Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "In vitro analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
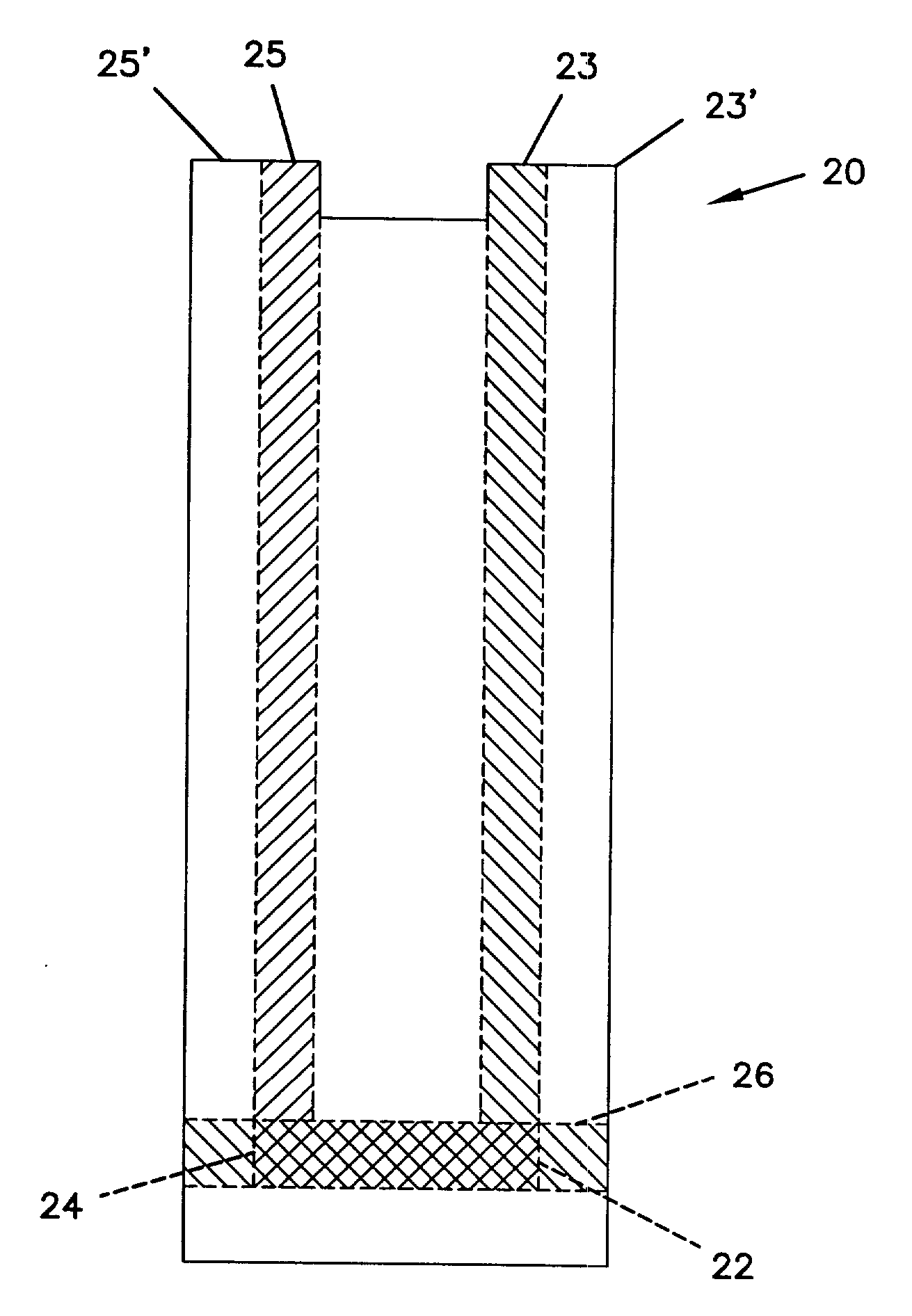
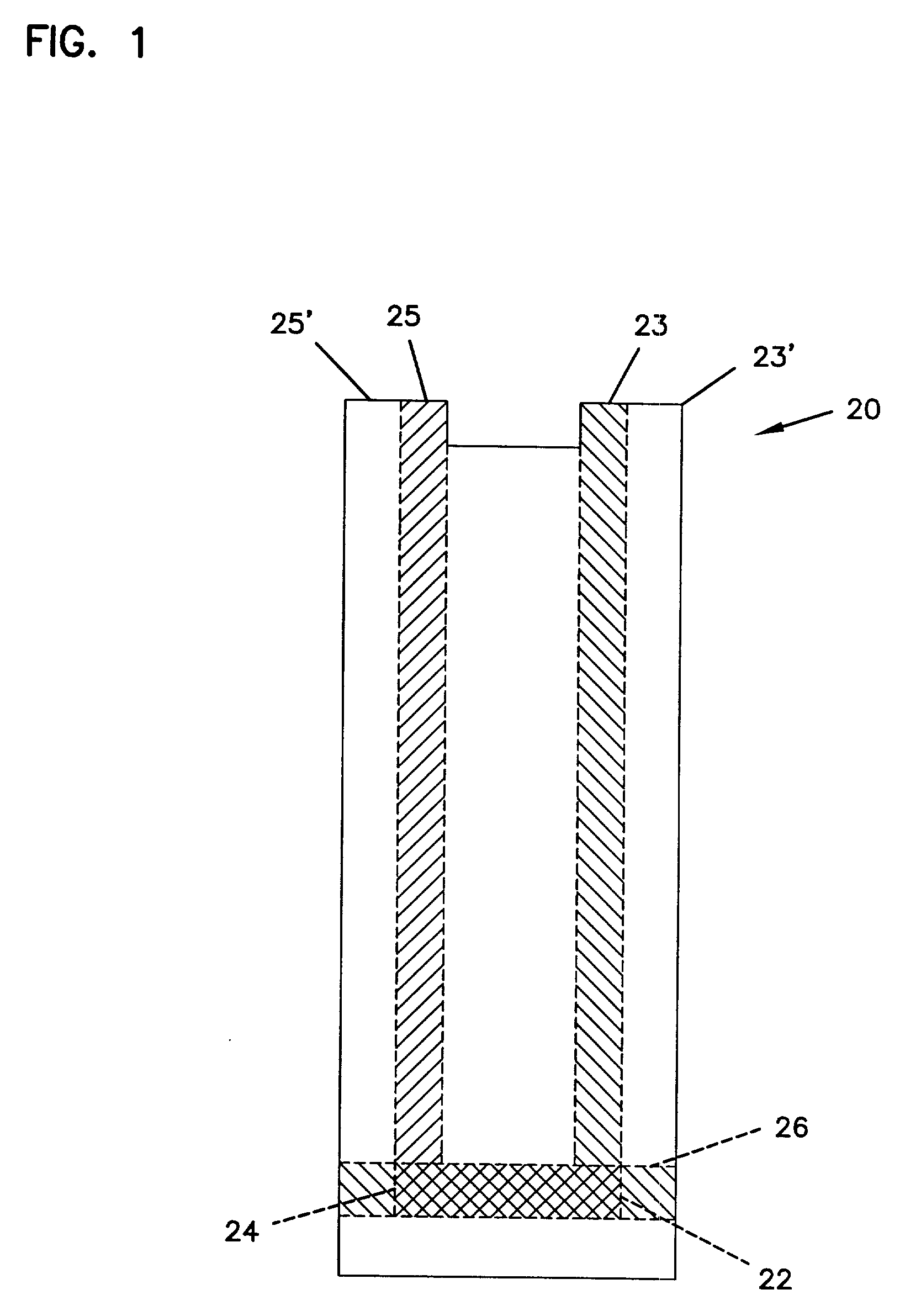
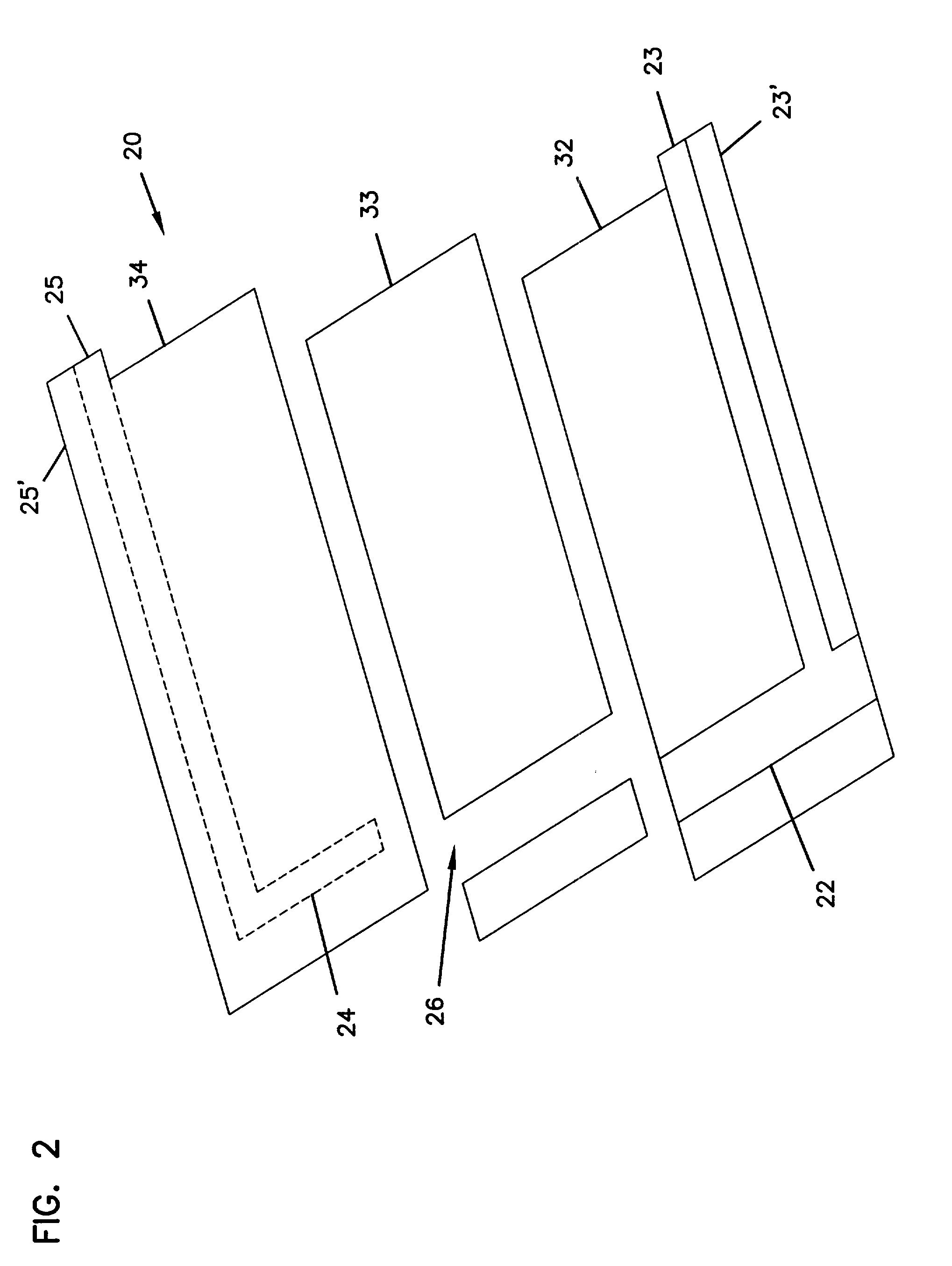
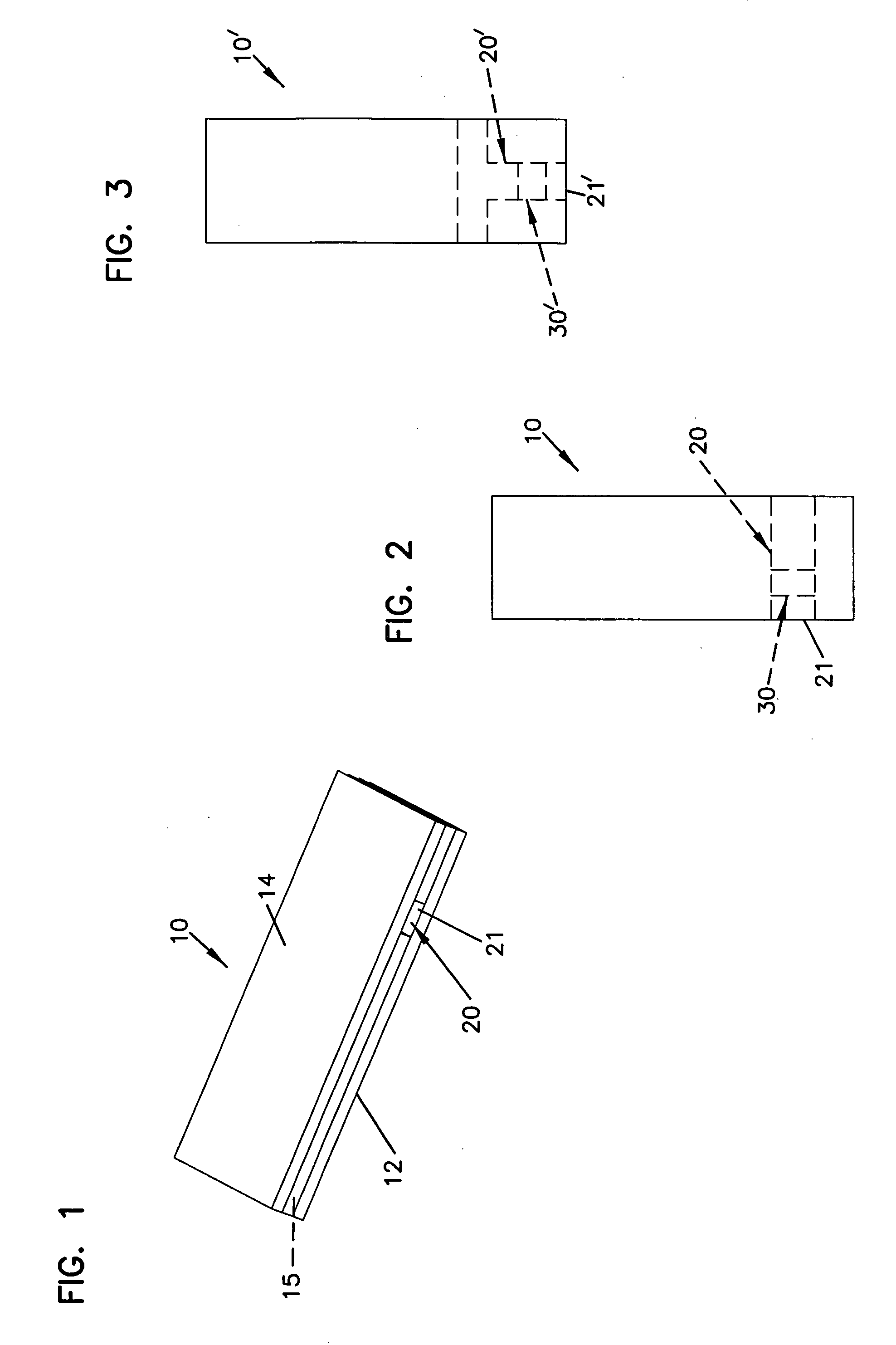
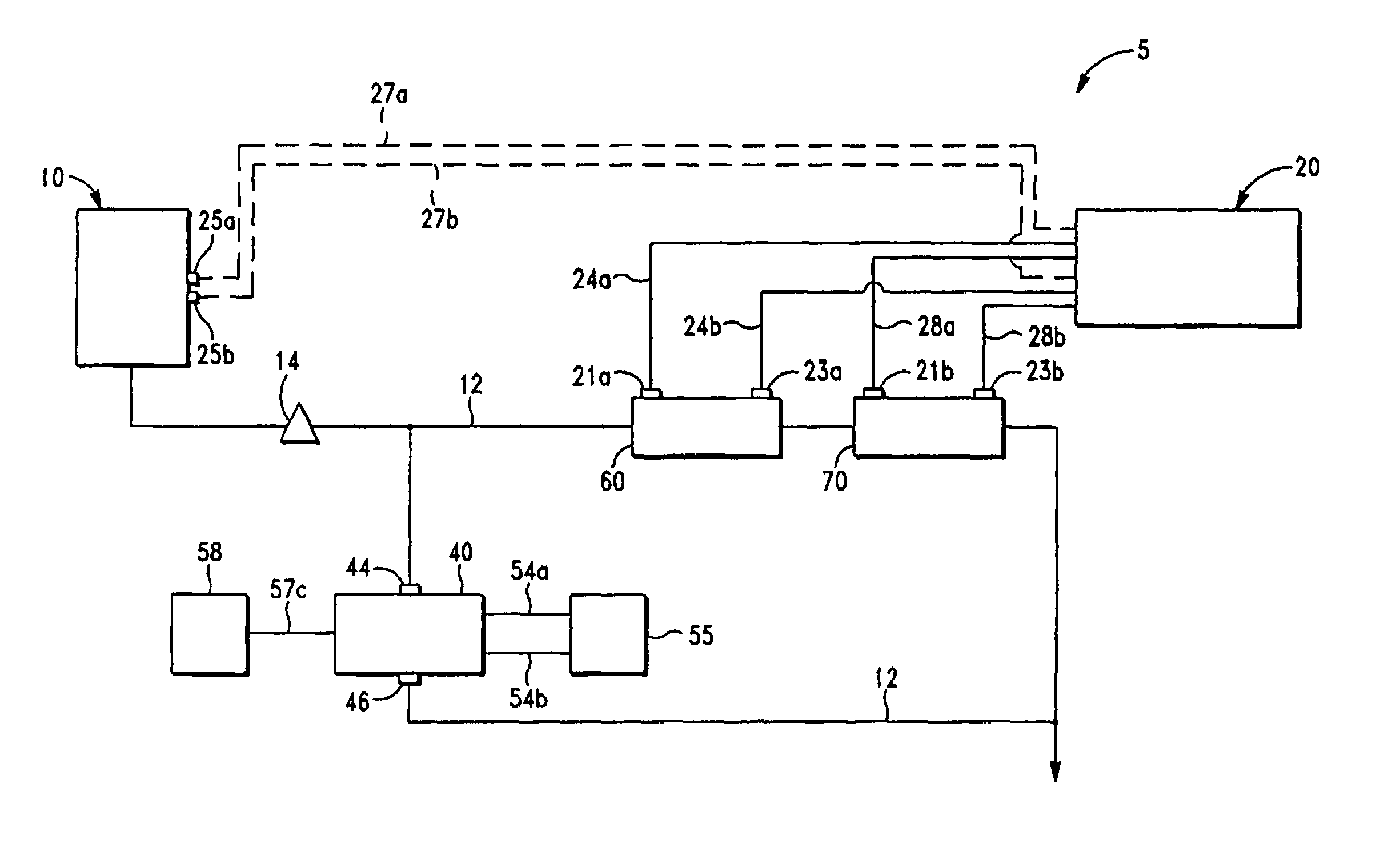
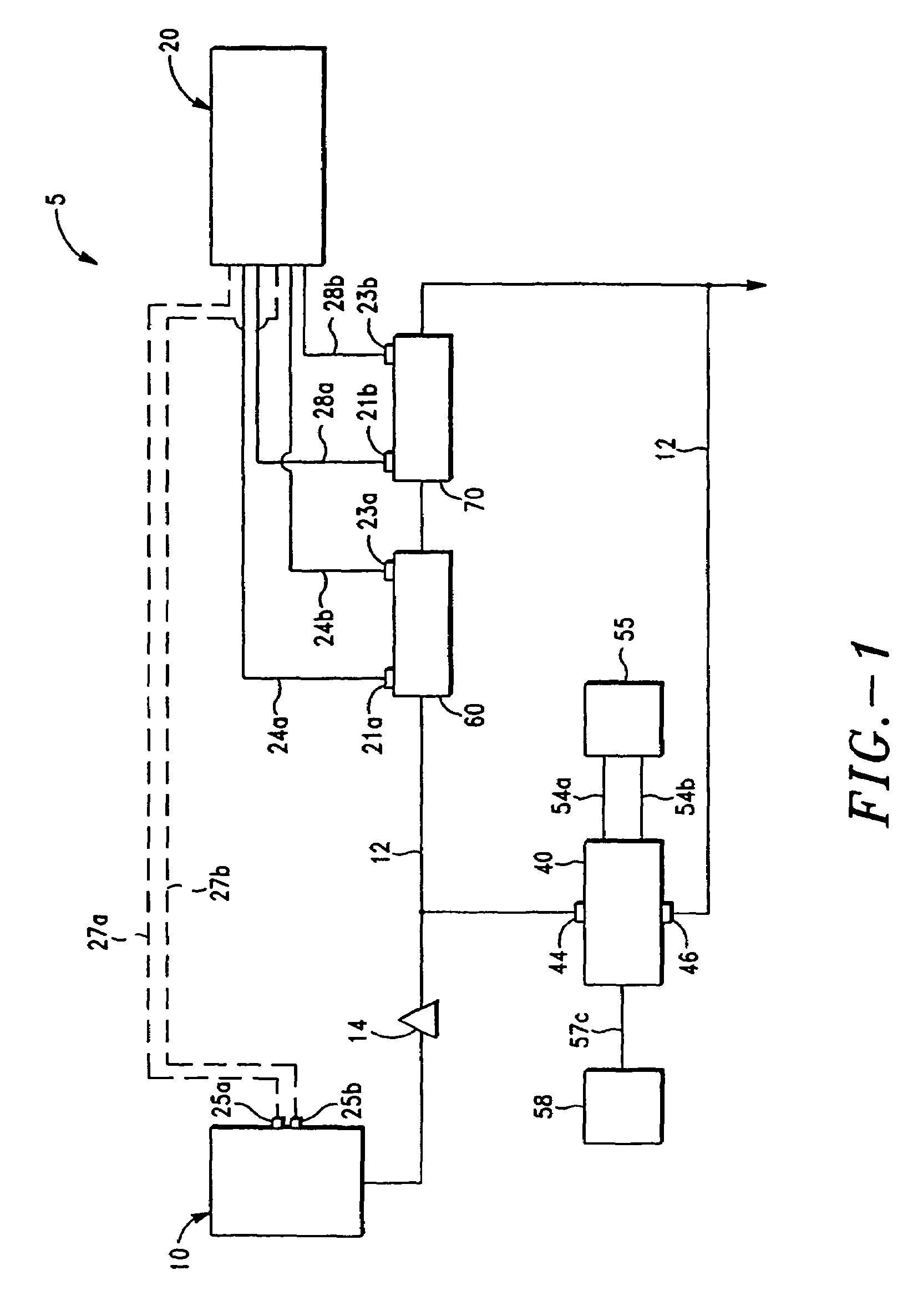
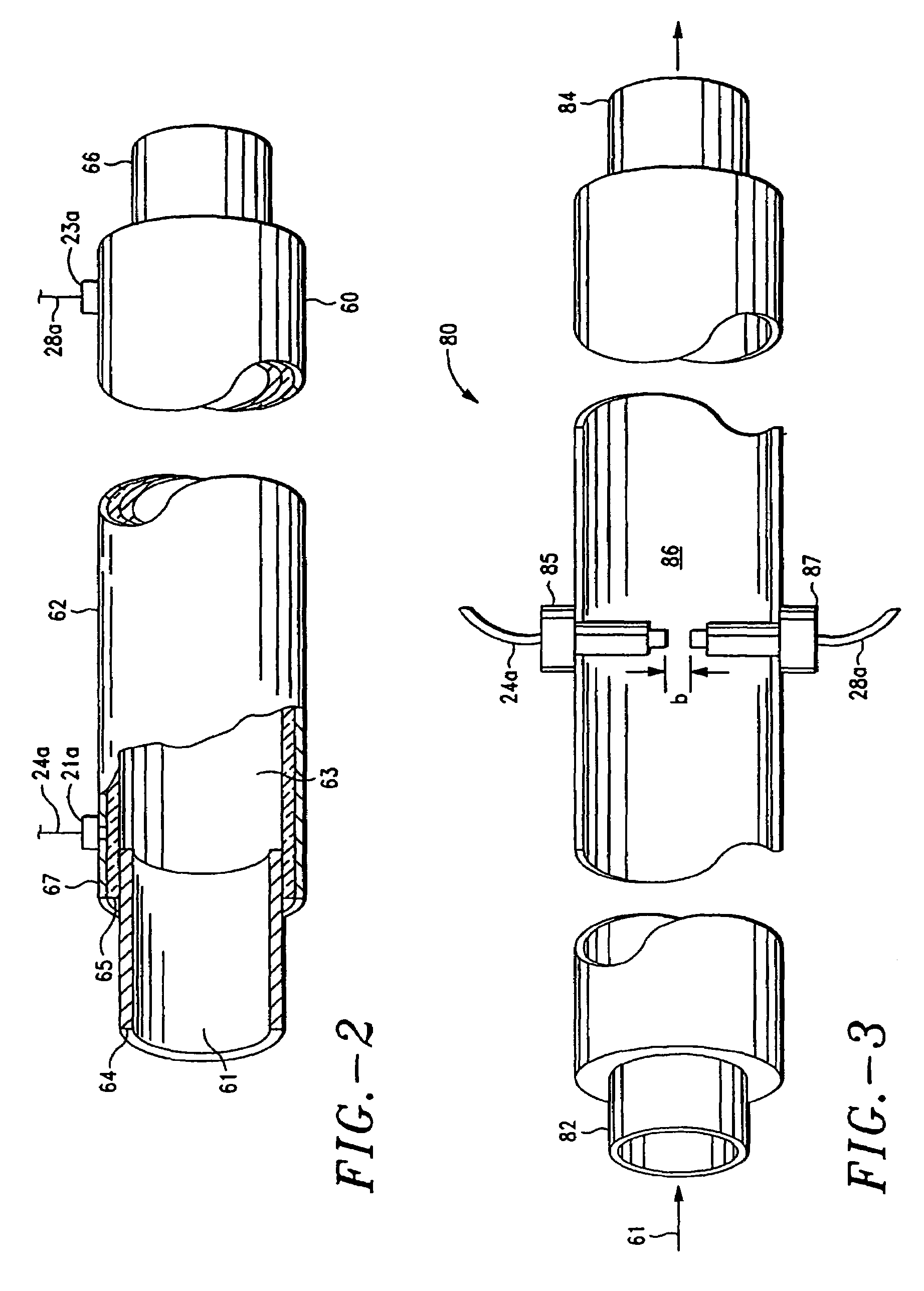
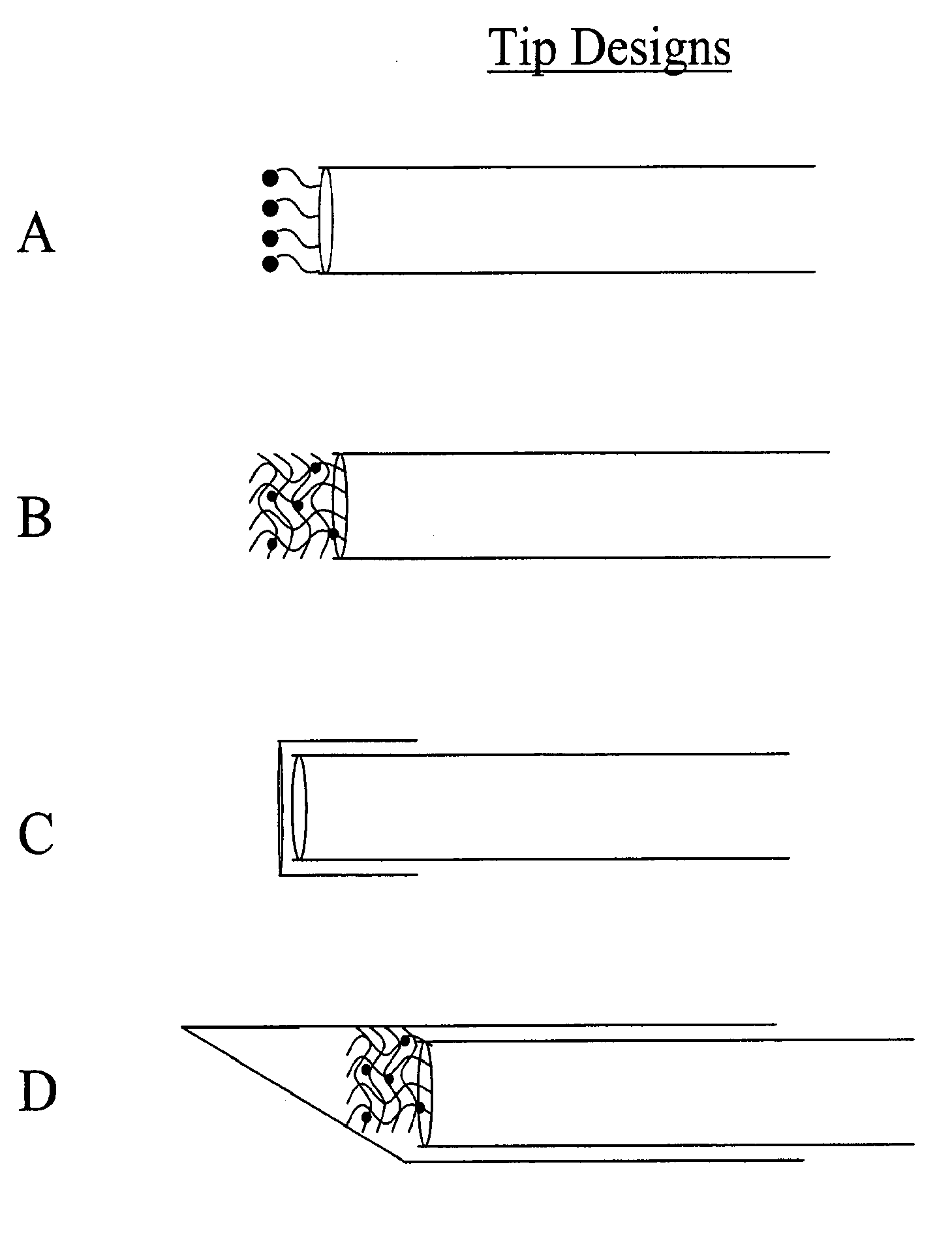
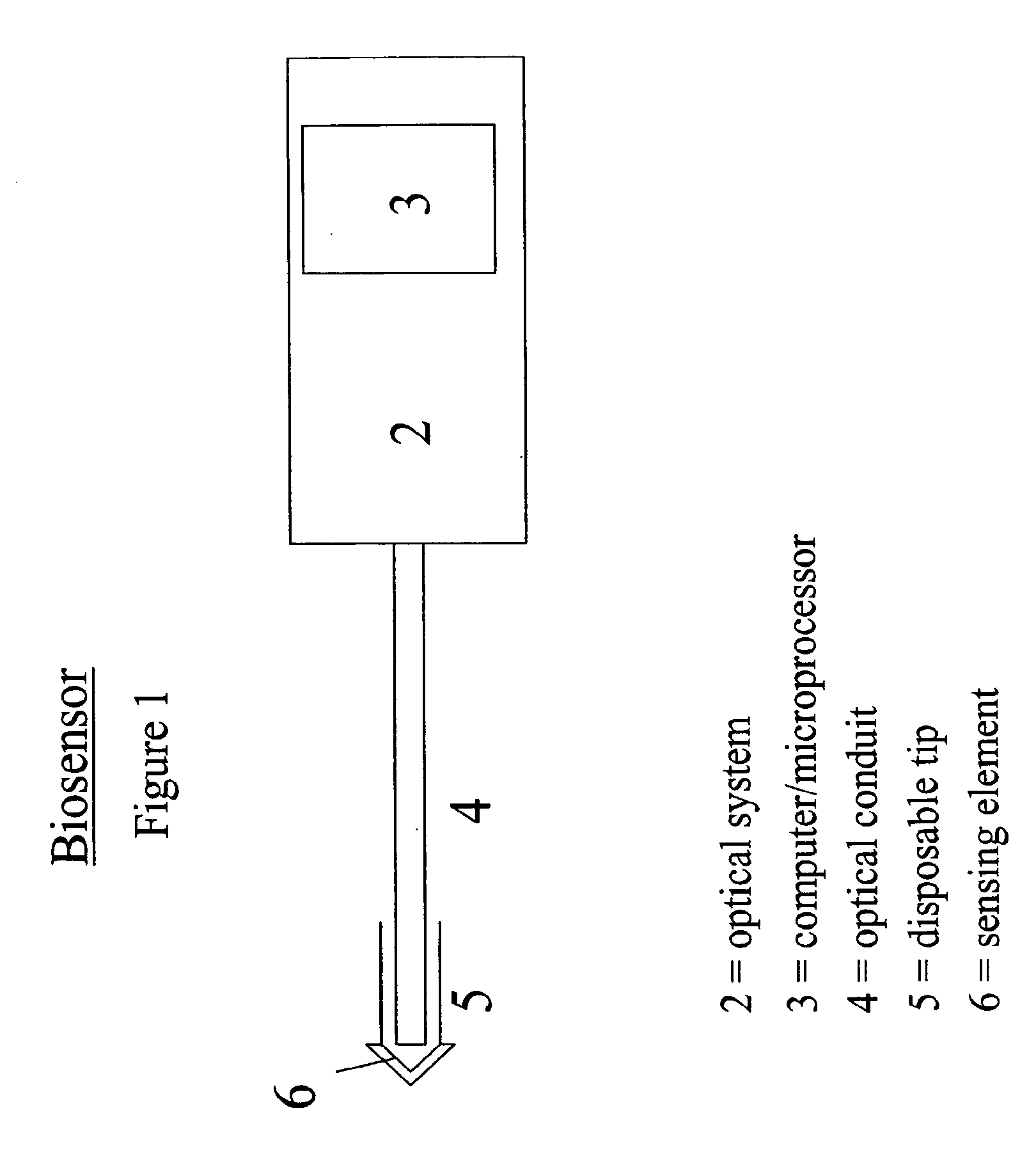
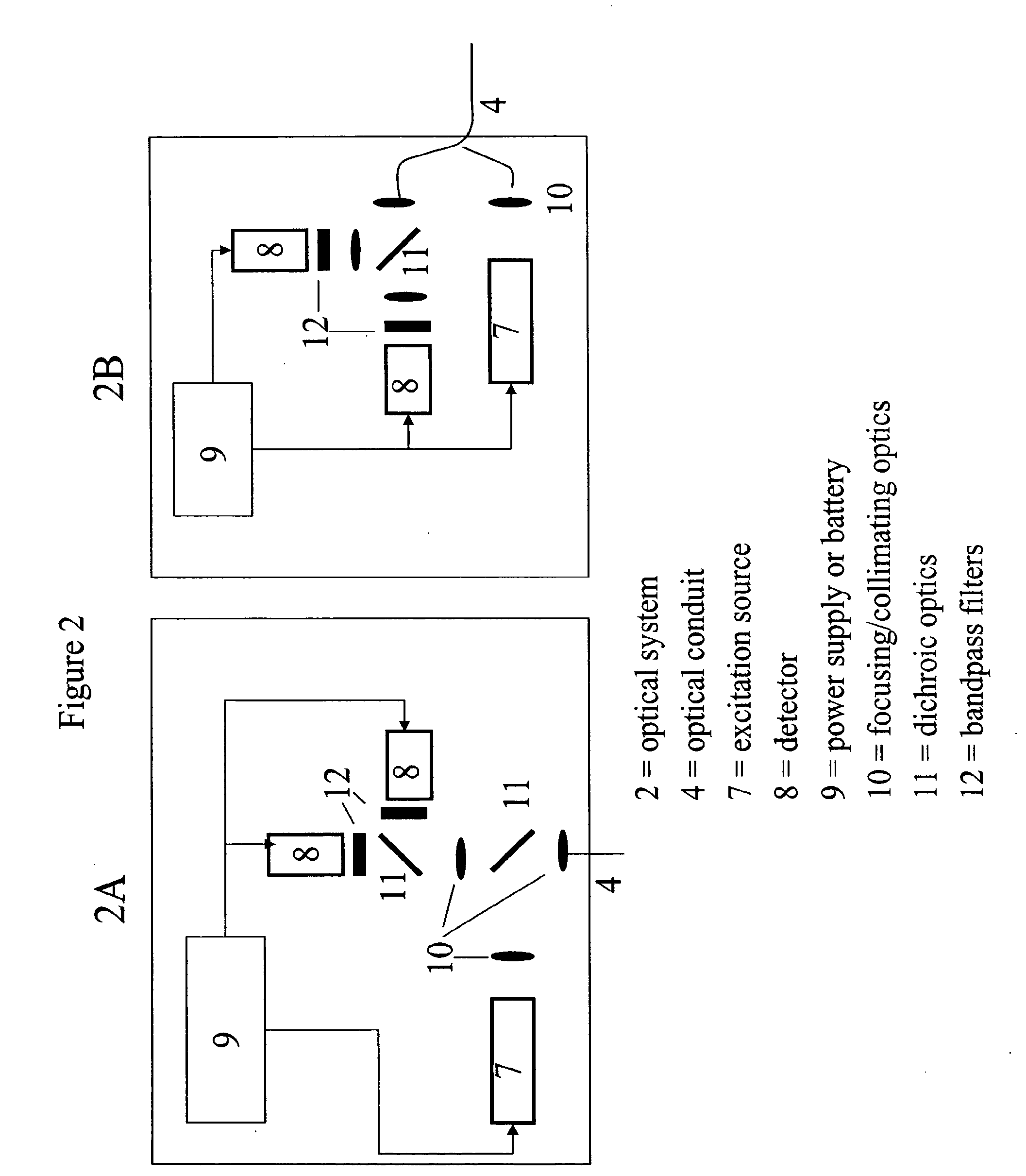
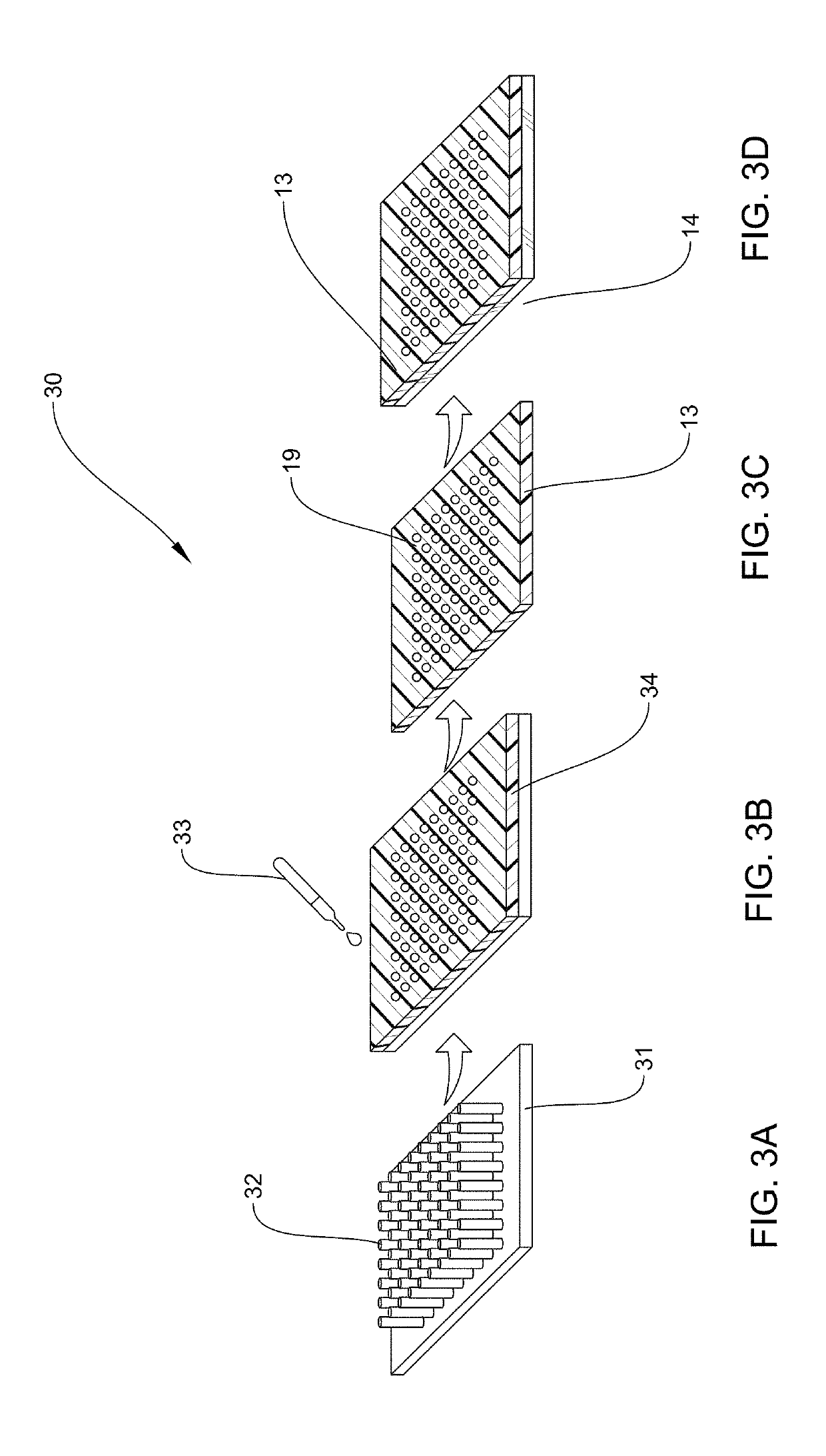
Small Volume in Vitro Analyte Sensor and Methods
InactiveUS20020148739A2Efficient and reliable methodEfficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBlood serumBiological fluid
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A small volume sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
In vitro analyte sensor, and methods
InactiveUS20070056858A1Accurate and repeatable analysisImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteIn vitro analysis
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
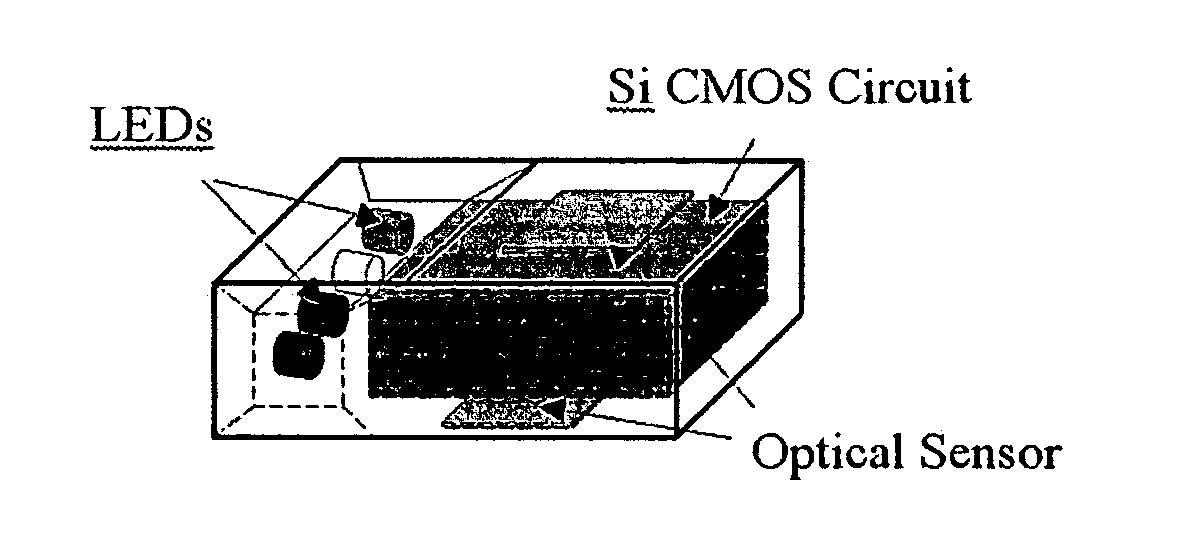
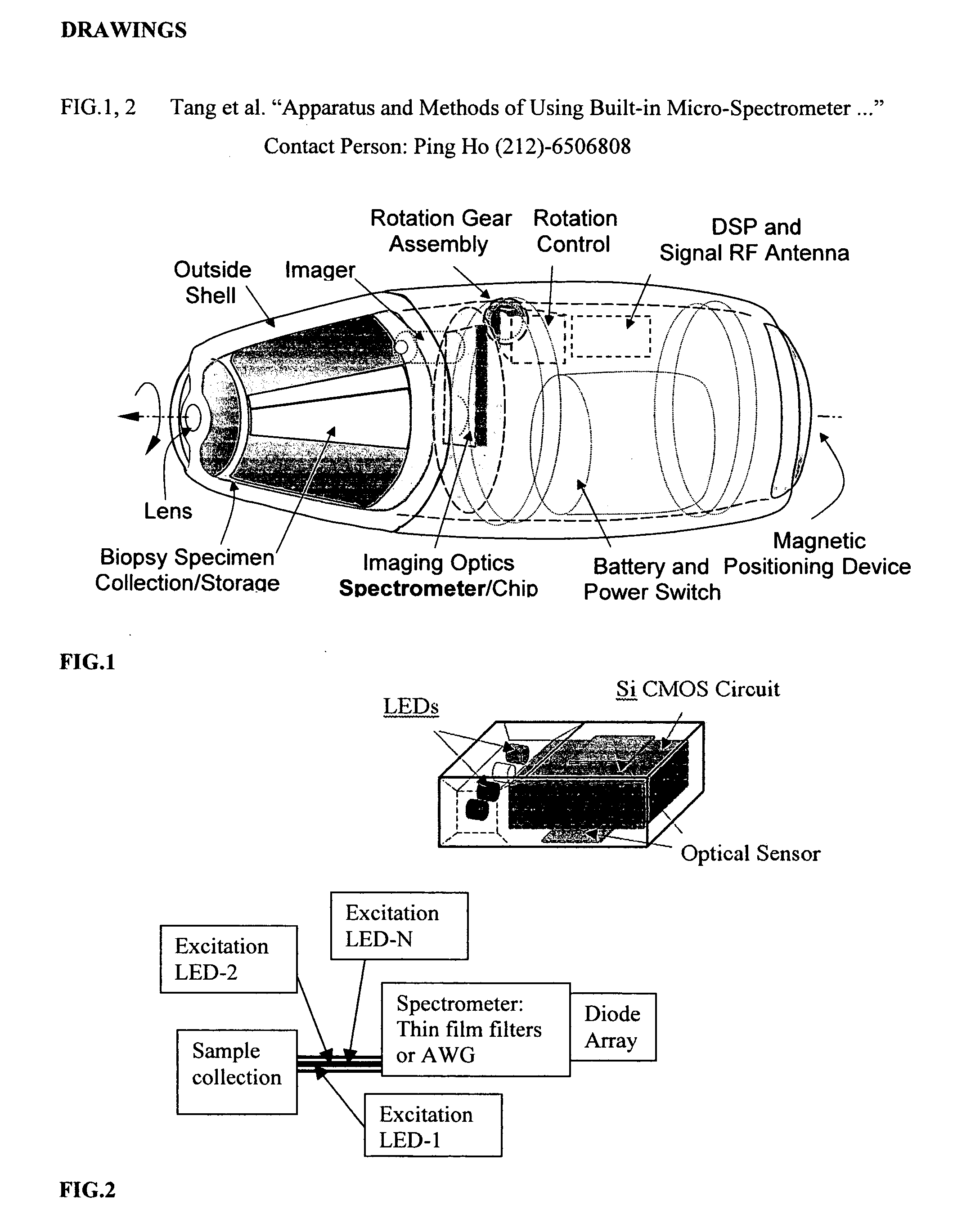
Positioning devices and methods for in vivo wireless imaging capsules
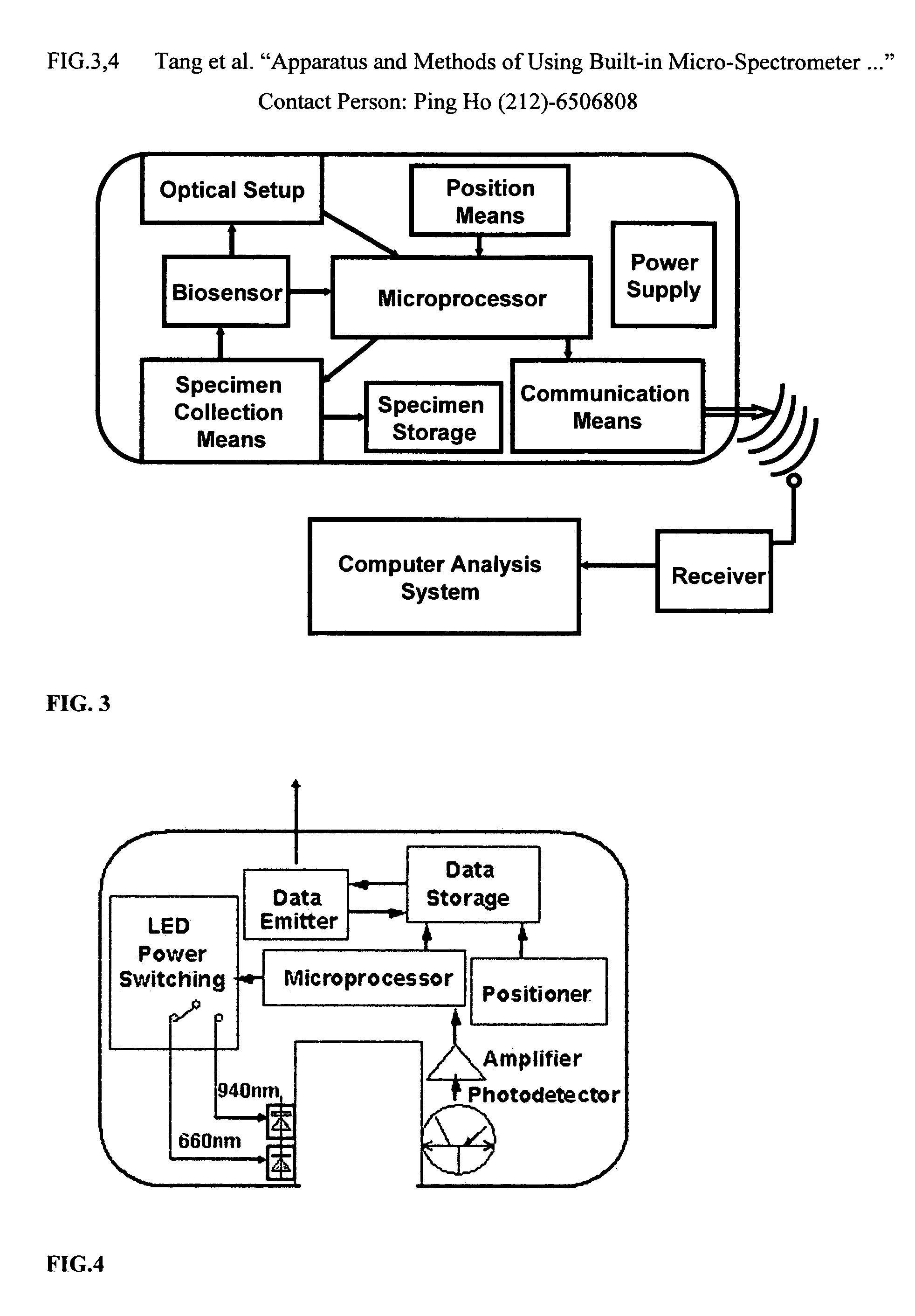
A wireless capsule as a disease diagnosis tool in vivo can be introduced into a biological body by a native and / or artificial open, or endoscope, or an injection. The information obtained from a micro-spectrometer, and / or an imaging system, or a micro-biosensor, all of which are built-in a wireless capsule, can be transmitted to the outside of the biological body for medical diagnoses. In addition, a real-time specimen collection device is integrated with the diagnostic system for the in-depth in vitro analysis
Owner:WANG LEMING +4
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050278945A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysisElectron transfer
A sensor utilizing a non-leachable or diffusible redox mediator is described. The sensor includes a sample chamber to hold a sample in electrolytic contact with a working electrode, and in at least some instances, the sensor also contains a non-leachable or a diffusible second electron transfer agent. The sensor and / or the methods used produce a sensor signal in response to the analyte that can be distinguished from a background signal caused by the mediator. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is typically provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
System and method for in vitro analysis of therapeutic agents
A system and method for in vitro analysis of therapeutic agents comprising a reservoir adapted to hold a therapeutic agent, a first flow cell having a first cell chamber adapted to receive at least a first sample of the therapeutic agent, a second flow cell having a second cell chamber adapted to receive at least a second sample of the therapeutic agent, the first flow cell having a first path length (be′) and the second flow cell having a second path length (be″), the first path length being substantially equal to a sensitivity factor (f)×be″, a membrane chamber having a biological cell membrane therein adapted to receive at least a third sample of the therapeutic agent, the membrane chamber being further adapted to detect the membrane potential of the biological cell membrane; and spectroscopic detection means for detecting the spectral characteristics of the first and second therapeutic agent samples.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Method for the Molecular Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer and Kit for Implementing Same
InactiveUS20100227317A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsProstate sampleIn vitro analysis
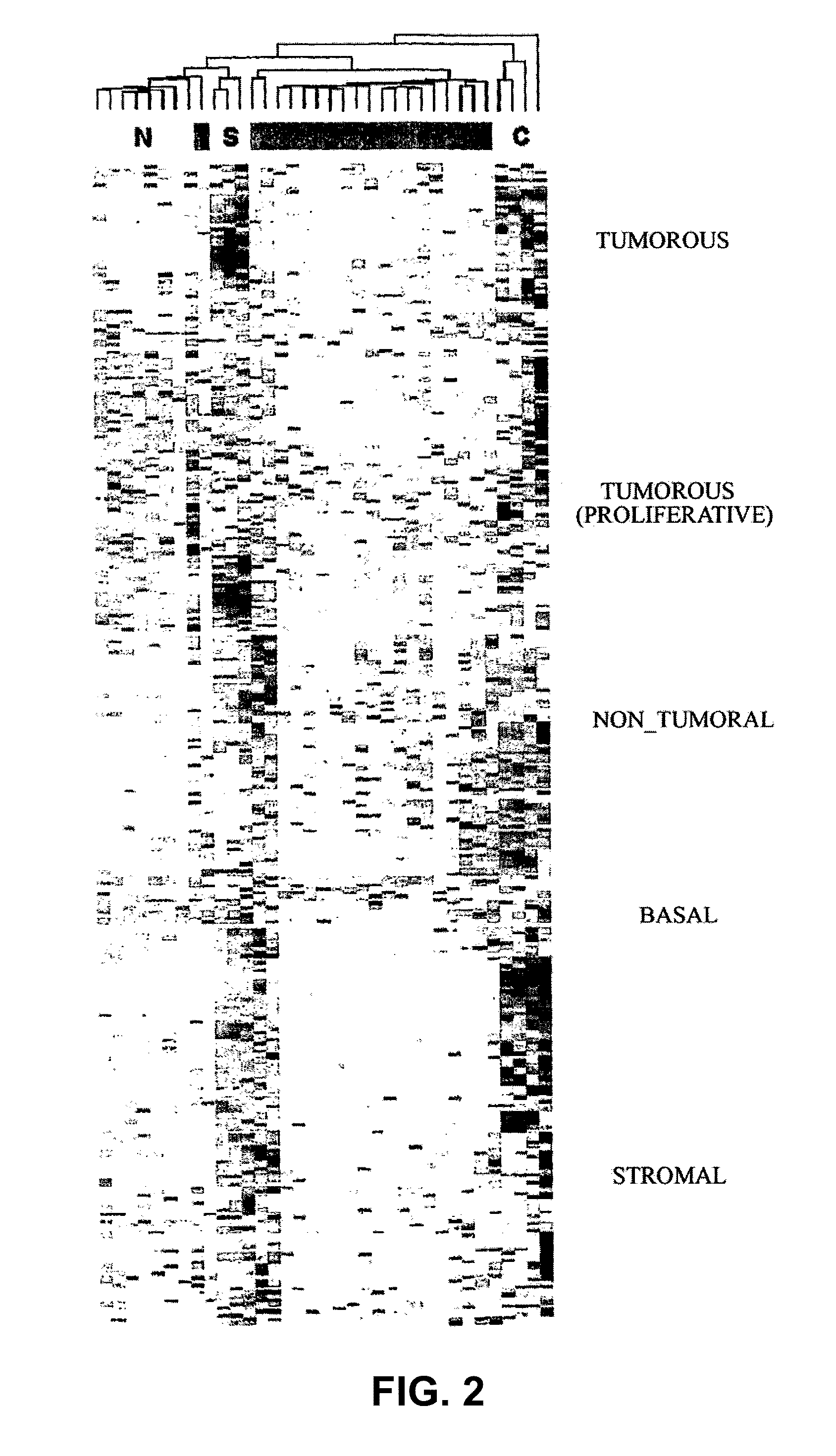
The invention relates to a method for the molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer, comprising the in vitro analysis of the overexpression or underexpression of combinations of genes that can distinguish, with high statistical significance, tumorous prostate samples from non-tumorous prostate samples. The invention also relates to a kit for the molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer, which can perform the above-mentioned detection.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA CLINIC PER A LA RECERCA BIOMEDICA +1
Unit cuvette for analyzing a biological fluid, automatic device for in vitro analysis
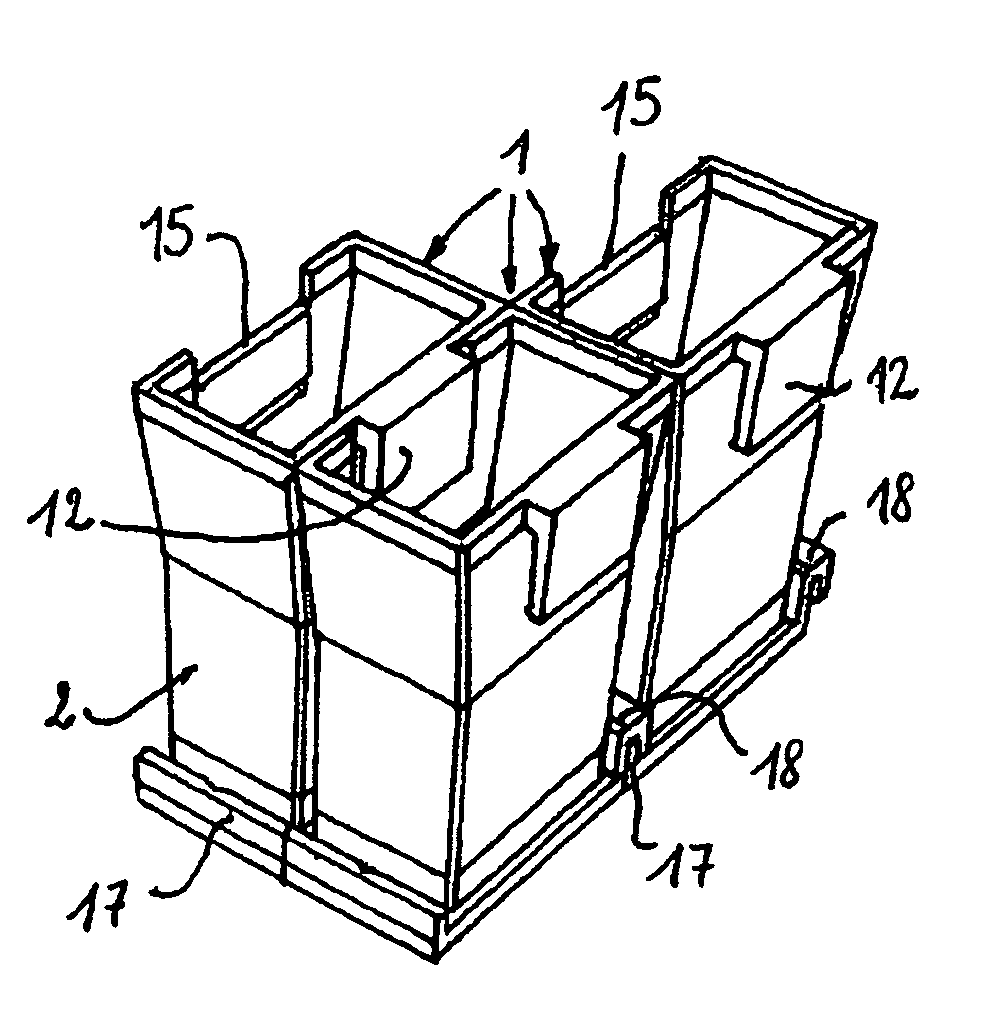
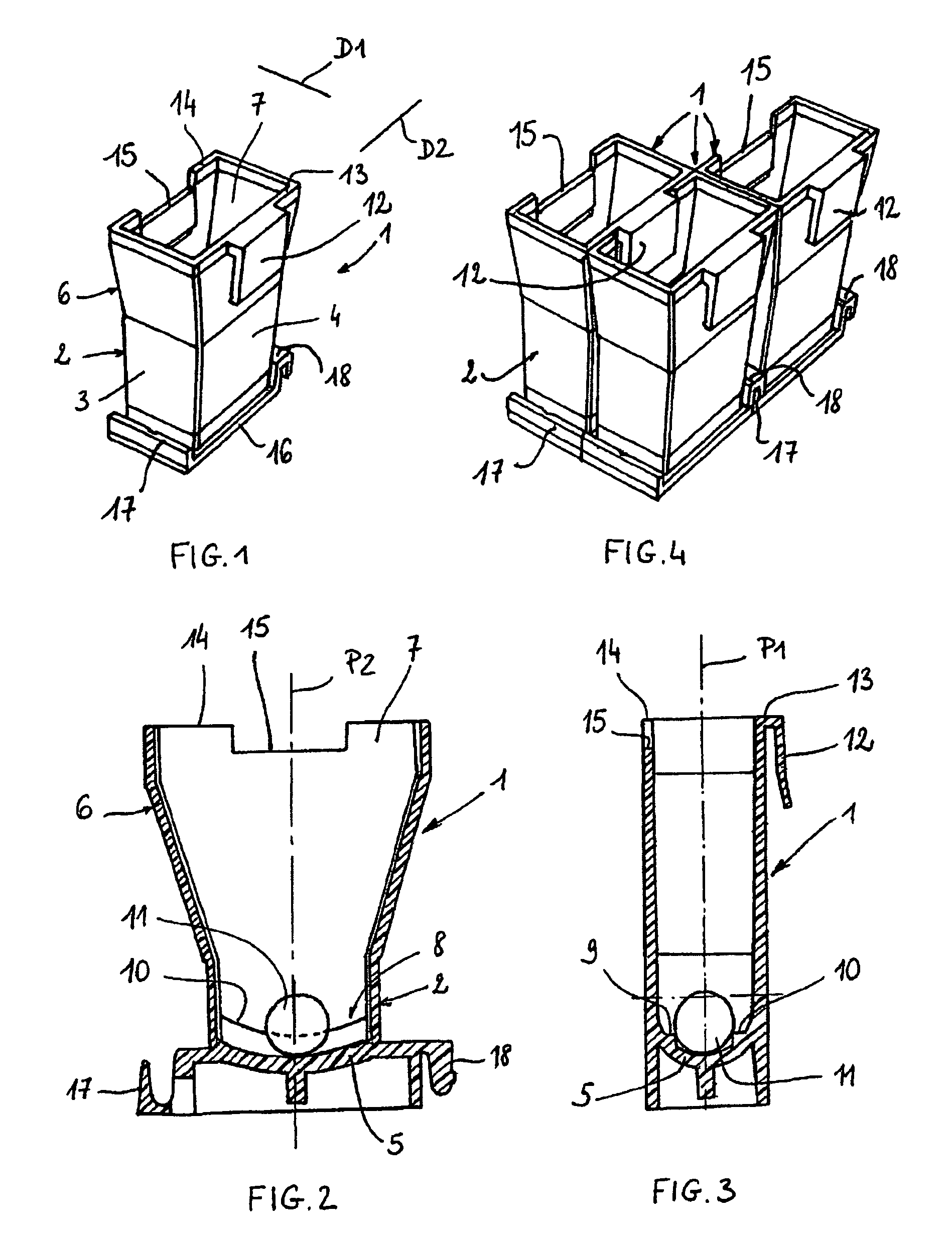
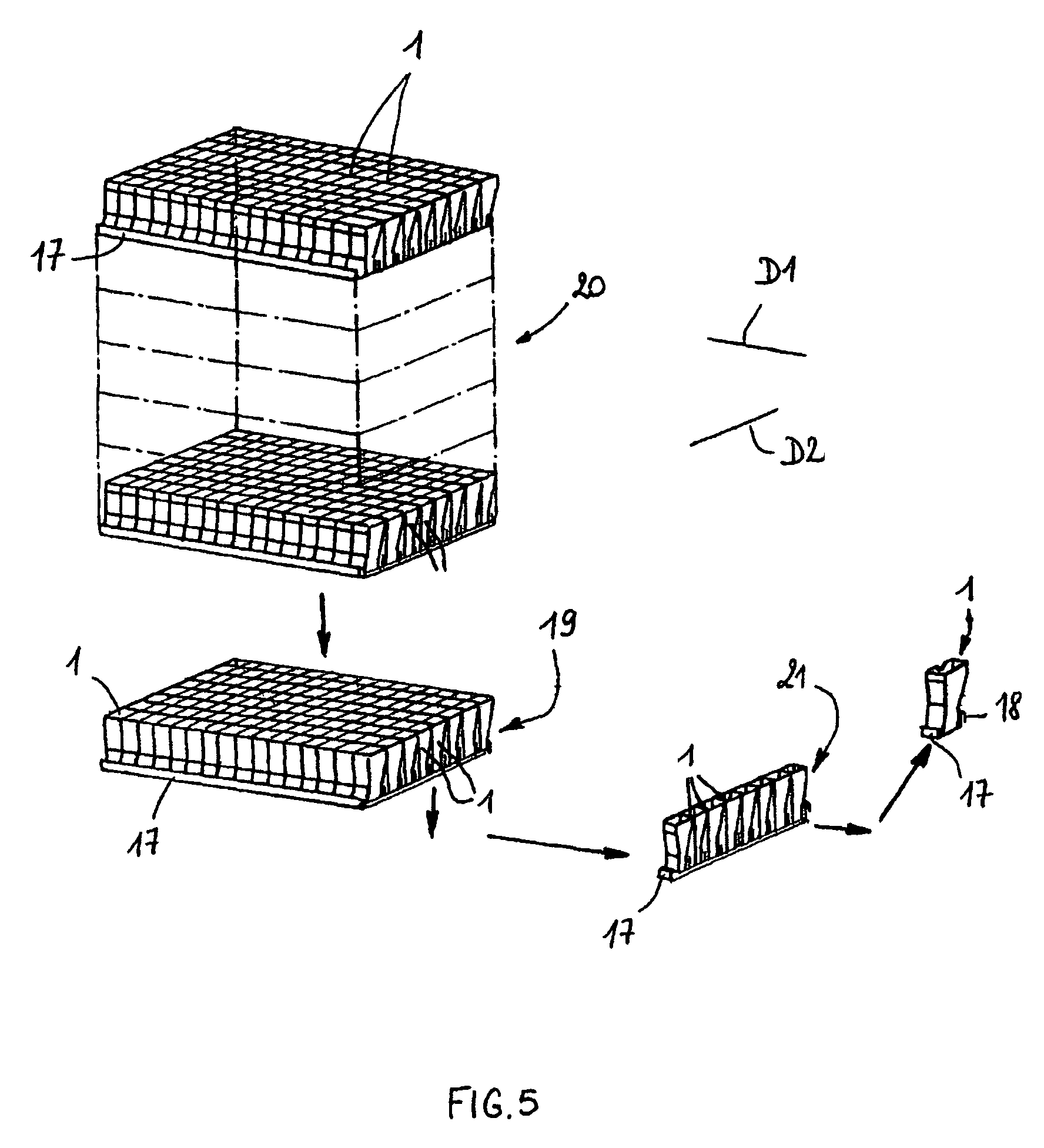
ActiveUS7959878B2Easy to storeEasy to usePharmaceutical containersMaterial analysis by optical meansCuvetteIn vitro analysis
The bottom of the cuvette comprises a curved raceway placed so as to guide the oscillating movement of a ball inserted into the cuvette. In addition, the cuvette comprises means of attachment, in two perpendicular directions, to adjacent unit cuvettes. The cuvettes can thus be stored as plates in a feed magazine of an analytical device. The analytical device comprises several stations placed around a rotary ring. Only where it is desired to determine the clotting time of the blood contained in the cuvette a ball is introduced into the latter, at a ball distribution post. The cuvette equipped in this way is then brought to a station where the test is carried out. The major advantage of the invention is the polyvalence of the cuvette and of the analytical device.
Owner:ALAIN ROUSSEAU +1
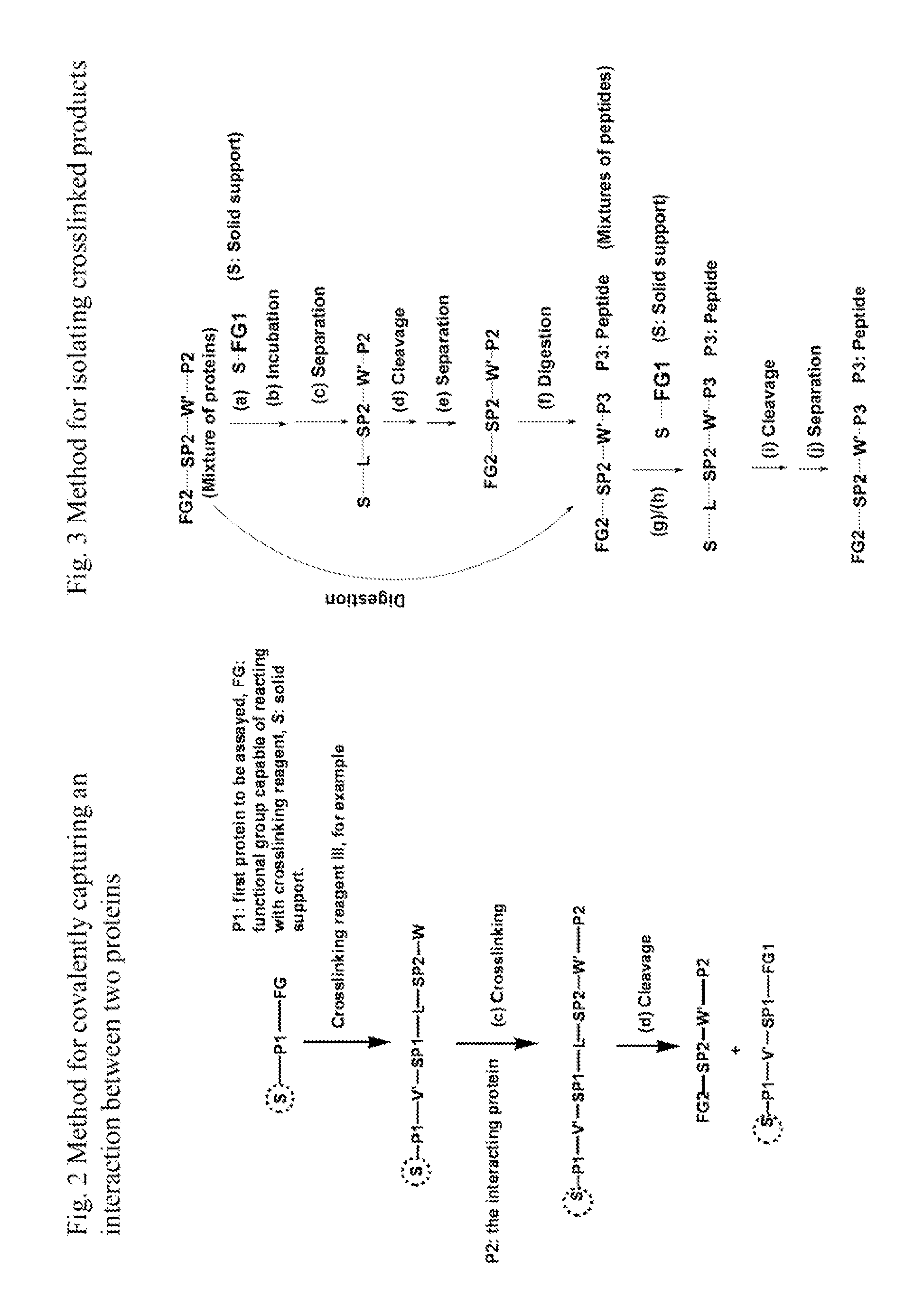
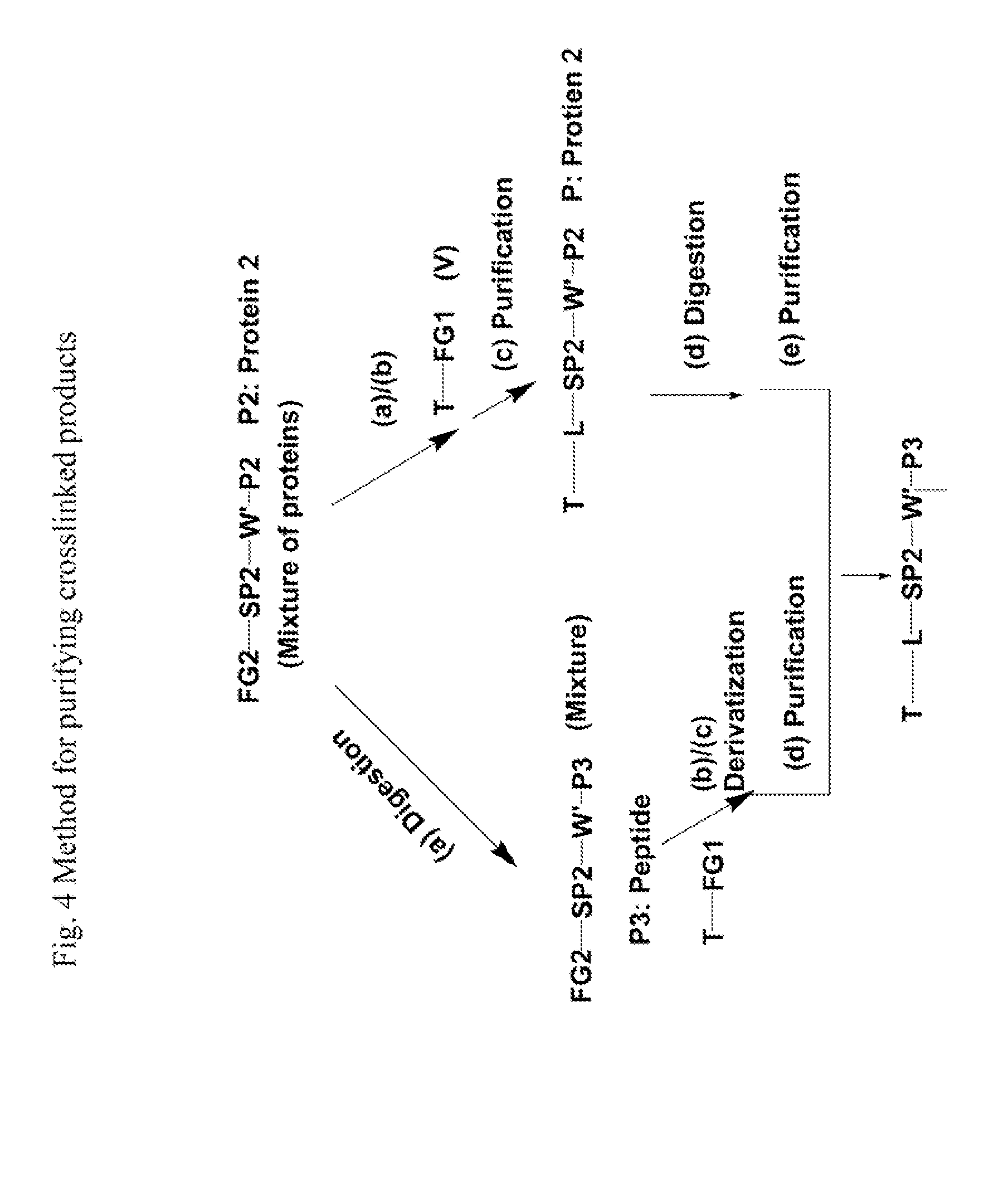
Crosslinking reagents, methods, and compositions for studying protein-protein interactions
InactiveUS20120322978A1Highly specific labelingNo side productsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesProduct baseIn vivo
The invention provides reagents, methods, and compositions for studying protein-protein interactions. The inventive system and methods allow the analysis of protein-protein interactions in vivo and in vitro. Advantages offered by various embodiments of the inventive system and methods compared to existing photocrosslinking approaches include, for example, (i) novel reversible crosslinking reagents that allow easy isolation, purification, and enrichment of the crosslinked products; (ii) trifluoromethyl phenyldiazirine- or perfluorinated phenylazide-based photocrosslinking reagents that provide high specific labeling, no side product, and higher photocrosslinking efficiency; (iii) versatile spacer groups that allow systematic contact site mapping; (iv) novel methods for isolating, purifying, and detecting crosslinked products based on the reversible-link chemistry; and (v) the ability to study the interaction sites in vitro, in situ, or in vivo.
Owner:CELLMOSAIC
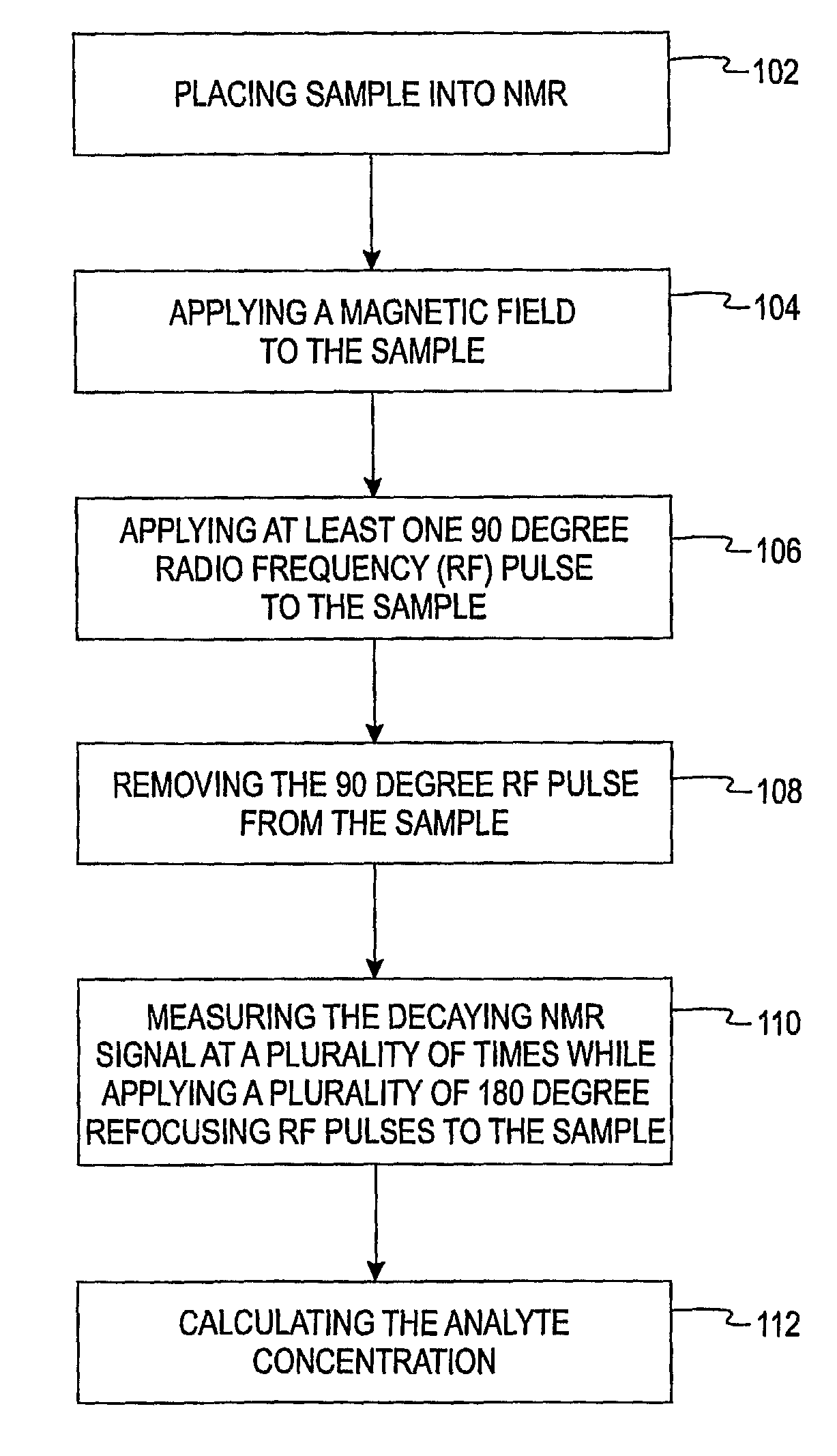
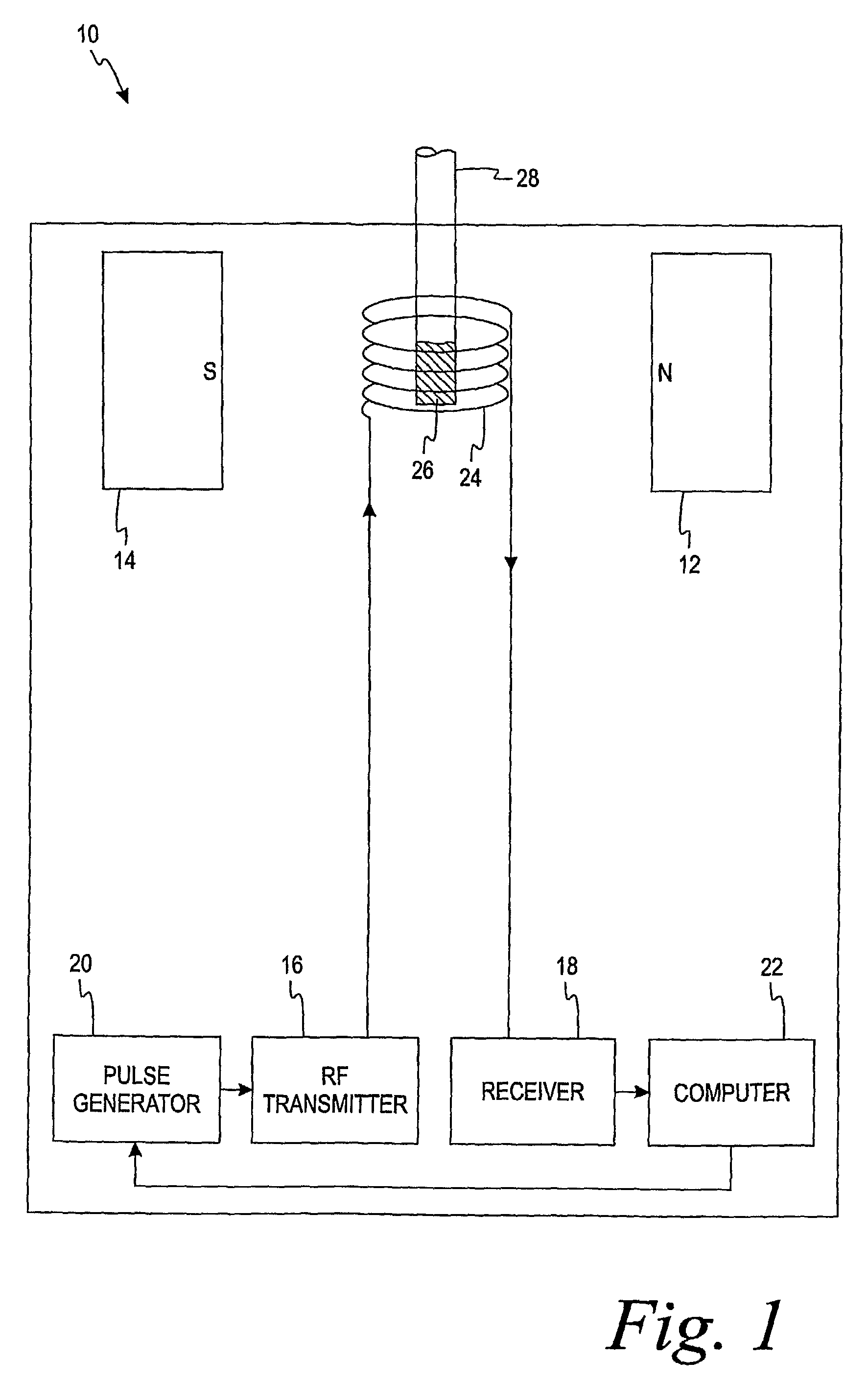
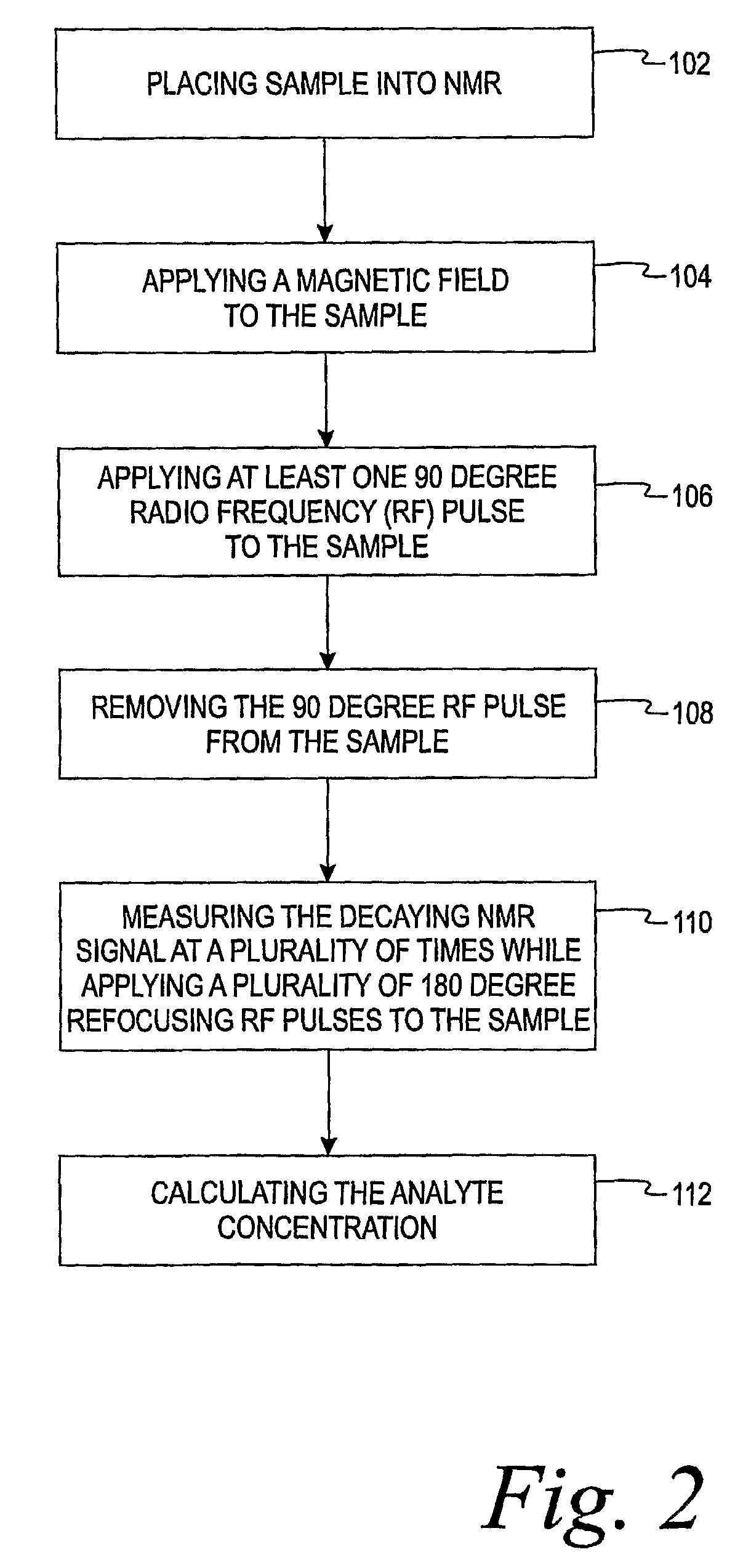
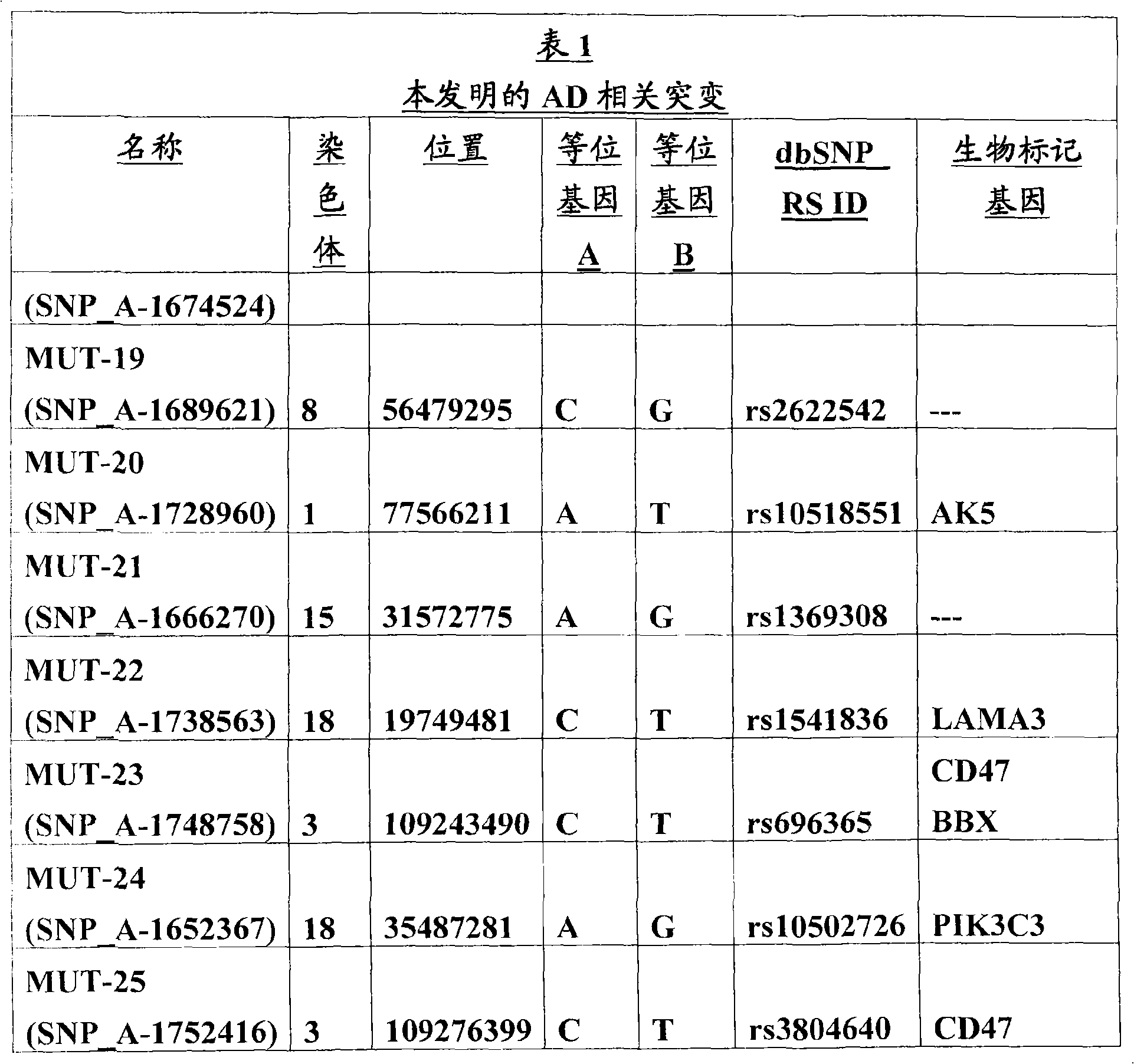
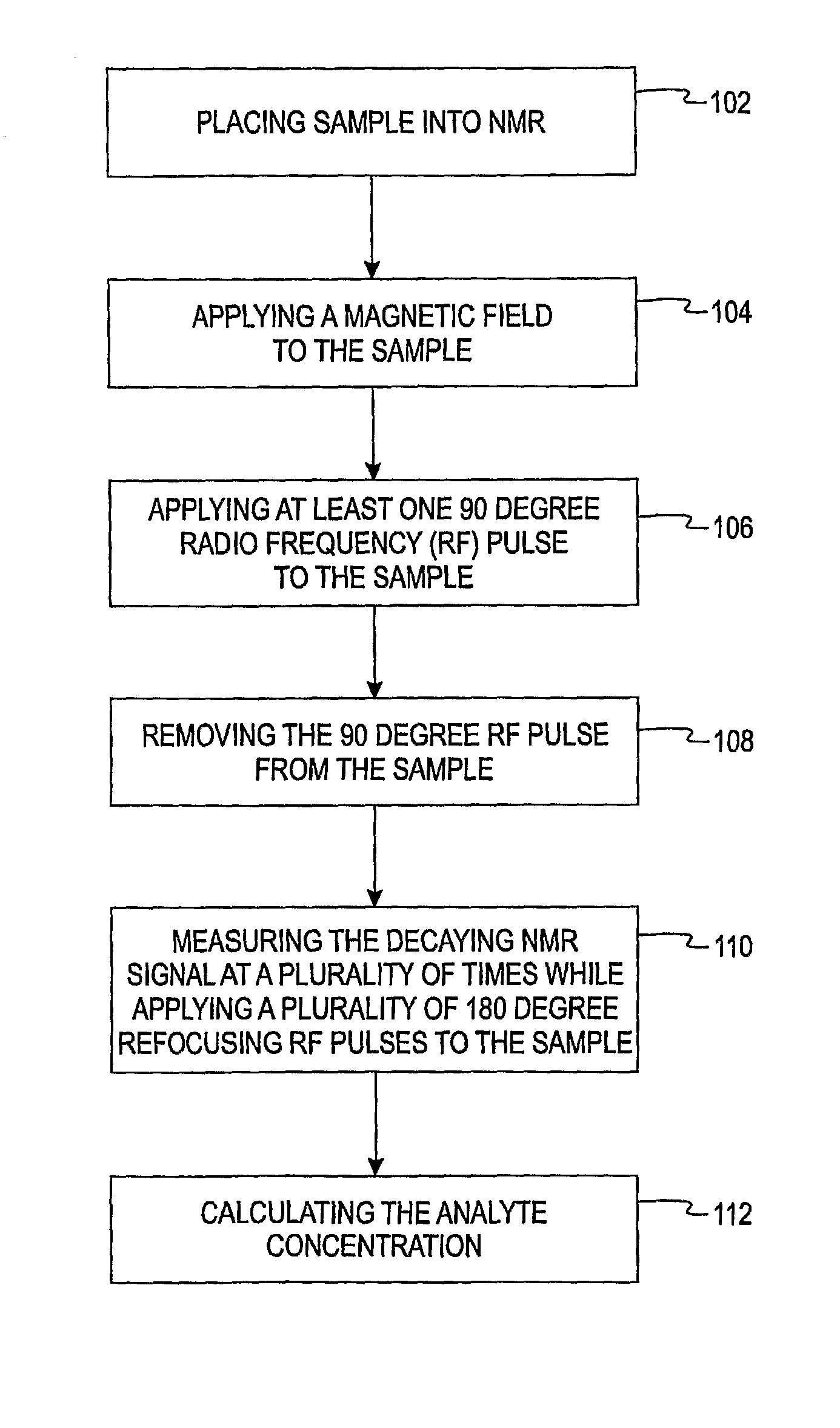
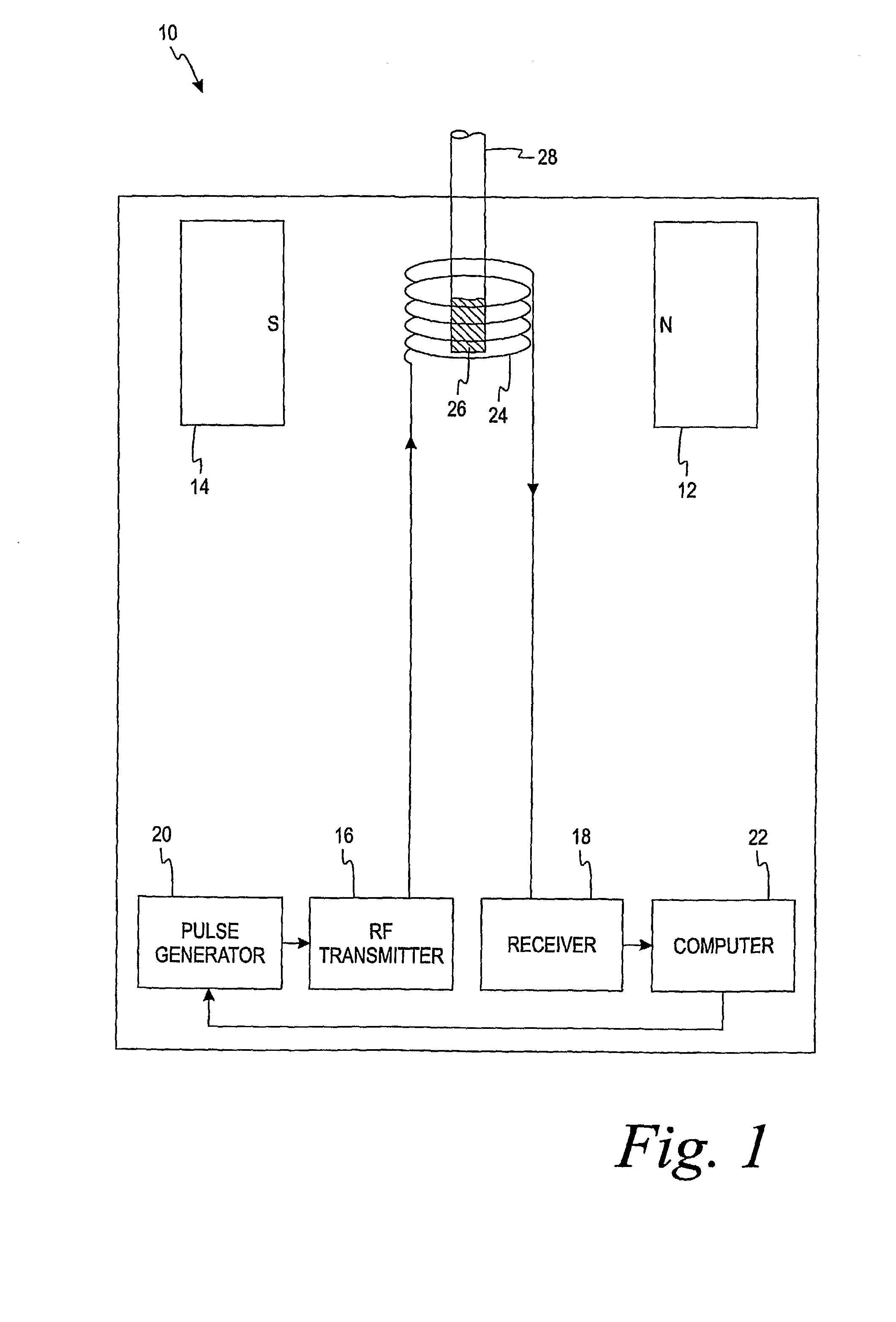
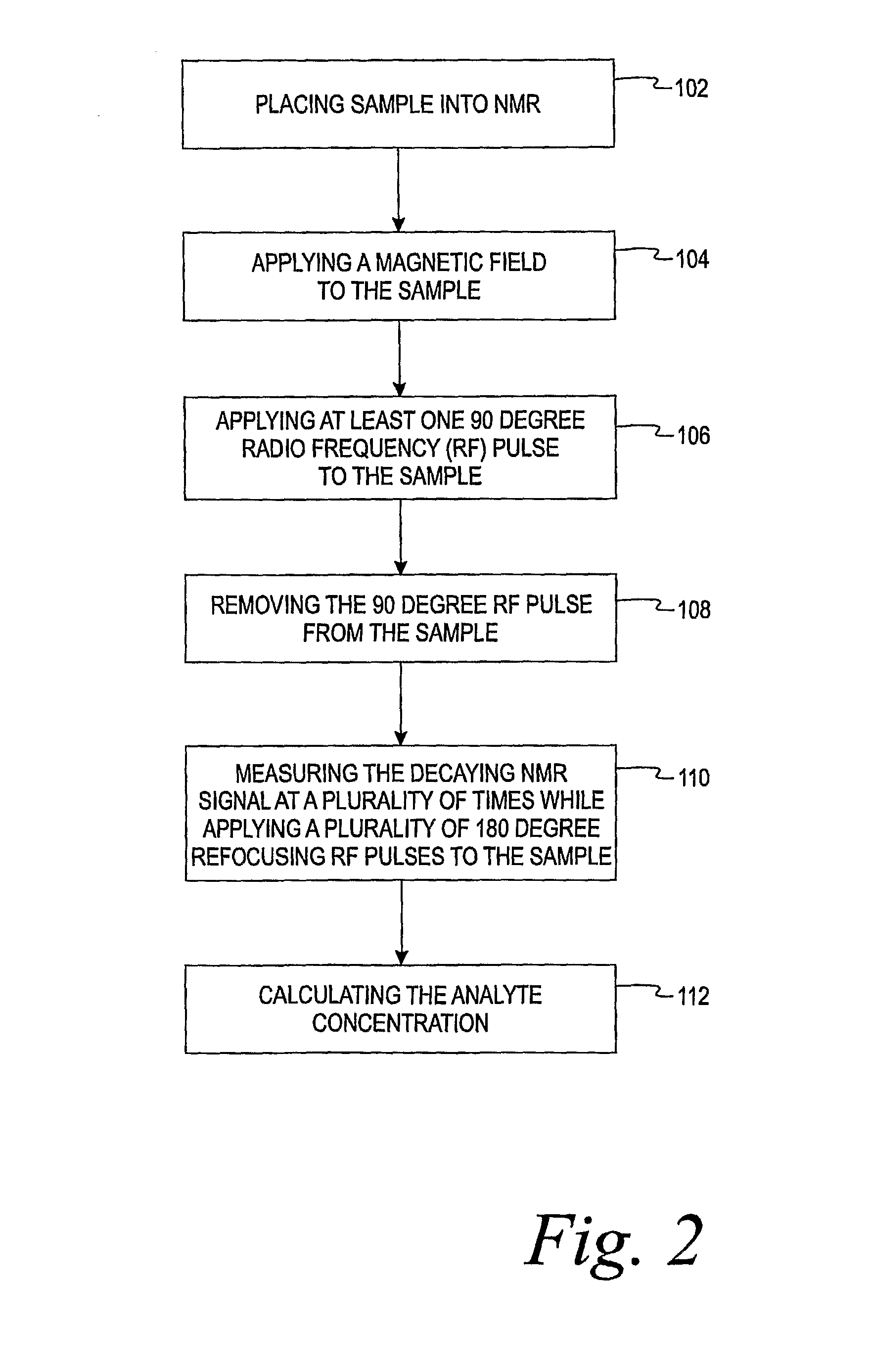
Methods of in vitro analysis using time-domain NMR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7550971B2Magnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSpectroscopyRadio frequency
An in vitro method of determining an analyte concentration of a sample includes placing the sample into a low-field, bench-top time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance (TD-NMR) spectrometer. The NMR spectrometer is tuned to measure a selected type of atom. A magnetic field is applied to the sample using a fixed, permanent magnet. At least one 90 degree radio-frequency pulse is applied to the sample. The radio-frequency pulse is generally perpendicular to the magnetic field. The 90 degree radio-frequency pulse is removed from the sample so as to produce a decaying NMR signal. The decaying NMR signal is measured at a plurality of times while applying a plurality of 180 degree refocusing radio-frequency pulses to the sample. The analyte concentration is calculated from the plurality of measurements associated with the decaying NMR signal and a selected model.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
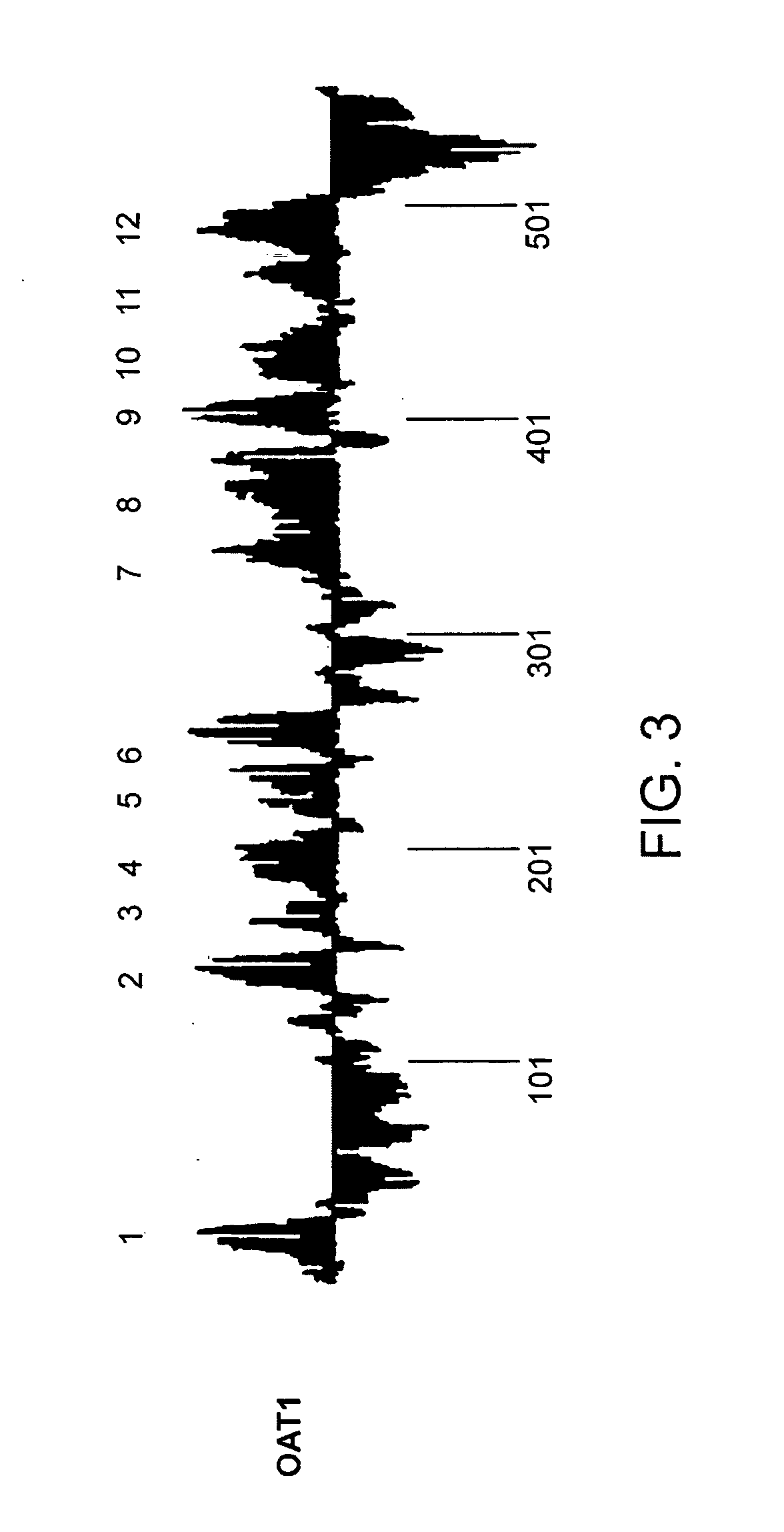
Method for screening using an OAT1 transporter protein
A protein capable of transporting organic anions having amino acid sequences represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2 or amino acid sequences derived therefrom by deletion, substitution or addition of one or more amino acid residues; and a gene coding for the protein. The protein and gene therefore are useful in vitro analysis of drug release and drug—drug interactions and development of method for screening drugs useful for preventing nephrotoxicity.
Owner:FUJI BIOMEDIX +2
System for in vitro analysis of fluid dynamics on contact lenses via phase shifting interferometry
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Method and Device for the in Vitro Analysis for MRNA of Genes Involved in Haematological Neoplasias
InactiveUS20120157329A1Accurate classificationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesHematological TumorIn vitro analysis
Method and device for the in vitro analysis of mRNA of genes involved in hematological neoplasias. The device, composed of probes which specifically hybridize with genes involved in hematological neoplasias, designed so that its behaviour in the hybridization is similar, permits the evaluation of the mRNA level in biological samples taken from subjects suspected to be suffering from hematological neoplasia and facilitating the comparison between the different samples and their grouping by similarity in the gene expression patterns, especially when the probes are disposed in the form of microarray. The application of the method of the invention to obtain and process data of gene expression differences from the device of the invention permits the identification of genes significant for distinguishing samples associated to hematological neoplasias, facilitates the diagnosis of neoplasias as CLL and permits making a prognosis of the evolution thereof.
Owner:GIRALDO CASTELLANO PILAR +2
In vivo device and method for researching GI tract processes, microbes, and variables associated with illnesses and diseases
An interactive research device comprised of an orally ingested capsule with pockets rendering the capsule capable of sampling intestinal tracts (gut) substances and microbes before, during and after delivery of system perturbation substances and methods of use and associate system are described. Sensors are provided to simultaneously measure, monitor, record, and transmit data in real time obtained from within the exact vicinity of substance deployment and location of microbial assisted digestive processes. In vivo collected samples are also collected and preserved for in vitro analysis. Digestive processes and dysfunctions involving proteins that result in “gluten sensitivities” and dozens of gut-based diseases that develop in stages, and have been mysteries for over 2,000 years, can be analyzed. The capabilities were developed to permit research within the heretofore inaccessible and important regions of the small intestine where villi functions are compromised, and in the upper colon. Special focus includes determining roles microbes and their byproduct substances in cascade play in autoimmune system responses and diseases.
Owner:SHUCK L ZANE
Biomarkers for alzheimer's disease progression
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Methods of In Vitro Analysis Using Time-Domain Nmr Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20080088308A1Magnetic measurementsMicrobiological testing/measurementSpectroscopyRadio frequency
An in vitro method of determining an analyte concentration of a sample includes placing the sample into a low-field, bench-top time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance (TD-NMR) spectrometer. The NMR spectrometer is tuned to measure a selected type of atom. A magnetic field is applied to the sample using a fixed, permanent magnet. At least one 90 degree radio-frequency pulse is applied to the sample. The radio-frequency pulse is generally perpendicular to the magnetic field. The 90 degree radio-frequency pulse is removed from the sample so as to produce a decaying NMR signal. The decaying NMR signal is measured at a plurality of times while applying a plurality of 180 degree refocusing radio-frequency pulses to the sample. The analyte concentration is calculated from the plurality of measurements associated with the decaying NMR signal and a selected model.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Fiber optic device for sensing analytes
InactiveUS20080198358A1Reduce power consumptionExtended service lifeSamplingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Applications of small molecular compound Salubrinal in drugs for treating or preventing osteoporosis and osteopenia diseases
InactiveCN111568904APromote differentiationPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseIn vivo
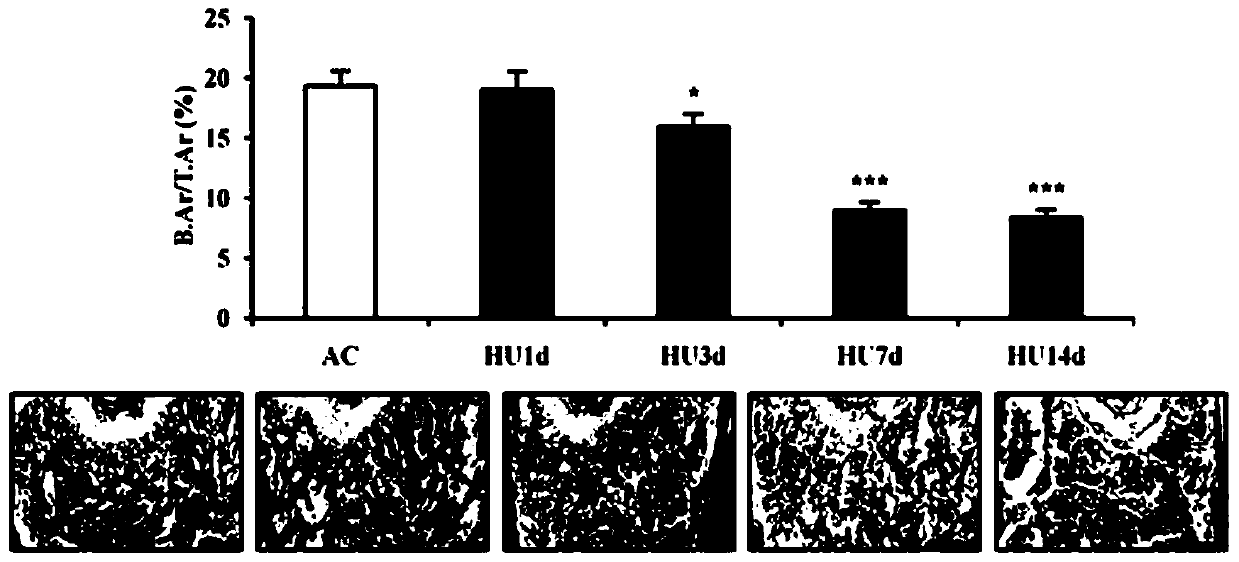
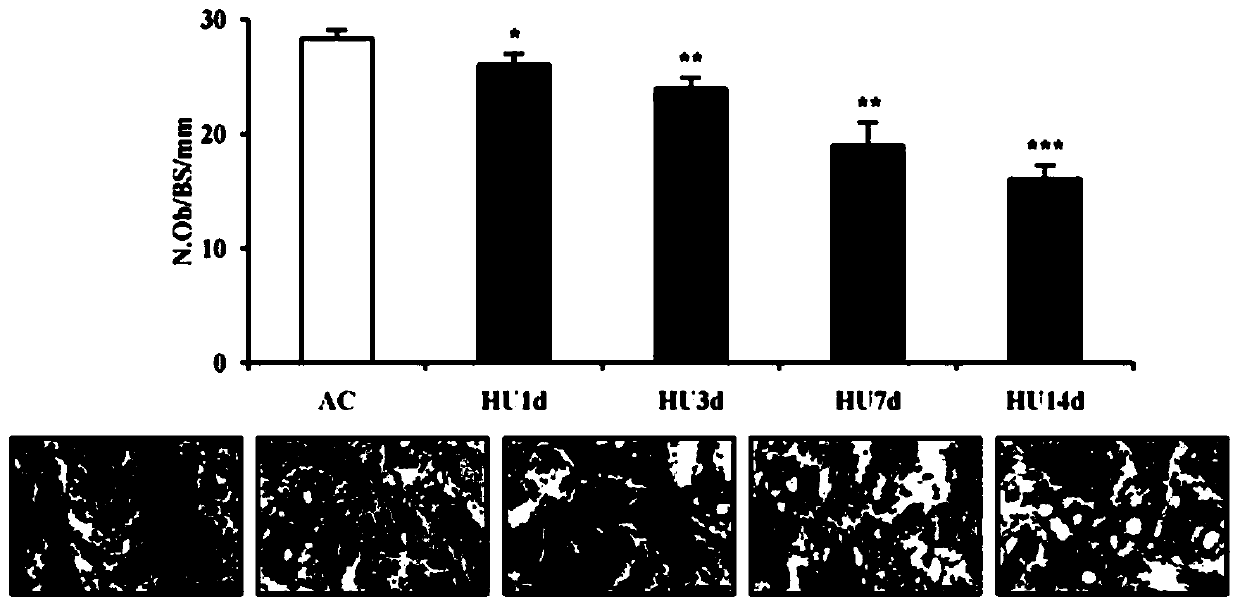
The invention discloses applications of a small molecular compound Salubrinal in drugs for treating or preventing osteoporosis and osteopenia diseases. Through the utilization of a mouse model of postmenopausal osteoporosis caused by OVX ovariectomy, a mouse model of disuse osteoporosis caused by tail suspension, in vivo and in vitro analysis of primary bone marrow-derived cells and the indicationof cell line-based experimental results, Salubrinal administration can effectively relieve OVX related symptoms, stimulate the differentiation of osteoblasts and inhibit the development of osteoclasts. Through the indication of precise molecular mechanism of the Salubrinal, the Salubrinal can be applied to drugs for treating or preventing osteopenia diseases caused by postmenopausal osteoporosis,disuse osteoporosis and other factors.
Owner:张平
Cell preserving fluid for in-vitro analysis and detection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113966737AReduce autolytic spoilageImprove integrityDead animal preservationAnticoagulant AgentIn vitro analysis
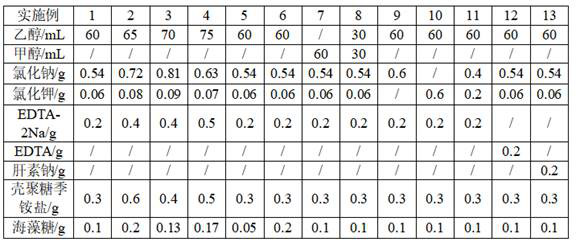
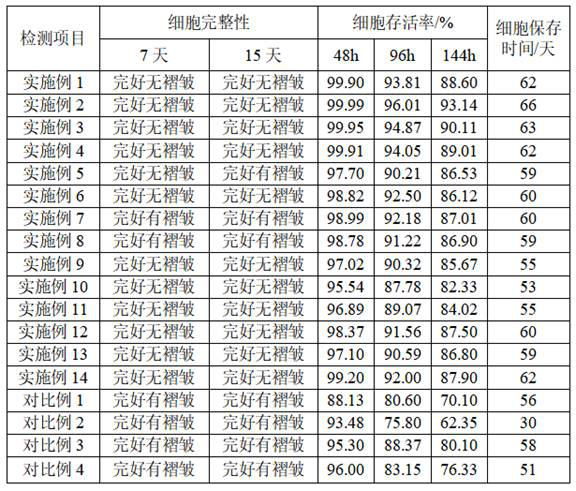
The invention relates to the technical field of biological preserving fluid, in particular to cell preserving fluid for in-vitro analysis and detection and a preparation method thereof. The cell preserving fluid is prepared from the following components in a concentration range: 60 to 75 v / v percent of a cell fixing agent, 0.6 to 0.9 g / 100 mL of an osmotic pressure regulator, 0.2 to 0.5 g / 100 mL of an anticoagulant, 0.3 to 0.6 g / 100 mL of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt and 0.05 to 0.2 g / 100 mL of trehalose; and the solvent is ultra-pure water, and the pH value is 7.0-7.6. A small amount of trehalose and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt are combined, so that the protective effect can be effectively enhanced, autolysis decay of cells is effectively reduced, and the integrity of cell preservation is improved. When the cell preserving fluid is prepared, ultra-pure water is used for dissolving components except the cell curing agent, the dissolving effect of the components can be effectively improved, the uniform and stable cell preserving fluid is obtained, and batch production of the cell preserving fluid is facilitated.
Owner:深圳市华晨阳科技有限公司
White spot syndrome virus gene VP28, recombinant protein, polyclonal antibody, preparation method and application
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering of molecular biology, relates to a nucleotide sequence of a procambarus clarkii white spot syndrome virus gene VP28, an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence and a codon-optimized nucleotide sequence and particularly relates to a preparation method for recombinant expression of a protein WSSVVP28 and preparation of a rabbitpolyclonal antibody. Through the recombinant-expressed protein WSSVVP28, a structure and functions of the protein can be further analyzed in vitro; and furthermore, due to the preparation of the polyclonal antibody, a foundation can be settled for further detecting the content of WSSV in procambarus clarkii bodies.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Application of quantum dot fluorescent probe to visual detection of Hg < 2 + > in cells and human blood
InactiveCN111303877ACorrection errorIncrease signal strengthMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFluoProbesMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum dot fluorescent probe fluorescence detection, and especially relates to an application of a quantum dot fluorescent probe in visual detection ofHg < 2 + > in cells and human blood. The quantum dot fluorescent probe comprises silicon dioxide microspheres and 10Ca / 6Tb: Bi2O2S nanocrystalline and aminated fluorescent carbon quantum dots, wherein the surface of the silicon dioxide microspheres is aminated and then is modified with a layer of 10Ca / 6Tb: Bi2O2S nanocrystal, and the outer layer of the 10Ca / 6Tb: Bi2O2S nanocrystal is further coated and modified with aminated fluorescent carbon quantum dots. The quantum dot fluorescent probe adopts SiO2 (at) 10Ca / 6Tb: SiO2 (at) 10Ca / 6Tb fluorescent probe, dual emission fluorescence can be realized, the quantum dot fluorescent probe can be used for a ratiometric fluorescence analysis method and does not depend on expensive instruments when being used for in-vitro analysis and can completelyperform quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis by naked eyes, can detect the fluorescence ratio intensity under two emission wavelengths or excitation wavelengths, can well correct errors causedby environment detection and improves the signal intensity.
Owner:杭州众道光电科技有限公司
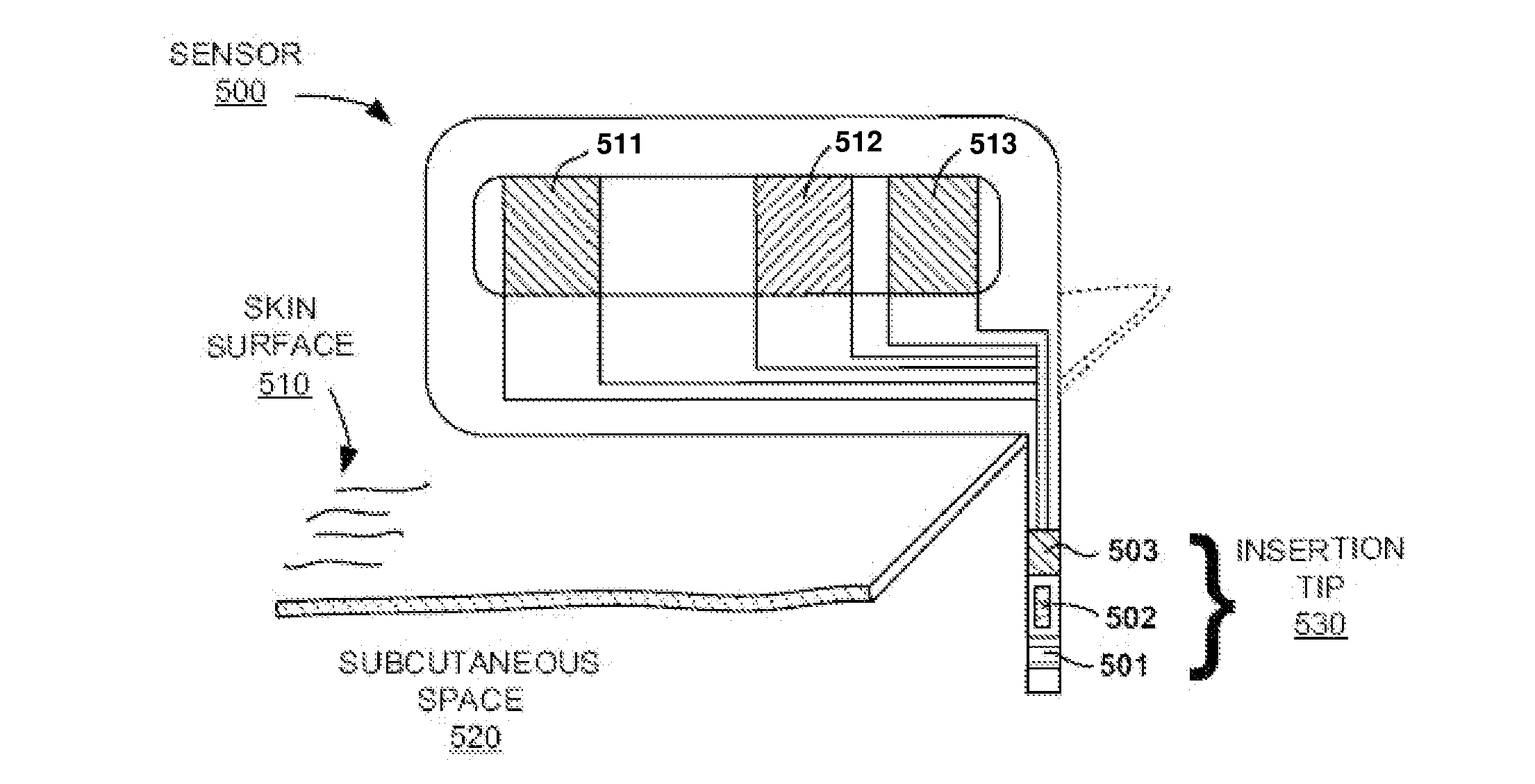
Analyte sensors with a sensing surface having small sensing spots
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to analyte determining methods and devices (e.g., electrochemical analyte monitoring systems) that have a sensing surface that includes two or more sensing elements disposed laterally to each other, where the sensing surface is on a working electrode of in vivo and / or in vitro analyte sensors, e.g., continuous and / or automatic in vivo monitoring using analyte sensors and / or test strips. Also provided are systems and methods of using the, for example electrochemical, analyte sensors in analyte monitoring.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Animal model for verifying acute virus hepatitis and establishment method of animal model
InactiveCN107384964AProve complex relationsImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsInsulin resistanceIndividual animal
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, and discloses an animal model for verifying acute virus hepatitis and an establishment method of the animal model. The establishment method comprises the following steps: randomly dividing 240 clean male rats which are 240-350g respectively into a normal control group and an acute virus hepatitis model group; performing cell culture; performing inoculation and modeling; performing RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) micro-array gene detection; performing expression experiment and analysis; and establishing an animal model for verifying acute virus hepatitis. The establishment method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being simple to operate and low in cost, a drug-resistant liver cancer HepG2 cell model is high in stability, high in autophagy activity and beneficial to in-vitro analysis, can be applied to early-stage diagnosis kits for drug resistance of liver cancer cells and can be used for screening medicines for improving autophagy activity of liver cancer, and thus the drug resistance states of the liver cancer cells can be effectively improved. Tests show that the drug-resistant liver cancer HepG2 cell model established by using the establishment method has insulin resistance longer than 96 hours.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
In vivo micro-invasive investigation device including a metal guide
The device has a microinvasive or micro-sampling investigating system comprising a flexible metallic guide with an end containing a series of pits. The pits are directly coupled to a specific reactive group of a substrate, where the end is perforated. Another end of the metallic guide is used to maneuver the metallic guide and associated with an aspiration system. A removable protection system e.g. flexible catheter, is arranged at the former end of the metallic guide. An independent claim is also included for a method for detecting ex vivo of a substrate present in a tissue or organ.
Owner:BIOSTEMS LTD
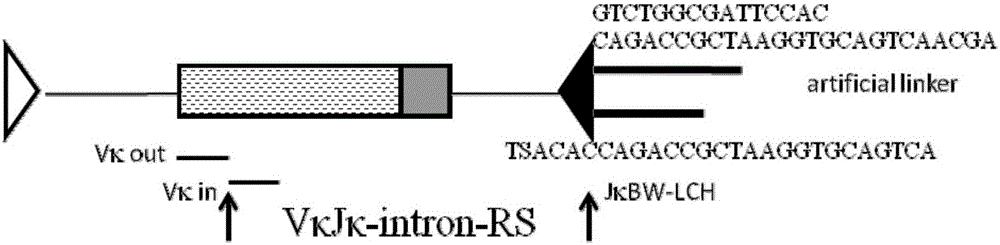
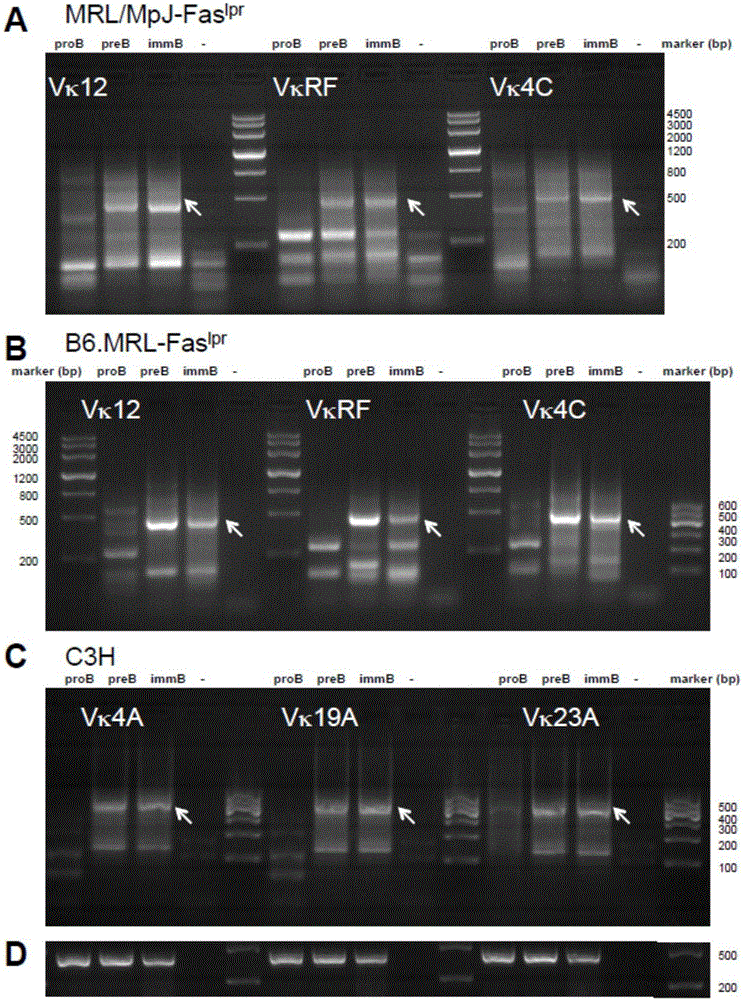
Method for analyzing intermediate product of secondary rearrangement of Igk gene and kit
InactiveCN106191262AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vitro analysisIntron
The invention relates to a method for analyzing an intermediate product of secondary rearrangement of an Igk gene and a kit. The kit consists of an artificially designed oligodeoxynucleotide linker, 6 pairs of upstream primers and a downstream primer; a first rearrangement fragment VkJk-intron-RS which is replaced in the secondary rearrangement of the Igk gene is captured and amplified by using a ligation mediated-PCR (lm-pcr) technology. The kit disclosed by the invention can be applied to in vitro analysis of the generation efficiency of the secondary rearrangement of the Igk gene and research on a molecular mechanism which generates the secondary rearrangement of the Igk gene.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
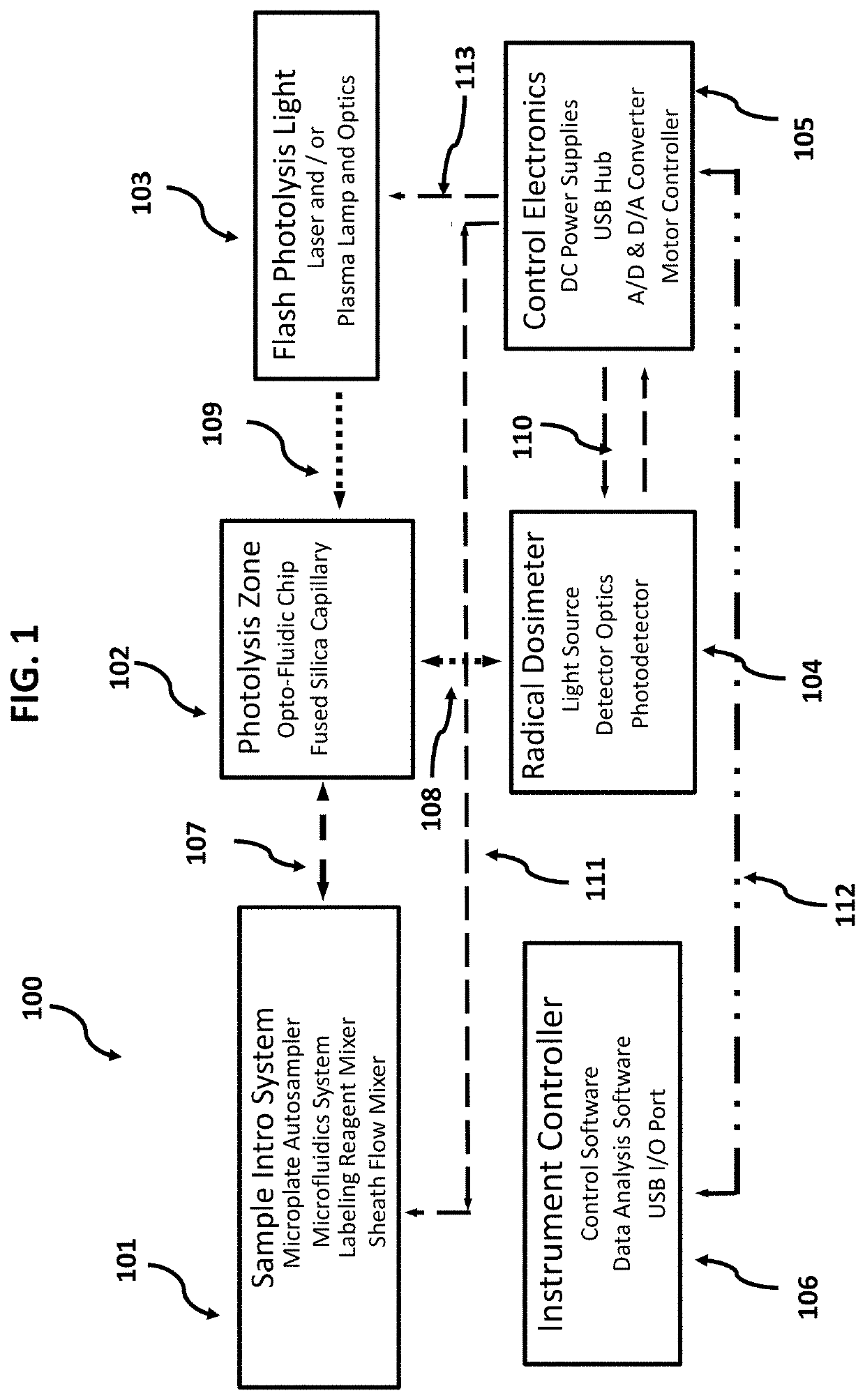
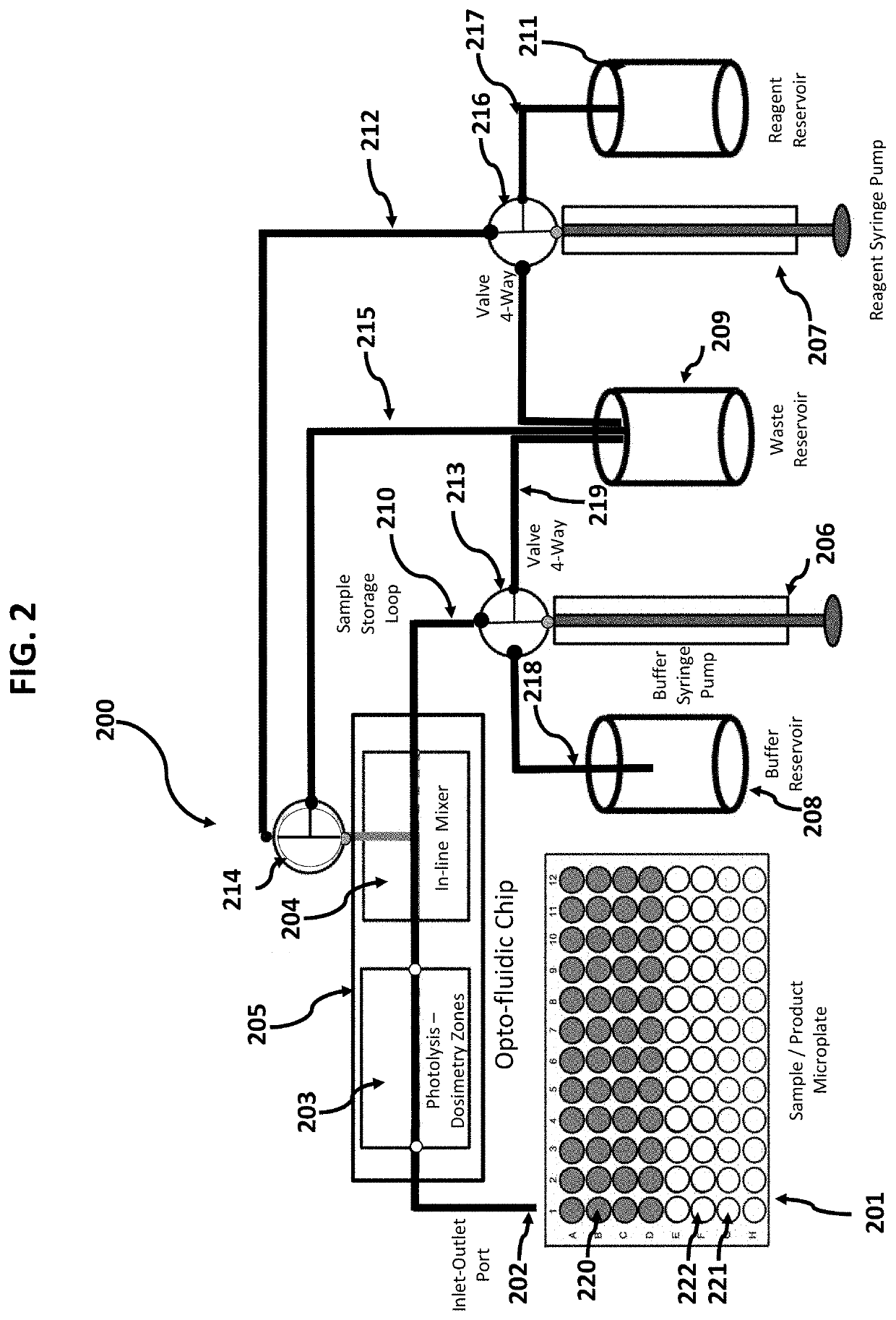
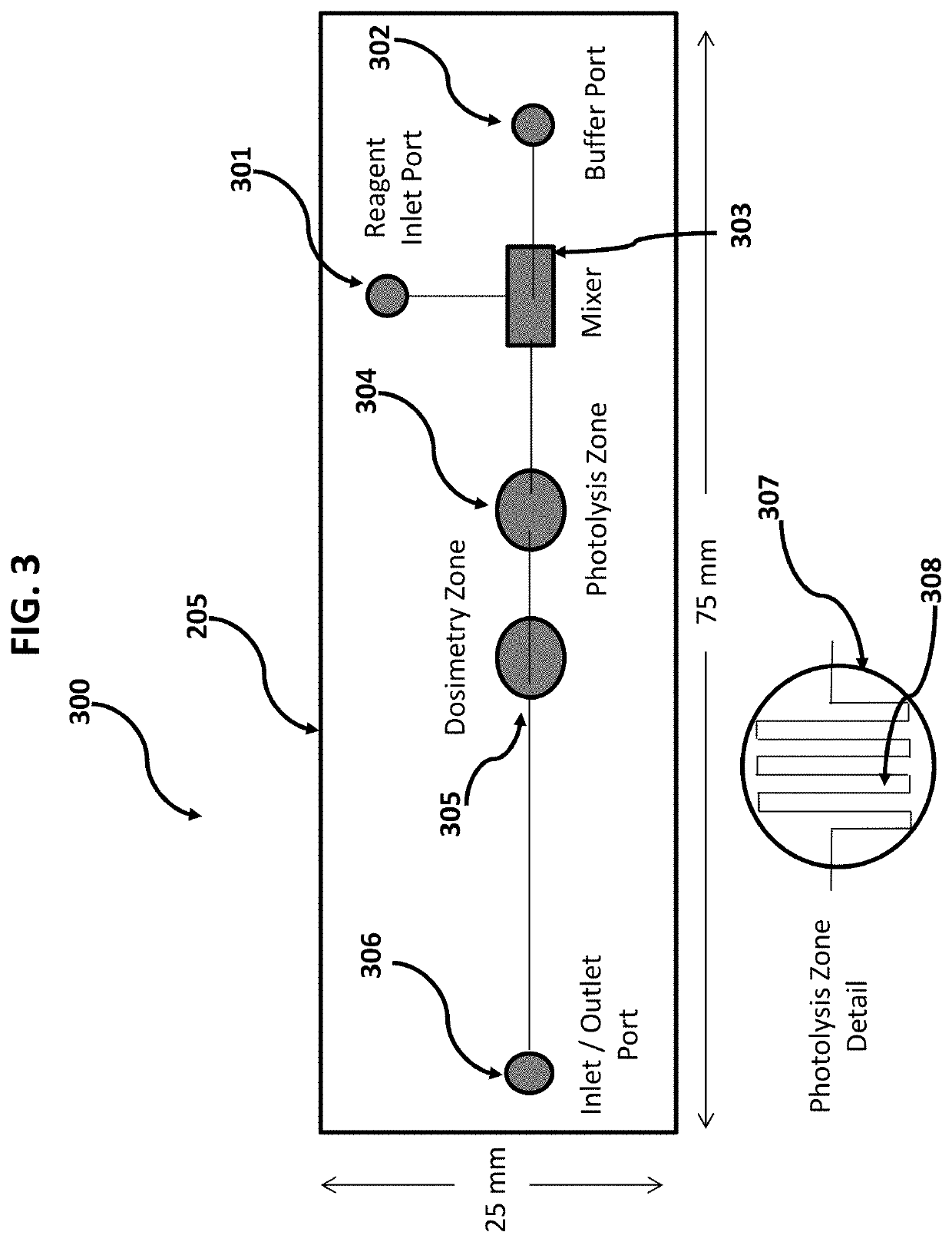
Opto-Fluidic Array for Radical Protein Foot-Printing
PendingUS20220080418A1Increase heightEasy to controlLaboratory glasswaresFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn vitro analysisProtein structure
Systems and methods of in vivo and in vitro radical protein foot-printing using an opto-fluidic array are presented. These teachings may be used to, for example, study three-dimensional protein structure or bio-kinetics. Radical dosimetry including an optional intrinsic standard is used. Real-time feedback based on an internal standard provides comparability between different experiments and in vivo and in vitro analysis results in data that is representative of actual biological conditions.
Owner:GENNEXT TECH INC
Interdigitated electrodes for in vitro analysis of cells
ActiveUS20190162688A1Reduce undesired background noiseHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vitro analysisSensing applications
Described are interdigitated electrodes, which may optionally be plasmonic, useful for in vitro biosensing applications. Such devices may significantly reduce undesired background noise by separating the excitation source (light) from the detection signal (current), and thereby, leading to higher sensitivity for bioanalysis compared with conventional interdigitated electrodes. Also described are methods of making such interdigitated electrodes, which allow a substrate, which may optionally be plasmonic, to be tuned not only to maximize the targeted interaction of the cells with the nanoscale geometry, but also for the excitation wavelength to minimize biological sample interference.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Analyte Sensors Comprising High-Boiling Point Solvents
ActiveUS20130189421A1Improve distribution uniformityPeptide/protein ingredientsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIn vitro analysisElectrochemistry
Generally, embodiments of the present disclosure relate to analyte determining methods and devices (e.g., electrochemical analyte monitoring systems) that have improved uniformity of distribution of the sensing layer by inclusion of a high-boiling point solvent, where the sensing layer is disposed proximate to a working electrode of in vivo and / or in vitro analyte sensors, e.g., continuous and / or automatic in vivo monitoring using analyte sensors and / or test strips. Also provided are systems and methods of using the, for example electrochemical, analyte sensors in analyte monitoring.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods and systems for in-vitro analysis of biological cells and/or microorganisms
ActiveUS8552383B2Avoid disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological cellMicroorganism
Methods for in-vitro analysis of biological cells and / or microorganisms to determine characteristics such as: degree of differentiation, cell type, donor individuals, culture conditions, purity, lack of natural characteristic, or additional characteristics in comparison to natural characteristics. The methods include the steps of: (a) projecting infrared radiation on a sample; (b) recording spectral characteristics of the sample; (c) deriving a Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FT-IR) from the collected spectral characteristics; (d) generating a derivative transformation of the FT-IR spectrum; (e) comparing said derivative transformation with a derivative of a reference FT-IR spectrum; (f) identifying deviations of said derivative from said reference derivative; and (g) providing an analysis of said characteristics based on the presence of said deviations. In addition, the invention relates to an apparatus for carrying out the disclosed methods.
Owner:TETEC TISSUE ENG TECH
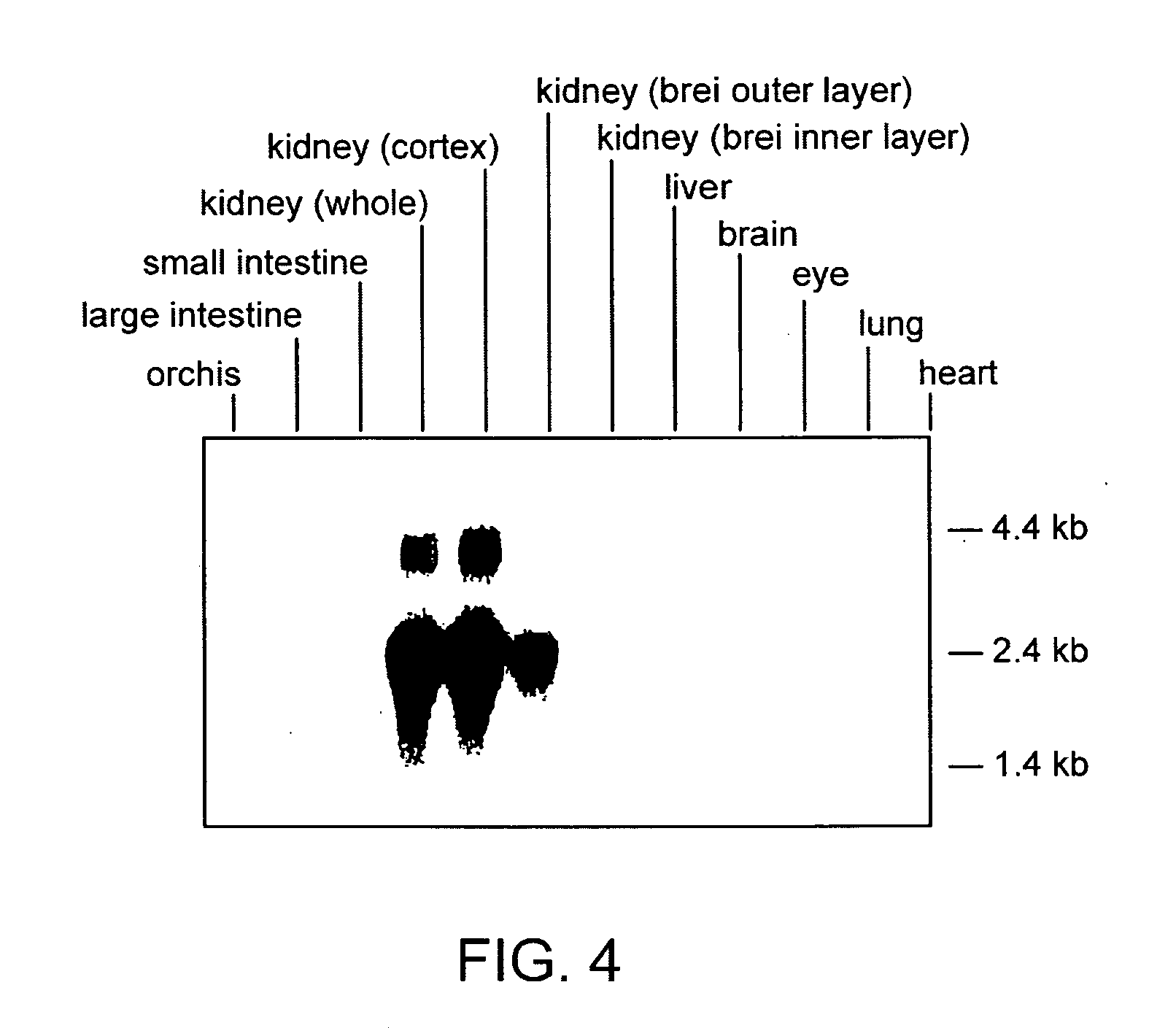
Organic anion transporter and gene coding for the same
InactiveUS20060057677A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesDrug-drug interactionIn vitro analysis
A protein capable of transporting organic anions having amino acid sequences represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2 or amino acid sequences derived therefrom by deletion, substitution or addition of one or more amino acid residues; and a gene coding for the protein. The protein and gene therefor are useful in vitro analysis of drug release and drug-drug interactions and development of methods for screening drugs useful for preventing nephrotoxicity.
Owner:FUJI BIOMEDIX
Positioning base, dark chamber and in vitro detection and analysis device using the dark chamber
ActiveCN104713863BReduce volumeStable positionMachine supportsCo-operative working arrangementsIn vitro analysisEngineering
The invention relates to a positioning base used for accommodating and positioning a detection card in an in vitro detection and analysis device. The positioning base includes a first positioning mechanism and a second positioning mechanism. An open positioning groove is opened on the upper surface of the positioning base. The positioning groove forms an opening on the side of the positioning base for inserting the detection card. The positioning groove includes an inner bottom surface and a pair of inner side surfaces. A first receiving groove is opened on the inner bottom surface to accommodate the first positioning mechanism. A second accommodating groove is opened on one of the inner surfaces for accommodating the second positioning mechanism. The first positioning mechanism and the second positioning mechanism are used to jointly position the inserted detection card. The invention also relates to a dark chamber using the positioning base and an in vitro detection and analysis device using the dark chamber.
Owner:JIANGSU LIANGDIAN TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com