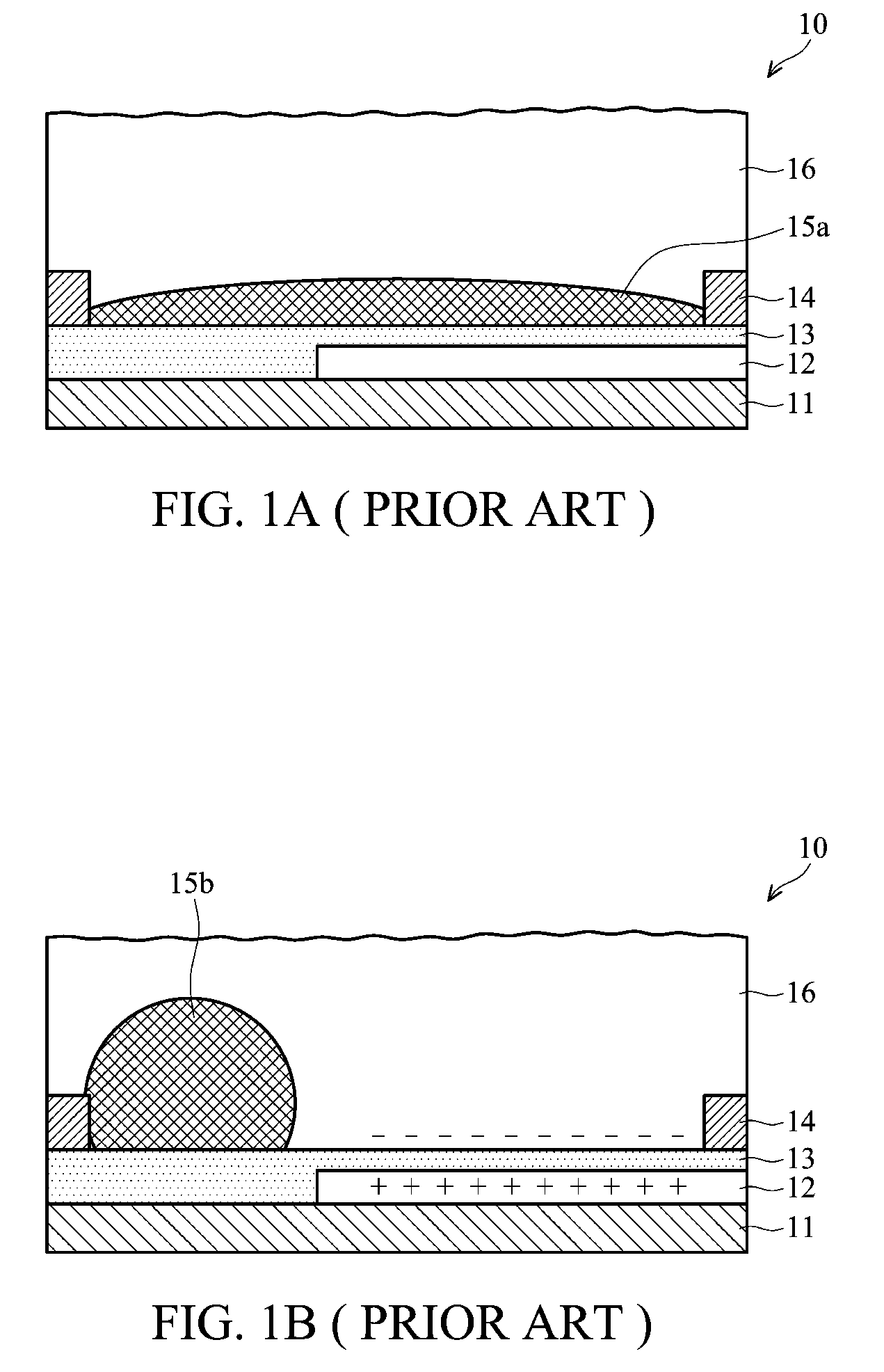
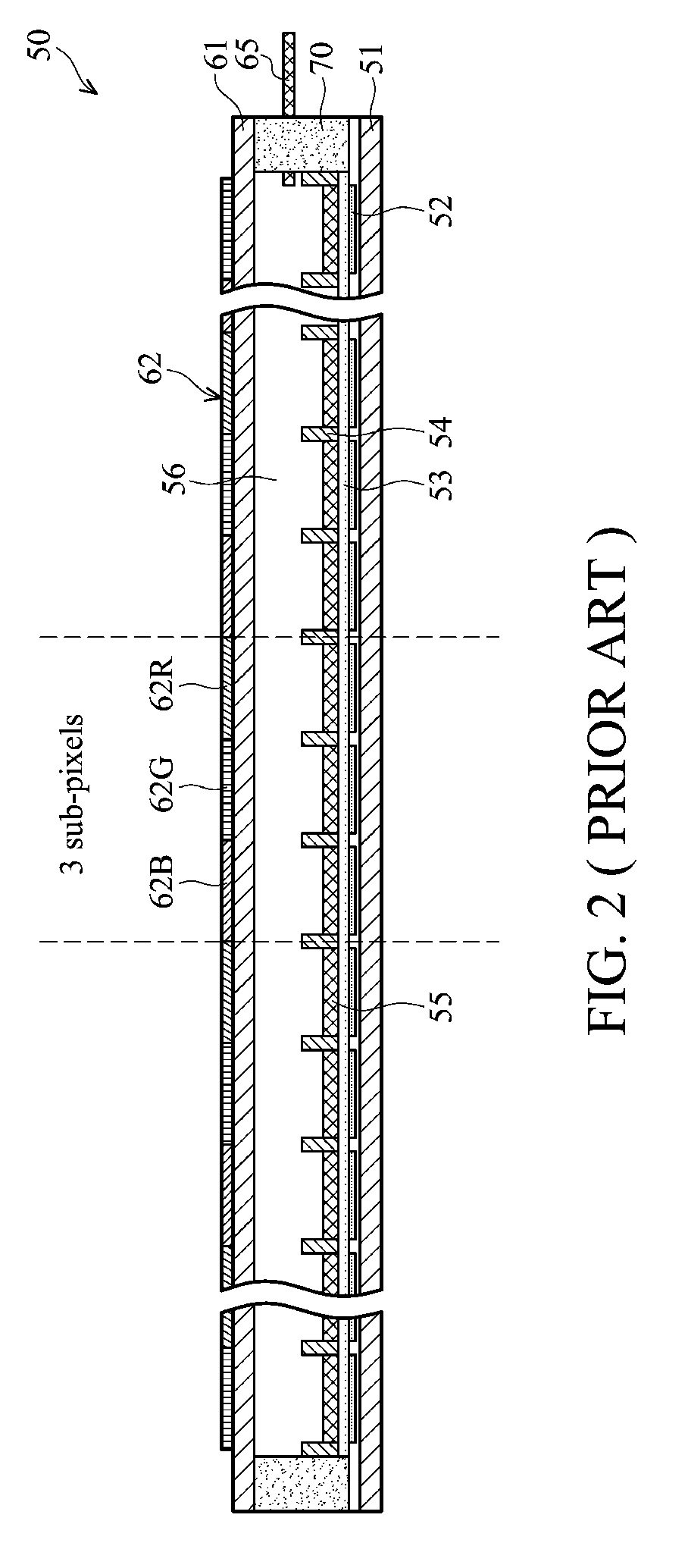
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
317 results about "Fluid layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
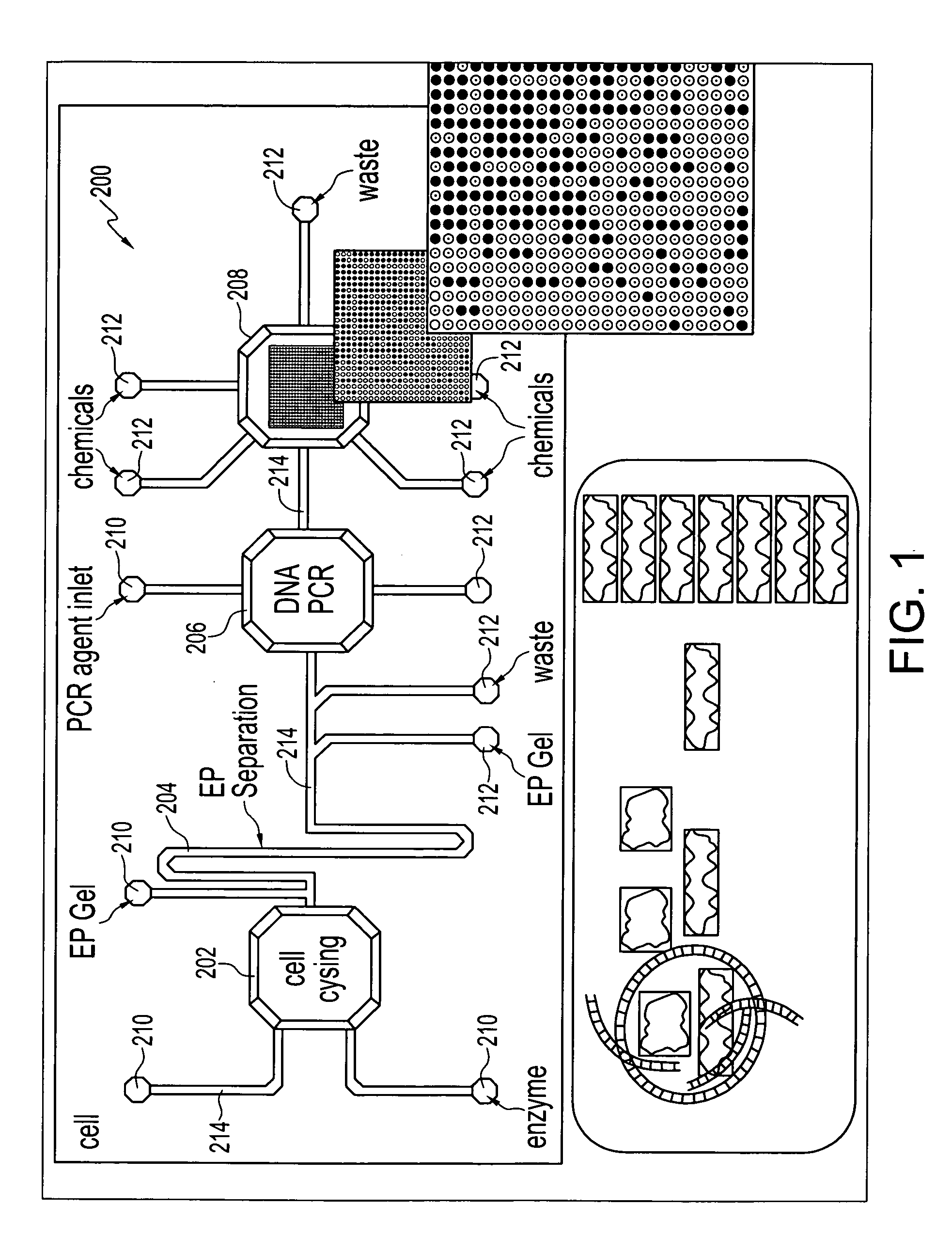
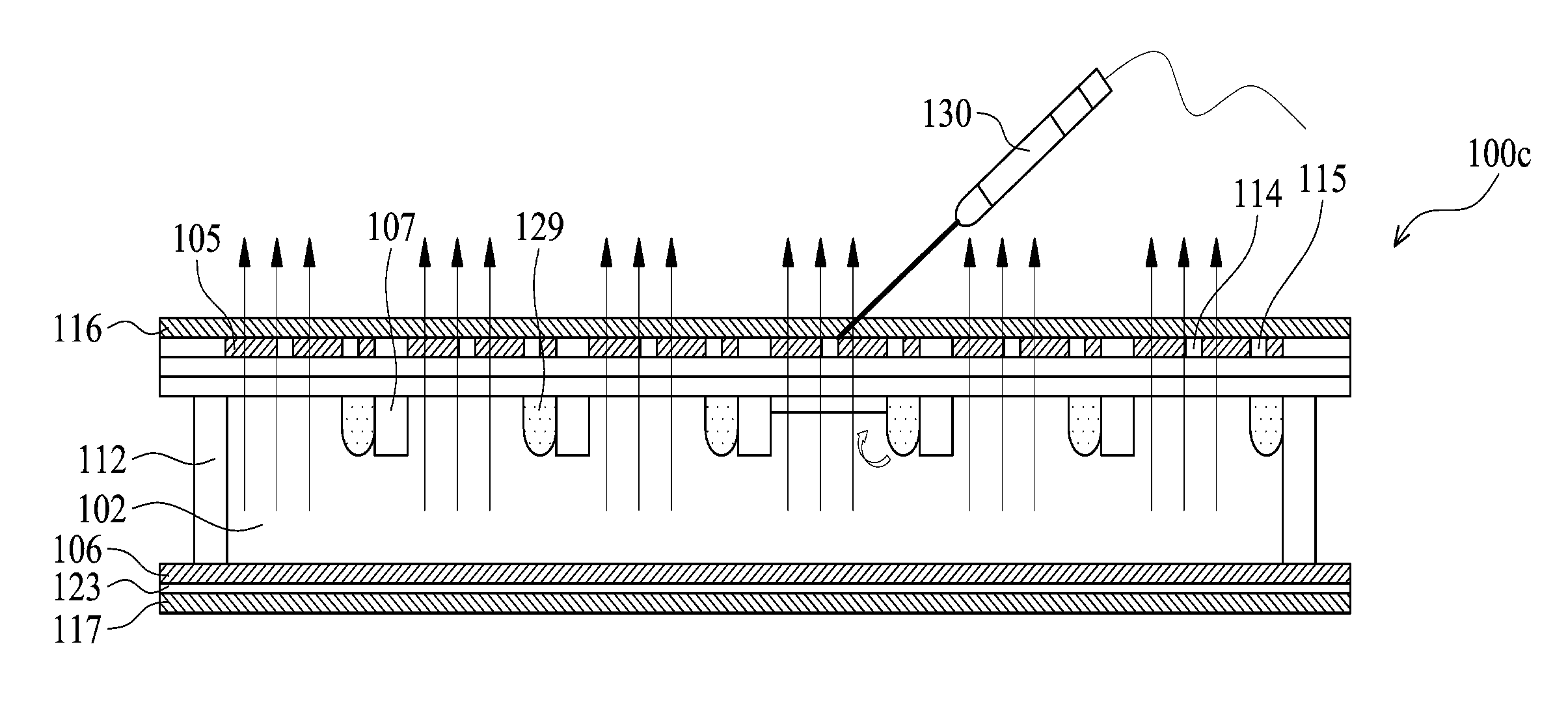
Instrument with microfluidic chip
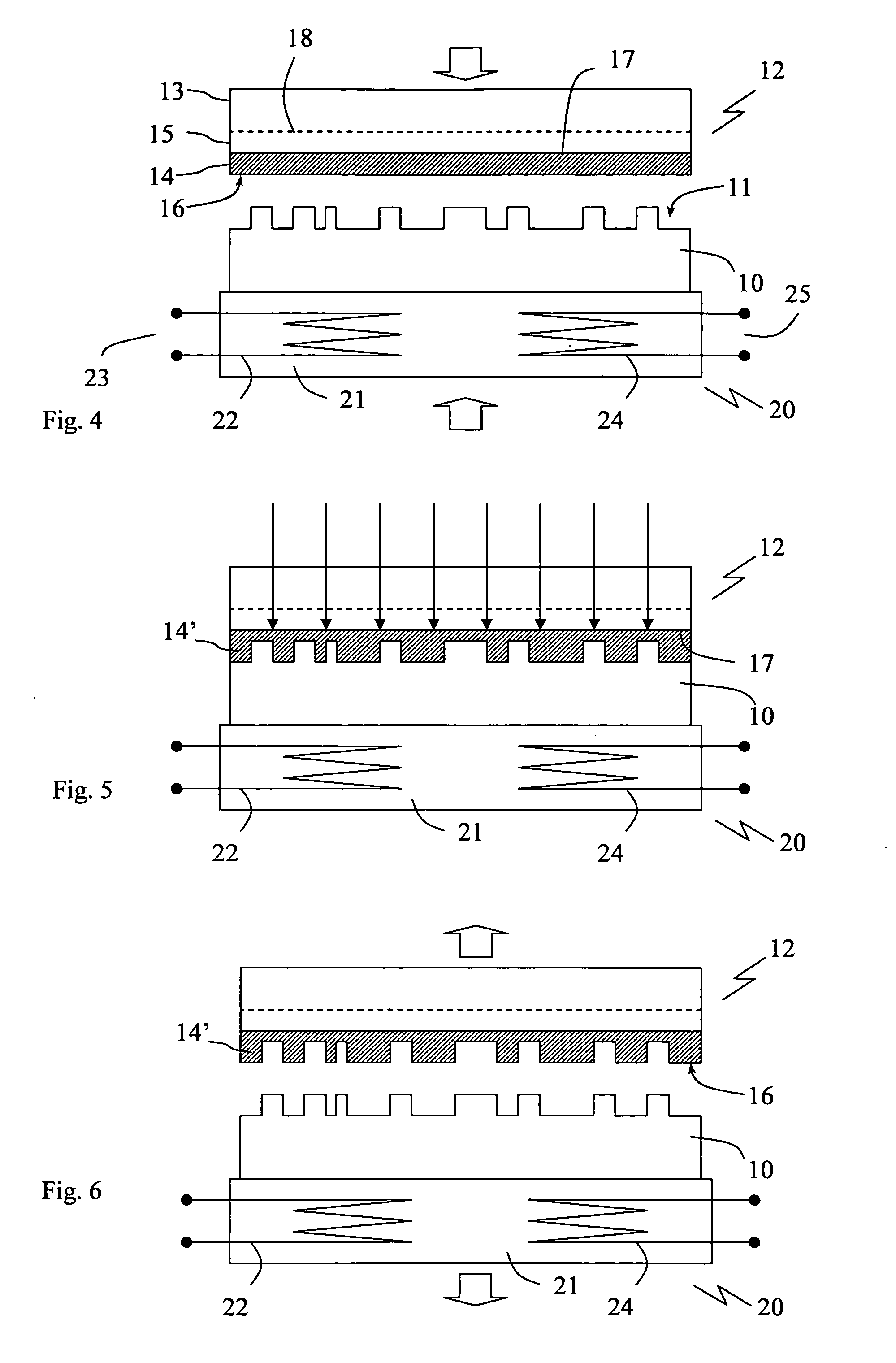
ActiveUS20100165784A1Well mixedShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow mixersFluidicsDiaphragm valve
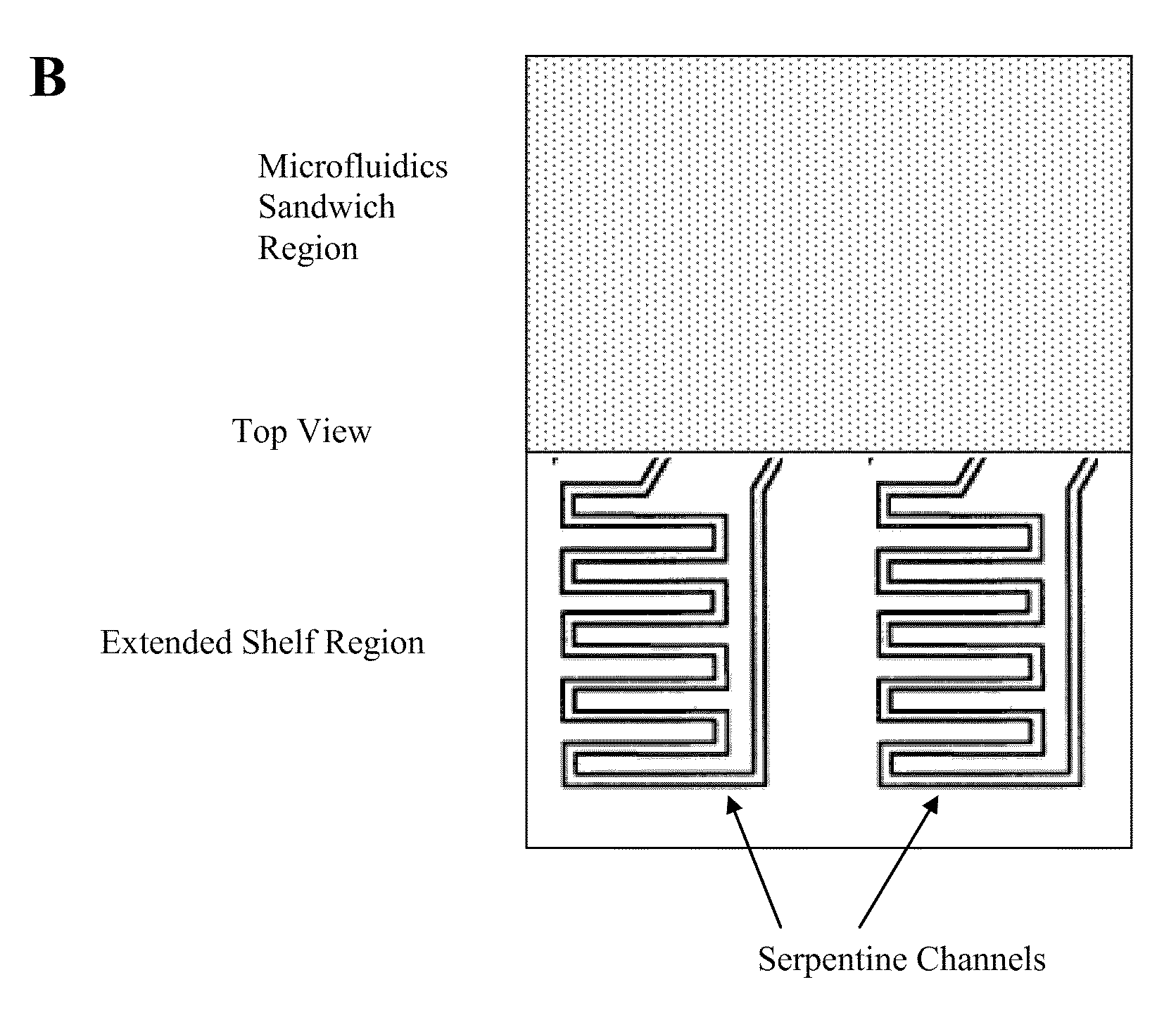
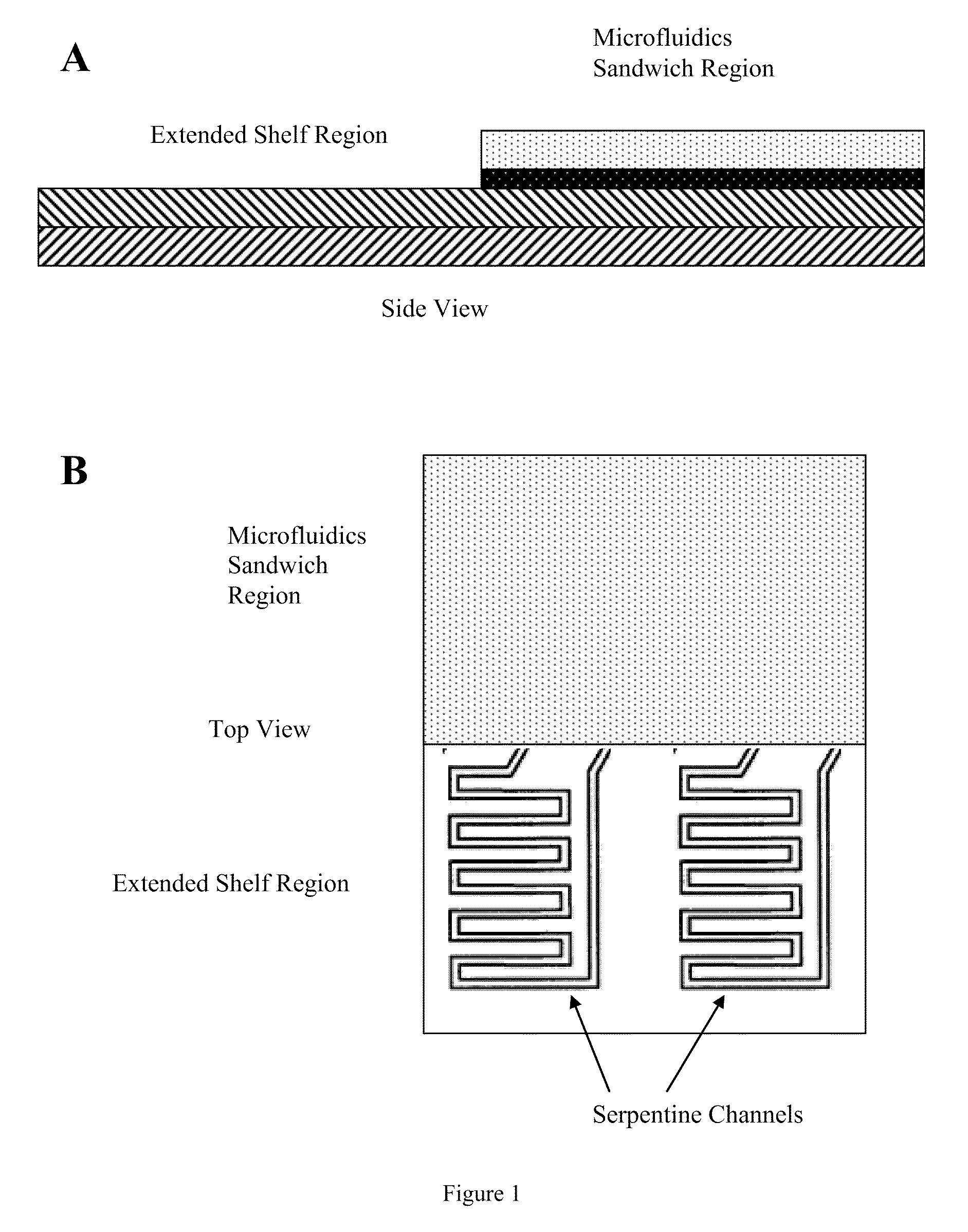
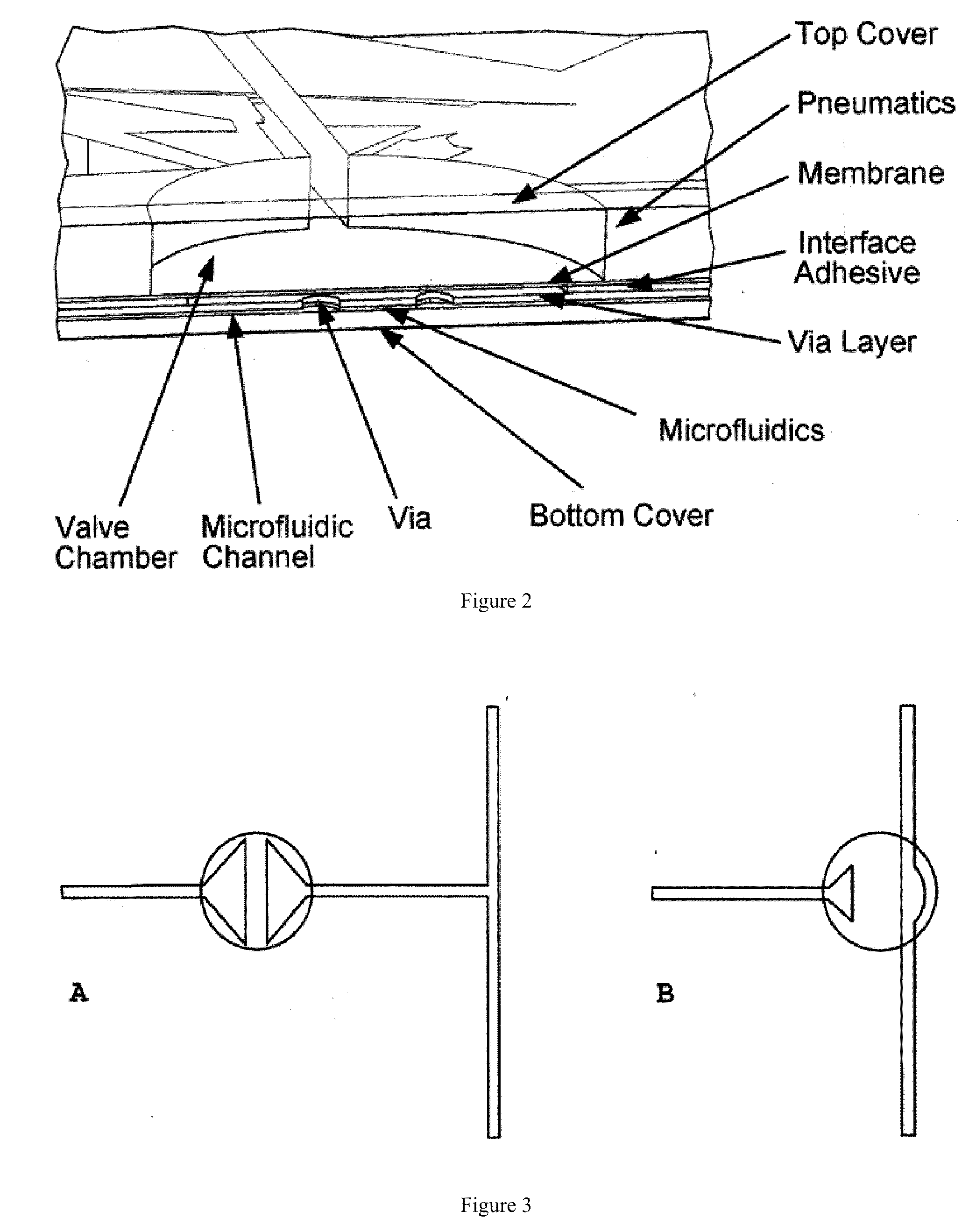
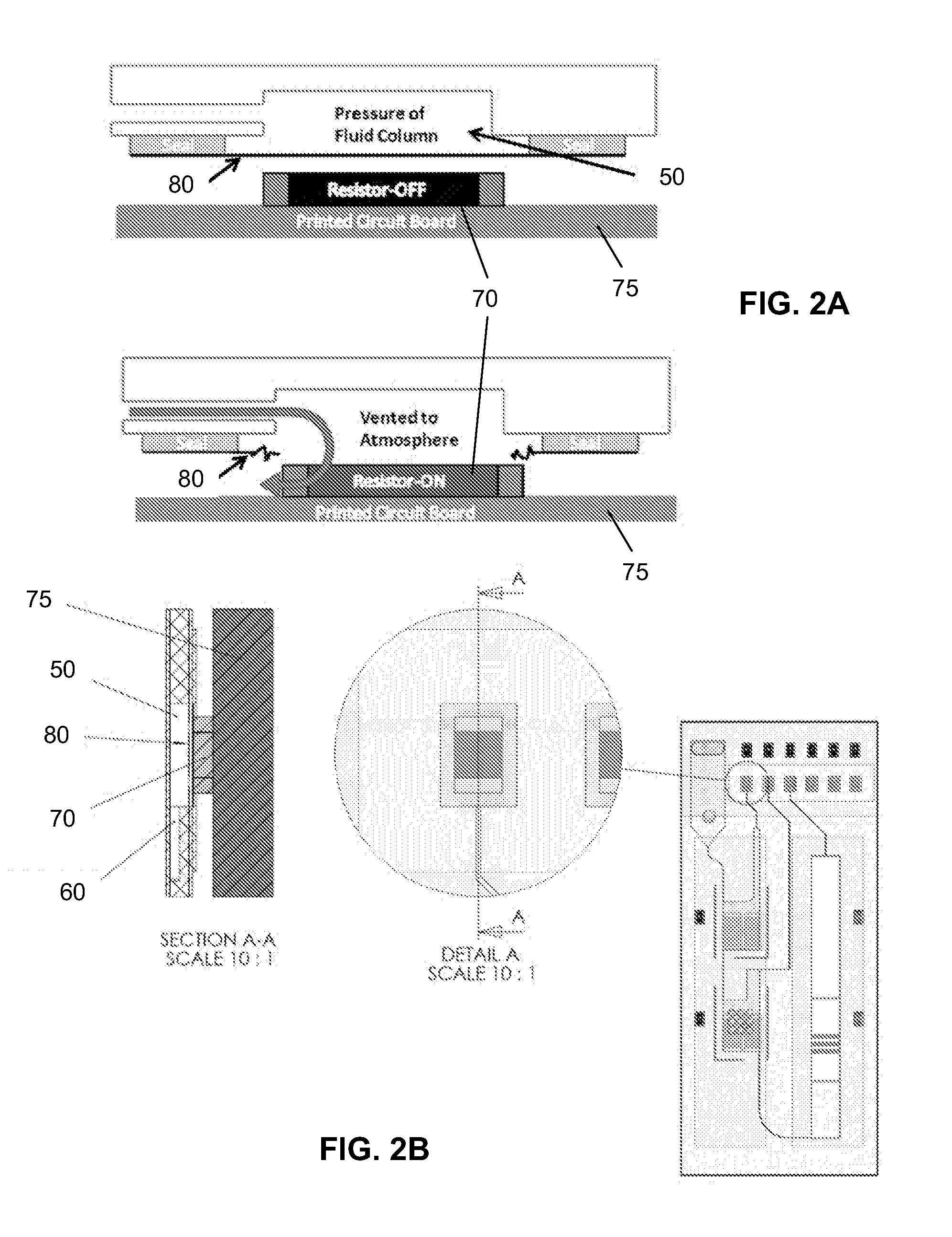
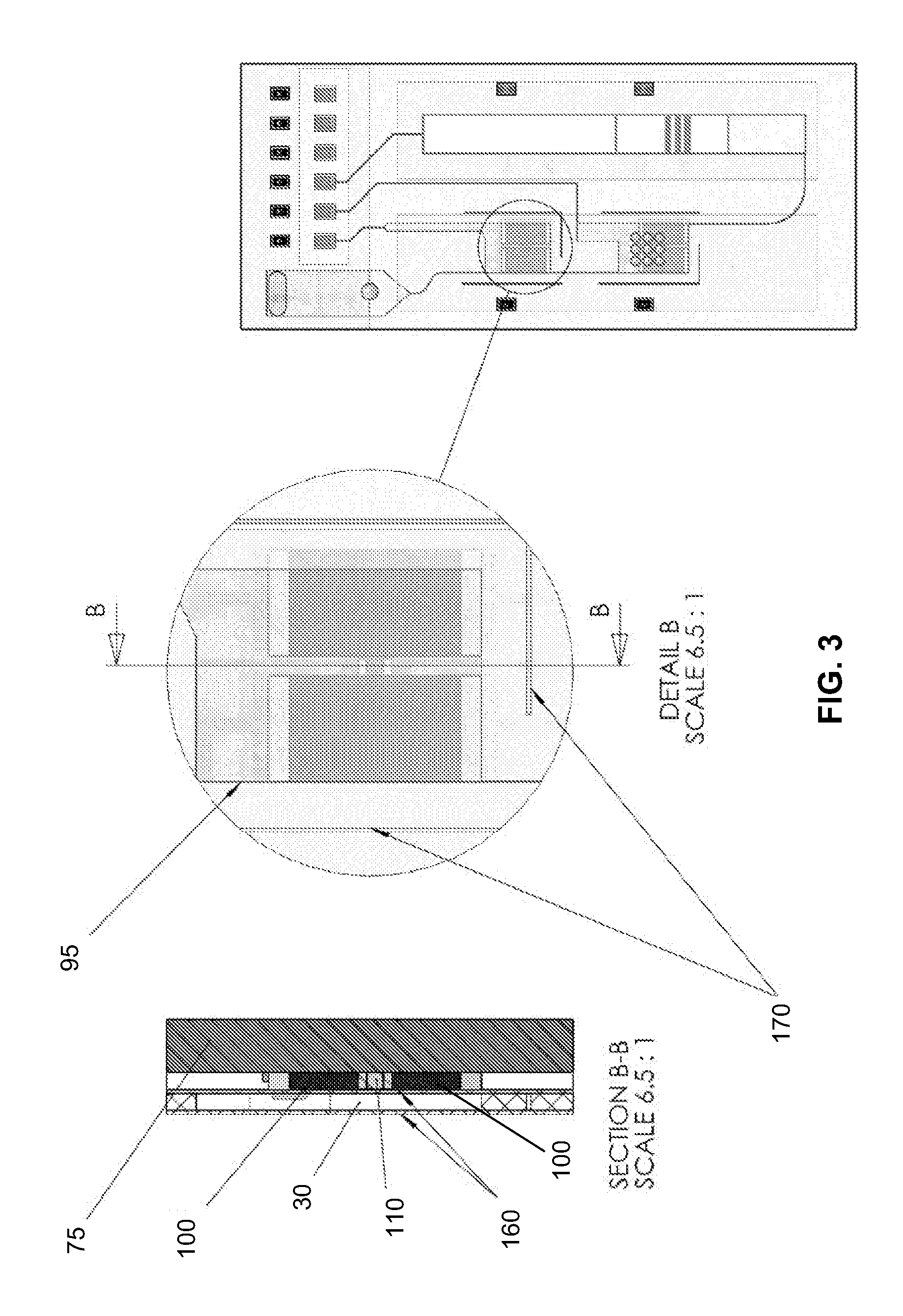
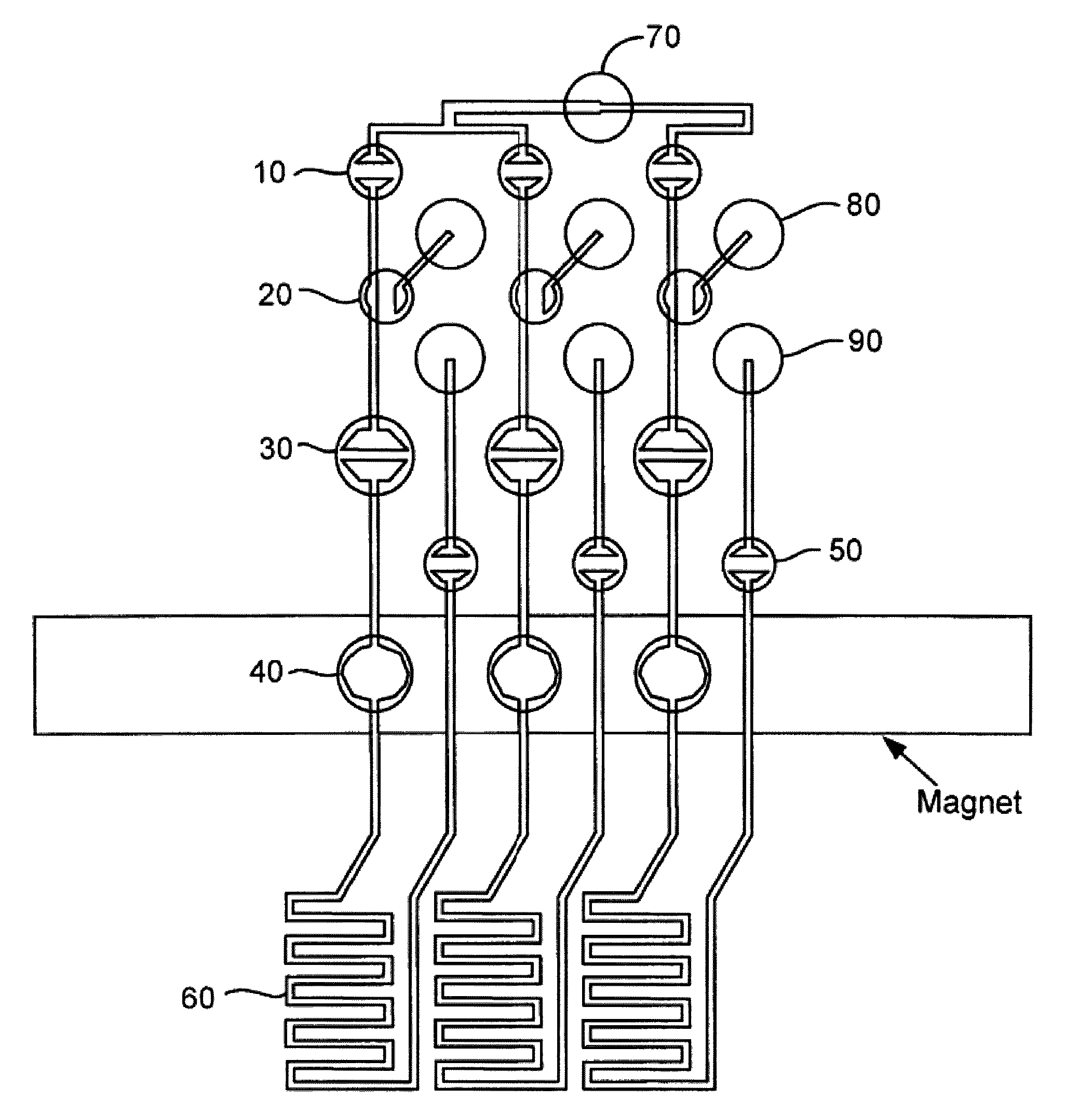
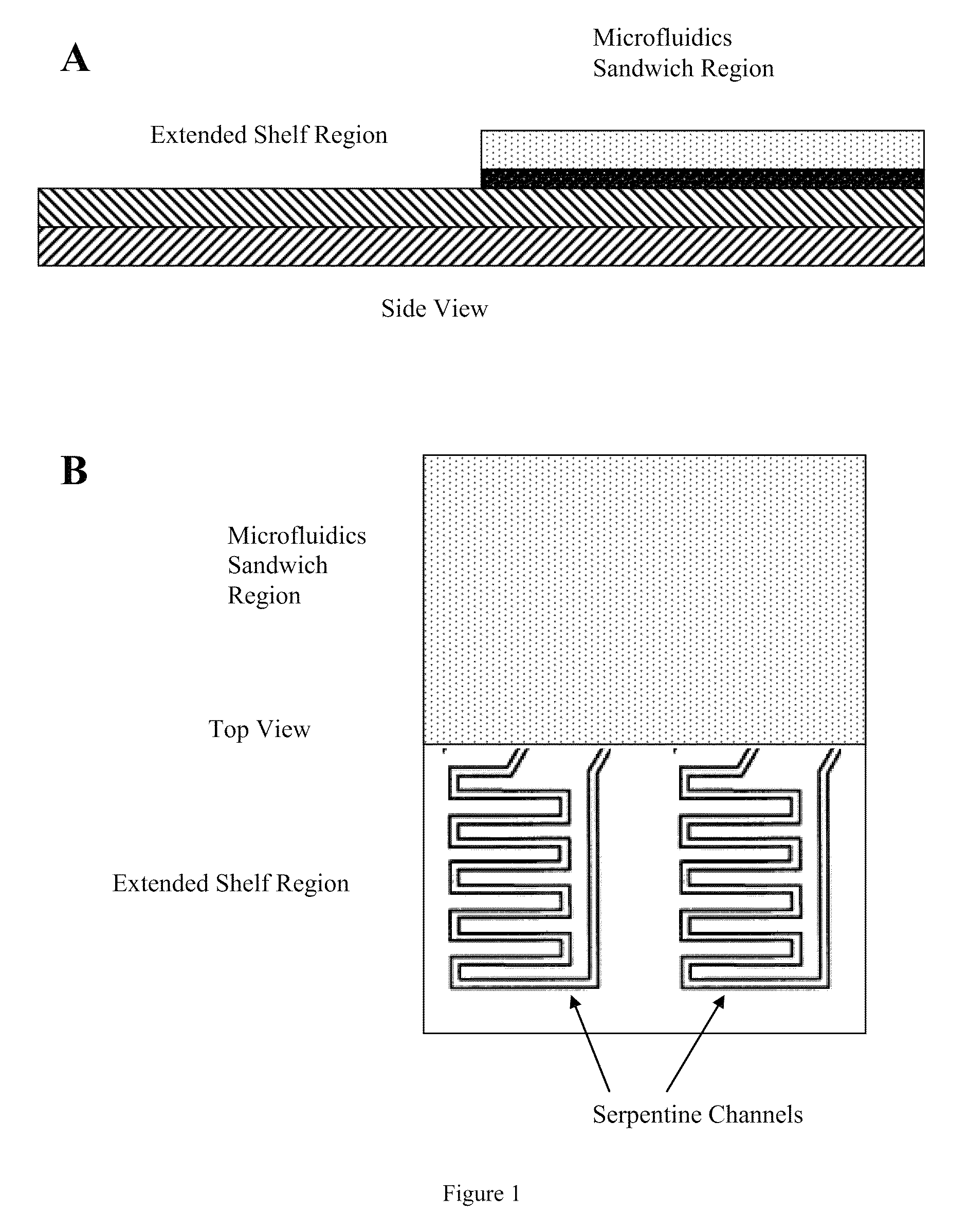
This invention provides microfluidic devices that comprise a fluidics layer having microfluidic channels and one or more regulating layers that regulate the movement of fluid in the channels. The microfluidic devices can be used to mix one or more fluids. At least a portion of the fluidics layer can be isolated from the regulating layer, for example in the form of a shelf. Such isolated portions can be used as areas in which the temperature of liquids is controlled. Also provided are instruments including thermal control devices into which the microfluidic device is engaged so that the thermal control device controls temperature in the isolated portion, and a movable magnetic assembly including magnets with shields so that a focused magnetic field can be applied to or withdrawn from the isolated portion or any other portion of the microfluidic device. Also provided are methods of mixing fluids. The methods include stacking a plurality of alternating boluses of different liquids in a microfluidic channel, and moving the stacked boluses through the channel. In another method, the boluses are moved into a diaphragm valve having a volume able to accommodate several boluses, and then pumping the liquids out of the valve.
Owner:INTEGENX
Microfluidic systems and components
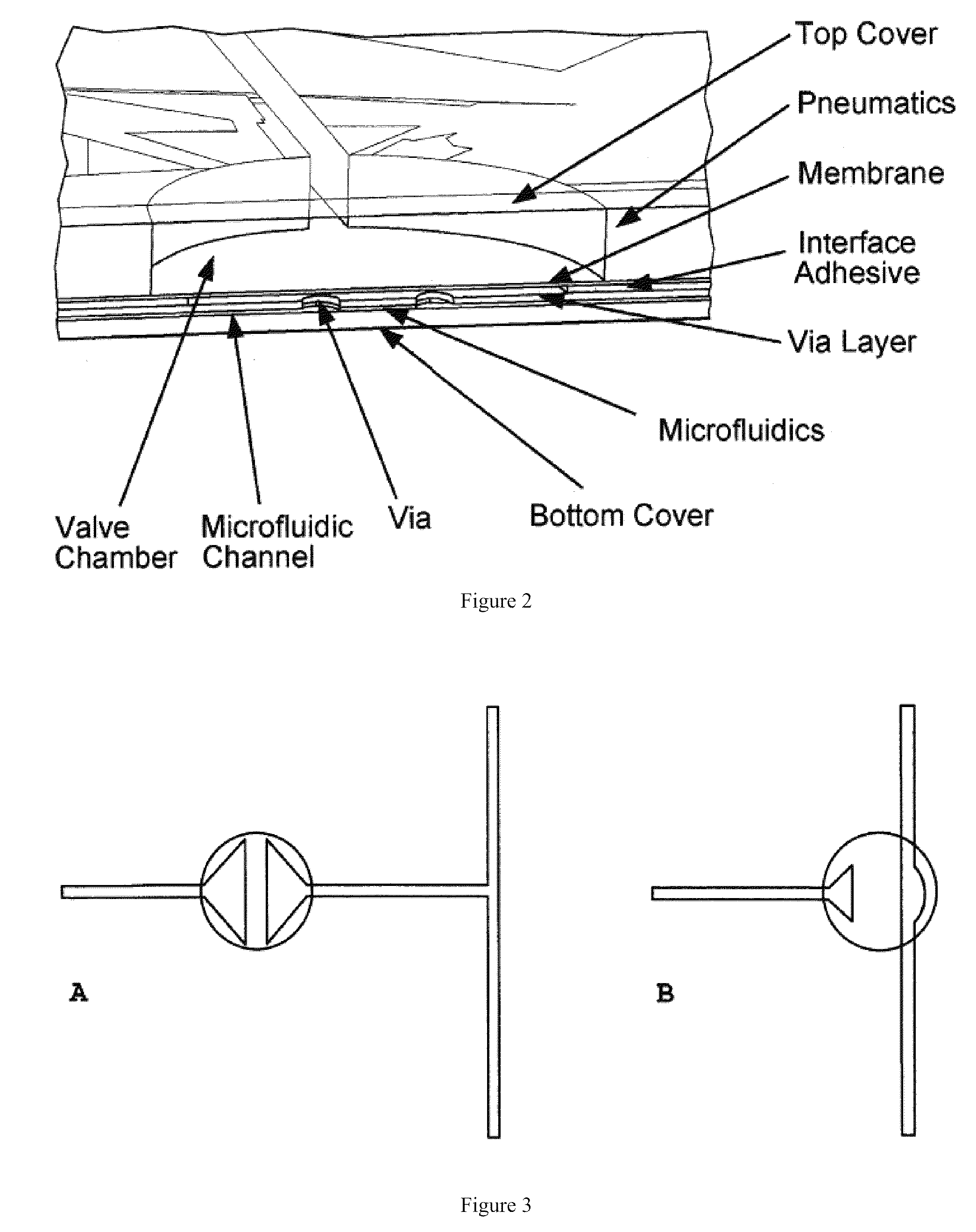
Microfluidic systems and components. A microfluidic system includes one or more functional units or microfluidic chips, configured to perform constituent steps in a process and interconnected to form the system. A multi-layer microfluidic system includes a separate dedicated fluid layer and dedicated electromechanical layer connected via through-holes. Electromechanical components are formed on the electromechanical layer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
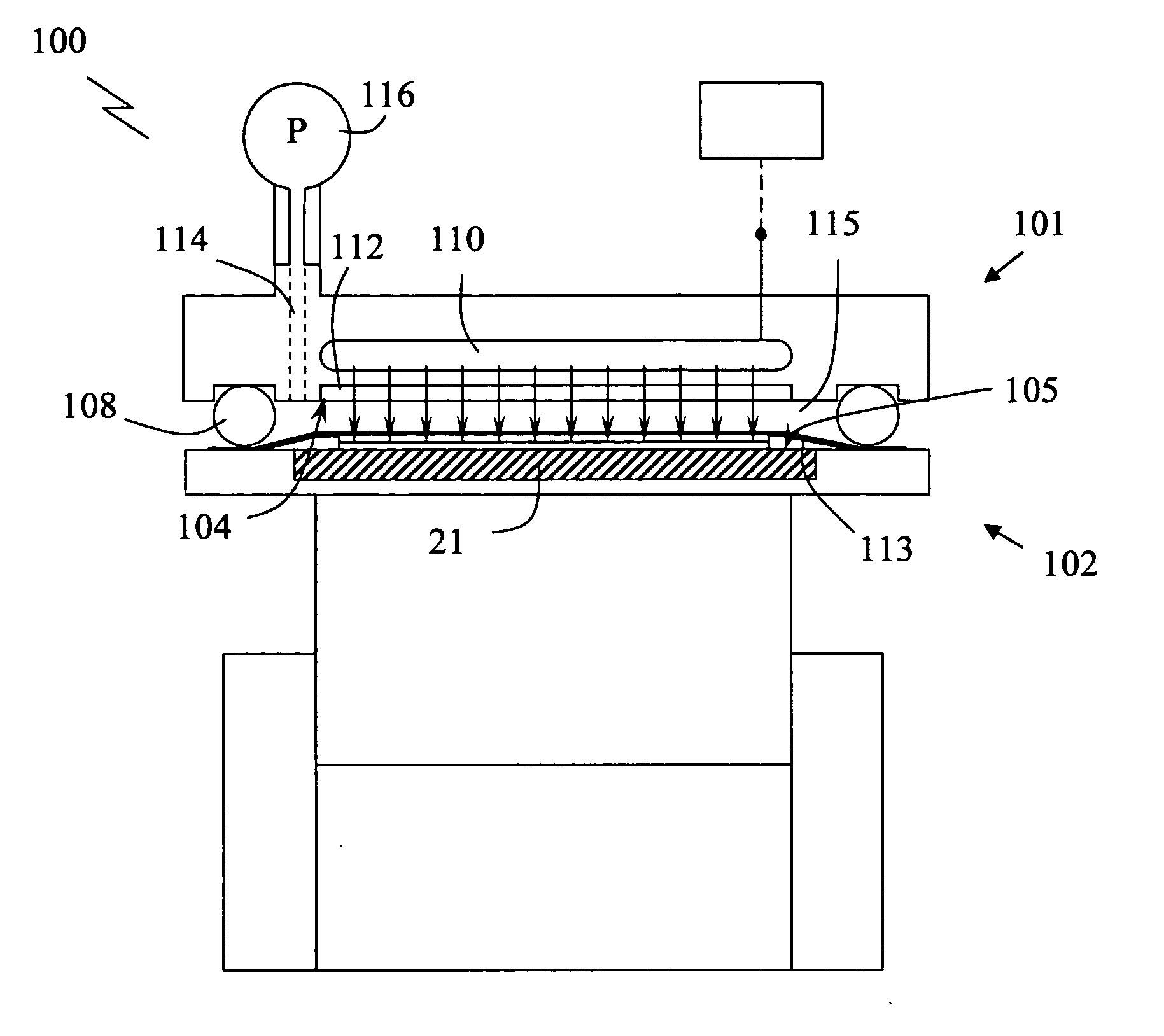
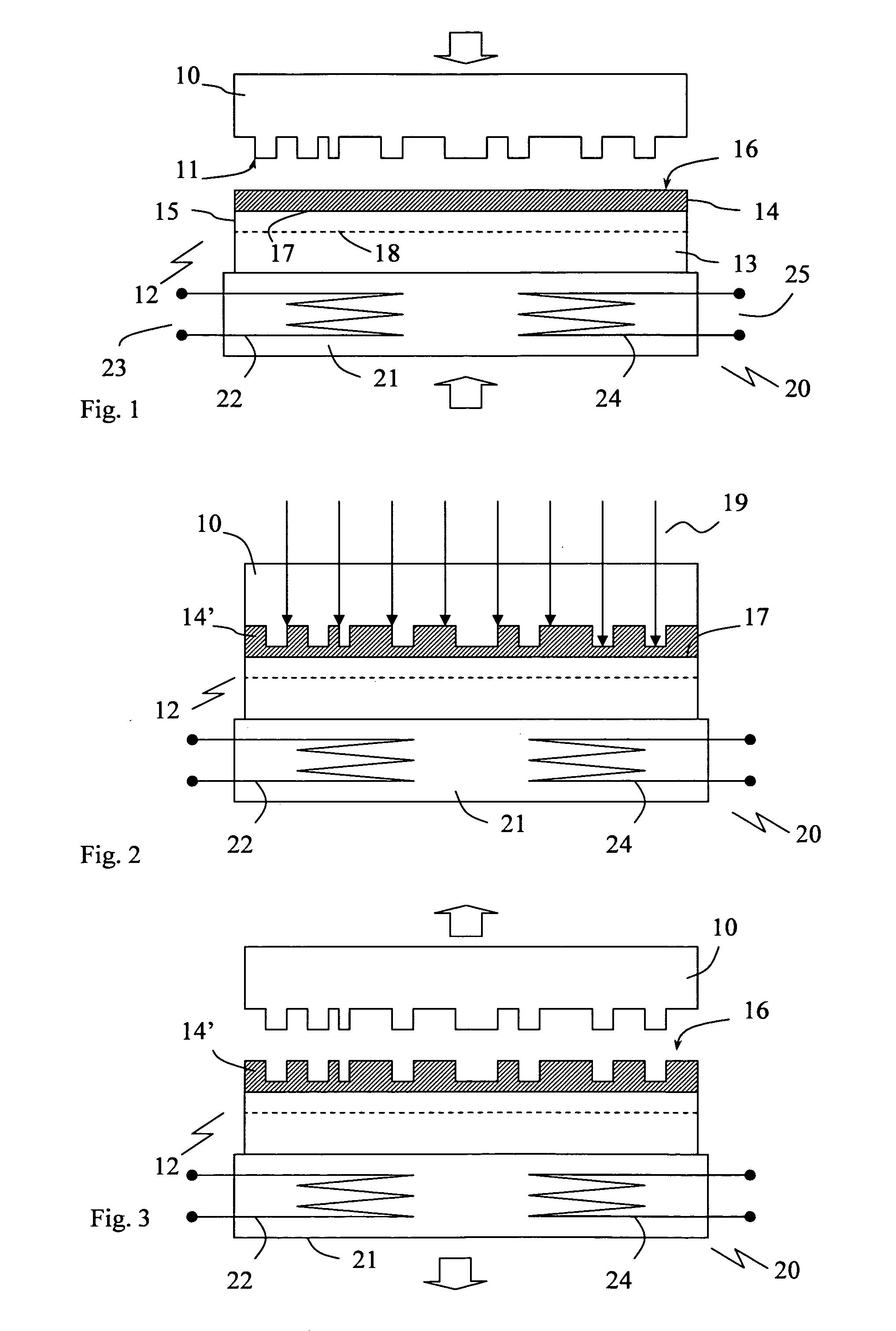
Device and method for lithography
InactiveUS20050274693A1Cost-effective and more versatileAdded fabricationDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsSurface layerFluid layer
Apparatus and method for transferring a pattern from a template (10) having a structured surface to a substrate (12) carrying a surface layer of a radiation polymerisable fluid (14). The apparatus comprises a first main part (101) and a second main part (102) having opposing surfaces (104;105), means for adjusting a spacing (115) between said main parts, support means (106) for supporting said template and substrate in mutual parallel engagement in said spacing with said structured surface facing said surface layer, a radiation source (110) devised to emit radiation into said spacing. A cavity (115) has a first wall comprising a flexible membrane (113) devised to engage said template or substrate, and means (114;116) are provided for applying an adjustable overpressure to a medium present in said cavity, whereby an even distribution of force is obtained over the whole of the contact surface between the substrate and the template. The apparatus further includes a heater device having a surface facing said spacing, for heating either fluid layer (14).
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Method and device for measuring concentration of specific component
ActiveUS7215982B2Easy and stable measurementScattering properties measurementsRefuse receptaclesBiological bodyFluid layer
The present invention provides easy and stable measurement of the concentration of a specific component contained in a living body, even when a fluid such as water, saliva or sweat is present between an optical element and the living body or when the measurement is taken at a plurality of measuring parts of a living body. In the measurement of the present invention, a calibration line to be used to correct the influence of a change of a fluid layer present between a living body and an optical element is determined, a measured value is corrected based on the calibration line and the concentration is obtained from the corrected value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
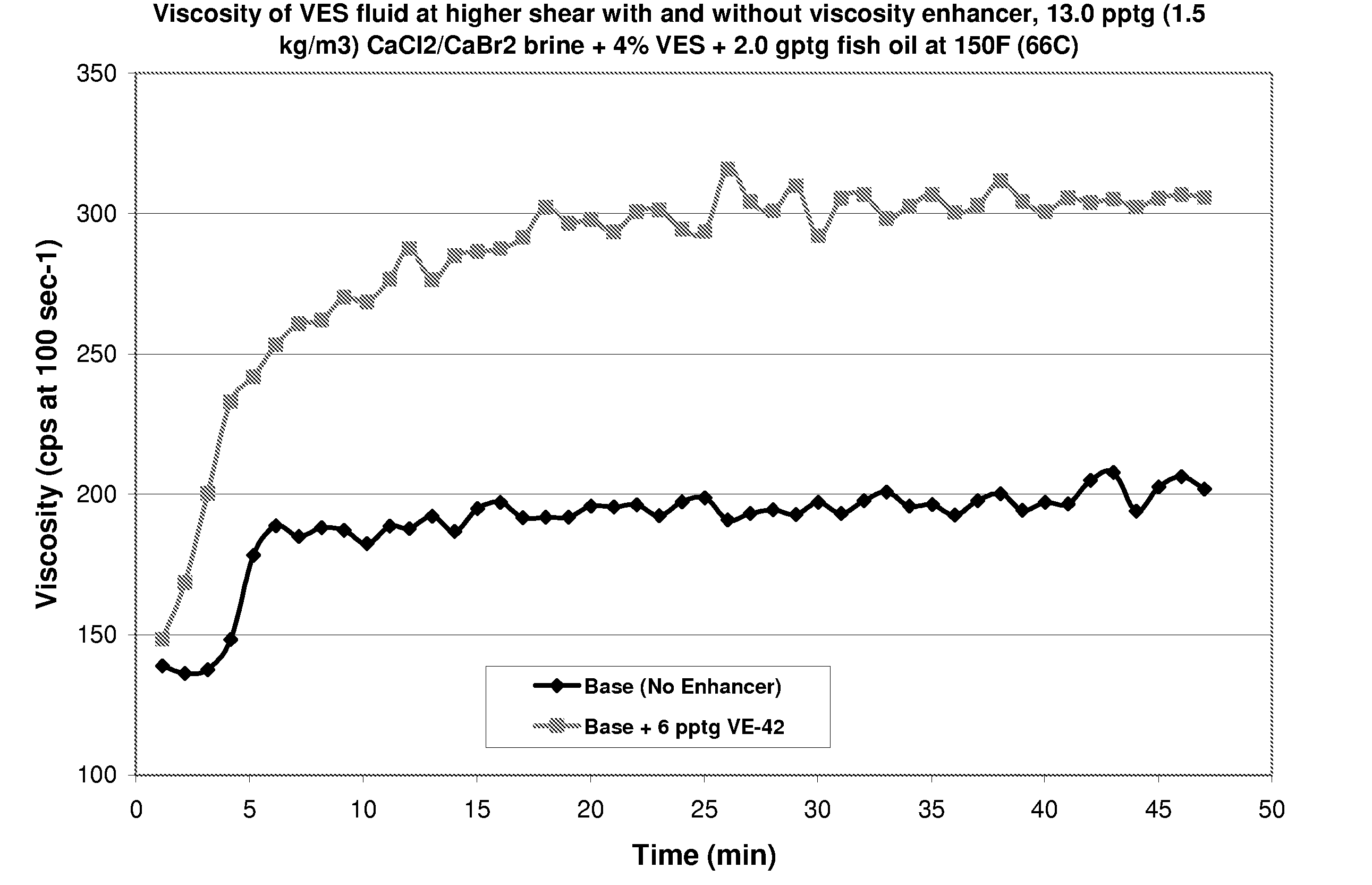
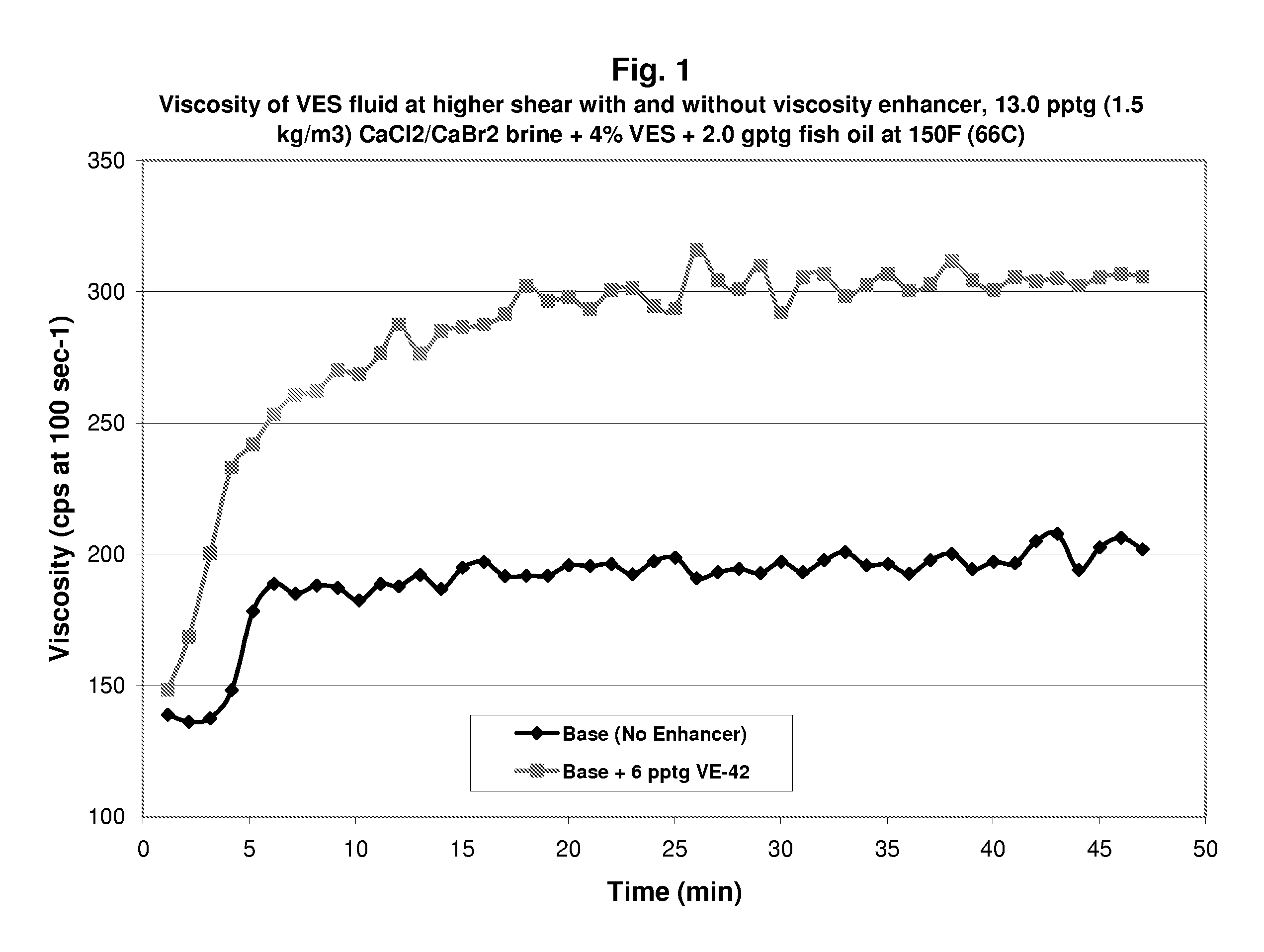
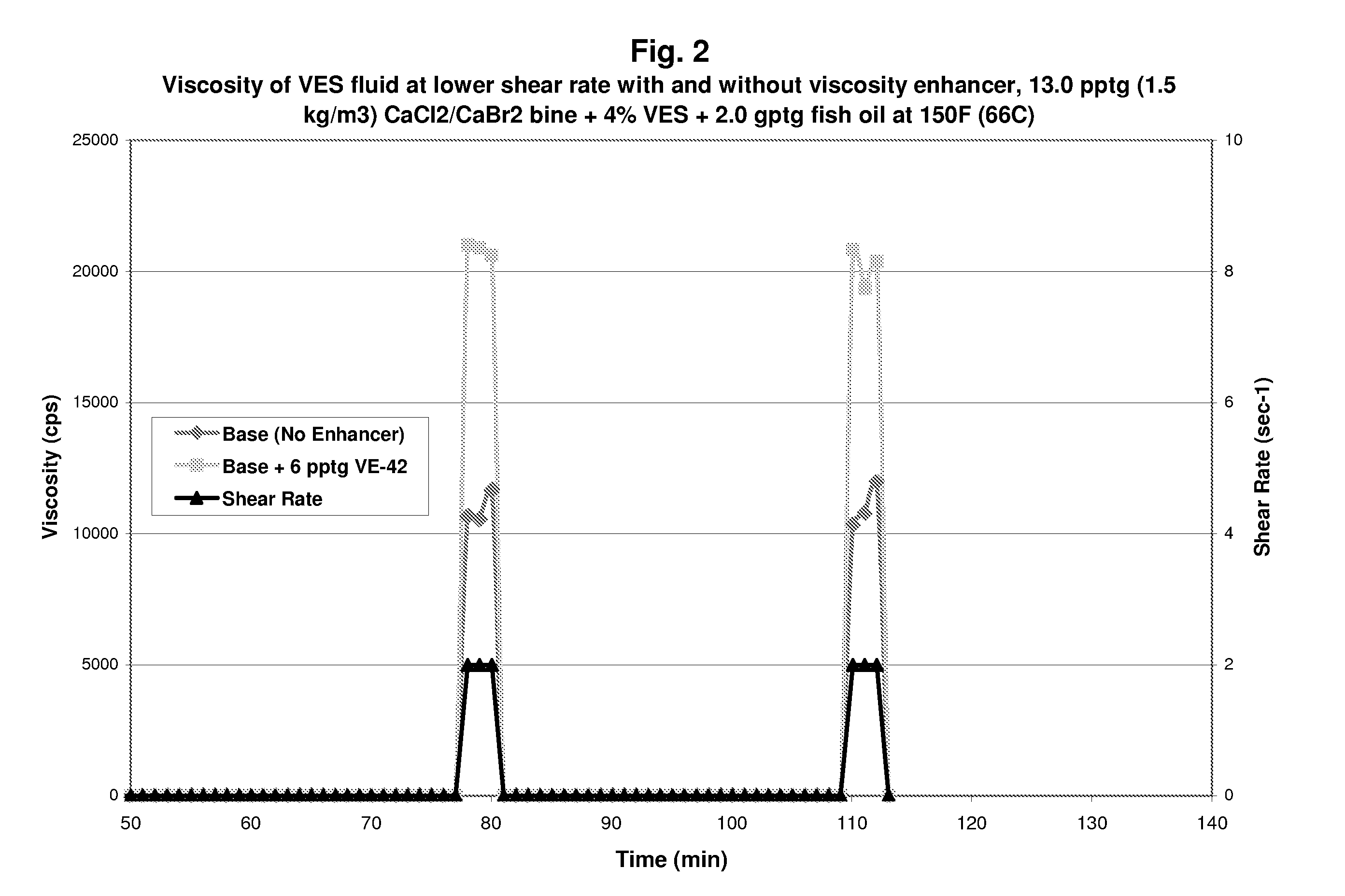
Methods and Compositions for Diverting Acid Fluids in Wellbores
InactiveUS20070151726A1Easily and readily recoveredEasy to produceFluid removalFlushingFluid viscosityFluid layer
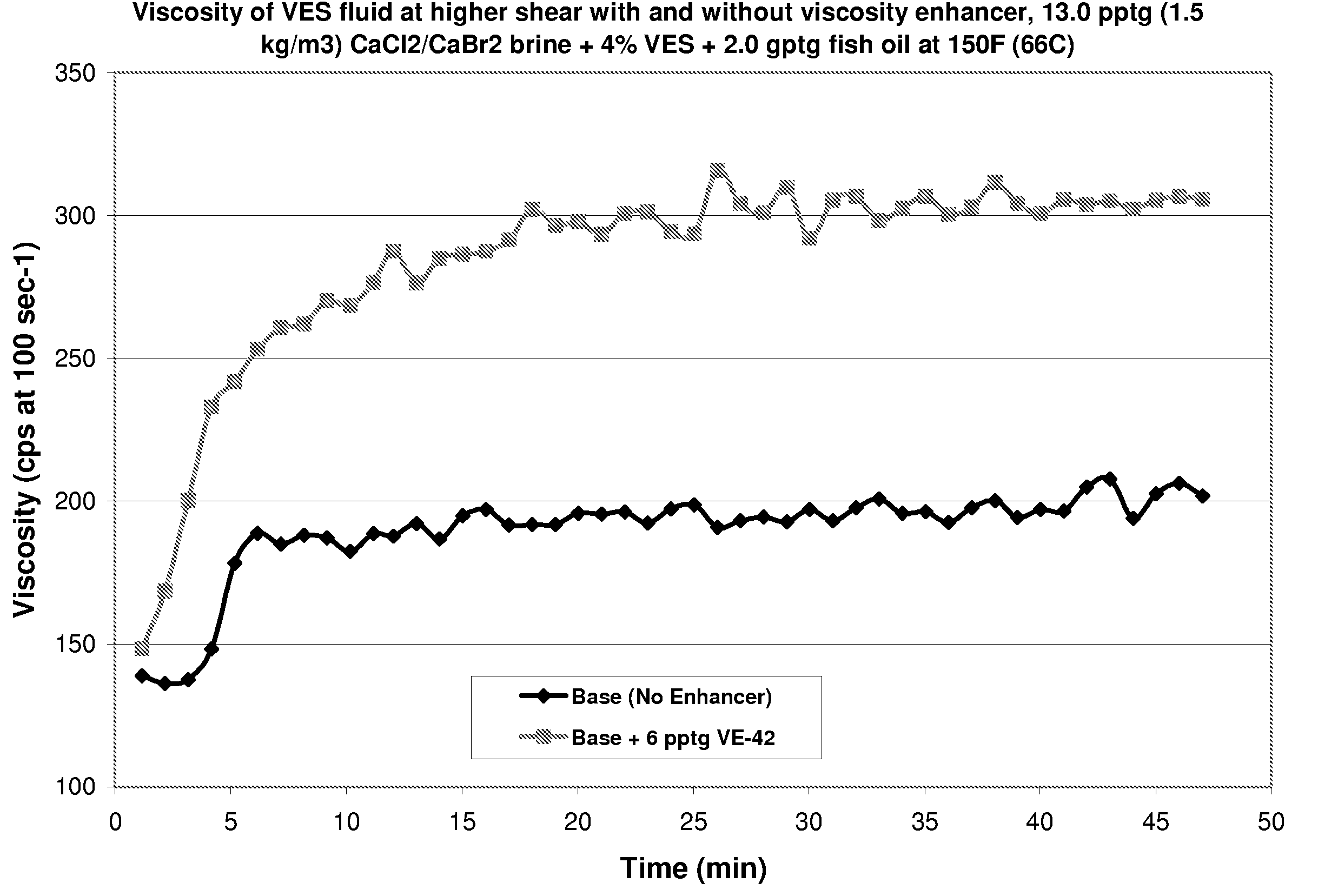
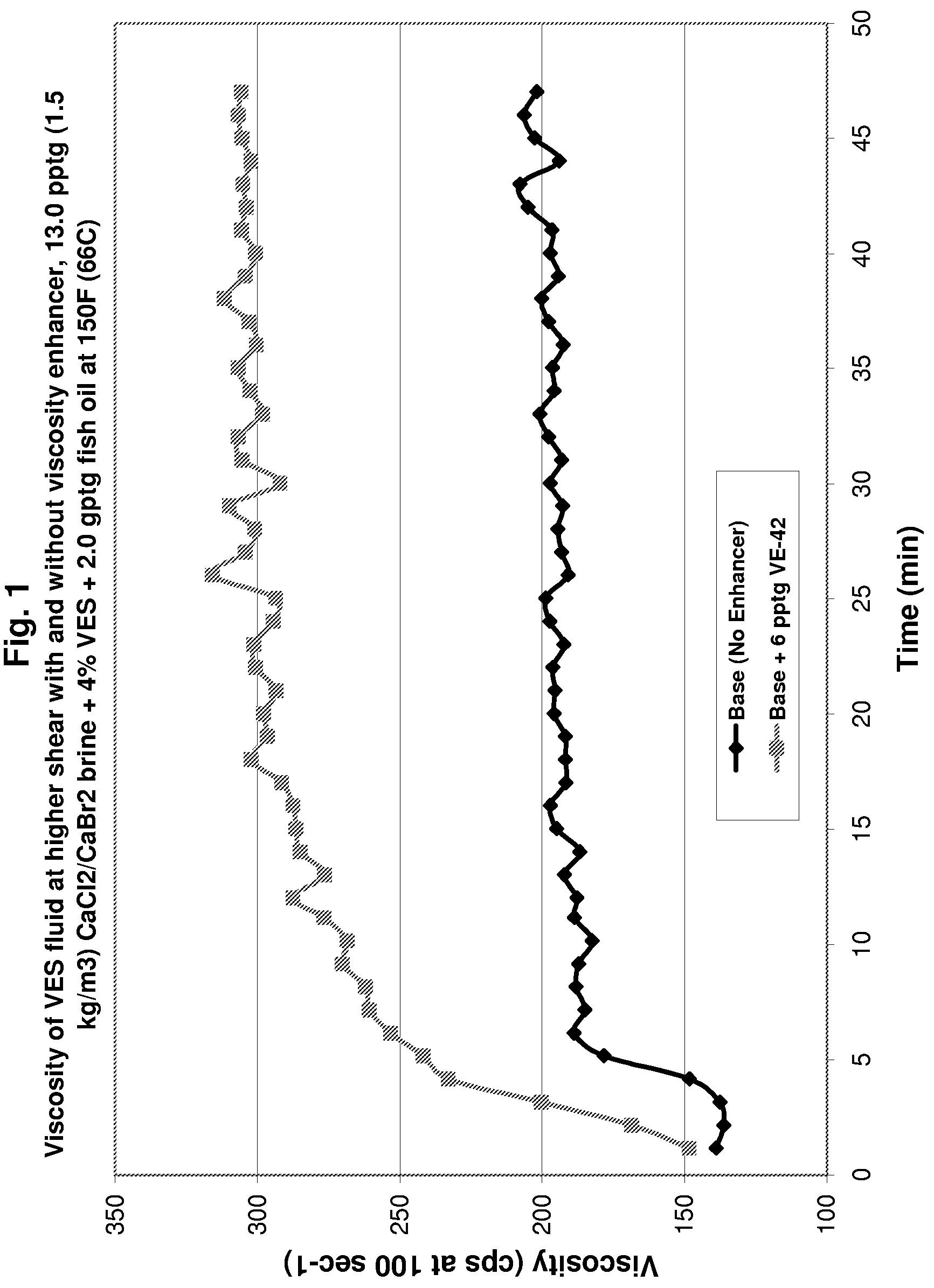
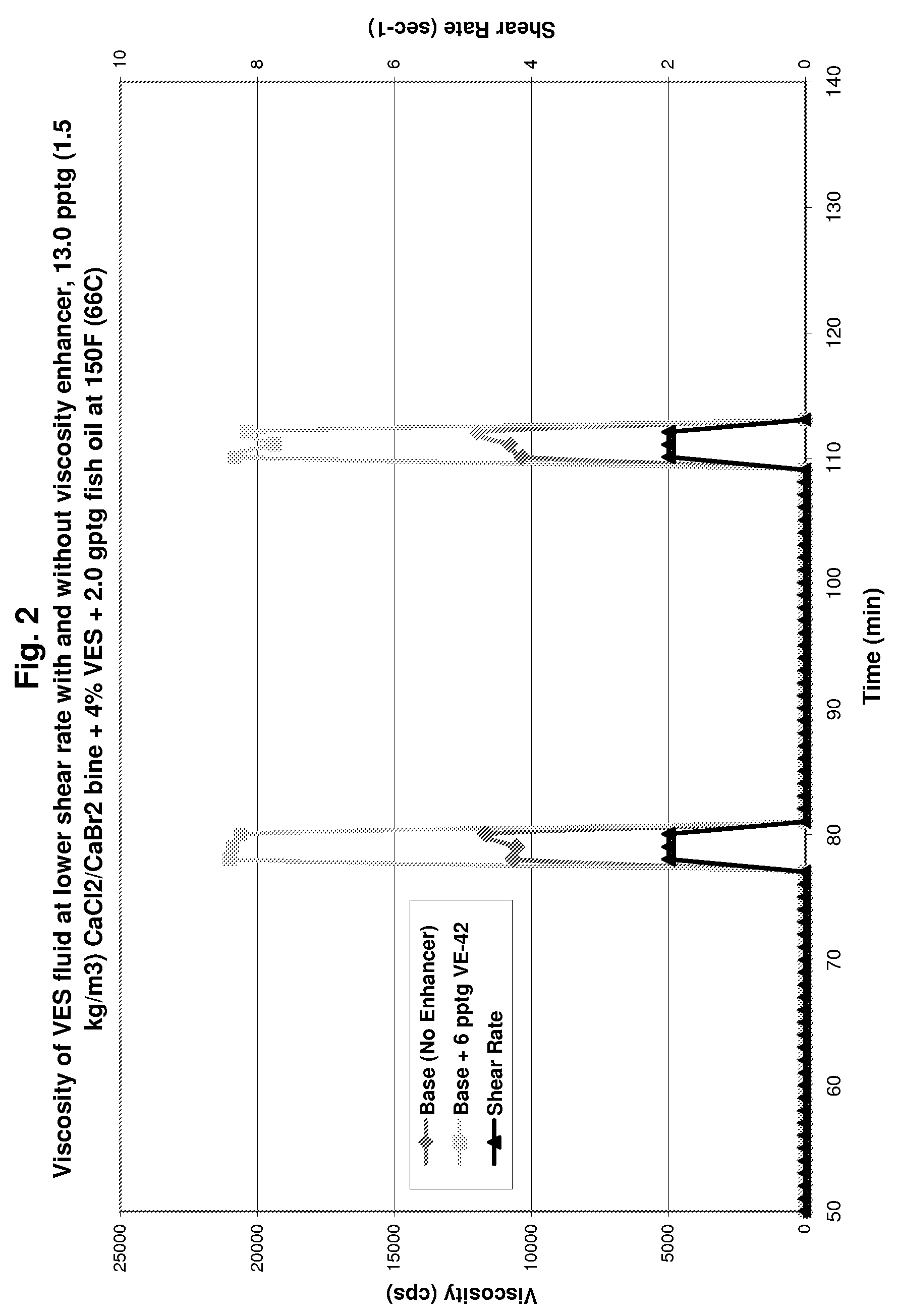
Viscoelastic surfactant (VES) gelled aqueous fluids containing a VES, an internal breaker, and optionally a viscosity enhancer are useful as diverting fluid for directing placement of an acid into a subterranean formation, where the acid is injected subsequent to introducing the VES gelled fluid. These VES-based diverting fluids have faster and more complete clean-up than polymer-based diverting fluids. The viscosity enhancers may include pyroelectric particles and / or piezoelectric particles. The VES gelled fluid may optionally contain a fluid loss agent which increases the viscosity of the fluid and / or facilitates development of an external viscous VES fluid layer (e.g. a pseudo-filter cake) on the formation face. The VES gelled fluid may also optionally contain an agent that stabilizes the viscosity of the fluid, for instance at high temperatures, such as MgO, Mg(OH)2, CaO, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and the like.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
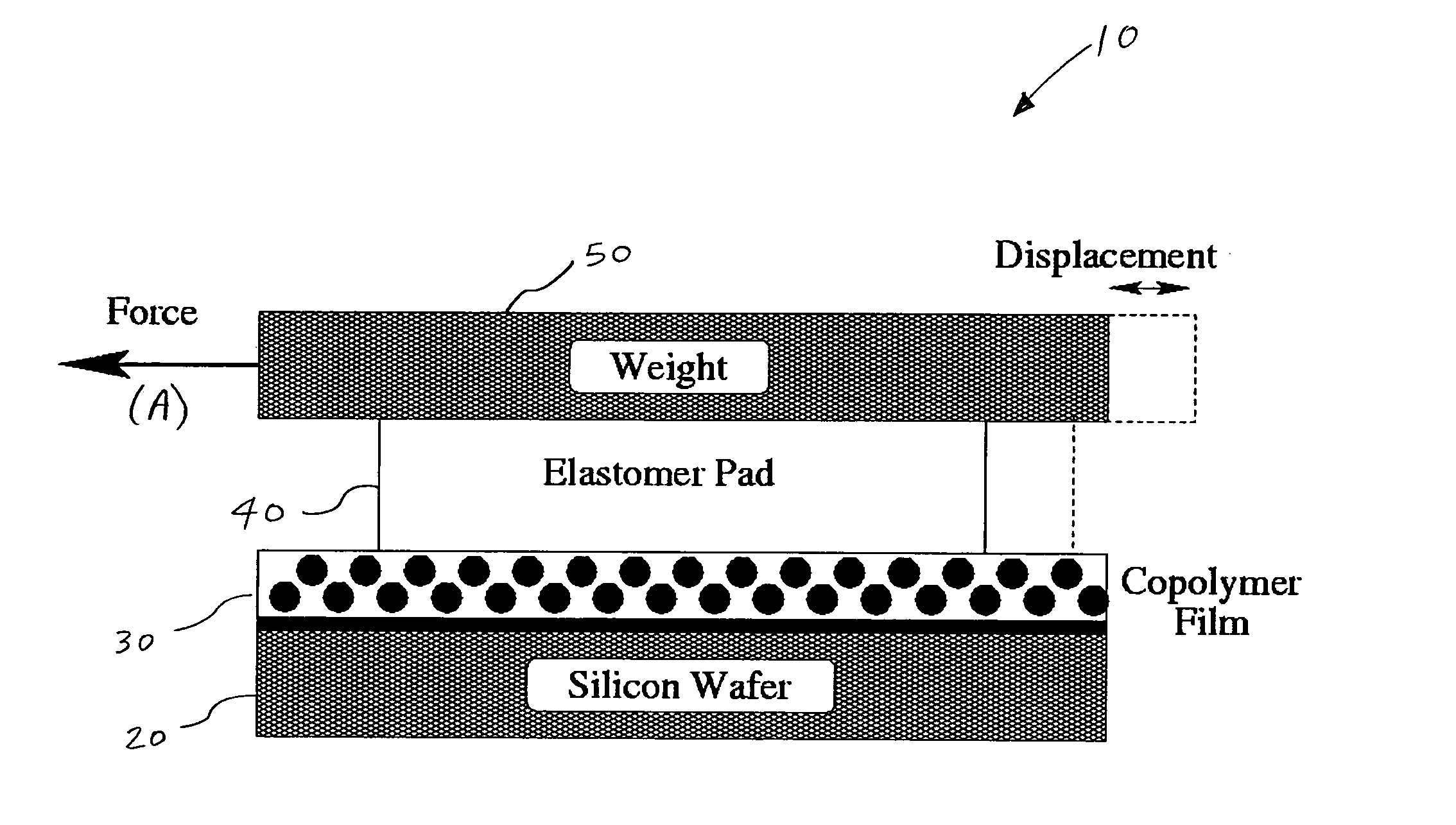
Method and apparatus for providing shear-induced alignment of nanostructure in thin films
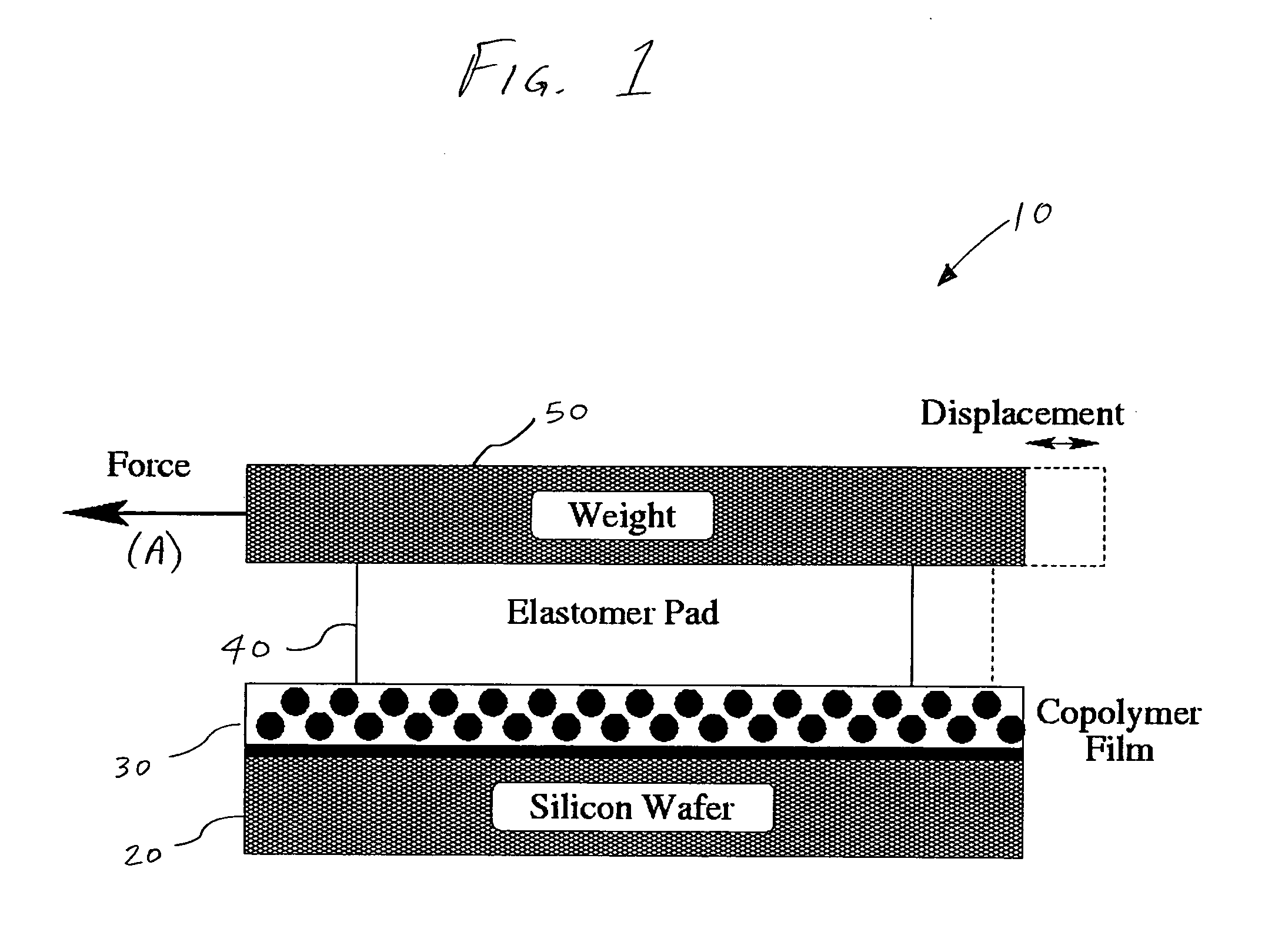
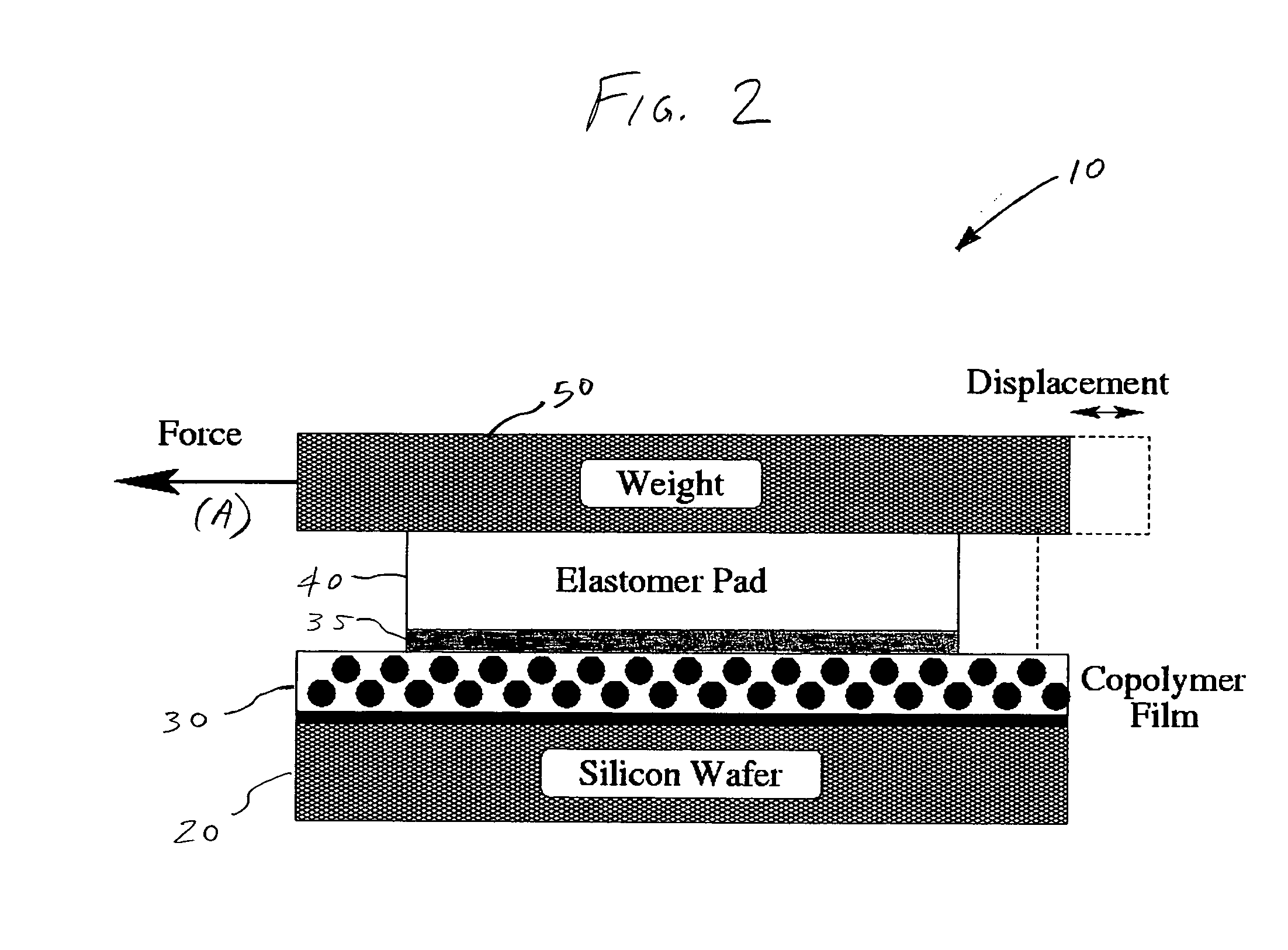
A method and apparatus is disclosed for providing shear-induced alignment of nanostructures, such as spherical nanodomains, self-assembled nanodomains, and particles, in thin films, such as block copolymer (BCP) thin films. A silicon substrate is provided, and a thin film is formed on the substrate. A pad is then applied to the thin film, and optionally, a weight can be positioned on the pad. Optionally, a thin fluid layer can be formed between the pad and the thin film to transmit shear stress to the thin film. The thin film is annealed and the pad slid in a lateral direction with respect to the substrate to impart a shear stress to the thin film during annealing. The shear stress aligns the nanostructures in the thin film. After annealing and application of the shear stress, the pad is removed, and the nanostructures are uniformly aligned.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method and system for microfluidic device and imaging thereof
InactiveUS7695683B2Improve accuracyAccurate focusMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresControl layerFluid layer
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Light-enhancing structure for electrophoretic display
The present invention is directed to a display device comprising a display fluid layer sandwiched between a first substrate layer and a second substrate layer, and a light-enhancing layer between the display fluid layer and the second substrate layer. The light-enhancing structure can enhance the colors displayed by the display device, especially the colors displayed through lateral switching of the charged pigment particles in an electrophoretic fluid.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Electrowetting display devices
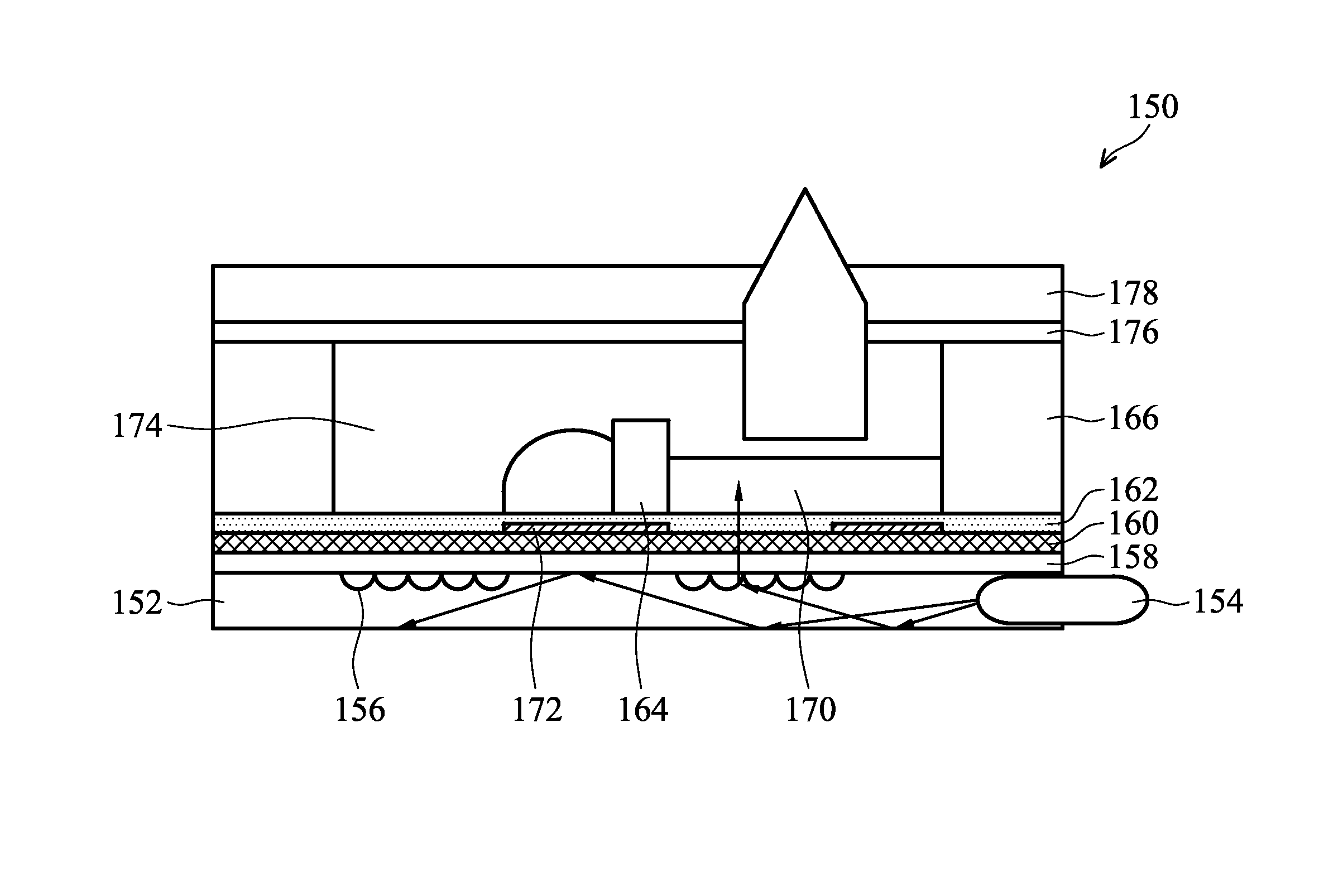
Electrowetting devices (EWD) are presented. The electrowetting device includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer interposed therebetween. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A first partition structure is disposed on the first substrate; thereby defining a plurality of color sub-pixels. A dye and / or a pigment substance is doped in one of the polar fluid layer and the non-polar fluid layer. A luminescence substance is doped in one of the polar fluid layer and the non-polar fluid layer. An emission module (also known as an excitation module) is disposed underlying the bottom of the first substrate. The colors of the non-polar fluid layer in the neighboring sub-pixels are different.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method of forming ceramic beads
InactiveUS20040007789A1Reduce blemishesGood dispersionGranulation by liquid drop formationCeramic shaping apparatusMetallurgyFluid layer
A method of forming substantially spherical ceramic beads that includes conveying an aqueous ceramic slurry to a nozzle tip that is immersed in an inert water-immiscible fluid layer. The nozzle tip is spaced a predetermined distance away from a rotating disk that is also immersed in the immiscible fluid layer. The rotating disk creates a shear force that at the nozzle tip that dislodges droplets of the aqueous ceramic slurry from the nozzle tip into the immiscible fluid layer. Once dislodged, the droplets assume a substantially spherical shape and a substantially mono-modal size distribution. The droplets are permitted to pass from the immiscible fluid layer into an aqueous gelling solution wherein the droplets are converted into rigid beads. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the rigid beads are recovered from the gelling solution, washed, and then sintered to obtain a density of greater than about 98% of theoretical density and a sphericity of greater than about 0.95. The method can be used to fabricate substantially spherical zirconia-containing beads having a diameter within the range of from about 0.1 mm to about 2.0 mm that are useful, for example, as grinding media.
Owner:CERCO
Electrowetting Display Devices
Electrowetting display devices are presented. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a transparent polar fluid layer and an opaque non-polar fluid layer insoluble with each other and interposed between the first and second substrates. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second transparent electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A dielectric layer is disposed on the second transparent electrode. A reflective plate structure is interposed between the second transparent electrode and the second substrate, thereby defining a reflective region and a transmission region. A backlight plate is disposed on the back of the second substrate. During operation, the opaque non-polar fluid converges, therefore, exposing equal areas of reflective region and transmission region.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Integrated device for nucleic acid detection and identification
ActiveUS20140045191A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceDocking station
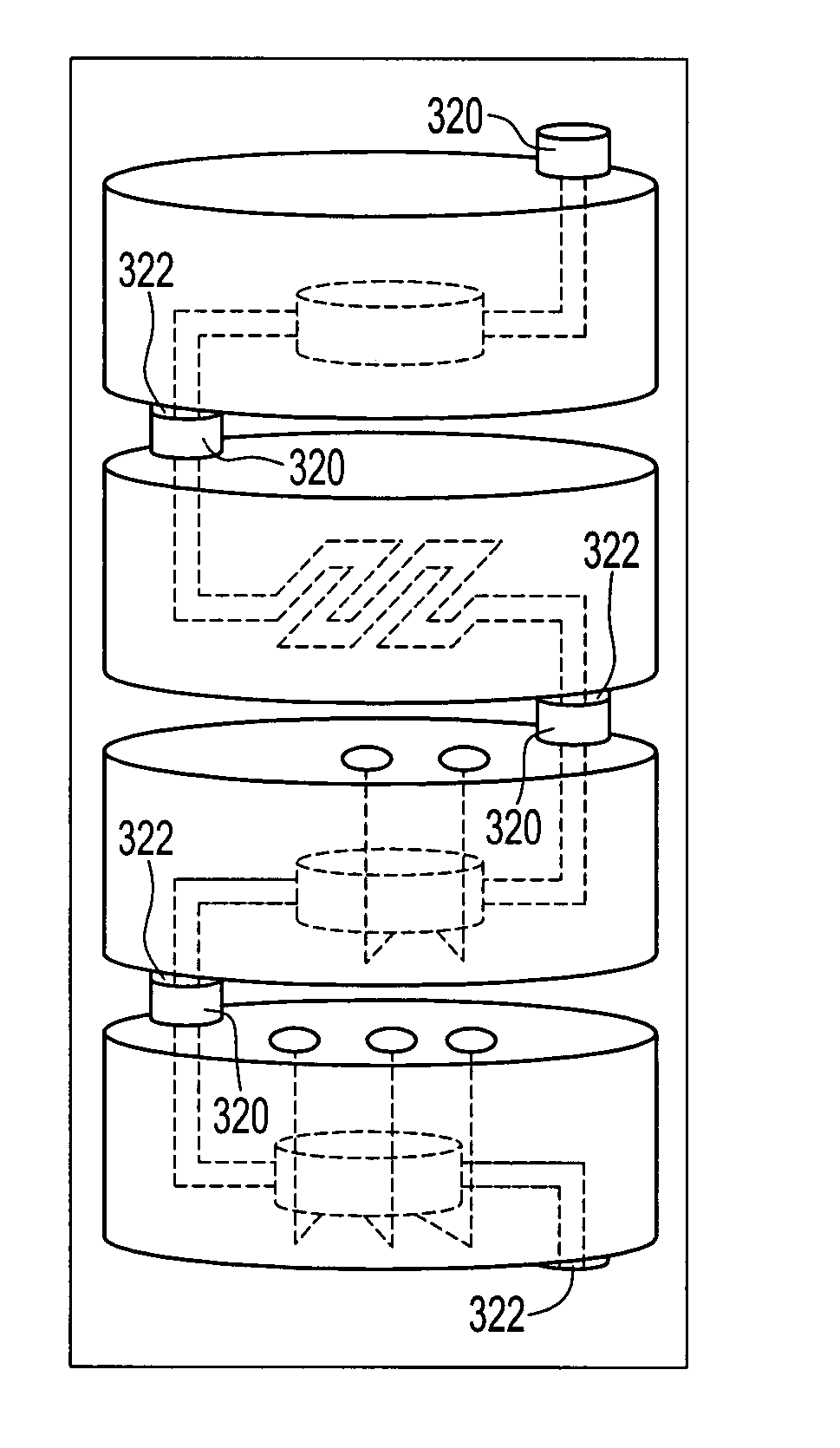
A disposable assay platform for detecting a target nucleic acid comprising multiple chambers and a method for operating the assay platform. Solutions containing the target nucleic acid move from one chamber to the next chamber by opening a vent pocket. The resulting pressure change enables the solution to flow to the next chamber. The platform comprises an electronic layer and one or more fluid layers bonded together. All heating operations can be performed by using resistive heating elements in the platform. All cooling operations are preferably passive. The platform is preferably operated when in a vertical orientation and can be docked to an external docking station that controls the operation of the platform.
Owner:MESA BIOTECH
Microfluidic methods
This invention provides microfluidic devices that comprise a fluidics layer having microfluidic channels and one or more regulating layers that regulate the movement of fluid in the channels. The microfluidic devices can be used to mix one or more fluids. At least a portion of the fluidics layer can be isolated from the regulating layer, for example in the form of a shelf. Such isolated portions can be used as areas in which the temperature of liquids is controlled. Also provided are instruments including thermal control devices into which the microfluidic device is engaged so that the thermal control device controls temperature in the isolated portion, and a movable magnetic assembly including magnets with shields so that a focused magnetic field can be applied to or withdrawn from the isolated portion or any other portion of the microfluidic device. Also provided are methods of mixing fluids. The methods include stacking a plurality of alternating boluses of different liquids in a microfluidic channel, and moving the stacked boluses through the channel. In another method, the boluses are moved into a diaphragm valve having a volume able to accommodate several boluses, and then pumping the liquids out of the valve.
Owner:INTEGENX
Methods and compositions for diverting acid fluids in wellbores
InactiveUS7527102B2Easily and readily recoveredEasy to produceFluid removalFlushingFluid viscosityFluid layer
Viscoelastic surfactant (VES) gelled aqueous fluids containing a VES, an internal breaker, and optionally a viscosity enhancer are useful as diverting fluid for directing placement of an acid into a subterranean formation, where the acid is injected subsequent to introducing the VES gelled fluid. These VES-based diverting fluids have faster and more complete clean-up than polymer-based diverting fluids. The viscosity enhancers may include pyroelectric particles and / or piezoelectric particles. The VES gelled fluid may optionally contain a fluid loss agent which increases the viscosity of the fluid and / or facilitates development of an external viscous VES fluid layer (e.g. a pseudo-filter cake) on the formation face. The VES gelled fluid may also optionally contain an agent that stabilizes the viscosity of the fluid, for instance at high temperatures, such as MgO, Mg(OH)2, CaO, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and the like.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Semiconductor surface modification
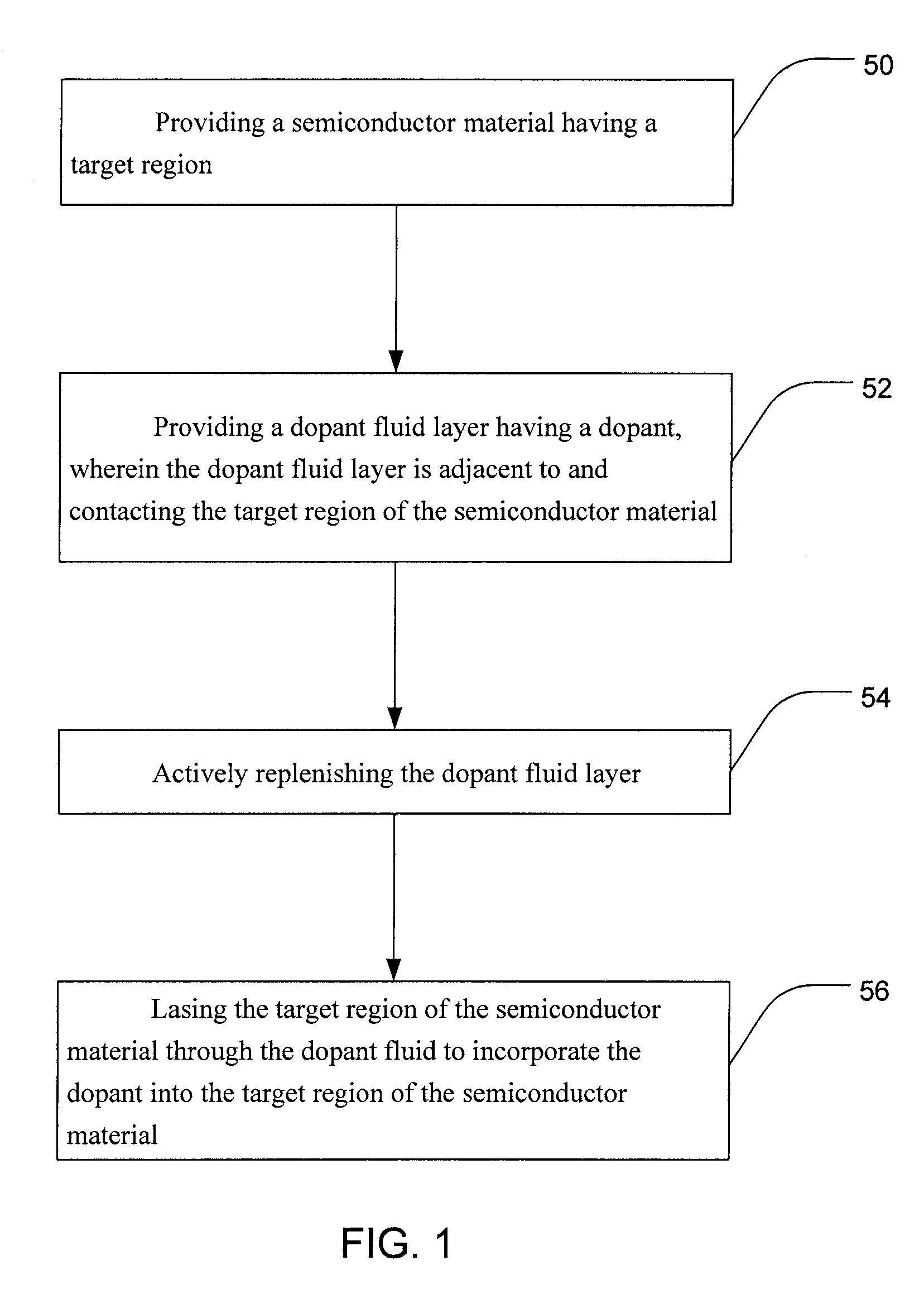
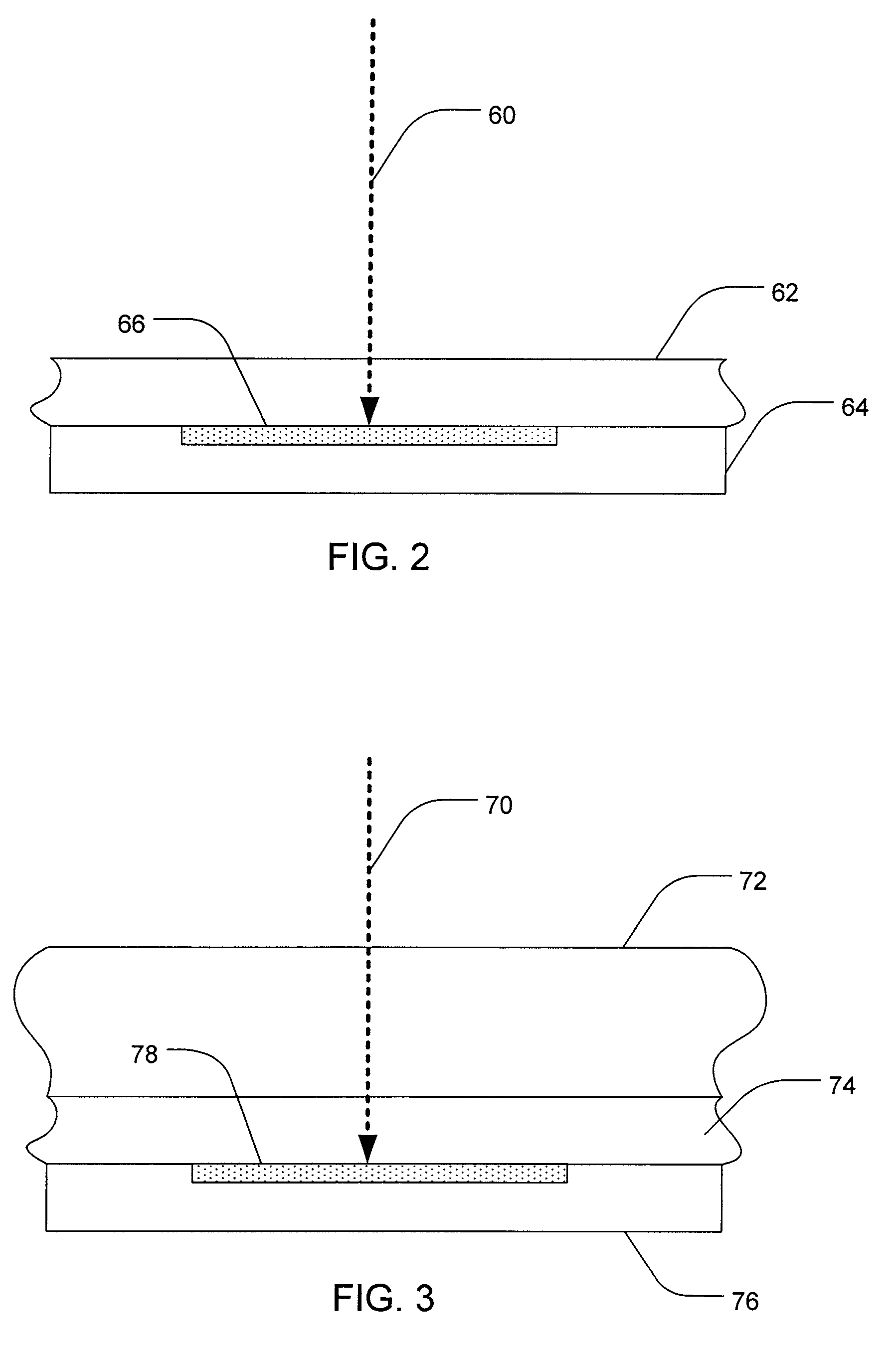
ActiveUS8207051B2Improve efficiency and reliabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDopantSemiconductor materials
Methods, systems, and devices associated with surface modifying a semiconductor material are taught. One such method includes providing a semiconductor material having a target region and providing a dopant fluid layer that is adjacent to the target region of the semiconductor material, where the dopant fluid layer includes at least one dopant. The target region of the semiconductor material is lased so as to incorporate the dopant or to surface modify the semiconductor material. During the surface modification, the dopant in the dopant fluid layer is actively replenished.
Owner:SIONYX
Fluid motion device for accelerating and energy-saving
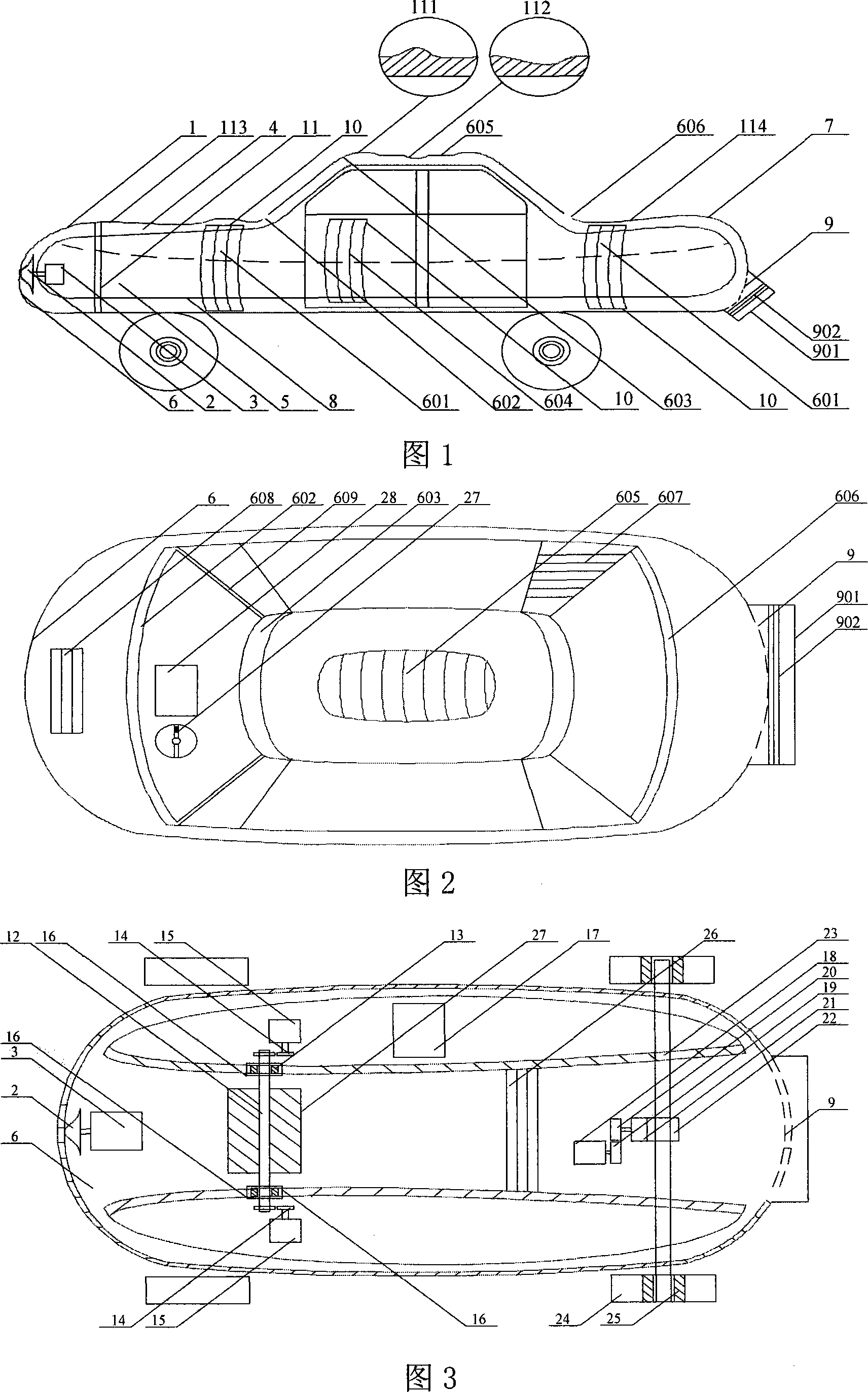
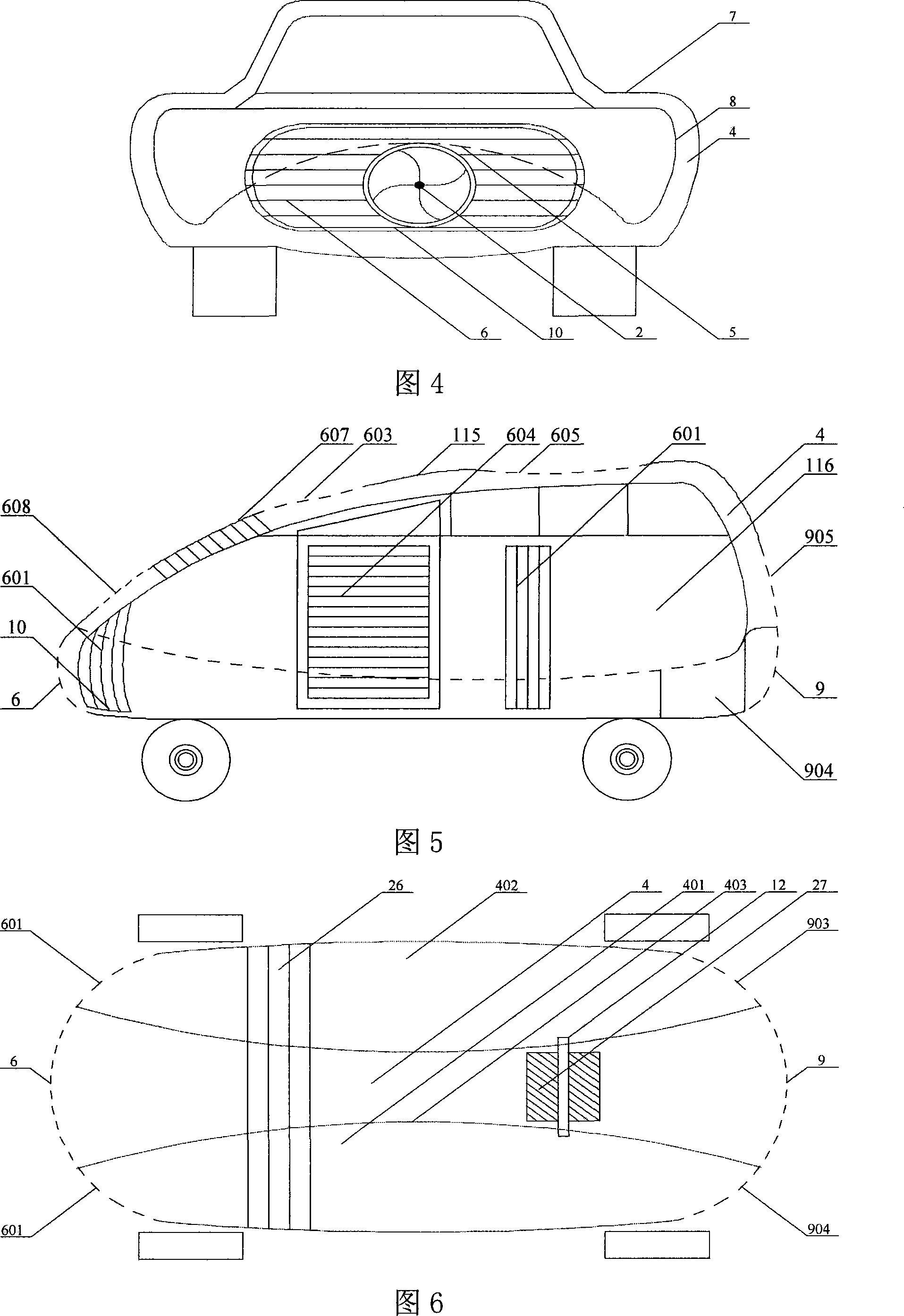
InactiveCN101195348ASimple structureEasy to introduceWatercraft hull designPropulsive elementsEngineeringRocket
Provided is an accelerating and energy-saving moving device, a certain distance and a fluid layer are positioned between an outer case and an inner case of the device, the fluid layer is fore-and-aft communicated with a leading-in port arranged at the front end and a leading-out port mounted at the rear end, at least one leading-in port and one balance port which are arranged on the surrounding case body of the outer case are communicated with the fluid layer, the leading-in port, the balance port and the leading-in port which is arranged at the front end receive forward fluid, and the forward fluid is discharged from the leading-out port which is disposed at the middle portion or rear end of the device after passing through the fluid layer. An impeller and a generator are driven by the fluid layer to replenish energy source for fuel power and to drive a motor, a speed reducer, a differential mechanism and two half-spindles via a control panel, and the moving device is further driven to move. The invention further discloses energy-saving devices which employ the method, such as cars, trains, ships, submarines, airplanes, missiles, rockets and the like, the invention is in particular applicable to cars and trains. The resistance of a moving body in moving can be greatly reduced with the employment of the invention, and the energy consumption is greatly lowered, thereby the moving body can be accelerated extremely rapidly.
Owner:朱晓义
Method and devices for prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers
ActiveUS20130019873A1Constricts compressionConstrict compressionOperating chairsVibration massageFluid layerPressure Sores/Ulcers
Method and devices for the prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers are described in which a portable support assembly may be worn by a bed-stricken individual around particular regions of the body where pressure ulcers tend to form. The portable support assembly may generally include one or more individual fluid filled pods which are enclosed entirely within an inner fluid pad localized along a central portion. Both the one or more pods and inner fluid pad are then enclosed entirely by another layer of fluid within an outer fluid pad which extends over the entire assembly. Each of the fluid layers may be secured to an outer shell which is relatively stiffer than the fluid layers and may restrict or limit the expansion or movement of the fluid pods and / or fluid pads.
Owner:PRS MEDICAL TECH
Method for selectively anchoring and exposing large numbers of nanoscale structures
Methods for fastening nanoscale structures within an anchoring structure to form a nanostructure composite and nanostructure composites formed therefrom. A primary fluid layer is formed on an anchoring substrate. Nanostructures are provided on an initial substrate, the nanostructures having a defined height and orientation with respect to the initial substrate. The nanostructures are introduced to a desired depth in the primary fluid layer, such that the orientation of the nanostructures relative to the growth substrate is substantially maintained. The primary fluid layer comprises one or more fluid layers. Ones of multiple fluid layers are selected such that when altered to form an anchoring structure, a portion of the anchoring structure can be removed, permitting exposure of at least a portion of the nanostructures from the anchoring structure in which they are affixed. The growth substrate is removed. Ends or other parts of nanostructures may be exposed from the anchoring structure.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Electrowetting display devices and fabrication methods thereof
InactiveUS7746540B2Simplify the manufacturing processSimple structureCoatingsSpecial surfacesFluid layerDisplay device
Electrowetting display devices and fabrication methods thereof are presented. The electrowetting display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer insolvable to each other and interposed between the first and second substrates. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A dielectric layer is disposed on the second electrode. A hydrophilic partition wall structure is directly disposed on the dielectric layer defining a plurality of pixel regions. A layer of low surface energy material is disposed on the dielectric layer within each of the pixel region.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Nonlinear and multidirectional irregular wave and internal wave generating system and control method therefor
ActiveCN105758617AReduce distanceImprove wave making accuracyHydrodynamic testingEngineeringAccuracy and precision
The invention relates to the technical field of hydrodynamic experiment and search, and more specifically, relates to a nonlinear and multidirectional irregular wave and internal wave generating system and a control method therefor, wherein the system is used for generating high-precision nonlinear multidirectional irregular waves and internal waves in a pool. The system based on vertical multilayer and horizontal multi-plate control comprises a test pool (comprising a wave absorbing segment), a computer control drive system, a mechanical transmission system, a wave generating plate system (vertical multiple plates and horizontal multiple groups), and a wave height monitoring system. There are two fluid layers with different densities in the test pool during wave generating, or there is one fluid layer in the test pool otherwise. The system achieves the simulation of the nonlinear and multidirectional irregular waves and internal waves in the pool through the simultaneous control of a plurality of groups of horizontally arranged vertical multi-plate wave generating mechanisms and the different nonlinear vertical speed distribution of the two fluid layers or the single fluid layer, is higher in accuracy and precision, and meets the requirements of different tests.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Electrowetting display devices
InactiveUS20100225611A1Static indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingFluid layerDisplay device
Electrowetting display devices are provided. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer interposed between the first and second substrates. A first electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic bank structure is disposed on the first substrate, and a reflective layer is disposed on the second substrate, wherein the first substrate of the electrowetting display serves as a display face.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
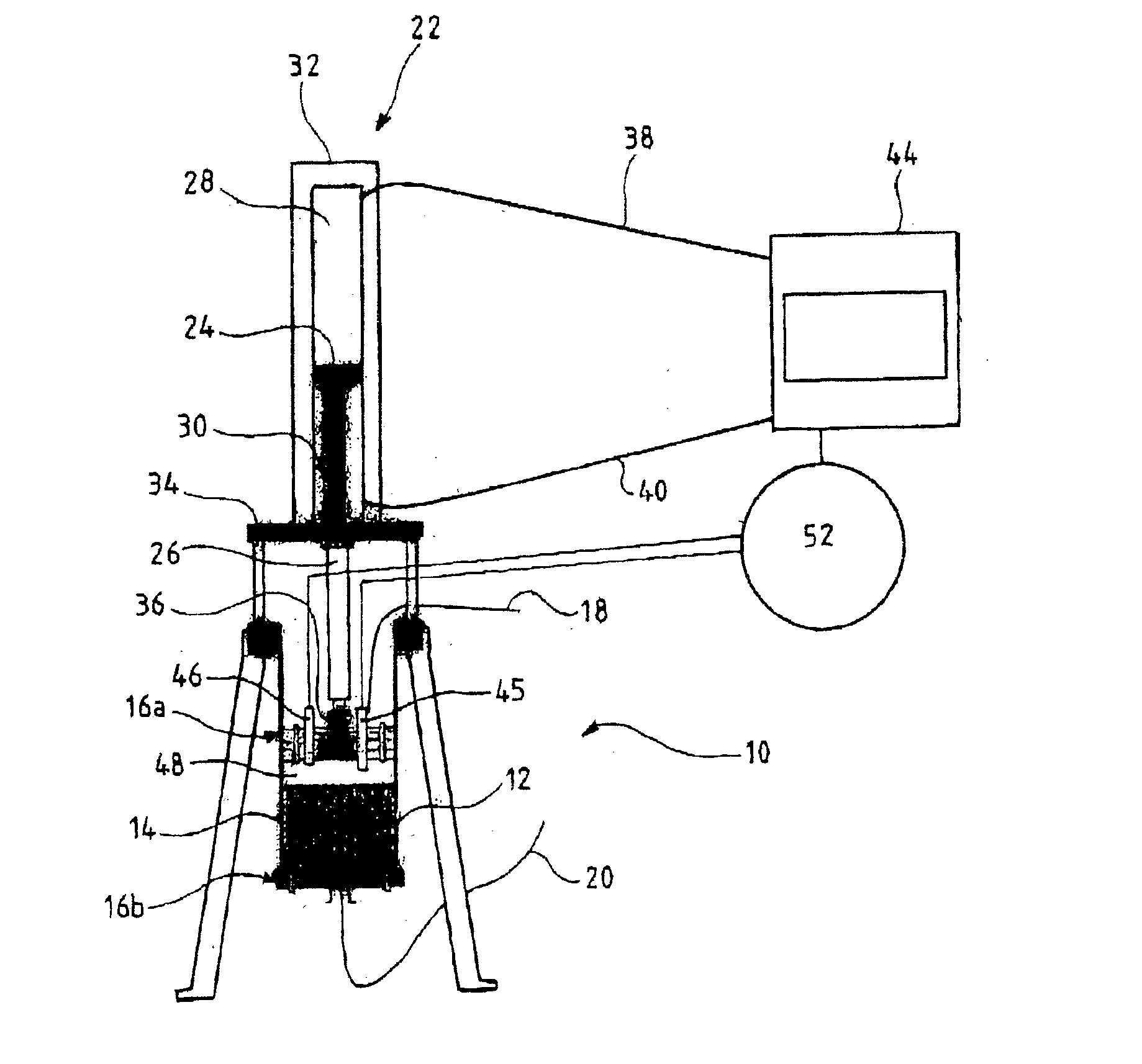
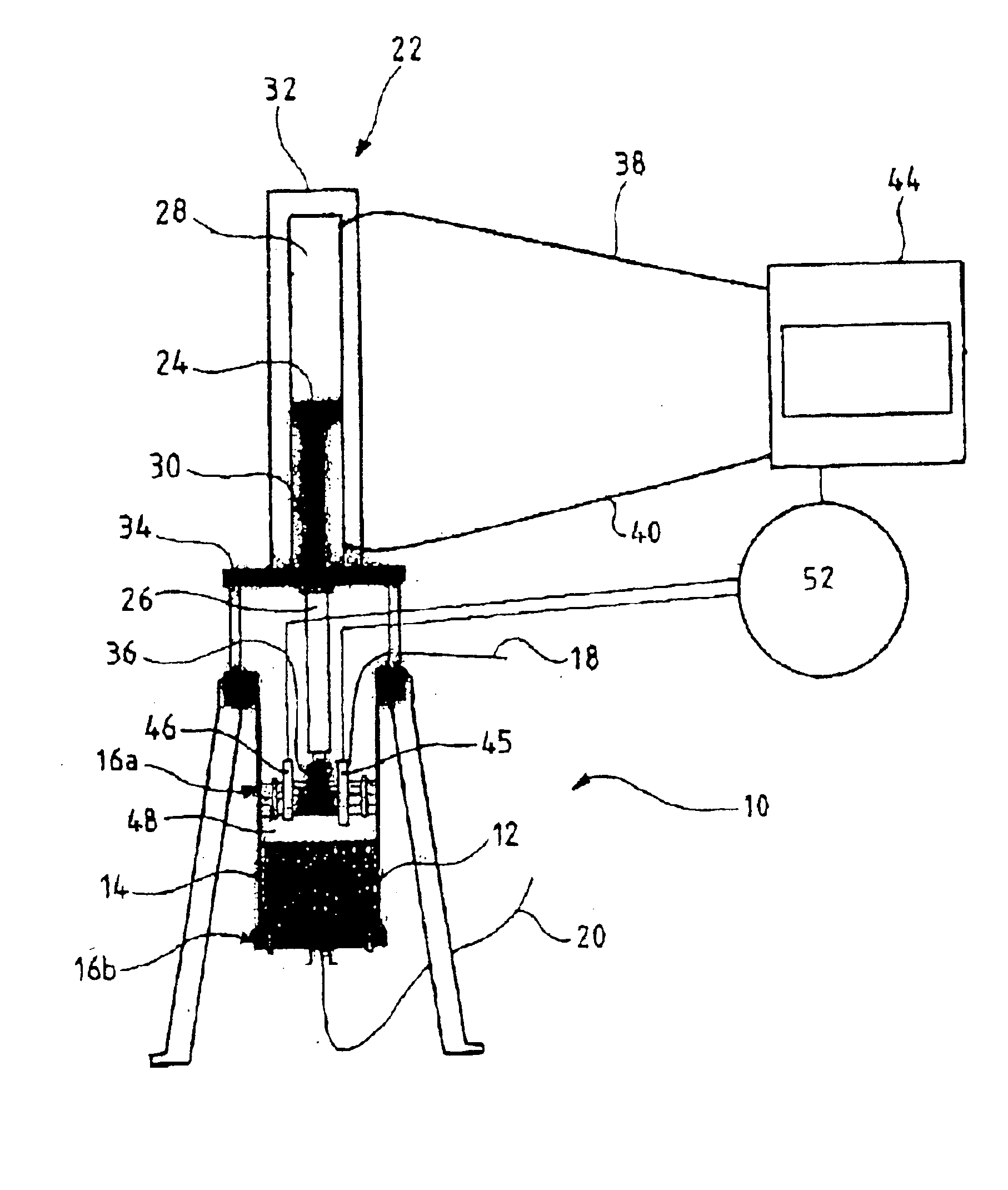
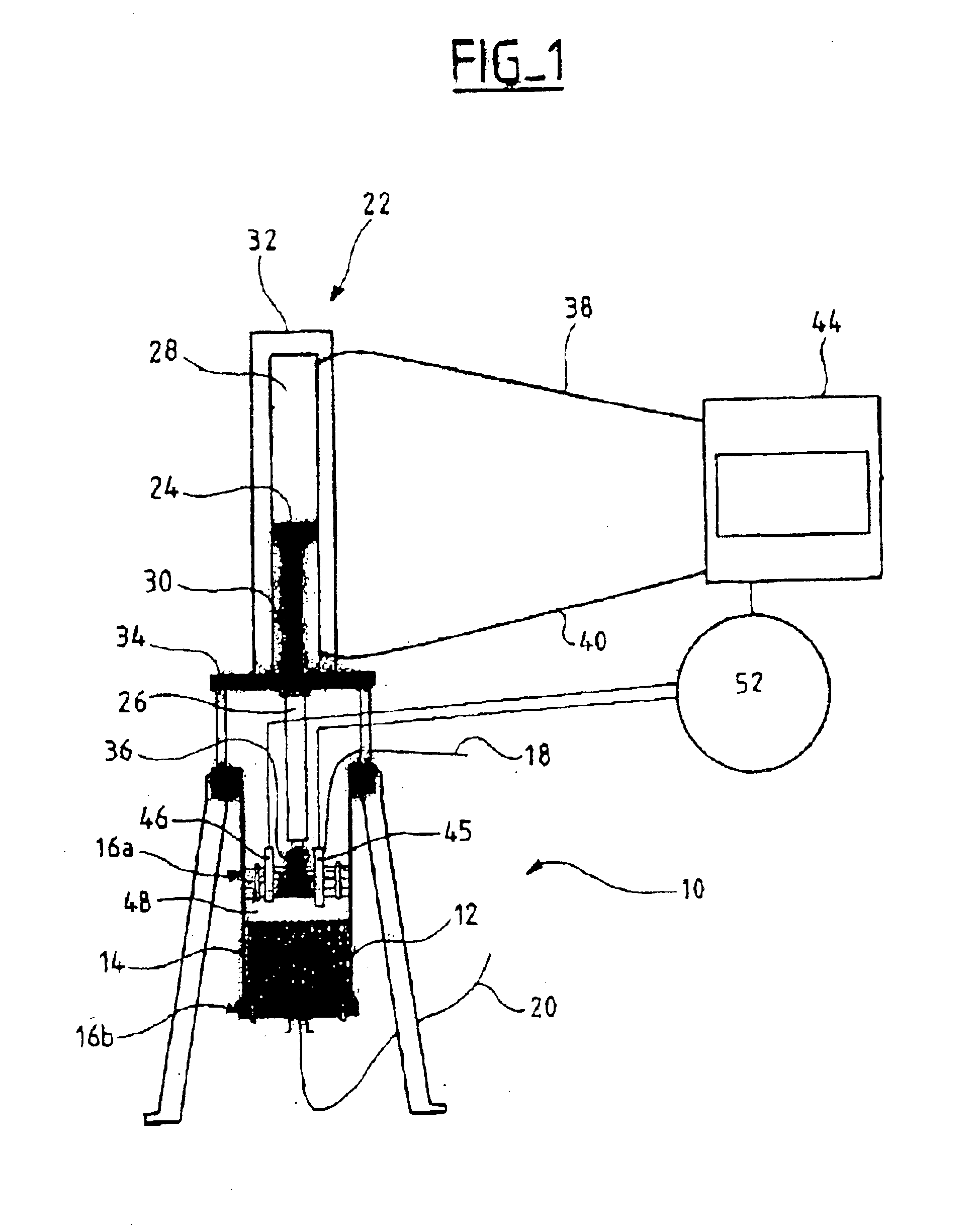
Protection of the chromatographic bed in dynamic axial compression chromatography devices
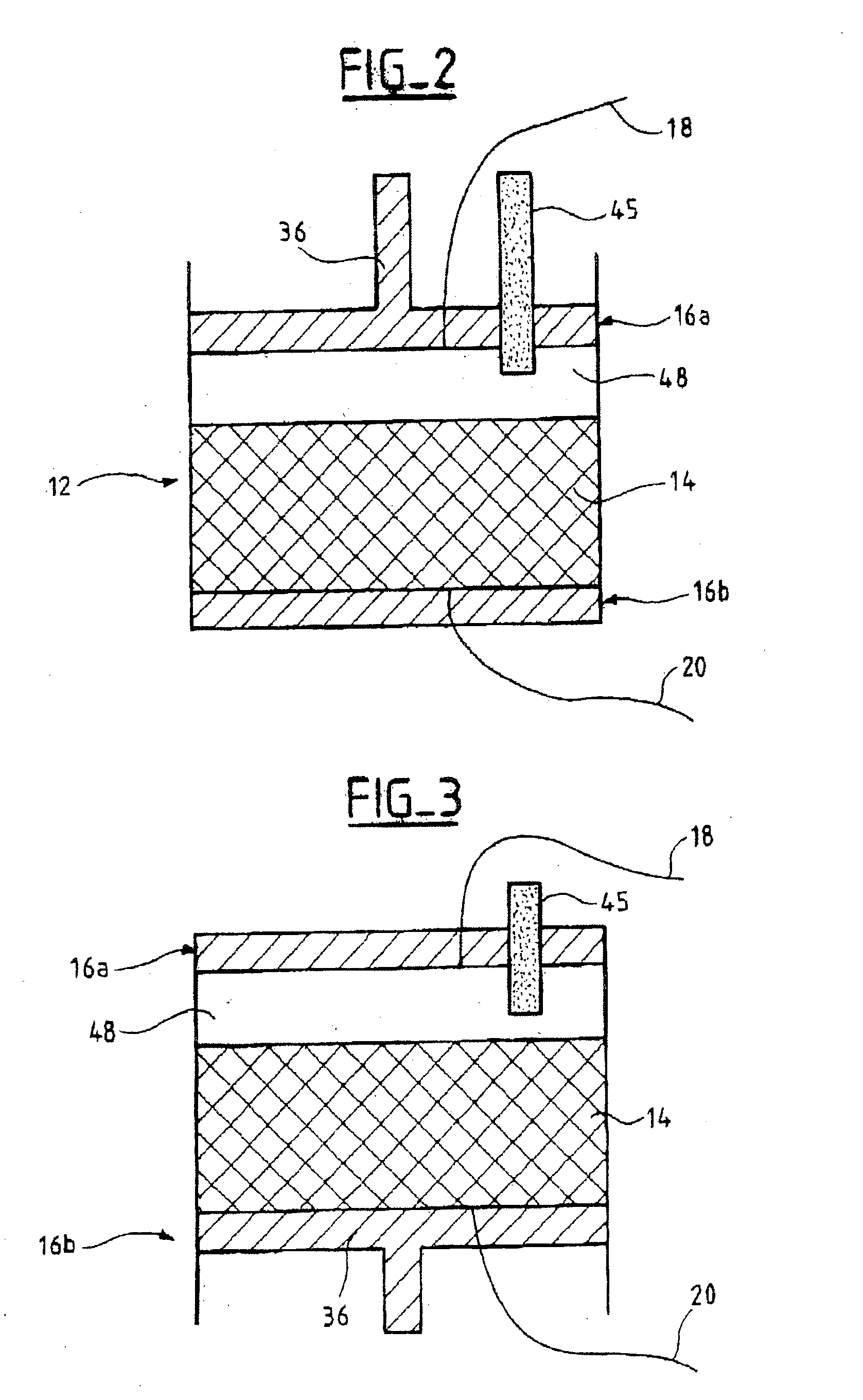
InactiveUS20040016701A1Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationAxial compression
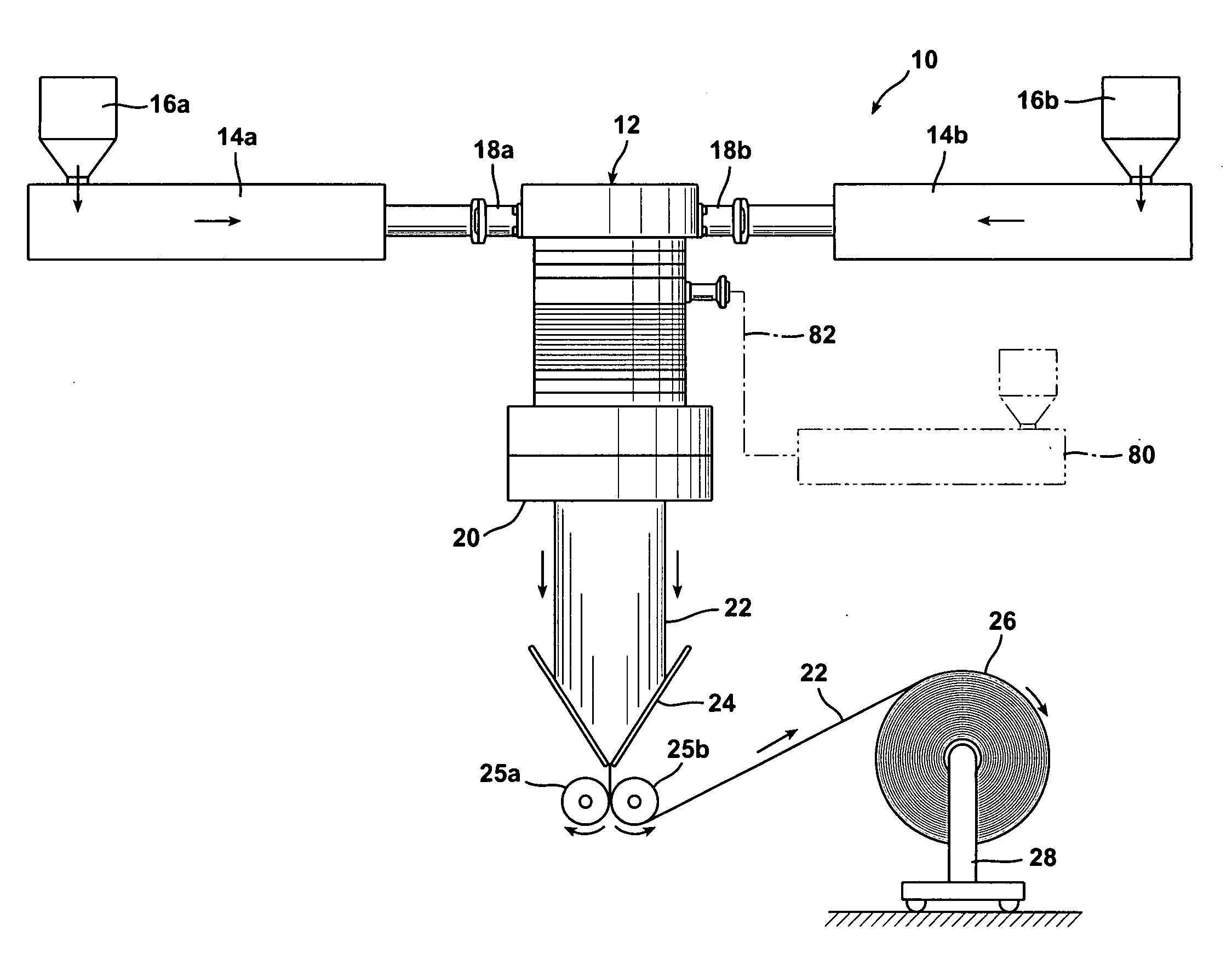
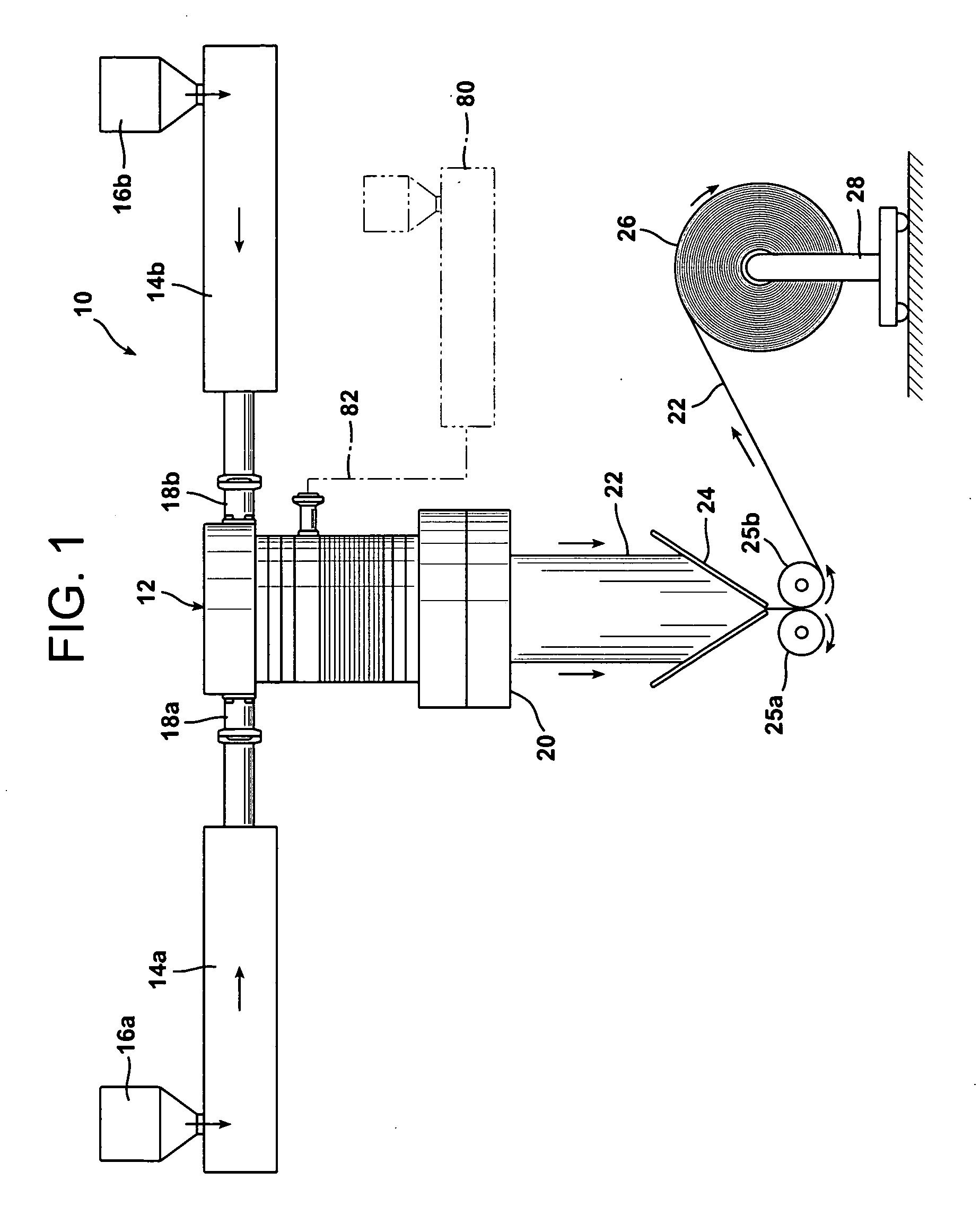
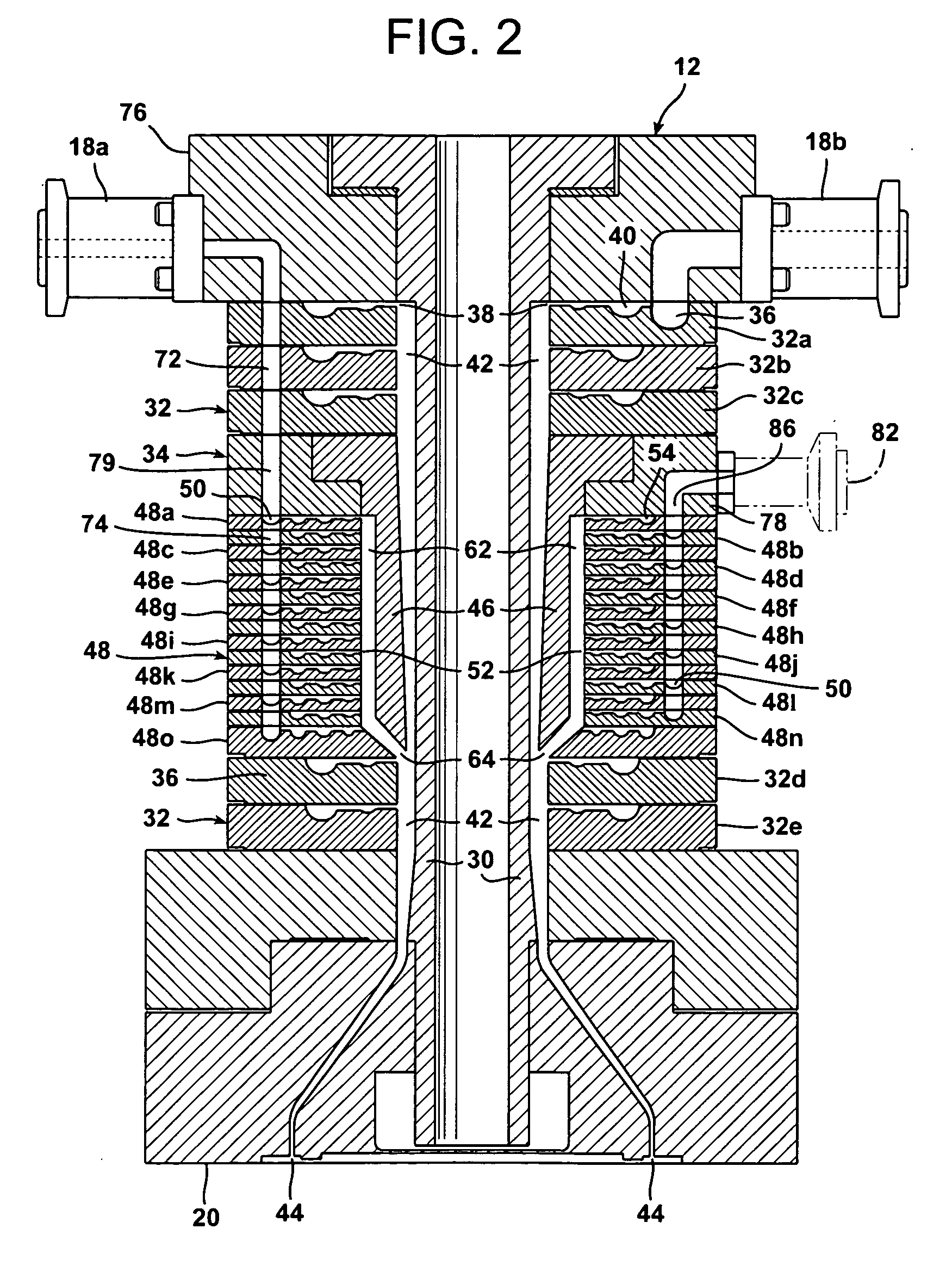
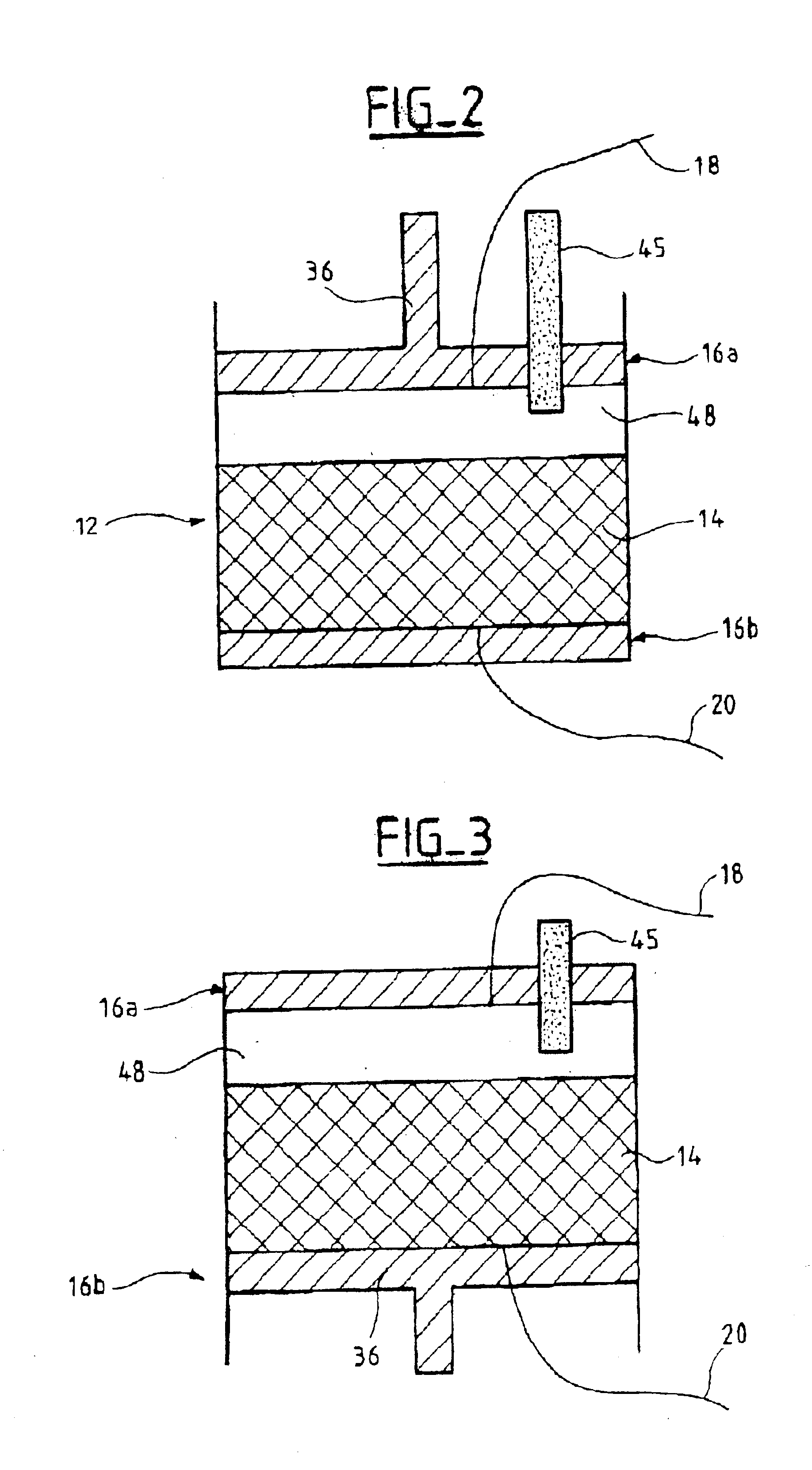
The invention relates to a chromatography device comprising: a column (12) intended to house, between its two ends (16a, 16b) a chromatographic bed (14) and a fluid to be chromatographed, a fluid layer (48) being defined between a surface of the bed (14) and one (16a) of the ends of the column (12); a piston (36) sliding in the column (12), the piston (36) being one of the ends (16a, 16b) of the column (12); at least a first probe (45, 46) for detecting the surface of the bed (14), the probe (45, 46) being mounted on the end (16a) of the column (12) defining the layer (48); and means (52) for adjusting the position of the piston (36) according to the detection of the surface of the bed (14) by the probe (45, 46). The invention also relates to processes for separating at least two compounds of a fluid to be chromatographed and to methods of adjusting the position of the piston with respect to the surface of the chromatographic bed using the chromatography device. The invention has the advantage of allowing effective separation of the compounds of the fluid to be chromatographed while ensuring that the bed is protected.
Owner:NOVASEP SA
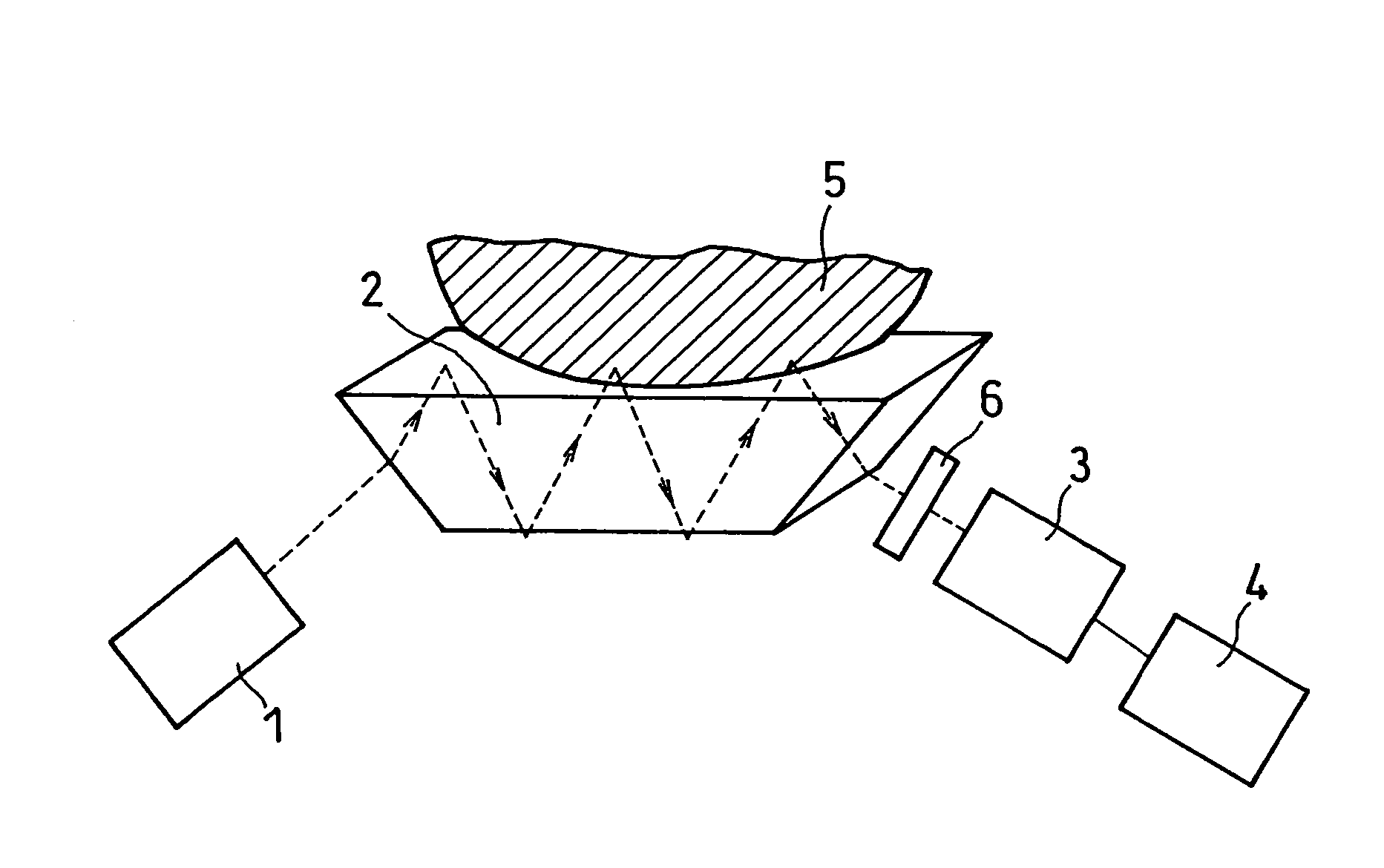
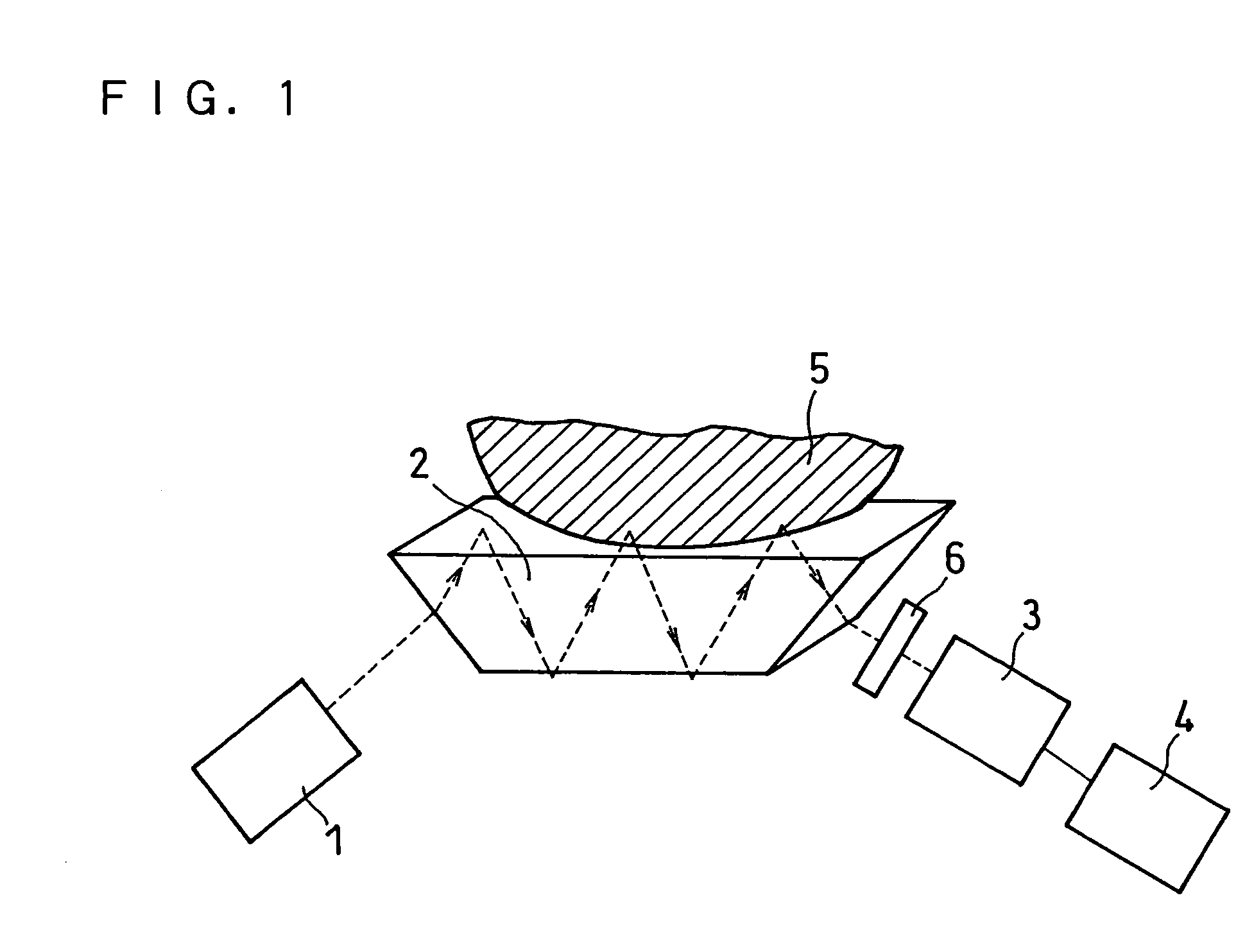
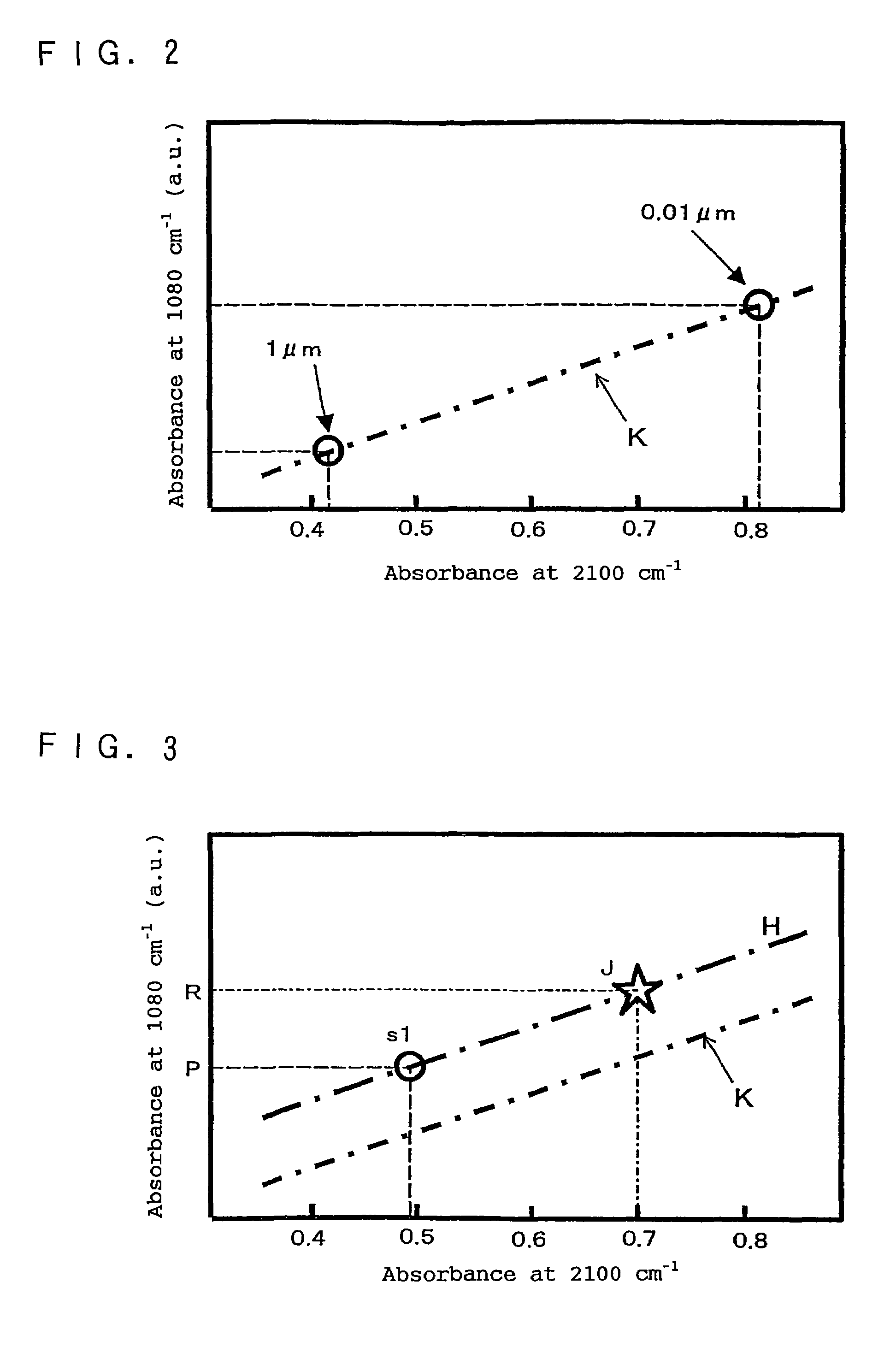
Ultrasonic inspection method
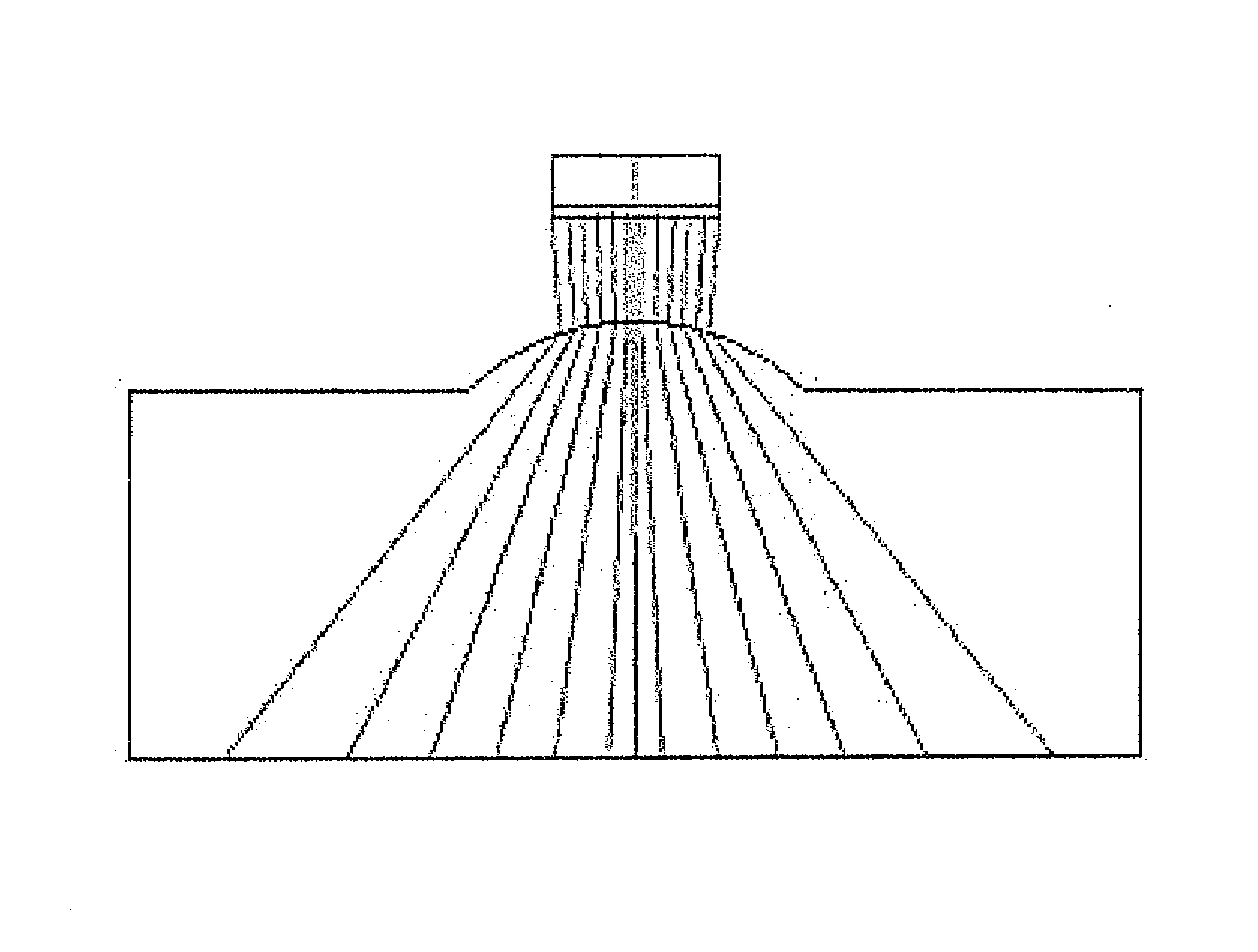
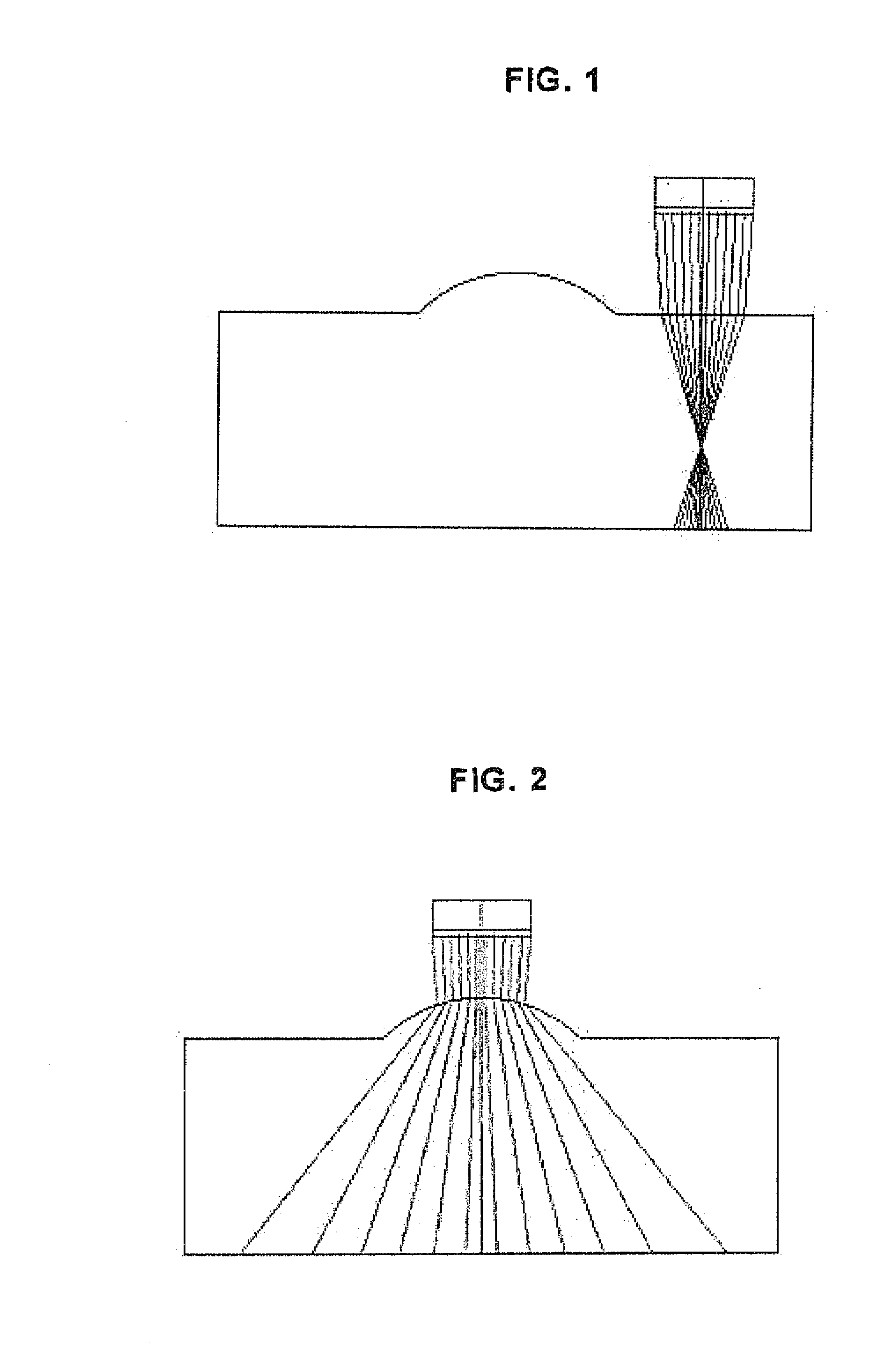
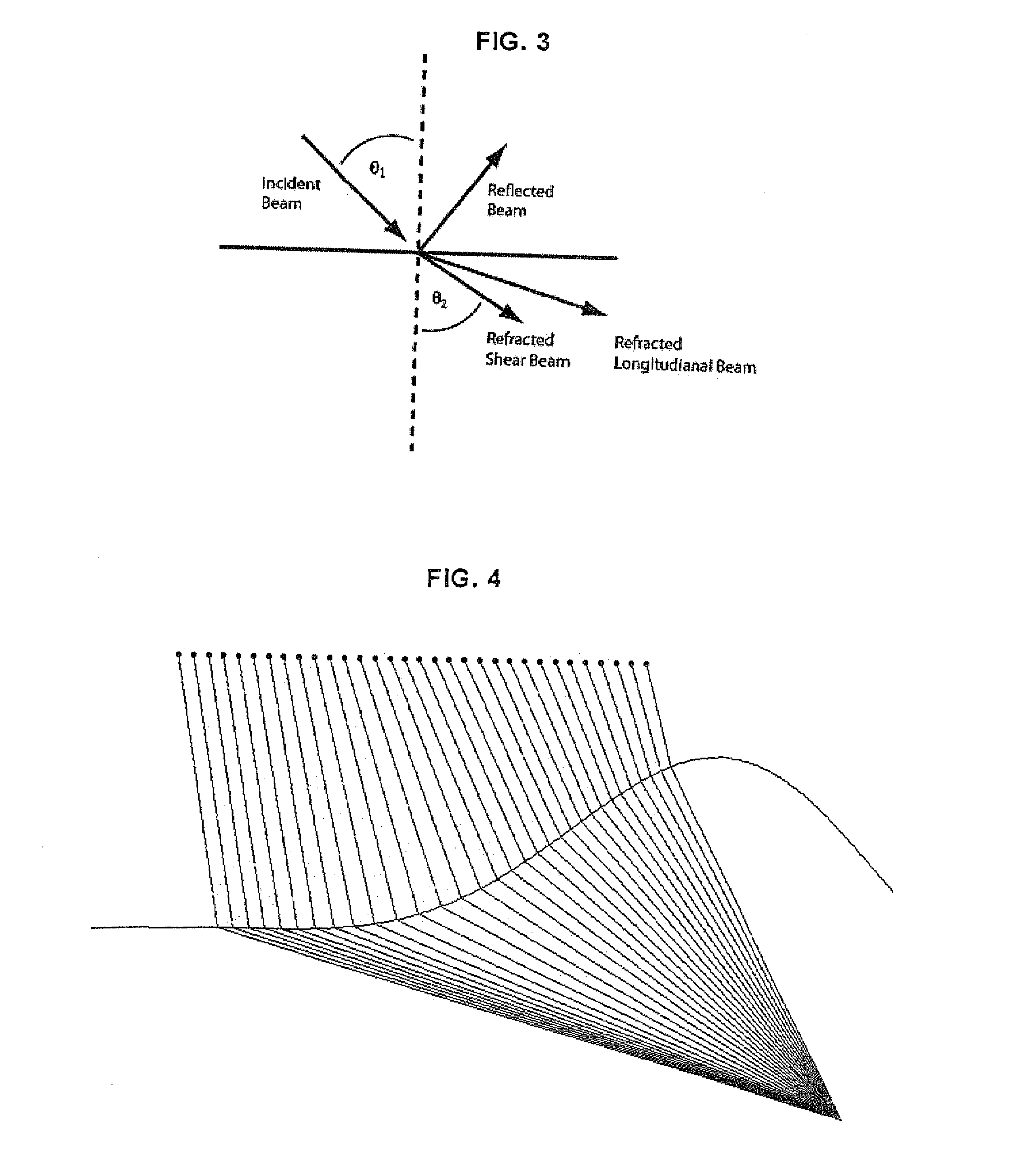
ActiveUS20080121040A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalUltrasound sonographyLight beam
A method for ultrasonically inspecting components with wavy or uneven surfaces. A multi-element array ultrasonic transducer is operated with a substantial fluid layer, such as water, between the array transducer and the component surface. This fluid layer may be maintained by immersing the component in liquid or by using a captive couplant column between the probe and the component surface. The component is scanned, measuring the two dimensional surface profile using either a mechanical stylus, laser, or ultrasonic technique. Once an accurate surface profile of the component's surface has been obtained, data processing parameters are calculated for processing the ultrasonic signals reflected from the interior of the component that eliminate beam distortion effects and reflector mis-location that would otherwise occur due to the uneven surfaces.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
Color electrowetting display (EWD) devices
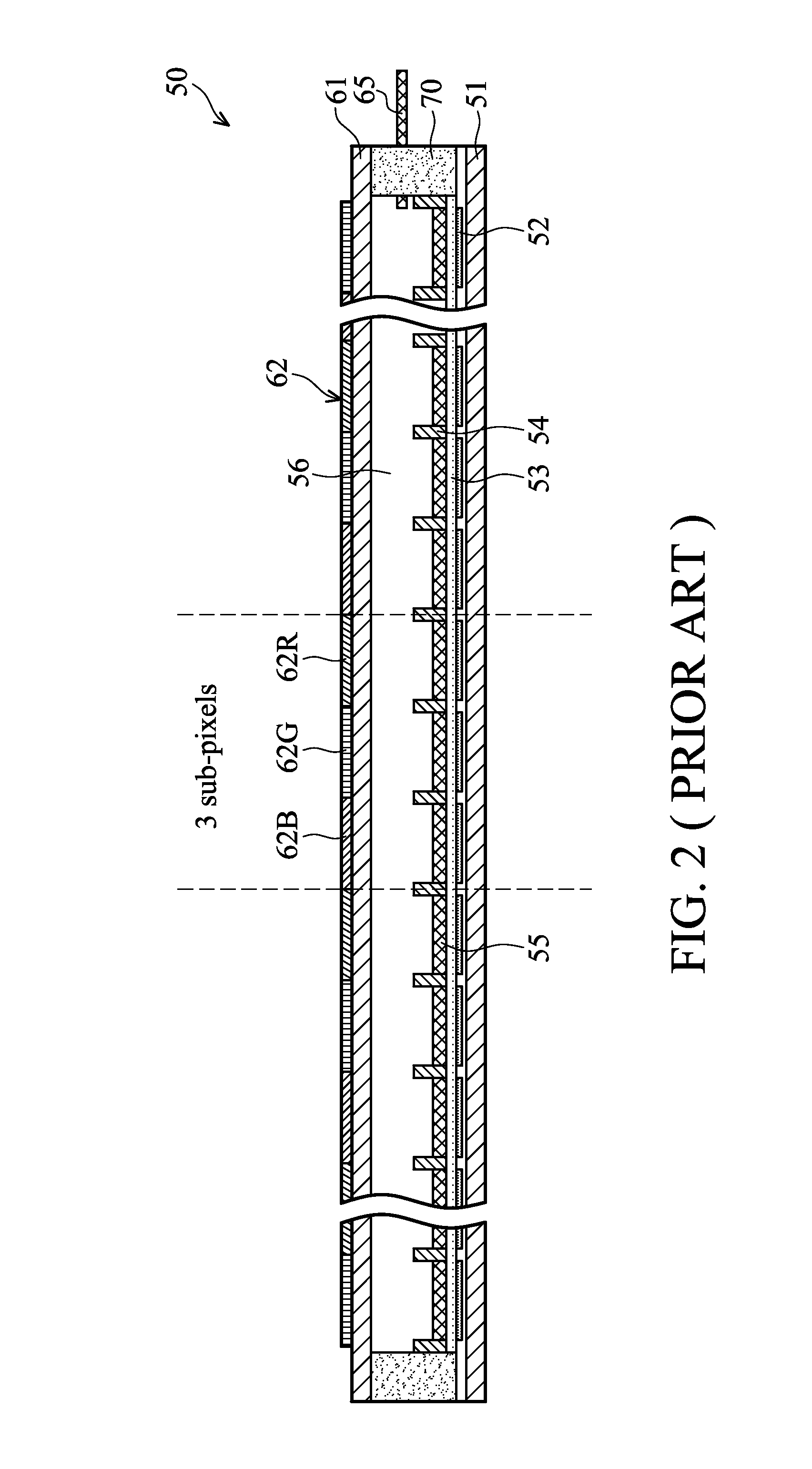
Electrowetting display devices are presented. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a color non-polar fluid layer interposed therebetween. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic partition structure is disposed on the second substrate, thereby defining a plurality of sub-pixels. The color electrowetting display further includes an array of color pixel regions. Each pixel region consists of a set of primary color sub-pixel. Each color sub-pixel corresponds to one of different color non-polar fluid layers, and each of the different color non-polar fluid layers is isolated from each other. The colors of non-polar fluid layer in the neighboring sub-pixels are different.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Protection of the chromatographic bed in dynamic axial compression chromatography devices
InactiveUS6843918B2Improve efficiencyMaintain validityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesChromatographic separationAxial compression
The invention relates to a chromatography device comprising:a column (12) intended to house, between its two ends (16a, 16b) a chromatographic bed (14) and a fluid to be chromatographed, a fluid layer (48) being defined between a surface of the bed (14) and one (16a) of the ends of the column (12);a piston (36) sliding in the column (12), the piston (36) being one of the ends (16a, 16b) of the column (12);at least a first probe (45, 46) for detecting the surface of the bed (14), the probe (45, 46) being mounted on the end (16a) of the column (12) defining the layer (48); andmeans (52) for adjusting the position of the piston (36) according to the detection of the surface of the bed (14) by the probe (45, 46).The invention also relates to processes for separating at least two compounds of a fluid to be chromatographed and to methods of adjusting the position of the piston with respect to the surface of the chromatographic bed using the chromatography device.The invention has the advantage of allowing effective separation of the compounds of the fluid to be chromatographed while ensuring that the bed is protected.
Owner:NOVASEP SA
Water curtain apparatus and method
ActiveUS7296785B2Lighting and heating apparatusUsing liquid separation agentEvaporative coolerFluid layer
Owner:HAYDEN JOHN B
Methods and apparatus using electrostatic atomization to form liquid vesicles
InactiveUS20070120280A1High transfection efficiencyUniform physicochemical propertyGlass/slag layered productsSeparation processesLipid formationFood flavor
The methods of the invention employ electrostatic atomization to form a compound droplet of at least two miscible fluids. The compound droplet comprises a core of a first fluid and a layer of a second fluid completely surrounding the core. The first fluid contains the agent to be encapsulated and the second fluid contains an encapsulating agent. The first and second liquids are miscible. The encapsulated droplets can contain a variety of materials including, but not limited to, polynucleotides such as DNA and RNA, proteins, bioactive agents or drugs, food, pesticides, herbicides, fragrances, antifoulants, dyes, oils, inks, cosmetics, catalysts, detergents, curing agents, flavors, fuels, metals, paints, photographic agents, biocides, pigments, plasticizers, propellants and the like and components thereof. The droplets can be encapsulated by a variety of materials, including, but not limited to, lipid bilayers and polymer shells. An additional complete or partial layer of a third fluid can be formed on the outside of the second fluid layer. The third fluid can contain a targeting or steric stabilizing agent.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Method and devices for prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers
ActiveUS20130174855A1Reduce morbidityPromote blood circulationOperating chairsVibration massageFluid layerBiomedical engineering
Method and devices for the prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers are described in which a portable support assembly may be worn by a bed-stricken individual around particular regions of the body where pressure ulcers tend to form. The portable support assembly may generally include one or more individual fluid filled pods which are enclosed entirely within an inner fluid pad localized along a central portion. Both the one or more pods and inner fluid pad are then enclosed entirely by another layer of fluid within an outer fluid pad which extends over the entire assembly. Each of the fluid lavers may be secured to an outer shell which is relatively stiffer than the fluid layers and may restrict or limit the expansion or movement of the fluid pods and / or fluid pads.
Owner:PRS MEDICAL TECH
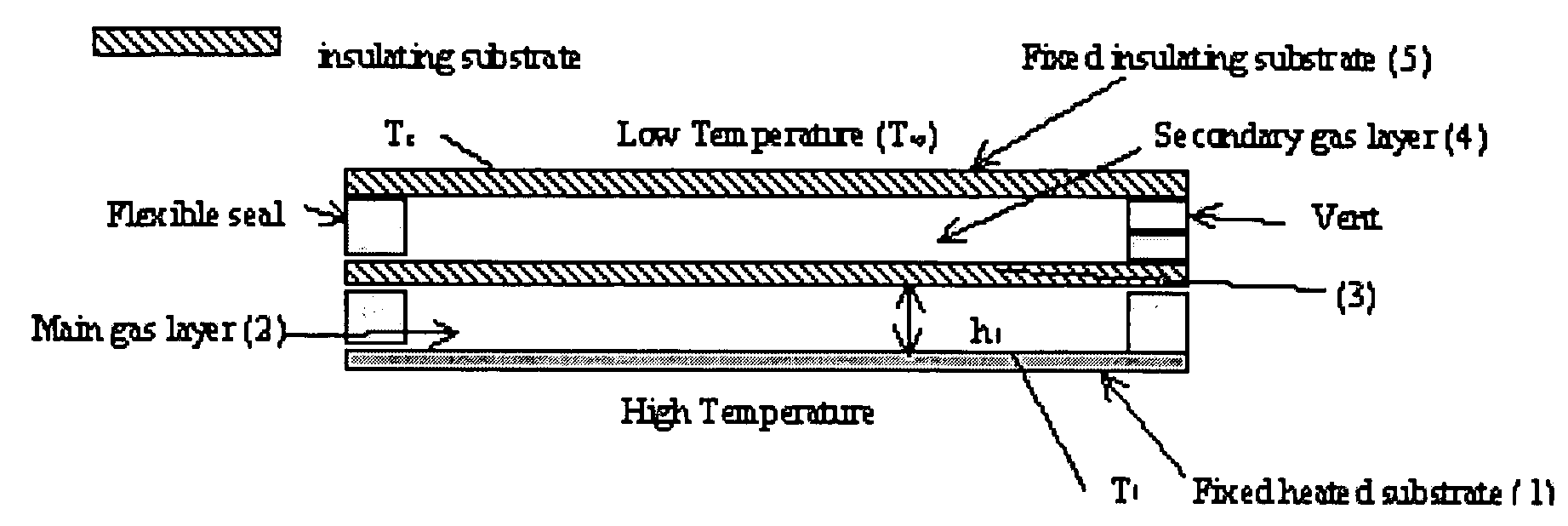
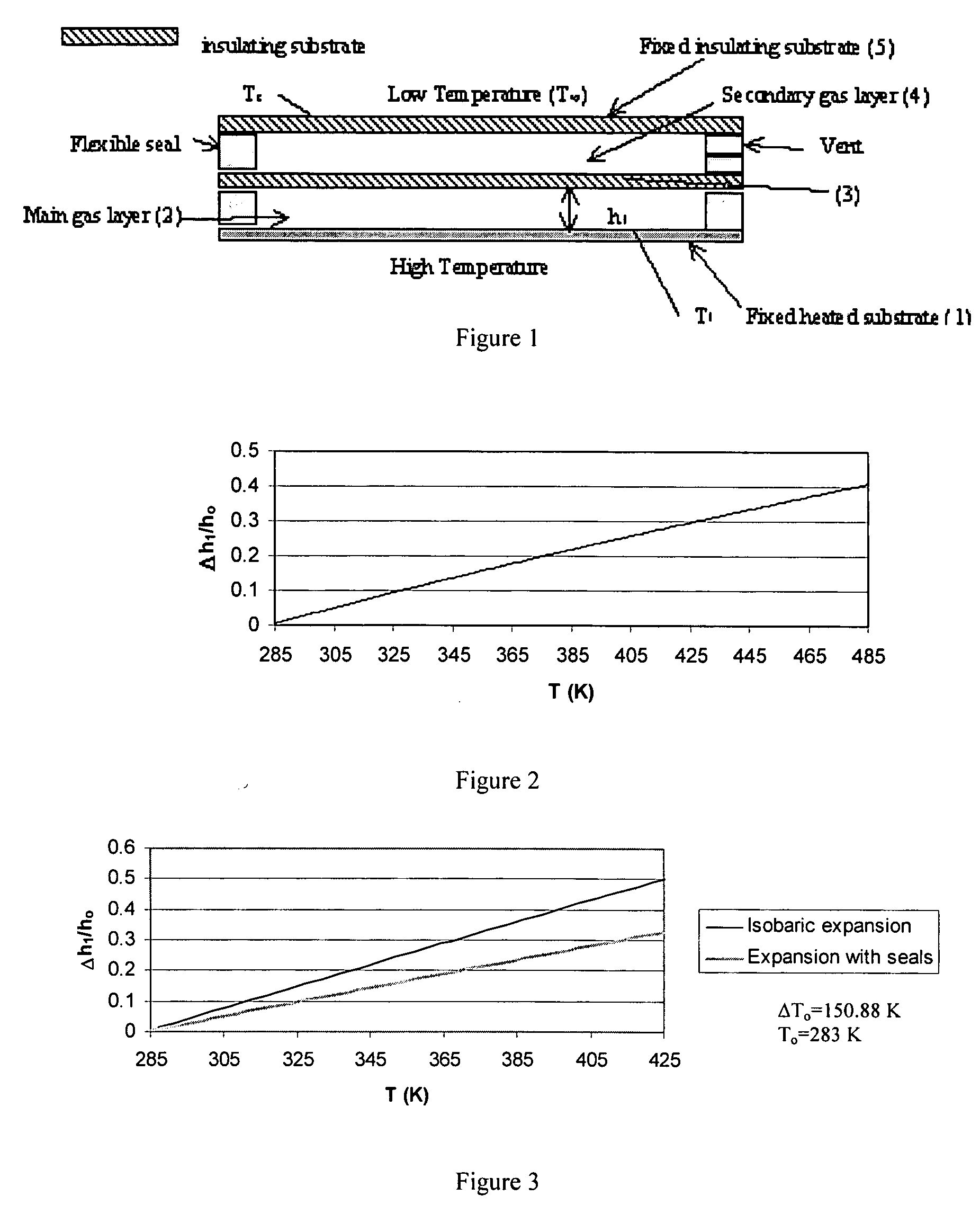
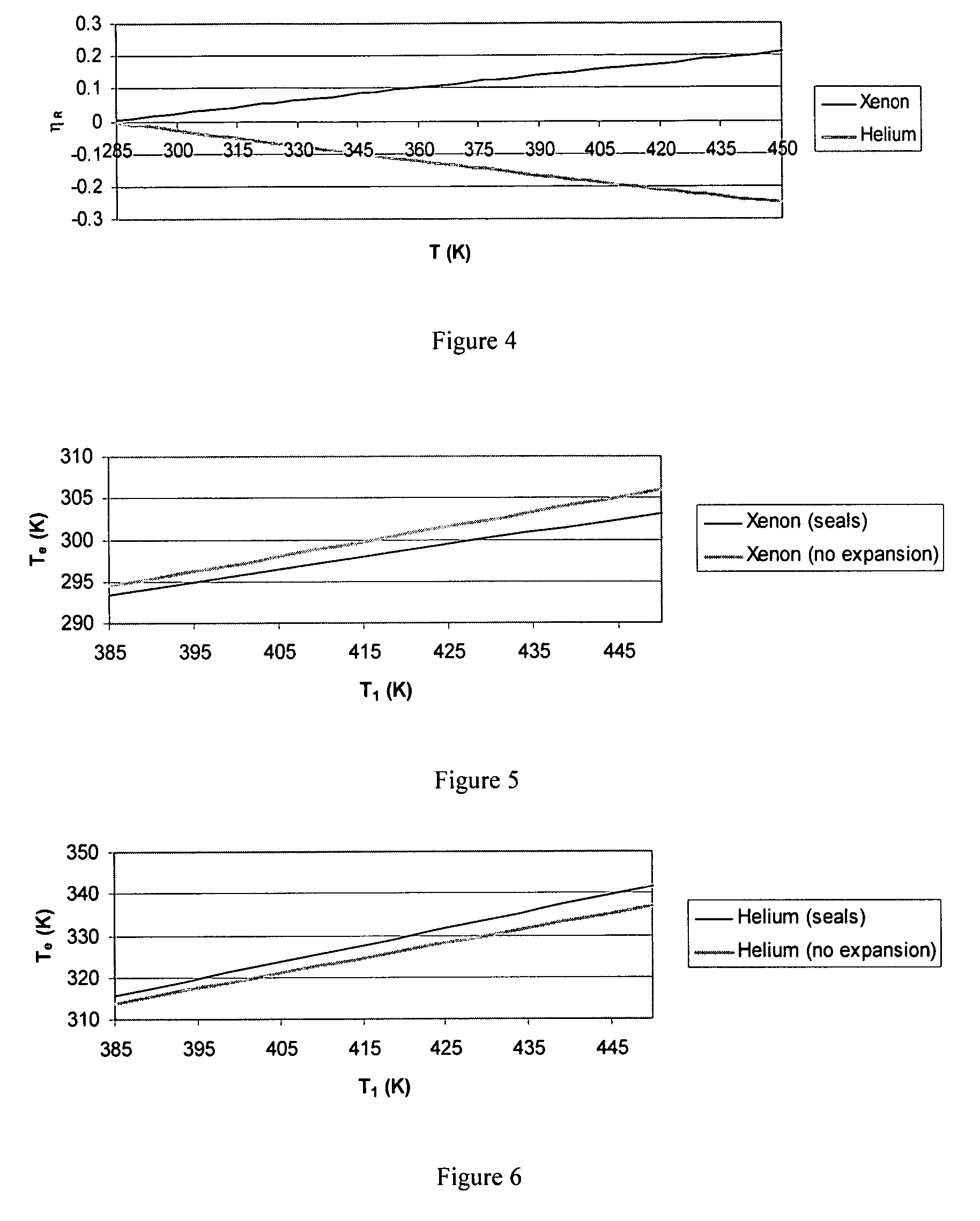
Methods and devices comprising flexible seals, flexible microchannels, or both for modulating or controlling flow and heat
InactiveUS20070084940A1Save heatReduce leakageMaterial nanotechnologyTemperature control without auxillary powerFluid layerEngineering
Disclosed herein are devices comprising at least one flexible seal, at least one flexible complex seal having at least one closed cavity containing a fluid, or a combination thereof. The devices may comprise at least one immobile and inflexible substrate and at least one mobile and inflexible substrate capable of movement due to the flexible seal, the flexible complex seal, or both. The flexible complex seals comprise at least one closed cavity comprising a fluid, such as a gas or a liquid. As disclosed, the presence or absence of heat will cause the mobile and inflexible substrate to move. The movement will increase or decrease the fluid amount or fluid flow rate in the primary fluid layer. Also disclosed are methods for enhancing the insulating properties of insulating assemblies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com