Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Polar fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
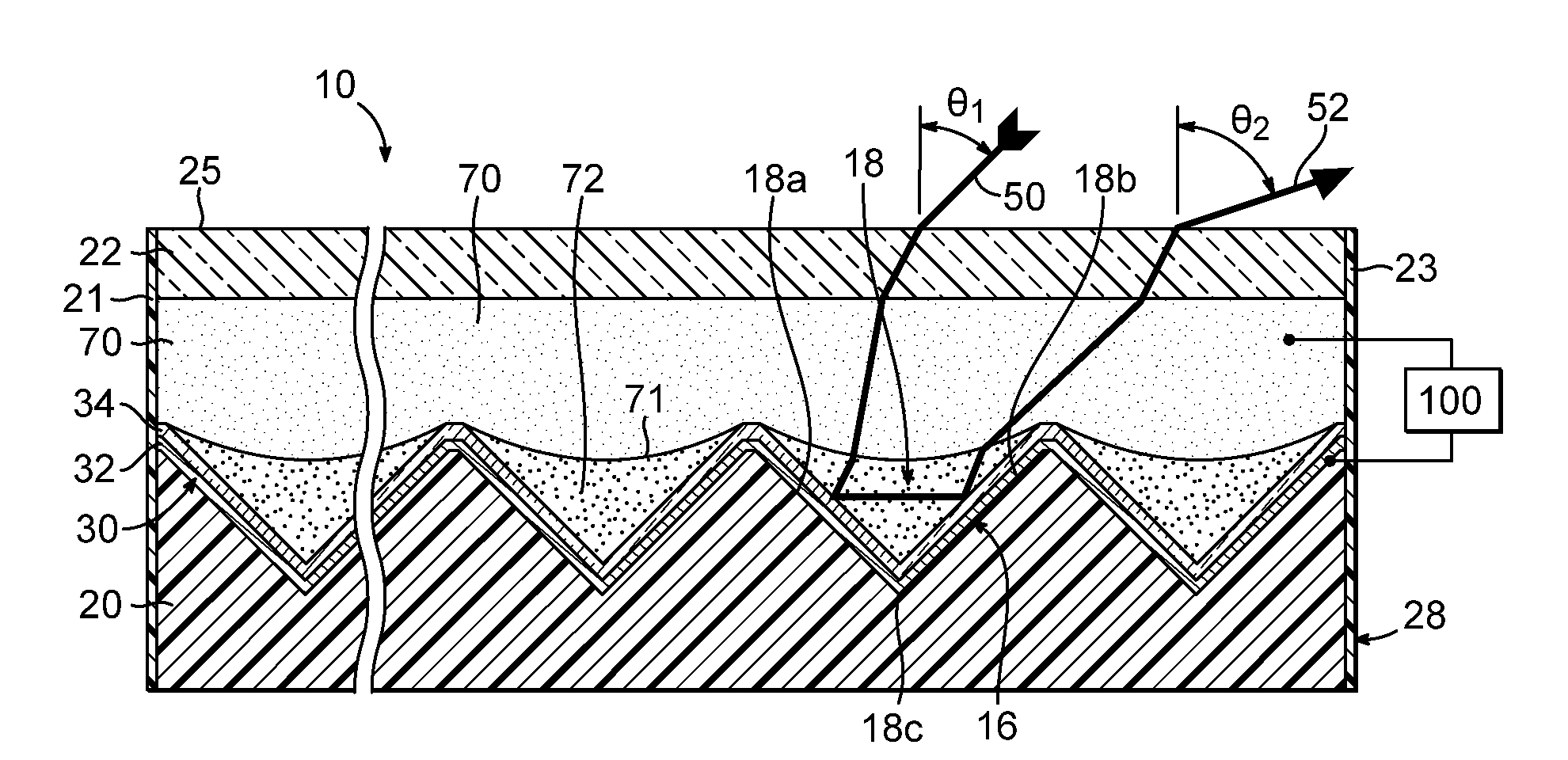
If the fluid is such that the torques within it arise only as the moments of direct forces we shall call it nonpolar. A polar fluid is one that is capable of transmitting stress couples and being subjected to body torques, as in polyatomic and certain non-Newtonian fluids.
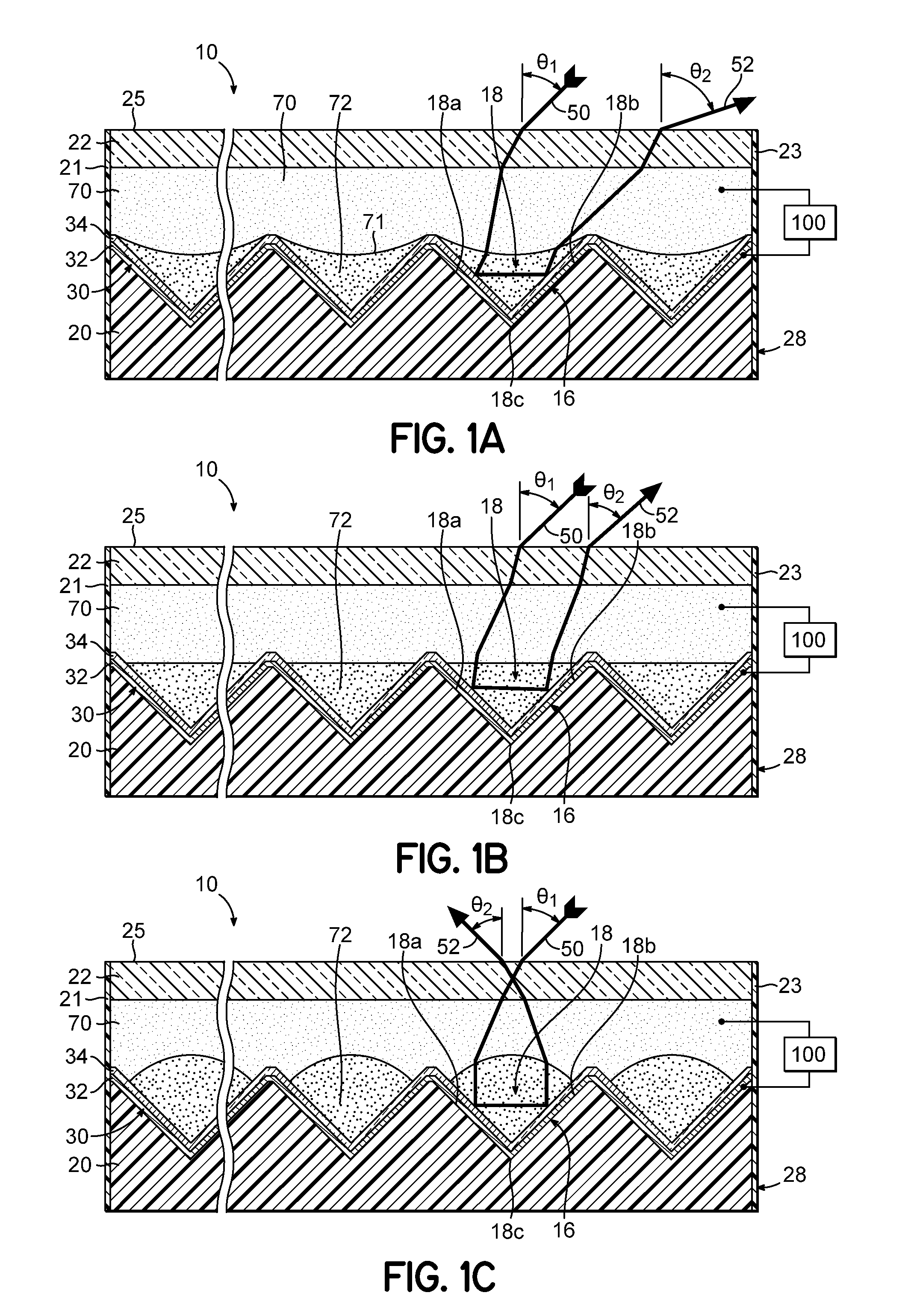
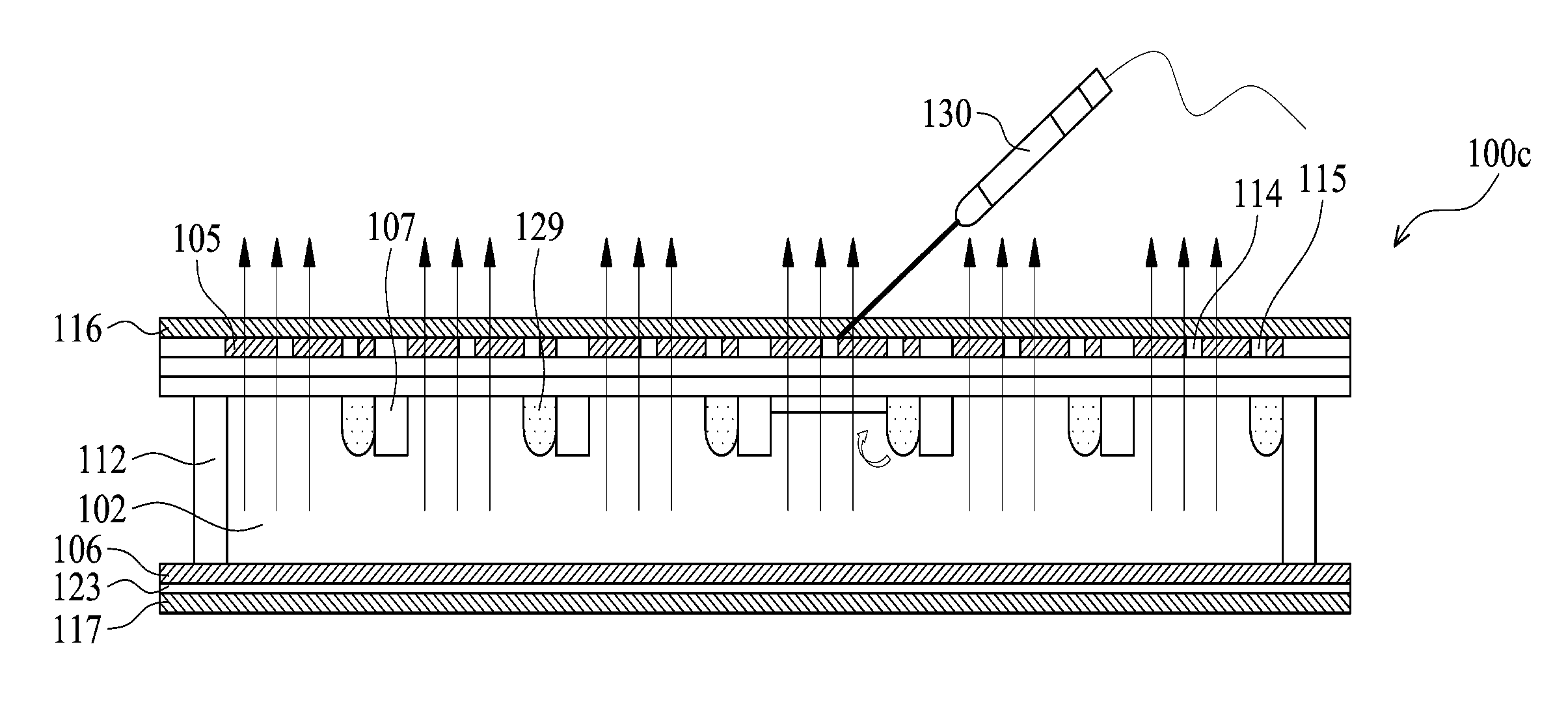
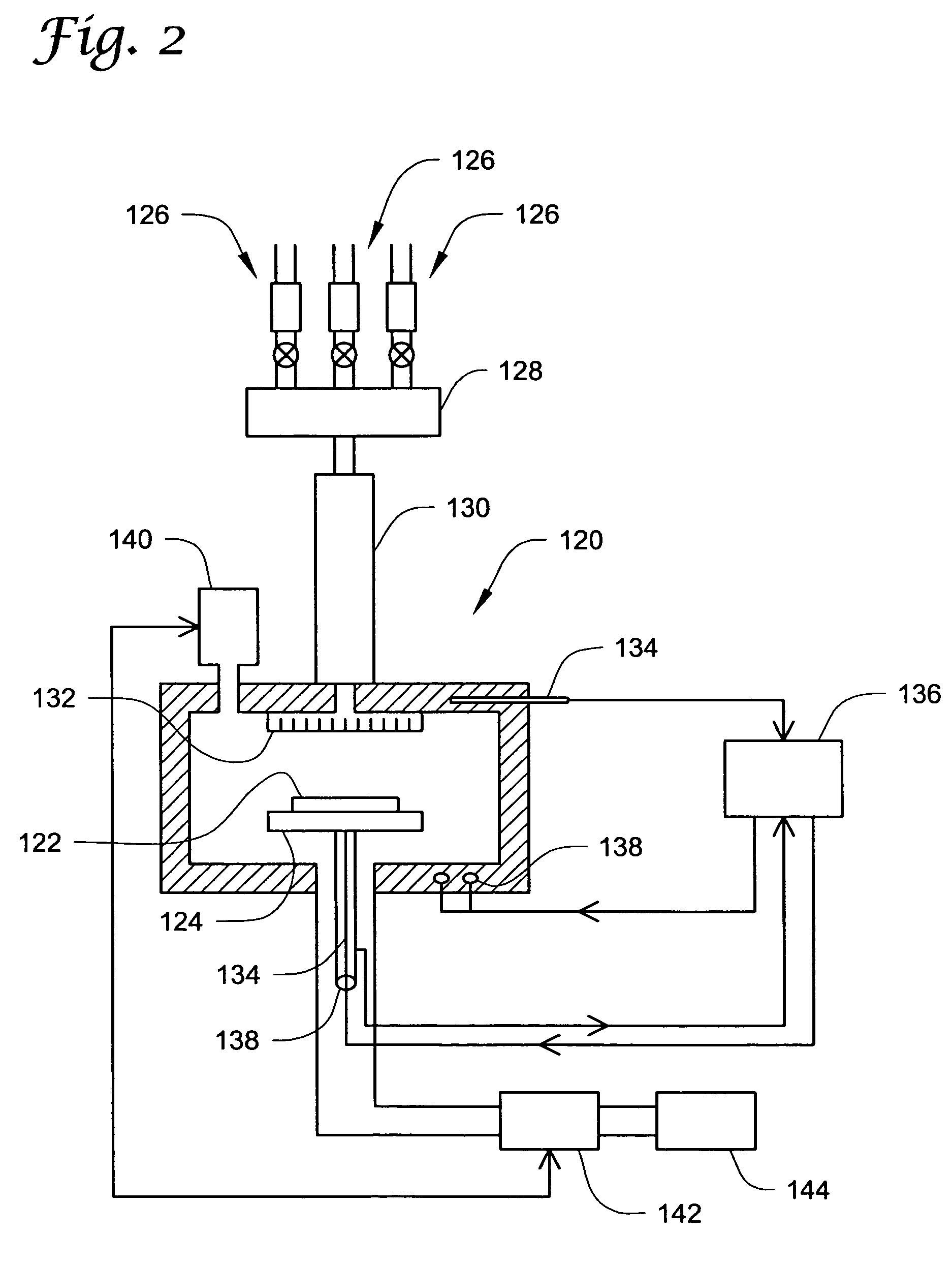
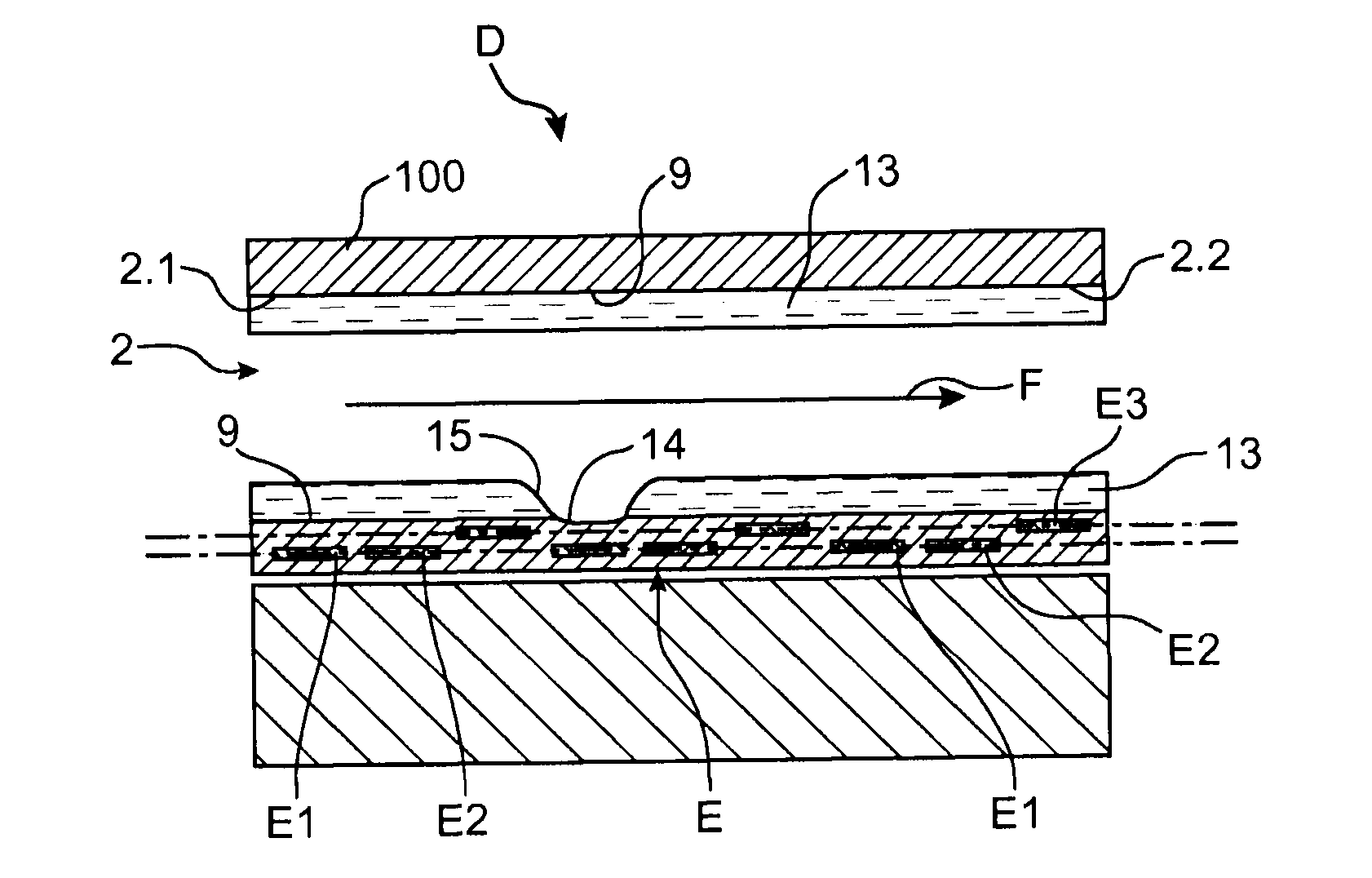
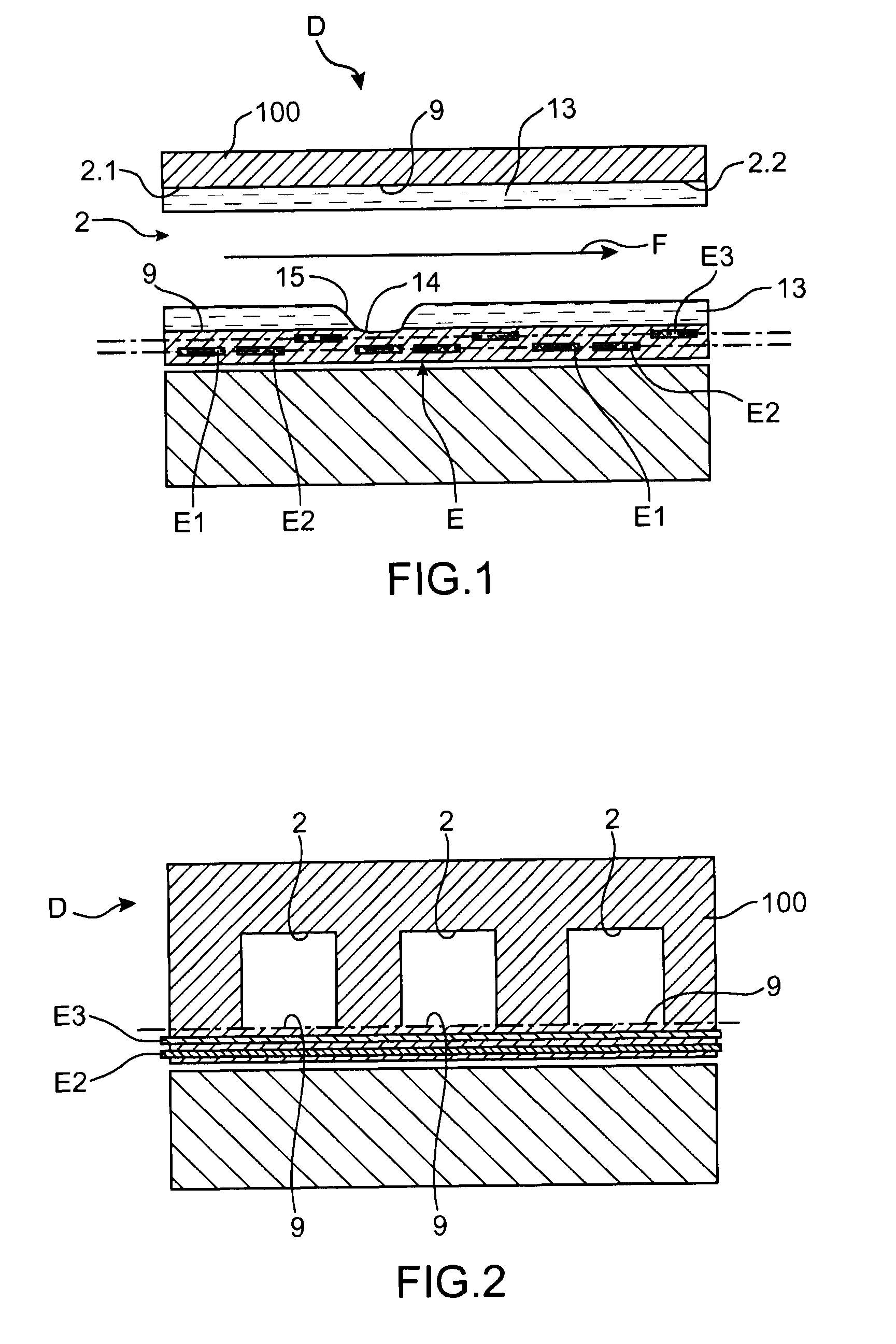
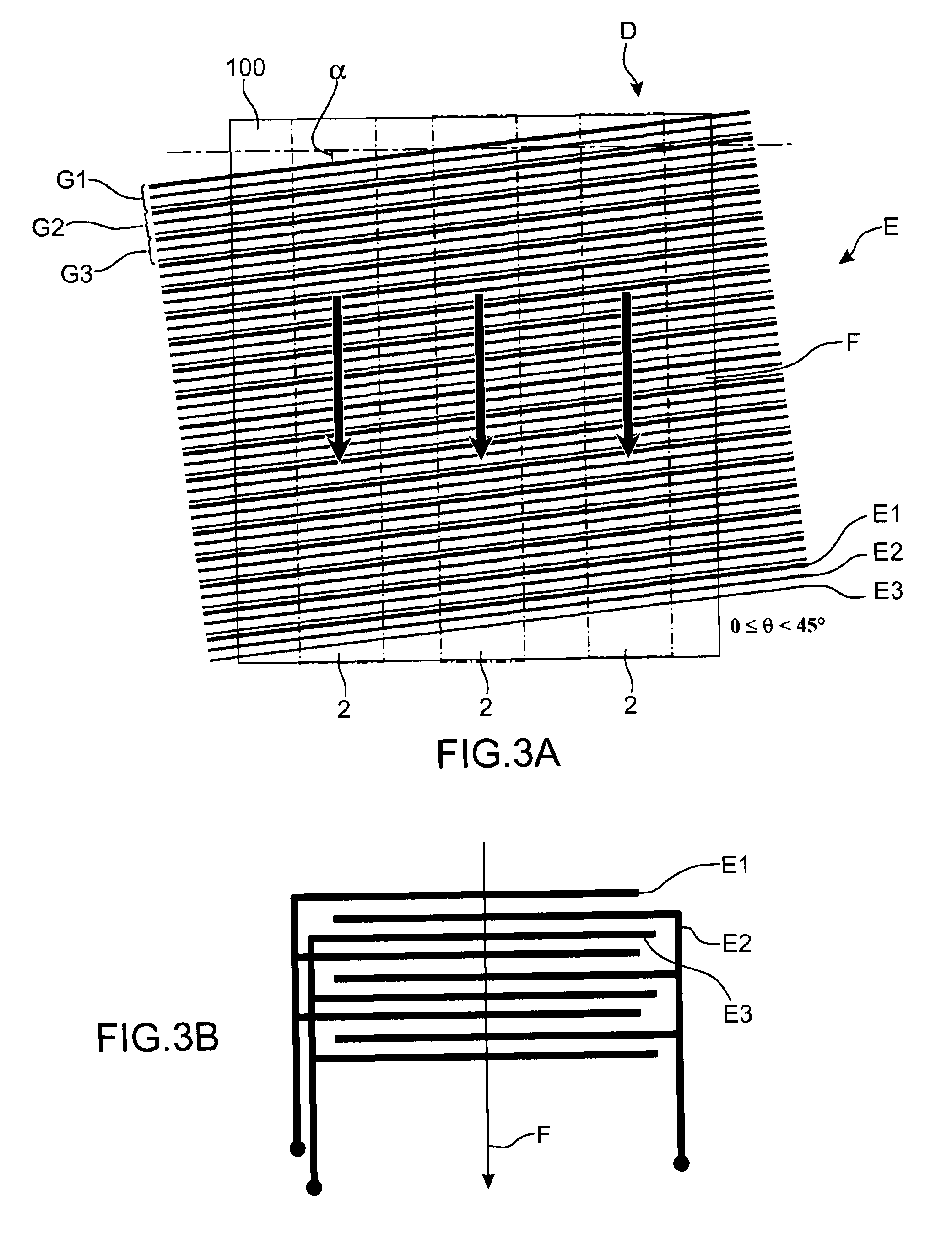
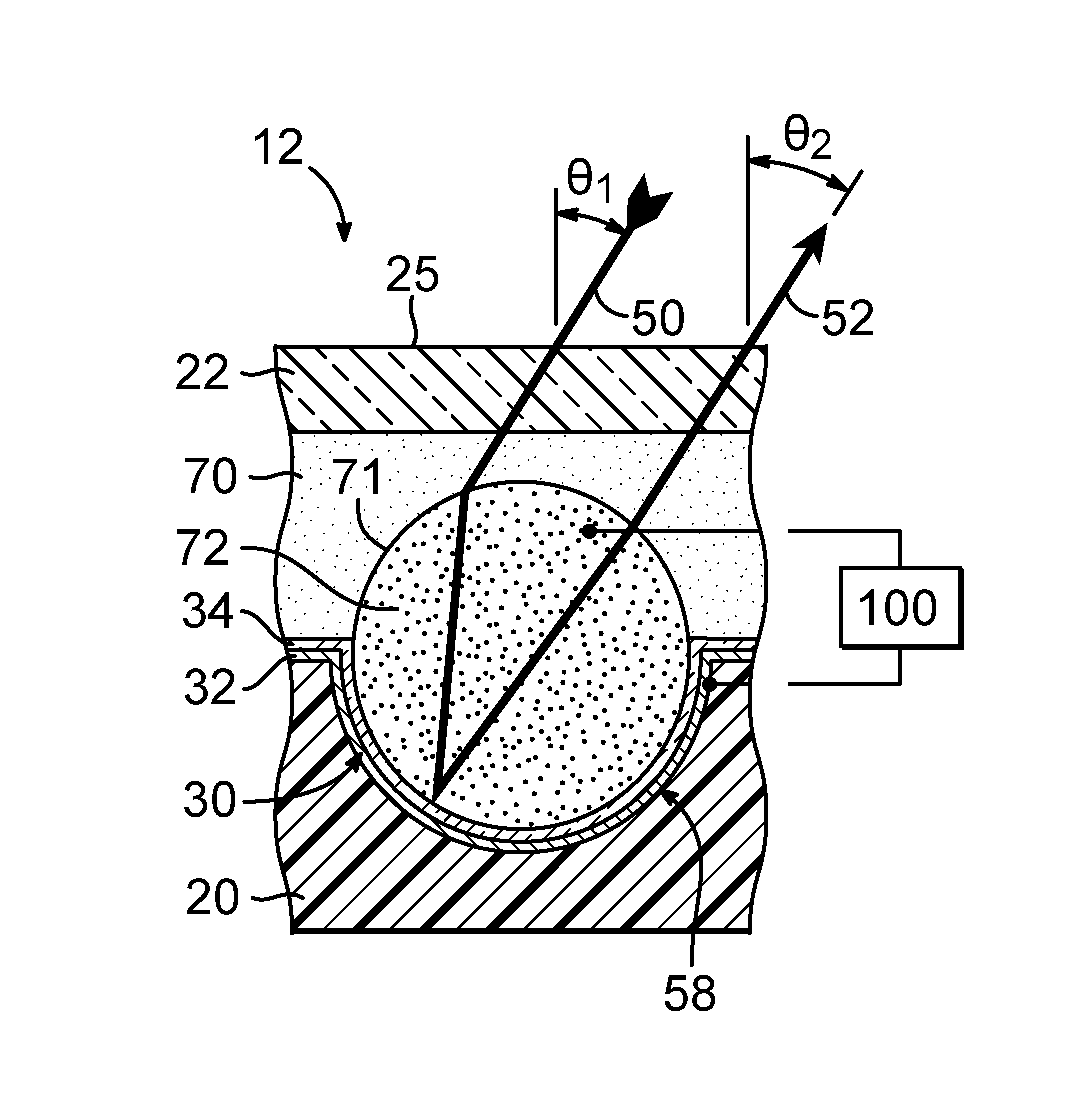
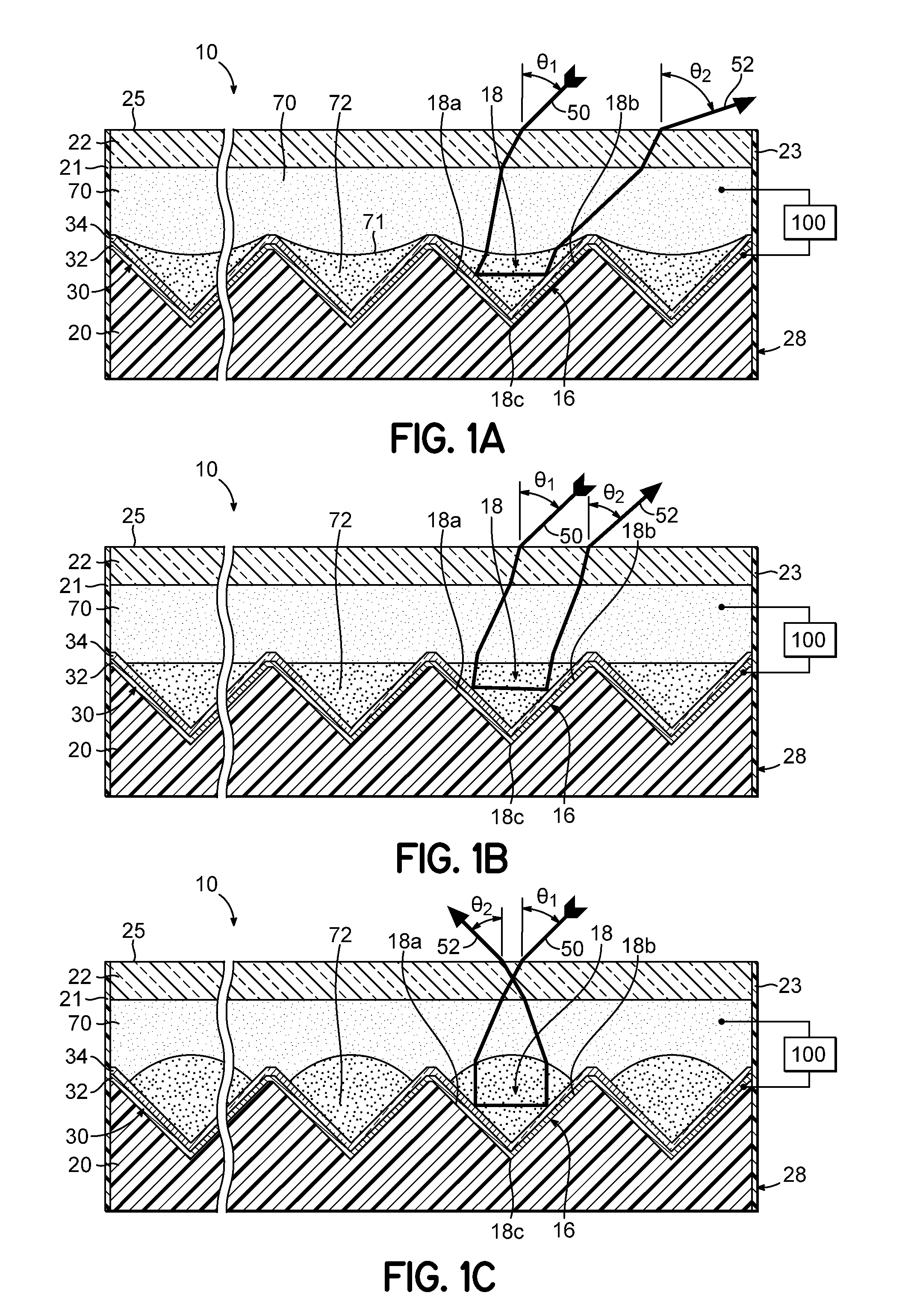
Electrowetting Display Devices
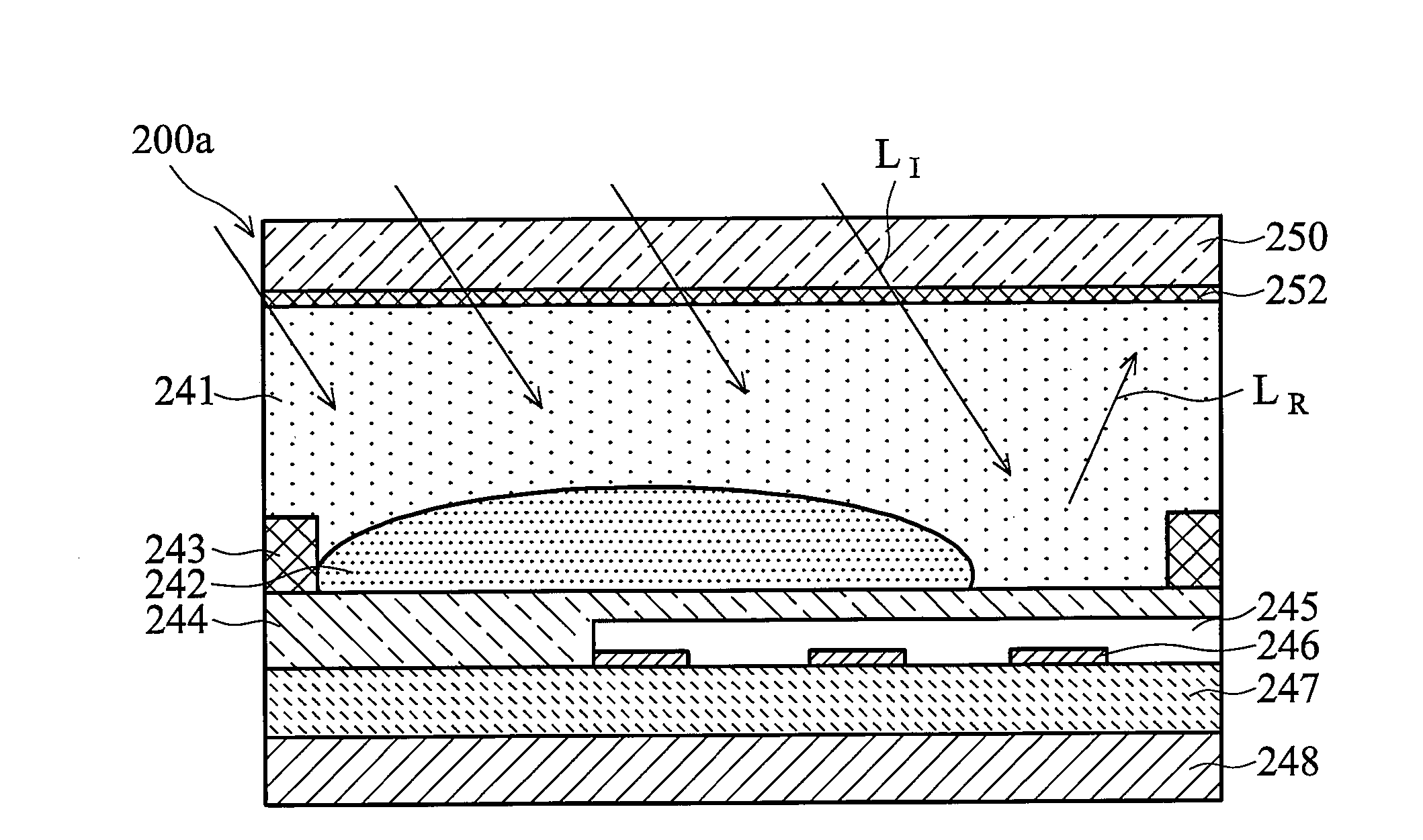
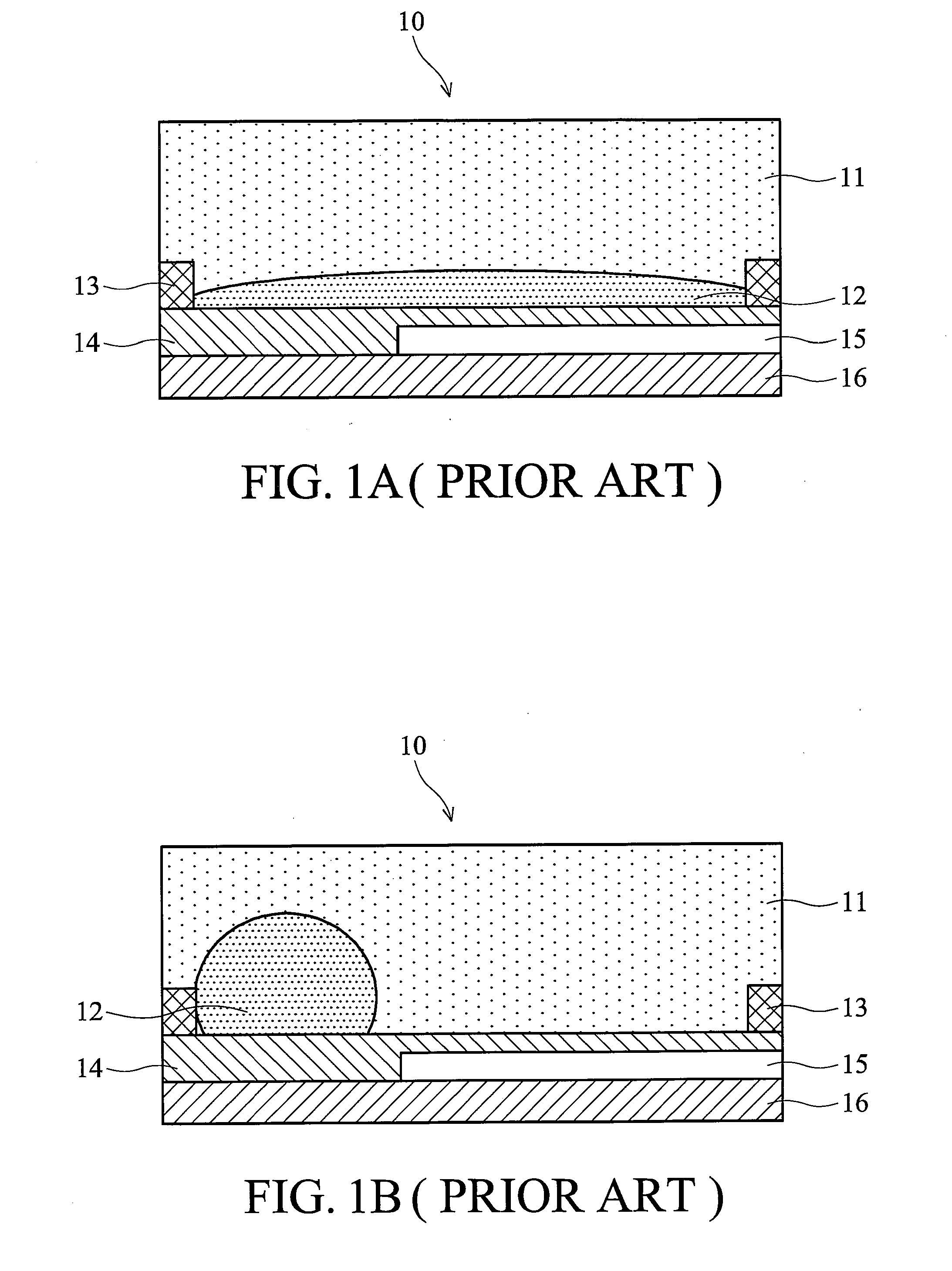
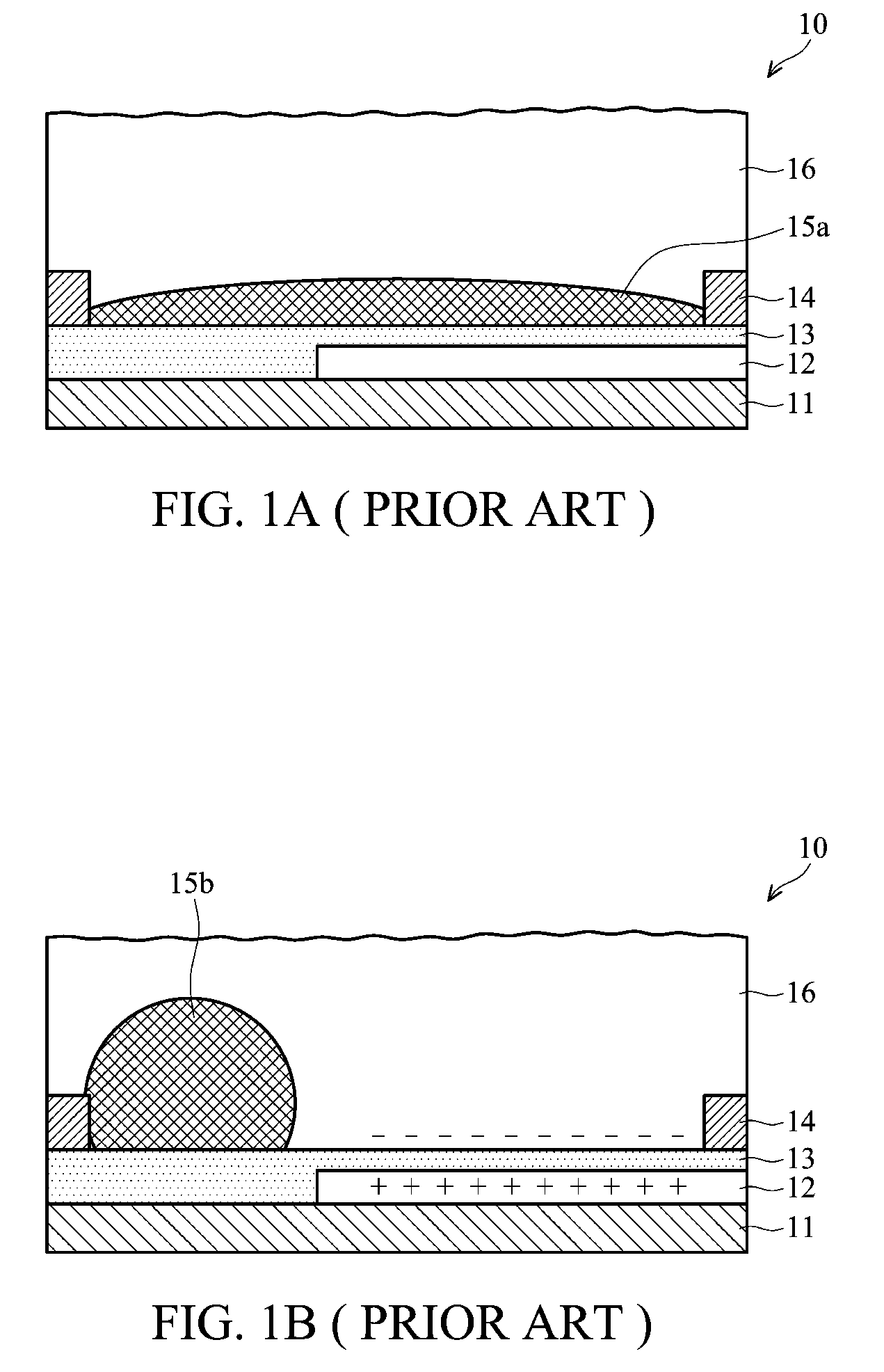
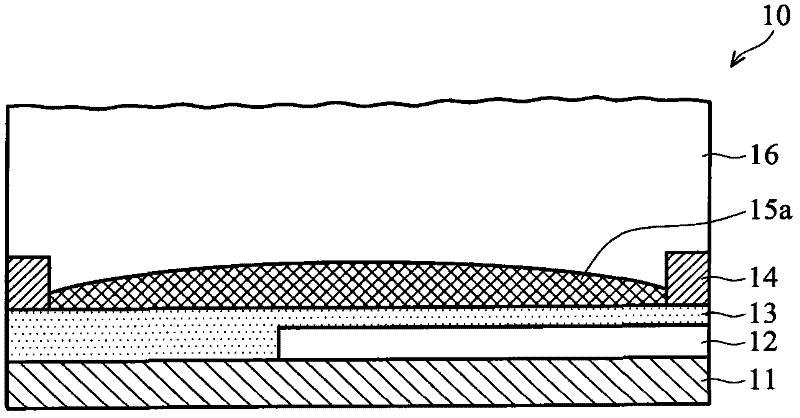
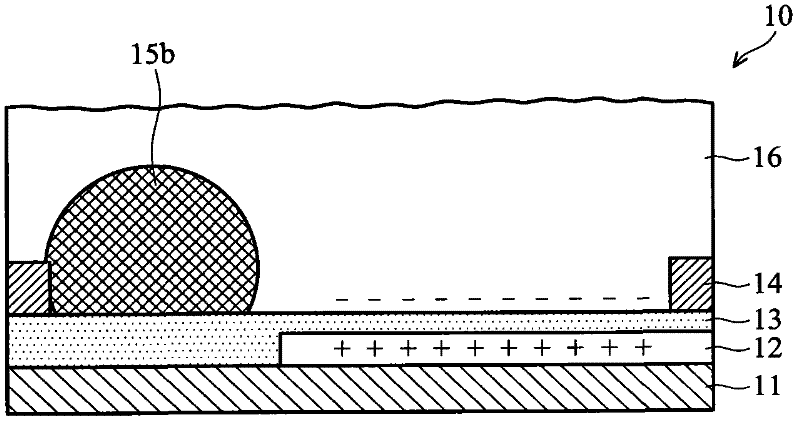
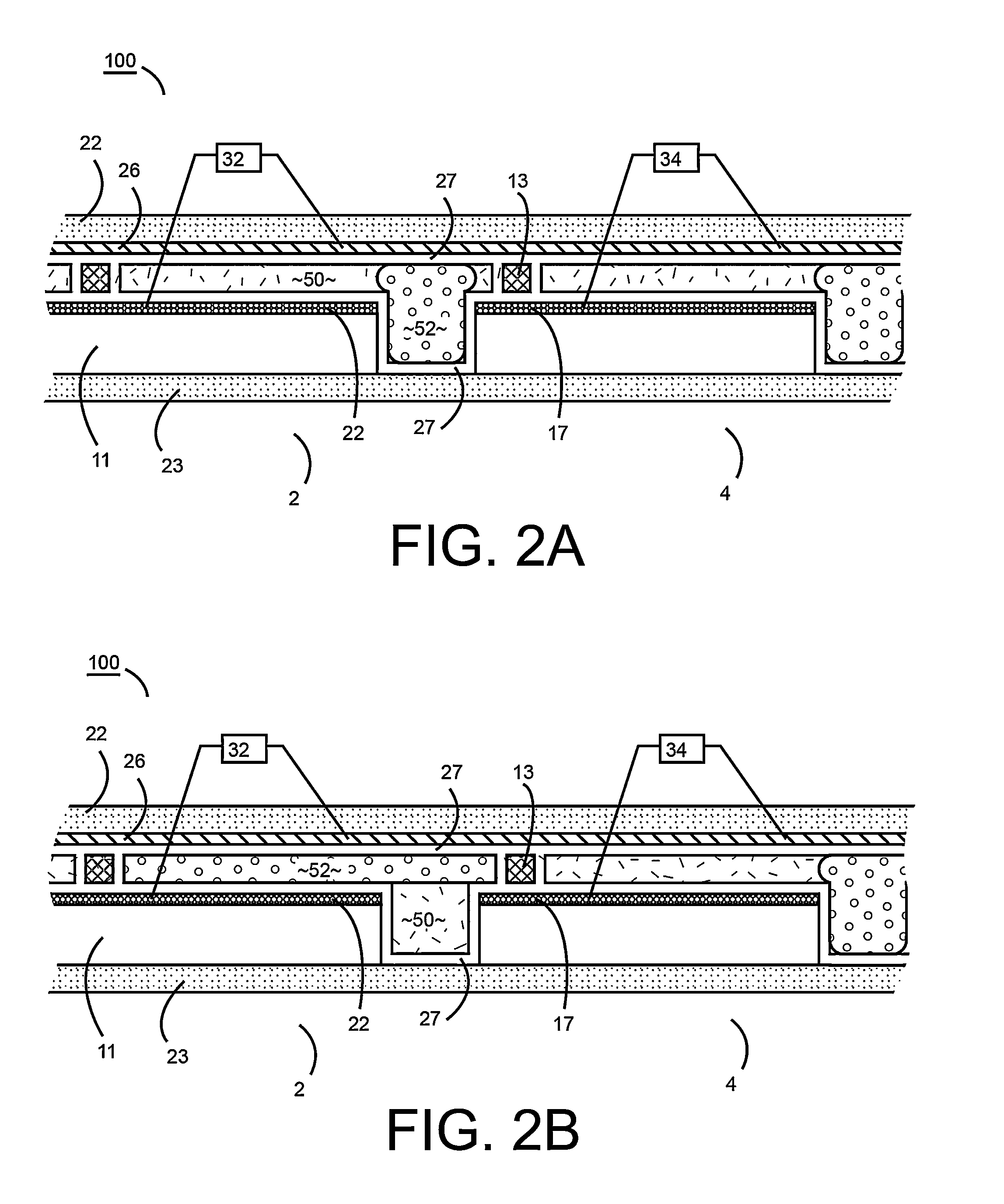
Electrowetting display devices are presented. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a transparent polar fluid layer and an opaque non-polar fluid layer insoluble with each other and interposed between the first and second substrates. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second transparent electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A dielectric layer is disposed on the second transparent electrode. A reflective plate structure is interposed between the second transparent electrode and the second substrate, thereby defining a reflective region and a transmission region. A backlight plate is disposed on the back of the second substrate. During operation, the opaque non-polar fluid converges, therefore, exposing equal areas of reflective region and transmission region.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Electrofluidic imaging film, devices, and displays, and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20120081777A1Optical lossReduce eliminateVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureOptical elementsElectricityDisplay device
A device and method of making and using the same. The device includes first and second substrates that are spaced to define a fluid space. Polar and non-polar fluids occupy the fluid space. A first electrode, with a dielectric layer, is positioned on the first substrate and electrically coupled to at least one voltage source, which is configured to supply an electrical bias to the first electrode. The fluid space includes at least one fluid splitting structure that is configured to facilitate the movement of the non-polar fluid into a portion of the polar fluid. Fluid splitting structure assisted movement of the non-polar fluid splits the polar fluid.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Advanced thermal properties of a suspension with graphene nano-platelets (GNPS) and custom functionalized f-gnps
InactiveUS20140312263A1Improve thermal performanceMinimal negative mechanical effectHeat-exchange elementsPower electronicsElectric power
A method for producing nanofluids with multilayered graphene nanoplatelets for providing improved heat transfer coolant fluids. A method for optimizing the concentration of nanoplatelets based on their morphology that allows achieving high thermal conductivity and low viscosity thus resulting in high heat transfer coefficient. A method is provided to functionalize as received graphene nanoplatelets by oxidaitively treating the multilayered graphene / nanothin graphite to generate highly dispensable nanoparticles for suspension in polar fluids for cooling thermal sources, such as power electronics and other heat transfer cooling applications.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
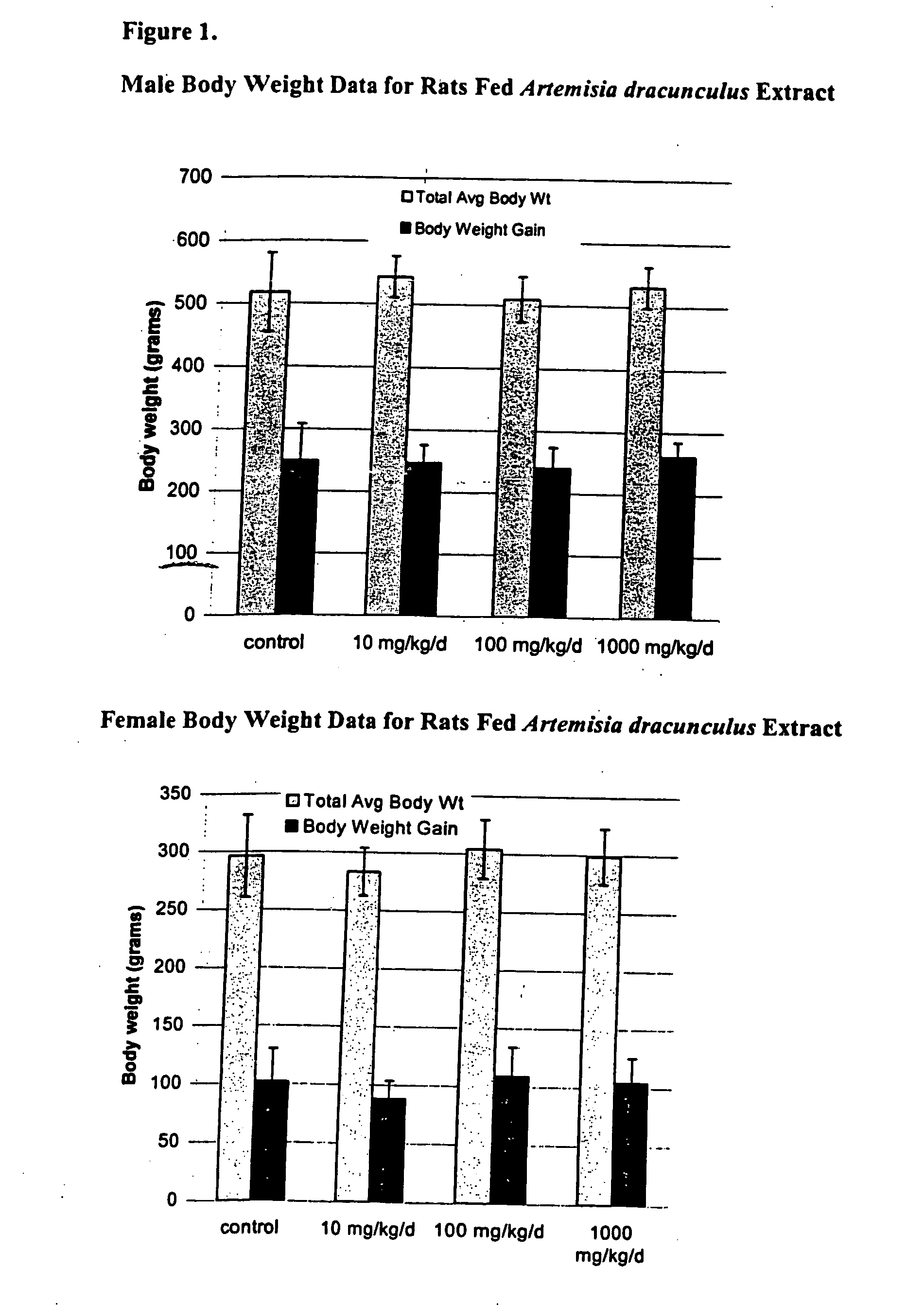
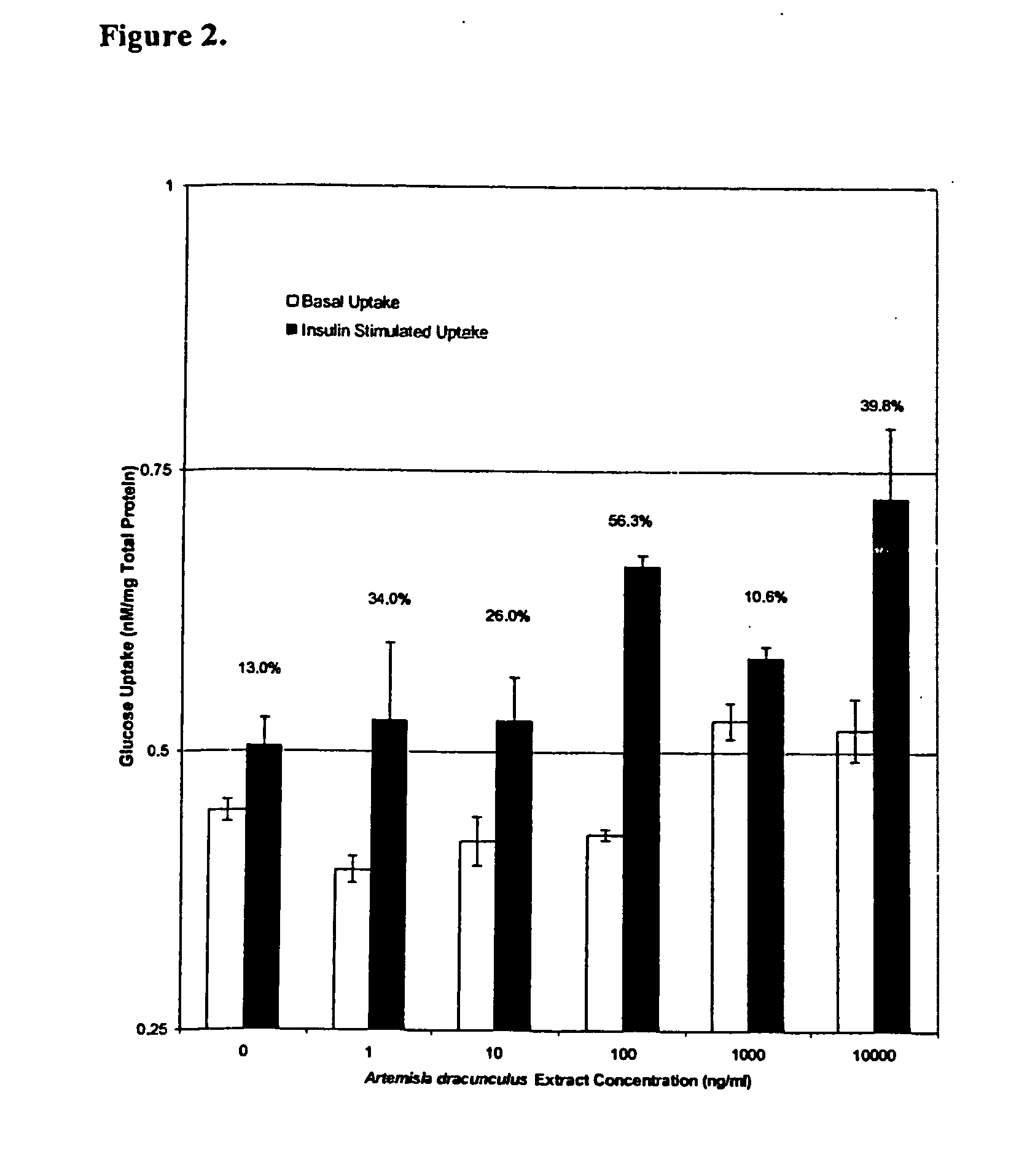
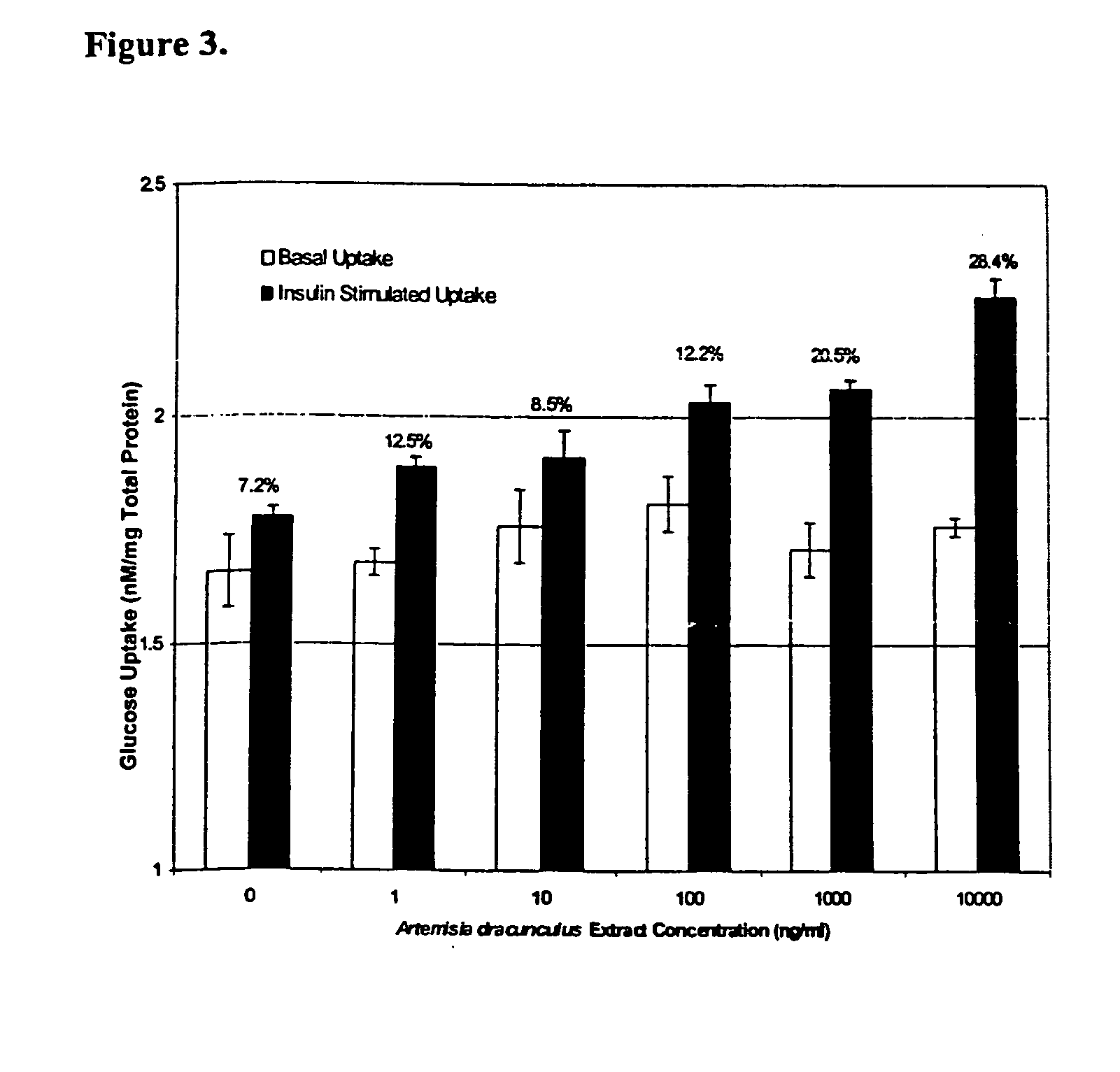
Methods for treating disorders using plant extracts
InactiveUS20050069598A1High affinityInhibit gastric emptyingAntibacterial agentsBiocideMammalFractionation
The present invention provides materials and methods relating to mildly polar fluid extracts of plant materials, such as Artemisia plant species, useful in methods for treating diabetes and methods for modulating the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and in methods for modulating phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) activity in a diabetes-specific manner. The extracts are generally non-toxic and non-mutagenic and may be administered to diabetics with beneficial effect on blood glucose levels. The extracts may also be administered to non-diabetics without deleterious effect. The plants are easily grown with a minimum of time, labor, and cost. Extracts are inexpensively and quickly prepared without the need for fractionation to remove potentially deleterious compounds, and the extracts may be administered to mammals such as humans through various routes, in a variety of forms, and at convenient concentrations.
Owner:RIBNICKY DAVID M +1
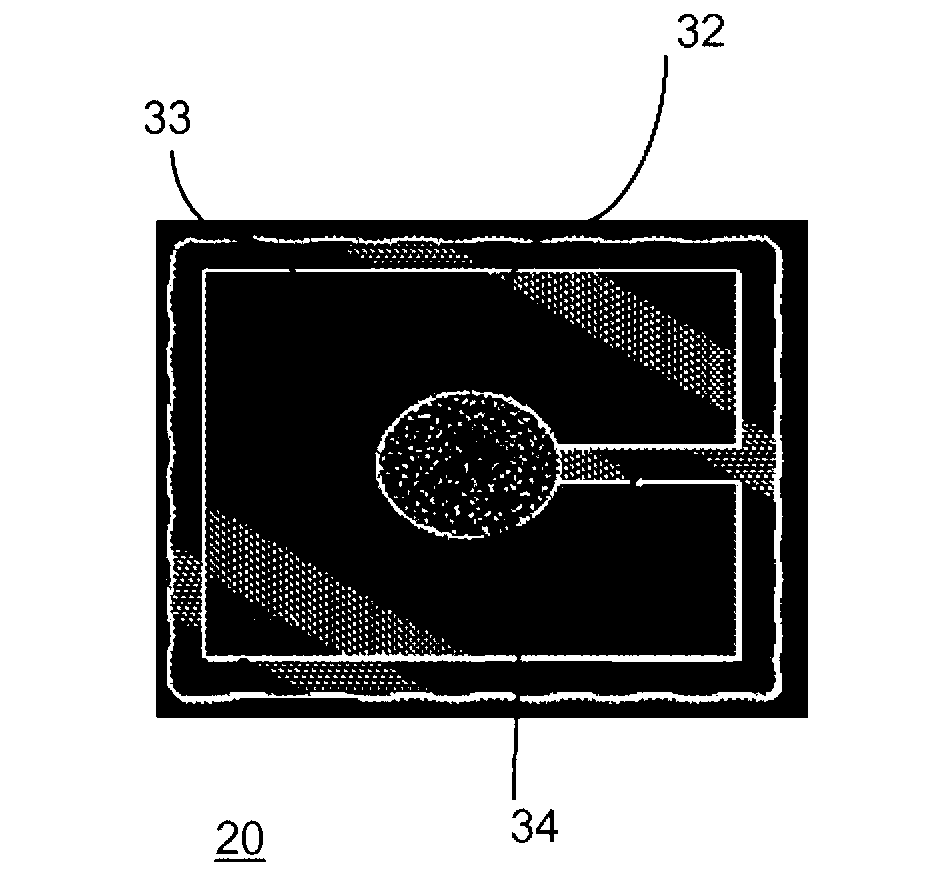
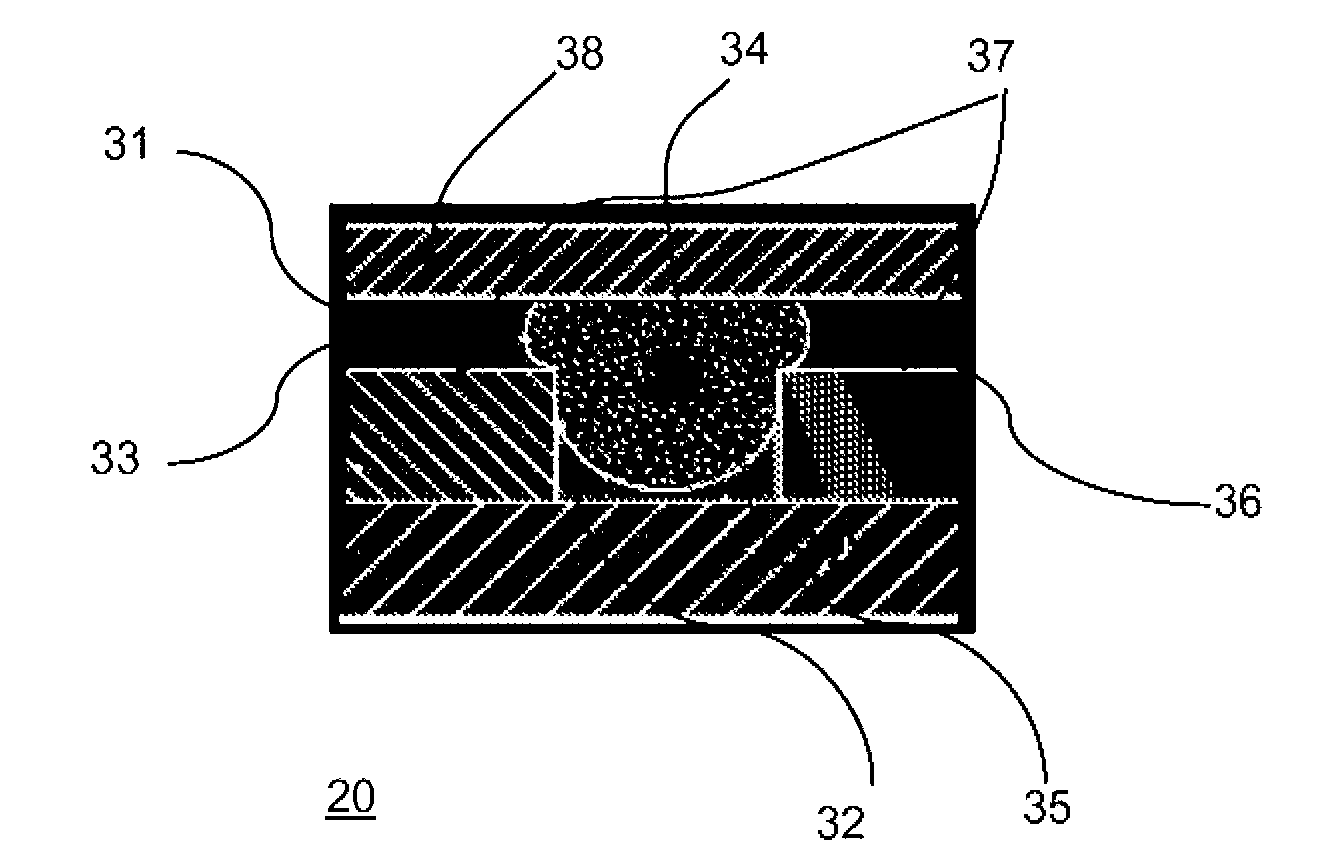
Electrowetting retroreflector devices, systems, and methods
Switchable retroreflector devices that are modulated via electrowetting. The devices include an electrically-conductive polar fluid and a non-polar fluid that is immiscible with the polar fluid. The polar and the non-polar fluids differ in at least one optical property. The fluids are contained in a fluid vessel, or an array of fluid vessels. The fluids are at least partially viewable. A voltage source is configured to selectively apply an electromechanical force to the polar fluid causing repositioning and / or geometrical change of the fluids such that retroreflection in created, or suppressed, by optical refraction or by optical attenuation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Electrowetting display devices and fabrication methods thereof
InactiveUS7746540B2Simplify the manufacturing processSimple structureCoatingsSpecial surfacesFluid layerDisplay device
Electrowetting display devices and fabrication methods thereof are presented. The electrowetting display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer insolvable to each other and interposed between the first and second substrates. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A dielectric layer is disposed on the second electrode. A hydrophilic partition wall structure is directly disposed on the dielectric layer defining a plurality of pixel regions. A layer of low surface energy material is disposed on the dielectric layer within each of the pixel region.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Electrowetting display devices
InactiveUS20100225611A1Static indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingFluid layerDisplay device
Electrowetting display devices are provided. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer interposed between the first and second substrates. A first electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic bank structure is disposed on the first substrate, and a reflective layer is disposed on the second substrate, wherein the first substrate of the electrowetting display serves as a display face.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Electrofluidic chromatophore (EFC) display apparatus
InactiveUS20130141405A1Increase the cell apertureLarge aperture EFDCathode-ray tube indicatorsPrinted circuit manufacturePolar fluidNon polar
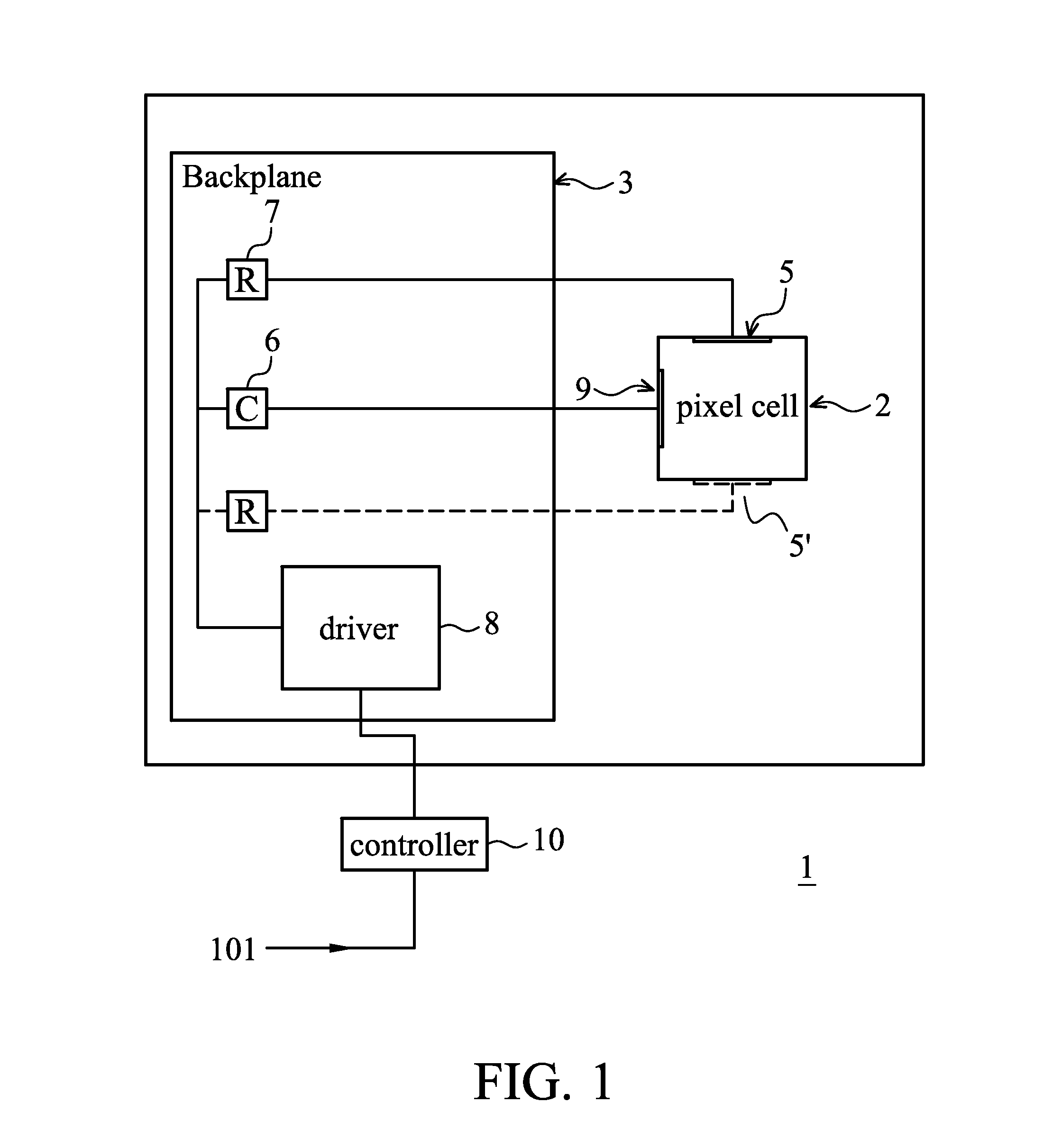
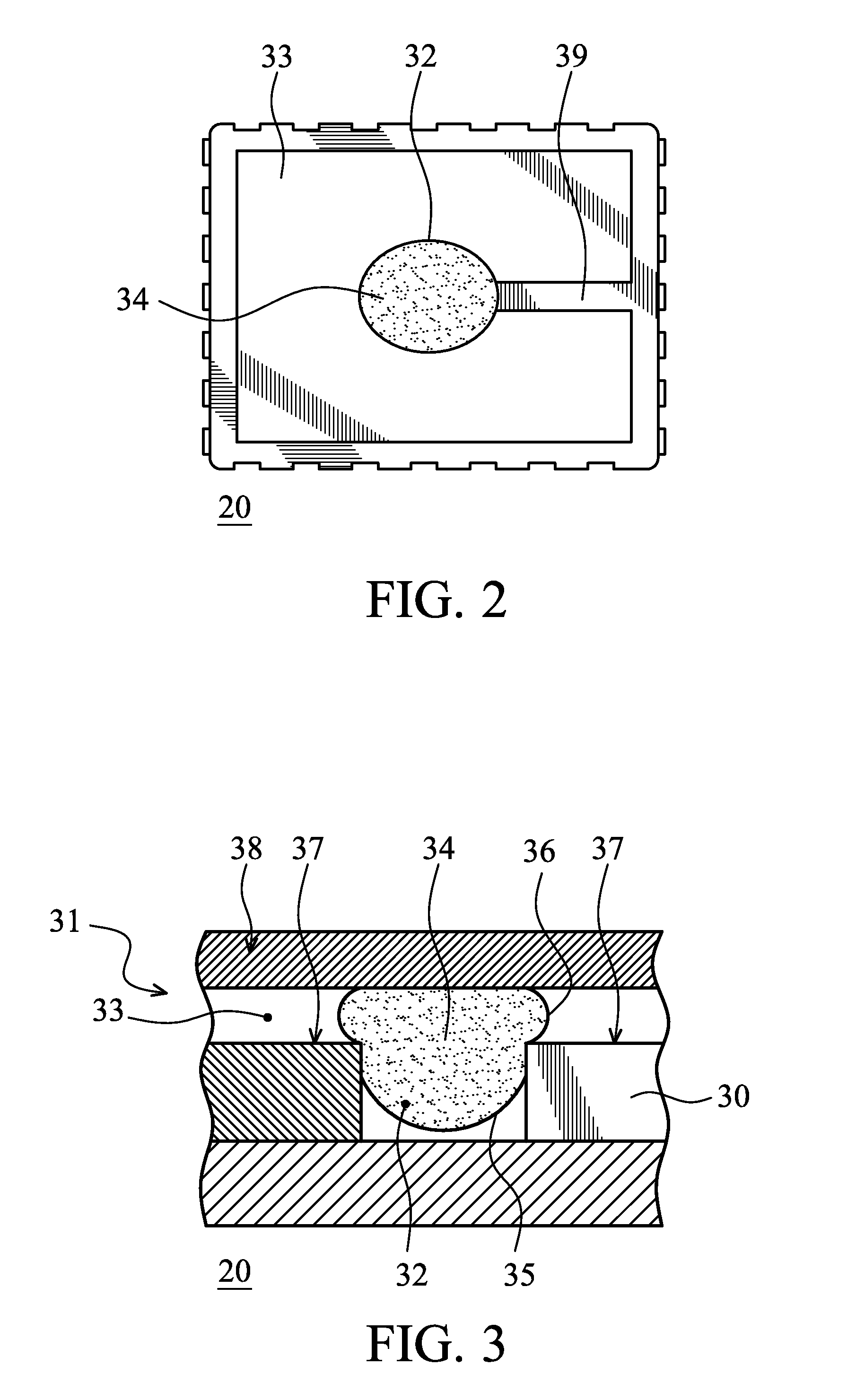
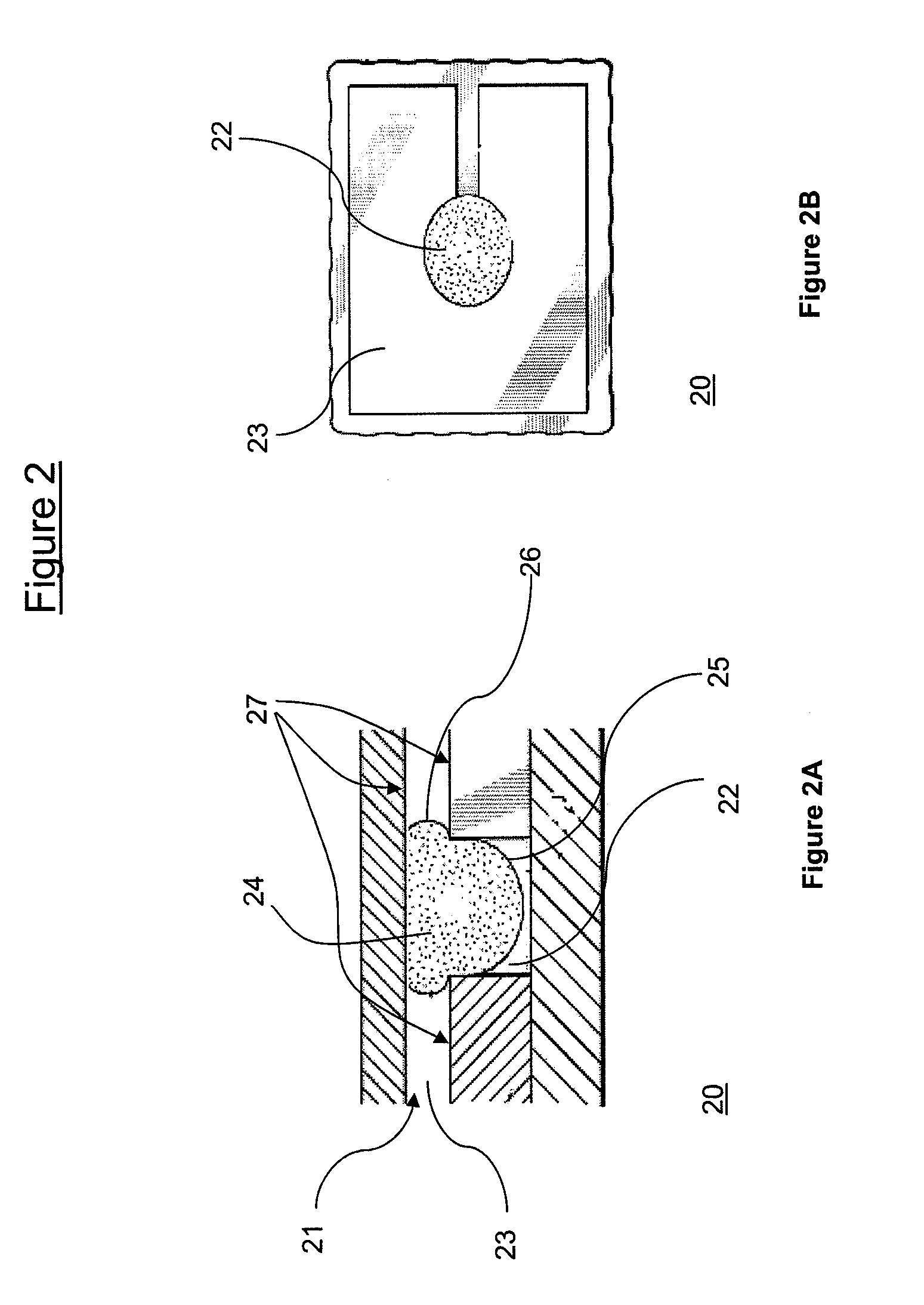
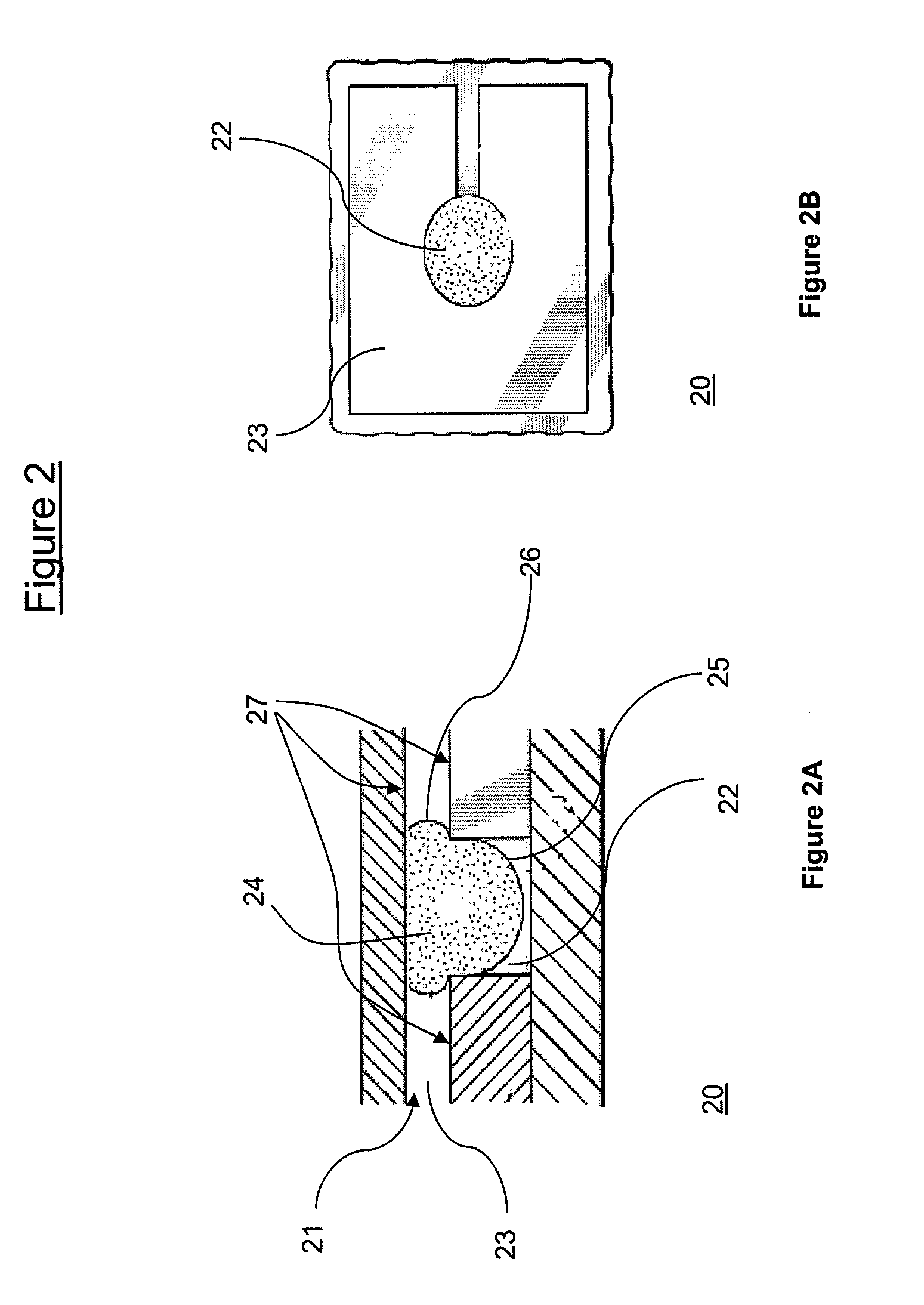
A display apparatus includes a plurality of electrofluidic chromatophore (EFC) pixel cells. Each pixel cell includes a fluid holder for holding a polar fluid and a non-polar fluid having differing display properties, the fluid holder including a reservoir having an orifice with a small visible area projected in the direction of a viewer onto the polar fluid, and a channel with a geometry having a large visible area projected in the direction of a viewer onto the polar fluid. The channel is connected to the reservoir via said orifice so as to enable free movement of the polar fluid and non-polar fluid between the channel and the reservoir. The reservoir is formed in a laminated resin structure of homogenous resin film layers, including an orifice film layer and a reservoir film layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
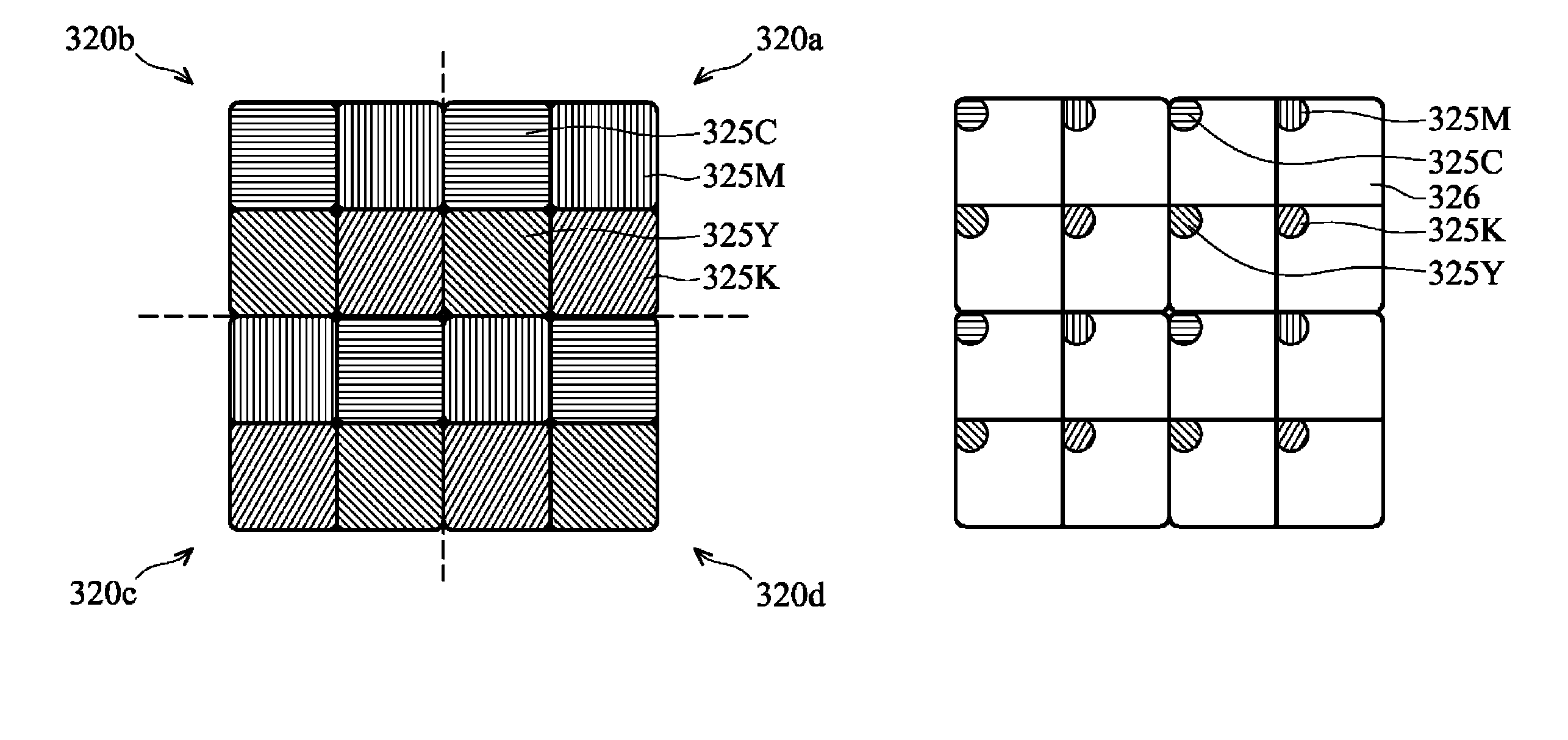
Color electrowetting display (EWD) devices
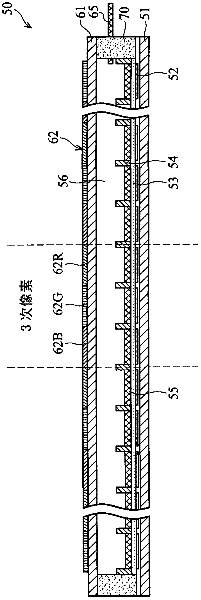
Electrowetting display devices are presented. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a color non-polar fluid layer interposed therebetween. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic partition structure is disposed on the second substrate, thereby defining a plurality of sub-pixels. The color electrowetting display further includes an array of color pixel regions. Each pixel region consists of a set of primary color sub-pixel. Each color sub-pixel corresponds to one of different color non-polar fluid layers, and each of the different color non-polar fluid layers is isolated from each other. The colors of non-polar fluid layer in the neighboring sub-pixels are different.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Display Apparatus Comprising Electrofluidic Cells
ActiveUS20110025668A1Realistic voltage operating rangeReduced overall height dimensionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringPolar fluid
A display apparatus is described comprising a plurality of electrofluidic chromatophore (EFC) pixel cells. Each pixel cell comprises a fluid holder for holding a polar fluid and a non-polar fluid having differing display properties. The fluid holder comprises a fluid reservoir with a geometry having a small visible area onto the polar fluid, and a channel with a geometry having a large visible area onto the polar fluid. The channel is connected to the reservoir to enable free movement of the polar fluid and non-polar fluid between the channel and the reservoir. At least part of a surface of the channel comprises a wetting property responsive to a supply voltage. The pixel cell comprises at least one further pixel cell terminal that is coupled to a further electrode to supply a direct voltage to the pixel cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Display apparatus comprising electrofluidic cells
ActiveUS8279166B2Realistic voltage operating rangeReduced overall height dimensionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringPolar fluid
A display apparatus is described comprising a plurality of electrofluidic chromatophore (EFC) pixel cells. Each pixel cell comprises a fluid holder for holding a polar fluid and a non-polar fluid having differing display properties. The fluid holder comprises a fluid reservoir with a geometry having a small visible area onto the polar fluid, and a channel with a geometry having a large visible area onto the polar fluid. The channel is connected to the reservoir to enable free movement of the polar fluid and non-polar fluid between the channel and the reservoir. At least part of a surface of the channel comprises a wetting property responsive to a supply voltage. The pixel cell comprises at least one further pixel cell terminal that is coupled to a further electrode to supply a direct voltage to the pixel cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Composition containing fine silver particles, production method thereof, method for producing fine silver particles, and paste having fine silver particles
A composition containing fine silver particles which have a uniform particle size, can form a fine drawing pattern, and have a small environmental impact, a method for producing that composition, a method for producing fine silver particles, and a paste having fine silver particles are provided.The fine silver particles are produced by carrying out a fluid preparation step of preparing a reduction fluid, a silver reaction step, and a filtration / washing step.The reaction step is carried out by adding an aqueous silver nitrate fluid to a reduction fluid whose temperature has been increased to a range between 40 and 80° C.The aqueous silver nitrate fluid is added at a stretch.The composition containing fine silver particles is produced by dispersing the composition containing the fine silver particles in a polar fluid.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Smart display devices
InactiveUS20110007046A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDisplay device
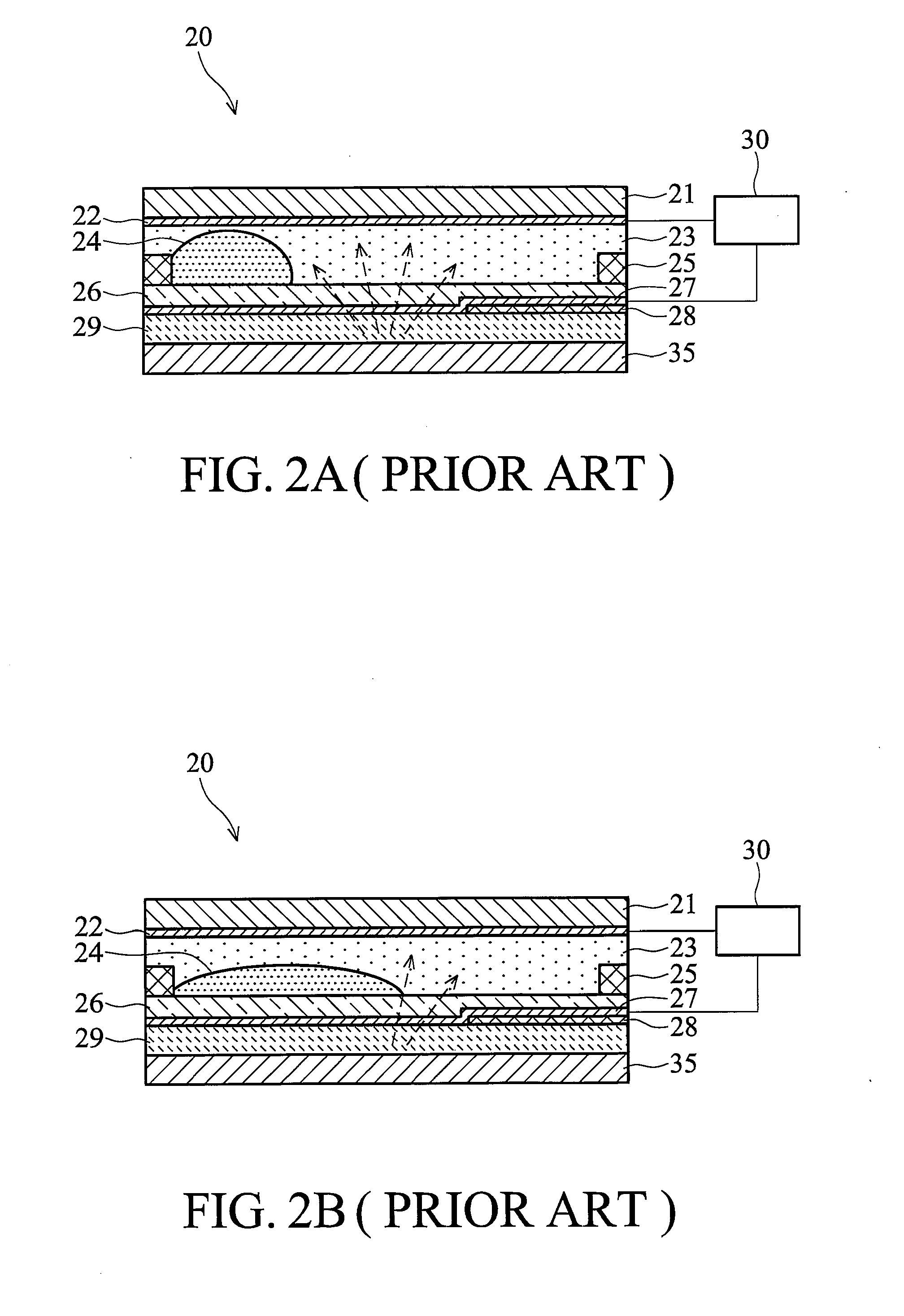
Smart display devices are presented. The smart display device includes an electrowetting panel, a photo-detector device, and a panel driving control device, wherein the photo-detector device detects environmental light such that the electrowetting panel is driven by the panel driving control device accordingly. The electrowetting panel has an array of pixels, wherein each pixel includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer interposed between the first and second substrates. A first electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic bank structure is disposed between the first and the second substrates.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Electrowetting display devices
ActiveCN102411203AHigh image qualityReduce manufacturing complexityOptical elementsElectricityFluid layer
Electrowetting devices (EWD) are presented. The electrowetting device includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a non-polar fluid layer interposed therebetween. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A first partition structure is disposed on the first substrate; thereby defining a plurality of color sub-pixels. A dye and / or a pigment substance is doped in one of the polar fluid layer and the non-polar fluid layer. A luminescence substance is doped in one of the polar fluid layer and the non-polar fluid layer. An emission module (also known as an excitation module) is disposed underlying the bottom of the first substrate. The colors of the non-polar fluid layerin the neighboring sub-pixels are different.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Polar fluid removal from surfaces using supercritical fluids
InactiveUS20060254612A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticulatesSimple Organic Compounds
A method for removing polar fluids from the surface of a substrate using a supercritical fluid is described. Substrates that may be cleaned include microelectronic devices such as integrated circuits, micro-electro mechanical devices, and optoelectronic devices. The surfaces of these devices may include foamed polymers, such as those used as dielectric material. Supercritical fluids useful for removal of polar fluids generally include an oxygen-containing organic compound in the supercritical state. The removal of polar fluids using supercritical fluids may be supplemented by other cleaning methods using supercritical fluids to remove particulate matter from the surface of the substrate.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Color electrowetting display (EWD) devices
Electrowetting display devices are presented. The electrowetting display includes a first substrate and an opposing second substrate with a polar fluid layer and a color non-polar fluid layer interposed therebetween. A first transparent electrode is disposed on the first substrate. A second electrode is disposed on the second substrate. A hydrophilic partition structure is disposed on the second substrate, thereby defining a plurality of sub-pixels. The color electrowetting display further includes an array of color pixel regions. Each pixel region consists of a set of primary color sub-pixel. Each color sub-pixel corresponds to one of different color non-polar fluid layers, and each of the different color non-polar fluid layers is isolated from each other. The colors of non-polar fluid layer in the neighboring sub-pixels are different.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Heat exchange device with confined convective boiling and improved efficiency
InactiveUS20120180978A1Encouraging vapour evacuationCooling is improvedAir-treating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityEngineering
A heat exchange device with convective and confined boiling includes a channel in a substrate in contact with an element to be cooled, in which a polar fluid flows from upstream to downstream, a mechanism of movement of the fluid by convection in the channel imposing a direction of flow, and a device for movement by electro-wetting positioned between the channel and the element to be cooled to move the fluid in the channel. The channel includes an inner surface having low wettability with regard to the polar fluid. The mechanism of movement by electro-wetting includes electrodes and a controller to apply selectively a potential to the electrodes such that an electrostatic force gradient is applied to the fluid in the direction of flow.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electrically-controlled variable-focus liquid lens based on electrowetting-on-dielectric
The invention relates to an electric control focal variable fluid lens, based on the medium electric wetting, belonging to the optical focal variable lens. The invention comprises a hollow chamber that containing one conductive or insulated or part insulated ring and two fluids while it is clamped between the transparent basic plate and the transparent cover plate; the transparent basic plate is coated by the conductive film and hydrophobic insulated medium film with special patterns; the bottom of ring has hydrophilous nature, while the top and inner and outer walls have hydrophobic property; the bus of inner wall of ring is a straight line or curve which can be bended in any angle; the ring is parallel with the basic plate and the cover plate with some distance between them. The invention can make conductive or polar fluid in the center by themselves, with simple structure, lower cost, non mechanical movable elements, large focal variable range, high speed, clear image, and lower power consumption. It can be used in photo telephone, endoscope, etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
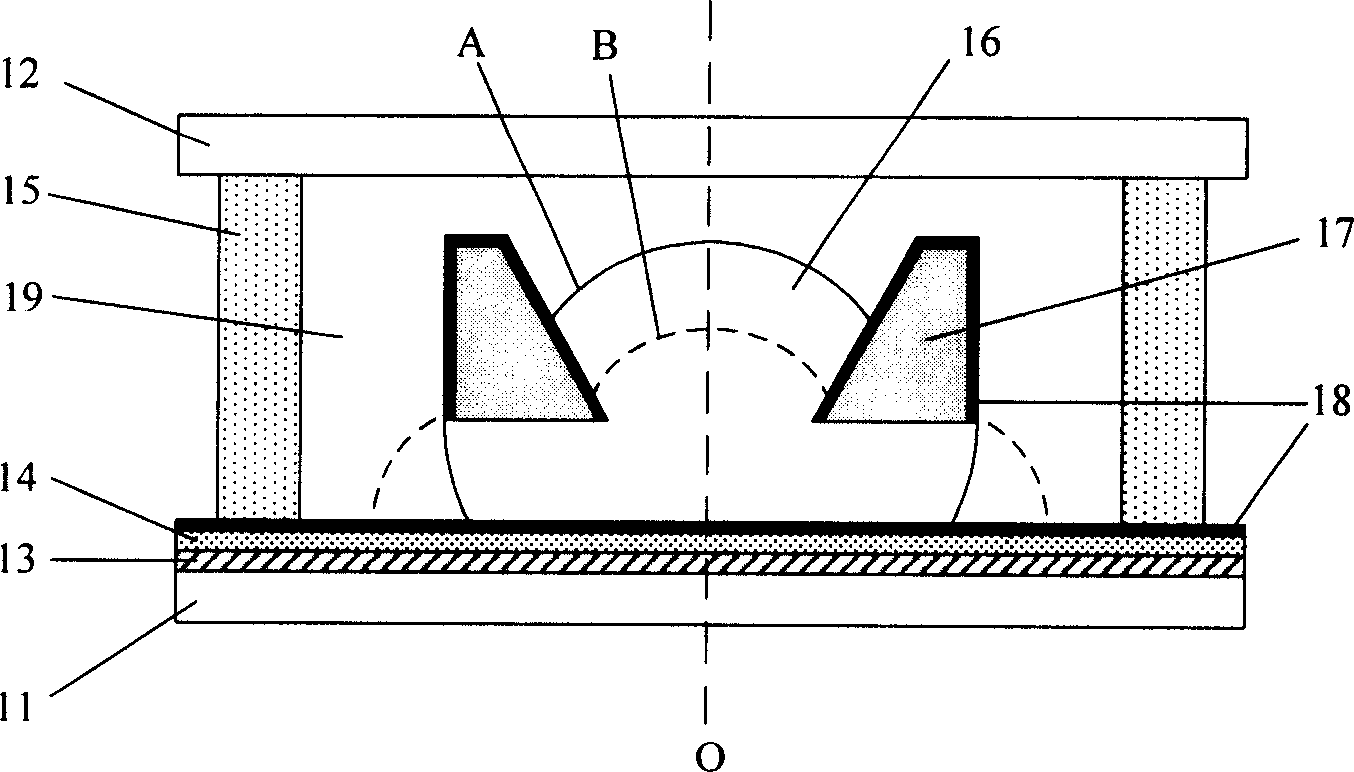
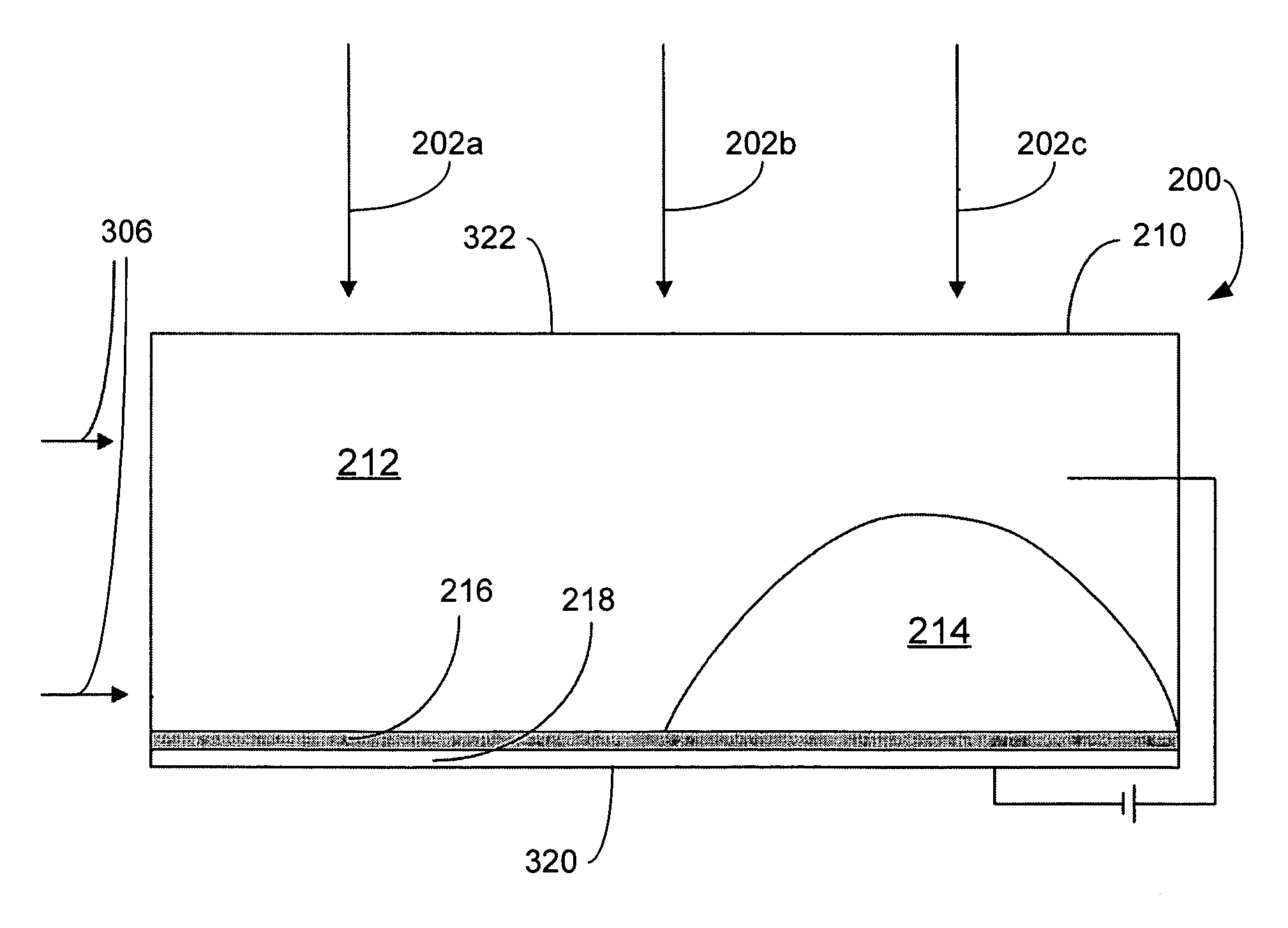
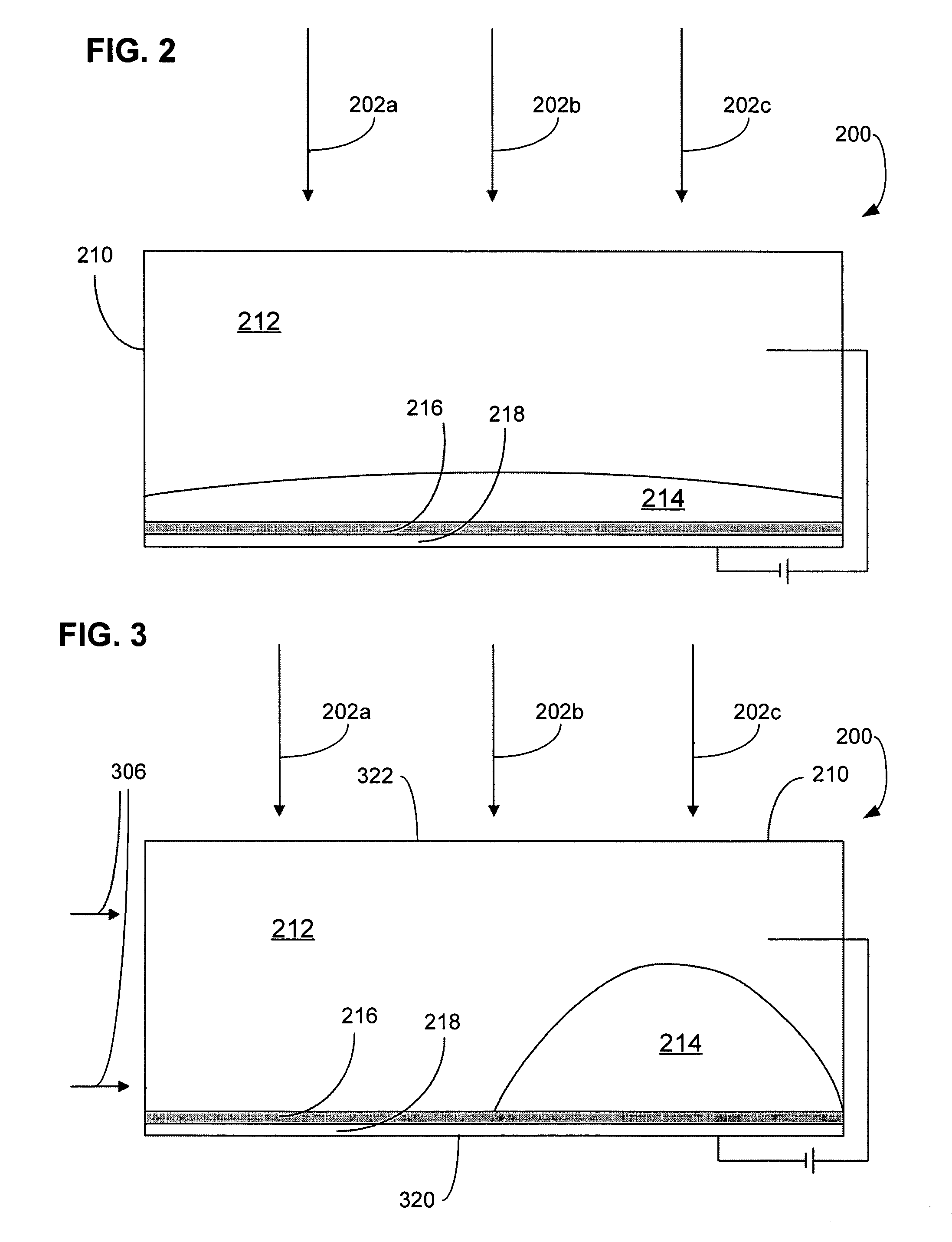
Controlled diffuse scattering for displays
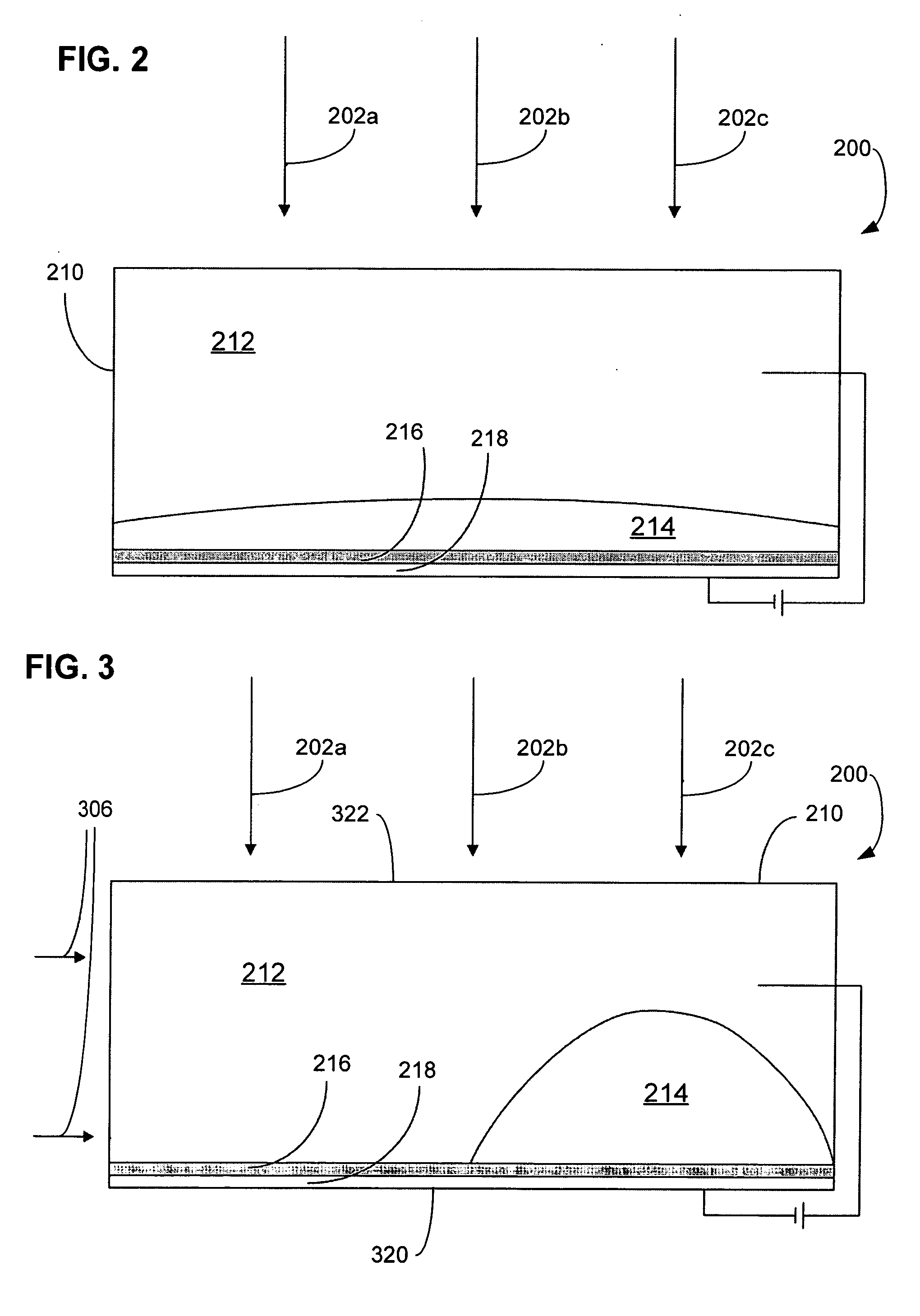
A display device comprising a pixel, where the pixel includes: (a) a polar fluid that is at least one of colored and black, (b) a non-polar fluid that is at least one of transparent and translucent, (c) a first substrate, (d) a second substrate arranged relative to the first substrate to define a channel occupied by the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid, wherein at least one of the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid is visible through at least one of the first substrate and the second substrate, (e) a reflector having a plurality of features, comprising at least one of concavities and projections, that alter an angle of reflected light from a specular reflection to provide the appearance of at least one of a diffuse reflection and a non-metallic reflection, where the reflector includes a hydrophobic coating causing the polar fluid that is at least one of colored and black to be non-wetting to the hydrophobic coating in the presence of the non-polar fluid, the display device also including a plurality of electrodes configured to cause repositioning of the polar fluid in the channel to displace at least a first portion of the non-polar fluid and a voltage source, where repositioning of the polar fluid occurs as a unified volume to retard reduced light reflection from the reflector in a portion of the channel where the polar fluid has been repositioned.
Owner:DEAN KENNETH A +2
Low oligomer conductive polyamide
The present invention relates to a low oligomer conductive polyamide composition, and articles of manufacture useful in the art of the transport of fluids such as solvents, polar fluids and fuels for applications such as fuel hoses or tubing for internal combustion engines. The material in the hose which is in contact with the fuel must be resistant to the extraction of materials from the hose which precipitate into the fuel or have the potential to clog fuel filters, fuel injectors and the like which have extremely small orifices and, thus, low tolerance for particulates in the fuel. As used herein, the term “low precipitate polyamide” means that the polyamide has been washed or extracted to reduce the level of components such as oligomers (low molecular weight polyamide), solids or semi-solids which would otherwise be released by the polyamide after exposure to the transported fluid and / or precipitate into the fluid.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
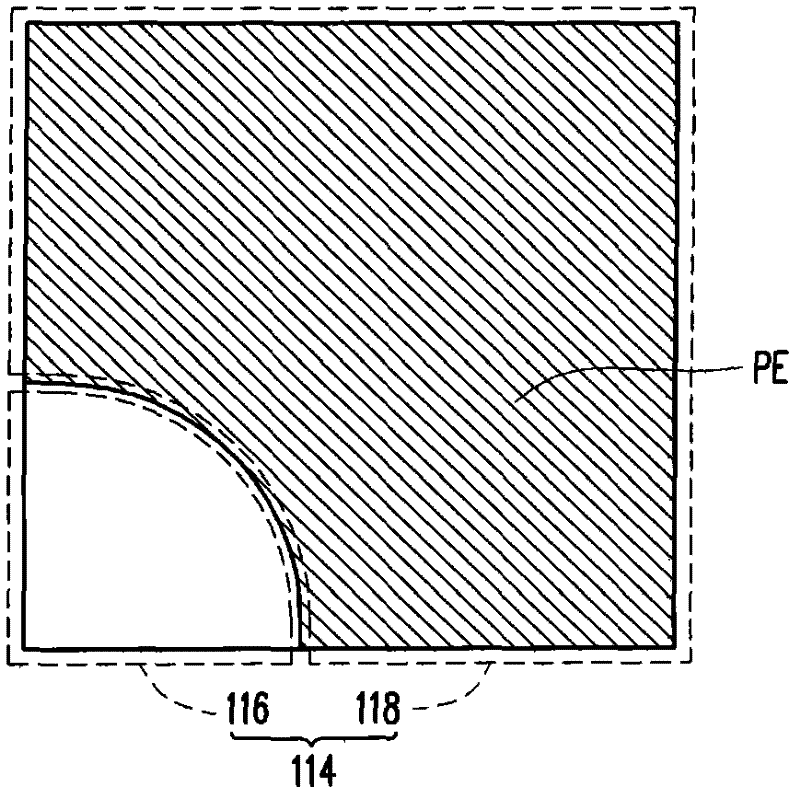
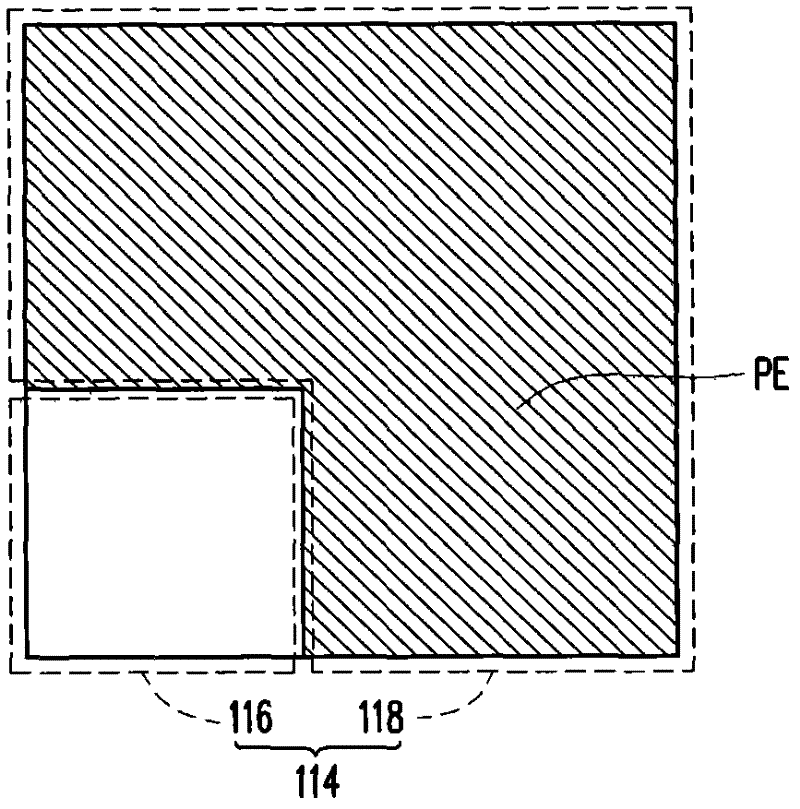
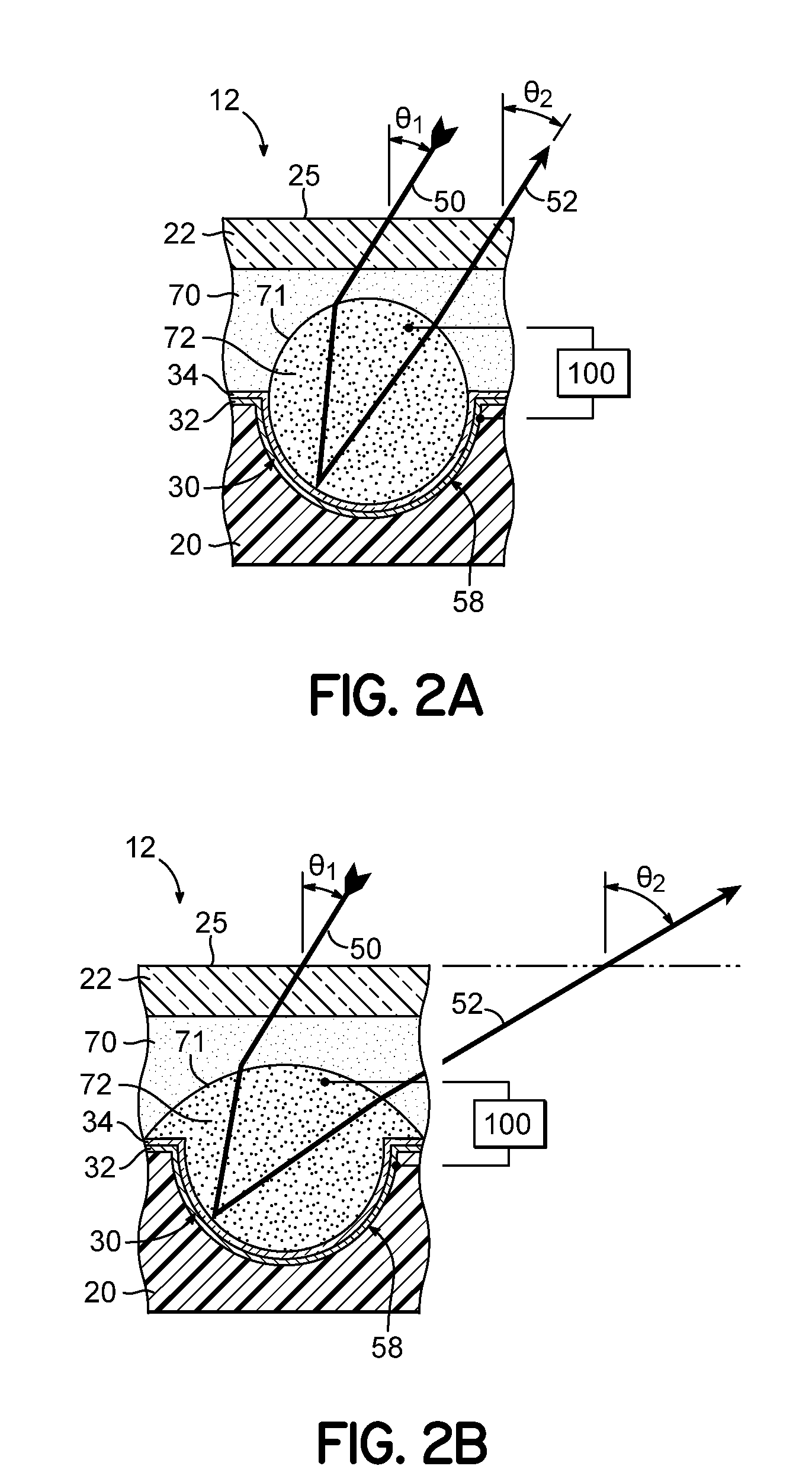
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060109435A1Difficult to controlEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPotential differenceRefractive index
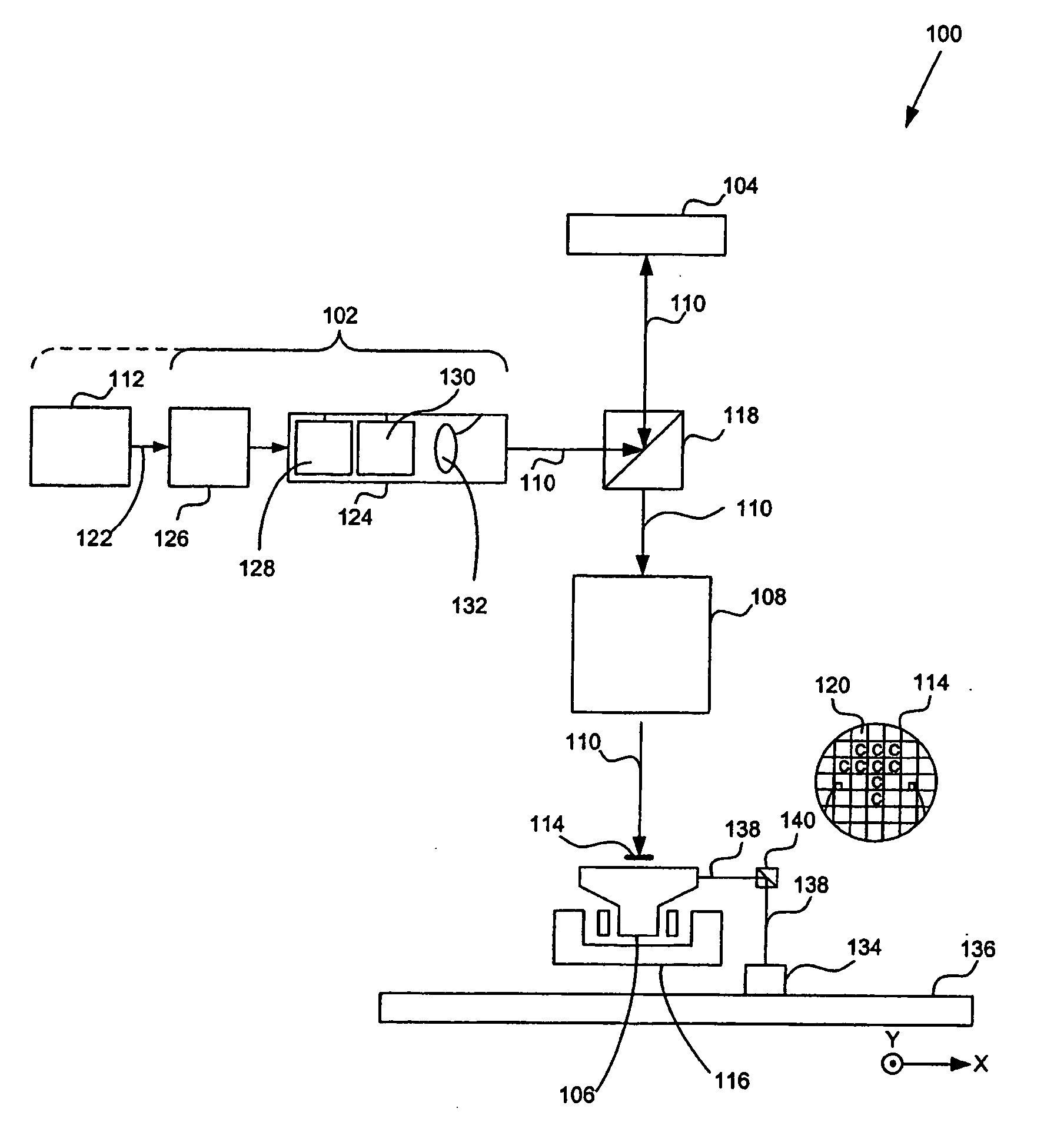
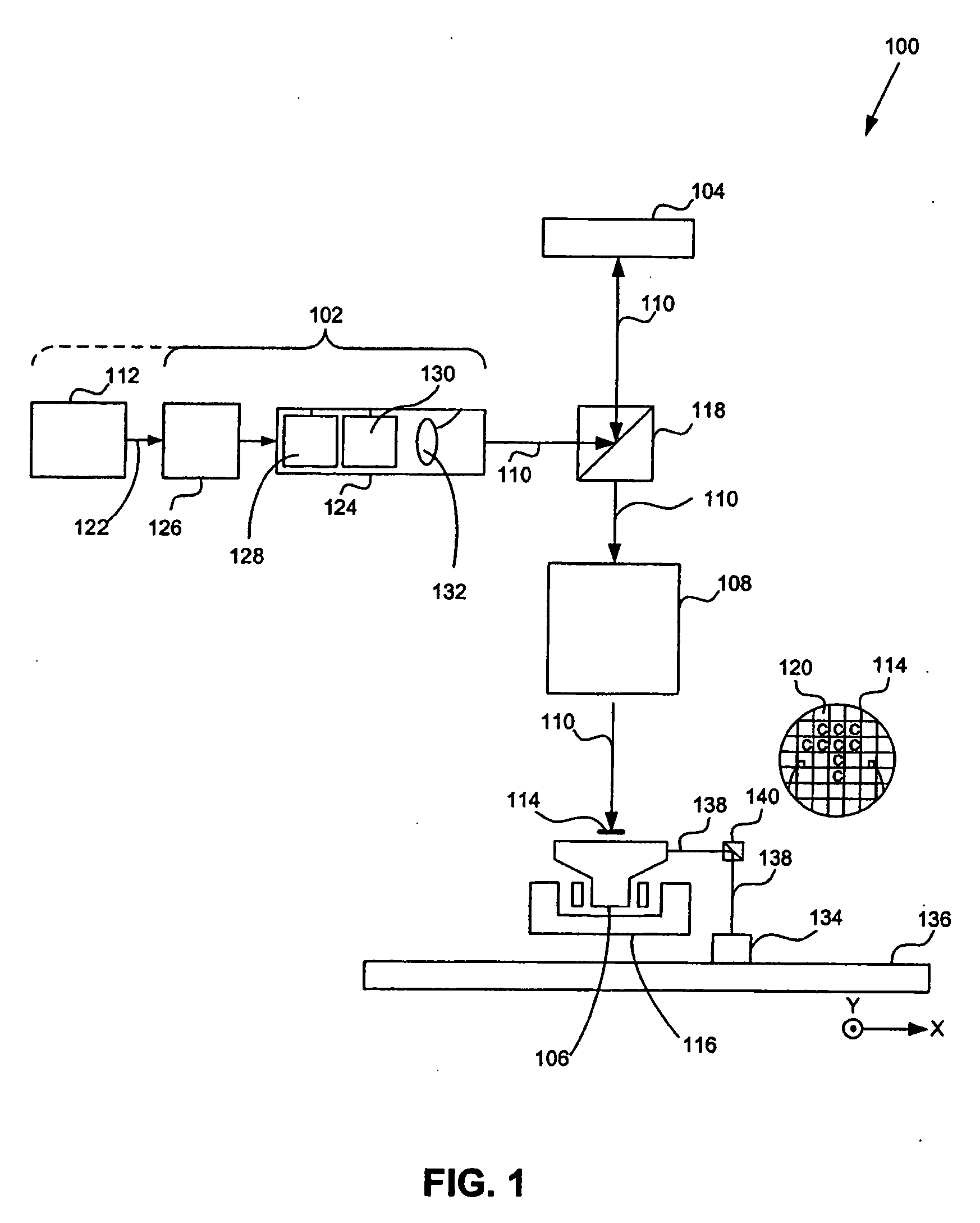
A lithographic apparatus includes a patterning device that patterns a projected beam. The patterning device includes an array of cells that contain a polar fluid, a non-polar fluid, and an electrode. A potential difference across the electrode and the polar fluid causes displacement of the non-polar fluid. Based on a difference in refractive index between the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid, a beam of light which passes through the cell will have its phase changed in dependence on the relative thickness on the polar and non-polar fluids and on their refractive indices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Electro-wetting display device
ActiveUS20120098812A1Reduce brightnessIncrease brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectricityDisplay device
An electro-wetting display device includes a polar fluid layer, a pixel electrode, a non-polar black fluid layer, a driving electrode, and a color fluid layer. The non-polar black fluid is deformed by a voltage difference between a voltage applied to the pixel electrode and a voltage applied to the polar fluid layer. the non-polar color fluid is deformed by a voltage difference between a voltage applied to the driving electrode and a voltage applied to the polar fluid layer. The driving electrode receives a voltage having a voltage level varied according to a display mode.
Owner:HYDIS TECH
Electrofluidic chromatophore (efc) display apparatus
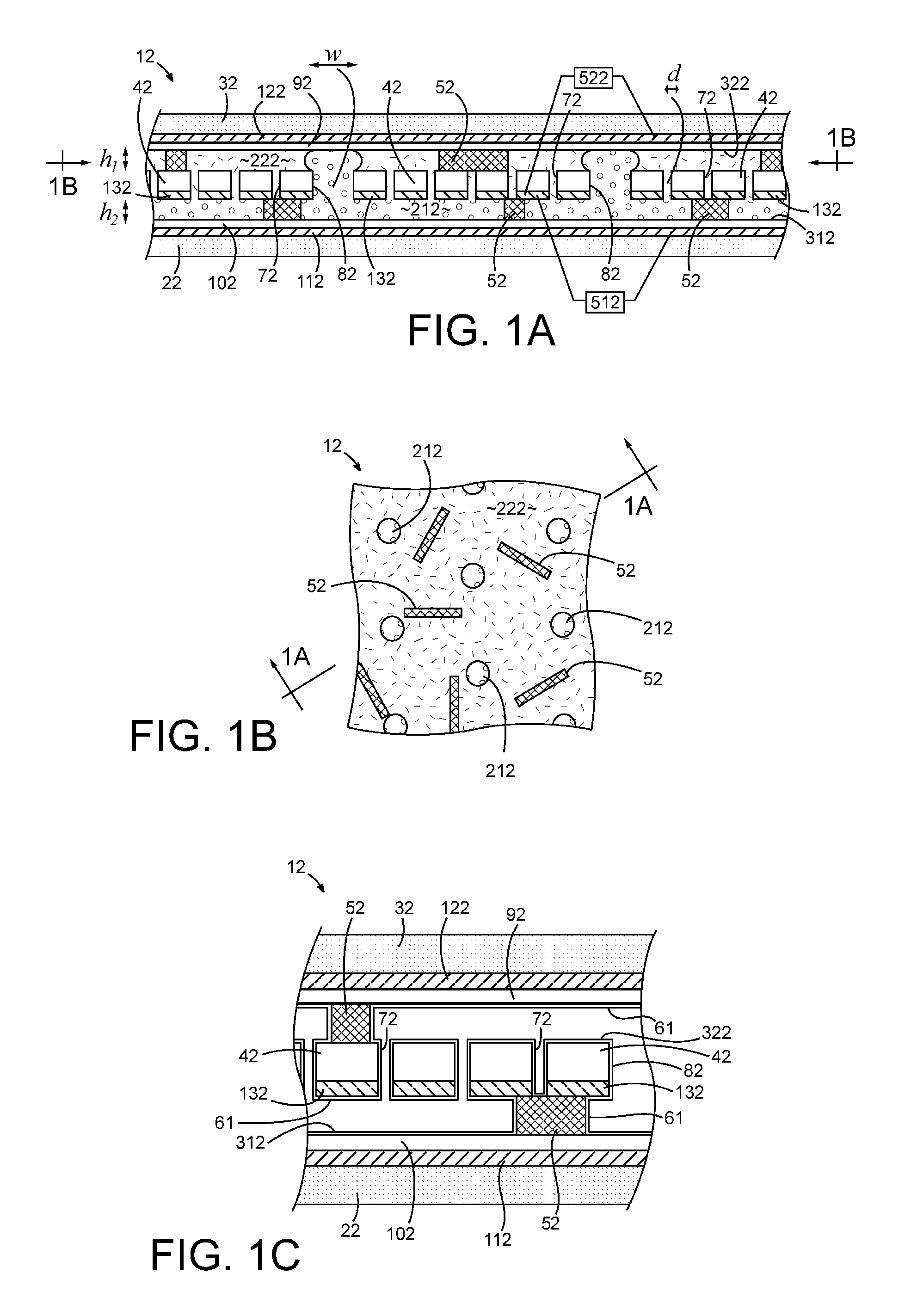
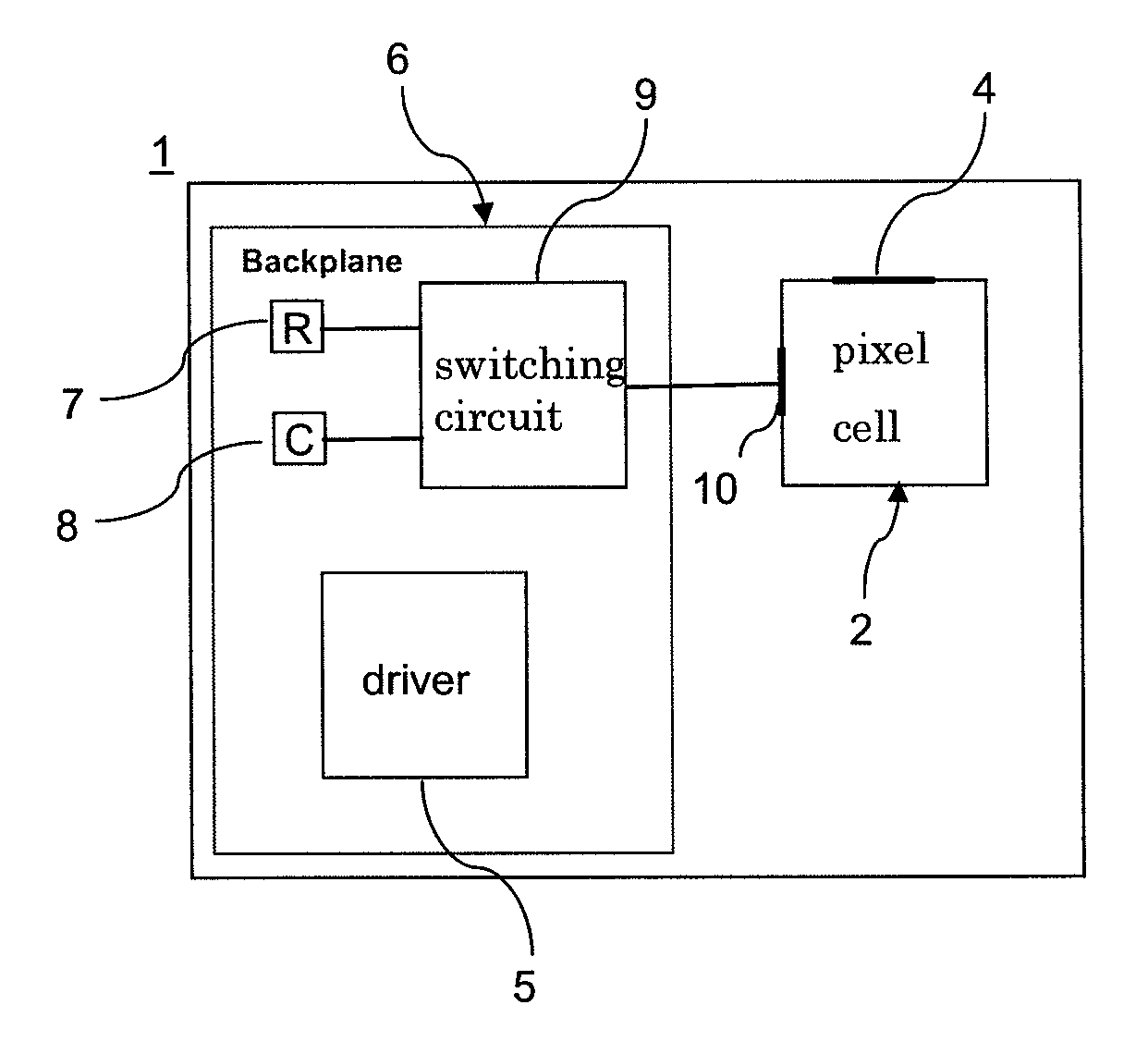
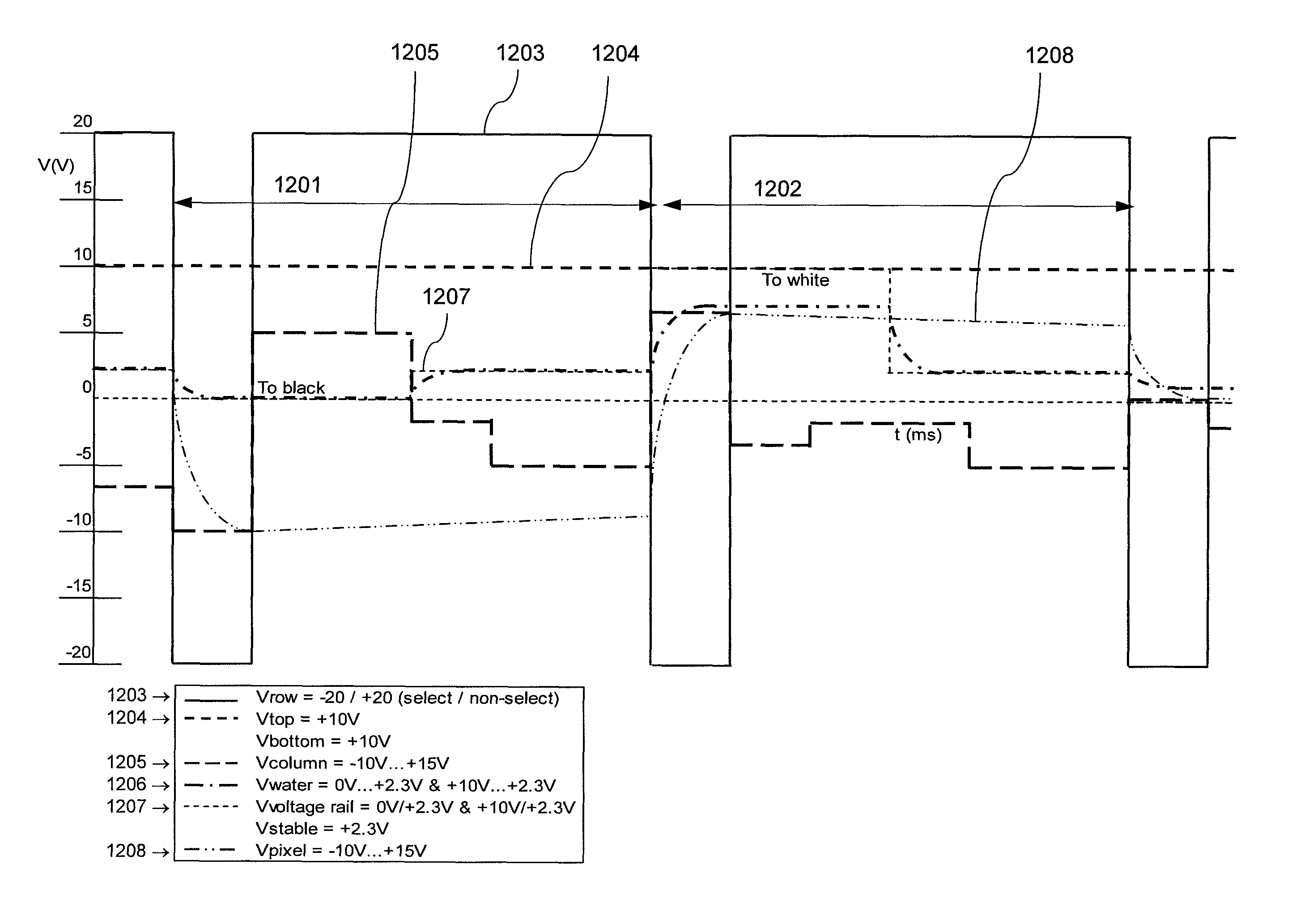
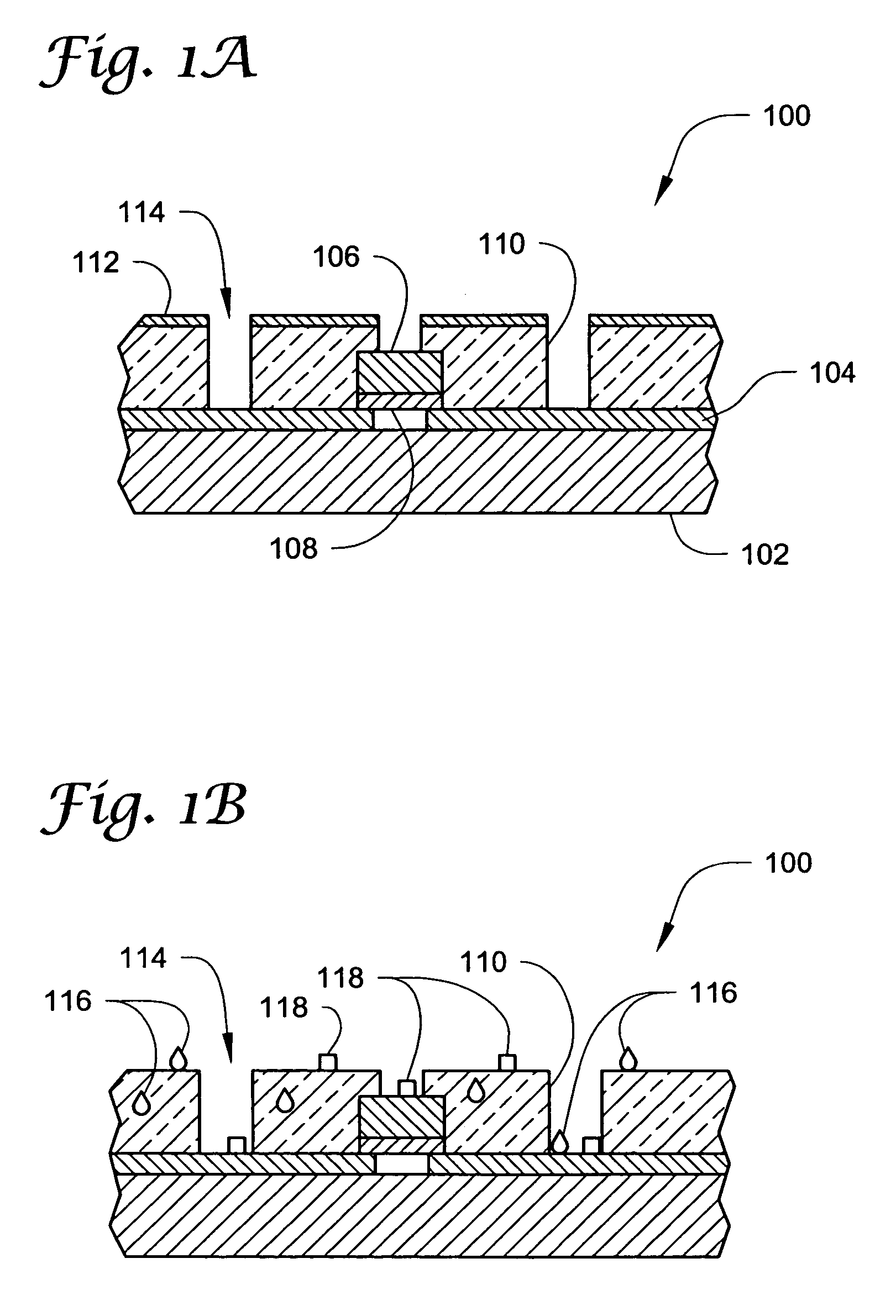
According to an aspect of the invention, there is provided a display apparatus comprising a plurality of electrofluidic chromatophore (EFC) pixel cells. Each pixel cell comprises a fluid holder for holding a polar fluid and a non-polar fluid having differing display properties, the fluid holder comprising a reservoir with a geometry having a small visible area projected in the direction of a viewer onto the polar fluid, and a channel with a geometry having a large visible area projected in the direction of a viewer onto the polar fluid. The channel is connected to the reservoir so as to enable free movement of the polar fluid and non-polar fluid between the channel and the reservoir. At least part of a surface of the channel comprises a wetting property responsive to a supply voltage over the pixel cell and defining (i) a stable region wherein the supply voltage stabilizes polar fluid in the channel; (ii) a fill region that controls filling of polar fluid in the channel and (iii) a retract region that controls retracting of polar fluid in the channel. At least two pixel cell terminals are configured to supply the supply voltage to at least part of the surface of the channel comprising the wetting property for supply voltage controlled channel movement of polar fluid. The display further comprises a driver operative to provide controlled column voltages and any of a predefined row select or non-select voltage. A circuit board comprises a row electrode and a column electrode each directly connecting the driver to the pixel cell terminals for supplying the supply voltage to the pixel cell terminals as a voltage difference between the row and column electrodes in a passive matrix configuration.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low pH development solutions for chemically amplified photoresists
InactiveUS20050208429A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistPhotoresist
A method for carrying out positive tone lithography with a carbon dioxide development system is carried out by: (a) providing a substrate, the substrate having a polymer resist layer formed thereon, (b) exposing at least one portion of the polymer resist layer to radiant energy causing a chemical shift to take place in the exposed portion and thereby form at least one light field region in the polymer resist layer while concurrently maintaining at least one portion of the polymer layer unexposed to the radiant energy to thereby form at least one dark field region in the polymer resist layer; (c) optionally baking the polymer resist layer; (d) contacting the polymer resist layer to a carbon dioxide solvent system, the solvent system comprising a polar group, under conditions in which the at least one light field region is preferentially removed from the substrate by the carbon dioxide solvent system as compared to the at least one dark field region; wherein the carbon dioxide solvent system comprises a first phase and a second phase, the first phase comprising carbon dioxide and the second phase comprising a polar fluid, with the at least one light field region being preferentially soluble in the polar fluid as compared to the at least one dark field region.
Owner:MT ACQUISITION HLDG LLC
Display
InactiveCN102385156AQuick responseStable grayscale drive displayOptical elementsDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display including a pixel array substrate, an opposite substrate and a fluid medium is provided. The pixel array substrate includes a first substrate including pixel regions and pixel structures disposed in the pixel regions. Each pixel region includes a distribution region of pixel electrode and a non-electrode region. A pixel electrode of the pixel structure is disposed in the distribution region of pixel electrode and has at least one slit extending from the non-electrode region toward the distribution region of pixel electrode. The opposite substrate includes a second substrate and a common electrode disposed on the second substrate and contacting a polar fluid. The fluid medium includes the polar fluid and a non-polar fluid and flows between the pixel array substrate and the opposite substrate. The non-polar fluid is contracted toward the non-electrode region when a voltage difference is generated between the pixel and the common electrodes.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for reversing gas humidity on surface of rock core by using cationic fluorocarbon surfactant
The invention relates to a method for reversing gas humidity on the surface of a rock core by using cationic fluorocarbon surfactant. The humidity reserving treatment agent used by the method contains the cationic fluorocarbon surfactant, a quaternary ammonium salt surfactant and a polar fluid, preferably FC911, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and water. The invention also provides a method for reversing the humidity on the surface of sandstone into gas humidity, which comprises: pumping a humidity reversing treatment agent which contains 0.1 to 1 weight percent of cationic fluorocarbon surfactant into a rock stratum of a gas oil well till the entire surface of the sandstone in the rock stratum is immersed in the humidity reversing treatment agent; and thus, realizing the reversion into the gas humidity on the surface of the rock core. The method can effectively reserve the liquid humidity on the surface of the sandstone into gas humidity. The method is simple, convenient and easy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Electrowetting retroreflector devices, systems, and methods
Switchable retroreflector devices that are modulated via electrowetting. The devices include an electrically-conductive polar fluid and a non-polar fluid that is immiscible with the polar fluid. The polar and the non-polar fluids differ in at least one optical property. The fluids are contained in a fluid vessel, or an array of fluid vessels. The fluids are at least partially viewable. A voltage source is configured to selectively apply an electromechanical force to the polar fluid causing repositioning and / or geometrical change of the fluids such that retroreflection in created, or suppressed, by optical refraction or by optical attenuation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS7002666B2Difficult to controlEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPotential differenceRefractive index
A lithographic apparatus includes a patterning device that patterns a projected beam. The patterning device includes an array of cells that contain a polar fluid, a non-polar fluid, and an electrode. A potential difference across the electrode and the polar fluid causes displacement of the non-polar fluid. Based on a difference in refractive index between the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid, a beam of light which passes through the cell will have its phase changed in dependence on the relative thickness on the polar and non-polar fluids and on their refractive indices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Electro-wetting display device
ActiveUS8730225B2Reduce brightnessIncrease brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceFluid layer
An electro-wetting display device includes a polar fluid layer, a pixel electrode, a non-polar black fluid layer, a driving electrode, and a color fluid layer. The non-polar black fluid is deformed by a voltage difference between a voltage applied to the pixel electrode and a voltage applied to the polar fluid layer. the non-polar color fluid is deformed by a voltage difference between a voltage applied to the driving electrode and a voltage applied to the polar fluid layer. The driving electrode receives a voltage having a voltage level varied according to a display mode.
Owner:HYDIS TECH CO LTD
Membrane for the Separation of a Mixture of a Polar Fluid and a Non-Polar Fluid and Methods for Use Thereof
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com