Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1344 results about "Radiant energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux (or power) with respect to time. The symbol Qₑ is often used throughout literature to denote radiant energy ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities). In branches of physics other than radiometry, electromagnetic energy is referred to using E or W. The term is used particularly when electromagnetic radiation is emitted by a source into the surrounding environment. This radiation may be visible or invisible to the human eye.
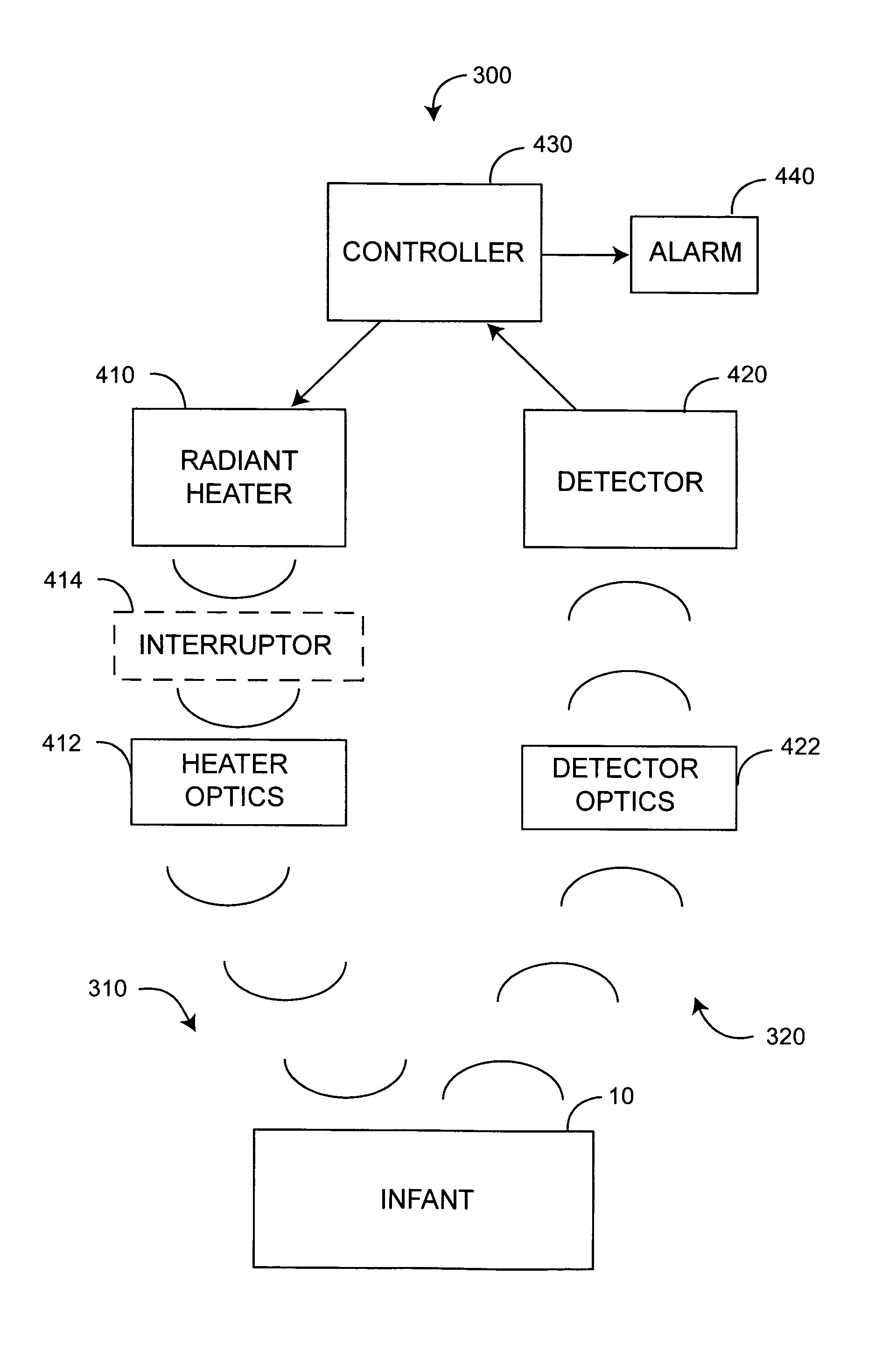
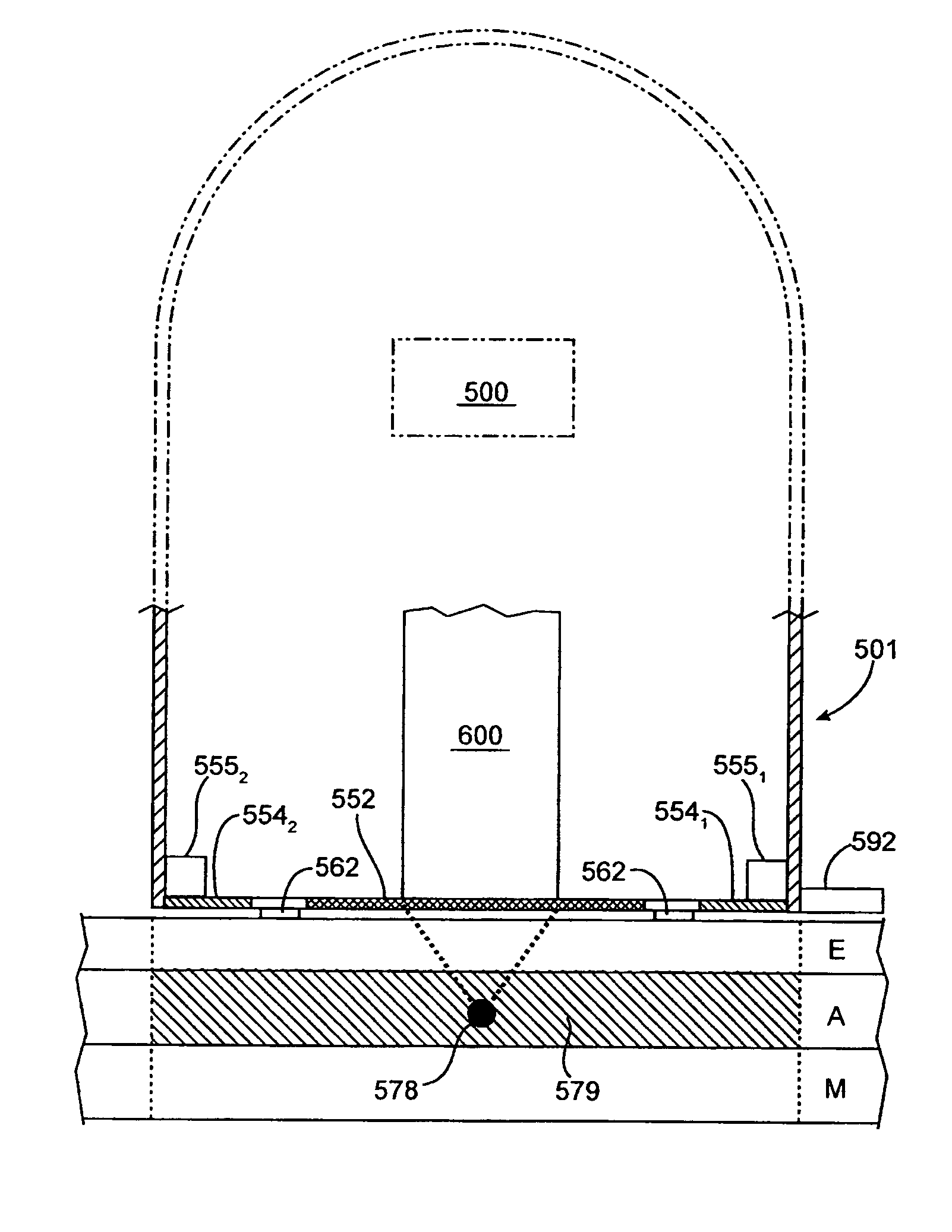
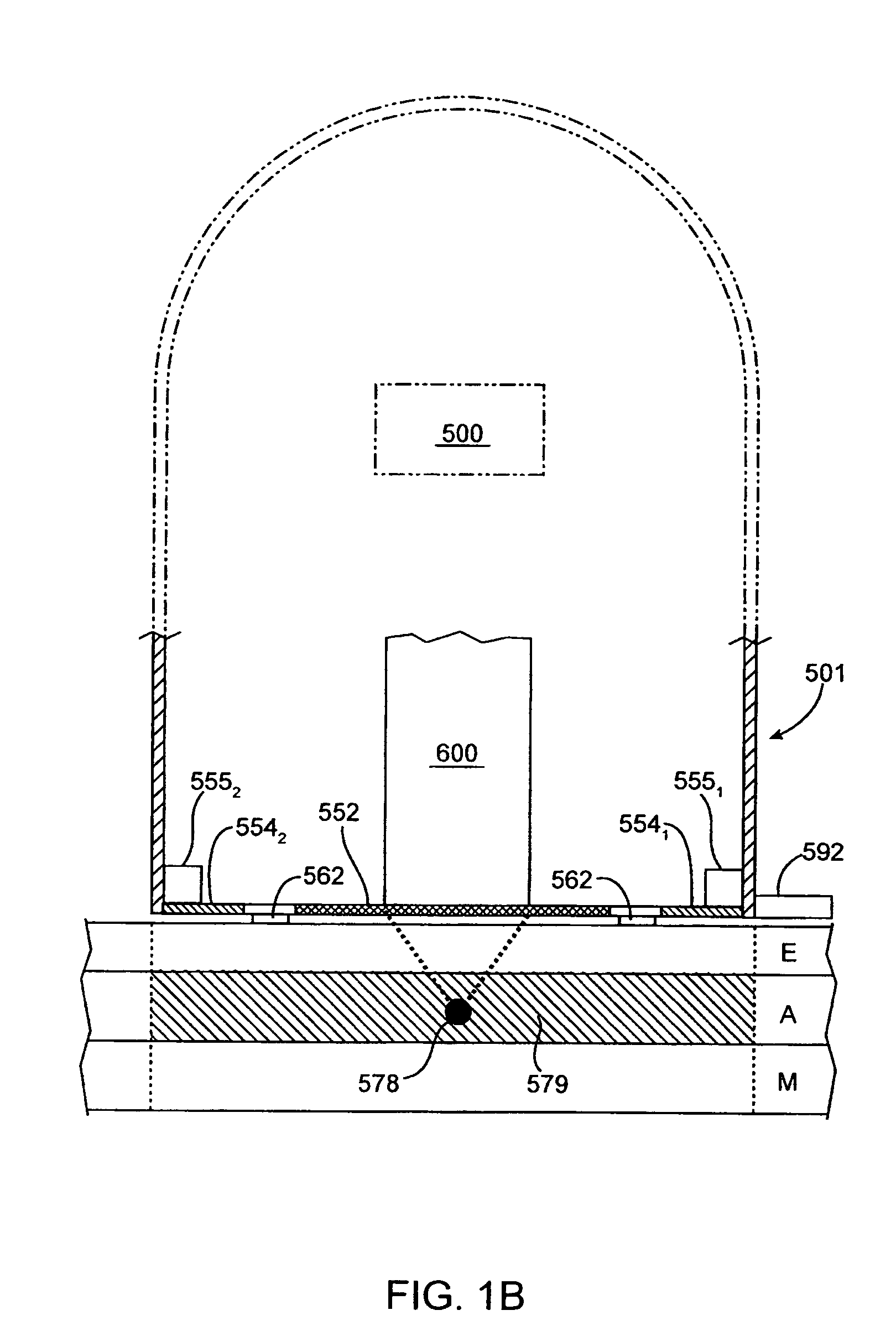
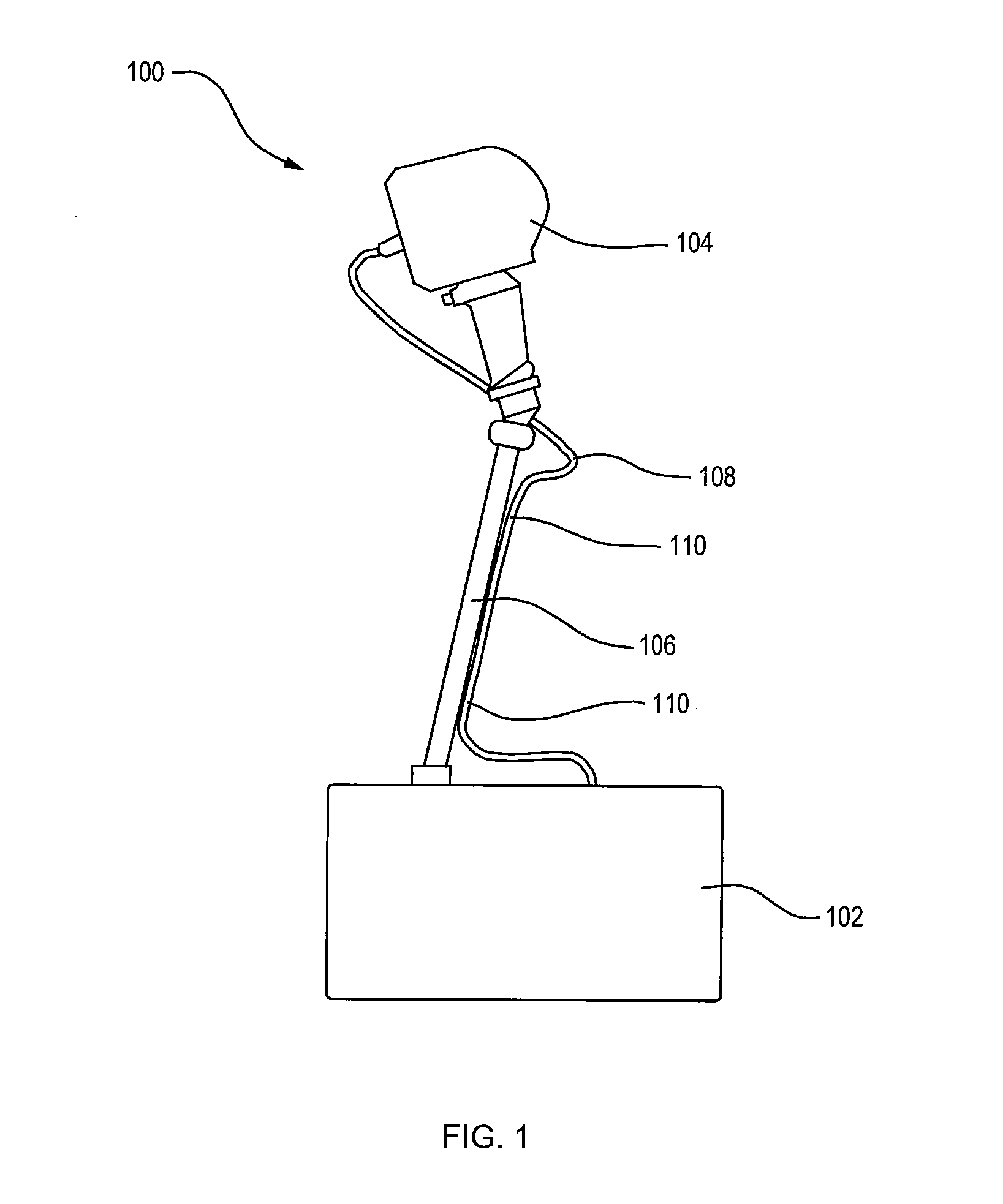
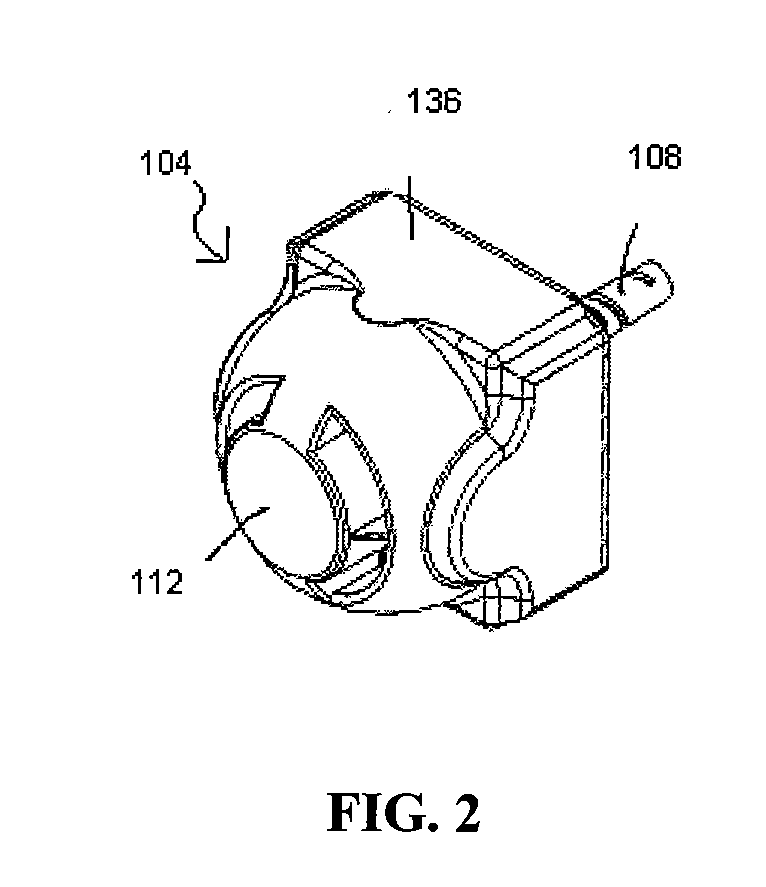
Remote sensing infant warmer
An infant is illuminated with heater radiant energy so as to warm the infant. A detector remotely senses infant radiated energy so as to determine the extent of infant warmth, and a controller responsive to the detector regulates the heater radiant energy accordingly. Skin-reflected heater radiant energy is limited at least during measurements of infant radiated energy.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
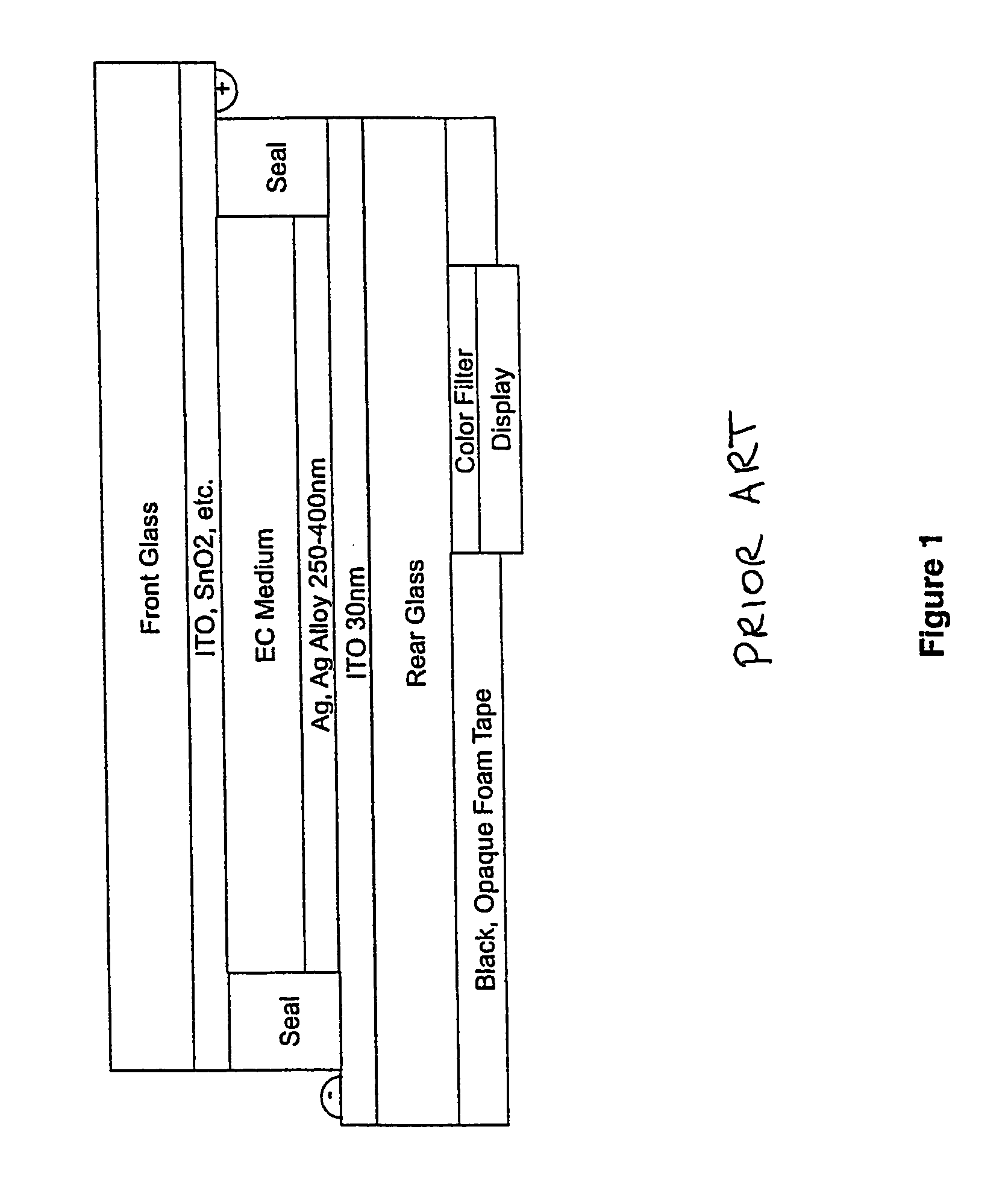
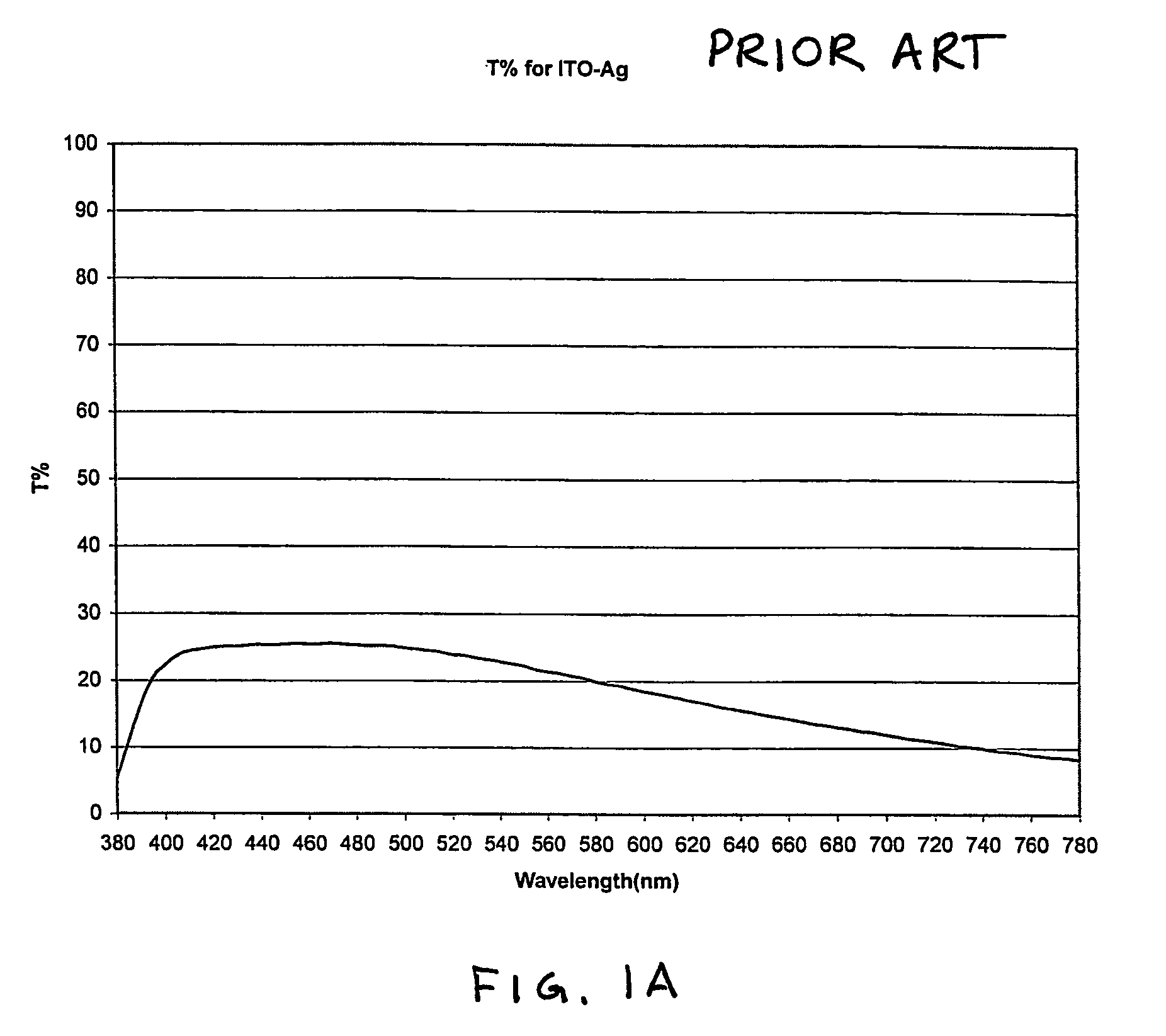
Mirror reflective element assembly
InactiveUS7274501B2Control interferenceImprove transmittanceMirrorsReflex reflectorsSpectral bandsRefractive index
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Film formation apparatus and methods including temperature and emissivity/pattern compensation
InactiveUS20070077355A1Good effectImprove absorption rateLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEmissivityRadiant heating
A film formation system 10 has a processing chamber 15 bounded by sidewalls 18 and a top cover 11. In one embodiment, the top cover 11 has a reflective surface 13 for reflecting radiant energy back onto a substrate 19, pyrometers 405 for measuring the temperature of the substrate 19 across a number of zones, and at least one emissometer 410 for measuring the actual emissivity of the substrate 19. In another embodiment, a radiant heating system 313 is disposed under the substrate support 16. The temperature of the substrate 19 is obtained from pyrometric data from the pyrometers 405, and the emissometer 410.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
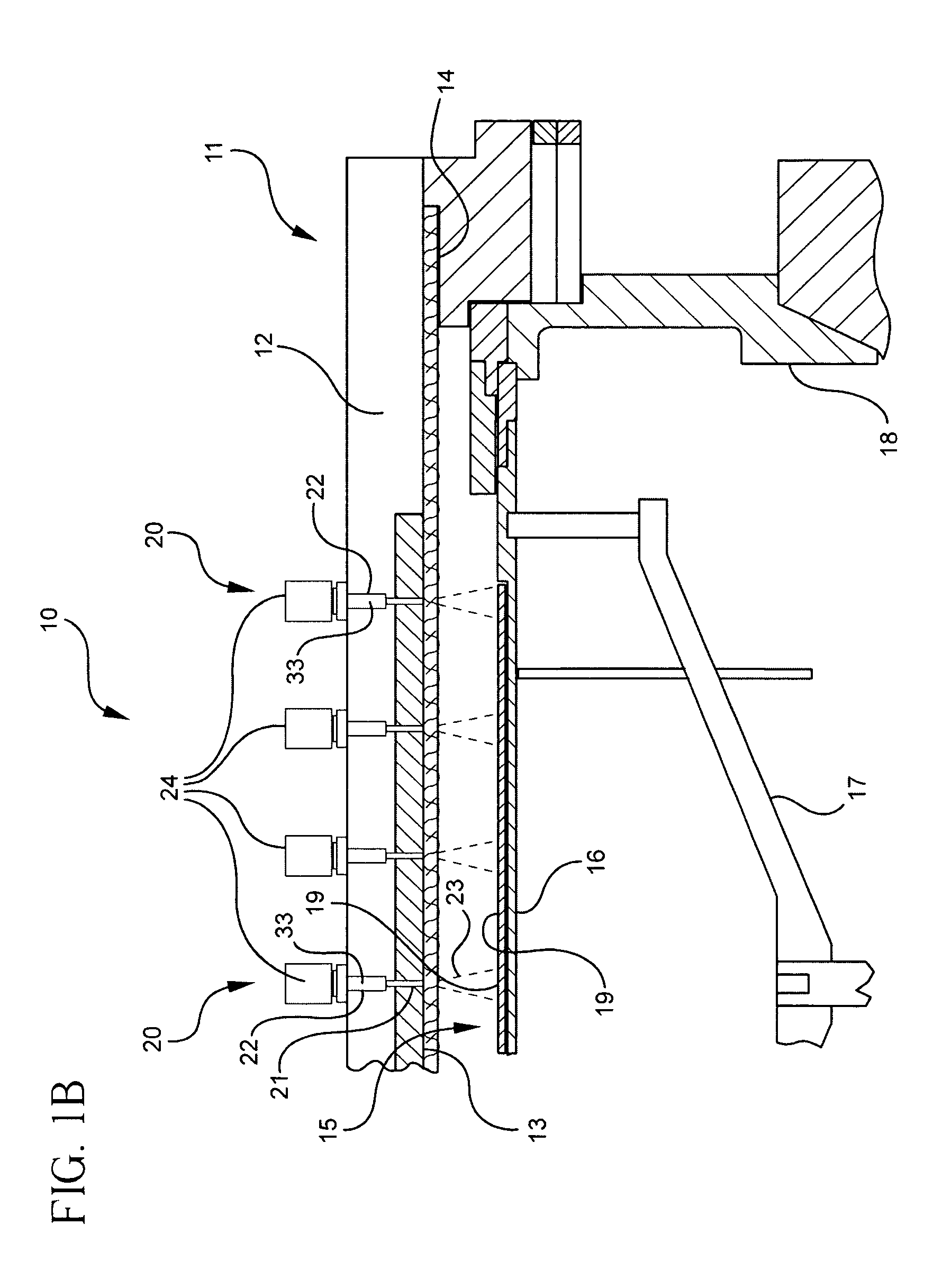
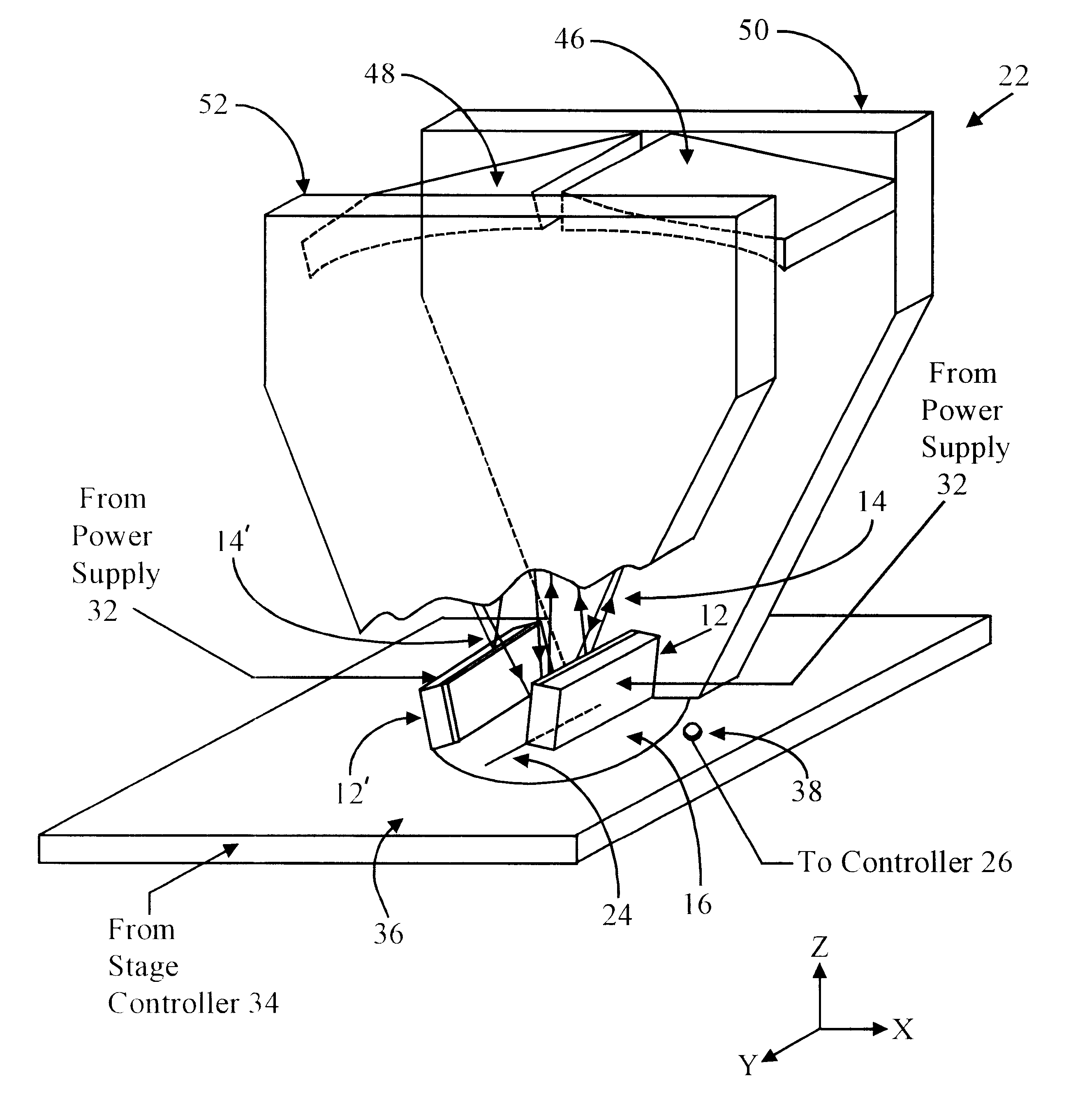
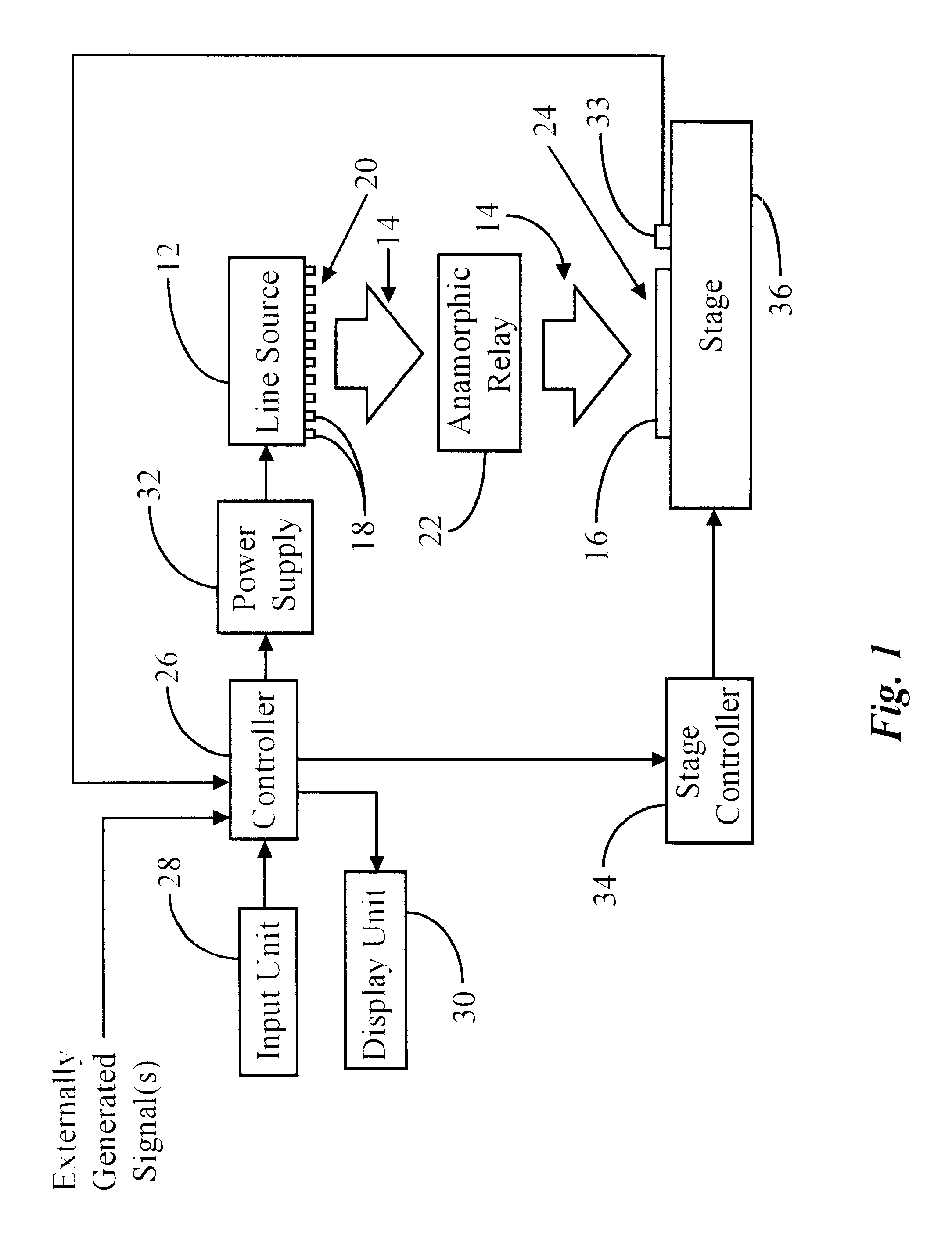
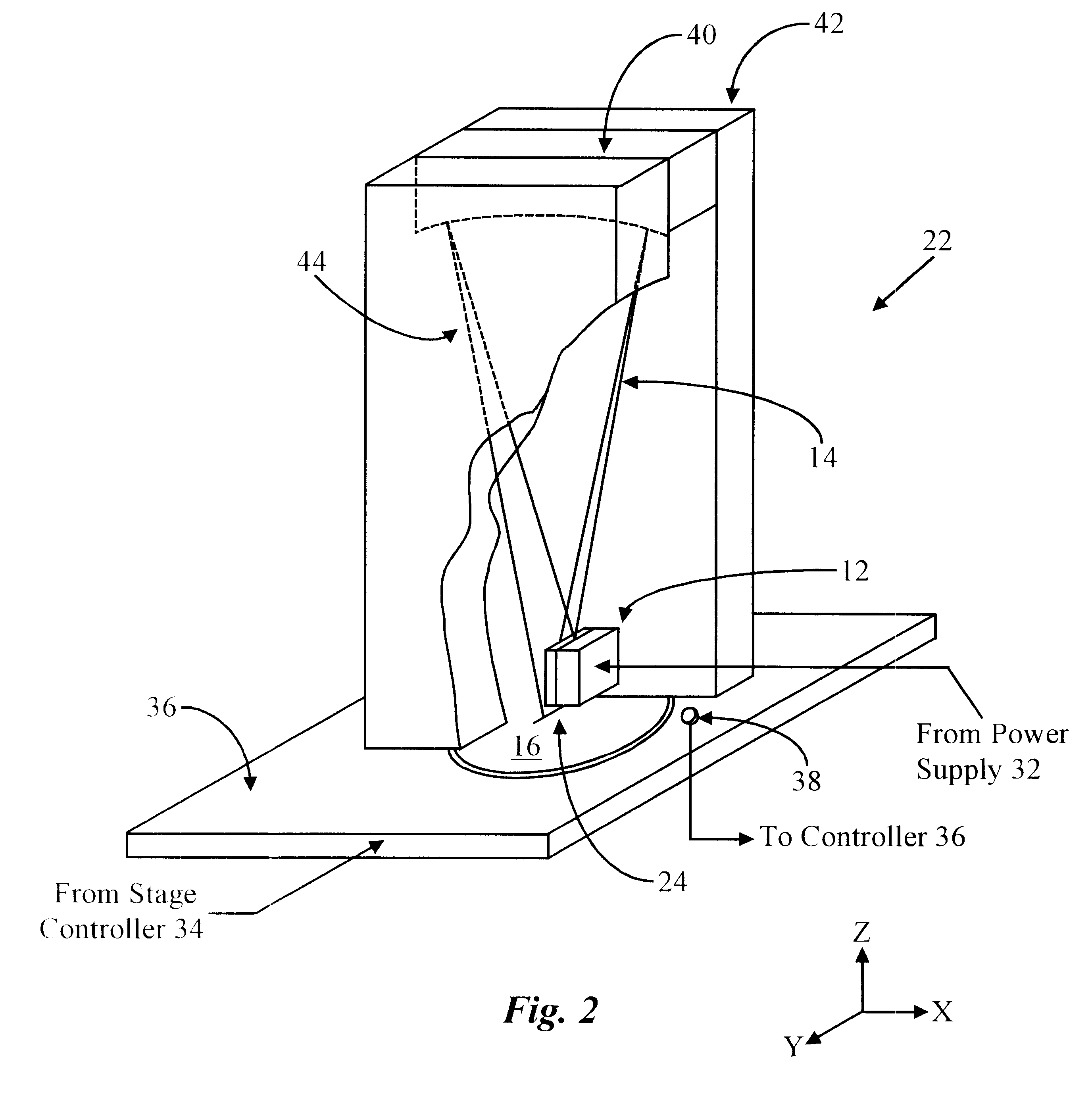
Apparatus having line source of radiant energy for exposing a substrate
InactiveUS6531681B1Easy constructionEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiant energyLaser diode
Radiant energy line source(s) (e.g., laser diode array) and anamorphic relay receiving radiant energy therefrom and directing that energy to a substrate in a relatively uniform line image. The line image is scanned with respect to the substrate for treatment thereof. Good uniformity is provided even when the line source is uneven. Optionally, delimiting aperture(s) located in the anamorphic relay focal plane and a subsequent imaging relay are includeable to permit substrate exposure in strips with boundaries between adjacent strips within scribe lines between circuits. An anamorphic relay focal plane mask with a predetermined pattern can be used to define portions of the substrate to be treated with the substrate and mask scanning motions synchronized with each other. Control of source output, and position / speed of the substrate, with respect to the line image, allows uniform dose and required magnitude over the substrate.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Staggered ribs on process chamber to reduce thermal effects
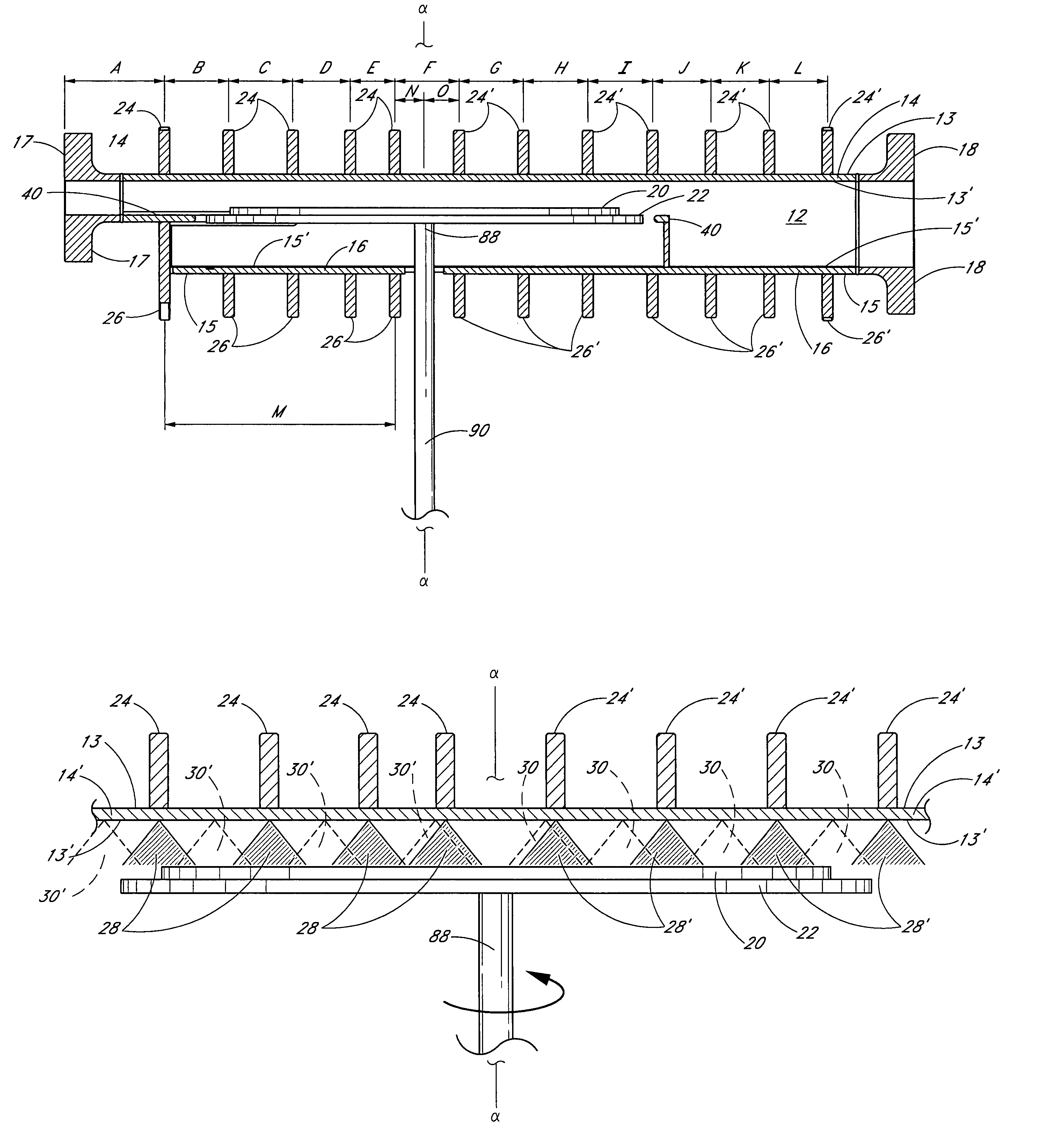
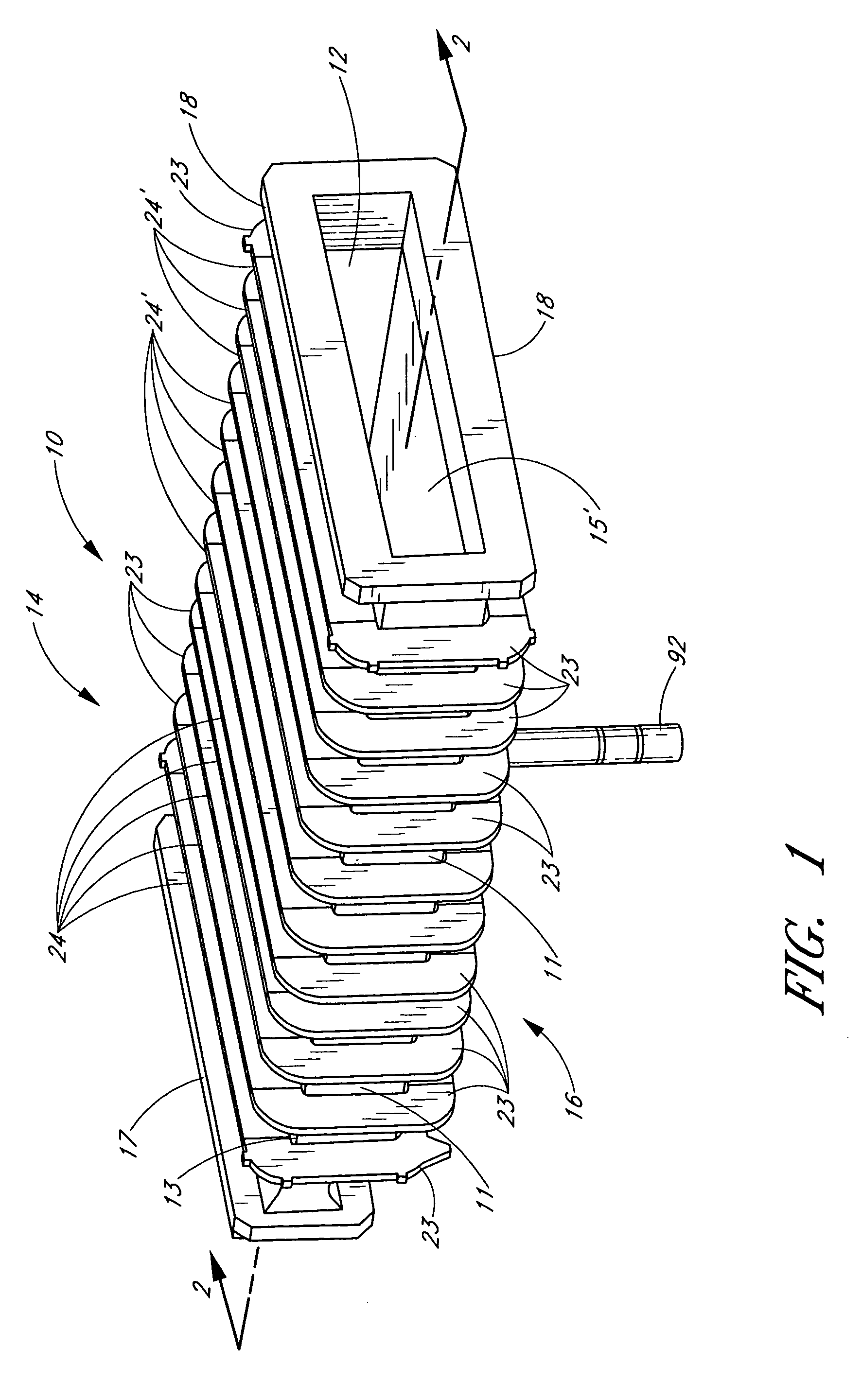
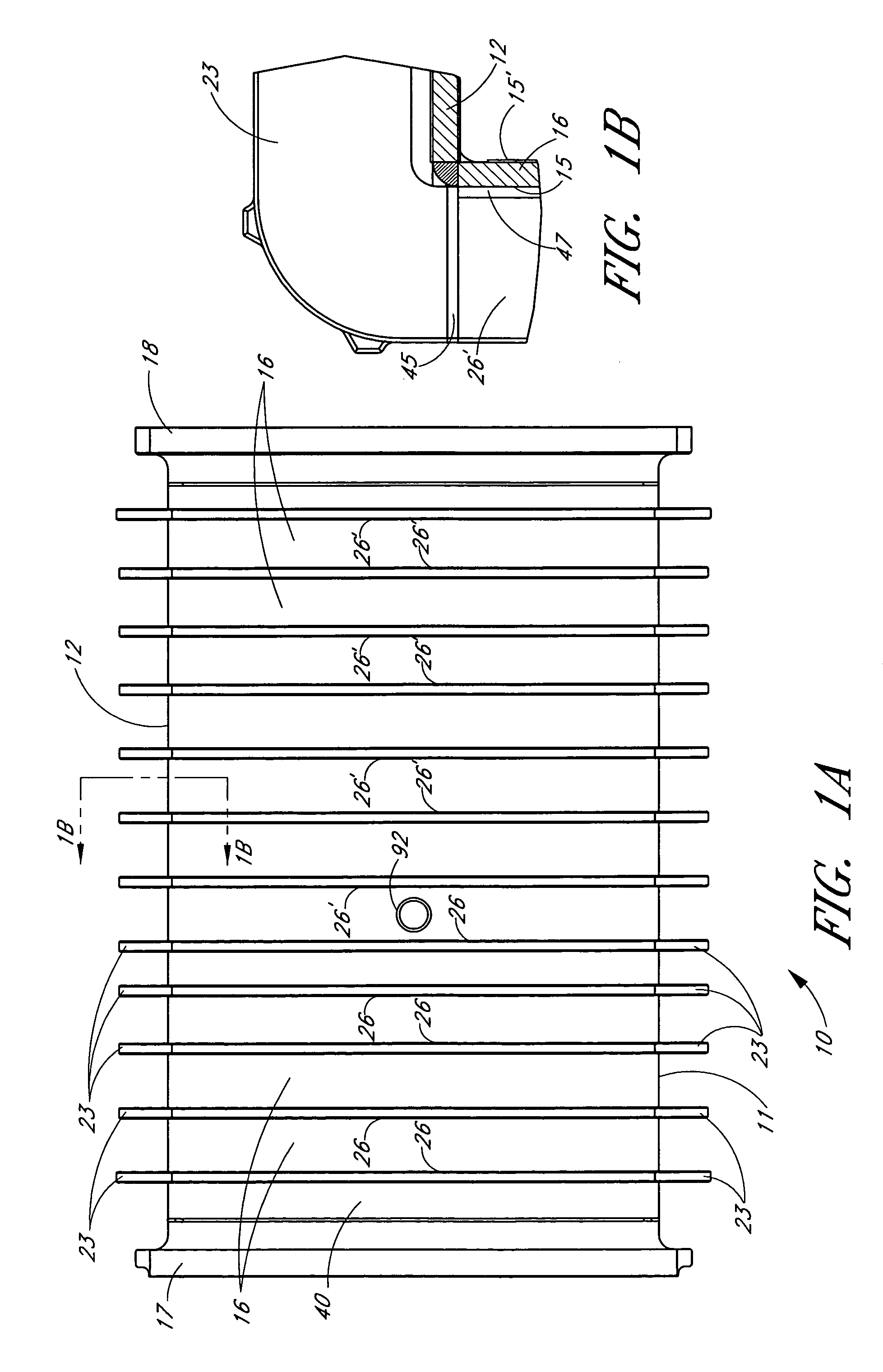
ActiveUS7108753B2Diffusion/dopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThermal effect
A semiconductor processing chamber having a plurality of ribs on an exterior surface of the chamber is provided. The ribs are positioned relative to the chamber such that shadows cast into the chamber by the ribs are offset from one another, thus more uniformly distributing radiant energy entering the chamber. In one embodiment, the ribs are positioned on the exterior surface of the chamber so that they have dissimilar radial distances from a center of the chamber. When a substrate rotates within the chamber, shadows produced by the ribs on a first side of the chamber fall substantially between secondary shadows produced by the ribs on a second side of the chamber. Likewise, shadows produced by the ribs on the second side of the chamber fall substantially between the secondary shadows produced by the ribs on the first side of the chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
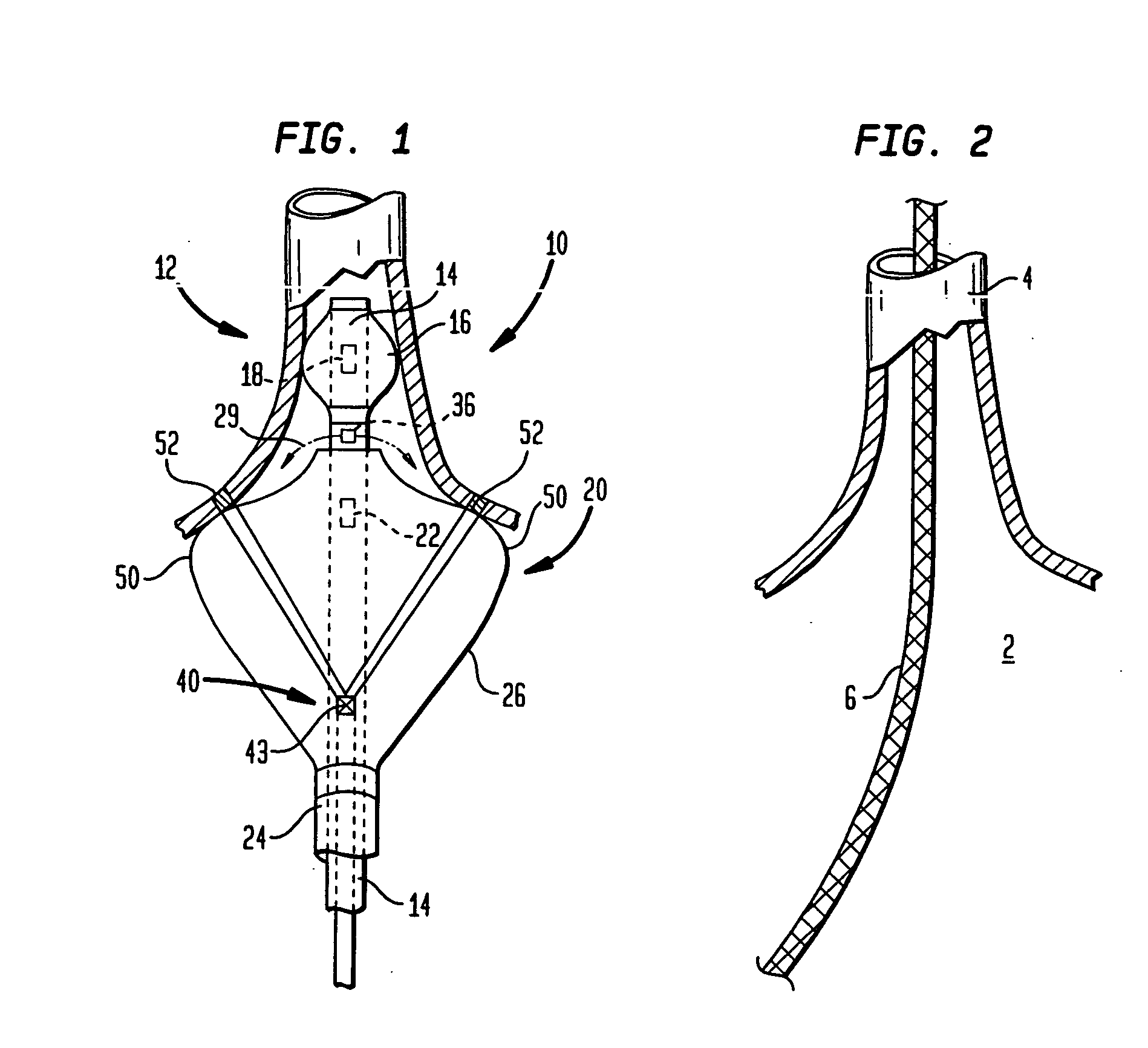
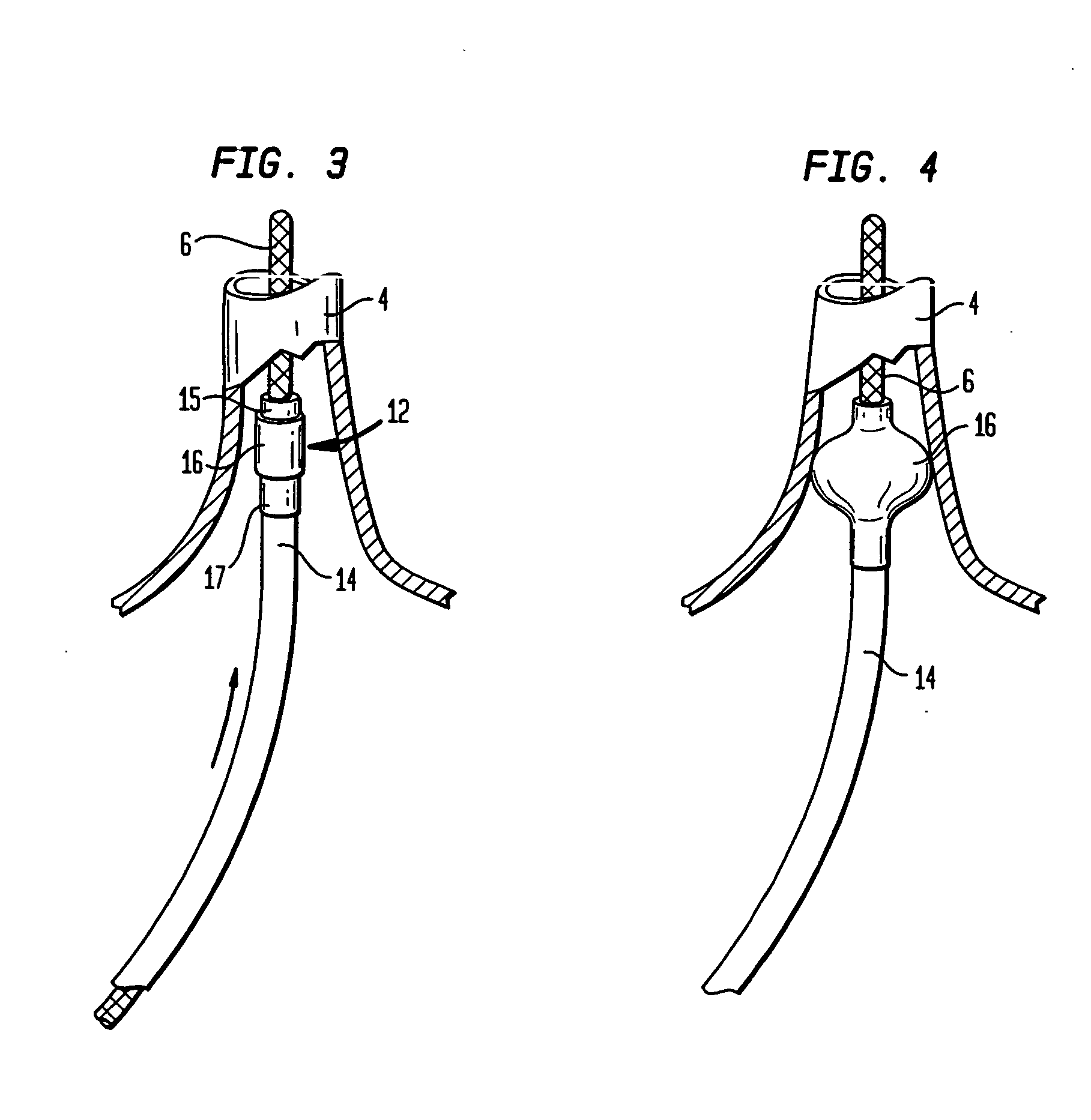
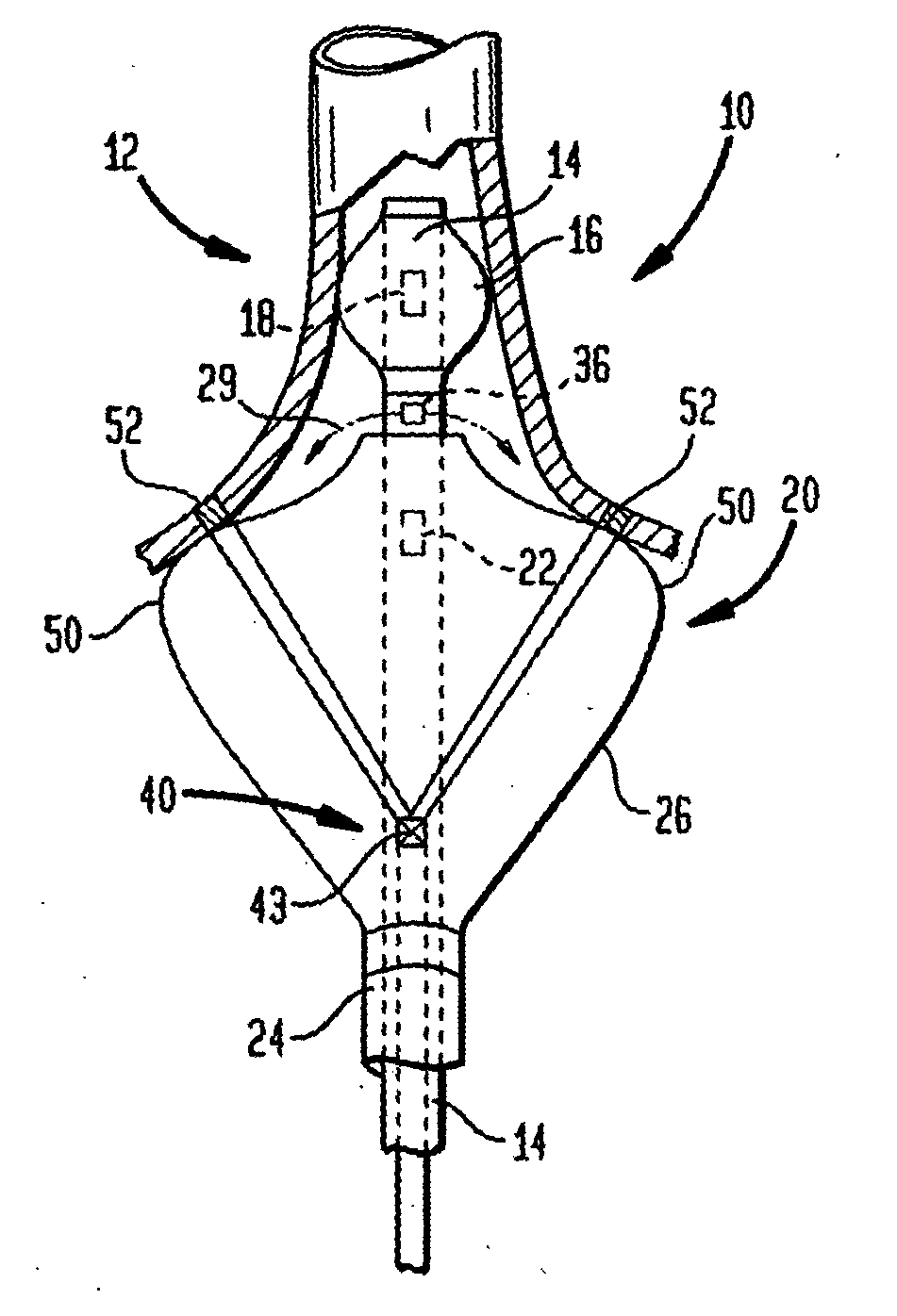
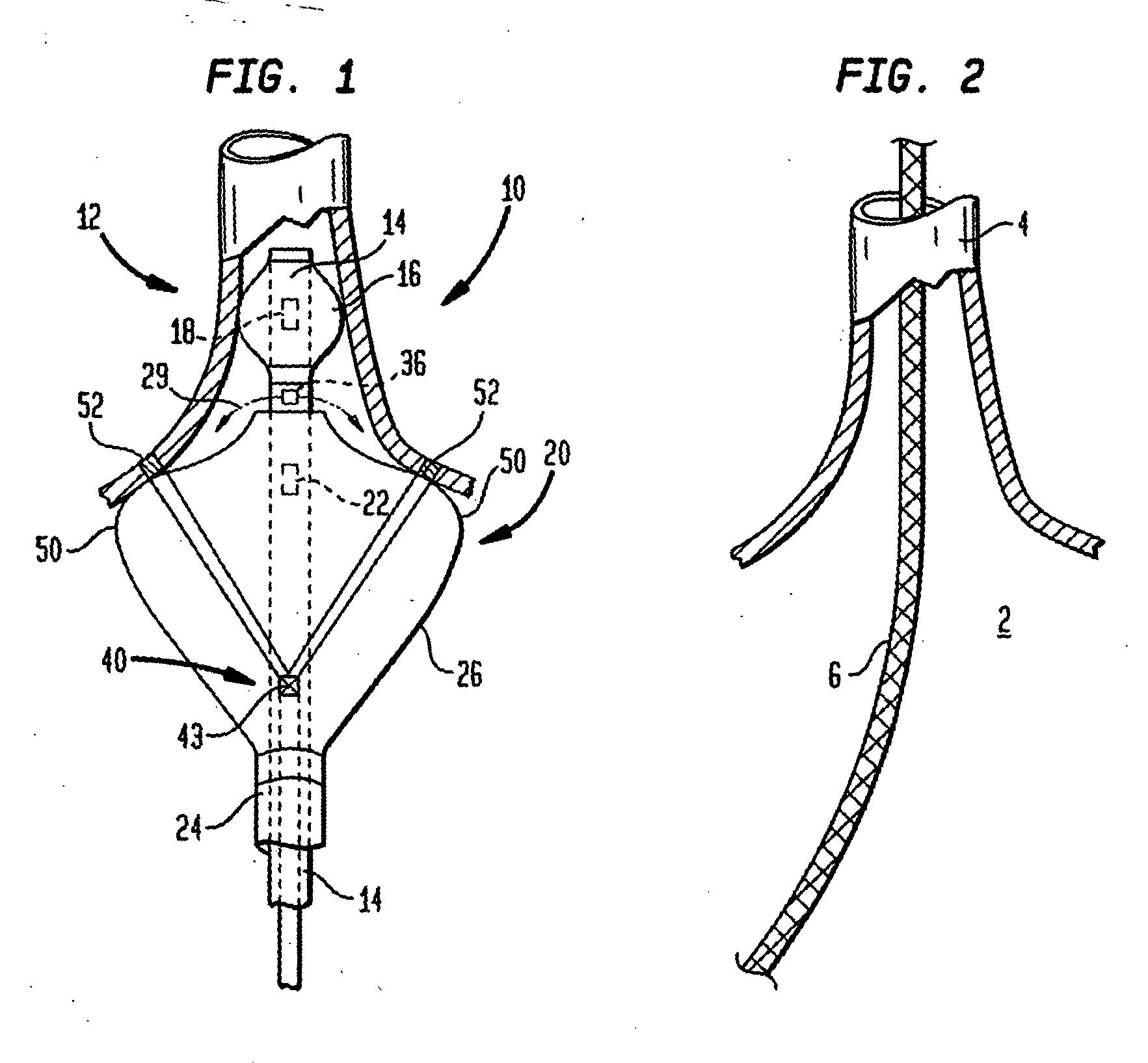
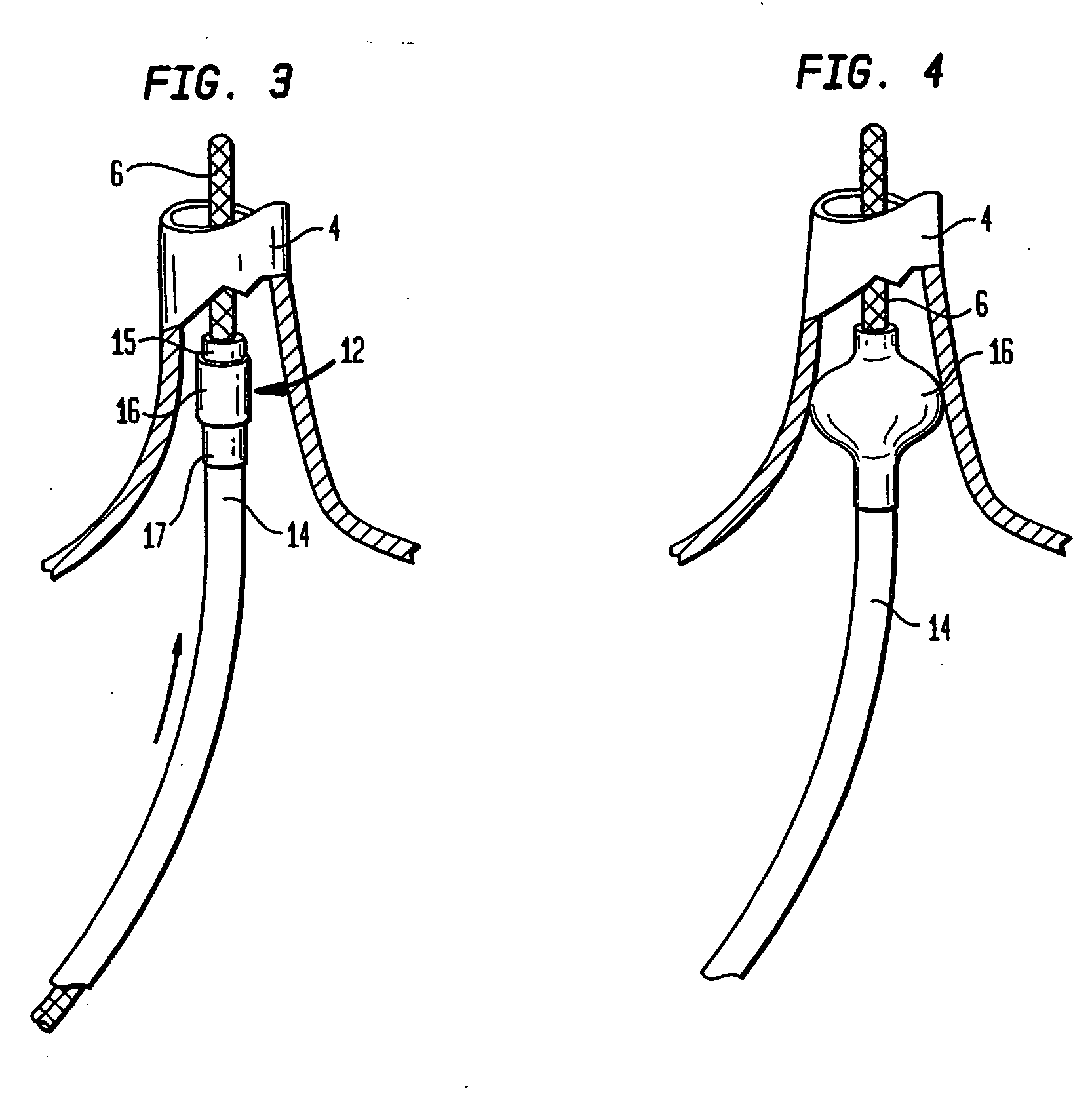
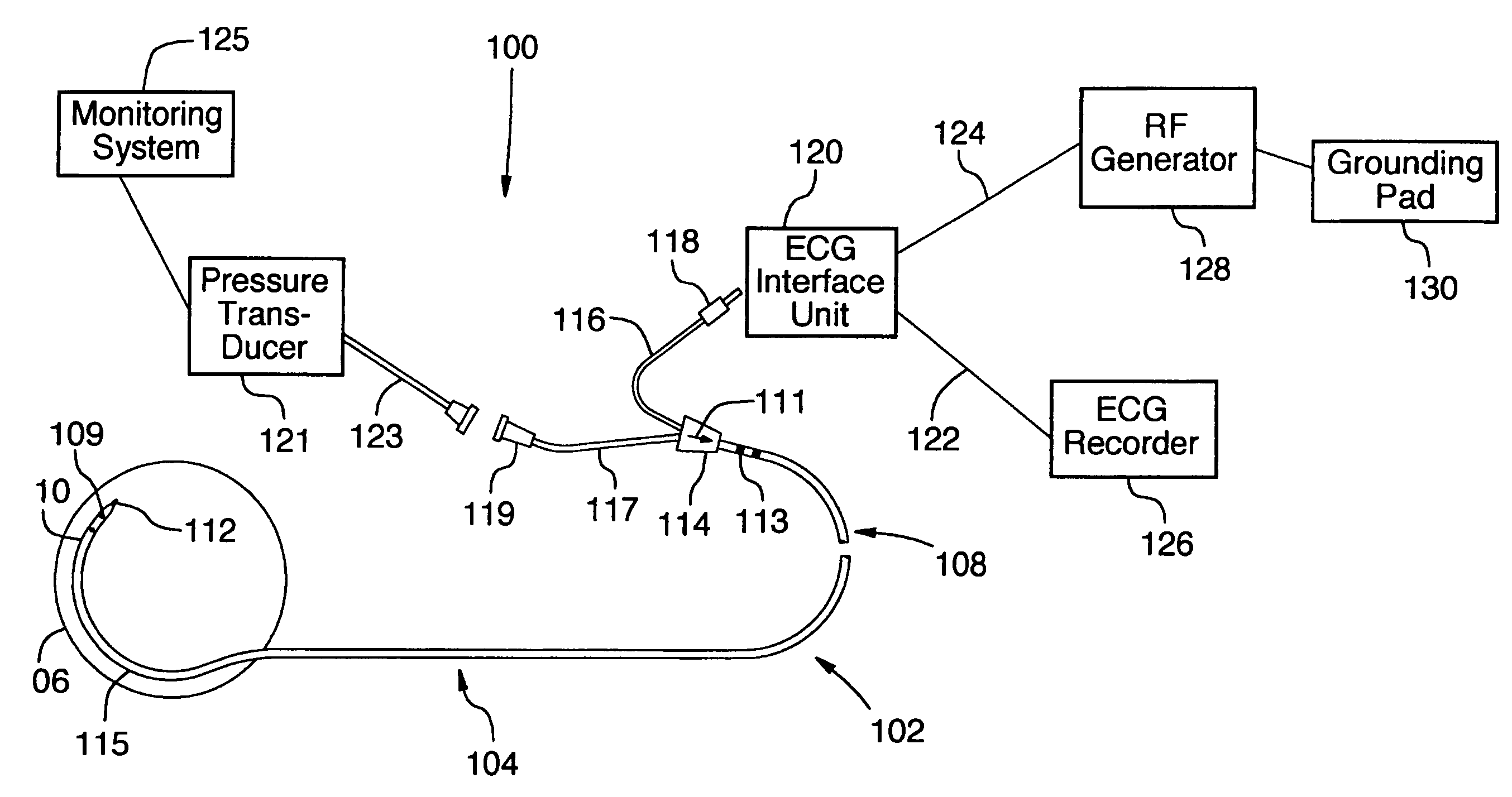
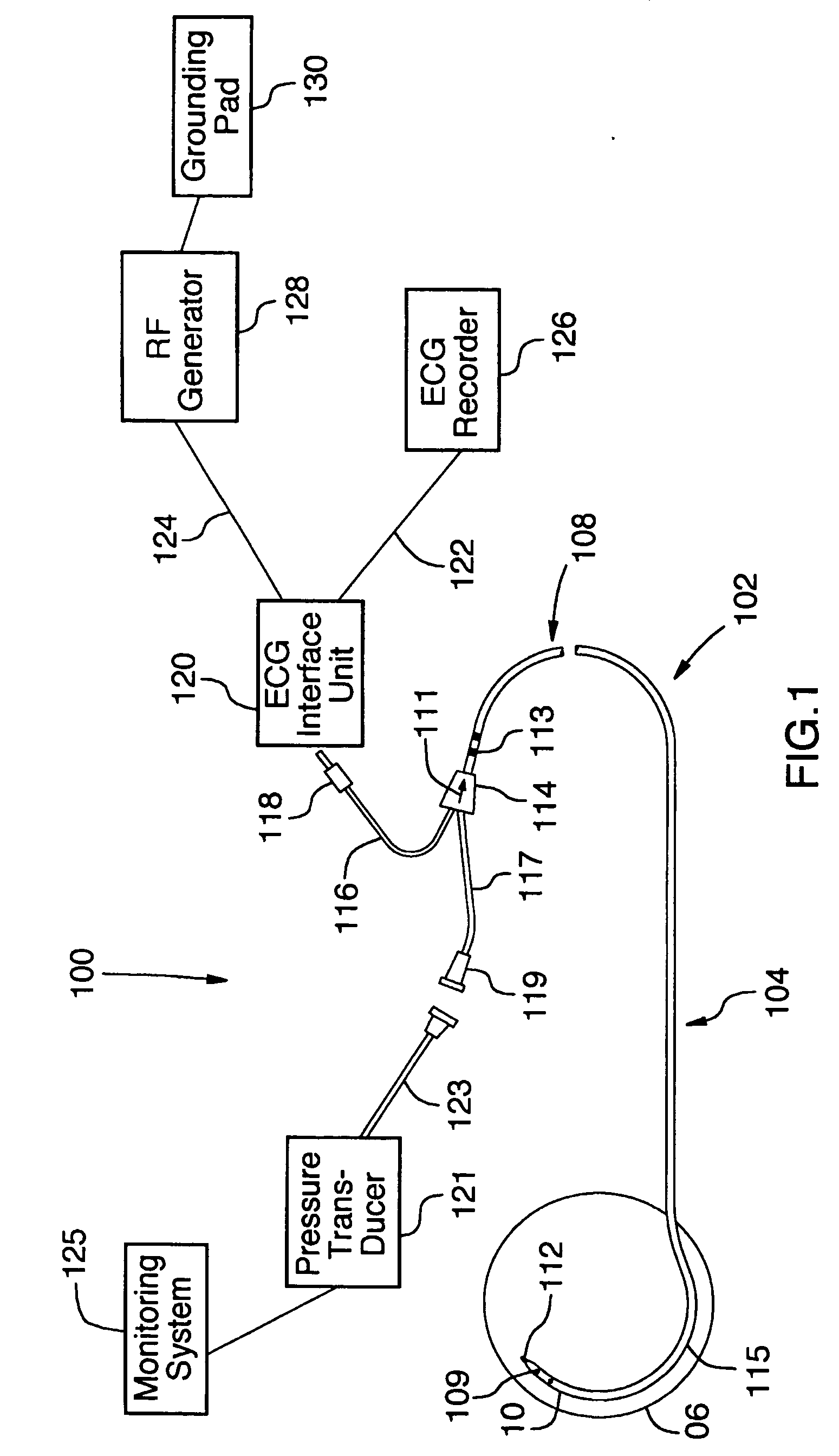
Coaxial catheter instruments for ablation with radiant energy
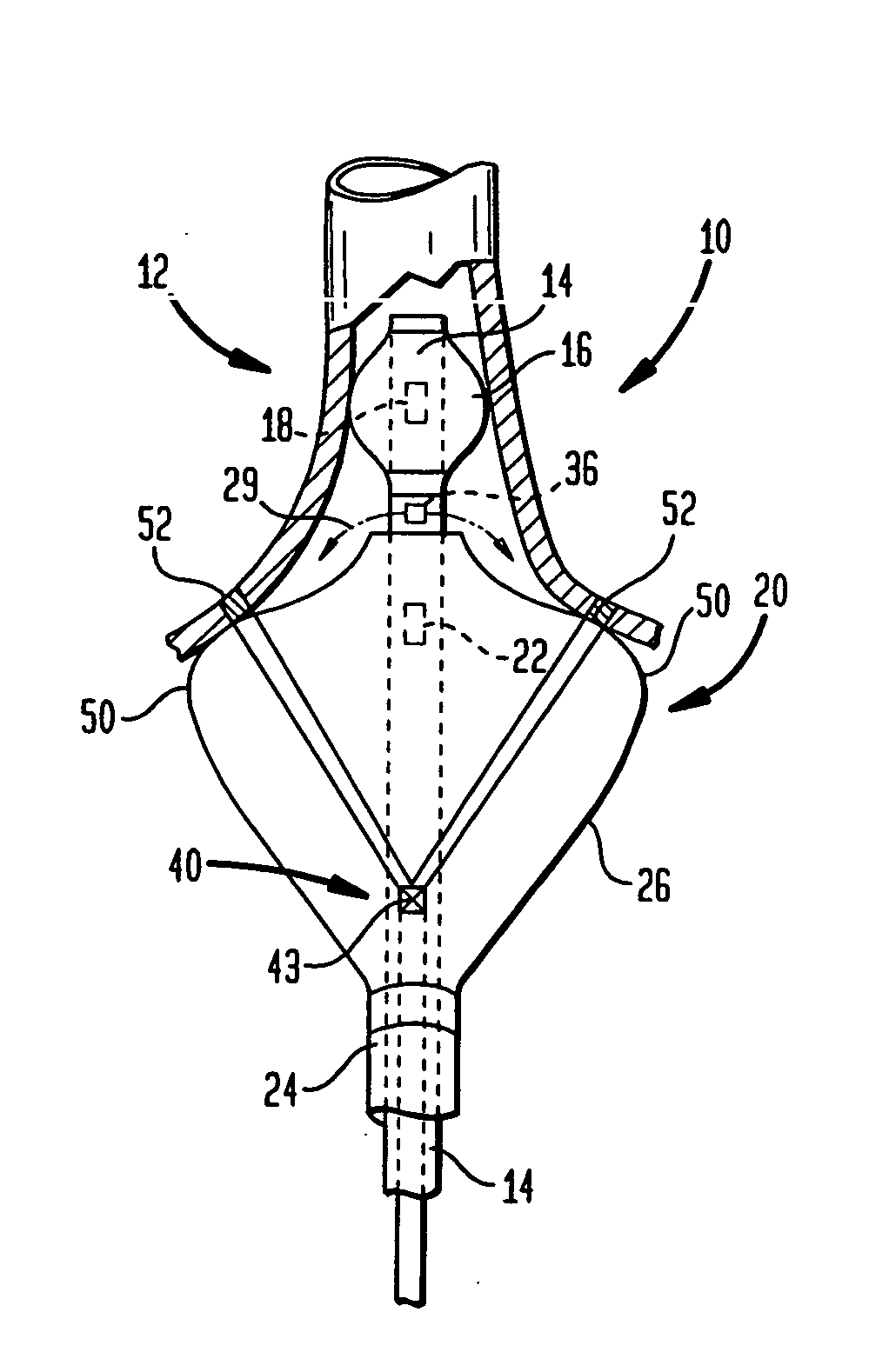
InactiveUS20050038419A9Rapid and effective photoablationLess timeStentsUltrasound therapyCoaxial catheterTarget tissue
Ablation methods and instruments are disclosed for creating lesions in tissue, especially cardiac tissue for treatment of arrhythmias and the like. Percutaneous ablation instruments in the form of coaxial catheter bodies are disclosed having at least one central lumen therein and having one or more balloon structures at the distal end region of the instrument. The instruments include an energy emitting element which is independently positionable within the lumen of the instrument and adapted to project radiant energy through a transmissive region of a projection balloon to a target tissue site. The instrument can optionally include at least one expandable anchor balloon disposed about, or incorporated into an inner catheter body designed to be slid over a guidewire. This anchor balloon can serve to position the device within a lumen, such as a pulmonary vein. A projection balloon structure is also disclosed that can be slid over the first (anchor balloon) catheter body and inflated within the heart, to define a staging from which to project radiant energy. An ablative fluid can also be employed outside of the instrument (e.g., between the balloon and the target region) to ensure efficient transmission of the radiant energy when the instrument is deployed. In another aspect of the invention, generally applicable to a wide range of cardiac ablation instruments, mechanisms are disclosed for determining whether the instrument has been properly seated within the heart, e.g., whether the device is in contact with a pulmonary vein and / or the atrial surface, in order to form a lesion by heating, cooling or projecting energy. This contact-sensing feature can be implemented by an illumination source situated within the instrument and an optical detector that monitors the level of reflected light. Measurements of the reflected light (or wavelengths of the reflected light) can thus be used to determine whether contact has been achieved and whether such contact is continuous over a desired ablation path.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
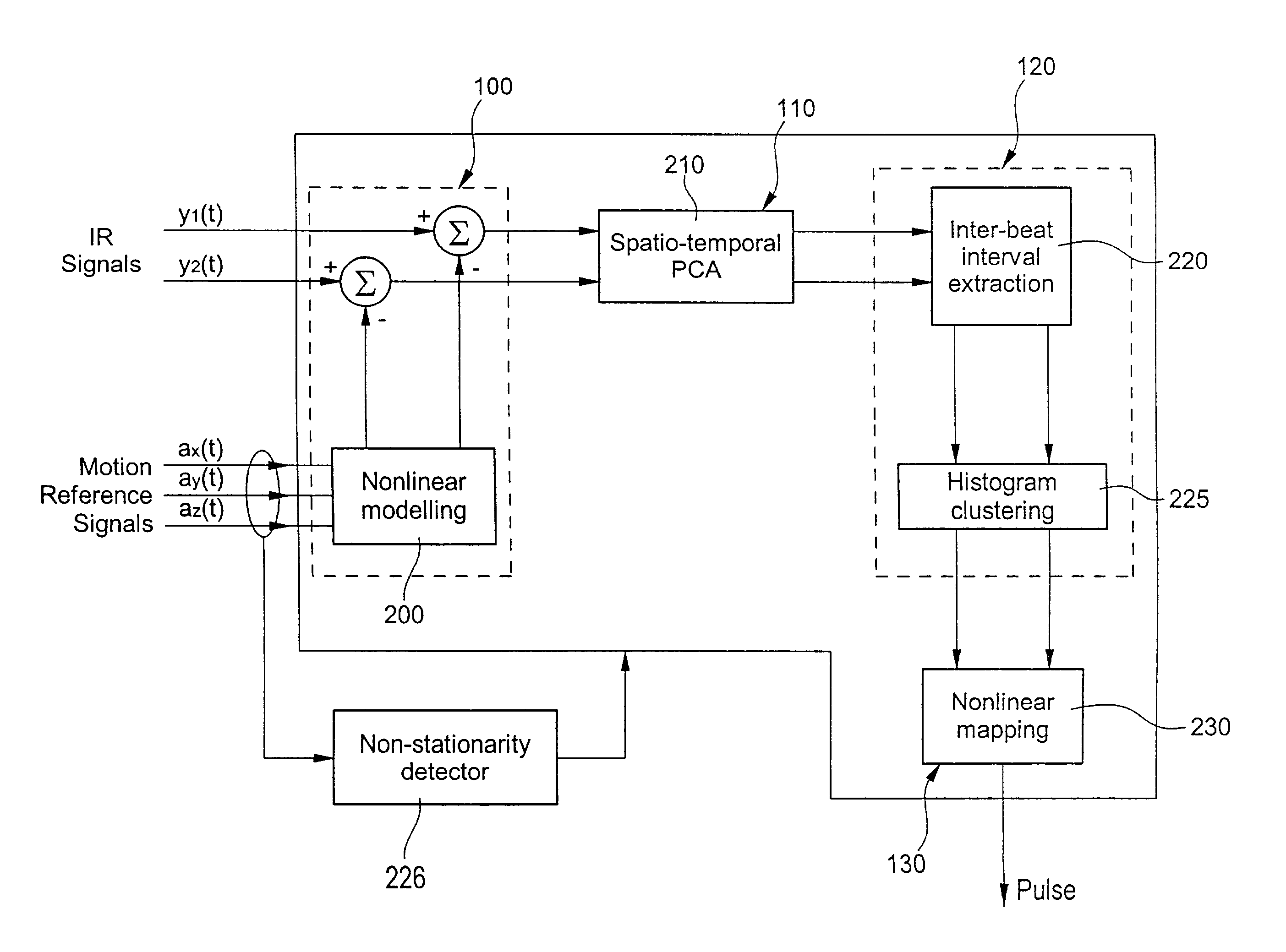
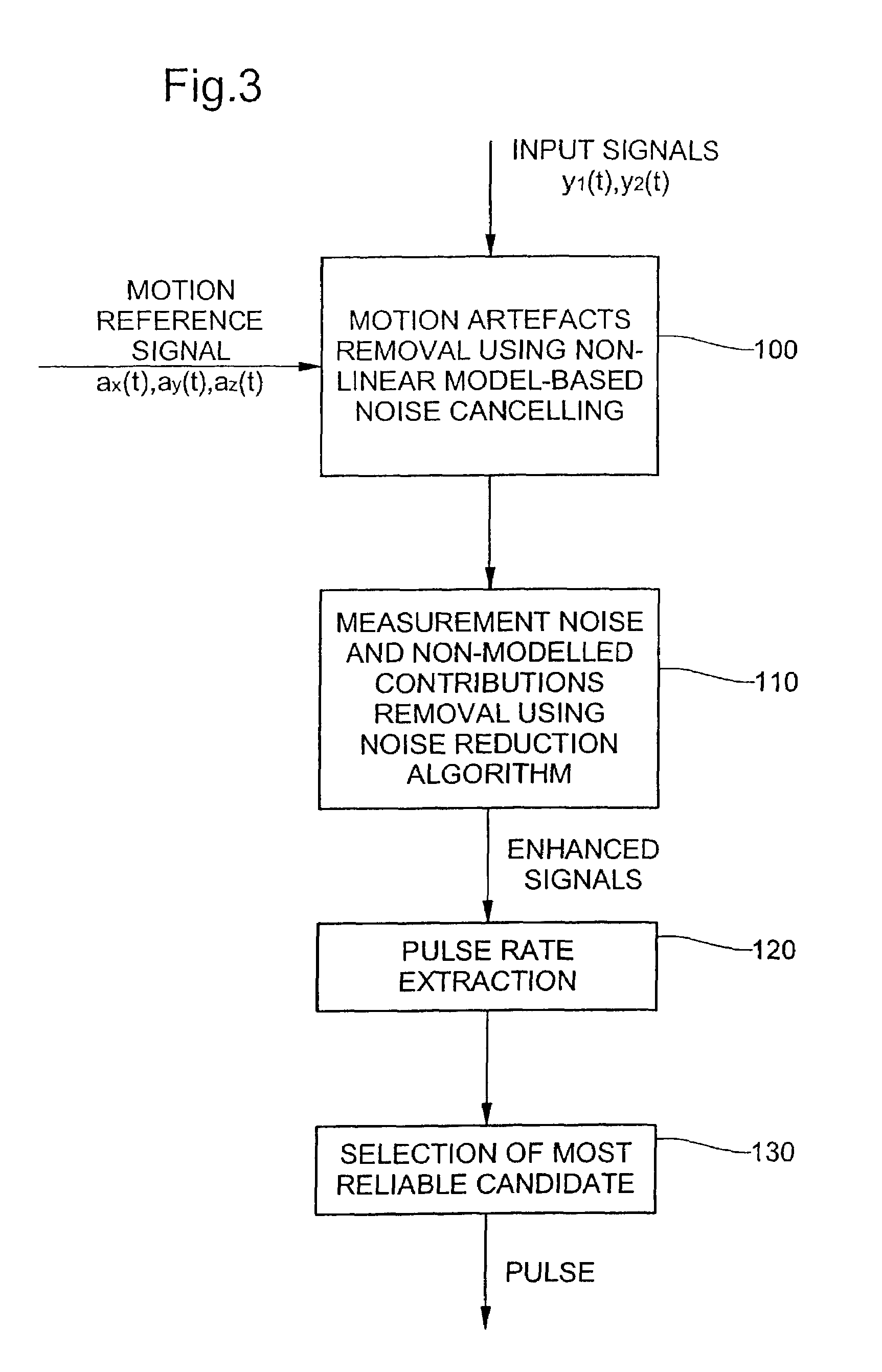
Method and device for pulse rate detection
InactiveUS7018338B2Accurately monitoring and detecting heart rateFully removedCatheterSensorsHuman bodyNoise reduction algorithm
Portable pulse rate detecting device for contact with human body tissue, including a light-emitting source for emitting radiant energy directed at through human body tissue; at least first and second light detectors for detecting intensity of radiant energy after propagation through human body tissue and for providing first and second input signals as a function of such propagation, a detecting device for providing a motion reference signal, and processing means for removing motion-related contributions from the first and second input signals and subtracting a calculated model based on the motion reference signal from each of the first and second input signals, wherein the processing means is also for removing measurement noise and residual non-modeled contributions from the first and second enhanced signals using a noise reduction algorithm.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC +1
Treatment of tissue volume with radiant energy
InactiveUS20070219605A1Reduce sensitivityLower power settingsUltrasound therapyDiagnostics using lightForms of energySpecific volume
Devices and methods for utilizing electromagnetic radiation and other forms of energy to treat a volume of tissue at depth are described. In one aspect, a device modulates the flux incident on surface tissue to control and vary the depth in the tissue at which an effective dose of radiant energy is delivered and, thereby, treat a specific volume of tissue. The methods and devices disclosed are used to perform various treatments, including treatments to relieve pain and promote healing of tissue.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Apparatus and method for production of three-dimensional models by spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6051179AFacilitate cross-linkingHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnalogue computers for control systemsSpatial light modulatorWide beam
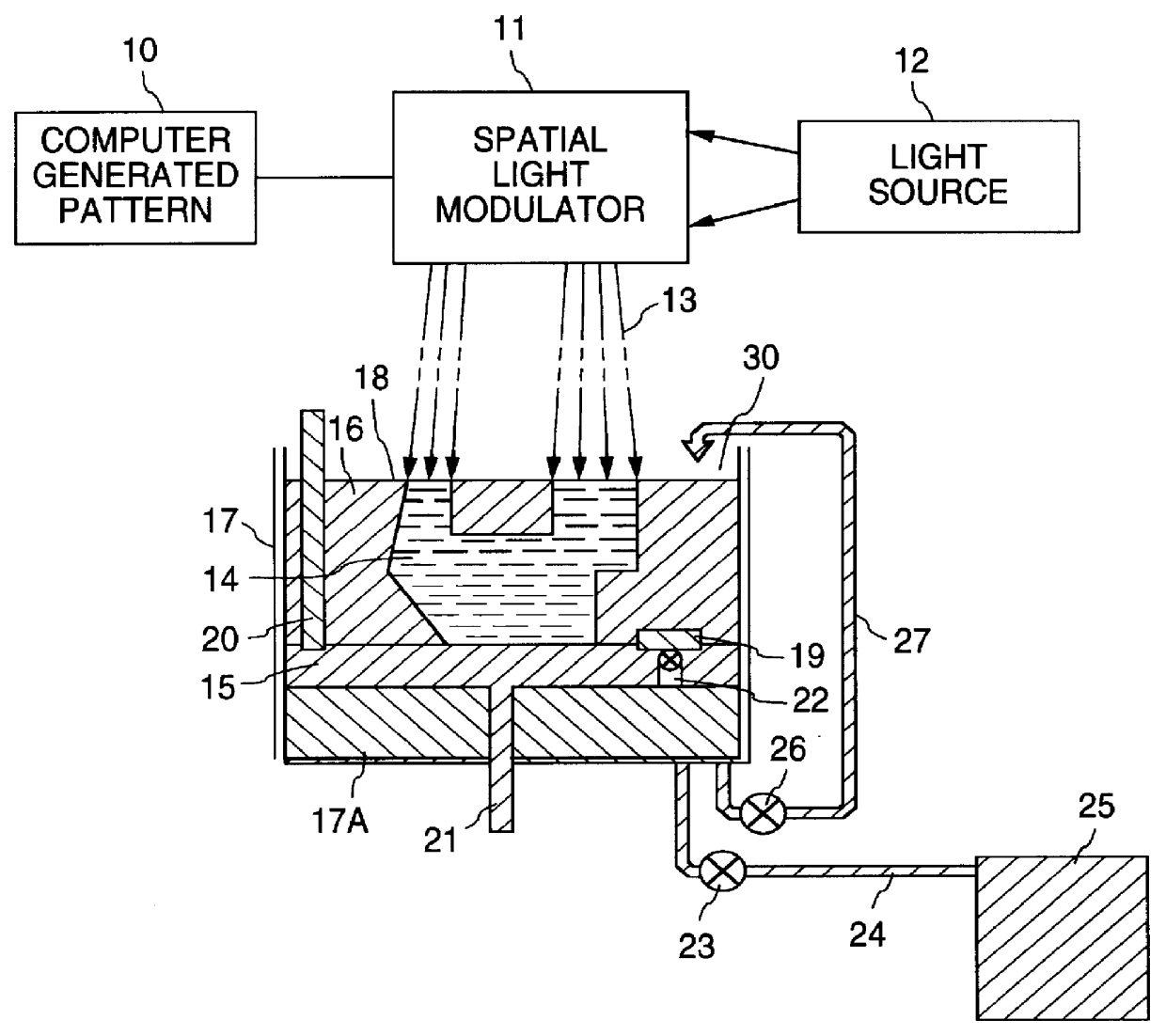
An apparatus and the method of its operation for rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional object which includes a radiant energy source of a wide beam of radiant energy of suitable intensity and wavelength for curing a layer of photo-curable resin contained in an open vat, a spatial light modulator (SLM) having an array of pixel elements which are individually digitally controllable by a computer, for modulating the radiant energy beam projected from the radiant energy source on a pixel by pixel basis, to form a series of time sequential images of the cross-sectional laminae of the object, an optical system for focusing each image formed by the SLM, one at a time, onto successive layers of photo-curable resin for predetermined exposure times to thereby form stacked laminae of cured resin, each lamina of cured resin being in the shape of a different one of the cross-sectional laminae, and a piston support for lowering each lamina of cured resin after it is formed by the SLM and for depositing a layer of resin corresponding to the thickness of one cross sectional lamina of the three-dimensional object before the step of projecting a new image by the SLM. The SLM, the piston support for lowering, and the optical system operate repeatedly and sequentially until a complete copy of the object is thereby produced.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
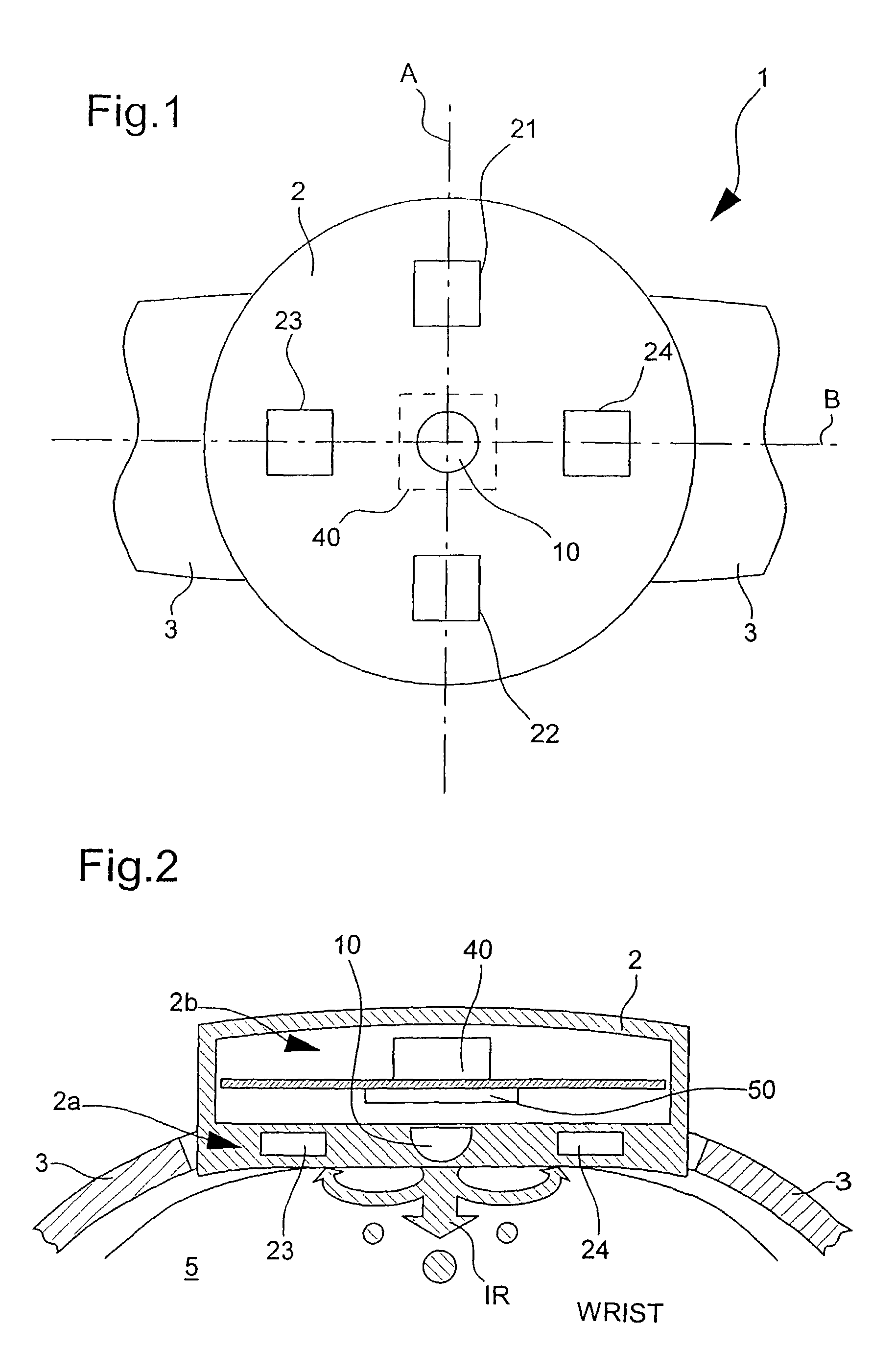
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS20050143662A1Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographySurgeryAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
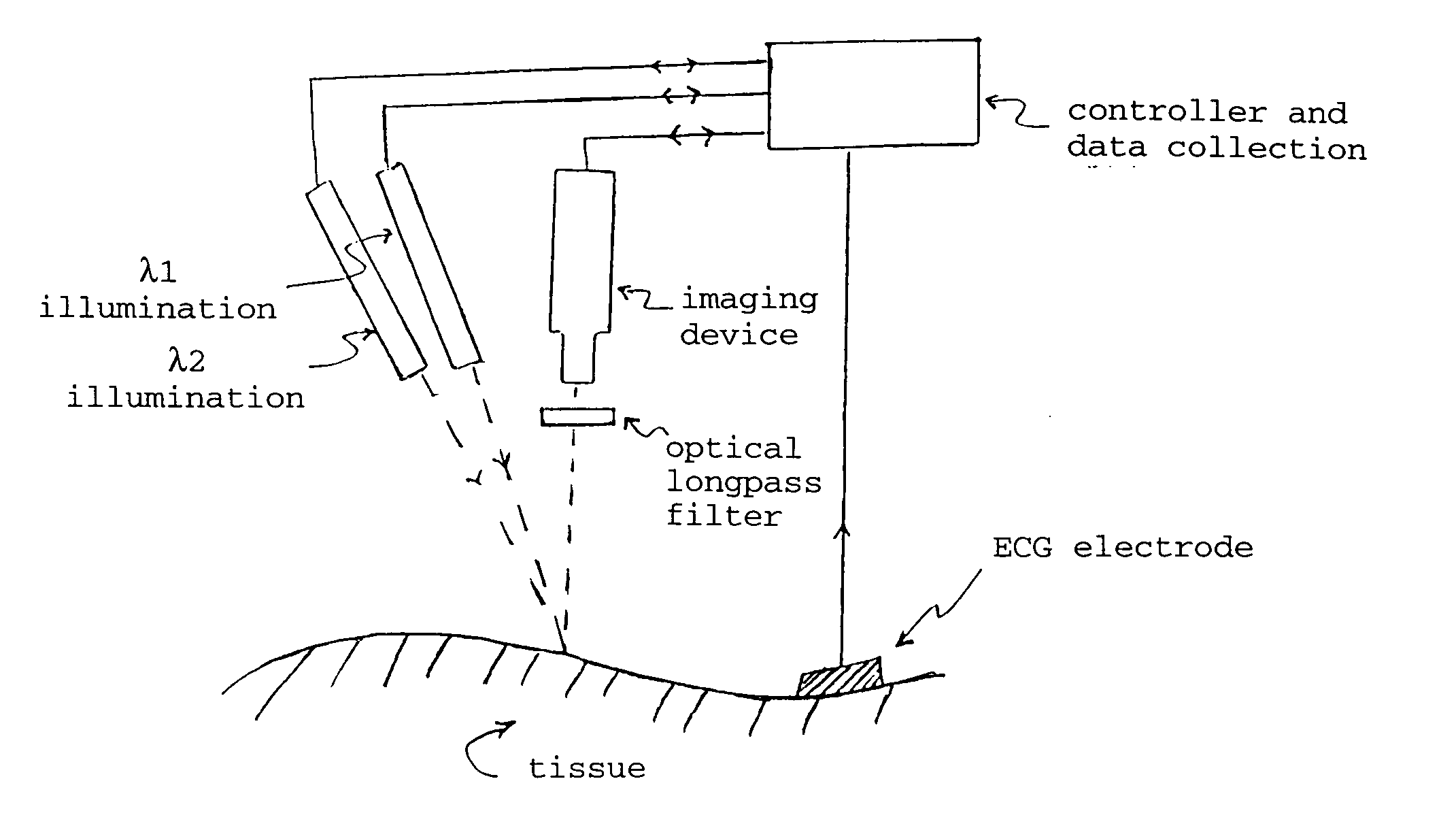
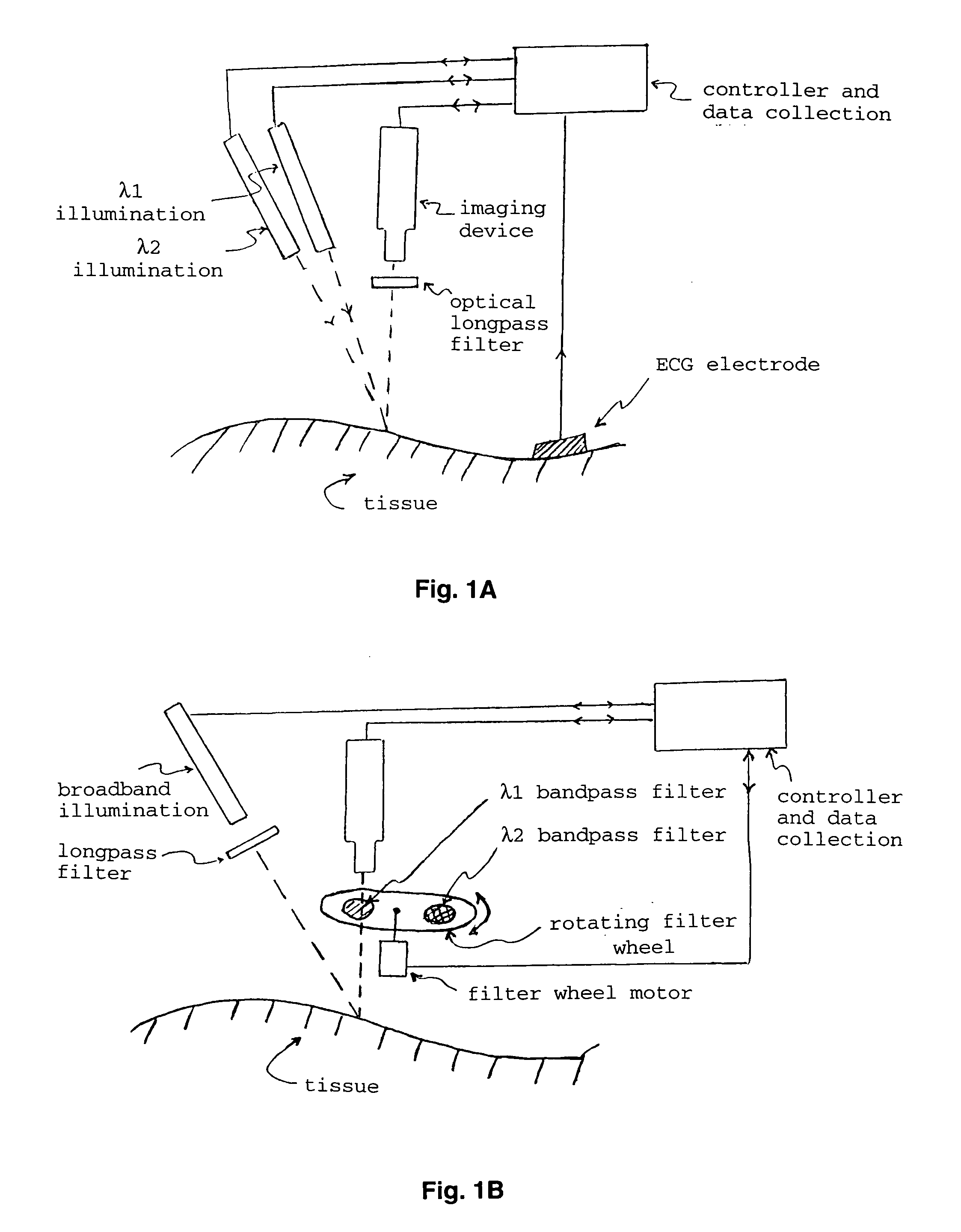
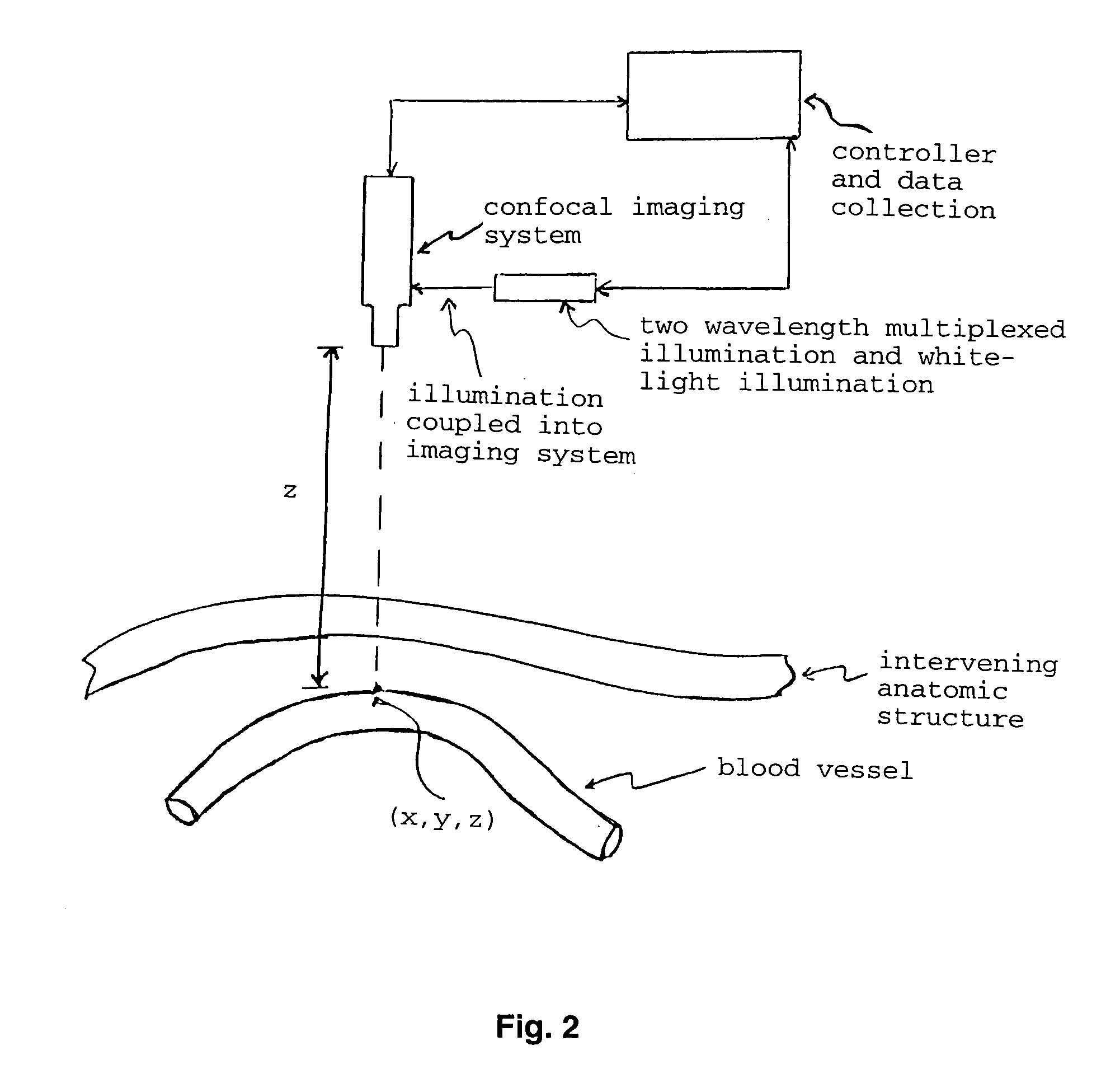
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
Solid state fluorine sensor system and method
InactiveUS6321587B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElectricityElectrical battery
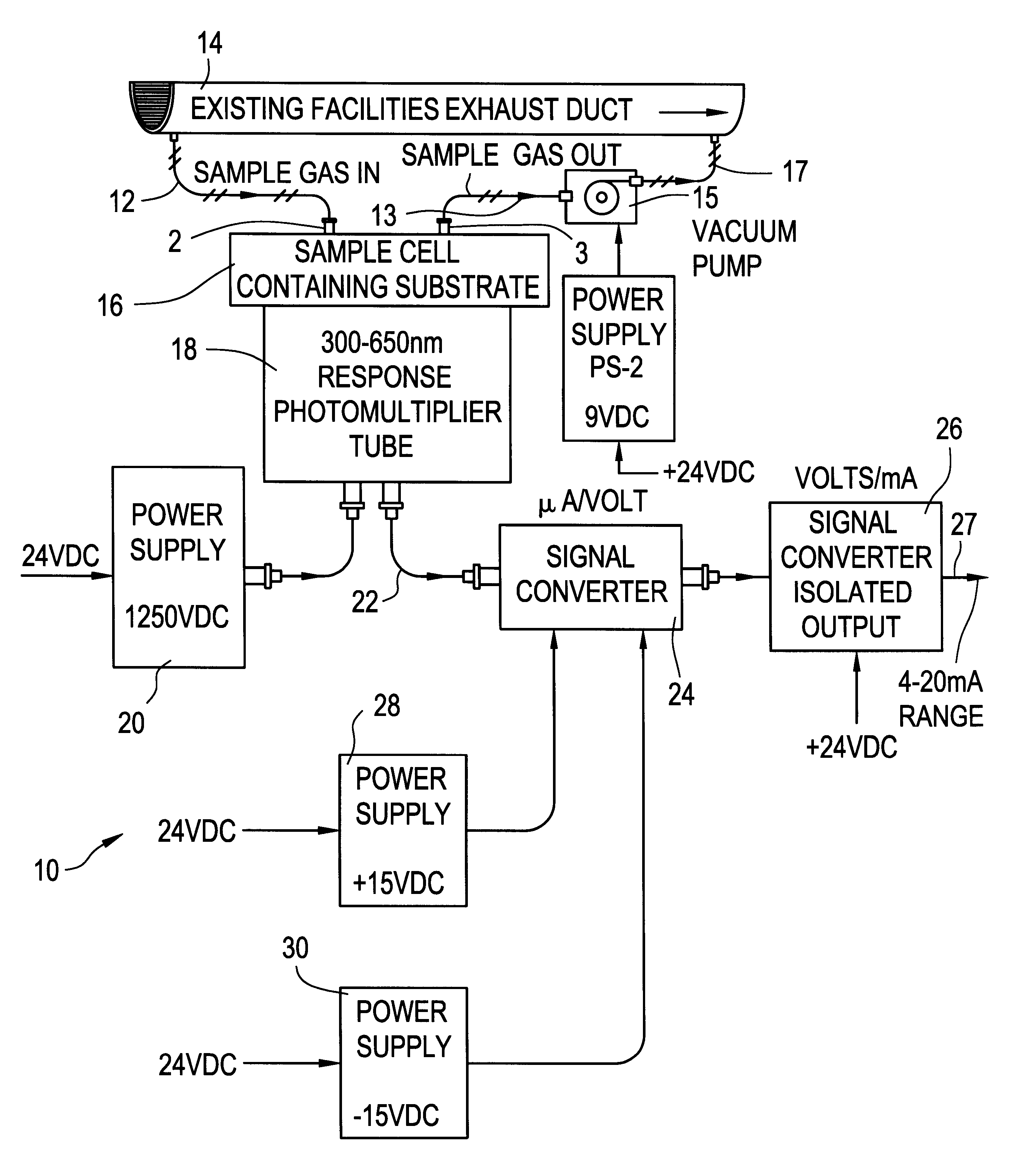
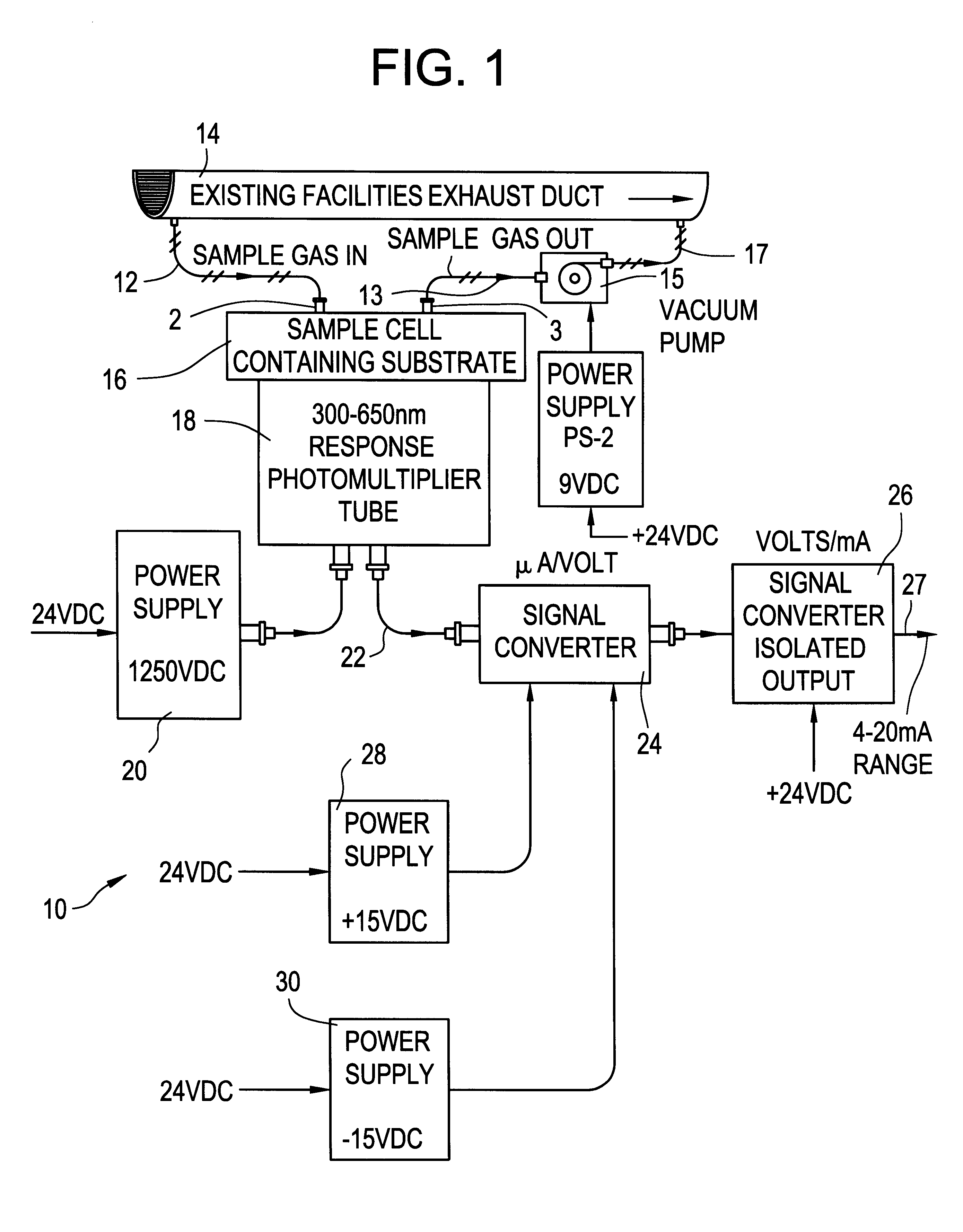
A gaseous fluorine detection system is provided which includes a generally enclosed sample cell containing a substrate comprising a material which interacts with fluorine gas to generate radiant energy. A gas sample of fluorine, the concentration levels of which are to be evaluated is flowed through the cell. A photomultiplier tube is positioned to receive the resulting radiant energy and generate an electrical output signal related to the level of said radiant energy. Means are provided for measuring the said photomultiplier output signal and relating same to the fluorine concentration of the gas sample provided to the cell.
Owner:RADIAN INT
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS6889075B2Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
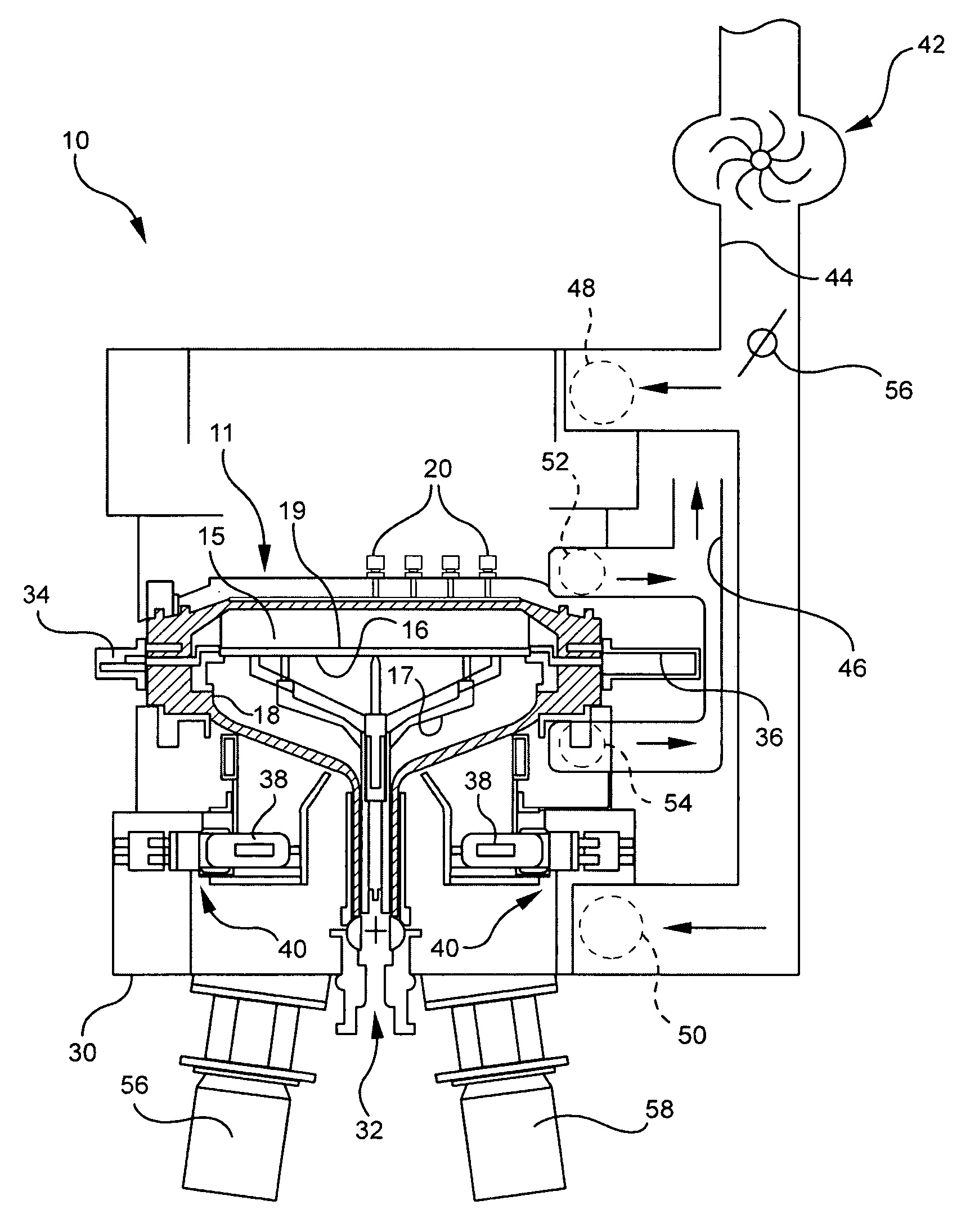
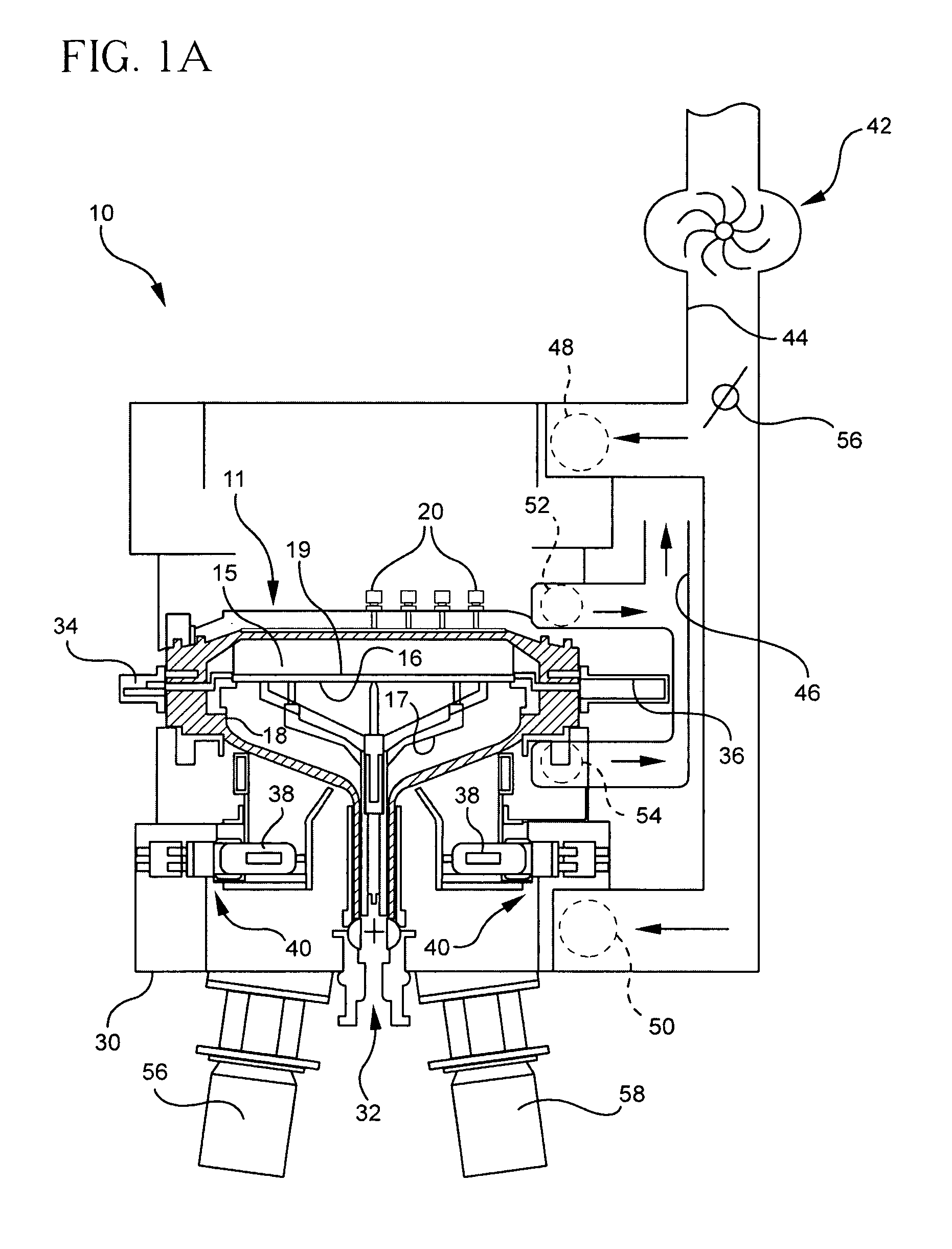
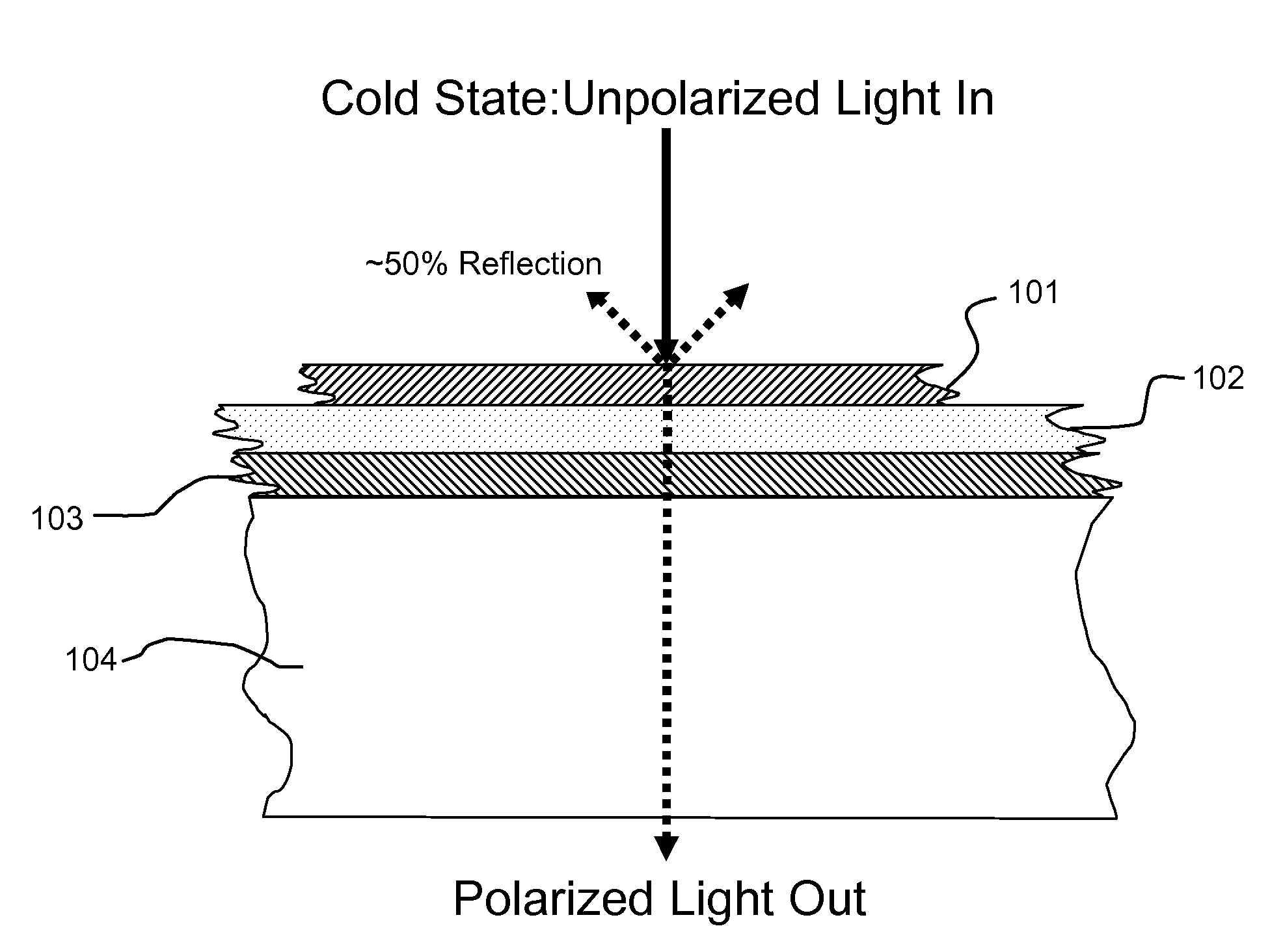
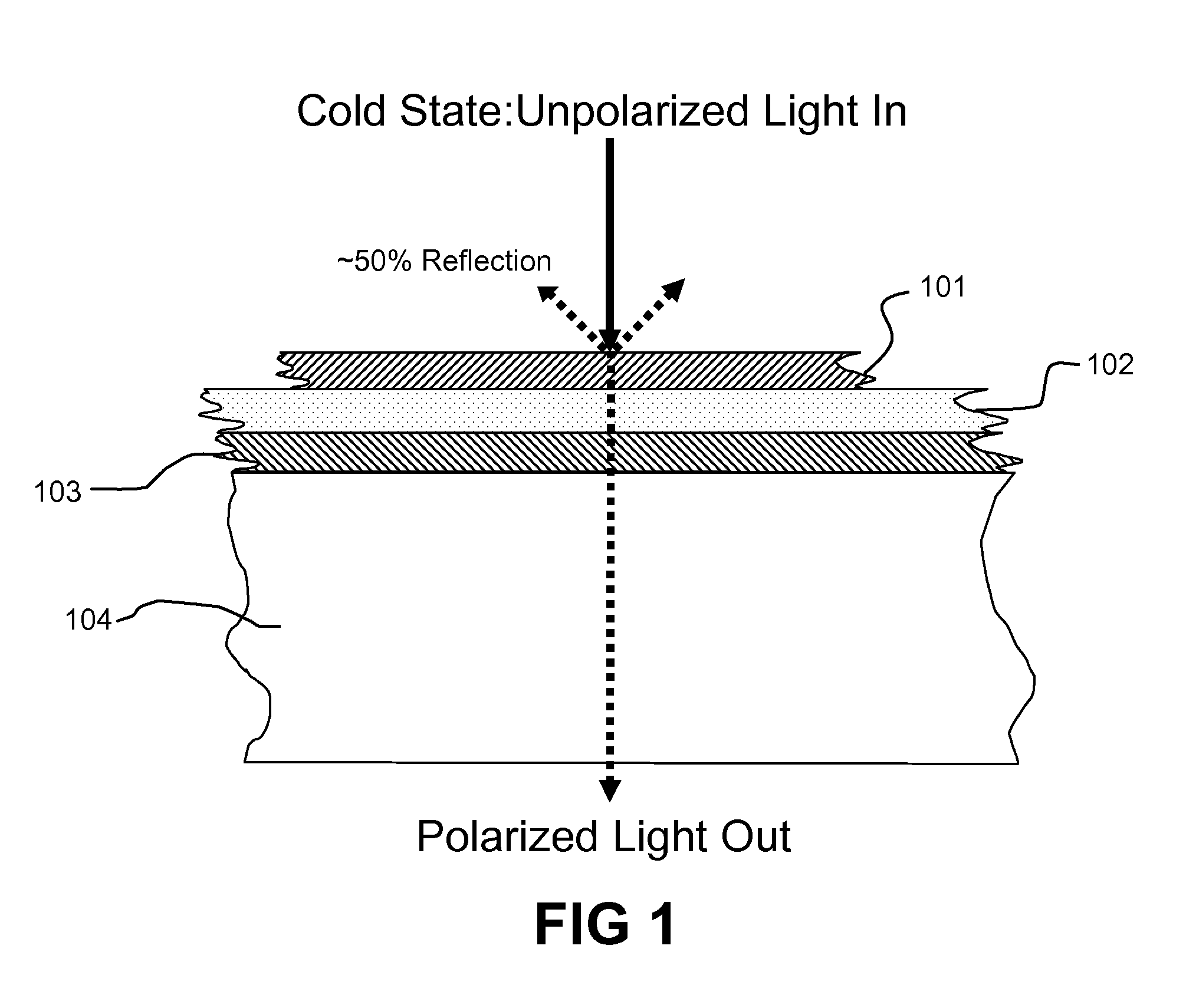
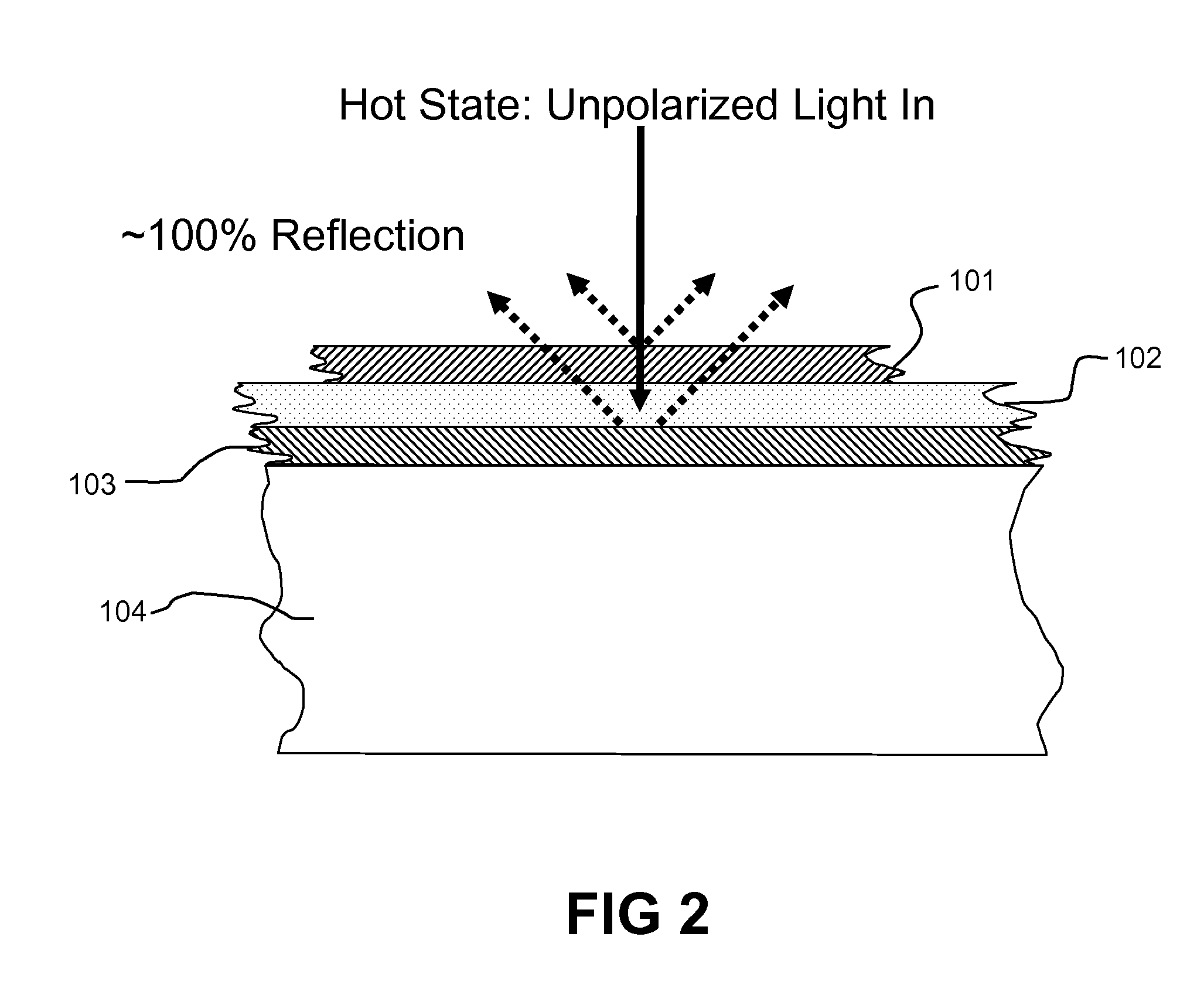
Thermally Switched Reflective Optical Shutter
The thermally switched reflective optical shutter is a self-regulating “switchable mirror” device that reflects up to 100% of incident radiant energy above a threshold temperature, and reflects up to 50% of incident radiant energy below a threshold temperature. Control over the flow of radiant energy occurs independently of the thermal conductivity or insulating value of the device, and may or may not preserve the image and color properties of incoming visible light. The device can be used as a construction material to efficiently regulate the internal temperature and illumination of buildings, vehicles, and other structures without the need for an external power supply or operator signals. The device has unique aesthetic optical properties that are not found in traditional windows, skylights, stained glass, light fixtures, glass blocks, bricks, or walls. The device can be tailored to transmit sufficient visible light to see through in both the transparent and reflective states, while still providing significant control over the total energy transmission across the device.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
Radiant Energy Conversion System
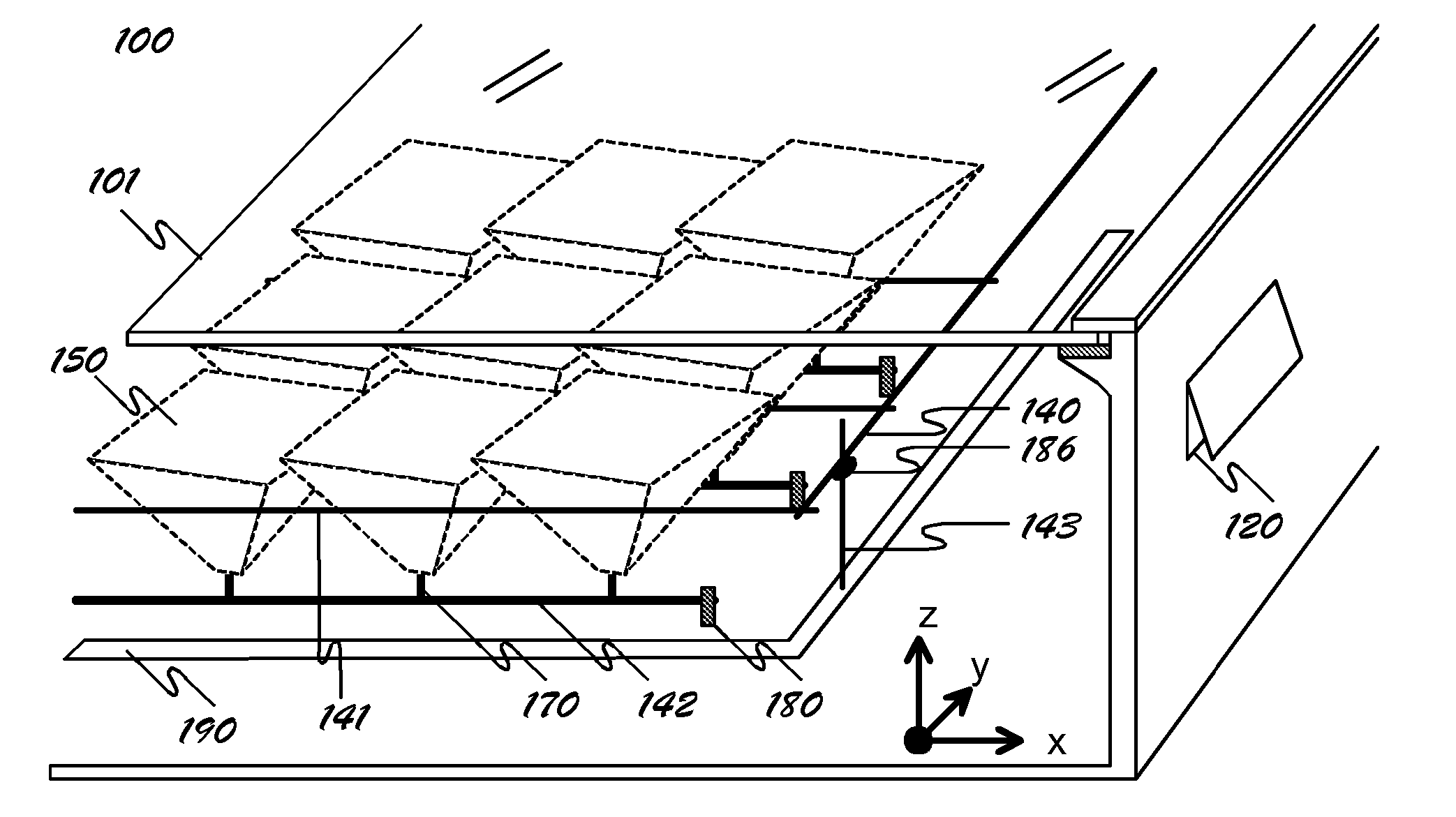
InactiveUS20070070531A1Improve conversion efficiencyLow usagePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEnvironmental effectEngineering
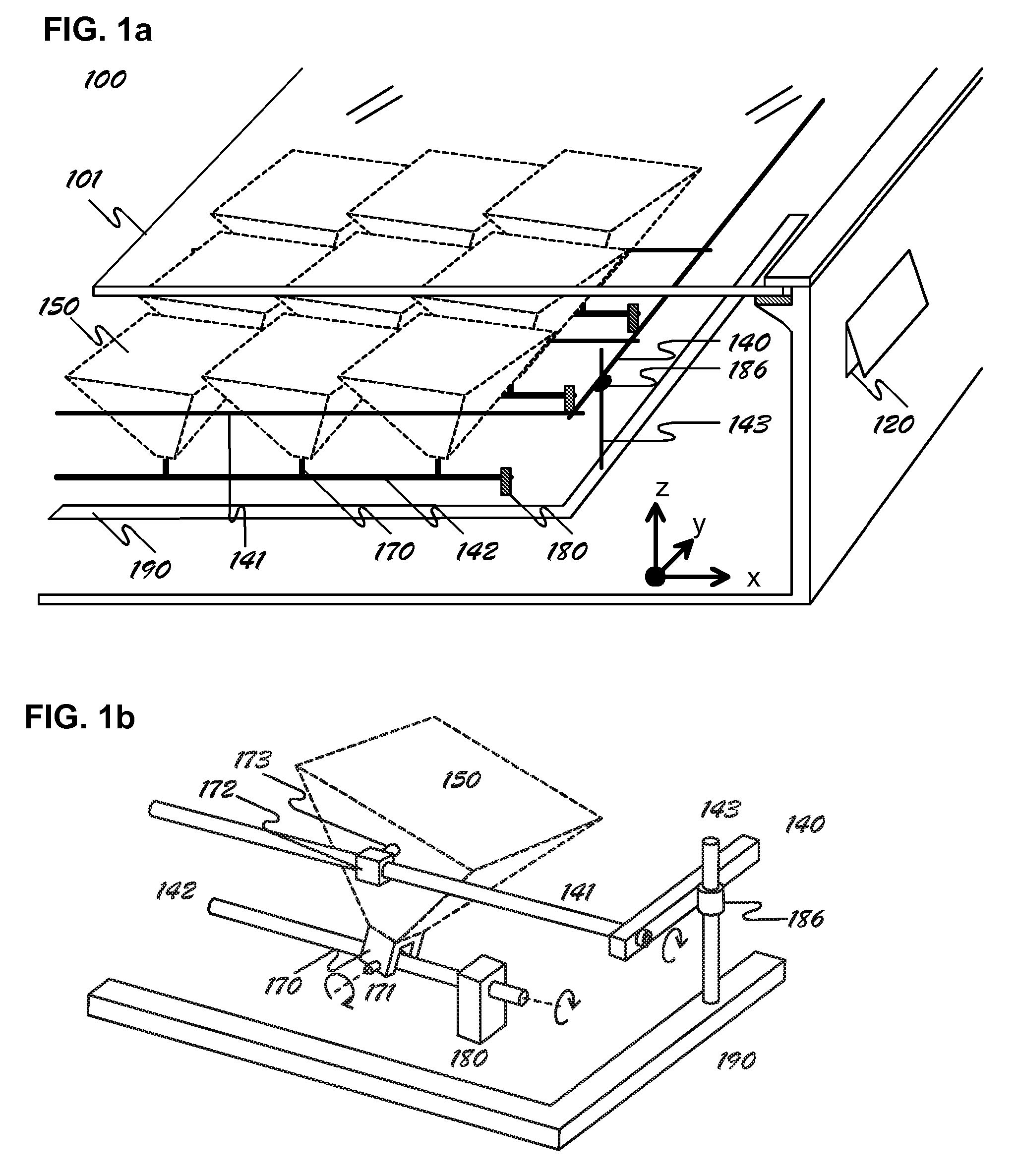
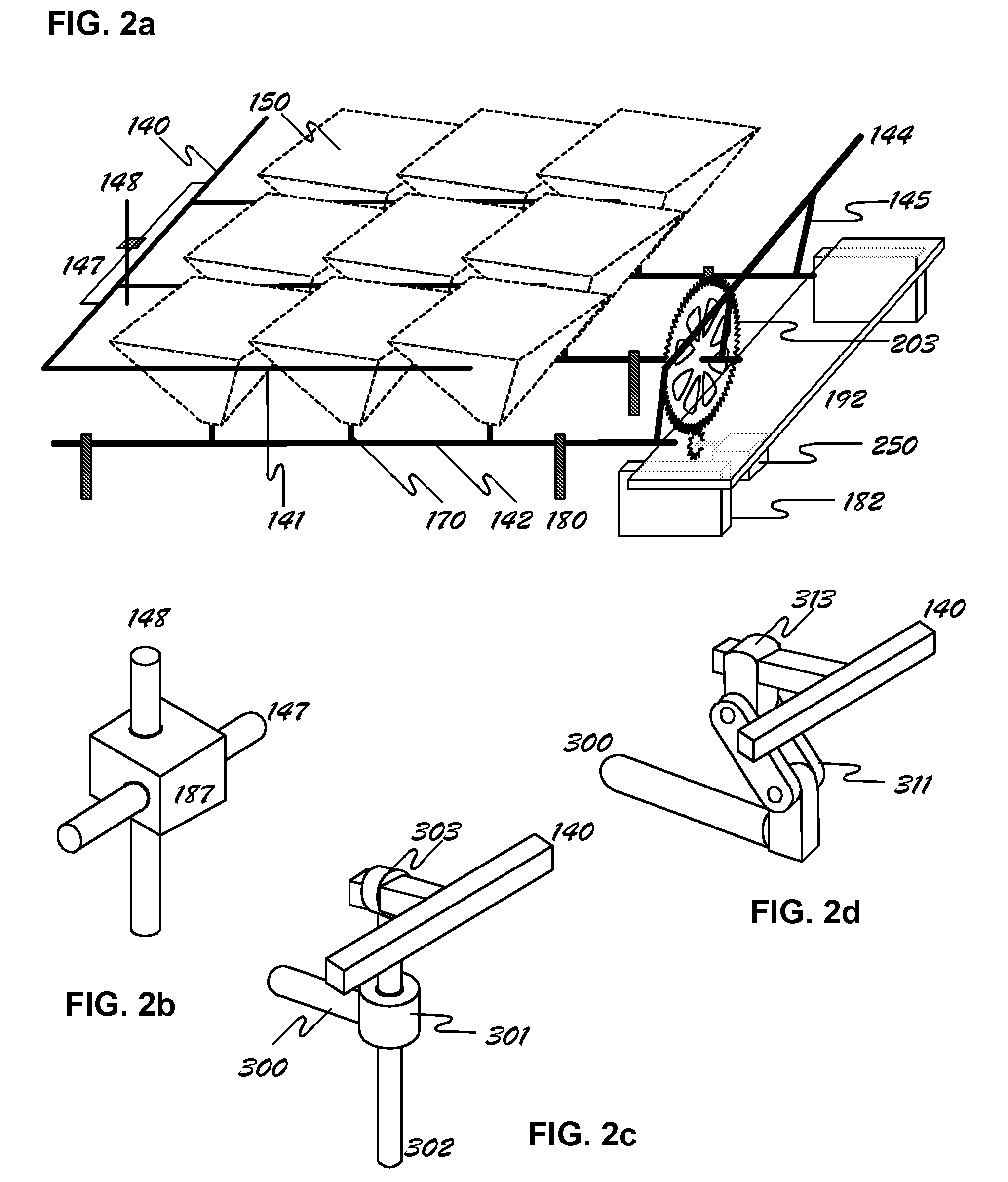
A radiant energy concentrating or collimating system comprising an enclosure that shields its contents from environmental effects while allowing radiant energy to transmit through its top window; a plurality of energy concentrating or collimating assemblies, each on its own pivot mechanism and each comprising a plurality of optics, a support structure and an energy conversion device that is mounted on a heat dissipating structure; a drive mechanism controlled by a microprocessor to rotate the said energy concentrating or collimating assemblies on two orthogonal axes in unison so the assemblies are oriented towards desired direction at any given time.
Owner:INLAND MARINE IND +1
Treatment of tissue with radiant energy
InactiveUS20070219604A1Not to damageReduce sensitivityUltrasound therapyDiagnostics using lightForms of energyMedicine
Devices and methods for utilizing electromagnetic radiation and other forms of energy to treat a volume of tissue at depth are described. In one aspect, a device modulates the flux incident on surface tissue to control and vary the depth in the tissue at which an effective dose of radiant energy is delivered and, thereby, treat a specific volume of tissue. The methods and devices disclosed are used to perform various treatments, including treatments to relieve pain and promote healing of tissue.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Extensible linear light emitting diode illumination source
InactiveUS6880952B2Avoid catastrophic failureImprove reliabilityMechanical apparatusLighting support devicesPower cableDirect illumination
A compact, energy-efficient extensible illumination source combines the reliability advantages of light emitting diodes (LEDs) with the brightness of conventional lighting. High reliability of the LEDs provides trouble-free operation over a long hour lifetime. This high-output light source can be used in direct lighting applications or for backlighting for translucent materials. The illumination source includes LED printed wire board segments that may be configured to form a light line of any length. The segments are mounted on a inner mounting base which also serves as a first stage heat sink for the LEDs. The illumination source includes a linear mirror for reflecting radiant energy away from the LEDs to produce a uniform linear illumination pattern. A window provides mechanical protection for the LEDs and may be used for diffusing or filtering light from the LEDs. An integral base in contact with the inner mounting base also serves as a heat sink and provides structural support for the illumination source. The integral base further includes channels and cavities for cooling the illumination source and for housing power cables.
Owner:WINTRISS ENG
System and method of evaluating uncoated turbine engine components
InactiveUS20080101683A1Gas-turbine engine testingMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveVision based systems
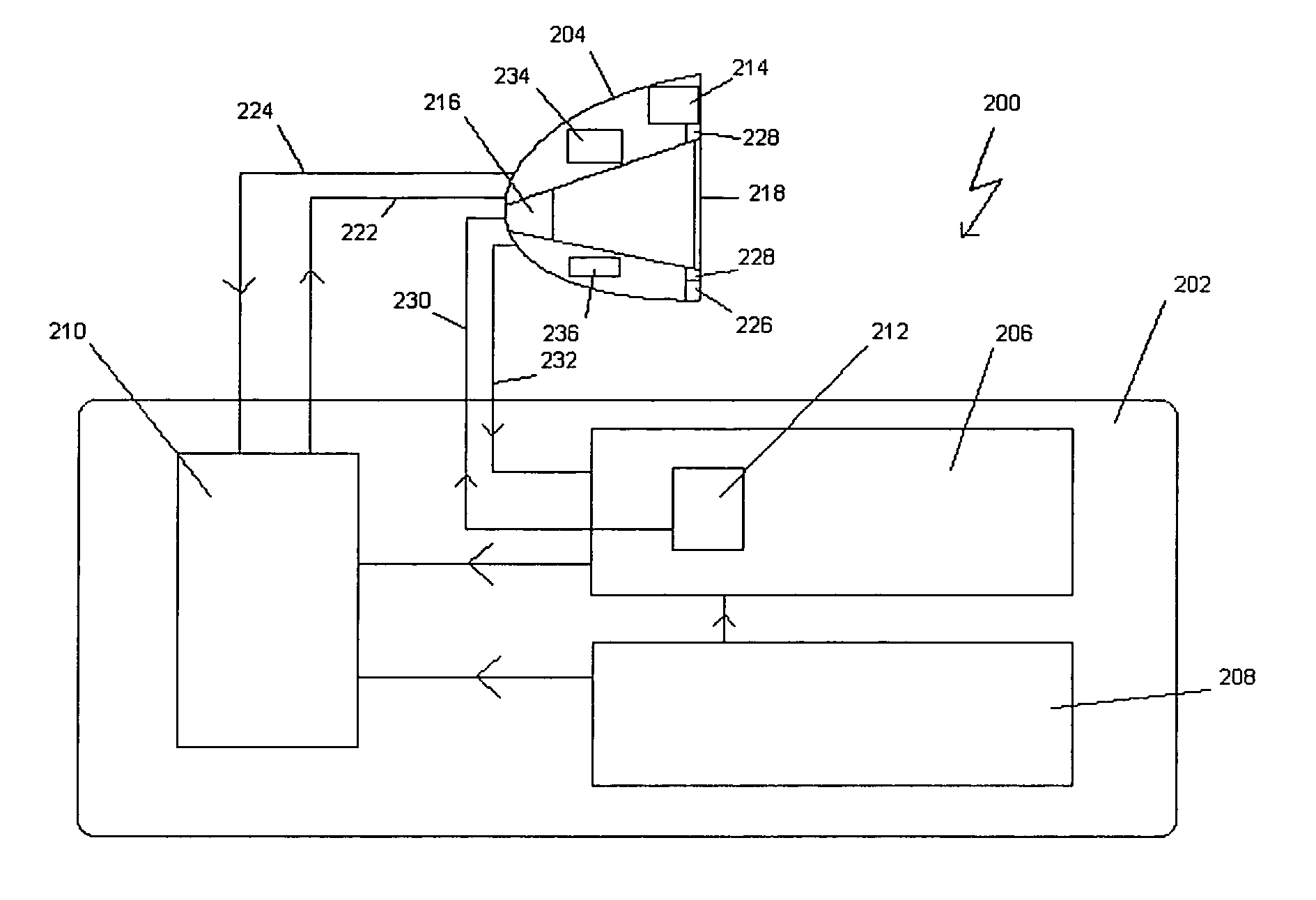
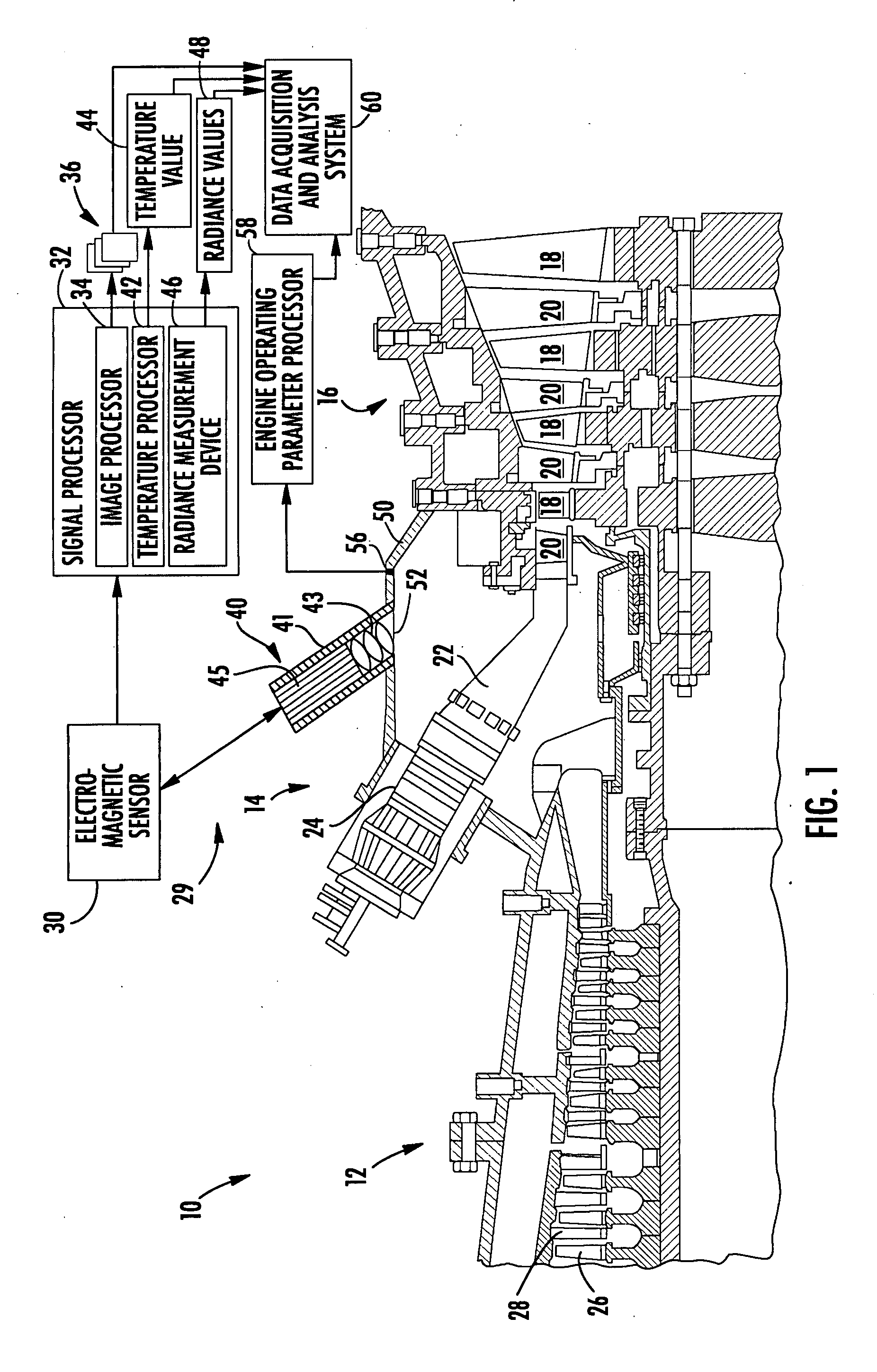
Aspects of the invention are directed to a visual-based system and method for non-destructively evaluating an uncoated turbine engine component. Aspects of the invention are well suited for high speed, high temperature components. Radiant energy emitted from an uncoated turbine engine component can be captured remotely and converted into a useful form, such as a high resolution image of the component. A plurality of images of the component can be captured over time and evaluated to identify failure modes. The system can also measure and map the temperature and / or radiance of the component. The system can facilitate the non-destructive evaluation of uncoated turbine components during engine operation without disassembly of the engine, thereby providing significant time and cost savings. Further, the system presents data to a user with sufficient context that allows an engine operator can evaluate the information with an increased degree of confidence and certainty.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Monolithic photovoltaic energy conversion device
InactiveUS20070137698A1Solid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A multijunction, monolithic, photovoltaic (PV) cell and device (600) is provided for converting radiant energy to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The PV cell includes an array of subcells (602), i.e., active p / n junctions, grown on a compliant substrate, where the compliant substrate accommodates greater flexibility in matching lattice constants to adjacent semiconductor material. The lattice matched semiconductor materials are selected with appropriate band-gaps to efficiently create photovoltage from a larger portion of the solar spectrum. Subcell strings (601, 603) from multiple PV cells are voltage matched to provide high output PV devices. A light emitting cell and device is also provided having monolithically grown red-yellow and green emission subcells and a mechanically stacked blue emission subcell.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Position tracking device
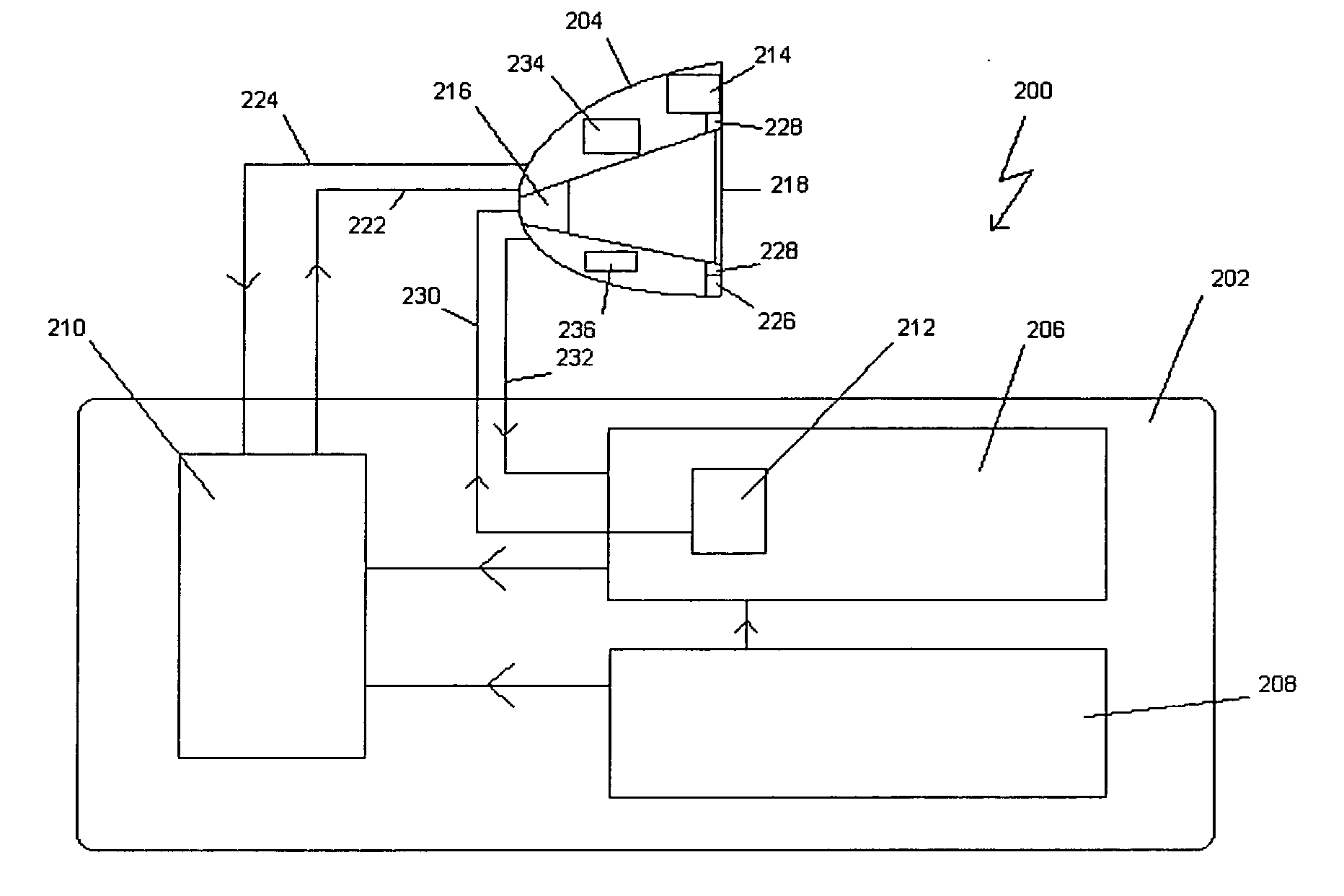
InactiveUS7532201B2Precision therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryOn boardLocation tracking
A position tracking device is disclosed combining one or more optical sensors in a housing with a medical device. The medical device may be an insertion device or one that produces radiant energy. The device may utilize an on-board processor or an external processor to track position data generated by the optical sensors and correlate the treatment regime of the medical device. Alternative embodiments and methods of use are also described.
Owner:LIPOSONIX
Treatment Of Tissue Volume With Radiant Energy
InactiveUS20070213792A1Reduce sensitivityLower power settingsUltrasound therapyDiagnostics using lightForms of energyMedicine
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Light or heat activated dental bleaching compositions
InactiveUS6387353B1Solve the lack of lifePromote decompositionCosmetic preparationsImpression capsBleachBiological activation
Dental bleaching compositions are made with a bleaching agent and a stable radiant-energy absorbing compound that acts as a bleaching agent activator. The dental bleaching compositions of the present invention can be one-part, pre-mixed compositions that do not require mixing at the time of treating a patient's teeth but which remain stable over time. The bleaching agent may consist of hydrogen peroxide, either in aqueous form or complexed with urea (carbamide peroxide) or sodium perborate. The bleaching agent activator includes hydrocarbons that are stable in the presence of the bleaching agent, which do not prematurely accelerate liberation of the bleaching agent, but which allow for selective activation of the bleaching agent by irradiation of the bleaching composition with radiant energy. The bleaching composition may optionally include a neutralizing agent to adjust the pH, a carrier to help provide proper consistency and potency, and a stabilizing agent to maintain maximum potency of the bleaching agent over time. The bleaching composition may also include a thickening agent to achieve a selected viscosity. The dental bleaching compositions may be adapted to be loaded into and delivered from a syringe.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Passive collimating tubular skylight
InactiveUS6363667B2Convenient lightingImproved passive tubular skylightsBuilding roofsCeilingsEngineeringSpecular reflection
A passive collimating tubular skylight consisting of a radiant energy-collecting aperture, a radiant energy-delivering aperture, and a radiant energy passageway between these two apertures, the passageway having a specularly reflective interior surface and a configuration to improve the collimation of the radiant energy passing therethrough. The skylight can be configured with the radiant energy-collecting aperture located above the roof of a building, oriented to collect sunlight; and equipped with a sealed weatherproof glazing, with the radiant energy-delivering aperture, or luminaire, located at ceiling level within the building, and equipped with a diffusing glazing; and with the reflective tubular light passageway constructed with a larger cross sectional area near the radiant energy-delivering aperture than near the radiant energy-collecting aperture. In complete accord with the second law of thermodynamics, and as proven by experimental results, the new passive collimating tubular skylight provides significant advantages over the prior art, including better solar energy collection, higher throughput optical efficiency, improved radiant energy collimation, enhanced interior illumination levels, and more precise positional control of the interior illumination.
Owner:ENTECH INC
Method of microwave processing ceramics and microwave hybrid heating system for same
InactiveUS20070023971A1Shorten the sintering timeOhmic-resistance heating detailsFurnace typesMicrowave ovenSusceptor
A method for sintering ceramic materials using a microwave hybrid heating system includes the steps of providing a ceramic member to be sintered, providing a microwave furnace, providing a thermal containment box comprising a material that is virtually transparent to microwave energy, providing at least one susceptor comprising a material that directly couples to microwave energy at room temperature substantially immediately within the thermal containment box, positioning the ceramic member within the thermal containment chamber proximate the susceptor, and irradiating the thermal containment box with microwave energy. The susceptor couples to the microwave energy and generates heat within the thermal containment box and the temperature of the ceramic member increases to the microwave coupling-trigger temperature, at which time the ceramic member couples directly to the microwave energy and is directly sintered by the microwave energy in cooperation with radiant energy from the one susceptor.
Owner:ALFRED UNIVERSITY
Methods for ablation with radiant energy
InactiveUS20060253113A1Rapid and efficient creationRapid and effective photoablationStentsUltrasound therapyCoaxial catheterTarget tissue
Ablation methods and instruments are disclosed for creating lesions in tissue, especially cardiac tissue for treatment of arrhythmias and the like. Percutaneous ablation instruments in the form of coaxial catheter bodies are disclosed having at least one central lumen therein and having one or more balloon structures at the distal end region of the instrument. The instruments include an energy emitting element which is independently positionable within the lumen of the instrument and adapted to project radiant energy through a transmissive region of a projection balloon to a target tissue site. The instrument can optionally include at least one expandable anchor balloon disposed about, or incorporated into an inner catheter body designed to be slid over a guidewire. This anchor balloon can serve to position the device within a lumen, such as a pulmonary vein. A projection balloon structure is also disclosed that can be slid over the first (anchor balloon) catheter body and inflated within the heart, to define a staging from which to project radiant energy. An ablative fluid can also be employed outside of the instrument (e.g., between the balloon and the target region) to ensure efficient transmission of the radiant energy when the instrument is deployed. In another aspect of the invention, generally applicable to a wide range of cardiac ablation instruments, mechanisms are disclosed for determining whether the instrument has been properly seated within the heart, e.g., whether the device is in contact with a pulmonary vein and / or the atrial surface, in order to form a lesion by heating, cooling or projecting energy. This contact-sensing feature can be implemented by an illumination source situated within the instrument and an optical detector that monitors the level of reflected light. Measurements of the reflected light (or wavelengths of the reflected light) can thus be used to determine whether contact has been achieved and whether such contact is continuous over a desired ablation path.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
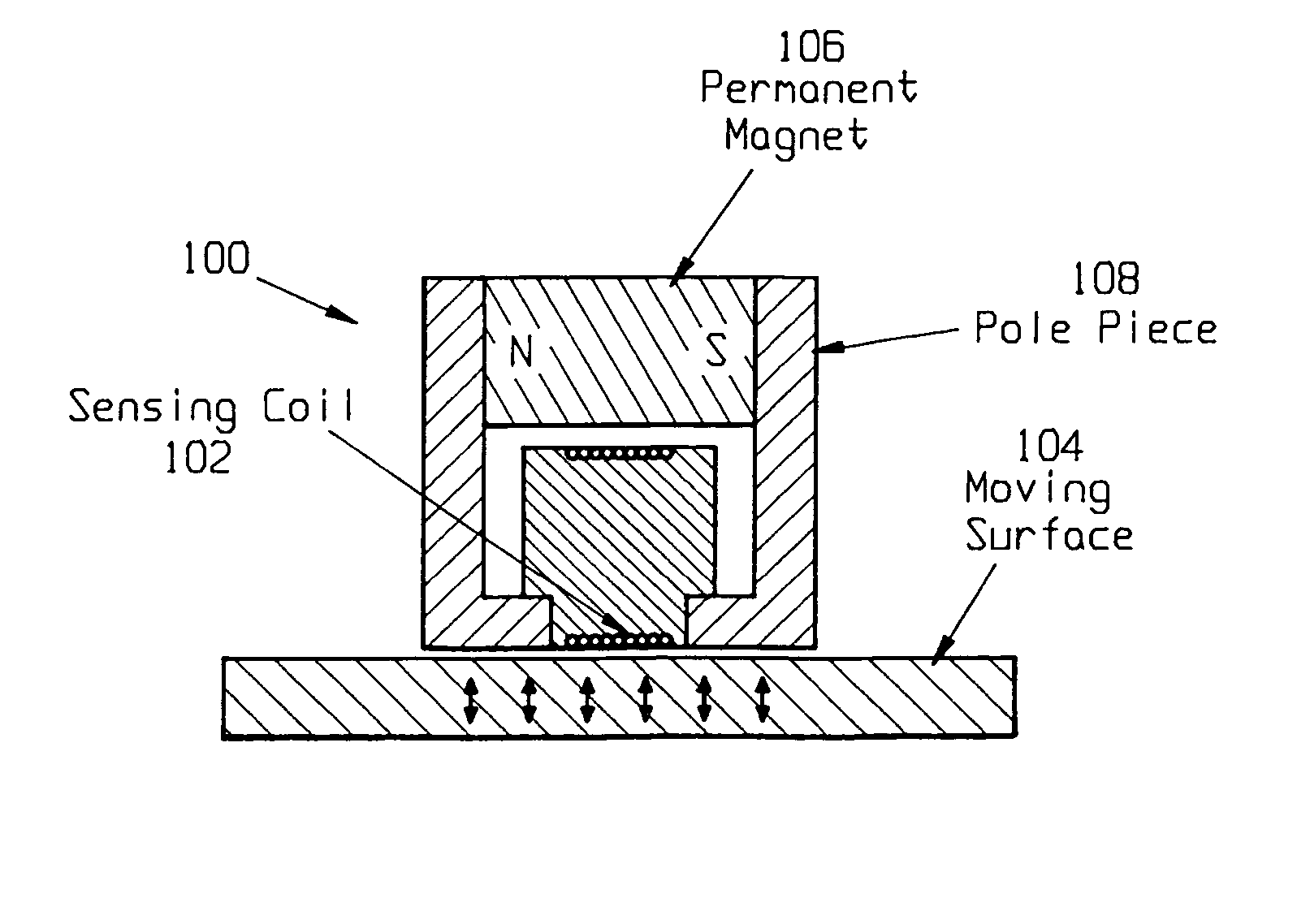
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS20090312956A1Detect degradationAvoid severe repairThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
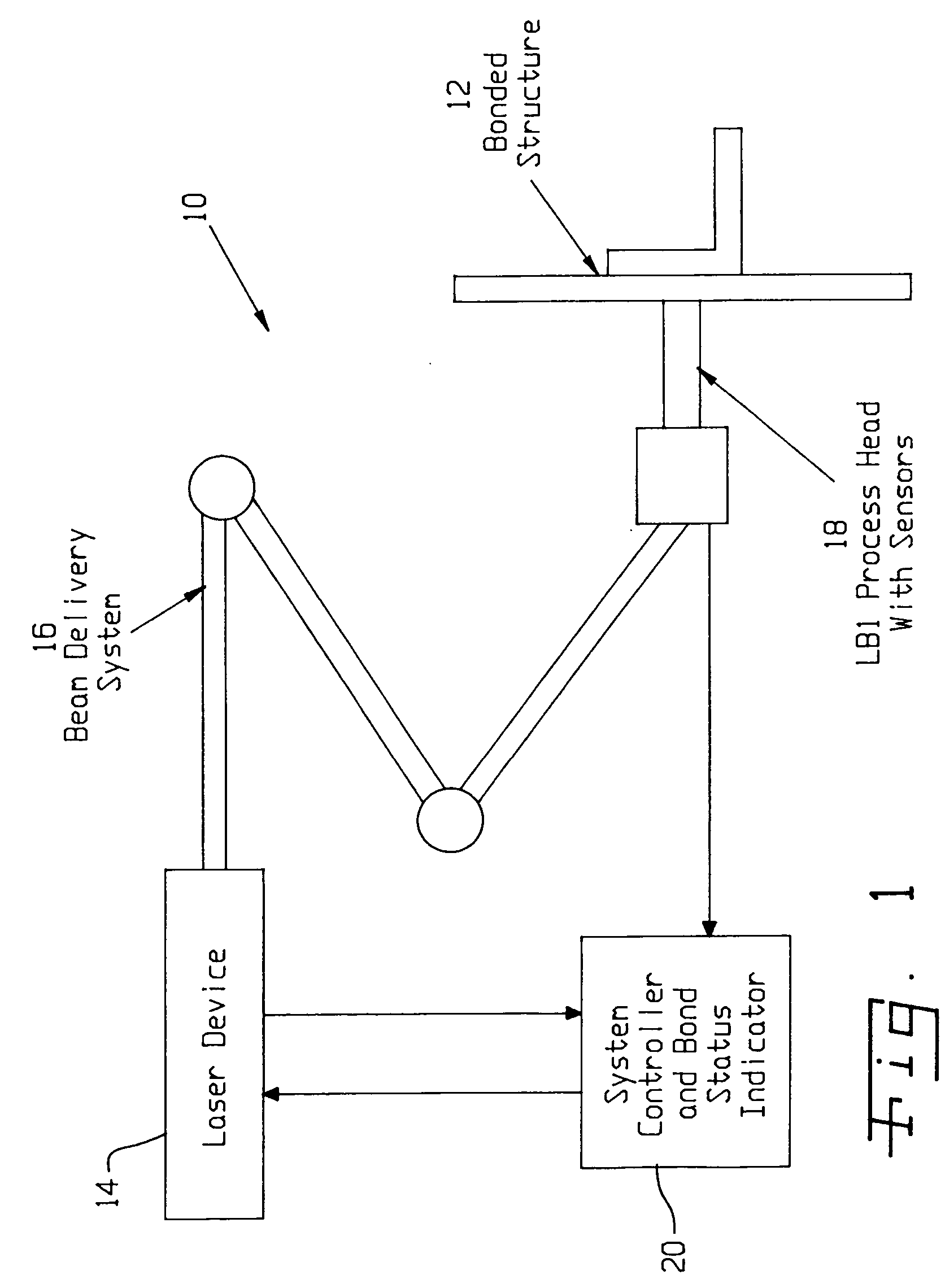
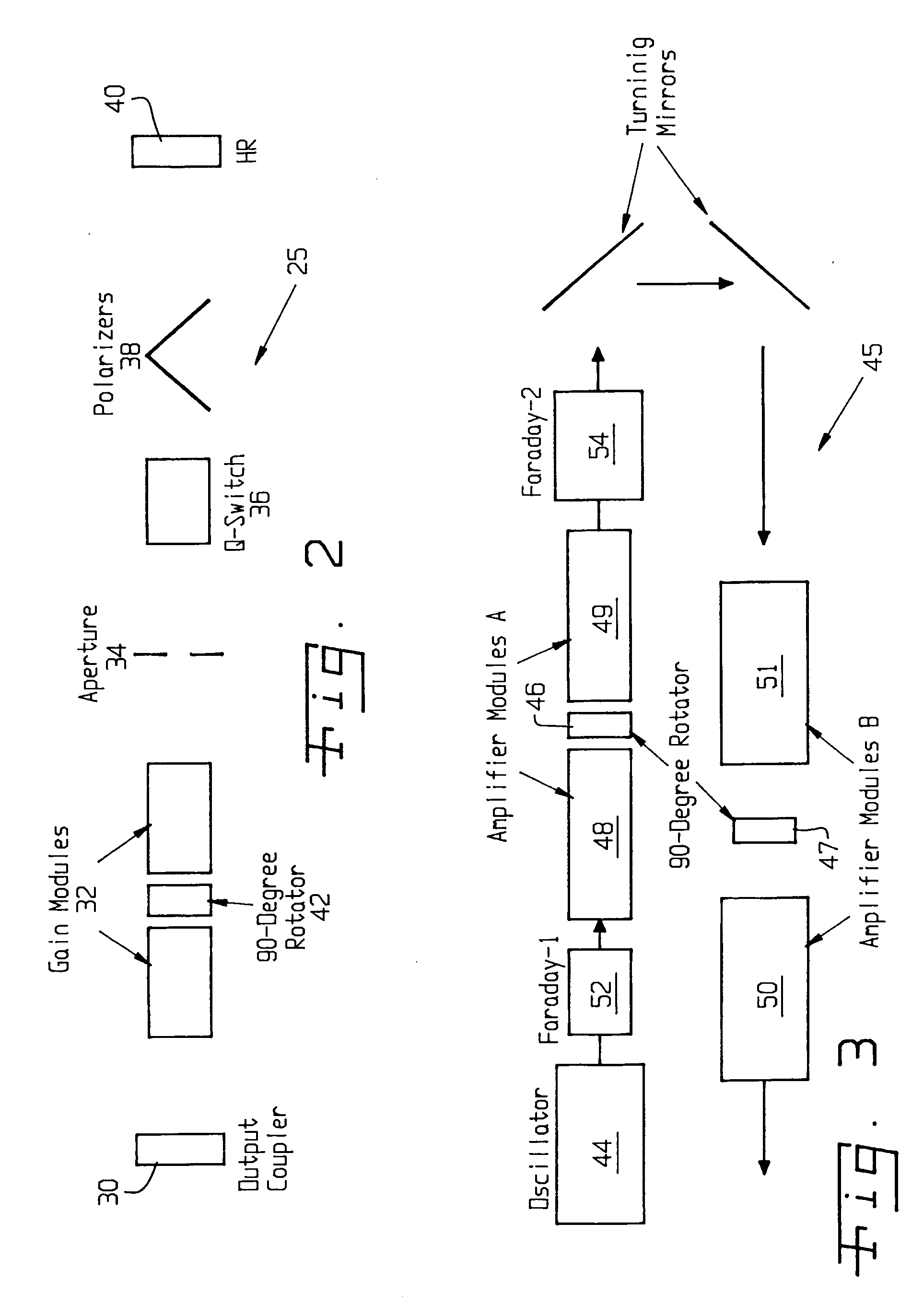
Laser system and method for non-destructive bond detection and evaluation
ActiveUS20050120803A1Easy to collectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesNon destructiveLight beam
A system for evaluating the integrity of a bonded joint in an article includes a laser configured in a laser shock processing arrangement to perform a laser shock processing treatment on the article. A beam delivery system employs an articulated arm assembly to communicate the radiant energy emitted by the laser to a process head proximate the article. The laser shock processing treatment causes the formation of shockwaves that propagate through the article, inducing internal stress wave activity that characteristically interacts with the bonded joint. A sensor detects a stress wave signature emanating from the article, which is indicative of the integrity of the bond. A detector such as a non-contact electromagnetic acoustic transducer provides a measure of the stress wave signature in the form of surface motion measurements.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
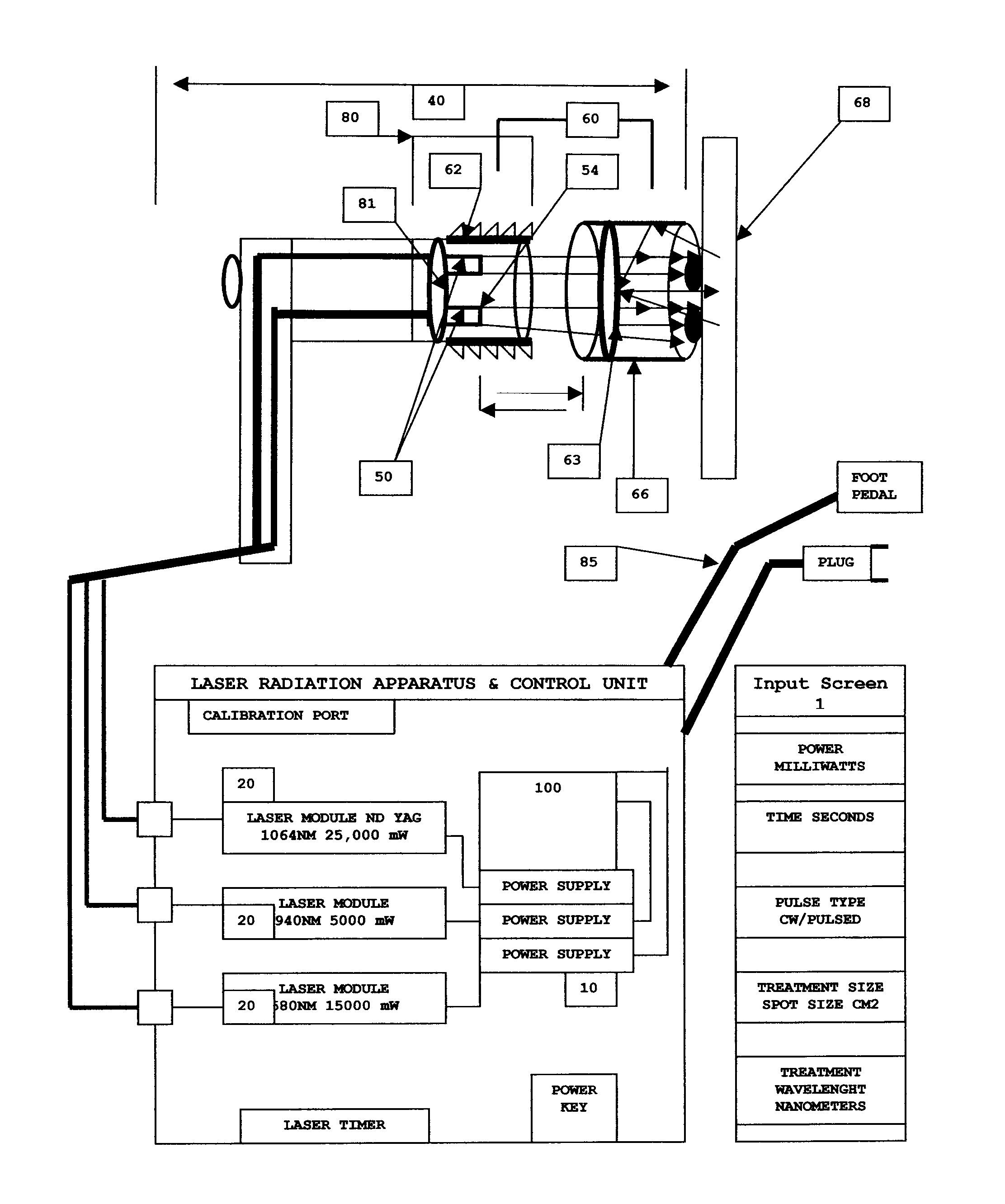
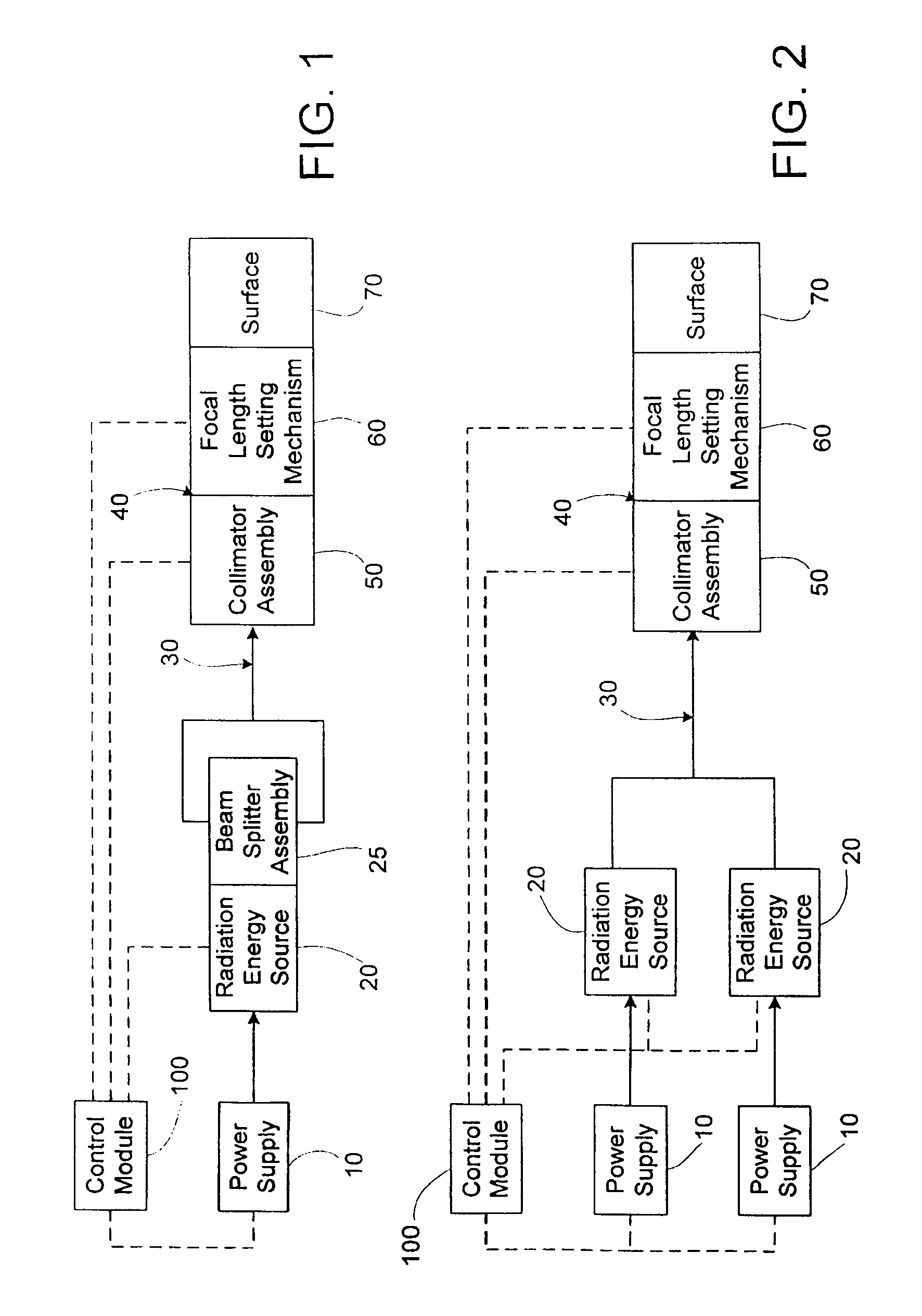
Apparatus and method for performing radiation energy treatments
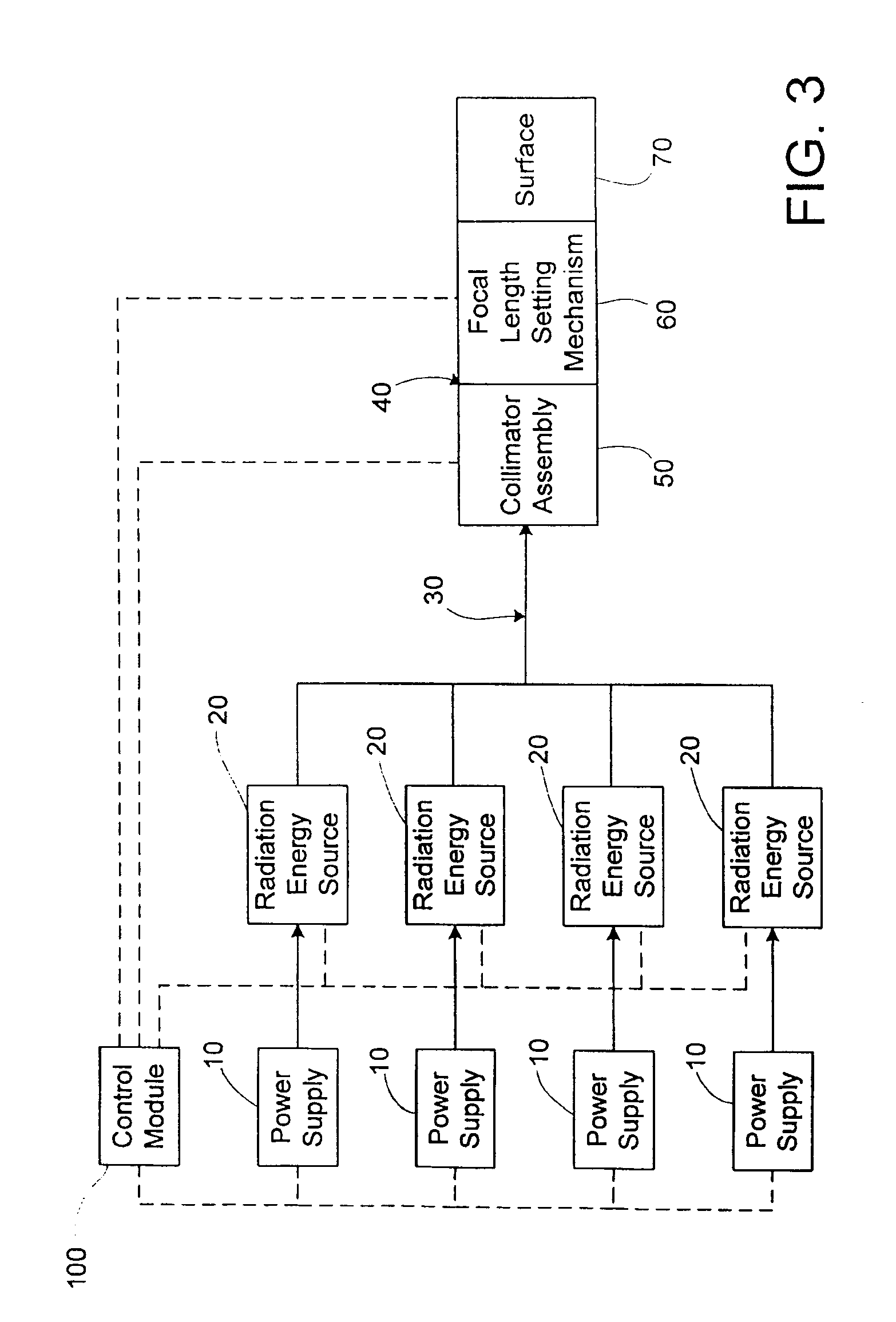
InactiveUS8287524B2Improve efficiencyImprove securitySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyFiberTherapeutic effect
An apparatus and method to apply photo-stimulation, photo-dynamic therapy and / or ablation laser treatment to biological tissue. The apparatus includes a plurality of radiation energy sources, preferably laser beams. Additionally, the apparatus allows either a single wavelength or a combination of various wavelengths, either coincidentally or adjacently, to be utilized to achieve a desired treatment effect. Laser beams are transmitted to the treatment area by one or more fiber optic cables which terminate at an assembly structured to collimate the emitted radiation prior to application to the tissue. In addition, the apparatus includes a focal length setting mechanism which assures that a constant, fixed distance exists between the point of discharge of the laser beam and the biological tissue, thus assuring a constant energy density at the point of application. A method is presented for applying photo-stimulation, photocollagen stimulation and / or ablation laser treatment utilizing the above apparatus.
Owner:SIEGEL JERRY
Medical fluid heater using radiant energy
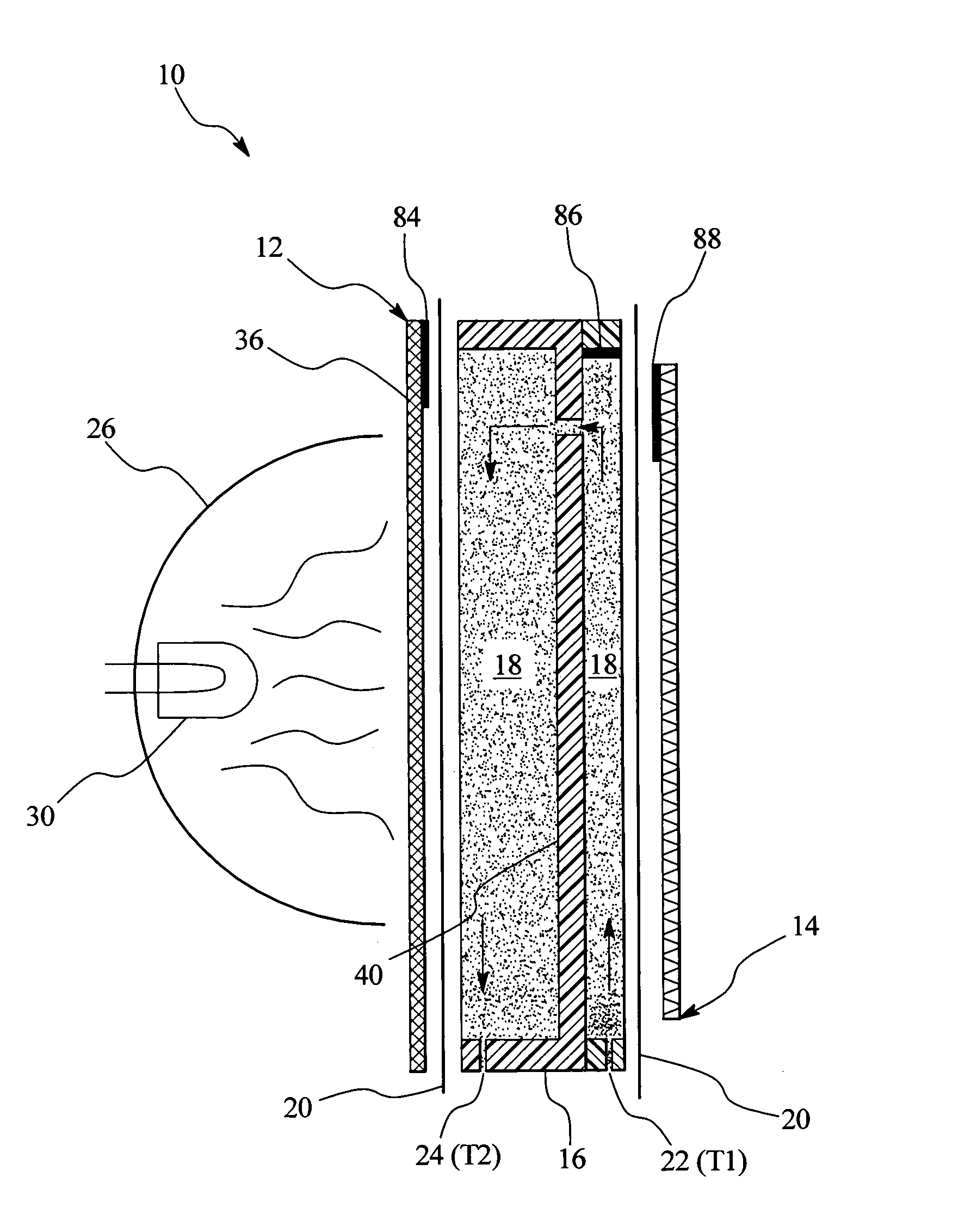
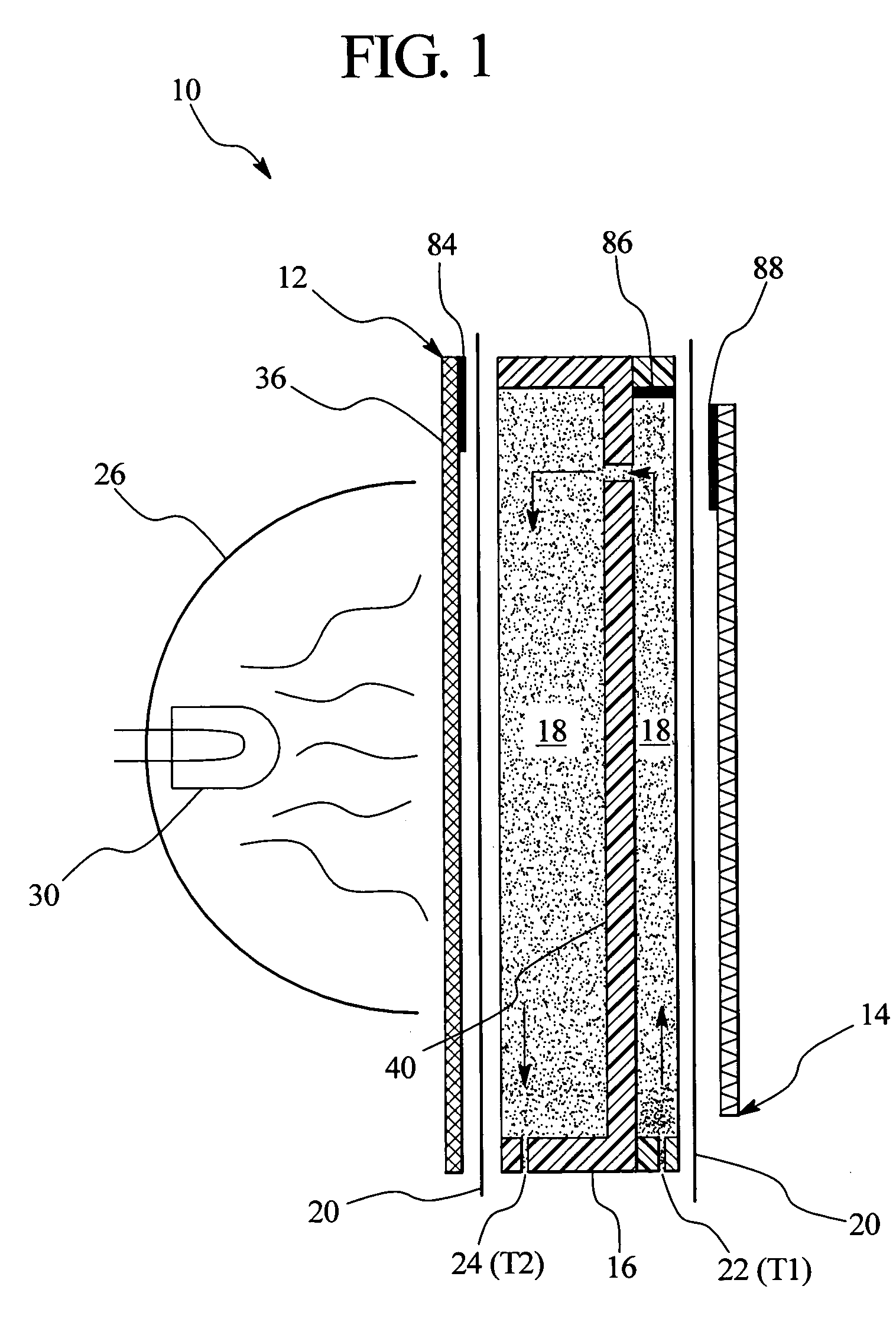
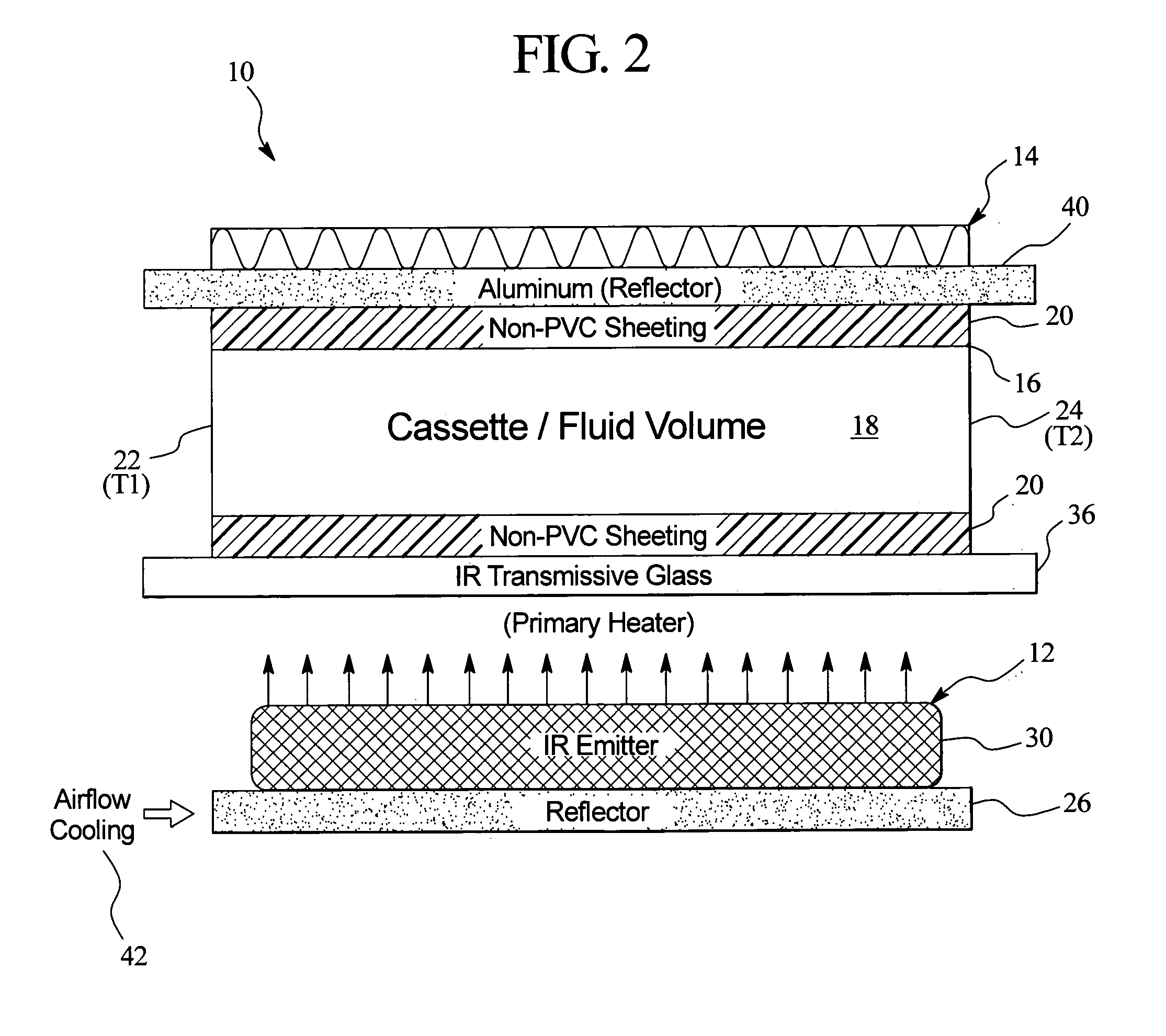
InactiveUS7153285B2Simple systemSimple methodMedical devicesIntravenous devicesEngineeringDialysis fluid
An in-line fluid heater for heating fluid, such as dialysis fluid for use in dialysis therapy is provided. The fluid heater is a dual heater having a primary infrared heater and a secondary plate heater. A controller is operatively connected to the infrared heater and to the plate heater and operates one or both of the infrared heater and the plate heater to maintain a temperature of the fluid.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method of surgical perforation via the delivery of energy
A method of surgical perforation via the delivery of electrical, radiant or thermal energy comprising the steps of: introducing an apparatus comprising an energy delivery device into a patient's heart via the patient's superior vena cava; positioning the energy delivery device at a first location adjacent material to be perforated; and perforating the material by delivering energy via the energy delivery device; wherein the energy is selected from the group consisting of electrical energy, radiant energy and thermal energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Self-illuminated sighting device
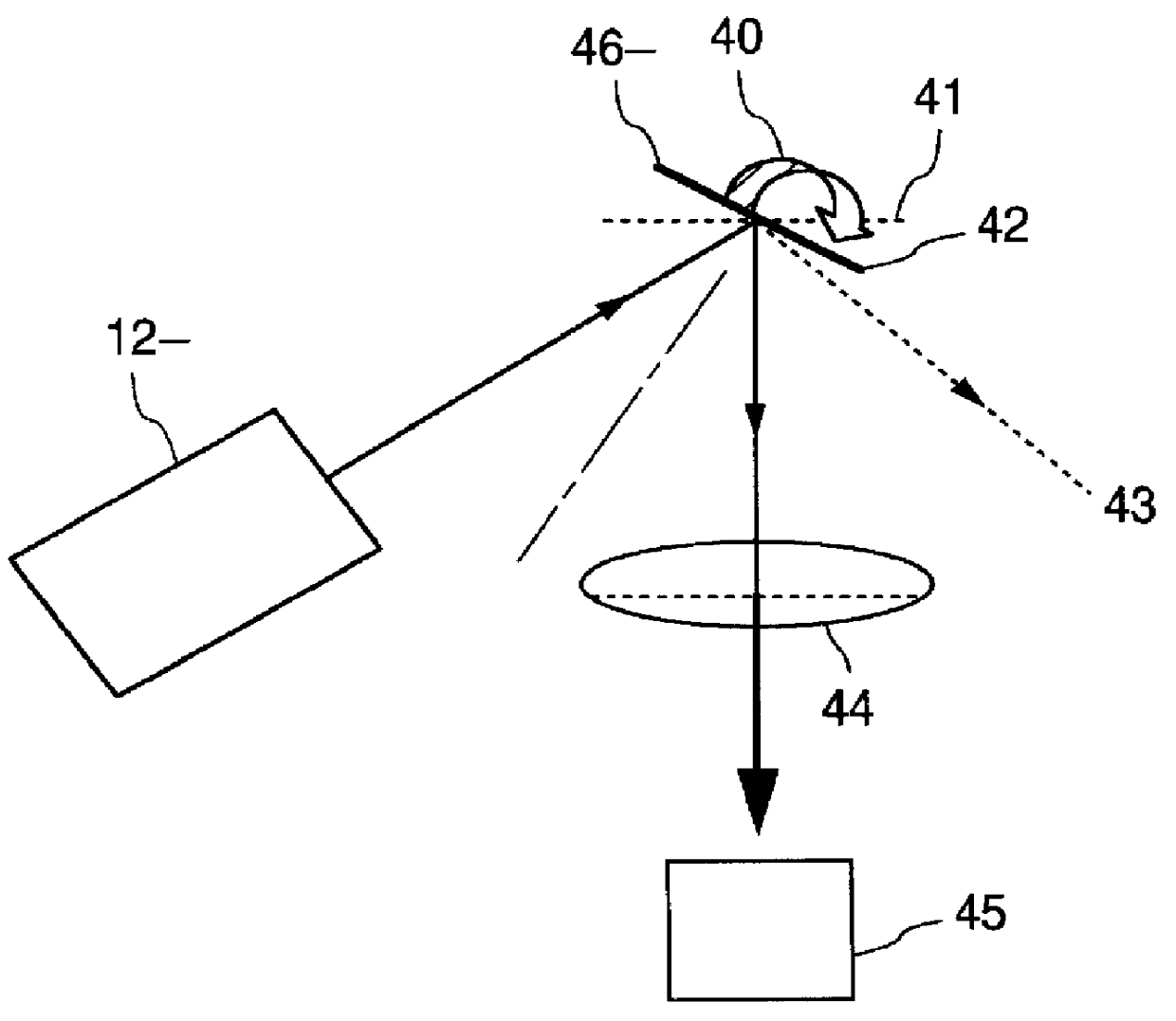
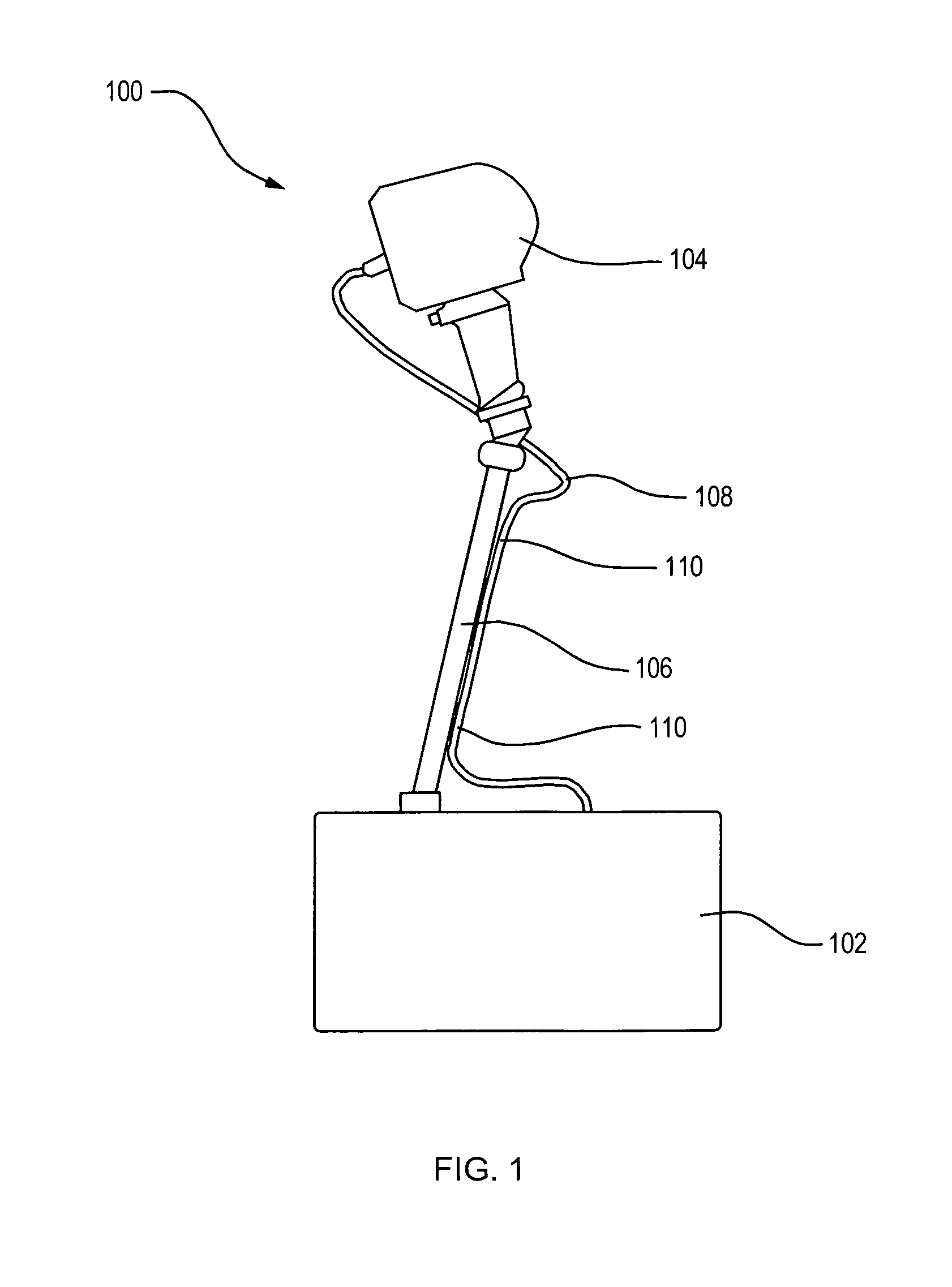
An illuminated sighting device includes a capsule with an integrally formed lens that is adapted to face rearwardly for viewing by a user. An elongate light collector is positioned within the hollow interior of the capsule and is formed such that light can be gathered along its length and transmitted to its ends. One of the light collector ends is located adjacent to the first lens and defines a sight point or dot. An artificial light source is located within the capsule hollow interior and is oriented for projecting radiant energy into the second light collector end so that the sight point is viewable during dark or low light conditions.
Owner:GOOD SPORTSMAN MARKETING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com