Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
776 results about "Optical efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enhanced LCD backlight
ActiveUS20060056166A1Improved backlight assemblyAvoid less flexibilityElectric discharge tubesDiffusing elementsCompression moldingEllipsoidal particle
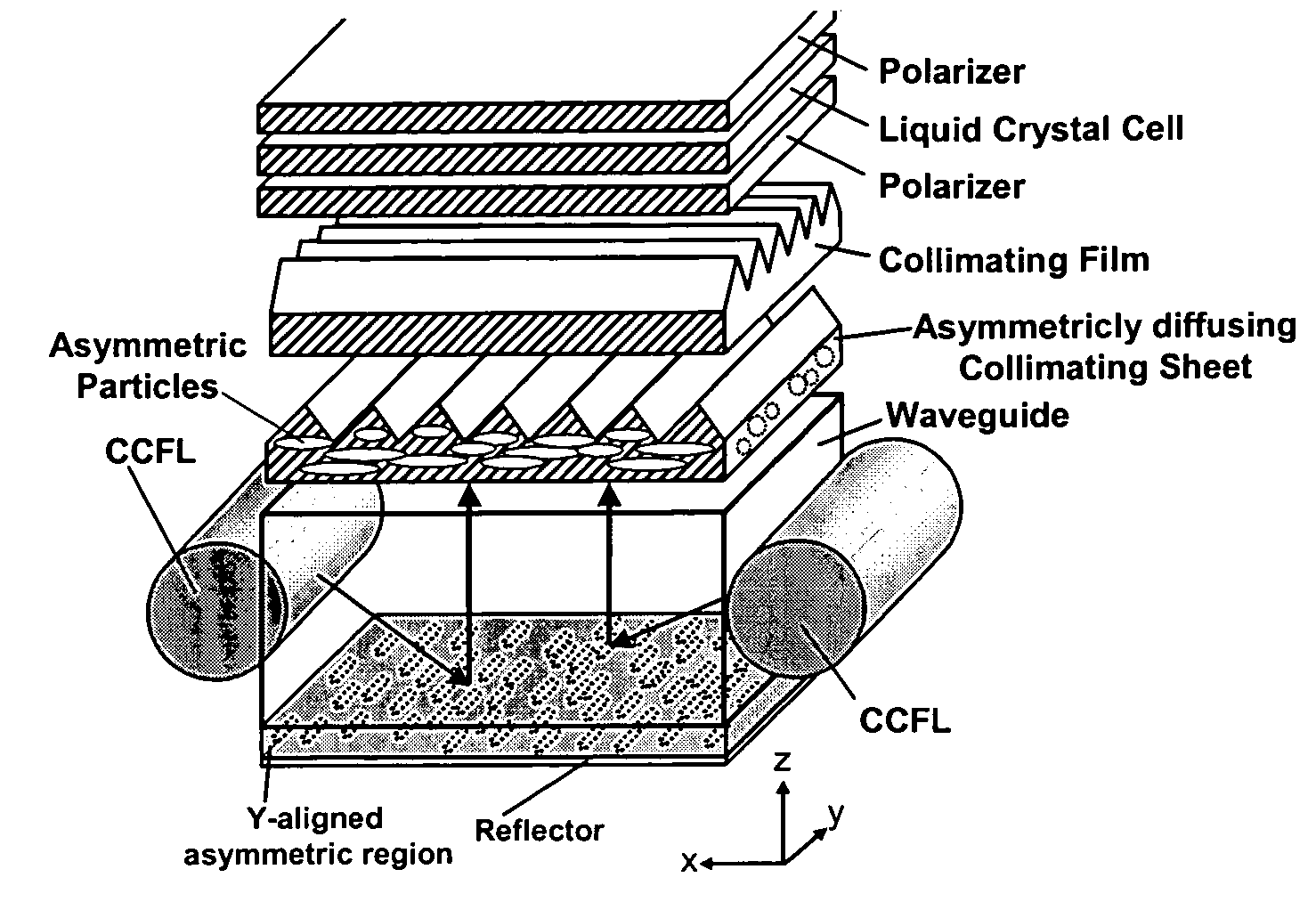
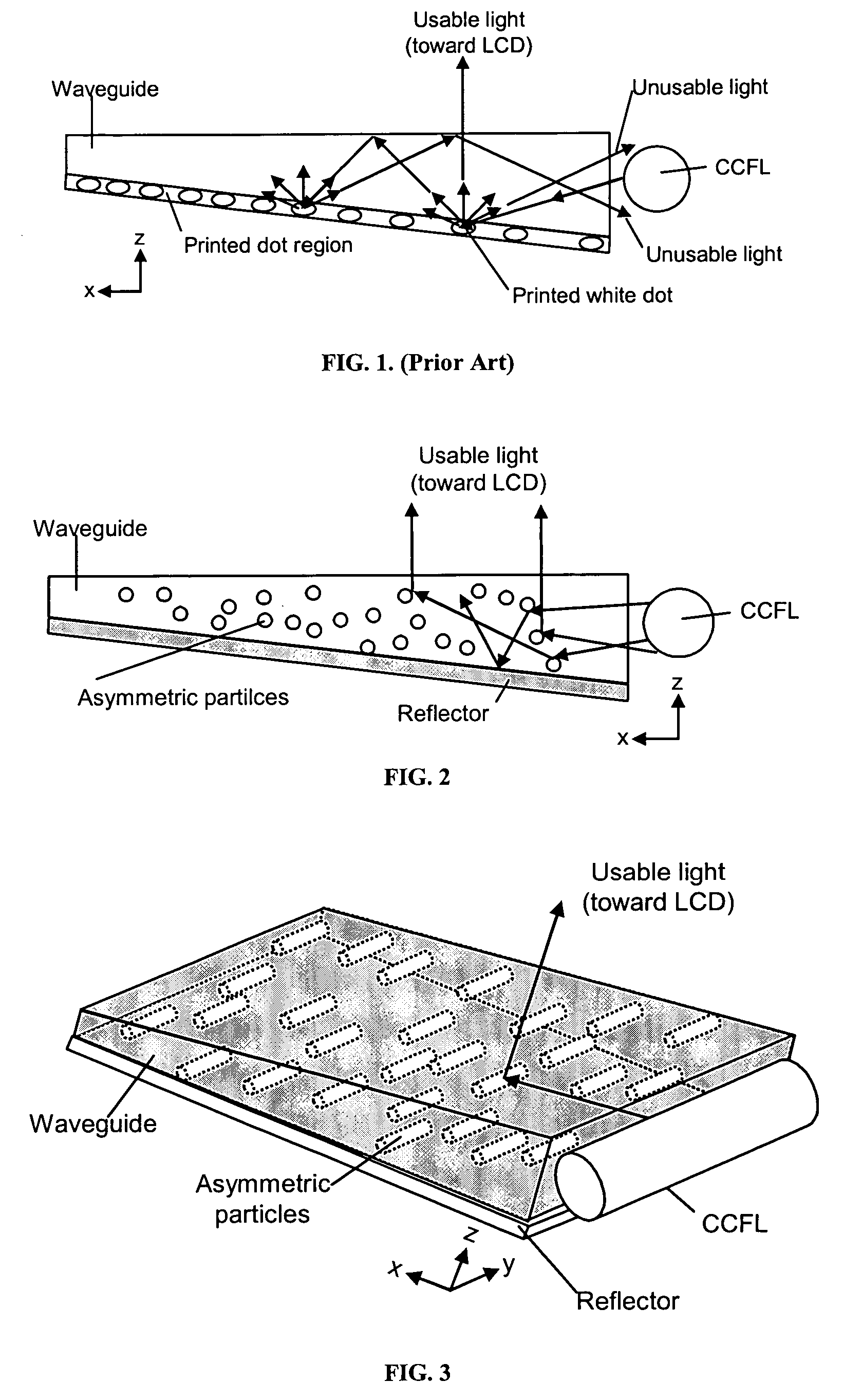
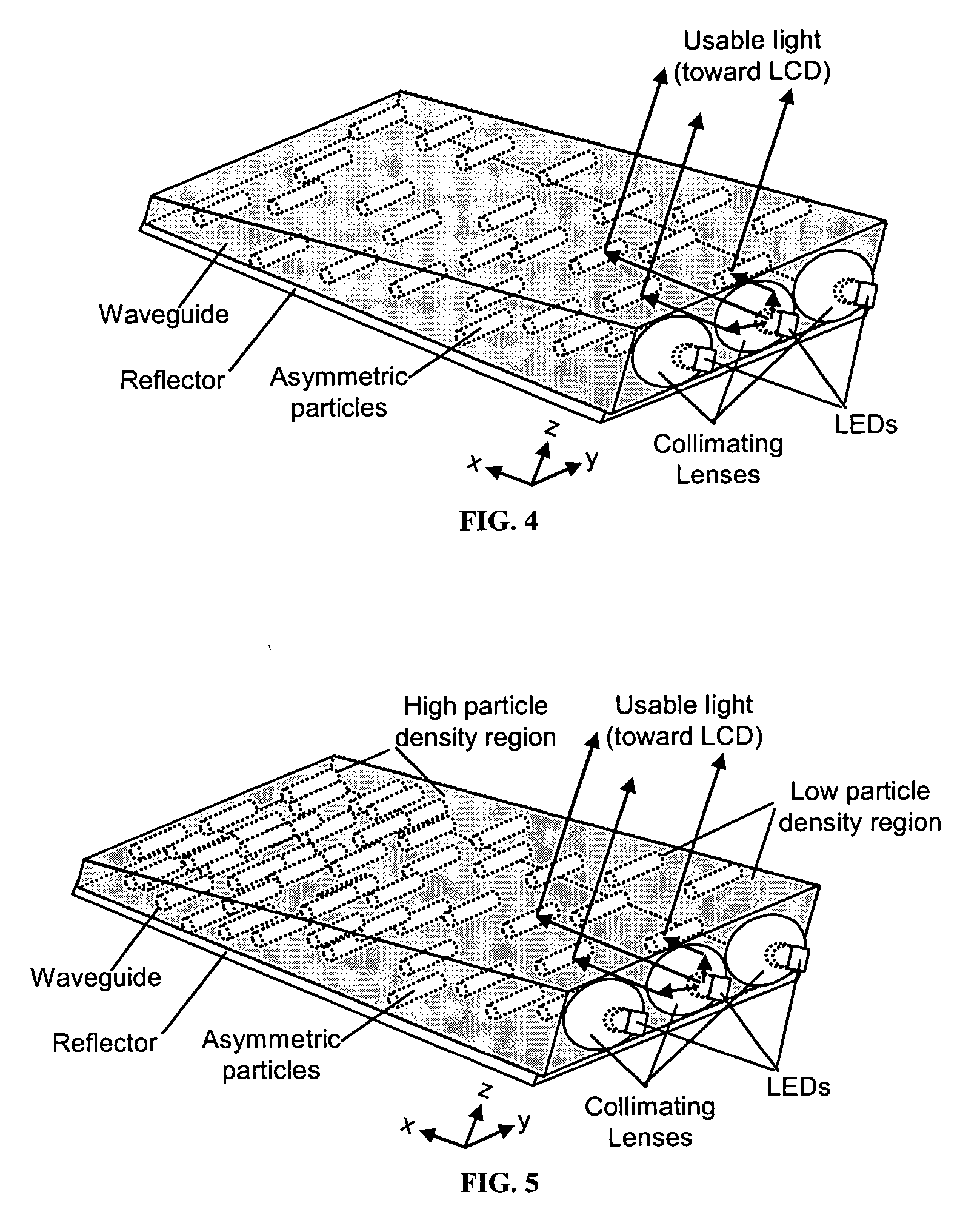
The present invention provides an improved light guide with inherently more flexibility for display system designers and higher optical efficiency. By using a light guide containing substantially aligned non-spherical particles, more efficient control of the light scattering can be achieved. One or more regions containing ellipsoidal particles may be used and the particle sizes may vary between 2 and 100 microns in the smaller dimension. The light scattering regions may be substantially orthogonal in their axis of alignment. Alternatively, one or more asymmetrically scattering films can be used in combination with a backlight light guide and a reflector to produce an efficient backlight system. The light guides may be manufactured by embossing, stamping, or compression molding a light guide in a suitable light guide material containing asymmetric particles substantially aligned in one direction. The light scattering light guide or non-scattering light guide may be used with one or more light sources, collimating films or symmetric or asymmetric scattering films to produce an efficient backlight that can be combined with a liquid crystal display or other transmissive display. By maintaining more control over the scattering, the efficiency of the recycling of light by using reflective polarizers can also be increased.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS DEV FINANCE AGENCY
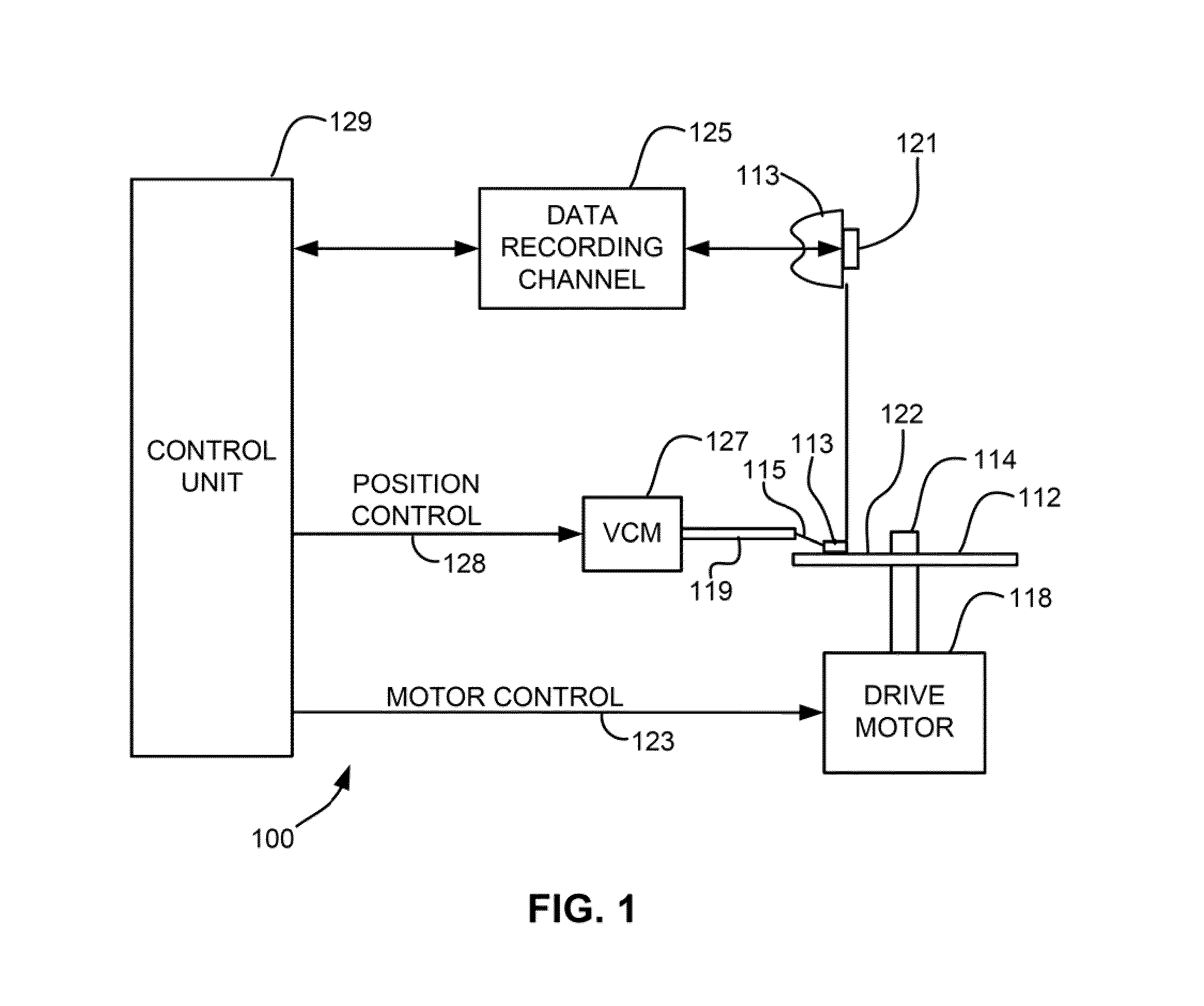
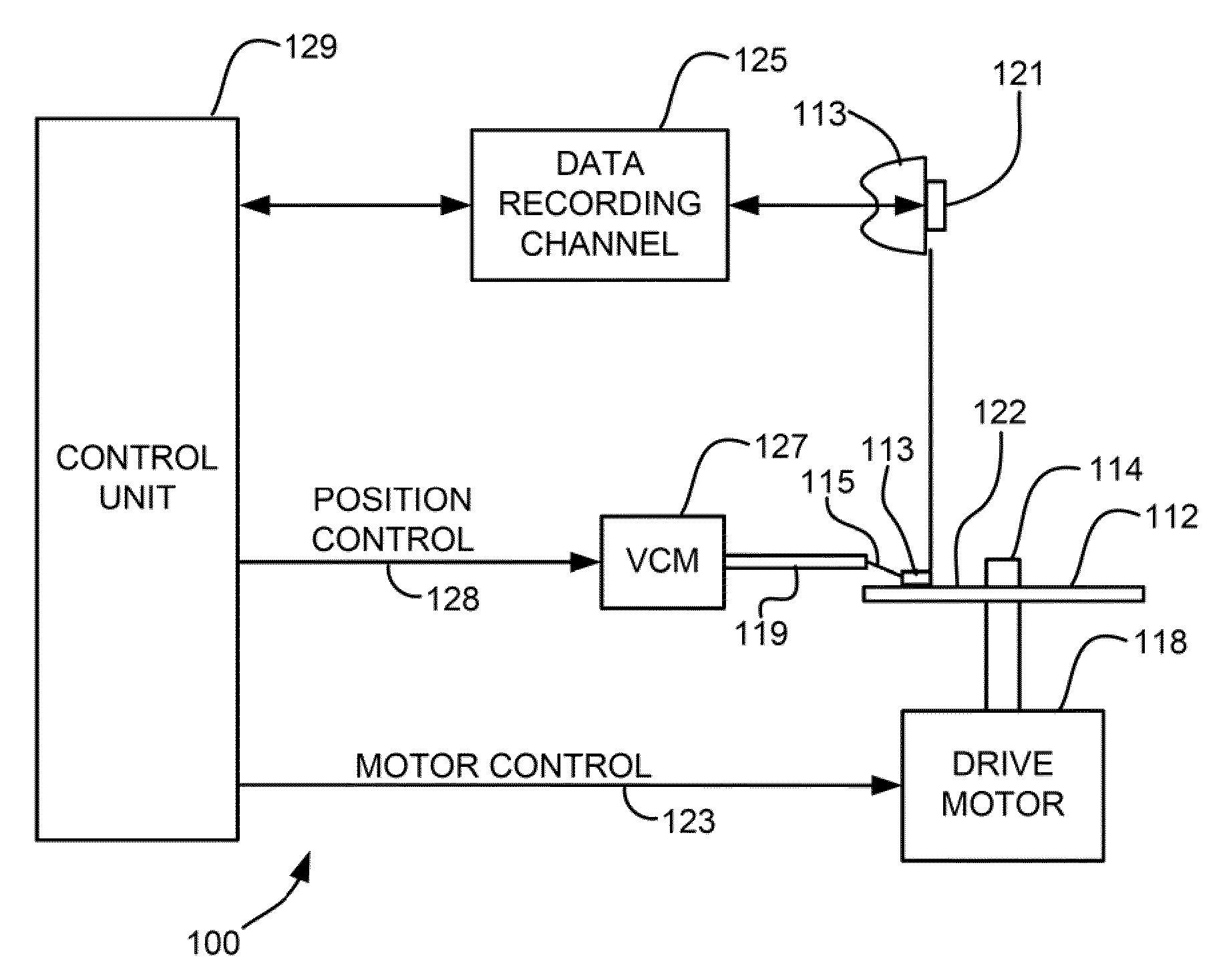
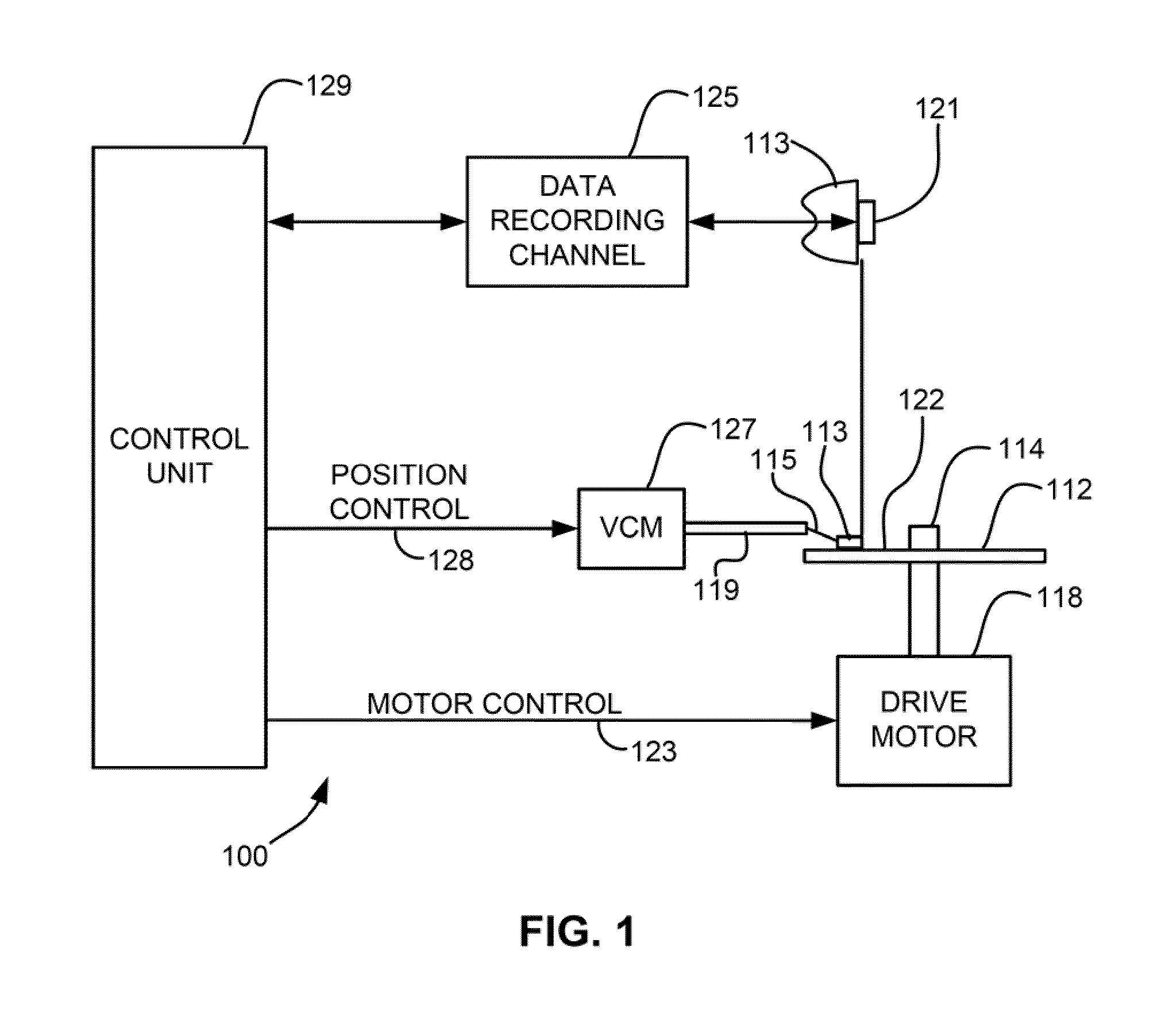
Method and system for enhancing optical efficiency for an EAMR head
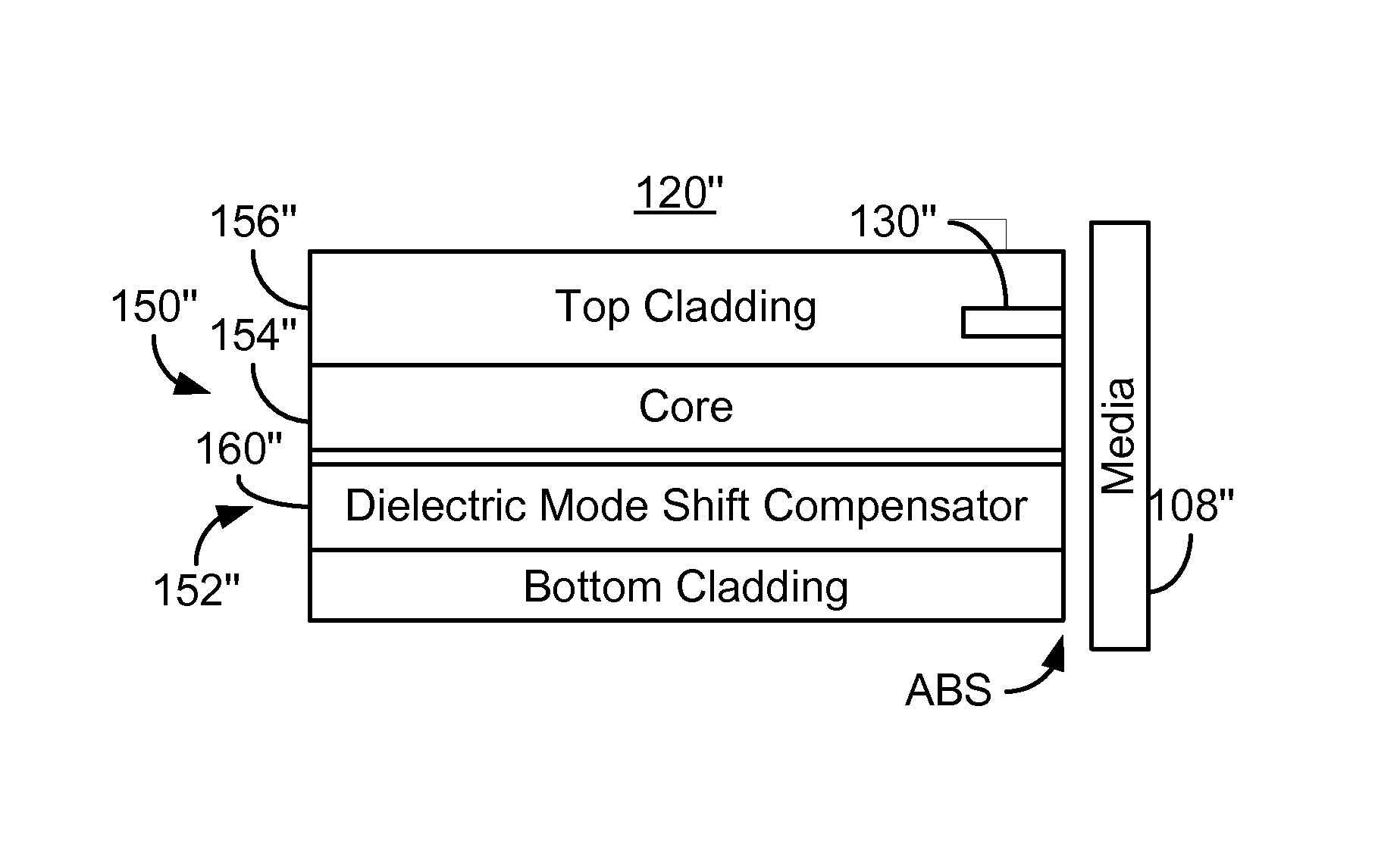
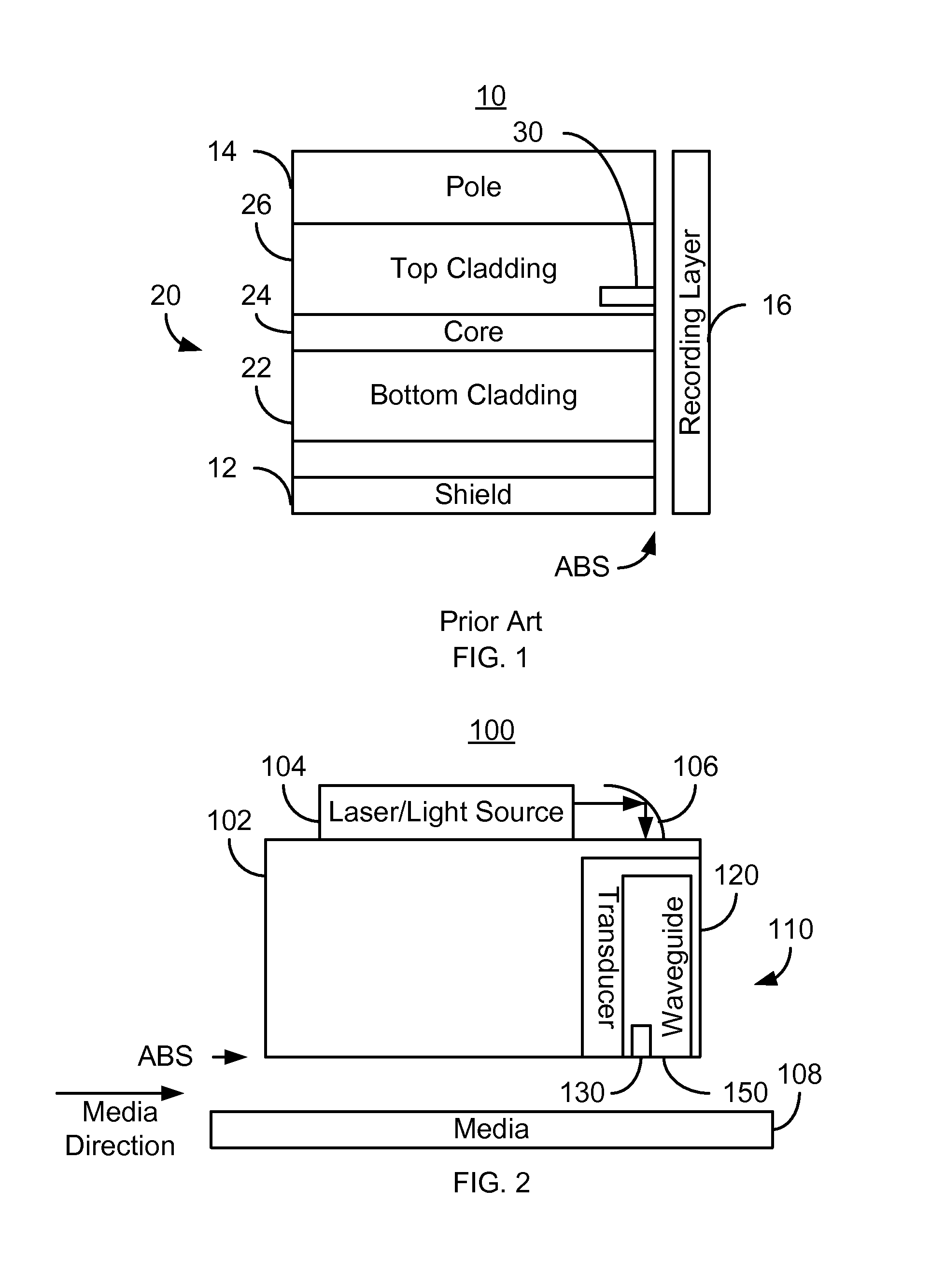
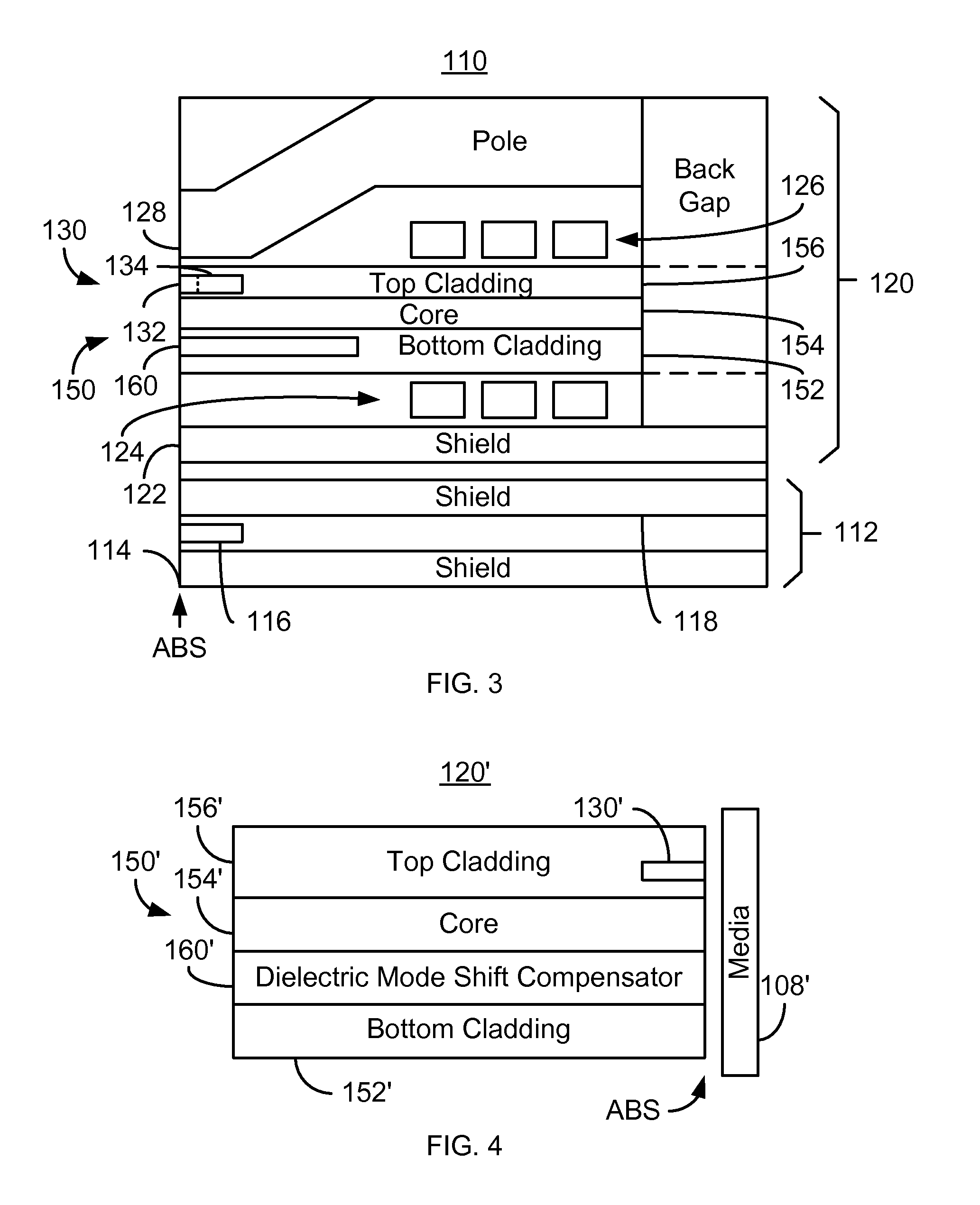
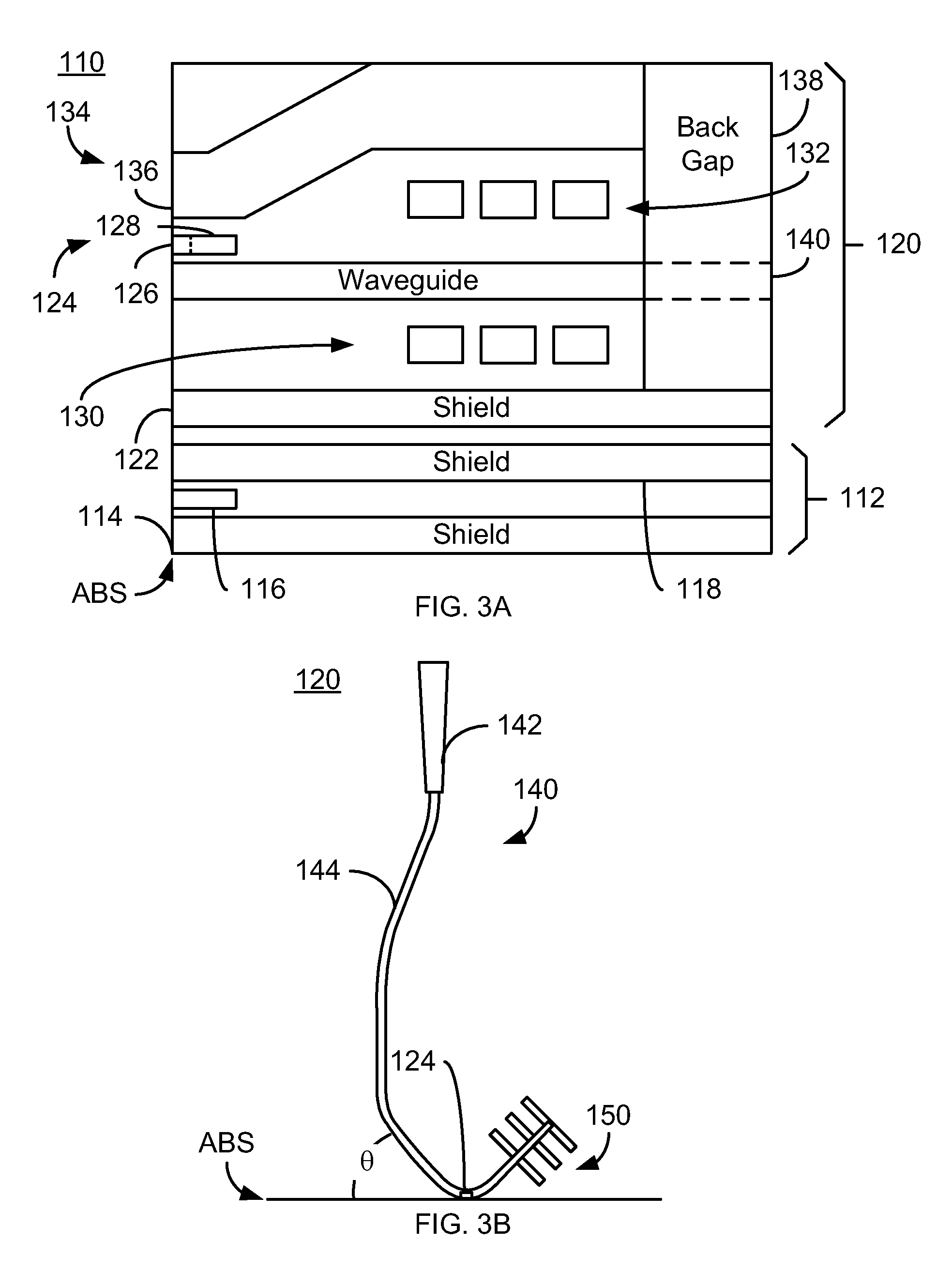
A method and system for providing an EAMR transducer and a waveguide used therein are described. The EAMR transducer is coupled with a laser that provides energy. The EAMR transducer also has an ABS that resides in proximity to a media during use. The EAMR transducer includes a waveguide, a write pole to write to a region of the media, coil(s) for energizing the write pole, and a near field transducer (NFT) proximate to the ABS for focusing the energy onto the media. The waveguide includes a mode shift compensator, first and second cladding layers, and a core between the cladding layers. The core directs energy from the laser toward the ABS and has a core index of refraction. The core is also between the mode shift compensator and the NFT. The mode shift compensator has a mode shift compensator index of refraction less than the core index of refraction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
EAMR head having improved optical coupling efficiency
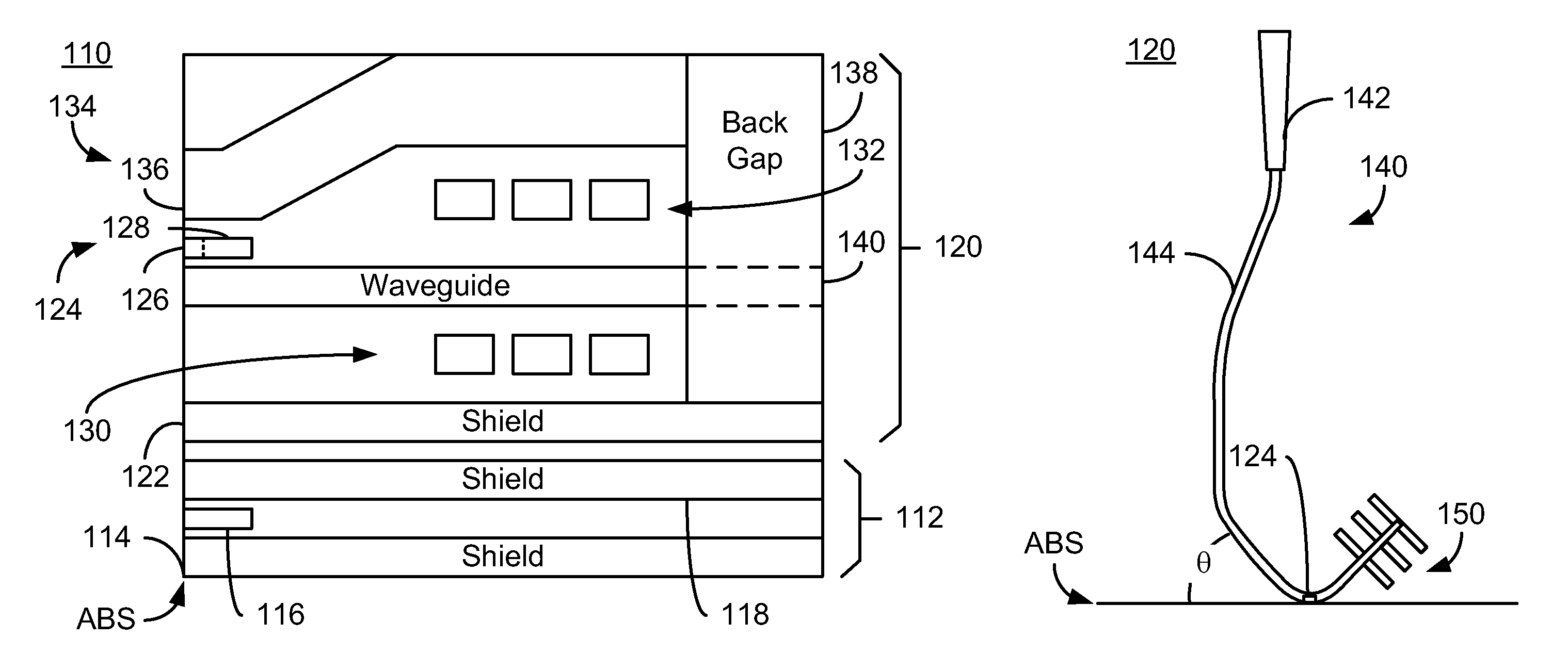
A method and system provide an EAMR transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS) that resides near a media during use. The EAMR transducer includes a write pole, coil(s), a near field transducer (NFT), a waveguide, and a reflective grating. The write pole writes to a region of the media. The coil(s) energize the write pole. The NFT is proximate to the ABS and focuses the energy onto the media. The waveguide is configured to direct the energy from the laser toward the NFT at an incident angle with respect to the ABS. A first portion of the energy reflects off of the ABS at a reflected angle. The reflective grating receives the first portion of the energy at the reflected angle from the ABS and reflects a second portion of the energy toward the ABS. The NFT resides between at least part of the waveguide and the reflective grating.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
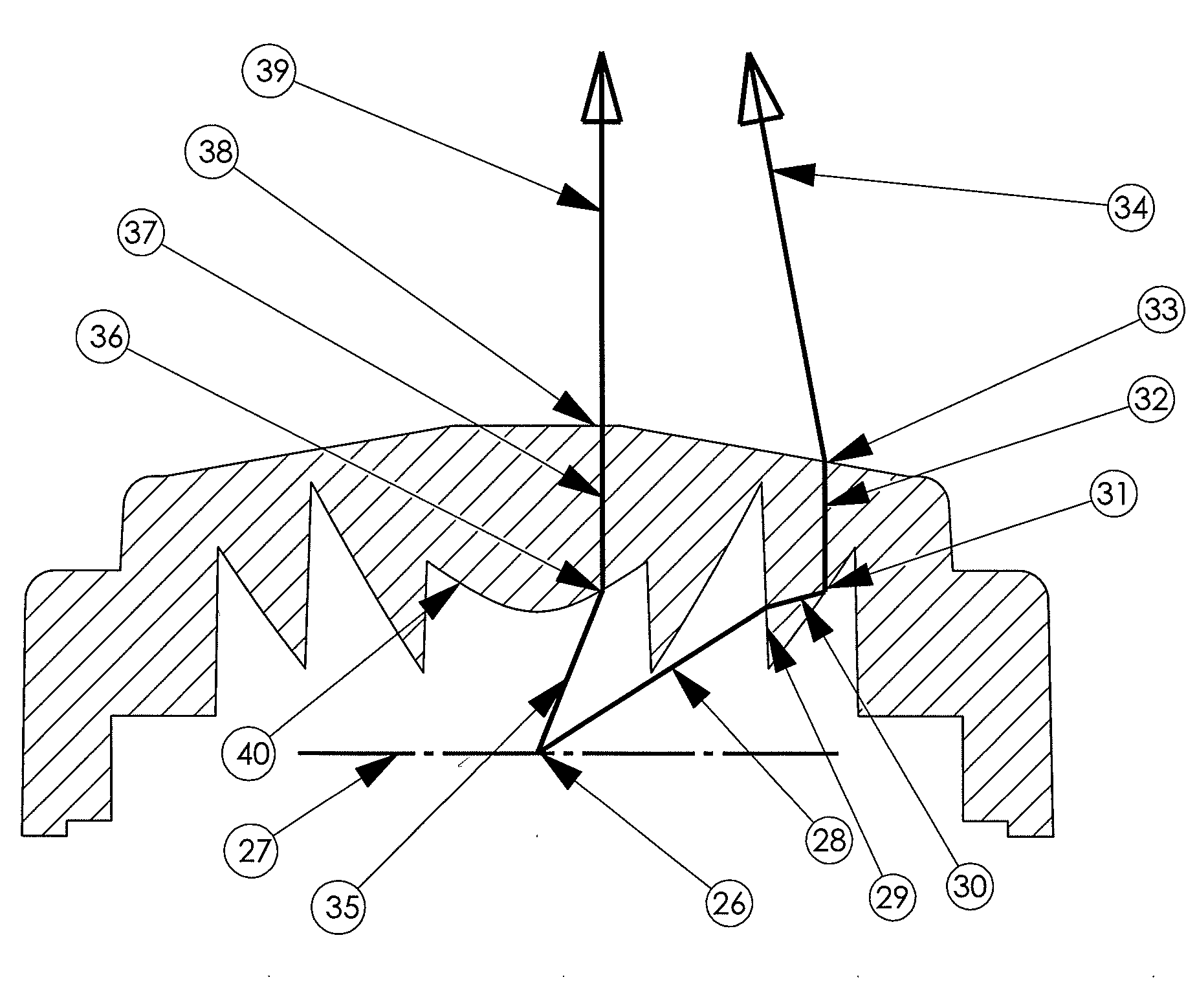
Surface mountable light emitting diode assemblies packaged for high temperature operation
InactiveUS20060006405A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface mountingEngineering
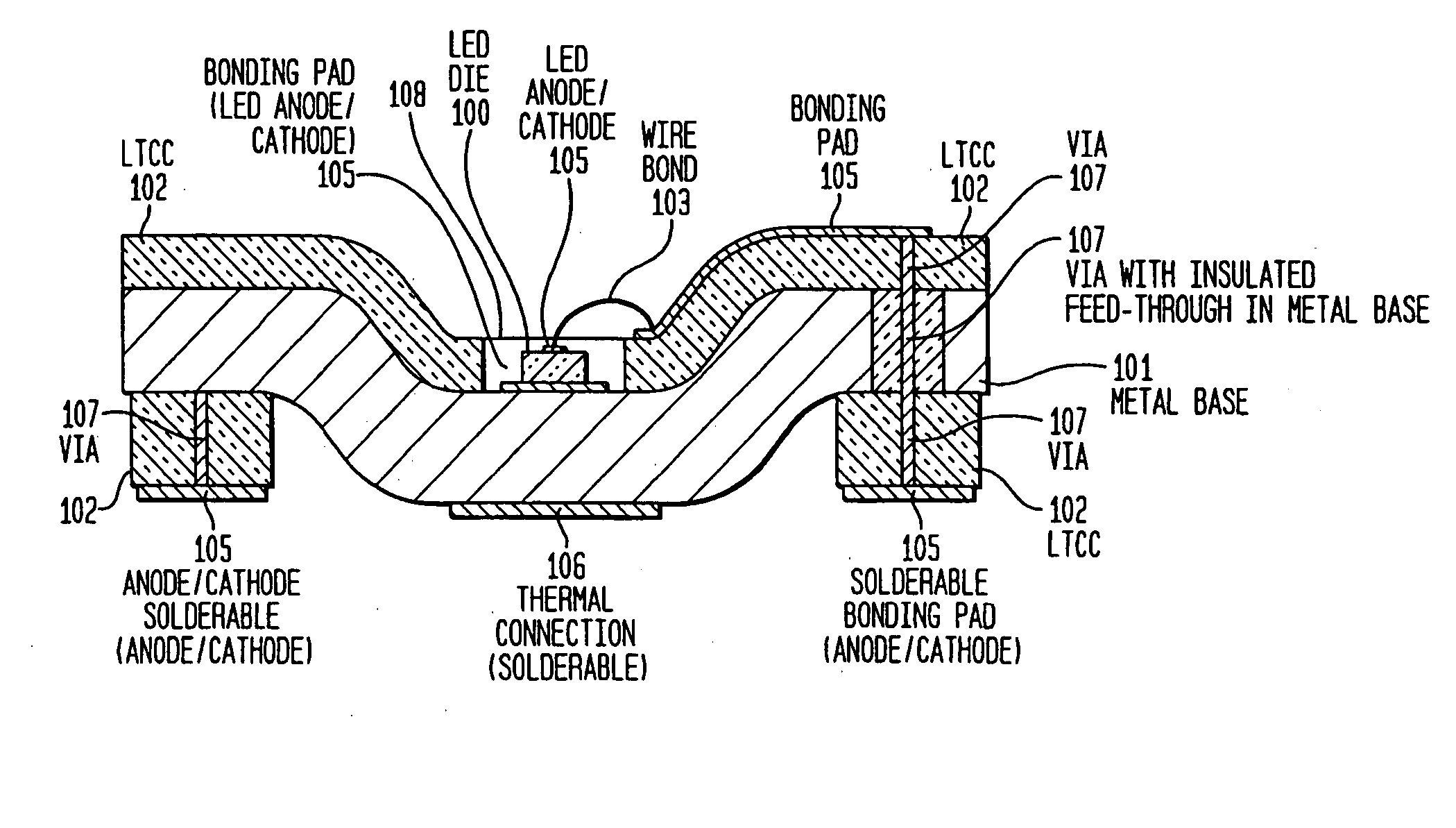
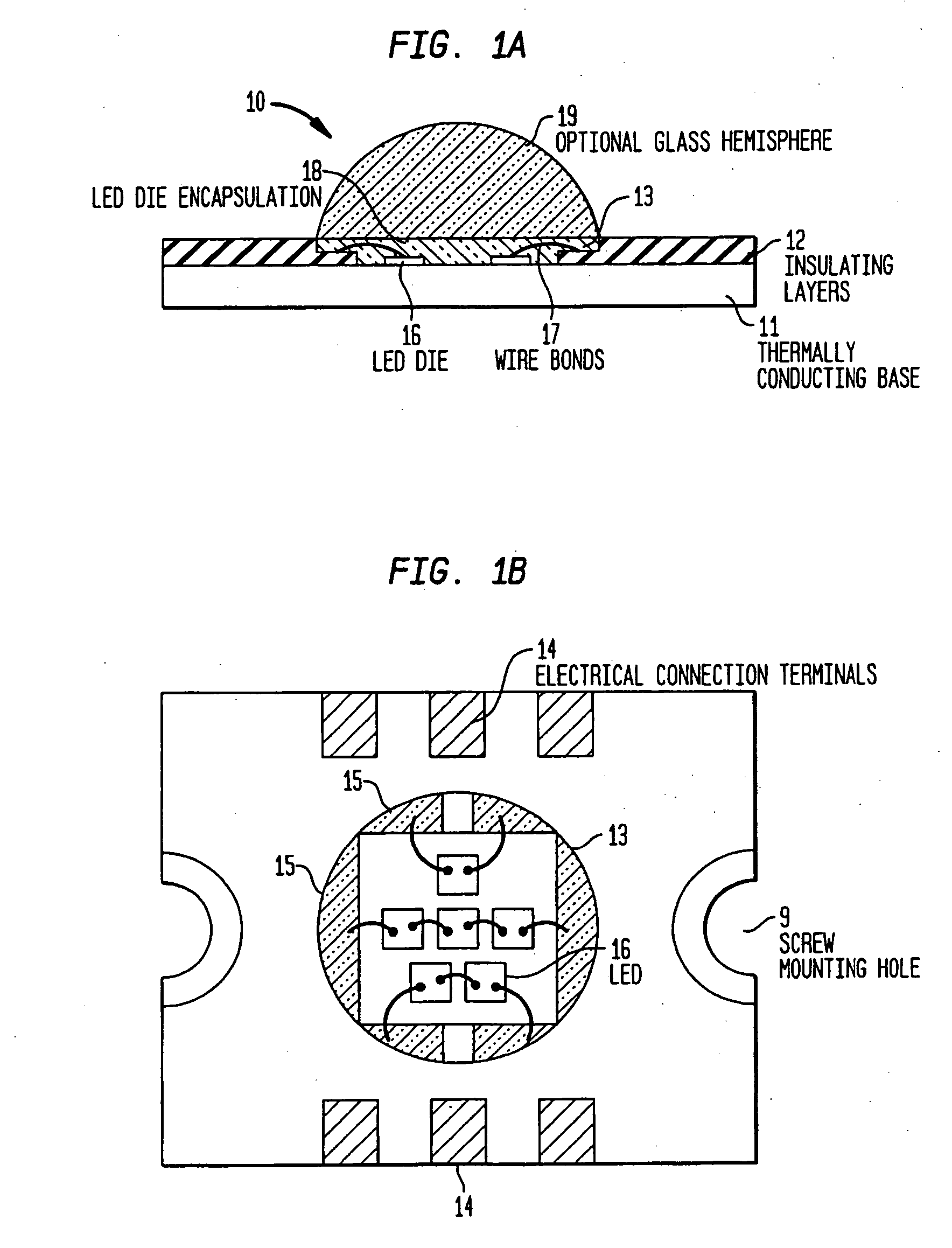
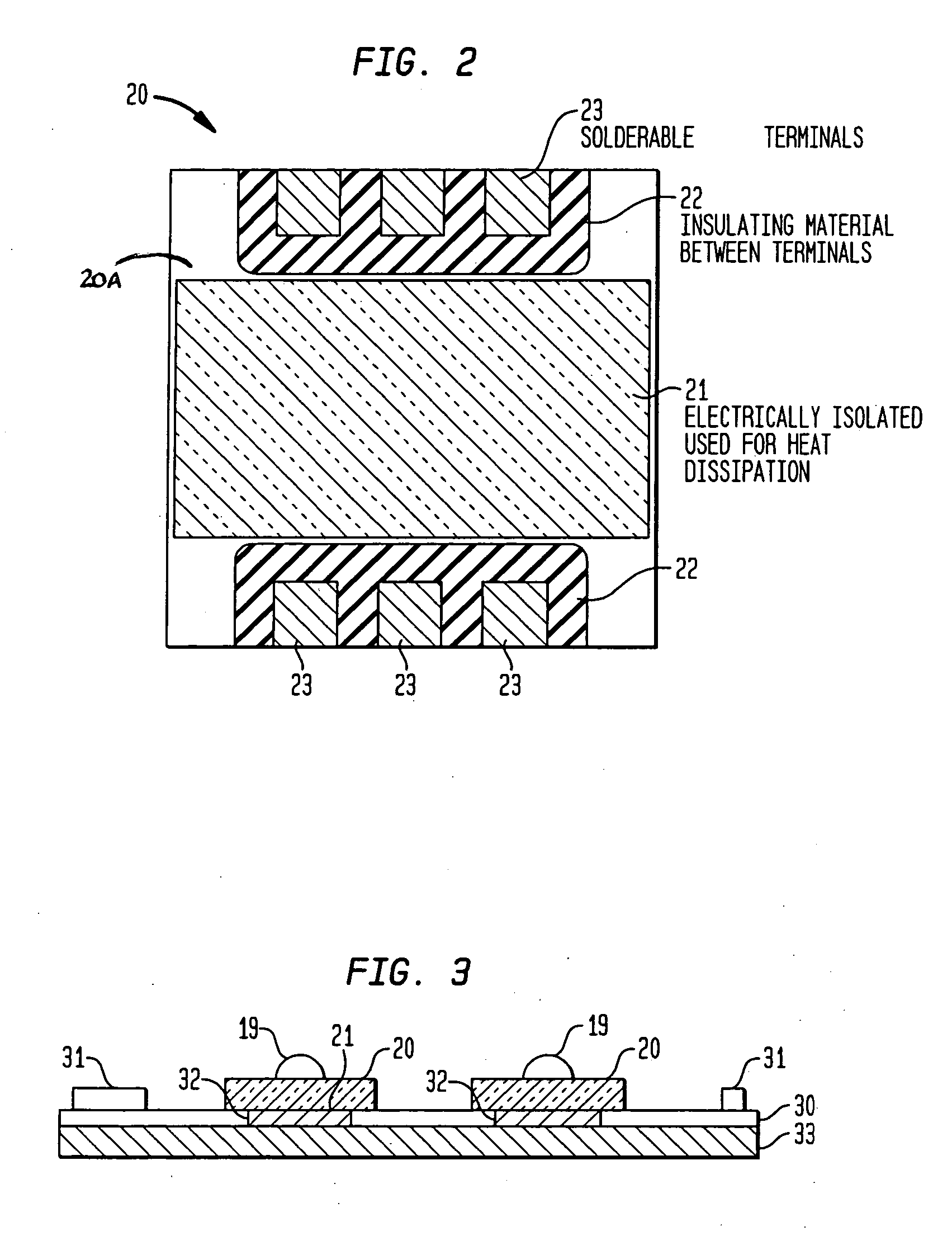
Light emitting diode (LED) assemblies packaged for high temperature operation and surface mounting. In particular, the LED assemblies according to the present invention are constructed to include a thermally conducting base and an optically efficient cavity that provides protection for the LED assembly and maximizes light extraction. The LED assemblies are particularly adapted for easy and efficient surface mounting or bolt down assembly mounting in high temperature environments.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Beam focusing and scanning system using micromirror array lens
ActiveUS20050264867A1Increase speedLarge focal length variationMirrorsMountingsLight beamProjection plane
A beam focusing and scanning system using a micromirror array lens (optical system) includes a light source configured to emit light and a micromirror array lens, including at least one micromirror, optically coupled to the light source, configured to reflect the light onto a projection medium (projection plane). The optical system also includes at least one actuating component coupled to the at least one micromirror, configured to move the at least one micromirror to enable the at least one micromirror to focus the light on the projection medium. The advantages of the present invention include high speed variable focusing and scanning, large focal length variation, phase compensation, high reliability and optical efficiency, low power consumption and low cost.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Passive collimating tubular skylight
InactiveUS6363667B2Convenient lightingImproved passive tubular skylightsBuilding roofsCeilingsEngineeringSpecular reflection
A passive collimating tubular skylight consisting of a radiant energy-collecting aperture, a radiant energy-delivering aperture, and a radiant energy passageway between these two apertures, the passageway having a specularly reflective interior surface and a configuration to improve the collimation of the radiant energy passing therethrough. The skylight can be configured with the radiant energy-collecting aperture located above the roof of a building, oriented to collect sunlight; and equipped with a sealed weatherproof glazing, with the radiant energy-delivering aperture, or luminaire, located at ceiling level within the building, and equipped with a diffusing glazing; and with the reflective tubular light passageway constructed with a larger cross sectional area near the radiant energy-delivering aperture than near the radiant energy-collecting aperture. In complete accord with the second law of thermodynamics, and as proven by experimental results, the new passive collimating tubular skylight provides significant advantages over the prior art, including better solar energy collection, higher throughput optical efficiency, improved radiant energy collimation, enhanced interior illumination levels, and more precise positional control of the interior illumination.
Owner:ENTECH INC
Illumination system
InactiveUS6863401B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceLighting system
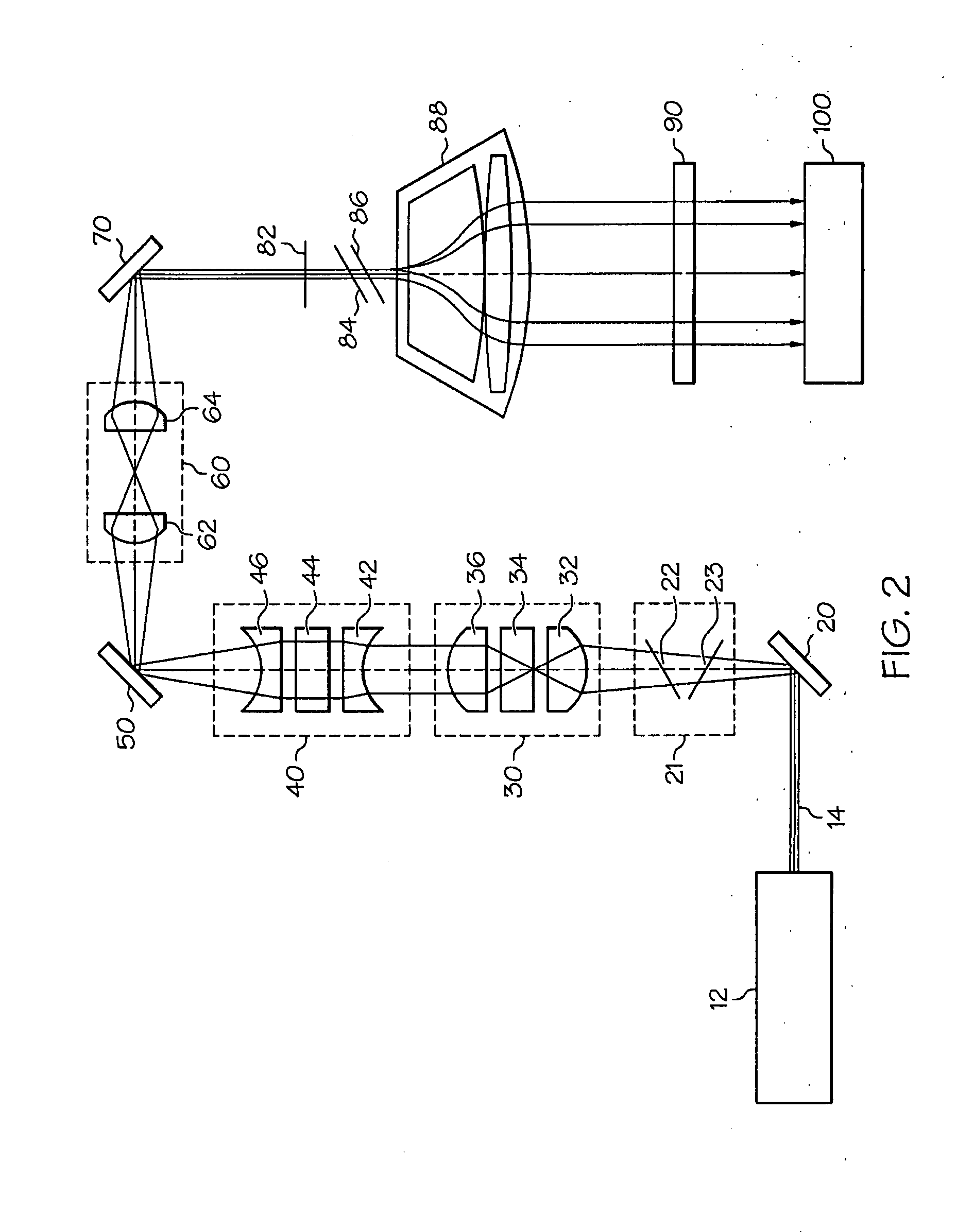
The addition of DMD illumination modulator(s) 702 in series with projection SLM(s) 706 / 709 to produce high-performance projection displays with improved optical efficiency, reliability, and lower maintenance requirements. This approach eliminates the vibration, audible noise, and safety problems associated with high speed rotating color filter wheels 203 commonly used in SLM projectors and controls the light applied to individual areas of the projection SLM(s).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Display apparatus
ActiveUS20110032209A1Excellent optical propertiesSolid-state devicesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureCapacitanceEngineering
A display apparatus having an improved optical efficiency and a touch panel function, the display apparatus including a substrate; a display unit formed on the substrate and including a plurality of pixels; an encapsulation substrate disposed facing the display unit to encapsulate the display unit; an electrostatic capacitive pattern layer formed on the encapsulation substrate; and a black matrix layer formed between the substrate and the encapsulation substrate, and disposed to surround the plurality of pixels, wherein the plurality of pixels are disposed to correspond to the electrostatic capacitive pattern layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
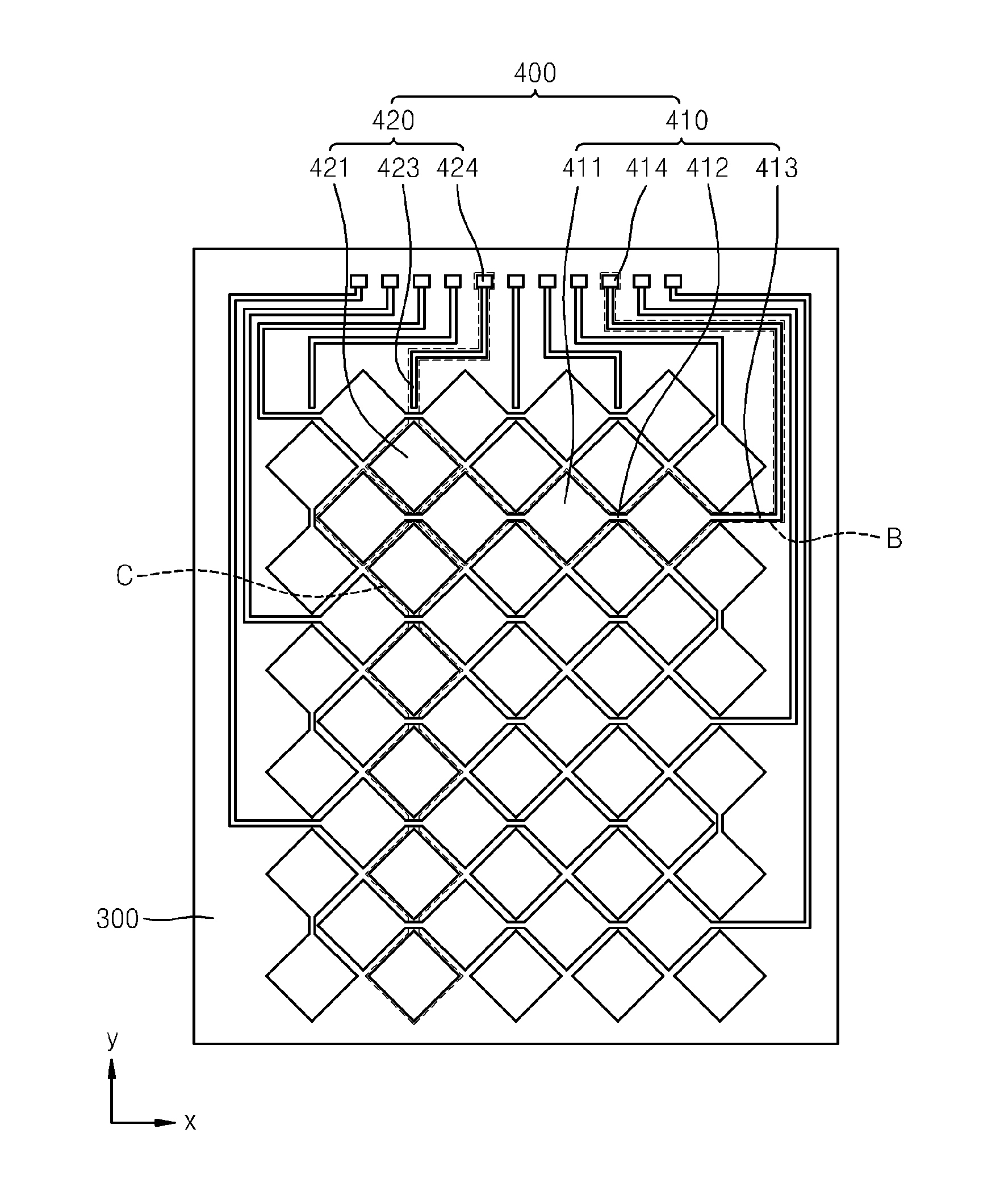
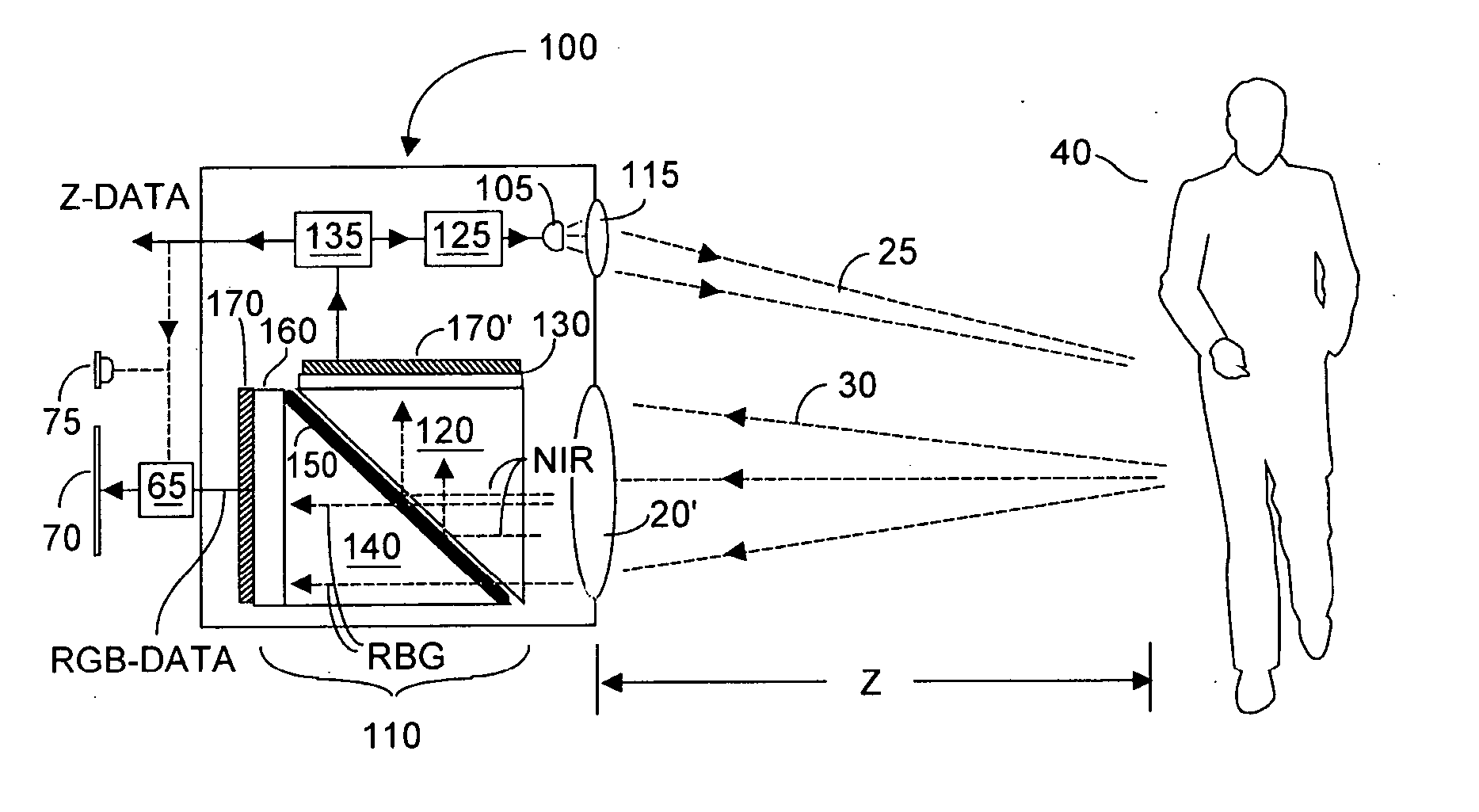
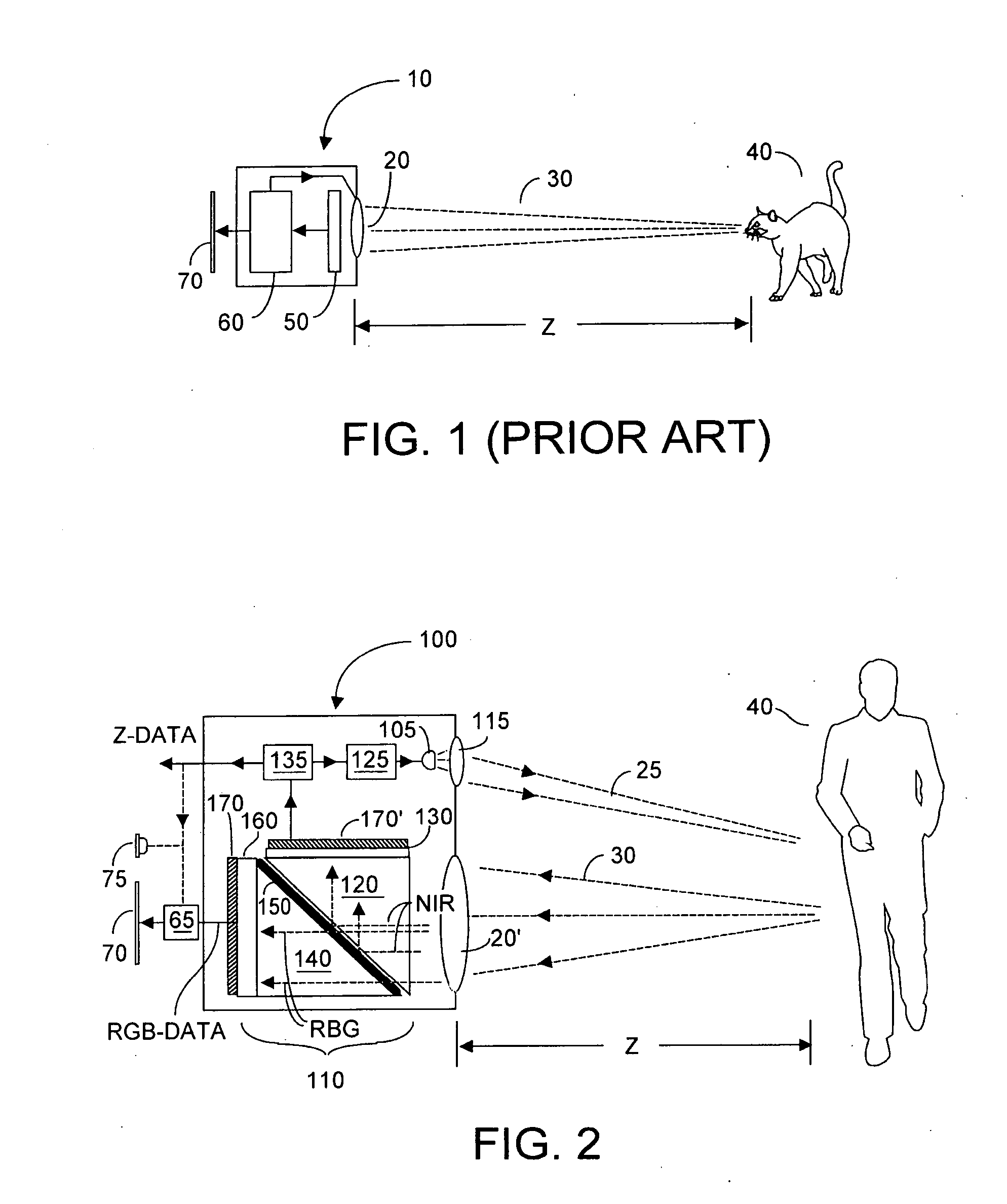
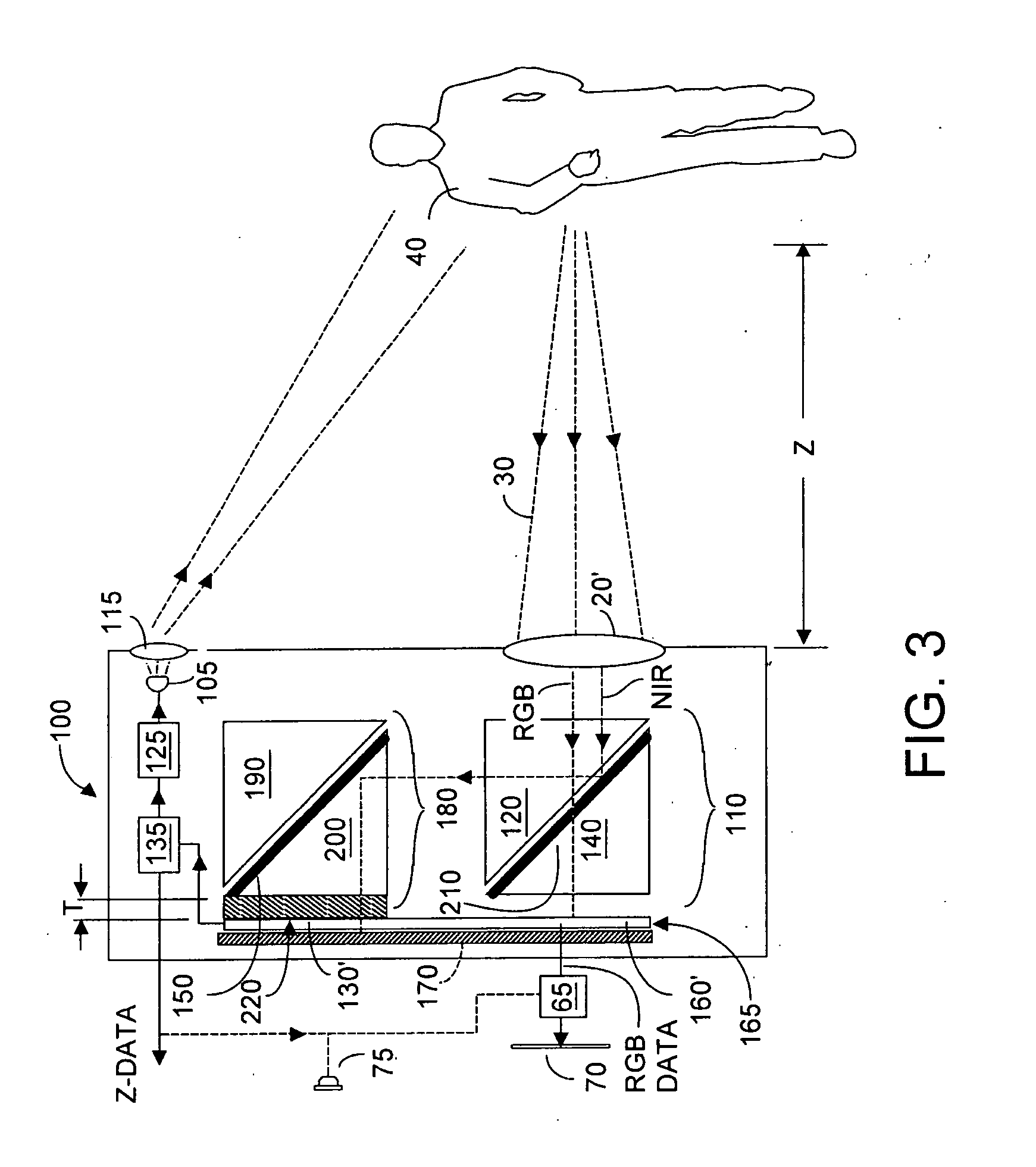
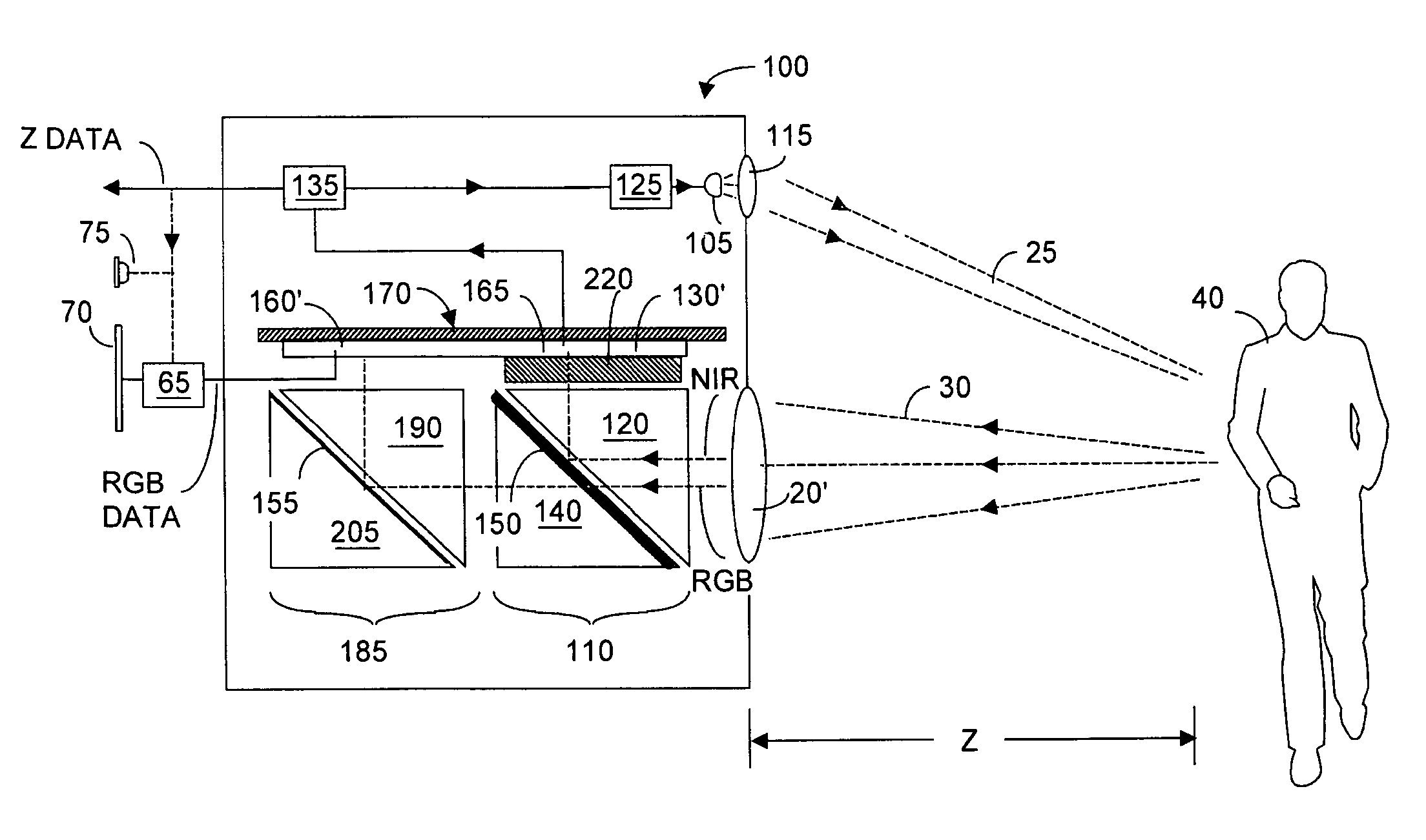
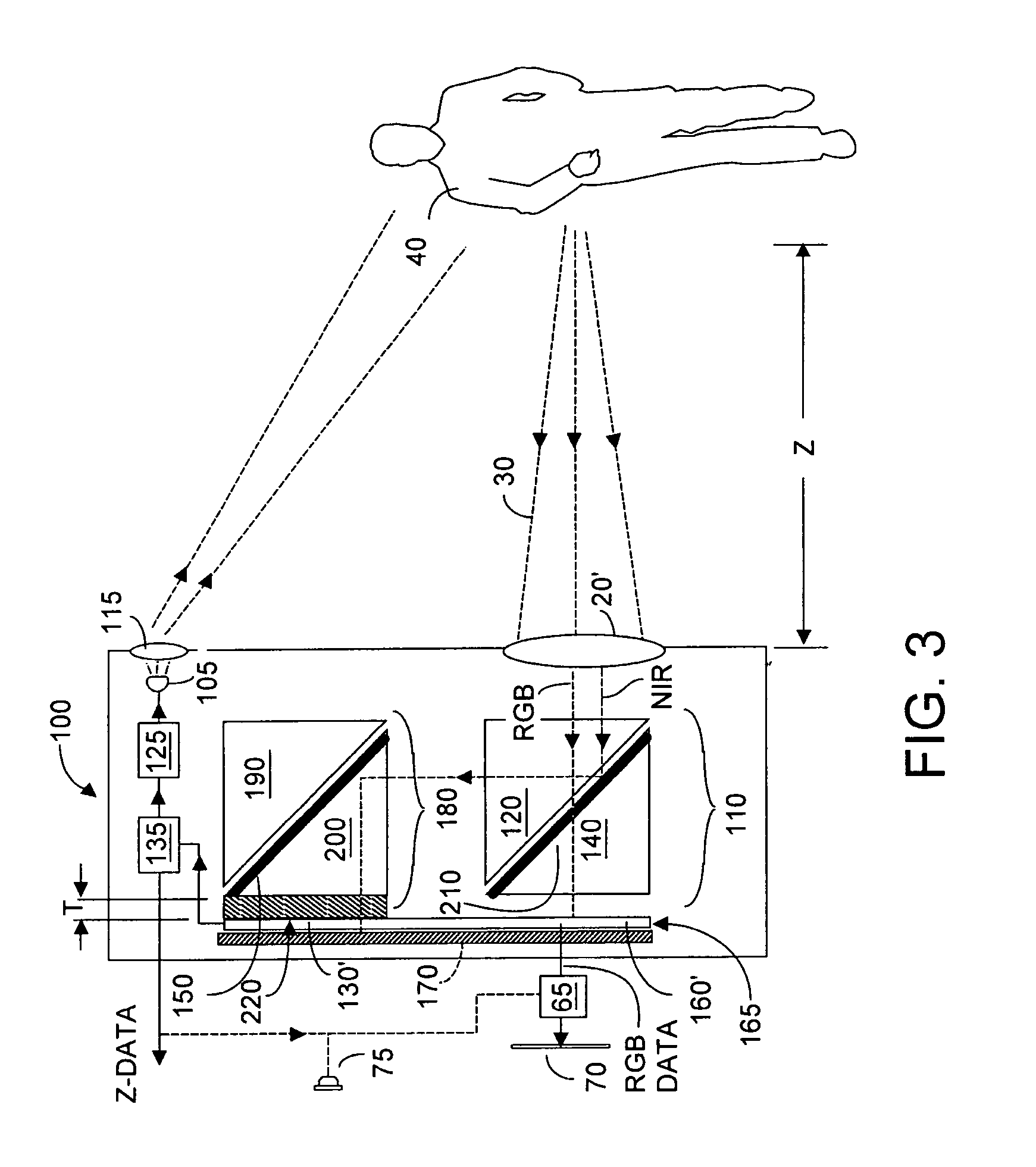
Single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor
ActiveUS20050285966A1Quick identificationHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersBeam splitterSpectral bands
An RGB-Z sensor is implementable on a single IC chip. A beam splitter such as a hot mirror receives and separates incoming first and second spectral band optical energy from a target object into preferably RGB image components and preferably NIR Z components. The RGB image and Z components are detected by respective RGB and NIR pixel detector array regions, which output respective image data and Z data. The pixel size and array resolutions of these regions need not be equal, and both array regions may be formed on a common IC chip. A display using the image data can be augmented with Z data to help recognize a target object. The resultant structure combines optical efficiency of beam splitting with the simplicity of a single IC chip implementation. A method of using the single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degrees of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS6934073B1Improve reflectivityIncrease the effective reflection areaNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCamera lensDegrees of freedom
A micromirror array lens consists of many micromirrors with one degree of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation and actuating components. As a reflective variable focal length lens, the array of micromirrors makes all lights scattered from one point of an object have the same periodic phase and converge at one point of image plane. As operational methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known semiconductor microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known semiconductor microelectronics technologies.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Light emitting diode package employing lead terminal with reflecting surface
InactiveUS20080048201A1Improved light emissionWell formedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEngineeringHigh reflectivity
Disclosed is a light emitting diode (LED) package employing a lead terminal with a reflecting surface. The package includes first and second lead terminals that are spaced apart from each other. The first lead terminal has a lower portion with an LED chip mounting area, and at least one reflecting surface formed by being bent from the lower portion. Meanwhile, a package body supports the first and second lead terminals and forms a cavity through which the LED chip mounting area and the reflecting surface of the first lead terminal and a part of the second lead terminal are exposed. The first and second lead terminals extend outside of the package body. Accordingly, light emitted from an LED chip can be reflected on the reflecting surface with high reflectivity, so that the optical efficiency of the package can be improved.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
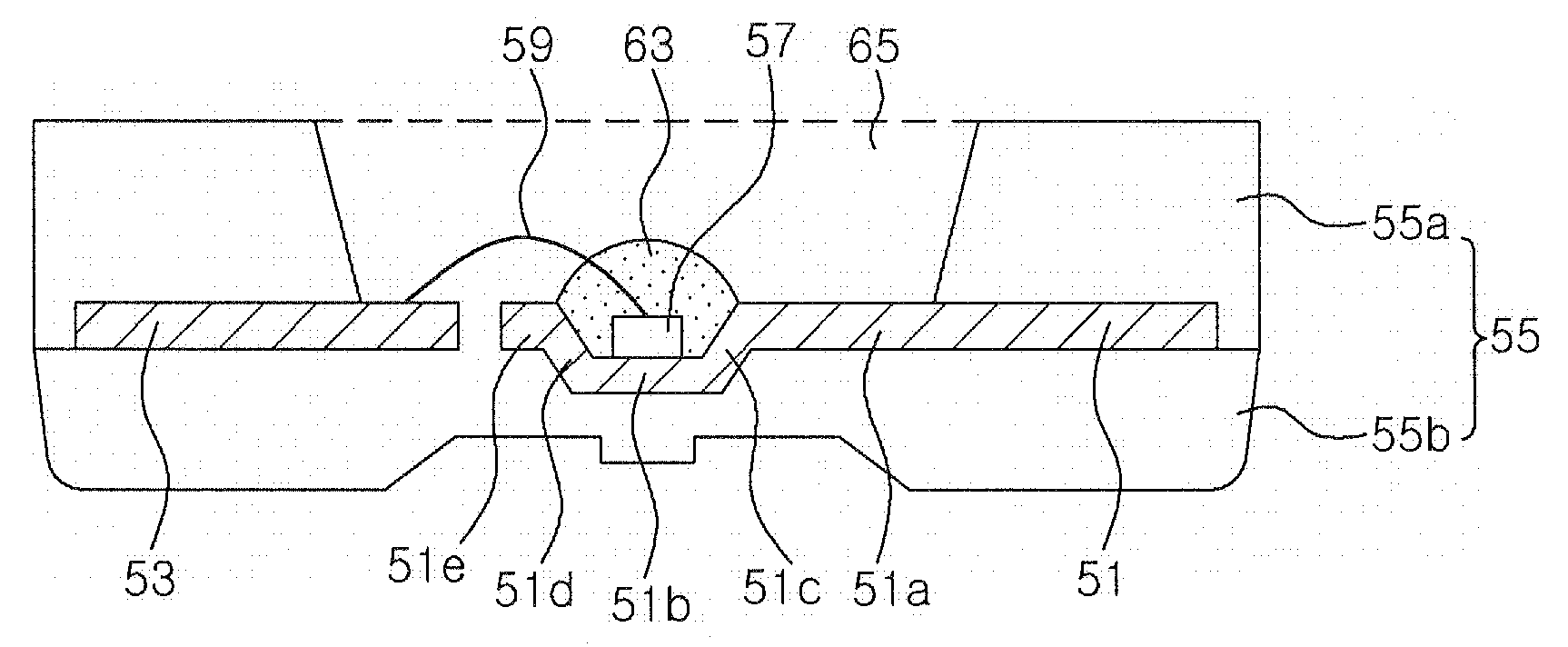
Joint design of thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and patterned media for high optical efficiency
ActiveUS20110096431A1Combination recordingPatterned record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A system according to one embodiment includes a magnetic recording medium having a magnetic layer with features in a discrete track configuration or a bit patterned configuration and an underlayer adjacent the magnetic layer, the underlayer comprising a material capable of forming surface plasmon resonance; and a magnetic head having: a writer for writing to the medium; and a near-field transducer for heating the medium for thermally assisted recording. Additional systems and methods are also presented.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS6999226B2Improve reflectivitySimple mechanical structure and actuating componentNon-linear opticsLensCamera lensMicromirror array
A variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with pure translation is invented. The lens consists of many micromirrors and actuating components. The array of micromirrors with pure translation makes all lights scattered from one point of an object have the same periodic phase and converge at one point of image plane by using Fresnel diffraction theory. The actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known semiconductor microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known semiconductor microelectronics technologies. The micromirror array can also form arbitrary shape and / or size of a lens.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Array of micromirror array lenses
ActiveUS7161729B2Increase the effective reflection areaImprove optical efficiencyMirrorsMountingsCamera lensOptical axis
An array of micromirror array lenses is invented. The micromirror array lens consists of many micromirrors and actuating components. Each micromirror array lens is variable focal length lens with high speed focal length change. The lens can have arbitrary type and / or size as desired and desired arbitrary optical axis and can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known microelectronics technologies. The actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known microelectronics technologies remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with two degrees of freedom rotation
ActiveUS7031046B2Simple mechanical structure and actuating componentLarge aberrationMirrorsMountingsDegrees of freedomMicromirror array
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Method and apparatus for creating optical images
ActiveUS20090086498A1Improve efficiencyLow costMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOptical axisWorking temperature
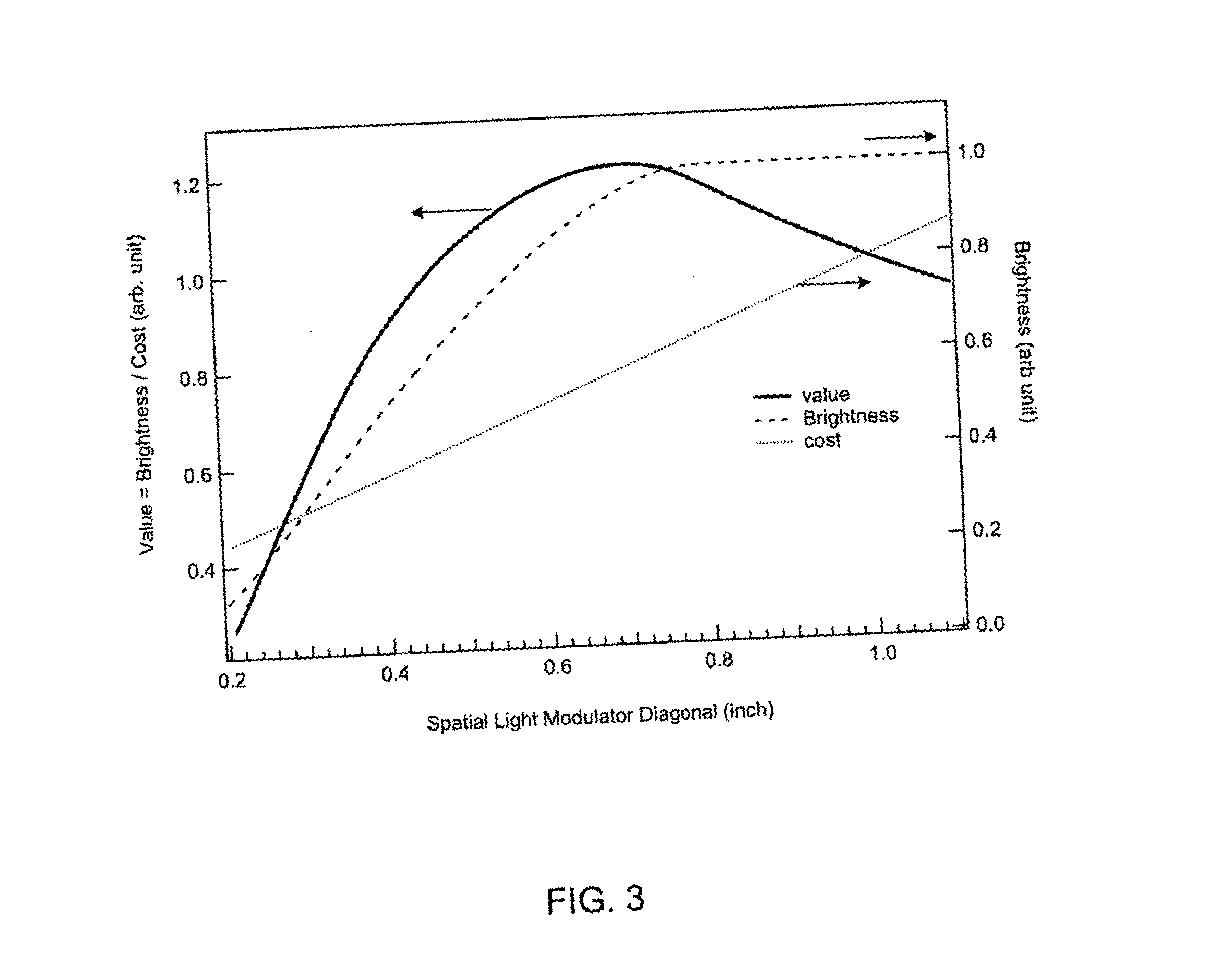
A device for creating a predetermined light output distribution having a substantially rectangular shape in angle space is provided having a lens with a revolved inner surface and a complex outer surface. The inner surface has a combination of reflective and refractive surface facets swept about an axis of revolution perpendicular to the optical axis of the device. The outer surface has a non-planar, non-circular, non-spherical shape. This outer surface generates an appropriate intensity distribution in a direction generally parallel to the major axis of the output rectangle and may also distribute energy generally parallelly to the minor axis of the output rectangle as well. The optical efficiency improvement in the design of this improved preferably LED-based product has several direct benefits including; increased reliability, lower operating temperature, reduced electrical requirements, greater product life and significantly reduced cost as compared to existing LED products. The resulting cost savings attendant with the implementation of the present invention makes high performance LED lamps more accessible to the general public and improves vehicle safety.
Owner:TECNIQ
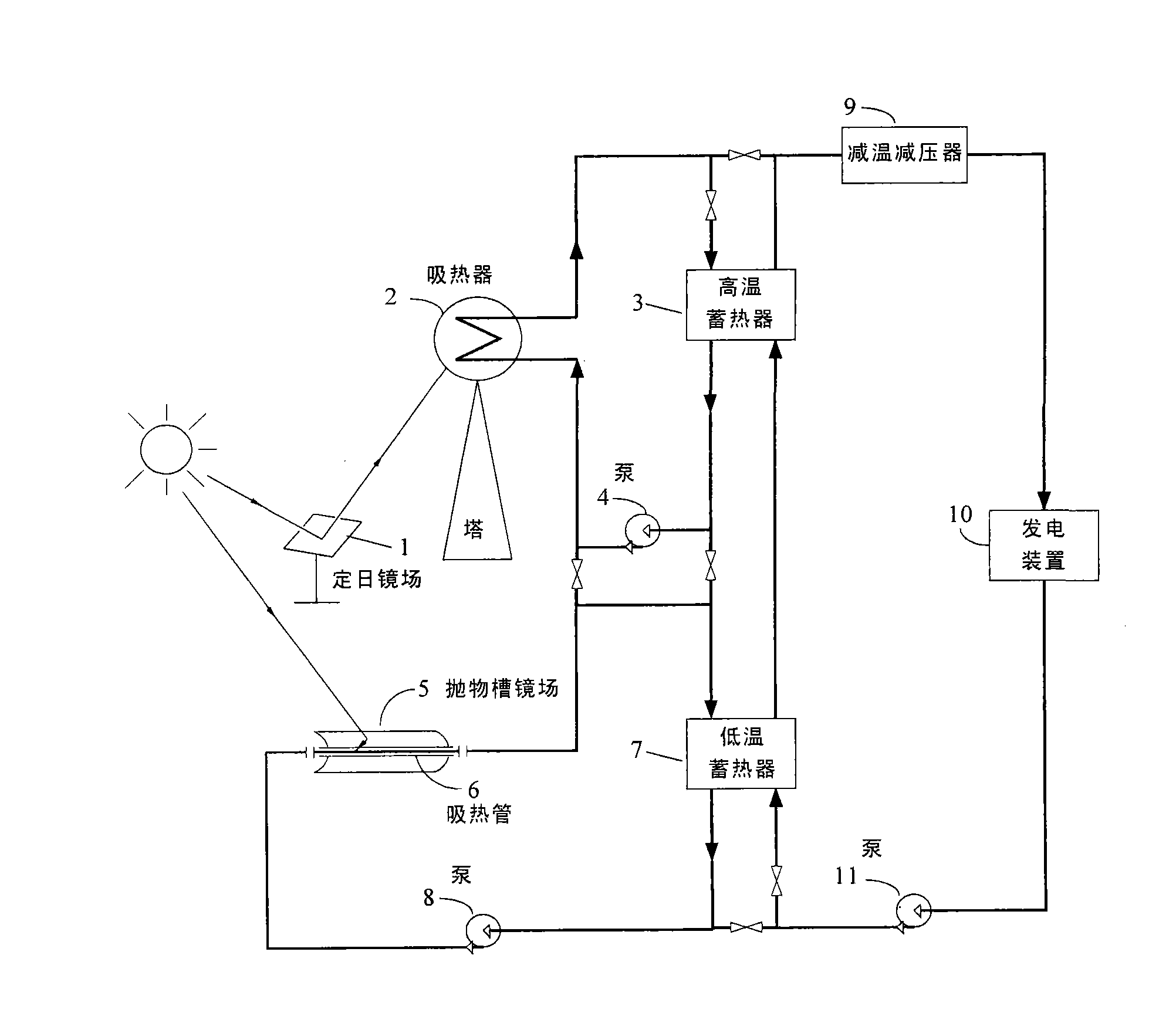
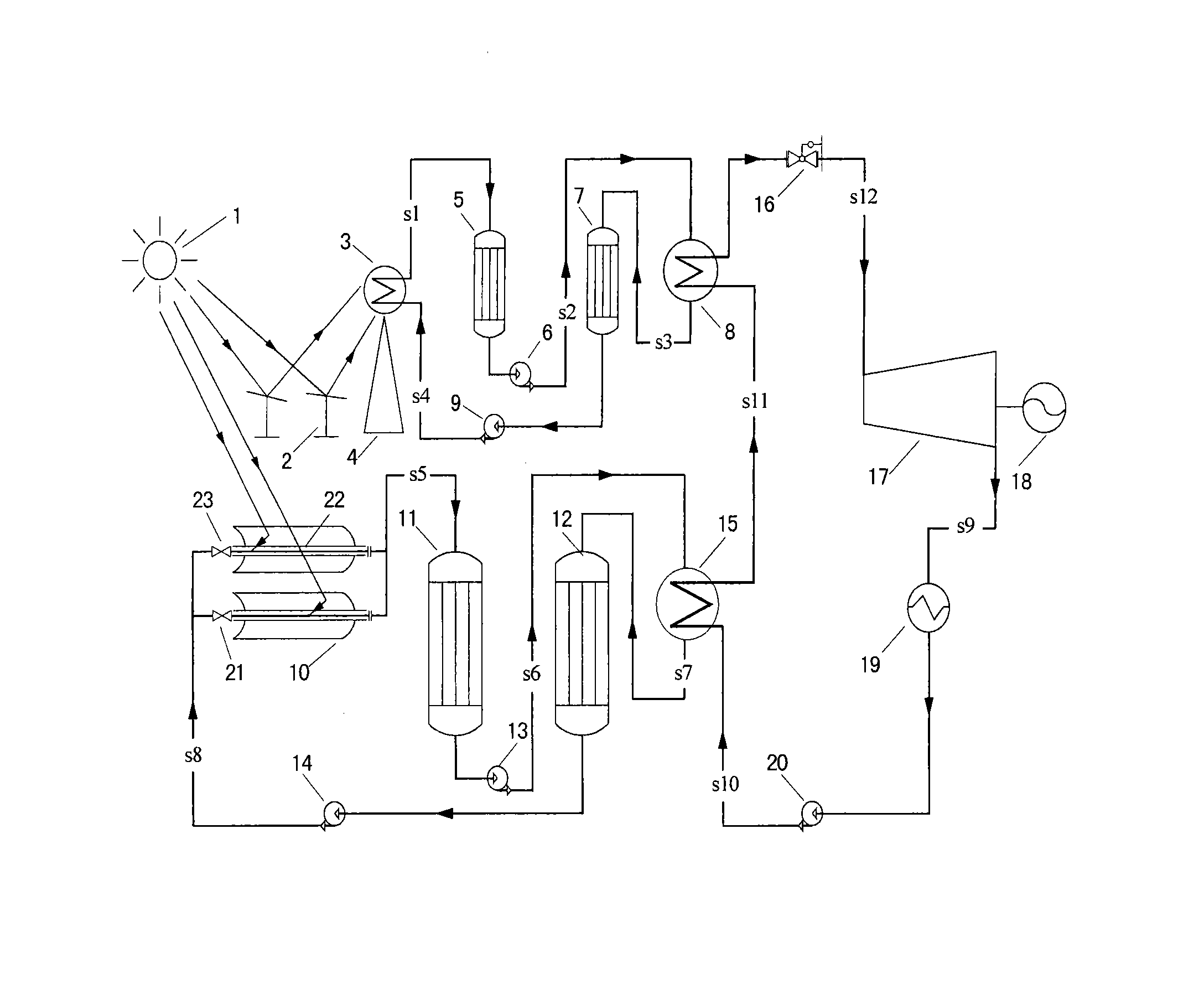
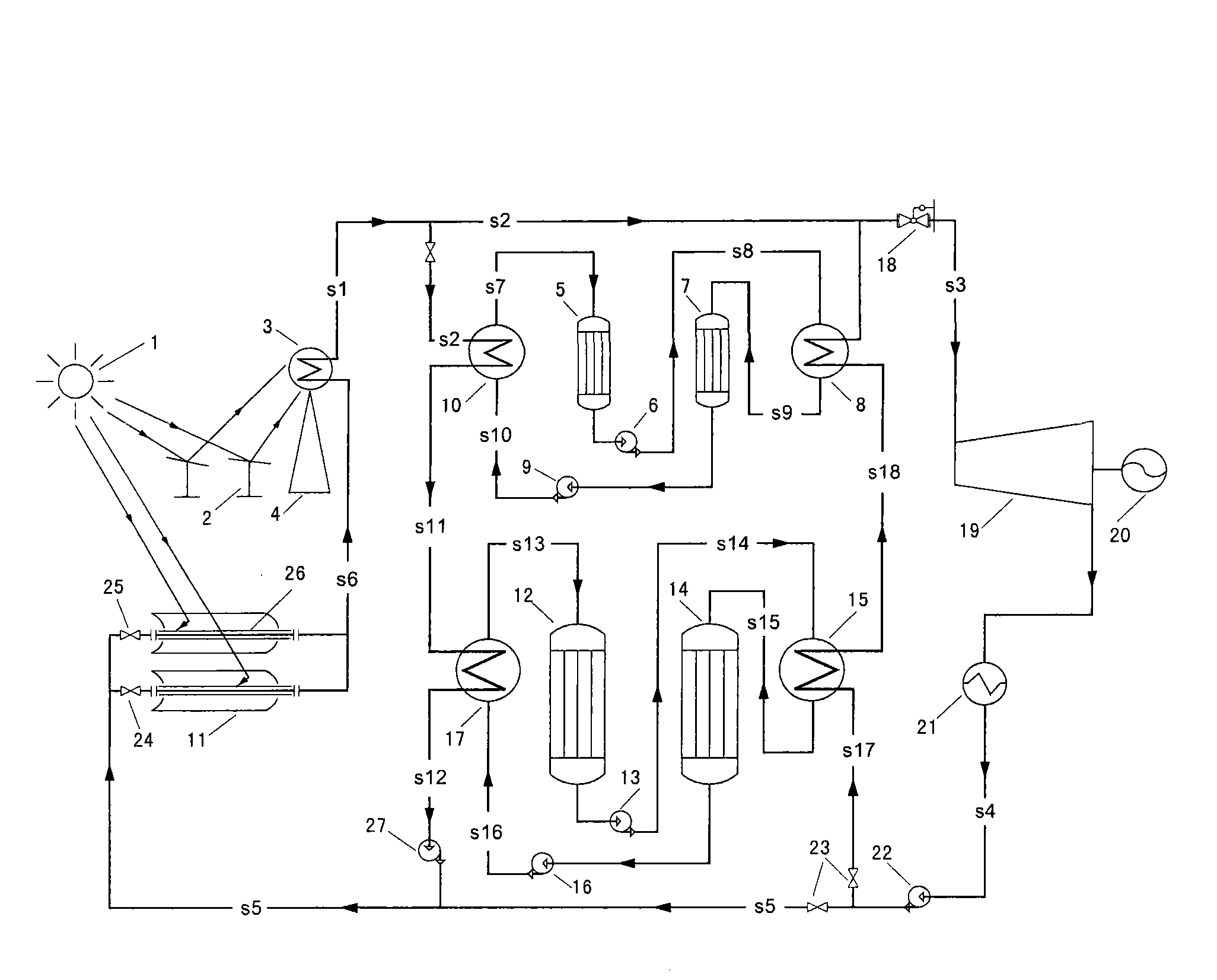
Groove-tower combined two-stage heat-storage solar-heat power generation system
InactiveCN101539123ALess investmentSave land areaSolar heating energyFrom solar energyThermal energyHeliostat
The invention discloses a groove-tower combined solar-heat power generation system, which comprises a subsystem for low-temperature groove-type heat collection and low-temperature heat storage, a subsystem for high-temperature tower-type heat collection and high-temperature heat storage, as well as a power generation subsystem, wherein the subsystem for low-temperature groove-type heat collection and low-temperature heat storage is used for receiving and gathering solar radiation energy, converting the received solar radiation energy into medium-temperature heat energy and conveying the medium-temperature heat energy to the subsystem for high-temperature tower-type heat collection and high-temperature heat storage or a low-temperature heat accumulator; the subsystem for high-temperature tower-type heat collection and high-temperature heat storage is used for receiving and gathering solar radiation energy, converting the received solar radiation energy into high-temperature heat energy and conveying the high-temperature heat energy to a power subsystem or a high-temperature heat accumulator; and the power subsystem is used for converting the received heat energy into electric energy and outputting the electric energy. The system solves the problems that a groove-type solar-heat power generation system is low in heat-collecting temperature and difficult to promote; the optical efficiency of a heliostat filed of a simple-tower solar-heat power generation system is greatly affected by the scale of power plants; and the simple-tower solar-heat power generation system is not easy to maximize. The system has the advantages of reducing initial cost and occupied area.
Owner:中金盛唐新能源科技(北京)有限公司
Single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor
ActiveUS8139141B2High resolutionQuick identificationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersBeam splitterSpectral bands
An RGB-Z sensor is implementable on a single IC chip. A beam splitter such as a hot mirror receives and separates incoming first and second spectral band optical energy from a target object into preferably RGB image components and preferably NIR Z components. The RGB image and Z components are detected by respective RGB and NIR pixel detector array regions, which output respective image data and Z data. The pixel size and array resolutions of these regions need not be equal, and both array regions may be formed on a common IC chip. A display using the image data can be augmented with Z data to help recognize a target object. The resultant structure combines optical efficiency of beam splitting with the simplicity of a single IC chip implementation. A method of using the single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors
ActiveUS20050264870A1Increase the number ofLower resistanceMirrorsMountingsDegrees of freedomRotational degrees of freedom
A variable focal length lens consists of many micromirrors with degrees of freedom rotation and / or degrees of freedom translation and actuating components. As operating methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the variable focal length lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. The lens can also be of a desired arbitrary shape and / or size. The micromirrors are arranged in a flat plane or in a curved plane with a predetermined curvature. The electrodes determining the position of the micromirrors can be made of material with high electrical conductivity, preferably metal. The surface material of the micromirror is made of a material with high reflectivity such as aluminum, silver, and gold, which are coated with multi-layer dielectric material or antioxidant.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Joint design of thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and patterned media for high optical efficiency
ActiveUS8031561B2Combination recordingPatterned record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingPatterned media
A system according to one embodiment includes a magnetic recording medium having a magnetic layer with features in a discrete track configuration or a bit patterned configuration and an underlayer adjacent the magnetic layer, the underlayer comprising a material capable of forming surface plasmon resonance; and a magnetic head having: a writer for writing to the medium; and a near-field transducer for heating the medium for thermally assisted recording. Additional systems and methods are also presented.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Micro-shutter device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100118413A1Improve optical efficiencyReduce light lossHollow inflatable ballsHollow non-inflatable ballsDisplay deviceEngineering
Micro-shutter device applicable to display devices including a flexible display device and method of manufacturing same are provided. Micro-shutter device includes membrane. Frame including receiving hole in its center portion is bonded to membrane. Transparent substrate is bonded to frame to encapsulate optical fluid received in receiving hole. Actuator varies refractive power produced by change in curvature of fluid lens formed in the center portion of the receiving hole due to bending of a periphery of the fluid lens. A reflector is disposed to correspond to the fluid lens and be spaced apart from the membrane, such that light intensity transferred to a user is adjusted depending on the refractive power produced by a change in curvature of the fluid lens. Therefore, the device has improved optical efficiency compared to using liquid crystal and a polarizing film, and can have a flexible structure for application to a flexible display device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optoelectrical Connector
ActiveUS20120020629A1Inhibition of attachmentCoupling deterioratesCoupling light guidesElectricityElectrical connection
In an optoelectrical connector that is composed of a plug including an insertion fitting part and a receptacle including a housing space into which the insertion fitting part of the plug is inserted, the plug is provided with an optical connection part (an optical member) on a front end of the insertion fitting part and an electric connection part (terminals) more rearward than the optical connection part. The receptacle is provided with an optical connection part (an optical member) on the deep side of the housing space and an electric connection part (movable contact pieces of terminals) more frontward than the optical connection part. A shutter is formed on the immediate front of the optical connection part of the receptacle and the shutter opens in the optical connection. Deterioration of optical coupling efficiency caused by attachment of metal abrasion powder, which is generated in a slide between the electrical connection parts in the electrical connection, to the optical connection parts, is prevented.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Light emitting diode package having dual lens structure and backlight for liquid crystal display device implementing the same
InactiveUS20080278655A1Effective diffusionSpread widelySolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display (LCD) device in which low power LEDs with a dual lens structure re configured for application in a backlight device to increase the optical efficiency at low power, thus enhancing the brightness, such LCD device including: a lower cover; PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) disposed on the lower cover for receiving power from the exterior; a main body mounted on the PCBs; R, G and B LED (Light Emitting Diode) devices disposed on the main body for emitting light; a first lens having a first curvature and mounted on the main body and housing the R, G and B LED devices; a second lens covering the outside of the first lens and having an inner curved surface with a second curvature having a varying radius of curvature, and an outer curved surface with a third curvature, wherein the second curvature of the inner curved surface is gradually increased from an edge portion toward a central portion; and a liquid crystal panel spaced apart from the second lens by a certain interval and to which light is provided.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Encapsulation of photovoltaic cells
This invention relates to a photovoltaic cell module and a process of applying a silicone based hot melt encapsulant material (102a, 104a) onto photovoltaic cells (103a) to form a photovoltaic cell module. There is provided a photovoltaic array with more efficient manufacturing and better utilization of the solar spectrum by using silicone hot melt sheets (102a, 104a) to give a silicone encapsulant photovoltaic device with the process ease of an organic encapsulant but the optical and chemical advantages of a silicone encapsulant. There is further provided a method for fabricating photovoltaic cells with increased throughput and optical efficiency when compared to prior art encapsulation methods. The preferred silicone material is provided in flexible sheet with hot melt properties and low surface tack.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Beam focusing and scanning system using micromirror array lens
A beam focusing and scanning system using a micromirror array lens (optical system) includes a light source configured to emit light and a micromirror array lens, including at least one micromirror, optically coupled to the light source, configured to reflect the light onto a projection medium (projection plane). The optical system also includes at least one actuating component coupled to the at least one micromirror, configured to move the at least one micromirror to enable the at least one micromirror to focus the light on the projection medium. The advantages of the present invention include high speed variable focusing and scanning, large focal length variation, phase compensation, high reliability and optical efficiency, low power consumption and low cost.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
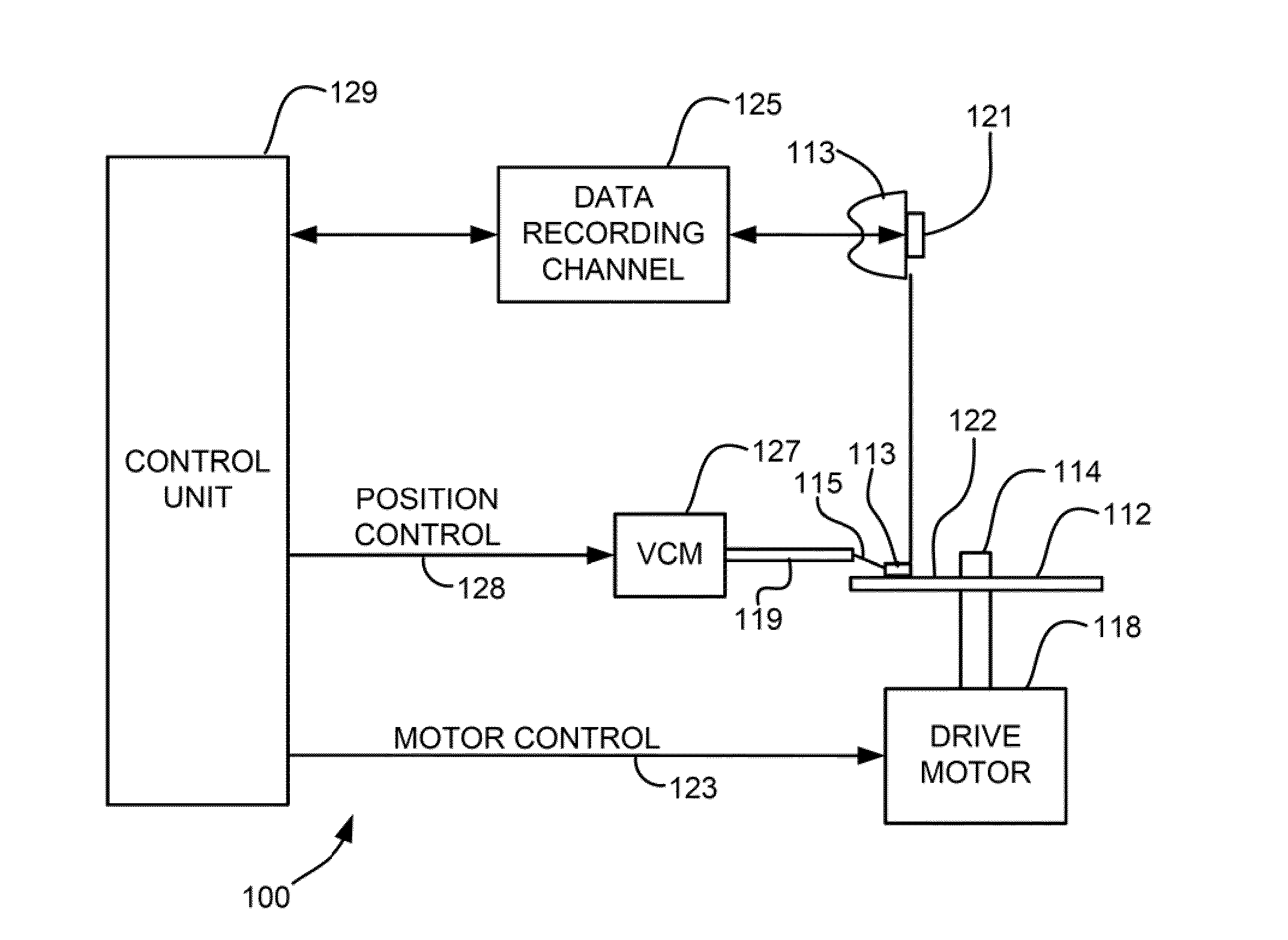
Optical pickup and optical recording and/or reproducing apparatus adopting the same
InactiveUS20060002247A1Improve optical efficiencyIncrease speedRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupLight spot
An optical pickup and an optical recording and / or reproducing apparatus adopting the same are provided. The optical pickup includes an optical unit, first and second objective lenses, and an optical path switching unit. The optical unit illuminates light onto an information storage medium and receives light reflected from the information storage medium to detect an information signal and / or an error signal. The first and the second objective lenses focus incident light to form a light spot on an information storage surface of the information storage medium. The optical path switching unit selectively directs the light incident from the optical unit to one of the first and second objective lenses. In the optical pickup, since the light quantity directed to a plurality of objective lenses may be maximized, optical efficiency is increased and thus high-speed operation may be attained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission-reflection blue-phase liquid crystal display with corrugated electrode
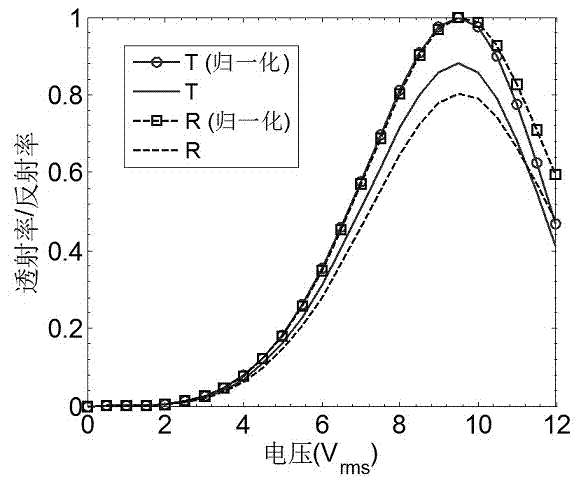
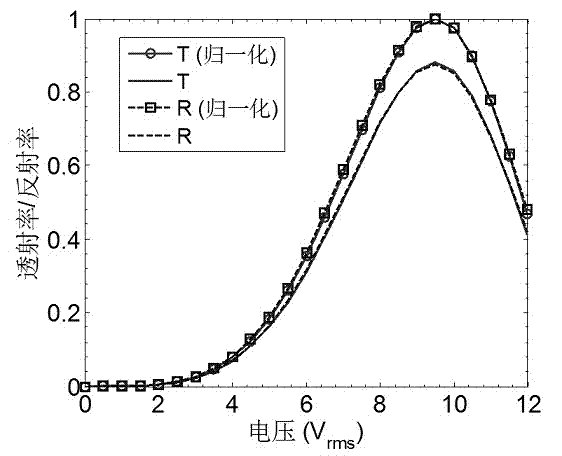
InactiveCN102231027AImprove matchLow working voltageNon-linear opticsLayer thicknessOptical efficiency
The invention discloses a transmission-reflection blue-phase liquid crystal display with a corrugated electrode. The liquid crystal display comprises an upper substrate, a transparent corrugated public electrode, a liquid crystal layer, a transparent corrugated pixel electrode, a lower substrate and a reflecting layer, wherein the upper substrate and the lower substrate are arranged in parallel and are partitioned into transmission regions and reflection regions; and the transmission regions and the reflection regions are made of the same blue-phase liquid crystal material. By adopting the following two schemes, the phase delay between the transmission region and the reflection region can be balanced and the transmission-reflection blue-phase liquid crystal display can be realized. In thescheme I: the same corrugated electrode inclination angle, i.e., alpha T=alpha R, is adopted for the transmission regions and the reflection regions, but different liquid crystal layer thicknesses, i.e., dT is less than dR, are adopted. In the scheme II: the same liquid crystal layer thickness, i.e., dT=dR, is adopted for the transmission regions and the reflection regions, but different corrugated electrode inclination angles, i.e., alpha T is more than alpha R, are adopted. Due to the adoption of the corrugated electrode in the transmission-reflection blue-phase liquid crystal display, the working voltage is reduced, the optical efficiency is increased, and the electrooptic property curves of the transmission regions and the reflection regions are well matched. Due to the adoption of the corrugated electrode, the manufacturing process is easier.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
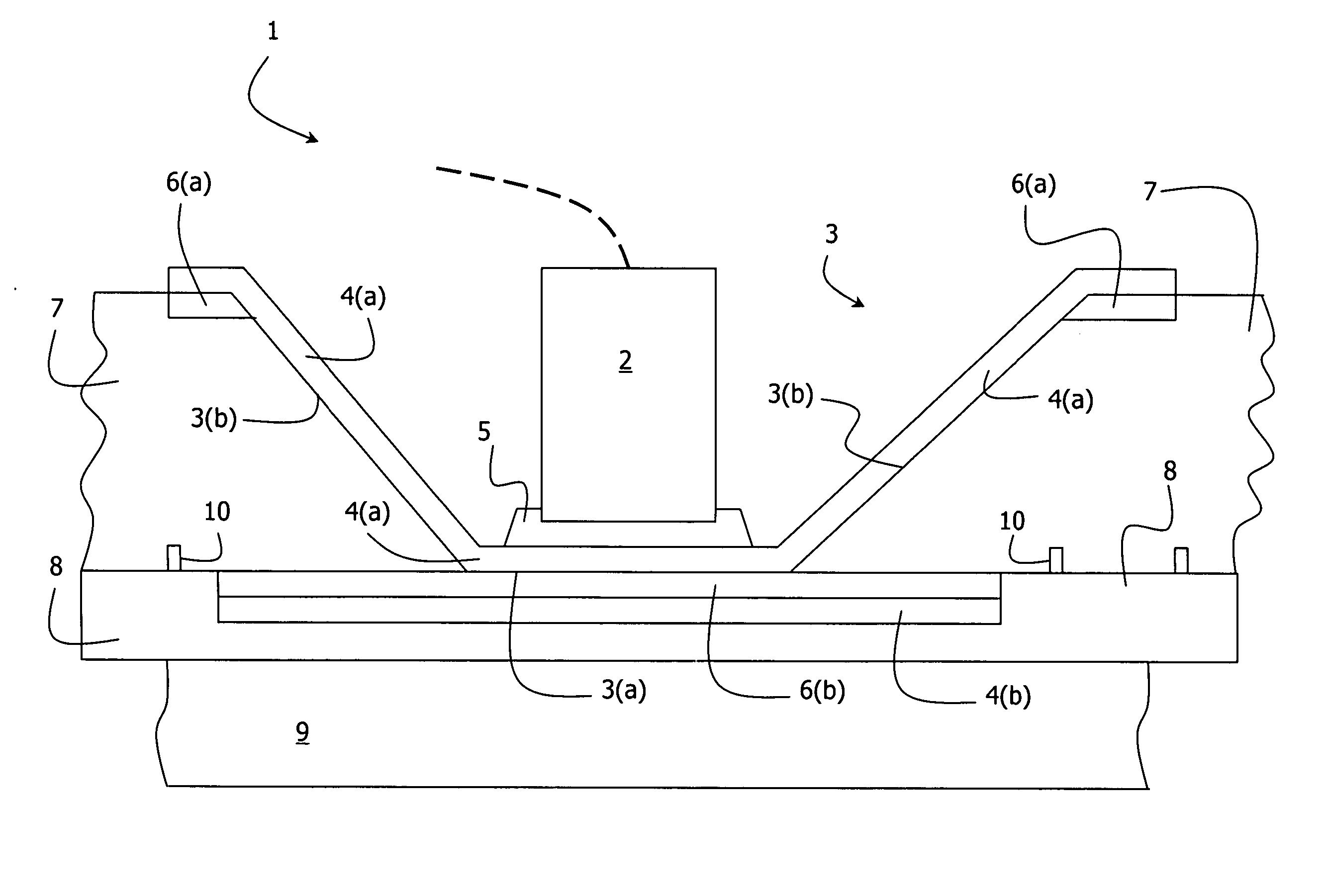
Illuminator and production method
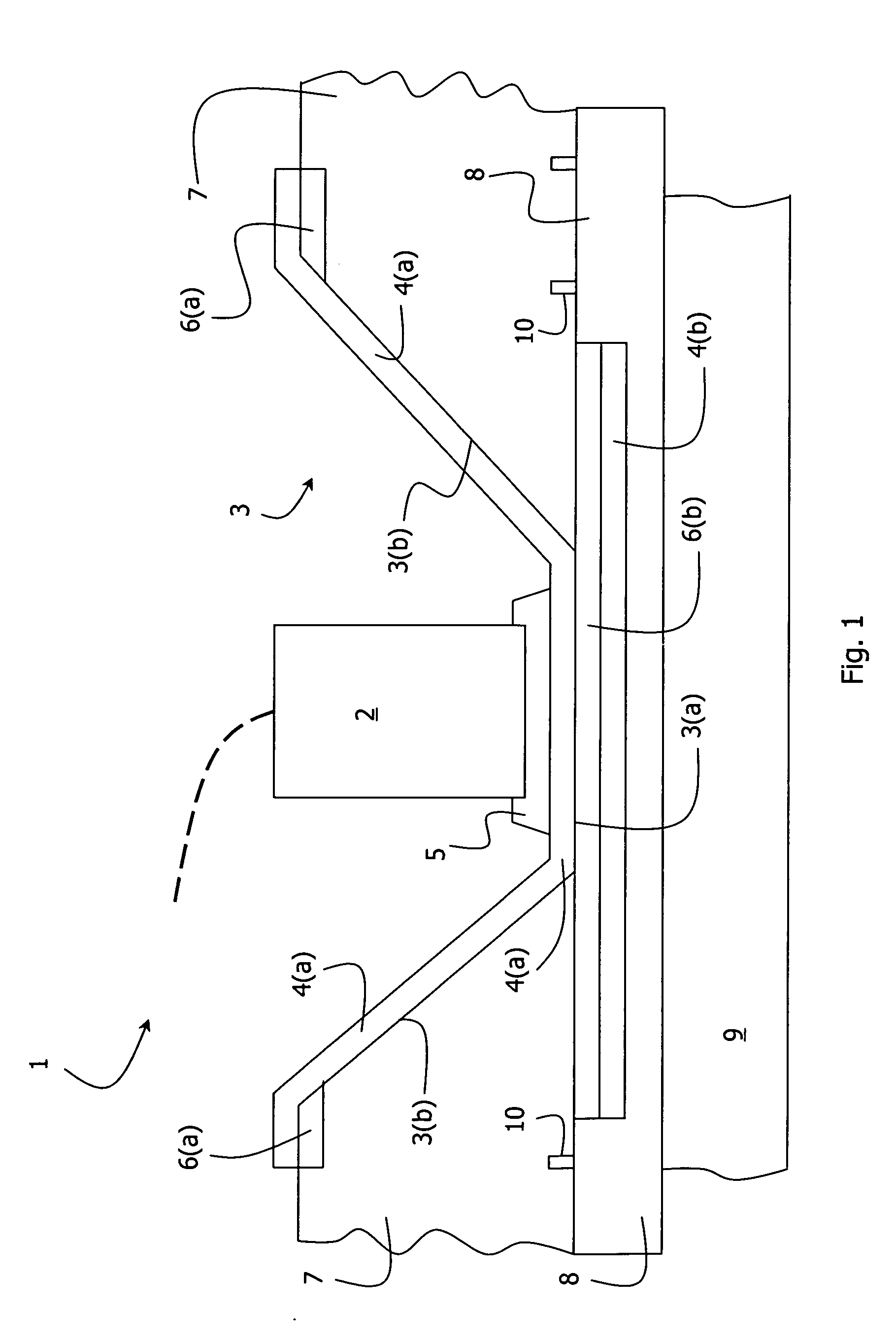
InactiveUS20060018120A1Printed circuit detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsCopper conductorEngineering
An illuminator (1) has an array of cavities (3) are drilled in a substrate having an FR4 electrically insulating body (7) plated with copper conductors (6(a), 6(b)). Further patterning of the substrate provided electrical conductors (3(b)) in the cavities to act as both part of the light drive circuit and reflectors in the cavities. The drilling is performed to the full depth of the FR4 body (7) until underneath plating (6(b)) is reached. A further Cu plating (4(b)) is applied on the platings (6(b)) so that they together form a heat spreader under each cavity (3). A layer (8) of resin incorporating thermally conductive particles is bonded to the underside surfaces, both of the FR4 (7) and of the platings (4(b)). A heat sink (9) is bonded to the layer (8). Good optical efficiency and thermal dissipation is achieved, despite the fact that conventional PCT processing techniques are used.
Owner:STOCKERYALE IRL
Laser optical system
InactiveUS20080151951A1Simple designSmall sizeLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designLuminous flux
A compact optical system is provided for delivering laser radiation with high optical efficiency and uniformity. The optical system includes, in order of the propagation of light, a refractive beam expander to adjust beam size and energy density, a beam flattening module to increase throughput and beam uniformity, an anamorphic corrector to equalize ray distribution in both axes, an attenuator assembly to adjust beam intensity, galvanometer mirrors to scan the beam across a substrate surface, and a focusing lens containing a plurality of refractive elements to deliver the beam at the substrate plane. The laser optical system shapes the laser source beam to increase its effective width for greater productivity in manufacturing, and reduces peak intensity to minimize substrate damage. The laser optical system design is optimized for maximum transmission and optical efficiency for low cost operation with a small laser.
Owner:UVTECH SYST
Micromirror having reduced space between hinge and mirror plate of the micromirror
InactiveUS20050088719A1Small dimensionImprove optical efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpatial light modulatorEngineering
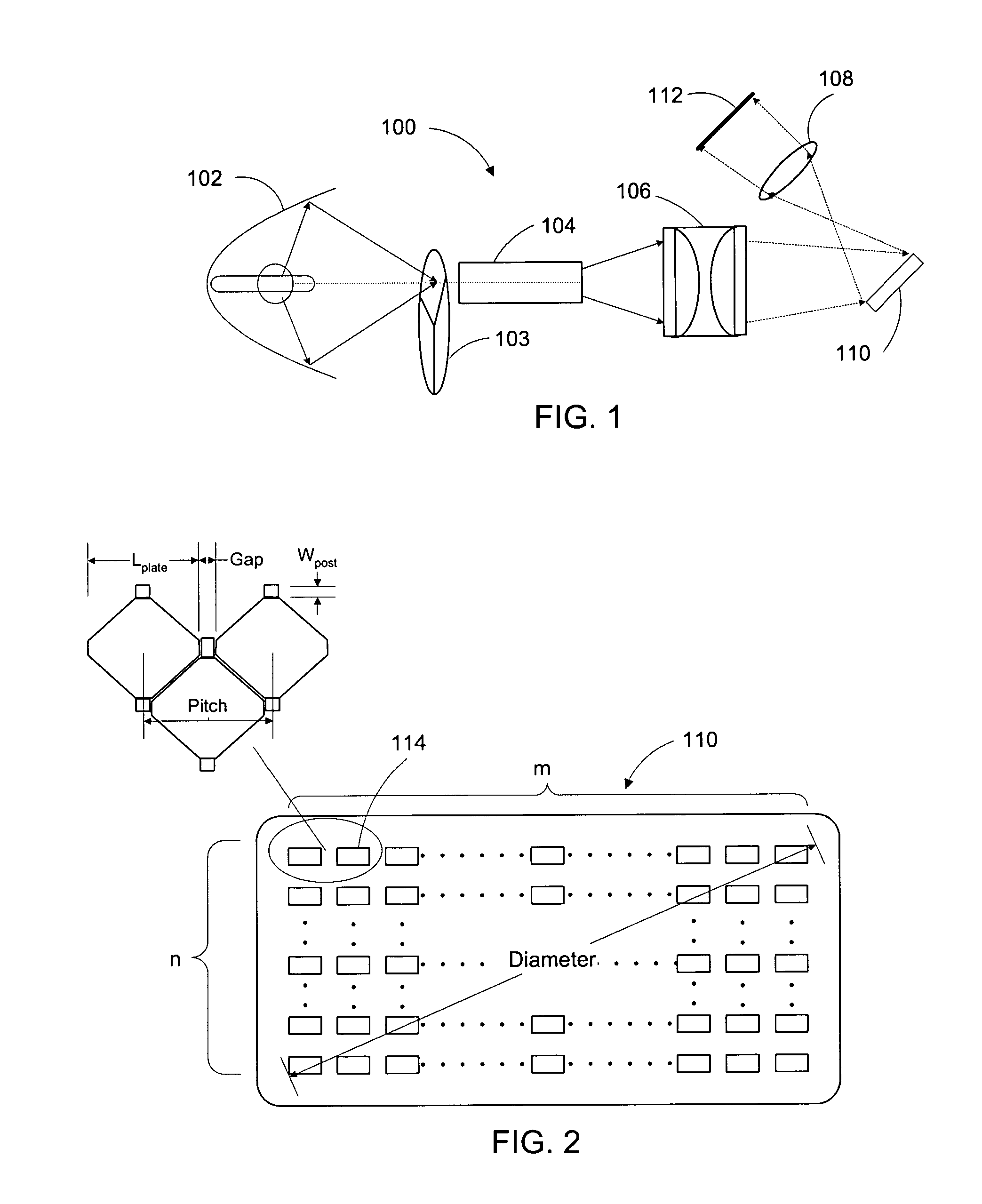
A spatial light modulator is disclosed, along with a method for making such a modulator that comprises an array of micromirror devices. The center-to-center distance and the gap between adjacent micromirror devices are determined corresponding to the light source being used so as to optimize optical efficiency and performance quality. The micromirror device comprises a hinge support formed on a substrate and a hinge that is held by the hinge support. A mirror plate is connected to the hinge via a contact, and the distance between the mirror plate and the hinge is determined according to desired maximum rotation angle of the mirror plate, the optimum gap and pitch between the adjacent micromirrors. In a method of fabricating such spatial light modulator, one sacrificial layer is deposited on a substrate followed by forming the mirror plates, and another sacrificial layer is deposited on the mirror plates followed by forming the hinge supports. The two sacrificial layers are removed via the small gap between adjacent mirror devices with spontaneous vapor phase chemical etchant. Also disclosed is a projection system that comprises such a spatial light modulator, as well as a light source, condensing optics, wherein light from the light source is focused onto the array of micromirrors, projection optics for projecting light selectively reflected from the array of micromirrors onto a target, and a controller for selectively actuating the micromirrors in the array.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com