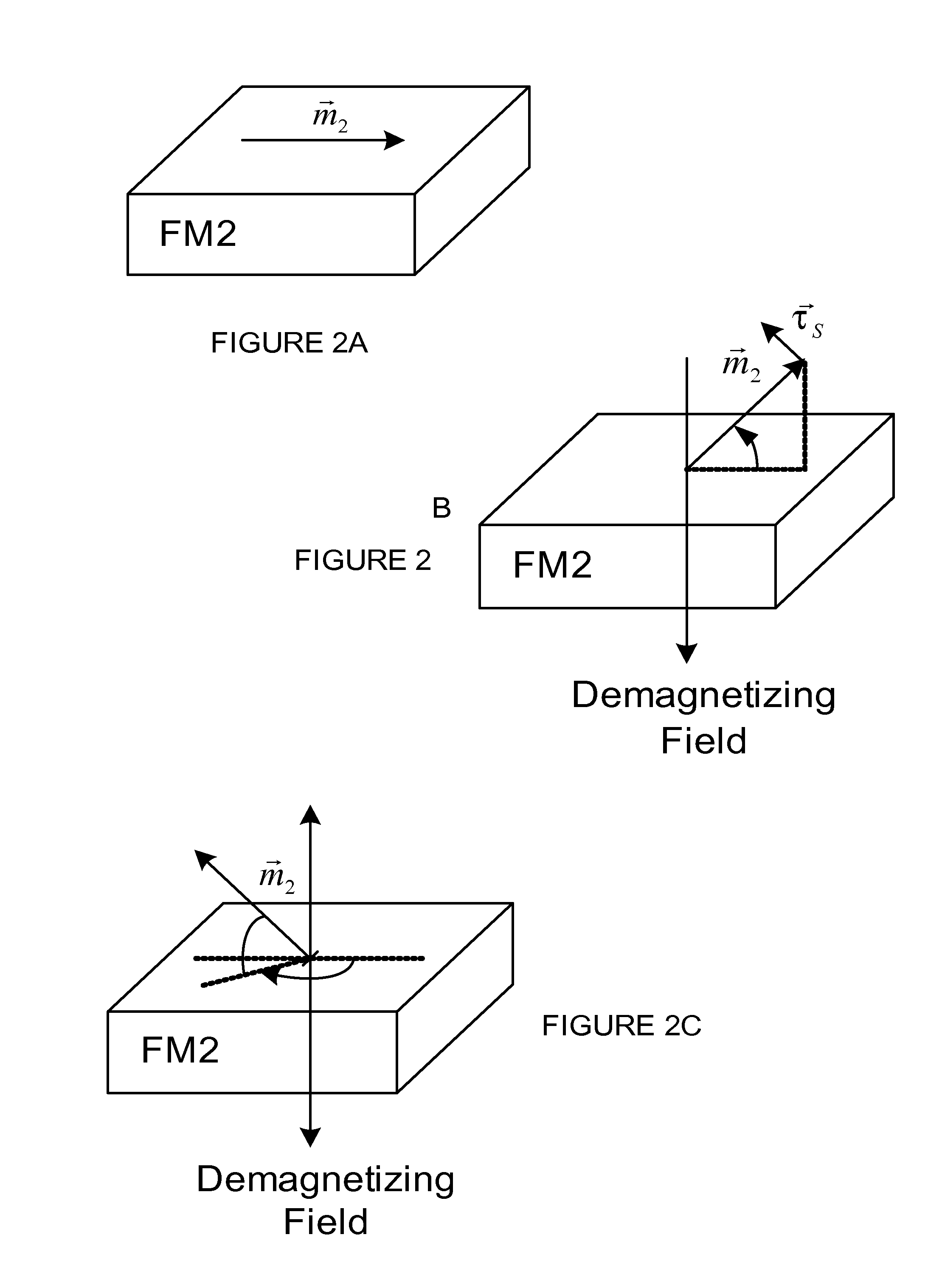
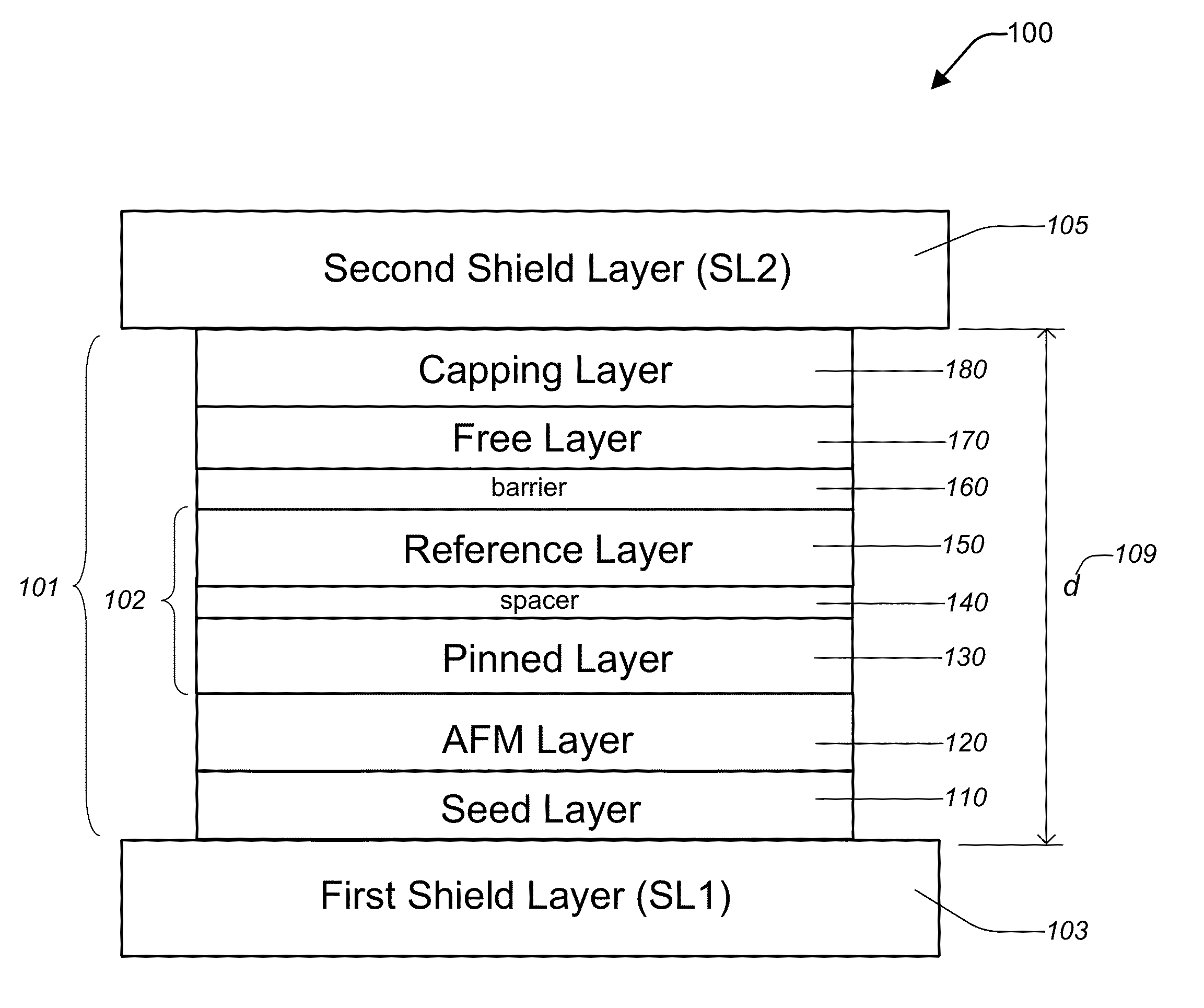
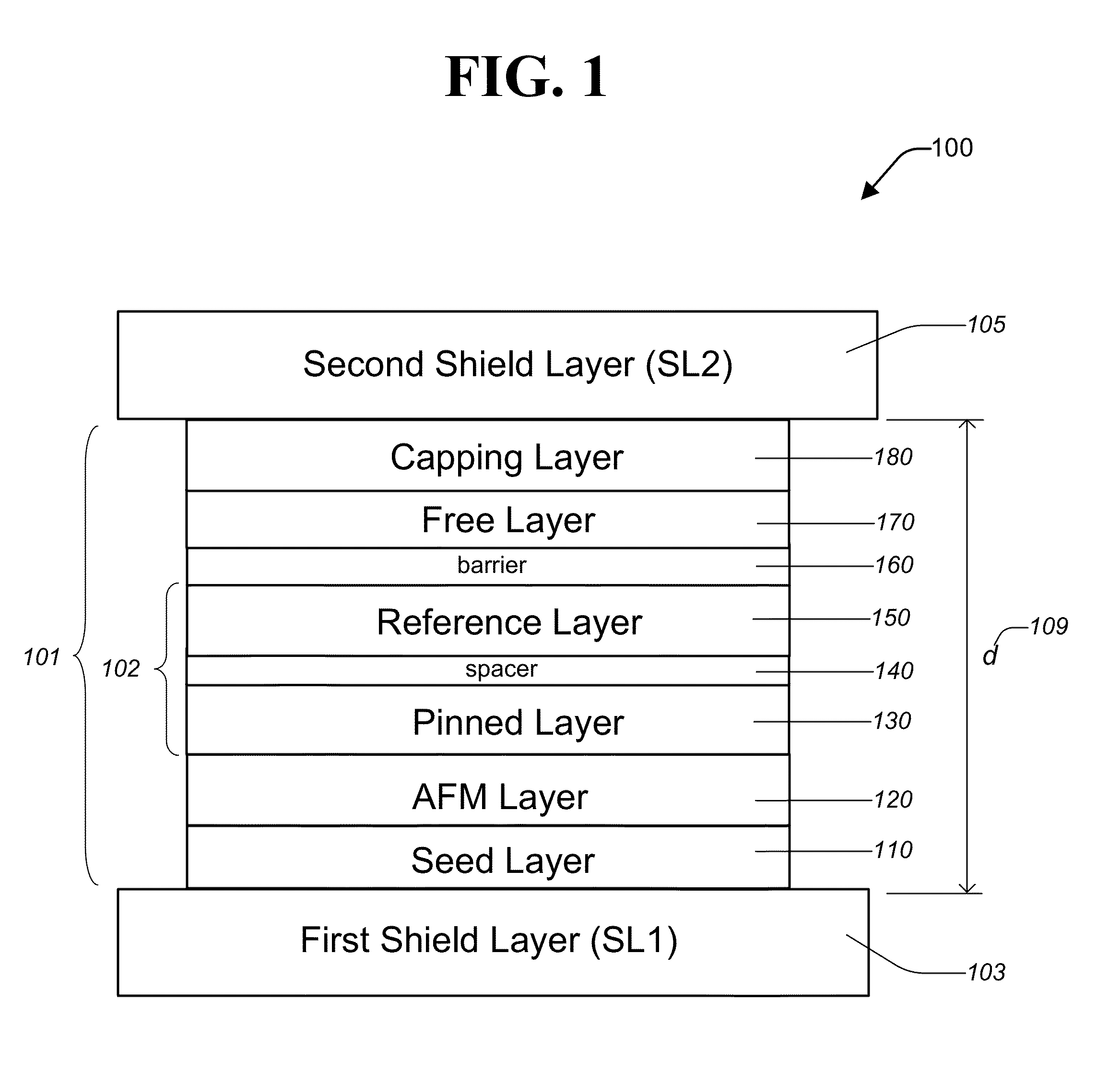
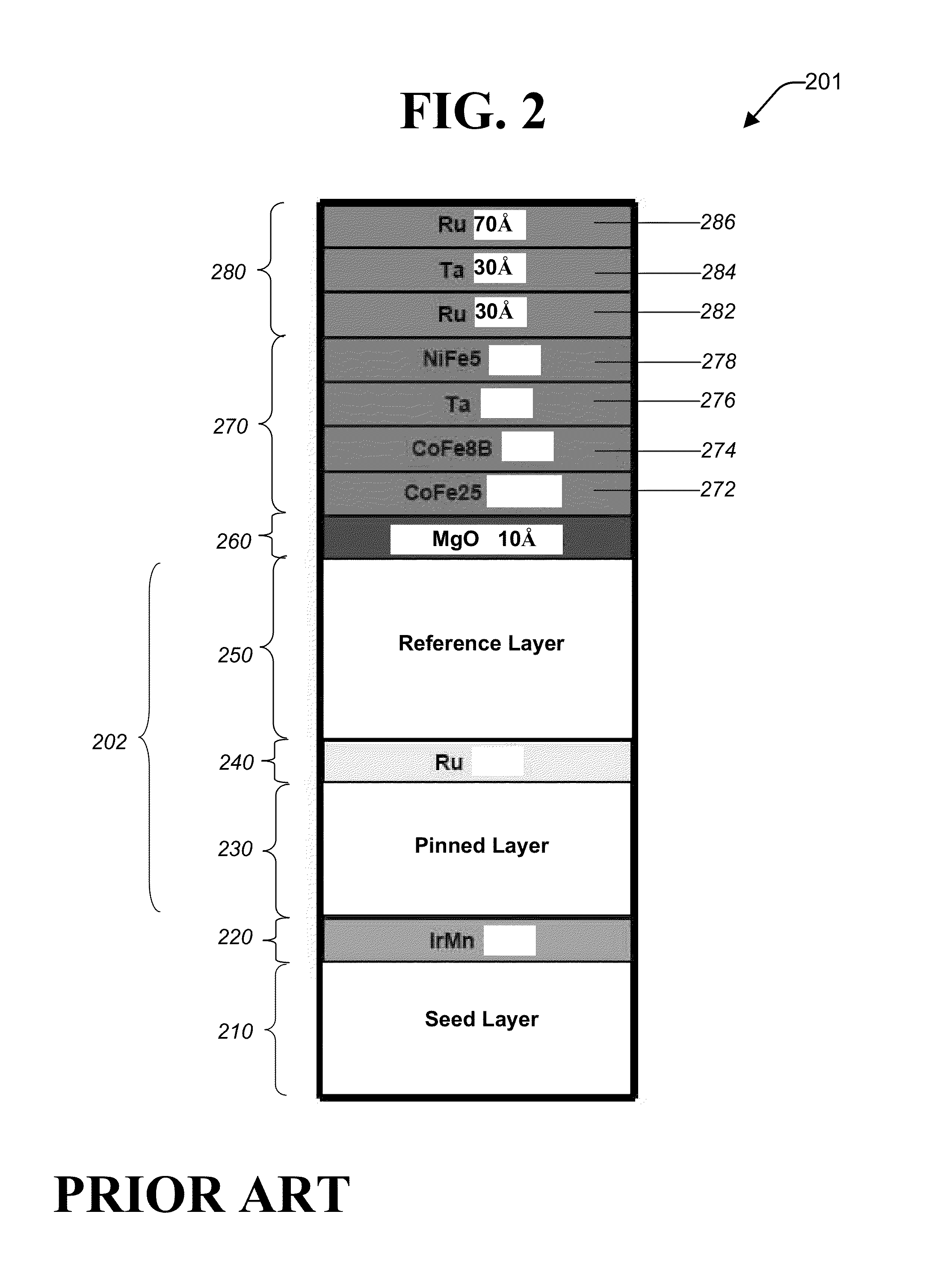
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5851 results about "Magnetic layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermally-assisted magnetic random access memory (MRAM)
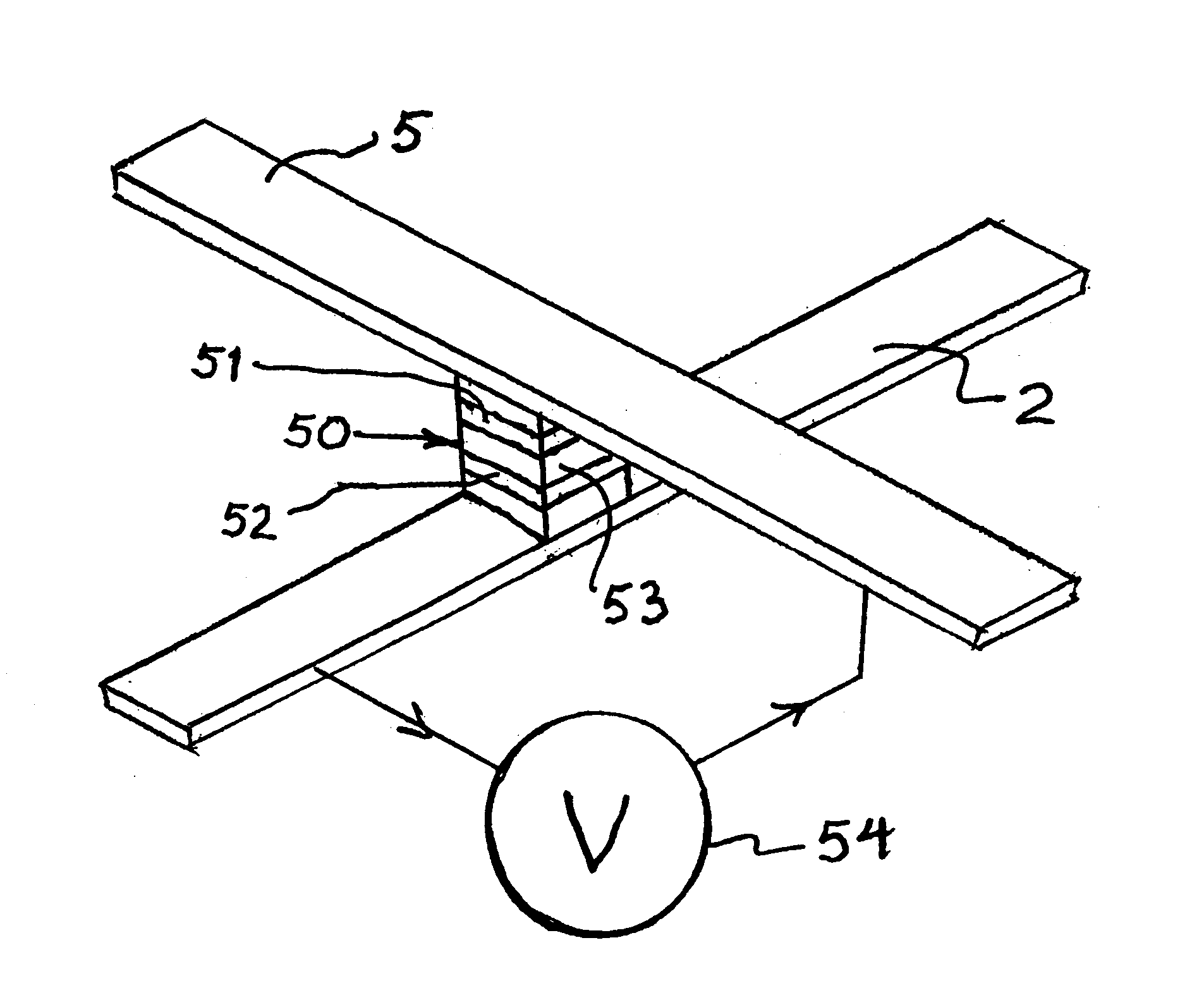
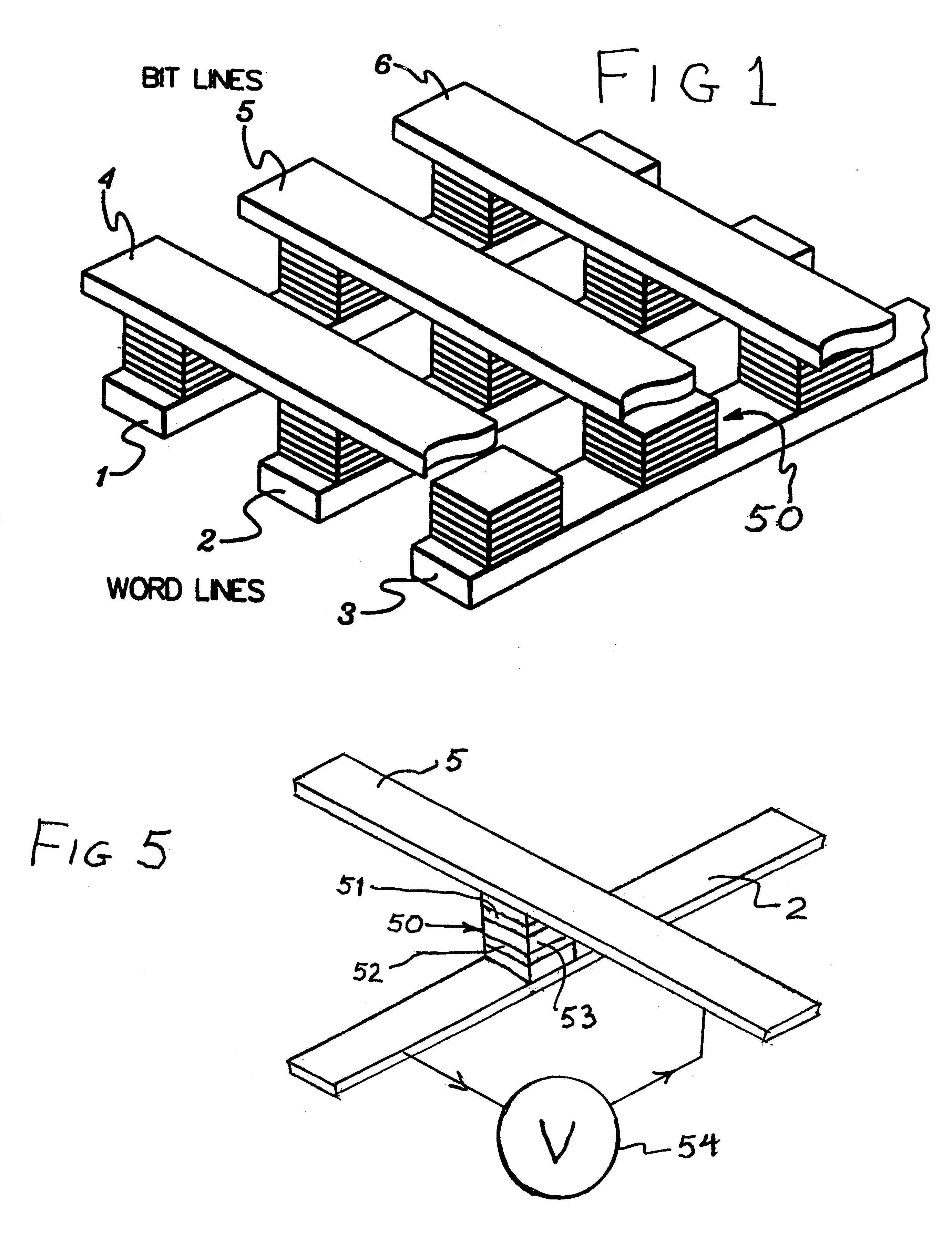
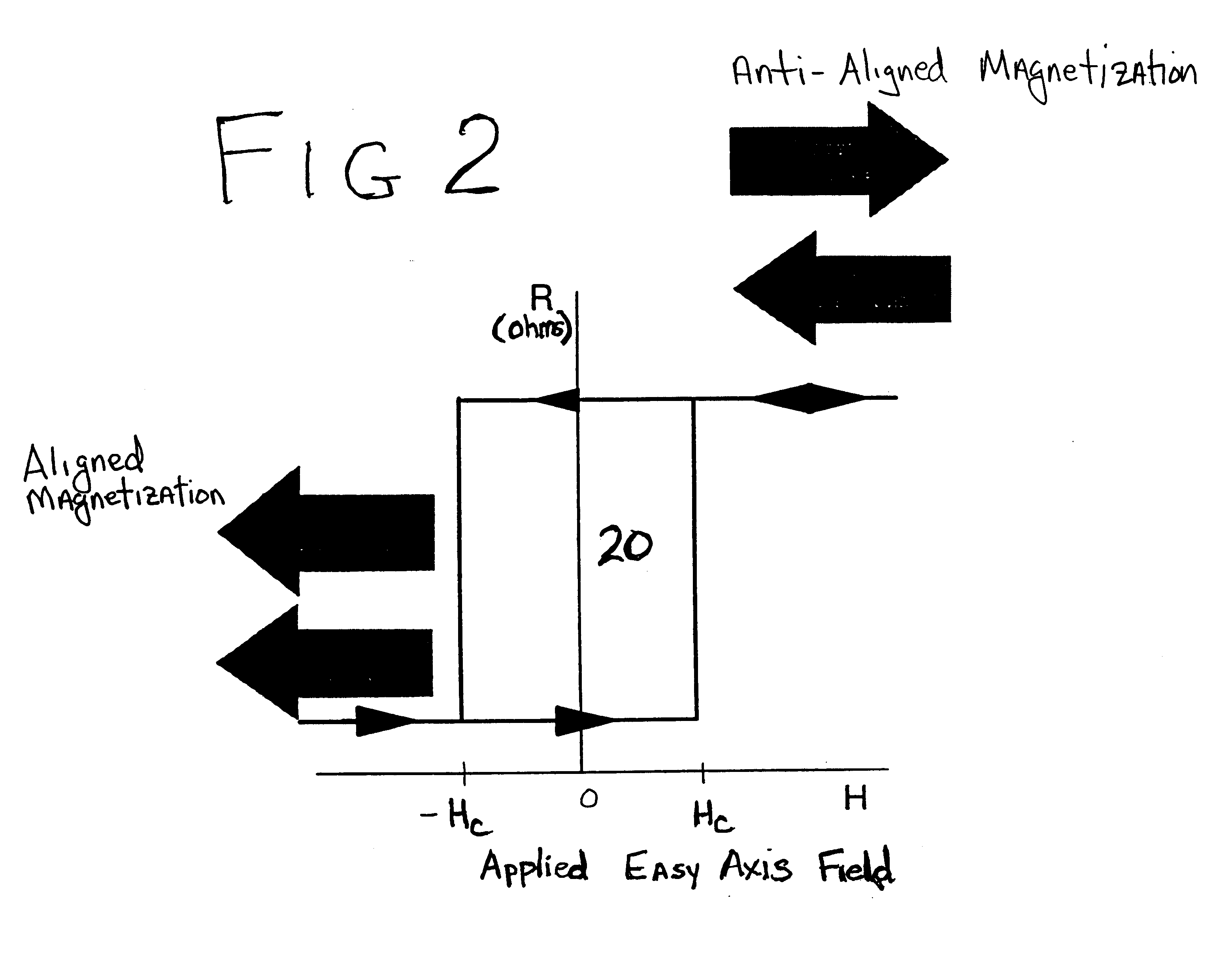
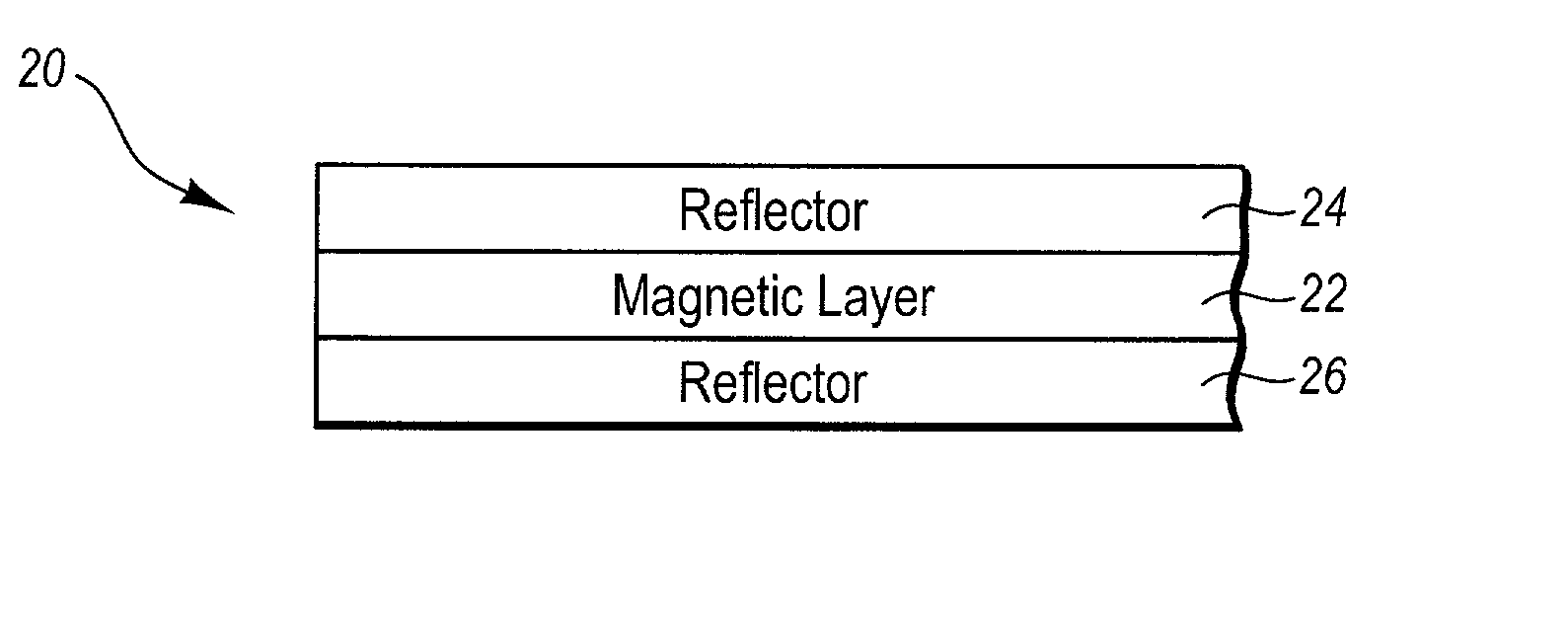
It is important to ensure good selectivity of a single magnetic tunnel junction storage cell within a memory array without affecting nearby storage cells. For this purpose, this memory array of storage cells preferably comprises a) an array of electrically conducting bit lines and electrically conducting word lines which form intersections therebetween, b) a storage cell disposed at each of said intersections, each storage cell comprising at least one reversible magnetic region or layer characterized by a magnetization state which can be reversed by applying thereto a selected external magnetic field, said reversible magnetic layer comprising a material whose magnetization state is more easily reversed upon a change in the temperature thereof, and c) a temperature change generator for changing the temperature of said reversible magnetic layer of only a selected one of said array of storage cells at any moment. To select a cell, it is preferable to select a cell by using a brief pulse of tunnelling current between the intersecting bit and word lines at that cell in order to provide sufficient Joule heating to facilitate a change in the magnetization state of its reversible magnetic layer, which preferably comprises a ferrimagnetic material.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-layered magnetic pigments and foils
InactiveUS20020160194A1High chromaIncreased durabilityPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsPattern printingLiquid mediumColor shift
Multilayered magnetic pigment flakes and foils are provided. The pigment flakes can have a symmetrical coating structure on opposing sides of a magnetic core, or can be formed with encapsulating coatings around the magnetic core. The magnetic core can be a magnetic layer between reflector or dielectric layers, a dielectric layer between magnetic layers, or only a magnetic layer. Some embodiments of the pigment flakes and foils exhibit a discrete color shift so as to have distinct colors at differing angles of incident light or viewing. The pigment flakes can be interspersed into liquid media such as paints or inks to produce colorant compositions for subsequent application to objects or papers. The foils can be laminated to various objects or can be formed on a carrier substrate.
Owner:FLEX PRODUCTS INC
Alignable diffractive pigment flakes
Diffractive pigment flakes are selectively aligned to form an image. In one embodiment, flakes having a magnetic layer are shaped to facilitate alignment in a magnetic field. In another embodiment, the flakes include a magnetically discontinuous layer. In a particular embodiment, deposition of nickel on a diffraction grating pattern produces magnetic needles along the grating pattern that allow magnetic alignment of the resulting diffractive pigment flakes. Color scans of test samples of magnetically aligned flakes show high differentiation between illumination parallel and perpendicular to the direction of alignment of the magnetic diffractive pigment flakes.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
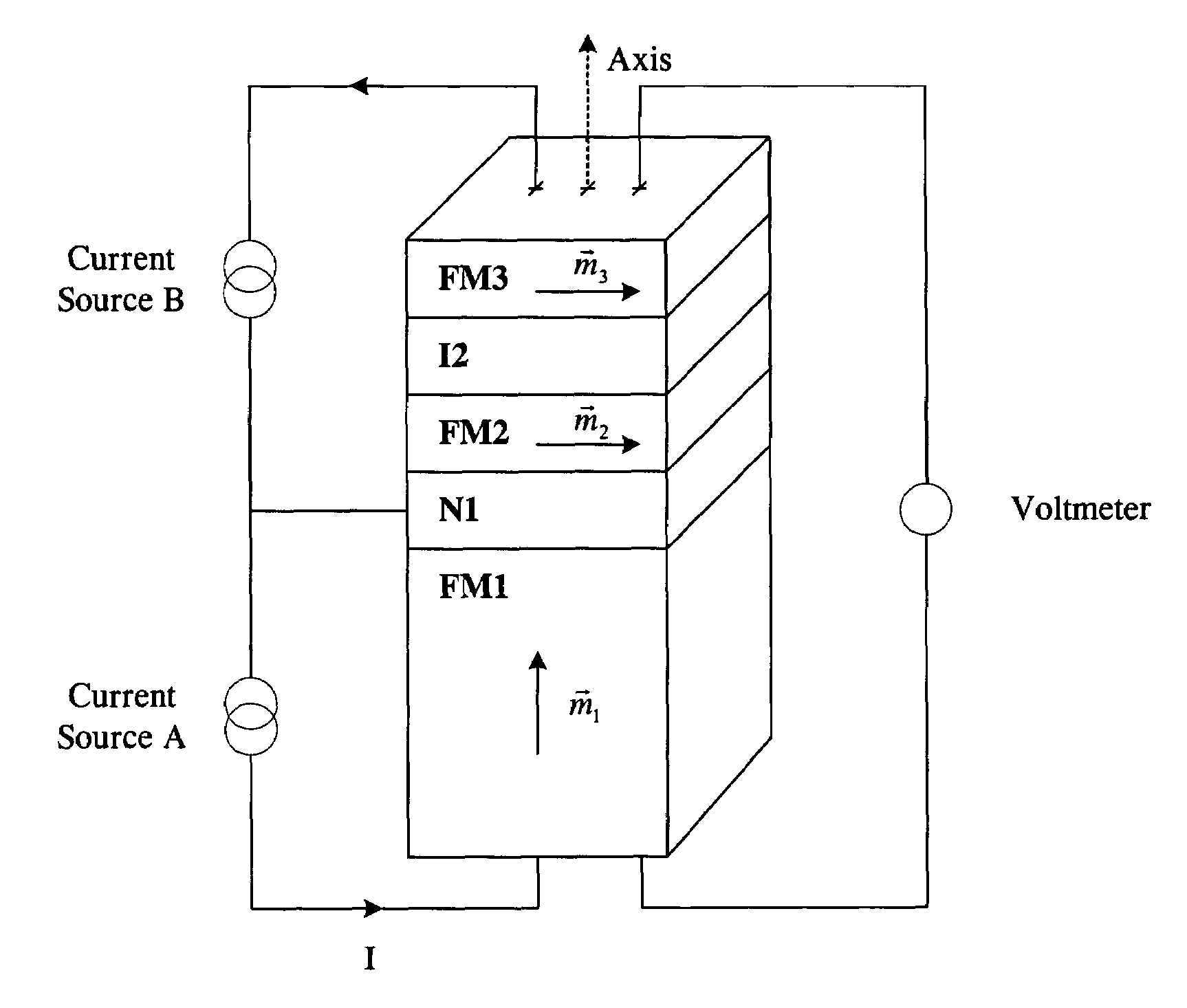
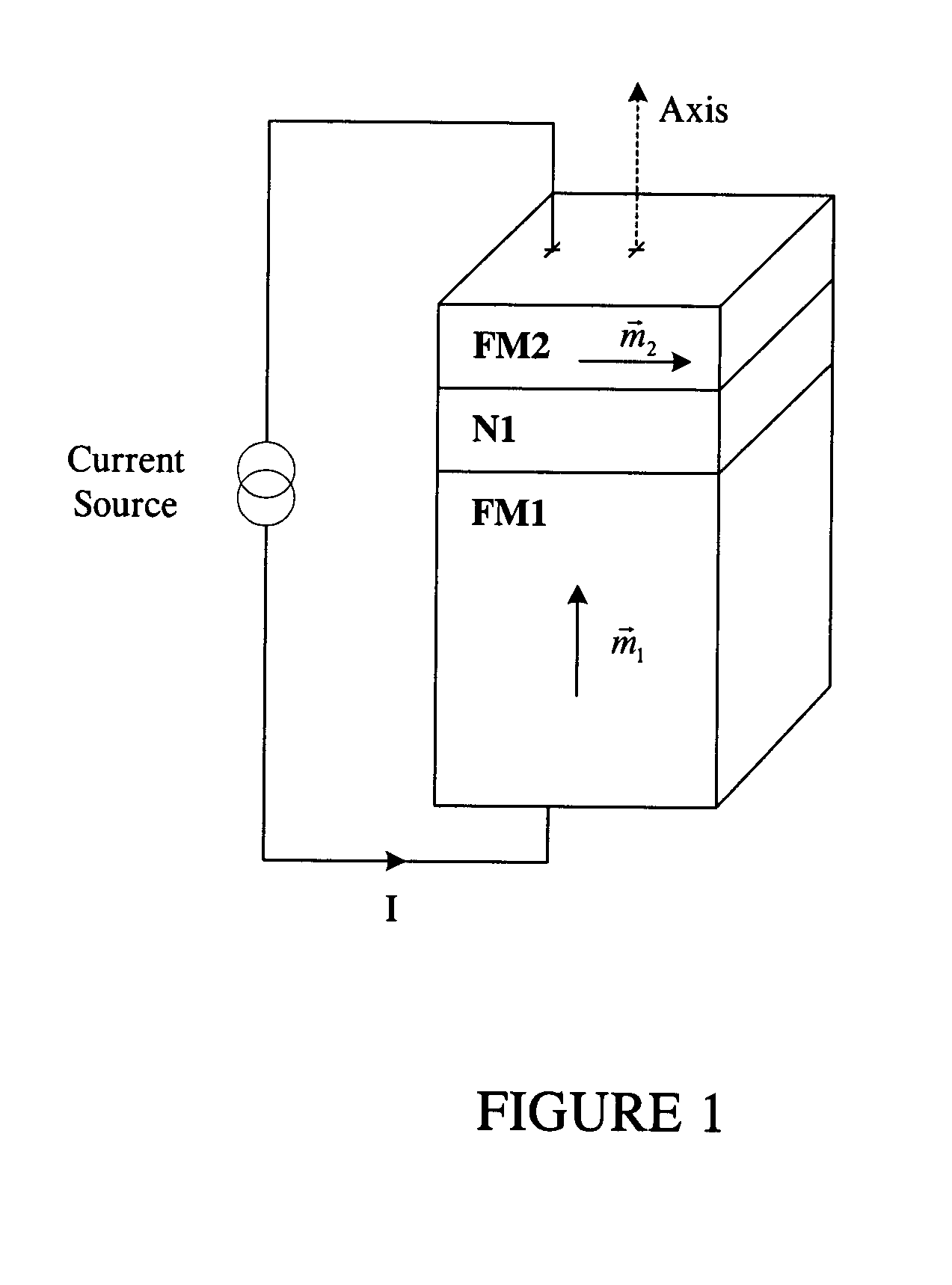
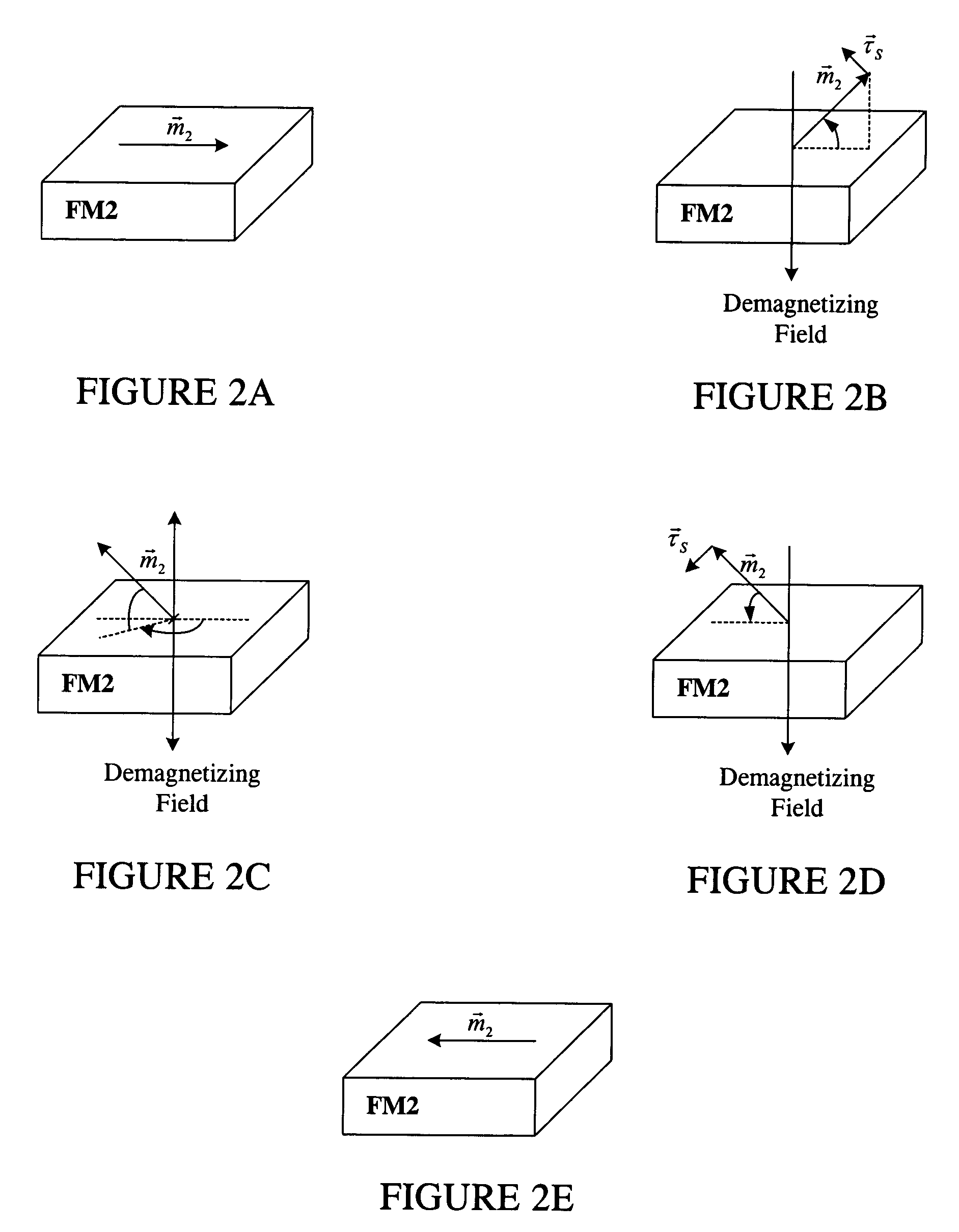
Thermally stable magnetic elements utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6838740B2Improve performanceImprove thermal stabilityTransistorNanomagnetismAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
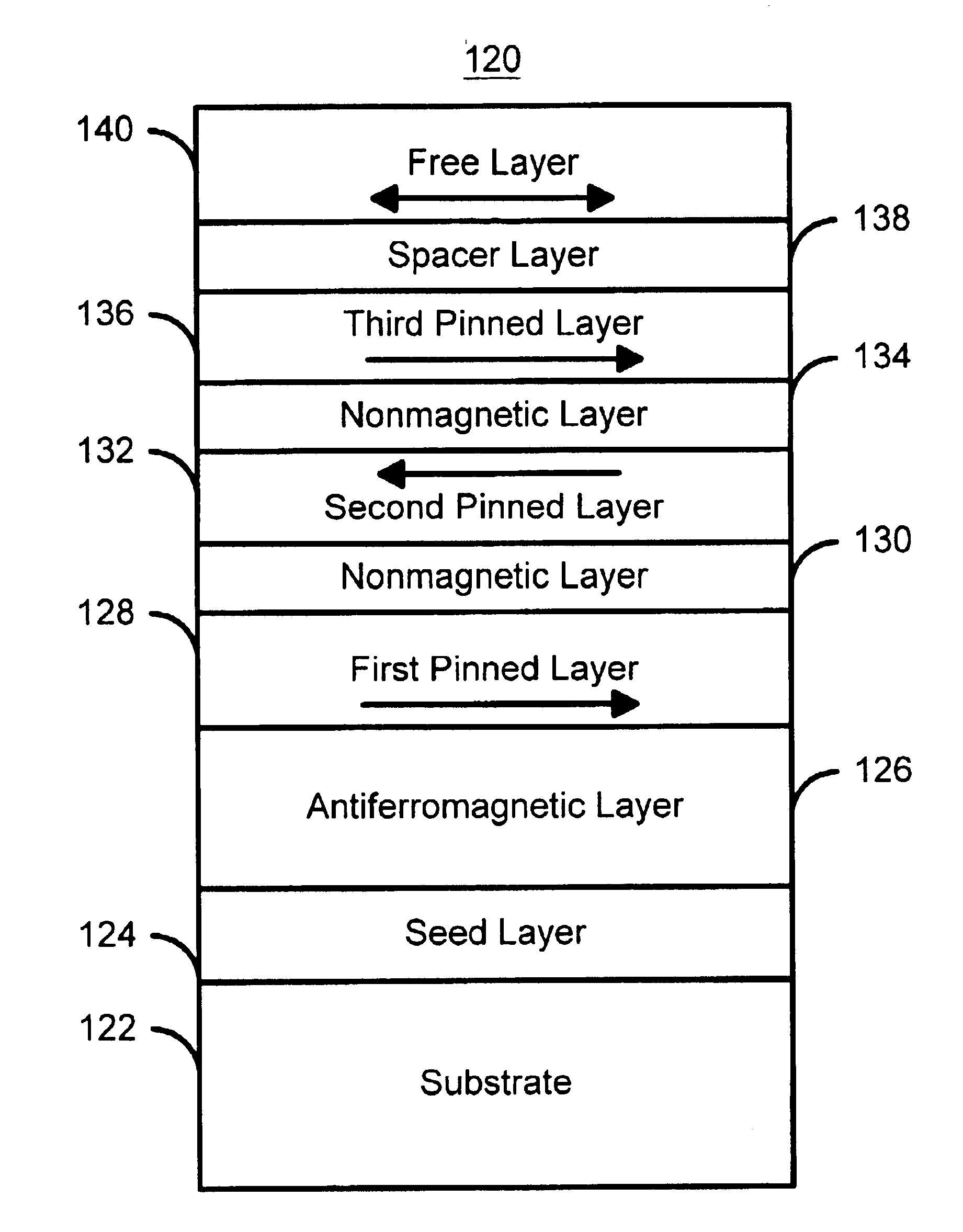
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while being thermally stable and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first, second and third pinned layers, first and second nonmagnetic layers, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layers. The first, second and third pinned layers are ferromagnetic and have first, second and third magnetizations pinned in first, second and third directions. The first and second nonmagnetic layers include first and second diffusion barriers, respectively. The first and second nonmagnetic layers are between the first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers, respectively. The first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers are antiferromagnetically coupled. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and resides between the free layer and the third pinned layer. In addition, performance can be further improved by doping Co containing ferromagnetic layers with Cr and / or Pt.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
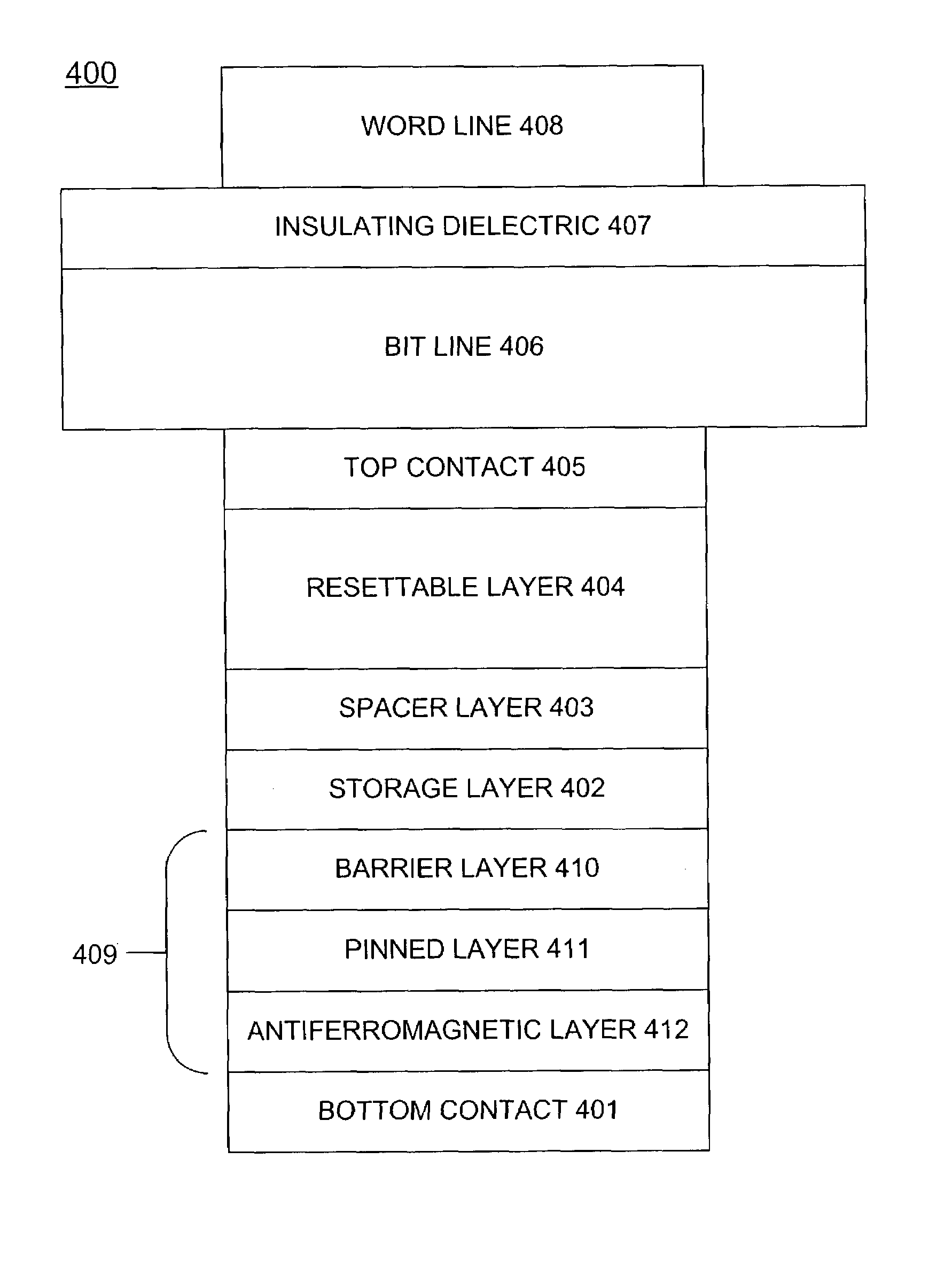
Spin-transfer multilayer stack containing magnetic layers with resettable magnetization
InactiveUS7190611B2Minimizing densityReduce process complexityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesHigh densitySpin transfer
A magnetic element for a high-density memory array includes a resettable layer and a storage layer. The resettable layer has a magnetization that is set in a selected direction by at least one externally generated magnetic field. The storage layer has at least one magnetic easy axis and a magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element. An alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure formed from a tunneling barrier layer, a pinned magnetic layer and an antiferromagnetic layer that pins the magnetization of the pinned layer in a predetermined direction. Another alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure that is formed from a tunneling barrier layer and a second resettable layer having a magnetic moment that is different from the magnetic moment of the resettable layer of the basic embodiment.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
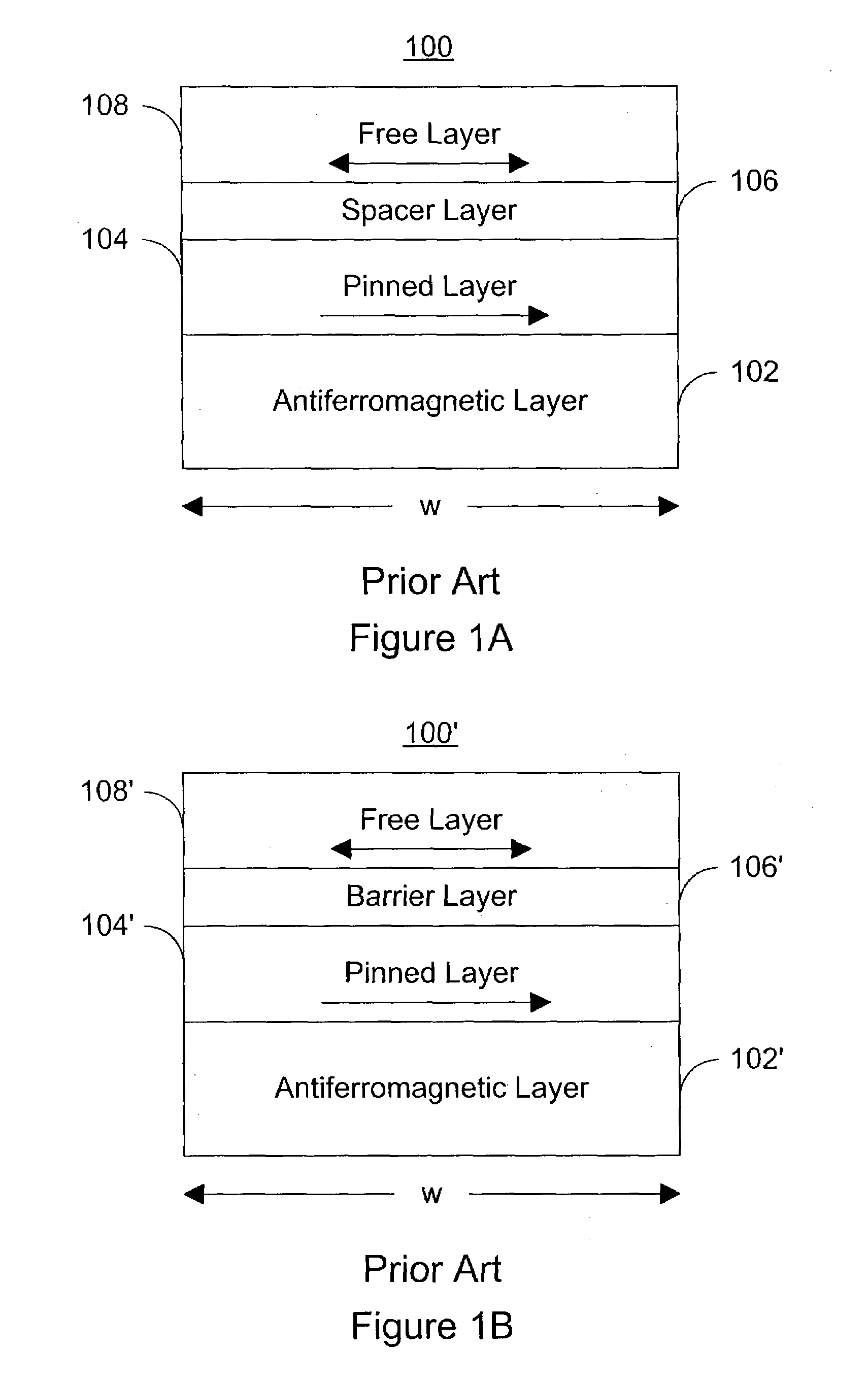
Magnetic tunneling junction configuration and a method for making the same
InactiveUS6897532B1Reduce the temperatureAvoid depositionTransistorNanomagnetismEngineeringGobio gobio obtusirostris
A method for forming a magnetic tunneling junction (MJT) is provided. In some embodiments, the method may include patterning one or more magnetic layers to form an upper portion of a MTJ. The method may further include patterning one or more additional layers to form a lower portion of the MTJ. In some cases, the lower portion may include a tunneling layer of the MTJ having a width greater than the upper portion. In addition, in some embodiments the method may further include patterning an electrode below the lower portion. In some cases, the electrode may include a lowermost layer with a thickness equal to or less than approximately 100 angstroms. In addition or alternatively, the electrode may have a width greater than the width of the tunneling layer. In yet other embodiments, the method may include forming spacers along the sidewalls of the upper and / or lower portions.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
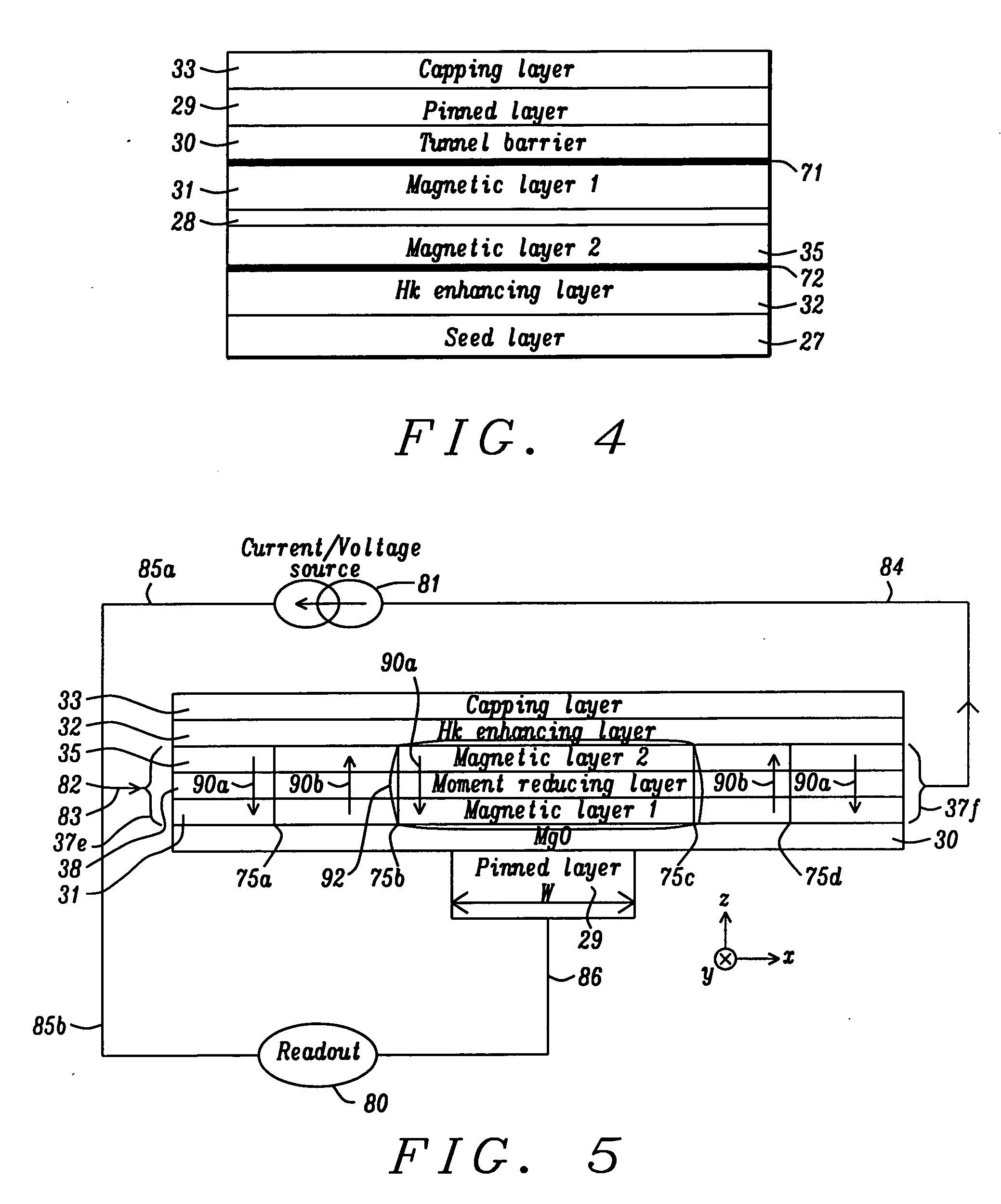
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120280336A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh MR ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
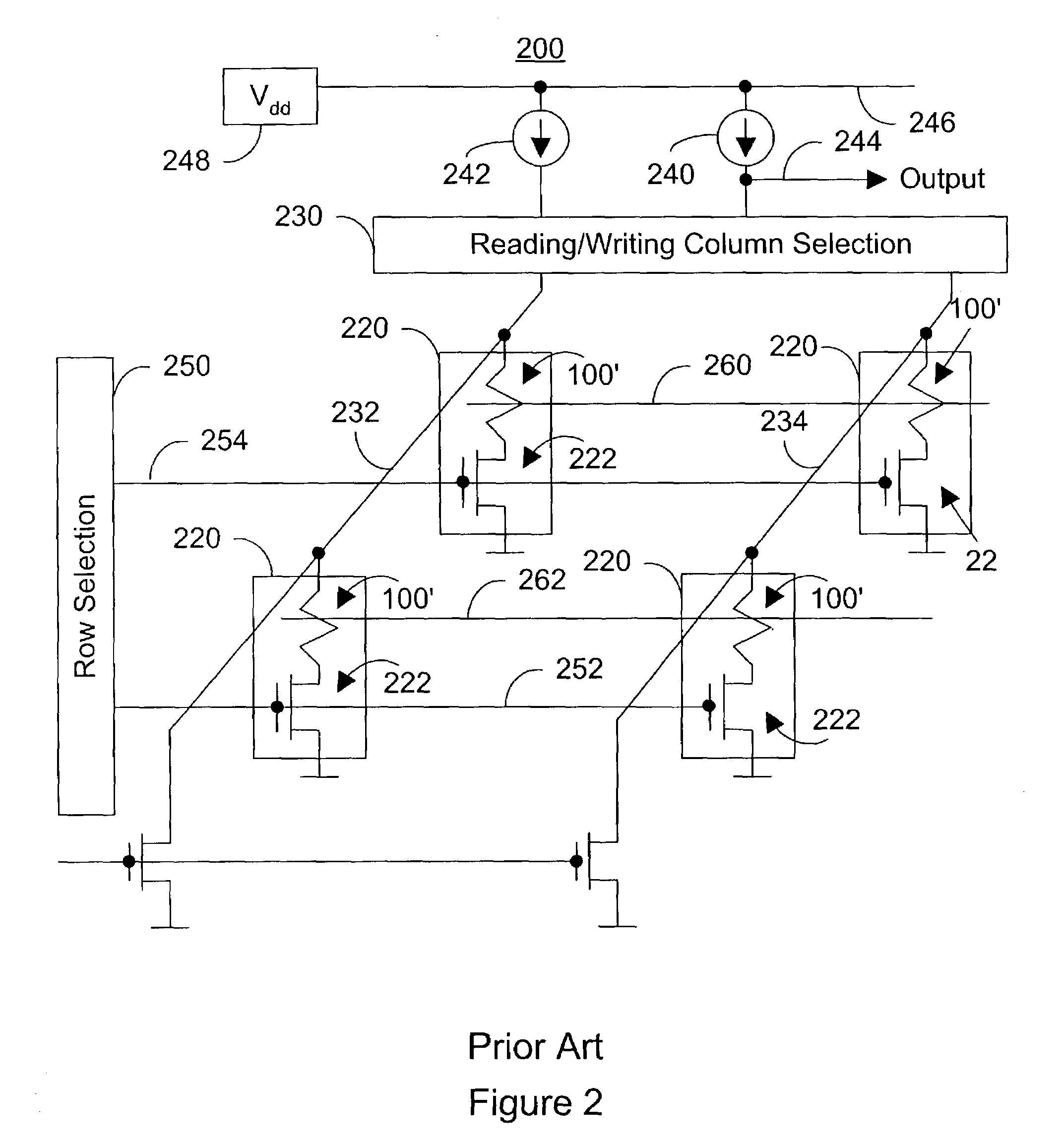
Magnetic tunnel junction memory device
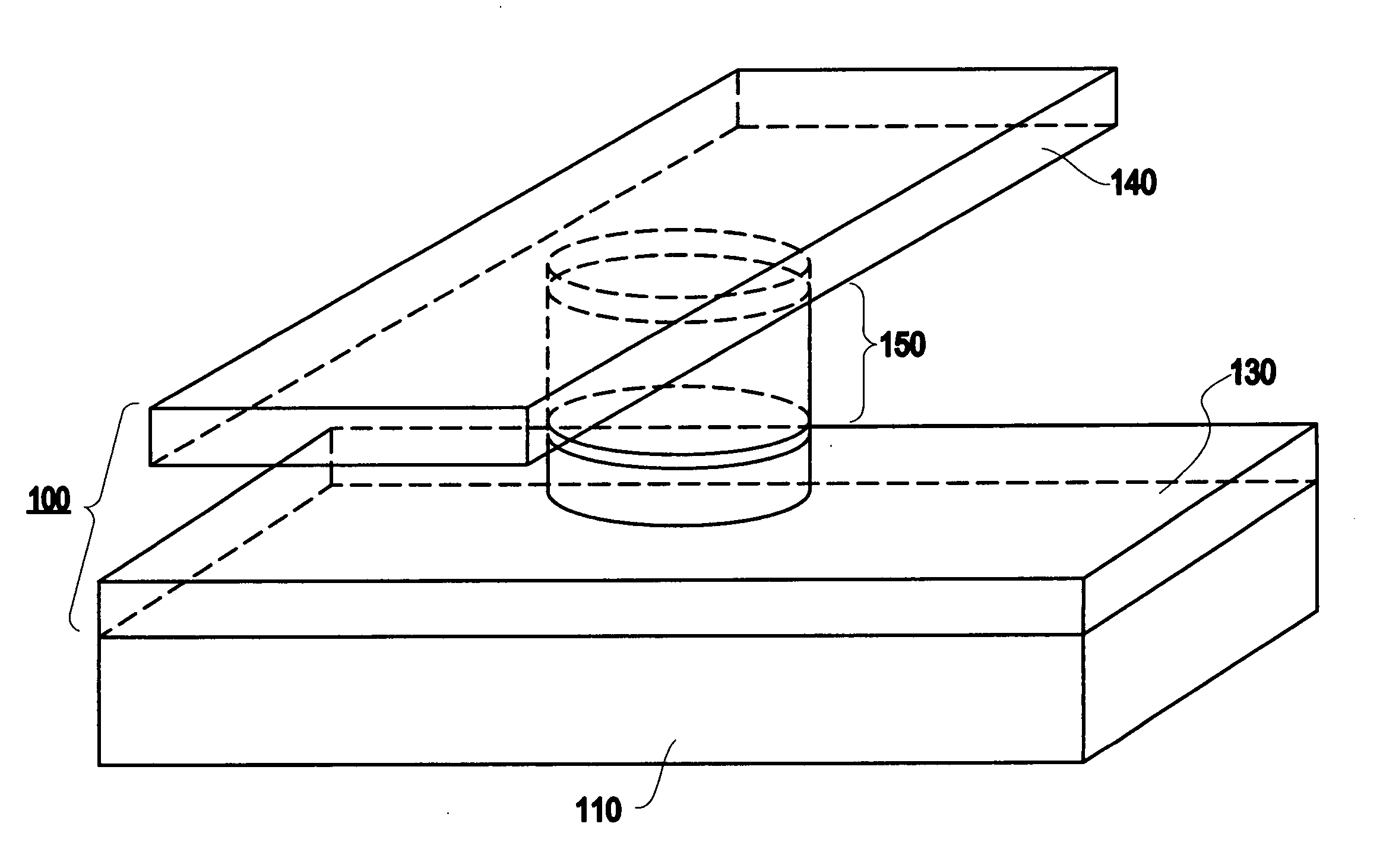
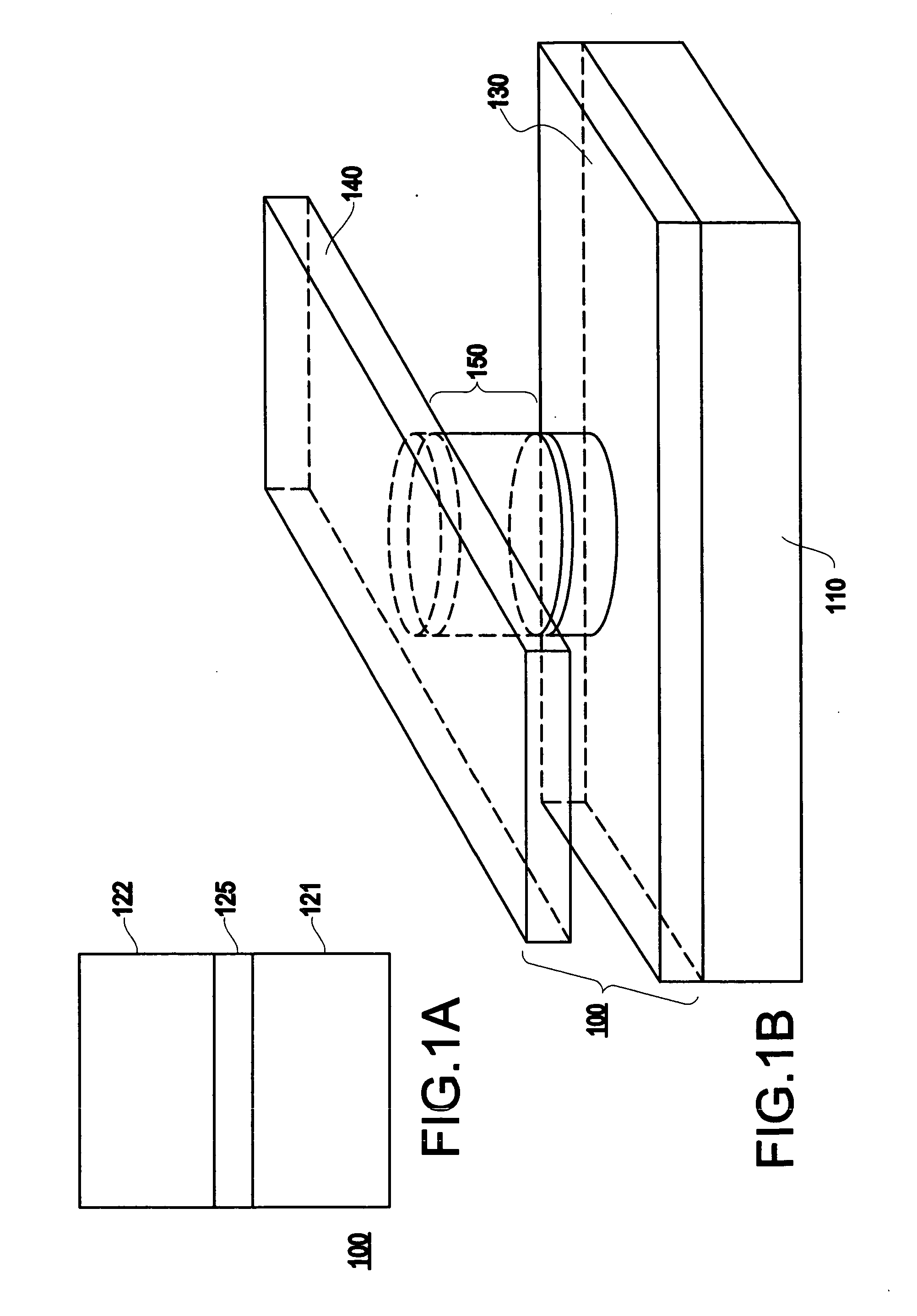
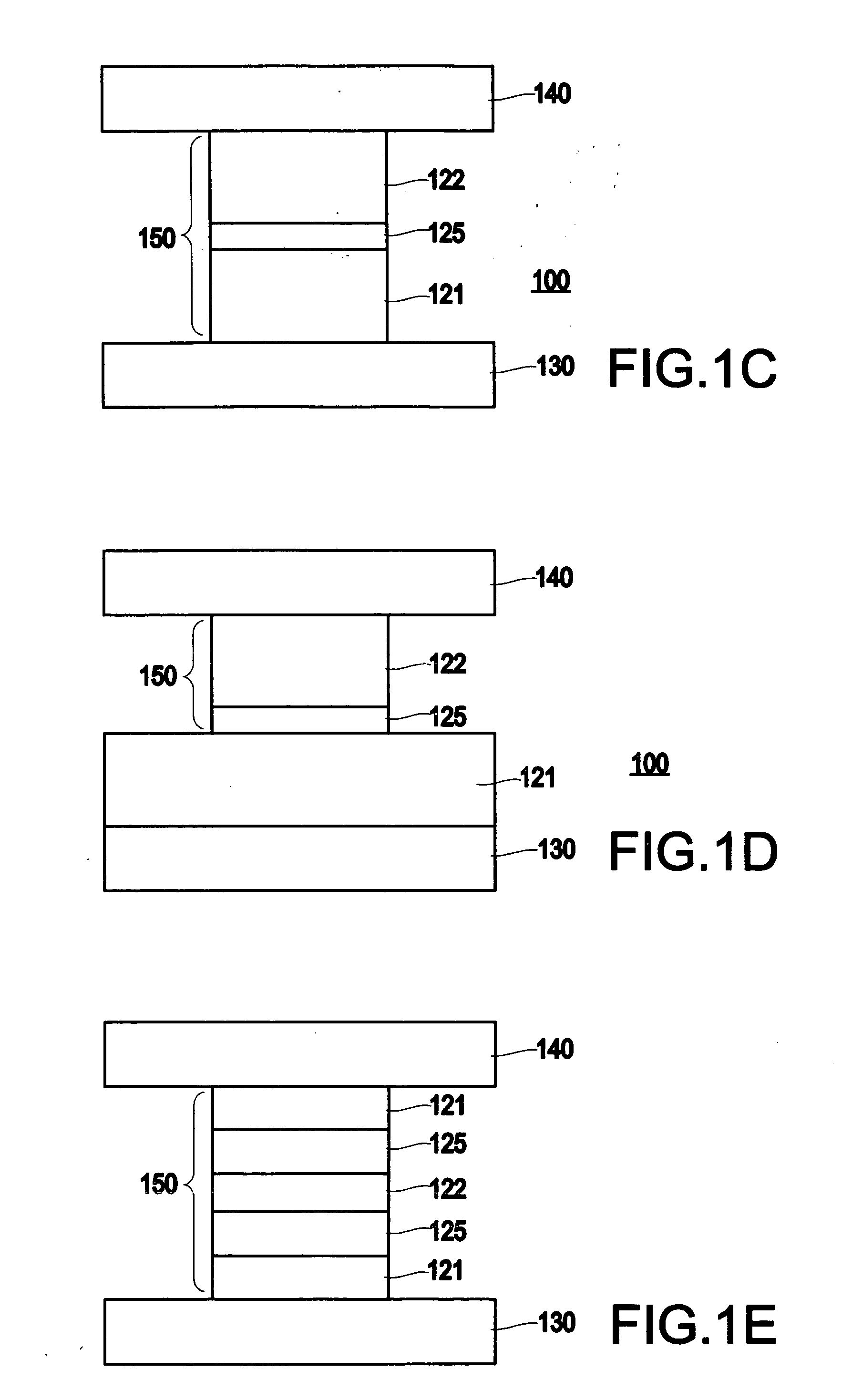
InactiveUS6845038B1Improve permeabilityLow resistivityDigital storageBit linePerpendicular magnetization
A memory cell for magnetic random access memory devices based on a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) memory element with a perpendicular orientation of magnetization in pinned and free magnetic layers, and a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between the pinned and free layers. The memory cell can include the MTJ memory element, a magnetic flux guide in series with selection devices, such as a bit line, a word line, and a transistor. The magnetic flux guide can have two electrically conductive magnetic portions with the MTJ memory element positioned between the magnetic portions. The MTJ memory element is magnetically isolated from the magnetic flux guide by thin non-magnetic conductive spacers. The MTJ memory element is arranged in a vertical space between the intersecting bit and word lines at their intersection region. The memory cell also includes write and excitation lines. The write line is parallel to the bit line and the excitation line is parallel to the word line. The write and excitation lines also intersect each other and define a corner. The MTJ memory element is positioned in the corner of the intercepting write and excitation lines.
Owner:SHUKH ALLA MIKHAILOVNA
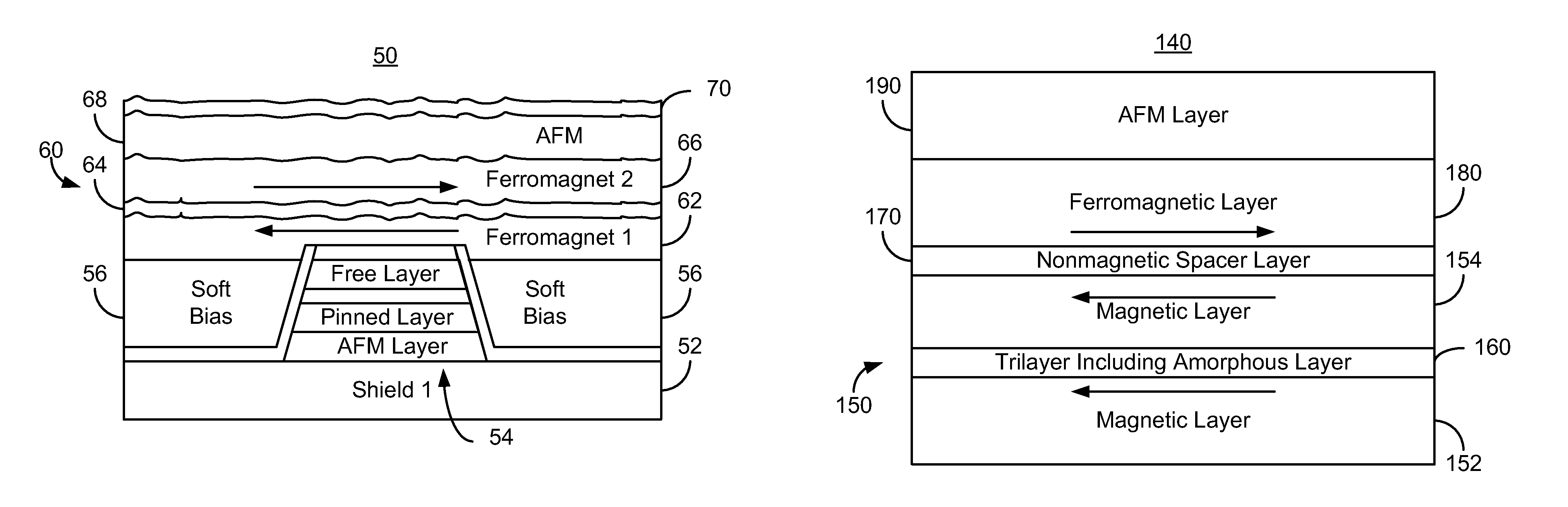
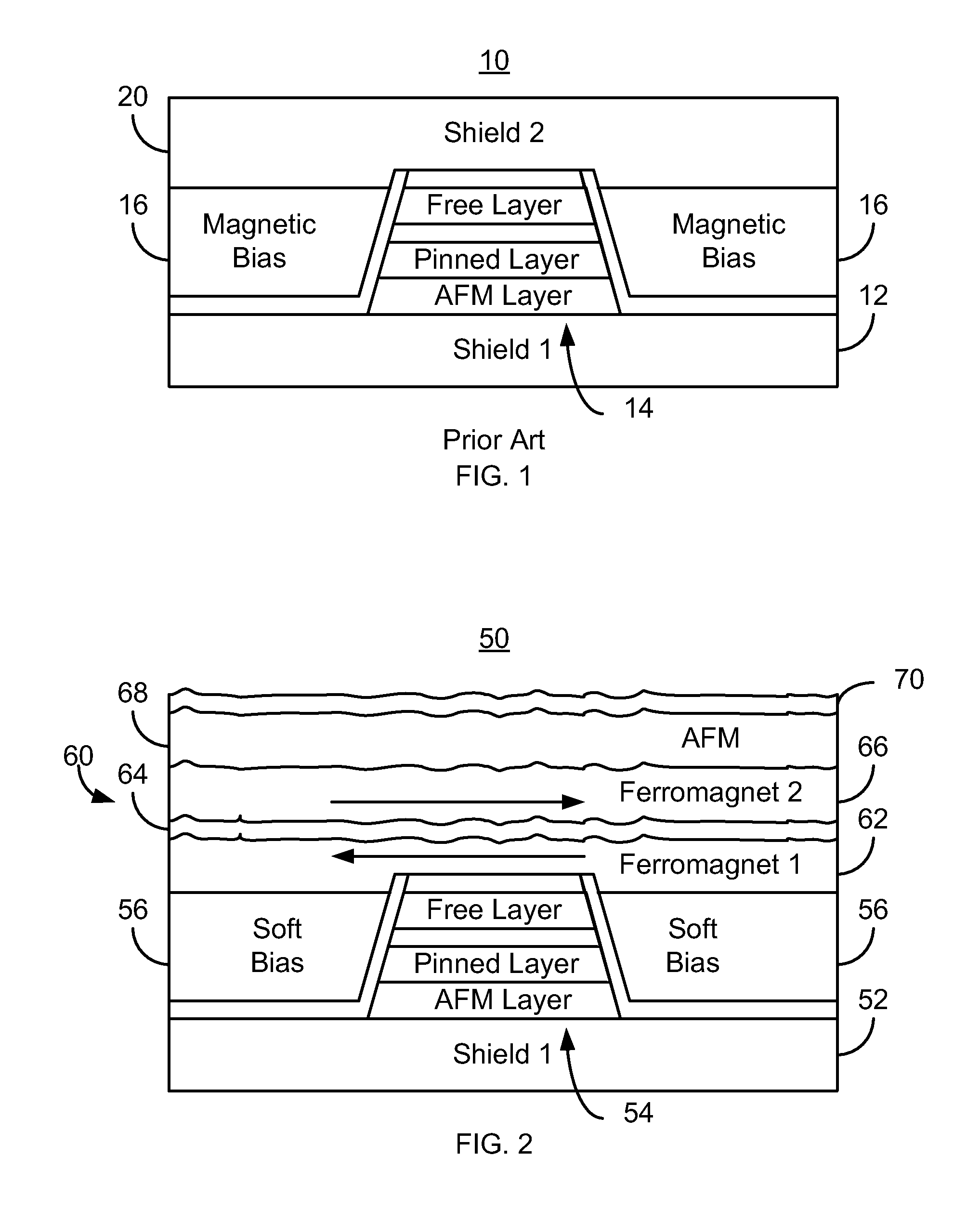
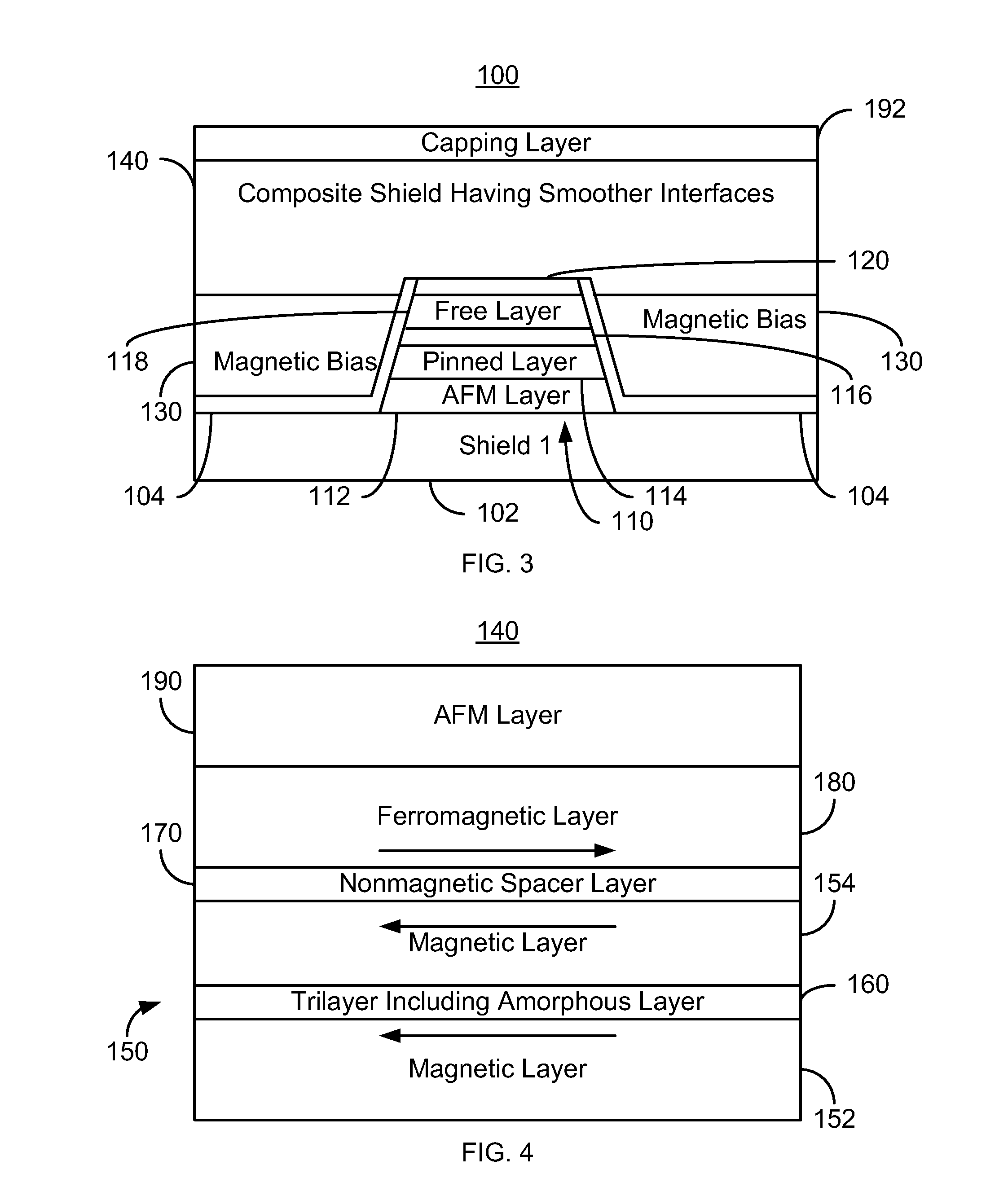
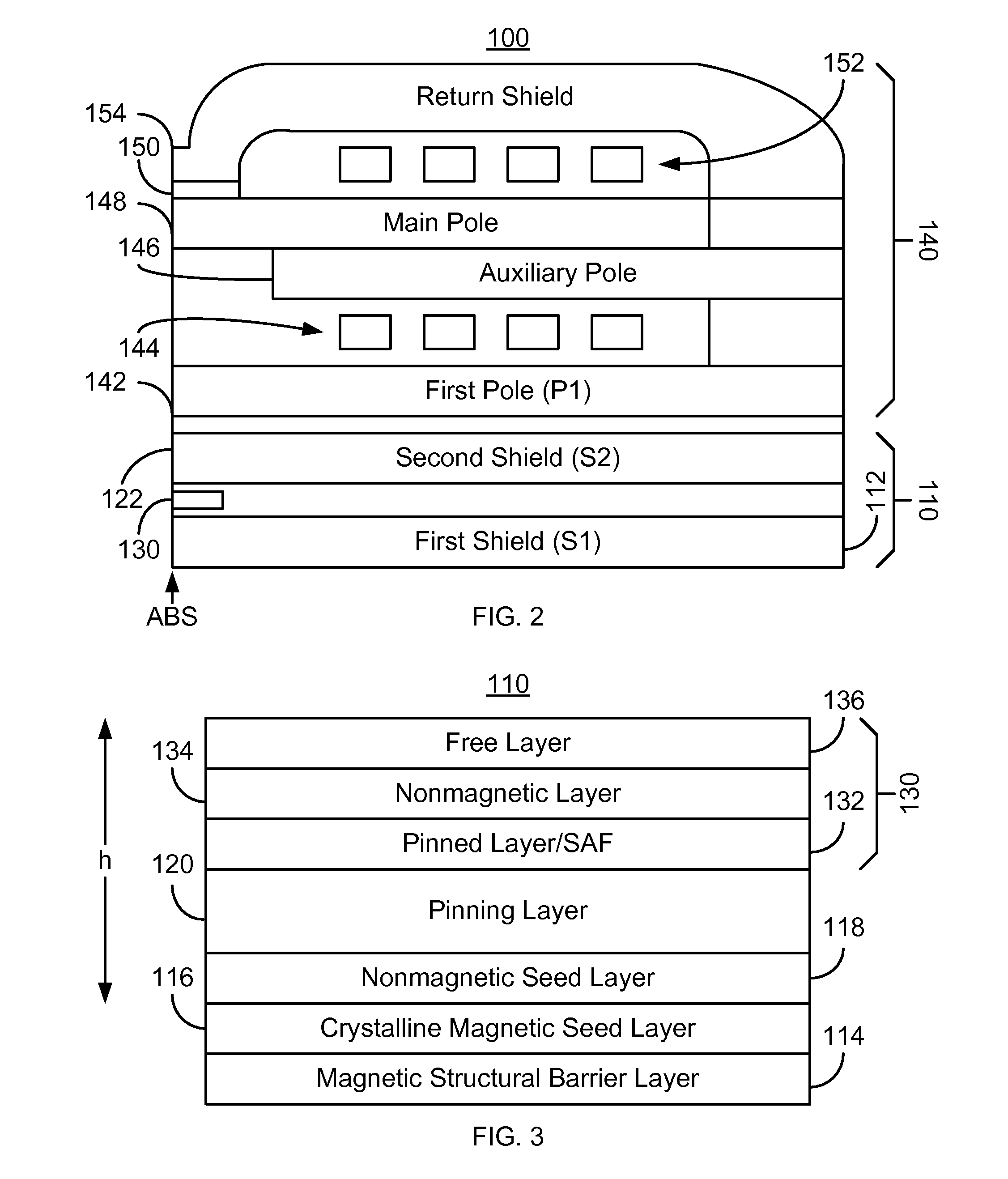
Method and system for providing a read transducer having a composite magnetic shield with smooth interfaces
A method and system provide a magnetic transducer including first and second shields, a read sensor, and magnetic bias structure(s) adjacent to the read sensor. The read sensor and magnetic bias structure(s) are between the shields. The second shield includes first and second ferromagnetic layers, a nonmagnetic spacer layer and a pinning layer. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the first and second ferromagnetic layers. The first ferromagnetic layer is between the read sensor and the nonmagnetic spacer layer. The pinning layer is adjacent to the second ferromagnetic layer. The first and second ferromagnetic layers are coupled antiparallel. The first ferromagnetic layer includes magnetic layers interleaved with trilayer(s). Each magnetic layer includes crystalline grains. The trilayer(s) include an amorphous nonmagnetic layer less than three Angstroms thick. Thus, the magnetic layers are ferromagnetically coupled but the crystalline grains in different magnetic layers are decoupled.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic write head with high moment magnetic thin film formed over seed layer
A magnetic write head includes a seed layer and a magnetic layer on the seed layer. The seed layer includes seed-layer grains having either a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [111] direction or a hexagonal-close-packed (hcp) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [0001] direction. The magnetic layer includes magnetic-layer grains having a body-centered-cubic (bcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [110] direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8535817B2Excellent characteristicsIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMetallurgyNon magnetic
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder and a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder in this order on a nonmagnetic support, whereinthe magnetic layer comprises a nonmagnetic powder of which coefficient of variation CV of a particle size distribution as denoted by the following formula (1):CV(%)=σ / φ×100 (1)is less than 20 percent, andthe magnetic layer has a thickness being equal to or less than 0.1 μm and falling within a range of 1.1≦φ / t≦8.0, wherein σ denotes a standard deviation of a particle diameter, φ denotes an average particle diameter of the nonmagnetic powder comprised in the magnetic layer being expressed in μm, and t denotes a thickness of the magnetic layer being expressed in μm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and system for providing a read sensor having a low magnetostriction free layer
ActiveUS8194365B1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic transducersMagnetic layer
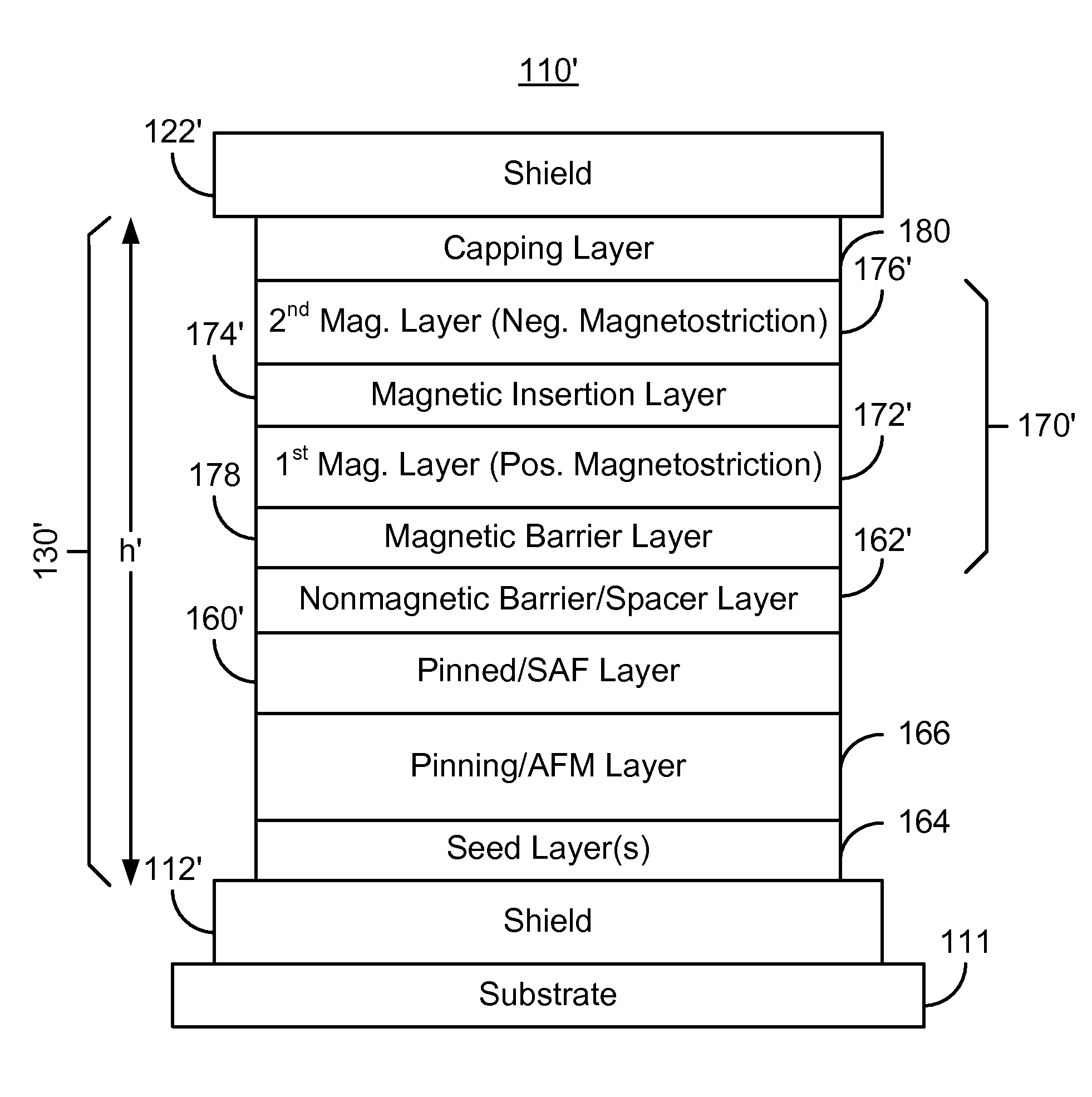
A method and system for providing a magnetic structure in magnetic transducer is described. The magnetic structure includes a pinned layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a free layer. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer includes a first magnetic layer, a second magnetic layer, and a magnetic insertion layer between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The first magnetic layer has a first magnetostriction. The second magnetic layer has a second magnetostriction opposite to the first magnetostriction. The magnetic insertion layer provides a growth texture barrier between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
ActiveUS20080304176A1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic poles
A magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole, and a spin oscillation device including a first magnetic layer having at least one magnetic material layer, a second magnetic layer having at least one magnetic material layer, and a first nonmagnetic layer provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are antiferromagnetically coupled and / or magnetostatically coupled to each other. The first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are laminated in a direction generally parallel to a medium facing surface and generally parallel to a side surface of the recording magnetic pole intersecting with the medium facing surface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
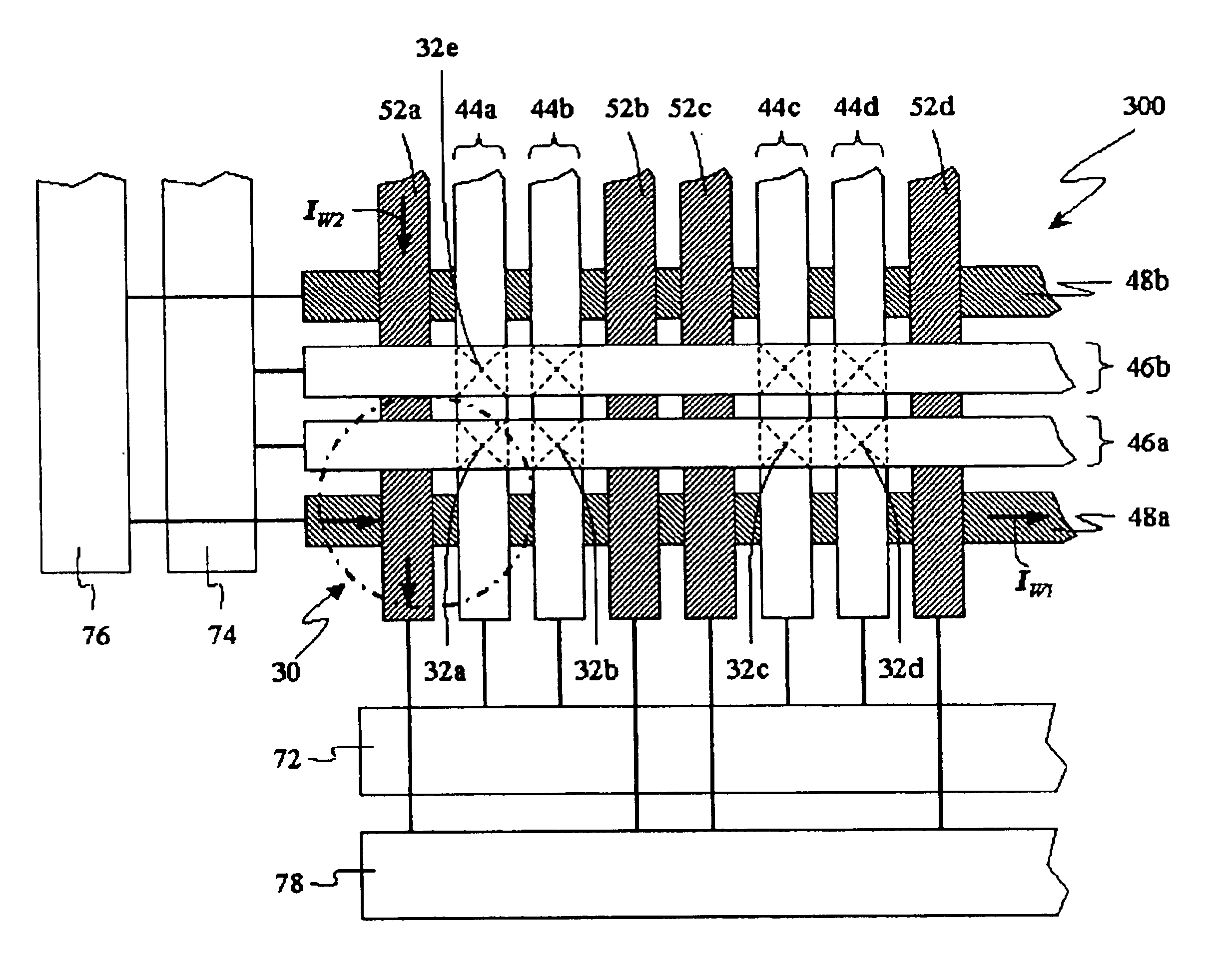
High speed low power annular magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS20080112094A1Operational advantageReduce the required powerRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A high speed and low power method to control and switch the magnetization direction and / or helicity of a magnetic region in a magnetic device for memory cells using spin polarized electrical current. The magnetic device comprises a reference magnetic layer with a fixed magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer with a changeable magnetic helicity. The fixed magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are preferably separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the reference layer includes an easy axis perpendicular to the reference layer. A current can be applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Magnetoresistive sensors having an improved free layer
ActiveUS8498084B1Reduce thicknessGilbert damping constantMagnetic measurementsRecord information storageSpin polarizationCobalt
A magnetoresistive sensor having a novel free layer and a method of producing the same are disclosed. The magnetoresistive sensor comprises a pinned layer, a barrier layer disposed over the pinned layer, and a free layer disposed over the barrier layer. The free layer comprises a first magnetic layer disposed over the barrier layer. The first magnetic layer has a positive spin polarization, a positive magnetostriction, and a polycrystalline structure. The free layer further comprises a second magnetic layer disposed over the first magnetic layer. The second magnetic layer has a negative magnetostriction and comprises at least cobalt (Co) and boron (B).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
TMR read head structures with differential stripe heights
InactiveUS8194366B1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic layerElectrical and Electronics engineering
A tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) read head and a method of producing the same are disclosed. A free layer having a free layer stripe height is provided, the free layer having a first side and a second side. A tunneling barrier layer is formed adjacent to the first side of the free layer, the tunneling barrier layer having a first side and a second side, the second side of the tunneling barrier layer facing the first side of the free layer. A pinned stack is formed adjacent to the first side of the tunneling barrier layer. The pinned stack comprises at least one magnetic layer having a current path stripe height that is less than the free layer stripe height.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spin-valve type magnetoresistance sensor and thin-film magnetic head
A method and apparatus of a spin-type magnetoresistance sensor having a free and pinned magnetic layer stacked with a non-magnetic interposed layer are disclosed. Specifically, the spin-valve type magnetoresistance sensor of the present invention is equipped with a free ferromagnetic layer, a pinned ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic spacer layer which is sandwiched between the aforementioned ferromagnetic layers, an anti-ferromagnetic layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned pinned ferromagnetic layer and which is used to pin the direction of magnetization of said pinned ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic back layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned free ferromagnetic layer and which is stacked on the opposite side the free ferromagnetic layer from the aforementioned nonmagnetic spacer layer, and an electron-reflective layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned back layer and which is stacked on the opposite side of the back layer from the aforementioned free ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for providing a magnetic transducer having improved shield-to-shield spacing
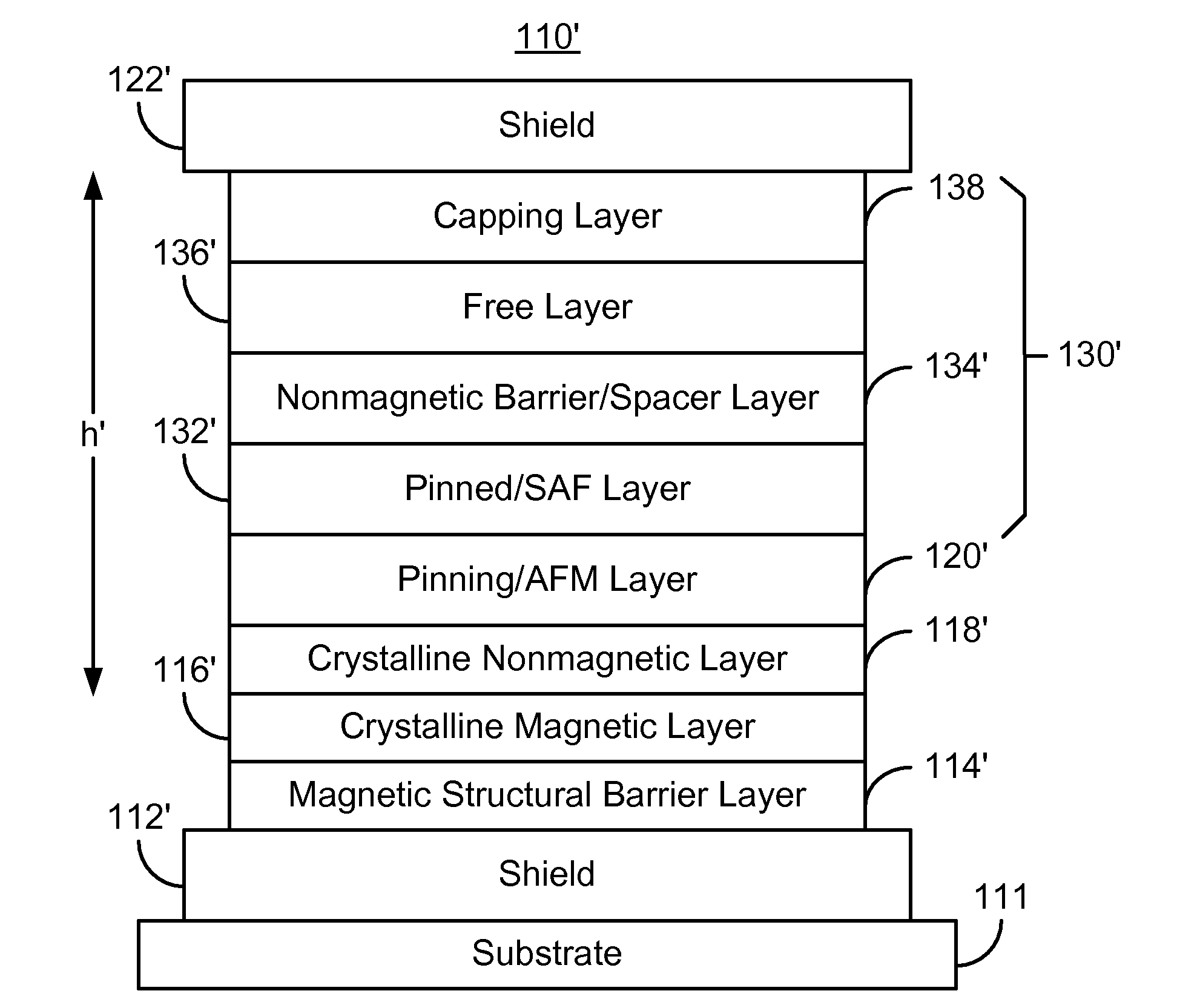
InactiveUS8537502B1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic transducersNon magnetic
A method and system for providing a magnetic transducer is described. The method and system include providing a magnetic structural barrier layer and a crystalline magnetic layer on the magnetic structural barrier layer. The magnetic structural barrier layer may reside on a shield. The method and system also include providing a nonmagnetic layer on the crystalline magnetic layer. A pinning layer is provided on the nonmagnetic layer. Similarly, a pinned layer is provided on the pinning layer. The pinning layer is magnetically coupled with the pinned layer. The method and system also include providing a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the pinned layer and the free layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
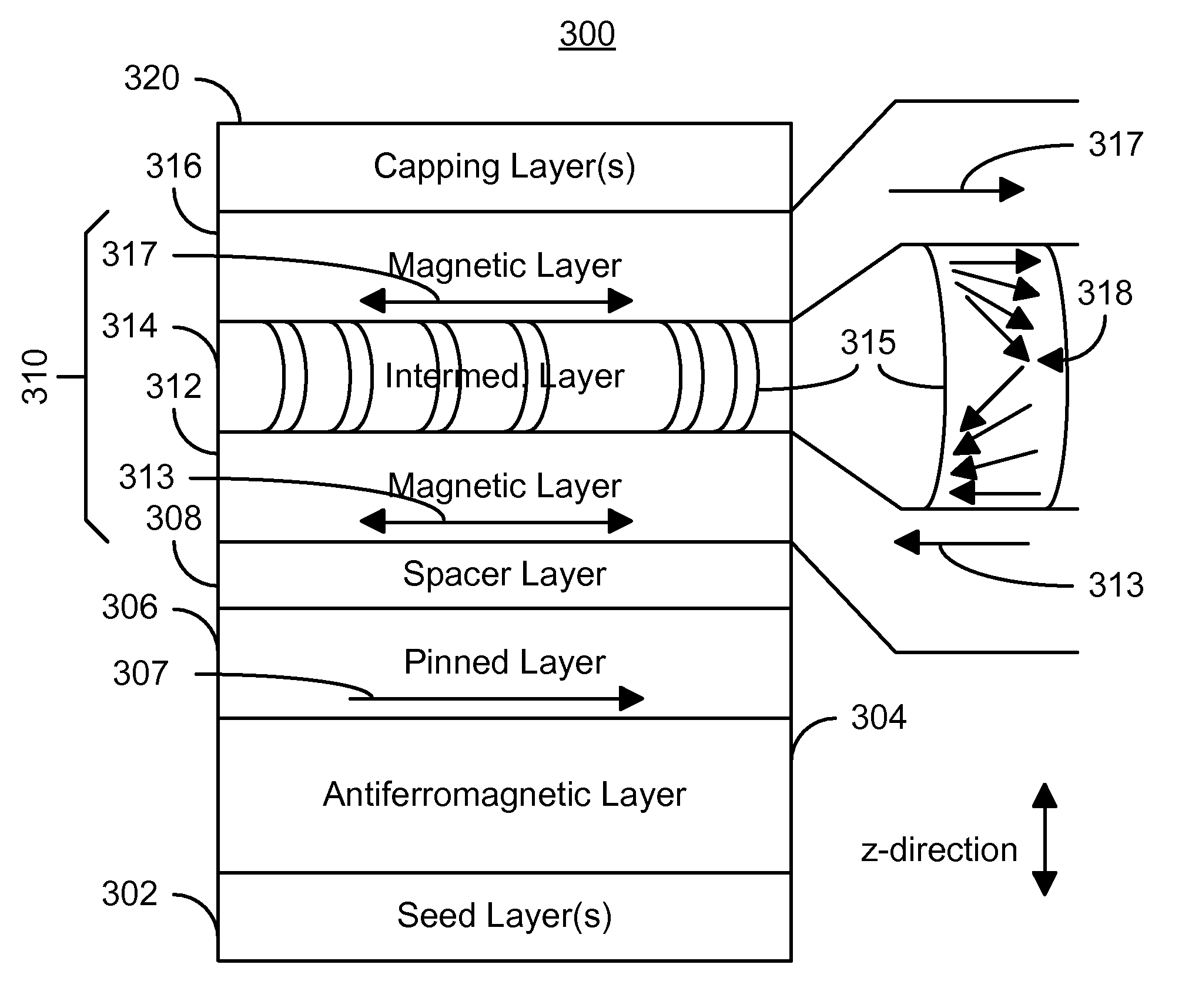
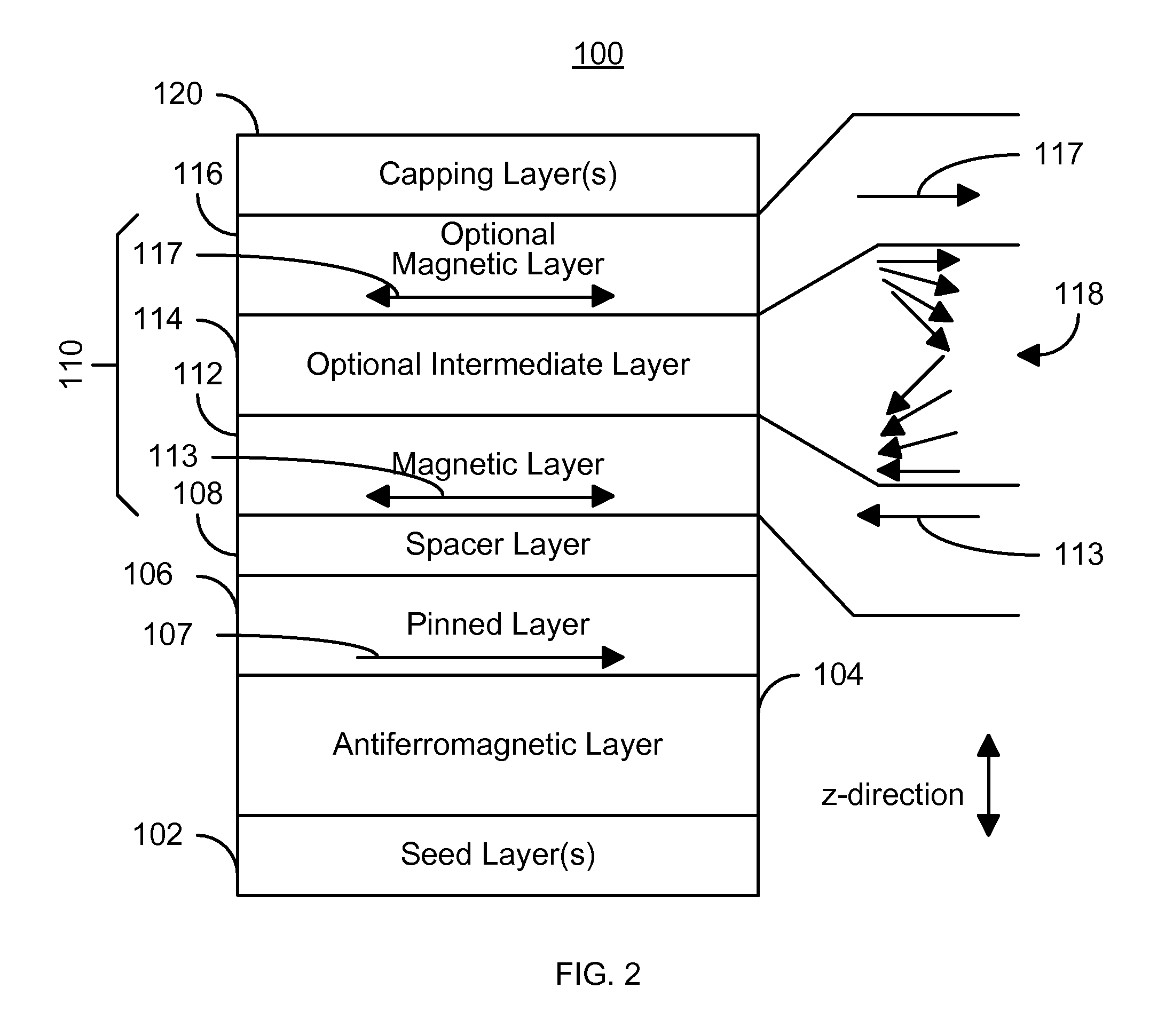
Method and system for providing domain wall assisted switching of magnetic elements and magnetic memories using such magnetic elements
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is described. The magnetic element includes a pinned layer, a spacer layer, and a free layer. The spacer layer is nonferromagnetic and resides between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer includes a first magnetic layer and at least one of a second magnetic layer and an intermediate layer. The intermediate layer would reside between the first and second magnetic layers. The free layer also includes at least one domain wall therein during switching. In addition, the magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched at least in part due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20120045664A1Superior recording/reproducing characteristicSuperior characteristic transportMaterials with ironRecord information storageNon magneticHexane
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention is a magnetic recording medium including a non-magnetic substrate; a non-magnetic layer that is formed on one of principal surfaces of the non-magnetic substrate and contains a non-magnetic powder, a binder, and a lubricant; and a magnetic layer that is formed on a principal surface of the non-magnetic layer opposite to the non-magnetic substrate and contains a magnetic powder and a binder. The magnetic powder has an average particle size between 10 inn and 35 nm inclusive. The lubricant is migratable to the magnetic layer and forms a lubricant layer on a surface of the magnetic layer when a pressure is applied to the magnetic layer. When spacing of the surface of the magnetic layer before and after washing the lubricant with n-hexane is measured with a TSA (Tape Spacing Analyzer), the value of the spacing after washing is 3 to 10 nm, and the value of the spacing before washing is 1 to 5 nm smaller than the value of the spacing after washing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Spin valve magnetoresistance sensor and thin film magnetic head
A spin valve magnetoresistance sensor of a thin film magnetic head. In one embodiment, a spin valve magnetoresistance sensor is provided with a spin valve film, in which a base layer including a first base film of Ta or some other nonmagnetic metal and, on top of this, a second base film of an alloy represented by NiFeX (where X is at least one element selected from among Cr, Nb, Rh) is formed on a substrate, and on top of this are formed by layering a free magnetic layer and pinned magnetic layer arranged to enclose a nonmagnetic conductive layer, as well as an antiferromagnetic layer, the second base film has an fcc (face-centered cubic) structure and also has a (111) orientation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Electrowetting electrode device with electromagnetic field for actuation of magnetic-bead biochemical detection system
InactiveUS20050056569A1Reduce dissipationEnhanced magnetic forceMaterial thermal conductivityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityMagnetic bead
A detecting device for biochemical detections is provided. The detecting device includes a first substrate, a magnetic layer located on the first substrate, an isolation layer located on the magnetic layer, at least a first electrode located on the isolation layer, a first dielectric layer located on the first electrode, a first hydrophobic layer located on the first dielectric layer, a second substrate, at least a second electrode located on the second substrate and having a cathode and an anode, a second dielectric layer located on the second electrode and a second hydrophobic layer located on the second dielectric layer. The first electrode is zigzag-shaped, and the cathode and the anode of the second electrode are comb-shaped and interlaced with each other.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Magnetic signal reproduction system and magnetic signal reproduction method
InactiveUS20090027812A1Stable reproduction propertyDeterioration of reproduction propertyManufacture unitary devices of plural headsRecord information storageIridiumAlloy
The magnetic signal reproduction system comprises a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support and a reproduction head, wherein a number of protrusions equal to or greater than 10 nm in height on the magnetic layer surface, as measured by an atomic force microscope, ranges from 50 to 2500 / 10,000 μm2, a quantity of lubricant on the magnetic layer surface, denoted as a surface lubricant index, ranges from 0.5 to 5.0, a surface abrasive occupancy of the magnetic layer ranges from 2 to 20 percent, the reproduction head is a magnetoresistive magnetic head comprising a spin-valve layer, the spin-valve layer comprises a magnetization free layer, a magnetization pinned layer and an antiferromagnetic layer, and the antiferromagnetic layer is comprised of alloy comprising iridium and manganese, and the reproduction head comes in sliding contact with the magnetic recording medium during signal reproduction.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Microfabricated system for magnetic field generation and focusing
InactiveUS20050275497A1Easily of circuitryWell formedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDielectricMicro coil
A method of forming, in or on a Si substrate, planar micro-coils with coil windings of high aspect ratio (>3) and a wide variety of geometric shapes. The micro-coils may be formed on a Si substrate and be embedded in a dielectric, or they may be formed in trenches within a Si substrate. The micro-coils may have field enhancing ferromagnetic pillars rising above the micro-coil plane, formed at positions of maximum magnetic field strength and the micro-coils may also include magnetic layers formed beneath the substrate and contacting the pillars to form a substantially closed pathway for the magnetic flux. The substrate may be thinned to membrane proportions. These micro-coils produce strong magnetic fields with strong field gradients and can be used in a wide variety of processes that involve the exertion of strong magnetic forces at small distances or the creation of magnetic wells for trapping and manipulating small particles.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Magnetic tape
InactiveUS20070230054A1Shorten the trackSimple resultRecord information storageTape carriersMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
A magnetic tape including: a nonmagnetic support; a substantially nonmagnetic layer containing nonmagnetic powder and a binder; and a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and a binder, in this order, wherein the magnetic tape has a coefficient of temperature expansion of from 0 to 10×10−6 / ° C. and a coefficient of humidity expansion of 0 to 7×10−6 / % RH each in a transverse direction of the magnetic tape, and the magnetic tape has a dimensional deformation amount of from 0.01 to 0.06% in the transverse direction in case of applying a tensile stress of 1N to the magnetic tape at 60° C. for 50 hours in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium with improved magnetic anisotropy field
InactiveUS20100035085A1High HcExcellent crystallographic C axis orientationMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyAlloy
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprising a substrate, a soft underlayer, a seed layer, a non-magnetic FCC NiW alloy underlayer, a non-magnetic HCP underlayer, and a magnetic layer. We have discovered that the combination of a seed layer comprising Ta and a NiW alloy underlayer uniquely improves media recording performance and thermal stability by achieving excellent coercivity of the thin bottom magnetic recording layer and narrow C axis orientation distribution.
Owner:WD MEDIA
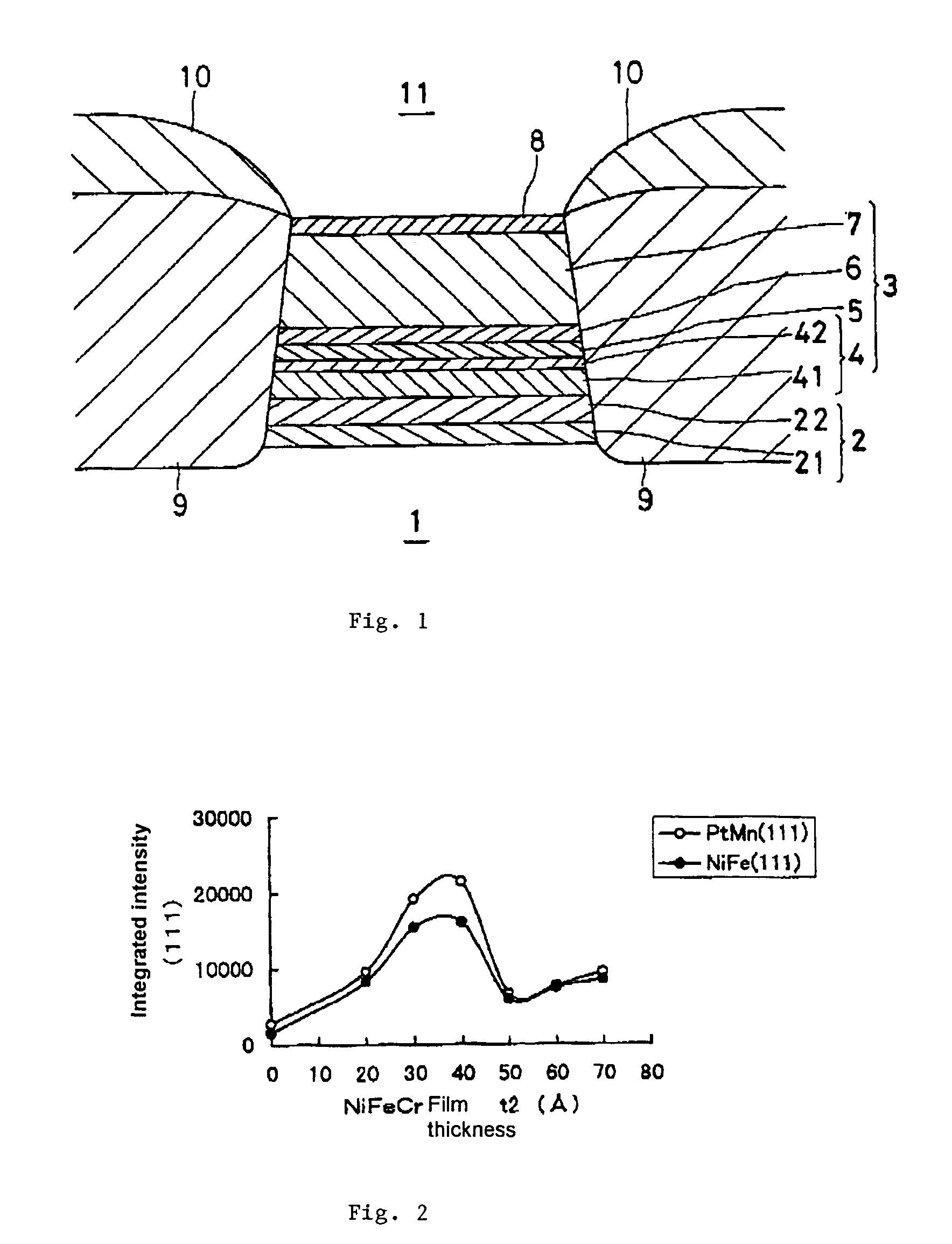
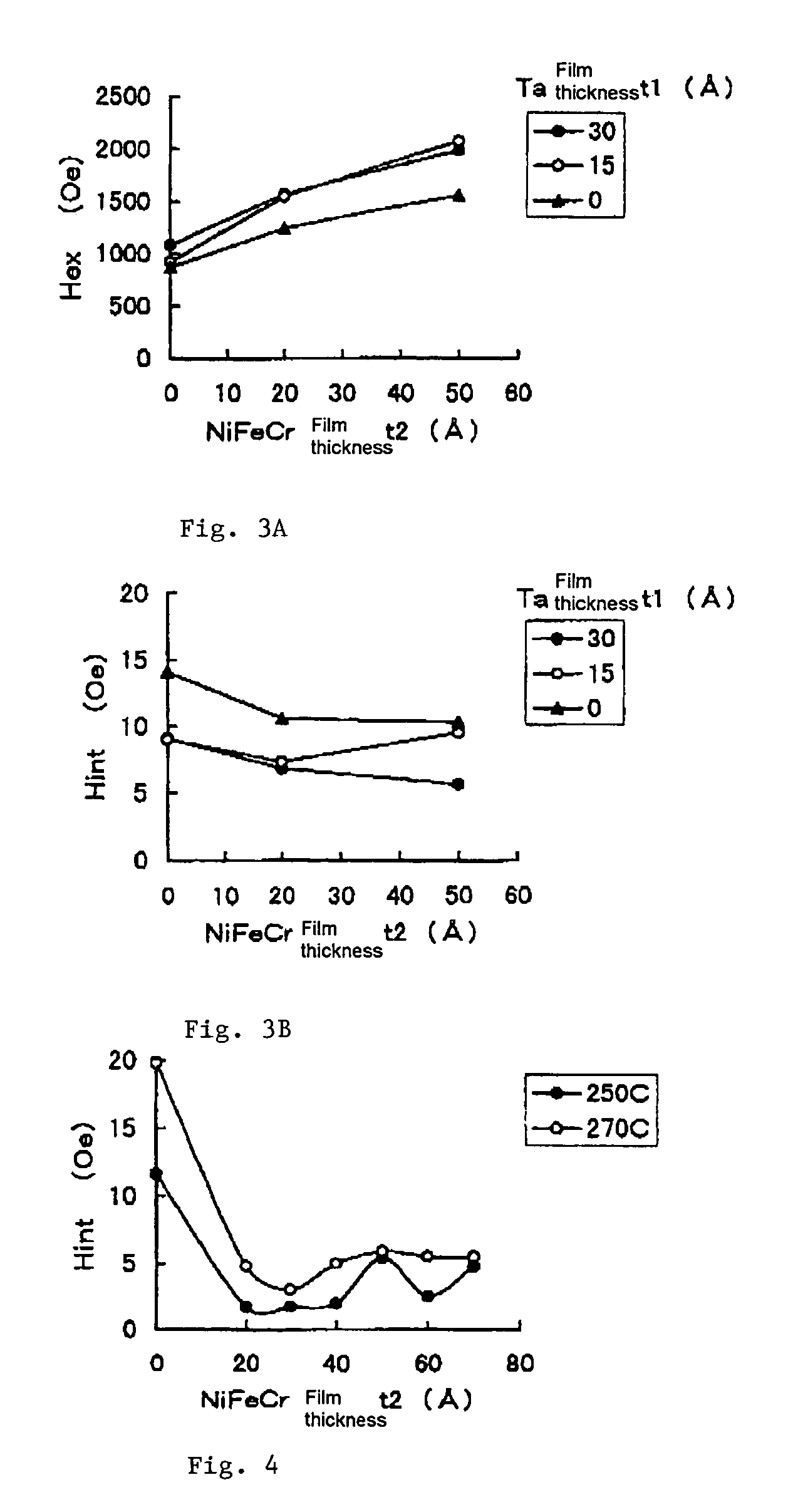
Magnetic recording medium, method for producing thereof, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
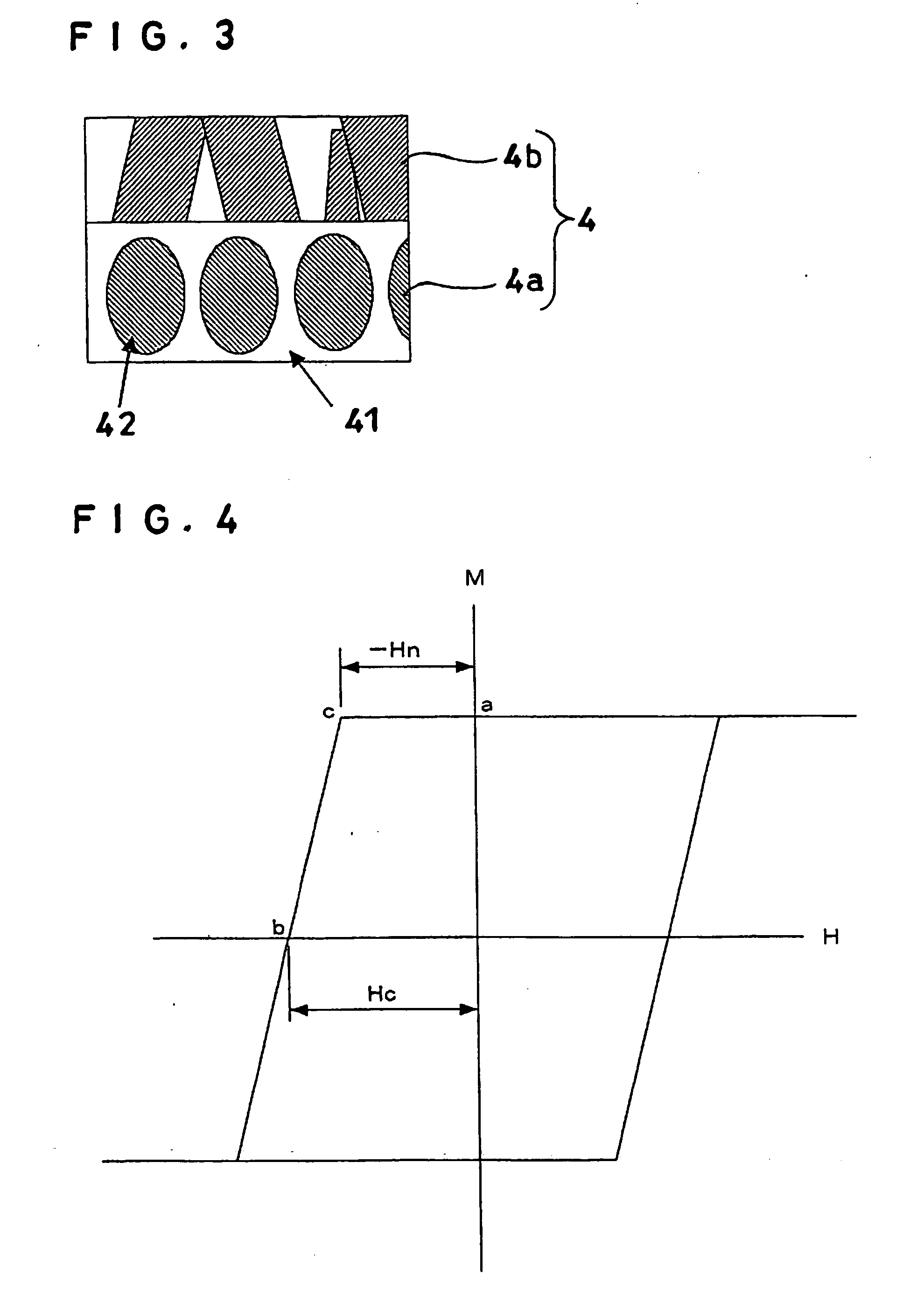
A magnetic recording medium which is provided on a nonmagnetic substrate 1 with at least an orientation-controlling layer 3 for controlling the orientation of a layer formed directly thereon, a perpendicularly magnetic layer 4 having an easily magnetizing axis oriented mainly perpendicularly relative to the nonmagnetic substrate 1, and a protective layer 5 and characterized in that the perpendicularly magnetic layer 4 includes two or more magnetic layers, that at least one of the magnetic layers is a layer 4a having Co as a main component and containing Pt as well and containing an oxide and that at least another of the magnetic layers is a layer 4b having Co as a main component and containing Cr as well and containing no oxide.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK +1
Magnetic Tunnel Junctions Using Amorphous Materials as Reference and Free Layers
ActiveUS20060098354A1Improve barrier propertiesImprove performanceNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsBoronTunnel junction
Magnetic tunnel junctions are constructed from a MgO or Mg—ZnO tunnel barrier and amorphous magnetic layers in proximity with, and on respective sides of, the tunnel barrier. The amorphous magnetic layer preferably includes Co and at least one additional element selected to make the layer amorphous, such as boron. Magnetic tunnel junctions formed from the amorphous magnetic layers and the tunnel barrier have tunneling magnetoresistance values of up to 200% or more.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com