Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74123 results about "Si substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Si Substrate. Si substrates are promising materials for the heteroepitaxial growth of diamond due to their scalability, coefficient of thermal expansion, and cost.
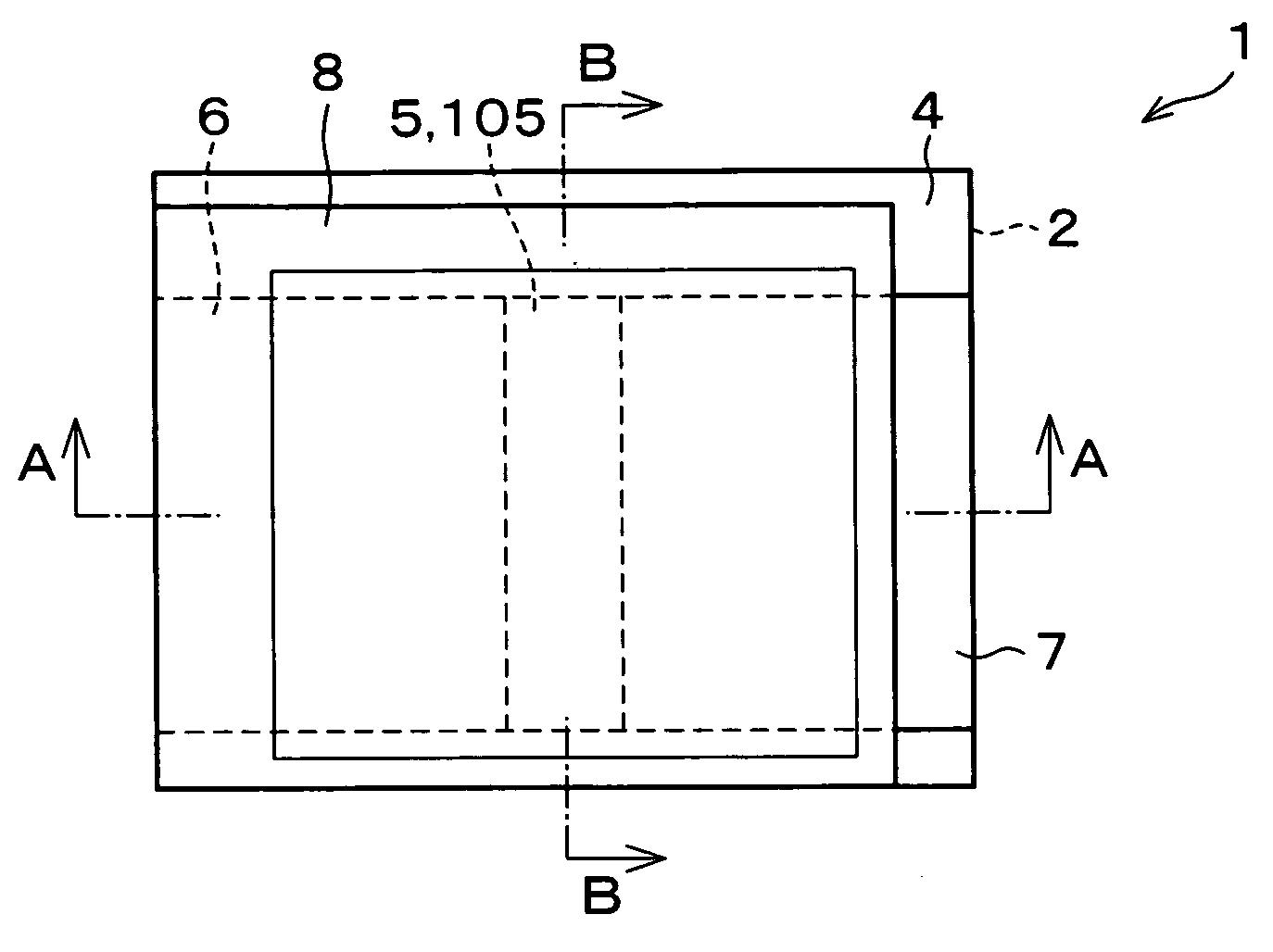
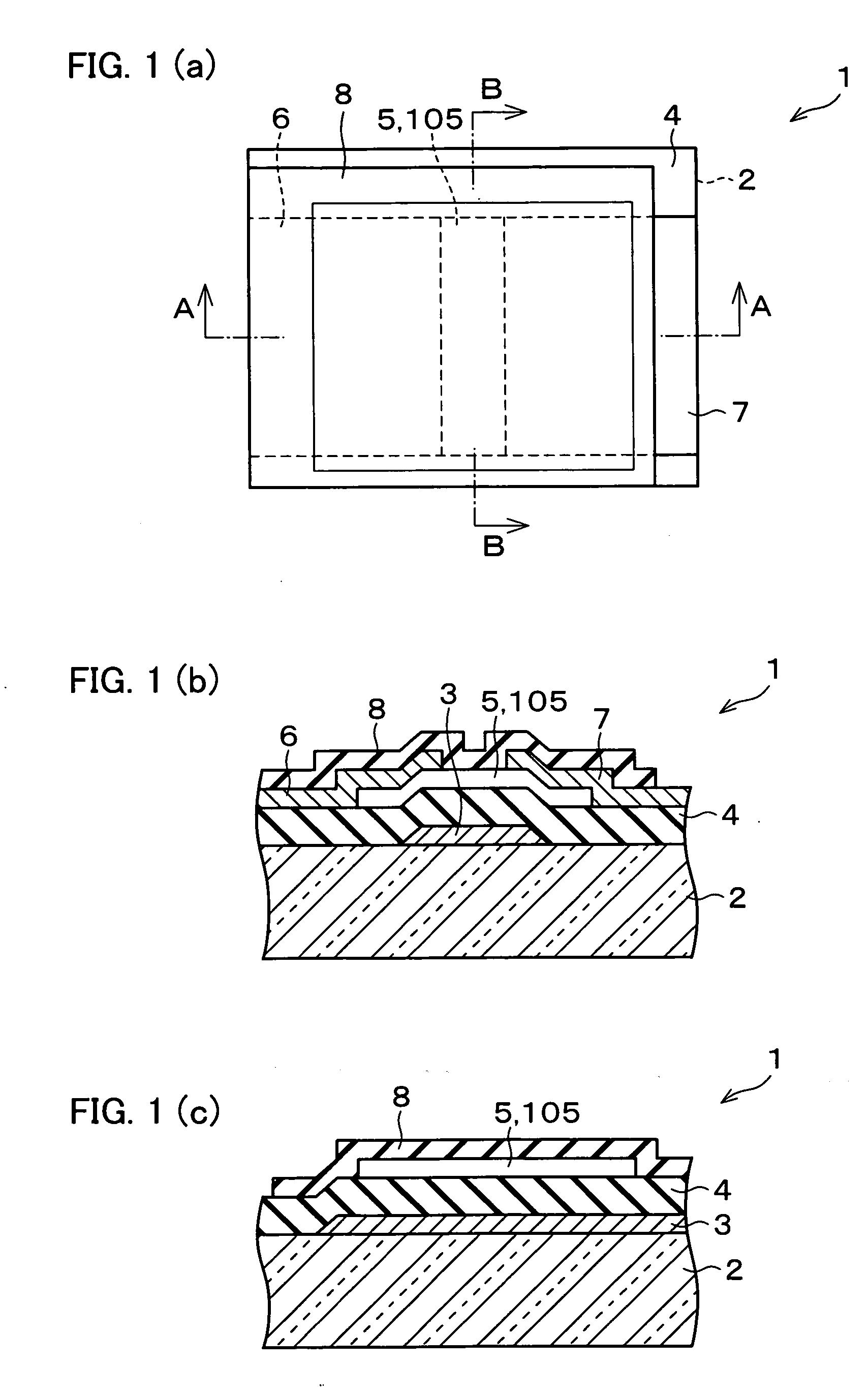
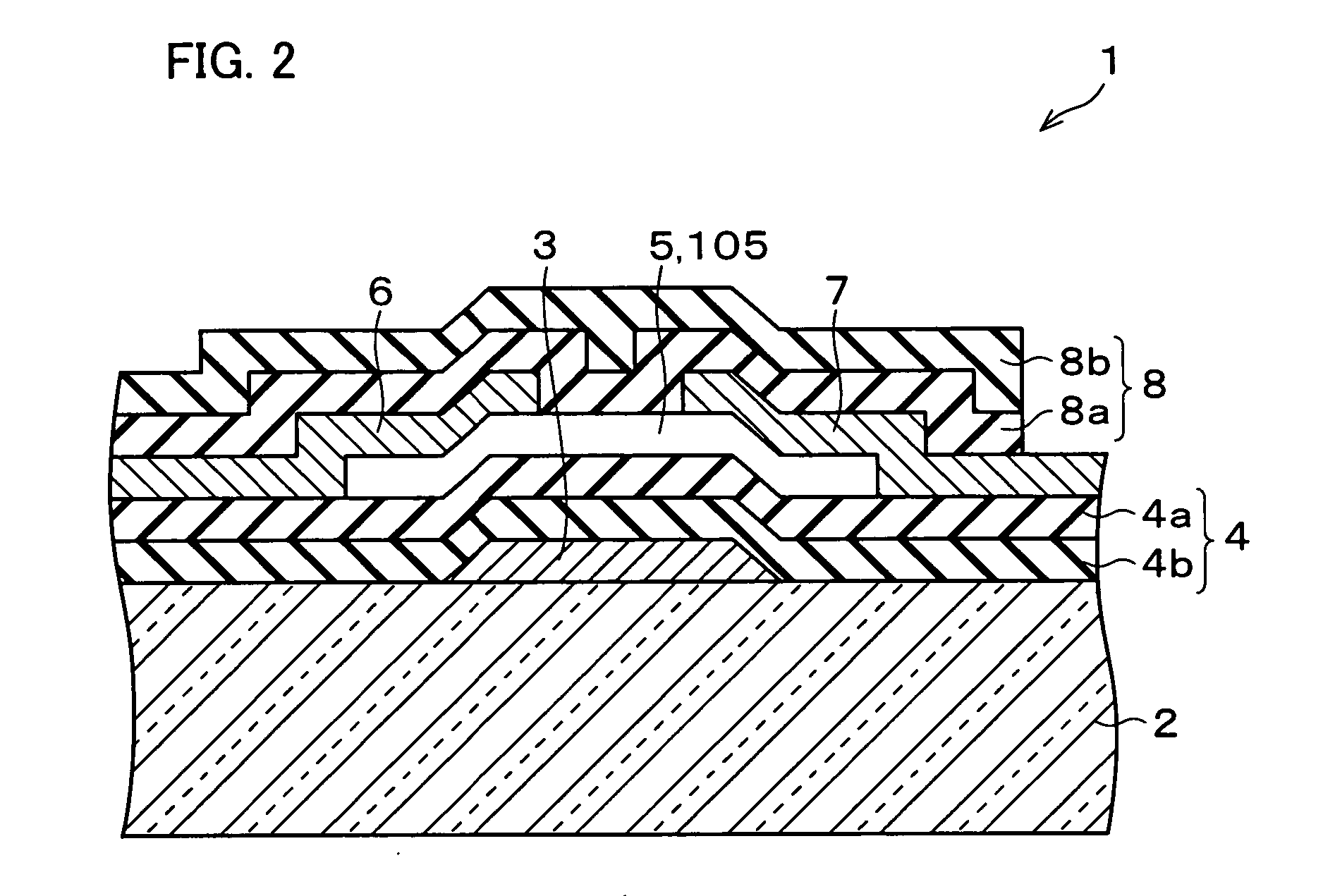
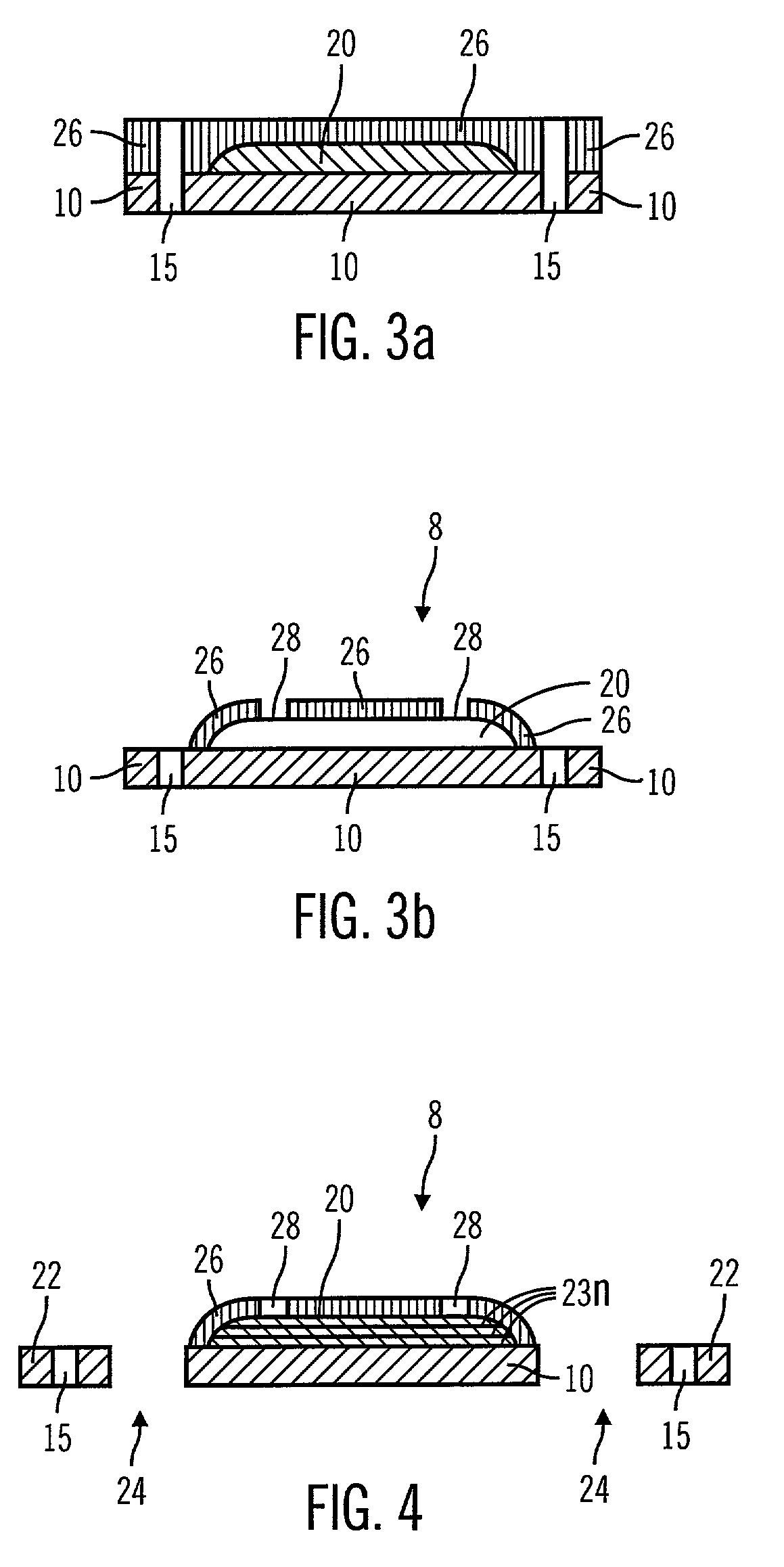
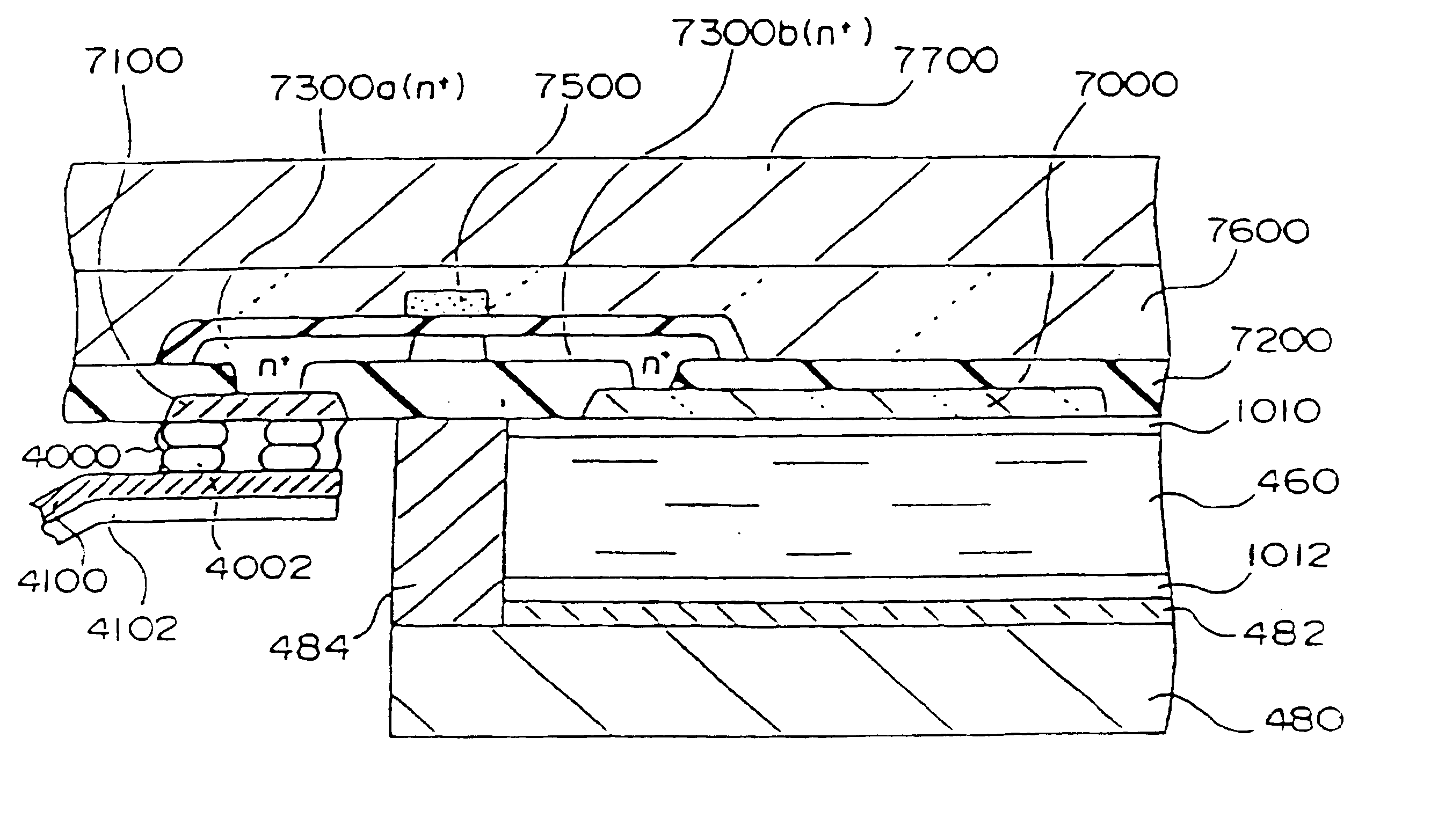
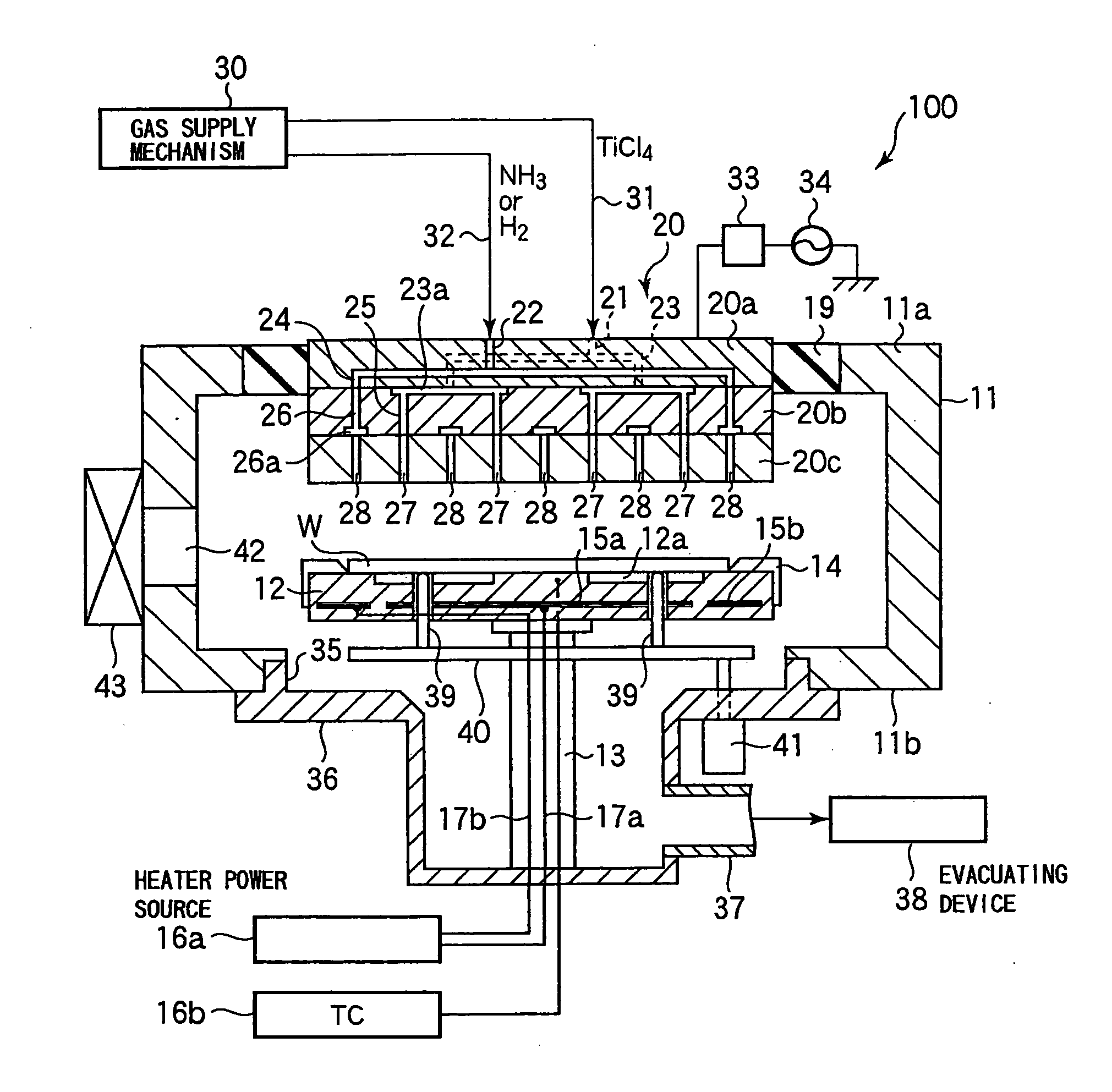
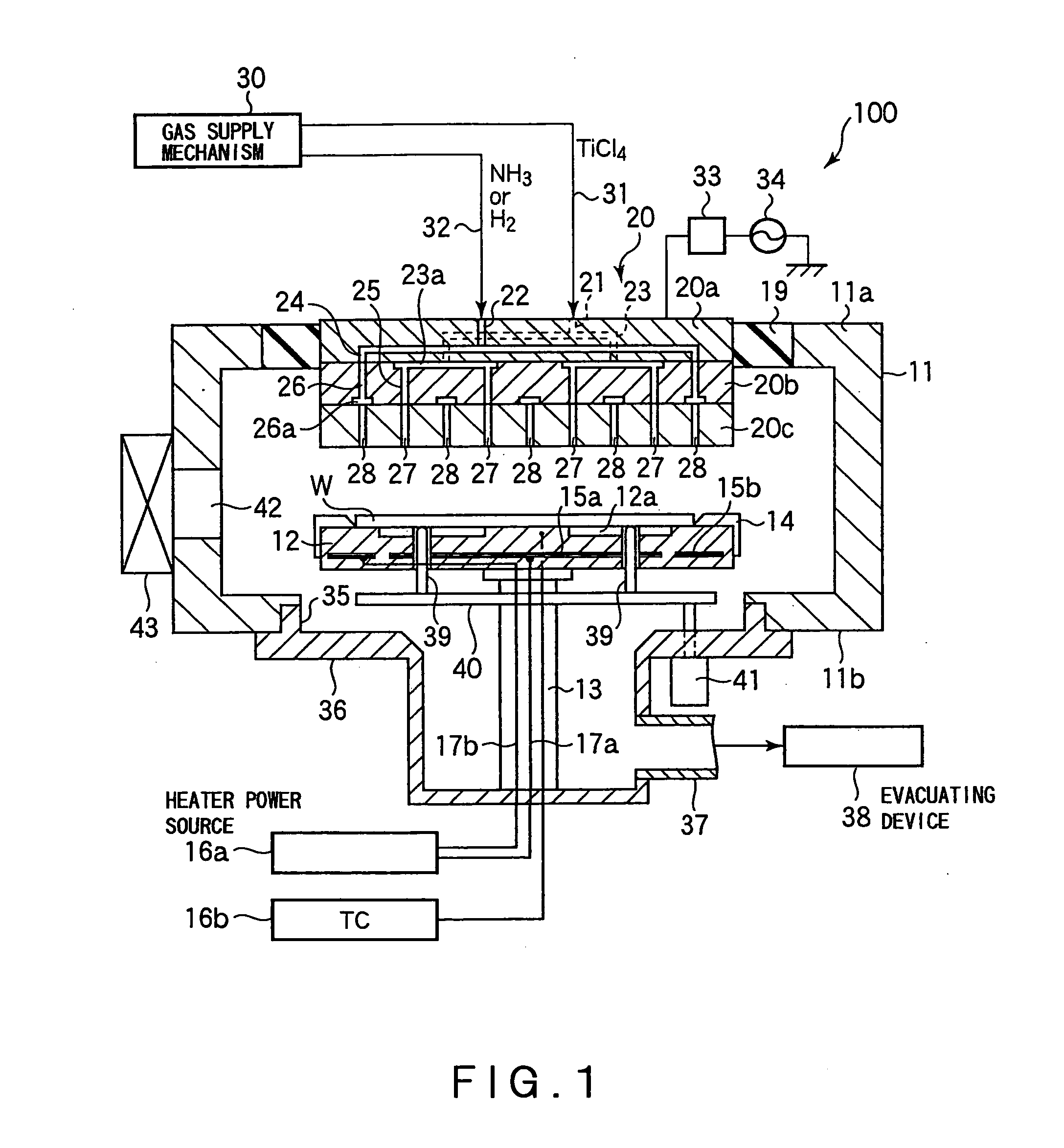
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
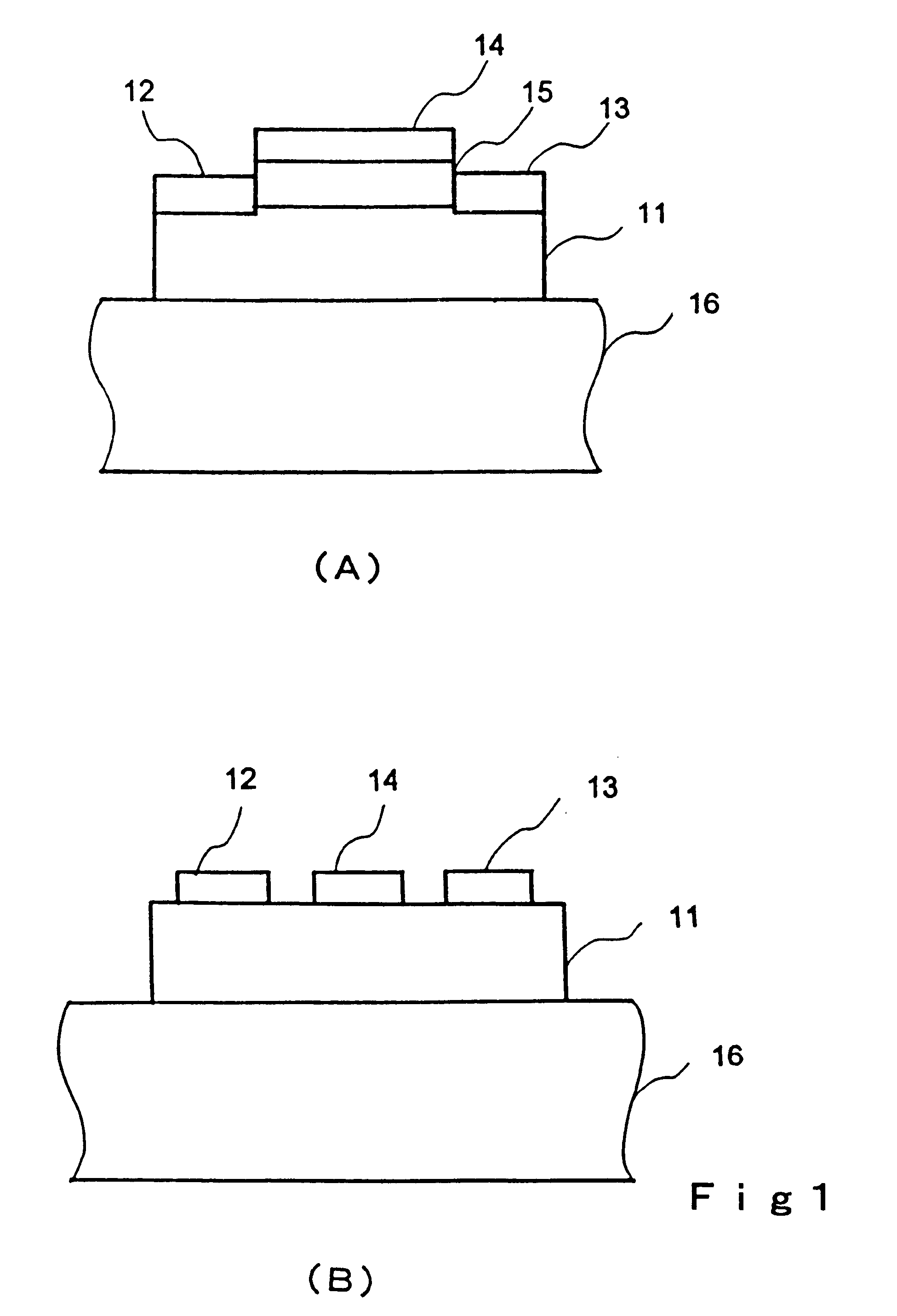
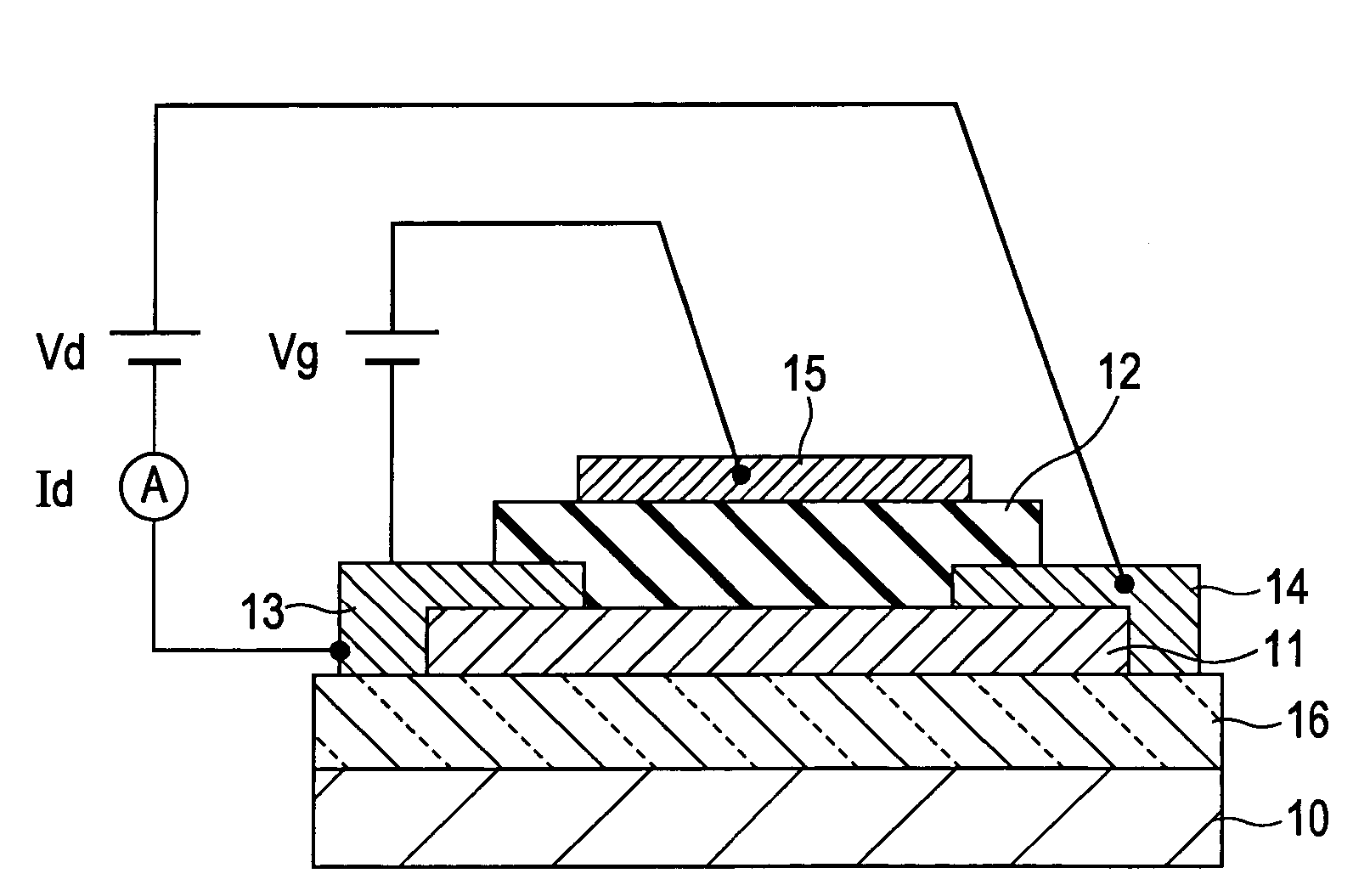
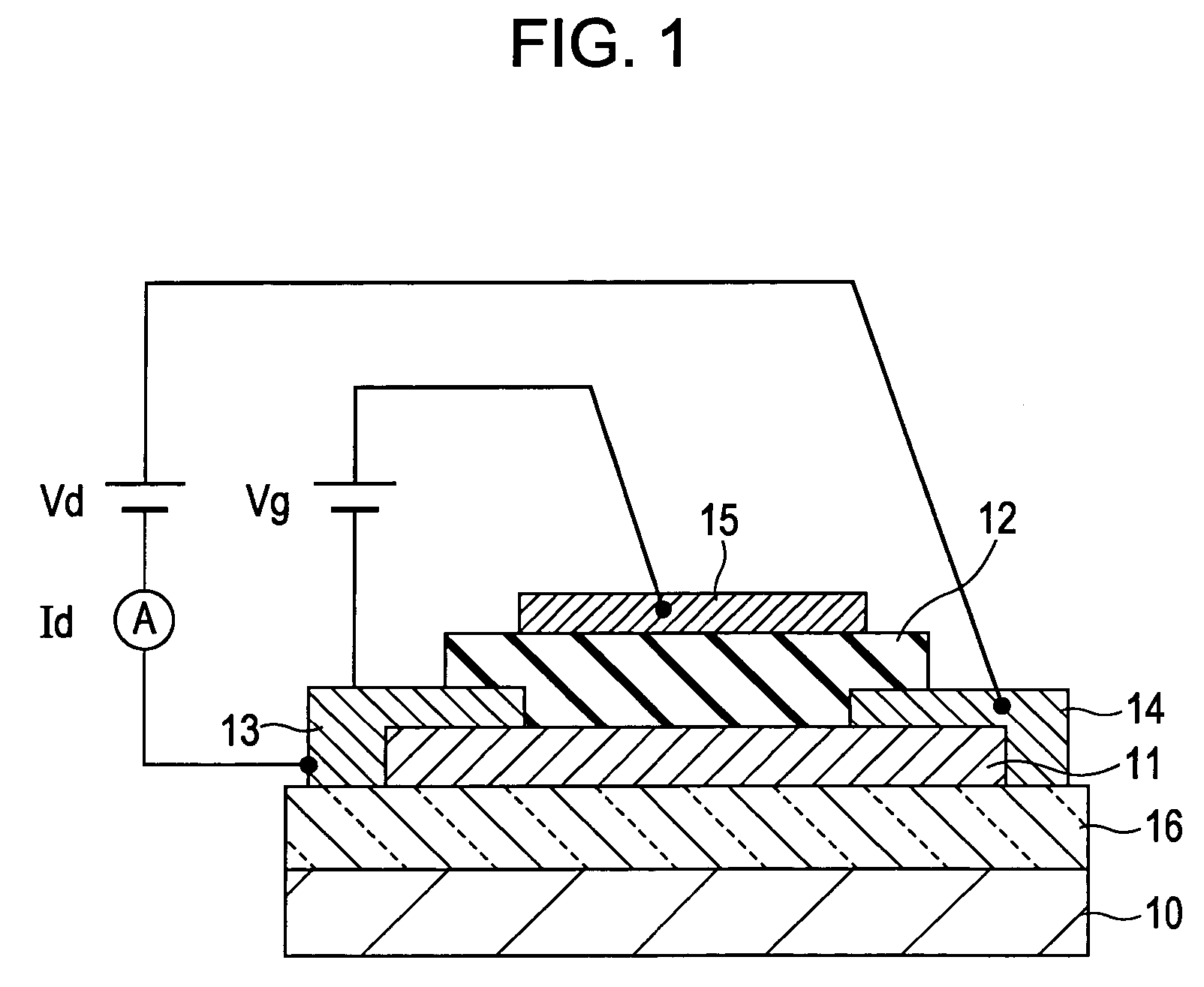
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Transistor and semiconductor device
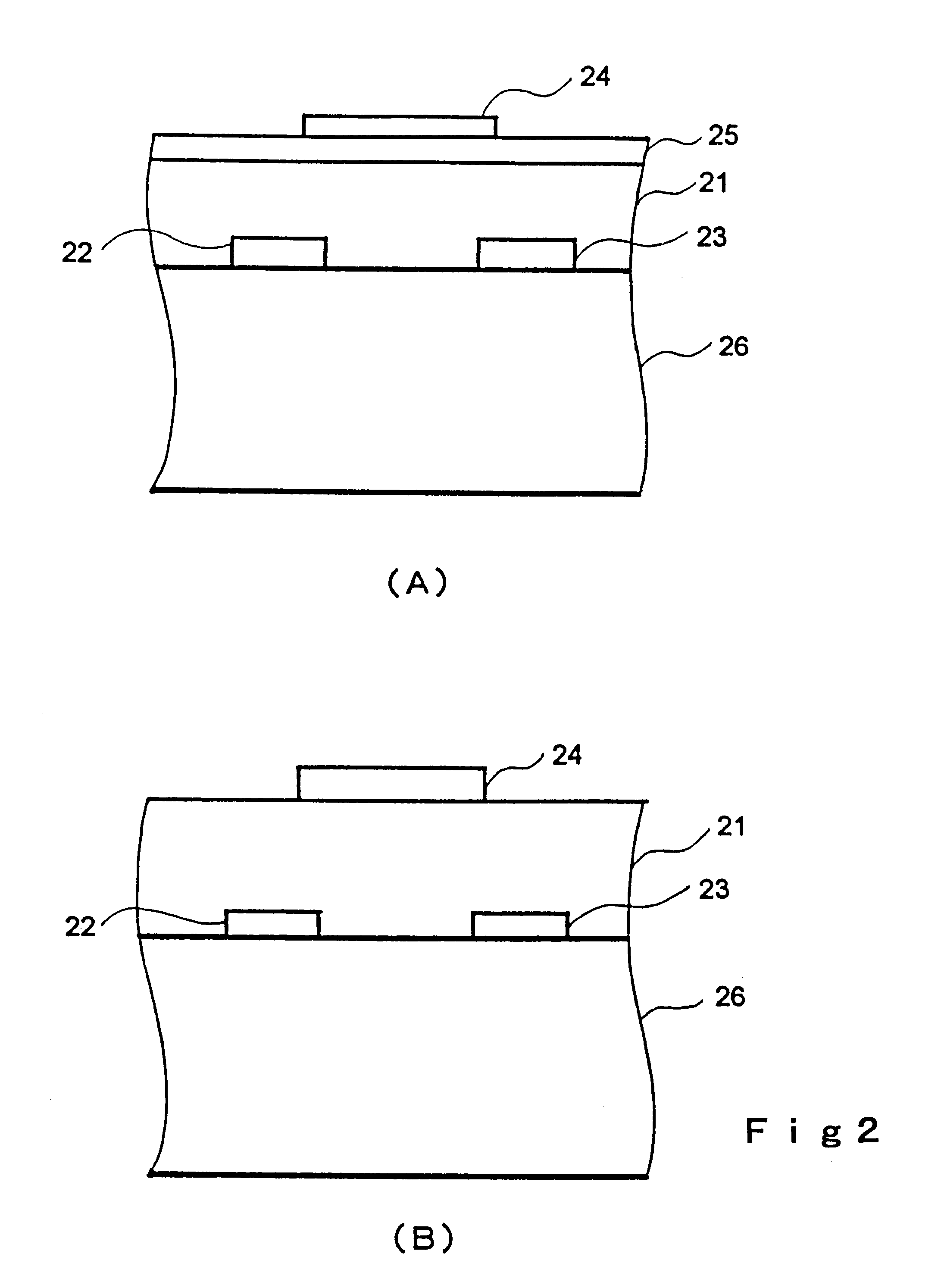
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Color el display and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080129195A1Quality improvementHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
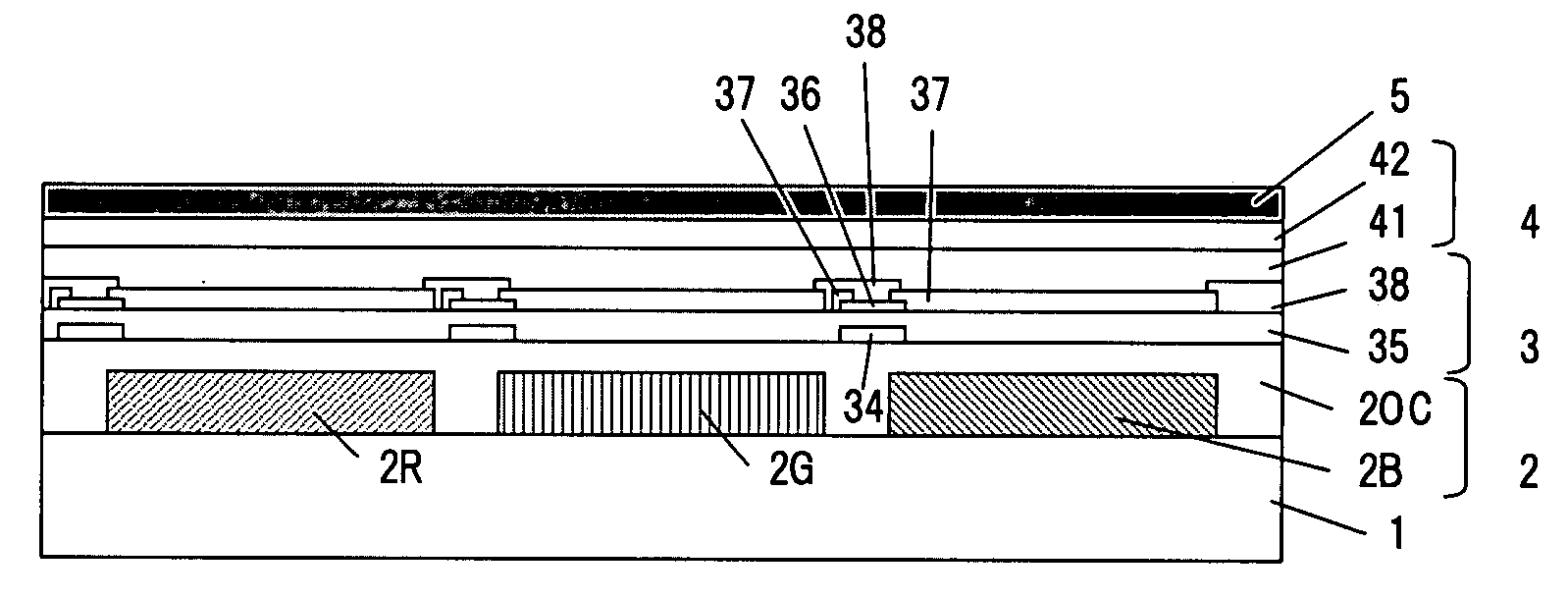
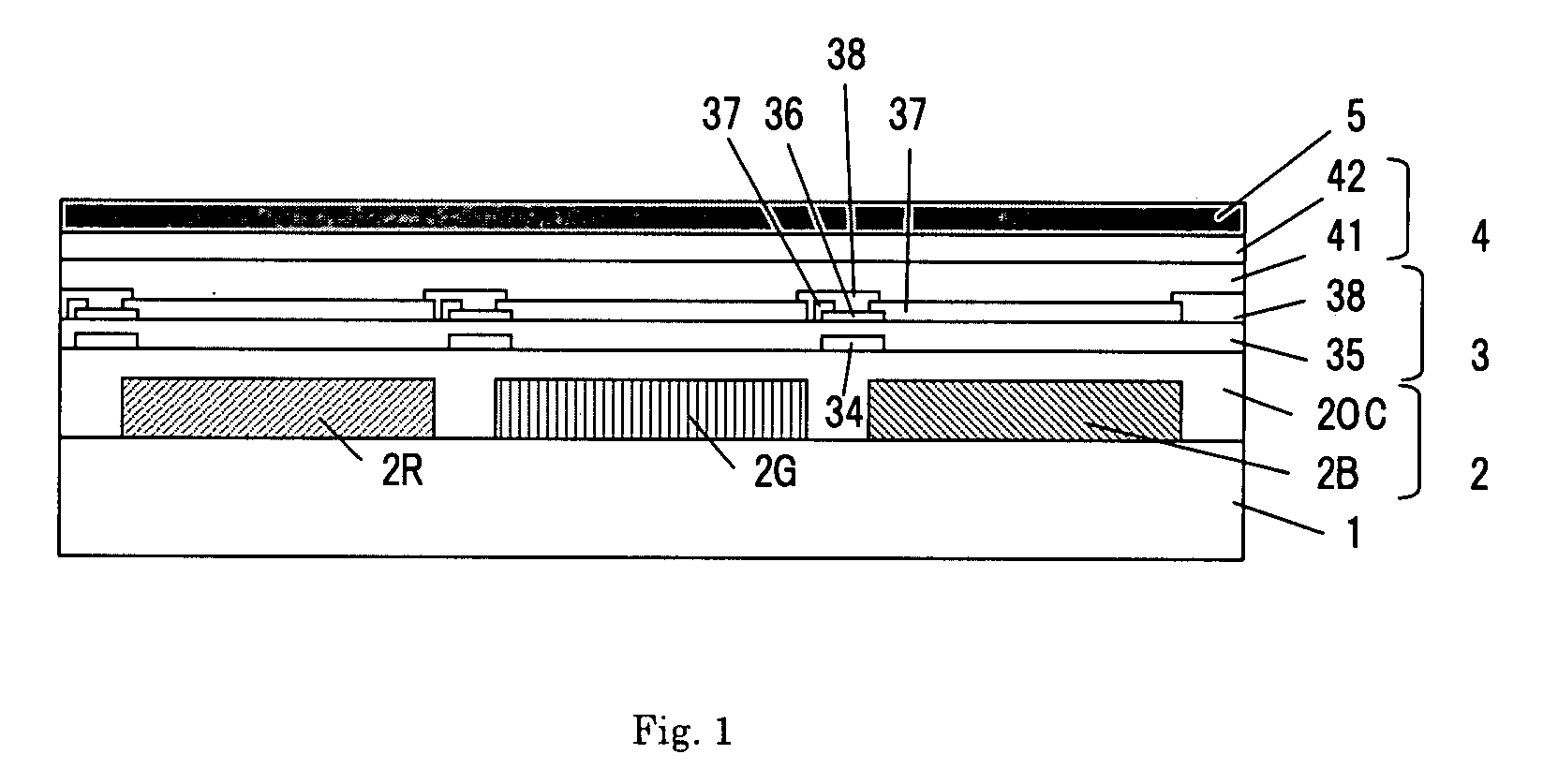
One embodiment of the present invention is a color EL display characterized in that at least color filters, a thin film transistor circuit, an organic EL layer, and a common electrode are laminated in this order on a transparent substrate. Another embodiment of the invention is a method for producing a color EL display comprising the steps of forming color filters or a transparent substrate; forming a thin film transistor circuit; forming an organic EL layer; and forming a common electrode, wherein process temperatures of the steps of forming the thin film transistor circuit and subsequent steps are 200° C. or less.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Thin-film transistor and thin-film diode having amorphous-oxide semiconductor layer
ActiveUS7453087B2High light transmittanceHigh transparencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin-film diodeRefractive index
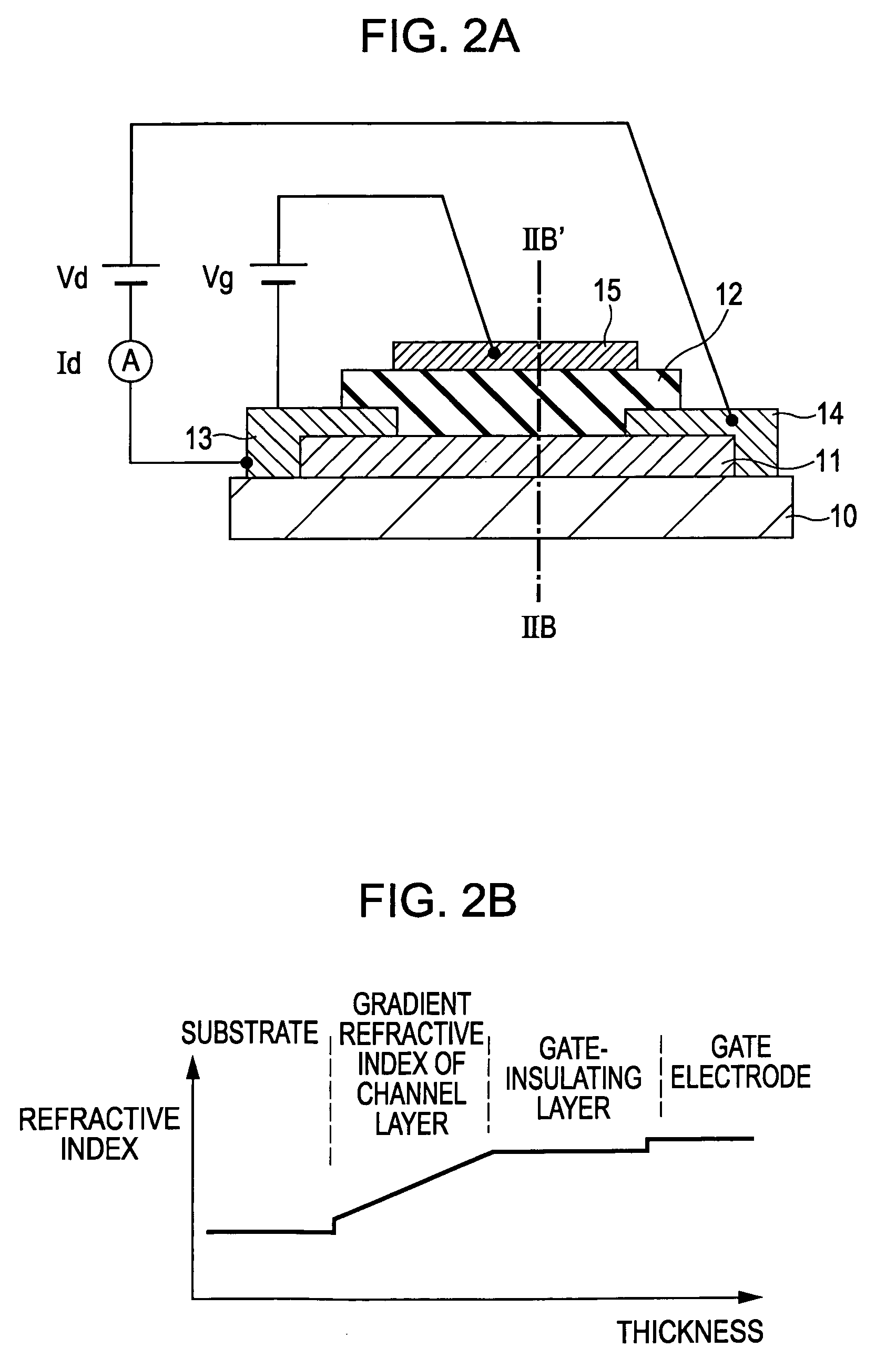
A thin-film transistor including a channel layer being formed of an oxide semiconductor transparent to visible light and having a refractive index of nx, a gate-insulating layer disposed on one face of the channel layer, and a transparent layer disposed on the other face of the channel layer and having a refractive index of nt, where there is a relationship of nx>nt. A thin-film transistor including a substrate having a refractive index of no, a transparent layer disposed on the substrate and having a refractive index of nt, and a channel layer disposed on the transparent layer and having a refractive index of nx, where there is a relationship of nx>nt>no.
Owner:CANON KK
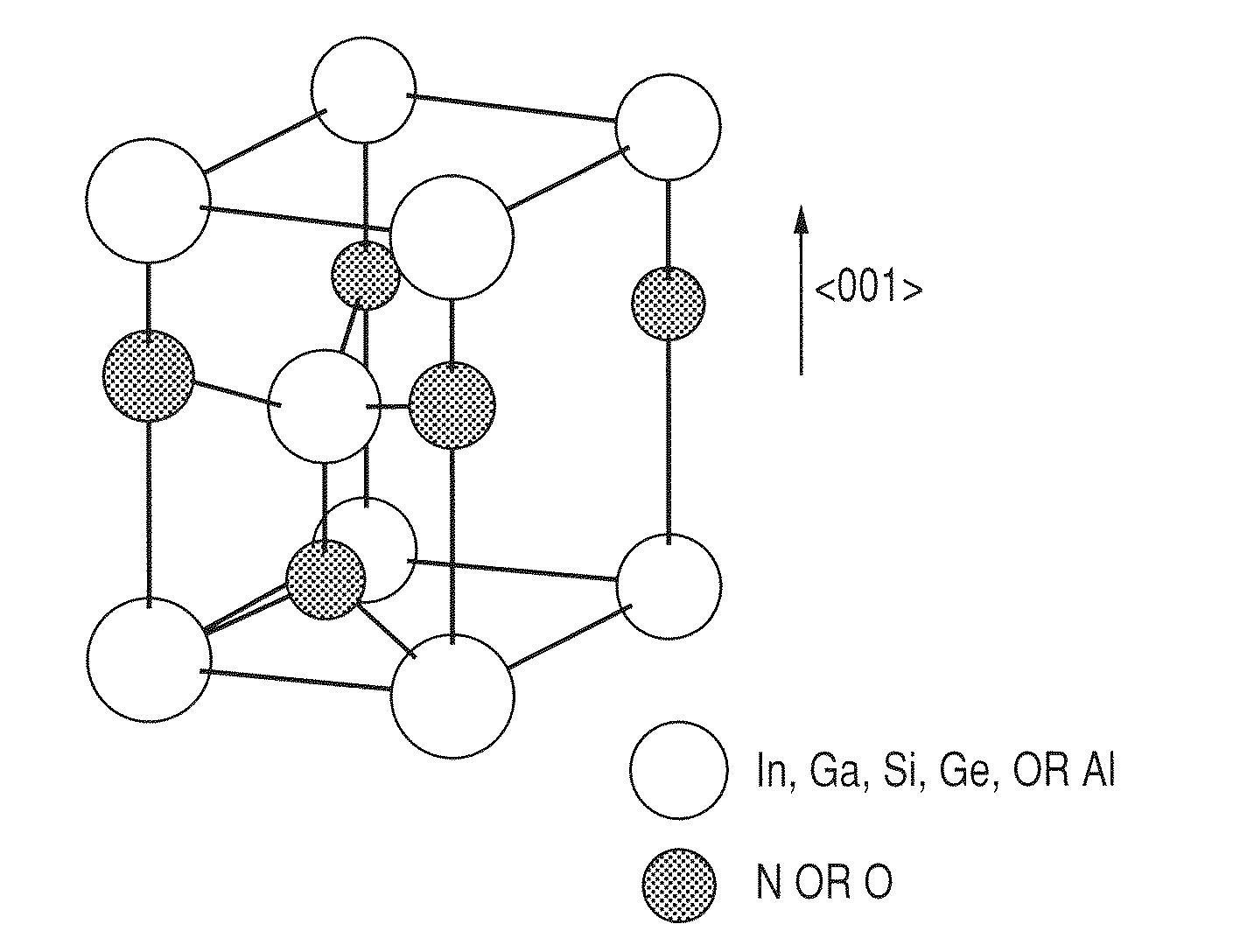
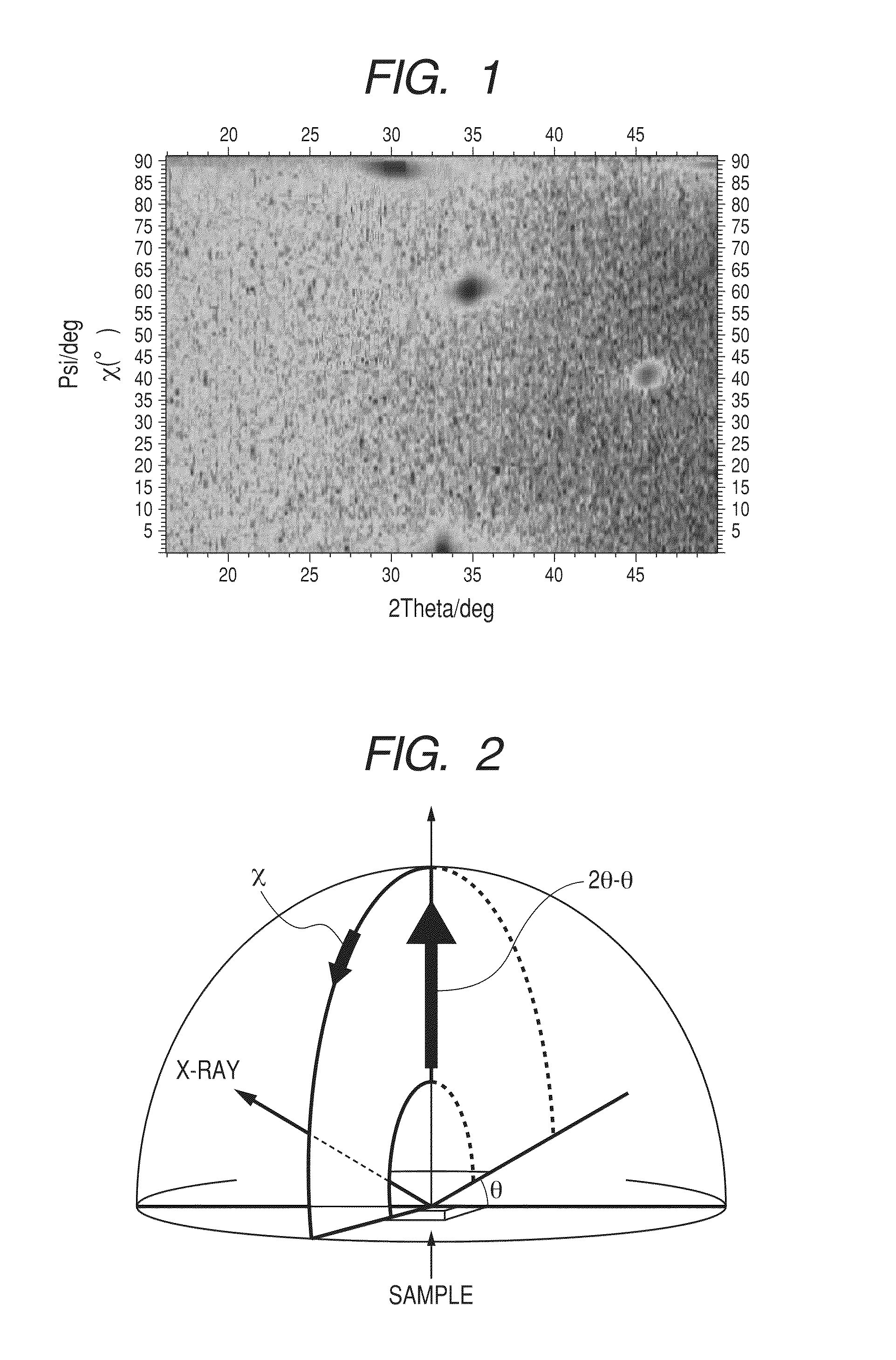
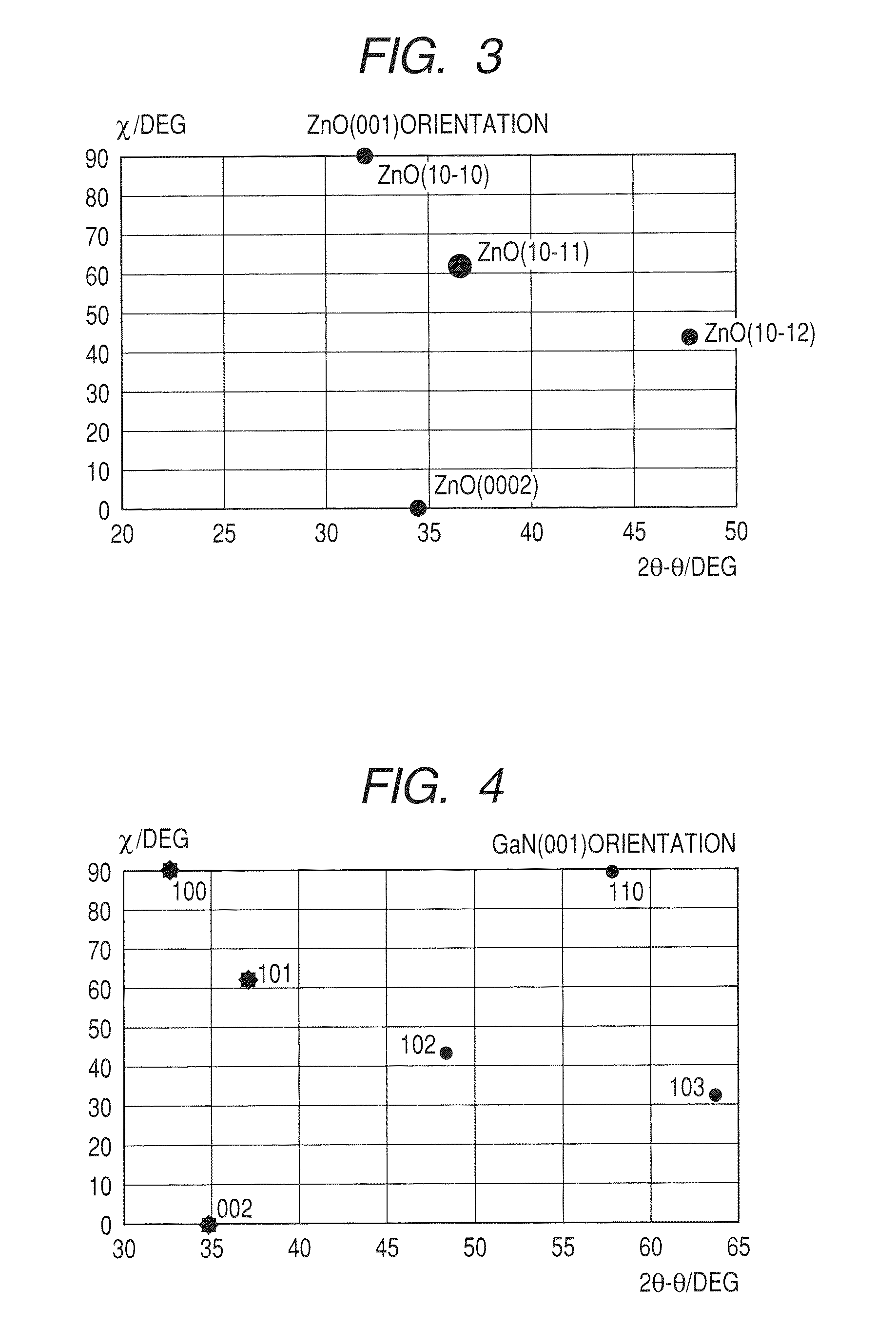
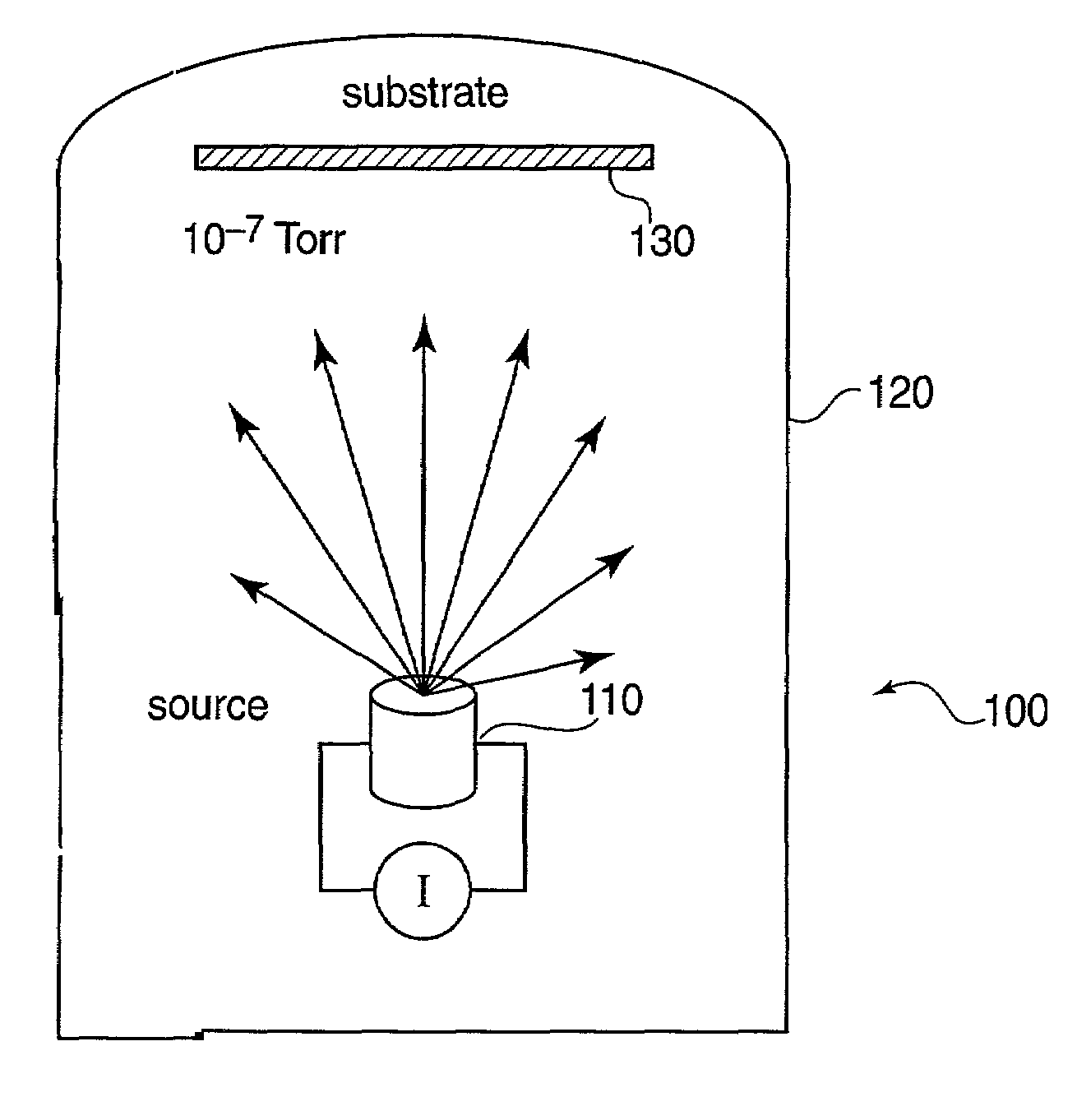
Substrate for growing wurtzite type crystal and method for manufacturing the same and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100092800A1Low costHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingNitrideSemiconductor
A laminated structure comprises a first layer comprising a crystal with six-fold symmetry, and a second layer comprising a metal oxynitride crystal formed on the first layer, wherein the second layer comprises at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Si, Ge and Al, N, O and Zn, as main elements, and wherein the second layer has in-plane orientation.
Owner:CANON KK
Process and apparatus for organic vapor jet deposition
ActiveUS7431968B1Good directionSharp pixelVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOrganic filmVacuum chamber
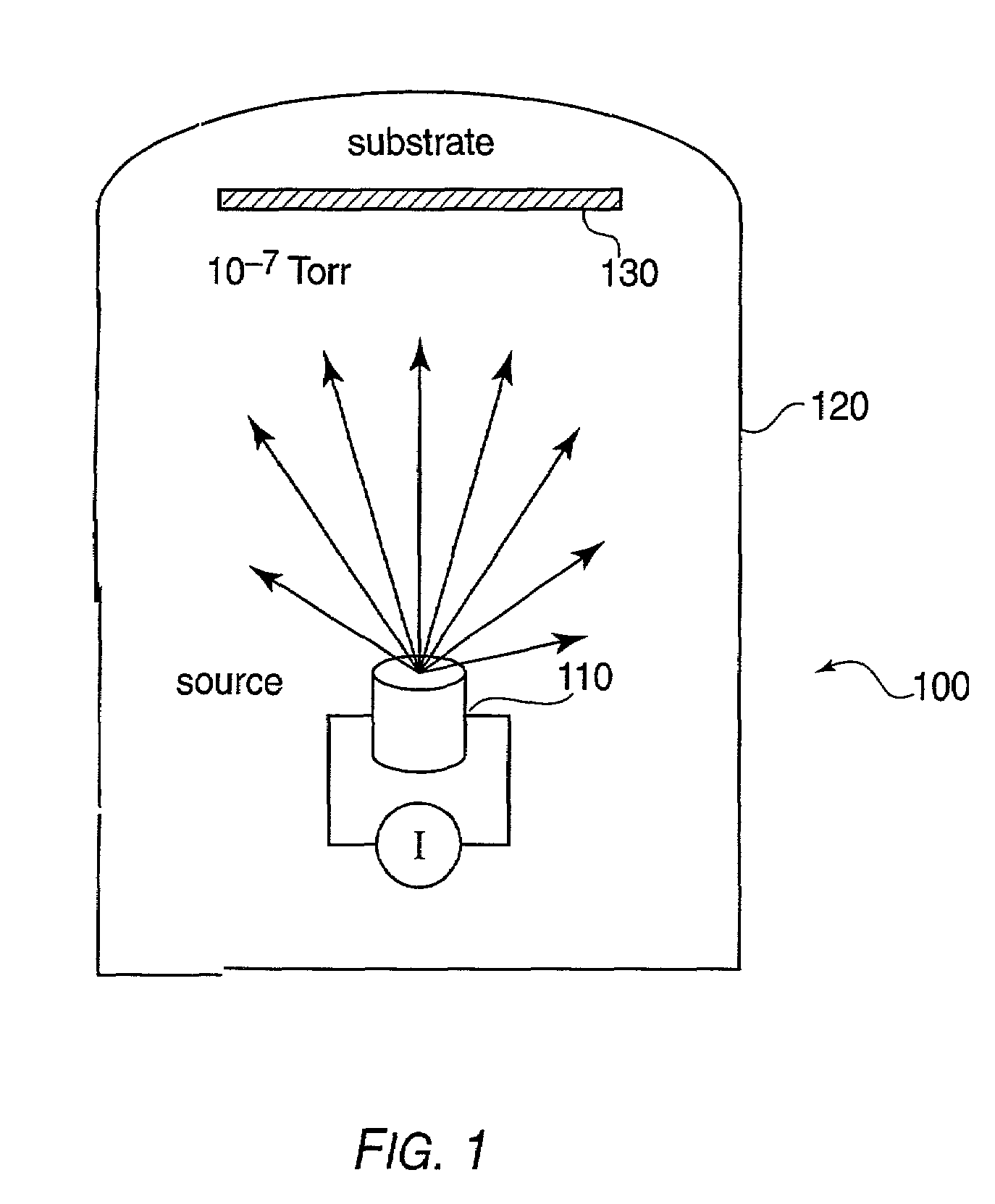
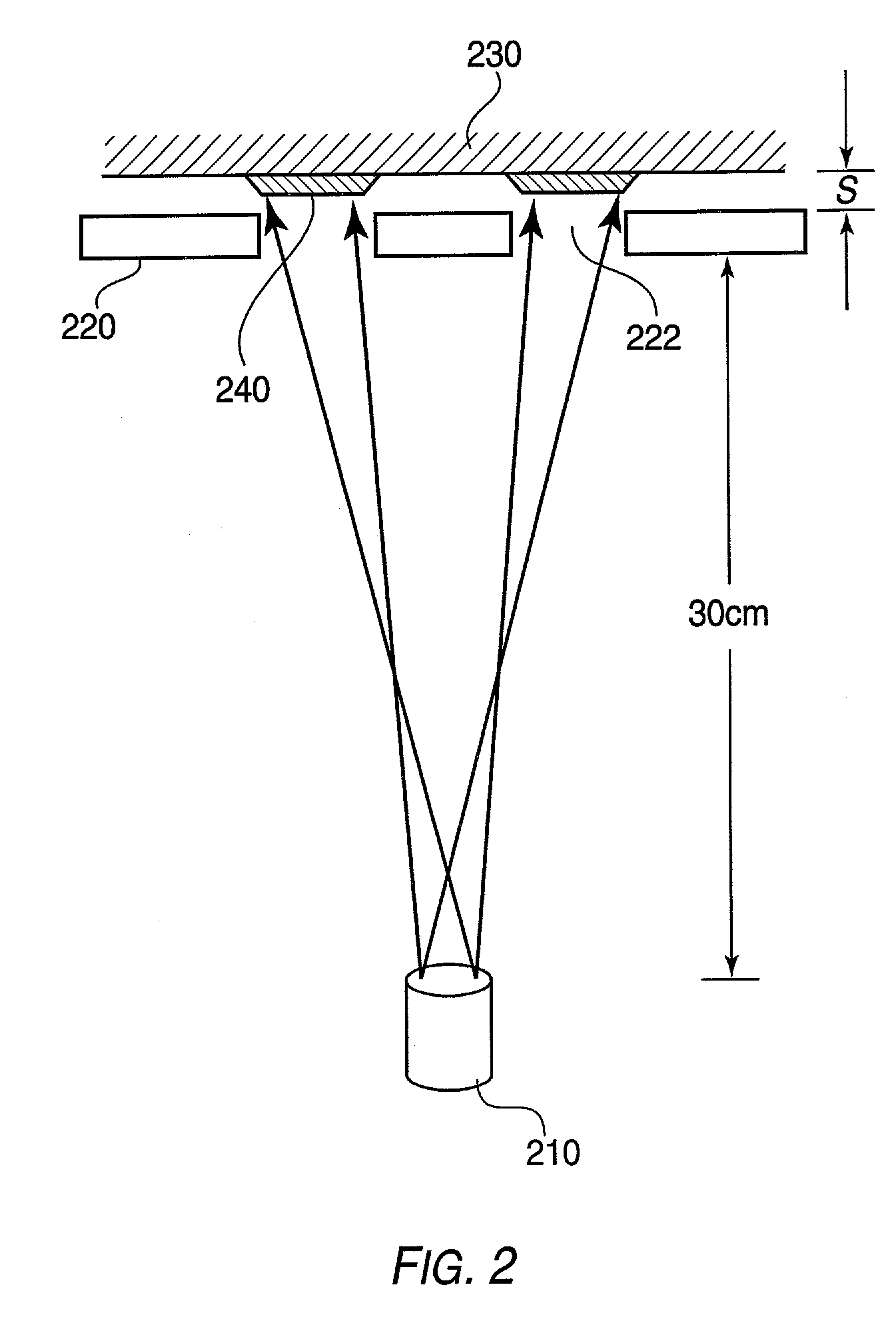
A method of fabricating an organic film is provided. A non-reactive carrier gas is used to transport an organic vapor. The organic vapor is ejected through a nozzle block onto a cooled substrate, to form a patterned organic film. A device for carrying out the method is also provided. The device includes a source of organic vapors, a source of carrier gas and a vacuum chamber. A heated nozzle block attached to the source of organic vapors and the source of carrier gas has at least one nozzle adapted to eject carrier gas and organic vapors onto a cooled substrate disposed within the vacuum chamber.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Analyte sensor method of making the same
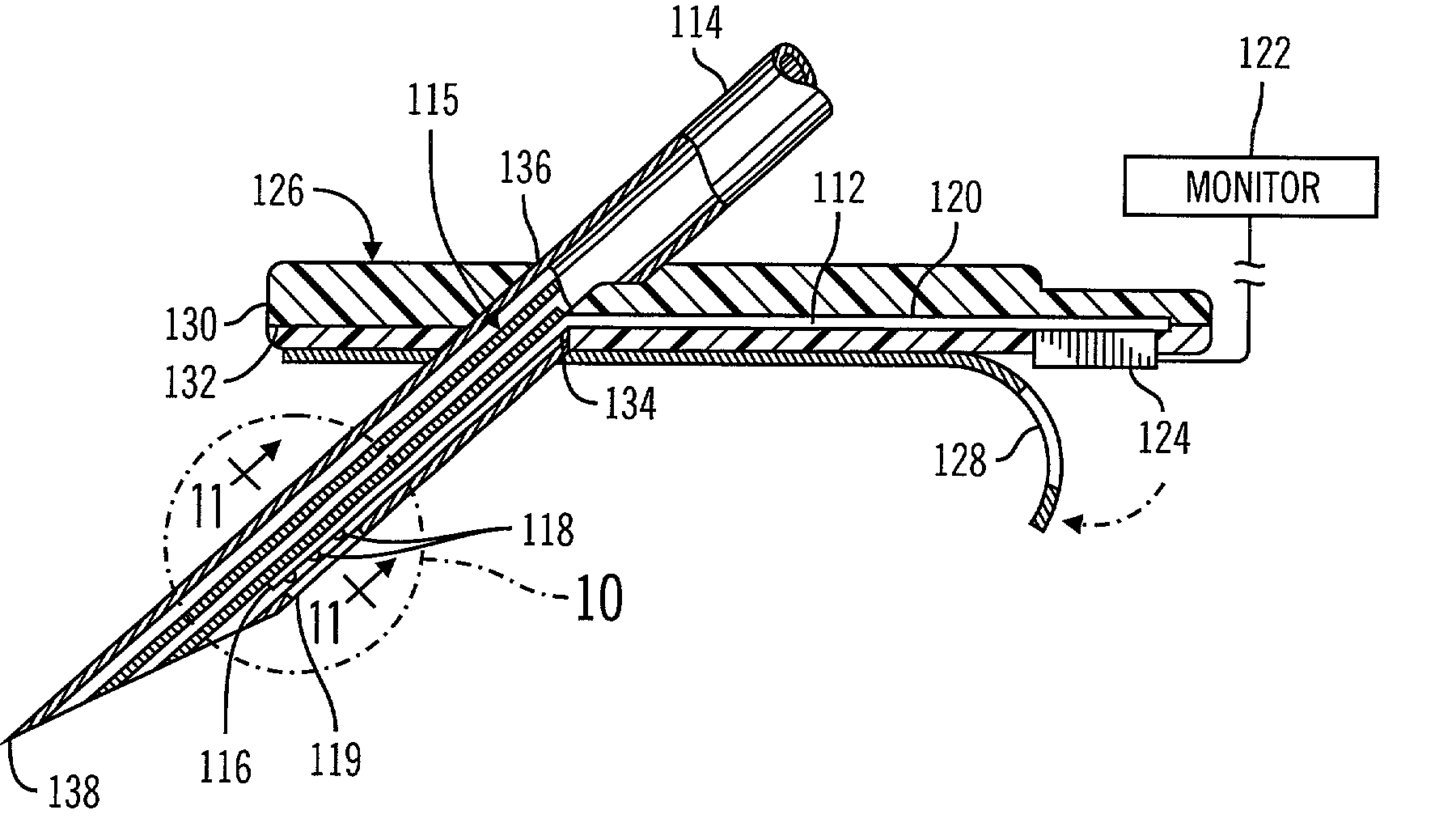
A sensor and method of making the same for implantation in a body that includes a substrate with notches cut in the substrate to form a necked down region in the substrate; and at least one sensor electrode formed from one or more conductive layers. Preferably, the thickness of the substrate ranges from approximately 25μ to 350μ, but the thickness of the substrate can range from 5μ to 750μ. The sensor may be incorporated in to a sensor assembly includes a slotted needle having a slot. The notches creating the necked down region allow the substrate to slide into the slotted needle, which that has the slot narrow enough to permit passage of the necked down region. However, a non-necked down region of the substrate is prevented from pulling out of the slotted needle through the slot. The slot of the slotted needle may also permit the necked down region of the substrate to slide down the slot.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
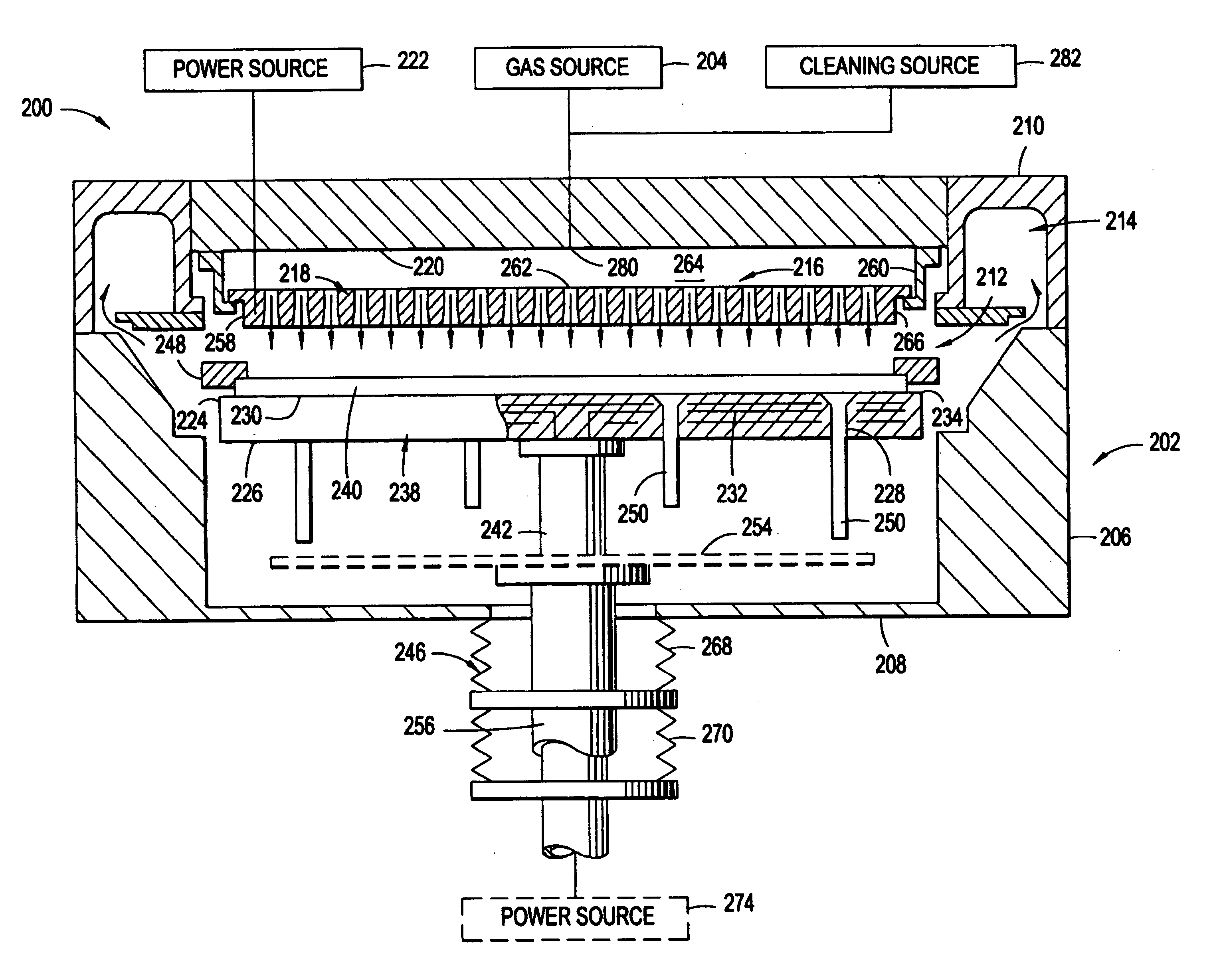
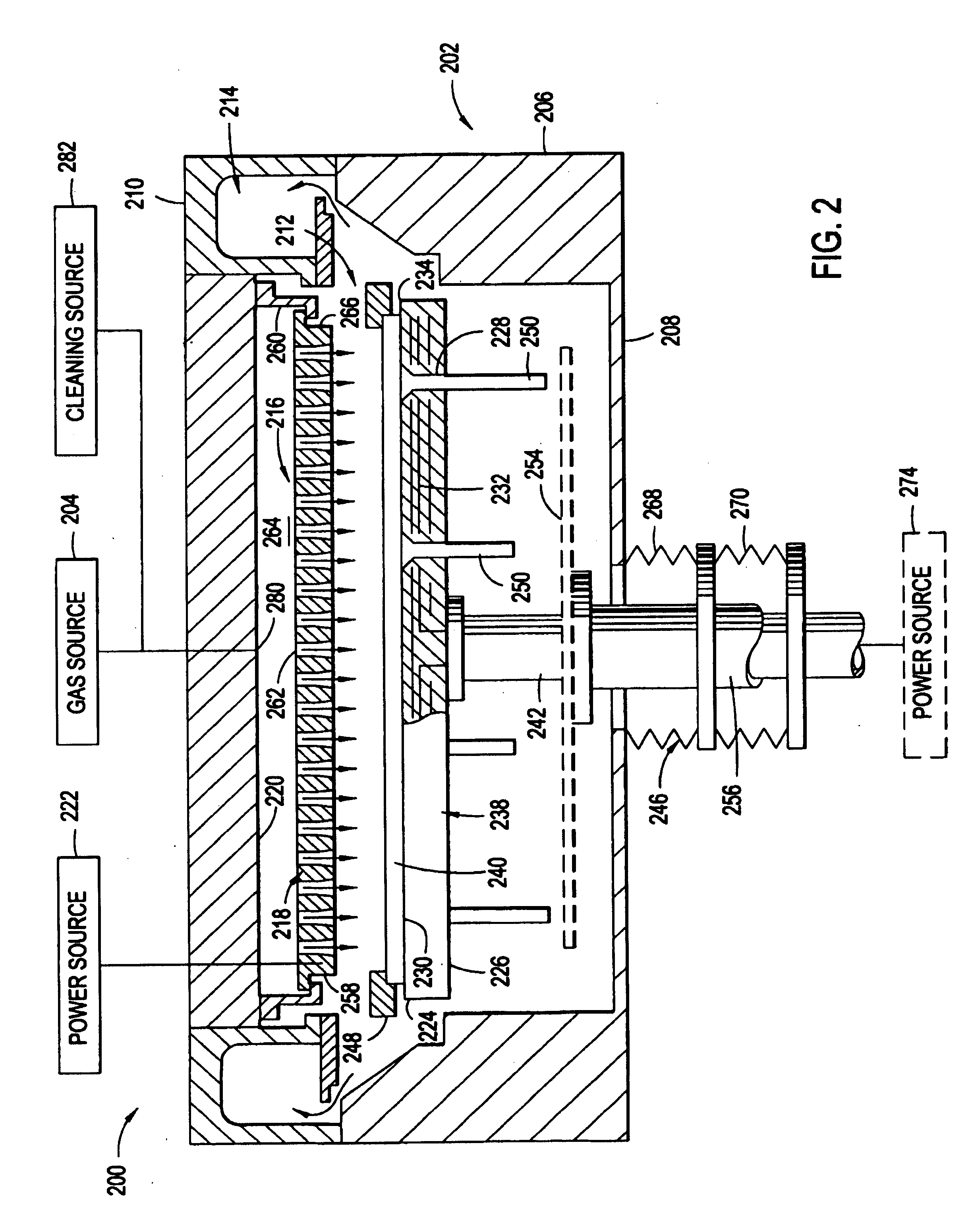
Plasma uniformity control by gas diffuser hole design
ActiveUS20050251990A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
Embodiments of a gas diffuser plate for distributing gas in a processing chamber are provided. The gas distribution plate includes a diffuser plate having an upstream side and a downstream side, and a plurality of gas passages passing between the upstream and downstream sides of the diffuser plate. The gas passages include hollow cathode cavities at the downstream side to enhance plasma ionization. The depths, the diameters, the surface area and density of hollow cathode cavities of the gas passages that extend to the downstream end can be gradually increased from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate to improve the film thickness and property uniformity across the substrate. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can be created by bending the diffuser plate toward downstream side, followed by machining out the convex downstream side. Bending the diffuser plate can be accomplished by a thermal process or a vacuum process. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can also be created computer numerically controlled machining. Diffuser plates with gradually increasing diameters, depths and surface areas of the hollow cathode cavities from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate have been shown to produce improved uniformities of film thickness and film properties.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
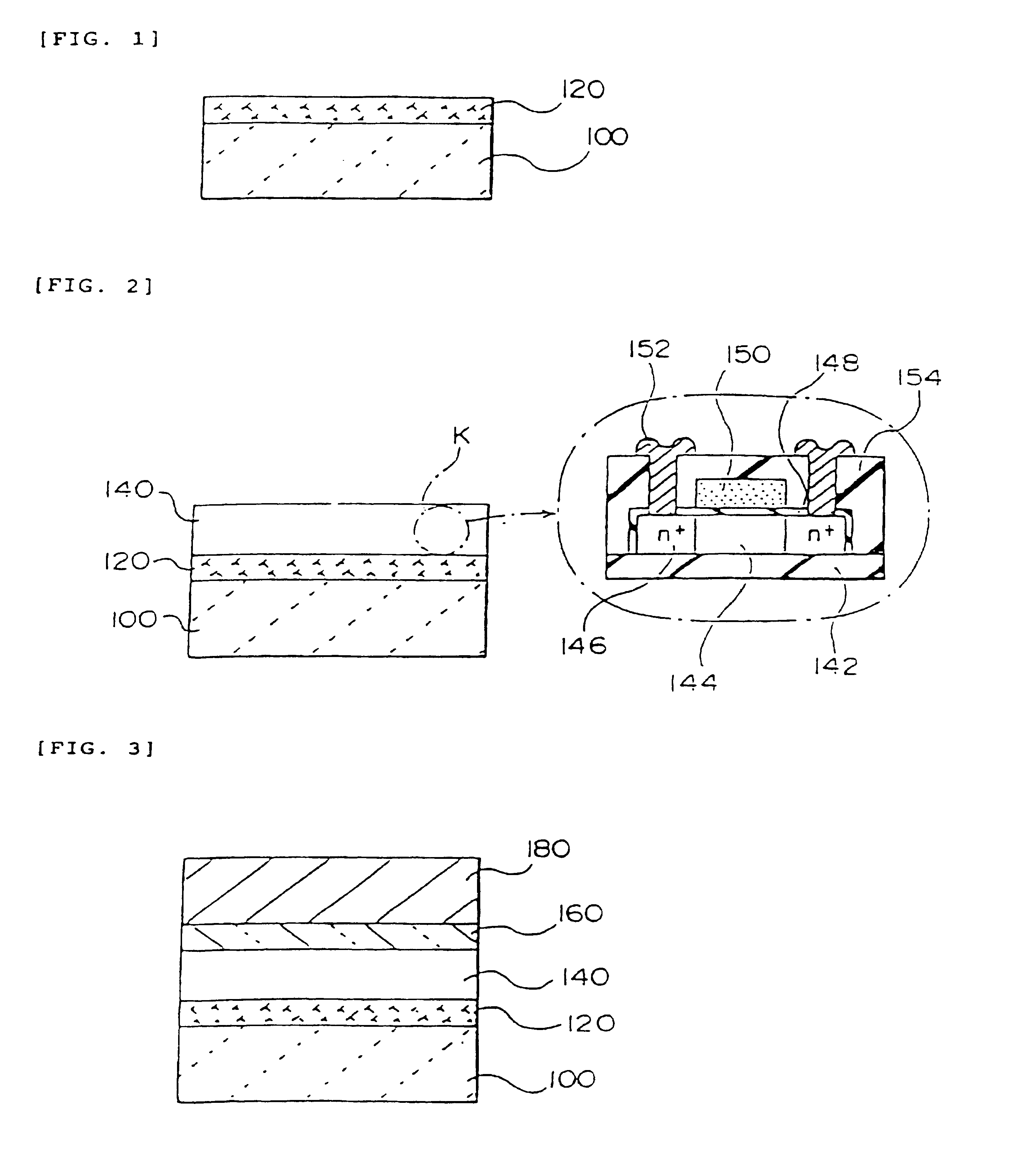
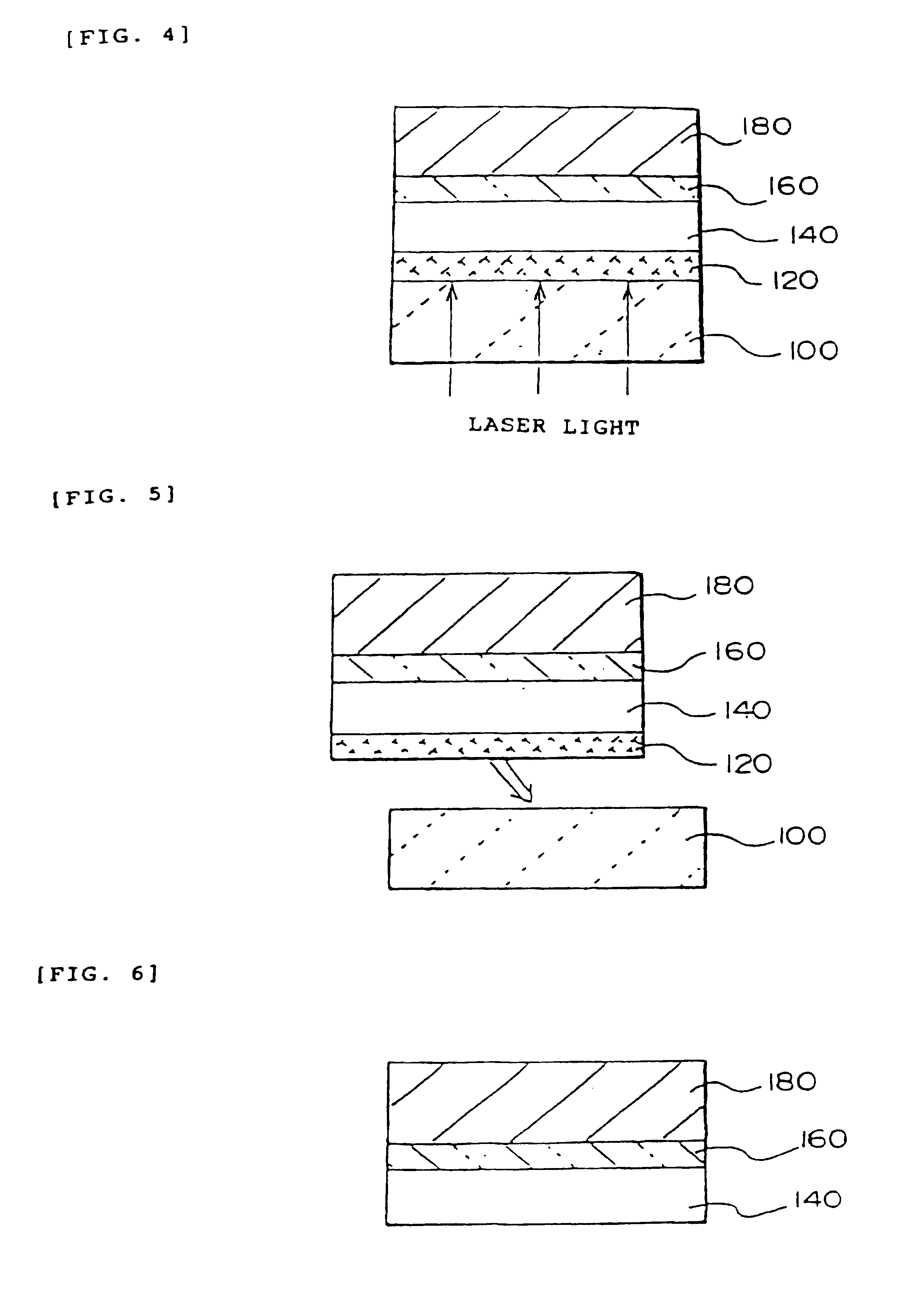
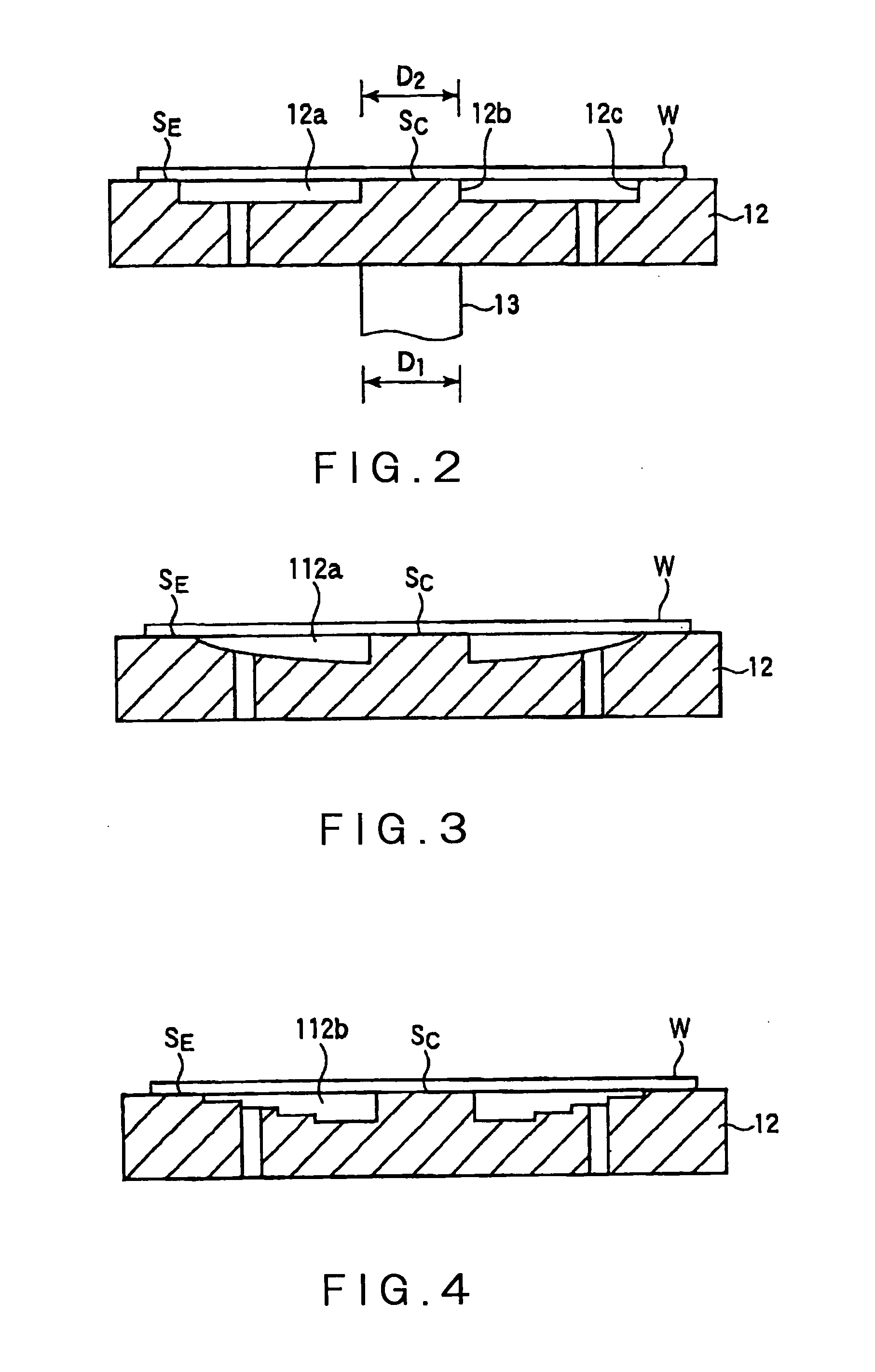
Manufacturing method of active matrix substrate, active matrix substrate and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUSRE38466E1Property for applicationMaintain good propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayActive matrix
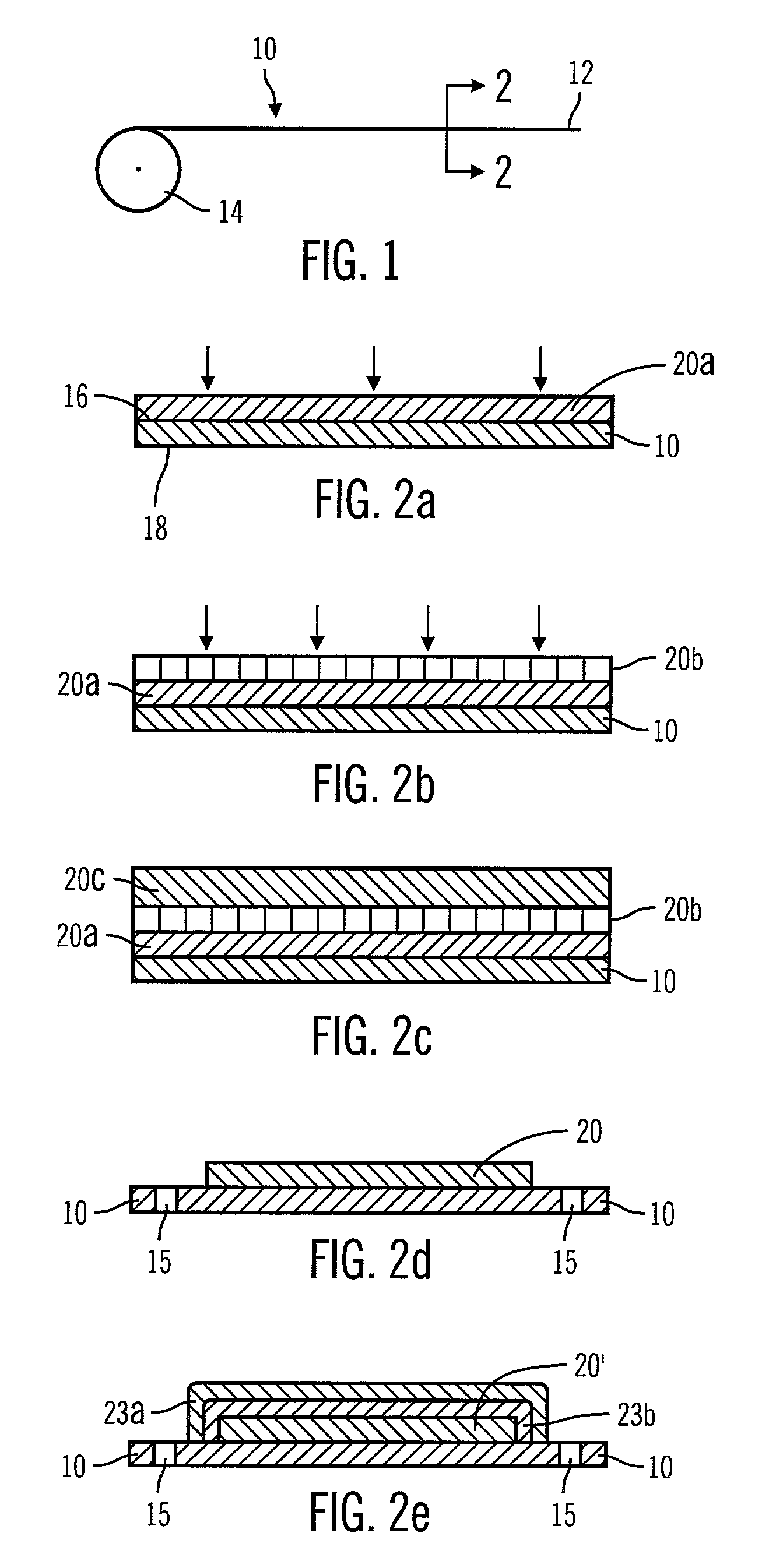
A method of manufacturing an active matrix substrate is provided that uses a technique of transferring a thin film device. In forming thin film transistors and pixel electrodes on an original substrate before transfer, an insulator film such as an interlayer insulation film or the like, is previously removed before the pixel electrodes are formed. Further, the original substrate is separated by exfoliation to transfer the device to a transfer material to cause the pixel electrodes to partially appear in the surface or the vicinity of the surface of the device. This portion permits application of a voltage to a liquid crystal through the pixel electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
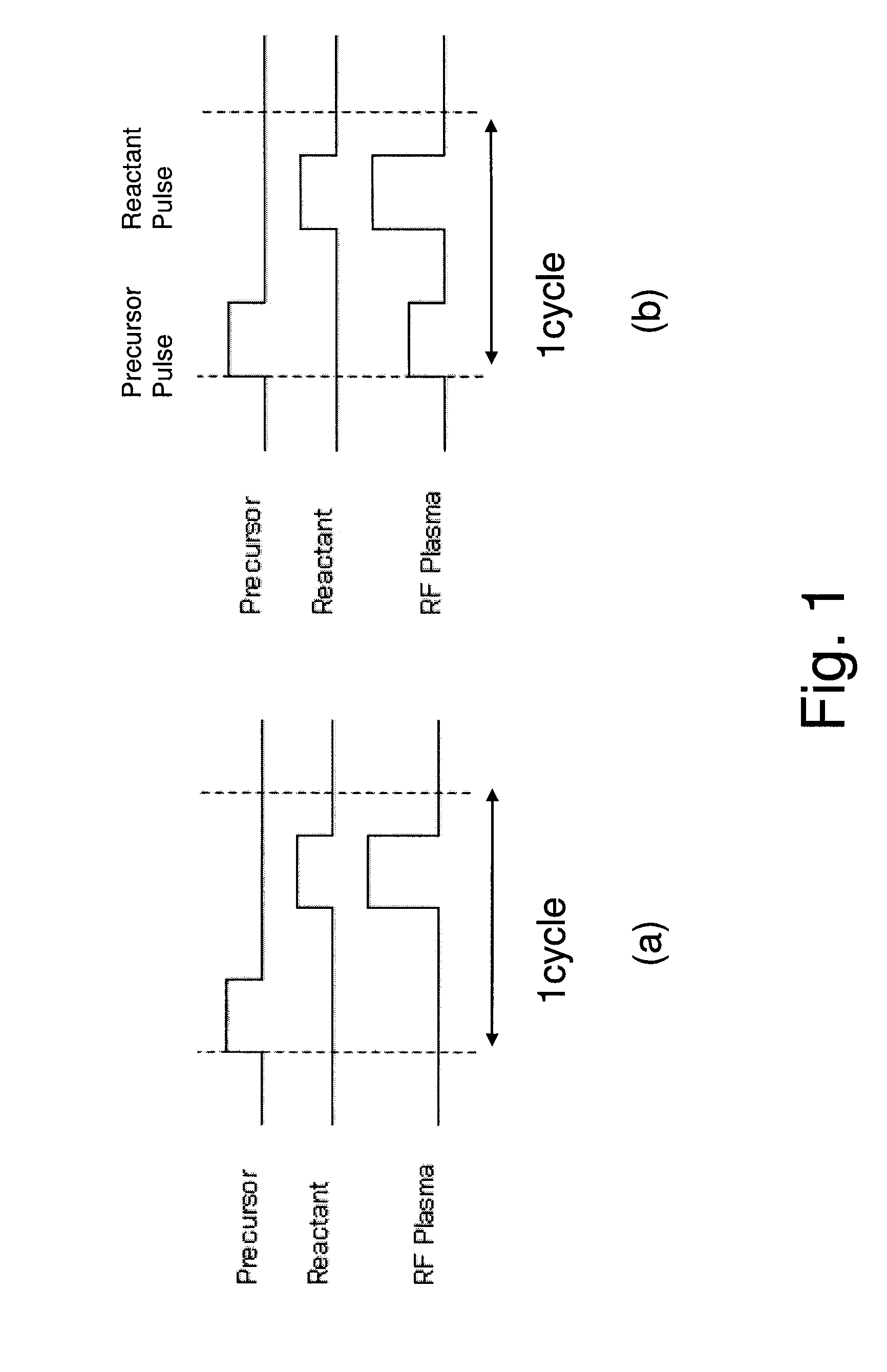
Method of Forming Insulation Film by Modified PEALD
ActiveUS20100124621A1Increase coverageImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringPhysical chemistry
Owner:ASM JAPAN
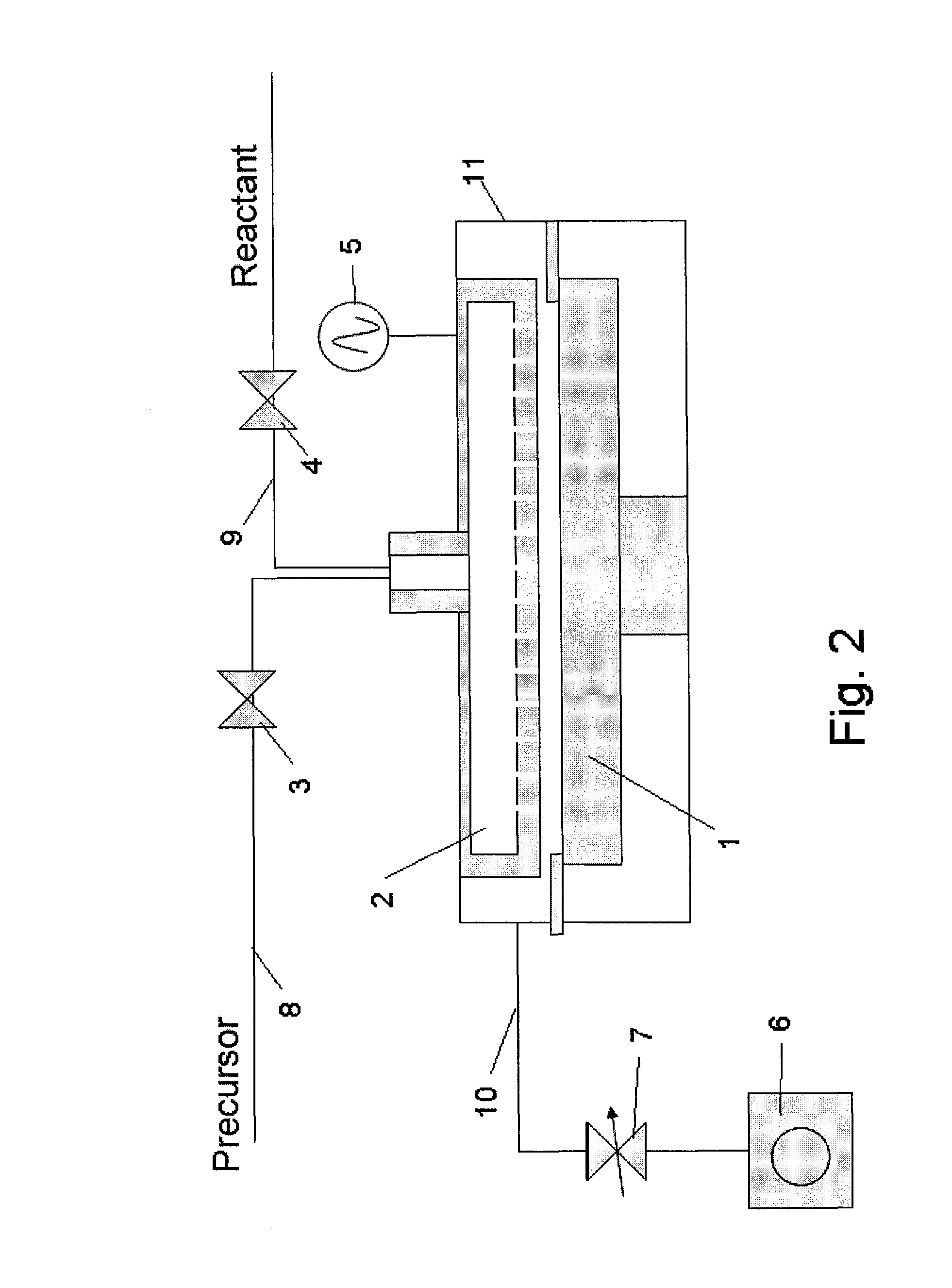
Deposition apparatus
ActiveUS20090156015A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingProduct gasEngineering
A deposition apparatus configured to form a thin film on a substrate includes: a reactor wall; a substrate support positioned under the reactor wall; and a showerhead plate positioned above the substrate support. The showerhead plate defines a reaction space together with the substrate support. The apparatus also includes one or more gas conduits configured to open to a periphery of the reaction space at least while an inert gas is supplied therethrough. The one or more gas conduits are configured to supply the inert gas inwardly toward the periphery of the substrate support around the reaction space. This configuration prevents reactant gases from flowing between a substrate and the substrate support during a deposition process, thereby preventing deposition of an undesired thin film and impurity particles on the back side of the substrate.
Owner:ASM KOREA LTD
Atomic layer deposition method of depositing an oxide on a substrate
The invention includes atomic layer deposition methods of depositing an oxide on a substrate. In one implementation, a substrate is positioned within a deposition chamber. A first species is chemisorbed onto the substrate to form a first species monolayer within the deposition chamber from a gaseous precursor. The chemisorbed first species is contacted with remote plasma oxygen derived at least in part from at least one of O2 and O3 and with remote plasma nitrogen effective to react with the first species to form a monolayer comprising an oxide of a component of the first species monolayer. The chemisorbing and the contacting with remote plasma oxygen and with remote plasma nitrogen are successively repeated effective to form porous oxide on the substrate. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Process chamber for dielectric gapfill
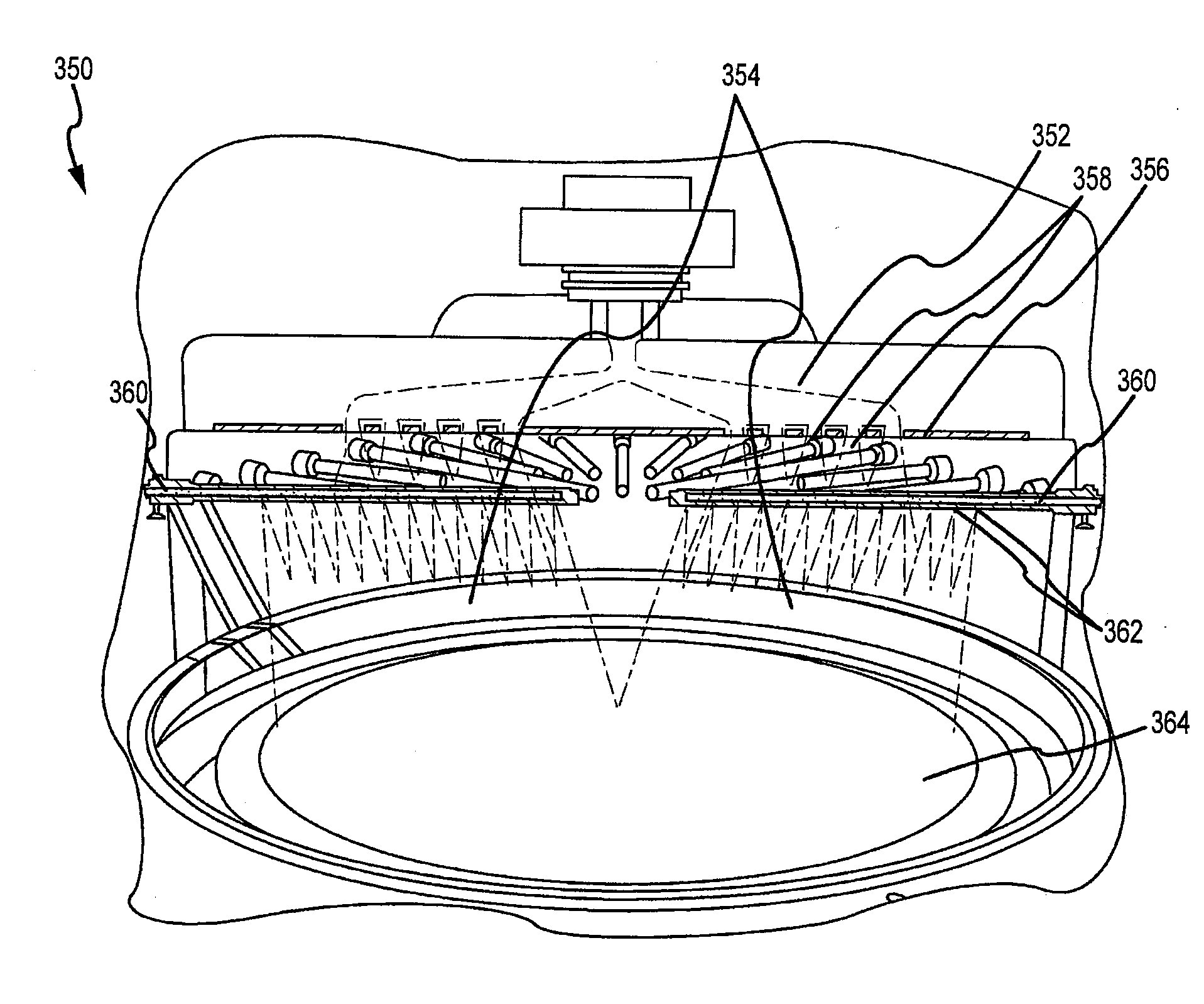
InactiveUS20070281106A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaDistribution system
A system to form a dielectric layer on a substrate from a plasma of dielectric precursors is described. The system may include a deposition chamber, a substrate stage in the deposition chamber to hold the substrate, and a remote plasma generating system coupled to the deposition chamber, where the plasma generating system is used to generate a dielectric precursor having one or more reactive radicals. The system may also include a precursor distribution system that includes at least one top inlet and a plurality of side inlets. The top inlet may be positioned above the substrate stage and the side inlets may be radially distributed around the substrate stage. The reactive radical precursor may be supplied to the deposition chamber through the top inlet. An in-situ plasma generating system may also be included to generate the plasma in the deposition chamber from the dielectric precursors supplied to the deposition chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Capillary electroflow apparatus and method
The present invention concerns an apparatus for conducting a microfluidic process. The apparatus comprises integral first and second plates. The first plate comprises an array of sample receiving elements for receiving a plurality of samples from an array of sample containers and dispensing the samples. The second plate comprises a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. Also disclosed is a method for processing an array of samples. At least a portion of each sample in an array of sample wells is simultaneously transferred to a corresponding array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels by means of a corresponding array of sample receiving elements that is in integral fluid communication with the array of microfluidic networks. The samples are then processed. Also disclosed is a device for conducting a microfluidic process wherein the device comprising a planar substrate having a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. A plurality of such devices may be present on a continuous sheet. The invention further includes kits for carrying out microfluidic processes comprising an apparatus as described above.
Owner:ACLARA BIOSCIENCES INC
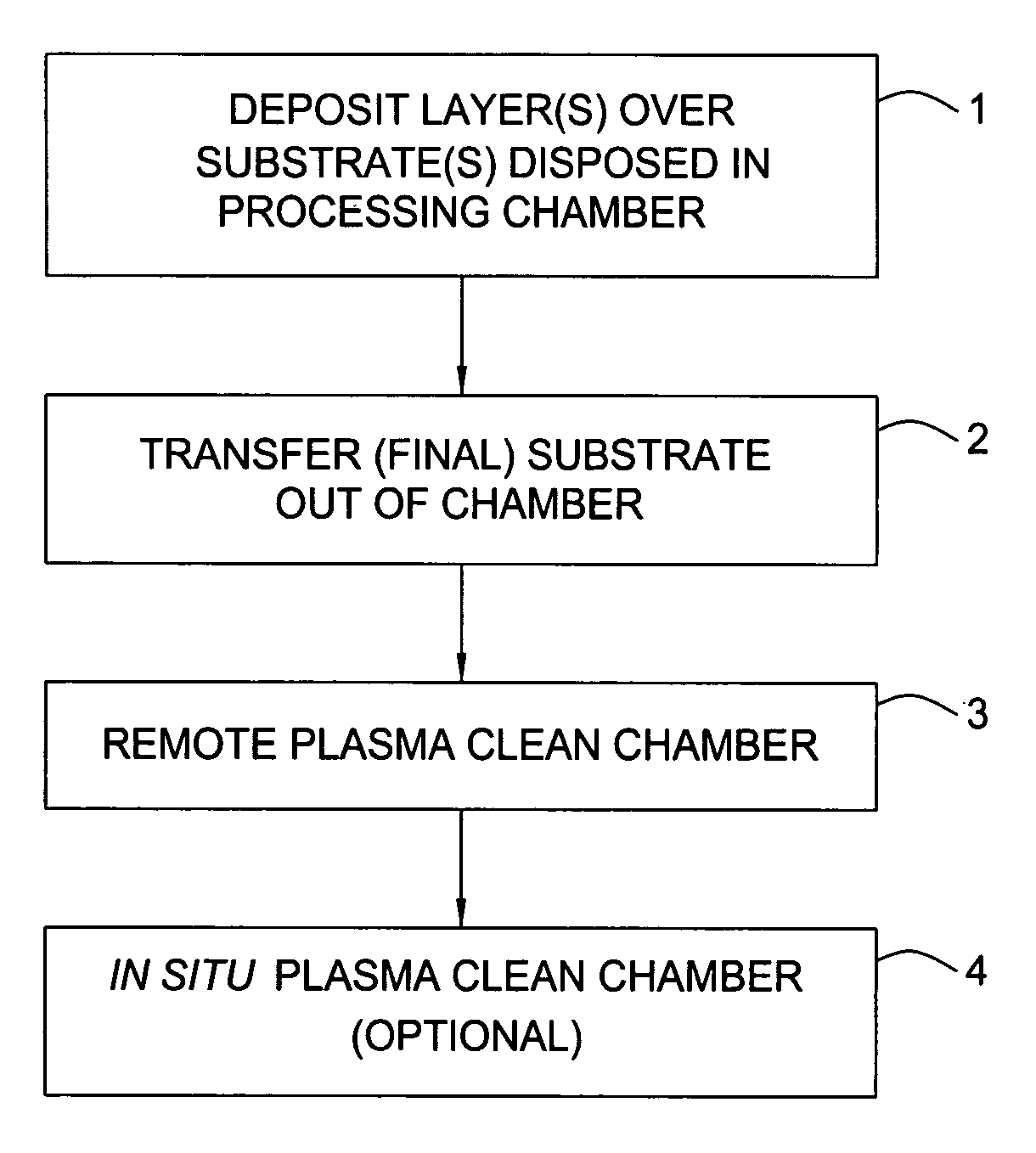
High-power dielectric seasoning for stable wafer-to-wafer thickness uniformity of dielectric CVD films
InactiveUS20060093756A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCleaning methods
A method for seasoning a deposition chamber wherein the chamber components and walls are densely coated with a material that does not contain carbon prior to deposition of an organo-silicon material on a substrate. An optional carbon-containing layer may be deposited therebetween. A chamber cleaning method using low energy plasma and low pressure to remove residue from internal chamber surfaces is provided and may be combined with the seasoning process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Forming Substrate Structure by Filling Recesses with Deposition Material
InactiveUS20100041179A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsMaterials science
Owner:VEECO ALD
Lithographic Focus and Dose Measurement Using A 2-D Target
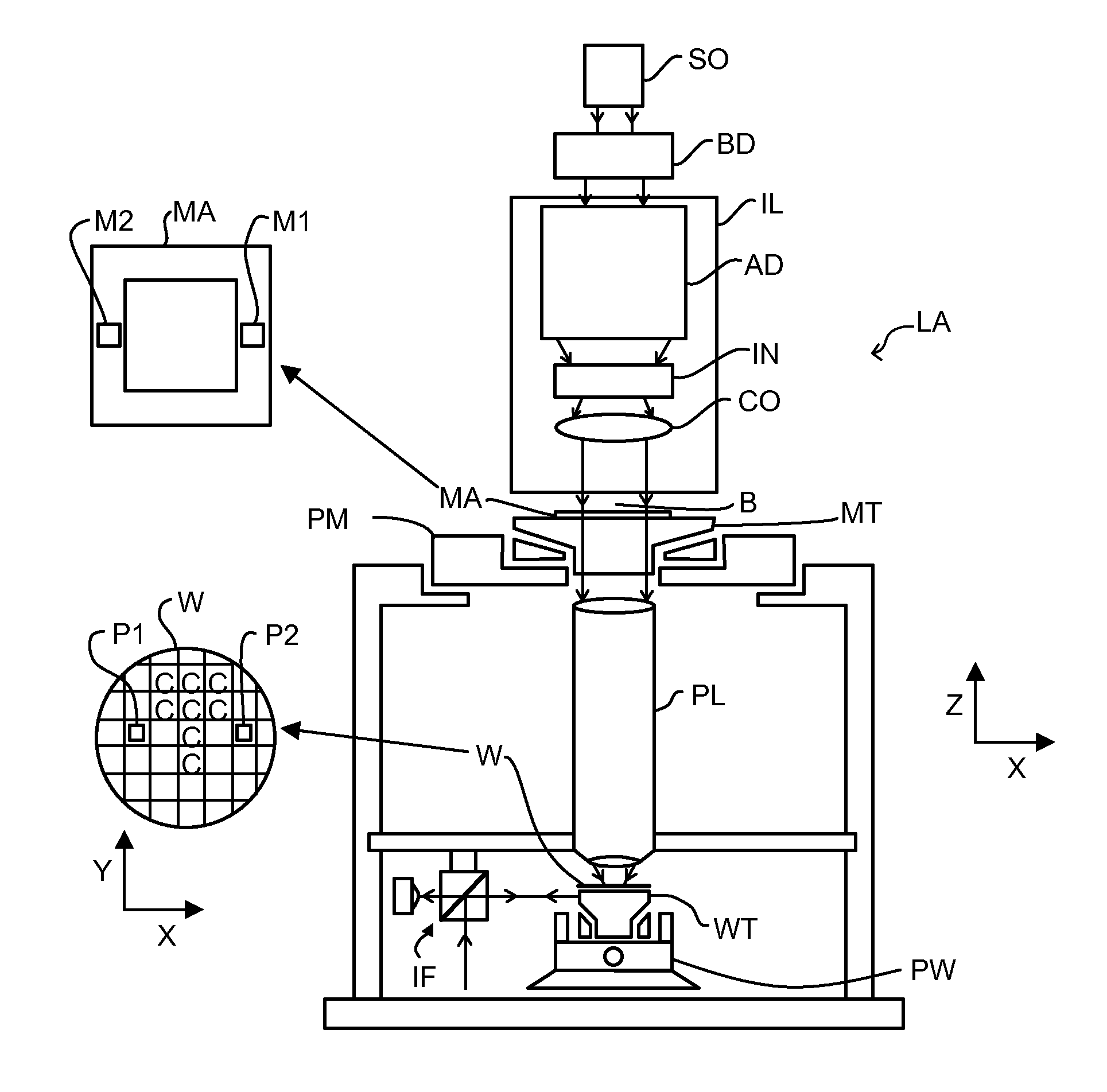
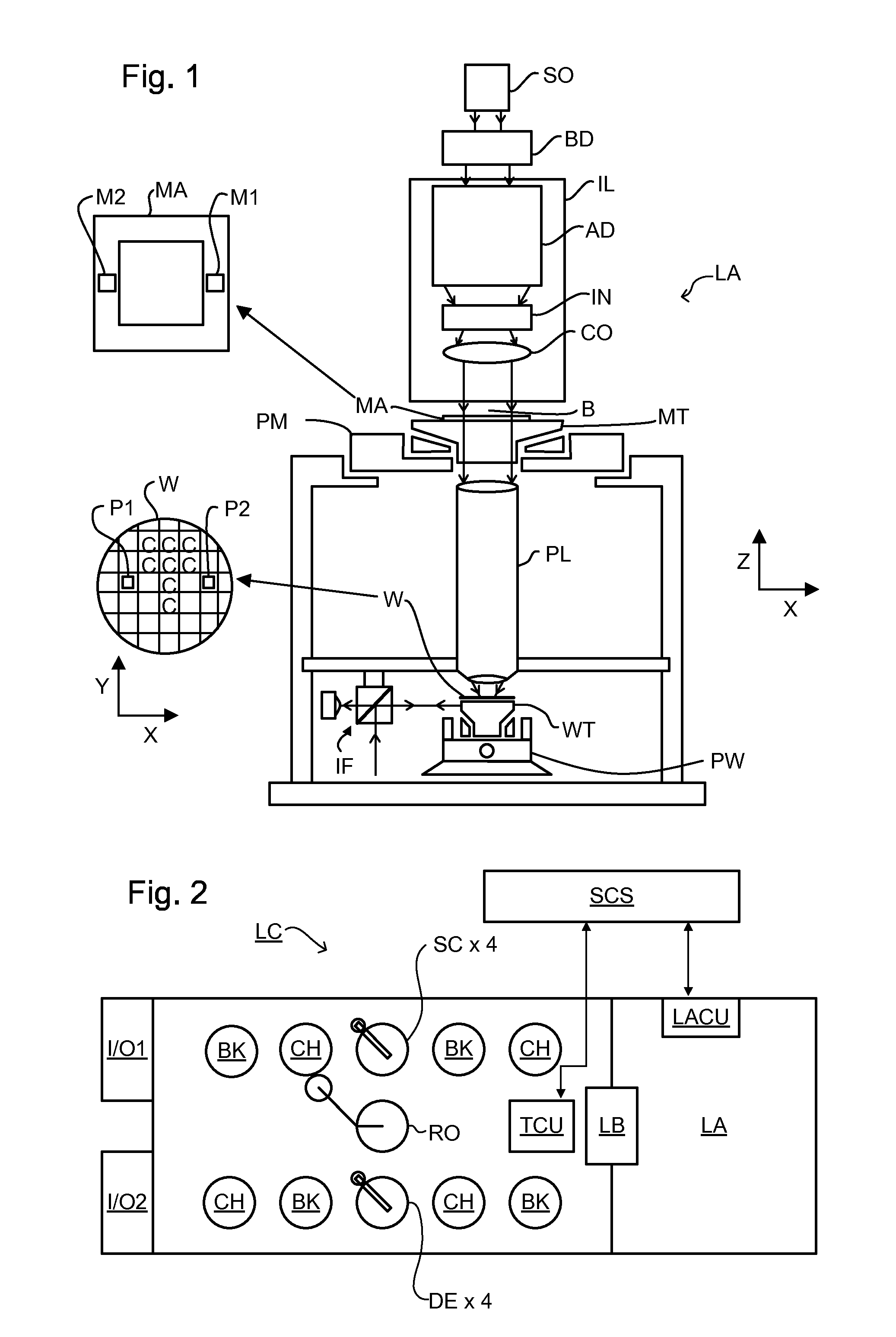
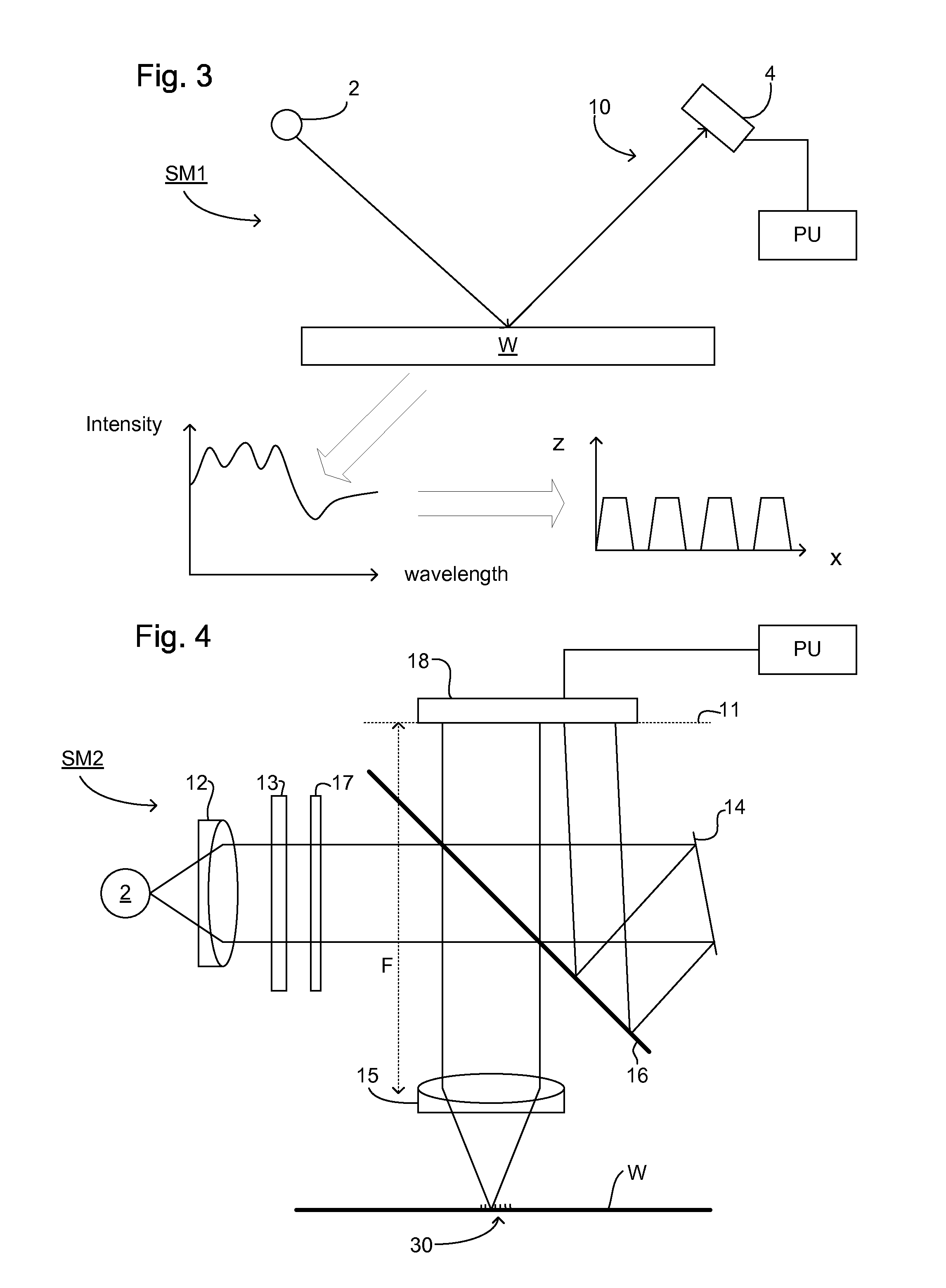
ActiveUS20110249244A1Minimize overall surface areaArea minimizationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiologyScatterometer
In order to determine whether an exposure apparatus is outputting the correct dose of radiation and its projection system is focusing the radiation correctly, a test pattern is used on a mask for printing a specific marker onto a substrate. This marker is then measured by an inspection apparatus, such as a scatterometer, to determine whether there are errors in focus and dose and other related properties. The test pattern is configured such that changes in focus and dose may be easily determined by measuring the properties of a pattern that is exposed using the mask. The test pattern may be a 2D pattern where physical or geometric properties, e.g., pitch, are different in each of the two dimensions. The test pattern may also be a one-dimensional pattern made up of an array of structures in one dimension, the structures being made up of at least one substructure, the substructures reacting differently to focus and dose and giving rise to an exposed pattern from which focus and dose may be determined.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
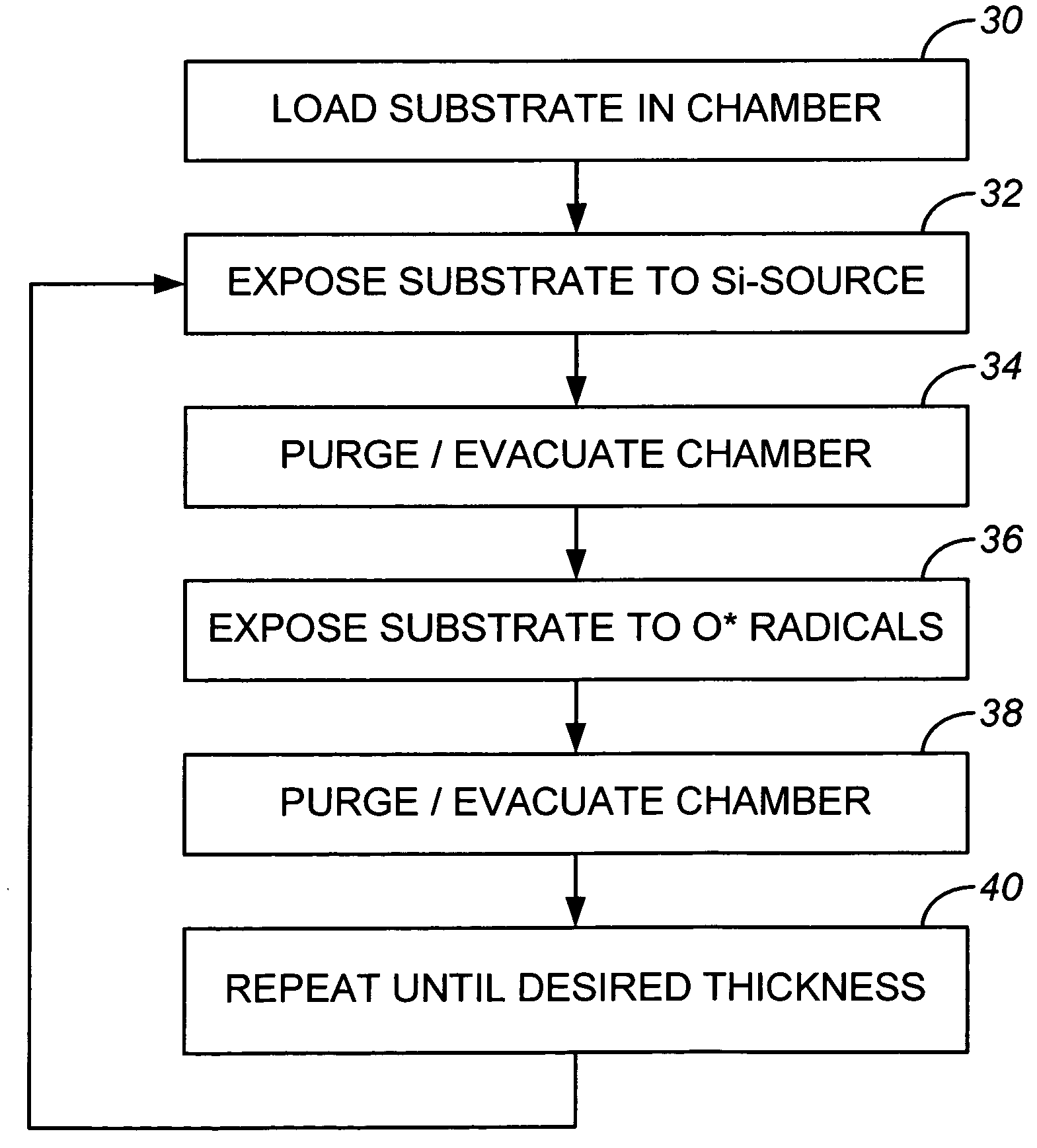
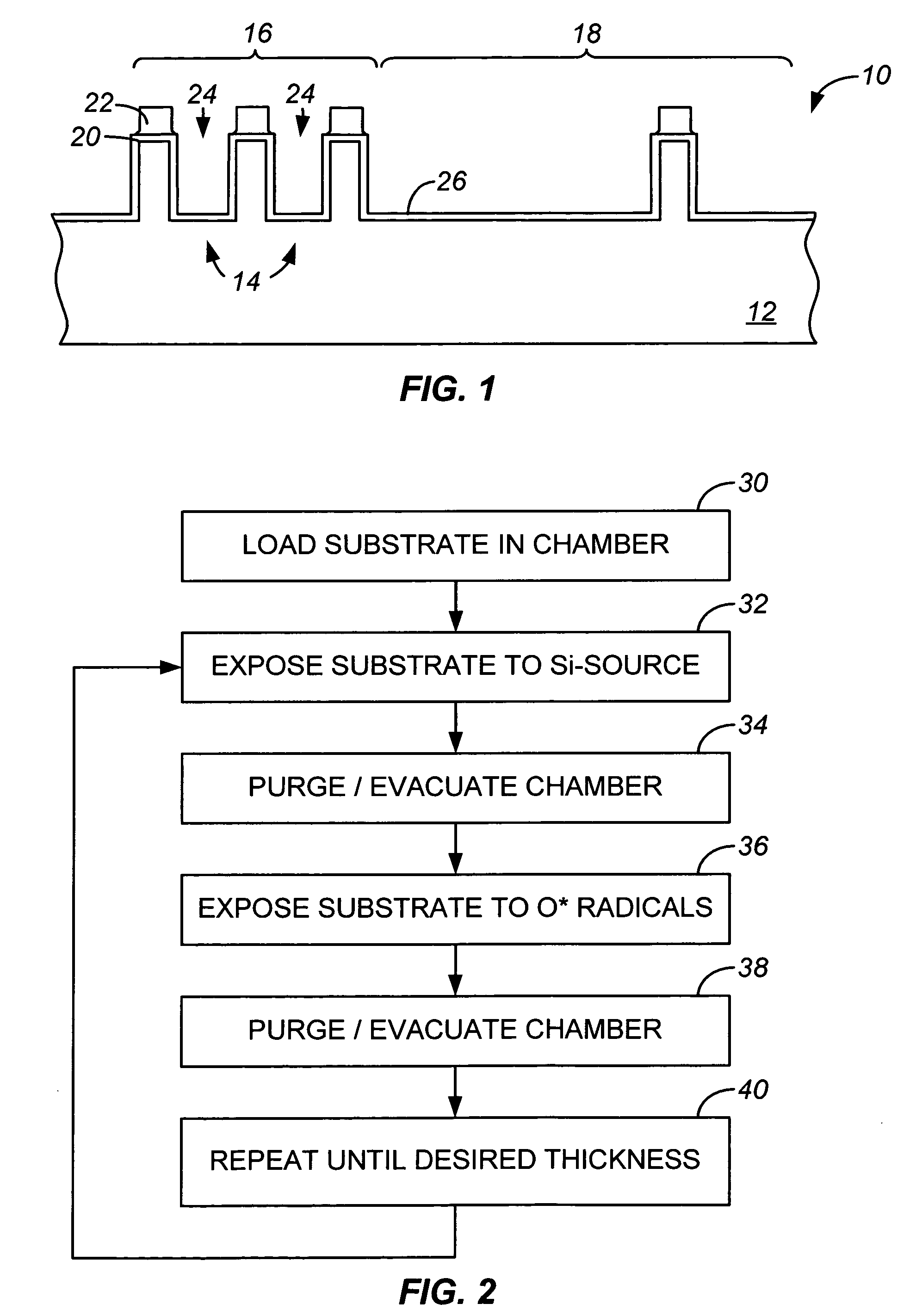
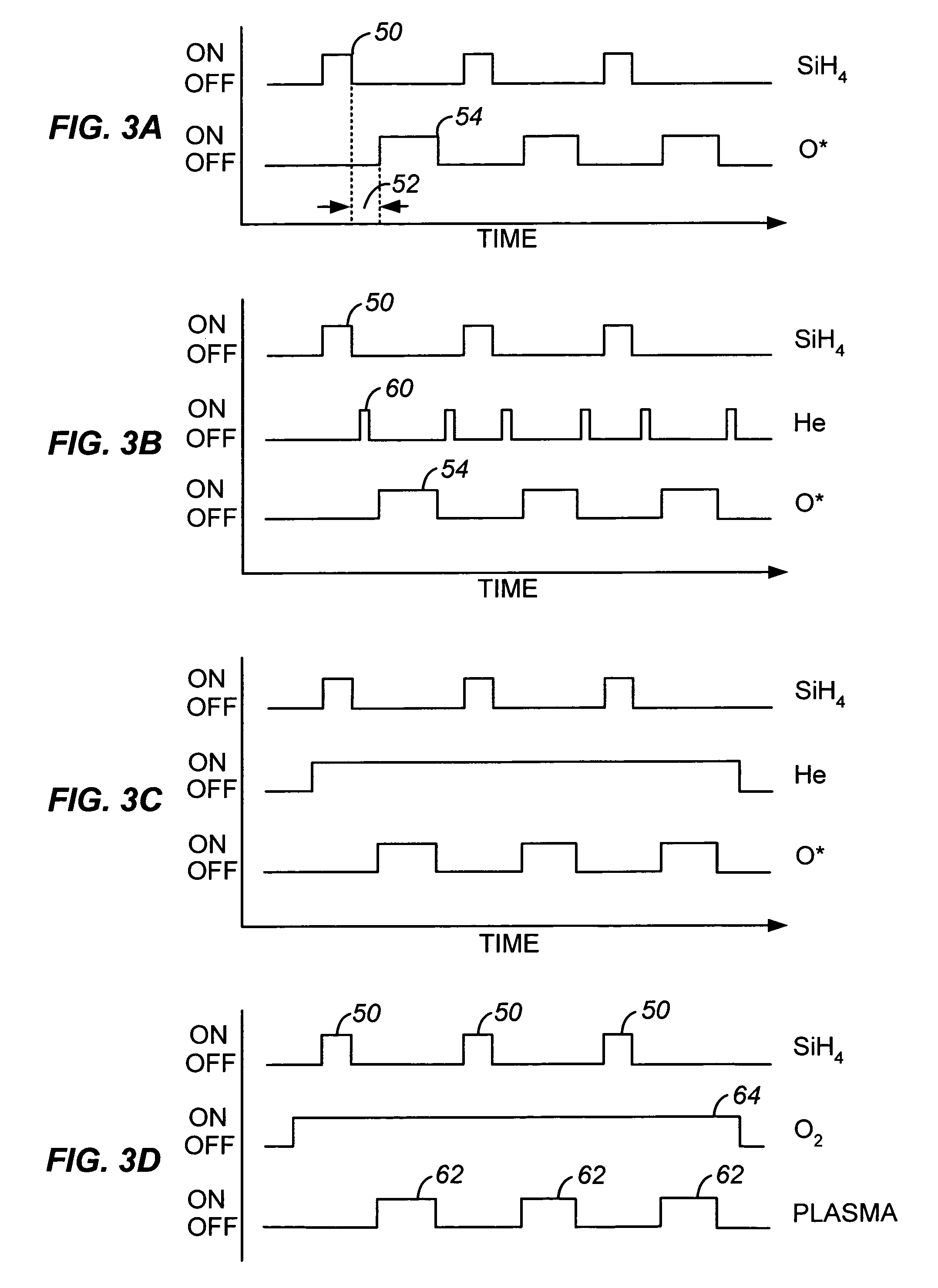
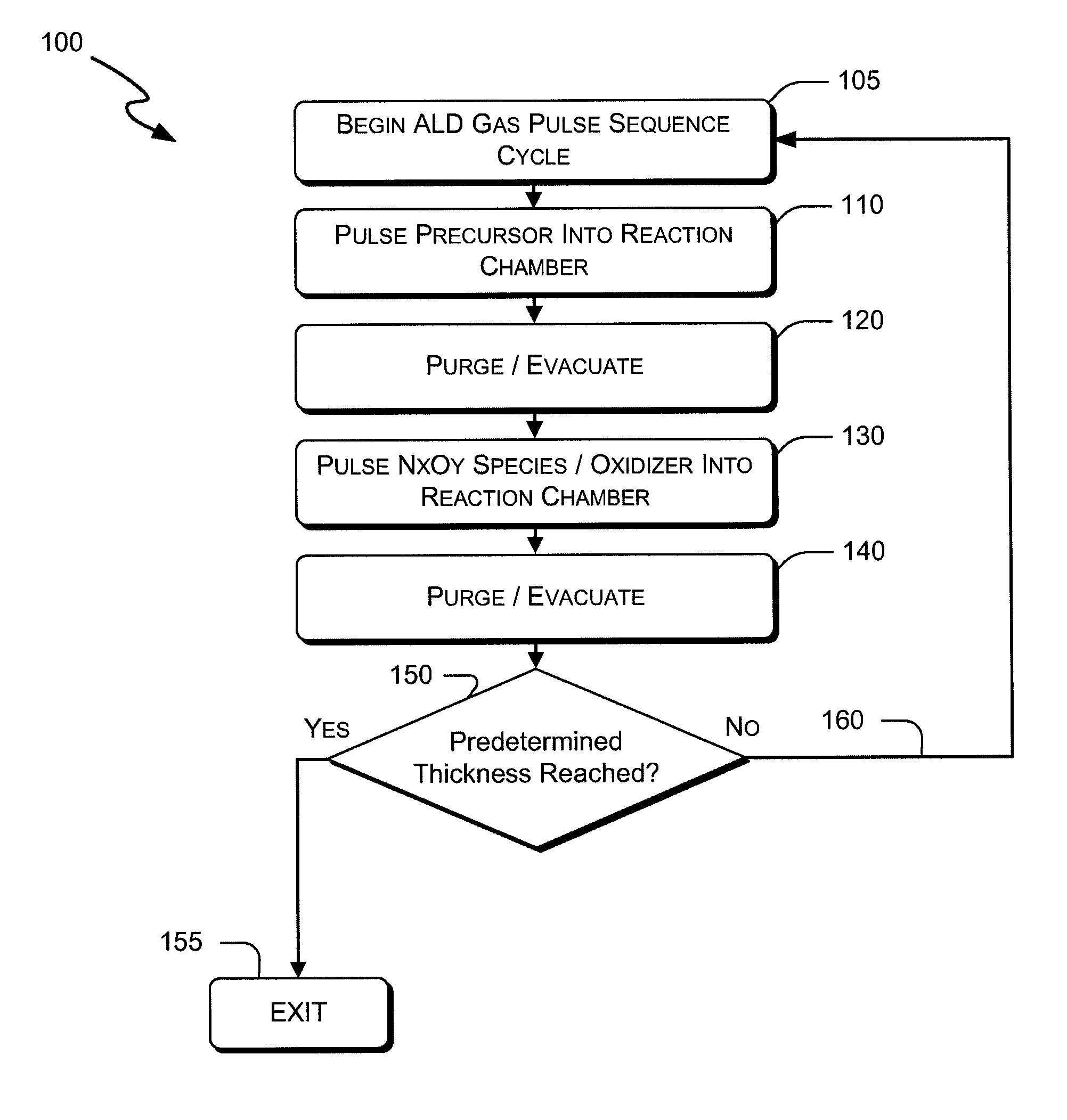
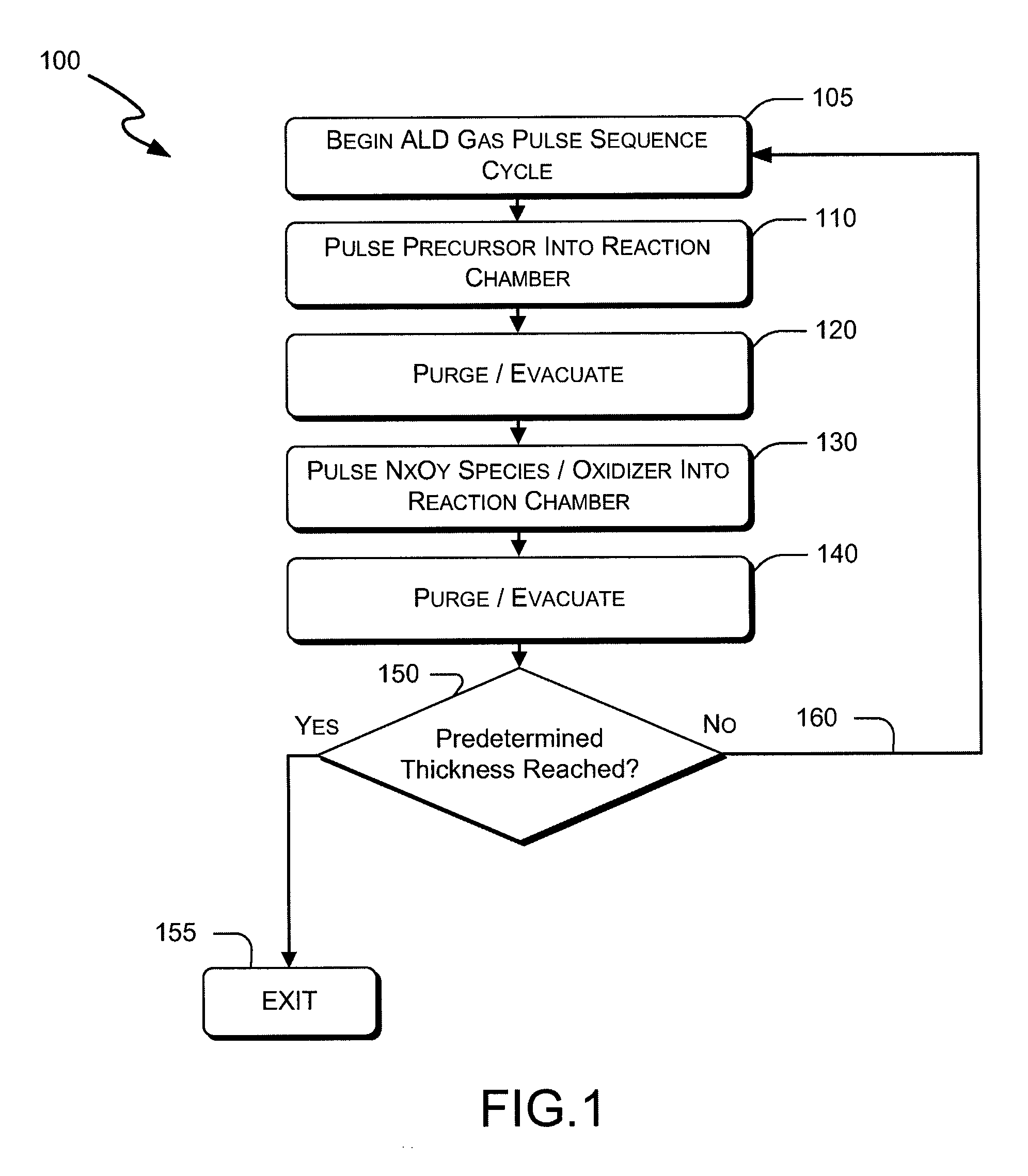
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
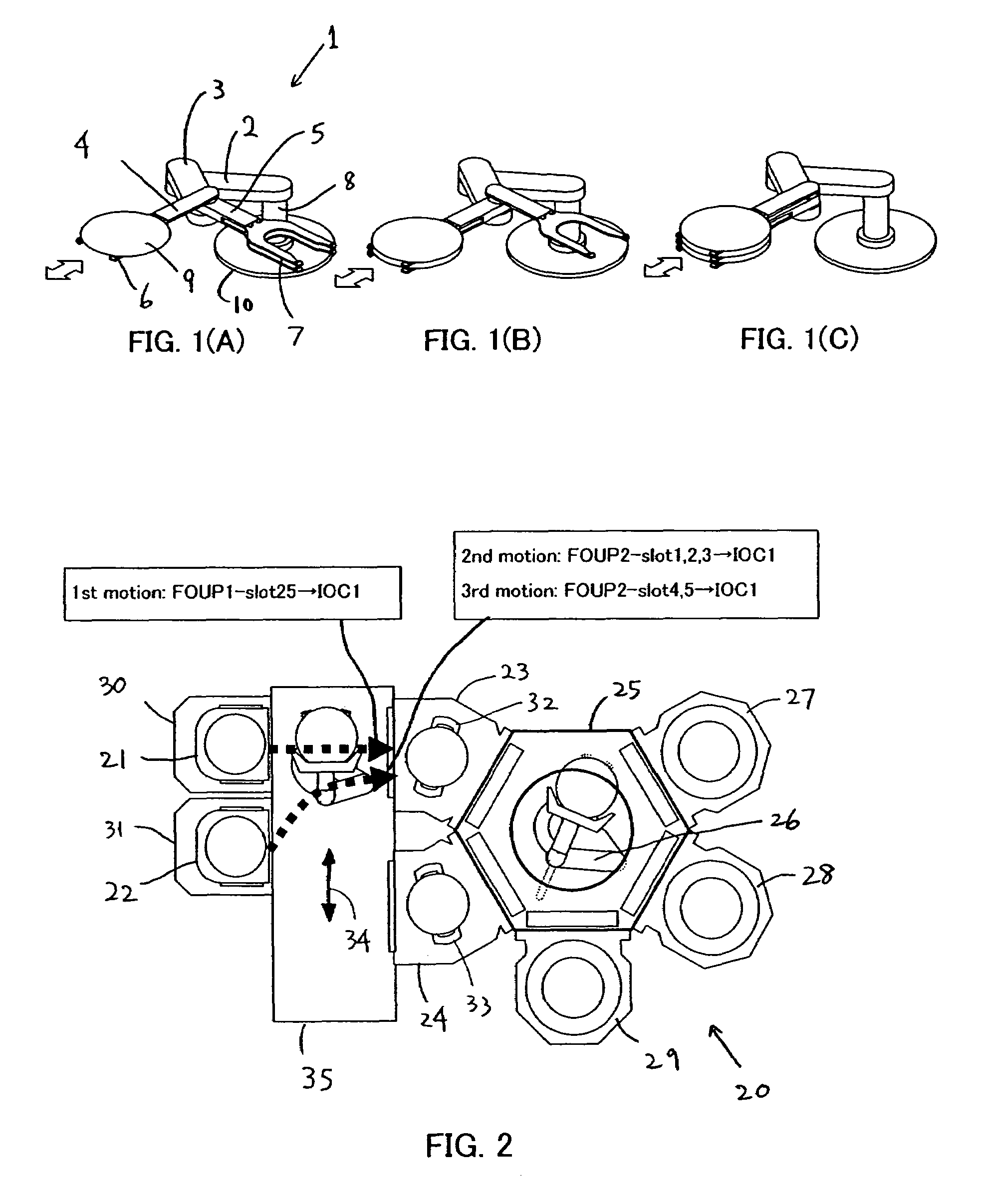
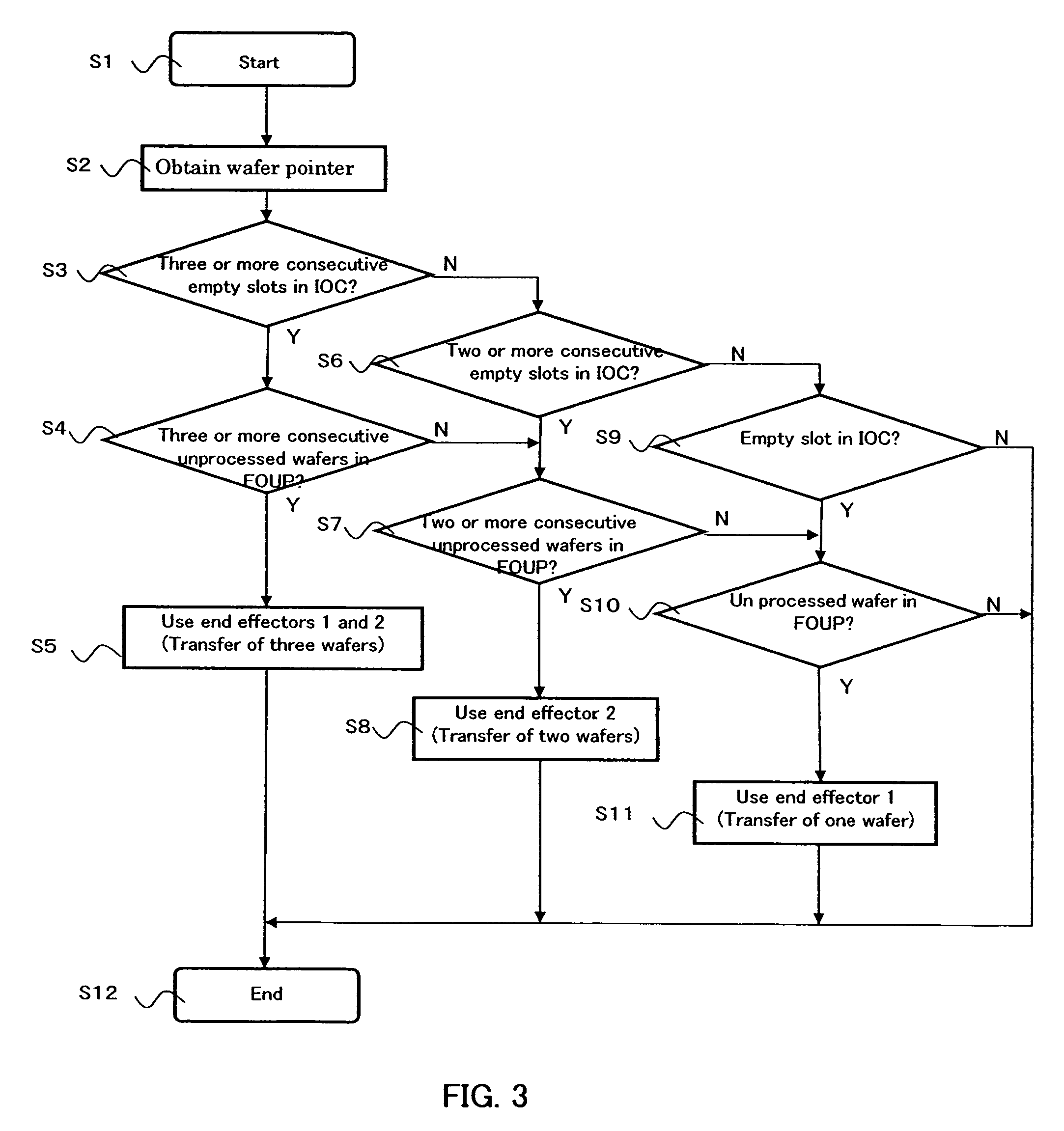
Semiconductor substrate transfer apparatus and semiconductor substrate processing apparatus equipped with the same
A semiconductor substrate transfer apparatus for transferring semiconductor substrates from a first container to a second container, includes: multiple end effectors; at least one robot arm with which the multiple end effectors are independently rotatably joined; and a controller storing software including instructions to judge which end effector or end effectors in the multiple end effectors are to be selected based on a distribution status of substrates stored in the first and second containers and to rotate the selected end effector(s) for unloading a substrate or substrates from the first container and loading the substrate or substrates to the second container.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Substrate susceptors for receiving semiconductor substrates to be deposited upon and methods of depositing materials over semiconductor substrates
In one implementation, a substrate susceptor for receiving a semiconductor substrate for selective epitaxial silicon-comprising depositing thereon, where the depositing comprises measuring emissivity of the susceptor from at least one susceptor location in a non-contacting manner, includes a body having a front substrate receiving side, a back side, and a peripheral edge. At least one susceptor location from which emissivity is to be measured is received on at least one of the front substrate receiving side, the back side, and the edge. Such at least one susceptor location comprises an outermost surface comprising a material upon which selective epitaxial silicon will not deposit upon during selective epitaxial silicon depositing on a semiconductor substrate received by the susceptor for at least an initial thickness of epitaxial silicon depositing on said substrate. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
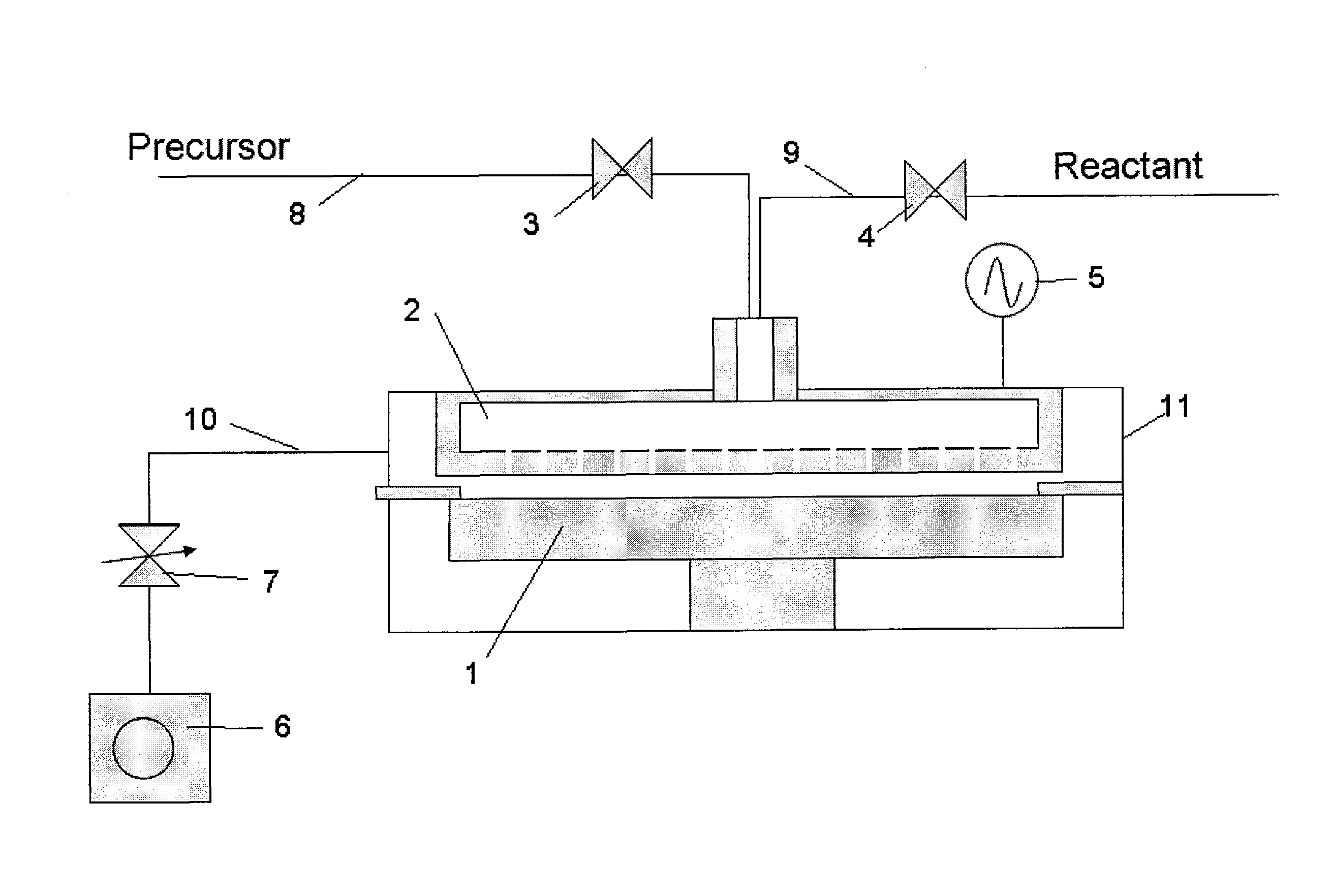
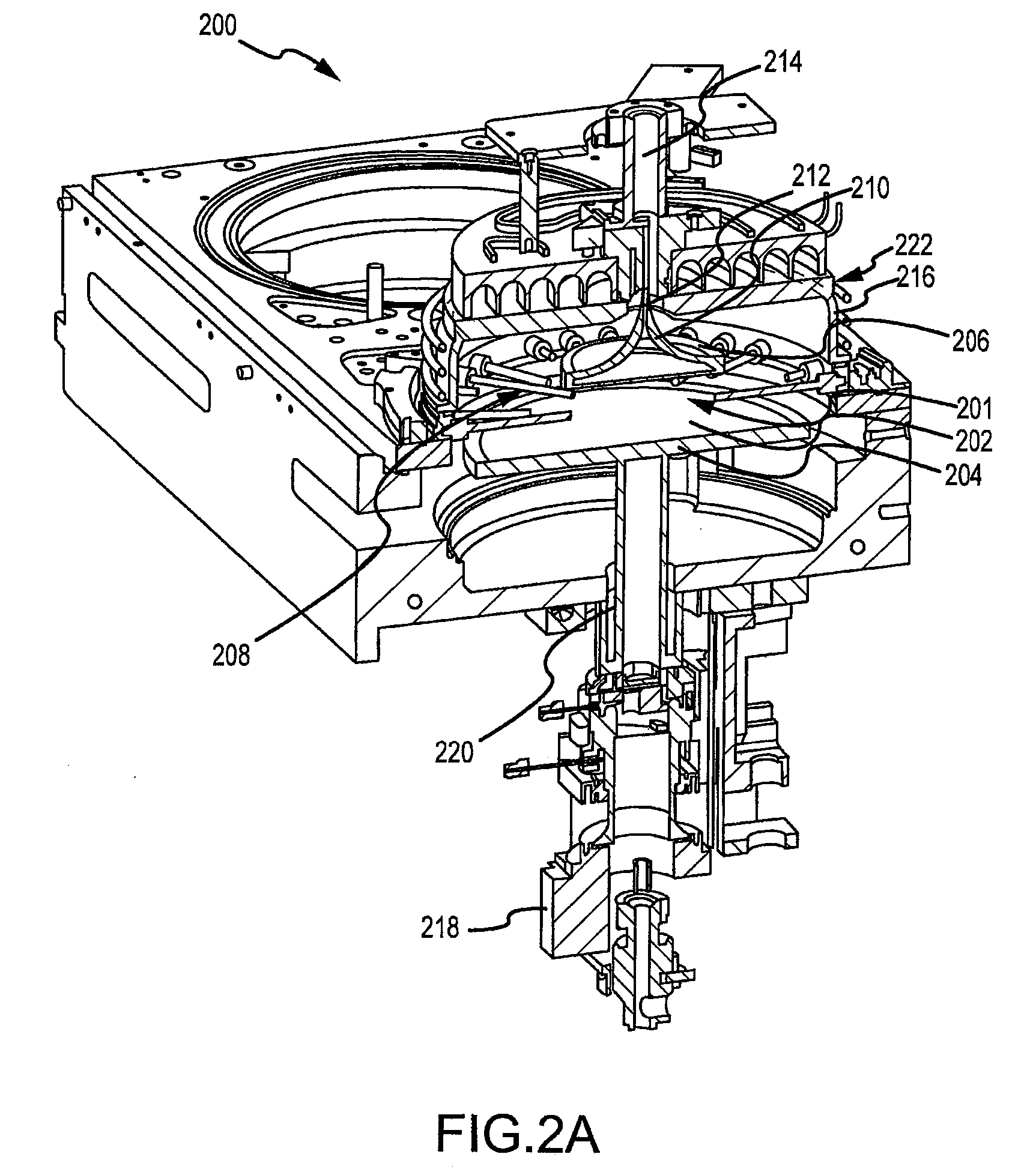
Continuous flow deposition system
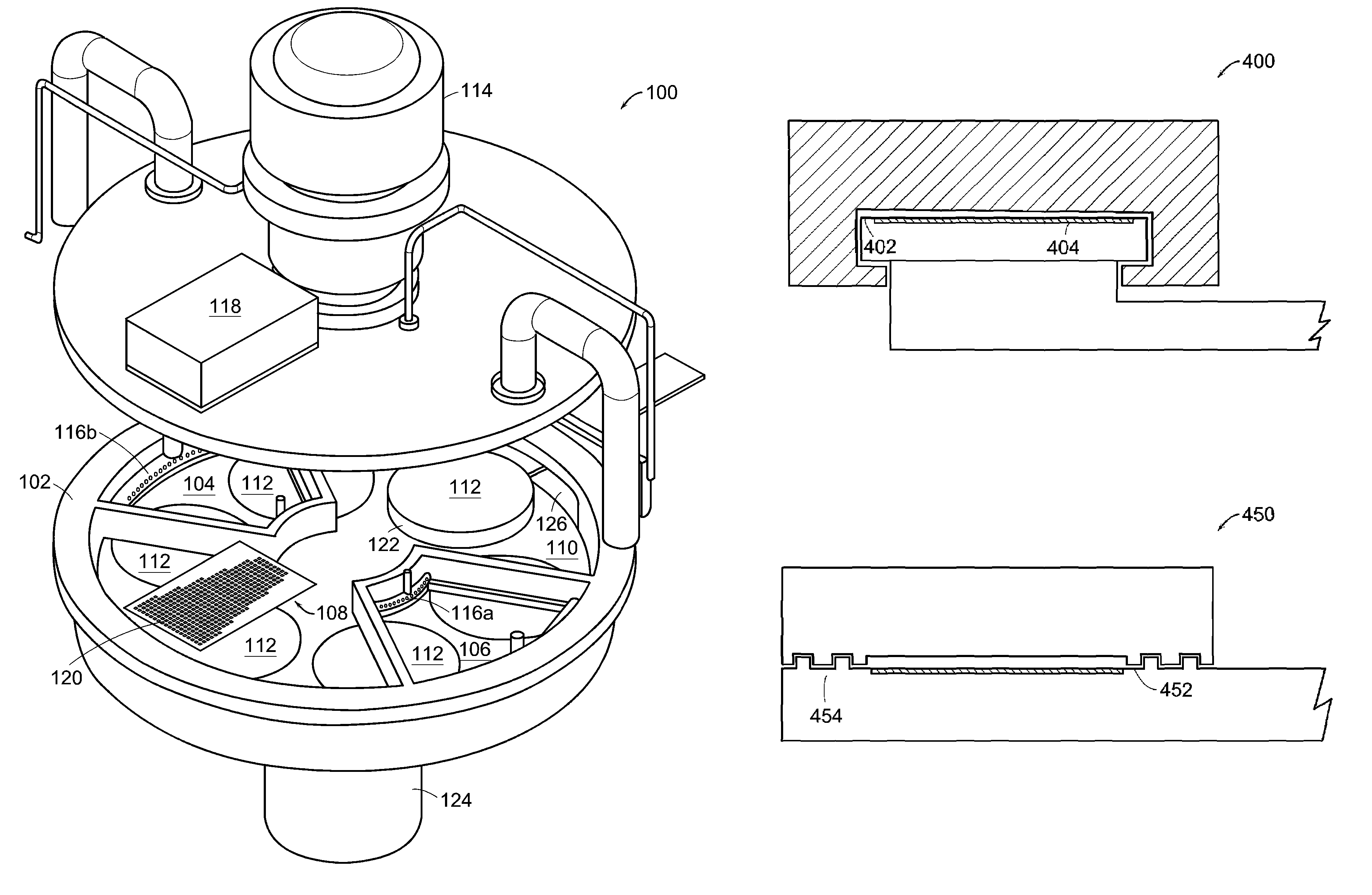
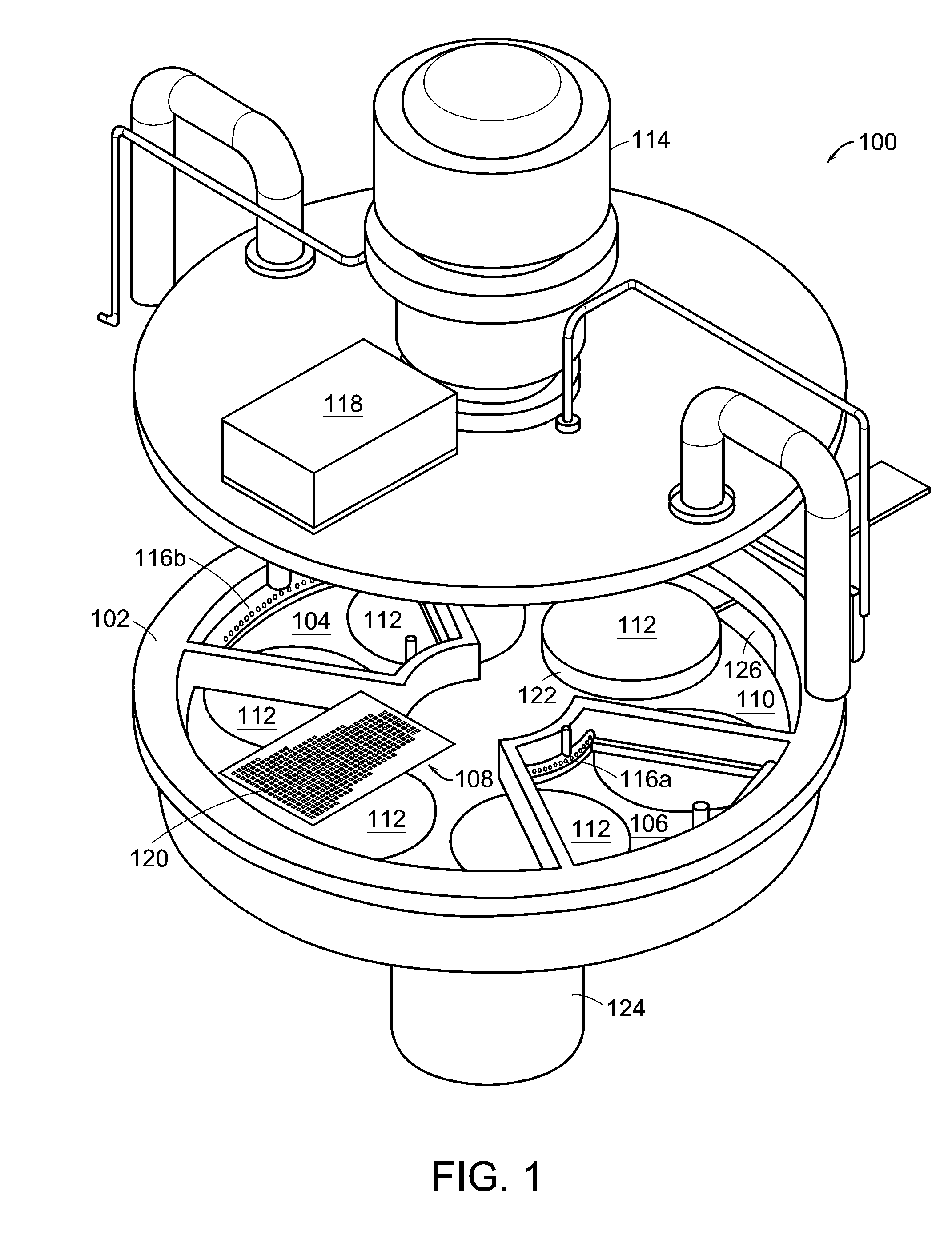
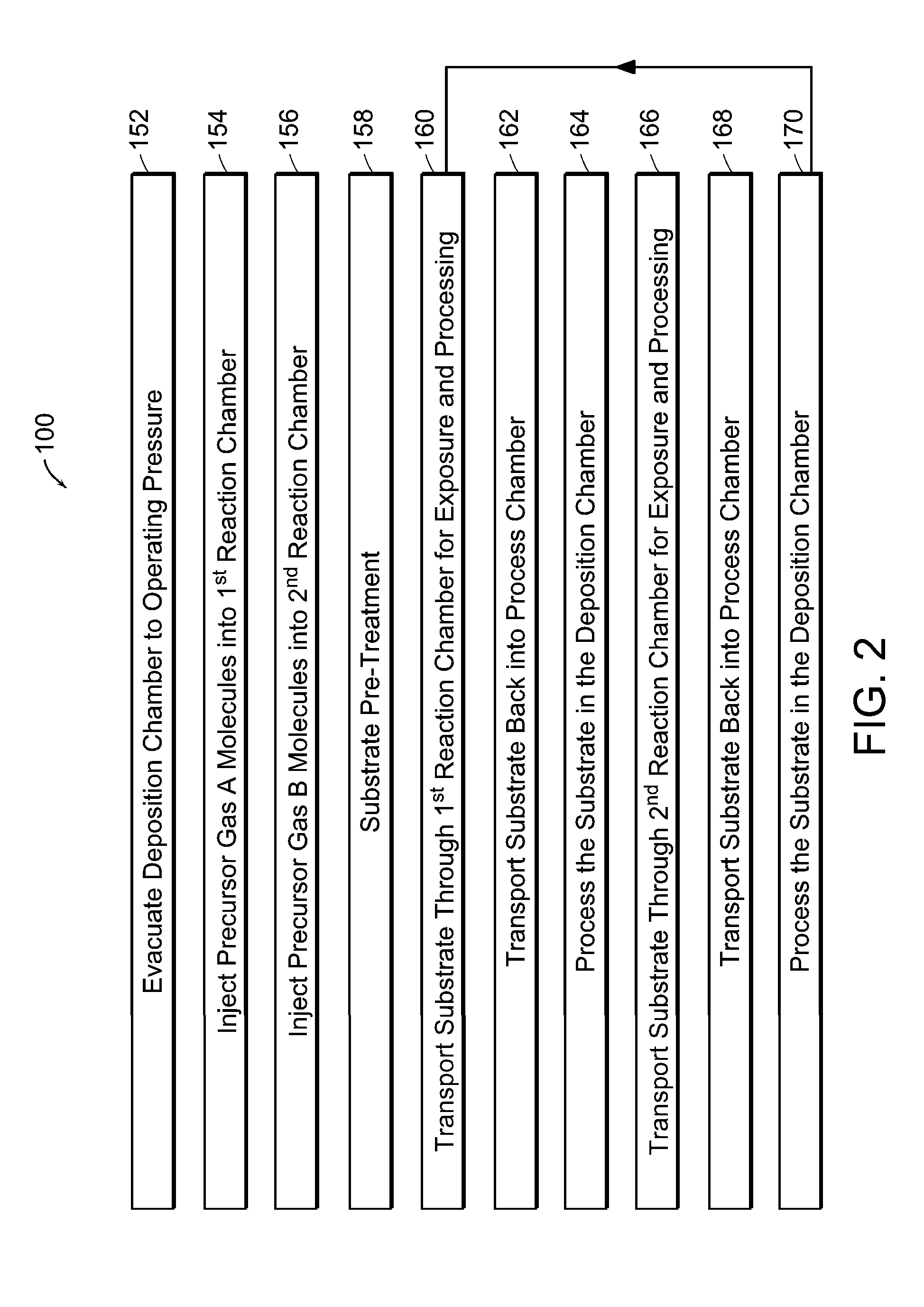
An atomic layer deposition system is described that includes a deposition chamber. A first and second reaction chamber are positioned in the deposition chamber and contain a first and a second reactant species, respectively. A monolayer of the first reactant species is deposited on a substrate passing through the first reaction chamber. A monolayer of the second reactant species is deposited on a substrate passing through the second reaction chamber. A transport mechanism transports a substrate in a path through the first reaction chamber and through the second reaction chamber, thereby depositing a film on the substrate by atomic layer deposition. The shape of the first and the second reaction chambers are chosen to achieve a constant exposure of the substrate to reactant species when the transport mechanism transports the substrate in the path through the respective reaction chambers at the constant transport rate.
Owner:VEECON INSTR
Method of selective coverage of high aspect ratio structures with a conformal film
ActiveUS7625820B1High aspect ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMetallurgySilicon oxide
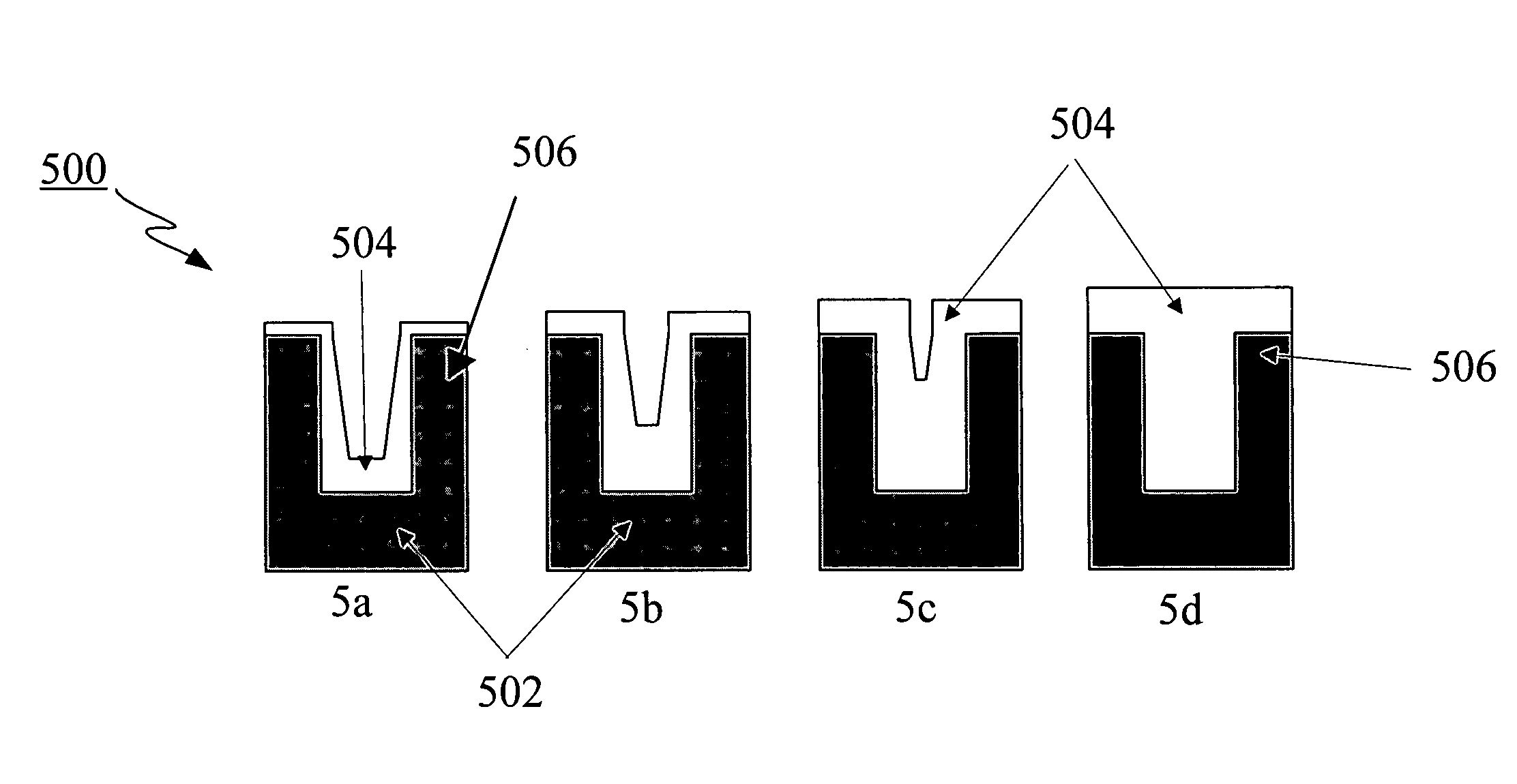
Methods for forming thin dielectric films by selectively depositing a conformal film of dielectric material on a high aspect ratio structure have uses in semiconductor processing and other applications. A method for forming a dielectric film involves providing in a deposition reaction chamber a substrate having a gap on the surface. The gap has a top opening and a surface area comprising a bottom and sidewalls running from the top to the bottom. A conformal silicon oxide-based dielectric film is selectively deposited in the gap by first preferentially applying a film formation catalyst or a catalyst precursor on a portion representing less than all of the gap surface area. The substrate surface is then exposed to a silicon-containing precursor gas such that a silicon oxide-based dielectric film layer is preferentially formed on the portion of the gap surface area. The preferential application of the catalyst or catalyst precursor may occur either at the top of the gap, for example to form a sacrificial mask, or at the bottom of the gap to create a seamless and void-free gap fill.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of controlling the film properties of a CVD-deposited silicon nitride film
InactiveUS20060019502A1Increase wet etch rateEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricGas composition
We have discovered that adding H2 to a precursor gas composition including SiH4, NH3, and N2 is effective at improving the wet etch rate and the wet etch rate uniformity across the substrate surface of a-SiNx:H films which are deposited on a substrate by PECVD. Wet etch rate is an indication of film density. Typically, the lower the wet etch rate, the denser the film. The addition of H2 to the SiH4 / NH3 / N2 precursor gas composition did not significantly increase the variation in deposited film thickness across the surface of the substrate. The a-SiNx:H films described herein are particularly useful as TFT gate dielectrics in the production of flat panel displays. The uniformity of the film across the substrate enables the production of flat panel displays having surface areas of 25,000 cm2 and larger.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming conformal dielectric film having Si-N bonds by PECVD
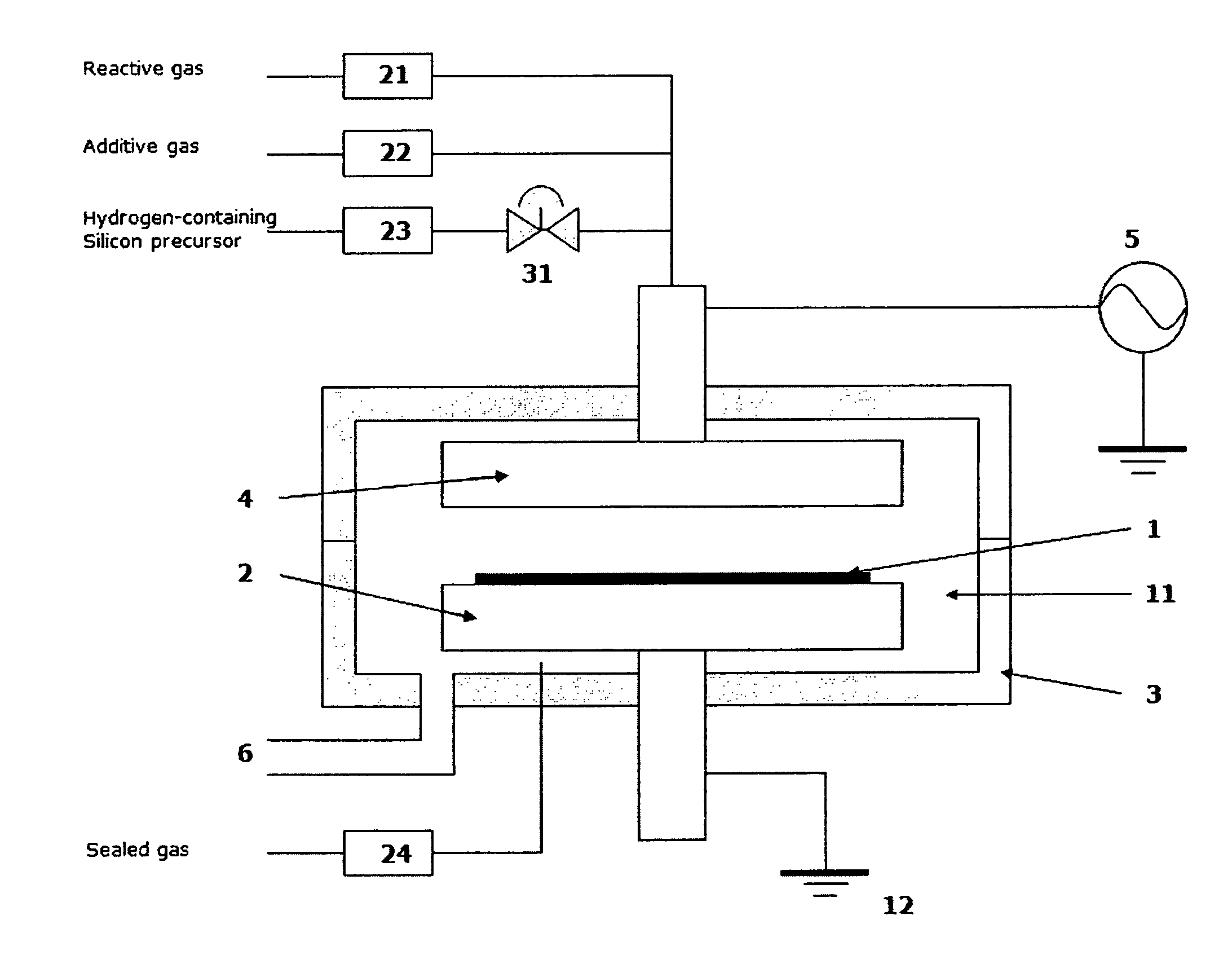
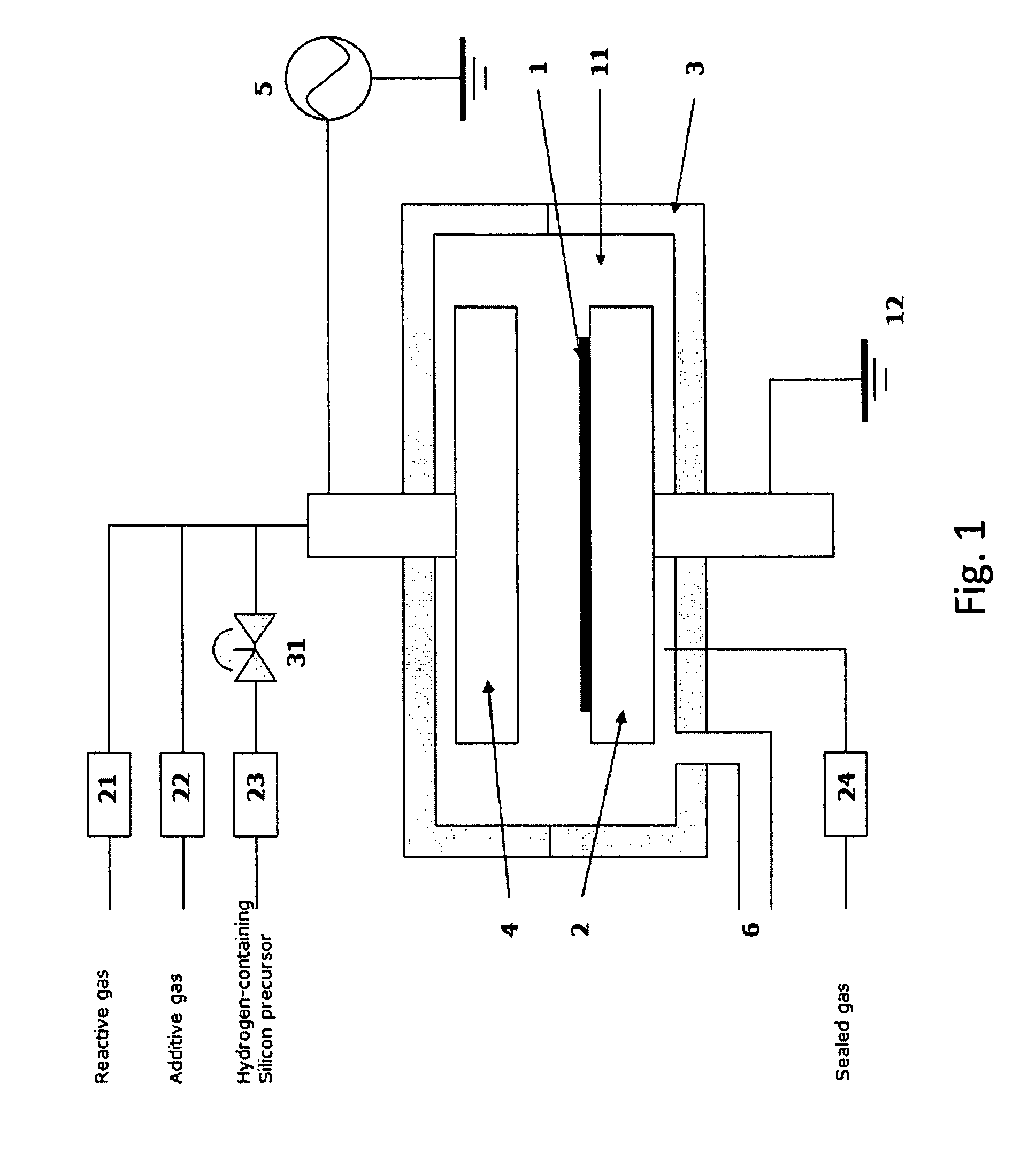
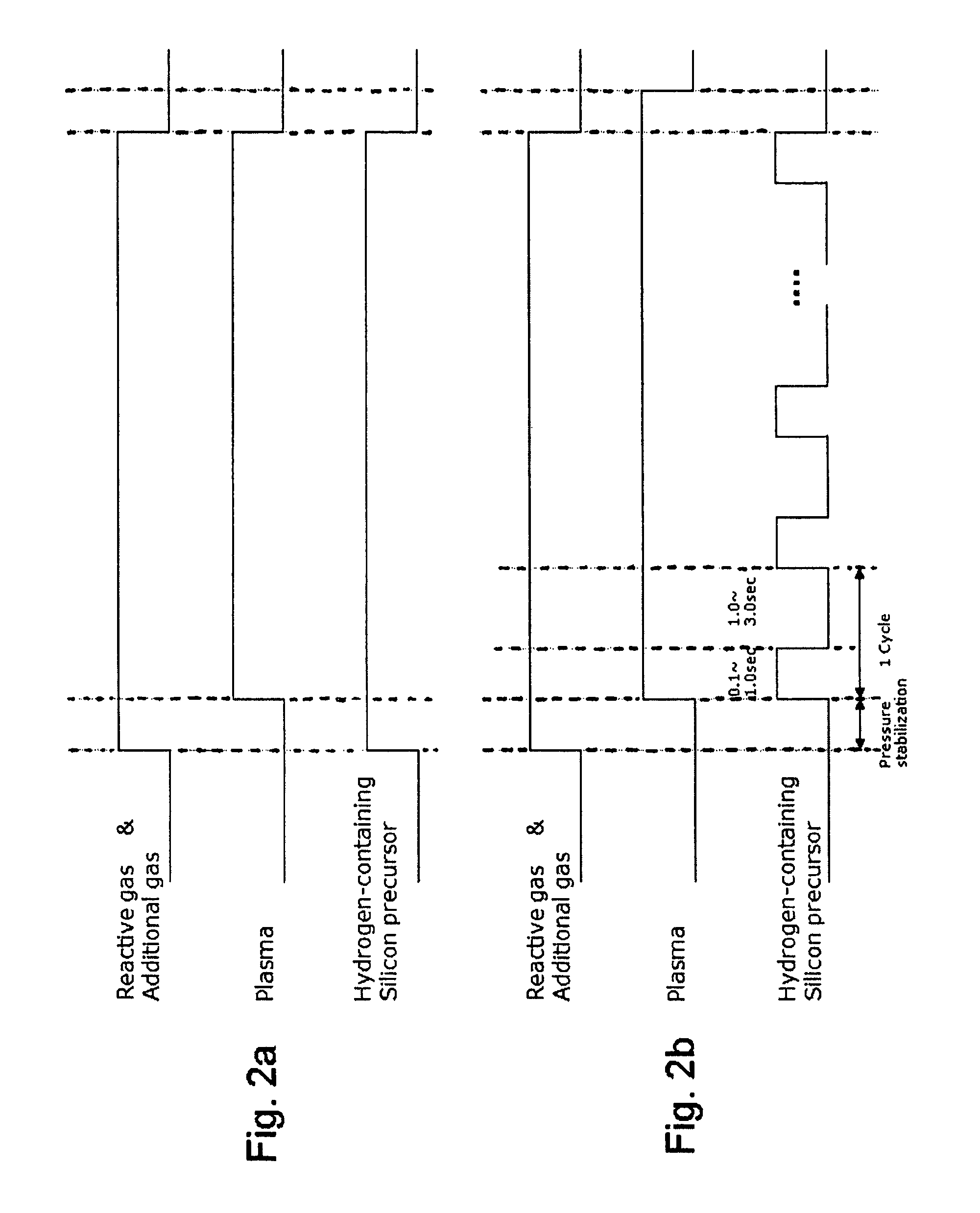
A method of forming a conformal dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and an additive gas into a reaction space inside which a semiconductor substrate is placed; applying RF power to the reaction space; and introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses into the reaction space wherein a plasma is excited, thereby forming a conformal dielectric film having Si—N bonds on the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Substrate processing apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and reaction vessel
InactiveUS20080173238A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingIn planeProduct gas
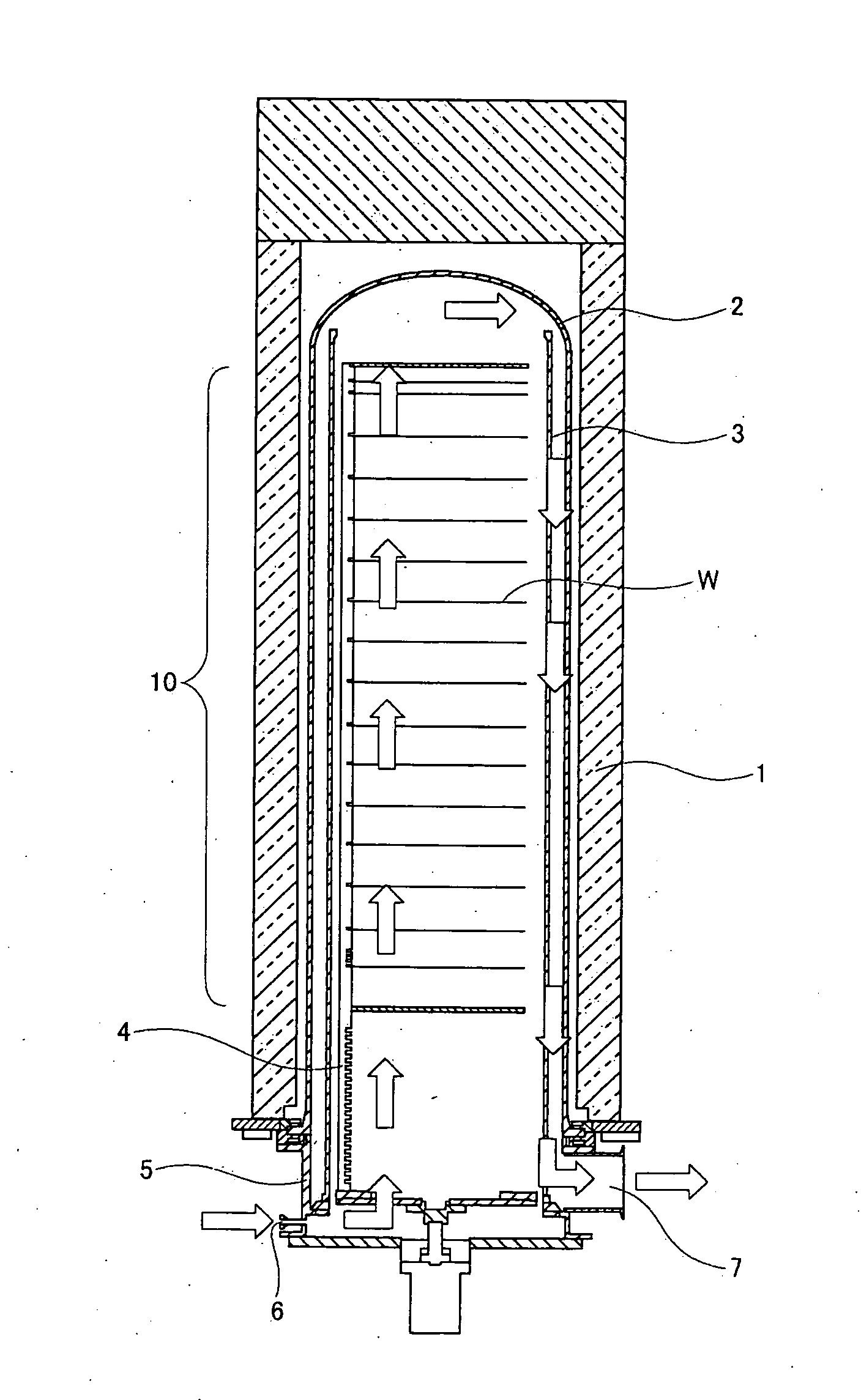
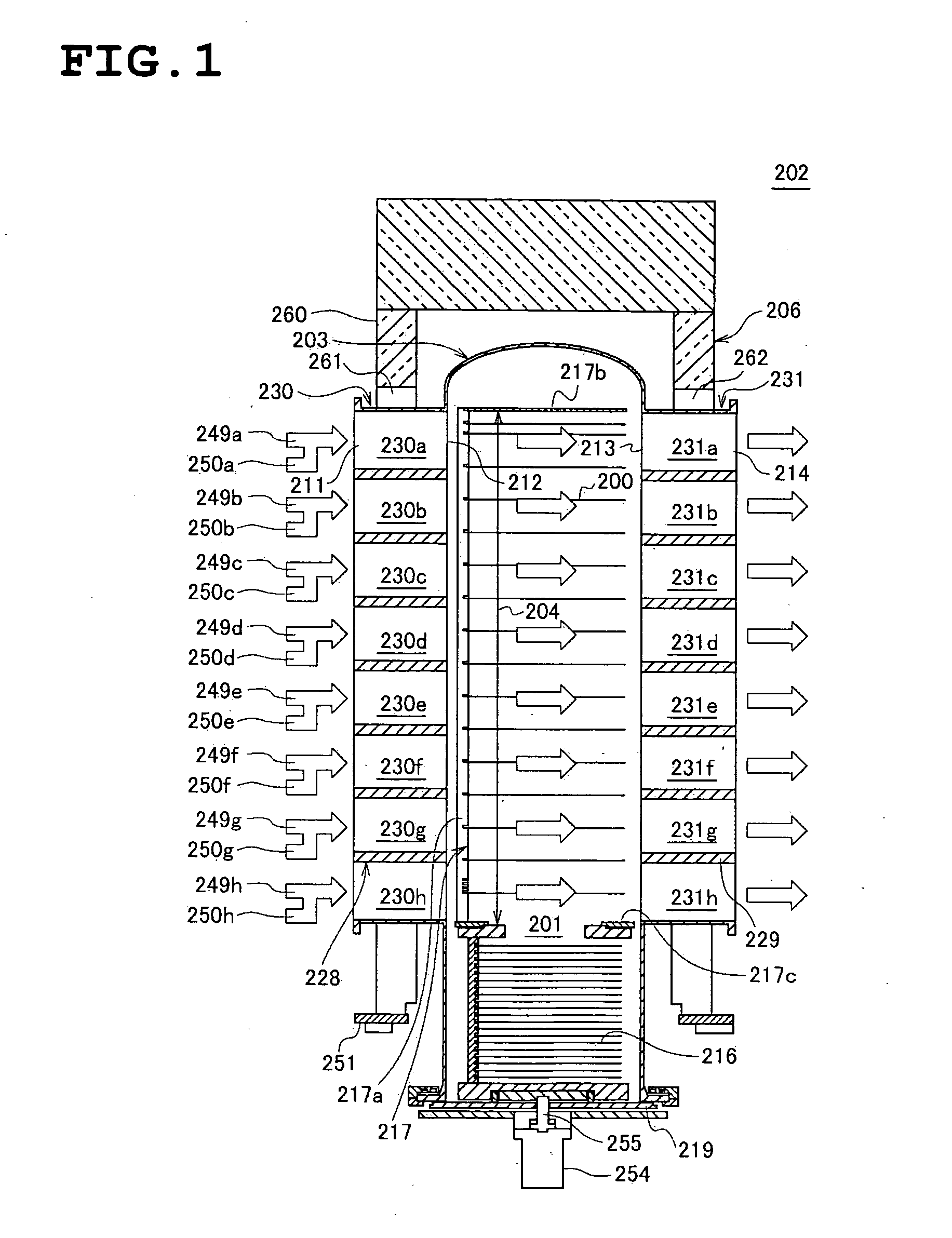
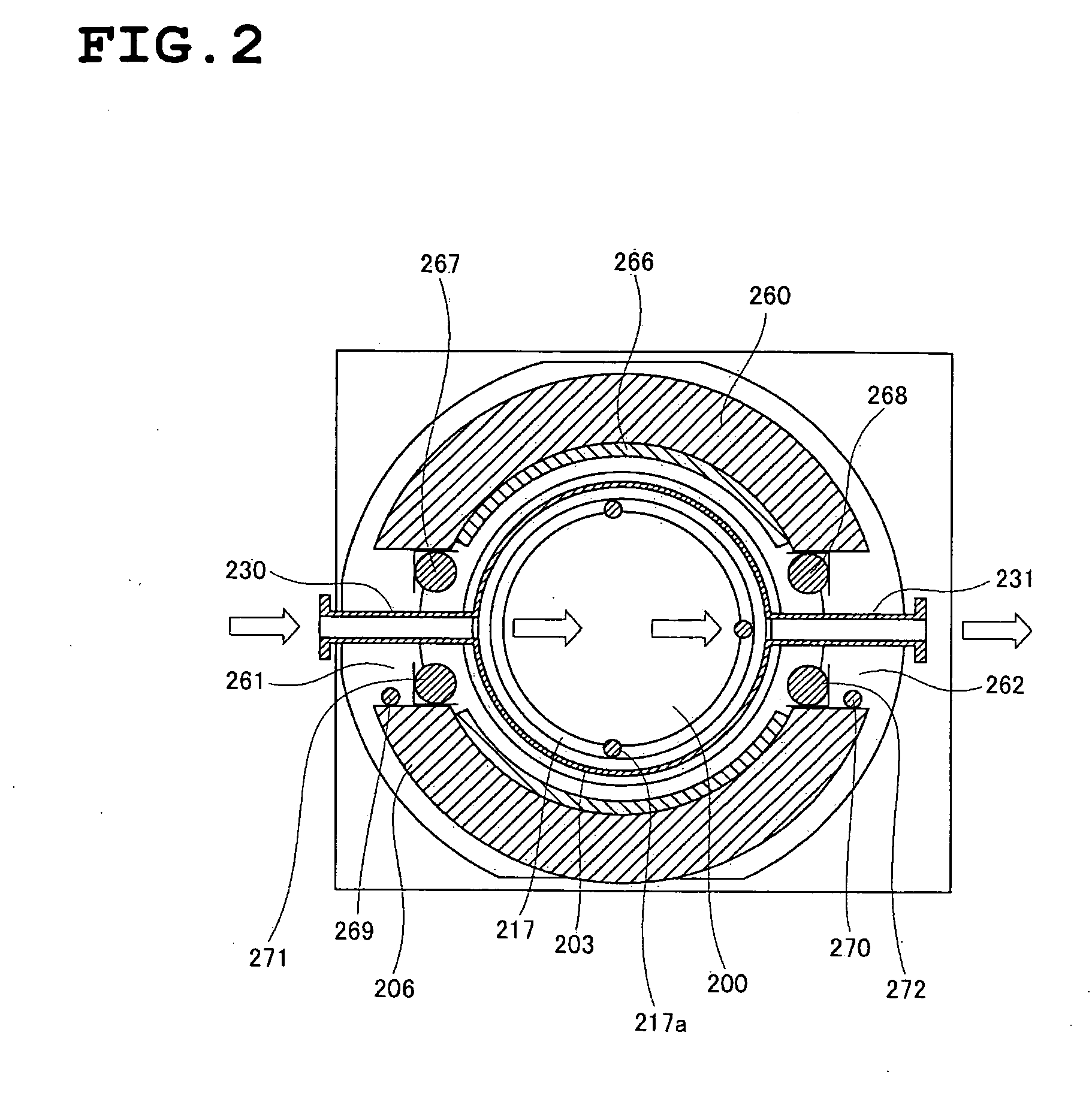
A substrate processing apparatus that affords improved uniformity to in-plane wafer and interwafer film thickness of a large number of wafers on which a film is simultaneously formed, having: a reaction tube having in an interior thereof a processing chamber in which a plurality of substrates disposed in a direction perpendicular to a substrate processing surface can be processed; and a heating device provided to surround an outer circumference of the reaction tube, a gas inlet tube being provided on a side face of the reaction tube in a region for processing a substrate inside the reaction tube, so as to reach at least an outside of the heating device; and a gas spouting port being disposed in this gas inlet tube in a slit form so as to straddle at least a plurality of the substrates in a direction perpendicular to the substrate processing surface, for spouting gas from the gas inlet tube into the processing chamber.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
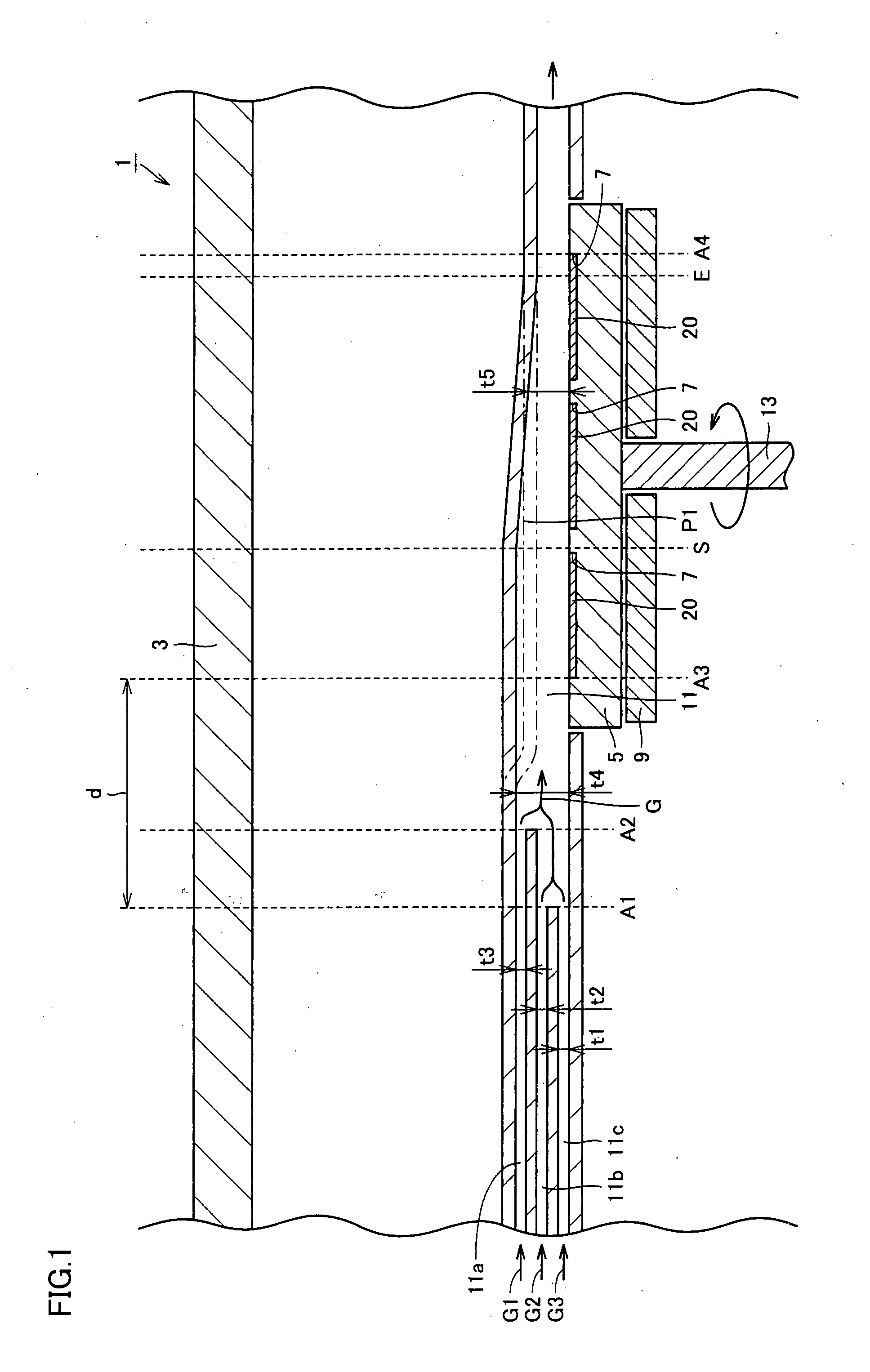
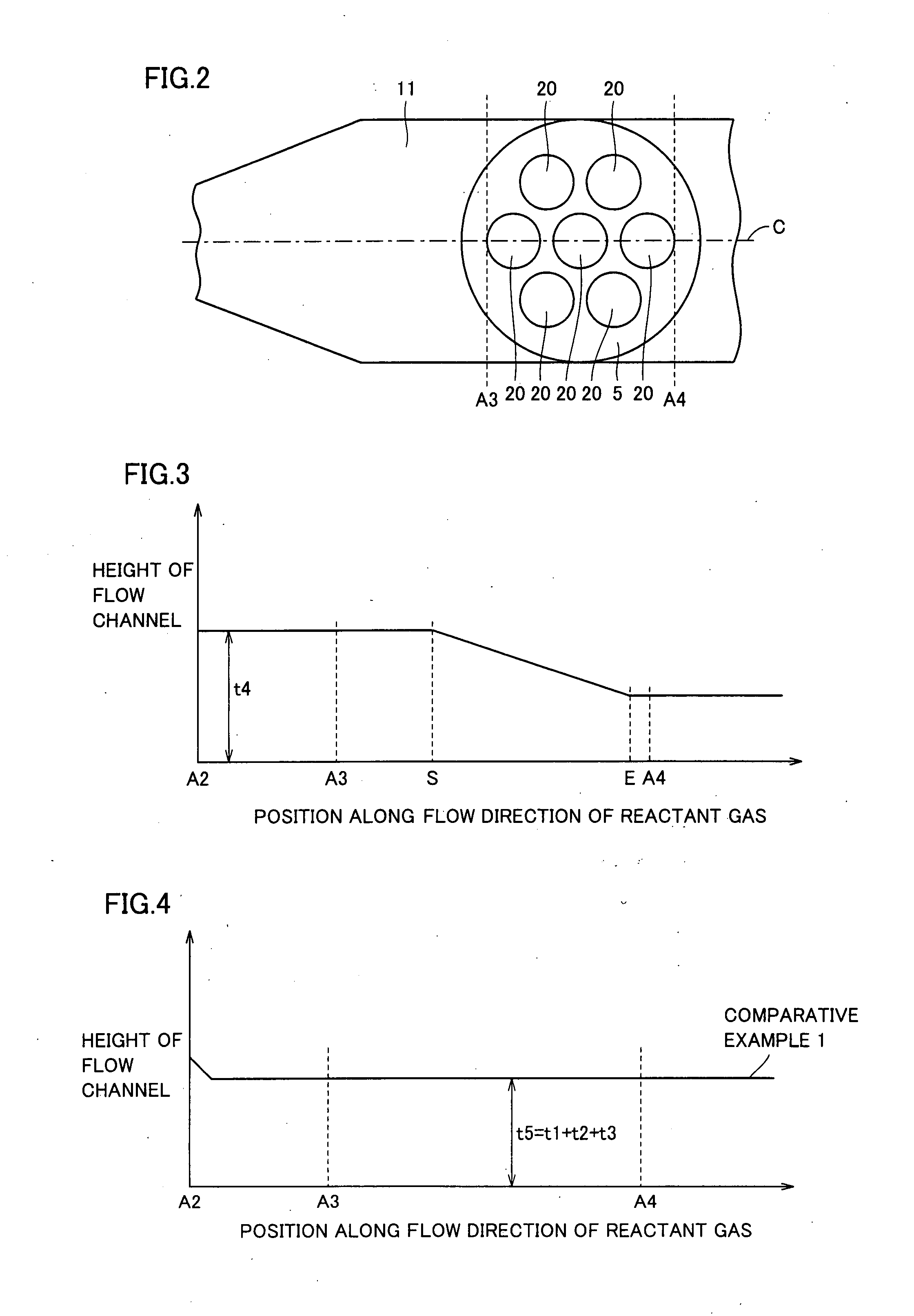
Metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment
InactiveUS20080006208A1Uniform film thicknessImprove formation efficiencyAfter-treatment apparatusFrom chemically reactive gasesSusceptorProduct gas
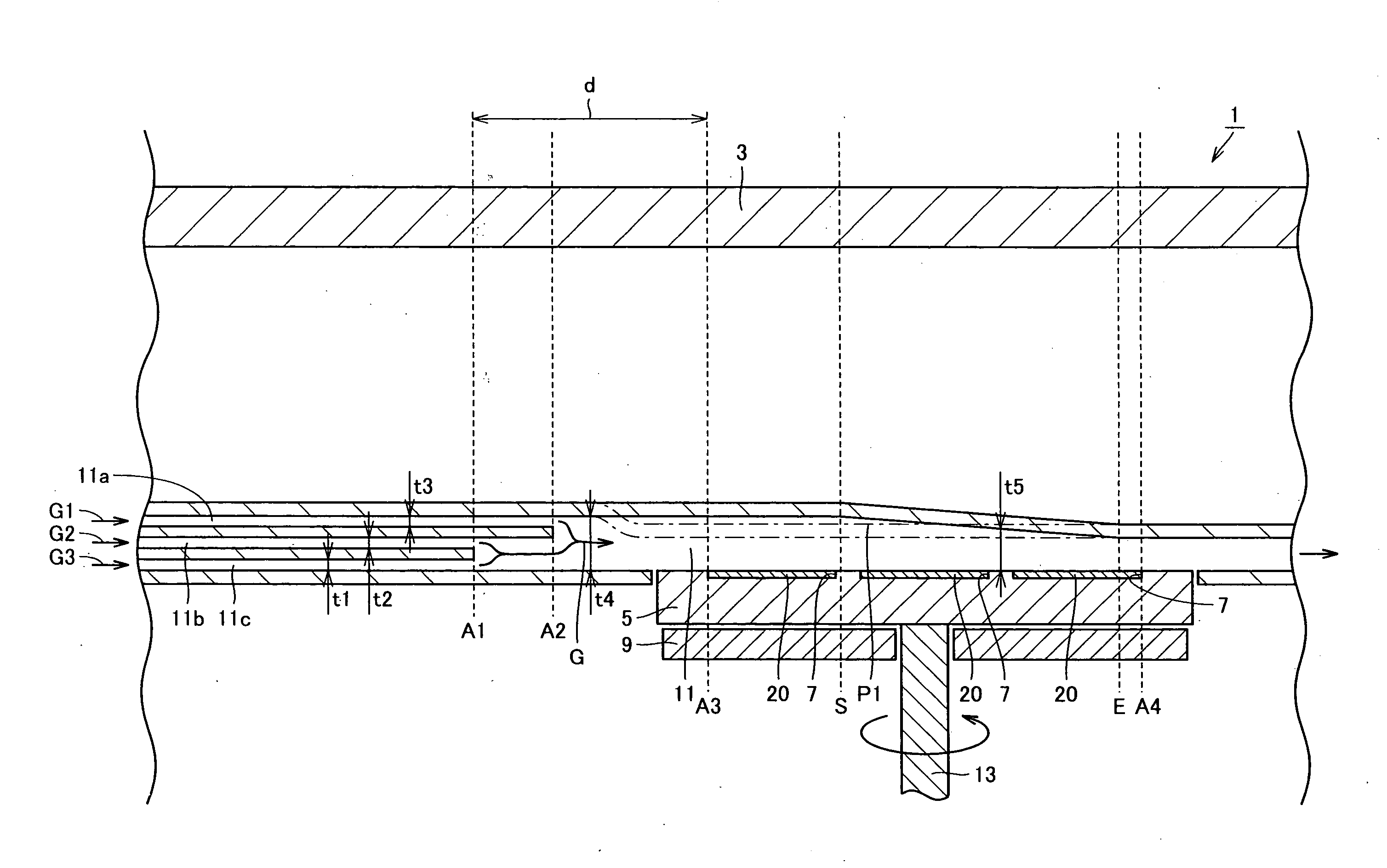
Metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment is metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment for forming a film on a substrate by using a reactant gas, and includes a susceptor heating the substrate and having a holding surface for holding the substrate, and a flow channel for introducing the reactant gas to the substrate. The susceptor is rotatable with the holding surface kept facing an inner portion of the flow channel, and a height of the flow channel along a flow direction of the reactant gas is kept constant from a position to a position, and is monotonically decreased from the position to the downstream side. It is thereby possible to improve film formation efficiency while allowing the formed film to have a uniform thickness.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
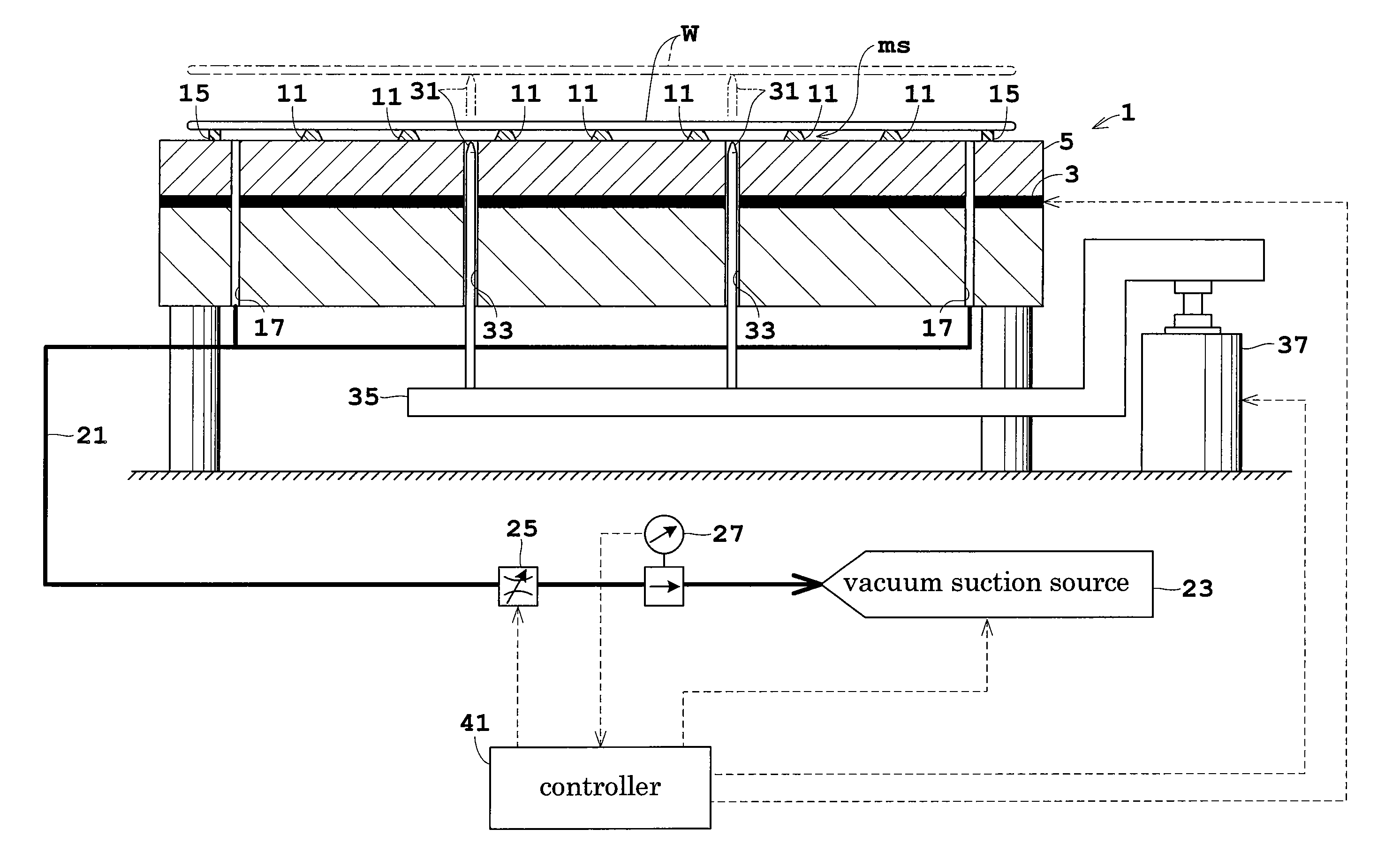
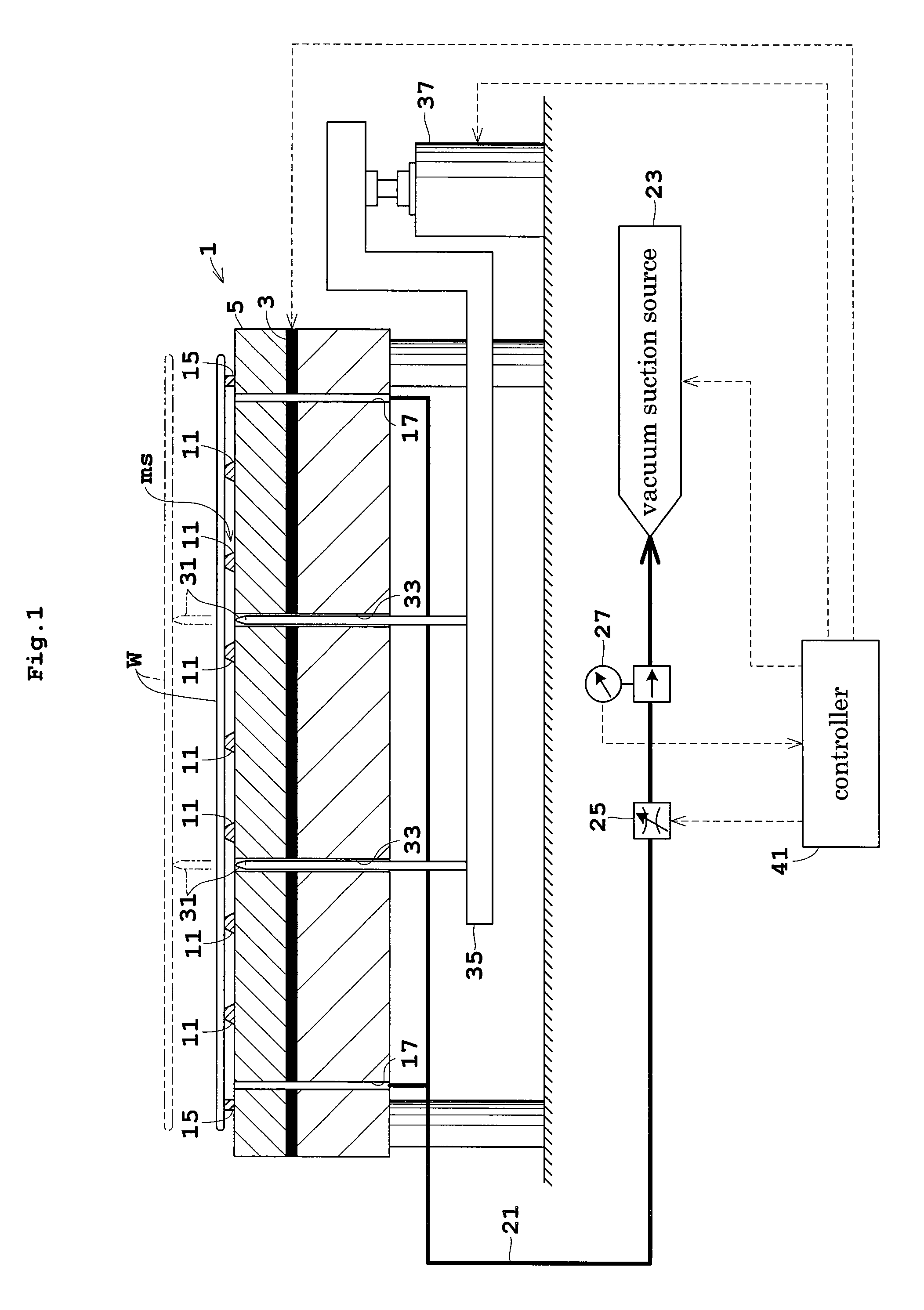
Substrate heat treatment apparatus
A substrate heat treatment apparatus includes a heat-treating plate having a flat upper surface, support devices formed of a heat-resistant resin for contacting and supporting a substrate, a seal device disposed annularly for rendering gastight a space formed between the substrate and heat-treating plate, and exhaust bores for exhausting gas from the space. The support devices are formed of resin, and the upper surface of the heat-treating plate is made flat, whereby a reduced difference in the rate of heat transfer occurs between contact parts and non-contact parts on the surface of the substrate. Consequently, the substrate is heat-treated effectively while suppressing variations in heat history over the surface of the substrate.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
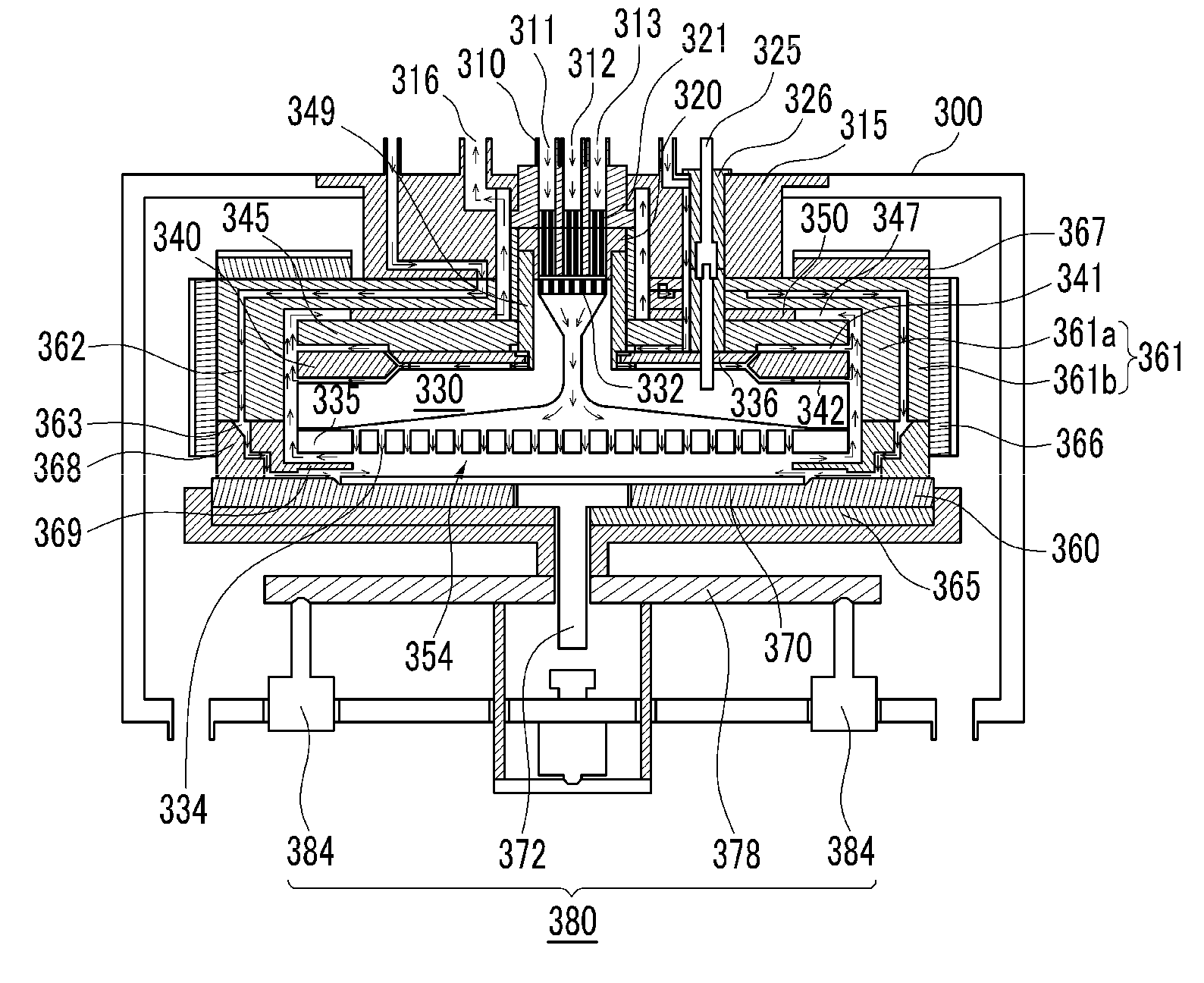
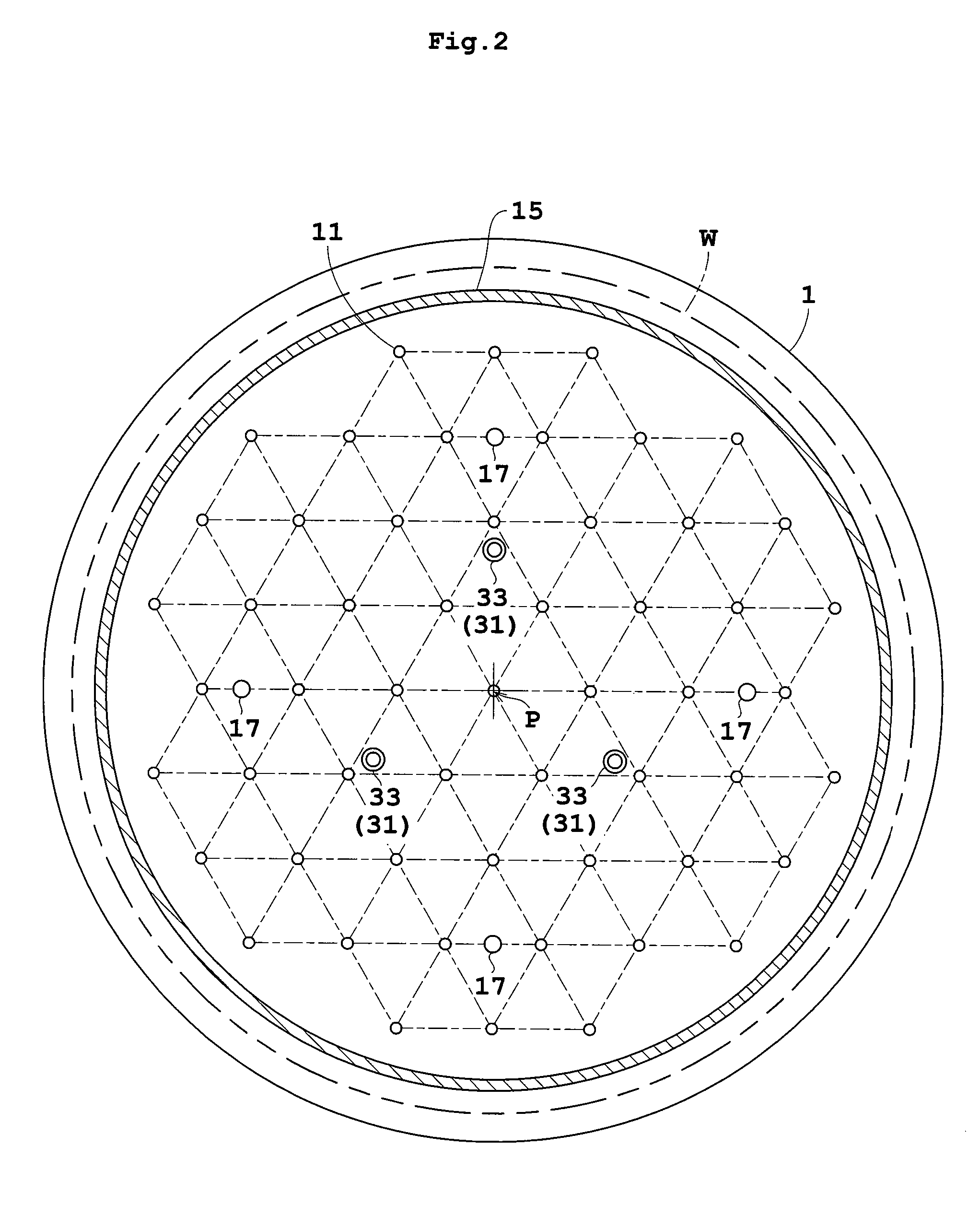
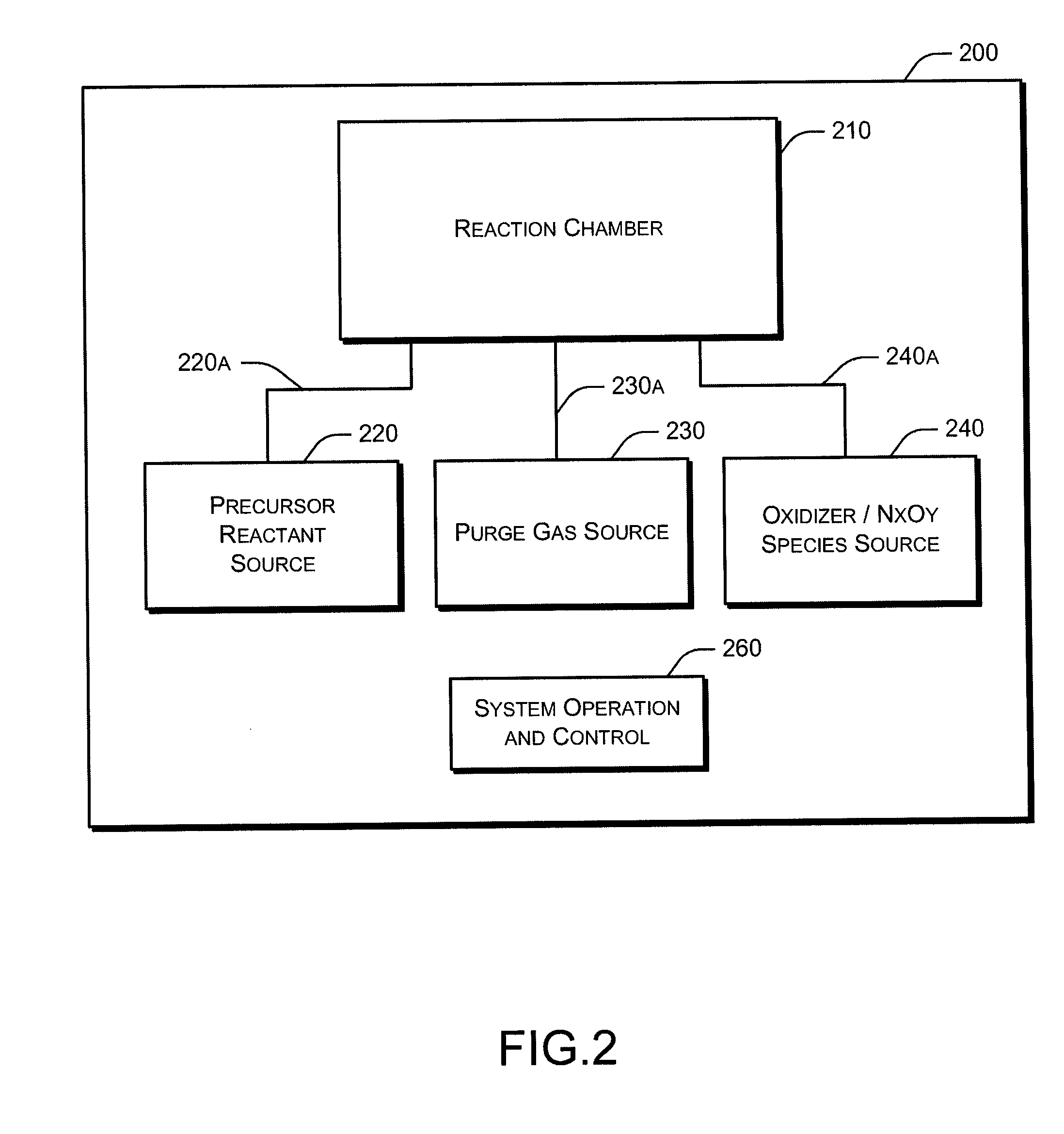
Systems and methods for thin-film deposition of metal oxides using excited nitrogen-oxygen species
ActiveUS8877655B2Enhance growth rate and uniformityUniform growthLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to a process and system for depositing a thin film onto a substrate. One aspect of the invention is depositing a thin film metal oxide layer using atomic layer deposition (ALD).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Substrate Processing Apparatus and Substrate Mount Table Used in the Apparatus
InactiveUS20100162956A1Achieving temperature uniformityEliminate the effects ofElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureSusceptor
Disclosed is a susceptor which achieves uniform temperature distribution of a wafer placed on the susceptor, and also disclosed is a substrate processing apparatus provided with the susceptor. An annular recess 12a is formed in an intermediate portion between the central portion and the peripheral portion of a wafer support surface of the susceptor 12. Due to the provision of the recess, the substrate heating effect by thermal radiation from the susceptor is suppressed in the intermediate portion. The geometrical dimension of the recess is determined taking the chamber internal pressure into consideration.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
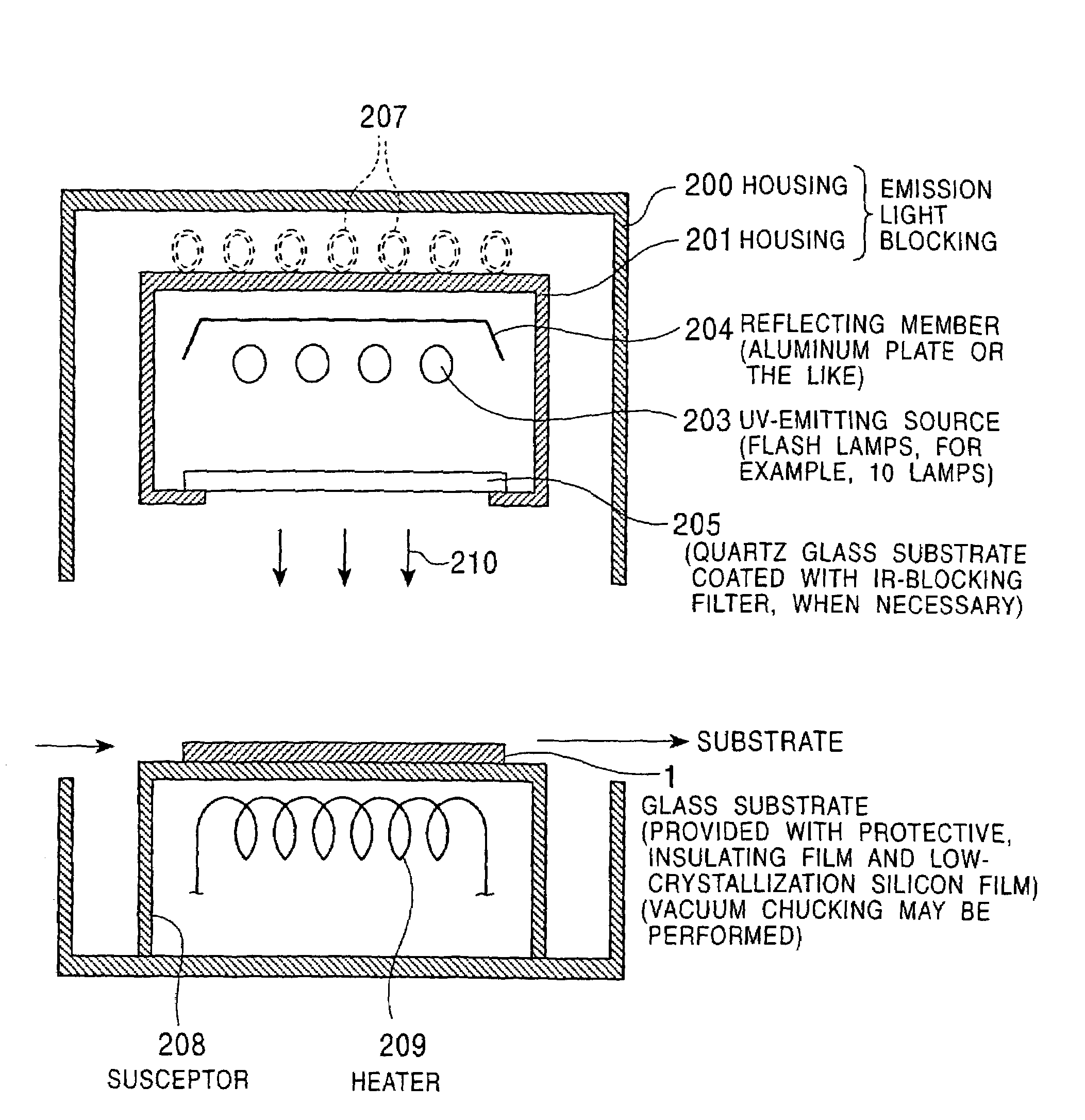
Semiconductor thin film forming method, production methods for semiconductor device and electrooptical device, devices used for these methods, and semiconductor device and electrooptical device
InactiveUS7183229B2Promote crystallizationTransistorDrying solid materials with heatSingle crystalCrystallinity
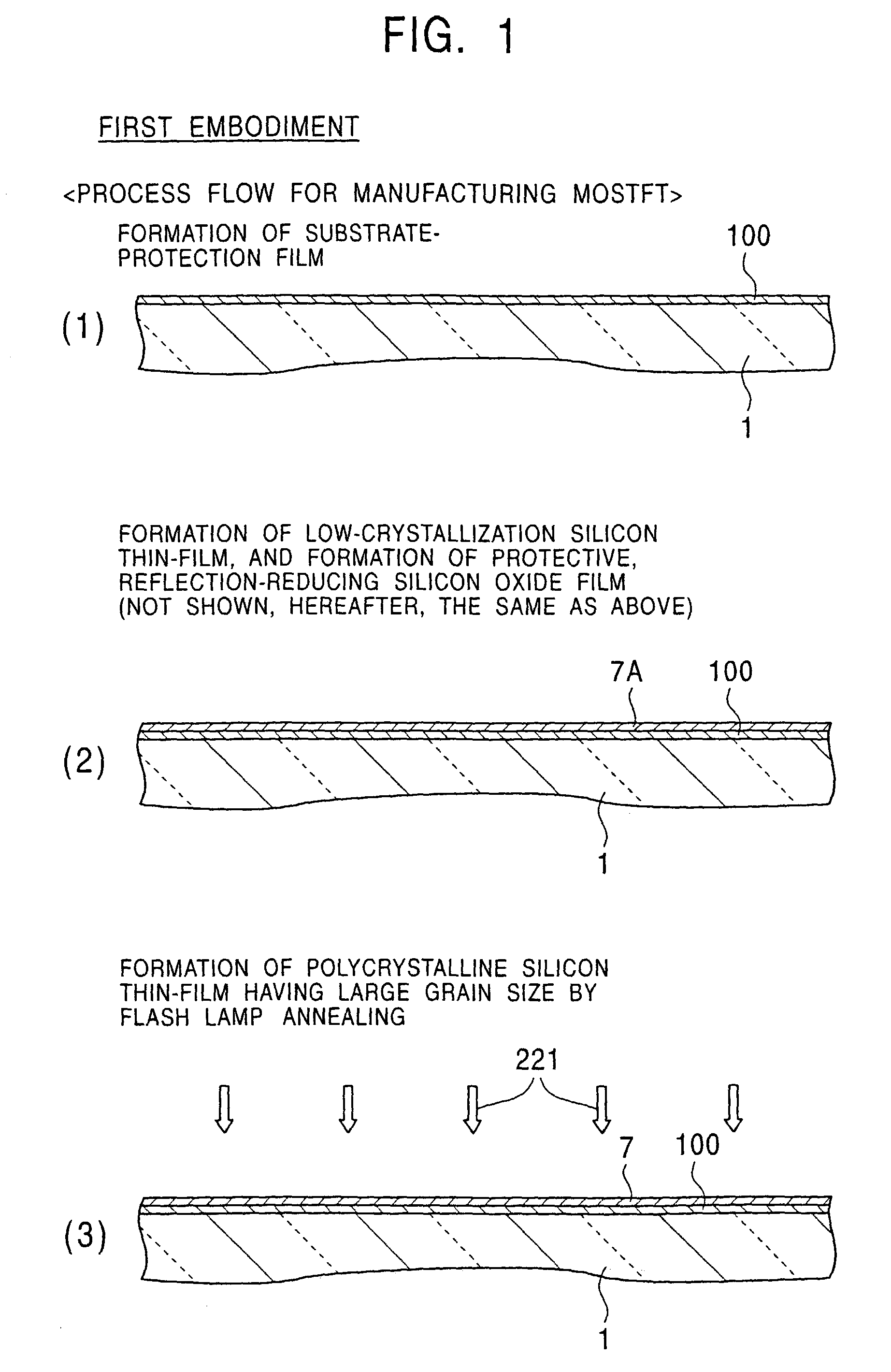
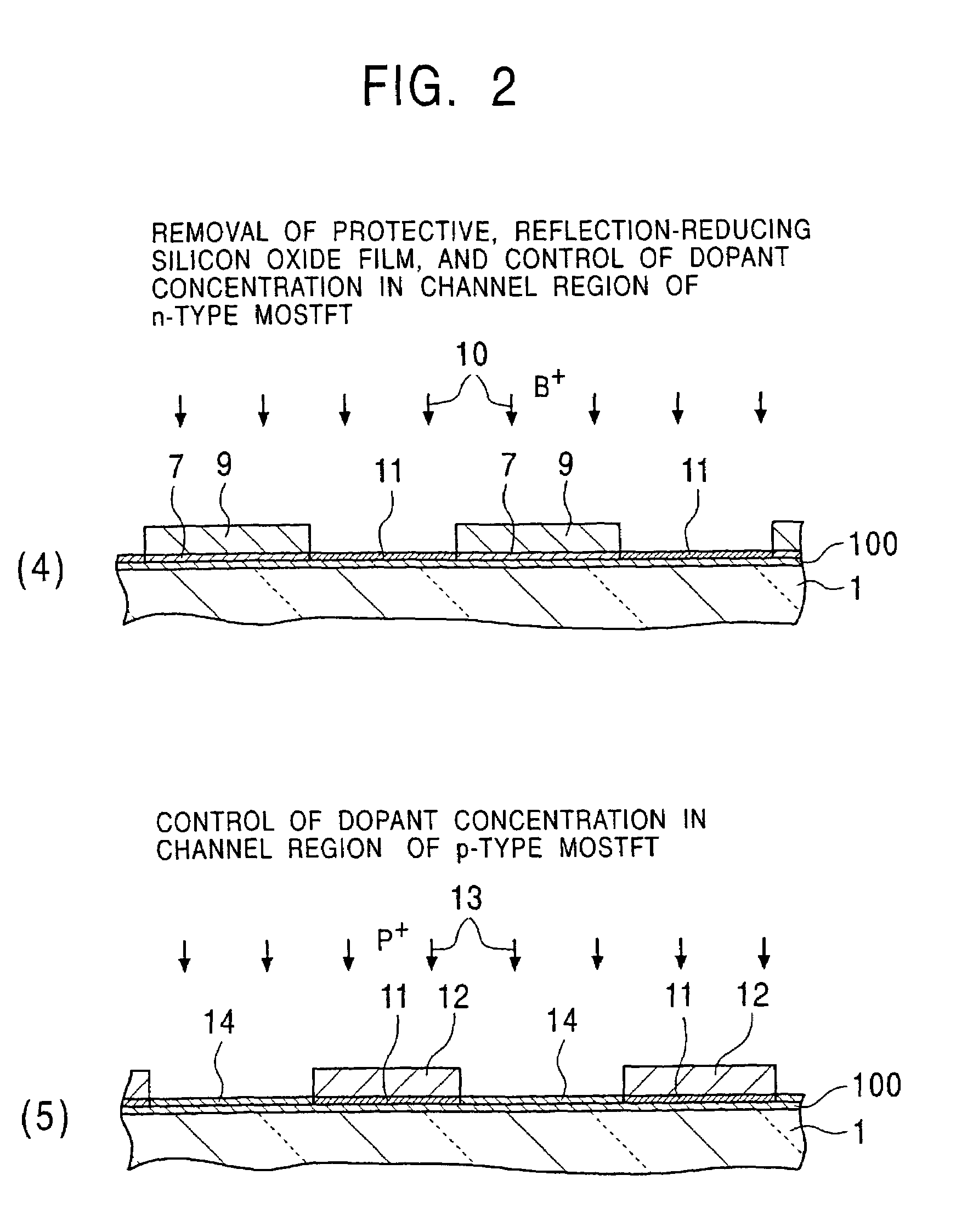
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for easily forming a polycrystalline semiconductor thin-film, such as polycrystalline silicon having high crystallinity and high quality, or a single crystalline semiconductor thin-film at inexpensive cost, the crystalline semiconductor thin-film having a large area, and to provide an apparatus for processing the method described above. In forming a polycrystalline (or single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7), such as a polycrystalline silicon thin-film, having high crystallinity and a large grain size on a substrate (1), or in forming a semiconductor device having the polycrystalline (or single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7) on the substrate (1), a method comprises forming a low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film (7A) on the substrate (1), and subsequently heating and cooling this low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film (7A) to a fusion, a semi-fusion, or a non-fusion state by flash lamp annealing to facilitate the crystallization of the low-crystallization semiconductor thin-film, whereby a polycrystalline (single crystalline) semiconductor thin-film (7) is obtained. A method for forming the semiconductor device and an apparatus for processing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com