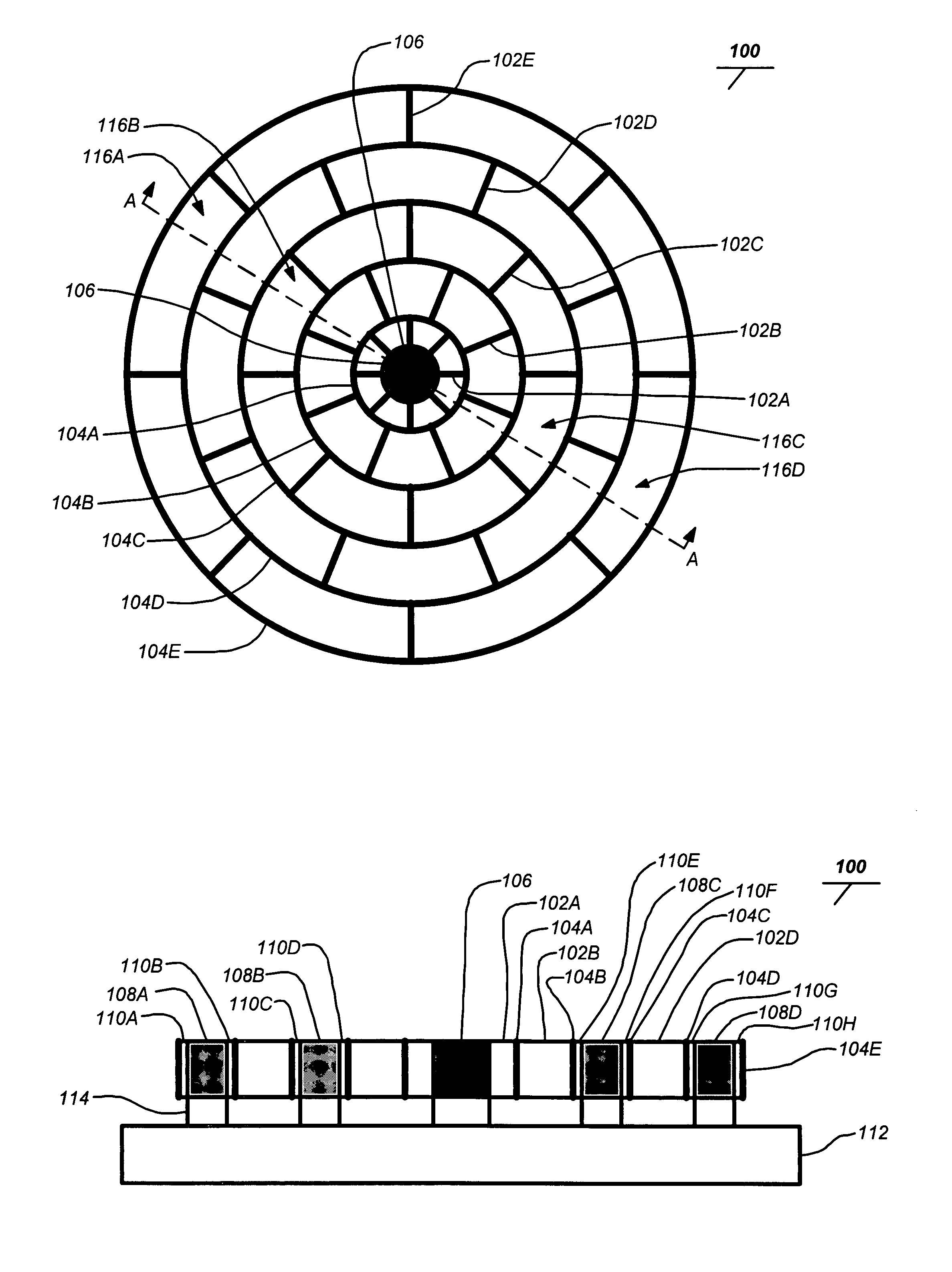
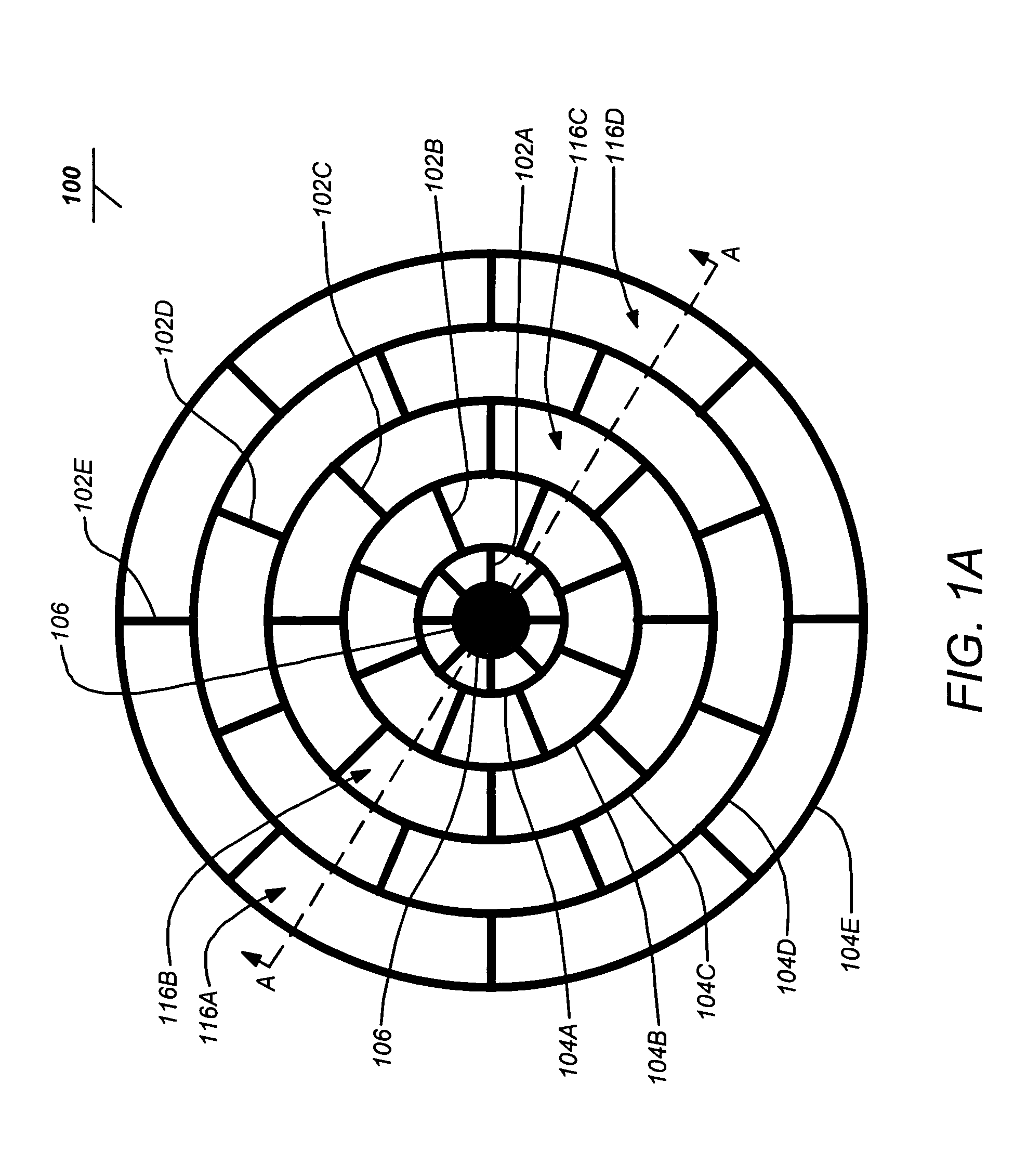
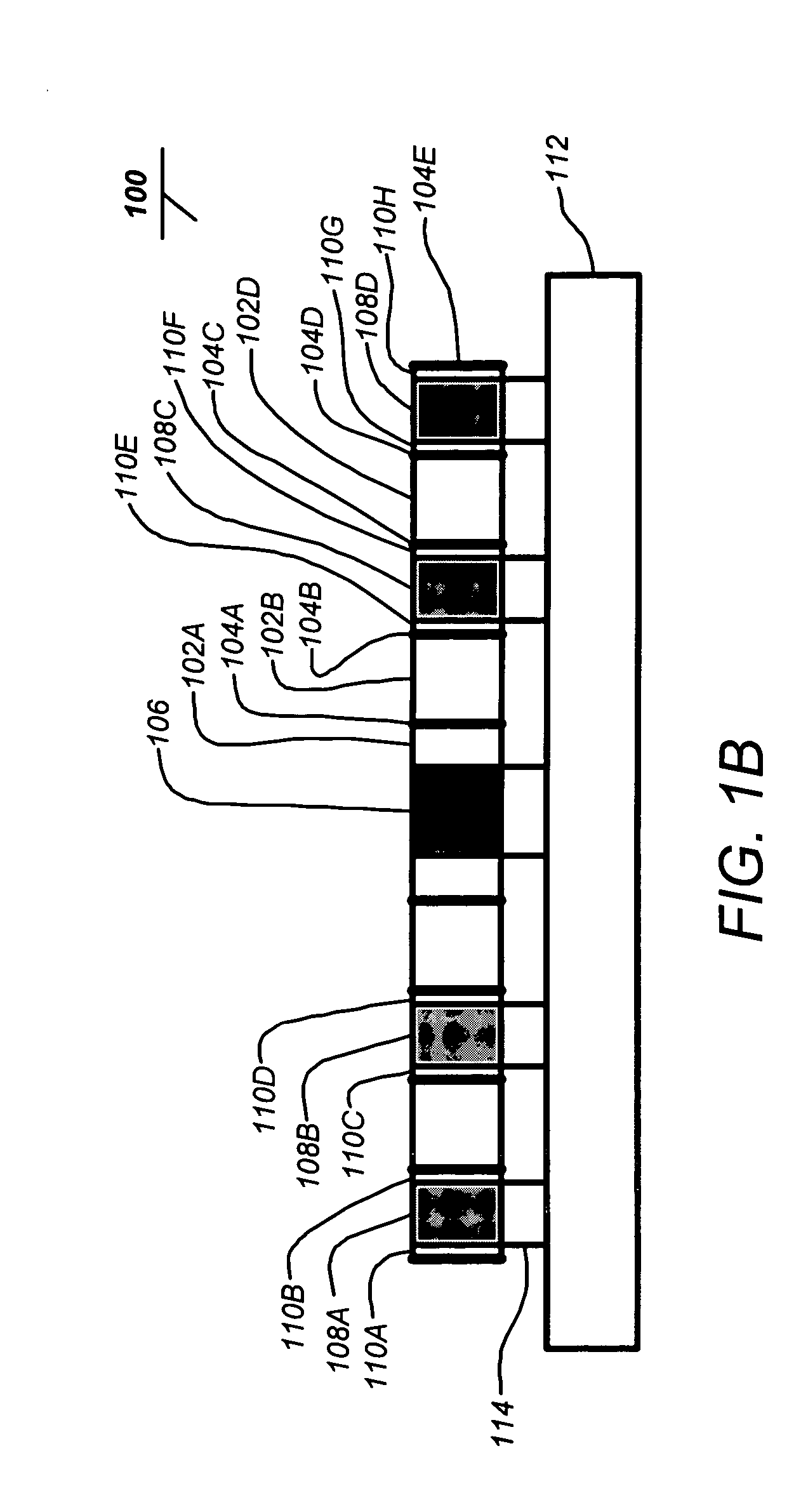
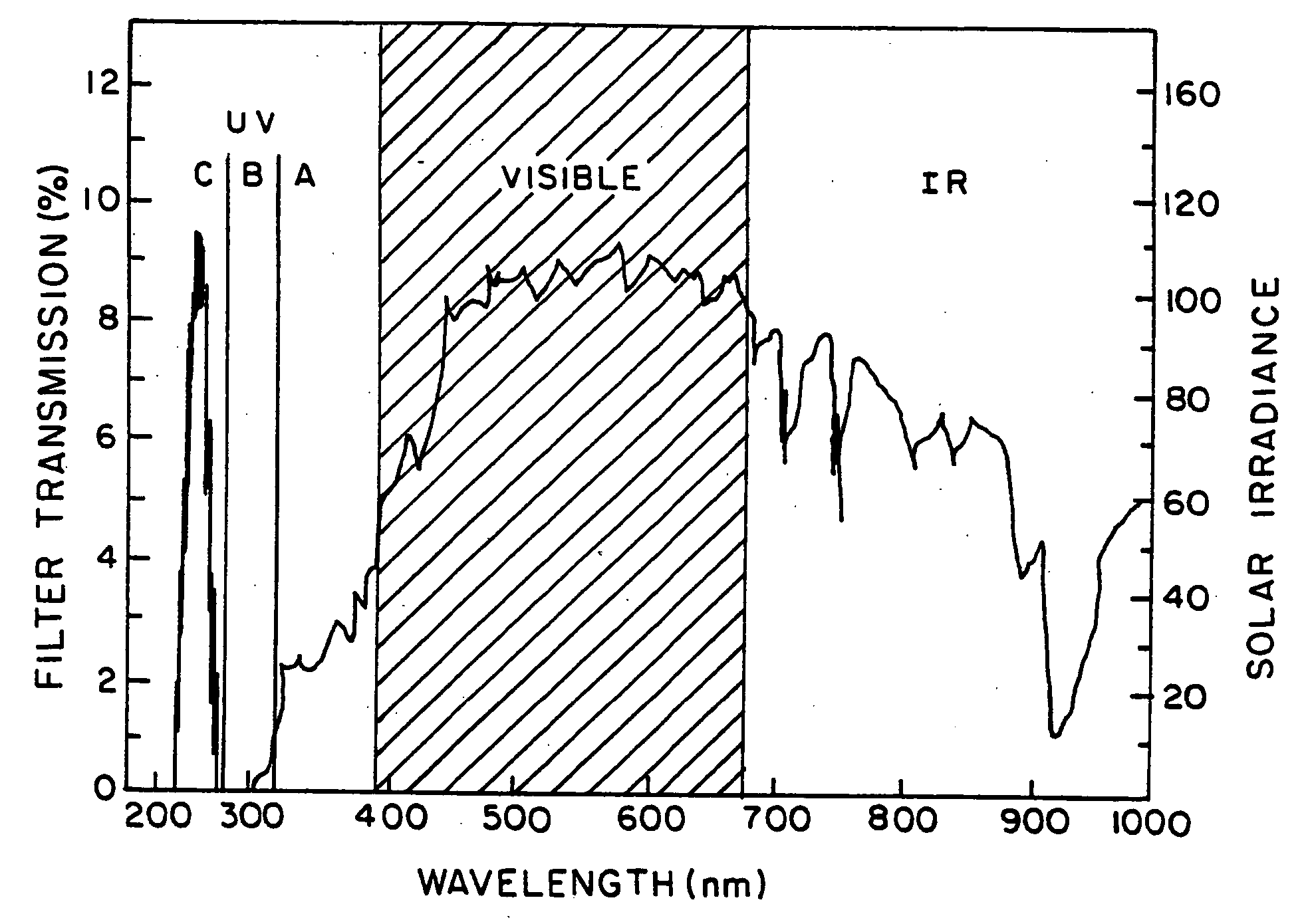
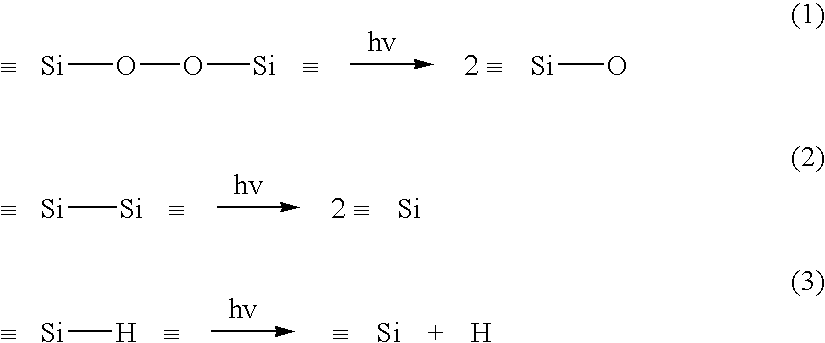Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3004 results about "Silica glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silica Glass - Characteristics. Silica glass is a kind of glass as the name is implied, but silica glass is composed of by almost only SiO 2, while, on the other hand, other glasses are composed of by various kinds of elements.
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
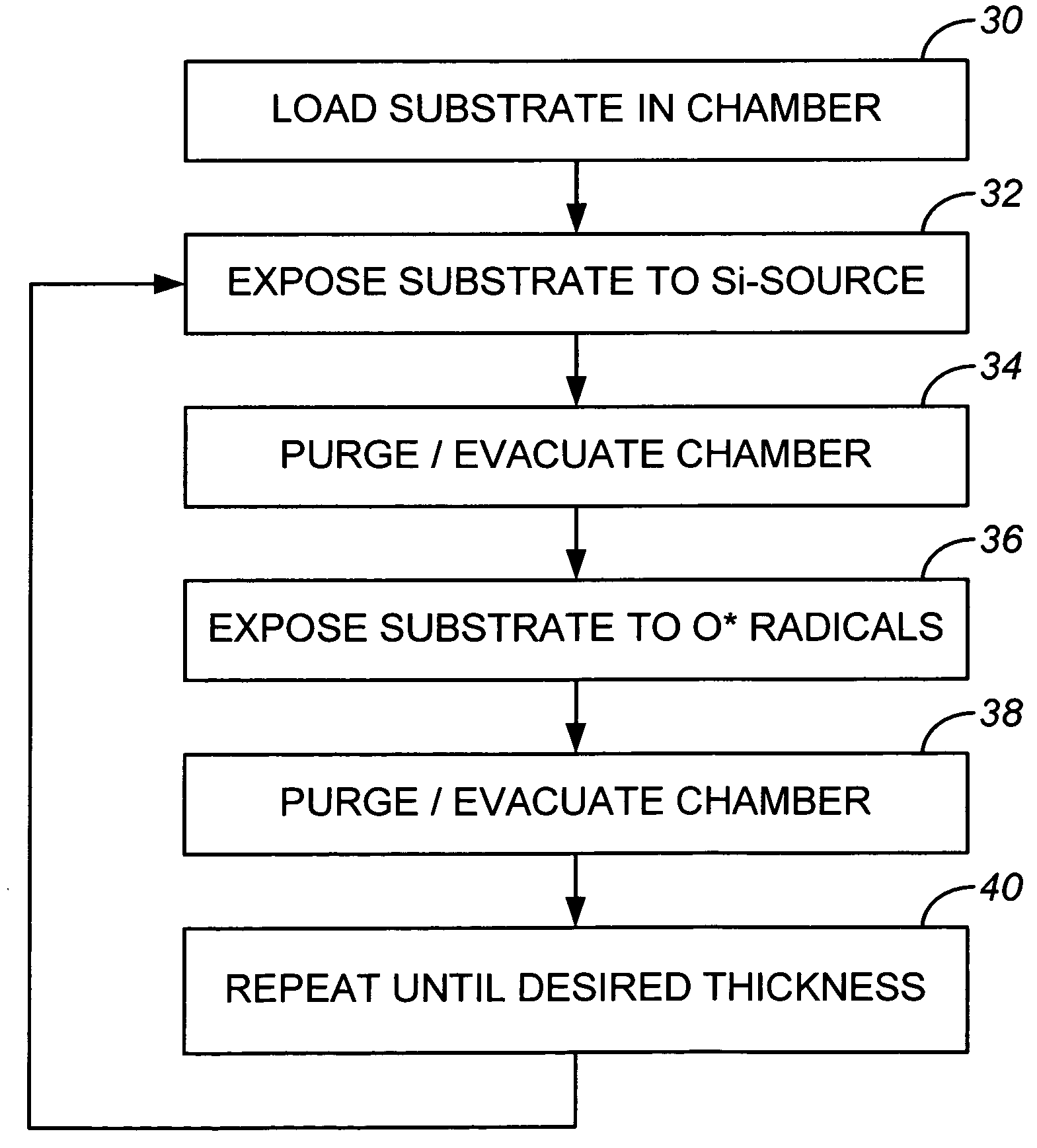
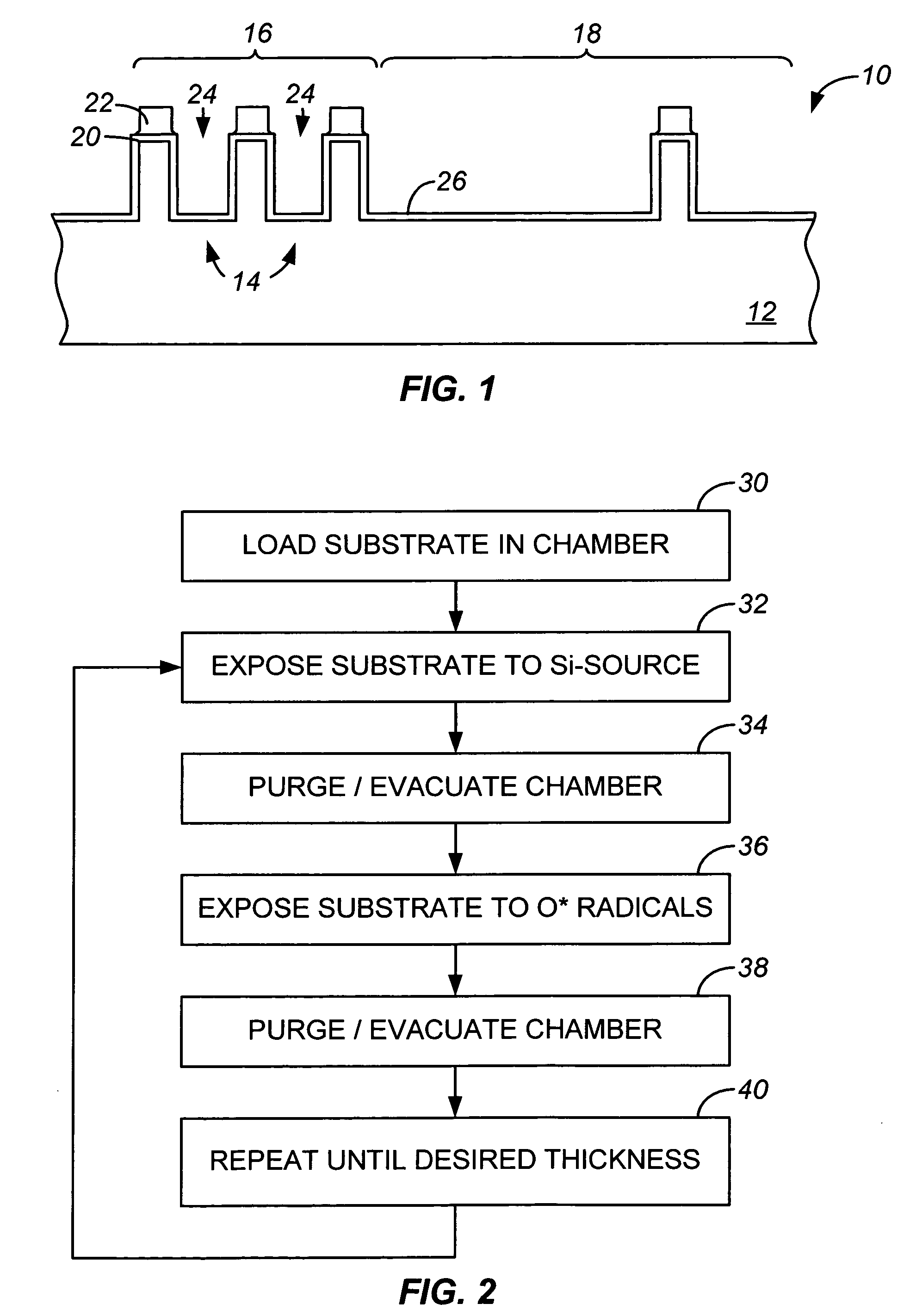
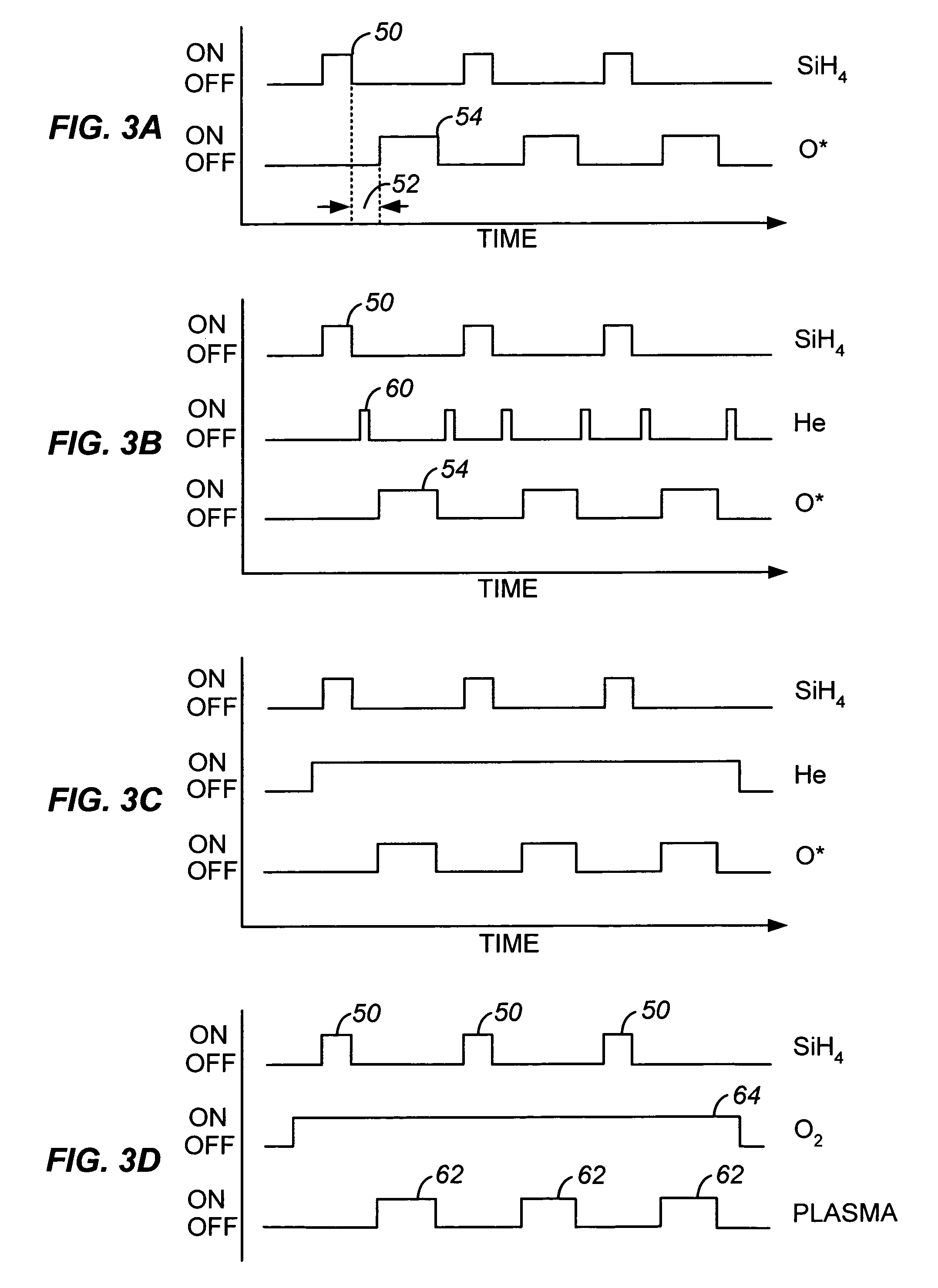
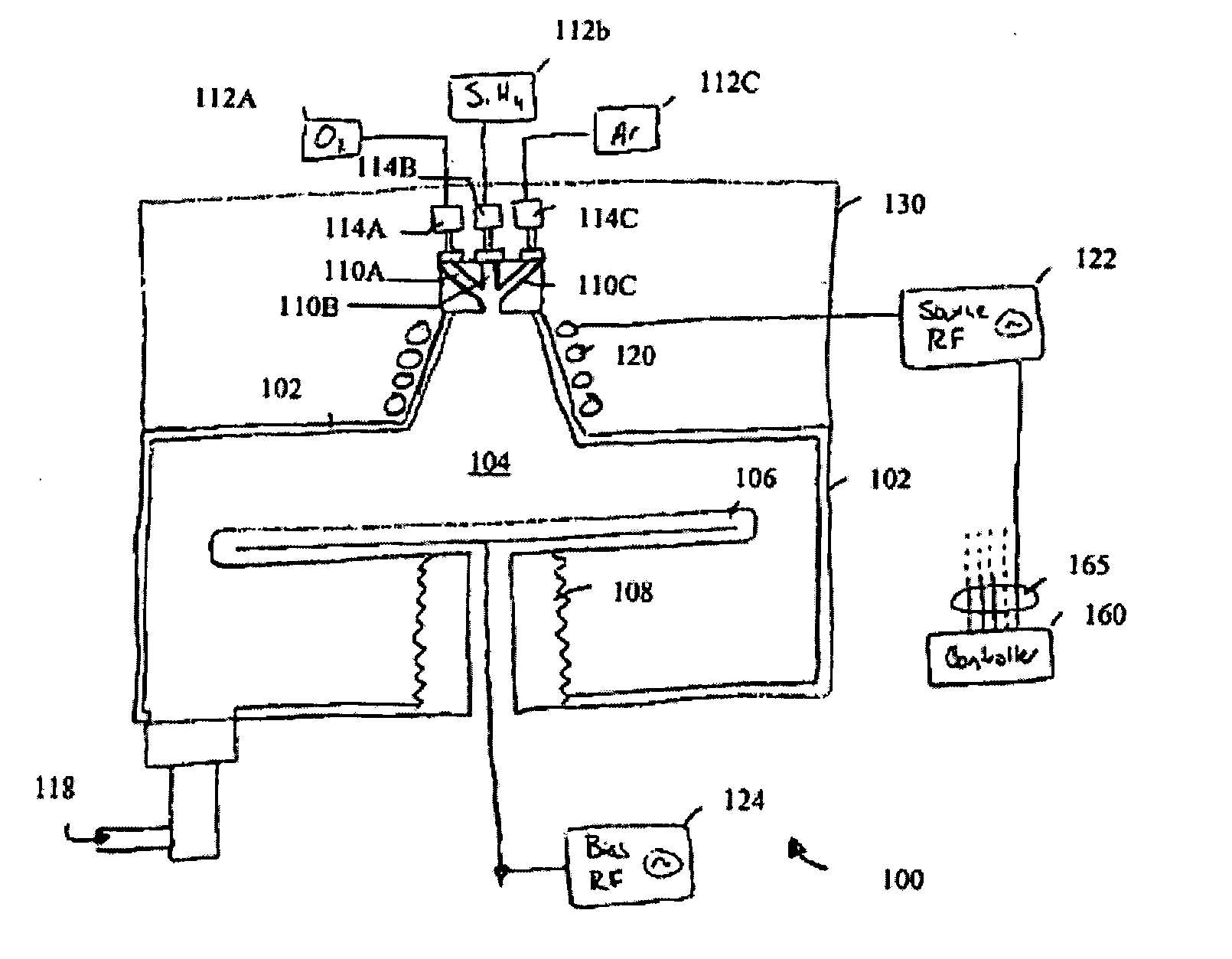
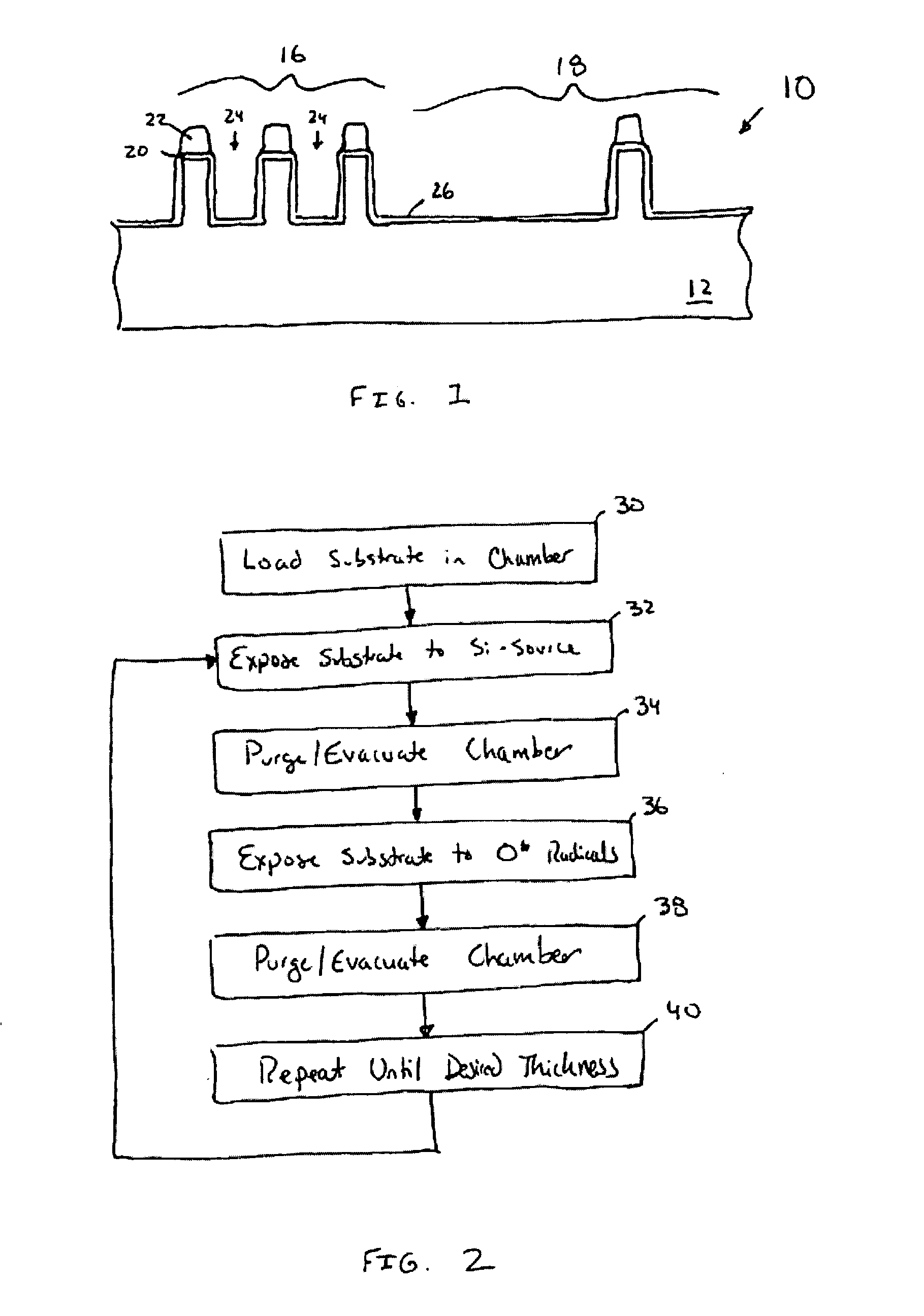
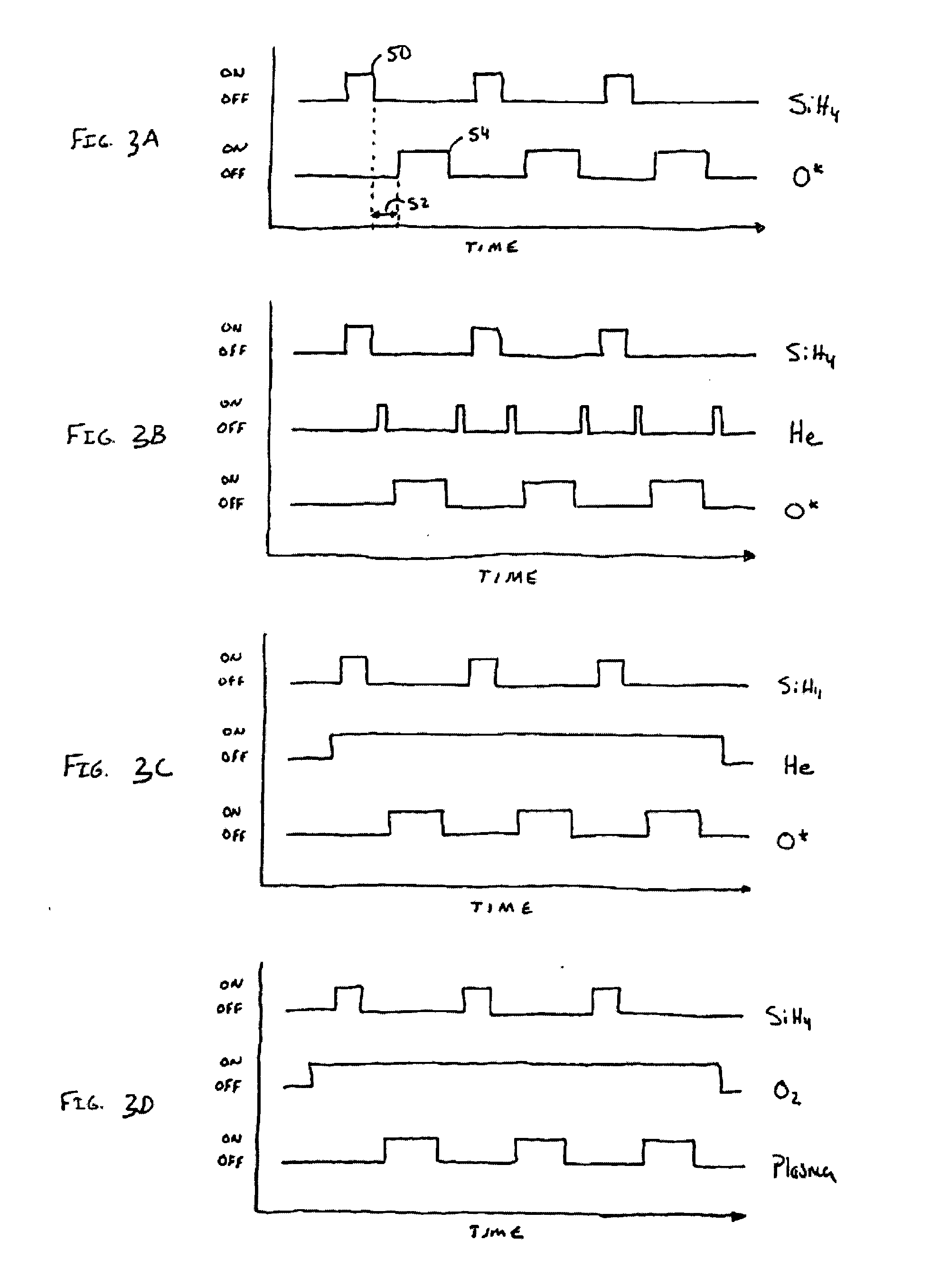
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
InactiveUS20050019494A1High aspect ratioGood effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxygenSilicon dioxide
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of doping silica glass with an alkali metal, and optical fiber precursor formed therefrom
A method of making an optical fiber precursor includes generating vapors from an alkali metal source comprising compound containing oxygen and one or more alkali metals and applying the vapors to a surface of a glass article comprising silica at a temperature that promotes diffusion of the alkali metal into the surface of the glass article. An optical fiber has a core comprising silica and an alkali metal oxide of the form X2O, where X is selected from the group consisting of K, Na, Li, Cs, and Rb, wherein a concentration of the alkali metal oxide along a length of the core is uniform.
Owner:CORNING INC
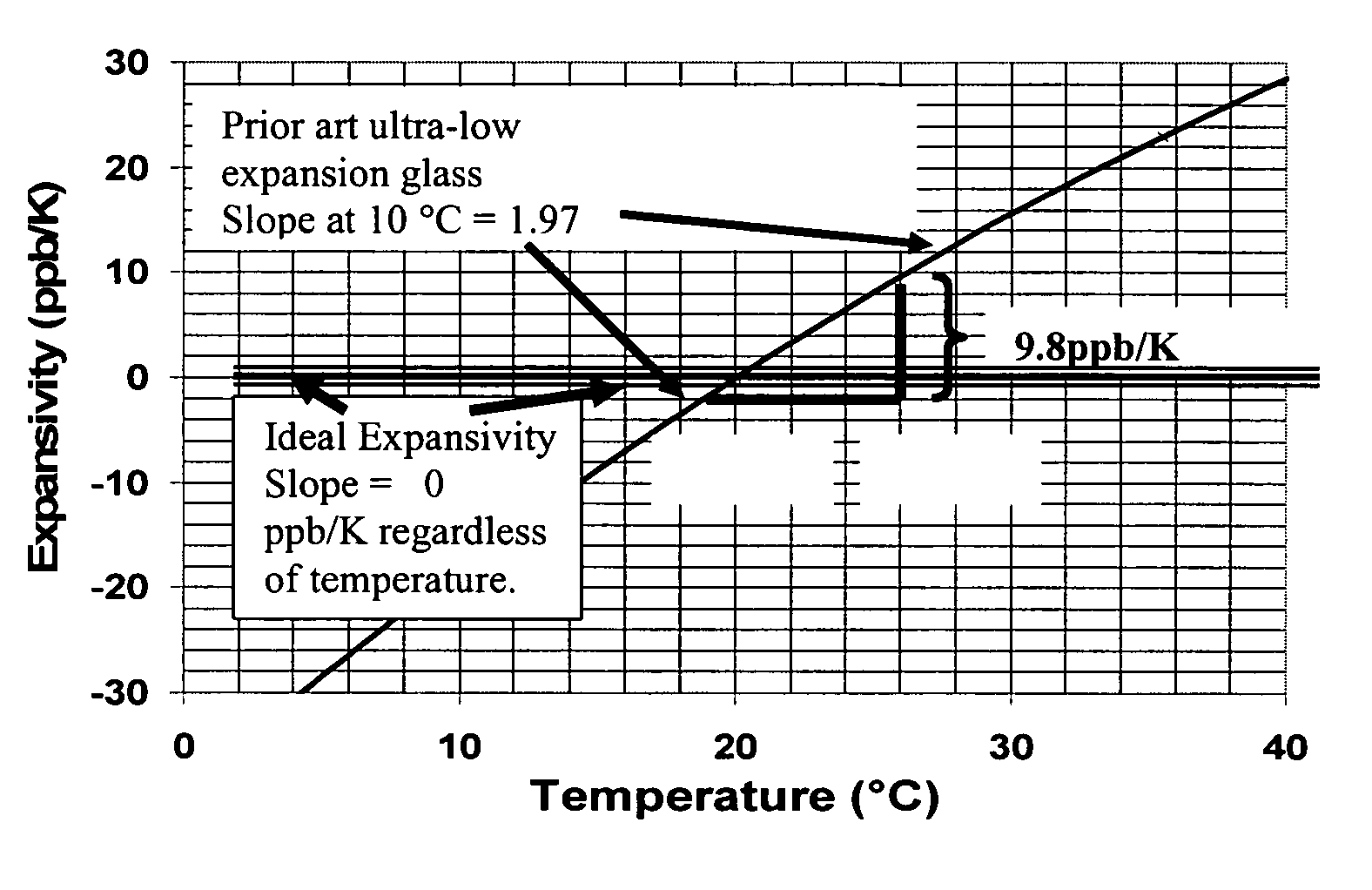
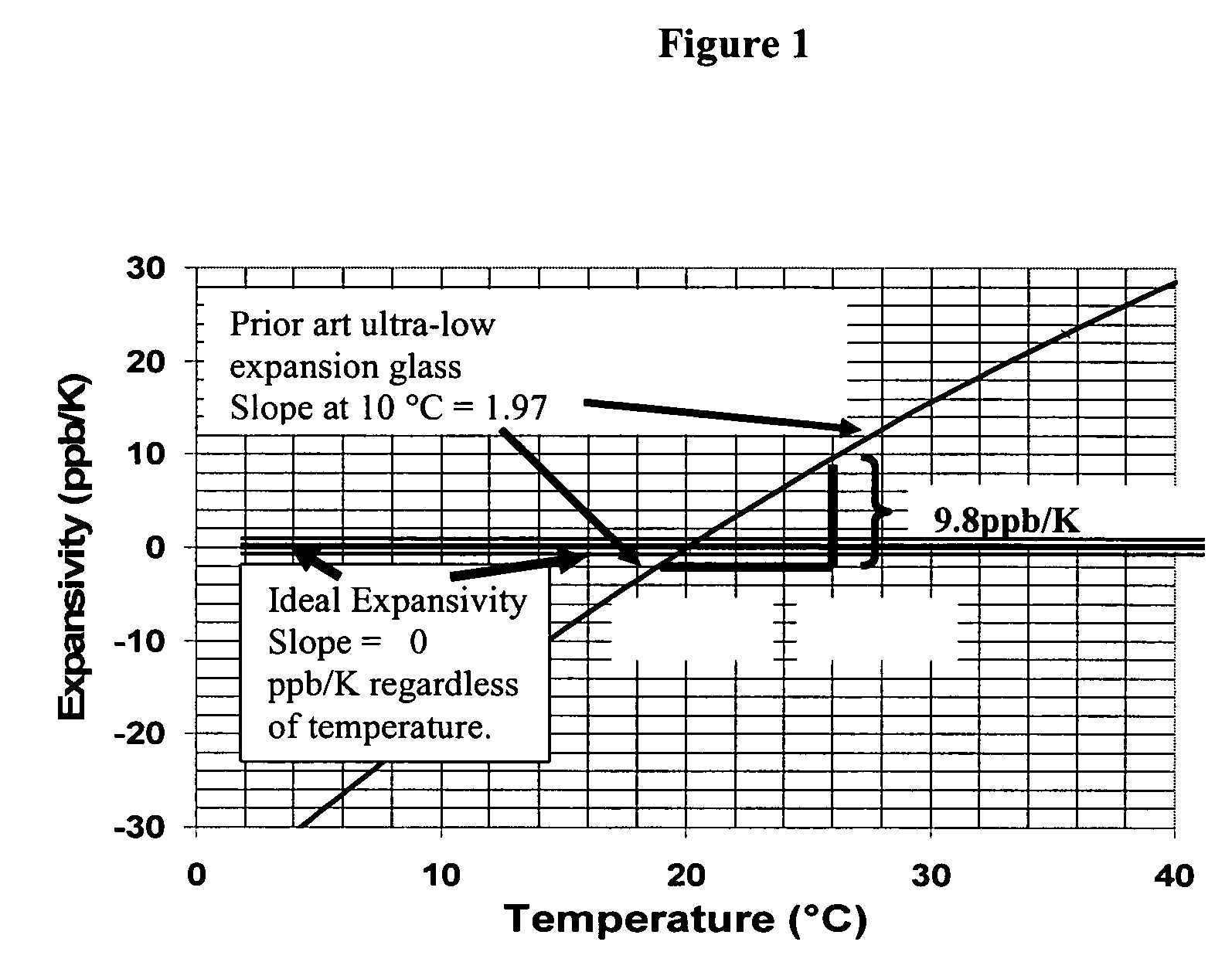
Adjusting expansivity in doped silica glasses
InactiveUS20060179879A1Low viscosityGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersDopantUltra low expansion glass
The invention is directed to ultra-low expansion glasses to which adjustments have been made to selected variables in order to improve the properties of the glasses, and particularly to lower the expansivity of the glasses. The glasses are titania-doped silica glasses. The variables being adjusted include an adjustment in β-OH level; an adjustment to the cooling rate of the molten glass material through the setting point; and the addition of selected dopants to impact the CTE behavior.
Owner:CORNING INC
Coated optical fibers having strippable primary coatings and processes for making and using same
InactiveUS6014488ACleanly strippableHigh modulusGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusFiberSilicon dioxide
PCT No. PCT / US98 / 01289 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 1, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 1, 1998 PCT Filed Jan. 23, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 33081 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 30, 1998The invention relates to coated optical fibers which are coated with a particular radiation-cured primary coating layer composition. The fibers which are coated comprises a glass core and a glass cladding layer. The core, for example may comprises silica doped with oxides of germanium or phosphorous and the cladding, a pure or doped silicate such as fluorosilicate. Alternatively, the fibers may comprises a polymerclad silica glass core. Examples of such claddings include organosiloxanes such as polydimethylsiloxane or a fluorinated acrylic polymer.
Owner:HEXION INC
Optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray, optical fiber probe, and method of manufacturing the optical fiber probe
InactiveUS6944380B1High light transmittanceResistant to deteriorationGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusFiberHydrogen
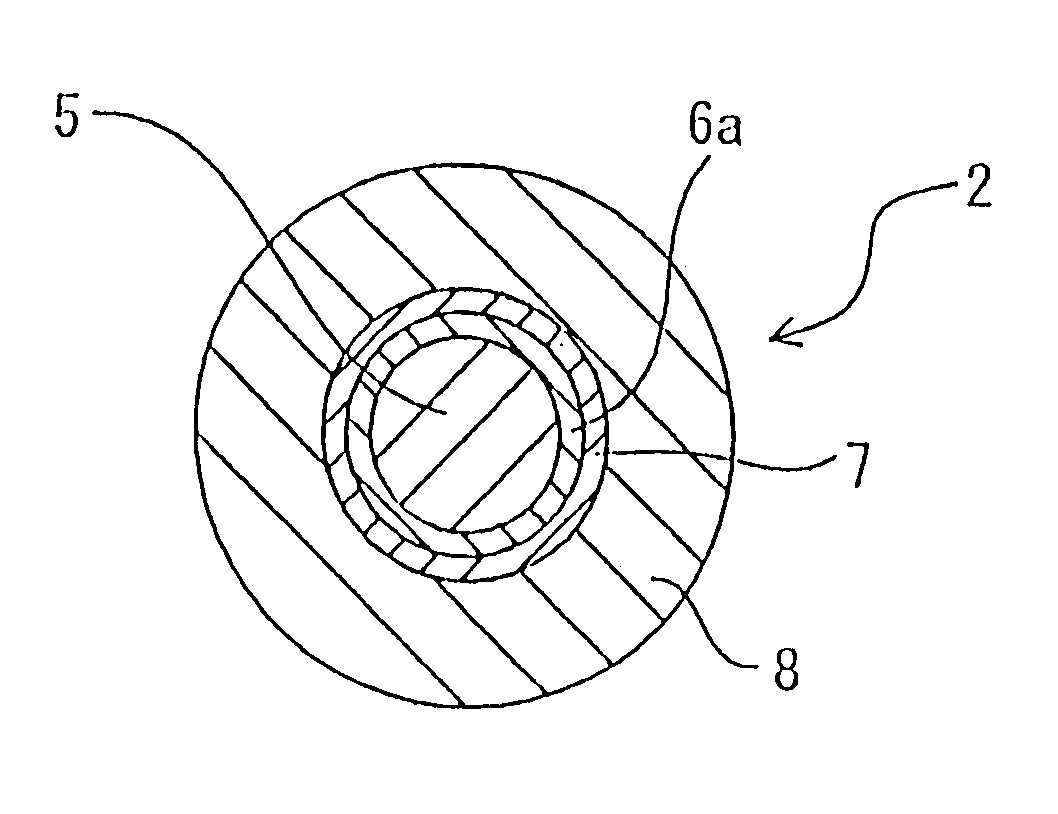
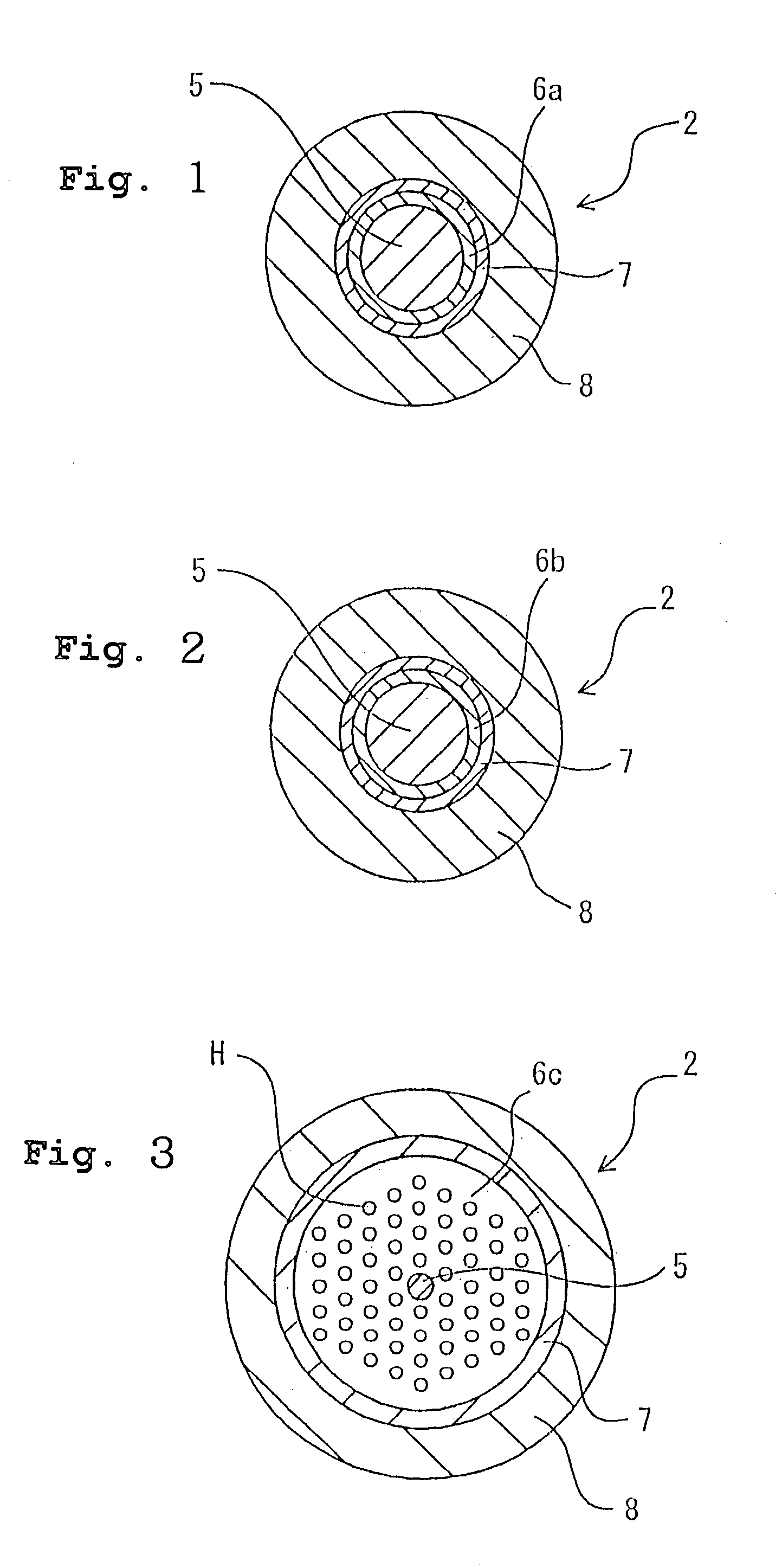
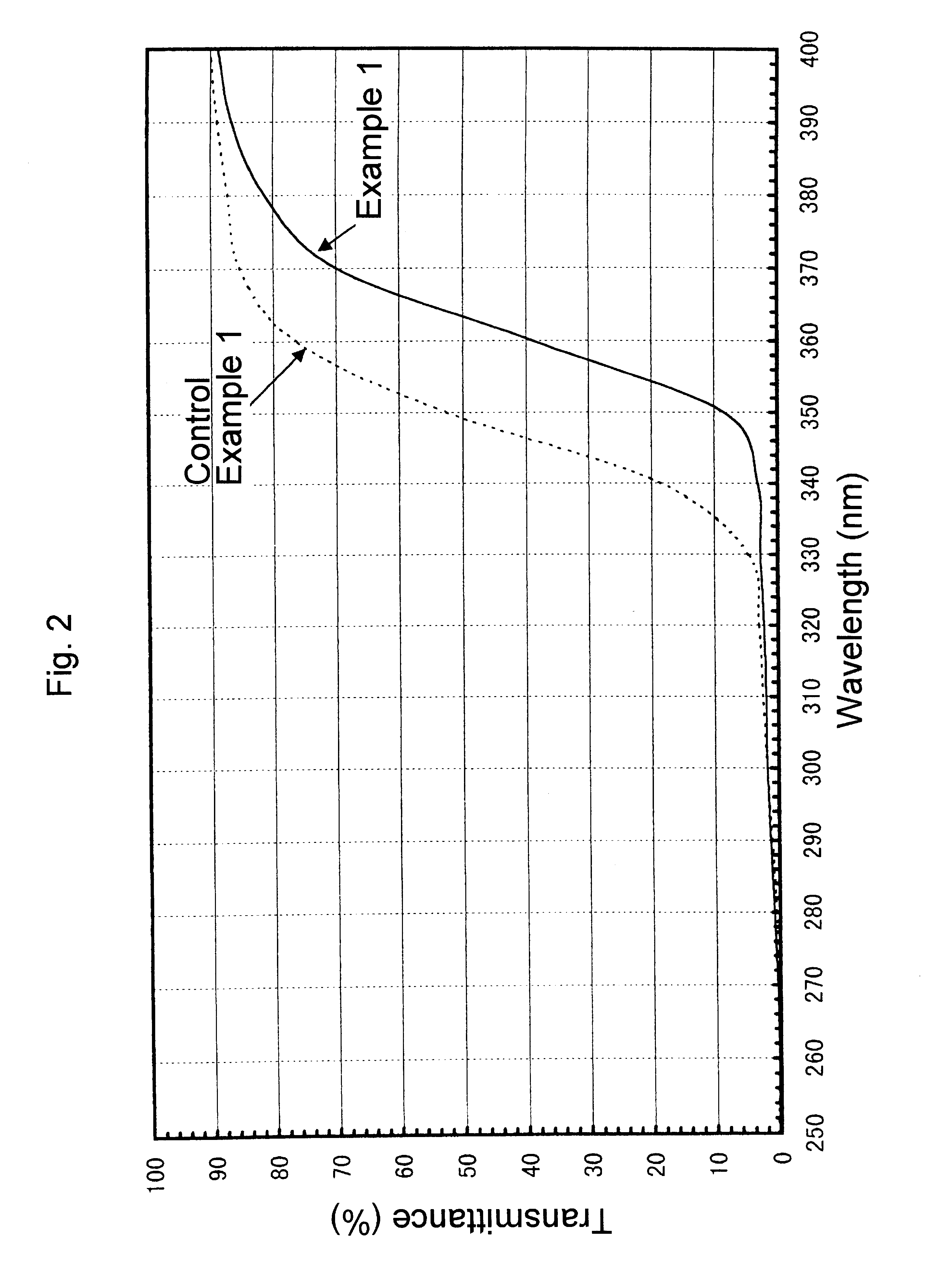
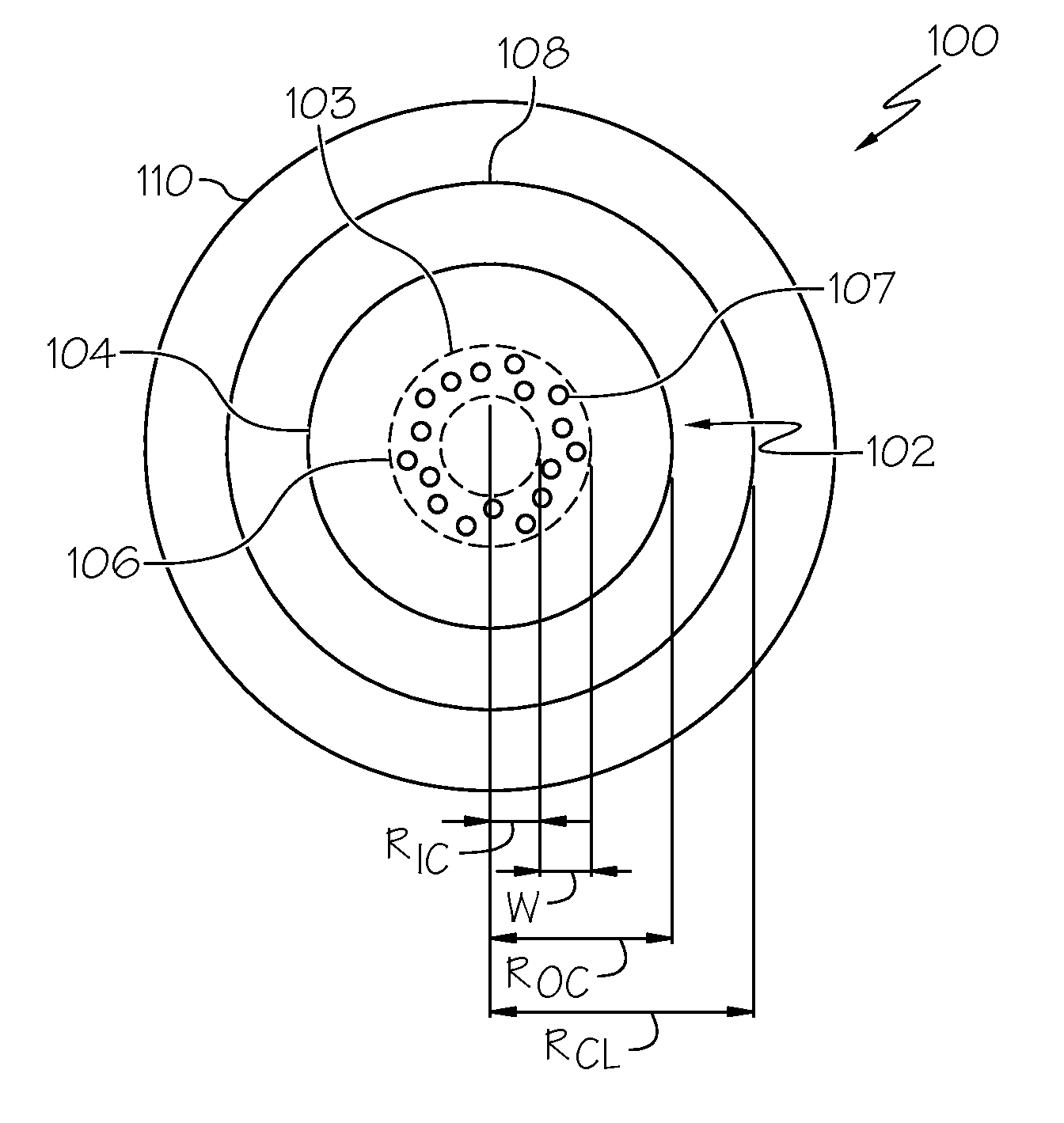
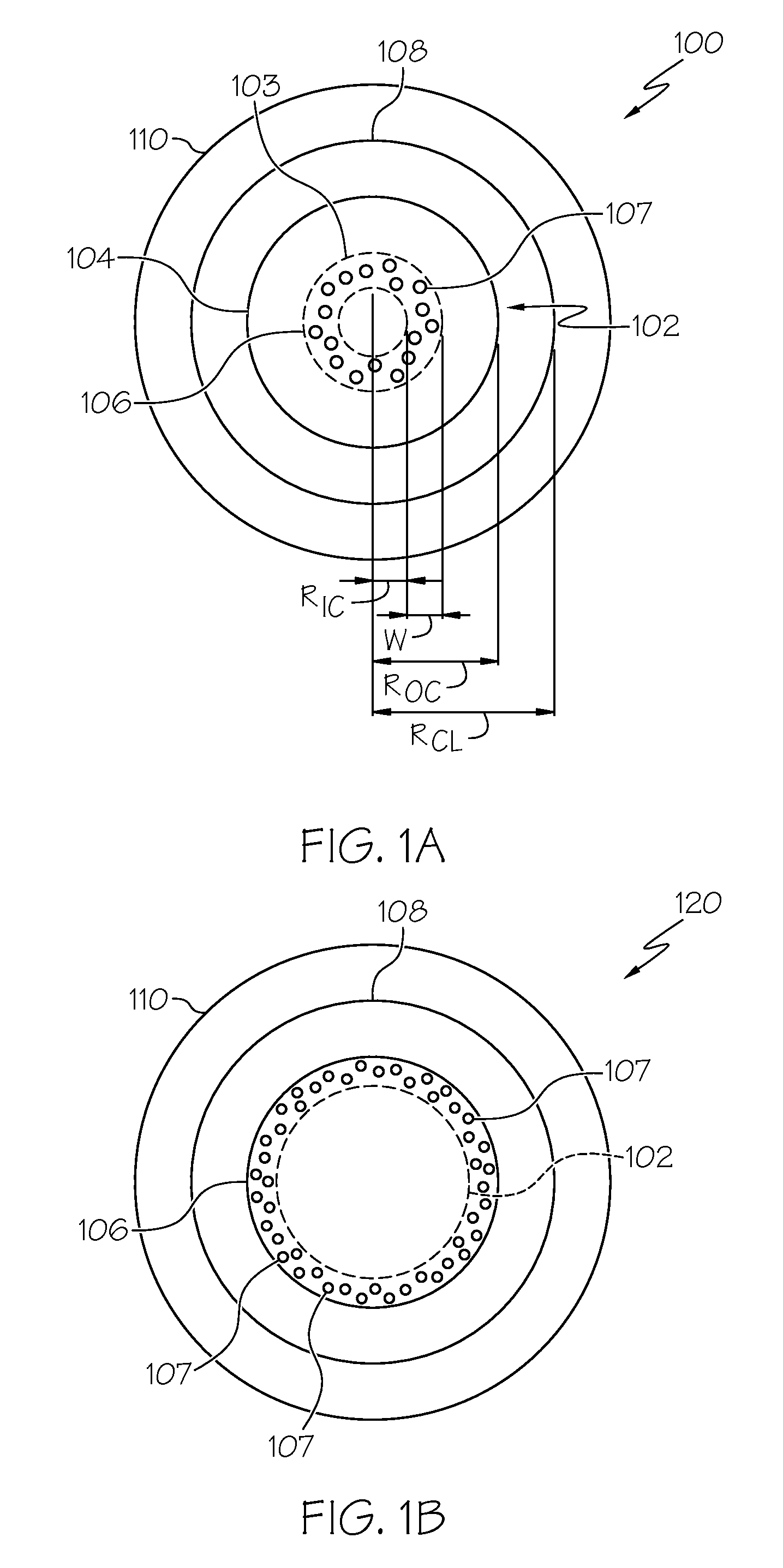
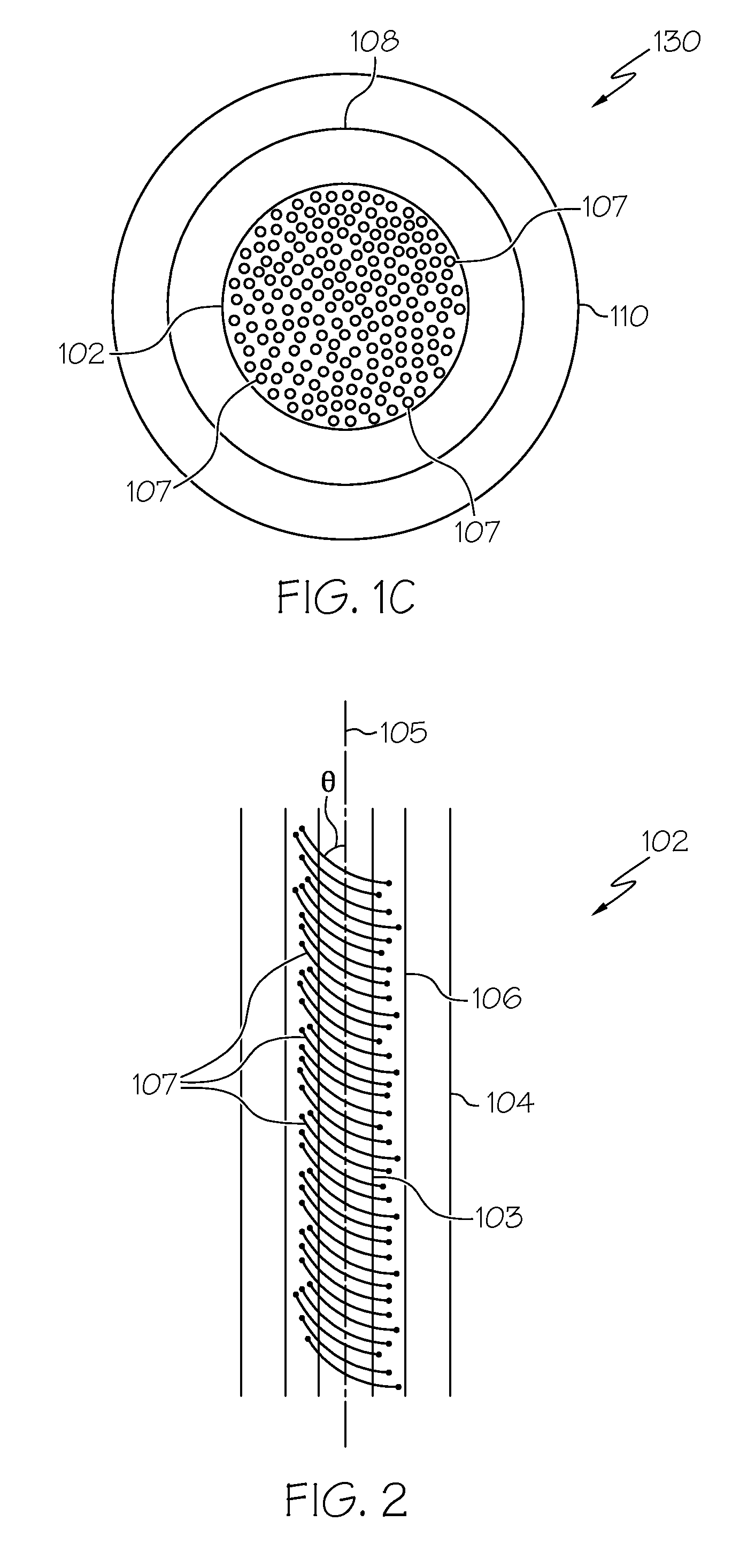
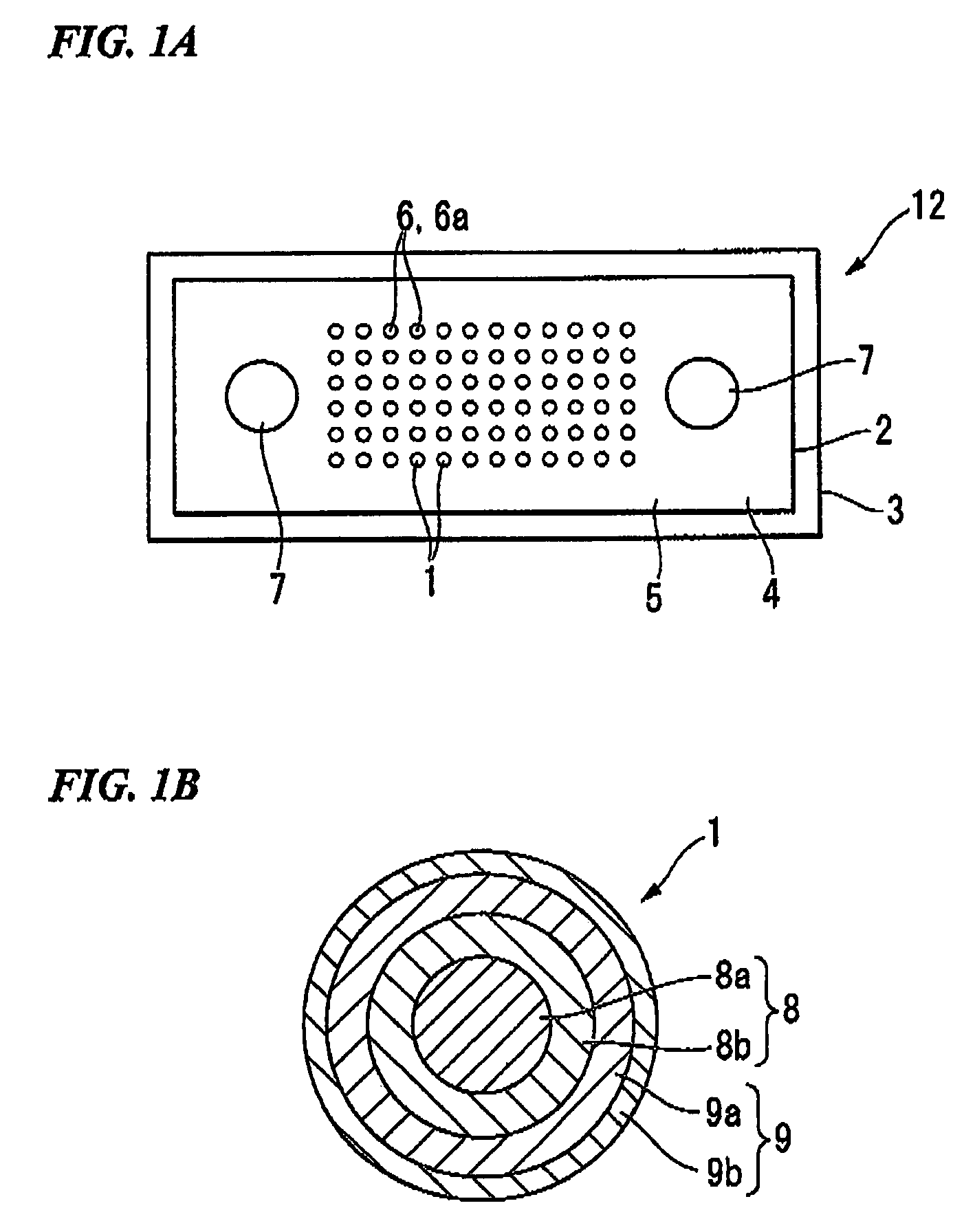
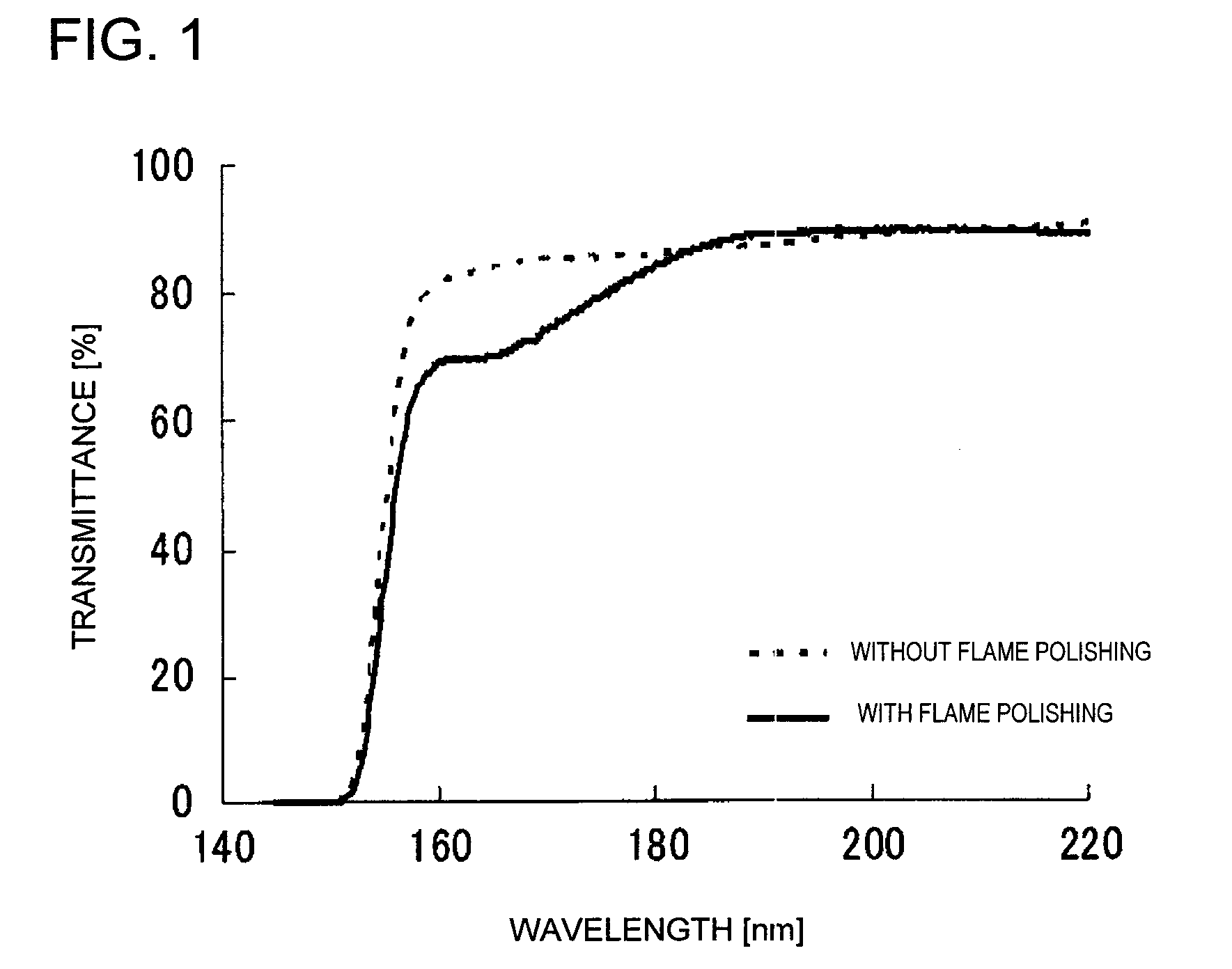
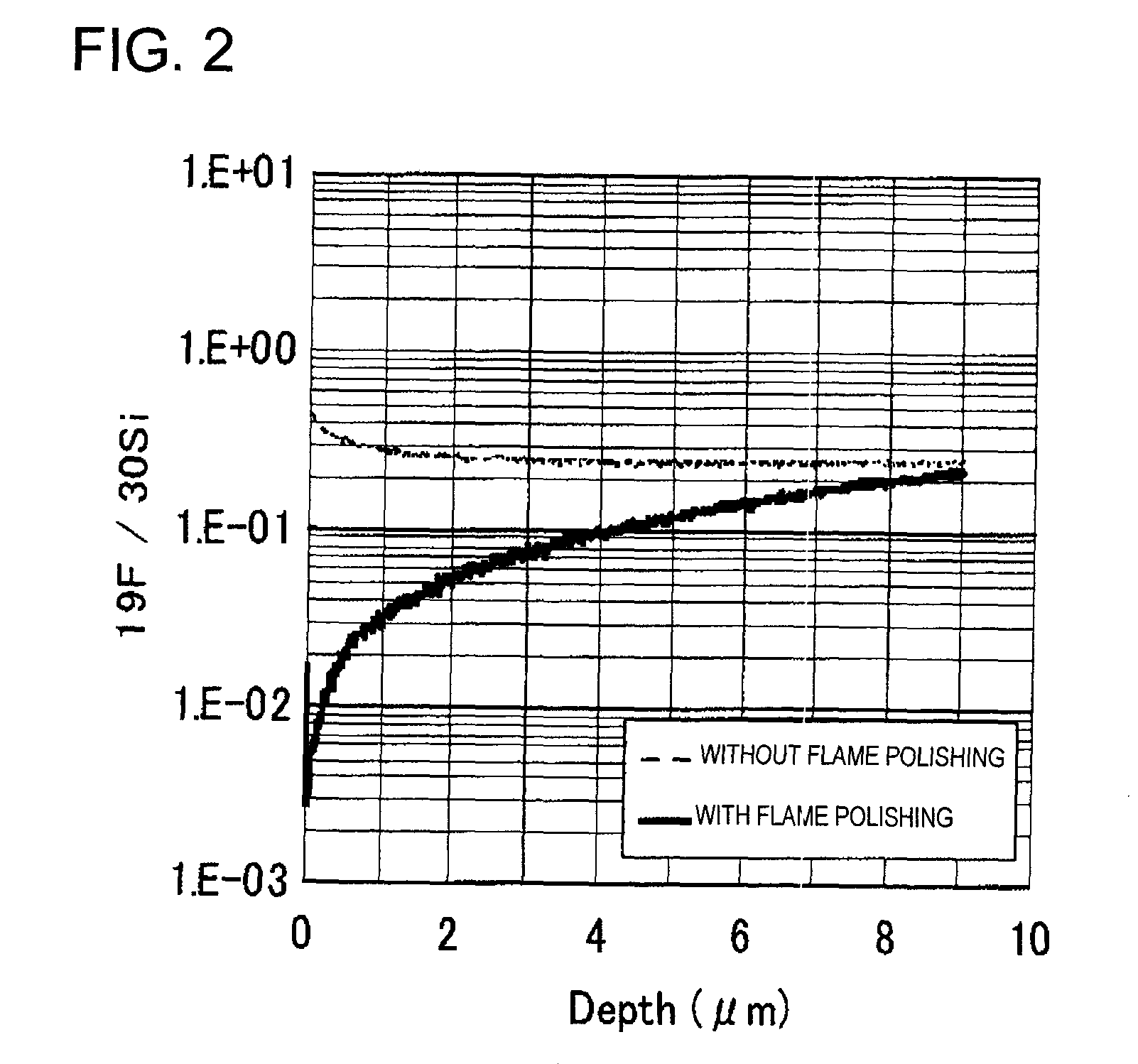
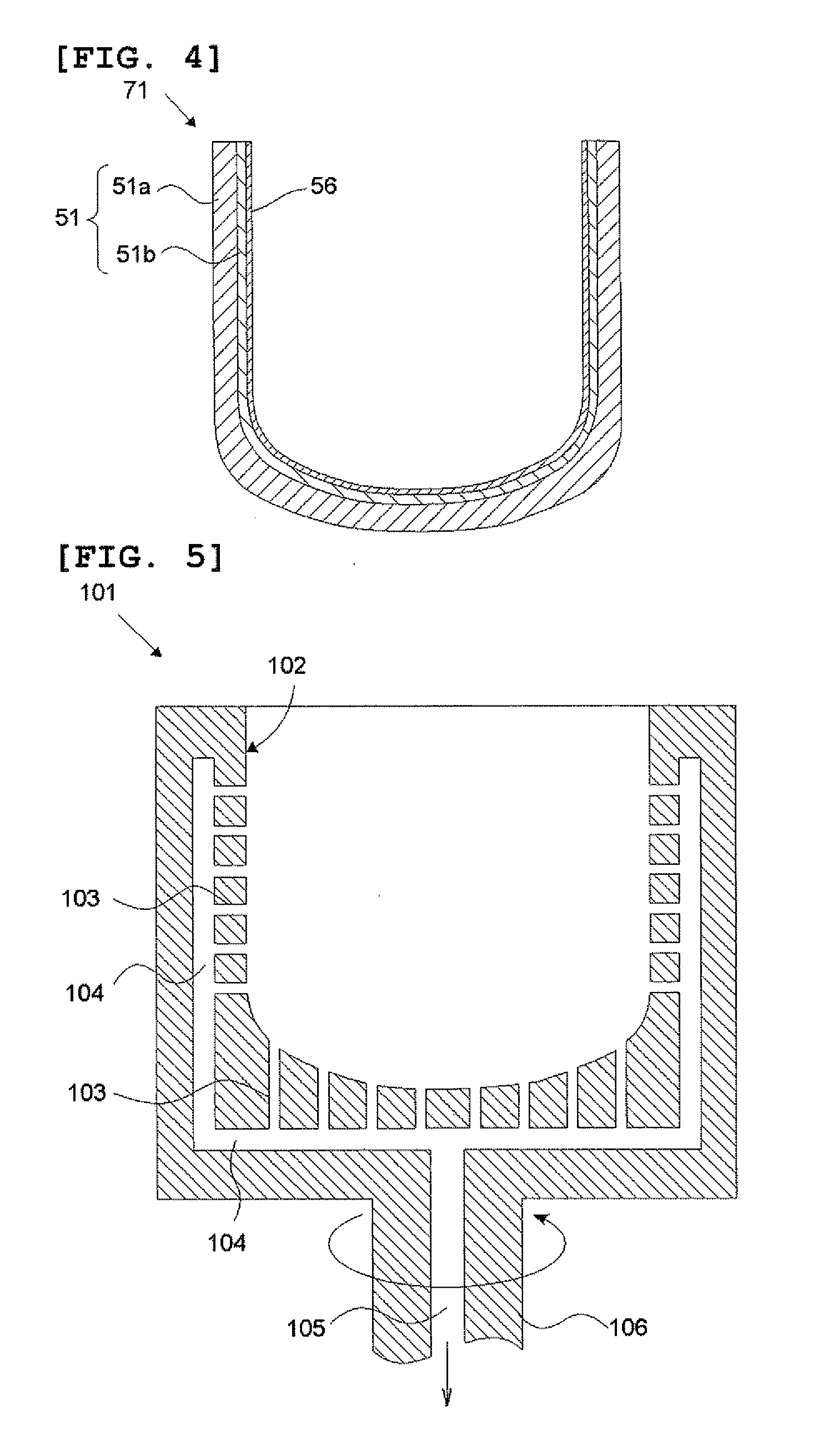
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has an improve transmittance and is prevented from deterioration by ultraviolet ray with which it is irradiated. It is another object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber probe which can propagate vacuum ultraviolet ray and deep ultraviolet ray at a high transmittance, is deteriorated only to a limited extent when irradiated with ultraviolet ray and can be etched to have a desired shape of the sharpened section at the fiber end.The present invention provides the optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has a core 5 of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine and a clad 6a of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine or boron, a clad 6b of a resin which transmits ultraviolet ray or a clad 6c having air holes H. The clad may be coated with a protective layer and further with a covered layer for protection. In particular, the core, clad and protective layer have a high transmittance for ultraviolet ray and resistance to ultraviolet ray with which they are irradiated, when treated with hydrogen.An optical fiber probe 1 has an optical fiber 2 provided with a sharpened section 3 at the end, which is sharpened with an etchant solution, the sharpened section 3 being coated with a light-shielding metallic film 4.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime silica glass
An ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime-silica glass as well as glass bottles formed out of the glass are disclosed which, while maintaining high transmittance to light in the visible region and thereby allowing the contents to be seen clearly, absorbs ultraviolet radiation and thus prevents coloration, discoloration, fading in color or deterioration of the flavor of the contents caused by ultraviolet radiation. The glass is characterized in that its composition includes, in % by weight, SO3 . . . 0.15-0.4%; Cerium oxide . . . 0.2-1% (calculated as CeO2); Fe2O3 . . . 0.01-0.08%; FeO . . . 0-0.008%; Manganese oxide . . . 0.01-0.08% (calculated as MnO); and Cobalt oxide . . . 0-0.0005% (calculated as CoO).
Owner:NIHON YAMAMURA GLASS CO LTD
Light Diffusing Fibers and Methods for Making the Same
Light diffusing optical fibers and methods for producing light diffusing optical fibers are disclosed. In one embodiment, a light diffusing optical fiber includes a core portion formed from silica glass and comprising a plurality of helical void randomly distributed in the core portion of the optical fiber and wrapped around the long axis of the optical fiber. A pitch of the helical voids may vary along the axial length of the light diffusing optical fiber in order to achieve the desired illumination along the length of the optical fiber. A cladding may surround the core portion. Light guided by the core portion is scattered by the helical voids radially outward, through the cladding, such that the light diffusing optical fiber emits light with a predetermined intensity over an axial length of the light diffusing optical fiber, the light diffusing optical fiber having a scattering induced attenuation loss greater than about 0.2 dB / m at a wavelength of 550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Isolated planar mesogyroscope
InactiveUS7168318B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsIn planeThermal expansion
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Optical filter comprising solar blind dyes and UV-transparent substrates
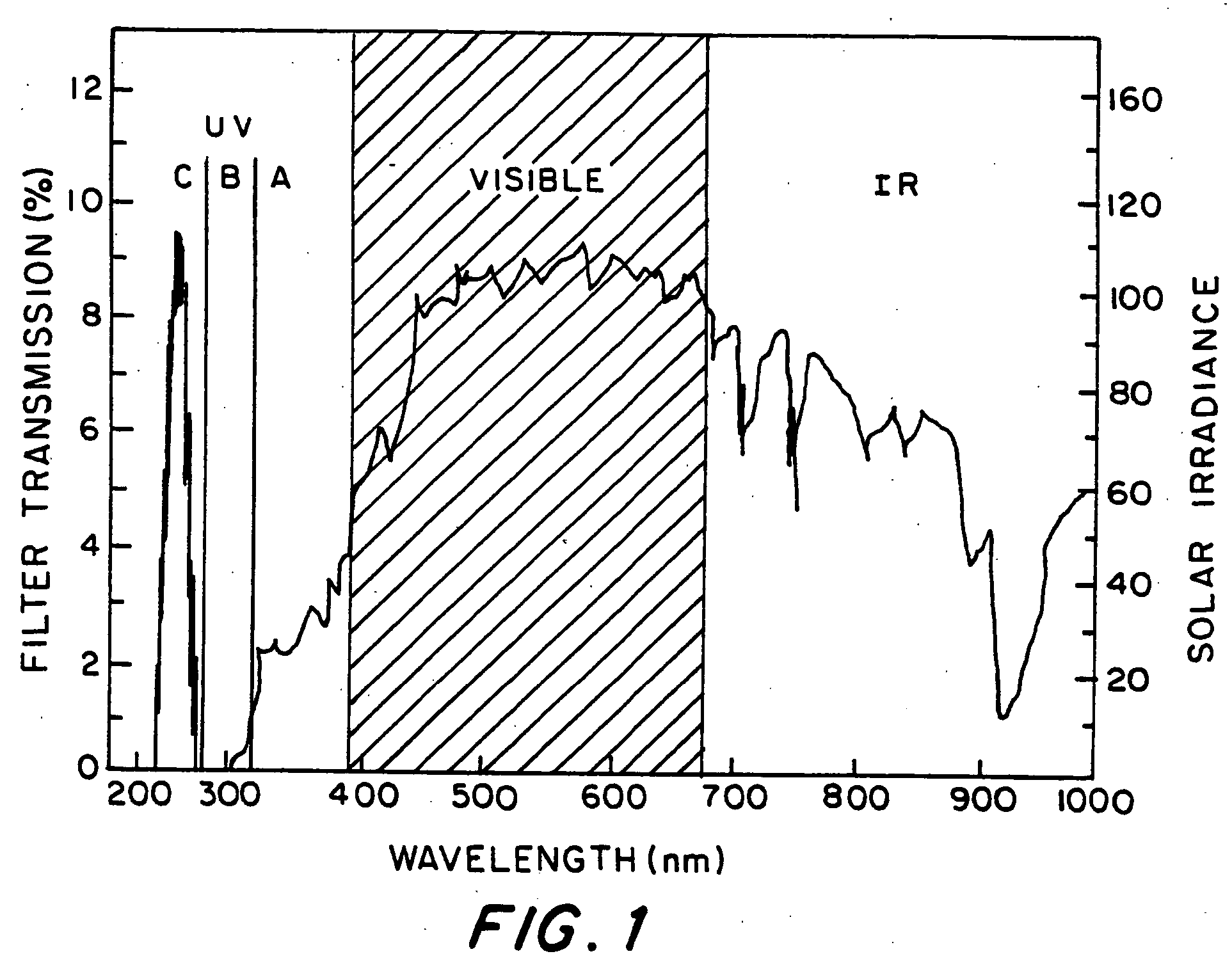
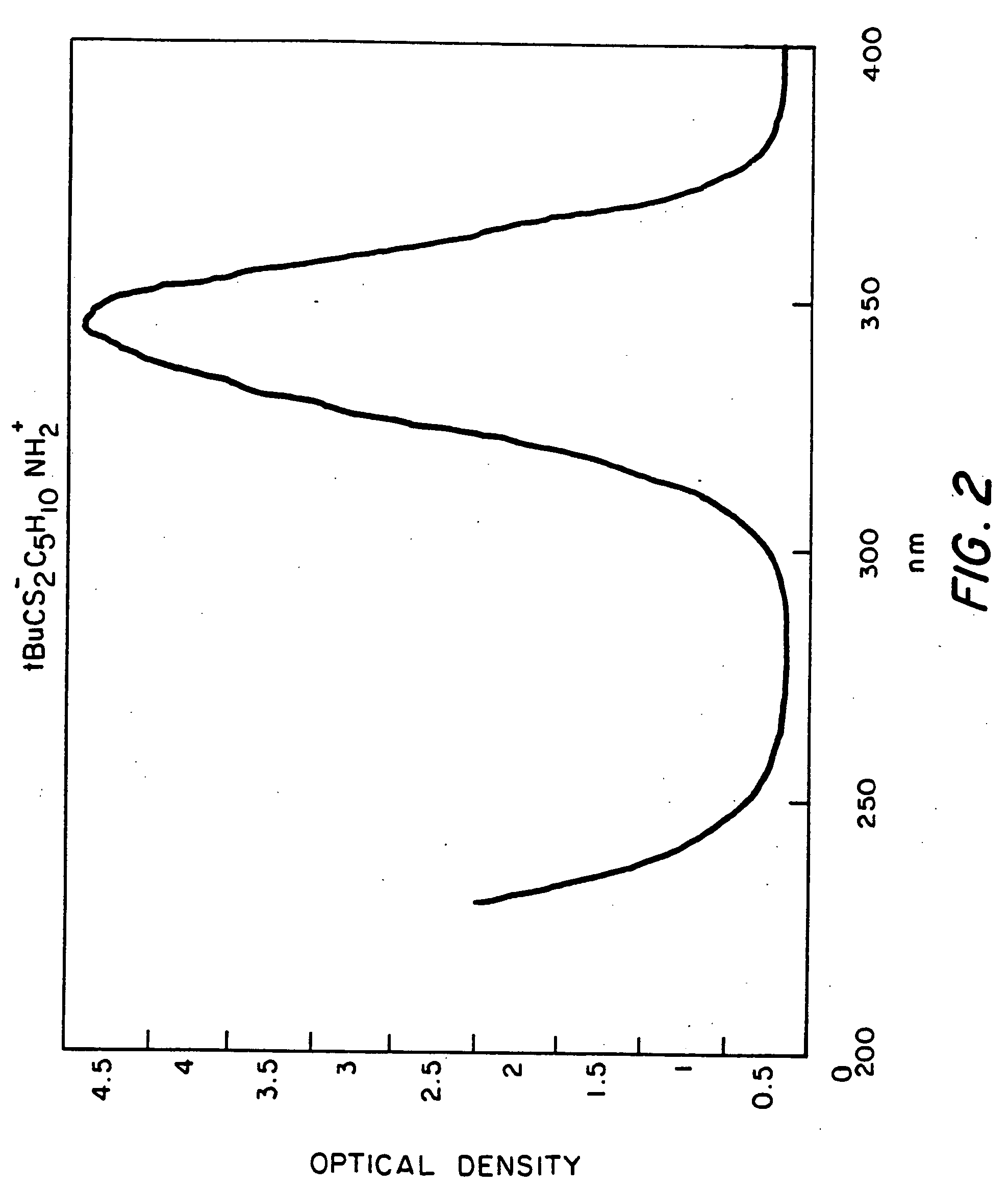
The invention provides an optical filter comprising: a. an organic, solar blind filter dye; and b. a UV-transparent, non-scattering and chemically stable substrate. The substrate may be a UV-transparent nanoporous silica glass solid having pores that are substantially filled with a UV-transparent solvent, which has been selected to dissolve said dye and also to match the refractive index of the nanoporous silica glass solid. Alternatively, the substrate may be a UV-transparent inorganic salt compressed to form a solid body. The invention also provides for methods of making these embodiments and an optical device comprising such an optical filter. The filter provides an efficient solar blind filter that is chemically and dimensionally stable.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Synthetic quartz glass for optical member and its production method
ActiveUS20060183623A1Suppress compactionSlow changeGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersOxygen deficientLength wave
A synthetic quartz glass for an optical member which is free from compaction and rarefaction is obtained. A synthetic quartz glass for an optical member to be used for an optical device employing a light having a wavelength of at most 400 nm and at least 170 nm as a light source, which contains substantially no oxygen excess defects, dissolved oxygen molecules nor reduction type defects, which has a chlorine concentration of at most 50 ppm and a OH group concentration of at most 100 ppm, and which contains oxygen deficient defects within a concentration range of at most 5×1014 defects / cm3 and at least 1×1013 defects / cm3. The fluorine concentration is preferably at most 100 ppm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Substrate for EUV mask blanks
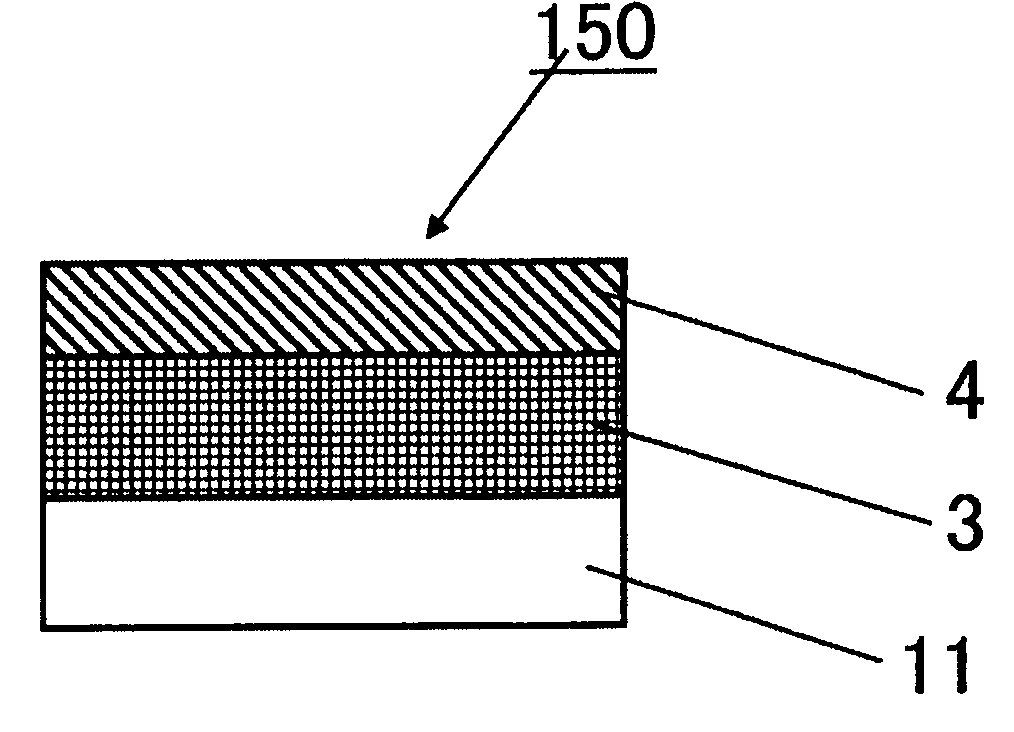
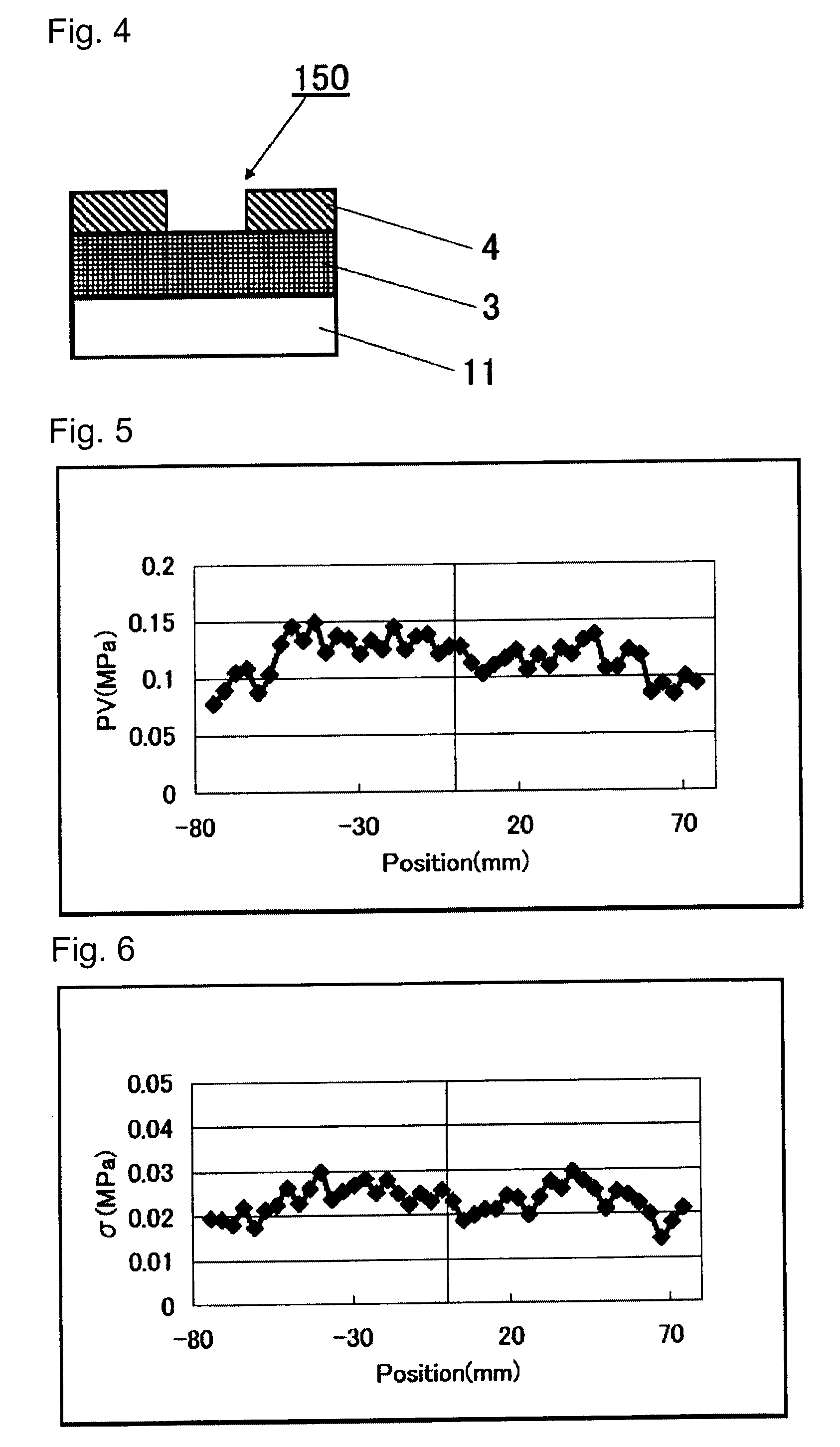
ActiveUS20100028787A1Improve flatnessNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessQuartz
A substrate that is suitable for an EUV mask or an EUV mask blank and excellent in flatness, is provided.A substrate for an EUV mask blank, which is made of a silica glass containing from 1 to 12 mass % of TiO2, wherein the surface roughness (rms) in a surface quality area of the substrate is at most 2 nm, and the maximum variation (PV) of the stress in the surface quality area of the substrate is at most 0.2 MPa.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Process of making rare earth doped optical fibre
InactiveUS20040187524A1Reduce in quantityNumber of step involvedMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreDip-coatingSoot
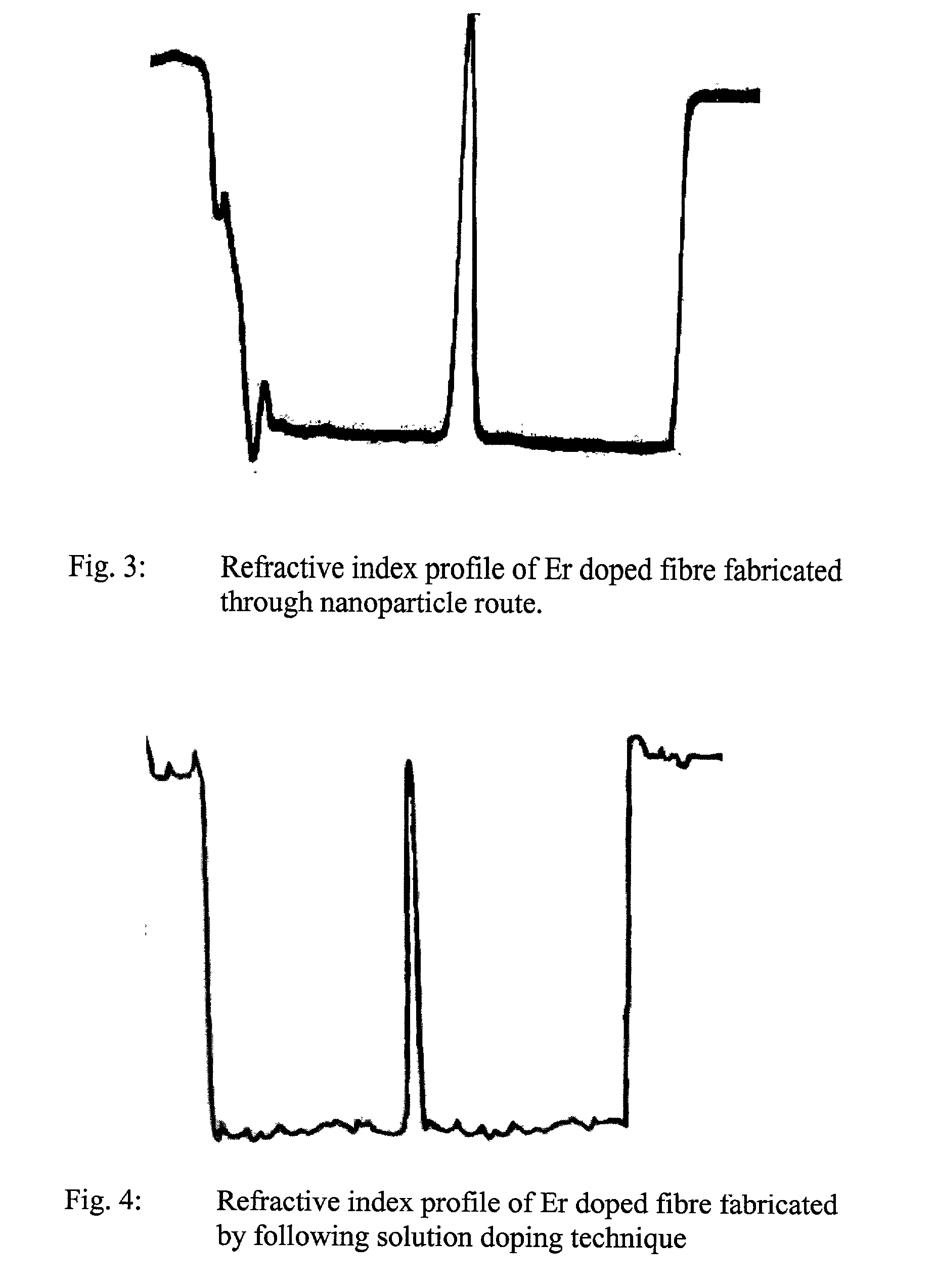
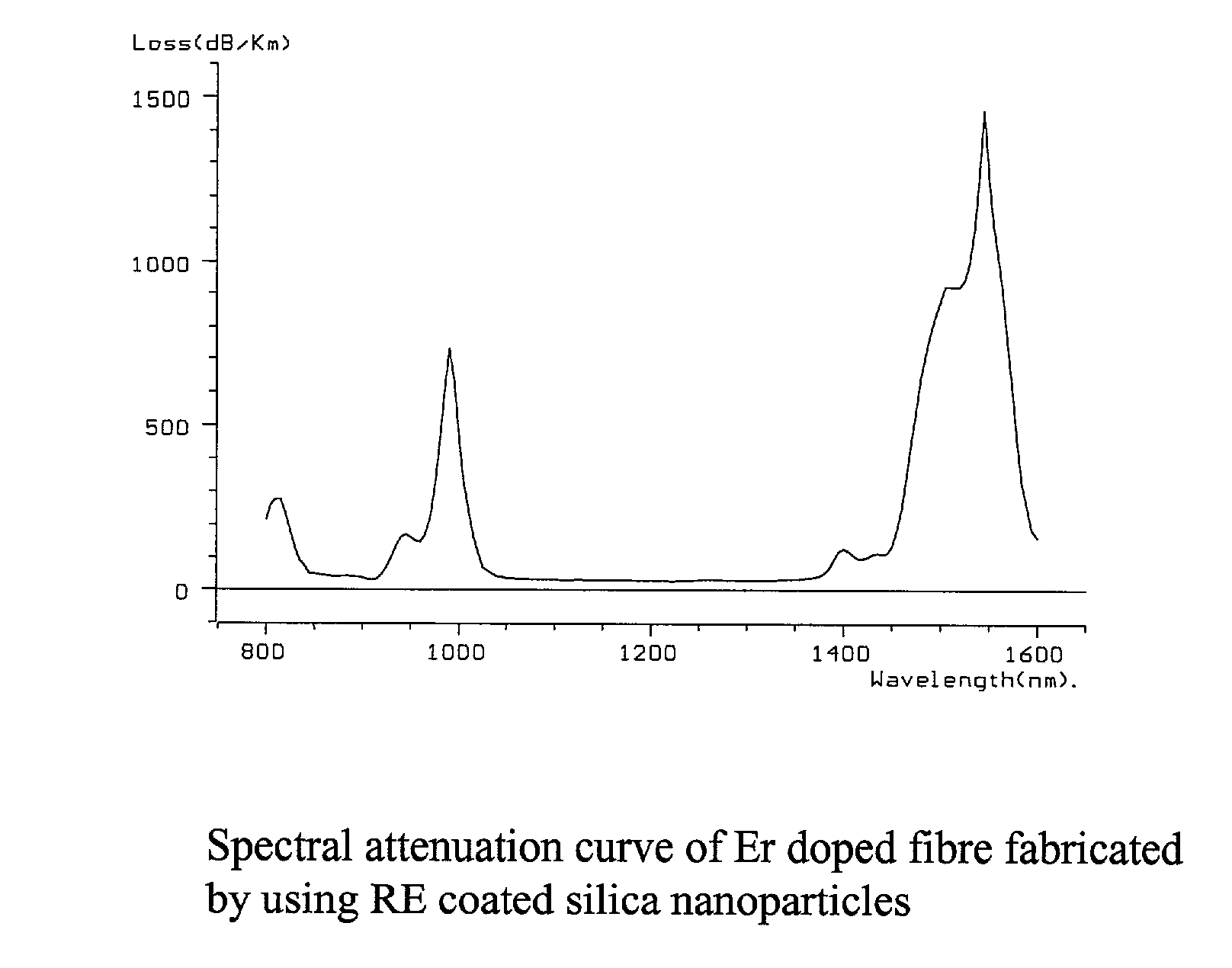
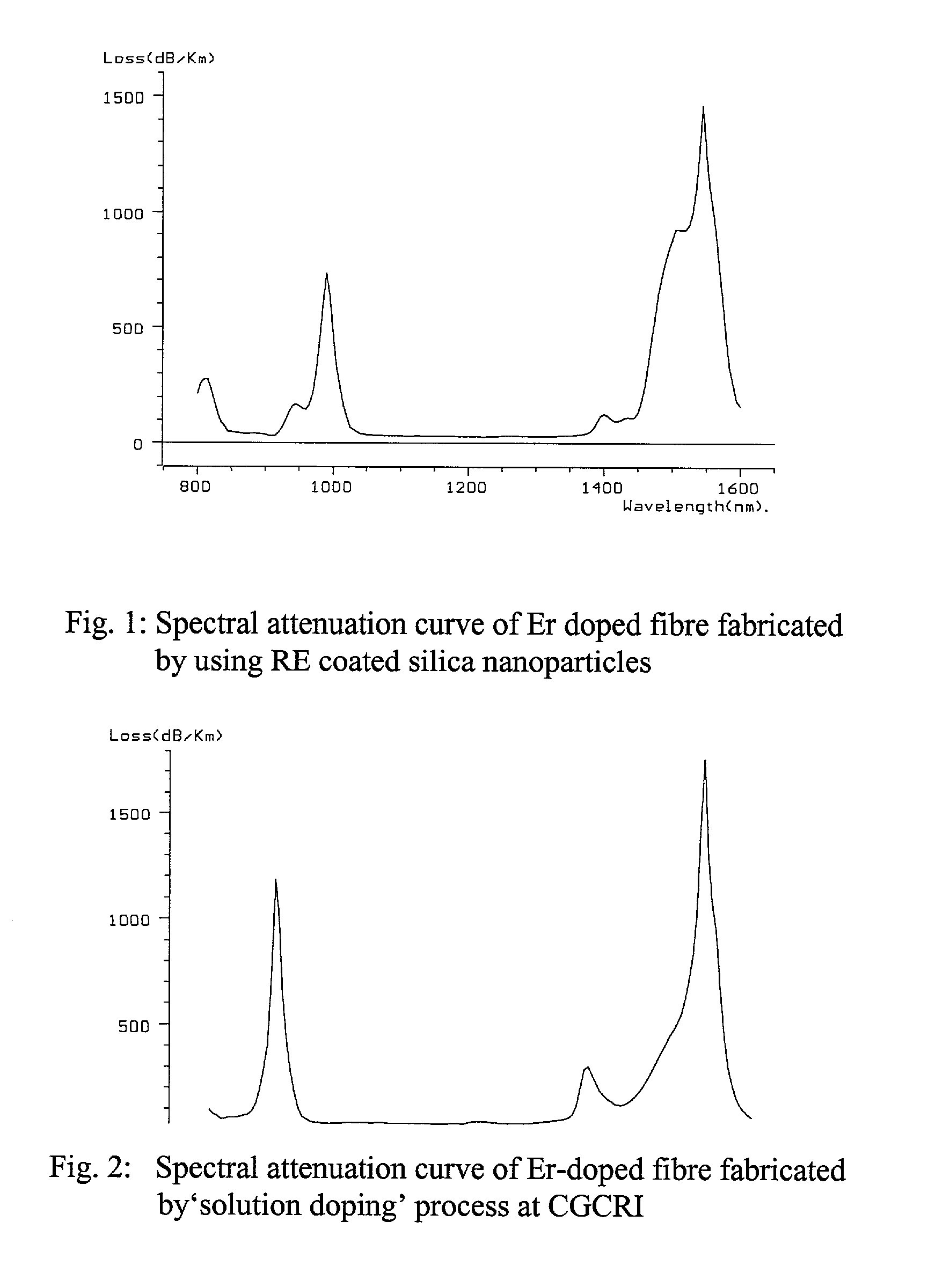
The present invention discloses a process for making rare earth (RE) doped optical fibre by using RE oxide coated silica nanoparticles as the precursor materia, more particularly the method of the present invention involves preparation of stable dispersions (sol) of RE oxide coated silica nanoparticles at ambient temperature and applying a thin coating on the inner surface of silica glass tube following dip coating technique or any other conventional methods, of the said silica sol containing suitable dopants selected from Ge, Al, P, etc., the coated tubes were further processed into optical preforms by following MCVD technique and fiberised in desired configuration, the novelty lies in eliminating the step of the formation of porous soot layer at high temperature by CVD process inside a fused silica glass tube for formation of the core and also in the elemination of the incorporation of the rare earth ions into the porous soot layer following the solution doping technique or other conventional methods, the direct addition of RE oxides in the sol eliminates the formation of microcrystalites and clusters of rare earth ions and prevents change in composition including variation of RE concentration in the core which results in increase in the reproducibility and reliability of the process to a great extent, further the addition of Ge(OET)4 at ambient temperature in the silica sol reduces the quantity of GeCl4 which is required at high temperature to achieve the desired Numerical Aperture.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Transparent, colorless low-titania beta-quartz glass-ceramic material
Owner:EUROKERA SOC & NOM COLLECTIF
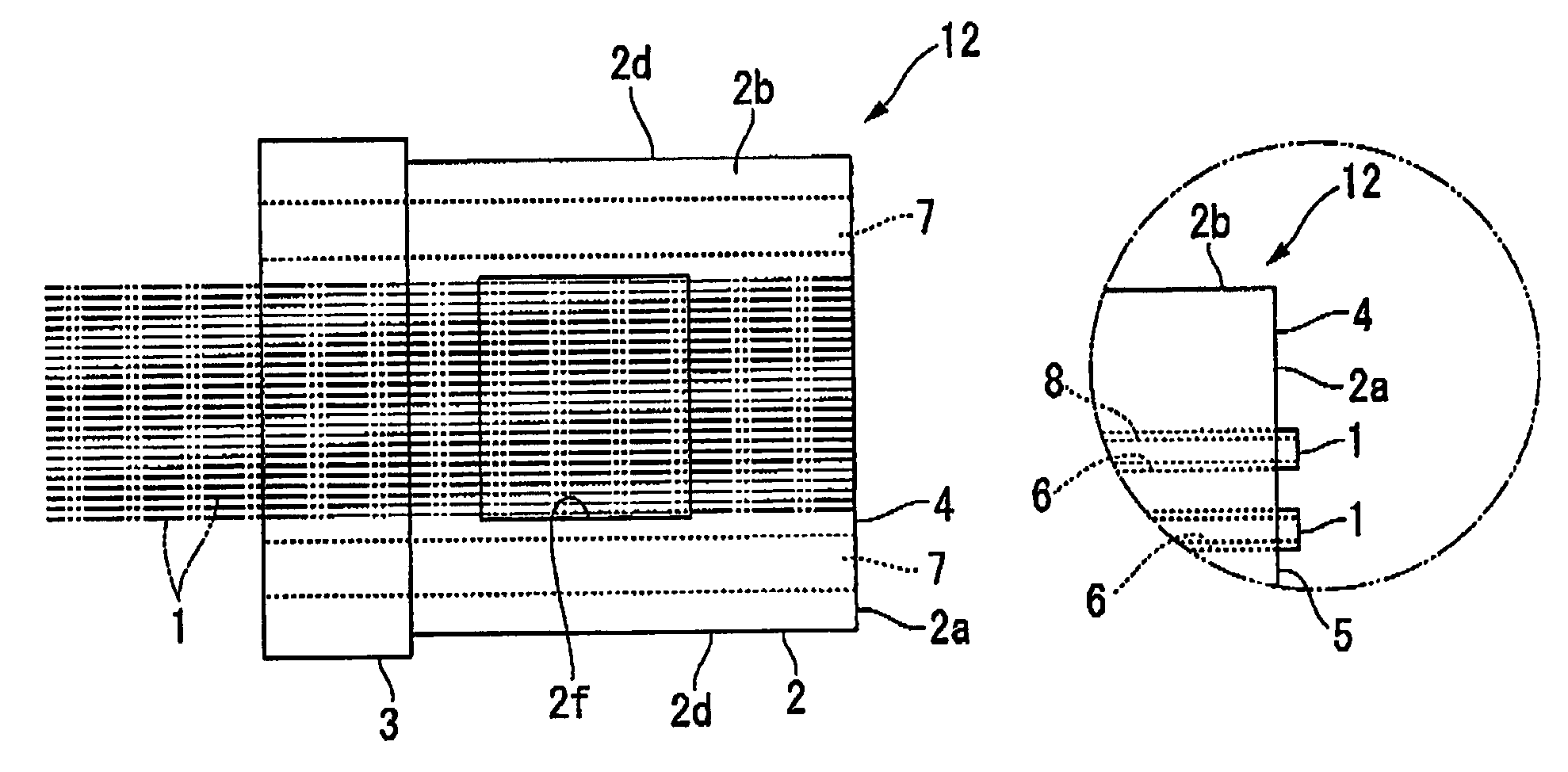
Optical connector with optical fiber
In an optical connector with optical fibers in which silica glass optical fibers with resin coating layers remaining attached are connected in optical fiber openings of a ferrule made from resin, at least a part of the resin coating layer of the optical fiber is glued to an inner face of the optical fiber opening, an outer diameter of the resin coating layer of the optical fiber is less than or equal to 125 μm, and the Young's modulus of the resin coating layer is less than the Young's modulus of the ferrule, and the Young's modulus of the resin coating layer is 1500 to 10000 MPa.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Method for preparing Cu2Se thermoelectric material by low-temperature solid-phase reaction
InactiveCN102674270ALow costControl compositionChemical industryBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsMuffle furnace
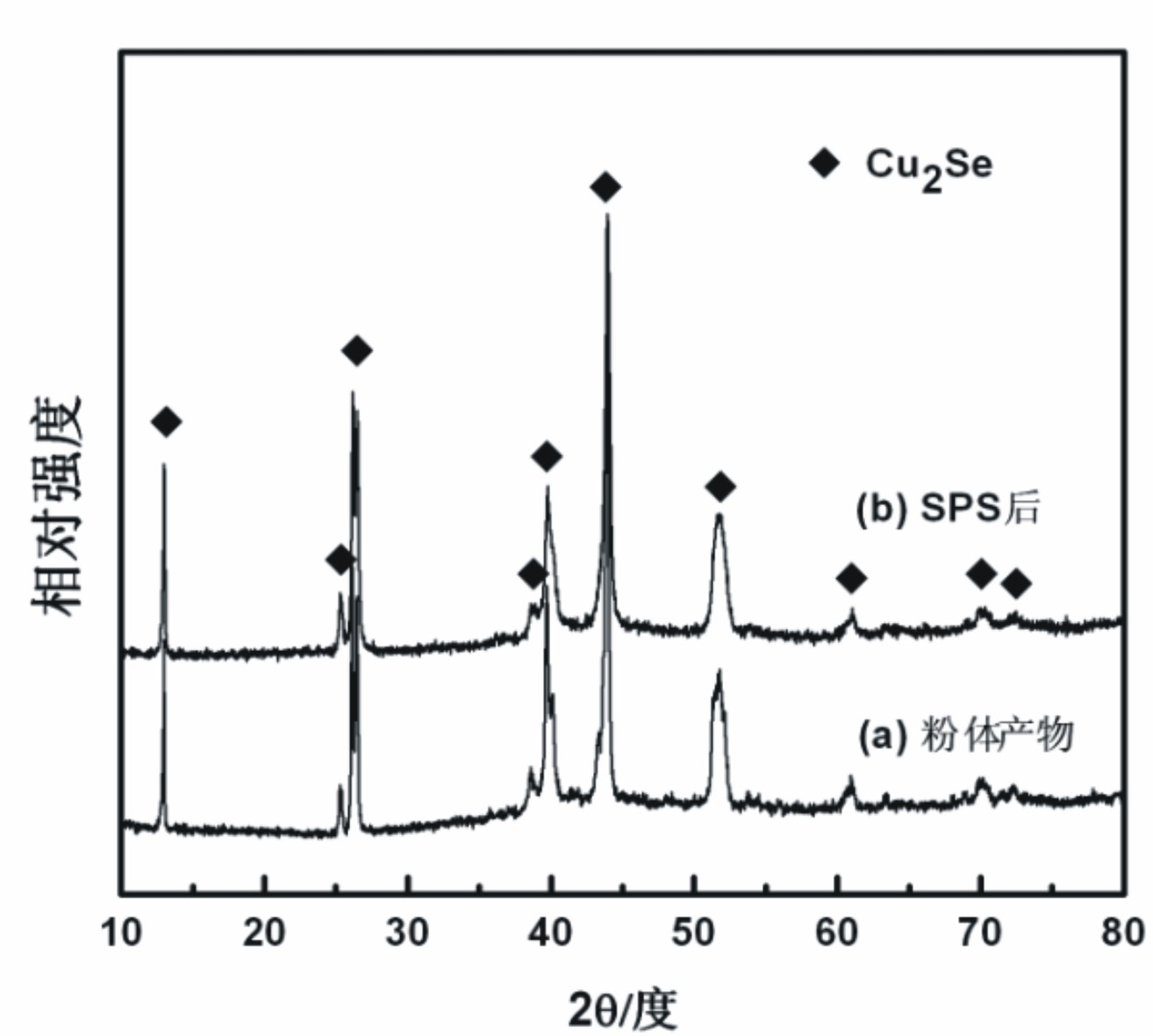
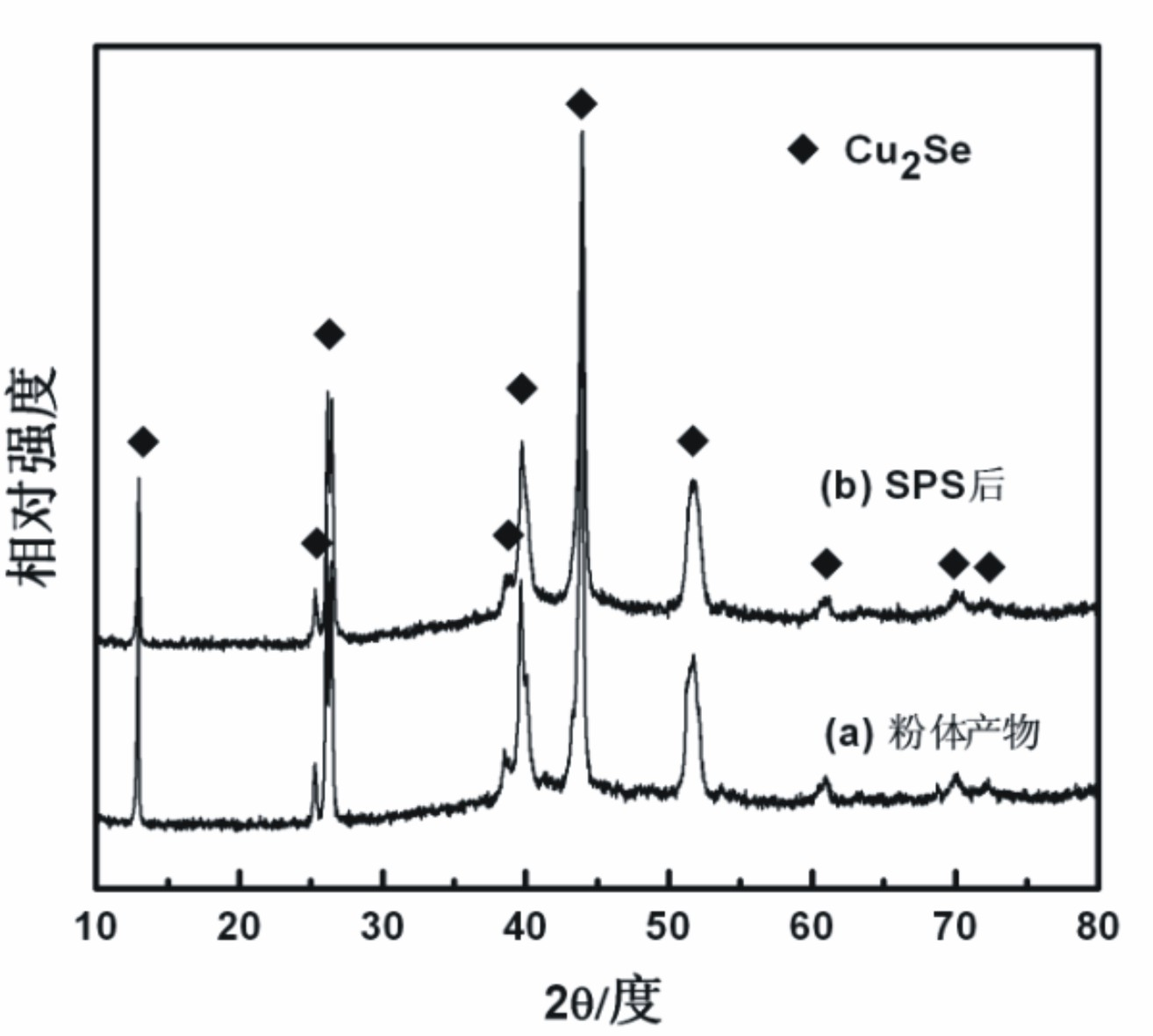
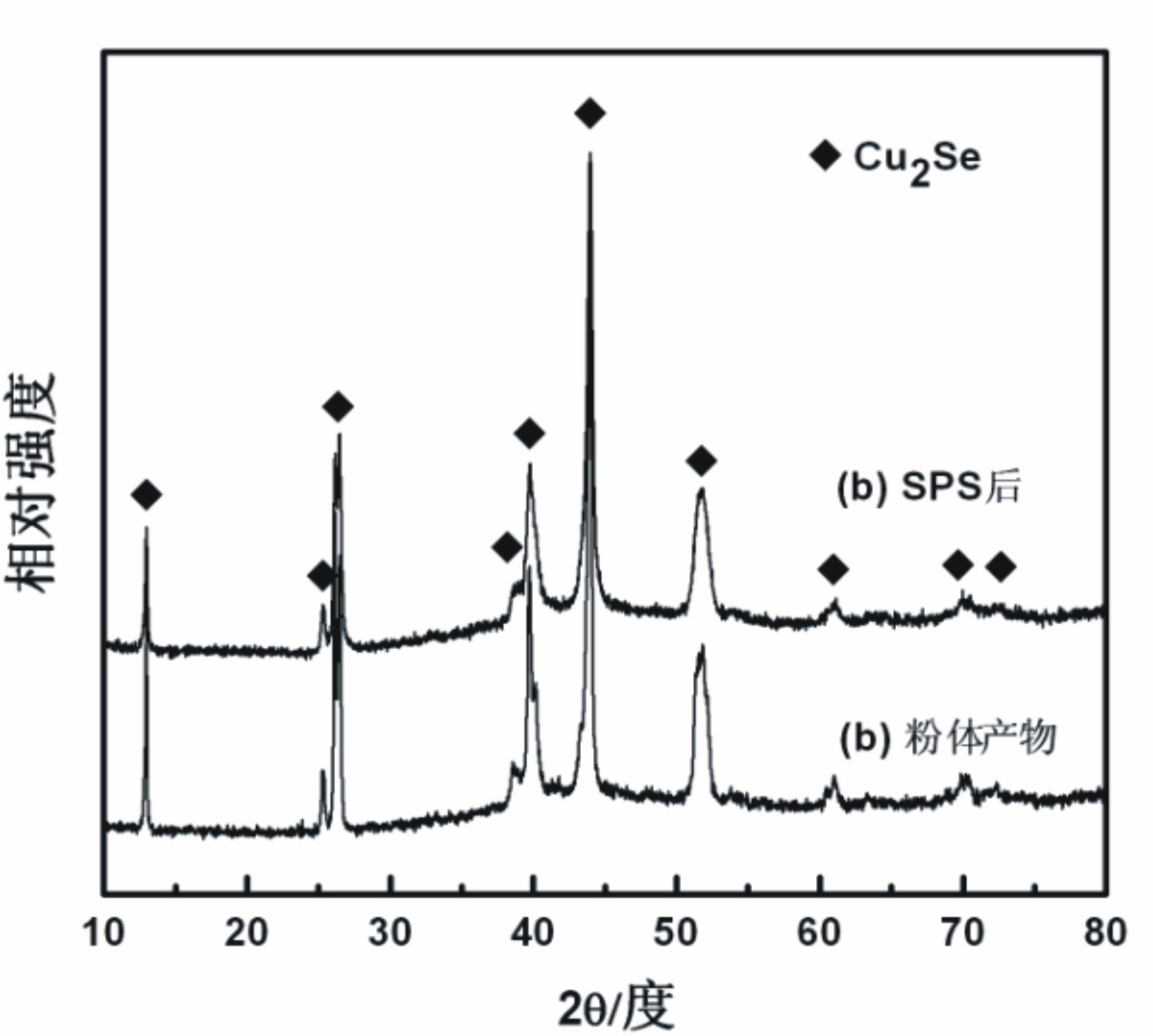
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Cu2Se thermoelectric material. The method for preparing the Cu2Se thermoelectric material by the low-temperature solid-phase reaction is characterized by comprising the following step: 1) weighing Cu powder and Se powder according to the molar ratio of 2:1 and mixing the Cu powder and the Se powder uniformly to obtain mixed powder, wherein the Cu powder and the Se powder serve as raw materials; 2) pressing the mixed powder into a block body by using tablet press, placing the block body into a graphite crucible, vacuumizing, sealing into a quartz glass tube, placing into a muffle furnace, performing solid-phase reaction at the temperature of between 650 and 750 DEG C for 12 to 24 hours, and grinding the obtained product into powder; and 3) performing spark plasma sintering on the powder obtained in the step 2) to obtain a compact block body, namely the Cu2Se thermoelectric material. By the method, the raw materials have low cost; the reaction temperature is low; energy is saved; and the materials are fed according to the stoichiometric ratio of the Cu2Se, so the product composition can be controlled precisely; and the repeatability is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Energy-transmitting or ultraviolet light-transmitting optical fiber preform and production process thereof
InactiveUS20090208760A1Reduce transmission lossIncreased durabilityGlass making apparatusGlass/slag layered productsHigh energyUltraviolet lights
The present invention is to provide an optical fiber preform suitable for the production of an energy-transmitting or ultraviolet light-transmitting optical fiber, which has an excellent transmittance of a high-energy light of 50 KW / cm2 or more in terms of laser peak power or an ultraviolet light, to be transmitted through the optical fiber and which exhibits excellent durability that causes almost no deterioration by the irradiation with those two lights; and a production process thereof. The present invention relates to an energy-transmitting or ultraviolet light-transmitting optical fiber preform, having a core and a cladding each comprising a silica glass, wherein the core has an average OH concentration of 0 to 10 ppm, an average O2 concentration of ≦1015 molecules / cm3, an average ODC (I) concentration of ≦1013 defects / cm3, an average ODC (II) concentration of ≦1012 defects / cm3 and an average F concentration of ≦1,000 ppm, and the cladding has an average OH concentration of 0 to 10 ppm, an average F concentration of ≧7,000 ppm, an average O2 concentration of ≦1016 molecules / cm3, an average ODC (I) concentration of ≦1013 defects / cm3 and an average ODC (II) concentration of ≦1012 defects / cm3.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
UV sterilizer
InactiveUS20070274879A1Energy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesRadiationUVC RadiationUv disinfection
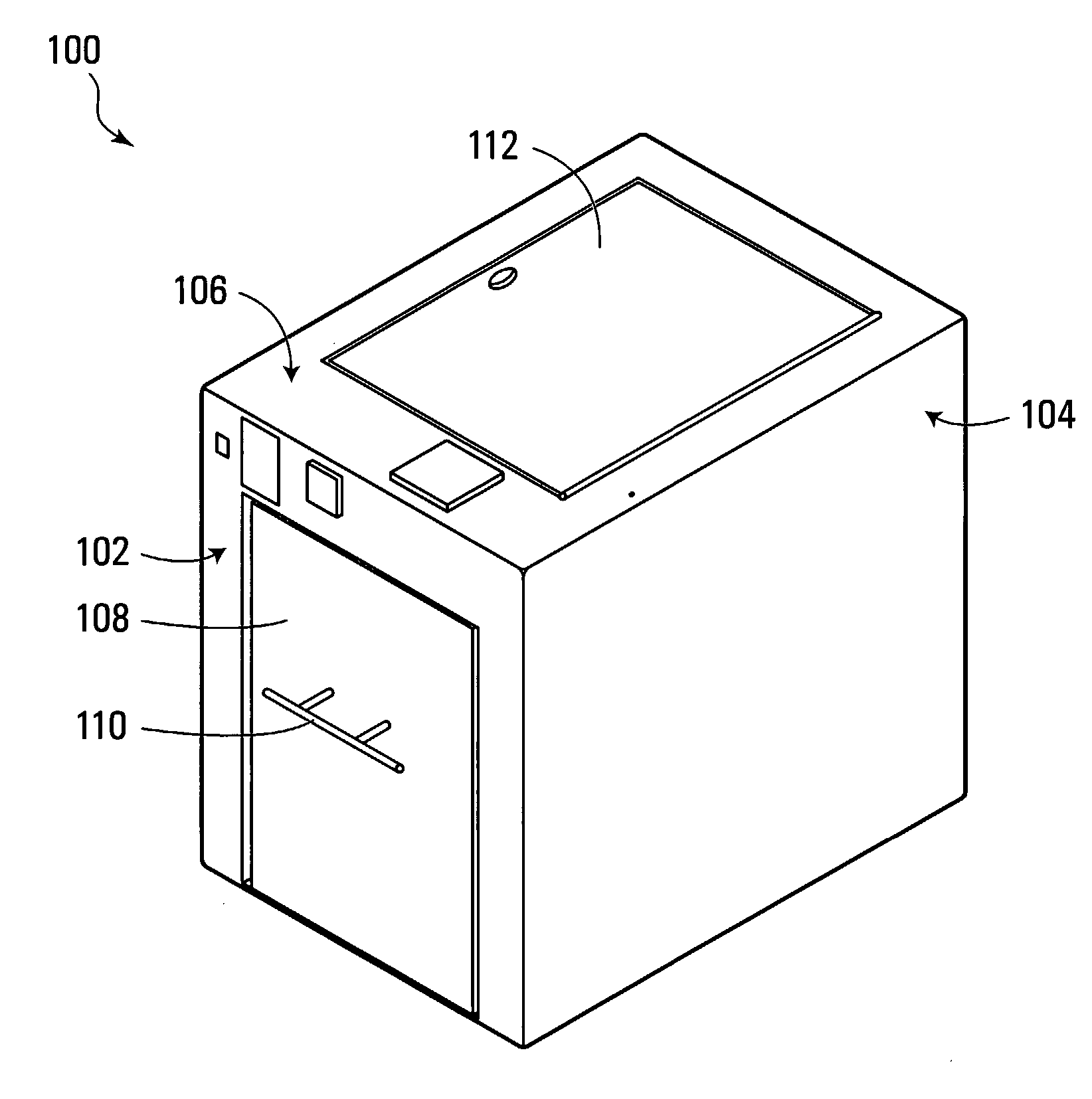
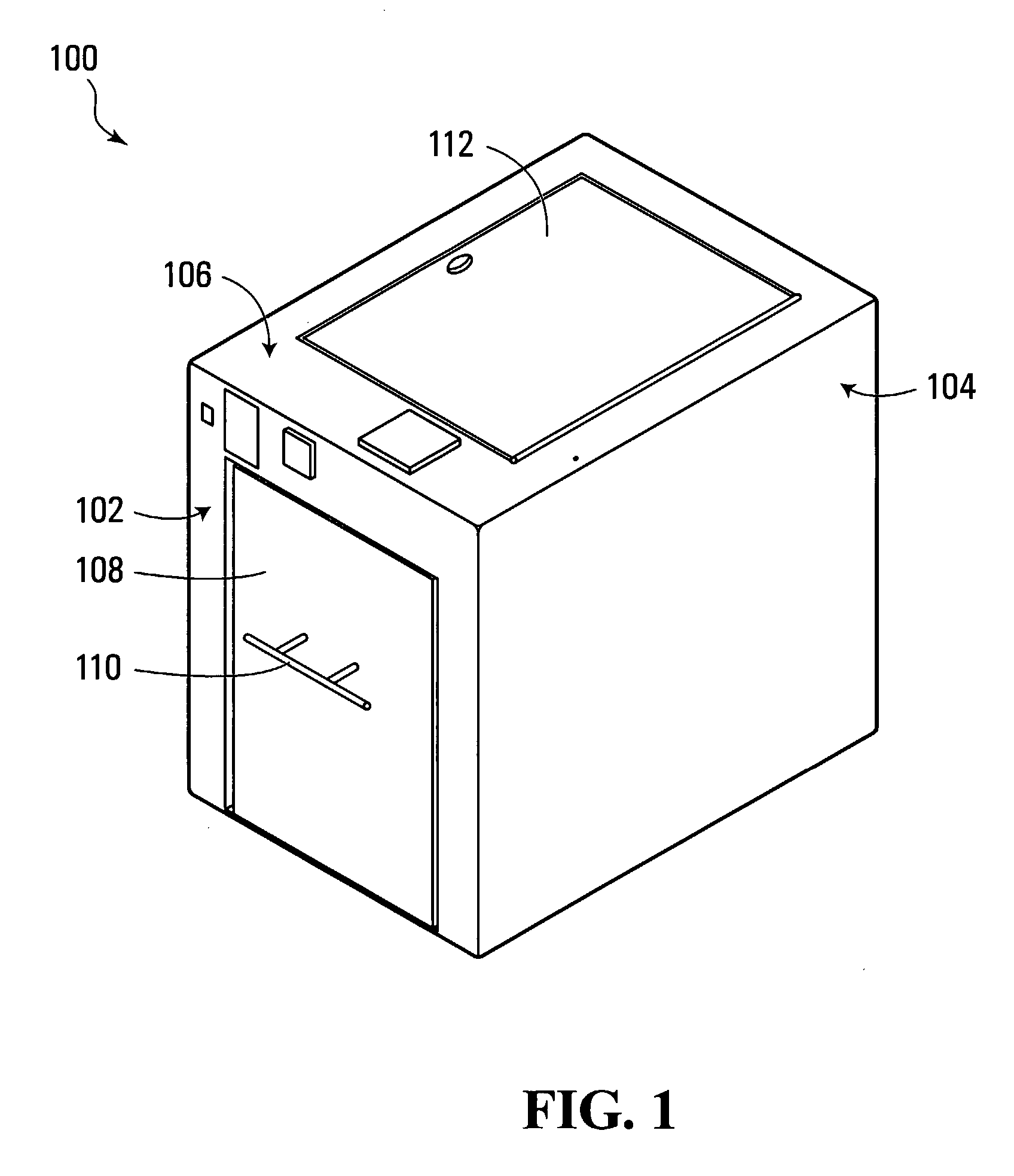
A box-type sterilizer using C-band Ultra-Violet (UVC) radiation is based on a hollow rectangular box with a door on one end. Mounted proximate to the interior surfaces of the box are lamps that, when powered, produce UVC radiation. In operation, an object to be sterilized is placed inside the box, the door is closed and the lamps are briefly powered. Any DNA-based organisms present on the object to be sterilized are killed by the UVC radiation. Cross tubes of quartz glass, which are transparent to UVC radiation, are used to support the object to be sterilized and separate the object to be sterilized from the lamps on the bottom interior surface. Cross tubes of quartz glass are also used to separate the object to be sterilized from the lamps on the other interior surfaces.
Owner:UV LIGHT SCI GROUP
Synthetic silica glass optical material having high resistance to laser induced damage
InactiveUS7534733B2Decrease in levelGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersHigh resistanceLength wave
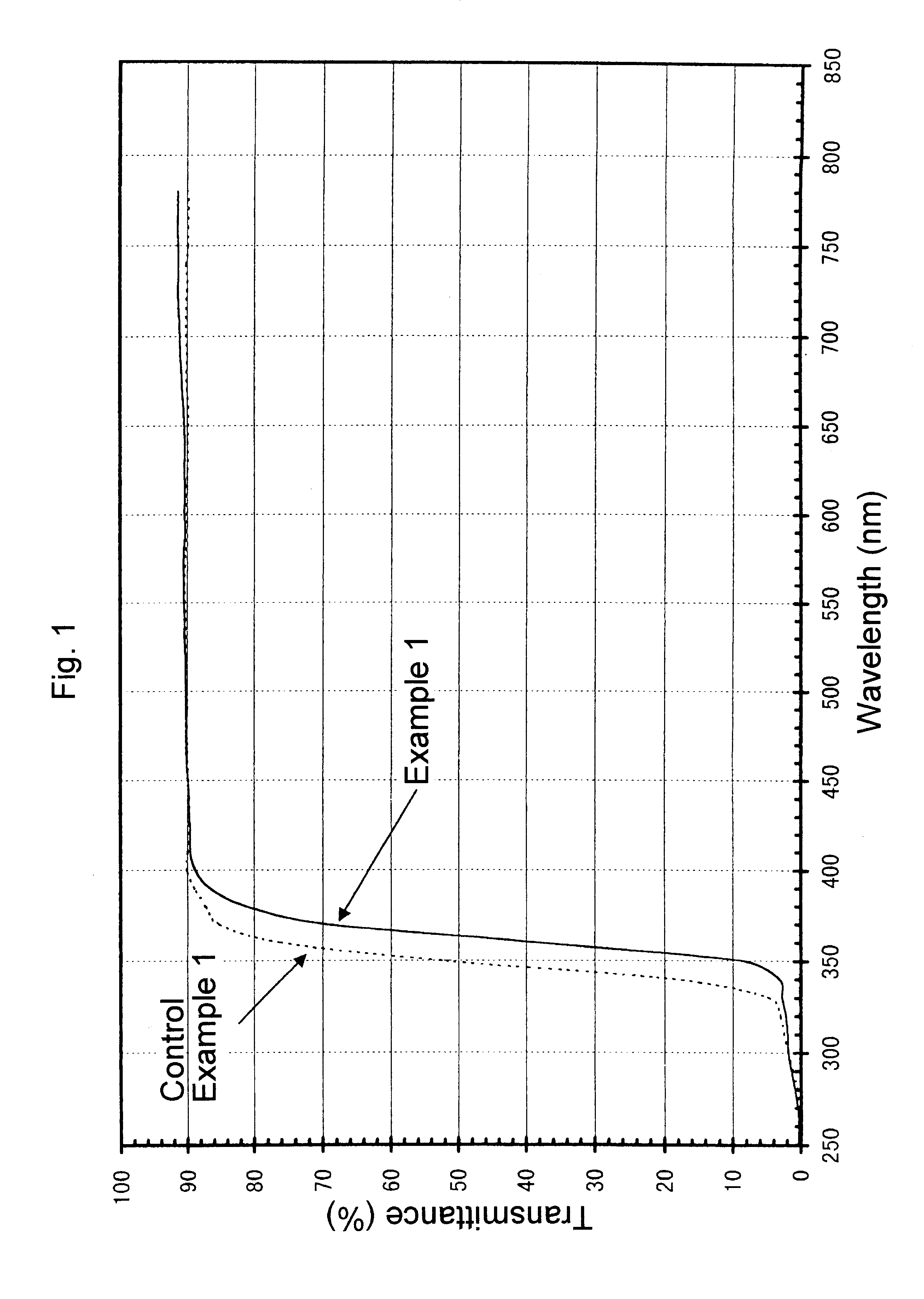
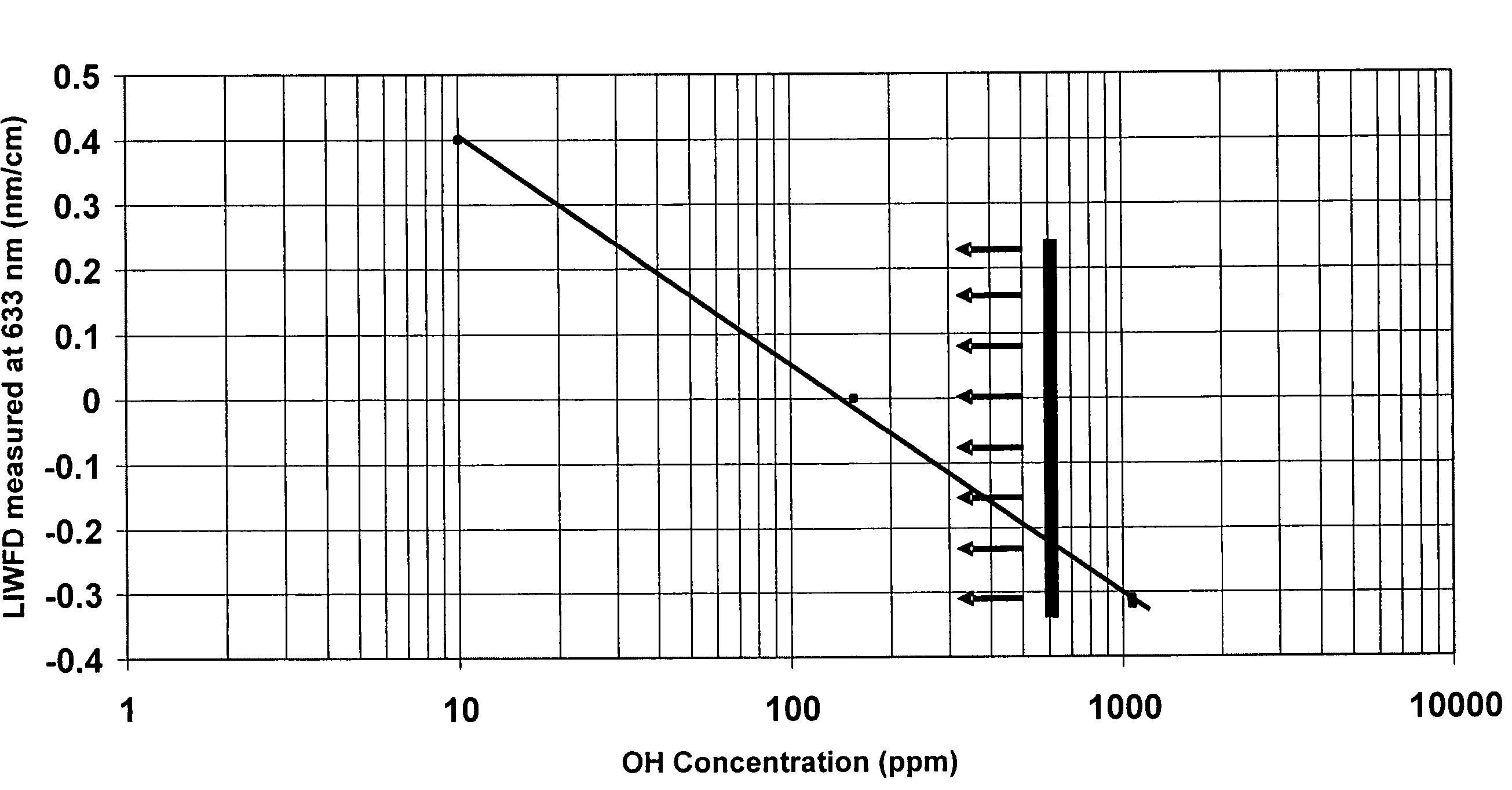
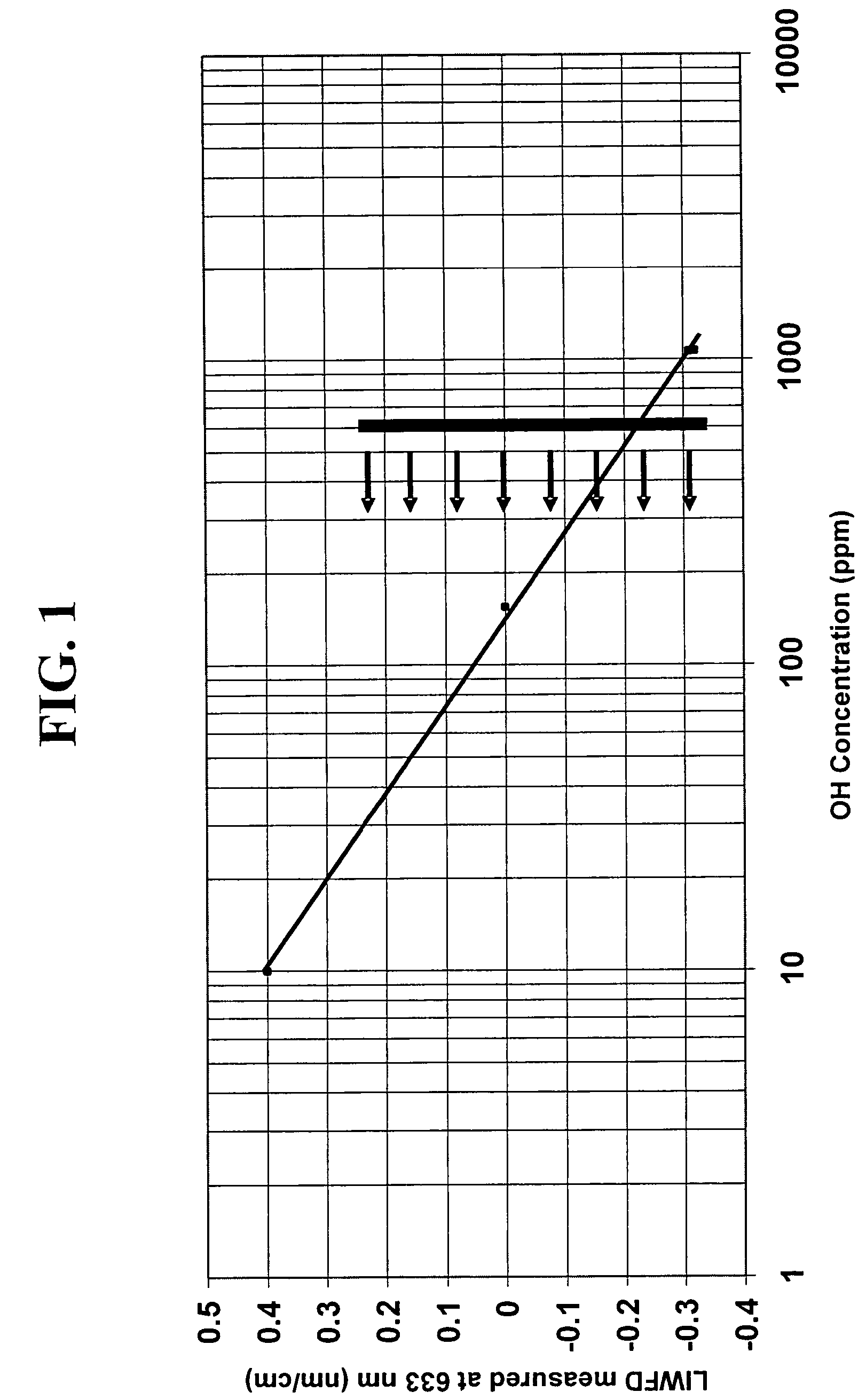
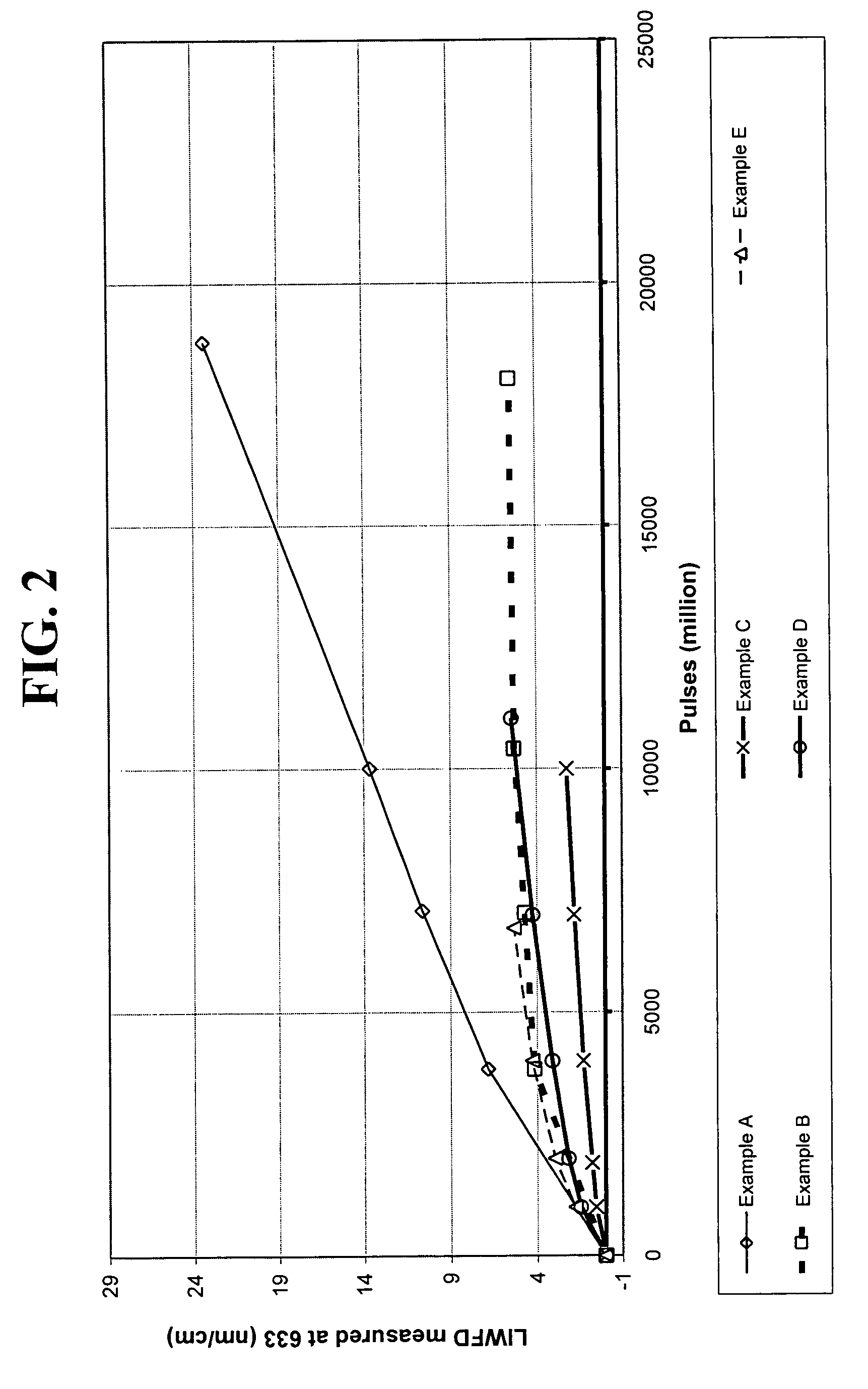
Disclosed is a synthetic silica glass optical material having high resistance to optical damage by ultraviolet radiation in the ultraviolet wavelength range, particularly in the wavelength less than about 250 nm and particularly, exhibiting a low laser induced wavefront distortion; specifically a laser induced wavefront distortion, measured at 633 nm, of between about −1.0 and 1.0 nm / cm when subjected to 10 billion pulses of a laser operating at approximately 193 nm and at a fluence of approximately 70 μJ / cm2. The synthetic silica glass optical material of the present invention comprises OH concentration levels of less than about 600 ppm, preferably less than 200 ppm, and H2 concentration levels less than about 5.0×1017 molecules / cm3,and preferably less than about 2.0×1017 molecules / cm3.
Owner:CORNING INC
Isolated planar mesogyroscope
ActiveUS20050172714A1Reduce frequencyEffect of errorAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsIn planeThermal expansion
An inertial sensor includes a mesoscaled disc resonator comprised of micro-machined substantially thermally non-conductive wafer with low coefficient of thermal expansion for sensing substantially in-plane vibration, a rigid support coupled to the resonator at a central mounting point of the resonator, at least one excitation electrode within an interior of the resonator to excite internal in-plane vibration of the resonator, and at least one sensing electrode within the interior of the resonator for sensing the internal in-plane vibration of the resonator. The inertial sensor is fabricated by etching a baseplate, bonding the substantially thermally non-conductive wafer to the etched baseplate, through-etching the wafer using deep reactive ion etching to form the resonator, depositing a thin conductive film on the through-etched wafer. The substantially thermally non-conductive wafer may comprise a silicon dioxide glass wafer, which is a silica glass wafer or a borosilicate glass wafer, or a silicon-germanium wafer.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Silica glass containing TiO2 and process for its production
ActiveUS20070042893A1High light transmittanceHigh transparencyCharging furnaceGlass reforming apparatusVitrificationTransmittance
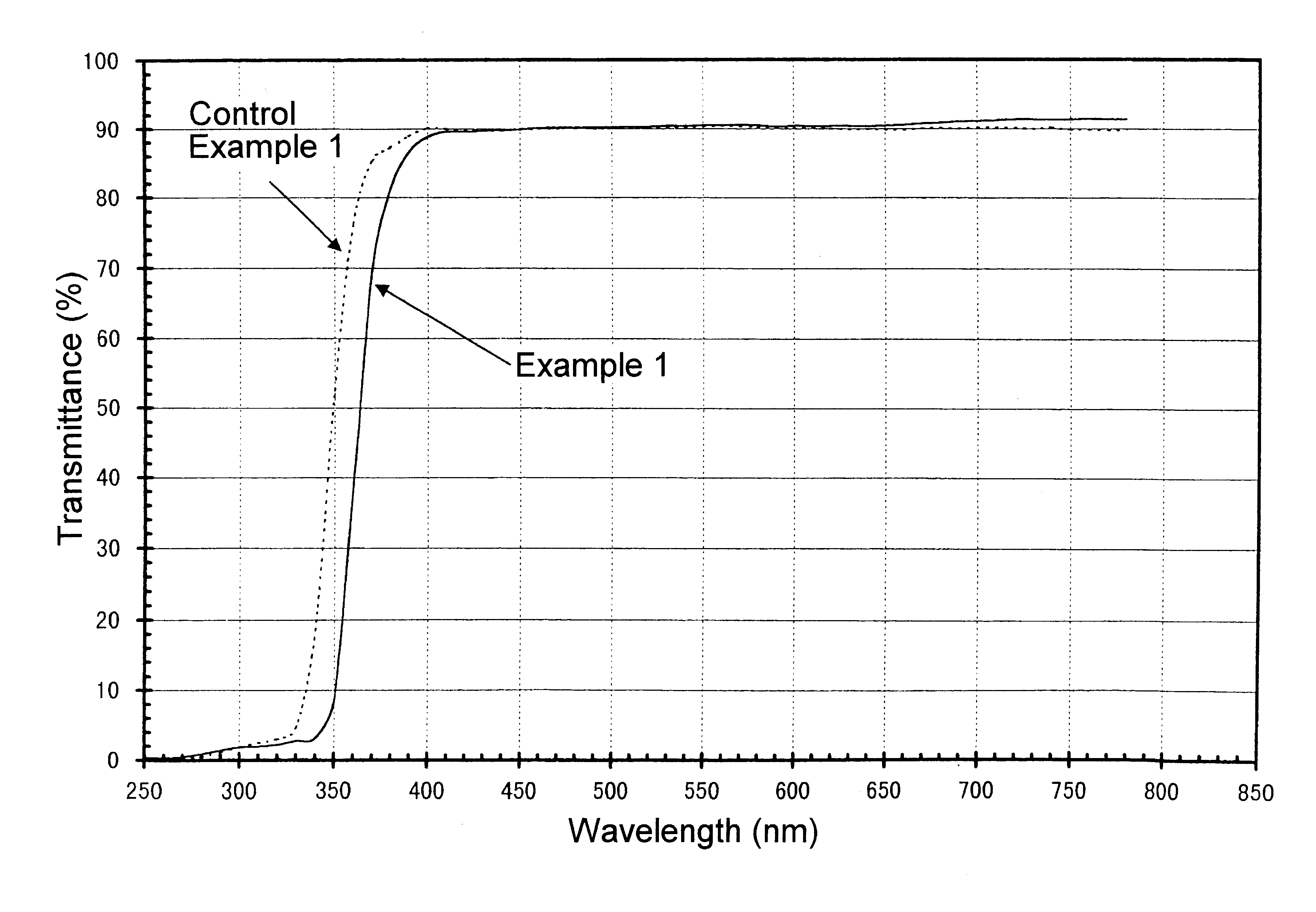
It is to provide a silica glass containing TiO2, having a wide temperature range wherein the coefficient of thermal expansion is substantially zero. A silica glass containing TiO2, which has a TiO2 concentration of from 3 to 10 mass %, a OH group concentration of at most 600 mass ppm and a Ti3+ concentration of at most 70 mass ppm, characterized by having a fictive temperature of at most 1,200° C., a coefficient of thermal expansion from 0 to 100° C. of 0±150 ppb / ° C., and an internal transmittance T400-700 per 1 mm thickness in a wavelength range of from 400 to 700 nm of at least 80%. A process for producing a silica glass containing TiO2, which comprises porous glass body formation step, F-doping step, oxygen treatment step, densification step and vitrification step.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Purification method in process of production of high-pure quartz sand as raw material of quartz glass
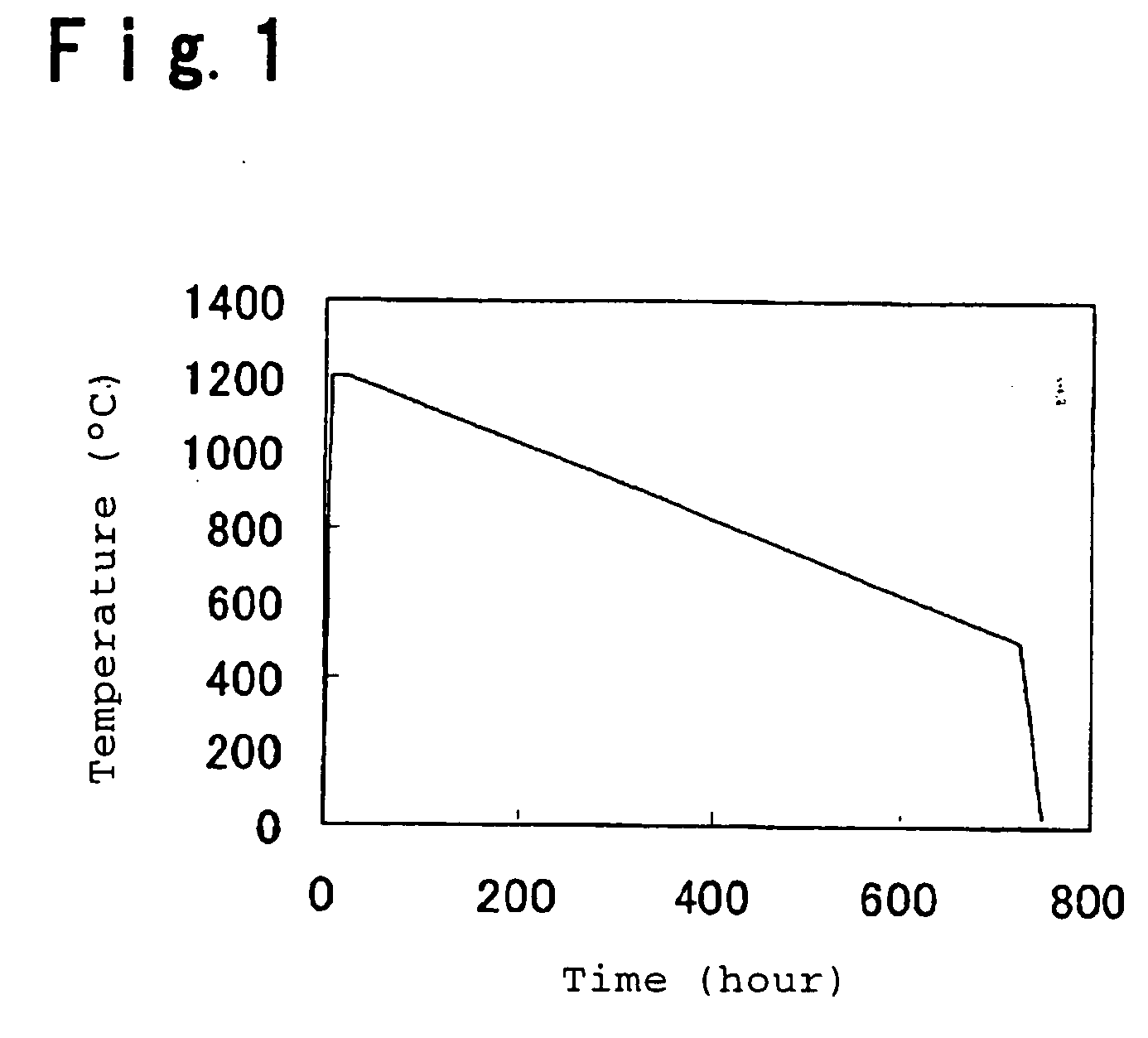
InactiveCN101337767AHigh purityHigh activitySilicaGlass shaping apparatusPurification methodsImpurity
The invention discloses a purification method in the production of high-purity quartz sand applied to the raw materials of quartz glass. Through effectively eliminating hydroxyl group and gaseous-liquid inclusion in a natural quartz, the raw material of the quartz glass hyphen, the high-purity quartz sand produced by a common vein quartz, is realized, thereby achieving the effective control to key quality indexes such as air bubbles and air lines in a quartz glass product, and breaking the high dependency to the quality of an ore in the prior process art, so that the availability of vein quartz resources in a quartz glass industry is improved to above 80 percent from about 5 percent; the content of the high-purity quartz sand SiO2 produced by the common vein quartz ore reaches above 99.99 percent; and the total amount of the foreign impurities of thirteen metallic elements is less than 25 to 30 ppm.
Owner:江苏阳山硅材料科技有限公司
Optical device
InactiveUS6888994B2Non-linear effectEasy lithographic reproductionPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
In order to create an optical device with a photonic band gap extending in two dimensions and with very uniform properties in any direction and for any polarisation state, to within 1%, air holes are etched within a substrate of low refractive index material such silicon oxynitride or silica glass. The ratio of air hole area to the remainder of the substrate is low, being less than 35%. The air holes define a quasicrystal structure, having twelve fold symmetry, being based on a square-triangle system. In another development, an etched substrate with a regular crystal structure or quasicrystal structure exhibits a non-linear refractive index. Two adjacent areas in such a substrate have different lattice properties, or have defects in the lattices, to create a unidirectional transmission path (diode action). A further beam of light may be used to modulate the transmission path by reason of the non-linear refractive index.
Owner:NANOGAN
Waveguide pair with cladding
PCT No. PCT / GB97 / 00040 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 12, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 12, 1999 PCT Filed Jan. 8, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 25636 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 17, 1997A planar waveguide structure has, supported on a lower refractive index buffer layer (5), a pair of optical cores (1, 2) that, over at least a portion of their length, are closely spaced. These cores are covered with a layer (6) of cladding material comprising boron and phosphorus doped silica glass deposited by PECVD as a succession of individually annealed layers in order to minimize the incidence of voids in the deposit between the cores.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS UK +1
Multi-core optical fiber
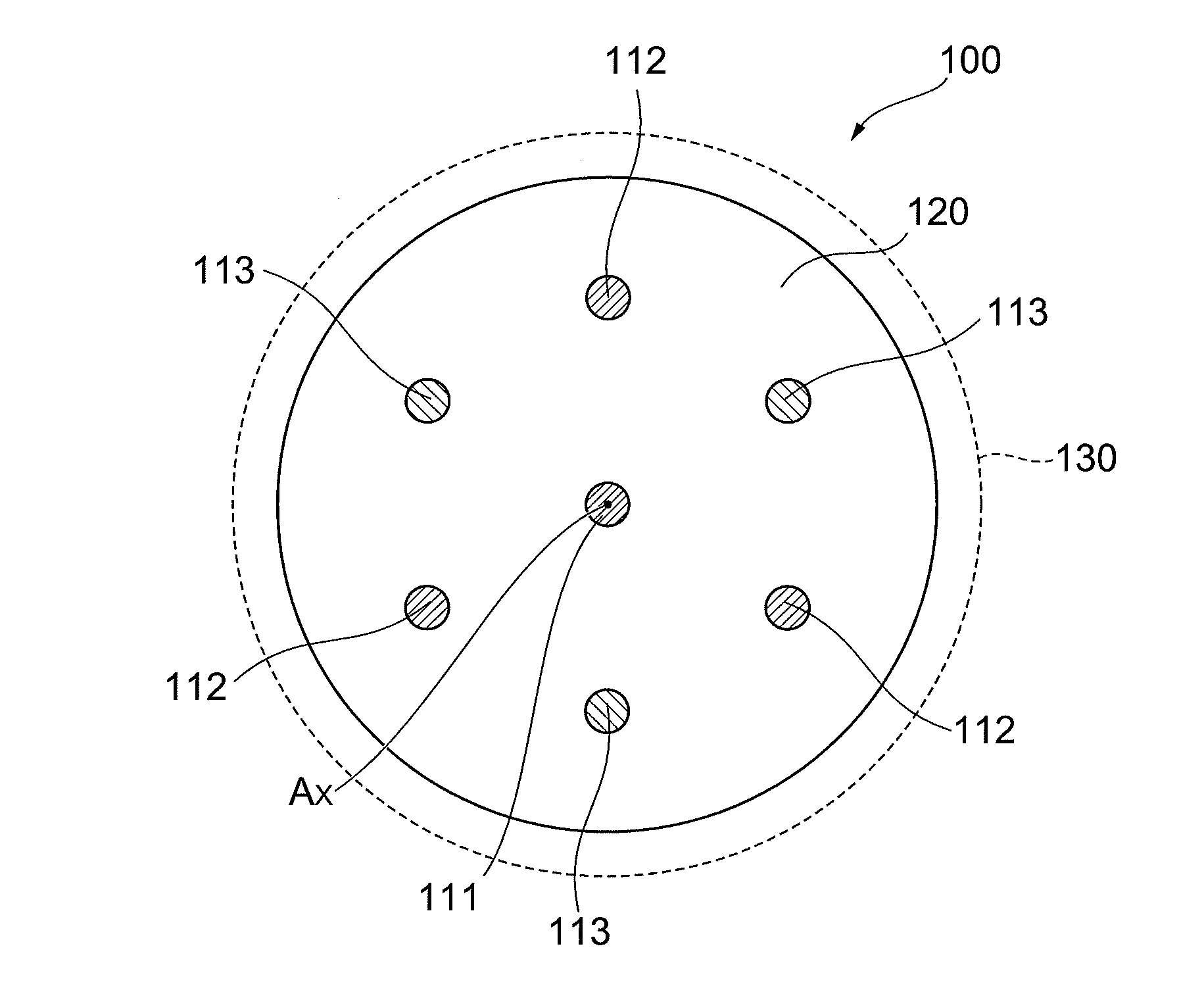
InactiveUS20110222828A1Reduce crosstalkReduce nonlinearityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingMulticore optical fibreTransmission lossSilicon dioxide
The present invention relates to a multi-core optical fiber having a structure for reducing transmission loss and nonlinearity. The multi-core optical fiber comprises plural cores extending along a center axis direction, and a cladding surrounding the peripheries of the plural cores. The cladding is comprised of silica glass doped with fluorine, and each of the plural cores is comprised of silica glass doped with chlorine or pure silica glass.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Methods for making optical fiber preforms and microstructured optical fibers
InactiveUS20090126407A1Glass deposition burnersGlass fibre productsRefractive indexChemical vapor deposition
A method of making an optical fiber preform includes depositing silica glass on the inside of a tube substrate via a plasma chemical vapor deposition (PCVD) operation. The parameters of the PCVD operation are controlled such that the silica glass deposited on the interior of the tube substrate contains a non-periodic array of voids in a cladding region of the optical fiber preform. The optical fiber preform may be used to produce an optical fiber having a core and a void containing cladding. The core of the optical fiber has a first index of refraction and the cladding has a second index of refraction less than that of the core.
Owner:CORNING INC
High-Precision Optical Surface Prepared by Sagging from a Masterpiece
InactiveUS20080099935A1Produced cost-effectivelyImprove spectral responseHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotomechanical apparatusFlat glassFree form
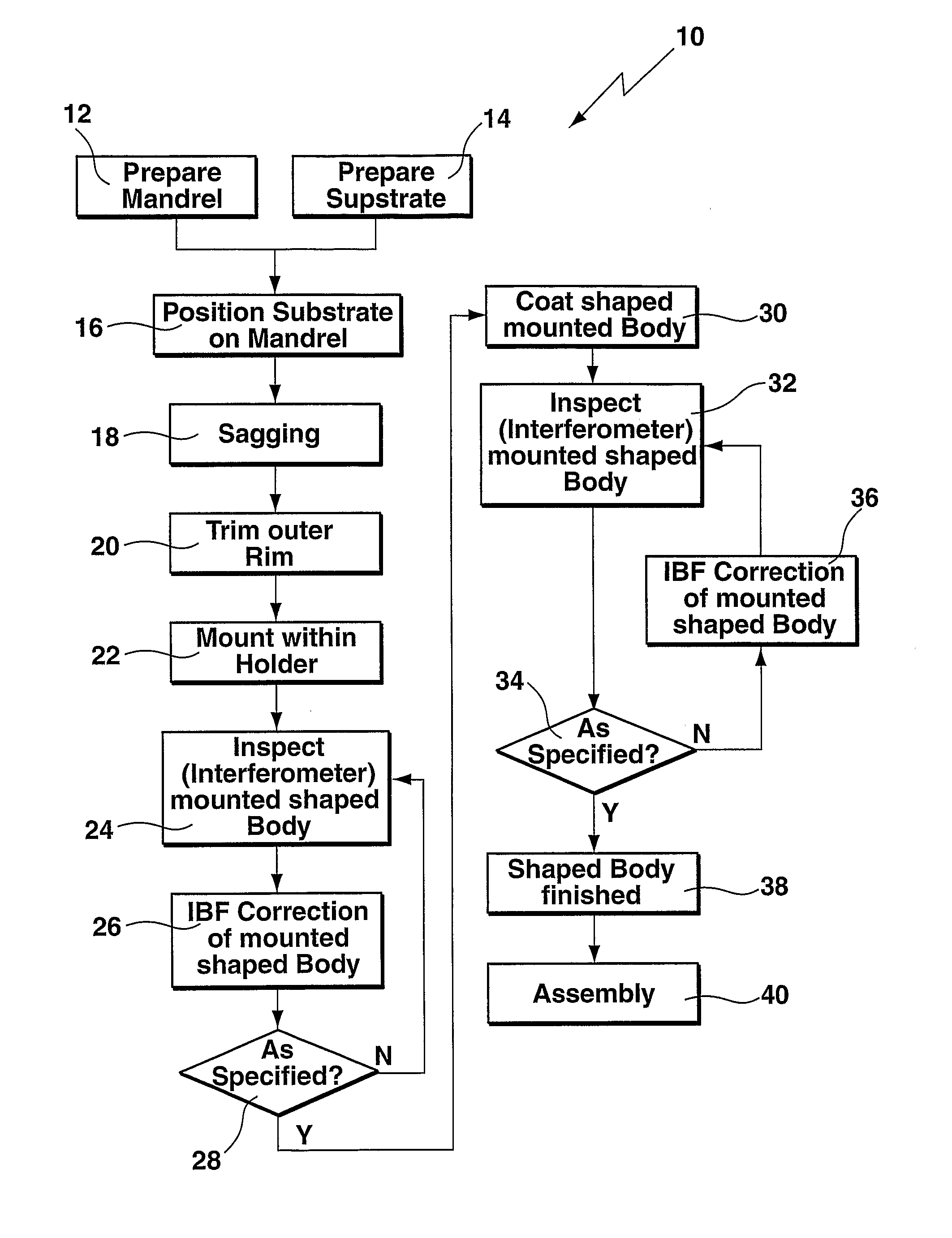
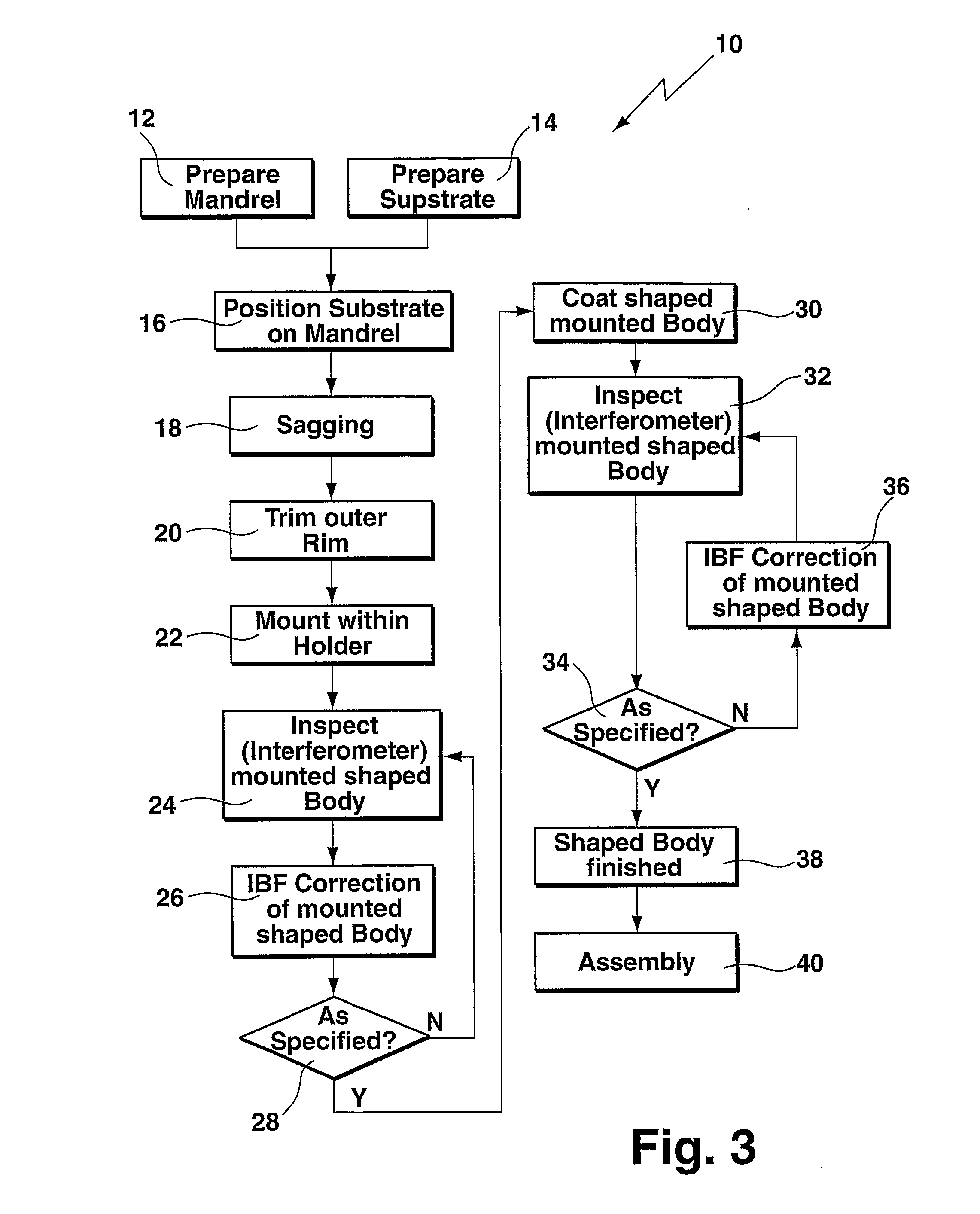
A method of making a high-precision optical surface which may be used either as a Wolter-type segment in an X-ray mirror system or in a collector of a EUVL system or as a spherical, aspherical, or free form normal or grazing incidence mirror in an EUVL system is prepared by sagging a thin flat glass sheet onto a masterpiece, in particular a mandrel, made from a temperature-resistant material, such as an alumina based ceramic or a keatite glass ceramic. The glass sheet is polished to the desired surface roughness (14), is positioned to an upper surface of the masterpiece (16), and is heated (18) to effect sagging onto the upper surface of the masterpiece for generating a shaped body. Thereafter, the shaped body is cooled and removed from the masterpiece, is mounted within a holder (22), is inspected for deviations from the specification (24) preferably using interferometric measurements, and is corrected for defects (26), preferably using ion beam figuring.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Gap filling with a composite layer
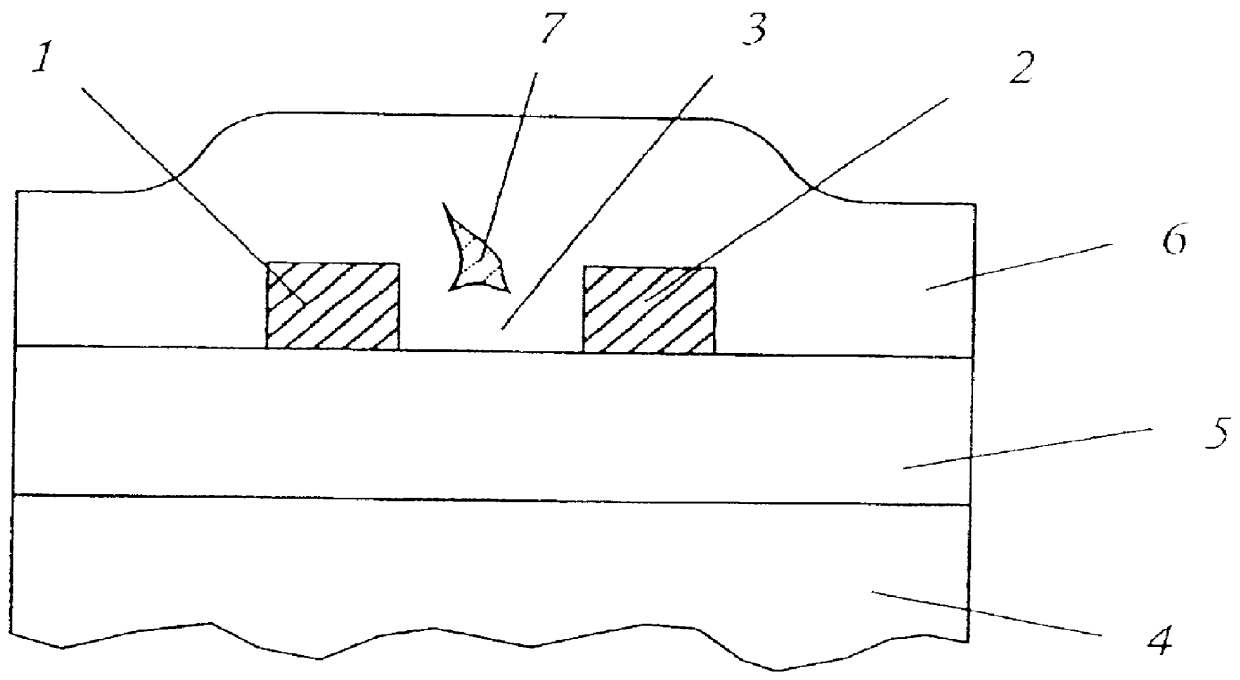
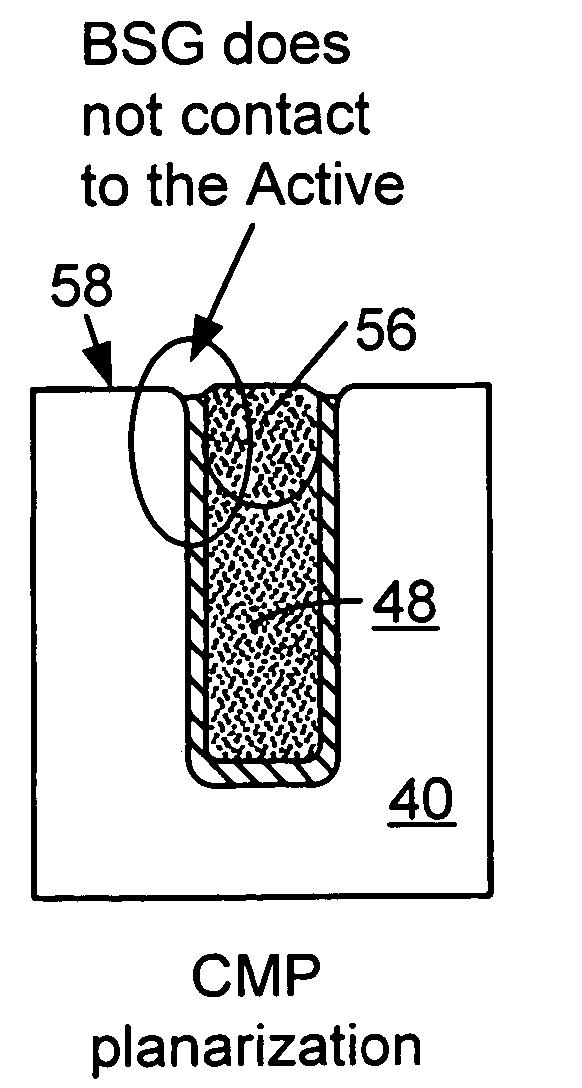
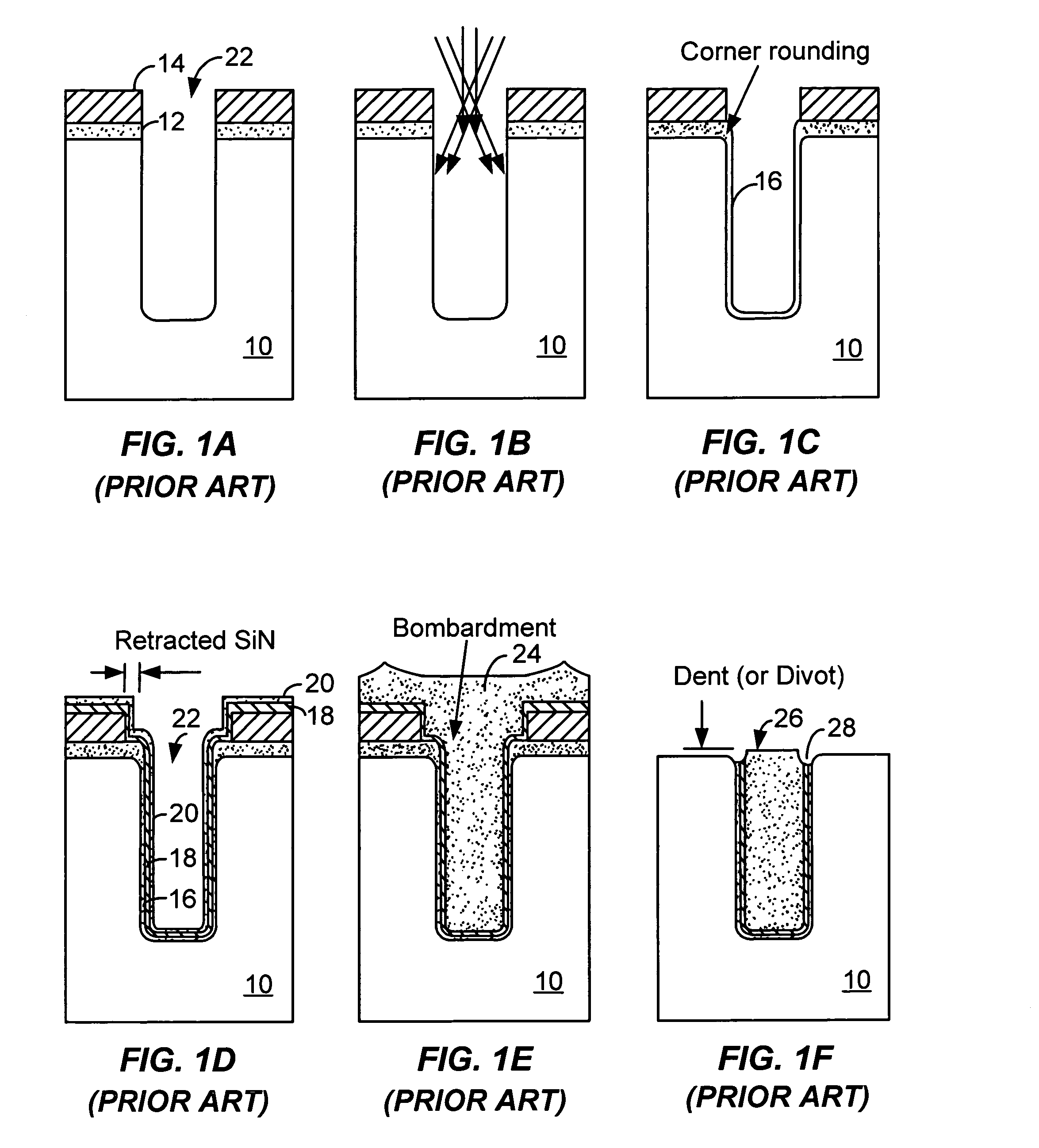
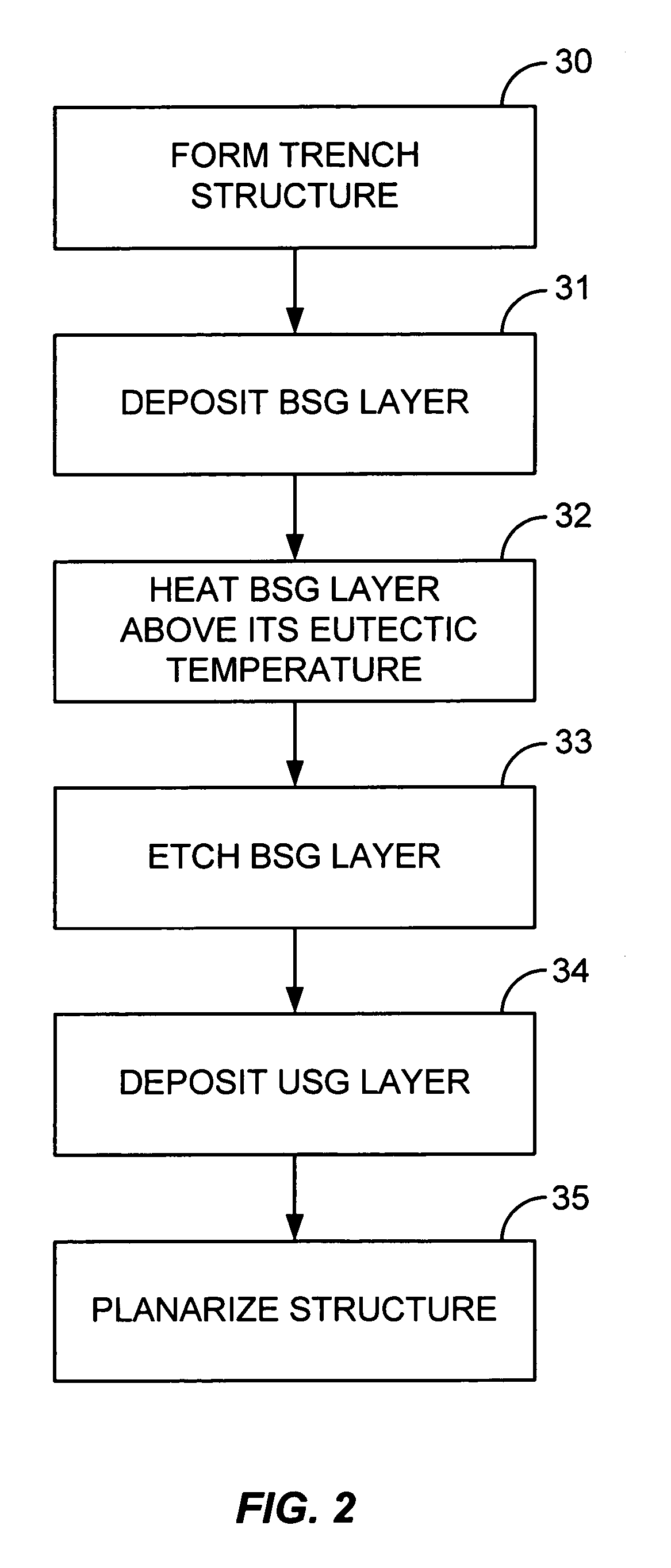
A method of filling a gap formed between adjacent raised surfaces on a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises depositing a boron-doped silica glass (BSG) layer over the substrate to partially fill the gap using a thermal CVD process; exposing the BSG layer to a steam ambient at a temperature above the BSG layer's Eutectic temperature; removing an upper portion of the BSG layer by exposing the layer to a fluorine-containing etchant; and depositing an undoped silica glass (USG) layer over the BSG layer to fill the remainder of the gap.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Silica container and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20110272322A1Increased durabilitySuppress generationAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthHydrogenFused glass
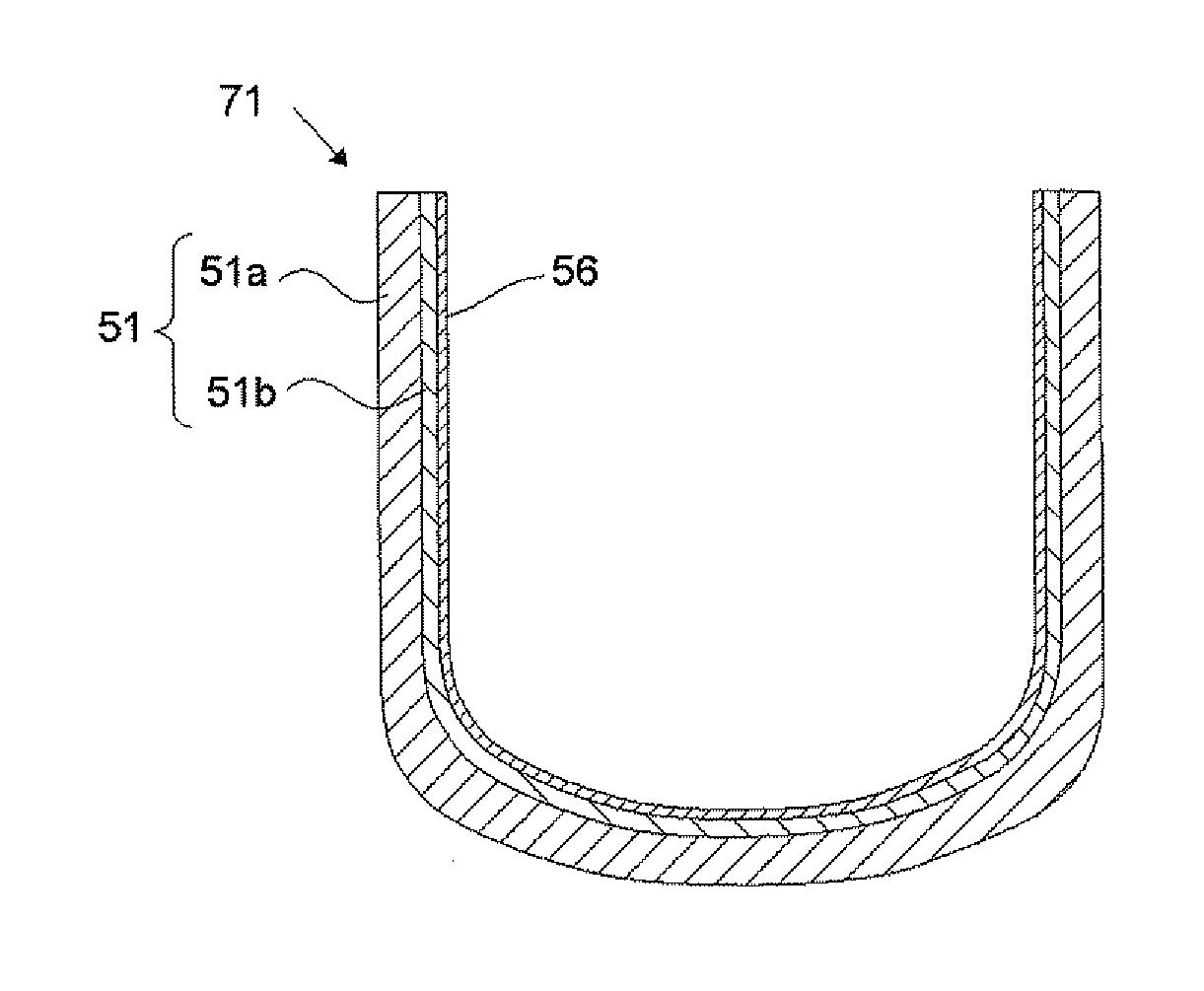
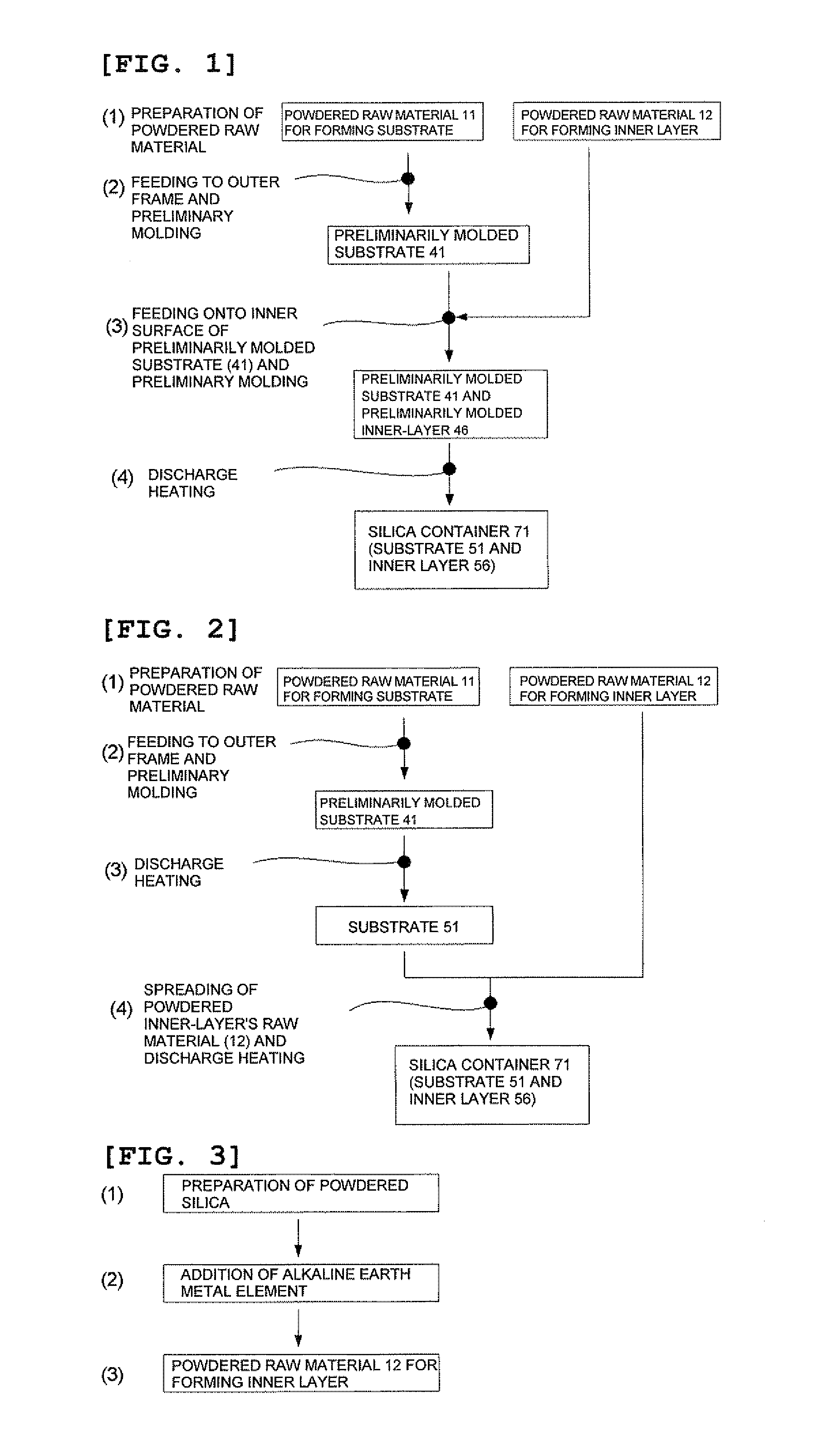
The present invention is a method for producing a silica container having a substrate containing gaseous bubbles in its outer peripheral part and an inner layer comprised of a transparent silica glass formed on an inner surface of the substrate, wherein a powdered raw material for forming a substrate containing Li, Na, and K with the total concentration of 50 or less ppm by weight and a powdered raw material for forming an inner layer containing Ca, Sr, and Ba with the total concentration of 50 to 2000 ppm by weight are prepared; a preliminarily molded substrate is formed in a frame; a preliminarily molded inner layer is formed on an inner surface of the preliminarily molded substrate; and the preliminarily molded substrate and molded inner layer are heated from inside thereof by a discharge-heat melting method under a gas atmosphere containing a hydrogen gas or a helium gas or a gas mixture thereof with the ratio of more than 10% by volume thereby making an outer peripheral part of the preliminarily molded substrate to a sintered body and an inner peripheral part of the preliminarily molded substrate and the preliminarily molded inner layer to a fused glass body. With this, a method for producing a silica container, producible with a low cost and having a high durability and dimensional precision, and a container of this sort can be provided.
Owner:SHIN ETABU QUARTZ PRODS
Prepreg and printed wiring board using thin quartz glass cloth
ActiveUS20090266591A1Low dielectric constantLoss tangentSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsGlass fiberDielectric loss
It is an object of the present invention to provide a high frequency-capable printed wiring board material reduced in the dielectric loss tangent, weight, thickness and cost without compromising the workability, and provide electronic components using the same. The present invention provides a prepreg obtained by using a quartz glass cloth composed of low-density quartz glass fibers as a base material and impregnating the cloth with a thermosetting resin composition having a low dielectric loss tangent, and provides electronic components using a cured product of the prepreg as an insulating layer.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com