Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4779results about "Glass shaping apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Use of amorphous carbon film as a hardmask in the fabrication of optical waveguides
Methods are provided for forming optical devices, such as waveguides, with minimal defect formation. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for forming a waveguide structure on a substrate surface including forming a cladding layer on the substrate surface, forming a core layer on the cladding layer, depositing an amorphous carbon hardmask on the core layer, forming a patterned photoresist layer on the amorphous carbon hardmask, etching the amorphous carbon hardmask, and etching the core material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fused glassy particulates obtained by flame fusion
InactiveUS6254981B1Efficient meltingFast heat transferSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsParticulatesSuspended particles
The disclosure describes methods for producing bulk, particulate material that includes solid, generally ellipsoidal particles. Irregularly shaped feed particles with average particle sizes of up to 25 microns on a volume basis are dispersed in at least a portion of a combustible gas mixture by application of force and / or fluidizing agents. The combustible mixture with particles in suspension is then delivered, while controlling agglomeration or re-agglomeration of the particles, to at least one flame front. There, the mixture and suspended particles are uniformly distributed across the surface(s) of and passed through the flame front(s) with a high concentration of particles in the mixture. This flame front and the resultant flame(s) with suspended particles are located in at least one "wall free" zone. In such zone(s) the flame(s) may expand while the particles are maintained in dispersion and heated, with controlled and highly efficient application of heating energy. At least partial fusion occurs within at least the surfaces of the particles at high thermal efficiencies, while agglomeration of particles during fusion is inhibited.
Owner:3M CO
Hybrid optical/electronic structures fabricated by a common molding process
InactiveUS7391572B2Improve thermal performanceEasy alignmentOptical articlesGlass shaping apparatusElectricityElectronic structure
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte and production process thereof
InactiveUS20070231704A1Increase battery capacitySimple and convenient manufactureSecondary cellsSolid electrolyte cellsPorosityLithium metal
A lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte formed by sintering a molding product containing an inorganic powder and having a porosity of 10 vol % or less, which is obtained by preparing a molding product comprising an inorganic powder as a main ingredient and sintering the molding product after pressing and / or sintering the same while pressing, the lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte providing a solid electrolyte having high battery capacity without using a liquid electrolyte, usable stably for a long time and simple and convenient in manufacture and handling also in industrial manufacture in the application use of secondary lithium ion battery or primary lithium battery, a solid electrolyte having good charge / discharge cyclic characteristic in the application use of the secondary lithium ion battery a solid electrolyte with less water permeation and being safe when used for lithium metal-air battery in the application use of primary lithium battery, a manufacturing method of the solid electrolyte, and a secondary lithium ion battery and a primary lithium battery using the solid electrolyte.
Owner:OHARA
Composite and its use
InactiveUS6248344B1Rapid ossificationQuick upgradeDental implantsNervous disorderMaterials scienceCompound s
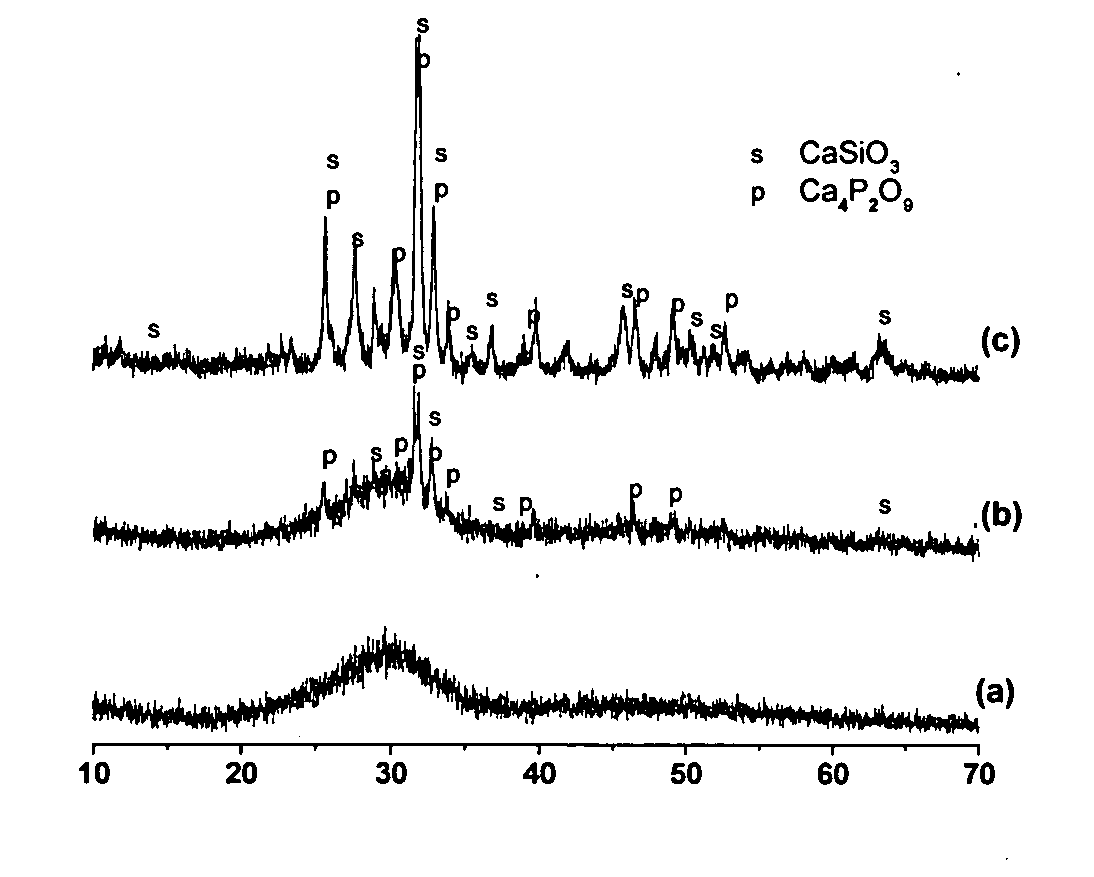
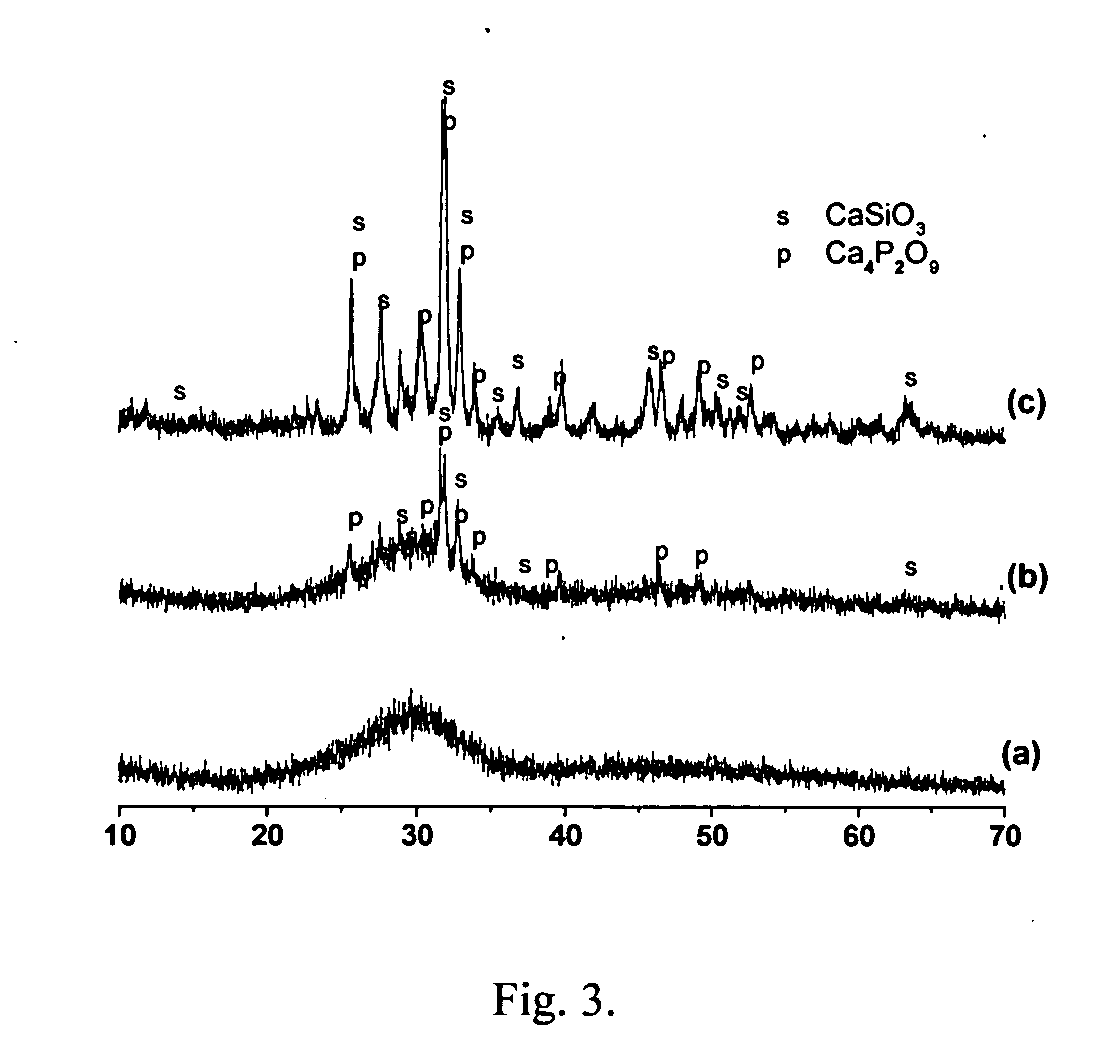
A porous composite suitable for filling a recess or a through-passing hole in an implant. The composite includes particles A prepared from a bioactive material and particles B prepared from a non-bioactive material or weakly bioactive material, which is sintratable with the bioactive material, such that particles A and particles B have been sintered together to a porous composite. Particles A and particles B are essentially homogeneous in size. Also disclosed is an implant which contains a core and the composite.
Owner:VIVOXID
Hybrid organic-inorganic planar optical waveguide device
InactiveUS6144795AReduce stressAvoid deformationGlass shaping apparatusCoatingsHybrid materialOxygen
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 22760 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 10, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 10, 1999 PCT Filed Dec. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 26315 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 18, 1999A planar optical device is formed on a substrate (12) and comprising an array of waveguide cores (14) and a cladding layer (16) formed contiguously with the cores. At least one of the array of waveguide cores (14) and the cladding layer (16) is an inorganic-organic hybrid material that comprises an extended matrix containing silicon and oxygen atoms with at least a fraction of the silicon being directly bonded to substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon atoms. In accordance with other embodiments of the invention, a method of forming an array of cores comprises the steps of preparing a core composition precursor material; partially hydrolyzing and polymerizing the material; forming an array of waveguide cores under conditions effective to form an inorganic-organic hybrid material that comprises an extended matrix containing silicon and oxygen atoms with at least a fraction of the silicon being directly bonded to substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon atoms.
Owner:CORNING INC
Hybrid organic-inorganic planar optical waveguide device
InactiveUS6511615B1Reduce stressStress induced polarization effects can be minimizedOptical articlesGlass shaping apparatusOptical radiationSilanes
A planar optical device is formed on a substrate. The device comprises an array of waveguide cores which guide optical radiation. A cladding layer is formed contiguously with the array of waveguide cores to confine the optical radiation to the array of waveguide cores. At least one of the array of waveguide cores and cladding layer is an inorganic-organic hybrid material that comprises an extended matrix containing silicon and oxygen atoms with at least a fraction of the silicon atoms being directly bonded to substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon moieties. This material can be designed with an index of refraction between 1.4 and 1.55 and can be deposited rapidly to thicknesses of up to 40 microns. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, a method for forming a planar optical device obviates the need for a lithographic process. Illustratively, a method for forming an array of cores comprises the steps of: (1) preparing a waveguide core composition precursor material comprising at least one silane and a source of hydrocarbon moiety, (2) partially hydrolyzing and polymerizing the waveguide core precursor material to form a waveguide core composition, (3) using a mold, forming an array of waveguide cores comprising the waveguide core composition, and (4) completing hydrolysis and polymerization of the waveguide core composition under conditions effective to form an inorganic-organic hybrid material that comprises an extended matrix containing silicon and oxygen atoms with at least a fraction of the silicon atoms being directly bonded to substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon moieties. A cladding layer is then deposited over the array of waveguide cores. The use of the mold to pattern the array of waveguide cores obviates the need for a lithographic process.
Owner:CORNING INC
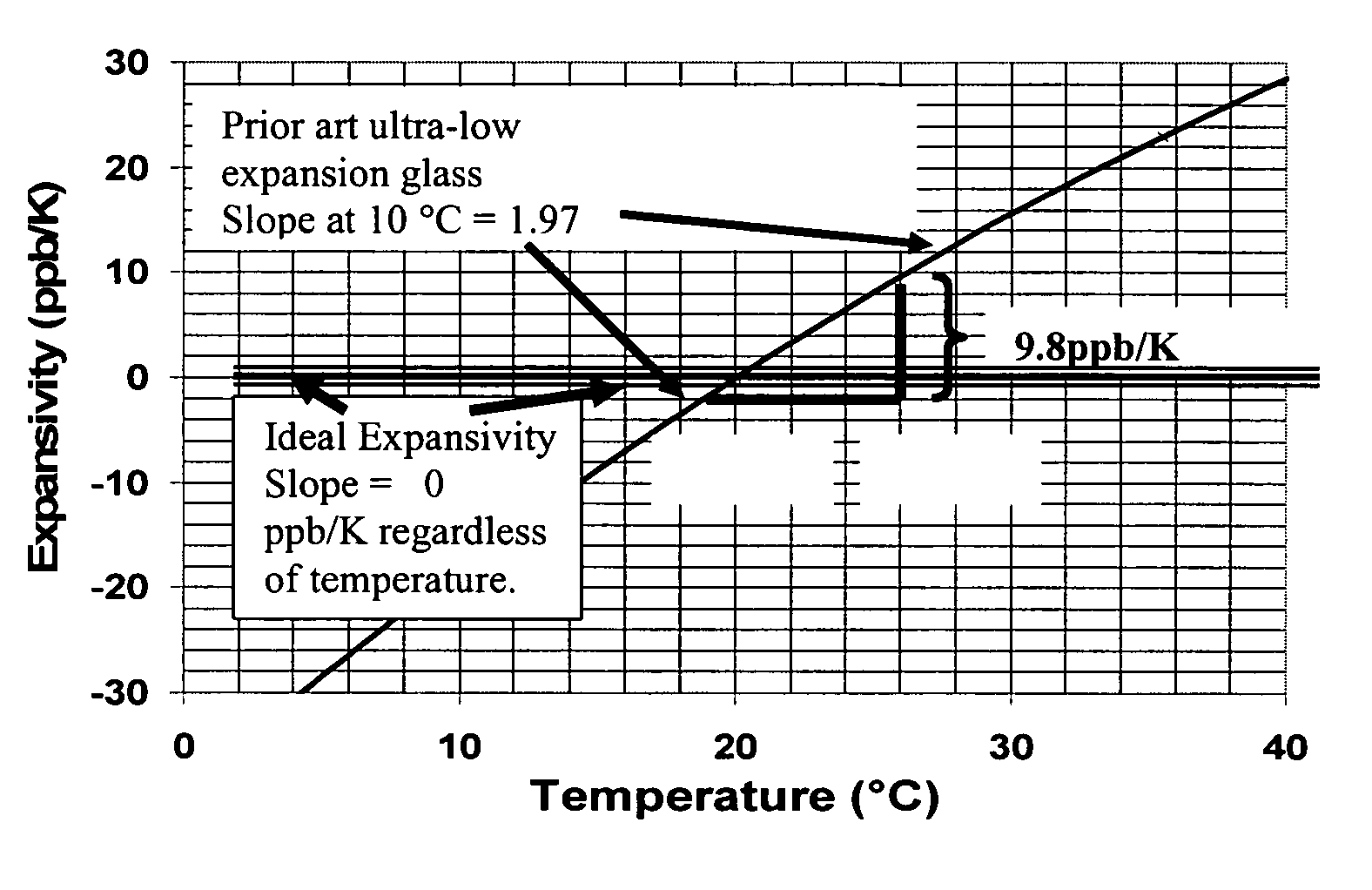
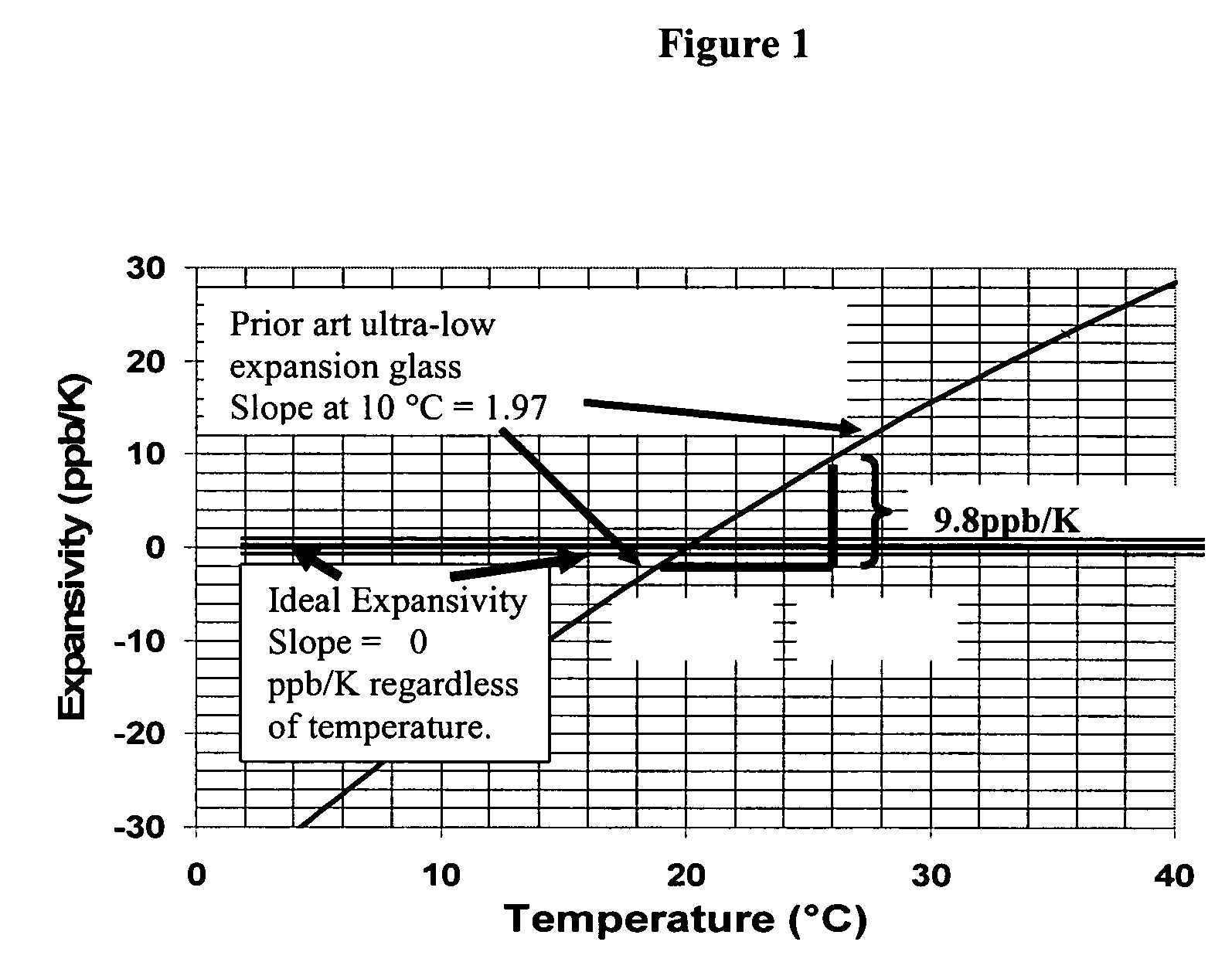
Adjusting expansivity in doped silica glasses
InactiveUS20060179879A1Low viscosityGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersDopantUltra low expansion glass
The invention is directed to ultra-low expansion glasses to which adjustments have been made to selected variables in order to improve the properties of the glasses, and particularly to lower the expansivity of the glasses. The glasses are titania-doped silica glasses. The variables being adjusted include an adjustment in β-OH level; an adjustment to the cooling rate of the molten glass material through the setting point; and the addition of selected dopants to impact the CTE behavior.
Owner:CORNING INC
High-strength dental restorations
InactiveUS20050127544A1Improve adhesionHigh strengthHair accessoriesImpression capsDental ProductHigh intensity
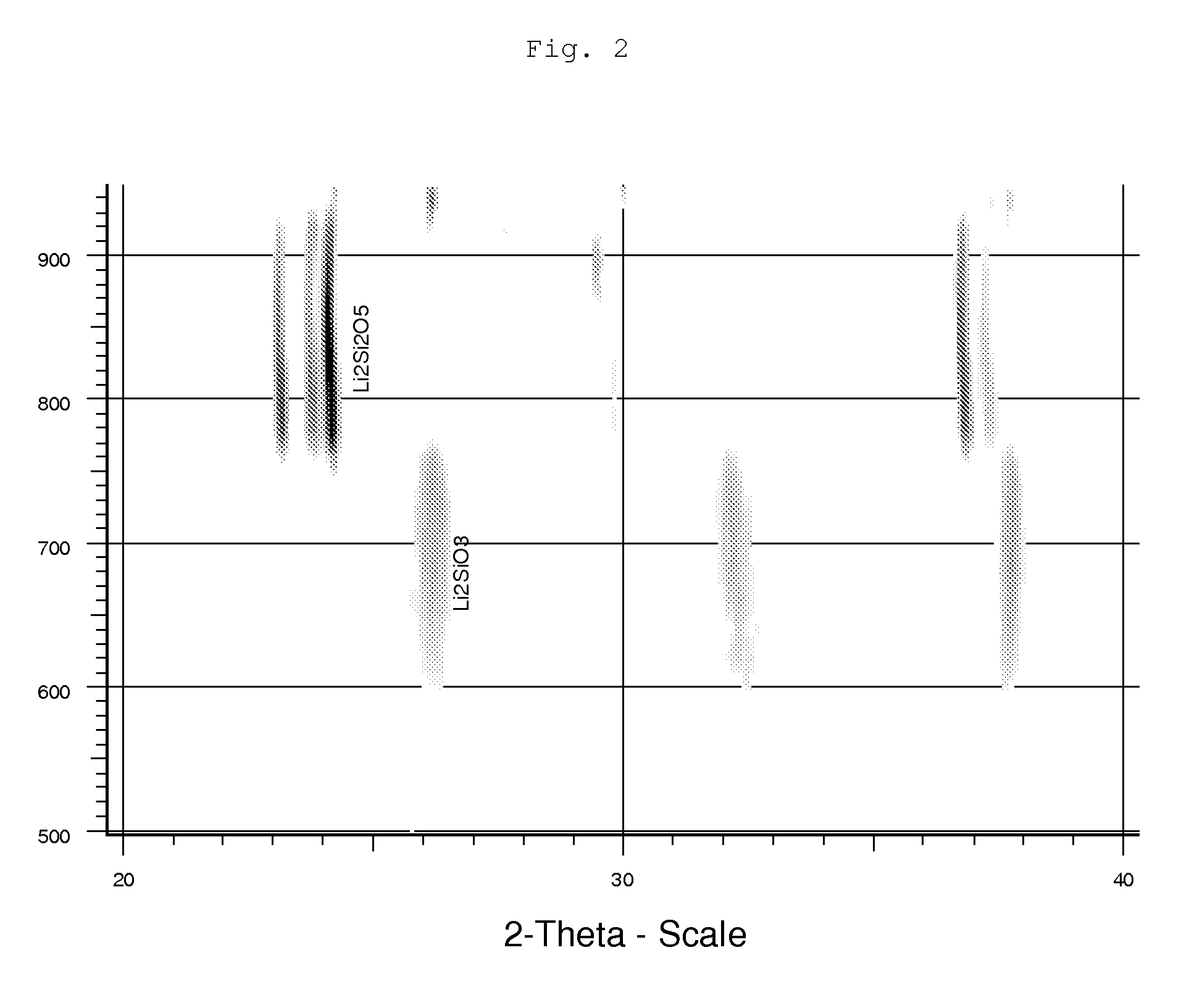
Lithium disilicate based glass-ceramics contain high strength ceramic components for use in the manufacture of dental products. The glass-ceramics have good pressability, i.e., the ability to be formed into dental products by heat-pressing using commercially available equipment. The strength of the dental articles is increased with the inclusion of the high strength ceramic components.
Owner:ARDENT
Method of making a glass fiber preform with adjusting a spacing while increasing acceleration of a starting glass powder
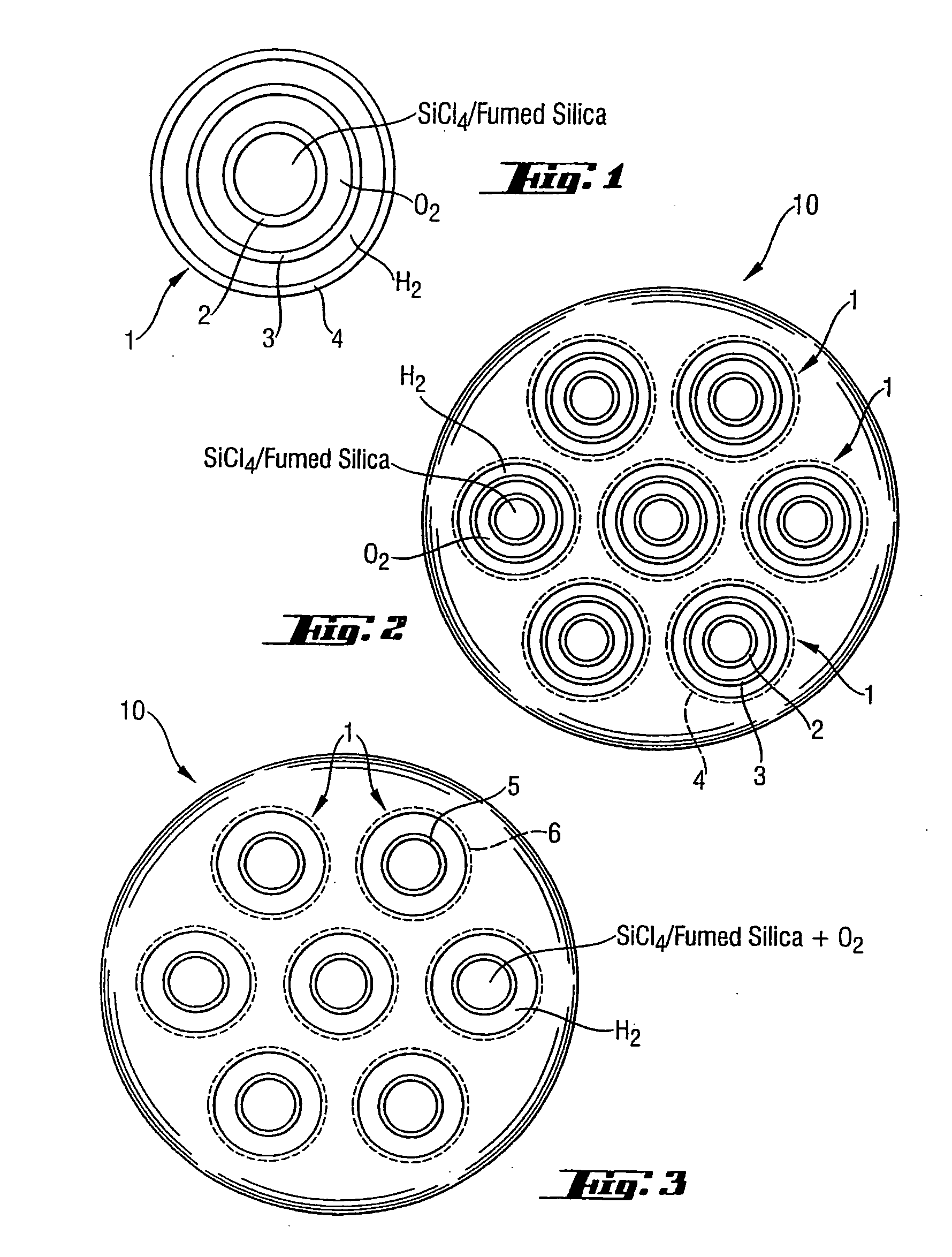
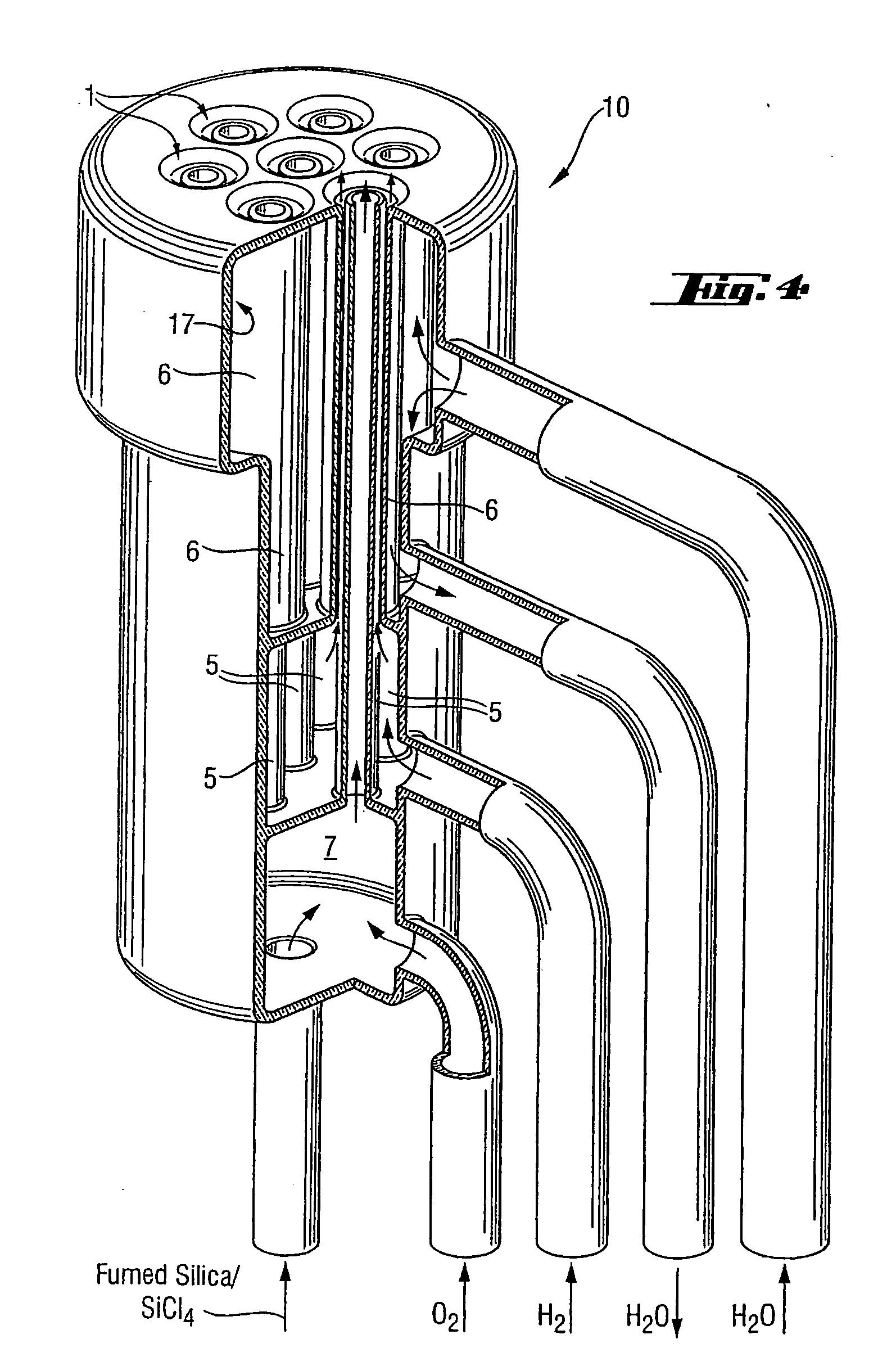
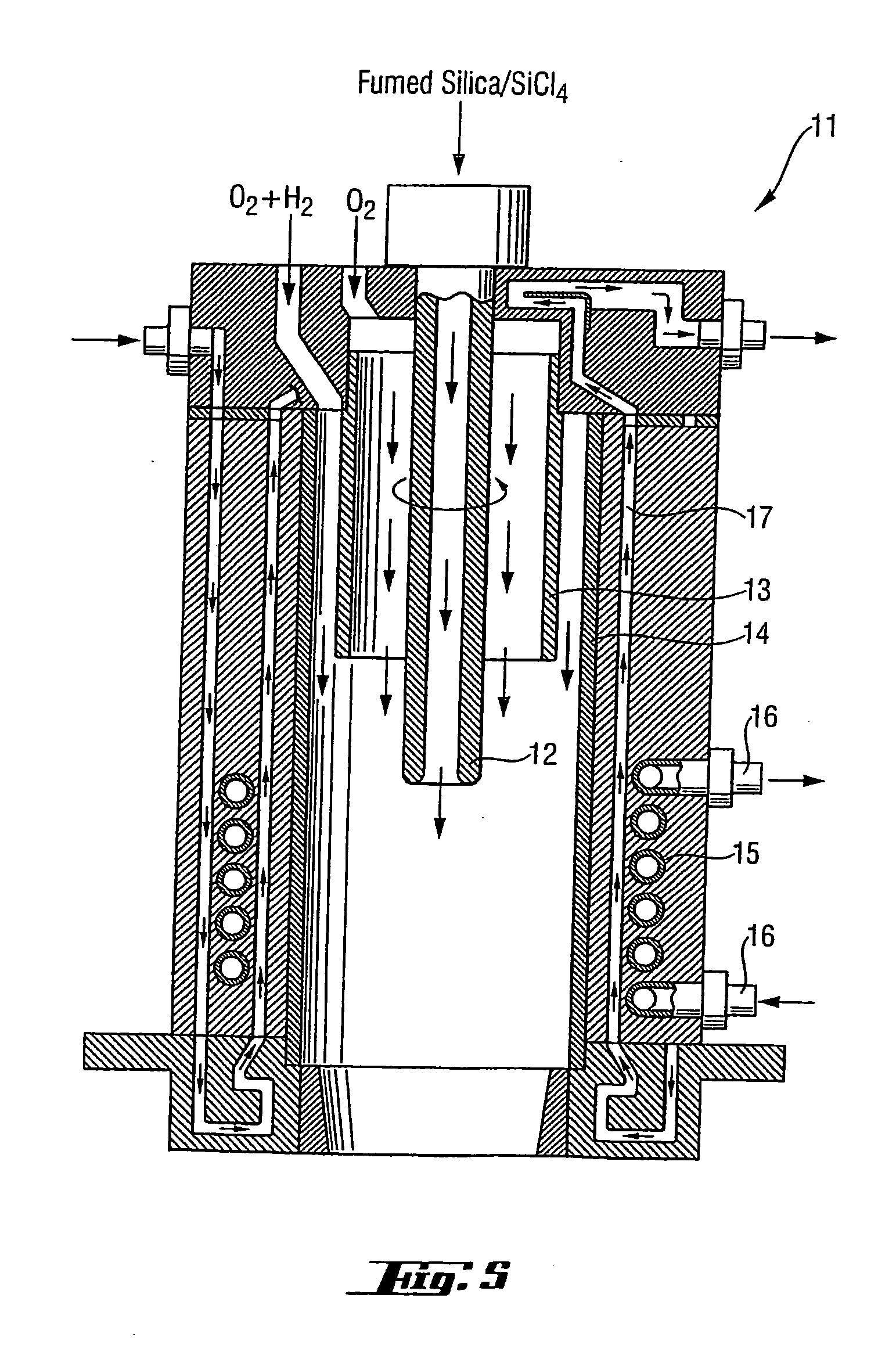
InactiveUS6202447B1Material analysis by optical meansGlass shaping apparatusGlass fiberOffset distance
The invention relates to manufacturing glass fiber preforms. It relates to a method comprising rotating preform about its own axis, and displacing a plasma torch in translation relative to the preform in a direction parallel to the axis of the preform, the axes of the flame and of the preform and being offset by a certain distance, and then inserting glass powder into the plasma flame under gravity. According to the invention, the glass powder is accelerated before penetrating into the plasma flame by means of an accelerator gas, and the offset distance between the axes is reduced with increasing acceleration of the powder. The invention is applicable to manufacturing glass fibers, and in particular optical fibers.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Quartz glass jig for processing apparatus using plasma
InactiveUS6869898B2High-quality semiconductor devicesLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass shaping apparatusAbrasive blastingEtching
An object of the present invention is to provide a quartz glass jig, which, when employed in a processing apparatus using plasma, is less in generation of abnormal etching and particles and low in contamination with impurities. This object is obtained by a quartz glass jig for a processing apparatus using plasma, wherein a surface of the jig is subjected to grinding or a sandblast processing and has a surface roughness Ra in the range of from 2 μm to 0.05 μm, and microcracks of grinding marks formed during the grinding or sandblast processing have a depth of 50 μm or less.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
High-purity silica powder, and process and apparatus for producing it
Use of a flame hydrolysis apparatus for preparing fumed silica particles or a plasma torch apparatus for sintering fumed silica particles to fused silica particles is capable of producing highly pure silica with non-silicon metal impurities less than 500 pb, when at least an inner nozzle is constructed of a silicon-containing material having a low level of non-silicon metal impurities. Preferably, all surfaces in the respective apparatus which contact silica are of similar construction. The silica contains a low level of impurities as produced, without requiring further purification.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Lithium silicate glass ceramic and glass with ZrO2 content
ActiveUS20120248642A1Substantial deterioration in translucencyInhibition formationDental implantsWristbandsLithiumSolid Bond
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Sintered quartz glass products and methods for making same
InactiveUS6012304AReduce sinteringLonger sintering timeGlass shaping apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusSilica particleDevitrification
A number of unique processes are disclosed for manufacture of sintered high-purity quartz glass products in which a shaped silica body or preform is made from an aqueous slurry of micronized silica particles by gel casting, slip casting or electrophoretic deposition. The silica particles may comprise a major portion by weight of crystalline silica. In one embodiment of the invention the sintered quartz glass is transparent, substantially bubble-free and suitable for scientific or optical uses. In another embodiment the porous silica preform is fired in steam to increase the hydroxyl content and then nitrided in a nitrogen-hydrogen reducing atmosphere. A minute amount of chemically-combined nitrogen in the high-purity quartz glass is sufficient to provide a tremendous improvement in physical properties and an incredible increase in the resistance to devitrification.
Owner:LOXLEY TED A +2
Mould for processing glass container
InactiveCN101298357AGuaranteed StrengthReduce the temperatureGlass shaping apparatusBottleMaterials science
The invention provides a mold for processing a glass container and belongs to the technical field of mold. The mold includes a pair of half molds that are opposite to each other and have the same shape, and a mold cavity is formed in each half mold. The mold is characterized in that vertical through ventilation holes which are communicated with each other are alternatively distributed around the mold cavity at the height direction of the half molds. The invention has the advantages that the bottle temperature can be cooled effectively due to the through ventilation holes around the mold cavity at the height direction, thus preventing the bottle from being deformed by high temperature and guaranteeing the strength of the half molds.
Owner:CHANGSHU WEIHENG MOLD MFG
Method for producing sulfide glass or sulfide glass ceramic capable of conducing lithium ion, and whole solid type cell using said glass ceramic
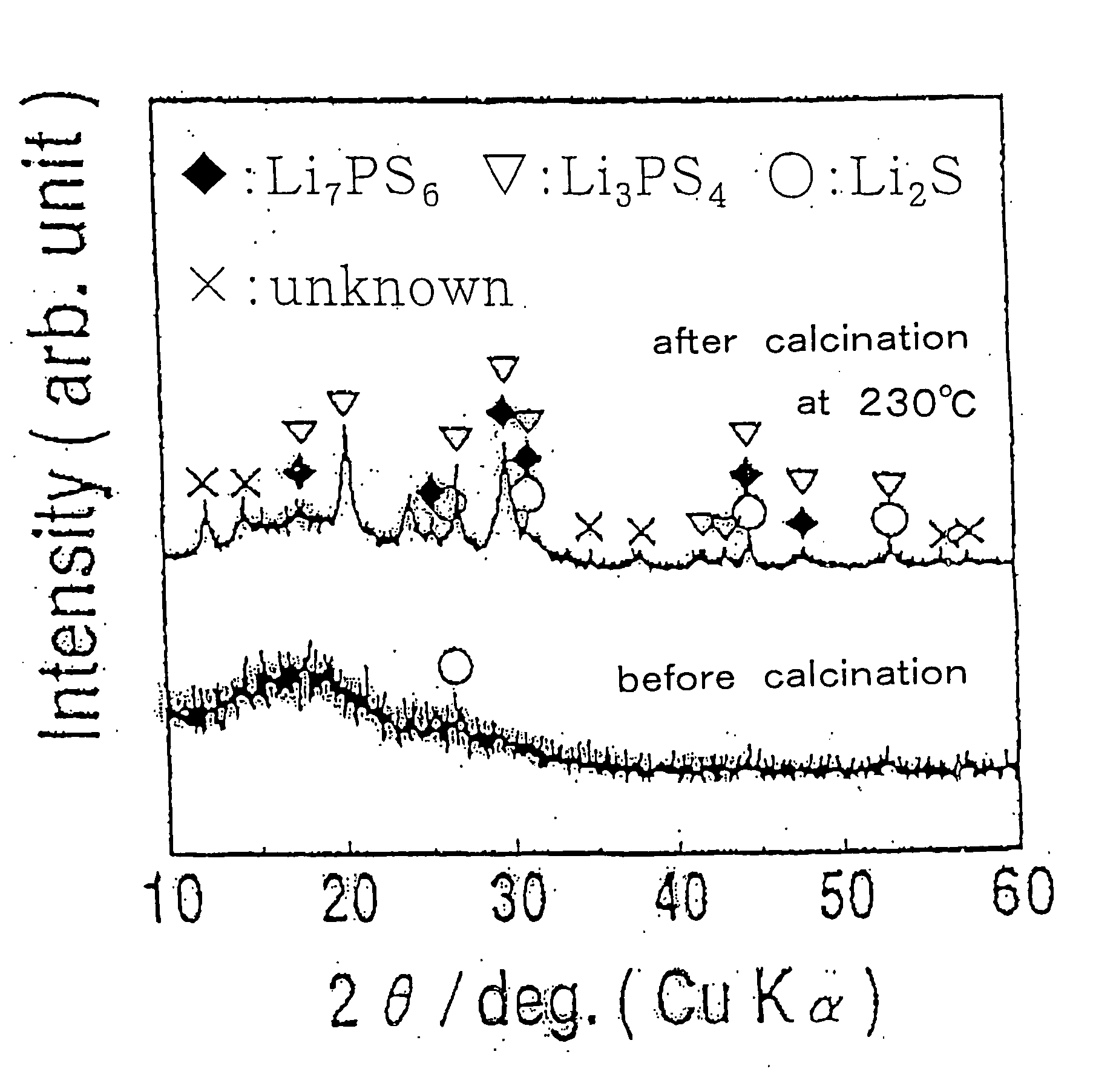
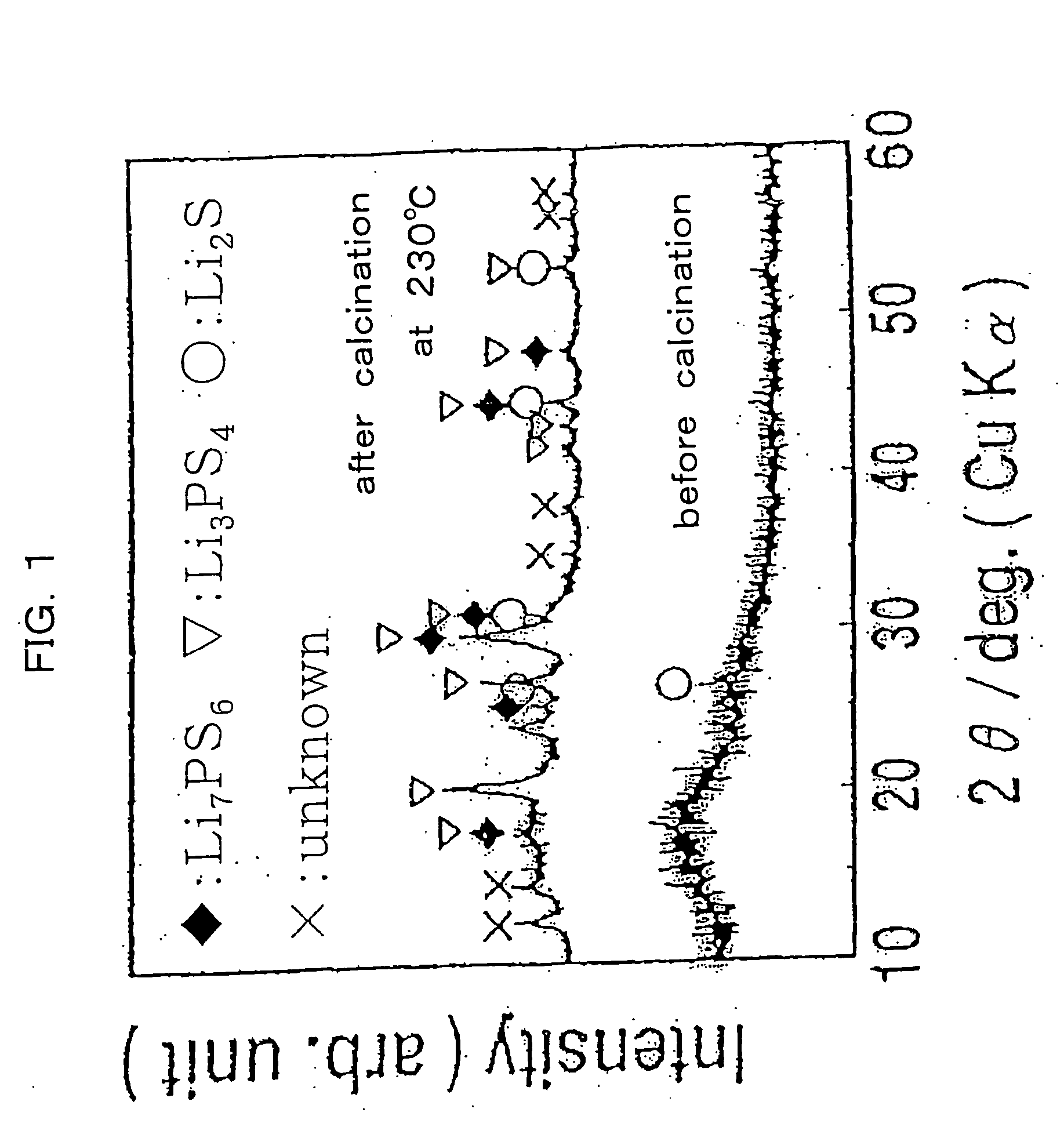
InactiveUS20050107239A1Simple and convenient and easily availableSolid electrolytesConductive materialMetallic lithiumSulfur
The present invention relates to a process for producing sulfide glass or sulfide glass ceramic each capable of conducting a lithium ion, comprising subjecting metallic lithium, sulfur as a simple substance and phosphorus as a simple substance as starting raw materials, which constitute the sulfide glass and sulfide glass ceramic, to mechanical milling to thereby convert them into sulfide glass or sulfide glass ceramic; and a whole solid type cell using the above-mentioned sulfide glass ceramic as a solid electrolyte. According to the present invention, it is made possible to produce sulfide glass and sulfide glass ceramic which are each capable of conducting a lithium ion and which have high electroconductivity at room temperature by a simple and advantageous process from starting raw materials being easily available and inexpensive.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
Nano glass powder and use thereof, particularly multicomponent glass powder with a mean particle size of less than 1 [mu]m
InactiveCN101094818AReduce the temperatureRelieve pressureMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusMetallurgyGlass-ceramic
The invention relates to a glass powder or a glass-ceramic powder comprising multicomponent glasses with at least three elements, and is characterized in that the glass powder or a glass-ceramic powder has a mean particle size of less than 1 mum, preferably less than 0.1 mum, particularly preferred less than 10 nm.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Synthetic quartz glass for optical member and its production method
ActiveUS20060183623A1Suppress compactionSlow changeGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersOxygen deficientLength wave
A synthetic quartz glass for an optical member which is free from compaction and rarefaction is obtained. A synthetic quartz glass for an optical member to be used for an optical device employing a light having a wavelength of at most 400 nm and at least 170 nm as a light source, which contains substantially no oxygen excess defects, dissolved oxygen molecules nor reduction type defects, which has a chlorine concentration of at most 50 ppm and a OH group concentration of at most 100 ppm, and which contains oxygen deficient defects within a concentration range of at most 5×1014 defects / cm3 and at least 1×1013 defects / cm3. The fluorine concentration is preferably at most 100 ppm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Al2O3-rare earth oxide-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030126803A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3-rare earth oxide-ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Substrate for EUV mask blanks
ActiveUS20100028787A1Improve flatnessNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessQuartz
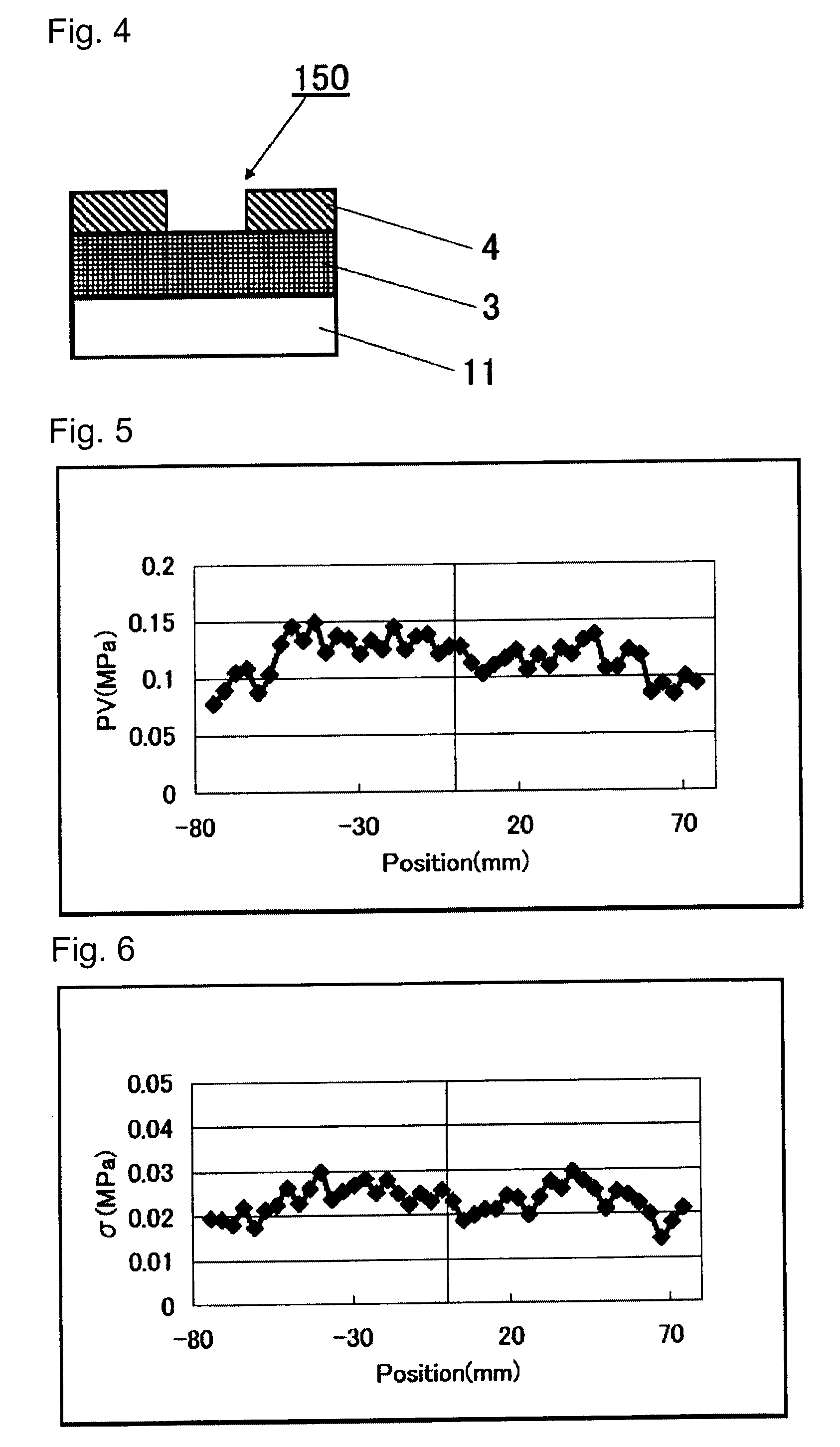
A substrate that is suitable for an EUV mask or an EUV mask blank and excellent in flatness, is provided.A substrate for an EUV mask blank, which is made of a silica glass containing from 1 to 12 mass % of TiO2, wherein the surface roughness (rms) in a surface quality area of the substrate is at most 2 nm, and the maximum variation (PV) of the stress in the surface quality area of the substrate is at most 0.2 MPa.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Ceramic materials, abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030126802A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentGlass-ceramicMaterials science
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of making a jacketed preform for optical fibers using OVD
InactiveUS7089765B2Cost effective productionReduce lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGlass shaping apparatusProduction rateDopant
On the basis of a known process for the production of a preform for an optical fiber for optical data transmission technology, the productivity of the process for the production of complex refractive index profiles is to be improved by providing a quartz glass substrate tube which exhibits different doping in radial direction, introducing a core glass made of synthetic quartz glass into the substrate tube and covering the substrate tube with a jacket tube. A substrate tube suitable therefor is also being provided which tube requires less core glass material for the production of the preform, whether during the internal deposition or for the core glass rod in the rod-in-tube technique. Regarding the process it is proposed according to the invention that a substrate tube be used which was obtained by vitrification of a porous tube-shaped SiO2 blank, the substrate tube being provided with a core glass layer which is produced in that to the first radial portion of the SiO2 blank there is added before the vitrification a first dopant which increases the refractive index of quartz glass. The substrate tube according to the invention has in the radial direction regions of different doping whereby it incorporates a core glass layer which has a refractive index of at least 1.459.
Owner:HERAEUS TENEVO
Abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030115805A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentAbrasive
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods to fabricate nano-macro porous glass using a water soluble pore former
Provided herein are methods for preparing nano-macroporous glass articles, such as bioscaffolds, from starting materials such as phosphosilicate glasses made by melt-quench methods, mixed with a soluble pore former such as a sugar, followed by steps of dissolving, heating, and leaching to yield a glass composition having a highly interconnected system of both macropores and large scale nanoporosity.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Inductively-coupled plasma source
ActiveUS7969096B2Energy efficiencyMaximize efficiencyElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsInductively coupled plasmaInductance
A method and apparatus for exciting gas that involves generating an alternating magnetic field unidirectionally through a magnetic core defining a gap, across the gap and through a plasma vessel that includes dielectric material. The magnetic field induces an electric field in the plasma vessel that generates the plasma.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Resorbable macroporous bioactive glass scaffold and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20070162151A1Excellent bioactivityImprove biodegradabilityBone implantGlass shaping apparatusBioactive glassChemistry
A resorbable, macroporous bioactive glass scaffold comprising approximately 24-45% CaO, 34-50% SiO2, 0-25% Na2O, 5-17% P2O5, 0-5% MgO and 0-1% CaF2 by mass percent, produced by mixing with pore forming agents and specified heat treatments.
Owner:NOVABONE PRODS
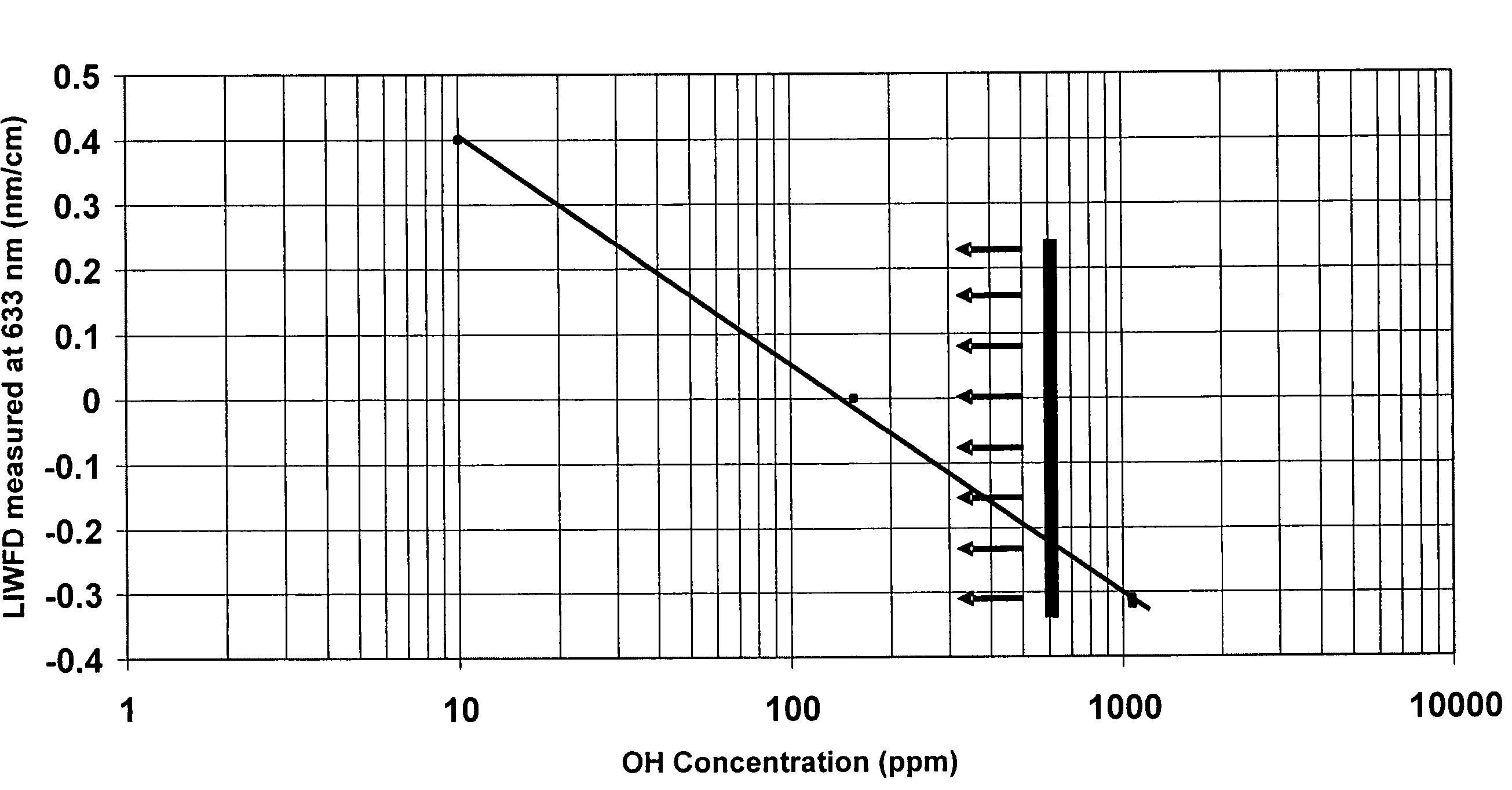
Synthetic silica glass optical material having high resistance to laser induced damage
InactiveUS7534733B2Decrease in levelGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersHigh resistanceLength wave
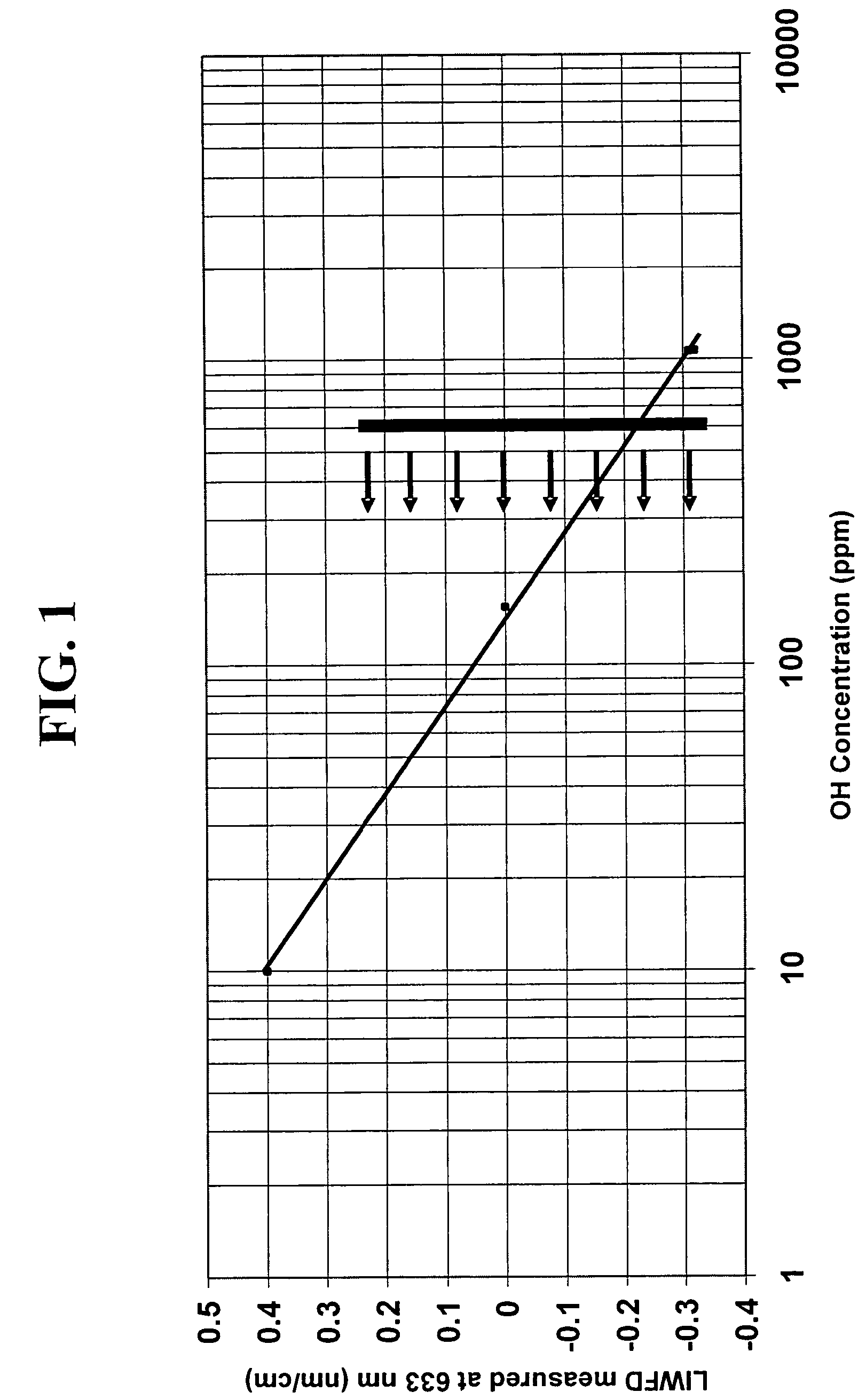
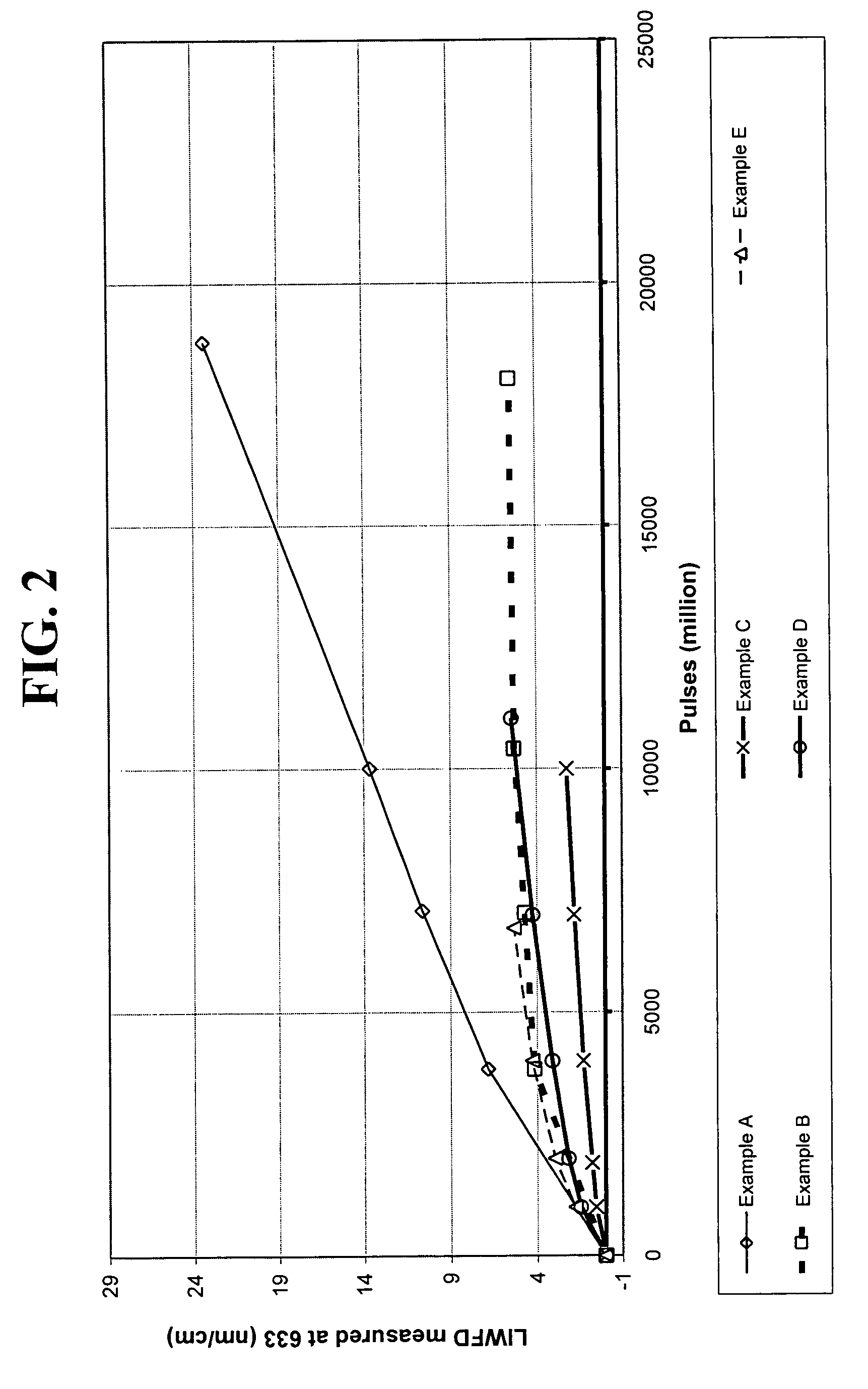
Disclosed is a synthetic silica glass optical material having high resistance to optical damage by ultraviolet radiation in the ultraviolet wavelength range, particularly in the wavelength less than about 250 nm and particularly, exhibiting a low laser induced wavefront distortion; specifically a laser induced wavefront distortion, measured at 633 nm, of between about −1.0 and 1.0 nm / cm when subjected to 10 billion pulses of a laser operating at approximately 193 nm and at a fluence of approximately 70 μJ / cm2. The synthetic silica glass optical material of the present invention comprises OH concentration levels of less than about 600 ppm, preferably less than 200 ppm, and H2 concentration levels less than about 5.0×1017 molecules / cm3,and preferably less than about 2.0×1017 molecules / cm3.
Owner:CORNING INC
Soft chemical preparation method for hollow glass micro-balloon, prepared hollow glass micro-balloon and application thereof
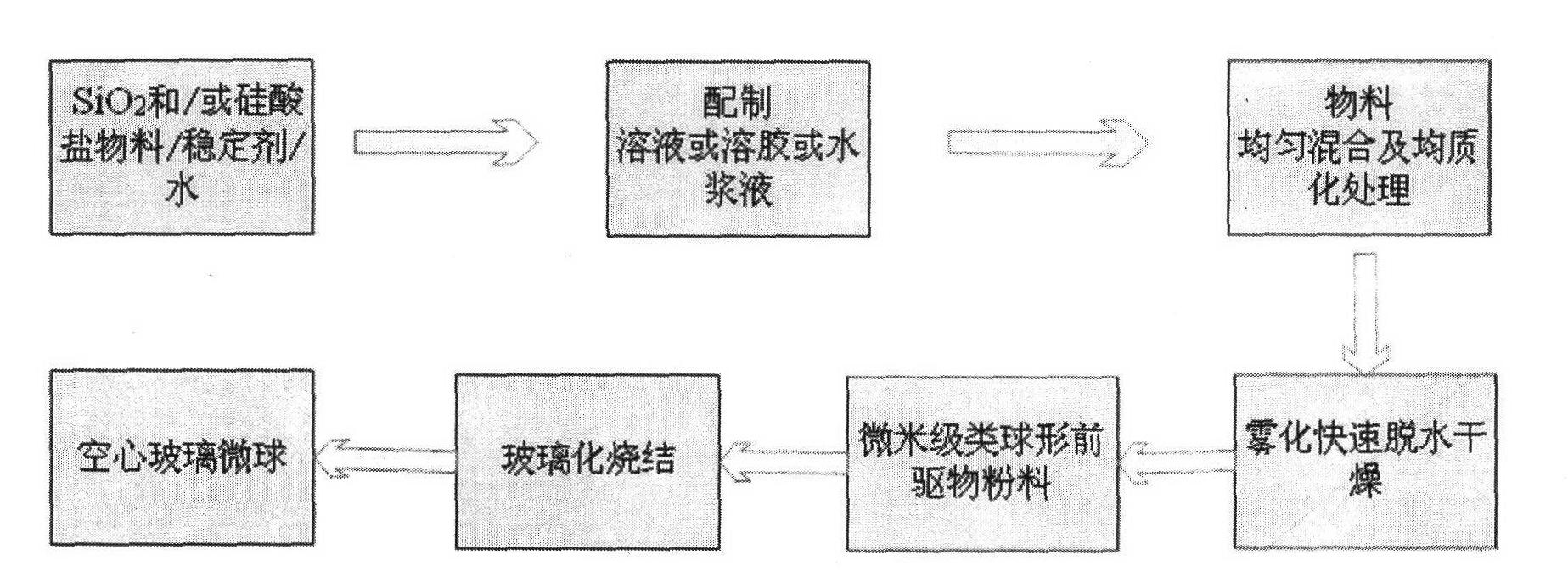
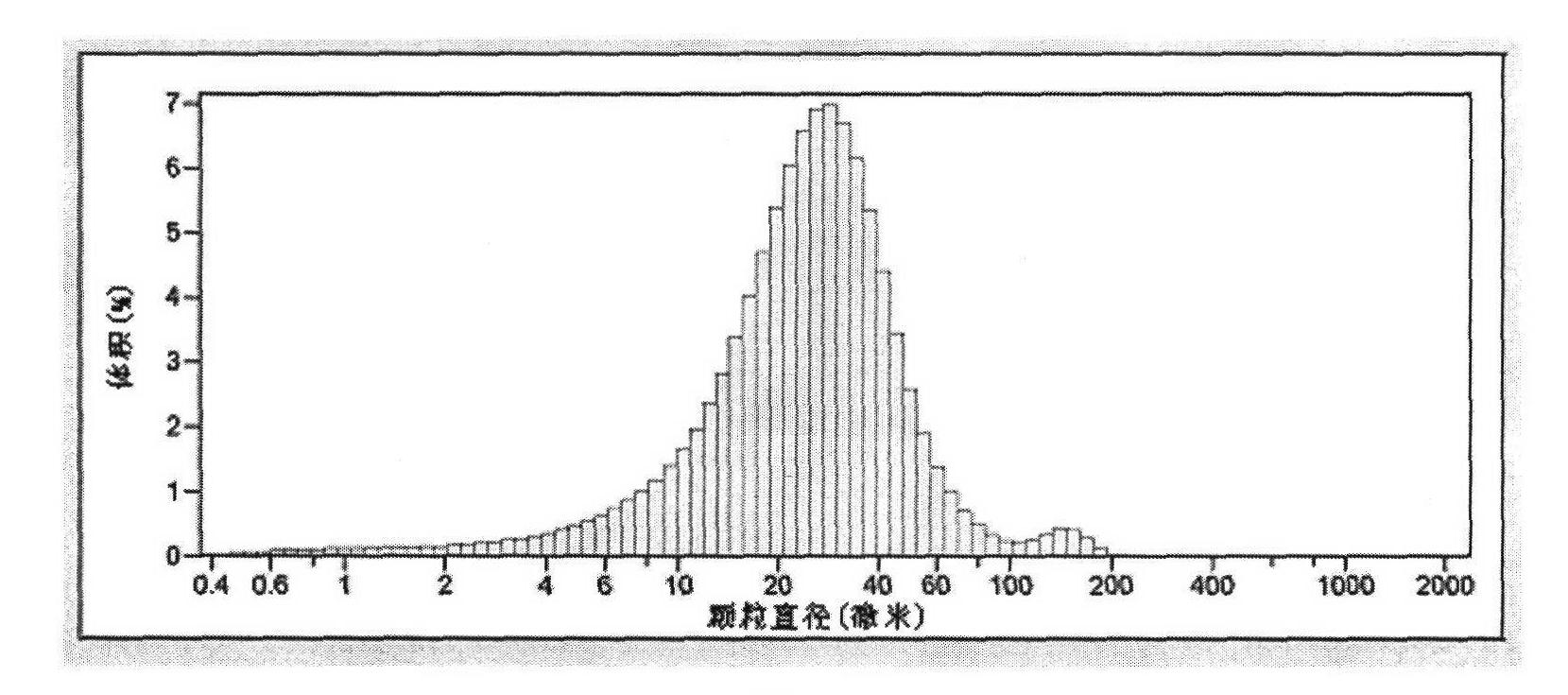
ActiveCN102583973AHigh strengthHigh compressive strengthGlass shaping apparatusMicron scalePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of a soft chemical method. According to the invention, the method is used for overcoming the defects that the traditional solid-phase glass powder method for preparing a hollow glass micro-balloon is high in energy consumption, long in technical process and difficult in controlling grain size distribution and the hollow glass micro-balloon prepared according to a liquid-phase atomizing method is high in alkalinity, easy to absorb water, high in strength and easy to break, and the like. A liquid material system is compounded through a chemical reaction; after the system is homogenized, the system is quickly atomized, dewatered and dried, thereby obtaining approximate spherical precursor powder with required grain size and corresponding distribution; and the powder is treated under high temperature at 600-1100 DEG C, thereby obtaining a micron-scale hollow glass micro-balloon with the volume floating rate being above 90%, the SiO2 content (weight) being 55-88%, the true density being 0.1-0.7g / cm<3> and the compression strength being 1-50MPa. The method is low in energy consumption, free from fusion and sintering, and high in yield. The prepared hollow glass micro-balloon is high in compression strength, light in weight, low-alkali, waterproof, excellent in fluidity and dispersibility, and suitable for various high-performance light compound materials.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
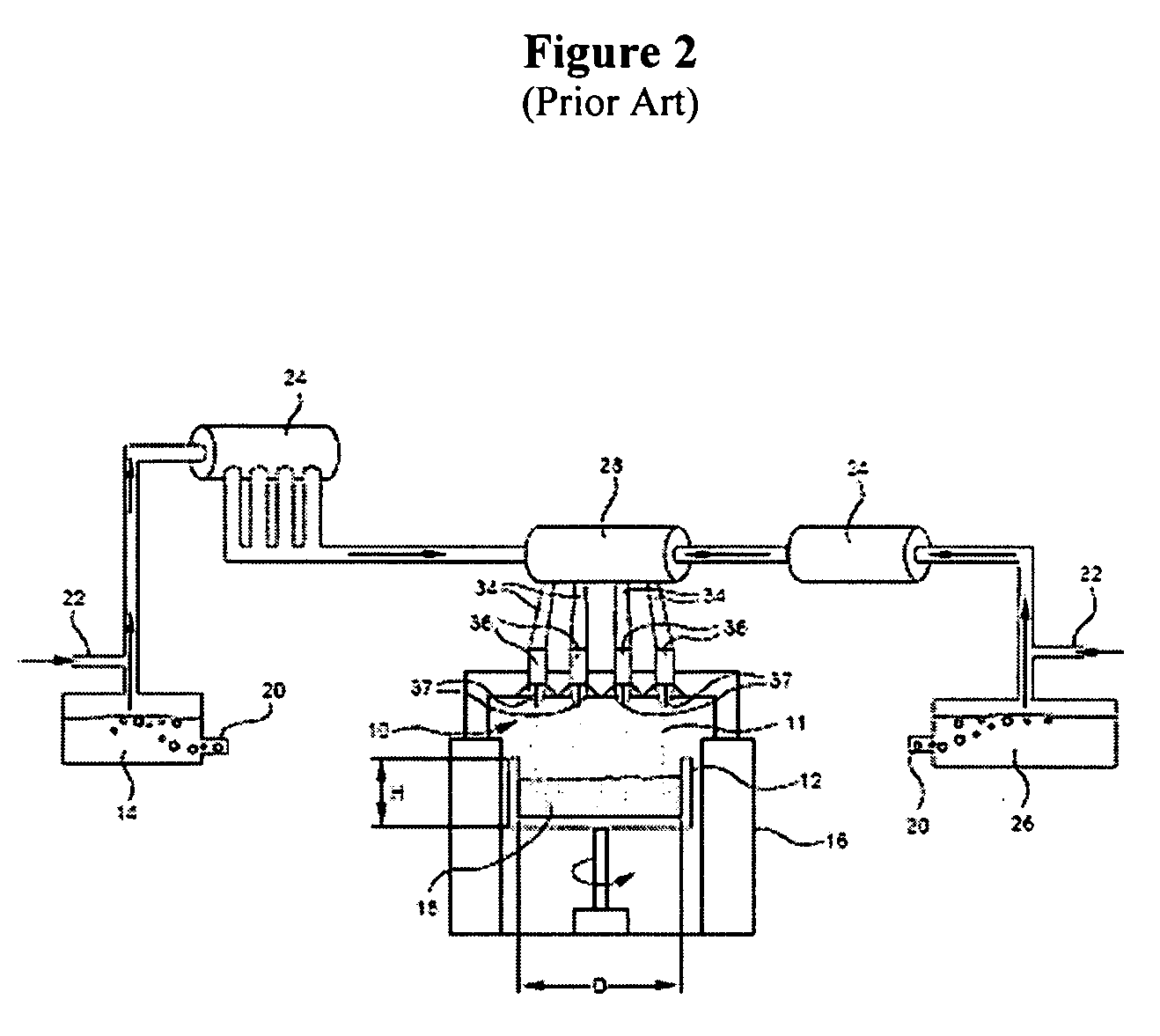
Method of producing oxide soot using a burner with a planar burner face
InactiveUS6837076B2Accurate and efficient depositionIncrease back pressureOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSilicaChemical reactionCombustor
A burner and a method for producing an inorganic soot such as silica comprising a plurality of substantially planar layers having multiple openings therethrough formed by a micromachining process. The openings are in fluid communication with a precursor inlet and a gas inlet to permit the gas and the precursor to flow through and exit the burner. The burner produces a flame from a combustible gas in which the precursor undergoes a chemical reaction to form the soot.
Owner:CORNING INC
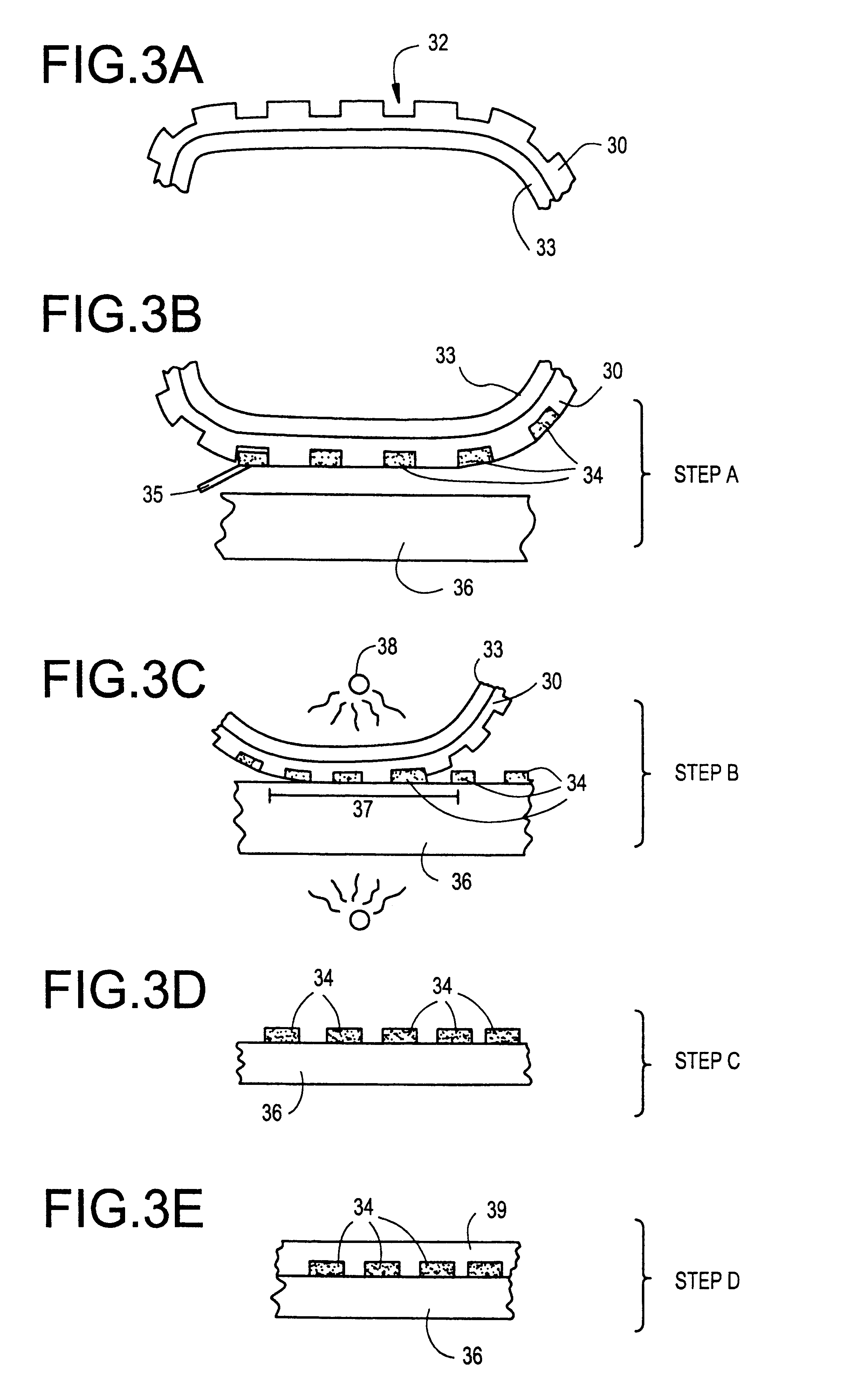
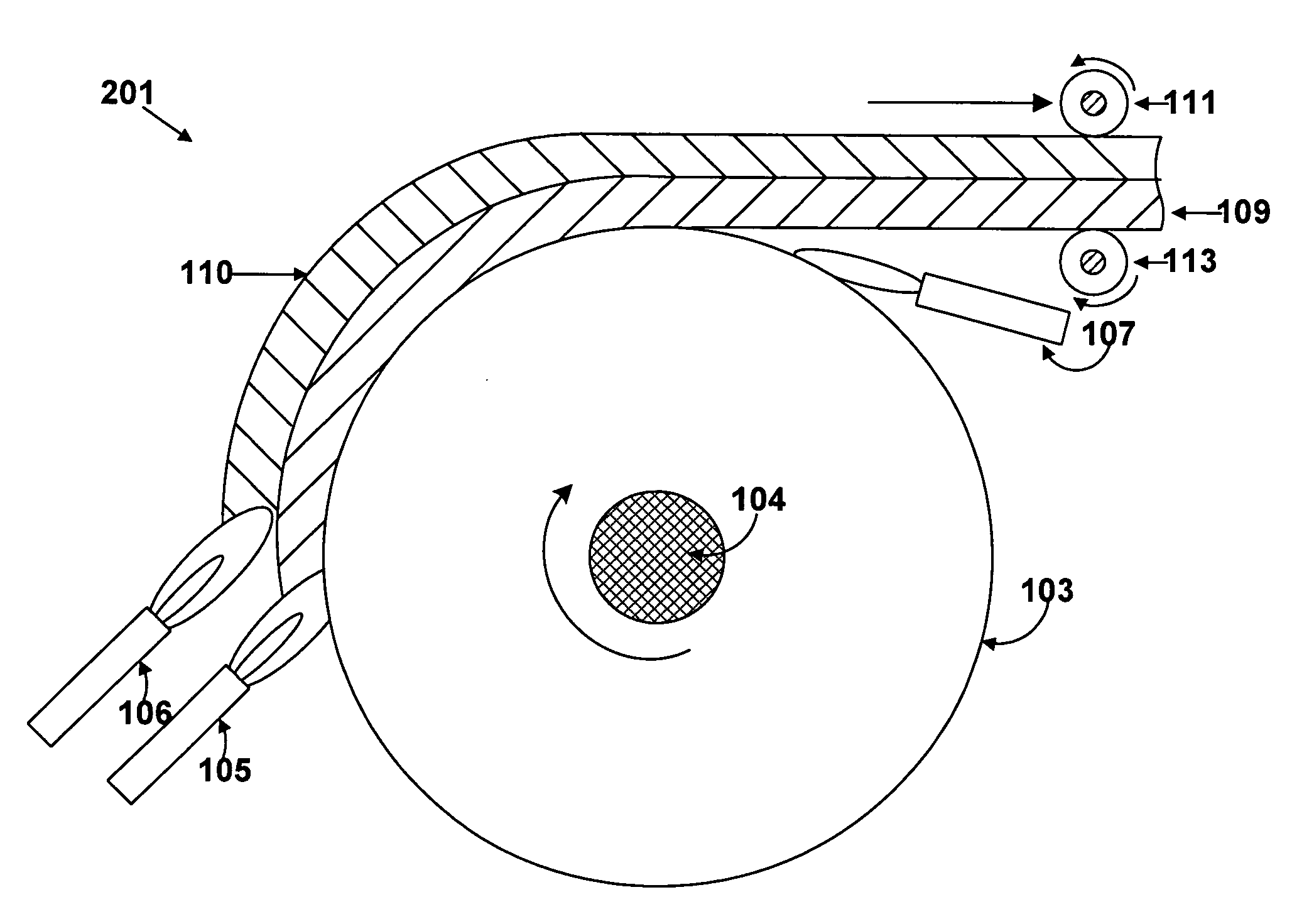
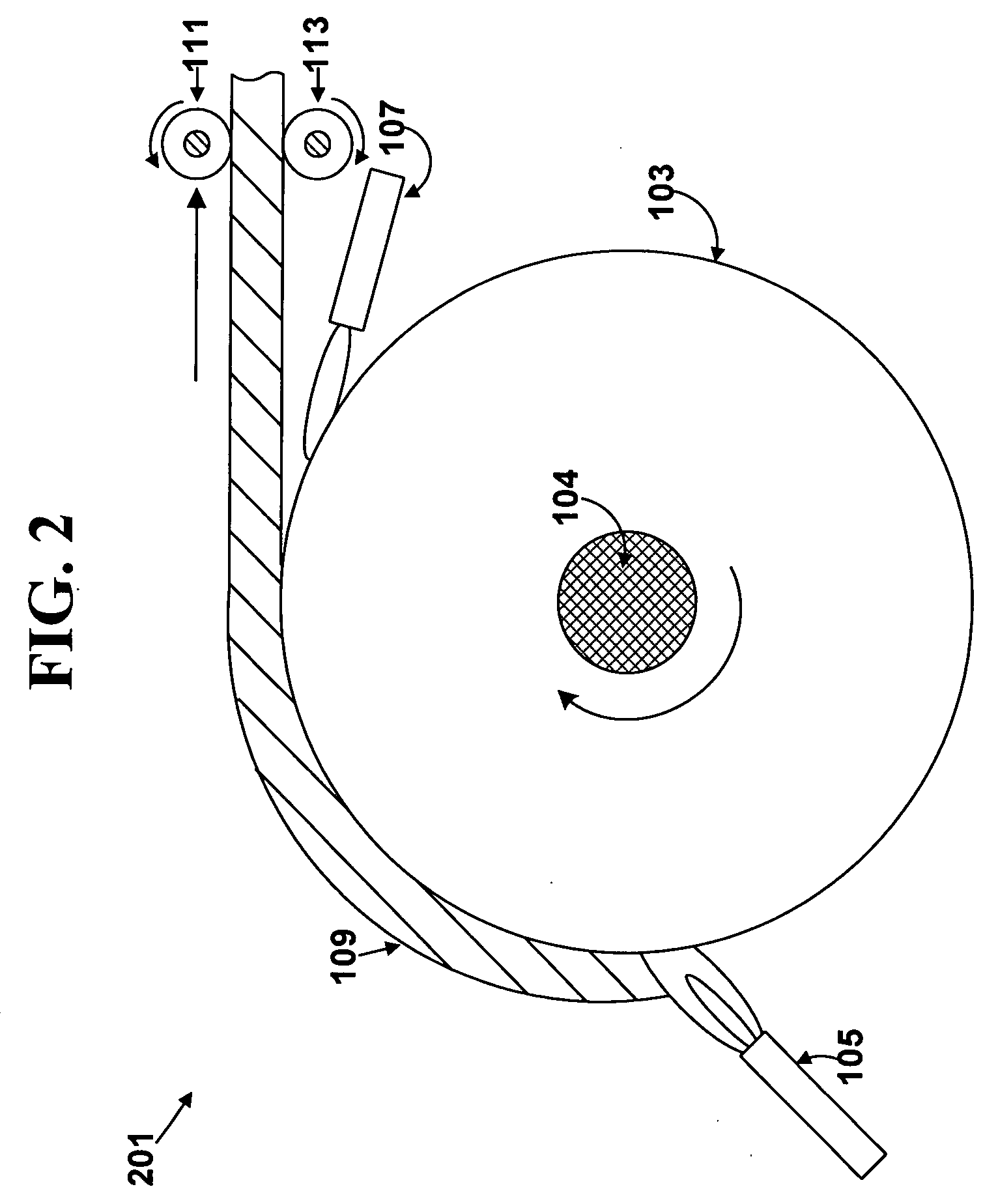
Process and apparatus for making glass sheet
ActiveUS20080280057A1Improve thickness uniformityUniform thicknessMolten spray coatingGlass shaping apparatusMetallurgyFritted glass
An apparatus and process for making glass soot sheet and sintered glass sheet. Glass soot particles are deposited on a curved deposition surface of a rotating drum to form a soot sheet. The soot sheet is then released from the deposition surface. The soot sheet can be sintered into a consolidated glass. The soot sheet and the sintered glass can be sufficiently long and flexible to be reeled into a roll.
Owner:CORNING INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com