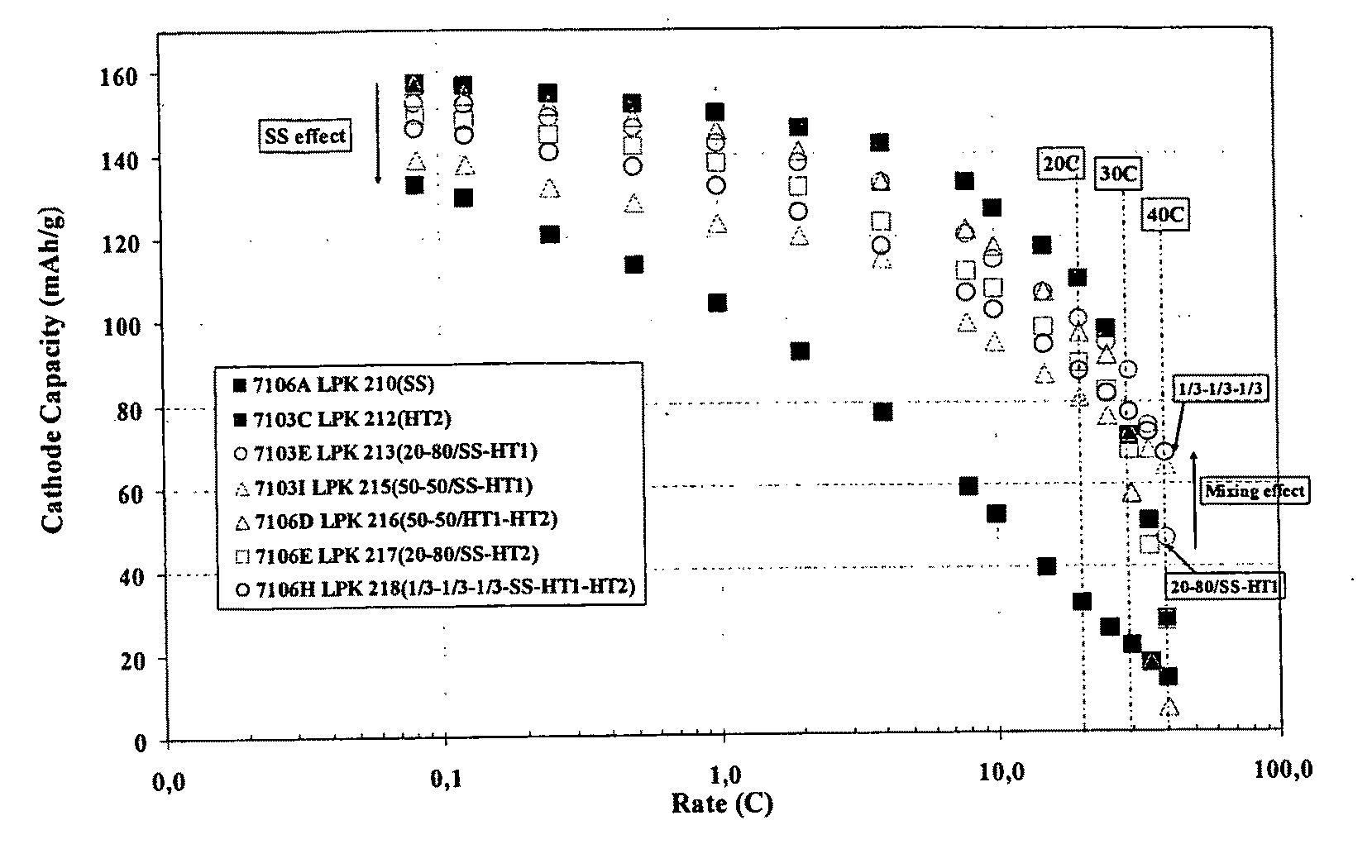
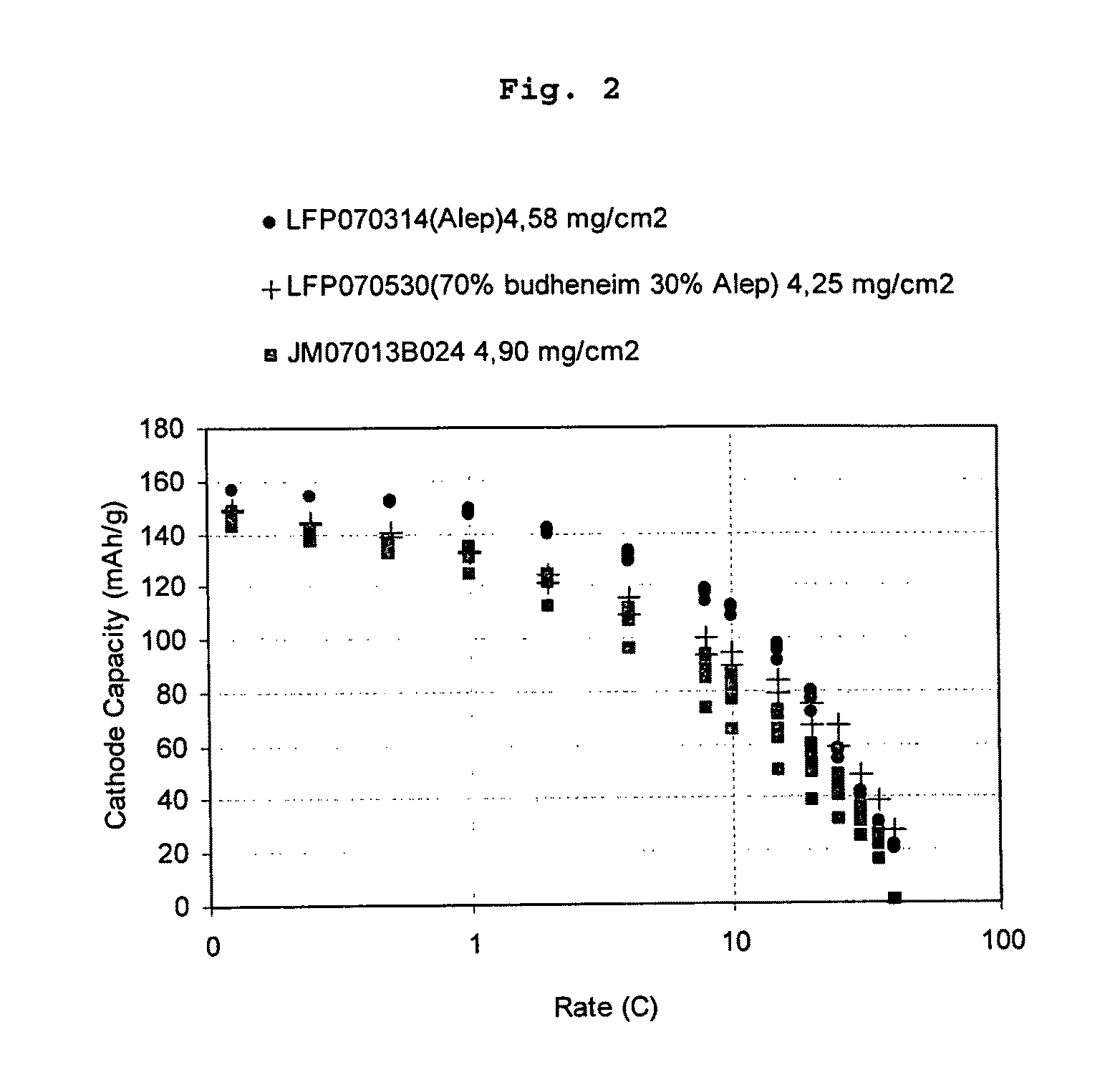
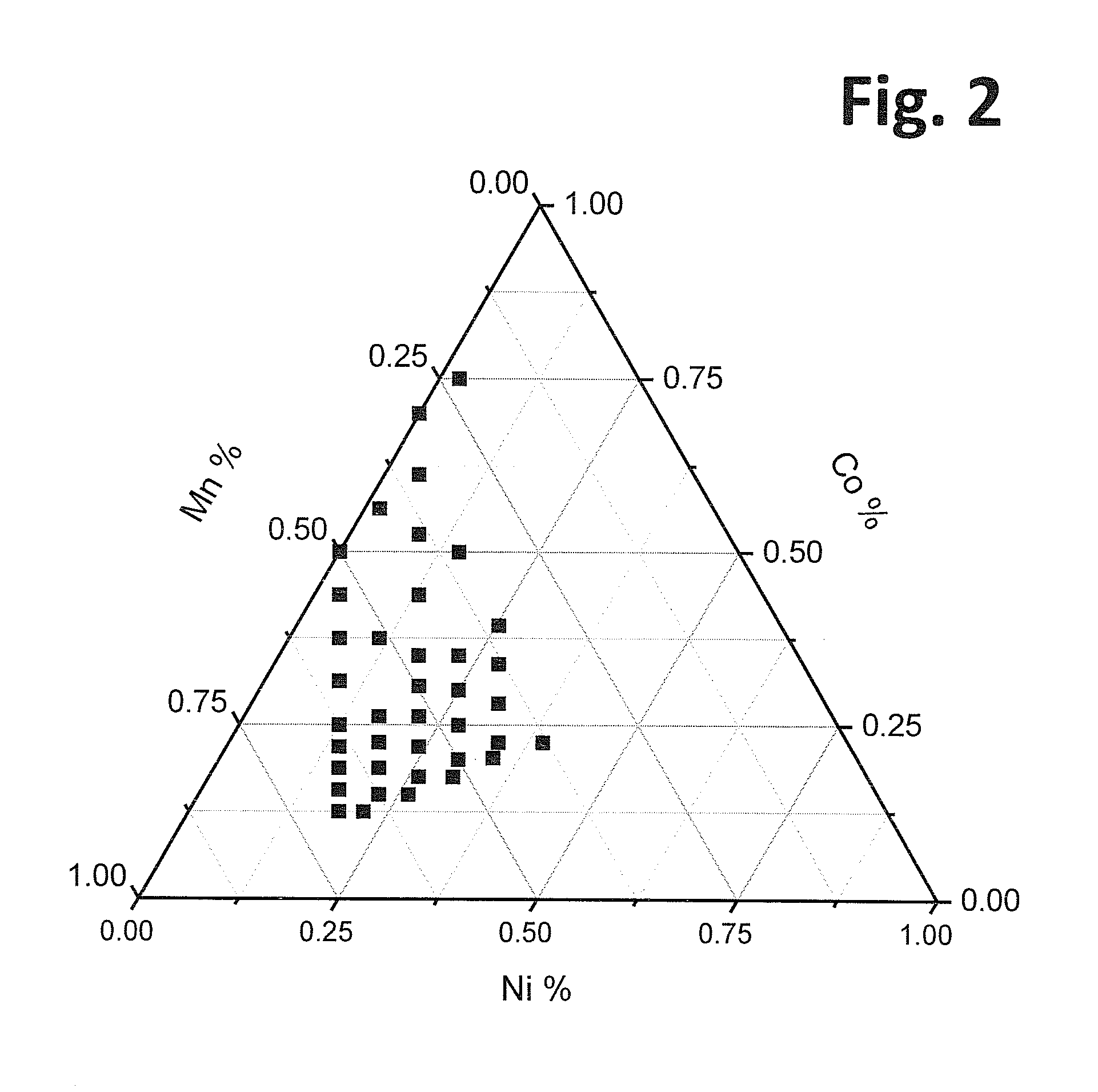
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2937 results about "Lithium metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
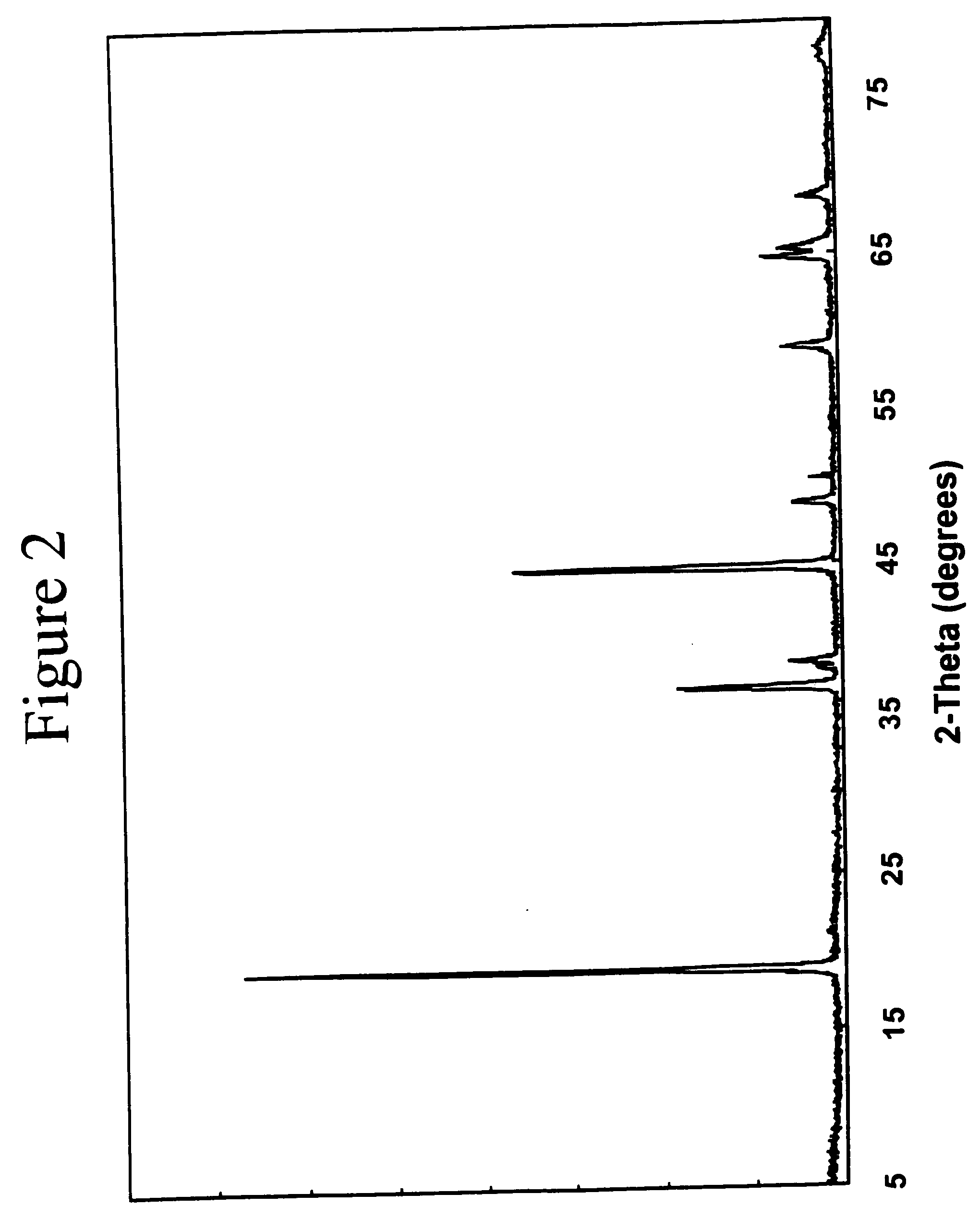
Lithium is an alkali metal. It is silver-white in pure form and so soft it can be cut with a butter knife. It has one of the lowest melting points and a high boiling point for a metal. Lithium metal burns white, though it imparts a crimson color to a flame.
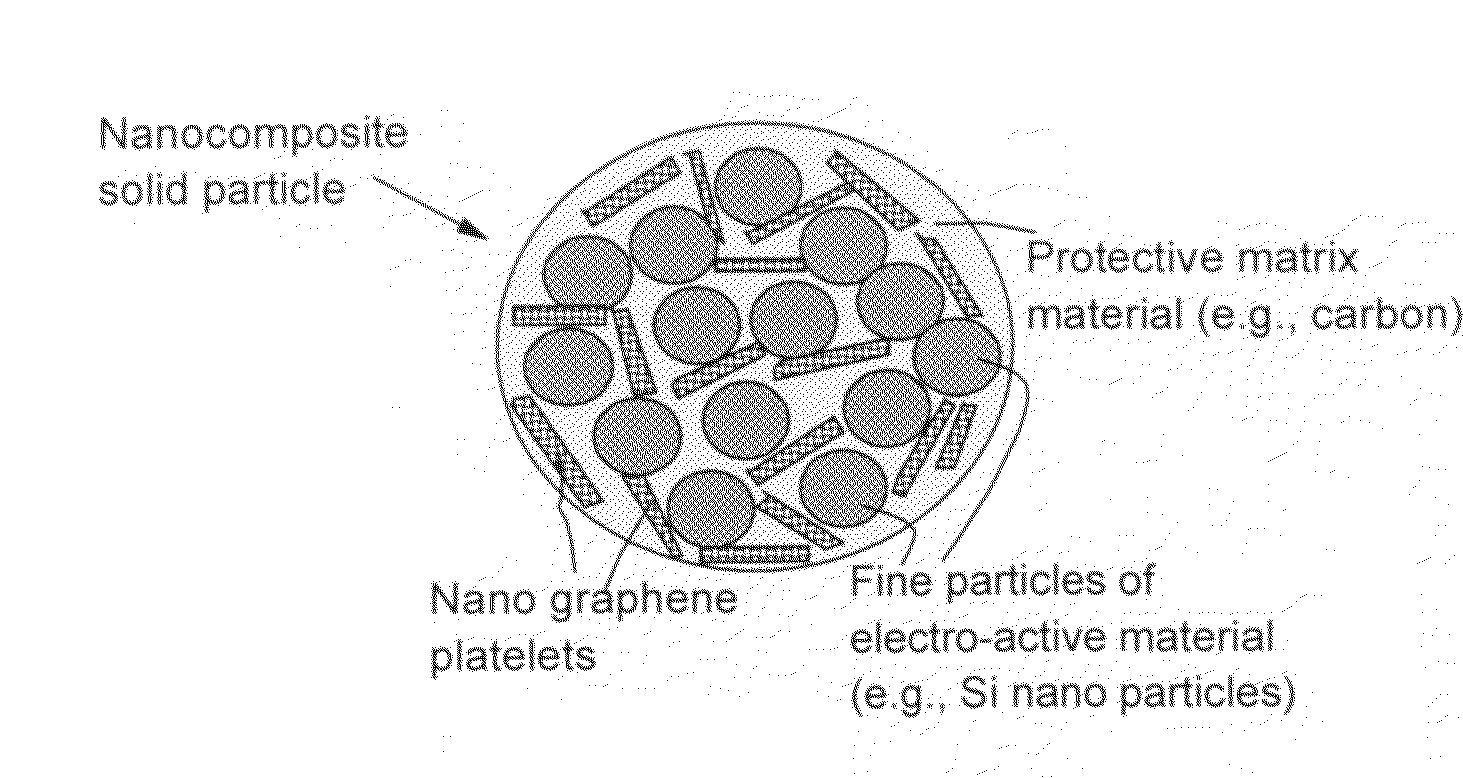
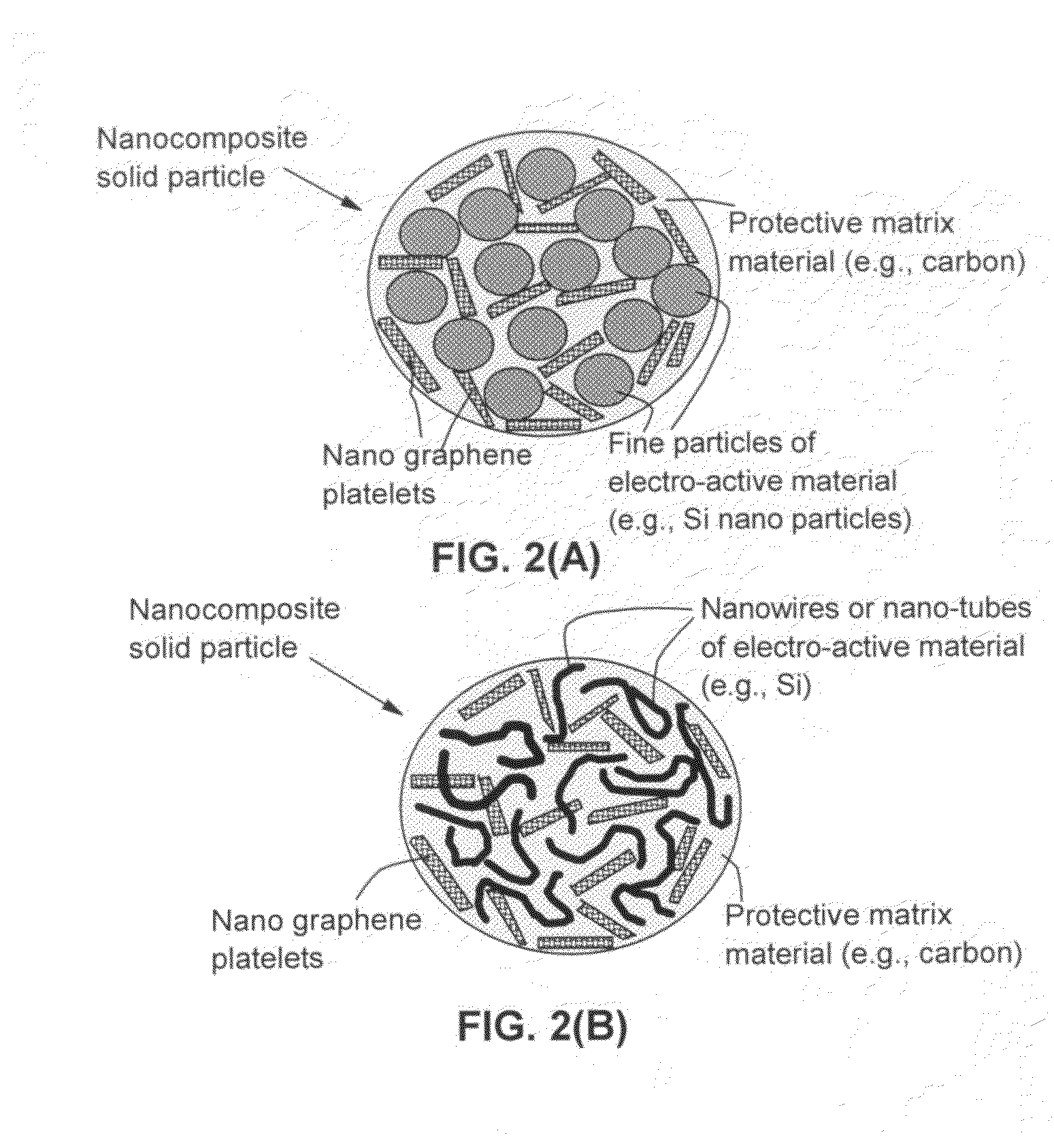
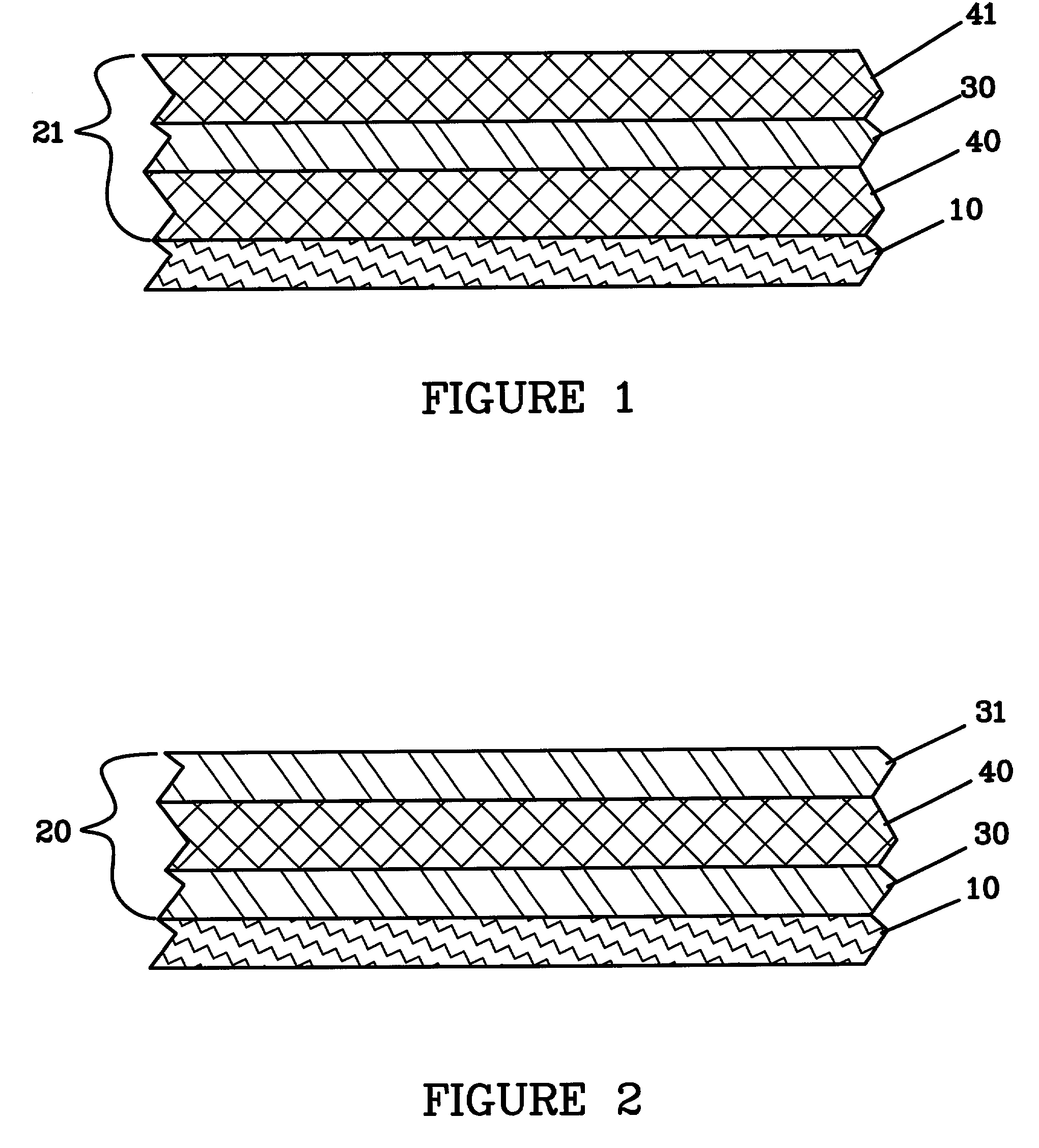
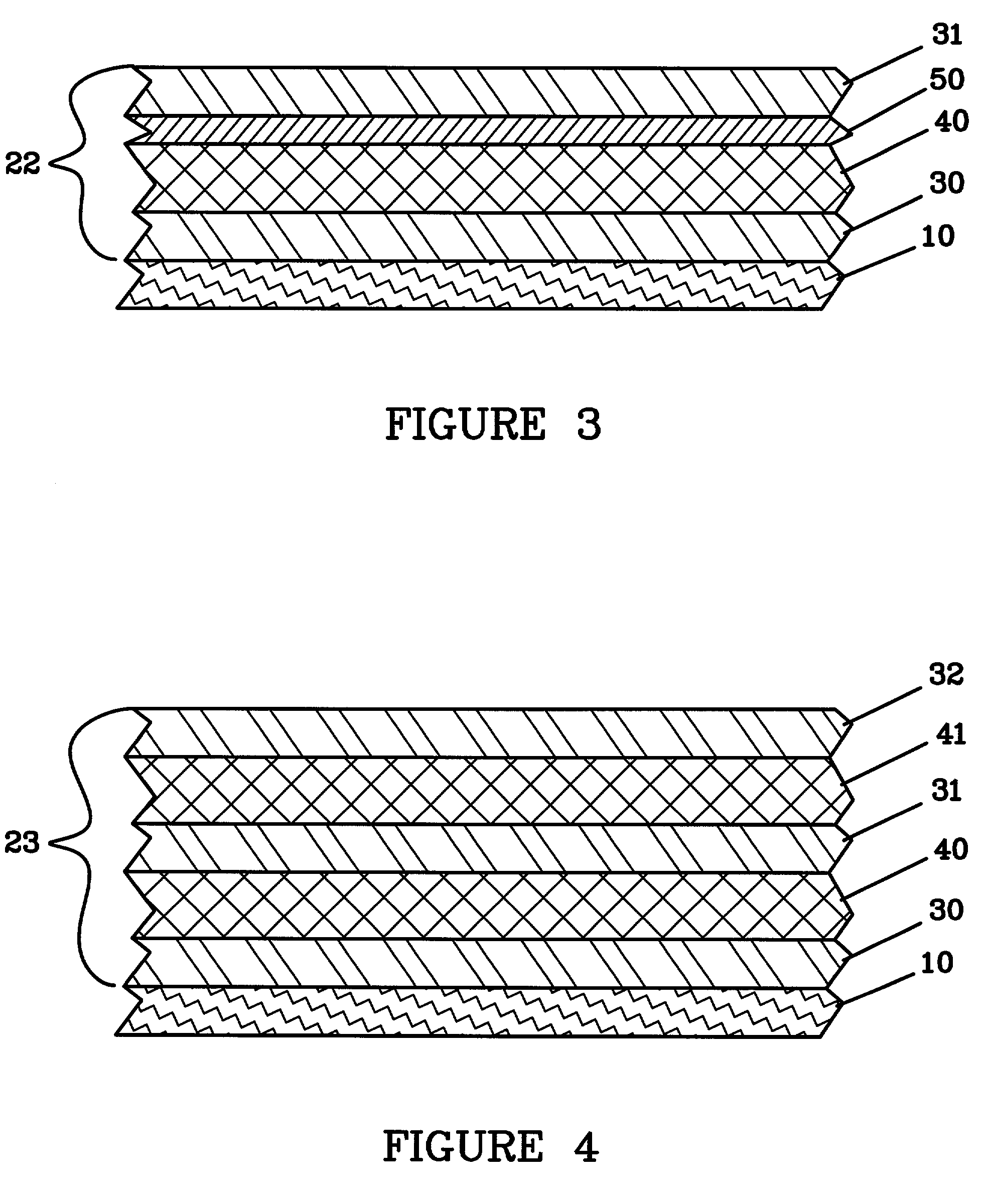
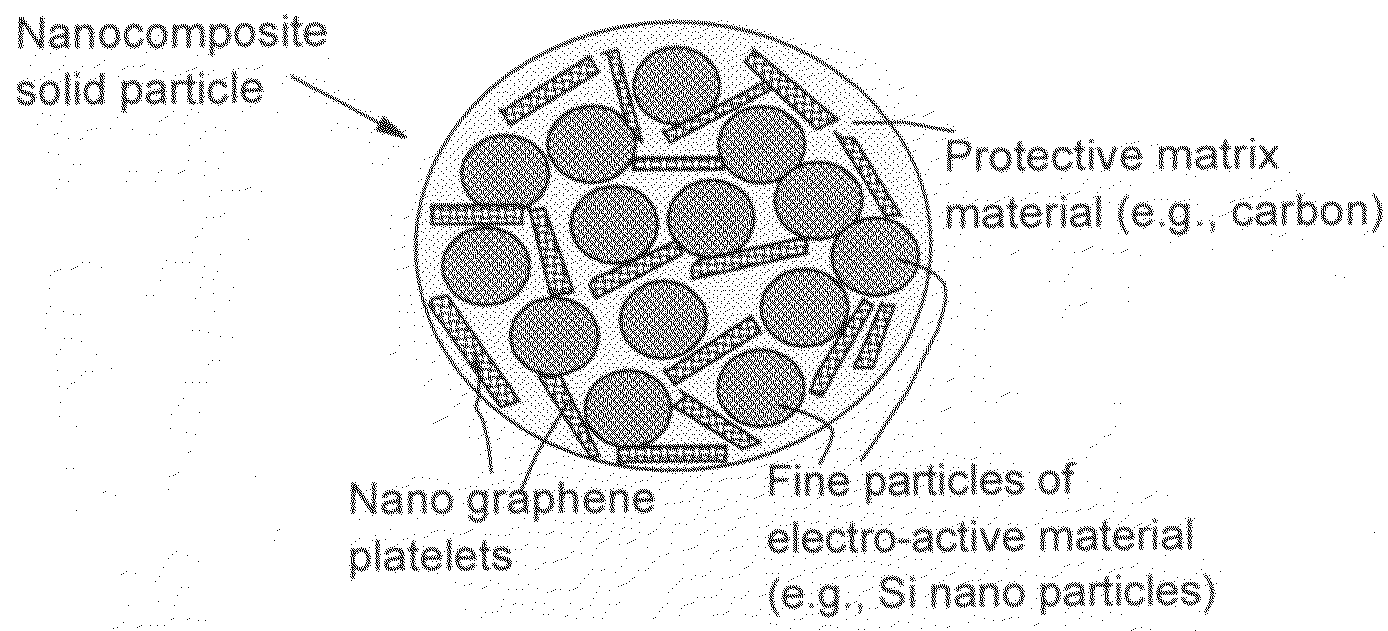
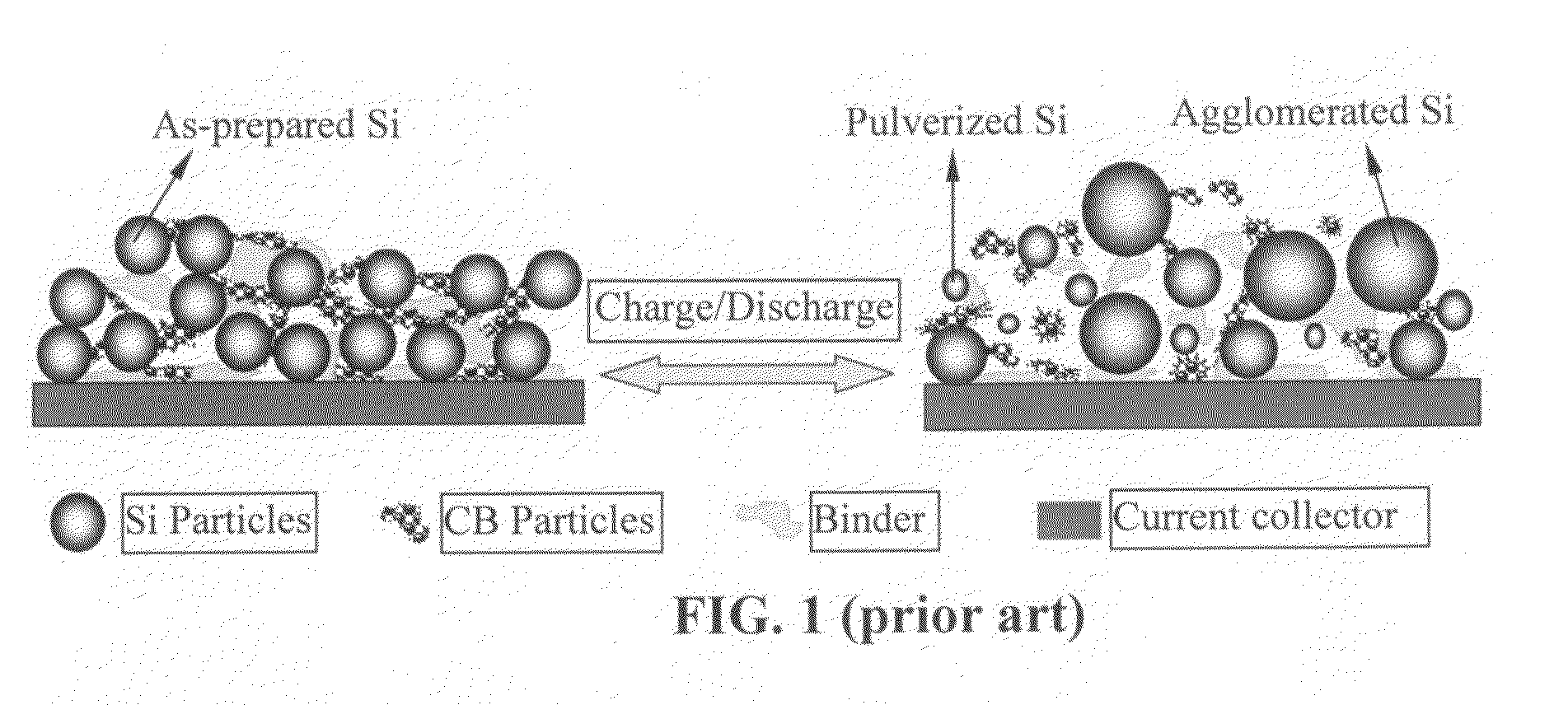
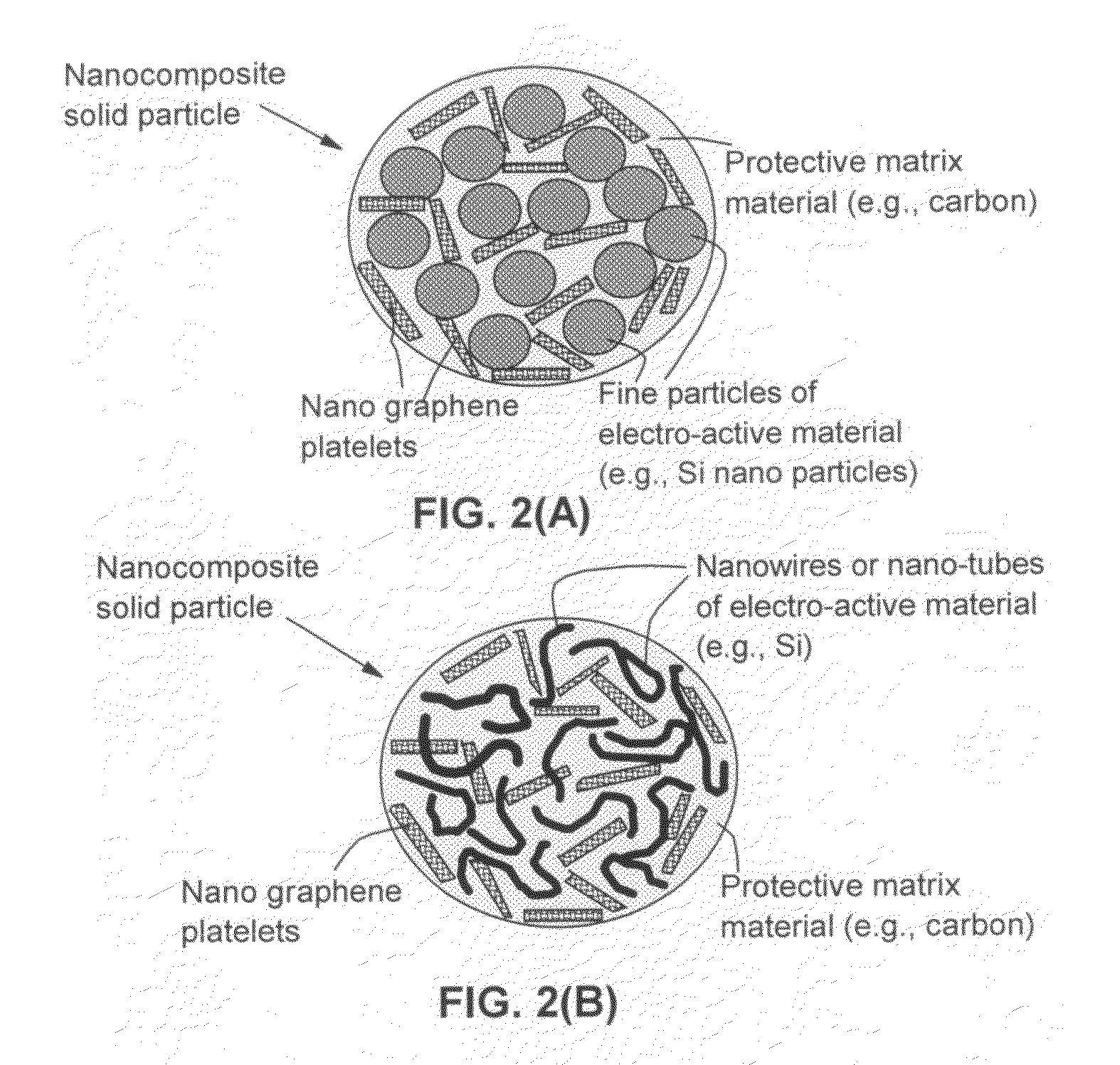
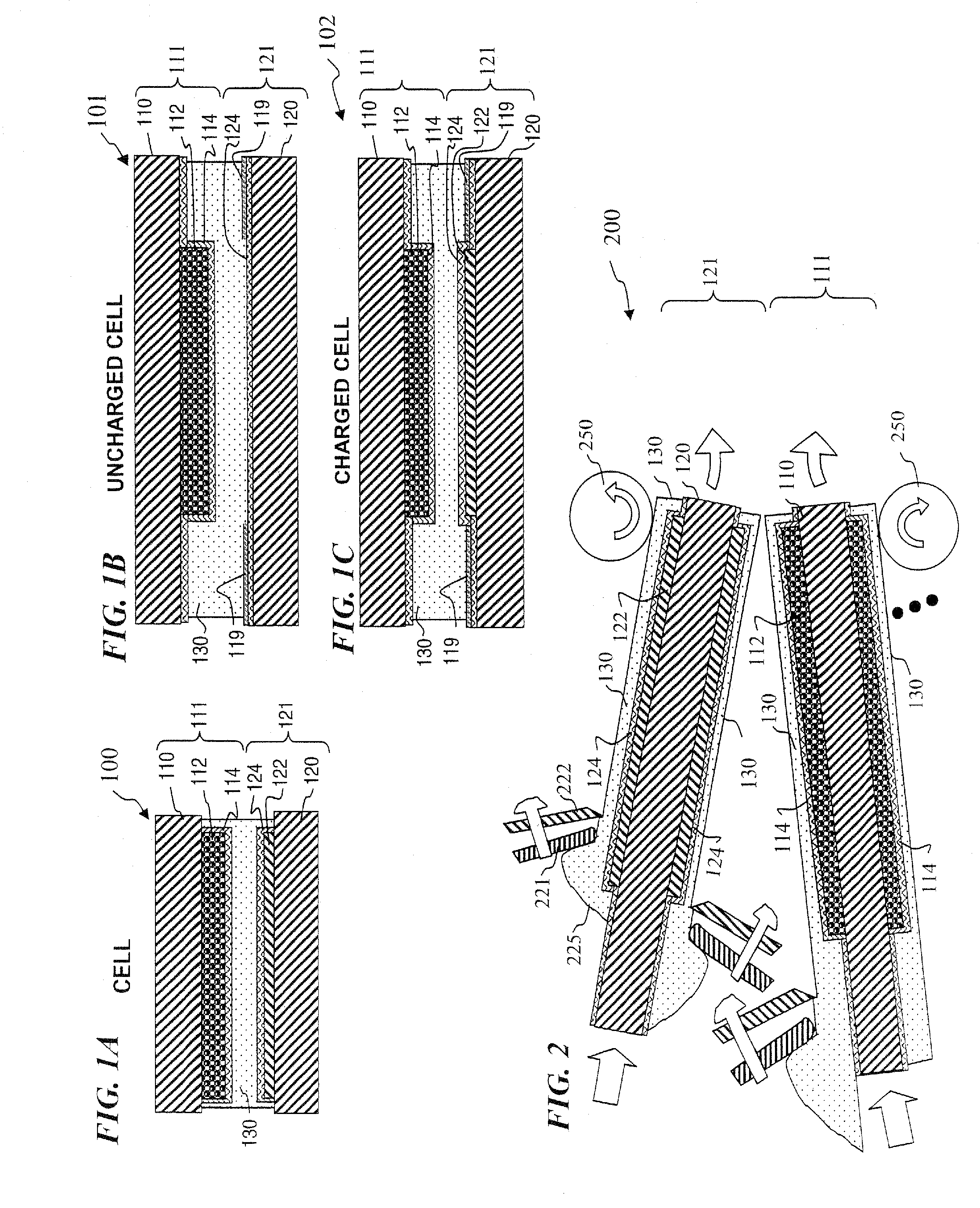
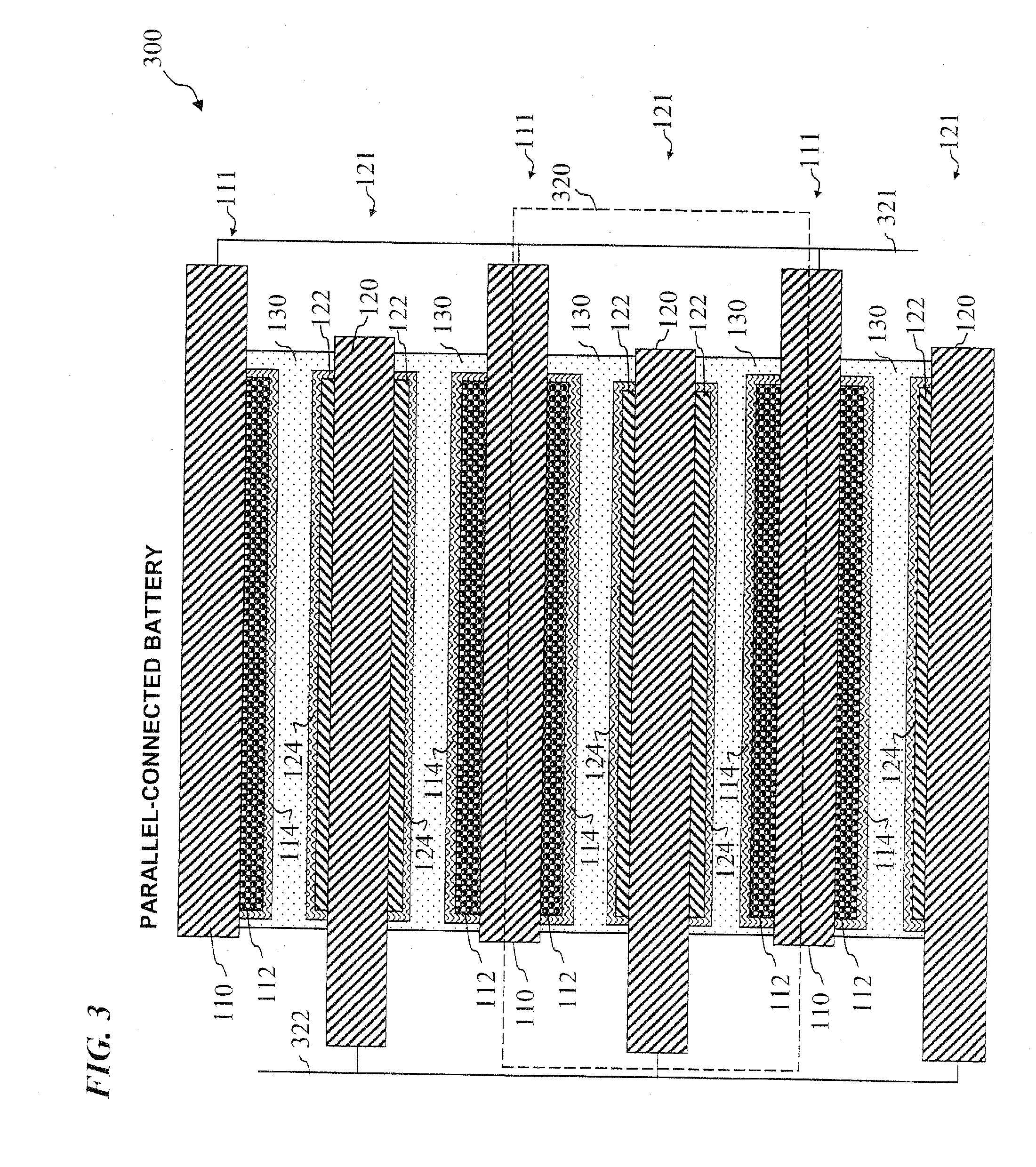
Nano graphene reinforced nanocomposite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100143798A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthActive material electrodesSecondary cellsLithium metalNanocomposite
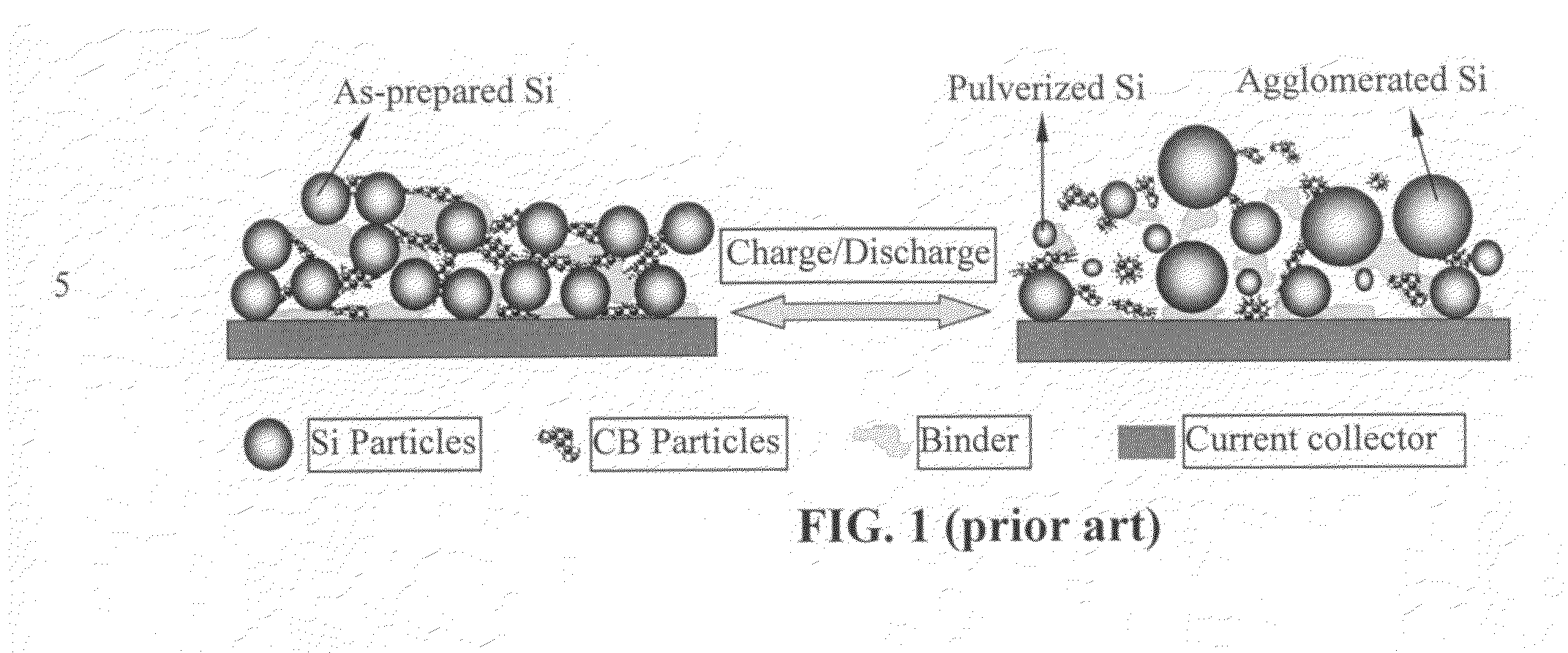
A solid nanocomposite particle composition for lithium metal or lithium ion battery electrode applications. The composition comprises: (A) an electrode active material in a form of fine particles, rods, wires, fibers, or tubes with a dimension smaller than 1 μm; (B) nano graphene platelets (NGPs); and (C) a protective matrix material reinforced by the NGPs; wherein the graphene platelets and the electrode active material are dispersed in the matrix material and the NGPs occupy a weight fraction wg of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, the electrode active material occupies a weight fraction wa of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, and the matrix material occupies a weight fraction wm of at least 2% of the total nanocomposite weight with wg+wa+wm=1. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon, polymeric carbon, or meso-phase carbon. Such a solid nanocomposite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling stability. For a cathode application, the resulting lithium metal or lithium ion battery exhibits an exceptionally high cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lithium anodes for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS7247408B2Light weightFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalReactive gas
Provided is an anode for use in electrochemical cells, wherein the anode active layer has a first layer comprising lithium metal and a multi-layer structure comprising single ion conducting layers and polymer layers in contact with the first layer comprising lithium metal or in contact with an intermediate protective layer, such as a temporary protective metal layer, on the surface of the lithium-containing first layer. Another aspect of the invention provides an anode active layer formed by the in-situ deposition of lithium vapor and a reactive gas. The anodes of the current invention are particularly useful in electrochemical cells comprising sulfur-containing cathode active materials, such as elemental sulfur.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100176337A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsFiberLithium metal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and reagents for enhancing the cycling efficiency of lithium polymer batteries
InactiveUS6017651AImprove efficiencyElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrochemical processing of electrodesLithium metalSulfur electrode
Batteries including a lithium electrode and a sulfur counter electrode that demonstrate improved cycling efficiencies are described. In one embodiment, an electrochemical cell having a lithium electrode and a sulfur electrode including at least one of elemental sulfur, lithium sulfide, and a lithium polysulfide is provided. The lithium electrode includes a surface coating that is effective to increase the cycling efficiency of said electrochemical cell. In a more particular embodiment, the lithium electrode is in an electrolyte solution, and, more particularly, an electrolyte solution including either elemental sulfur, a sulfide, or a polysulfide. In another embodiment, the coating is formed after the lithium electrode is contacted with the electrolyte. In a more particular embodiment, the coating is formed by a reaction between the lithium metal of the lithium electrode and a chemical species present in the electrolyte.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS7135252B2Improve structural stabilityImprove stabilityZirconium compoundsSecondary cellsLithium metalOxidation state
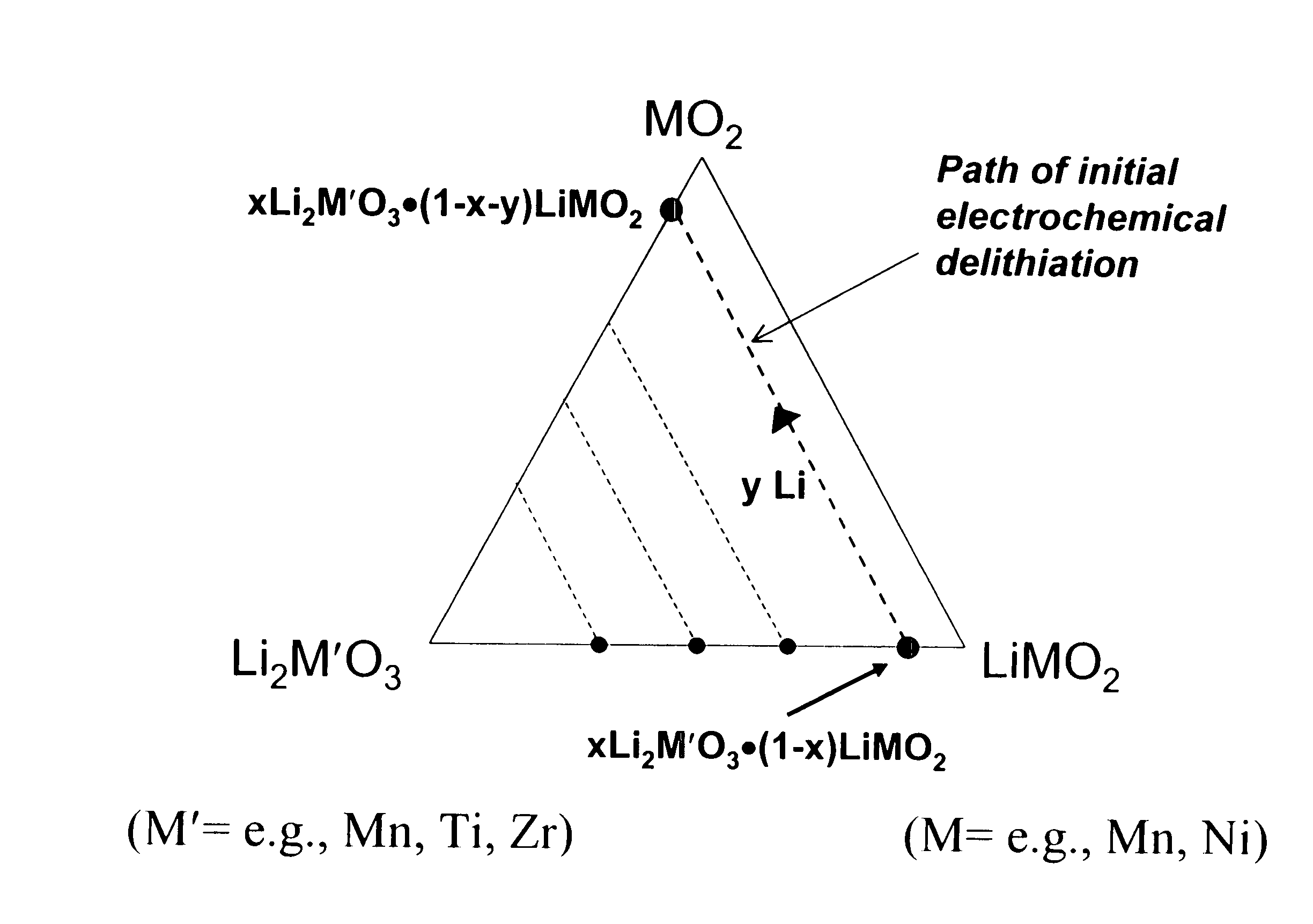
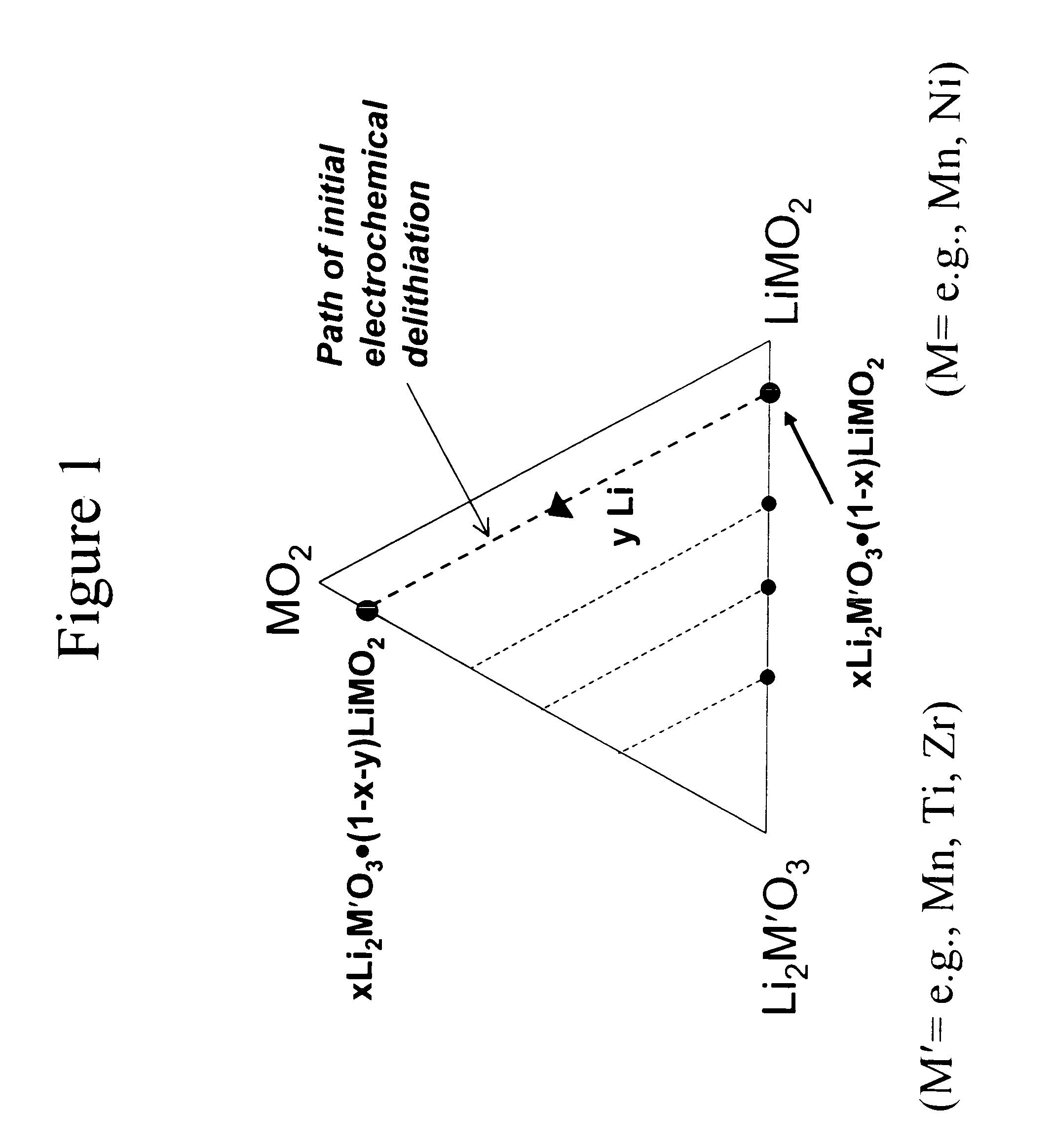
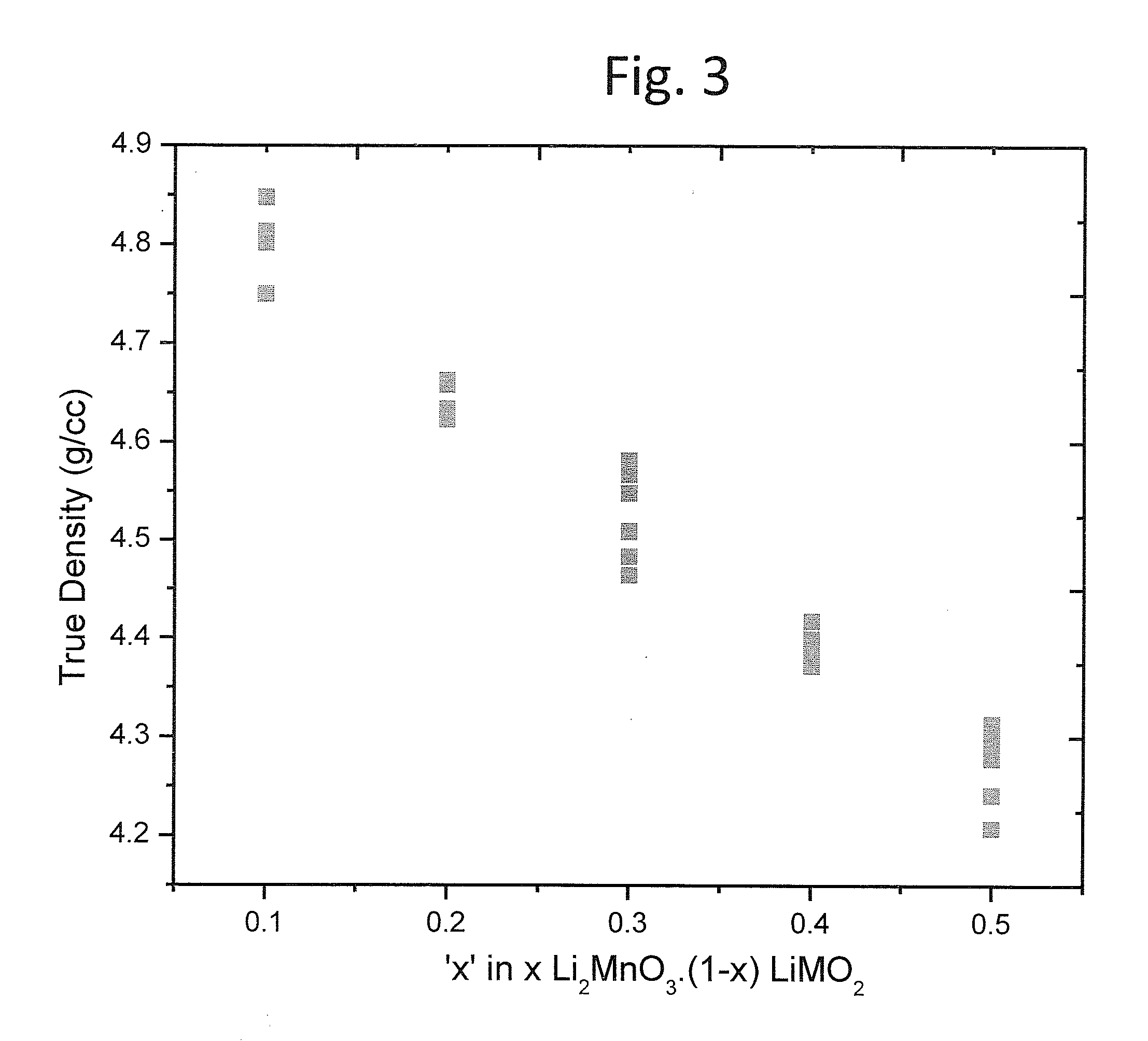
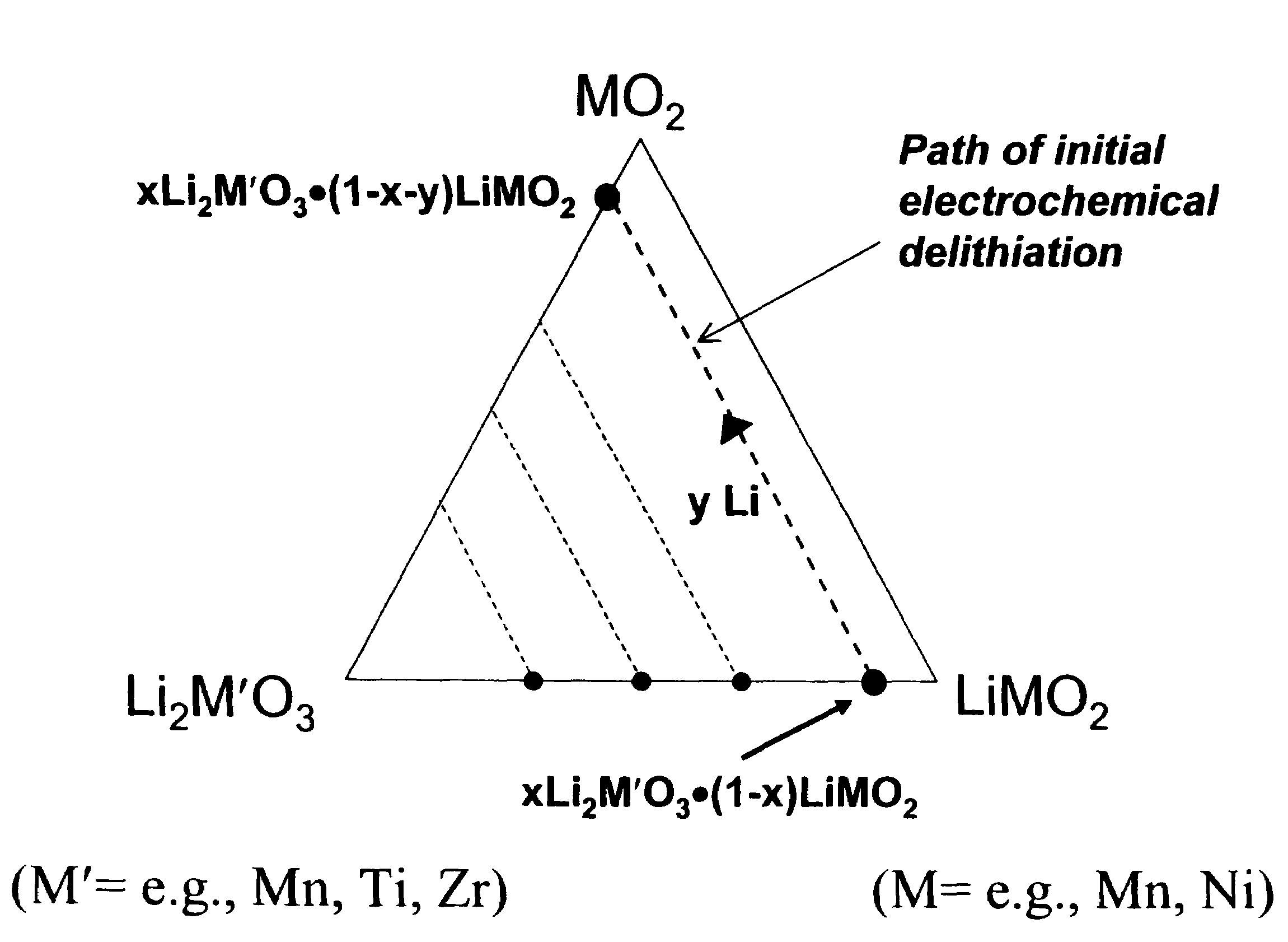
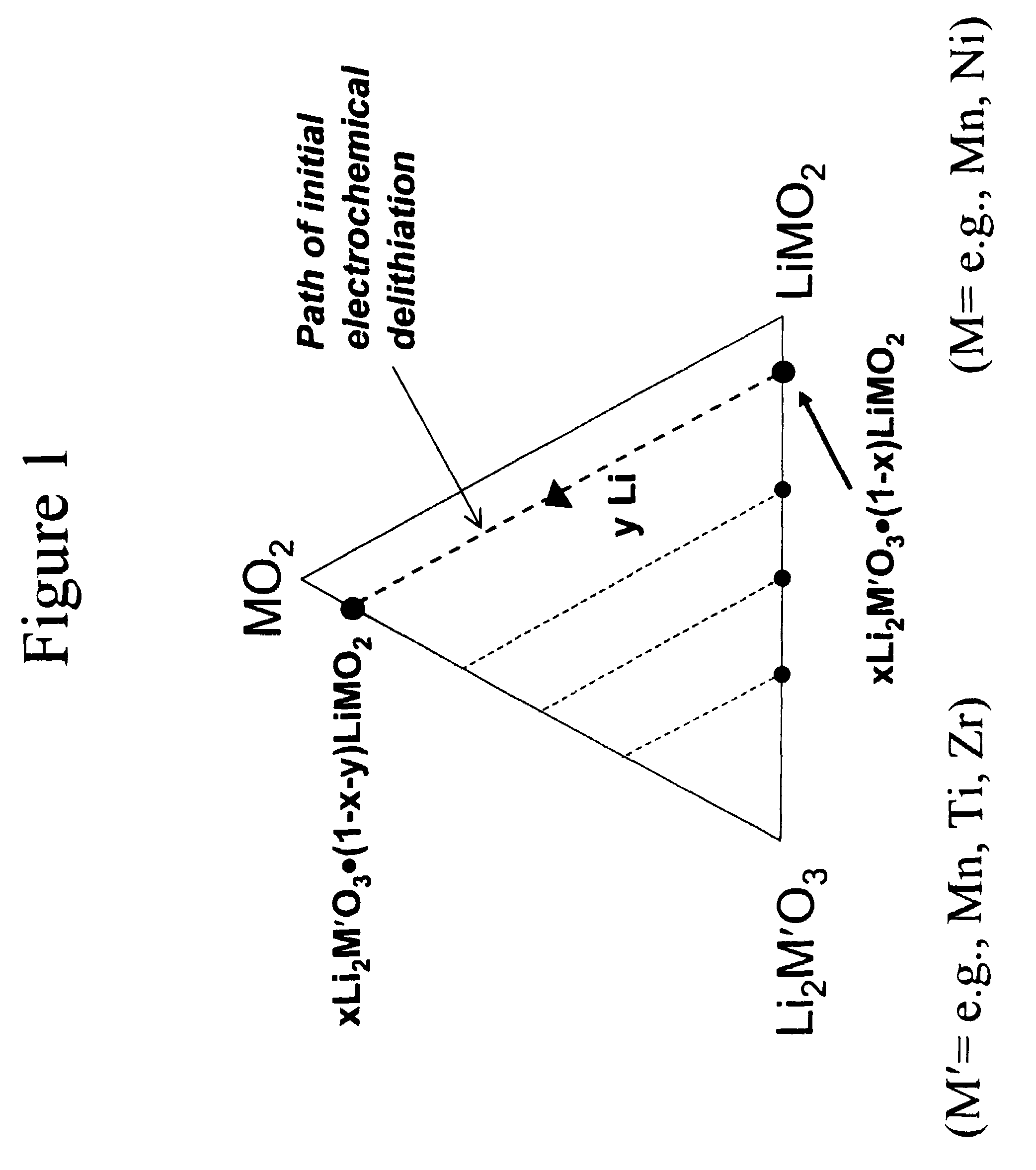
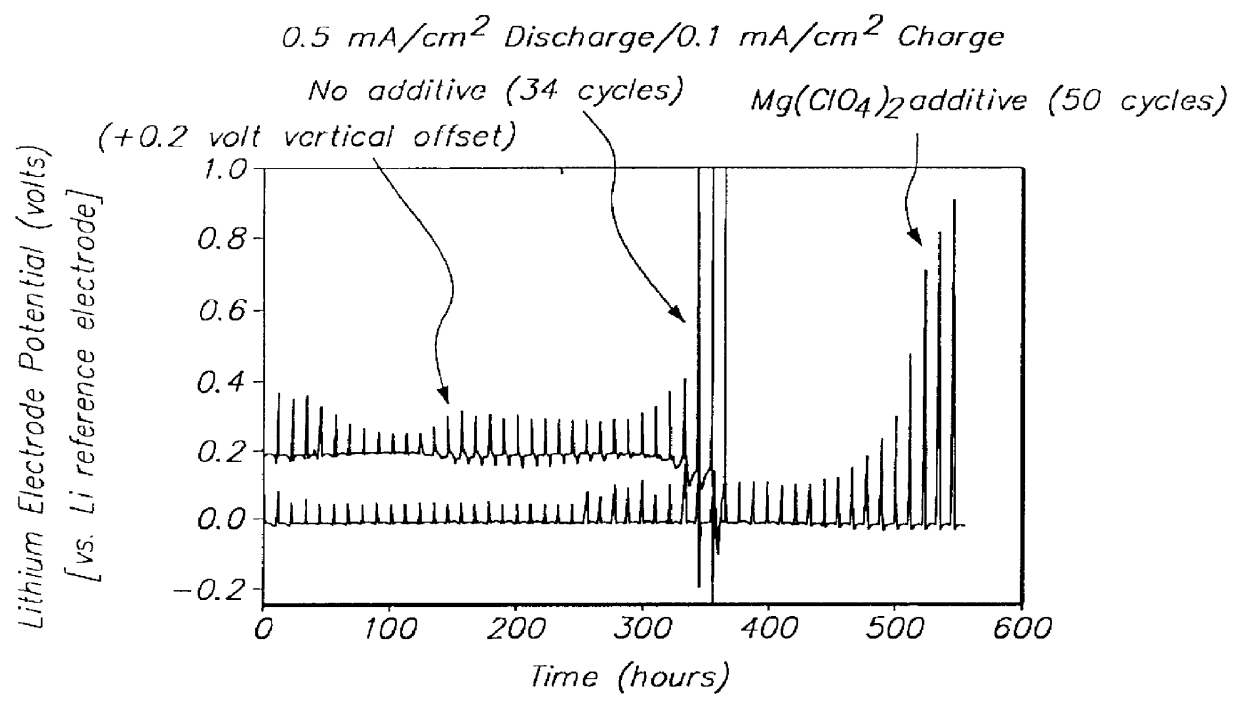
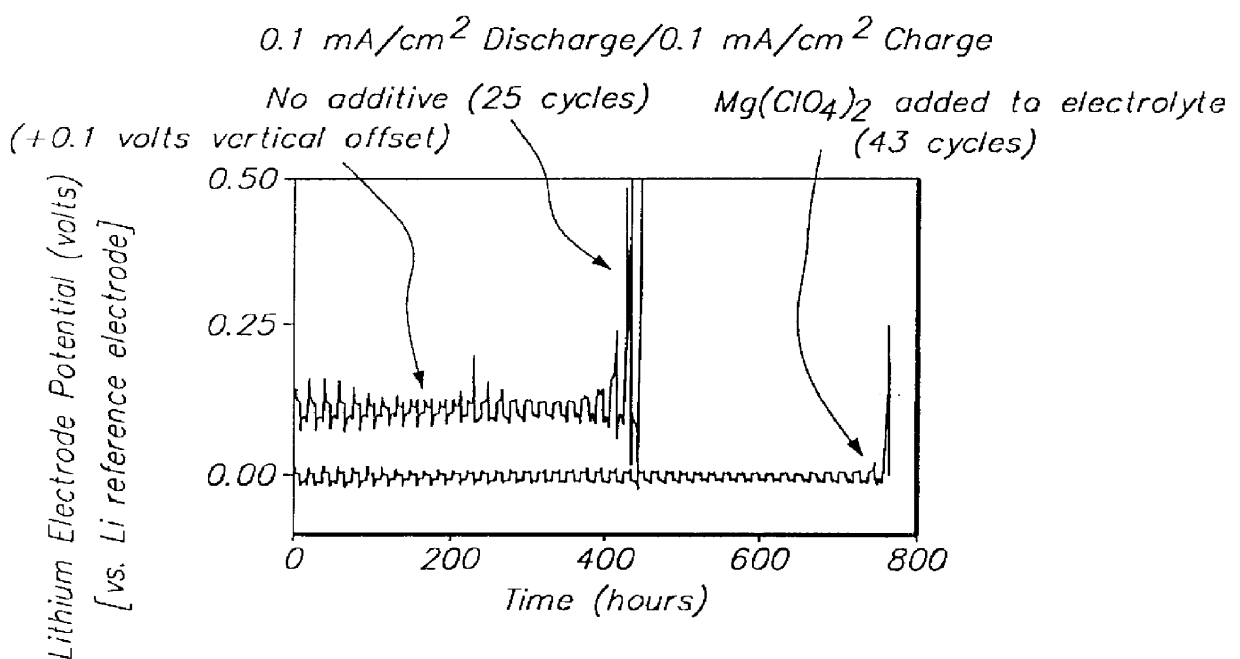
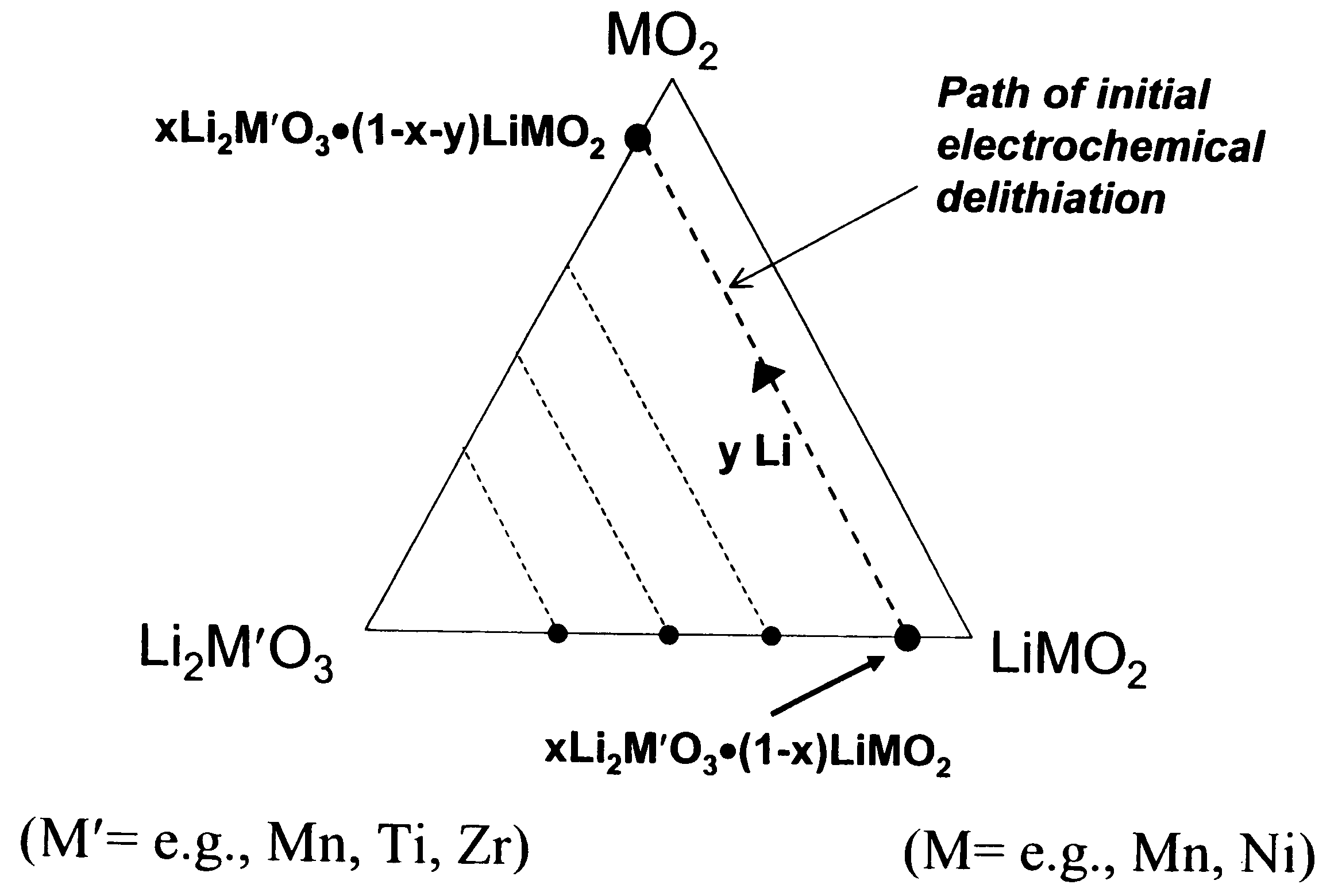
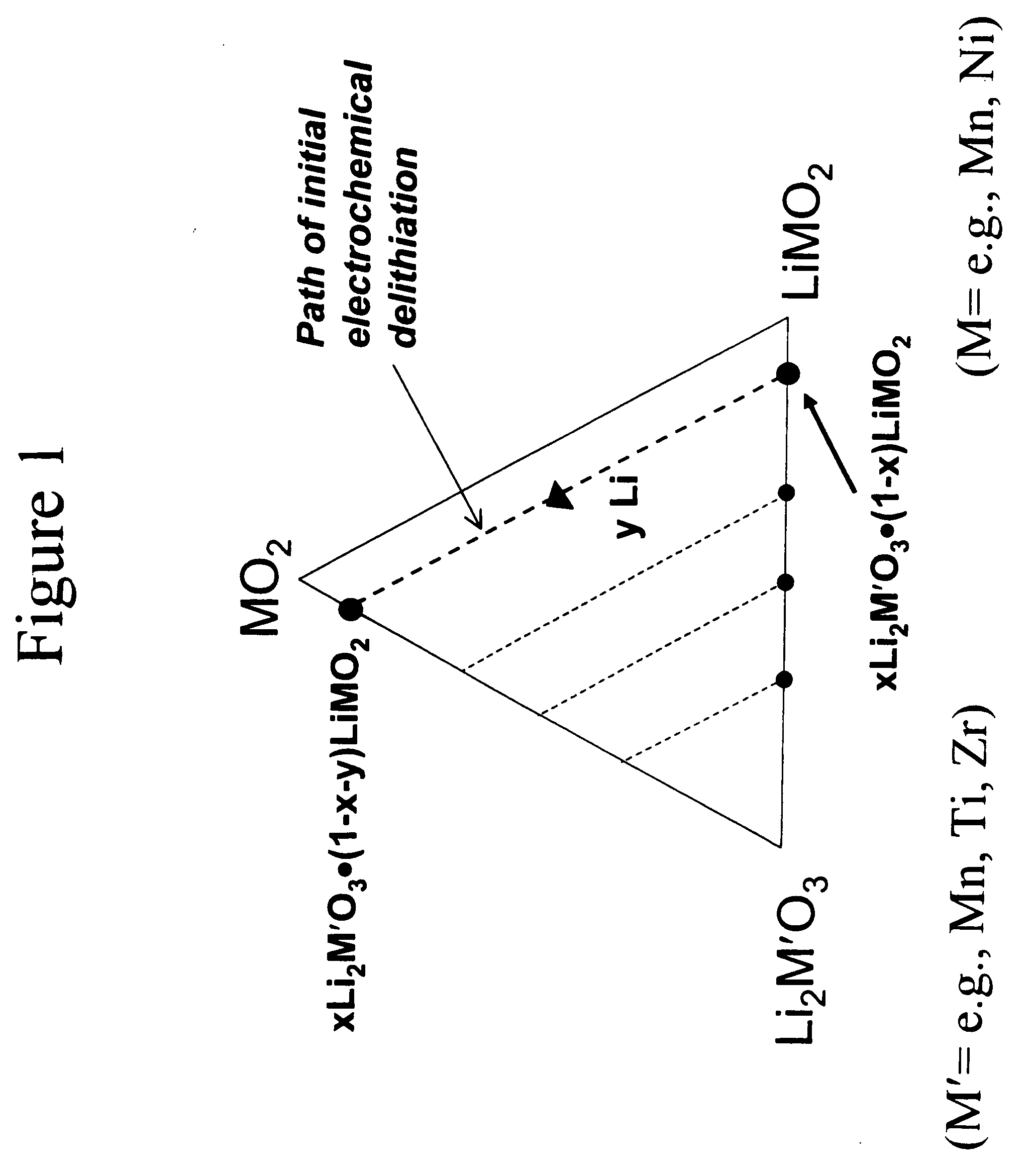
A lithium metal oxide positive electrode for a non-aqueous lithium cell is disclosed. The cell is prepared in its initial discharged state and has a general formula xLiMO2.(1-x)Li2M′O3 in which 0<x<1, and where M is more than one ion with an average trivalent oxidation state and with at least one ion being Ni, and where M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state. Complete cells or batteries are disclosed with anode, cathode and electrolyte as are batteries of several cells connected in parallel or series or both.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE +1
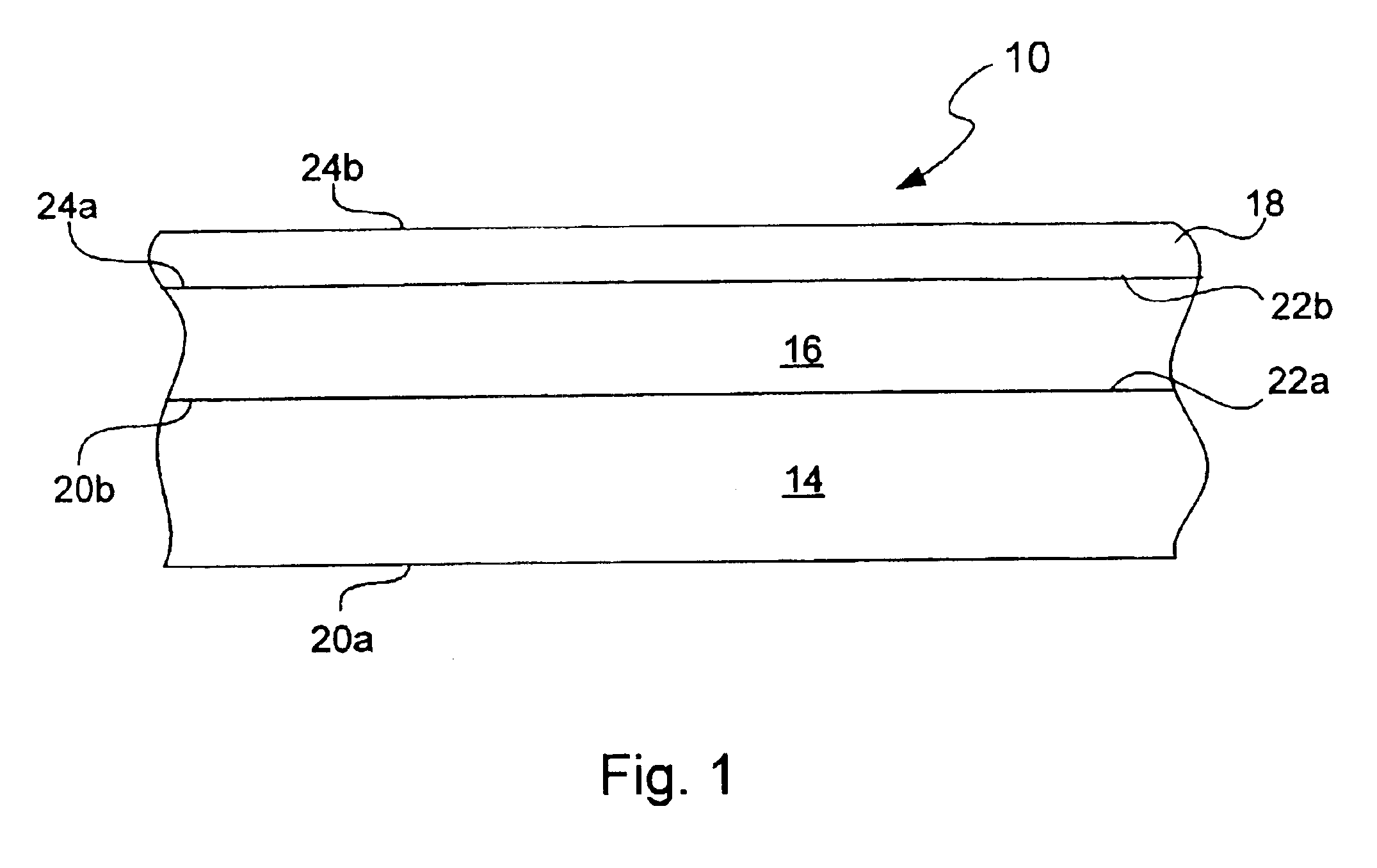
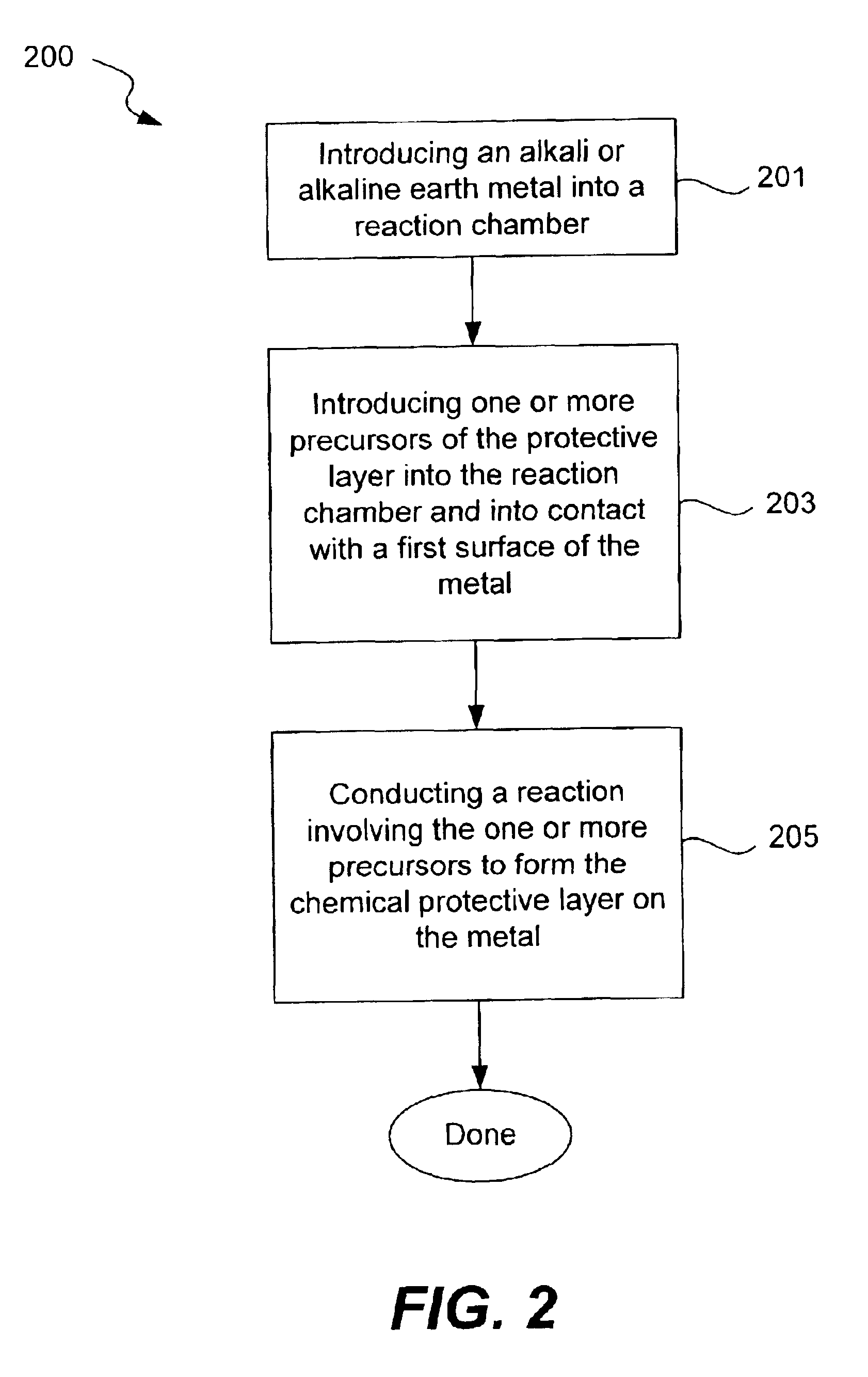
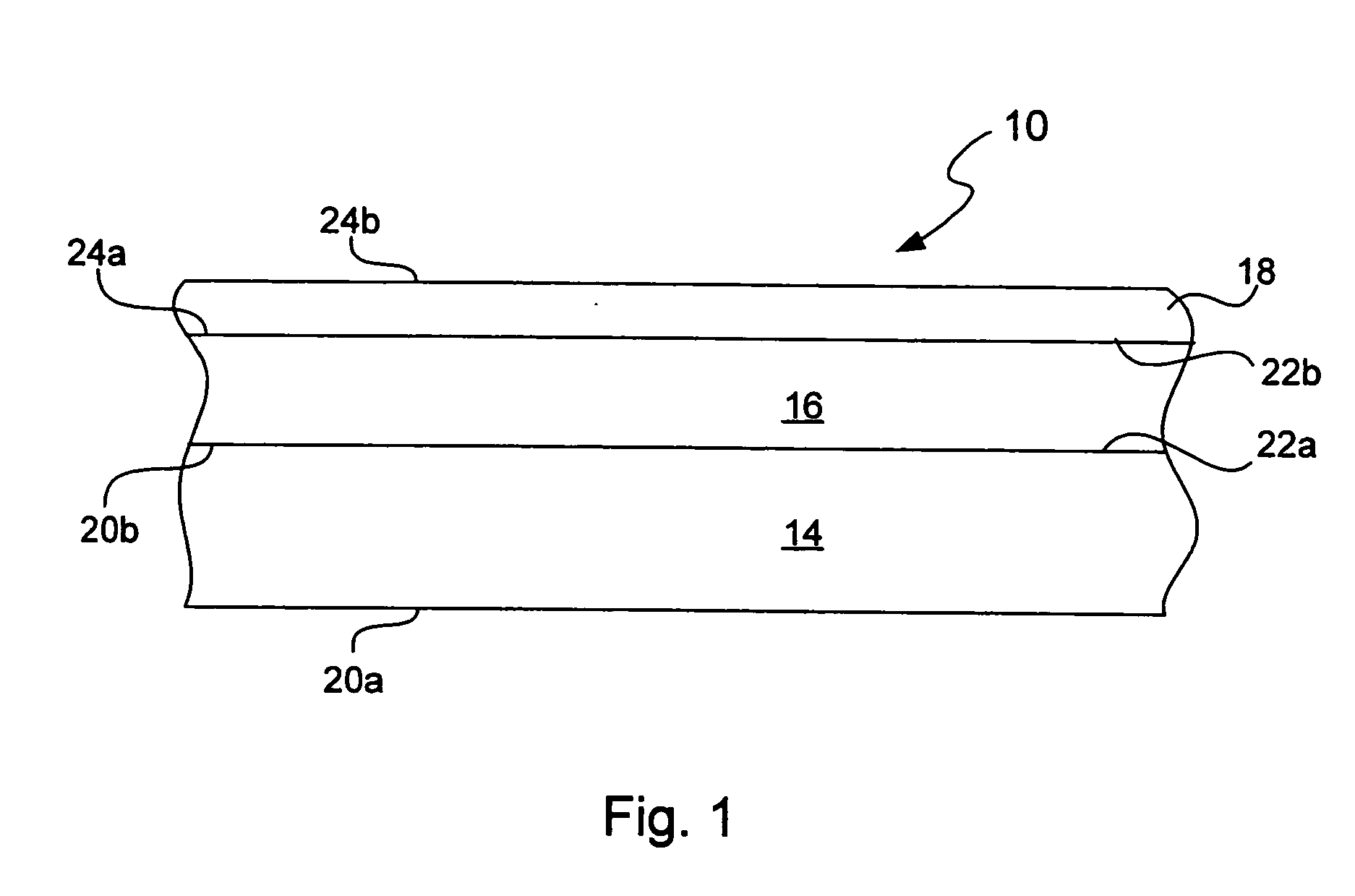
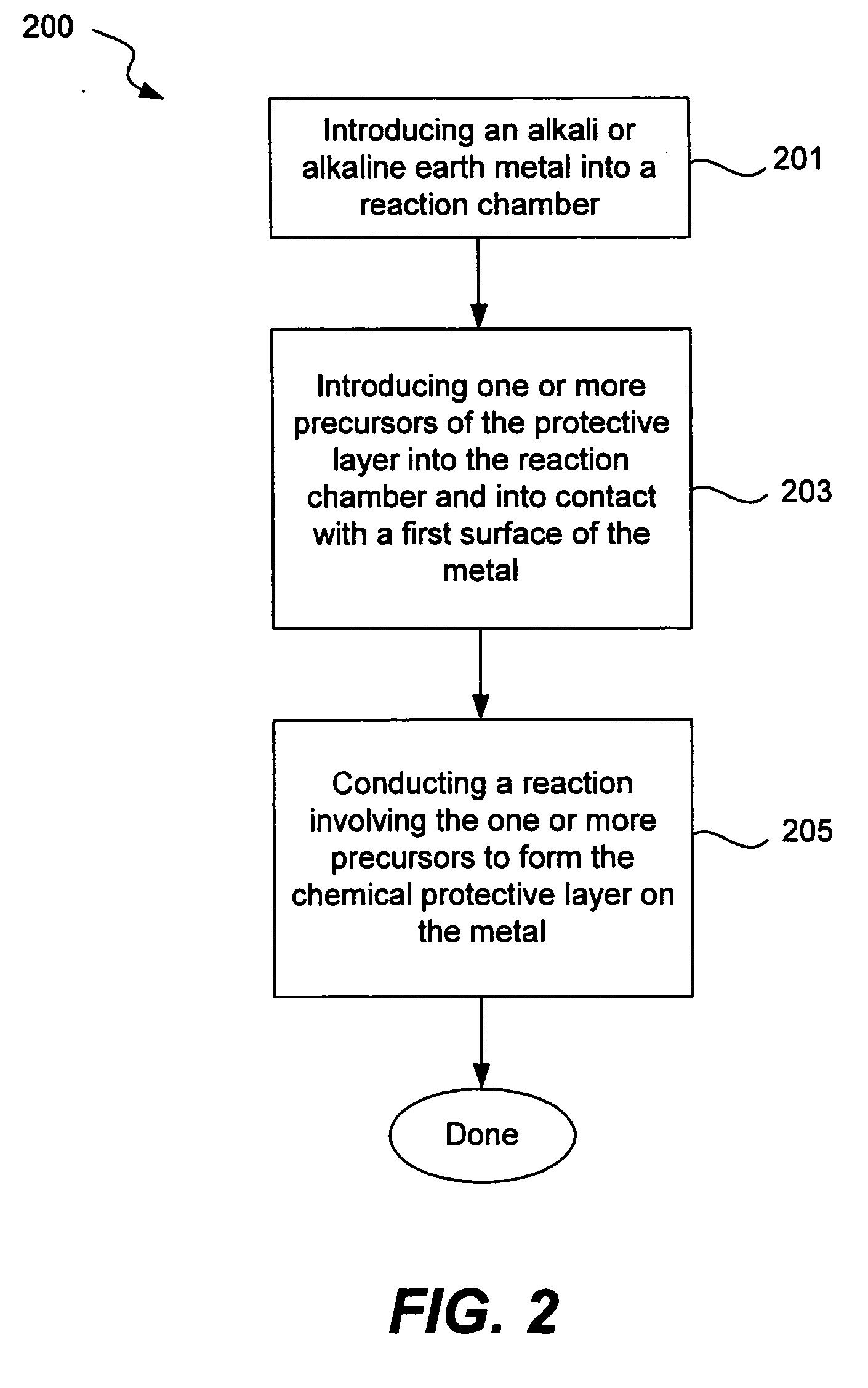
Chemical protection of a lithium surface
InactiveUS6911280B1Easy to produceSimple processElectrochemical processing of electrodesFinal product manufactureAlkaline earth metalLithium metal
Disclosed are compositions and methods for alleviating the problem of reaction of lithium or other alkali or alkaline earth metals with incompatible processing and operating environments by creating a ionically conductive chemical protective layer on the lithium or other reactive metal surface. Such a chemically produced surface layer can protect lithium metal from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen or moisture in ambient atmosphere thereby allowing the lithium material to be handled outside of a controlled atmosphere, such as a dry room. Production processes involving lithium are thereby very considerably simplified. One example of such a process in the processing of lithium to form negative electrodes for lithium metal batteries.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Negative electrode for lithium metal battery and lithium metal battery comprising the same
InactiveUS20050095504A1Improving life-cycle characteristicInhibit side effectsFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesCross-linkMetallic lithium
The present invention relates to a negative electrode for a lithium metal battery and a lithium metal battery comprising the same. The negative electrode of the present invention comprises a negative active material layer of metallic lithium or a lithium alloy, and a passivation layer formed on the negative active material layer. The passivation layer has a structure comprising a 3-dimensionally cross-linked polymer network matrix penetrated by linear polymers. The passivation layer formed on the surface of the negative electrode reduces reactivity of the negative electrode and stabilizes the surface, so that it offers a lithium metal battery having superior life cycle characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Lithium metal dispersion in electrodes
InactiveUS20050130043A1High specific capacityPromote circulationElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrode thermal treatmentLithium metalHost material
Electrodes, such as anodes and cathodes, can include a host material that is prelithiated or undergoes lithiation upon electrolyte introduction into a battery. Lithiation of the host material can occur by the agitation of lithium metal and a host material, the agitation of a lithium metal powder and a host material at a temperature greater than room temperature, the application of pressure to a lithium metal and host material mixture, contact of the host material with molten lithium metal, the lamination of lithium foil or lithium mesh onto an electrode containing the host material, or by lamination of lithium metal or mesh onto an electrode at elevated temperatures.
Owner:AEA TECH BATTERY SYST +1
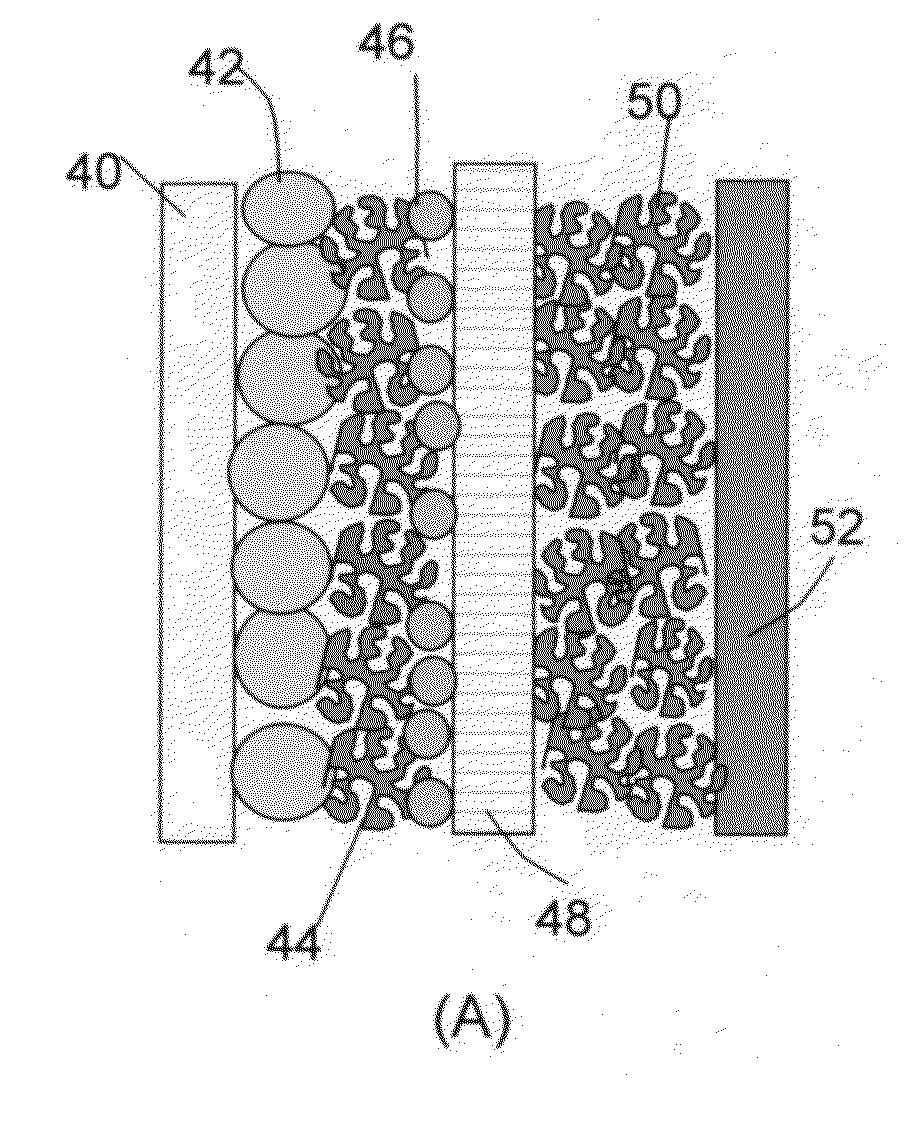
Hybrid electrode and surface-mediated cell-based super-hybrid energy storage device containing same
PendingUS20130171502A1Primary cell to battery groupingMaterial nanotechnologyHigh energyLithium metal
The present invention provides a multi-component hybrid electrode for use in an electrochemical super-hybrid energy storage device. The hybrid electrode contains at least a current collector, at least an intercalation electrode active material storing lithium inside interior or bulk thereof, and at least an intercalation-free electrode active material having a specific surface area no less than 100 m2 / g and storing lithium on a surface thereof, wherein the intercalation electrode active material and the intercalation-free electrode active material are in electronic contact with the current collector. The resulting super-hybrid cell exhibits exceptional high power and high energy density, and long-term cycling stability that cannot be achieved with conventional supercapacitors, lithium-ion capacitors, lithium-ion batteries, and lithium metal secondary batteries.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
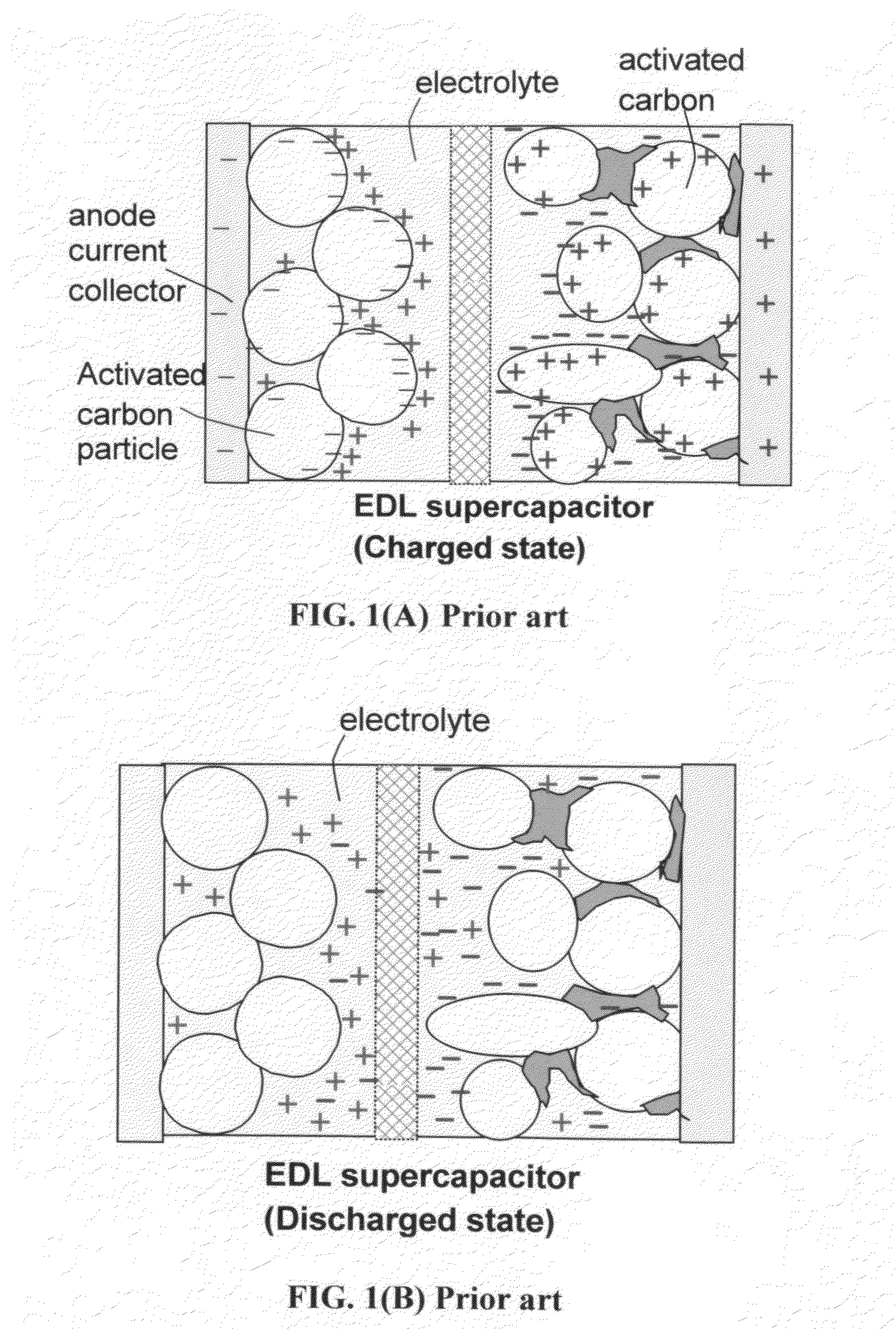
Lithium metal-sulfur and lithium ion-sulfur secondary batteries containing a nano-structured cathode and processes for producing same
ActiveUS20110165466A1High specific capacityImprove the immunityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrochemical processing of electrodesSpecific energyLithium metal
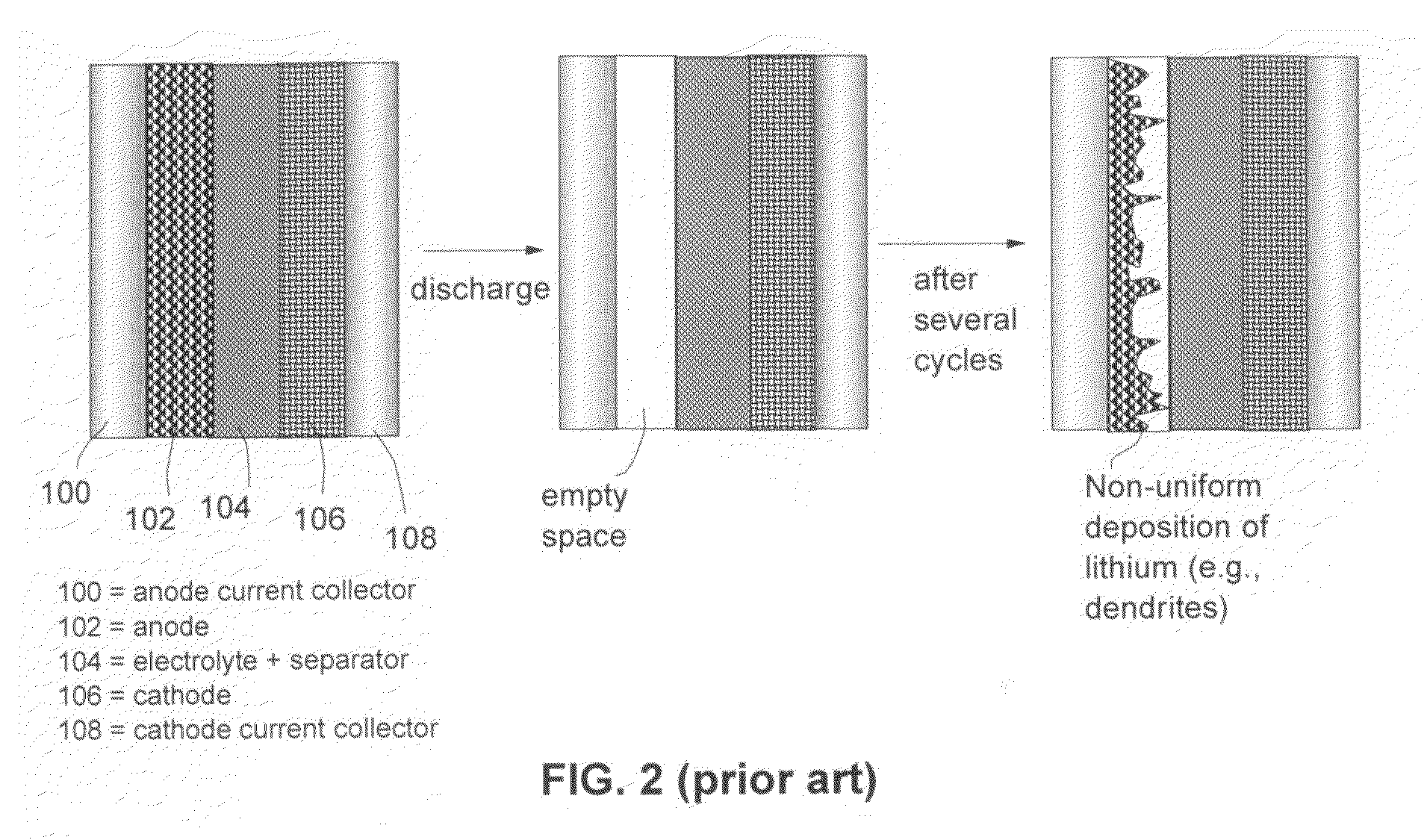
An electrochemical cell comprising an anode, electrolyte or an electrolyte / separator combination, and a nano-structured cathode, wherein the cathode comprises: (a) an integrated nano-structure of electrically conductive nanometer-scaled filaments that are interconnected to form a porous network of electron-conducting paths comprising pores with a size smaller than 100 nm (preferably smaller than 10 nm), wherein the filaments have a transverse dimension less than 500 nm (preferably less than 100 nm); and (b) powder or salt of lithium-containing sulfide (lithium polysulfide) disposed in the pores, or a thin coating of lithium-containing sulfide deposited on a nano-scaled filament surface wherein the lithium-containing sulfide is in contact with, dispersed in, or dissolved in electrolyte liquid and the lithium-containing sulfide-to-filament weight ratio is between 1 / 10 and 10 / 1 which is measured when the cell is in a fully discharged state. The cell exhibits an exceptionally high specific energy and a long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Lithium alloy/sulfur batteries
Electrochemical cells including anode compositions that may enhance charge-discharge cycling efficiency and uniformity are presented. In some embodiments, alloys are incorporated into one or more components of an electrochemical cell, which may enhance the performance of the cell. For example, an alloy may be incorporated into an electroactive component of the cell (e.g., electrodes) and may advantageously increase the efficiency of cell performance. Some electrochemical cells (e.g., rechargeable batteries) may undergo a charge / discharge cycle involving deposition of metal (e.g., lithium metal) on the surface of the anode upon charging and reaction of the metal on the anode surface, wherein the metal diffuses from the anode surface, upon discharging. In some cases, the efficiency and uniformity of such processes may affect cell performance. The use of materials such as alloys in an electroactive component of the cell have been found to increase the efficiency of such processes and to increase the cycling lifetime of the cell. For example, the use of alloys may reduce the formation of dendrites on the anode surface and / or limit surface development.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte and production process thereof
InactiveUS20070231704A1Increase battery capacitySimple and convenient manufactureSecondary cellsSolid electrolyte cellsPorosityLithium metal
A lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte formed by sintering a molding product containing an inorganic powder and having a porosity of 10 vol % or less, which is obtained by preparing a molding product comprising an inorganic powder as a main ingredient and sintering the molding product after pressing and / or sintering the same while pressing, the lithium ion conductive solid electrolyte providing a solid electrolyte having high battery capacity without using a liquid electrolyte, usable stably for a long time and simple and convenient in manufacture and handling also in industrial manufacture in the application use of secondary lithium ion battery or primary lithium battery, a solid electrolyte having good charge / discharge cyclic characteristic in the application use of the secondary lithium ion battery a solid electrolyte with less water permeation and being safe when used for lithium metal-air battery in the application use of primary lithium battery, a manufacturing method of the solid electrolyte, and a secondary lithium ion battery and a primary lithium battery using the solid electrolyte.
Owner:OHARA
Application of force in electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20100035128A1Improve performancePrimary cell to battery groupingCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersRough surfaceChemical reaction
The present invention relates to the application of a force to enhance the performance of an electrochemical cell. The force may comprise, in some instances, an anisotropic force with a component normal to an active surface of the anode of the electrochemical cell. In the embodiments described herein, electrochemical cells (e.g., rechargeable batteries) may undergo a charge / discharge cycle involving deposition of metal (e.g., lithium metal) on a surface of the anode upon charging and reaction of the metal on the anode surface, wherein the metal diffuses from the anode surface, upon discharging. The uniformity with which the metal is deposited on the anode may affect cell performance. For example, when lithium metal is redeposited on an anode, it may, in some cases, deposit unevenly forming a rough surface. The roughened surface may increase the amount of lithium metal available for undesired chemical reactions which may result in decreased cycling lifetime and / or poor cell performance. The application of force to the electrochemical cell has been found, in accordance with the invention, to reduce such behavior and to improve the cycling lifetime and / or performance of the cell.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Coated positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20110111298A1Secondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium metalInorganic composition
High specific capacity lithium rich lithium metal oxide materials are coated with inorganic compositions, such as metal fluorides, to improve the performance of the materials as a positive electrode active material. The resulting coated material can exhibit an increased specific capacity, and the material can also exhibit improved cycling. The materials can be formed while maintaining a desired relatively high average voltage such that the materials are suitable for the formation of commercial batteries. Suitable processes are described for the synthesis of the desired coated compositions that can be adapted for commercial production.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
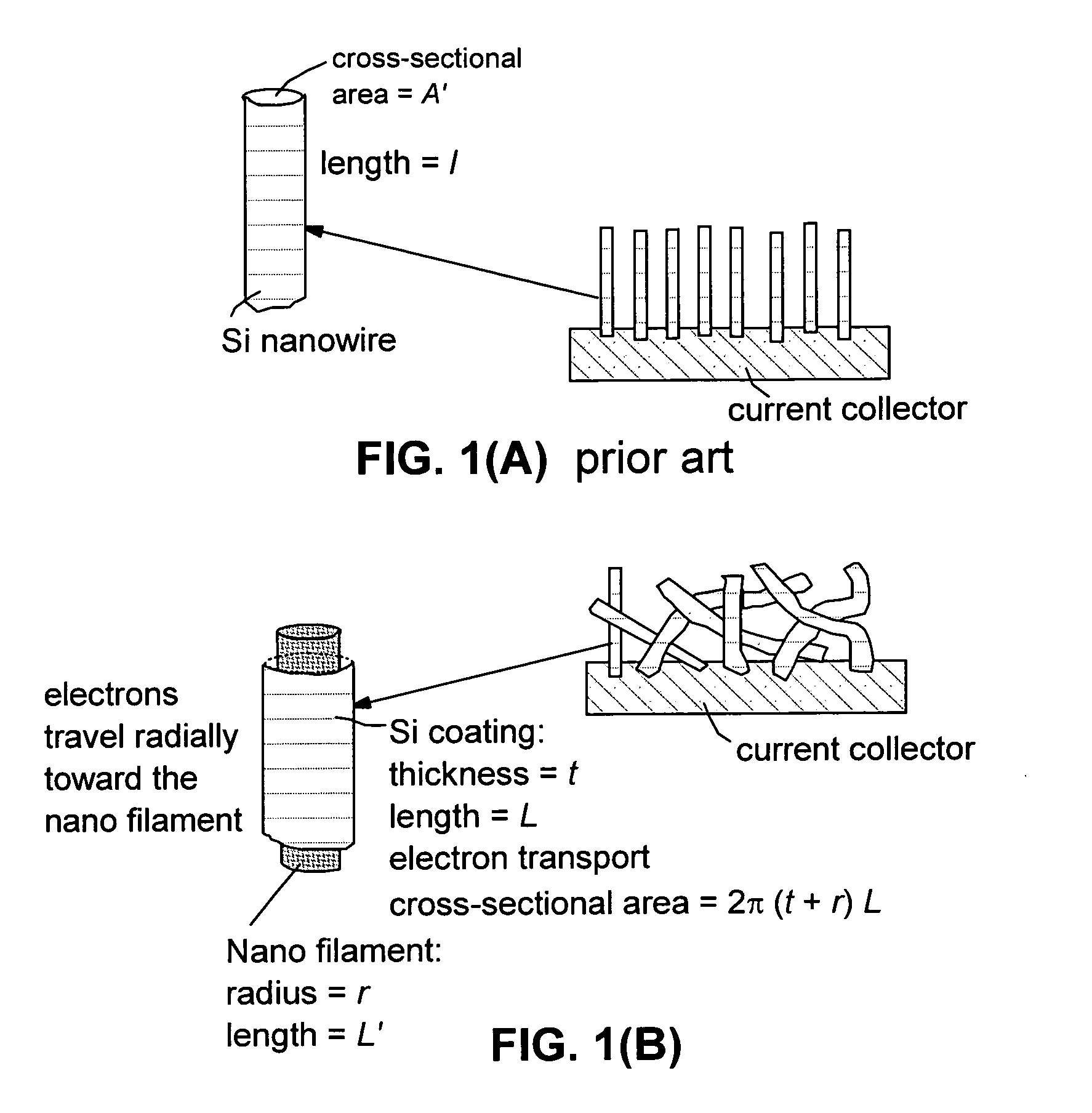
Nano-structured anode compositions for lithium metal and lithium metal-air secondary batteries
ActiveUS20110104571A1High specific capacityHigh reversible capacityFuel and primary cellsConductive materialLithium metalAlloy
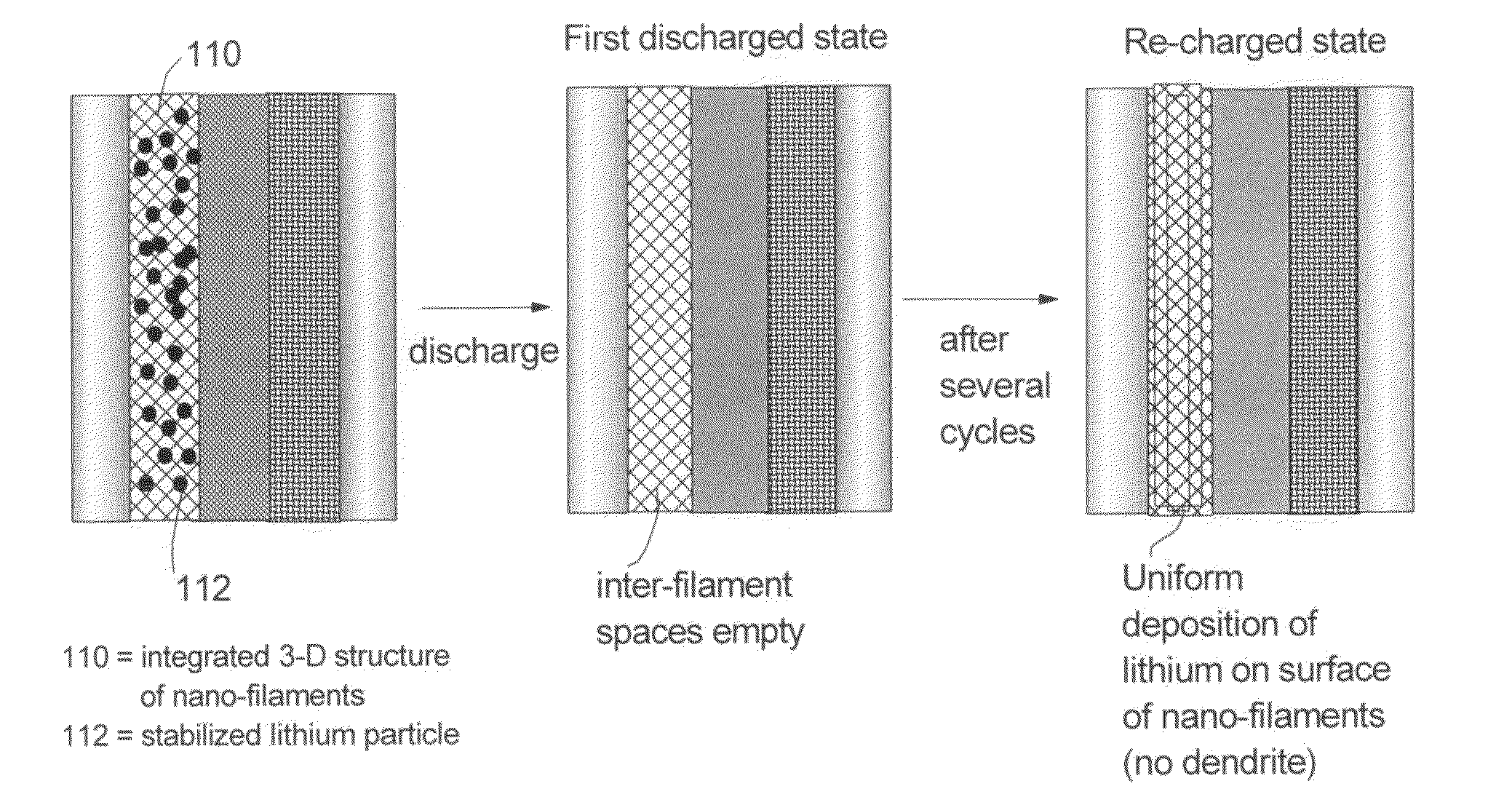
This invention provides a nano-structured anode composition for a lithium metal cell. The composition comprises: (a) an integrated structure of electrically conductive nanometer-scaled filaments that are interconnected to form a porous network of electron-conducting paths comprising interconnected pores, wherein the nano-filaments have a transverse dimension less than 500 nm; and (b) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles of lithium, a lithium alloy, or a lithium-containing compound wherein at least one of the particles is surface-passivated or stabilized and the weight fraction of these particles is between 1% and 99% based on the total weight of these particles and the integrated structure together. Also provided is a lithium metal cell or battery, or lithium-air cell or battery, comprising such an anode. The battery exhibits an exceptionally high specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Chemical protection of a lithium surface
InactiveUS20050186469A1Easy to produceEasy to processElectrochemical processing of electrodesFinal product manufactureAlkaline earth metalLithium metal
Disclosed are compositions and methods for alleviating the problem of reaction of lithium or other alkali or alkaline earth metals with incompatible processing and operating environments by creating a ionically conductive chemical protective layer on the lithium or other reactive metal surface. Such a chemically produced surface layer can protect lithium metal from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen or moisture in ambient atmosphere thereby allowing the lithium material to be handled outside of a controlled atmosphere, such as a dry room. Production processes involving lithium are thereby very considerably simplified. One example of such a process is the processing of lithium to form negative electrodes for lithium metal batteries.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Lithium anodes for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20060222954A1Light weightFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalReactive gas
Provided is an anode for use in electrochemical cells, wherein the anode active layer has a first layer comprising lithium metal and a multi-layer structure comprising single ion conducting layers and polymer layers in contact with the first layer comprising lithium metal or in contact with an intermediate protective layer, such as a temporary protective metal layer, on the surface of the lithium-containing first layer. Another aspect of the invention provides an anode active layer formed by the in-situ deposition of lithium vapor and a reactive gas. The anodes of the current invention are particularly useful in electrochemical cells comprising sulfur-containing cathode active materials, such as elemental sulfur.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Prelithiated current collector and secondary lithium cells containing same
ActiveUS20130045427A1Reduce capacityMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitorsLithium metalLithium sulfur
The present invention provides a battery or supercapacitor current collector which is prelithiated. The prelithiated current collector comprises: (a) an electrically conductive substrate having two opposed primary surfaces, and (b) a mixture layer of carbon (and / or other stabilizing element, such as B, Al, Ga, In, C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, Sb, Bi, Te, or a combination thereof) and lithium or lithium alloy coated on at least one of the primary surfaces, wherein lithium element is present in an amount of 1% to 99% by weight of the mixture layer. This current collector serves as an effective and safe lithium source for a wide variety of electrochemical energy storage cells, including the rechargeable lithium cell (e.g. lithium-metal, lithium-ion, lithium-sulfur, lithium-air, lithium-graphene, lithium-carbon, and lithium-carbon nanotube cell) and the lithium ion based supercapacitor cell (e.g, symmetric ultracapacitor, asymmetric ultracapacitor, hybrid supercapacitor-battery, or lithium-ion capacitor).
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Lithium iron phosphate cathode materials with enhanced energy density and power performance
InactiveUS20090155689A1Powerful performanceHigh discharge ratePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesFiberPhosphate
The invention is related to a cathode material comprising particles having a lithium metal phosphate core and a pyrolytic carbon deposit, said particles having a synthetic multimodal particle size distribution comprising at least one fraction of micron size particles and one fraction of submicron size particles, said lithium metal phosphate having formula LiMPO4 wherein M is at least Fe or Mn.Said material is prepared by method comprising the steps of providing starting micron sized particles and starting submicron sized particles of at least one lithium metal phosphate or of precursors of a lithium metal phosphate; mixing by mechanical means said starting particles; making a pyrolytic carbon deposit on the lithium metal phosphate starting particles before or after the mixing step, and on their metal precursor before or after mixing the particles; optionally adding carbon black, graphite powder or fibers to the said lithium metal phosphate particles before the mechanical mixing.
Owner:PHOSTECH LITHIUM
Layer-layer lithium rich complex metal oxides with high specific capacity and excellent cycling
Lithium rich and manganese rich lithium metal oxides are described that provide for excellent performance in lithium-based batteries. The specific compositions can be engineered within a specified range of compositions to provide desired performance characteristics. Selected compositions can provide high values of specific capacity with a reasonably high average voltage. Compositions of particular interest can be represented by the formula, xLi2MnO3.(1−x)LiNiu+ΔMnu−ΔCowAyO2. The compositions undergo significant first cycle irreversible changes, but the compositions cycle stably after the first cycle.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Lithium anodes for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS6936381B2Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalCrosslinked polymers
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS7468223B2Improve electronic conductivityLess costlyLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium metalOxidation state
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
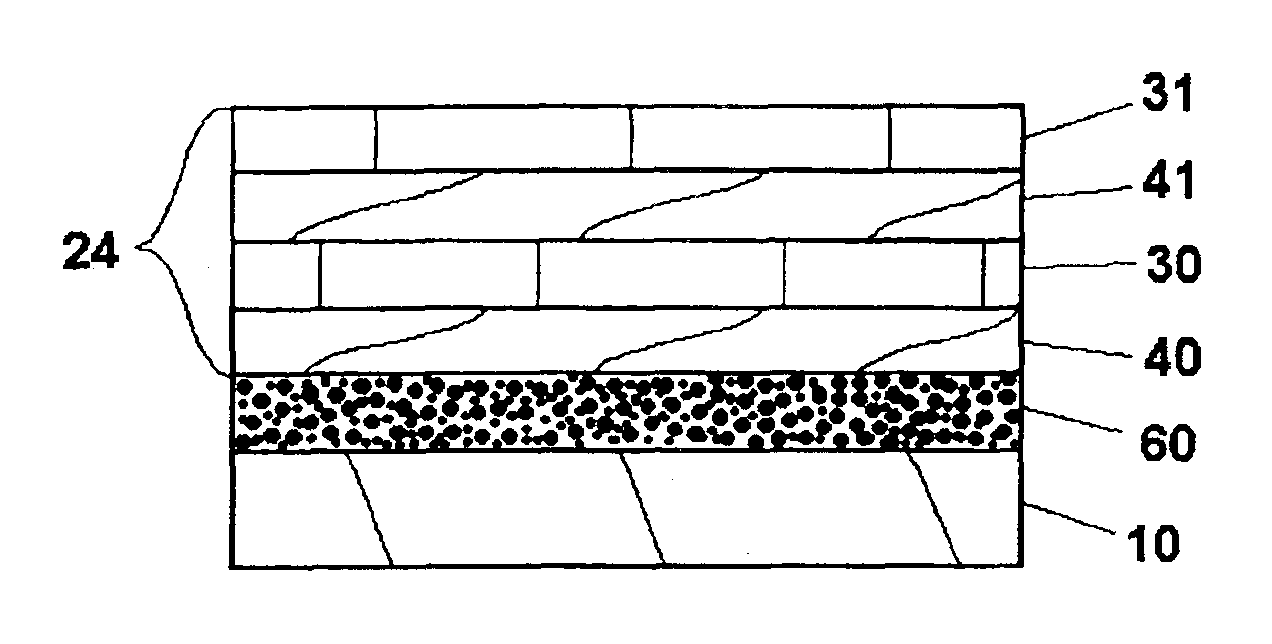
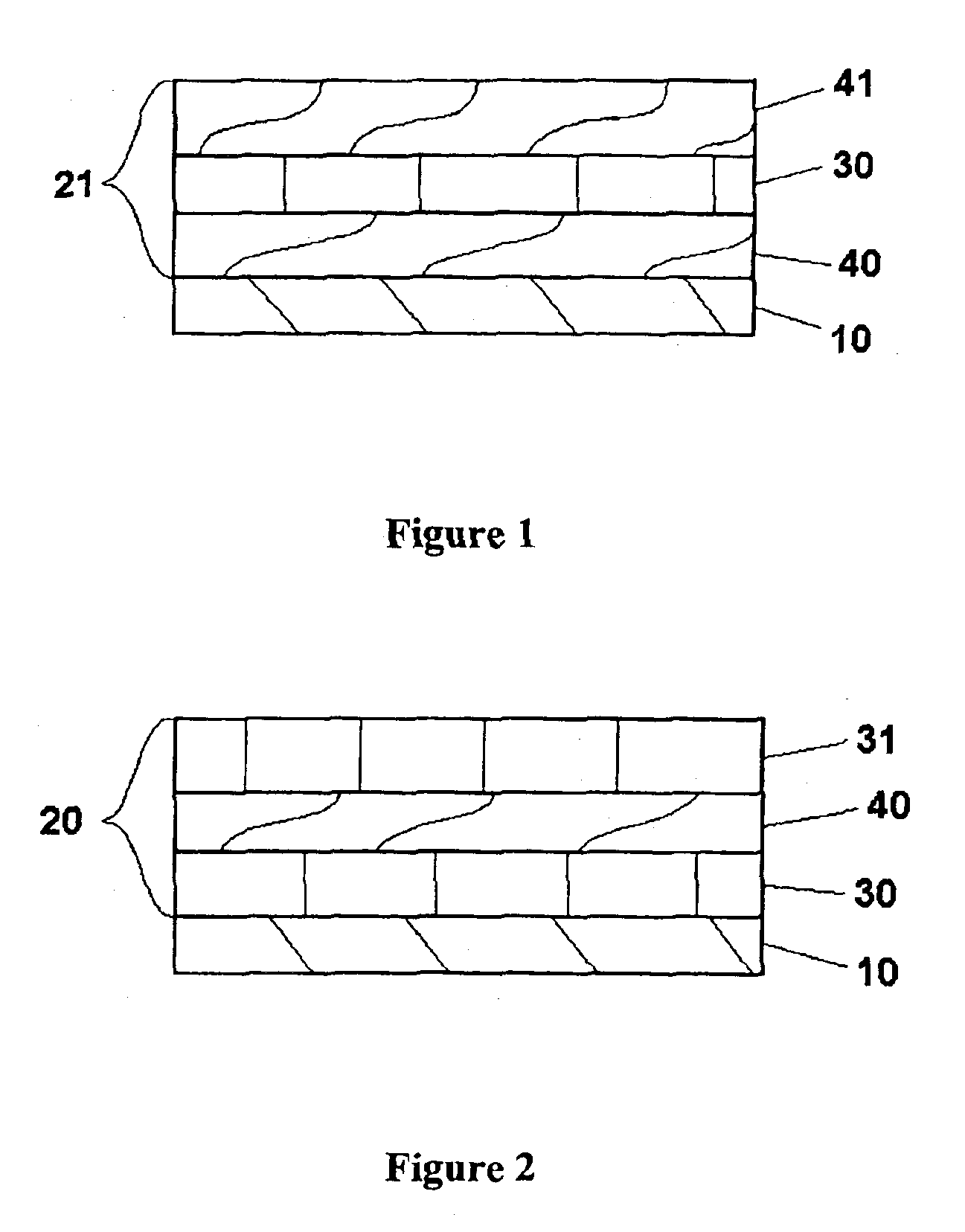
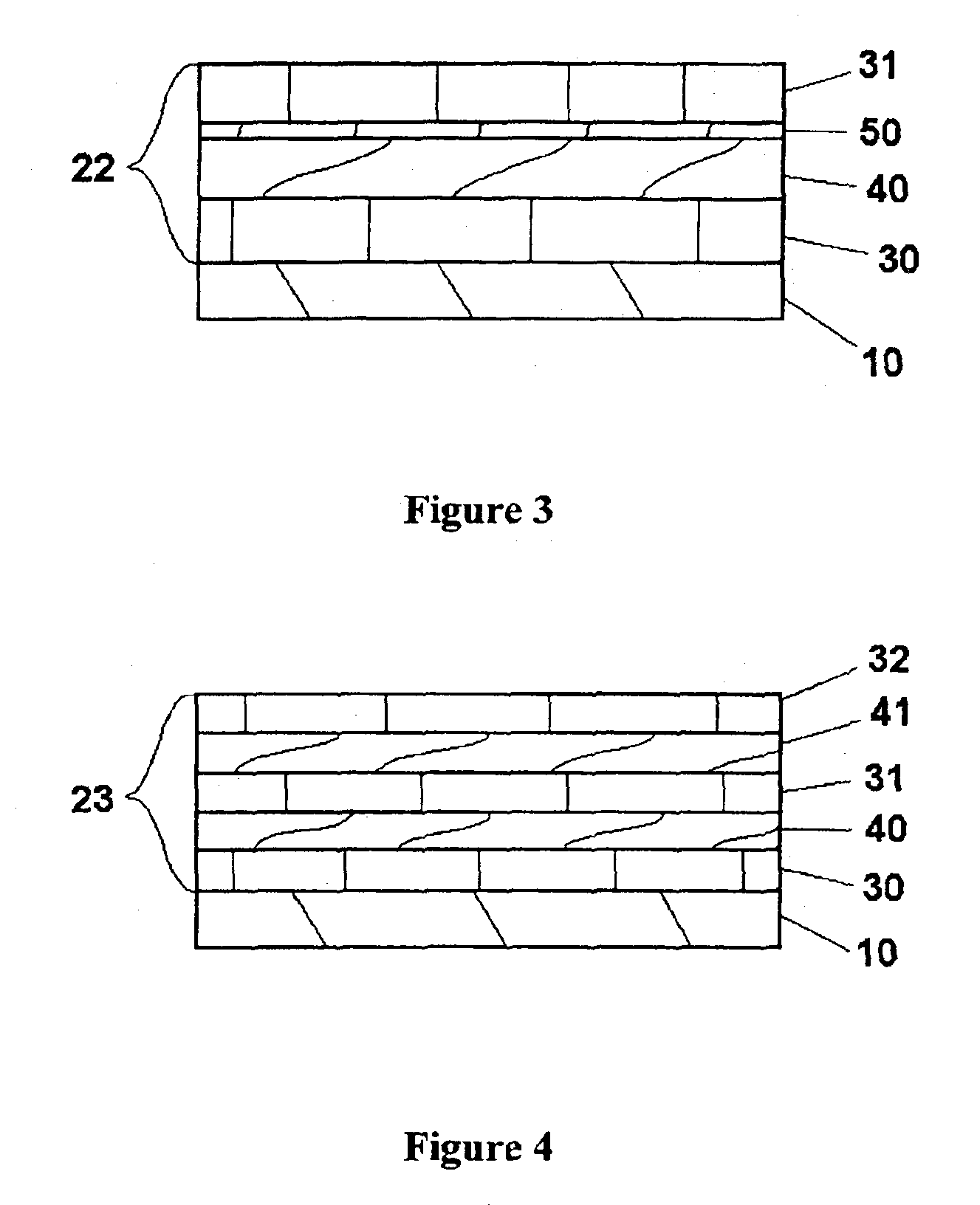
THIN-FILM BATTERIES WITH POLYMER AND LiPON ELECTROLYTE LAYERS AND METHOD
InactiveUS20070015061A1Improve environmental resistanceInhibition formationFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalPolymer gel
A method and apparatus for making thin-film batteries having composite multi-layered electrolytes with soft electrolyte between hard electrolyte covering the negative and / or positive electrode, and the resulting batteries. In some embodiments, foil-core cathode sheets each having a cathode material (e.g., LiCoO2) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, and foil-core anode sheets having an anode material (e.g., lithium metal) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, are laminated using a soft (e.g., polymer gel) electrolyte sandwiched between alternating cathode and anode sheets. A hard glass-like electrolyte layer obtains a smooth hard positive-electrode lithium-metal layer upon charging, but when very thin, have randomly spaced pinholes / defects. When the hard layers are formed on both the positive and negative electrodes, one electrode's dendrite-short-causing defects on are not aligned with the other electrode's defects. The soft electrolyte layer both conducts ions across the gap between hard electrolyte layers and fills pinholes.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
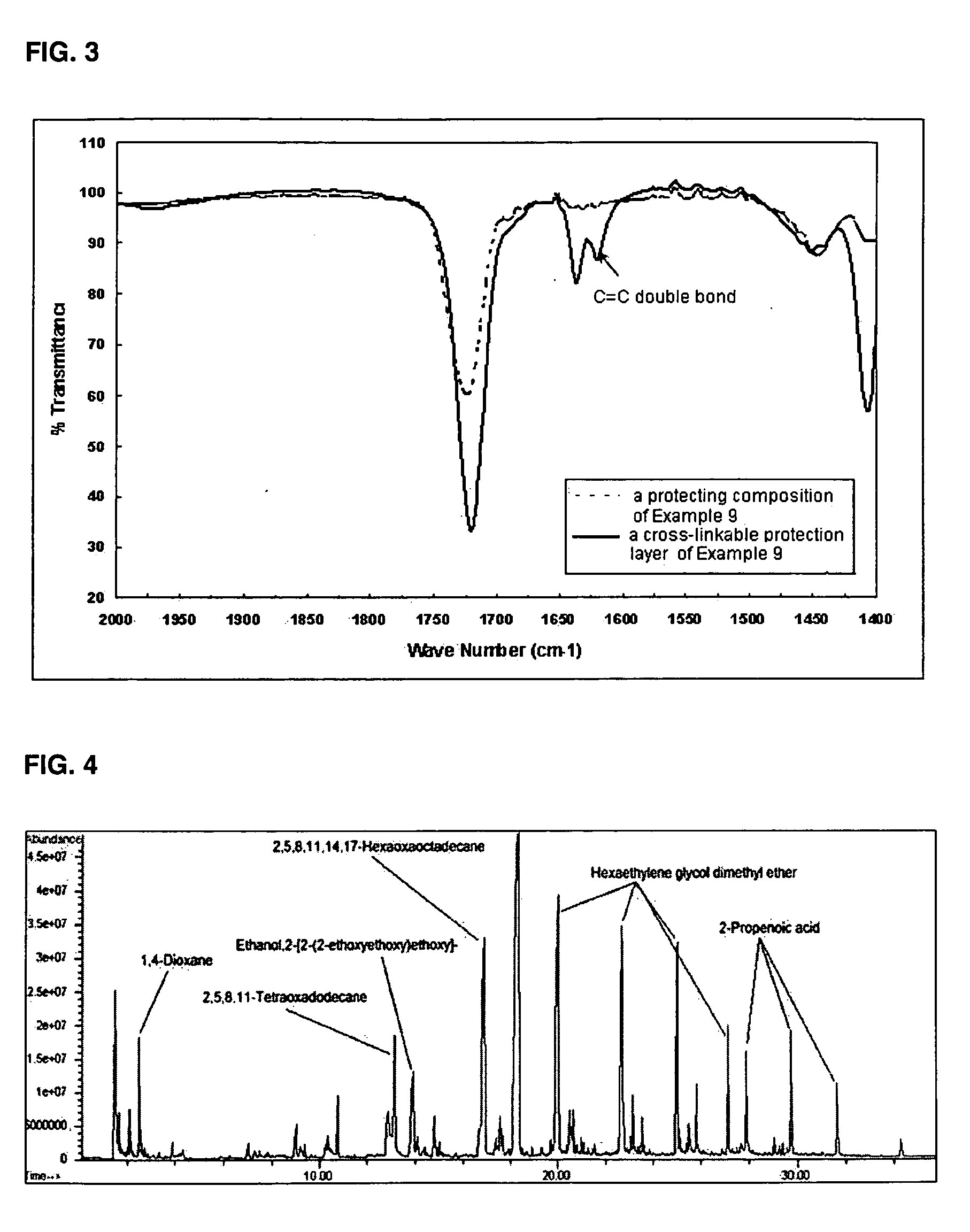
Composition for protecting negative electrode for lithium metal battery, and lithium metal battery fabricated using same
InactiveUS20050042515A1Improve cycle lifeInhibit side effectsFinal product manufactureNegative electrodesLithium metalPlasticizer
Disclosed is a composition for protecting a negative electrode for a lithium metal battery including a multifunctional monomer having at least two double bonds for facilitating cross-linking, a plasticizer, and at least one alkali metal salt.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Method of producing hybrid nano-filament electrodes for lithium metal or lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090169725A1High reversible capacityLower internal resistanceElectrochemical processing of electrodesElectrode thermal treatmentChemical LinkageFiber
Disclosed is a method of producing a hybrid nano-filament composition for use in a lithium battery electrode. The method comprises: (a) providing an aggregate of nanometer-scaled, electrically conductive filaments that are substantially interconnected, intersected, physically contacted, or chemically bonded to form a porous network of electrically conductive filaments, wherein the filaments comprise electro-spun nano-fibers that have a diameter less than 500 nm (preferably less than 100 nm); and (b) depositing micron- or nanometer-scaled coating onto a surface of the electro-spun nano-fibers, wherein the coating comprises an electro-active material capable of absorbing and desorbing lithium ions and the coating has a thickness less than 10 μm (preferably less than 1 μm). The same method can be followed to produce an anode or a cathode. The battery featuring an anode or cathode made with this method exhibits an exceptionally high specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Thin-film batteries with soft and hard electrolyte layers and method
InactiveUS20070015060A1Improve environmental resistanceInhibition formationFinal product manufactureConductive materialLithium metalPolymer gel
A method and apparatus for making thin-film batteries having composite multi-layered electrolytes with soft electrolyte between hard electrolyte covering the negative and / or positive electrode, and the resulting batteries. In some embodiments, foil-core cathode sheets each having a cathode material (e.g., LiCoO2) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, and foil-core anode sheets having an anode material (e.g., lithium metal) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, are laminated using a soft (e.g., polymer gel) electrolyte sandwiched between alternating cathode and anode sheets. A hard glass-like electrolyte layer obtains a smooth hard positive-electrode lithium-metal layer upon charging, but when very thin, have randomly spaced pinholes / defects. When the hard layers are formed on both the positive and negative electrodes, one electrode's dendrite-short-causing defects on are not aligned with the other electrode's defects. The soft electrolyte layer both conducts ions across the gap between hard electrolyte layers and fills pinholes.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Methods and reagents for enhancing the cycling efficiency of lithium polymer batteries
InactiveUS6165644AImprove efficiencyElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrochemical processing of electrodesLithium metalSulfur electrode
Batteries including a lithium electrode and a sulfur counter electrode that demonstrate improved cycling efficiencies are described. In one embodiment, an electrochemical cell having a lithium electrode and a sulfur electrode including at least one of elemental sulfur, lithium sulfide, and a lithium polysulfide is provided. The lithium electrode includes a surface coating that is effective to increase the cycling efficiency of said electrochemical cell. In a more particular embodiment, the lithium electrode is in an electrolyte solution, and, more particularly, an electrolyte solution including either elemental sulfur, a sulfide, or a polysulfide. In another embodiment, the coating is formed after the lithium electrode is contacted with the electrolyte. In a more particular embodiment, the coating is formed by a reaction between the lithium metal of the lithium electrode and a chemical species present in the electrolyte.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS20060099508A1Improve structural stabilityImprove stabilityLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium metalOxidation state
A lithium metal oxide positive electrode for a non-aqueous lithium cell is disclosed. The cell is prepared in its initial discharged state and has a general formula xLiMO2.(1−x)Li2M′O3 in which 0<x<1, and where M is one or more ion with an average trivalent oxidation state and with at least one ion being Mn or Ni, and where M′ is one or more ion with an average tetravalent oxidation state. Complete cells or batteries are disclosed with anode, cathode and electrolyte as are batteries of several cells connected in parallel or series or both.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Electrode structure and method for making the same
Electrode structures, and more specifically, electrode structures for use in electrochemical cells, are provided. The electrode structures described herein may include one or more protective layers. In one set of embodiments, a protective layer may be formed by exposing a lithium metal surface to a plasma comprising ions of a gas to form a ceramic layer on top of the lithium metal. The ceramic layer may be highly conductive to lithium ions and may protect the underlying lithium metal surface from reaction with components in the electrolyte. In some cases, the ions may be nitrogen ions and a lithium nitride layer may be formed on the lithium metal surface. In other embodiments, the protective layer may be formed by converting lithium to lithium nitride at high pressures. Other methods for forming protective layers are also provided.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
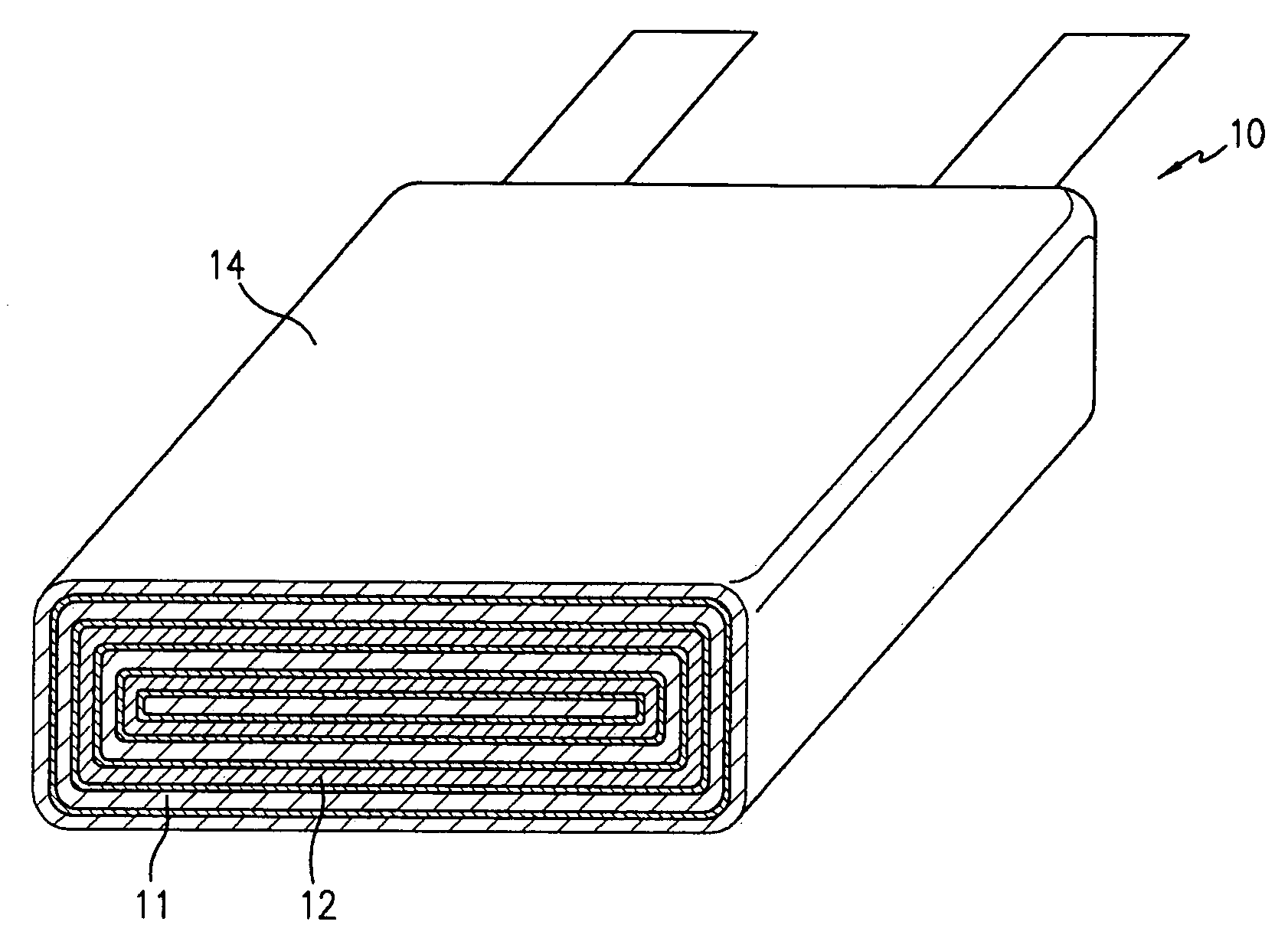
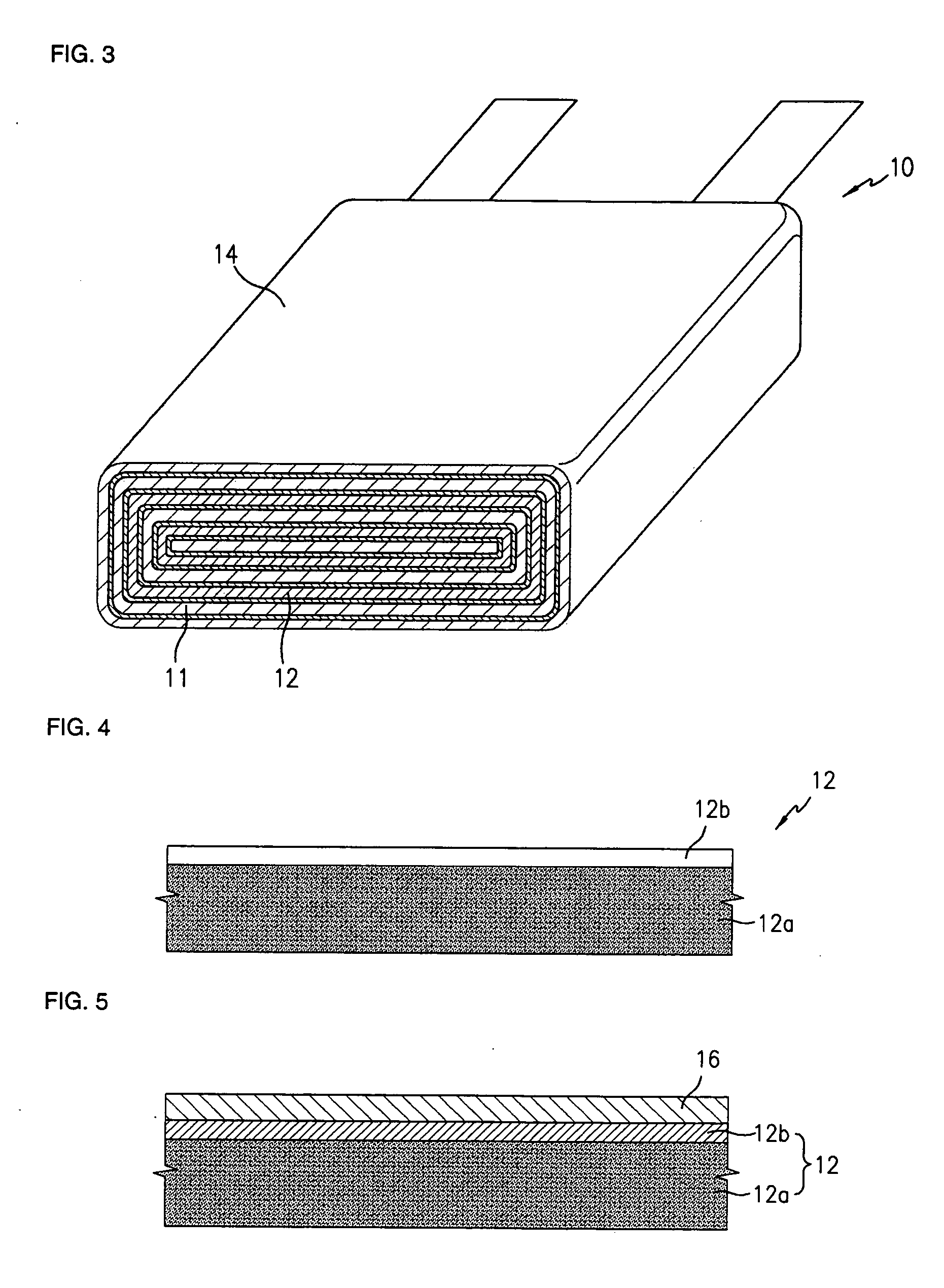
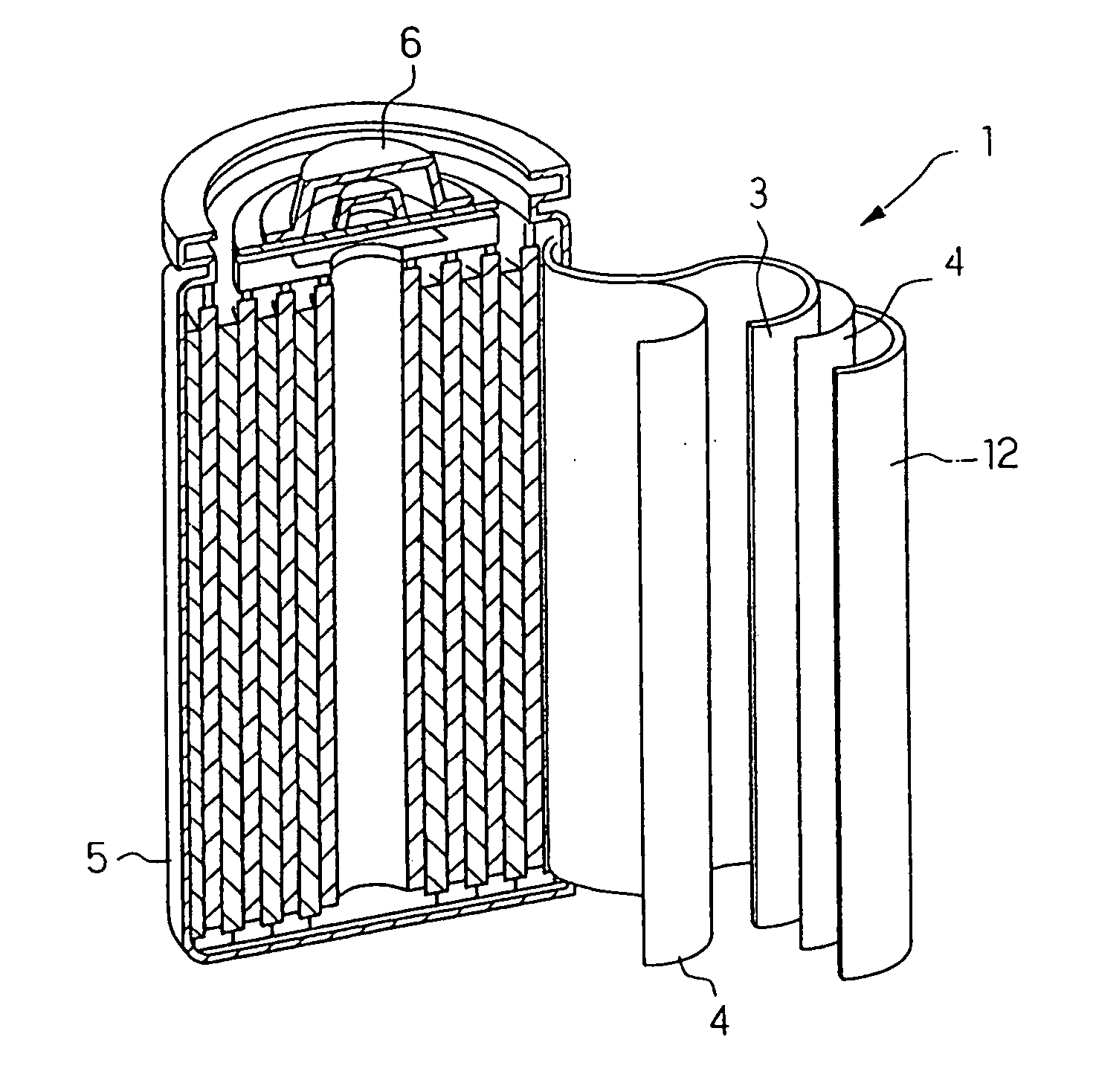
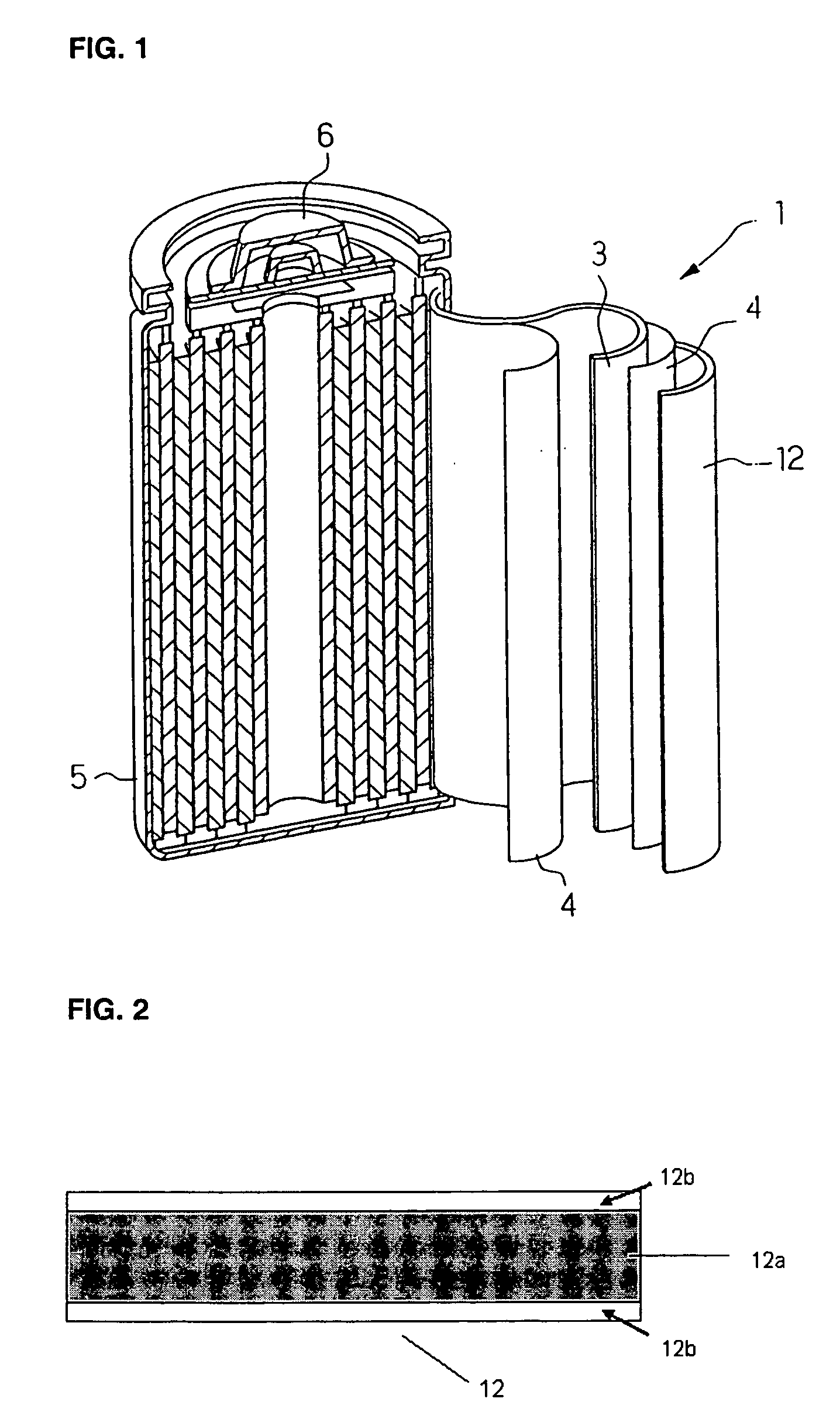
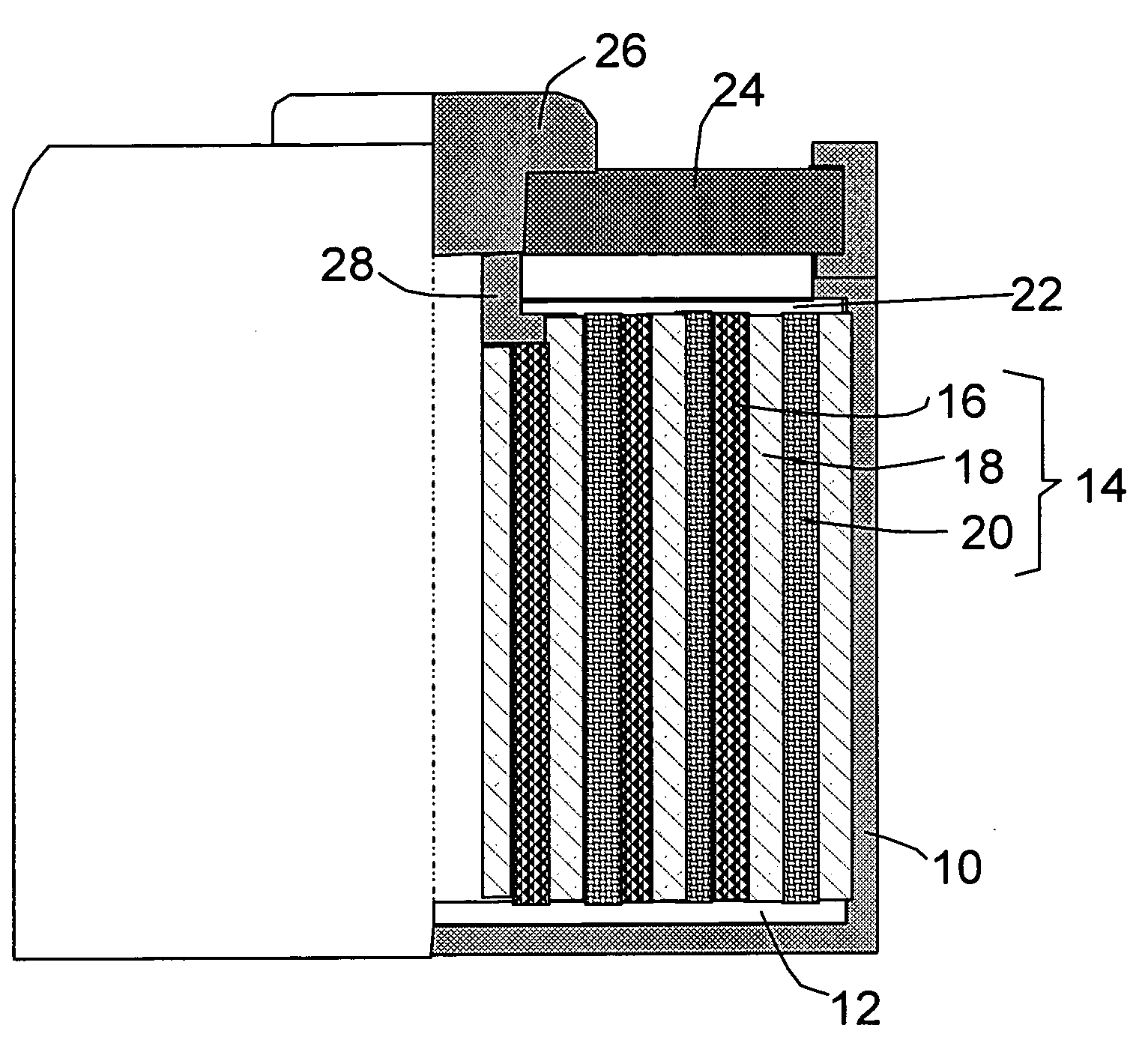
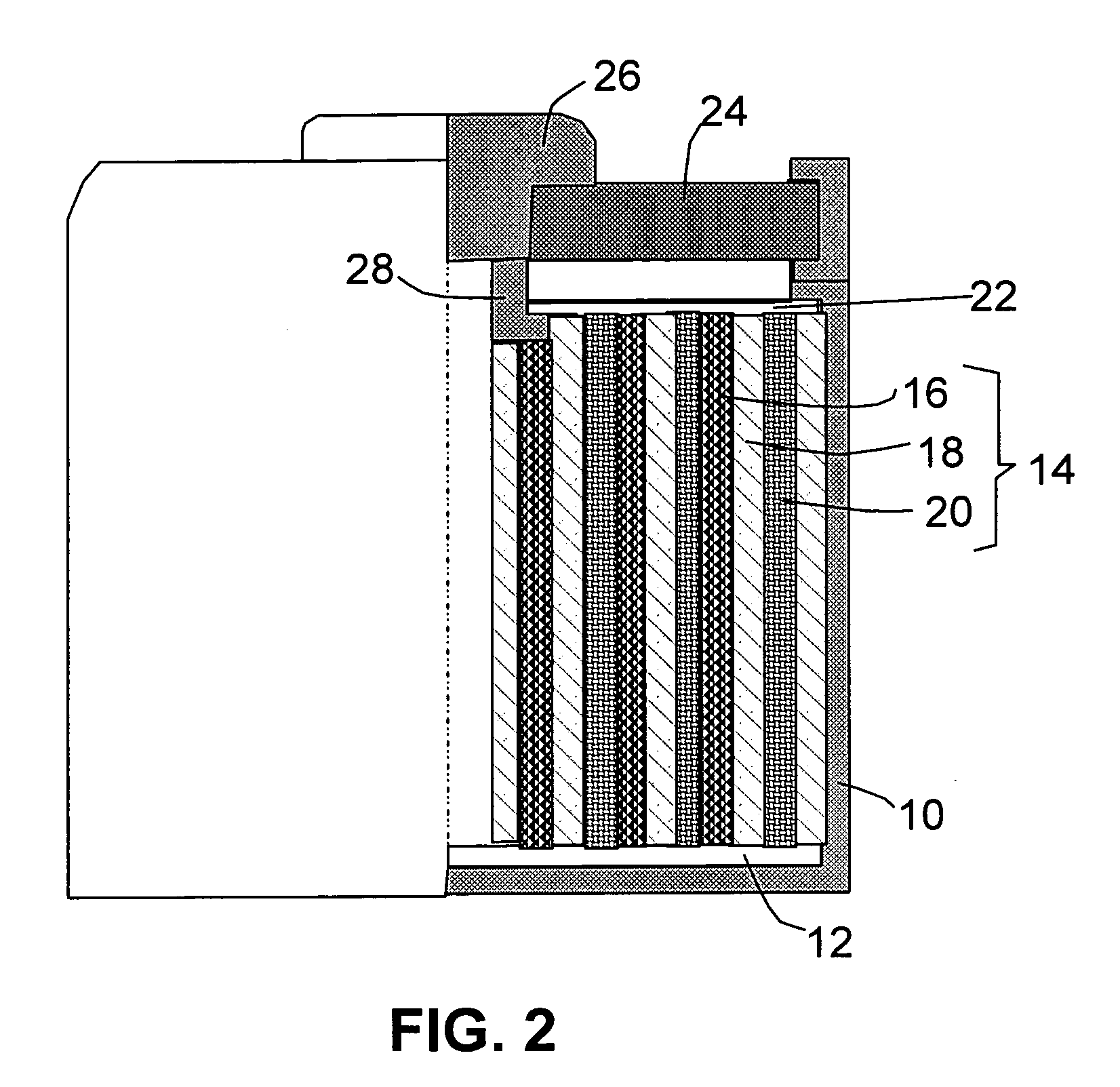
Secondary battery
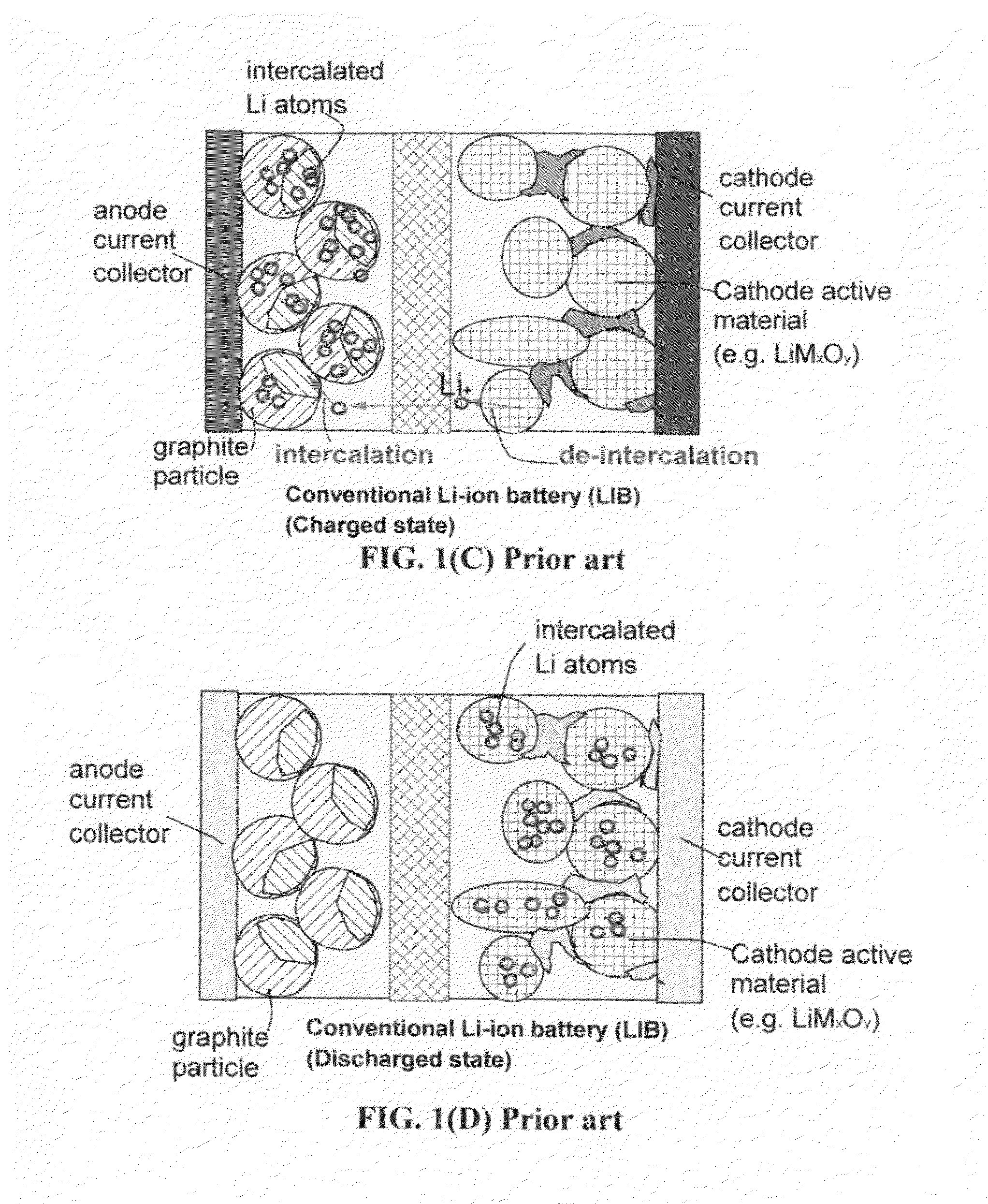
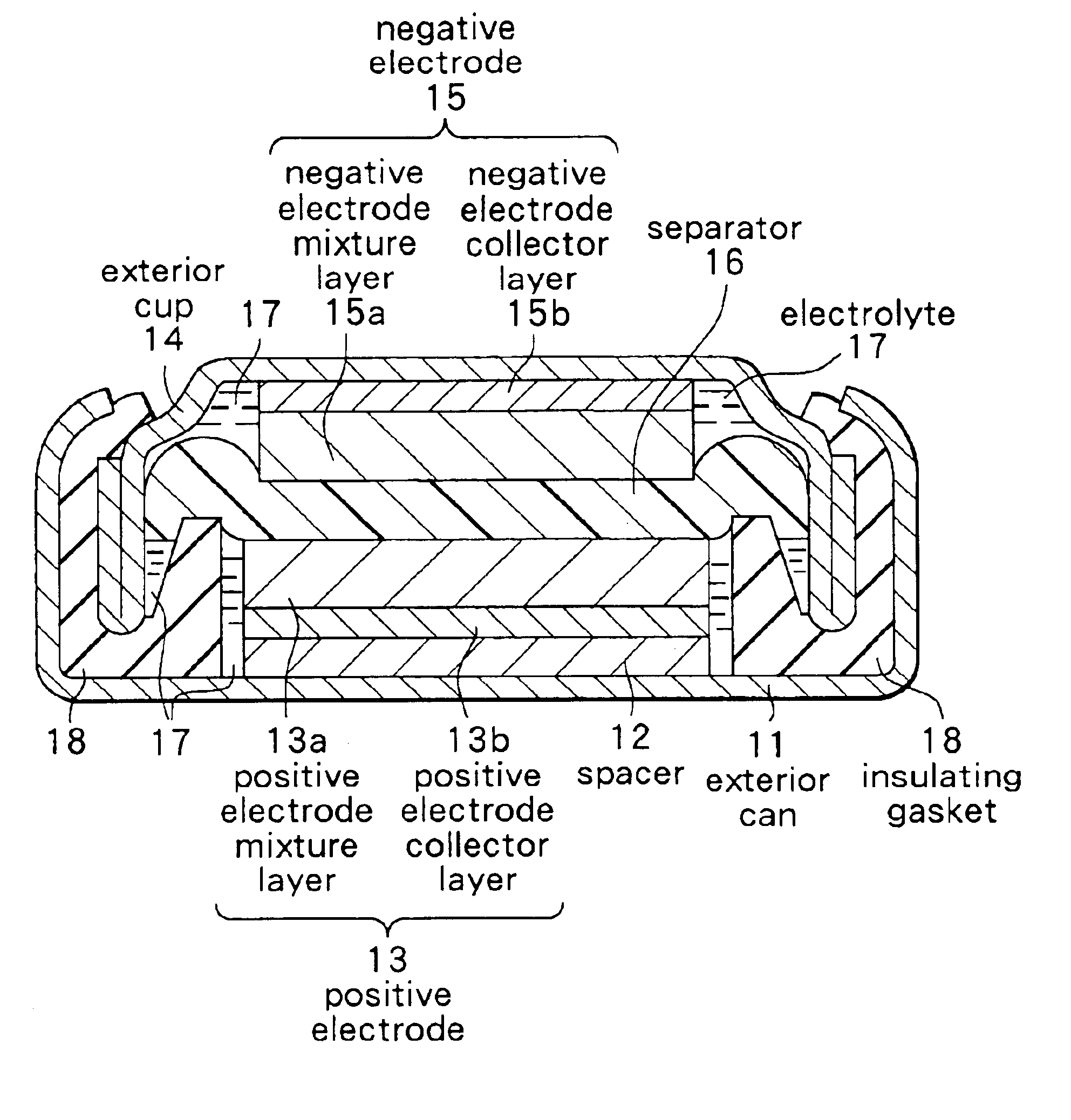
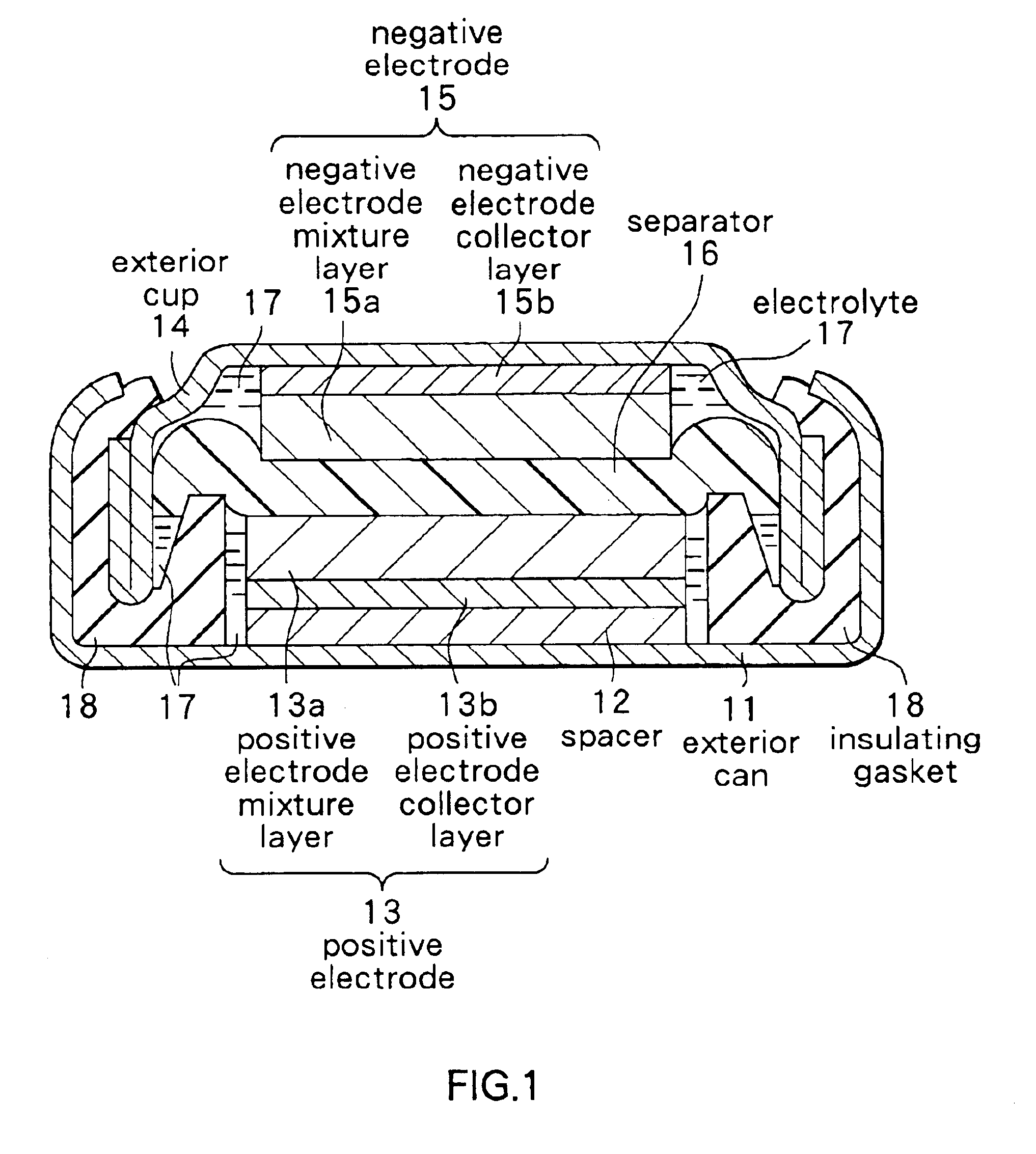
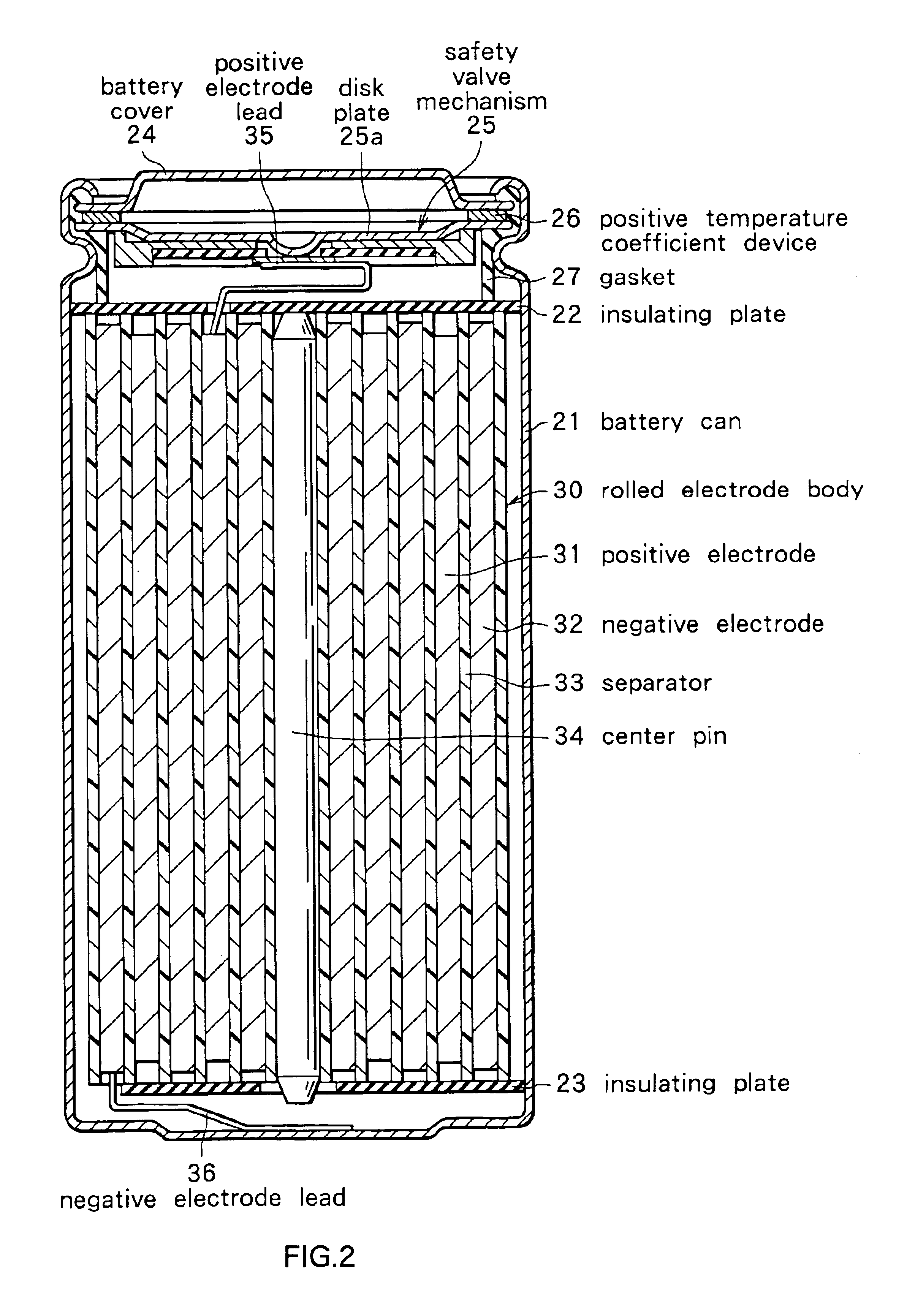
Provided is a secondary battery in which high energy density can be obtained and charging / discharging cycle characteristic can be improved. A positive electrode (13) and a negative electrode (15) are stacked with a separator (16) interposed therebetween, and are enclosed inside an exterior can (11) to which an electrolyte is injected. The negative electrode (15) contains a negative electrode material capable of occluding / releasing lithium in an ionic state. Thereby, lithium metal precipitates in the negative electrode (15) in a state where the open circuit voltage is lower than the overcharge voltage. In other words, lithium is occluded in an ionic state in a negative electrode material capable of occluding / releasing lithium in the beginning of charging, and then lithium metal precipitates on the surface of the negative electrode material thereafter during charging. The amount of precipitation of lithium metal is preferable to be from 0.05 to 3.0 times, both inclusive, the ability of charging capacity of the negative electrode material capable of occluding / releasing lithium. Thereby, a high energy density and an excellent cycle characteristic can be obtained.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com