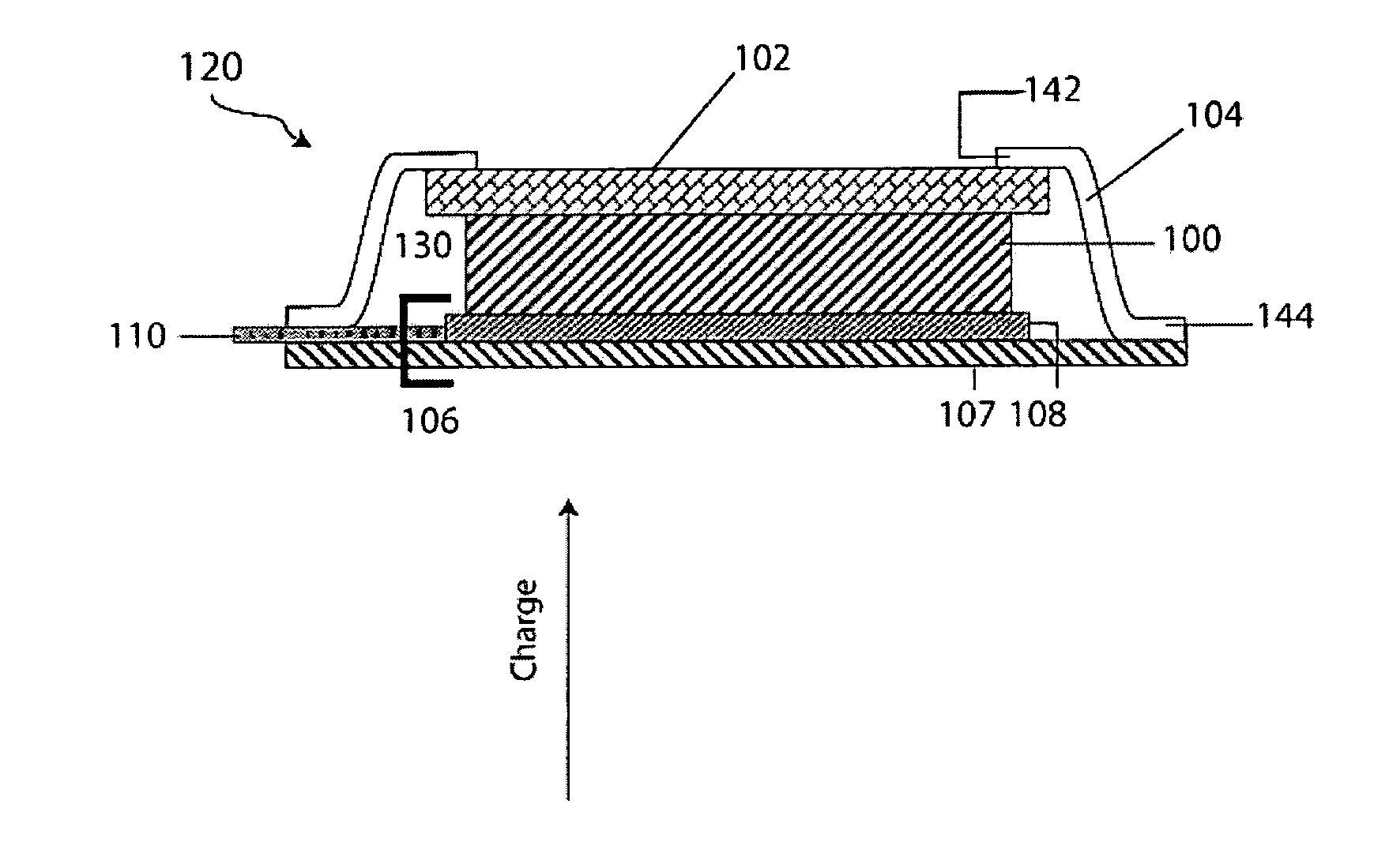
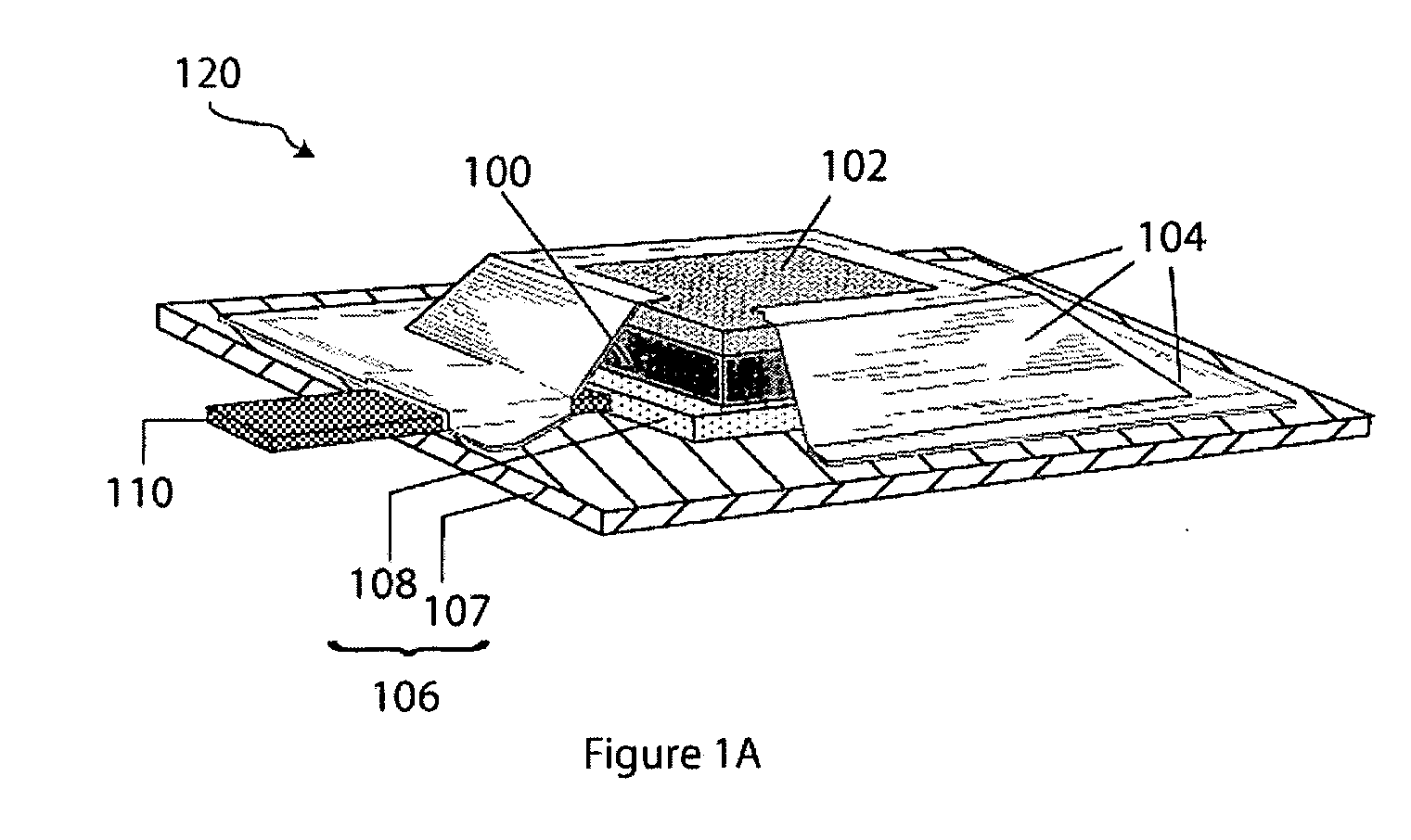
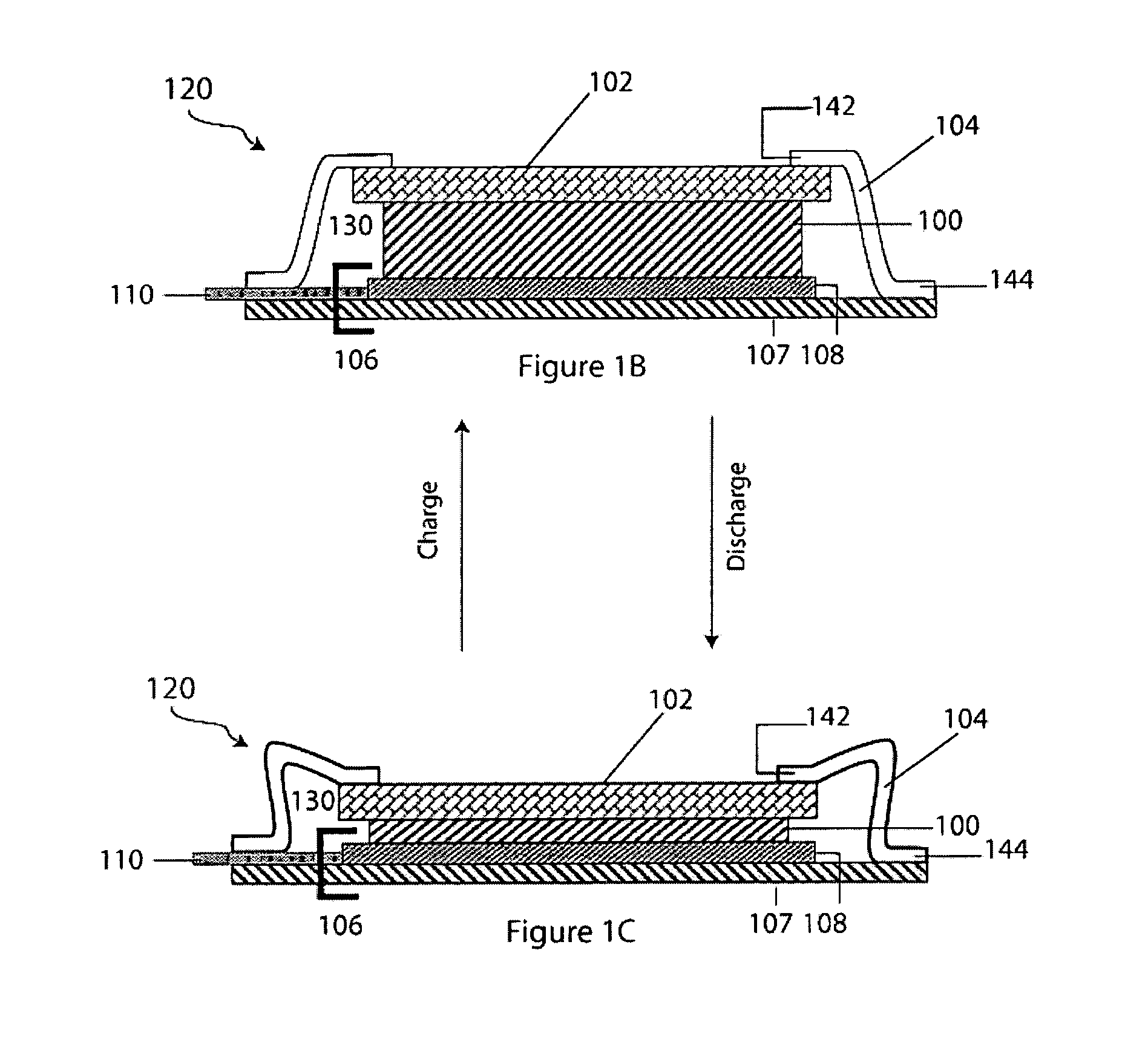
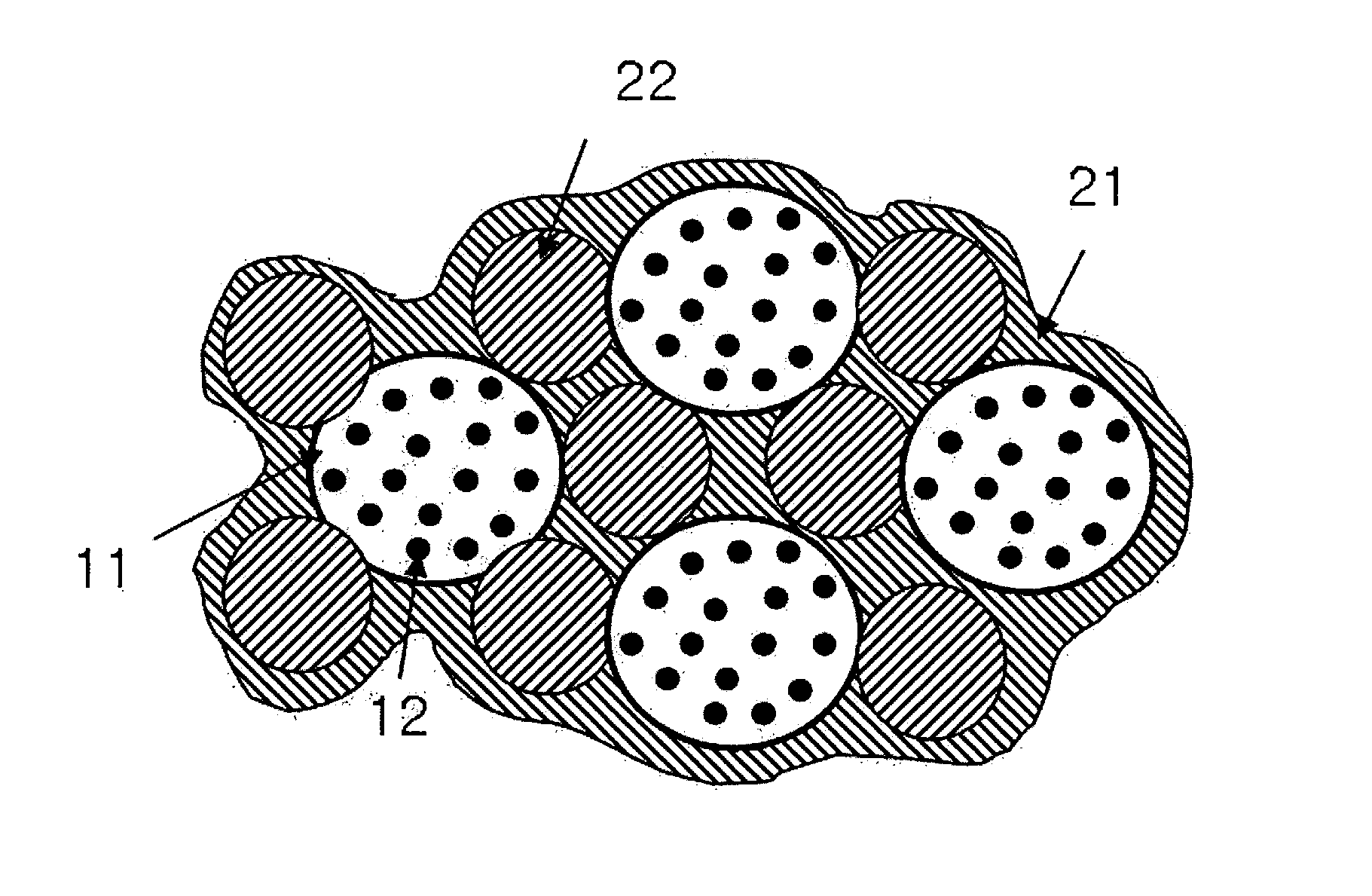
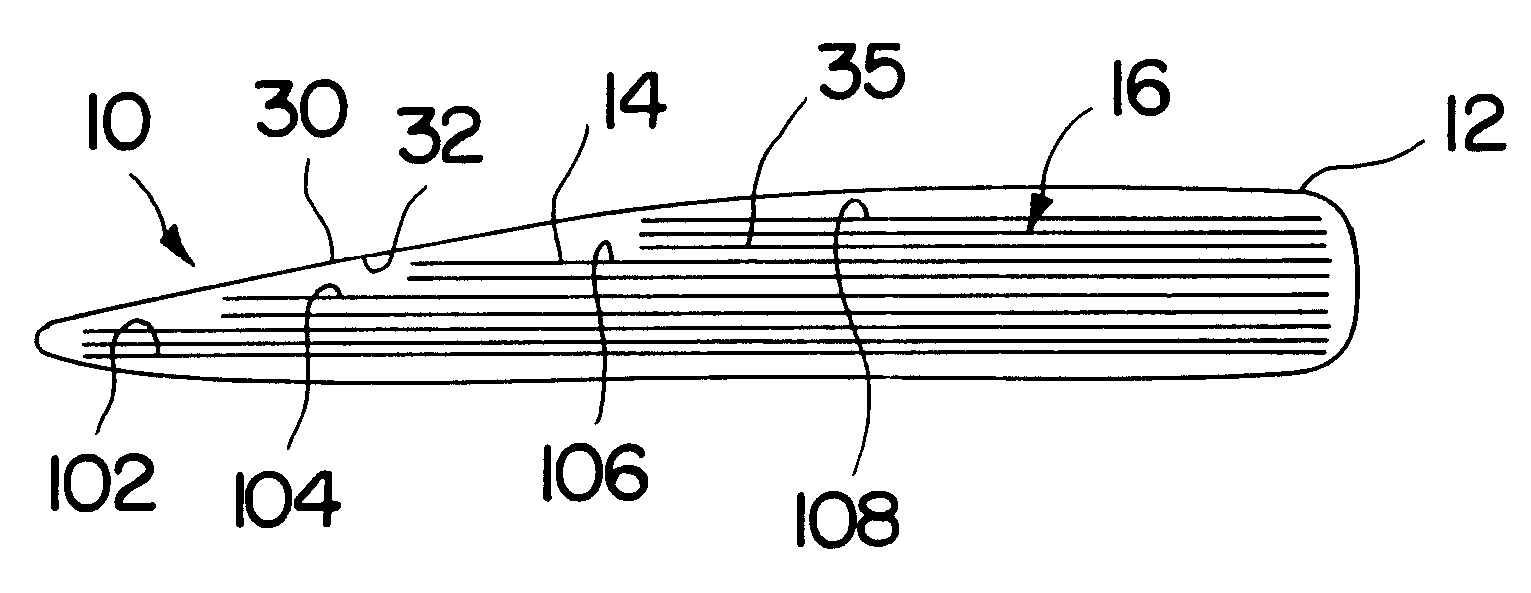
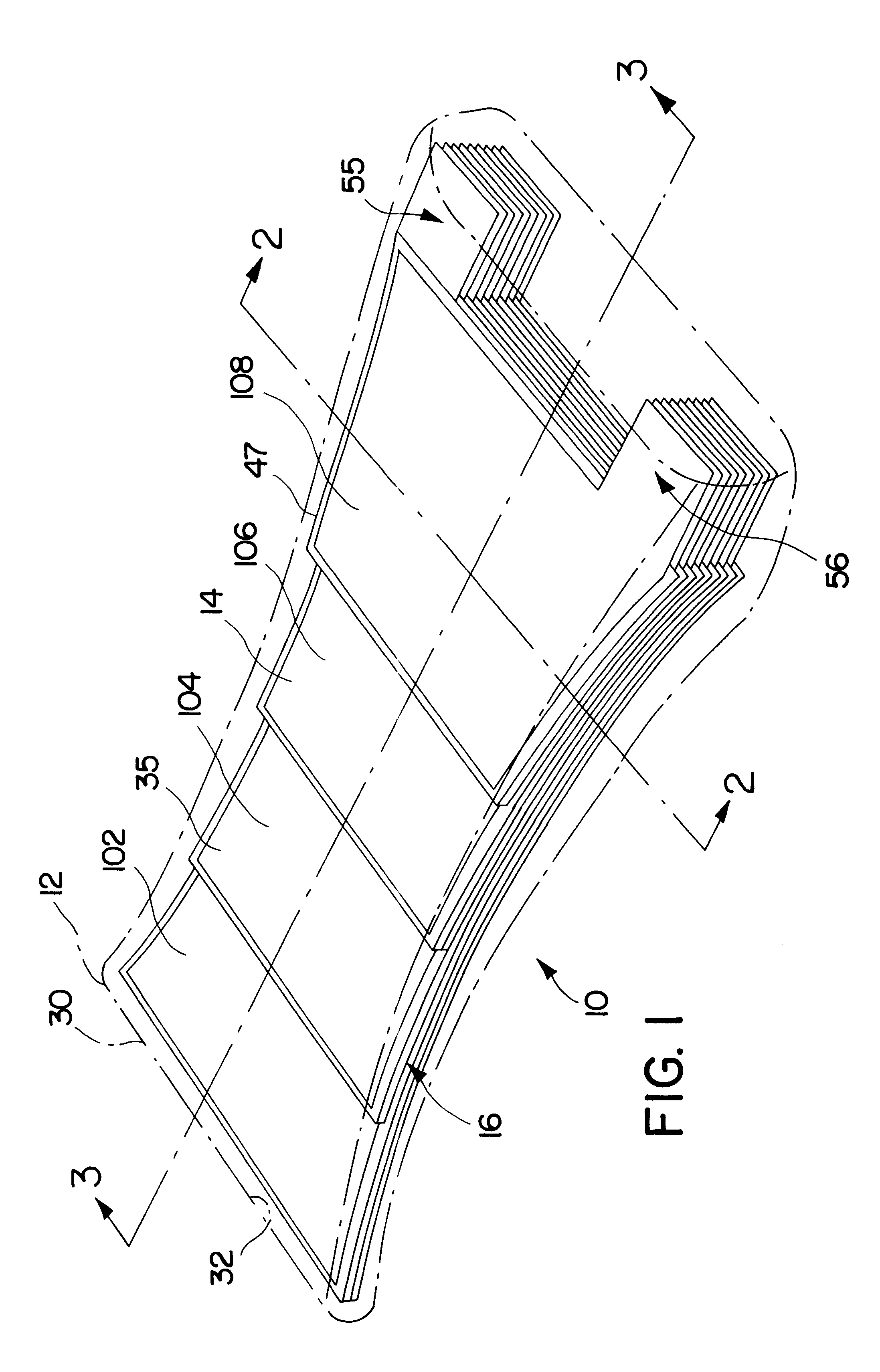
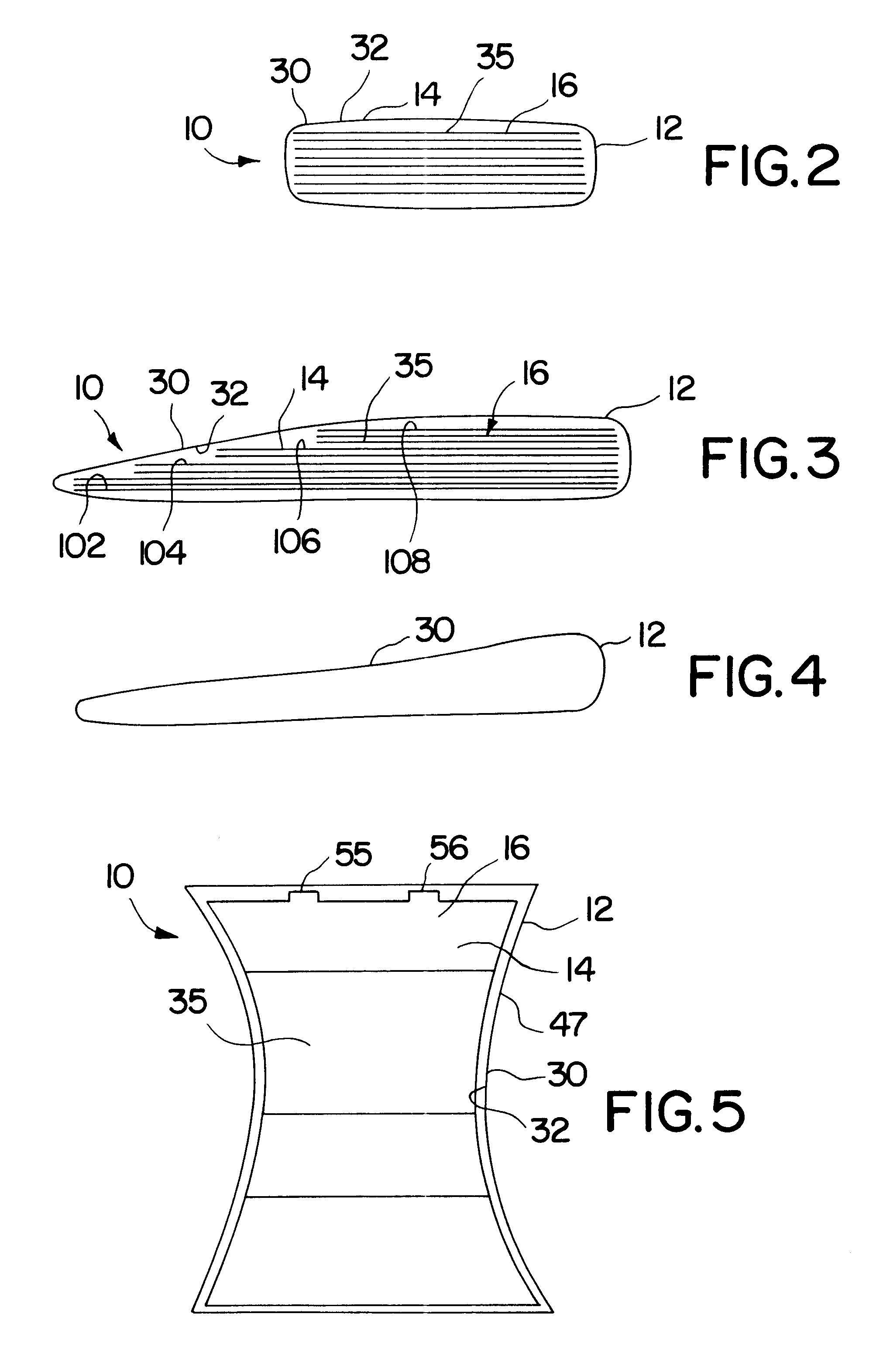
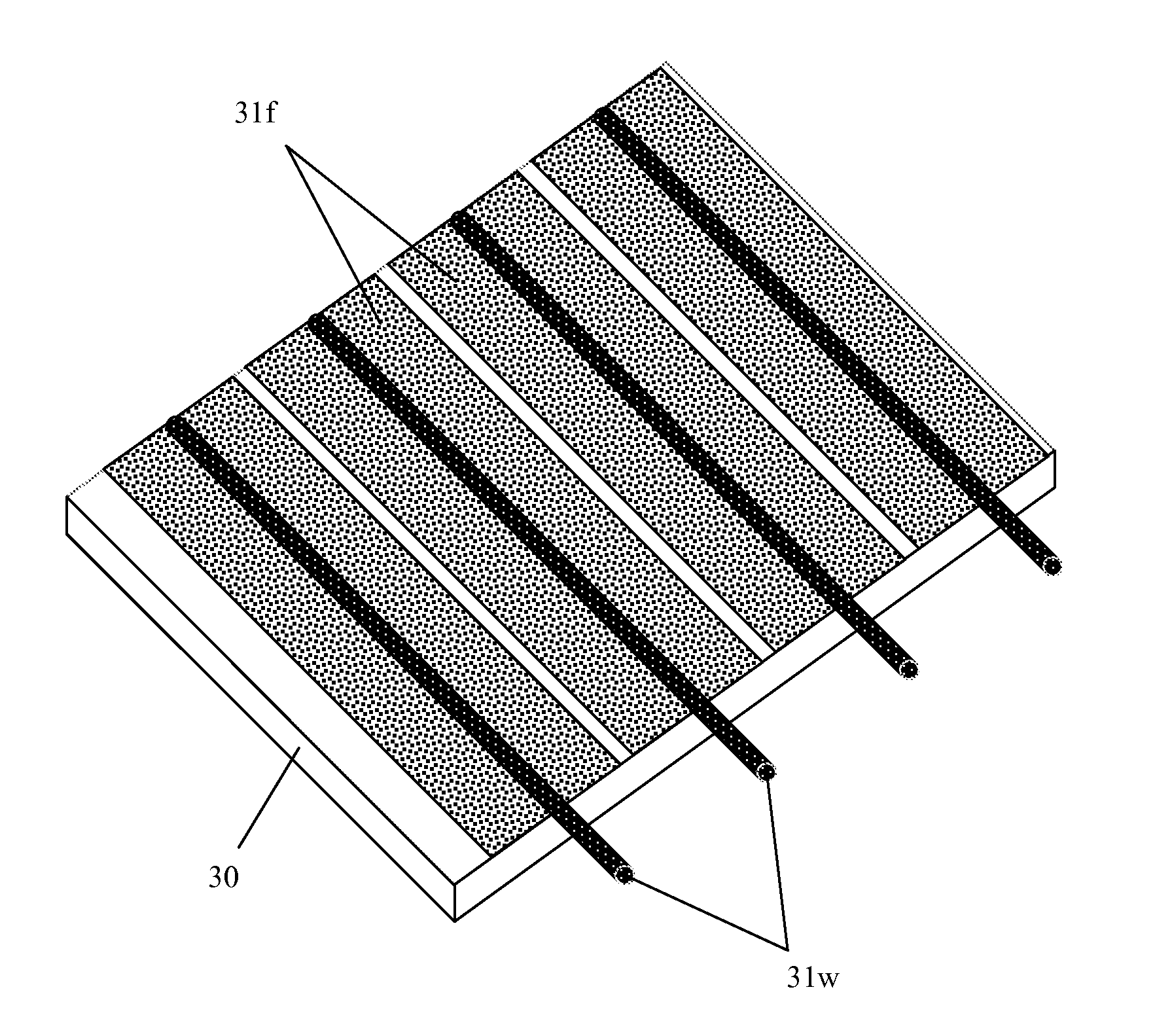
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9218results about "Active material electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
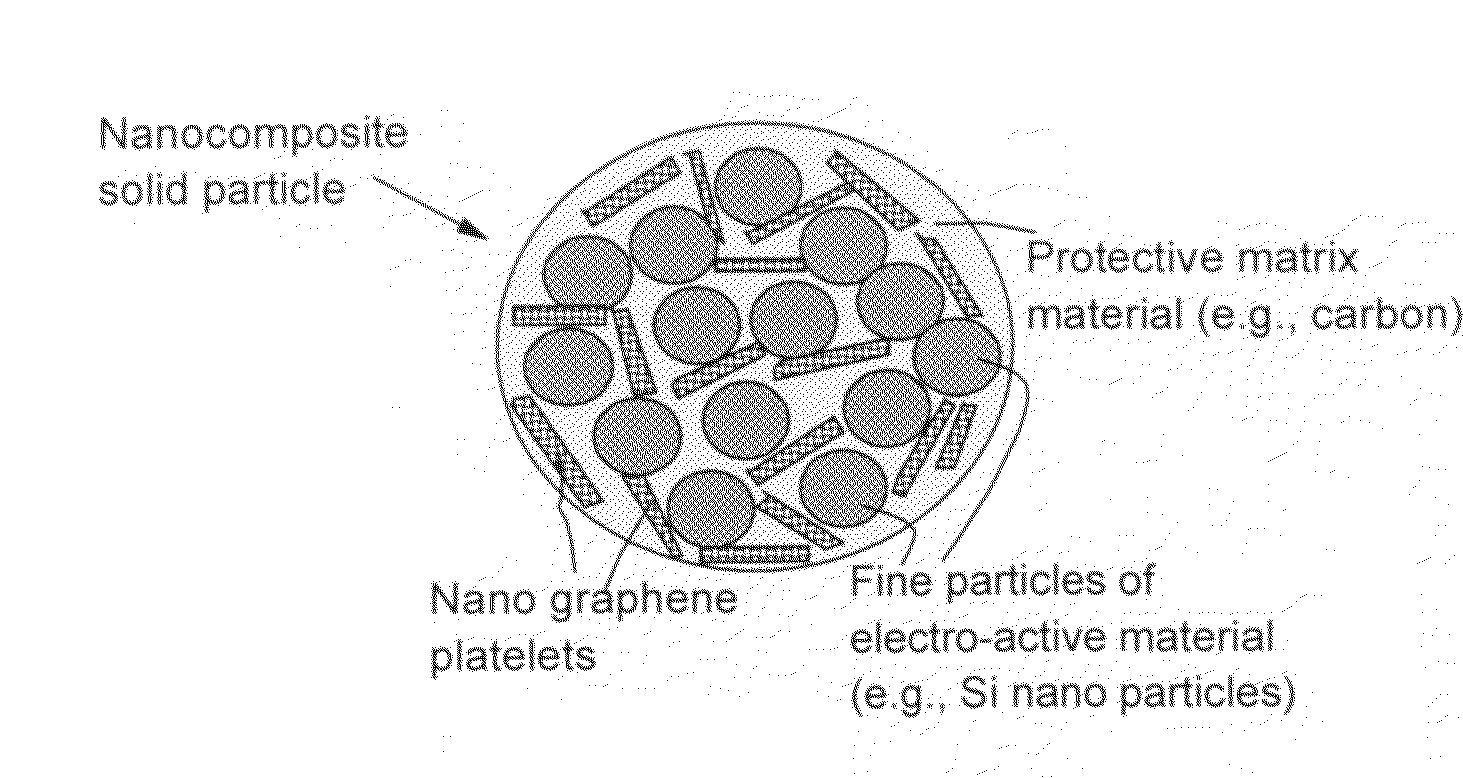
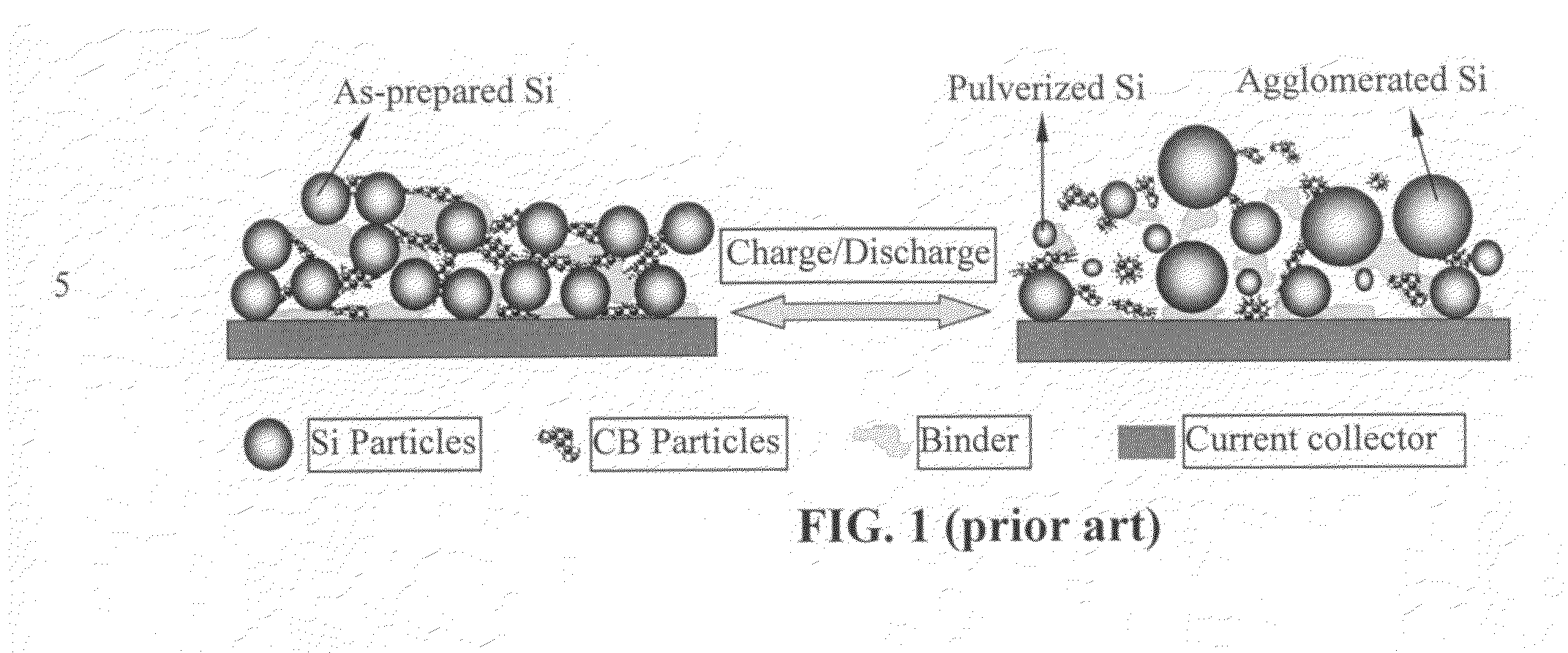
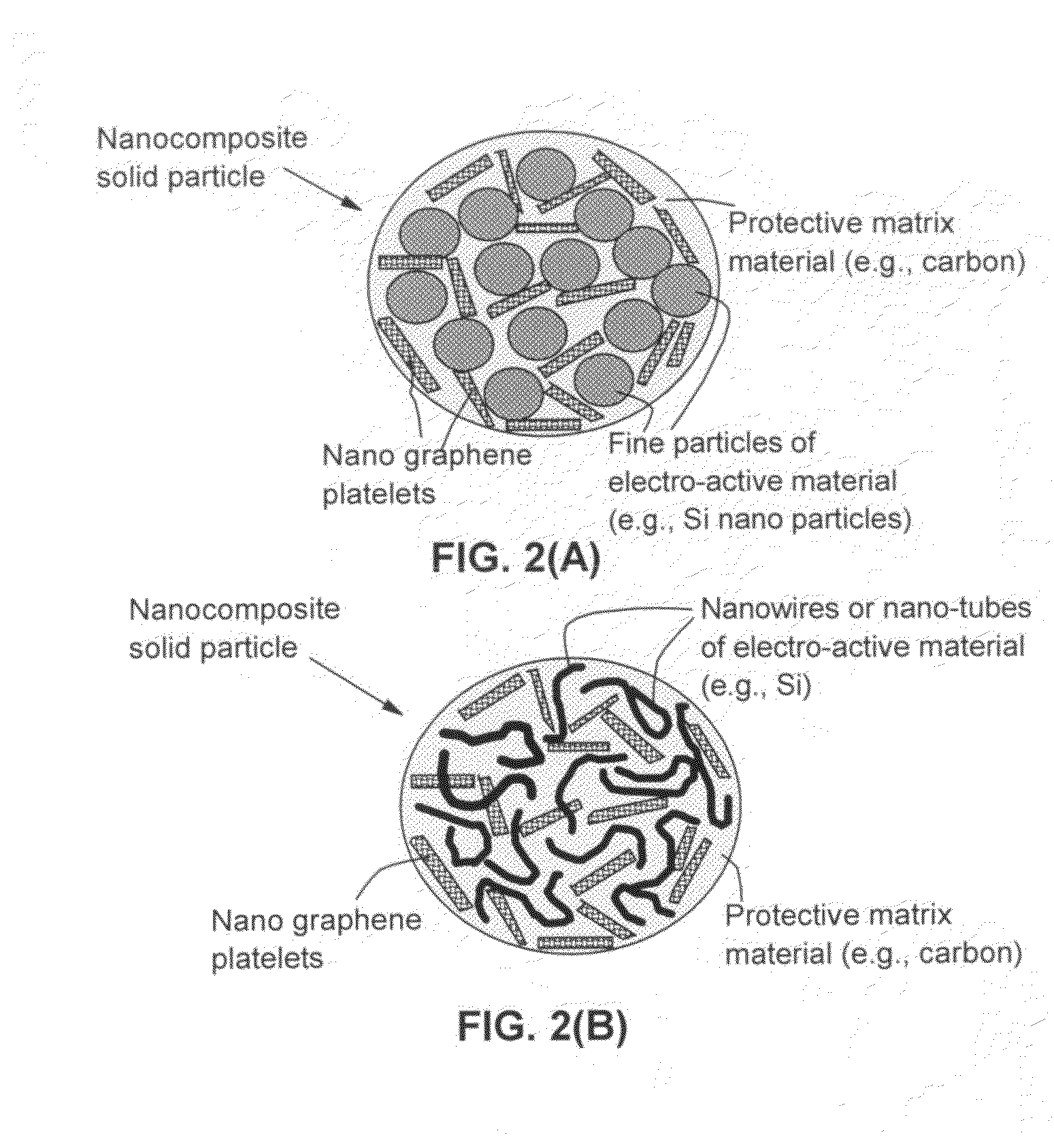
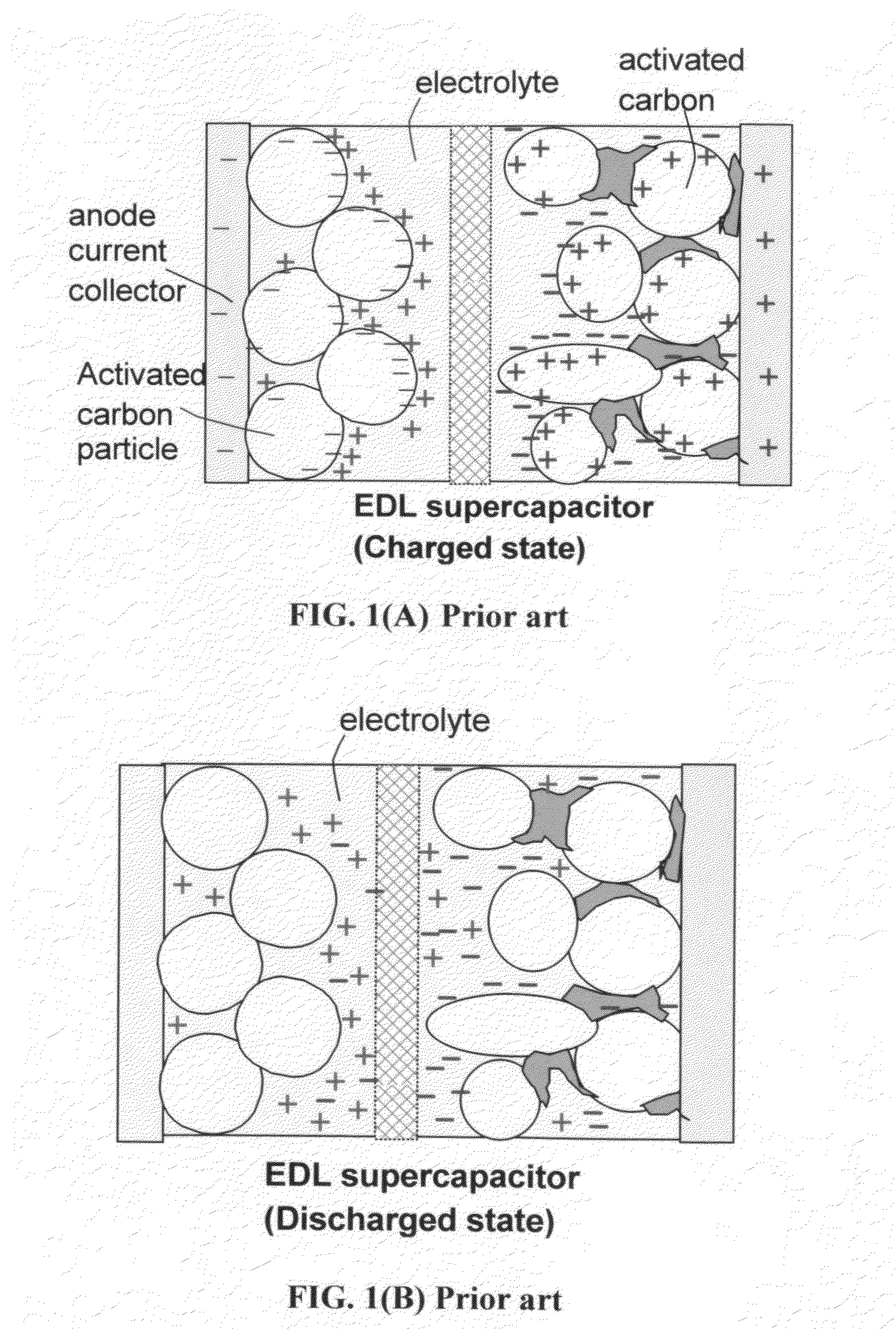
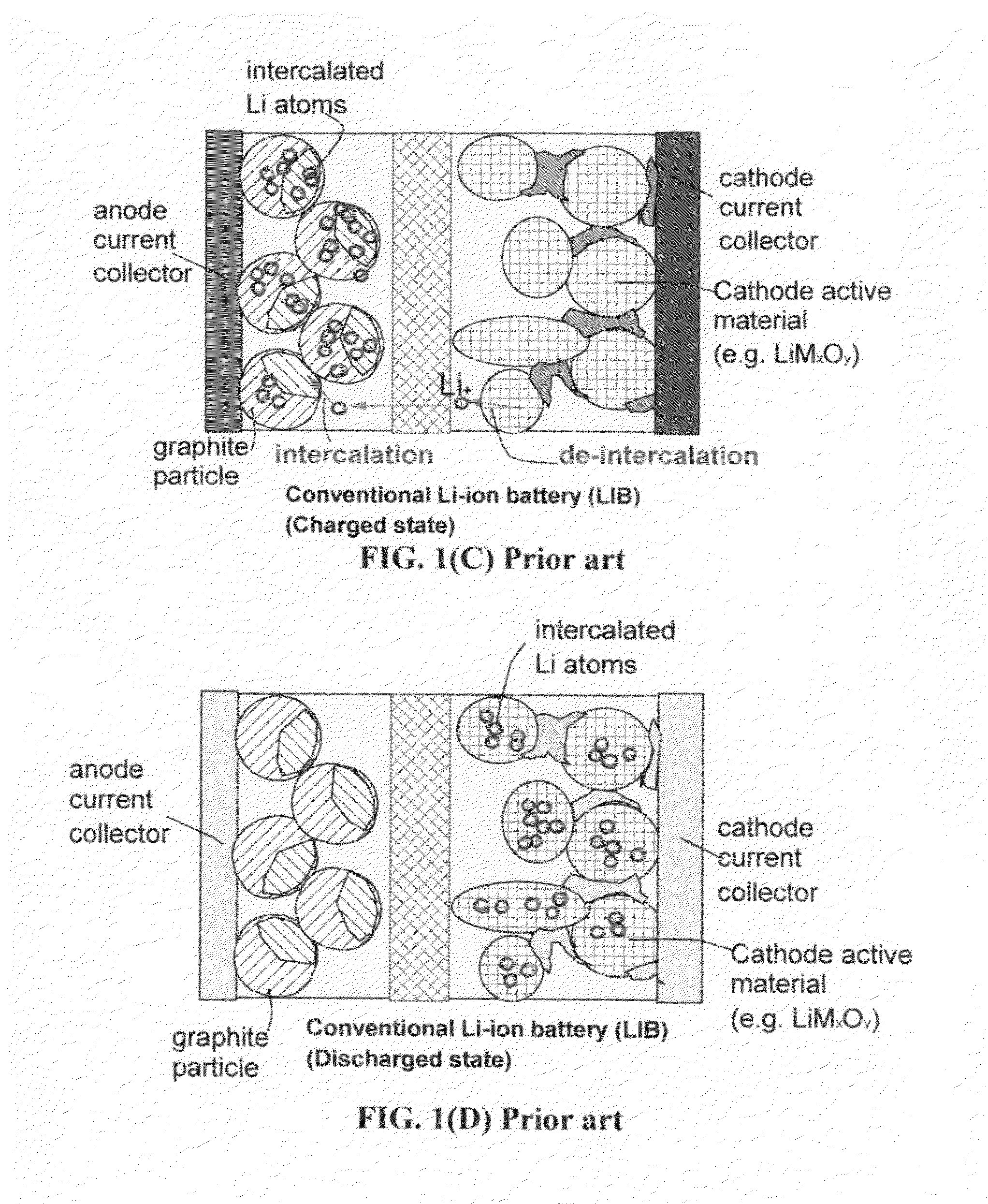
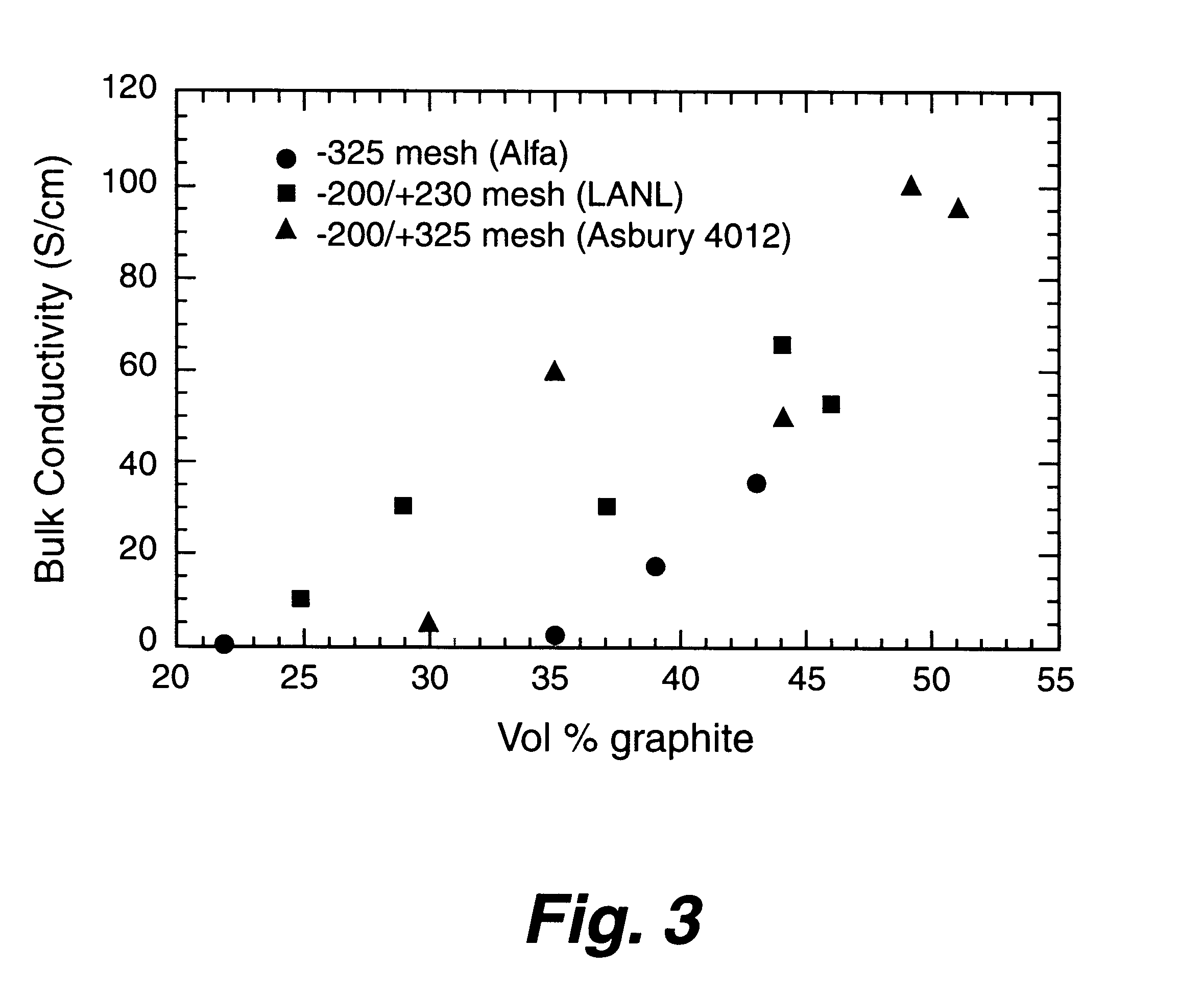
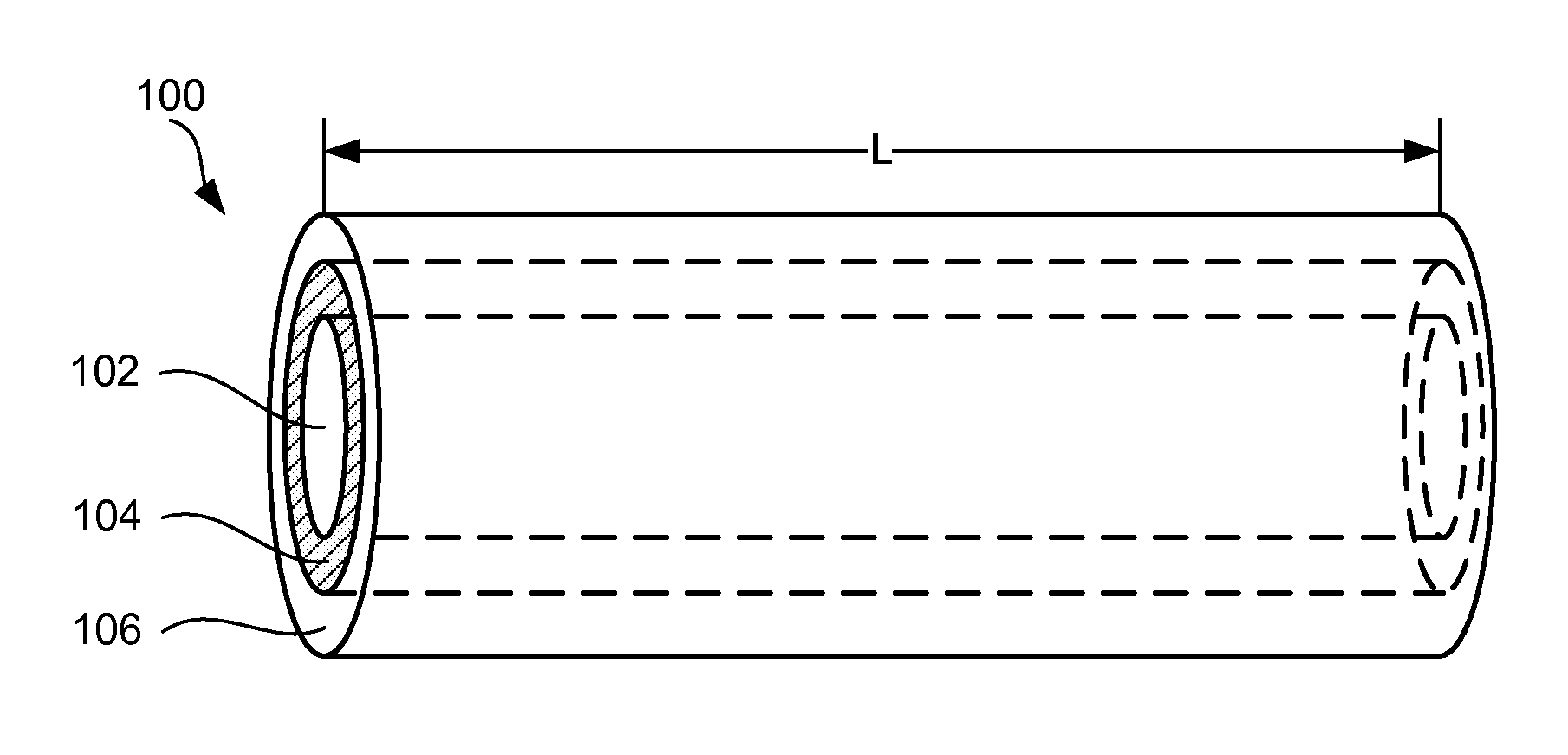
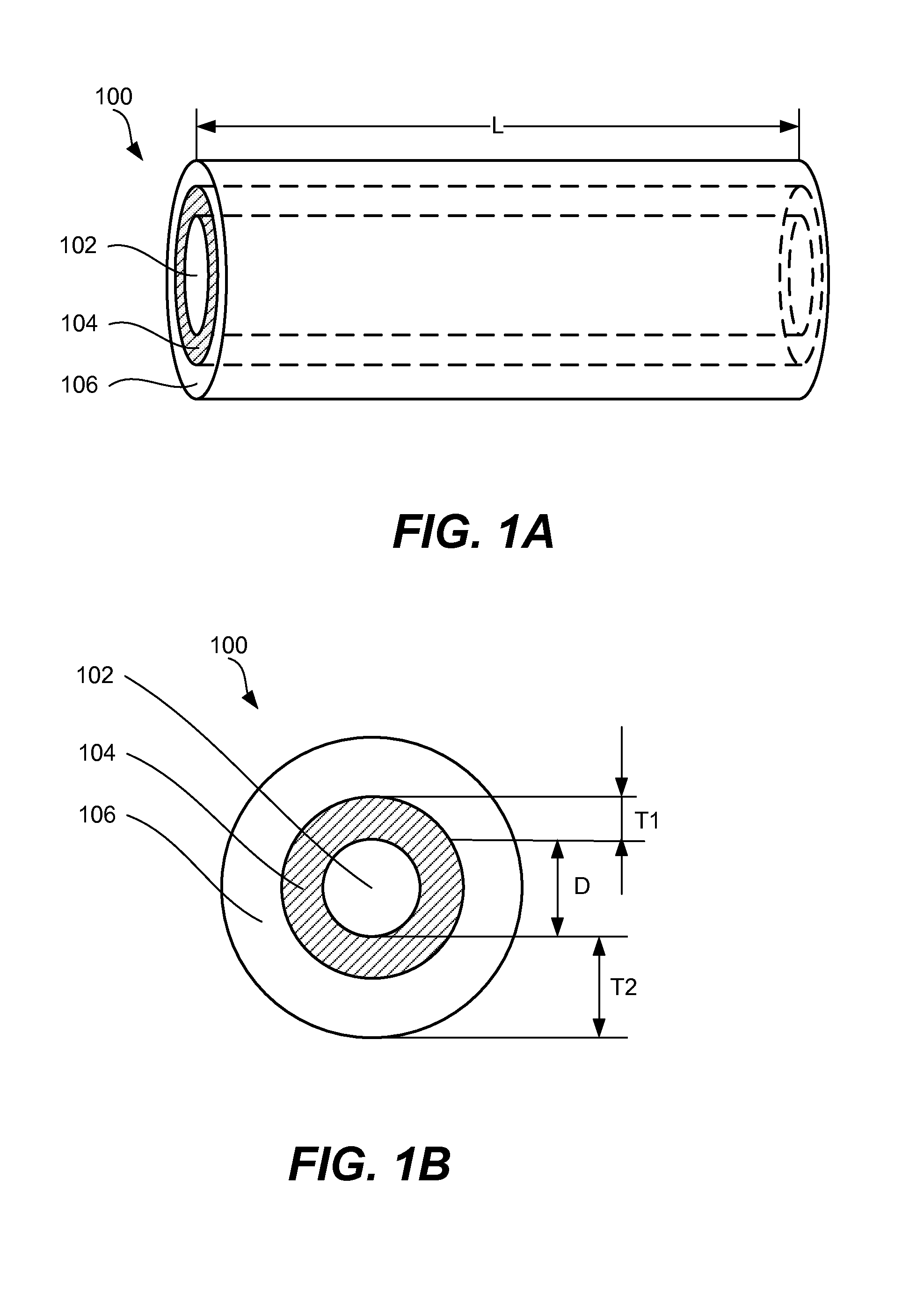
Nano graphene reinforced nanocomposite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100143798A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthActive material electrodesSecondary cellsLithium metalNanocomposite
A solid nanocomposite particle composition for lithium metal or lithium ion battery electrode applications. The composition comprises: (A) an electrode active material in a form of fine particles, rods, wires, fibers, or tubes with a dimension smaller than 1 μm; (B) nano graphene platelets (NGPs); and (C) a protective matrix material reinforced by the NGPs; wherein the graphene platelets and the electrode active material are dispersed in the matrix material and the NGPs occupy a weight fraction wg of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, the electrode active material occupies a weight fraction wa of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, and the matrix material occupies a weight fraction wm of at least 2% of the total nanocomposite weight with wg+wa+wm=1. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon, polymeric carbon, or meso-phase carbon. Such a solid nanocomposite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling stability. For a cathode application, the resulting lithium metal or lithium ion battery exhibits an exceptionally high cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Materials and configurations for scalable microbial fuel cells
ActiveUS20070259217A1Raise the potentialTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesActive material electrodesElectricityMicrobial fuel cell
Devices for production of electricity and / or hydrogen gas are provided by the present invention. In particular, microbial fuel cells for production of electricity and modified microbial fuel cells for production of hydrogen are detailed. A tube cathode is provided which includes a membrane forming a general tube shape. An anode is provided which has a specific surface area greater than 100 m2 / m3. In addition, the anode is substantially non-toxic to anodophilic bacteria. Combinations of particular anodes and cathodes are included in microbial fuel cells and modified microbial fuel cells.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Hdp-cvd multistep gapfill process
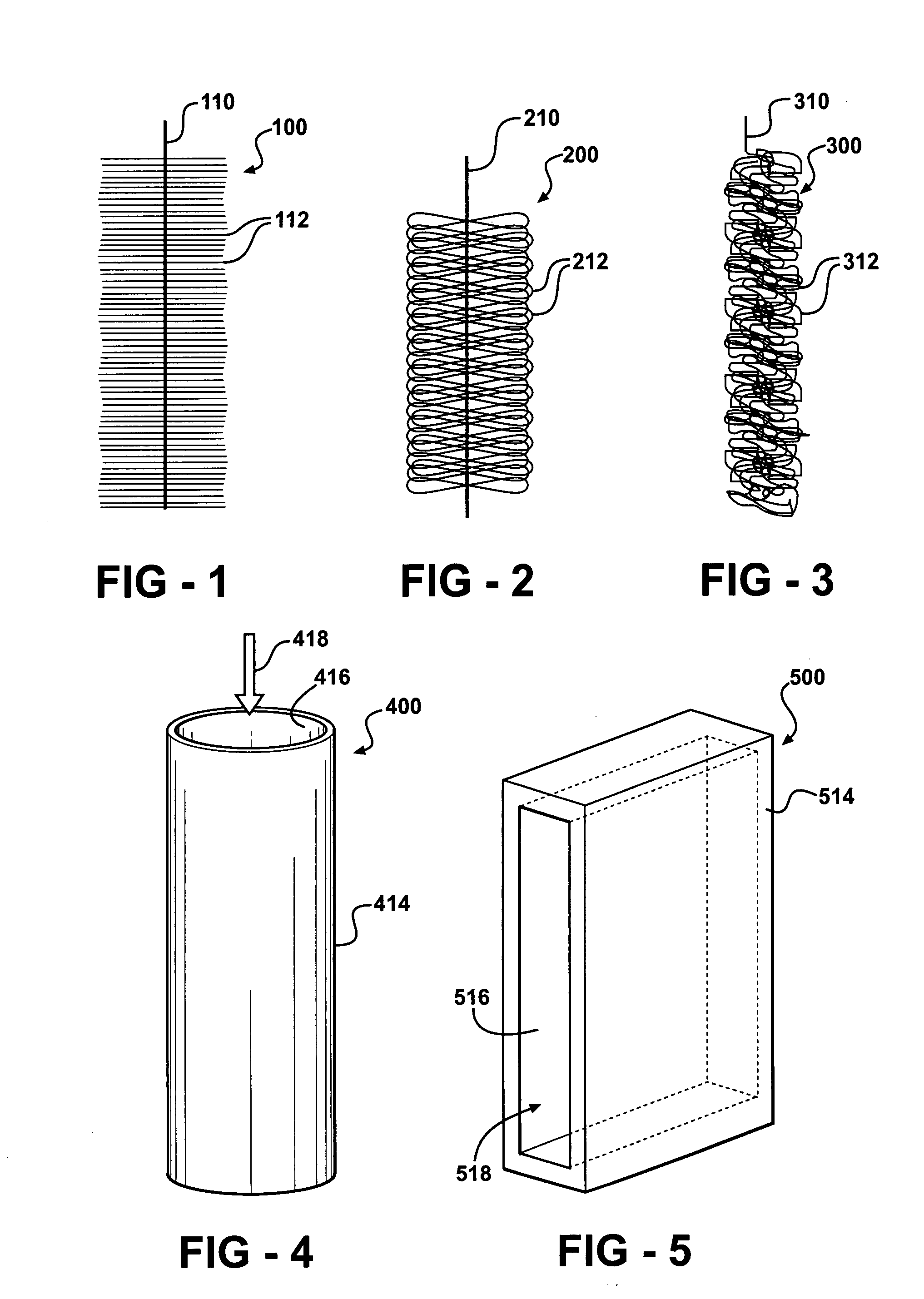
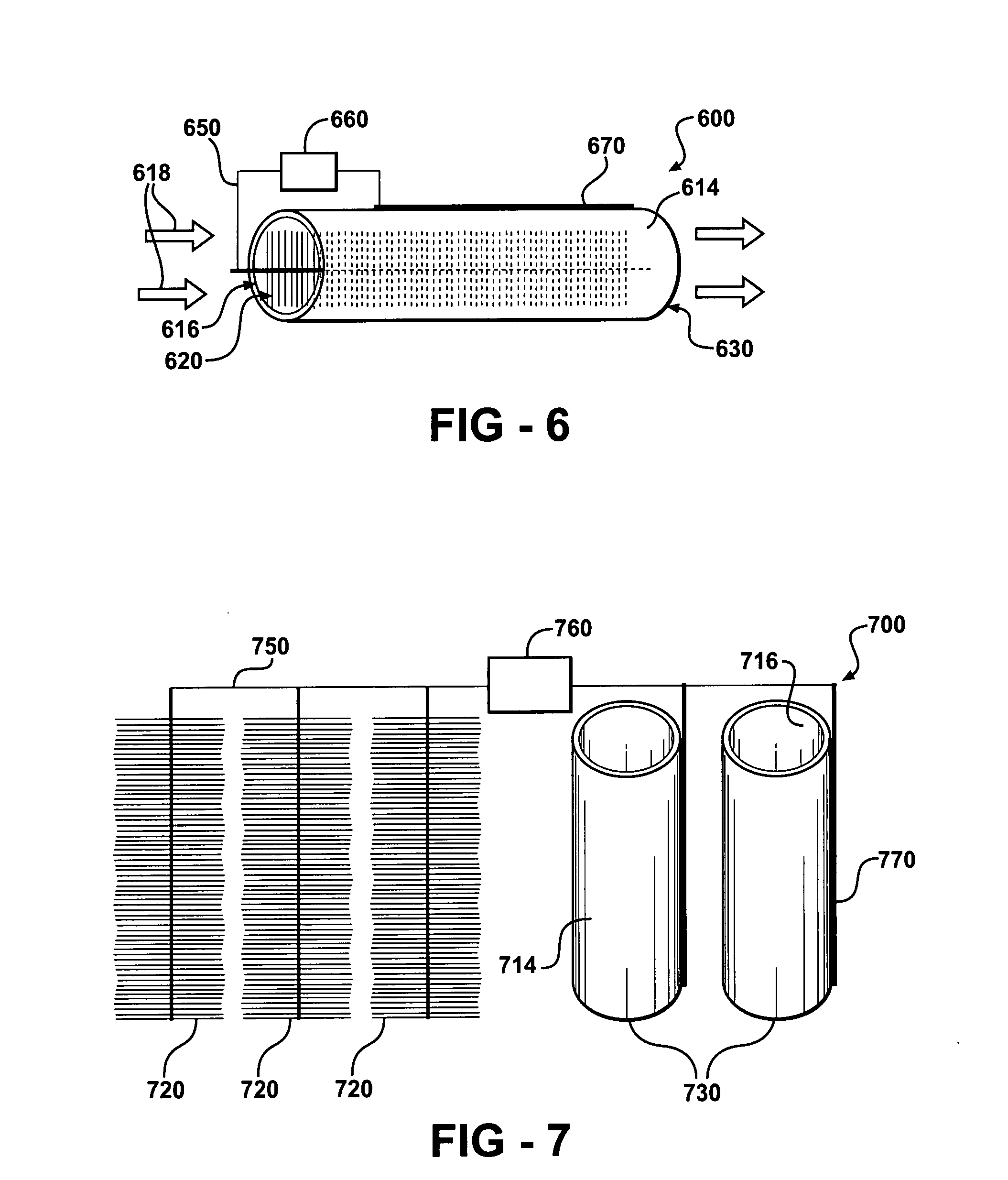
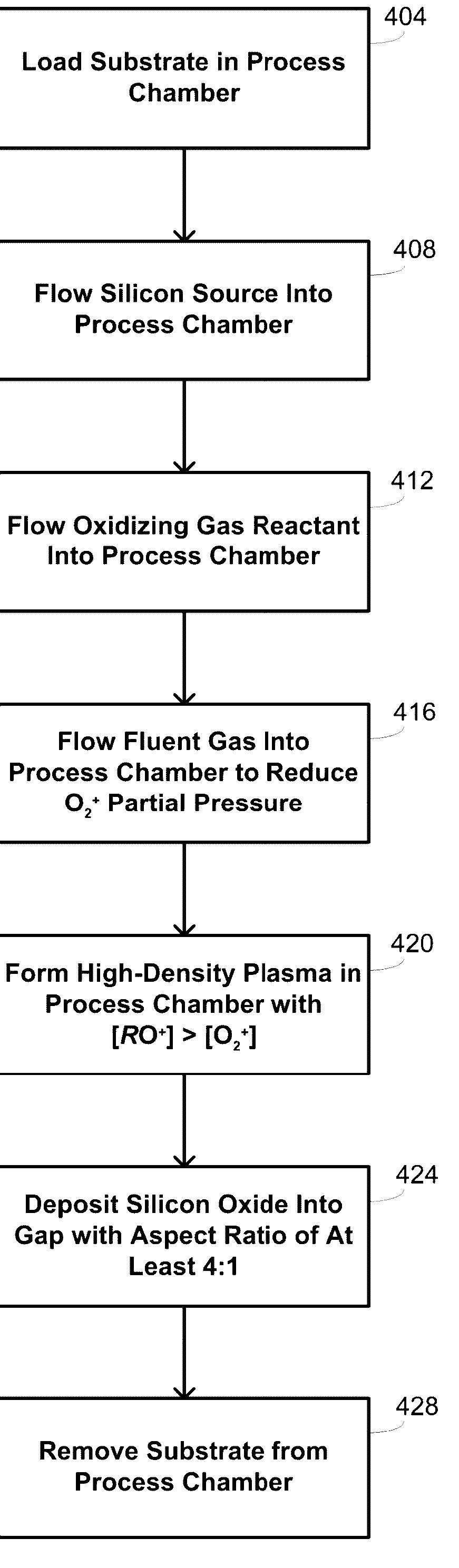
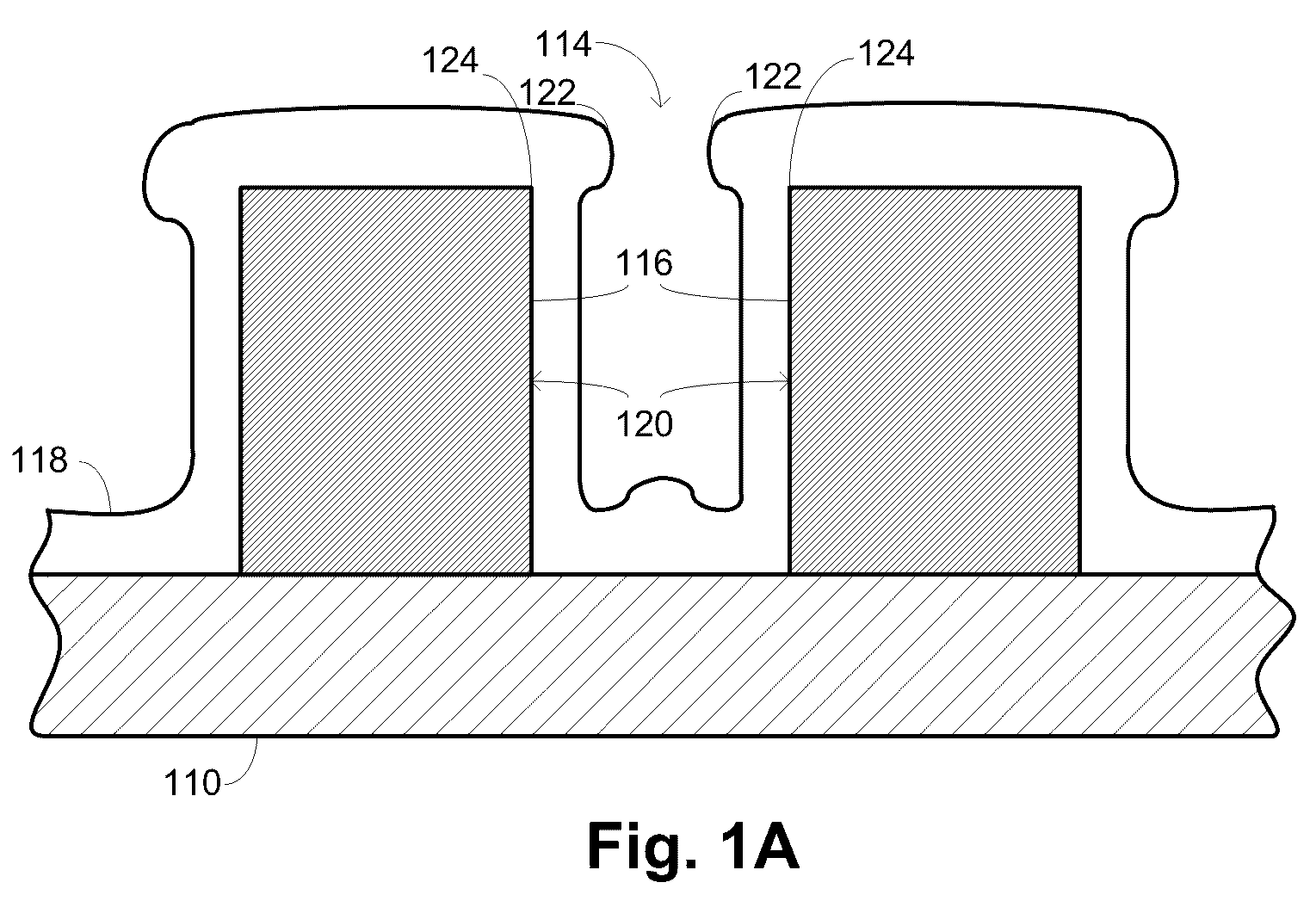
InactiveUS20040245091A1Reduce molecular weightReduced sputtering characteristicVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingProduct gasChemistry
Abstract of the Disclosure A gapfill process is provided using cycling of HDP-CVD deposition, etching, and deposition step. The fluent gas during the first deposition step includes an inert gas such as He, but includes H2 during the remainder deposition step. The higher average molecular weight of the fluent gas during the first deposition step provides some cusping over structures that define the gap to protect them during the etching step. The lower average molecular weight of the fluent gas during the remainder deposition step has reduced sputtering characteristics and is effective at filling the remainder of the gap.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electroactive high storage capacity polyacetylene-co-polysulfur materials and electrolytic cells containing same
InactiveUS6117590AHigh storage capacity per unit weightFacilitates electron transportElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrochemical cellElectrode material
The present invention relates to novel electroactive energy storing polyacetylene-co-polysulfur (PAS) materials of general formula (C2Sx)n wherein x is greater than 1 to about 100, and n is equal to or greater than 2. This invention also relates to novel rechargeable electrochemical cells containing positive electrode materials comprised of said polyacetylene-co-polysulfur materials with improved storage capacity and cycle life at ambient and sub-ambient temperatures.
Owner:THE BANK OF NEW YORK +1
Mesoporous network electrode for electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20040131934A1Simplifies production of cellFull penetrationMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesLithiumNanoparticle
A high kinetics rate electrochemical cell in which at least one of the electrodes is composed of a mesostructural electroactive material comprising nanoparticles forming a three-dimensional framework structure of mesoporous texture having a bicontinuous junction of large specific surface area with the electrolyte. A low temperature method of preparation of the electrodes employs a high-speed deposition of the electrically active material in the form of a thin film. The application of said electrodes in high power lithium ion insertion batteries, photovoltaic cells, supercapacitors and fast electrochromic devices is disclosed.
Owner:FRANCOIS SUGNAUX
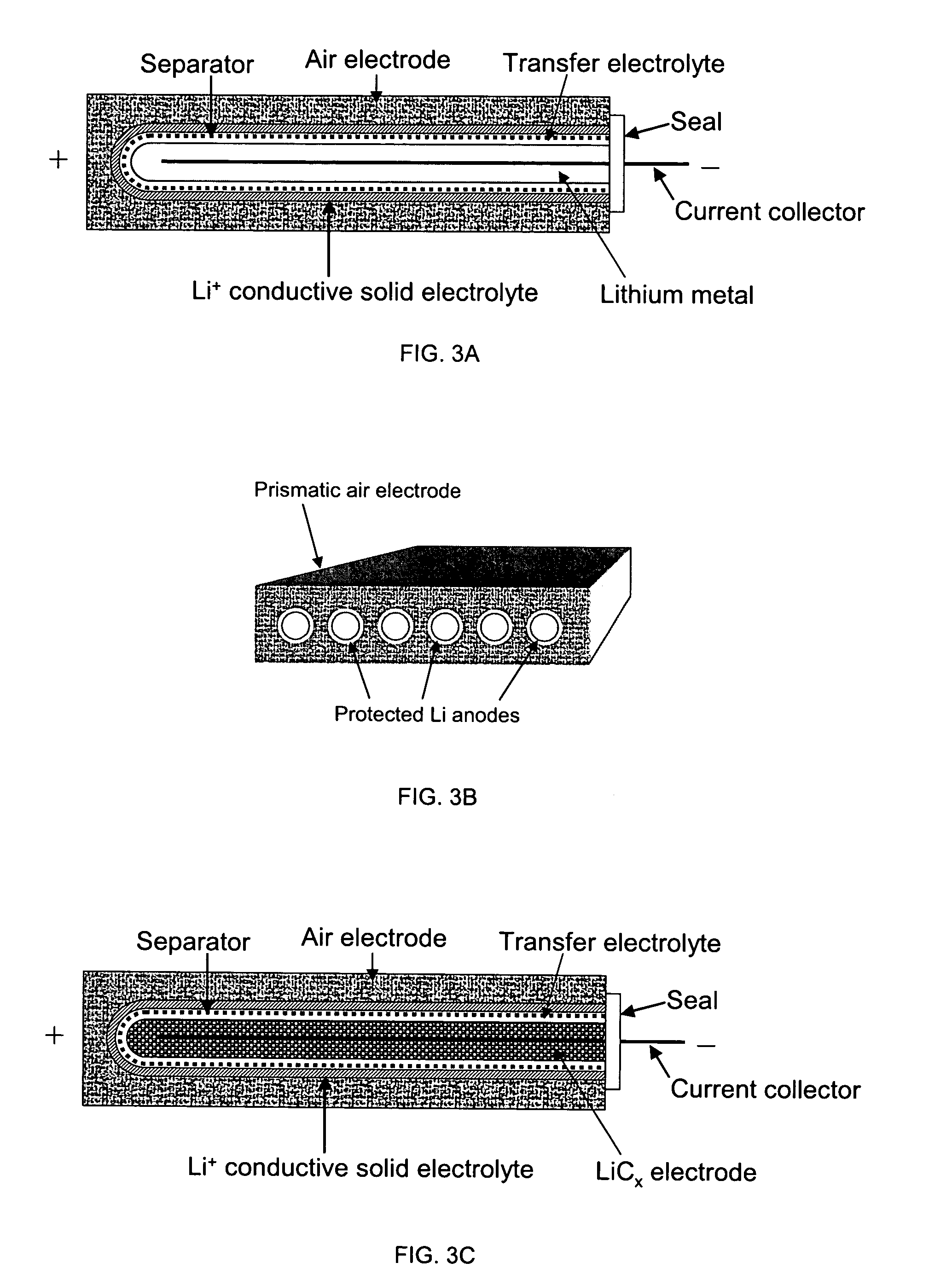
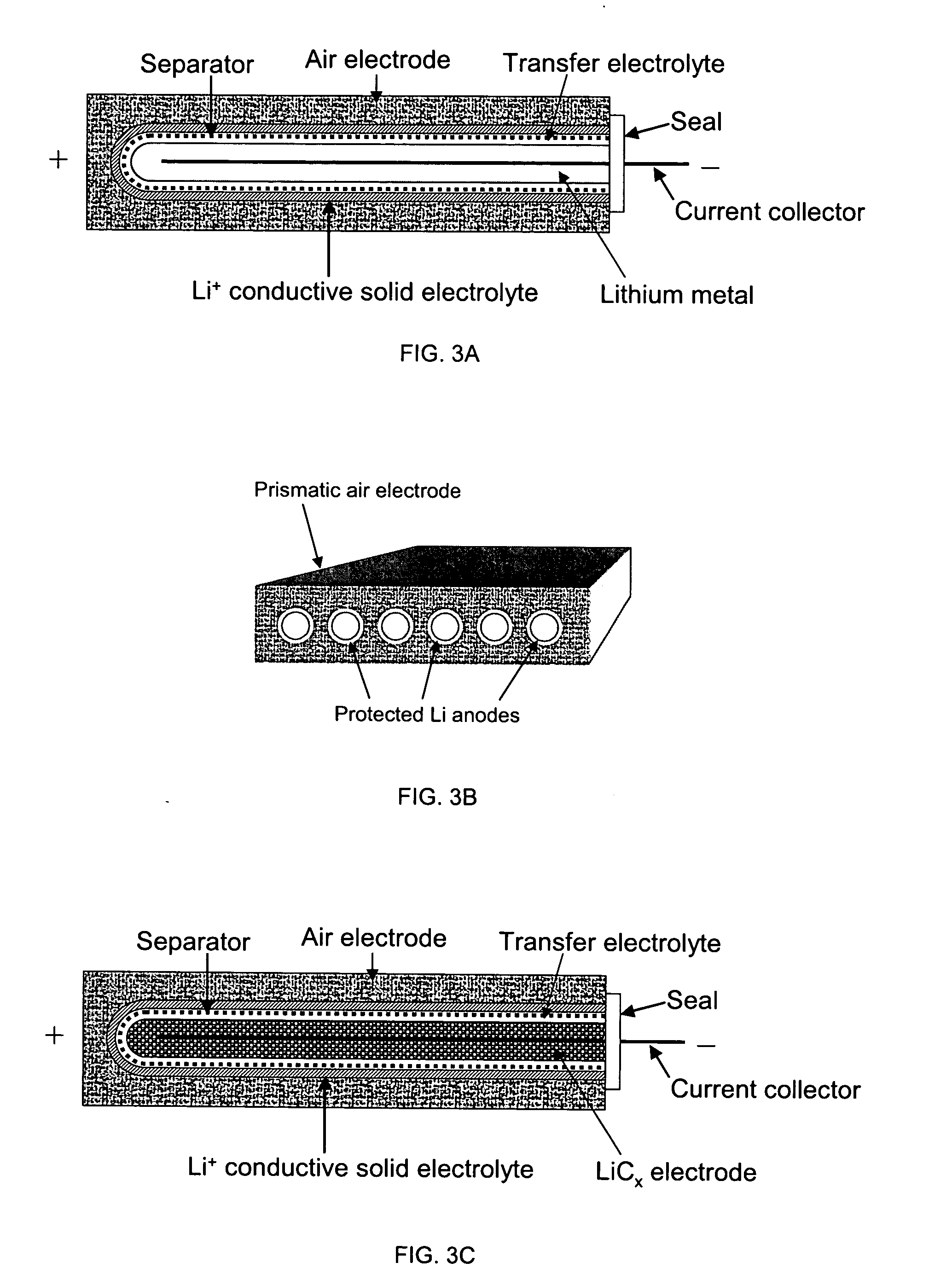
Protected active metal electrode and battery cell structures with non-aqueous interlayer architecture
ActiveUS7282295B2Avoid harmful reactionsFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsMetal electrodesBattery cell
Active metal and active metal intercalation electrode structures and battery cells having ionically conductive protective architecture including an active metal (e.g., lithium) conductive impervious layer separated from the electrode (anode) by a porous separator impregnated with a non-aqueous electrolyte (anolyte). This protective architecture prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the impervious layer, which may include aqueous or non-aqueous liquid electrolytes (catholytes) and / or a variety electrochemically active materials, including liquid, solid and gaseous oxidizers. Safety additives and designs that facilitate manufacture are also provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
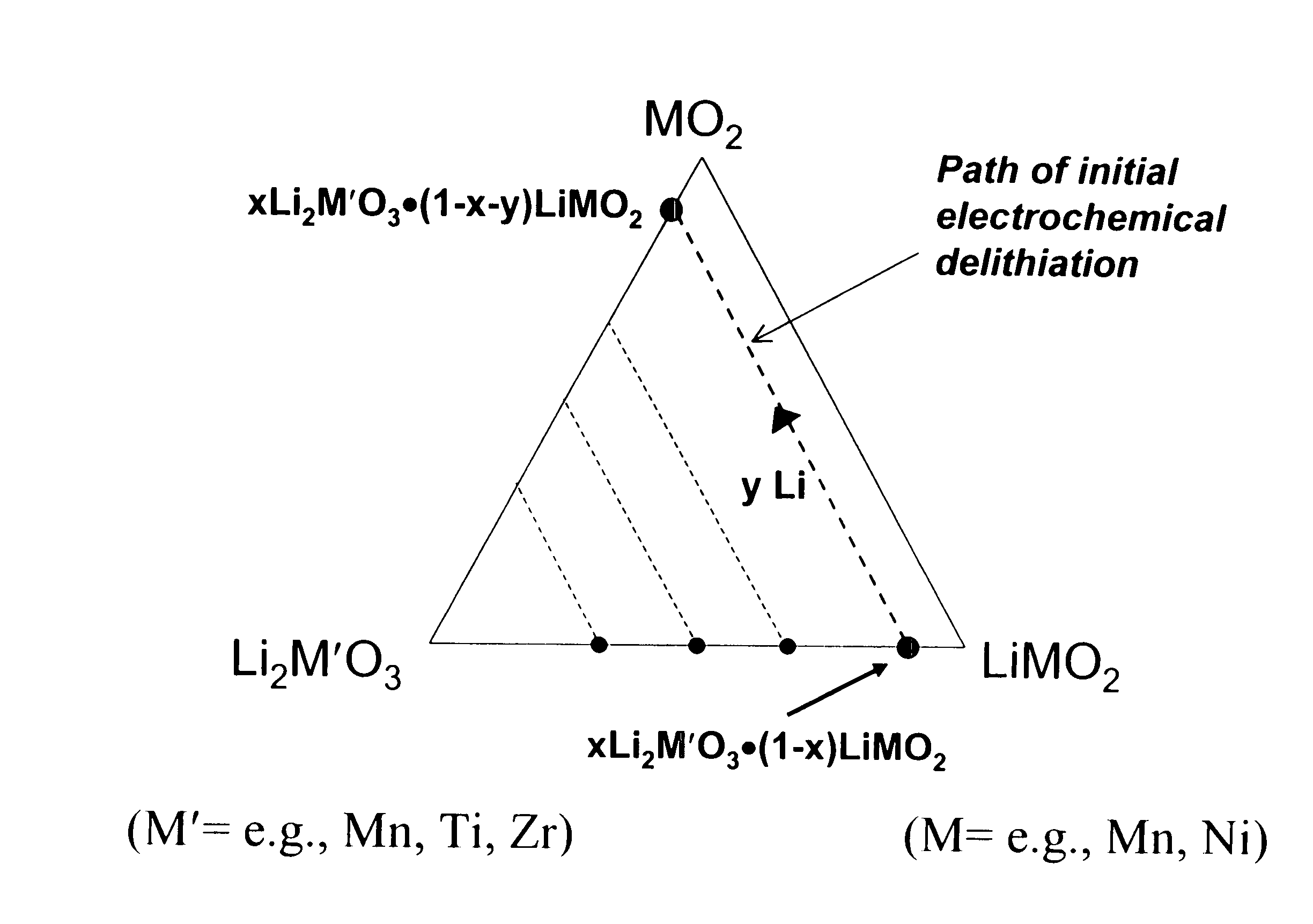
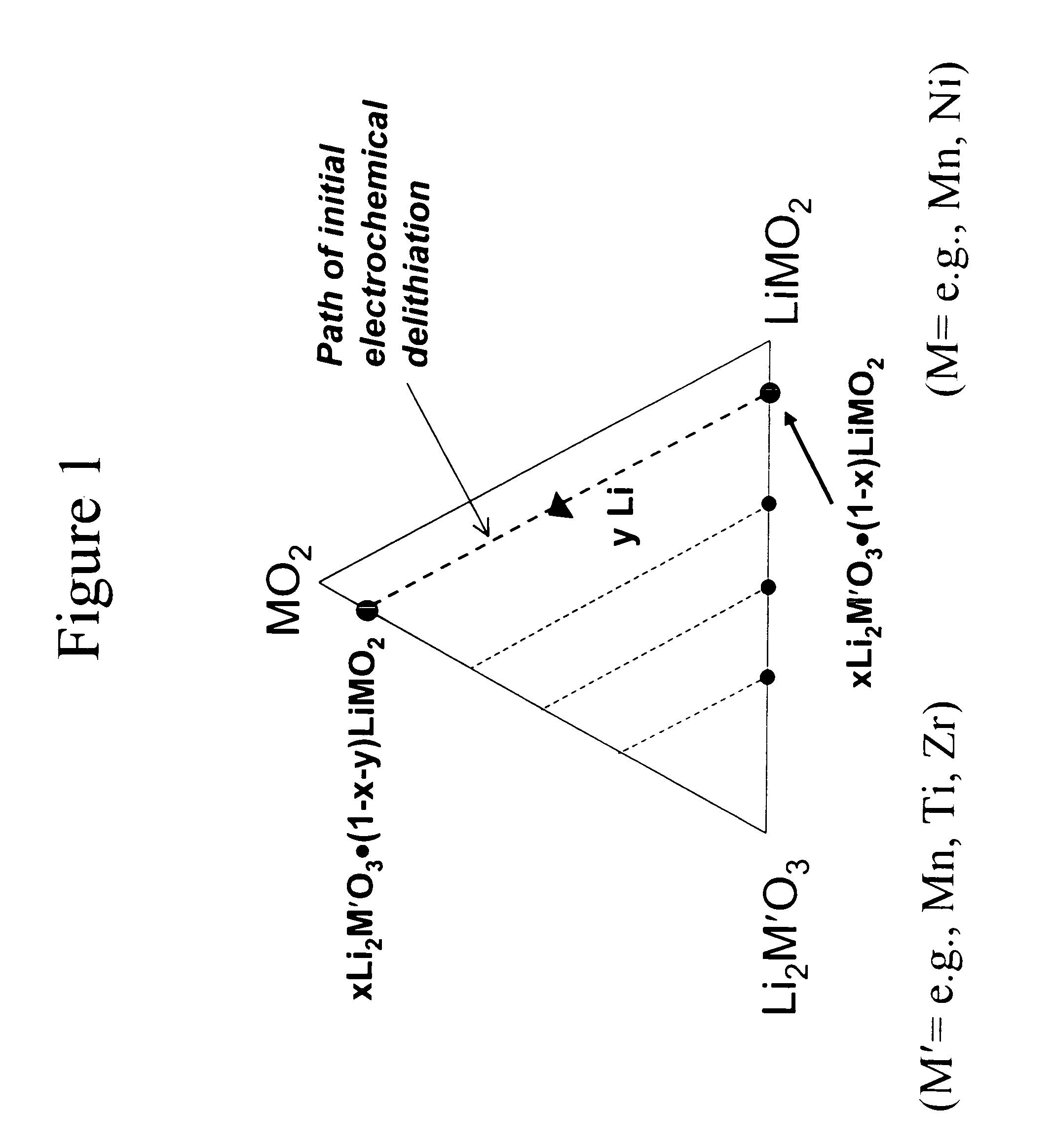
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS7135252B2Improve structural stabilityImprove stabilityZirconium compoundsSecondary cellsLithium metalOxidation state
A lithium metal oxide positive electrode for a non-aqueous lithium cell is disclosed. The cell is prepared in its initial discharged state and has a general formula xLiMO2.(1-x)Li2M′O3 in which 0<x<1, and where M is more than one ion with an average trivalent oxidation state and with at least one ion being Ni, and where M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state. Complete cells or batteries are disclosed with anode, cathode and electrolyte as are batteries of several cells connected in parallel or series or both.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE +1
Protected active metal electrode and battery cell structures with non-aqueous interlayer architecture
ActiveUS20050175894A1Avoid harmful reactionsHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesMetal electrodesBattery cell
Active metal and active metal intercalation electrode structures and battery cells having ionically conductive protective architecture including an active metal (e.g., lithium) conductive impervious layer separated from the electrode (anode) by a porous separator impregnated with a non-aqueous electrolyte (anolyte). This protective architecture prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the impervious layer, which may include aqueous or non-aqueous liquid electrolytes (catholytes) and / or a variety electrochemically active materials, including liquid, solid and gaseous oxidizers. Safety additives and designs that facilitate manufacture are also provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
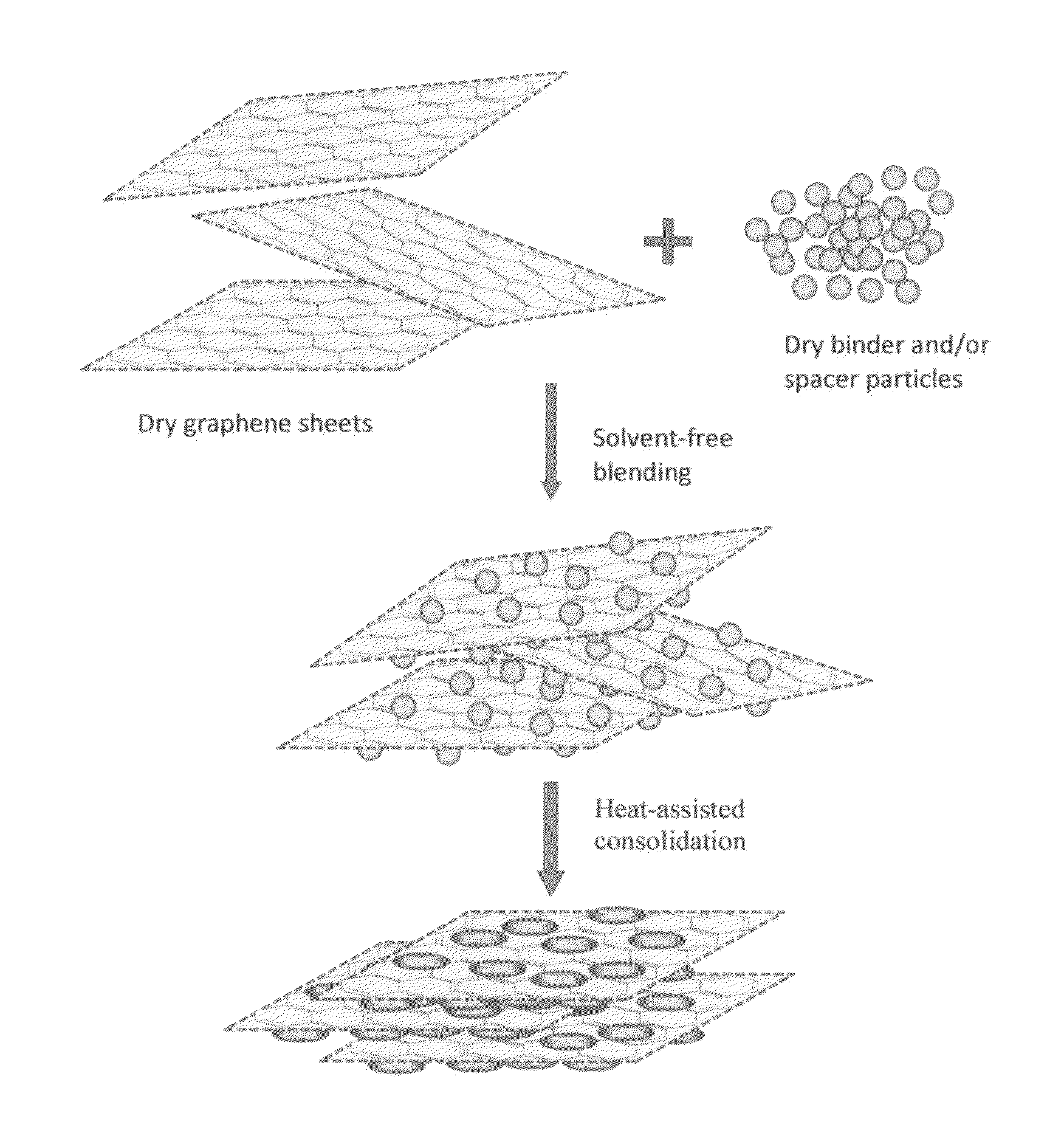
Solvent-free process based graphene electrode for energy storage devices
PendingUS20140030590A1Inexpensive and durable and highly reliableHigh capacitanceMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene flakeSolvent free
Disclosed is an electrode for an electrochemical energy storage device, the electrode comprising a self-supporting layer of a mixture of graphene sheets and spacer particles and / or binder particles, wherein the electrode is prepared without using water, solvent, or liquid chemical. The graphene electrode prepared by the solvent-free process exhibits many desirable features and advantages as compared to the corresponding electrode prepared by a known wet process. These advantages include a higher electrode specific surface area, higher energy storage capacity, improved or higher packing density or tap density, lower amount of binder required, lower internal electrode resistance, more consistent and uniform dispersion of graphene sheets and binder, reduction or elimination of undesirable effect of electrolyte oxidation or decomposition due to the presence of water, solvent, or chemical, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Hybrid anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090117466A1Superior multiple-cycle behaviorSmall capacity fadeAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialHybrid materialSodium-ion battery
The present invention provides an exfoliated graphite-based hybrid material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing alkali or alkaline metal ions (particularly, lithium ions); and (b) exfoliated graphite flakes that are substantially interconnected to form a porous, conductive graphite network comprising pores, wherein at least one of the particles or coating resides in a pore of the network or attached to a flake of the network and the exfoliated graphite amount is in the range of 5% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating is in the range of 95% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, excellent reversible capacity, and long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Powder material, electrode structure using the powder material, and energy storage device having the electrode structure
InactiveUS20080003503A1Fast chargingIncrease energy densityNon-metal conductorsElectrode manufacturing processesElectrical conductorHigh energy
A powder material which can electrochemically store and release lithium ions rapidly in a large amount is provided. In addition, an electrode structure for an energy storage device which can provide a high energy density and a high power density and has a long life, and an energy storage device using the electrode structure are provided. In a powder material which can electrochemically store and release lithium ions, the surface of particles of one of silicon metal and tin metal and an alloy of any thereof is coated by an oxide including a transition metal element selected from the group consisting of W, Ti, Mo, Nb, and V as a main component. The electrode structure includes the powder material. The battery device includes a negative electrode having the electrode structure, a lithium ion conductor, and a positive electrode, and utilizes an oxidation reaction of lithium and a reduction reaction of lithium ion.
Owner:CANON KK
Hybrid electrode and surface-mediated cell-based super-hybrid energy storage device containing same
PendingUS20130171502A1Primary cell to battery groupingMaterial nanotechnologyHigh energyLithium metal
The present invention provides a multi-component hybrid electrode for use in an electrochemical super-hybrid energy storage device. The hybrid electrode contains at least a current collector, at least an intercalation electrode active material storing lithium inside interior or bulk thereof, and at least an intercalation-free electrode active material having a specific surface area no less than 100 m2 / g and storing lithium on a surface thereof, wherein the intercalation electrode active material and the intercalation-free electrode active material are in electronic contact with the current collector. The resulting super-hybrid cell exhibits exceptional high power and high energy density, and long-term cycling stability that cannot be achieved with conventional supercapacitors, lithium-ion capacitors, lithium-ion batteries, and lithium metal secondary batteries.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
Composite bipolar plate for electrochemical cells
A bipolar separator plate for fuel cells consists of a molded mixture of a vinyl ester resin and graphite powder. The plate serves as a current collector and may contain fluid flow fields for the distribution of reactant gases. The material is inexpensive, electrically conductive, lightweight, strong, corrosion resistant, easily mass produced, and relatively impermeable to hydrogen gas. The addition of certain fiber reinforcements and other additives can improve the properties of the composite material without significantly increasing its overall cost.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Separation of electrolytes
Methods and articles relating to separation of electrolyte compositions within lithium batteries are provided. The lithium batteries described herein may include an anode having lithium as the active anode species and a cathode having sulfur as the active cathode species. Suitable electrolytes for the lithium batteries can comprise a heterogeneous electrolyte including a first electrolyte solvent (e.g., dioxolane (DOL)) that partitions towards the anode and is favorable towards the anode (referred to herein as an “anode-side electrolyte solvent”) and a second electrolyte solvent (e.g., 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME)) that partitions towards the cathode and is favorable towards the cathode (and referred to herein as an “cathode-side electrolyte solvent”). By separating the electrolyte solvents during operation of the battery such that the anode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the anode and the cathode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the cathode, the battery can benefit from desirable characteristics of both electrolyte solvents (e.g., relatively low lithium reactivity of the anode-side electrolyte solvent and relatively high polysulfide solubility of the cathode-side electrolyte solvent).
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Compliant seal structures for protected active metal anodes
ActiveUS20070037058A1Reduced ionic contact areaReduce the total massPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrode manufacturing processesOptoelectronicsAnodic protection
Protected anode architectures have ionically conductive protective membrane architectures that, in conjunction with compliant seal structures and anode backplanes, effectively enclose an active metal anode inside the interior of an anode compartment. This enclosure prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment external to the anode compartment, which may include aqueous, ambient moisture, and / or other materials corrosive to the active metal. The compliant seal structures are substantially impervious to anolytes, catholyes, dissolved species in electrolytes, and moisture and compliant to changes in anode volume such that physical continuity between the anode protective architecture and backplane are maintained. The protected anode architectures can be used in arrays of protected anode architectures and battery cells of various configurations incorporating the protected anode architectures or arrays.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery, a method of preparing the same, and a rechargeable lithium battery comprising the same
ActiveUS20050233213A1Improved cycle-life characteristic and charge and discharge characteristicIncrease chanceElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsHigh rateSilicon oxide
The present invention relates to a negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery, which includes a silicon-based composite having a silicon oxide of the form SiOX where x≦1.5 and at least one element selected from the group consisting of B, P, Li, Ge, Al, and V, and a carbonaceous material. The negative active material of the present invention can improve the cycle-life and high-rate charge / discharge characteristics of a rechargeable lithium battery.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Electrode for rechargeable lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS7192673B1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsInhibition formationElectrode manufacturing processesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAmorphous siliconMaterials science
An electrode for a rechargeable lithium battery which includes a thin film composed of active material that expands and shrinks as it stores and releases lithium, e.g., a microcrystalline or amorphous silicon thin film, deposited on a current collector, characterized in that said current collector exhibits a tensile strength (=tensile strength (N / mm2) per sectional area of the current collector material×thickness (mm) of the current collector) of not less than 3.82 N / mm.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
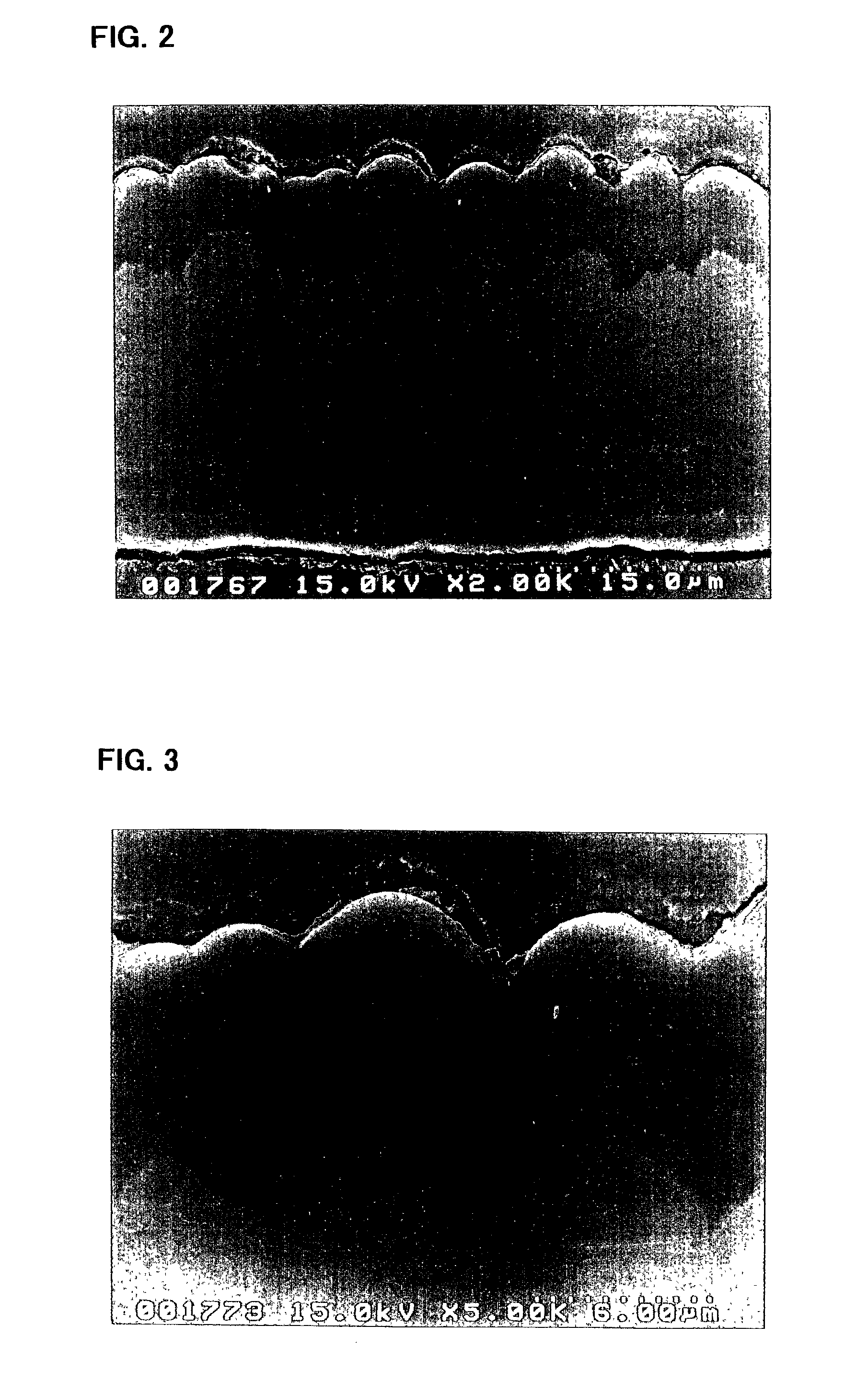
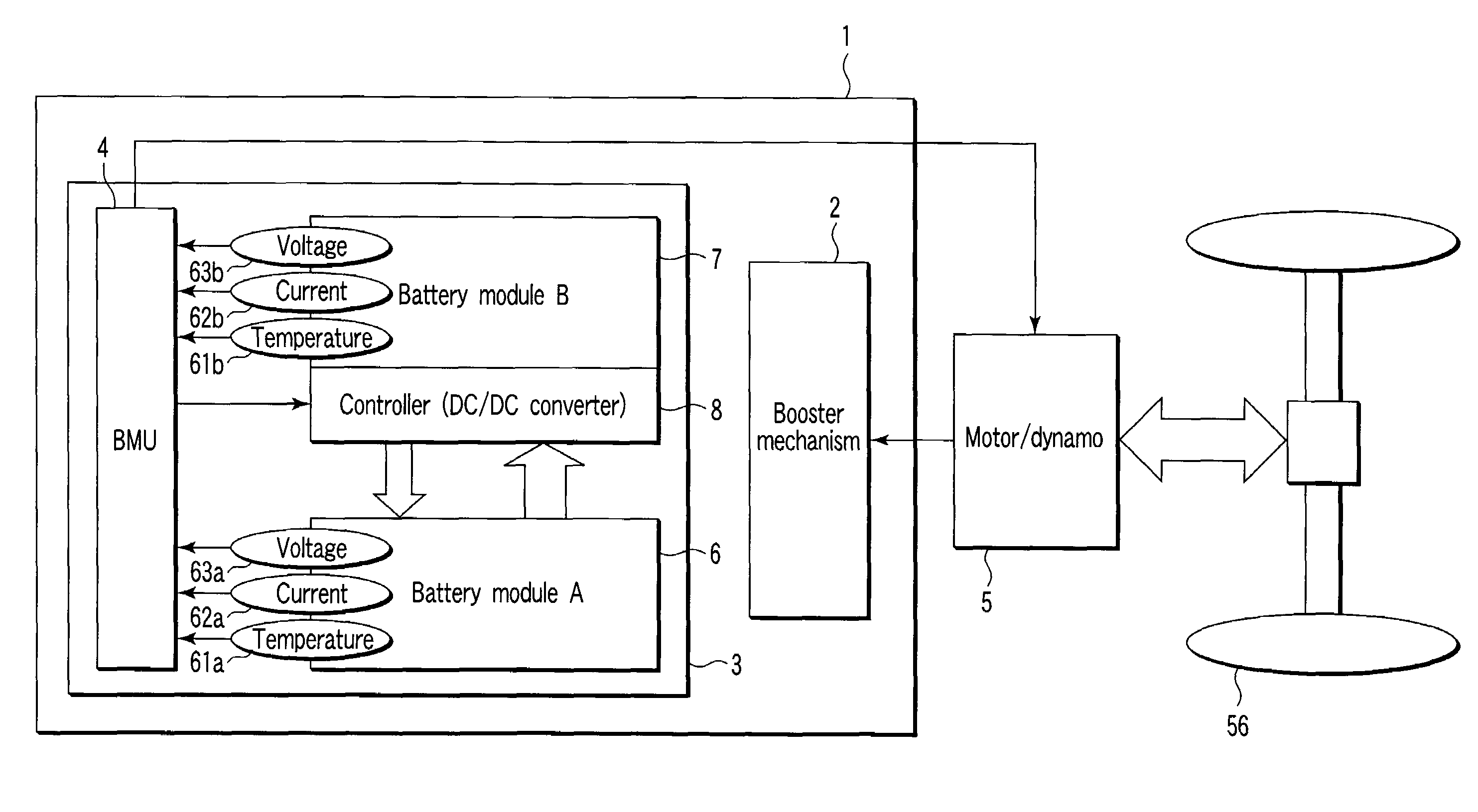
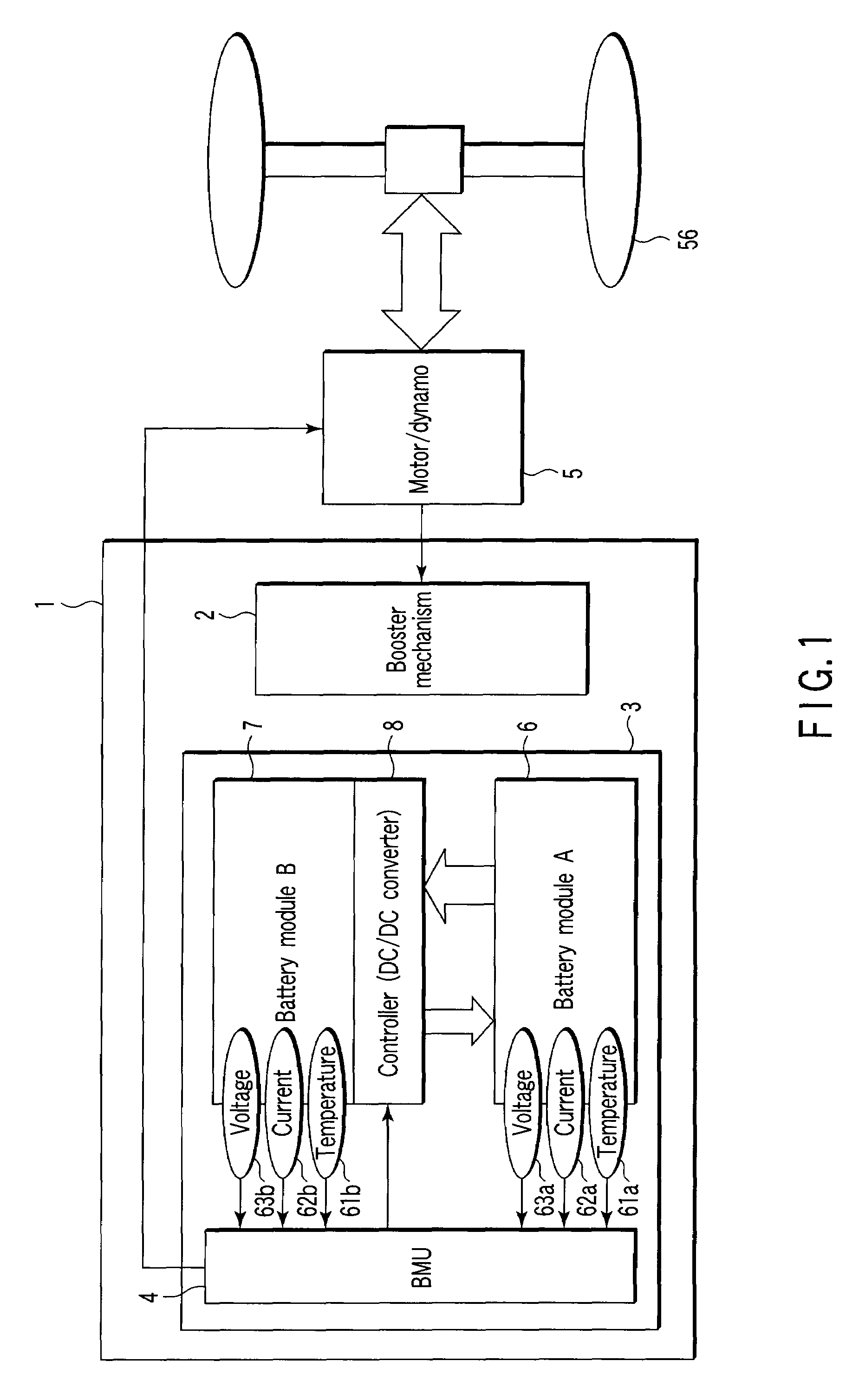
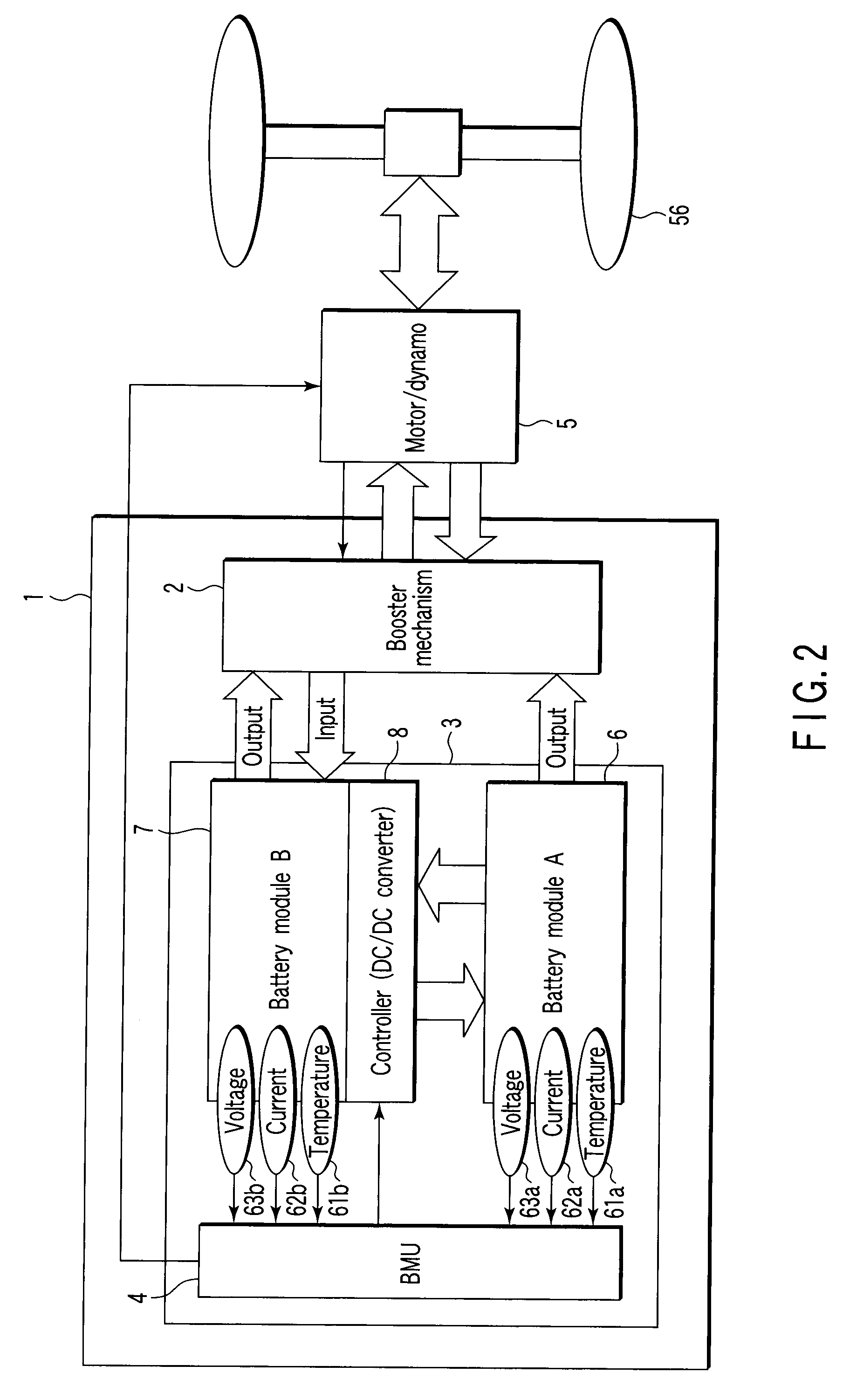
Storage battery system, on-vehicle power supply system, vehicle and method for charging storage battery system
ActiveUS20070284159A1Efficient chargingKeep for a long timeBatteries circuit arrangementsRailway vehiclesLithiumElectrical battery
A storage battery system includes a battery module A with a first nonaqueous electrolyte battery including a negative-electrode material which has an average grain size of 2 μm or more and is used to occlude and discharge lithium ions, a battery module B with a second nonaqueous electrolyte battery set at a lithium-ion-occluding potential of 0.4V (vs.Li / Li) or more, and including a negative-electrode material which has an average grain size of primary particles of 1 μm or less and is used to occlude lithium ions, and a controller configured to intermittently connect the module A to the module B to intermittently supply power from the module A to the module B to set a charge state and a discharge depth of the second nonaqueous electrolyte battery within a range of 10 to 90%, when no power is supplied to the module B at least from an outside.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
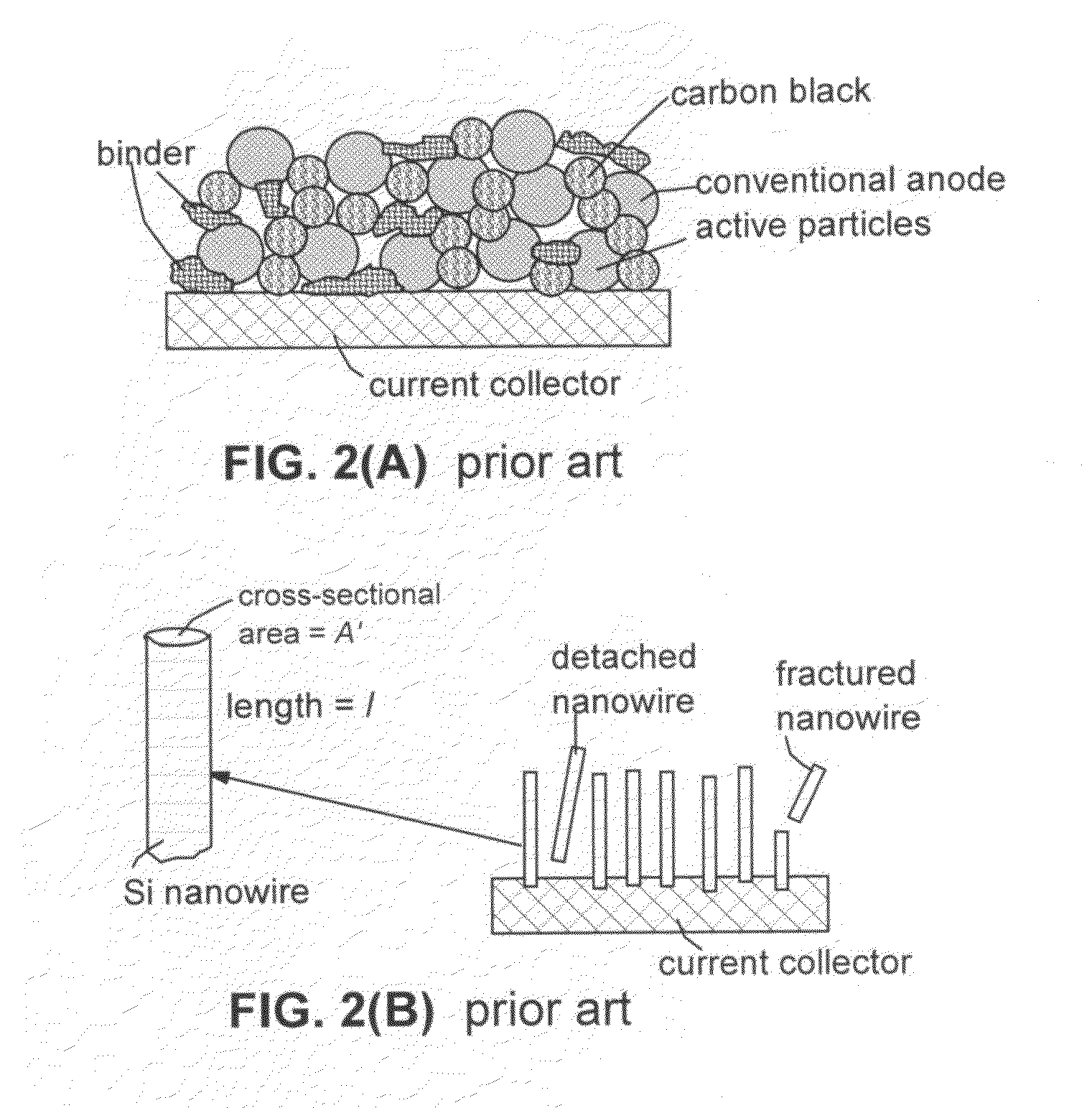
Core-shell high capacity nanowires for battery electrodes
InactiveUS20100330421A1Large capacityInhibition formationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanowireElectrochemistry
Provided are nanostructures containing electrochemically active materials, battery electrodes containing these nanostructures for use in electrochemical batteries, such as lithium ion batteries, and methods of forming the nanostructures and battery electrodes. The nanostructures include conductive cores, inner shells containing active materials, and outer shells partially coating the inner shells. The high capacity active materials having a stable capacity of at least about 1000 mAh / g can be used. Some examples include silicon, tin, and / or germanium. The outer shells may be configured to substantially prevent formation of Solid Electrolyte lnterphase (SEI) layers directly on the inner shells. The conductive cores and / or outer shells may include carbon containing materials. The nanostructures are used to form battery electrodes, in which the nanostructures that are in electronic communication with conductive substrates of the electrodes.
Owner:AMPRIUS INC
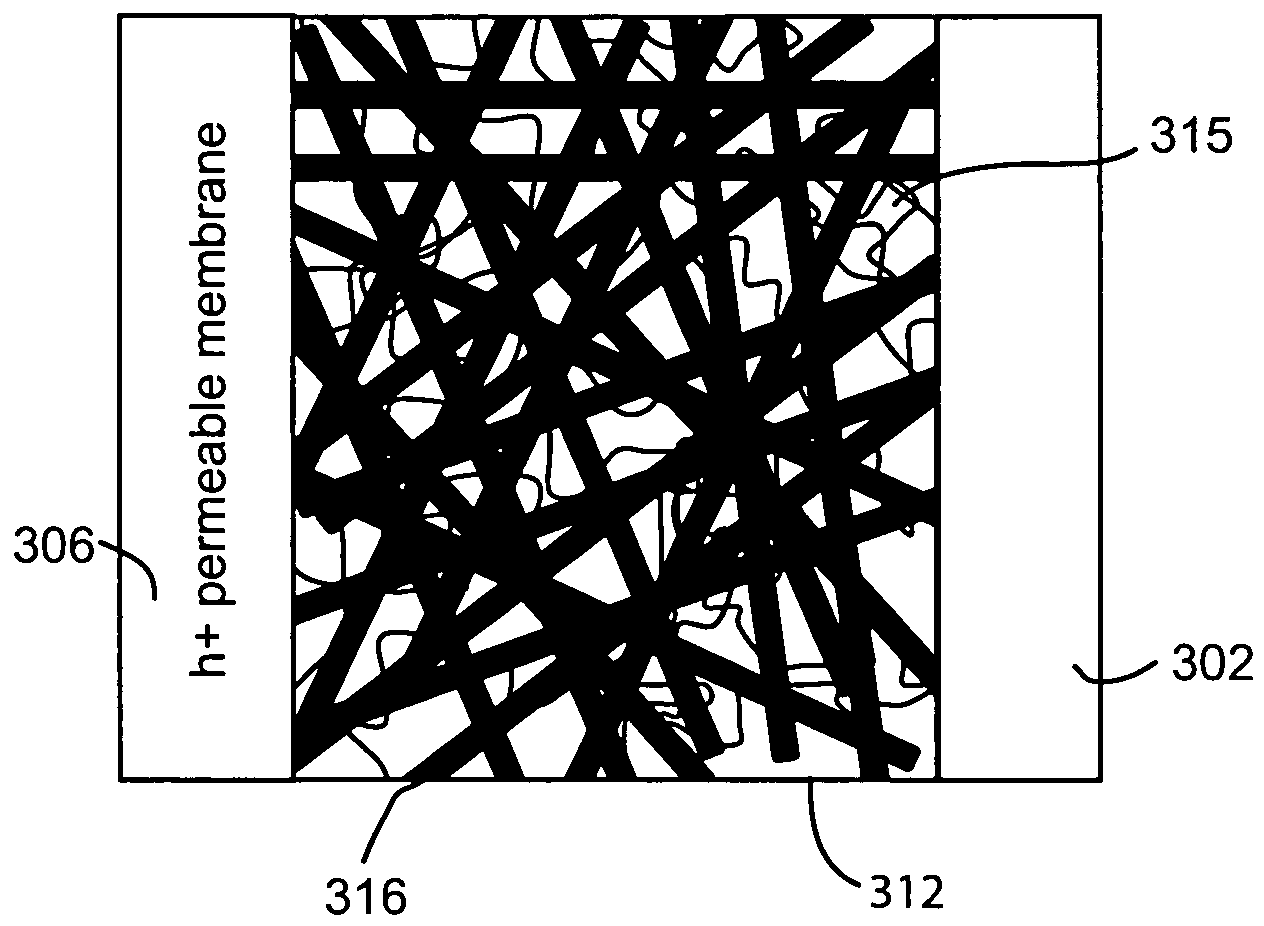
Nanowire-based membrane electrode assemblies for fuel cells
ActiveUS7179561B2High rateLow costMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureNanowirePtru catalyst
The present invention discloses nanowires for use in a fuel cell comprising a metal catalyst deposited on a surface of the nanowires. A membrane electrode assembly for a fuel cell is disclosed which generally comprises a proton exchange membrane, an anode electrode, and a cathode electrode, wherein at least one or more of the anode electrode and cathode electrode comprise an interconnected network of the catalyst supported nanowires. Methods are also disclosed for preparing a membrane electrode assembly and fuel cell based upon an interconnected network of nanowires.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Active metal electrolyzer
InactiveUS20050100793A1Effective isolationReduce environmental pollutionPhotography auxillary processesElectrode manufacturing processesElectrolysisAqueous electrolyte
Electro-winning of active metal (e.g., lithium) ions from a variety of sources including industrial waste, and recycled lithium and lithium-ion batteries is accomplished with an electrolyzer having a protected cathode that is stable against aggressive solvents, including water, aqueous electrolytes, acid, base, and a broad range of protic and aprotic solvents. The electrolyzer has a highly ionically conductive protective membrane adjacent to the alkali metal cathode that effectively isolates (de-couples) the alkali metal electrode from solvent, electrolyte processing and / or cathode environments, and at the same time allows ion transport in and out of these environments. Isolation of the cathode from other components of a battery cell or other electrochemical cell in this way allows the use of virtually any solvent, electrolyte and / or anode material in conjunction with the cathode. The electrolyzer can be configured and operated to claim or reclaim lithium or other active metals from such sources.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Secondary lithium ion battery containing a prelithiated anode
ActiveUS20100173198A1High specific capacityLong charge-discharge cycle lifeSecondary cellsActive material electrodesCharge dischargeGraphene
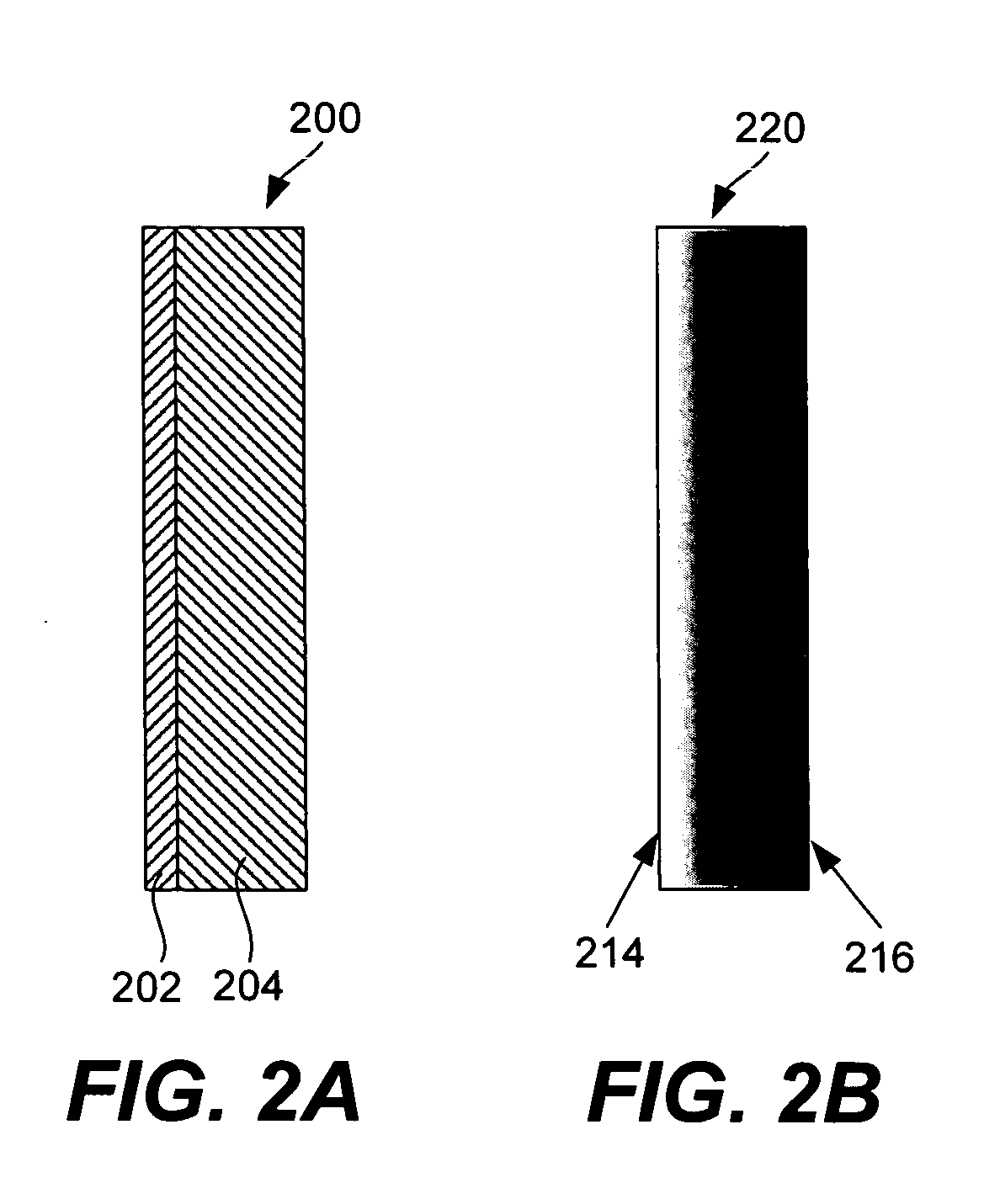
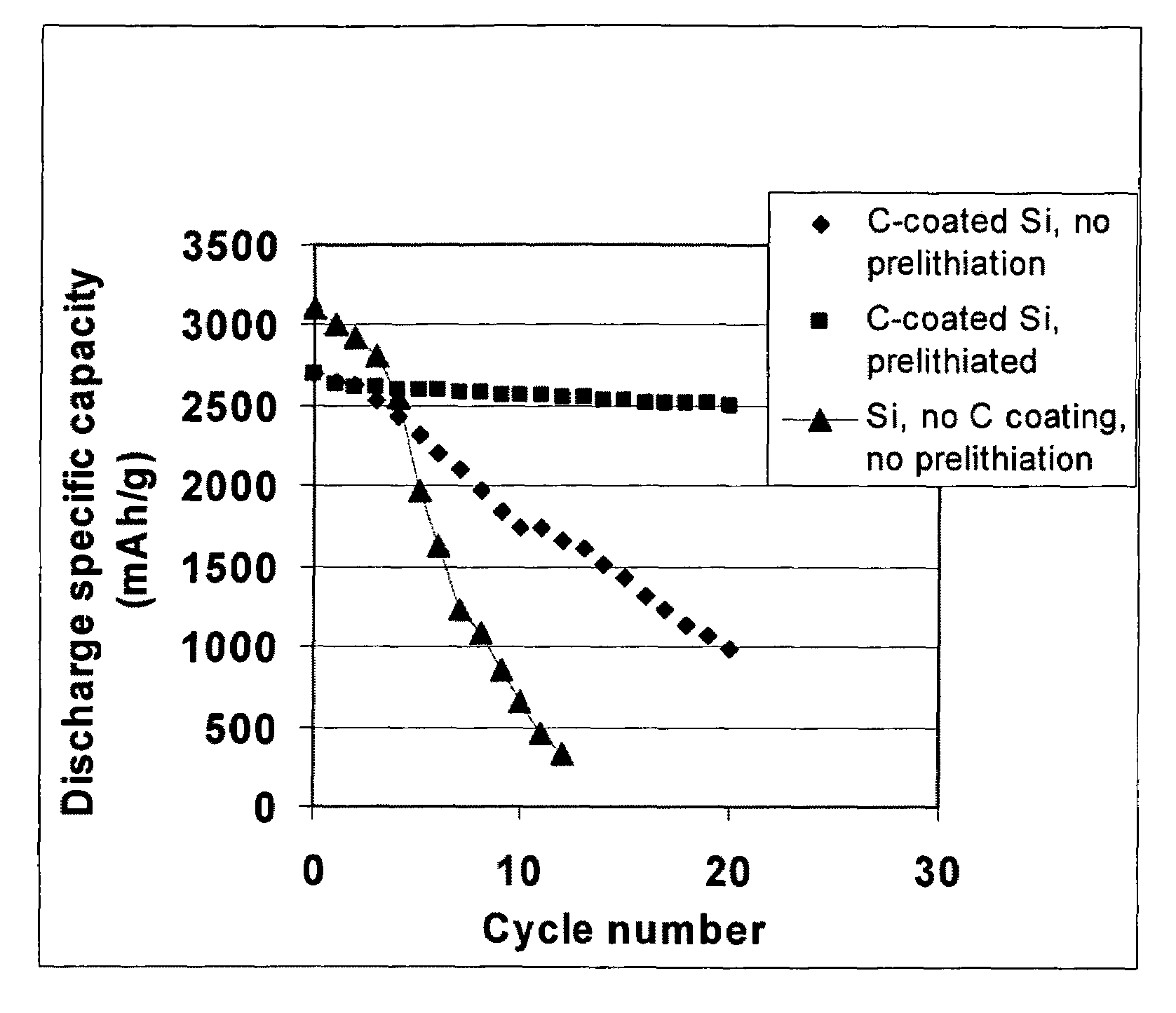
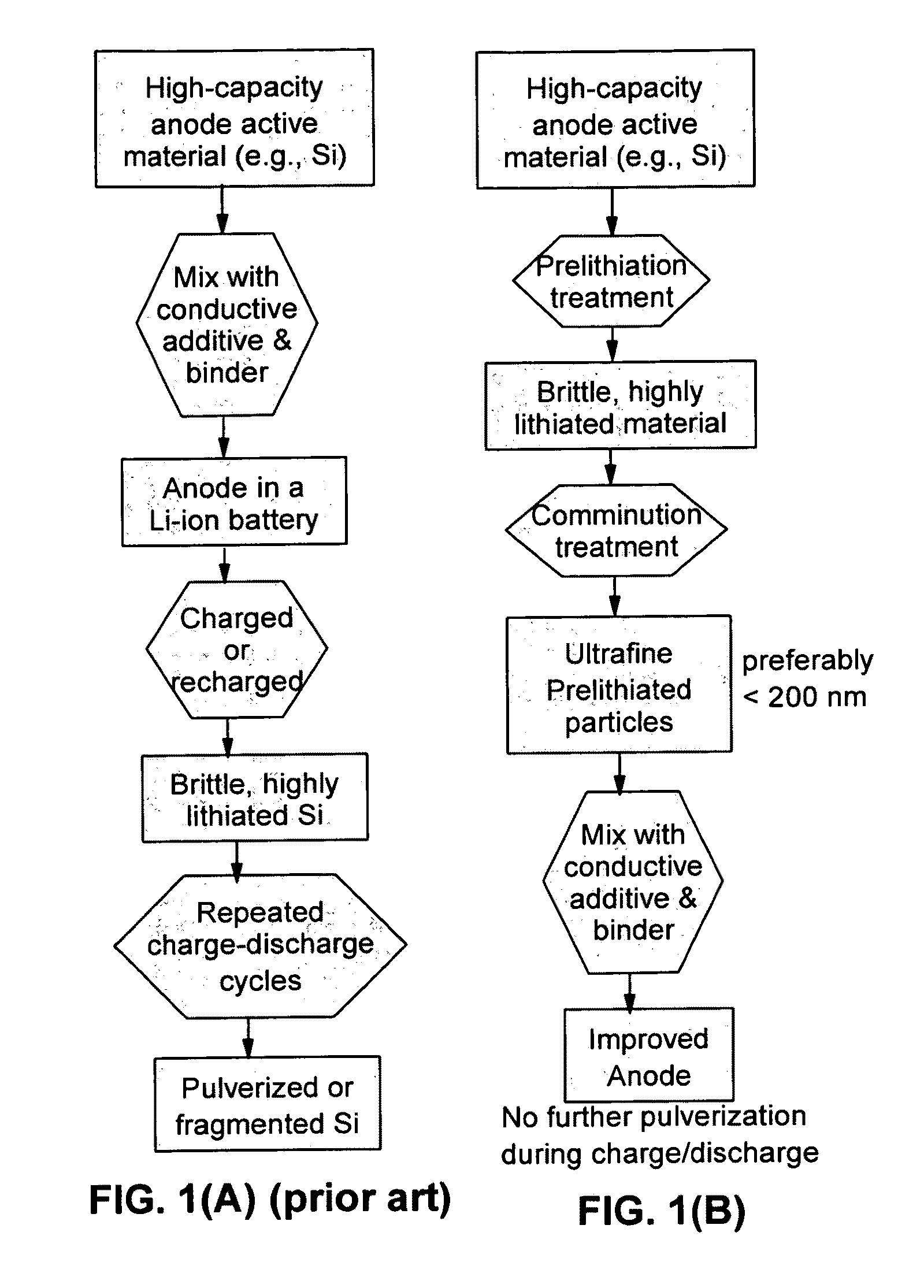
The present invention provides a lithium ion battery that exhibits a significantly improved specific capacity and much longer charge-discharge cycle life. In one preferred embodiment, the battery comprises an anode active material that has been prelithiated and pre-pulverized. This anode may be prepared with a method that comprises (a) providing an anode active material (preferably in the form of fine powder or thin film); (b) intercalating or absorbing a desired amount of lithium into the anode active material to produce a prelithiated anode active material; (c) comminuting the prelithiated anode active material into fine particles with an average size less than 10 μm (preferably <1 μm and most preferably <200 nm); and (d) combining multiple fine particles of the prelithiated anode active material with a conductive additive and / or a binder material to form the anode. Preferably, the prelithiated particles are protected by a lithium ion-conducting matrix or coating material. Further preferably, the matrix material is reinforced with nano graphene platelets.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
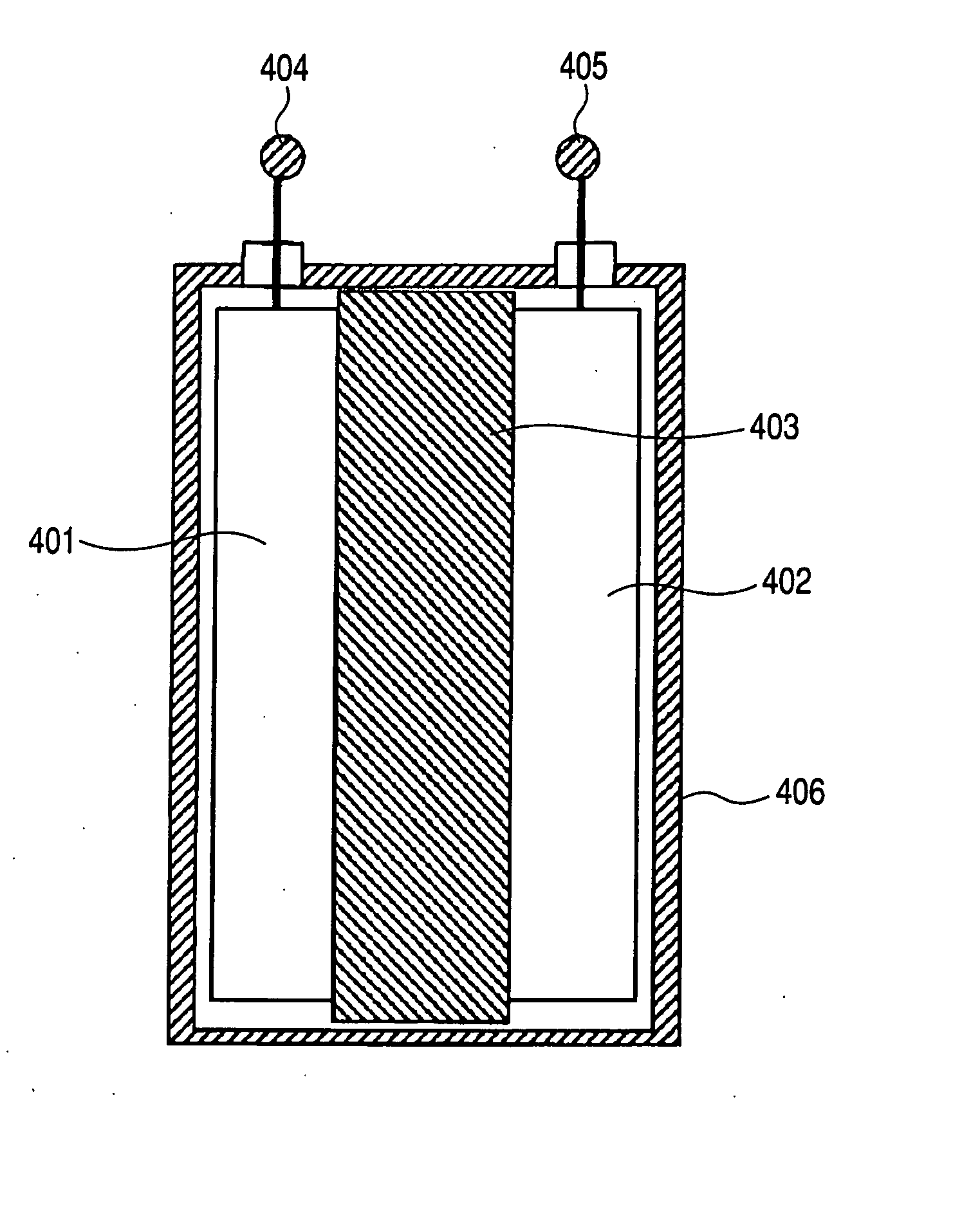
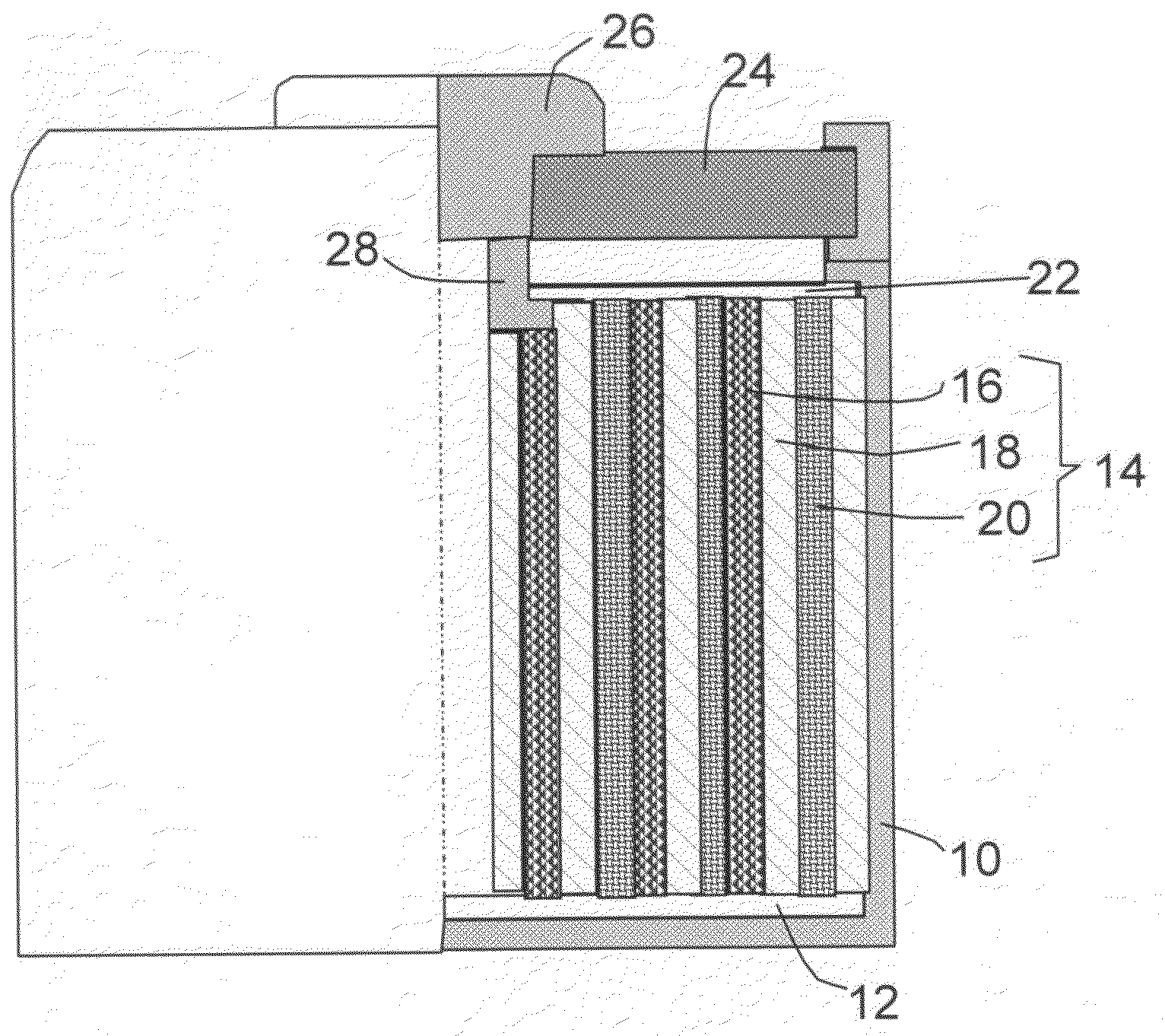
Three dimensional free form battery apparatus
A battery apparatus comprising a casing, at least two stacked lithium ion cells a member for maximizing the utilization of the casing and a member for precluding inadvertent deformation of the casing. The casing includes a non-uniform inner periphery. Each of at least two stacked lithium ion cells is positioned within the casing. The utilization maximizing member maximizes the utilization of the inner periphery of the casing by facilitating the independent shaping of each of the at least two stacked lithium ion cells to confirm to the inner periphery. As a result, the shape of one cell does not limit or dictate the shape of any other cell. The deformation precluding member is associated with each of the at least two lithium ion cells, and, substantially precludes inadvertent deformation of the casing by the at least two lithium ion cells, during cell cycling and storage. The invention further includes a process for fabricating a battery apparatus.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Electroded Sheet for a Multitude of Products
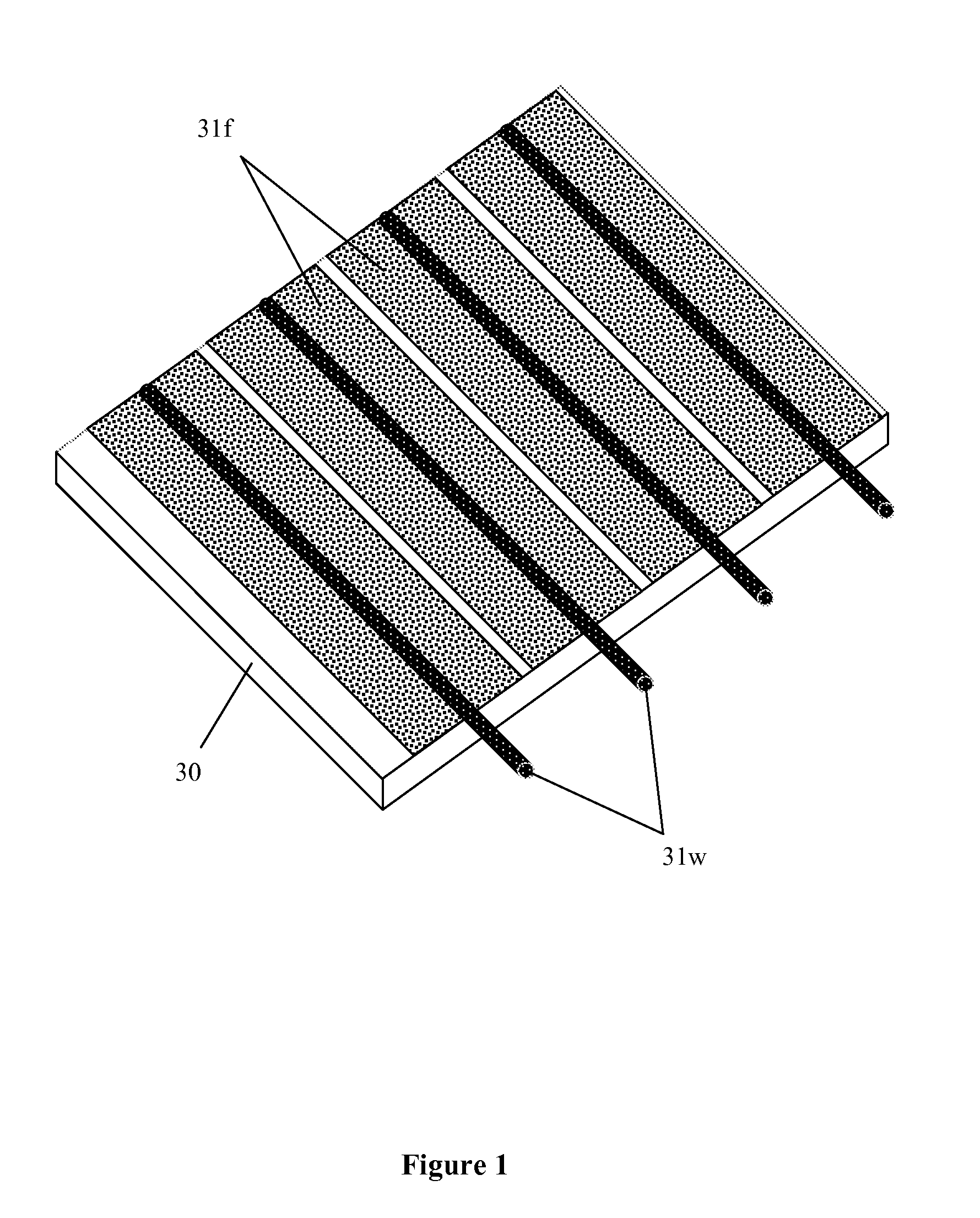
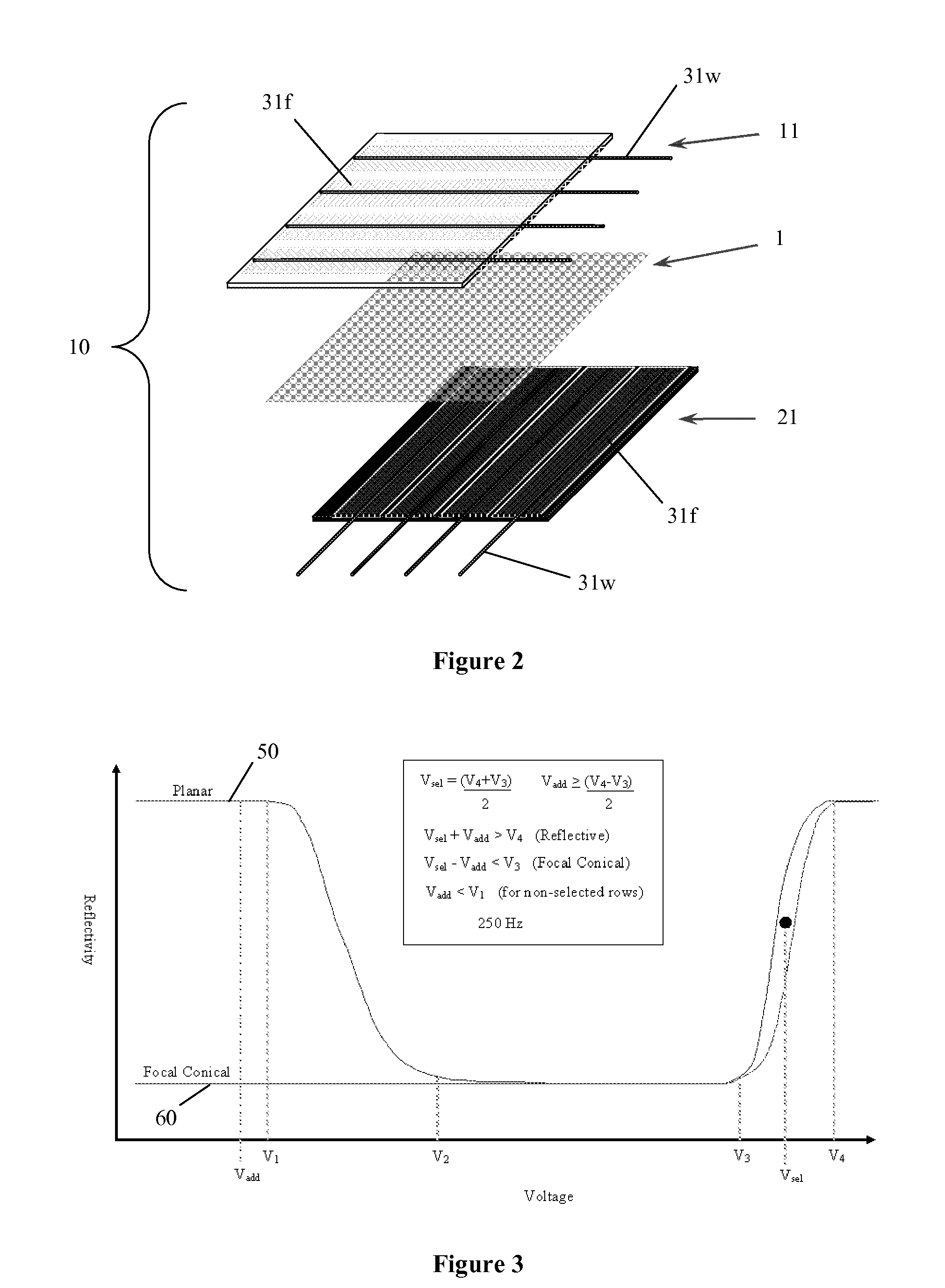
InactiveUS20120105370A1Increase capacitanceLarge displayLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectronic form
eSheets create a multitude of different products. One embodiment is a projected capacitive touch sensor created by embedding orthogonal arrays of coated metal wires into the surface of a polymer sheet or onto the back of a projector screen. To increase the capacitance of the electrodes or pixels in the sensor, transparent conductive electrodes can be electrically connected to the wire electrodes. Another embodiment is a reflective, energy-efficient display formed by sandwiching a reflective cholesteric liquid crystal (Ch. LC) material between electroded sheet substrates. The eSheet Ch. LCD is pressure sensitive and can be written on using a finger or stylus. The eSheet Ch. LCD can then be read using the wire electrodes in the eSheet LCD.
Owner:NUPIX
Method for preparing electrode material for lithium battery
InactiveUS6887511B1Improve adhesionReduce expansionElectrode carriers/collectorsVacuum evaporation coatingAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
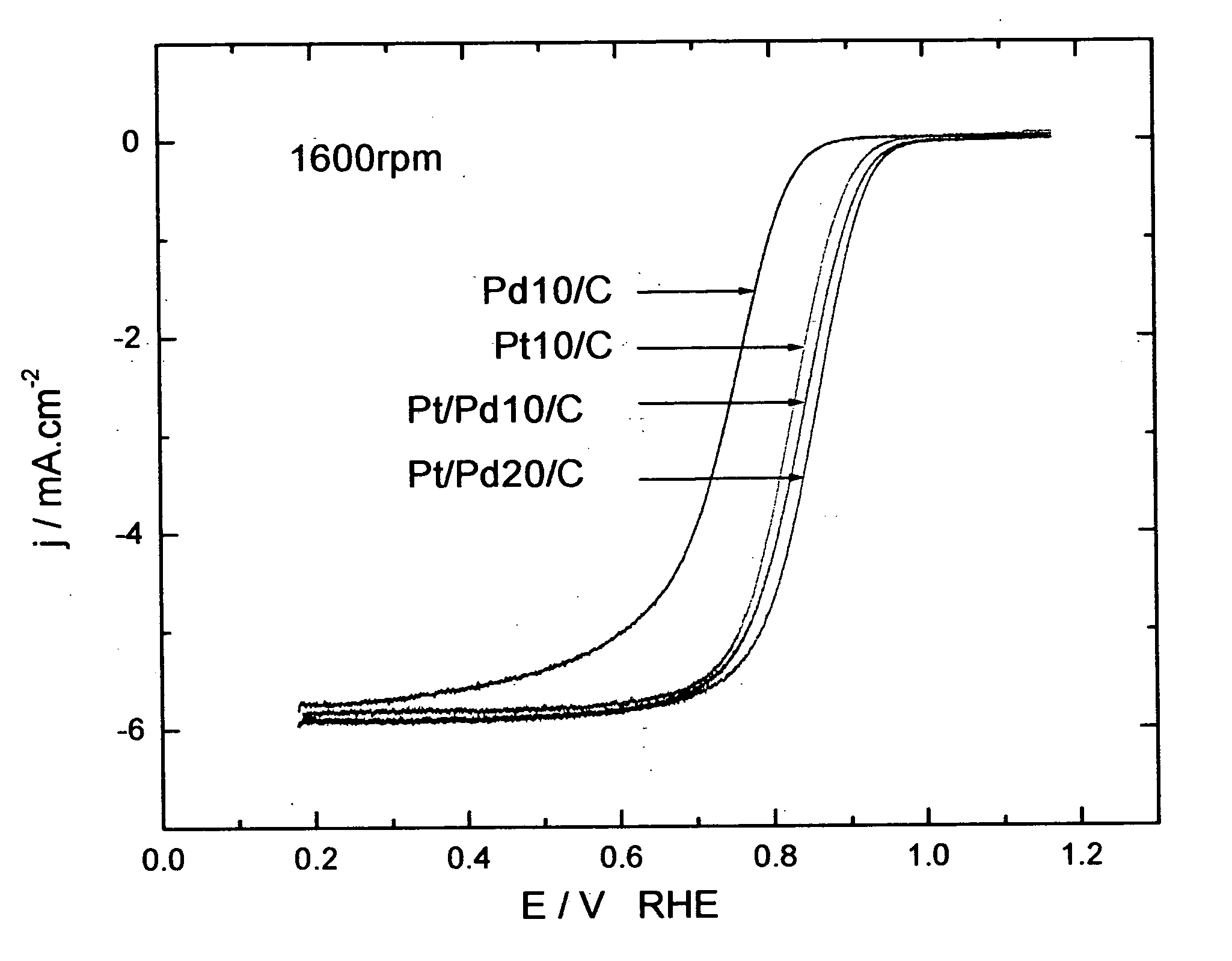
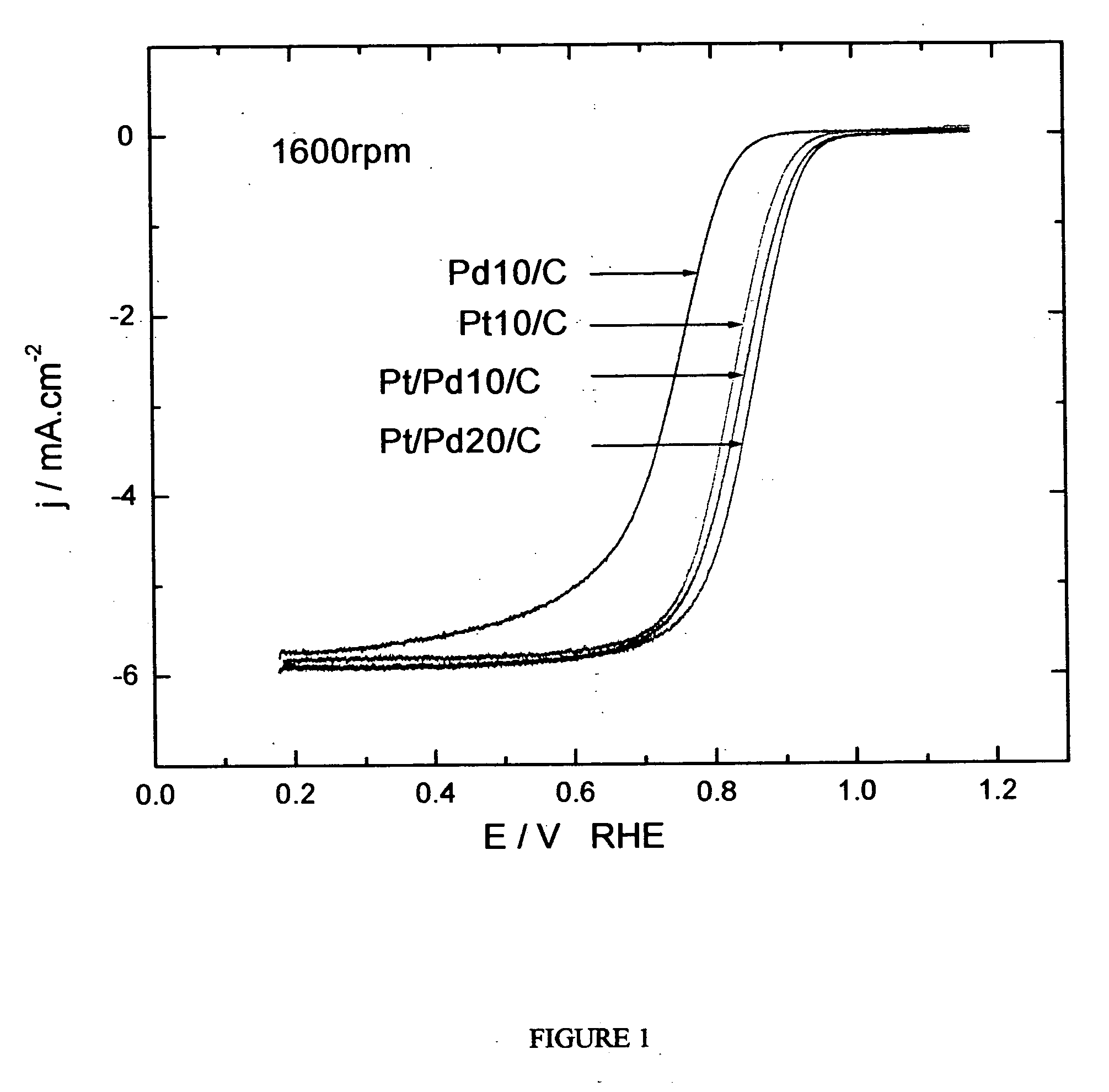
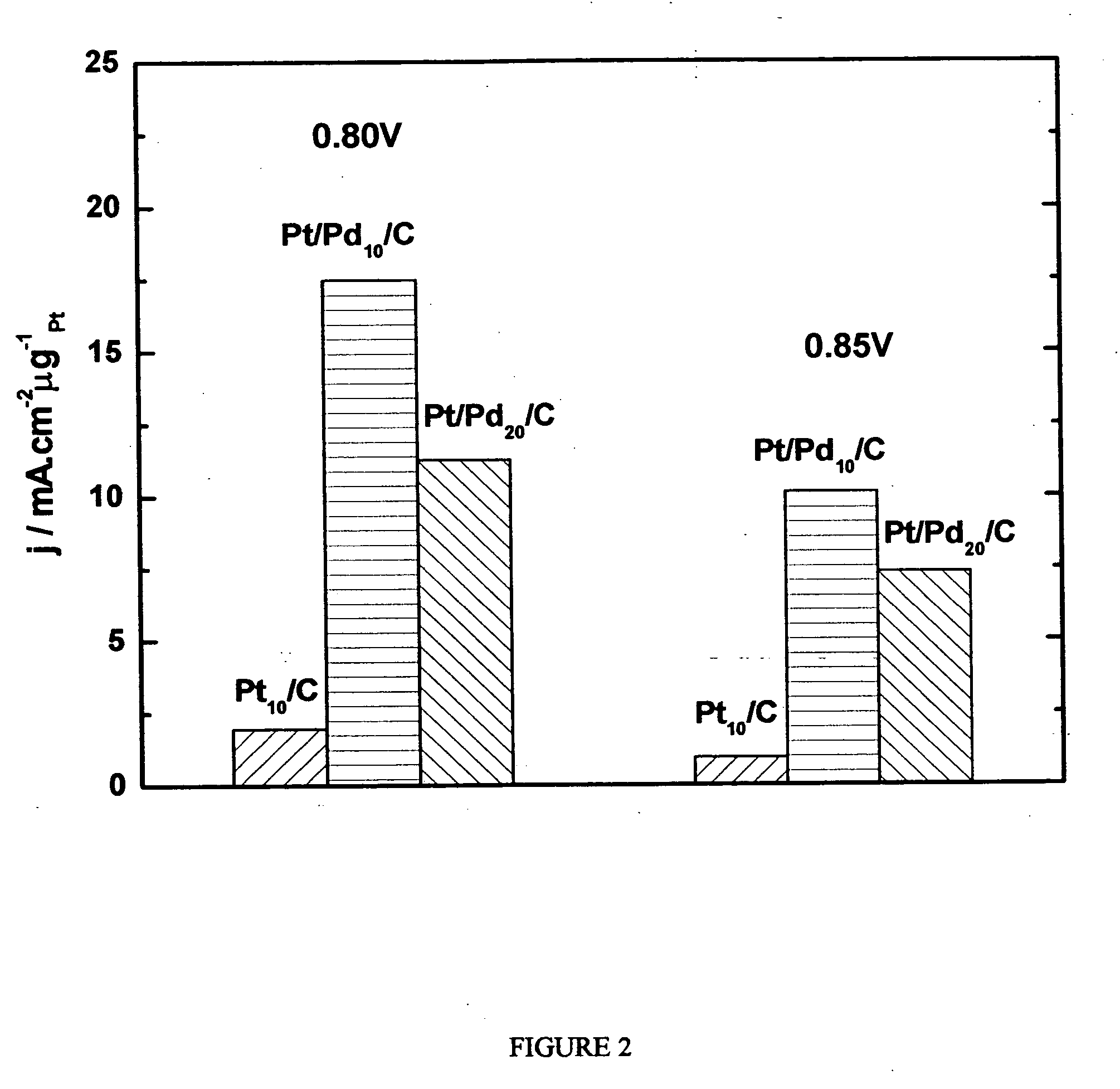
Electrocatalysts having platinum monolayers on palladium, palladium alloy, and gold alloy nanoparticle cores, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070031722A1Improved oxygen-reducing catalytic activityLow platinum loadingMetal-working apparatusActive material electrodesRheniumGold alloys
The invention relates to platinum-coated particles useful as fuel cell electrocatalysts. The particles are composed of a noble metal or metal alloy core at least partially encapsulated by an atomically thin surface layer of platinum atoms. The invention particularly relates to such particles having a palladium, palladium alloy, gold alloy, or rhenium alloy core encapsulated by an atomic monolayer of platinum. In other embodiments, the invention relates to fuel cells containing these electrocatalysts and methods for generating electrical energy therefrom.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
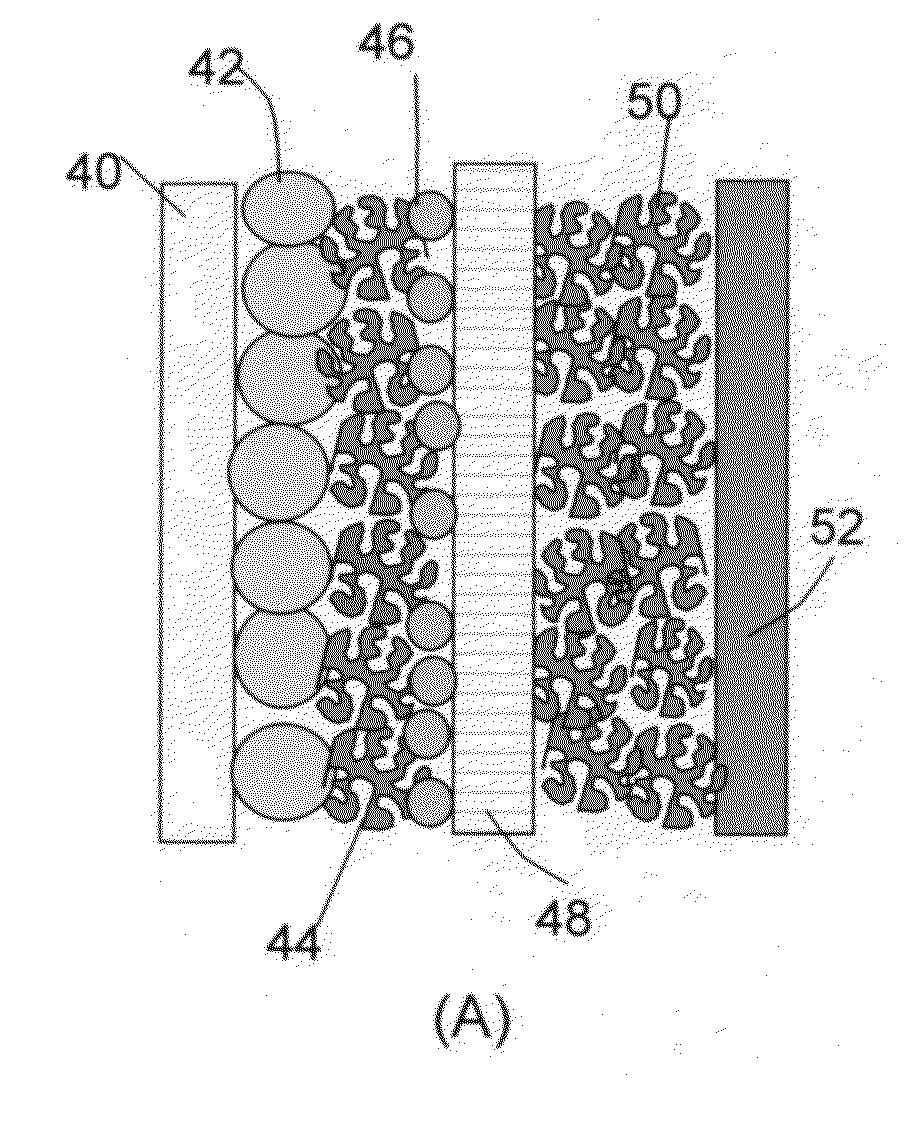
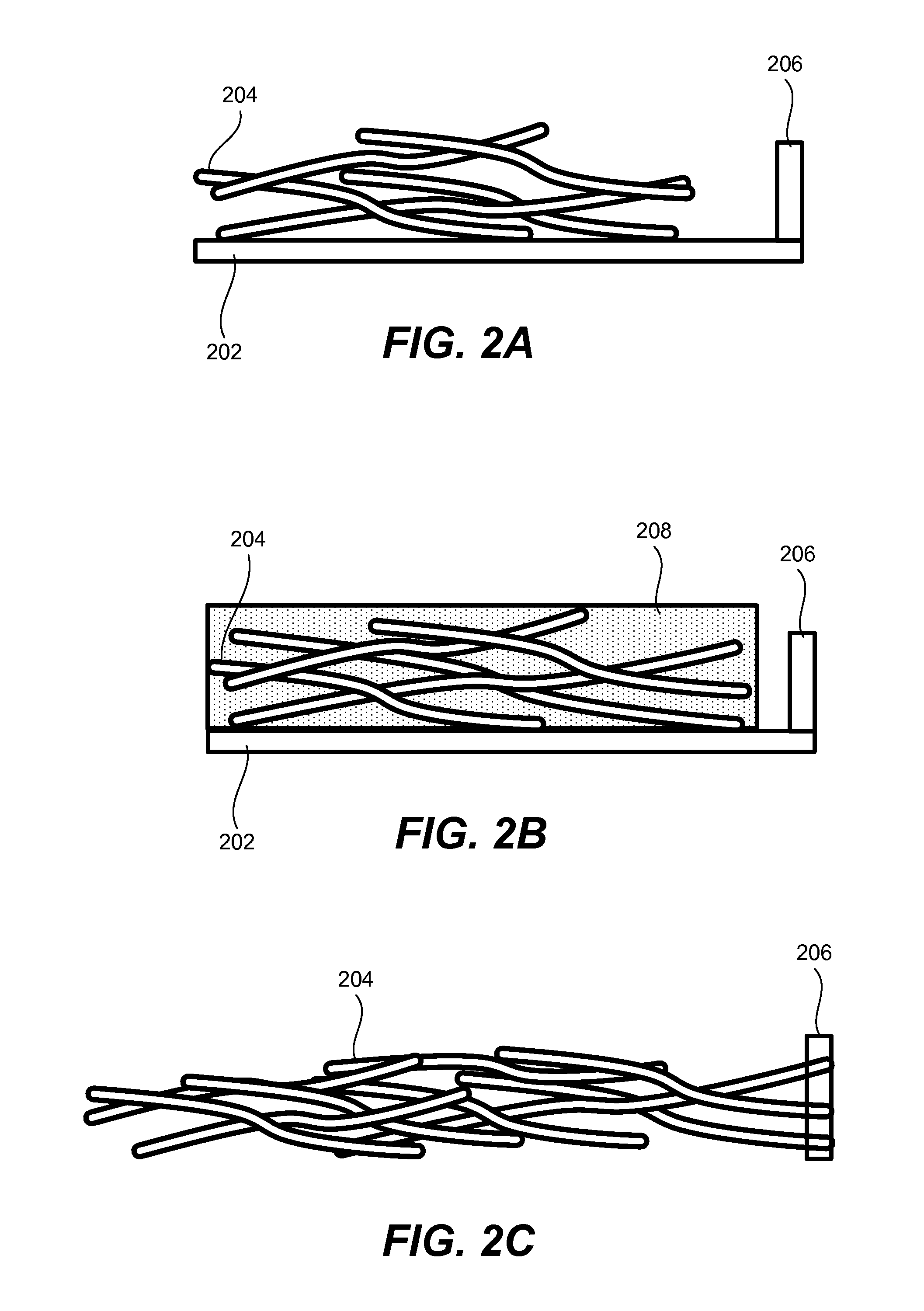
Hybrid nano-filament anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090169996A1Superior multiple-cycle behaviorImprove cycle lifeElectrochemical processing of electrodesElectrode thermal treatmentLithium-ion batteryNanometre
This invention provides a hybrid nano-filament composition for use as an electrochemical cell electrode. The composition comprises: (a) an aggregate of nanometer-scaled, electrically conductive filaments that are substantially interconnected, intersected, or percolated to form a porous, electrically conductive filament network comprising substantially interconnected pores, wherein the filaments have an elongate dimension and a first transverse dimension with the first transverse dimension being less than 500 nm (preferably less than 100 nm) and an aspect ratio of the elongate dimension to the first transverse dimension greater than 10; and (b) micron- or nanometer-scaled coating that is deposited on a surface of the filaments, wherein the coating comprises an anode active material capable of absorbing and desorbing lithium ions and the coating has a thickness less than 20 μm (preferably less than 1 μm). Also provided is a lithium ion battery comprising such an electrode as an anode. The battery exhibits an exceptionally high specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, negative electrode material, and making method
ActiveUS20090239151A1Improve cycle performanceImprove efficiencyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsActive material electrodesSilicon oxideSilicon particle
A negative electrode material comprising an active material and 1-20 wt % of a polyimide resin binder is suitable for use in non-aqueous electrolyte secondary batteries. The active material comprises silicon oxide particles and 1-50 wt % of silicon particles. The negative electrode exhibits improved cycle performance while maintaining the high battery capacity and low volume expansion of silicon oxide. The non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery has a high initial efficiency and maintains improved performance and efficiency over repeated charge / discharge cycles by virtue of mitigated volumetric changes during charge / discharge cycles.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Release system for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20110068001A1Active material electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesEngineeringElectrochemical cell
Electrochemical cells, and more specifically, release systems for the fabrication of electrochemical cells are described. In particular, release layer arrangements, assemblies, methods and compositions that facilitate the fabrication of electrochemical cell components, such as electrodes, are presented. In some embodiments, methods of fabricating an electrode involve the use of a release layer to separate portions of the electrode from a carrier substrate on which the electrode was fabricated. For example, an intermediate electrode assembly may include, in sequence, an electroactive material layer, a current collector layer, a release layer, and a carrier substrate. The carrier substrate can facilitate handling of the electrode during fabrication and / or assembly, but may be released from the electrode prior to commercial use.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Non-sintered type thin electrode for battery, battery using same and process for same
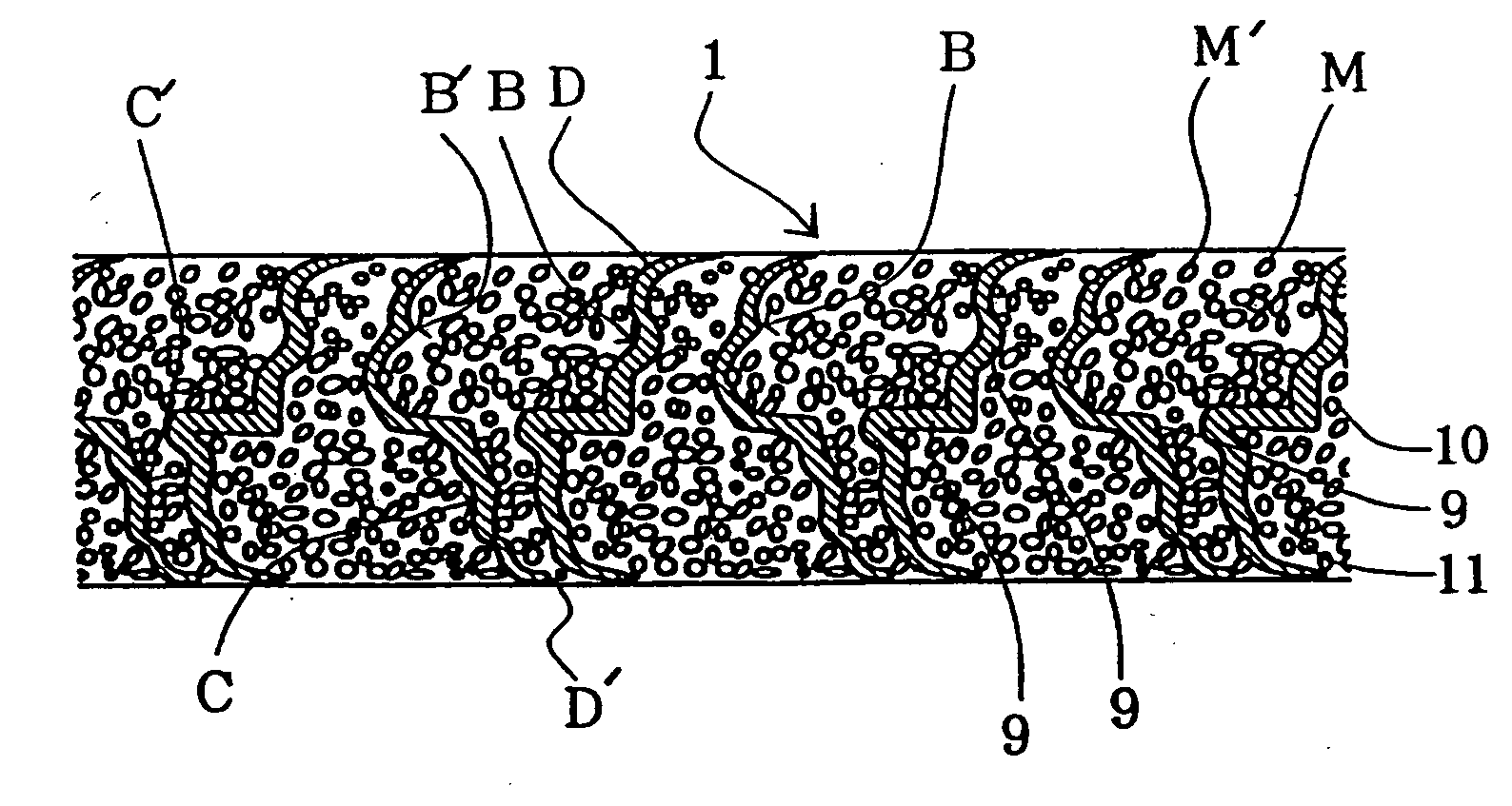
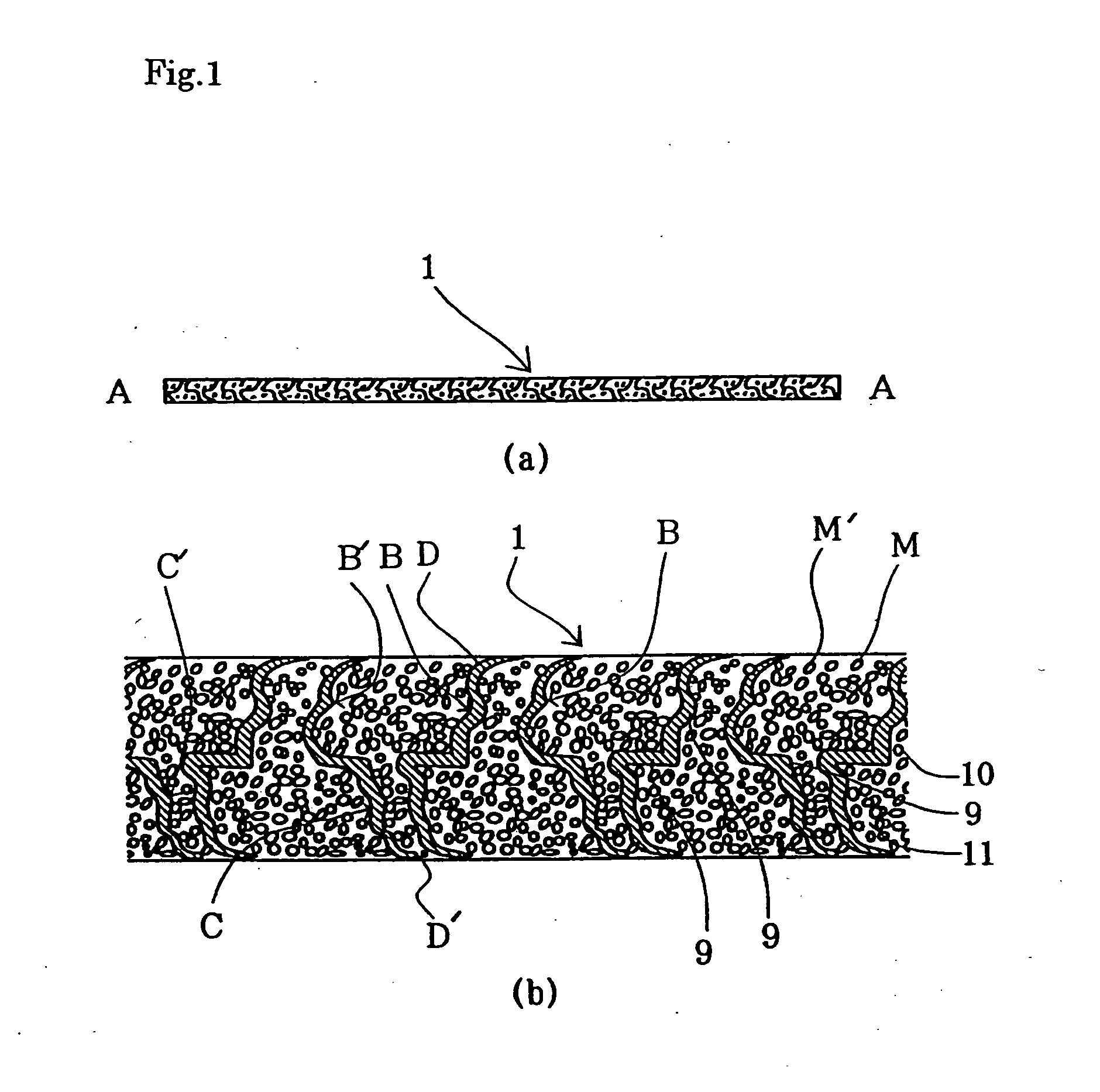
InactiveUS20050019664A1Prevent peelingPrevent materialElectrode carriers/collectorsActive material electrodesElectrical batteryEngineering
An electrode substrate is formed by mechanically processing a nickel foil so as to be made three dimensional through the creation of concave and convex parts, and then, this substrate is filled with active material or the like so that an electrode is manufactured, wherein the above described concave and convex parts are rolling pressed so as to incline in one direction. Furthermore, an electrode for secondary battery is formed by using the above described method.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Popular searches
Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes Biochemical fuel cells Energy based wastewater treatment Solid electrolyte fuel cells Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Solid state diffusion coating Alkaline accumulator electrodes Secondary cells charging/discharging Electrochemical machining apparatus Electrical-based auxillary apparatus
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com