Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1324results about "Treatment by combined electrochemical biological processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
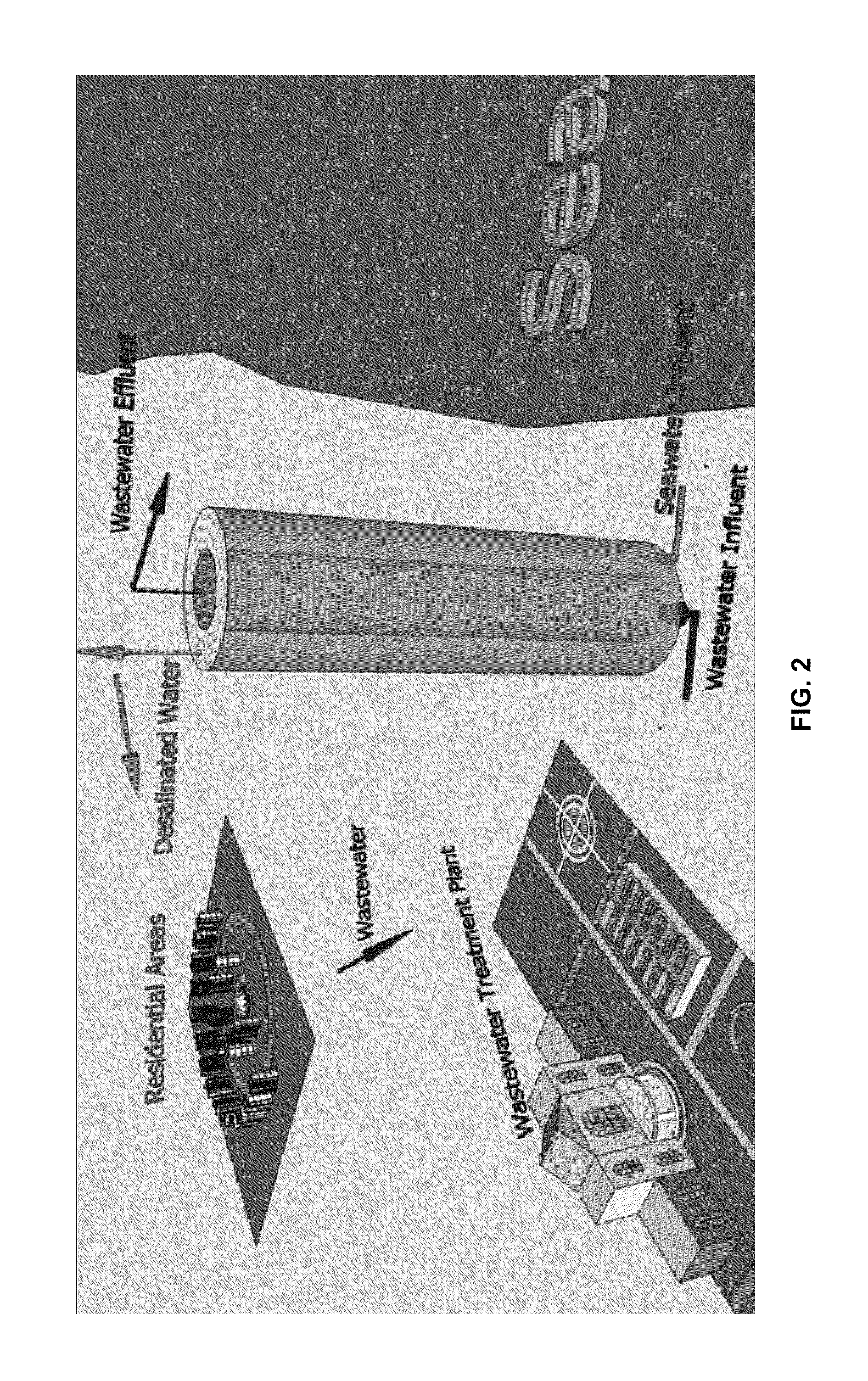
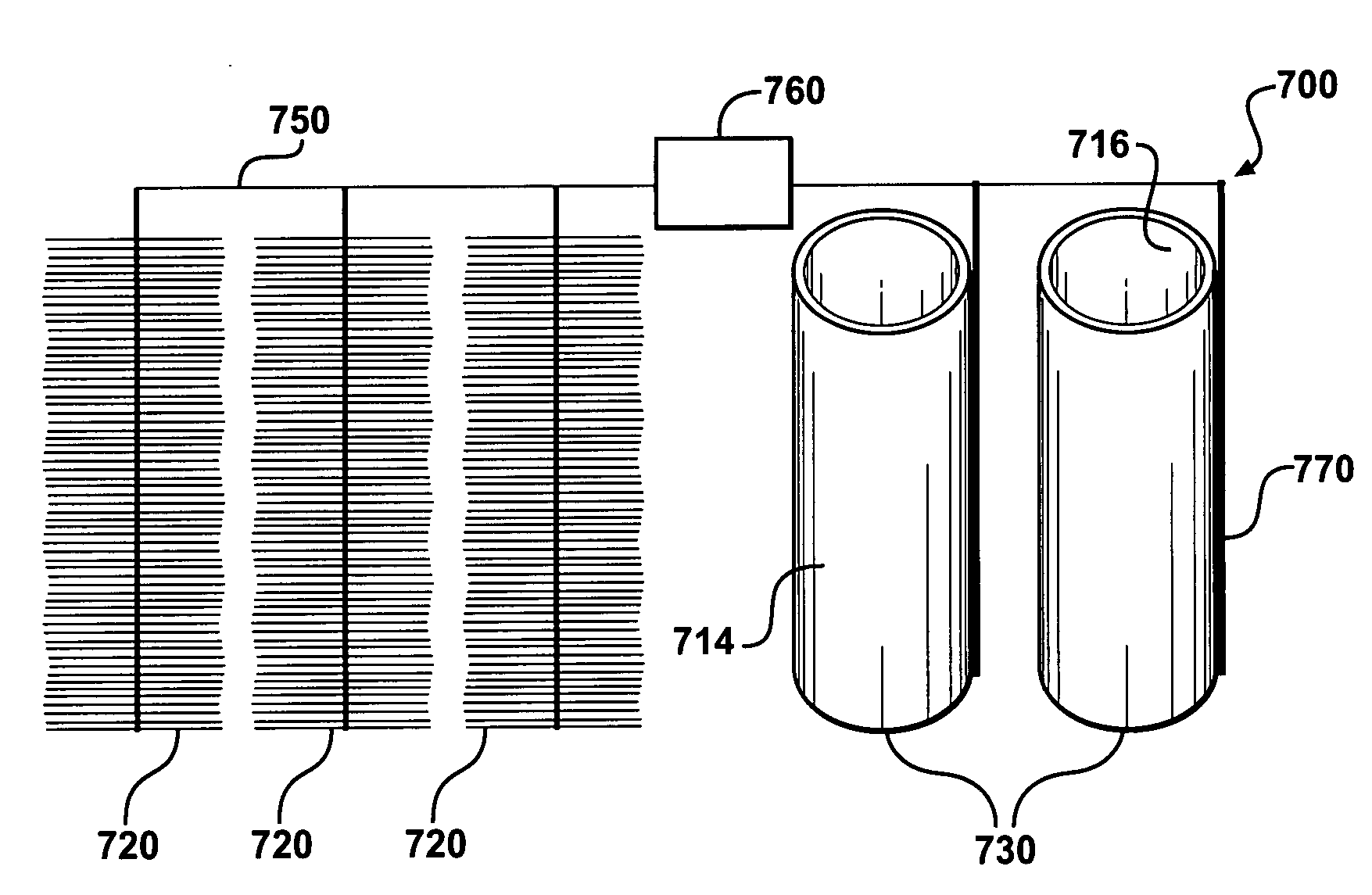
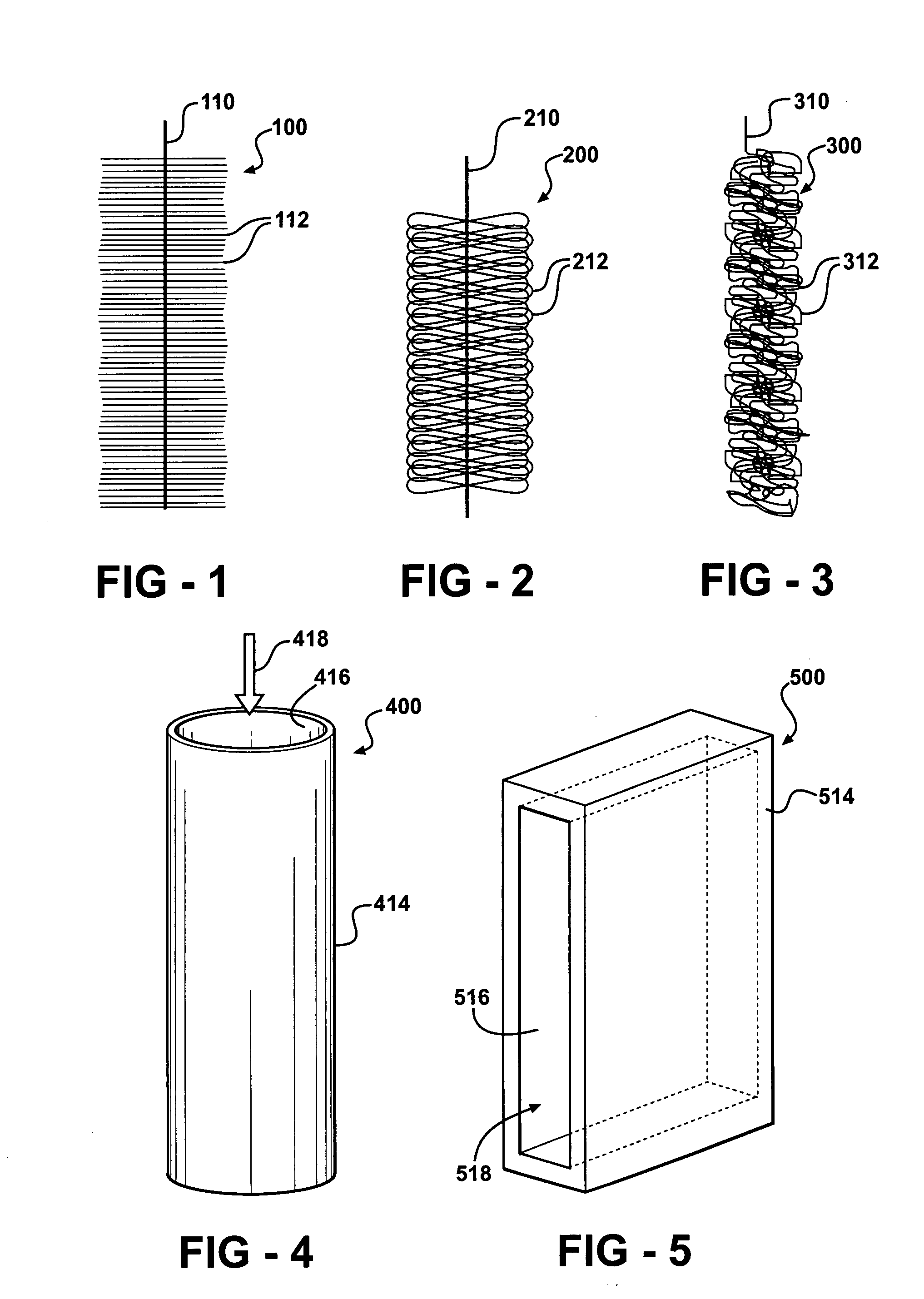
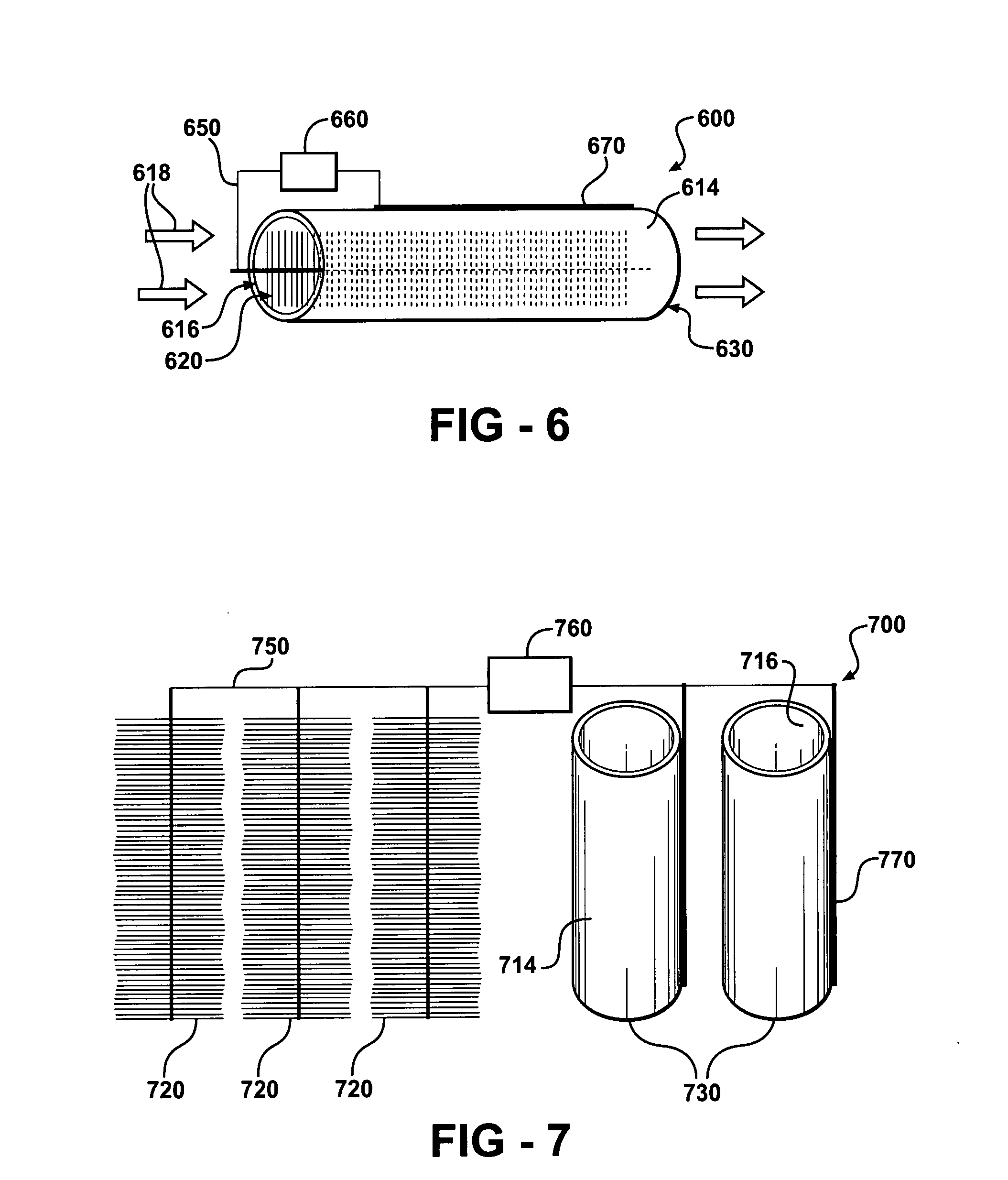
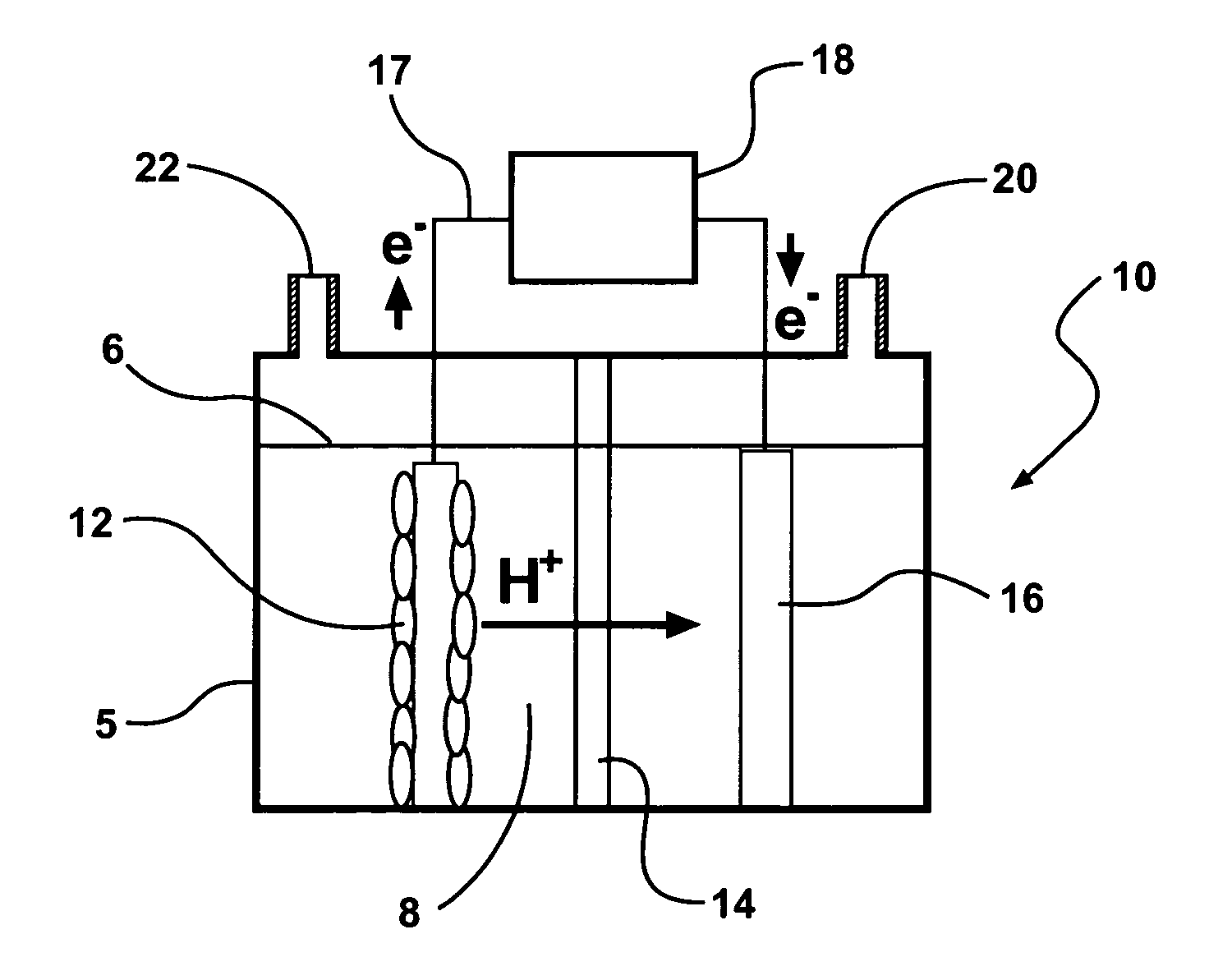
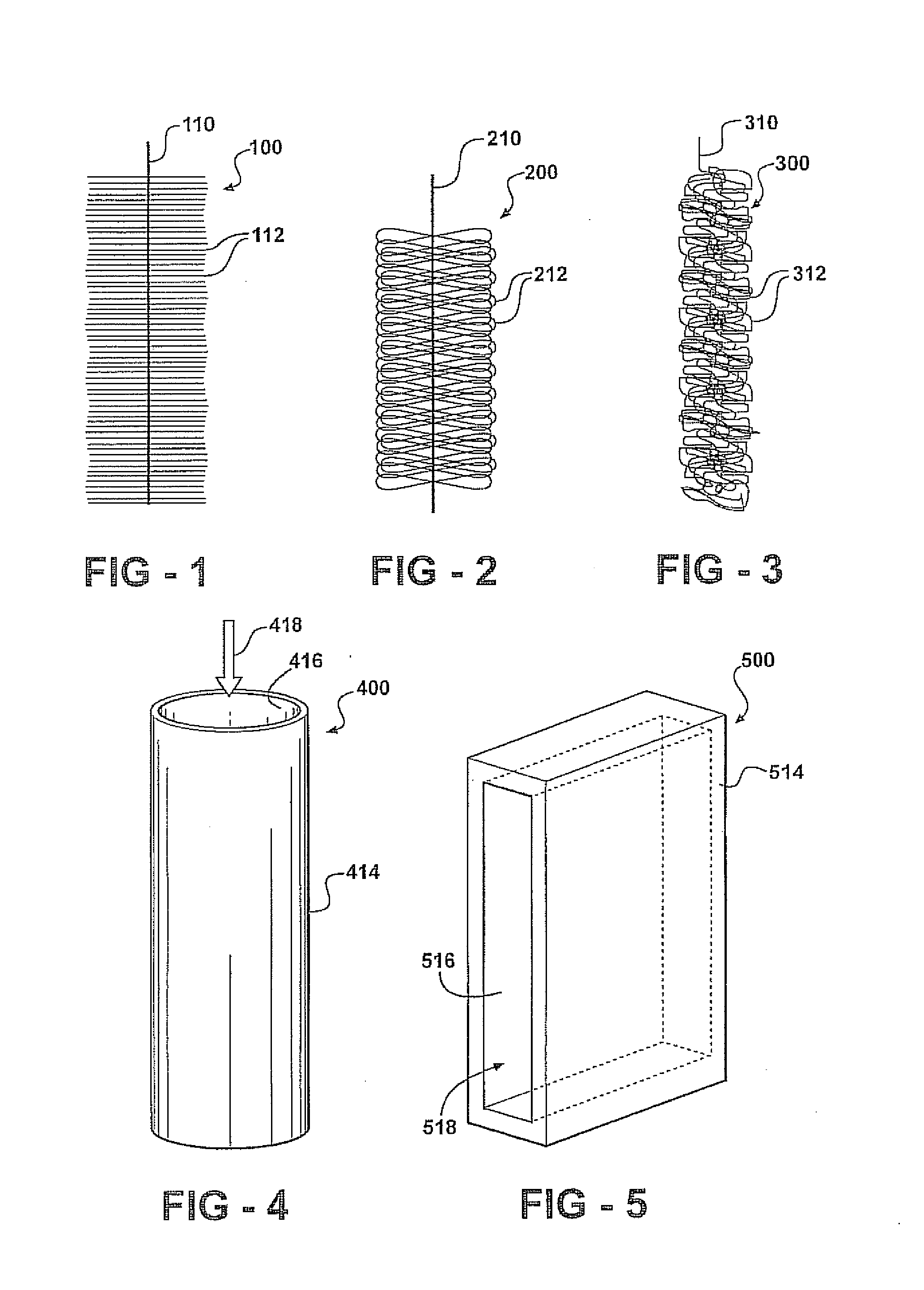
Materials and configurations for scalable microbial fuel cells
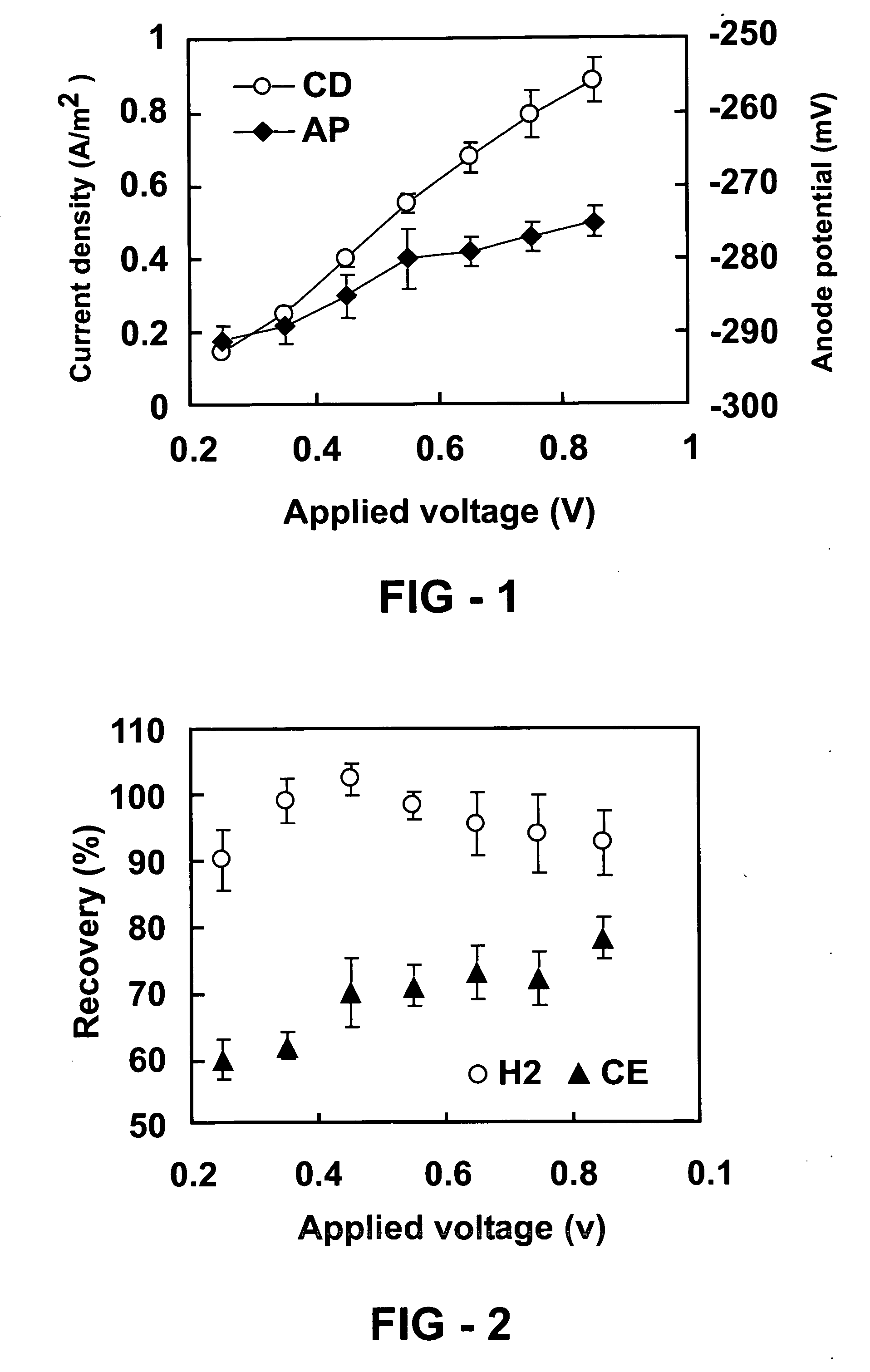
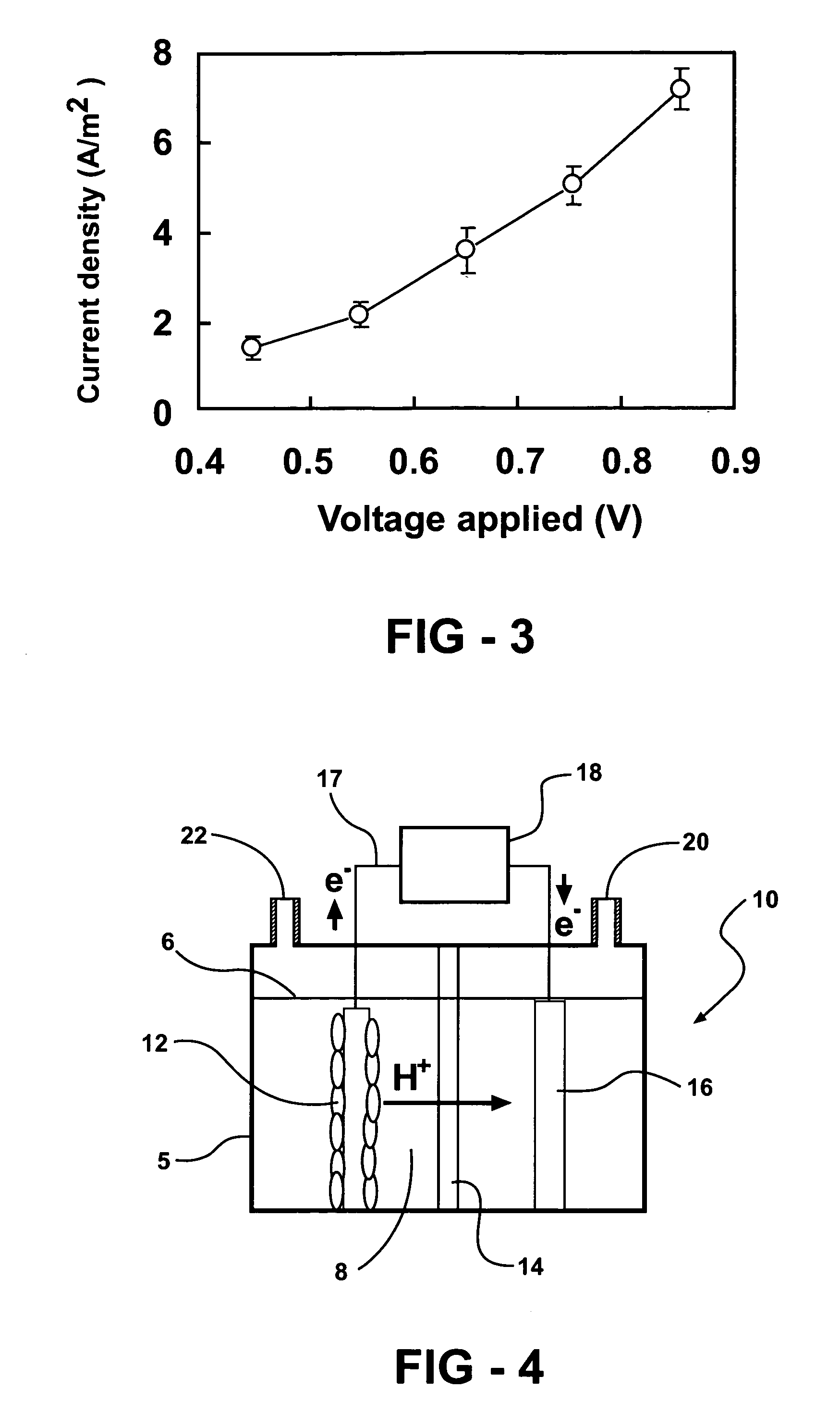
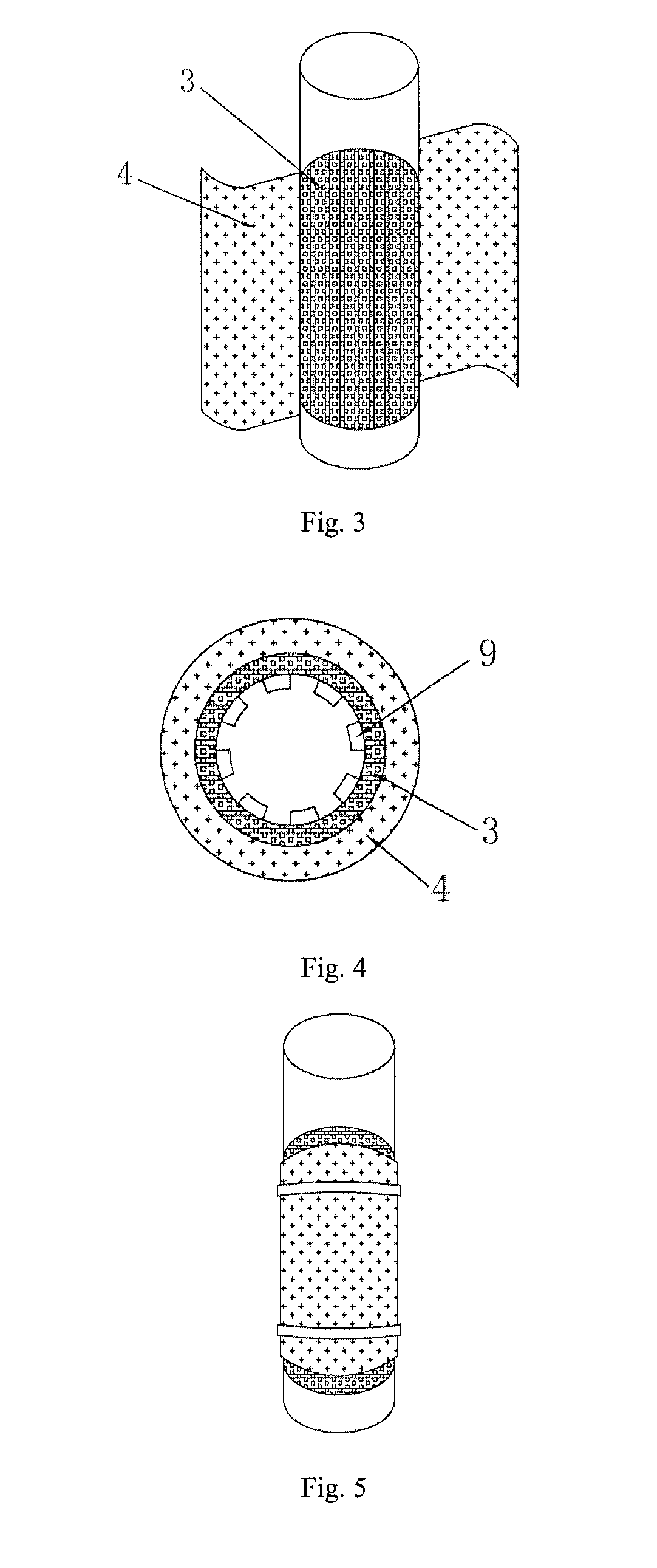
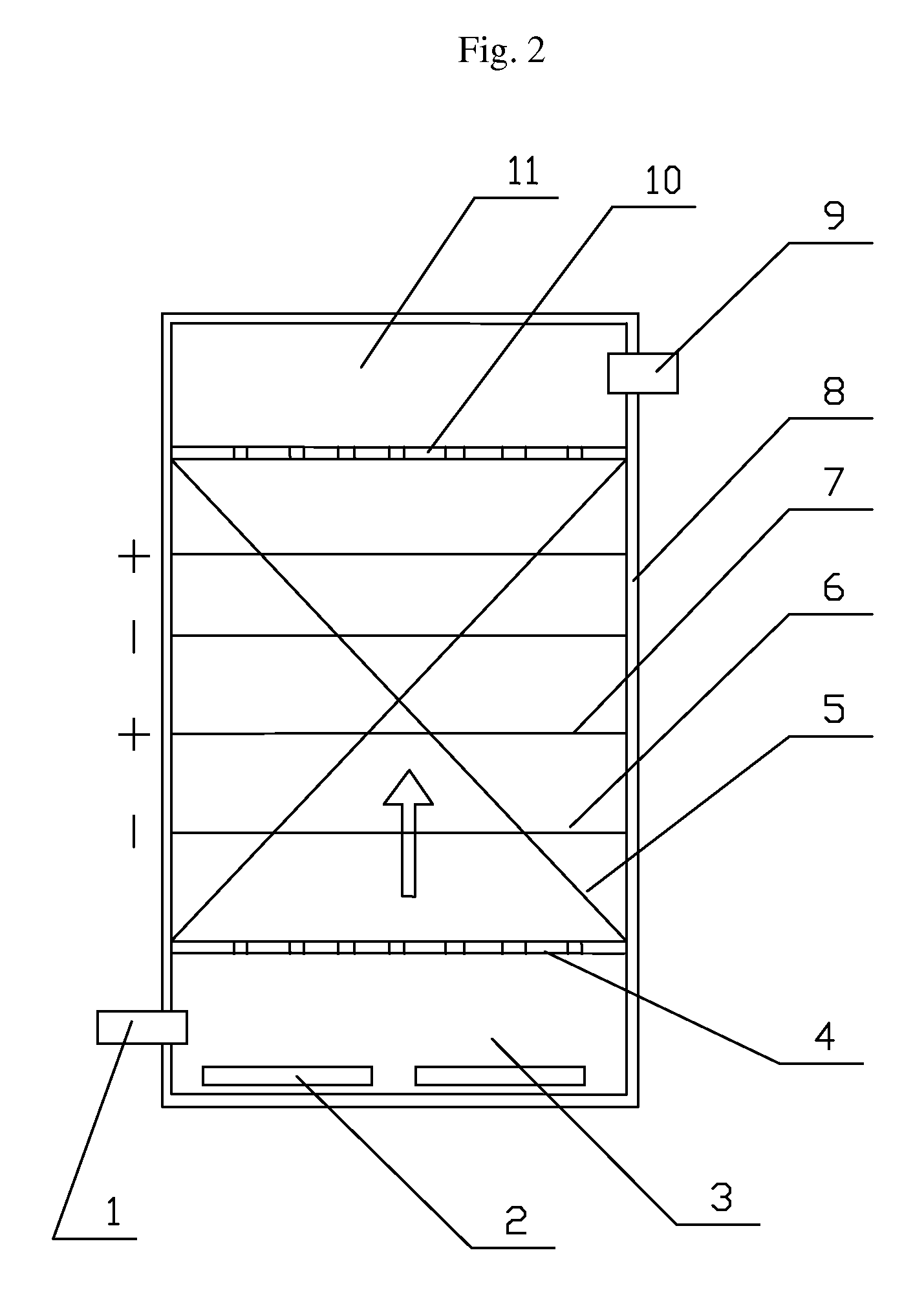
ActiveUS20070259217A1Raise the potentialTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesActive material electrodesElectricityMicrobial fuel cell
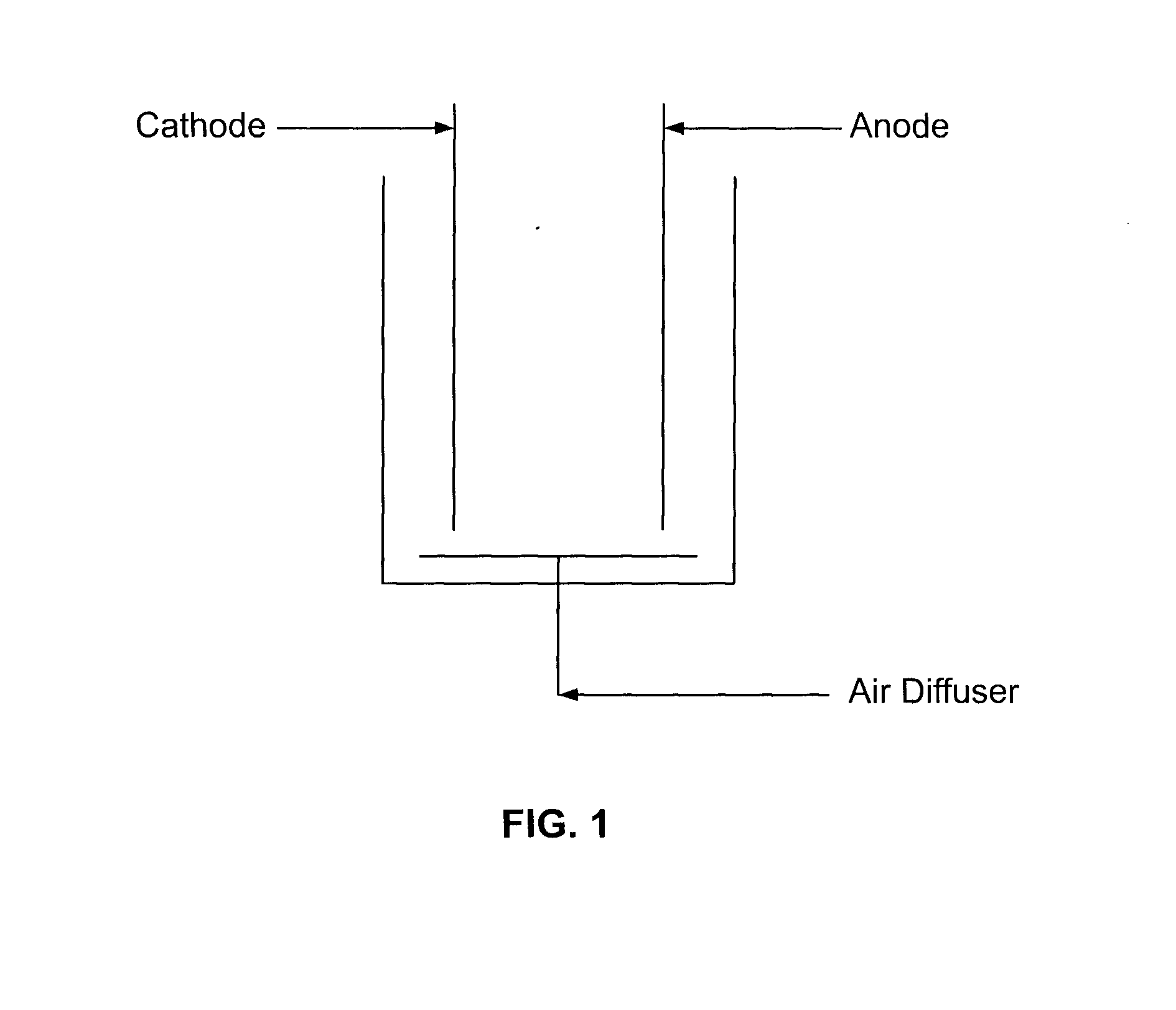
Devices for production of electricity and / or hydrogen gas are provided by the present invention. In particular, microbial fuel cells for production of electricity and modified microbial fuel cells for production of hydrogen are detailed. A tube cathode is provided which includes a membrane forming a general tube shape. An anode is provided which has a specific surface area greater than 100 m2 / m3. In addition, the anode is substantially non-toxic to anodophilic bacteria. Combinations of particular anodes and cathodes are included in microbial fuel cells and modified microbial fuel cells.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
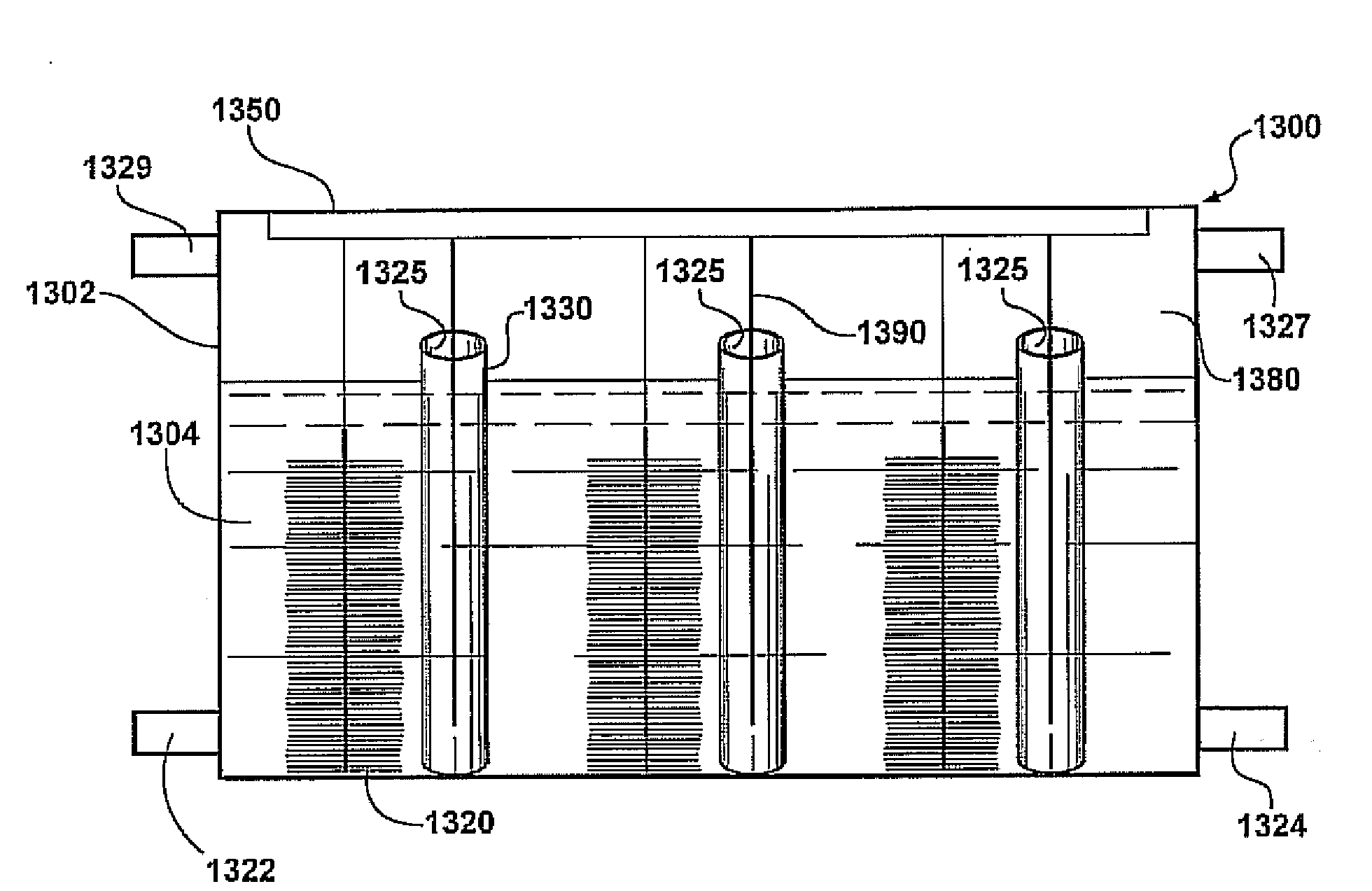
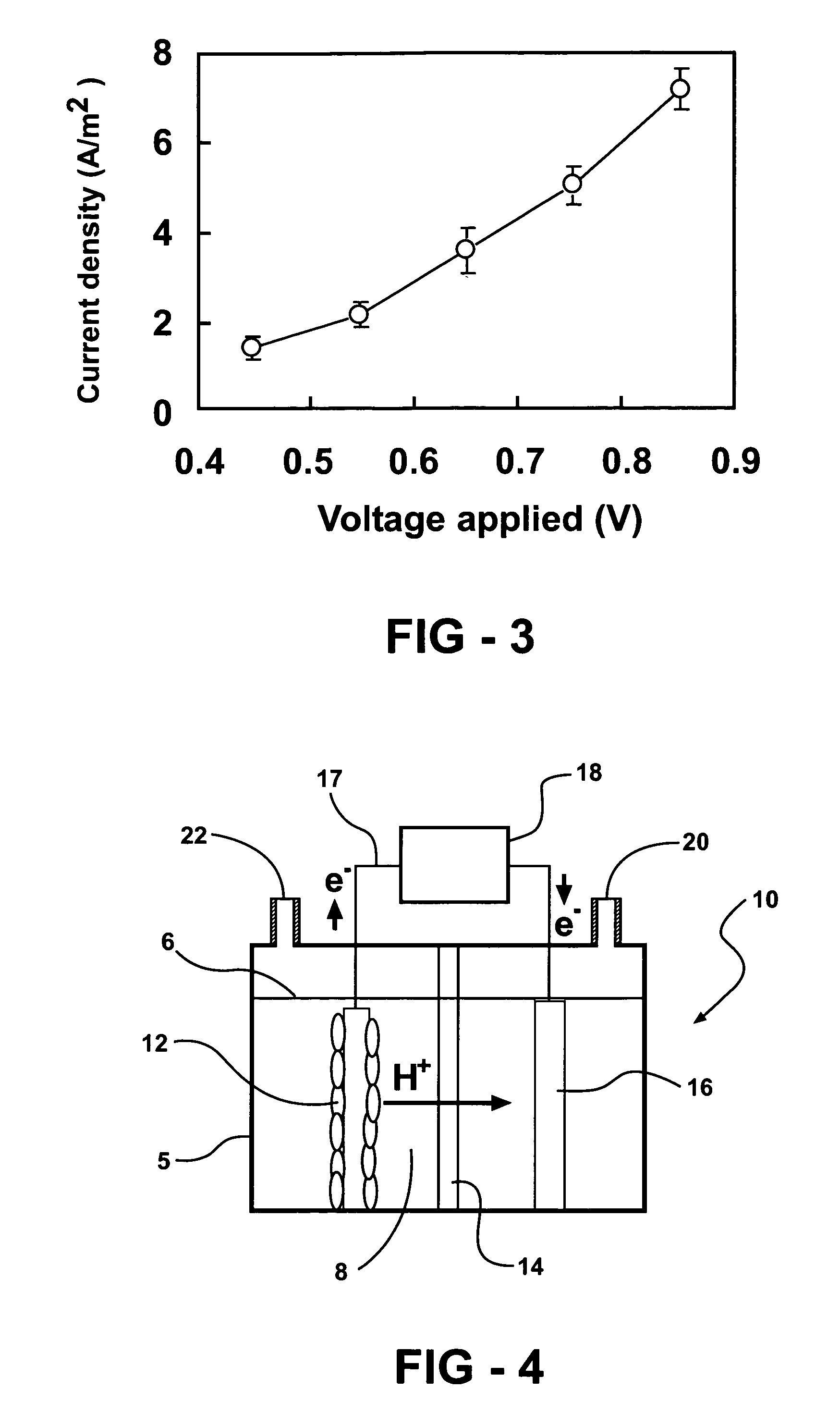
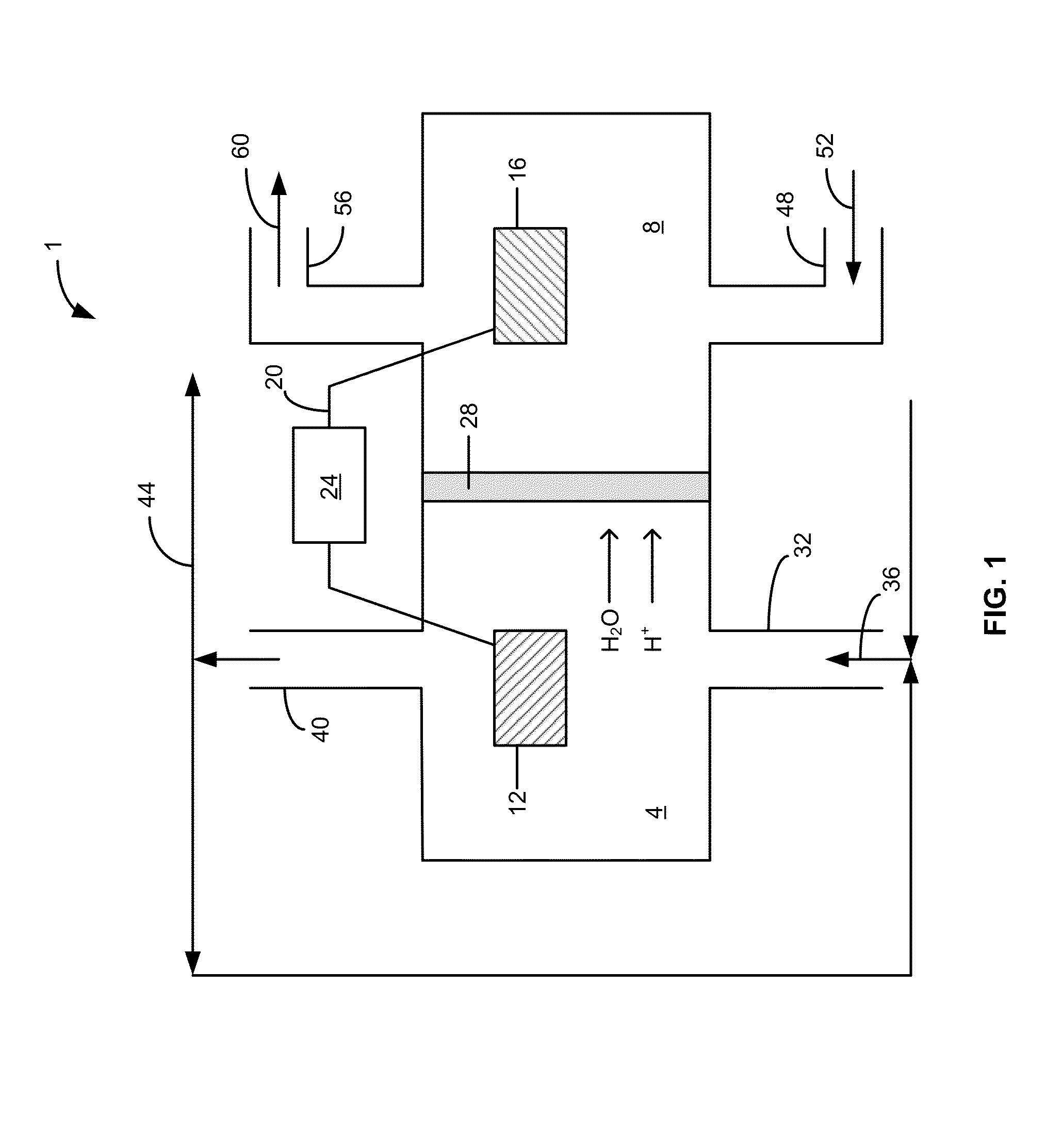
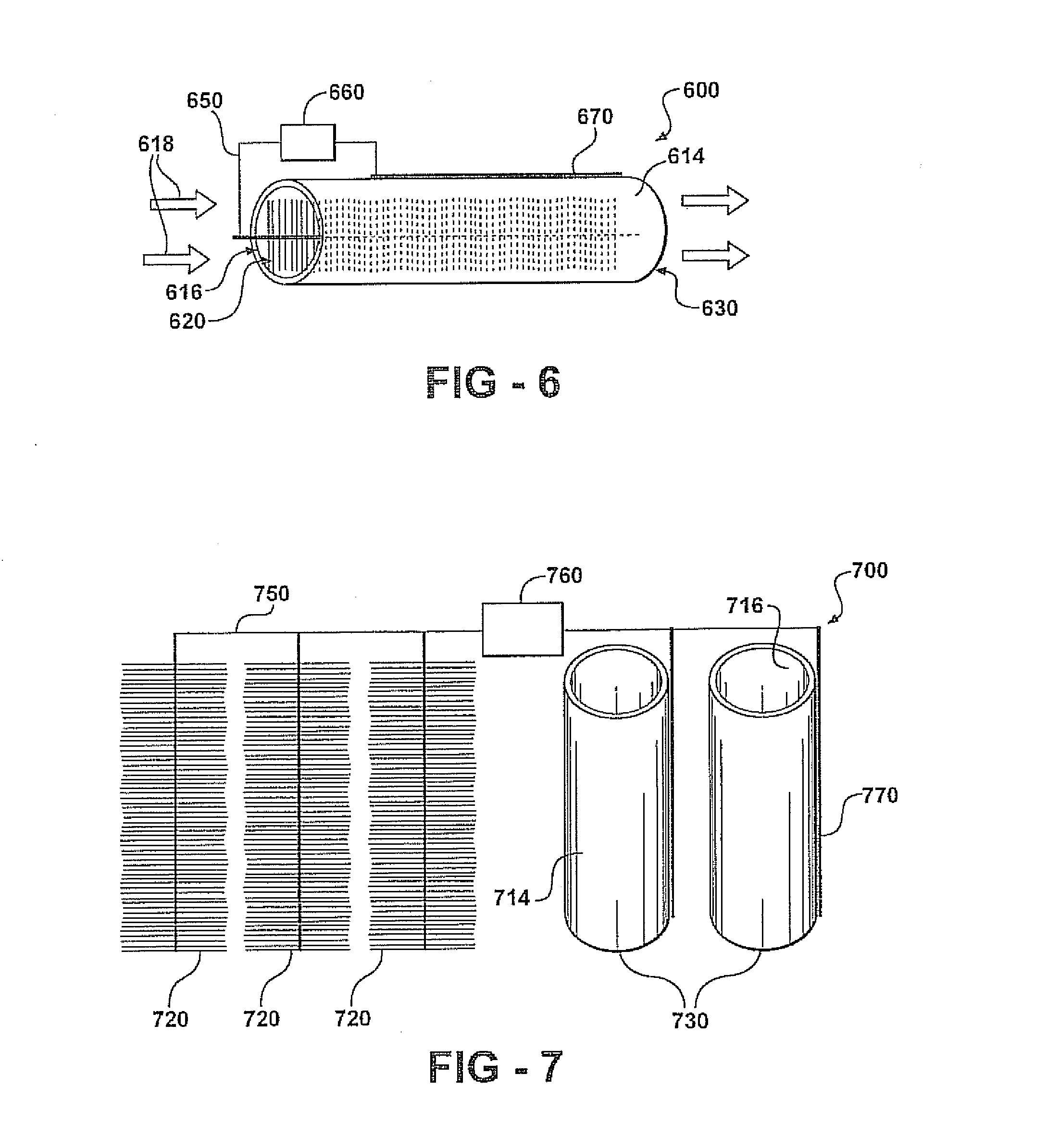
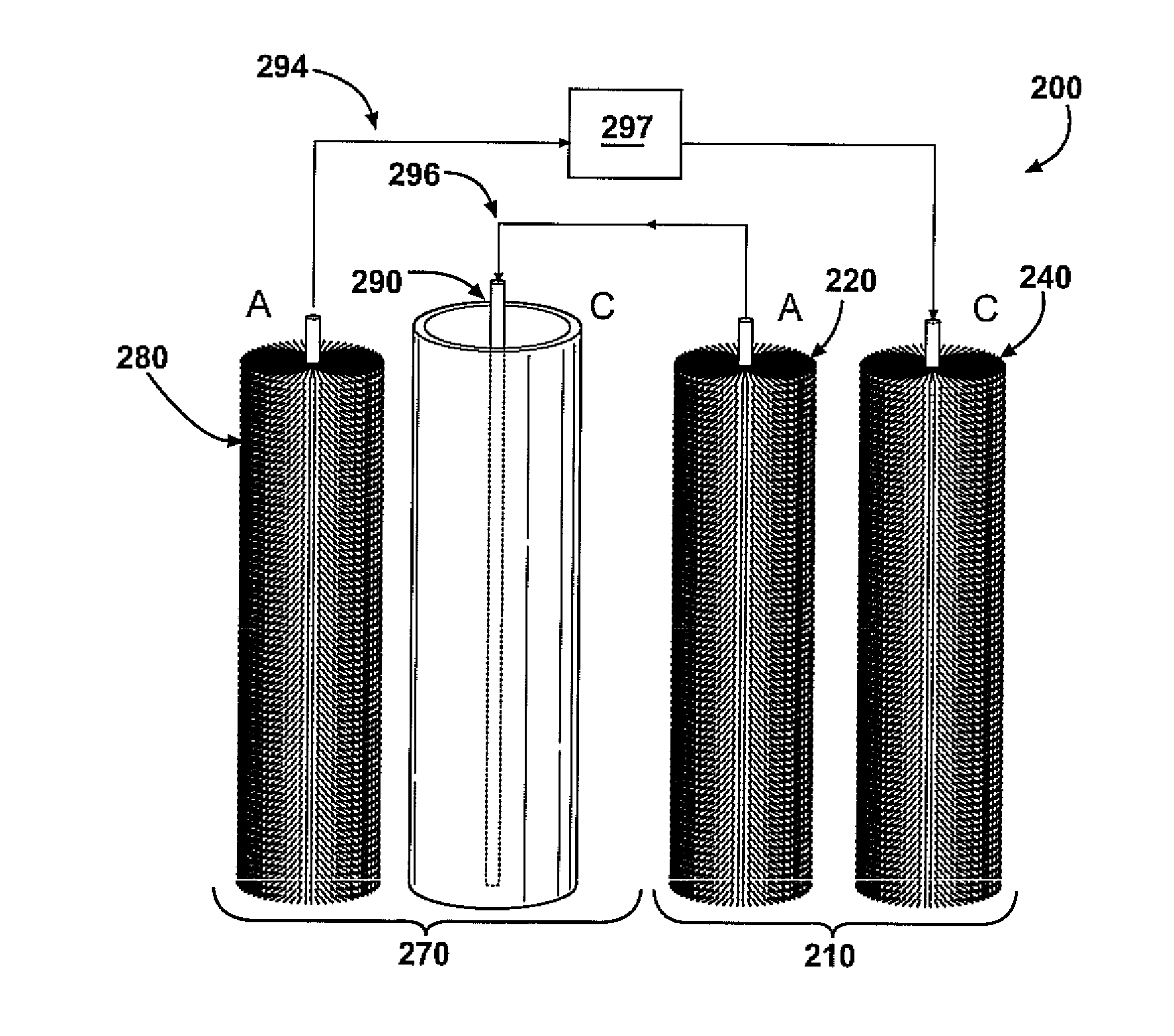
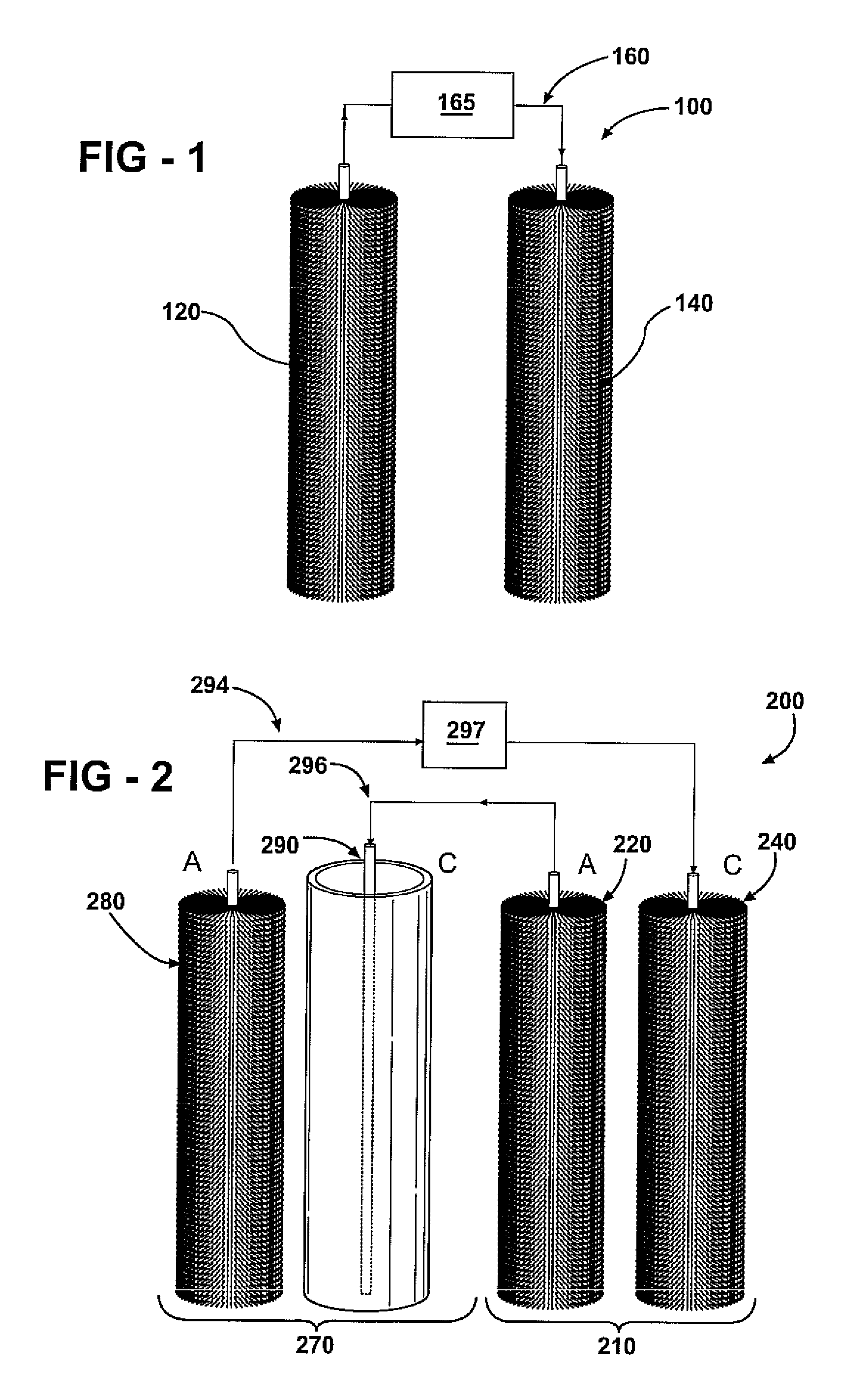
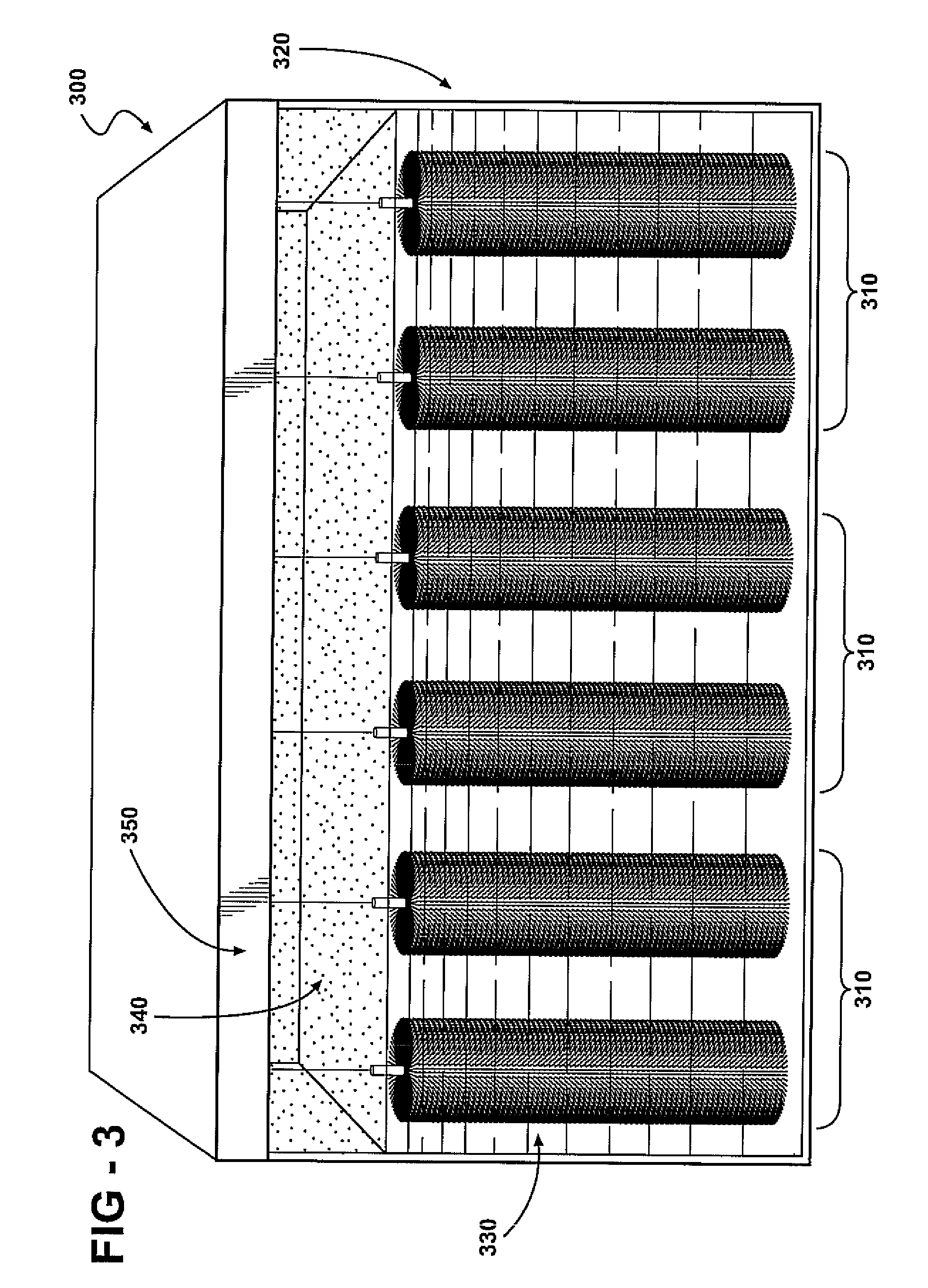
Bio-electrochemically assisted microbial reactor that generates hydrogen gas and methods of generating hydrogen gas
ActiveUS20060011491A1Provide supportGrowth inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrogen
Systems and processes for producing hydrogen using bacteria are described. One detailed process for producing hydrogen uses a system for producing hydrogen as described herein, the system including a reactor. Anodophilic bacteria are disposed within the interior of the reactor and an organic material oxidizable by an oxidizing activity of the anodophilic bacteriais introduced and incubated under oxidizing reactions conditions such that electrons are produced and transferred to the anode. A power source is activated to increase a potential between the anode and the cathode, such that electrons and protons combine to produce hydrogen gas. One system for producing hydrogen includes a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reactor and an exterior of the reaction chamber. An anode is provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber and a cathode is also provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber. The cathode is spaced apart at a distance in the range between 0.1-100 centimeters, inclusive, from the anode. A conductive conduit for electrons is provided which is in electrical communication with the anode and the cathode and a power source for enhancing an electrical potential between the anode and cathode is included which is in electrical communication at least with the cathode. A first channel defining a passage from the exterior of the reaction chamber to the interior of the reaction chamber is also included.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Electrodes and methods for microbial fuel cells
InactiveUS20080292912A1Raise the potentialImprove performanceTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCell electrodesMicrobial fuel cellFuel cells
Methods of improving a performance parameter of a microbial fuel cell are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include heating an electrode and exposing the heated electrode to ammonia gas to produce a treated electrode characterized by an increased positive surface charge on the electrode surface. Improved performance parameters include increased maximum power density, increased coulombic efficiency, increased volumetric power density and decreased microbial fuel cell operation time to achieve maximum power density
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Bio-electrochemically assisted microbial reactor that generates hydrogen gas and methods of generating hydrogen gas
ActiveUS7491453B2Growth inhibitionLower internal resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrogenProton
Systems and processes for producing hydrogen using bacteria are described. One detailed process for producing hydrogen uses a system for producing hydrogen as described herein, the system including a reactor. Anodophilic bacteria are disposed within the interior of the reactor and an organic material oxidizable by an oxidizing activity of the anodophilic bacteria is introduced and incubated under oxidizing reactions conditions such that electrons are produced and transferred to the anode. A power source is activated to increase a potential between the anode and the cathode, such that electrons and protons combine to produce hydrogen gas. One system for producing hydrogen includes a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reactor and an exterior of the reaction chamber. An anode is provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber and a cathode is also provided which is at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber. The cathode is spaced apart at a distance in the range between 0.1-100 centimeters, inclusive, from the anode. A conductive conduit for electrons is provided which is in electrical communication with the anode and the cathode and a power source for enhancing an electrical potential between the anode and cathode is included which is in electrical communication at least with the cathode. A first channel defining a passage from the exterior of the reaction chamber to the interior of the reaction chamber is also included.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
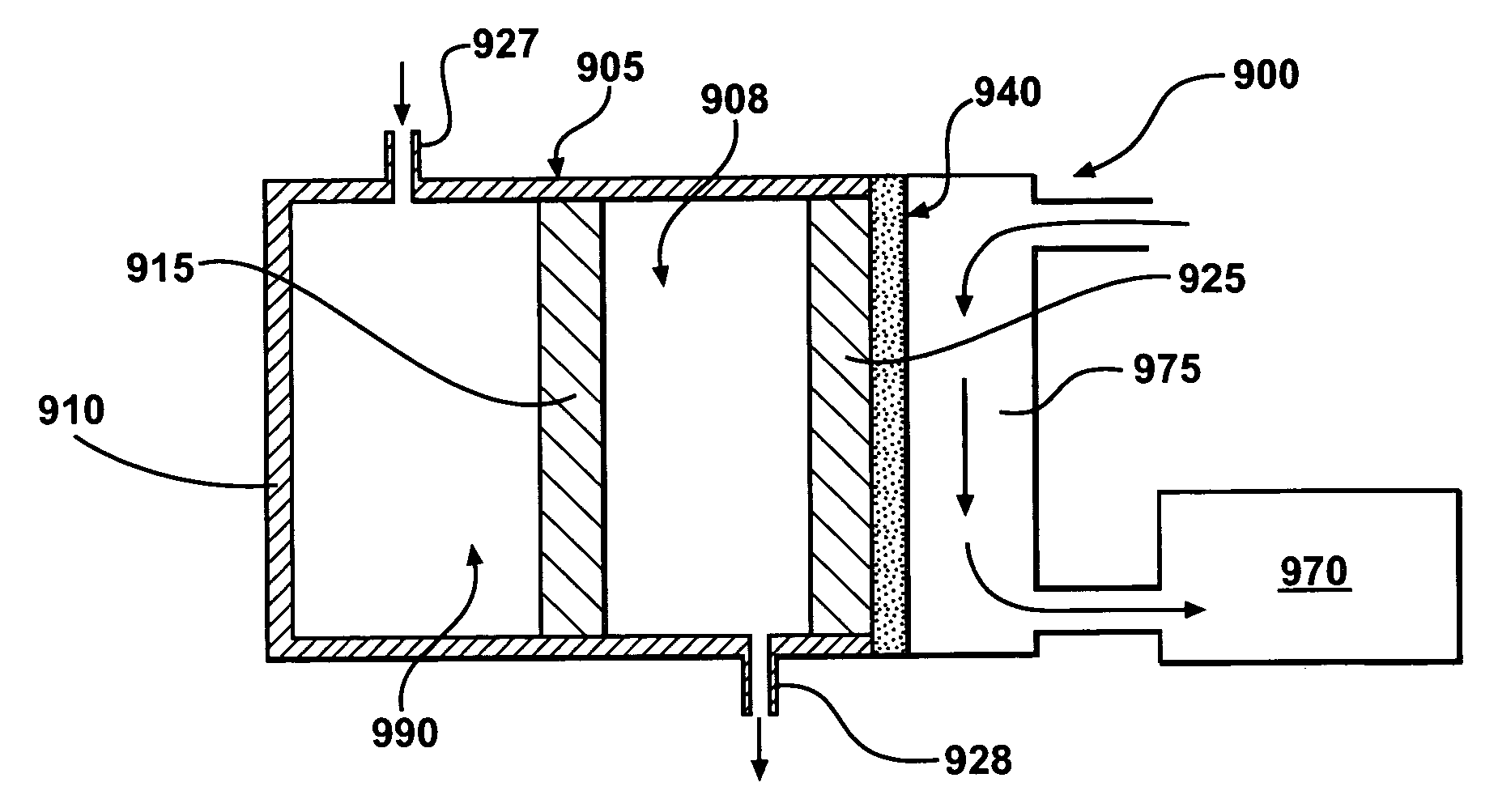
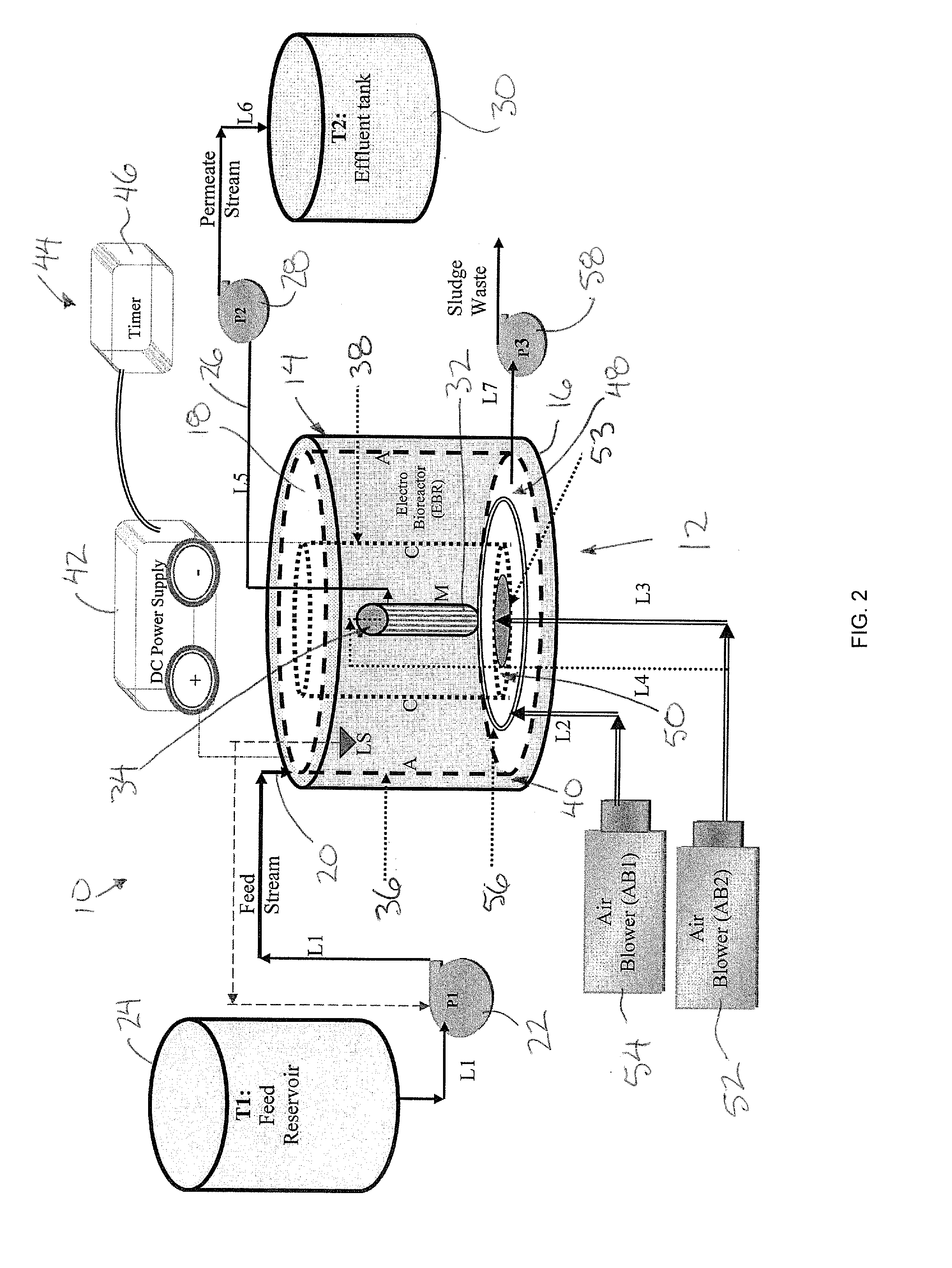
Wastewater Treatment System and Method
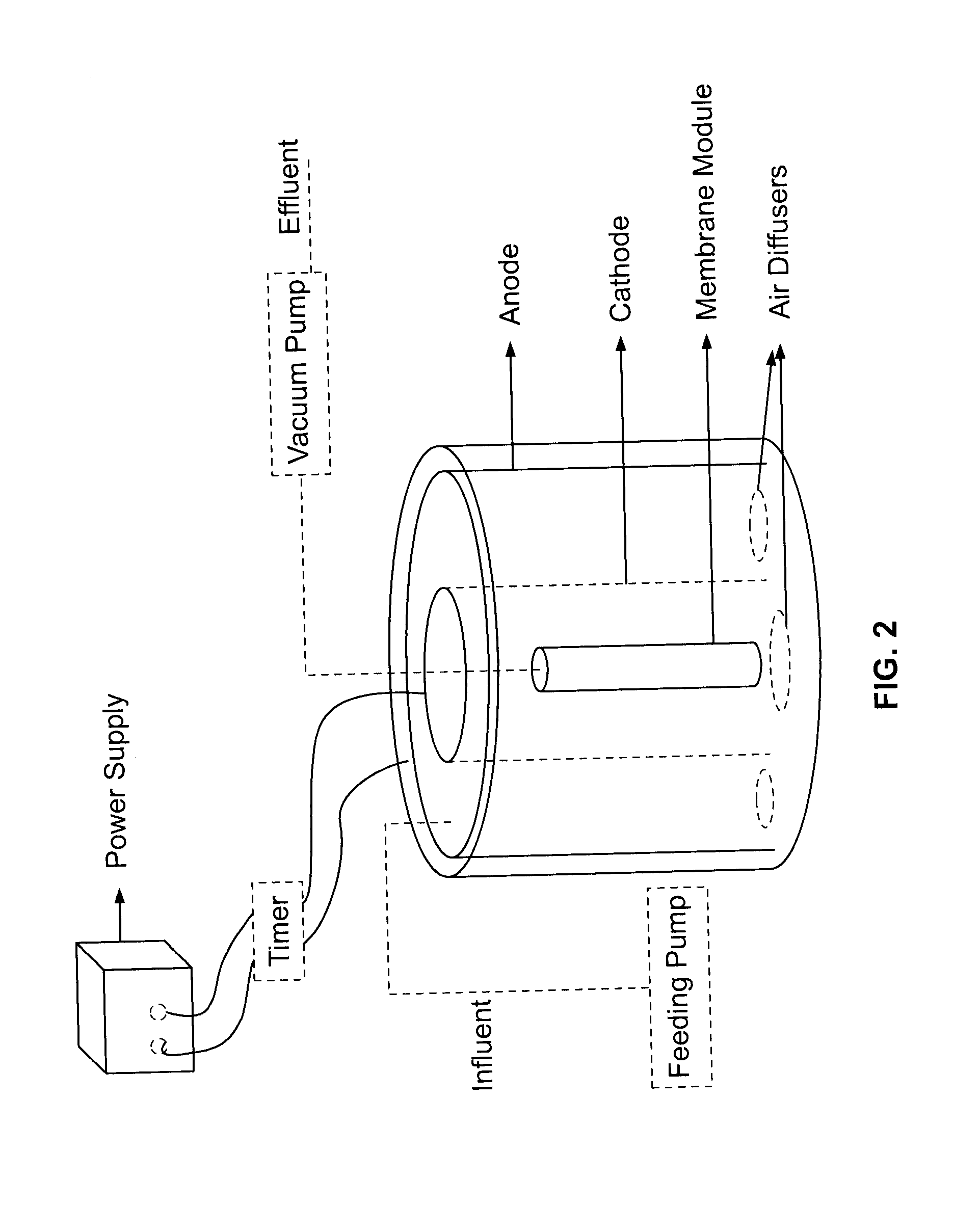
ActiveUS20100051542A1Reduce operating costsQuality improvementTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesFiltration membraneMedicine
A wastewater treatment system and method comprises a treatment chamber having a filtration membrane spanning an effluent outlet of the chamber and a pair of electrodes in the treatment chamber so as to be in communication with the wastewater. An electrical potential difference is applied between the electrodes such that one of the electrodes functions as an anode and one of the electrodes functions as a cathode. A flow of fluid is induced out of the treatment chamber through the filtration membrane to the effluent outlet. Accordingly the treatment chamber is arranged to biologically treat the wastewater, electrochemically treat the wastewater and mechanically filter the wastewater through the filtration membrane commonly therein.
Owner:ELEKTOROWICZ MARIA +2
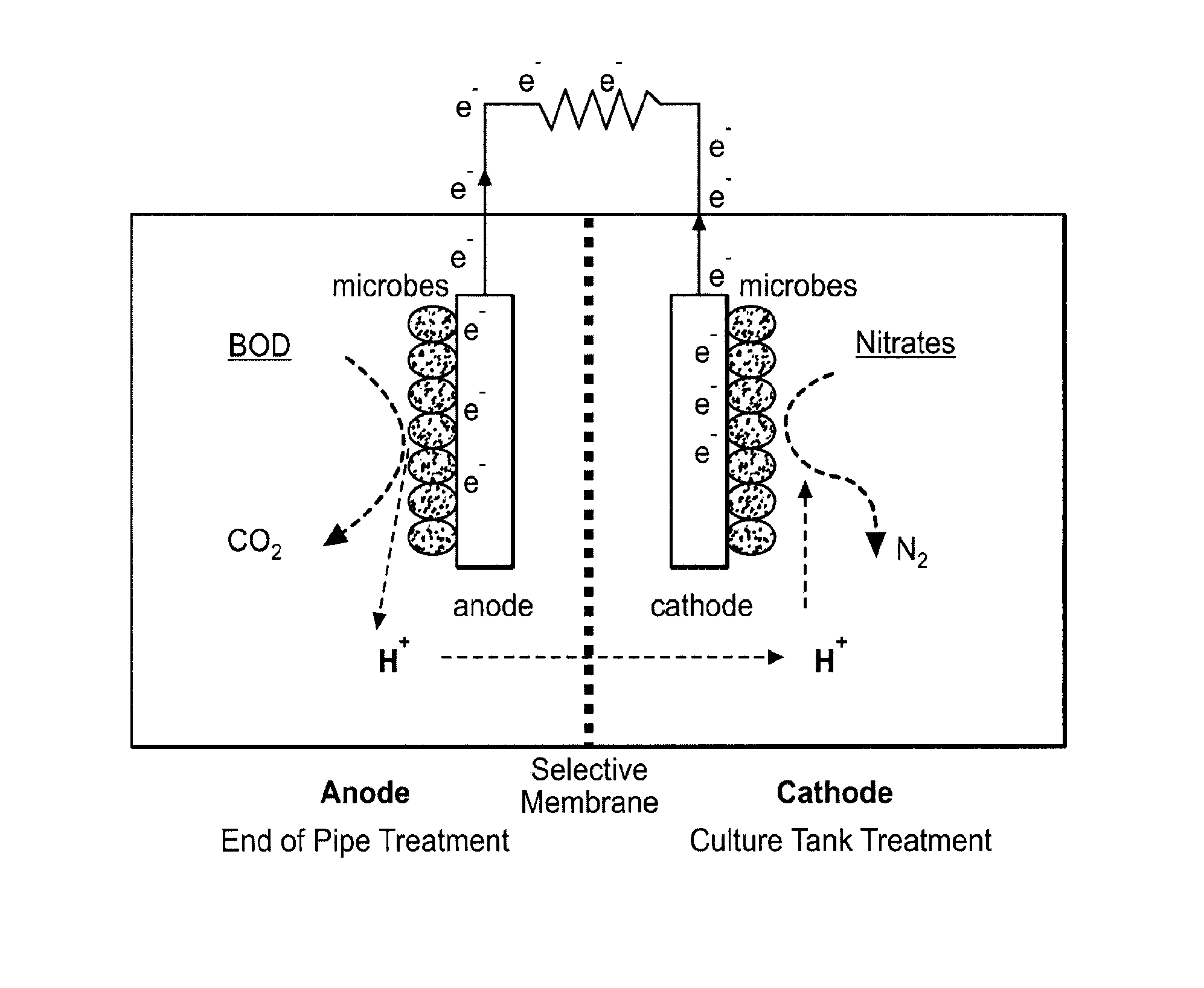
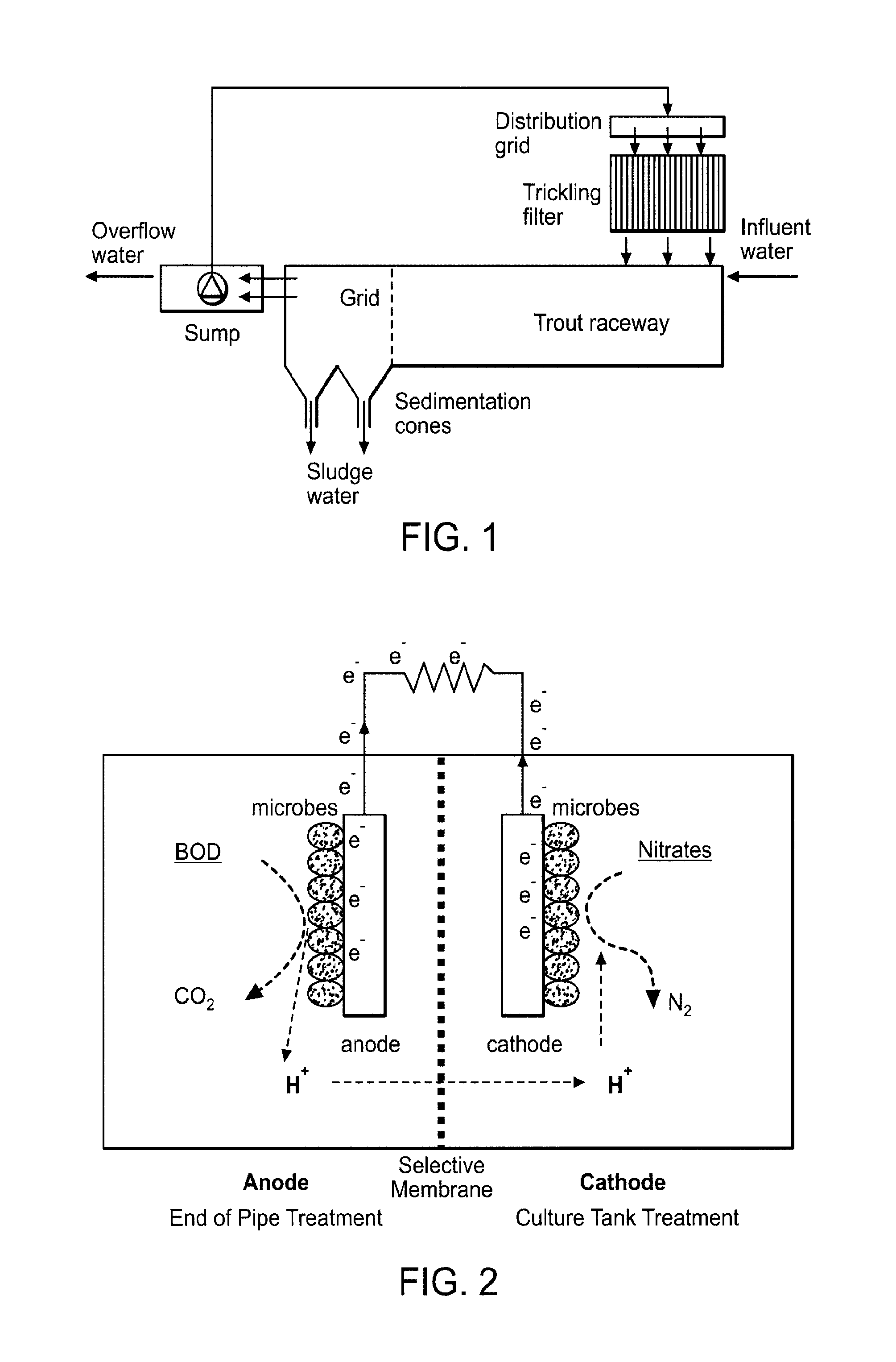
Denitrification and ph control using bio-electrochemical systems
ActiveUS20130112601A1Simple methodReduce compoundingWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesChemical oxygen demandNitrate
The present invention provides reactor designs, component designs, and operating schemes for removing nitrates and chemical oxygen demand from any suitable wastewater stream. The invention also provides reactor designs, component designs, and operating schemes designed to modify and improve pH and water quality in wastewater streams.
Owner:CAMBRIAN INNOVATION
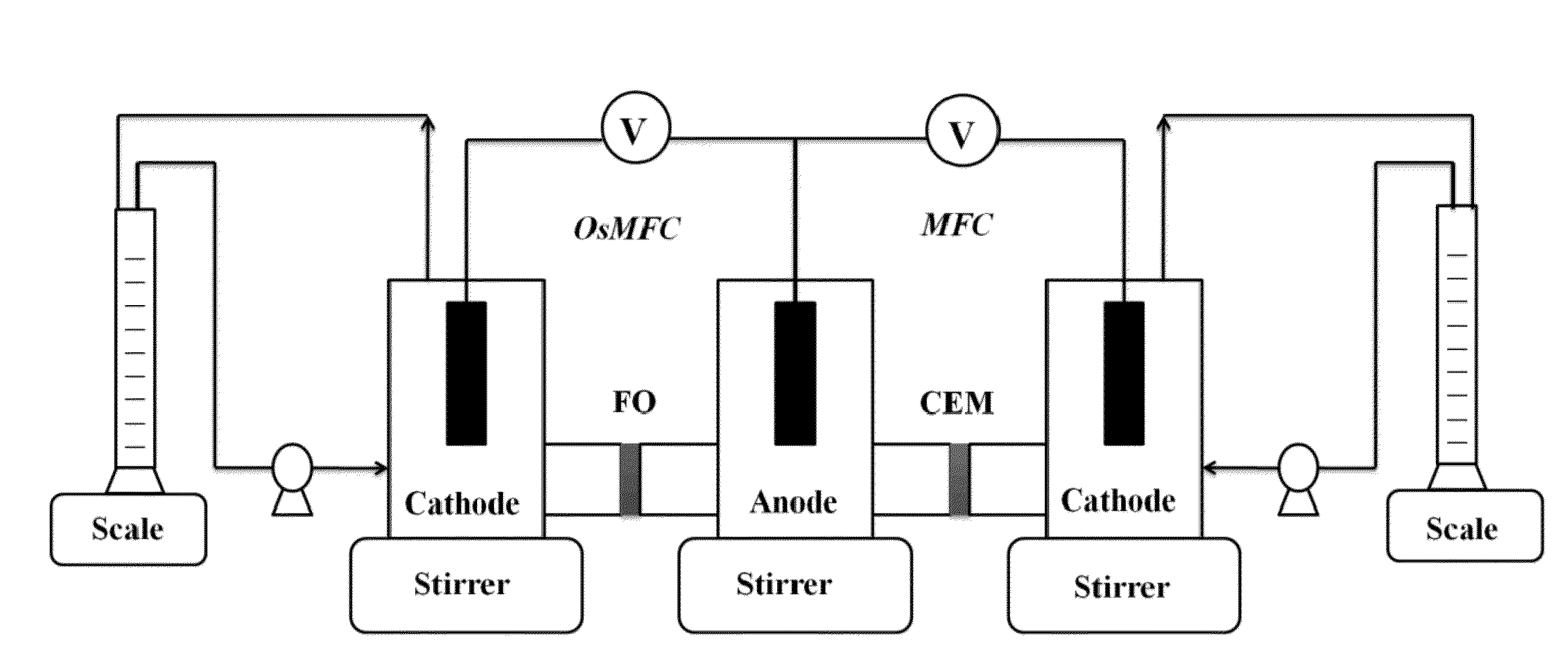
Osmotic bioelectrochemical systems
A bioelectrochemical system includes an anode, a saline solution chamber, and a cathode. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber containing an aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The saline solution chamber contains a draw solution and is separated from the anode chamber by a forward osmosis membrane. Water diffuses across the forward osmosis membrane from the aqueous reaction mixture to the draw solution.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
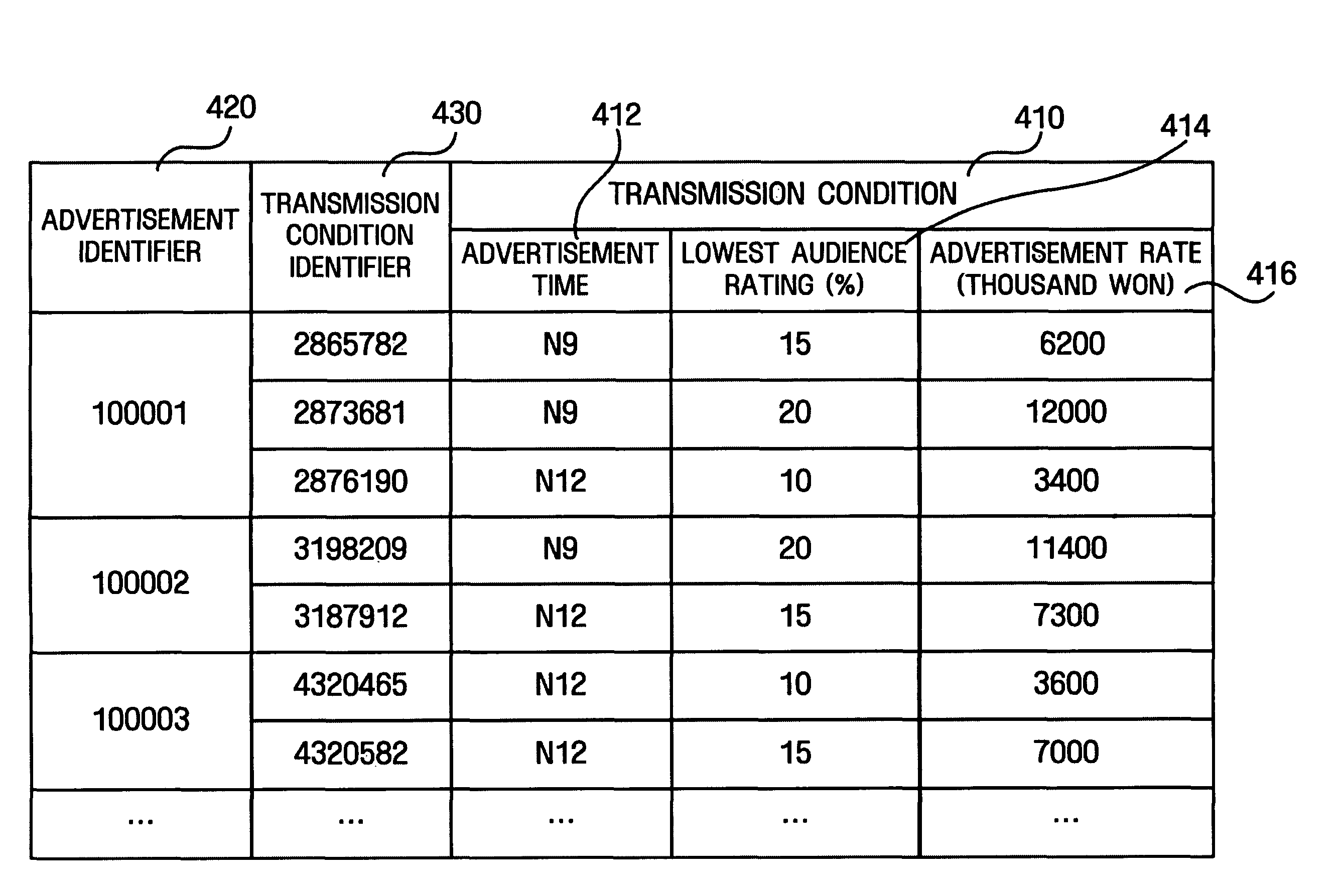
System and method of dynamically allocating advertisement according to audience rating
InactiveUS8205226B2Television system detailsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWorld Wide Web
A method and system are provided for allocating a dynamic advertisement according to audience ratings. The method includes selecting an advertisement broadcast to be transmitted based on broadcast viewing information of users and a transmission condition, and providing the selected advertisement broadcast.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for heavy metal elimination or precious metal recovery using microbial fuel cell
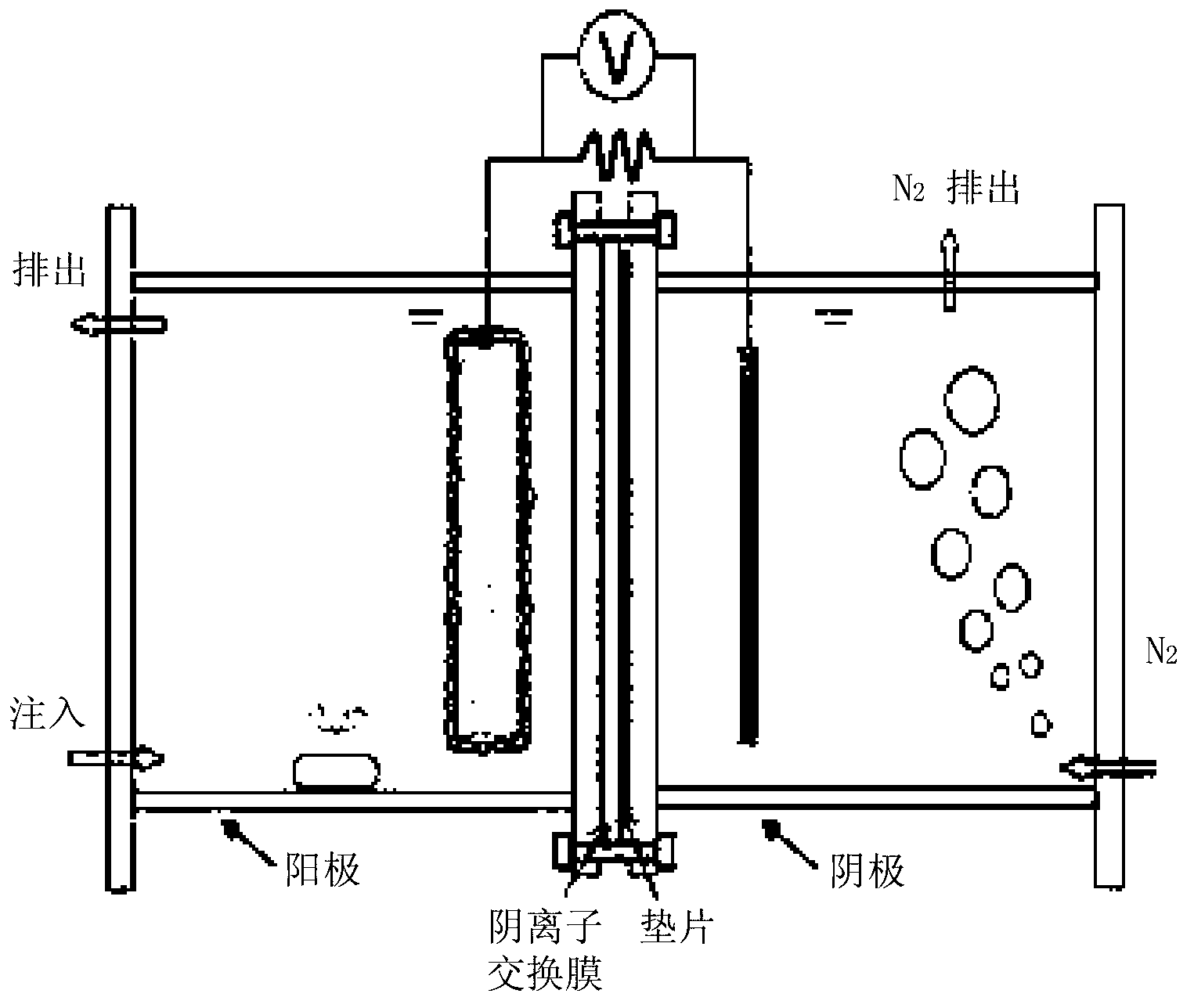
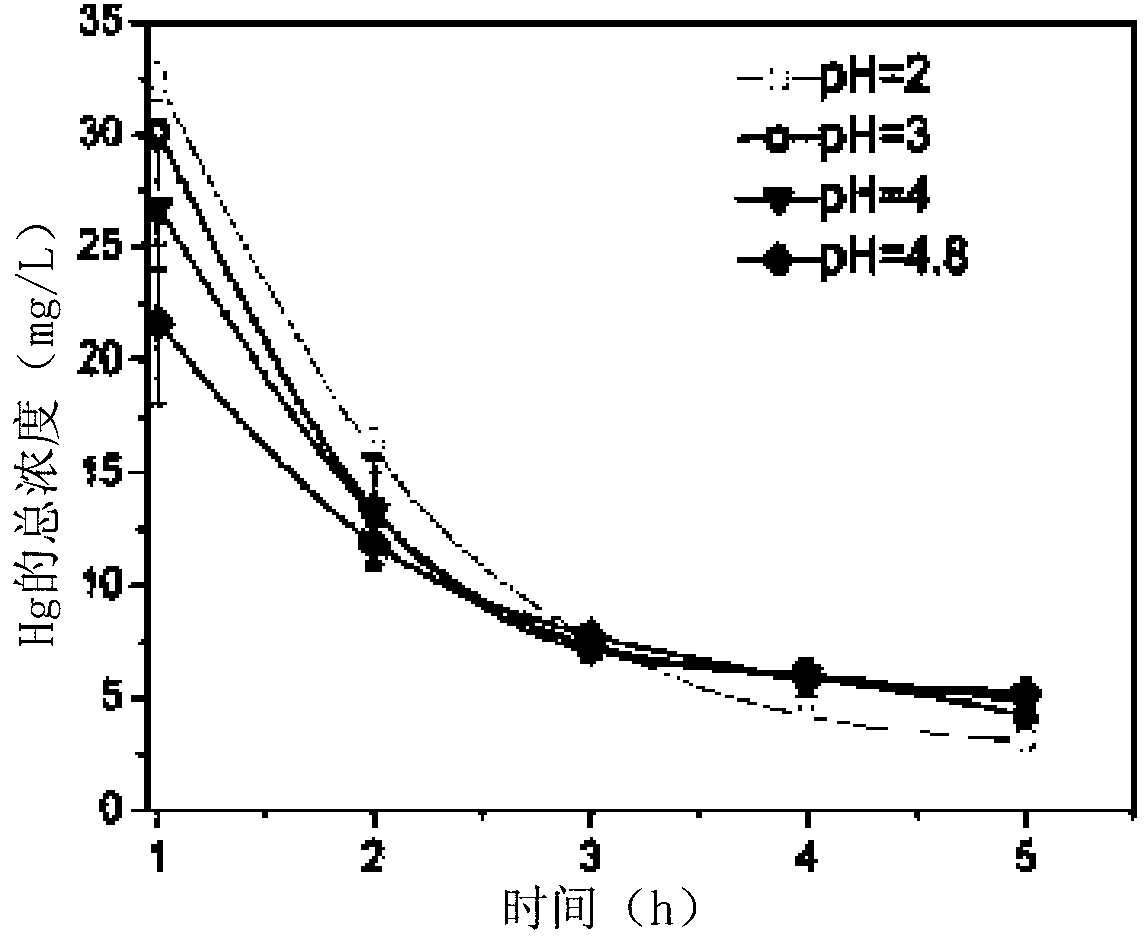
InactiveCN103153883AGood removal effectEfficient recyclingWater treatment parameter controlTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesMicrobial fuel cellElectricity
The present invention relates to a method in which a microbial fuel cell (MFC) is used in order to produce electrical power while also either eliminating a heavy metal or recovering a precious metal from waste water containing the heavy metal or the precious metal, and, more particularly, the invention has advantages including effective elimination of Hg2+ in the form of a solid precipitate or deposit of Hg or Hg2Cl2, and, incidentally, power is produced, by-products are rendered harmless and long-term economic operation is achieved.
Owner:RM TECH
Electrodes and methods for microbial fuel cells
InactiveUS20100151279A1Raise the potentialImprove performanceTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCell electrodesMicrobial fuel cellFuel cells
Methods of improving a performance parameter of a microbial fuel cell are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include heating an electrode and exposing the heated electrode to ammonia gas to produce a treated electrode characterized by an increased positive surface charge on the electrode surface. Improved performance parameters include increased maximum power density, increased coulombic efficiency, increased volumetric power density and decreased microbial fuel cell operation time to achieve maximum power density
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
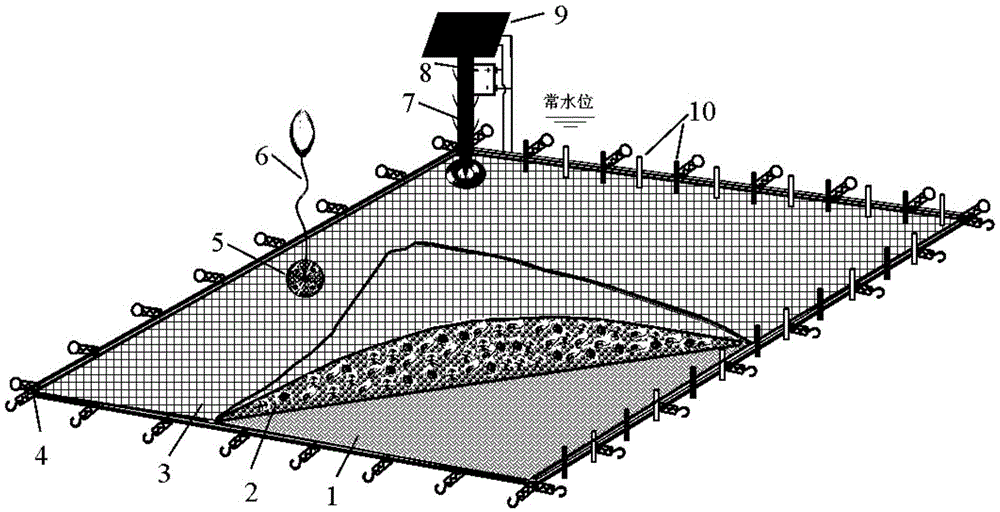
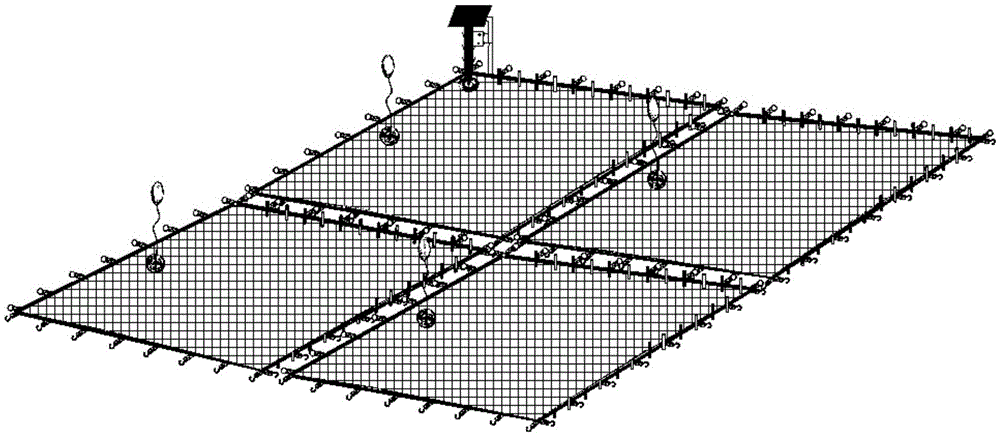
Polluted sediment ecological coverage carpet capable of inhibiting original algae from revival and growth and application method thereof
ActiveCN105645563AExtended service lifeReduce the amount of adsorption saturationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCoastlines protectionFiberEutrophication
The invention provides a polluted sediment ecological coverage carpet capable of inhibiting original algae from revival and growth and an application method thereof, belonging to the field of sediment in-situ restoration and algae control of a eutrophied water body. The invention aims to solve the problems of ecological potential safety hazards, low restoration efficiency, incapability of reutilization and the like in the existing sediment coverage technique. The ecological coverage carpet comprises a thin fiber inverted filter layer, a biological-matrix combined restoration layer, a fabric layer, a quick connection hook, an embedded matrix frame, floaters, stay piles, a microcurrent electrolyzer, solar panels and electrodes. The application method comprises the following steps: analyzing the varieties of algae hypopuses and pollutants in the superficial deposit, selecting the restoration region, laying in the dormancy interval that blue algae do not revive to the water body, analyzing the pollutant content and adsorption characteristics of the adsorptive filter material in the embedded matrix frame, and determining whether to replace the filler or reap the plants. The carpet can be used in sediment improvement and ecological restoration in lakes, ponds, landscape water and other polluted water bodies.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Process for the production of chemicals
InactiveUS20110315560A1Maintain steady stateIncrease ratingsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesFinal product manufactureChemical compoundReducing equivalent
A process for producing one or more chemical compounds comprising the steps of providing a bioelectrochemical system having an anode and a cathode separated by a membrane, the anode and the cathode being electrically connected to each other, causing oxidation to occur at the anode and causing reduction to occur at the cathode to thereby produce reducing equivalents at the cathode, providing the reducing equivalents to a culture of microorganisms, and providing carbon dioxide to the culture of microorganisms, whereby the microorganisms produce the one or more chemical compounds, and recovering the one or chemical compounds.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
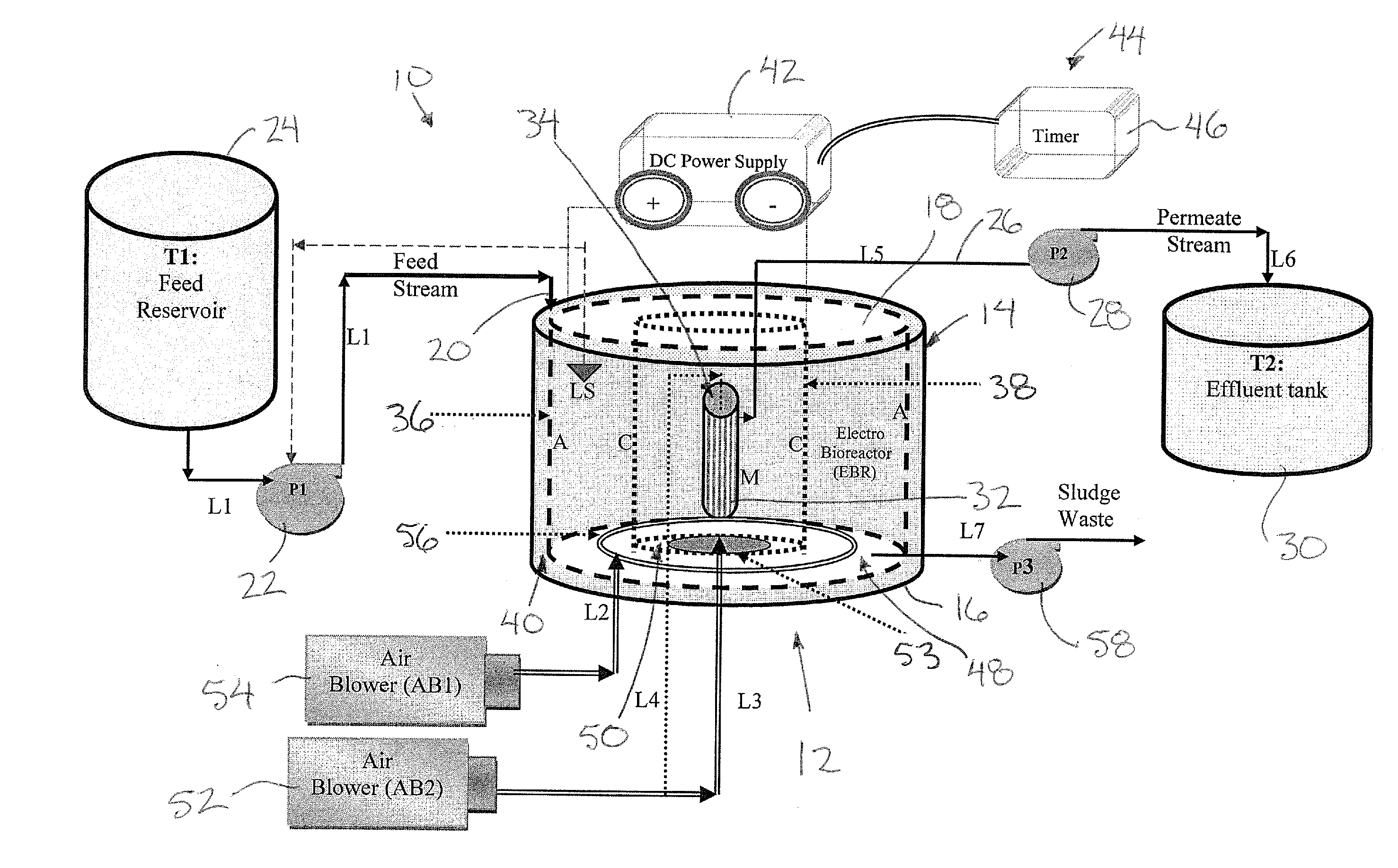
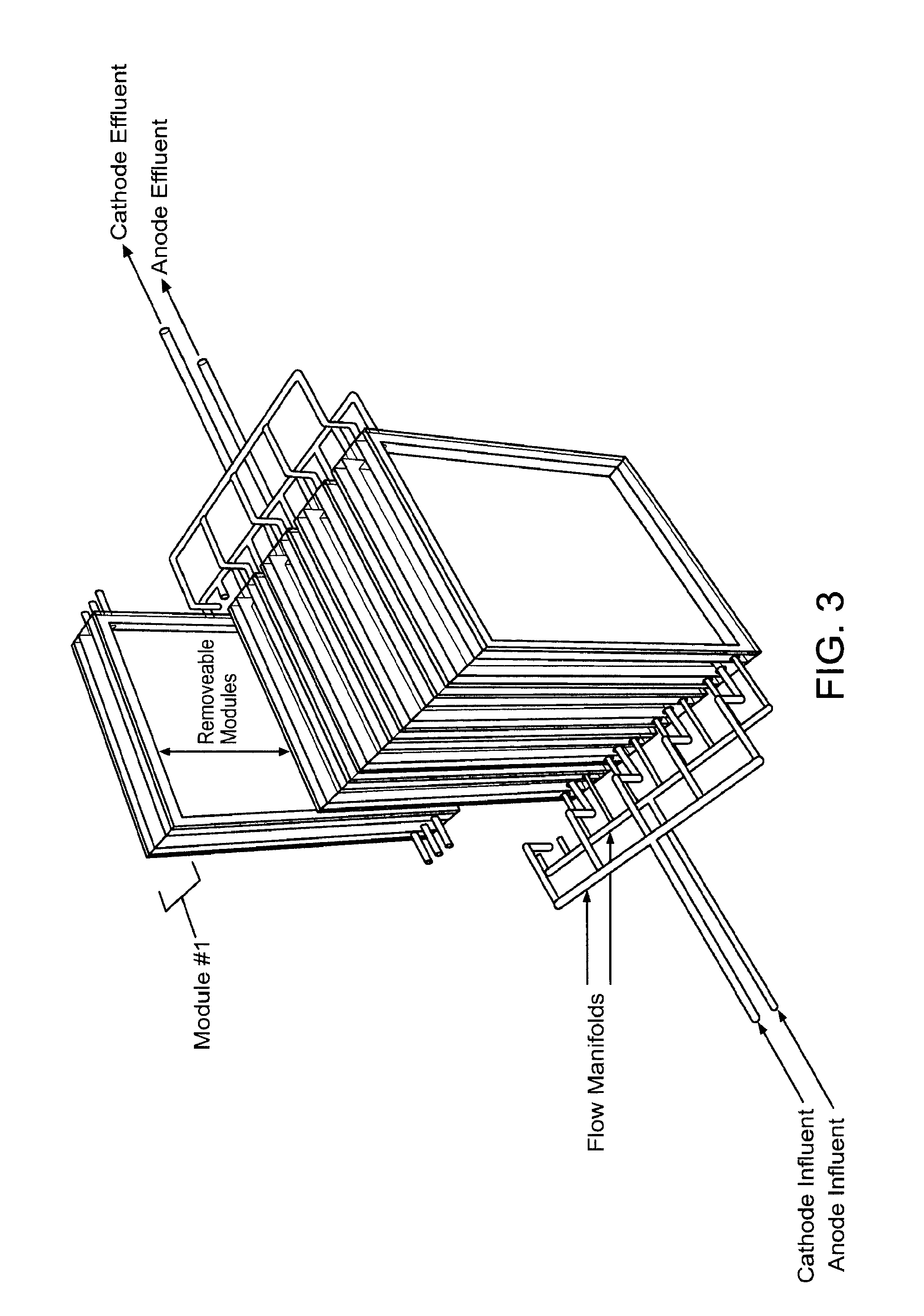
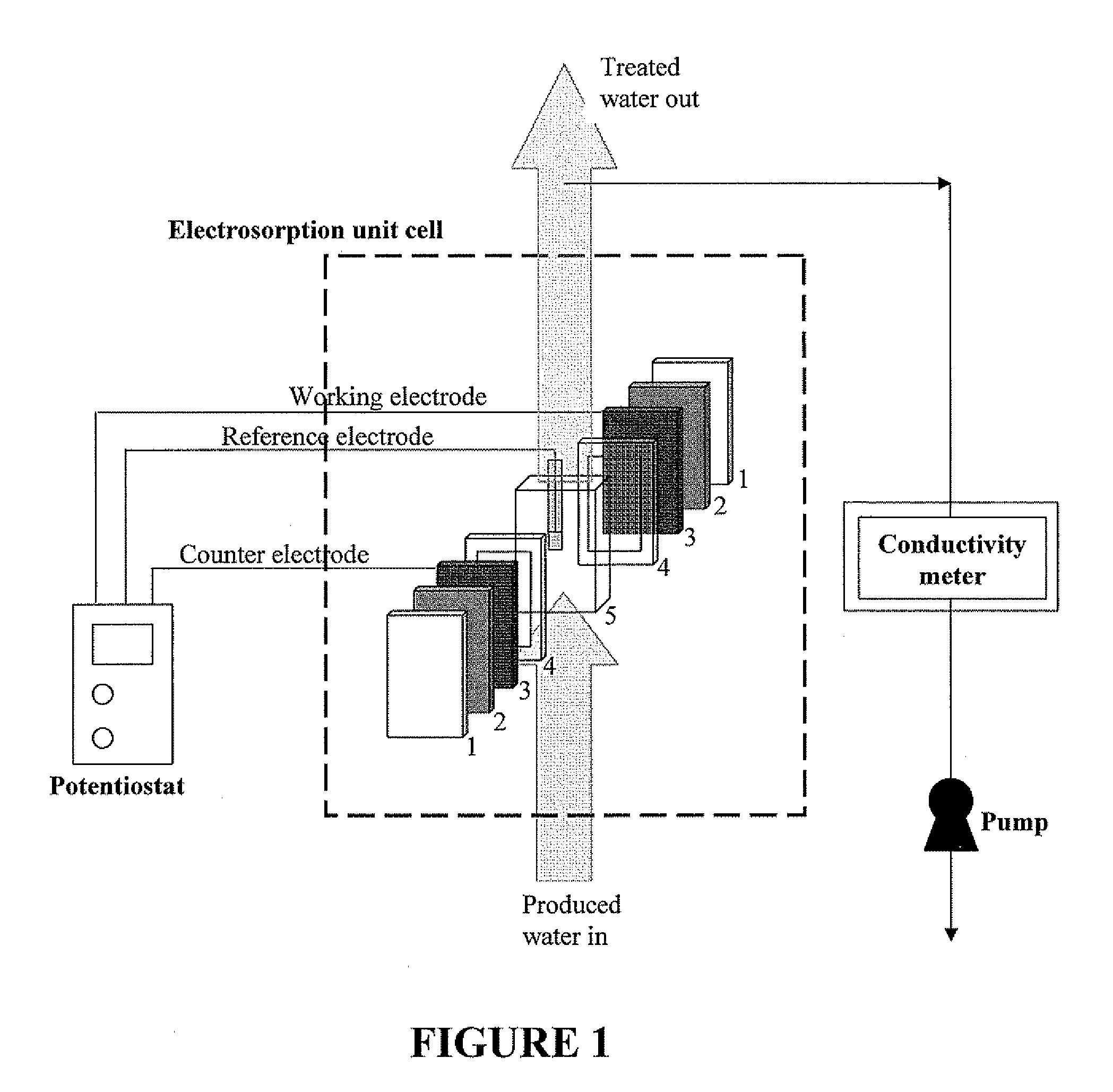
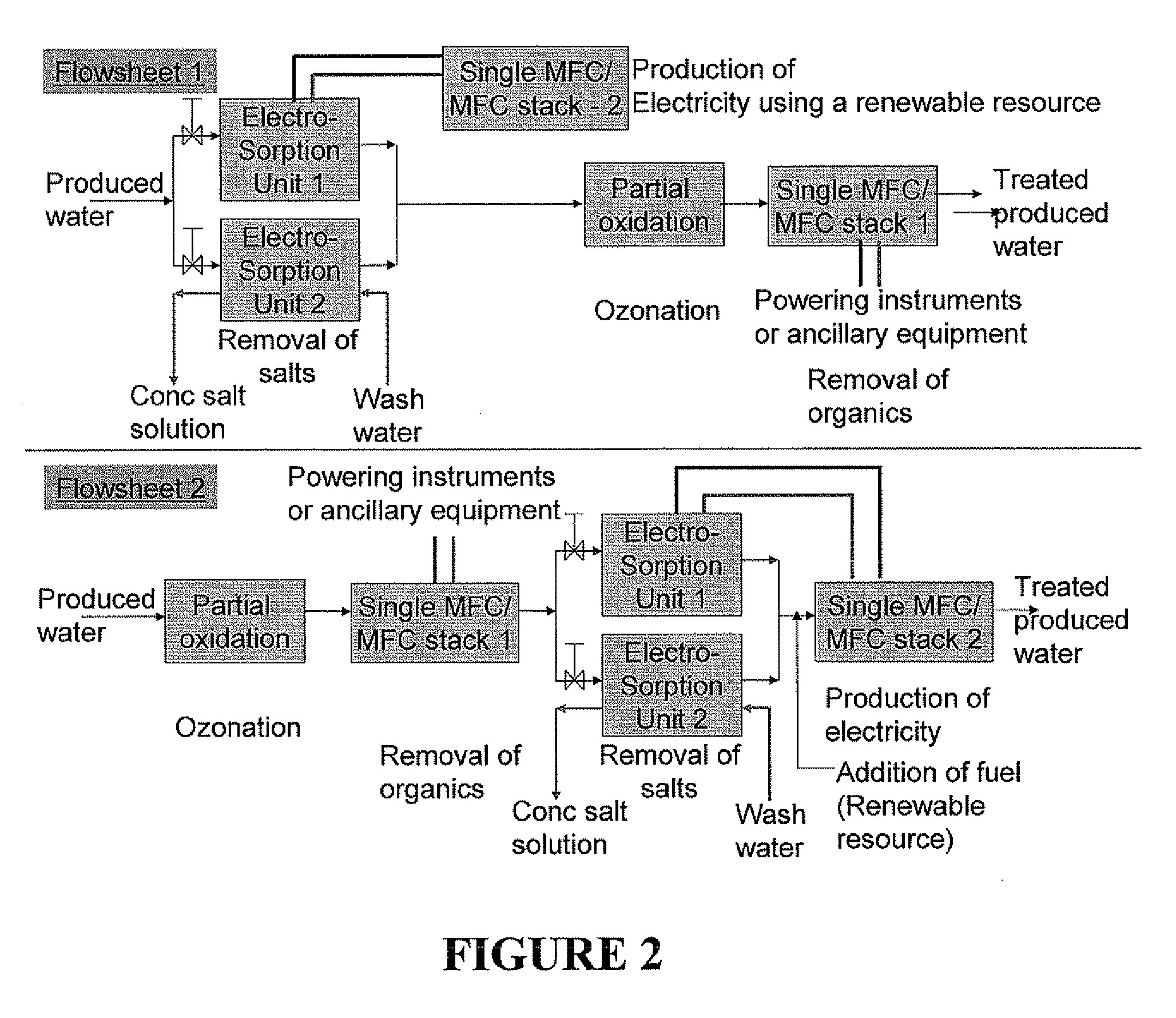
Bio-electrochemical system for treating wastewater
ActiveUS20130299400A1Simple and robust systemIncreasing wastewater treatment rateTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSpecific water treatment objectivesWastewaterBioelectrochemistry
The invention relates to bio-electrochemical systems for treating wastewater, and sour gas produced by anaerobic digestion of organic material. The invention further relates to novel anode / cathode pairing schemes, and electric and hydraulic architectures for use in bio-electrochemical systems.
Owner:CAMBRIAN INNOVATION
Integrated membrane system for distributed water treatment
InactiveUS20130032533A1Easy to operateLess-effectiveTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesChloramine BPh control
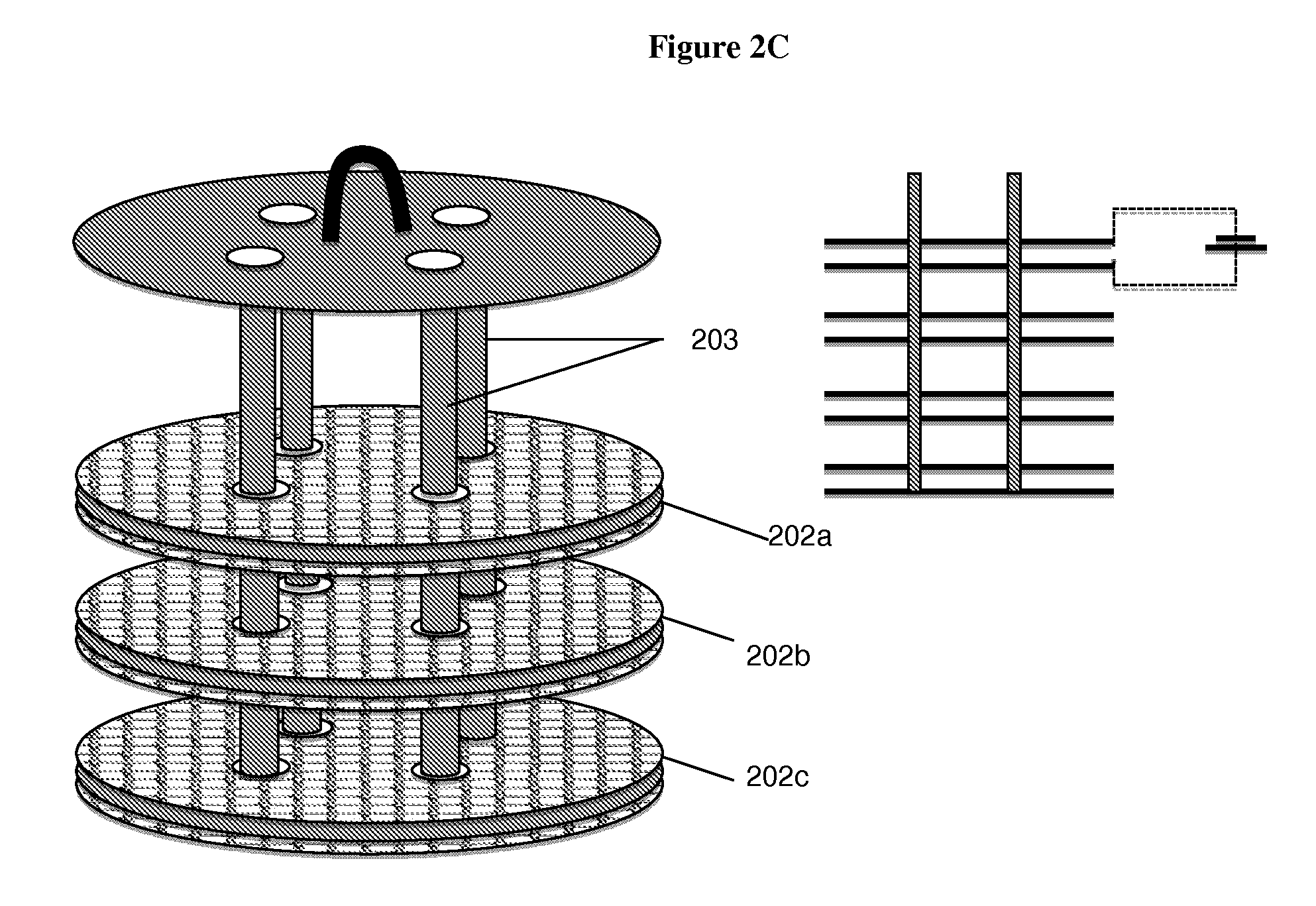
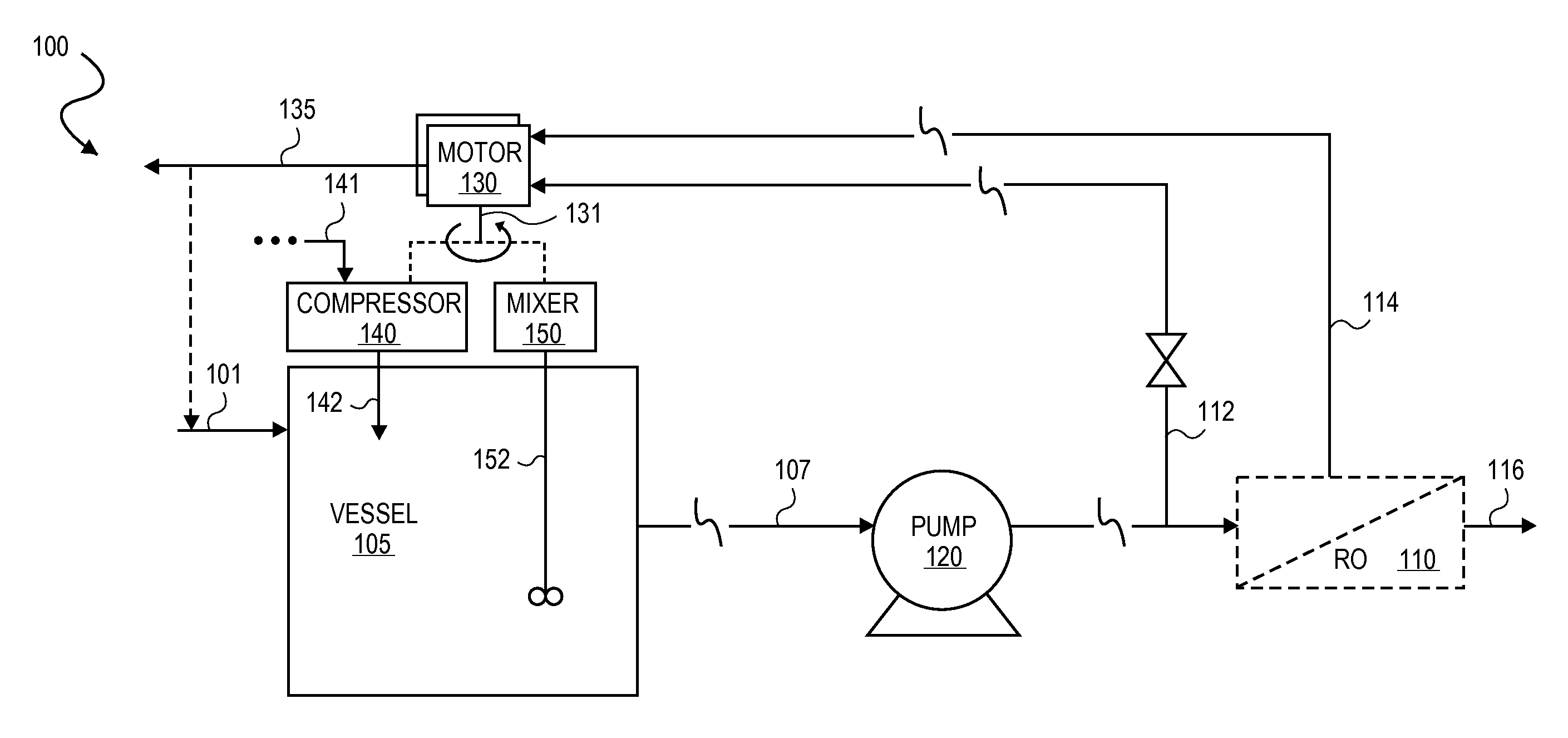
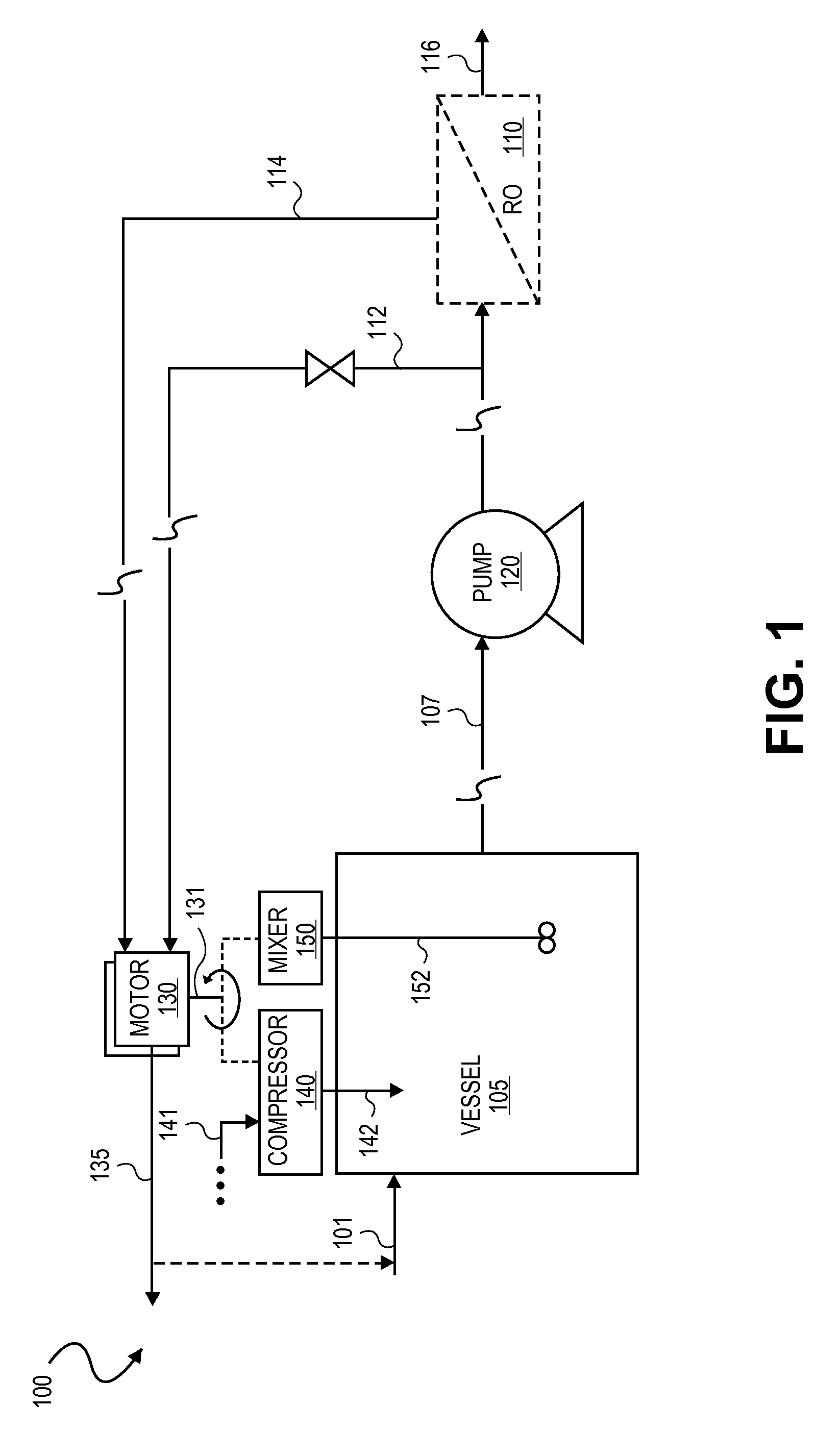
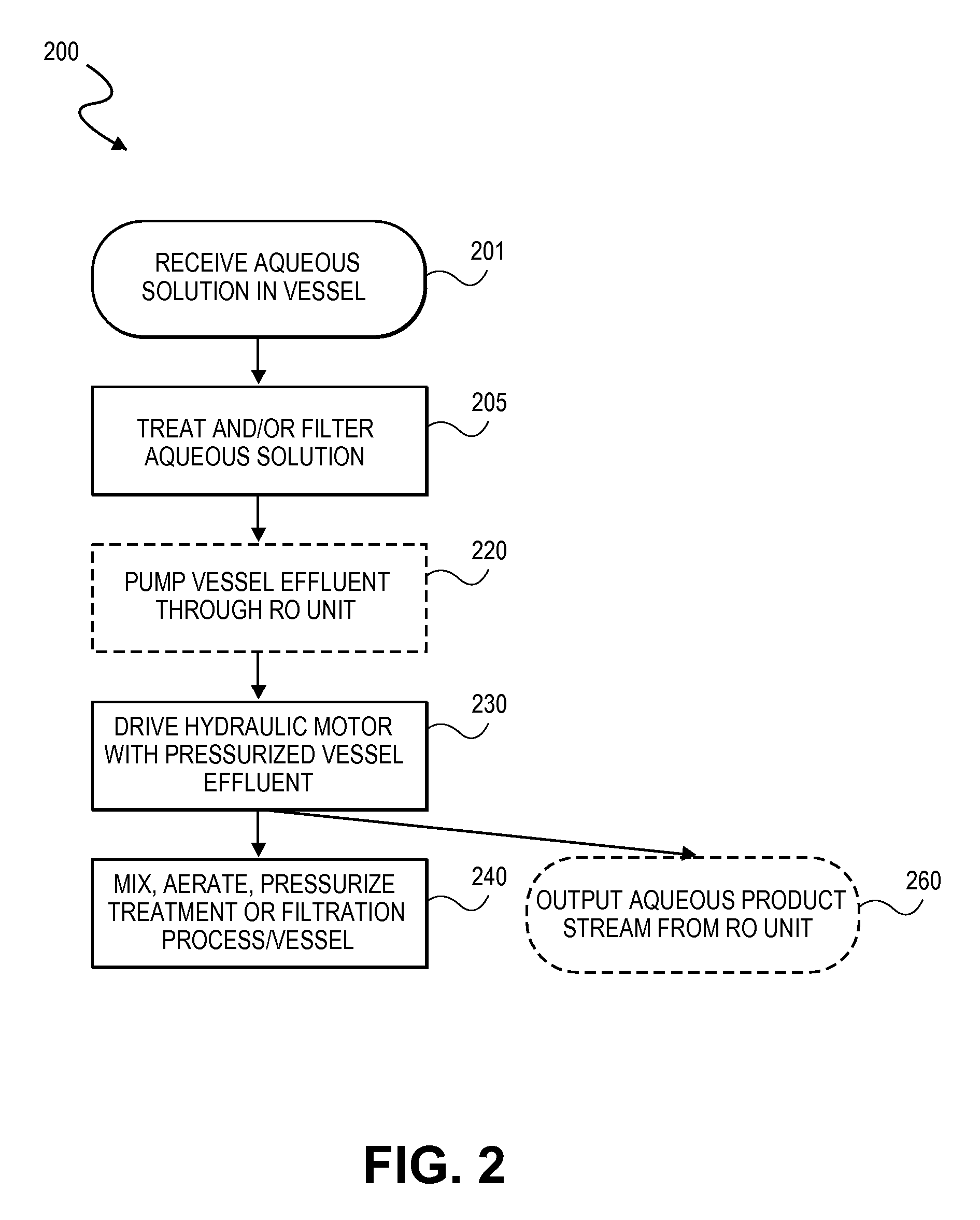
Integrated membrane treatment systems for treatment of an aqueous solution. In embodiments, components, such as an MBR, are integrated with means to recover energy from the system, for example from an RO concentrate, to operate the other components. In embodiments including biological treatment, RO is integrated with other components, such as an MBR with the ROs ability to remove inorganic nitrogen enabling biological treatment to be performed with only partial nitrification and the MBR operated without active pH control. In embodiments, RO is integrated with a chlorine generator to convert chlorides present in the RO concentrate for an in-situ source of oxidizing biocides for disinfection purposes. Chloramines may be generated in-situ from residual ammonia and chlorides in the RO reject. In embodiments, carrier media is employed in a membrane tank to enhance removal of residual organics by the MBR and to also improve effectiveness of membrane scouring.
Owner:ENVEERA
Integrated photo-bioelectrochemical systems
ActiveUS20130017415A1Treatment by combined electrochemical biological processesBiochemical fuel cellsOrganic compoundBioreactor
A bioelectricalchemical system includes an anode, an algal bioreactor, and a cathode. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber containing a first aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The algal bioreactor contains a second aqueous reaction mixture including one or more nutrients and one or more algae for substantially removing the nutrients from the second aqueous reaction mixture. The cathode is at least partially positioned within the algal bioreactor.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
Microbial fuel cell treatment of fuel process wastewater
ActiveUS20100200495A1Improve economyAmenable to operatingTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityMicrobial fuel cell
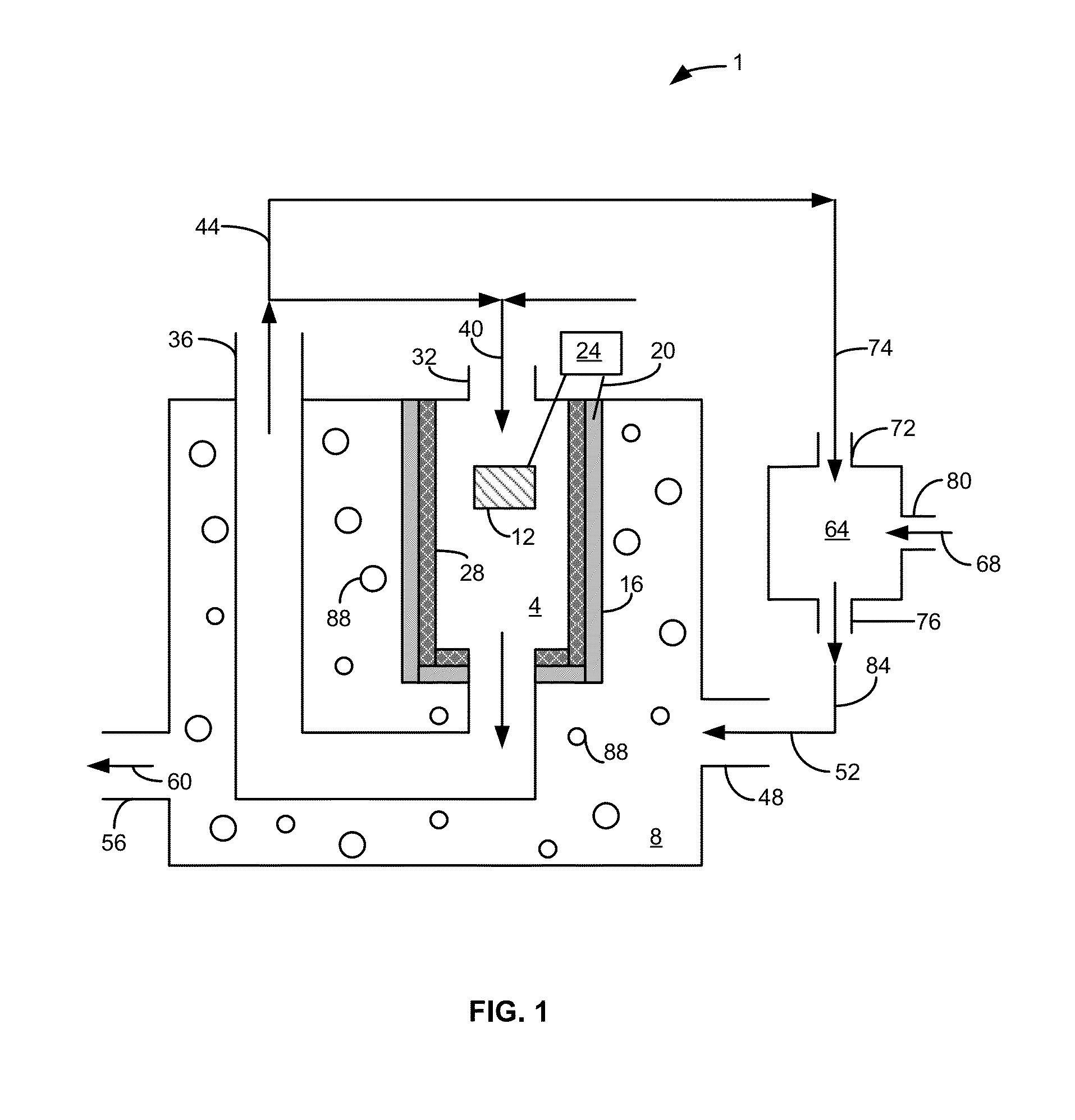
The present invention is directed to a method for cleansing fuel processing effluent containing carbonaceous compounds and inorganic salts, the method comprising contacting the fuel processing effluent with an anode of a microbial fuel ell, the anode containing microbes thereon which oxidatively degrade one or more of the carbonaceous compounds while producing electrical energy from the oxidative degradation, and directing the produced electrical energy to drive an electrosorption mechanism that operates to reduce the concentration of one or more inorganic salts in the fuel processing effluent, wherein the anode is in electrical communication with a cathode of the microbial fuel cell. The invention is also directed to an apparatus for practicing the method.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Processes and apparatuses for removal of carbon, phosphorus and nitrogen
ActiveUS20150001094A1Increased cost of infrastructureUpgrade effluent qualityWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesActivated sludgeElectricity
There are provided processes for treating wastewater. The processes can comprise treating a mixture comprising the wastewater and an activated sludge, in a single reactor, with an electric current having a density of less than about 55 A / m2, by means of at least one anode and at least one cathode that define therebetween an electrical zone for treating the mixture; exposing the mixture to an intermittent ON / OFF electrical exposure mode to the electric current in which an OFF period of time is about 1 to about 10 times longer than an ON period of time; and maintaining an adequate oxidation-reduction potential in the single reactor. Such processes allow for substantial removal of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus from the wastewater in the single reactor of various forms and for obtaining another mixture comprising a treated wastewater and solids.
Owner:VALORBEC S E C +1
Methods and Systems for Enhanced Oxidative and Reductive Remediation
ActiveUS20120070696A1Accelerates the biodegradation processEnhancing transformation of inorganic chemicalsCellsPolycrystalline material growthEngineeringConductive materials
Enhanced contaminant degradation systems via rapid transfer of electrons in an environment or matrix through bioelectrochemical electron transfer circuitry, electron transfer conduit and conductive materials. Specialized circuitry may be used with respect to the anode, cathode, and transmission line design including floating cathodes, anchored anodes, and the like.
Owner:ADVANCED ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
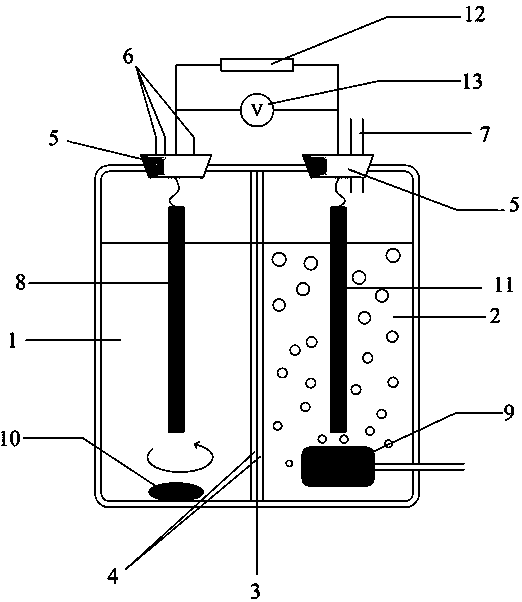
Microbial fuel cell based method for treatment and detection of chromium-containing electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN104386826AAvoid toxic effectsNo pollution in the processTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsHigh concentrationSodium acetate
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell based method for treatment and detection of chromium-containing electroplating wastewater. The steps include: 1) injecting anaerobic sludge and a sodium acetate solution into an anode chamber of a two-chambered microbial fuel cell to inoculate microorganisms, injecting a cathode liquid into a cathode chamber, and connecting resistance at the cathode and the anode to form a closed loop, reacting the cell in a thermotank, injecting sodium acetate into the anode chamber each day till the output voltage is stable; 2) changing the anode chamber solution to an oxygen removed anode liquid, and changing the cathode solution to chromium-containing wastewater; and 3) after starting, adjusting the pH value of wastewater, injecting the wastewater into the cathode chamber, connecting the external resistance and starting the treatment process. The method provided by the invention realizes no direct contact of microorganisms and hexavalent chromium, avoids poisoning of hexavalent chromium on microorganisms, and makes microbiological treatment of high concentration hexavalent chromium wastewater become possible. The standard redox potential of hexavalent chromium is 1.33V, the microbial fuel cell is utilized to treat hexavalent chromium wastewater, and the purposes of synchronous wastewater treatment and electric energy recovery are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and devices for in-situ treatment of sediment simultaneous with microbial electricity generation
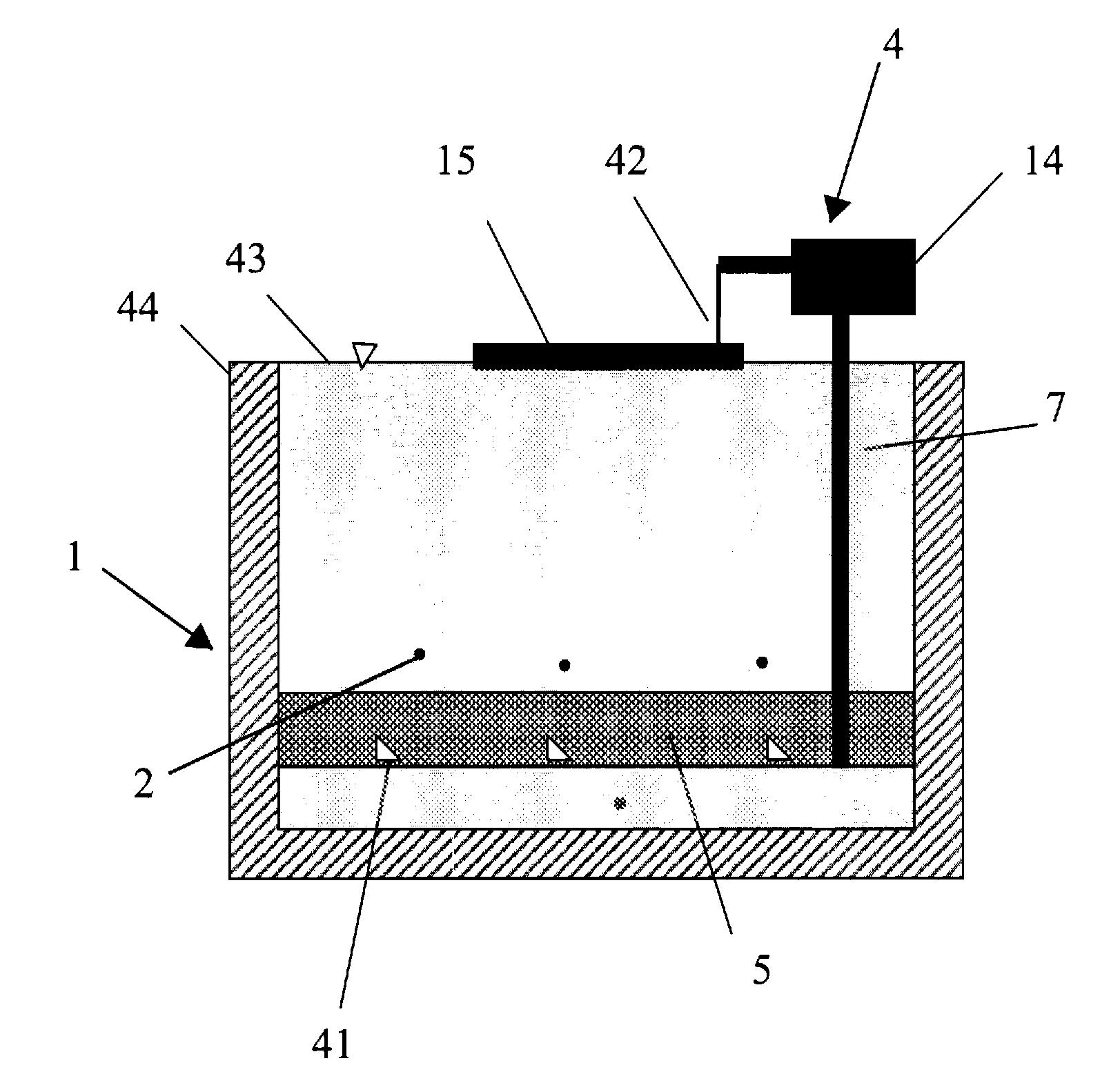
ActiveUS20120276418A1Easy to placeGood effectTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesFinal product manufactureEnvironmental resistanceMicrobial fuel cell
A method for in-situ treatment of sediment simultaneous with microbial electricity generation is provided, comprising steps of constructing a microbial fuel cell, placing the microbial fuel cell in the sediment, forming a cell circuit, and cultivating microorganisms to generate electrical power. The method overcomes shortcomings found in the prior art and uses organics in the sediment as fuels to in-situ treat the sediment with simultaneous electricity generation. A device for implementing the method is also provided, which can be expanded in different directions as needed and is easy to maintain during long-term operation. The device has many advantages including compact structure, easy operation, low cost, high output power density, significant reduction in sediment COD, no influence on water flow, and environment-friendly
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
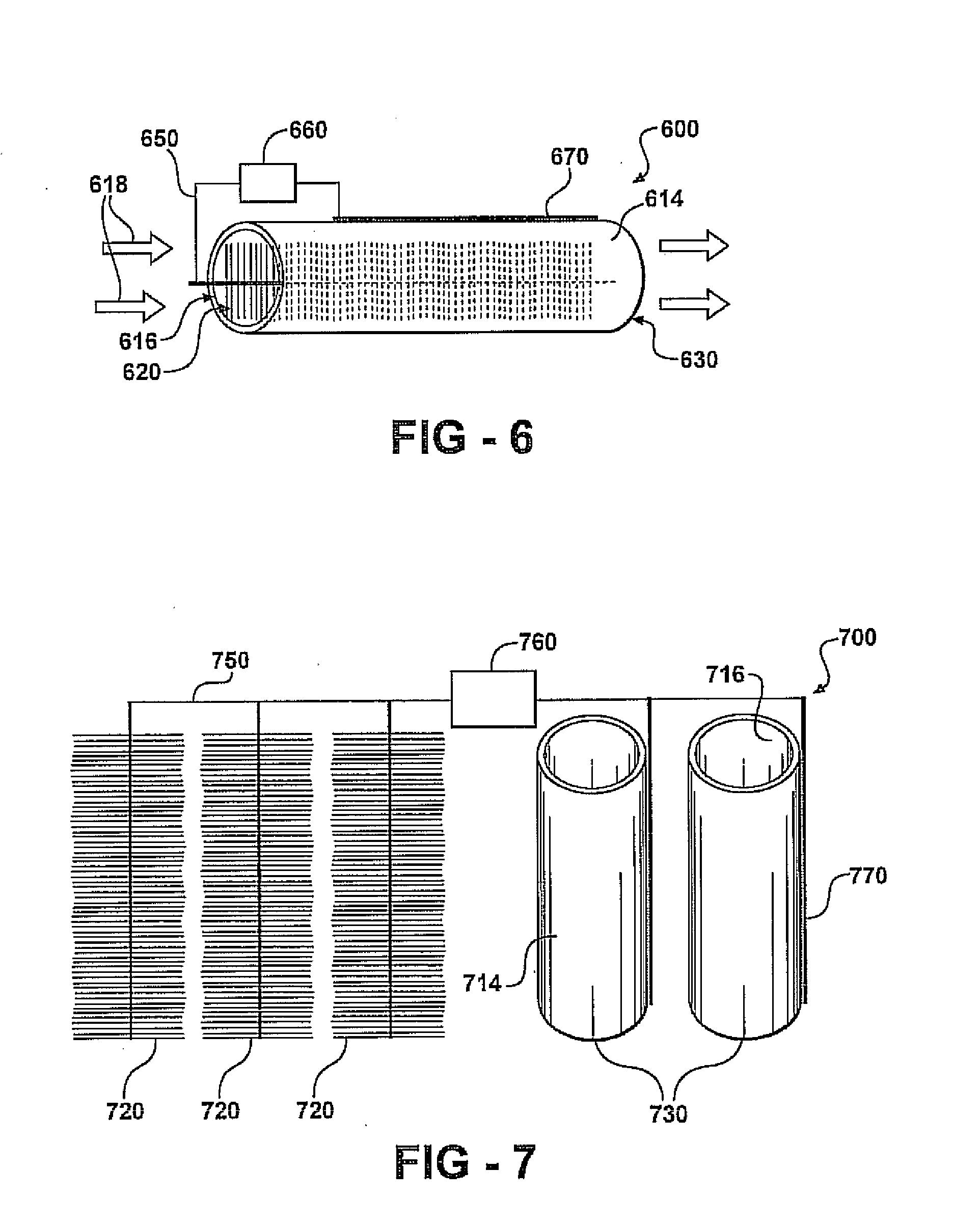
Electrohydrogenic reactor for hydrogen gas production
ActiveUS7922878B2CellsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesElectricityInterior space
A system for hydrogen gas generation is provided according to the present invention which includes a hydrogen gas electrode assembly including a first anode in electrical communication with a first cathode; a microbial fuel cell electrode assembly including a second anode in electrical communication with a second cathode, the microbial fuel cell electrode assembly in electrical communication with the hydrogen gas electrode assembly for enhancing an electrical potential between the first anode and the first cathode. A single chamber housing contains the hydrogen gas electrode assembly at least partially in the interior space of the housing.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
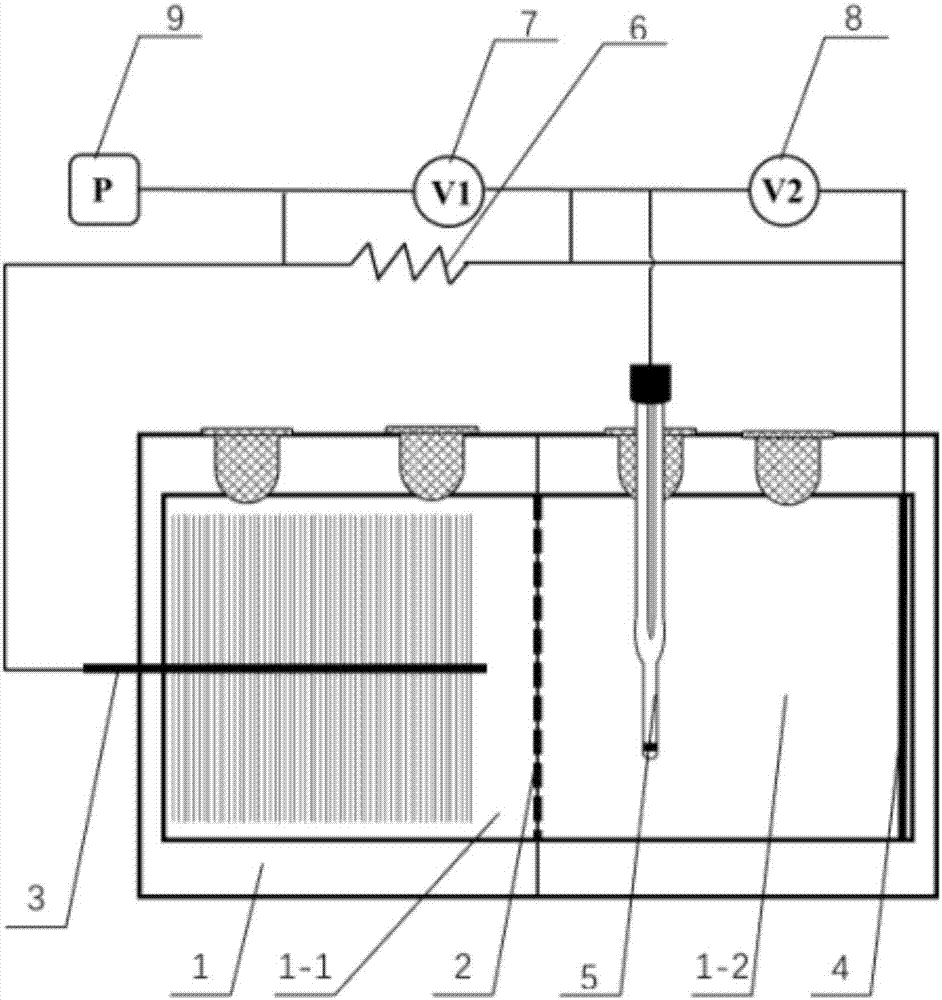
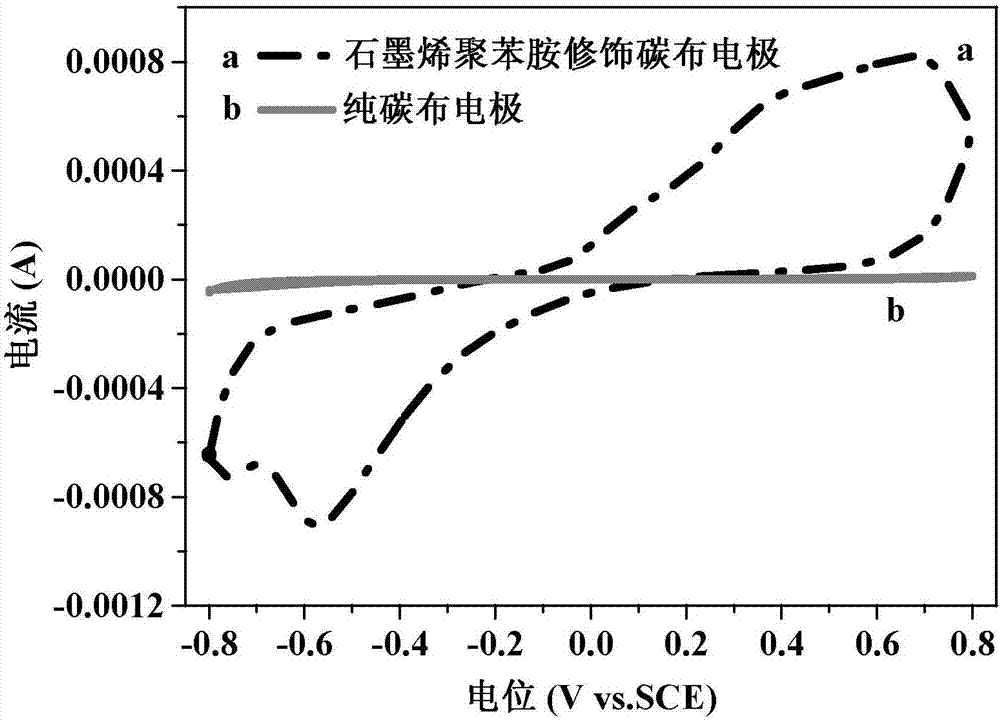
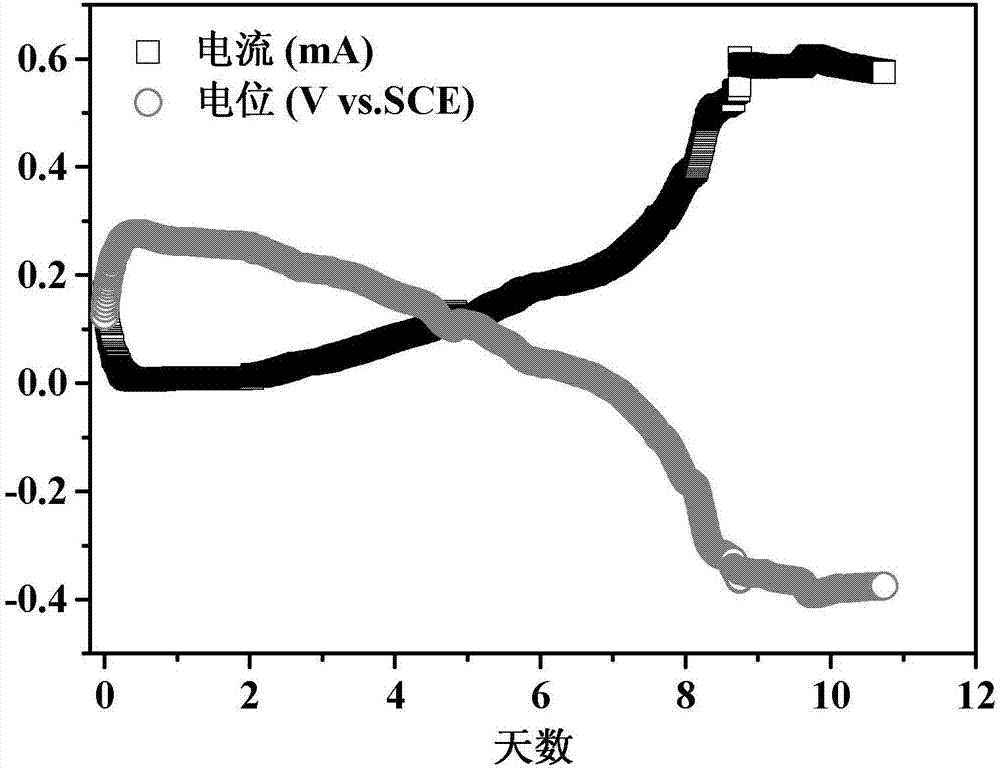
Preparation of graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material, and method for accelerating acclimation of bio-anode
InactiveCN106941179AImprove transfer efficiencyLower resistanceTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCell electrodesModified carbonWastewater
The invention provides preparation of a graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material, and a method for accelerating the acclimation of a bio-anode, and relates to electrode preparation and bio-anode acclimation. A purpose of the present invention is to solve the technical problem of poor electron transfer efficiency of existing bioelectrochemical anode. The graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material preparation method comprises: loading graphene oxide onto a carbon cloth, immersing into a sodium borohydride solution, reducing, immersing into an aniline monomer solution, adding a curing agent solution in a dropwise manner, and polymerizing to obtain the graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material. According to the present invention, with the application of the graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material as the anode in the bioelectrochemical system reactor, the operation is performed after the starting until the output potential is stable so as to complete the acclimation; and the graphene polyaniline modified carbon cloth electrode material can be used in wastewater treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
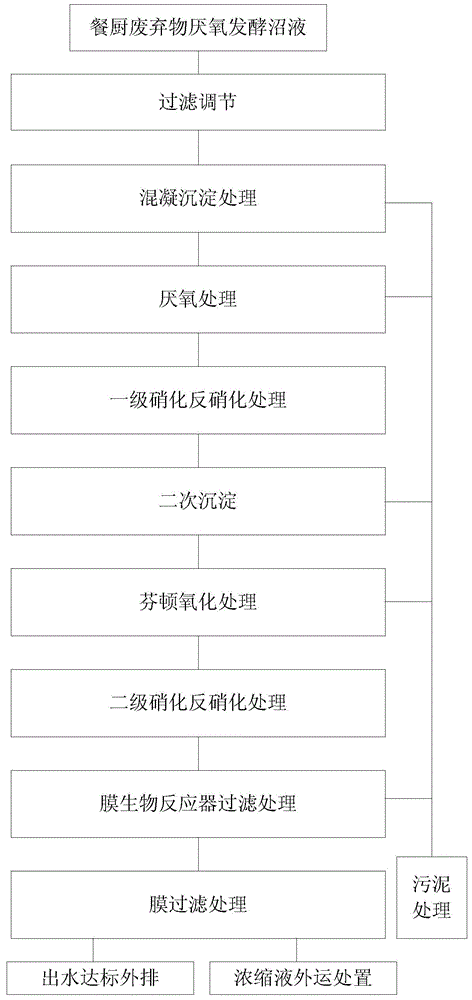
Treatment system and method for biogas slurry produced from anaerobic fermentation of kitchen waste
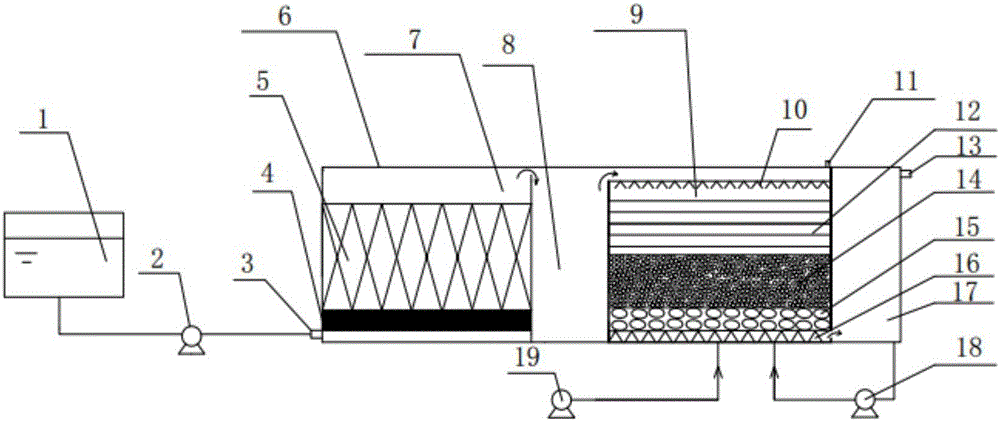
InactiveCN104478175AGuarantee water qualityGuaranteed uptimeTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWaste based fuelFiltrationWater quality
The invention discloses a treatment system and method for biogas slurry produced from anaerobic fermentation of kitchen waste. The system comprises a filtering and adjusting treatment unit, a coagulating sedimentation treatment unit, an anaerobic treatment unit, a primary nitrification and denitrification treatment unit, a secondary sedimentation tank, a Fenton oxidation treatment unit, a secondarynitrification and denitrification treatment unit, a membrane bioreactor filtration treatment unit, a membrane filtration treatment unit and a sludge treatment unit. The method comprises the main following steps: (1), hydraulic screen sieving and water quality and quantity adjustment; (2), coagulating sedimentation treatment; (3), anaerobic treatment; (4), primary nitrification and denitrification treatment; (5), Fenton oxidation treatment; (6), secondarynitrification and denitrification treatment; (7), membrane bioreactor filtration treatment and (8), membrane filtration treatment. The treatment method is resistant to impact load, the system operates stably, the treatment effect is good, pollutant discharge is greatly reduced, and the method has broad applicationprospect.
Owner:BEIJING SOUND ENVIRONMENTAL ENG +1
Electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system
ActiveCN105906051AEfficient couplingAccelerate reaction mass transfer efficiencyTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsSmall footprintElectrochemistry
The invention discloses an electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system. The system comprises a microorganism electrolytic tank shell, a sealed cover, a microorganism positive electrode, a microorganism negative electrode and a power supply, wherein the sealed cover covers the microorganism electrolytic tank shell to form a closed space; the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode are connected with a negative electrode and a positive electrode of the power supply respectively, a short-distance nitrification microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism positive electrode, and denitrification methane anaerobic oxidation microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism negative electrode; the side, close to the microorganism positive electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water inlet, and the side, close to the microorganism negative electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water outlet. An inorganic carbon source put-in opening is formed in the position, close to the microorganism negative electrode, between the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode. By means of one electrolytic tank, short-distance nitrification, electrochemical methane production and methane anaerobic oxidation are effectively coupled, reaction mass transfer efficiency is accelerated, occupied area is small, and capital construction investment is small.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
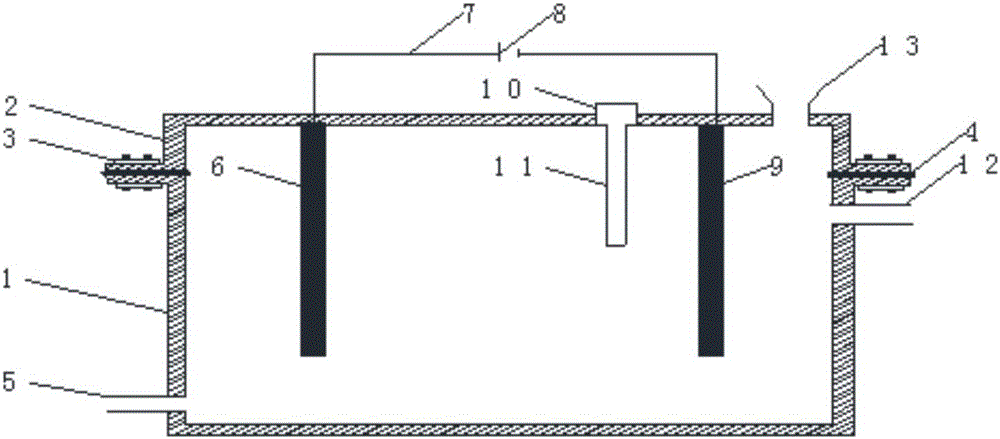
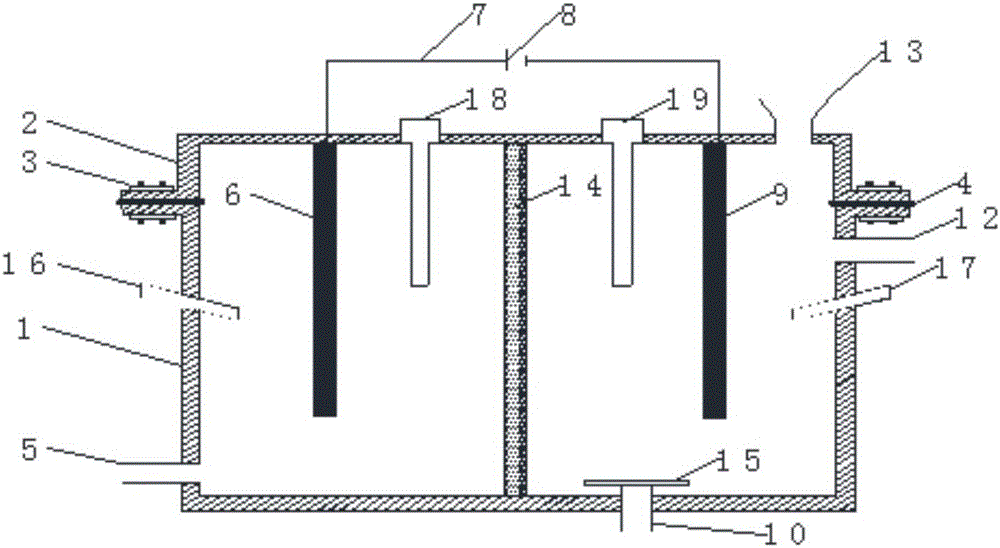
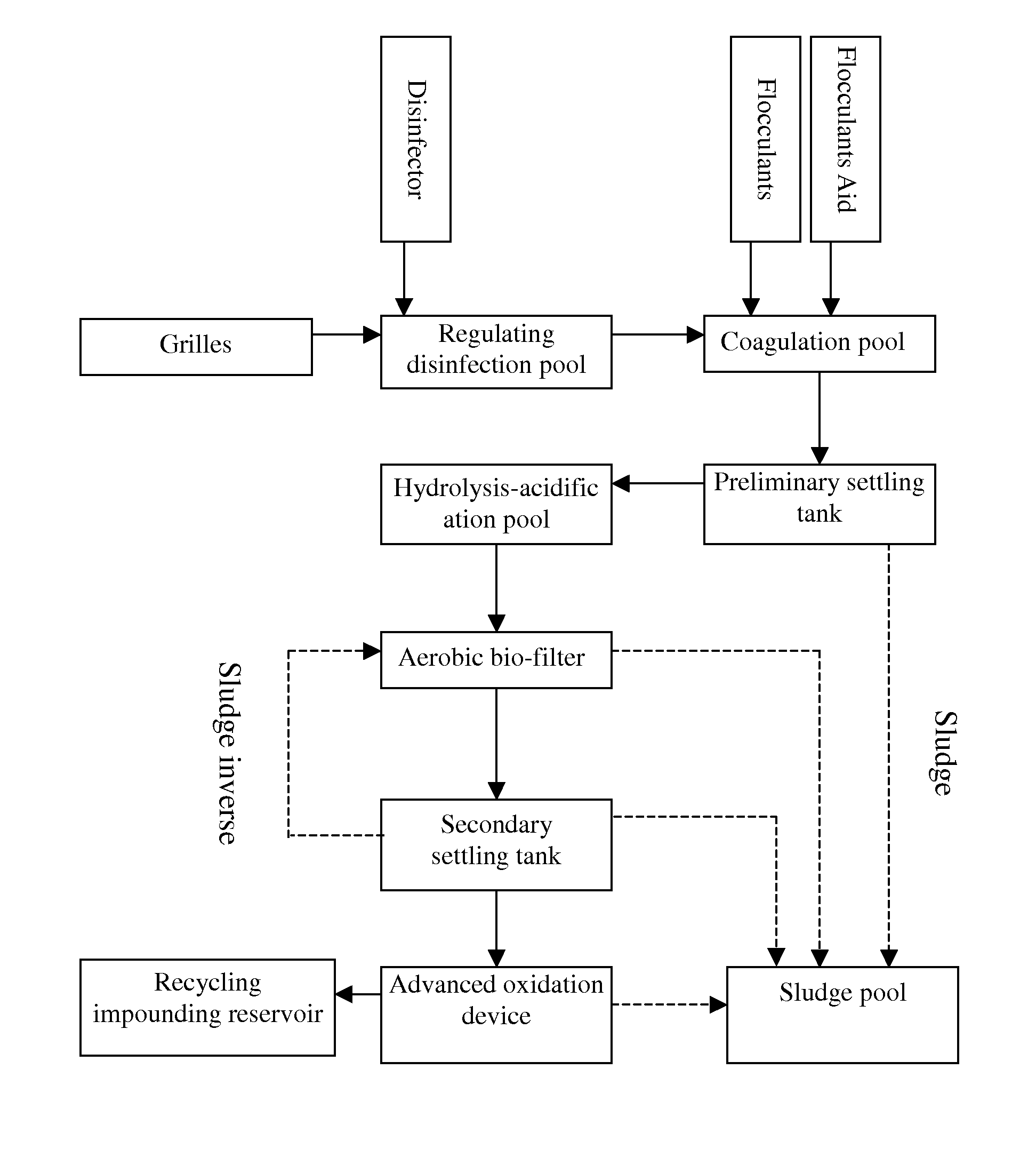
Wastewater purifying system in hospitals
InactiveUS20090166280A1Reduce pollutant loadGood treatment effectTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSludgeBiological oxidation
This invention relates a wastewater purifying system in hospitals, comprising interconnected grilles, a regulating disinfection pool, a coagulation pool, a preliminary settling tank, a hydrolysis-acidification pool, an aerobic bio-filter, a secondary settling tank, an advanced oxidation device, a sludge pool and a recycling impounding reservoir. The regulating disinfection pool is used to accumulate original wastewater released from every source and the advanced oxidation device is used to oxidize remained organic matters into inorganic molecules via chemical and biochemical methods or via physical methods and could be an electric biological oxidation treatment device. This system possesses high purifying degree and purified water from this system can be used as reclaimed water.
Owner:BEIJING JINAOHUARONG TECH
Microbial fuel cell artificial wetland electrogenesis in-situ utilization water purification method
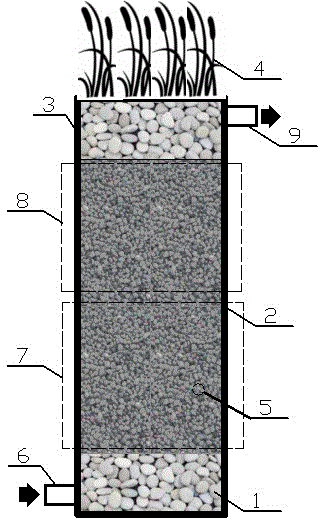
InactiveCN105540860ASolving the problem of low organic loadsEfficient degradationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesConstructed wetlandPurification methods
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell artificial wetland electrogenesis in-situ utilization water purification method. A microbial fuel cell artificial wetland electrogenesis in-situ utilization water purification device is set up, sewage flows in from a water inlet pipe at the bottom, and flows upwards into the bottom of a bed body after passing through a water distributing area, an anaerobic environment of the bottom layer of the bed body forms an anode region of a microbial fuel cell artificial wetland, an electrogenesis microorganism oxidizing organic substrate releases electrons and protons, the electrons are conducted upwards to the surface layer of the bed body through conductive filler, the protons are conducted upwards to the surface layer of the bed body through the sewage, an aerobic / hypoxia region of the surface layer serves as a cathode region of the microbial fuel cell artificial wetland, oxygen or nitrogen oxide and the like serving as electron acceptors are subjected to an oxidation reaction, and output water after being treated flows out through a water outlet pipe. The problems that as the distance between the two poles of a microbial fuel cell artificial wetland of a traditional external circuit is too large, internal resistance is too large, the electrogenesis rate is low and the purification effect is poor, and purification performance is promoted.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Autotrophic/heterotrophic denitrification-based integrated nitrogen removal apparatus and nitrogen removal method thereof
ActiveCN106396097AEffluent total nitrogen is stableLow costTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater treatment compoundsNitrogen removalElectrolysis
The invention discloses an autotrophic / heterotrophic denitrification-based integrated nitrogen removal apparatus and method, and belongs to the technical field of water treatment. A main reaction device is divided into an autotrophic denitrification area, a heterotrophic denitrification area and a buffer cavity. The device is provided with a liquid inlet, a liquid outlet and a gas outlet, and the liquid inlet is connected with the autotrophic denitrification area; the liquid outlet and the gas outlet are connected with the heterotrophic denitrification area; the device keeps the autotrophic denitrification area and the heterotrophic denitrification area mutually independent through the buffer cavity, and a micro-electrolysis filler layer and a sulfur / limestone filler layer are arranged in the autotrophic denitrification area; and a biomass vinasse layer is arranged in the heterotrophic denitrification area to improve the C / N ratio of wastewater and promote the heterotrophic denitrification nitrogen removal process. A solid-phase autotrophic denitrification coupled heterotrophic denitrification technology is adopted to remove nitrogen from the wastewater, so compared with routine single nitrogen removal technologies based on heterotrophic denitrification, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of high nitrogen removal efficiency, low cost and stable quality of outlet water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Method for coupling of PVDF/carbon fiber-based MFe2O4 photocatalysis conductive filtering membrane and MBR/MFC
ActiveCN106000130AImprove processing efficiencyEnergy-saving and efficient processingMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberFiltration
The invention belongs to the fields of new energy and environment pollution control and discloses a method for coupling of a PVDF / carbon fiber-based MFe2O4 photocatalysis conductive filtering membrane and MBR / MFC. The membrane is used as the cathode of a microbial fuel cell (MFC), pollutant removal efficiency is improved through the cathode and photocatalysis under the powder generation driving of a biological anode, and finally membrane filtration is conducted to discharge water to achieve energy-efficient treatment of wastewater. A method for preparing the PVDF / carbon fiber-based MFe2O4 photocatalysis conductive filtering membrane comprises the steps of adding carbon nano powder and MFe2O4 photocatalyst to PVDF casting membrane solution in sequence, coating the surface of a carbon fiber cloth with the mixture by a certain thickness, and preparing the PVDF / carbon fiber-based MFe2O4 photocatalysis conductive filtering membrane with the phase inversion method. In an H type MFC, by placing the membrane on the cathode of the cell, energy-efficient treatment of wastewater can be achieved through biological power generation, photocatalysis and membrane filtration.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and operating method for deep denitrification and toxicity reduction of wastewater
InactiveUS20190389756A1Rapidly and efficiently removedIncrease profitTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesToxicity reductionElectrolysis
Disclosed is an apparatus and an operating method for deep denitrification and toxicity reduction of wastewater. The apparatus comprises a regulation tank, an aeration biofilter, an ozone reaction tank, an ozone generation and diffusion device, and a denitrification biofilter. By the coupling reaction treatment of microorganisms, ozone, electrolysis and denitrification, an effect of refractory organic contaminants and nitrate nitrogen removal, deep denitrification and toxicity reduction can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
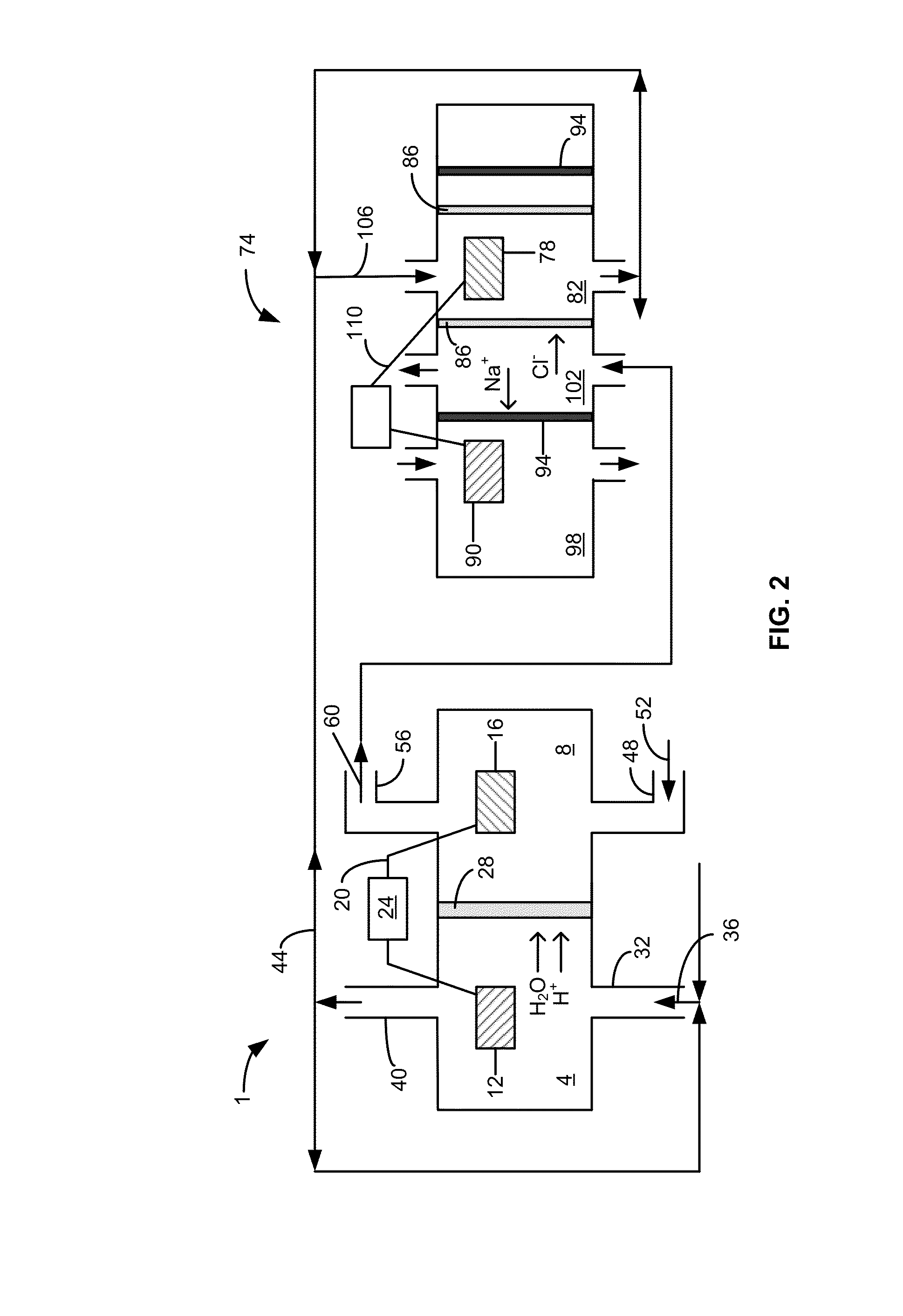
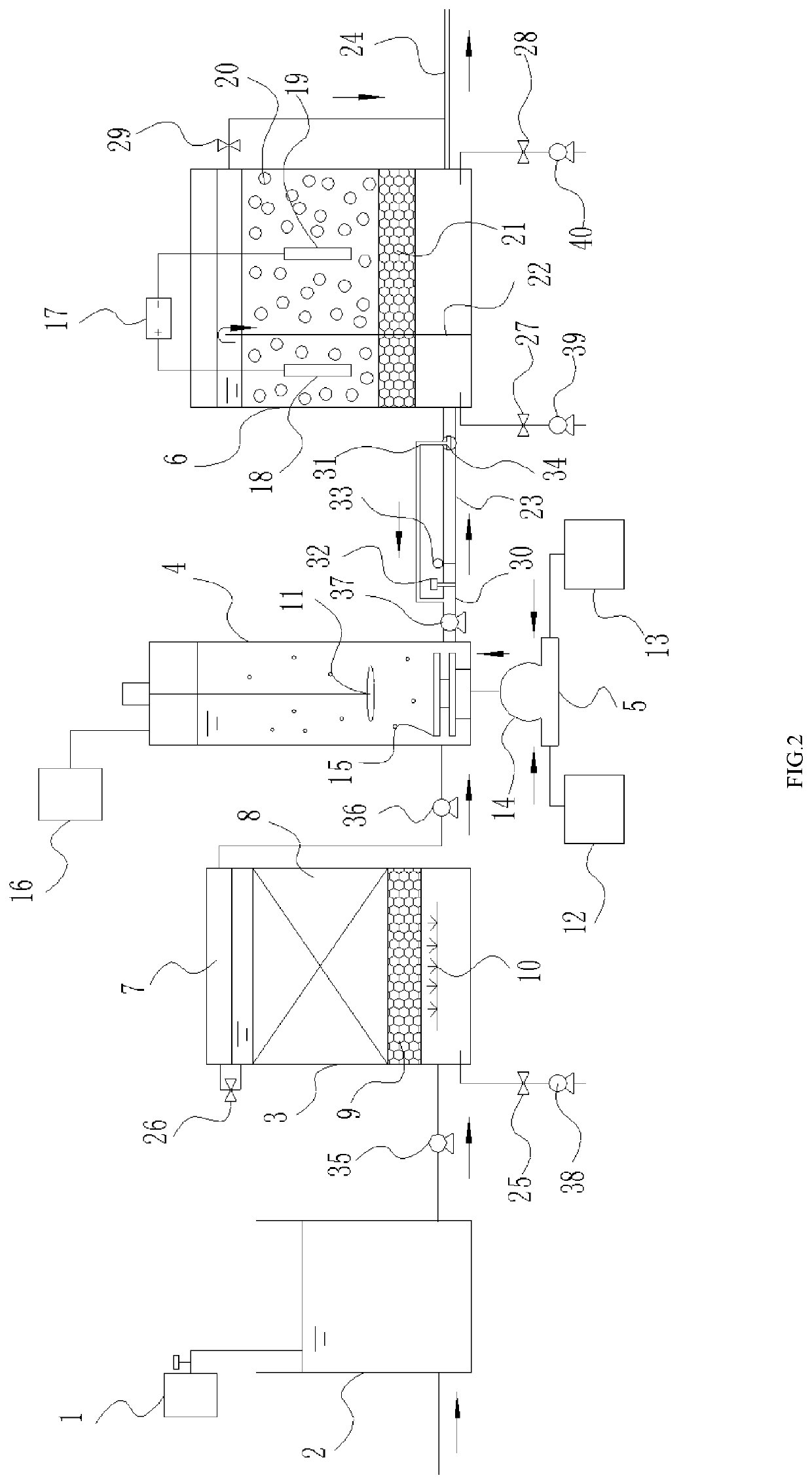
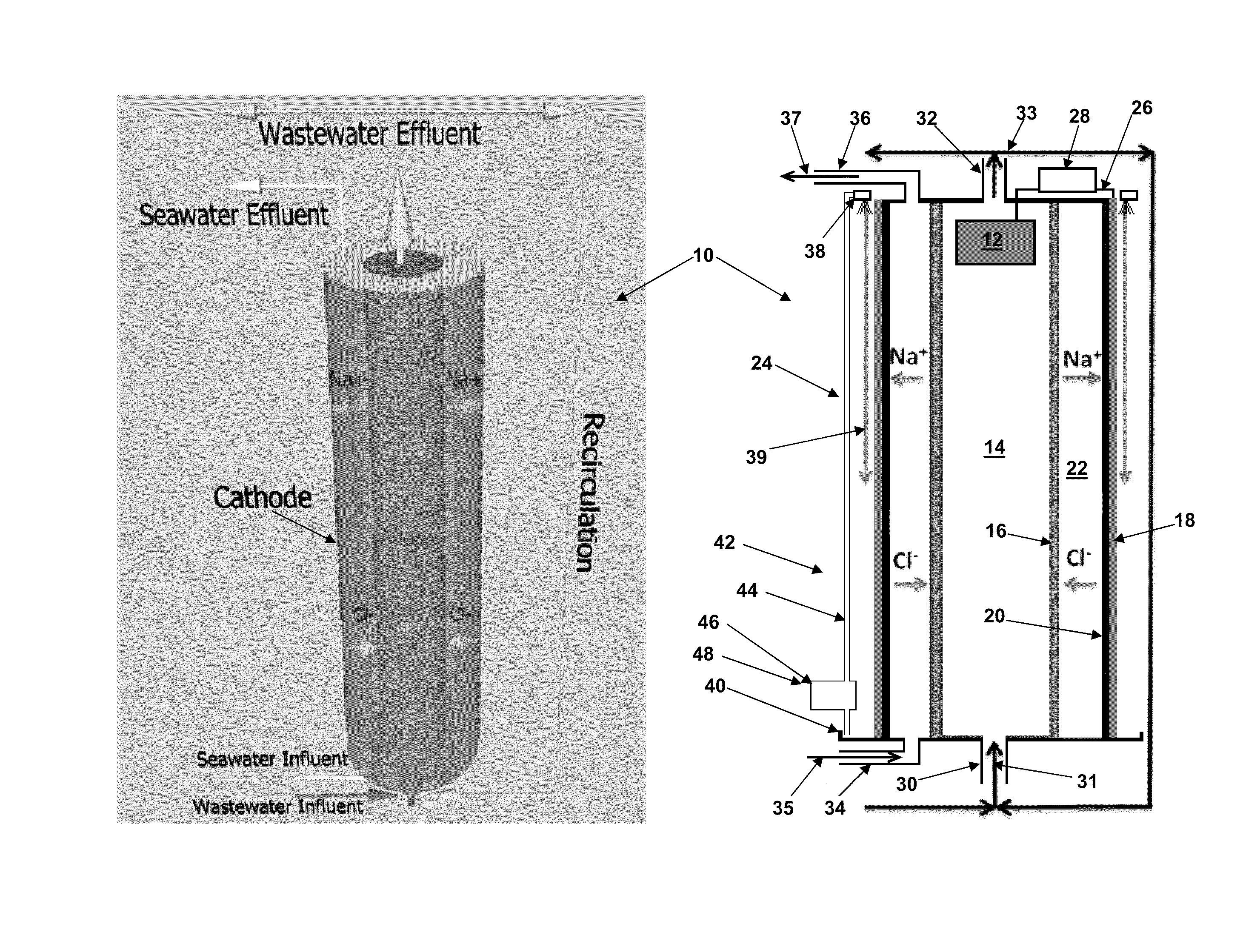
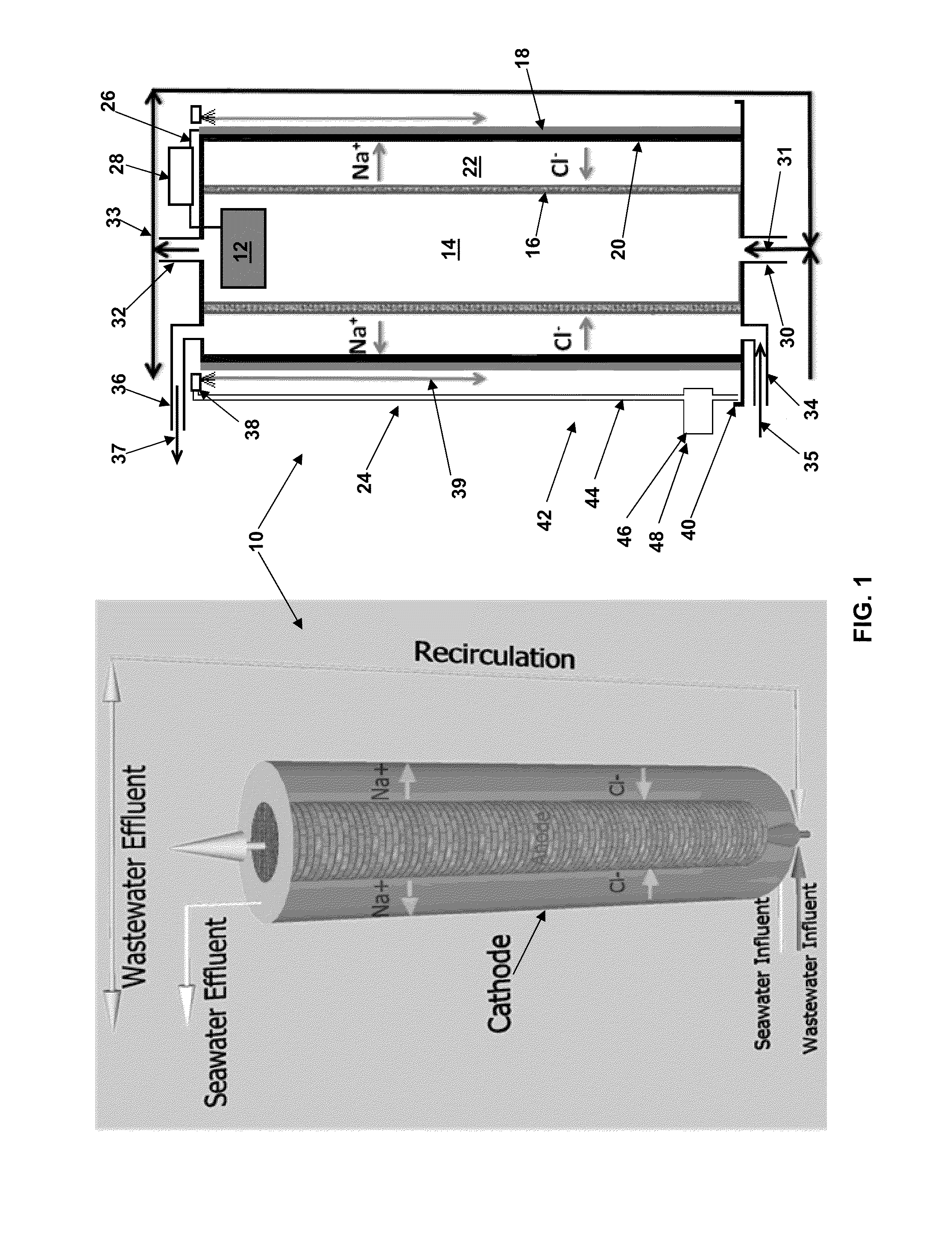
Microbial desalination cells
InactiveUS20110311887A1Other chemical processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSimple Organic CompoundsDesalination
A microbial desalination cell includes an anode, a cathode, a saline solution chamber and a cathode rinsing assembly. The anode is at least partially positioned within an anode chamber for containing an aqueous reaction mixture including one or more organic compounds and one or more bacteria for oxidizing the organic compounds. The cathode is directly exposed to air. The saline solution chamber is positioned between the anode and the cathode, and is separated from the anode by an anion exchange material and from the cathode by a cation exchange material. The cathode rinsing assembly is for rinsing the cathode with a catholyte.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com