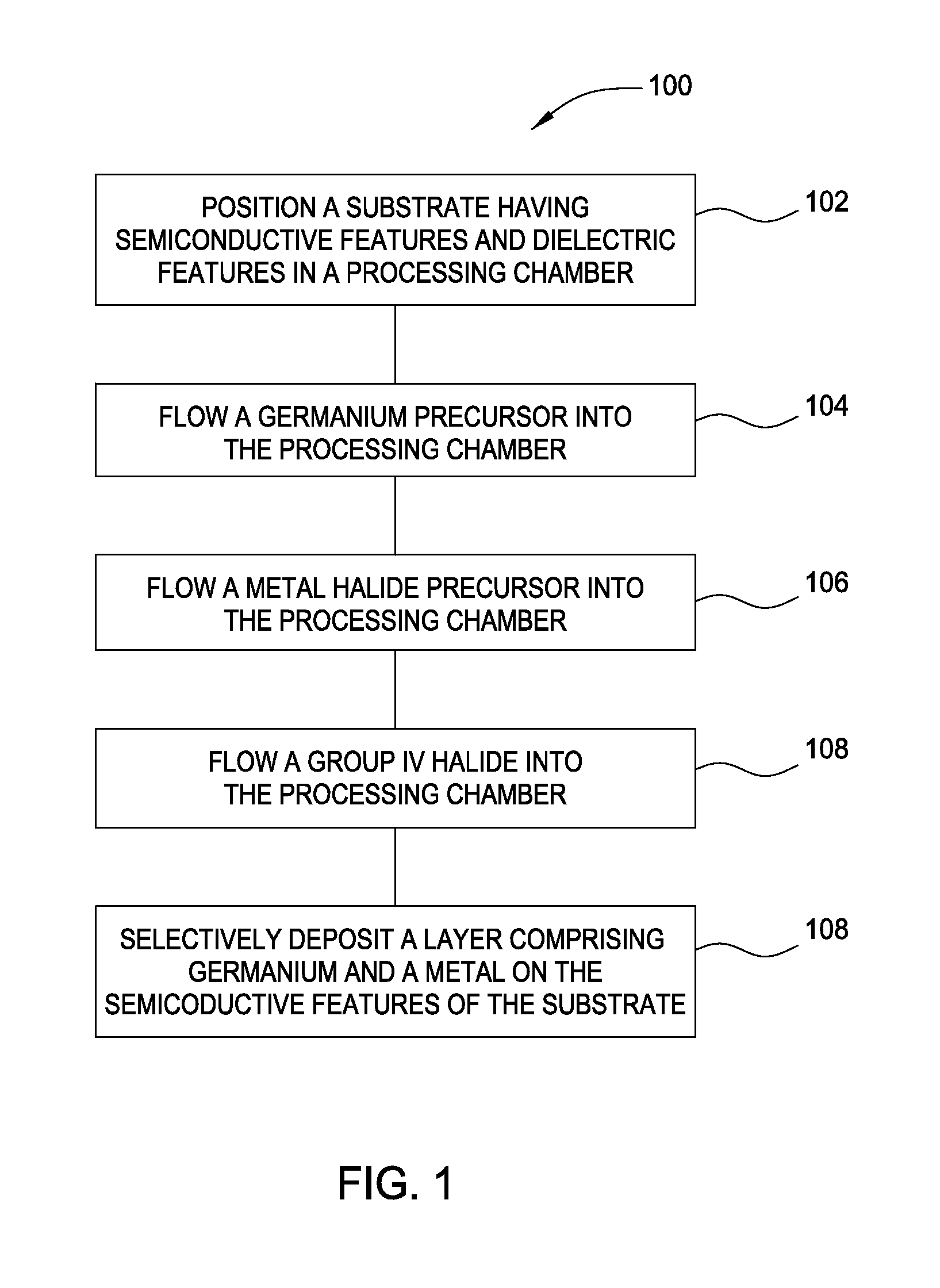
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43795 results about "Phosphorus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). With few exceptions, minerals containing phosphorus are in the maximally oxidized state as inorganic phosphate rocks.
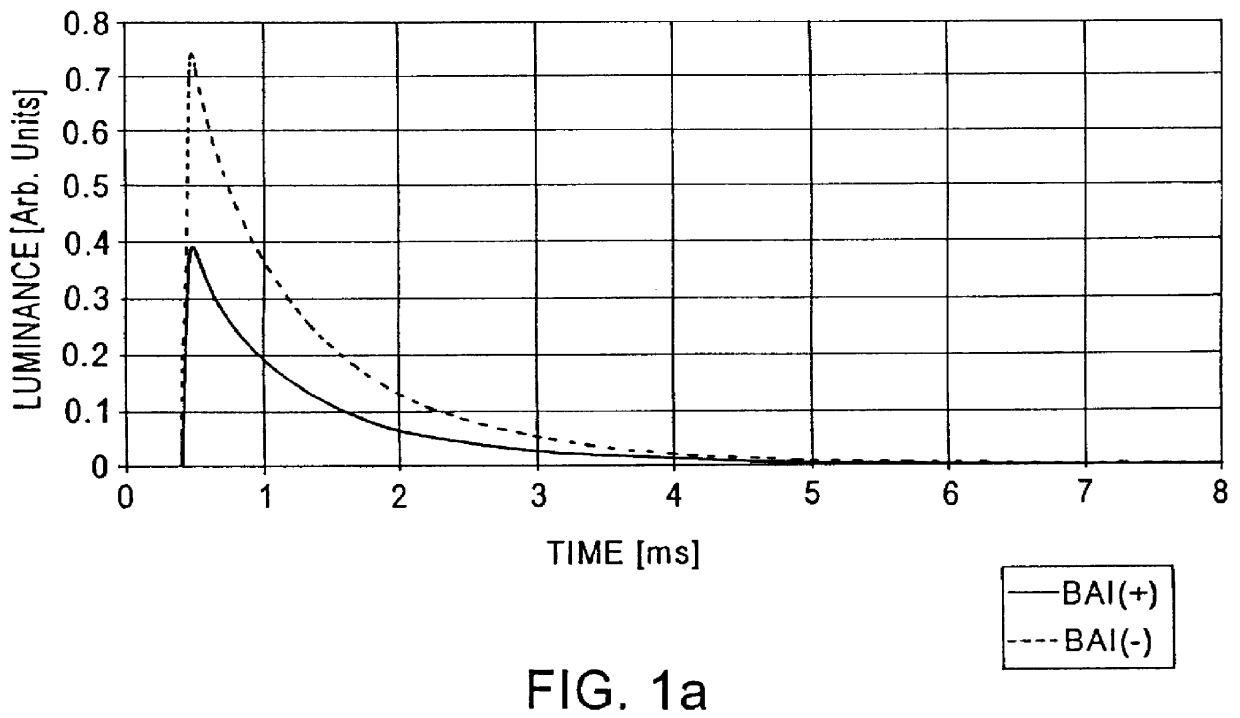
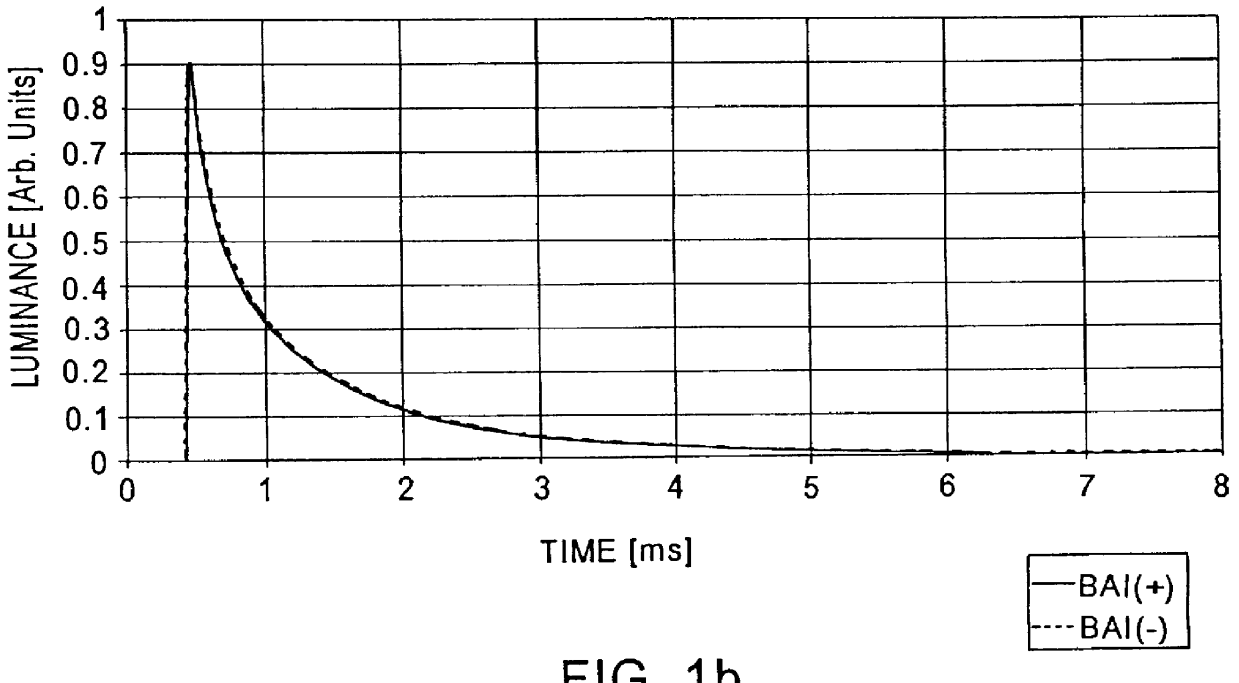
Red emitting phosphor materials for use in LED and LCD applications
ActiveUS7358542B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorPhosphate
Phosphor compositions including those having the formulas A2-xEuxW1-yMoyO6, where A is selected from Y, Gd, Lu, La, and combinations thereof; and where 0.5≦x≦1.0, 0.01≦y≦1.0; MmOnX, wherein M is selected from the group of Sc, Y, a lanthanide, an alkali earth metal and mixtures thereof; X is a halogen; 1≦m≦3; and 1≦n≦4, and wherein the lanthanide doping level can range from 0.1 to 40% spectral weight; and Eu3+ activated phosphate or borate phosphors. Also disclosed are light emitting devices including a light source and at least one of the above phosphor compositions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6165824ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystallinityCrystal growth
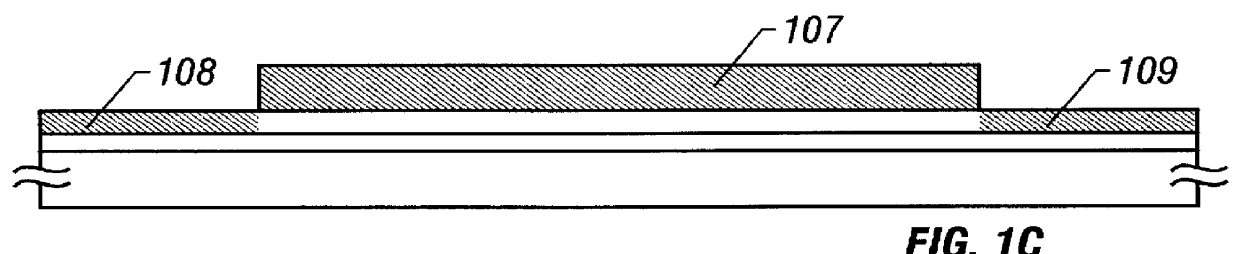
A crystal growth 301 is carried out by diffusing a metal element, and a nickel element is moved into regions 108 and 109 which has been doped with phosphorus. An axis coincident with the moving directions 302 and 303 of the nickel element at this time is made to coincide with an axis coincident with the direction of the crystal growth, and a TFT having the regions as channel forming regions is manufactured. In the path of the region where nickel moved, since high crystallinity is obtained in the moving direction, the TFT having high characteristics can be obtained by this way.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light sources with nanometer-sized VUV radiation-absorbing phosphors
A light source comprises: (a) a source of plasma discharge that emits electromagnetic radiation, a portion of which has wavelengths shorter than about 200 nm; and (b) a phosphor composition that comprises particles, each of the particles comprising at least a first phosphor and at least a second phosphor, the phosphor composition is disposed such that the first phosphor absorbs substantially the portion of EM radiation having wavelengths shorter than about 200 nm, and the first phosphor emits EM radiation having wavelengths longer than about 200 nm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
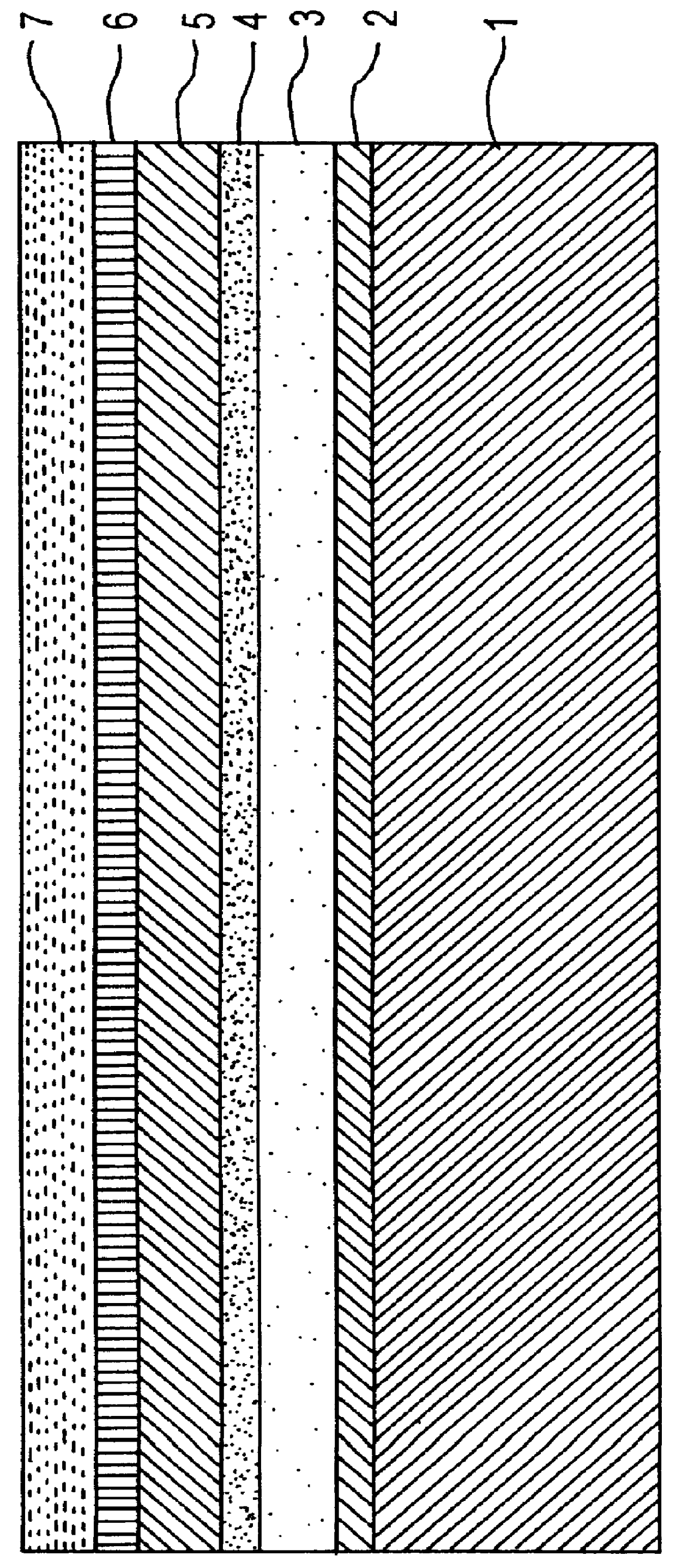
Luminescent ceramic for a light emitting device
ActiveUS7361938B2Less sensitive to temperatureLess scatteringDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorLength wave
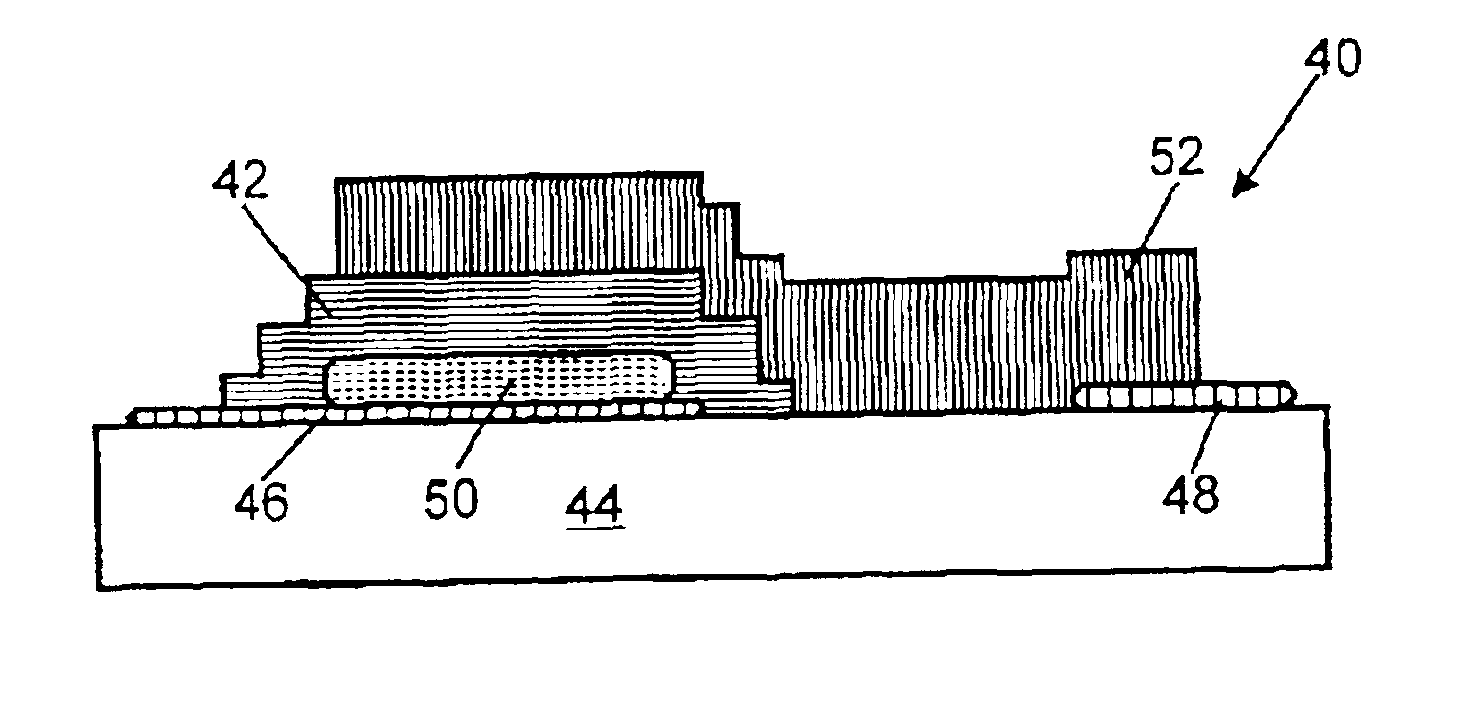
A semiconductor light emitting device comprising a light emitting layer disposed between an n-type region and a p-type region is combined with a ceramic layer which is disposed in a path of light emitted by the light emitting layer. The ceramic layer is composed of or includes a wavelength converting material such as a phosphor. Luminescent ceramic layers according to embodiments of the invention may be more robust and less sensitive to temperature than prior art phosphor layers. In addition, luminescent ceramics may exhibit less scattering and may therefore increase the conversion efficiency over prior art phosphor layers.
Owner:LUMILEDS
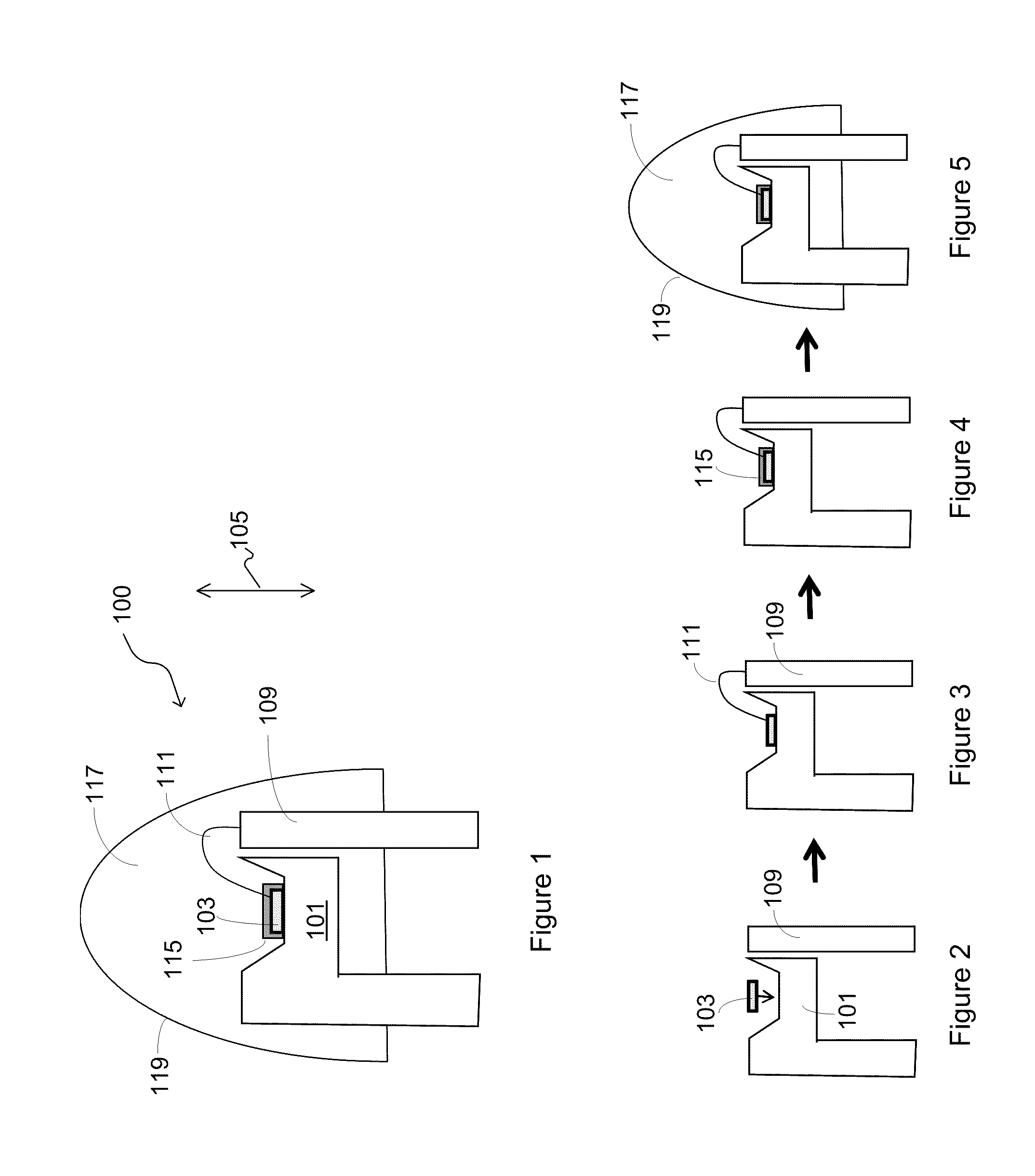
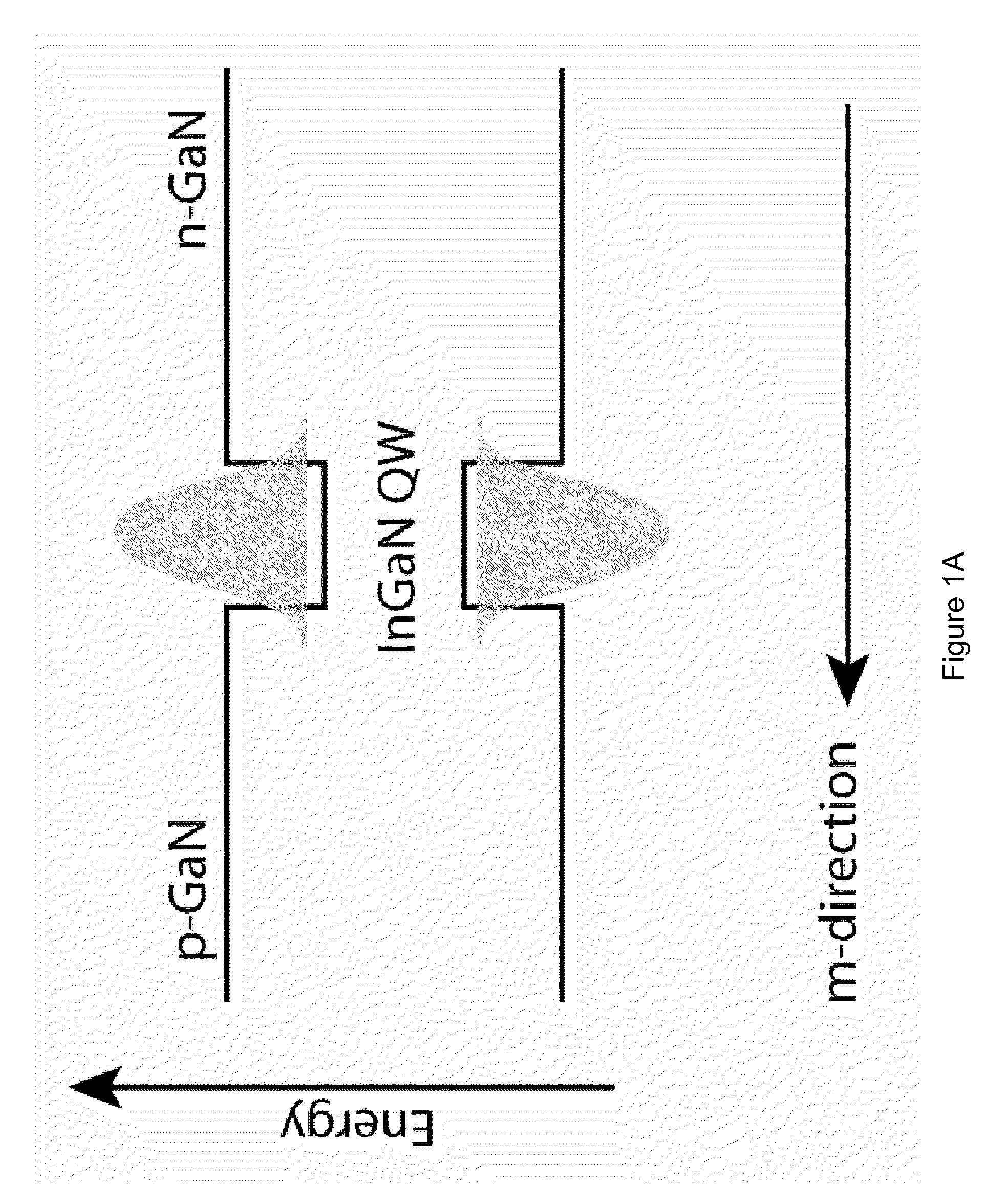
White light devices using non-polar or semipolar gallium containing materials and phosphors
ActiveUS20100025656A1Easy to implementImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorQuantum well
A packaged light emitting device. The device includes a substrate member comprising a surface region and one or more light emitting diode devices overlying the surface region. In a specific embodiment, at least one of the light emitting diode device is fabricated on a semipolar or nonpolar GaN containing substrate. The one or more light emitting diode devices are fabricated on the semipolar or nonpolar GaN containing substrate emits substantially polarized emission of one or more first wavelengths. At least at least one of the light emitting diode devices comprise a quantum well region, which is characterized by an electron wave function and a hole wave function. In a specific embodiment, the electron wave function and the hole wave function are substantially overlapped within a predetermined spatial region of the quantum well region. In a specific embodiment, the device has a thickness of one or more entities formed overlying the one or more light emitting diode devices. The one or more entities are excited by the substantially polarized emission and emitting electromagnetic radiation of one or more second wavelengths.
Owner:SLT TECH
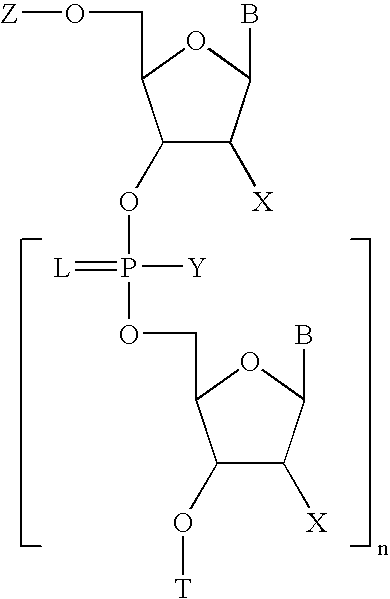
Methods for synthesis of oligonucleotides
Improved methods for synthesis of oligonucleotides and other phosphorus-linked oligomers are disclosed. The methods include the use of aromatic solvents, alkyl aromatic solvents, halogenated aromatic solvents, halogenated alkyl aromatic solvents, or aromatic ether solvents to achieve deprotection of protected hydroxyl groups.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
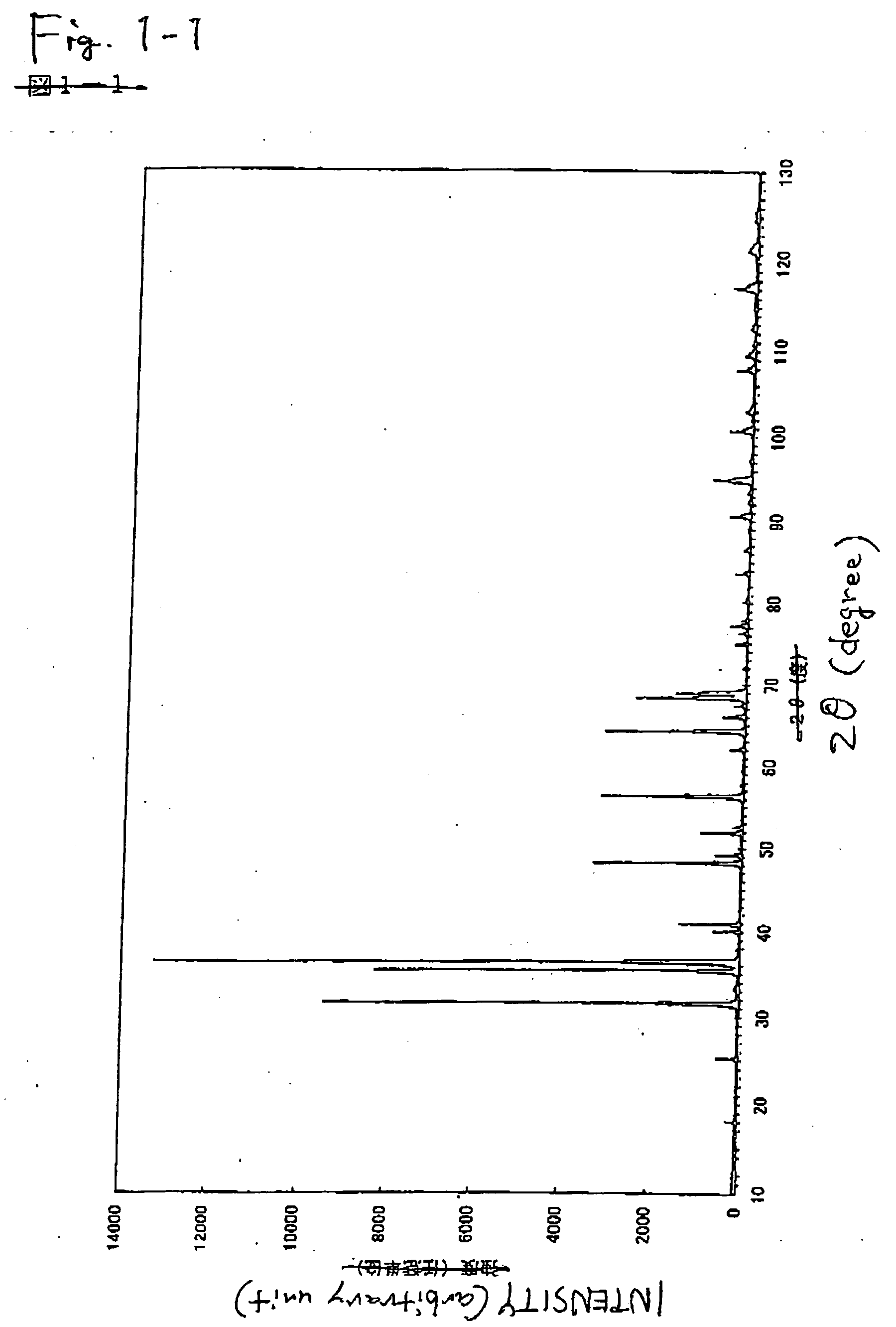
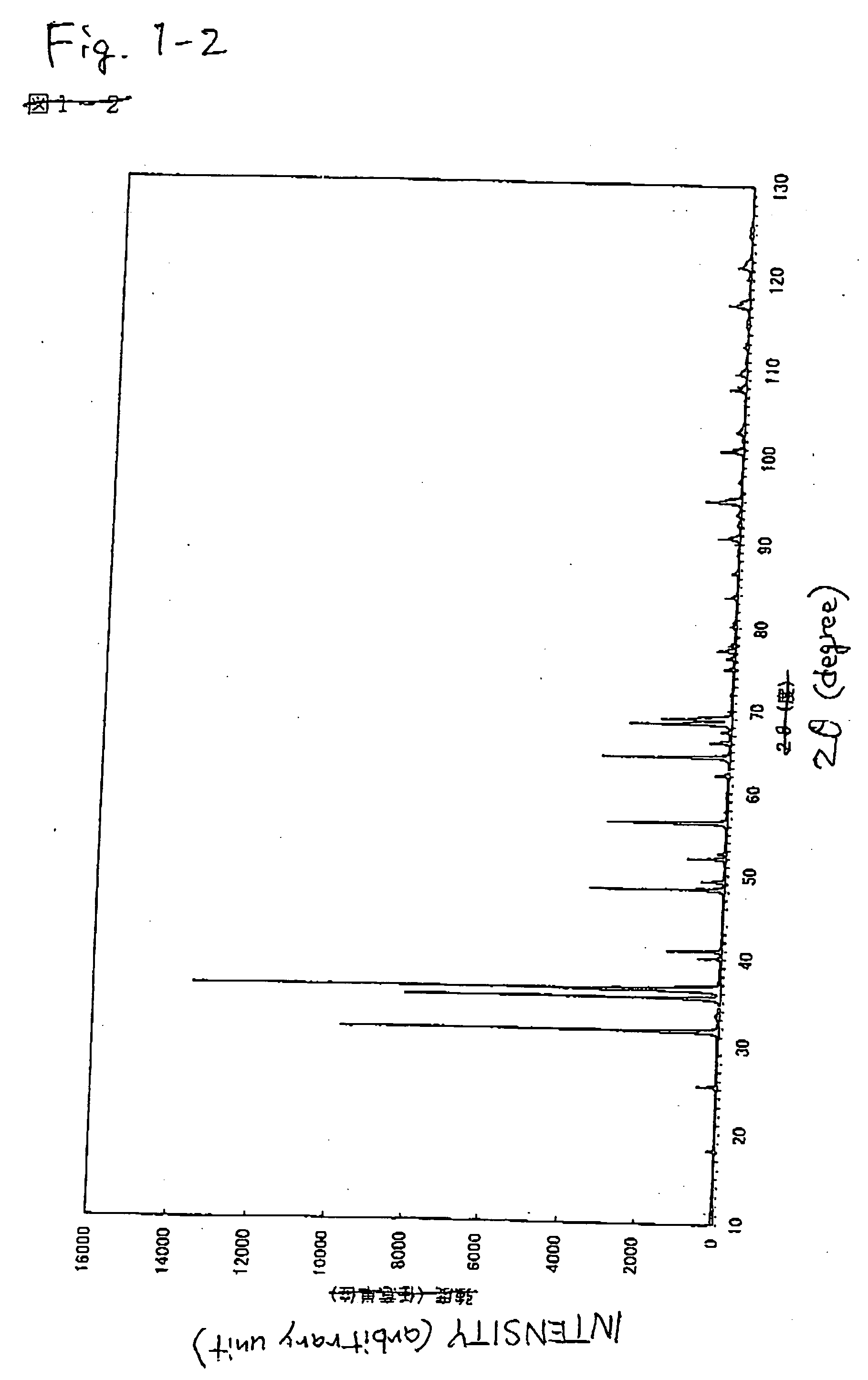
Red Nitride Phosphor and Production Method Thereof
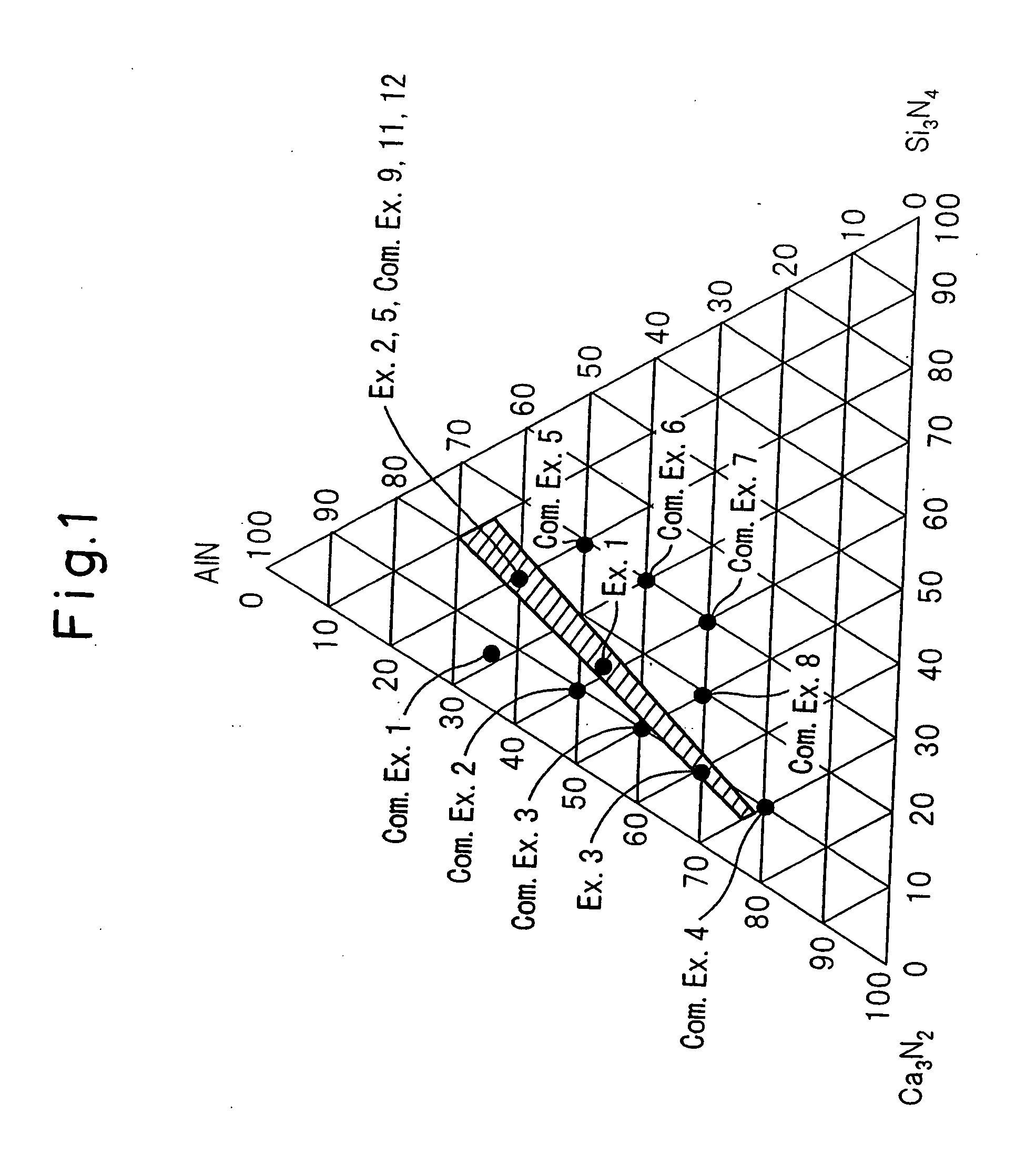
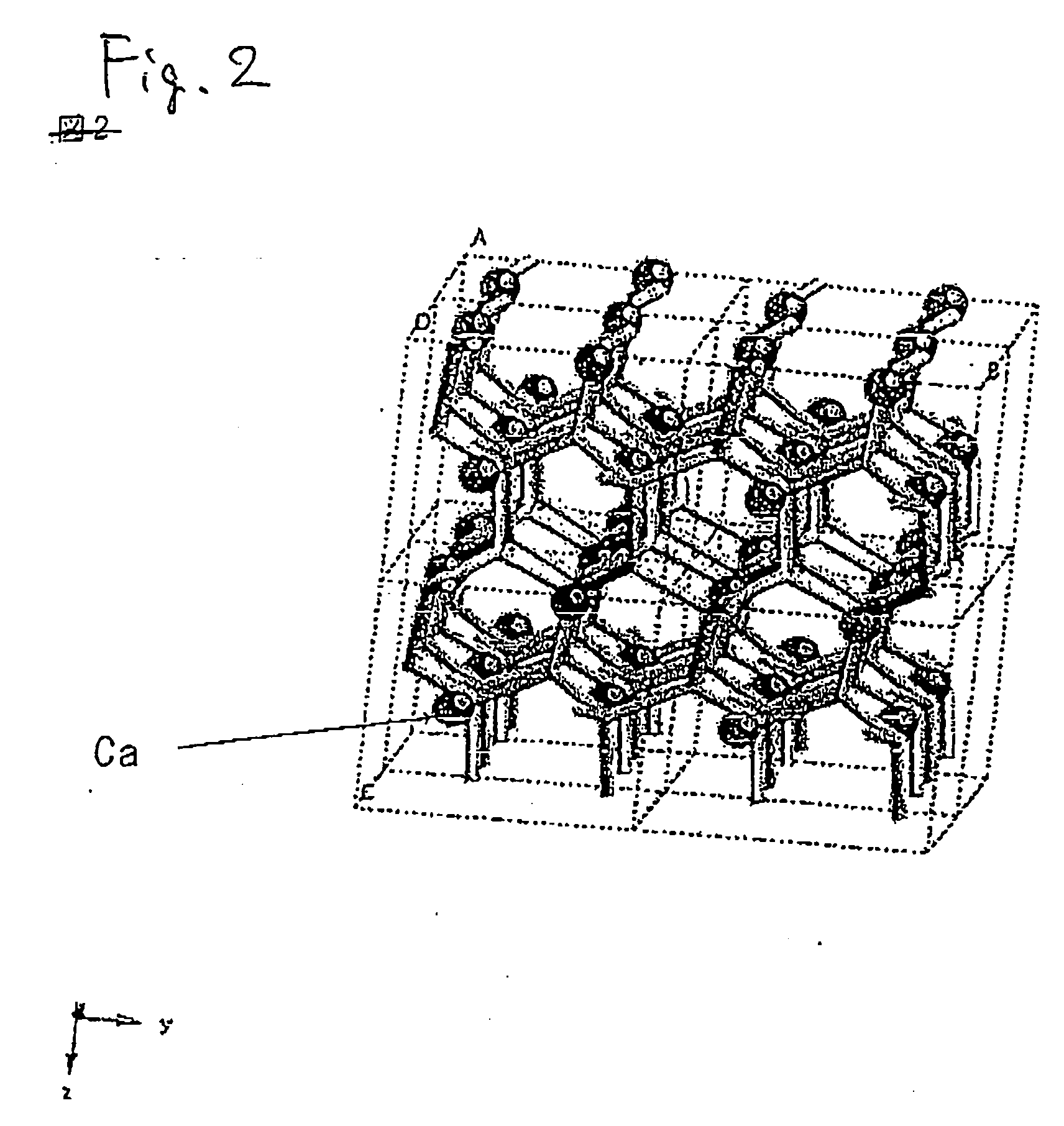
A red phosphor where the crystal phase constituting the phosphor is monoclinic Eu-activated CaAlSiN3. A red phosphor which is Eu-activated CaAlSiN3 powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm or less as measured in the non-pulverized state by the laser scattering particle size distribution analysis. A light-emitting device comprising a blue light-emitting element, a yellow phosphor capable of converting the blue light emitted from the blue light-emitting element into yellow light, and the above-described red phosphor capable of converting the blue light emitted from the blue light-emitting element into red light. A method for producing Eu-activated CaAlSiN3, comprising firing a raw material powder comprising Ca3N2, AlN, Si3N4 and EuN at 1,400 to 2,000° C. in a nitrogen-containing atmosphere, the Ca3N2, AlN and Si3N4 giving a composition falling in the region surrounded by a straight line connecting the following four points A to D in the composition diagram of FIG. 1 and EuN being contained in an amount of 0.01 to 10 parts by weight as Eu per 100 parts by weight in total of Ca3N2, AlN and Si3N4.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
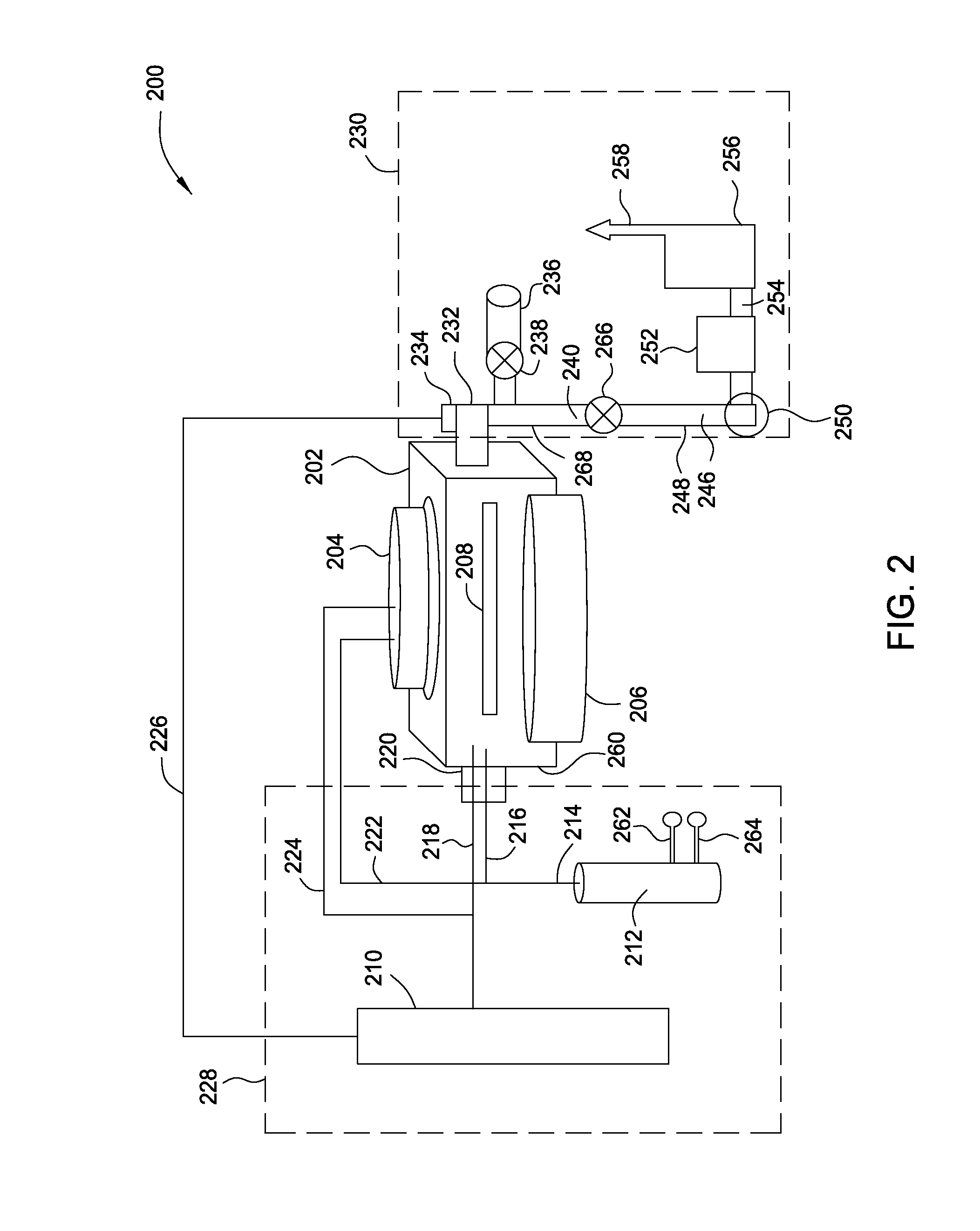
Method and apparatus for germanium tin alloy formation by thermal CVD
InactiveUS20130280891A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelective depositionLiquid metal
A method and apparatus for forming semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers is described. A germanium precursor and a metal precursor are provided to a chamber, and an epitaxial layer of germanium-metal alloy, optionally including silicon, is formed on the substrate. The metal precursor is typically a metal halide, which may be provided by evaporating a liquid metal halide, subliming a solid metal halide, or by contacting a pure metal with a halogen gas. A group IV halide deposition control agent is used to provide selective deposition on semiconductive regions of the substrate relative to dielectric regions. The semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers may be doped, for example with boron, phosphorus, and / or arsenic. The precursors may be provided through a showerhead or through a side entry point, and an exhaust system coupled to the chamber may be separately heated to manage condensation of exhaust components.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Phosphor and light-emitting equipment using phosphor
ActiveUS20070007494A1Increase brightnessGood colorOther chemical processesNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsFluorescenceRare earth
An object of the present invention is to provide an inorganic phosphor having fluorescence properties emitting an orange or red light which has a longer wavelength as compared with the cases of conventional sialon phosphors activated with a rare earth. The invention relates to a design of white light-emitting diode rich in a red component and having good color-rendering properties by employing a solid solution crystal phase phosphor which uses as a host crystal an inorganic compound having the same crystal structure as that of a CaSiAlN3 crystal phase and to which M Element (wherein M Element is one or two or more elements selected from the group consisting of Mn, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb) is added as an emission center.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Systems and methods for converting illumination
InactiveUS20050041424A1Improve performanceQuick changeMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsSynthetic materialsPhosphor
An illumination system according to the principles of the invention may include a first LED and a carrier material. The carrier material may be comprised of plastic, synthetic material, polymer, latex, rubber or other material. The carrier material may also contain a phosphor, fluorescent material, organic fluorescent material, inorganic fluorescent material, impregnated phosphor, phosphor particles, phosphor material, YAG:Ce phosphor, or other material for converting electromagnetic radiation into illumination or visible light.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
Conductive lithium storage electrode
A compound comprising a composition Ax(M′1-aM″a)y(XD4)z, Ax(M′1-aM″a)y(DXD4)z, or Ax(M′1-aM″a)y(X2D7)z, and have values such that x, plus y(1-a) times a formal valence or valences of M′, plus ya times a formal valence or valence of M″, is equal to z times a formal valence of the XD4, X2D7, or DXD4 group; or a compound comprising a composition (A1-aM″a)xM′y(XD4)z, (A1-aM″a)xM′y(DXD4)z(A1-aM″a)xM′y(X2D7)z and have values such that (1-a)x plus the quantity ax times the formal valence or valences of M″ plus y times the formal valence or valences of M′ is equal to z times the formal valence of the XD4, X2D7 or DXD4 group. In the compound, A is at least one of an alkali metal and hydrogen, M′ is a first-row transition metal, X is at least one of phosphorus, sulfur, arsenic, molybdenum, and tungsten, M″ any of a Group IIA, IIIA, IVA, VA, VIA, VIIA, VIIIA, IB, IIB, IIIB, IVB, VB, and VIB metal, D is at least one of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, or a halogen, 0.0001<a≦0.1, and x, y, and z are greater than zero. The compound can have a conductivity at 27° C. of at least about 10−8 S / cm. The compound can be a doped lithium phosphate that can intercalate lithium or hydrogen. The compound can be used in an electrochemical device including electrodes and storage batteries and can have a gravimetric capacity of at least about 80 mAh / g while being charged / discharged at greater than about C rate of the compound.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Light emitting film, luminescent device, method for manufacturing light emitting film and method for manufacturing luminescent device
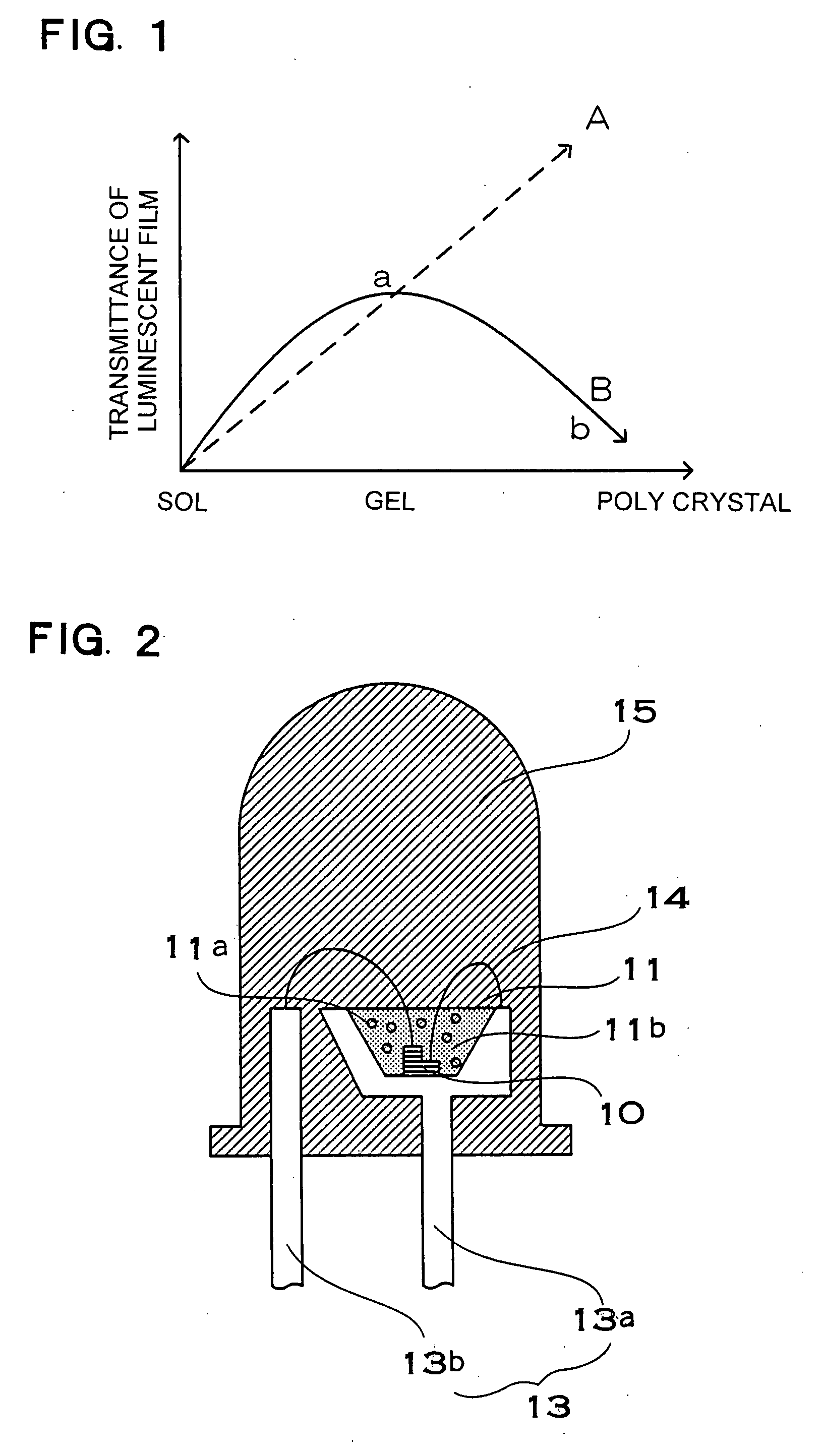
InactiveUS20060170332A1High light-outgoing efficiencyHardness is easy to controlDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorTransmittance
The present invention provides a reliable, long-life phosphor, or the like, which is prevented from darkening due to aging. A light emitting apparatus has a light emitting element and a phosphor layer. The phosphor layer has a phosphor excited by light from the light emitting element, and a binder which binds the phosphor. The binder is hydroxide oxide gel obtained by curing sol of a hydroxide oxide mixed with sol containing at least one metallic element selected from the group consisting of Al, Y, Gd, Lu, Sc, Ga, In, and B. Transmittance of hydroxide oxide in a gel state is higher than the transmittance in the polycrystal state where the sol-gel reaction is proceeded. In addition, the content of hydroxyl group or water of crystallization in the hydroxide oxide is 10% or less by weight.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Transmissive optical elements including transparent plastic shell having a phosphor dispersed therein, and methods of fabricating same
A transmissive optical element is fabricated by filling a mold with molten liquid that includes a transparent plastic and a phosphor additive, and allowing the molten liquid to solidify to produce the transmissive optical element having phosphor dispersed therein. Accordingly, a separate phosphor coating or phosphor-containing encapsulant need not be used. Transmissive optical elements include a shell made of transparent plastic with a phosphor dispersed therein. The phosphor may be uniformly and / or nonuniformly dispersed in the shell.
Owner:CREELED INC
Additive formulation for lubricating oils
InactiveUS7285516B2Reduce the amount requiredOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSulfurPhosphorus
Lubricating oils containing an additive formulation including at least one sulphonate, saligenin and salixarate detergent provide improved wear performance and decreased sulphur and phosphorus emissions.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Deposited semiconductor structure to minimize N-type dopant diffusion and method of making
ActiveUS20060087005A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantSemiconductor structure
In deposited silicon, n-type dopants such as phosphorus and arsenic tend to seek the surface of the silicon, rising as the layer is deposited. When a second undoped or p-doped silicon layer is deposited on n-doped silicon with no n-type dopant provided, a first thickness of this second silicon layer nonetheless tends to include unwanted n-type dopant which has diffused up from lower levels. This surface-seeking behavior diminishes when germanium is alloyed with the silicon. In some devices, it may not be advantageous for the second layer to have significant germanium content. In the present invention, a first heavily n-doped semiconductor layer (preferably at least 10 at % germanium) is deposited, followed by a silicon-germanium capping layer with little or no n-type dopant, followed by a layer with little or no n-type dopant and less than 10 at % germanium. The germanium in the first layer and the capping layer minimizes diffusion of n-type dopant into the germanium-poor layer above.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
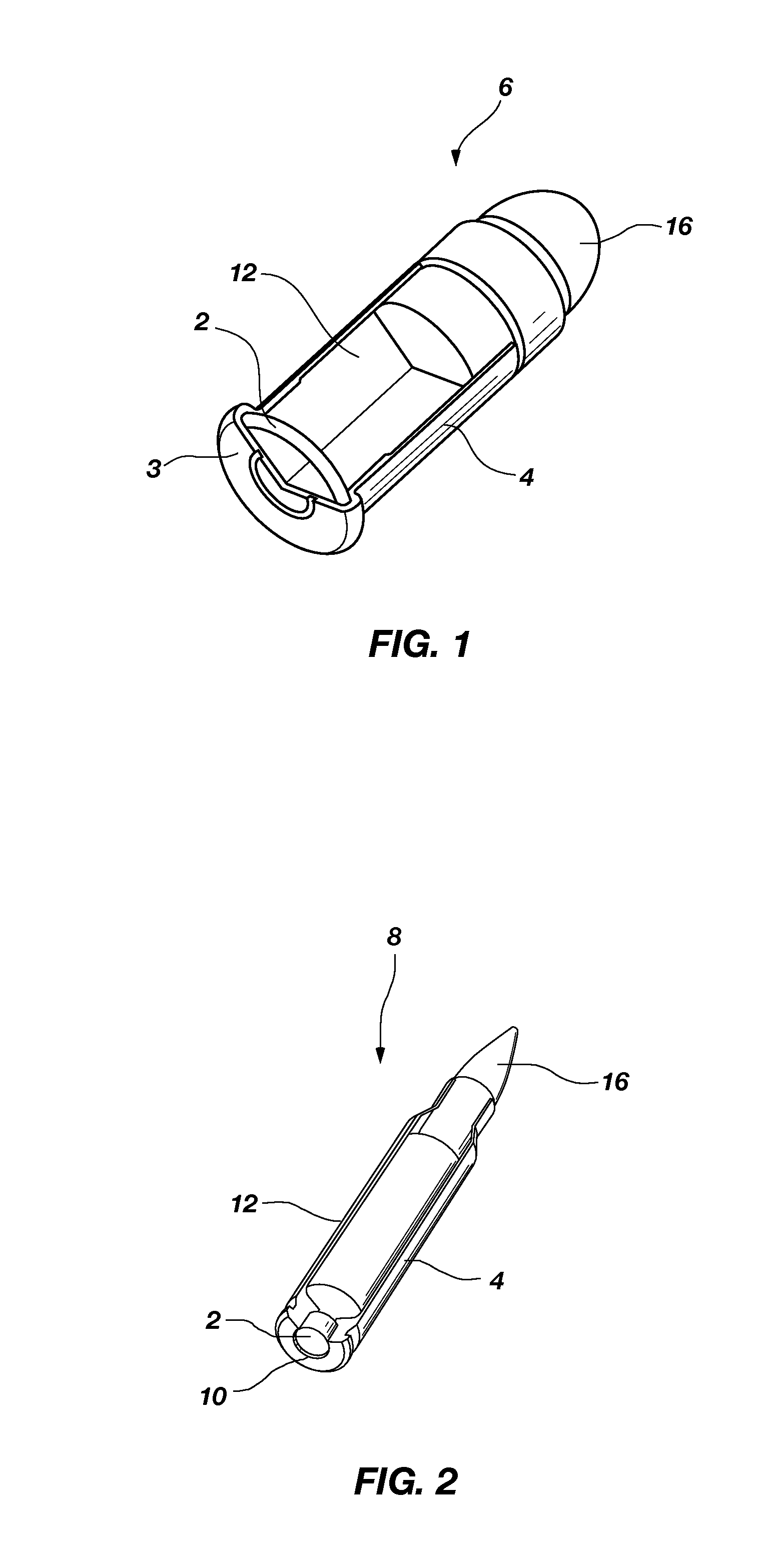
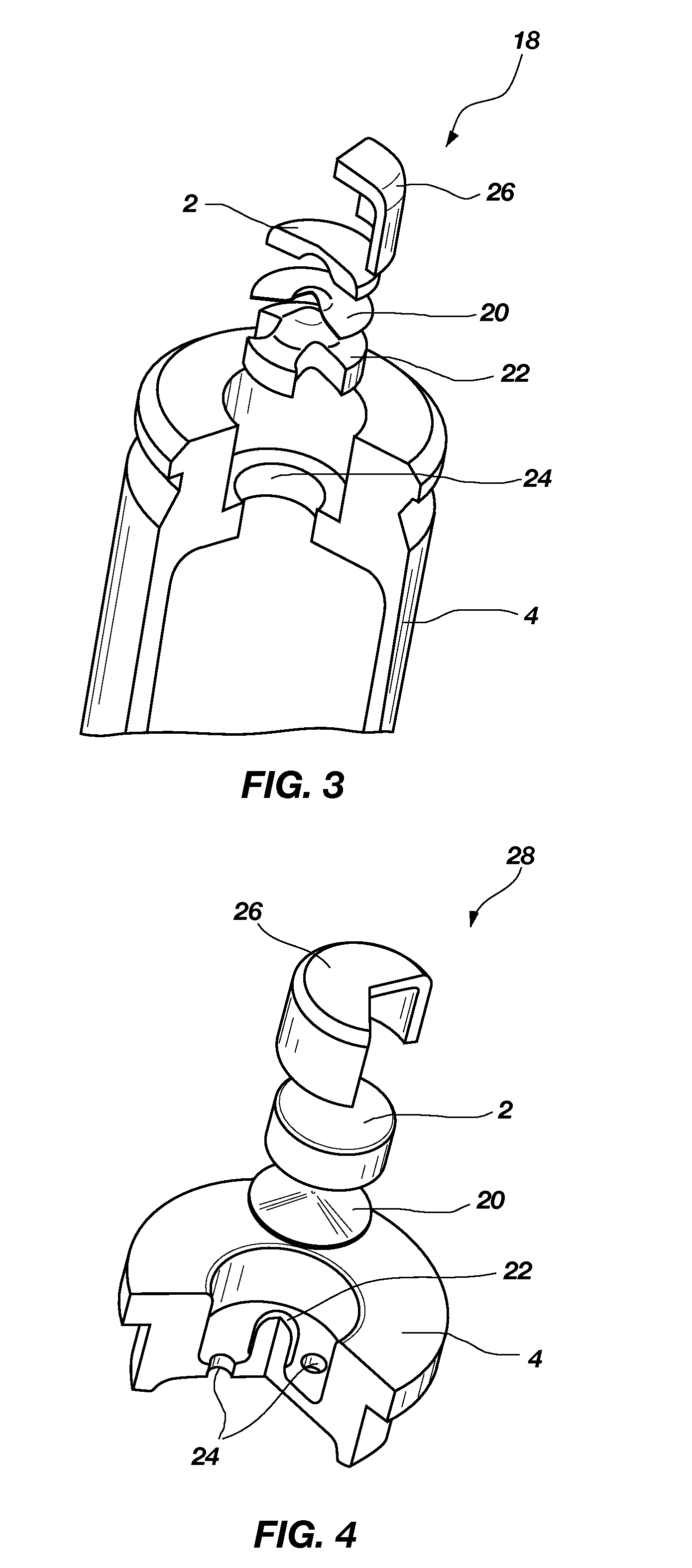
Nontoxic, noncorrosive phosphorus-based primer compositions and an ordnance element including the same
A primer composition that includes red phosphorus having an acid scavenger and a polymer thereon. The primer composition includes at least one other component that is substantially free of lead. The other component is at least one oxidizer, or at least one oxidizer and at least one of at least one secondary explosive composition and at least one energetic binder. The primer composition optionally includes at least one element having an ionic charge to ionic radius ratio of 4 or of 8, such as magnesium, zirconium, aluminum, silicon, titanium, tungsten, alloys thereof, and combinations thereof. The red phosphorus and the at least one oxidizer are present in the primer composition at approximately stoichiometric amounts. An ordnance element including the primer composition is also disclosed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
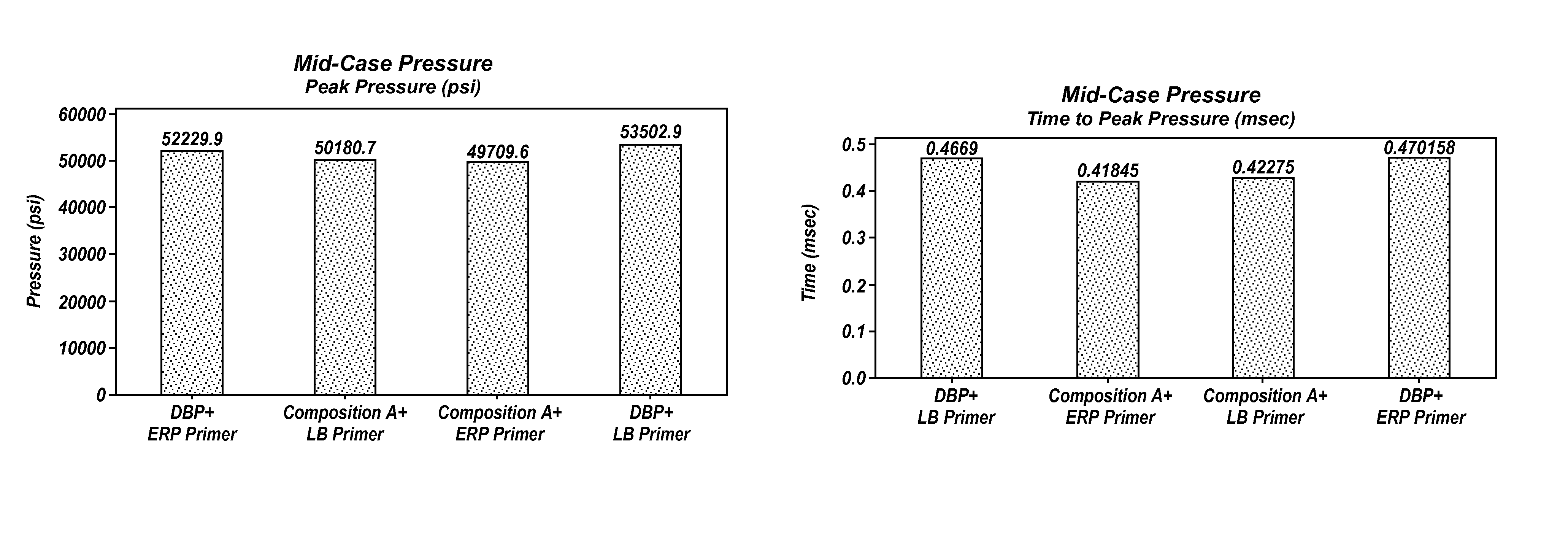
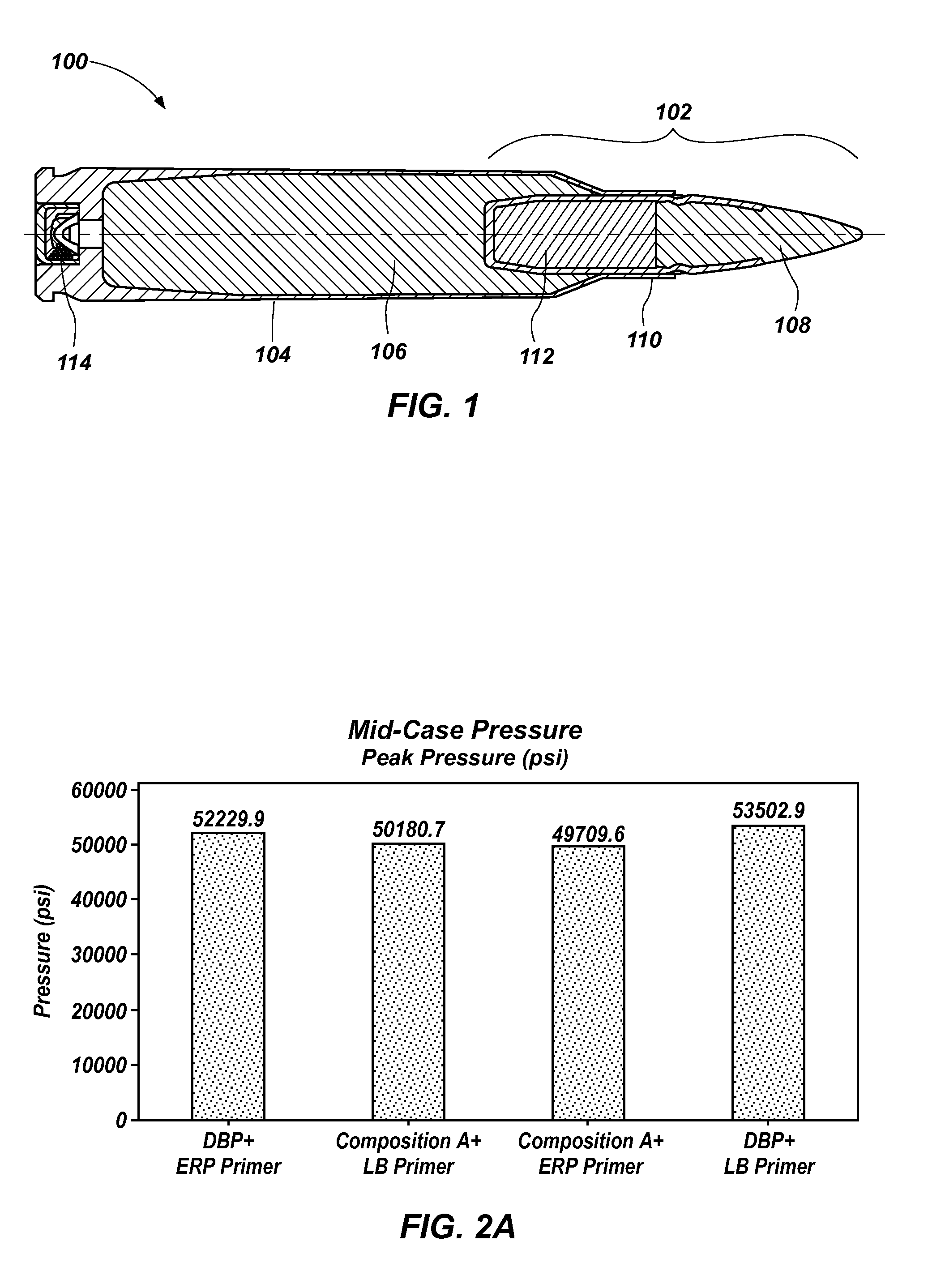
Propellant compositions including stabilized red phosphorus, a method of forming same, and an ordnance element including the same
Propellant compositions include an energetic binder, such as nitrocellulose, and a stabilized, encapsulated red phosphorous as a ballistic modifier. The propellant composition may additionally include an energetic plasticizer, such as nitroglycerine. For example, the propellant composition may be formed by mixing a double or multi base propellant that includes nitrocellulose plasticized with nitroglycerine with the stabilized, encapsulated red phosphorus. The propellant compositions may be substantially lead-free and may exhibit improved ballistic properties. Methods of forming such propellant compositions and an ordnance device including such propellant compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Bidirectional photothyristor chip, optical lighting coupler, and solid state relay
ActiveUS7423298B2Improving luminous sensitivityCoupling device detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenSolid-state relay
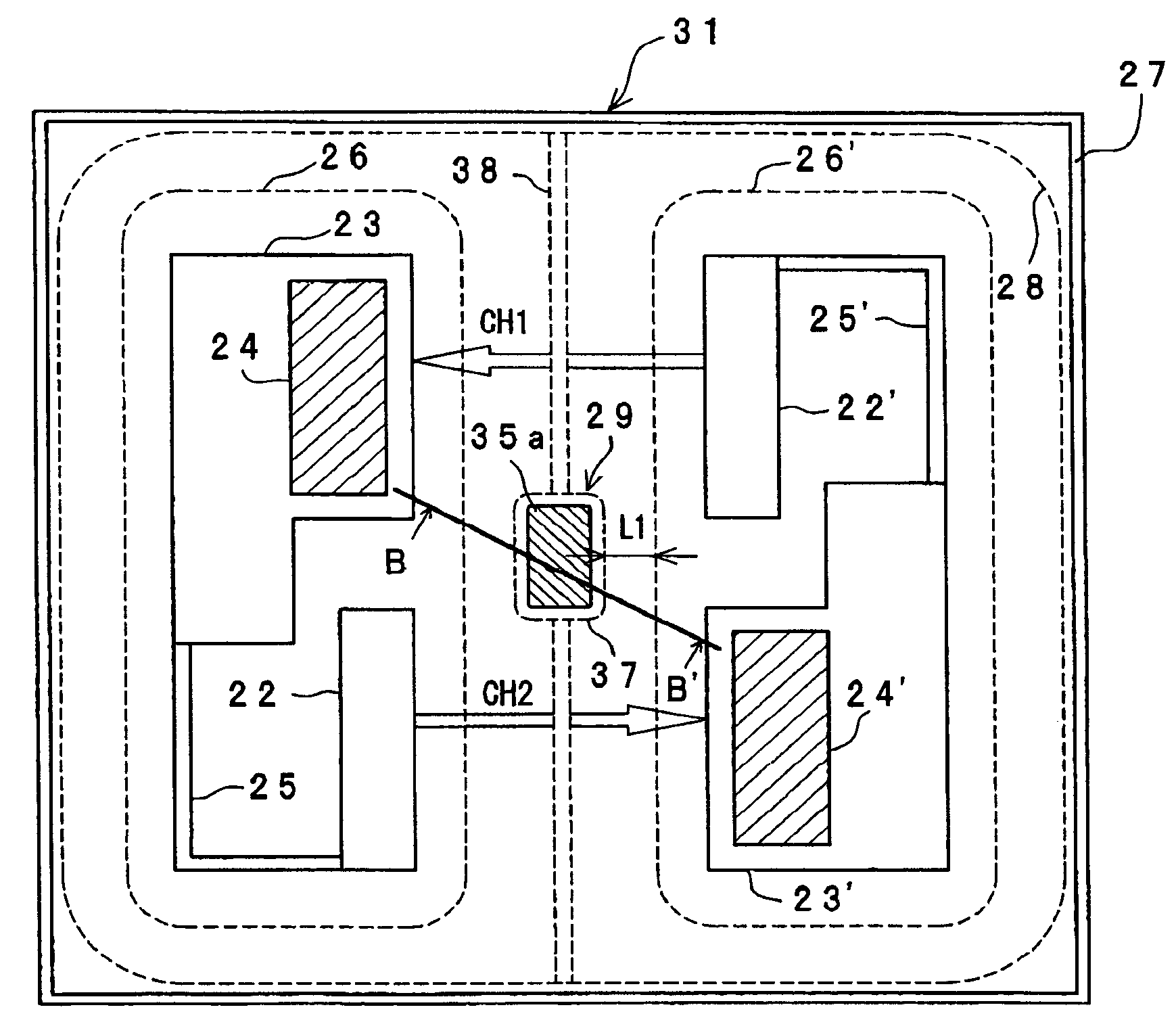
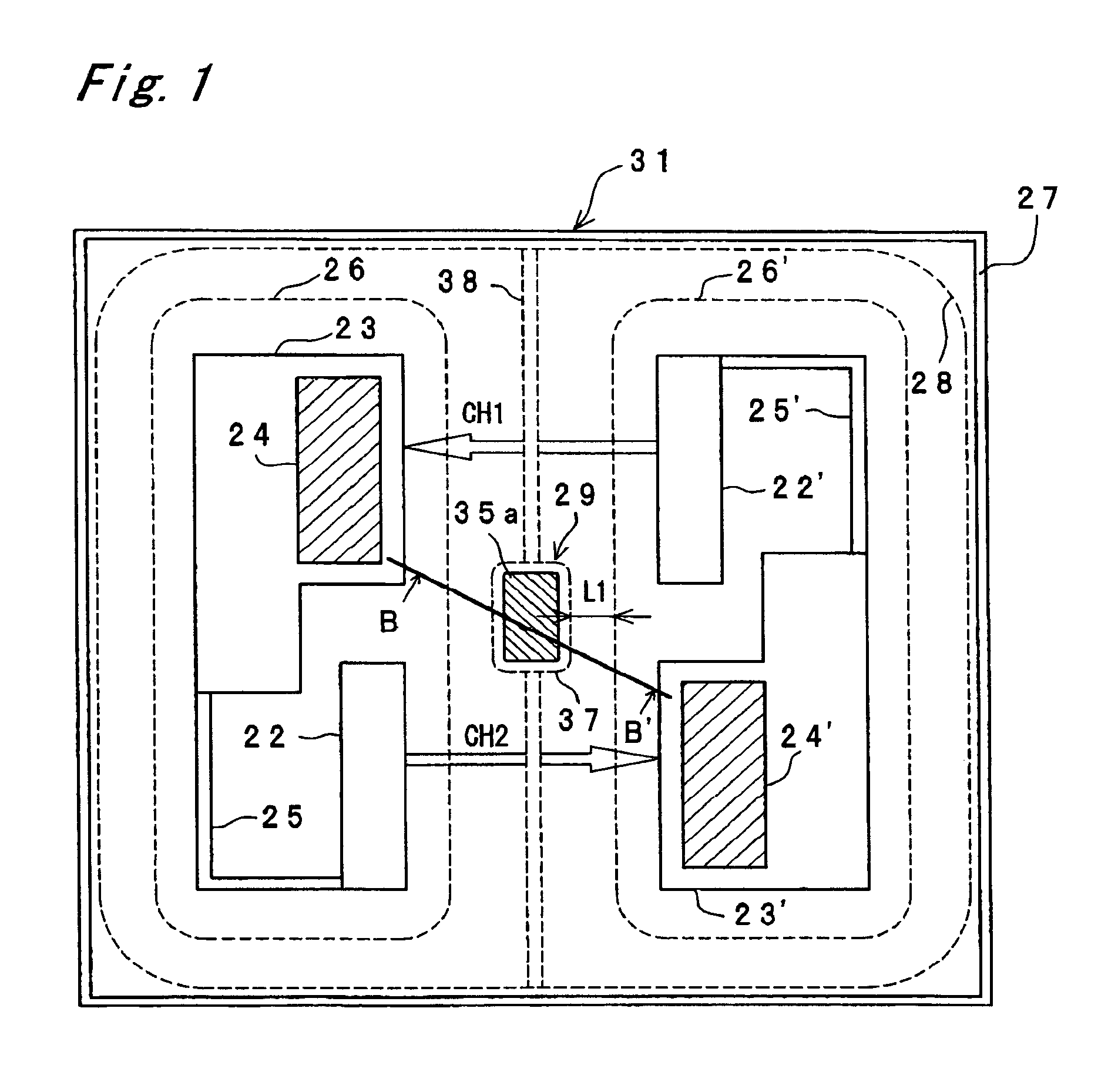
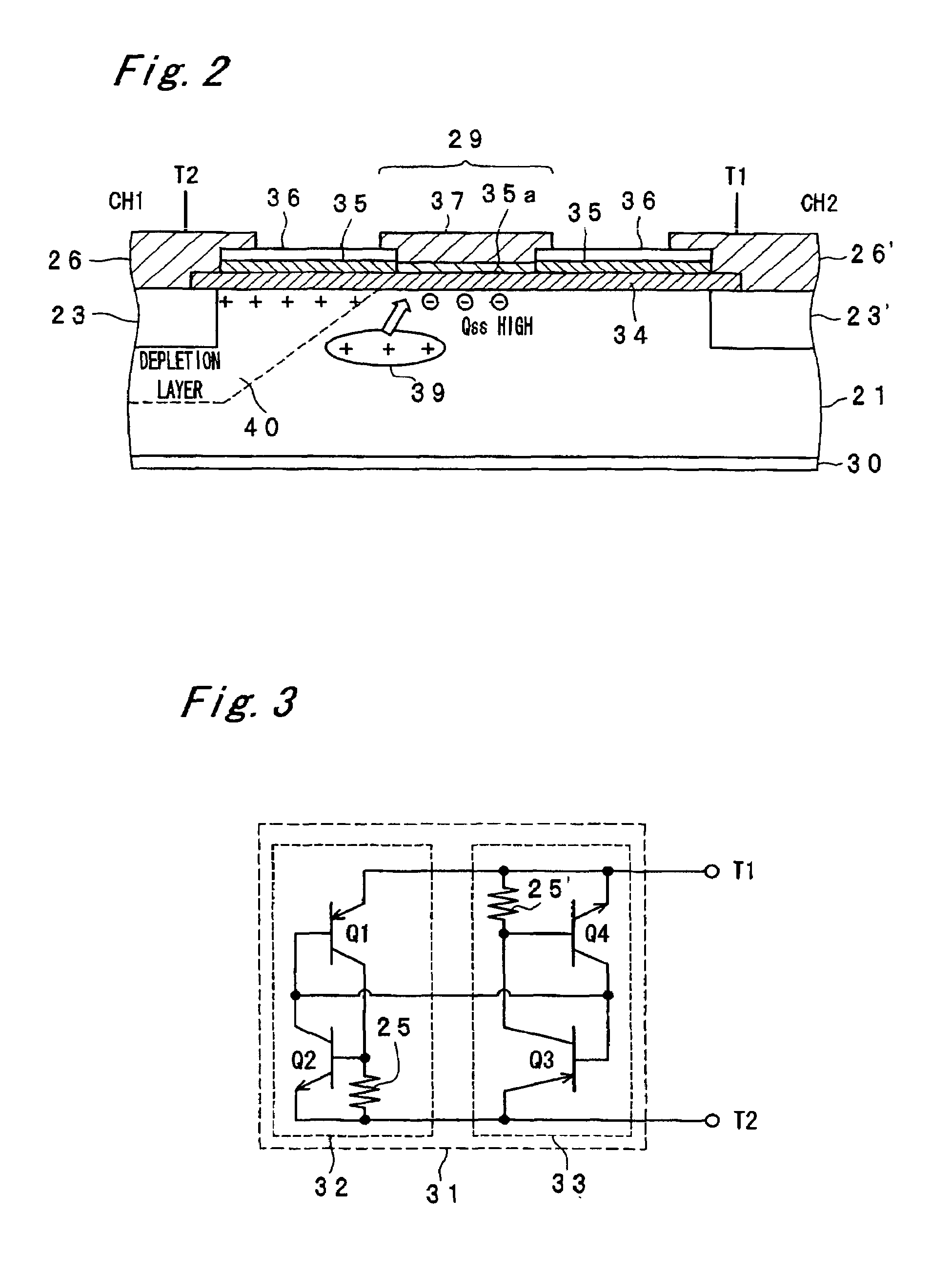
Two operation channels CH1 and CH2 of a bidirectional photothyristor chip 31 are disposed away from each other so as not to intersect with each other. In between a P-gate diffusion region 23 on the left-hand side and a P-gate diffusion region 23′ on the right-hand side on an N-type silicon substrate, and in between the CH1 and the CH2, a channel isolation region 29 comprised of an oxygen doped semi-insulating polycrystalline silicon film 35a doped with phosphorus is formed. Consequently, a silicon interface state (Qss) in the vicinity of the channel isolation region 29 on the surface of the N-type silicon substrate increases, so that holes or minority carriers in the N-type silicon substrate are made to disappear in the region. This makes it possible to prevent such commutation failure that when a voltage of the inverted phase is applied to the CH2 side at the point of time when the CH1 is turned off, the CH2 is turned on without incidence of light, and this allows a commutation characteristic to be enhanced.
Owner:SHARP KK
Illumination system housing multiple LEDs and provided with corresponding conversion material
InactiveUS7132785B2Improve performanceQuick changeMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsSynthetic materialsPhosphor
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
Methods of Forming Integrated Circuit Devices Having Ion-Cured Electrically Insulating Layers Therein
ActiveUS20090098706A1Quality improvementDegree of reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic orderEngineering
Methods of forming integrated circuit devices include forming a trench in a surface of semiconductor substrate and filling the trench with an electrically insulating region having a seam therein. The trench may be filled by depositing a sufficiently thick electrically insulating layer on sidewalls and a bottom of the trench. Curing ions are then implanted into the electrically insulating region at a sufficient energy and dose to reduce a degree of atomic order therein. The curing ions may be ones selected from a group consisting of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), boron (B), arsenic (As), carbon (C), argon (Ar), germanium (Ge), helium (He), neon (Ne) and xenon (Xe). These curing ions may be implanted at an energy of at least about 80 KeV and a dose of at least about 5×1014 ions / cm2. The electrically insulating region is then annealed at a sufficient temperature and for a sufficient duration to increase a degree of atomic order within the electrically insulating region.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nano particles and molecules
ActiveUS7090355B2Avoid viewingDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsColor imageWavelength filter
A system and a method of a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion (FC) of nano-particles and molecules are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a color image display system consists of a light source equipped with two-dimensional scanning hardware and a FC display screen board. The FC display screen board consists of a transparent fluorescence display layer, a wavelength filtering coating, and an absorption substrate. In another preferred embodiment, two mechanisms of light excitation are utilized. One of the excitation mechanisms is up-conversion where excitation light wavelength is longer than fluorescence wavelength. The second mechanism is down-conversion where excitation wavelength is shorter than fluorescence wavelength. A host of preferred fluorescence materials for the FC screen are also disclosed. These materials fall into four categories: inorganic nanometer sized phosphors; organic molecules and dyes; semiconductor based nano particles; and organometallic molecules. These molecules or nano-particles are incorporated in the screen in such a way that allows the visible transparency of the screen. Additionally, a preferred fast light scanning system is disclosed. The preferred scanning system consists of dual-axes acousto-optic light deflector, signal processing and control circuits equipped with a close-loop image feedback to maintain position accuracy and pointing stability of the excitation beam.
Owner:SUN INNOVATIONS
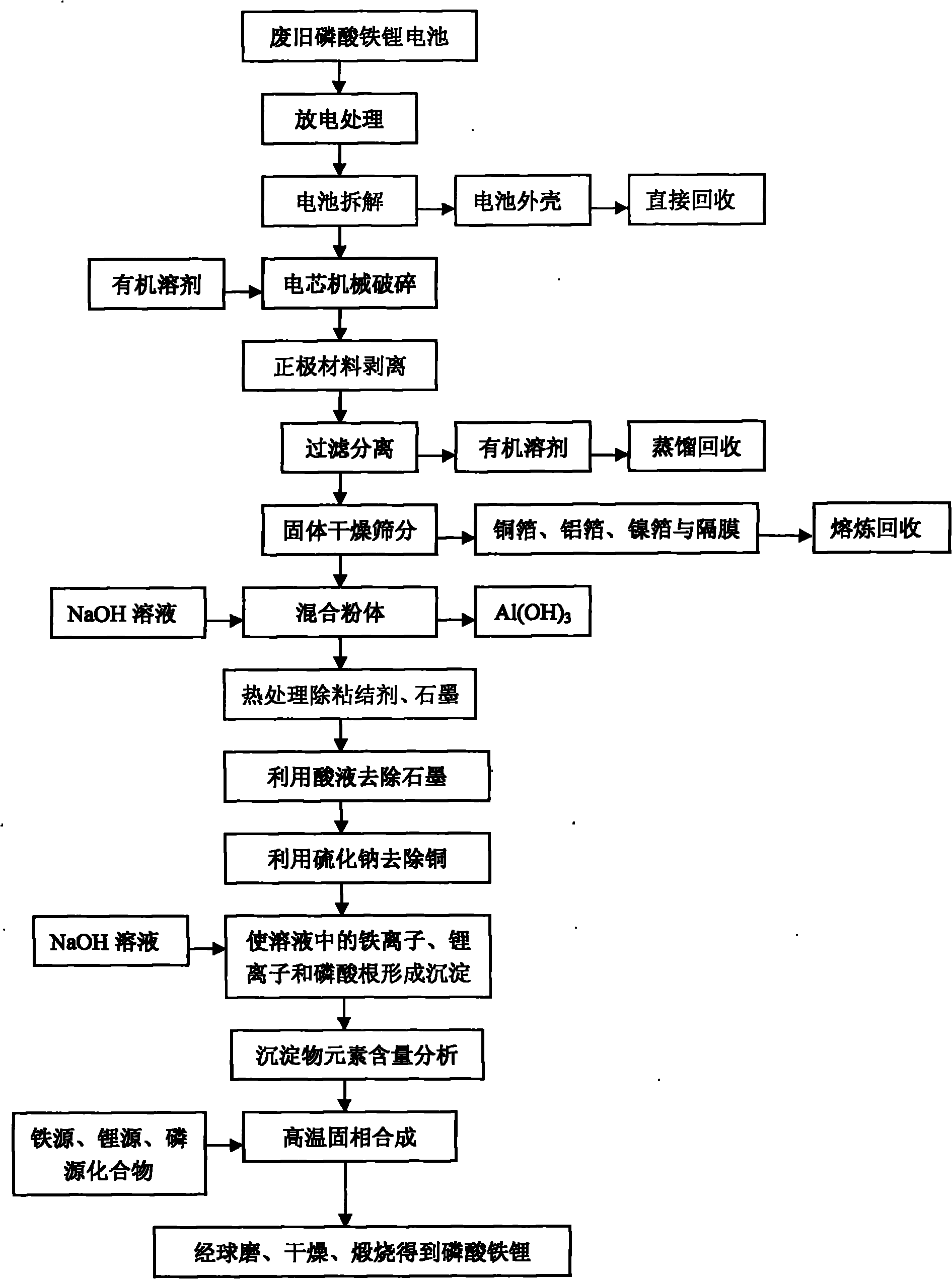
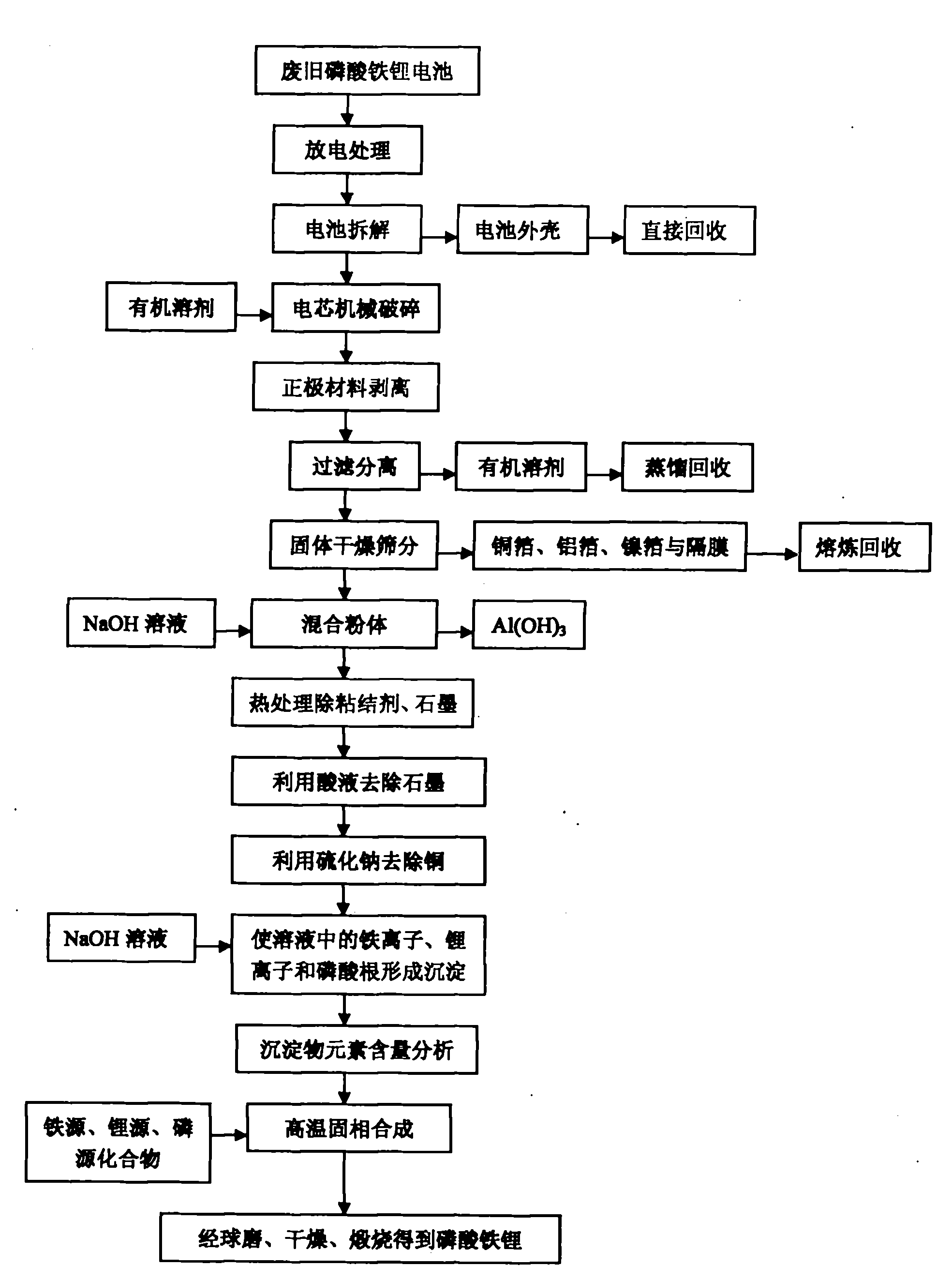
Comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN101847763AImprove performanceLow priceWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAdhesiveCalcination
The invention provides a comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, which has simple and reasonable process, low recovering cost and high added value. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing an organic solvent to dissolve an adhesive on battery cell fragments, and realizing the separation of lithium iron phosphate material and clean aluminum and copper foils through screening, wherein the aluminum and copper foils are recovered by smelting; utilizing a NaOH solution to remove residual aluminum foil scraps in the lithium iron phosphate material, and removing graphite and remaining adhesive by heat treatment; after dissolving the lithium iron phosphate with acid, utilizing sodium sulphide to remove copper ions, and utilizing the NaOH solution or ammonia solution to allow iron, lithium and phosphorus ions in the solution to generate sediments; adding iron source, lithium source or phosphorus source compounds to adjust the molar ratio of iron, lithium and phosphorus; and finally adding a carbon source, and obtaining a lithium iron phosphate cathode material through ball milling and calcination in inert atmosphere. After the treatment of the steps, the recovery rate of valuable metals in the batteries is more than 95%, and the comprehensive recovery rate of the lithium iron phosphate cathode material is more than 90%.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
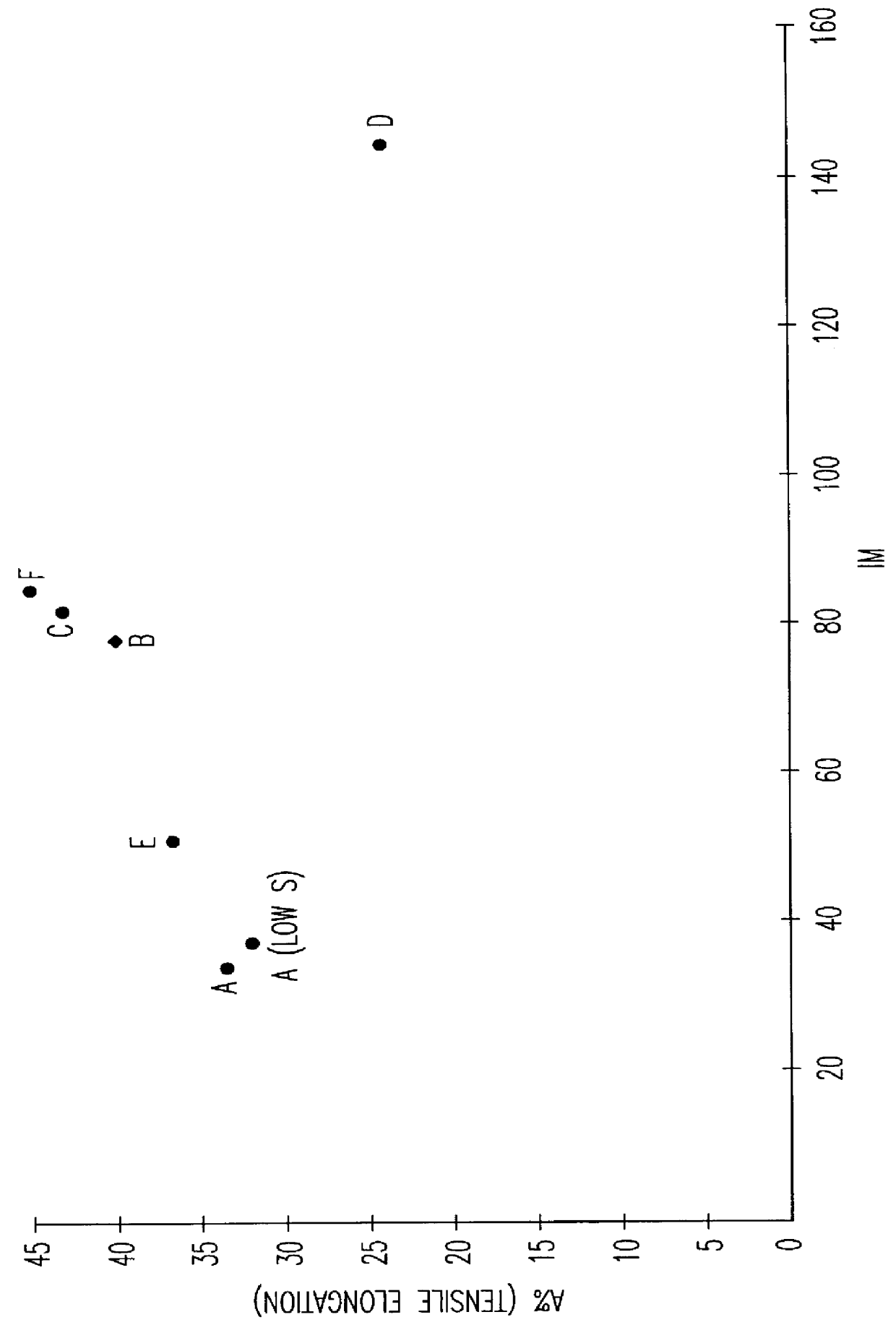
Austenoferritic stainless steel having a very low nickel content and a high tensile elongation
InactiveUS6096441ALow nickel contentImproved general propertyHeat treatment process controlElectric furnaceSulfurManganese
An austenoferritic stainless steel with high tensile elongation includes iron and the following elements in the indicated weight amounts based on total weight: carbon<0.04% 0.4%<silicon<1.2% 2%<manganese<4% 0.1%<nickel<1% 18%<chromium<22% 0.05%<copper<4% sulfur<0.03% phosphorus<0.1% 0.1%<nitrogen<0.3% molybdenum<3% the steel having a two-phase structure of austenite and ferrite and comprising between 30% and 70% of austenite, wherein Creq=Cr %+Mo %+1.5 Si % Nieq=Ni %+0.33 Cu %+0.5 Mn %+30 C %+30 N % and Creq / Nieq is from 2.3 to 2.75, and wherein IM=551-805(C+N)%-8.52 Si %-8.57 Mn %-12.51 Cr %-36 Ni %-34.5 Cu %-14 Mo %, IM being from 40 to 115.
Owner:UGITECH
Thin film battery and electrolyte therefor
A solid amorphous electrolyte composition for a thin-film battery. The electrolyte composition includes a lithium phosphorus oxynitride material containing a sulfide ion dopant wherein the atomic ratio of sulfide ion to phosphorus ion (S / P) in the electrolyte ranges greater than 0 up to about 0.2. The composition is represented by the formula: where 2x+3y+2z=5+w, x ranges from about 3.2 to about 3.8, y ranges from about 0.13 to about 0.46, z ranges from greater than zero up to about 0.2, and w ranges from about 2.9 to about 3.3. Thin-film batteries containing the sulfide doped lithium oxynitride electrolyte are capable of delivering more power and energy than thin-film batteries containing electrolytes without sulfide doping.
Owner:OAK RIDGE MICRO ENERGY
Ultrastable Y-type RE molecular sieve active component and its prepn process
InactiveCN1506161AReasonable matching activityIncreased hydrogen transfer activityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveActive component
The active component of ultrastable Y-type RE molecular sieve is composite modified Y-zeolite containing RE oxide 8-25 wt%, P 0.1-3.0 wt% and sodium oxide 0.3-2.5 wt%, and with degree of crystallization 30-55 % and unit cell parameter 2.455-2.477 nm. It is prepared with Y-zeolite as material and through the steps of exchange with RE and the first roasting to obtain RE-Na Y-zeolite; reaction with RE, reaction with P-containing compound, and the second roasting. The ultrastable Y-type RE molecular sieve is used as the active component of cracking catalyst and has the obvious effect of lowering olefin content in gasoline and the features of resulting in moderate coke yield and high diesel oil yield. The preparation process is simple and high in the utilization of the modifying elements.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Solar control coated glass
InactiveUS6596398B1Efficient use ofLow emissivityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsControl layerLow emissivity
A solar-control glass that has acceptable visible light transmission, absorbs near infrared wavelength light (NIR) and reflects midrange infrared light (low emissivity mid IR) along with a preselected color within the visible light spectrum for reflected light is provided. Also provided is a method of producing the improved, coated, solar-controlled glass. The improved glass has a solar energy (NIR) absorbing layer comprising tin oxide having a dopant such as antimony and a low emissivity control layer (low emissivity) capable of reflecting midrange infrared light and comprising tin oxide having fluorine and / or phosphorus dopant. A separate iridescence color suppressing layer as described in the prior art is generally not needed to achieve a neutral (colorless) appearance for the coated glass, however an iridescence suppressing layer or other layers may be combined with the two layer assemblage provided by the present invention. If desired, multiple solar control and / or multiple low emissivity layers can be utilized. The NIR layer and the low emissivity layer can be separate portions of a single tin oxide film since both layers are composed of doped tin oxide. A method of producing the coated solar control glass is also provided.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Solar control coated glass
A solar-control glass that has acceptable visible light transmission, absorbs near infrared wavelength light (NIR) and reflects midrange infrared light (low emissivity mid IR) along with a preselected color within the visible light spectrum for reflected light is provided. Also provided is a method of producing the improved, coated, solar-controlled glass. The improved glass has a solar energy (NIR) absorbing layer comprising tin oxide having a dopant such as antimony and a low emissivity control layer (low emissivity) capable of reflecting midrange infrared light and comprising tin oxide having fluorine and / or phosphorus dopant. A separate iridescence color suppressing layer as described in the prior art is generally not needed to achieve a neutral (colorless) appearance for the coated glass, however an iridescence suppressing layer or other layers may be combined with the two layer assemblage provided by the present invention. If desired, multiple solar control and / or multiple low emissivity layers can be utilized. The NIR layer and the low emissivity layer can be separate portions of a single tin oxide film since both layers are composed of doped tin oxide. A method of producing the coated solar control glass is also provided.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Biodegradable polymers, compositions, articles and methods for making and using the same
Biodegradable polymer compositions that degrade in vivo into non-toxic residues are described. In part, the present invention is directed to such polymers containing phosphorus and desaminotyrosyl L-tyrosine linkages in the polymer backbone. Processes for preparing such polymers, compositions containing such polymers and biologically active substances, articles useful for implantation or injection into the body fabricated from the compositions, and methods for controllably releasing biologically active substances using the polymers, are also described.
Owner:JOHNS HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of growing a ZnS:Mn phosphor layer for use in thin-film electroluminescent components
InactiveUS6113977AImprove electroluminescence performanceSimple manufacturing processElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganozinc compoundFluorescence
The invention relates to a method of growing a ZnS:Mn phosphor layer suitable for use in thin-film electroluminescent components. According to the method, the ZnS:Mn phosphor layer is grown on a substrate by means of the ALE method using volatile zinc, sulfur and manganese compounds as the precursors. According to the invention, an organozinc compound such as diethylzinc or dimethylzinc is used as precursor for zinc, hydrogen sulfide or an organosulfur compound is used as precursor for sulfur, and an organomanganese compound or organic manganese complex compound is used as precursor for manganese. The invention provides a display component with drive-voltage-symmetrical light emission and stable characteristics of luminance level and turn-on voltage.
Owner:PLANAR SYSTEMS +1
Cracking catalyst for petroleum hydrocarbon, and preparation method
A cracking catalyst for petroleum hydrocarbon is proportionally prepared from clay, aluminum oxide prepared from alpha-AlO(OH), Y-type molecular sieve containing RE and P and silicon oxide. Its advantages are strong power to convert heavy oil and high output rate of diesel oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com