Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Diethylzinc" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
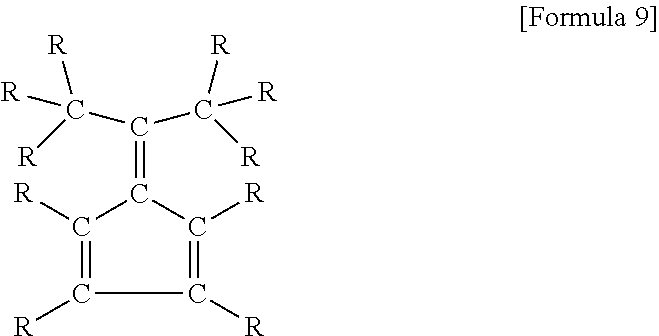
Diethylzinc (C₂H₅)₂Zn, or DEZ, is a highly pyrophoric and reactive organozinc compound consisting of a zinc center bound to two ethyl groups. This colourless liquid is an important reagent in organic chemistry. It is available commercially as a solution in hexanes, heptane, or toluene, or as a pure liquid.
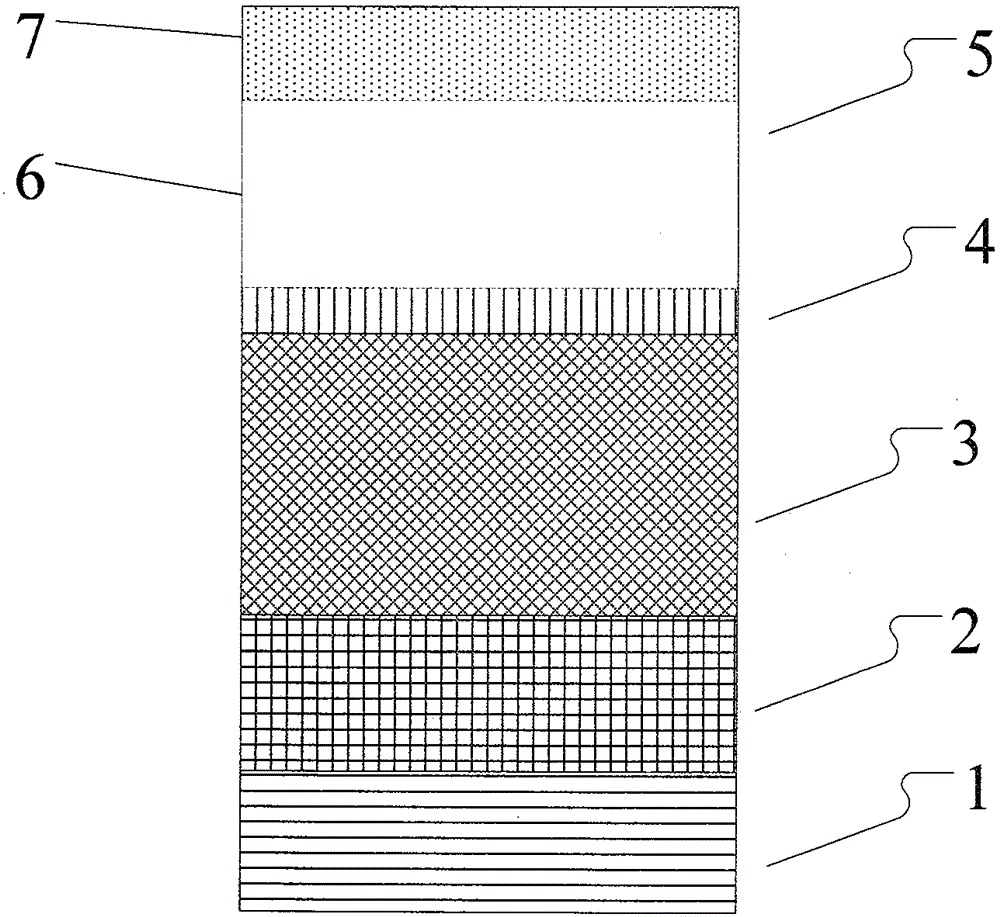
Method of growing a ZnS:Mn phosphor layer for use in thin-film electroluminescent components
InactiveUS6113977AImprove electroluminescence performanceSimple manufacturing processElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganozinc compoundFluorescence
The invention relates to a method of growing a ZnS:Mn phosphor layer suitable for use in thin-film electroluminescent components. According to the method, the ZnS:Mn phosphor layer is grown on a substrate by means of the ALE method using volatile zinc, sulfur and manganese compounds as the precursors. According to the invention, an organozinc compound such as diethylzinc or dimethylzinc is used as precursor for zinc, hydrogen sulfide or an organosulfur compound is used as precursor for sulfur, and an organomanganese compound or organic manganese complex compound is used as precursor for manganese. The invention provides a display component with drive-voltage-symmetrical light emission and stable characteristics of luminance level and turn-on voltage.
Owner:PLANAR SYSTEMS +1
Process For Producing Zno Transparent Conductive Film By Mocvd (Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) Method
InactiveUS20080032044A1Low costEliminate useChemical vapor deposition coatingPhotovoltaic energy generationWater vaporGas phase
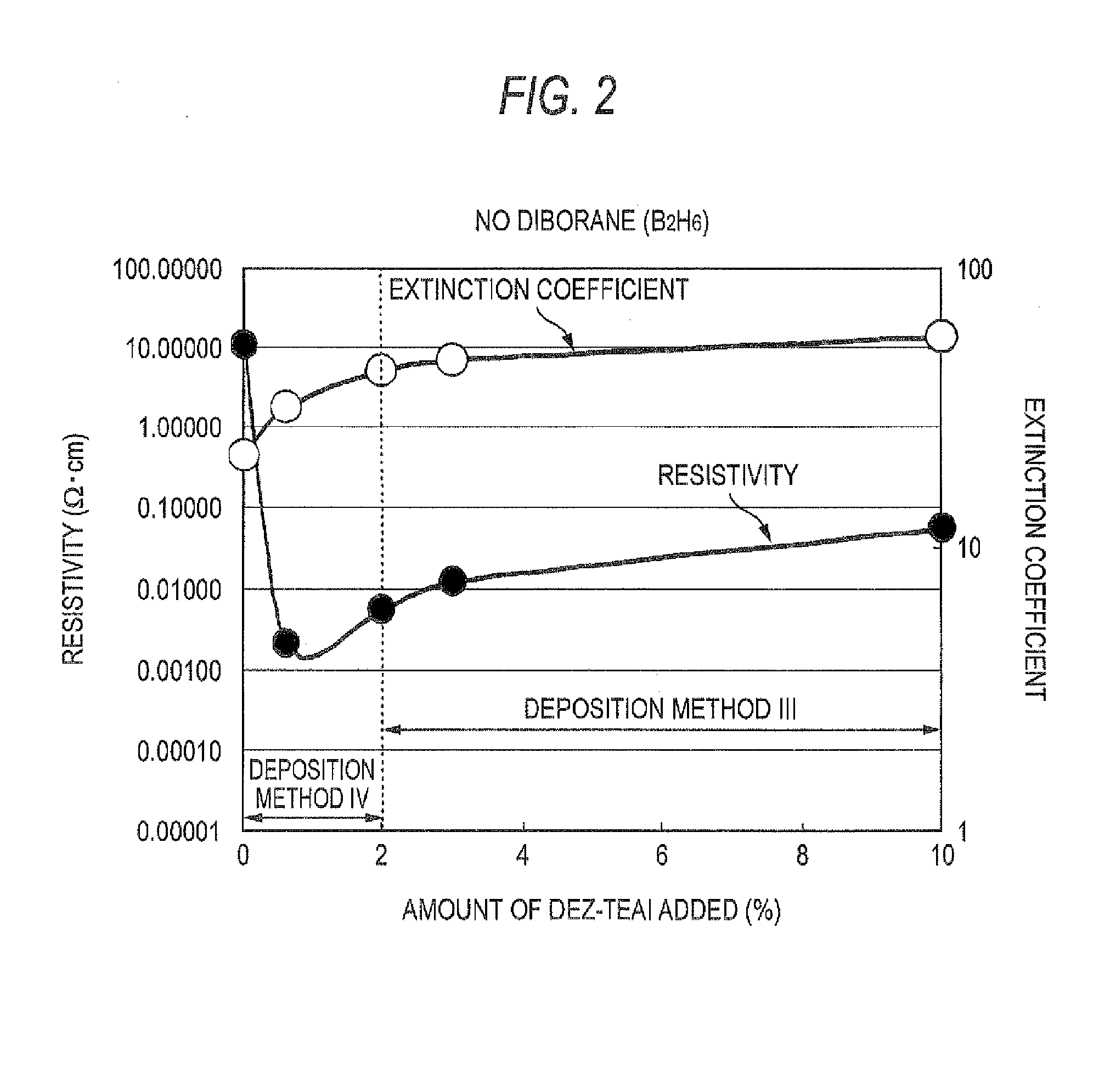
The triethylaluminum contained as an impurity in low-purity raw-material diethylzinc, which is inexpensive, is utilized as an additive to reduce the cost of film formation. Diethylzinc having a low purity (99.99-98% or 99.99-90%) is used as a raw material to produce a ZnO transparent conductive film by the MOCVD (metal-organic chemical vapor deposition) method. Water vapor (H2O) is used as an oxidizing agent and the triethylaluminum contained as an impurity in the raw material is utilized as an additive (diborane is further added as an additive) to cause the diethylzinc, the water vapor (H2O), and the triethylaluminum (and the diborane) to undergo a vapor-phase reaction to produce a ZnO transparent conductive film.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Zinc oxide film method and structure for CIGS cell
InactiveUS8168463B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingZincDiethylzinc
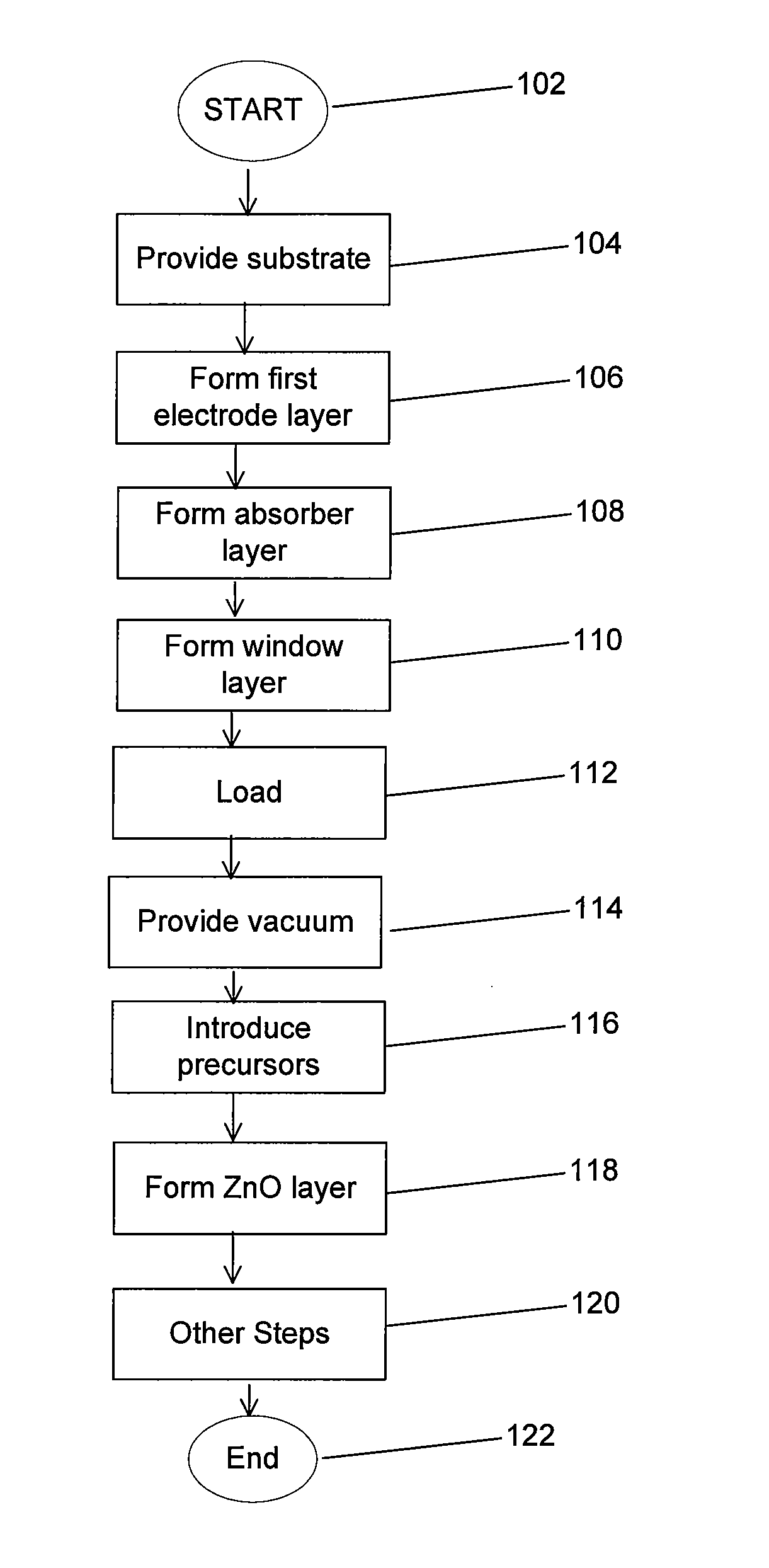
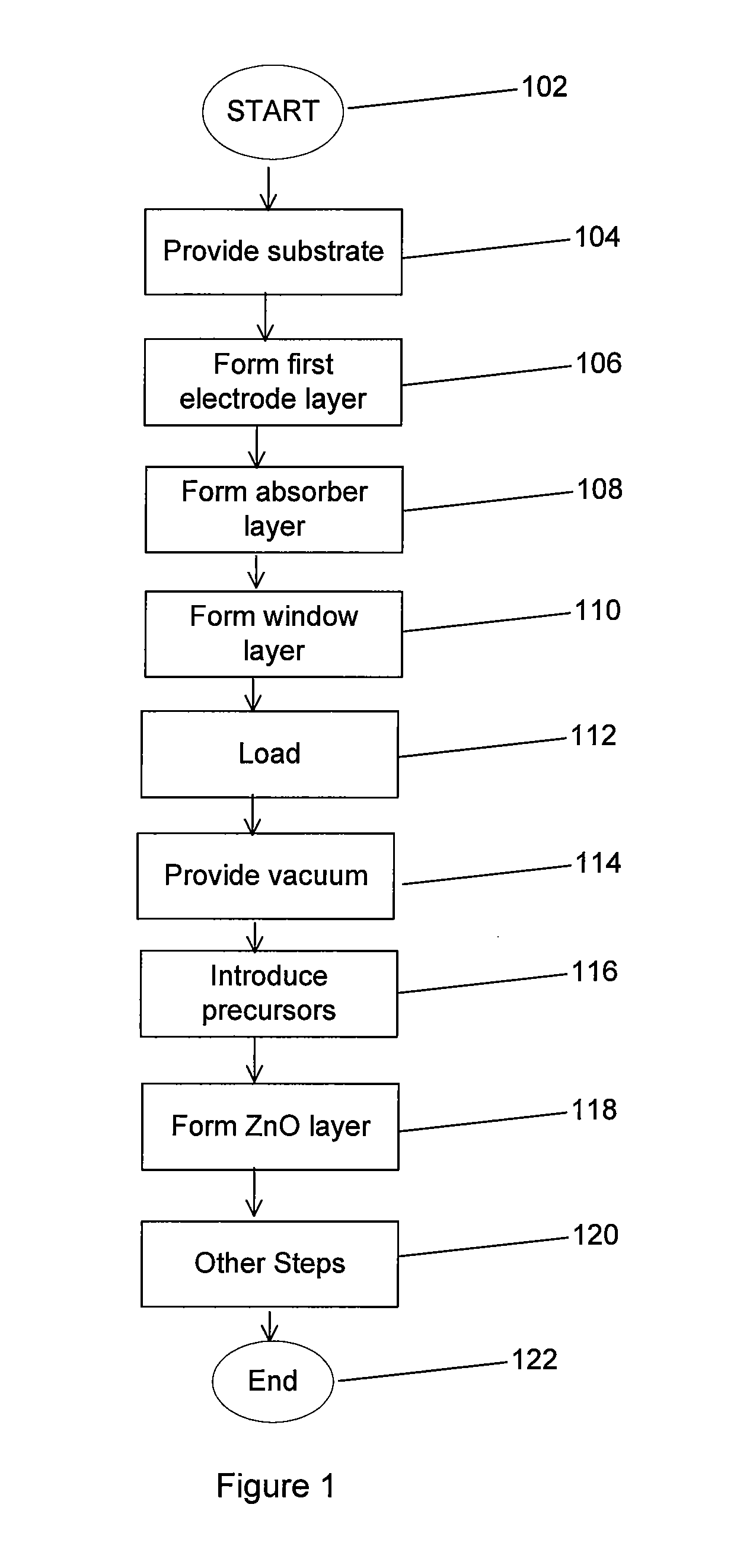
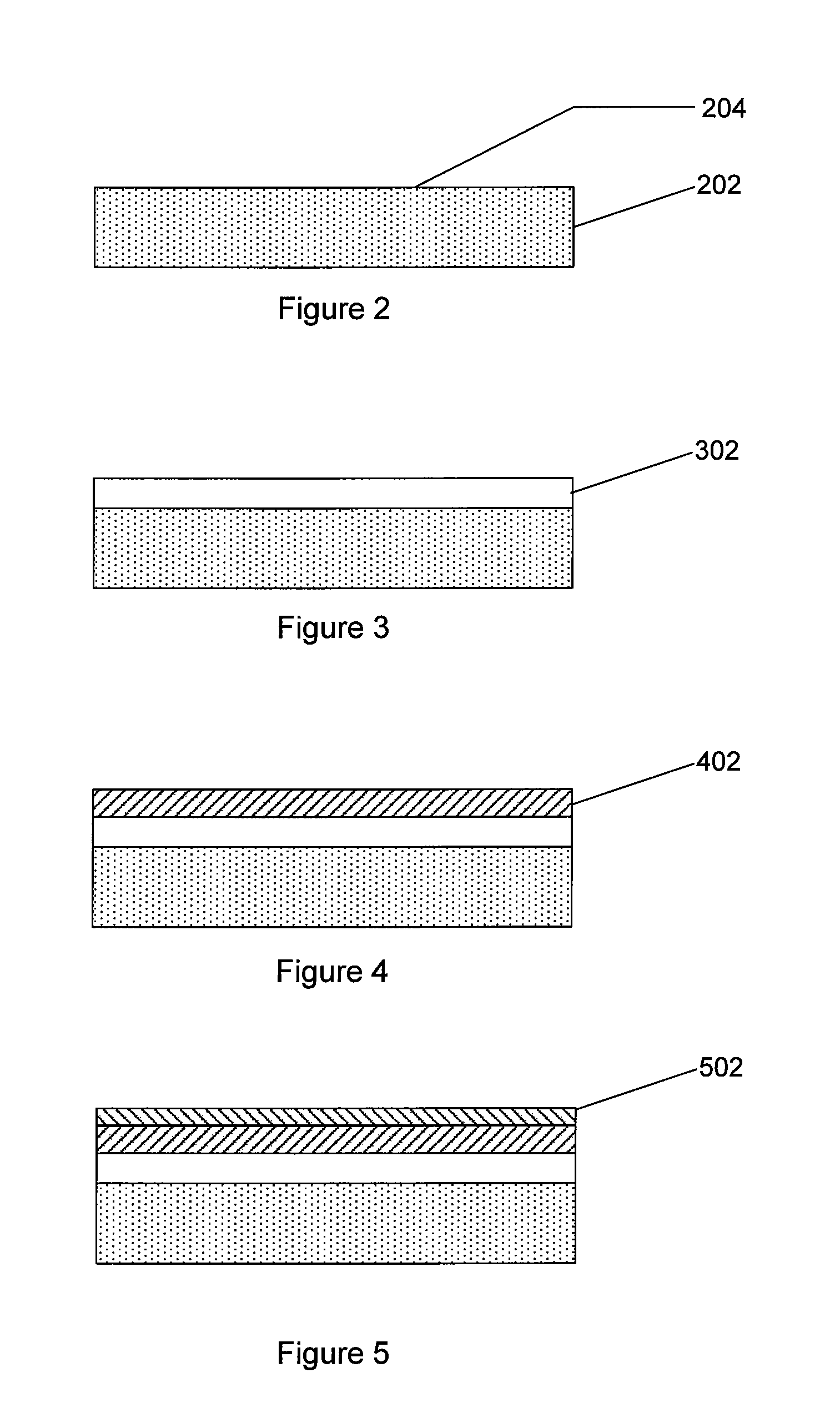
A method for fabricating a thin film photovoltaic device. The method includes providing a substrate comprising an absorber layer and an overlying window layer. The substrate is loaded into a chamber and subjected to a vacuum environment. The vacuum environment is at a pressure ranging from 0.1 Torr to about 0.02 Torr. In a specific embodiment, a mixture of reactant species derived from diethylzinc species, water species and a carrier gas is introduced into the chamber. The method further introduces a diborane species using a selected flow rate into the mixture of reactant species. A zinc oxide film is formed overlying the window layer to define a transparent conductive oxide using the selected flow rate to provide a resistivity of about 2.5 milliohm-cm and less and an average grain size of about 3000 to 5000 Angstroms.
Owner:CM MFG
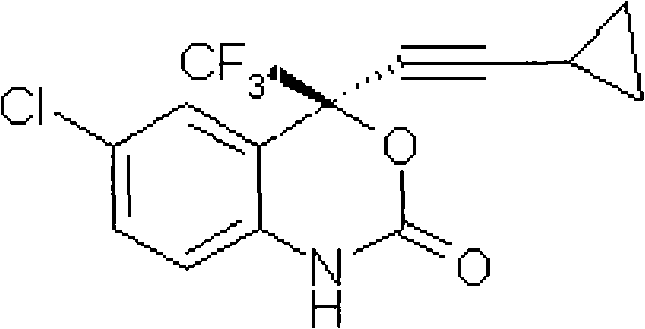
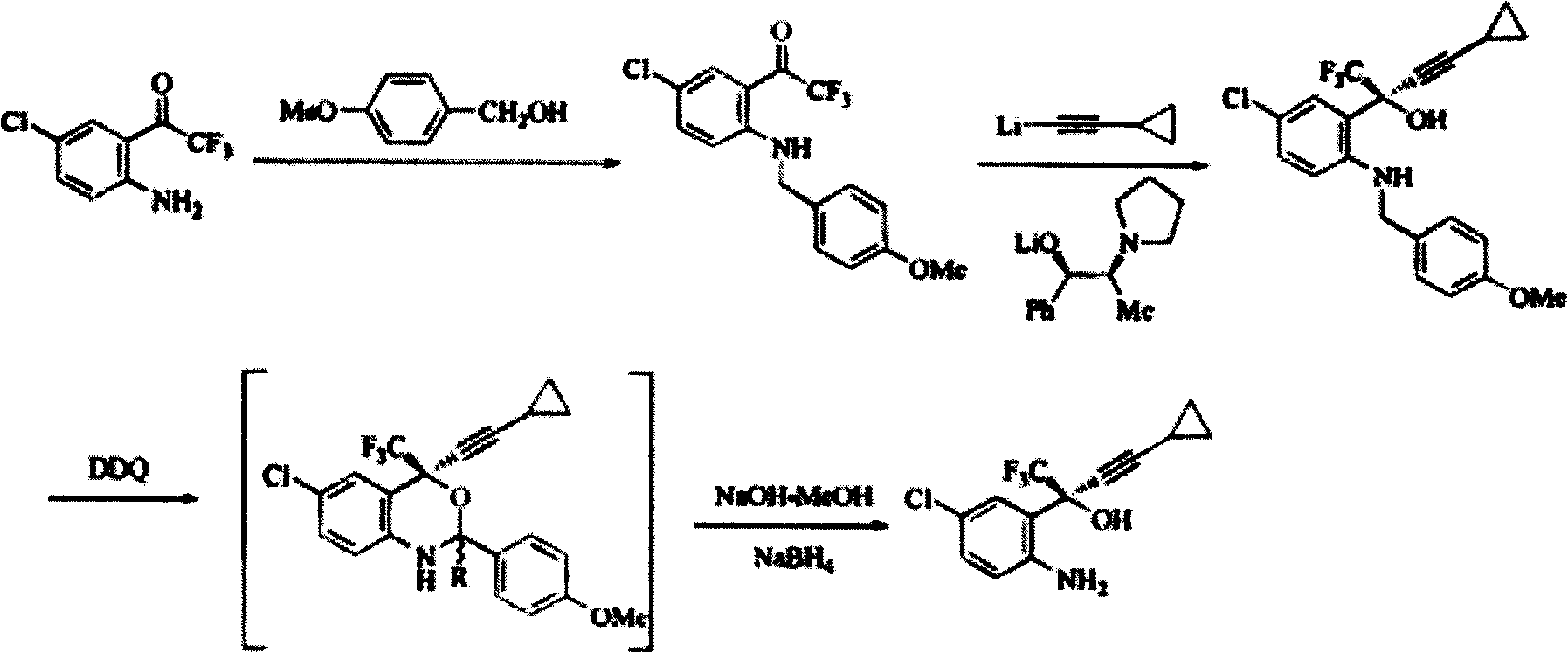
Method for preparing chiral cylopropyl acetenyl tertiary alcohol compound
InactiveCN101786959ALow costSuitable for industrial productionOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationTrifluorideButyl lithium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a chiral cylopropyl acetenyl tertiary alcohol compound.The steps of the method are as follows: (a) cylopropyl ethylnen or other derivatives react with a chiral induction reagent, a chirality auxiliary reagent and zinc halide in an organic solvent under the action of an alkaline reagent so as to obtain a zinc complex; (b) addition reaction is carried out between the obtained zinc complex and 5-chlorin-2-amino trifluoro-benzophenone; (c) (S)-2-amino-5-chlorin-alpha-cylopropyl ethylnen-alpha-benzyl alcohol trifluoride is collected from reaction liquid. Compared with butyl lithium and diethylzinc, the alkaline reagent adopted in the invention is safer; in addition, the cheap zinc halide is used as a ligand, which greatly reduces the cost. Therefore, the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACEBRIGHT PHARMA GRP +1
Method for producing amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide thin film by atomic layer deposition
InactiveCN102618843ASimple processLow deposition temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtomic layer depositionMaterials science
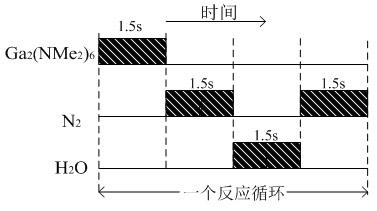
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits, and particularly discloses a method for growing an amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide thin film by the ALD (atomic layer deposition) technique. The method mainly includes the steps: using diethylzinc as a reaction source for growing ZnO, and using water or hydrogen peroxide as oxidant; using Ga2 (NMe2)6 as a reaction source for growing Ga2O3, and using water as oxidant; growing In2O3 for multiple cycles, using cyclopentadienylindium as a reaction source for growing In2O3, and using mixture of water and oxygen or ozone as oxidant; and repeating the steps for multiple times as required to obtain an IGZO thin film of certain thickness. The temperature of a reaction chamber in growth is controlled within a range of from 100 DEG C to 300 DEG C. In addition, the steps above are free to order and combine. The IGZO thin film grown by the method is high in uniformity, density and shape retention, suitable for large-area disposition, and widely applicable to the fields of thin film transistors, thin film transistor memories and transparent electronic devices.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
ZnO:B film grown by utilizing MOCVD (Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) gradient doping technology and application
InactiveCN102168256ARefine the grain sizeReduce absorptionFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
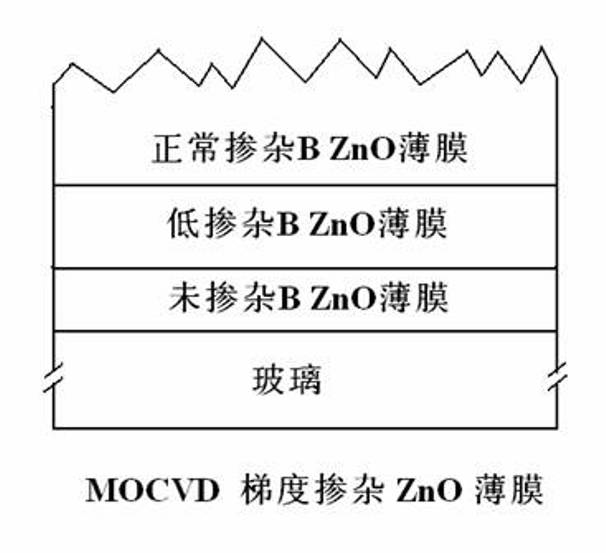
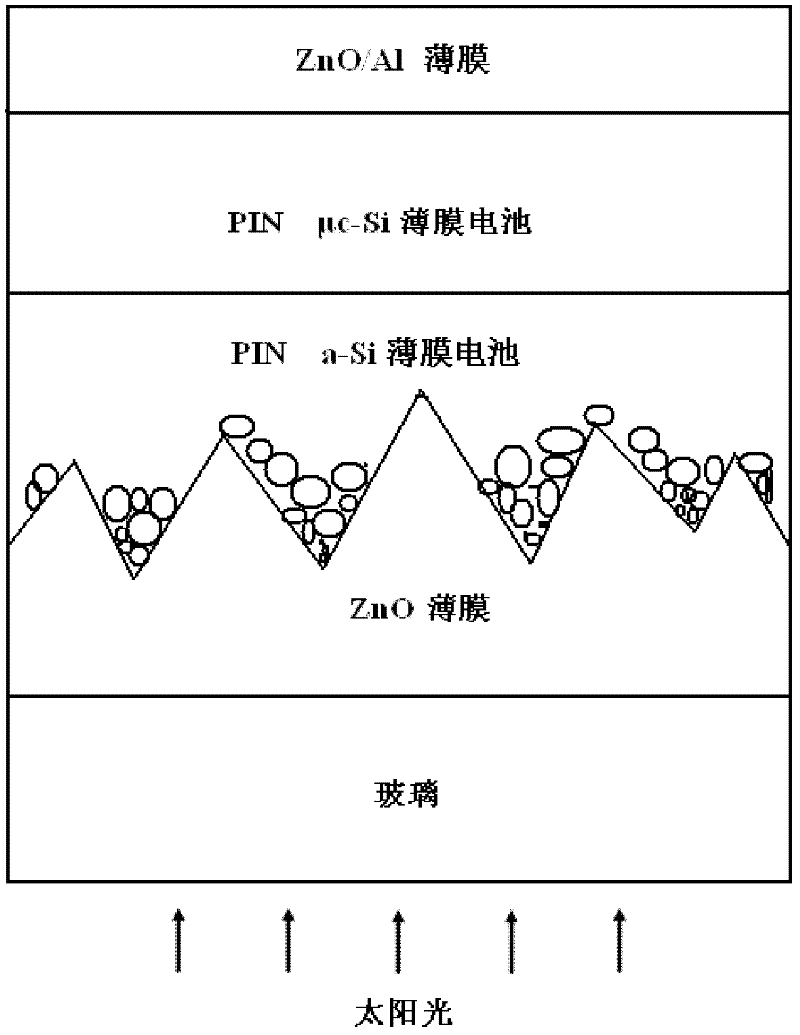
The invention relates to a ZnO:B film grown by utilizing an MOCVD (Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) gradient doping technology. By utilizing the MOCVD technology, using a glass base sheet as a substrate, using diethylzinc and water as raw materials and using borane as doping gas, a ZnO transparent conducting film without doping B or doping less B grows on the glass base sheet; then, ZnO grows by sectional gradient doping on the basis of the film by utilizing the MOCVD technology as well to prepare the glass base sheet / undoped B or low B doped ZnO / normal B doped ZnO transparent conducting film. The invention has the advantage of realizing the ZnO film with large grain size and high visible light and near-infrared transmissivity by growing undoped or low B doped ZnO film at the initial period and then adopting doping under the normal condition. The film is suitable for being applied to a p-i-n type Si-based film solar cell, especially an a-Si / muc-Si laminated film solar cell andcan further improve the performance of an Si film cell.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film for photocatalysis
The invention provides a preparation method of a zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film for photocatalysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: heating to 100-200 DEG C in the rough vacuum of below 20PMa, and cleaning a reaction cavity; cleaning a substrate, drying the substrate, introducing a precursor tetrakis (dimethylamino)titanium to the reaction cavity to pulse for 3 seconds, and cleaning; pulsing steam, and cleaning the steam to finish one cycle of titanium oxide deposition; introducing a precursor diethyl zinc to pulse for 2 seconds, and cleaning; introducing the steam to pulse for 4 seconds, and cleaning to finish one cycle of zinc oxide deposition; and forming a large cycle by a plurality of cycles of the titanium oxide deposition and one cycle of the zinc oxide deposition, and annealing at the temperature of 450 DEG C for 2 hours after a plurality of large cycles are finished, i.e., the zinc oxide doped titanium oxide film deposition process is finished. The film is precise and adjustable in thickness and component and excellent in optical transmittance and photocatalysis efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Method for synthesis of polylactide polyol by lactide and polyol
InactiveCN103396535ALow viscosity average molecular weightHigh viscosity average molecular weightTin dioxidePropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for obtaining polylactide polyol by a way of ring-opening polymerization of lactide with lactide and a polyol as direct raw materials. The method includes the following steps: A, lactide purification: a crude product lactide is purified, and lactide with the content of more than 99.5% and the optical purity of more than 99% is obtained; B, synthesis of polylactide polyol: the purified lactide and the polyol are added into a reaction kettle, then a catalyst is added according to a lactide weight ratio of 0.5 / 1000-1 / 1000 into the reaction kettle for polymerization, and polylactide polyol with the viscosity average molecular weight of 100-5000 is obtained, wherein the catalyst is a composite catalyst comprising one or more of zinc lactate, zinc oxide, zinc powder, diethyl zinc, tin lactate, tin oxide, tin dioxide, stannous oxide, stannous lactate, stannous octoate, stannous chloride, tin powder, propionic acid or tetrabutyl titanate. The method has simple process and easy operation, is suitable for industrialized production applications, and has no 'three wastes' emissions.
Owner:SHENZHEN ESUN IND
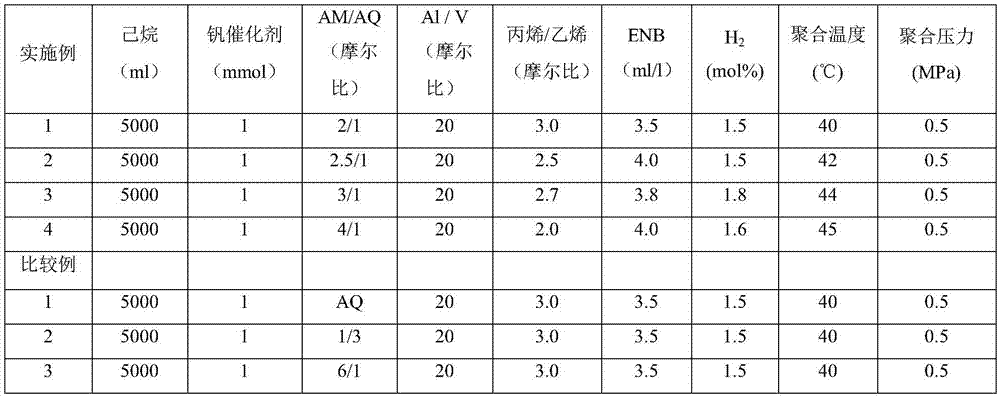
Poly(ethylene-r-norbornene/ethylene) segmented copolymer synthesized by utilizing chain shuttling method
The invention discloses a poly(ethylene-r-norbornene / ethylene) segmented copolymer synthesized by utilizing a chain shuttling method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing amixed catalyst; adding polymerization monomers and regulating a polymerization temperature; adding a promoter and a chain shuttling agent; adding a catalyst for performing chain shuttling polymerization; terminating the polymerization reaction; and precipitating and drying the polymer solution. Diethyl zinc is selected as the chain shuttling agent, an ethylene / norbornene random chain segment synthesized from a Rac-ethyl bridged zirconium dichloride diindene catalyst serves as a soft segment, a polyethylene segment synthesized from a Rac-3-tert-butyl substituted methyl bridged zirconium dichloride diindene catalyst serves as a hard segment, and the poly(ethylene-r-norbornene / ethylene) segmented copolymer is synthesized for the first time. The method and the substance are not reported in many technologies, and conditions are provided for realizing wide application of the novel material.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of high-purity ZnO/BiVO4 heterogeneous micro-ribbon
ActiveCN107190362AEffective regulatory structureEffective Regulatory ComponentsInorganic material artificial filamentsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsDiisopropyl azodicarboxylateElectrospinning
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-purity ZnO / BiVO4 heterogeneous micro-ribbon, and belongs to the technical field of the micro-ribbon. The preparation method includes steps of dissolving polyvinylpyrrolidone, bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, bis(acetylacetone) vanadium oxide and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate in a mixed solvent; stirring and mixing under a room temperature to form a precursor spinning fluid; performing electrostatic spinning on the precursor spinning fluid to obtain a solid precursor micro-ribbon; placing the solid precursor micro-ribbon in an atomic layer deposition system; reacting with water by diethylzinc; after circulation, depositing ZnO on the surface of the precursor micro-ribbon; performing high-temperature calcination on the precursor micro-ribbon coated with ZnO to obtain the ZnO / BiVO4 heterogeneous micro-ribbon material. Compared with the prior art, the method uses diethylzinc to strongly react with water and generate ZnO; through changing the circulation frequency in the atomic layer deposition system, the structure and component of the ZnO / BiVO4 heterogeneous micro-ribbon are effectively controlled.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
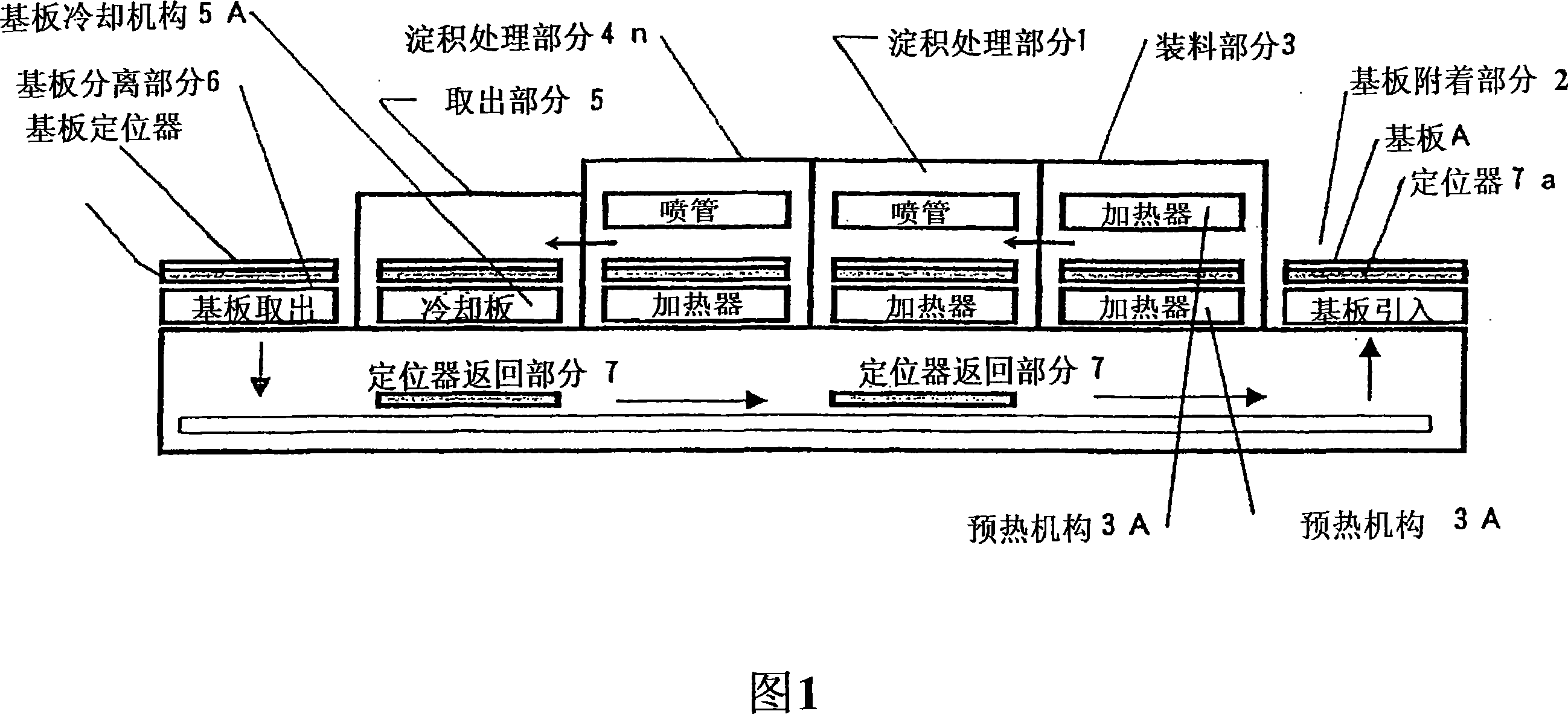
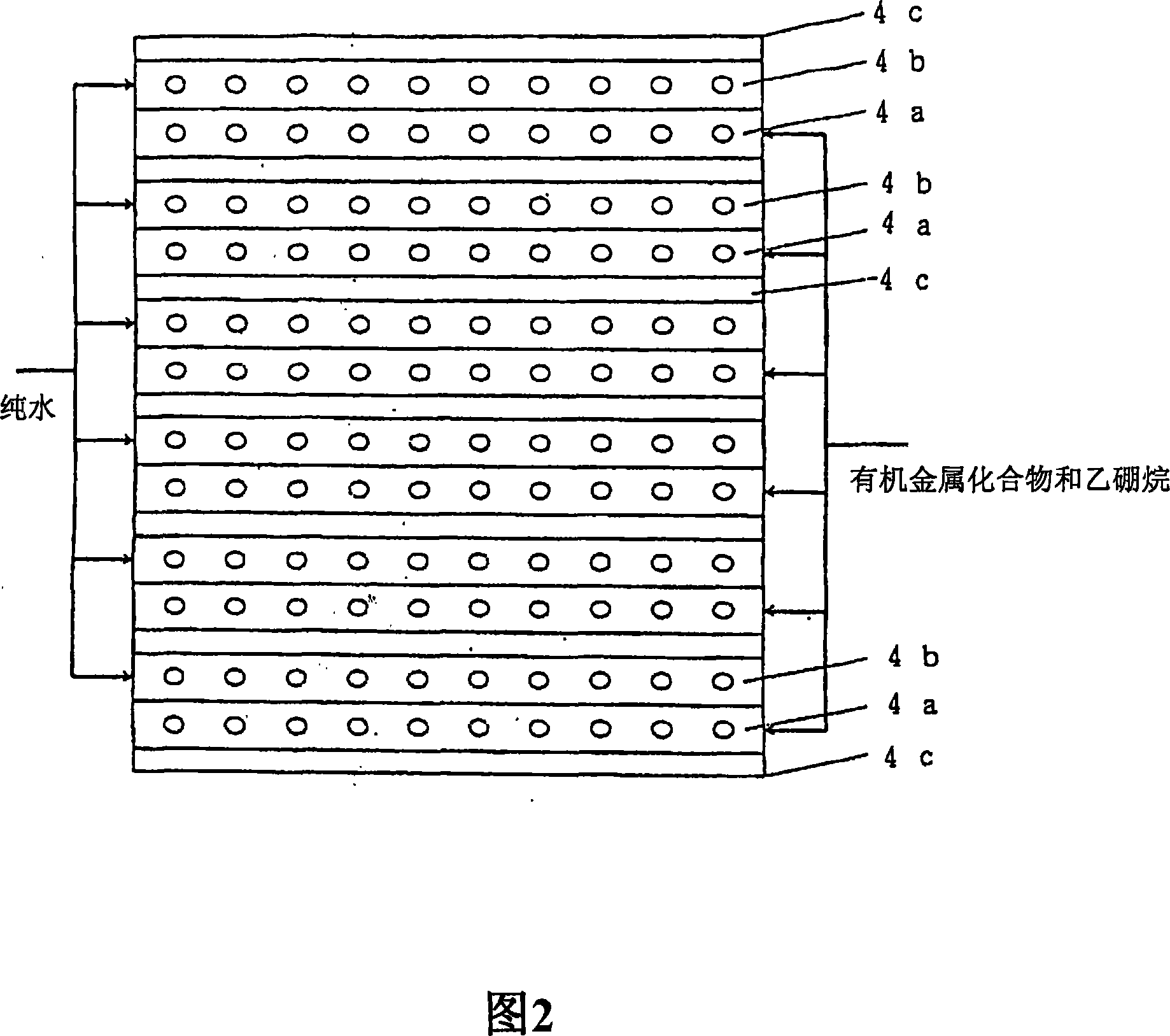
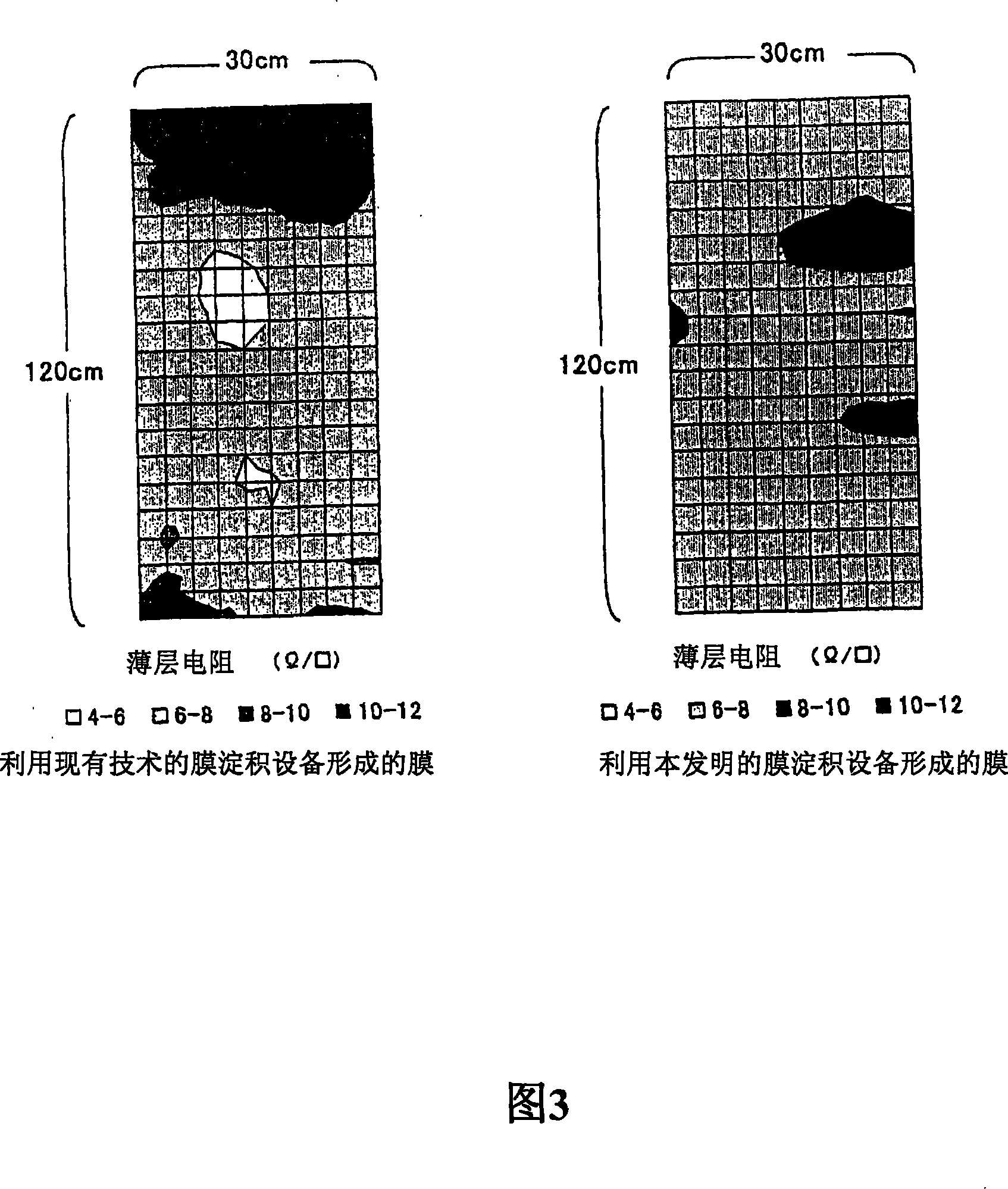
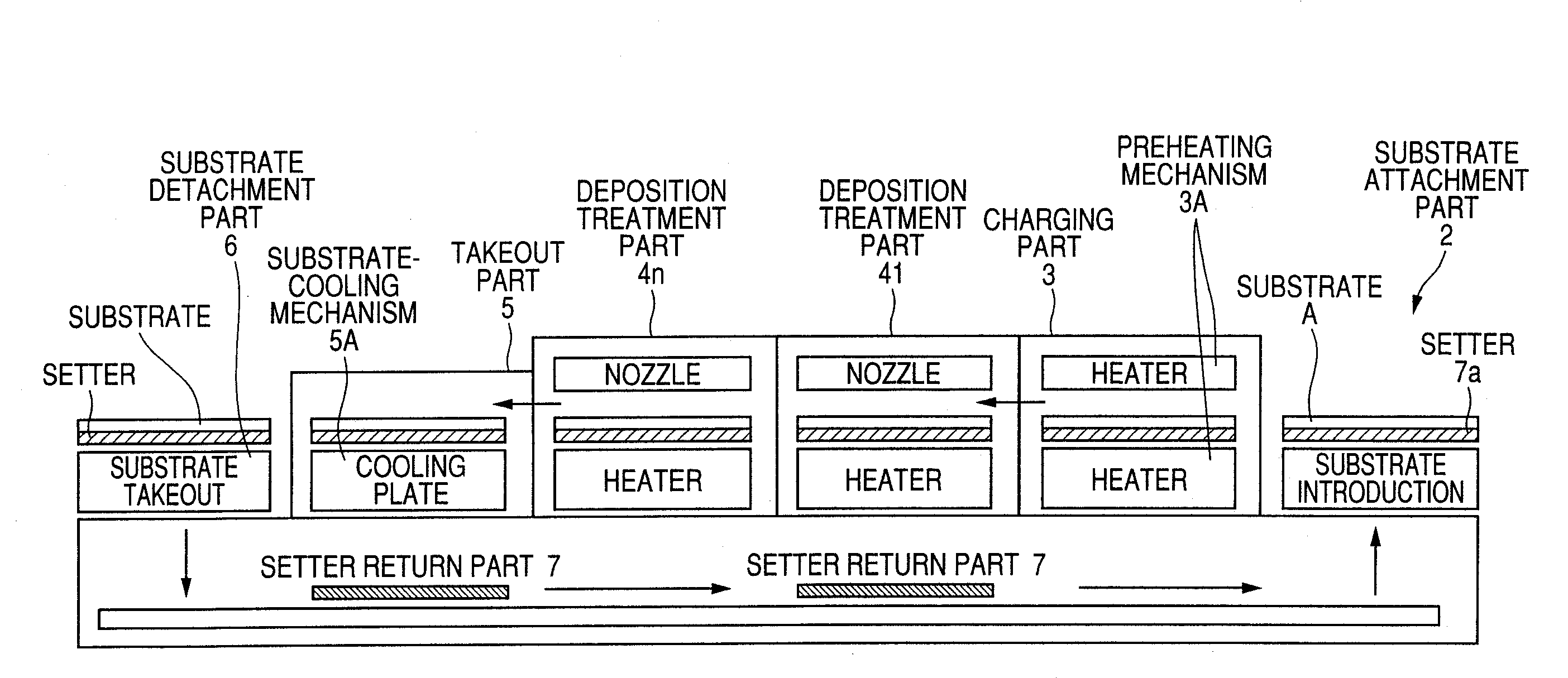
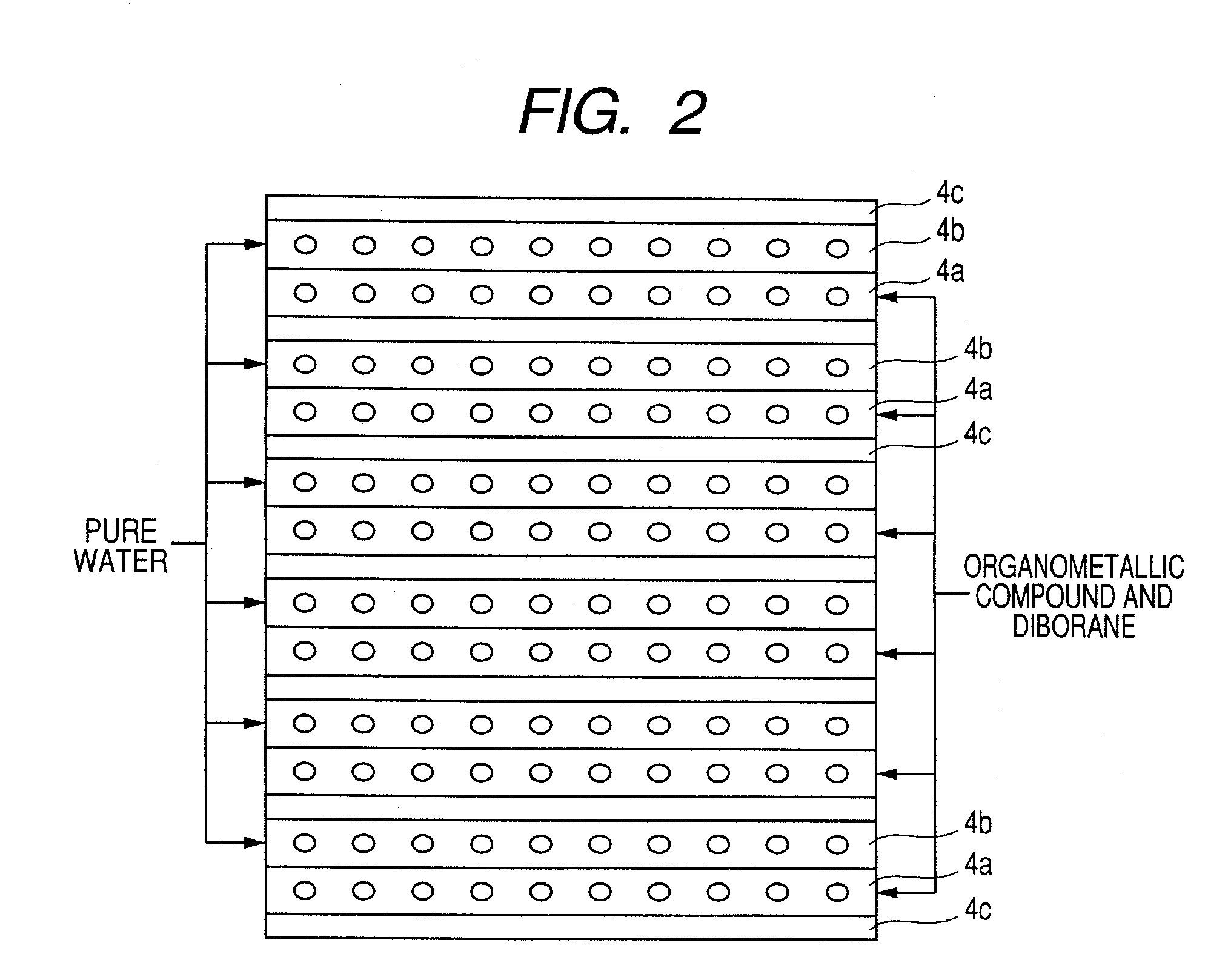
Transparent conductive film deposition apparatus, film deposition apparatus for continuous formation of multilayered transparent conductive film, and method of forming the film
InactiveUS20090203194A1Reduce necessityImprove utilization efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseTransparent conducting film
Raw materials are economized and a film deposition rate is improved while maintaining film evenness and high film quality.A film deposition apparatus for the continuous formation of a multilayered transparent conductive film is provided which comprises a substrate attachment part, a charging part where evacuation is conducted, a multilayer deposition treatment part comprising two or more deposition treatment parts for forming a transparent conductive film on a substrate by the MOCVD method by reacting an organometallic compound (diethylzinc), diborane, and water in a vapor phase, a substrate takeout part, a substrate detachment part, and a setter return part where the substrate setter is returned to the substrate attachment part. Film deposition is successively conducted while moving a substrate sequentially through the parts to form a multilayered transparent conductive film on the substrate. Each deposition treatment part is equipped with nozzles for spraying the organometallic compound, diborane, and water and with a cooling mechanism for cooling the nozzles.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Ternary polymerization catalyst of norbornene, octafluorocyclopentene and styrene and ternary polymerization method
The invention relates to a ternary polymerization catalyst of norbornene, octafluorocyclopentene and styrene and a ternary polymerization method, wherein the catalyst is prepared through a following method comprising steps of: 1) dissolving neodymium trichloride, diethyl zinc and a ligand compound in a first solvent in a dried single-mouth glass bottle under an inert gas atmosphere; 2) sealing the mouth of the bottle by a latex pipe, performing a reaction at a constant temperature of 40-60 DEG C for 20-30 min to prepare a neodymium / zinc complex catalyst; 3) according to a ratio of 1:1:1, adding a norbornene monomer, an octafluorocyclopentene monomer and a styrene monomer into a high-pressure kettle which is vacuumized for several times and is filled with nitrogen, and adding a second solvent to dissolve the raw materials; 4) adding the neodymium / zinc complex catalyst, and carrying out a reaction at 20-90 DEG C for 0.1-6 MPa for 1-6 h; and 5) washing a reaction product to obtain a terpolymer. The raw materials of the catalyst are low in cost and are easy to obtain. The catalyst can generate catalytic activity at a low temperature and is high in catalytic efficiency. A product is very easy to wash and separate and the method is high in yield of the co-polymer.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method for ethylene-series random copolymer
The invention provides a preparation method for an ethylene-series random copolymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: subjecting a reaction vessel to waterless oxygen-free treatment with nitrogen in a vacuum state, then adding a solvent, ethylene, alpha-olefin, unconjugated diene and a molecular weight regulator, and carrying out uniform mixing under stirring; adding a main catalyst, a cocatalyst and an activator for polymerization; adding ethanol to terminate polymerization and then adding an antioxidant; subjecting a glue solution obtained in the previous step to desolventization, and separating glue so as to obtain the product ethylene-series random copolymer; and drying the product so as to obtain dry glue, wherein the dry glue contains 0.8 to 1 wt% of the antioxidant; the main catalyst is alcohol-modified vanadium oxytrichloride; the cocatalyst is a mixture of aluminum diethyl monochloride and triethyldialuminum trichloride; the molecular weight regulator is diethyl zinc or hydrogen; the solvent is aliphatic alkane, cycloalkane or an aromatic compound; the activator is ethyl trichloroacetate; and the antioxidant is 2,6-di-t-butyl-p-cresol.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Norbornene, vinyl ethyl ether and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether ternary copolymerized catalyst and ternary copolymerizing method
The invention relates to a norbornene, vinyl ethyl ether and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether ternary copolymerized catalyst and a ternary copolymerizing method. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: dissolving bis(cyclopentadiene) vanadium and ligand in a first solvent in a dried container at an inert gas atmosphere to obtain a mixed solution; dripping diethyl zinc into the mixed solution, and stirring for 30-60 minutes at 30-60 DEG C after dripping to obtain a vanadium-zinc complex catalyst; adding norbornene, vinyl ethyl ether and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether into an autoclave which is vacuumized for multiple times and inflated with nitrogen, adding a second solvent and dissolving; adding the vanadium-zinc complex catalyst, and reacting for 1-6 hours at certain temperature and pressure; and pouring the product obtain in reaction into a hydrochloric acid-containing alcohol solution, washing the precipitate to be neutral with alcohol, and drying in vacuum to obtain the norbornene, vinyl ethyl ether and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether ternary copolymerized catalyst.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
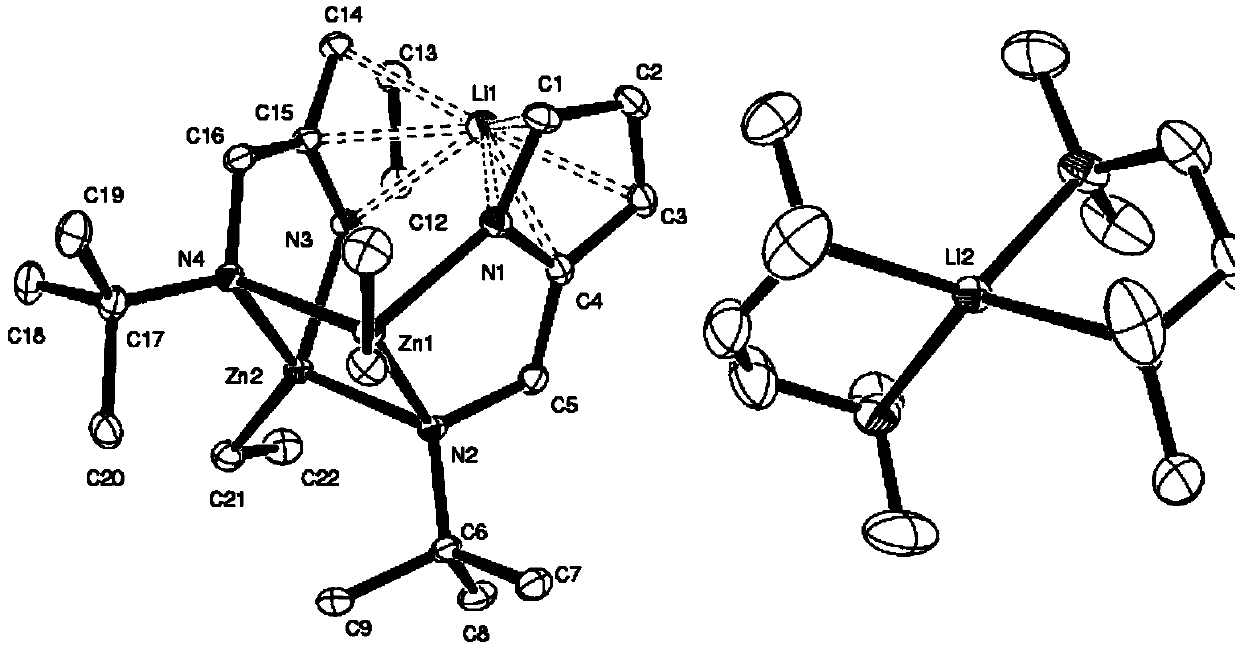
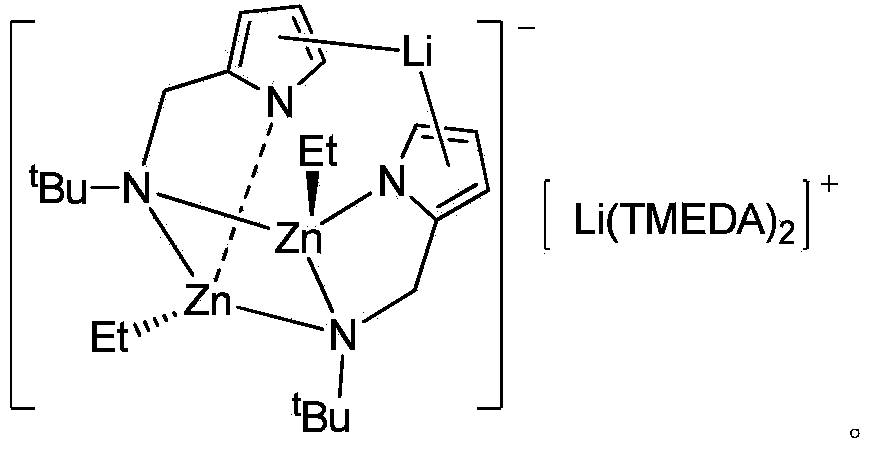
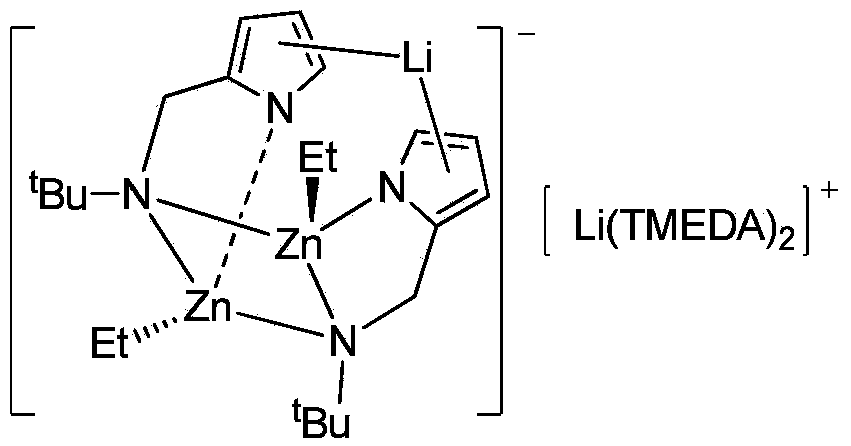
Aminopyrrole zinc-lithium bimetallic catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides an aminopyrrole zinc-lithium bimetallic catalyst, relates to lactide ring-opening polymerization, in particular to a zinc-lithium bimetallic catalyst by taking 2-tert-butyl-aminomethylpyrrole as a ligand. A preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: under protection of an inert gas and a condition of cold-water bath, using n-butyllithium to conduct lithiation on the aminopyrrole ligand, sequentially dropping diethyl zinc and TMEDA (Tetramethylethylenediamine) with equivalent amount in the obtained solution, after the reaction, filtering the reactant, carrying out vacuum concentration on the filtrate, and at last separating out colorless and transparent crystals. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple, convenient, easy to get the raw materials, mild in the reaction conditions; the obtained catalyst is of a higher catalytic activity on the lactide ring opening polymerization; the obtained polylactic acid is uniform in distribution of molecular weight, so that the catalyst is of a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Norbornene, styrene and maleic anhydride ternary polymerization catalyst and ternary polymerization method
The invention relates to a norbornene, styrene and maleic anhydride ternary polymerization catalyst and a ternary polymerization method. The norbornene, styrene and maleic anhydride ternary polymerization catalyst is characterized in that a preparation method of the catalyst comprises the steps of dissolving rhodium chloride, iethylzinc and a ligand compound into a first solvent in a single-neck glass bottle with a dry inert atmosphere, sealing the bottleneck, and keeping the constant temperature of 40-50 DEG C for 15-30 minutes to obtain a rhodium-zinc complex catalyst. The ternary polymerization method comprises the steps of adding norbornene monomers, styrenes and maleic anhydride monomers into the multiply vacuumized and dried single-neck glass bottle with the dry inert atmosphere according to the molar ratio of 1:1:1, and then, adding a second solvent to dissolve; and then, adding the rhodium-zinc complex catalyst, and reacting at the temperature of 20-90 DEG C for 1-8 hours. The catalyst provided by the invention is cheap and available in raw materials, capable of generating catalytic activity at a relatively low temperature, low in polymerization reaction temperature and high in catalytic efficiency; and in addition, the catalyst is easily washed and separated, and the yield of copolymers is high.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of surface acoustic wave filter in AlN/GAZO/self-supporting diamond film structure
InactiveCN103014653AHigh crystallinityMeet high frequencyImpedence networksChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface acoustic waveNitrogen gas
The invention belongs to the field of piezoelectric thin-film materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a surface acoustic wave filter in an AlN / GAZO / self-supporting diamond film structure. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning a self-supporting diamond film used as a substrate, sending the self-supporting diamond film into a vapor deposition reaction chamber, introducing nitrogen gas, trimethyl aluminum, trimethyl gallium and diethyl zinc into the reaction chamber to deposit a GAZO film with the thickness of 80-120nm on the substrate, introducing trimethyl aluminum to deposit an AlN thin film with the thickness of 800nm on the substrate carrying the GAZO film, cooling the inside of the vapor deposition reaction chamber to room temperature, and opening the deposition chamber to obtain the surface acoustic wave filter in an AlN / GAZO / self-supporting diamond film structure. The method provided by the invention is simple, the technique is easy to control, and the prepared piezoelectric thin-film device has the advantages of favorable uniformity and excellent acoustic speed transmission performance and can be used for manufacturing high-power high-frequency surface acoustic wave filters.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF ENG +1
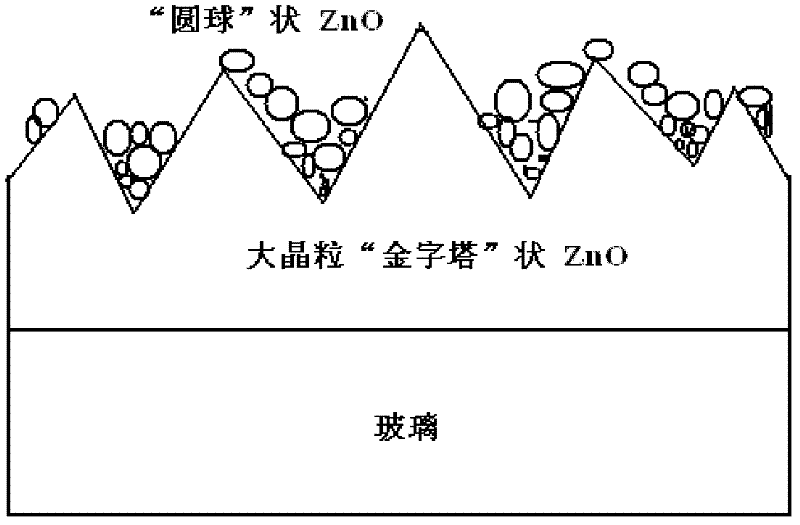
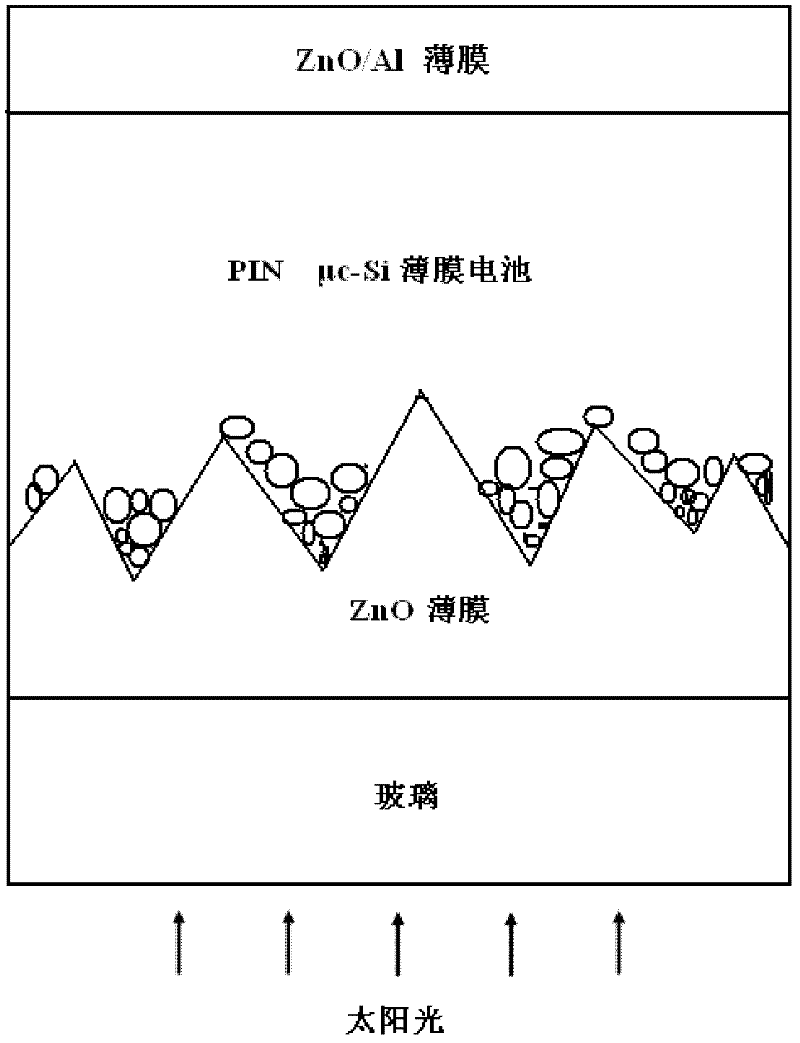
Preparation method and application of texture structure ZnO thin film on glass substrate
InactiveCN102418080AGood for light scatteringFacilitate the realization of depositionChemical vapor deposition coatingSemiconductor devicesTwo stepSilicon thin film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a texture structure ZnO thin film on a glass substrate. In the preparation method, by taking diethyl zinc and water as raw materials and taking borane (B2H6) as a doping gas, a texture structure Zno-TCO thin film is grown on the glass substrate by adopting a metal organic chemical vapor deposition method and using two specific steps of: firstly, growing a layer of a pyramid-like-shaped structure ZnO thin film with a large crystal grain size on the glass substrate; and secondly, growing a layer of round-ball-shaped ZnO thin film with a small crystal grain size on the ZnO thin film. The texture structure ZnO thin film on the glass substrate is used for a pin-type microcrystallite silicon thin film solar cell or an amorphous silicon / microcrystallite silicon laminated thin film solar cell. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process and convenience in large-area production and popularization; and by adopting a two-step method growing technology compatible with a process technique, light scattering of visible light and near-infrared region and the subsequent deposition of a silicon-based thin film are facilitated to realize and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell can be effectively improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
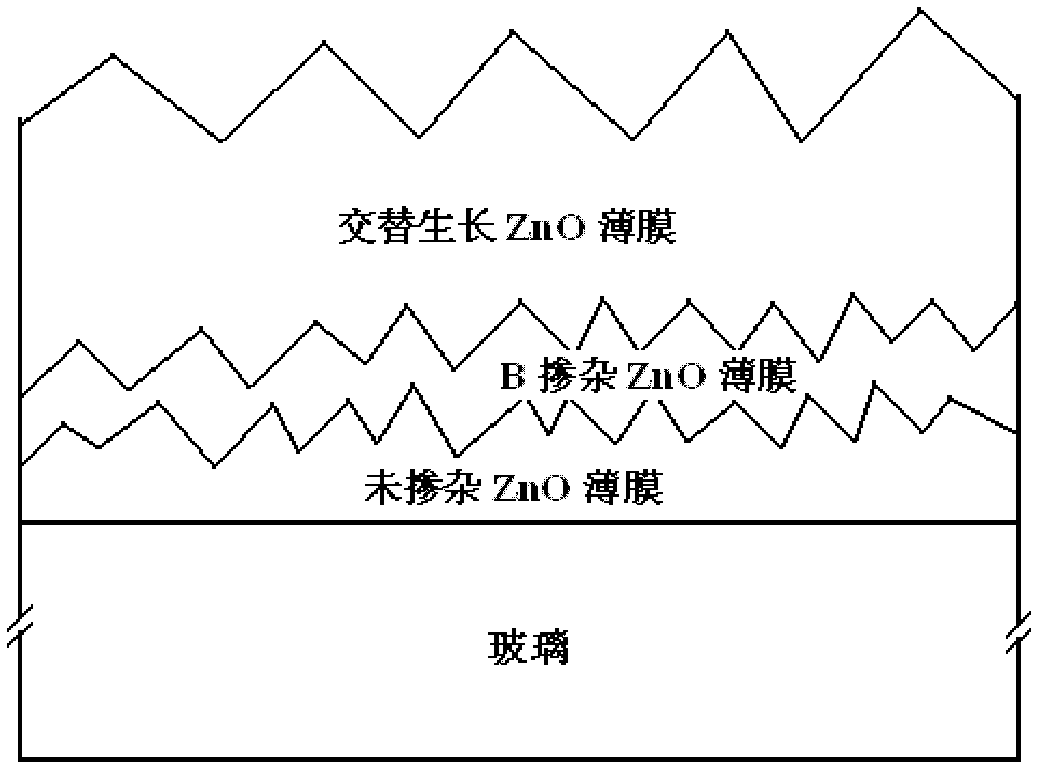
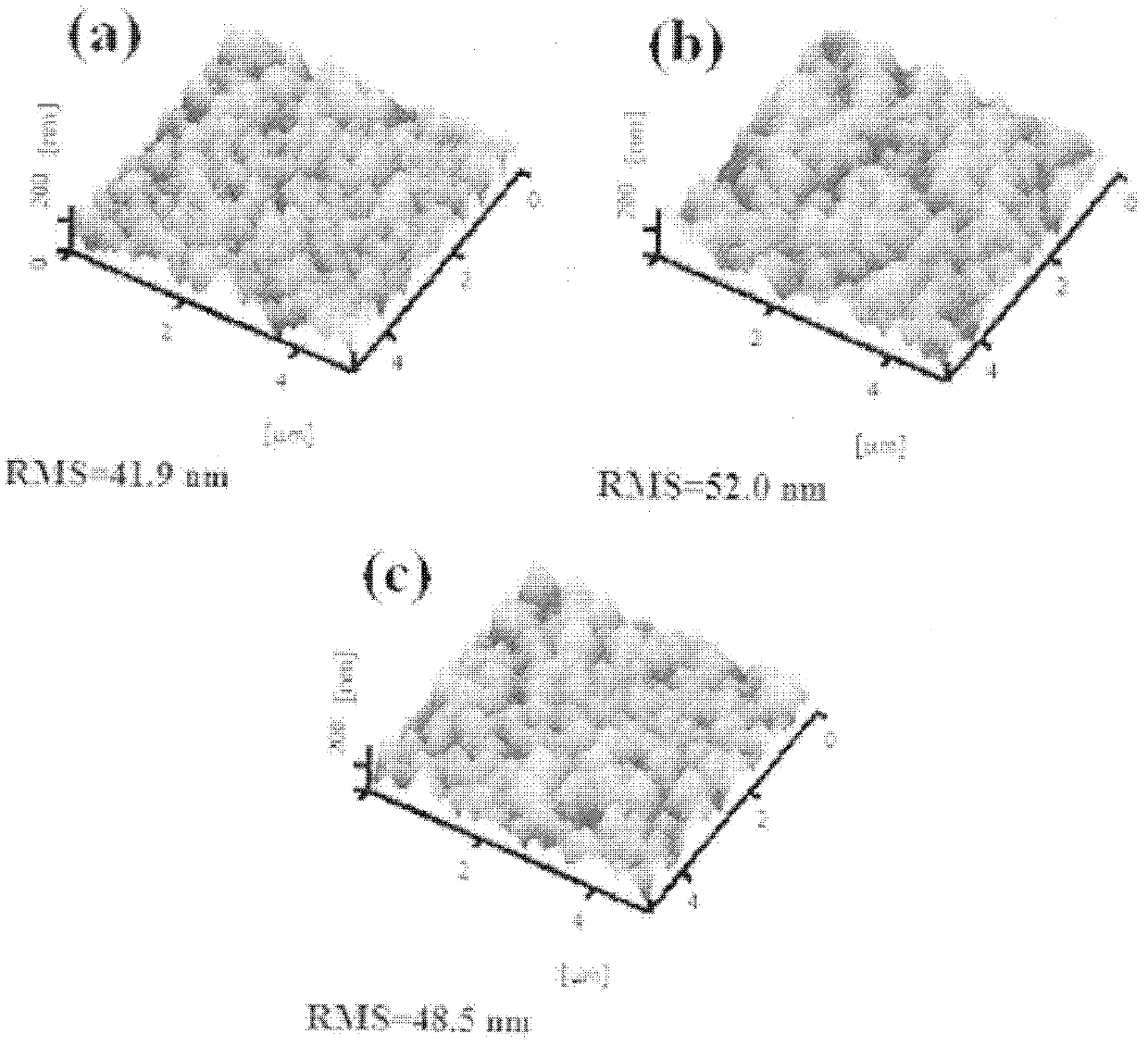
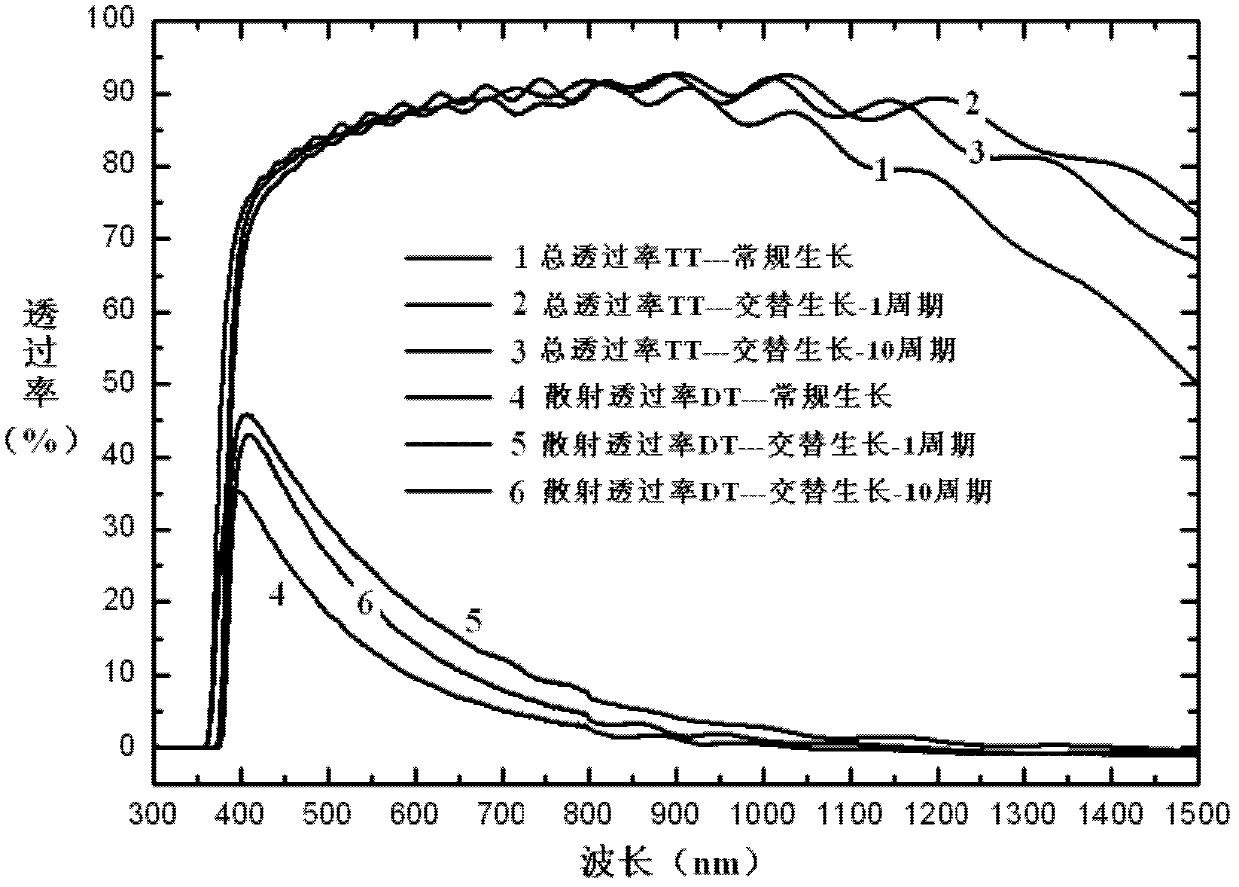
Suede-structured ZnO film prepared by alternative growth technology and application thereof
InactiveCN102433545AGood for light scatteringFacilitate the realization of depositionChemical vapor deposition coatingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenSource material
The invention provides a suede-structured ZnO film prepared by an alternative growth technology. A suede-structured ZnO-TCO (transparent conductive oxide) film is alternatively grown on a glass substrate by a metal organic chemical vapor deposition method based on diethylzinc and water as source materials and hydrogen used for diluting and doping a gas borane B2H6. The steps are as follows: 1) firstly, growing a layer of undoped ZnO film on the glass substrate; 2), then growing a B-doped type ZnO film on the undoped ZnO film; and 3) repeating the steps 1) and 2), so as to obtain a multi-layer overlapping-grown ZnO film. The suede-structured ZnO film has the advantages that the direct growth of the suede-structured ZnO film on the glass substrate can be realized by using an MOCVD (metal oxide chemical vapor deposition) technology; the preparation method has simple process, and is convenient for large-area production and popularization; through the alternative growth technology compatible to the process technology, the light scattering of visible light and neat infrared regions and subsequent deposition of a silicon-based film are facilitated; and the suede-structured ZnO film can be applied to a film solar battery, thereby effectively improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate
The invention belongs to the field of the synthesis of anti-hepatitis C virus medicines by using medical intermediates, and particularly relates to an asymmetric synthesis method of a medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate. The asymmetric synthesis method is mainly characterized in that (2R) or (2S)-1, 2-tert-butyl dicarbonate-2, 3-pyrrole alkene is used as a raw material, methylbenzene, benzene or trihalomethylbenzene is used as a solvent, diiodomethane, chlorobromomethane, dibromomethane or diethylzinc is used as a cyclopropanation reagent, and after reaction, the compound 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate is obtained. The asymmetric synthesis method has the advantages that synthesis steps are simple, the yield is high, the cost is low, the cyclopropanation reagent is wide in selectivity, the synthesis process is simple, convenient and practical, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
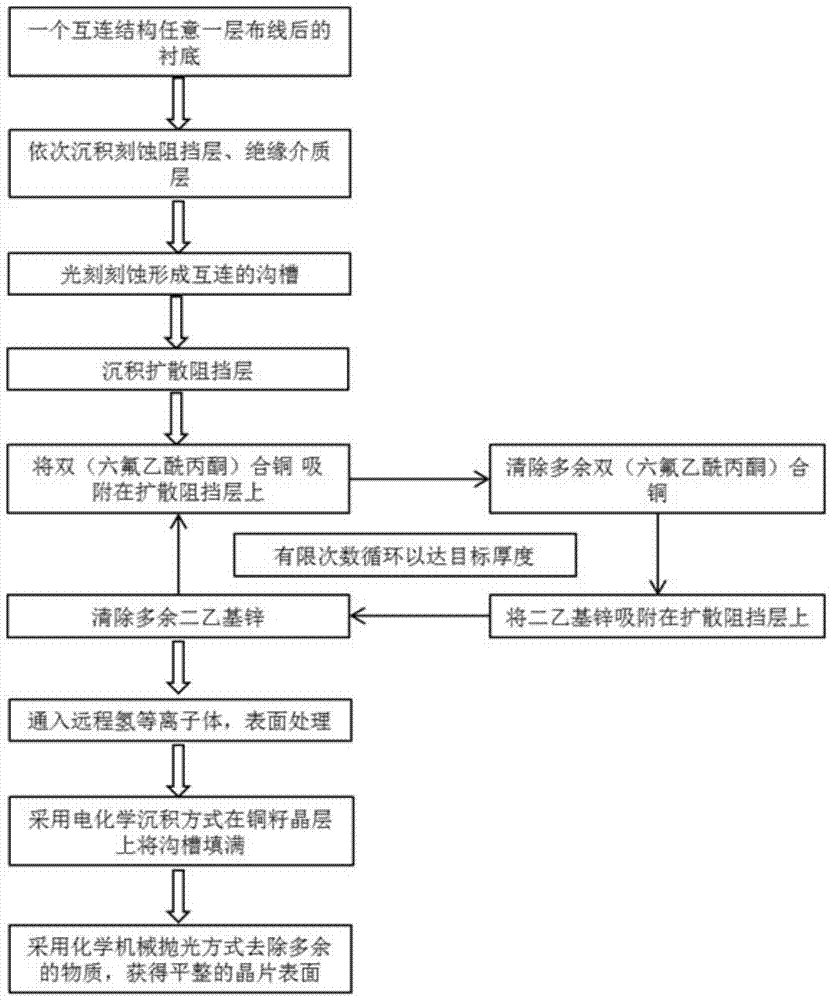
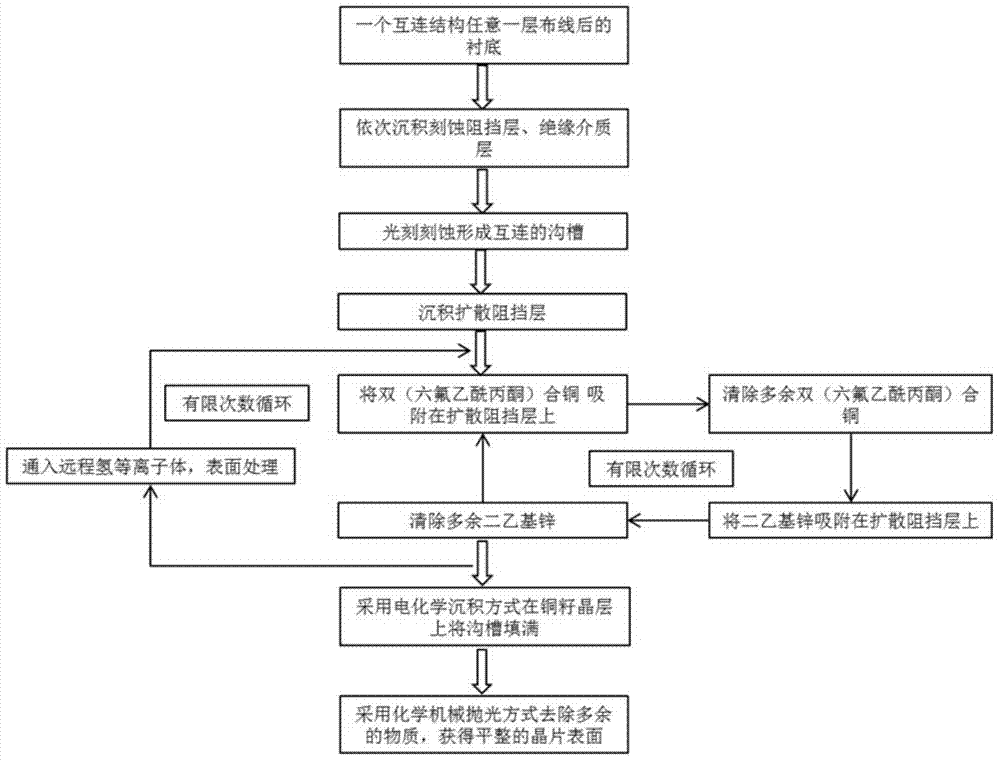
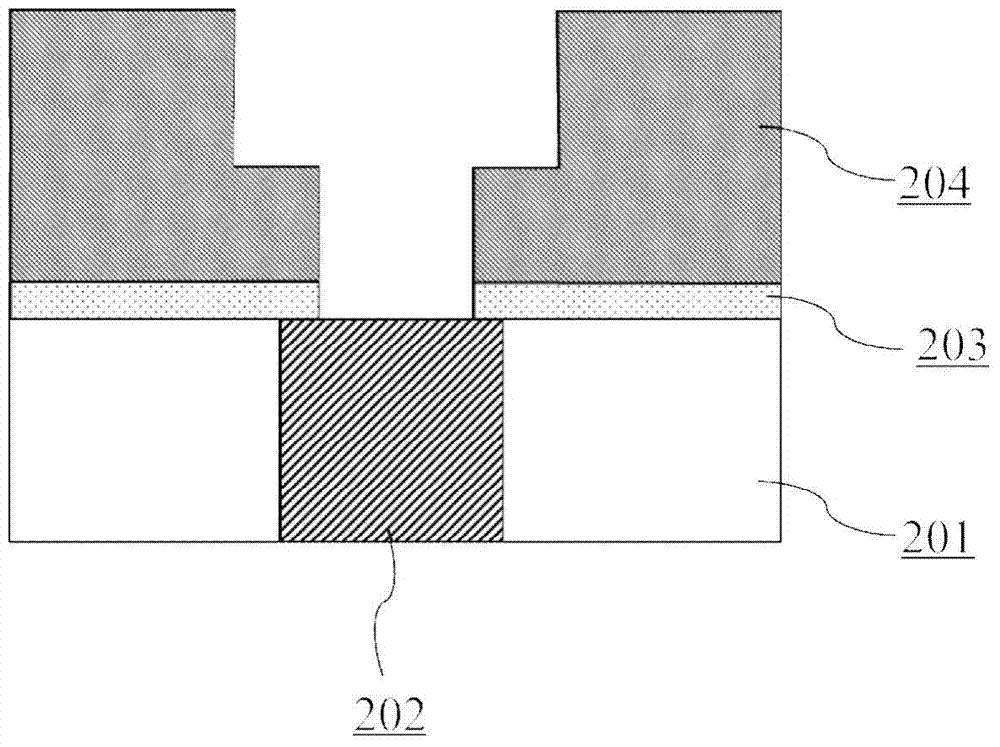
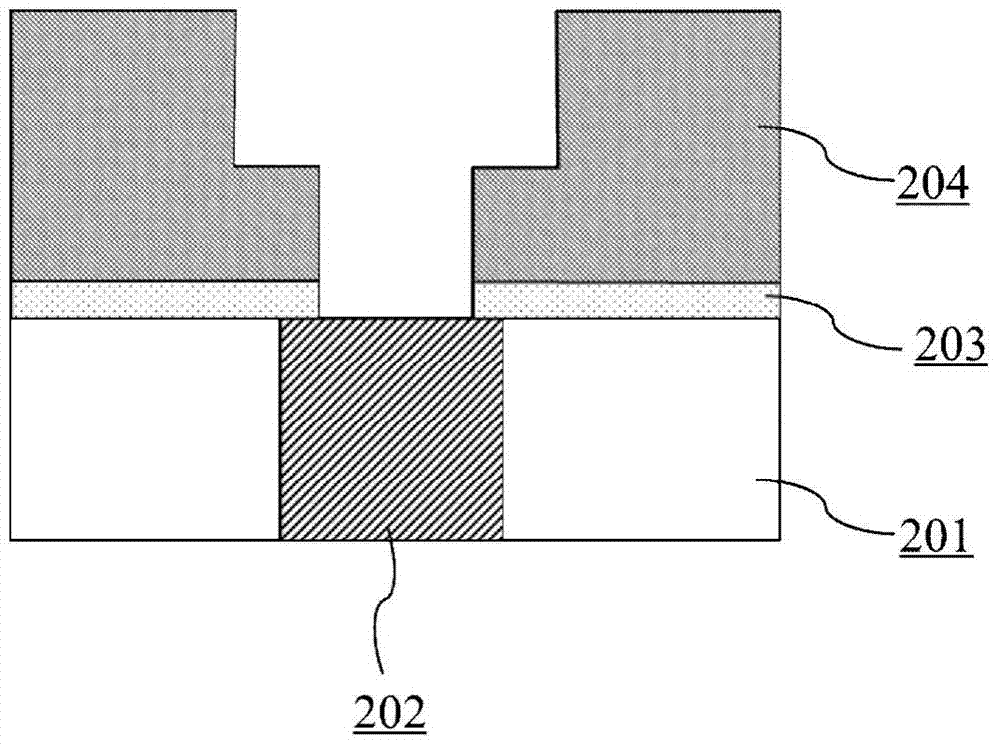
Method and application for preparing ultra-thin copper seed layer by processing surfaces of hydrogen plasmas
InactiveCN103681480AImprove performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHexafluoro-acetylacetonePhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits, specifically a method for preparing an ultra-thin copper seed layer by processing surfaces of remote hydrogen plasmas. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: absorbing bi(hexafluoro-acetylacetone) copper on a diffusion barrier layer to remove residual bi(hexafluoro-acetylacetone) copper; absorbing diethyl zinc on the diffusion barrier layer to remove residual diethyl zinc; repeating the above steps to achieve the target thickness of the ultra-thin copper seed layer; finally inputting the remote hydrogen plasmas to process the surface. With an ALD (Atomic Layer Deposition) method, the copper seed layer is grown, the thickness of the copper seed layer can be effectively controlled under lower technique temperature, and the copper seed layer has good groove filling performance; with remote hydrogen plasmas pulse, gas byproducts can be generated by reacting with impurities in a deposition film and are taken away through carrier gas, thus the quality of the deposition film is improved, the adhesion characteristic of electro-coppering and the copper seed layer is improved, and the reliability in the copper-connection application of the integrated circuits is kept.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Catalyst for catalyzing chain shuttle polymerization of ethylene and application thereof
InactiveCN102336850AReduce the impactInhibit sheddingIron organic compoundsBulk chemical productionPolymer scienceAluminoxane
The invention discloses a catalyst for catalyzing chain shuttle polymerization of ethylene and application thereof. The catalyst mainly comprises a main catalyst, a cocatalyst and a chain shuttle agent, wherein the main catalyst agent is a loaded bis(imino)pyridyl iron complex; the cocatalyst is modified methylaluminoxane; the chain shuttle agent is diethylzinc; the bis(imino)pyridyl iron complexis prepared by loading the bis(imino)pyridyl iron complex onto a modified magnesium chloride carrier; in the loaded catalyst, the molar ratio of the cocatalyst to the bis(imino)pyridyl iron complex is (100-500):1; and the molar ratio of the chain shuttle agent to the bis(imino)pyridyl iron complex is (300-800):1. When the catalyst is applied to an ethylene chain shuttle polymerization reaction, the polymerization reaction temperature can be remarkably increased, high activity is kept at the temperature 50-70 DEG C, the molecular weight of a polyethylene product is increased, and ethylene and terminal group-functionalized ethylene with narrow molecular weight distribution can be obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Chiral dinaphtholsiloxane derivatives and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101121725AEasy to take offEasy to getGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsBaylis–Hillman reactionBenzaldehyde
The invention relates to a chiral linking naphthol siloxane derivative connected by the 6, 6-propylamine amide methyl and the preparation method. The invention is characterized in the structural formula; therein, R is chosen from the - CH2OCH3,-CH3, -C12H25 or - C16H33. After the later graft or copolycondensation to be loaded on the mesoporous silicon dioxide, the chiral linking naphthol siloxane derivative provided in the invention can be used in a plurality of catalytic reactions, such as the asymmetric synthetic reaction of the diethyl zinc and the benzaldehyde, the asymmetric Baylis-Hillman reaction, and so on. Therein, the linking naphthol siloxane derivative protected by the methoxy methyl can be used to prepare the mesoporous material after the copolycondensation or the later graft to protect the easy doffing of the base groups, and can be directly used in the catalytic reaction; the linking naphthol siloxane derivative protected by the long-chain alkyl can be used as the siloxane modifying reagent and the surfactant at the same time to prepare the complex mesoporous material. In the synthesis method of the chiral linking naphthol siloxane derivative, the raw materials are easy to access; the synthesis process is simple and easy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing conversion efficiency of thin-film solar cell
InactiveCN105047750AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess equipmentChemical vapor deposition
The invention relates to the photovoltaic field of thin-film solar cells, and provides a method for increasing the conversion efficiency of a thin-film solar cell. The thin-film solar cell includes a substrate, a back electrode, a P-type light absorption layer, an N-type buffer layer and a window layer, wherein the back electrode, the P-type light absorption layer, the N-type buffer layer and the window layer are successively deposited on the substrate. The window layer includes an intrinsic layer and a doping conducting layer, the intrinsic layer is an intrinsic i-ZnO thin film, and the doping conducting laye ris aluminum-doping ZnO: AI thin film or a boron-doping ZnO:B thin film. The intrinsic layer and the doping conducting layer both have diethylzinc or dimethylzinc acting as zinc sources and are deposited to thin films by adopting a low pressure chemical vapor deposition method. The intrinsic layer and the doping conducting layer are successively deposited on the surface of the N-type buffer layer. The solar cell prepared by the method herein has the characteristics of high conversion efficiency, low requirements for technology and devices, easy mass-production and low cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG HANERGY THIN FILM SOLAR CO LTD
Method for preparing ultra-thin copper seed crystal layer on diffusion barrier layer and application thereof
InactiveCN103579100AThickness is effectively controlledReduce contact resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIntegrated circuit manufacturingThin membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuit manufacturing, and particularly relates to a method for preparing an ultra-thin copper seed crystal layer on a diffusion barrier layer and an application thereof. According to the method, an atomic layer deposition method is used for preparing the ultra-thin copper seed crystal layer, and the method includes the following steps that Cu (C5HF6O2)2 is adsorbed on the diffusion barrier layer, and the air flow is 100-500 standard milliliter per minute; diethylzinc is adsorbed on the diffusion barrier layer, and the air flow is 100-500 standard milliliter per minute. The method has the advantages that the ALD method is adopted for growing the copper seed crystal layer, under a lower process temperature, only a film with the thickness about 0.02-1nm is formed in each growth cycle, the thickness of the copper seed crystal layer can be effectively controlled, the groove filling performance is good, the adhesion property of electroplated copper and the copper seed crystal layer is improved, the reliability of the method in the integrated circuit copper interconnection application is maintained, and the method provides an ideal interconnection technology solution to technology nodes with the thickness below 22nm.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
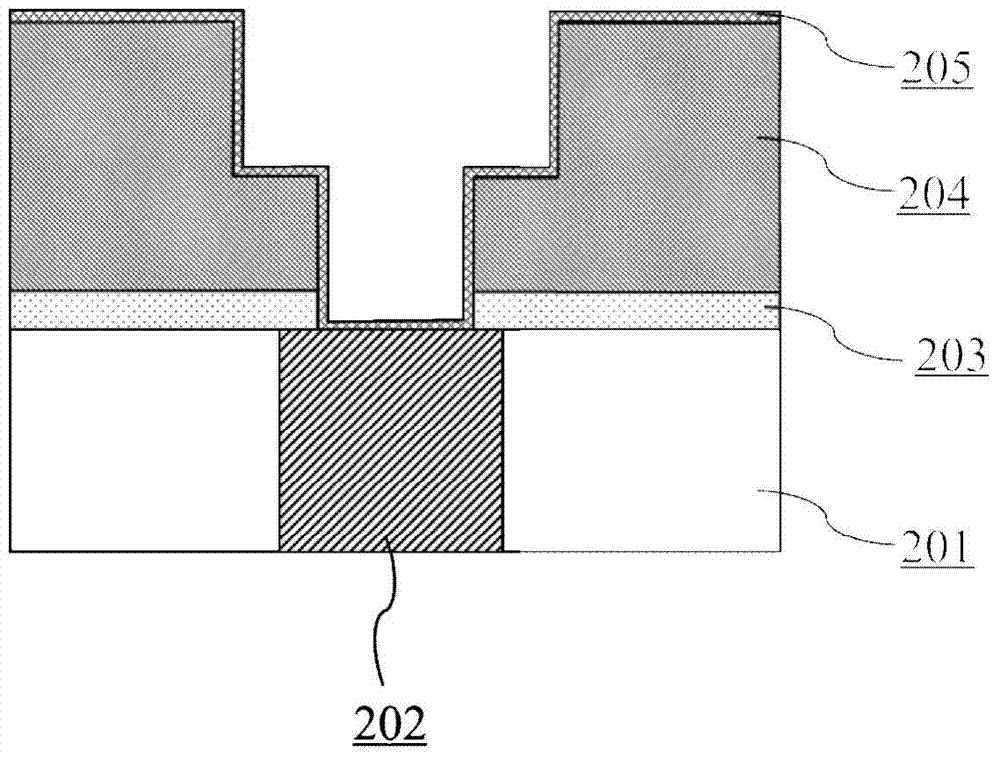
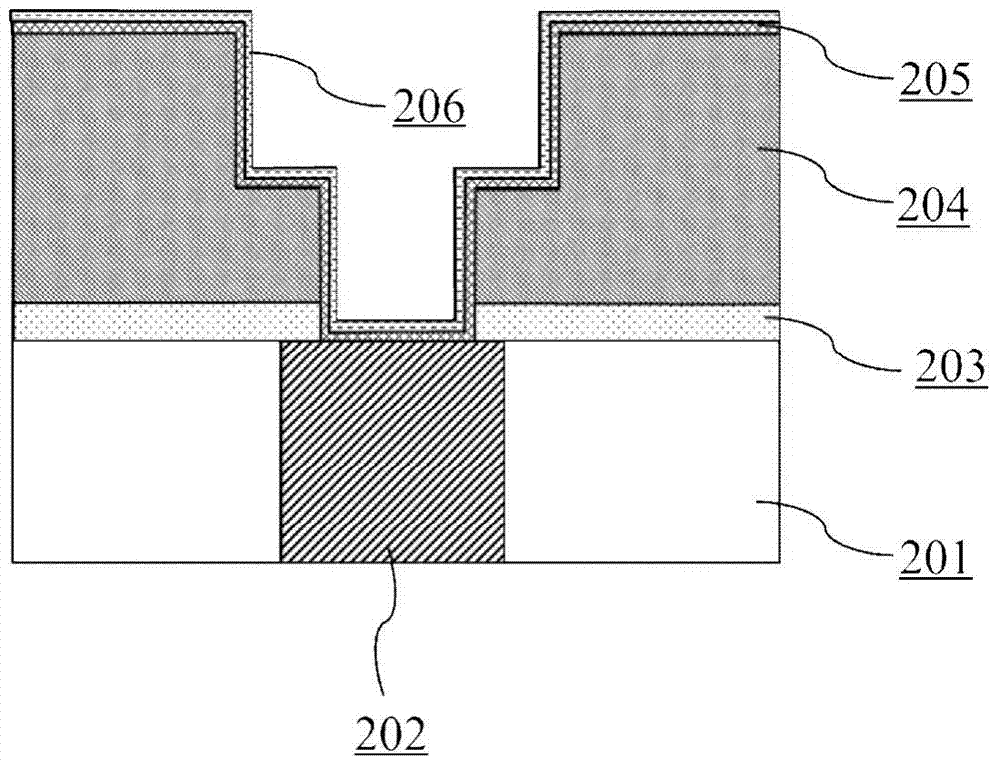
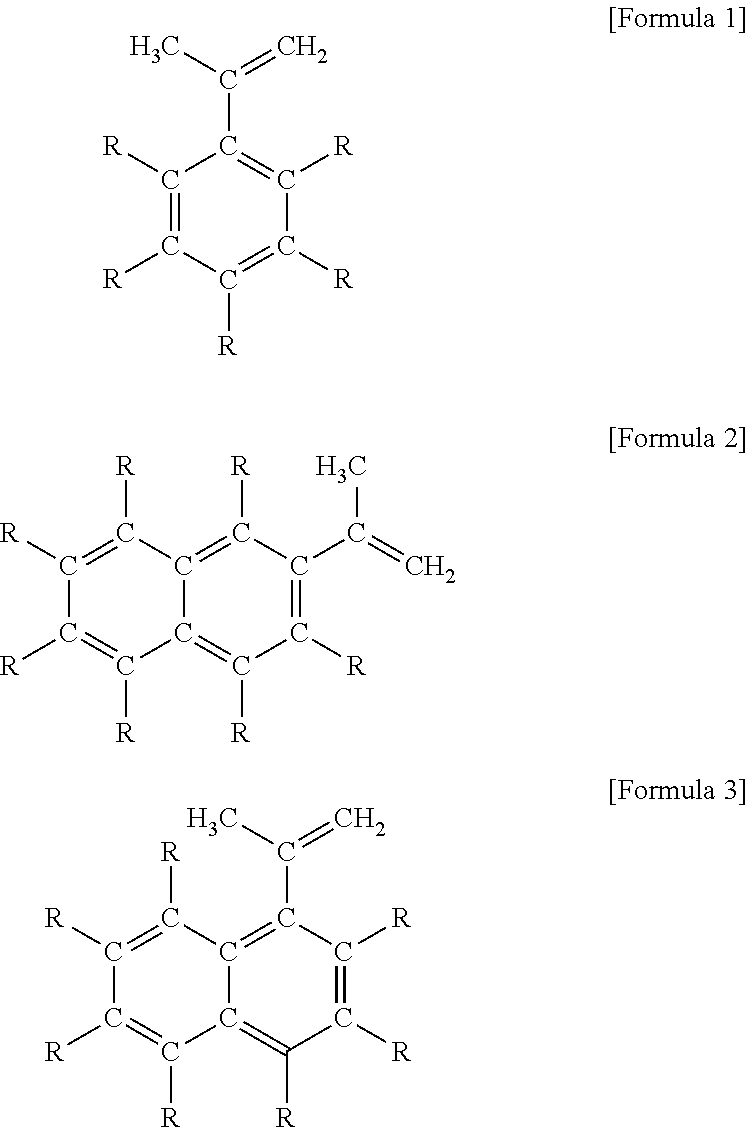
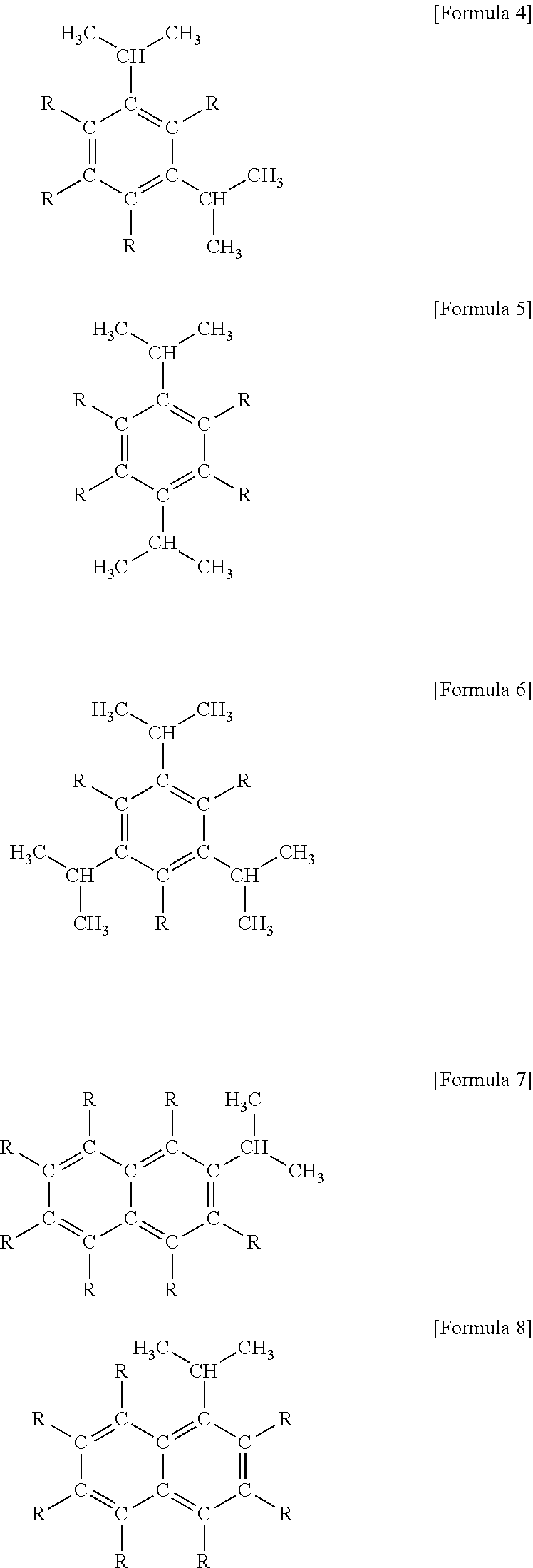
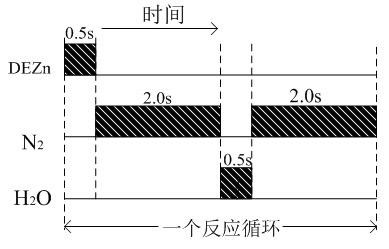
Diethylzinc composition, method for heat stabilization, and compound for heat stabilization
ActiveUS20120184432A1Improve thermal stabilityPrevent fall off in product purityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsZinc organic compoundsSide chainOrganic synthesis
[Object]To improve heat stability of diethylzinc which is used for a catalyst of polymerizing, an organic synthetic reaction reagent and a raw materials for providing a zinc film by MOCVD. And to offer the diethylzinc composition being superior in heat stability, even if it handles for a long term a metal zinc particle does not precipitate.[Solving Means]Use a diethylzinc composition added a compound which is added an aromatic compound as an additive which has isopropenyl group bonded as a side chain.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
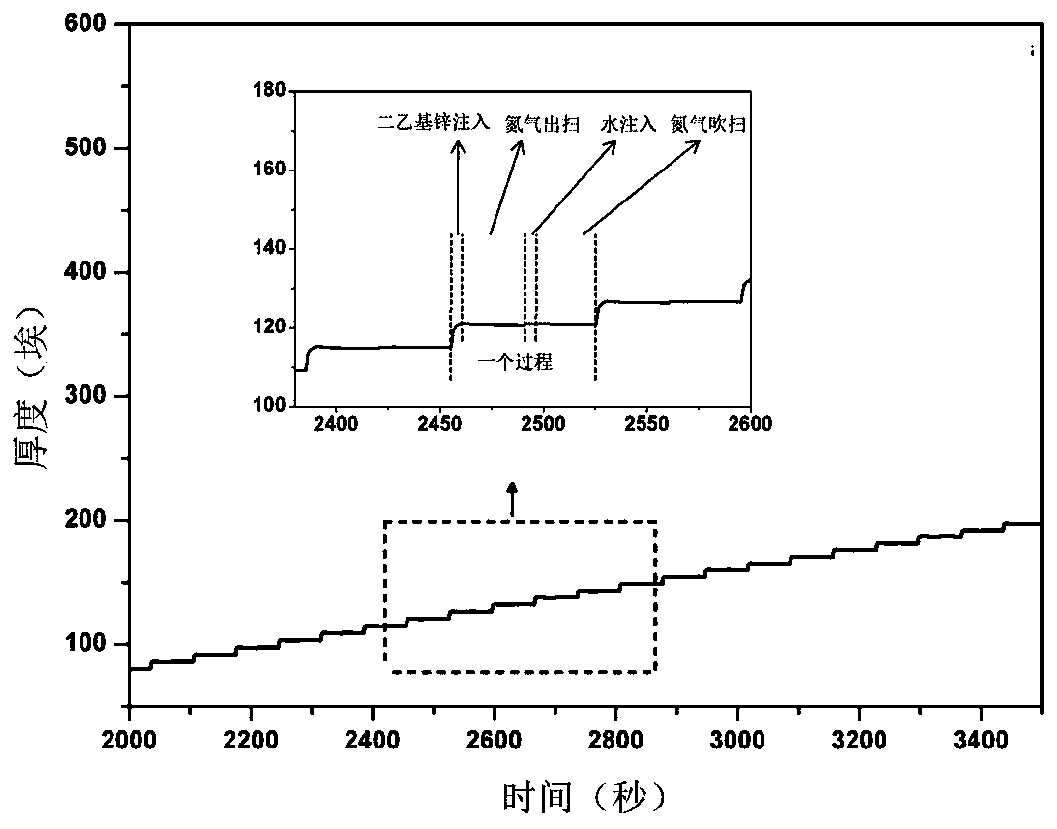
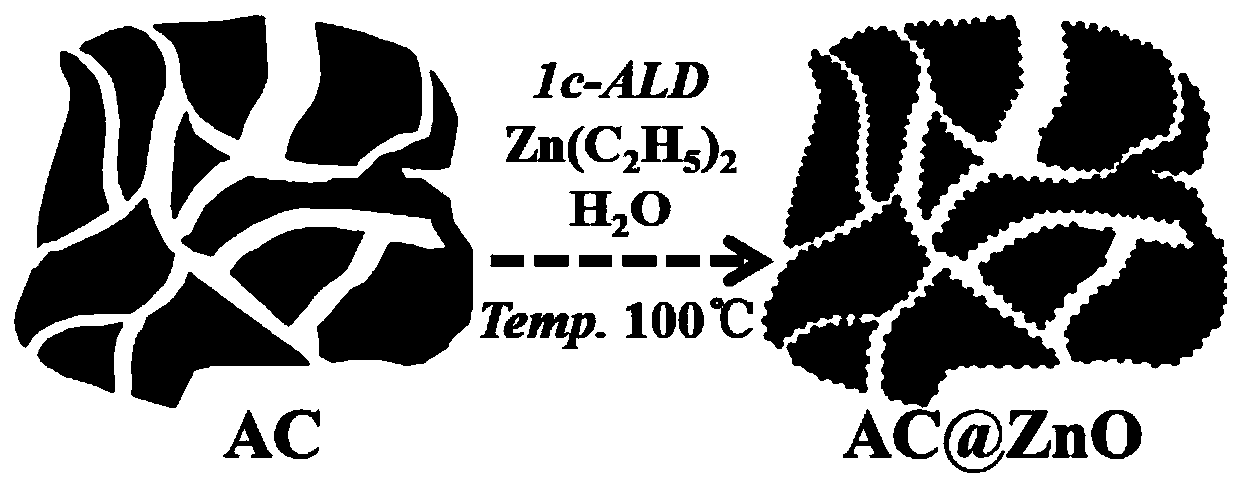
Combustion rate regulator for carbon-based zinc oxide composite propellant and low-temperature preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111499479ALower decomposition temperatureExcellent burning rate adjustment abilityChemical vapor deposition coatingNon-explosive/non-thermic compositionsChemical reactionCombustion
The invention provides a low-temperature preparation method of a combustion rate regulator for a carbon-based zinc oxide composite propellant, which mainly comprises the following steps: exposing a carbon-based substrate in diethyl zinc vapor to adsorb vapor molecules on the surface of the carbon-based substrate; blowing away part of physically adsorbed diethyl zinc molecules on the surface of thesubstrate from the surface of the substrate by using inert gas; exposing the carbon-based substrate to steam of water, so that steam molecules of the water and adsorbed diethyl zinc molecules are subjected to a chemical reaction; using inert gas for blowing away byproducts and redundant steam molecules on the surface of the substrate from the surface. The invention discloses a combustion rate regulator. Compared with a traditional combustion speed regulator and a carbon-based combustion speed regulator prepared by adopting other methods, the combustion rate regulator of the invention is excellent in combustion speed regulation capability, capable of effectively reducing the AP decomposition temperature and optimizing the energy release structure, is mild in preparation temperature, high in automation degree, good in safety performance, capable of being directly used without aftertreatment, easy to realize batch production and environmentally friendly.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Transparent conductive film forming apparatus, multilayer transparent conductive film continuously forming apparatus and method of film forming therewith
ActiveCN101107695AImprove efficiencyAvoid accumulationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransparent conducting filmEngineering
It is intended to attain an increase of film forming rate while saving raw materials and while maintaining a homogeneous high film quality. There is provided a multilayer transparent conductive film continuously forming apparatus, comprising a substrate mounting section; a charging section adapted for vacuum exhaust; a multilayer film forming treatment section including multiple film forming treatment areas capable of carrying out reaction of an organometallic compound (diethylzinc), diborane and water in a vapor phase and forming a transparent conductive film on a substrate according to the MOCVD process; a substrate ejection section; a substrate detaching section; and a setter return section capable of returning a substrate setter to the substrate mounting section, wherein while sequentially traveling the mentioned sections, a multilayer transparent conductive film is continuously formed on the substrate. Each of the film forming treatment areas is fitted with respective nozzles for injection of the organometallic compound, diborane and water and further fitted with cooling means for cooling them.
Owner:太阳能先锋株式会社
Preparation process of diethyl zinc
A process for preparing diethyl zinc includes such steps as activating and drying Zn powder, adding it along with cuporous iodide and a quarter of the mixture of iodoethane and bromoethane into reactor, adding finished diethyl zinc as trigger, heating, adding rest of said mixture, heating, stirring while reacting, vacuum distilling and collecting product at a temp lower than -35 deg.C.
Owner:大连保税区科利德化工科技开发有限公司
Ternary catalyst for preparing fatty group polycarbonate
The invention discloses a ternary catalyst for preparing fatty group polycarbonate, comprising three components of boron hydrogenation rare earth, zinc alkyls and glycerol, wherein the structure of the boron hydrogenation rare earth is M(BH4)3, and M is one of rare earth elements of Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Yb and Lu; the zinc alkyls is diethyl zinc, zinc n-propyl, zinc isopropyl, zinc normal-butyl, zinc isobutyl or zinc benzyl. The ternary catalyst has easy acquirement of raw materials, simple preparation method and low cost, the fatty group polycarbonate with the number-average molecular weight exceeding 16000 and the weight-average molecular weight exceeding 45000 can be prepared, and the carbon dioxide fixation rate exceeds 36%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
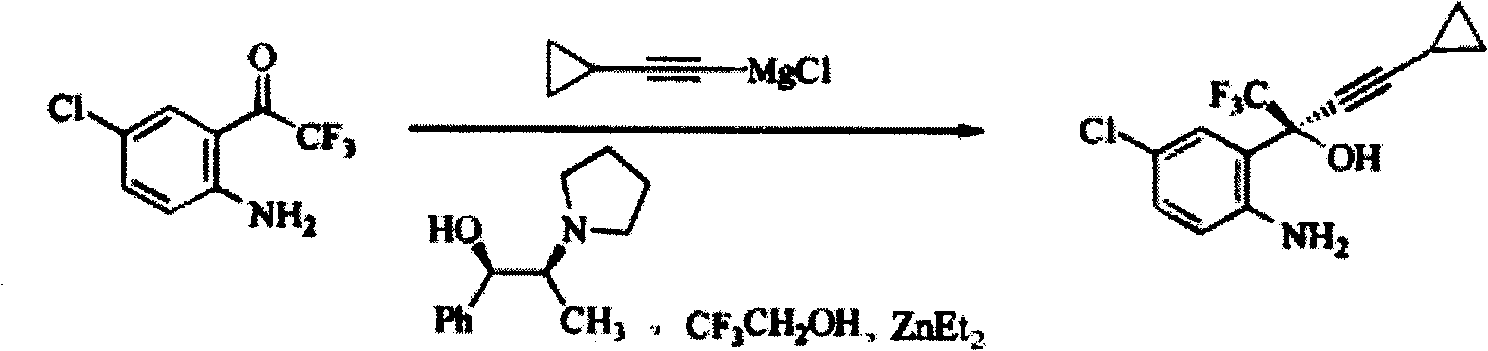







![Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1409fff9-d875-46f2-8f0b-566c63208a5f/BSA0000094785120000011.PNG)
![Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1409fff9-d875-46f2-8f0b-566c63208a5f/BSA0000094785120000021.PNG)
![Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate Asymmetric synthesis method of medical intermediate 2-azabicyclo [3. 1. 0] hexane-2, 3-tert-butyl dicarbonate](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1409fff9-d875-46f2-8f0b-566c63208a5f/BSA0000094785120000022.PNG)