Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7260 results about "Absorption layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
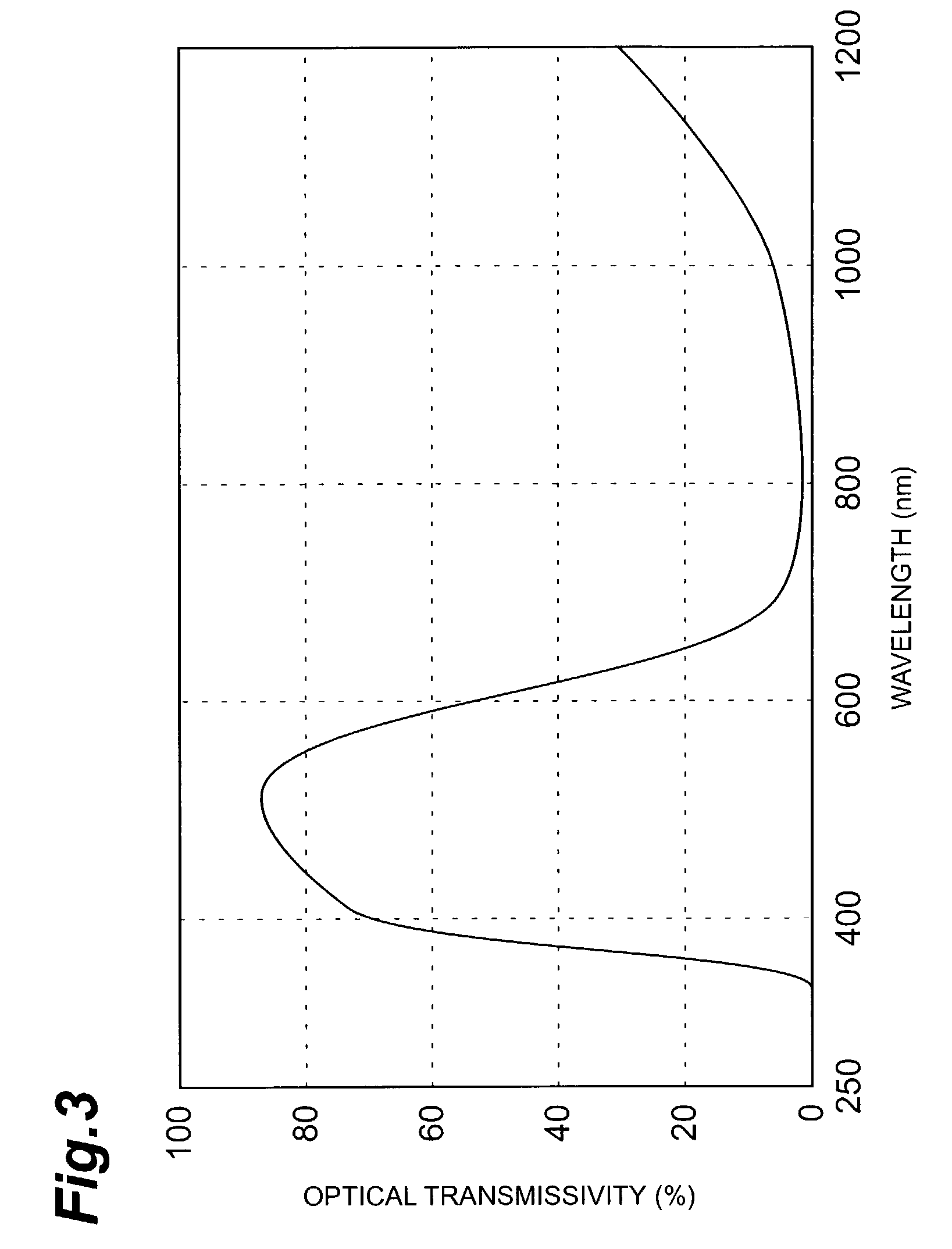
Absorption Layer Transmittance refers to the absorption of light at the transmitting surface by a given "layer", which allows further control over how specular materials appear without changing the medium's absorption properties (which is what usually creates the perceived colour).
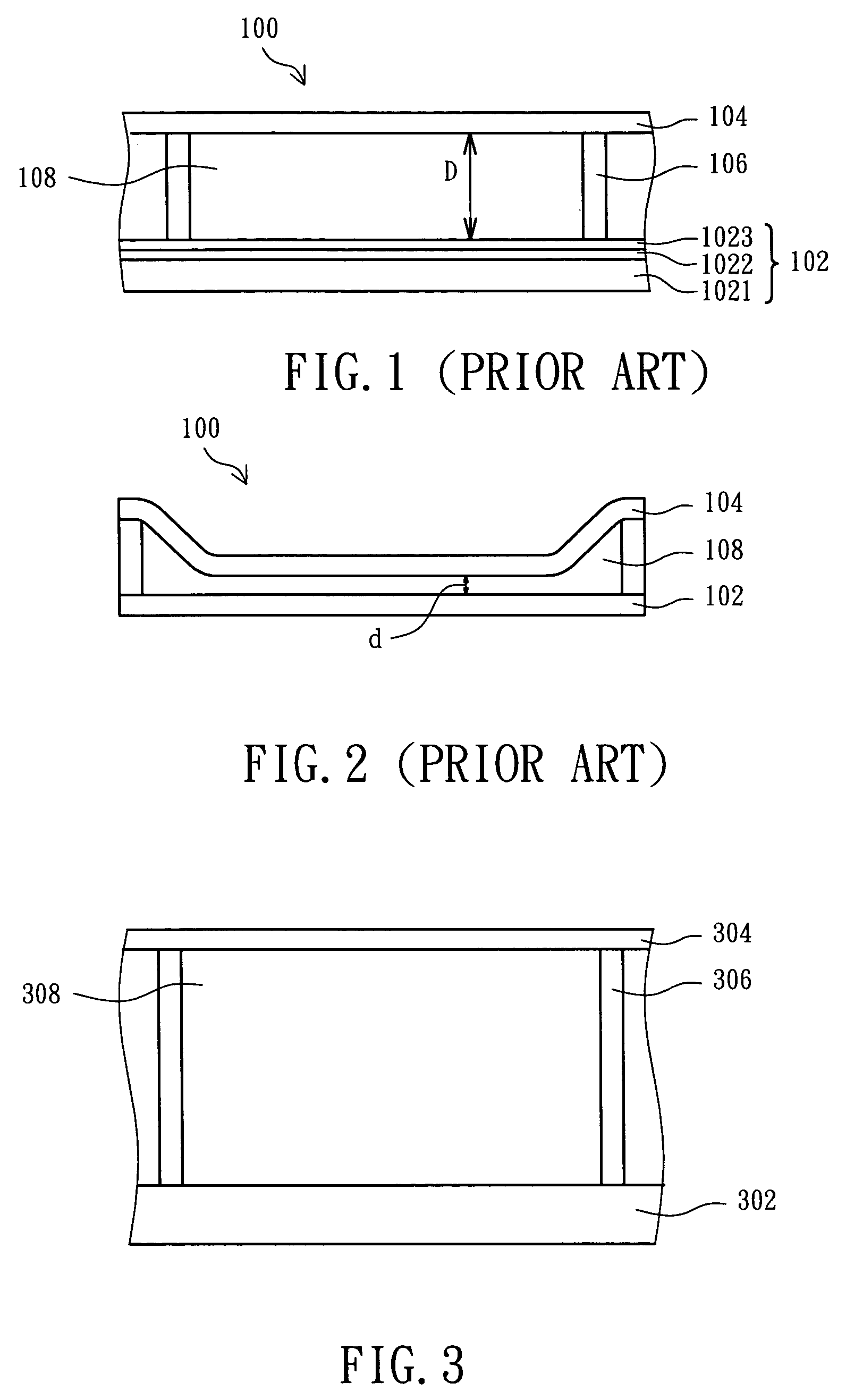
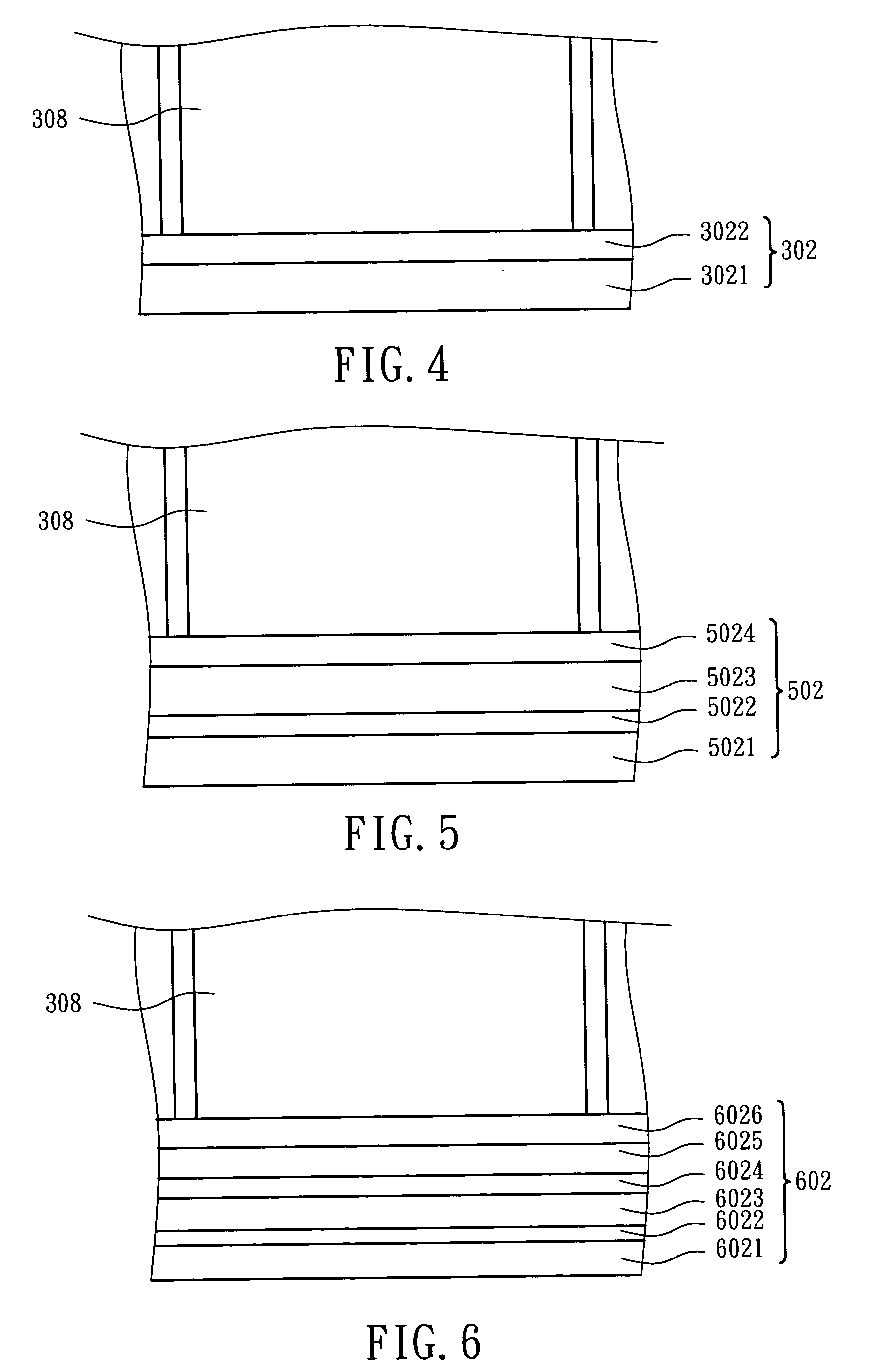
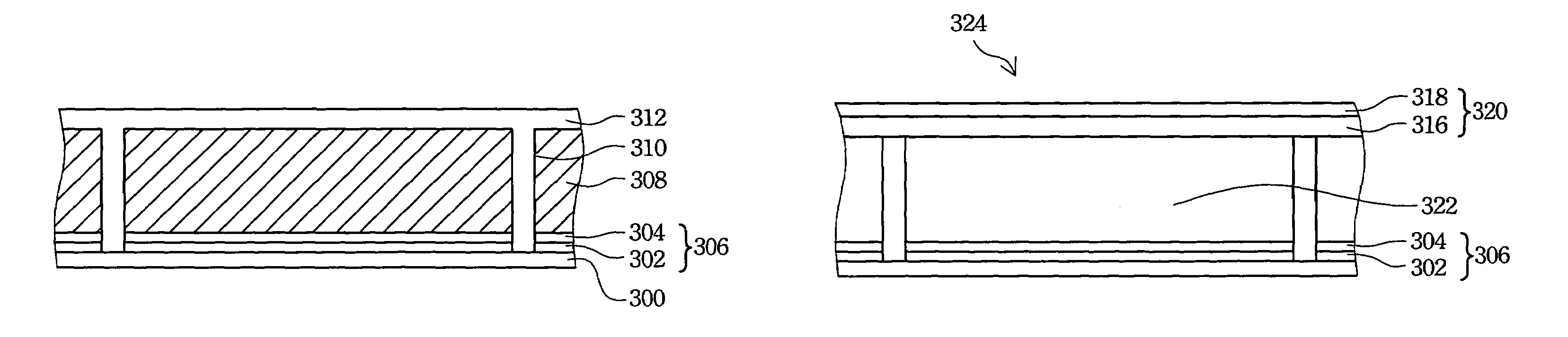
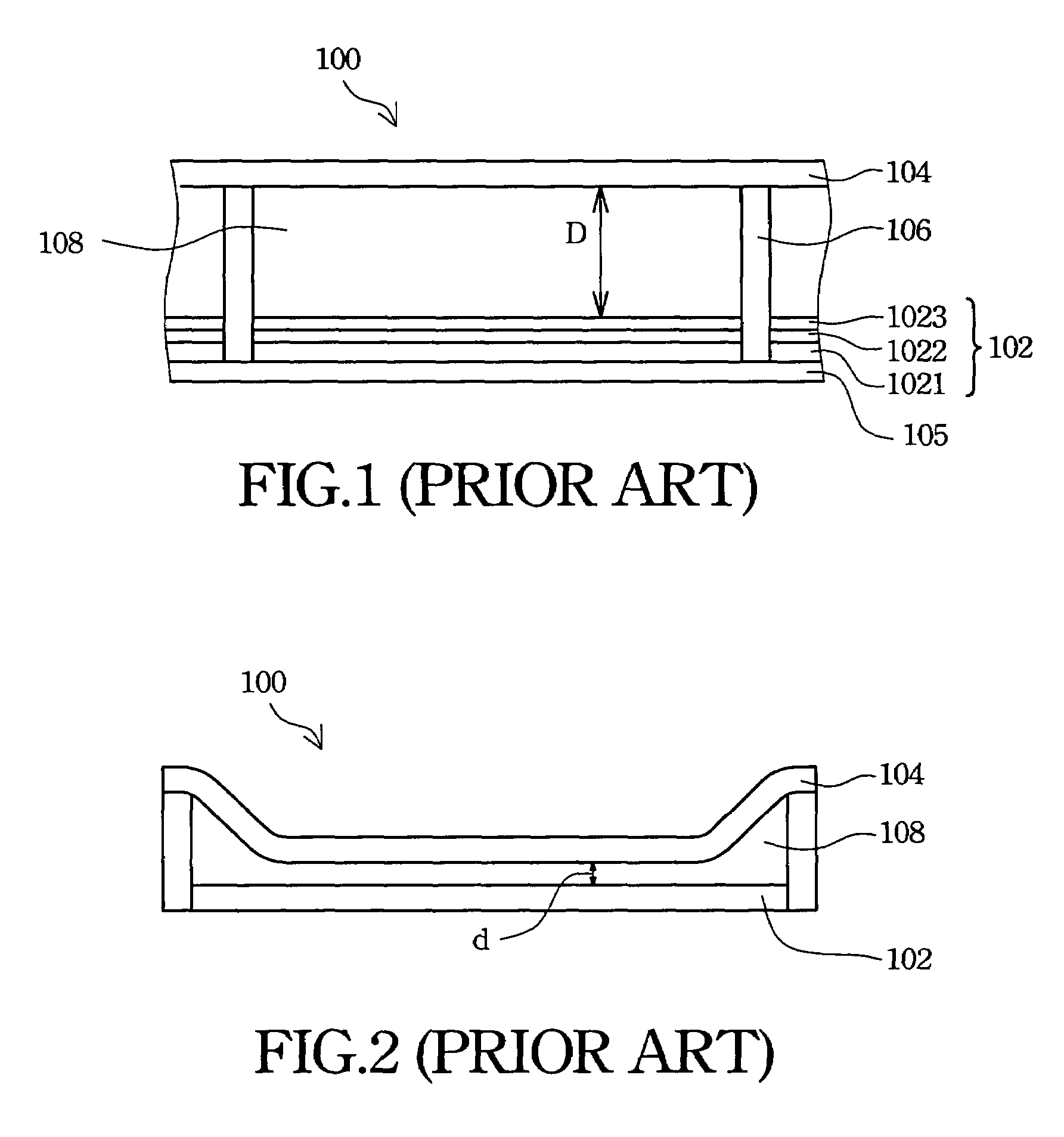
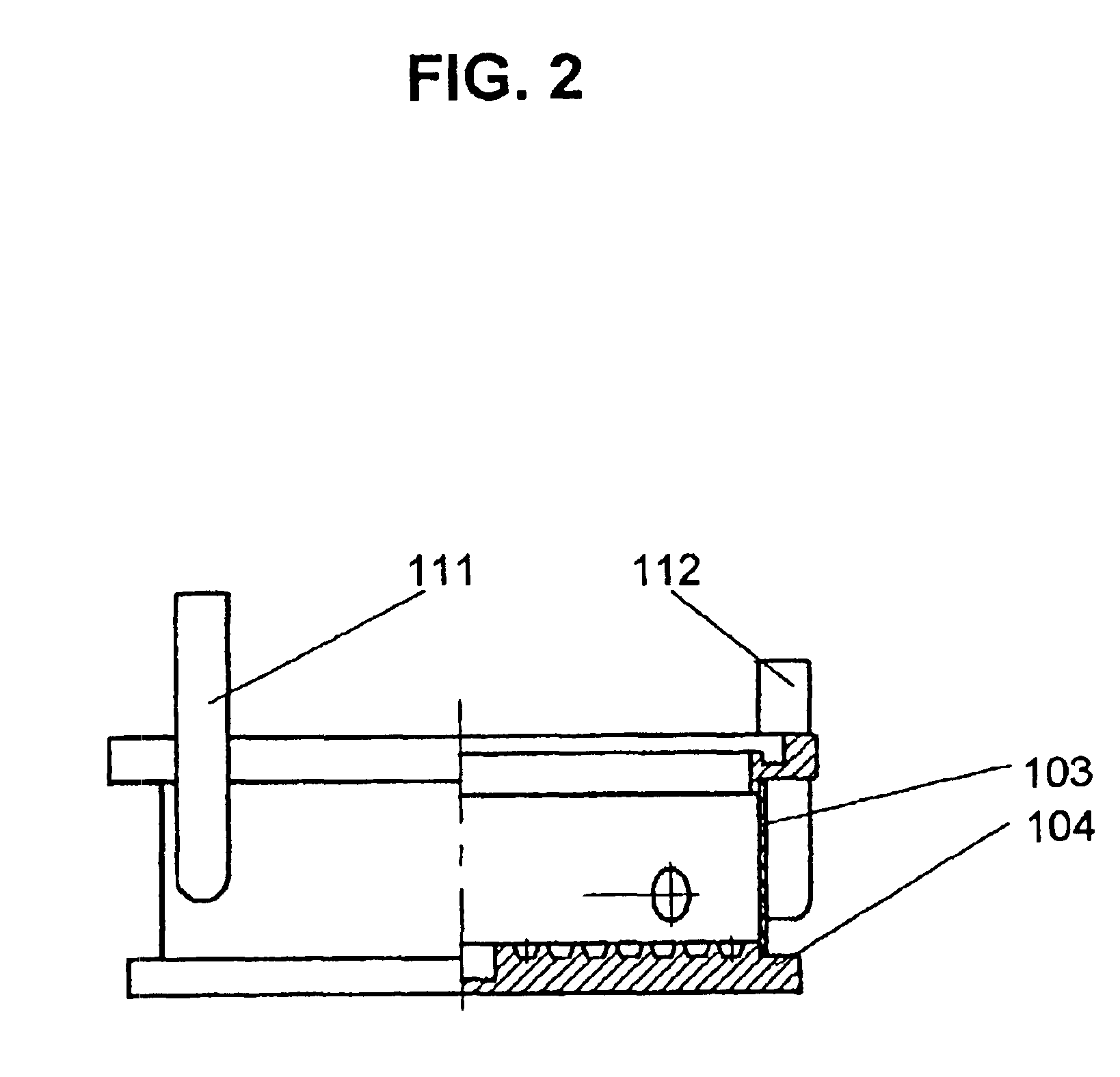
Glass substrate-holding tool
InactiveUS20120100464A1Avoid dustAvoid depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringScratching
To provide a glass substrate-holding tool which is capable of avoiding scratching to the deposition surface of a glass substrate and dusting thereby caused as well as scratching and deposition of foreign substances at a center portion of the rear surface of the substrate and which is capable of suppressing dusting from the holding tool itself at the time of forming a multi-layered reflection film and an absorptive layer.A glass substrate-holding tool having, formed on a surface of a flat base, a catching portion for catching and holding by van der Waals forces, wherein the catching portion is in contact with only the periphery of the glass substrate.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Semiconductor junction formation process including low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
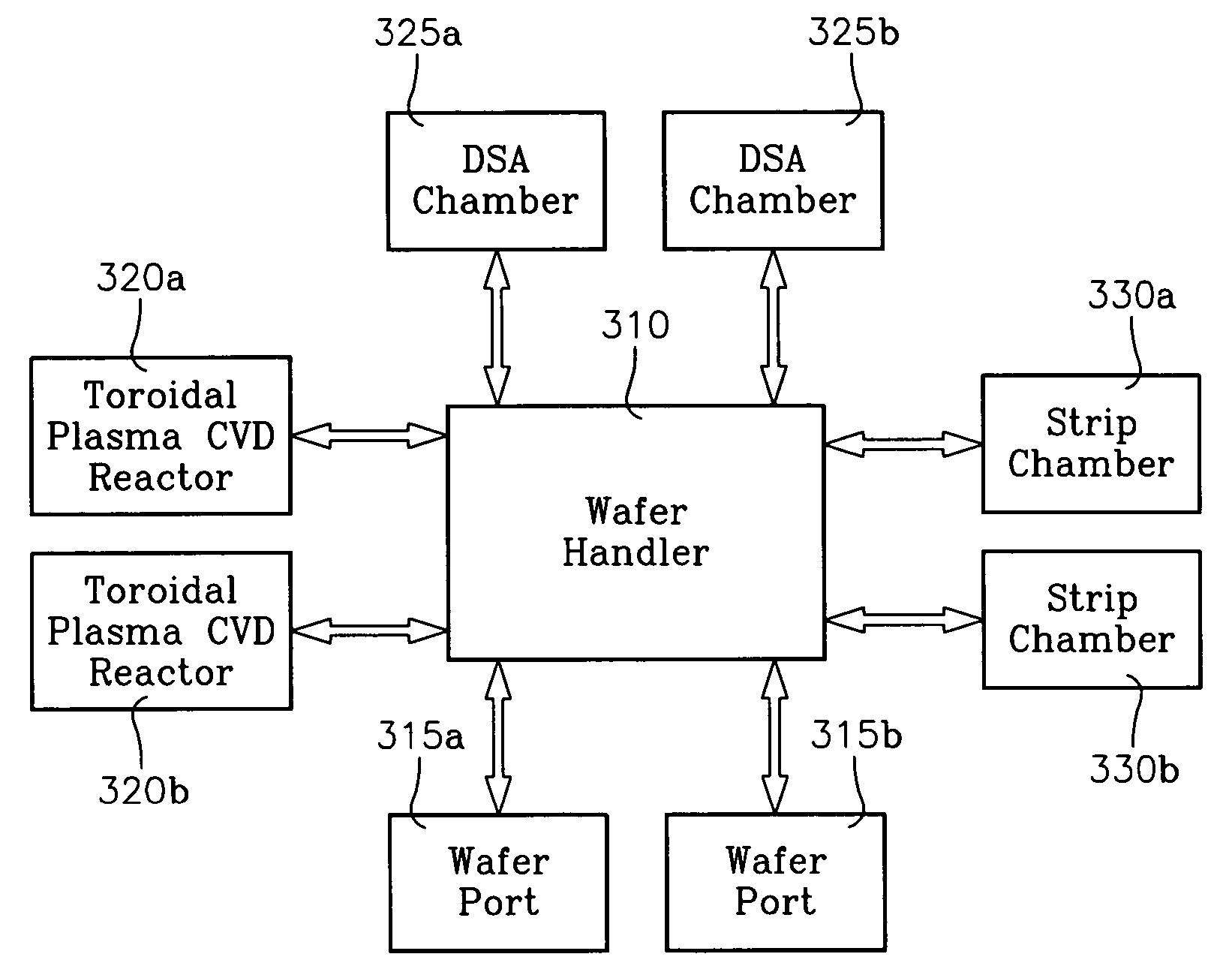
A method of forming semiconductor junctions in a semiconductor material of a workpiece includes ion implanting dopant impurities in selected regions of the semiconductor material, introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and optically annealing the workpiece so as to activate dopant impurities in the semiconductor material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Glass substrate-holding tool
InactiveUS8192901B2Avoid dustAvoid depositionPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForeign matterEngineering
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Process for low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
A method of processing a workpiece includes introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and exposing the workpiece to optical radiation that is at least partially absorbed in the optical absorber layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature absorption layer deposition and high speed optical annealing system
InactiveUS20060260545A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNuclear engineeringSemiconductor
An integrated system for processing a semiconductor wafer includes a toroidal source plasma reactor for depositing a heat absorbing layer, the reactor including a wafer support, a reactor chamber, an external reentrant toroidal conduit coupled to said chamber on generally opposing sides thereof, an RF source power applicator for coupling power to a section of said external reentrant conduit and a process gas source containing a heat absorbing material precursor gas. The integrated system further includes an optical annealing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
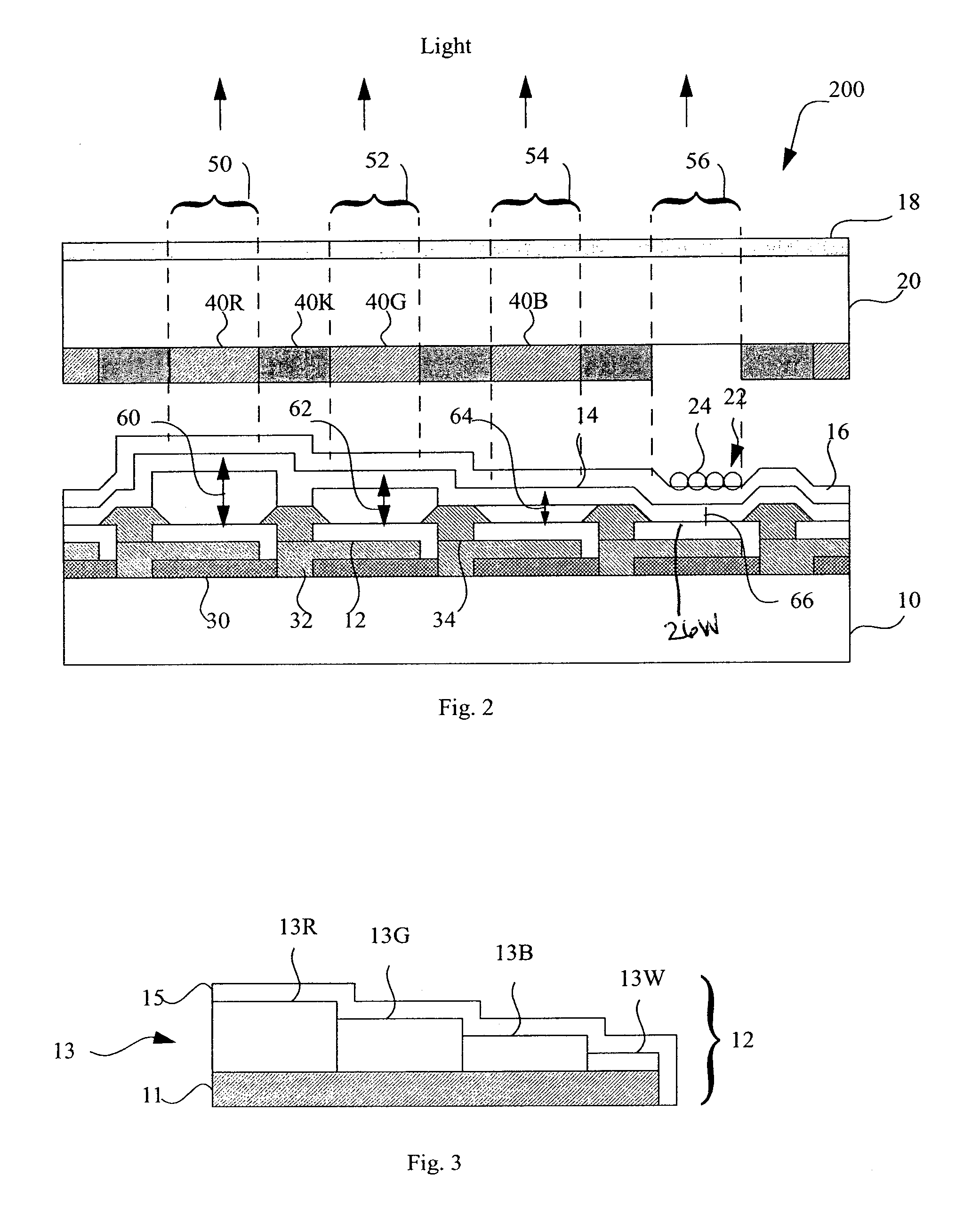
Structure of a light-incidence electrode of an optical interference display plate
InactiveUS20040175577A1Glass/slag layered productsNon-linear opticsLight reflectionMetallic materials
An optical interference display plate at least comprises a light-incidence electrode and a light-reflection electrode. The light-incidence electrode at least comprises an absorption layer and a dielectric layer. A material of the absorption layer does not comprises metallic material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Structure of an optical interference display unit
InactiveUS6958847B2Avoid pollutionIncreased process complexityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight reflectionReflective layer
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS20070032095A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorEngineering
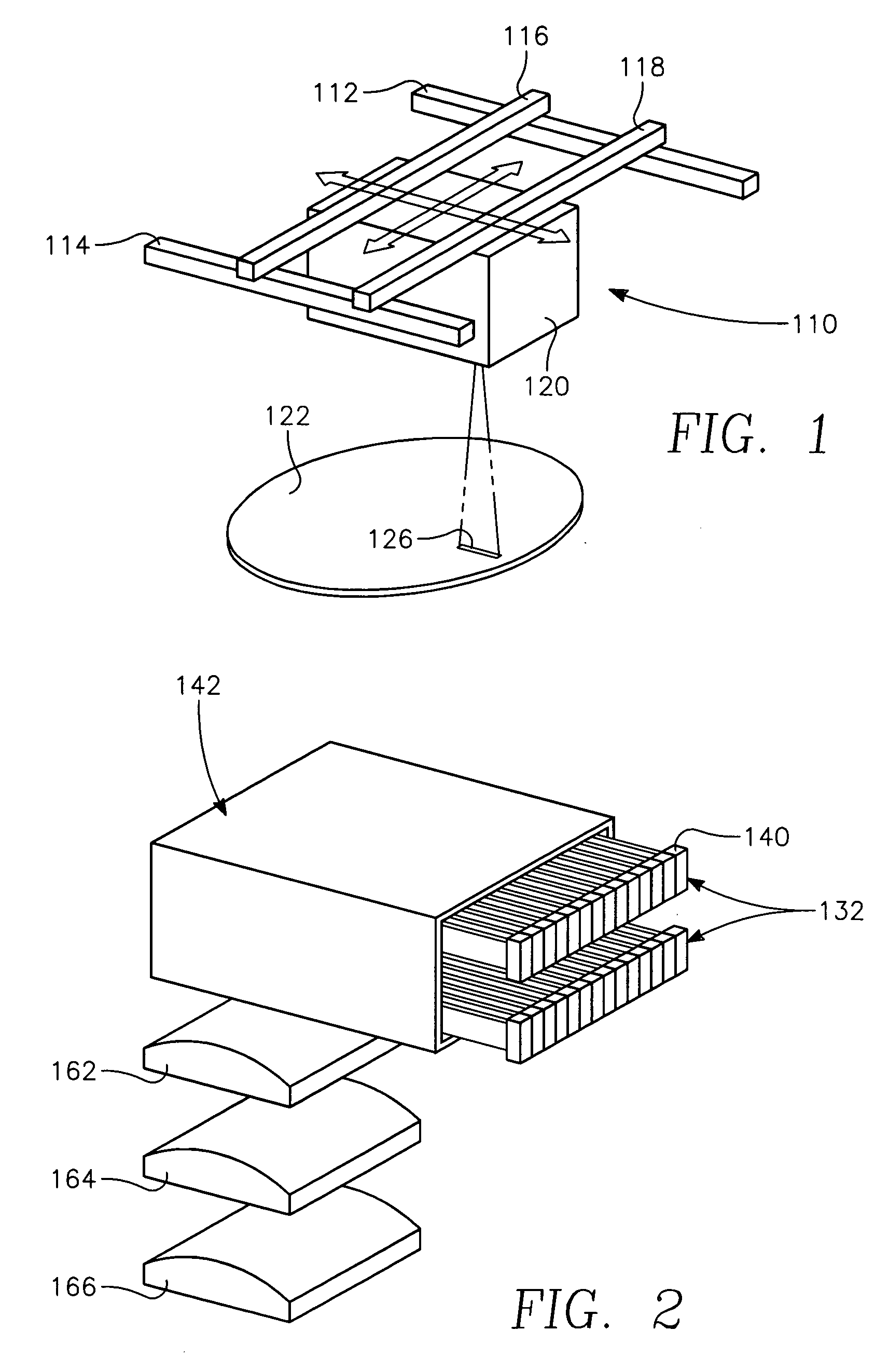
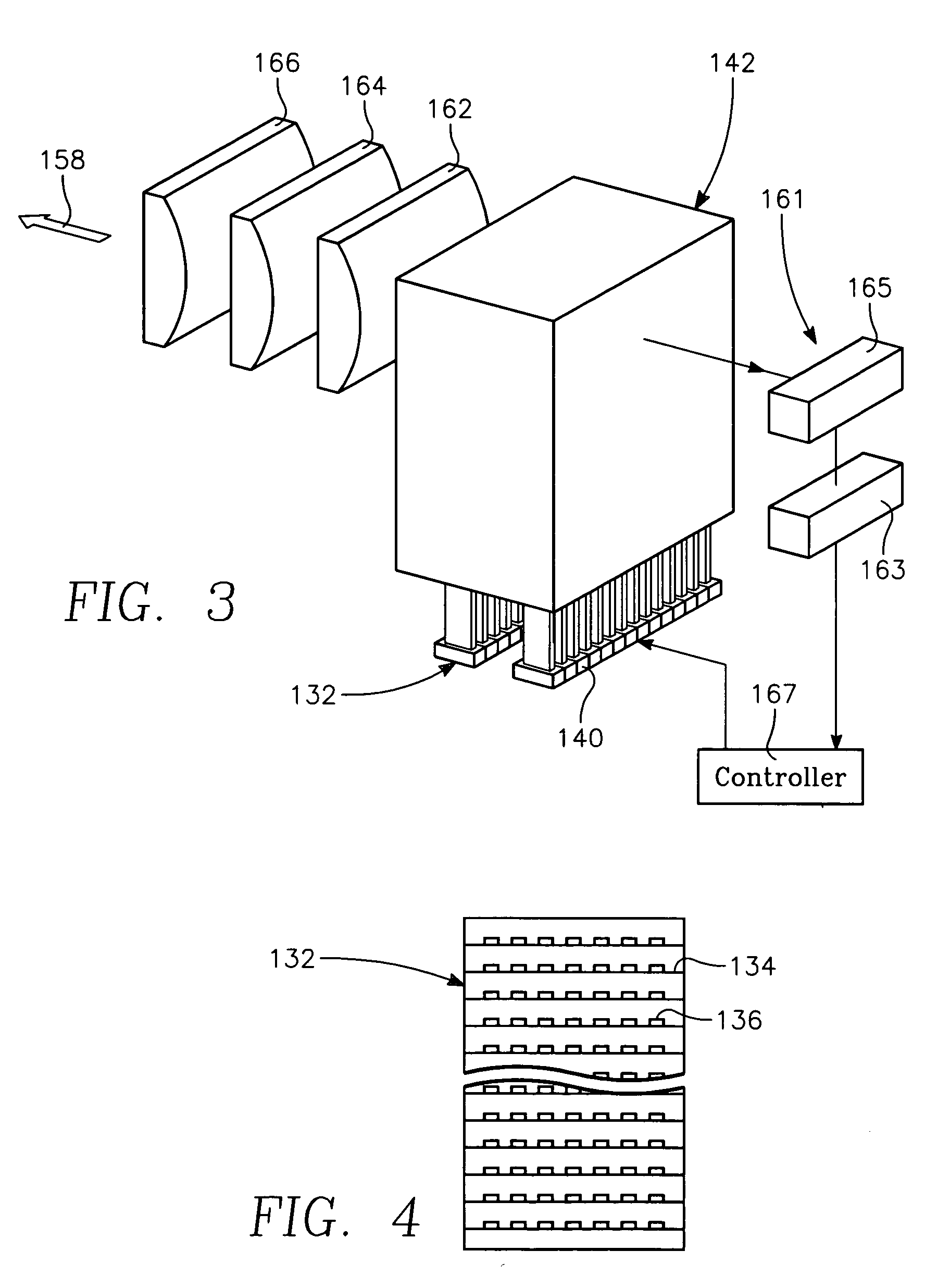
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
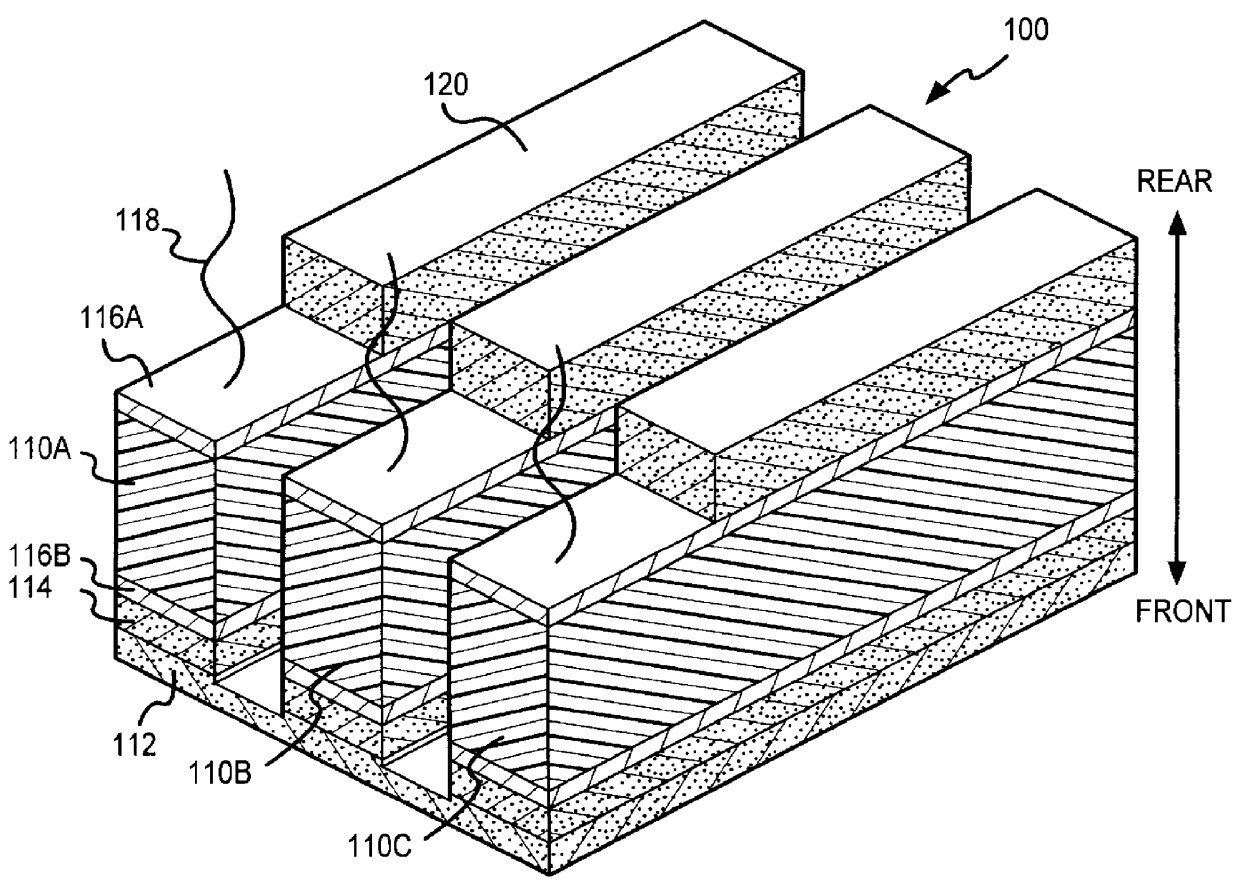
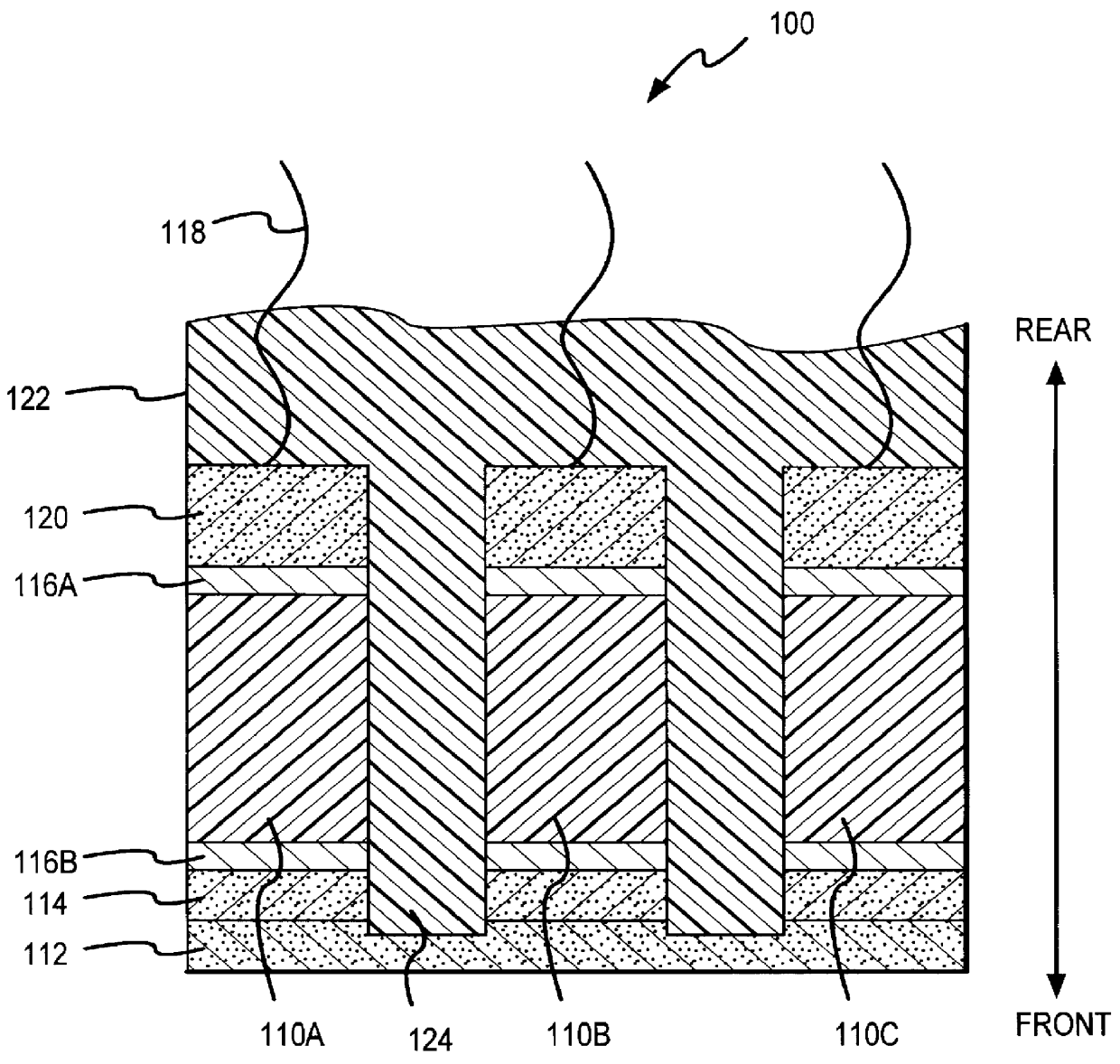
Wideband acoustic transducer
InactiveUS6049159AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAcoustic energyTransducer
A transducer according to various aspects of the present invention provides high fractional bandwidth with relatively low degradation of the pulse duration and sensitivity. The transducer includes a back matching layer behind the transducer material. The back matching layer is characterized by an impedance selected to transmit a selected portion of the backwards propagating acoustic energy to an absorption layer. The remaining acoustic energy is reflected in the desired direction of propagation. As a result, the transducer provides enhanced bandwidth without excessive loss of sensitivity or increase in pulse duration.
Owner:ARDENT SOUND
Formation of CIGS absorber layer materials using atomic layer deposition and high throughput surface treatment
An absorber layer may be formed on on a substrate using atomic layer deposition reactions. An absorber layer containing elements of groups IB, IIIA and VIB may be formed by placing a substrate in a treatment chamber and performing atomic layer deposition of a group IB element and / or one or more group IIIA elements from separate sources onto a substrate to form a film. A group VIA element is then incorporated into the film and annealed to form the absorber layer. The absorber layer may be greater than about 25 nm thick. The substrate may be coiled into one or more coils in such a way that adjacent turns of the coils do not touch one another. The coiled substrate may be placed in a treatment chamber where substantially an entire surface of the one or more coiled substrates may be treated by an atomic layer deposition process. One or more group IB elements and / or one or more group IIIA elements may be deposited onto the substrate in a stoichiometrically controlled ratio by atomic layer deposition using one or more self limiting reactions.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Solar control coated glass
A solar-control glass that has acceptable visible light transmission, absorbs near infrared wavelength light (NIR) and reflects midrange infrared light (low emissivity mid IR) along with a preselected color within the visible light spectrum for reflected light is provided. Also provided is a method of producing the improved, coated, solar-controlled glass. The improved glass has a solar energy (NIR) absorbing layer comprising tin oxide having a dopant such as antimony and a low emissivity control layer (low emissivity) capable of reflecting midrange infrared light and comprising tin oxide having fluorine and / or phosphorus dopant. A separate iridescence color suppressing layer as described in the prior art is generally not needed to achieve a neutral (colorless) appearance for the coated glass, however an iridescence suppressing layer or other layers may be combined with the two layer assemblage provided by the present invention. If desired, multiple solar control and / or multiple low emissivity layers can be utilized. The NIR layer and the low emissivity layer can be separate portions of a single tin oxide film since both layers are composed of doped tin oxide. A method of producing the coated solar control glass is also provided.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Thermal control interface coatings and pigments
The invention provides an optical structure with low chroma and brightness in the visible region and low emissivity in the infrared region. The optical structure includes an interference structure having an infrared reflective layer and an infrared absorbing thin film layer. These layers are in turn separated by a thin film spacer of a dielectric or semiconductor material. The reflectivity and transmission of the layers are selectively controlled through the thickness of the layers such that the visual reflectivity and color is independent of the infrared properties of the absorber and reflector layers.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP +1
LED device having improved contrast
ActiveUS20090051283A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight-emitting diodeOptical microcavity
A light-emitting diode device, including a substrate; and a reflective electrode and a semi-transparent electrode formed over the substrate and an unpatterned white light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the semi-transparent electrode, the reflective electrode, semi-transparent electrode, and unpatterned white-light-emitting layer forming an optical microcavity, and wherein either the reflective or semi-transparent electrodes is patterned to form a plurality of independently controllable light-emitting elements with at least one light-emitting element having no color filter. Color filters are formed over a side of the semi-transparent electrodes opposite the unpatterned white light-emitting layer in correspondence with the light-emitting elements, the color filters having at least two different colors. Additionally, a reflected-light absorbing layer is located over all of the light-emitting elements.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS20070281171A1Equal and good chemical and durabilityEqual and good and mechanical durabilityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLow emissivityGain coefficient
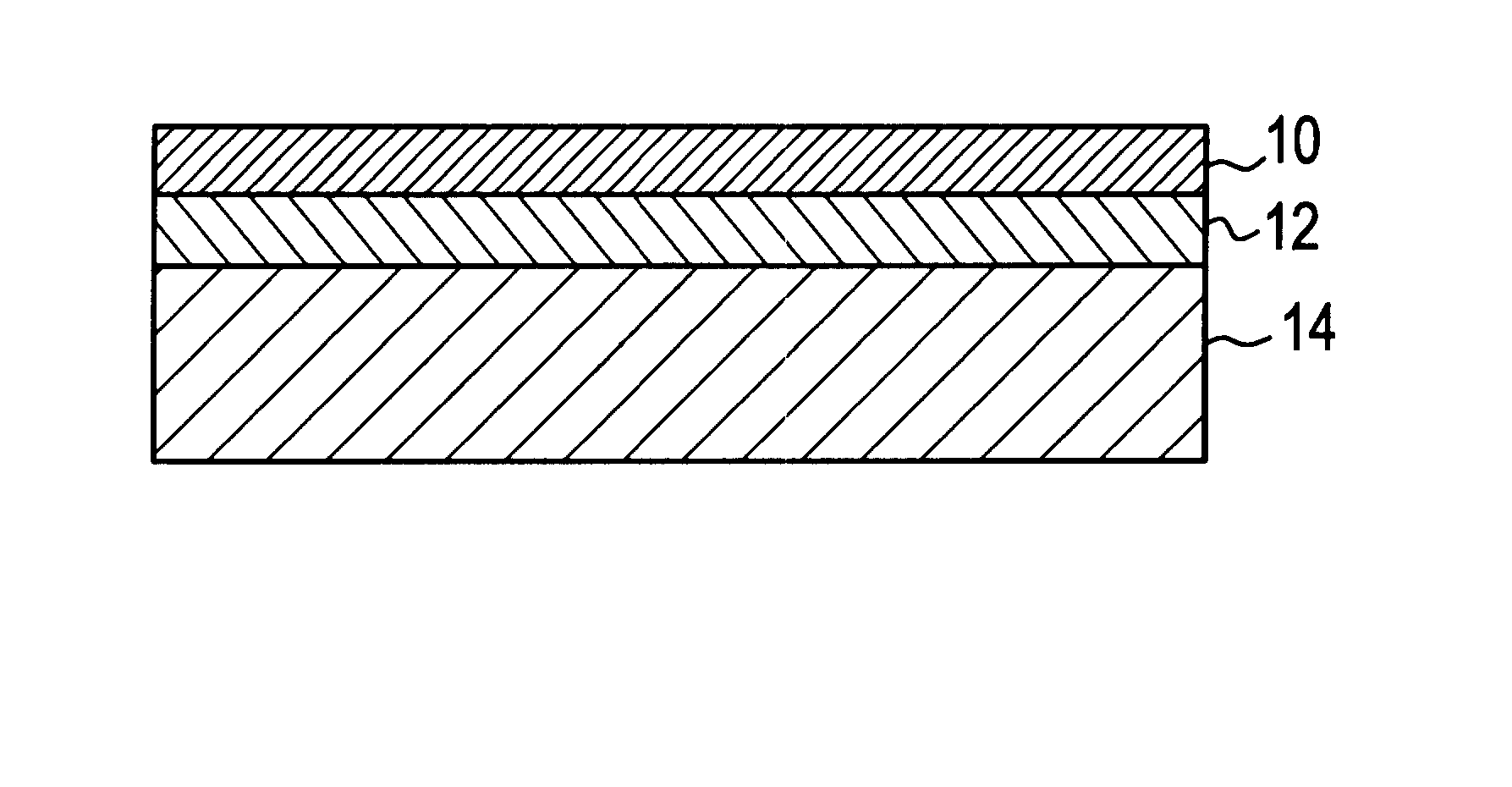
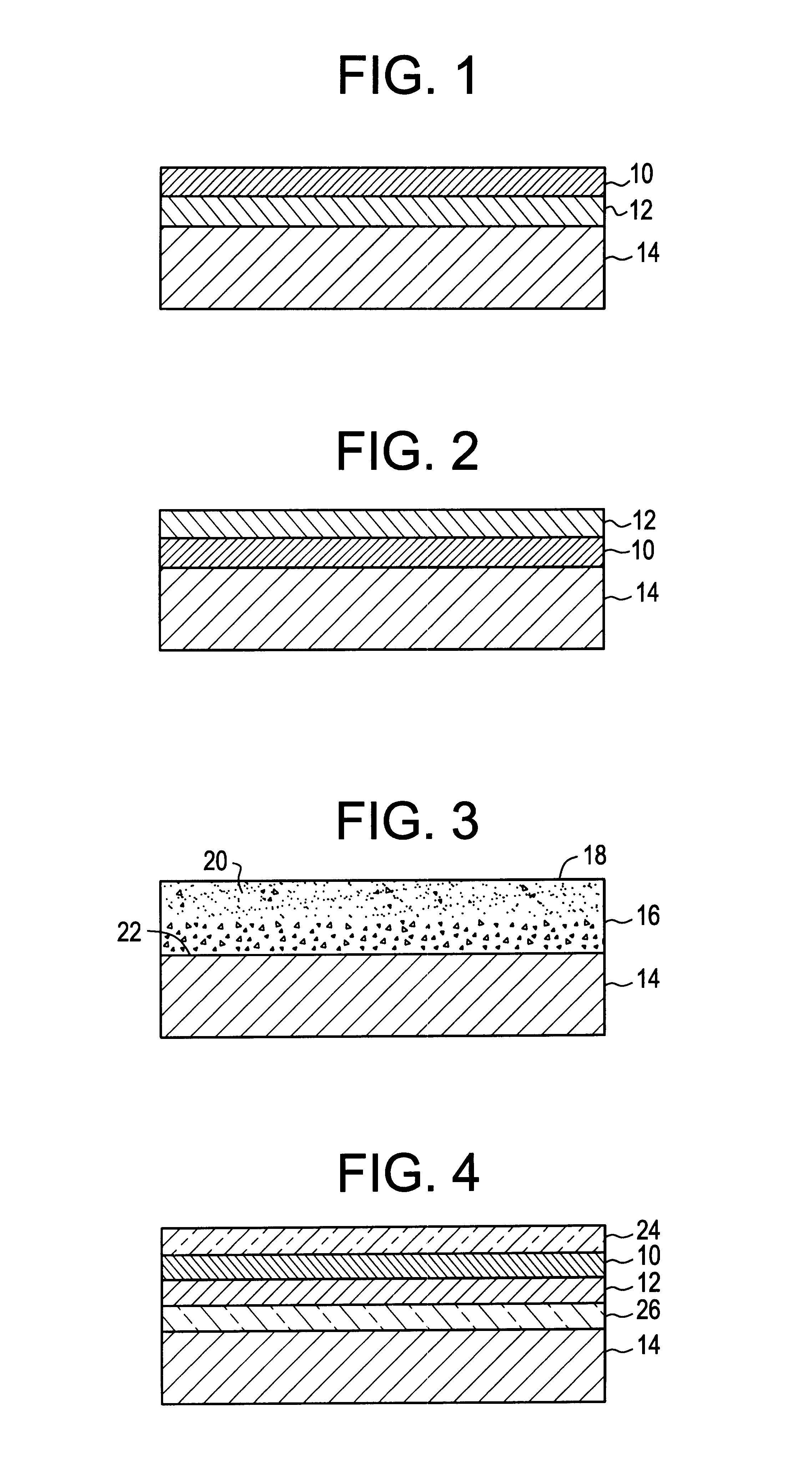
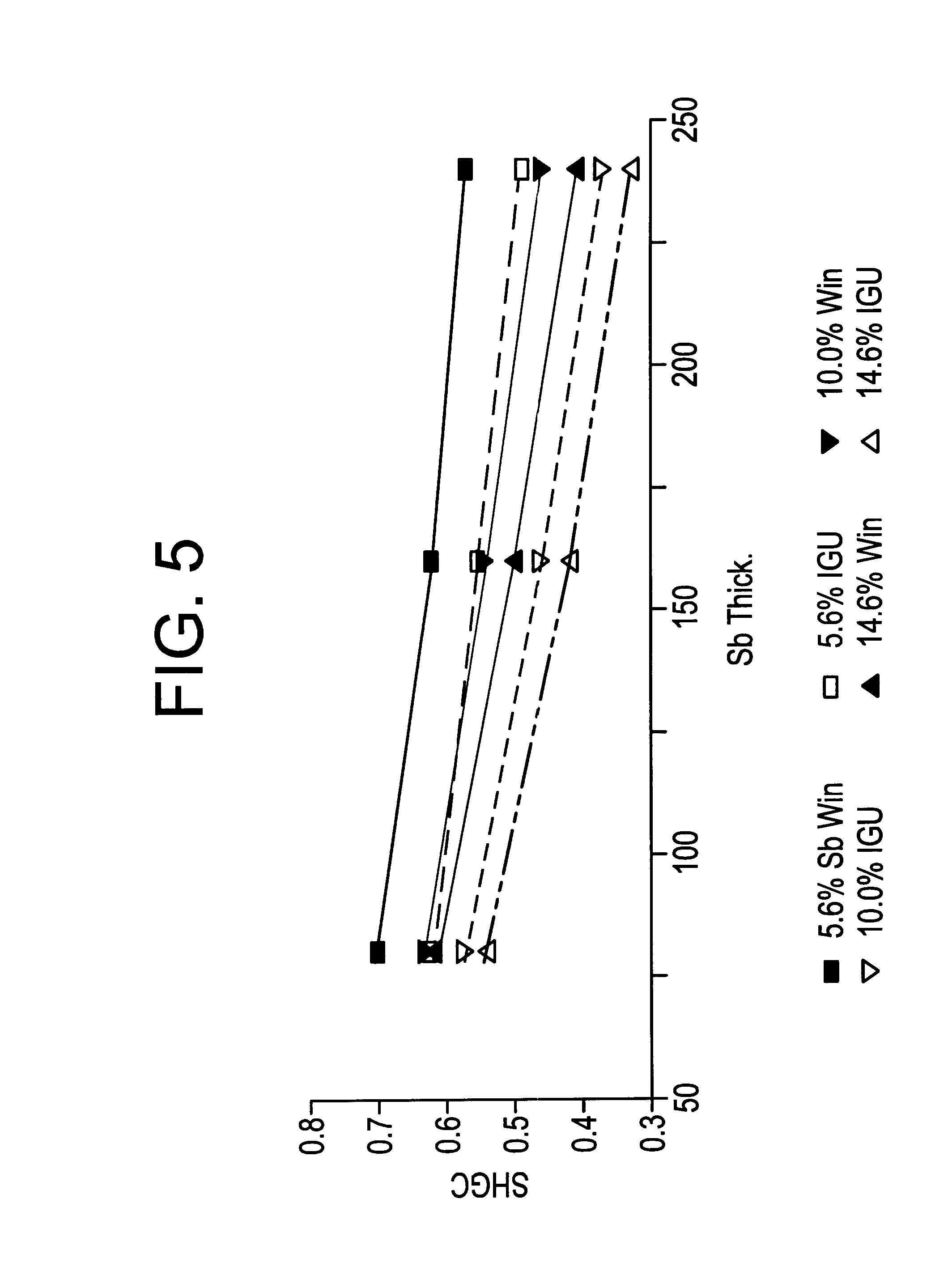
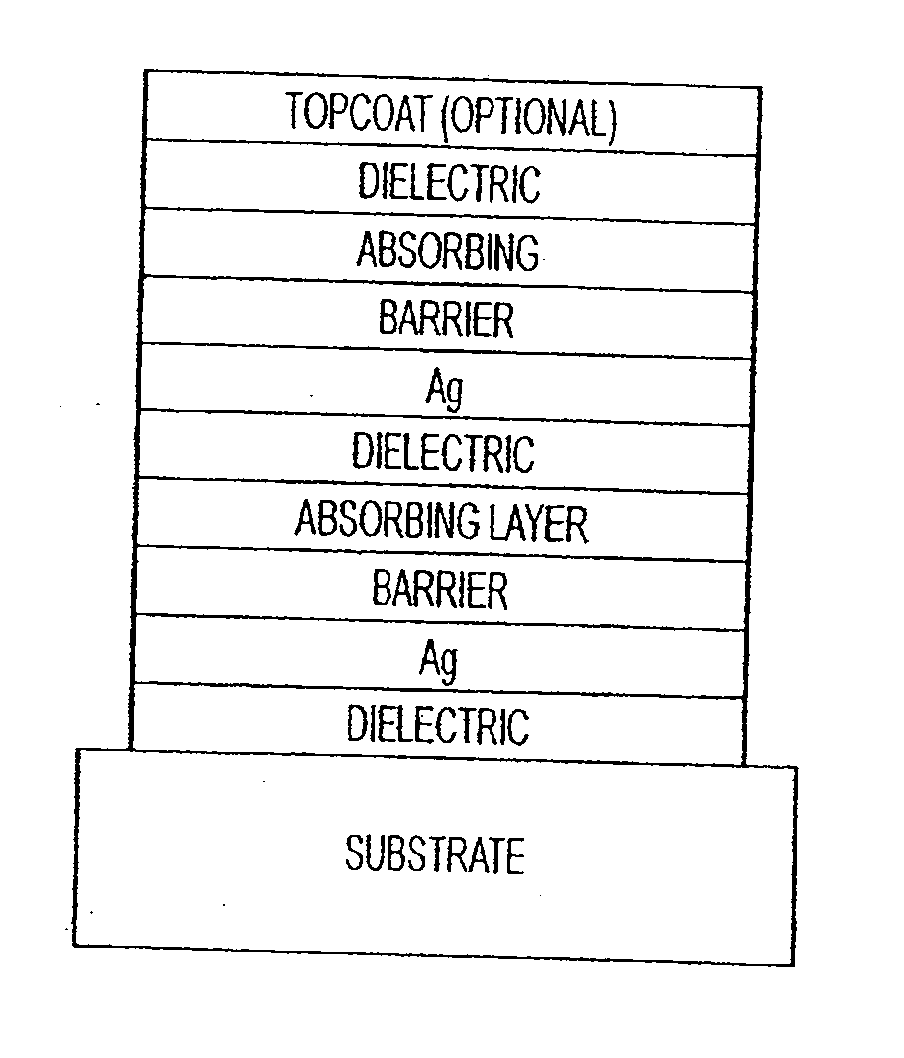
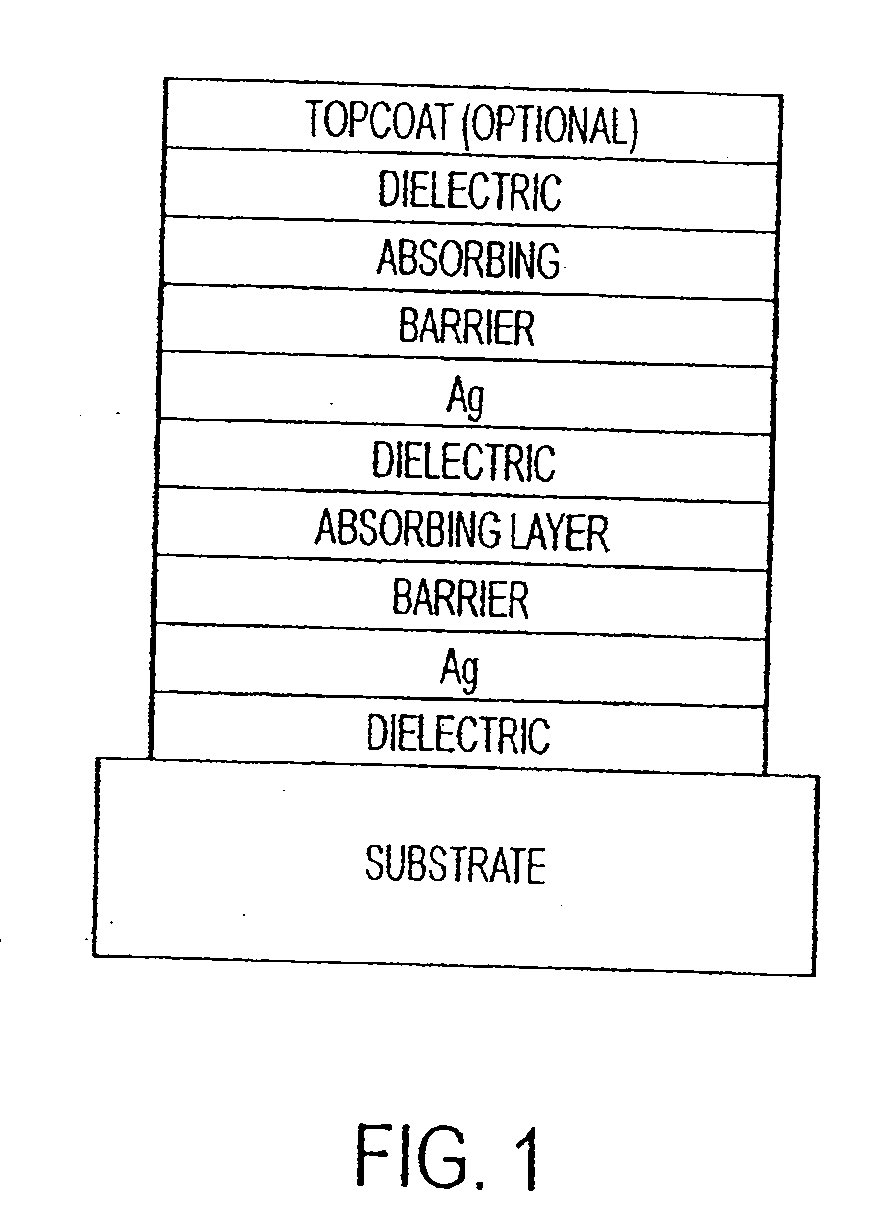
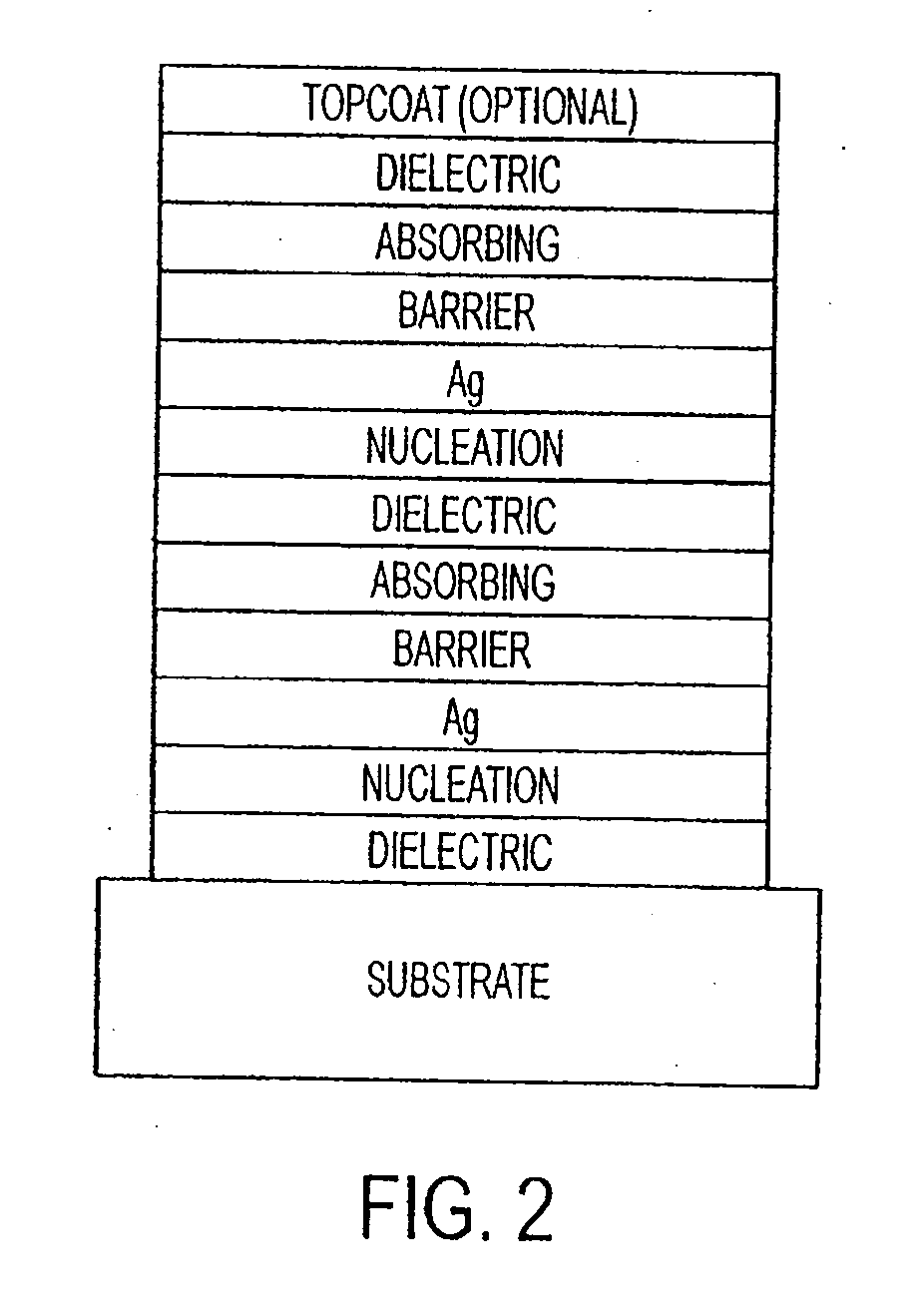
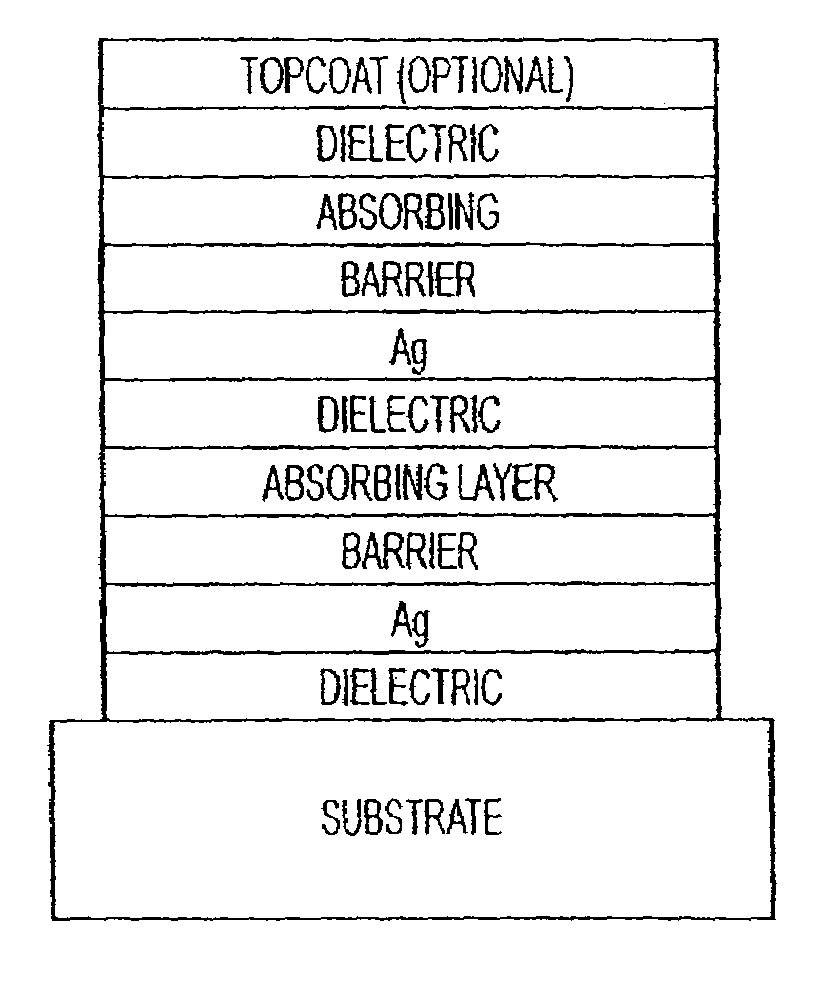
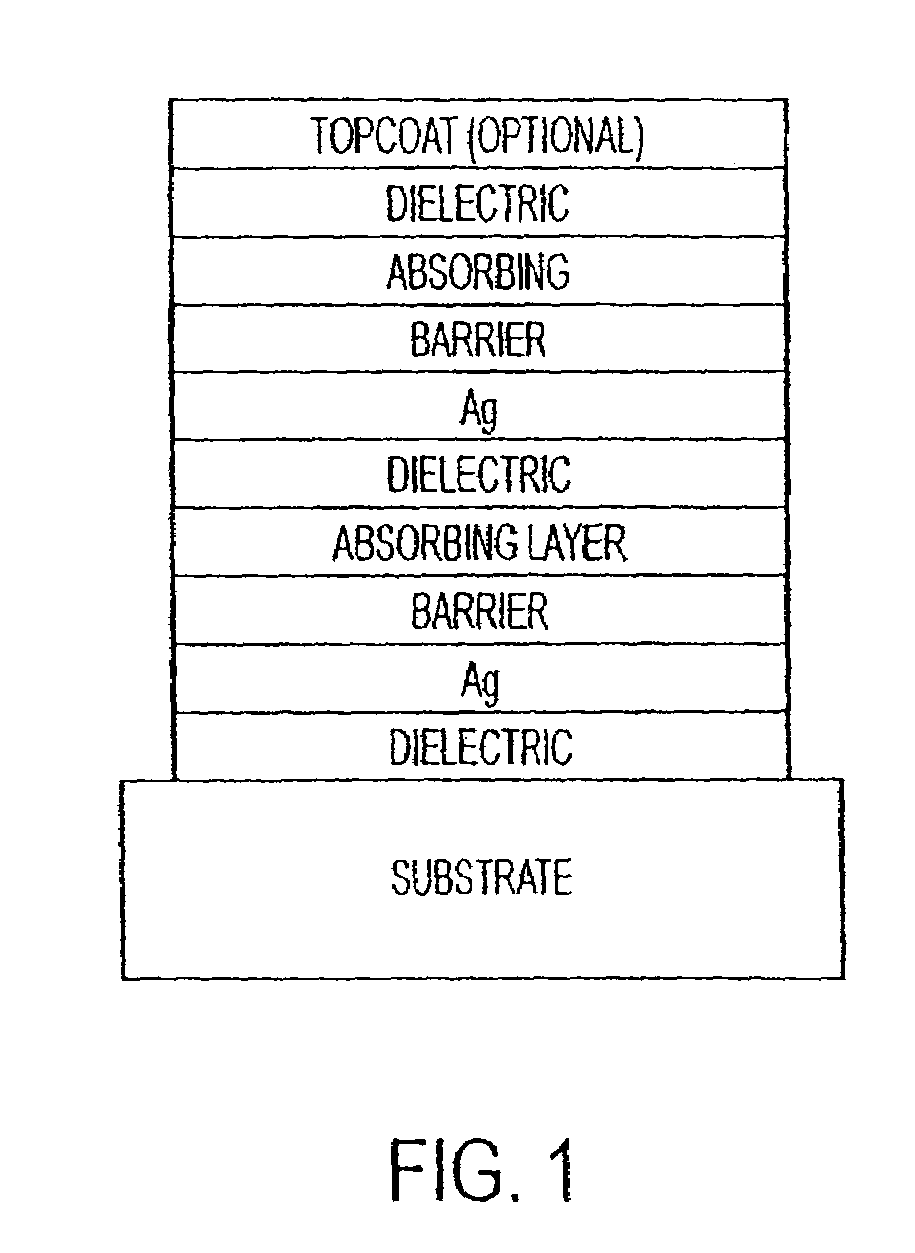
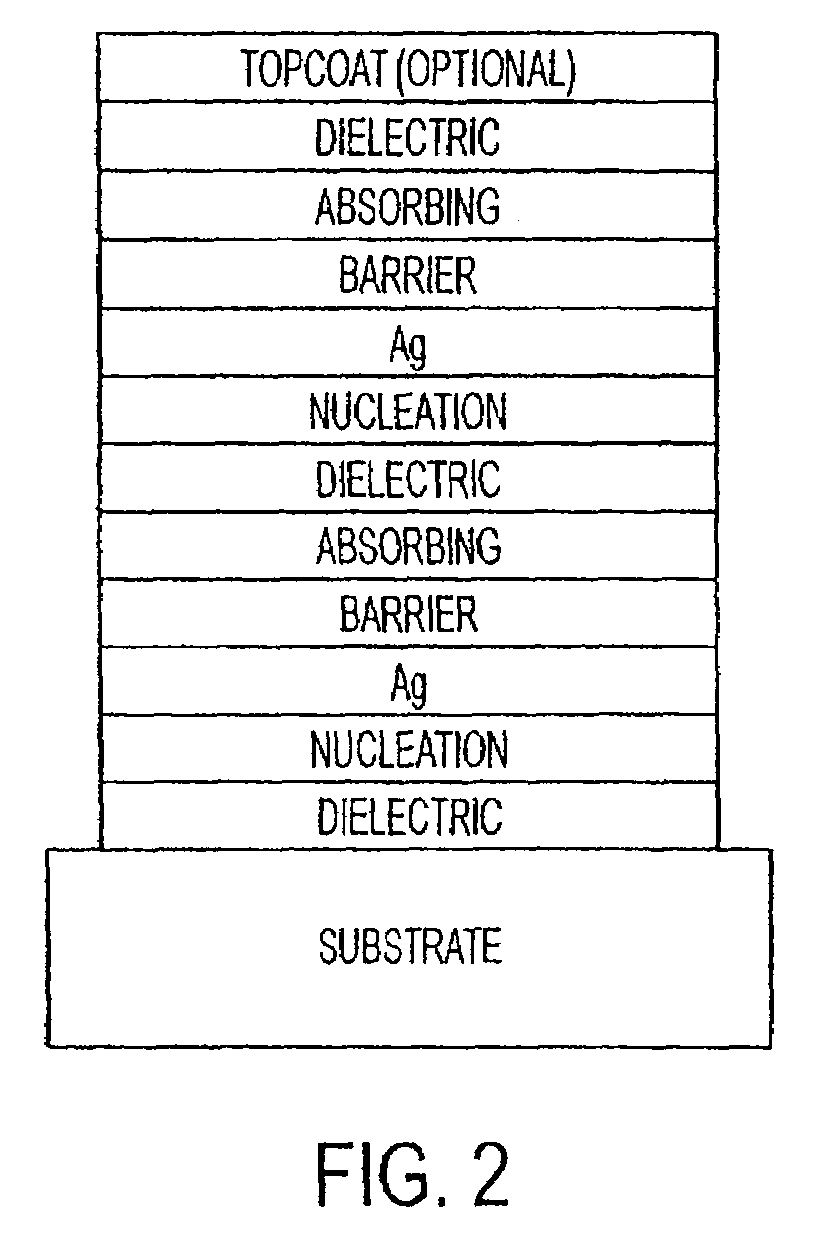
The invention provides low-emissivity stacks comprising at least one absorbing layer, said stacks being characterized by a low solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhanced aesthetics, mechanical and chemical durability, and a tolerance for tempering or heat strengthening. The invention moreover provides low-emissivity coatings comprising, in order outward from the substrate a first dielectric layer, a first Ag layer; a first barrier layer; a first absorbing layer; a second dielectric layer; a second Ag layer; a second absorbing layer; a third dielectric layer; and optionally, a topcoat layer, and methods for depositing such coatings on substrates.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Wire grid polarized and liquid crystal display device using the same
ActiveUS20080094547A1Brightness in display can be increasedLow costPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayOptical property
An image is displayed by modulating TM-polarized light between the polarizer 2 and the wire grid polarizer 18 through the variation of the optical characteristic of the liquid crystal layer 12 interposed between the transparent plate 4 and the transparent plate 26. Degradation of contrast in the bright ambience is avoided by providing an absorption layer for absorbing TE-polarized light on that surface of the wire grid polarizer 18 which faces the liquid crystal layer 12.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
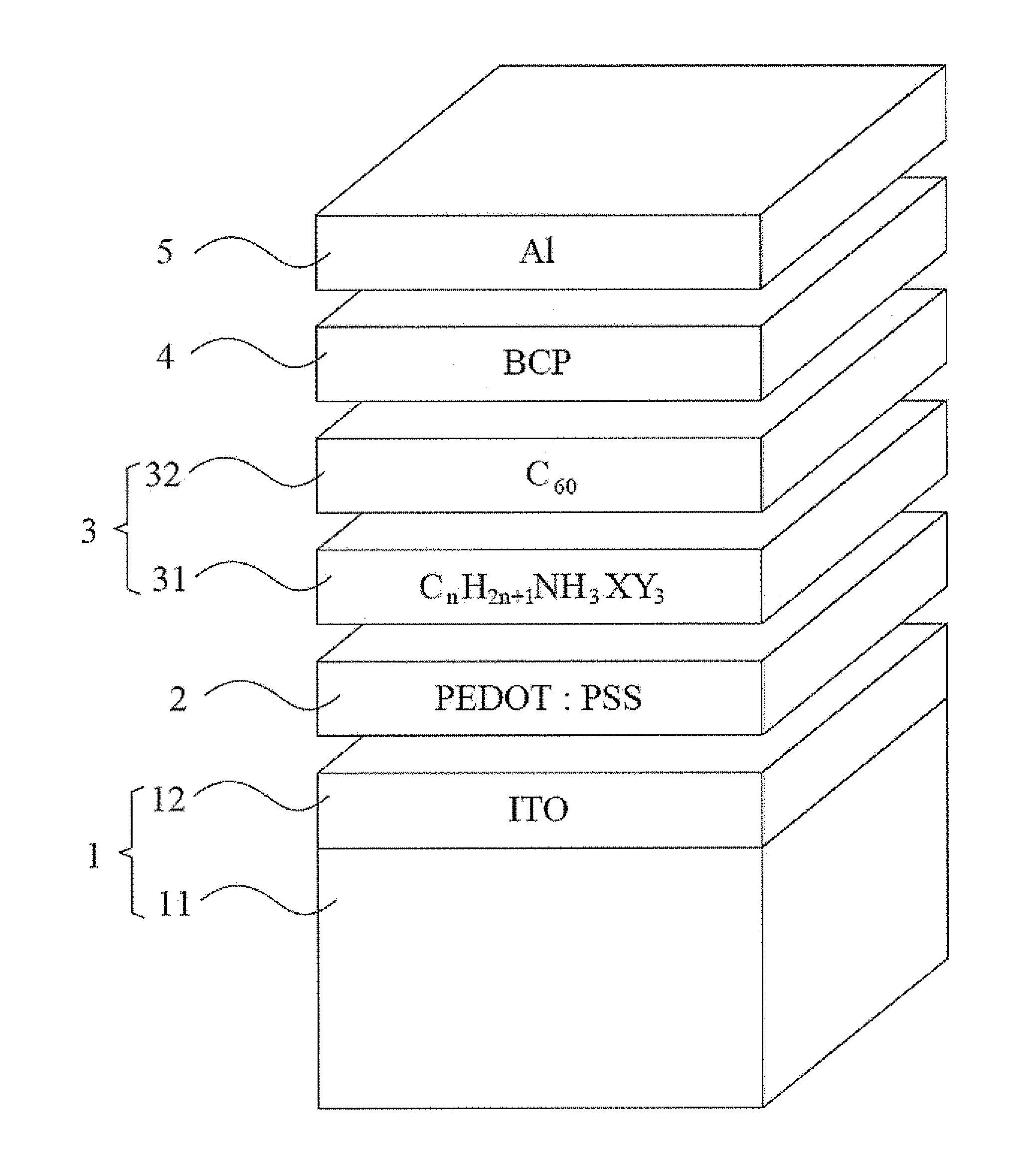
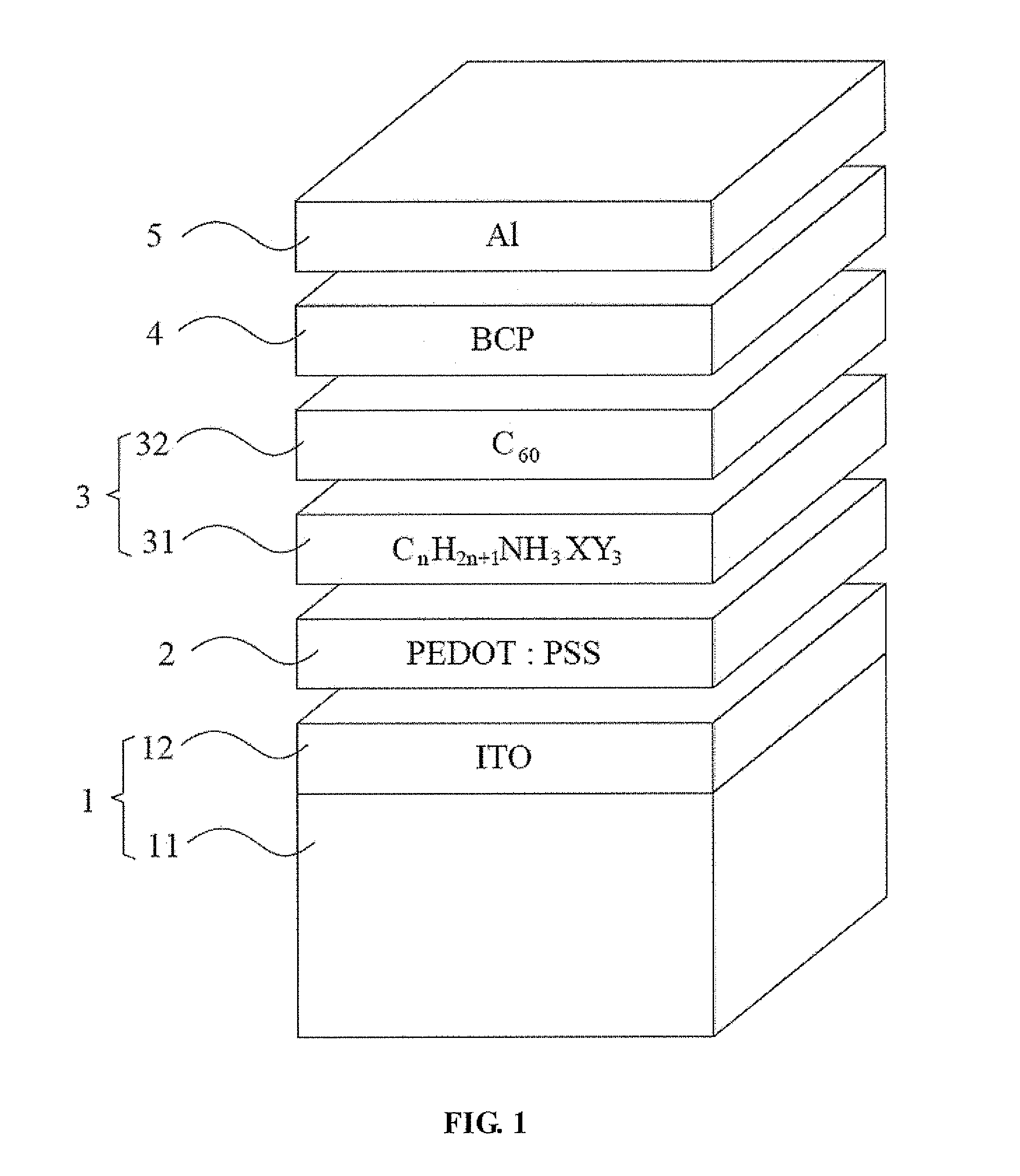
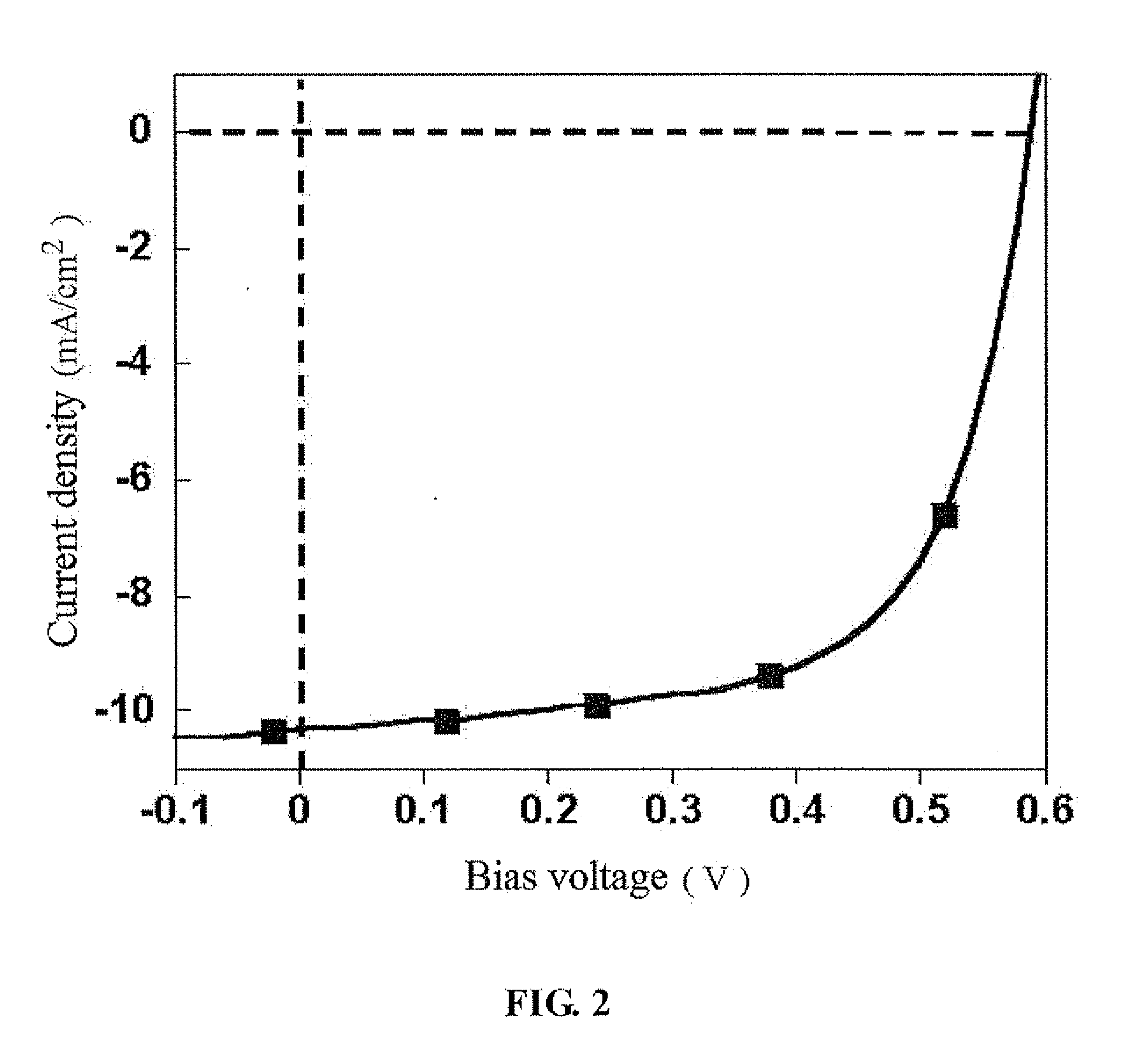
Hybrid organic solar cell with perovskite structure as absorption material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140332078A1Low costSimple processFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionOrganic solar cell
A hybrid organic solar cell (HOSC) with perovskite structure as absorption material and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The HOSC includes a conductive substrate, a hole transport layer, an active layer, a hole blocking layer and a negative electrode. The active layer has a light absorption layer (LAL) and an electron acceptor layer (EAL). The LAL is made of perovskite material represented by the following equation: CnH2n+1NH3XY3, n is positive integer form 1 to 9; X is Pb, Sn or Ge; and Y is at least one of I, Br or Cl. The EAL is made of at least one type of fullerene or derivatives thereof. A planar heterojunction (PHJ) is formed between the LAL and the EAL. The LAL has simple structure and fabricating process with relatively low cost, so that it is advantageous to carry out the mass production of HOSCs of flexible solid-state form.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Cis Compound Semiconductor Thin-Film Solar Cell and Method of Forming Light Absorption Layer of the Solar Cell
InactiveUS20070289624A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove productivityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationProduction rateAbsorption layer
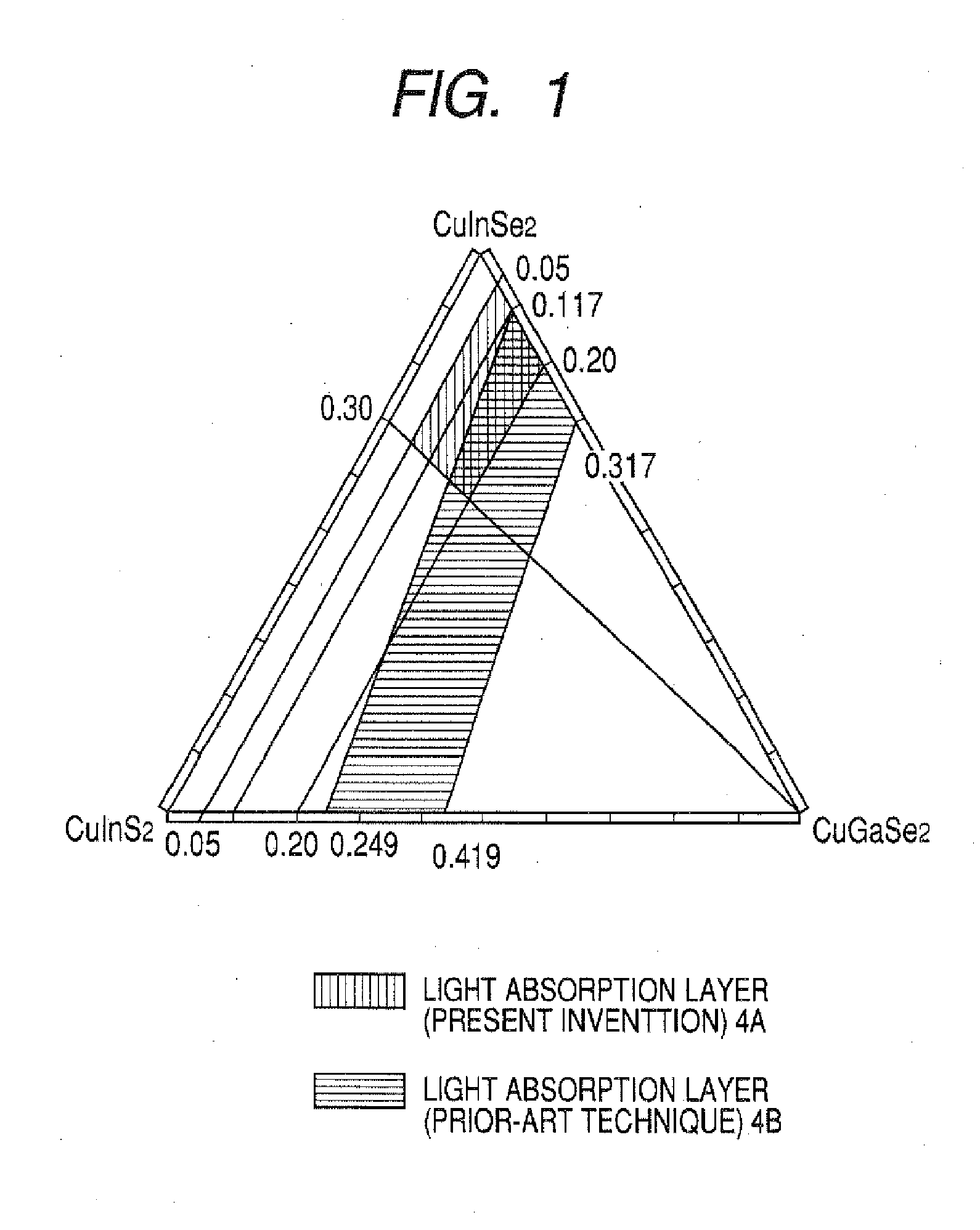
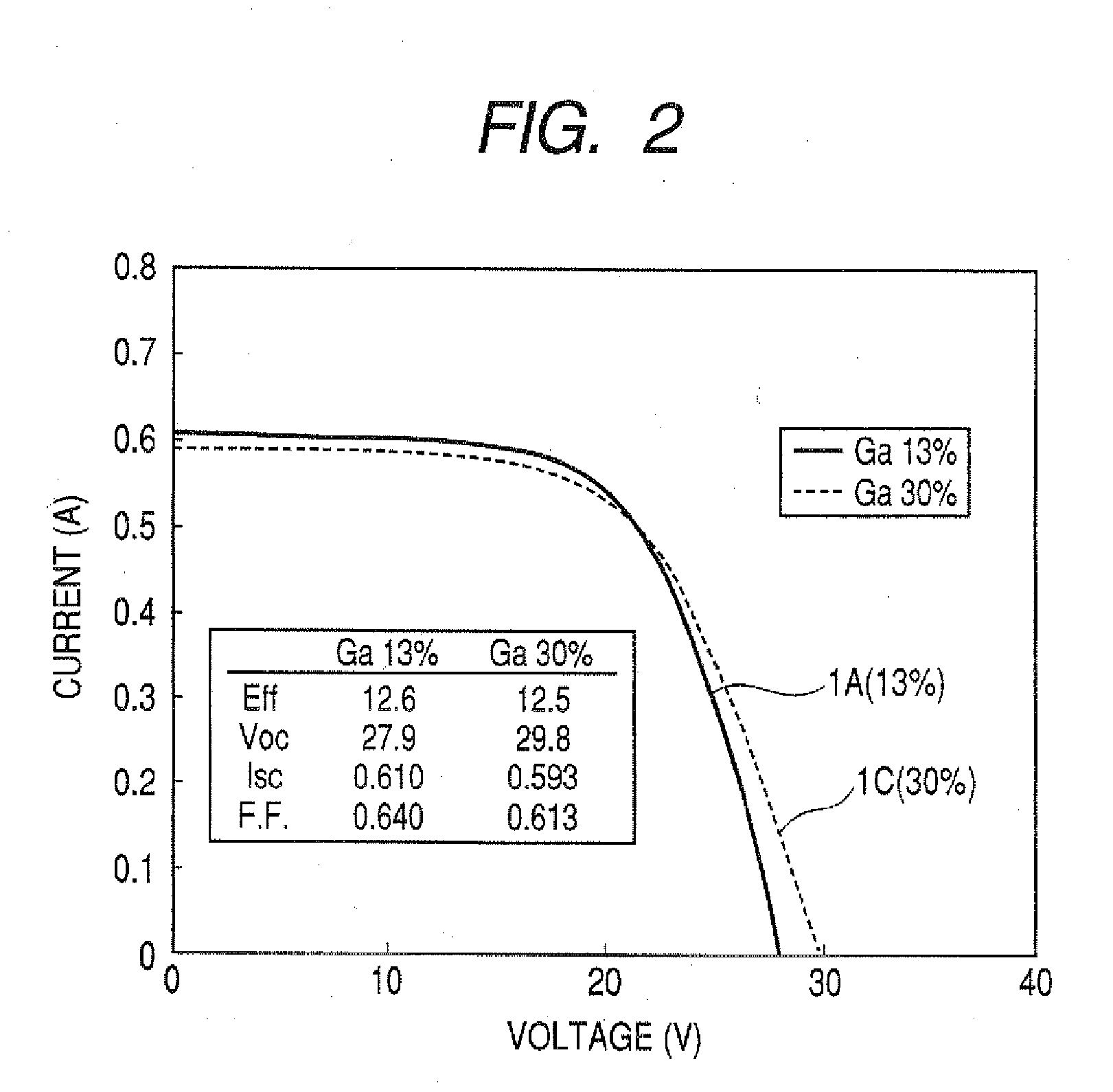
Film formation is conducted at a low temperature to improve conversion efficiency and productivity and to enable a wider choice of substrate materials to be used. The invention relates to the light absorption layer of a CIS compound semiconductor thin-film solar cell and to a method of forming the layer. The light absorption layer comprises a compound represented by Cux(In1-yGay)(Se1-zSz)2 and having a chalcopyrite type structure, the proportions of the components satisfying 0.86≦x≦0.98, 0.05≦y≦0.25, 0≦z≦0.3, x=αT+β, α=0.015y−0.00025, and β=−7.9y+1.105, provided that T (° C.) is anneal temperature and the allowable range for x is ±0.02. The layer is formed by the selenization method at a low temperature (about 500≦T≦550). As the substrate is used a soda-lime glass having a low melting point.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Method for Forming Light Absorption Layer of Cis Type Thin-Film Solar Cell
InactiveUS20080110495A1Good conditionSmooth circulationFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSulfurEngineering
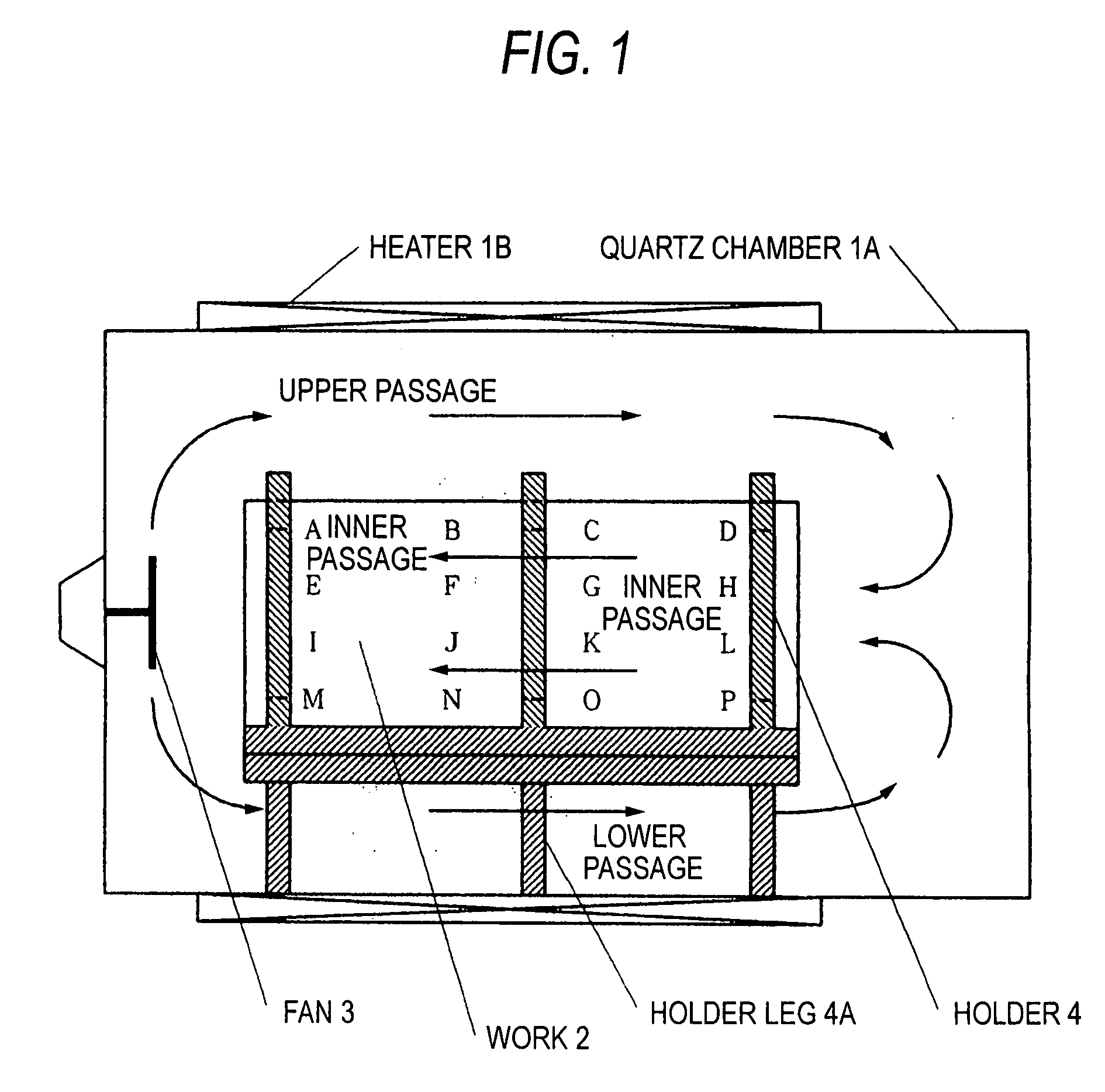
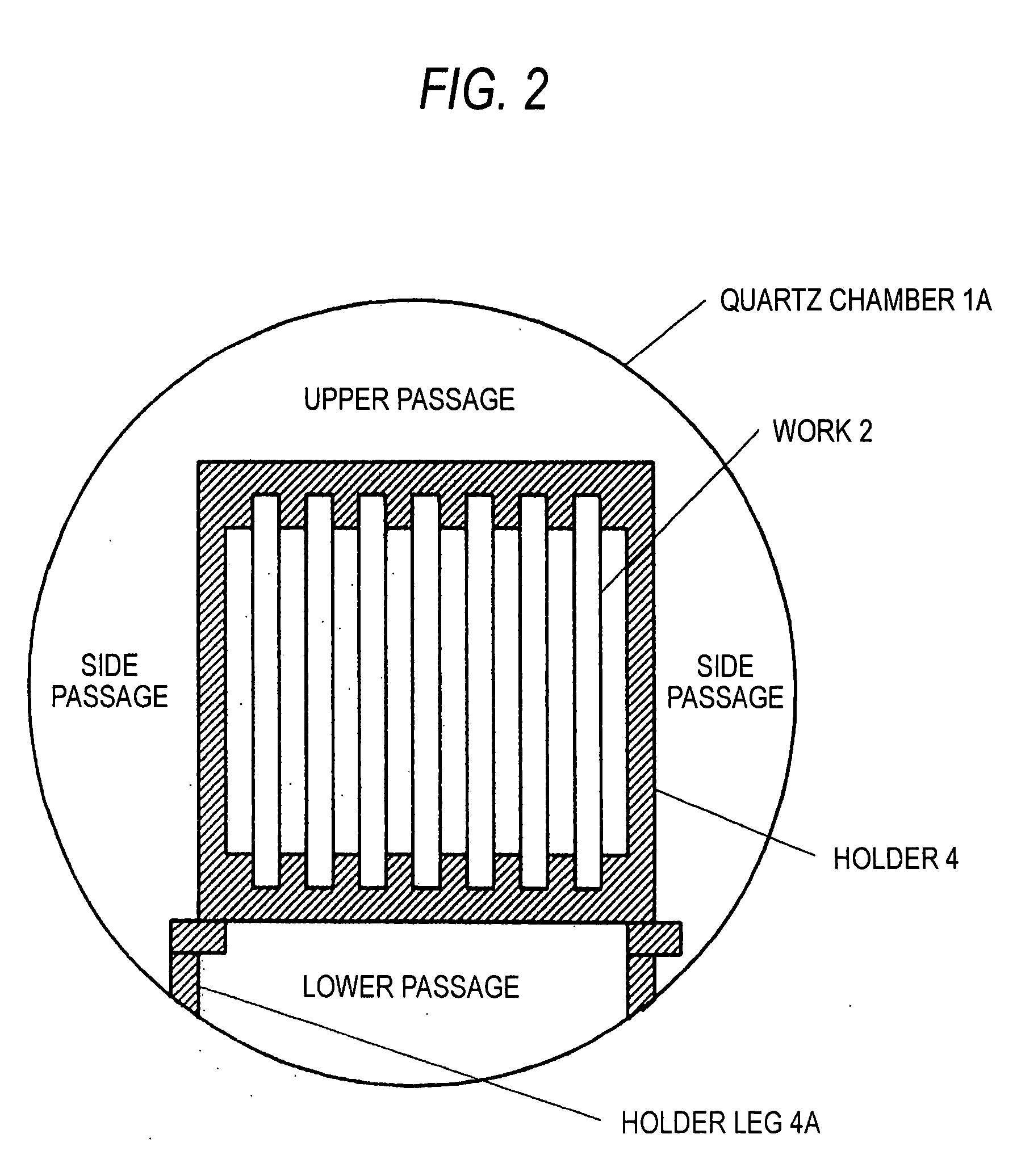
A simple device is used to make the temperature in an apparatus even and improve the state of being in contact with reactant gases, selenium, and sulfur.A fan 3 as a device for atmosphere homogenization is disposed in an apparatus, and the work is disposed in the manner which enables a reactant gas to circulate smoothly. Namely, flat platy works 2 are disposed apart from each other at a certain distance parallel to the direction of the major axis of the apparatus while keeping the plates vertical so that the apparatus has passages within the group of works and has gas passages over and under the works and on both sides thereof. Thus, each work is apt to come into contact with the reactant gases in the apparatus and the temperature in the apparatus is even. The state of being in contact with the reactant gases, selenium, and sulfur is improved.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
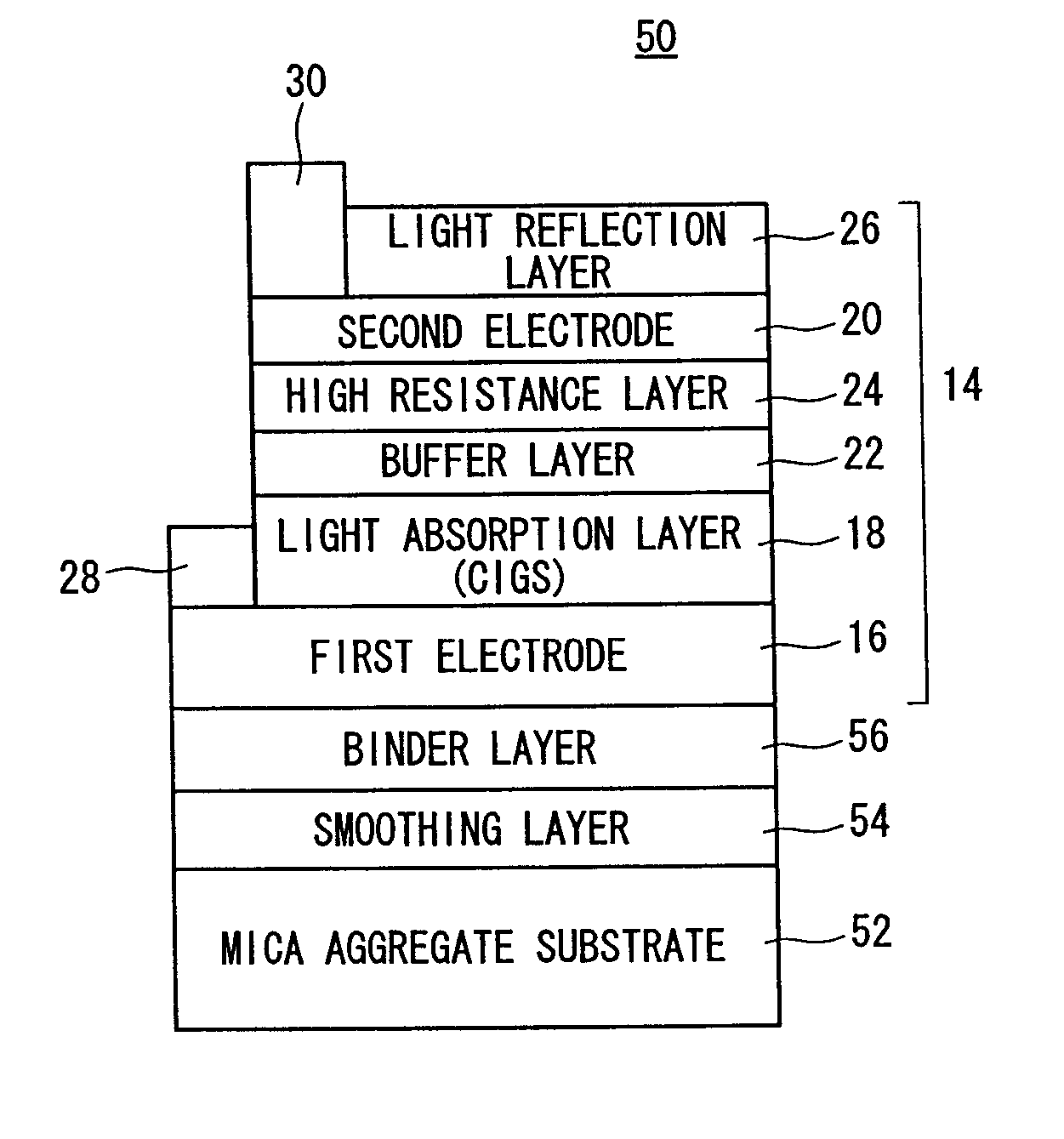
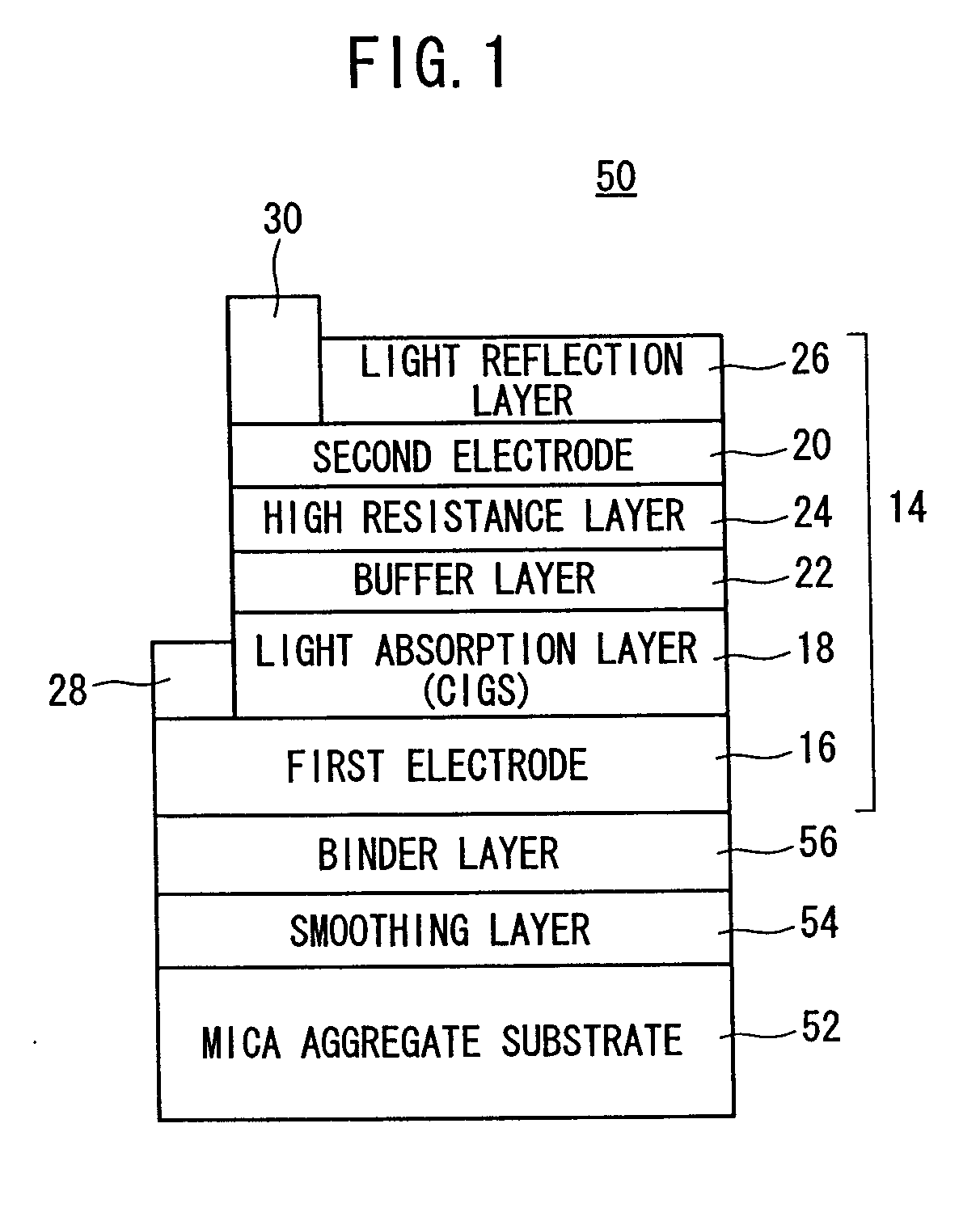
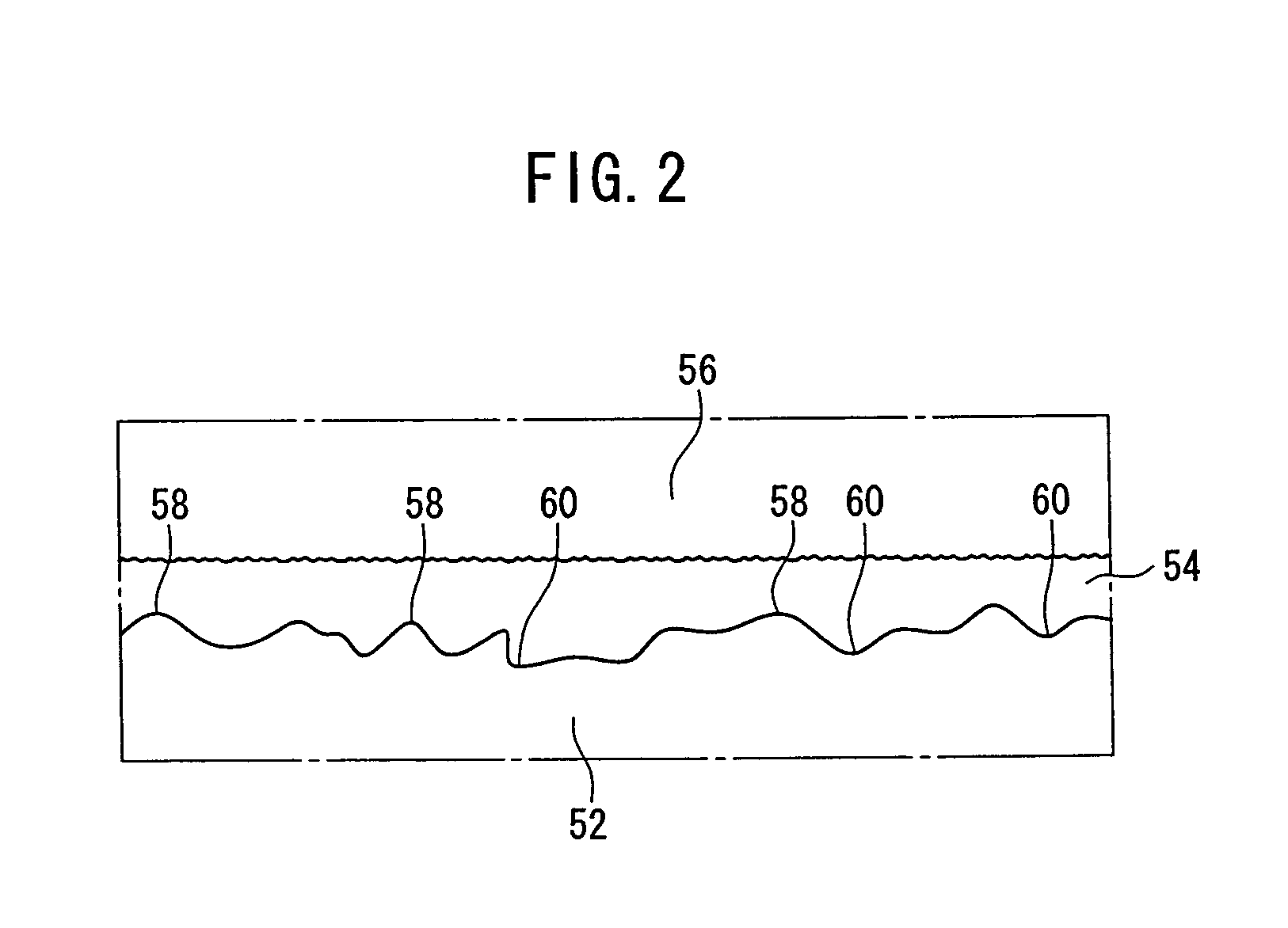
Chalcopyrite Type Solar Cell
InactiveUS20070209700A1Increase the open circuit voltageAvoid violationsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationParticulatesSolar cell
A chalcopyrite type solar cell has a mica aggregate substrate formed by binding mica particulates with a resin. A multilayer body consisting of a first electrode, a light absorption layer and a second electrode is formed on the mica aggregate substrate with a smoothing layer and a binder layer interposed between the substrate and the body. The smoothing layer is preferably made of SiN or SiO2, and the binder layer is made of TiN or TaN.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Absorbent product with improved instantaneous liquid adsorption, and improved fit
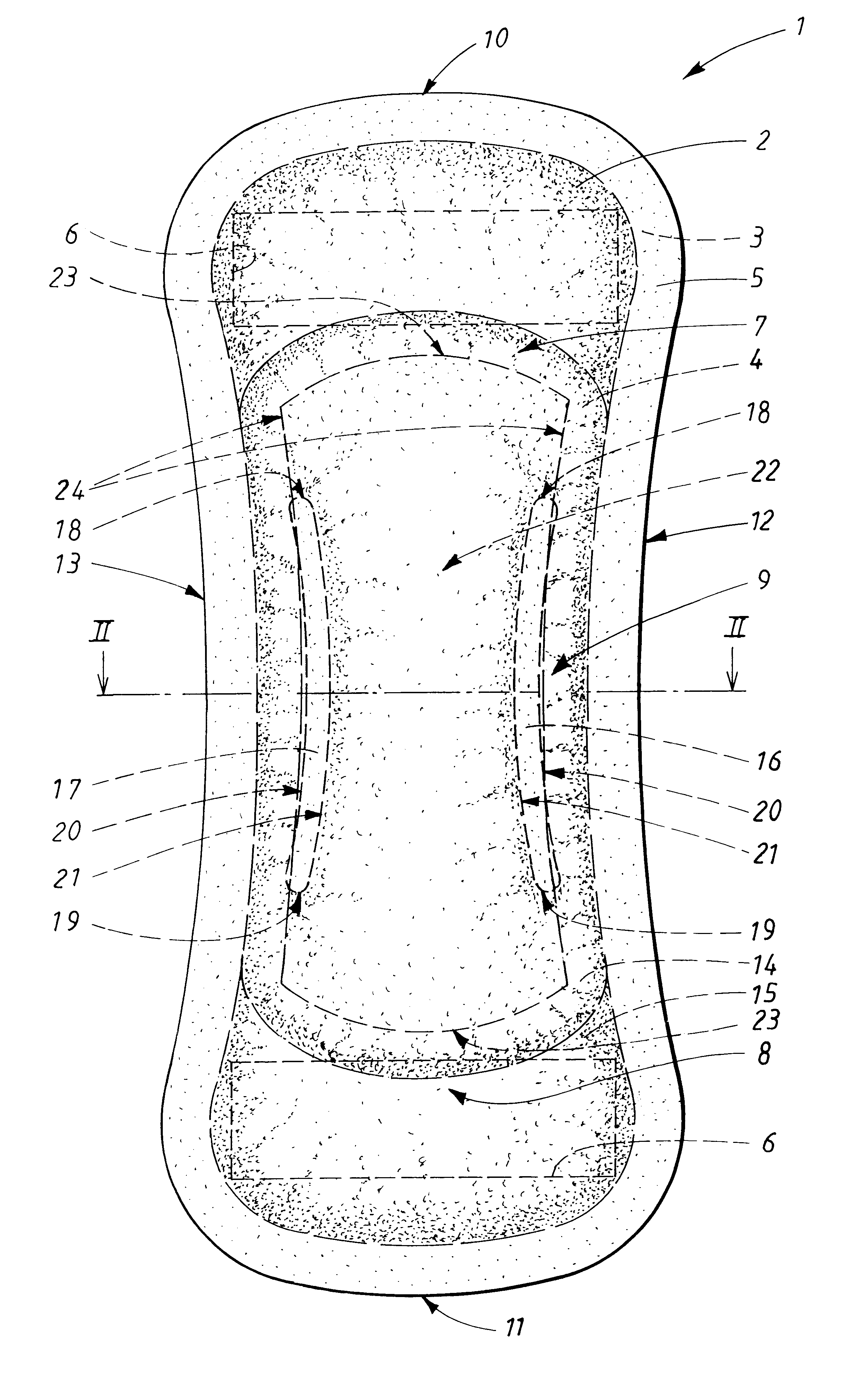
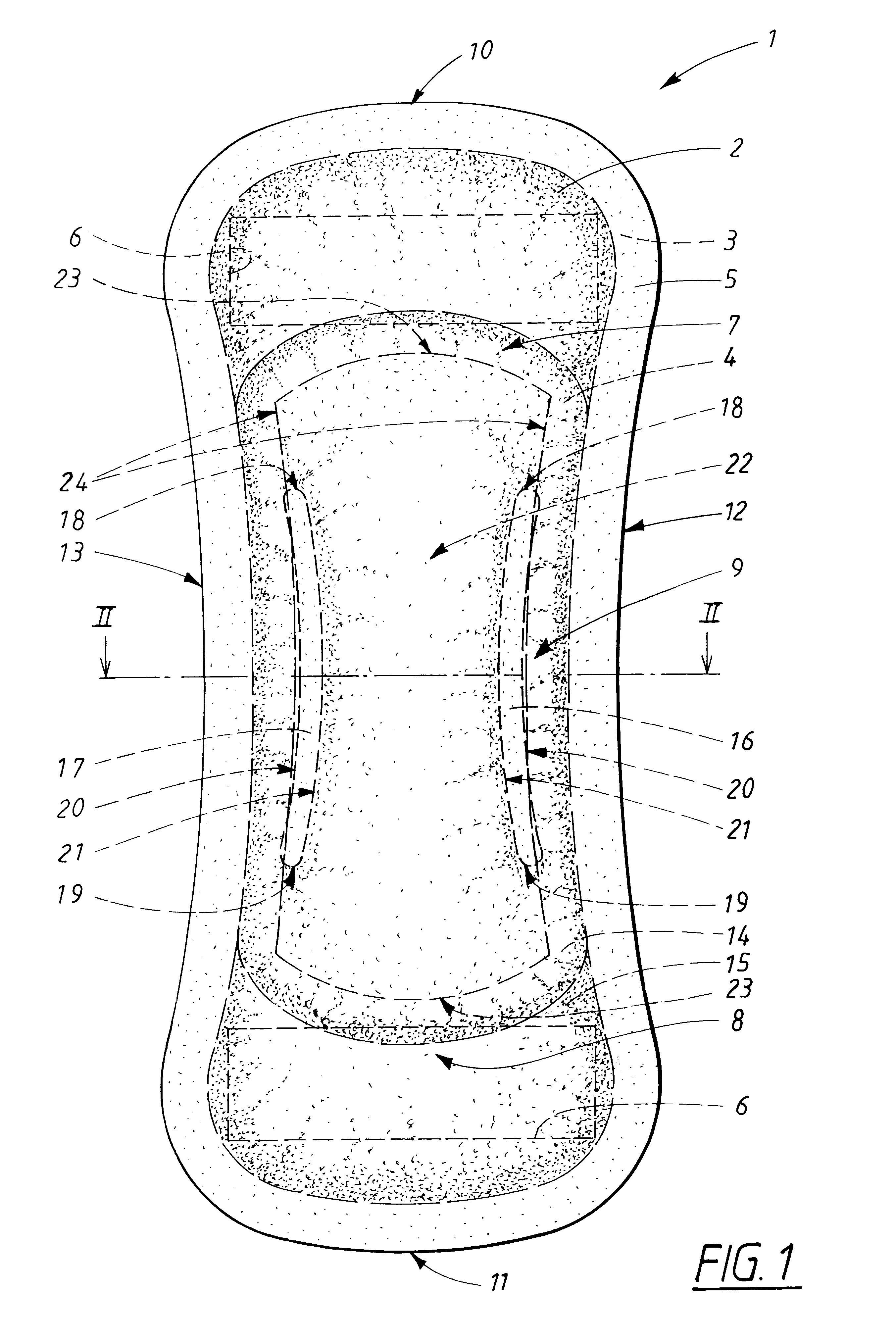
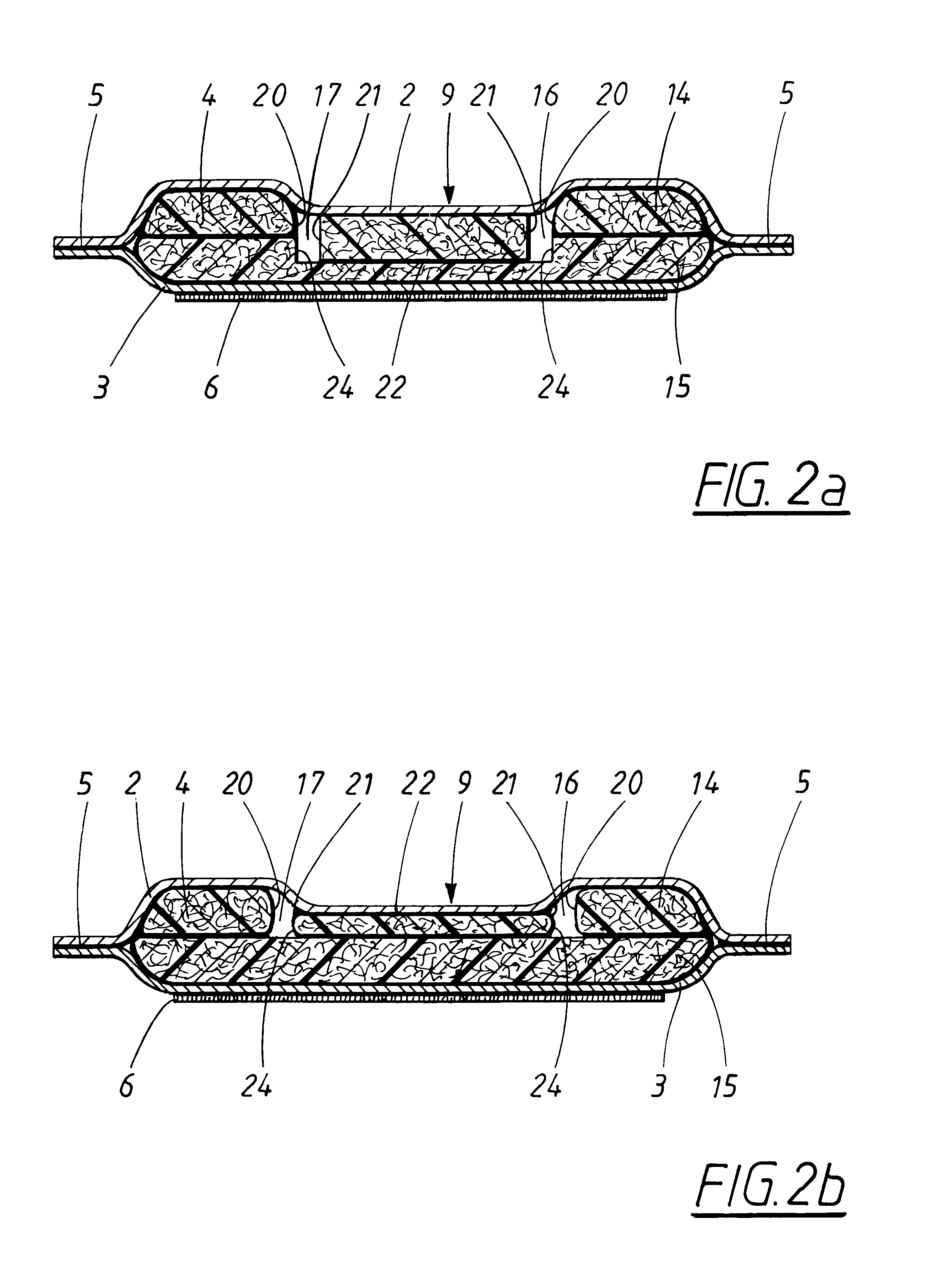
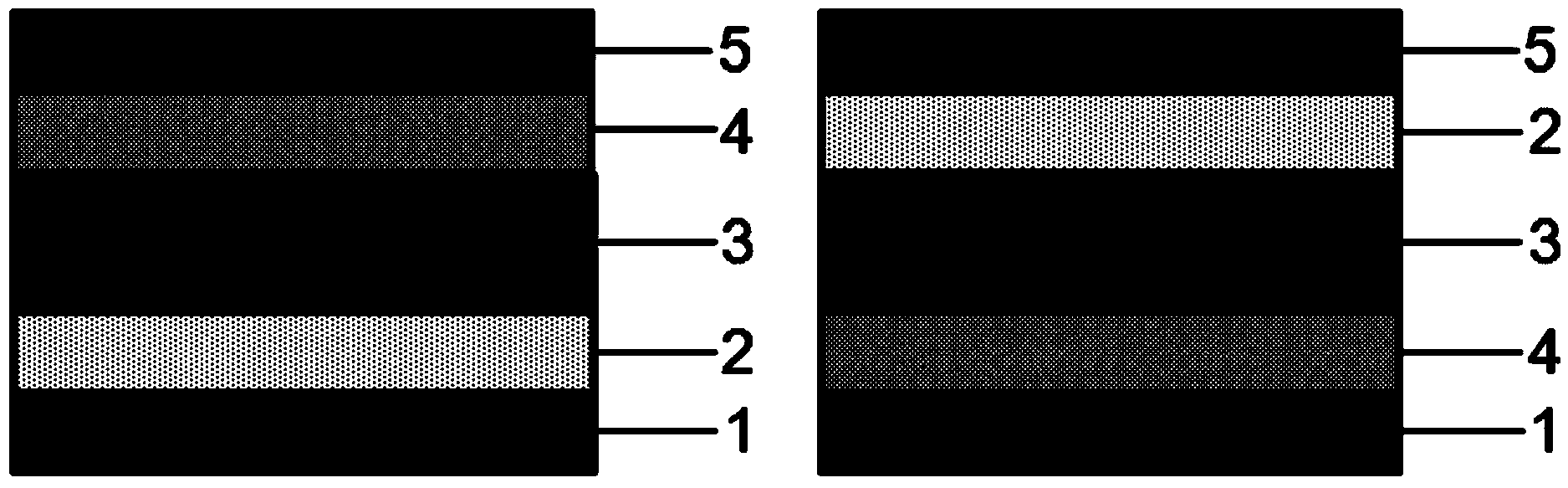
InactiveUS6605752B2Increases stability and deformation resistancePromote absorptionSanitary towelsBaby linensEngineeringAbsorption layer
An absorbent product which possesses two longitudinal side edges (12,13), two transverse end edges (10,11), a longitudinal centre line and a transverse centre line, and which comprises a liquid-permeable outer layer (2), a liquid-impermeable backing layer (3) and an absorption core (4) which is located between the outer layer (2) and the backing layer (3), with the absorption core (4) comprising a first and a second absorption layer (14,15), with the first absorption layer (14) being arranged behind the liquid-permeable outer layer (2) and the second absorption layer (15) being arranged between the first absorption layer (14) and the liquid-impermeable backing layer (3), with the first absorption layer (14) having two longitudinal channels (16,17), with each of the channels having an outer edge (20) closest to the corresponding longitudinal side edge (12,13) of the product and an inner edge (21) closest to the longitudinal centre line of the product. The two longitudinal channels (16,17) extend through the whole of the thickness of the first absorption layer (14), and a compressed area (22) is arranged between the longitudinal sides (12,13) of the absorbent product, wherein the distance between the side edges (24) of the compressed area (22) is smaller than or equal to the distance between the outer side edges (20) of the longitudinal channels (16,17).
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
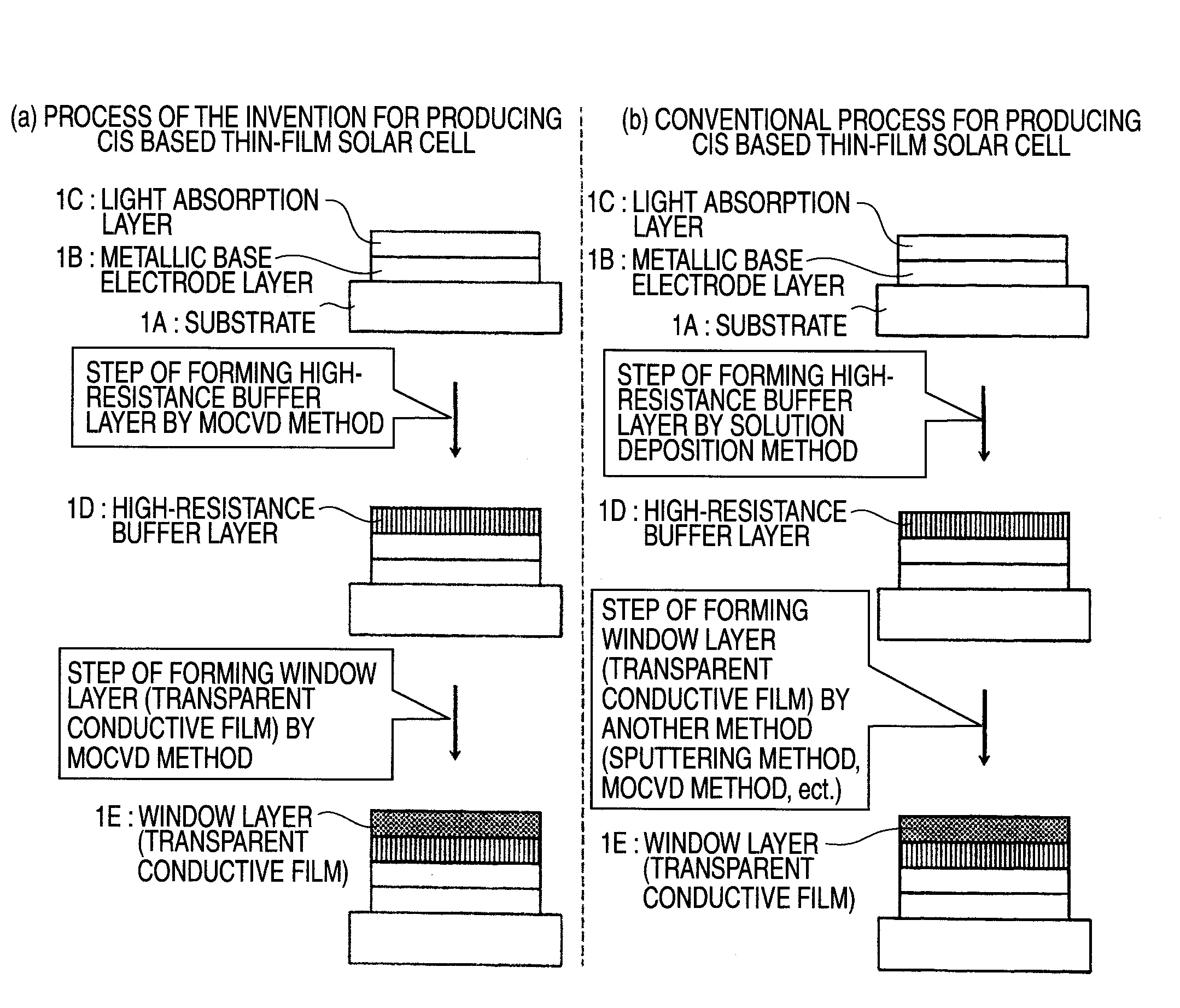
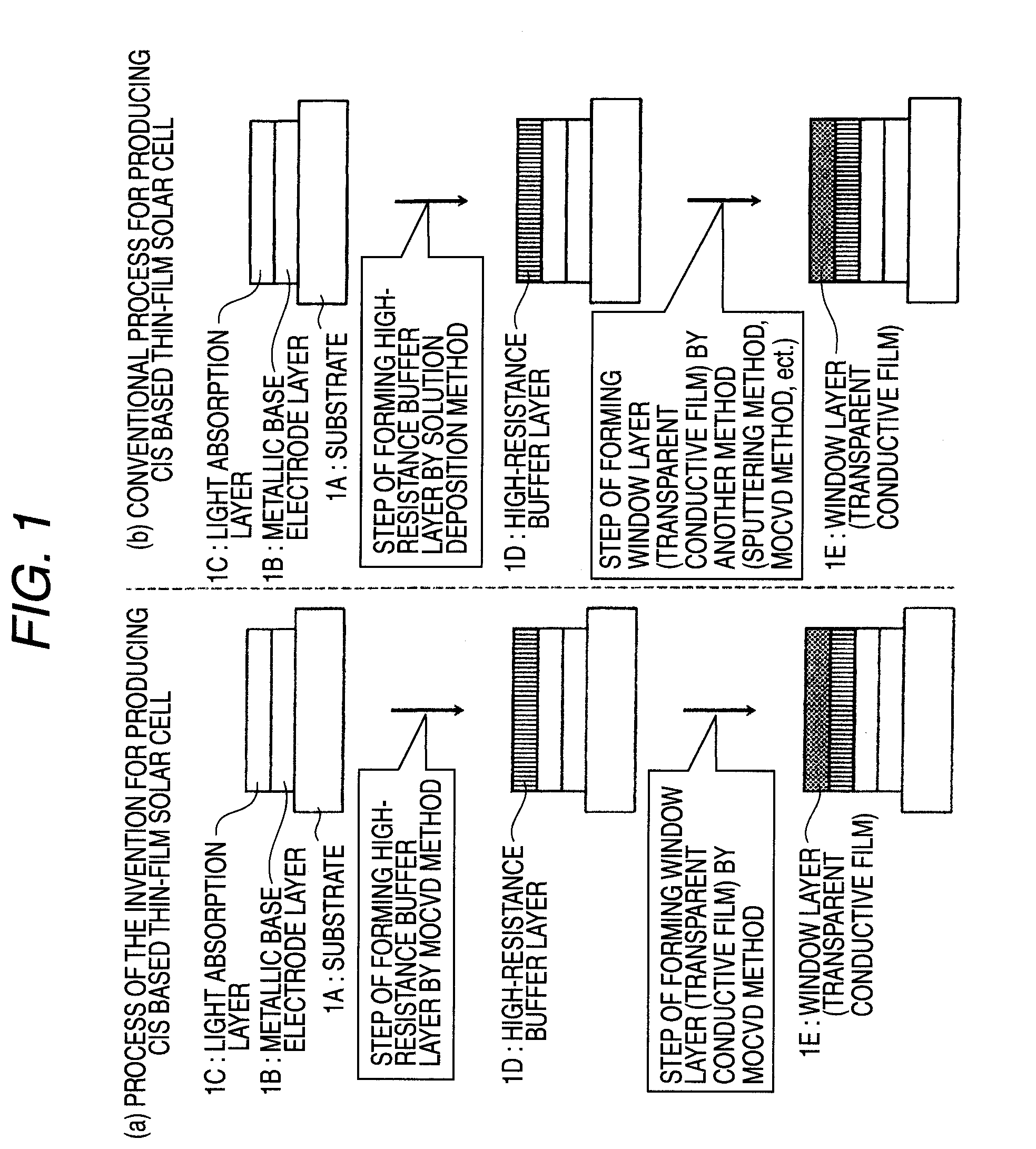
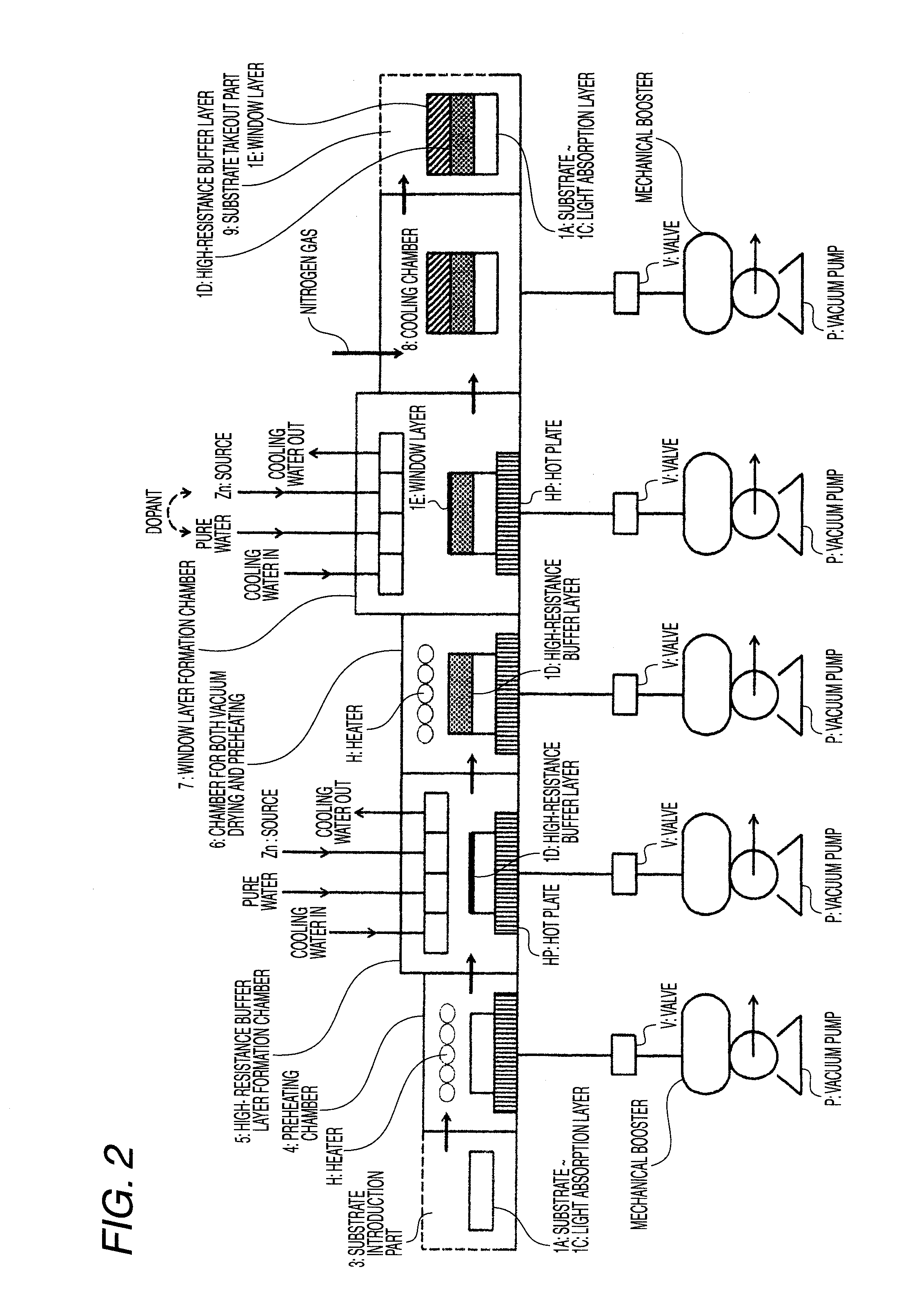
Method of Successive High-Resistance Buffer Layer/Window Layer (Transparent Conductive Film) Formation for CIS Based Thin-Film Solar Cell and Apparatus for Successive Film Formation for Practicing the Method of Successive Film Formation
ActiveUS20090087940A1Reduction in raw-material costLow cost of treatmentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceWork in process
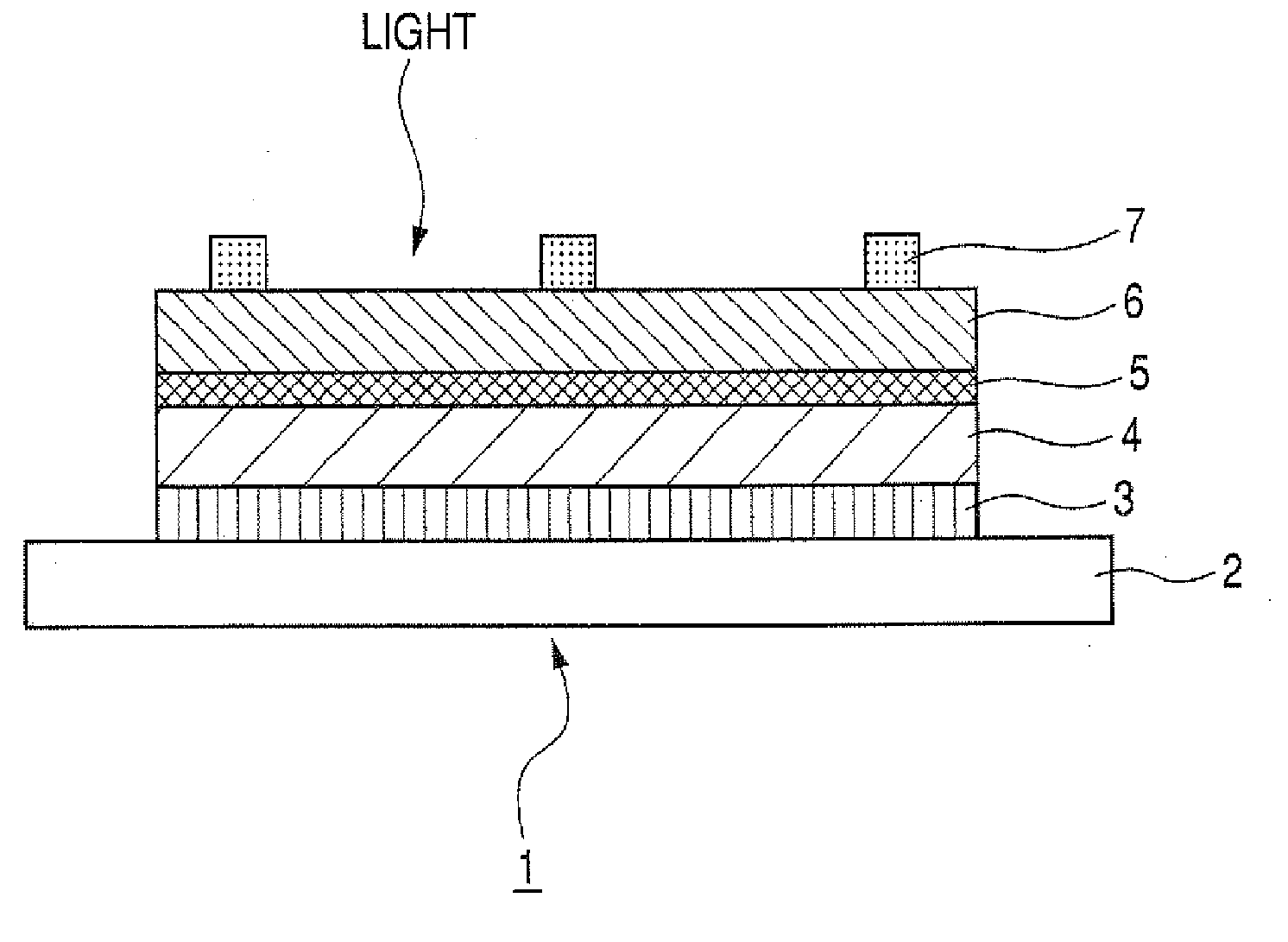
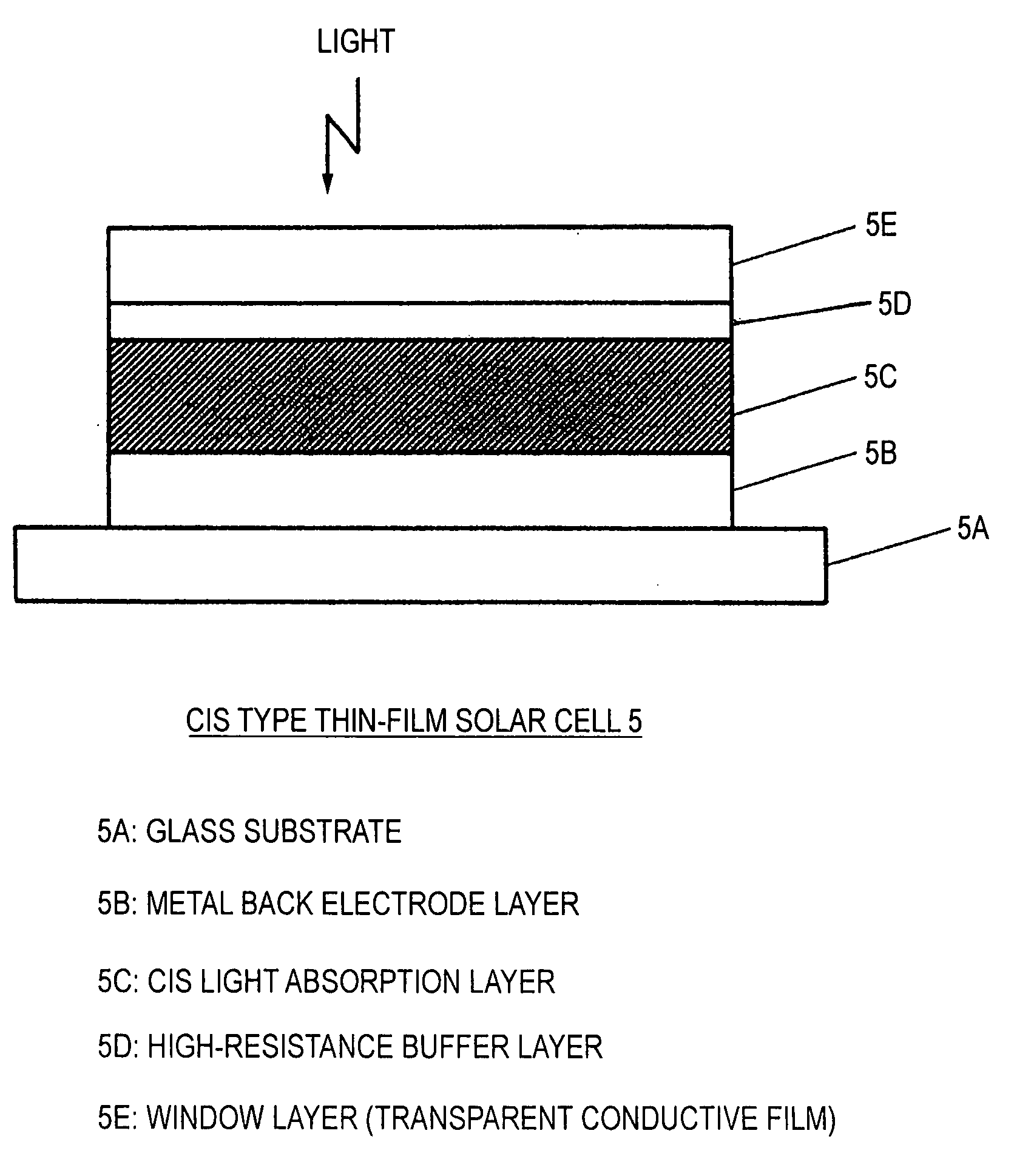
A high-resistance buffer layer and a window layer (transparent conductive film) are successively formed by the MOCVD method to obtain the same output characteristics as in conventional film deposition by the solution deposition method and to simplify a film deposition method and apparatus. Thus, the cost of raw materials and the cost of waste treatments are reduced to attain a considerable reduction in production cost.After a metallic base electrode layer 1B and a light absorption layer 1C are formed in this order on a glass substrate 1A, a high-resistance buffer layer 1D and a window layer 1E are successively formed in this order in a multi layer arrangement on the light absorption layer 1C of the resultant semifinished solar cell substrate by the MOCVD method. Consequently, a film deposition method and apparatus are simplified and the cost of raw materials and the cost of waste treatments can be reduced.
Owner:SOLAR FRONTIER
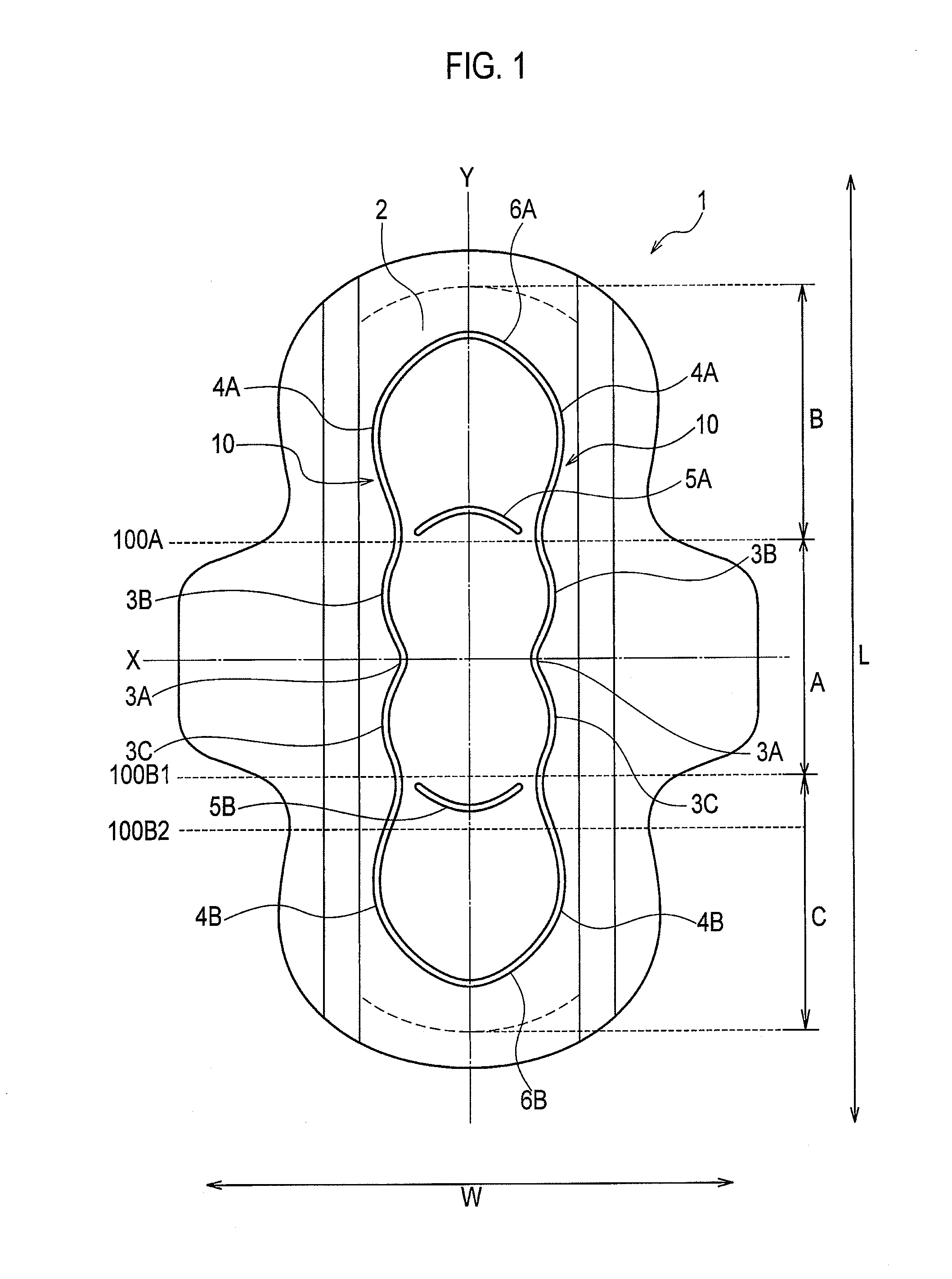
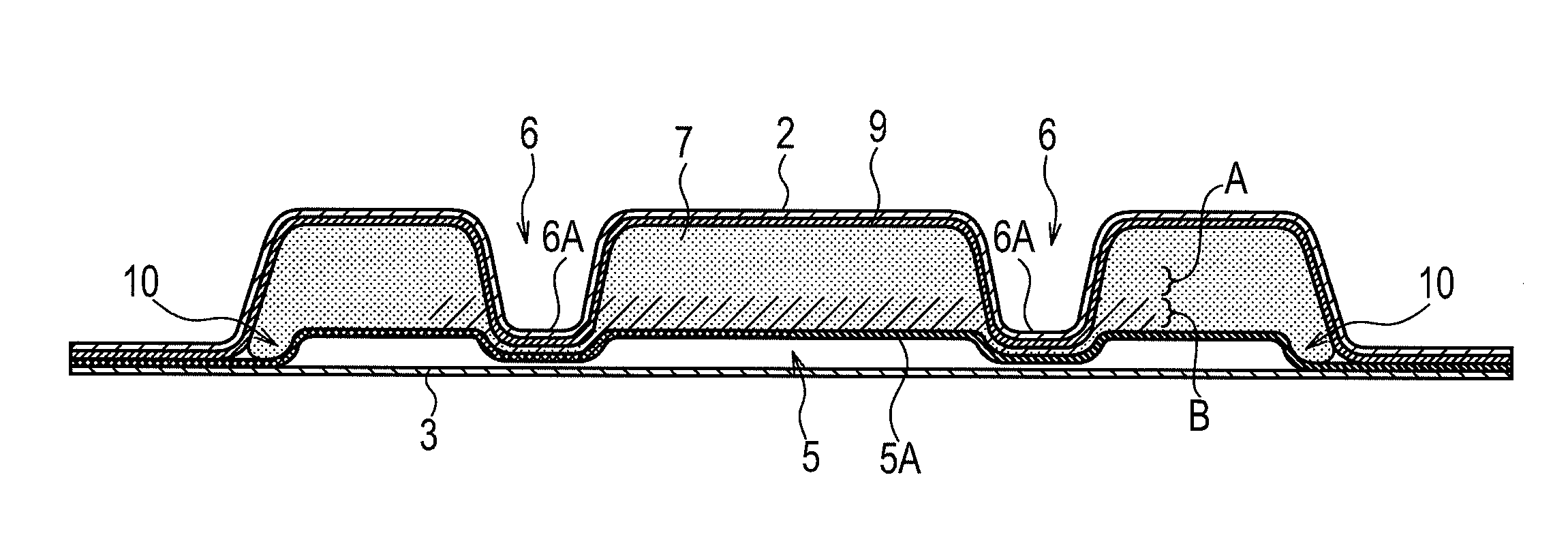
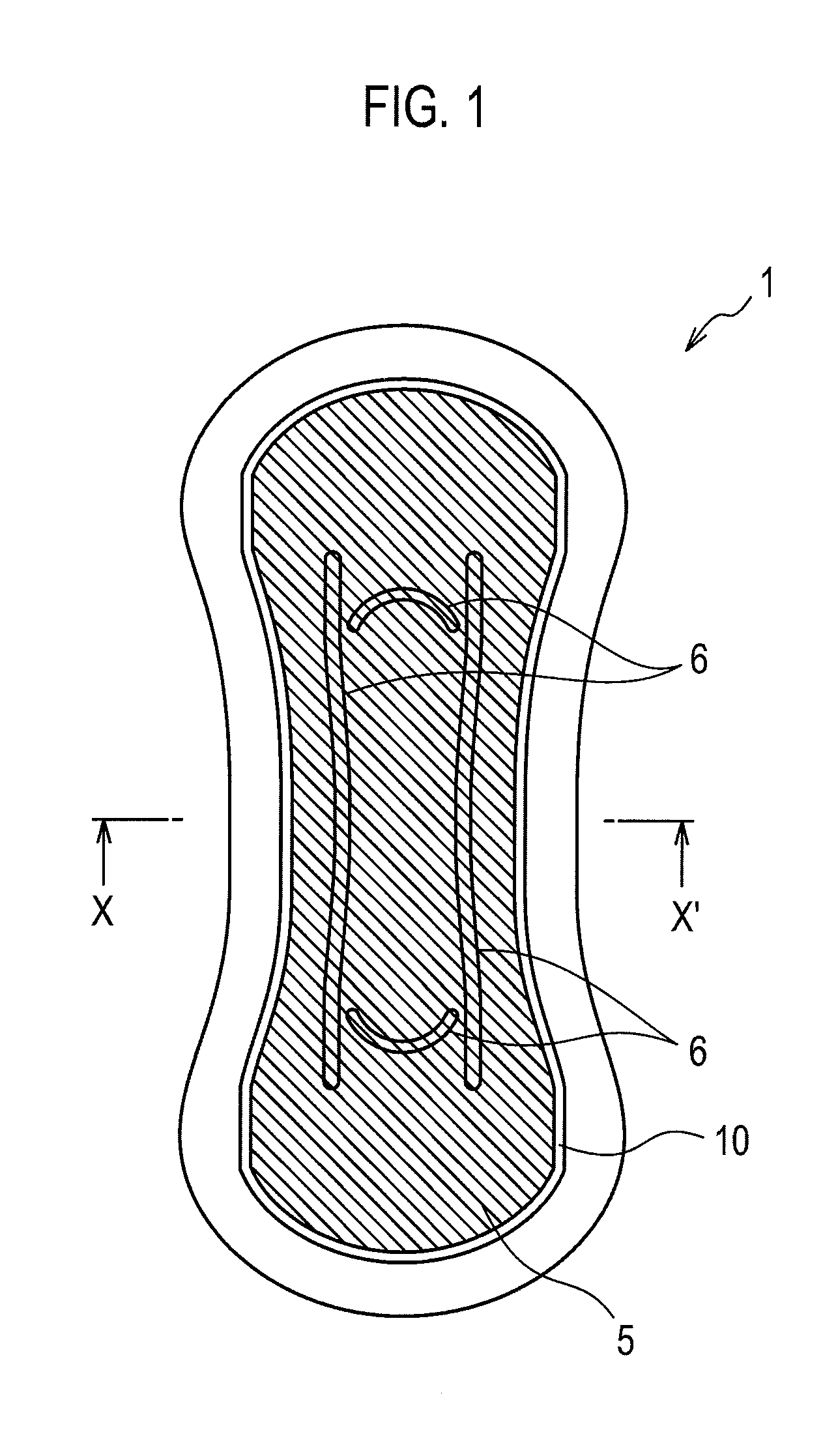
Absorbent article
An absorbent article includes a pair of grooves in which each of the grooves has a central region in the longitudinal direction has a first section which is formed so as to be curved in a convex manner at an inside of a widthwise direction of the absorption layer; a second section and a third section which is linked with each end of the first section and is formed so as to be curved in a convex manner at an outside of the widthwise direction. A radius of curvature of the first section is smaller than the radius of curvature of either the second section or the third section.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Avalanche photo-detector with high saturation power and high gain-bandwidth product
InactiveUS20050051861A1Reduce operating voltageReducing carrier transport timeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLow noiseCapacitance
An avalanche photo-detector (APD) is disclosed, which can reduce device capacitance, operating voltage, carrier transport time and dark current as well as increasing response speed and output power. Thus, an avalanche photo-detector (APD) with high saturation power, high gain-bandwidth product, low noise, fast response, low dark current is achieved. The APD includes an absorption layer with graded doping for converting an incident light into carriers, an undoped multiplication layer for multiplying current by means of receiving carriers, a doped field buffer layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the multiplication layer for concentrating an electric field in the multiplication layer when a bias voltage is applied, and an undoped drift layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the field buffer layer for capacitance reduction.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
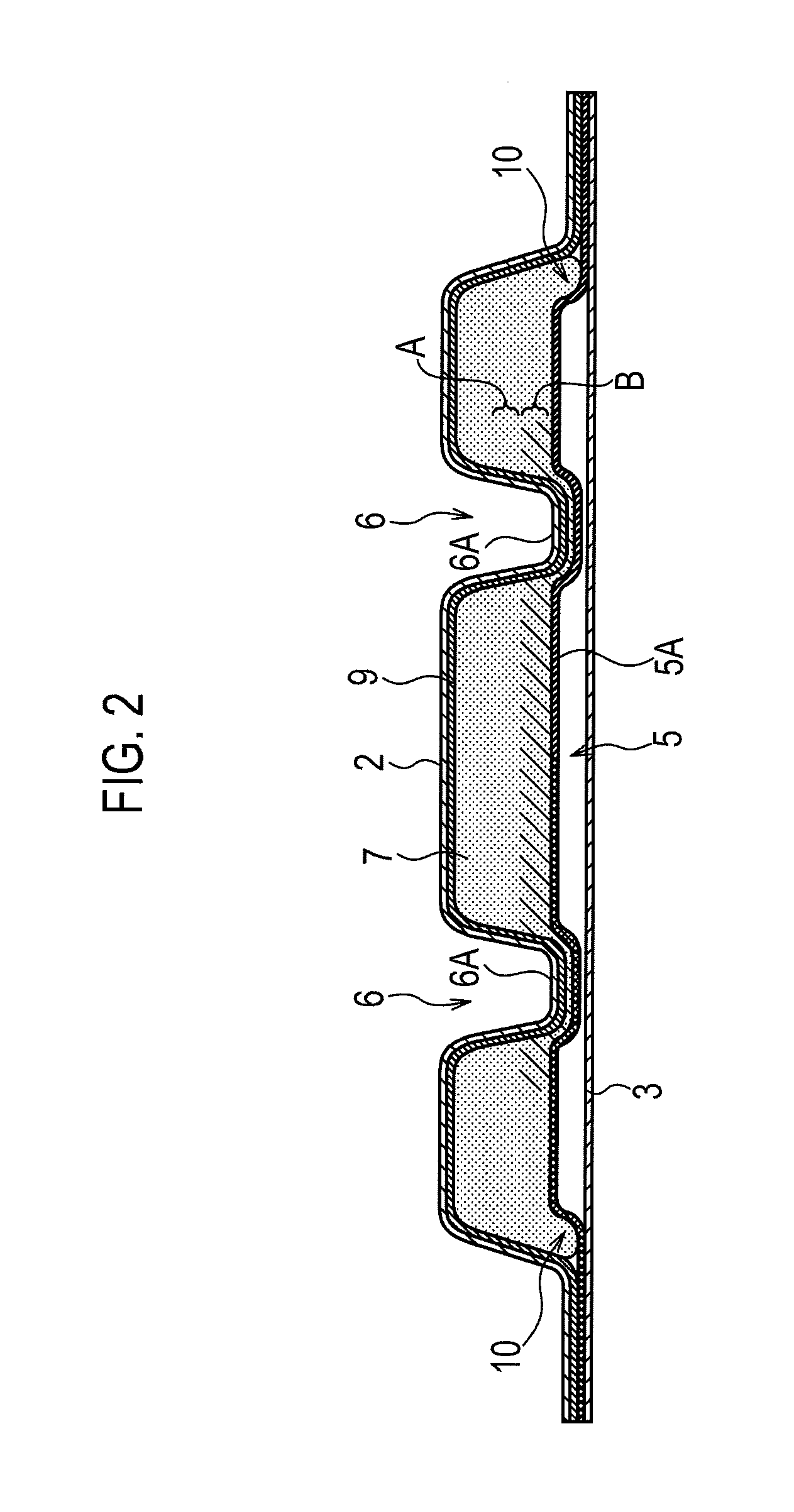
Absorbent article and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130035656A1Reduce wetted areaExcessive diffusionCeramic shaping apparatusSanitary towelsEngineeringAbsorption layer
An absorbent article having a compressed region formed by a compressing process in an absorption layer on a side facing to the backsheet; and a plurality of pressed grooves are formed by a pressing process in the absorption layer on a side facing to the topsheet, within a region opposed to the compressed region.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
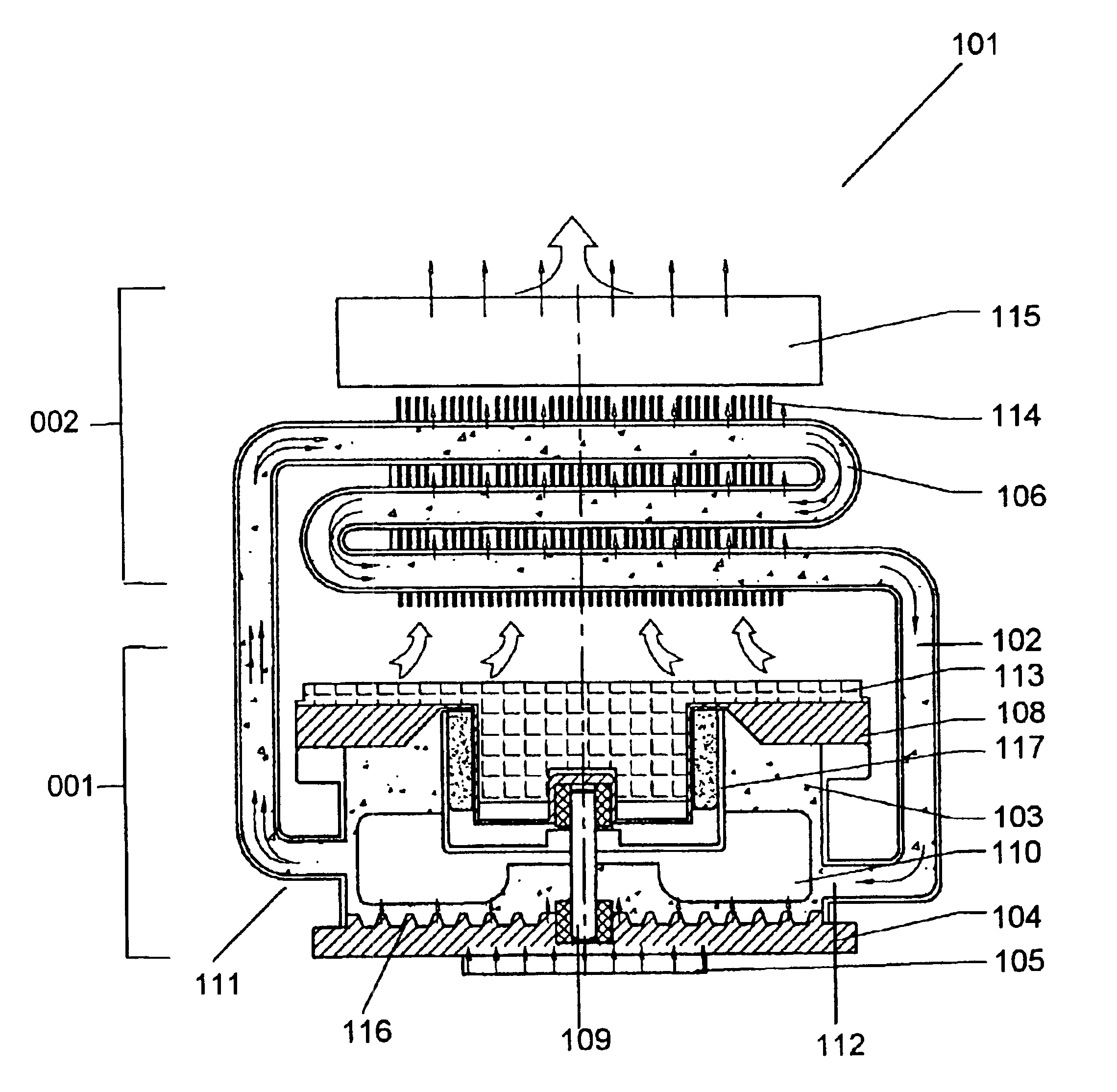
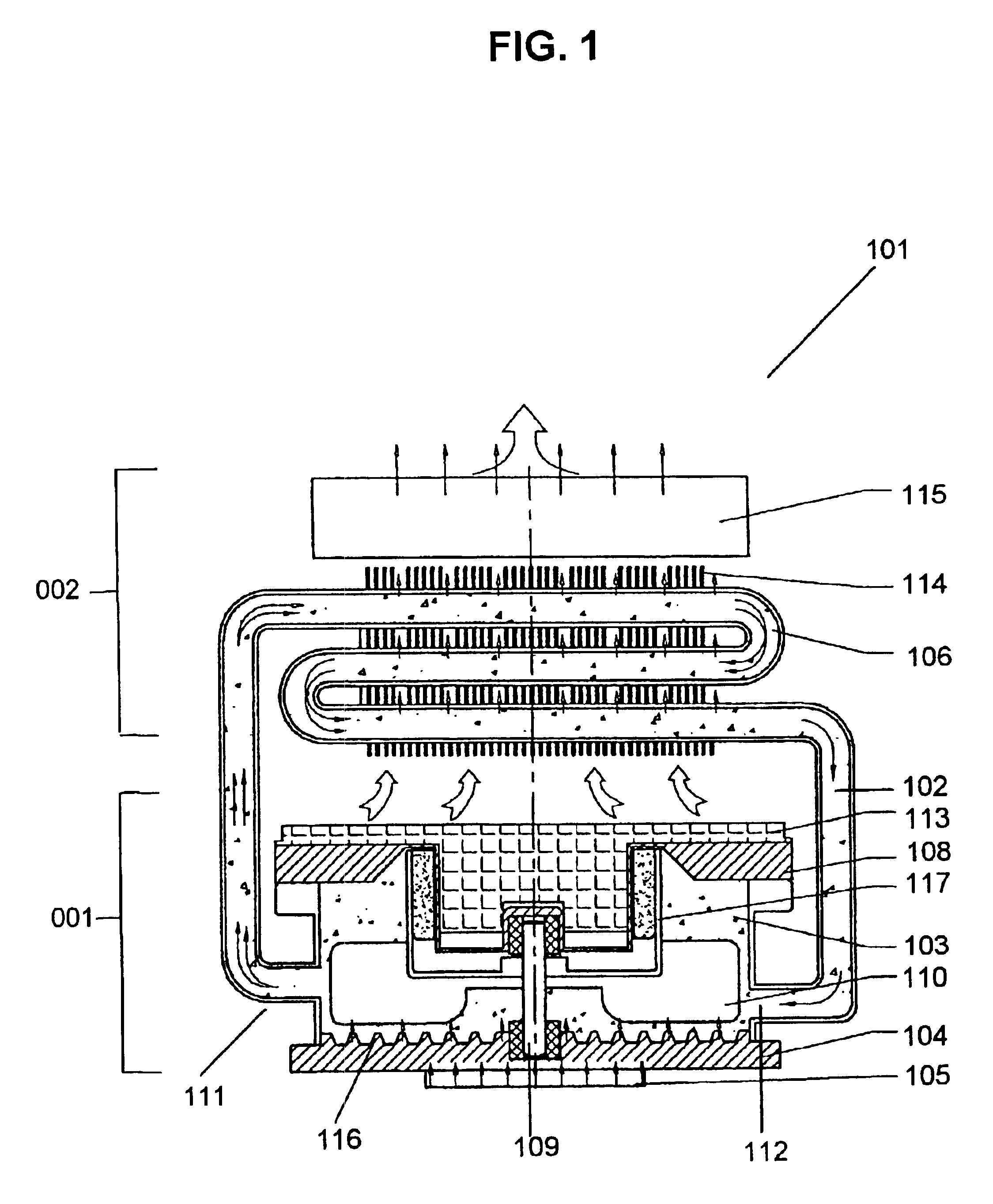
Integrated fluid cooling system for electronic components
InactiveUS6894899B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSystems designNuclear engineering
An improved cooling system designed for electronic components such as a central processing unit of a computer with an integrated unit comprising a radiation housing, an absorption housing having a coolant store unit, an absorption layer between the coolant store unit and the electronic component and a circulation generation unit which causes a coolant to flow from the coolant store unit to the absorption layer and back to the coolant store unit through a conduit.
Owner:HONG KONG CHEUNG TAT ELECTRICAL
Perovskite solar battery and preparing method thereof
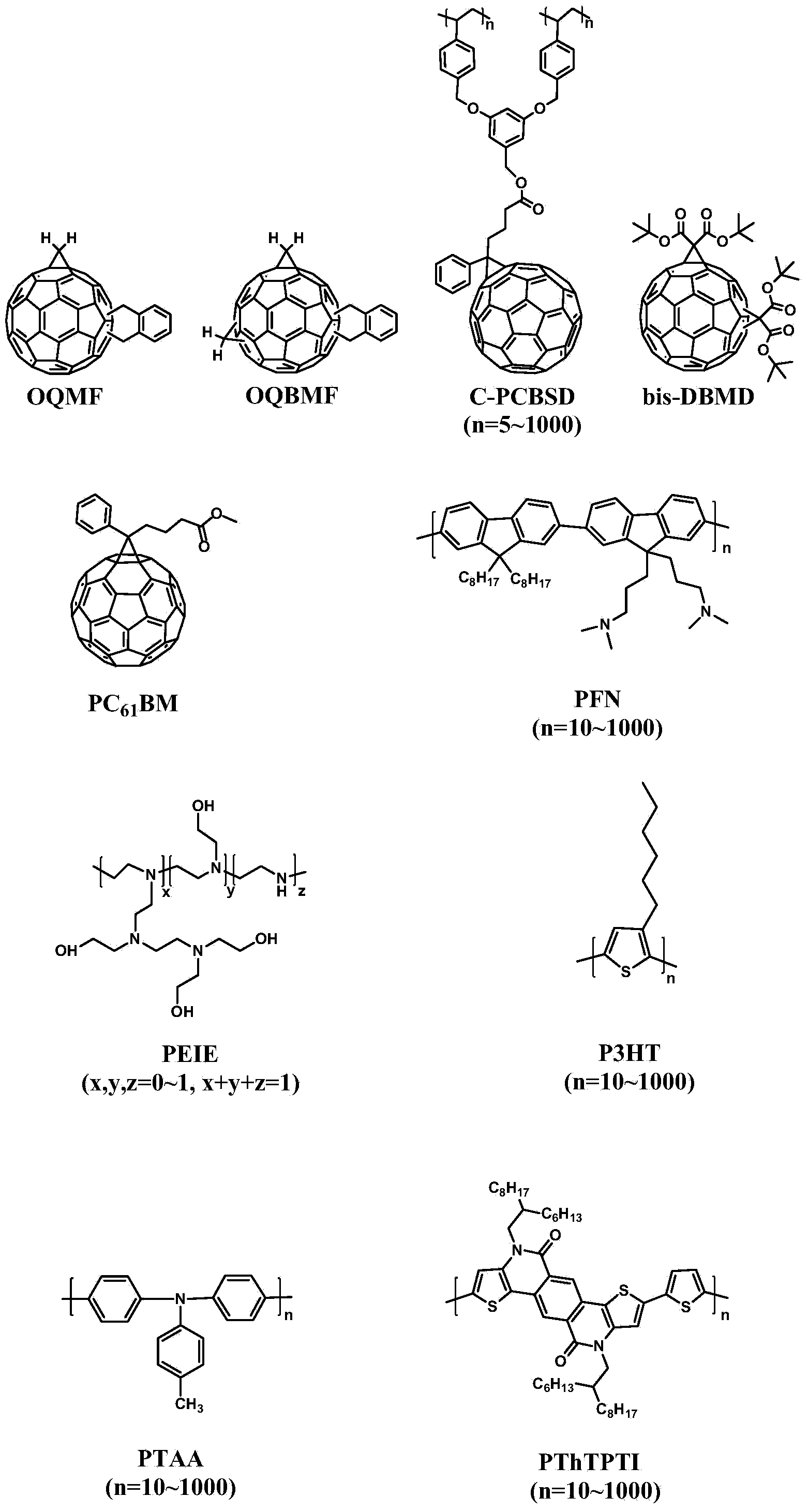
InactiveCN103855307ASimple processHigh industrial application valueFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionHole transport layer
The invention relates to a perovskite solar battery and a preparing method thereof. The perovskite solar battery comprises a transparent electrode, a hole transmission layer, a perovskite light absorption layer, an electronic transmission layer and a metal electrode. The hole transmission layer comprises at least one of PEDOT: PSS, P3HT, PTAA, PThTPTI, metallic oxide and graphene oxide. The electronic transmission layer comprises at least one of 58 pi-electronic fullerene PCBM, 56 pi-electronic fullerene OQMF, 54 pi-electronic fullerene OQBMF, PFN, PEIE, ZnO, TiO2, doped or modified ZnO or TiO2. The perovskite solar battery is high in energy exchange efficiency and low in cost and can be produced on a large scale, and the preparing method is simple in technology.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Perovskite solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104091888AEasy to prepareControllable parametersSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerovskite solar cellFill factor
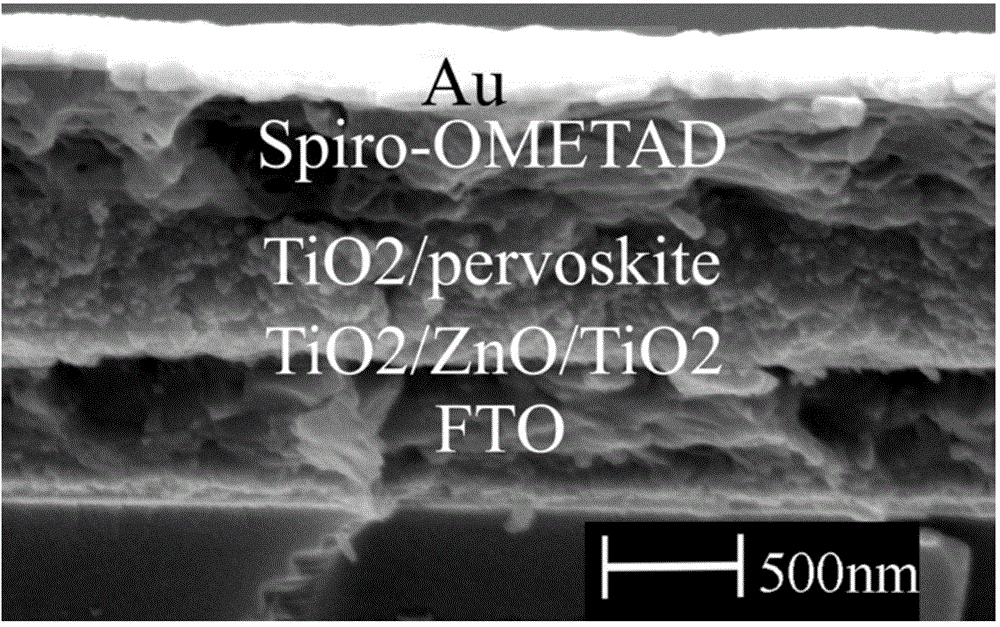
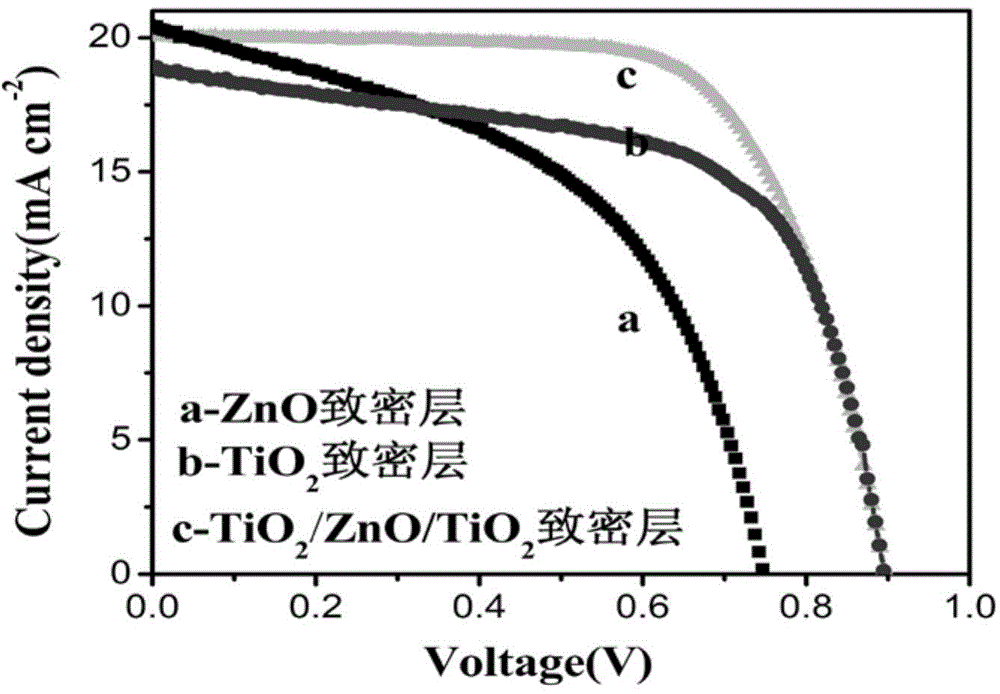
The invention relates to a perovskite solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The perovskite solar cell is composed of an FTO glass substrate, a sandwich structure TiO2 / ZnO / TiO2 compact layer, a TiO2 mesoporous / perovskite structure material active light absorption layer, a spiro-OMeTAD hole transferring layer and a gold electrode. Compared with the prior art, the sandwich structure TiO2 / ZnO / TiO2 compact layer combines with the advantages and disadvantages of TiO2 and ZnO, so that fill factors of the perovskite solar cell are improved to 70%, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency reaches 12.6%. Equipment for preparing the perovskite solar cell is simple, the preparing process is simple, control is easy, the cost is low, and the perovskite solar cell has a very good industrial application prospect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Optical filter and process for producing the same
InactiveUS7025908B1Improve stabilityHigh transparencyTransistorOther chemical processesPhosphoric Acid EstersIon content
The optical filter of the present invention is provided with a near infrared light absorption layer that contains a component composed of copper ions and a phosphoric ester compound expressed by the following Formula (10), in which the phosphorus atom content in the near infrared light absorption layer is 0.4 to 1.3 mol per mole of copper ions, and the copper ion content in the near infrared light absorption layer is 2 to 60 wt %. Thus keeping the phosphorus atom and copper ion content within specific ranges results in good near infrared light absorption and in improved moisture resistance whereby devitrification caused by whitening is suppressed
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS7659002B2Improve the overall coefficientIncreased durabilityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLow emissivityGain coefficient
Owner:CARDINAL CG
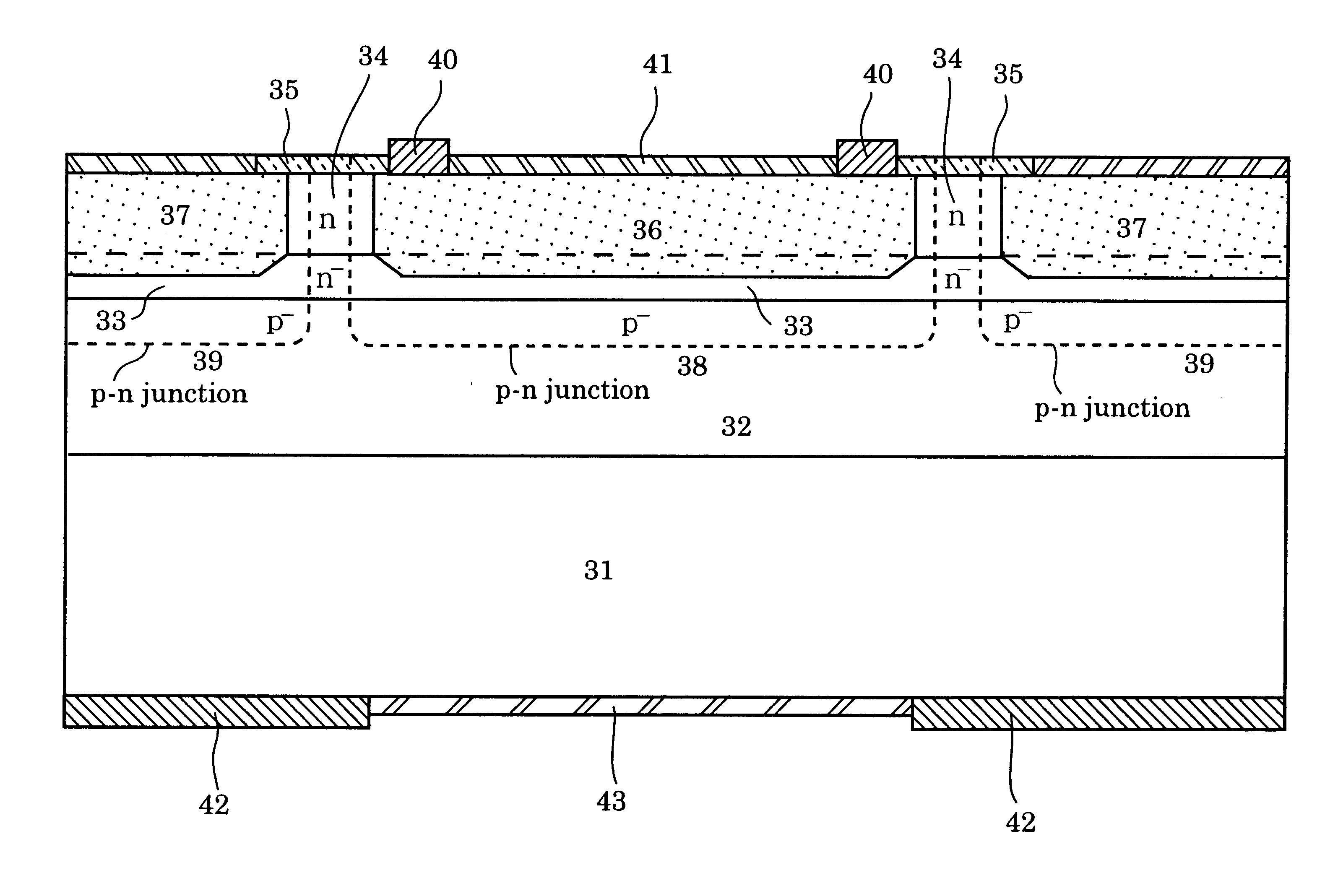
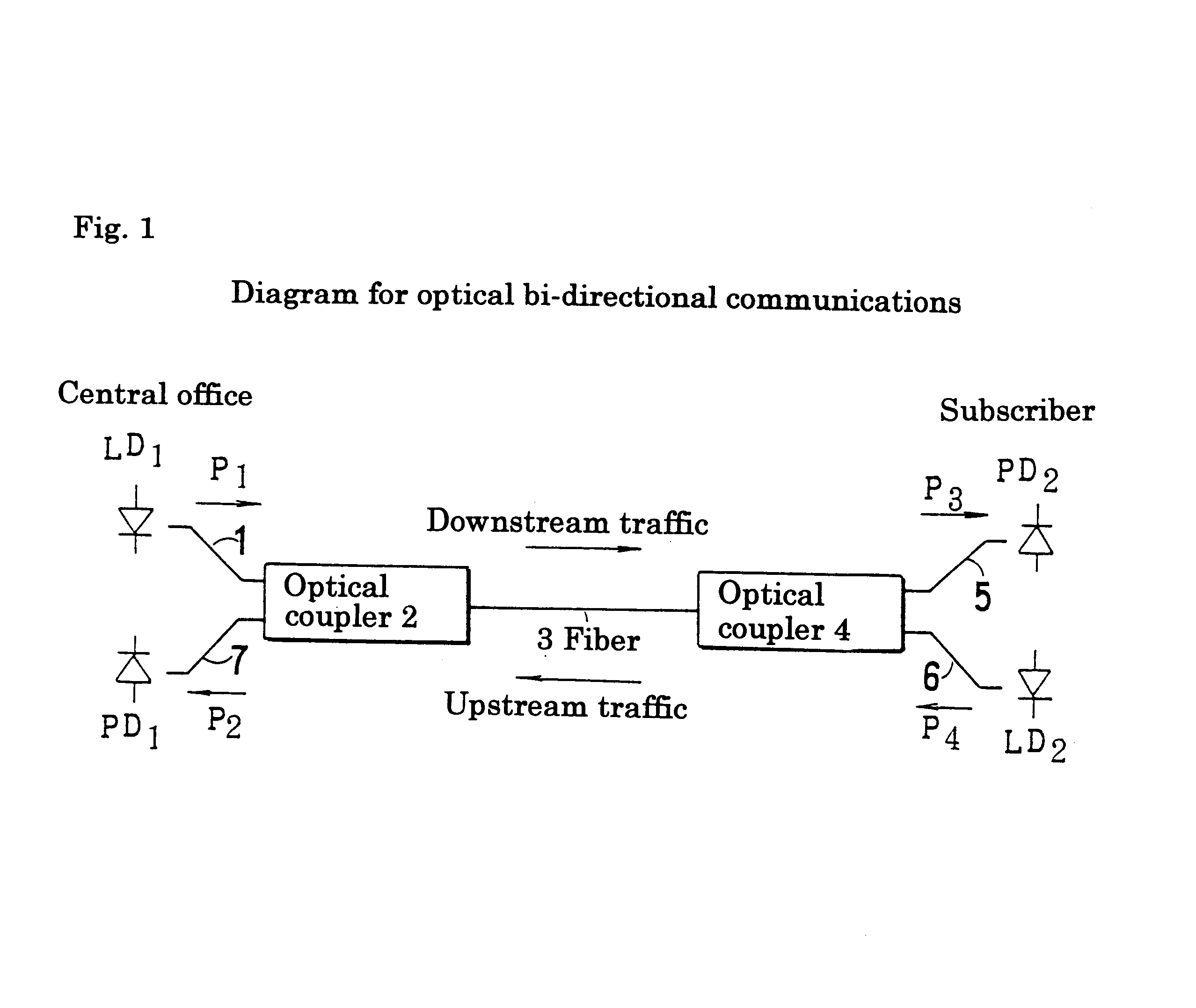
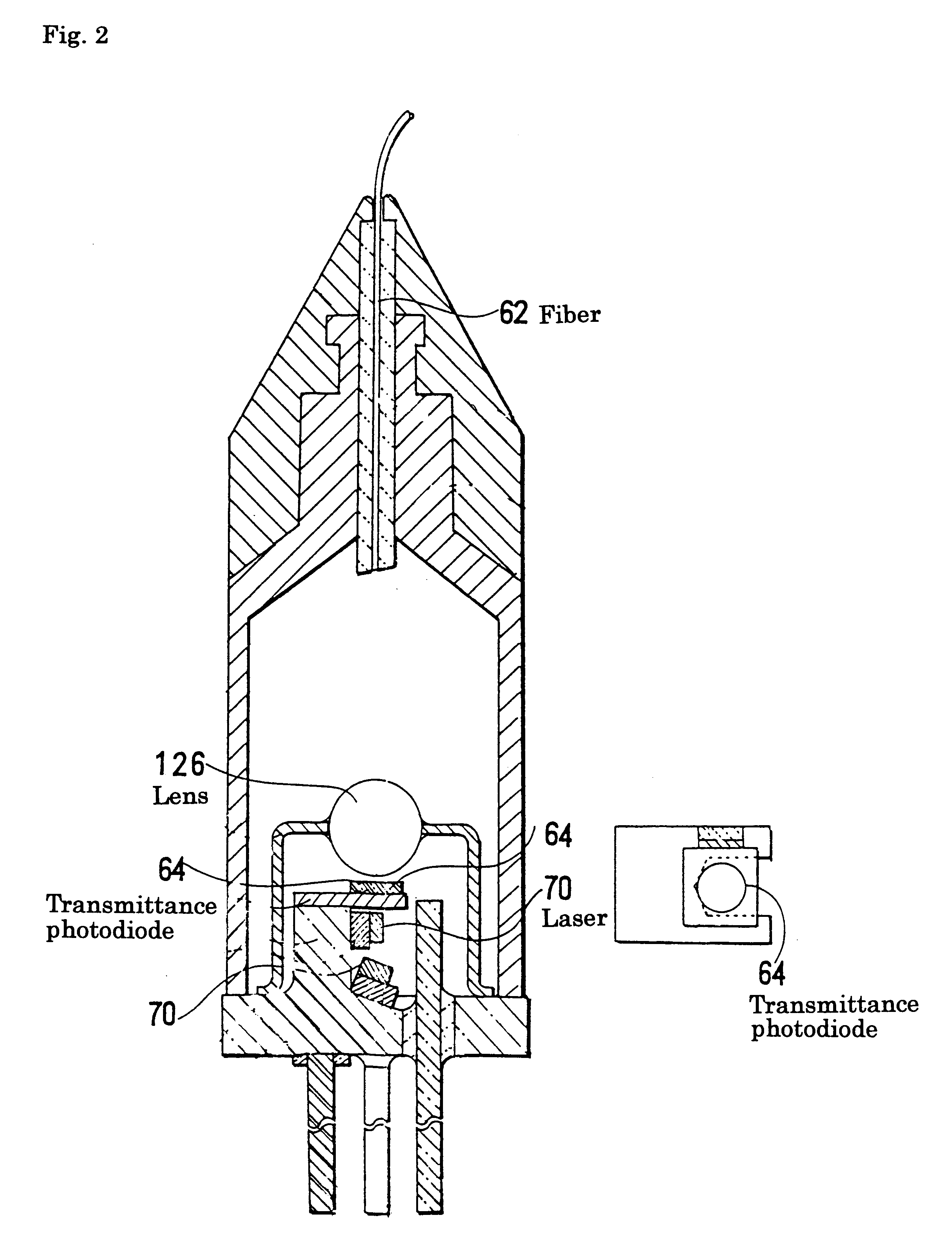
Photodiode with buffer layer
InactiveUS6218684B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A half-transmittance photodiode usable as a photodetector in receivers for "ping-pong transmission" is improved in temperature characteristic, so that a half-transmittance photodiode usable at low temperatures is available. A p-n junction is formed in a buffer layer, not in an absorption layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com