Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5249 results about "Central region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
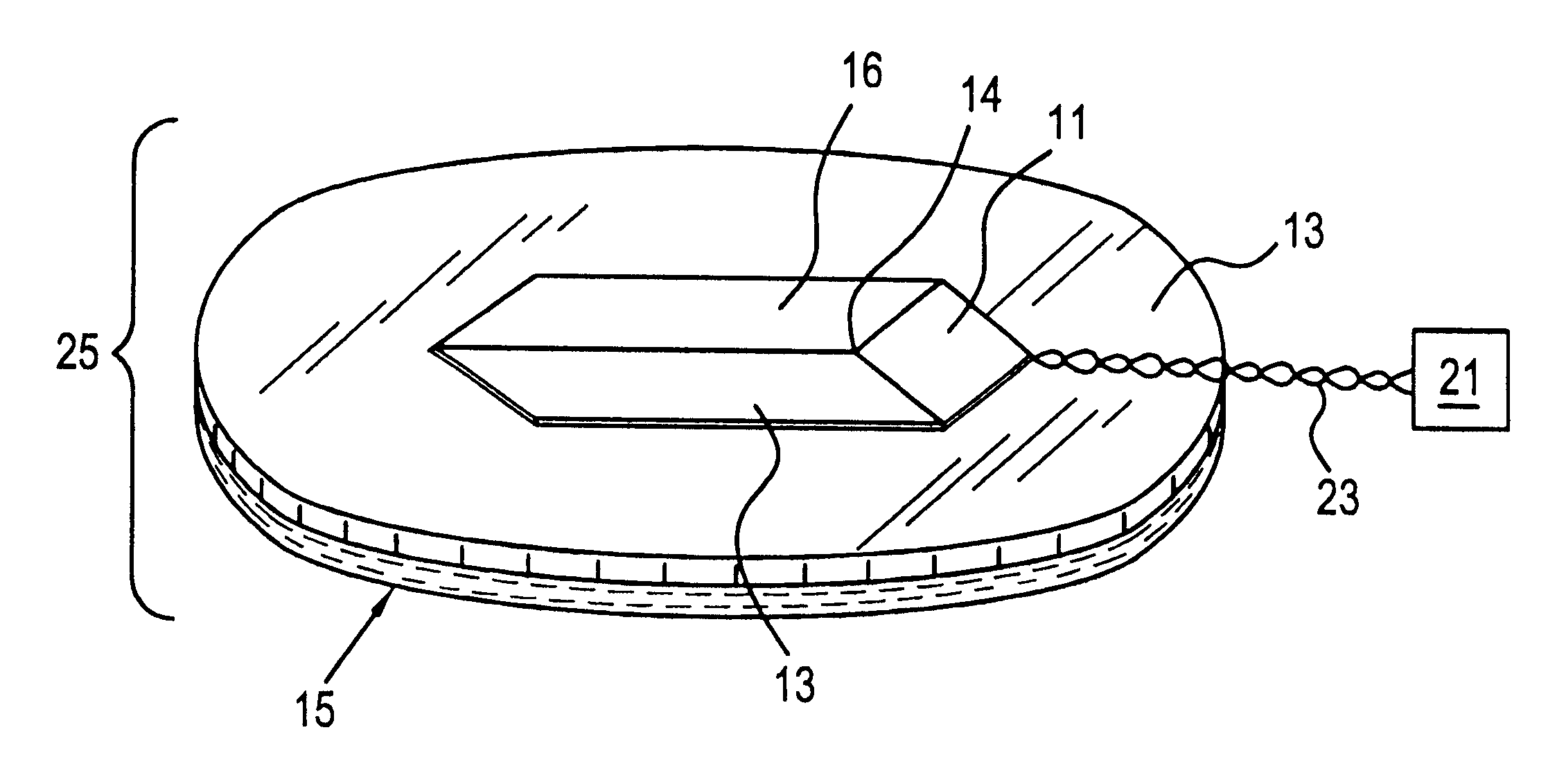
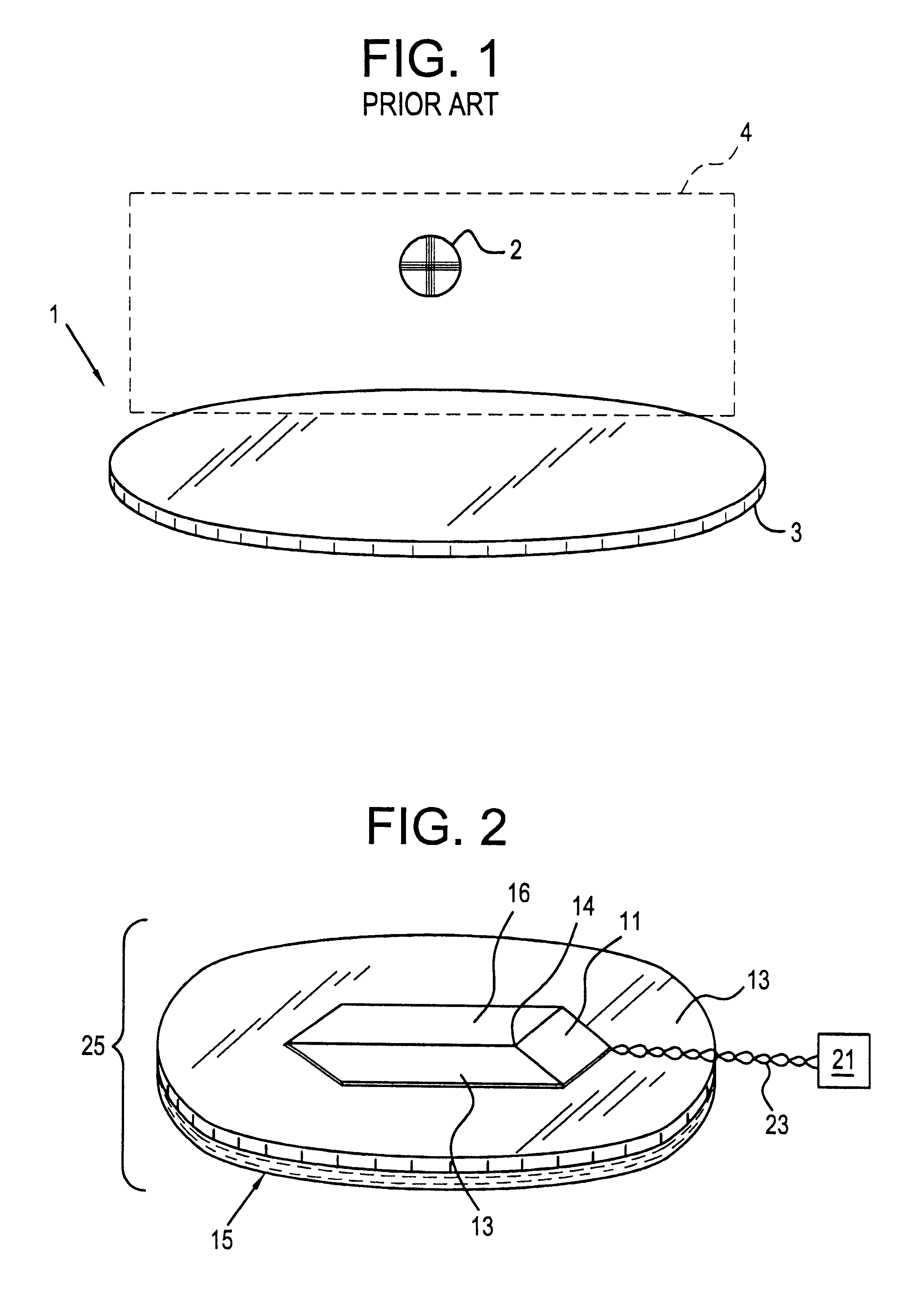
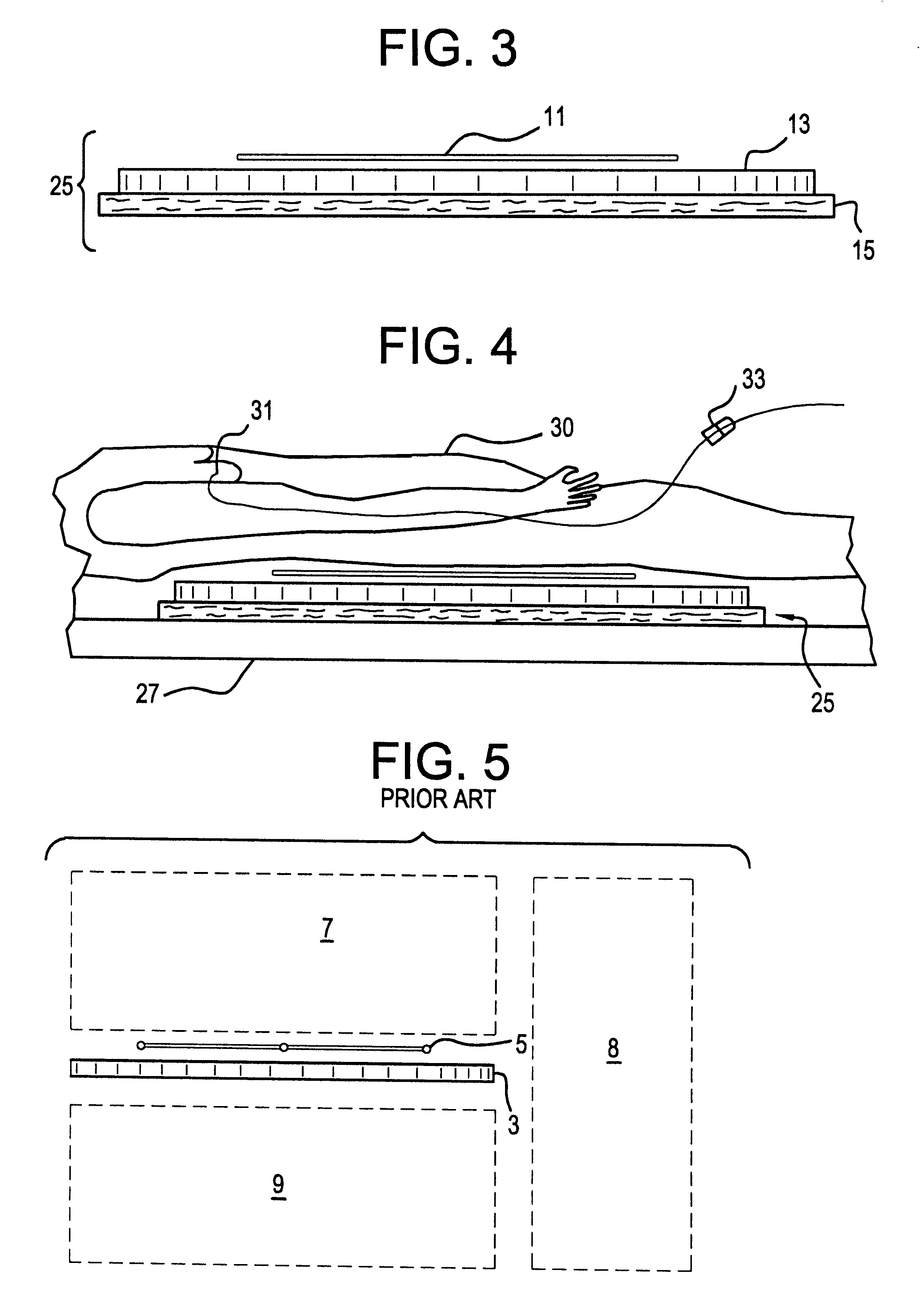
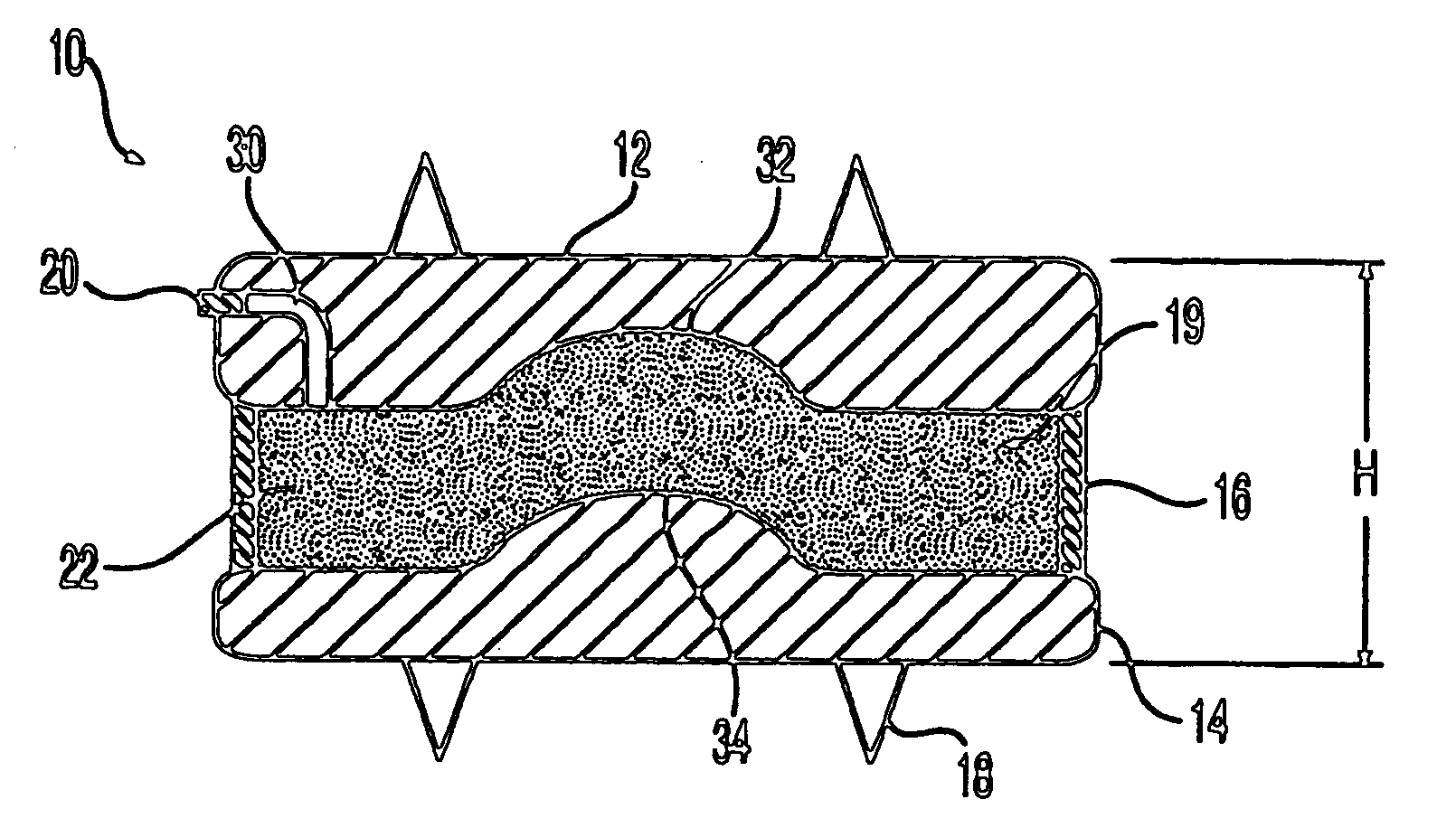
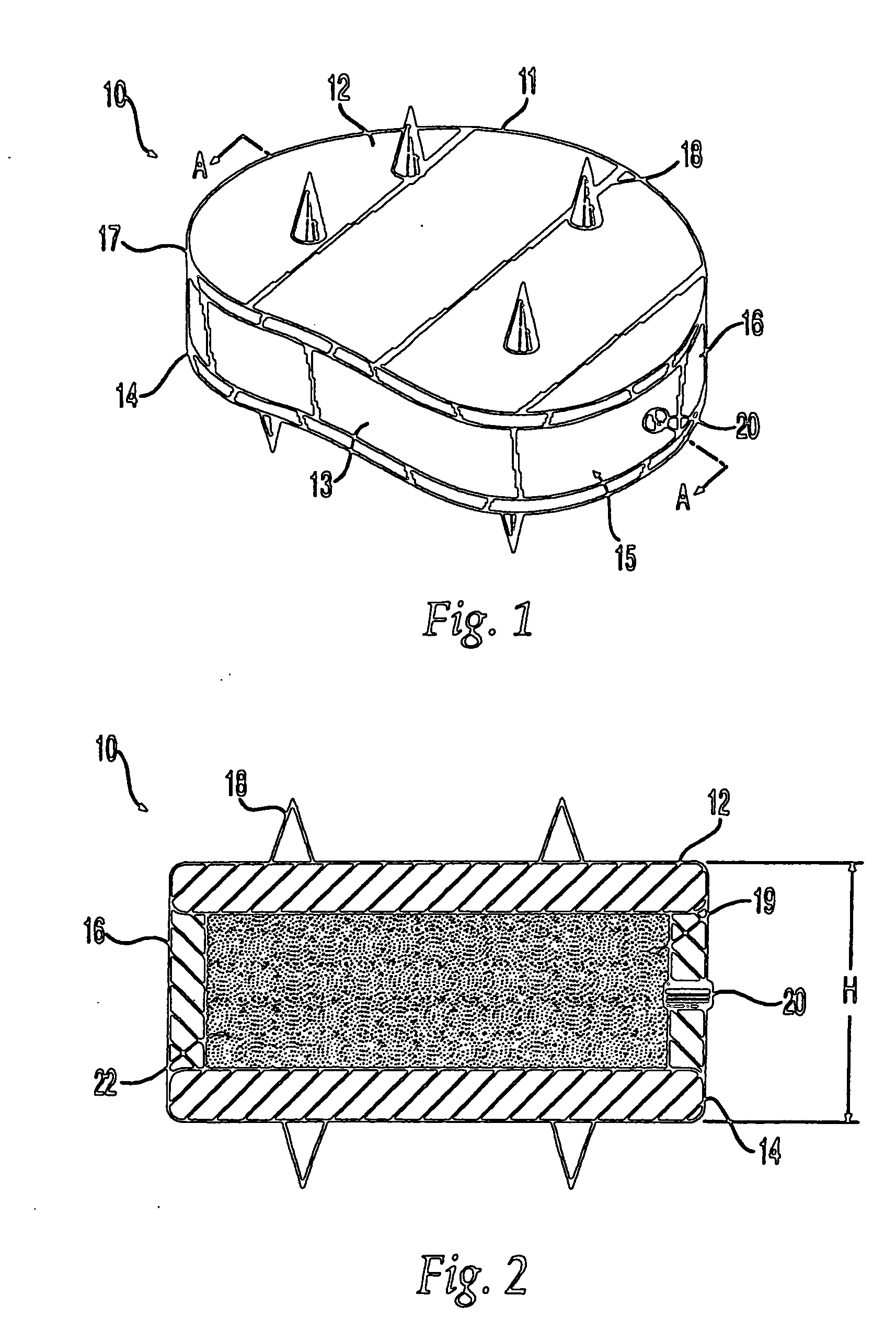
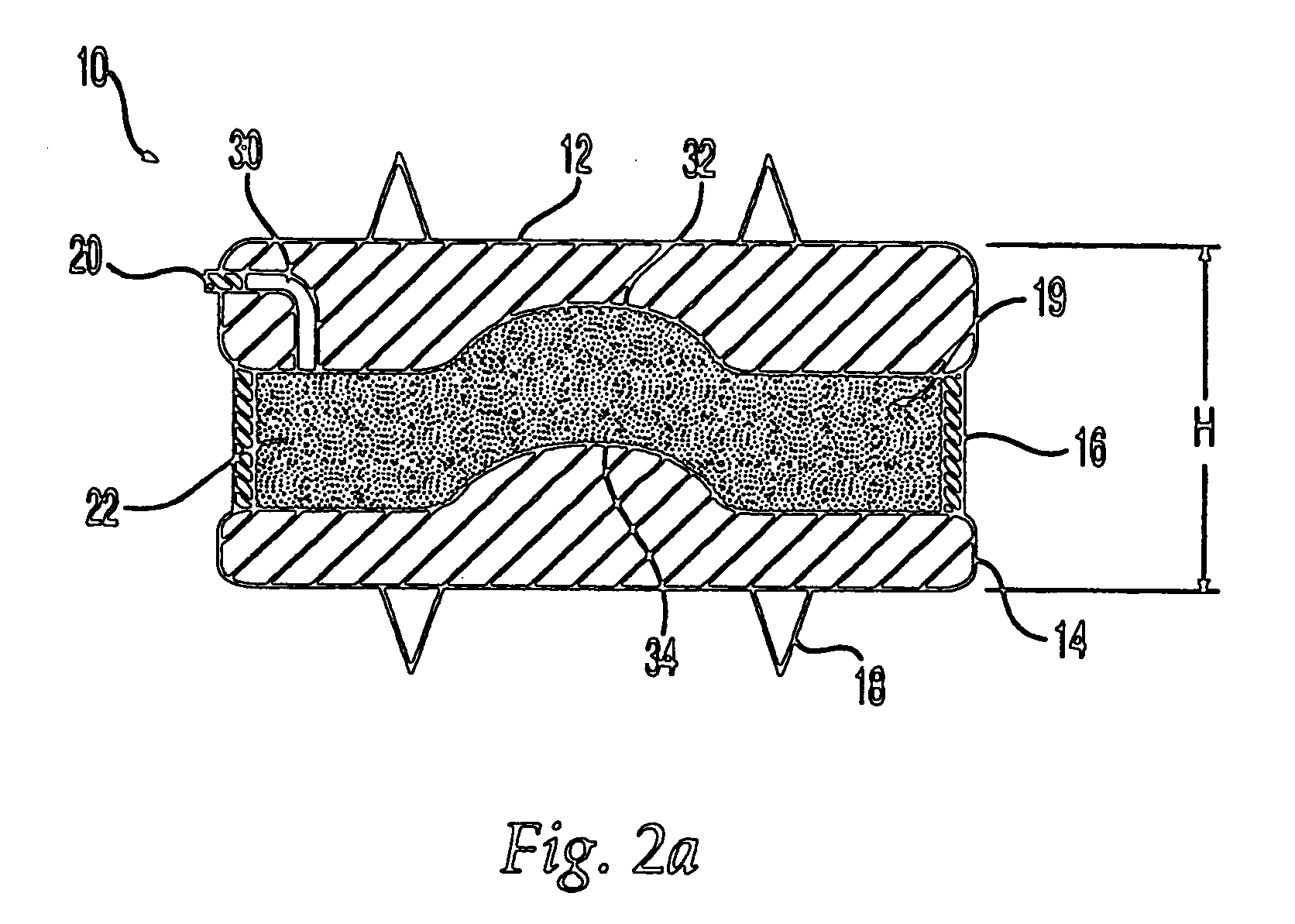
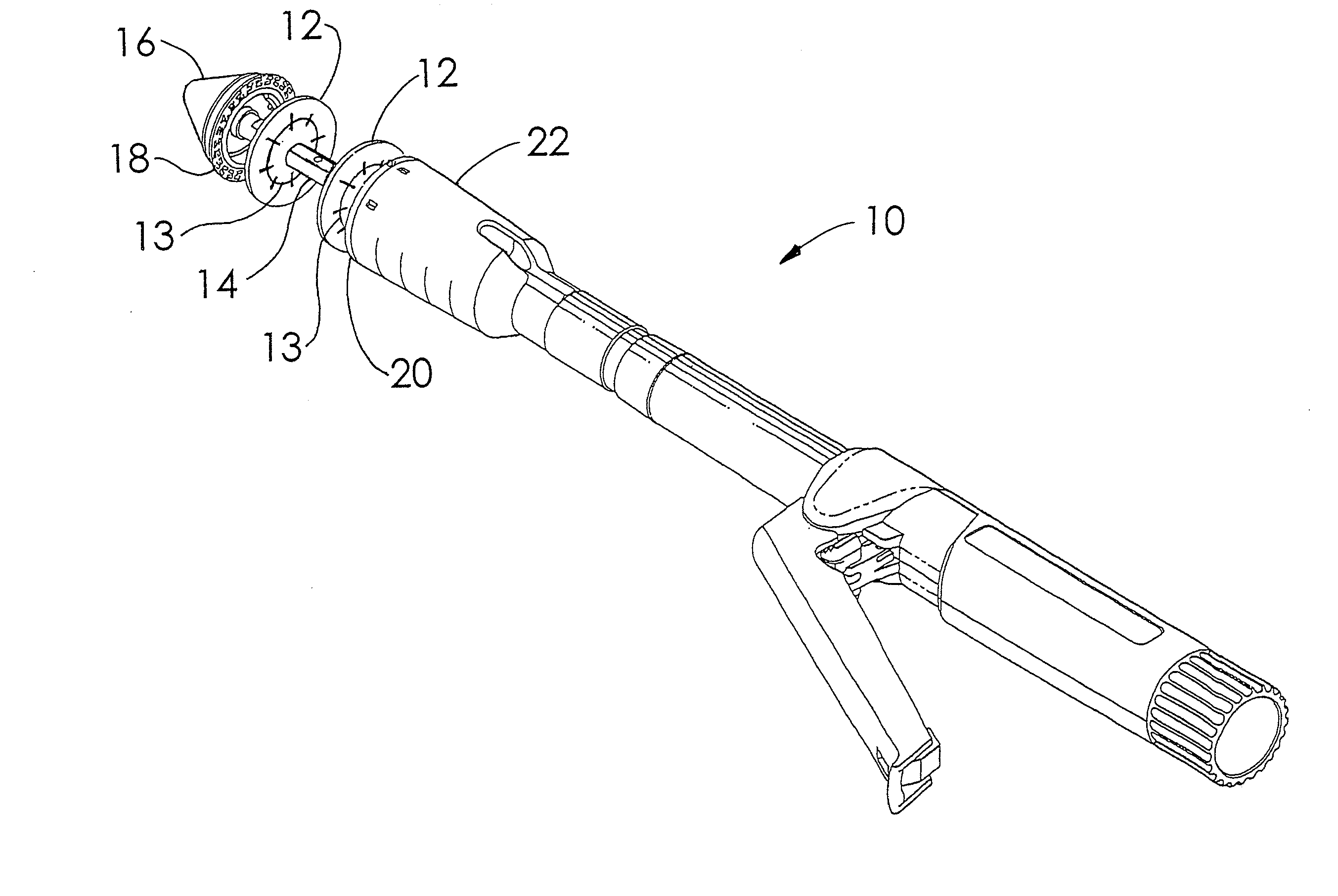
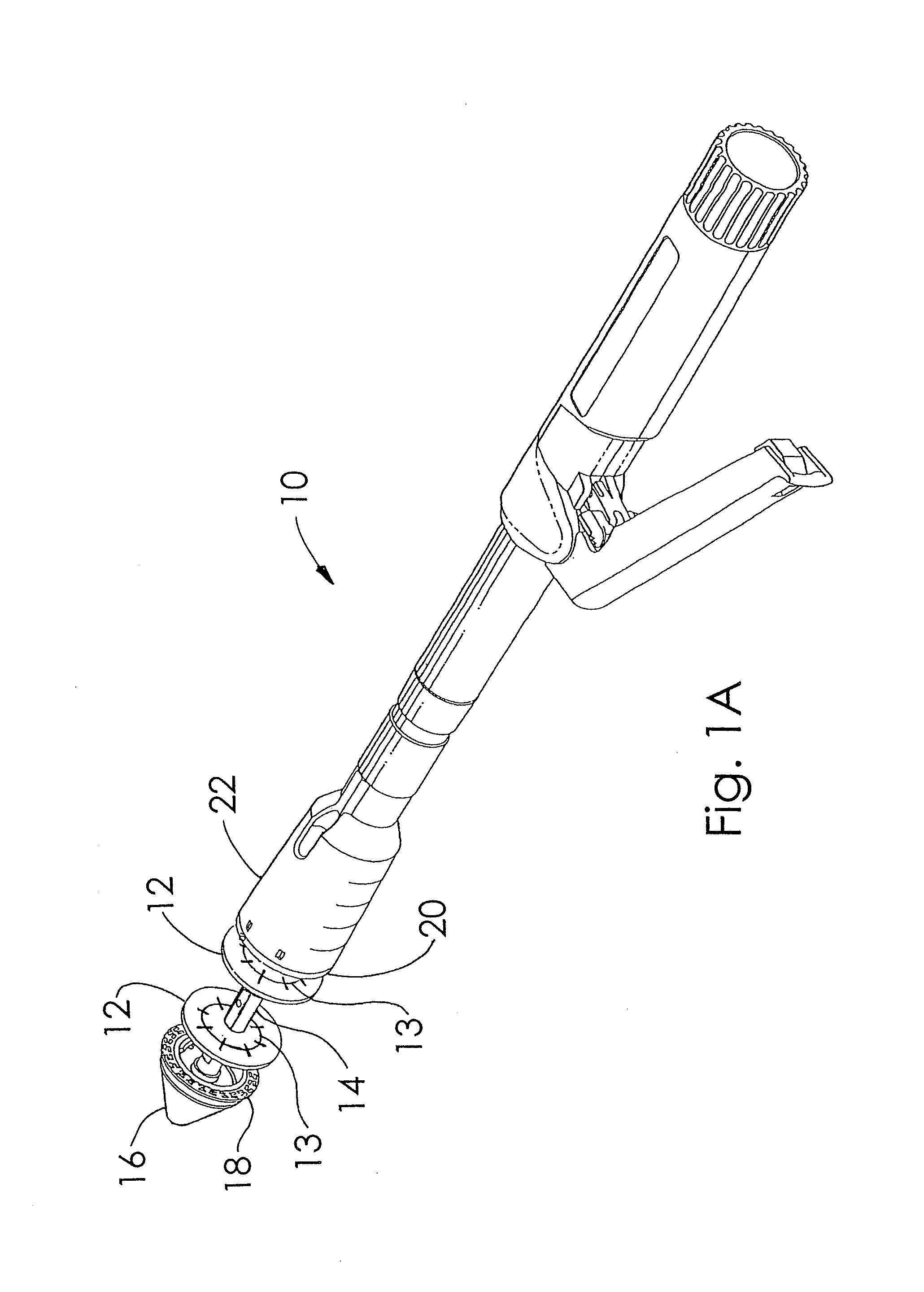
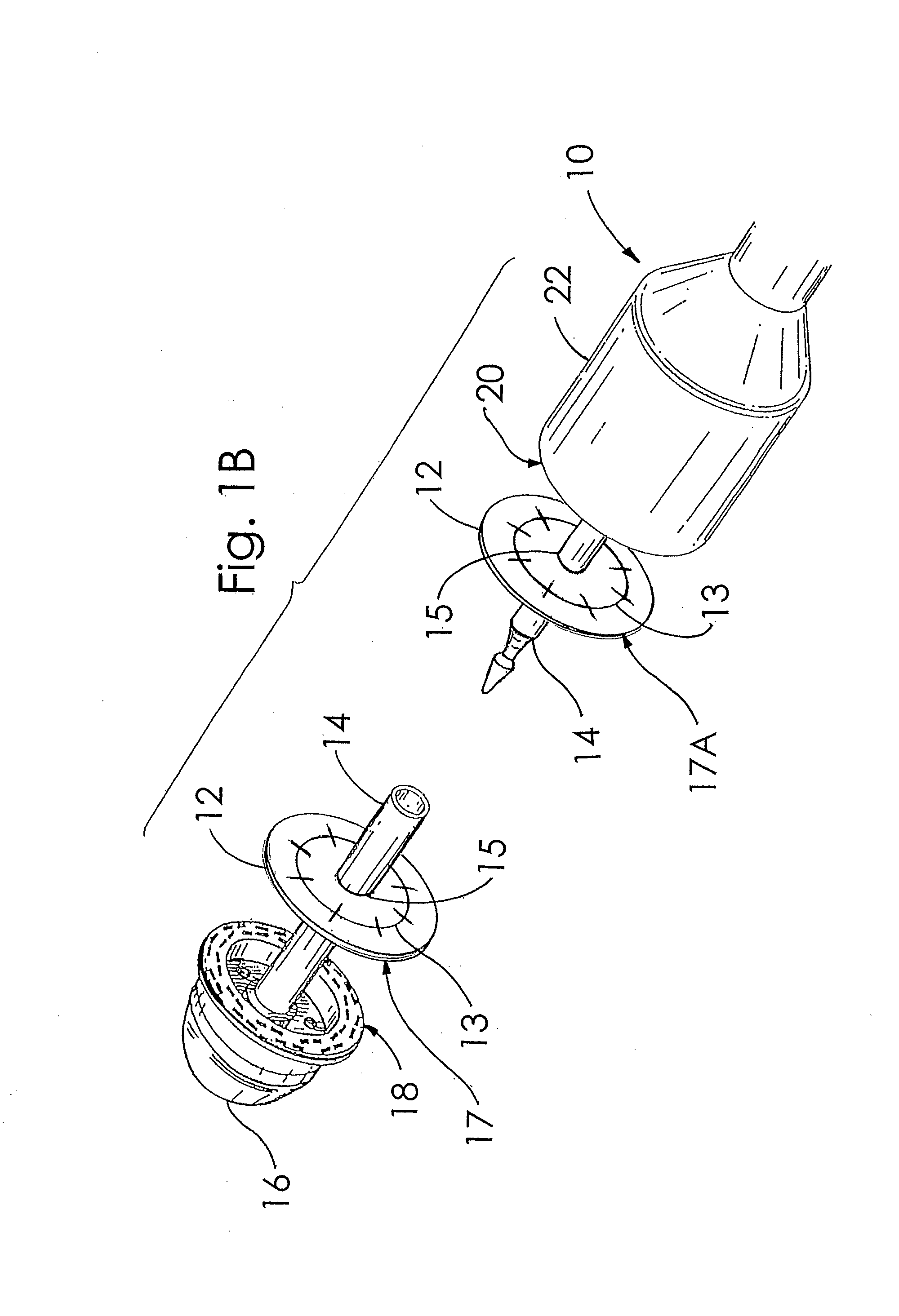
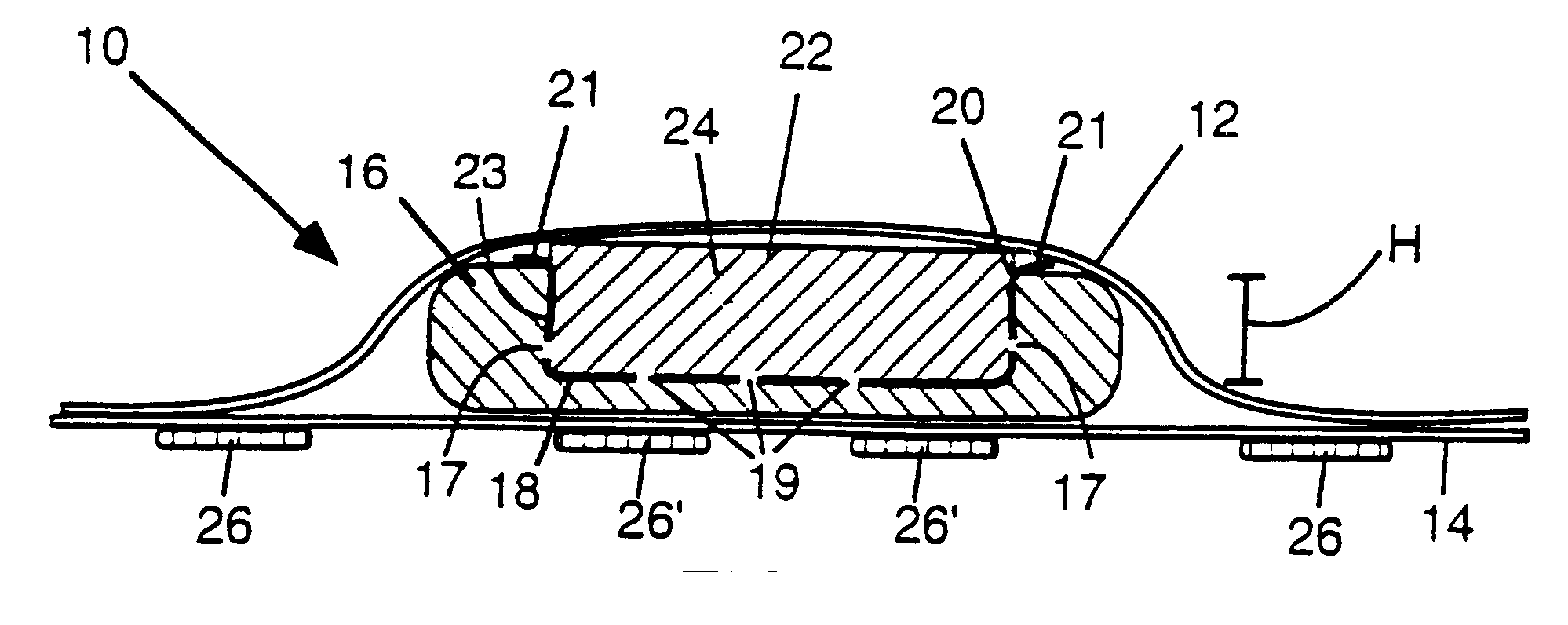
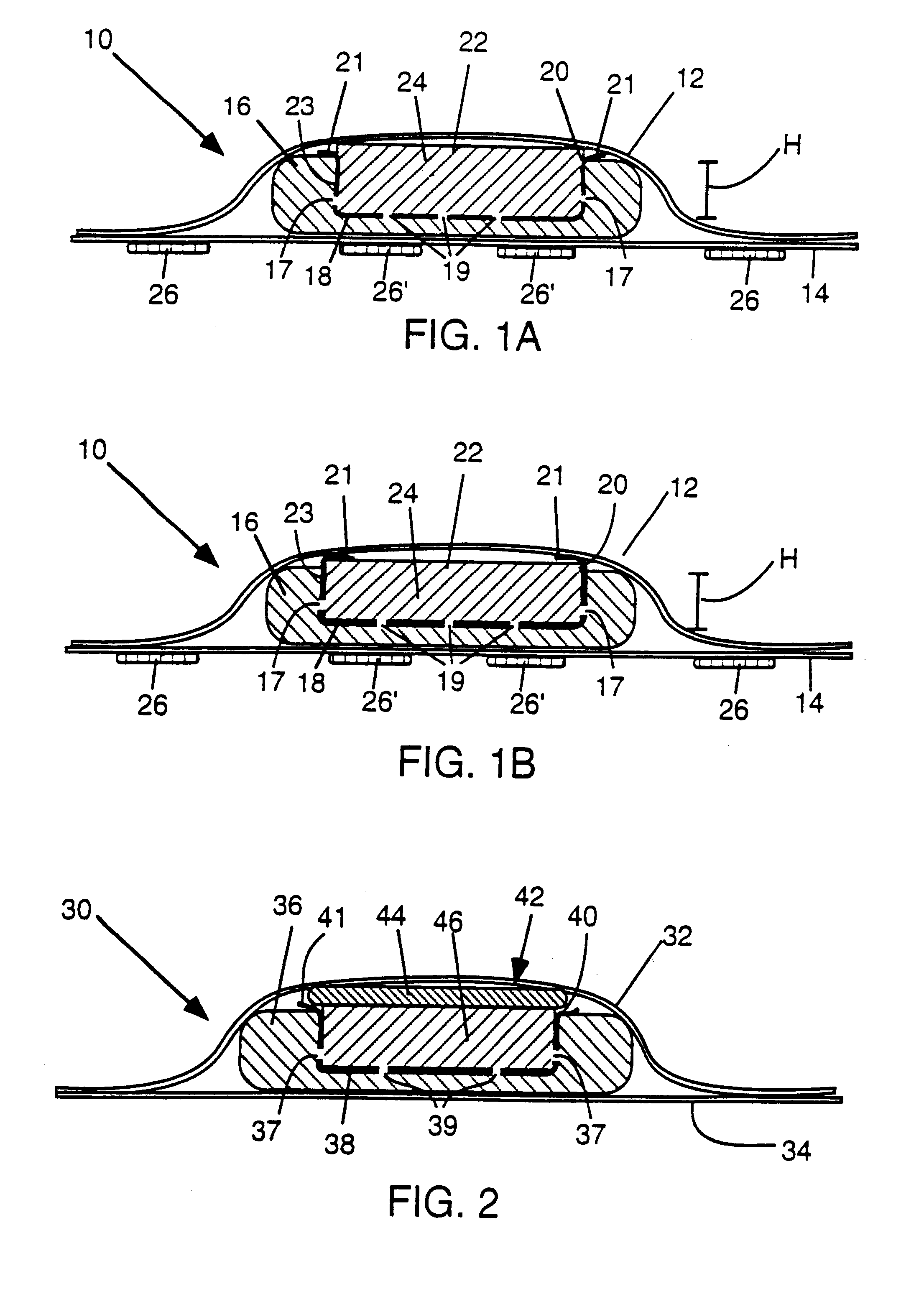
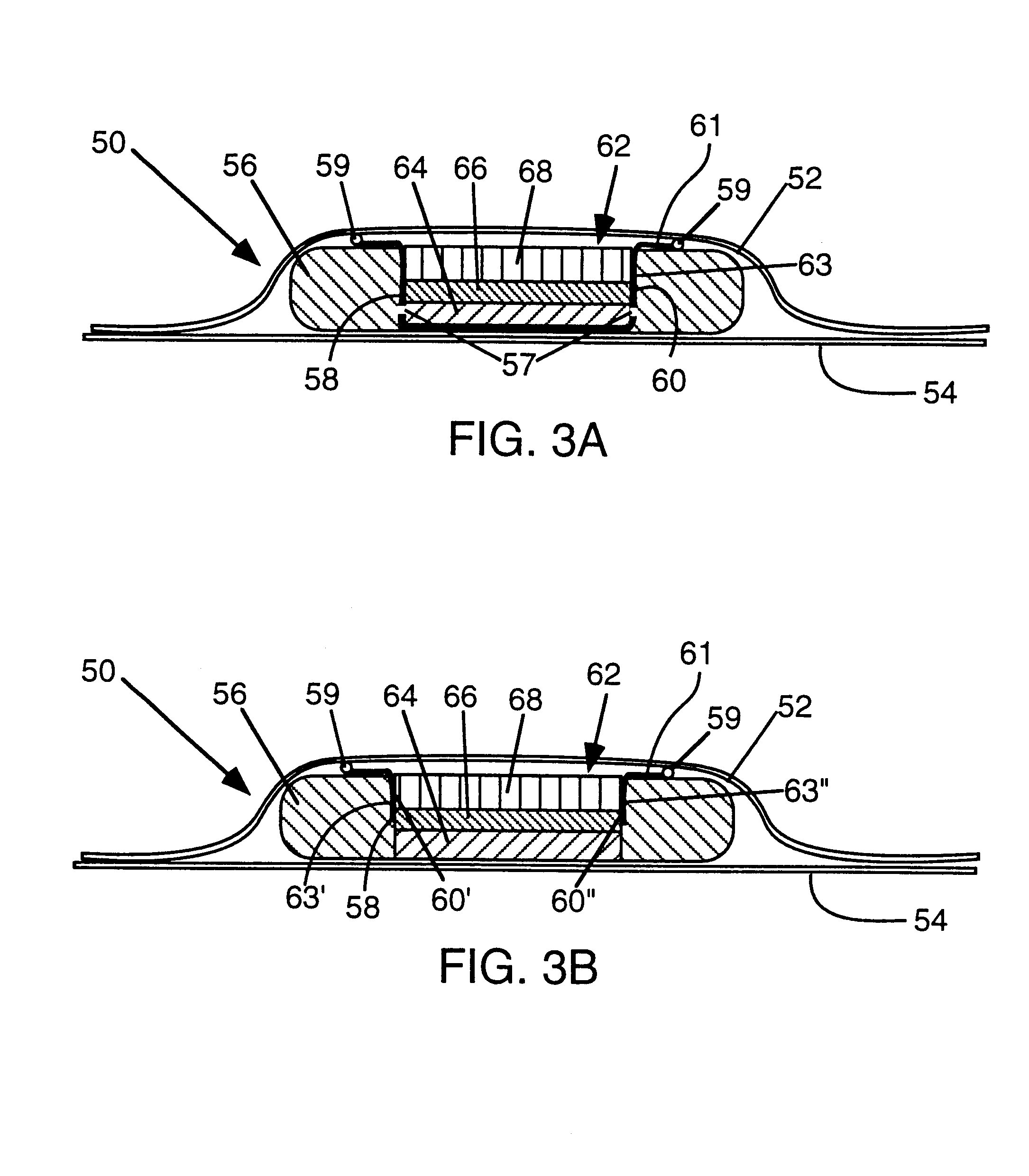
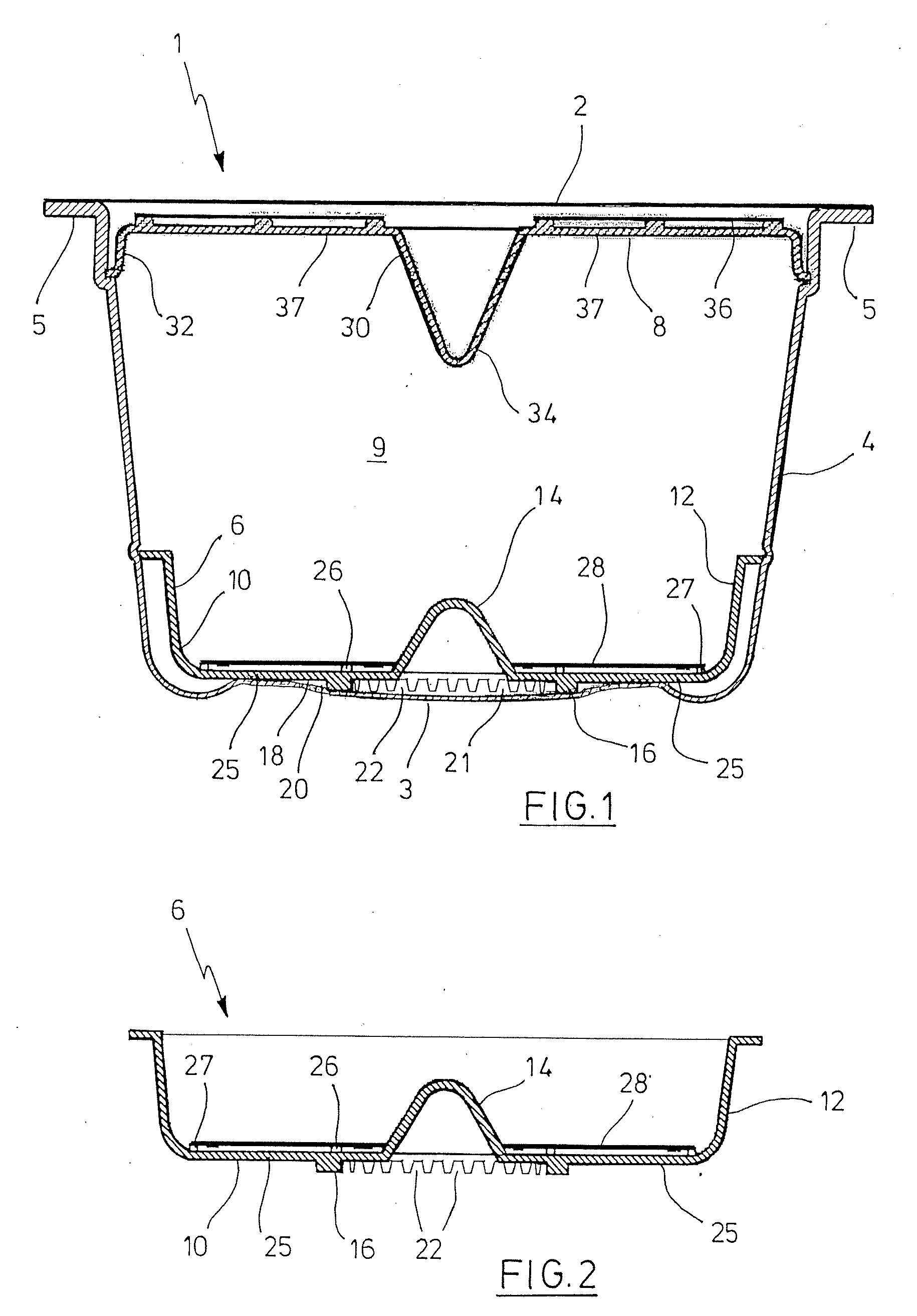
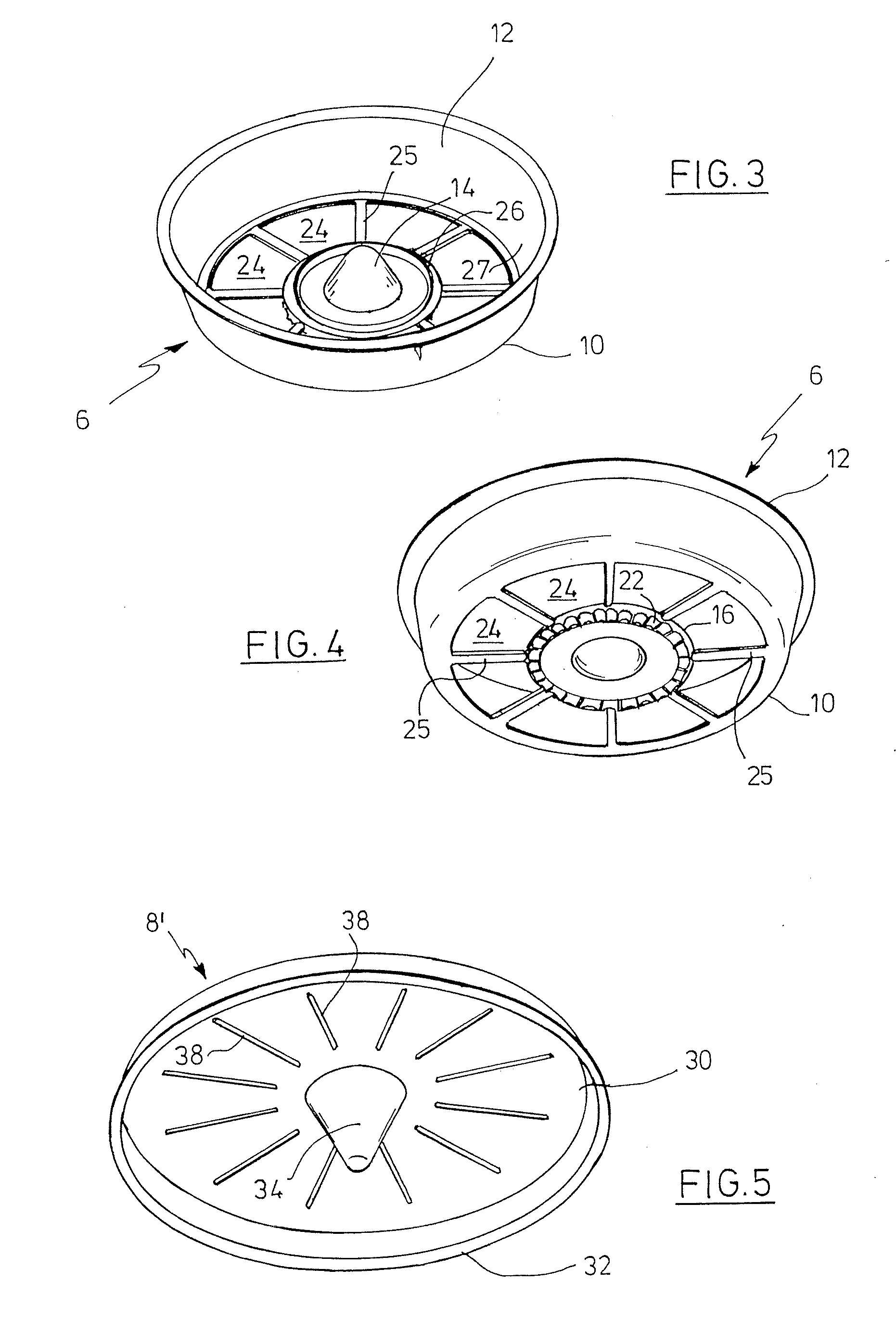
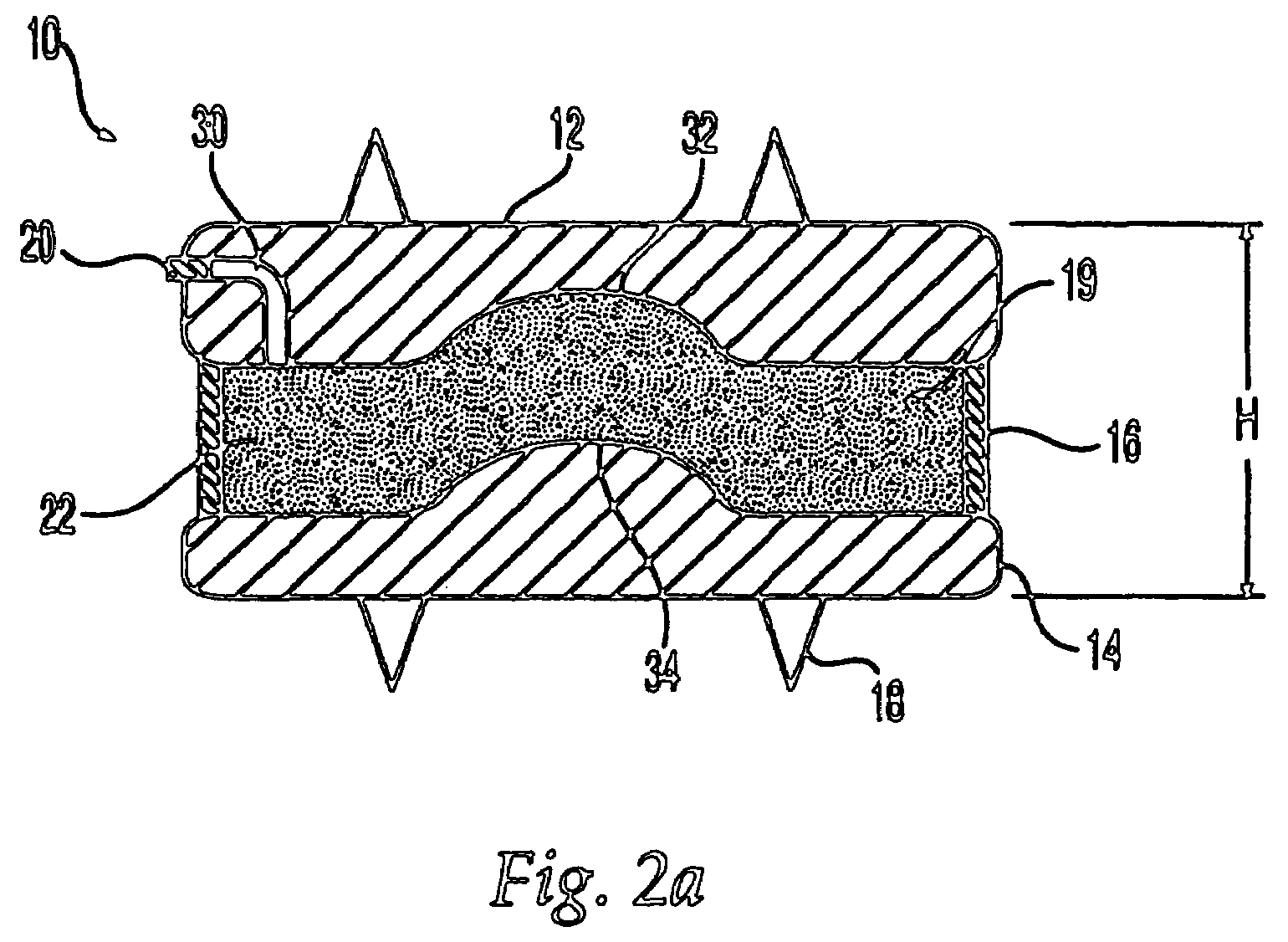
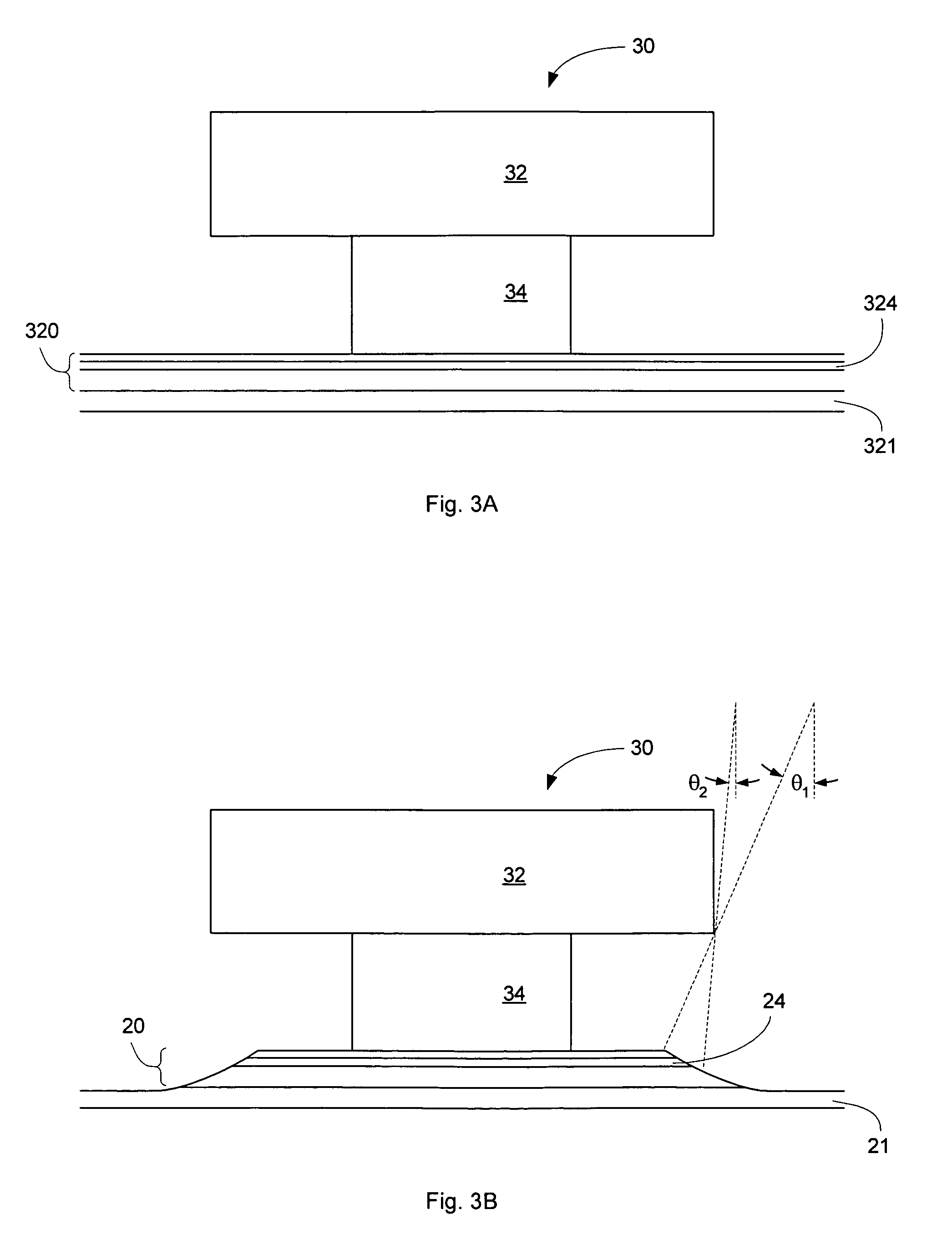
Circular stapler buttress
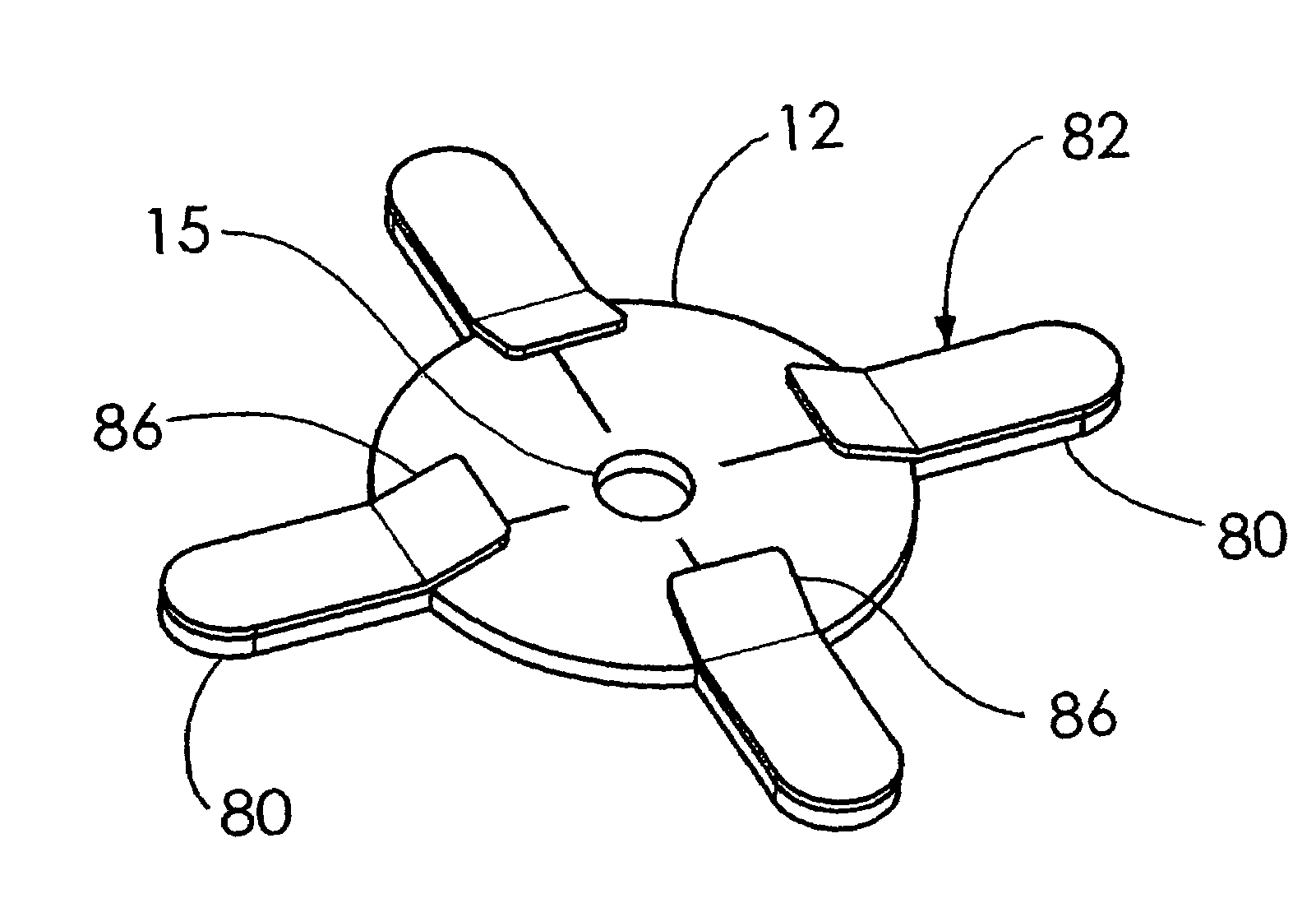
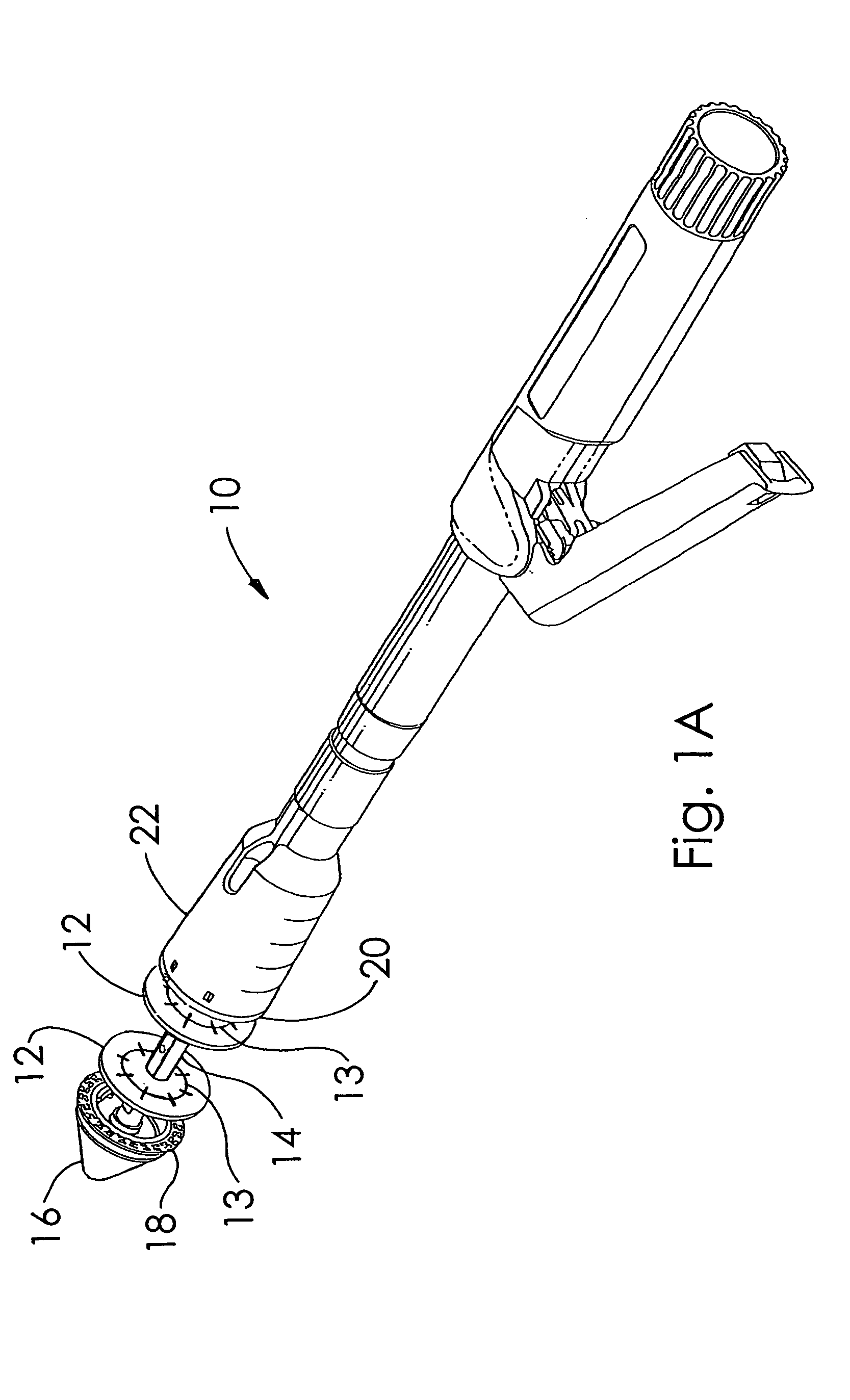
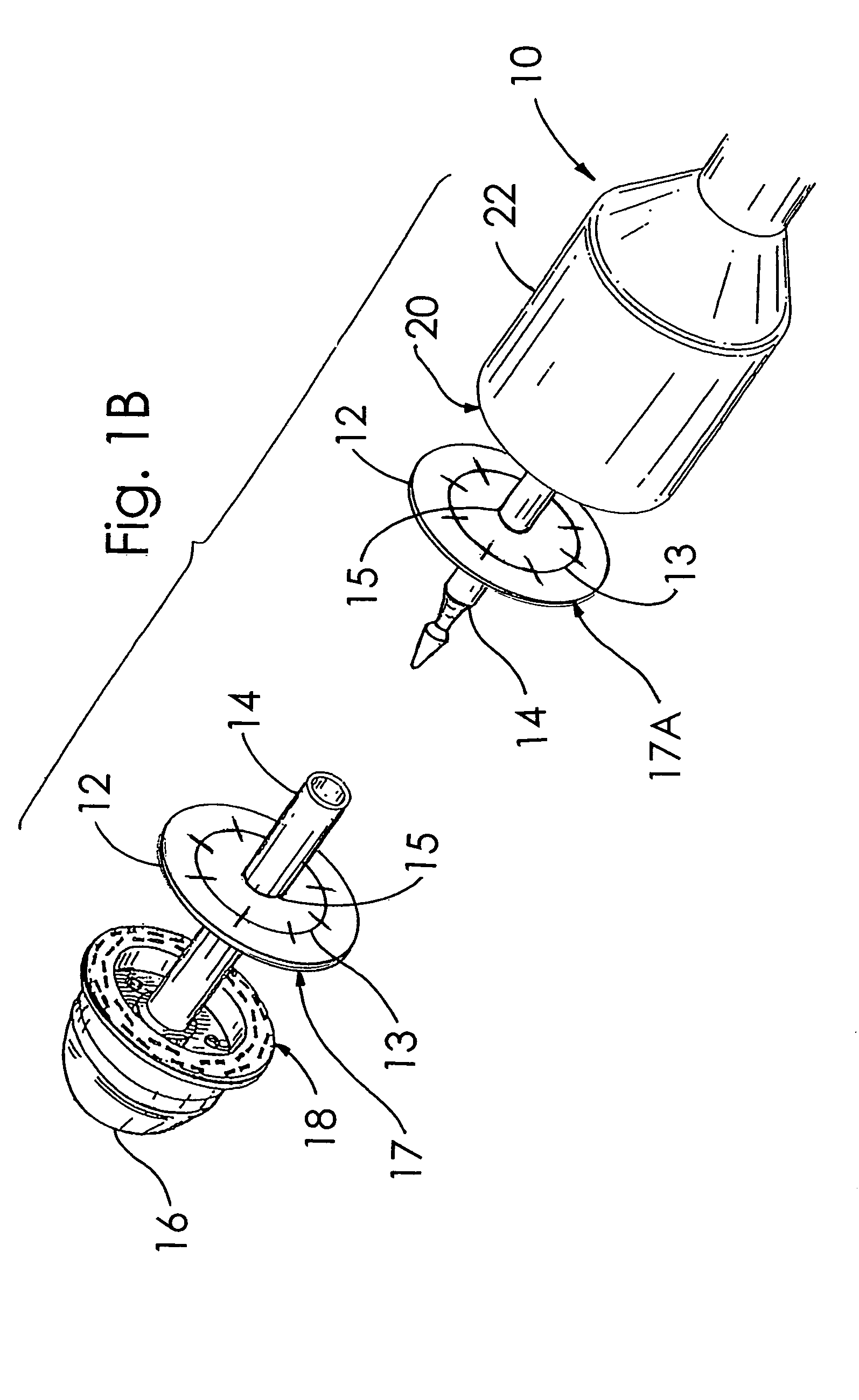
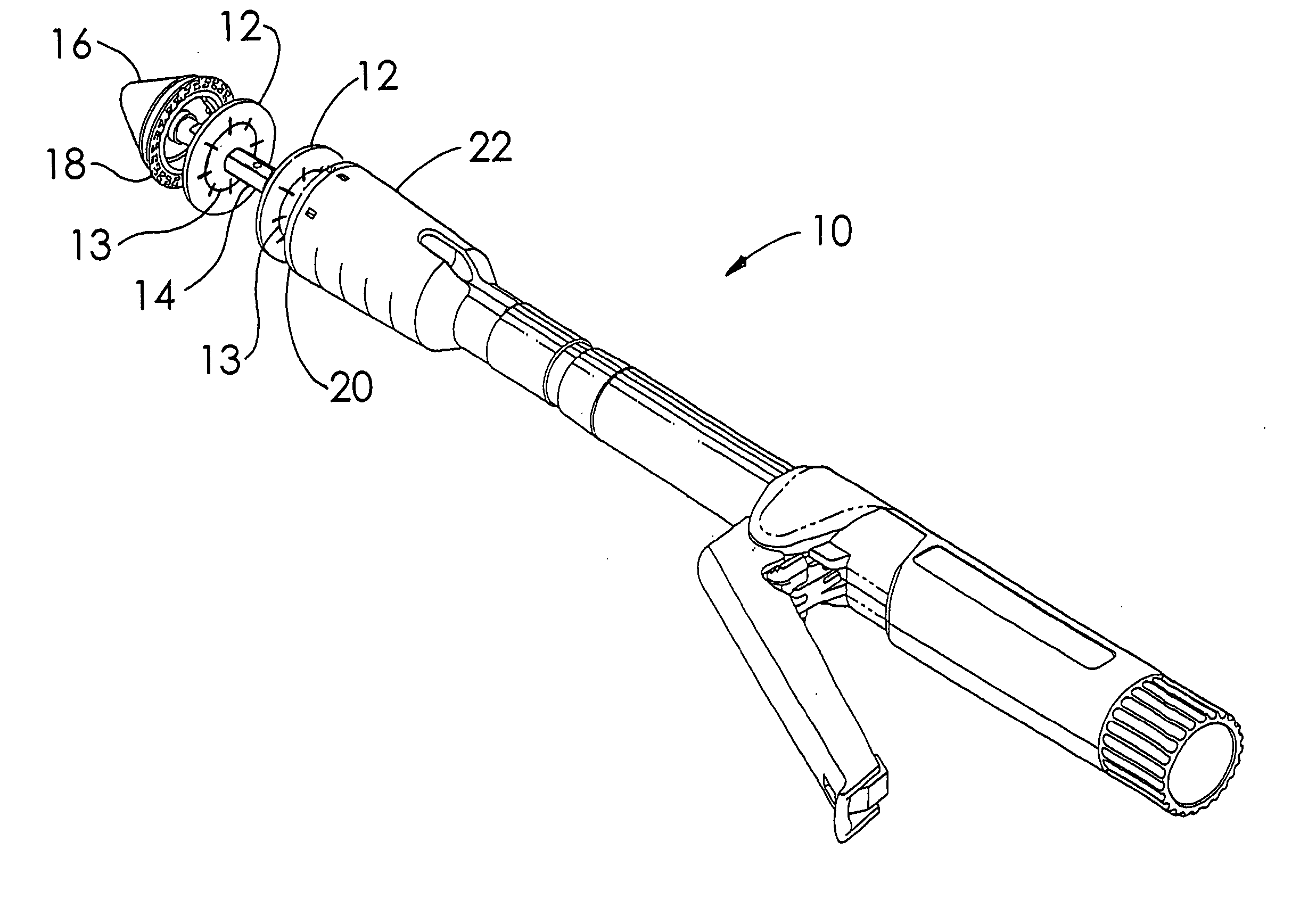
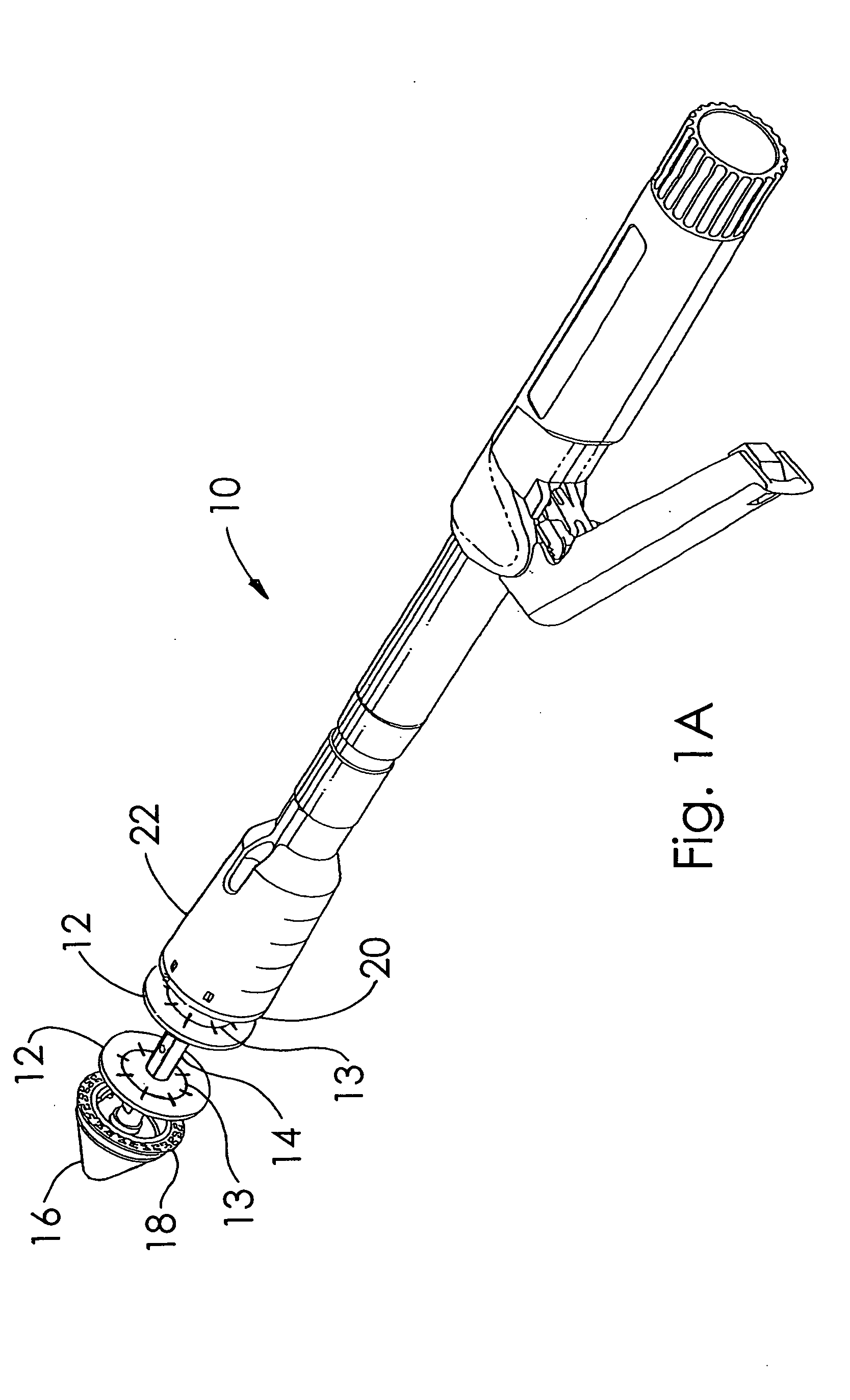
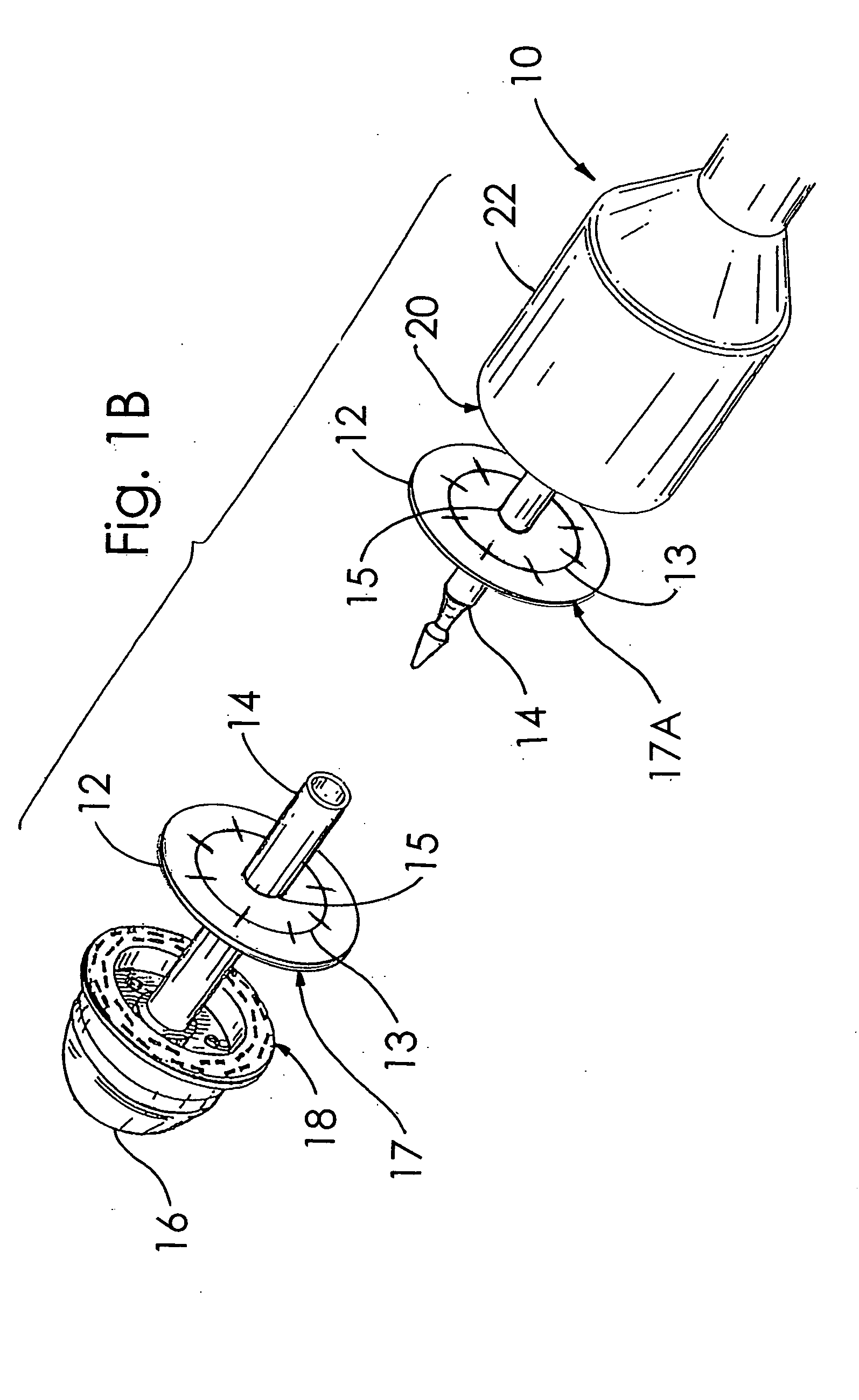
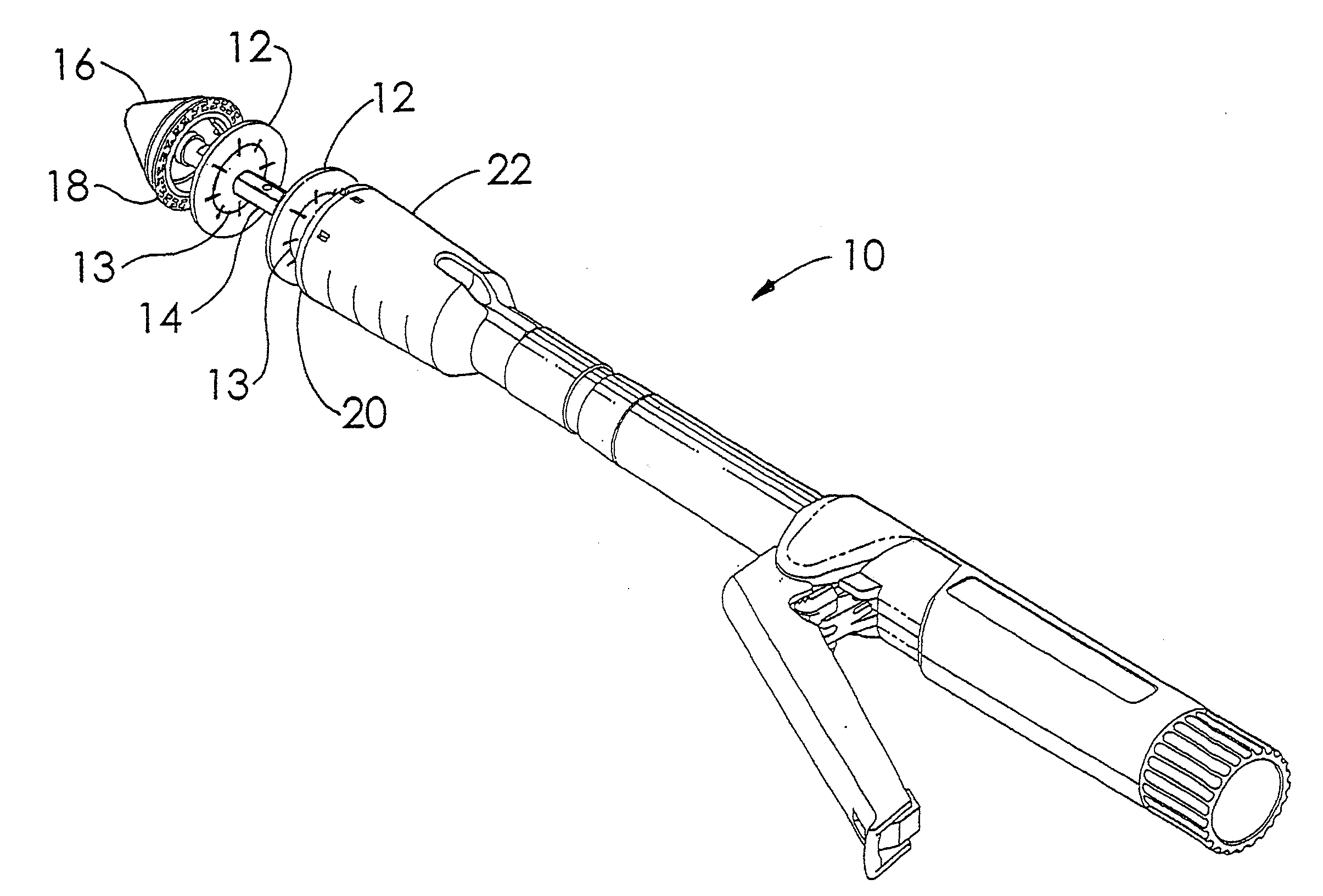
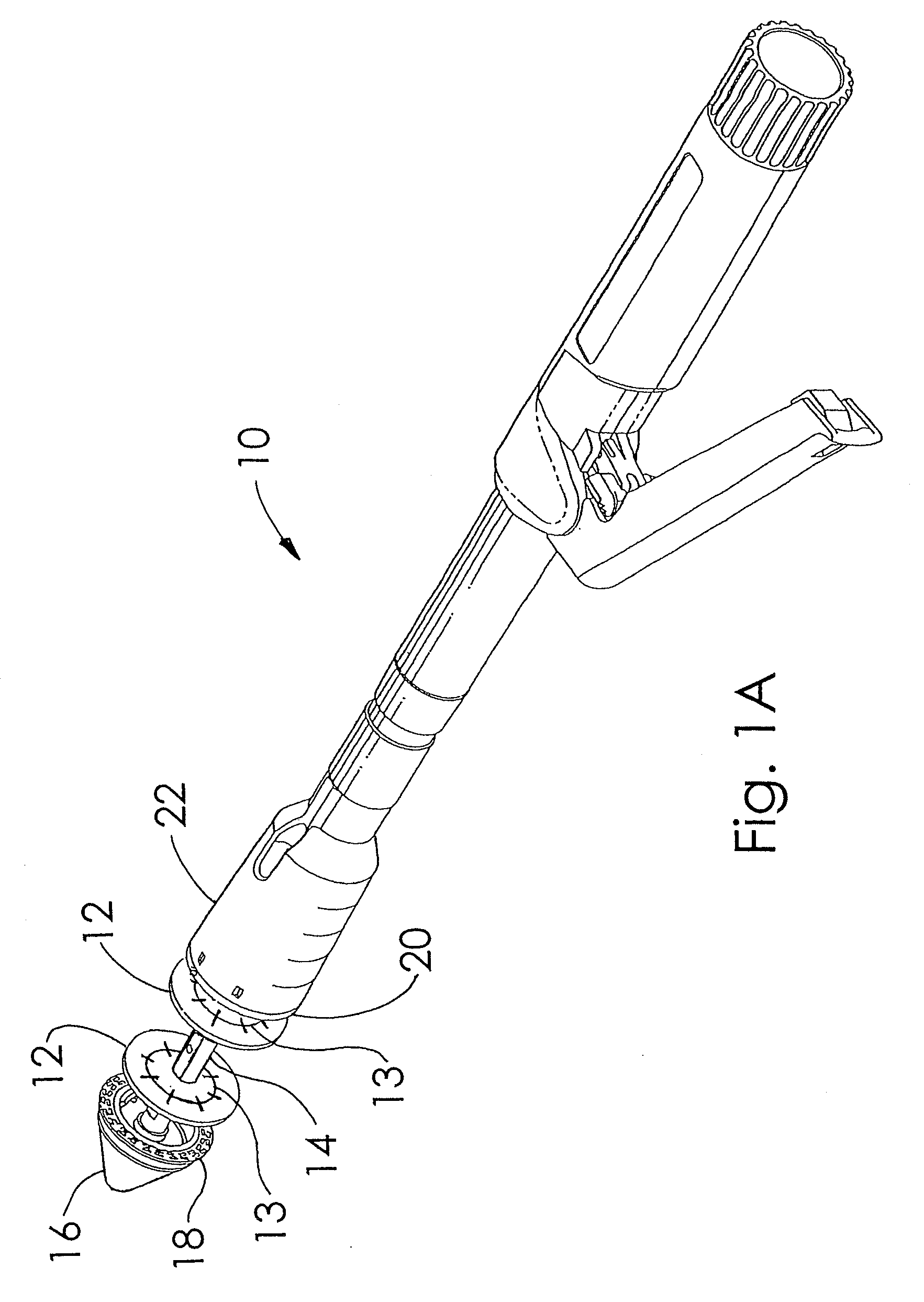
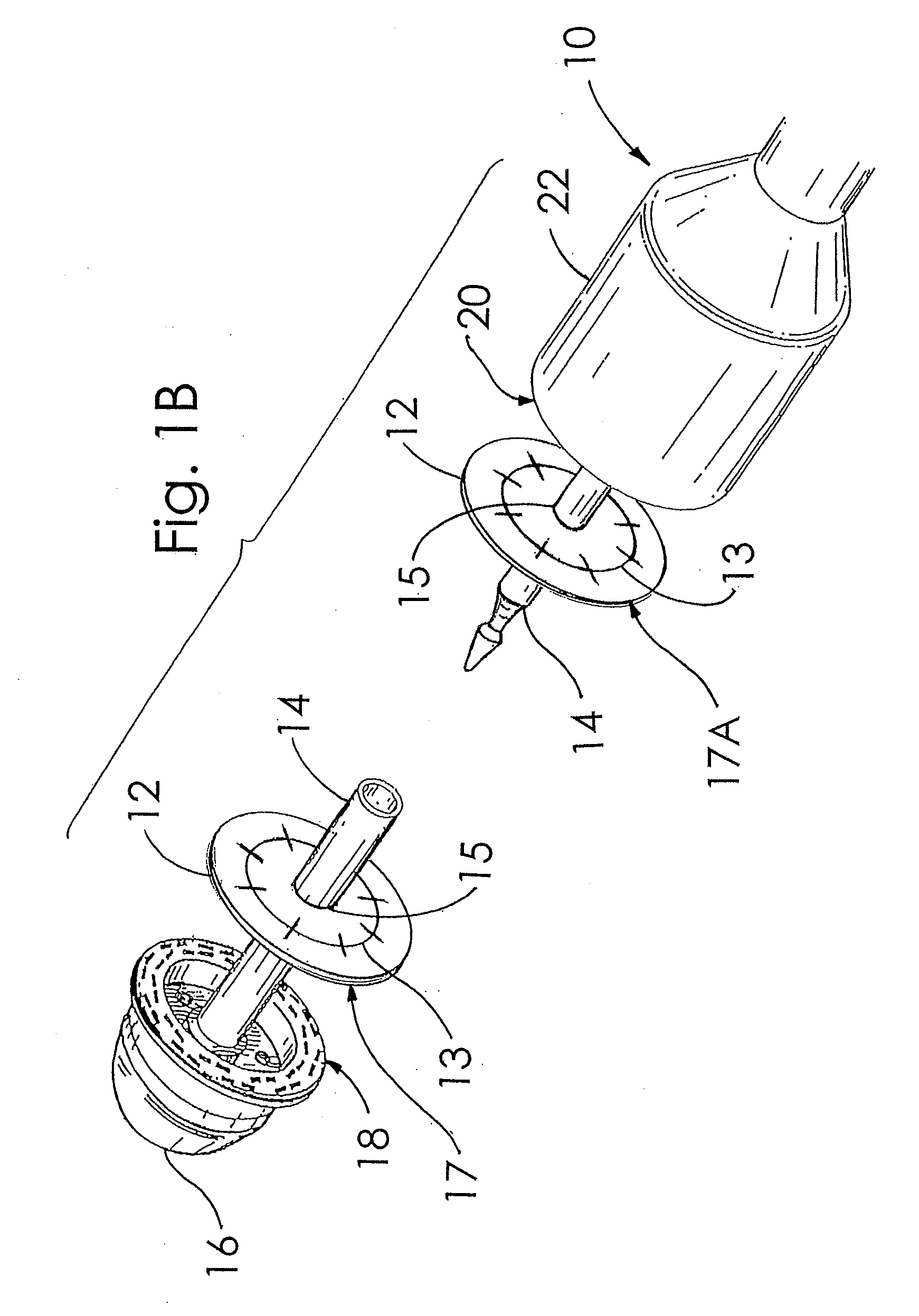
A buttress for use with circular surgical staplers that does not require adhesive to securely fasten the buttress to the stapler. Following cutting and stapling by the circular stapler, the buttress has an adaptive opening through its central region with a diameter smaller than the outer diameter of the stapler anvil. Because of relief features built into the buttress, the stapler anvil may be pulled through the buttress material without causing permanent alteration to the buttress. These relief features may be provided regardless of whether the buttress is made of inelastic or elastic materials. The buttress is generally circular in shape with an outer diameter sized to coincide with the outer diameter of the stapler body staple compression surface and the outer diameter of the anvil compression surface of a circular stapler with which it is used. Prior to surgical use, the buttress is attached to the stapler with disruptable portions extending from outer perimetal areas of the buttress.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Circular stapler buttress
A buttress for use with circular surgical staplers that does not require adhesive to securely fasten the buttress to the stapler. Following cutting and stapling by the circular stapler, the buttress has an adaptive opening through its central region with a diameter smaller than the outer diameter of the stapler anvil. Because of relief features built into the buttress, the stapler anvil may be pulled through the buttress material without causing permanent alteration to the buttress. These relief features may be provided regardless of whether the buttress is made of inelastic or elastic materials. The buttress is generally circular in shape with an outer diameter sized to coincide with the outer diameter of the stapler body staple compression surface and the outer diameter of the anvil compression surface of a circular stapler with which it is used. Prior to surgical use, the buttress is attached to the stapler with disruptable portions extending from outer perimetal areas of the buttress.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
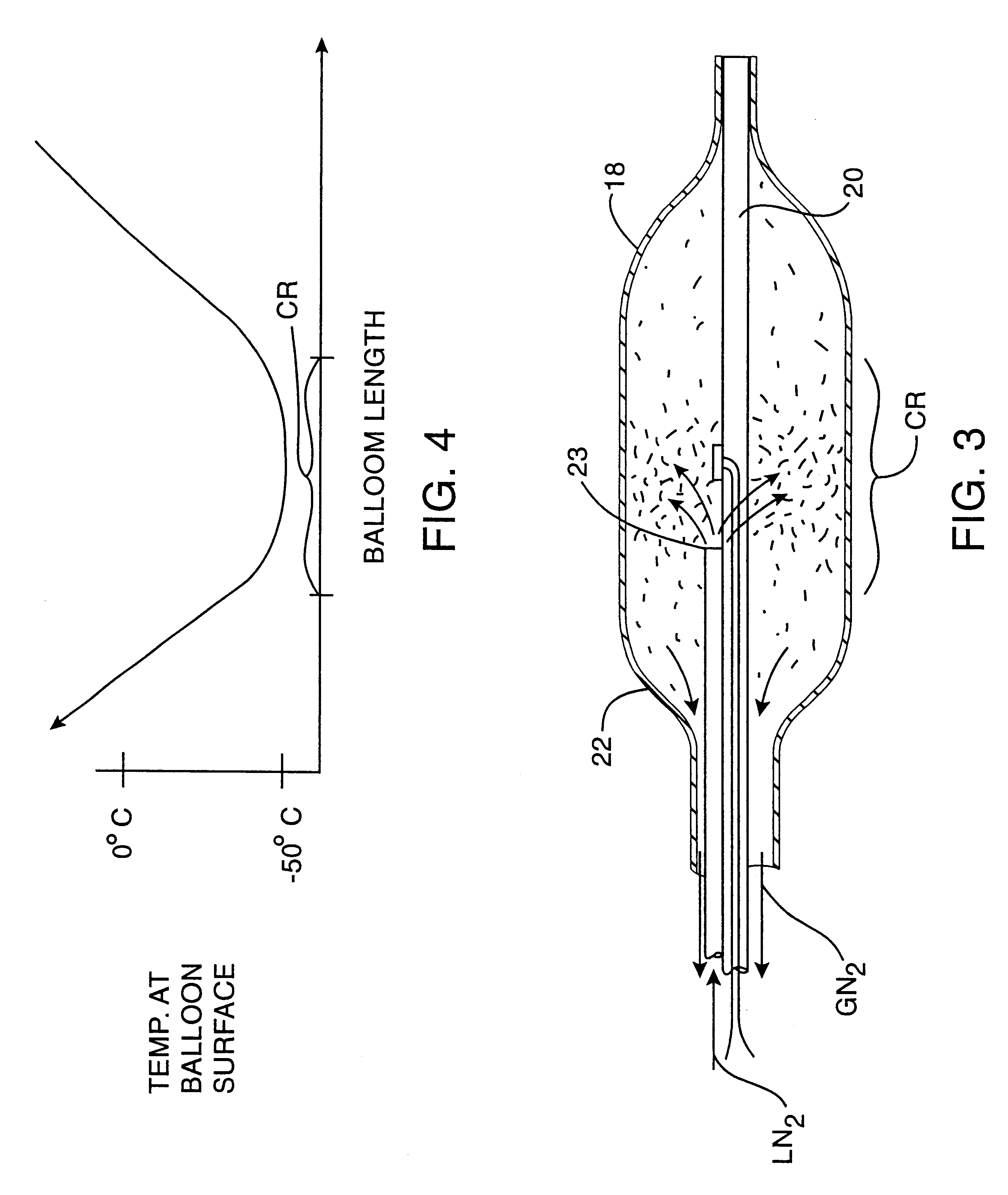
Apparatus and method for cryogenic inhibition of hyperplasia
InactiveUS6355029B1Enhanced inhibitory effectEasy to controlCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingPercutaneous angioplastyBalloon catheter
Post-angioplasty hyperplasia in blood vessels is treated using a cryosurgical balloon catheter. The balloon catheter is positioned at a target region within the blood vessel, and the balloon inflated by expanding a cryogenic fluid, such as liquid nitrogen, across an expansion orifice into a balloon. The balloon will be constructed so that cooling is achieved primarily in the central regions of the balloon, with the proximal and distal regions being less cold and acting to insulate adjacent regions of the blood vessel from excessive cooling.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Magnetic field permeable barrier for magnetic position measurement system
InactiveUS6246231B1SurgeryElectric/magnetic position measurementsOrientation measurementMetallic Object
A magnetic field position and orientation measurement system contains, confines and re-directs the magnetic field from one or more transmitters such that the fields are attenuated in areas outside of the operating volume in areas where metallic objects are commonly found. A thin barrier made of a highly permeable material such as ferrite or mumetal is placed on top of a conductive plate. The thickness of the permeable layer is from 0.01 inches to 0.25 inches while the conductive plate, preferably made of an aluminum alloy, may preferably be from {fraction (3 / 16)} of an inch to ¼ inch in thickness. On top of the permeable barrier, a rhombic three axis transmitter is placed. In the preferred embodiment, the transmitter consists of a PC board carrying the transmitter. PC boards having thicknesses varying from 0.03125-0.125 inches may be employed. Thus, the entire "stack" including the transmitter, the permeable barrier and the conductive plate may only be from ½ inch to ⅝ of an inch in thickness. The permeable barrier may have a flat, planar configuration. Alternatively, it may be made to resemble, in cross-section, a cake pan having a flat central region with uplifted peripheral edges. Alternatively, the permeable barrier may have a generally flat configuration with peripheral edges that taper outwardly from the top surface thereof to the bottom surface thereof with the taper making an angle with the bottom surface in the range of, preferably, 30° to 85°.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050197702A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantLigamentsCircular discAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and lordosis, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumber regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior at least partially filled with a fluid; a valve for injecting fluid into the interior of the disk; a central region having a stiffness that is preferably greater than the stiffness of the outer regions thus enabling the disc to pivot about the central region. The central pivot may be formed by a center opening, a central chamber, an inner core or a central cable.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
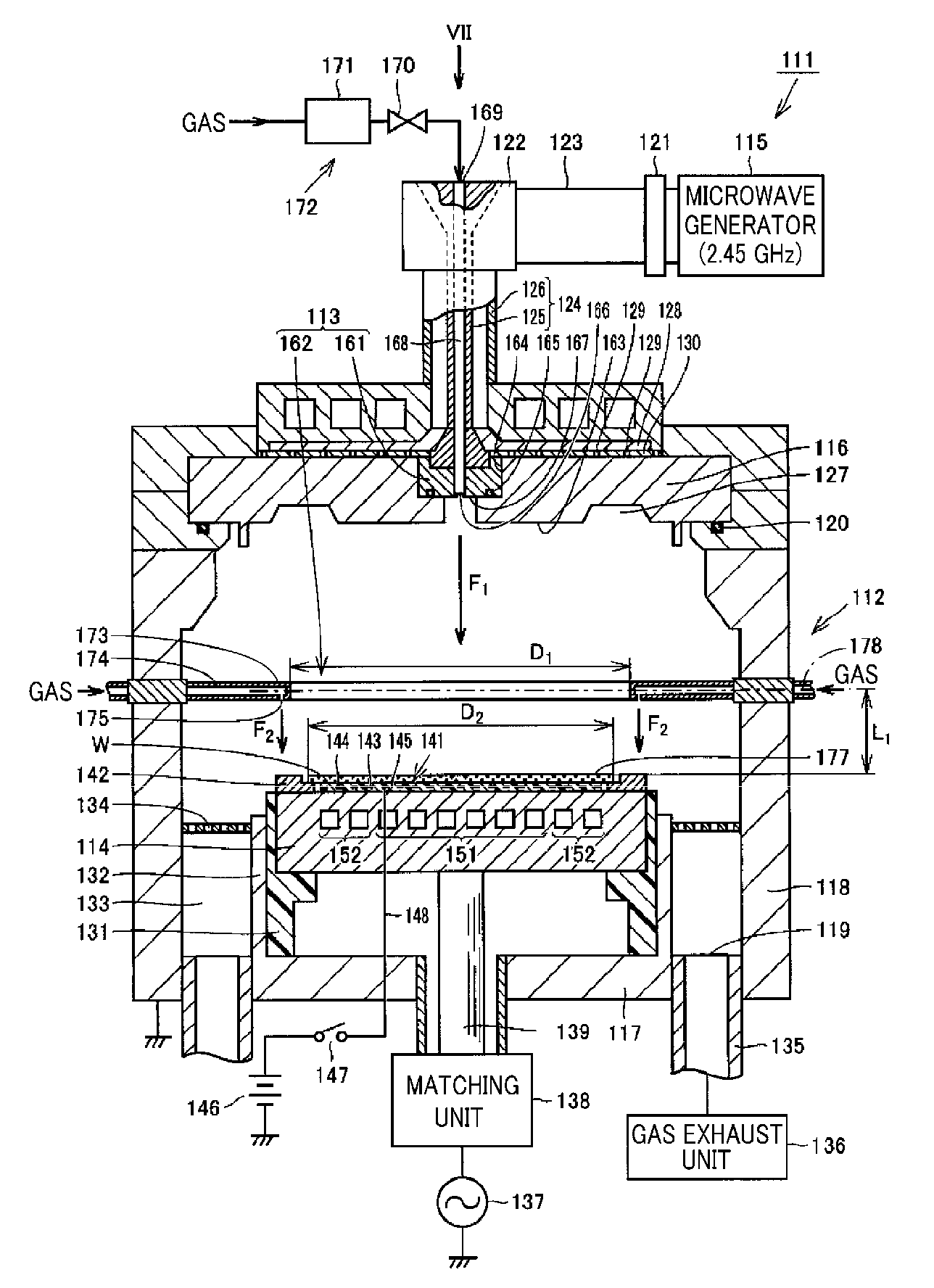
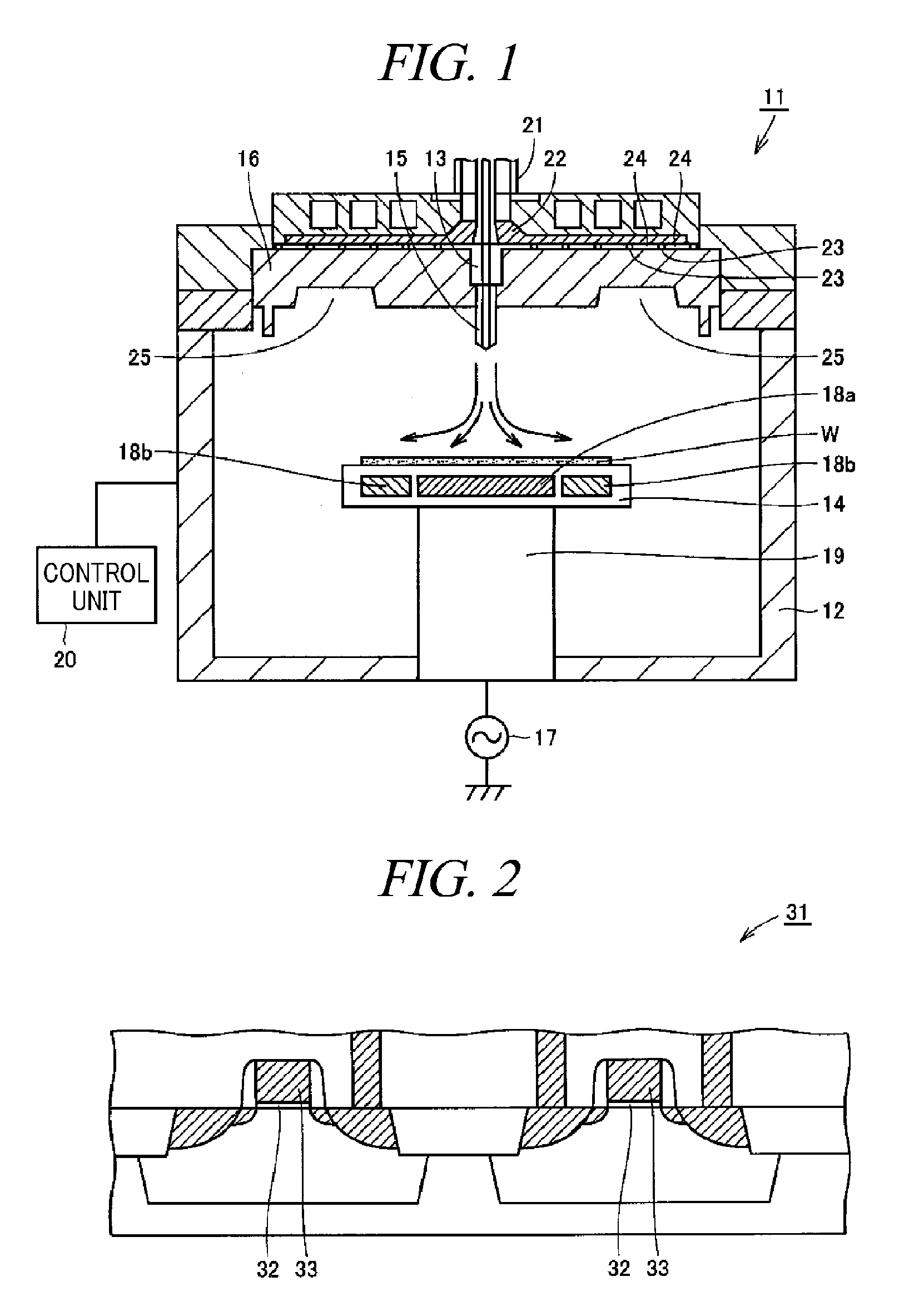
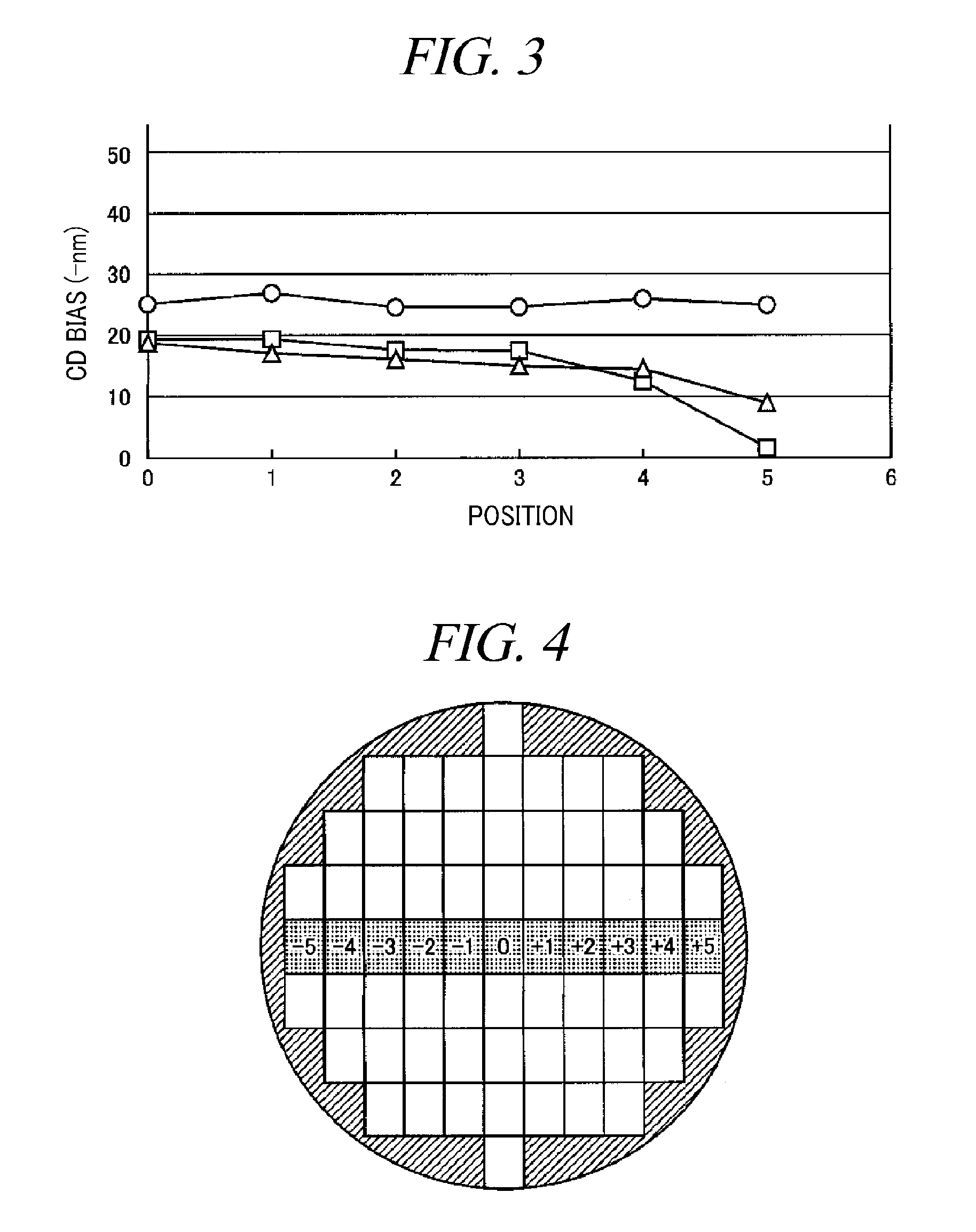
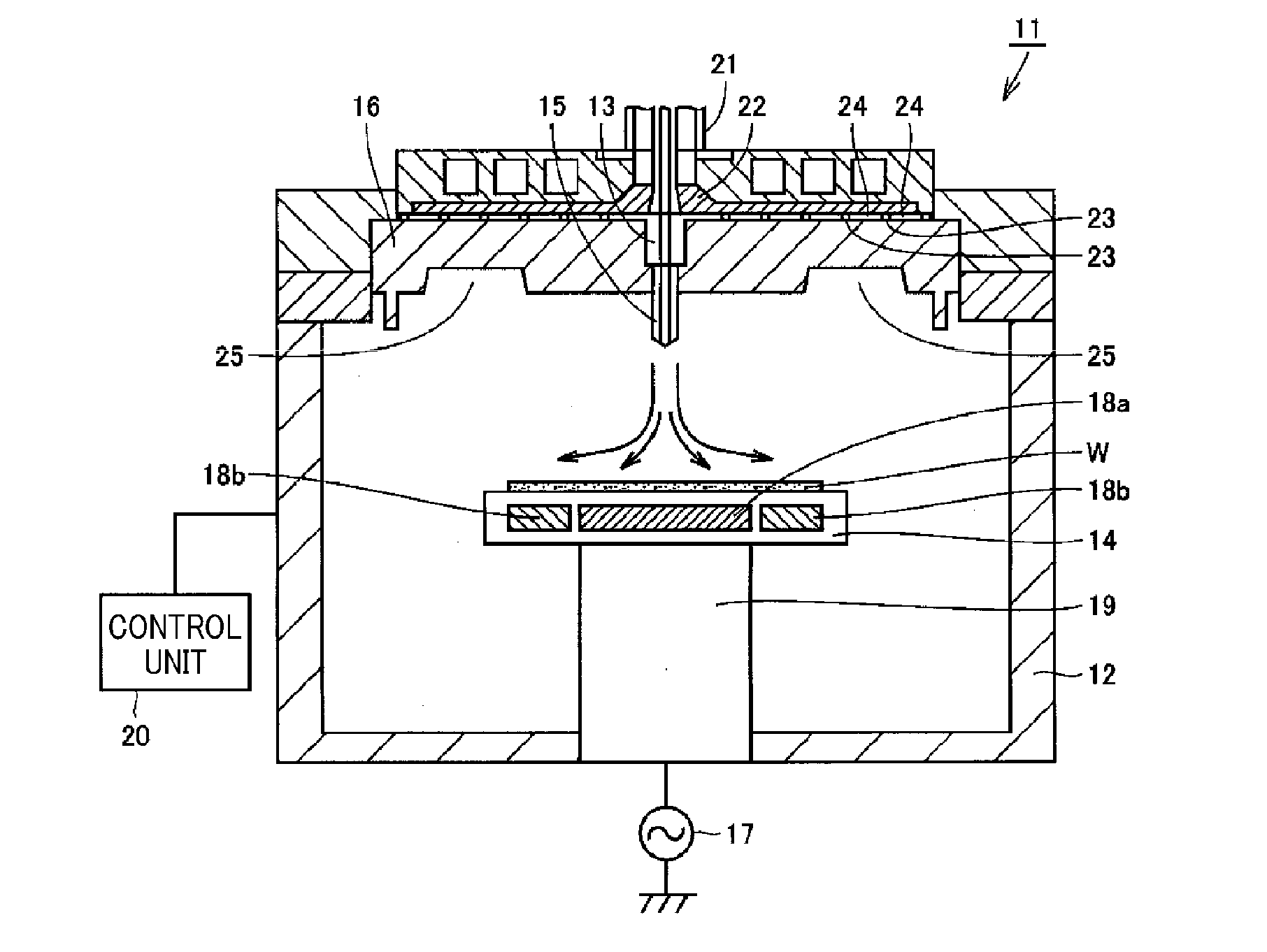
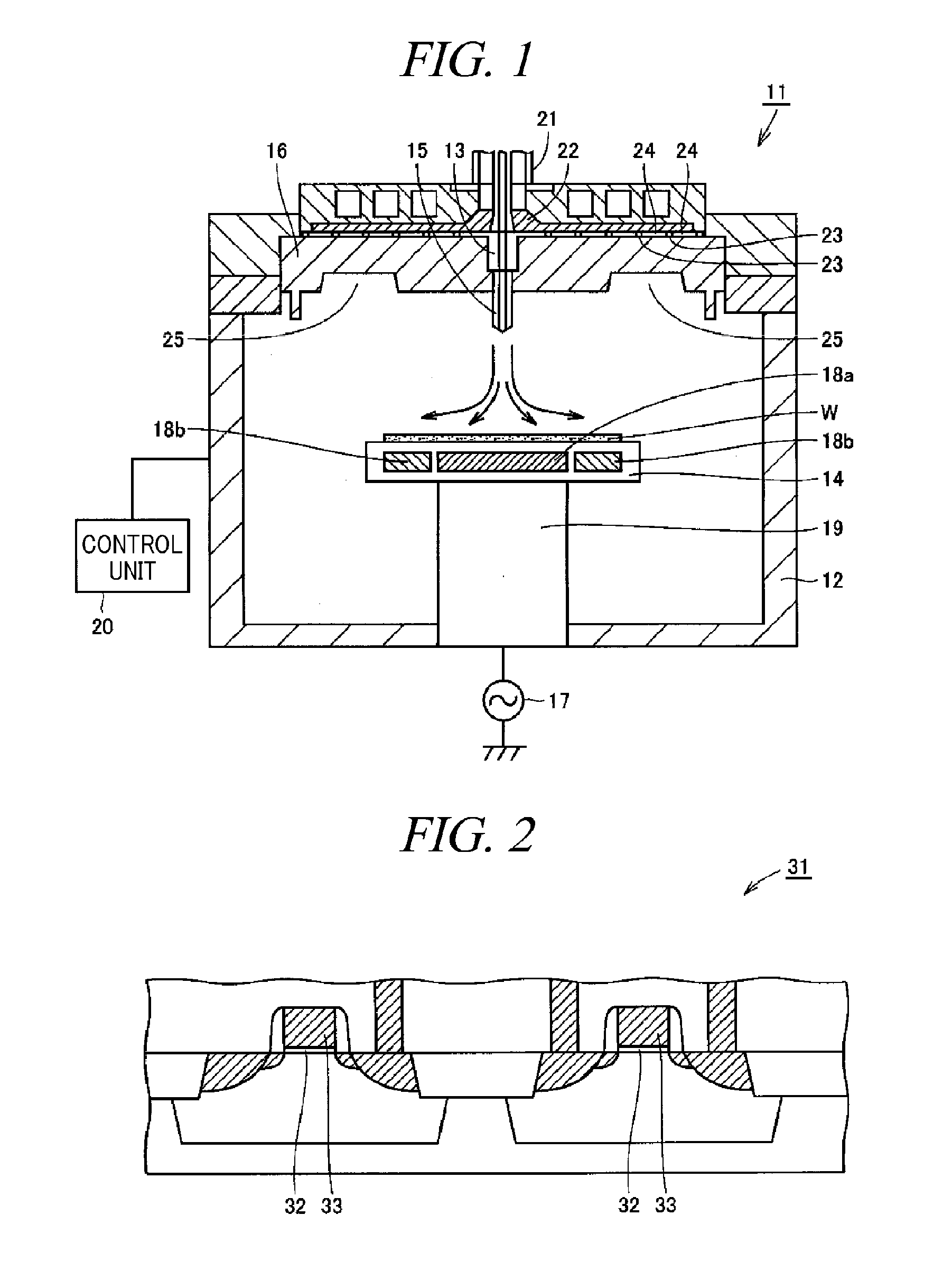
Plasma etching apparatus and plasma etching method
ActiveUS9263298B2Easy to controlUniform surfaceElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringGas supply
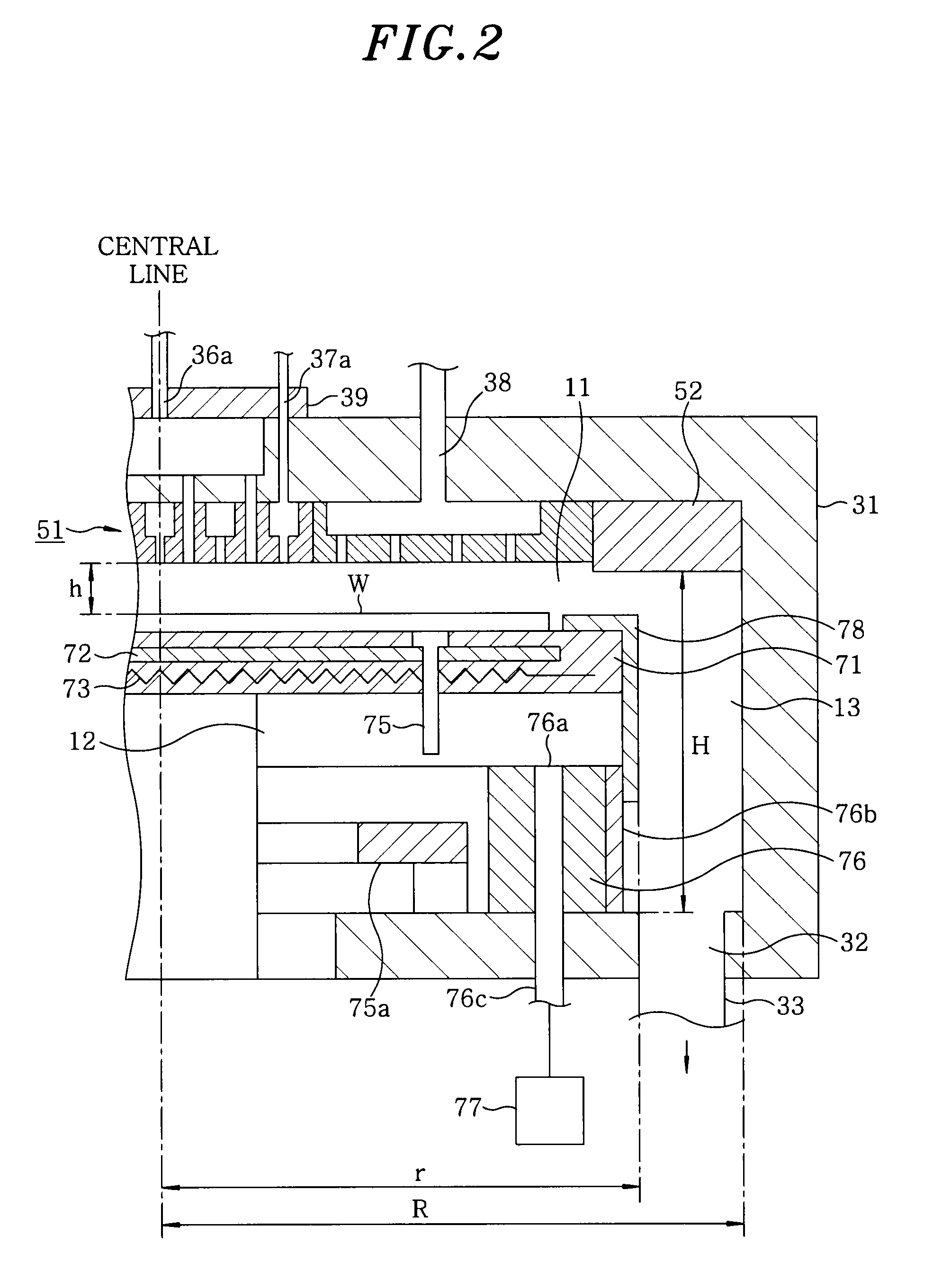
A plasma etching apparatus 11 includes a mounting table that holds a semiconductor substrate W thereon; a first heater 18a that heats a central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; a second heater 18b that heats an edge region around the central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; a reactant gas supply unit 13 that supplies a reactant gas for a plasma process toward the central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; and a control unit 20 that performs a plasma etching process on the semiconductor substrate W while controlling the first heater 18a and the second heater 18b to heat the central region and the edge region of the processing target substrate W held on the mounting table 14 to different temperatures.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
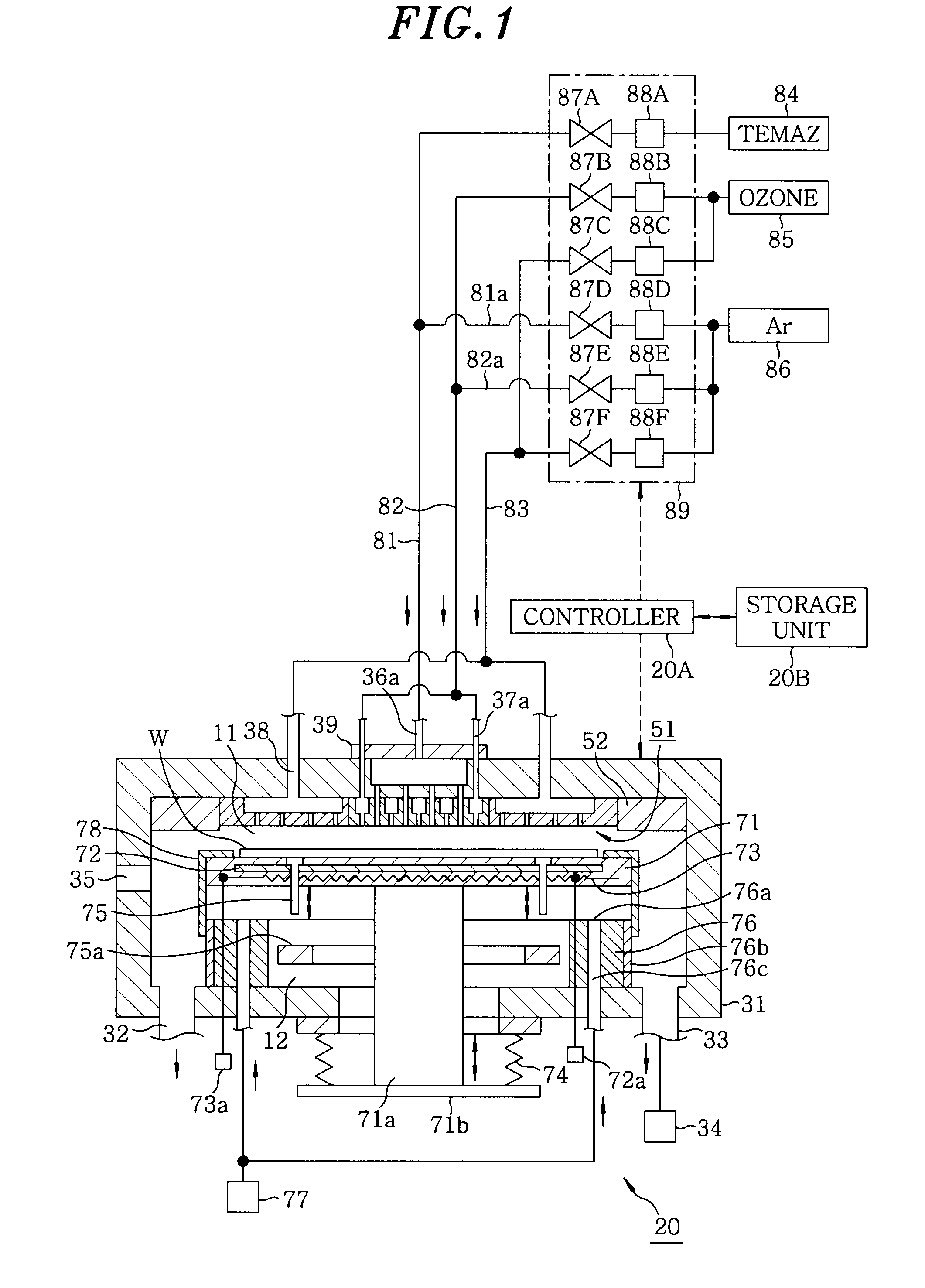
Film forming apparatus, film forming method and storage medium
ActiveUS20100119727A1Reduce gas volumeShorten the timeComputer controlPretreated surfacesEnergy supplyProduct gas
A film forming apparatus includes a processing chamber, and a mounting table disposed in the processing chamber to mount a substrate thereon. The film forming apparatus further includes a gas shower head having gas supply holes and including a central region facing a central portion of the substrate and a peripheral region facing a peripheral portion of the substrate, a first processing gas supply unit for supplying a first processing gas to the central region, a second processing gas supply unit for supplying a second processing gas to the central region, an energy supply unit for supplying energy to react the first processing gas with the second processing gas on the substrate, and a purge gas supply unit for supplying a purge gas to the central region and the peripheral region when one of the first and the second processing gas is switched by the other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
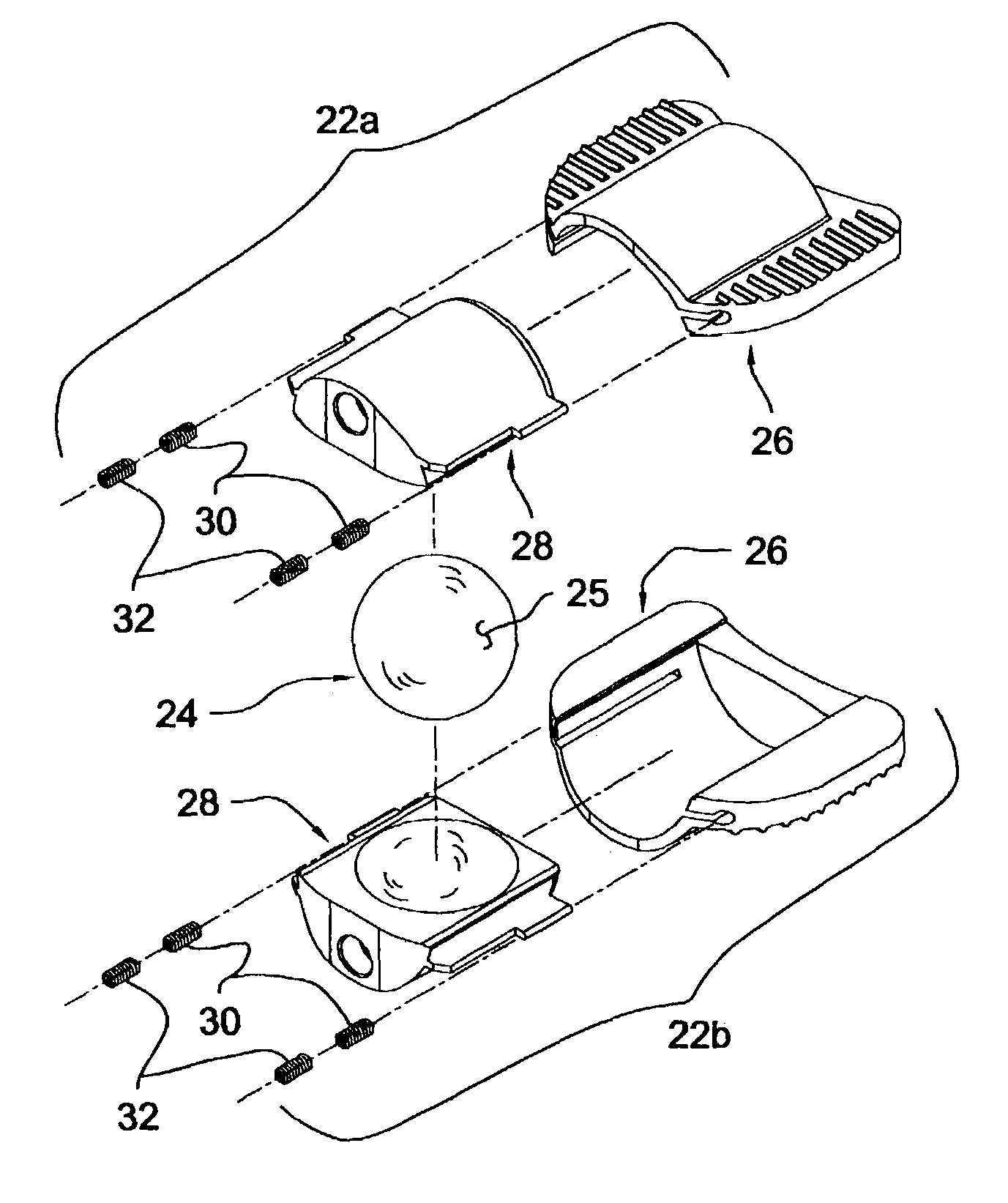
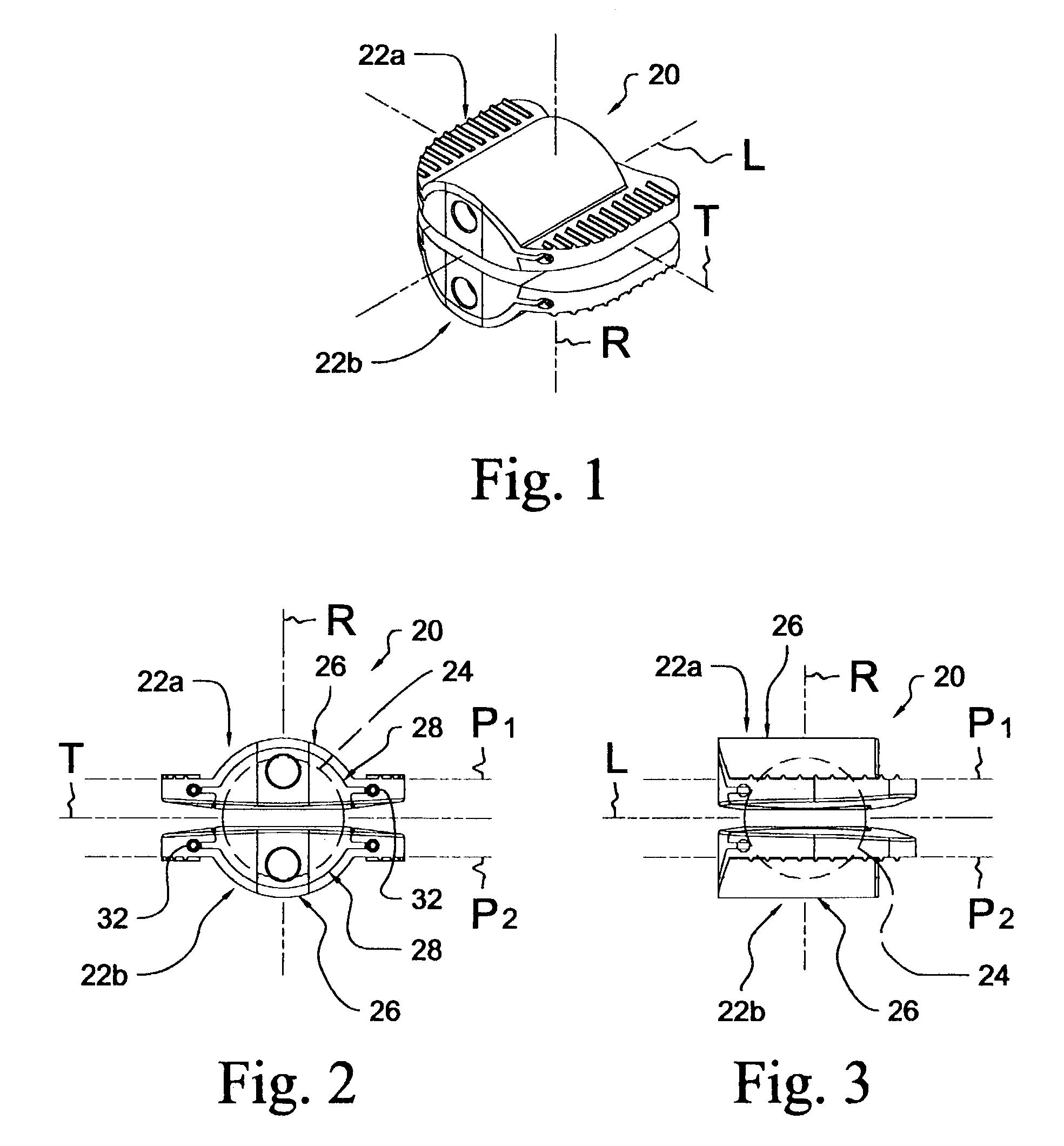
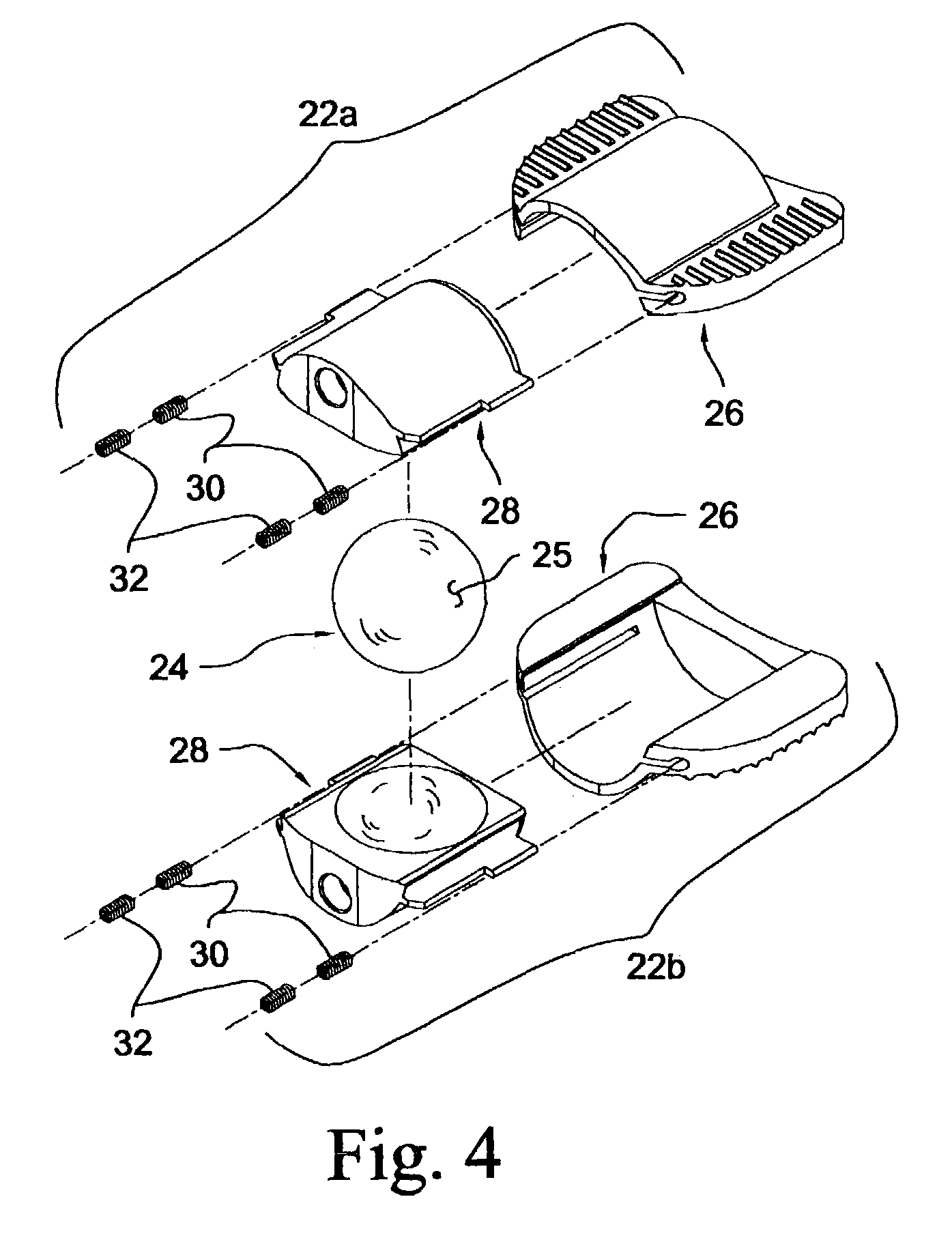
Articular disc prosthesis and method for implanting the same
InactiveUS7179294B2Simple methodInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsArticular surfacesArticular surface
An articular disc prosthesis and method of implanting the same within an intervertebral space between adjacent vertebral bodies. The prosthesis includes a pair of articular components and an articular ball disposed therebetween. Each of the articular components includes an outer shell portion and a removable inner insert portion. The insert portion includes a concave articular surface sized and shaped to receive a portion of the articular ball to provide articulating motion between the articular components. The outer shell portion includes a central hemi-cylindrical portion, a pair of laterally extending flanges, and an axially extending lip. Following removal of the natural intervertebral disc, a pair of hemi-cylindrical recesses are formed along a central region of the adjacent vertebral bodies to a predetermined depth. The prosthesis is implanted within the prepared disc space by axially displacing the hemi-cylindrical central portions of the articular components along the hemi-cylindrical recesses in the vertebral bodies. The lateral flanges and the axial lip of the articular components bear against the endplates of the adjacent vertebral bodies to stabilize the prosthesis and to prevent subsidence.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
High performance support-separator for communications cables
InactiveUS7098405B2Improve NEXT controlReduce needInsulated cablesOptical light guidesElectrical conductorHigh performance communication
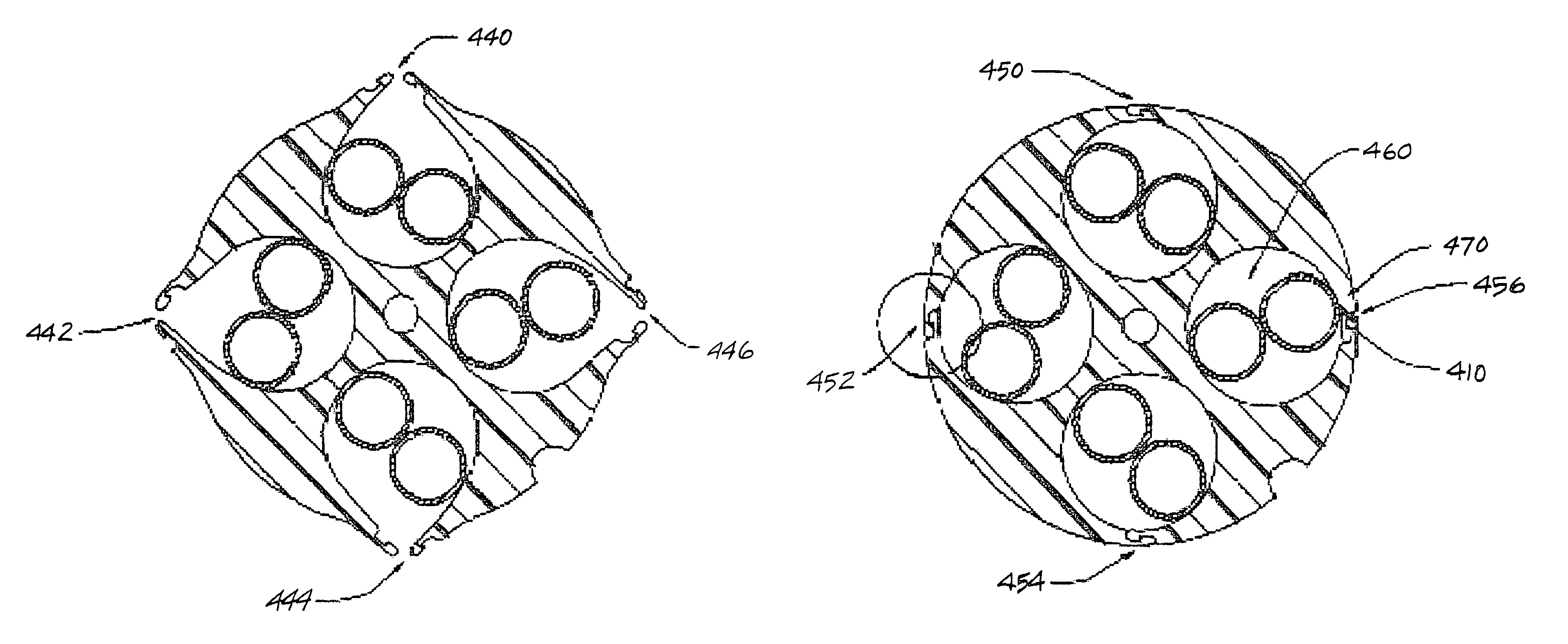
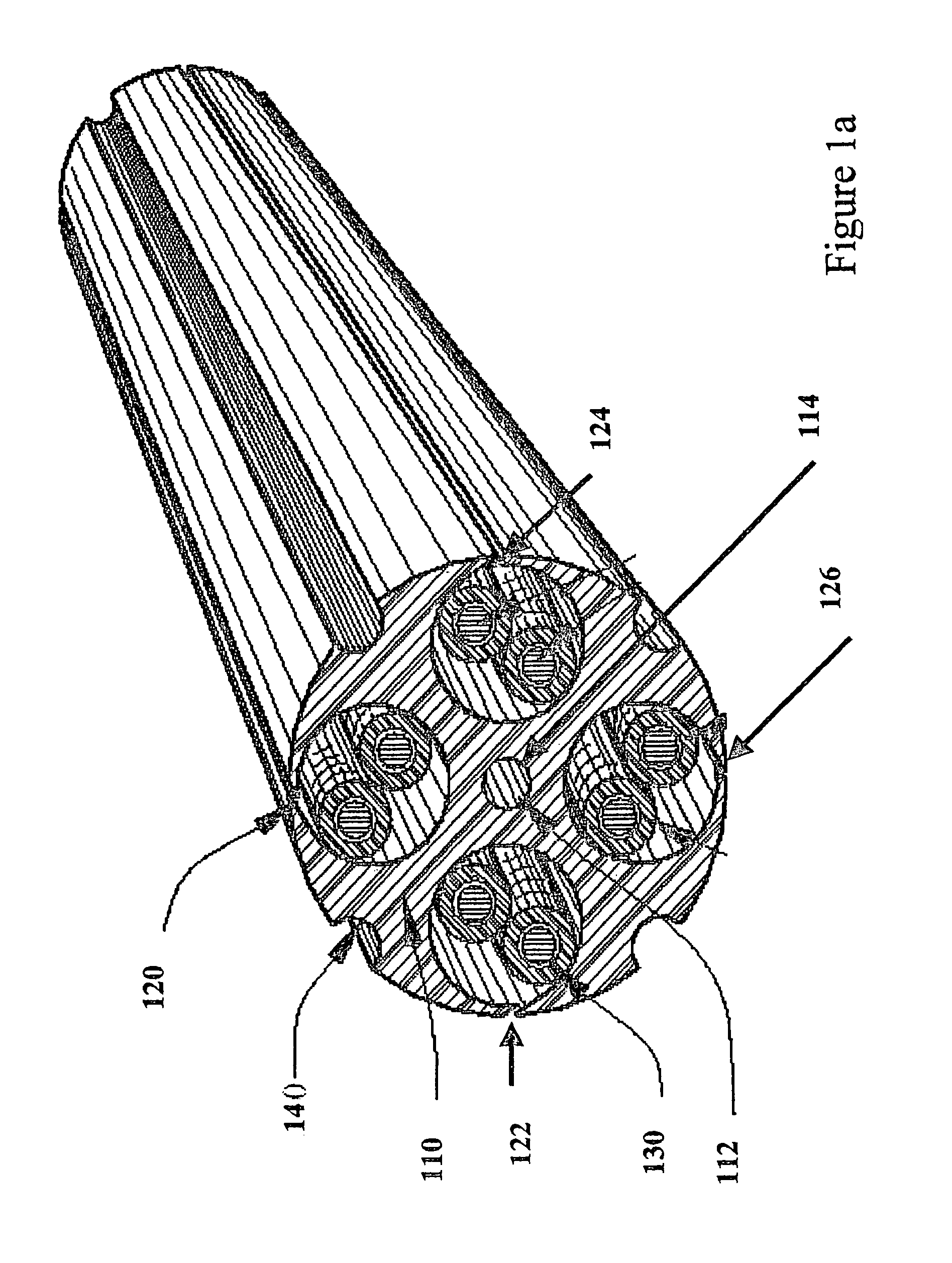
The present invention includes a high performance communications cable for transmission media that includes core support-separators which define clearance channels to maintain spacing between transmission media or transmission media pairs. The core support-separator can be either interior to a cable jacket or be employed singularly without the benefit of a jacket and extends along the longitudinal length of the communications cable. The core support-separator has a central region that may include flap-tops along the radial edge that are available for partial or complete sealing of the clearance channels during manufacturing operations. The central region may also include a hollow center portion and include various geometric shapes to provide proper spacing between conductors. Each of the defined clearance channels allow for disposal therein of metal conductors and / or optical fibers.
Owner:CABLE COMPONENTS GROUP
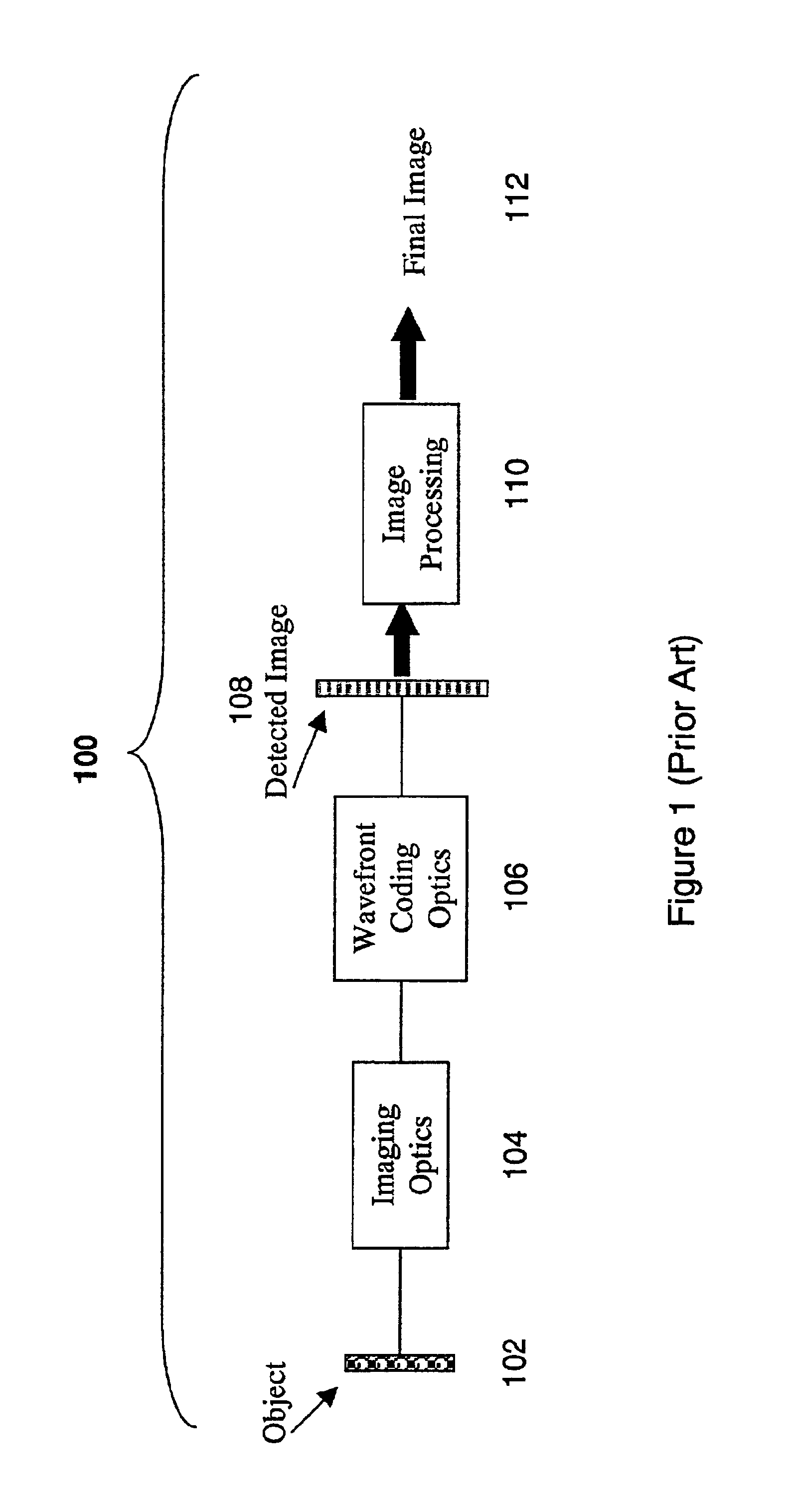
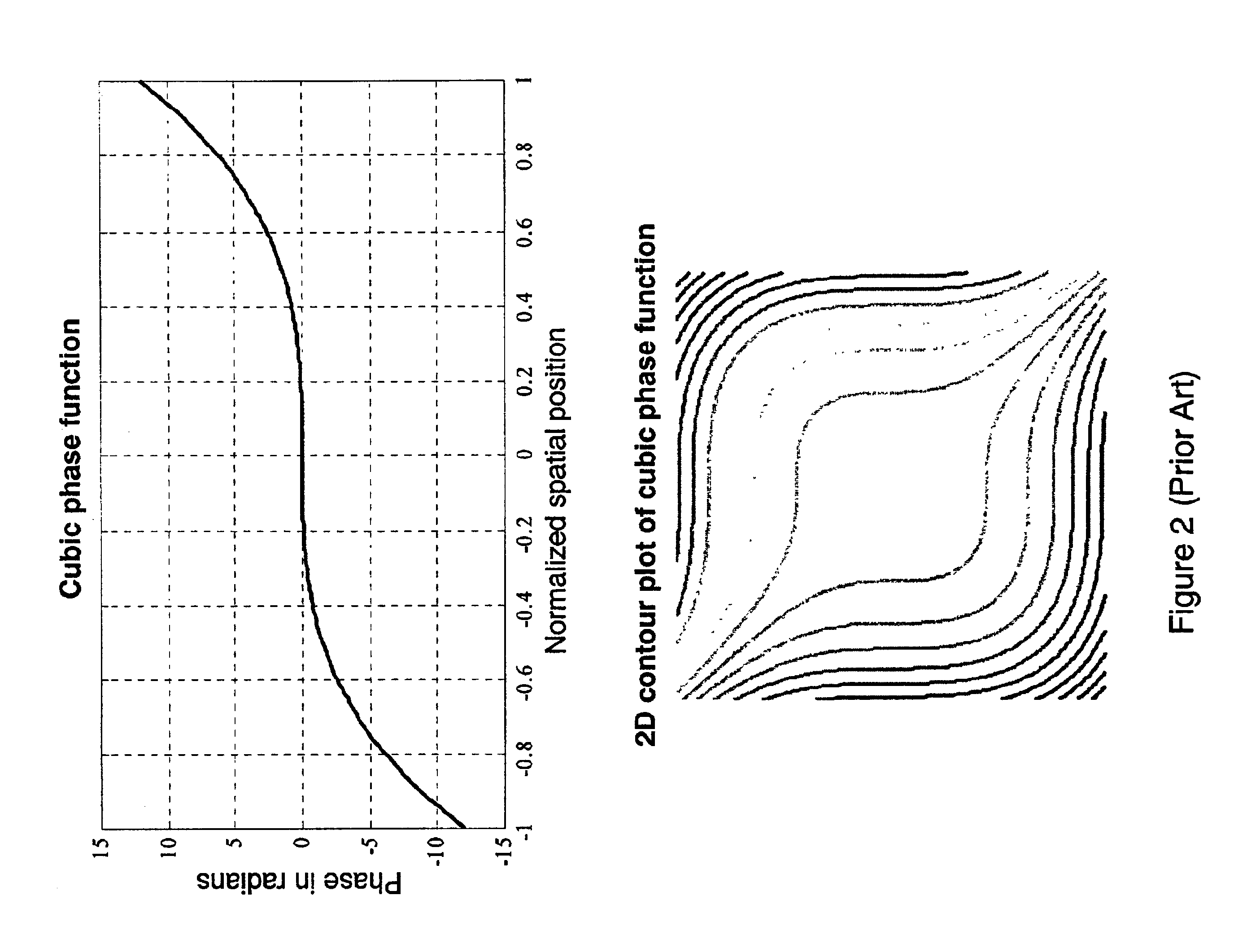
Wavefront coding optics
InactiveUS6842297B2Reduce aberrationIncrease valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansNegative phaseWavefront coding
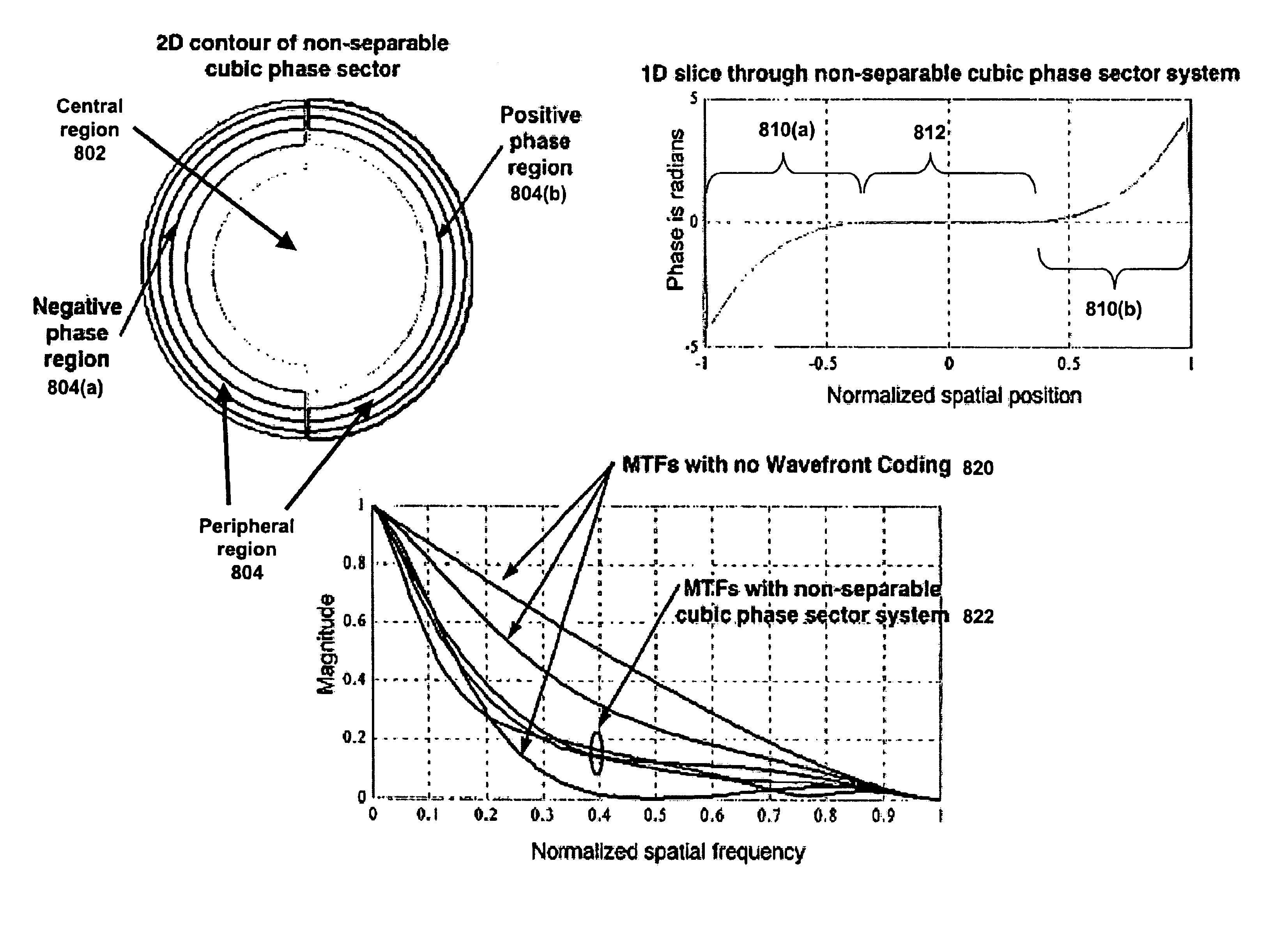
Improved Wavefront Coding Optics, which apply a phase profile to the wavefront of light from an object to be imaged, retain their insensitivity to focus related aberration, while increasing the heights of the resulting MTFs and reducing the noise in the final images. Such improved Wavefront Coding Optics have the characteristic that the central portion of the applied phase profile is essentially flat (or constant), while a peripheral region of the phase profile around the central region alternately has positive and negative phase regions relative to the central region.
Owner:CDM OPTICS +1
Hard mask arrangement
InactiveUS20060234138A1Reduce spacingIncrease processing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCarrying capacityLateral region
An interconnect connection structure having first and second interconnects and multiple connection elements that electrically connect the first interconnect to the second interconnect is described. The multiple connection elements are formed laterally in a lateral region of the first and second interconnects relative to an overlay orientation of the interconnects. A central region may be free of connection elements so that electro-migration properties of the connection structure are improved and the current-carrying capacity is increased.
Owner:FEHLHABER RODGER +1
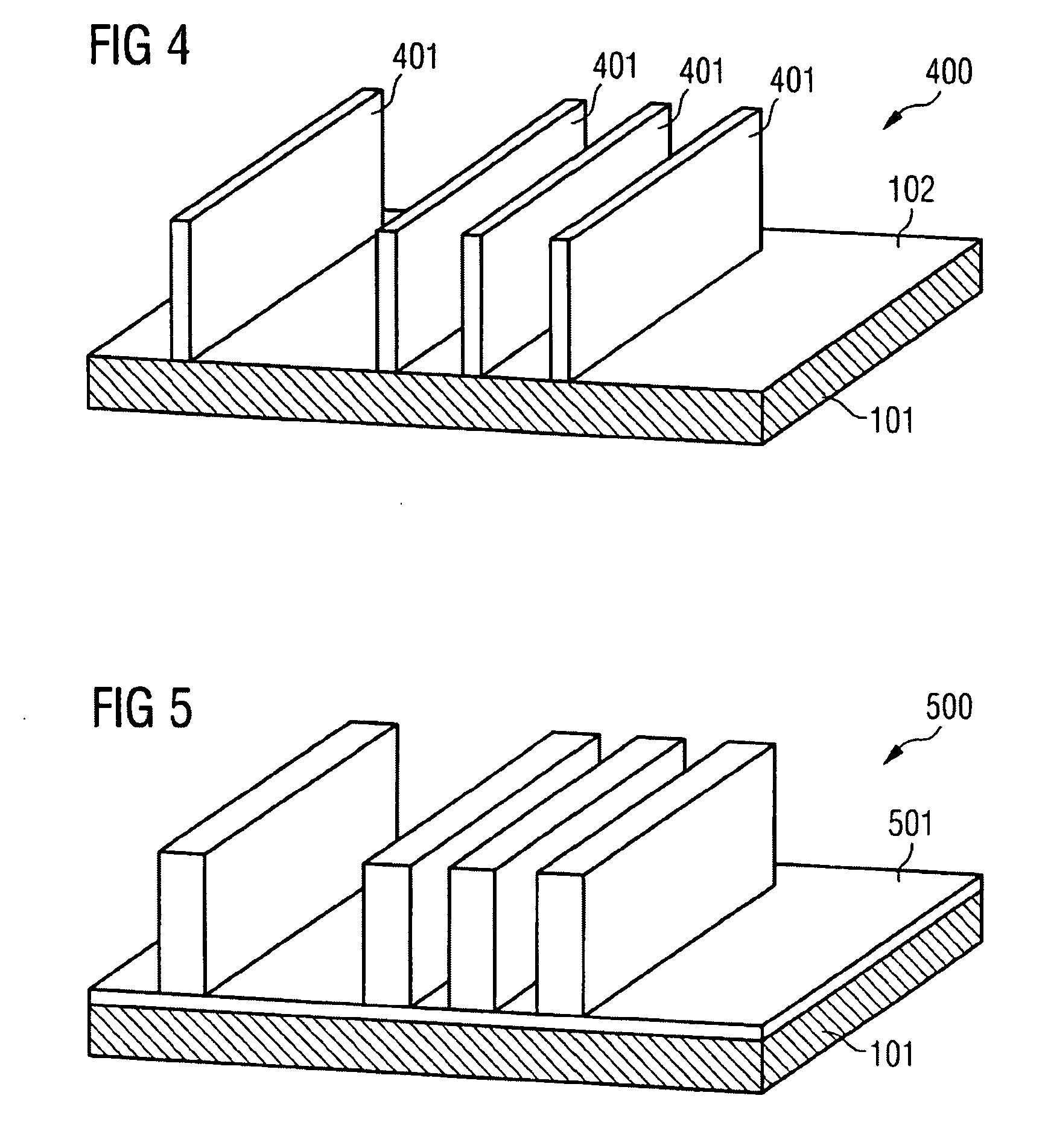
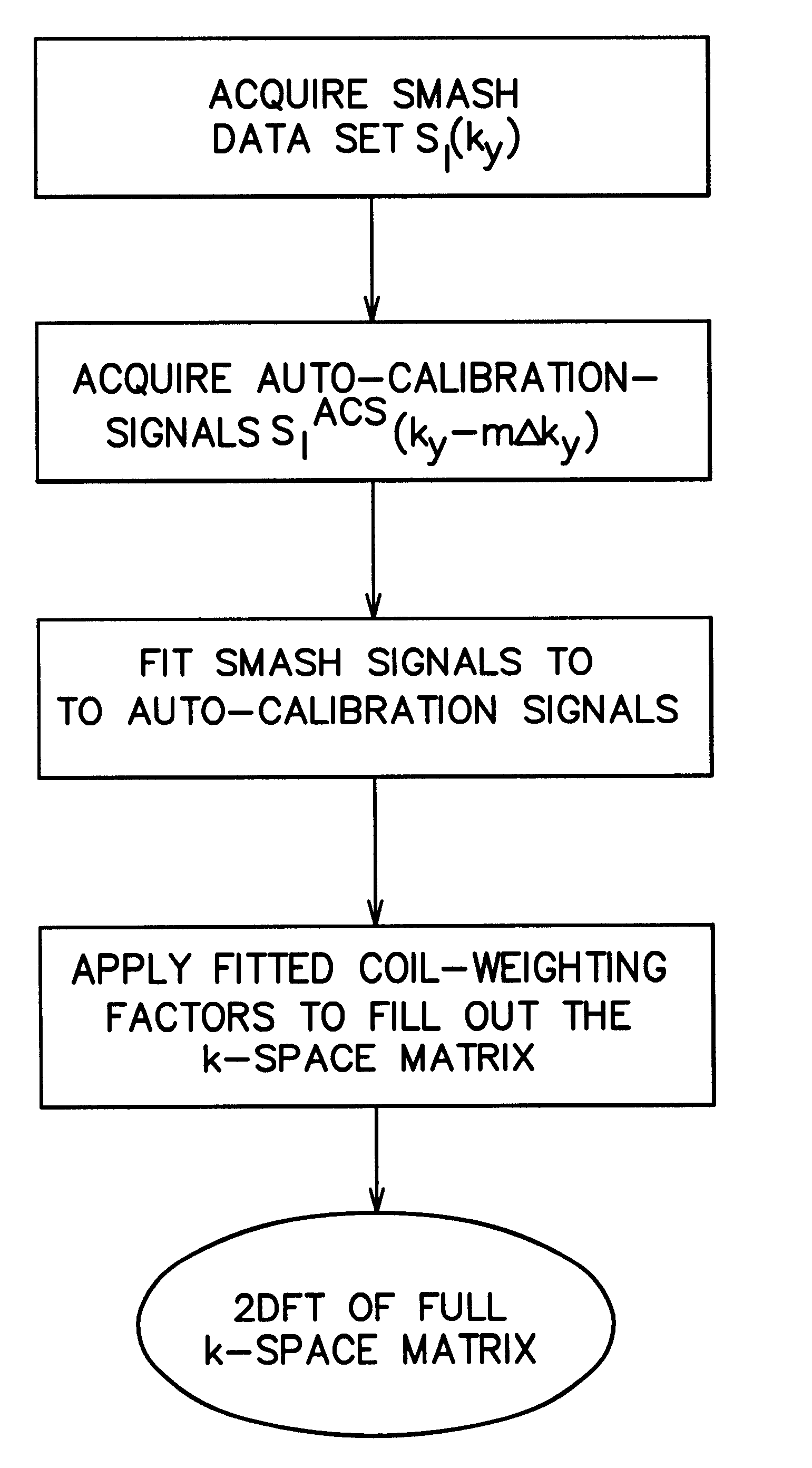
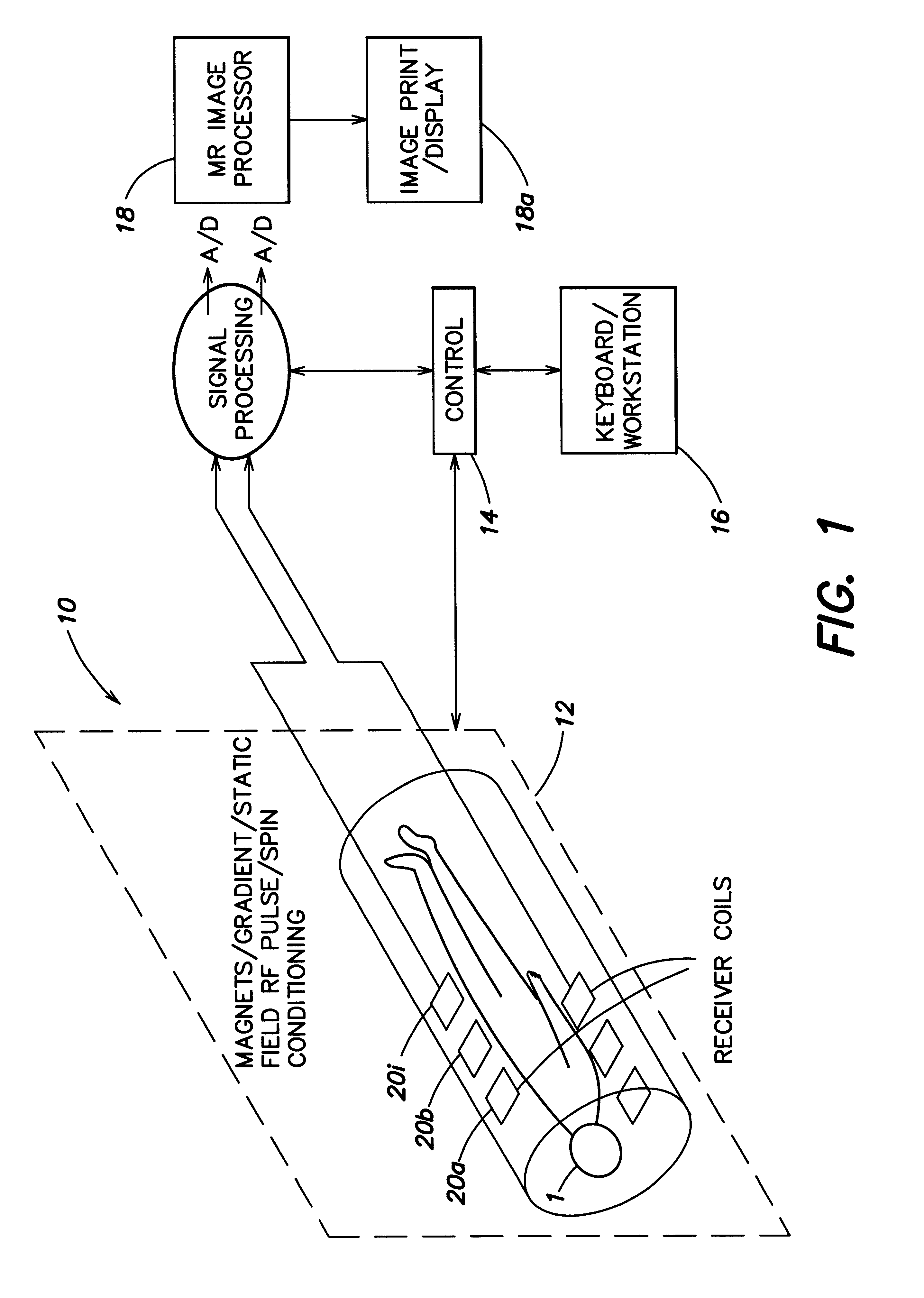
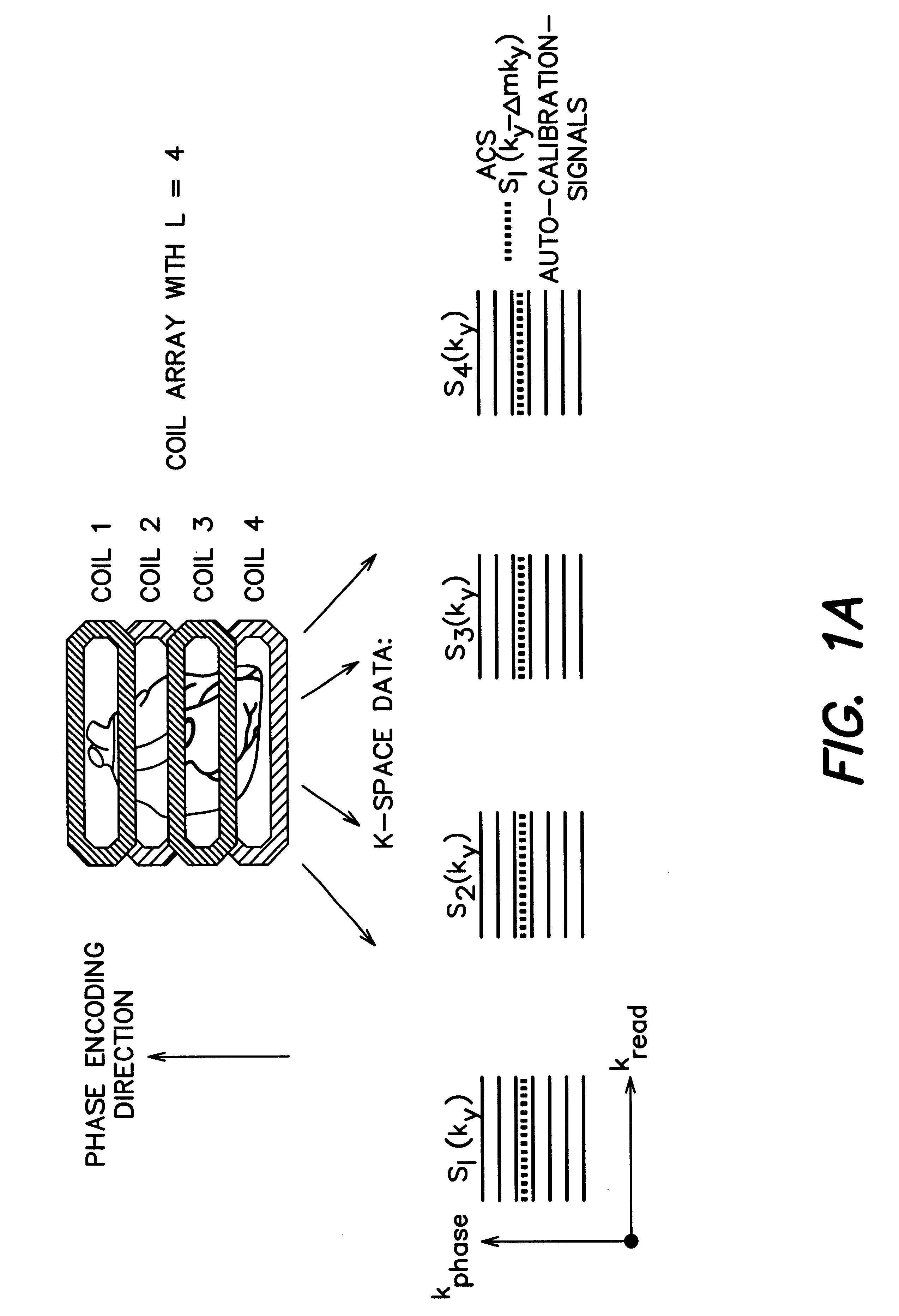
Coil array autocalibration MR imaging
InactiveUS6289232B1Shorten the timeEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData spaceIn vivo
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus and technique exploits spatial information inherent in a surface coil array to increase MR image acquisition speed, resolution and / or field of view. Magnetic resonance response signals are acquired simultaneously in the component coils of the array and, using an autocalibration procedure, are formed into two or more signals to fill a corresponding number of lines in the signal measurement data matrix. In a Fourier embodiment, lines of the k-space matrix required for image production are formed using a set of separate, preferably linear combinations of the component coil signals to substitute for spatial modulations normally produced by phase encoding gradients. One or a few additional gradients are applied to acquire autocalibration (ACS) signals extending elsewhere in the data space, and the measured signals are fitted to the ACS signals to develop weights or coefficients for filling additional lines of the matrix from each measurement set. The ACS lines may be taken offset from or in a different orientation than the measured signals, for example, between or across the measured lines. Furthermore, they may be acquired at different positions in k-space, may be performed at times before, during or after the principal imaging sequence, and may be selectively acquired to optimized the fitting for a particular tissue region or feature size. The in vivo fitting procedure is readily automated or implemented in hardware, and produces an enhancement of image speed and / or quality even in highly heterogeneous tissue. A dedicated coil assembly automatically performs the calibration procedure and applies it to measured lines to produce multiple correctly spaced output signals. One application of the internal calibration technique to a subencoding imaging process applies the ACS in the central region of a sparse set of measured signals to quickly form a full FOV low resolution image. The full FOV image is then used to determine coil sensitivity related information and dealias folded images produced from the sparse set.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Circular Stapler Buttress
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
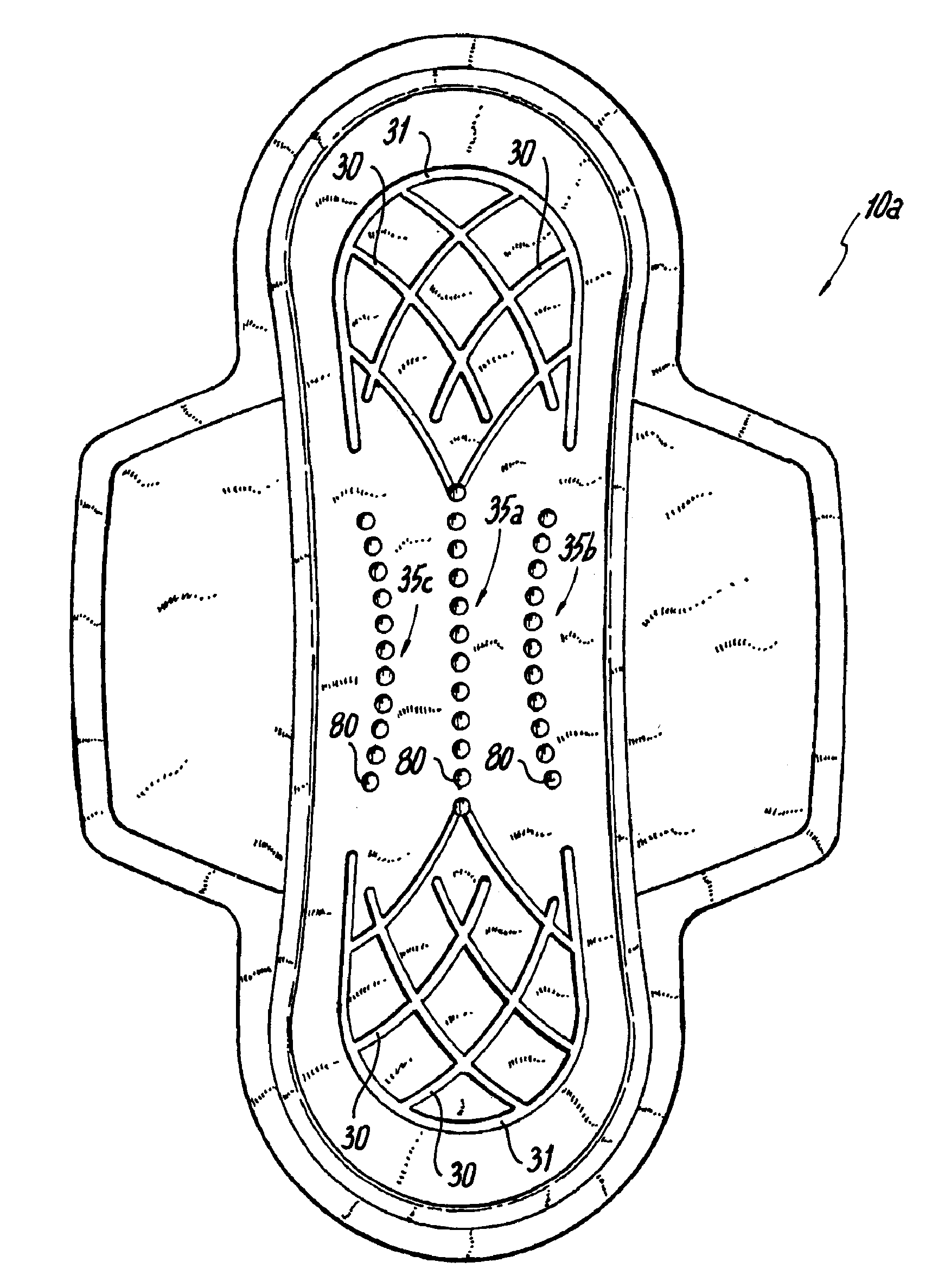
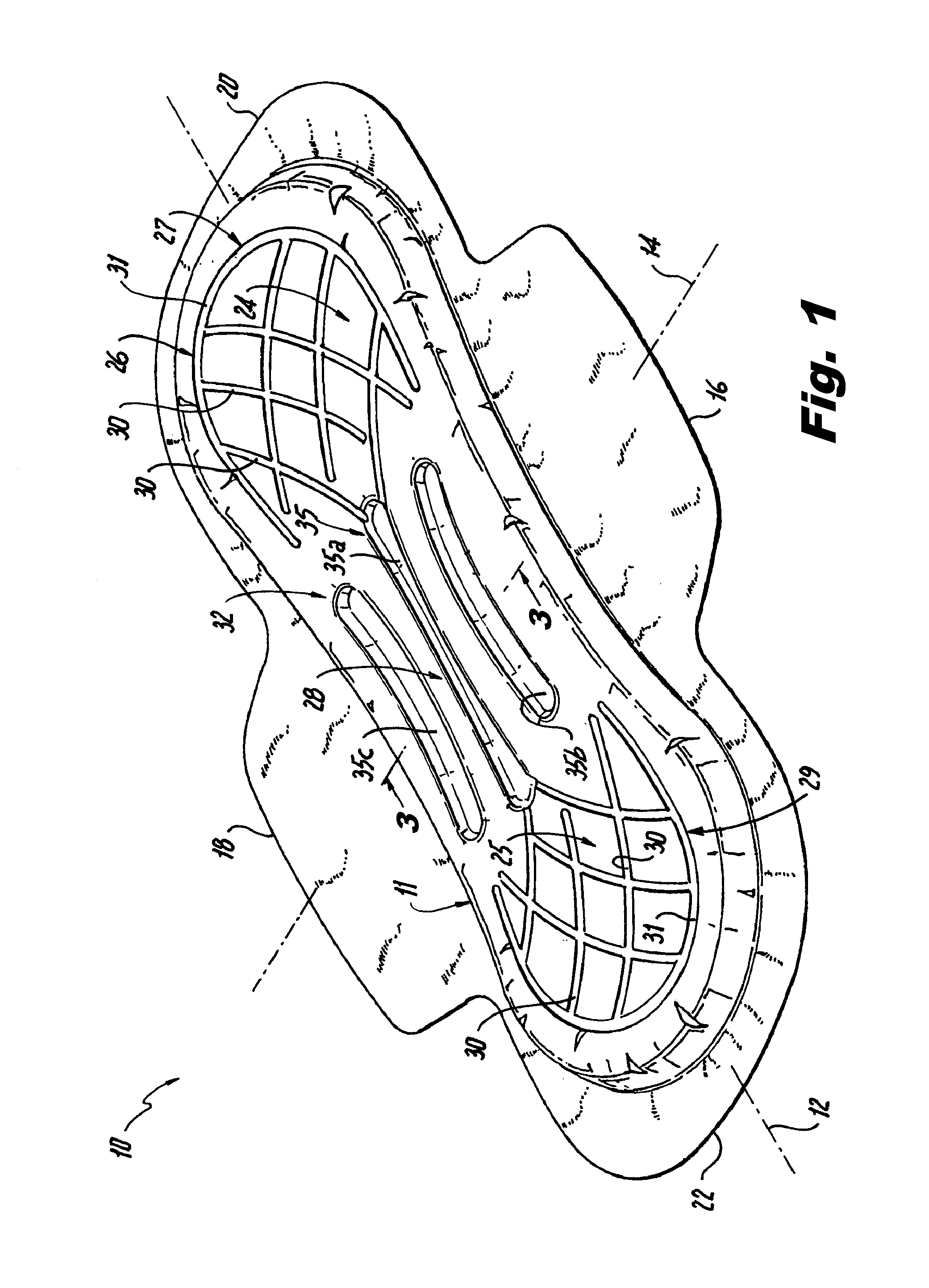
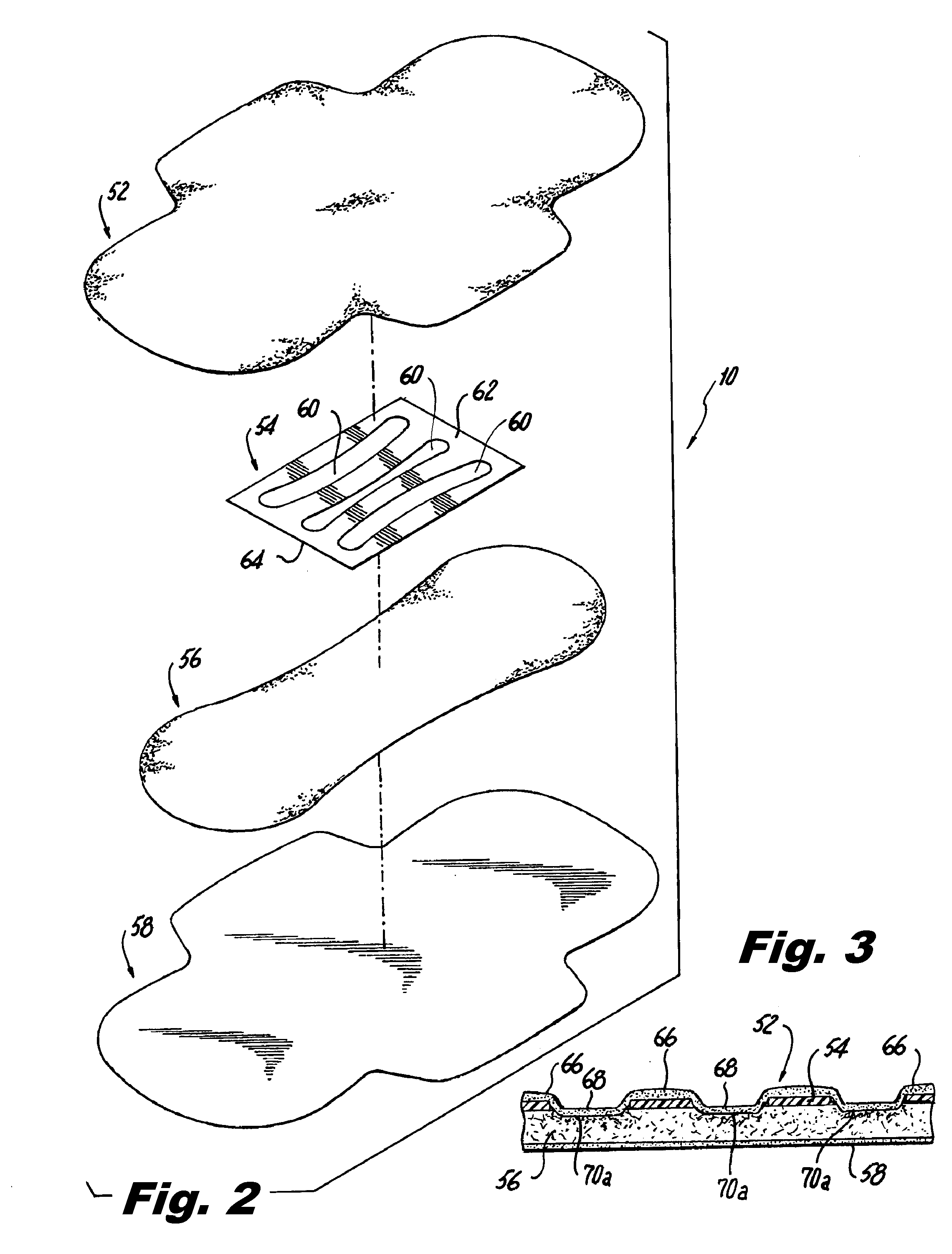
Absorbent article with center fill performance
InactiveUS6673982B1Reduce the possibilitySanitary towelsBaby linensAbsorbent materialMechanical engineering
An absorbent article comprising a central absorbent member and a lateral wicking barrier for inhibition of wicking from the central regions of the article to an outlying outer absorbent member. The wicking barrier has a vertical component for prevention of radial wicking in the plane of the article and thus promotes center filling of the article with fluid and reduces the likelihood of leaks from the sides of the article. The wicking barrier can also have a horizontal component to prevent leakage, redirect fluid flow, and improve fit and performance of the article. In one embodiment, the central absorbent member is a concentric absorbent structure having alternating rings of barrier material and absorbent material, including a spiral wound composite formed from a layer of barrier material wound with a layer of absorbent material and then sliced to provide a thin absorbent layer having high permeability in the thickness direction but low permeability in the plane due to the barrier material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Plasma etching apparatus and plasma etching method
ActiveUS20120012556A1Improve uniformityEasy to controlElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringSemiconductor
A plasma etching apparatus 11 includes a mounting table that holds a semiconductor substrate W thereon; a first heater 18a that heats a central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; a second heater 18b that heats an edge region around the central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; a reactant gas supply unit 13 that supplies a reactant gas for a plasma process toward the central region of the semiconductor substrate W held on the mounting table 14; and a control unit 20 that performs a plasma etching process on the semiconductor substrate W while controlling the first heater 18a and the second heater 18b to heat the central region and the edge region of the processing target substrate W held on the mounting table 14 to different temperatures.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Circular Stapler Buttress
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
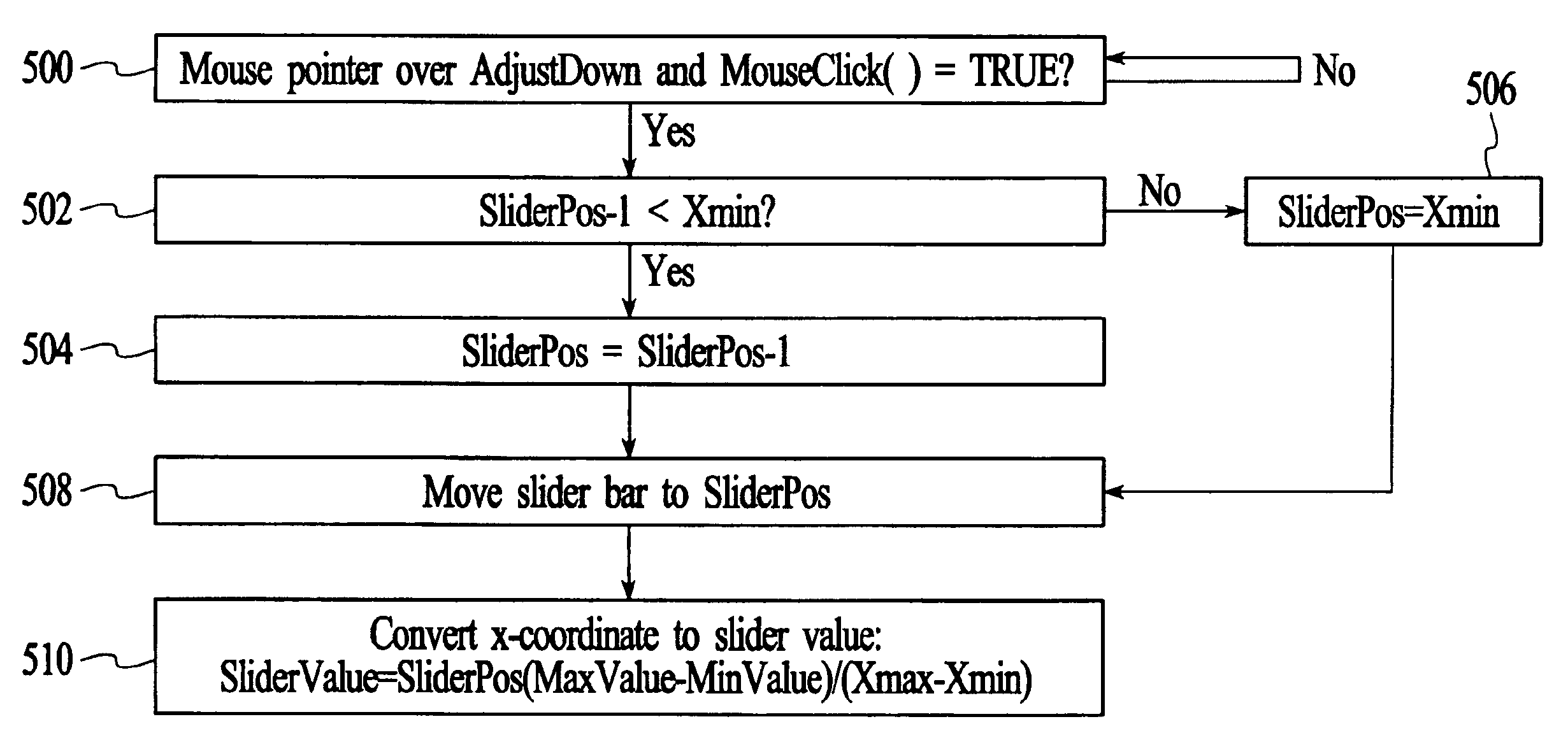
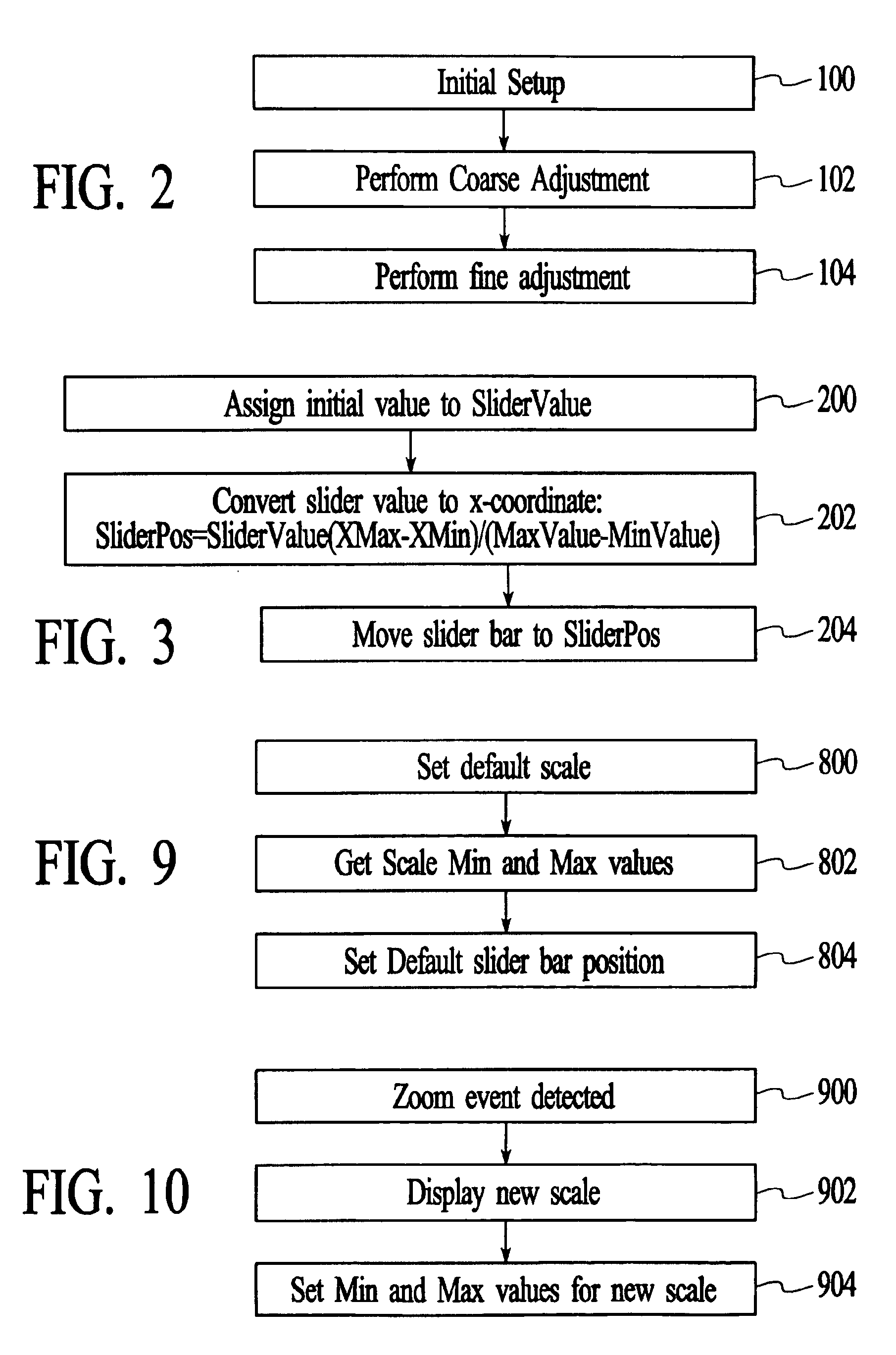
Method and system for adjusting settings with slider controls having variable sensitivity
InactiveUS6922816B1Improve intuitionVariable sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
Aspects for allowing adjustment of a setting via a slider bar displayed on a graphical user interface are provided. These aspects include providing a slider bar control button for the slider bar, and integrating fine and coarse adjustment control into the slider bar control button to allow precise manipulation of a value for the setting. The provision of a slider bar control button includes providing a thumbwheel control button with a central area for coarse adjustment control through repositioning of the thumbwheel control button, a top button substantially adjacent and above the central area for fine adjustment control to increase a setting value by a predetermined increment, and a bottom button substantially adjacent and below the central area for fine adjustment control to decrease a setting value by a predetermined increment. Alternatively, providing a slider bar control button includes providing a three section bar with a first section for coarse adjustment, a second section for fine adjustment up, and a third section for fine adjustment down. In yet another alternative, providing a slider bar control button includes providing a zoom control button that allows adjustment to a scale displayed for setting values and responds to separate selection interface means to increase and decrease the scale.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for examining, recording and analyzing dermatological conditions
InactiveUS6993167B1Minimise edge contributionDecrease shiftDiagnostics using lightSurgeryMelanomaHand held
A system for collecting, storing and displaying dermatological images for the purpose of monitoring and diagnosis of skin conditions and skin cancers, including melanoma. A hand-held unit illuminates a section of the patient's skin, and an imaging device generates imaging signals from light derived from a skin section. Pairs of light output ports in the hand-held unit are arranged such that their intensity distributions overlap at their half-intensity levels so that the resulting summation of their intensities has a flat central region. Three image stores are maintained, one for lesion images, one for “nearby skin” images, and one for reference-white images. The “nearby skin” images are used by the system software to automatically determine the skin / lesion border. The reference white images are used to set the dynamic range of the instrument and to compensate for lighting irregularities. Two images of the same lesion taken at different times may be displayed simultaneously so that changes in the lesion may be determined. The calibration system is designed so that image data taken on any of multiple machines built to the same specification will be corrected back to a common reference standard to ensure absolute accuracy in colour rendition.
Owner:POLARTECHNICS
Absorbent article with center fill performance
An absorbent article comprising a central absorbent member and a lateral wicking barrier for inhibition of wicking from the central regions of the article to an outlying outer absorbent member. The wicking barrier has a vertical component for prevention of radial wicking in the plane of the article and thus promotes center filling of the article with fluid and reduces the likelihood of leaks from the sides of the article. The wicking barrier can also have a horizontal component to prevent leakage, redirect fluid flow, and improve fit and performance of the article. In one embodiment, the central absorbent member is a concentric absorbent structure having alternating rings of barrier material and absorbent material, including a spiral wound composite formed from a layer of barrier material wound with a layer of absorbent material and then sliced.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Touch-sensing display panel
InactiveUS20130127790A1Reduce thicknessNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingTotal internal reflectionTouch Senses
A touch-sensing display panel, comprising a plurality of image-forming pixel elements; a planar light guide with a first refractive index, having a front surface forming a touch-sensing region and an opposite rear surface facing the pixel elements; a plurality of light emitters arranged at a peripheral region of the panel to emit light into the light guide for propagation therein through total internal reflection; a plurality of light detectors disposed at the peripheral region for receiving light from the light guide; and an optical layer disposed at the rear surface of the light guide to cover a plurality of the image-forming pixel elements in at least a central region of the panel, wherein said optical layer is configured to reflect at least a part of the light from the emitters impinging thereon from within the light guide.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Portion capsule
InactiveUS20070148290A1Increased Design PossibilitiesEasy piercingTransportation and packagingConfectioneryParticulatesBiomedical engineering
A portion capsule, which is suitable in particular for brewing coffee, has a capsule cover and a capsule base and is closed on all sides in the state in which it is supplied. It contains a particulate beverage substance which can be extracted by water. A screening device is arranged between the beverage substance and the capsule base. The screening device is spaced apart from the capsule base, in the central region of the latter, by means of an annular structure which defines an outer region and an inner region in the interspace between the screening device and capsule base. The outer region is connected to the inner region via through-openings.
Owner:TCHIBO
Intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS7563284B2Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantLigamentsAxial compressionRange of motion
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and lordosis, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumber regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior at least partially filled with a fluid; a valve for injecting fluid into the interior of the disk; a central region having a stiffness that is preferably greater than the stiffness of the outer regions thus enabling the disc to pivot about the central region. The central pivot may be formed by a center opening, a central chamber, an inner core or a central cable.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Wearable Glucometer
InactiveUS20070249916A1Large field of viewEasy alignmentMedical devicesIntravenous devicesAnalyteMedicine
Apparatus for assaying an analyte in blood in a patient's blood vessel comprising: a light provider comprising at least one light source that illuminates a tissue region in which a blood vessel is located with light that stimulates photoacoustic waves in the region; at least one acoustic transducer that generates signals responsive to the photoacoustic waves; a controller that receives the signals and processes them to determine which are responsive to photoacoustic waves that originate in the blood vessel and uses the determined signals to assay the analyte; wherein, the light provider and at least one transducer define a field of view that overlaps the blood vessel, said field of view having a central region and a lateral extent greater than about 4 mm.
Owner:GLUCON
Limb encircling therapeutic compression device
ActiveUS20050192524A1Short and useMinimal numberChemical protectionHeat protectionCompression deviceEngineering
A therapeutic compression garment made of flexible, foldable, light weight Velcro-type loop fabric having a central region for wrapping partially around a body part and a plurality of bands integrally connected to the central region and extending outwardly in opposite directions from both sides of the central region to cross each other and encompass the body part.
Owner:MEDI MFG INC
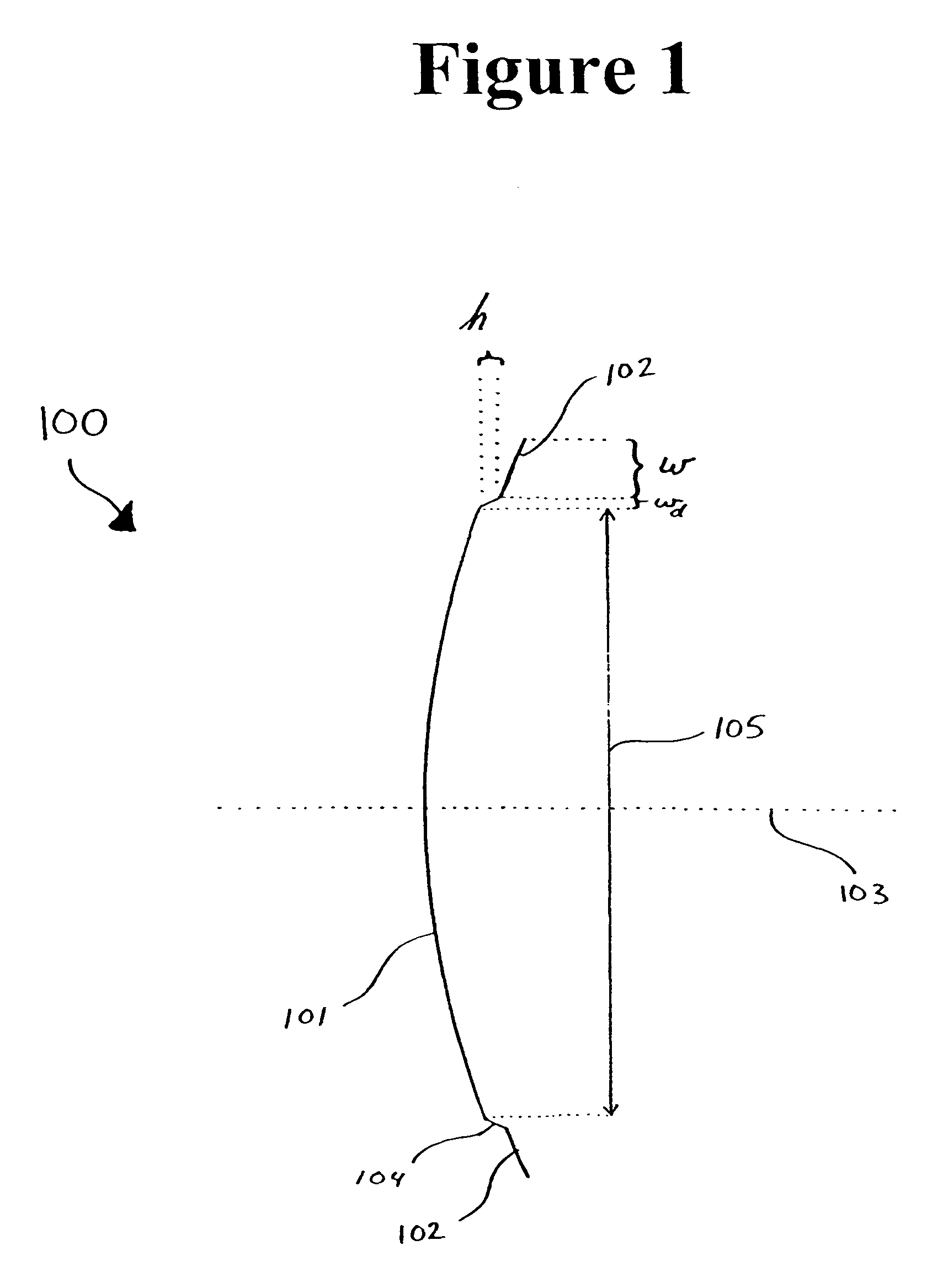
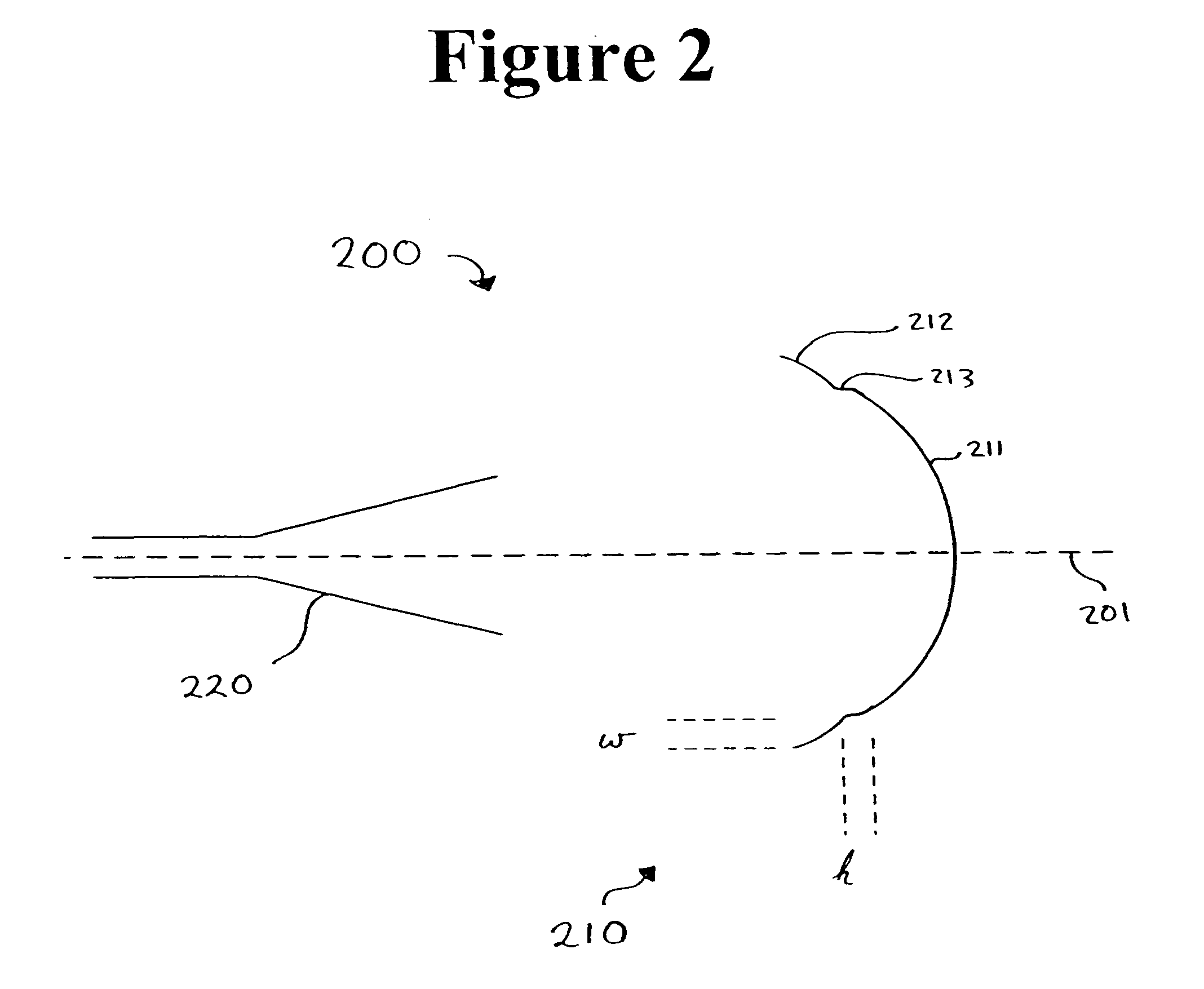
Stepped-reflector antenna for satellite communication payloads
ActiveUS7737903B1Reduce peak-to-edge gain variationImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsPhase shiftedEngineering
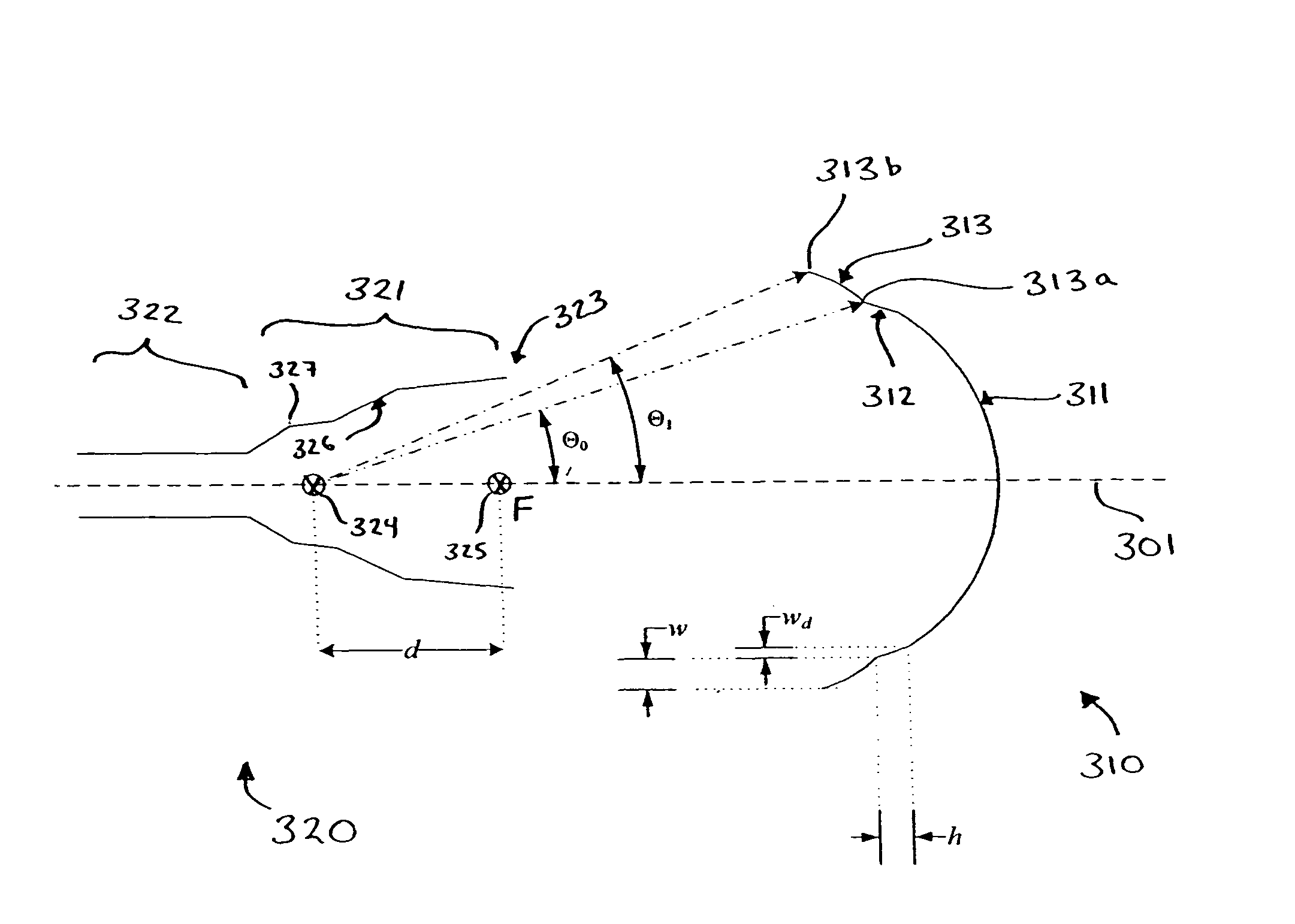
A stepped reflector for being illuminated by at least one multiple-band feed is provided. The reflector includes a central region and a first annular region with an annular width of w. The first annular region is axially stepped a height h above the central region, where h is approximately equal tom×[Φ±(ϕ(Θ=0)-ϕ(Θ=Θ0))]×π180×λ2π×12,where m is a positive odd integer, Φ is a desired amount of phase shift of an outer region of a phase front for reflecting off of the reflector, φ is a feed phase contribution for an angle Θ, and Θ0 is an angle formed between an axis of the at least one feed and a line connecting a phase center of the at least one feed and an inner edge of the at least one annular region.The central region and the annular region of the reflector may be parabolically curved or may alternately be shaped. The reflector may be fed by one or more multiple-band horn antennas.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for forming a hard bias structure in a magnetoresistive sensor
A method for forming a hard bias structure in a magnetoresistive sensor is disclosed. A magnetoresistive sensor having a soft magnetic bias layer, spacer layer, and a magnetoresistive layer, is formed over a substrate having a gap layer. A mask is formed over a portion of the magnetoresistive sensor structure to define a central region. The masked structure is ion milled to remove portions not shielded by the mask, to form the central region with sloped sides, and to expose a region of the gap layer laterally adjacent the sloped sides. A first underlayer is deposited onto at least the sloped sides at a high deposition angle. A second underlayer is deposited to at least partially overlap the first underlayer, and at a first lower deposition angle. A hard bias layer is deposited over at least a portion of the second underlayer, and at a second lower deposition angle.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Compact multi-band direction-finding antenna system
InactiveUS6480168B1Easy to transportEconomically manufacturedAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesMulti bandNon symmetric
An compact and rugged antenna system particularly suited to direction finding includes a plurality of antenna arrays for receiving respective frequency bands and colocated on a mast with separation between antenna arrays along the mast. The mast includes a coil wound of an insulator and functioning as a loaded inductor to shift the mast resonance out of the frequency band of the antenna system. A VHF dipole array having elements shaped to reduce scattering to UHF and SHF arrays is supported on movable arms which allow retraction that reduces height and provides mechanical protection to one or more other arrays as well as damping against vibration by contacting the mast with shaped portions of the dipole elements. The bowtie elements of the UHF array are angled at a central region to optimize array diameter at low UHF frequencies. A finned RF electronics housing is preferably provided which reduces solar loading and dissipates heat from antenna electronics. Asymmetrically keyed fittings are provided to permit accurate antenna system, array and element positioning and replaceable components and wiring, both internally and externally of the housing, is held in position to allow field repairs without recalibration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Absorbent article including a plurality of longitudinally extending channels
An absorbent article including a first end region, a second end region and a central region, a plurality of channels arranged in each of the first and second end regions, at least one channel arranged in the central region and extending in a longitudinal direction of the article, the at least one channel being connected at each end thereof to the plurality of channels in the first end region and the plurality of channels in the second end region.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC
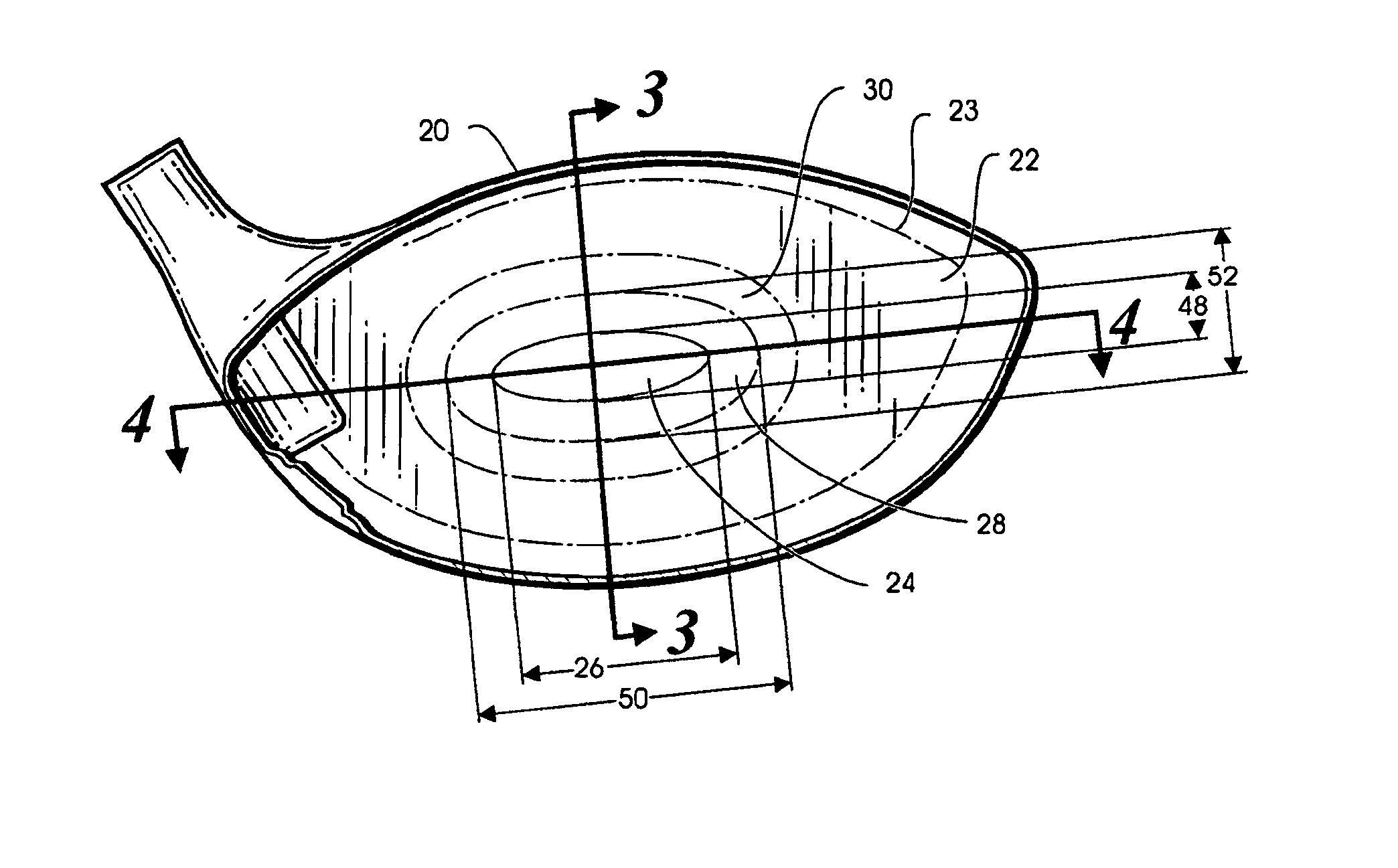
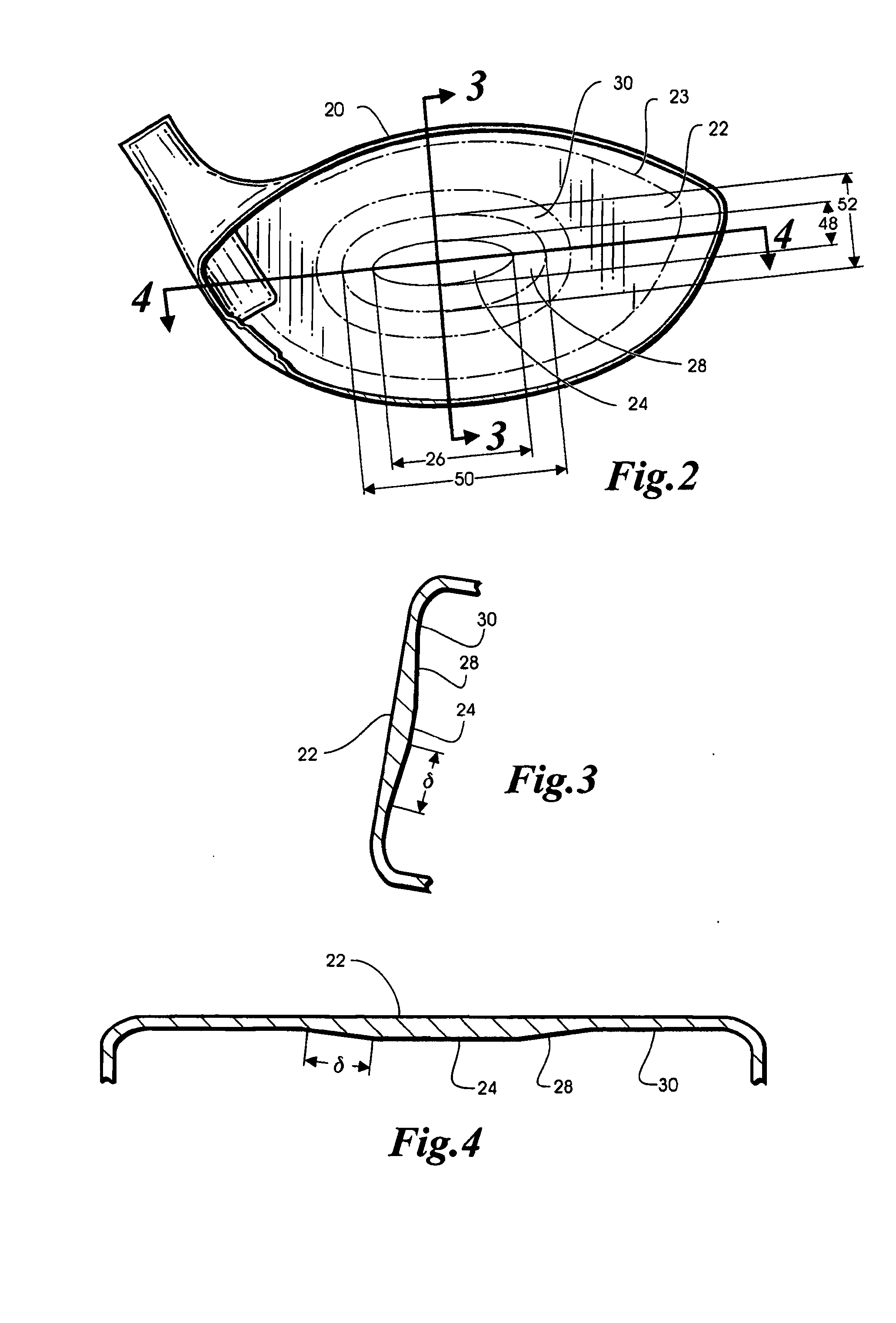
Method of manufacturing a golf club face
InactiveUS20080004133A1Improve uniformitySignificant timeMilling equipment detailsShaping cuttersEngineeringGolf Ball
Embodiments of methods of manufacturing a face plate for a golf cub are generally described herein. In one exemplary embodiment, a method for manufacturing a golf club face plate comprises: providing a face plate material, and milling the face plate material in an elliptical pattern to form a central region comprising, a first elliptical outer edge and a transition region extending from the first elliptical outer edge to a second elliptical outer edge. In this exemplary embodiment, each point along the second elliptical outer edge is displaced outward from the first elliptical outer edge by a predetermined distance. Other embodiments herein may be described and claimed.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
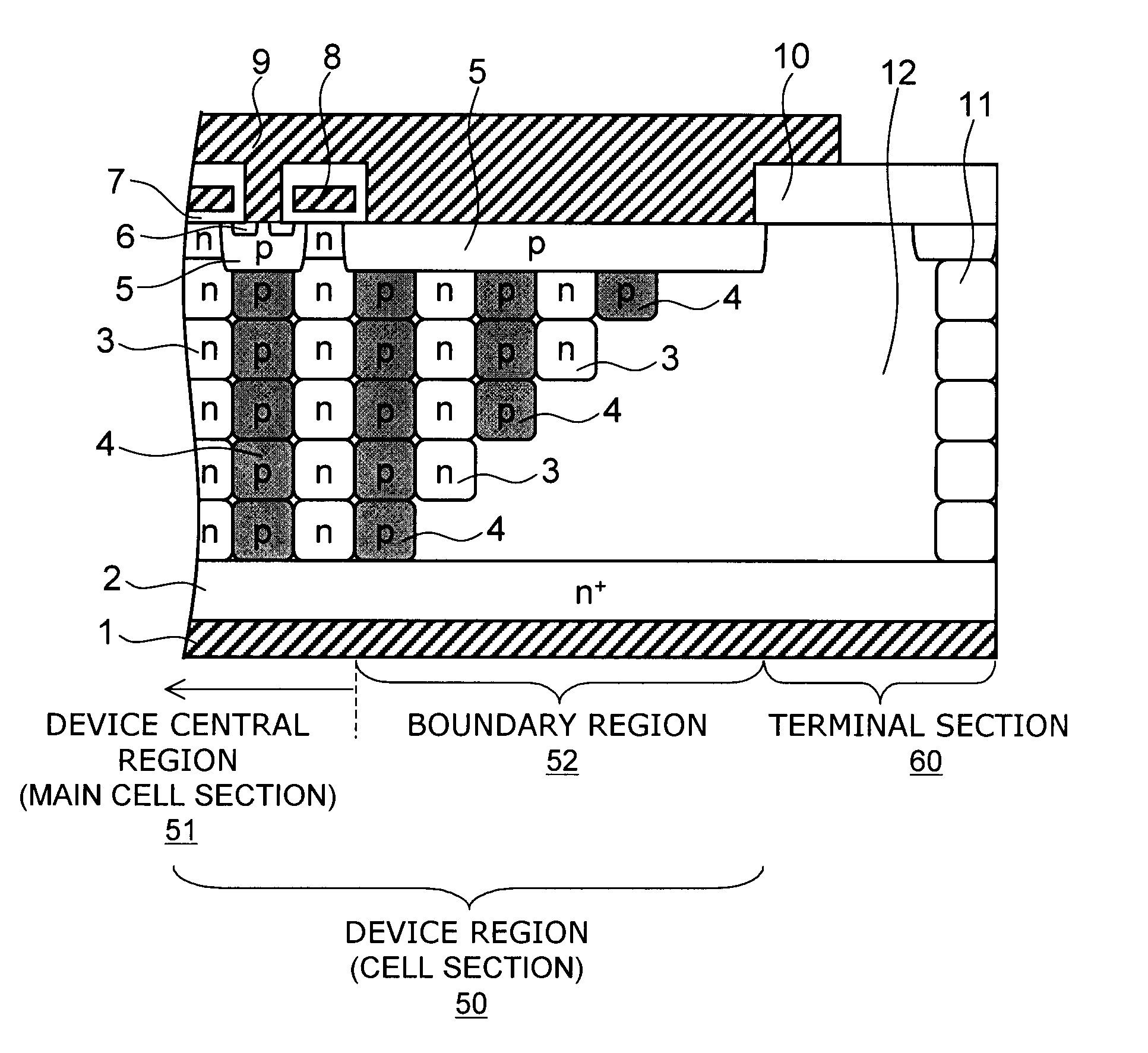
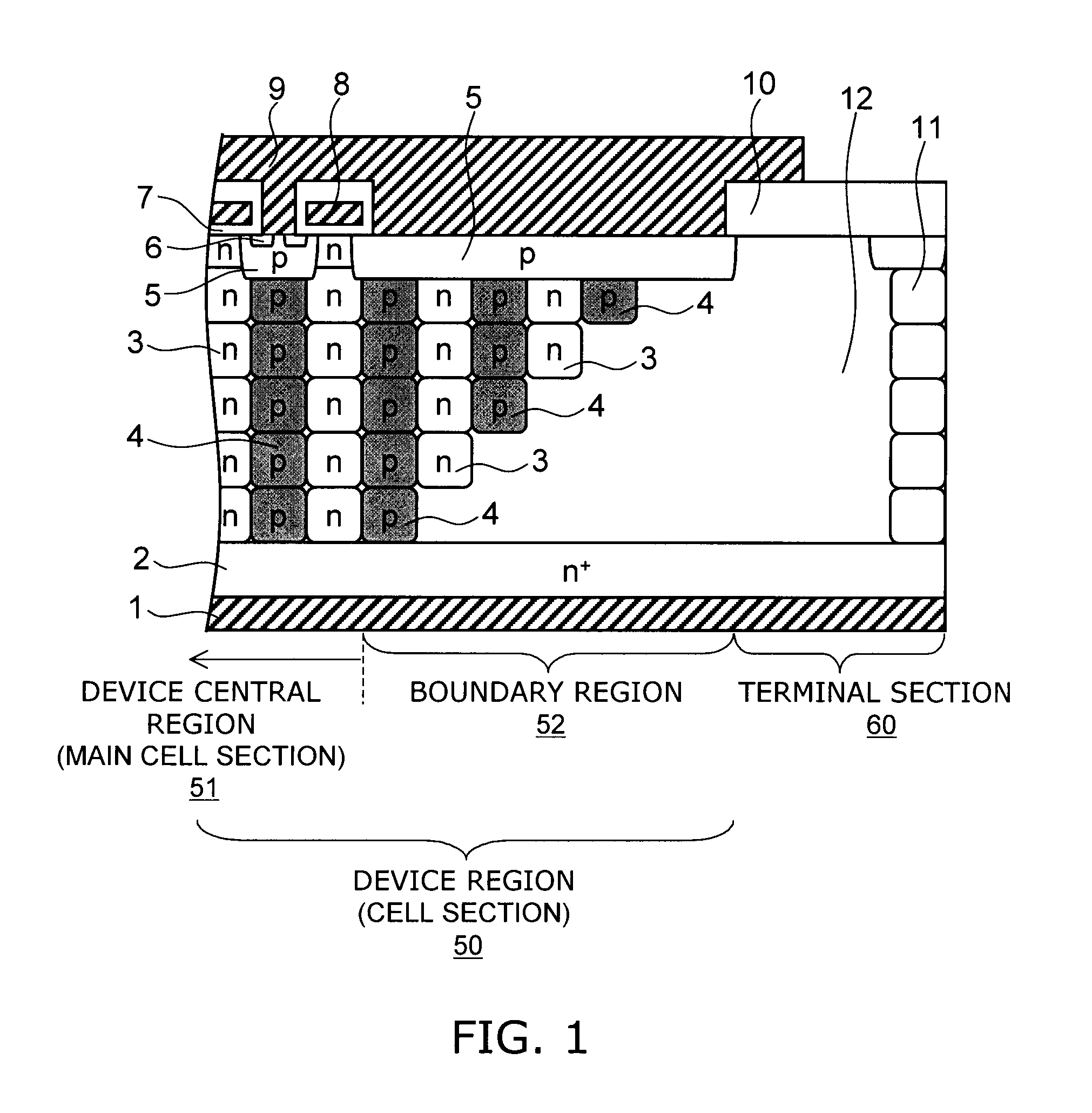
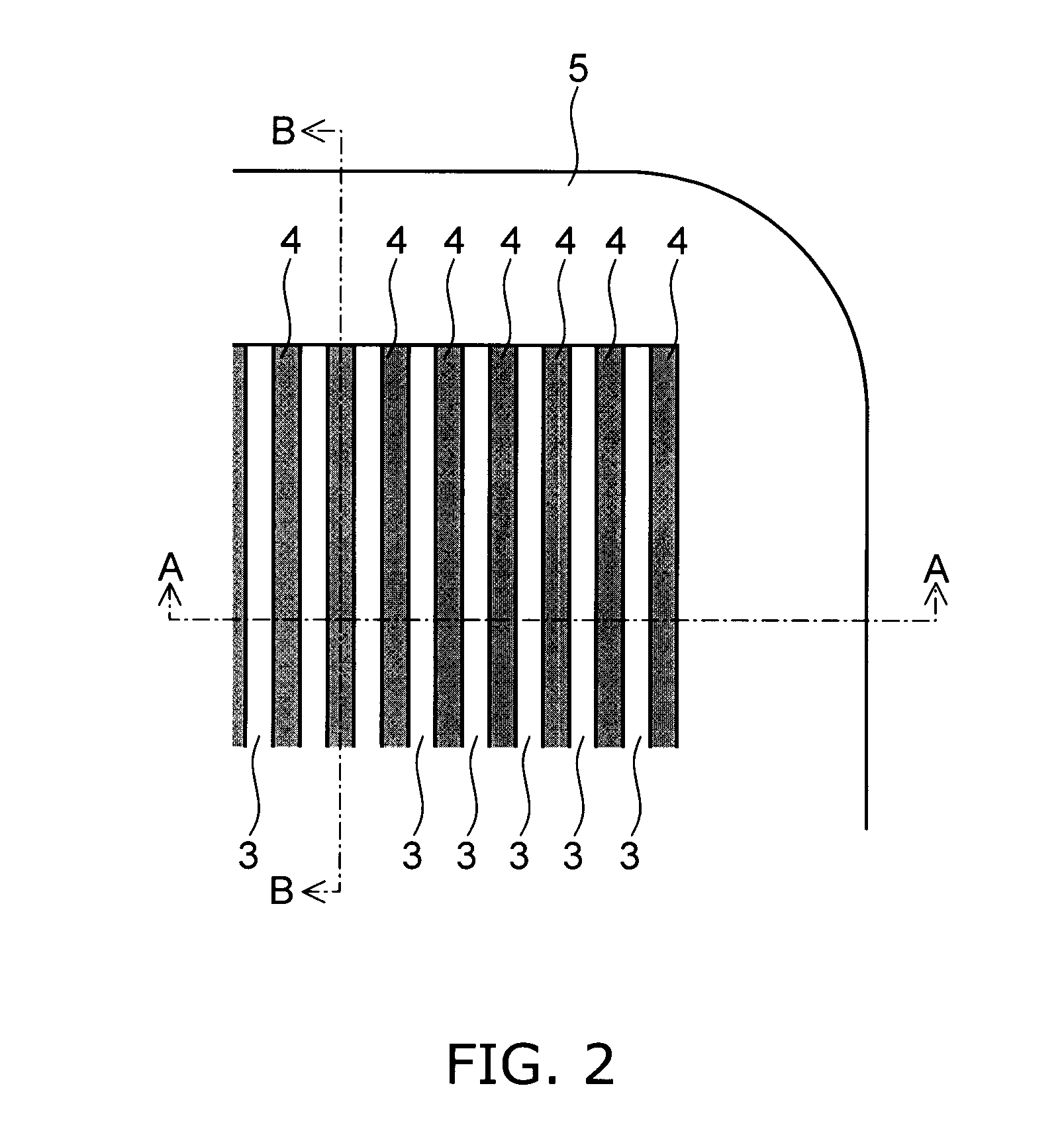
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070272979A1Reduce doping concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHigh resistanceDopant
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type; a first semiconductor pillar region of the first conductivity type provided on a major surface of the semiconductor layer; a second semiconductor pillar region of a second conductivity type provided adjacent to the first semiconductor pillar region on the major surface of the semiconductor layer, the second semiconductor pillar region forming a periodic arrangement structure substantially parallel to the major surface of the semiconductor layer together with the first semiconductor pillar region; a first main electrode; a first semiconductor region of the second conductivity type; a second semiconductor region of the first conductivity type; a second main electrode; a control electrode; and a high-resistance semiconductor layer provided on the semiconductor layer in an edge termination section surrounding the first semiconductor pillar region and the second semiconductor pillar region. The high-resistance semiconductor layer has a lower dopant concentration than the first semiconductor pillar region. A boundary region is provided between a device central region and the edge termination section. The first semiconductor pillar region and the second semiconductor pillar region adjacent to the high-resistance semiconductor layer in the boundary region have a depth decreasing stepwise toward the edge termination section.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com