Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
804 results about "Phase center" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
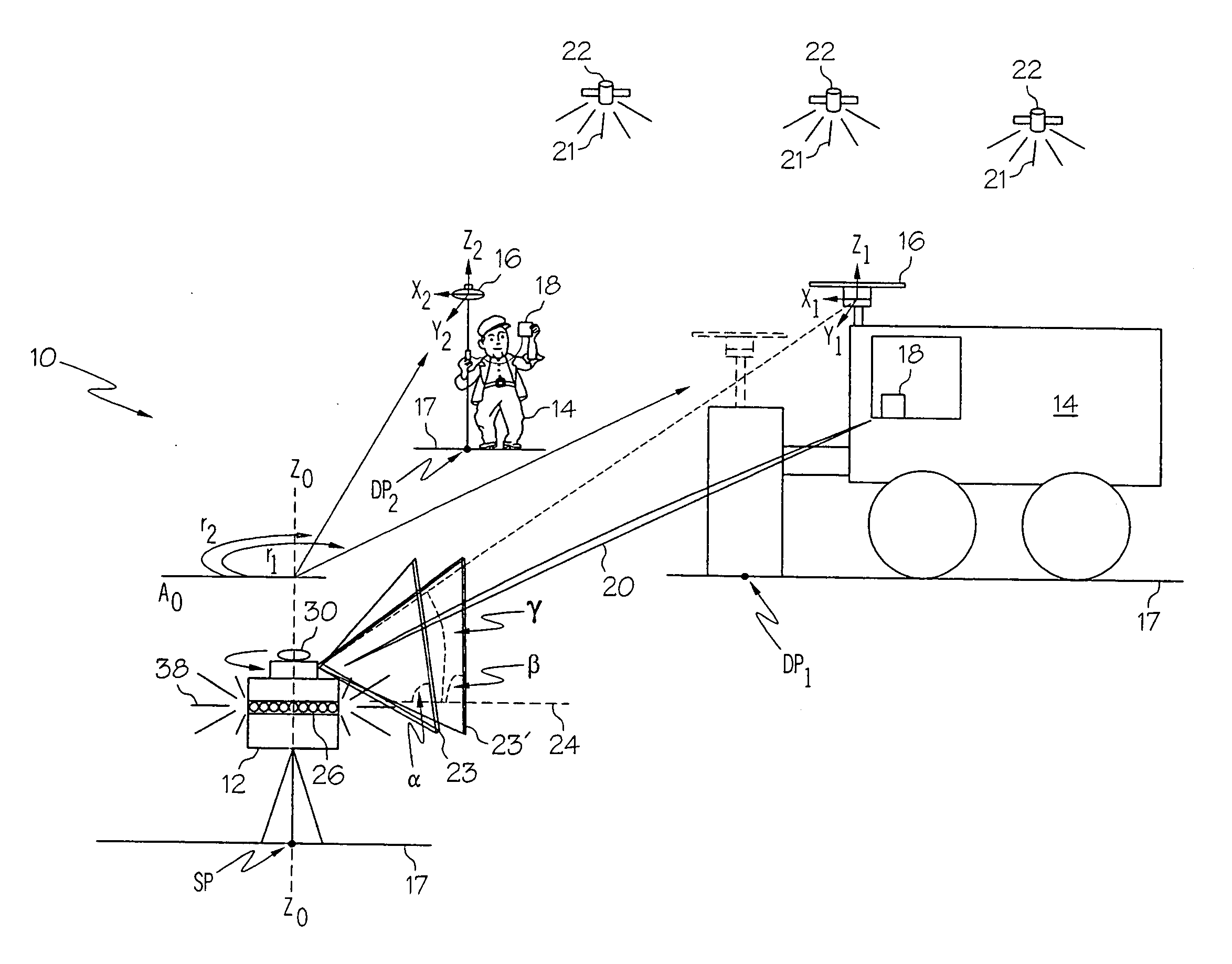
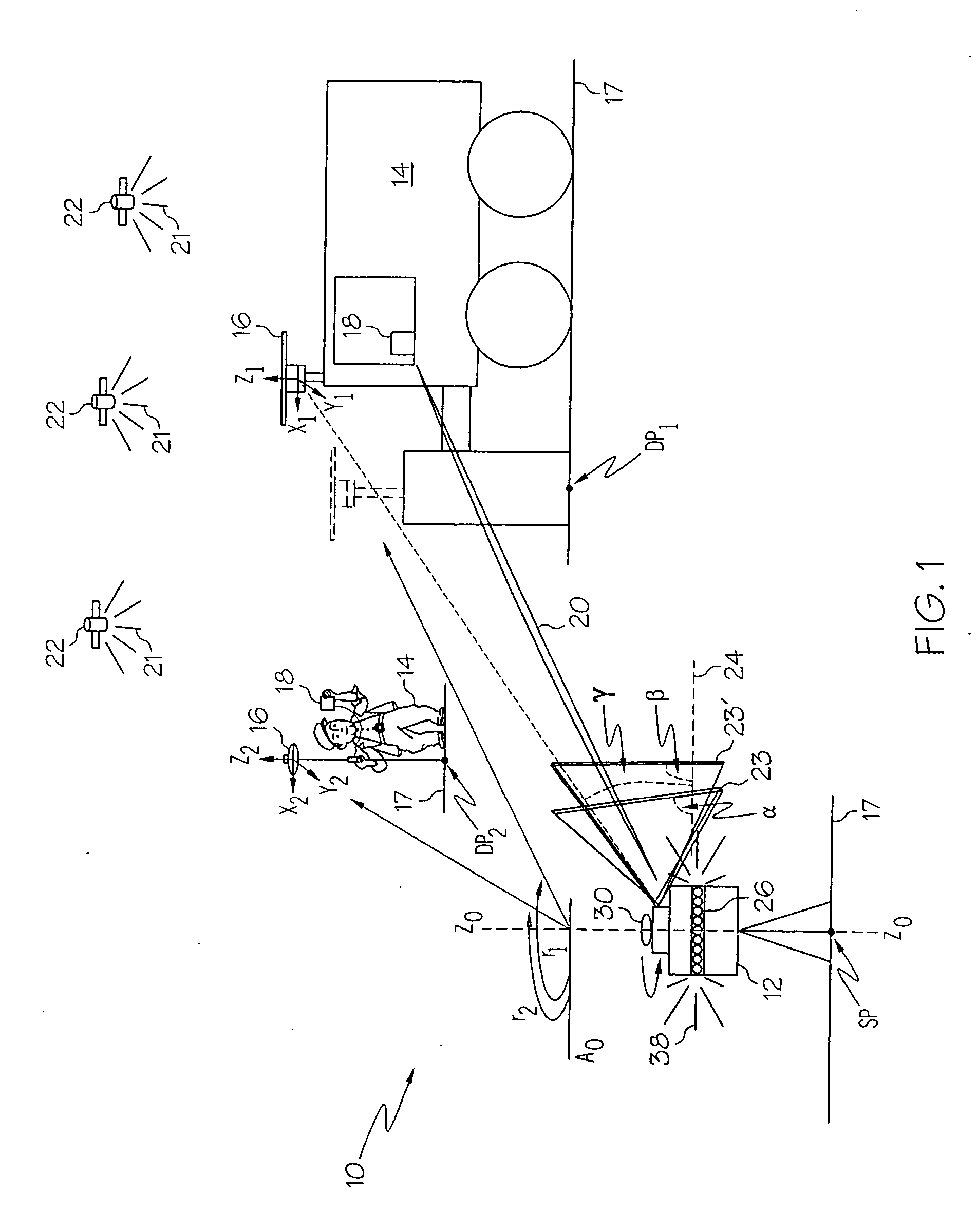
In antenna design theory, the phase center is the point from which the electromagnetic radiation spreads spherically outward, with the phase of the signal being equal at any point on the sphere. Apparent phase center is used to describe the phase center in a limited section of the radiation pattern.
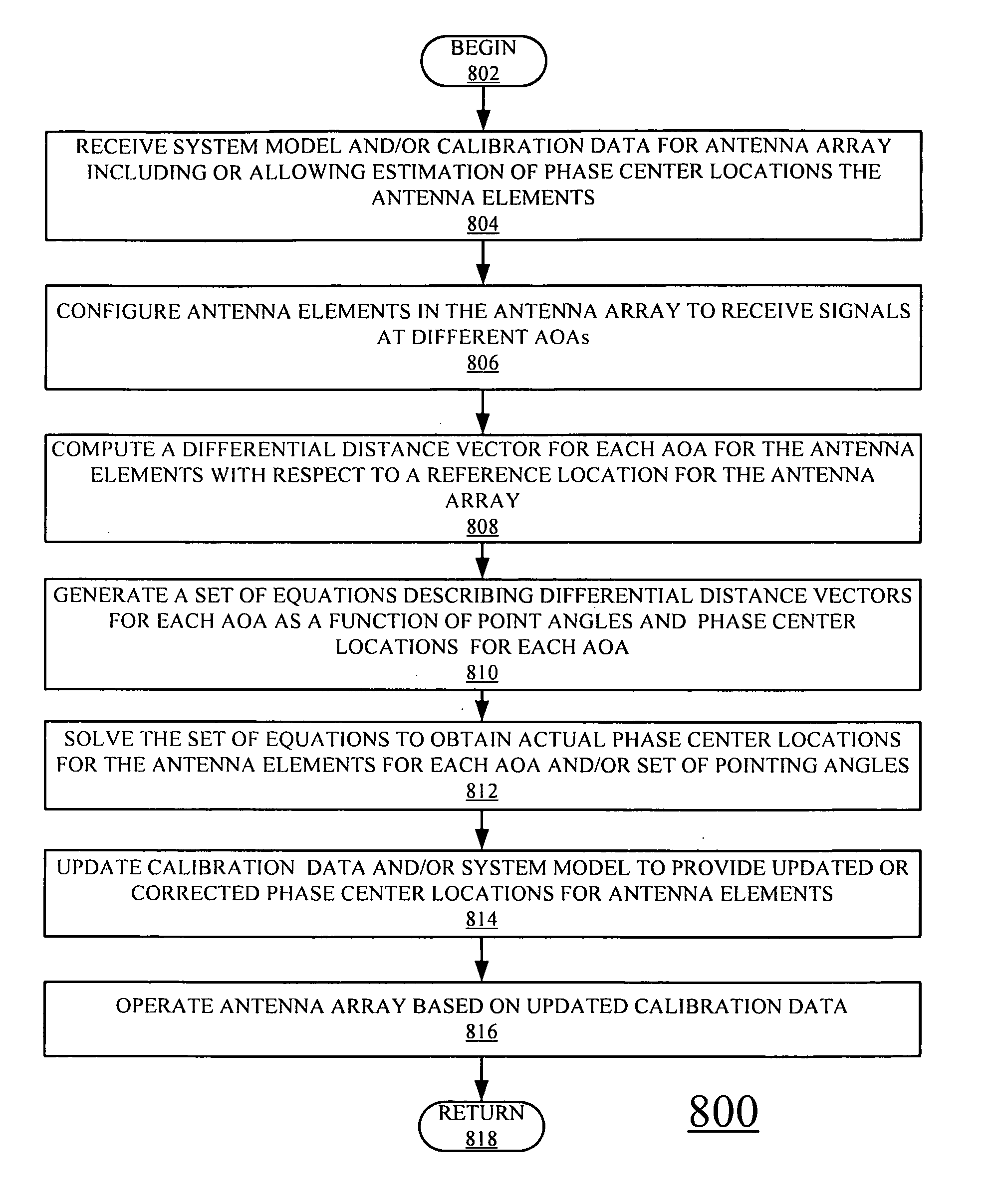
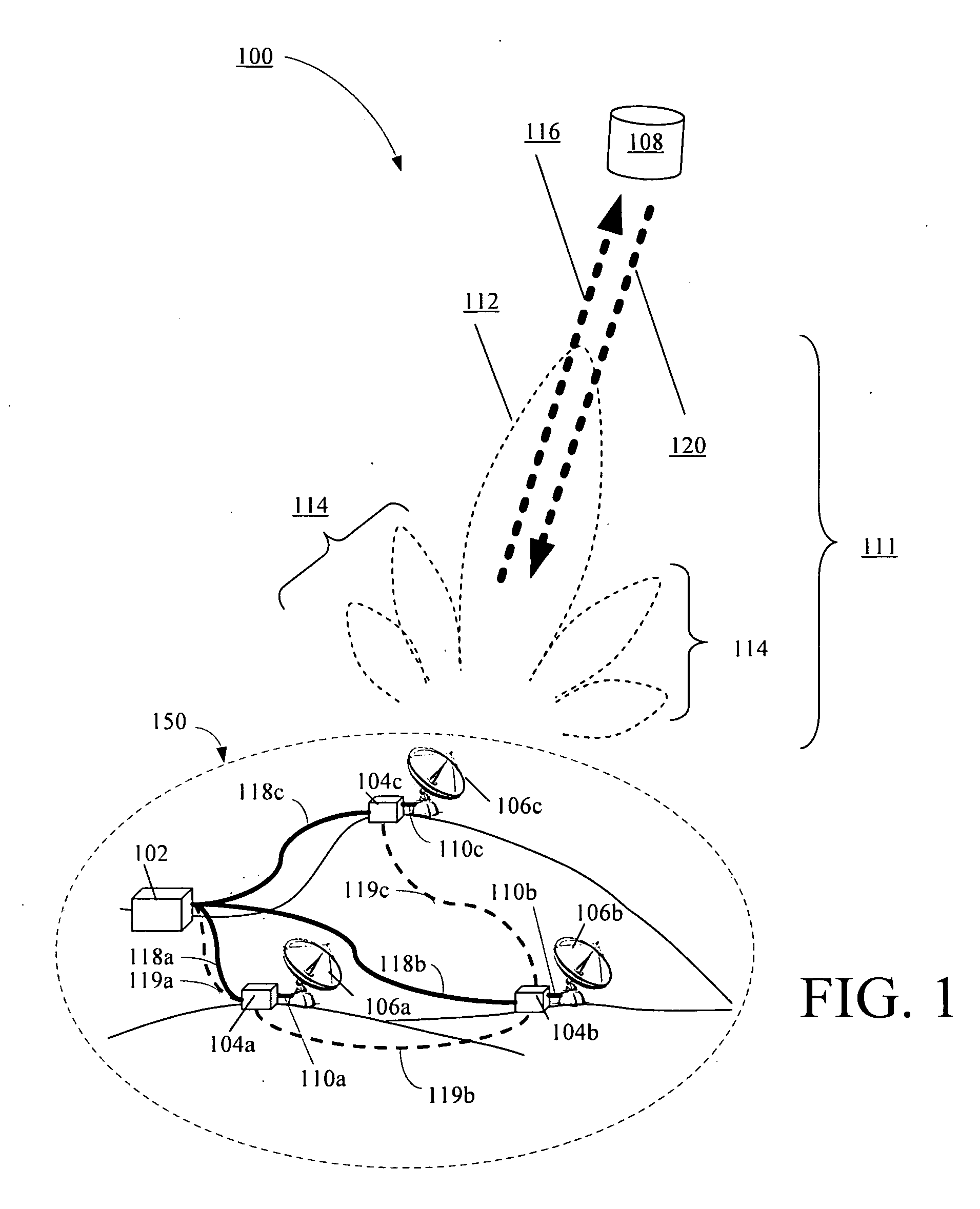
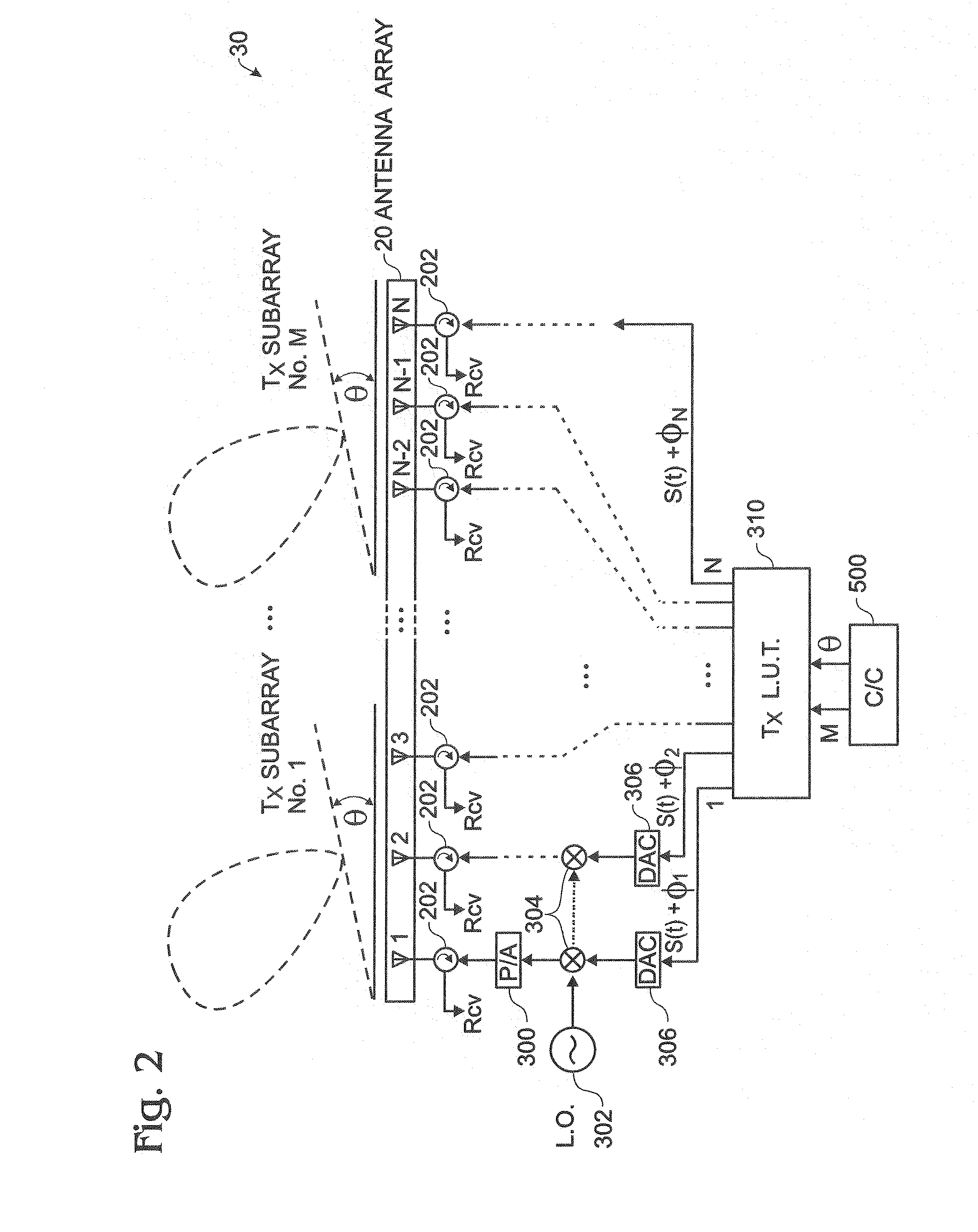
Systems and methods for determining element phase center locations for an array of antenna elements
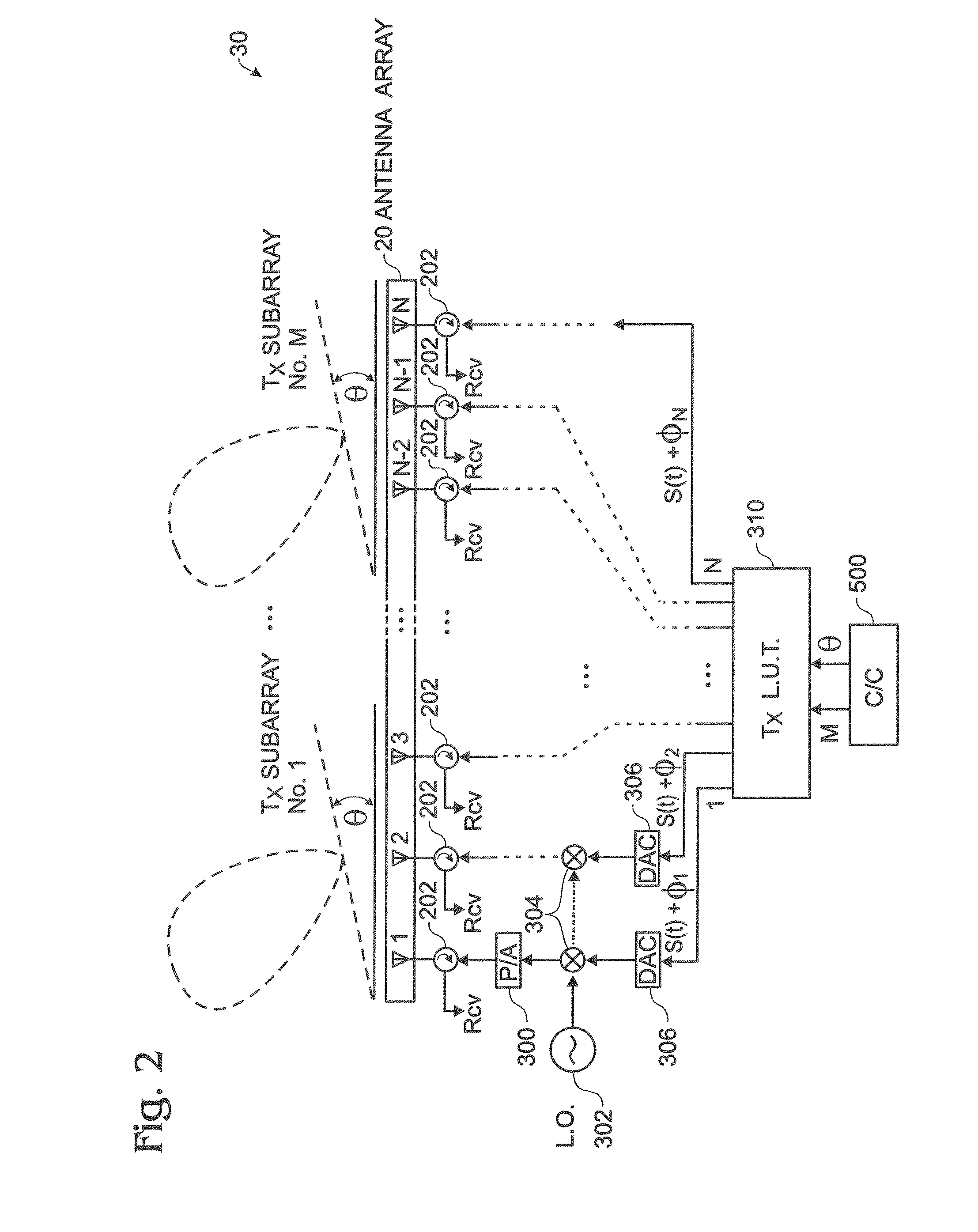
A method for operating a communications system is provided. The method includes receiving a plurality of signals at a plurality of antenna elements, the plurality of signals arriving at the array of antenna elements at a plurality of angles of arrival (AOAs) with respect to a reference location. The method also includes calculating a plurality of differential distance vectors between the plurality of antenna elements and the reference location, each of the plurality of differential distance vectors associated with one of the plurality of AOAs and at least one of the pluralities of signals. The method further includes obtaining a plurality of actual phase center locations for the plurality of antenna elements based on the plurality of differential distance vectors and the plurality of AOAs and providing a correction to configuration data for the array of antenna elements based at least on the plurality of actual phase center locations.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
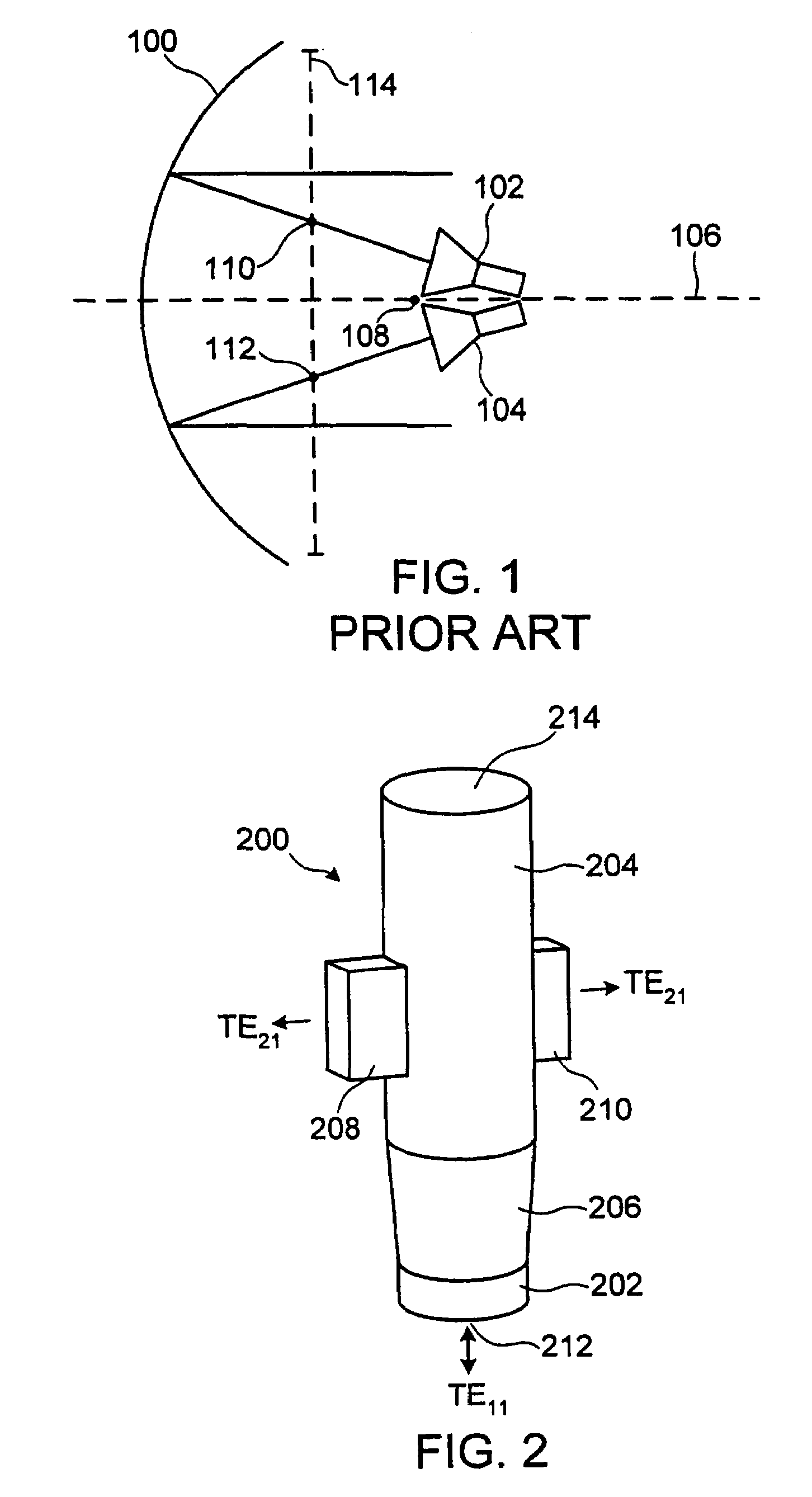
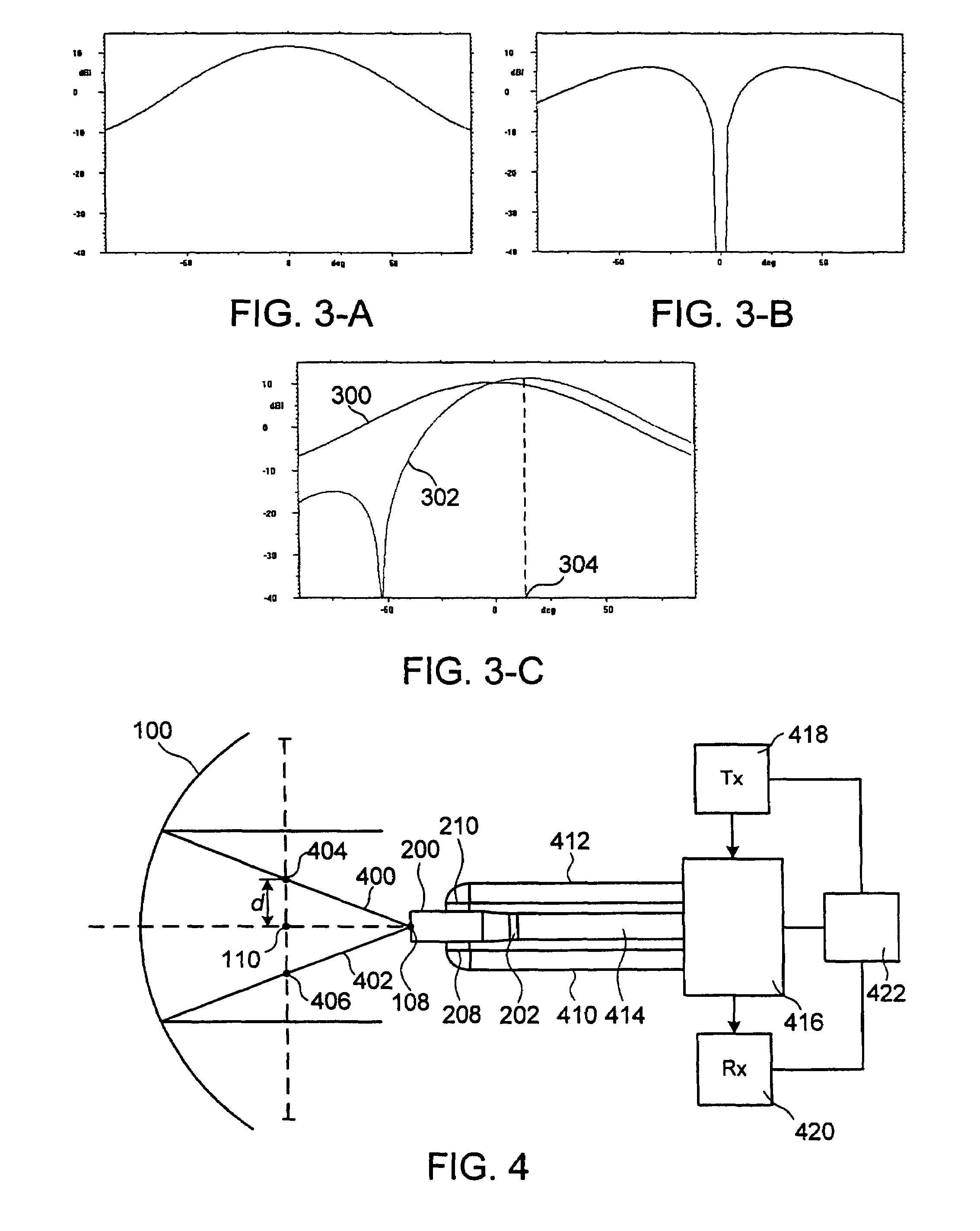
Multiple phase center feedhorn for reflector antenna
A feedhorn driving method and apparatus allows the establishment of multiple phase centers using only a single multimode feedhorn. At least two higher-order modes are extracted from the feedhorn and weighted in amplitude and phase. The phase center separation is established in accordance with an assigned weights. The feedhorn has application in i.a. moving target indication systems.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
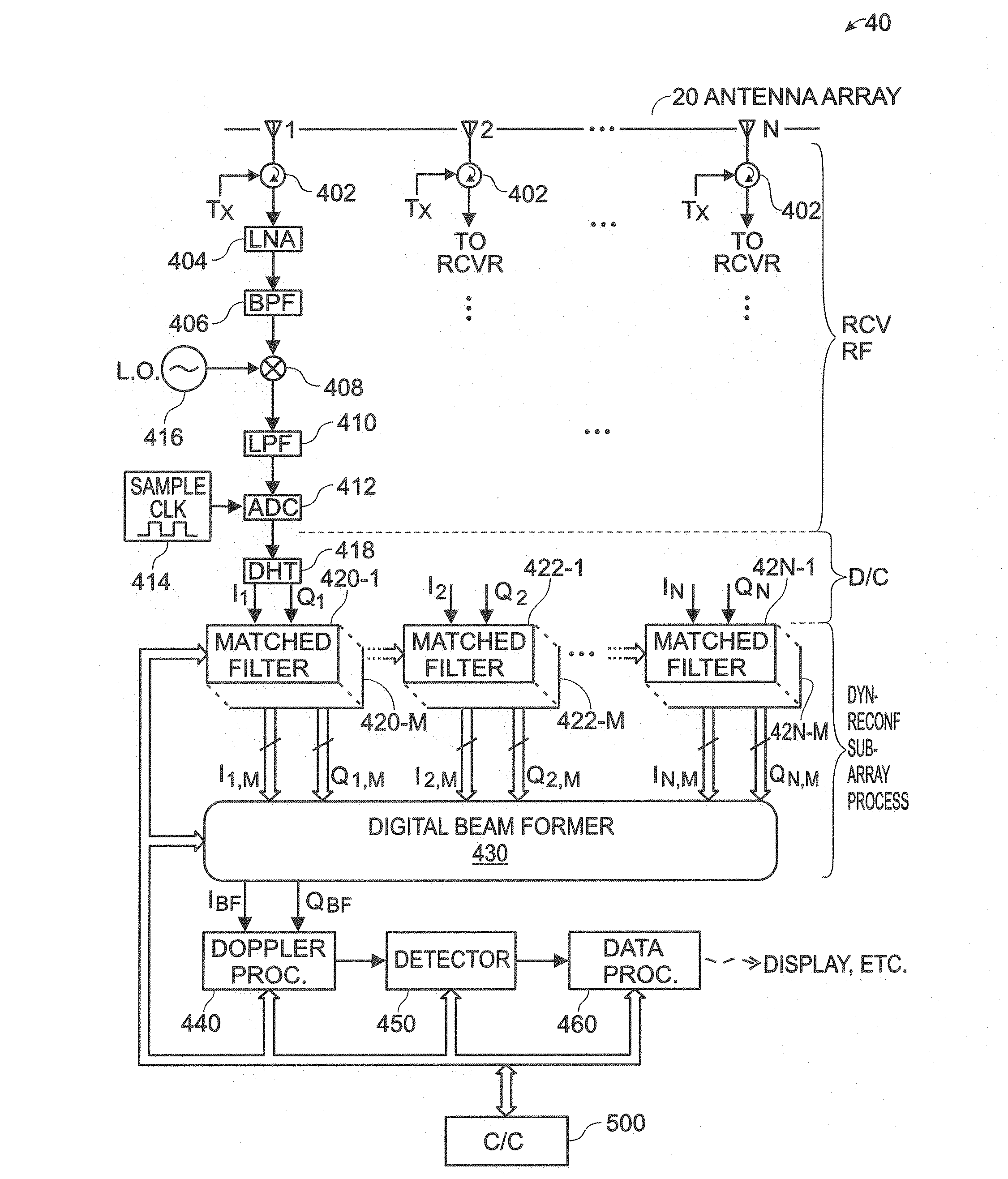
Radar architecture
ActiveUS20100328157A1Drawback can be obviatedAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsBeam pattern
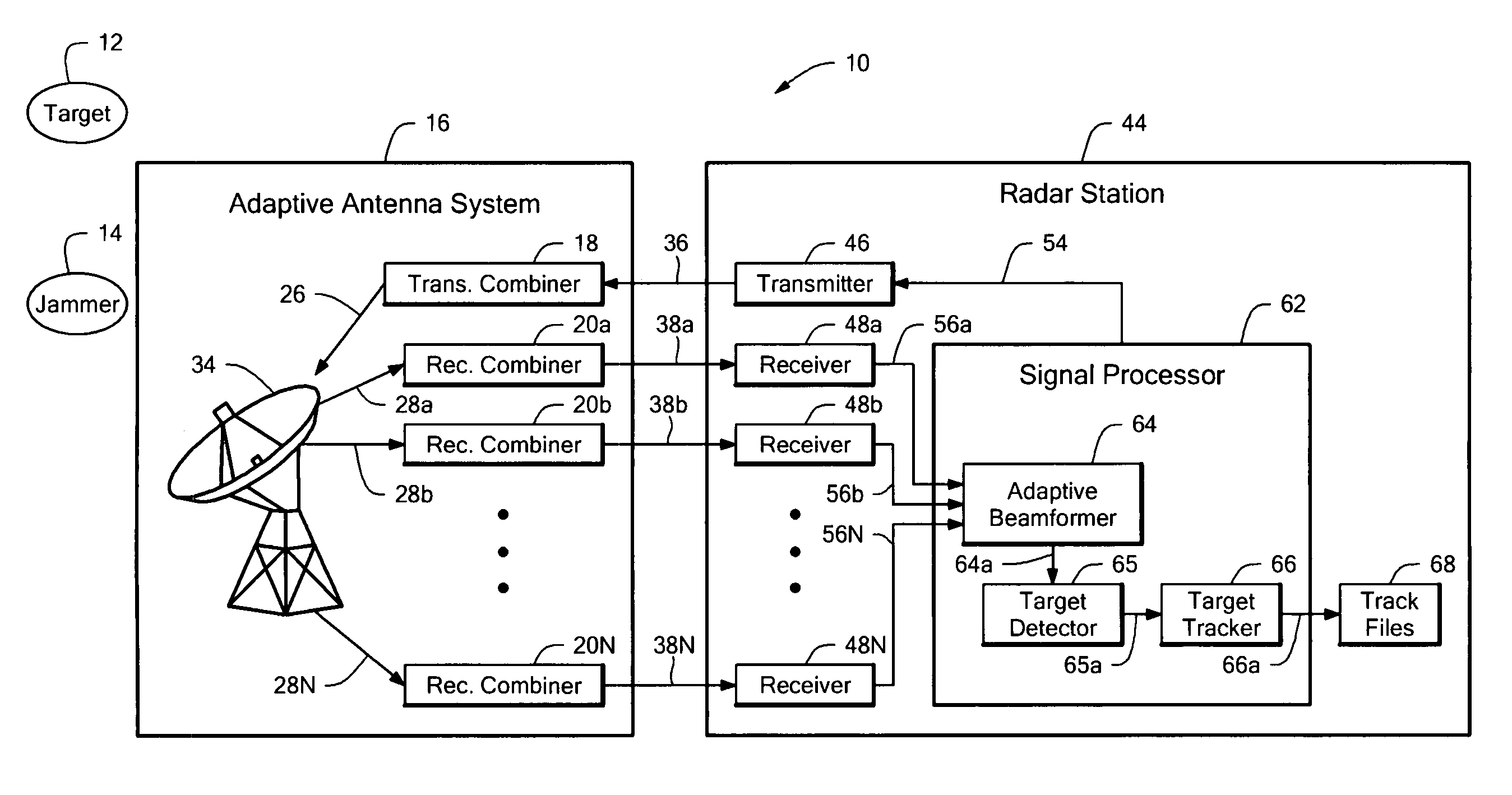
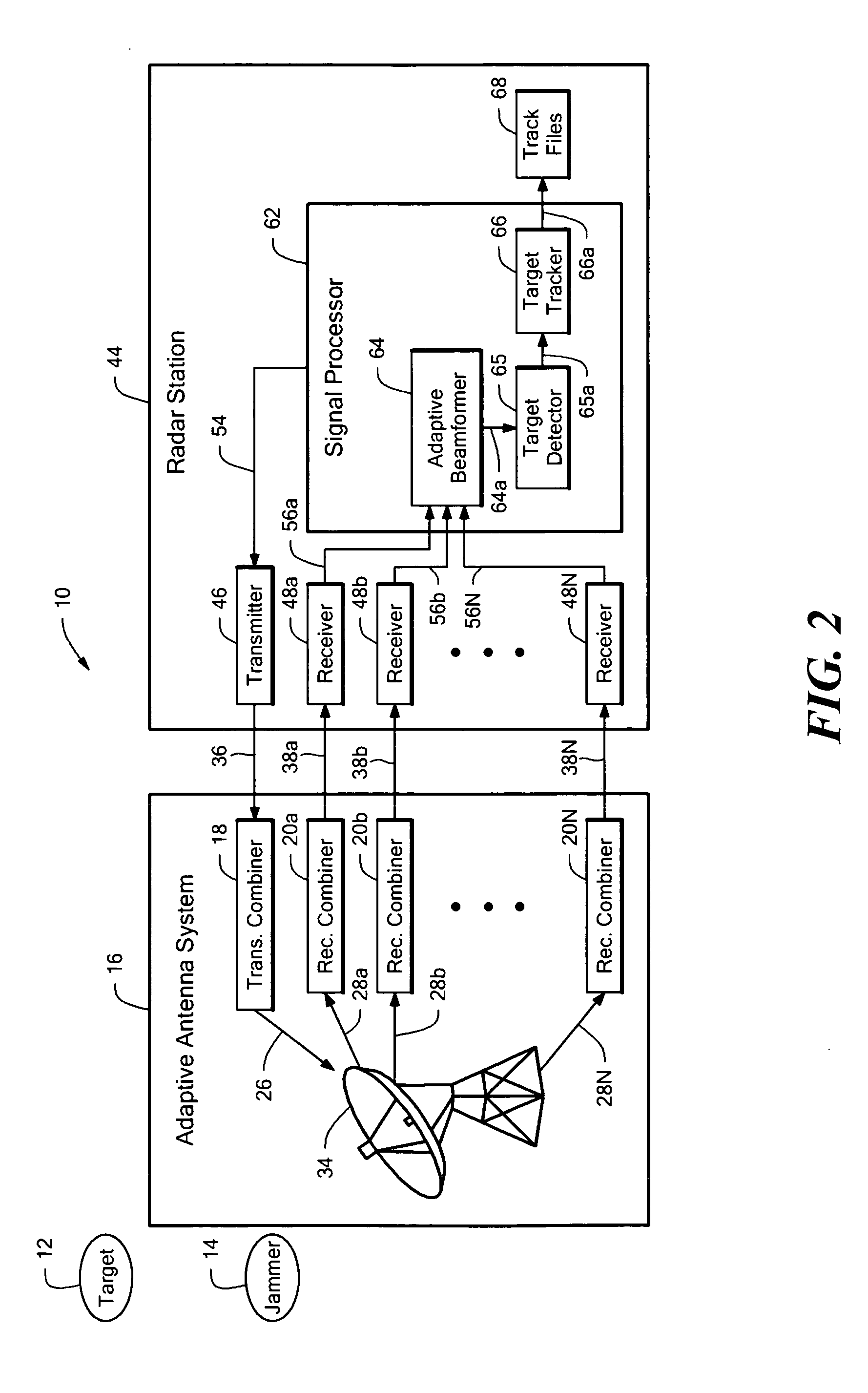
The present invention is directed to a radar system that includes an antenna array having a plurality of antenna elements and a plurality of transmit antenna phase centers. A transmitter portion is coupled to the antenna array. The transmitter portion is configured to transmit a plurality of transmit beams characterized by a transmit beam pattern. The transmit beam pattern has a predetermined transmit beamwidth that is a function of the number of orthogonal transmit waveforms. The predetermined transmit beamwidth substantially fills a predetermined angular volume. Each of the plurality of transmit beams includes a corresponding one of the plurality of orthogonal transmit waveforms. Each of the plurality of transmit beams is transmitted by a corresponding one of the plurality of transmit antenna phase centers. The number of orthogonal transmit waveforms is less than the plurality of antenna elements. A receiver portion is also coupled to the antenna array. The receiver portion is configured to extract a plurality of orthogonal receive signal components from a received signal provided by the antenna array. The plurality of orthogonal receive signal components corresponds to the plurality of orthogonal transmit waveforms. A plurality of extracted orthogonal receive signal components are digitally beam formed to implement a virtual antenna array and generate a receive signal having a receive beamwidth. The virtual antenna array includes a plurality of virtual antenna elements greater than the plurality of antenna elements. The receive beamwidth is a function of the plurality of virtual antenna elements.
Owner:SRC INC
Transmission/reception sources of electromagnetic waves for multireflector antenna
InactiveUS6861998B2Reduce sidelobeReducing side lobe level SLLLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsElectromagnetic wave transmissionWaveguide
The present invention relates to an electromagnetic wave transmission / reception source for a multireflector antenna of the Cassegrain type comprising longitudinal-radiation means operating in a first frequency band and an array of n radiating elements of the travelling-wave type operating in a second frequency band with the n radiating elements arranged symmetrically around the longitudinal-radiation means, the array and the longitudinal-radiation means having an approximately common phase centre, the array of n radiating elements being excited by a waveguide of polygonal cross section. The invention applies especially in satellite communication systems operating in the C-, Ku- or Ka-bands.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Stepped-reflector antenna for satellite communication payloads
ActiveUS7737903B1Reduce peak-to-edge gain variationImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsPhase shiftedEngineering
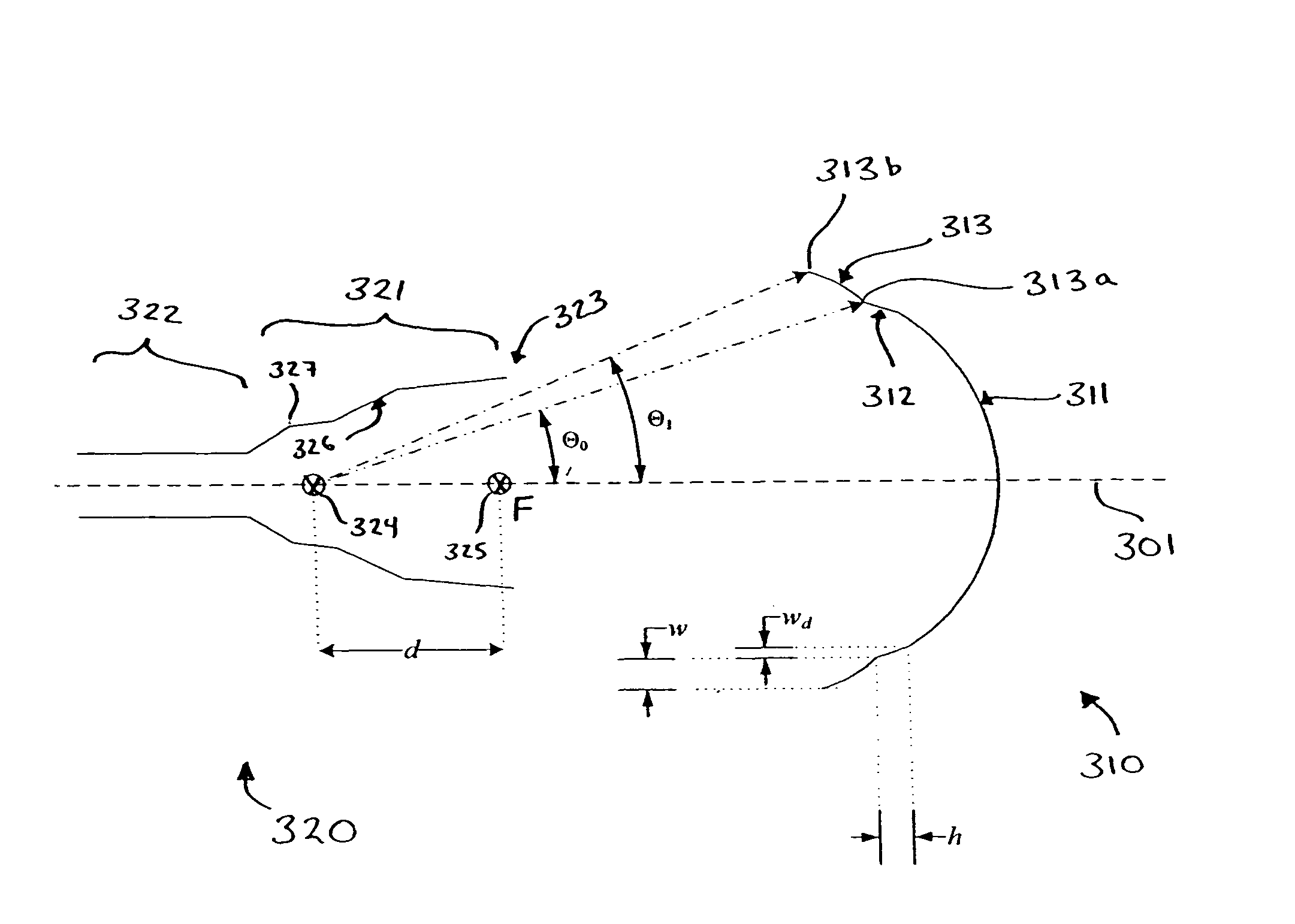
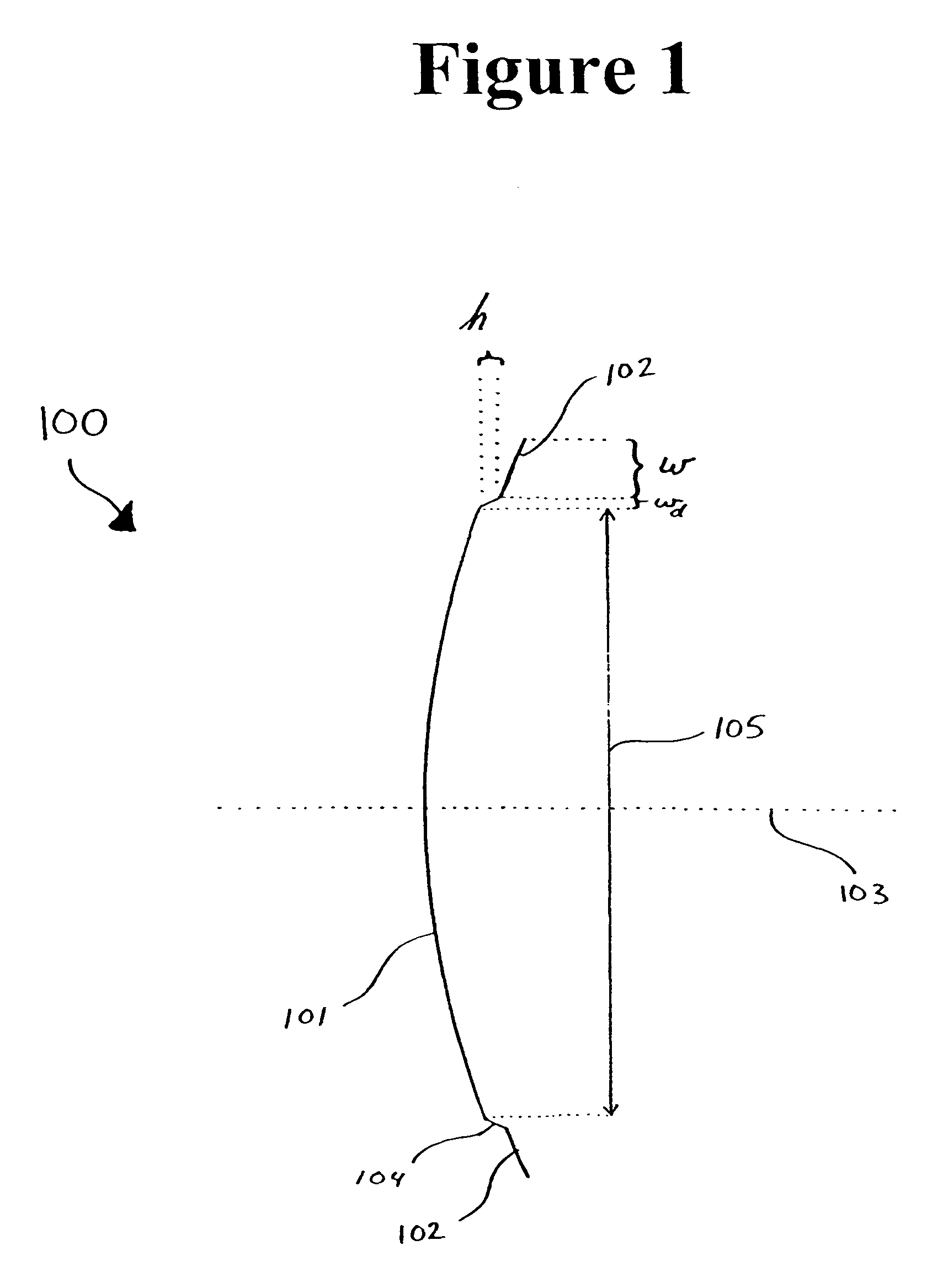
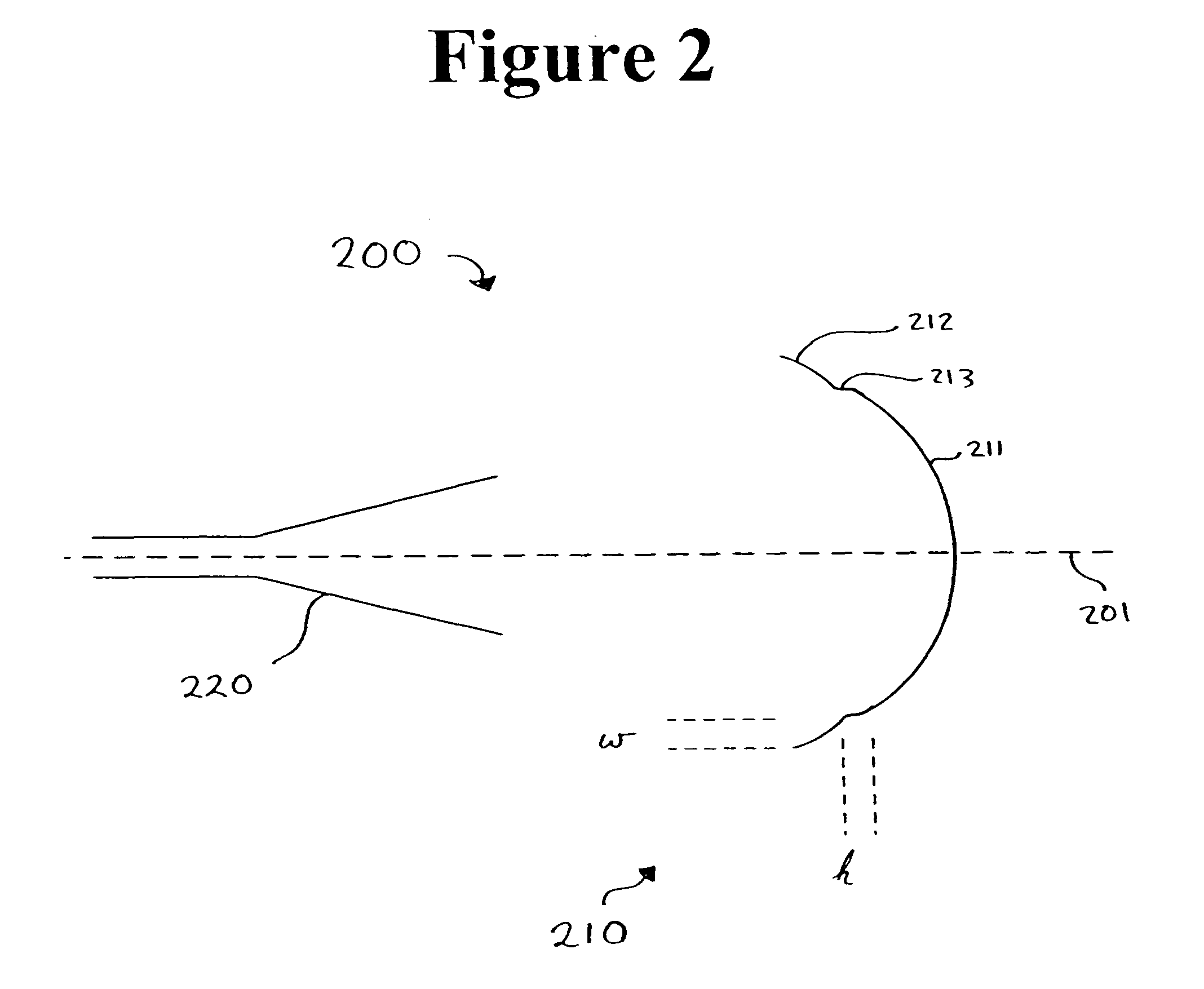
A stepped reflector for being illuminated by at least one multiple-band feed is provided. The reflector includes a central region and a first annular region with an annular width of w. The first annular region is axially stepped a height h above the central region, where h is approximately equal tom×[Φ±(ϕ(Θ=0)-ϕ(Θ=Θ0))]×π180×λ2π×12,where m is a positive odd integer, Φ is a desired amount of phase shift of an outer region of a phase front for reflecting off of the reflector, φ is a feed phase contribution for an angle Θ, and Θ0 is an angle formed between an axis of the at least one feed and a line connecting a phase center of the at least one feed and an inner edge of the at least one annular region.The central region and the annular region of the reflector may be parabolically curved or may alternately be shaped. The reflector may be fed by one or more multiple-band horn antennas.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
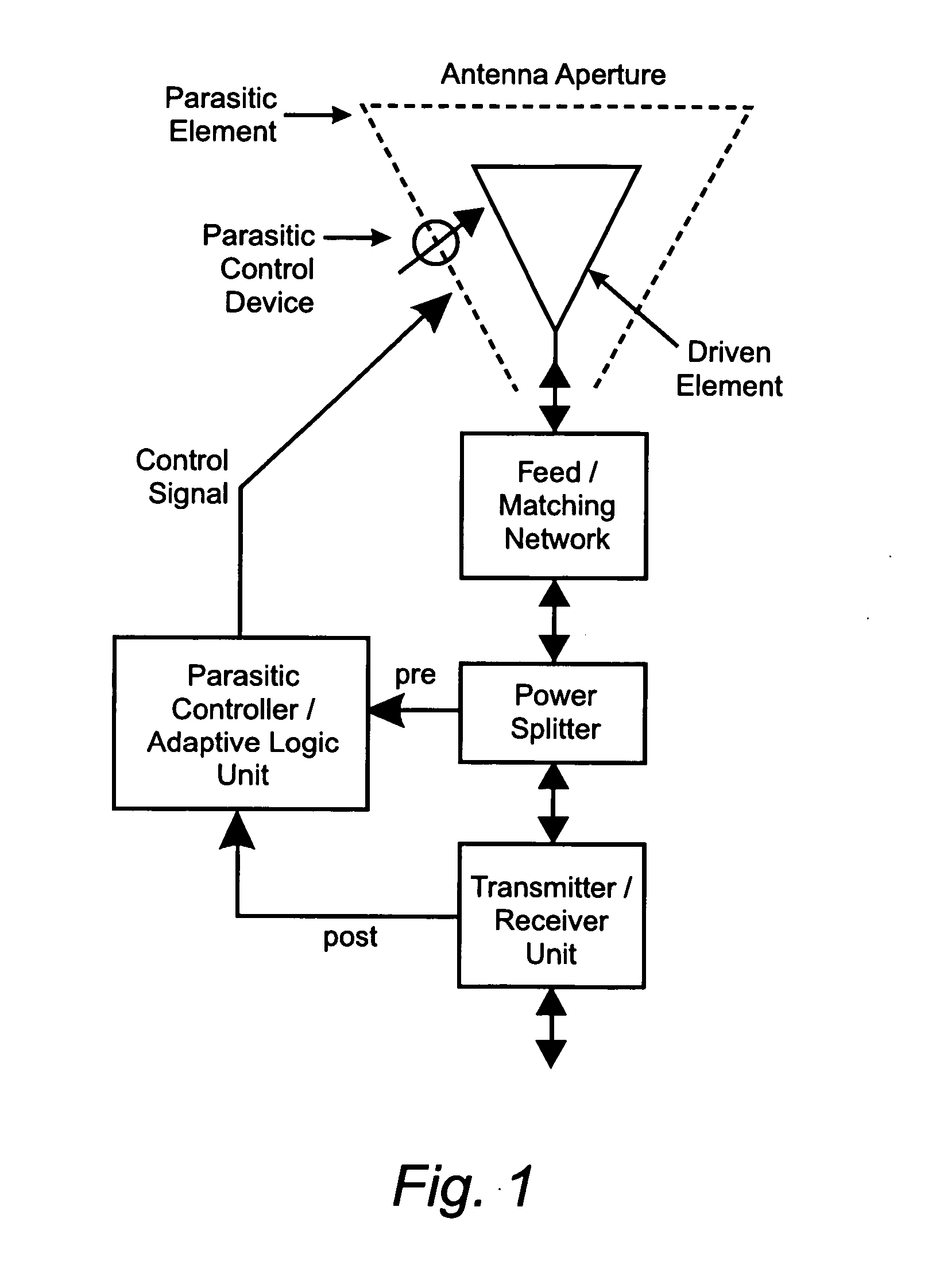
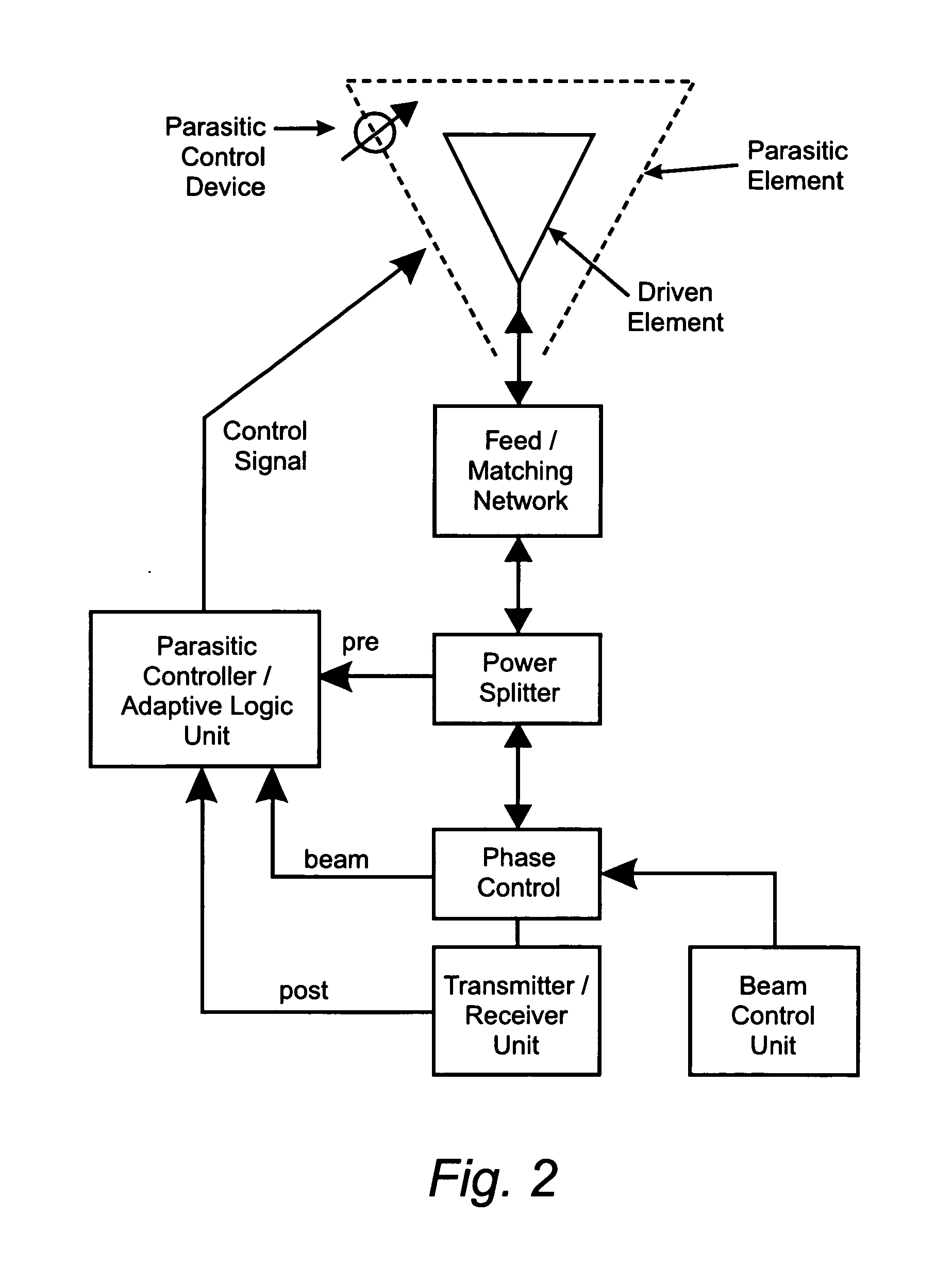
Reconfigurable parasitic control for antenna arrays and subarrays
InactiveUS20050088358A1Reduce decreaseScan angles can be increasedLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysEngineeringArray element
Reconfiguration of parasitically controlled elements in a phased array is used to expand the range of operational functions. Embedded array elements can be frequency tuned, and bandwidth can be improved by using reconfiguration to broaden the bandwidth of the embedded elements. For high gain arrays, beam squint can be a limiting factor on instantaneous bandwidth. Reconfiguration can alleviate this problem by providing control of the element phase centers. Scan coverage can be improved and scan blindness alleviated by controlling the embedded antenna patterns of the elements as well as by providing control of the active impedance as the beam is scanned. Applying limited phase control to the elements themselves can alleviate some of the complexity of the feed manifold. A presently preferred method of designing reconfigurable antennas is to selectively place controlled parasitic elements in the aperture of each of the antenna elements in the phased array. The parasitic elements can be controlled to change the operational characteristics of the antenna element. The parasitic elements are controlled by either switching load values in and out that are connected to the parasitic elements or are controlled by applying control voltages to variable reactance circuits containing devices such as varactors. The parasitic elements can be controlled by the use of a feedback control subsystem that is part of the antenna system which adjusts the RF properties of the parasitic components based on some observed metric. The controllable characteristics include directivity control, tuning, instantaneous bandwidth, and RCS.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
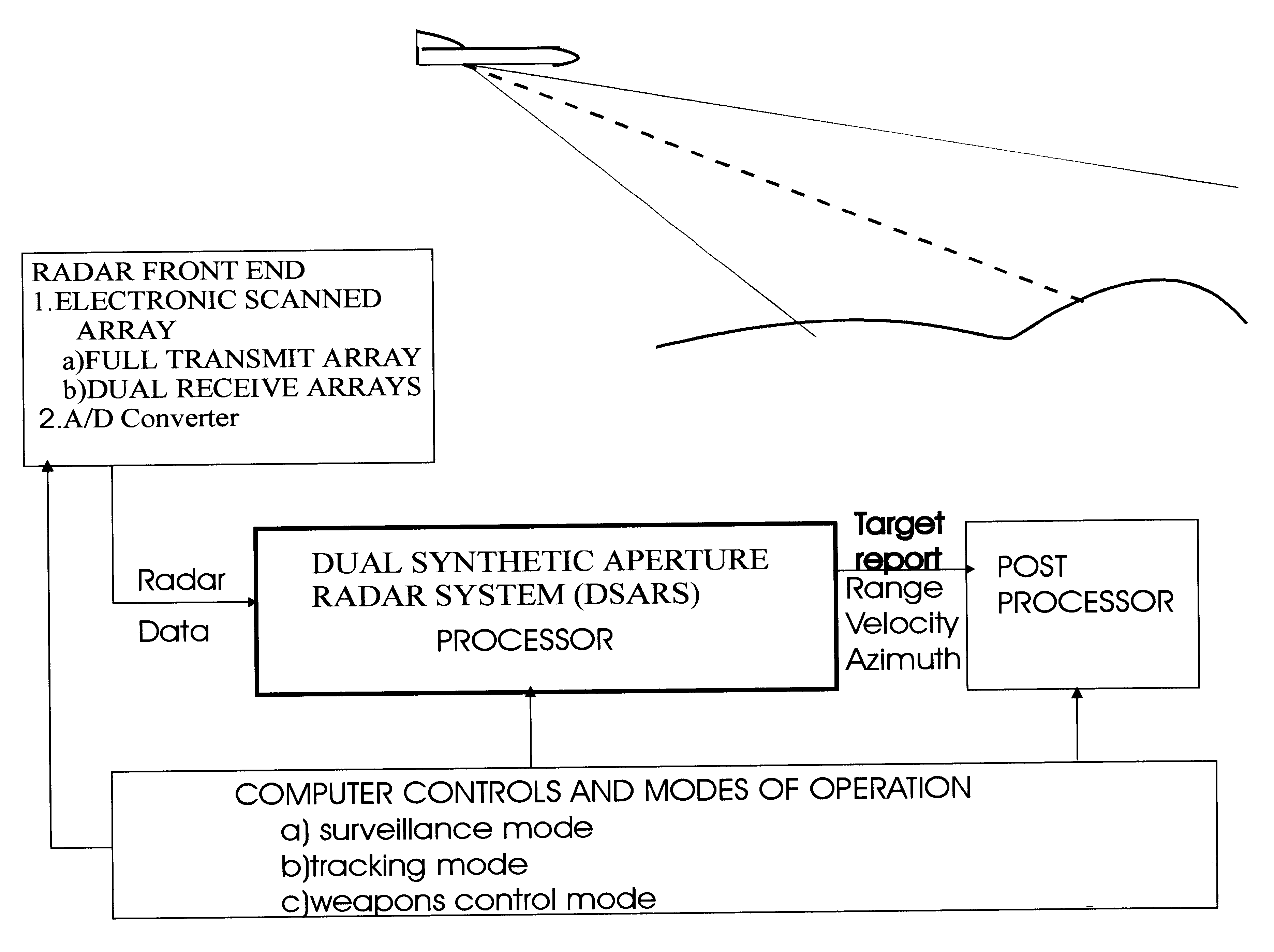
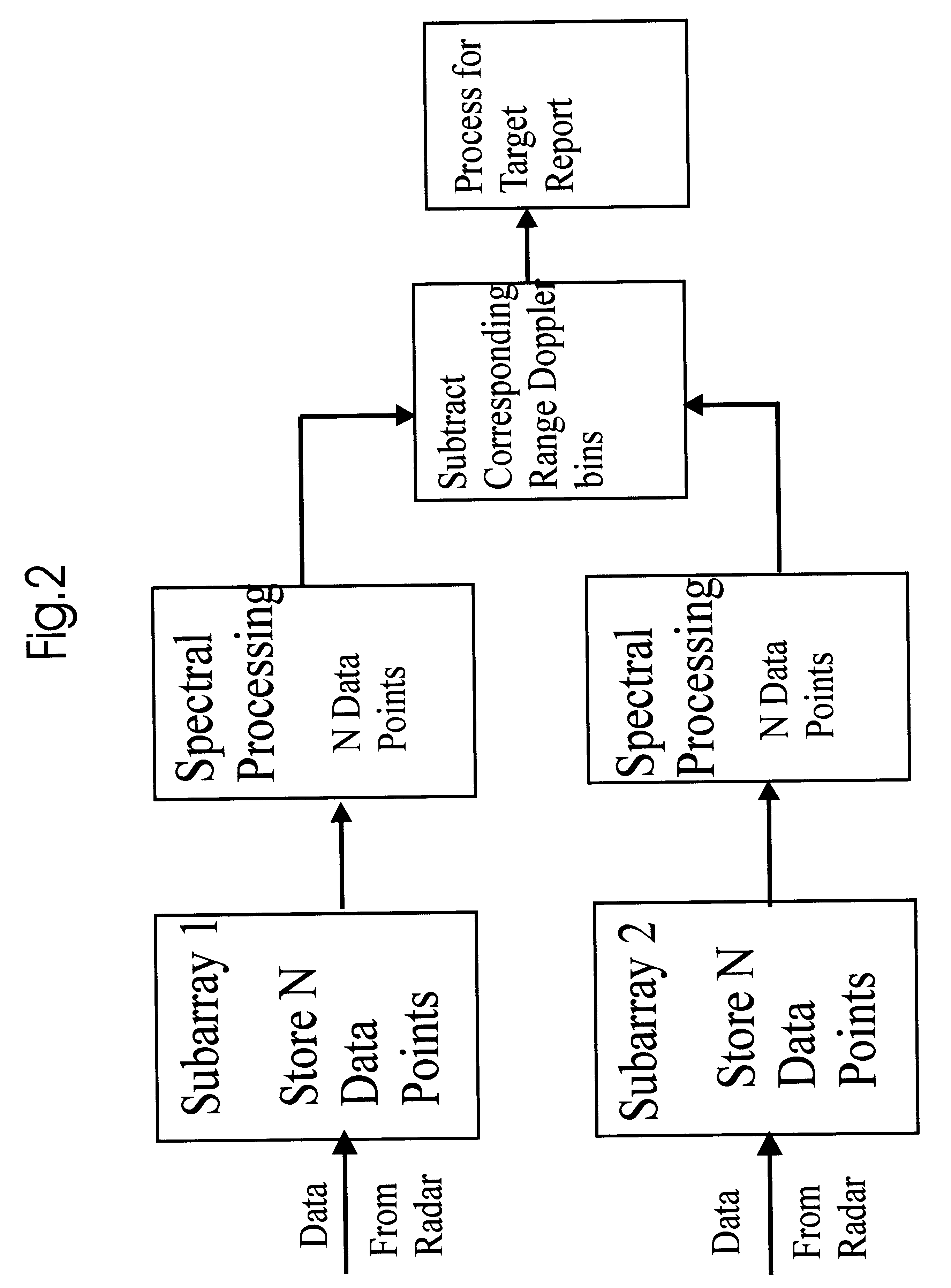
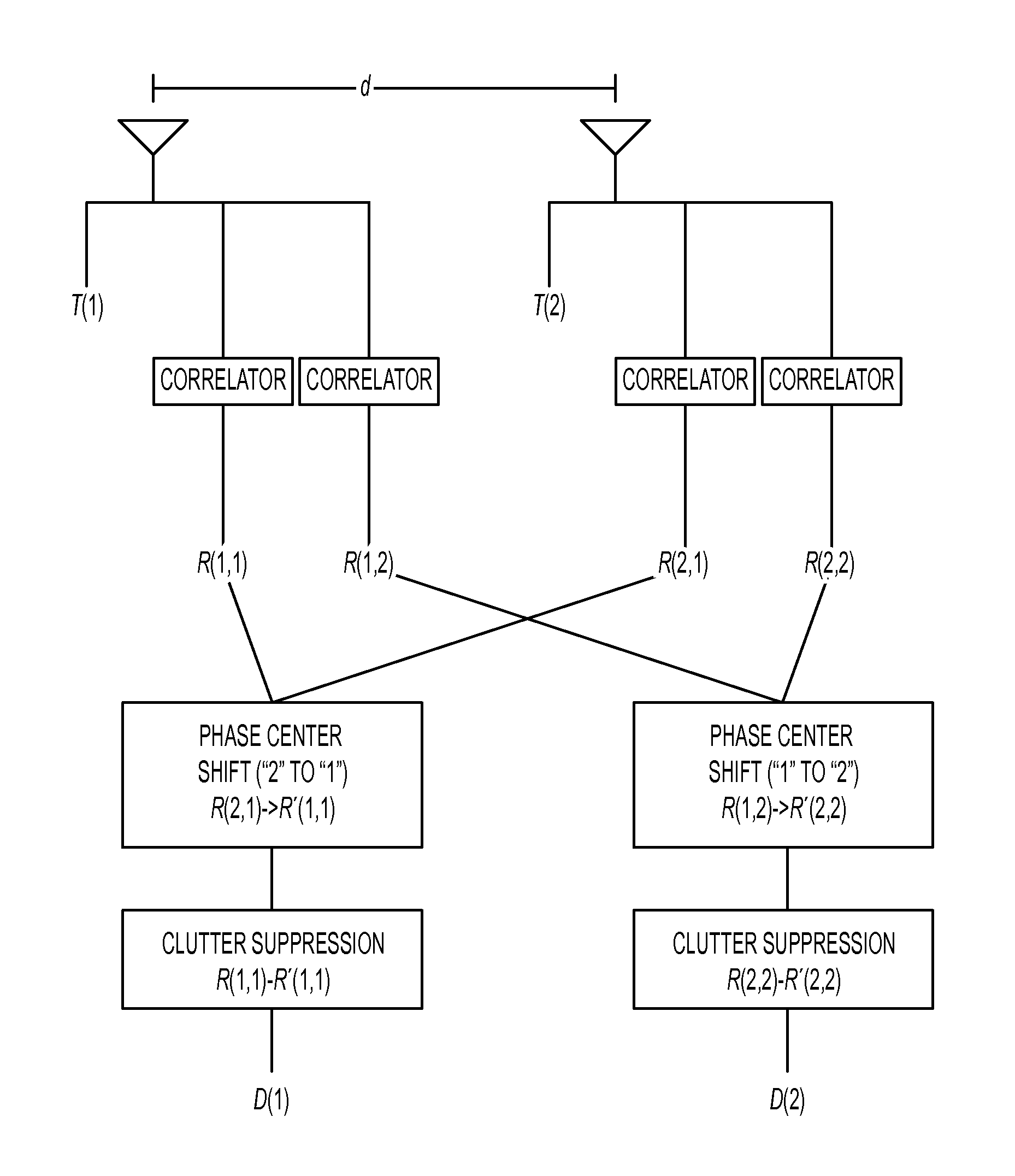
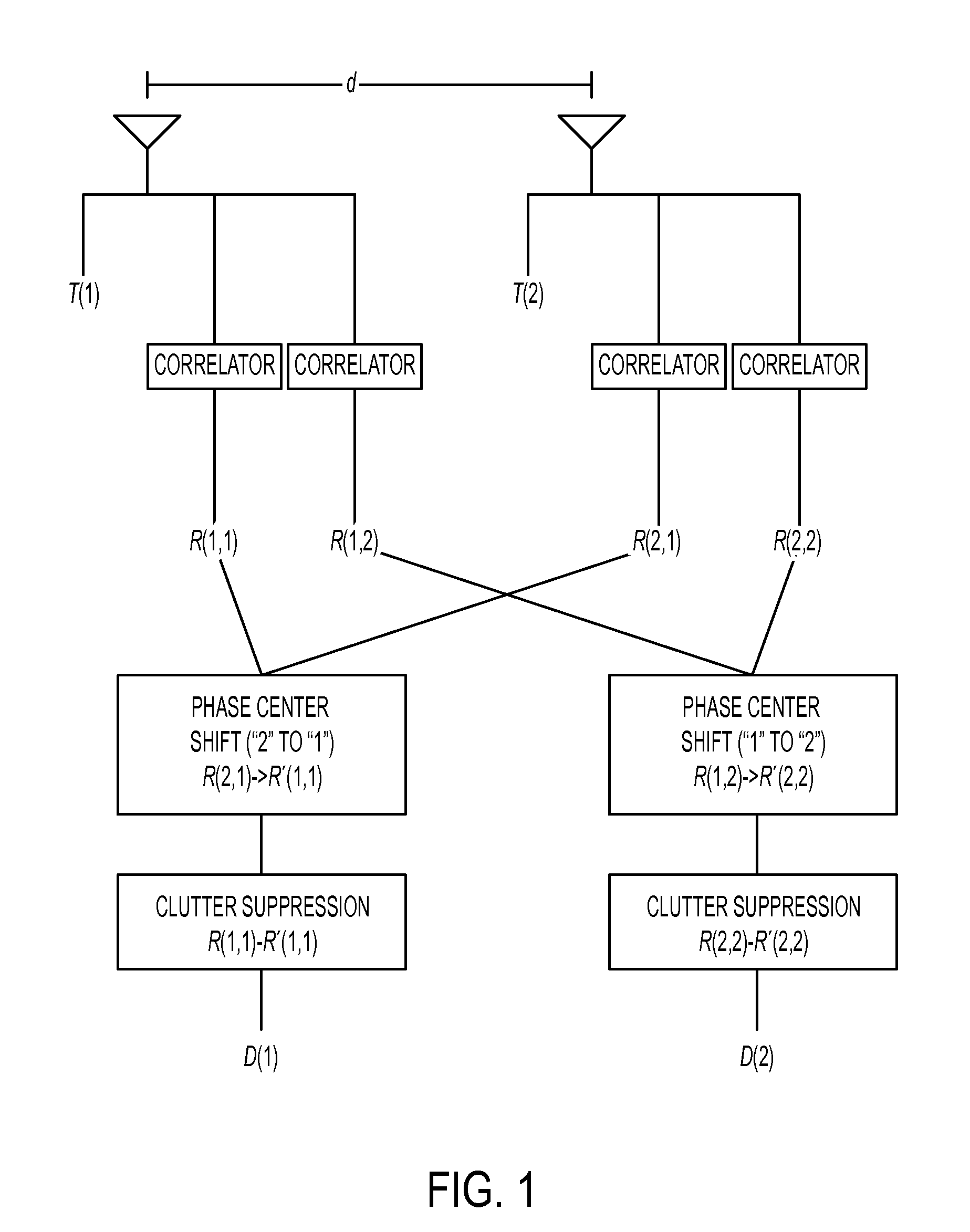
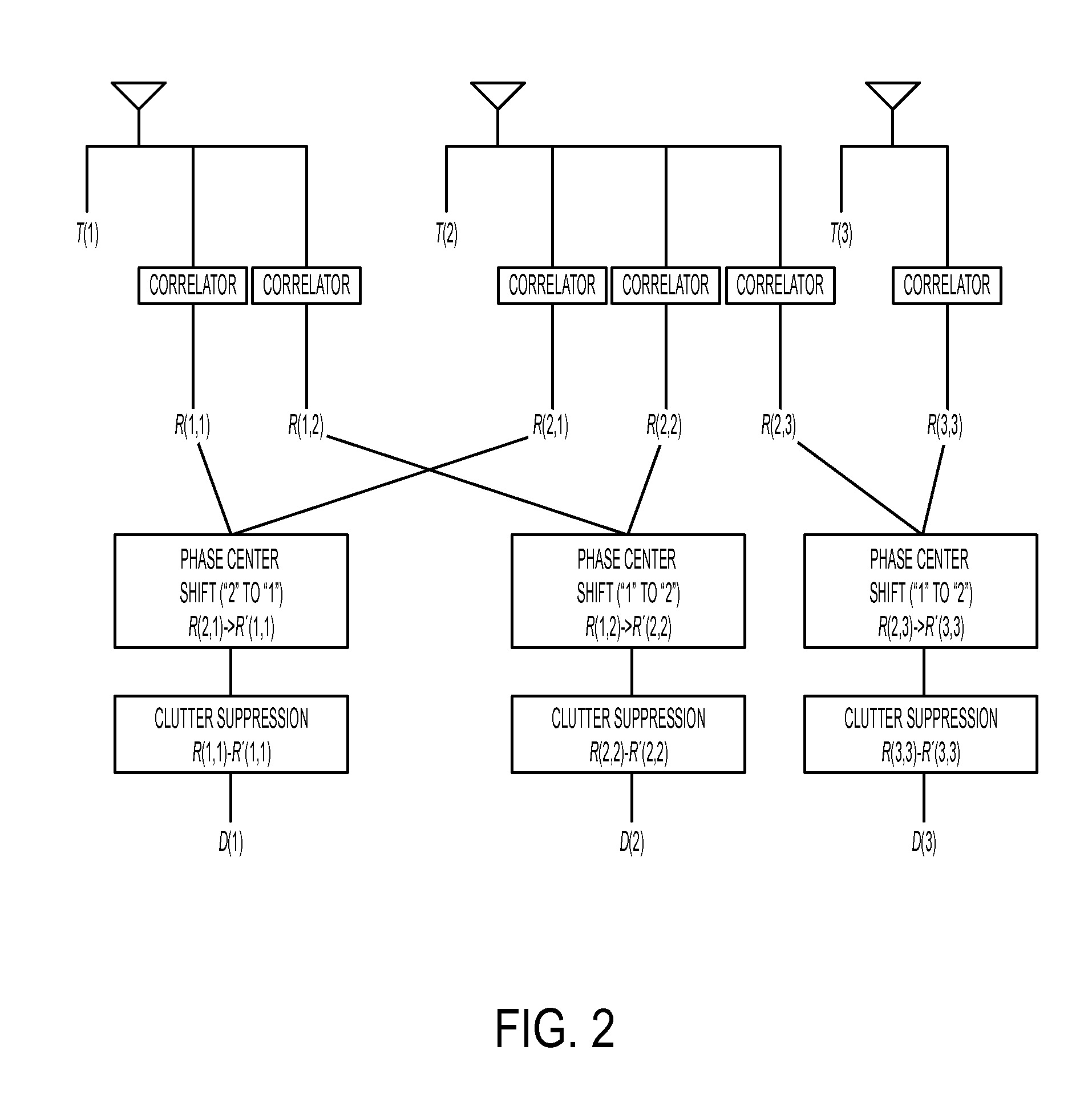
Dual synthetic aperture radar system
InactiveUS6633253B2Accurate angular positionAccurately radial velocityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumControl system
The dual synthetic aperture array system processes returns from the receiving arrays. The two identical receiving arrays employing displaced phase center antenna techniques subtract the corresponding spectrally processed data to cancel clutter. It is further processed that a moving target is detected and its velocity, angular position and range is measured, in or out of the presence of clutter. There are many techniques presented in the disclosure. These techniques are basically independent but are related based on common set of fundamental set of mathematical equations, understanding of radar principles and the implementations involved. These many techniques may be employed singly and / or in combination depending on the application and accuracy required. They are supported by a system that includes, optimization of the number of apertures, pulse repetition frequencies, DPCA techniques to cancel clutter, adaptive techniques to cancel clutter, motion compensation, weighting function for clutter and target, and controlling the system in most optimum fashion to attain the objective of the disclosure.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CATALDO THOMAS J
Methods And Systems For Multiple Input Multiple Output Synthetic Aperture Radar Ground Moving Target Indicator
A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system. The radar system includes spatially offset transmitting antennas simultaneously transmitting at least two distinguishable waveform signals and receiving antennas receiving incoming waveform returns for each of the distinguishable waveform signals. The radar system also includes a displaced phase center antenna (DPCA) processing unit adapted to perform processing on the incoming waveform returns, and a synthetic aperture radar processing unit adapted to produce a plurality of spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. The radar system also generates a plurality of clutter-suppressed signals using the spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. For each of two MIMO transmissions from spatially displaced transmitters, clutter is cancelled simultaneously in at least two spatially displaced receive channels via DPCA processing. This results in at least two spatially displaced but simultaneous clutter cancelled complex SAR images, which are combined in a monopulse processor to enhance target detection and unambiguously determine target angle.
Owner:SRC INC
Satellite differential positioning receiver using multiple base-rover antennas
ActiveUS20090189804A1Accurate measurementConvenient and accurateBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingTransceiverCentroid
A rover processor determines position of a rover based upon the interaction between multiple antennas located at the rover and multiple antennas located at a base. The rover antennas may include a rover master antenna having a phase center located at the centroid of the antennas patterns of at least two auxiliary rover antennas. The rover processor may determine the position of the rover master antenna based upon the relative positions of at least two rover antennas (e.g., the rover master antenna and at least one rover auxiliary antenna, or at least two rover auxiliary antennas) with respect to at least two antennas of a base transceiver.
Owner:JAVAD GNSS
Method of designing weight vectors for a dual beam antenna with orthogonal polarizations
ActiveUS20120212372A1Improved antenna radiation propertyImprove matchPolarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysDual beamLight beam
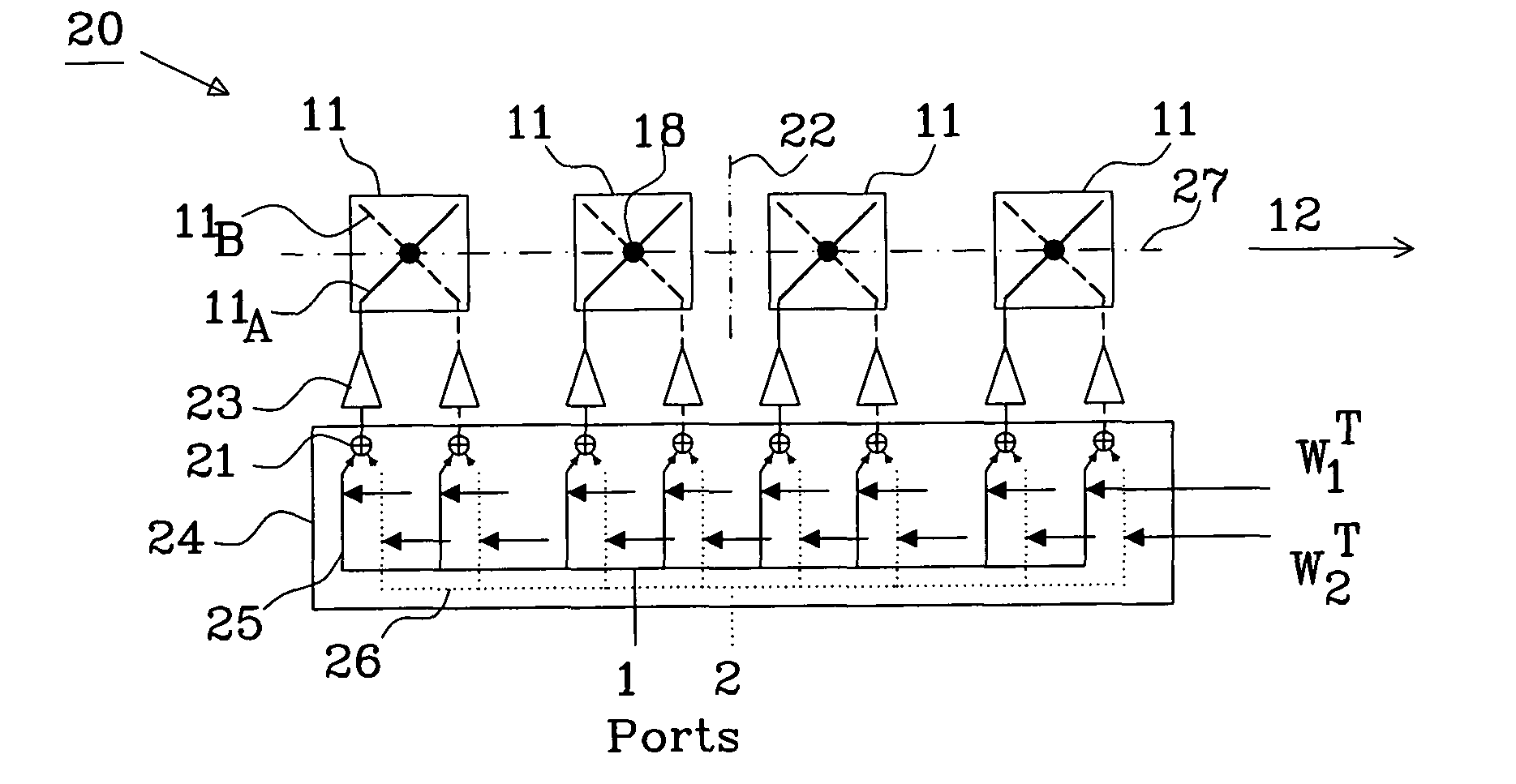
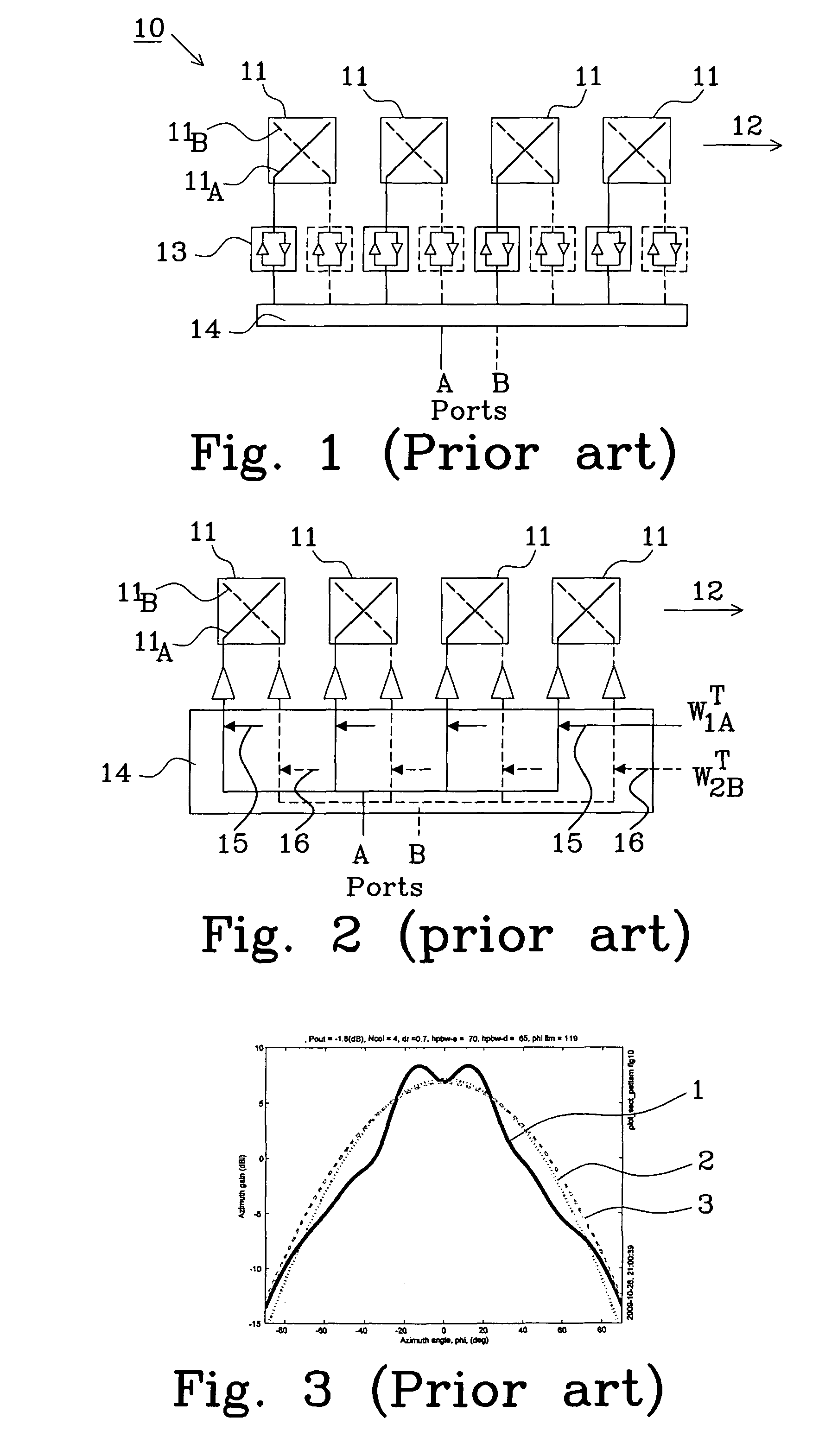
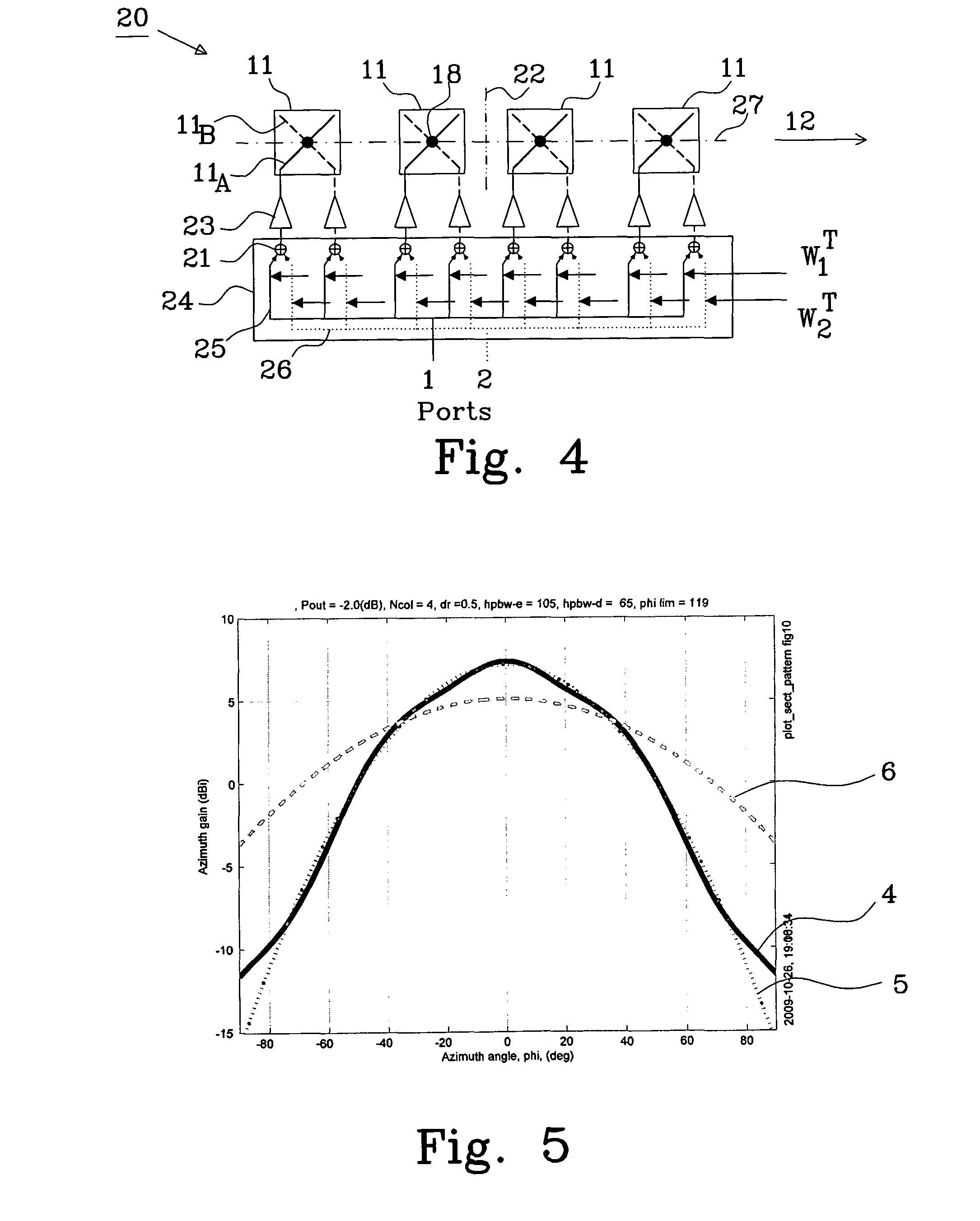
The present invention relates to a method of generating two beams, having orthogonal polarizations, covering a selected area using an antenna (20) comprising multiple dual-polarized array elements (11). Each dual-polarized array element having a first phase centre (18) associated with a first polarization and a second phase centre (18) associated with a second polarization. The method comprises: designing a first weight matrix having a first non-zero weight vector for the first polarization and a second non-zero weight vector for the second polarization, calculating a second weight matrix based on the weight vectors of the first weight matrix, and applying the first and second weight matrix to the dual-polarized array elements to generate a second beam covering the selected area.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Antenna with adjustable beam characteristics
ActiveUS20120319900A1Simple designPolarised antenna unit combinationsDifferential interacting antenna combinationsPhase shiftedLight beam
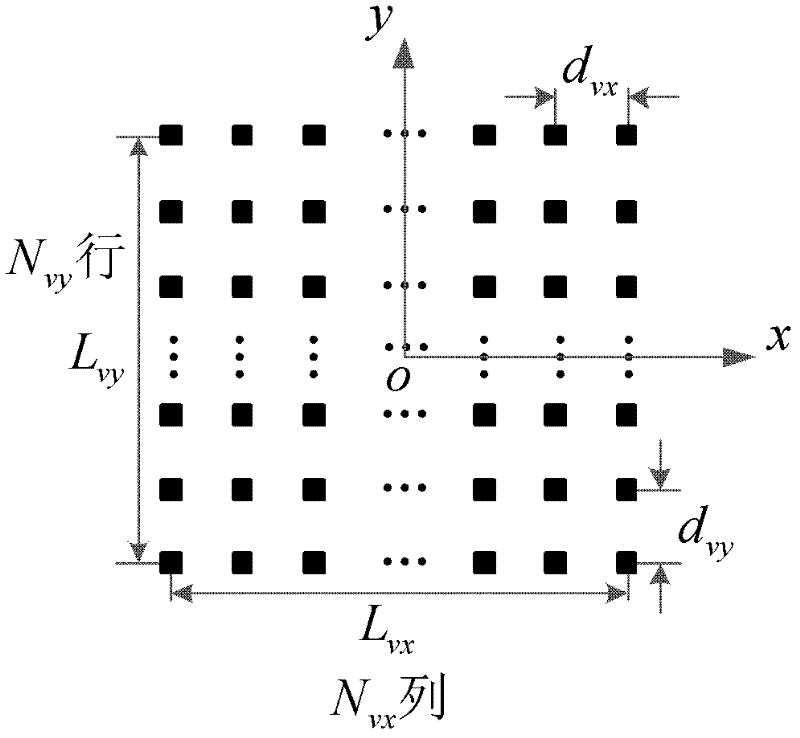
The present invention relates to an antenna comprising multiple array elements with a first and second feeding point, each associated with orthogonal polarizations, each array element has a first and second phase centre each associated with the orthogonal polarizations, the first and second phase centres of said array elements are arranged in at least two columns, and one antenna port connected to the first and second feeding points of at least two array elements with first phase centre and second phase centre arranged in the at least two columns via a respective feeding network. The feeding network comprises a beam forming network having a primary connection, connected to the antenna port, and at least four secondary connections. The beam forming network divides power between the first feeding point and the second feeding point and controls phase shift differences between the respective feeding points with phase centre arranged in different columns.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
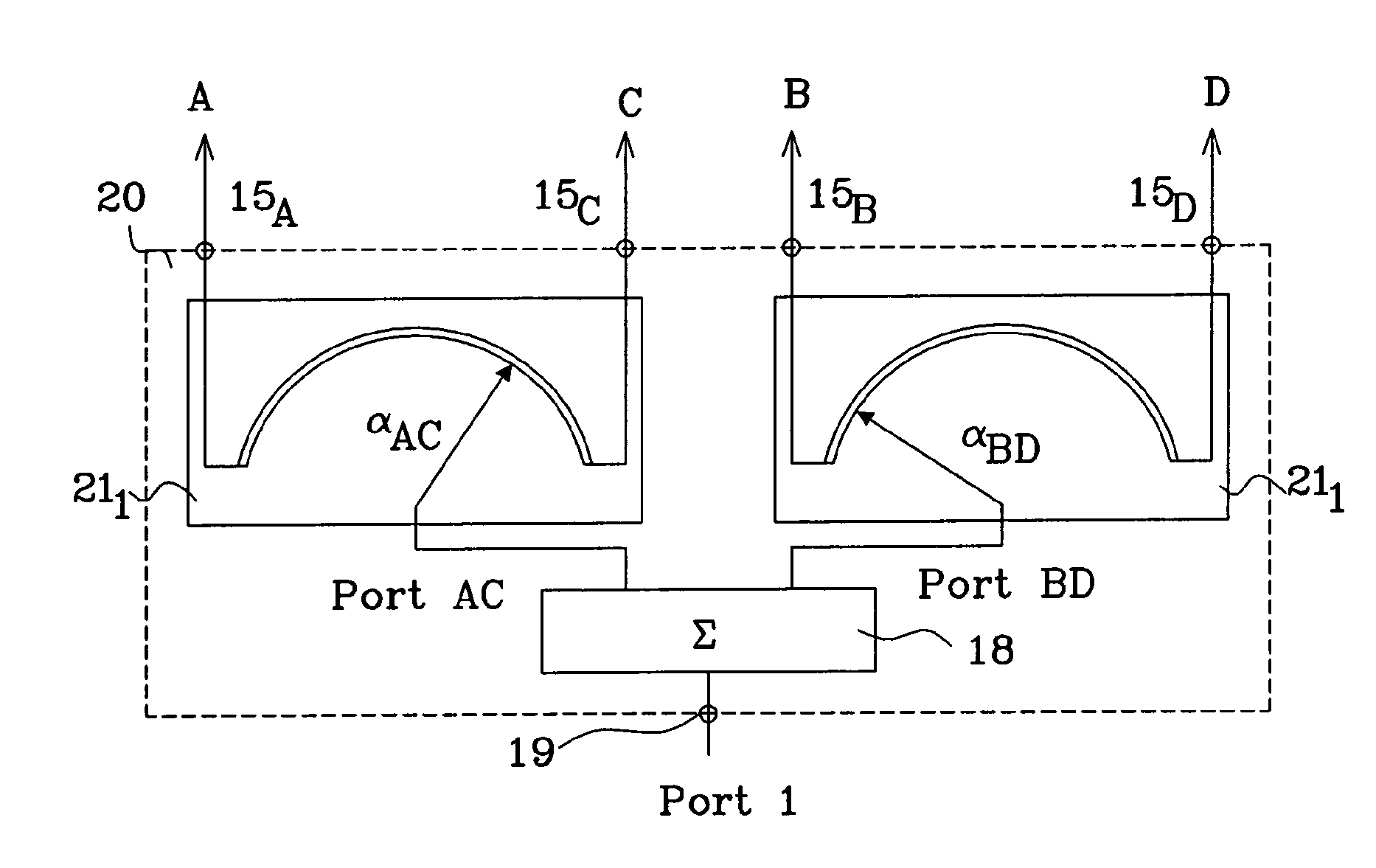
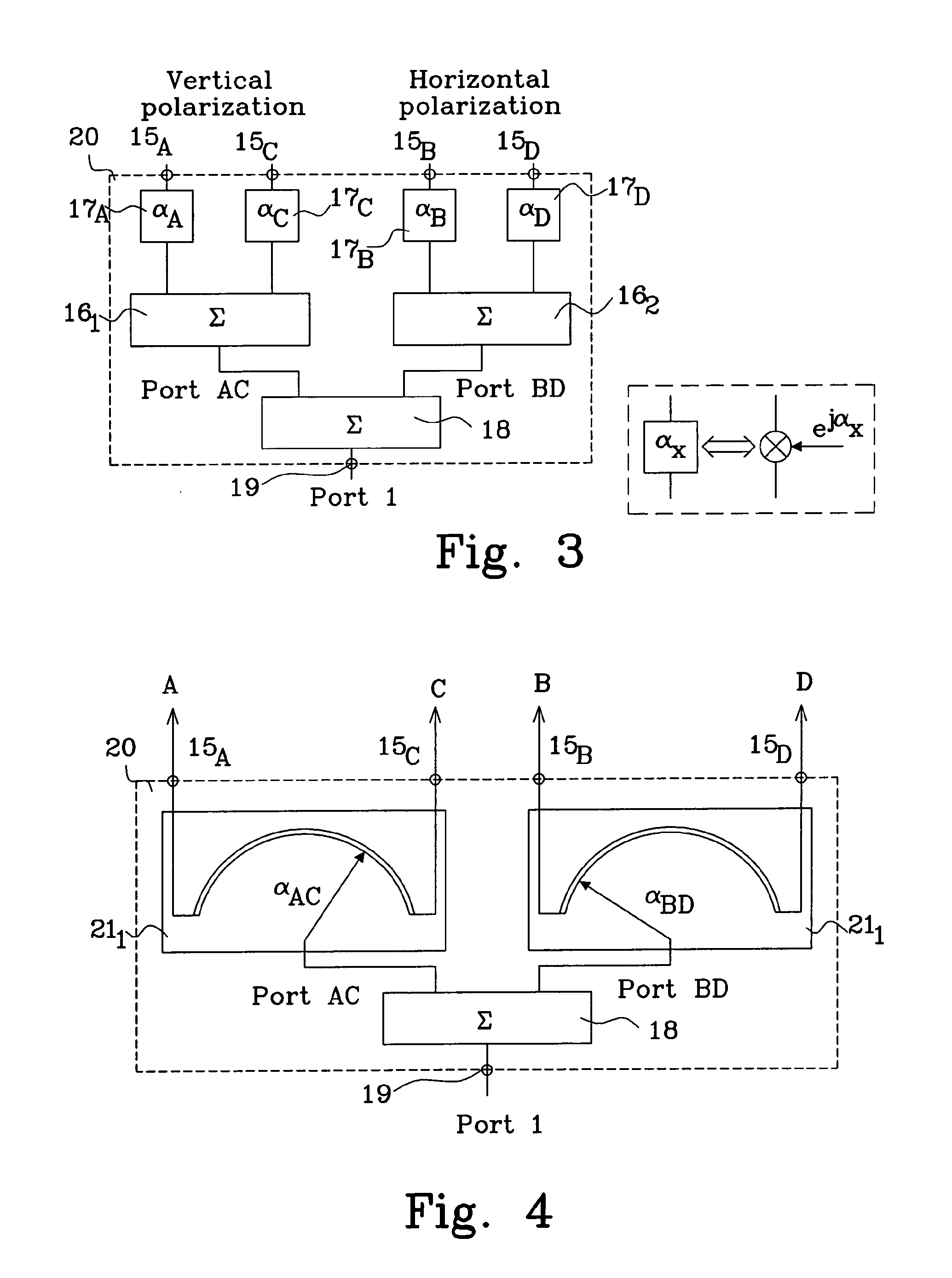
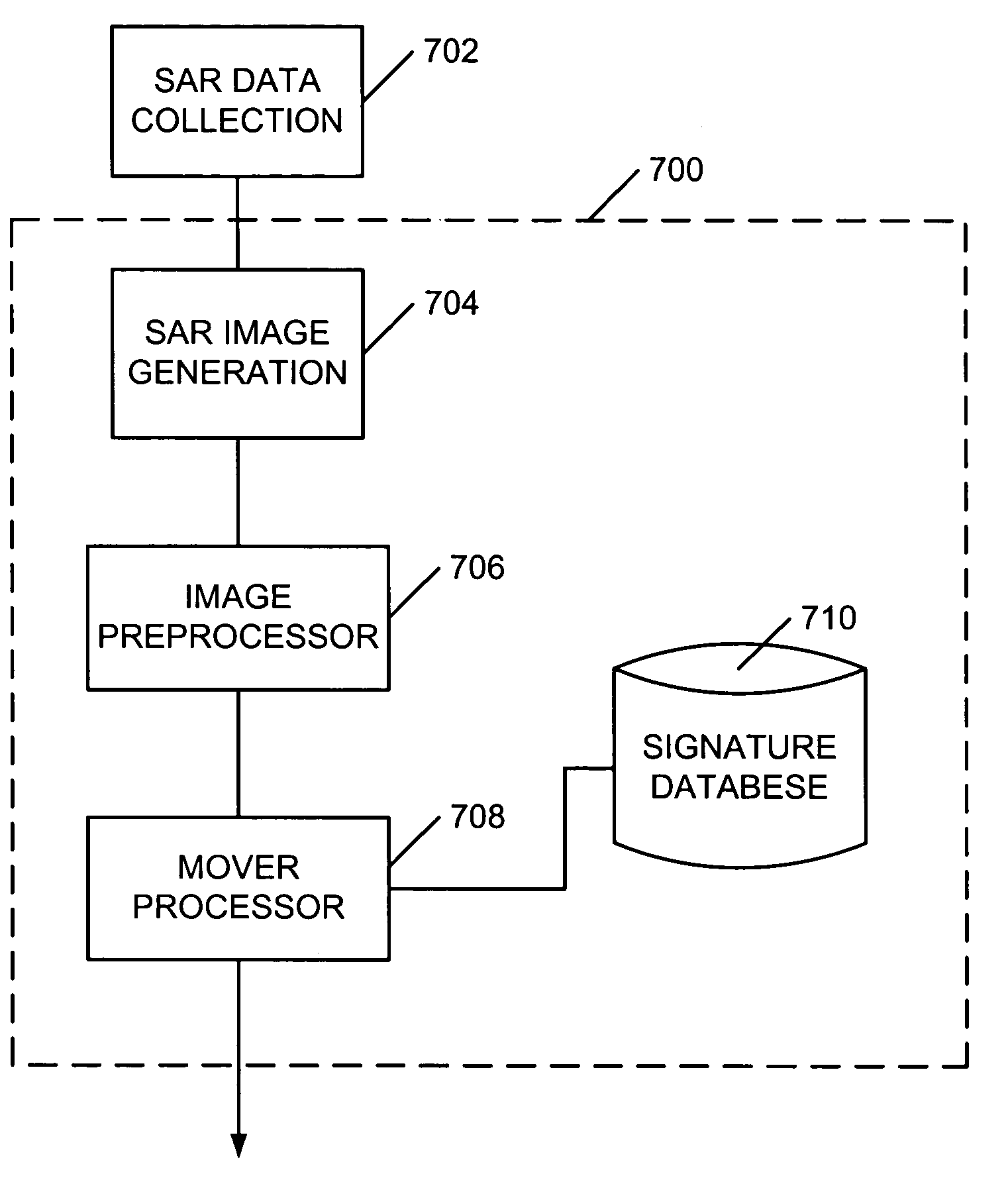
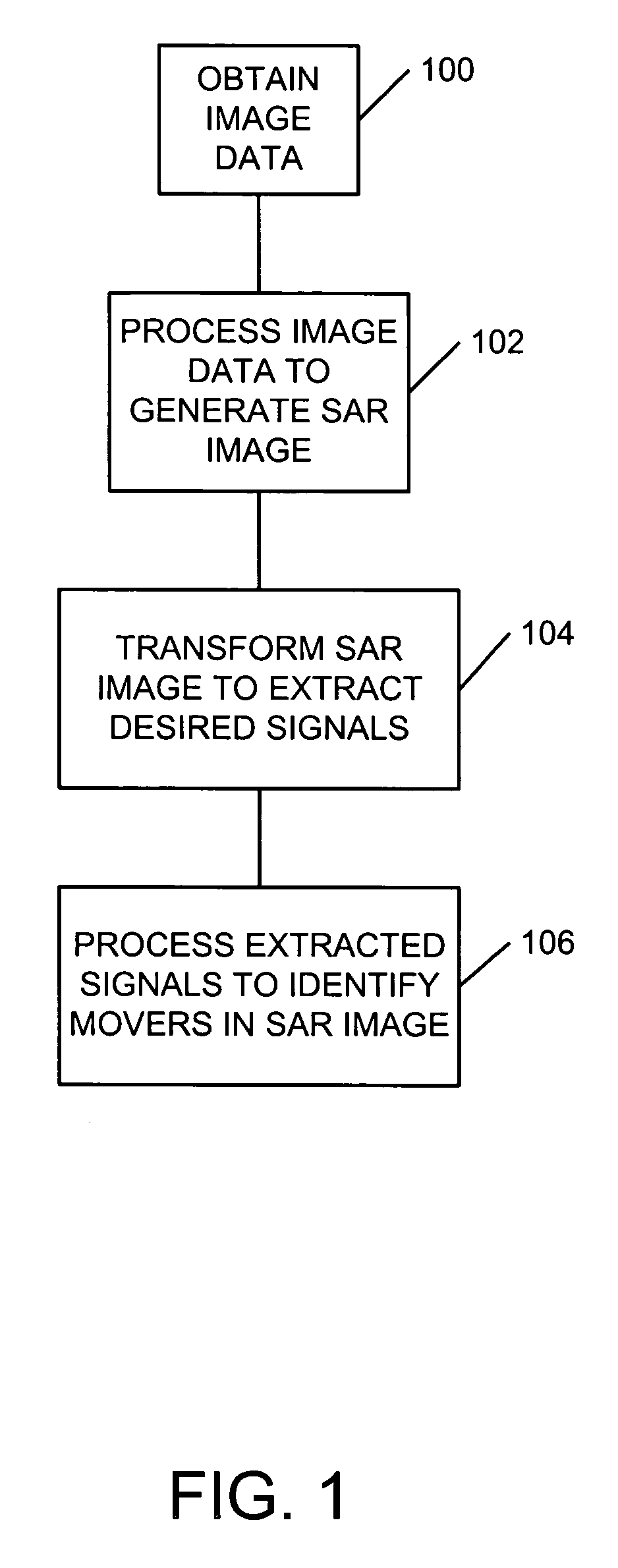
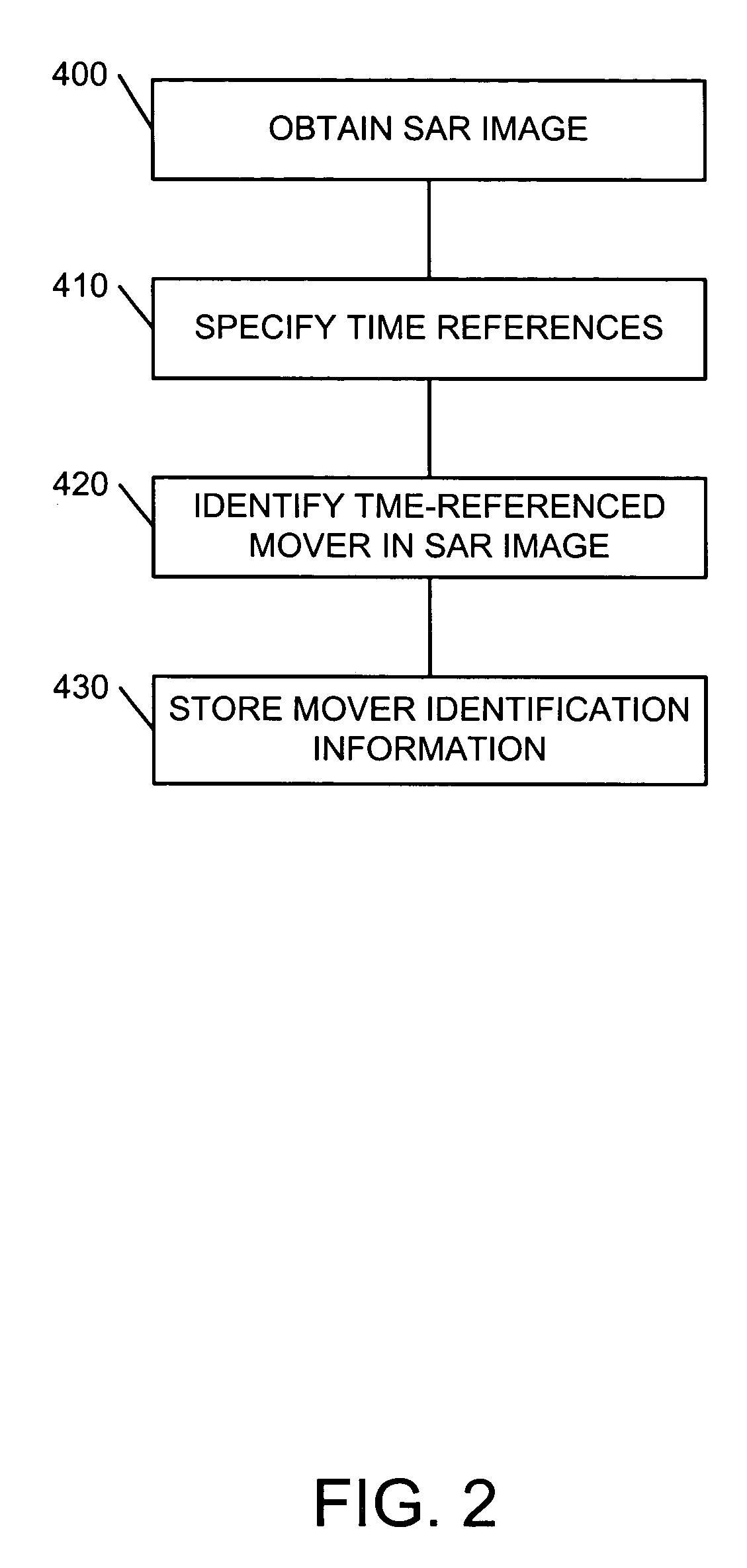
Identification and tracking of moving objects in detected synthetic aperture imagery
InactiveUS6943724B1Increase speedHigh sensitivityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObject basedTime profile
A method of tracking a moving object in an image created by use of a synthetic aperture includes identifying a plurality of receive phase centers for an image collector, obtaining a synthetic aperture image using the plurality of receive phase centers, and reading a signature of the moving object based on the synthetic aperture image, where the reading of the signature includes identifying, in the synthetic aperture image, as a function of image collection time, a presence of the moving object. The reading of the signature may also include identifying a changing position of the moving object, and may include associating a plurality of range difference values with respective ones of the plurality of phase centers. A signature of a scatterer may be formed using only its associated ΔR-versus-time profile. The presence of a mover in the image may be determined by filtering the image to detect all or part of a signature, or by using one or more signatures to train a neural network to observe the mover directly.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
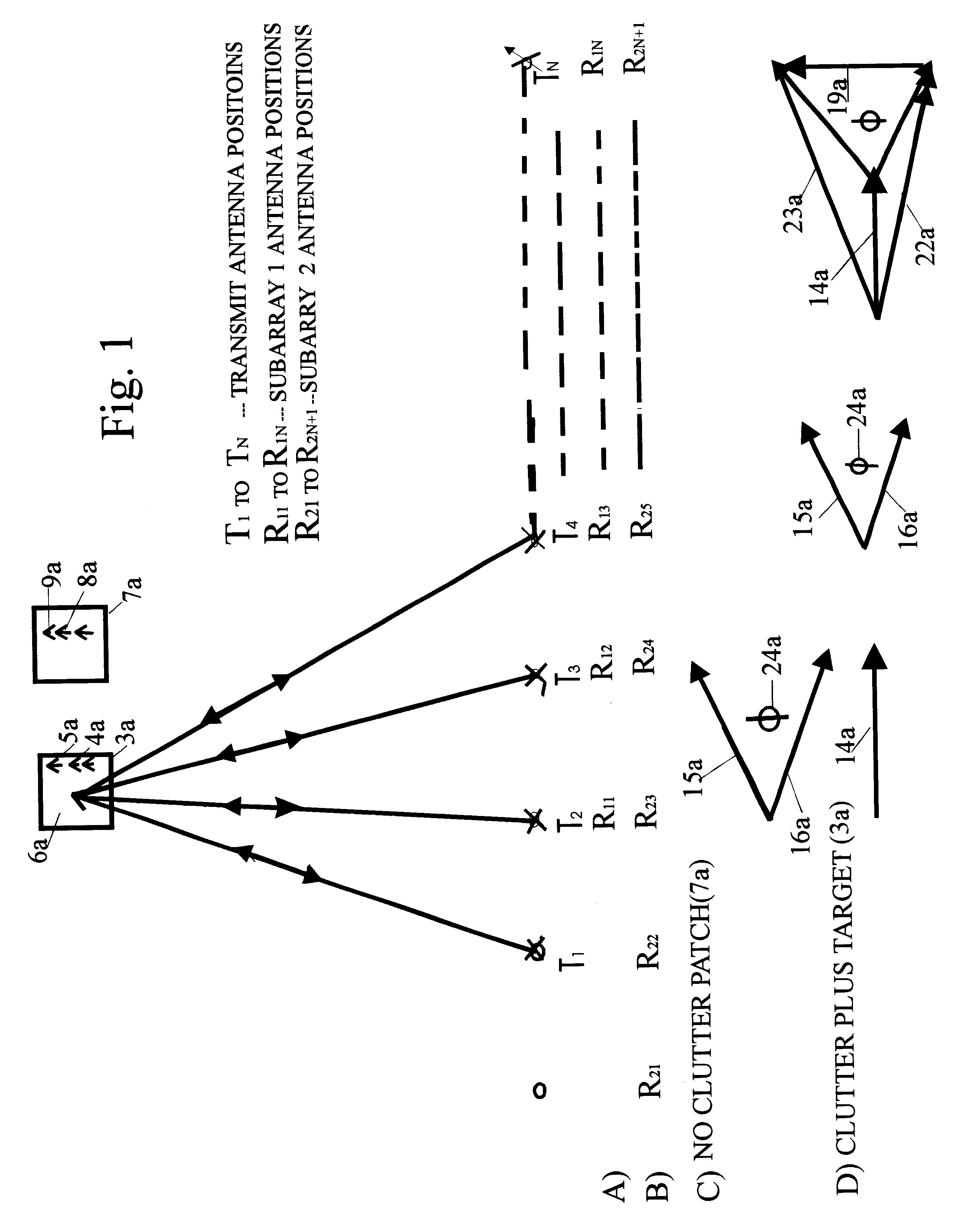
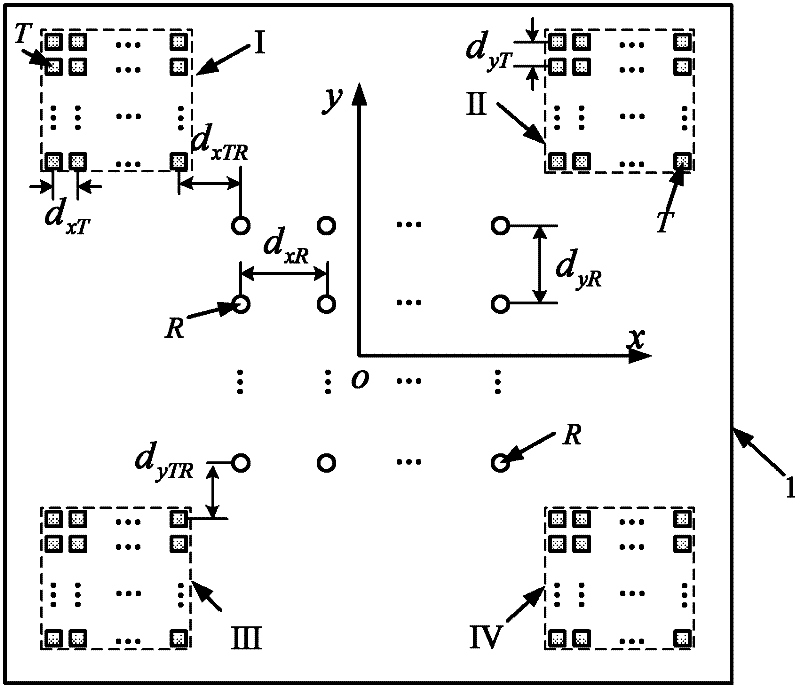
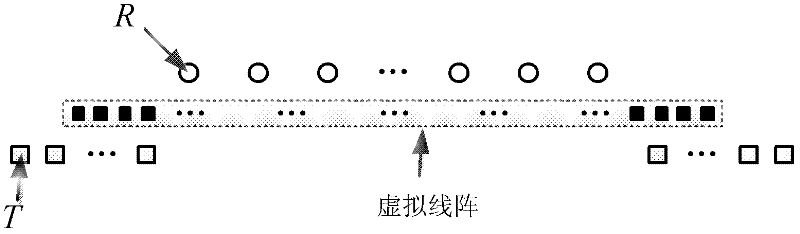
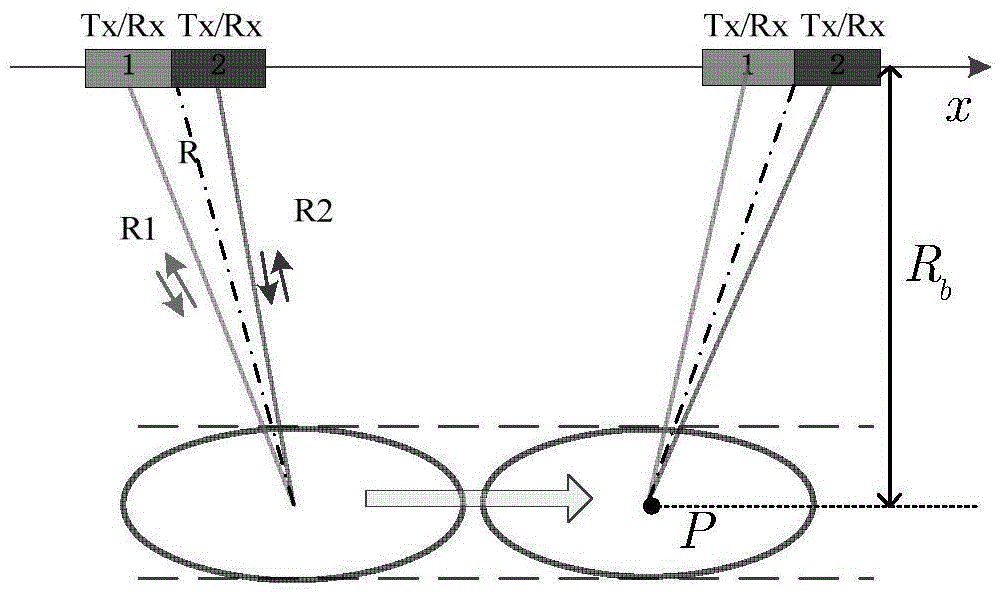
Method for constructing thinned MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) planar array radar antenna
ActiveCN102521472AReduce the number of needsSpecial data processing applicationsMimo antennaArray element
The invention provides a method for constructing a thinned MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) planar array radar antenna, which is on the basis of a phase center approximation principle and combines an MIMO antenna thought. The antenna arrangement optimal design is carried out by adopting the MIMO antenna thought. When all transmitting array elements simultaneously (or in turns) transmit orthogonal signals and receiving array elements simultaneously receive echo signals, a virtual planar array with uniform intervals is subjected to equivalence processing by utilizing the phase center approximation principle. According to the thinned MIMO planar array radar antenna constructed according to the invention, few transmitting antenna array elements and few receiving antenna array elements can be adopted and the equivalent full-array-element arrangement planar antenna array is virtually realized. Compared with the planar array antenna which is the same size as the equivalent virtual planar array and is directly arranged, the thinned MIMO planar array radar antenna constructed according to the method disclosed by the invention has the advantage of greatly reducing the requirement on the number of the array elements.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radio signal transmitter with multiple antennas for improved position detection
A radio frequency (RF) signal transmission device (the “device”) is used as a tracked target in a position tracking system (the “system”). In the preferred embodiments, the device's position is determined by analyzing the time difference of arrival of the device's RF signals received at multiple receivers which are part of the system. The device has two antennas spaced a known distance apart and the device alternately transmits on these antennas or can use code-division multiplexing for individual antenna's signal detection. The system detects the position of both antennas at their respective phase center and determines the distance between the two calculated antenna positions. By comparing the calculated distance to actual known distance the system can assess the quality of the calculated positions.
Owner:POSITION IMAGING
GPS antenna array and system for adaptively suppressing multiple interfering signals in azimuth and elevation
An antenna system has N antenna units stacked on a mast. Each unit has elements for responding to, e.g., GPS signals, and a phasing network that produces mutually orthogonal primary and auxiliary pattern modes at corresponding mode ports of the unit. A number of power dividers are each associated with a different mode, and each divider has N input ports coupled to the associated mode port of a corresponding antenna unit. The power divider associated with the primary pattern mode produces a reference beam and an auxiliary beam, and remaining power dividers produce different auxiliary beams. All beams have approximately both a common phase center and a common group delay center. An adaptive processor combines the reference and selected auxiliary beams to obtain a composite antenna reception pattern in which nulls are inserted at certain angles to suppress interfering signals, without degrading authentic signals arriving at other angles.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and apparatus for improved position, velocity, orientation or angular rate sensor
InactiveUS20050242991A1Position fixationSatellite radio beaconingAngular rate sensorProcessing element
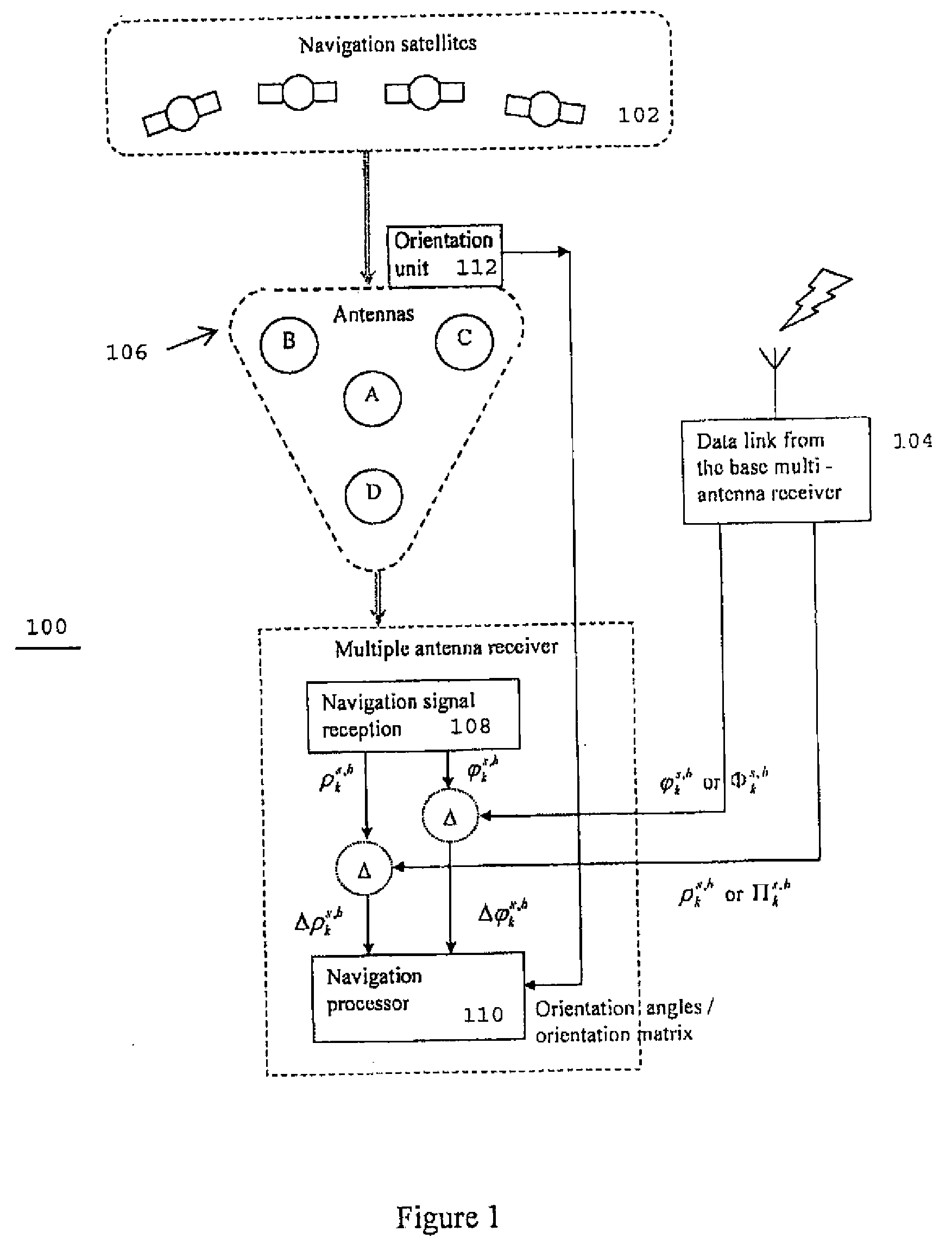
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver system includes a processing unit; and one or more antenna units for receiving GNSS signals, each of the antenna units having a phase center; one or more inertial sensor units each positioned substantially adjacent said phase centers; and at least one communication channel between each antenna unit and said processing unit.
Owner:NOVARIANT
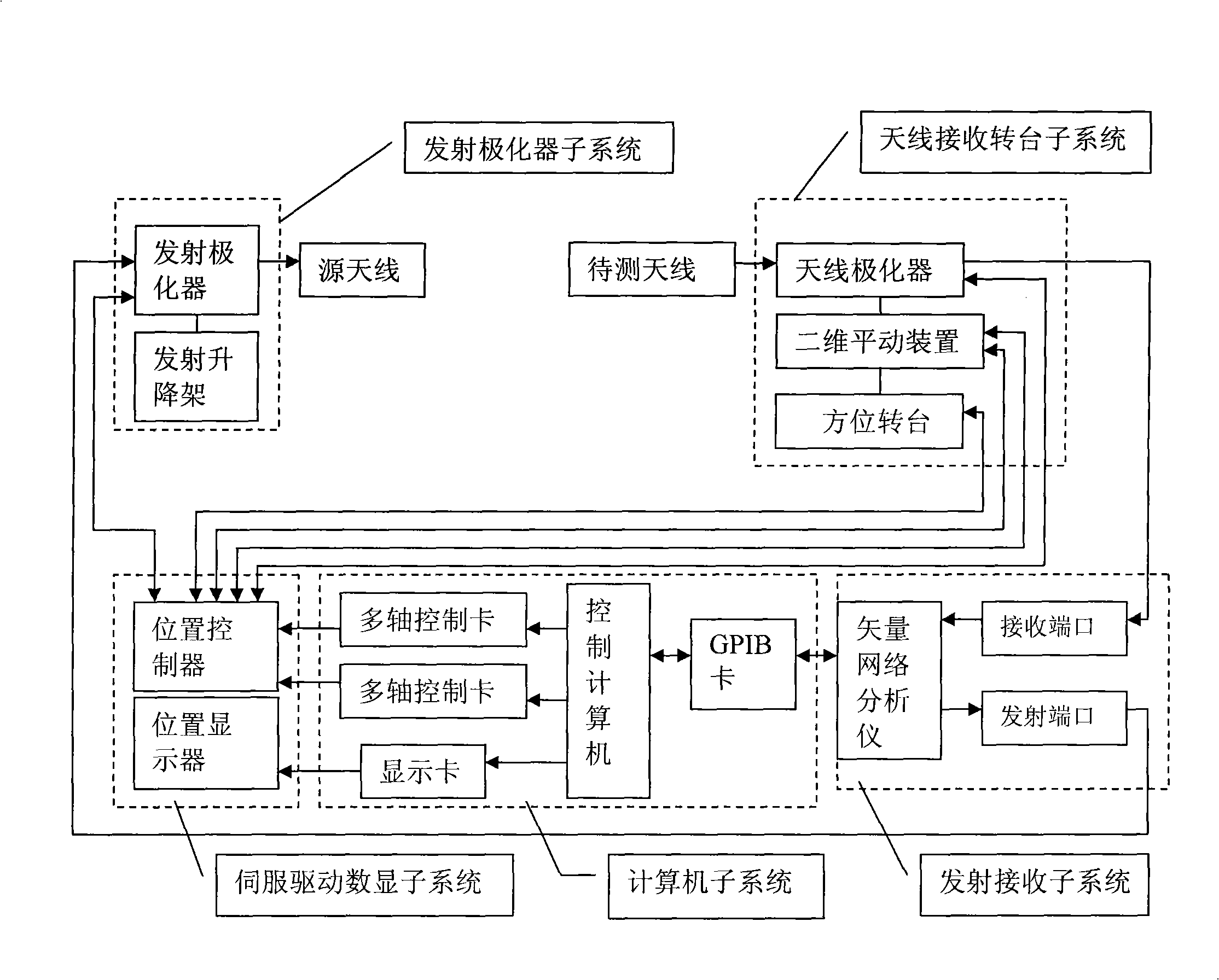
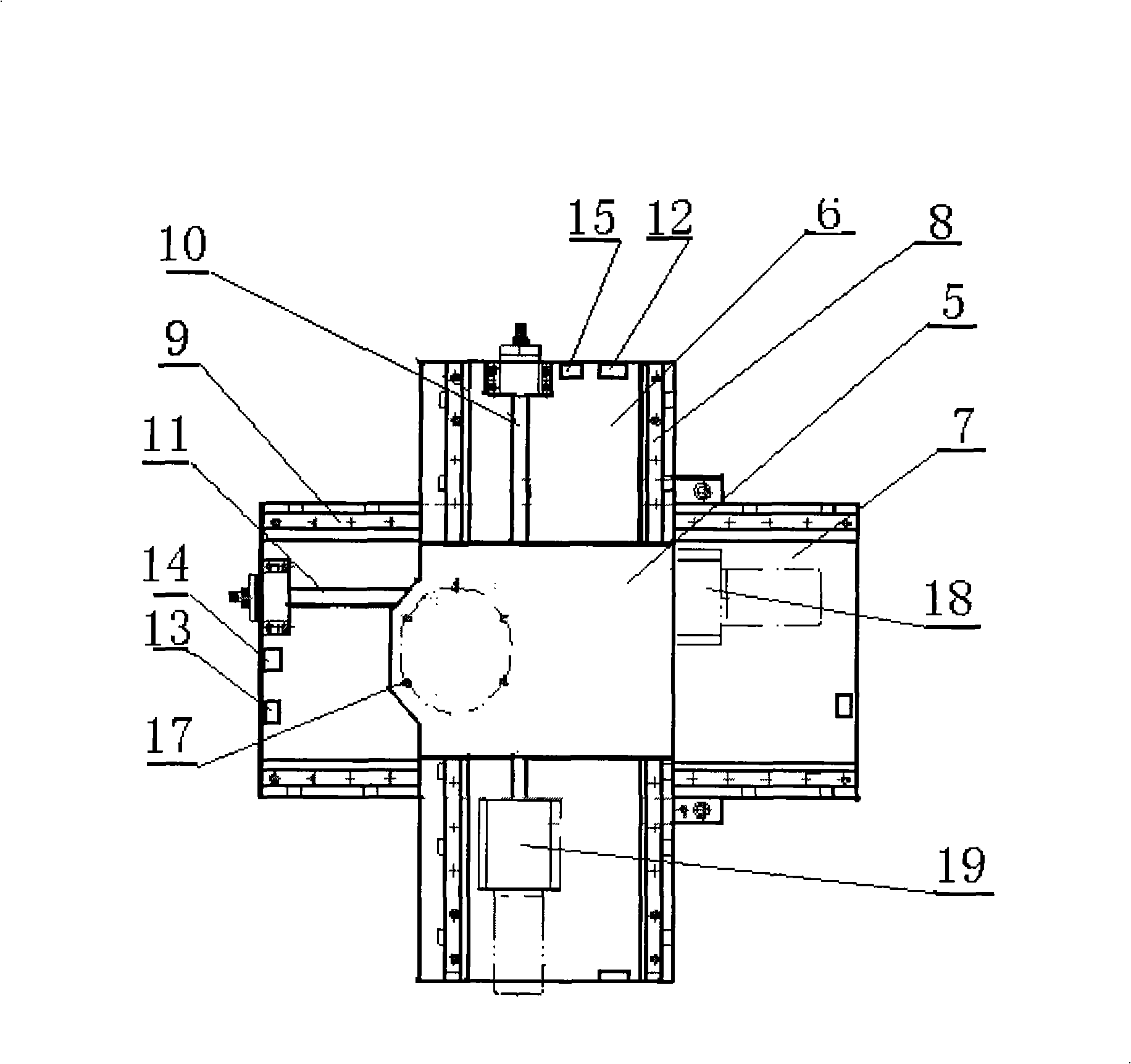
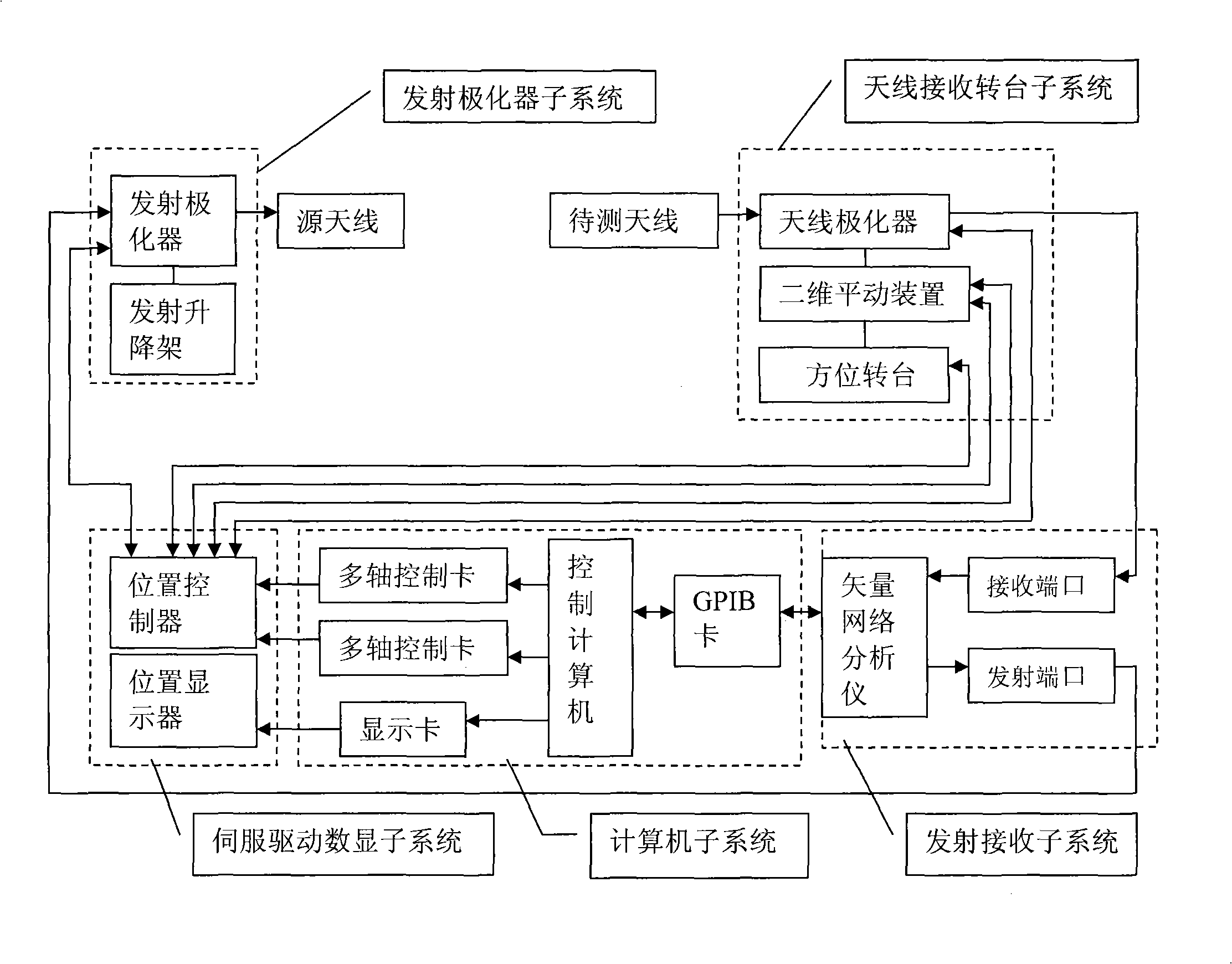
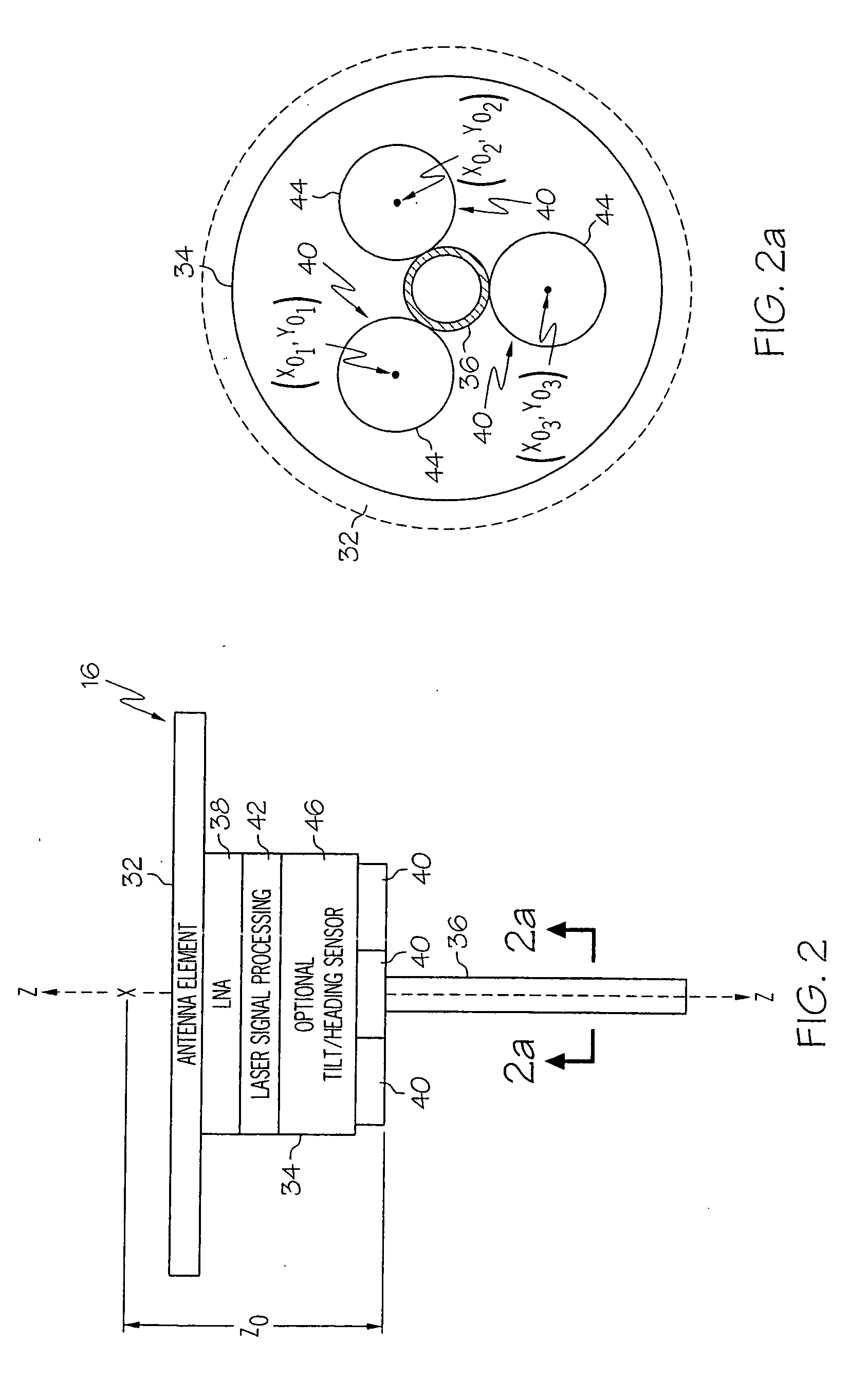
Automatic measuring system of antenna phase center
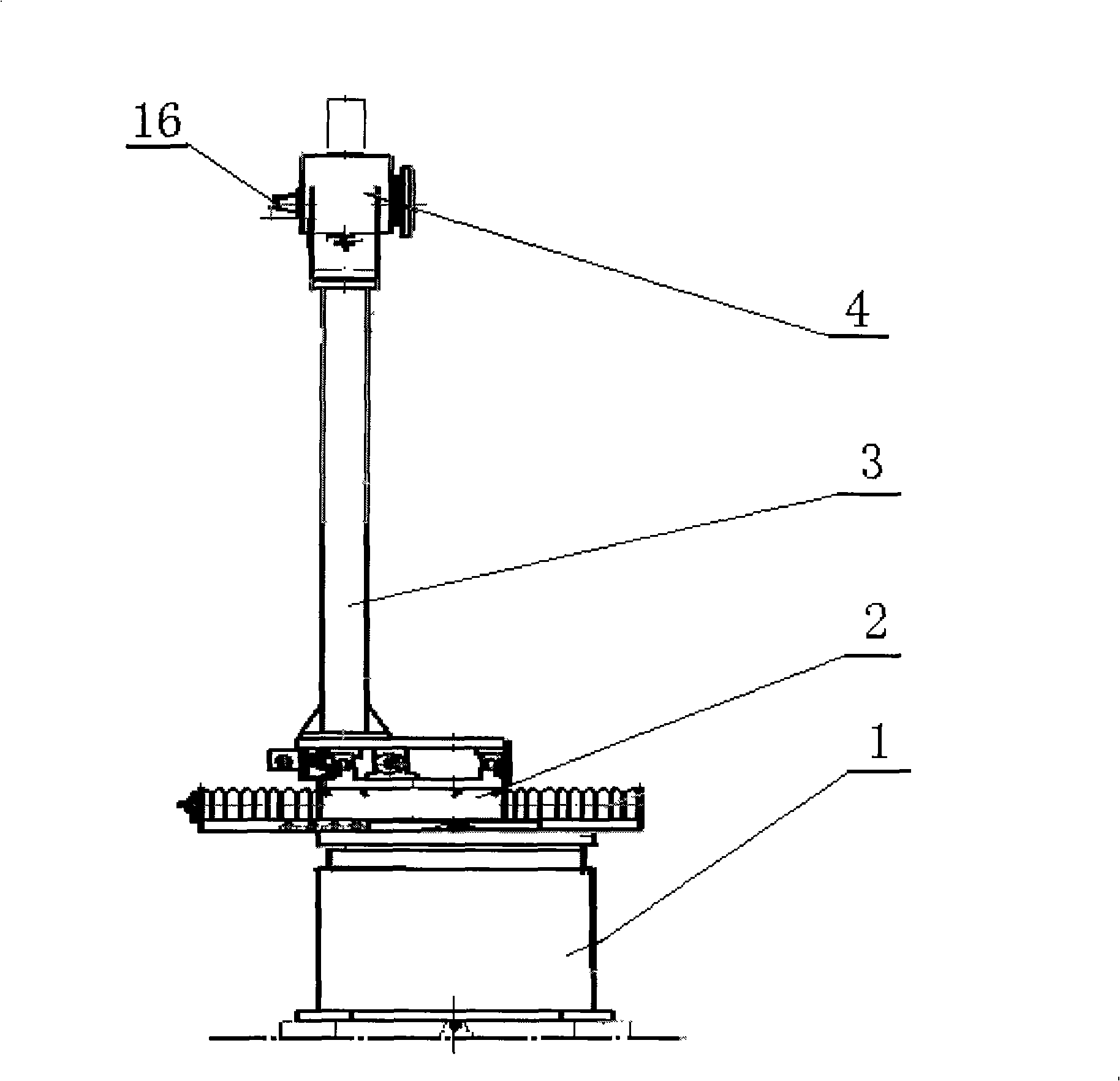
InactiveCN101320061AEnsure safetyStable positionAntenna radiation diagramsAntenna polarizationPolarizer
The invention discloses an automatic measuring system in the center of an antenna phase, which comprises an antenna receiving rotary table subsystem, an emission polarizer subsystem, an emission and reception subsystem, a servo drive digital display subsystem and a computer subsystem. The antenna receiving rotary table subsystem and the emission polarizer subsystem are both connected with the emission and reception subsystem, the servo drive digital display subsystem and the computer subsystem; wherein, the antenna receiving rotary table subsystem consists of a direction rotary table (1), a two-dimensional translation device (2), a bracket (3) and an antenna polarizer (4). The two-dimensional translation device (2) is positioned between the direction rotary table (1) and the antenna polarizer (4) and used for automatically adjusting the positions of an antenna and the rotating axis of the direction rotary table, thereby making the phase center of the antenna near the axle center of the rotary table and ensuring the stable positions of the rotating axis of the direction rotary table and the rotating axis of the antenna polarizer when the direction rotary table is rotating. The automatic measuring system provided by the invention has the advantage of high measuring automation and can be used to accurately mark the phase centers of antennas.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Repeater diversity system
InactiveUS6445904B1Improve reception performanceActive radio relay systemsRepeater circuitsEngineeringDiversity scheme
A repeater diversity system includes a null antenna having a given phase center and polarization for receiving a communications signal from a remote signal source, a donor antenna for transmitting a signal to a base station, and a diversity null antenna having the same phase center as the receive null antenna and a polarization orthogonal to the polarization of the main null antenna. A combining network is coupled to the main null antenna and the diversity null antenna for combining the signals therefrom and an uplink channel module is coupled with the combining network for delivering diversity combined receive signals to the donor antenna.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
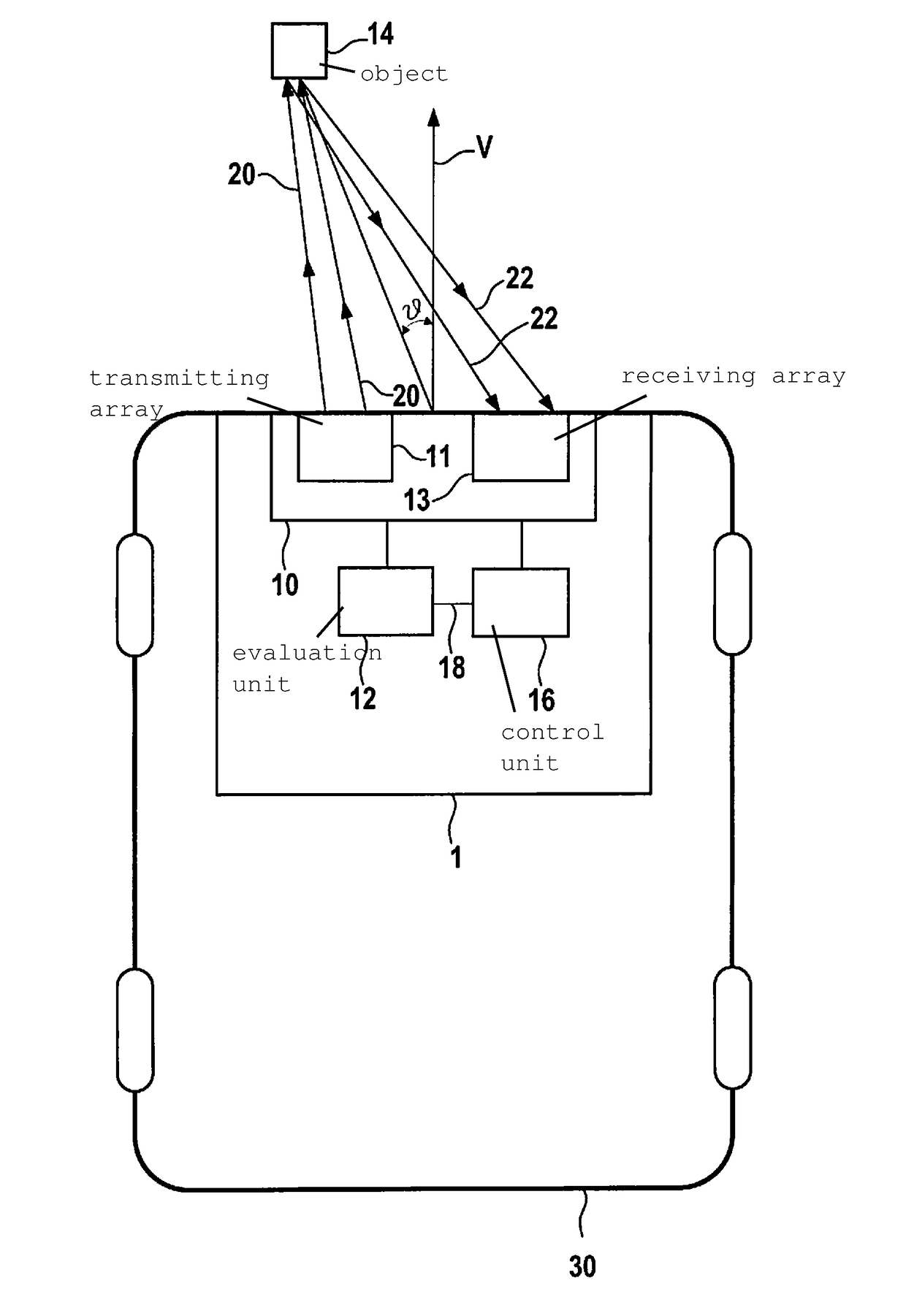
MIMO radar device for the decoupled determination of an elevation angle and an azimuth angle of an object and method for operating a MIMO radar device
ActiveUS20170307744A1Accurate measurementEase of evaluationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysElevation anglePhysics
A MIMO radar device for the decoupled determination of an elevation angle and azimuth angle of an object. The MIMO radar device includes an antenna array including multiple transmitting antennas, whose phase centers are situated spaced apart from one another along a first coordinate direction; and multiple receiving antennas, whose phase centers are situated spaced apart from one another along the first coordinate direction; the phase center of at least one of the transmitting antennas being spaced apart from the phase centers of the remaining transmitting antennas by an offset value along a second coordinate direction; the phase center of at least one of the receiving antennas being spaced apart from the phase centers of the remaining transmitting antennas by the offset value along the second coordinate direction; an evaluation unit to evaluate electromagnetic signals for the decoupled determination of the elevation angle and the azimuth angle of the object.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Antenna phase center measuring method based on moving reference point
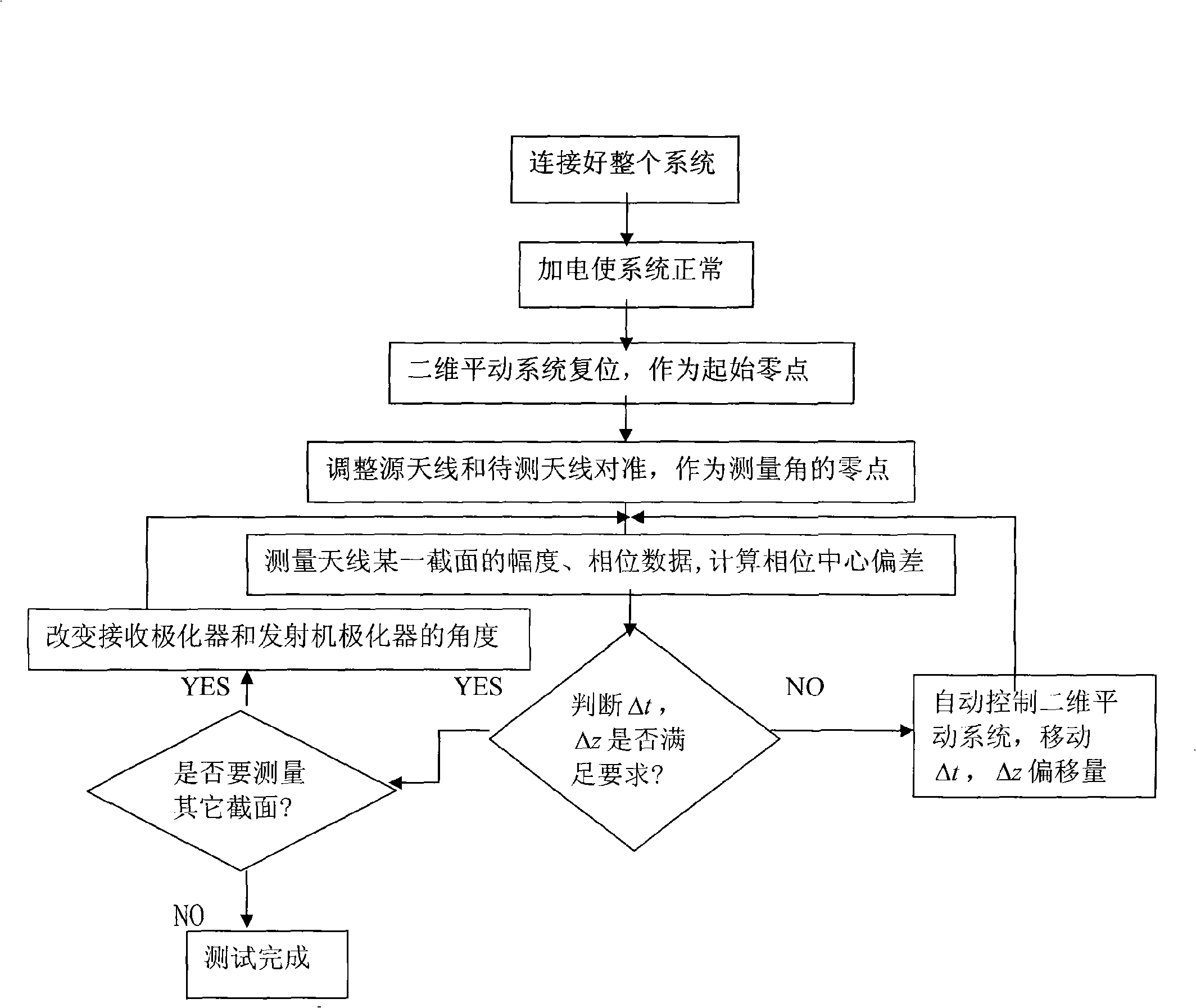
InactiveCN101320062AImprove test accuracyOvercoming the problem of poor measurement accuracyAntenna radiation diagramsAutomatic controlDesign phase
The invention discloses a method for measuring the phase center of an antenna, which is based on moving reference points. The method provided by the invention mainly solves the measuring problems of manual operation and artificial judgment. The method includes the following steps: in the measuring system, a measured antenna is adjusted to face an original antenna and is taken as the zero point of a measuring angle; the horizontal direction and the vertical direction of a two-dimensional translation device are controlled to reset and taken as the datum reference point of the phase center test; related parameter information is input and all moving shafts are controlled automatically, thereby collecting the amplitude and phase data of the measured antenna; the horizontal deviation and the longitudinal deviation of the phase center can be worked out by using the least square method and then can be determined whether the deviation of the phase center meets the deviation requirements of the designed phase center of the antenna; if not, the reference point of the antenna can be changed by automatically adjusting the horizontal coordinate and the vertical coordinate of the two-dimensional translation device according to the deviation value; the test can be repeated again and again until the horizontal deviation and the longitudinal deviation meet the requirements; and the final changed reference point can be taken as the phase center of the measured antenna. The method provided by the invention can automatically and accurately measure the phase center of an antenna.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Adaptive array
ActiveUS20060164284A1Easy to detectImprove tracking performanceCommunication jammingIndividually energised antenna arraysRadar systemsArray element
An adaptive antenna array has array elements arranged in element rows and element columns and subarrays arranged in subarray rows and subarray columns, for which the subarray phase centers have non-uniform spacing. The adaptive antenna array provides good detection and tracking performance when used in a radar system, while being inexpensive and easy to manufacture. A radar system and a method of adapting a radar array both employ the above described adaptive antenna array.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
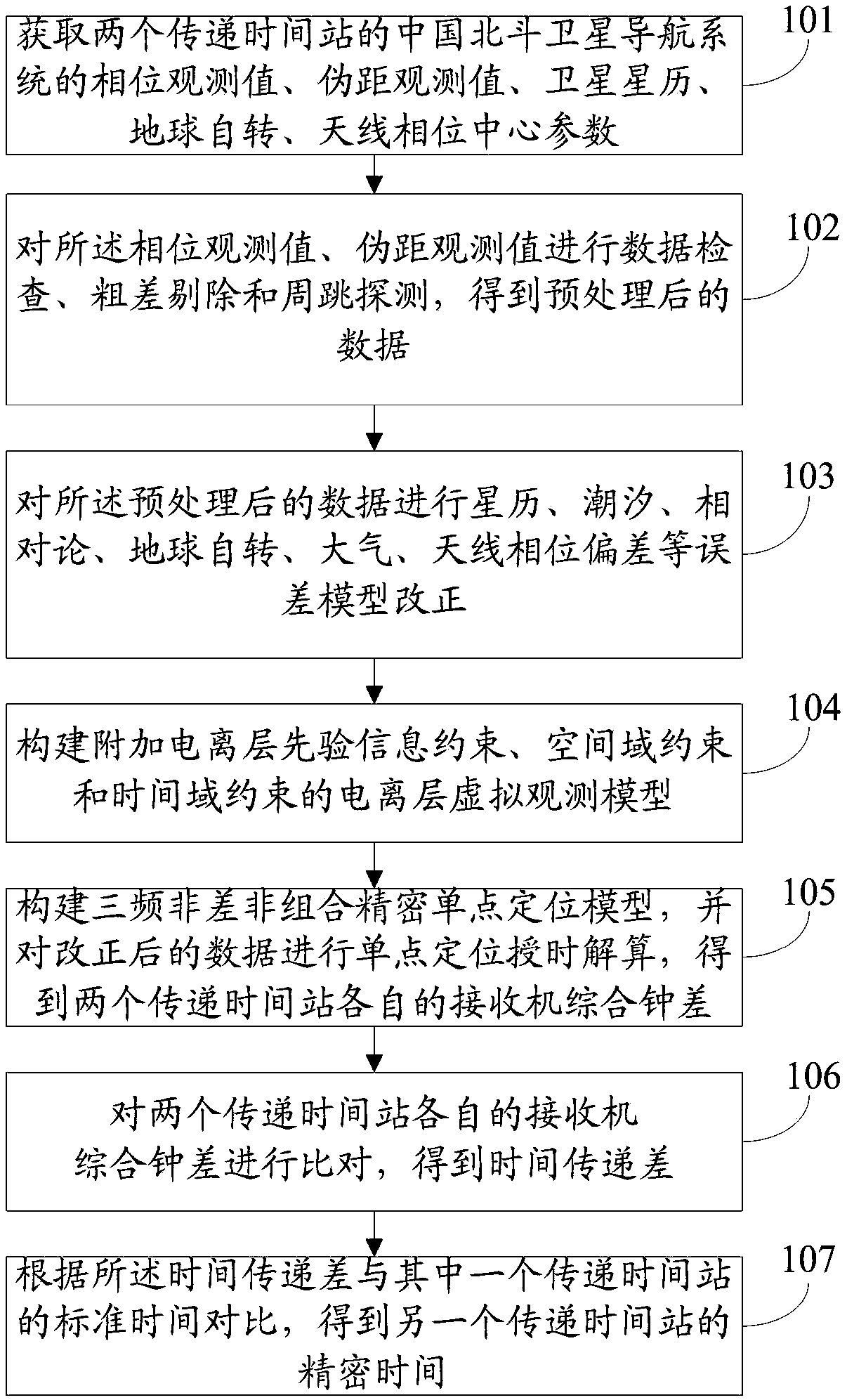
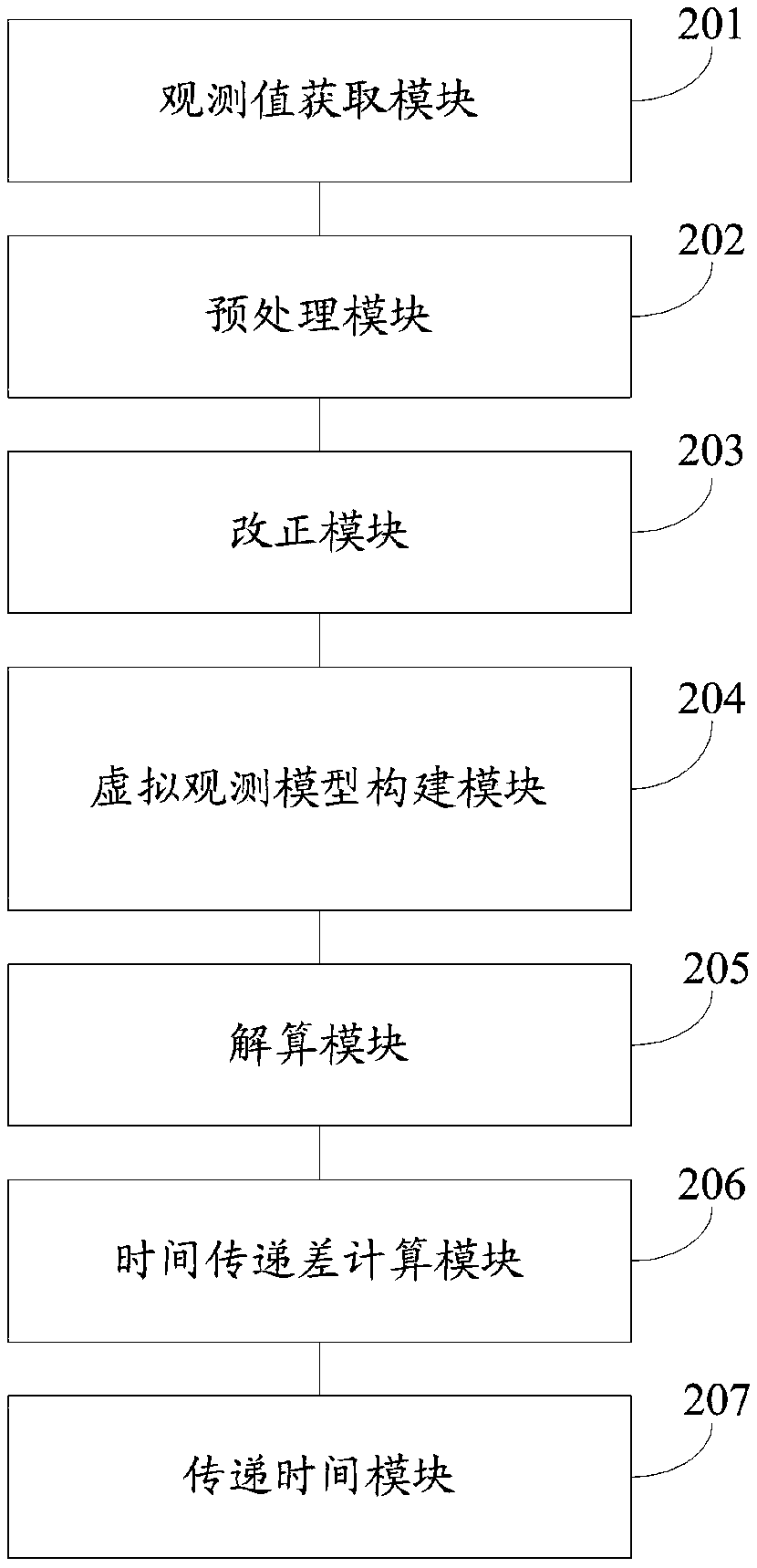
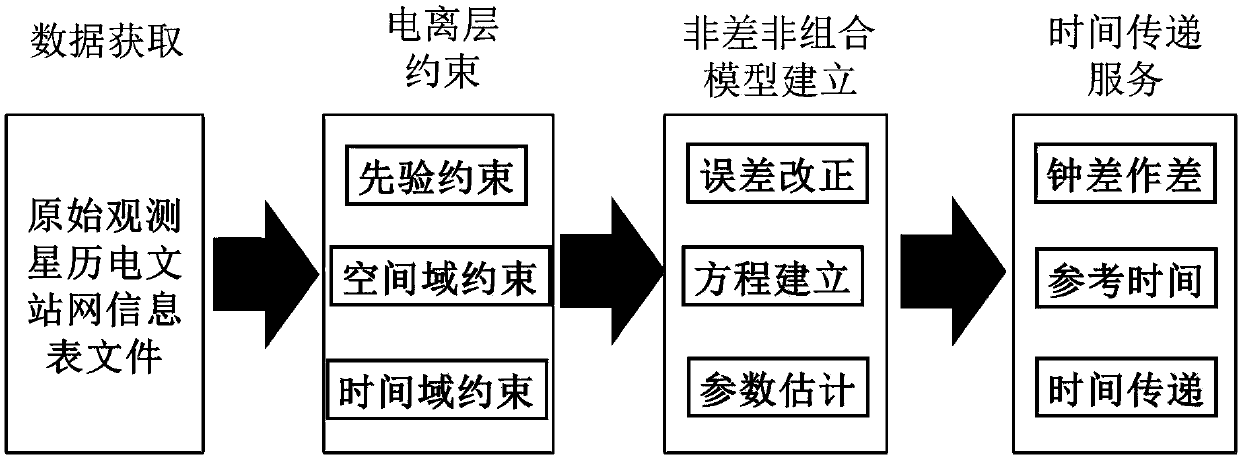
Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method
ActiveCN108919634AReduce observation noiseImprove time transfer accuracyRadio-controlled time-piecesEarth's rotationClock correction
The invention discloses a Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method. The method includes the steps that phase observation value, pseudo-range observation value, satellite ephemeris, earth rotation, antenna phase center and other parameters of China Beidou satellite navigation systems at two time transmission stations are obtained; data check, gross error reject and cycle slip detection are carried out, error models of ephemeris, tide, relativity, the earth rotation, atmosphere and antenna phase deviation are corrected; an ionospheric virtual observation model with additional ionospheric prior information constraints, spatial domain constraints and time domain constraints is constructed; and a three-frequency non-differentialnon-combinatorial precise single-point positioning model is constructed, a single-point positioning timing solution is carried out on corrected data, and comprehensive clock corrections of receivers of the two transmission time stations are obtained and compared to obtain a time transmission difference; and compared with standard time of one of the two transmission time stations, precise time of the other one of the two transmission time stations is obtained. According to the Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method, the observation noise can be reduced, and the accuracy and reliability of time transmission are improved.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radar architecture
ActiveUS8289203B2Drawback can be obviatedAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsBeam pattern
The present invention is directed to a radar system that includes an antenna array having a plurality of antenna elements and a plurality of transmit antenna phase centers. A transmitter portion is configured to transmit a plurality of transmit beams characterized by a transmit beam pattern. The transmit beam pattern has a predetermined transmit beamwidth that is a function of the number of orthogonal transmit waveforms. The number of orthogonal transmit waveforms is less than the plurality of antenna elements. A receiver portion is also coupled to the antenna array and is configured to extract a plurality of orthogonal receive signal components from a received signal provided by the antenna array. A plurality of extracted orthogonal receive signal components are digitally beam formed to implement a virtual antenna array and generate a receive signal having a receive beamwidth.
Owner:SRC INC
Navigation system using both GPS and laser reference
ActiveUS20070052950A1Slow down operationImprove precision controlAngle measurementPosition fixationLaser transmitterMachine control
A machine control system uses a laser system and global navigation satellite system to determine the position of the machine. The laser system has a laser detector positioned in a known and fixed relationship with the nominal phase center of a global navigation satellite antenna. The laser detector receives laser light transmitted from a laser transmitter. The outputs of the laser system and the global navigation satellite system are used together to determine the position of the transmitter prior to being used to determine the position of the machine.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
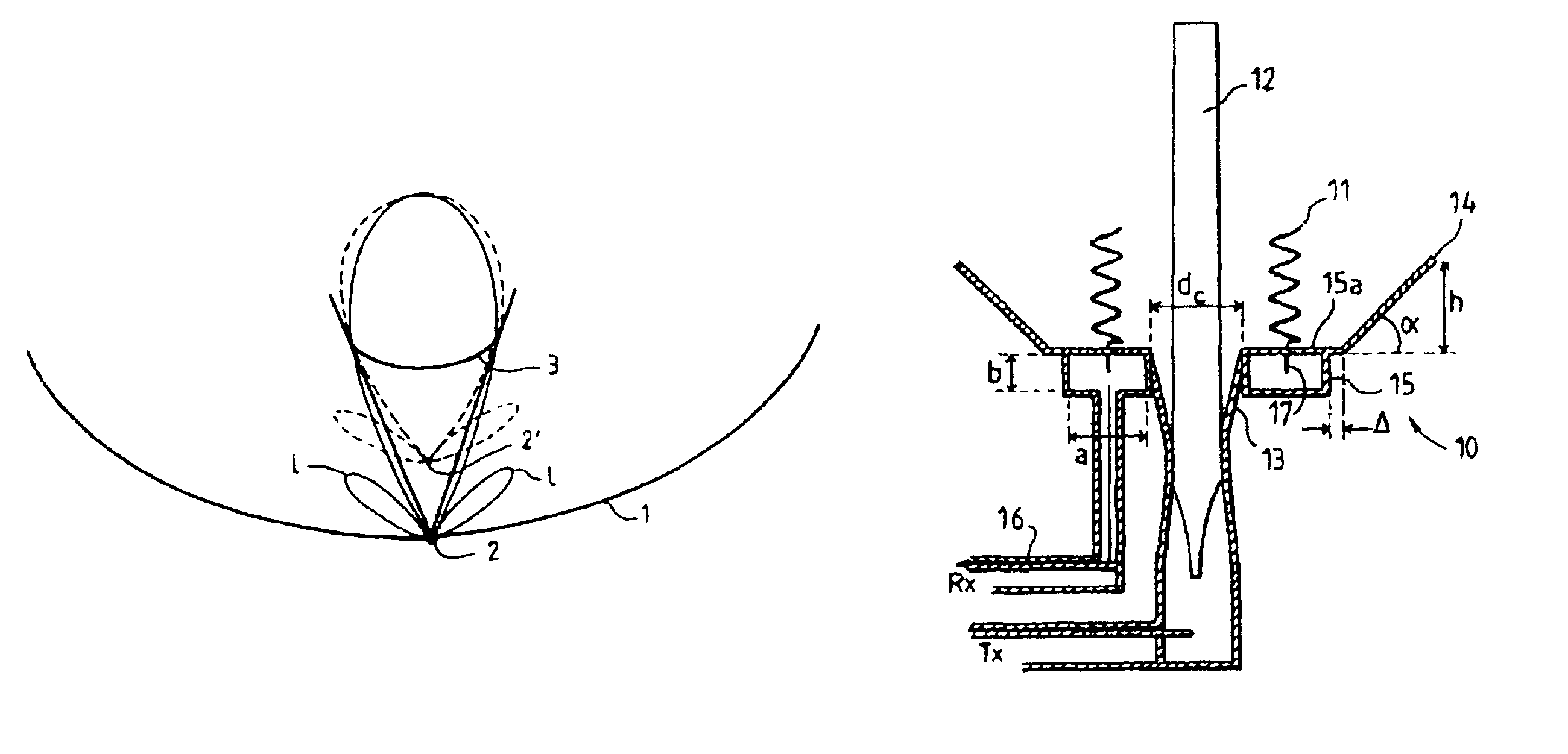
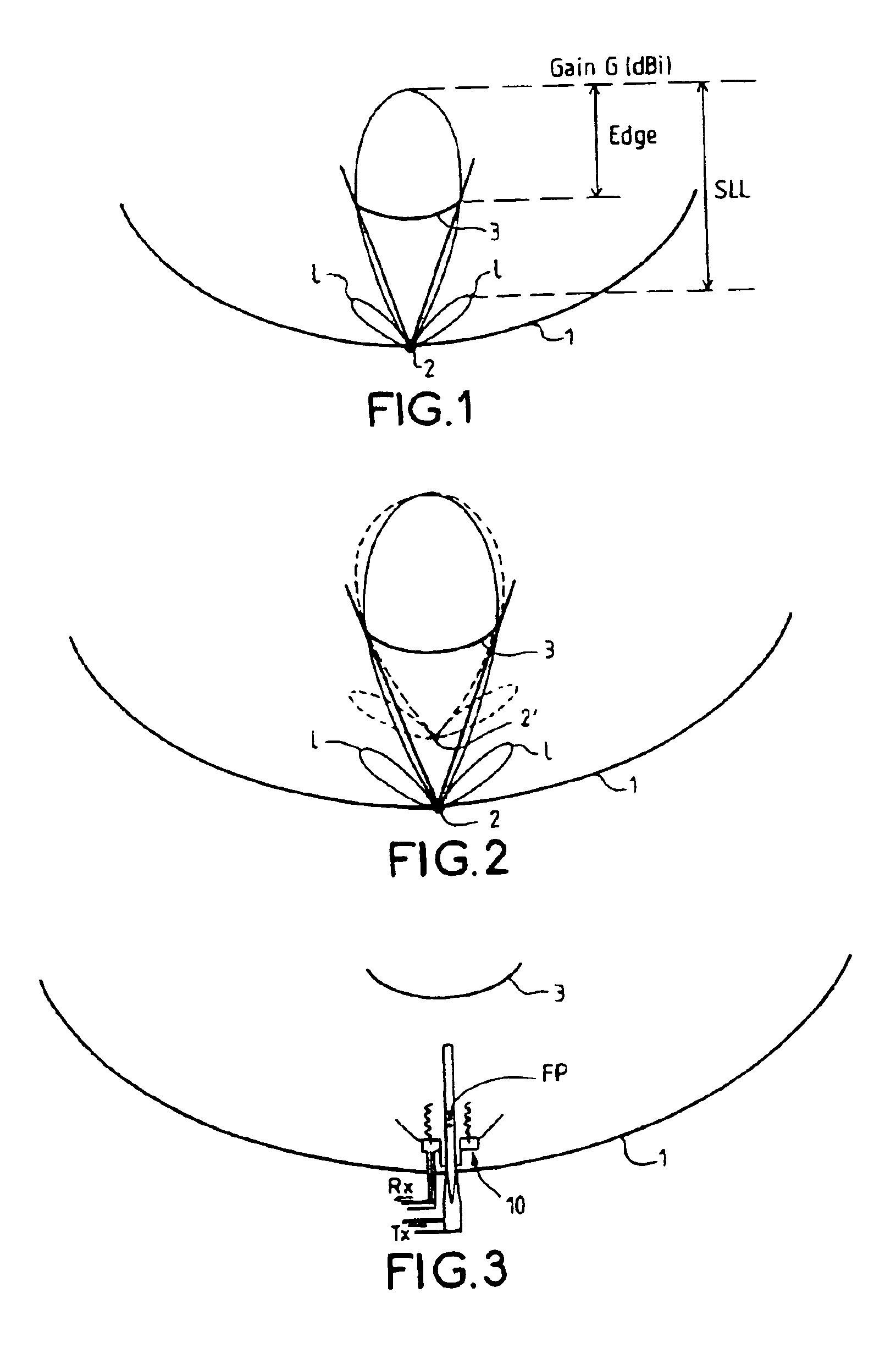
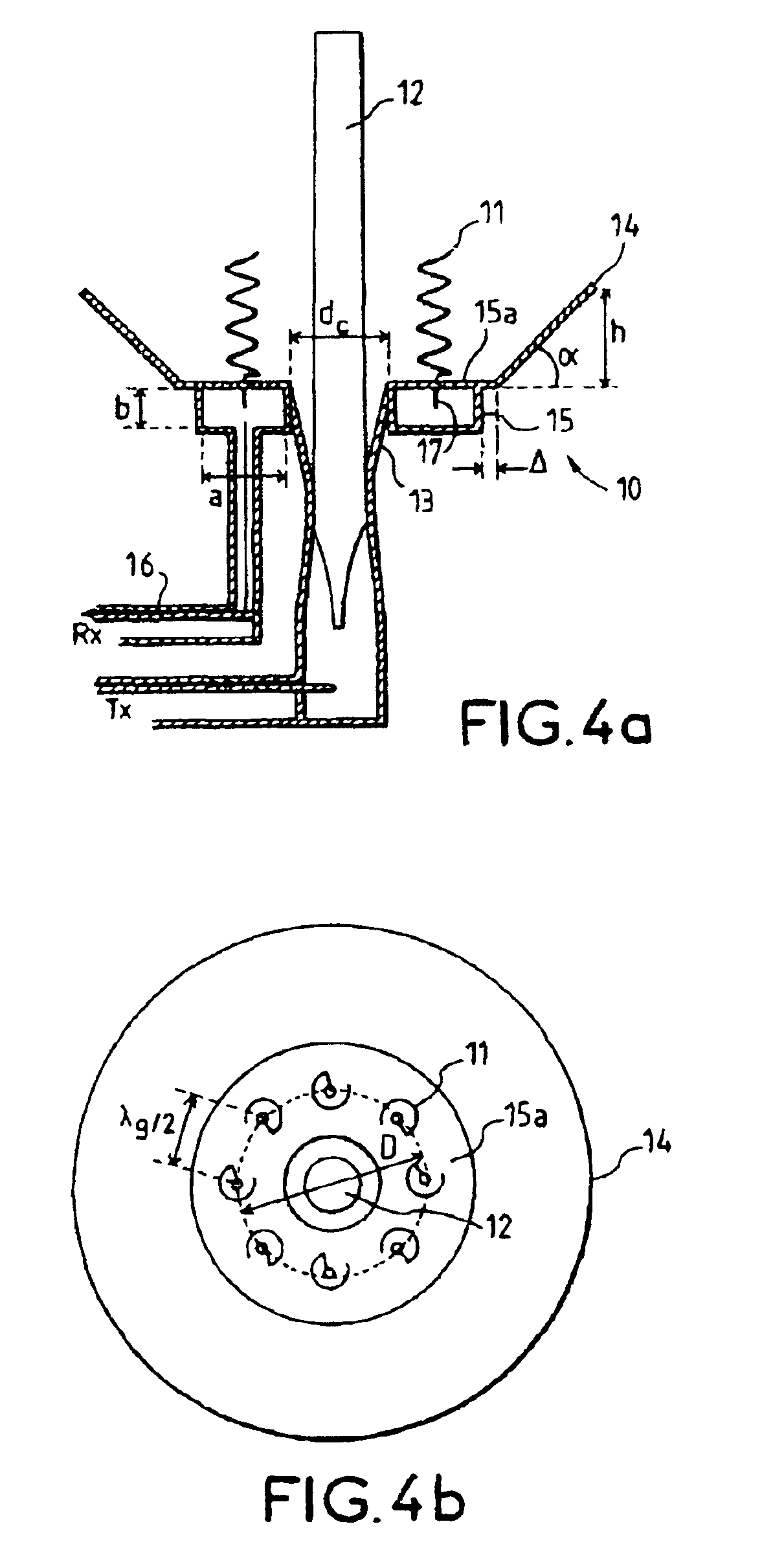
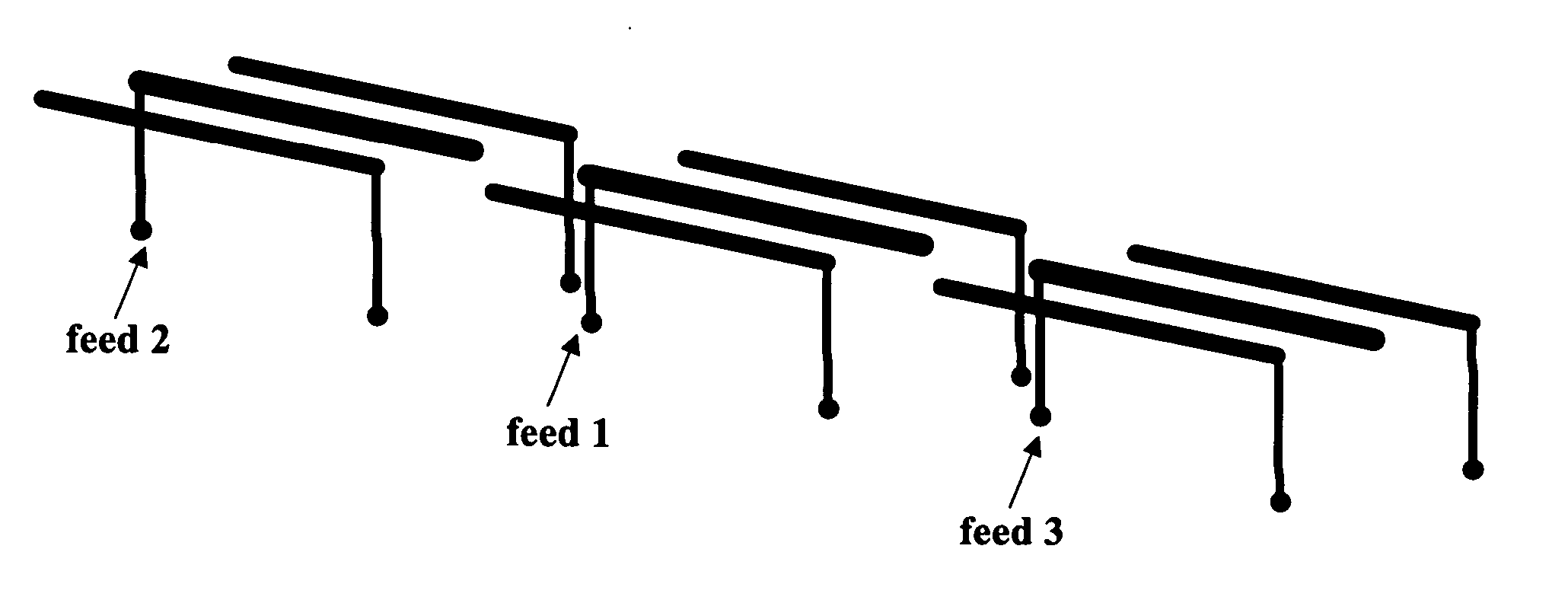
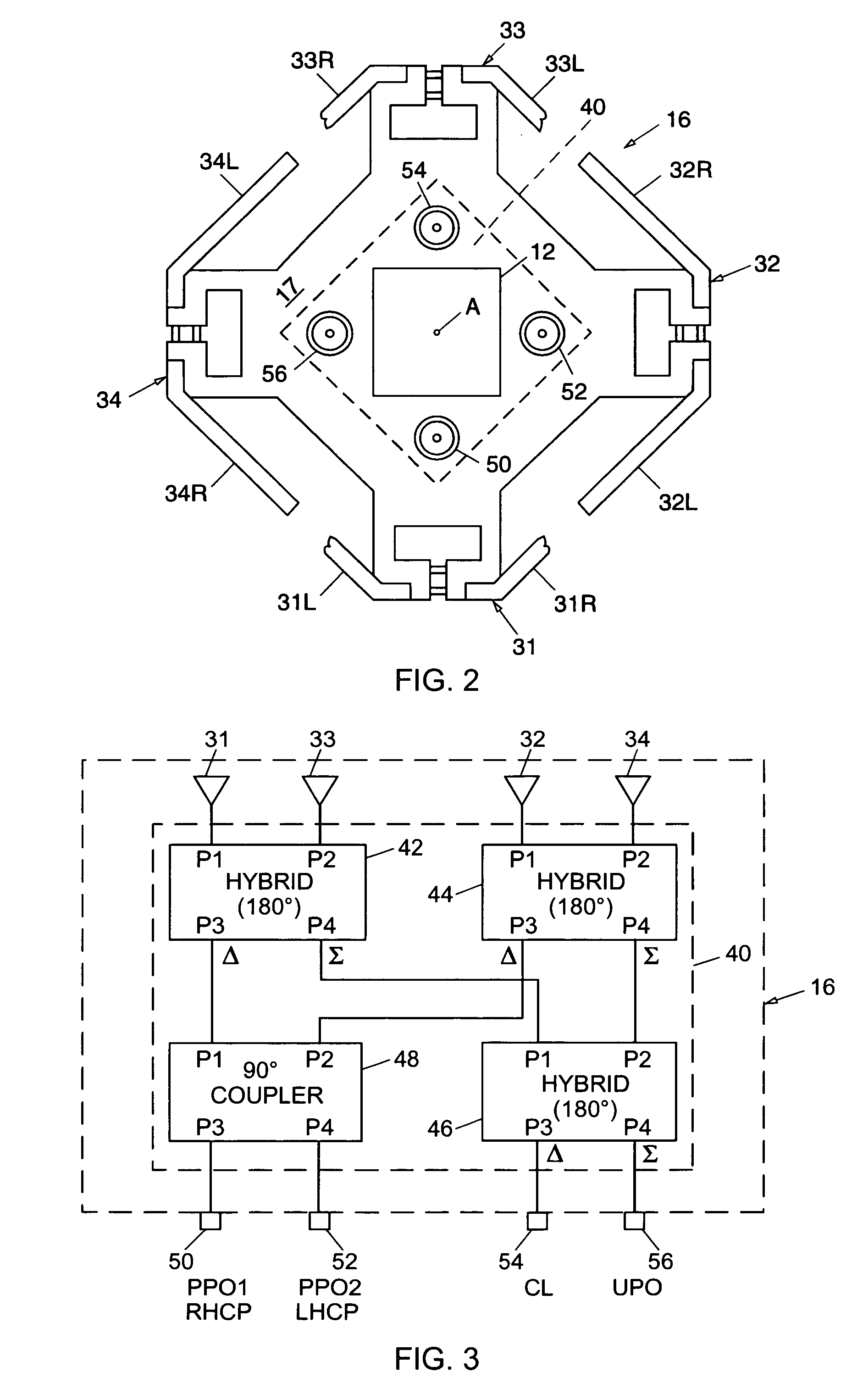
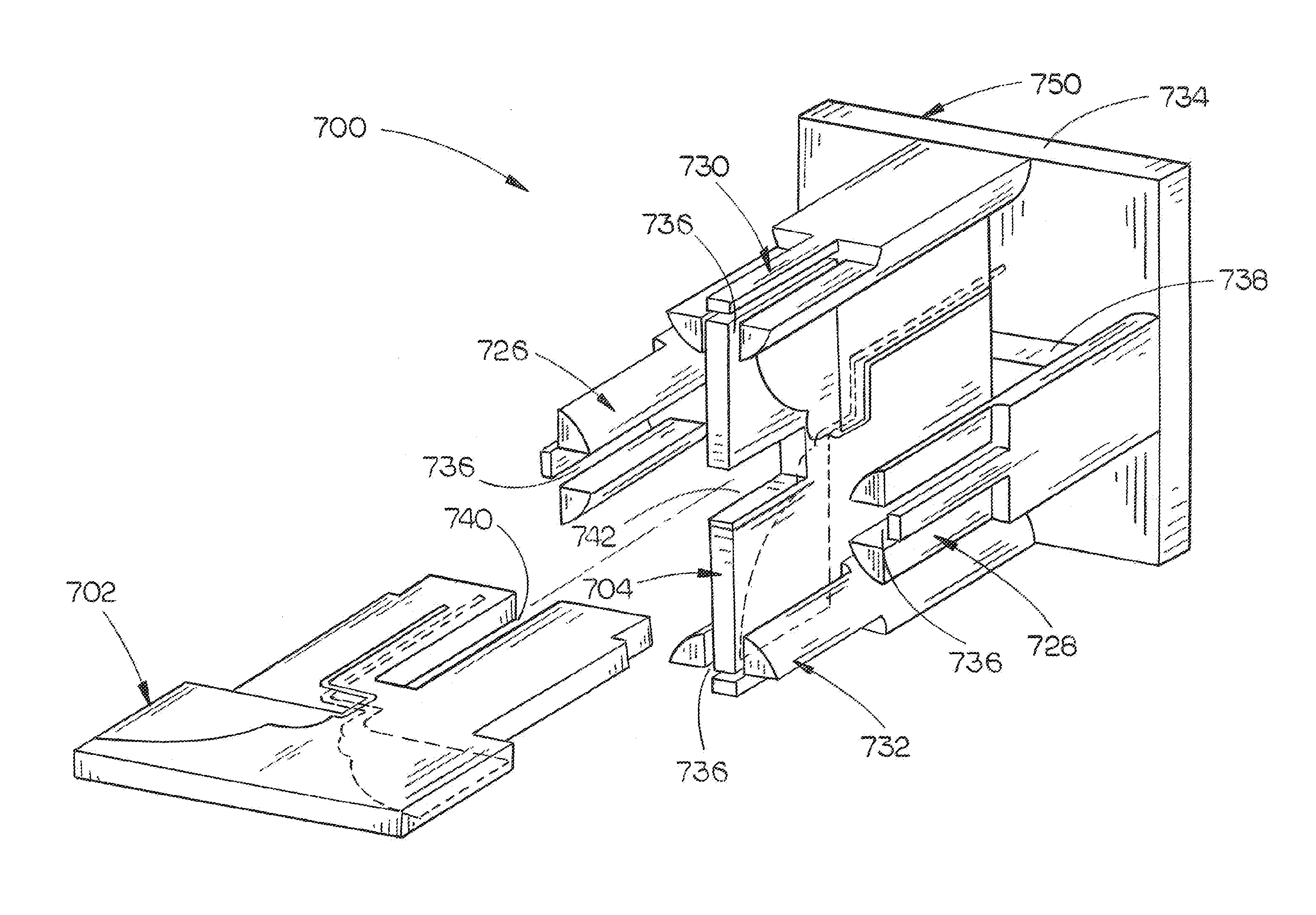
Phase center coincident, dual-polarization BAVA radiating elements for UWB ESA apertures
The present disclosure is directed to a dual polarized antenna array including a first BAVA (a horizontal polarization input), a second BAVA (a vertical polarization input), and a cradle assembly. The substrates of the first and second BAVAs each include a notched portion. The cradle assembly includes a base plate having four channel modules connected thereto. Edge portions of the substrates of the first and second BAVAs are received by the cradle assembly via channels of the channel modules and apertures of the base plate. The substrates of the BAVAs are interleaved via their notched portions so that the substrate of the second BAVA is an orthogonal orientation relative to the substrate of the first BAVA.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Multi-channel multi-sub-band sliding-spotlight-mode SAR imaging method
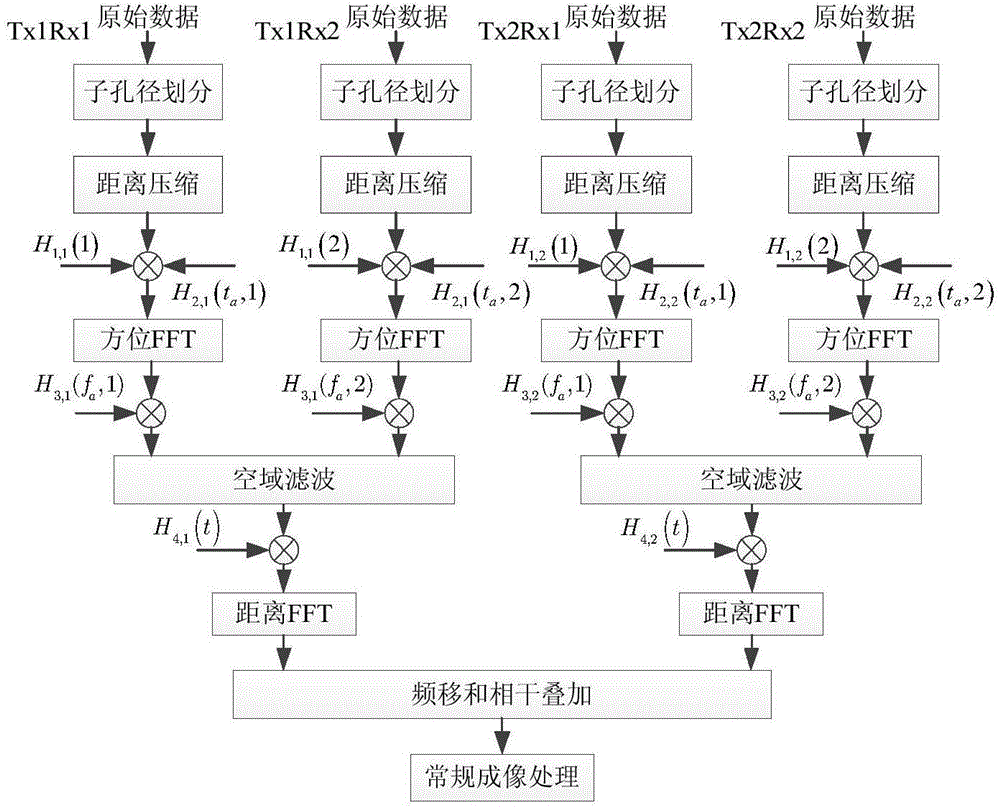
InactiveCN104865571AEfficient synthesisThe overall calculation is smallRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a multi-channel multi-sub-band sliding-spotlight-mode SAR imaging method. With the method, a problem of difficult orientation reconstruction and frequency band synthesis of the step-frequency multi-channel synthetic aperture radar under the sliding spotlight mode can be solved. The method is implemented by the following steps: firstly, carrying out sub aperture division on a multi-channel antenna and carrying out equivalent phase center error compensation and range direction pulse compression successively on an echo received y each sub aperture; secondly, carrying out doppler shift operation on the signal after the range direction pulse compression and moving the doppler shift to a doppler base band; thirdly, calculating a weight coefficient of spatial filtering; fourthly, carrying out doppler ambiguity resolution by using the spatial filtering weight coefficient and a base band signal; and fifthly, carrying out frequency band synthesis on the signal after doppler ambiguity resolution, and completing reconstruction of a two-dimensional frequency spectrum and carrying out imaging. According to the invention, the great amount of calculation of high-resolution wide surveying and mapping data can be avoided; the high resolution of the target at the wide swath can be improved; and the method can be used for SAR multi-channel multi-sub-band imaging of an airborne or spaceborne platform.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Simulation method of linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal
InactiveCN101295019AEasy to getImprove general performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a simulation method for a linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal, which comprises the following steps: simulated synthetic aperture radar system parameter information is set and read; the information parameter of a target is set; a simulated time is treated with discretization; the instantaneous positions of a radar platform and the target are respectively calculated, and a distance vector between a phase center and the target is obtained according to geometric position relation; a one-dimension echo signal is obtained by combining the echo signal mathematic model of the synthetic aperture radar and radar system parameters; the one-dimension signal is divided according to pulse repetition period and formatted into a two-dimension signal, the two-dimension signal with Na multiplied by Nr is obtained after the total data is stored, thus finishing the fine simulation of the linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal. The more accurate echo simulation signal can be obtained by utilizing the simulation method, and the simulation method is especially suitable for a frequency modulation continuous wave signal with high-speed movement, long distance and severe oblique observation condition of the radar and has more excellent realization efficiency, and stronger adaptability and compatibility.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for calibrating phase center of receiver antenna and apparatus thereof
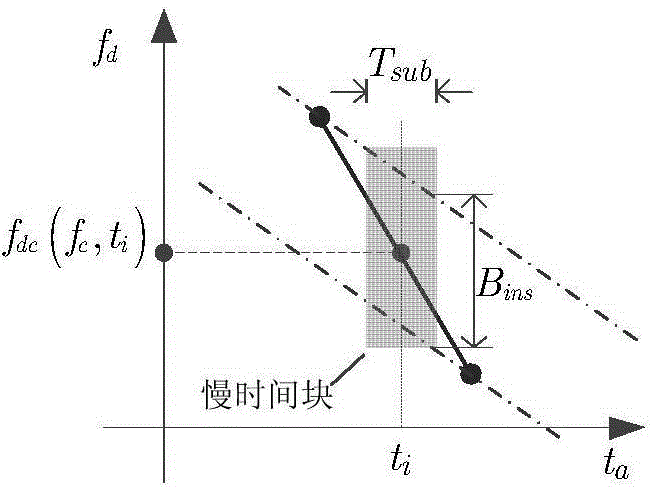
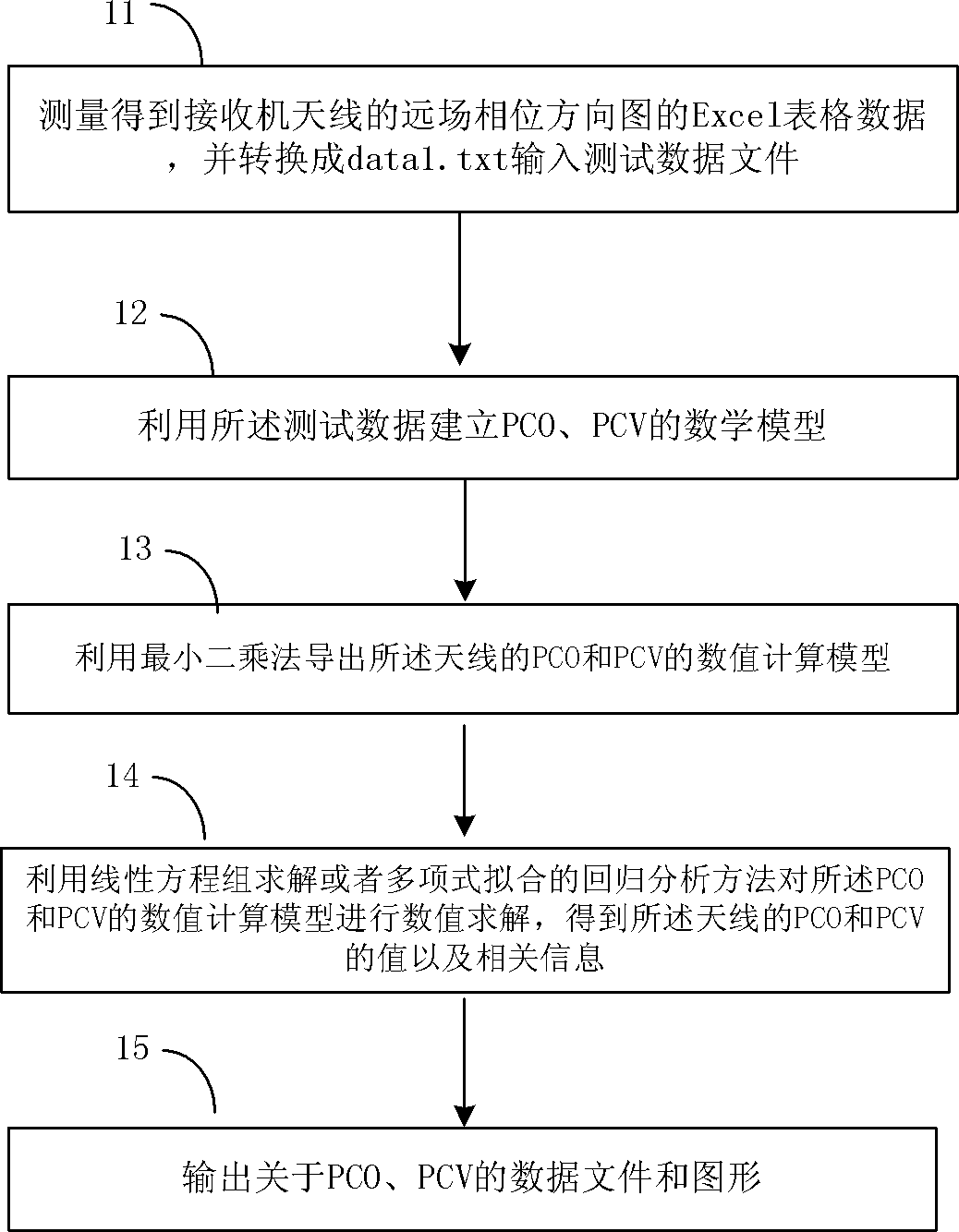
ActiveCN102323489AExact calibration valueCorrect measurement errorAntenna radiation diagramsObservational errorRegression analysis
An embodiment of the invention provides a method for calibrating a phase center of a receiver antenna and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps: measuring and obtaining far field phase directional diagram data of a receiver antenna and taking the far field phase directional diagram data as input test data; establishing mathematical models of Phrase Center Offset (PCO) andPhase Center Variation (PCV) of the receiver antenna by utilizing the input test data; exporting PCO and PCV value calculation models of the antenna by utilizing a least square method, and carrying out numerical solution on the PCO and PCV value calculation models by utilizing a linear equation group solution or polynomial fitting regression analysis method to obtain PCO and PCV values of the antenna. According to the embodiment of the invention, absolute positioning (phase) of PCO and PCV of the receiver antenna can be obtained, and a measurement error brought by antenna phase center change can be accurately corrected to raise measurement precision of a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver.
Owner:北京华力创通科技股份有限公司
Double frequency feed source
ActiveCN102394374AAchieving circular polarization of the radiation beamReduce interactionWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorImpedance matching
The invention relates to a double frequency feed source, which is applied to a ring-focus double-reflector antenna and works in S and X frequency bands. The S / X double frequency feed source adopts a way that a coaxial horn is nested, S frequency band is a coaxial horn, X frequency band is a five-section variable field angle multimode horn and is taken as an inner conductor of the S frequency bandcoaxial horn. By applying the double frequency feed source provided by the invention, the problems of wave beam equalization and impedance matching of the coaxial horn under a heavy calibre conditionare creatively solved, the double frequency feed source has the same illumination taper in the S frequency band and the X frequency band, the illumination taper at the temperature of 40 DEG C is minus 10dB to minus 13dB, an almost straight phase center is located in the two frequency bands, and efficiencies in the S frequency band and the X frequency band respectively reach up to 45% and 65%, thus the double frequency feed source provided by the invention is a high-efficiency double frequency feed source.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Method and system for obtaining an adaptive angle-doppler ambiguity function in MIMO radars
ActiveUS20200011968A1Enhanced low cost target detectionSuppressing angle-Doppler couplingDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguity functionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for obtaining an adaptive angle-Doppler ambiguity function (AF) for a target using multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar that includes a transmit antenna array having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes generating transmit signals for transmission by the transmit antenna array, the transmit signals defining at least a first transmit trajectory of a phase center within the transmit antenna array; transmitting the transmit signals using the transmit antenna array and receiving receive signals from the target, the receive signals resulting from the incidence of the transmit signals upon the target; and obtaining at least an angle-Doppler ambiguity function (AF) from the receive signals. The first transmit trajectory is such that, in operation, the phase center undergoes random phase center motion (PCM), such that a phase center position within the transmit antenna array varies randomly with time. A system for obtaining an AF is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV DU LUXEMBOURG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com