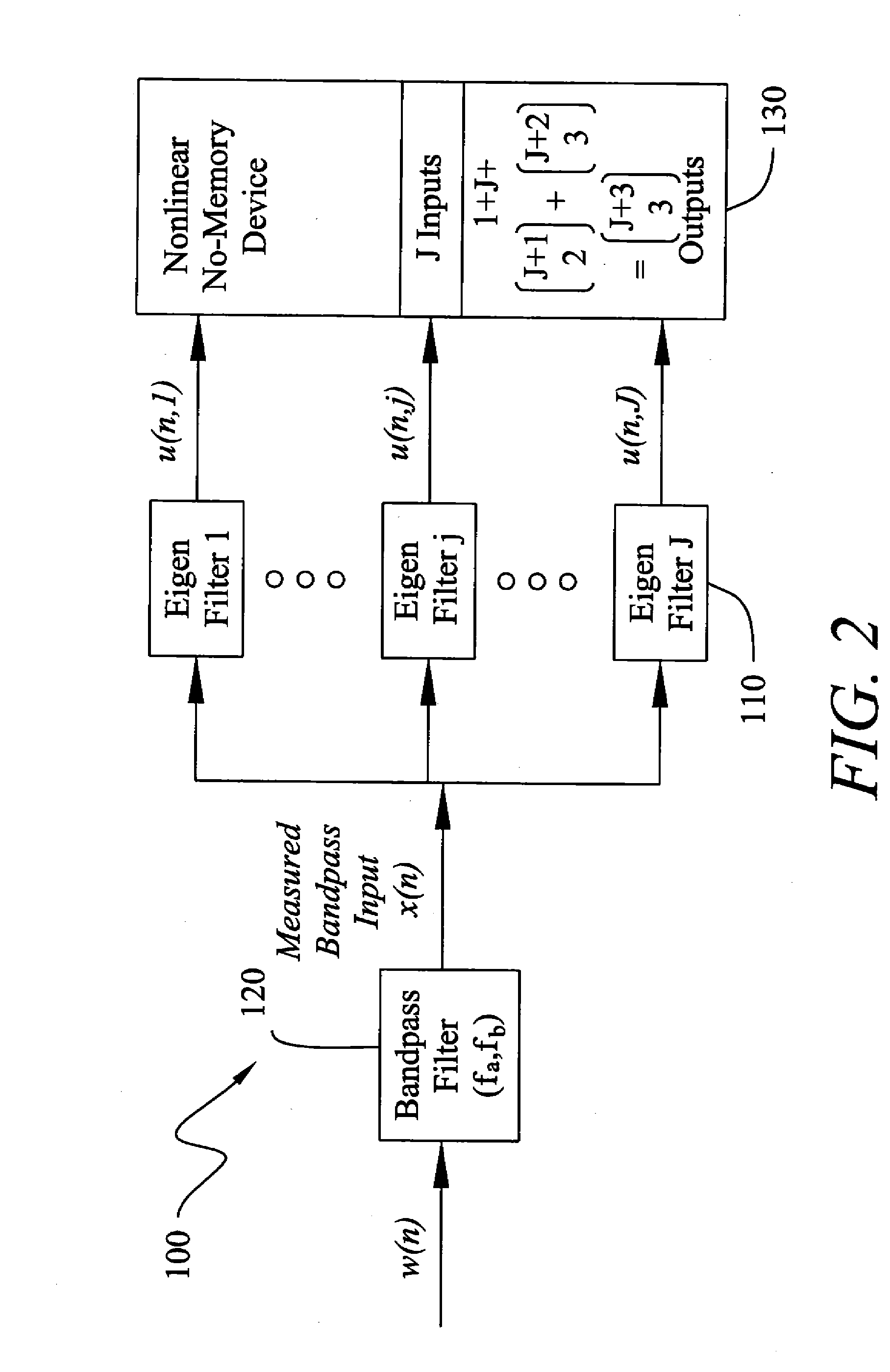
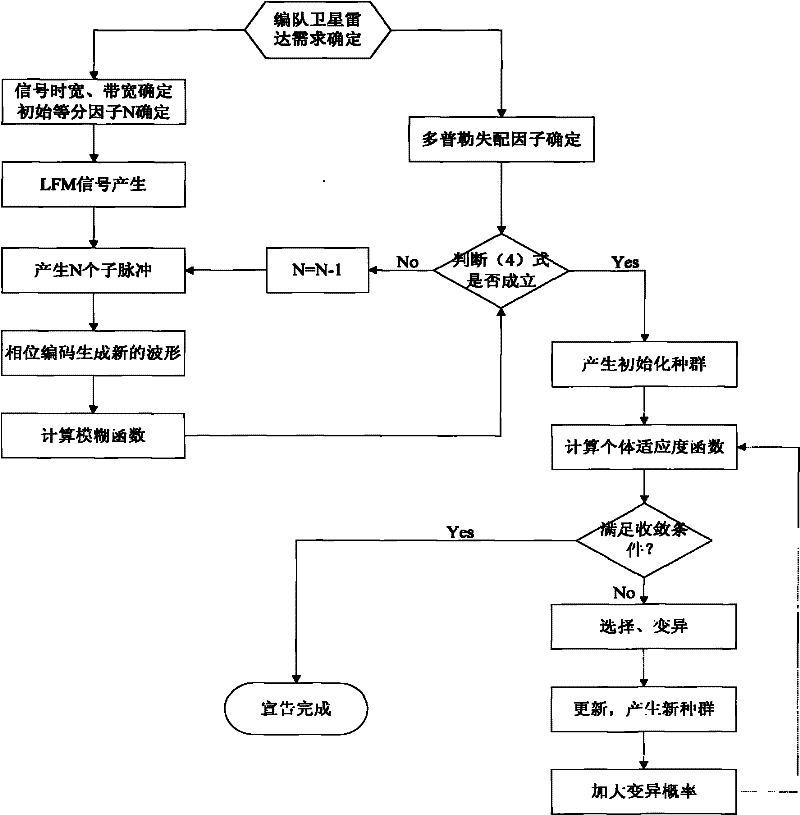
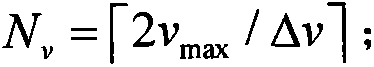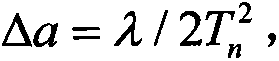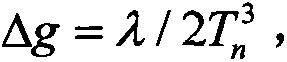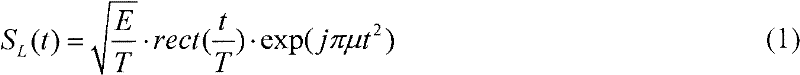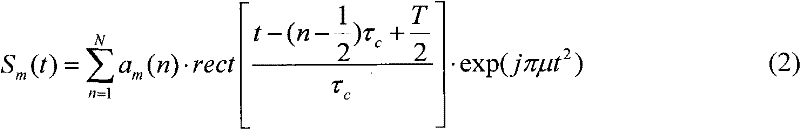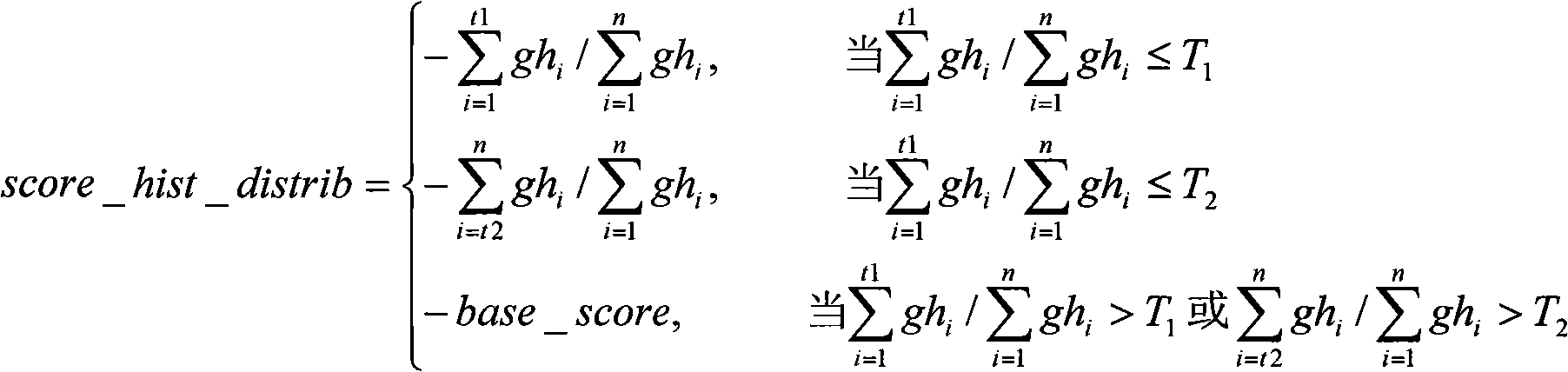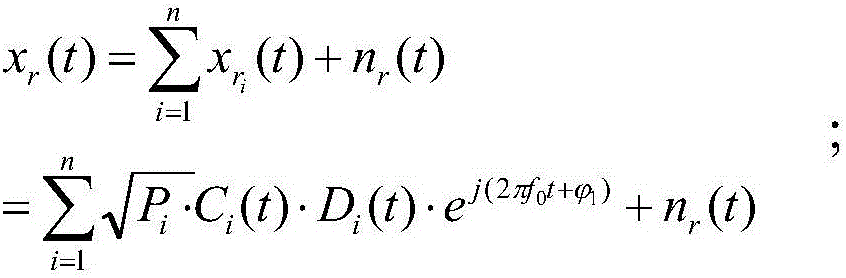Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
147 results about "Ambiguity function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
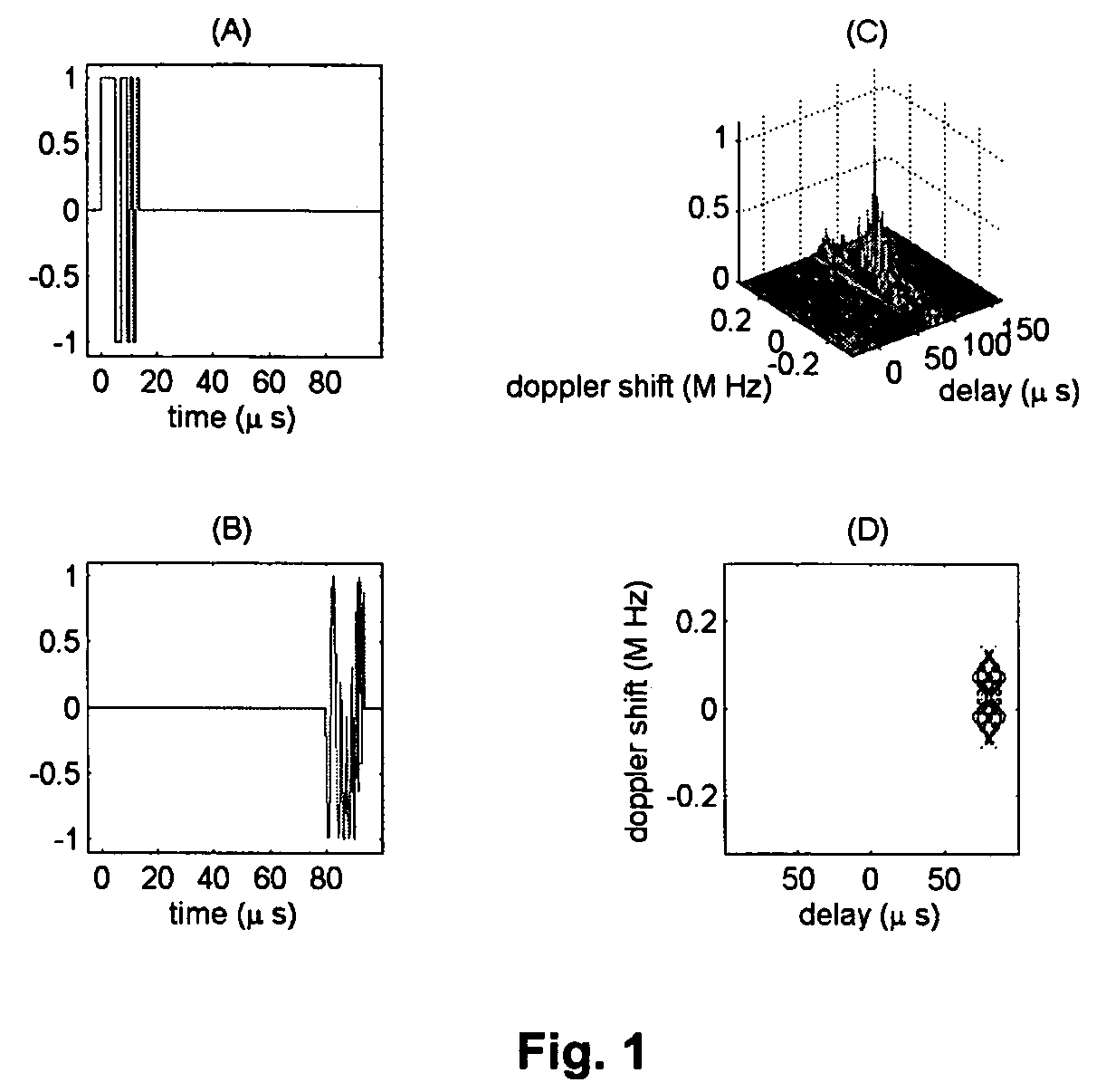
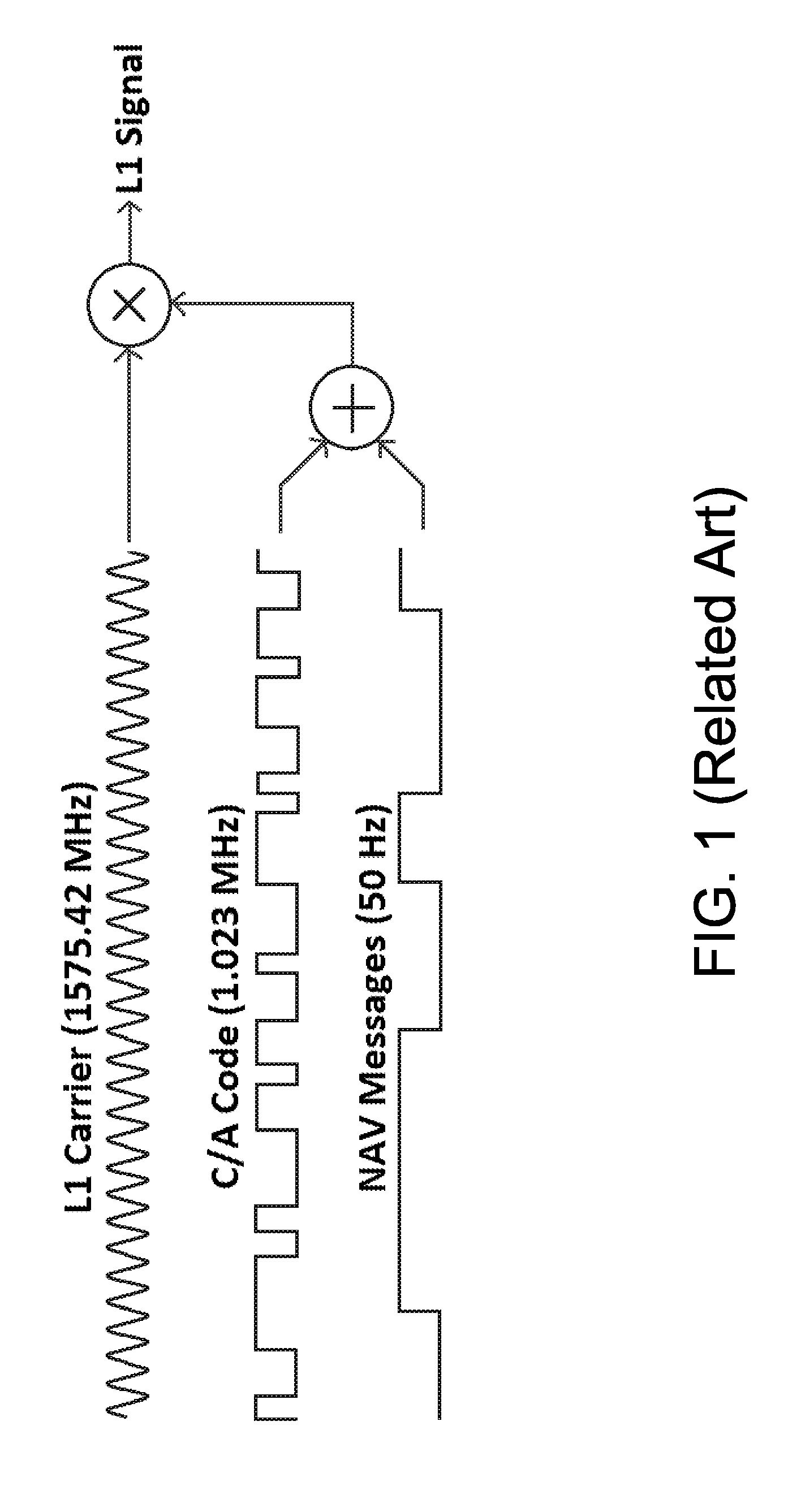
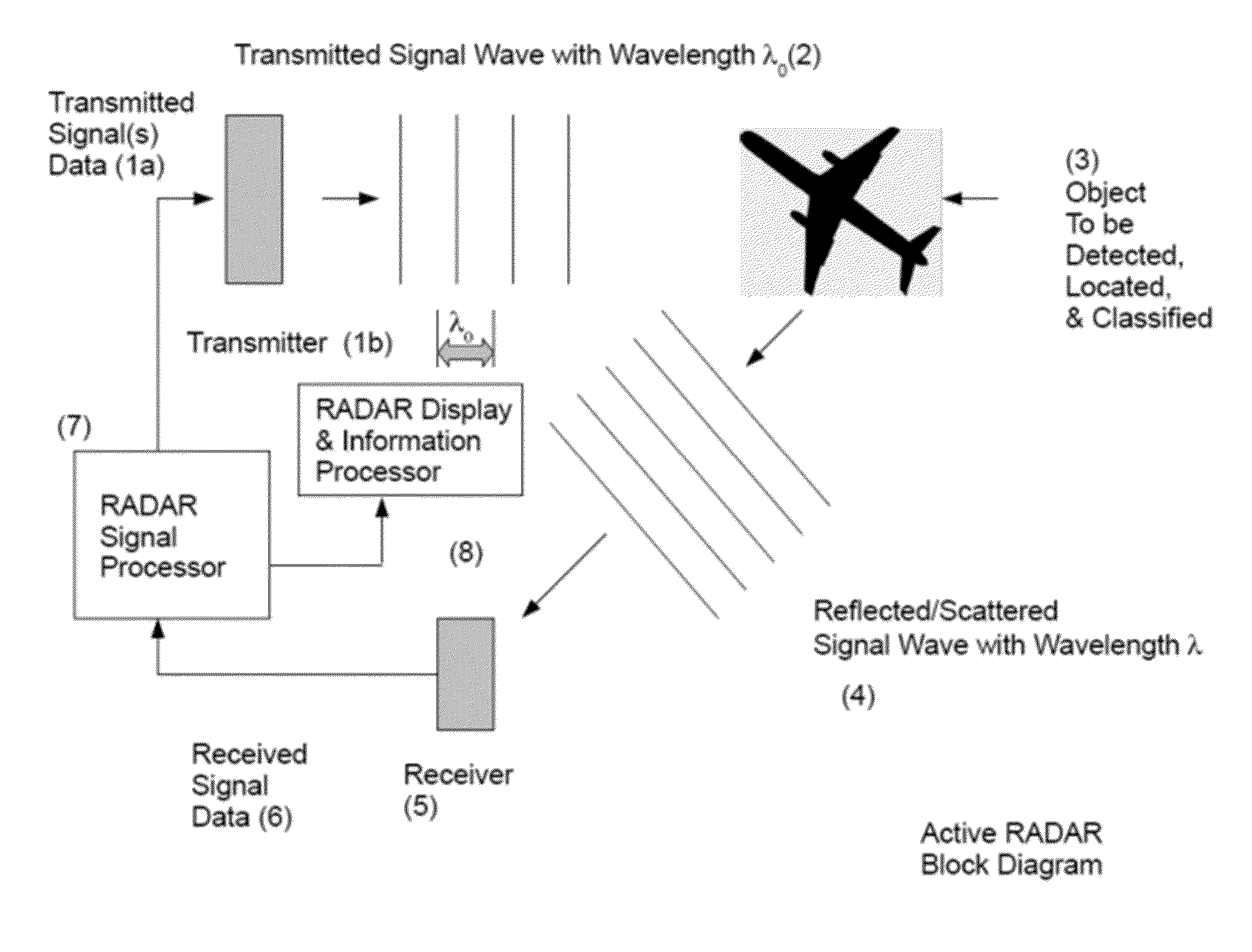
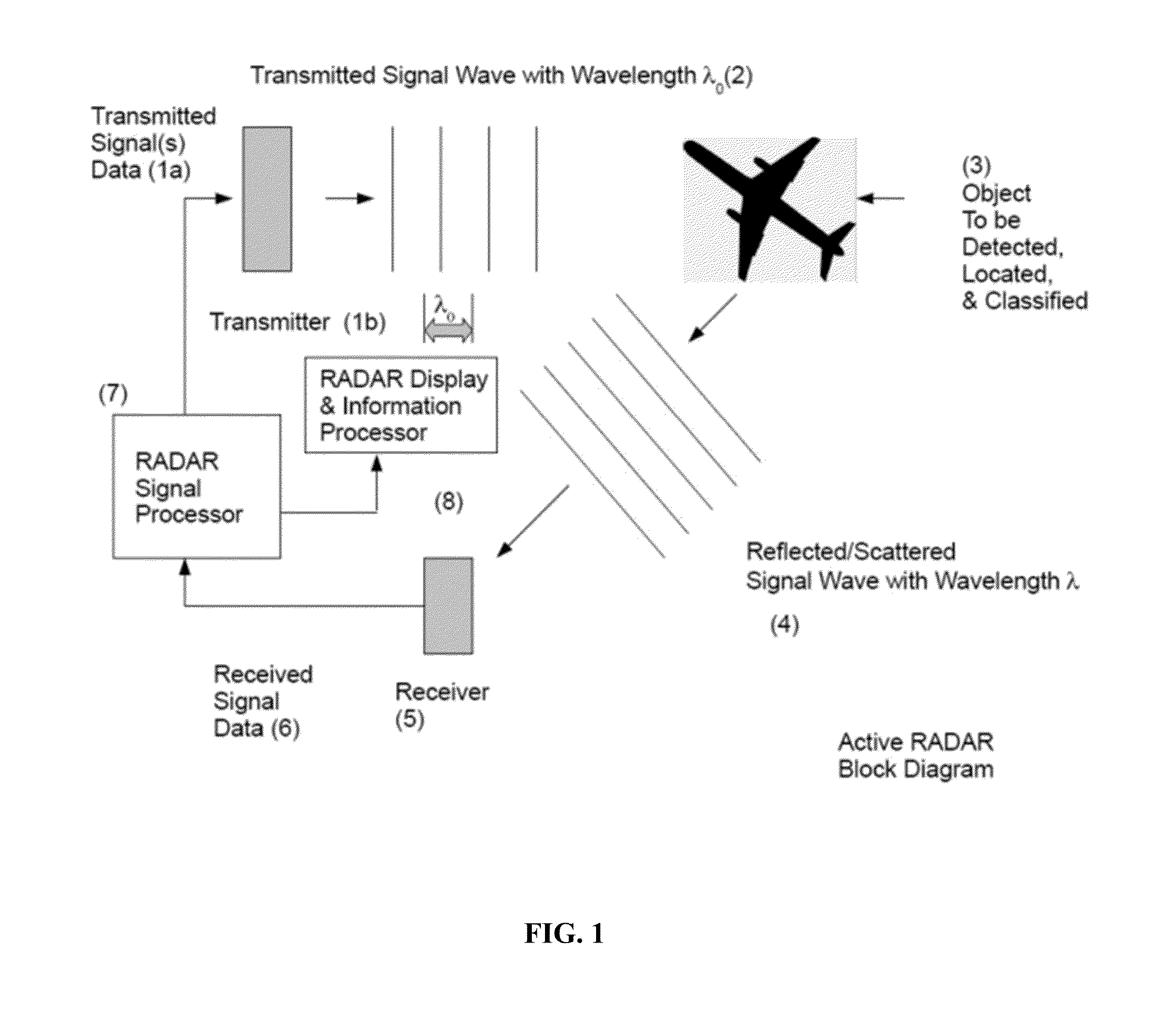
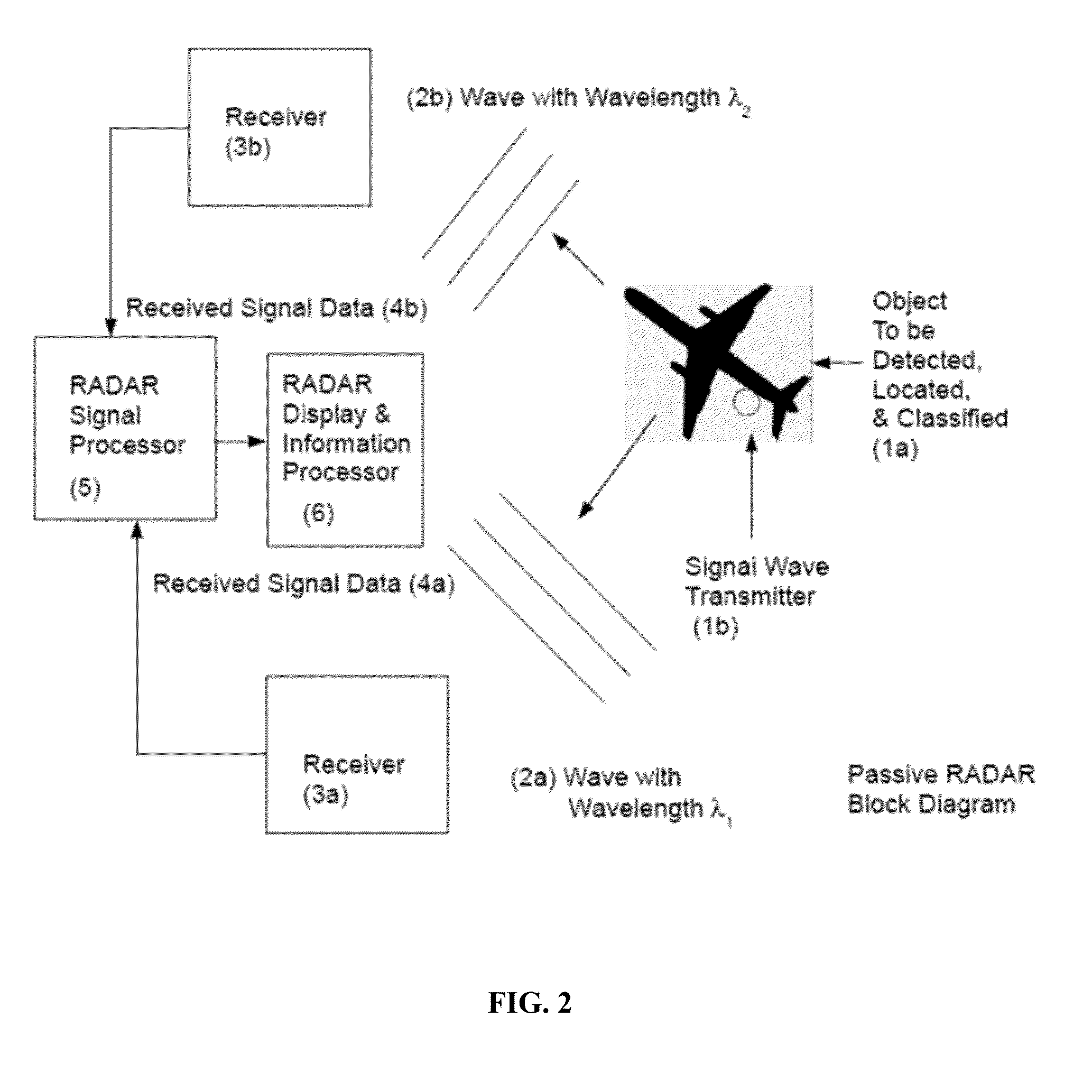
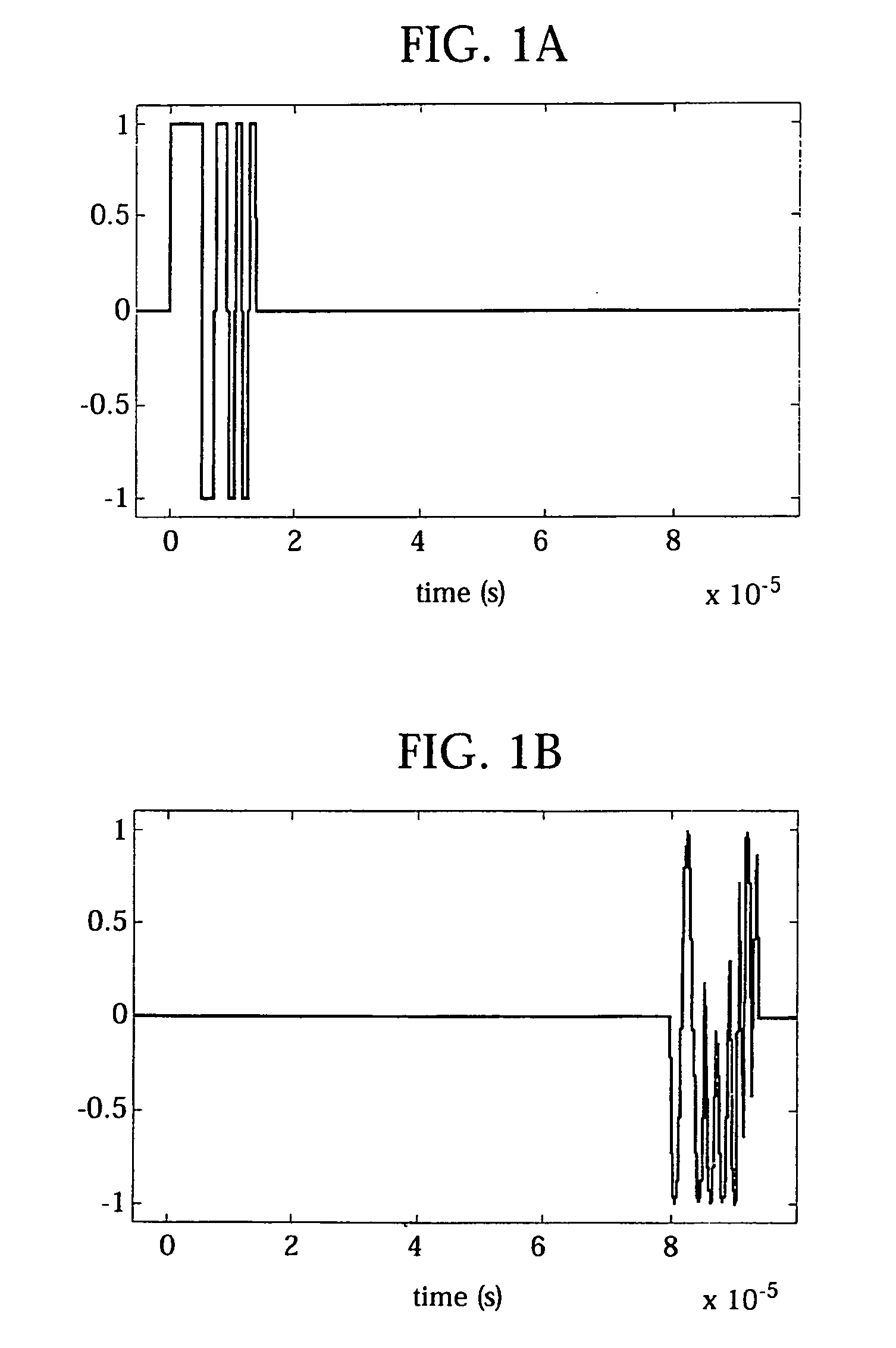
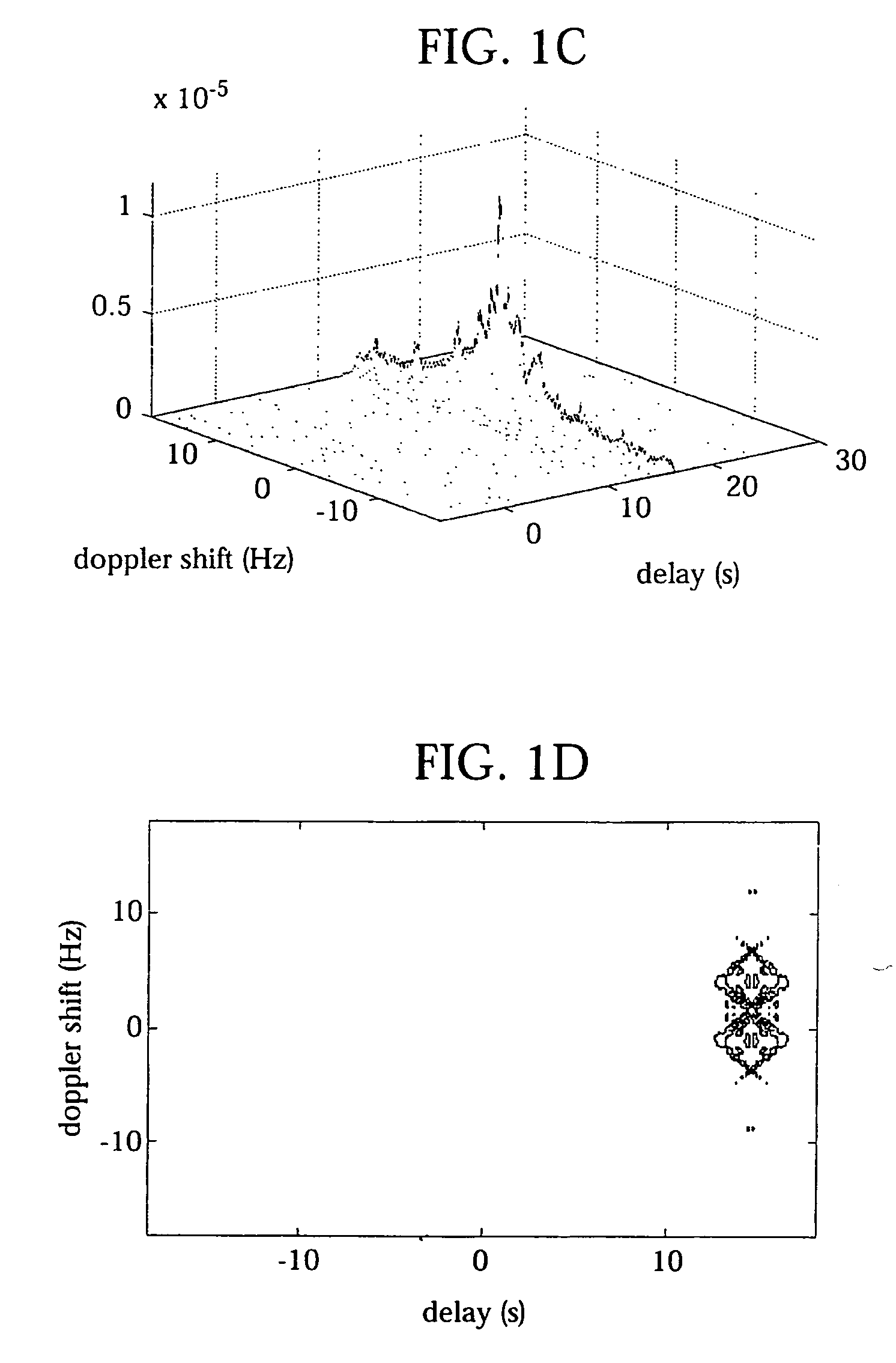
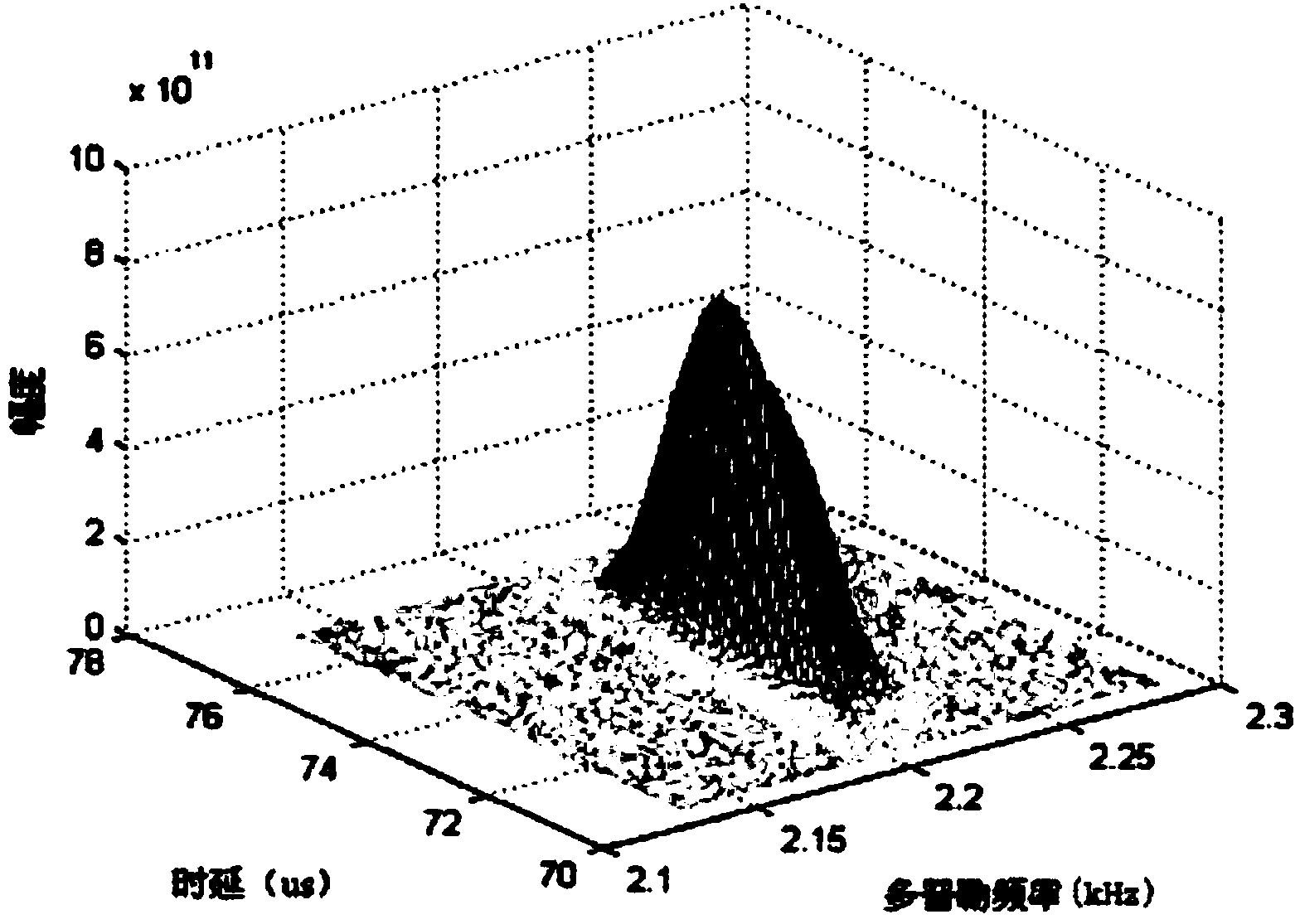
In pulsed radar and sonar signal processing, an ambiguity function is a two-dimensional function of time delay and Doppler frequency χ(τ,f) showing the distortion of a returned pulse due to the receiver matched filter (commonly, but not exclusively, used in pulse compression radar) due to the Doppler shift of the return from a moving target. The ambiguity function is determined by the properties of the pulse and the matched filter, and not any particular target scenario.
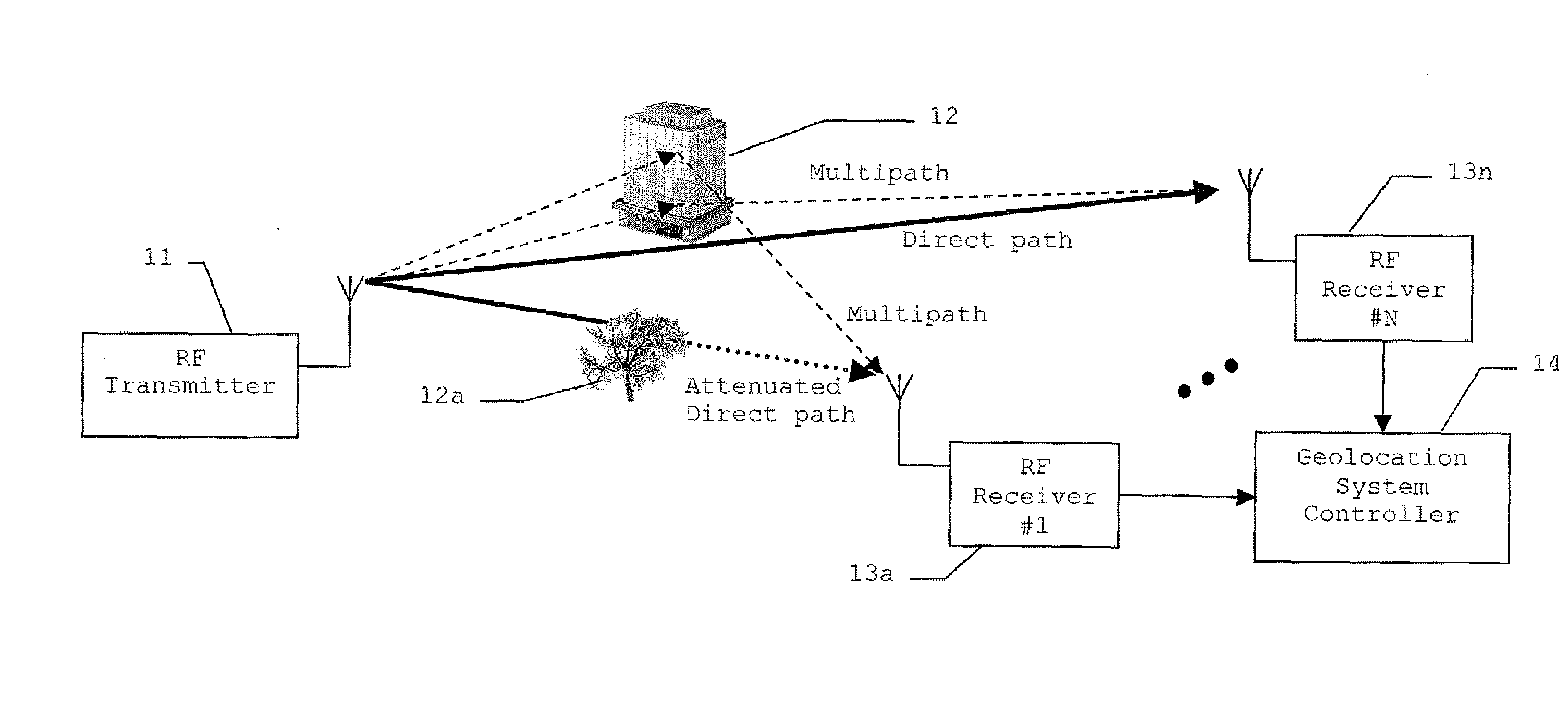
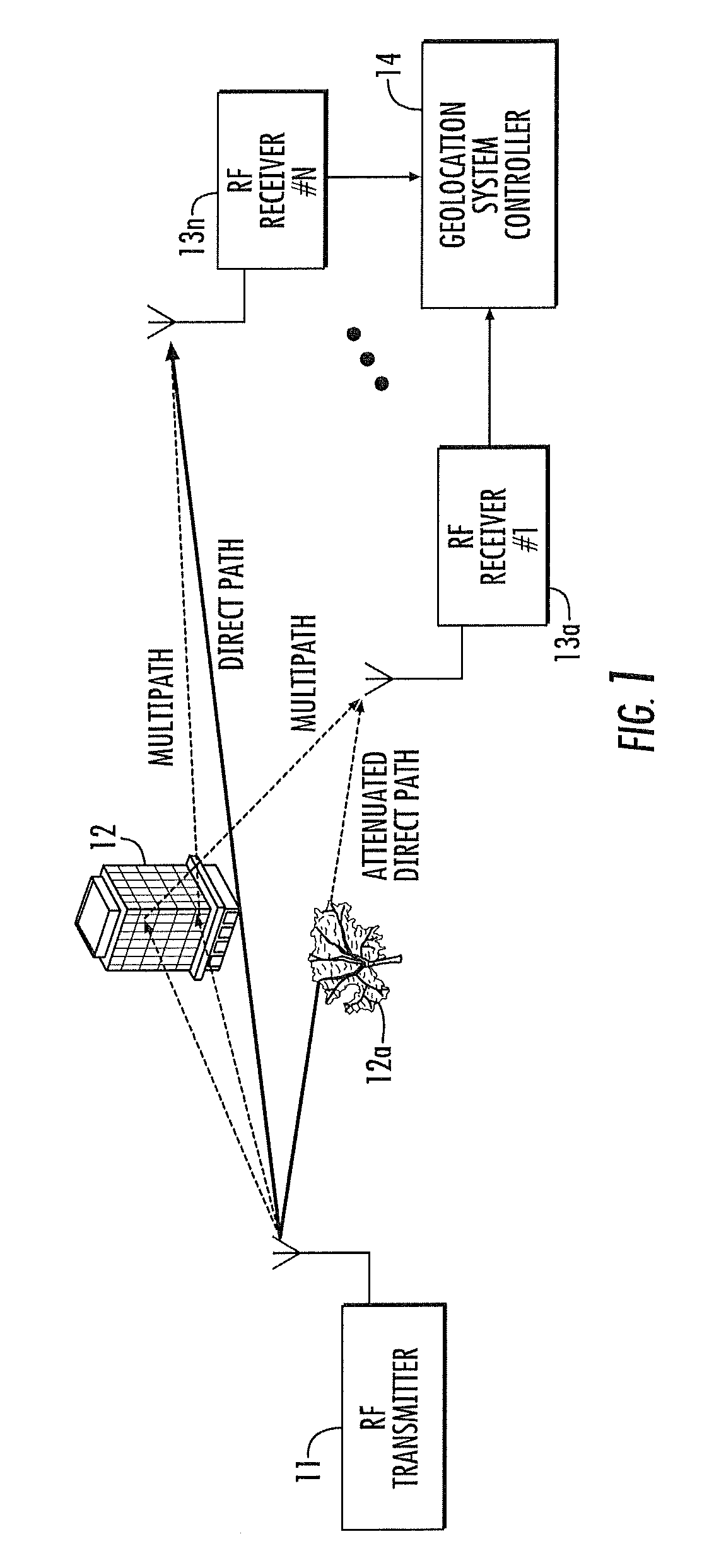
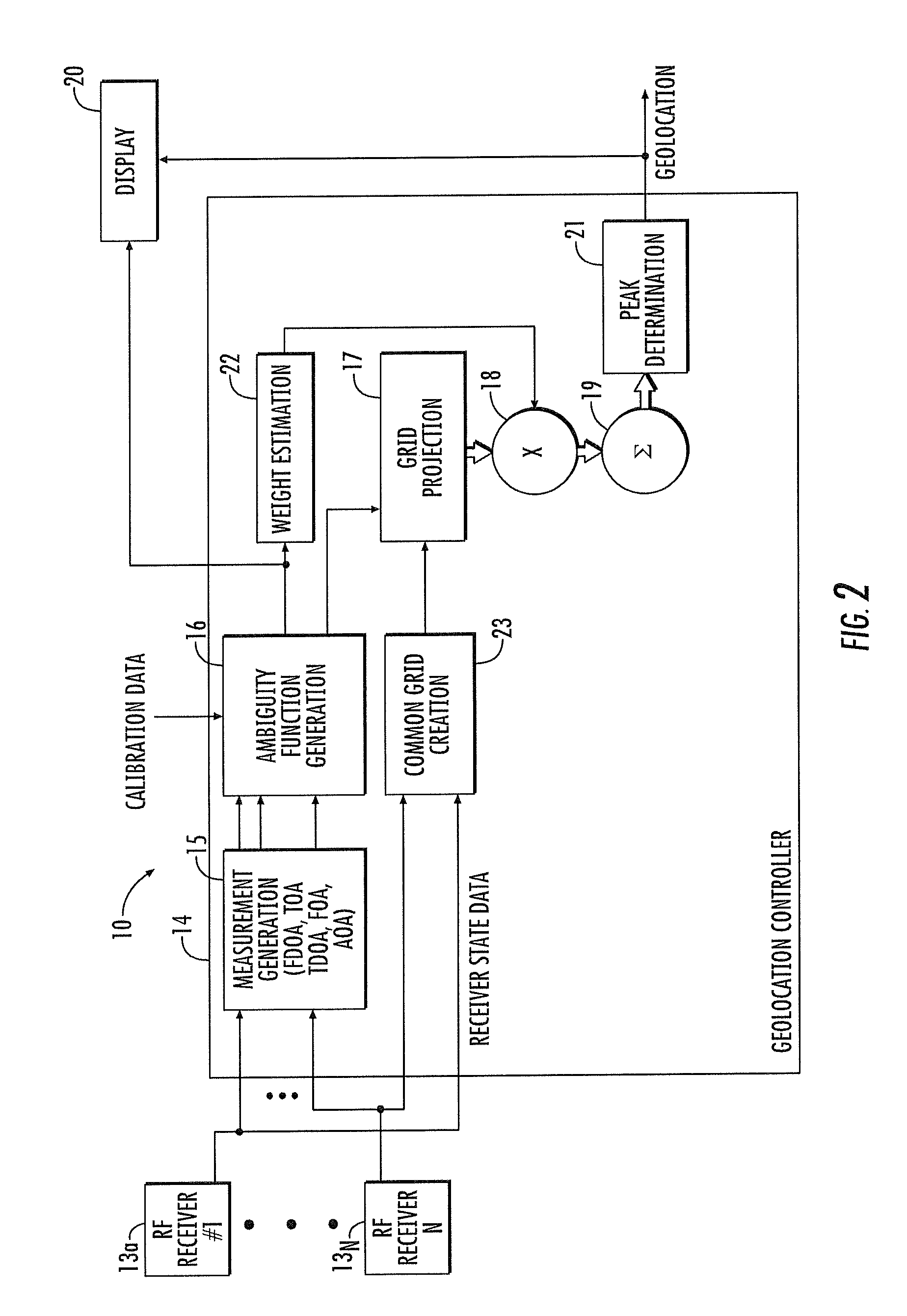
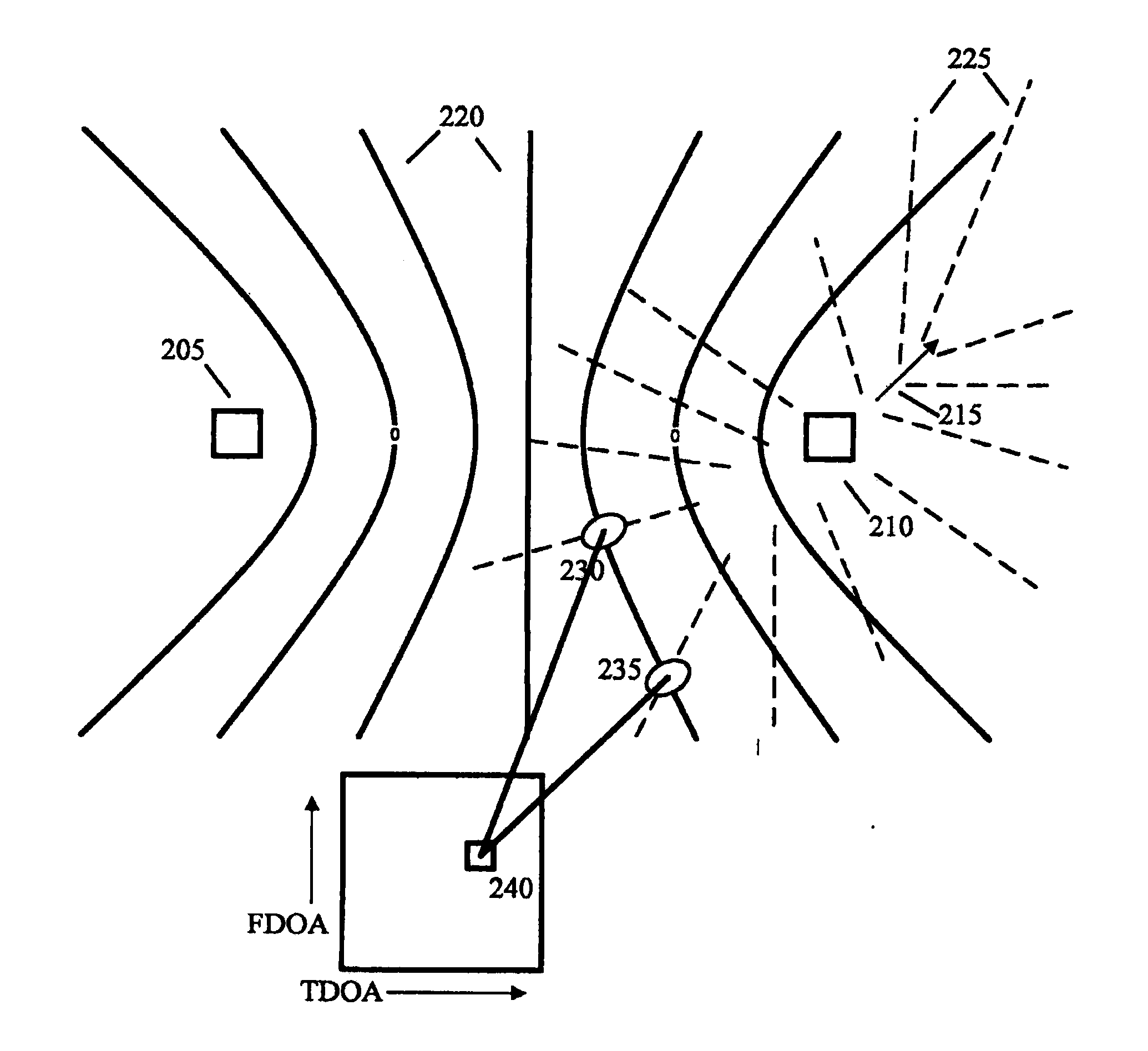
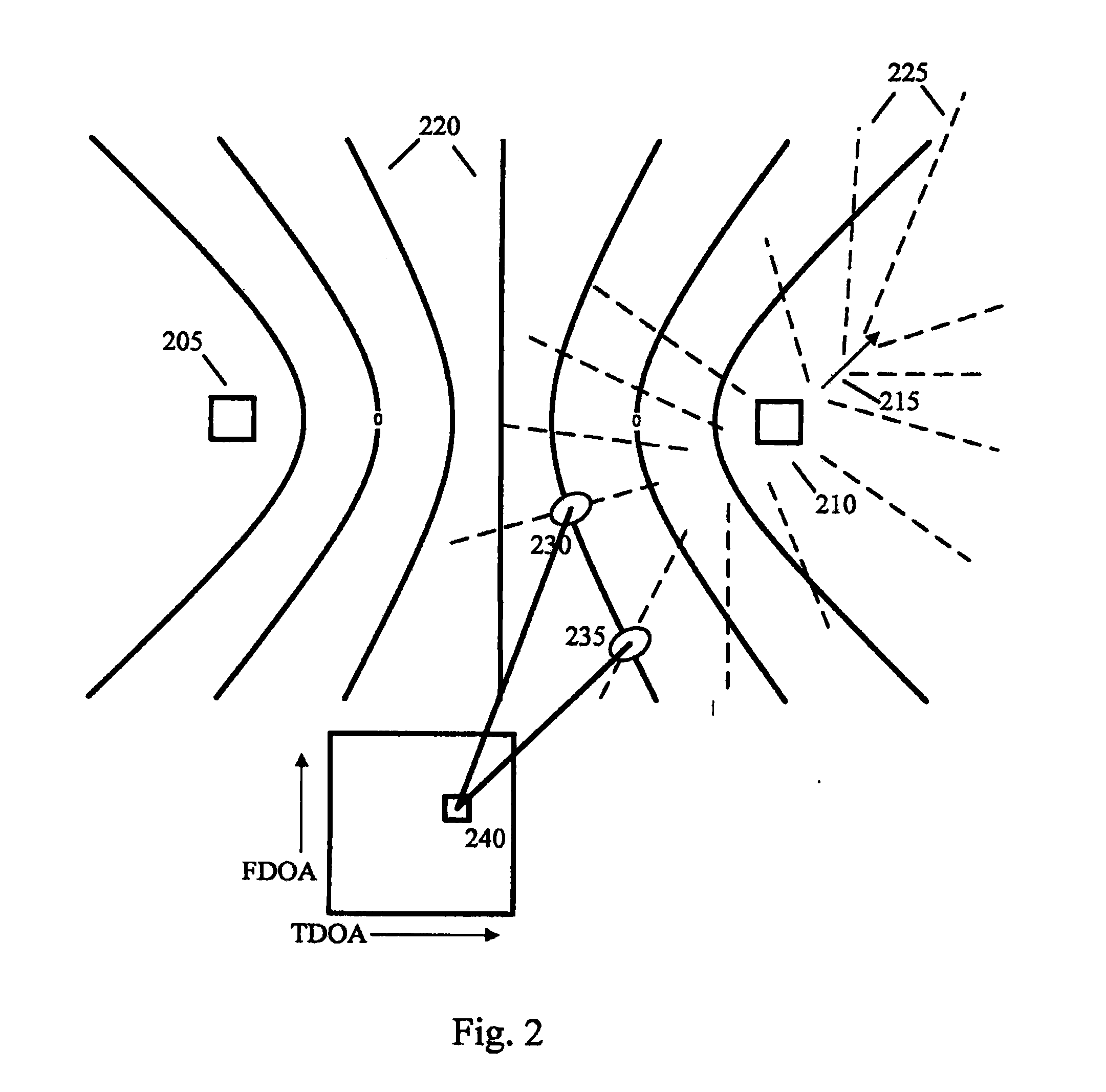
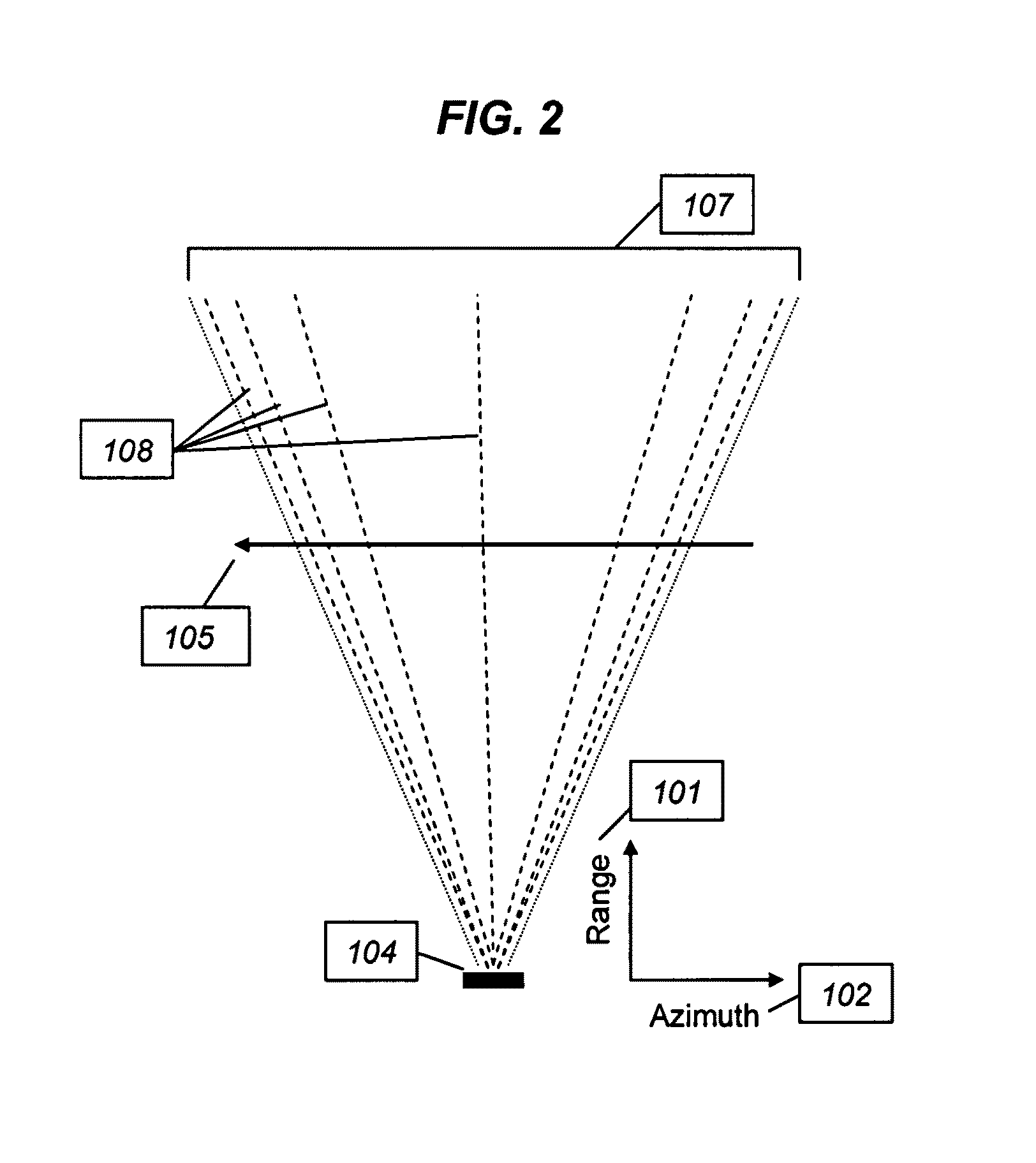
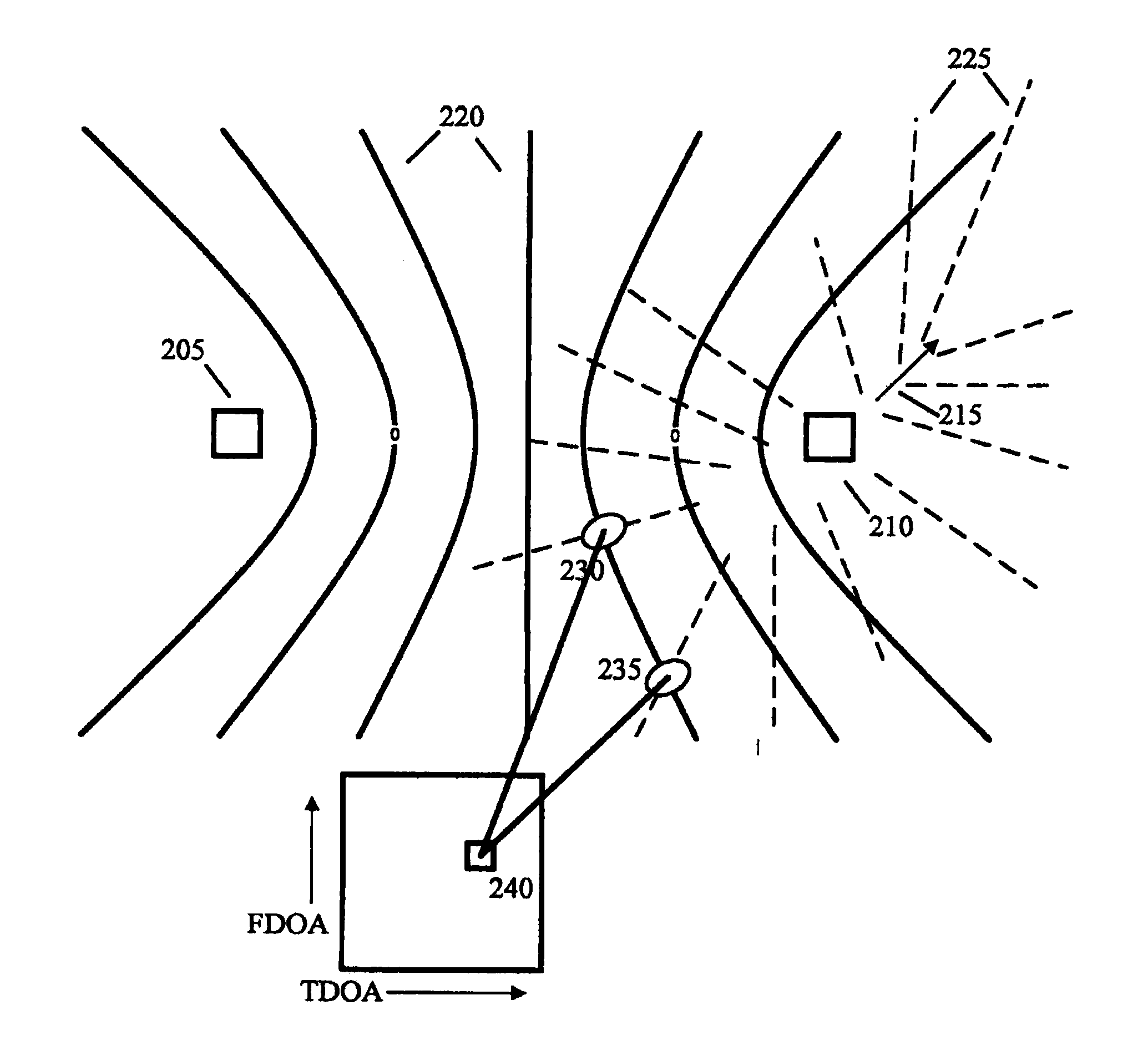
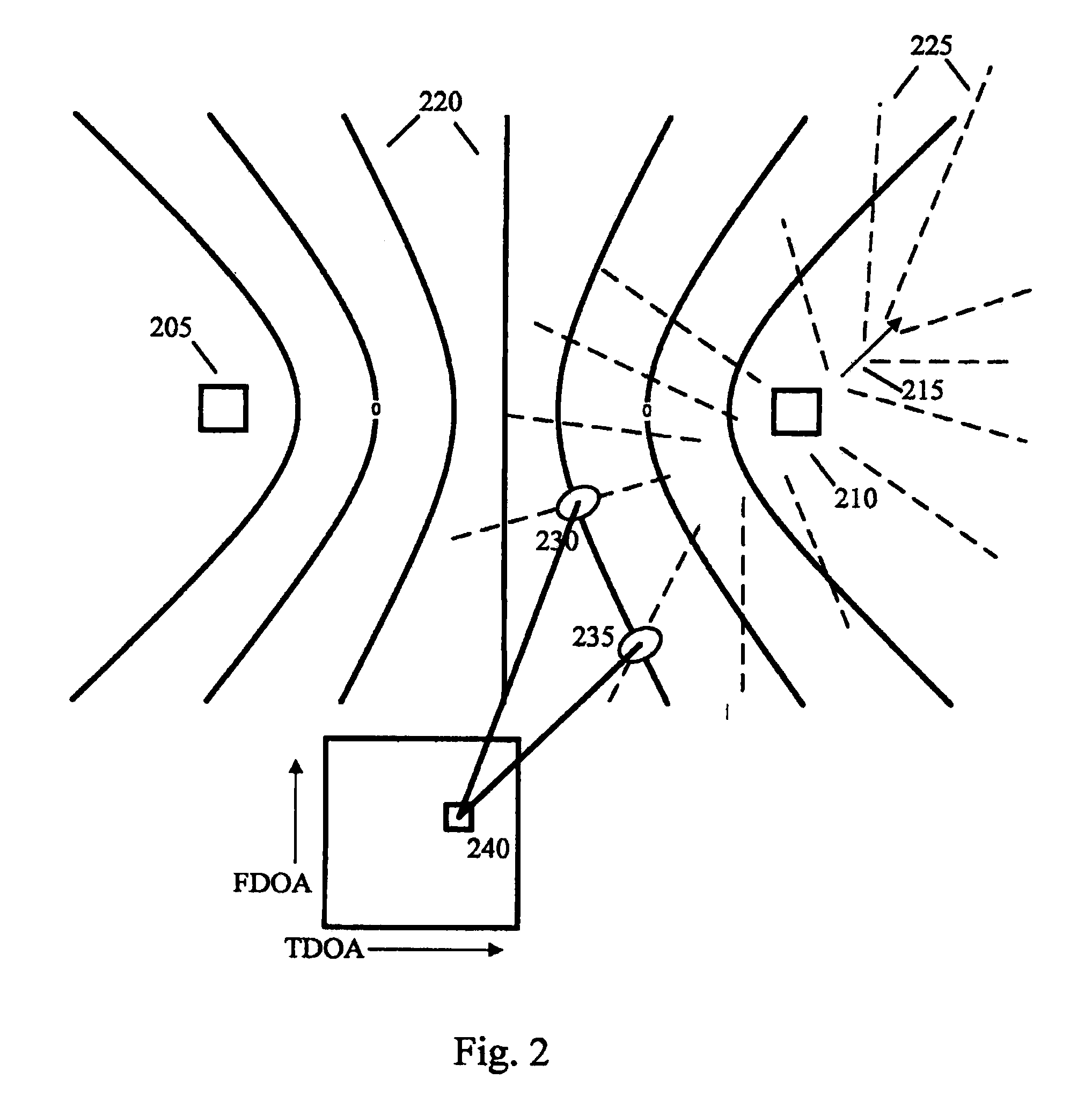
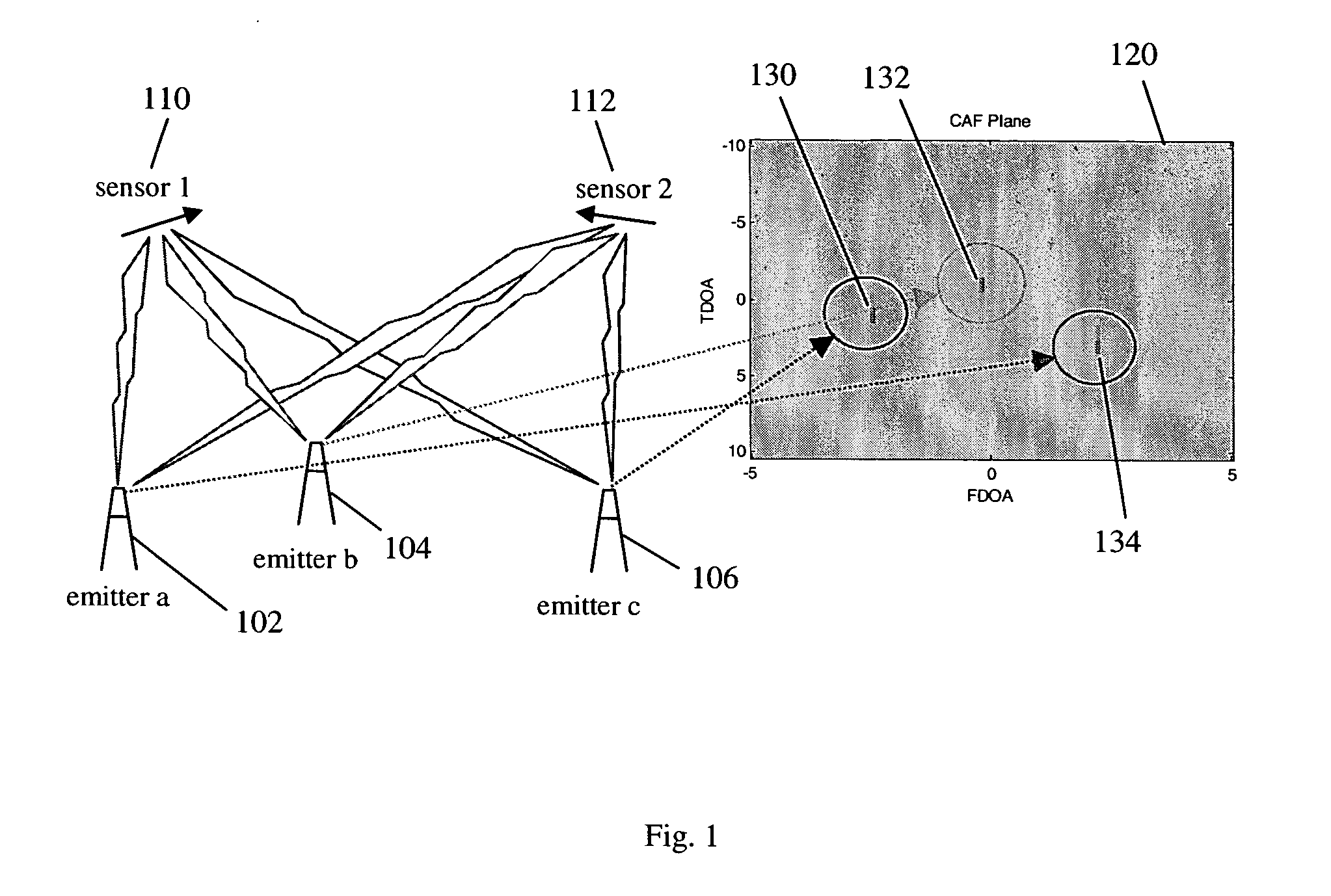
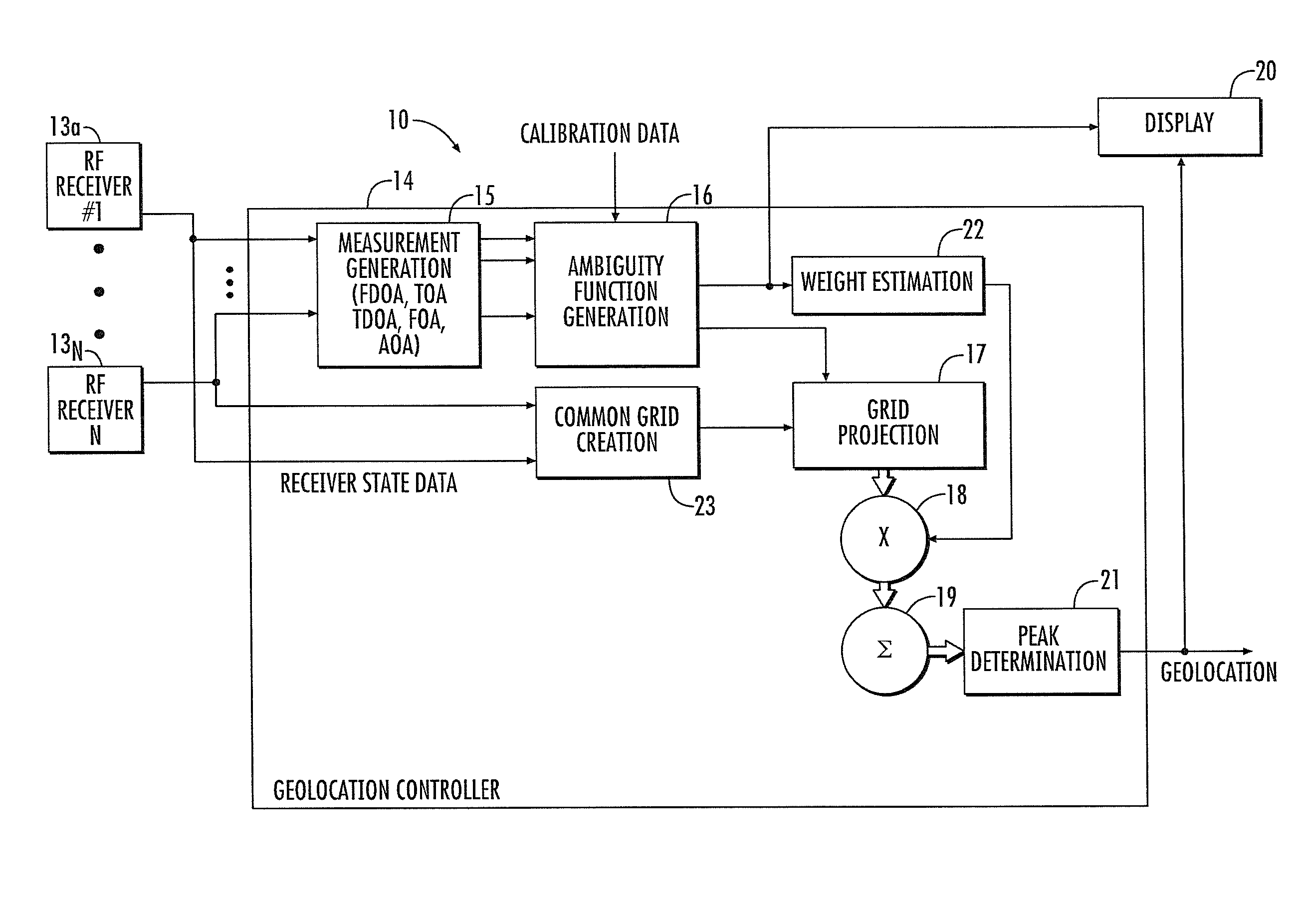
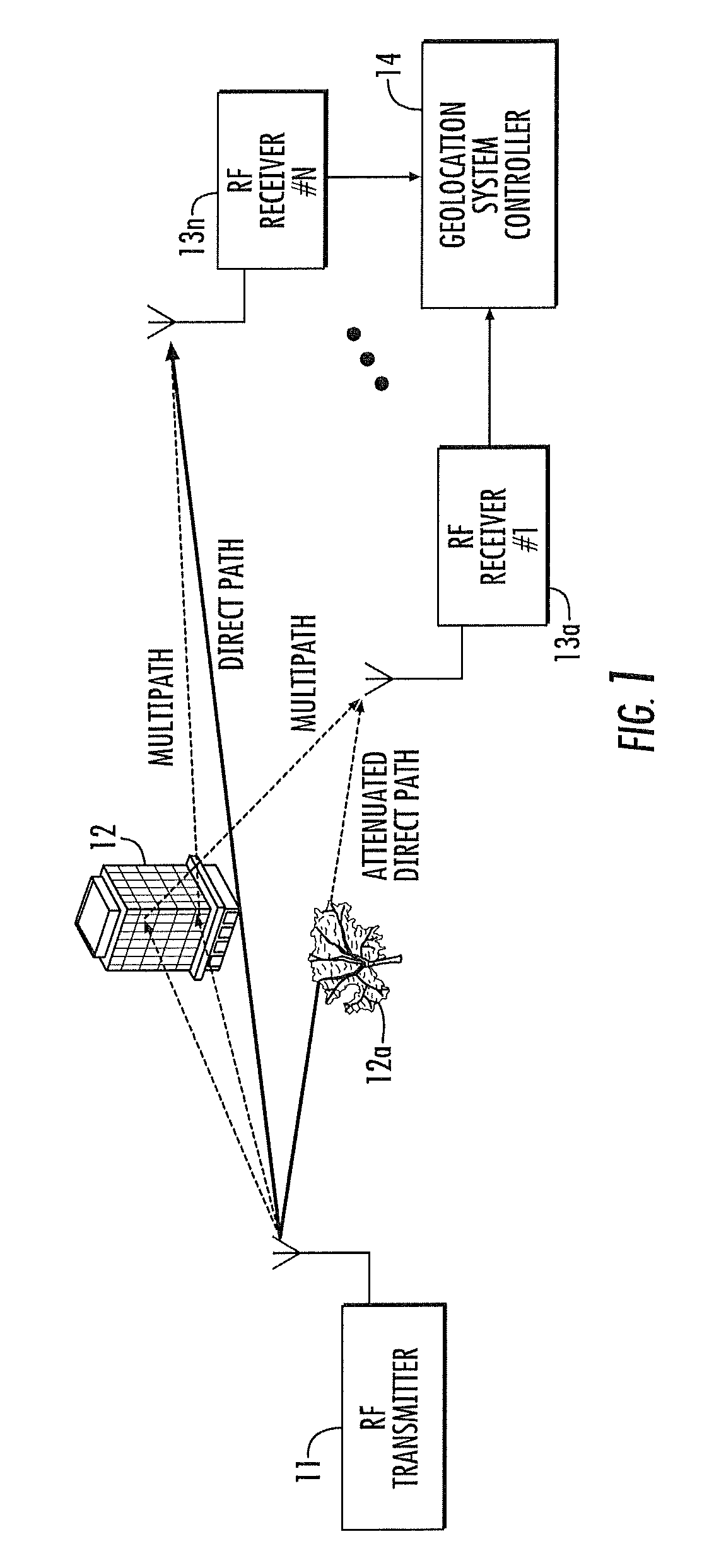
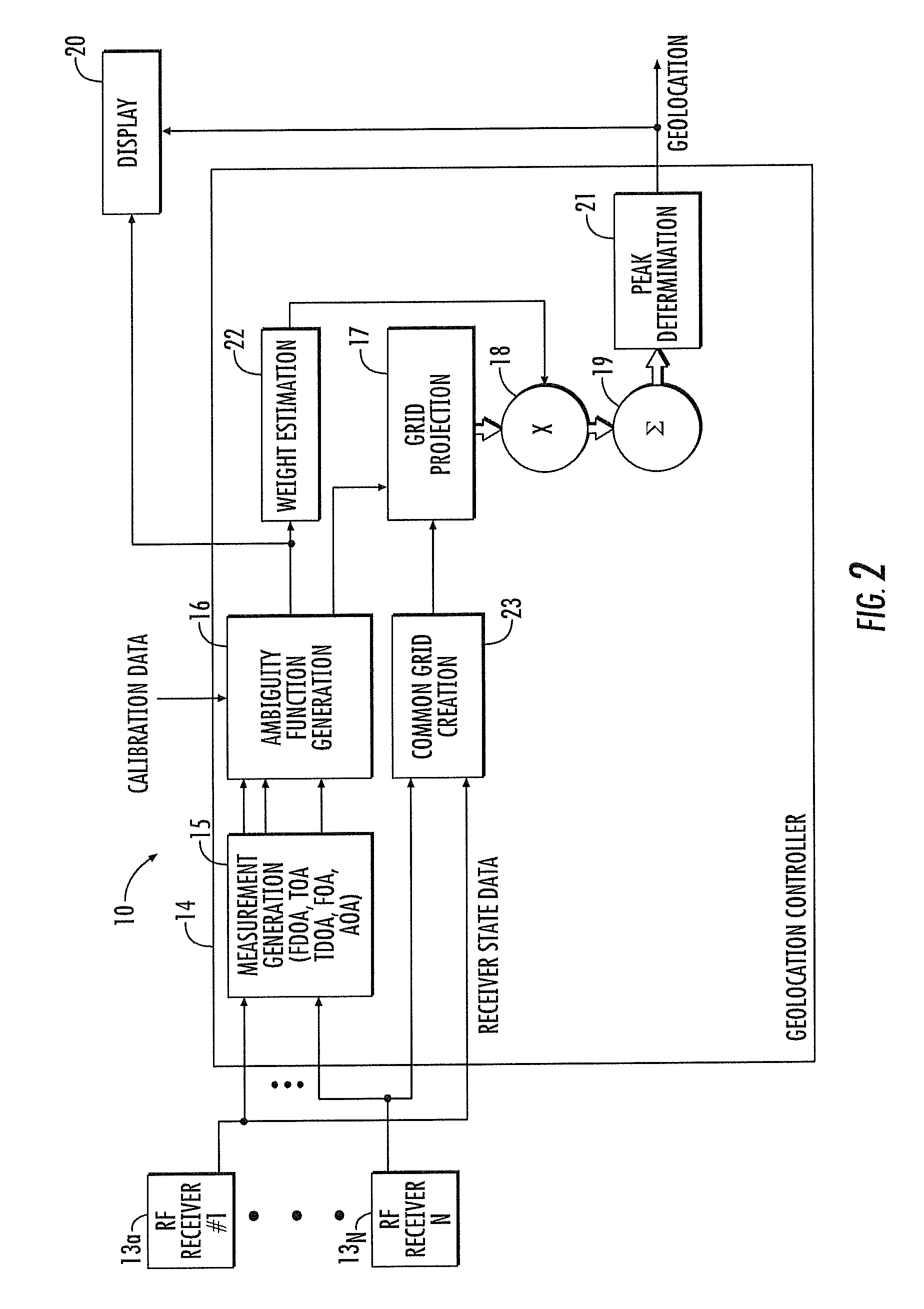
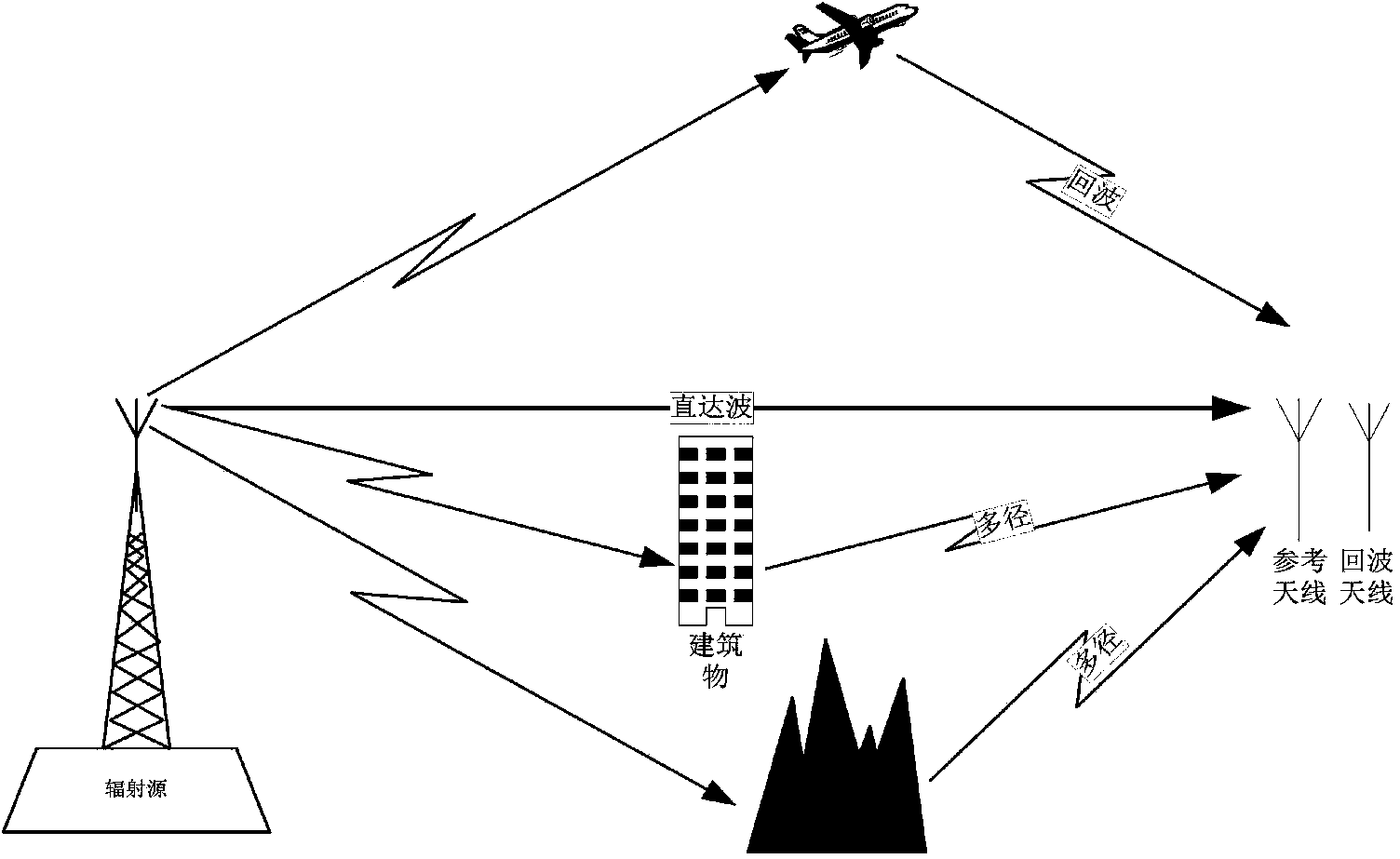
RF transmitter geolocation system and related methods
InactiveUS20100220011A1Improve accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesMultipath interferenceAmbiguity
A system for geolocating a radio frequency (RF) transmitter in the presence of multipath interference may include a plurality of RF receivers arranged in spaced relation. The system may also include a controller coupled to the plurality of receivers and configured to generate a plurality of measurements associated with the RF transmitter. The controller may also compute a plurality of ambiguity functions based upon the plurality of measurements and due to the multipath interference, and project the plurality of ambiguity functions onto a common geo-referenced grid. The controller may also detect a peak on the common geo-referenced grid indicative of a geolocation of the RF transmitter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
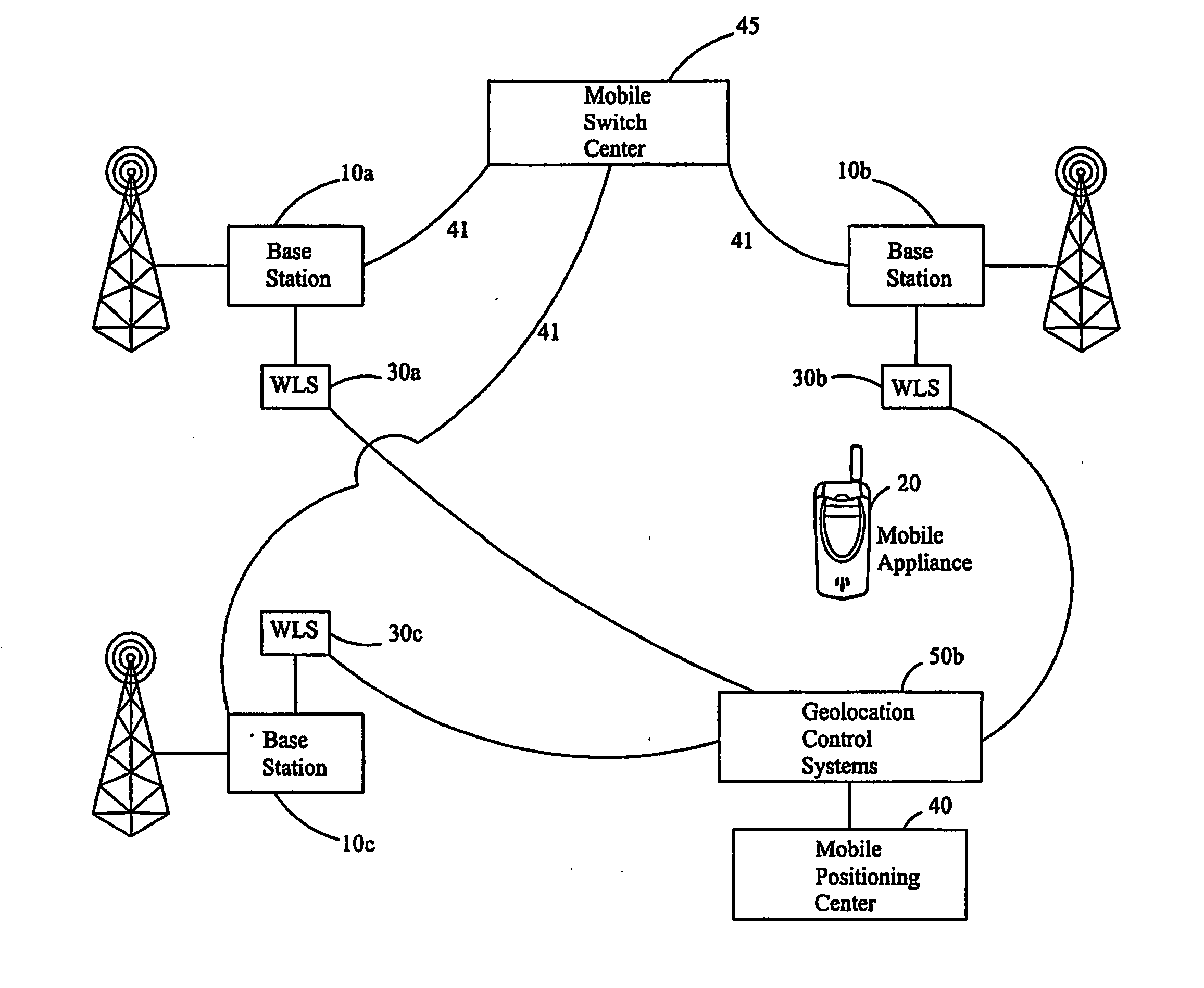
Method For Sparse Network Deployment Accuracy Enhancements
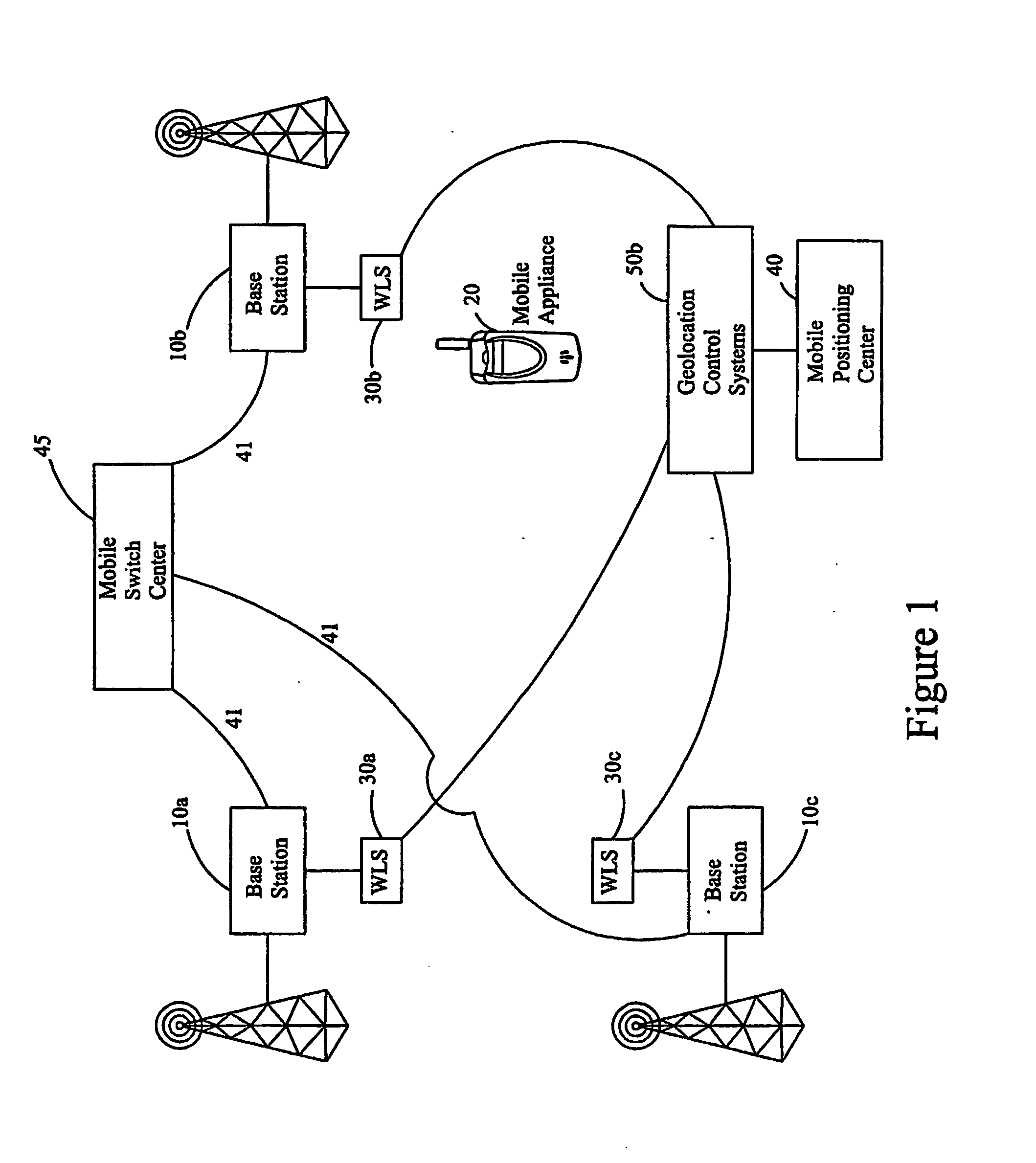
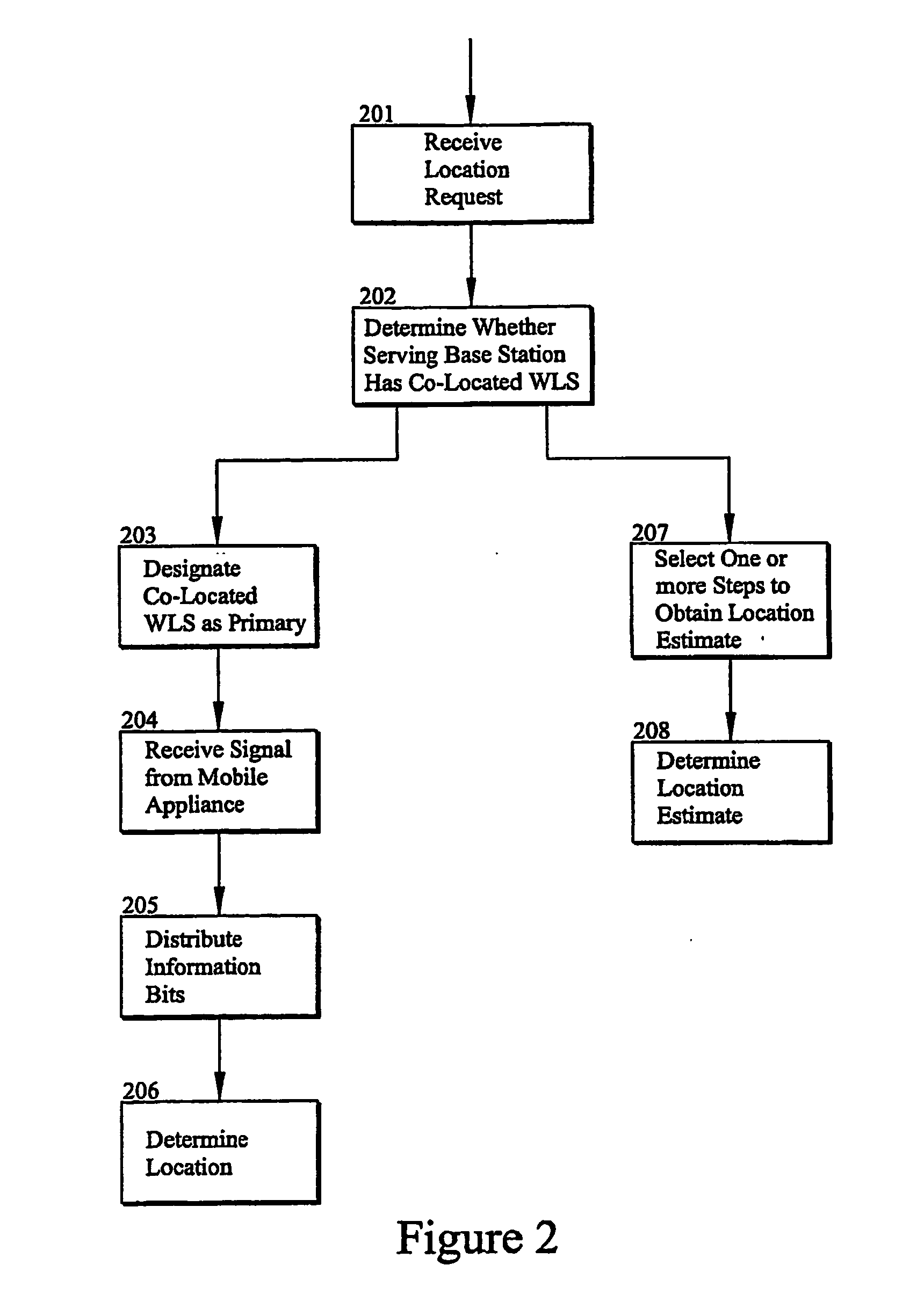
A method for use in a wireless communication system with a network overlay geolocation system having a sparse deployment network in which base stations of the wireless communication system may or may not have a co-located wireless location sensors (WLS). The method enables detection and measurement of a target mobile's signal independently from a primary WLS located at the base station serving the target mobile, which enable location estimated in previous “no location” areas. The method selects based on predetermined criteria from one or more of several techniques that aid in the detection and determining a location for the target mobile. The method selects from timing advance, power levels, pattern matching, EOTD, speed, and pseudo range measurements to estimate the location of the mobile. The method also uses ambiguity function processing to detect the signal and measure an attribute of the signal.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
System and method for detection and discrimination of targets in the presence of interference
InactiveUS7474258B1Reduce and eliminates time delay-Doppler shift ambiguity trade-offReduce or eliminates the time delay-Doppler shift ambiguity trade-offRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmAmbiguity
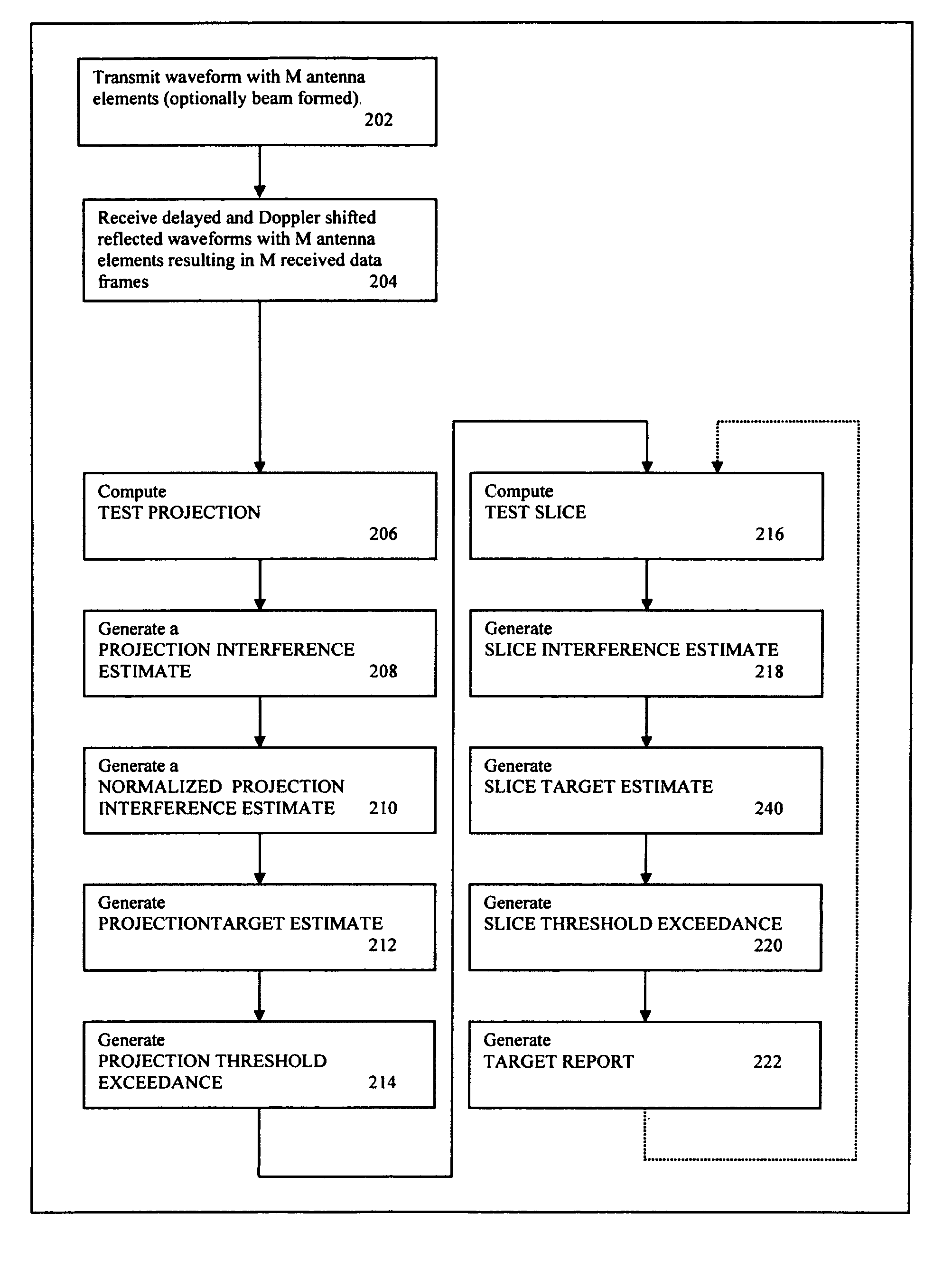
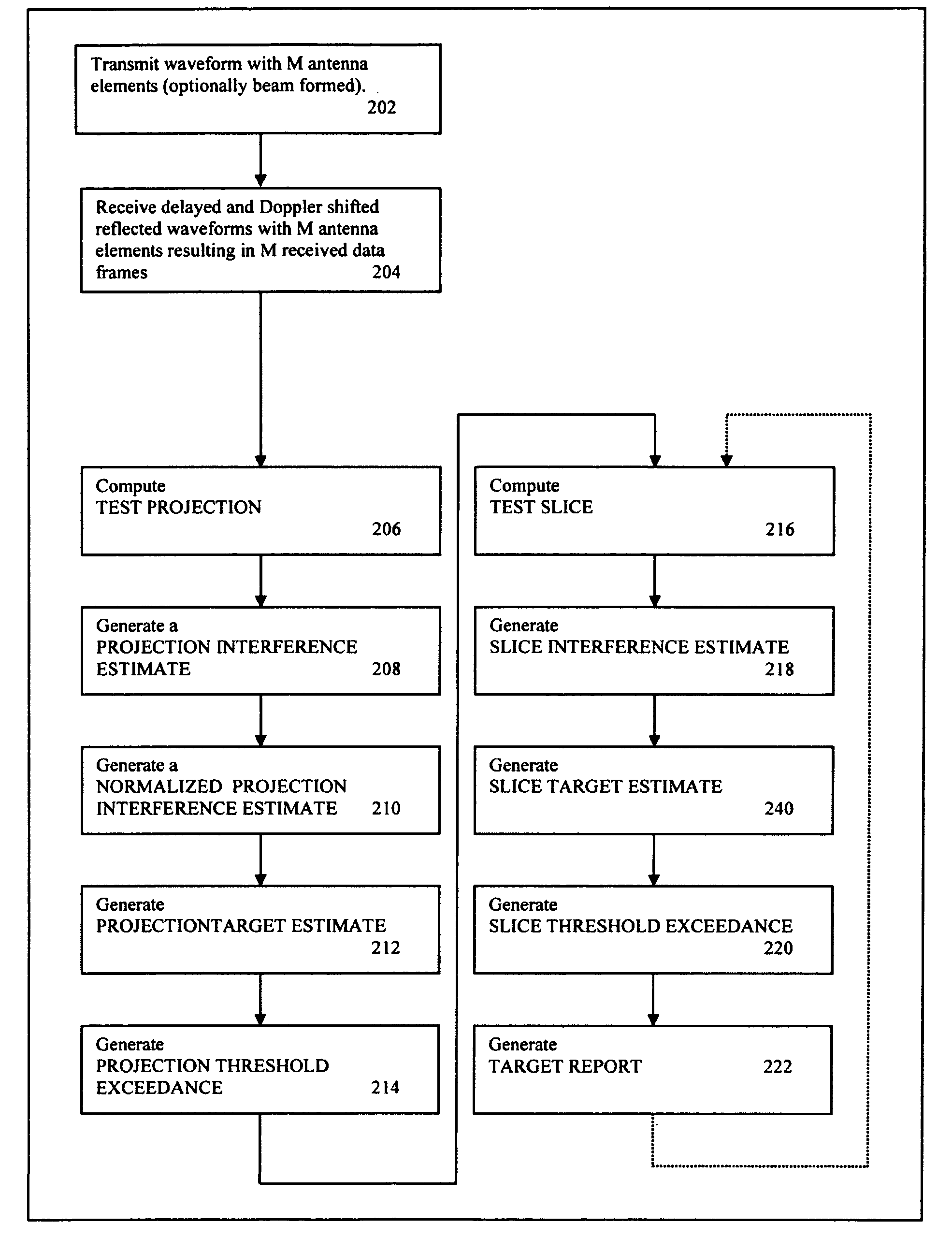
Systems and method of detection and discrimination of targets in the presence of interference are disclosed. A system transmits a signal and then receives signals including interference and reflections of transmitted signals. The system processes the received signals and transmitted signals to generate a 2D representation of the STAP cube with one of the dimensions collapsed. The system then reduces the interference contributions and identifies angle and Doppler component of potential targets. The system then computes slices, which are one dimensional representation of cross-ambiguity functions of the received and transmitted signals. It reduces the interference contributions in the slices and determines range components of the targets.
Owner:SIGNAL LABS
Methods for detection and tracking of targets
InactiveUS7317417B2Efficient and reliable detectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal correlationSignal delay
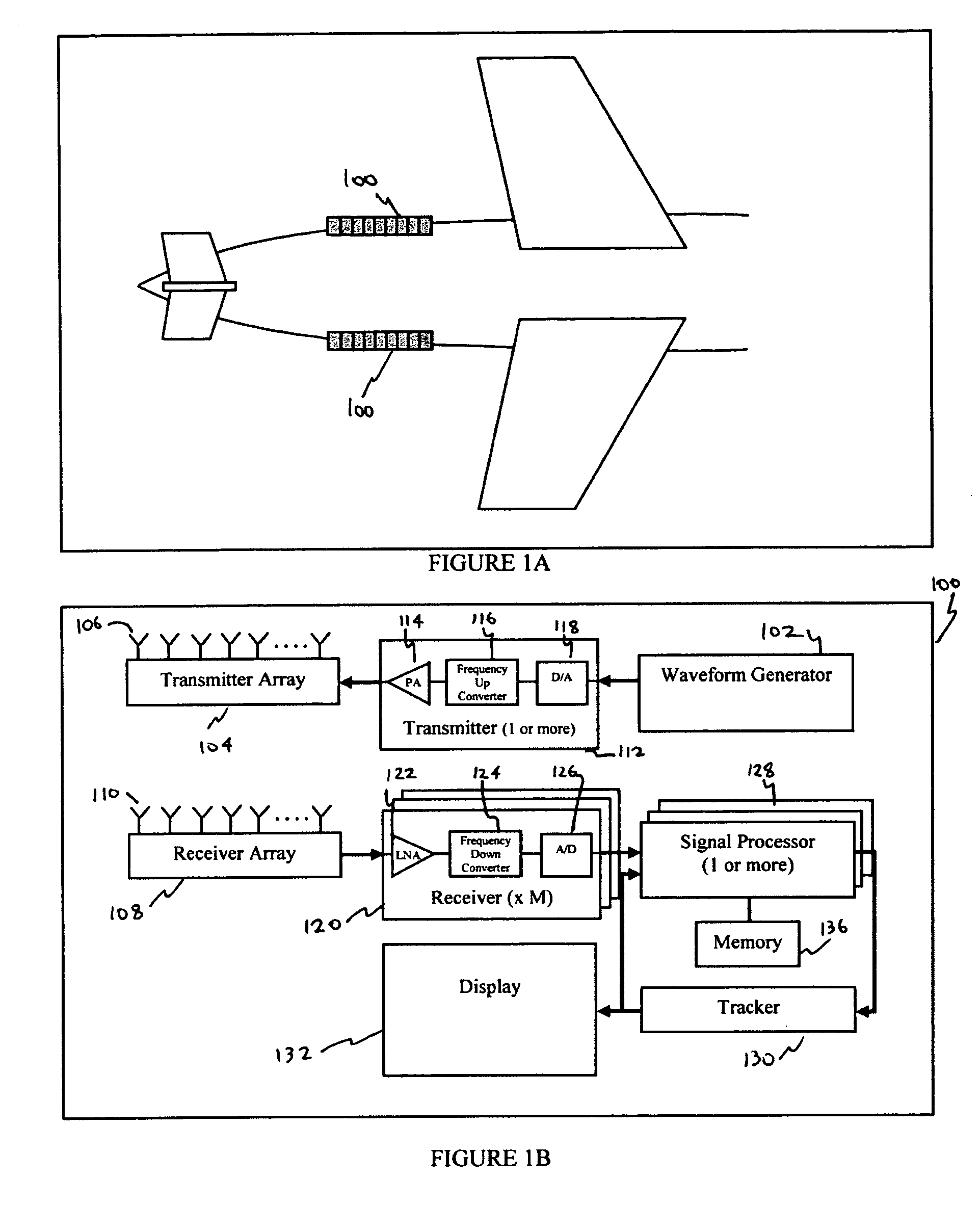
The present invention relates to active sensor applications, and more particularly is directed to efficient systems and methods for detection and tracking of one or more targets. The invention provides a method for receiving signals reflected from one or more targets, processing the received signals and the transmitted signal to compute two or more slices of the cross ambiguity function associated with the signals, and estimating the signal delay and the Doppler shit associated with the targets from the computed slices.
Owner:SIGNAL LABS
Method and system for high-accuracy differential tracking of global positioning system (GPS) receivers
Aspects of the present invention relate to methods and systems for high-accuracy differential tracking of global positioning system (GPS) receivers. In one embodiment, a network having multiple receivers is provided. The receivers are configured to communicate with each other. The receivers in the network are configured to measure raw satellite data, and to share the raw satellite data measured by each receiver. Each receiver is configured to process the measured raw satellite data with a Peak Ambiguity Function Value (AFV) Tracking Solution (PATS) to track relative motions of the neighboring receivers so as to derive relative location information for the plurality of receivers.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
System and method for detection and discrimination of targets in the presence of interference
InactiveUS20090027257A1Reduce or eliminates the time delay-Doppler shift ambiguity trade-offReduce peak power requirementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmAmbiguity
Systems and method of detection and discrimination of targets in the presence of interference are disclosed. A system transmits a signal and then receives signals including interference and reflections of transmitted signals. The system processes the received signals and transmitted signals to generate a 2D representation of the STAP cube with one of the dimensions collapsed. The system then reduces the interference contributions and identifies angle and Doppler component of potential targets. The system then computes slices, which are one dimensional representation of cross-ambiguity functions of the received and transmitted signals. It reduces the interference contributions in the slices and determines range components of the targets.
Owner:SIGNAL LABS
Beam phase modulation for improved synthetic aperture detection and estimation
InactiveUS20090066562A1Improve performanceSuppress ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSonificationSynthetic aperture sonar
Phase modulated beam patterns are substituted for the constant-phase versions that have been used in prior synthetic aperture systems. Relative movement between a radar / sonar / ultrasound platform and a point target causes a sequence of echoes from the point target to be phase and amplitude modulated by the beam pattern, as well as by the usual quadratic phase variation caused by range changes. Azimuth, range rate, and azimuth rate estimation, as well as detection in clutter, are substantially improved by appropriate beam pattern phase modulation, which is applied to the transmitter and / or receiver beam patterns. Phase modulated beam patterns are synthesized with array element weighting functions that are designed for high ambiguity function peak-to-sidelobe level, reduction of unwanted ambiguity ridge lines, and adequate spatial sampling. Two dimensional beam pattern phase modulation is useful when the relative motion between a transmit-receive array and multiple targets has both azimuth and elevation components.
Owner:CHIRP
Radar slightly-moving target detection method based on Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function
ActiveCN103344949AEfficient accumulationFlexible matchingWave based measurement systemsTarget signalPulse pressure
The invention relates to a radar slightly-moving target detection method based on a Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function (RLCAF) and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF comprises the following steps that (1) demodulation and pulse pressure are conducted on a radar echo in the distance direction so that in-pulse accumulation can be completed; (2) the type of a target to be detected is predicted, and parameters are initialized; (3) the distance and Doppler migration are compensated through the RLCAF and signal energy of a slightly-moving target is accumulated; (4) the parameters are traversed and searched, an RLCAF domain detection unit figure is established, and constant false-alarm detection is conducted; (5) target moving parameters are estimated and moving trace points are output. According to the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF, the advantages of an ambiguity function and the advantages of linear canonical transformation are combined, non-uniform velocity translational motion target signals or turning target signals can be flexibly matched and accumulated in a clutter background, the signal-to-clutter ratio is improved, range migration can be compensated through the extraction of a target observation value in a distance-slow-time plane, phase-coherent accumulation for a long time is completed, the detection capacity of radar to the slightly-moving target is improved, and therefore the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF is wide in applicability.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
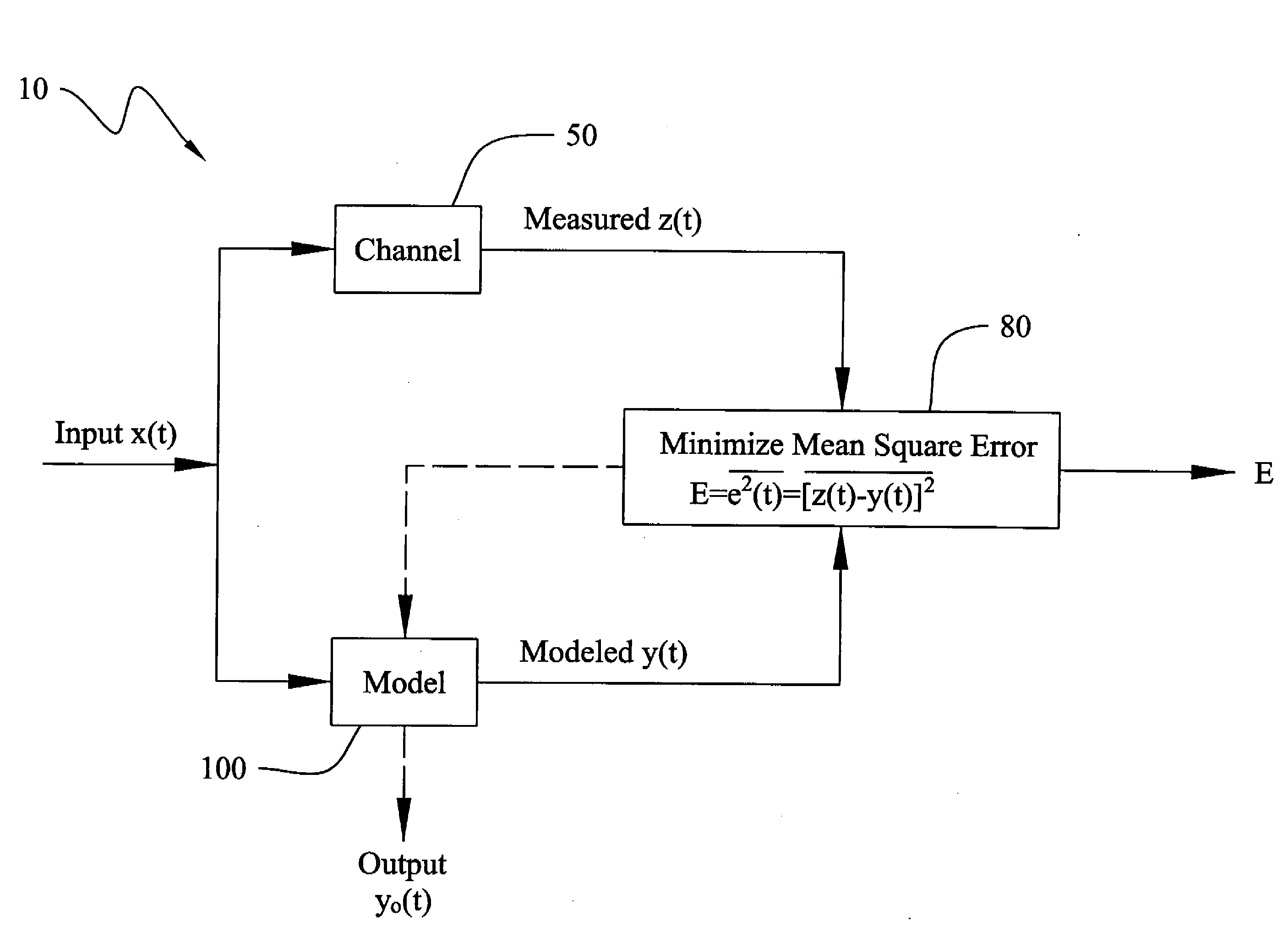
Method and Apparatus for Improved Active Sonar Using Singular Value Decomposition Filtering
InactiveUS20090003134A1Excellent performance resultGuarantee linear independenceAcoustic wave reradiationSingular value decompositionSonar
The invention is a method for improved active sonar using a singular value decomposition filtering and a Volterra-Hermite Basis Expansion to model real active sonar measurements. The fitting model minimizes the sum of the squared errors between a measured channel response, z(t), and model response, y(t), which is a fitted Volterra Series solution. The model requires as input an excitation waveform, x(t), to which is fitted the model response, y(t). A contracted broadband cross-ambiguity function is used to correct the excitation waveform for Doppler and range effects. Once completed, the modeled response can be used to determine the linearity or non-linearity of the channel effects. Appropriate measures can be utilized to reduce these effects on the measured channel response.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENT DIV NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL THE
Method and system for obtaining an adaptive angle-doppler ambiguity function in MIMO radars
ActiveUS20200011968A1Enhanced low cost target detectionSuppressing angle-Doppler couplingDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguity functionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for obtaining an adaptive angle-Doppler ambiguity function (AF) for a target using multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar that includes a transmit antenna array having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes generating transmit signals for transmission by the transmit antenna array, the transmit signals defining at least a first transmit trajectory of a phase center within the transmit antenna array; transmitting the transmit signals using the transmit antenna array and receiving receive signals from the target, the receive signals resulting from the incidence of the transmit signals upon the target; and obtaining at least an angle-Doppler ambiguity function (AF) from the receive signals. The first transmit trajectory is such that, in operation, the phase center undergoes random phase center motion (PCM), such that a phase center position within the transmit antenna array varies randomly with time. A system for obtaining an AF is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV DU LUXEMBOURG +1
Orthogonal waveform designing method for formation flying satellites SAR (synthetic aperture radar)
InactiveCN102540187AReduce autocorrelation sidelobesReduce cross-correlation peaksRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarPeak value
The invention relates to a waveform design for a formation flying satellites SAR (synthetic aperture radar), and provides an orthogonal waveform designing method which is used for carrying out phase encoding for linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals. The orthogonal waveform designing method includes generating a linear frequency modulation signal at first, dividing the linear frequency modulation signal into N parts according to equal time intervals to form N sub-pulses, carrying out random phase encoding for each sub-pulse by M times according to the number M of the formation flying satellites, establishing an ambiguity function expression, calculating cluster tolerance xi meeting formation flying satellite synthetic aperture radar Doppler mismatch, finding out a critical N value meeting requirements by the aid of a searching comparison method, finally selecting energy and functions which are in autocorrelation and cross-correlation as cost functions, namely fitness functions in genetic algorithm, searching code values of phase encoding of the various sub-pulses by the aid of the genetic algorithm, and finding out orthogonal waveforms after optimization at last. The waveforms have low autocorrelation side lobes, cross-correlation peak values, bandwidth occupation ratio and Doppler mismatch, and excellently suppress echo signal interferences among different space-borne SARs.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
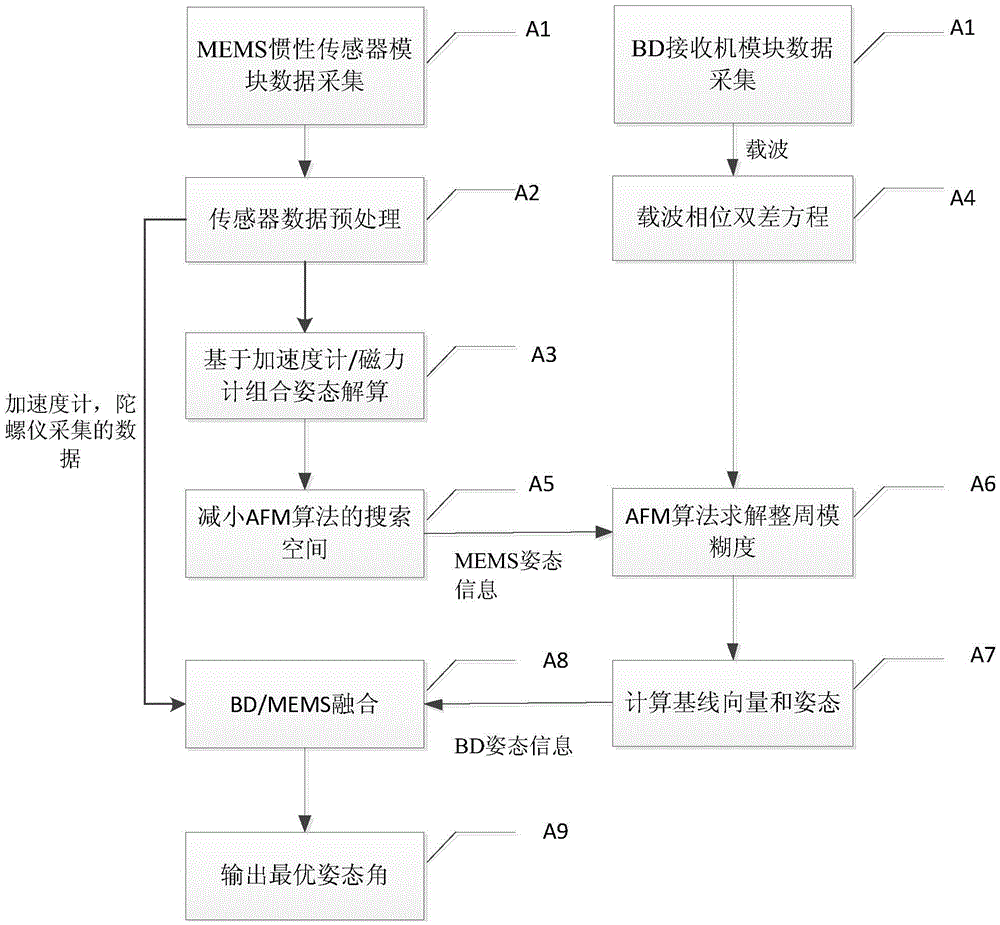
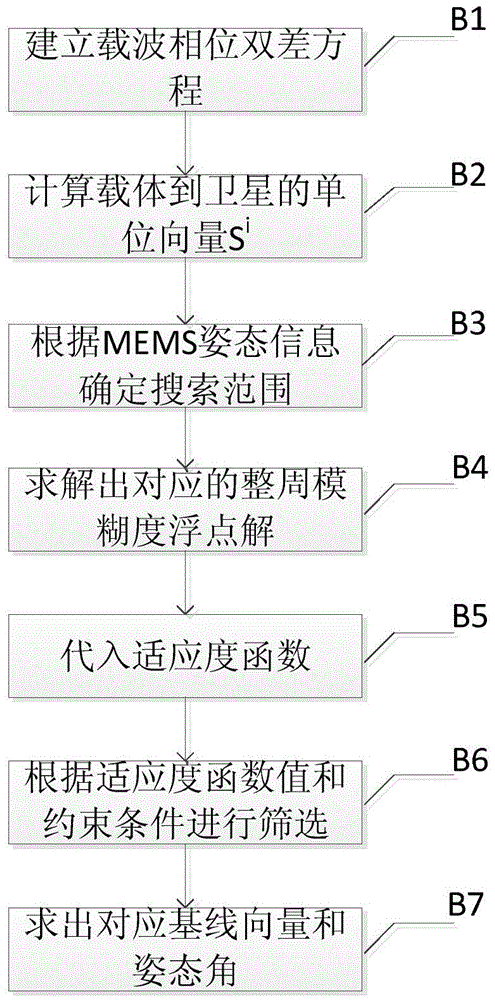
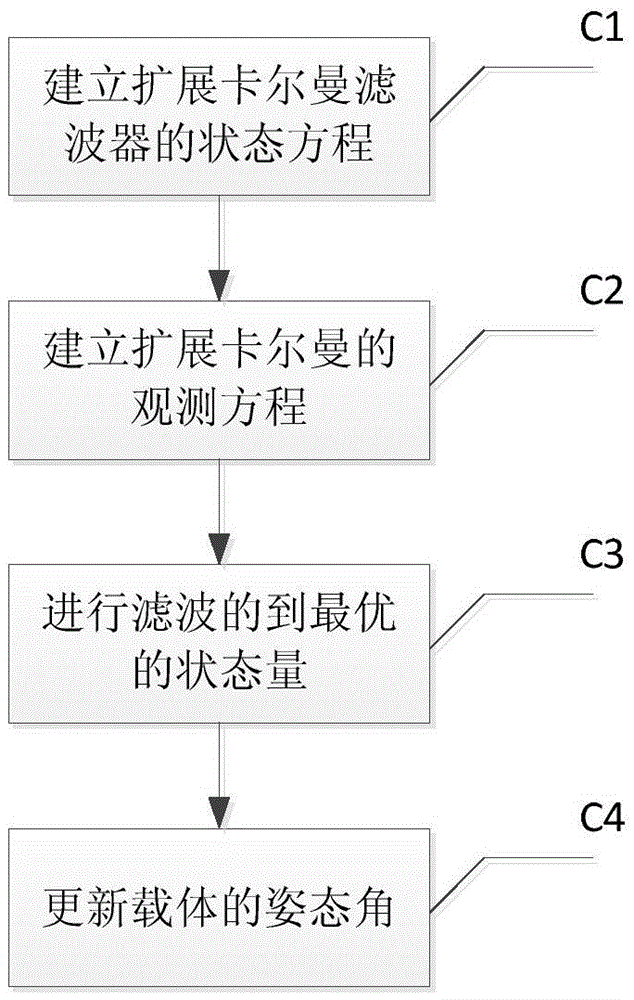
Low-cost high-precision BD/MEMS integration attitude measurement method
ActiveCN105607106ATroubleshoot insufficient not working properlyStrong real-timeNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterGyroscope
The invention relates to a low-cost high-precision BD / MEMS integration attitude measurement method, and belongs to the technical field of navigation. An MEMS inertia sensor module comprises a triaxial accelerometer, a triaxial gyroscope, and a triaxial magnetometer. A BD receiver module comprises two antennas and one integrated BD navigation chip. The method comprises the steps: solving a carrier attitude angle according to the information of an MEMS inertia sensor; solving the ambiguity of the whole cycle through the assistance of an AFM (ambiguity function method); and finally achieving the BD / MEMS integration attitude measurement through an expanded Kalman filter. The method solves a problem that a satellite attitude system cannot work normally under the condition that a BD signal is sheltered by an obstacle because of insufficient satellites, overcomes the difficulty, caused by signal lock loss, in solving the ambiguity of the whole cycle, and also solves a problem of accumulated errors of the gyroscope and the accelerometer. Compared with a conventional method, the method is higher in instantaneity and reliability and is higher in precision.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Locating system based on noisy type waveforms
InactiveUS8542145B2Limited extentReduce total powerCommunication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransmission channelRandom noise
The present invention relates to a system for locating non-cooperating objects by means of a random or pseudo-random noisy type waveform generator, an amplifier, of said waveforms and an antenna which radiates them towards the object, which object generates an electromagnetic echo which is detected by a passive subsystem of antennas and receivers. The time delay and Doppler shift values are determined in the latter subsystem and in turn forwarded from encoding and modulating blocks to a central processor which estimates the position and the speed of the object. The passive subsystem receives, through a transmission channel or storage element, the reference signal which represents the transmitted noisy type waveform and uses it for calculating the bi-dimensional cross correlation (ambiguity function), which permits to estimate the time delay and the Doppler shift.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
Radar moving target long-time phase-coherent accumulation detecting method based on RFRAF
ActiveCN103323829AEffective accumulationFlexible matching and accumulationWave based measurement systemsTarget signalRadar signal processing
The invention relates to a radar moving target long-time phase-coherent accumulation detecting method based on an RFRAF, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The method comprises the following steps that (1) radar echo data are demodulated, pulsed and compressed in the distance direction, and pulse accumulation is completed; (2) parameters are initialized; (3) the RFRAT is adopted to compensate distance and Doppler migration, and then long-time interpulse phase-coherent accumulation is completed: (4) the parameters are transversely searched, an RFRAT domain detecting unit map is constructed, and constant false alarm detection is conducted; (5) target moving parameters are estimated, and moving trace points are output. The advantages of the ambiguity function and fractional order Flourier transformation are synthesized, high order phase signals of a target generated in the moving process can be flexibly matched and accumulated, the distance and Doppler migration are compensated, accumulation and gain of a radar to complex moving target signals are improved, the capacity of detecting weak moving targets in strong clutters is possessed, the moving trace points of the target can be acquired, and popularization and application value are achieved.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
System utilizing CMMB (China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting) signal to detect target and method thereof
ActiveCN102707271ARandomNo electromagnetic pollutionWave based measurement systemsIntermediate frequencyData acquisition
The invention relates to a system utilizing CMMB (China mobile multimedia broadcasting) signals to detect a target and a method thereof. The system comprises a receiving antenna, an analog chassis with a signal simulating and receiving component, a CPCI (compact peripheral component interconnect) chassis with a signal acquisition and processing component, at least one disc array chassis with a signal storage component, a switchboard and a signal process for signal processing, which are connected in sequence. The analog reception adopts a scheme of secondary mixed frequency and fixed medium frequency; the data acquisition adopts a scheme of medium-frequency bandpass sampling and digital down-conversion; the data storage adopts a high-speed disc array; and the data processor is used for implementing such operations as signal reconstruction, channel correction, direct wave suppression, digital beam formation, inter-ambiguity function, peak detection, constant false alarm detection, positioning and tracking and the like, and final output of information of the target distance, speed and direction. The system has the following advantages of no need for frequency distribution, no electromagnetic pollution, high signal randomness, high signal interception performance, large signal bandwidth, high distance resolution, low research and maintenance cost, and high mobility.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Underwater moving target identification method
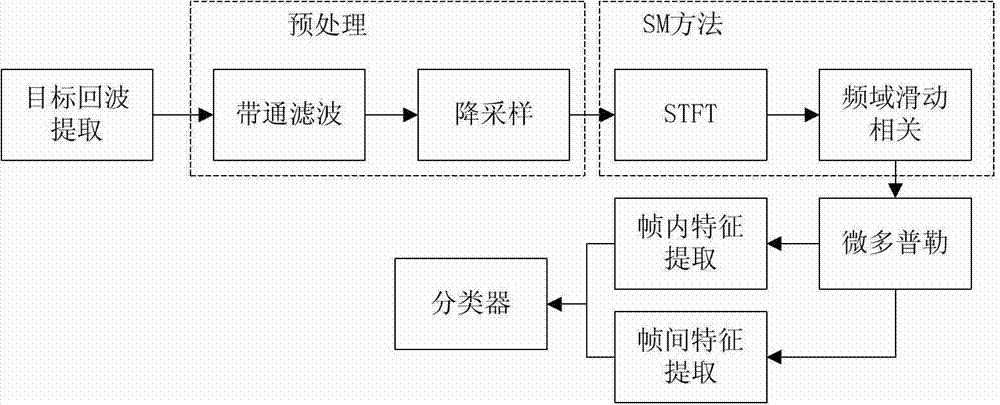
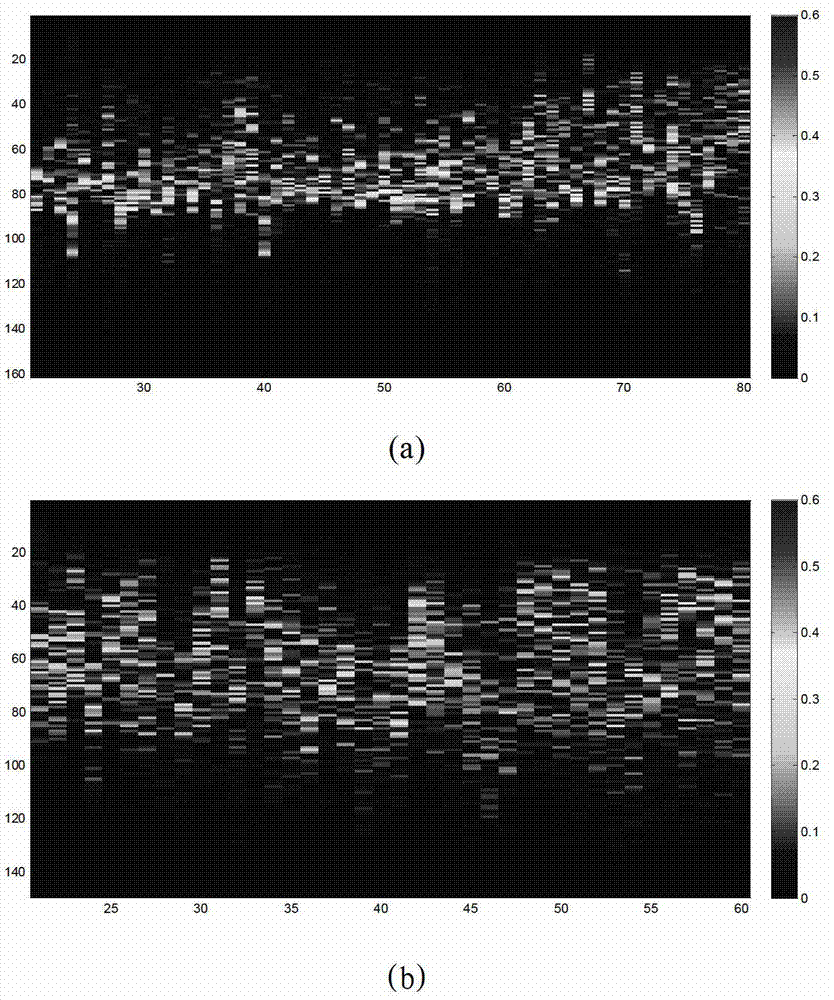
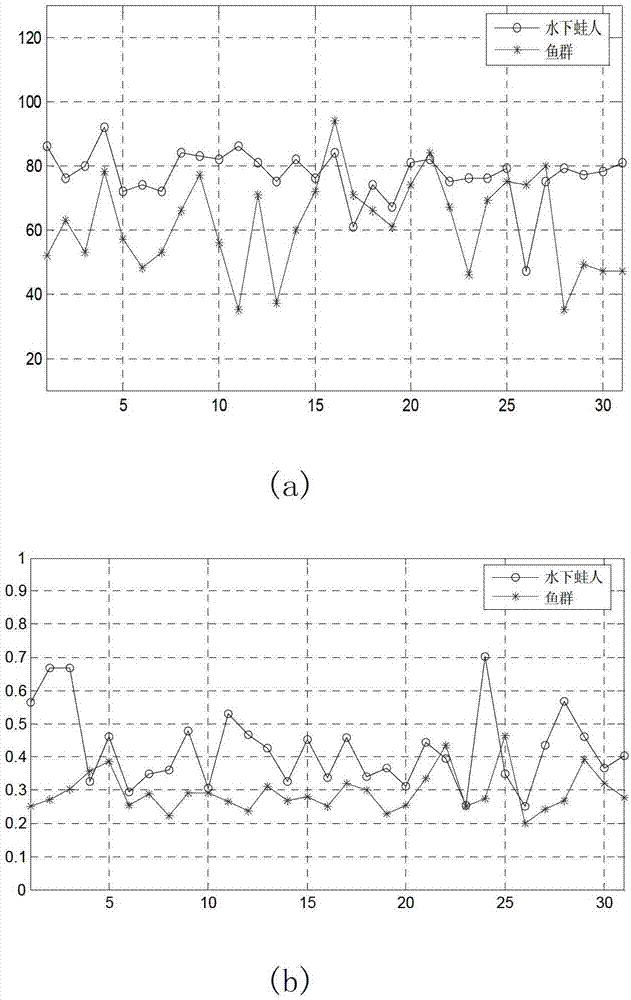
ActiveCN103091679AUnable to solve the problemImprove recognition stabilityAcoustic wave reradiationTarget signalSelf correlation
The invention relates to an underwater moving target identification method. The underwater moving target identification method includes the following steps: conducting preprocessing to target signals received by active sonar, conducting self-mixing (SM) time frequency processing to the target signals after being preprocessed, and extracting a micro-doppler spectrum; extracting intra-frame micro-doppler features and interframe micro-doppler features according to the micro-doppler spectrum; and classifying underwater moving targets based on the intra-frame micro-doppler features and the interframe micro-doppler features. The underwater moving target identification method extracts micro-doppler distribution feathers through echo waveform of underwater moving small target of an active high frequency sonar. A SM algorithm can produce self-correlation items which are identical with west data (WD), mutual disturbance terms cannot exist, the problem that micro-doppler variation restricted by linear frequency modulation (LFM) signal ambiguity function can not be achieved is solved, classification of underwater moving small target of active high frequency sonar single beam echo waveform is achieved, influences of a random channel are reduced through statistics stability of the interframe micro-doppler features, and identification stability is improved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radar using hermetic transforms
ActiveUS20150145716A1Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationPassive radarFrequency measurements
The systems and methods use Hermetic Transform processing to achieve higher resolution in space, time, and frequency measurements, leading to enhanced object detection, localization, and classification, and can improve several aspects of RADAR, including: phased-array beamforming, Doppler filter processing, pulse compression / replica correlation, and in the creation of higher resolution ambiguity function measurements for both multi-static active and passive RADAR.
Owner:HOBBIT WAVE
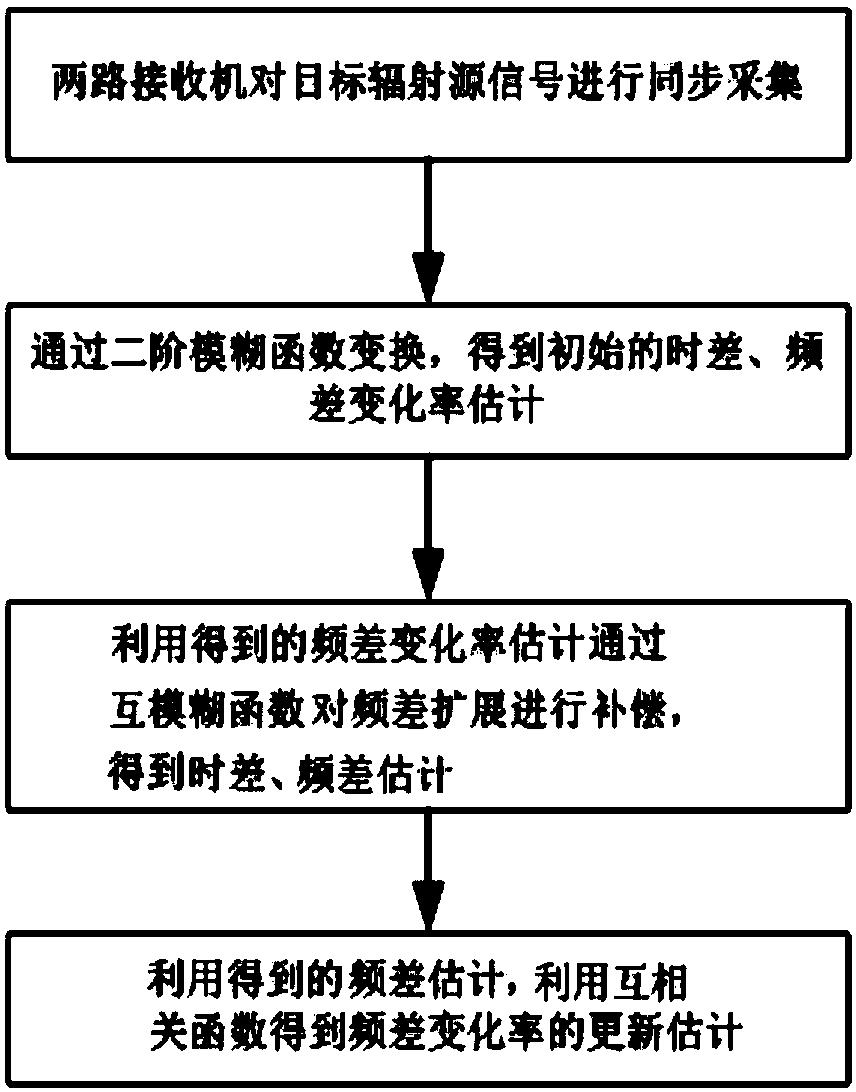
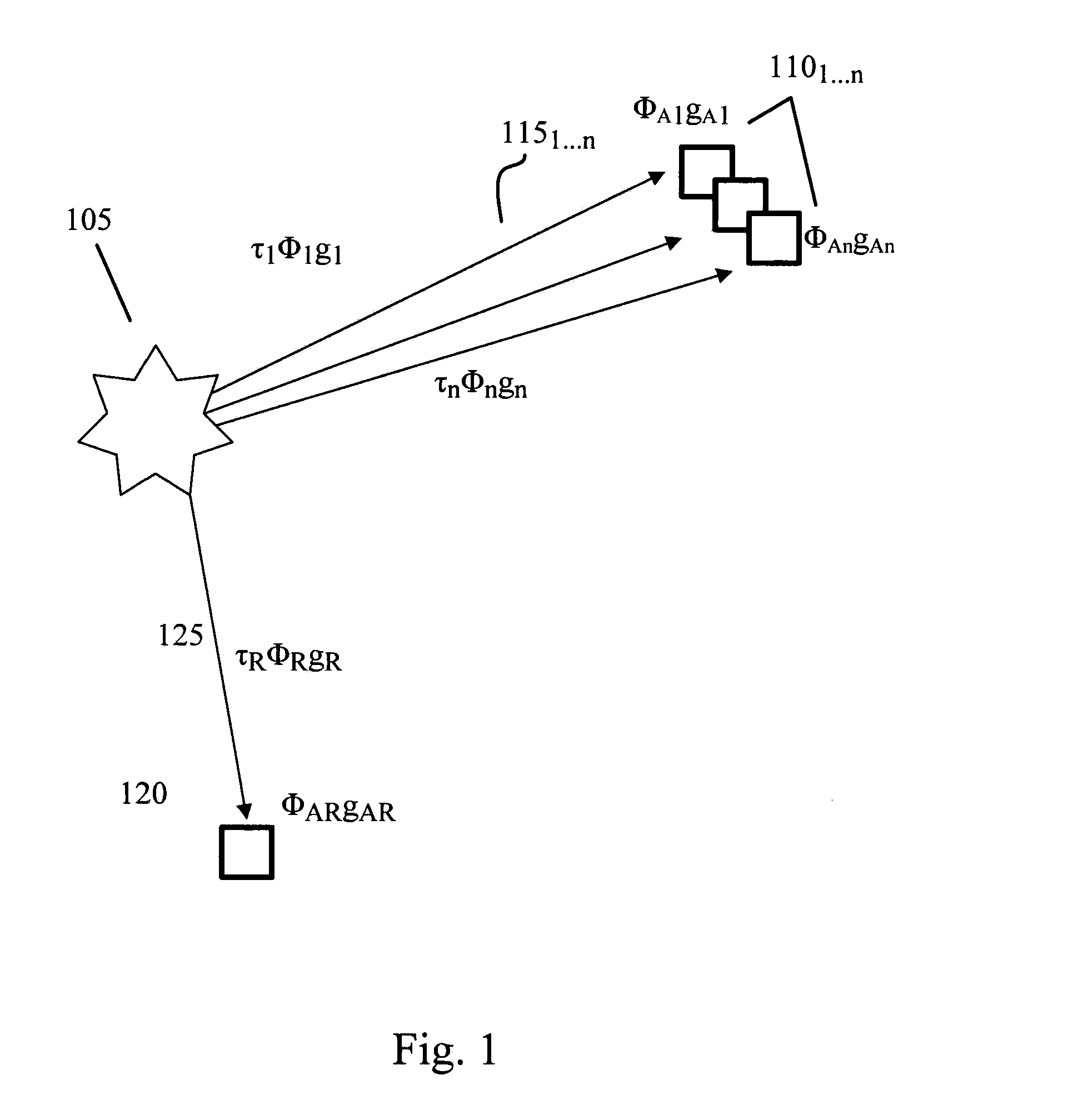
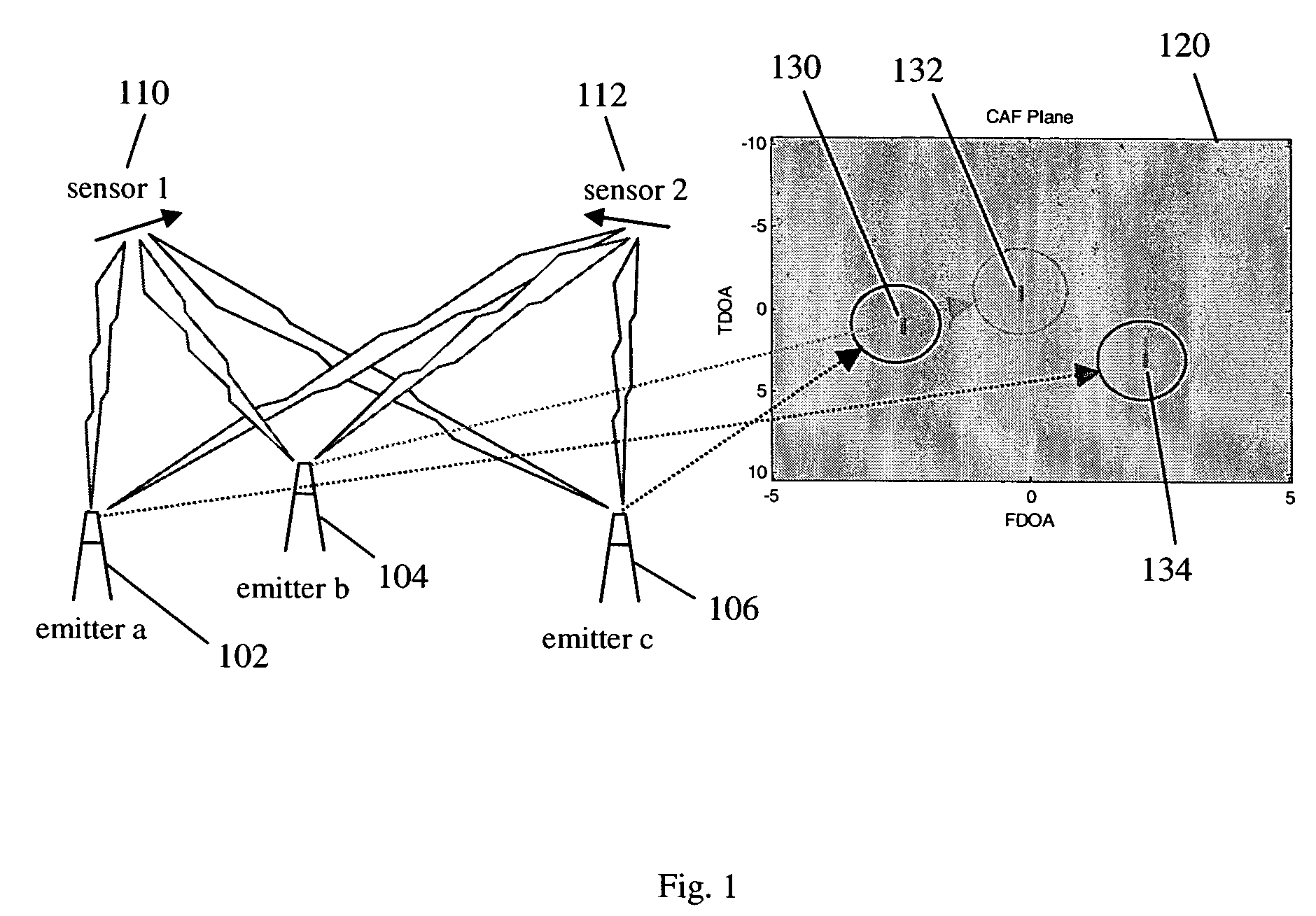
Time difference, frequency difference and frequency difference change rate joint estimation method
ActiveCN107607934AHigh precisionHigh positioning accuracyUsing reradiationEstimation methodsAmbiguity
The invention relates to a time difference, frequency difference and frequency difference change rate joint estimation method which comprises the following steps: (1) two receivers synchronously collect a target radiation source signal, wherein the digital signals collected are respectively s1(n) and s2(n); (2) mesh generation is carried out on the target radiation source signal in the time difference range and in the frequency difference change rate range respectively, a second-order ambiguity function H (Tau, f) is calculated for each mesh point, and the initial estimate (Tau-^, f-.^) of time difference and frequency difference change rate is obtained by searching for the module values of the second-order ambiguity functions H (Tau, f) of the mesh points; (3) compensation is made for frequency difference expansion through a cross ambiguity function CAF (Tau, f) according to the initial estimate f-.^ of frequency difference change rate to get new time difference estimate and frequencydifference estimate; and (4) new frequency difference change rate estimate is obtained through a frequency difference change rate cross correlation function according to the new frequency differenceestimate. The method of the invention is applicable to the passive location of time and frequency difference under high dynamic conditions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Quick implementation method for passive radar range migration compensation
InactiveCN104062640ASmall amount of calculationSimplify operation stepsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainConjugate transpose
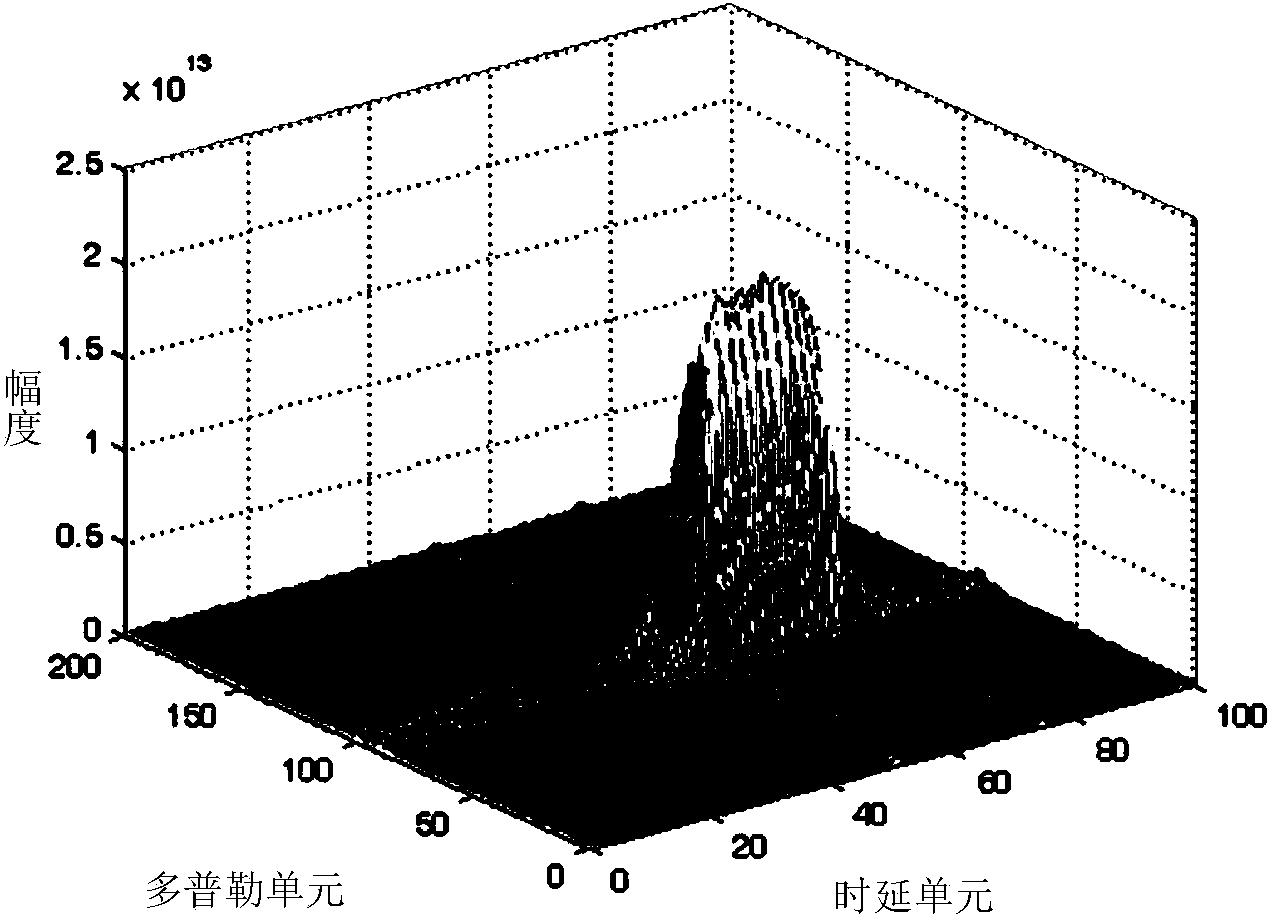
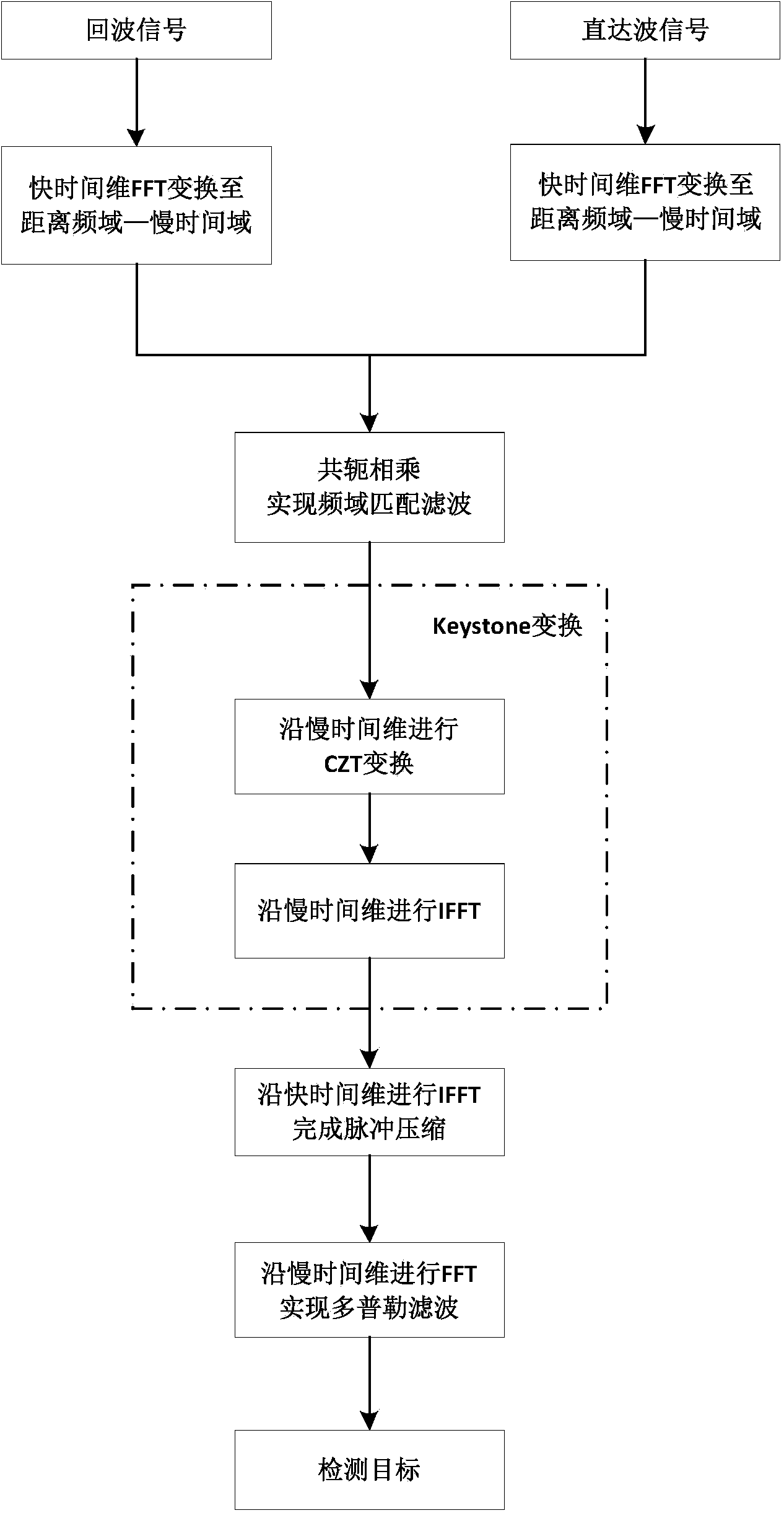
The invention relates to a quick implementation method for passive radar range migration compensation and belongs to the technical field of radar target detection. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a direct wave signal and an echo signal received by a passive radar antenna are segmented and rearranged into two-dimensional matrices; (2) each row of the direct wave and the echo wave is transformed to the frequency domain; (3) the transformed direct wave matrix is multiplied by the conjugate transpose of the transformed echo wave matrix; (4) each row is extracted after being processed by a low-pass filter; (5) each column is subjected to CZT; and (6) each row is transformed to the time domain, and a cross-ambiguity function result subjected to migration compensation is obtained. Compared with a conventional range migration compensation method based on CZT and IFFT to achieve keystone transform, the provided method reduces operation steps and the amount of computation substantially while the gain accumulated is almost the same.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Geo-Directed Adaptive Antenna Array
ActiveUS20120021687A1Dramatically relax the phase and/or amplitude calibration requirements of an antenna elementRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringTarget signalAmplitude response
Systems and methods for on-the-fly characterization of an arbitrary array of antenna elements are provided. An array of arbitrary antenna elements and a reference receiver is provided. A location for a target source of signals is provided or assumed. Cross ambiguity functions are computed between the signal received by the reference receiver and the signal received by each antenna element. The cross ambiguity functions are analyzed to determine the phase and amplitude response of the antenna array to signals originating from the location of the target source of signals.
Owner:RINCON RES CORP
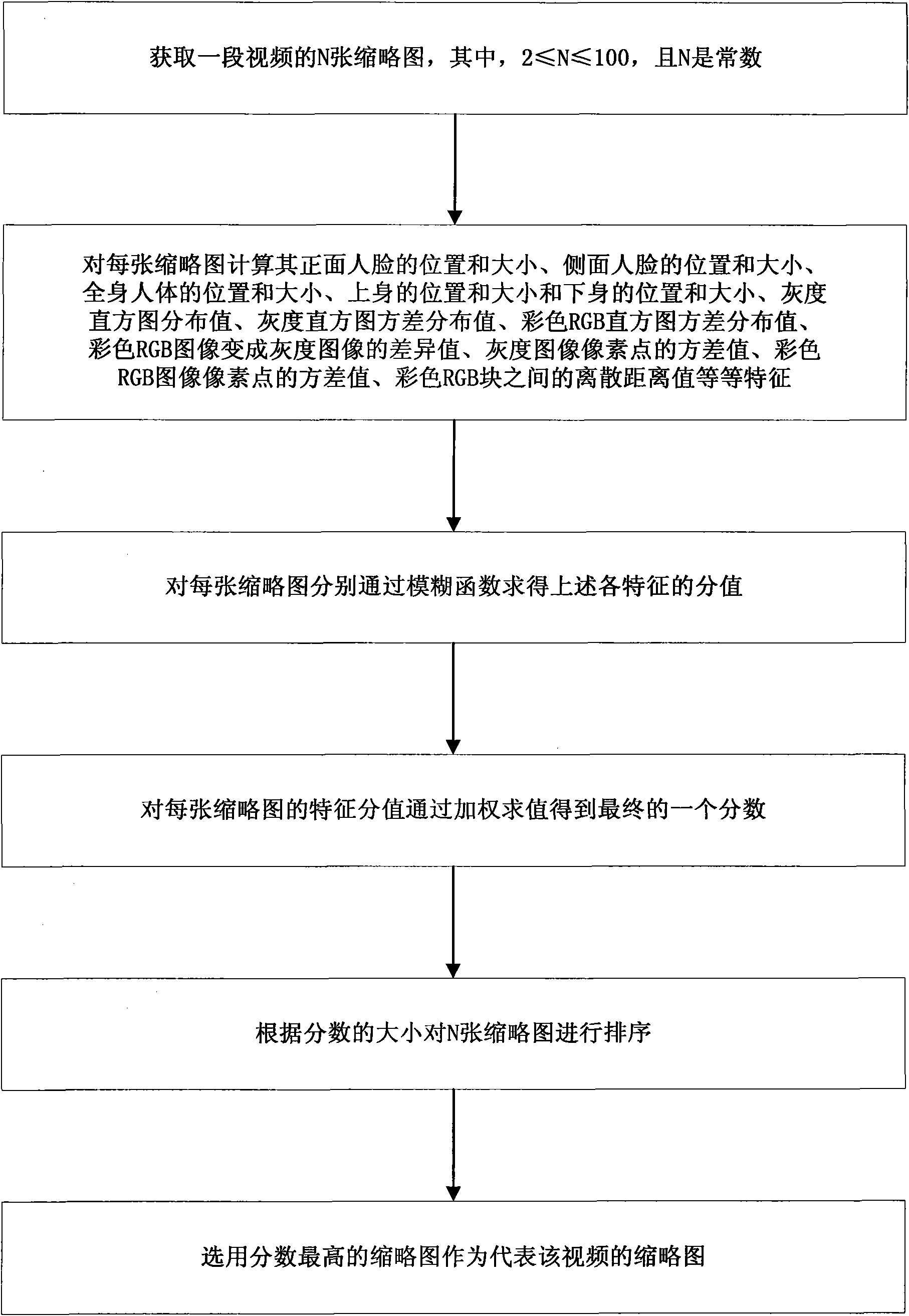
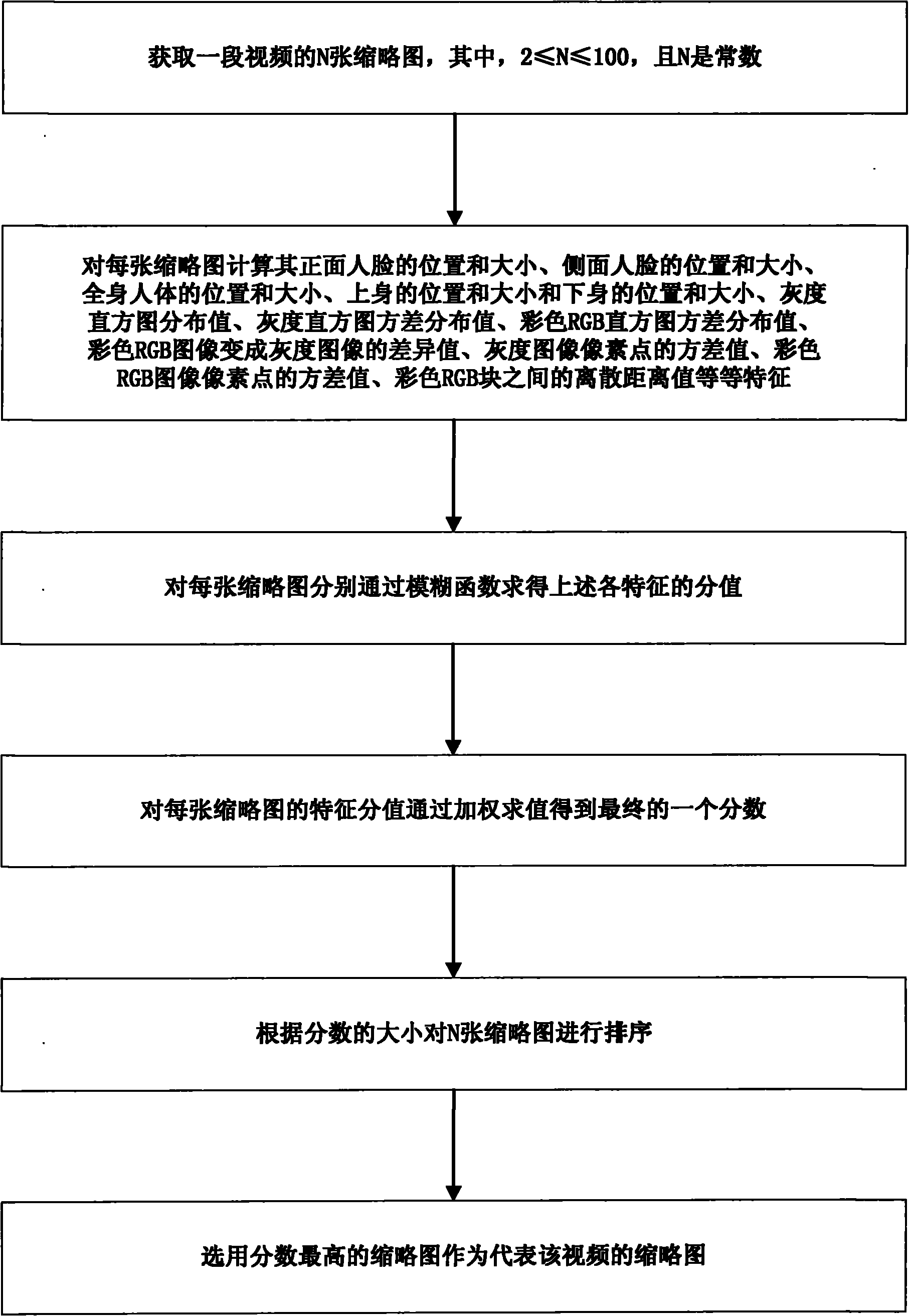
Intelligent selection method of video thumbnails
The invention discloses an intelligent selection method of video thumbnails, comprising the following steps: 1) acquiring N numbered thumbnails of a video, wherein N is more than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 100, and N is a constant; 2) calculating the characteristics of each thumbnail, such as frontal face position and size, profile face position and size, whole body position and size, upper body position and size, lower body position and size, gray level histogram distribution value, gray level histogram variance distribution value, colorful RGB histogram variance distribution value, difference value that a colorful RGB image is changed into a gray level image, the variance value of a gray level image pixel point, the variance value of the colorful RGB image pixel point, the dispersion distance value between the colorful RGB blocks, and the like; 3) calculating the characteristic values of each thumbnail respectively through ambiguity functions; 4) weighting and calculating the characteristic values of each thumbnail to obtain a final fraction; 5) sequencing the N numbered thumbnails according to the fraction of each thumbnail; and 6) selecting the thumbnail with the highest fraction as the thumbnail representing the video.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
Beam phase modulation for improved synthetic aperture detection and estimation
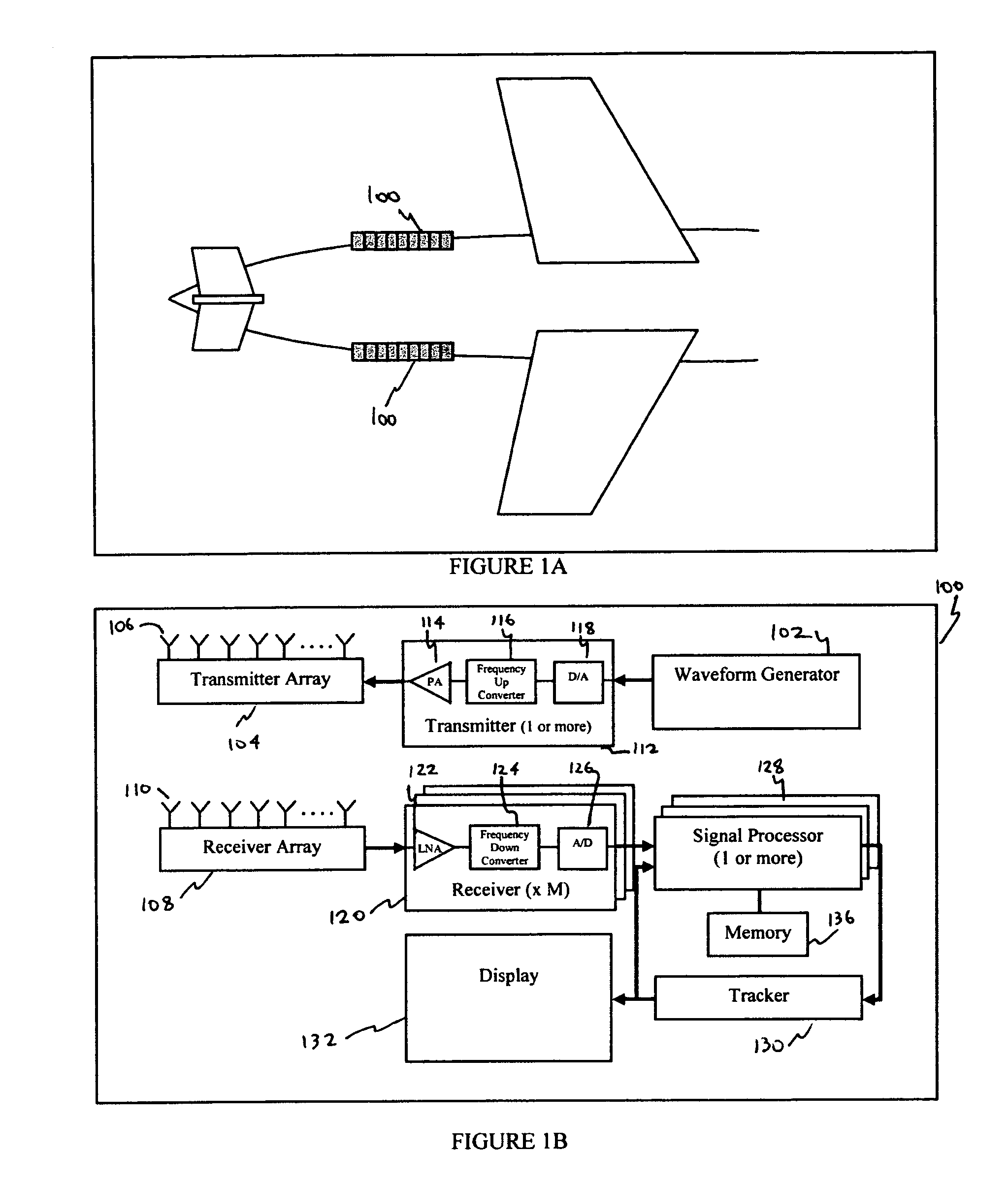
InactiveUS7701380B2Improve performanceSuppress ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSonificationAmbiguity
Owner:CHIRP
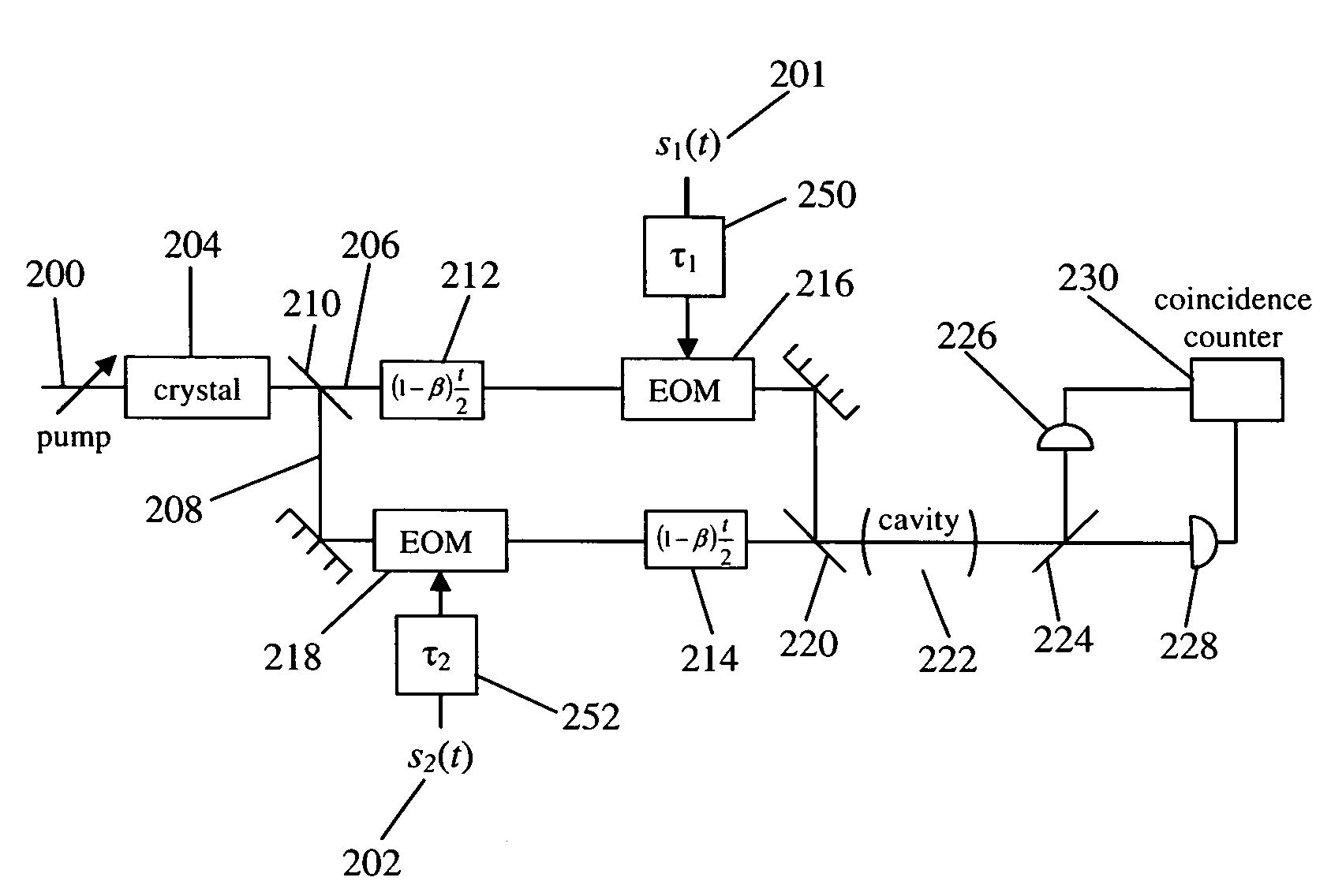
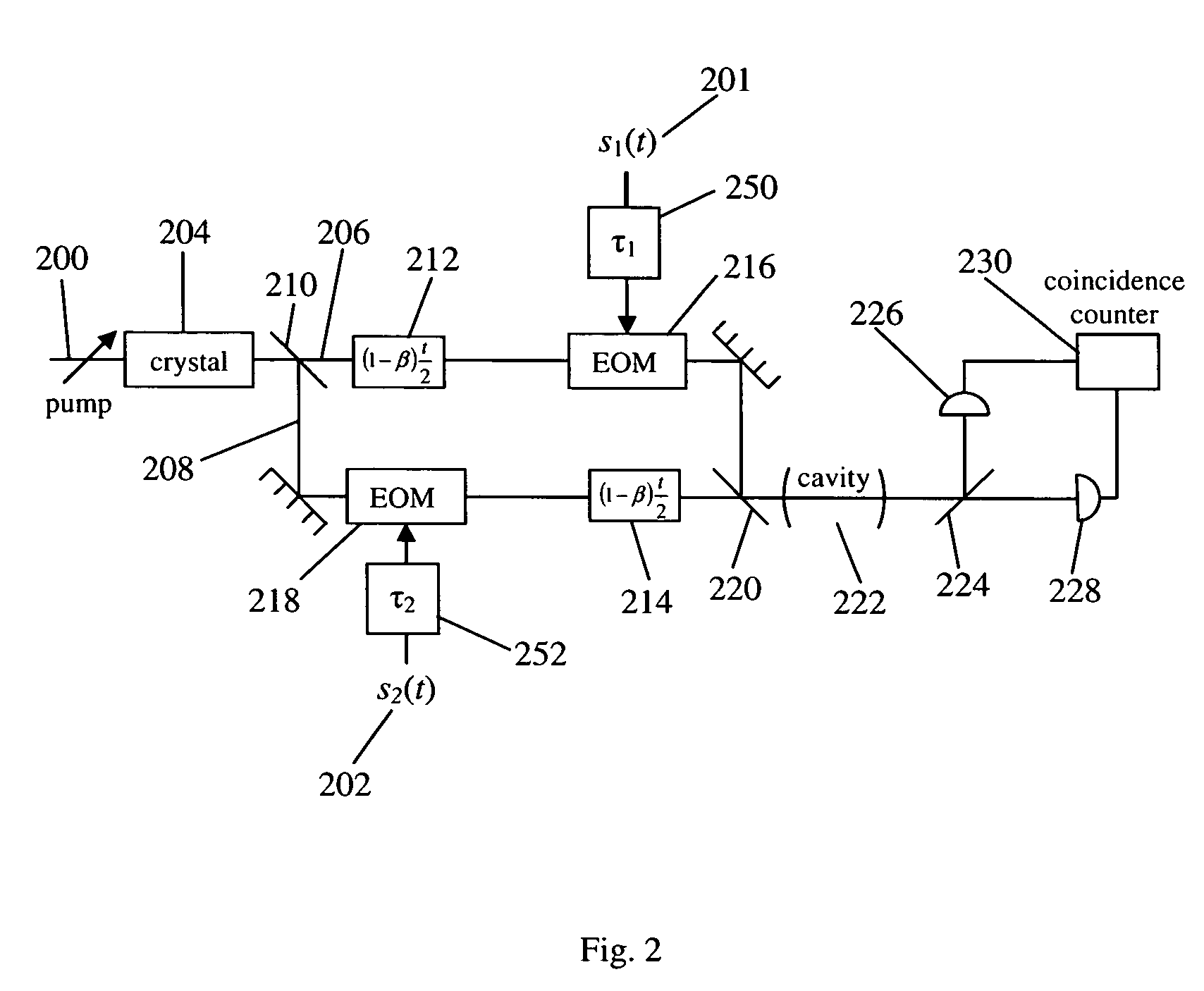
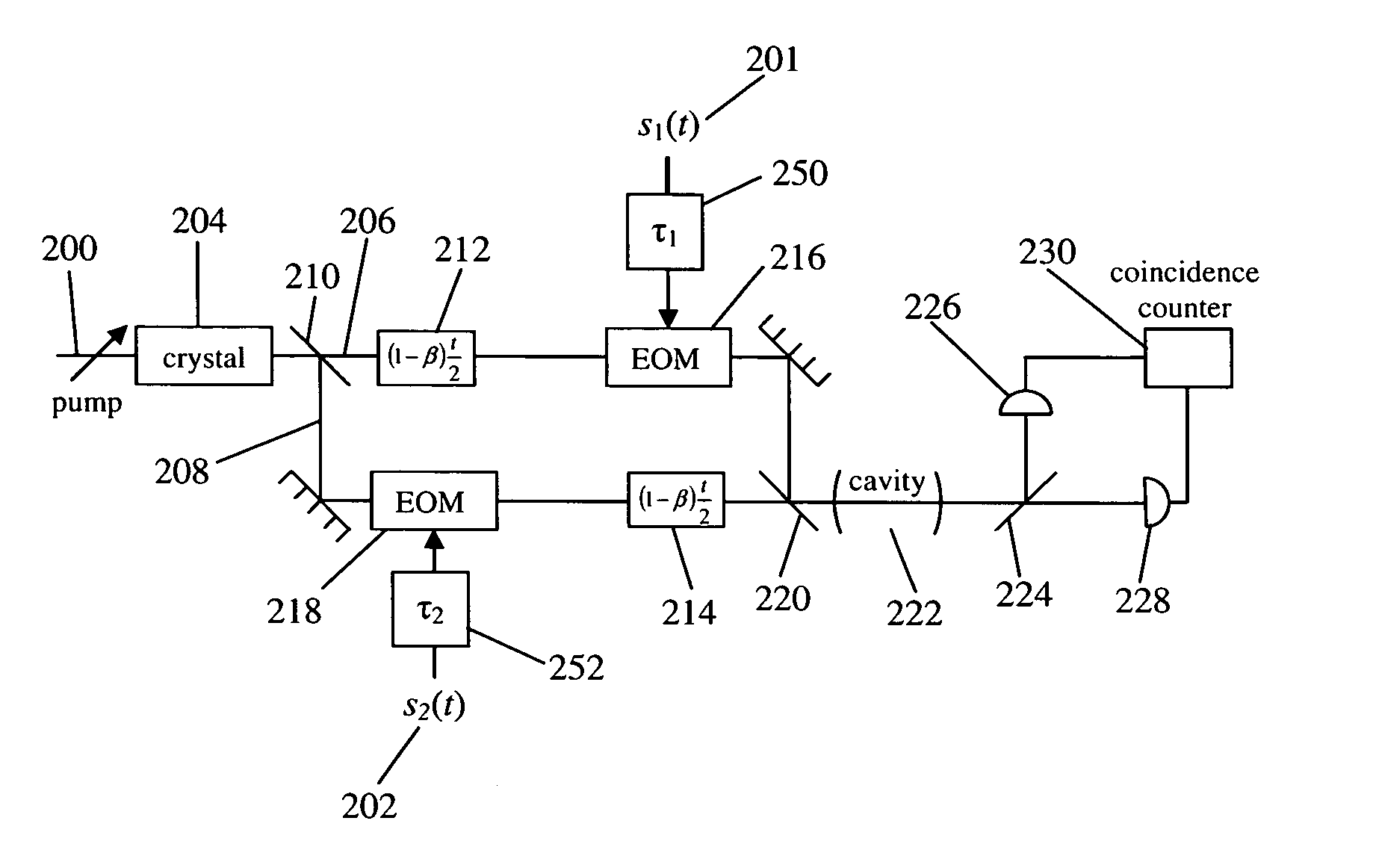
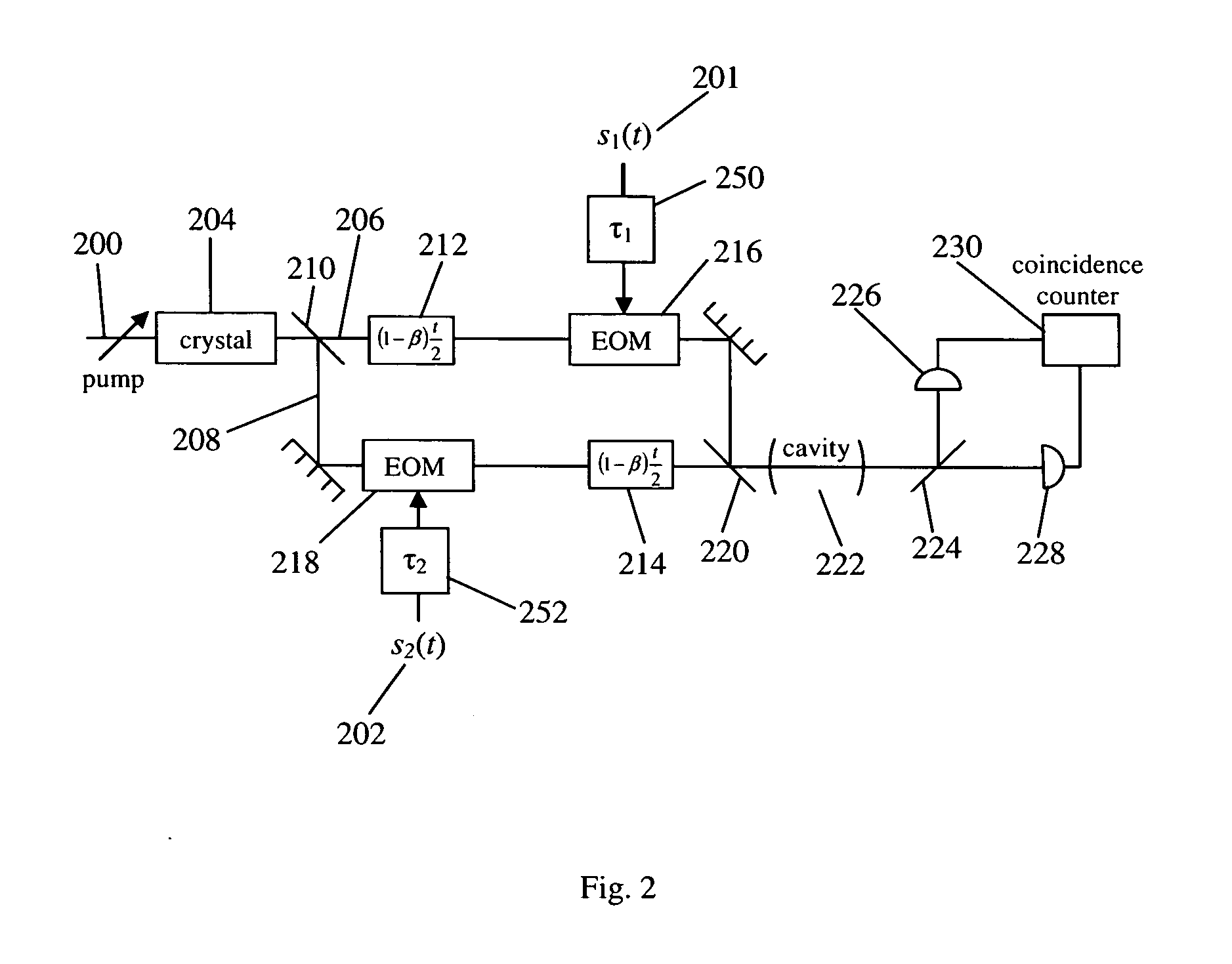
Quantum cross-ambiguity function generator
InactiveUS7304314B2Optical measurementsLuminescent dosimetersFunction generatorCondensed matter physics
A cross-ambiguity function generator (“CAF”) uses properties of quantum mechanics for computation purposes. The CAF has advantages over standard analog or digital CAF function generators, such as improved bandwidth. The CAF may be used for traditional geolocation or RADAR applications.
Owner:MDA INFORMATION SYST
Geo-directed adaptive antenna array
ActiveUS8565798B2Dramatically relax the phase and/or amplitude calibration requirements of an antenna elementRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringTarget signalAmplitude response
Systems and methods for on-the-fly characterization of an arbitrary array of antenna elements are provided. An array of arbitrary antenna elements and a reference receiver is provided. A location for a target source of signals is provided or assumed. Cross ambiguity functions are computed between the signal received by the reference receiver and the signal received by each antenna element. The cross ambiguity functions are analyzed to determine the phase and amplitude response of the antenna array to signals originating from the location of the target source of signals.
Owner:RINCON RES CORP
Quantum cross-ambiguity function generator
InactiveUS20050151093A1Luminescent dosimetersElectromagnetic transmissionFunction generatorCondensed matter physics
A cross-ambiguity function generator (“CAF”) uses properties of quantum mechanics for computation purposes. The CAF has advantages over standard analog or digital CAF function generators, such as improved bandwidth. The CAF may be used for traditional geolocation or RADAR applications.
Owner:MDA INFORMATION SYST
RF transmitter geolocation system and related methods
InactiveUS7911385B2Improve accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesMultipath interferenceAmbiguity
A system for geolocating a radio frequency (RF) transmitter in the presence of multipath interference may include a plurality of RF receivers arranged in spaced relation. The system may also include a controller coupled to the plurality of receivers and configured to generate a plurality of measurements associated with the RF transmitter. The controller may also compute a plurality of ambiguity functions based upon the plurality of measurements and due to the multipath interference, and project the plurality of ambiguity functions onto a common geo-referenced grid. The controller may also detect a peak on the common geo-referenced grid indicative of a geolocation of the RF transmitter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
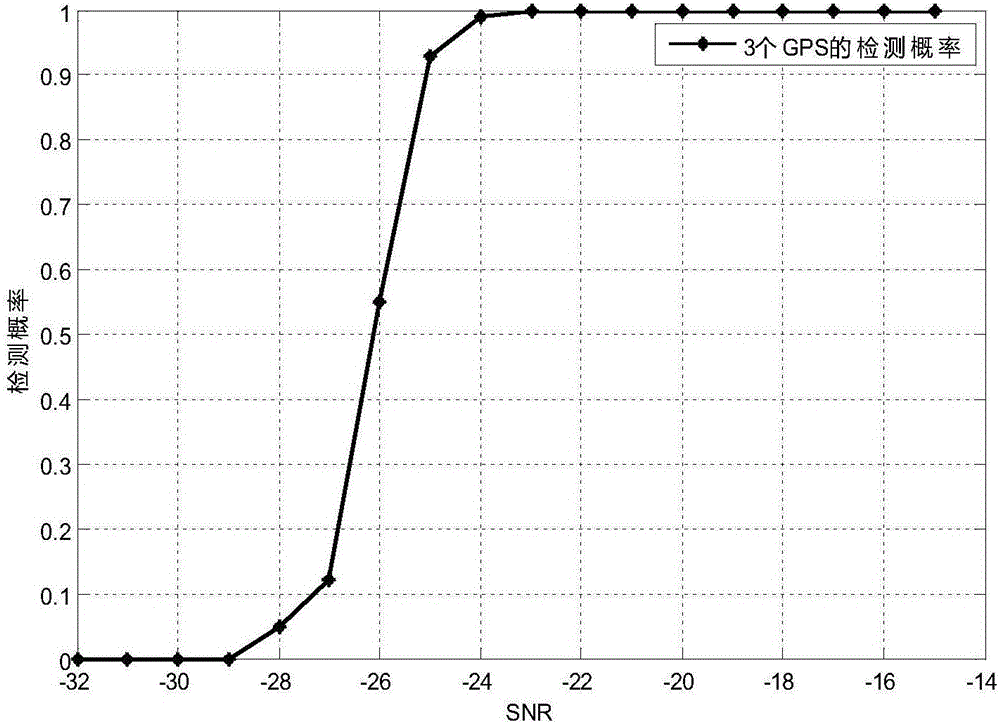
Method for detecting multiple GPS (global positioning system) satellite weak echo signals
The invention discloses a method for detecting multiple GPS (global positioning system) satellite weak echo signals. The method comprises steps as follows: a modulation parameter and a C / A code disclosed by a GPS are used for performing separation reconstruction on a GPS signal received by a reference channel, and a reference signal is obtained; direct waves and multiple paths of the direct waves are inhibited for the echo signals; circular cross-ambiguity function processing is performed on an echo channel signal and different reference signals respectively, and multiple delay-doppler spectra are obtained; the multiple delay-doppler spectra are subjected to TF-LV coordinate transformation, and multiple detection quantities are obtained and superposed; the best detection threshold is obtained according to probability distribution of the detection quantities and compared with peak values of the detection quantities, so that the multiple GPS satellite weak echo signals are detected. The method can have a good detection property for multiple GPS echo signals in a low signal-to-noise ratio environment.
Owner:GUILIN CHANGHAI DEV
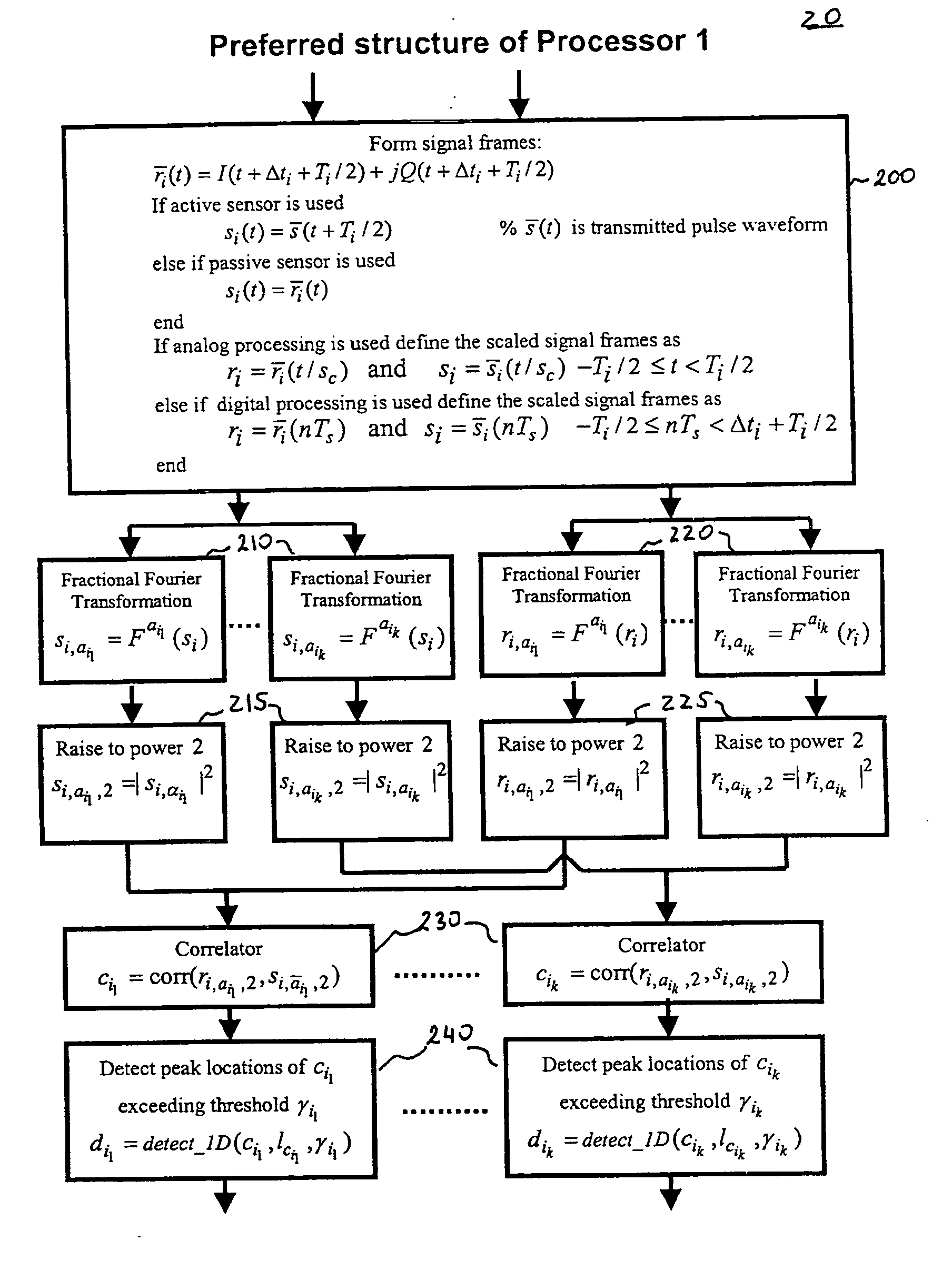
System and method for detection and tracking of targets
System and method for detection and tracking of targets, which in a preferred embodiment is based on the use of fractional Fourier transformation of time-domain signals to compute projections of the auto and cross ambiguity functions along arbitrary line segments. The efficient computational algorithms of the preferred embodiment are used to detect the position and estimate the velocity of signals, such as those encountered by active or passive sensor systems. Various applications of the proposed algorithm in the analysis of time-frequency domain signals are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGNAL LABS
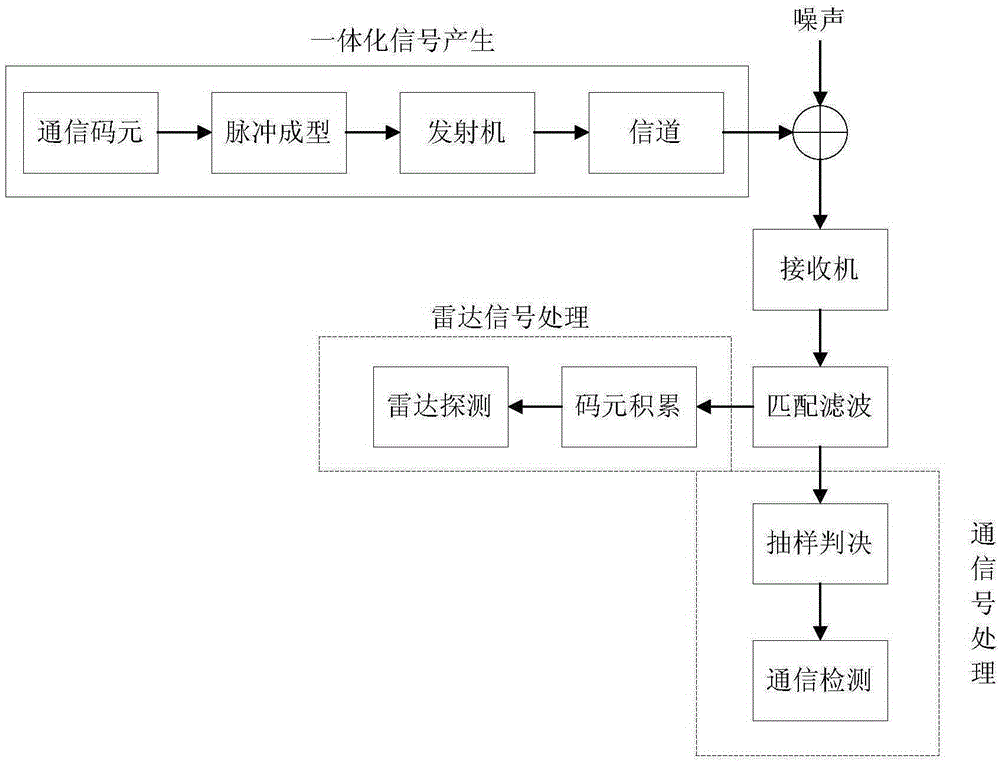
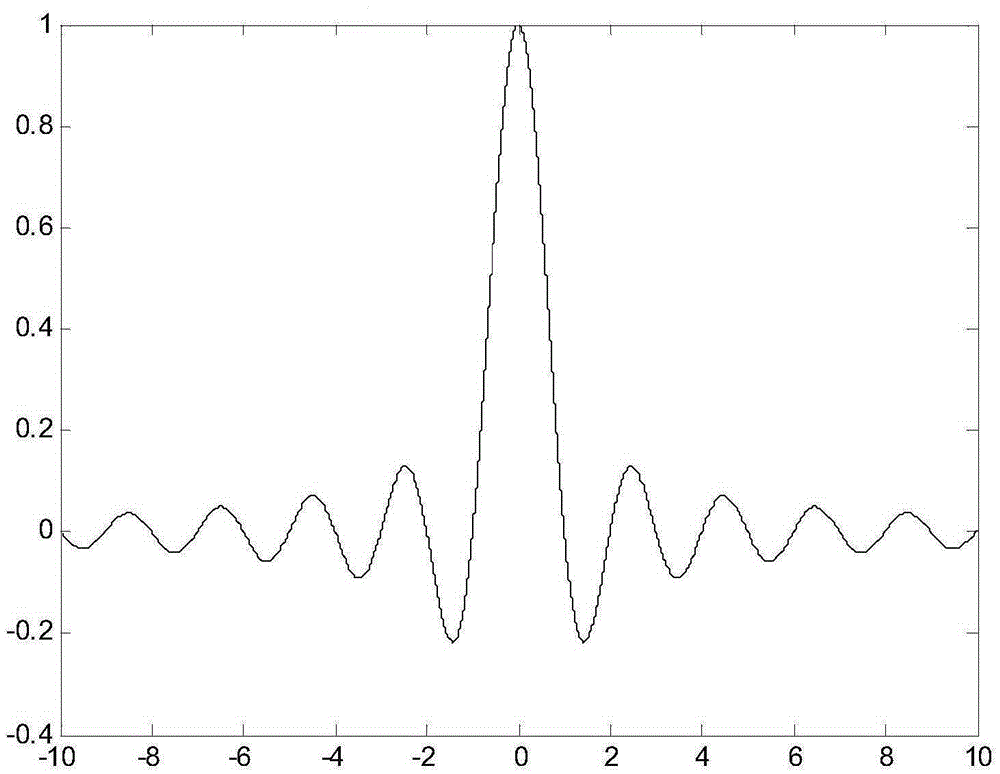
Radar-communication integrated realizing method
InactiveCN105425218ARealize integrationDoes not affect functionWave based measurement systemsBaseband system detailsTime delaysCoded element
The invention provides a radar-communication integrated realizing method. According to the radar-communication integrated realizing method, based on analysis on the characteristics of the ambiguity function of transmitted signals of a communication system, communication signals are directly transmitted when the number of transmitted code elements in one transmission period satisfies requirement; the communication code elements pass through a pulse type shaping filter; obtained signals are transmitted out through using a transmitter and by means of an antenna; a receiving end carries out radar detection processing on the signals directly using the communication signals; the receiving end carries out demodulation on the signals through a receiver, so that baseband signals can be obtained; the baseband signals pass through a matched filter, so that an output signal to noise ratio is maximum; if a function which is to be realized by the system is a communication function, sampling judgment is performed on the demodulated baseband signals, so that the communication function can be realized through communication code element information; and if a function which is to be realized by the system is a radar function, a certain code element accumulation is performed on the signals, so that high radar resolution can be obtained, and time delay and Doppler frequency are extracted through using related technologies, and a radar detection function can be finally realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Outer transmitter-based radar range migration compensation method based on frequency domain phase correction
InactiveCN103901419AImprove object detection performanceReduce computationWave based measurement systemsData acquisitionTransmitter
The invention relates to an outer transmitter-based radar range migration compensation method based on frequency domain phase correction and belongs to the technical field of radar target acquisition. The method comprises the steps that segment treatment is conducted on echo signals firstly; then echoes are converted to the frequency domain; phase correction is conducted on the echoes in the frequency domain to enable in-phase superposition of the signals to be achieved within the bandwidth and eliminate the influence of range migration; finally, the phase-corrected echoes are converted to the time domain through Fourier inversion, mutual ambiguity function calculation is conducted between the echoes and direct wave signals, and then a mutual ambiguity function diagram is obtained. According to the method, under the condition of a tracking mode (target speed is known) or that rough target speed is known, the accumulation gain of the method is similar to that of Keystone conversion, while the amount of calculation is far smaller.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com