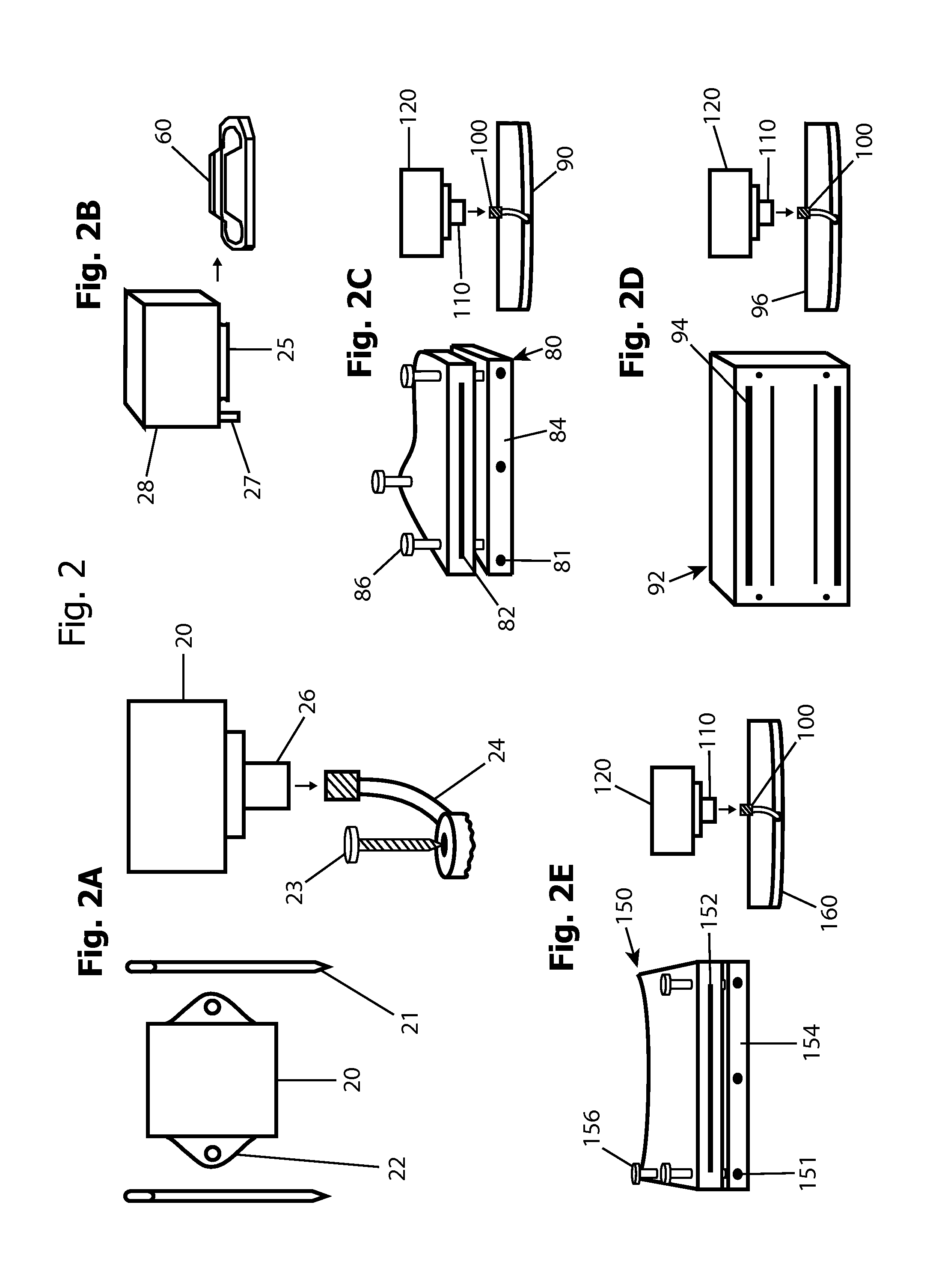
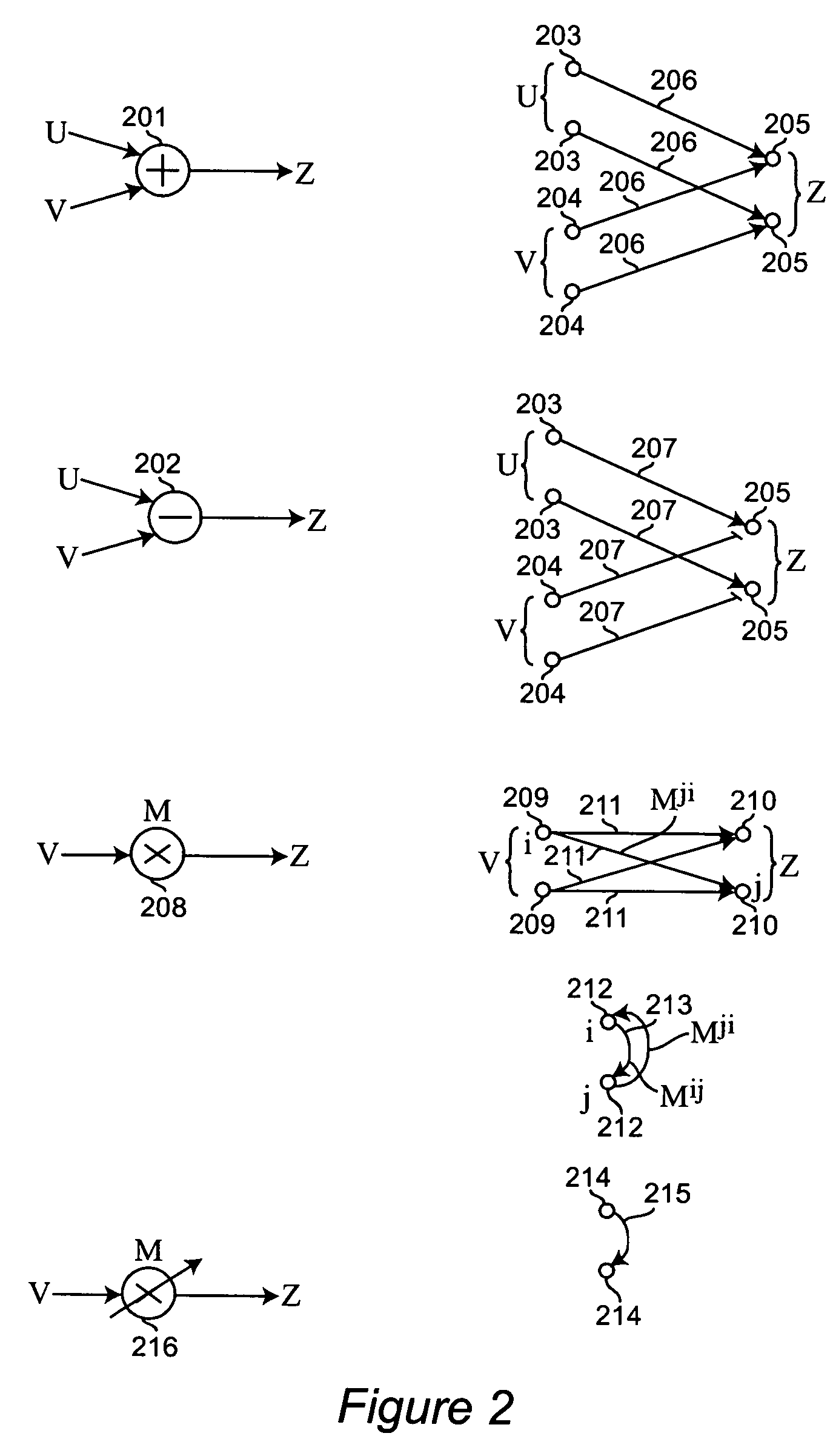
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2318 results about "Kaiman filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
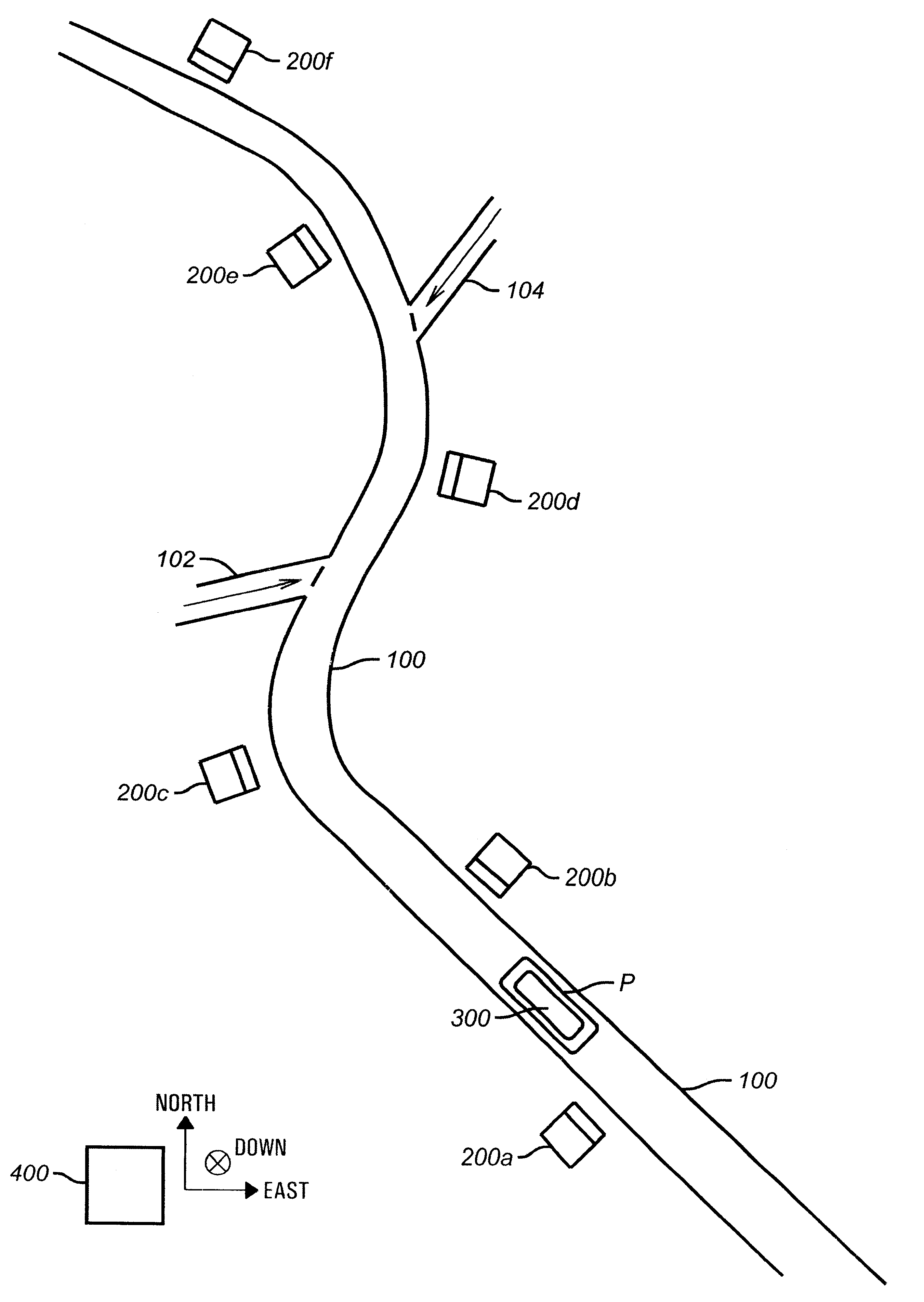
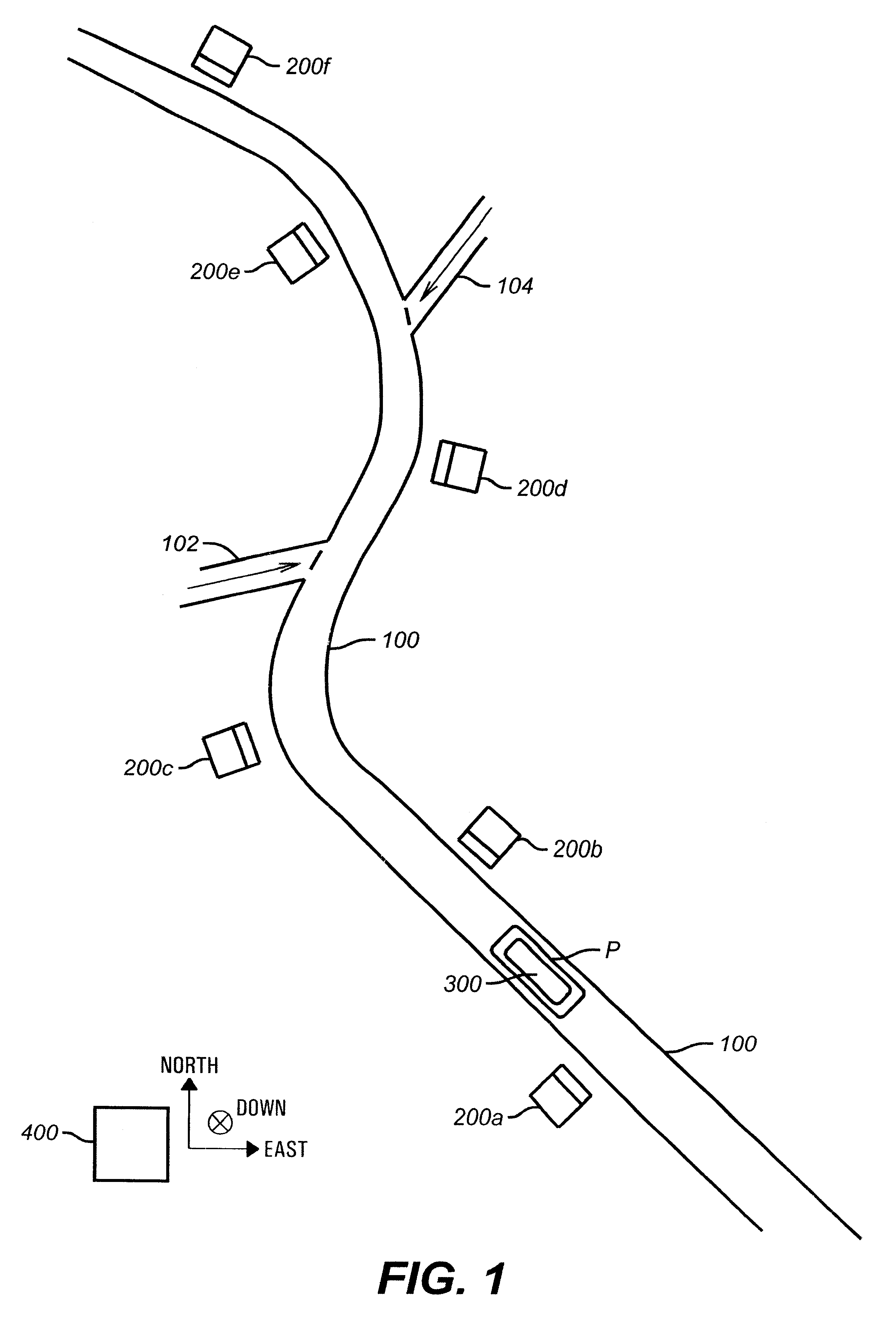
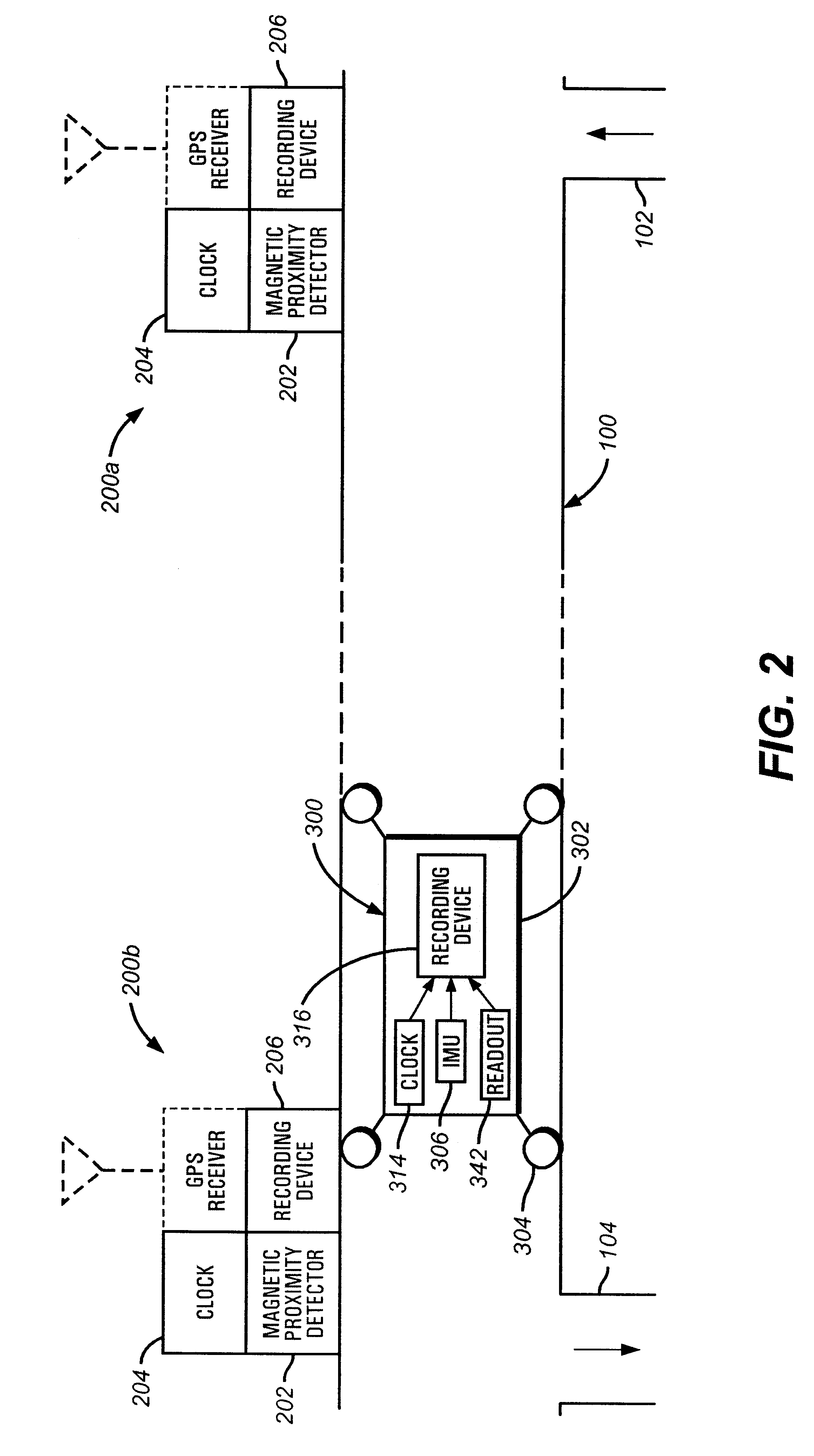
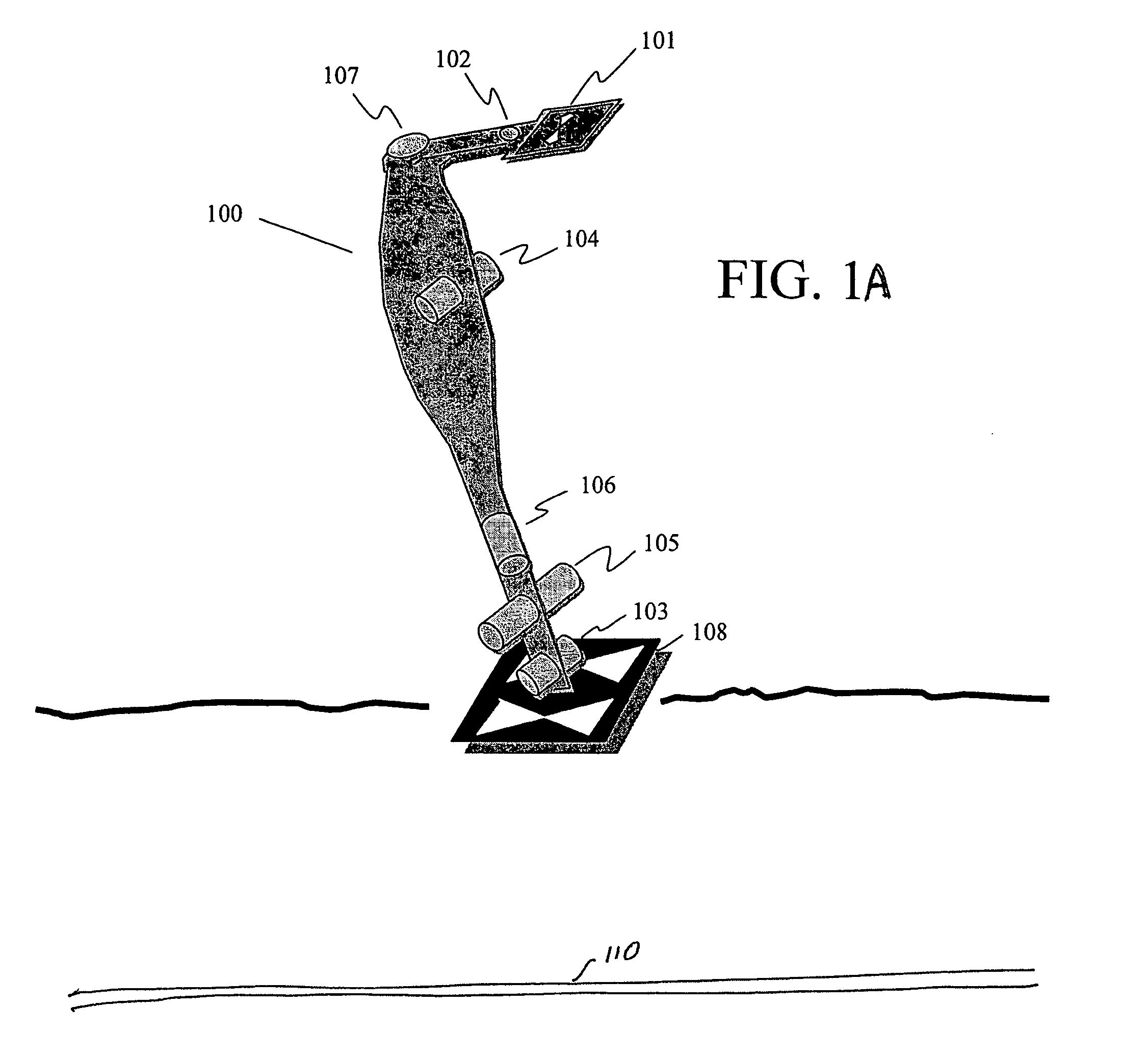
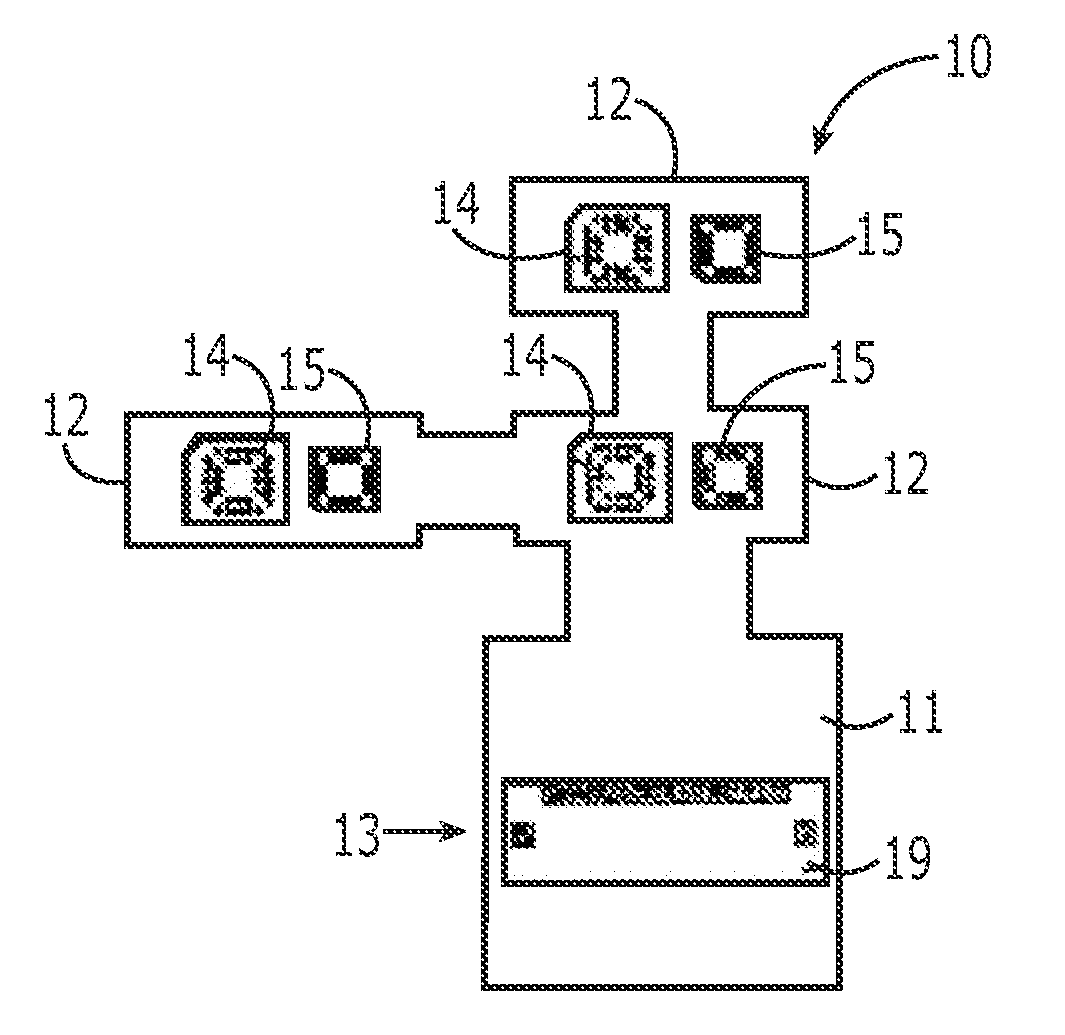
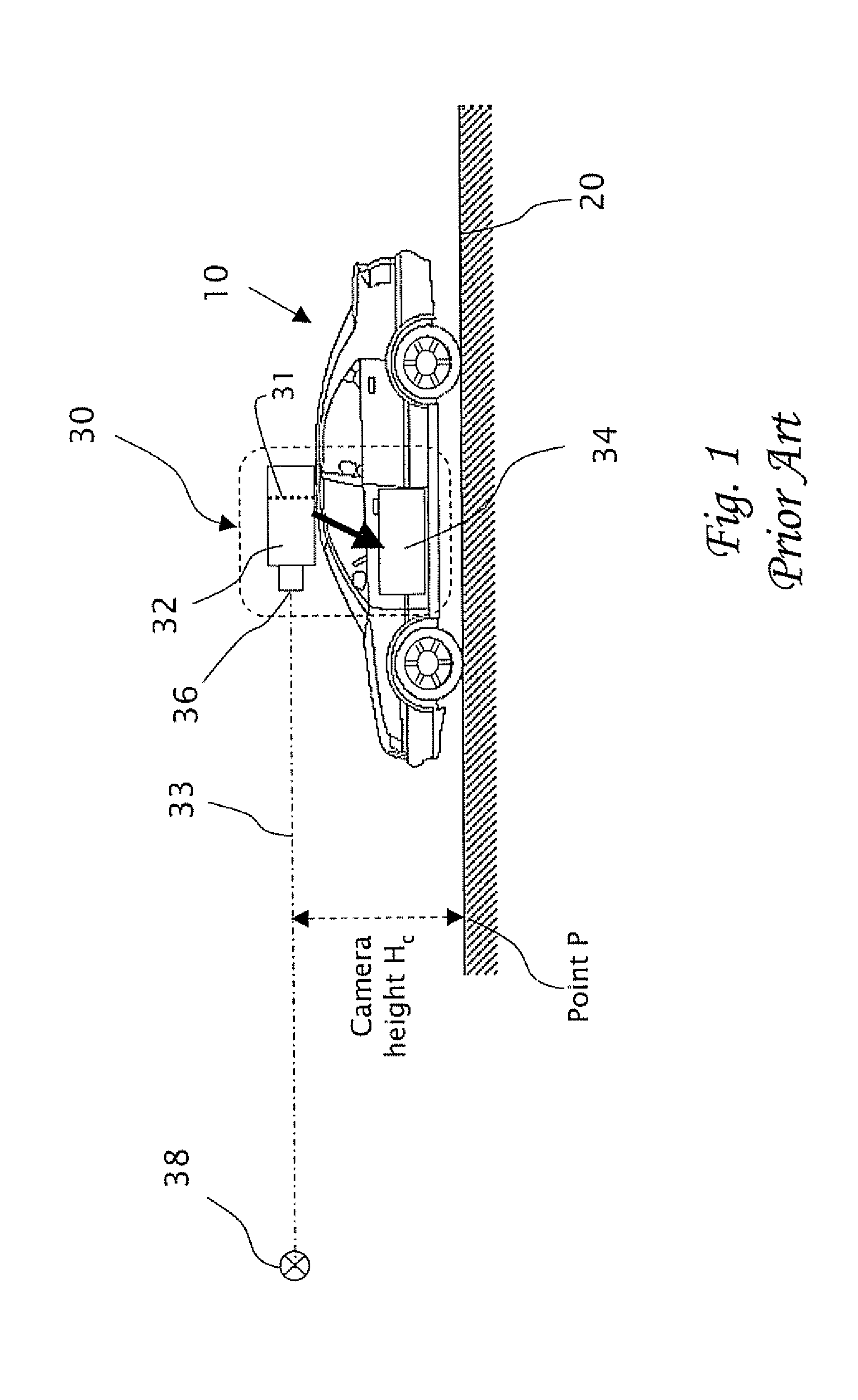
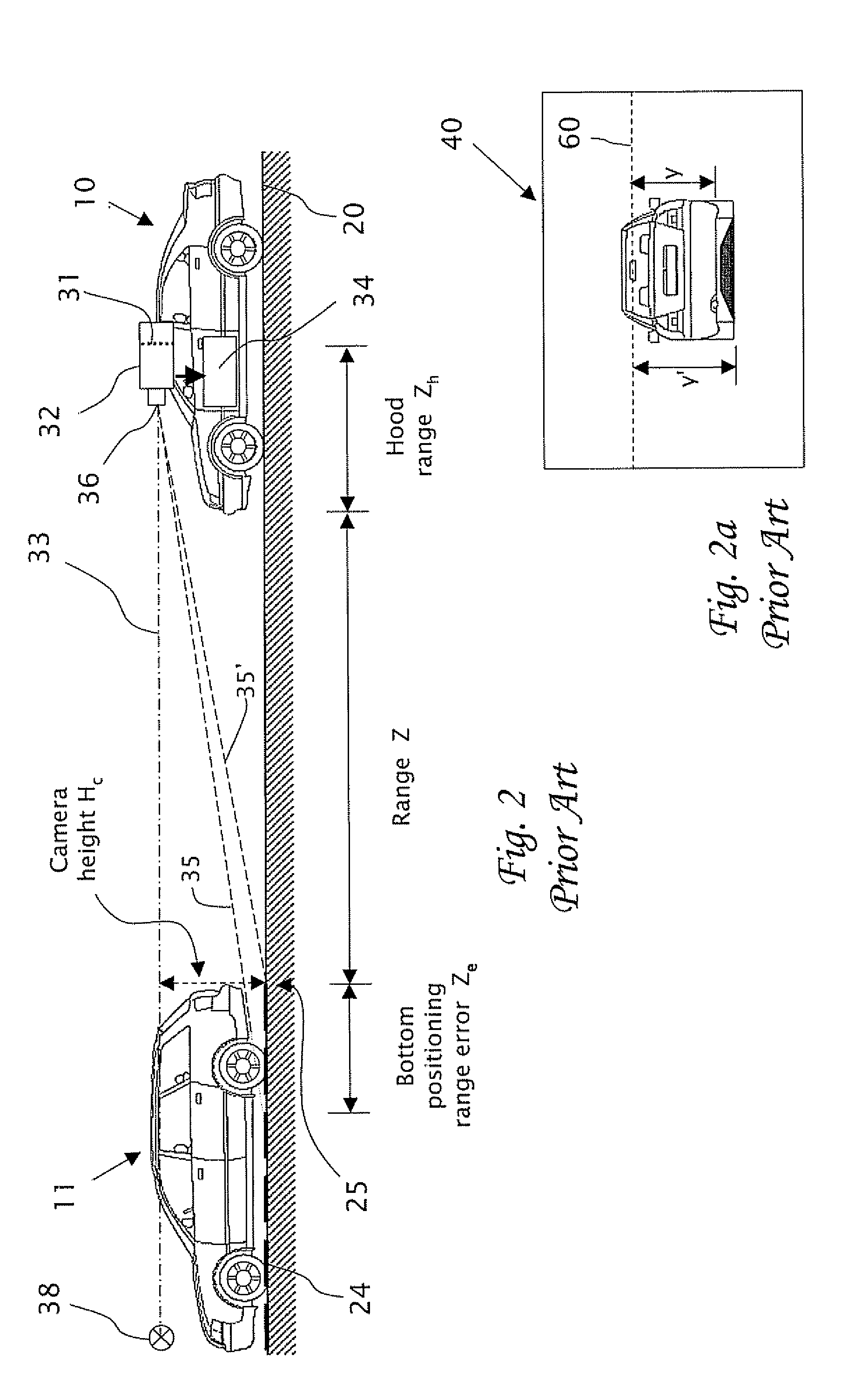
Method and apparatus for determining location of characteristics of a pipeline
InactiveUS6243657B1High degreeHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksKaiman filterComputerized system
A pipeline inspection and defect mapping system includes a pig having an inertial measurement unit and a pipeline inspection unit for recording pig location and defect detection events, each record time-stamped by a highly precise onboard clock. The system also includes several magloggers at precisely known locations along the pipeline, each containing a fluxgate magnetometer for detecting the passage of the pig along the pipeline and further containing a highly precise clock synchronized with the clock in the pig. The locations of the various magloggers are known in a north / east / down coordinate system through a differential global positioning satellite process. Finally, a postprocessing off-line computer system receives downloaded maglogger, inertial measurement, and odometer data and through the use of several Kalman filters, derives the location of the detected defects in the north / east / down coordinate frame. Consequently, a task of identifying sites for repair activity is much simplified.
Owner:PIPELINE INTEGRITY INT INC FORMERLY BRITISH GAS INSPECTION SERVICES INC +1
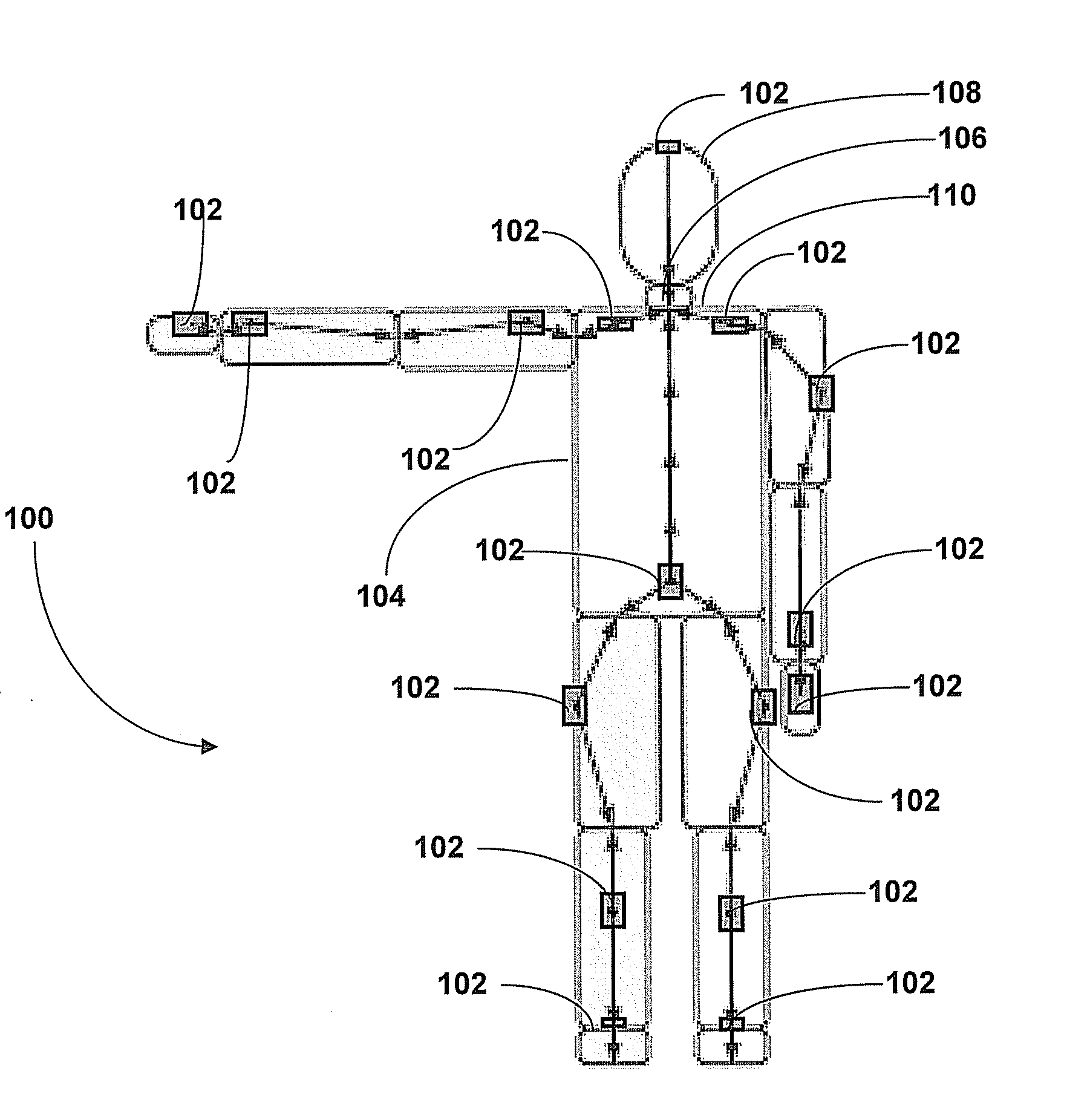
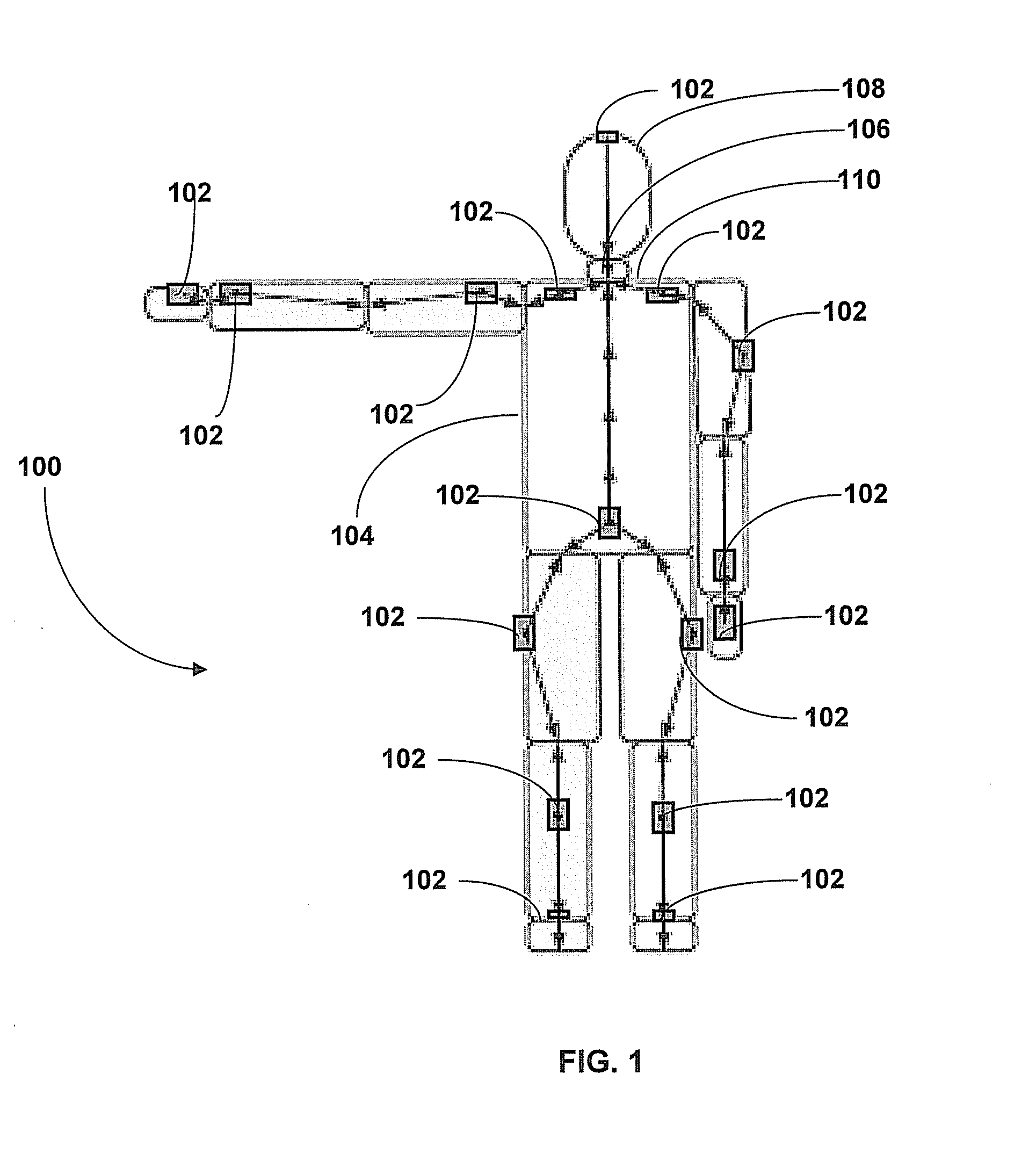
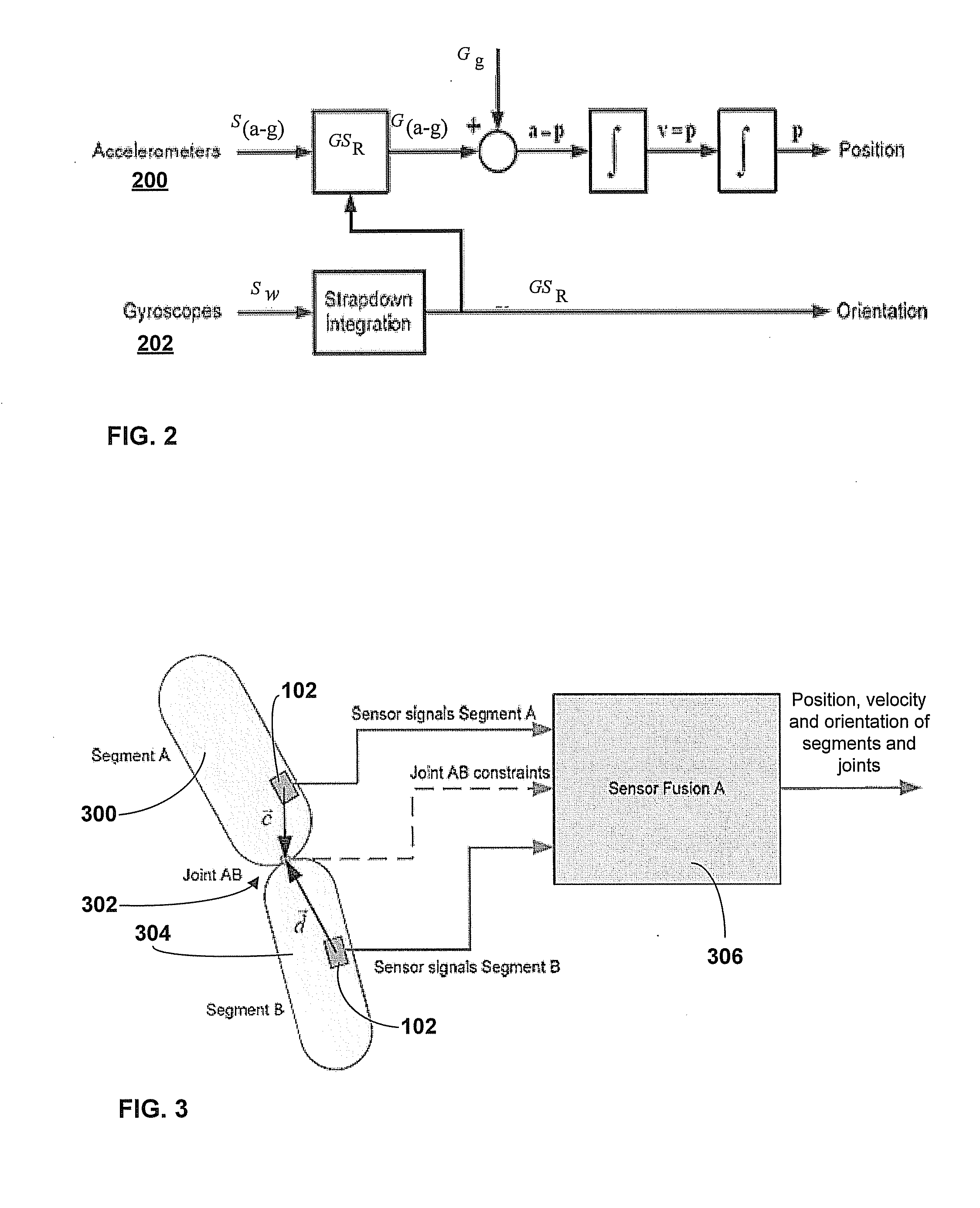
Motion Tracking System
ActiveUS20080285805A1High precisionAccurate recordProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationMovement trackingKalman filter
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
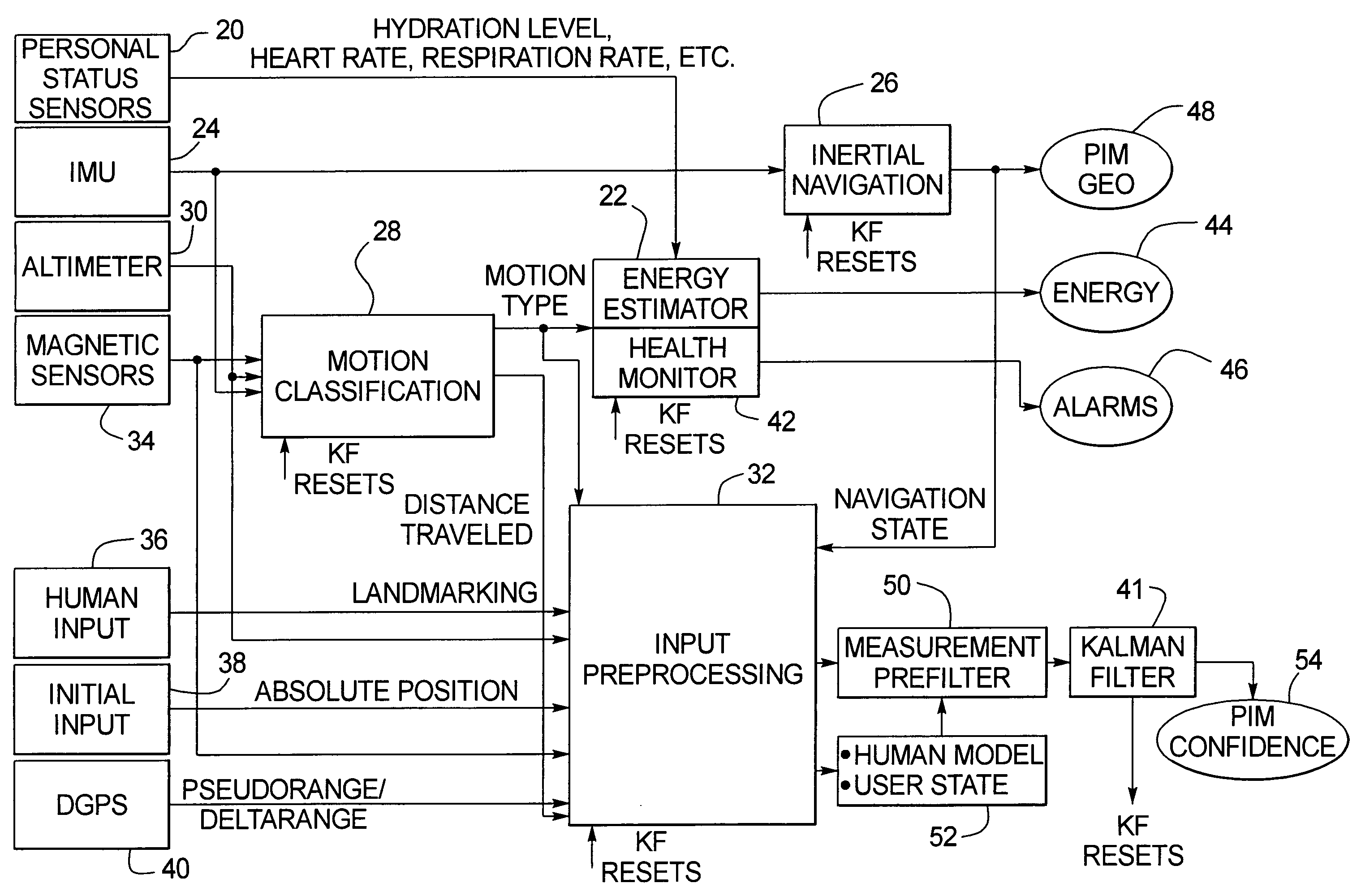
Human motion identification and measurement system and method
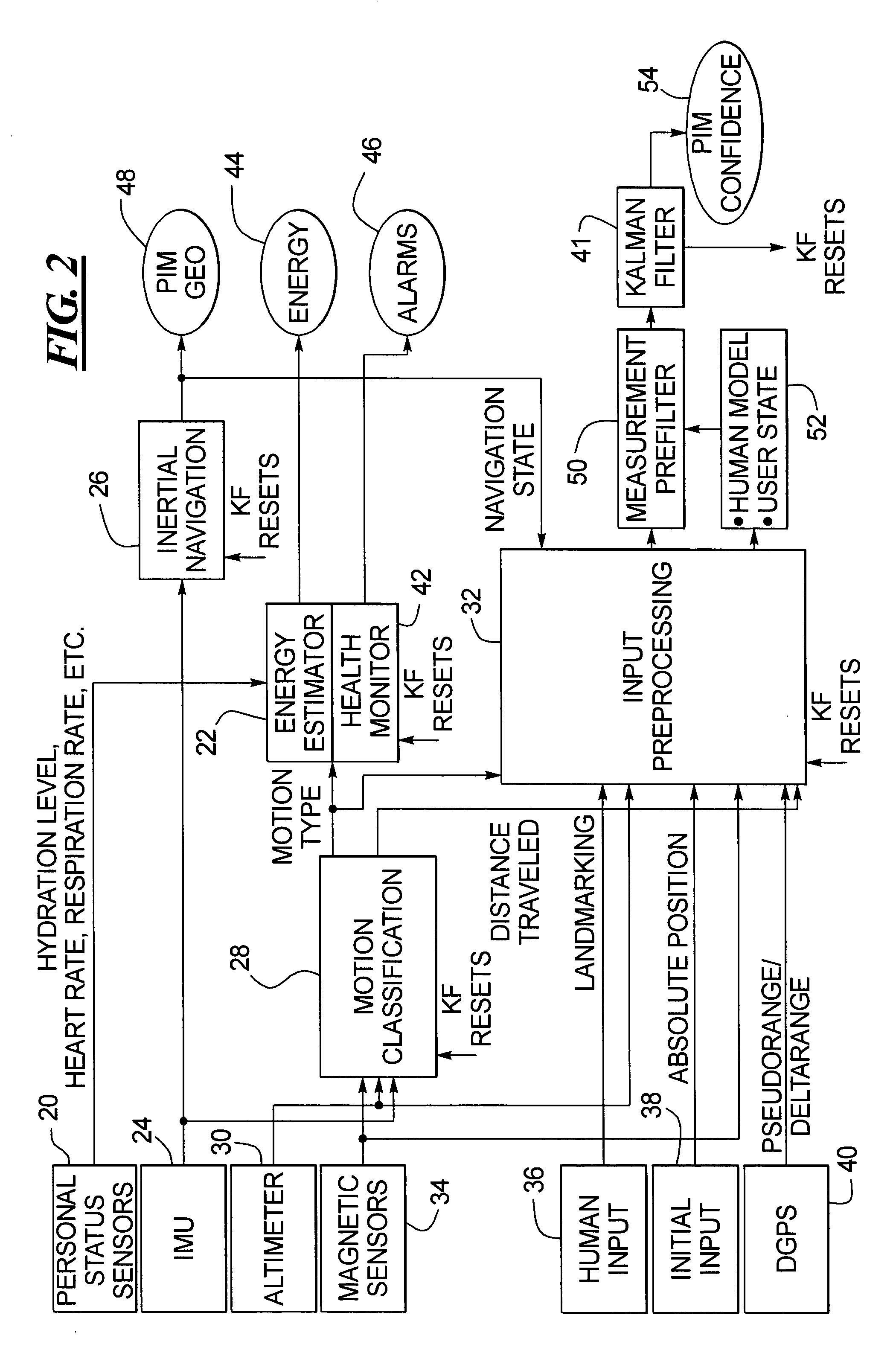
A system and method for classifying and measuring human motion senses the motion of the human and the metabolism of the human. A motion classification unit determines the motion type being carried out by the human and provides the motion classification information to an energy estimator and a health monitor. The energy estimator also receives the metabolism information and therefrom provides an estimate of energy expended by the human. The health monitor triggers an alarm if health related thresholds are traversed. The motion classification is also provided to a processing unit that in turn provides the data to a Kalman filter, which has an output that is provided as feedback to the motion classification unit, the energy estimator and health monitor. Altimeter, GPS and magnetic sensors may also be provided for monitoring the human motion, and initial input and landmark input data inputs are provided to the system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
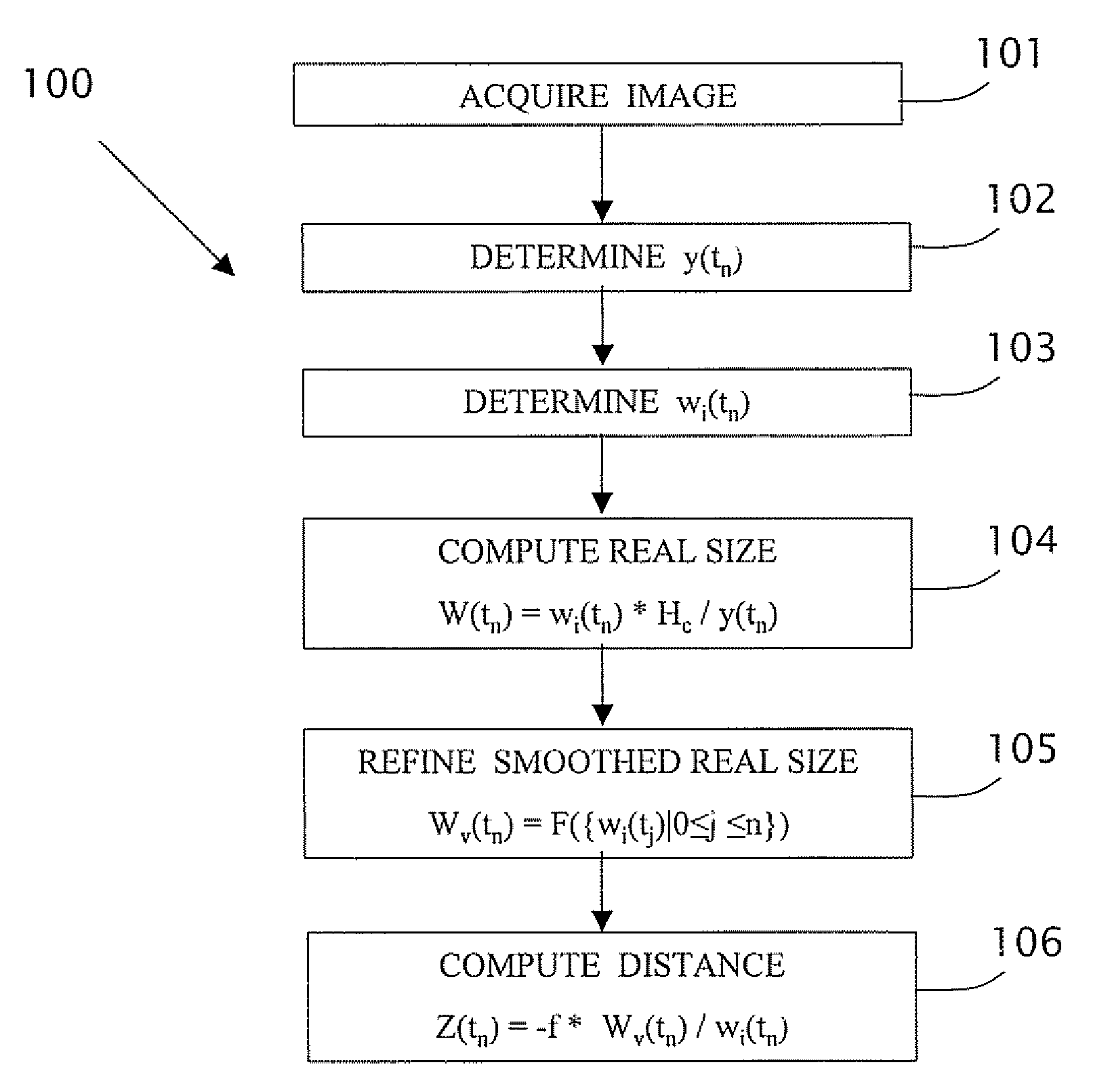
Estimating distance to an object using a sequence of images recorded by a monocular camera
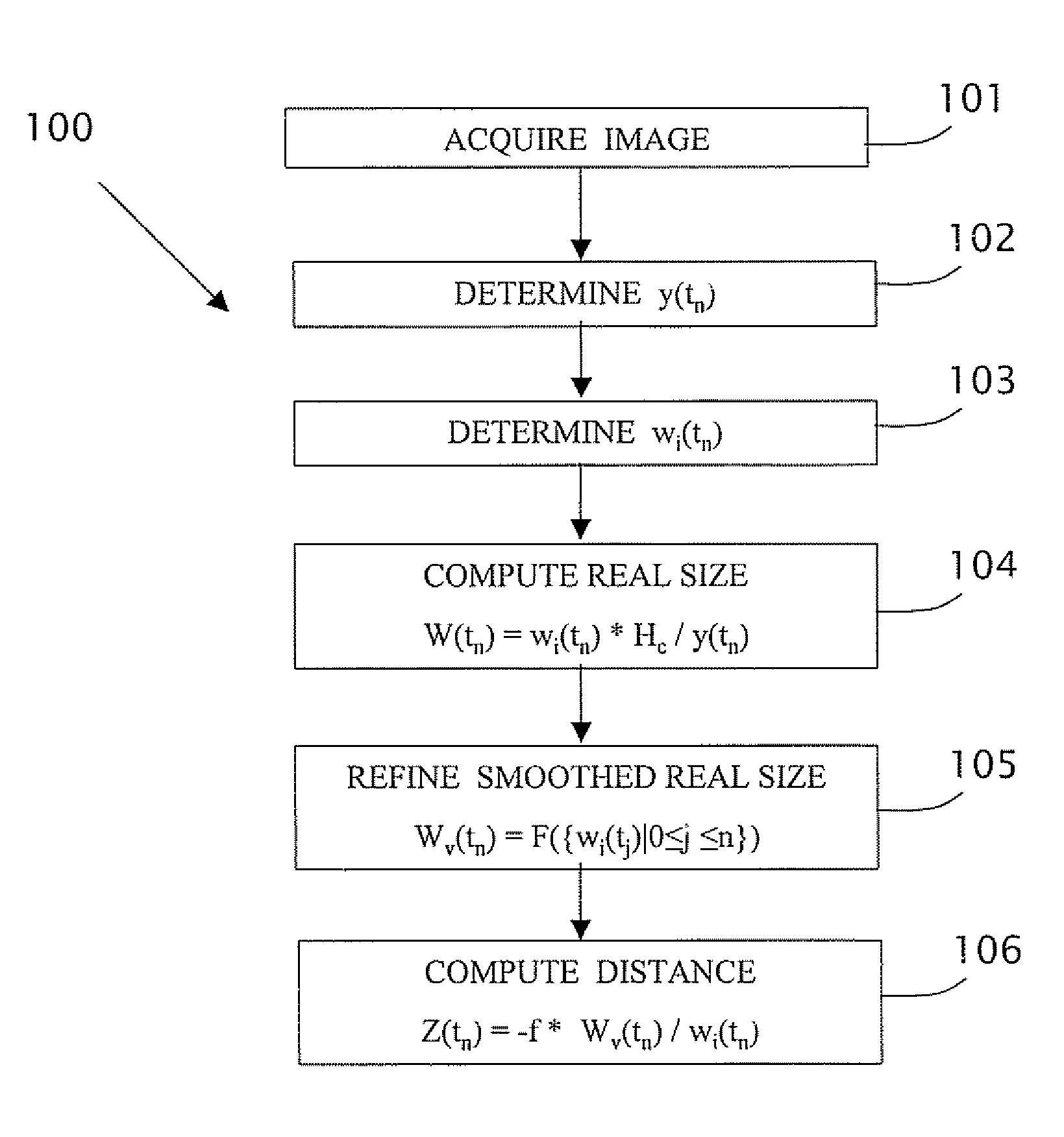
In a computerized system including a camera mounted in a moving vehicle. The camera acquires consecutively in real time image frames including images of an object within the field of view of the camera. Range to the object from the moving vehicle is determined in real time. A dimension, e.g. a width, is measured in the respective images of two or more image frames, thereby producing measurements of the dimension. The measurements are processed to produce a smoothed measurement of the dimension. The dimension is measured subsequently in one or more subsequent frames. The range from the vehicle to the object is calculated in real time based on the smoothed measurement and the subsequent measurements. The processing preferably includes calculating recursively the smoothed dimension using a Kalman filter.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
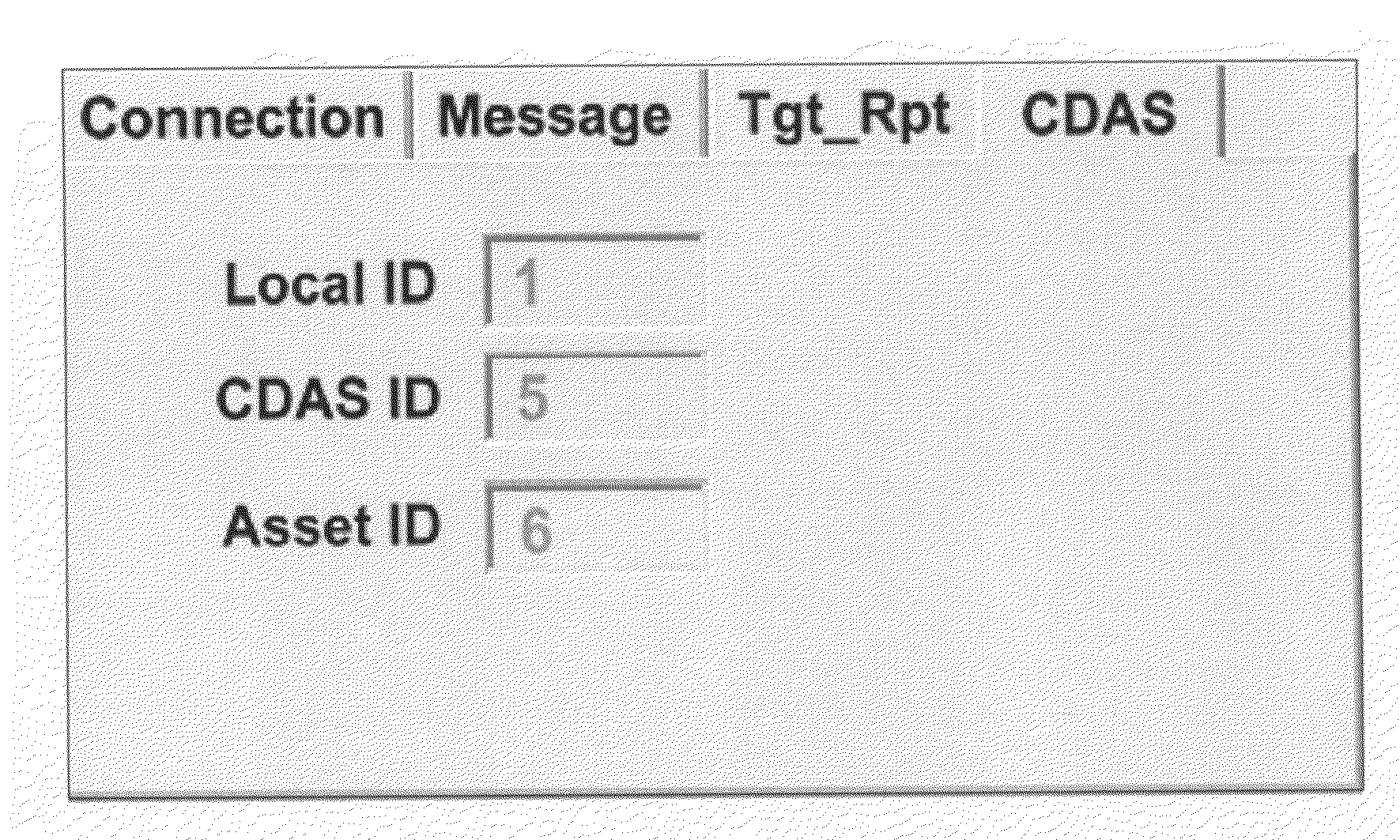
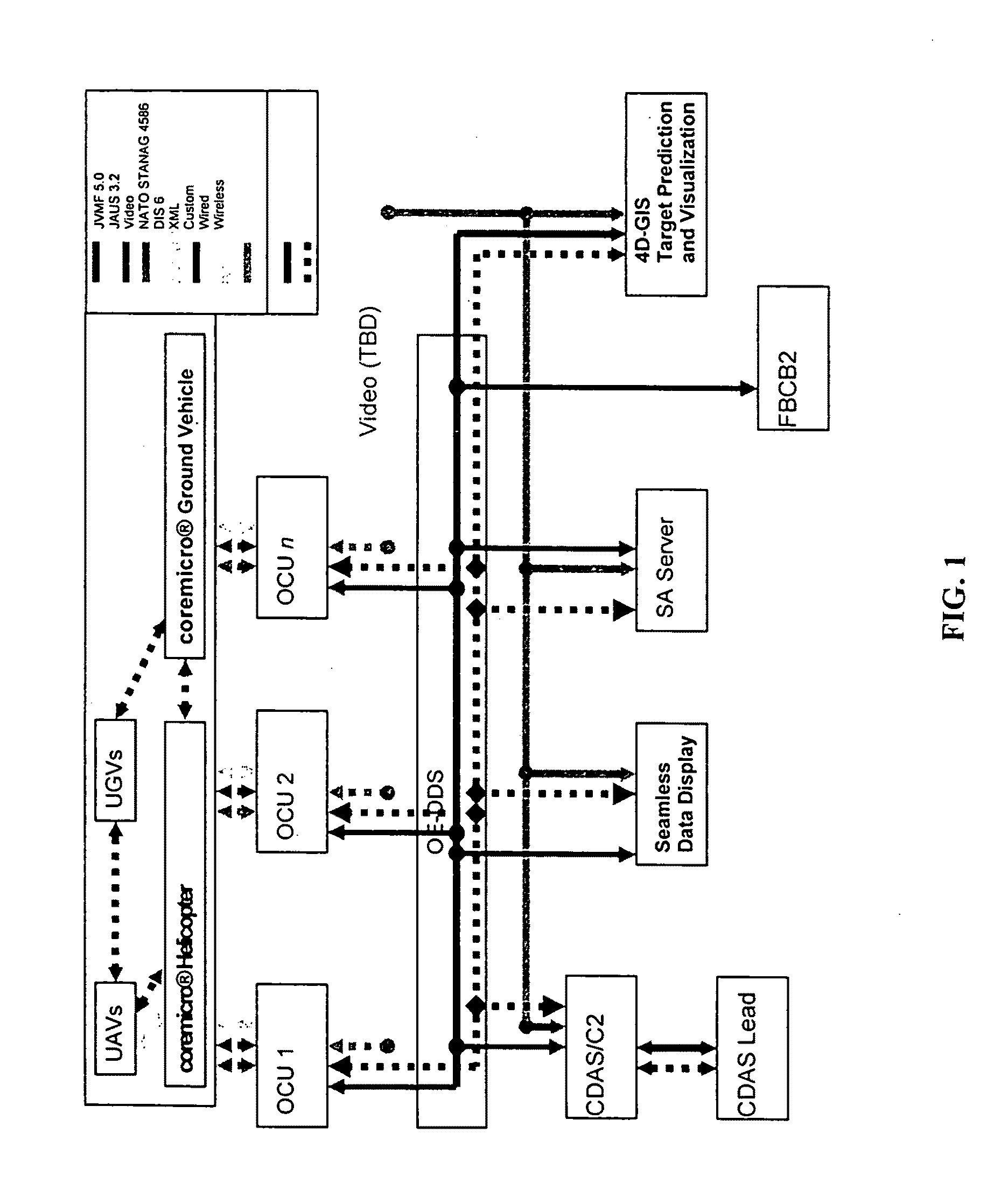
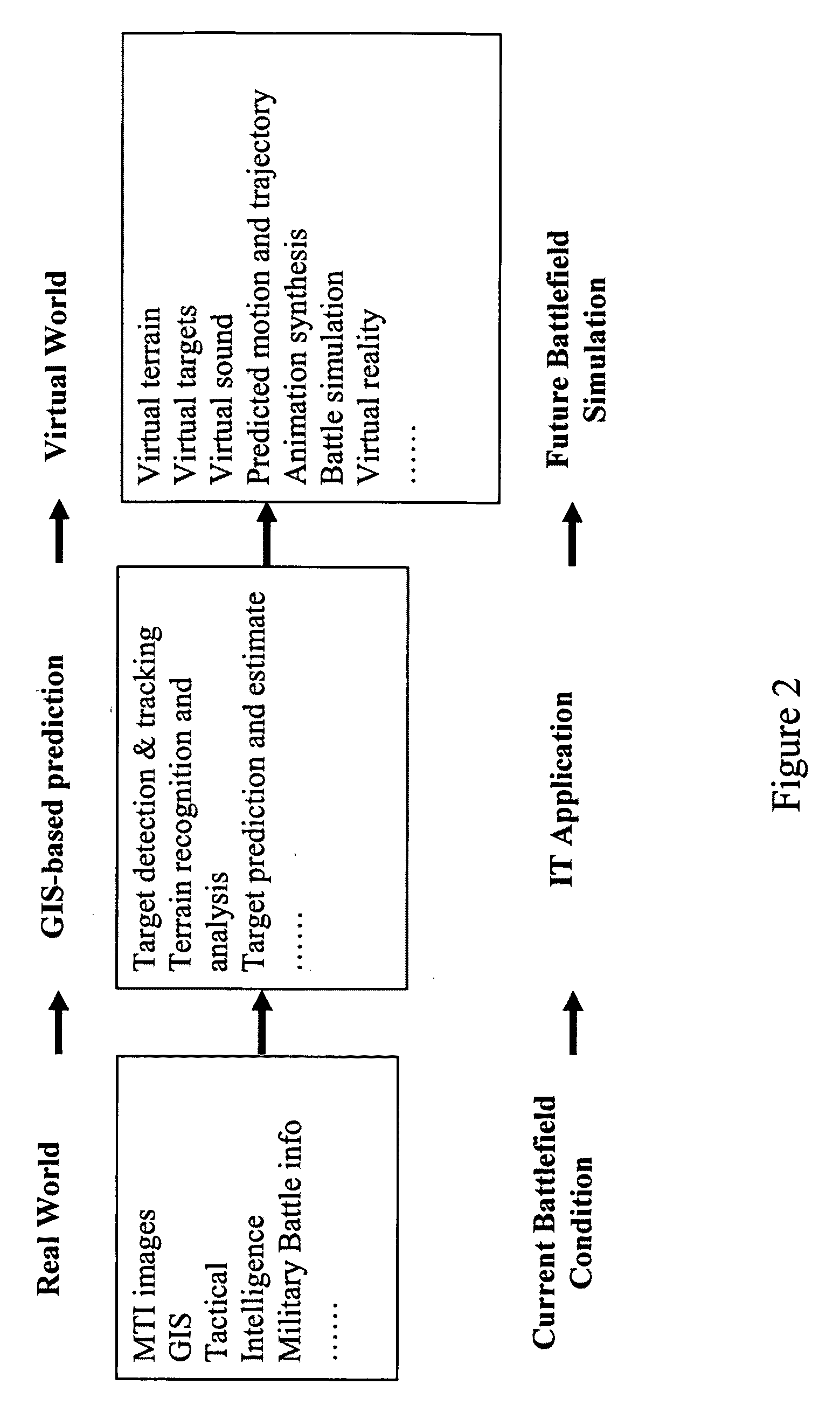
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS20090087029A1Enhanced degree of confidencePrecise processImage enhancementImage analysisMoving averageTerrain
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
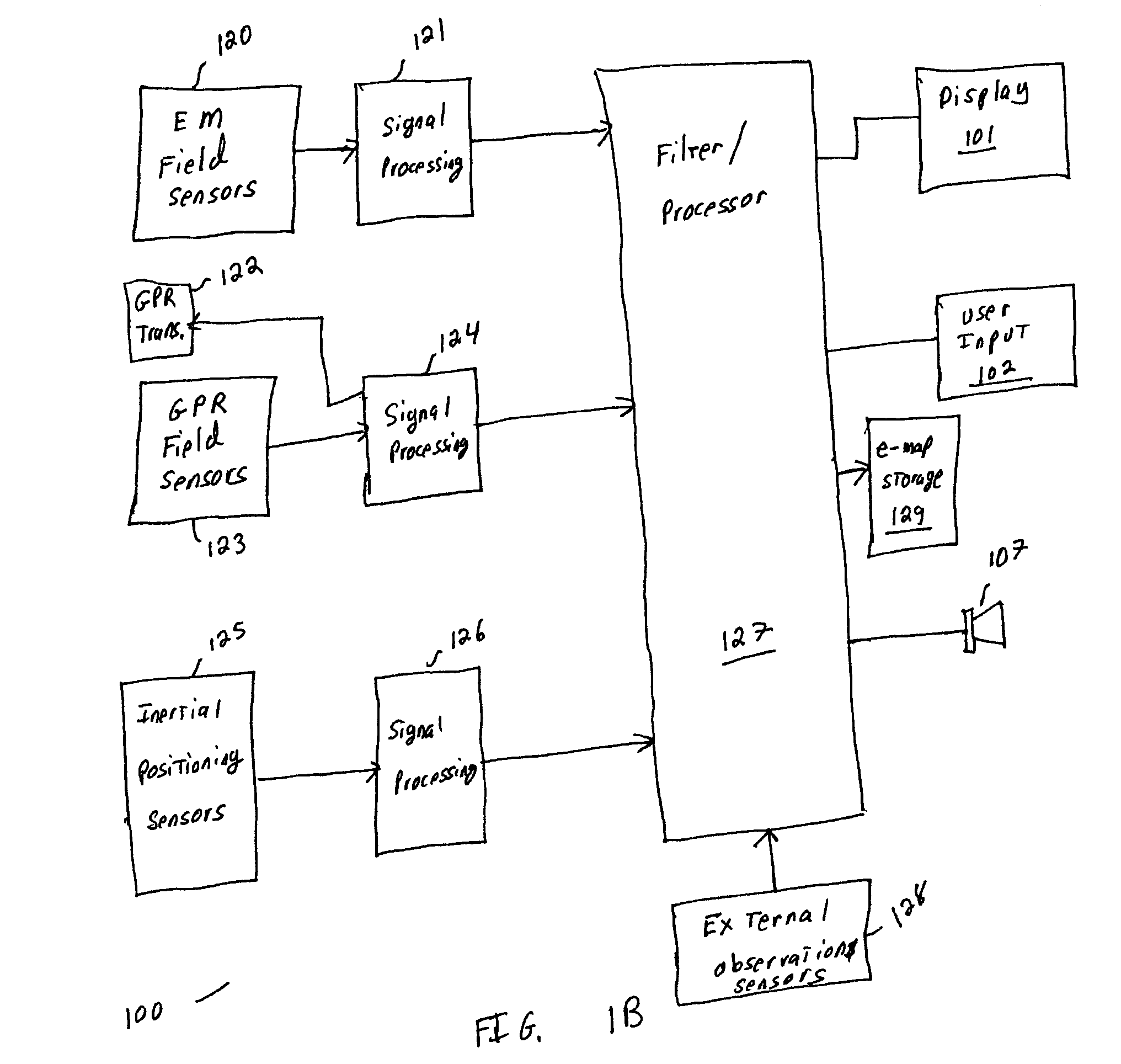
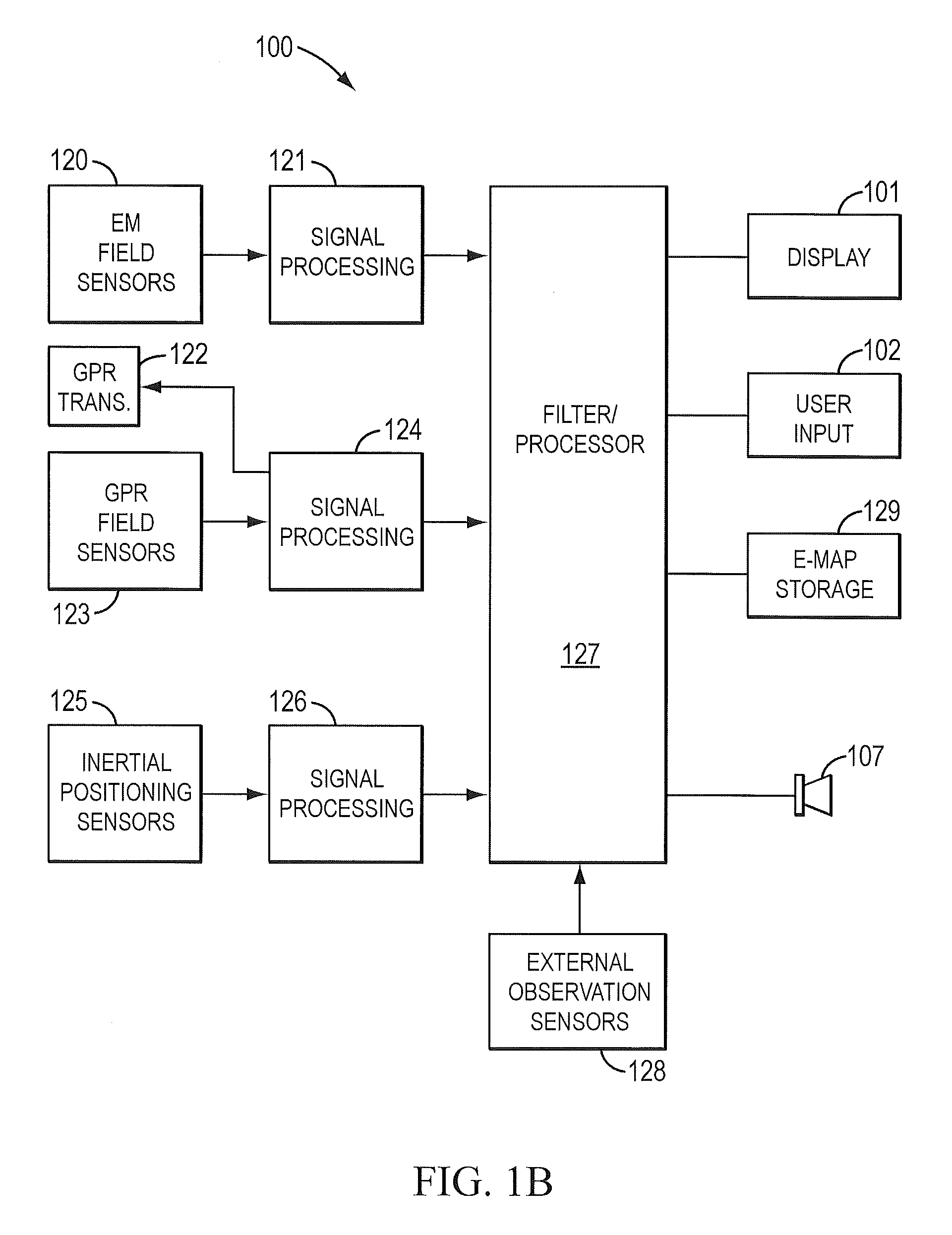
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS20060055584A1Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAccelerometerGyroscope
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
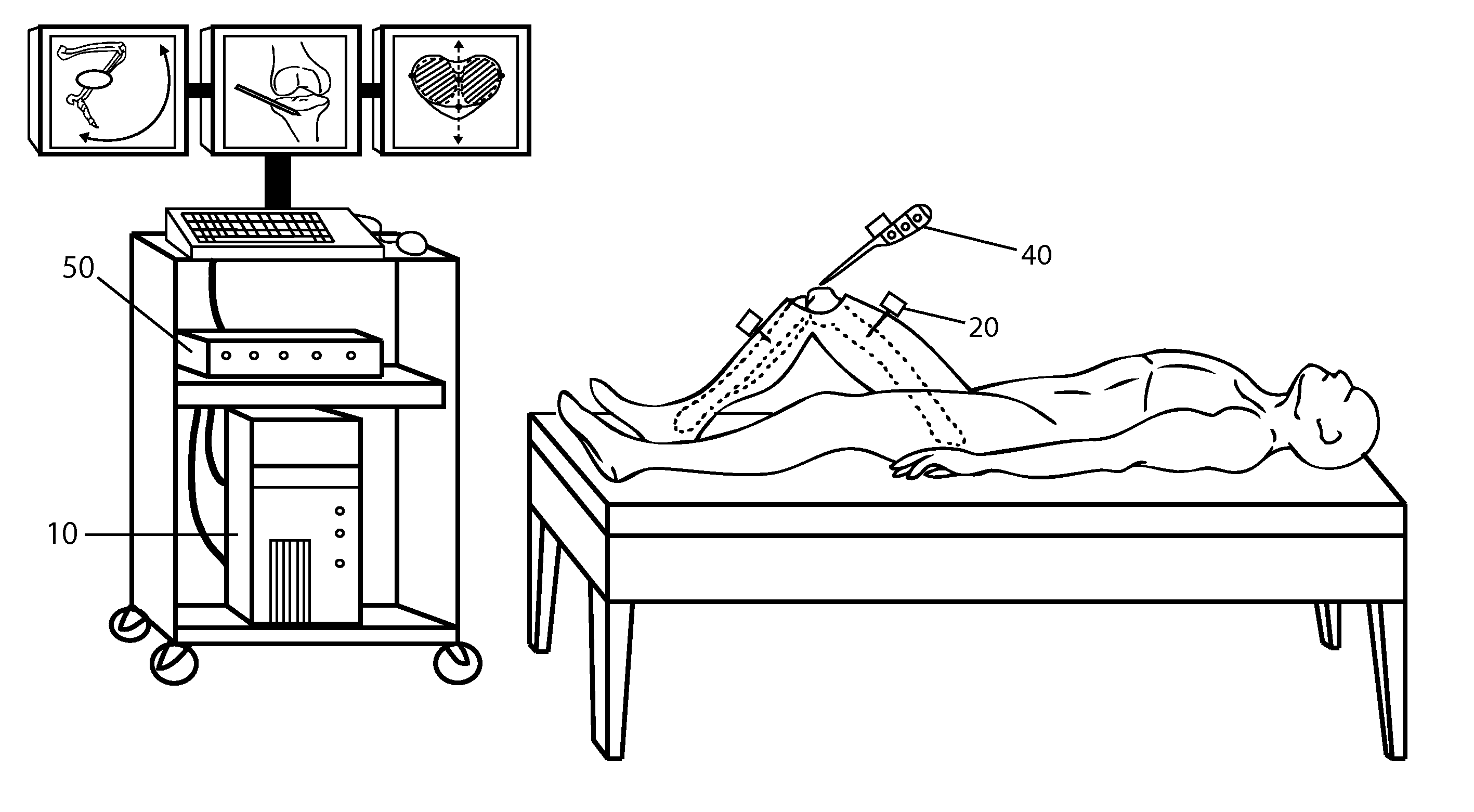
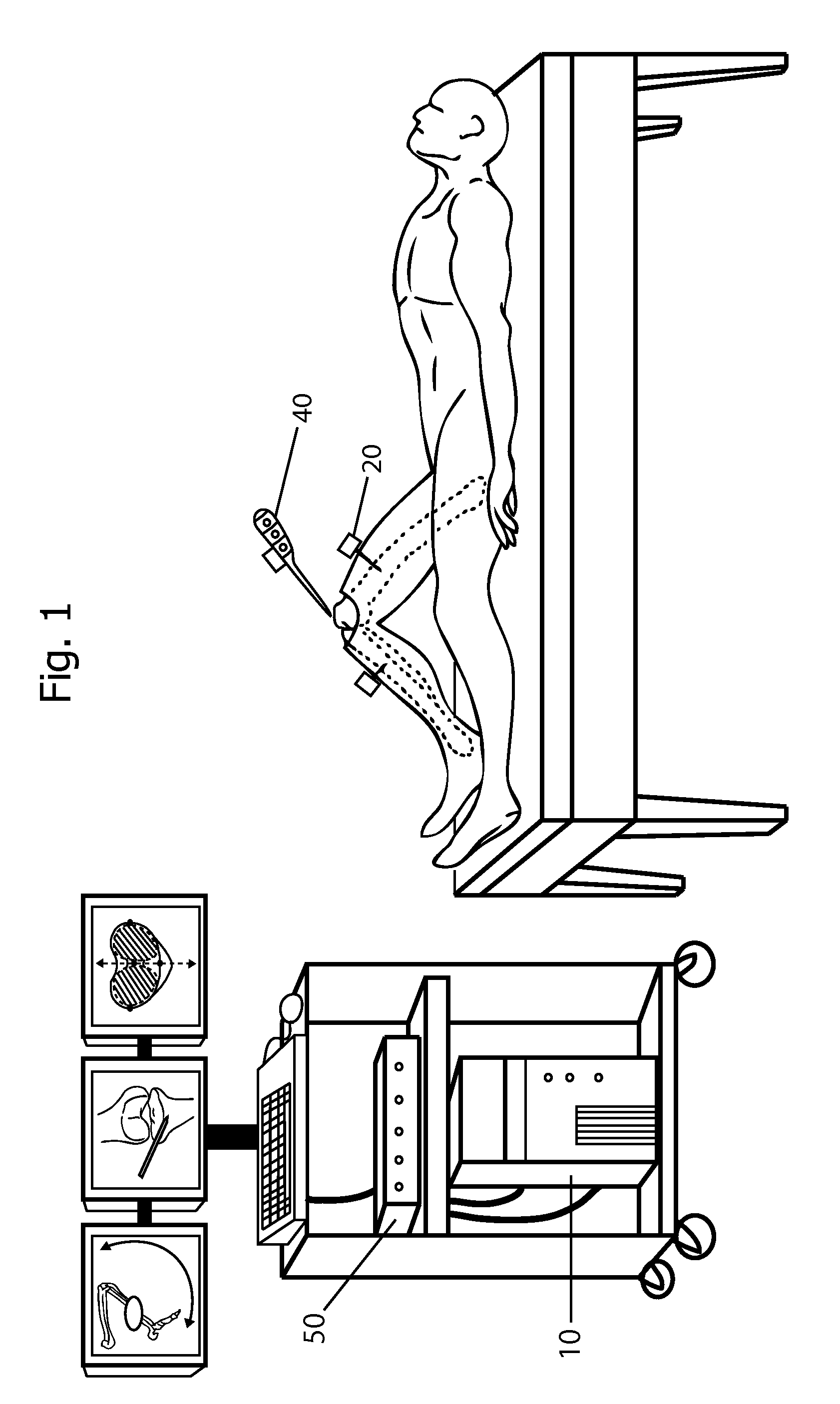
Inertial Sensor Based Surgical Navigation System for Knee Replacement Surgery
ActiveUS20110275957A1Improve accuracyGood precisionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationKnee JointNavigation system
An inertial sensor based surgical navigation system for knee replacement surgery is disclosed. Inertial sensors composed of six-degree-of-freedom inertial chips, whose measurements are processed through a series of integration, quaternion, and kalman filter algorithms, are used to track the position and orientation of bones and surgical instruments. The system registers anatomically significant geometry, calculates joint centers and the mechanical axis of the knee, develops a visualization of the lower extremity that moves in real time, assists in the intra-operative planning of surgical cuts, determines the optimal cutting planes for cut guides and the optimal prosthesis position and orientation, and finally navigates the cut guides and the prosthesis to their optimal positions and orientations using a graphical user interface.
Owner:BHANDARI SACHIN
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
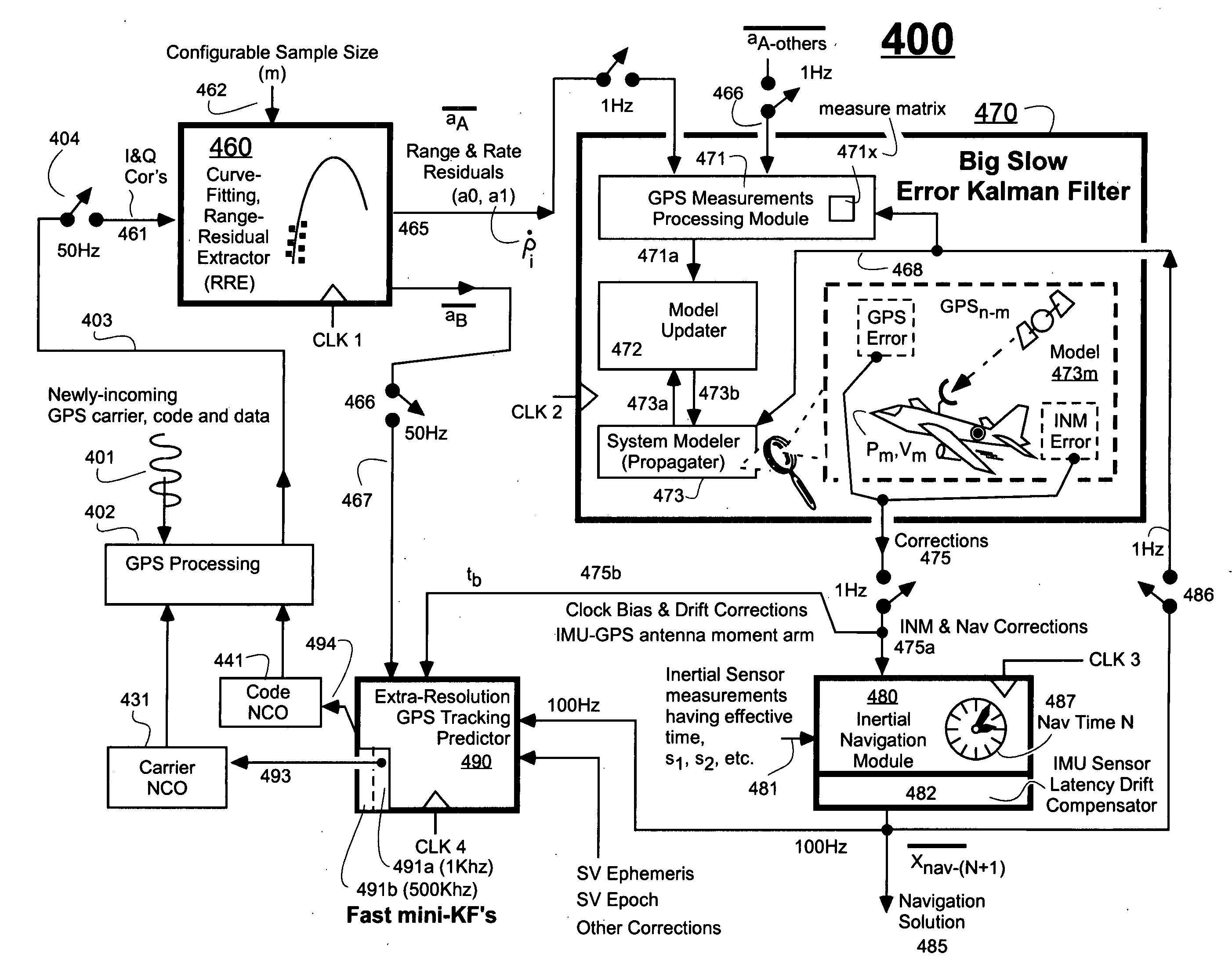
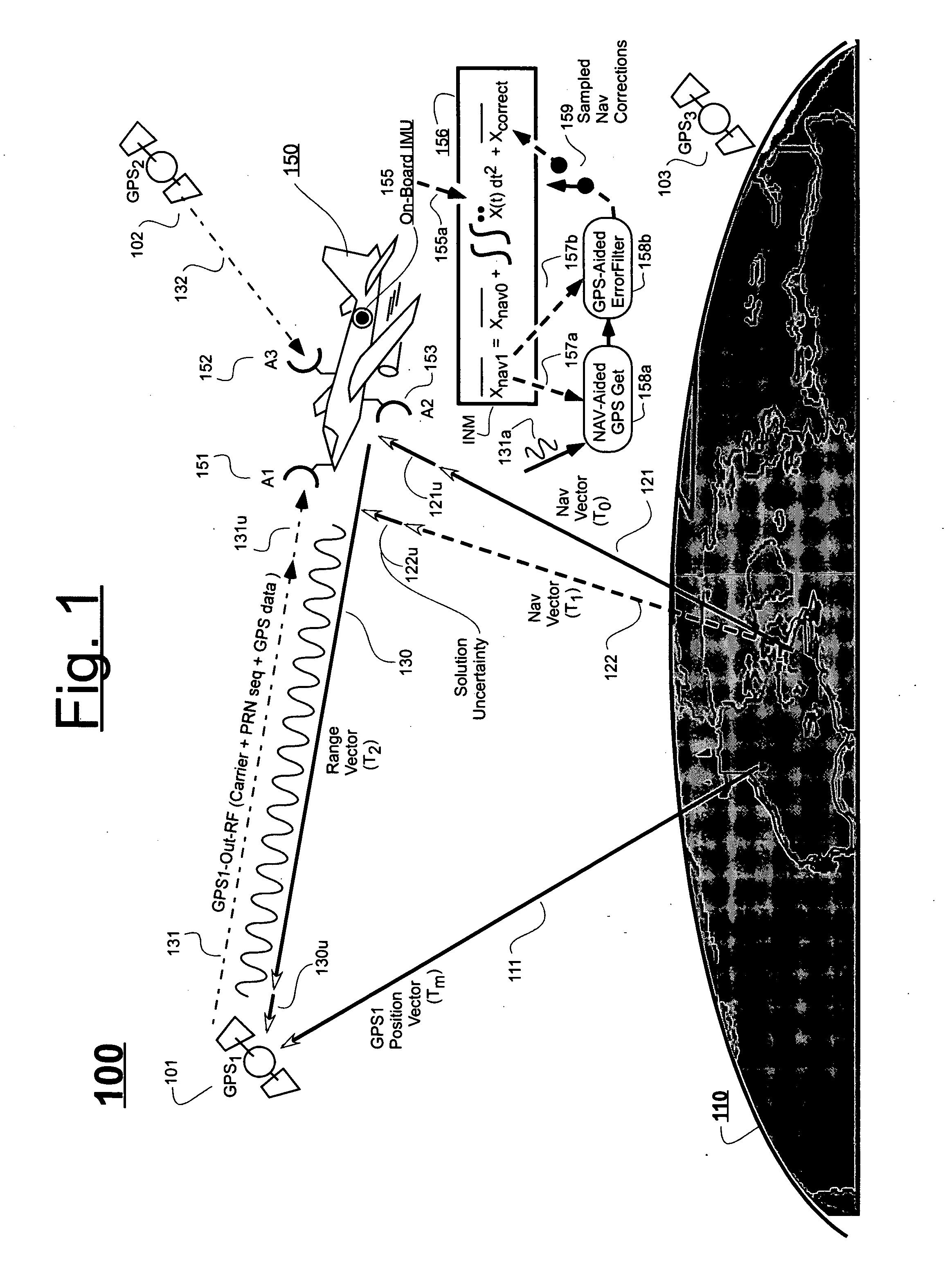
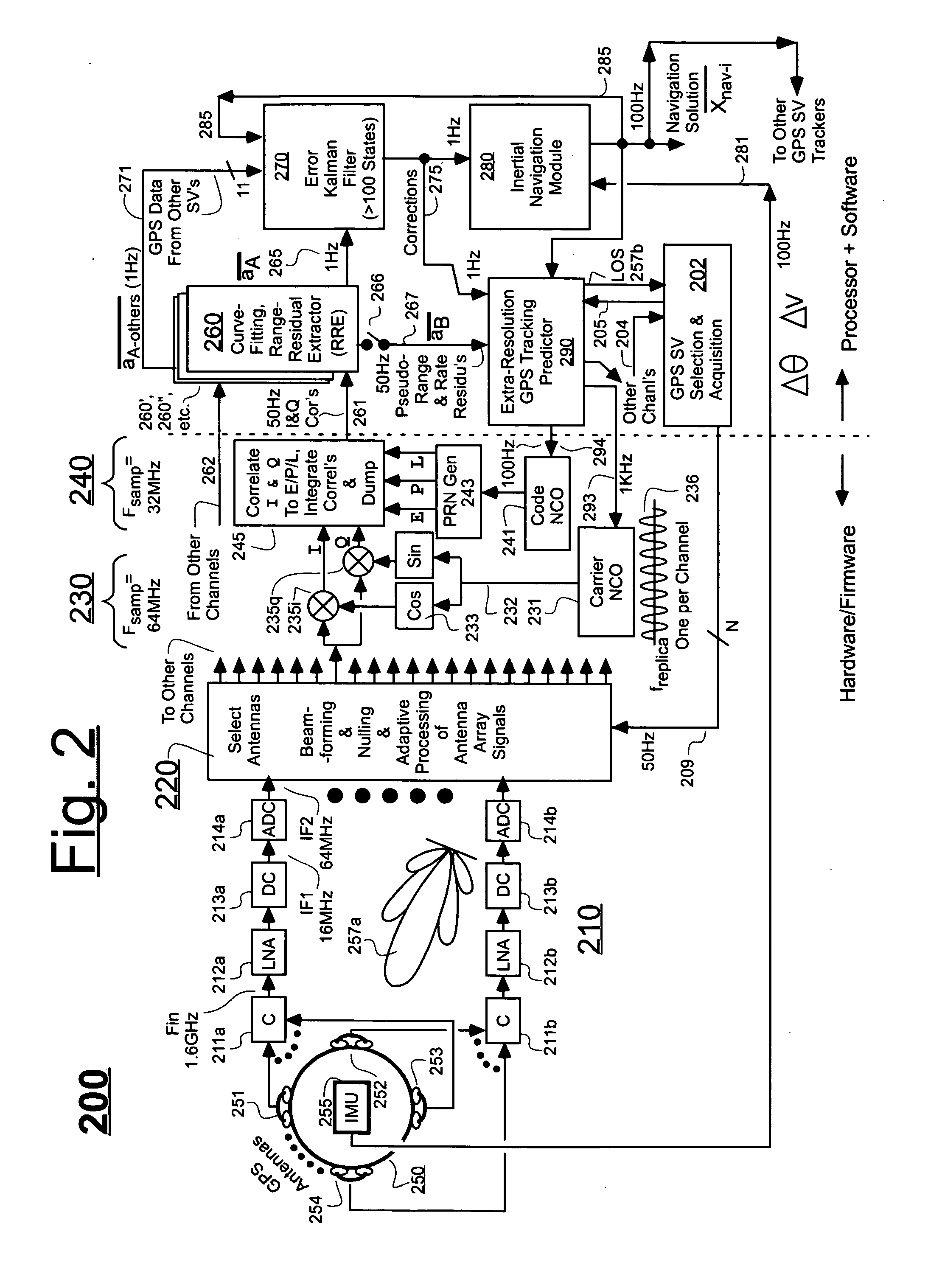
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
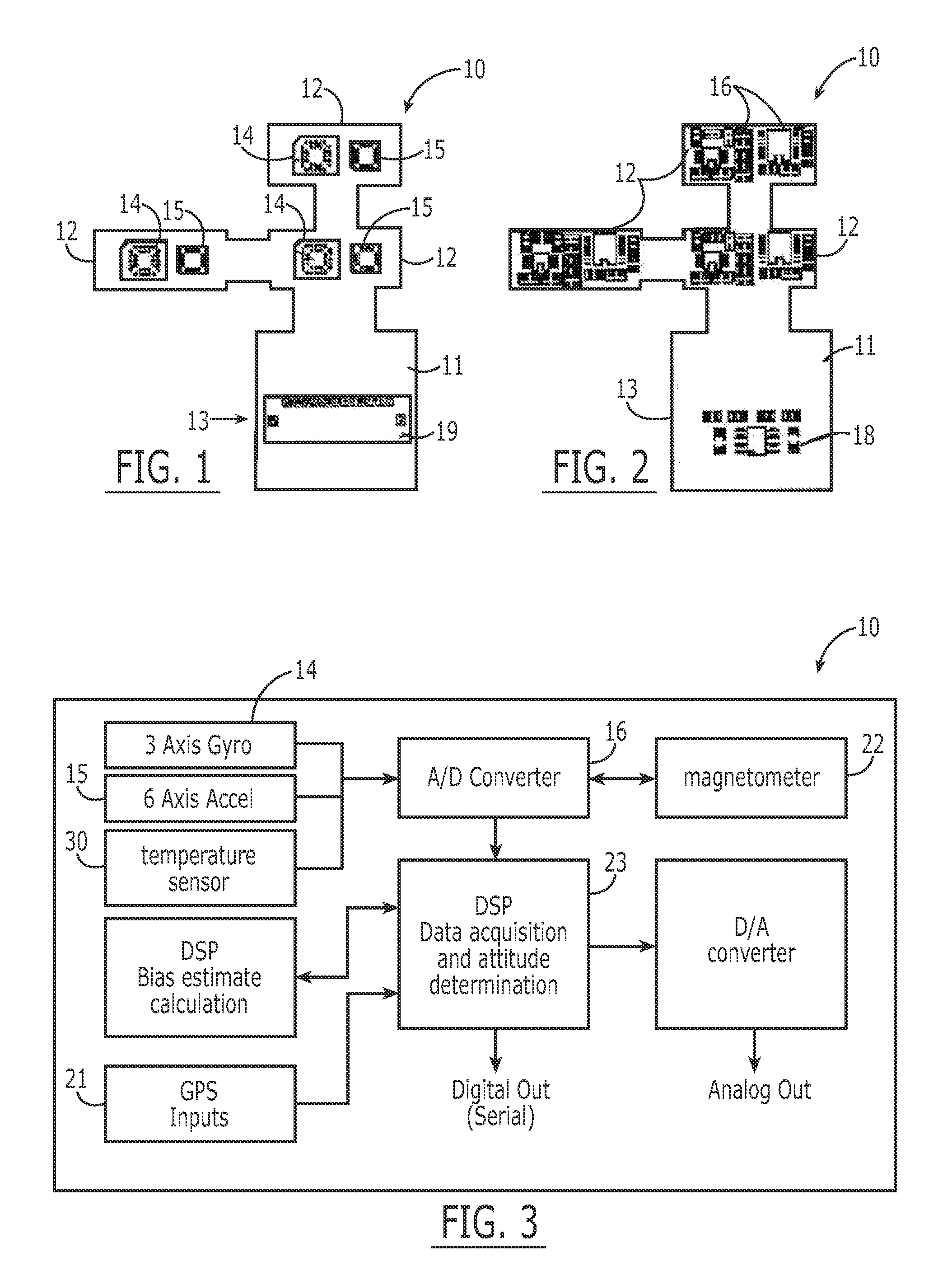
Miniaturized Inertial Measurement Unit and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20070032951A1Reduce noiseThe result is accurateNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingAccelerometer
A self-contained, integrated micro-cube-sized inertial measurement unit is provided wherein accuracy is achieved through the use of specifically oriented sensors, the orientation serving to substantially cancel noise and other first-order effects, and the use of a noise-reducing algorithm such as wavelet cascade denoising and an error correcting algorithm such as a Kalman filter embedded in a digital signal processor device. In a particular embodiment, a pair of three sets of angle rate sensors are orientable triaxially in opposite directions, wherein each set is mounted on a different sector of a base orientable normal to the other two and comprising N gyroscopes oriented at 360 / N-degree increments, where N≧2. At least one accelerometer is included to provide triaxial data. Signals are output from the angle rate sensors and accelerometer for calculating a change in attitude, position, angular rate, acceleration, and / or velocity of the unit.
Owner:JAYMART SENSORS
Estimating Distance To An Object Using A Sequence Of Images Recorded By A Monocular Camera
In a computerized system including a camera mounted in a moving vehicle. The camera acquires consecutively in real time image frames including images of an object within the field of view of the camera. Range to the object from the moving vehicle is determined in real time. A dimension, e.g. a width, is measured in the respective images of two or more image frames, thereby producing measurements of the dimension. The measurements are processed to produce a smoothed measurement of the dimension. The dimension is measured subsequently in one or more subsequent frames. The range from the vehicle to the object is calculated in real time based on the smoothed measurement and the subsequent measurements. The processing preferably includes calculating recursively the smoothed dimension using a Kalman filter.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
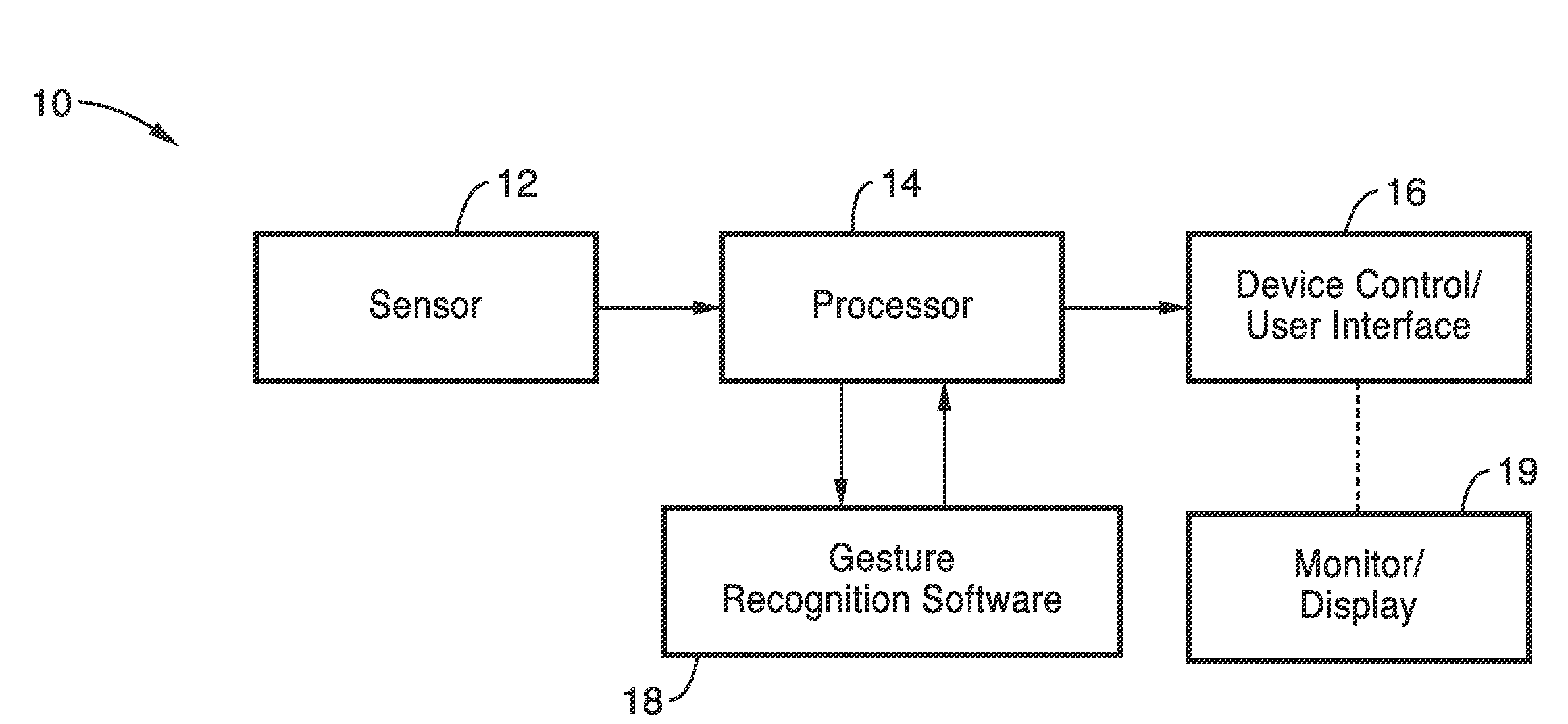
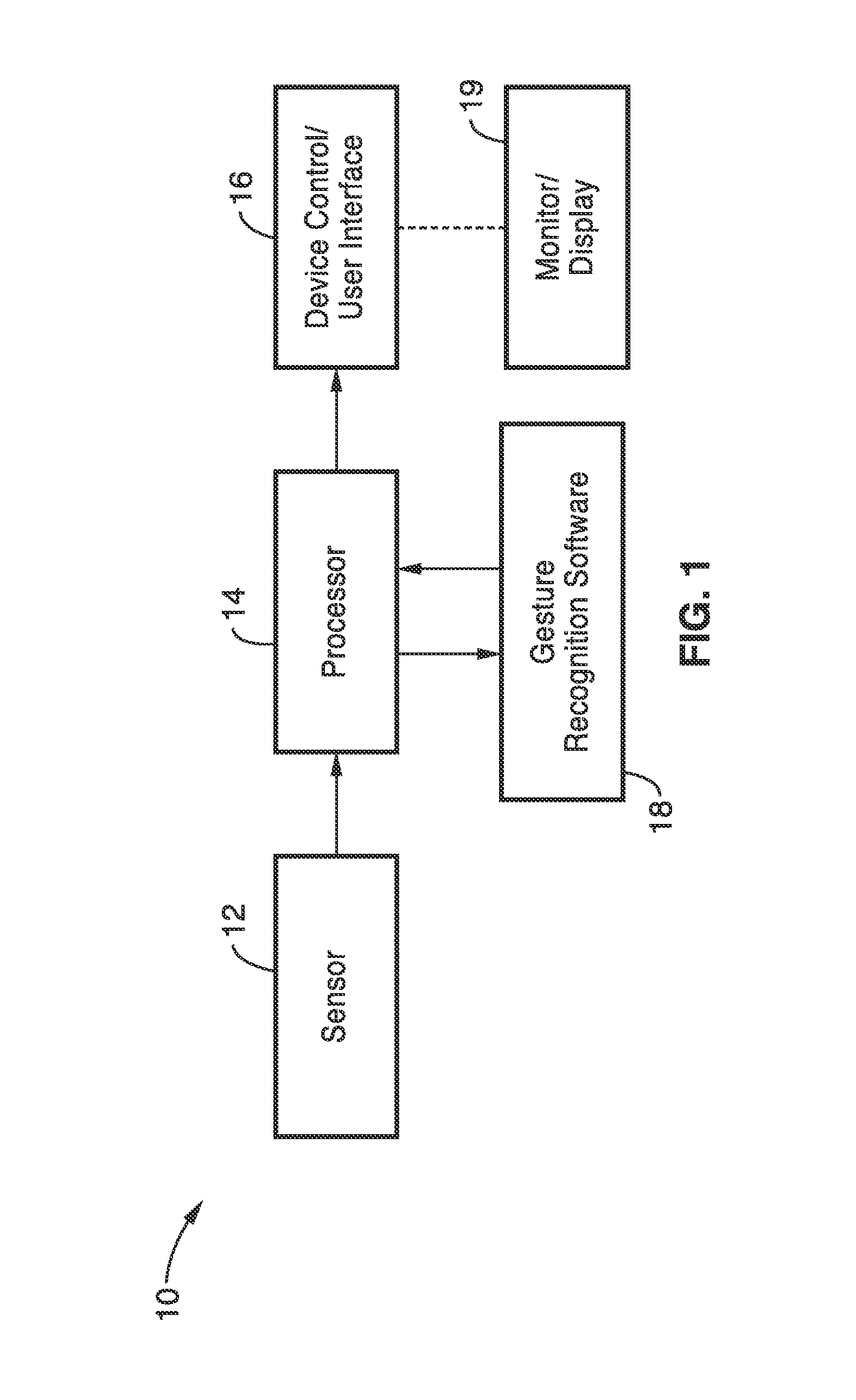
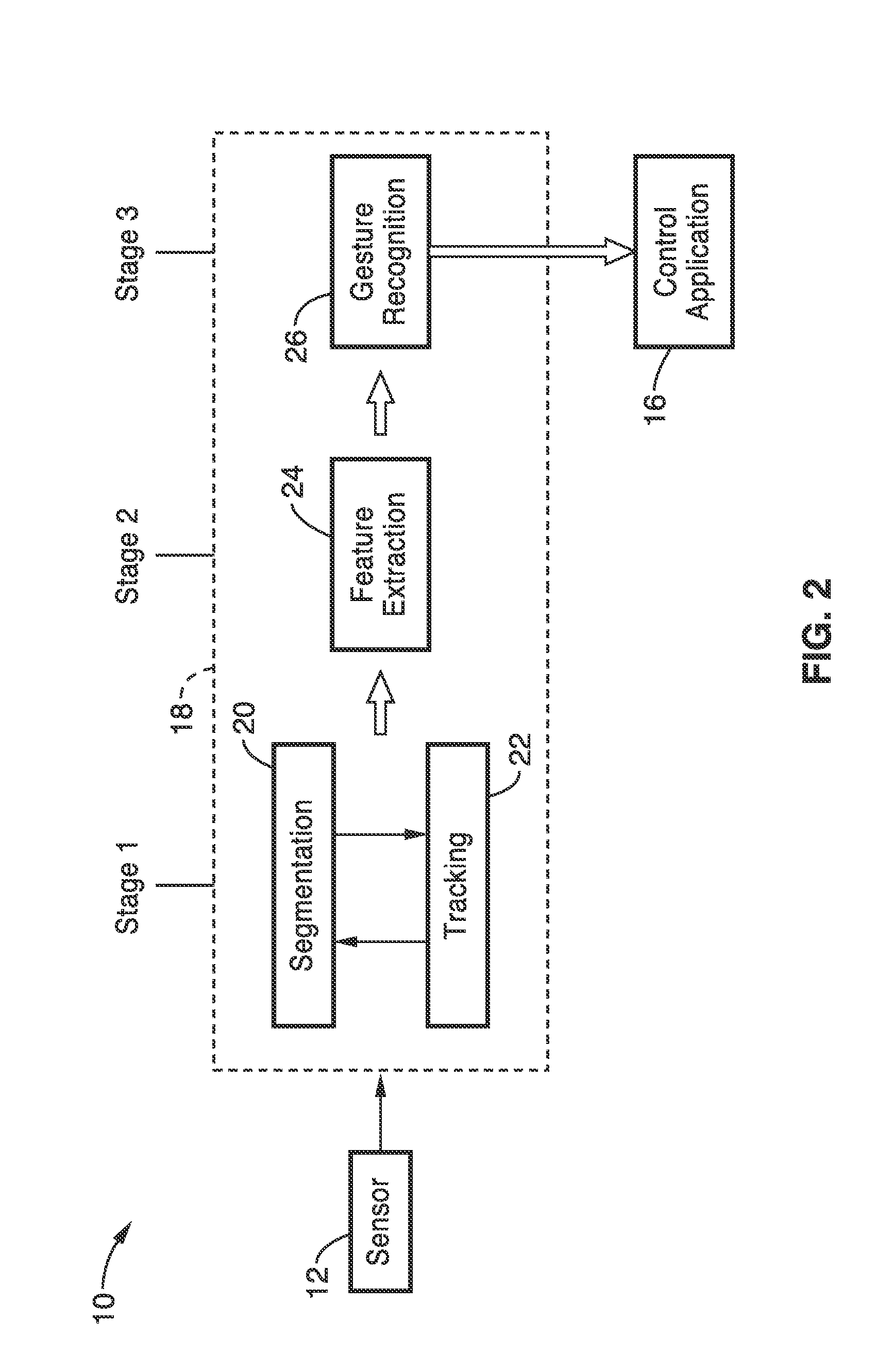
Gesture recognition system for TV control
ActiveUS20120069168A1Reduce computational complexityEasy to useImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionKaiman filter
A gesture recognition system using a skin-color based method combined with motion information to achieve real-time segmentation. A Kalman filter is used to track the centroid of the hand. The palm center, palm bottom, as well as the largest distance from the palm center to the contour from extracted hand mask are computed. The computed distance to a threshold is then compared to decide if the current posture is “open” or “closed.” In a preferred embodiment, the transition between the “open” and “closed” posture to decide if the current gesture is in “select” or “grab” state.
Owner:SONY CORP
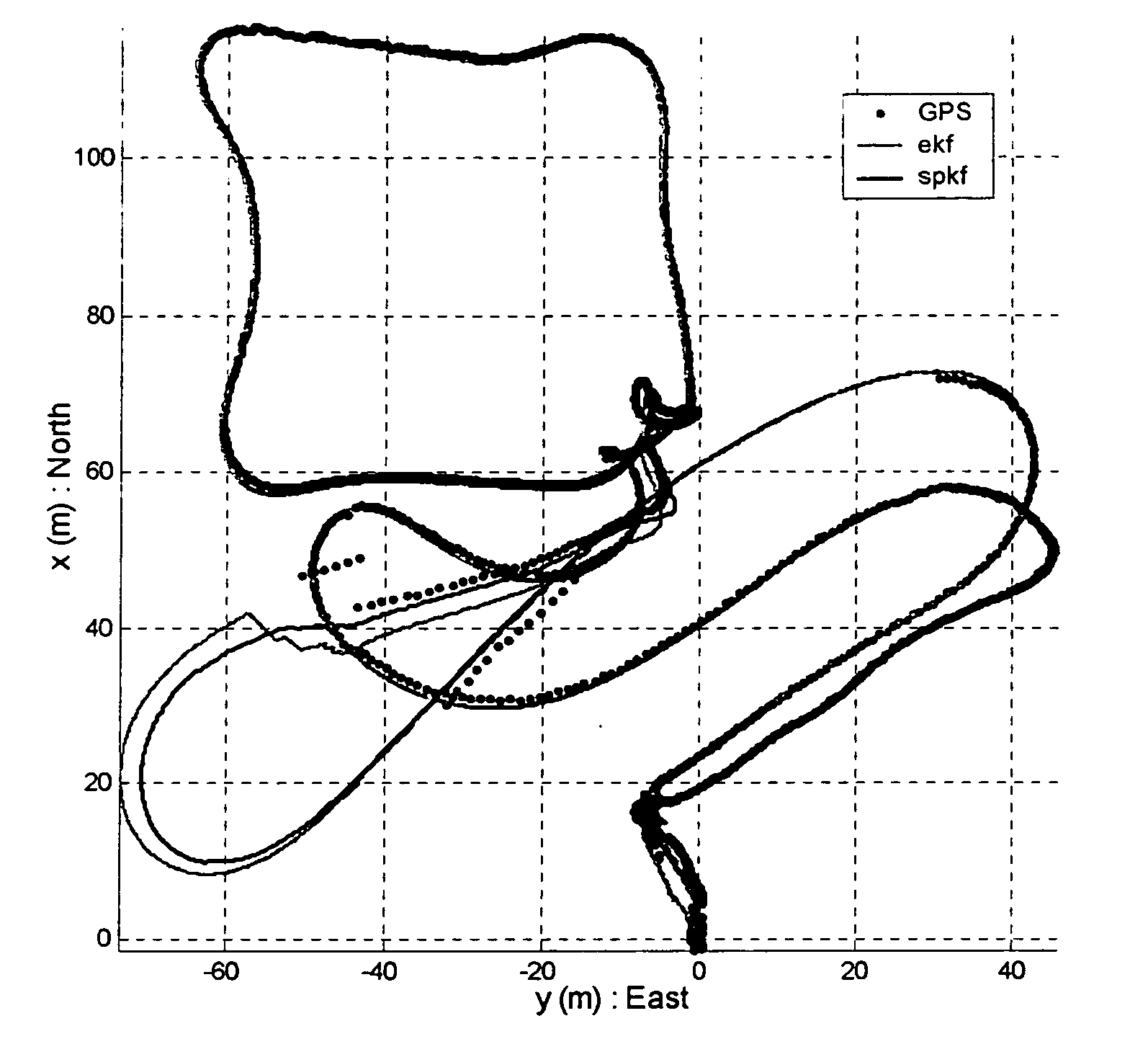
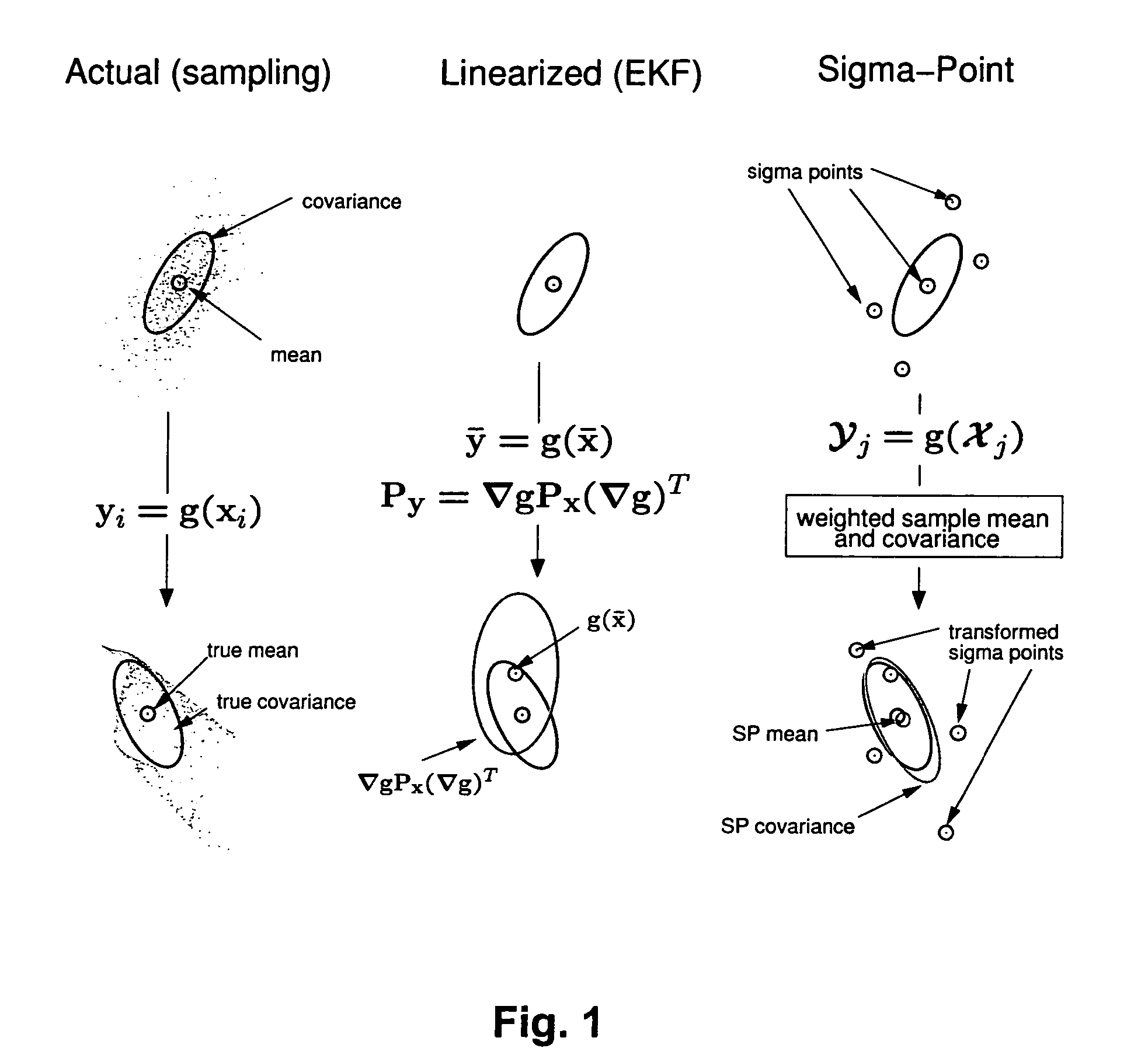
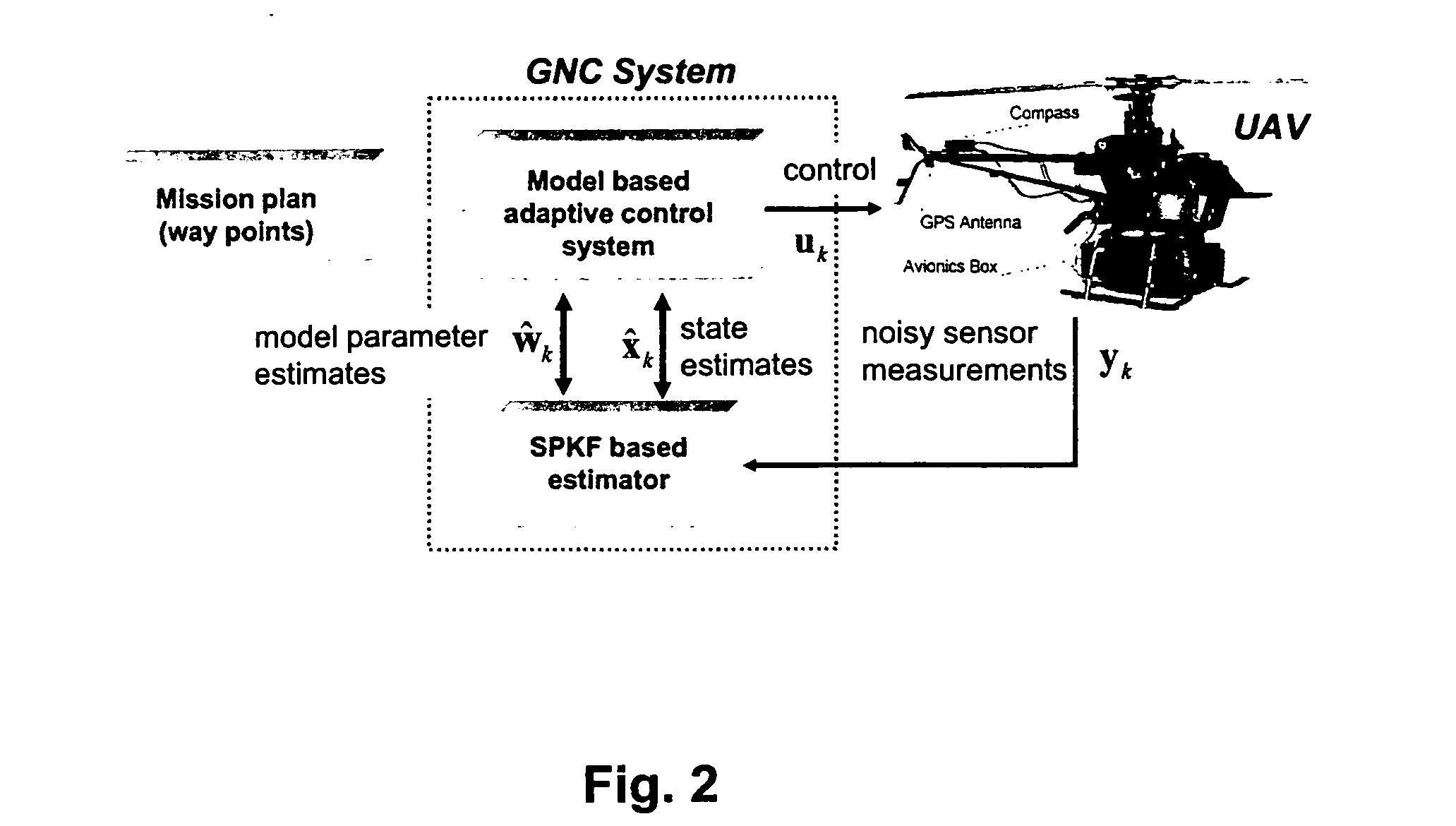
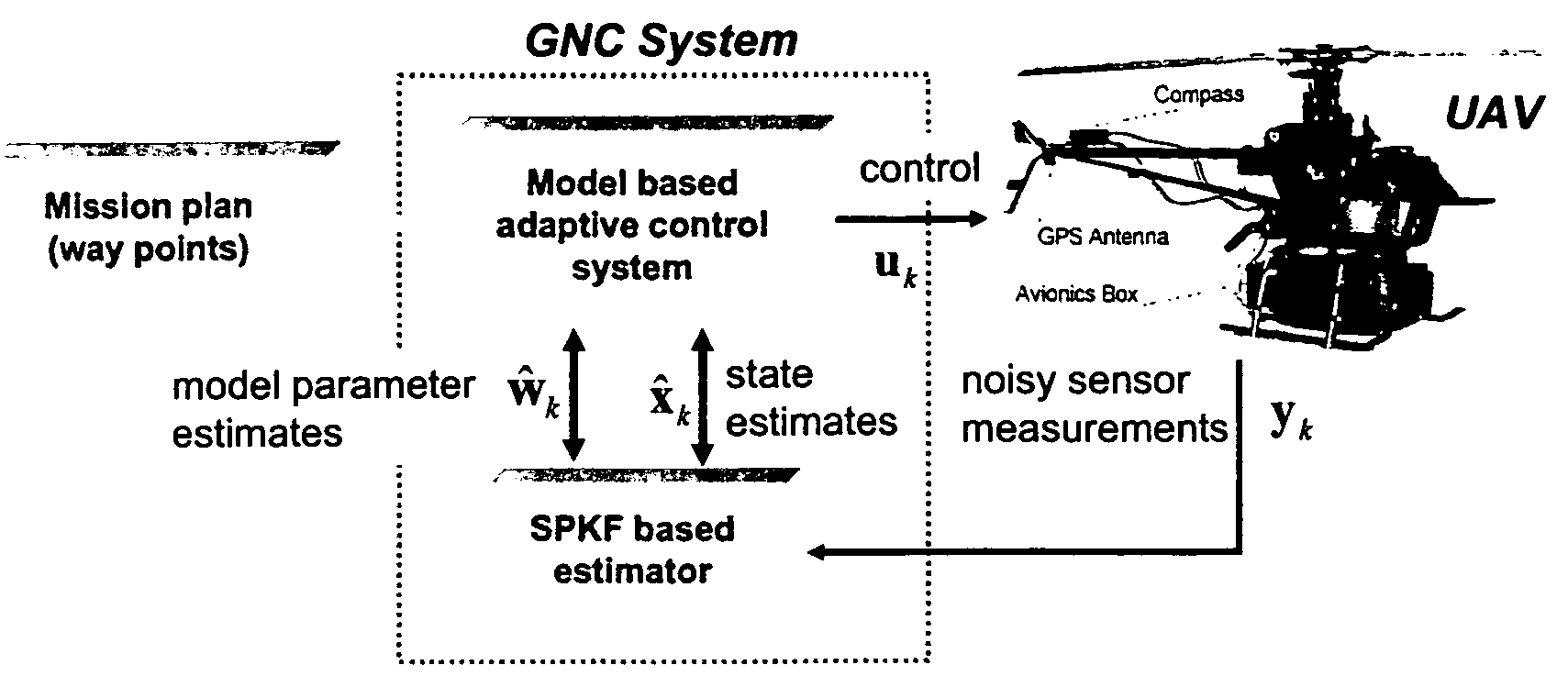
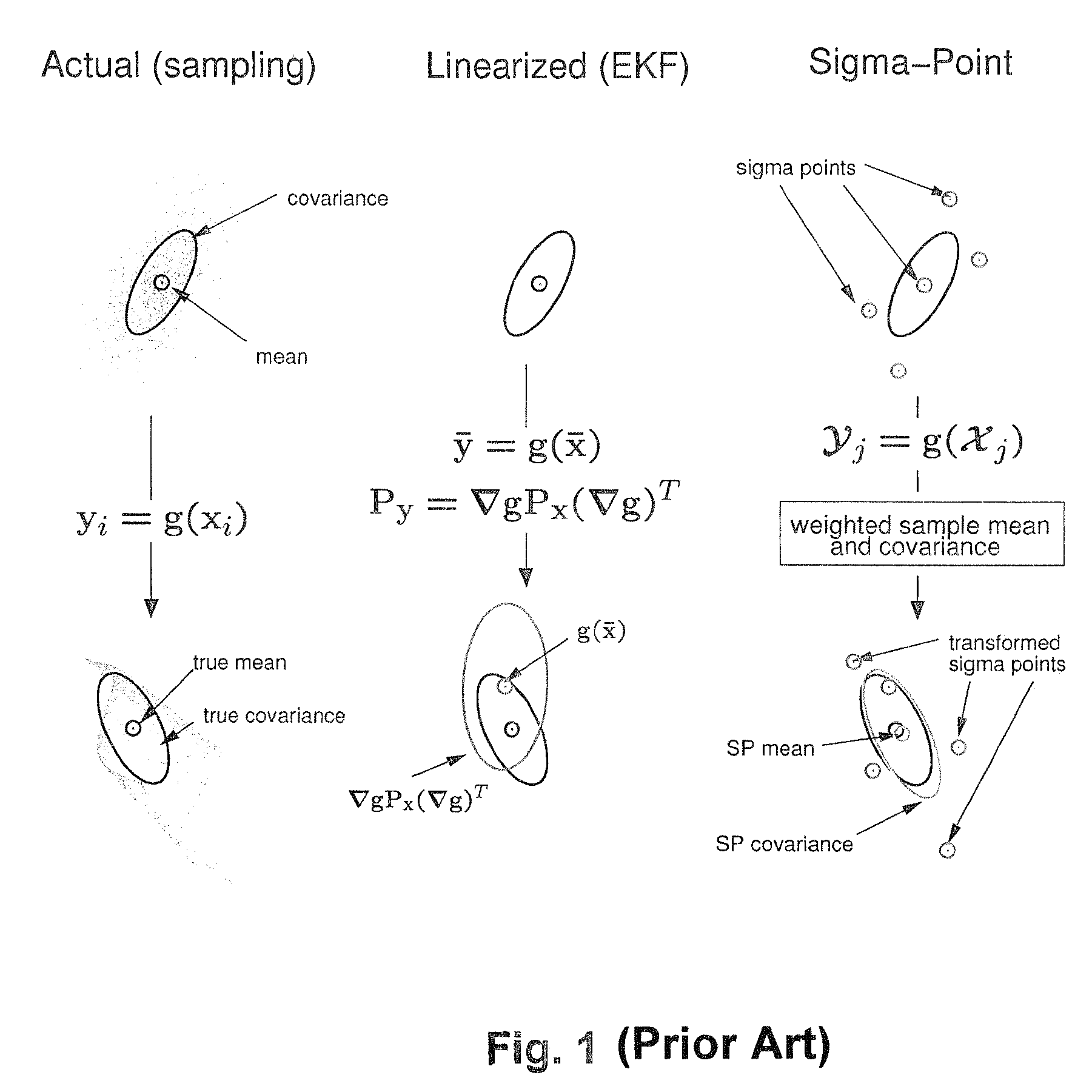
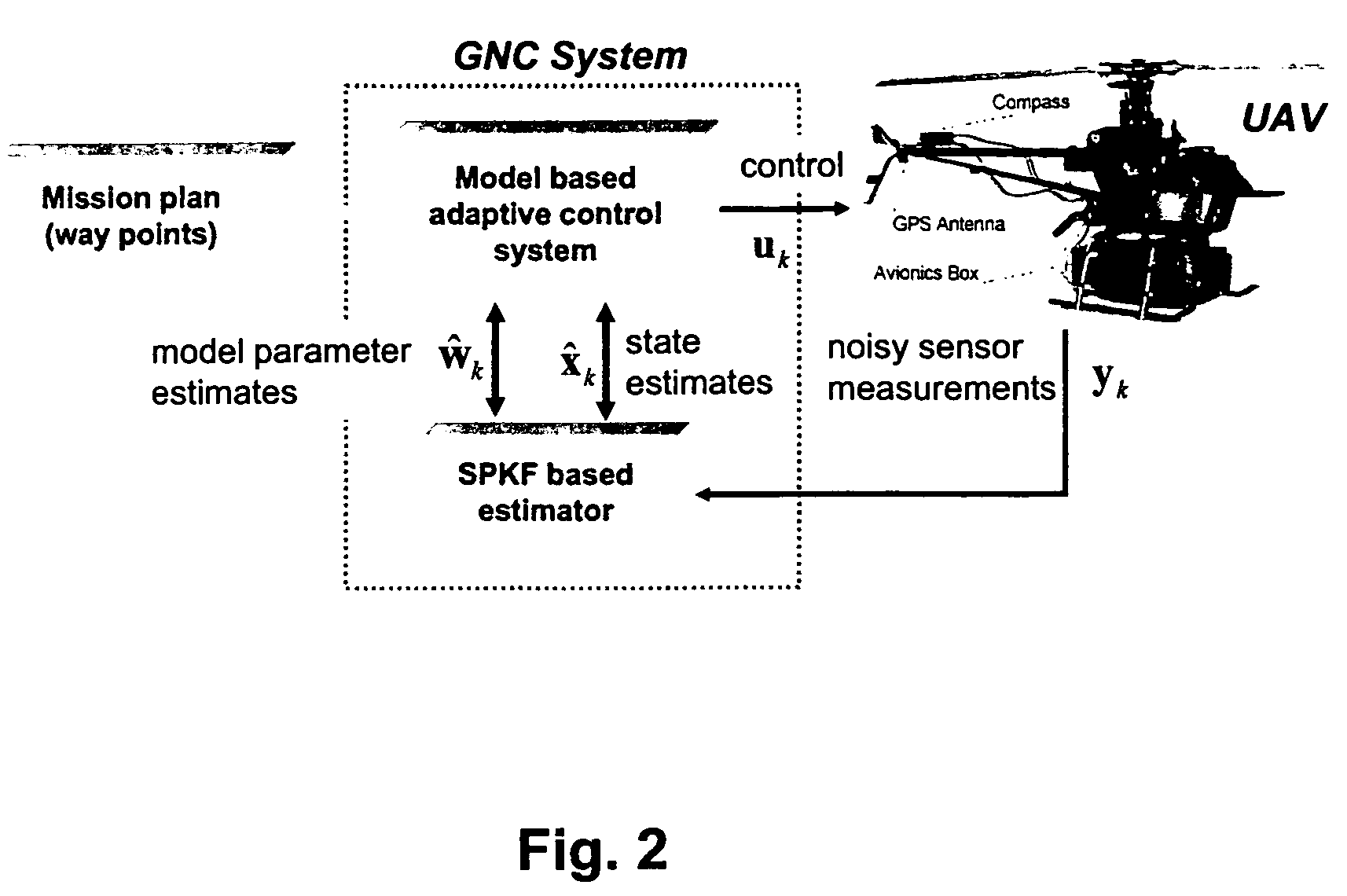
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS20050251328A1Improve estimation accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
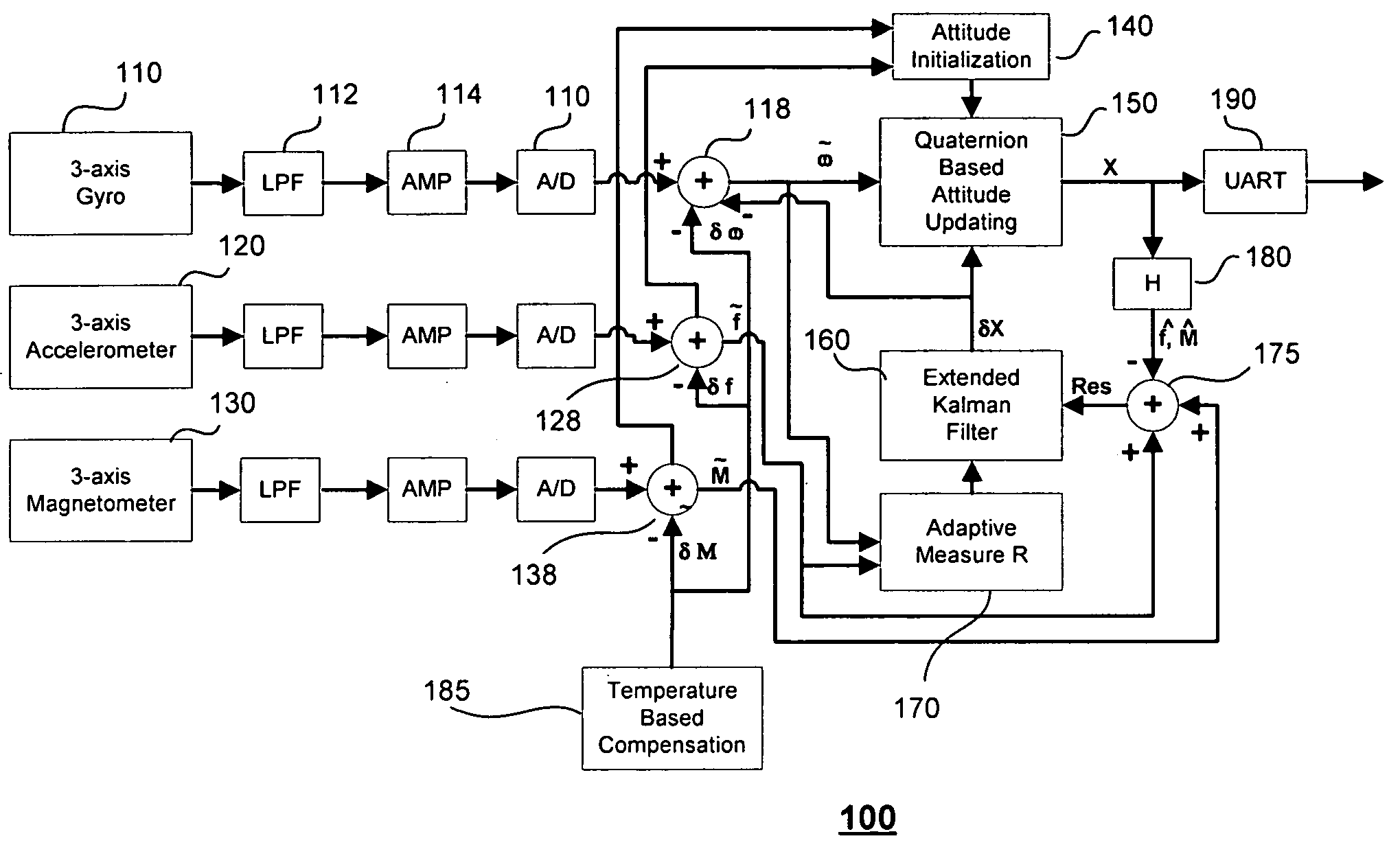
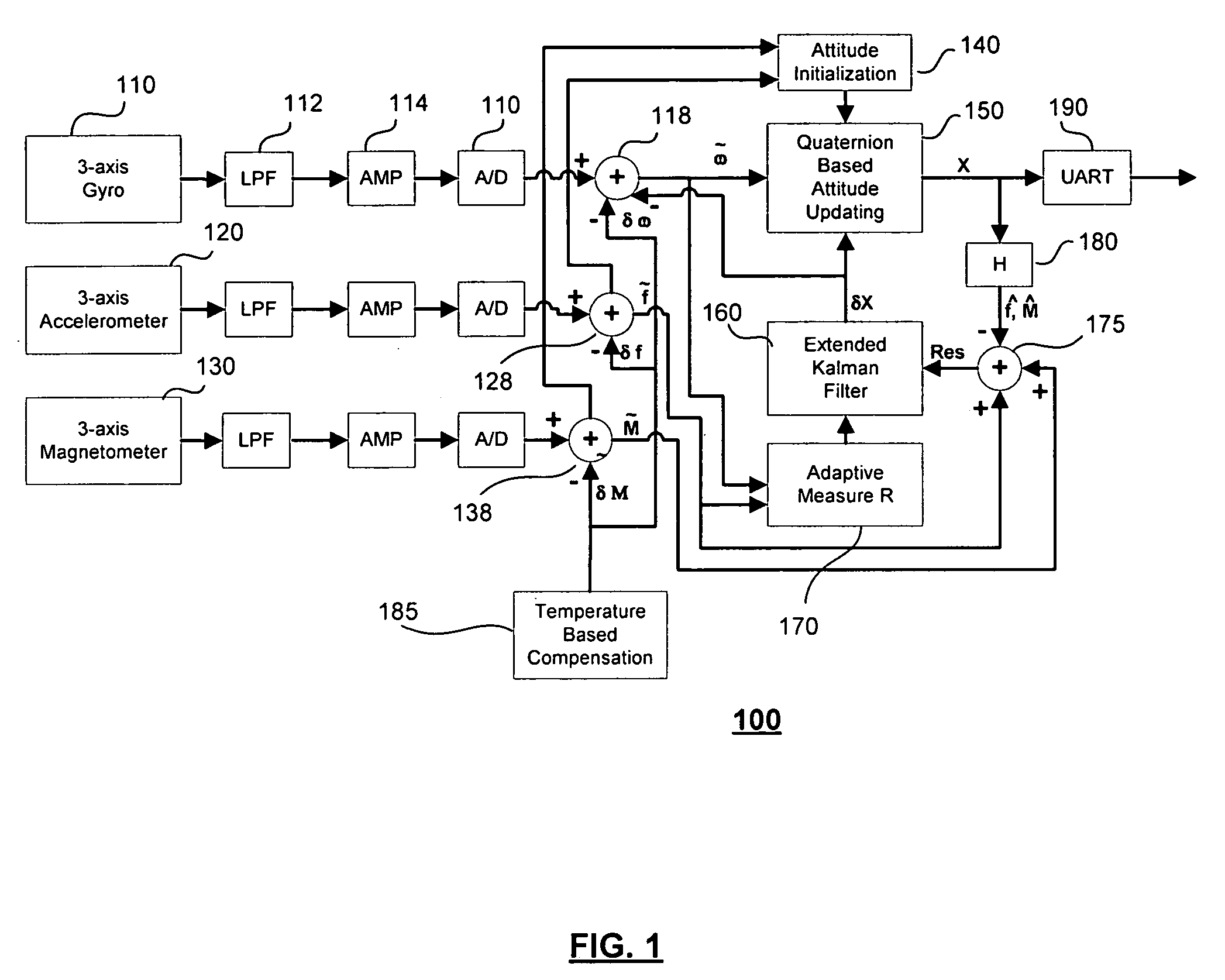
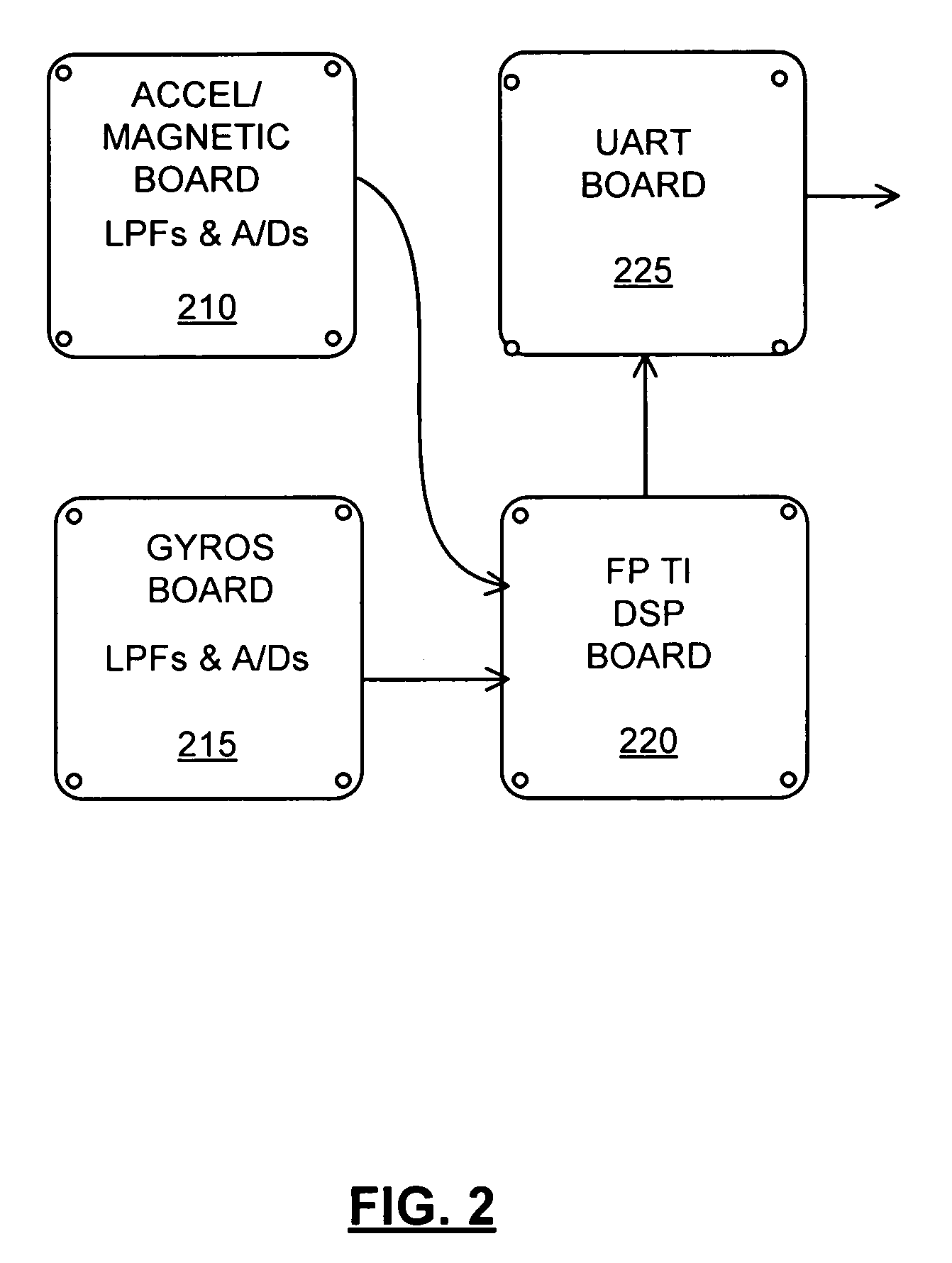
Method and apparatus for adaptive filter based attitude updating
InactiveUS20050240347A1Improve abilitiesConveniently implementedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterGyroscope
A six state Kalman filter is adapted based on a current acceleration mode of an INS device. Gyro measurements are used to determine the acceleration mode and the Kalman filter estimates bias and small angle error of the measurements based on the acceleration mode. The bias error corrects the gyro measurement and the small angle error is used along with the corrected gyro measurement to update an attitude sensed by the gyro.
Owner:YANG YUN CHUN
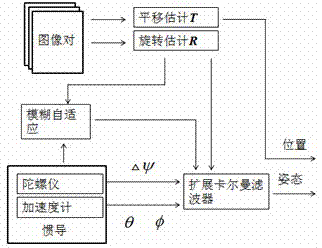
Machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method
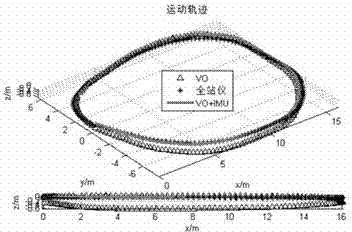
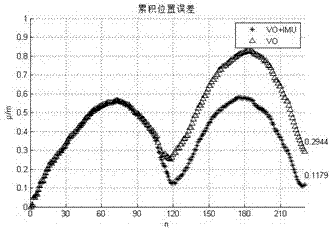
InactiveCN102538781AReduce cumulative errorHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionInertial navigation system
The invention discloses a machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method which comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring a mobile robot binocular camera image and triaxial inertial navigation data; distilling front / back frame image characteristics and matching estimation motion attitude; computing a pitch angle and a roll angle by inertial navigation; building a kalman filter model to estimate to fuse vision and inertial navigation attitude; adaptively adjusting a filter parameter according to estimation variance; and carrying out accumulated dead reckoning of attitude correction. According to the method, a real-time expanding kalman filter attitude estimation model is provided, the combination of inertial navigation and gravity acceleration direction is taken as supplement, three-direction attitude estimation of a visual speedometer is decoupled, and the accumulated error of the attitude estimation is corrected; and the filter parameter is adjusted by fuzzy logic according to motion state, the self-adaptive filtering estimation is realized, the influence of acceleration noise is reduced, and the positioning precision and robustness of the visual speedometer is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Neural networks for prediction and control
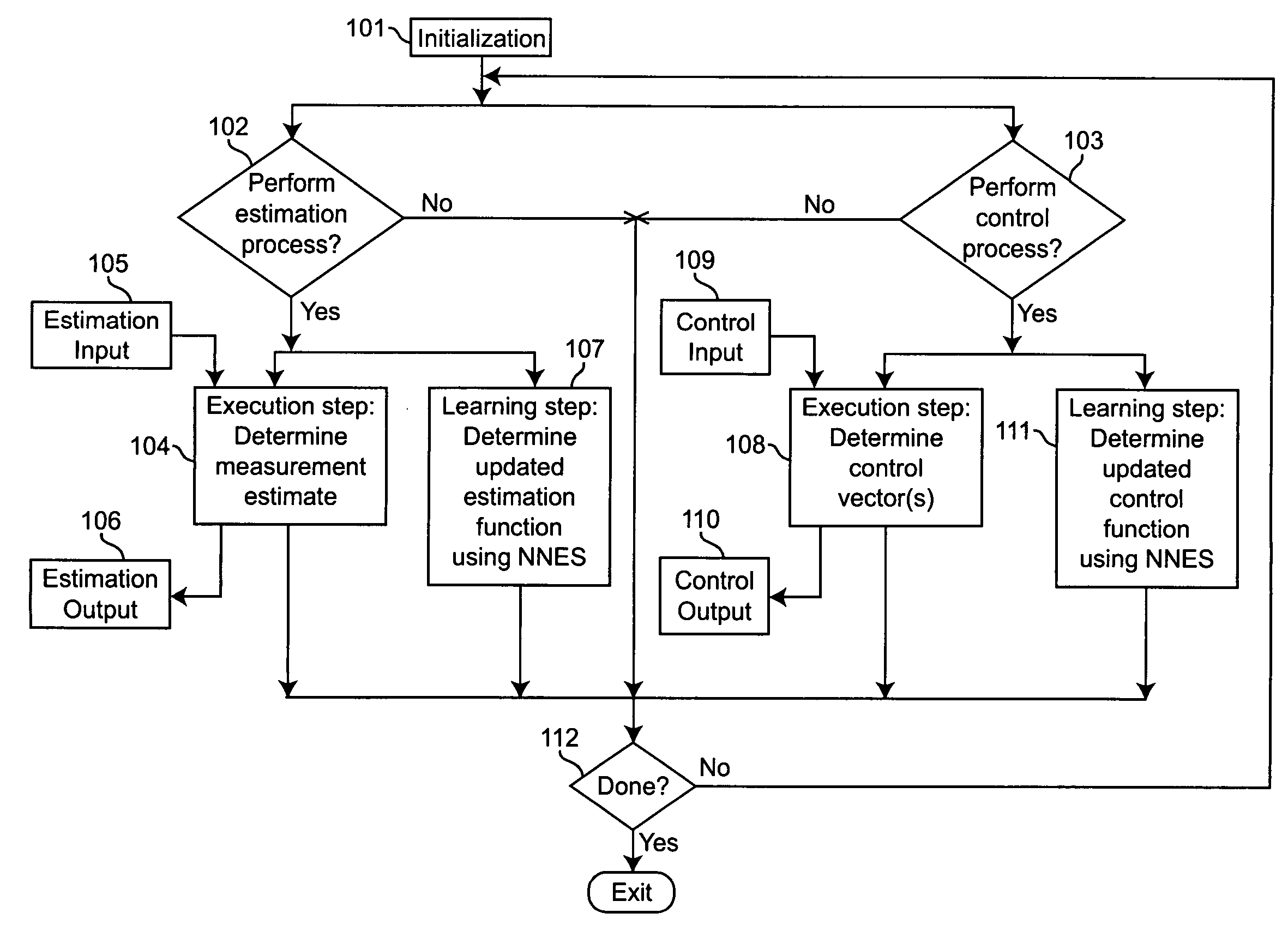
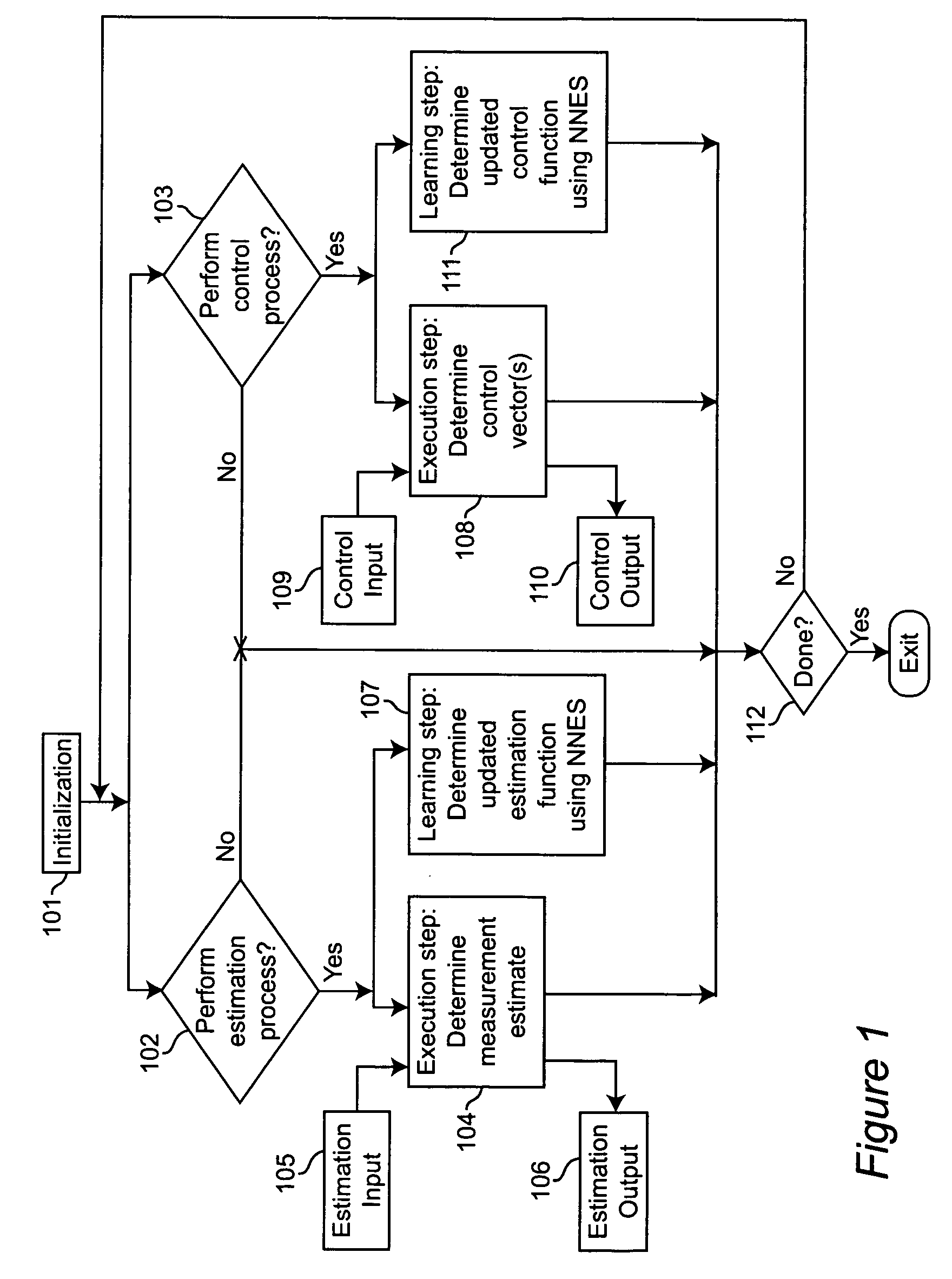
Neural networks for optimal estimation (including prediction) and / or control involve an execution step and a learning step, and are characterized by the learning step being performed by neural computations. The set of learning rules cause the circuit's connection strengths to learn to approximate the optimal estimation and / or control function that minimizes estimation error and / or a measure of control cost. The classical Kalman filter and the classical Kalman optimal controller are important examples of such an optimal estimation and / or control function. The circuit uses only a stream of noisy measurements to infer relevant properties of the external dynamical system, learn the optimal estimation and / or control function, and apply its learning of this optimal function to input data streams in an online manner. In this way, the circuit simultaneously learns and generates estimates and / or control output signals that are optimal, given the network's current state of learning.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
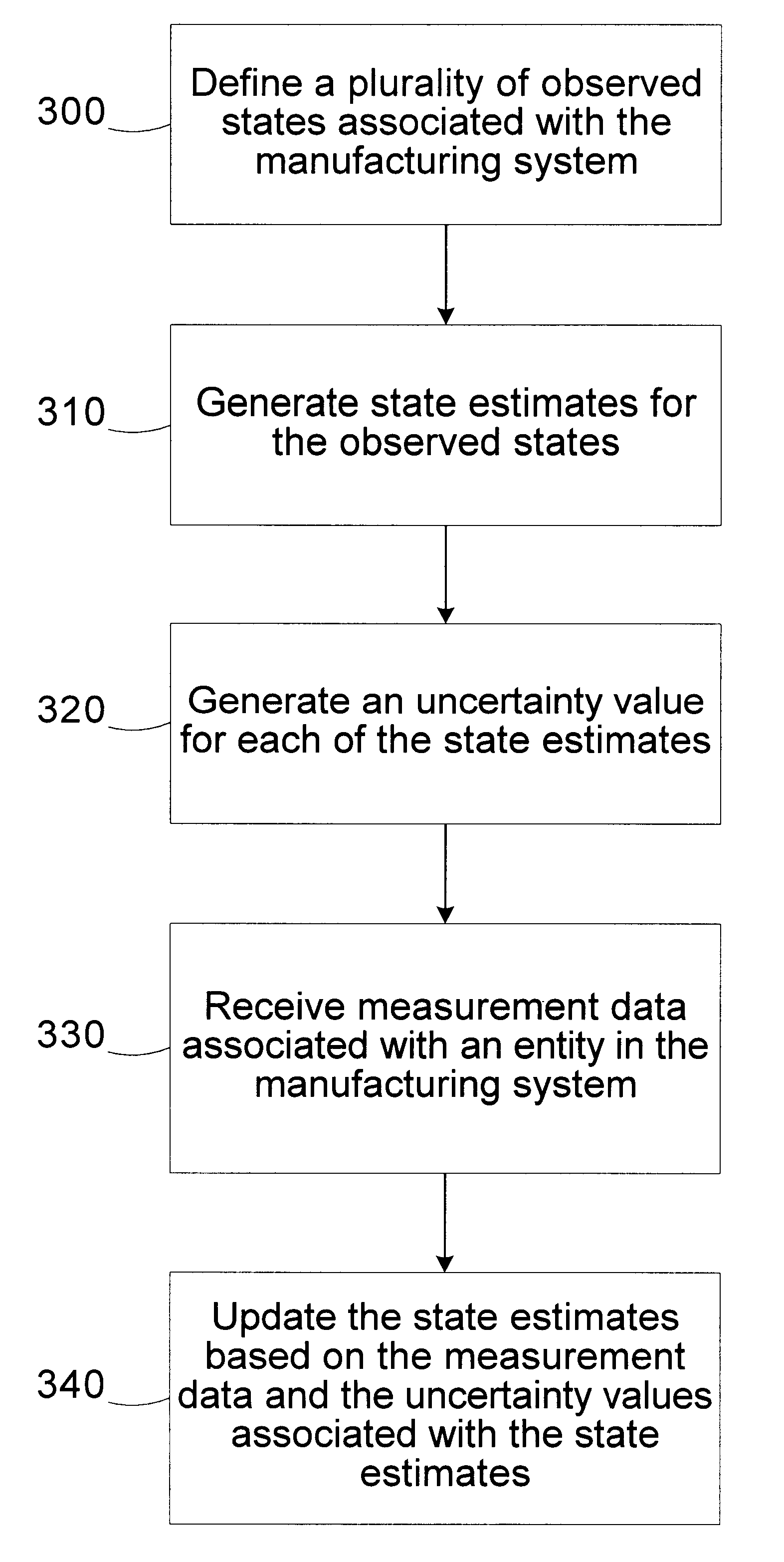
Kalman filter state estimation for a manufacturing system
InactiveUS6757579B1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsKaiman filterManufacturing systems
A method for monitoring a manufacturing system includes defining a plurality of observed states associated with the manufacturing system. State estimates are generated for the observed states. An uncertainty value is generated for each of the state estimates. Measurement data associated with an entity in the manufacturing system is received. The state estimates are updated based on the measurement data and the uncertainty values associated with the state estimates. A system for monitoring a manufacturing system includes a controller configured to define a plurality of observed states associated with the manufacturing system, generate state estimates for the observed states, generate an uncertainty value for each of the state estimates, receive measurement data associated with an entity in the manufacturing system, and update the state estimates based on the measurement data and the uncertainty values associated with the state estimates.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
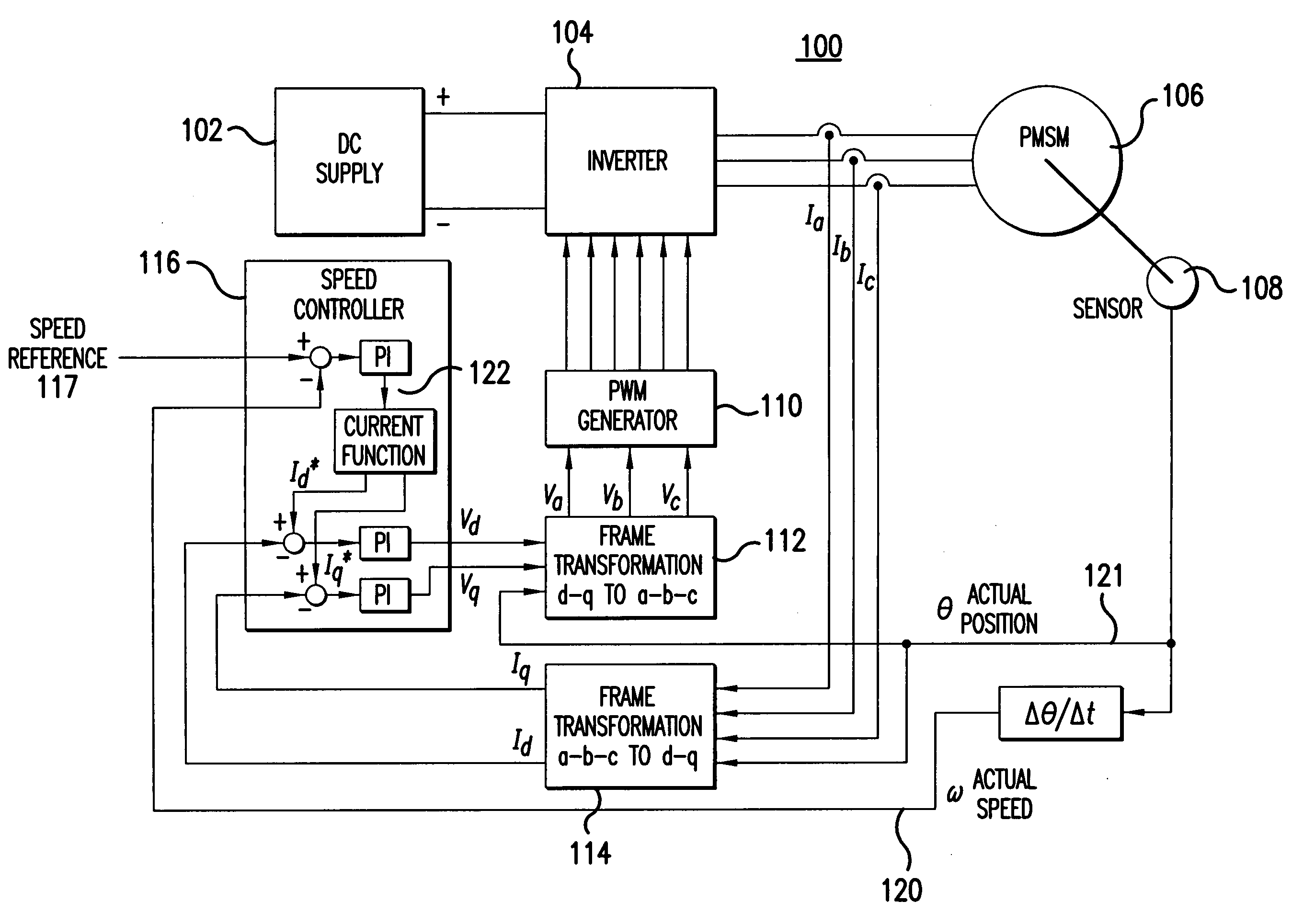
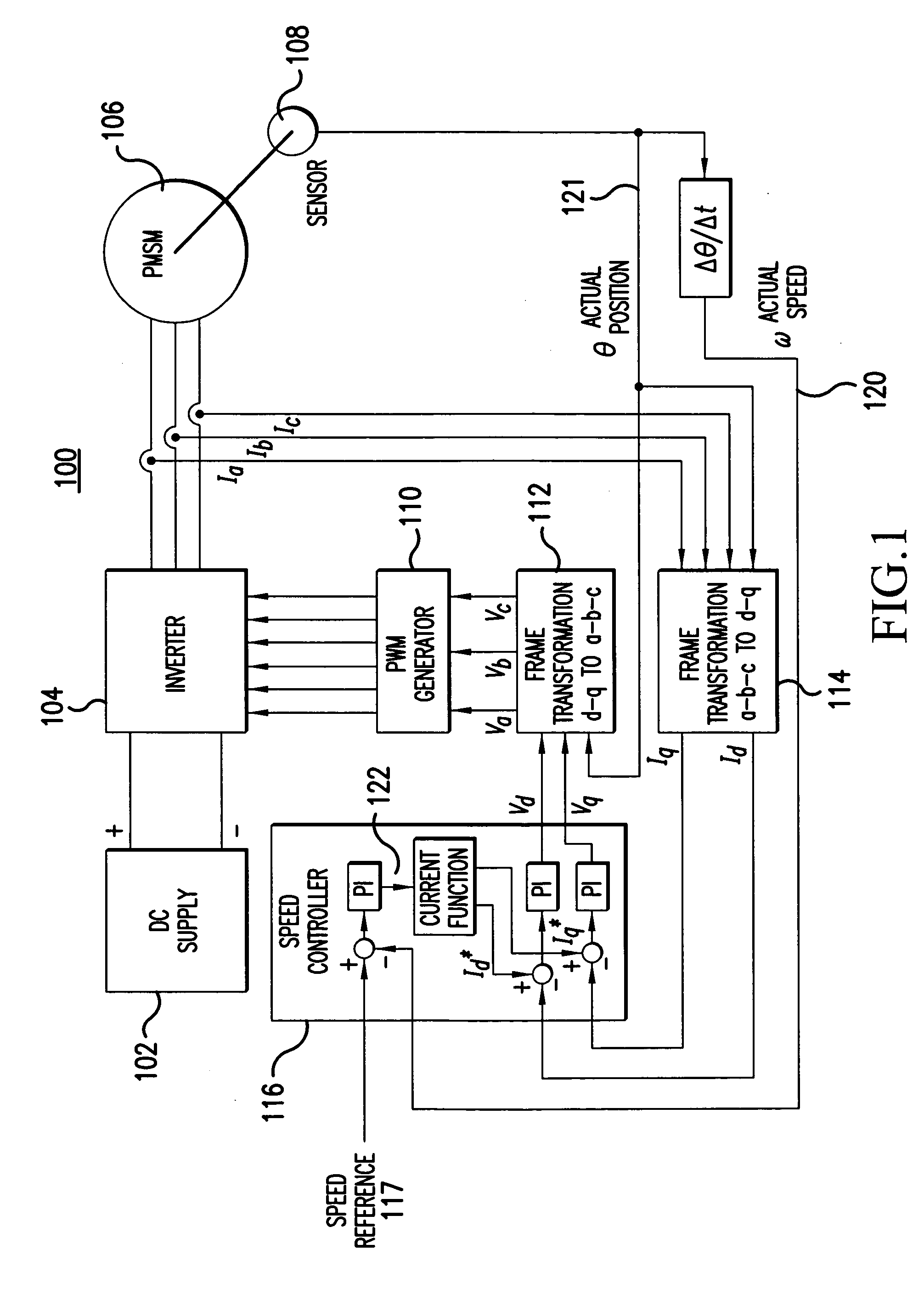
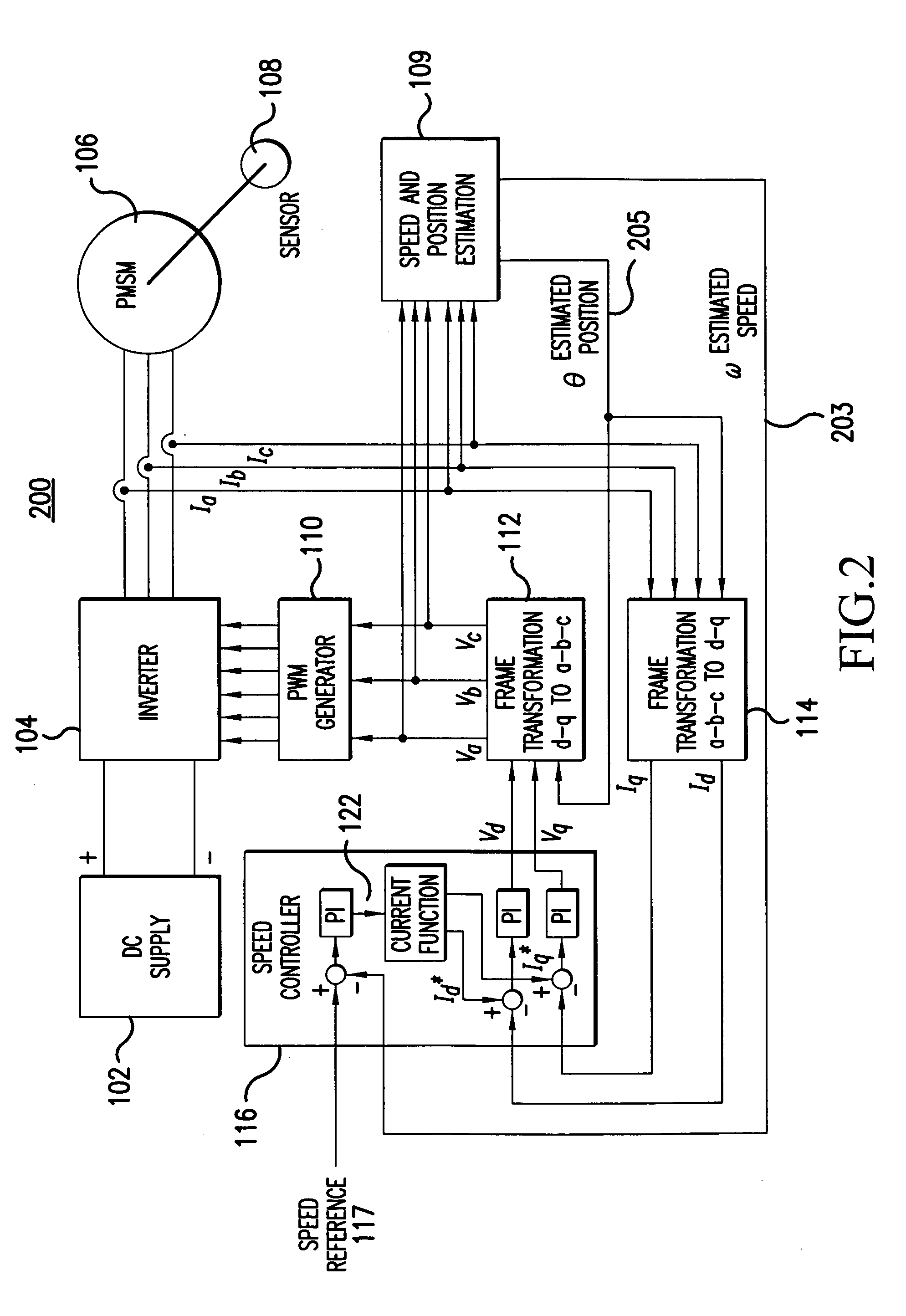
Sensorless control method and apparatus for a motor drive system
InactiveUS20050007044A1Quick calculationAccurate predictionDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlKaiman filterControl power
A method and apparatus provide a state observer control system 600 for a motor 106 that uses an extended Kalman filter 330 to predict initial rotor position and afterwards accurately predict rotor position and / or speed under variable types of loading conditions. A control system model 300 is generated that allows variable setting of an initial rotor position to generate estimated rotor position and speed as outputs. The control system model 300 includes an EKF (extended Kalman filter) estimator 330, speed controller 322, a current controller 324, and a variable load component 310. During operation, EKF estimator 330 estimates rotor speed 327 and position 333 based on reference voltages 402, 404 and currents 1325 generated by speed and current controllers 322, 324 and input from frame transformers 326, 328. Additionally, the reference currents and voltages 402, 404, 1325 are frame-transformed to be used as feedback signals 418, 346 in the system 600 and as drive signals to control power to be applied to a motor load 602.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
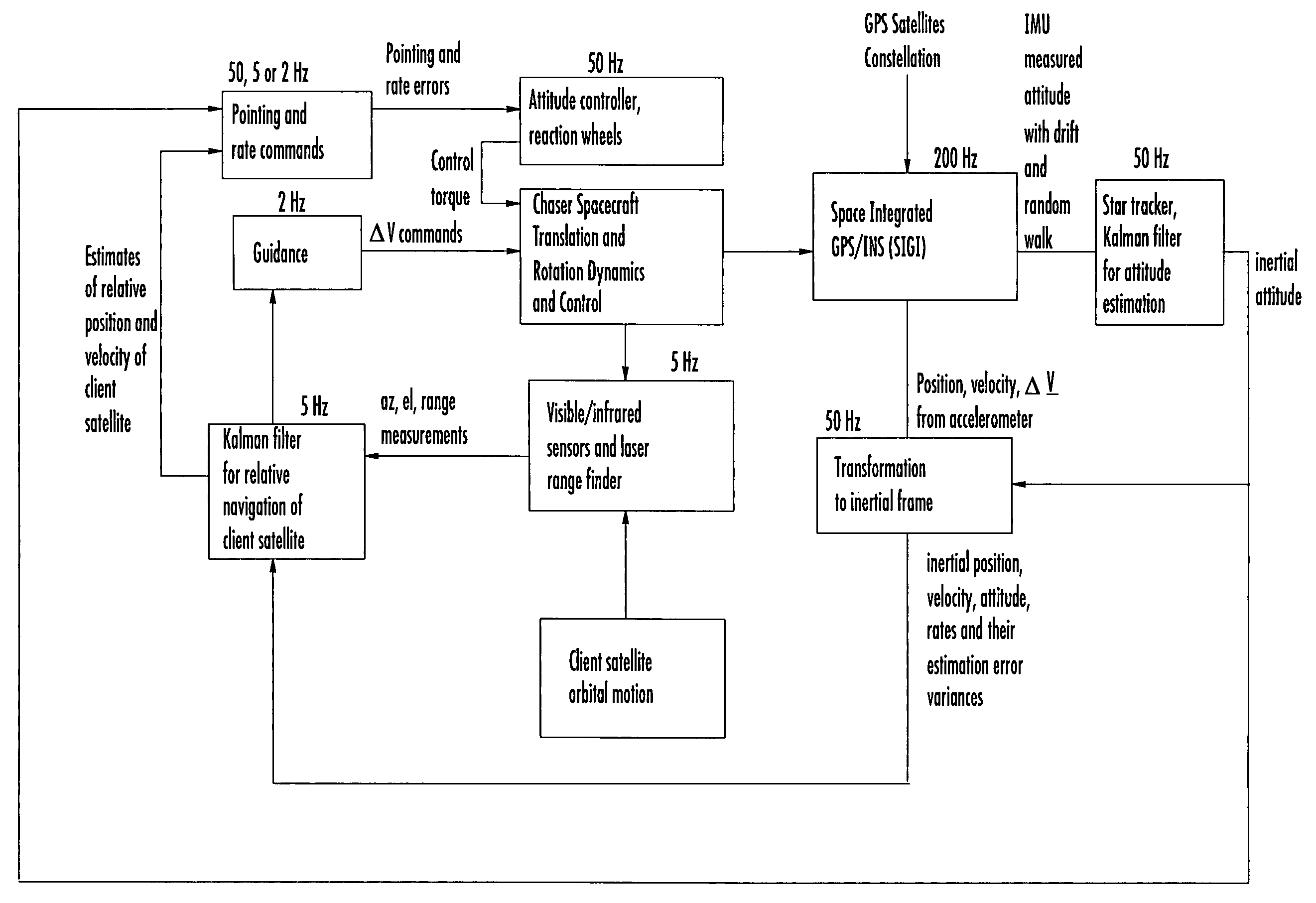
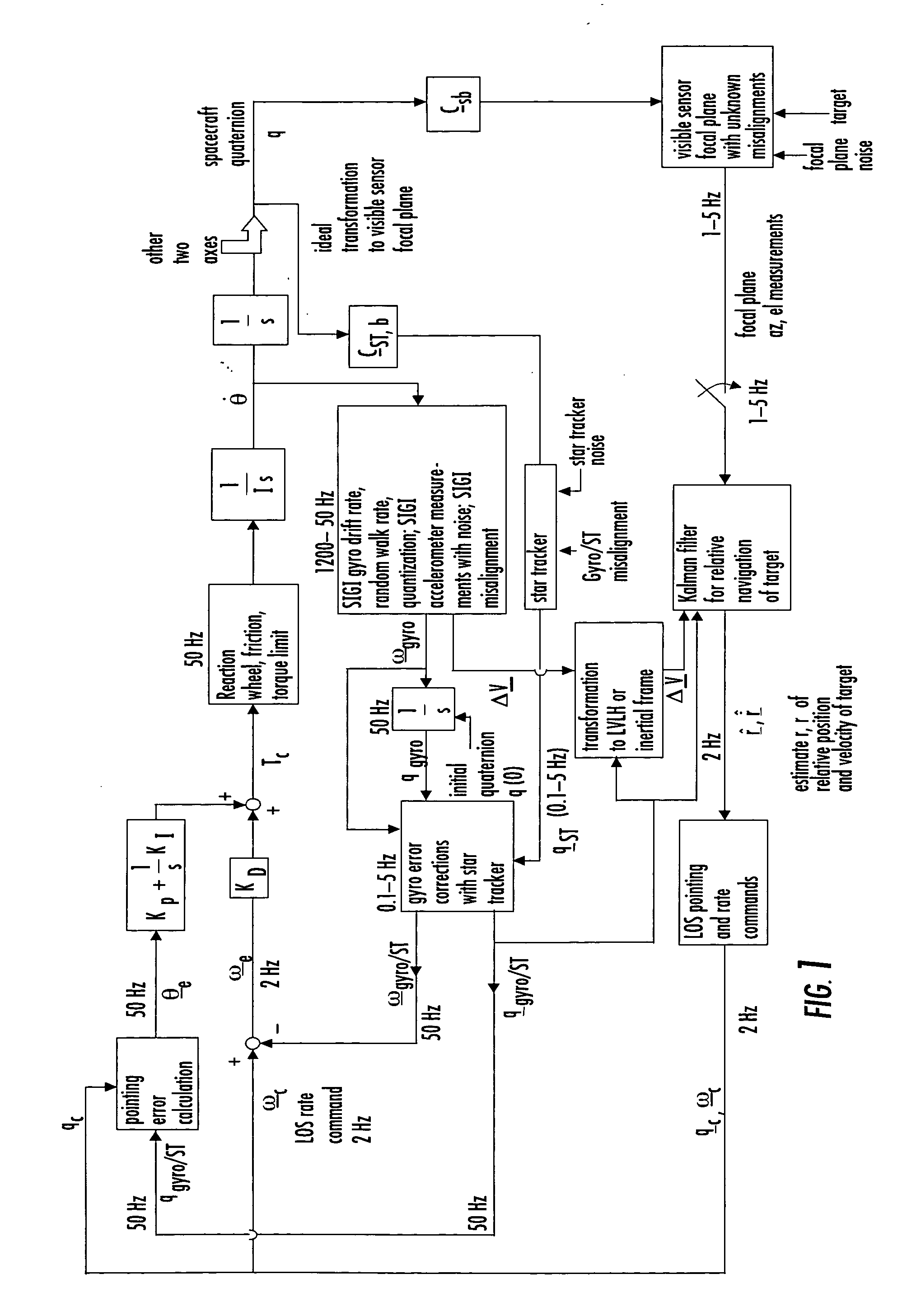
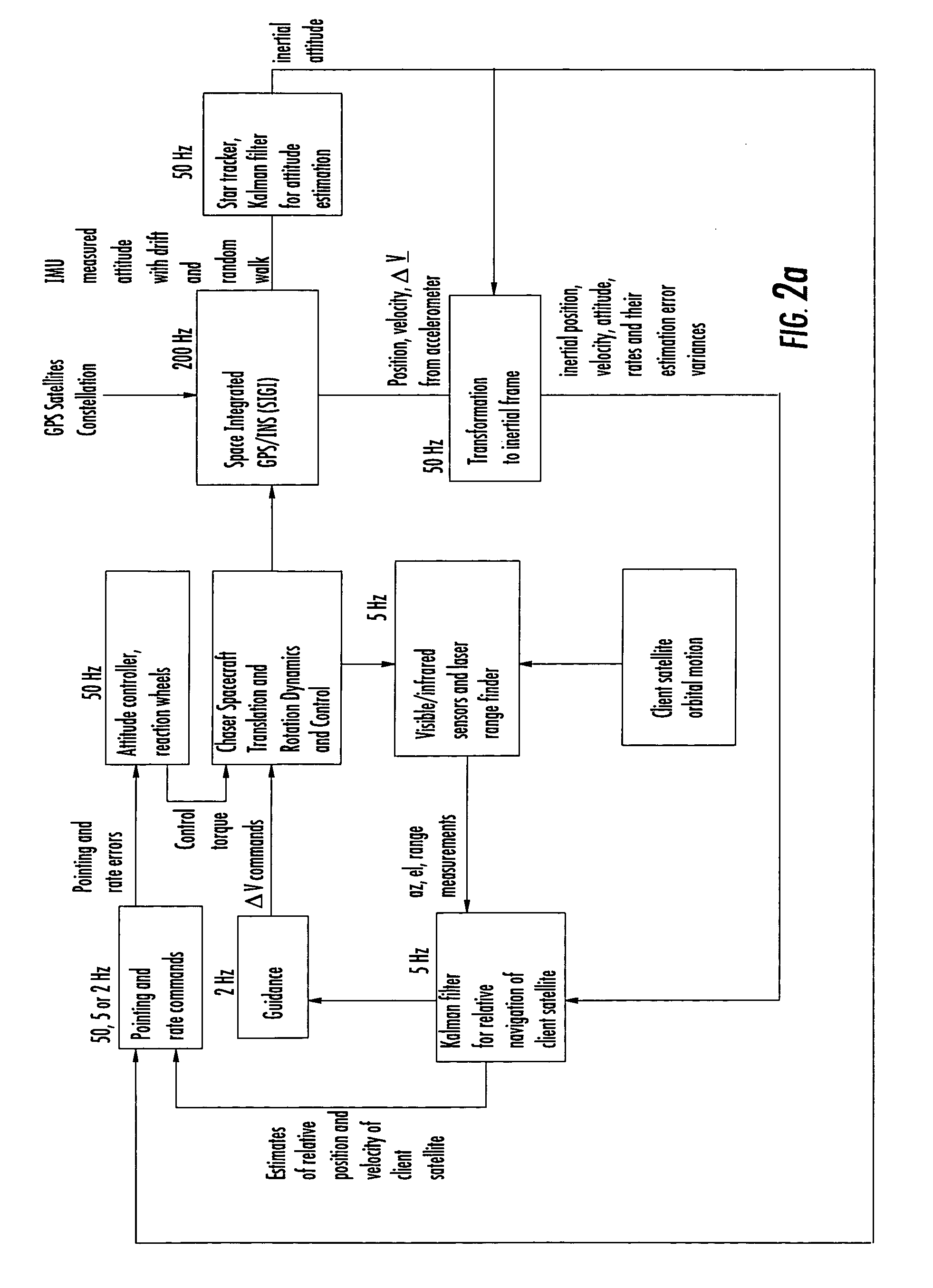
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
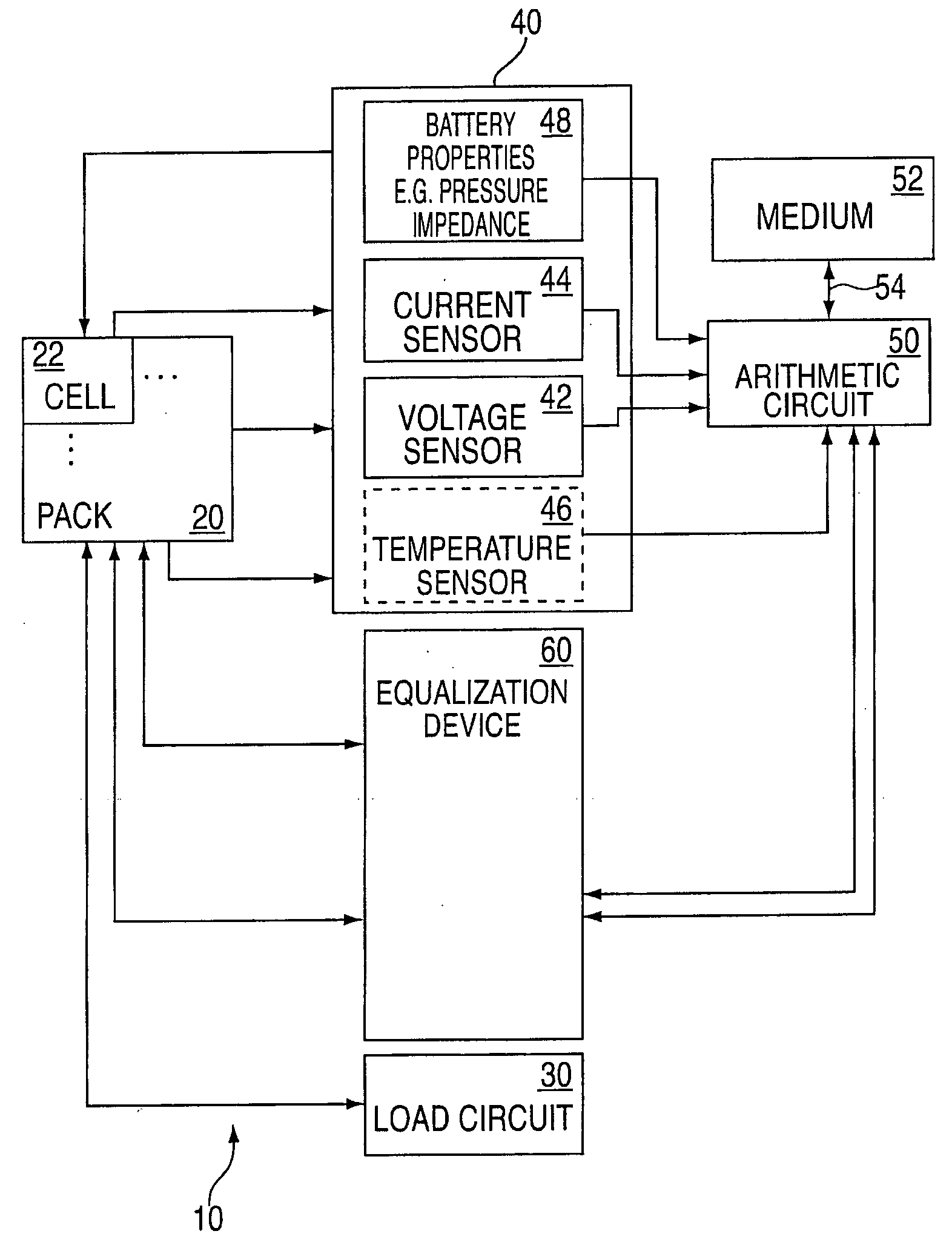
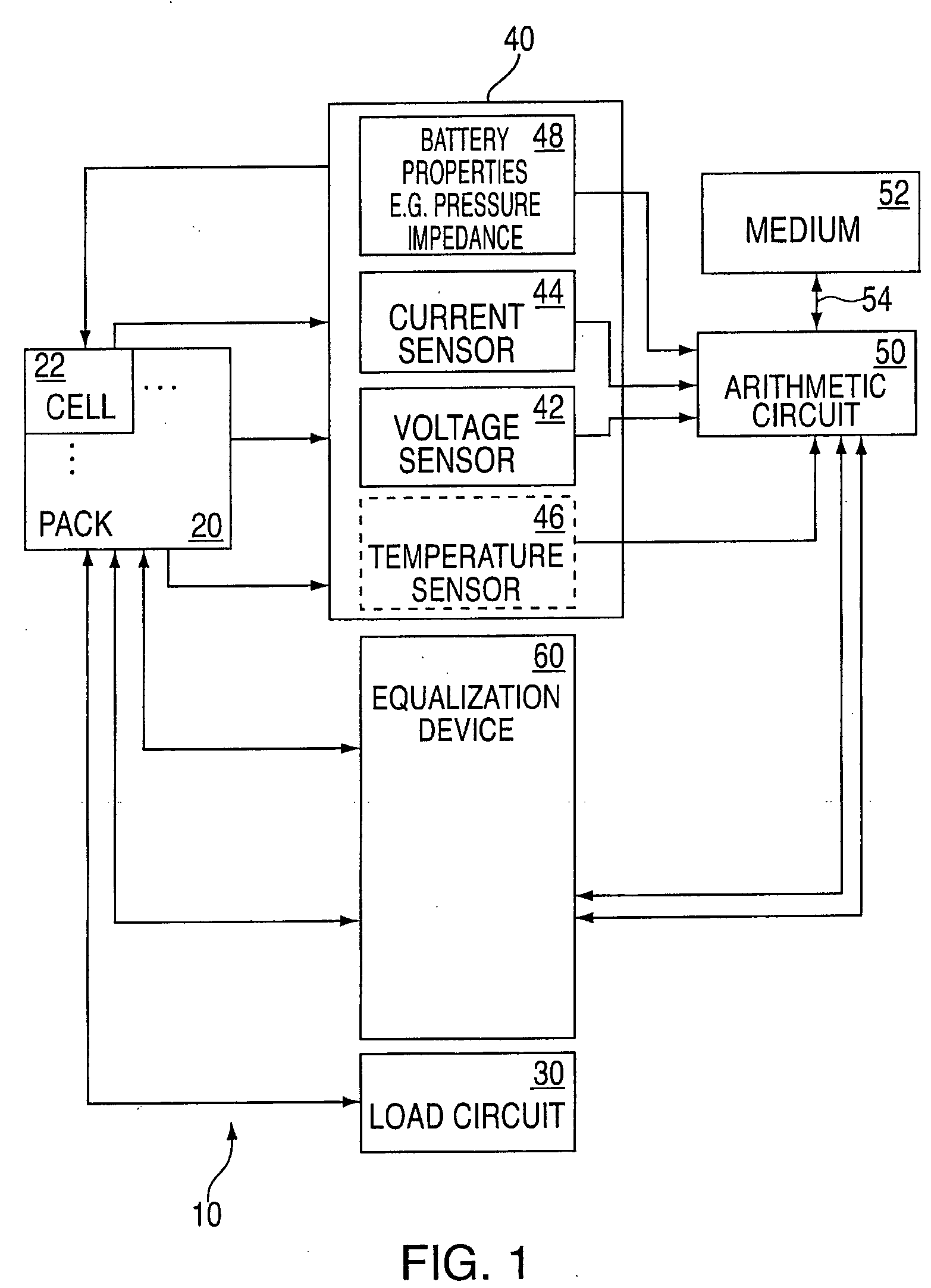
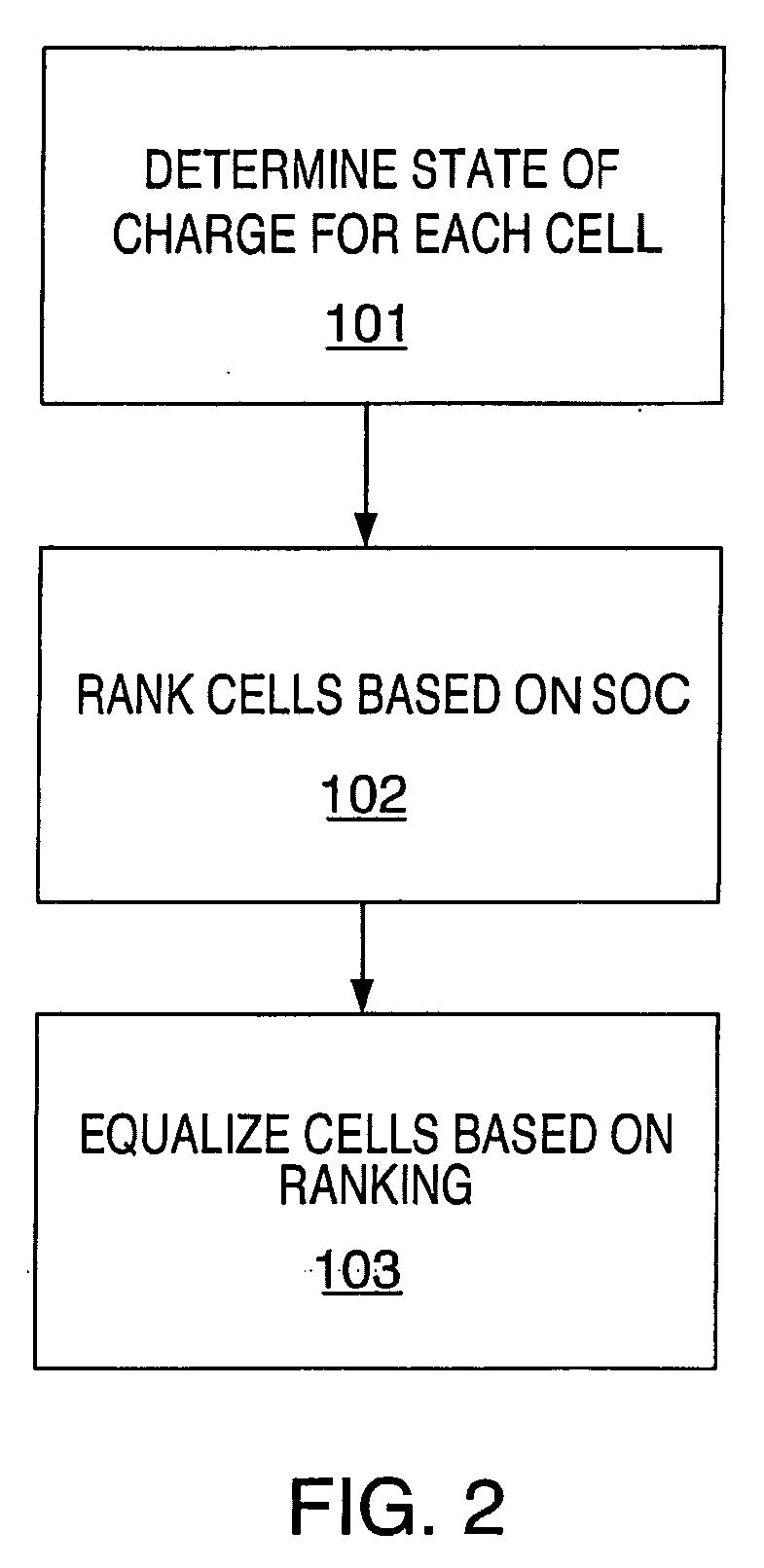
Method and system for cell equalization using state of charge
ActiveUS20060097698A1Easy to determineCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationKaiman filterBattery state of charge
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
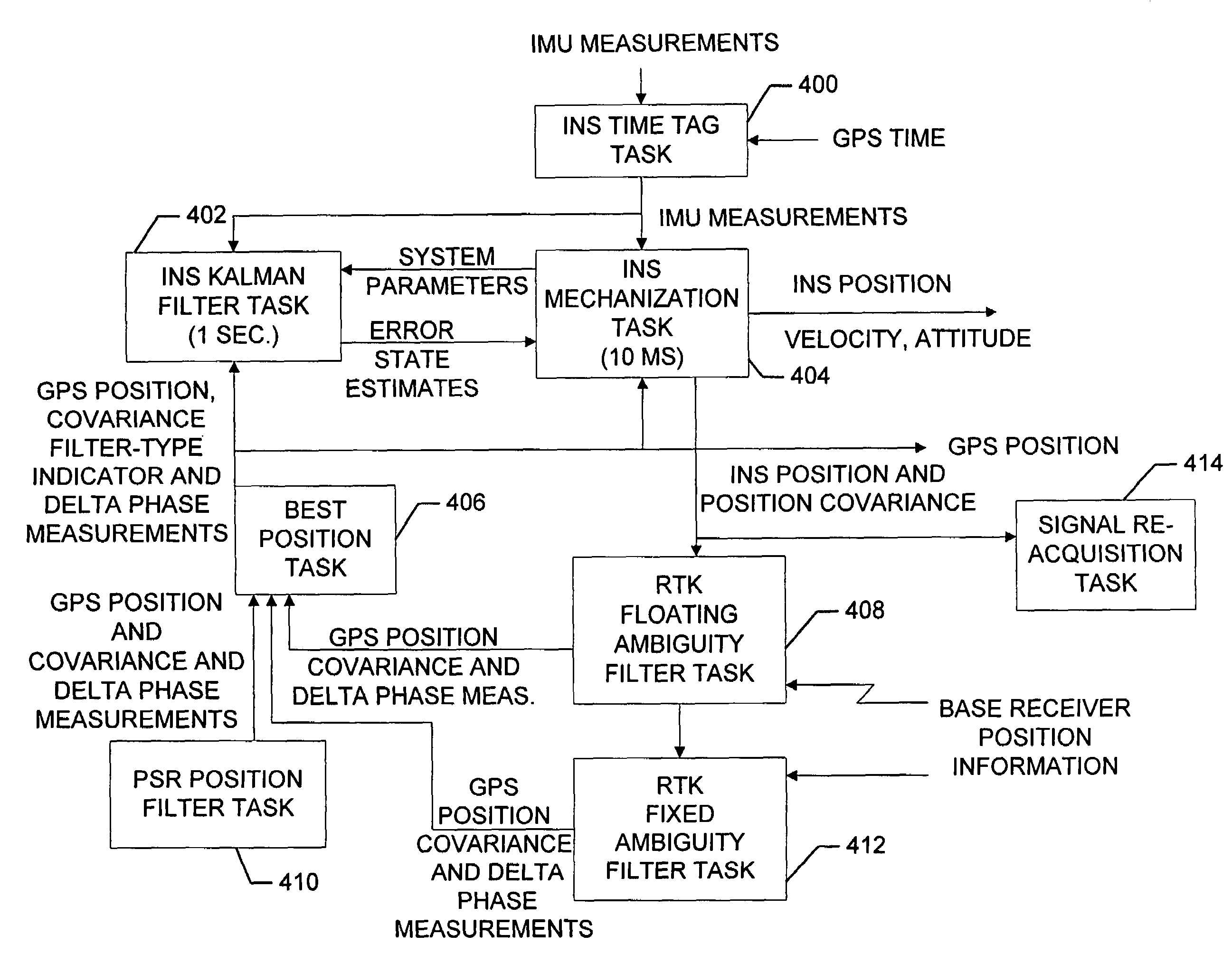
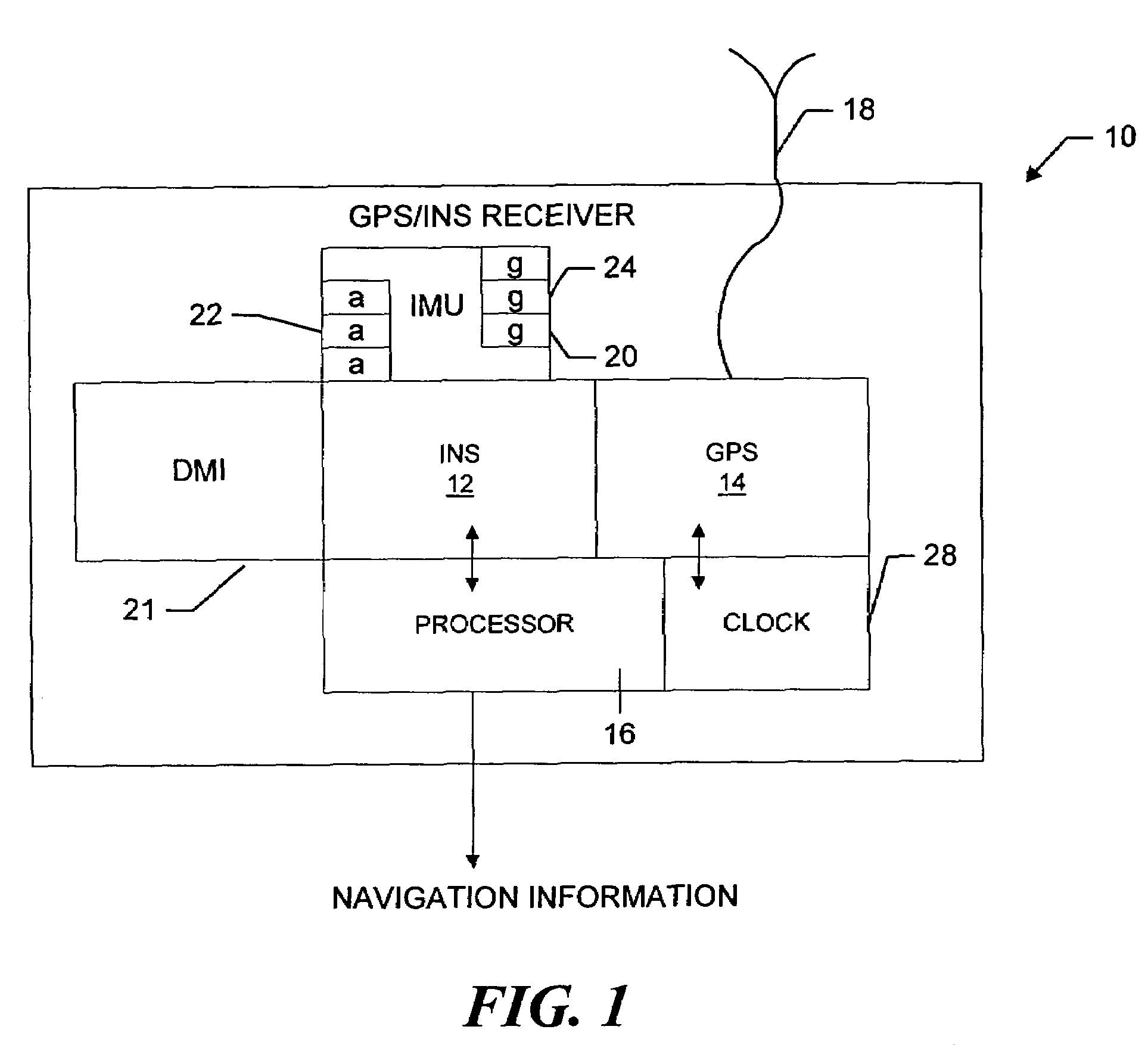
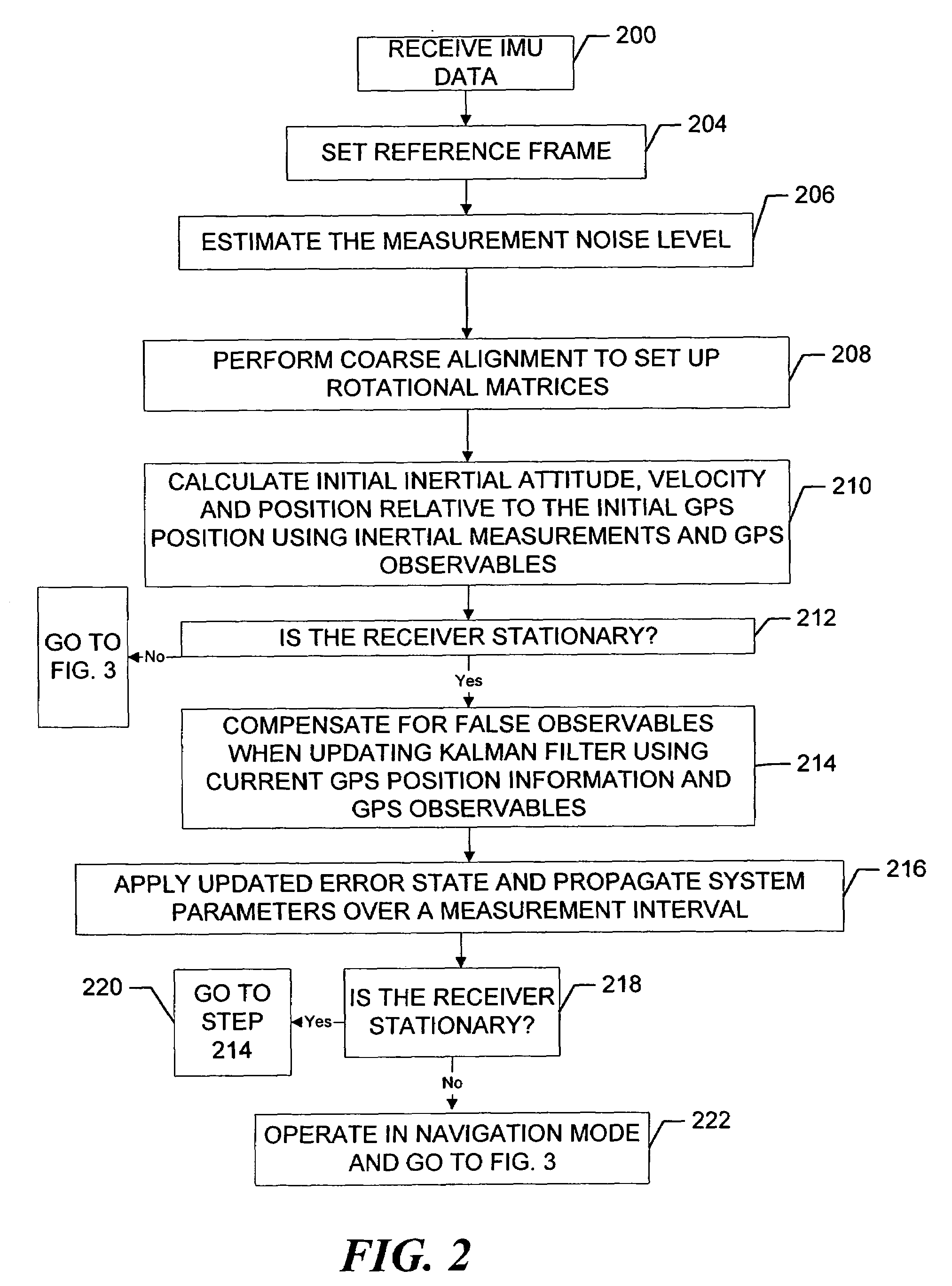
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
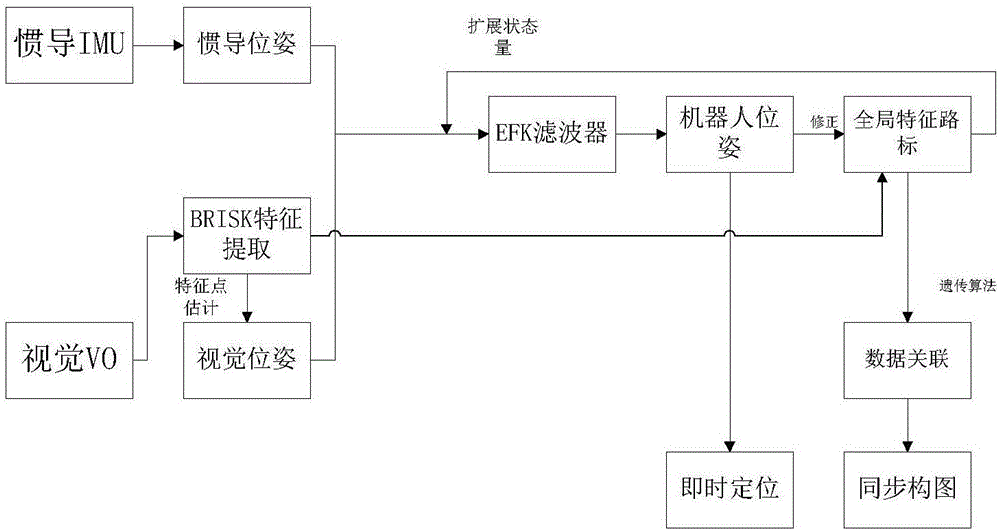
Vision-inertia integrated SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method based on genetic algorithm
ActiveCN106679648AHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSimultaneous localization and mappingKaiman filter
The invention discloses a vision-inertia integrated SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method based on a genetic algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: integrating a vision navigation coordinate system with an inertia navigation coordinate system, and calibrating parameters of a binocular camera so as to solve a three-dimensional space coordinate according to an image pixel coordinate; independently calculating by inertia navigation; calculating by vision navigation; integrating vision navigation information with inertia navigation information by using an extended Kalman filter, and building a system filter model; and observing global feature point road signs by using the binocular camera by taking localization locality into account, carrying out data association on map features based on the genetic algorithm, and feeding extended state vectors back to a filter. The method is capable of carrying out long-time and high-accuracy localization; the genetic algorithm is added for improving the data association of the map, so that the simultaneous mapping accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
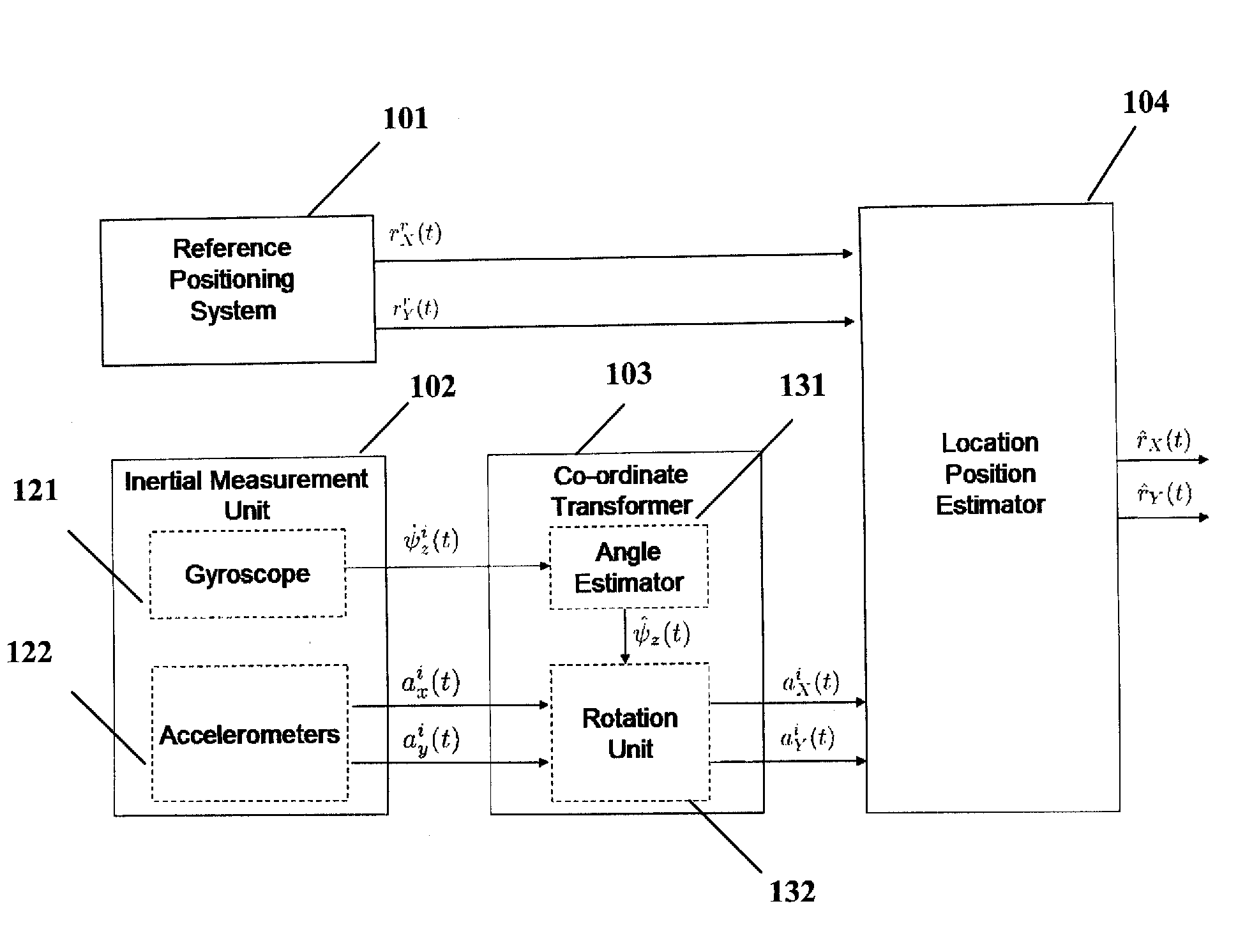
Apparatus and method for measuring the accurate position of moving objects in an indoor environment
ActiveUS20080004796A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlKaiman filterAccelerometer
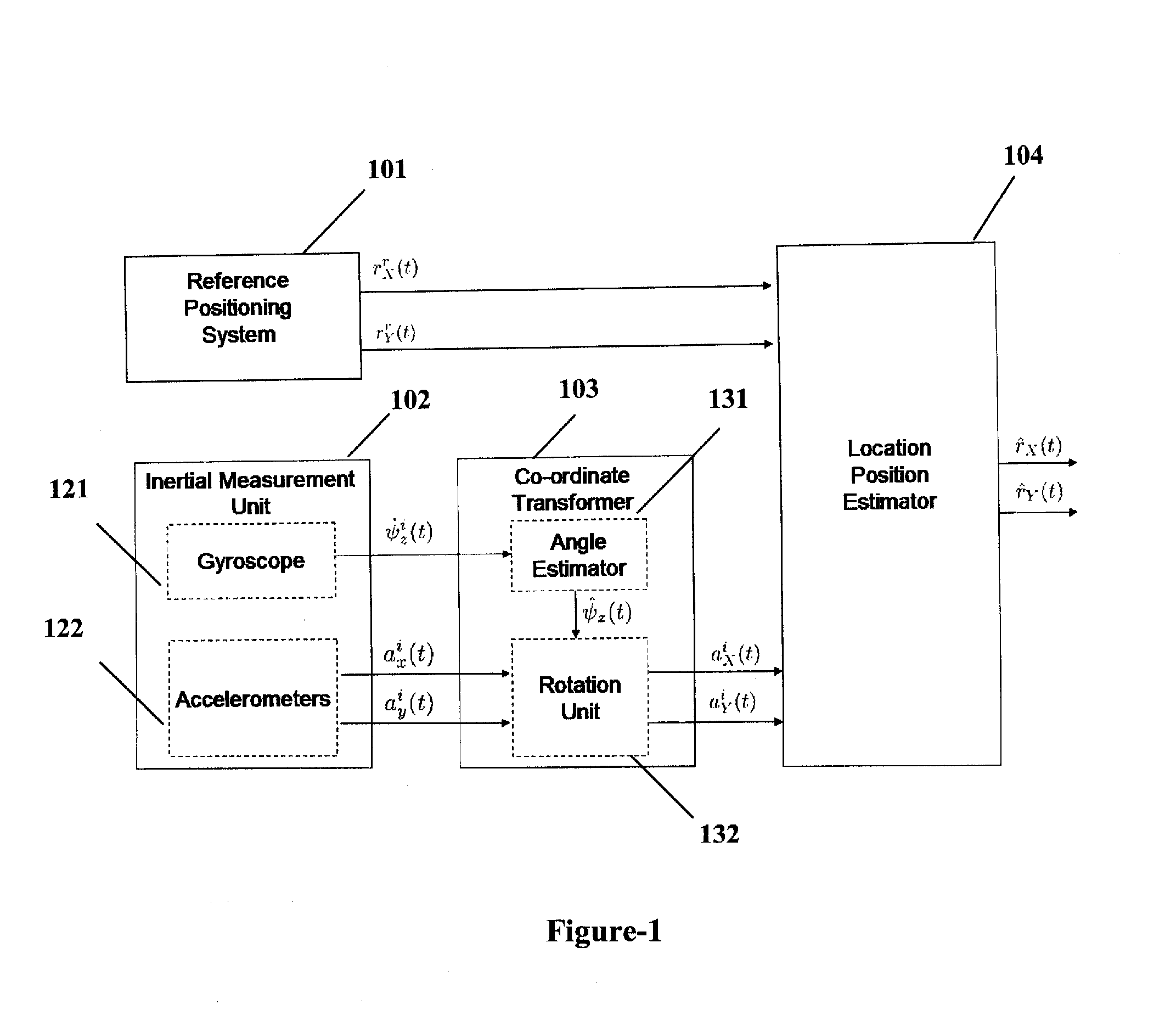
An apparatus and method is disclosed for efficiently sensing and tracking objects in an indoor environment by simultaneously measuring the object movement with an inertial navigation system and a reference location positioning system. By combining the measurements obtained with accelerometers, gyroscopes, angle estimators and the reference system using an extended Kalman filter based approach, a position estimate is obtained with high reliability and precision accuracy. Improvement in performance is obtained by the incorporation of dynamic mode switching and forward-backward smoothing in the location position estimator.
Owner:GENERAC POWER SYSTEMS
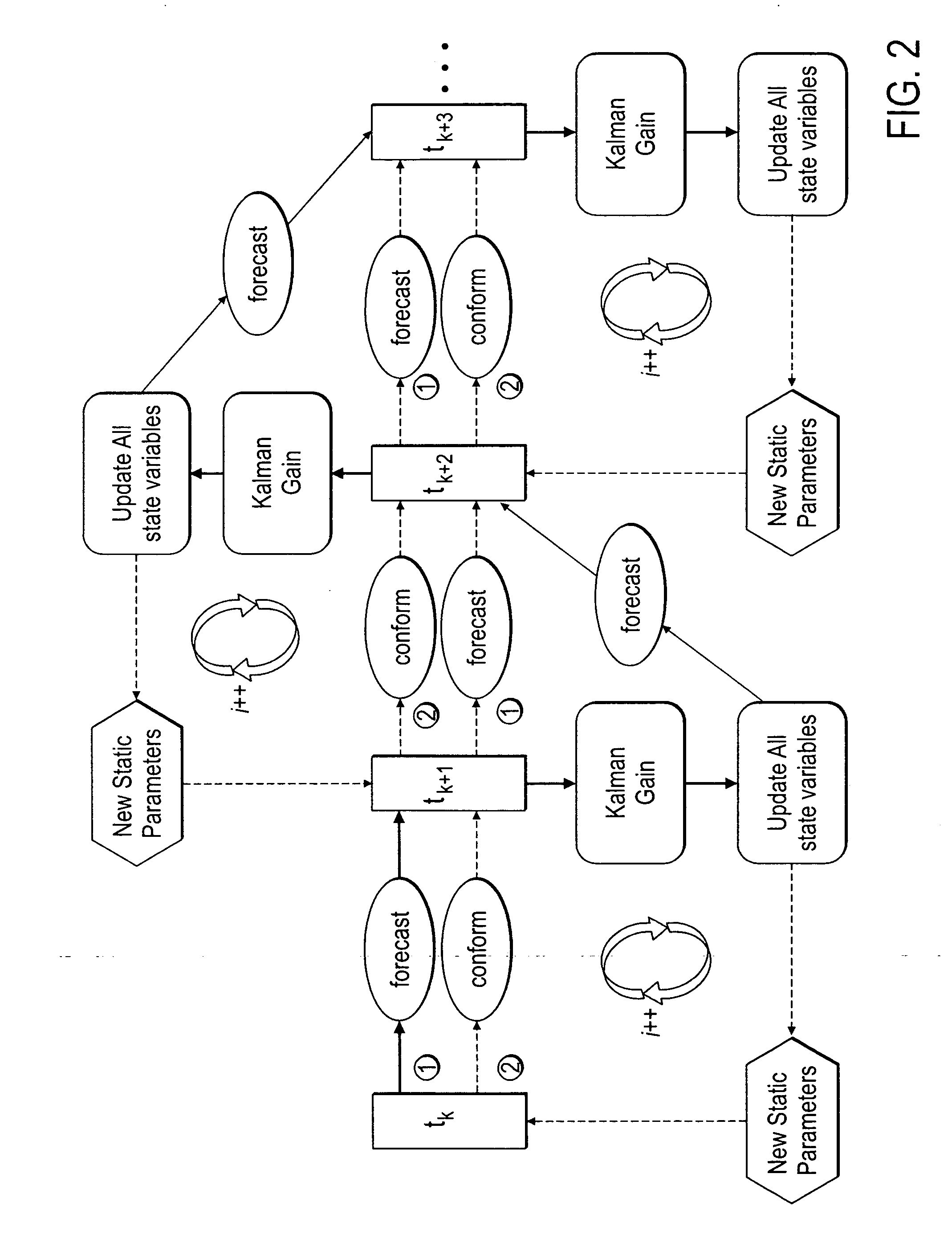
Method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filter
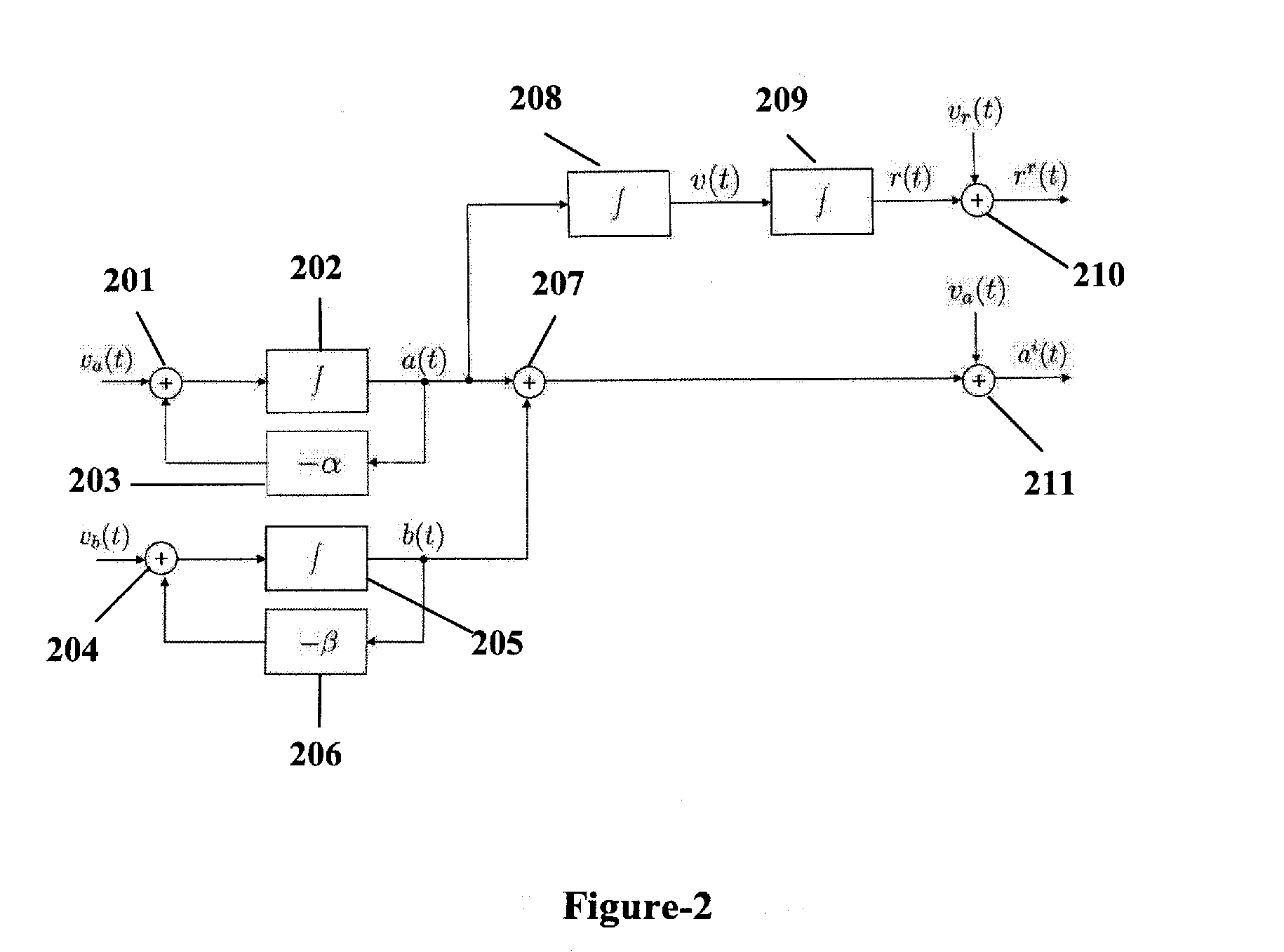
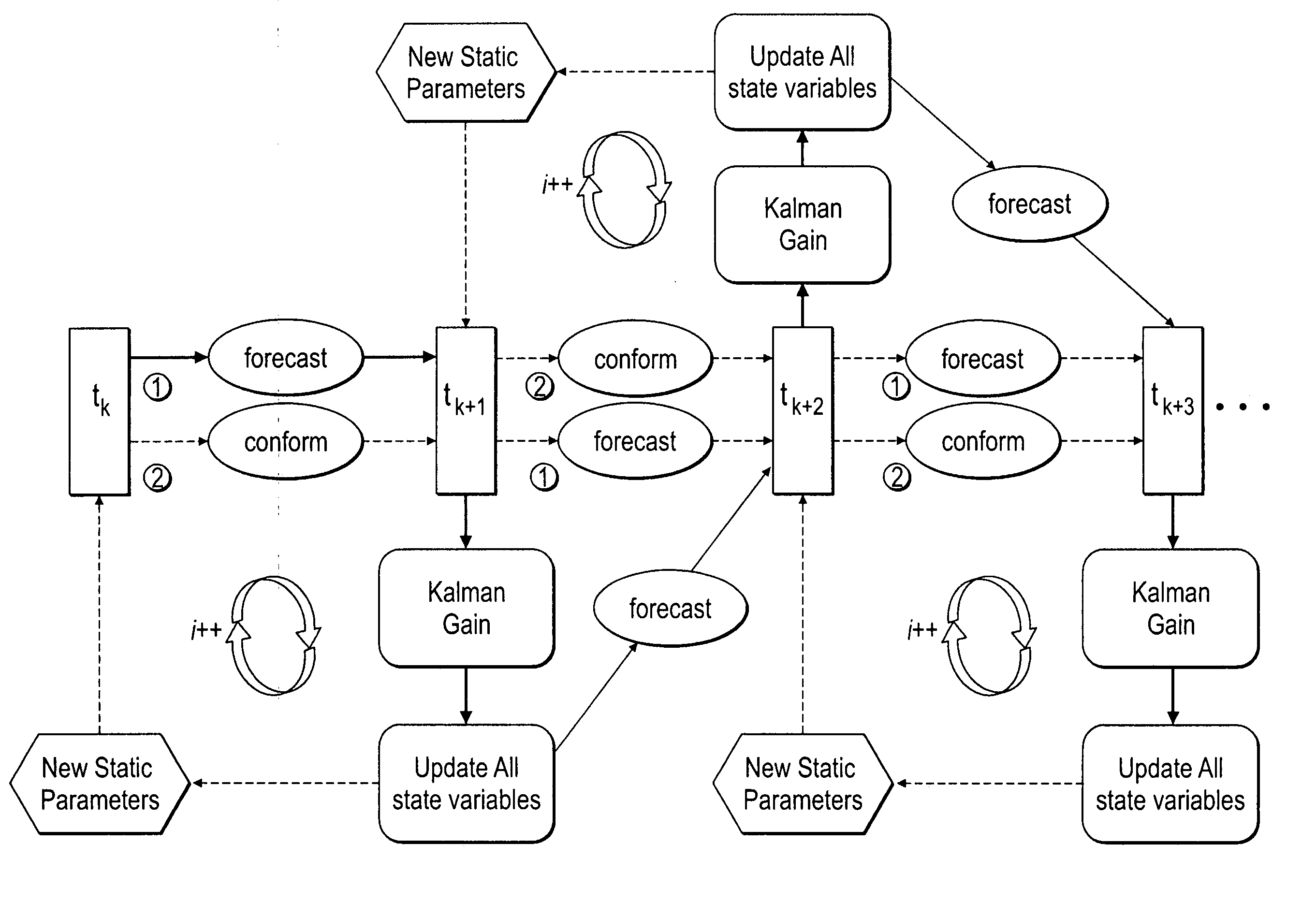
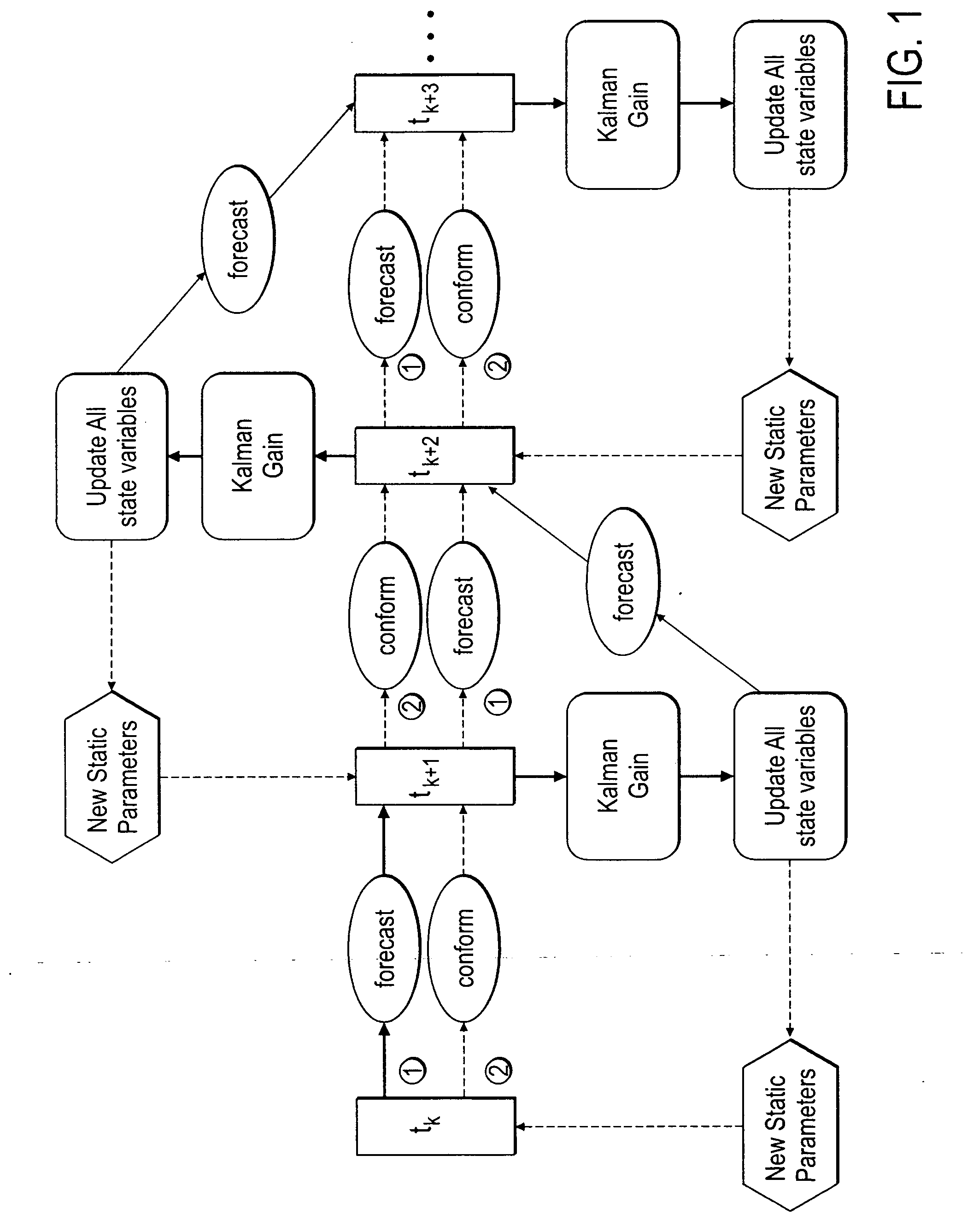
ActiveUS20070118346A1Reduce in quantityEnsure correct executionFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationKaiman filterState variable
A method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filters is described. The method includes a conforming step for bring bringing static and dynamic state variables into conformance with one another during a time step of the updating. Also, an iterative damping method is used in conjunction with the conformance step to account for nonGaussian and nonlinear features in a system. Also, a re-sampling method is described which reduces the ensemble size of reservoir models which are to be updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
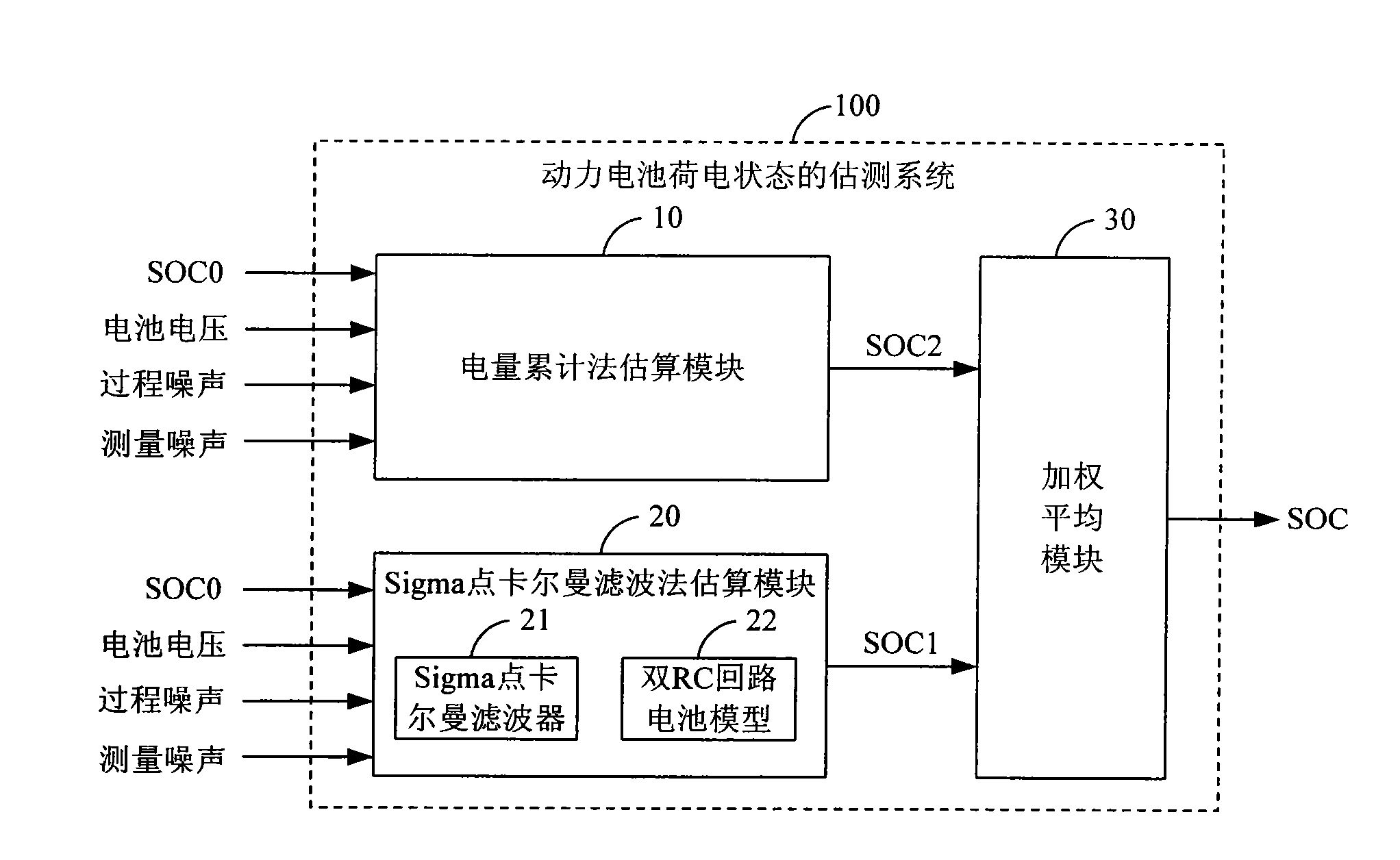
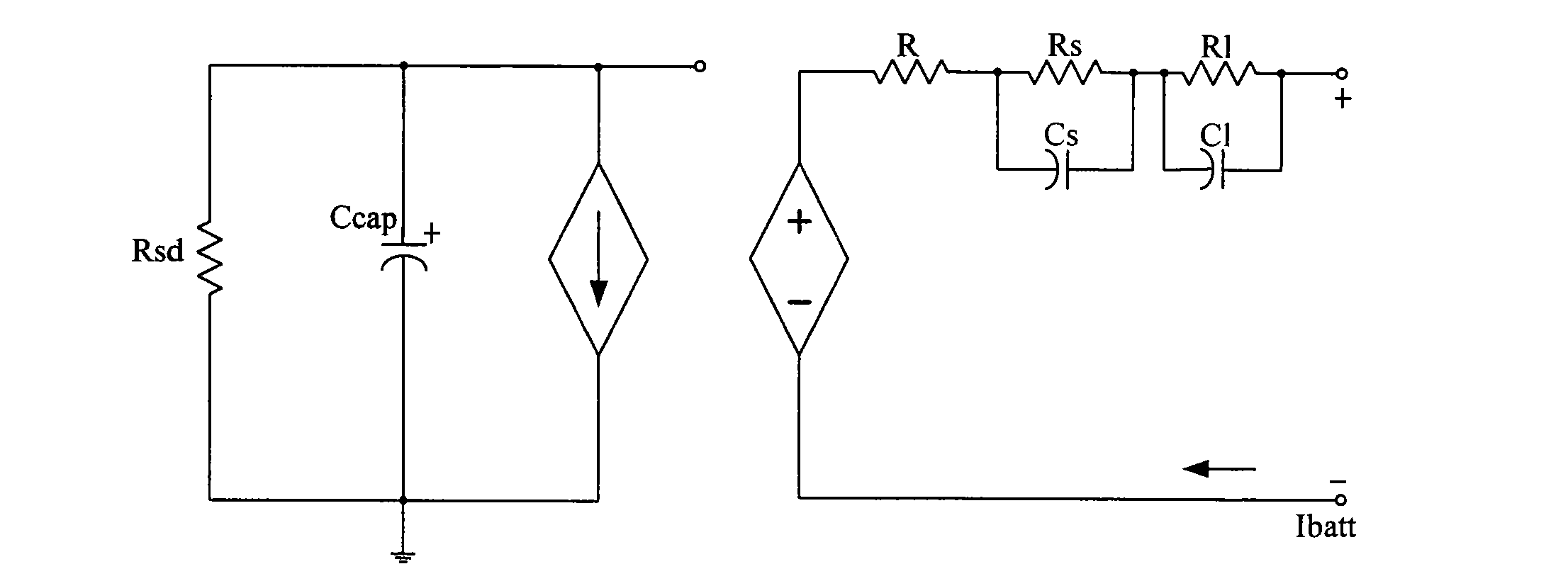
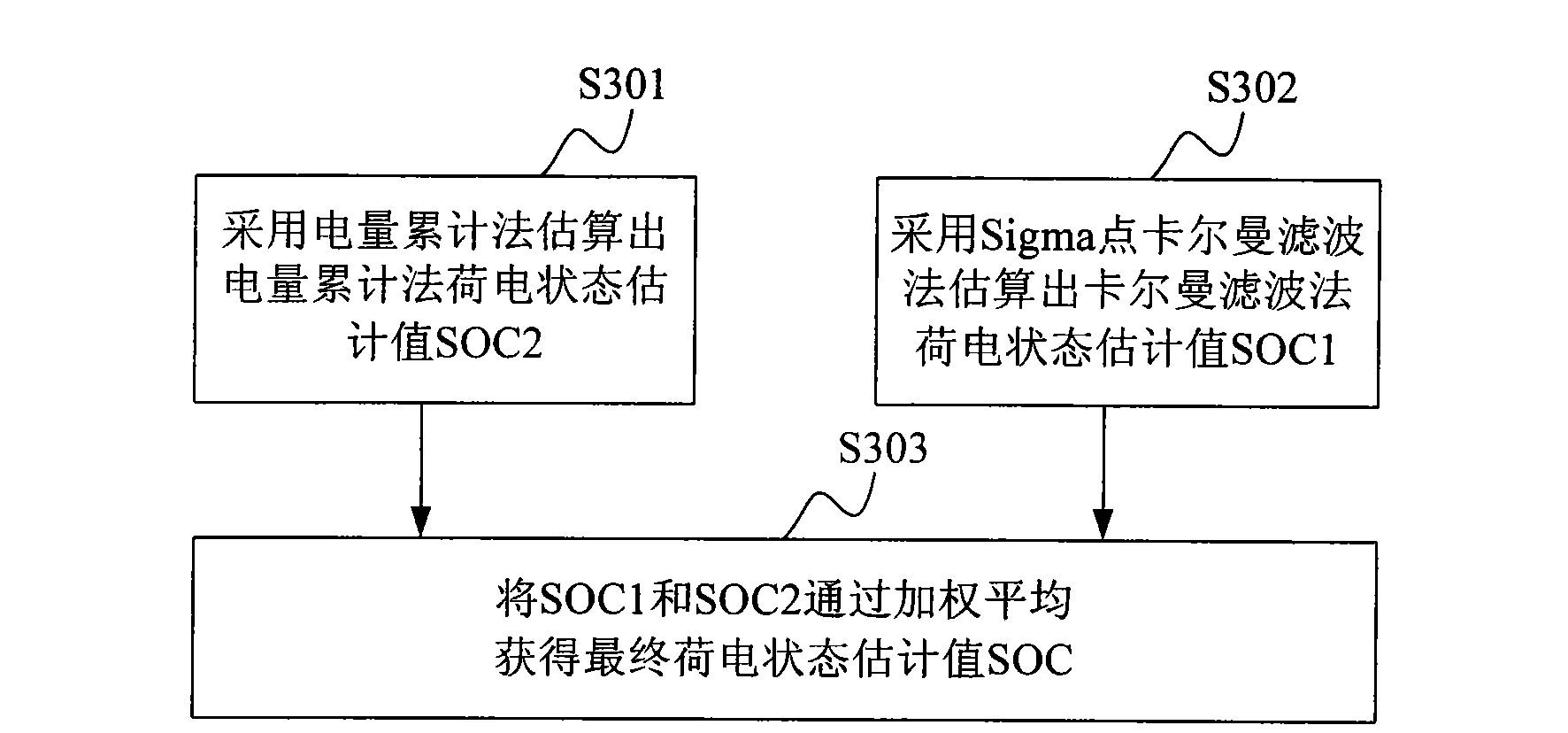
Estimation method and system of state of charge (SOC) of power battery
ActiveCN102062841AAvoid oscillationAvoid Cumulative ErrorsElectrical testingState of chargeWeighted average method
The invention discloses an estimation method of state of charge (SOC) of a power battery. The method comprises the following steps: estimating the SOC estimated value SOC2 of the power battery by an electricity accumulative method; taking a Sigma-point Kalman filter (SPKF) as a basic estimation tool, taking a dual-RC circuit battery model as a time and measurement update engine of the SPKF, and estimating the SOC estimated value SOC1 of the power battery by a Kalman filter method; and obtaining the final SOC estimated value SOC based on the SOC estimated value SOC2 by the electricity accumulative method and the SOC estimated value SOC1 by the Kalman filter method by utilizing a weighted average method. Correspondingly, the invention further discloses an estimation system of the SOC of thepower battery. The invention has the advantages of high SOC estimation accuracy, stable operation and the like, and is convenient in real-time estimation, thus being applicable to pure electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles in need of the power battery.
Owner:BEIQI FOTON MOTOR CO LTD
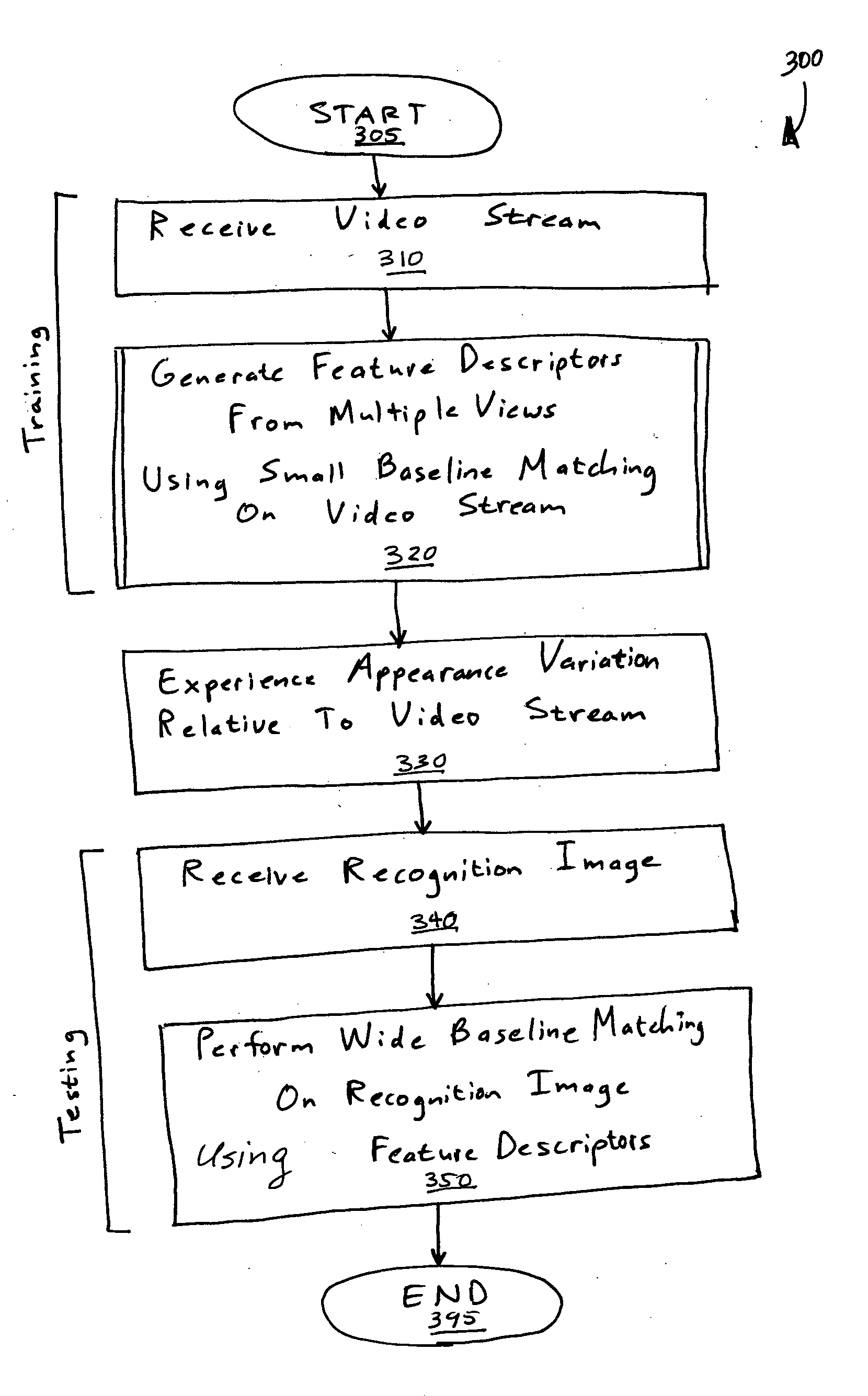
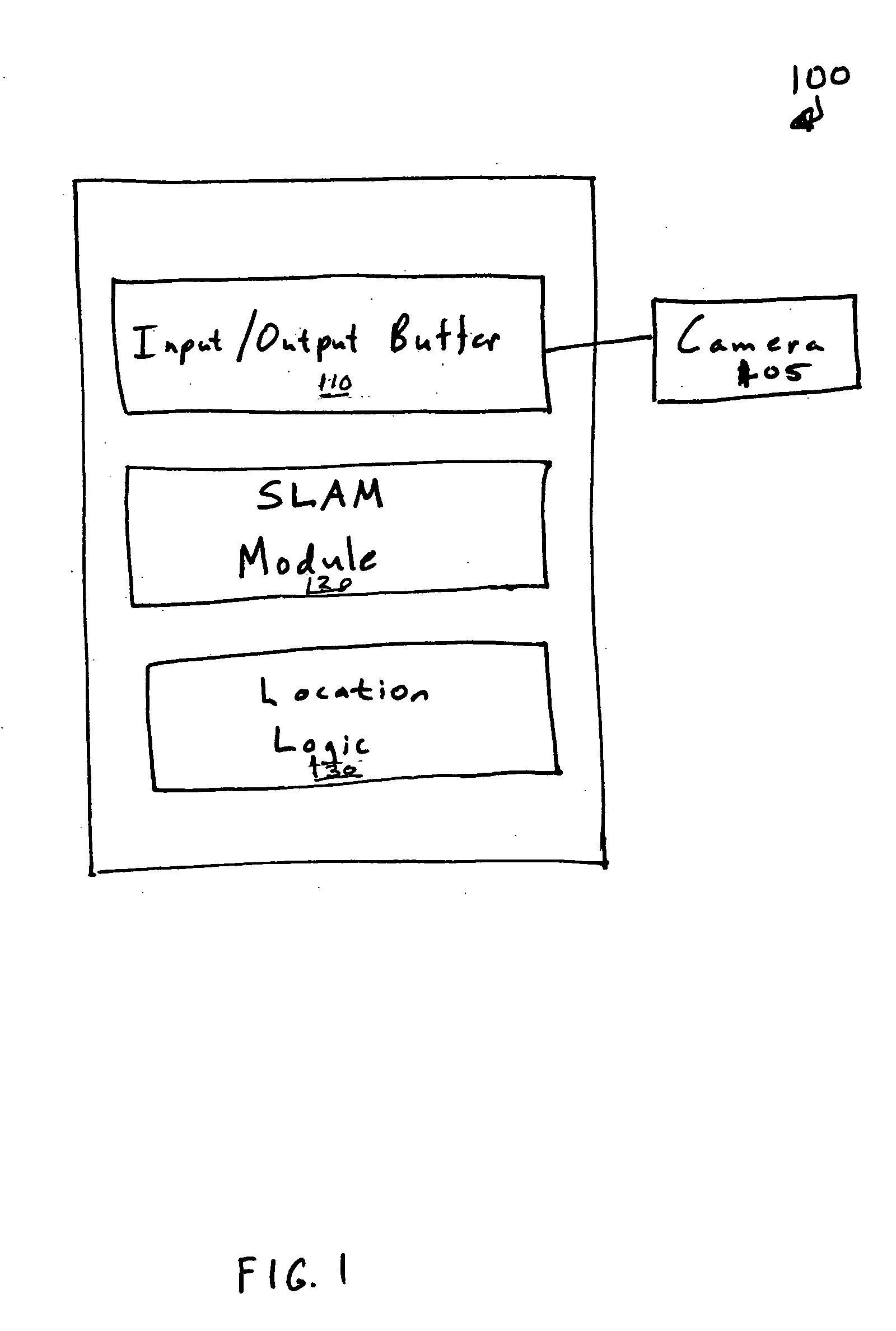
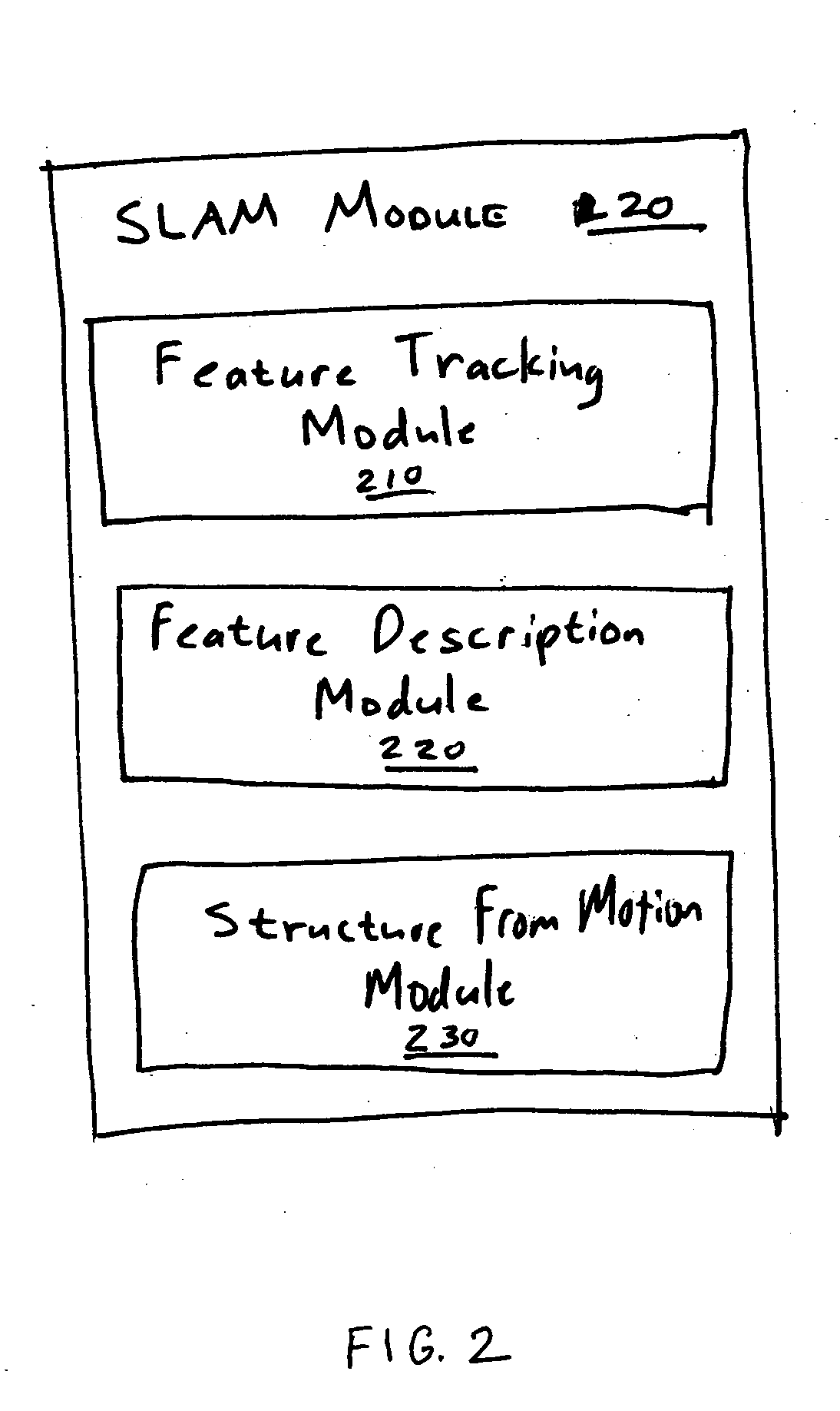
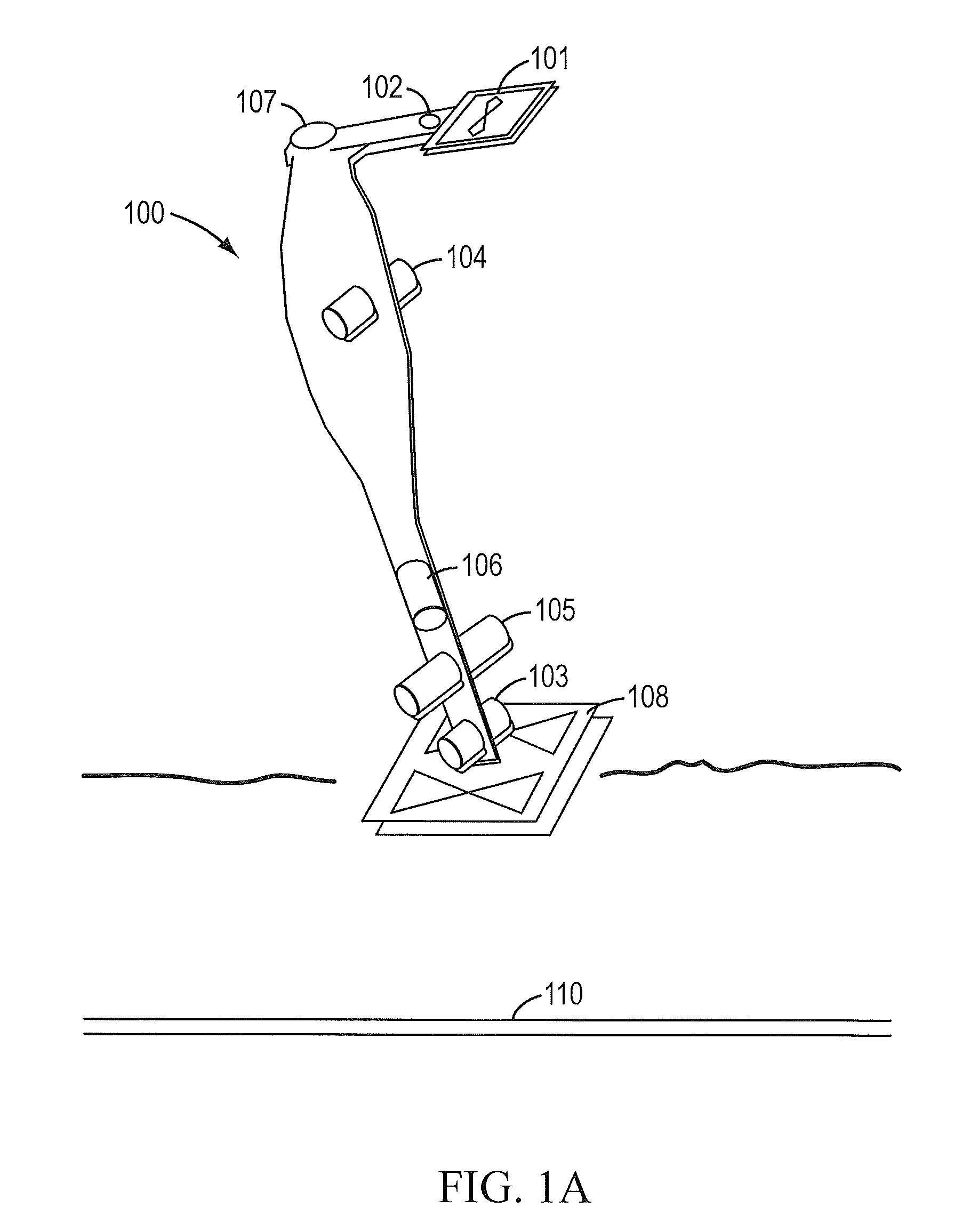
Simultaneous localization and mapping using multiple view feature descriptors
InactiveUS20050238200A1Efficiently build necessary feature descriptorReliable correspondenceThree-dimensional object recognitionKaiman filterKernel principal component analysis
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) utilizes multiple view feature descriptors to robustly determine location despite appearance changes that would stifle conventional systems. A SLAM algorithm generates a feature descriptor for a scene from different perspectives using kernel principal component analysis (KPCA). When the SLAM module subsequently receives a recognition image after a wide baseline change, it can refer to correspondences from the feature descriptor to continue map building and / or determine location. Appearance variations can result from, for example, a change in illumination, partial occlusion, a change in scale, a change in orientation, change in distance, warping, and the like. After an appearance variation, a structure-from-motion module uses feature descriptors to reorient itself and continue map building using an extended Kalman Filter. Through the use of a database of comprehensive feature descriptors, the SLAM module is also able to refine a position estimation despite appearance variations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS7834801B2Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingElectric/magnetic detectionGyroscopeAccelerometer
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS7289906B2Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
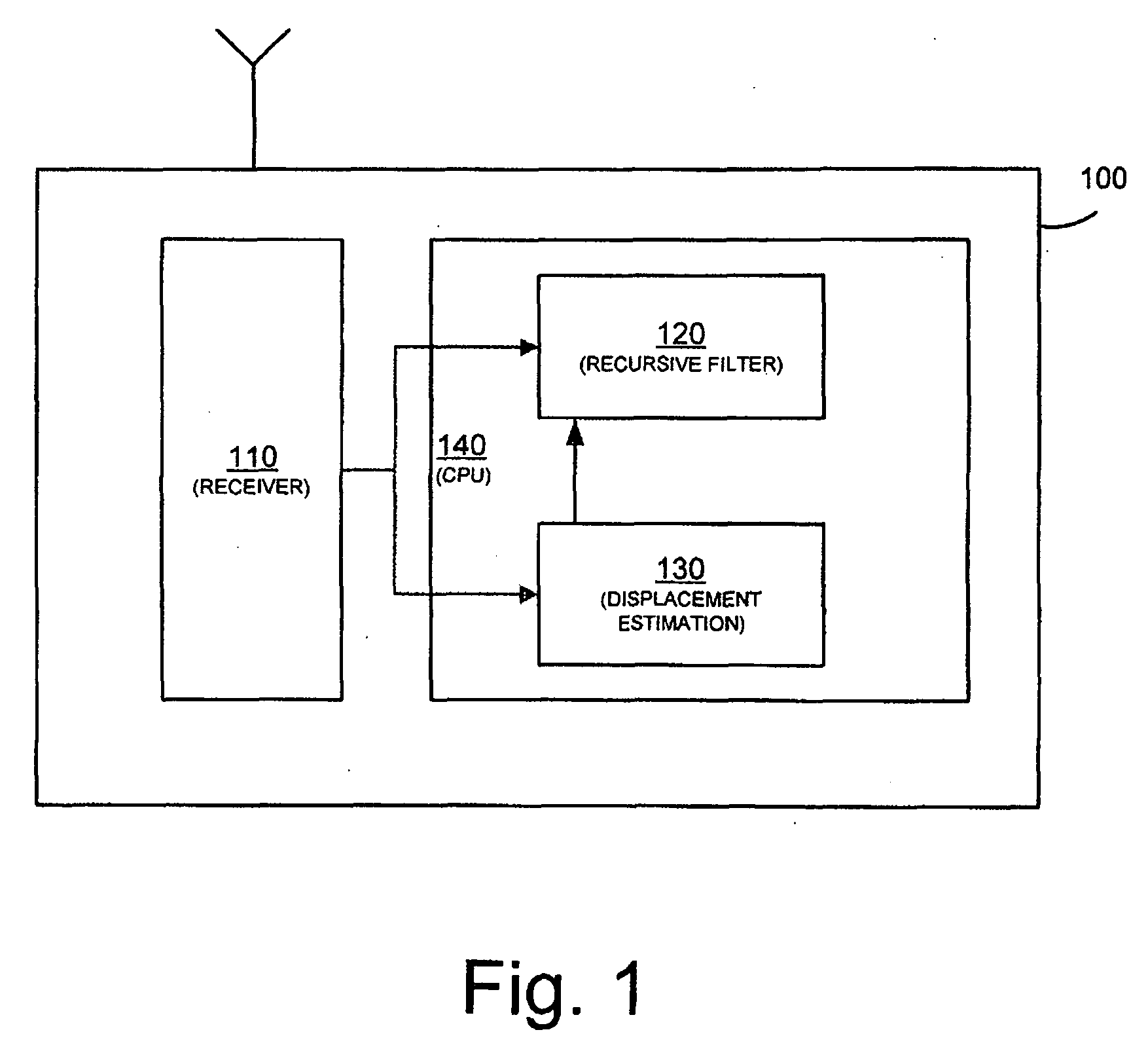
Position tracking device and method
ActiveUS20100141515A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterLocation tracking
The present application relates to tracking a position of a device, e.g. for detecting slow and rapid earth deformation, by making use of a recursive filter having the filter characteristic adapted to a detected type of motion. If the motion of the position tracking device is rapid, the filter characteristic is set such that the rapid motion can be tracked with the necessary speed. On the other hand, if the motion is slow, e.g. during times of a normal tectonic drift, the filter characteristic is set such that the motion is slowly tracked with the advantage of efficient noise reduction, i.e. noise in the input signal is effectively barred and does not pass through the filter to the output signal. Thus, in times of rapid motion the convergence speed of the filter output signal to the input signal is set high for fast convergence and in times of slow motion the convergence speed of the filter output signal to the input signal is set low for a slow convergence. The filter may be a Kalman filter.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
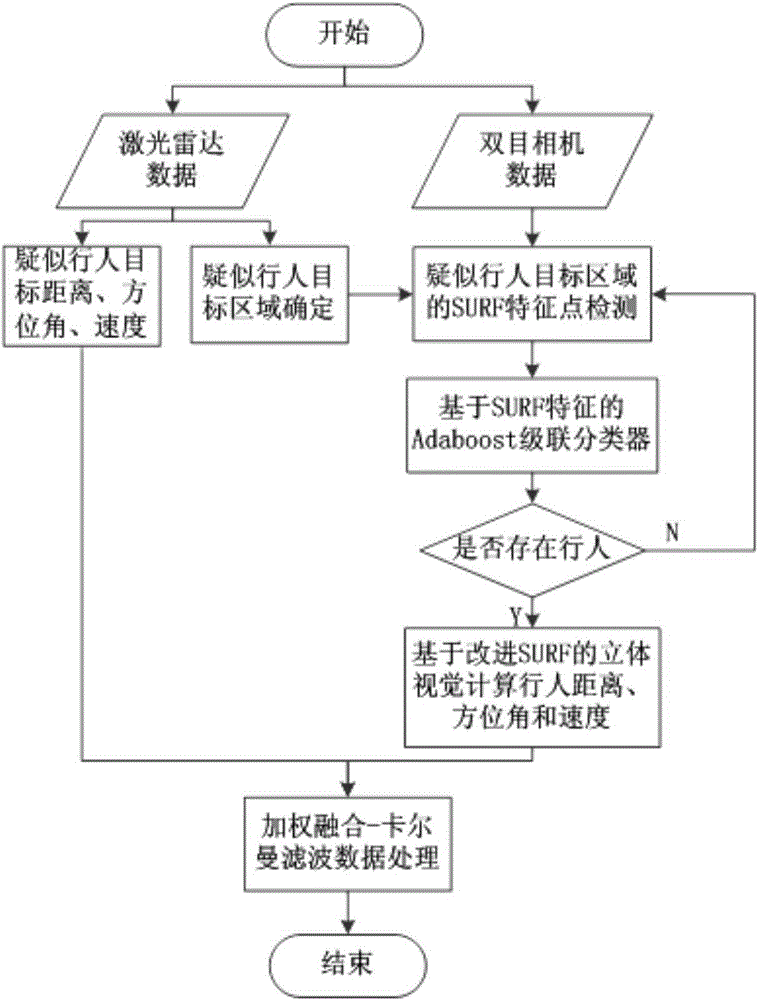
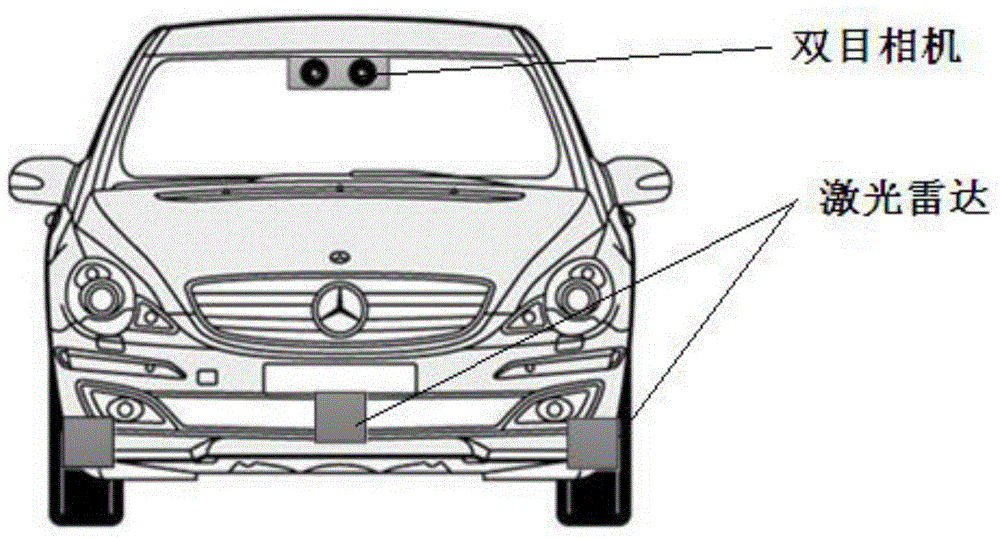
Detection method and system, based on laser radar and binocular camera, for pedestrian in front of vehicle
ActiveCN104573646AHigh measurement accuracyThe data is accurate and completeCharacter and pattern recognitionActive safetyVisual perception
The invention belongs to the field vehicle active safety, and particularly discloses a detection method and system, based on laser radar and binocular camera, for a pedestrian in front of vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: collection data of the front of the vehicle through the laser radar and the binocular camera; respectively processing the data collected by the laser radar and the binocular camera, so as to obtain the distance, azimuth angle and speed value of the pedestrian relative to the vehicle; correcting the information of the pedestrian through a Kalman filter. The method comprehensively utilizes a stereoscopic vision technology and a remote sensing technology, integrates laser radar and binocular camera information, is high in measurement accuracy and pedestrian detection accuracy, and can effectively reduce the occurrence rate of traffic accidents.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
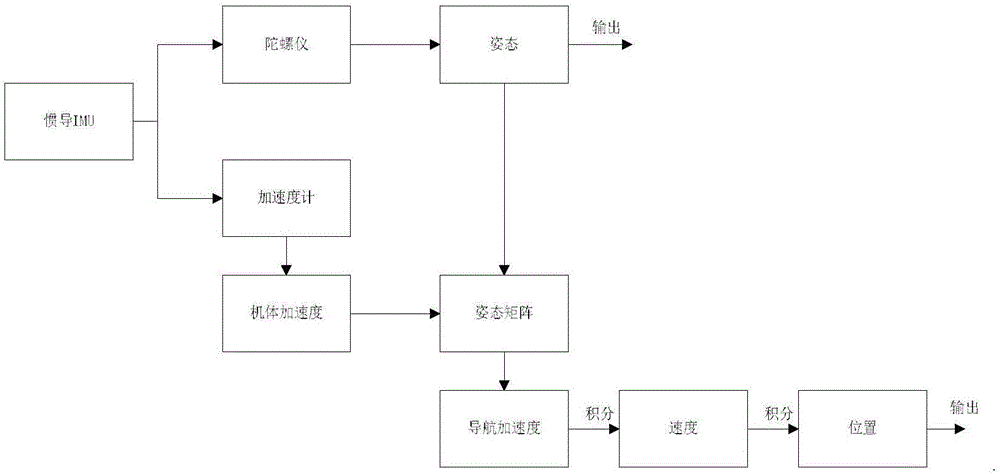
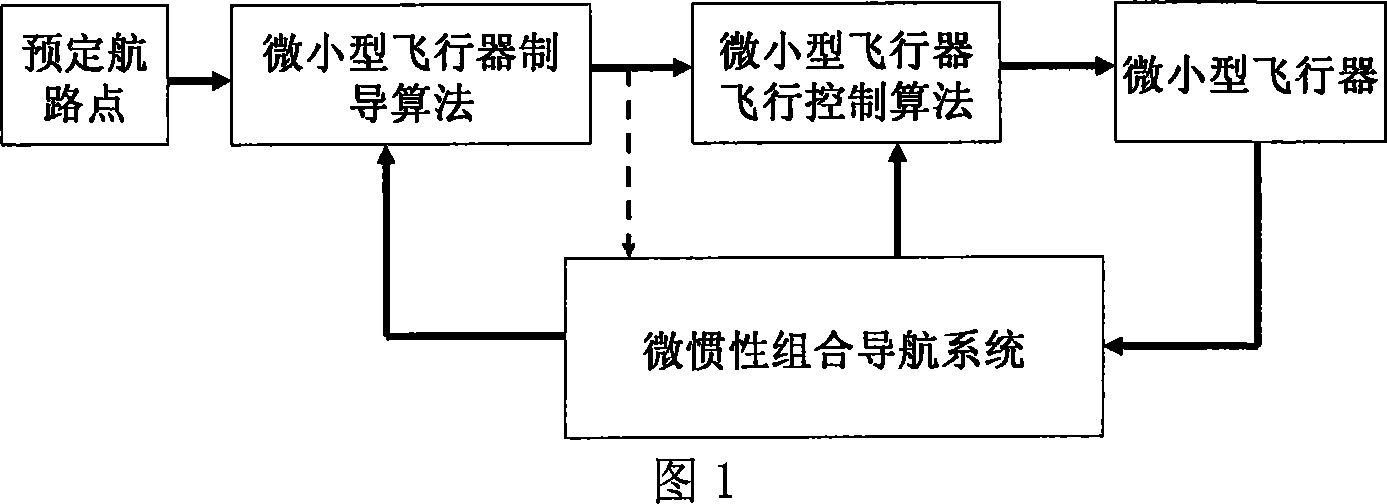
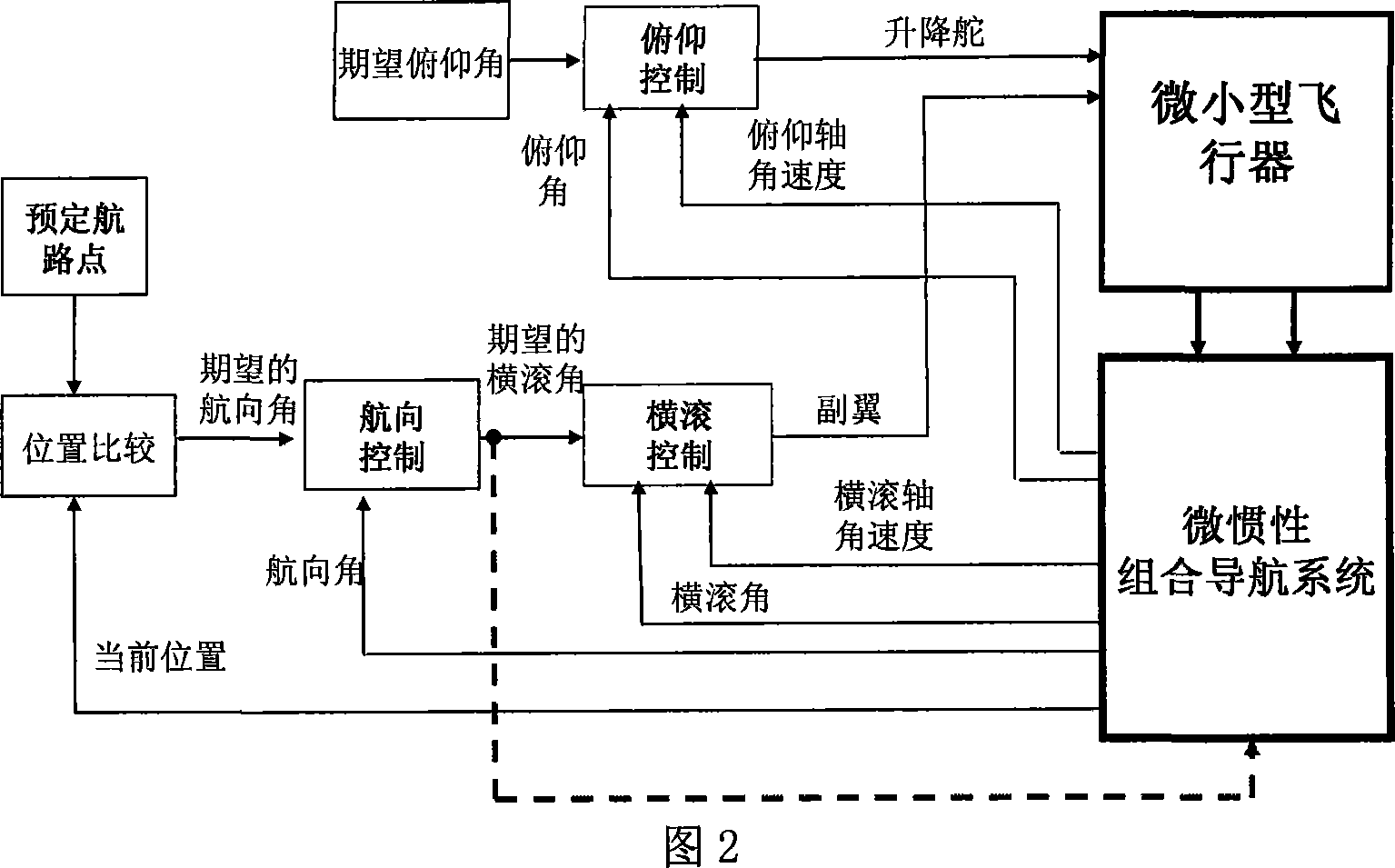
Attitude determination method of mini-aircraft inertial integrated navigation system
InactiveCN101033973AImprove flight qualityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGuidance systemAccelerometer
This invention relates to a kind of attitude definition method of micro inertia mixed navigation system of microminiature aero craft, belongs to microminiature vehicle attitude definition method. The method utilize guidance information, control Kalman filter noise matrices, to realize self-adapting adjust according to flight status; through parameter adjust to realize attitude definition of micro inertia mixed navigation system on dynamic airborne conditions; the specific process: through GNC closed loop circuit guidance algorithm, to gain aero craft barrel angle; through sensor picking, obtain vehicle rate and specific force; by strap inertial navigation algorithm to resolve out vehicle attitude, velocity and position information; by accelerometer and GPS data to count pose and position measurement information of aero craft; real-time compute horizontal attitude variance of Kalman filter observation noise matrices, through Kalman filter to estimate error of strap inertial guidance system; Amend above acquired pose, velocity and position information, and took as feedback information to import in control system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com