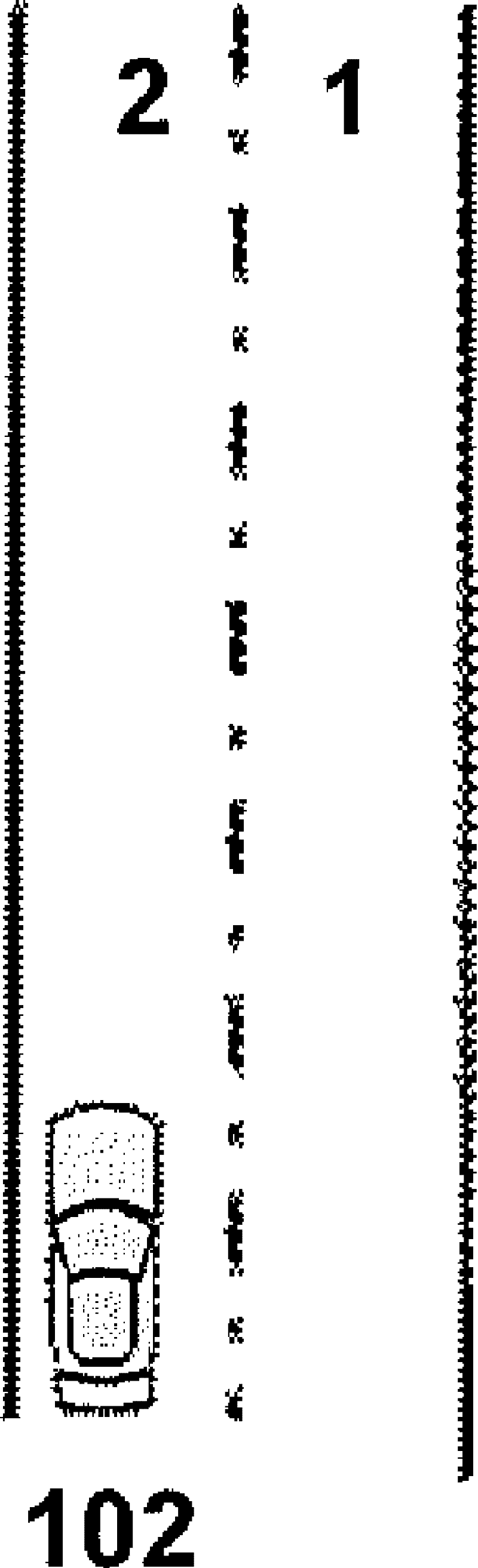Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2808 results about "Curve fitting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fit to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data.
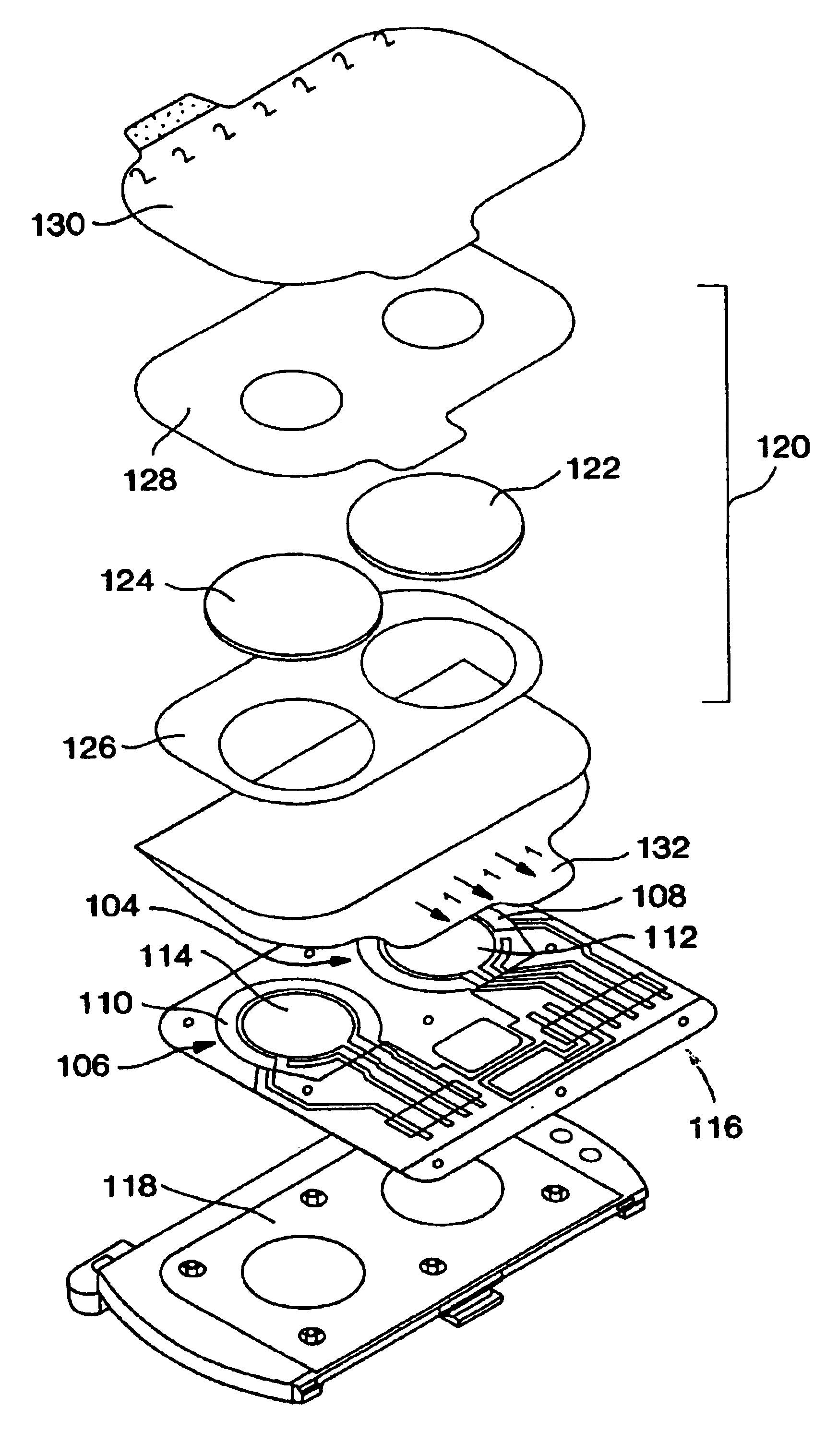
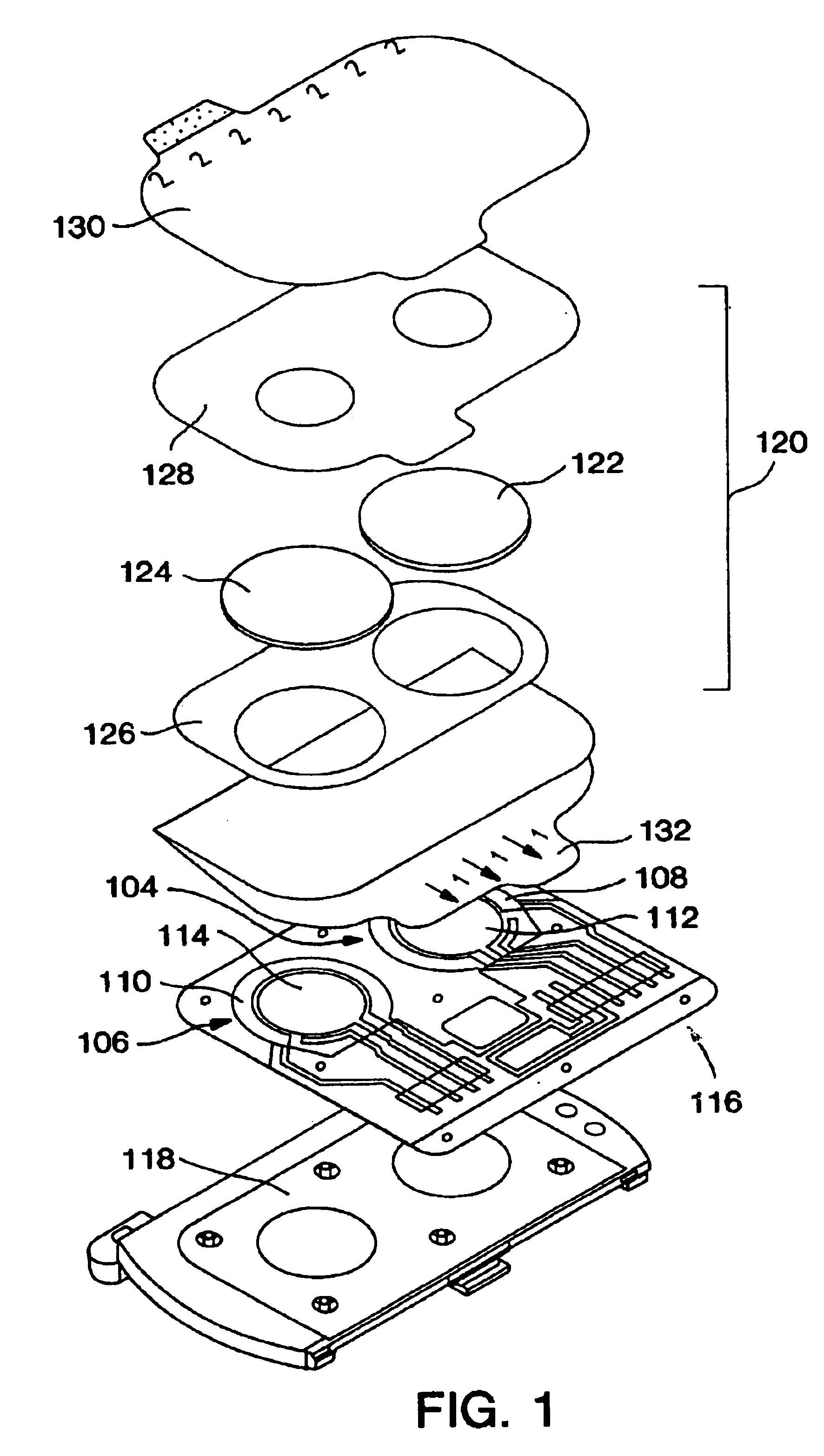
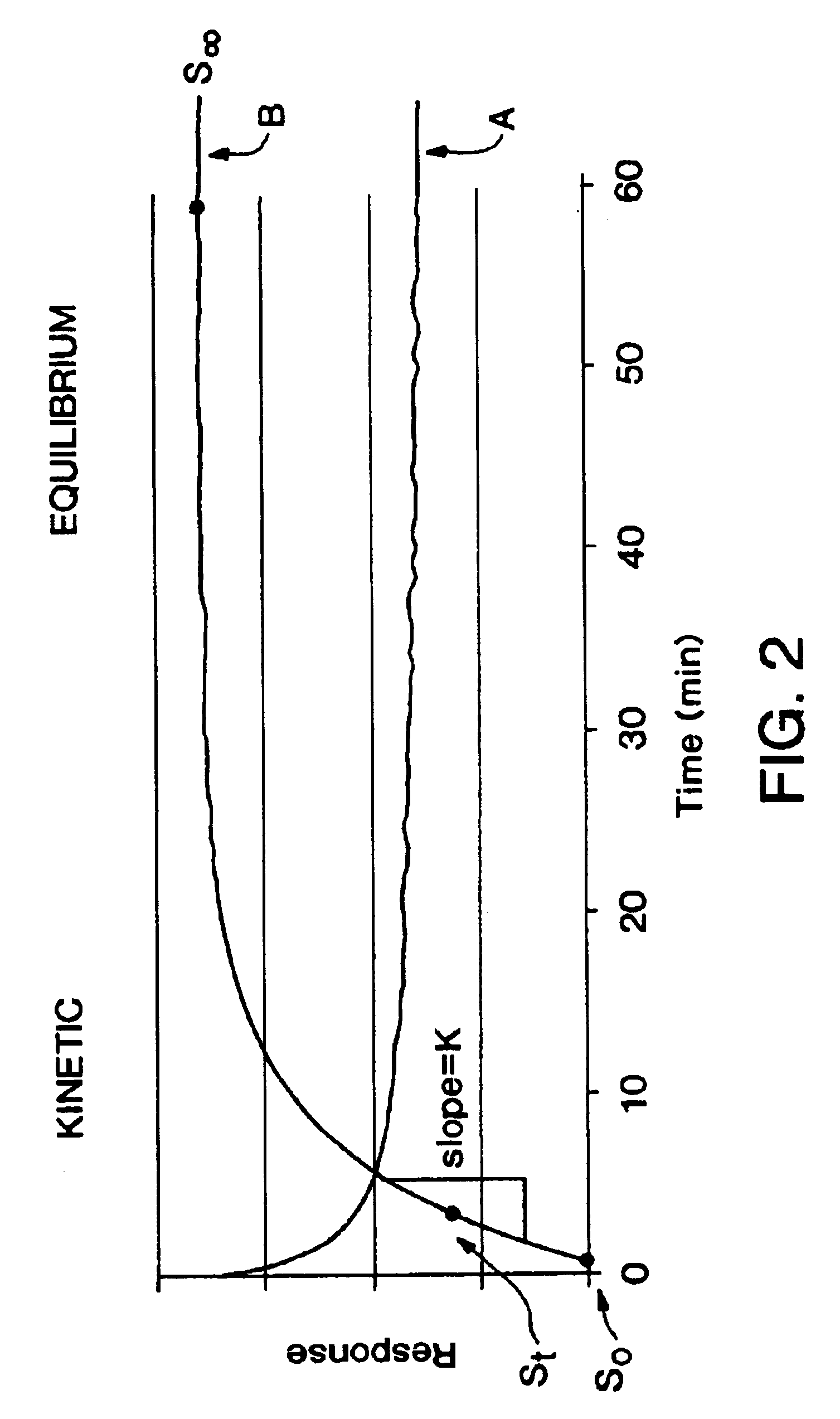
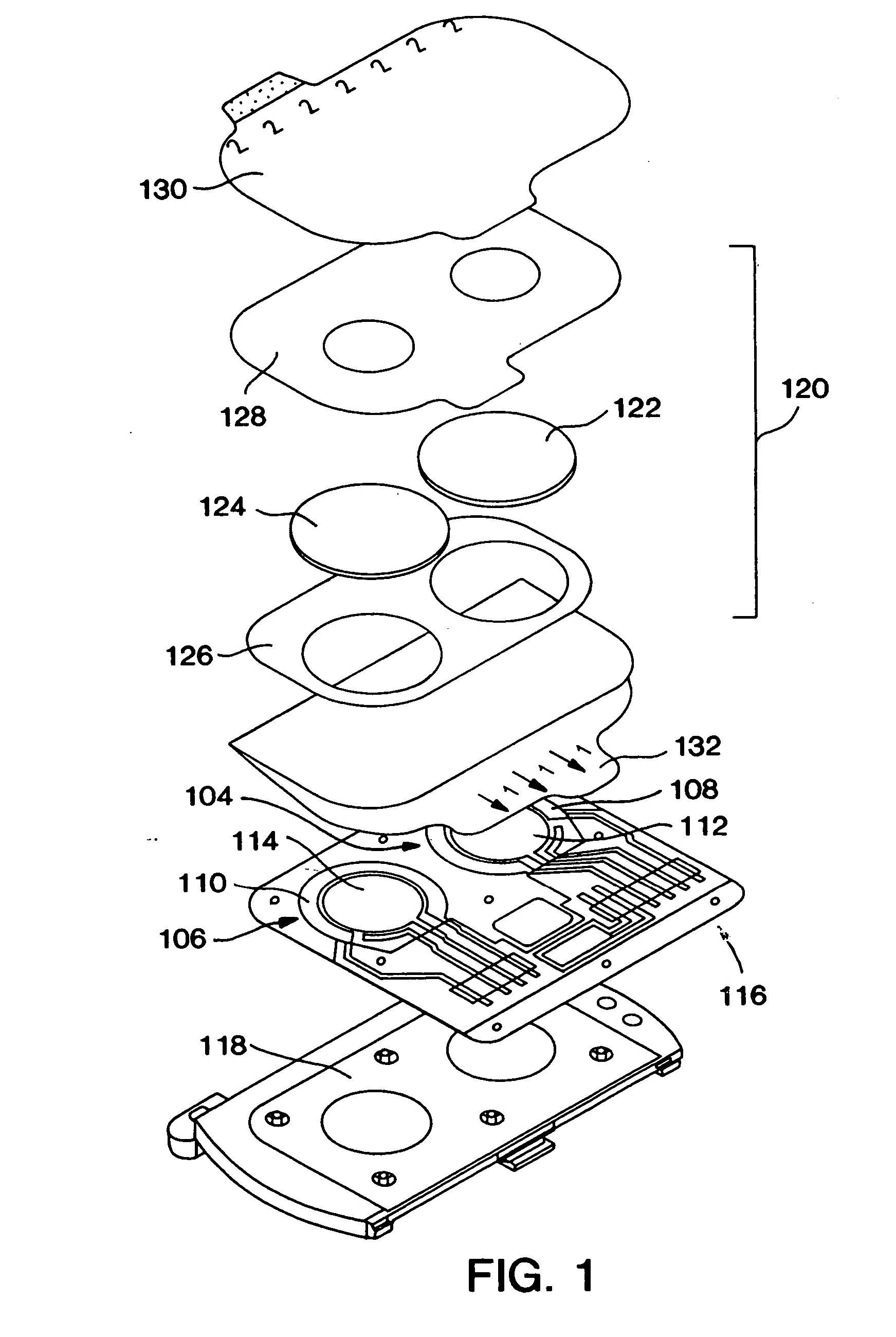
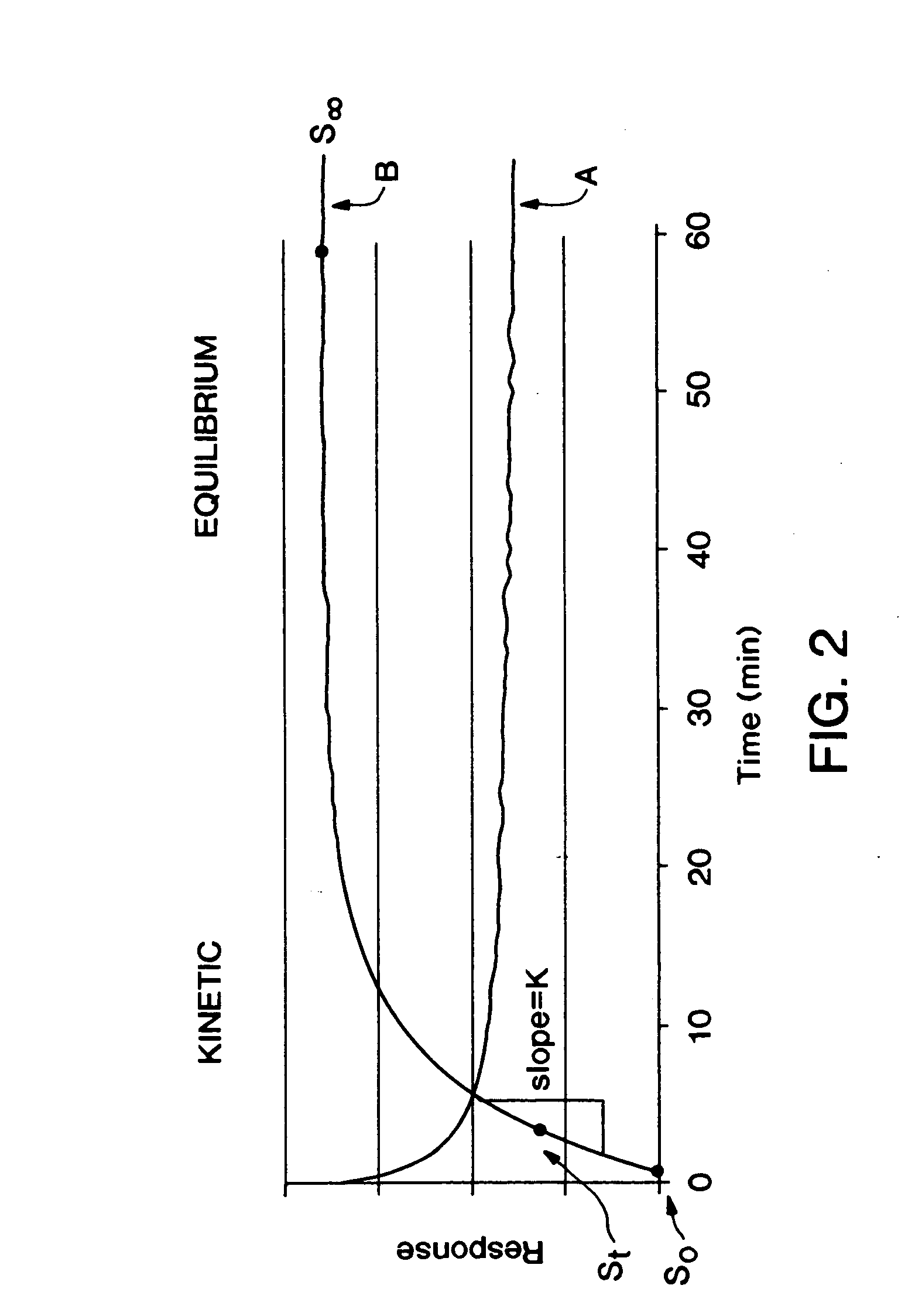
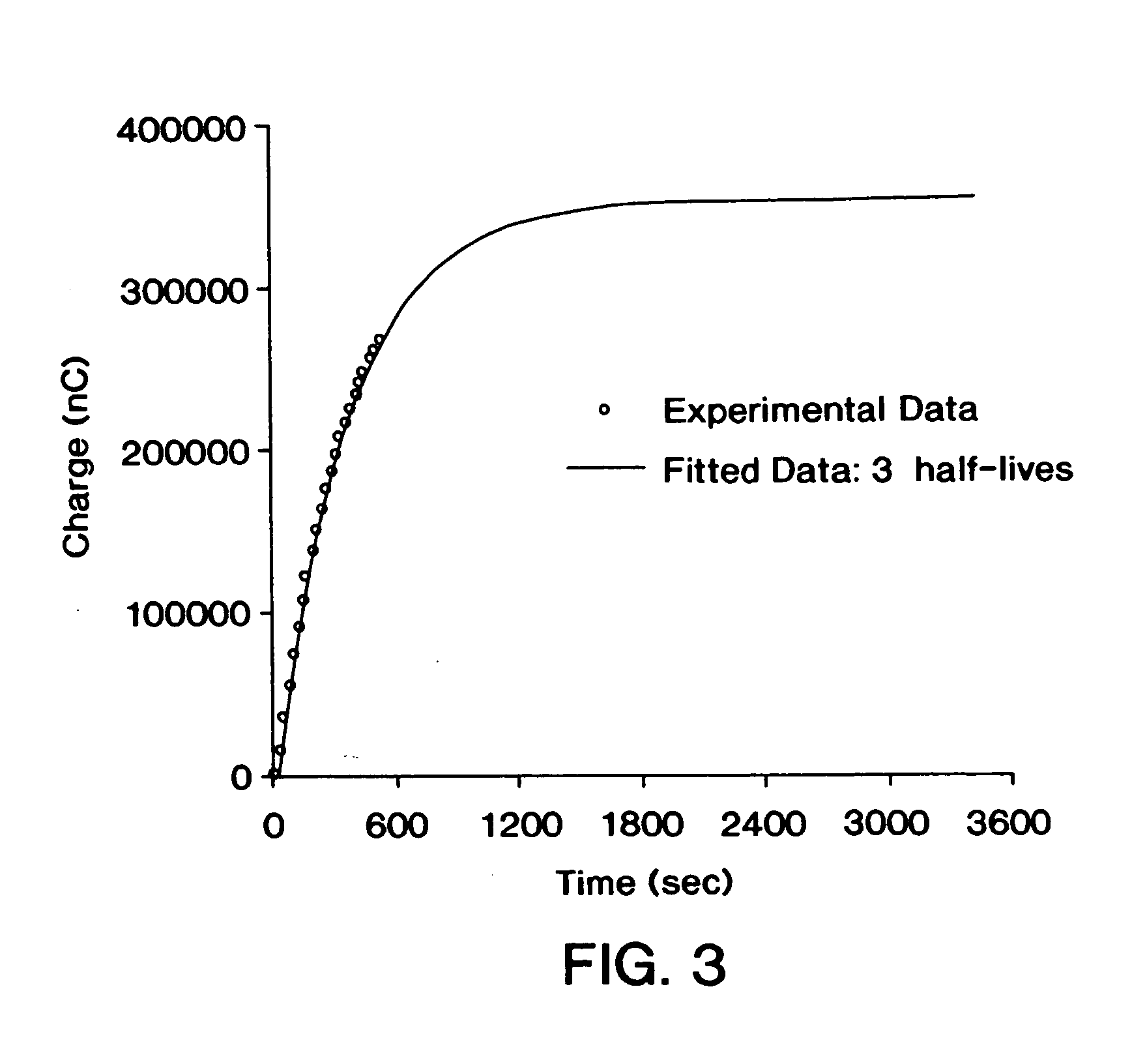
Methods for improving performance and reliability of biosensors
InactiveUS6885883B2Microbiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringCurve fittingMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a predictive-kinetic method for use with data processing of a sensor-generated signal, as well as, microprocessors and monitoring systems employing such a predictive-kinetic method. Data from a transient region of a signal is used with suitable models and curve-fitting methods to predict the signal that would be measured for the system at the completion of the reaction. The values resulting from data processing of sensor response using the methods of the present invention are less sensitive to measurement variables.
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
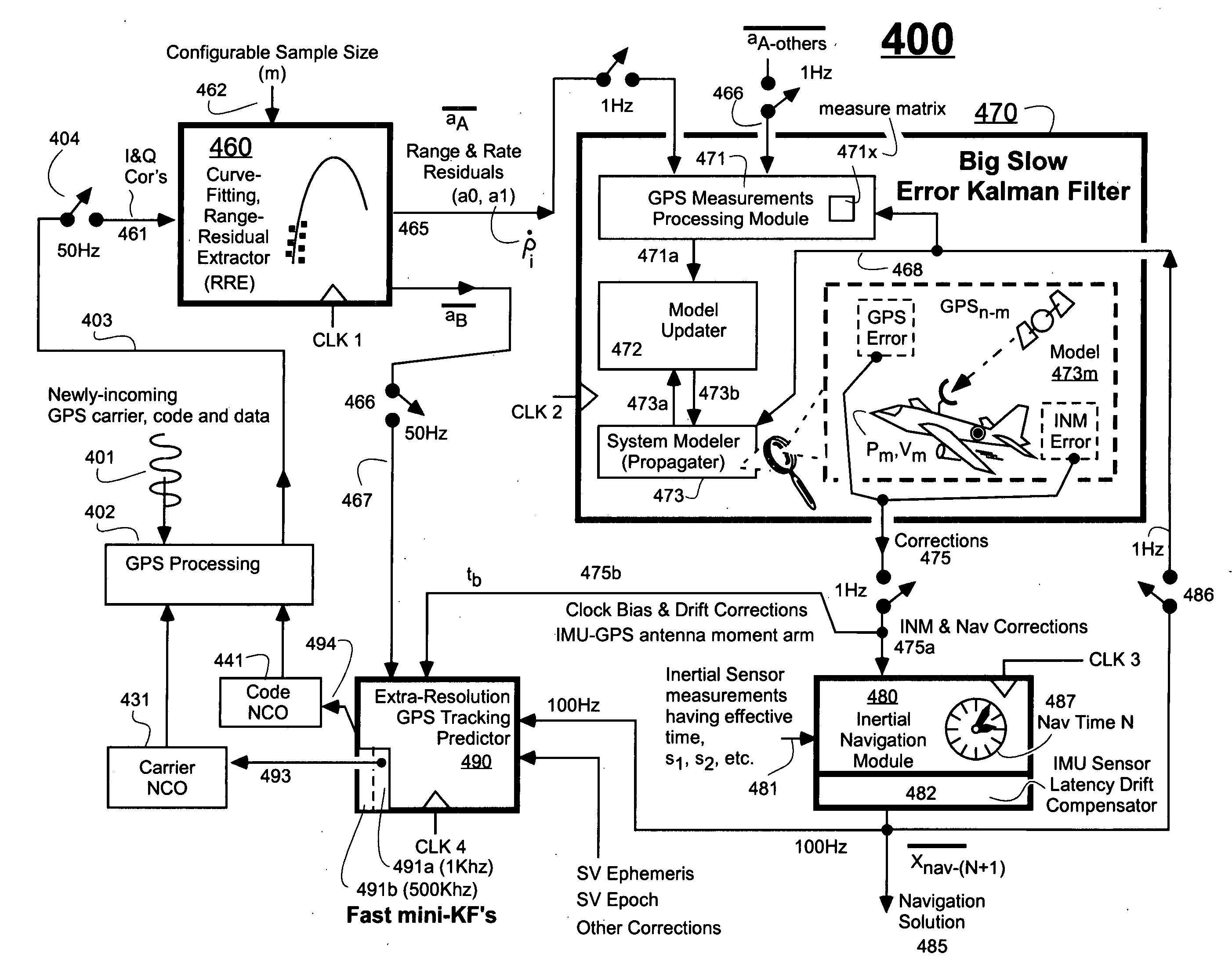
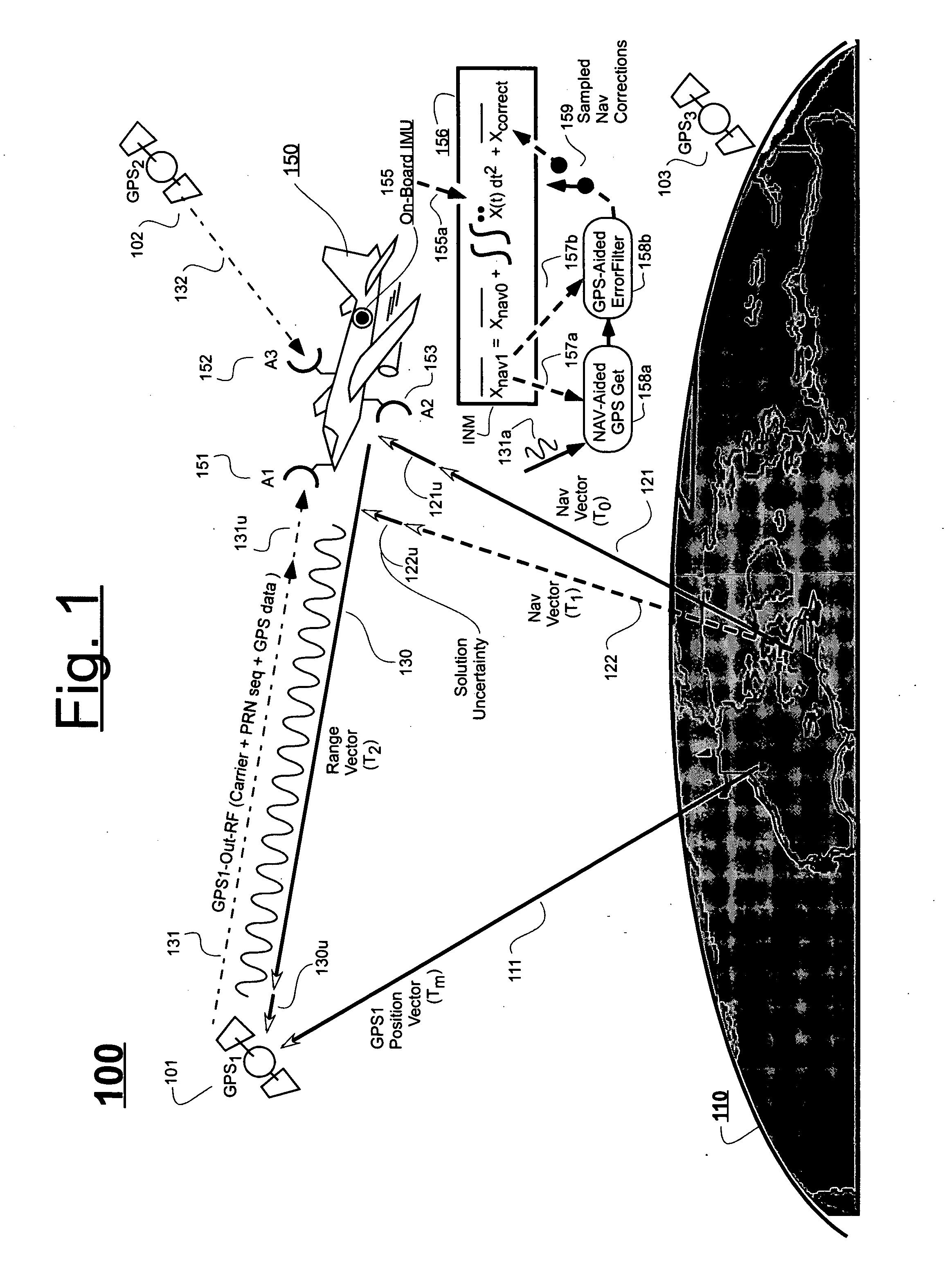
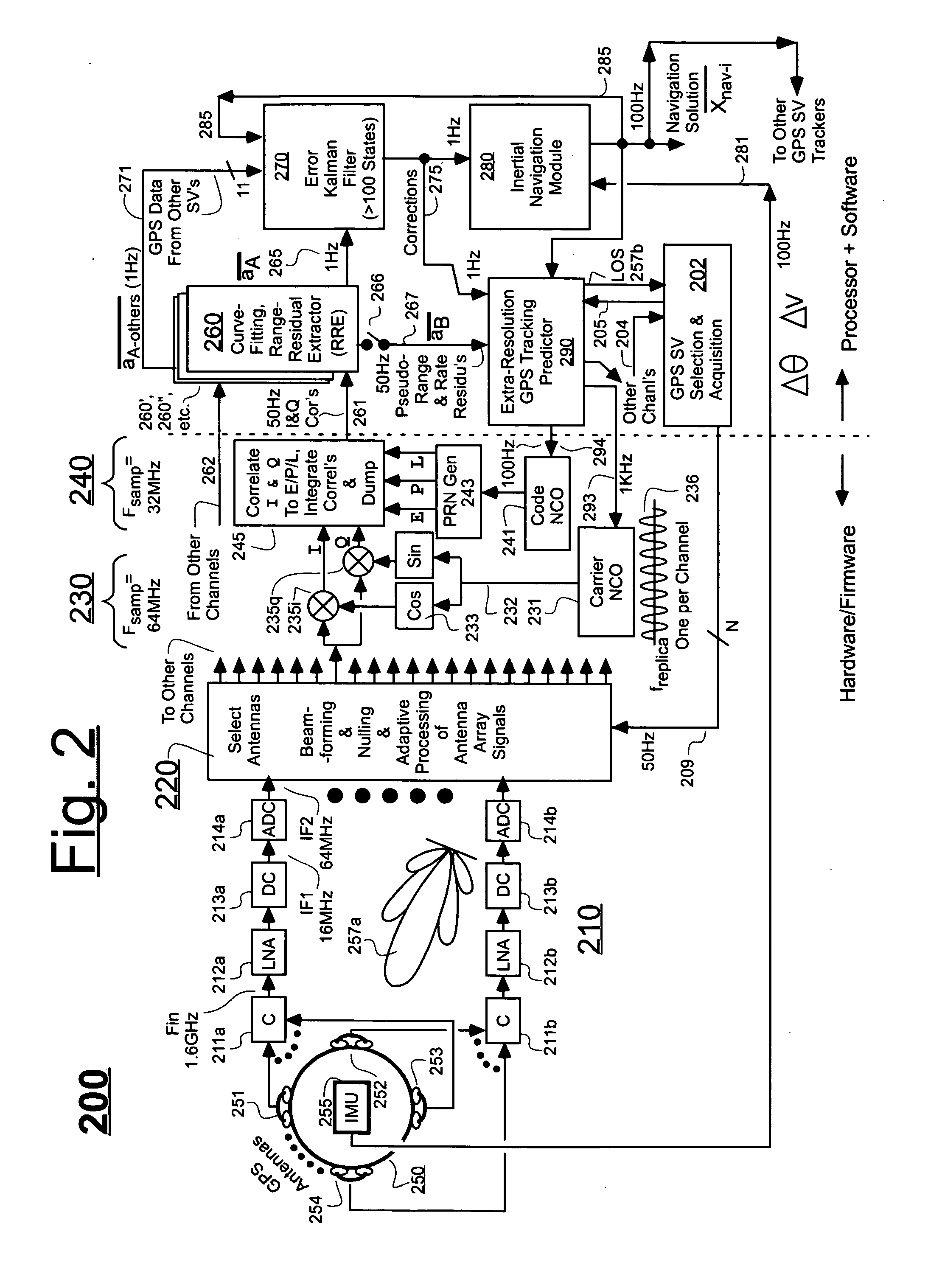
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Algorithmic compensation system and method therefor for a touch sensor panel
InactiveUS6506983B1Efficient mappingEfficient polynomial coefficient storageTransmission systemsUsing electrical meansCurve fittingTouchscreen
A general method is described for producing an inexpensive touchscreen system that provides accurate positional information and compensates for manufacturing variations without complicated sensor arrangements. Utilizing a set of sensed signals that are unique to each location on the touchscreen sensor, equations for X and Y are derived via curve fitting methods. The coefficients of the equations are stored with the sensor. During touchscreen operation the coefficients are used to calculate X and Y to the desired accuracy directly and independently.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
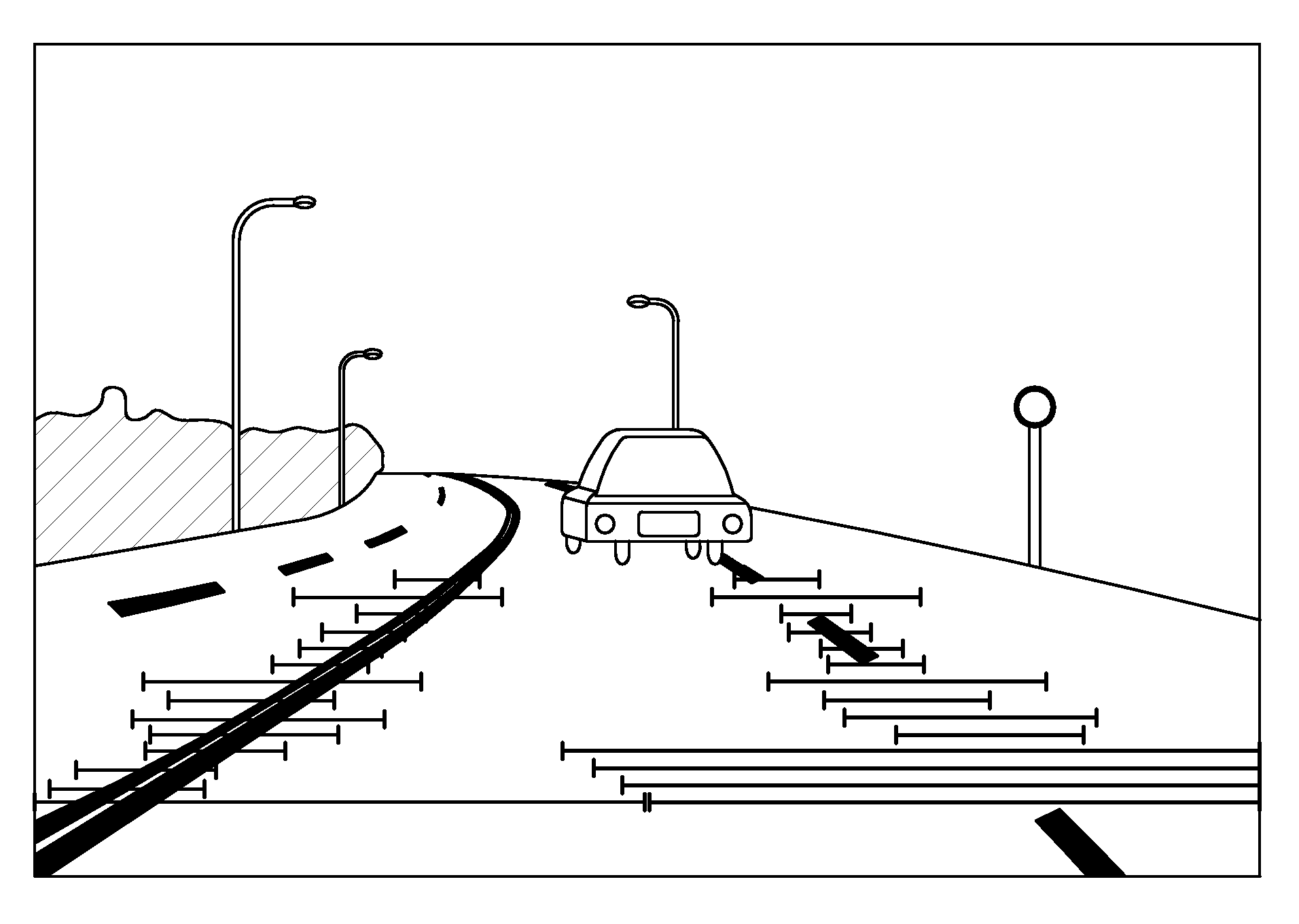
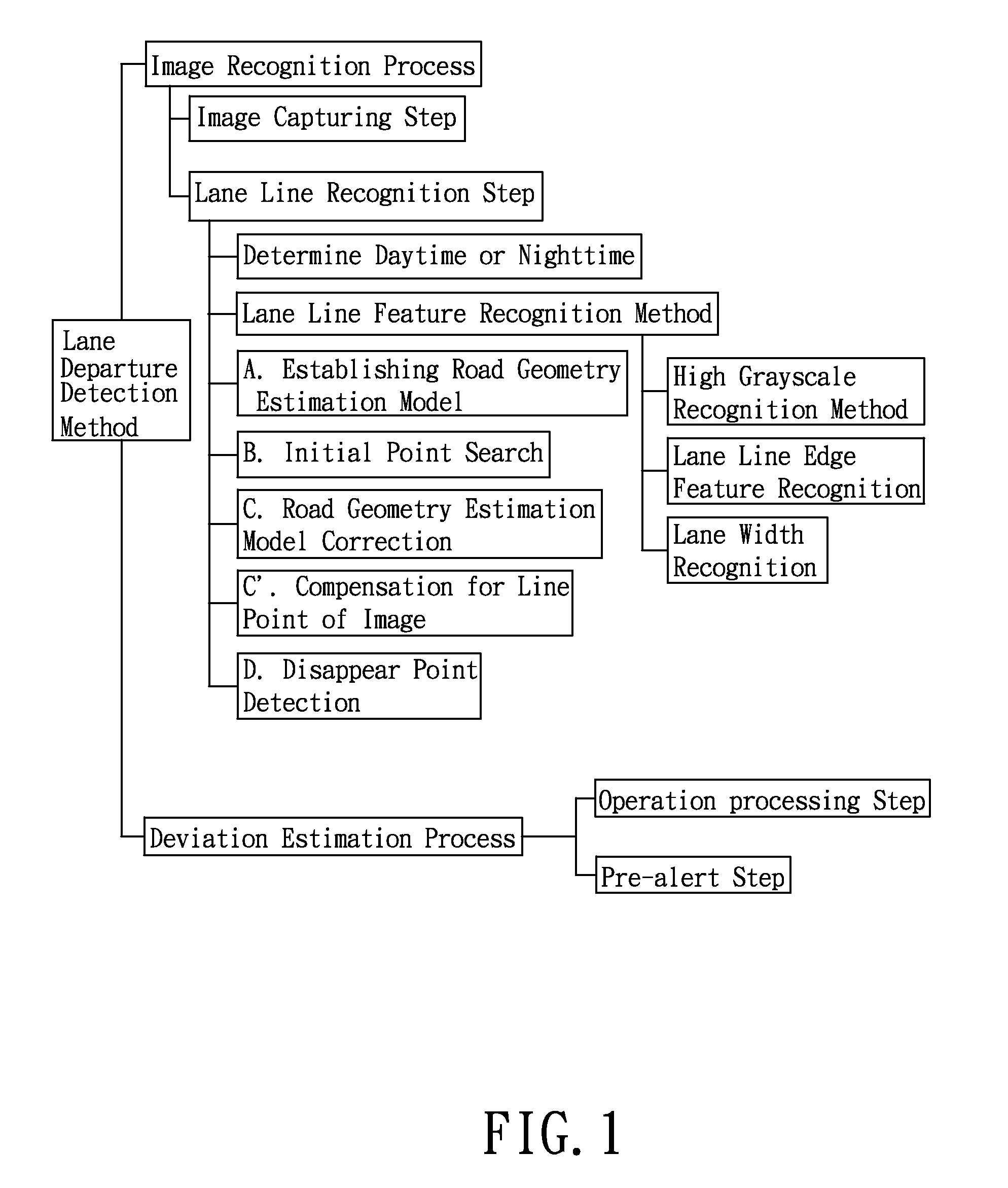
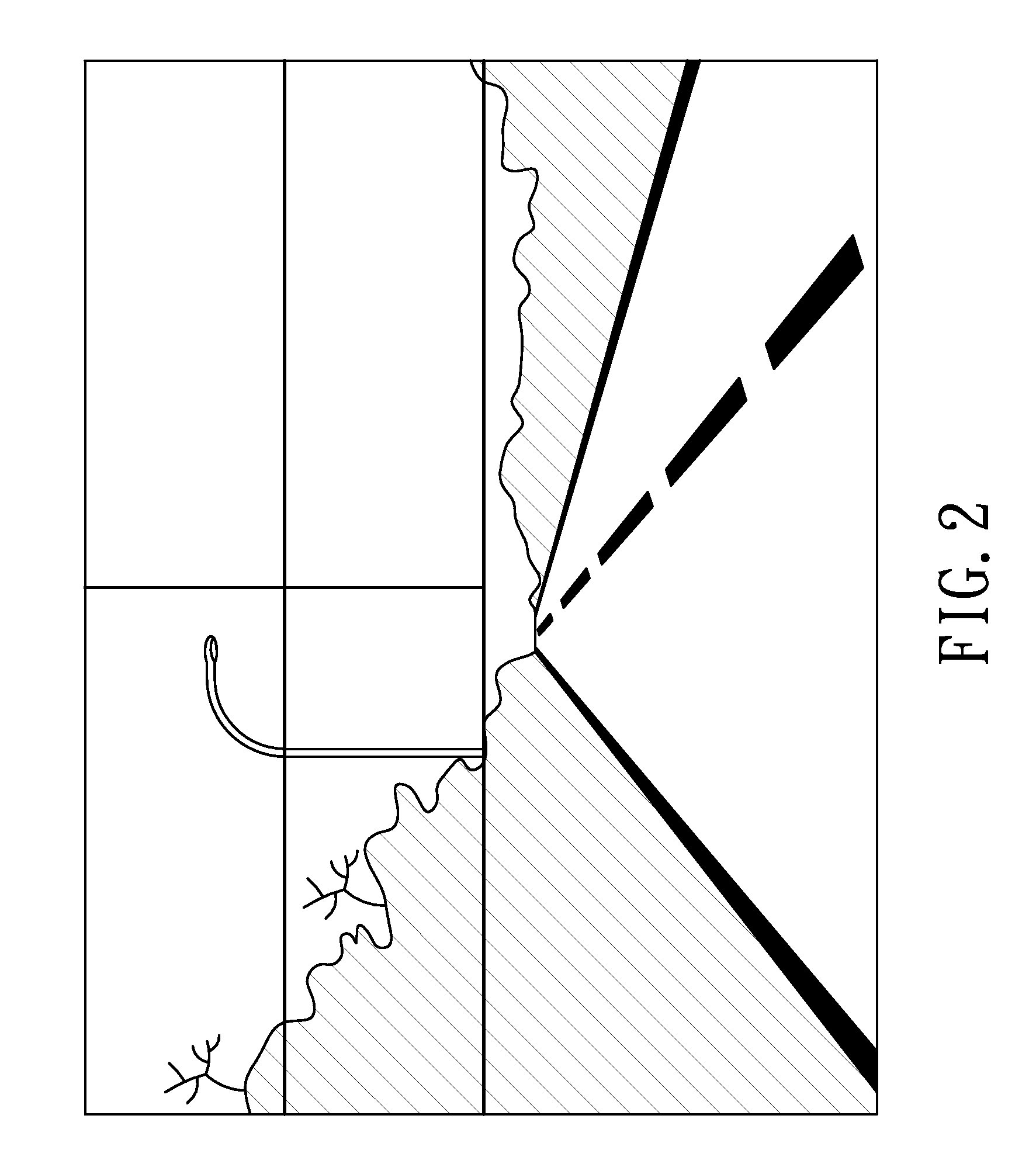
Method for detecting lane departure and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20100002911A1Improve shortcomingsResponse time is insufficientCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsDriver/operatorComputer graphics (images)
A method for detecting the lane departure of a vehicle includes an image recognition process and a deviation estimation process. The image recognition process includes the following steps: an image capturing step for capturing image frame data by using an image capturing unit; and a lane line recognition for analyzing the image frame data for determining the lane lines. By using a quadratic curve fitting equation, a plurality of lane line being detected so as to establish a road geometry estimation model. The road geometry estimation model is inputted into the deviation estimation process to detect the lane departure of the vehicle so as to alert the driver. Furthermore, an apparatus for detecting the deviation of the vehicle, comprising: an image capturing unit, a processing unit and a signal output unit.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE RES & TESTING CENT
Feature quantification from multidimensional image data
Techniques, hardware, and software are provided for quantification of extensional features of structures of an imaged subject from image data representing a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image. In one embodiment, stenosis in a blood vessel may be quantified from volumetric image data of the blood vessel. A profile from a selected family of profiles is fit to selected image data. An estimate of cross sectional area of the blood vessel is generated based on the fit profile. Area values may be generated along a longitudinal axis of the vessel, and a one-dimensional profile fit to the generated area values. An objective quantification of stenosis in the vessel may be obtained from the area profile. In some cases, volumetric image data representing the imaged structure may be reformatted to facilitate the quantification, when the structural feature varies along a curvilinear axis. A mask is generated for the structural feature to be quantified based on the volumetric image data. A curve representing the curvilinear axis is determined from the mask by center-finding computations, such as moment calculations, and curve fitting. Image data are generated for oblique cuts at corresponding selected orientations with respect to the curvilinear axis, based on the curve and the volumetric image data. The oblique cuts may be used for suitable further processing, such as image display or quantification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Active Alignment Using Continuous Motion Sweeps and Temporal Interpolation
Methods and apparatus for actively aligning a first optical element, such as a lens, to a second optical element, such as an image sensor, use continuous scans, even absent a synchronization signal from one of the optical elements. During a scan, timed position information about the scanned optical element is collected, and then a relationship between position of the scanned optical element and time is estimated, such as by fitting a curve to a set of position-time pairs. This relationship can then be used to estimate locations of the scanned optical element at times when image data or other alignment quality-indicating data samples are acquired. From this alignment quality versus location data, an optimum alignment position can be determined, and the scanned optical element can then be positioned at the determined alignment position.
Owner:AUTOMATION ENG
Apparatus and method for the complete characterization of optical devices including loss, birefringence and dispersion effects
InactiveUS6856400B1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical frequenciesCurve fitting
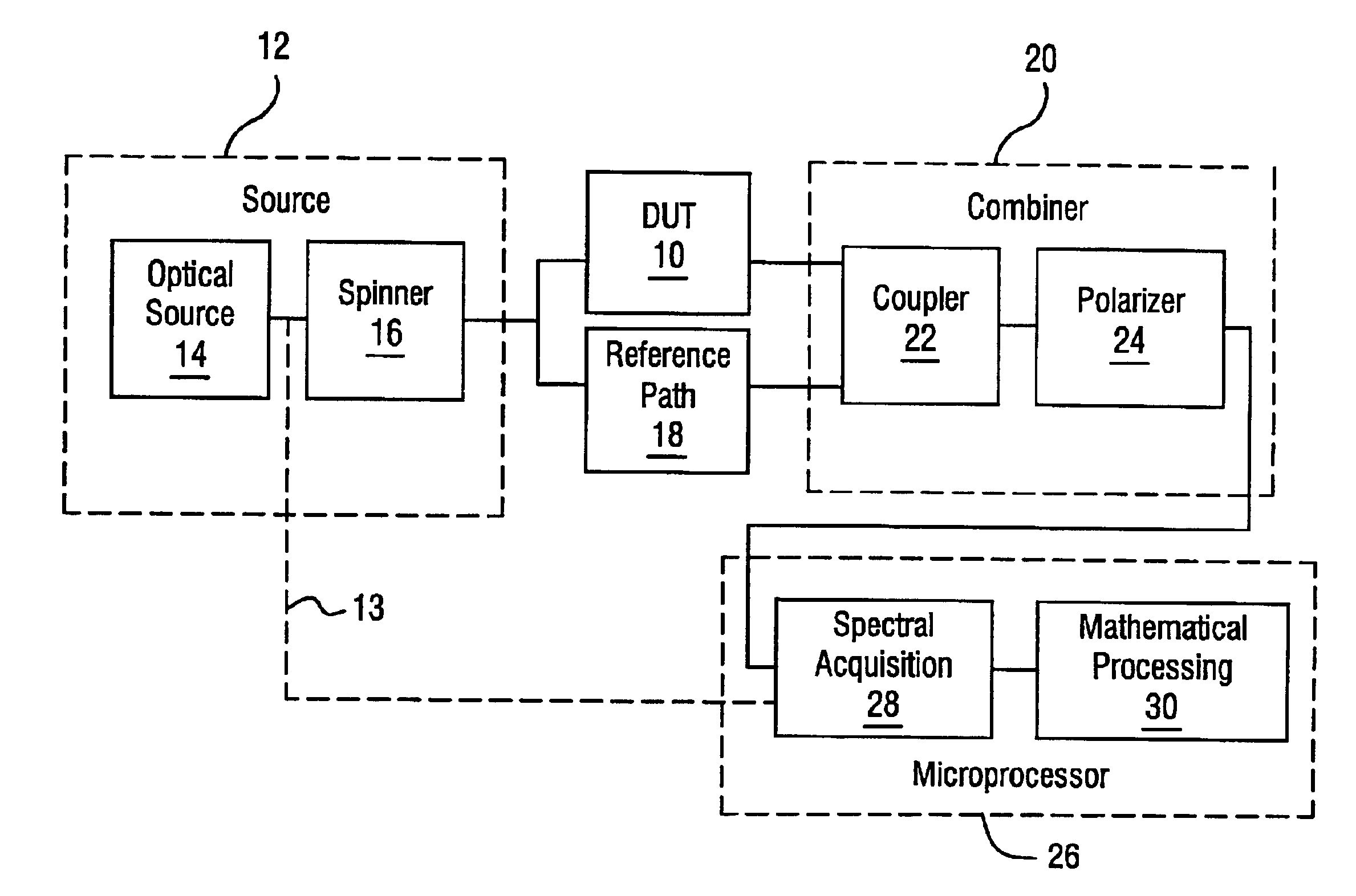
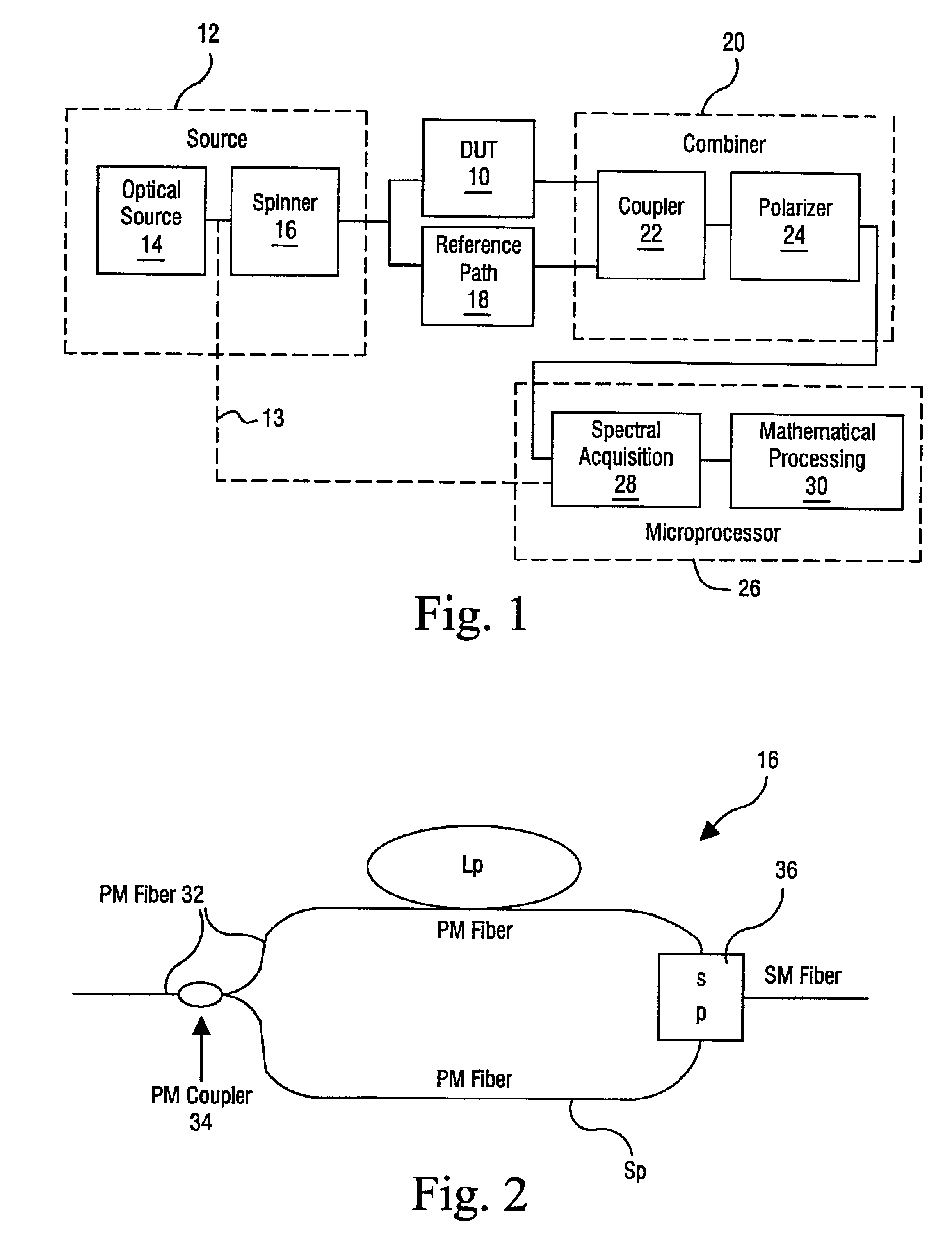
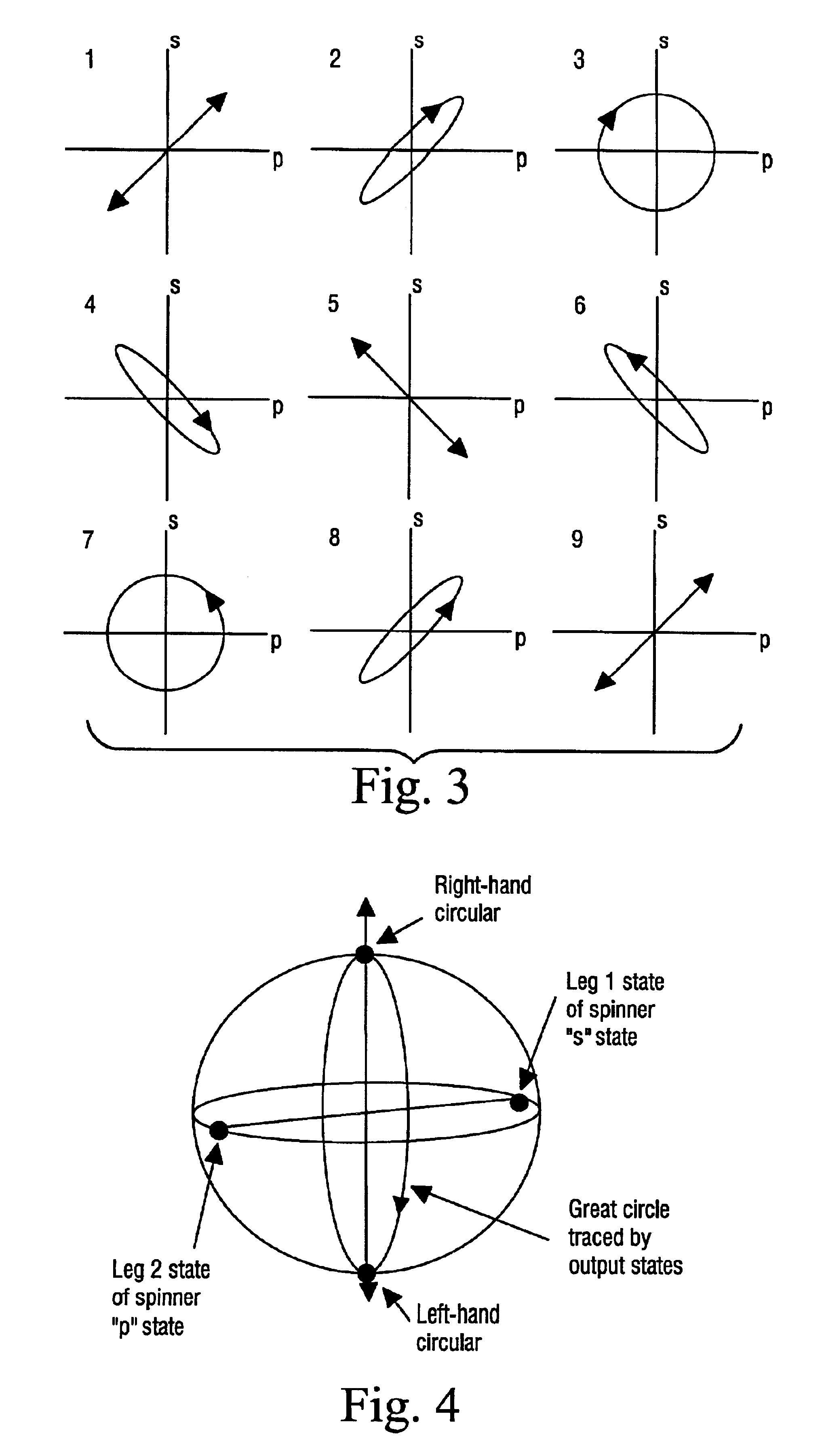
In order to characterize the optical characteristics of a device, a source of light having a variable frequency with a polarization state which varies linearly with frequency is provided as an input to the device under test. The input light is also passed through a known reference path and is added to the light output from the device under test in a beam combiner. The combined light for the frequencies of interest is split into two orthogonal polarizations which are then detected in a spectral acquisition apparatus and supplied to a microprocessor. The spectral measurements are digitized and curve-fitted to provide optical power versus optical frequency curves. Fourier transforms of each of the curves are calculated by the microprocessor. From the Fourier transforms, the four arrays of constants are calculated for the Jones matrix characterizing the device under test.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Methods for measuring analyte in a subject and/or compensating for incomplete reaction involving detection of the analyte
InactiveUS20050130249A1Microbiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteMonitoring system
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
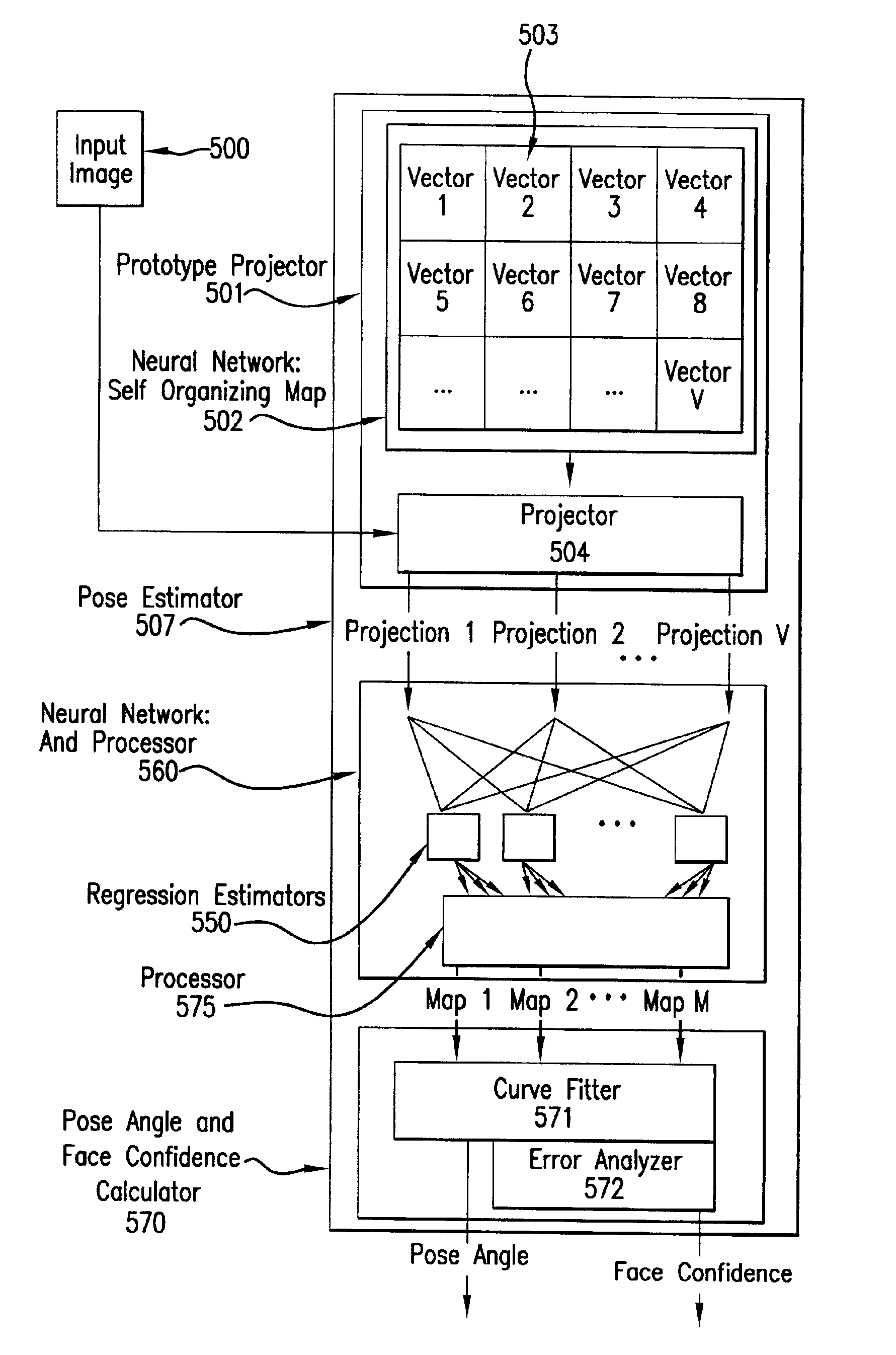
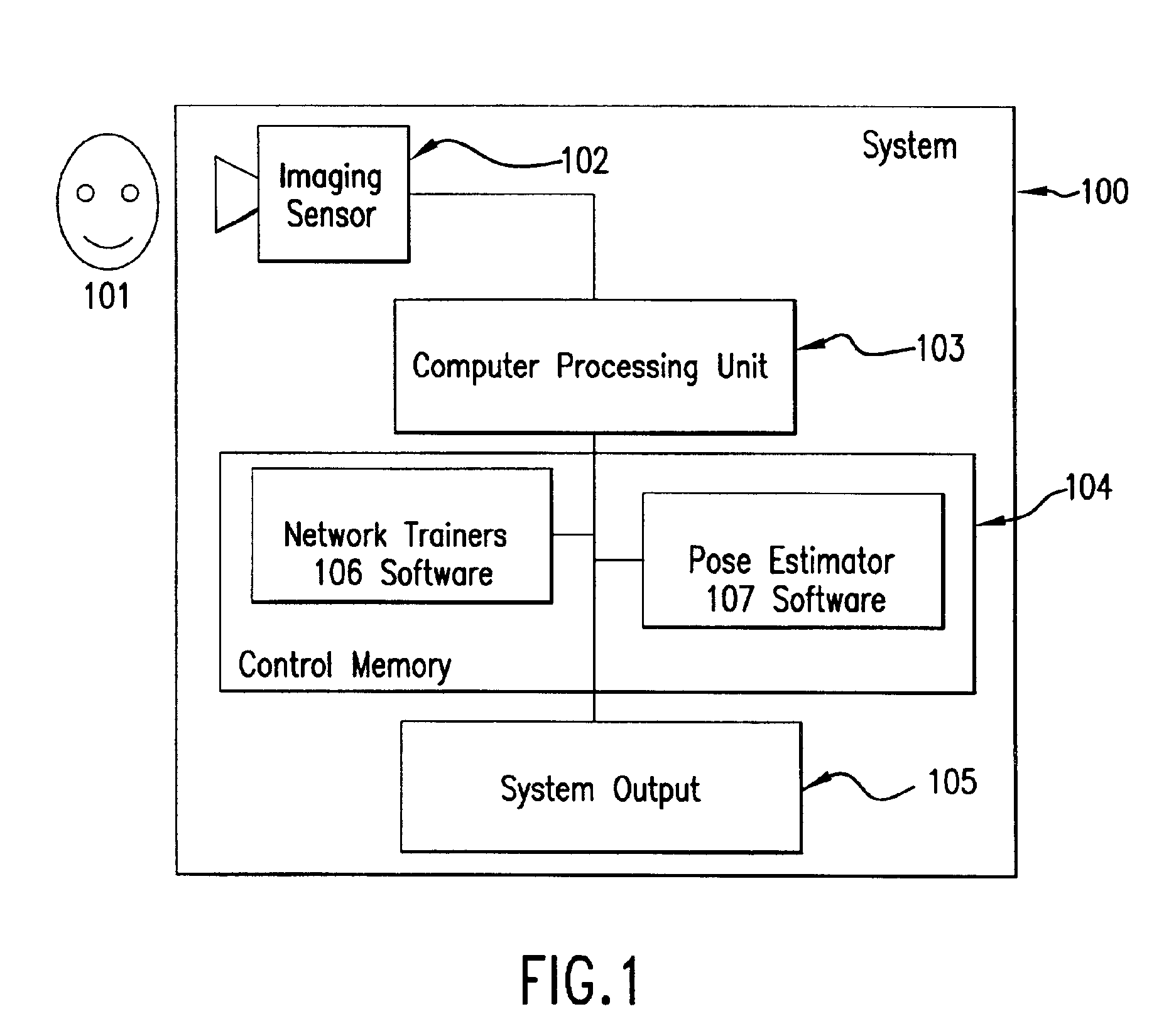
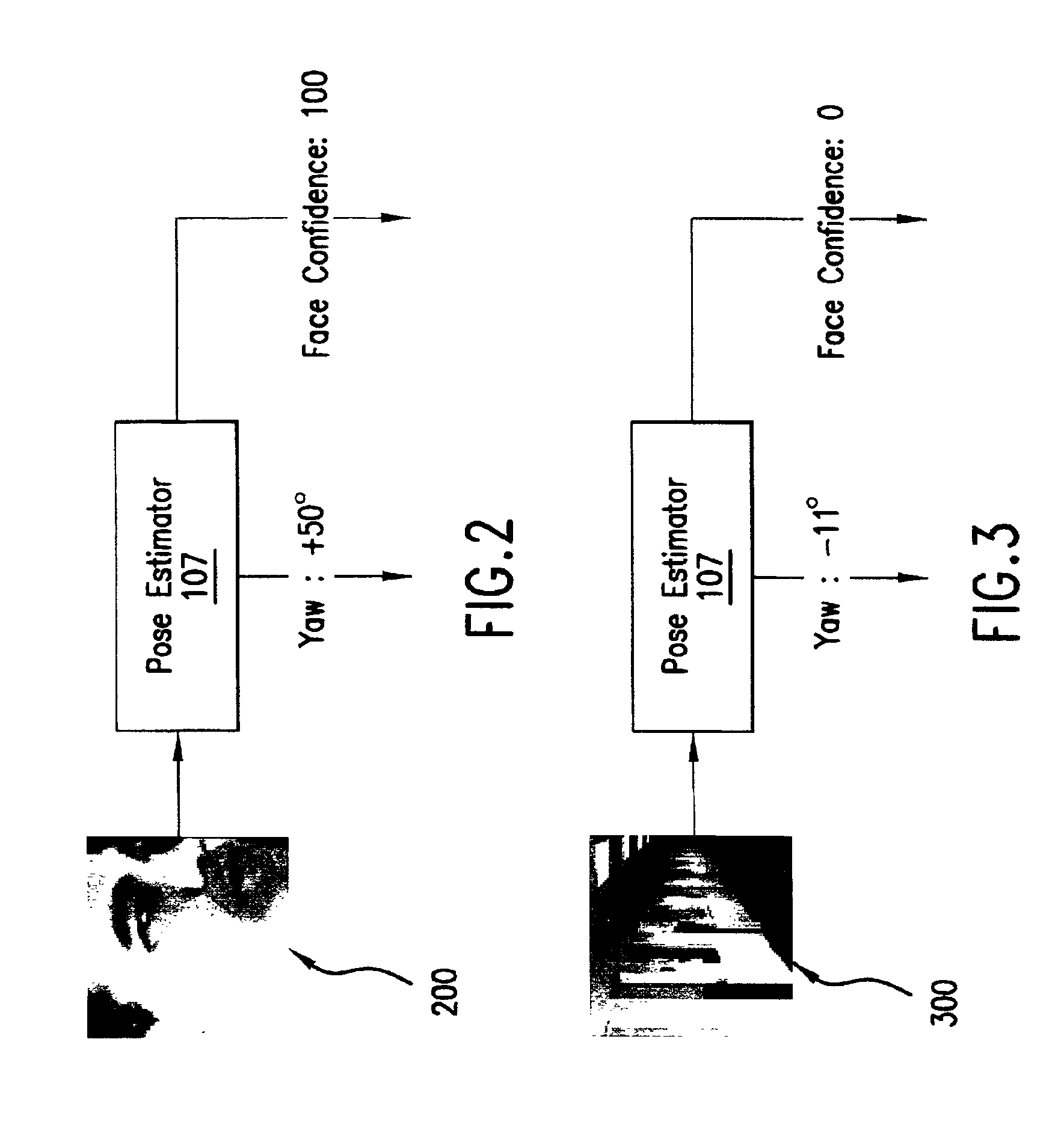
System and method for pose-angle estimation
InactiveUS6959109B2Reduces input image dimensionalityElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A system and method are disclosed for determining the pose angle of an object in an input image. In a preferred embodiment, the present system comprises a pose estimator having a prototype projector, a regression estimator, and an angle calculator. The prototype projector is preferably adapted to reduce the input image dimensionality for faster further processing by projecting the input pixels of the image onto a Self-Organizing Map (SOM) neural network. The regression estimator is preferably implemented as a neural network and adapted to map the projections to a pattern unique to each pose. The angle calculator preferably includes a curve fitter and an error analyzer. The curve fitter is preferably adapted to estimate the pose angle from the mapping pattern. The error analyzer is preferably adapted to produce a confidence signal representing the likelihood of the input image being a face at the calculated pose. The system also preferably includes two network trainers responsible for synthesizing the neural networks.
Owner:MORPHOTRUST USA
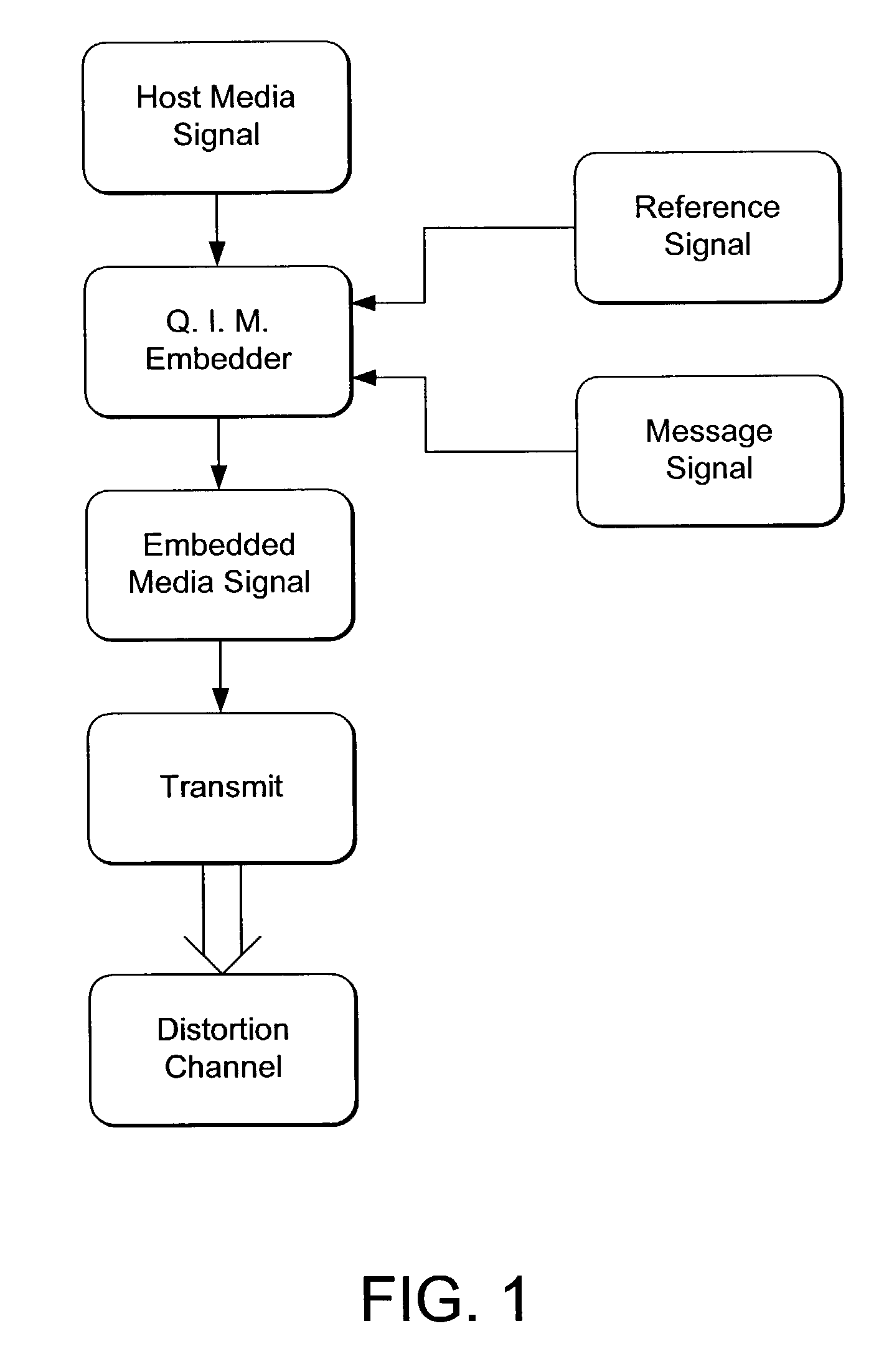
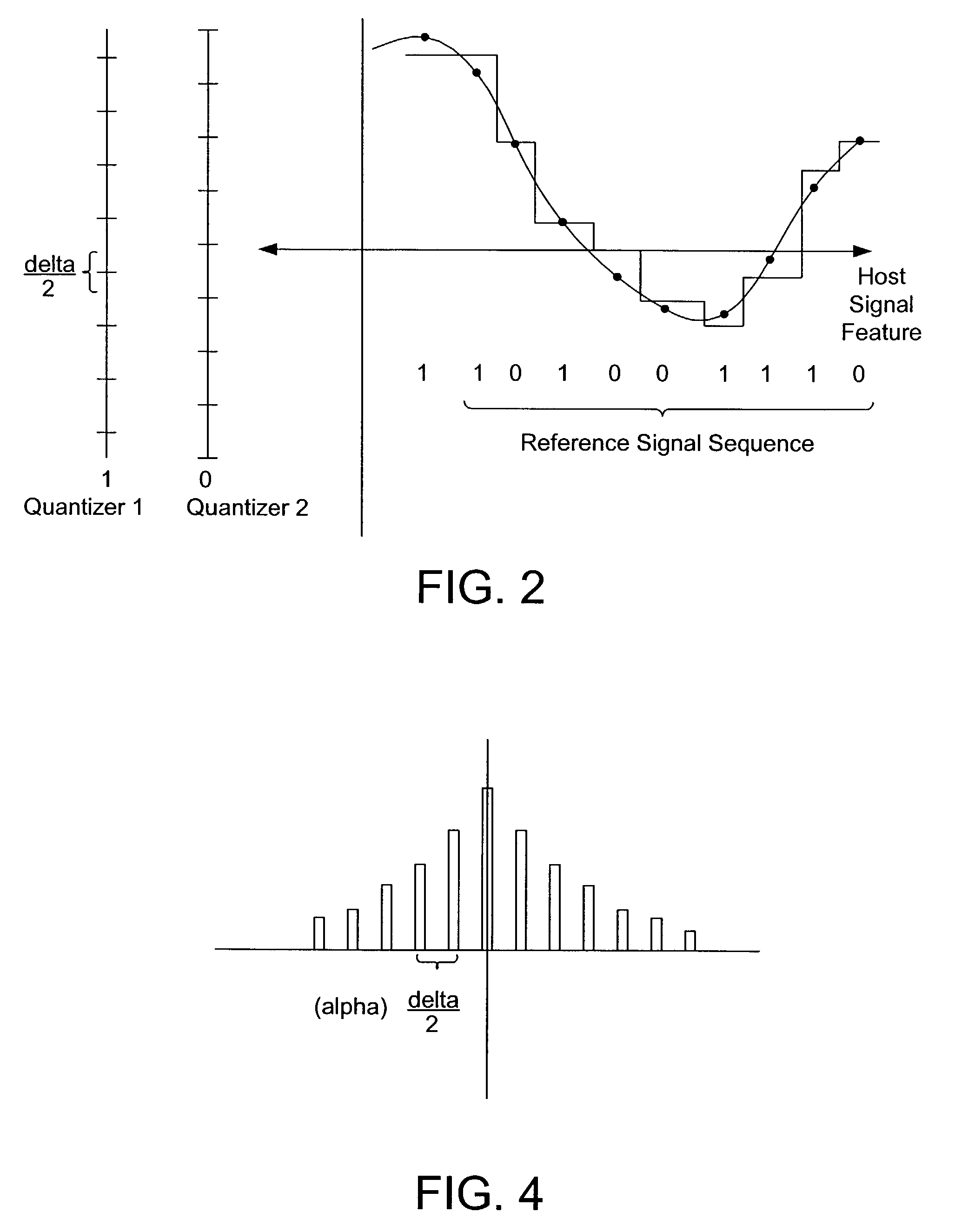
Media signal filtering for use in digital watermark reading
InactiveUS7076082B2Reduce errorsReduce the impactSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCircular referenceCurve fitting
A curve fitting method is used to synchronize a reader of embedded data in a media signal. A circular reference signal is embedded in the media signal. After geometric distortion of the media signal, the reference signal is distorted, yet still detectable. The amount of distortion is derived by detecting the reference signal, and applying a curve fitting method from which the distortion is calculated.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP (FORMERLY DMRC CORP)
Three-dimensional simultaneous multiple-surface method and free-form illumination-optics designed therefrom
InactiveUS20050086032A1Need be addressComputation using non-denominational number representationCondensersWavefrontFree form
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
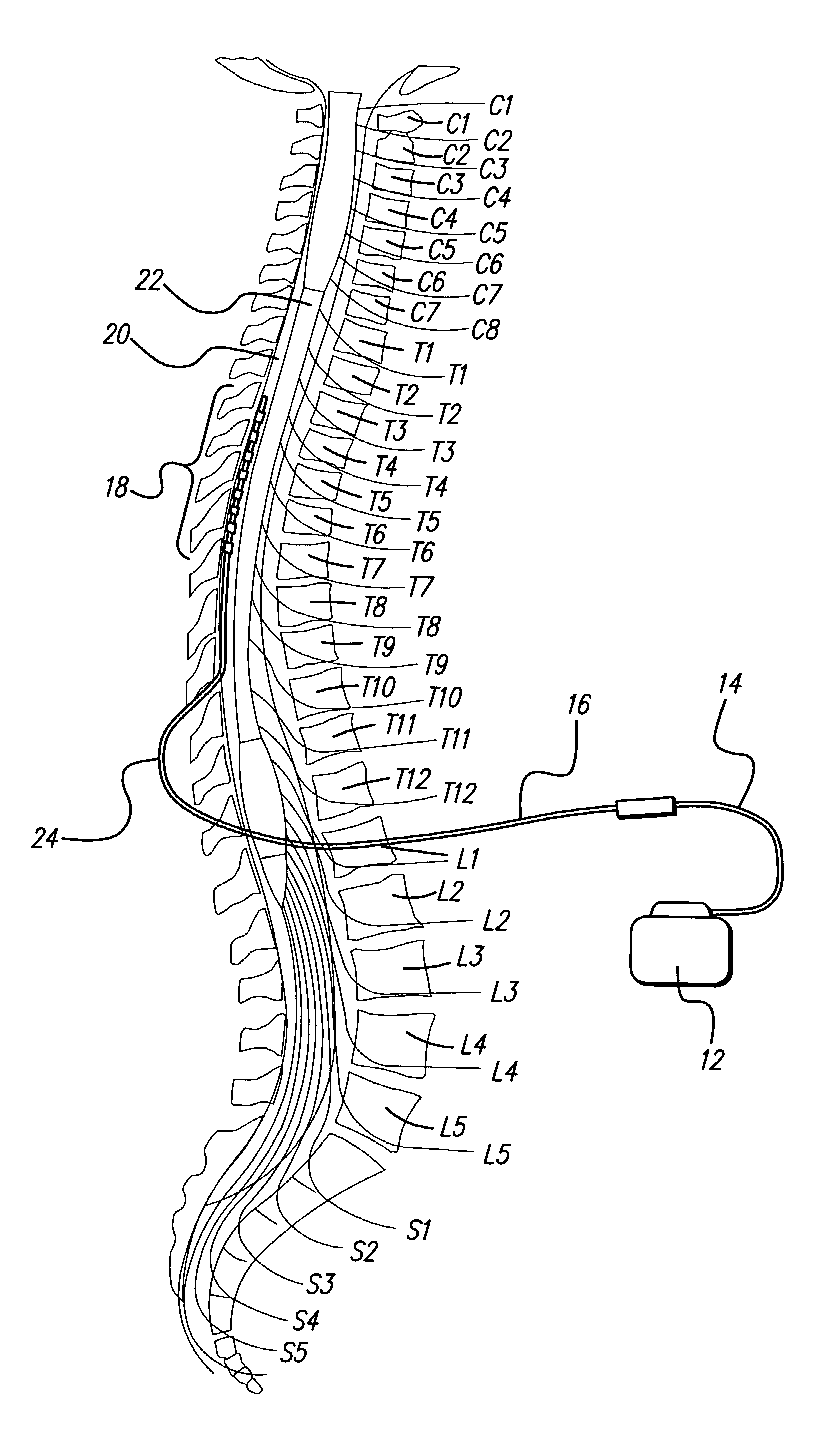
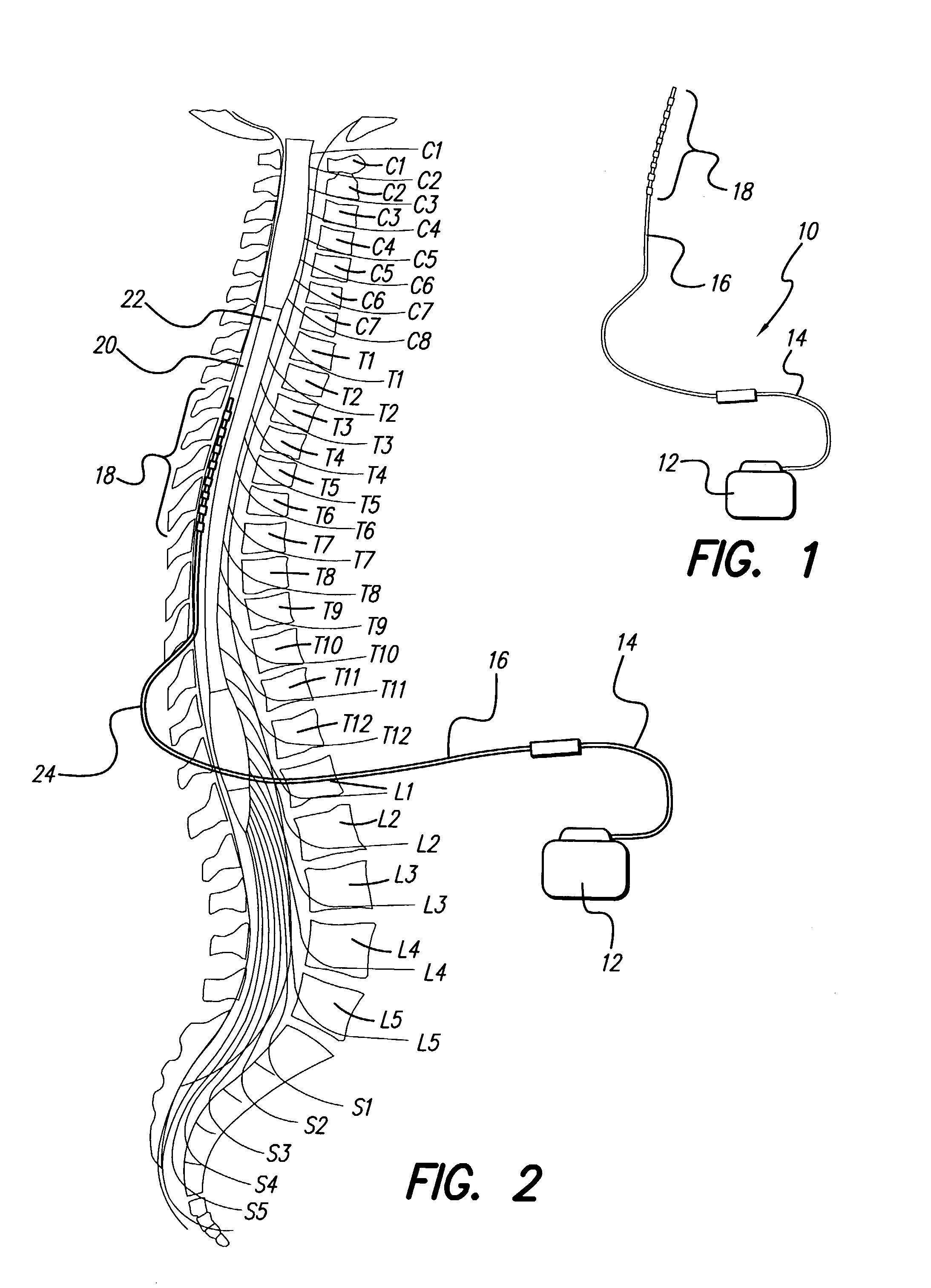
Method for increasing the therapeutic ratio/usage range in a neurostimulator
InactiveUS7127296B2Minimizing sensitivityExpand the scope of treatmentElectrotherapyCurve fittingIntensive care medicine
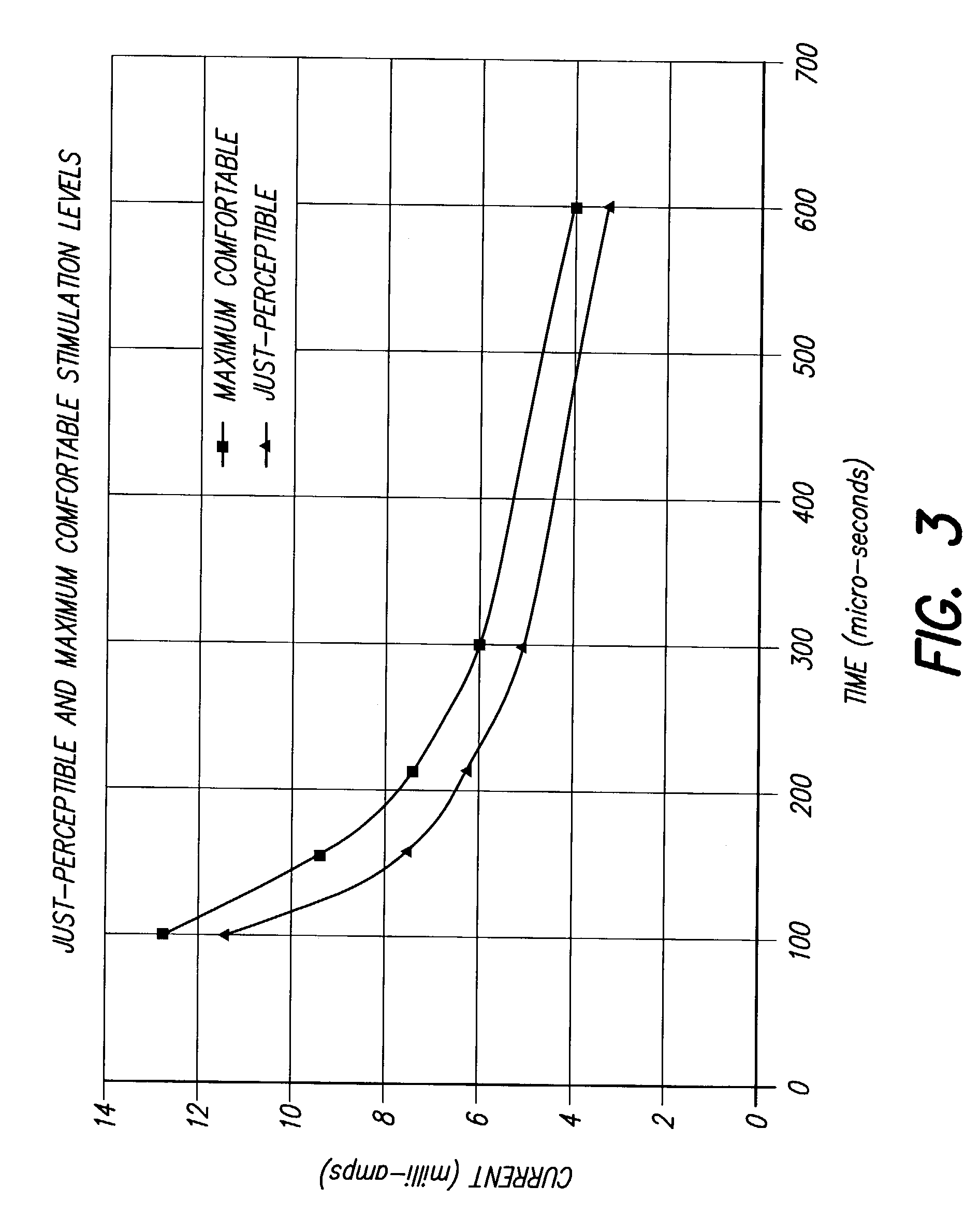
A system and method for patient control of the stimulation parameters of a Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) system, or other neurostimulation system, provides an increased Therapeutic Ratio (TR). Measurements of the just-perceptible stimulation level and the maximum-comfortable stimulation level are made for at least two values of pulse duration and two values of pulse amplitude. A Therapeutic Ratio is determined for stimulation level control strategies based on fixed pulse duration and variable pulse amplitude, and alternatively for fixed pulse amplitude and variable pulse duration. The control strategy providing the greatest therapeutic ratio is then selected for use by the patient. In an alternative embodiment, the pulse durations at the just-perceptible and maximum-comfortable stimulation levels are measured, and the pulse amplitudes at the just-perceptible and maximum-comfortable stimulation levels are determined using a curve-fitting process. Similarly, the pulse amplitudes may first be measured and the pulse widths determined using a curve-fitting process.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
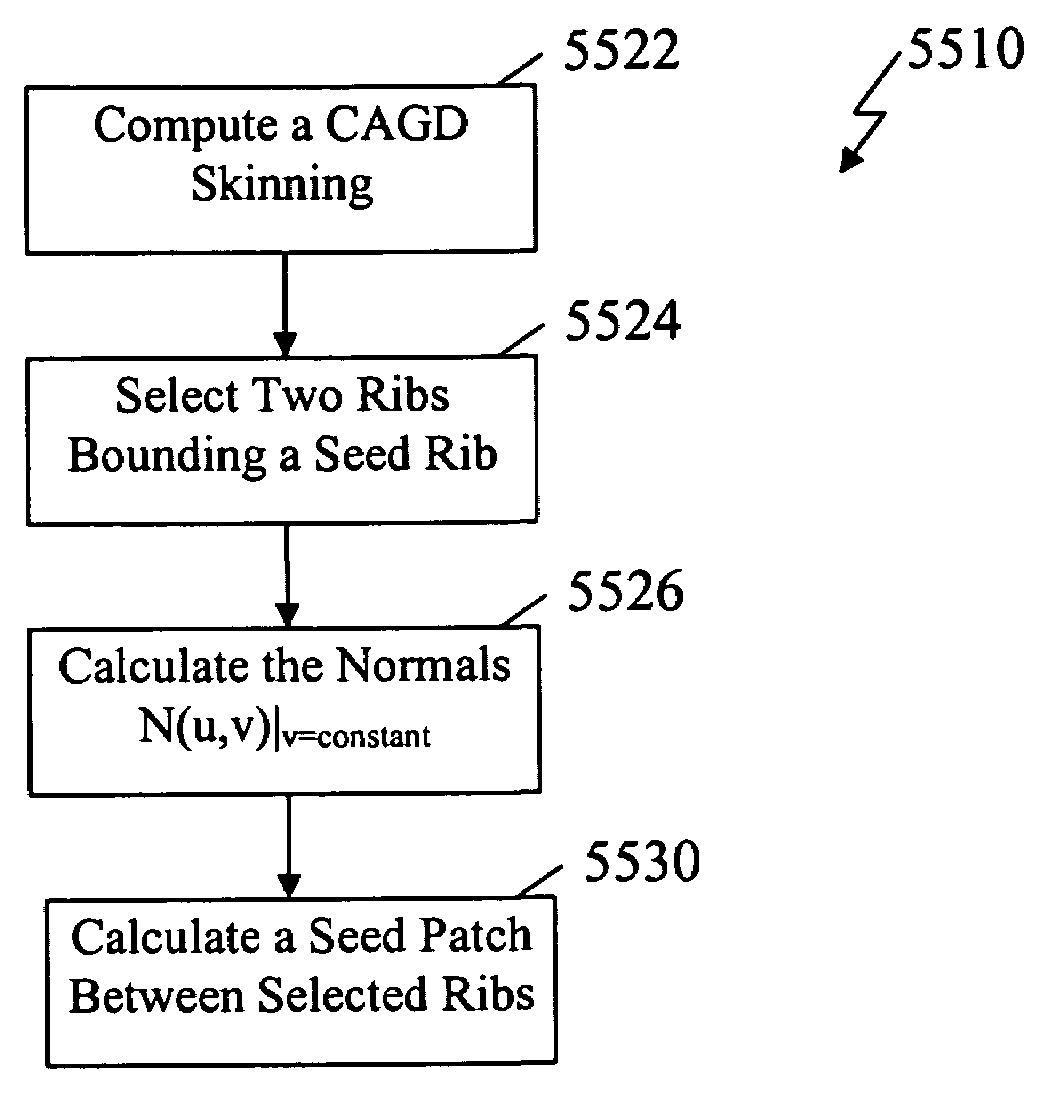
System and method of curve fitting
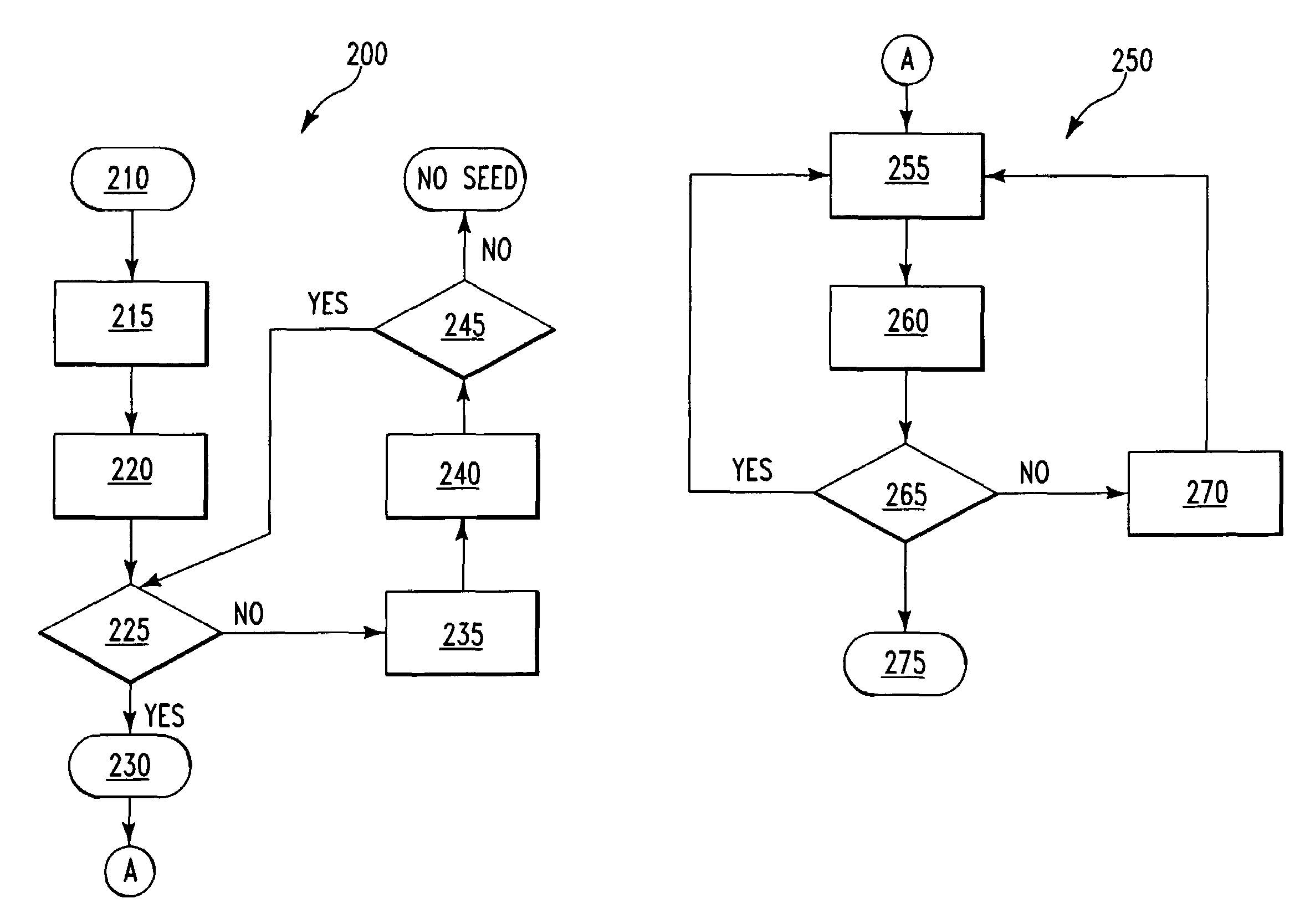
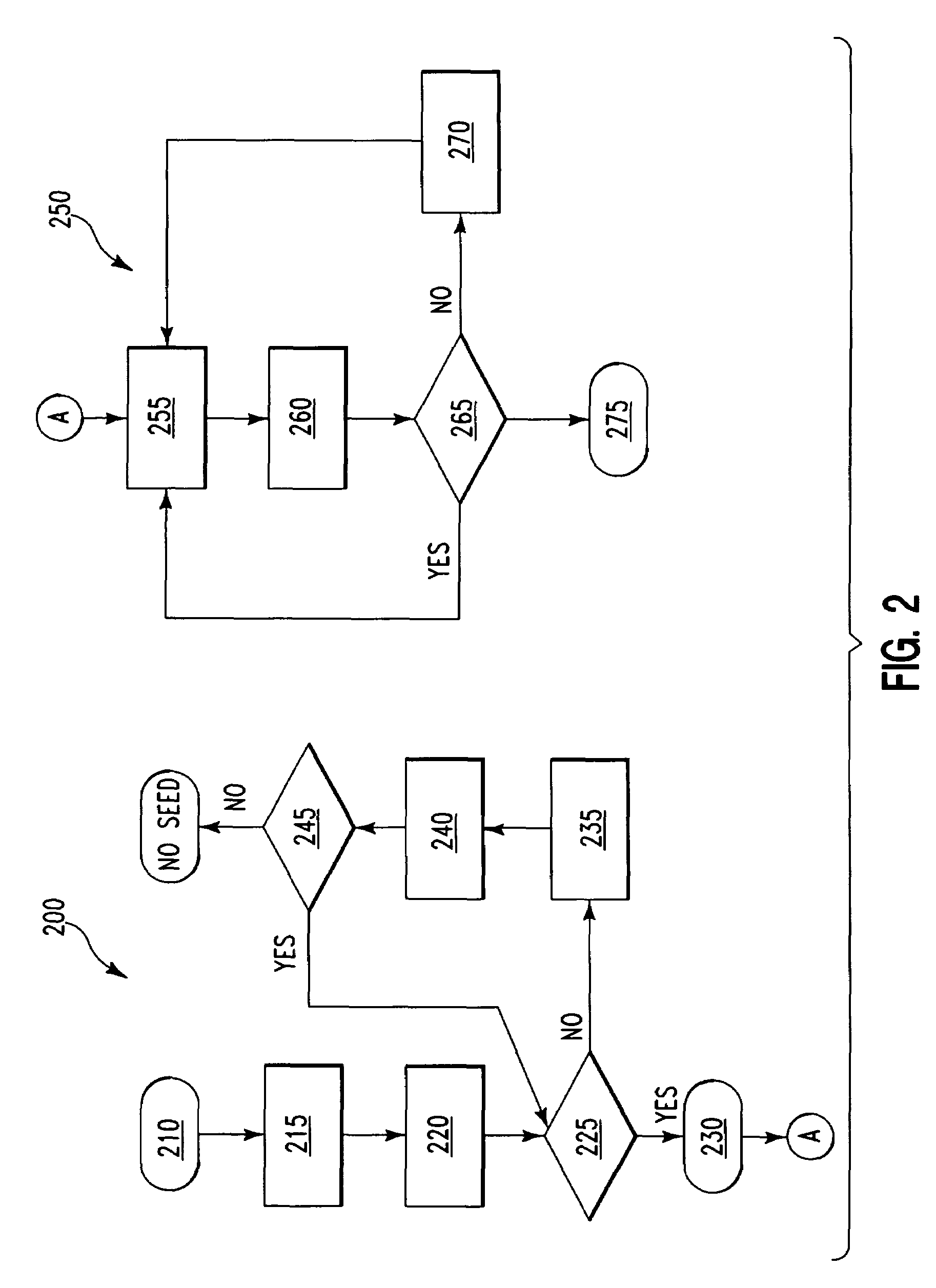
The invention relates to fitting a curve to a plurality of data points. A “seed curve” is determined from a first set of data points selected from the plurality of data points. From the remaining data points, data points are individually selected and a determination is made for each selected data point as to whether the data point is acceptable to be included with the first set of data points. When a data point is determined to be acceptable, the data point is included with the first set of data points to form another set of data points. After each of the other data points are evaluated for inclusion with the first set of data points, a best fit curve is determined from a final set of data points.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Three-dimensional simultaneous multiple-surface method and free-form illumination-optics designed therefrom
InactiveUS7460985B2Computation using non-denominational number representationCondensersWavefrontFree form
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
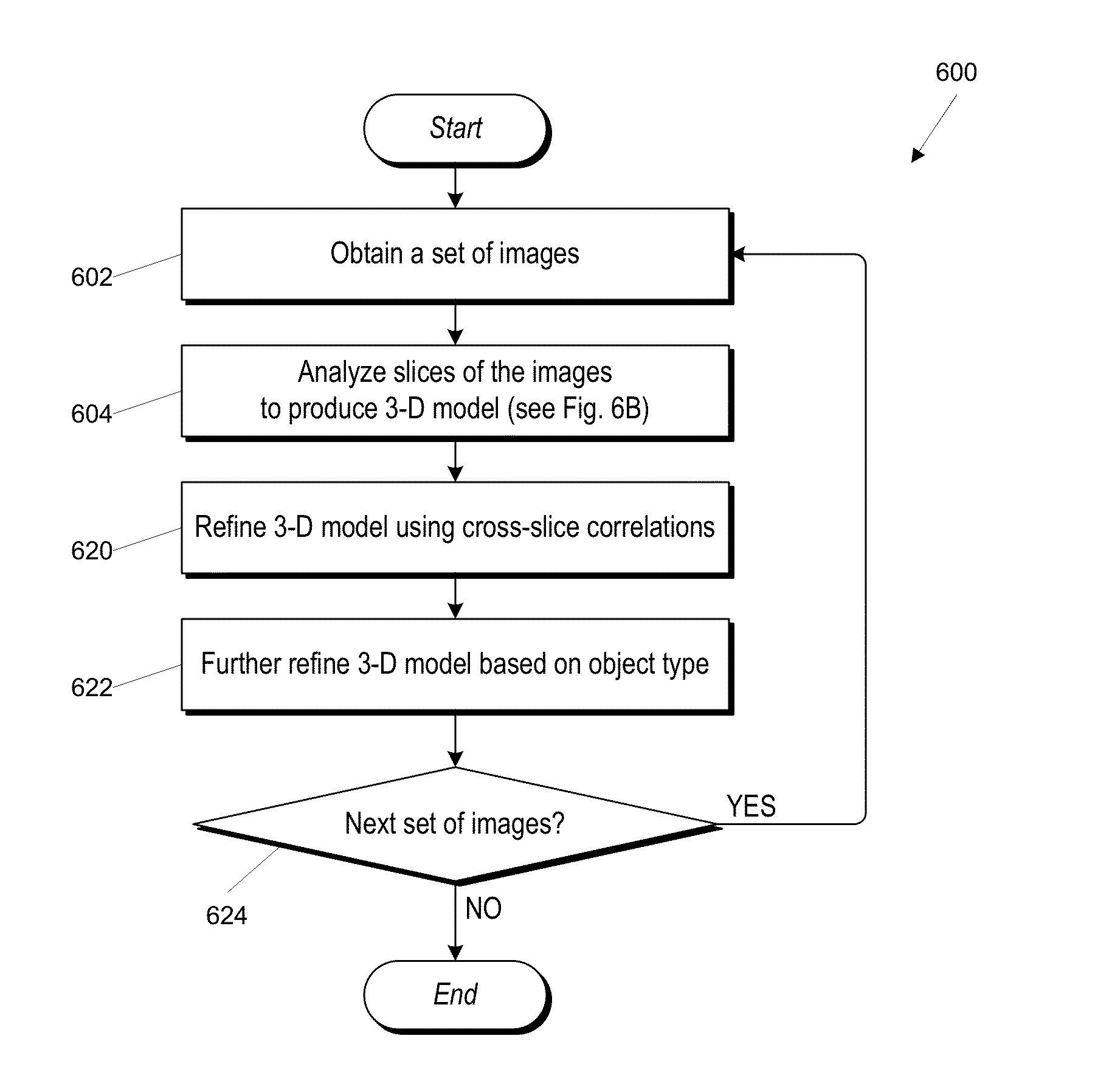
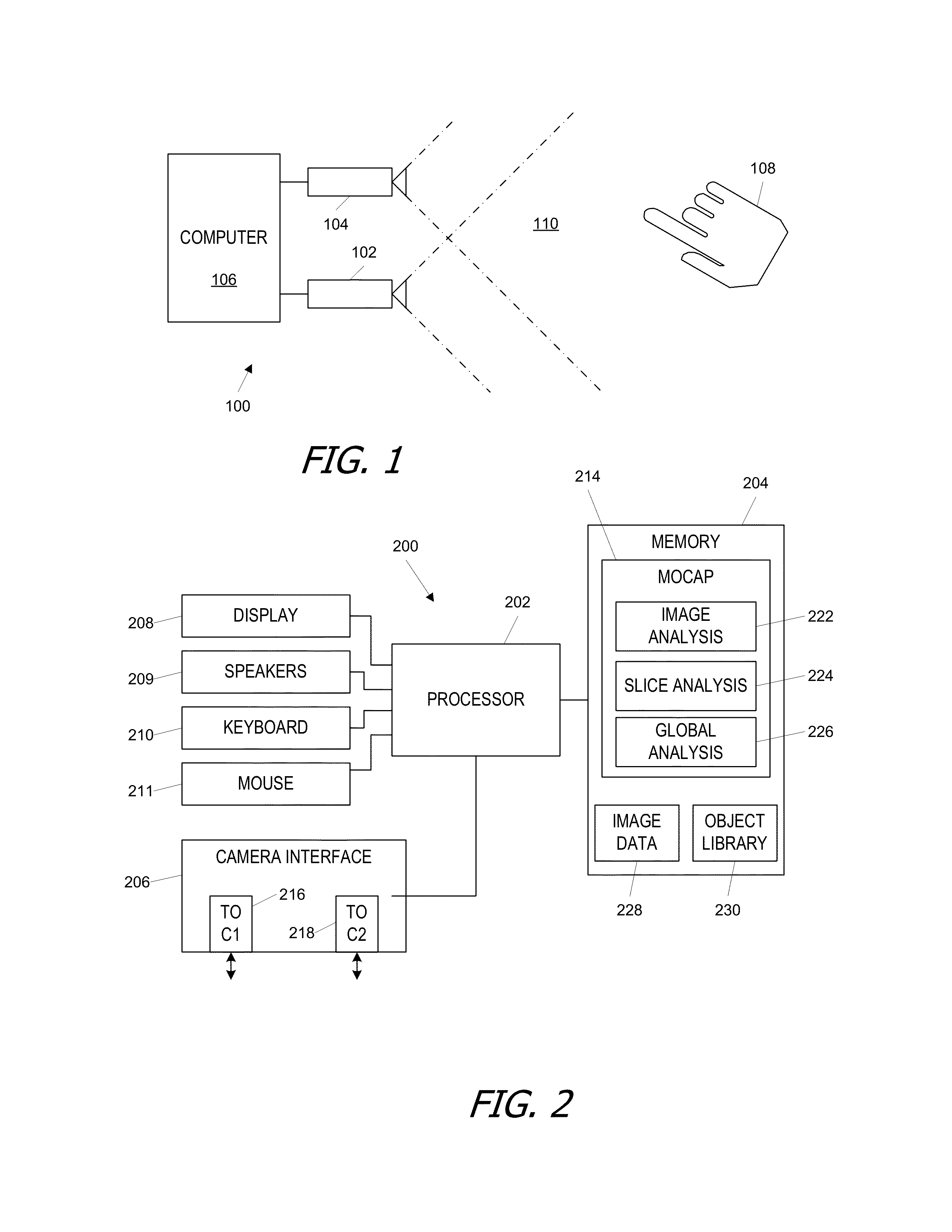
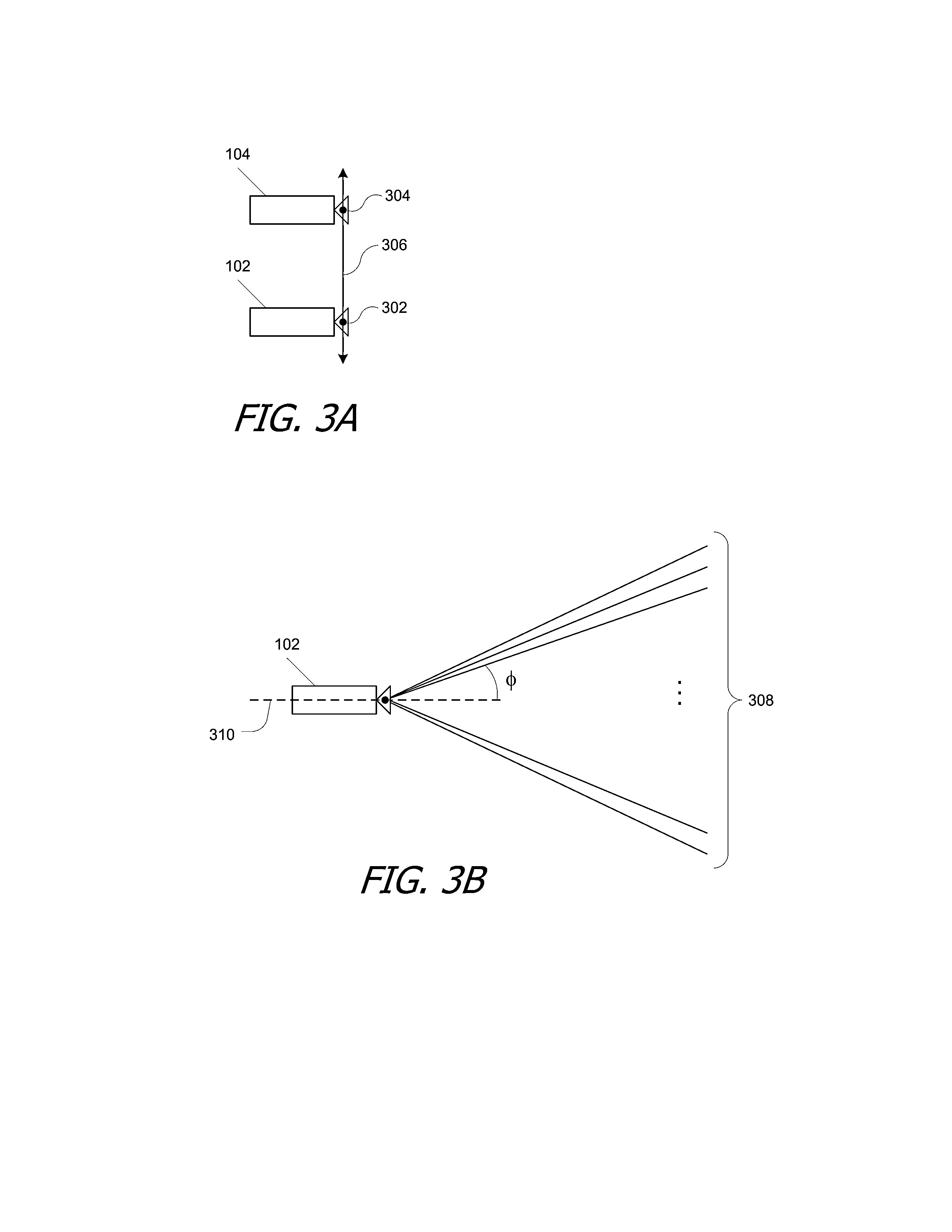
Motion capture using cross-sections of an object
InactiveUS20130182079A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsEllipseThree-dimensional space
An object's position and / or motion in three-dimensional space can be captured. For example, a silhouette of an object as seen from a vantage point can be used to define tangent lines to the object in various planes (“slices”). From the tangent lines, the cross section of the object is approximated using a simple closed curve (e.g., an ellipse). Alternatively, locations of points on an object's surface in a particular slice can also be determined directly, and the object's cross-section in the slice can be approximated by fitting a simple closed curve to the points. Positions and cross sections determined for different slices can be correlated to construct a 3D model of the object, including its position and shape. A succession of images can be analyzed to capture motion of the object.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP TWO LTD
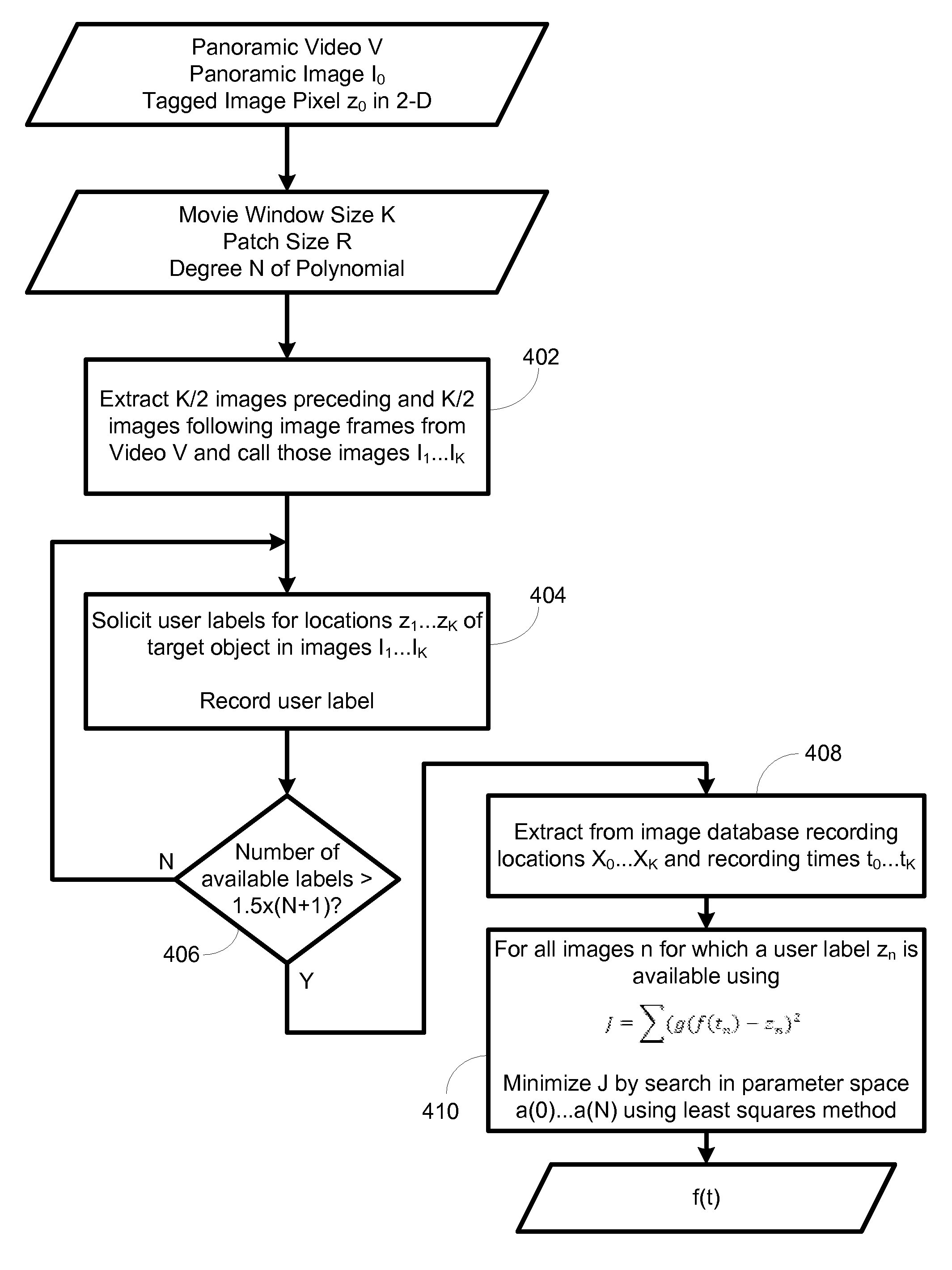
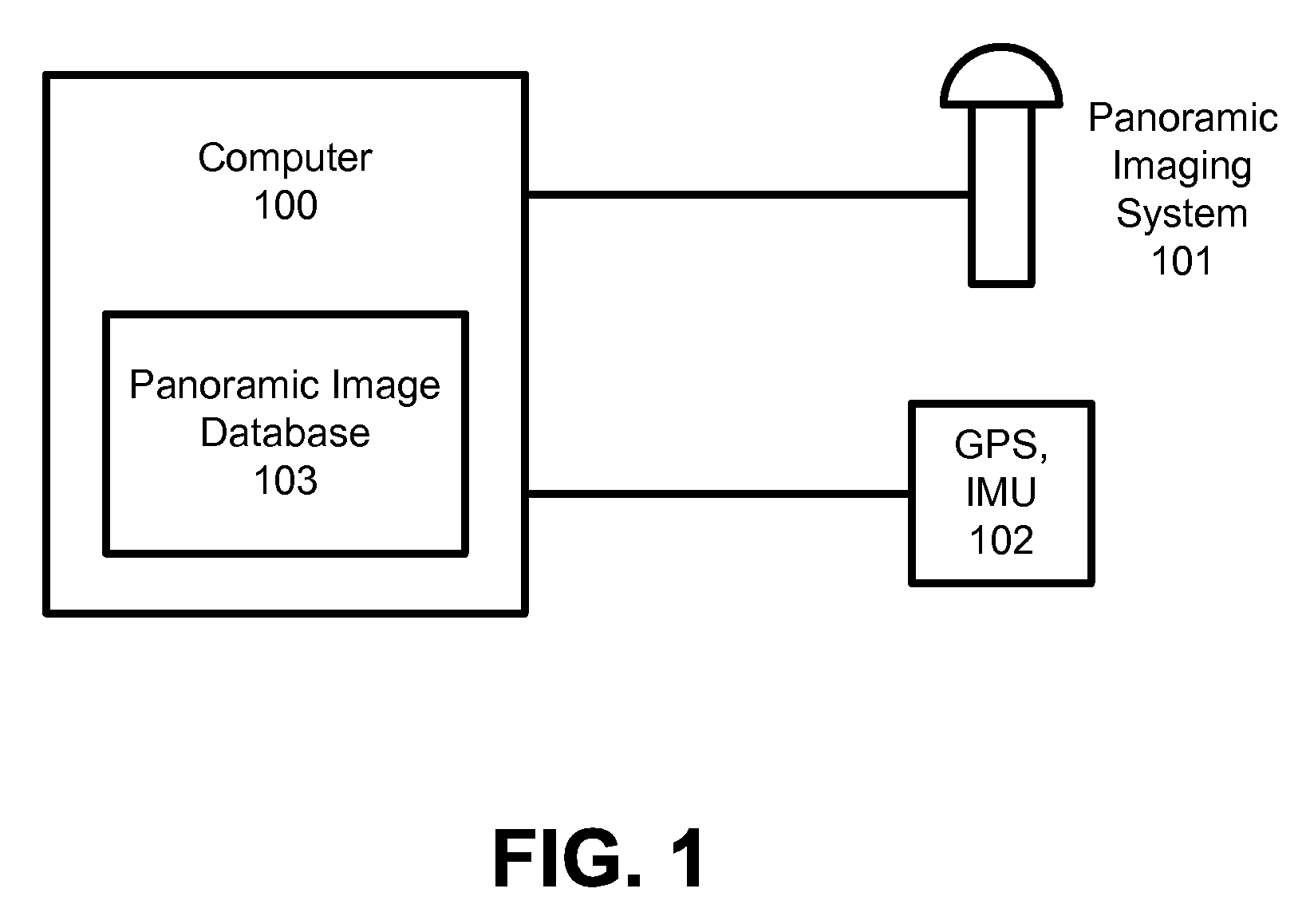
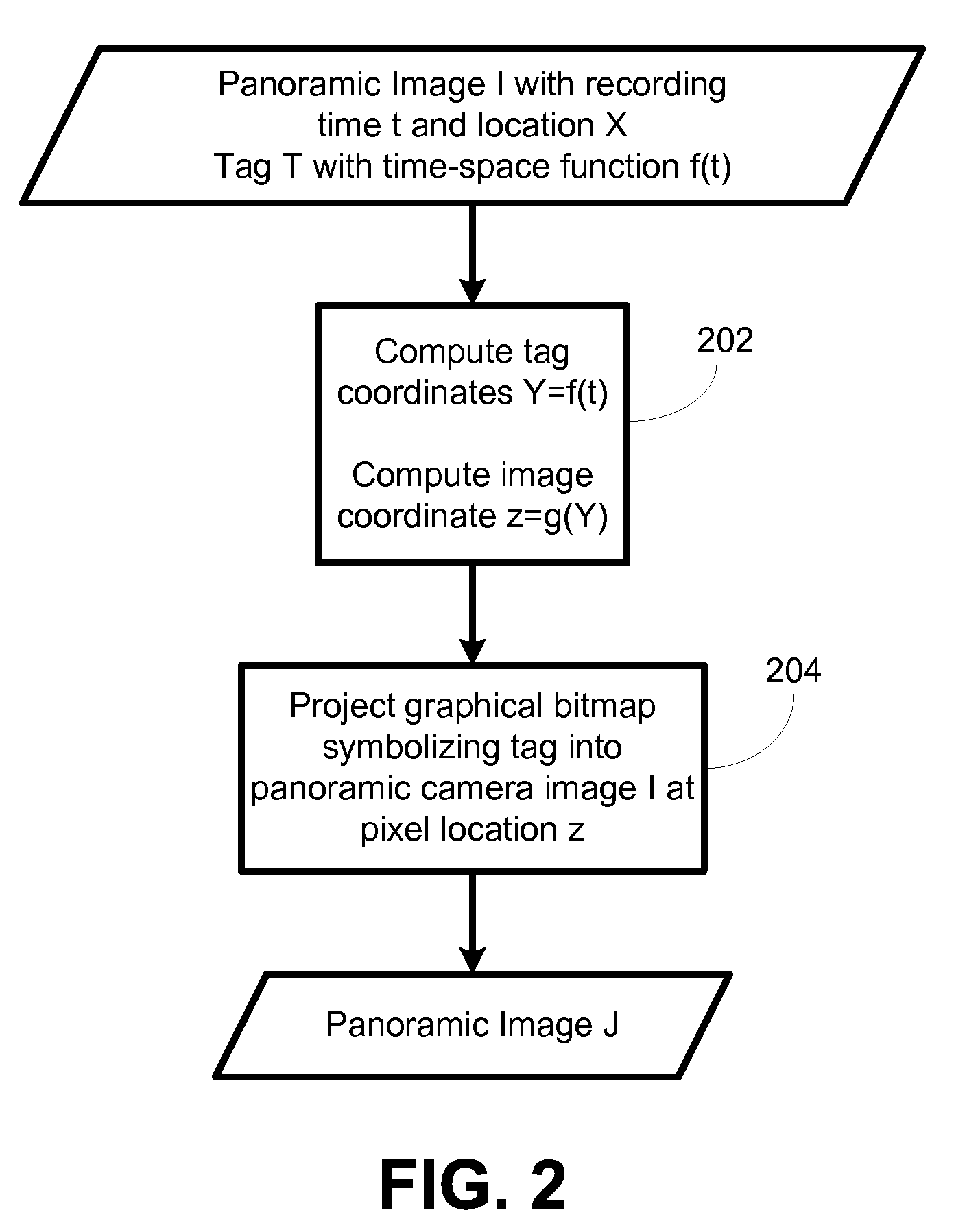
System and method for tagging objects in a panoramic video and associating functions and indexing panoramic images with same
A system and process for attaching tags to panoramic video. Tags provide information when viewing panoramic images, serve as references to specific actions and serve as reference for outside systems into a panoramic image database. Objects in a video can be tagged. It defines tags through 4-D time-space curves, which specify the 3-D location of a tagged object over time. It provides a user-friendly mechanism for defining said curves in panoramic video, which rely on curve fitting techniques to minimize the number of images to be labeled. It provides a mechanism for annotating tags with further information. When displaying tagged panoramic video, tags are graphically superimposed on the panoramic video feed using projective projection techniques. From this visualization, a user can then select a given tag and invoke an associated action. Additionally a mechanism whereby tags and associated user-provided information are used as index into panoramic image databases is provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
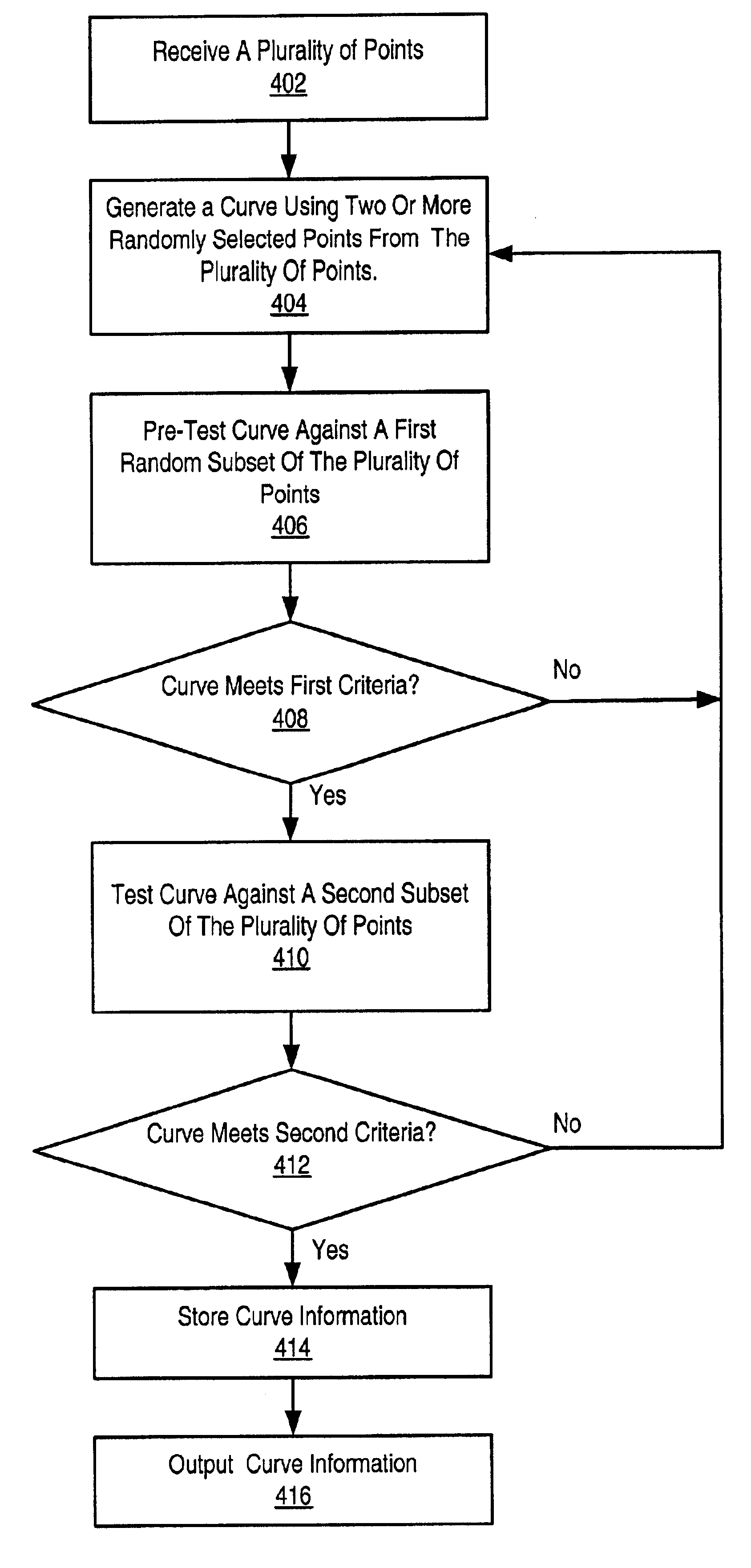
System and method for curve fitting using randomized techniques
InactiveUS6882958B2Improve method performanceAvoid calculationMeasurement devicesDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceCurve fitting
A system and method for performing a curve fit on a plurality of data points. In an initial phase, a subset Pmax of the plurality of points which represents an optimal curve is determined. This phase is based on a statistical model which dictates that after trying at most Nmin random curves, each connecting a randomly selected two or more points from the input set, one of the curves will pass within a specified radius of the subset Pmax of the input points. The subset Pmax may then be used in the second phase of the method, where a refined curve fit is made by iteratively culling outliers from the subset Pmax with respect to a succession of optimal curves fit to the modified subset Pmax at each iteration. The refined curve fit generates a refined curve, which may be output along with a final culled subset Kfinal of Pmax.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Empirical mode decomposition apparatus, method and article of manufacture for analyzing biological signals and performing curve fitting
InactiveUS6738734B1Easy to useAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDecompositionCurve fitting
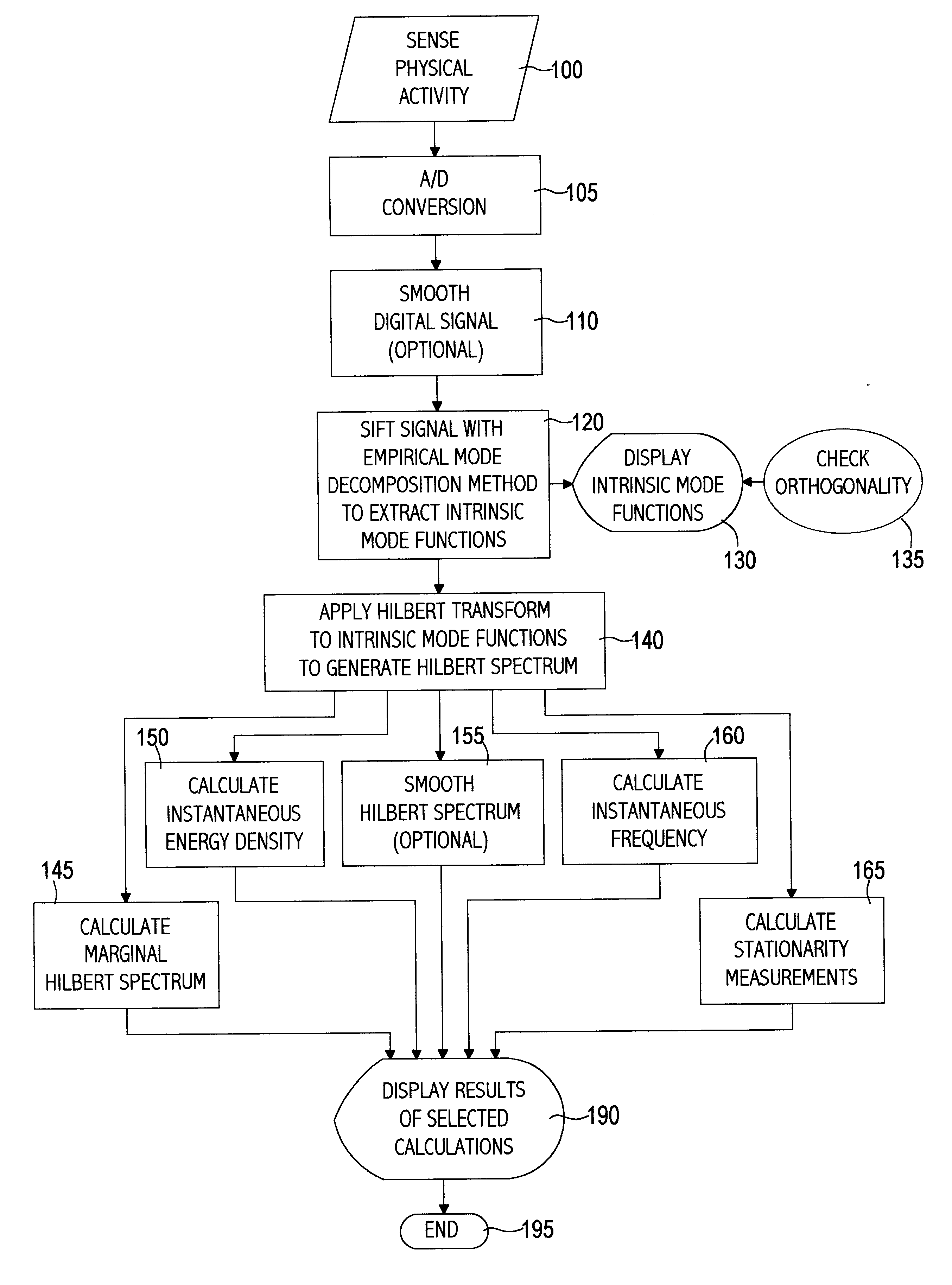
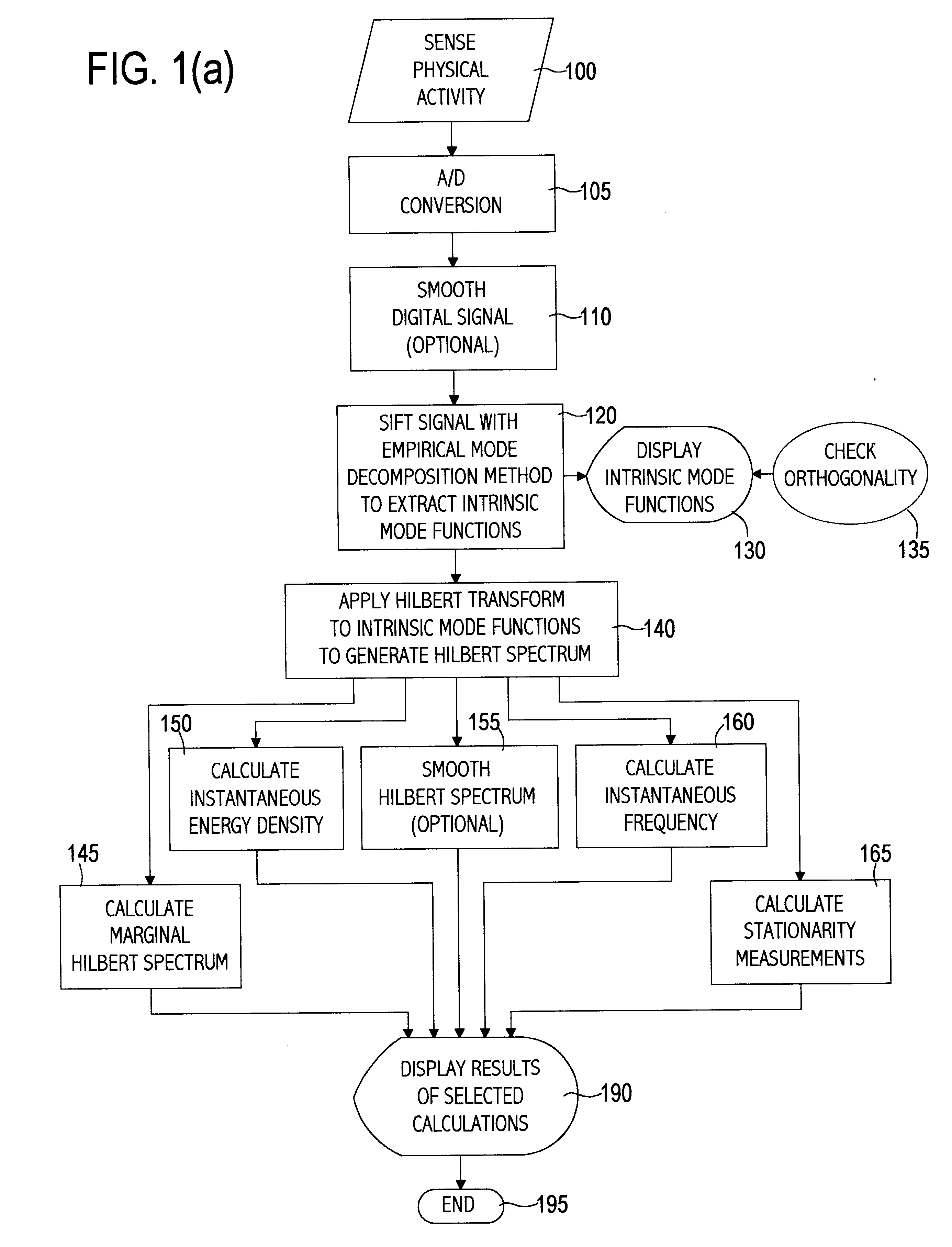
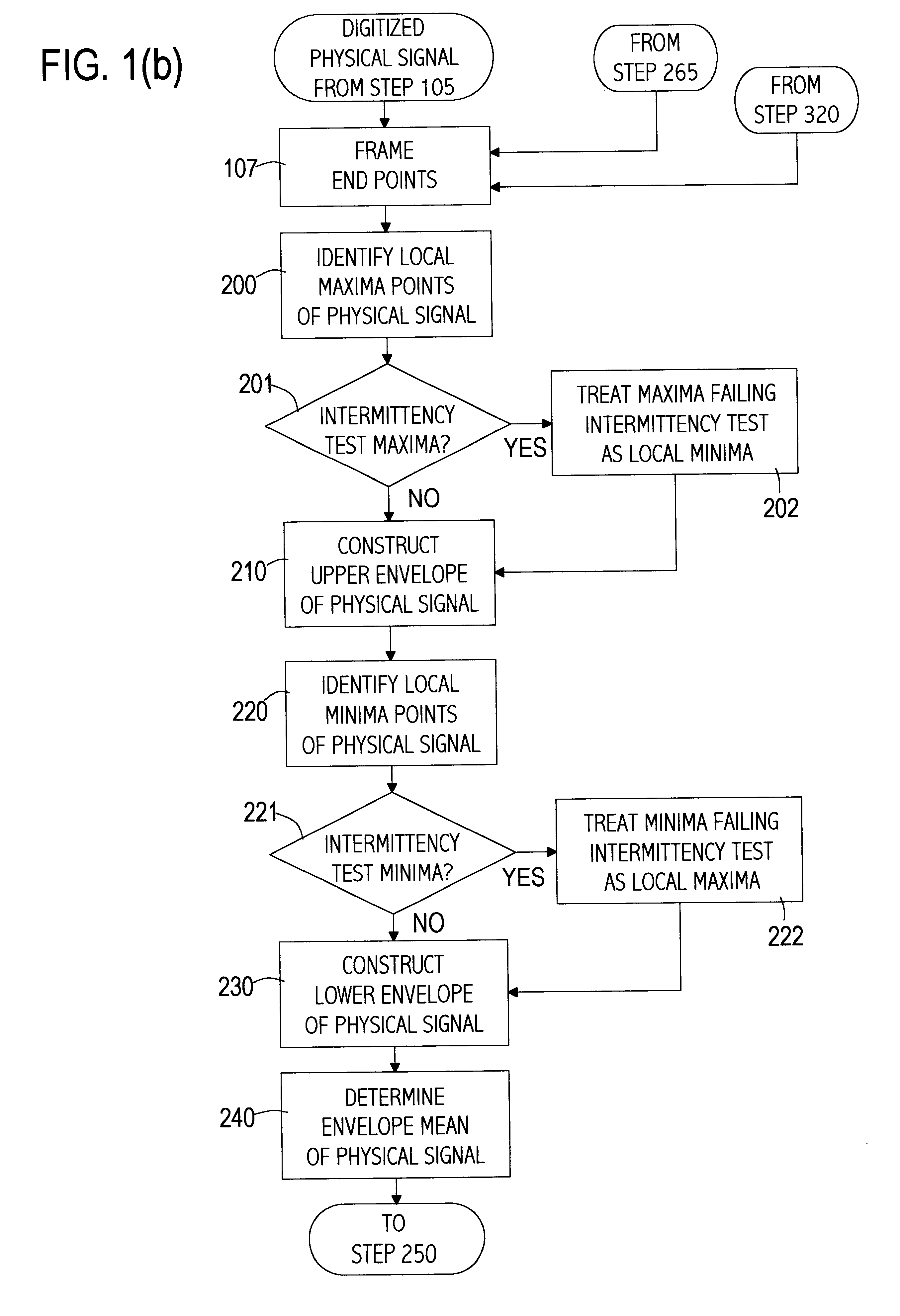
A computer implemented physical signal analysis method includes four basic steps and the associated presentation techniques of the results. The first step is a computer implemented Empirical Mode Decomposition that extracts a collection of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMF) from nonlinear, nonstationary physical signals. The decomposition is based on the direct extraction of the energy associated with various intrinsic time scales in the physical signal. Expressed in the IMF's, they have well-behaved Hilbert Transforms from which instantaneous frequencies can be calculated. The second step is the Hilbert Transform which produces a Hilbert Spectrum. Thus, the invention can localize any event on the time as well as the frequency axis. The decomposition can also be viewed as an expansion of the data in terms of the IMF's. Then, these IMF's, based on and derived from the data, can serve as the basis of that expansion. The local energy and the instantaneous frequency derived from the IMF's through the Hilbert transform give a full energy-frequency-time distribution of the data which is designated as the Hilbert Spectrum. The third step filters the physical signal by combining a subset of the IMFs. In the fourth step, a curve may be fitted to the filtered signal which may not have been possible with the original, unfiltered signal.
Owner:NASA
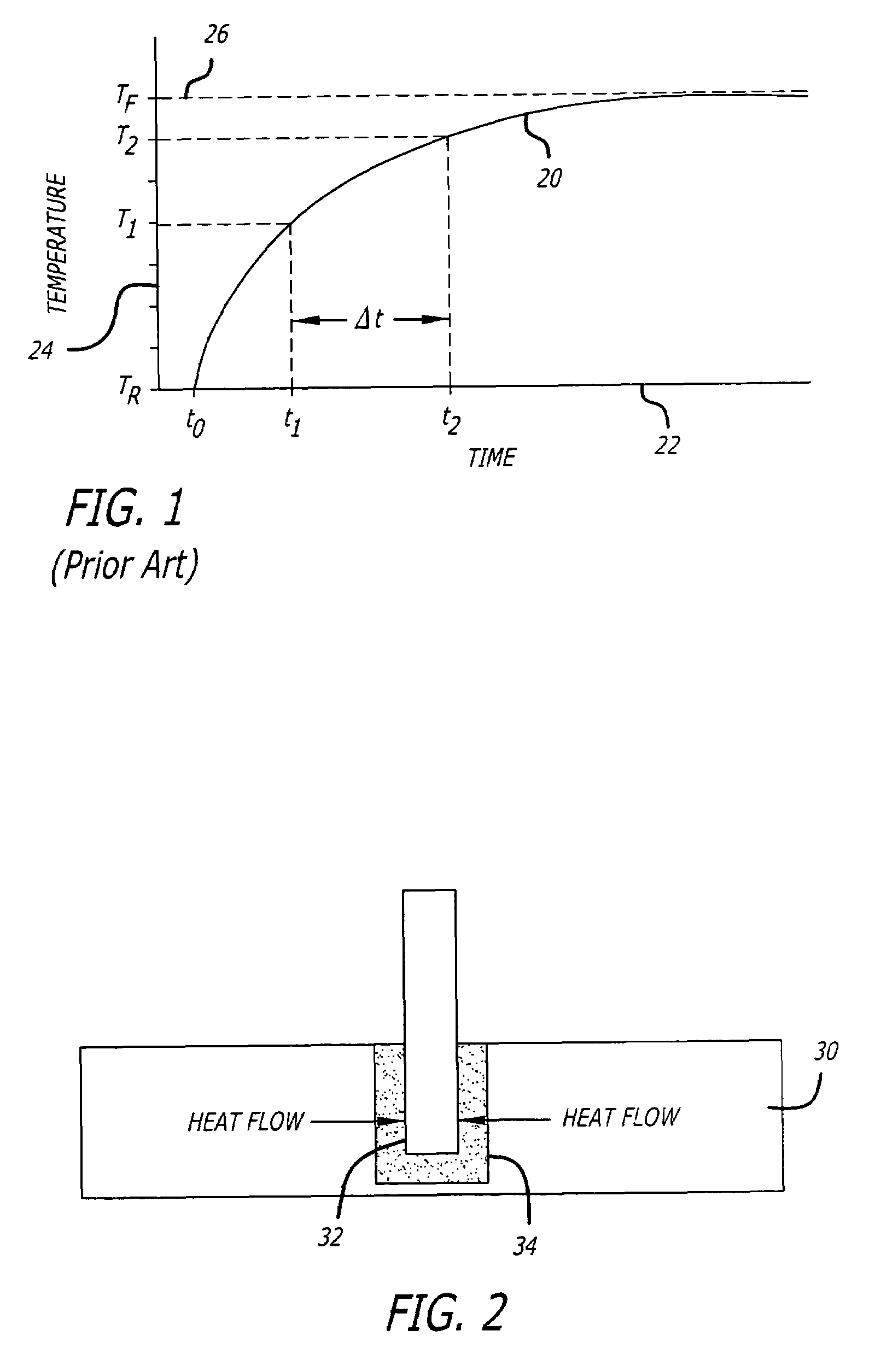
Temperature prediction system and method
ActiveUS7318004B2Little acquisitionLittle data dataThermometer detailsThermometer with A/D convertersStart timeCurve fitting
A thermometer system and method that rapidly predict body temperature based on the temperature signals received from a temperature sensing probe when it comes into contact with the body. A nonlinear, multi-parameter curve fitting process is performed and depending on the errors in the curve fit, parameters are changed or a prediction of the temperature is made. Criteria exist for the differences between the curve fit and the temperature data. The processor switches to a Continuous Monitor State if the curve fit over a limited number of time frames is unacceptable. Determining the start time on which the measurement time frame for prediction is based is performed by tissue contact threshold coupled with a prediction time delay.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
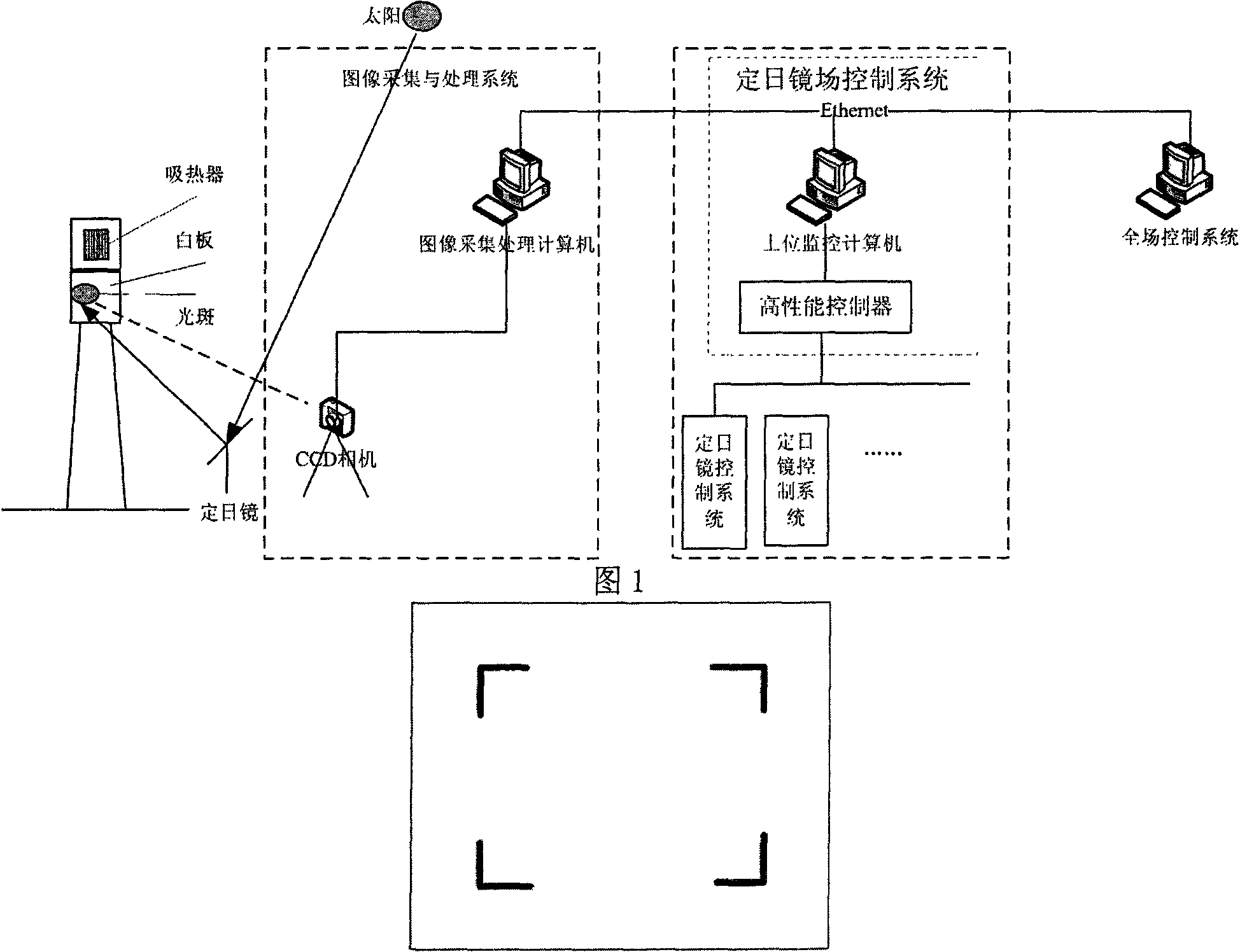
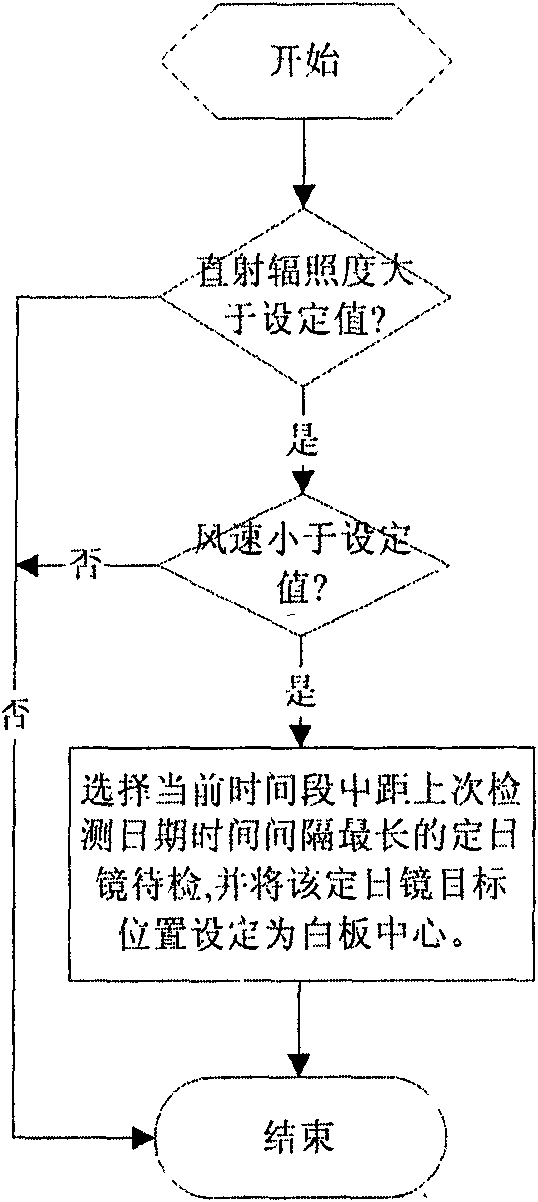
Heliostat tracking error correction method
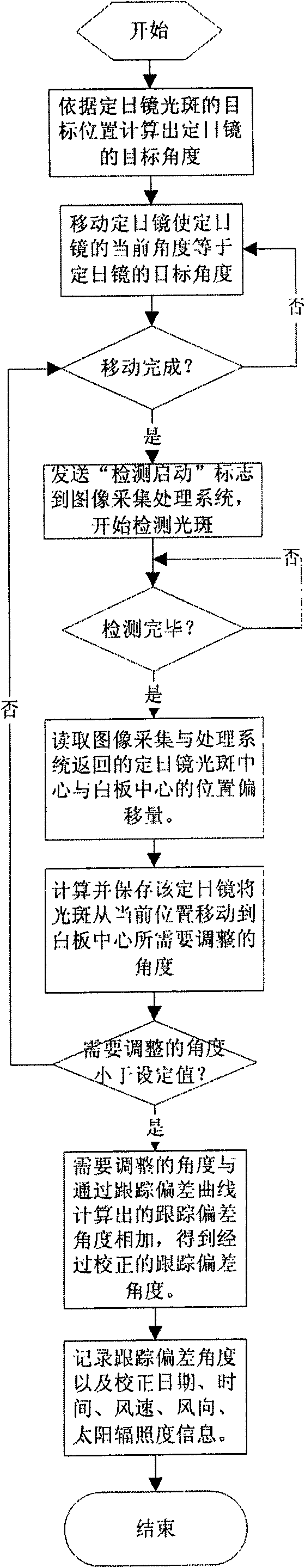
The invention discloses a heliostat tracking error correction method. Based on the characteristics that a heliostat tracking deviation angle has small variation in a short time and the tracking deviation angles at the same moment in the adjacent days have small variation, an image collecting and processing system is adopted to detect and obtain the tracking deviation angles of a certain heliostat at multiple moments in the whole day, or the tracking deviation angles obtained by the heliostat at multiple moments in one day or previous days are taken as the intraday tracking deviation angle; an intraday tracking deviation curve of the heliostat is obtained by the interpolation; according to the tracking deviation curve, the current angle of the heliostat is corrected to ensure that the facula of the heliostat can basically accurately be projected to a target position. The invention obtains the tracking deviation angles at multiple moments by detection of heliostat tracking error many days a year or many times a day; the everyday corresponding tracking deviation curve of each heliostat can be found by one-year or multiple-year tracking deviation angle data analysis treatment and curve fitting; and thus, the facula of the heliostat can be projected to the target position more accurately.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of constructing fine discrete road grid in urban drainage simulation system
InactiveCN103399990ARealize the expression of micro-topographic featuresBuild accuratelySpecial data processing applicationsTerrainMathematical model
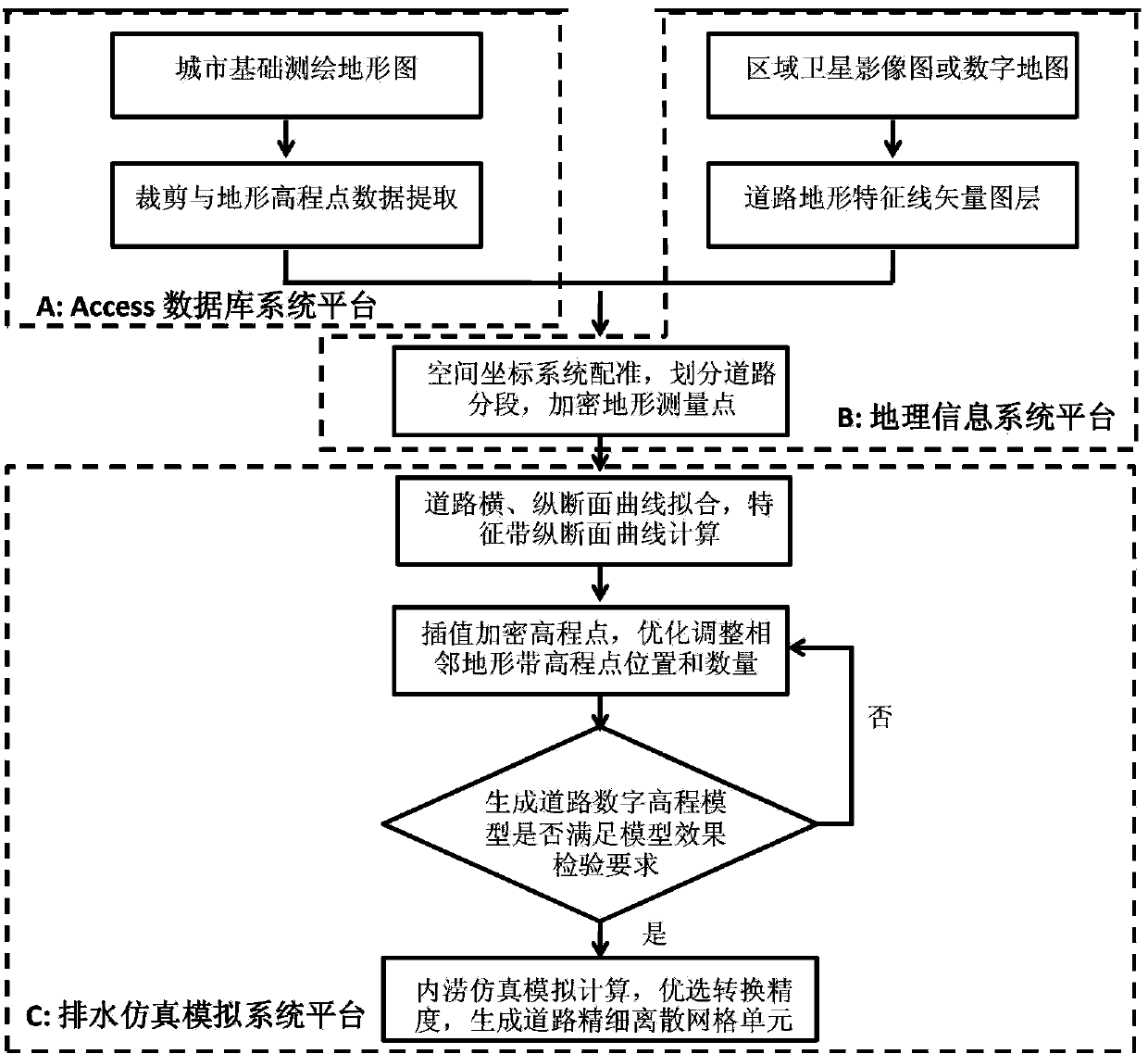
The invention relates to a method of constructing a fine discrete road grid in an urban drainage simulation system and belongs to the cross field of municipal engineering information technology, database technology and geologic information system technology. From the demand on construction of a waterlogging simulation model, under the restraint conditions in road design specifications and on the basis of conventional map measured elevation points, the number and positions of interpolation points are optimized under the drainage simulation system platform by the fitting method of local elevation change curves of cross-longitudinal road section and by road characteristic terrain vector layers according to mathematical model interpolation encryption plane and elevation information of physical road tomography; accordingly, a fine discrete road elevation grid unit is constructed, true tomographic road features are expressed quickly and economically, the demand on precise simulation of waterlogging models is met, especially the dredging and resisting actions of road micro-tomographic features upon waterflow can be correctly expressed, and the method is significant to promotion and application of the drainage simulation technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
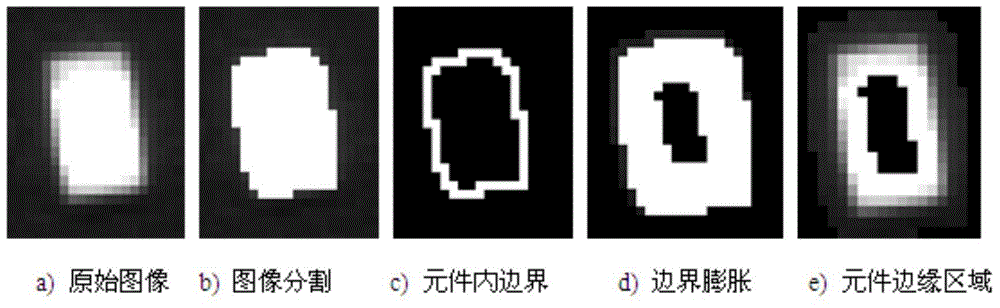
Detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining element center and deflection angle
ActiveCN104981105AFind out exactlyOvercoming complex shortcomingsPrinted circuit assemblingCircuit board tools positioningCurve fittingEdge extraction
A detecting and error-correcting method capable of rapidly and accurately obtaining an element center and a deflection angle is disclosed. Interested edge area can be rapidly and accurately found out through an automatic edge area extraction method based on combination of binary morphology and image reduction, and subsequent edge extraction image scope is minimized as possible. Pixel level edge is roughly positioned at first, and accordingly a sub-pixel edge is rapidly extracted by one-dimensional curve fitting method. The method overcomes the defect of complex algorithm of a conventional sub-pixel edge extraction algorithm based on two-dimensional images, and the time of extracting accurate sub-pixel edge can be shortened. Weighted least square rectangular edge fitting algorithm based on linear hazen paradigm can detect straight lines on any positions of an image, and effectively minimizes influence of outlier on fitting precision due to uneven edges. The central positions of a plurality of elements and deflect angles can be rapidly and accurately detected at once, and the efficiency of visual detection is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
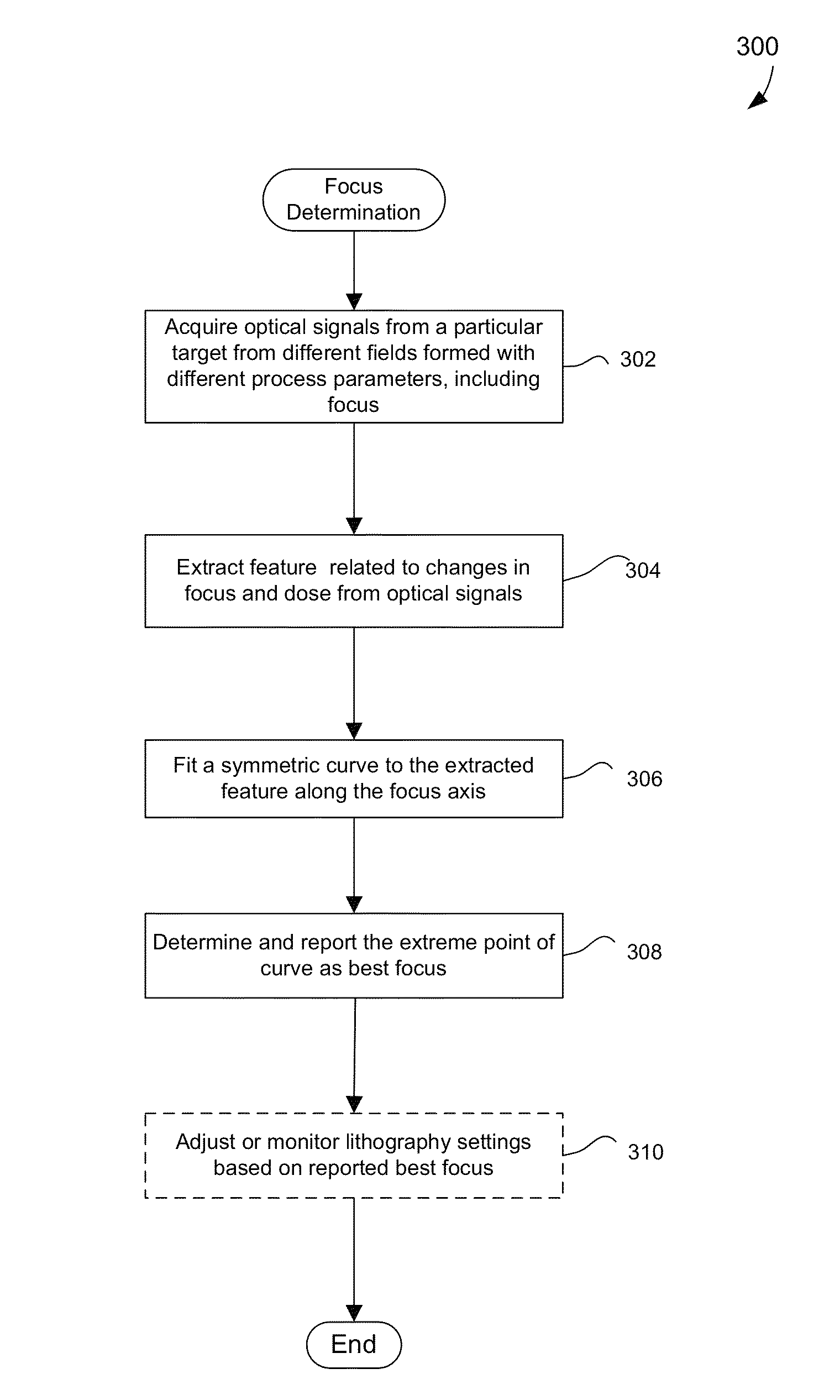
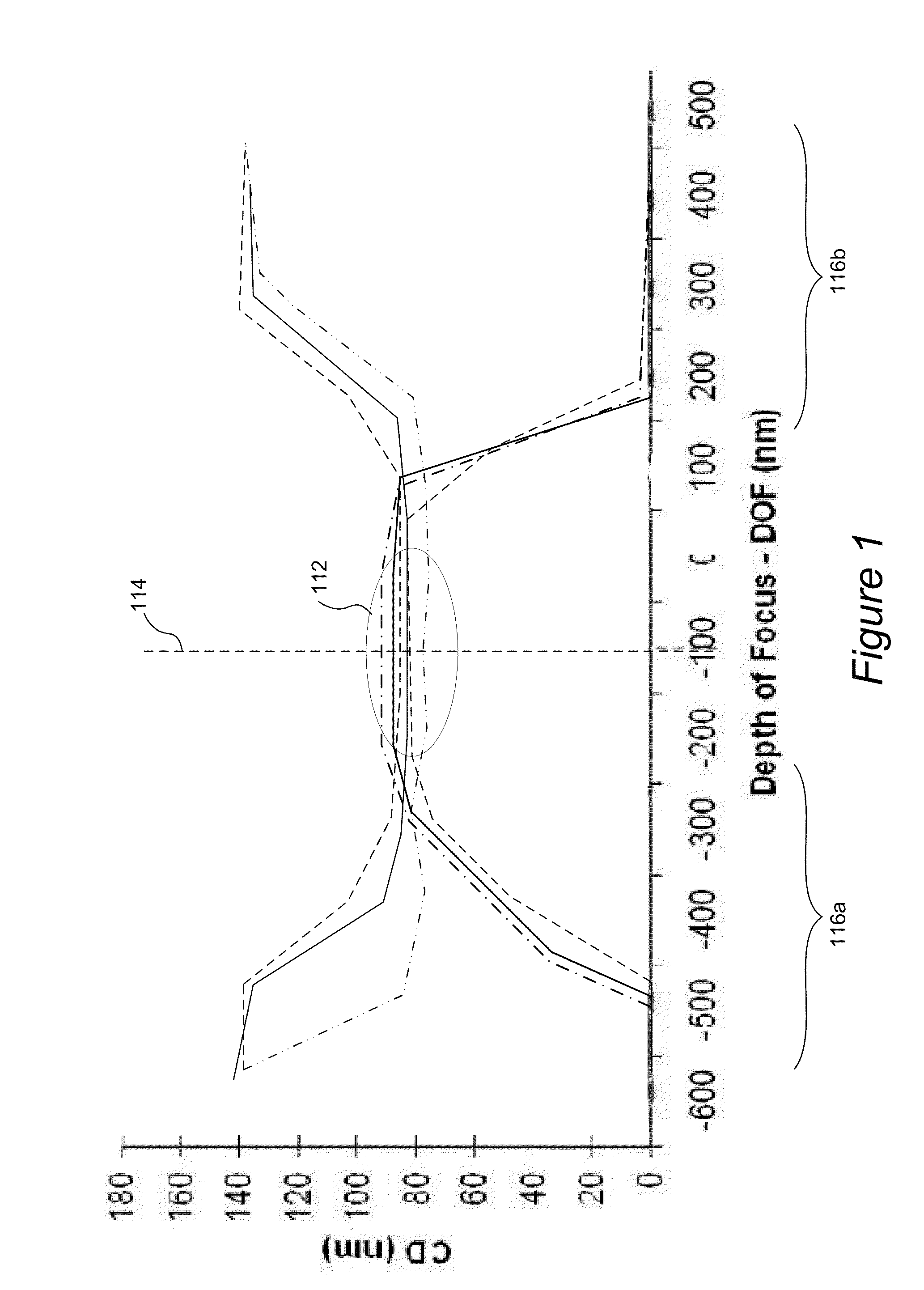
Methods and apparatus for determining focus
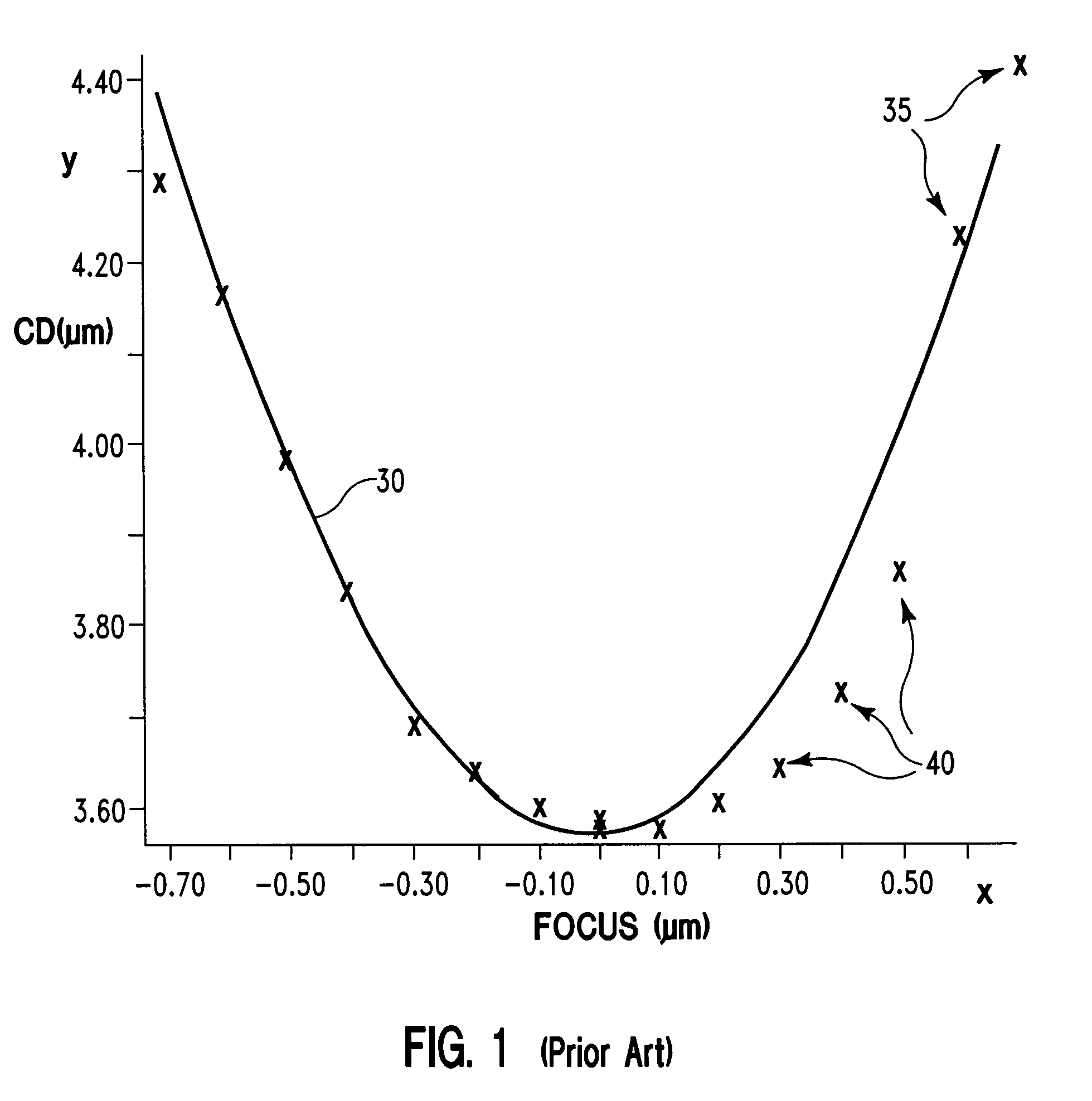
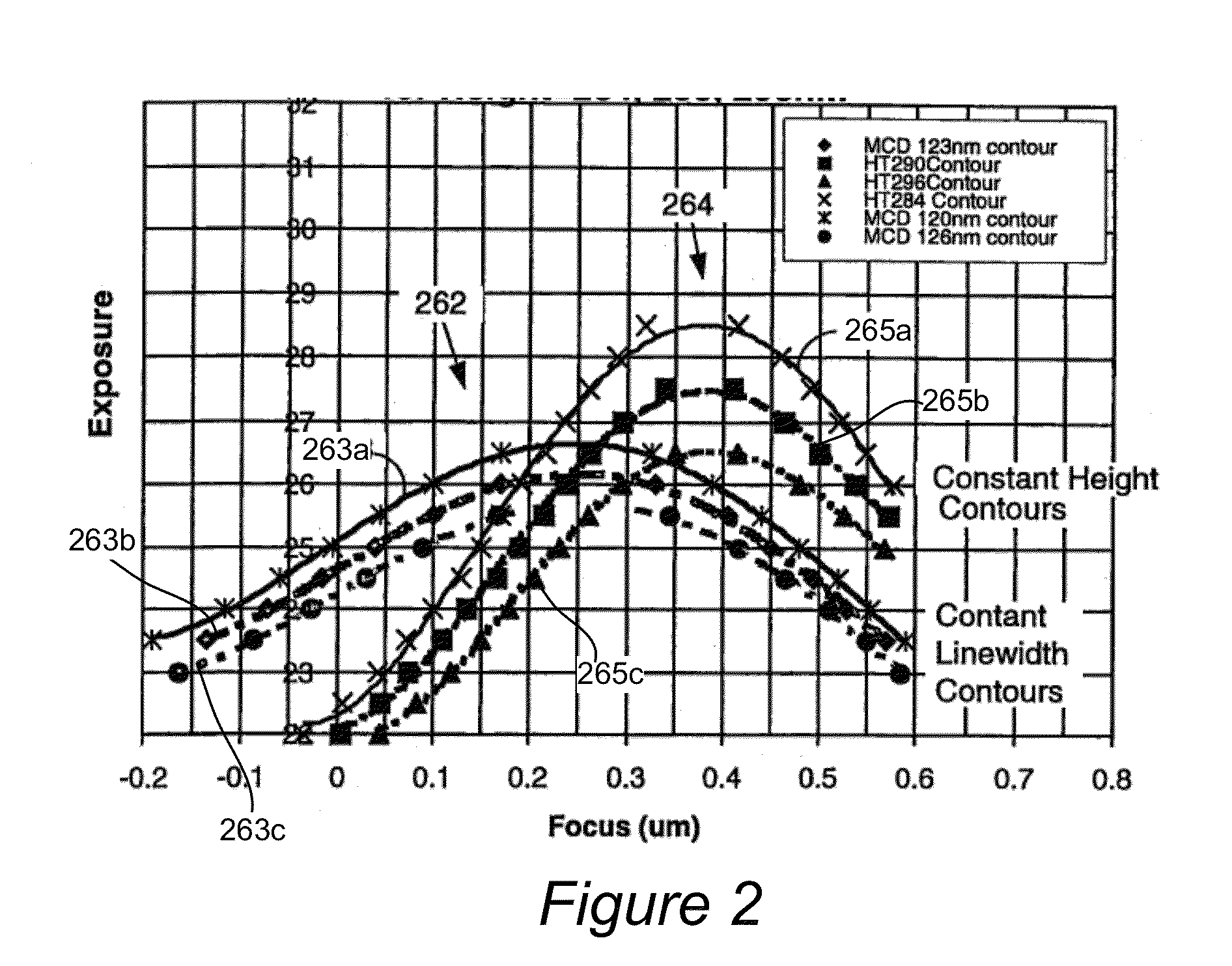
ActiveUS20150042984A1Well formedUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCurve fittingComputational physics
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for determining optimal focus for a photolithography system. A plurality of optical signals are acquired from a particular target located in a plurality of fields on a semiconductor wafer, and the fields were formed using different process parameters, including different focus values. A feature is extracted from the optical signals related to changes in focus. A symmetric curve is fitted to the extracted feature of the optical signals as a function of focus. An extreme point in the symmetric curve is determined and reported as an optimal focus for use in the photolithography system.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Reading voltage calculation in solid-state storage devices
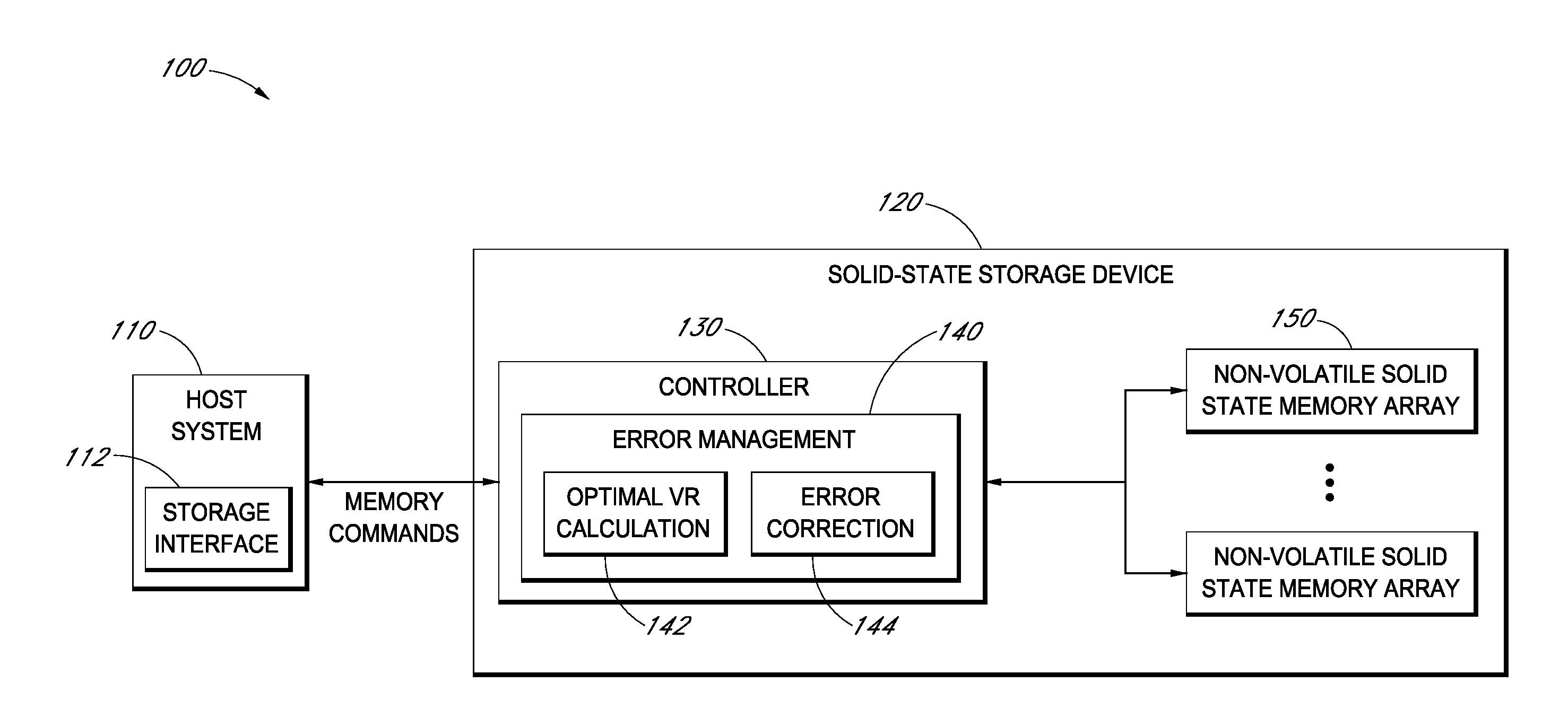
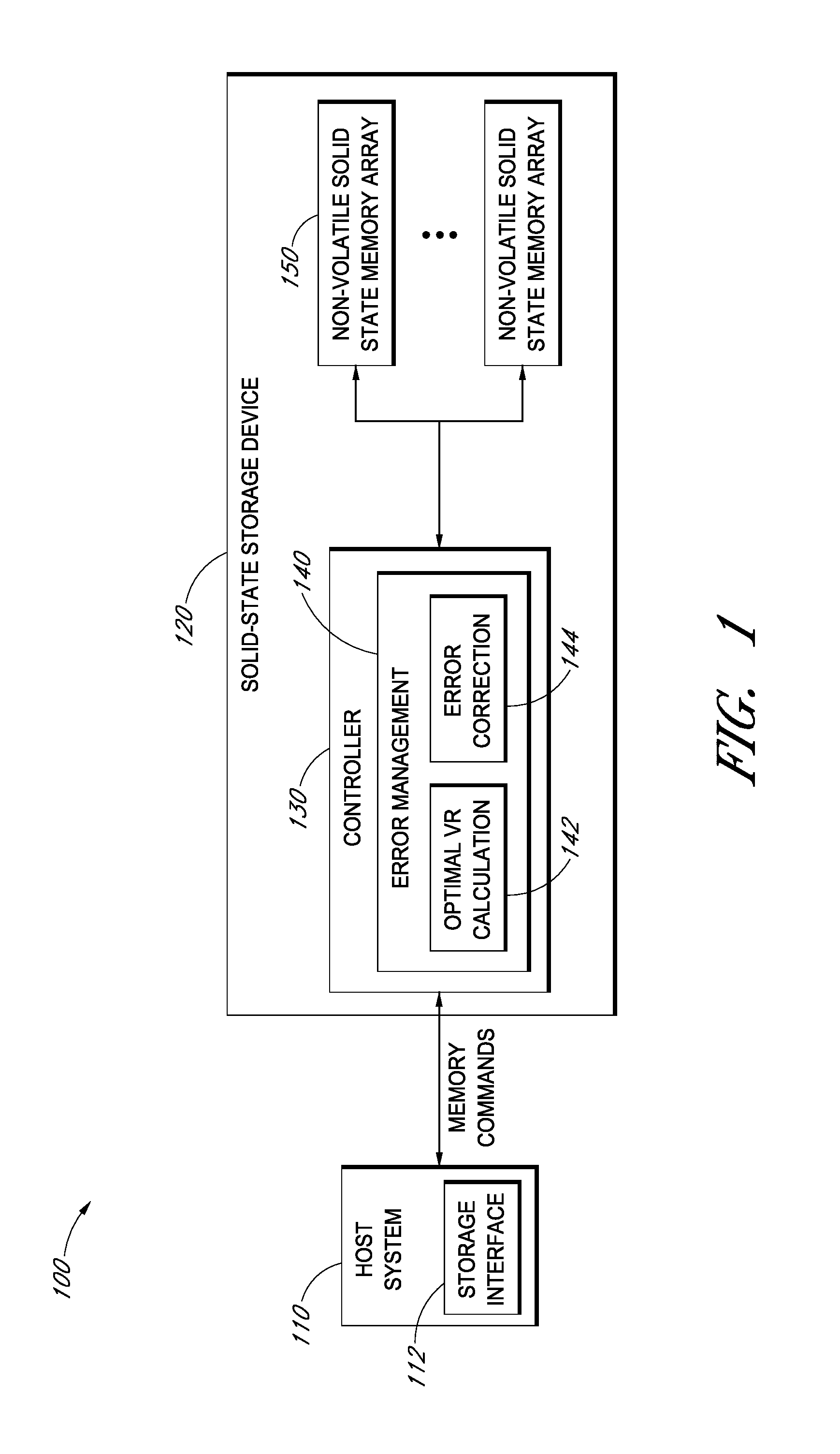
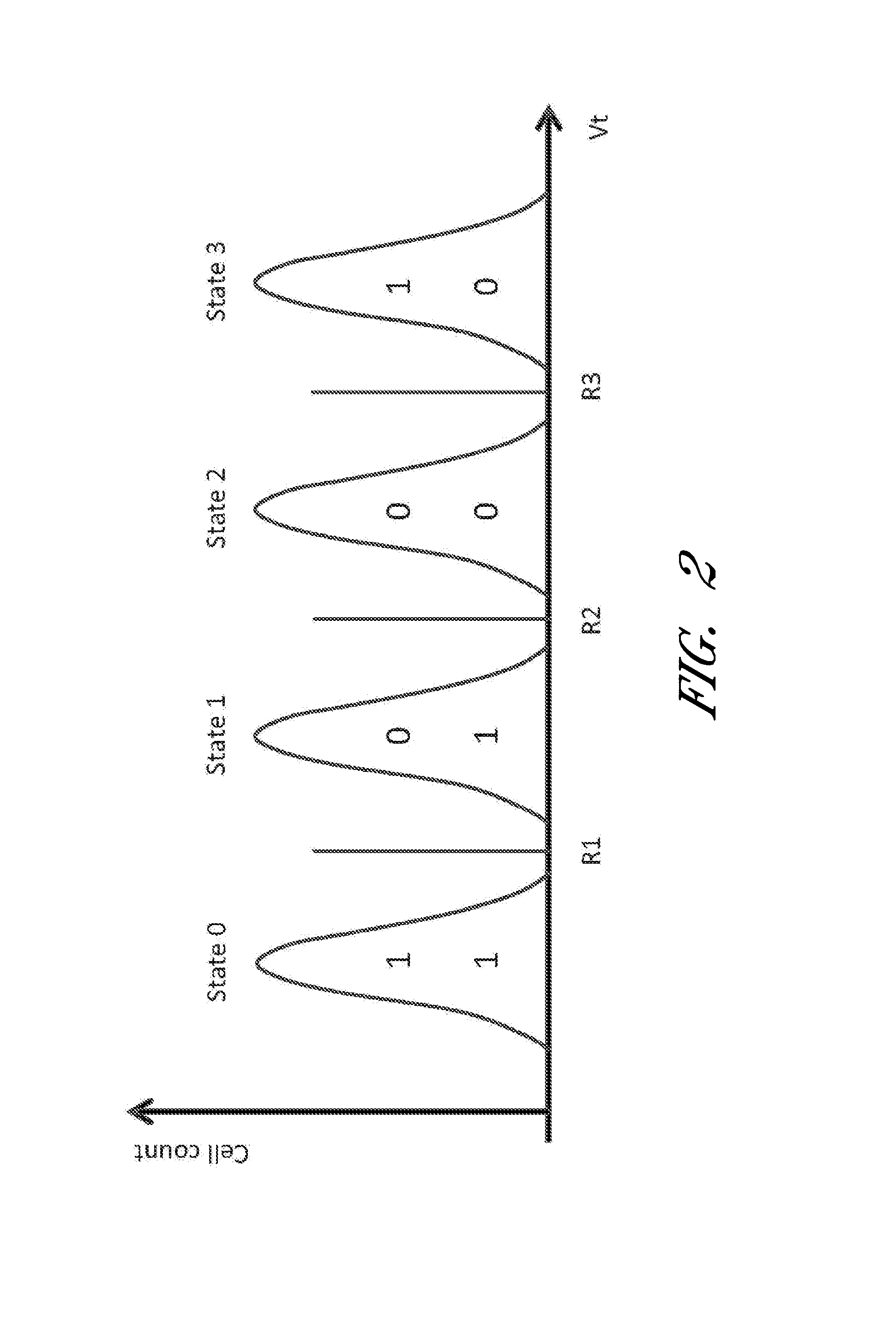
InactiveUS20140359202A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state storageComputer architecture
An error management system for a data storage device includes adjusted reading voltage level calculation functionality. Adjusted reading voltage level calculation may be based on the generation and use of an index in which data retention characteristics of a drive are used to look-up corresponding reading voltage levels. In certain embodiments, reading voltage level calculation is based at least in part on curve-fitting procedures / algorithms, wherein curves are fitted to bit error rate data points or cumulative memory cell distributions and are solved according to one or more algorithms to determine optimal reading voltage levels.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Adaptive pre-distortion method
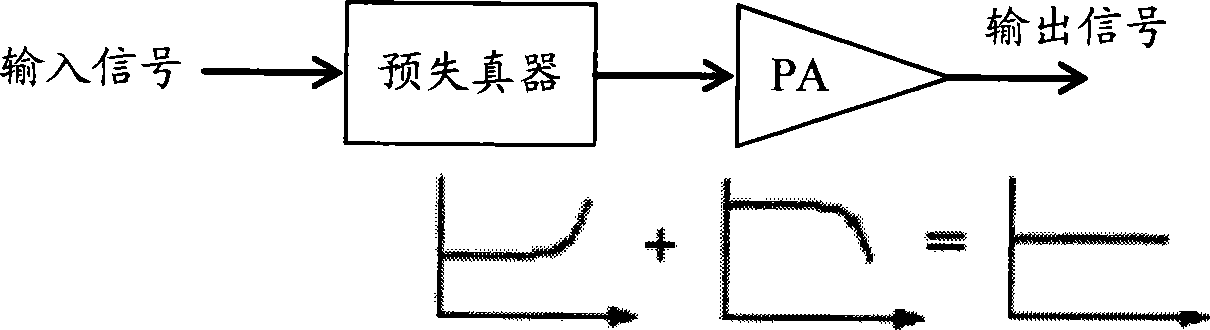
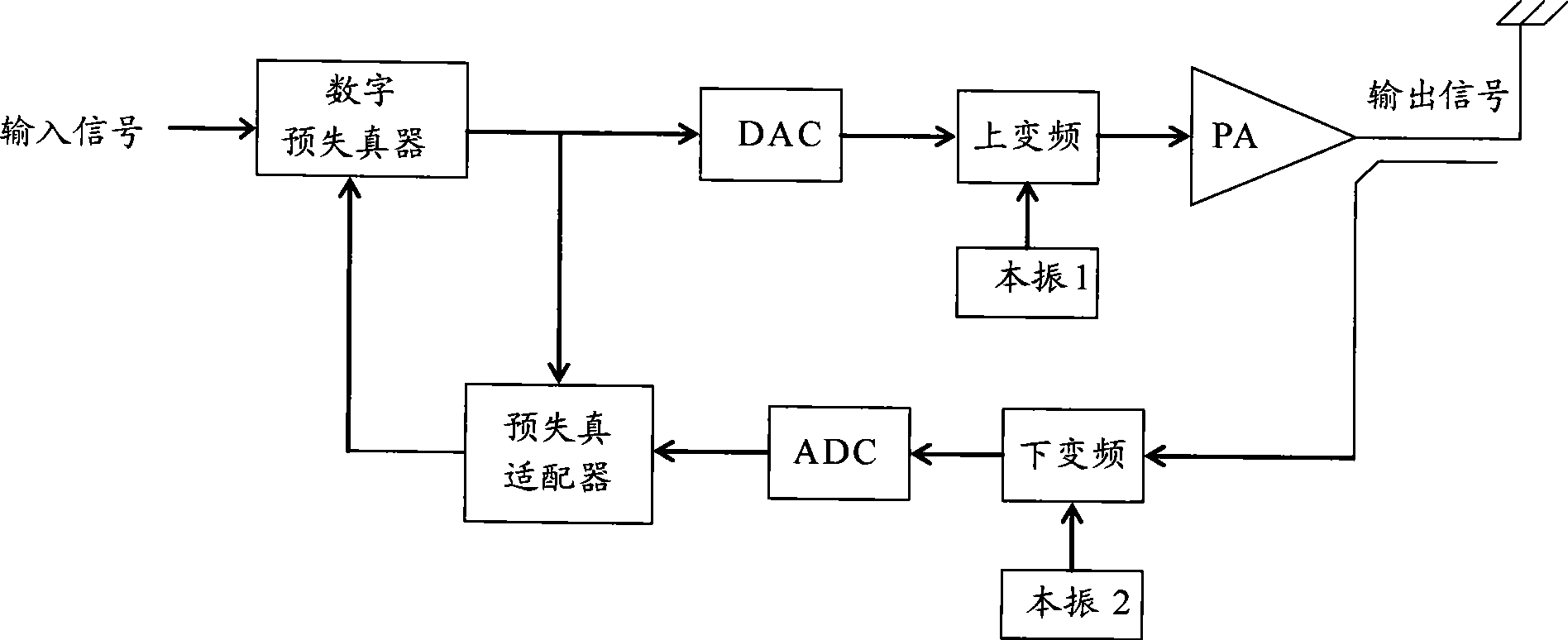
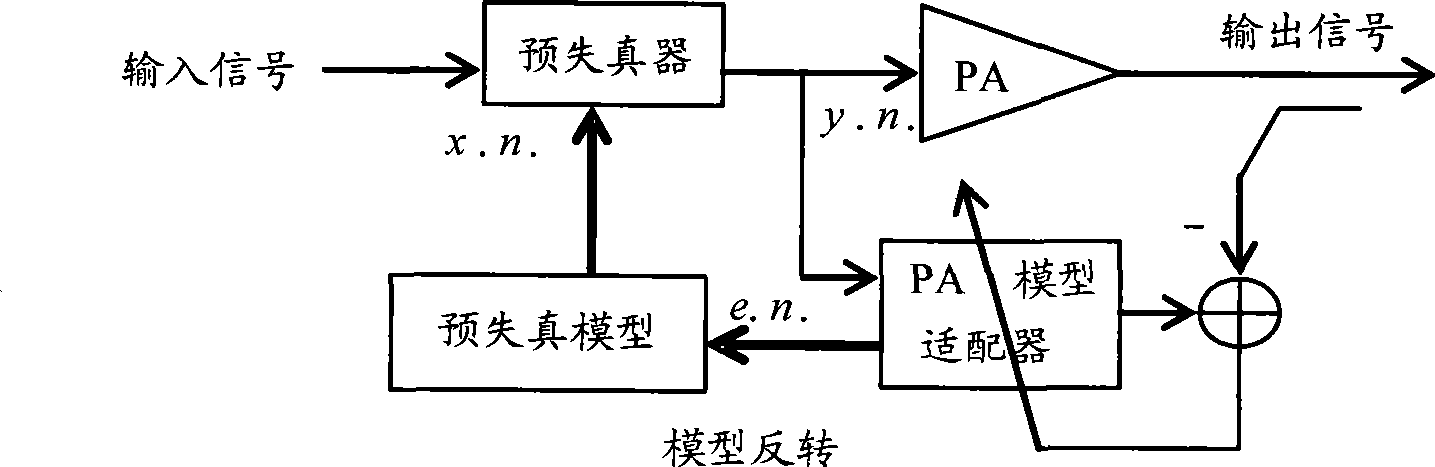
ActiveCN101459636ANo mistakesNo non-convergence problemAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSynchronising arrangementAudio power amplifierGate array
The invention discloses a self-adaptive predistortion method, which comprises the steps: collecting emission data and feedback data, calculating loop delay according to the emission data and the feedback data, carrying out time unifying to input signals according to the loop delay, compensating collected delay of the emission data and the feedback data according to the loop delay, estimating a predistortion model parameter, constructing a matrix according to the set predistortion model parameter, calculating a predistortion parameter corresponding to a power amplifier, adopting a curve fitting method to sample and quantize the predistortion parameter to obtain an LUT table, modifying the predistortion parameter in a digital predistorter according to the LUT table, carrying out digital predistortion to the input signals according to an LUT address and the predistortion parameter which is modified, and generating the LUT address according to the amplitude of the input signals. The technical scheme of the invention saves the hardware implementation cost and can be realized in an FPGA (programmable gate array) easily.
Owner:ZTE CORP
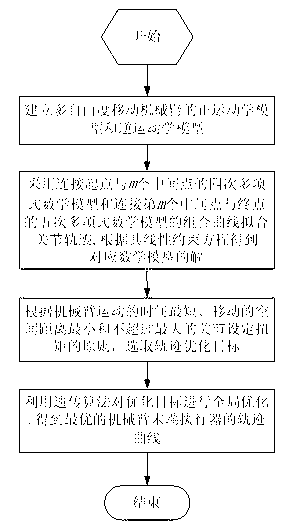
Genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for mobile mechanical arm
The invention relates to a genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for a mobile mechanical arm. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of first establishing a forward kinematic model and an inverse kinematic model of a multi-degree-of-freedom mobile mechanical arm; then fitting a joint trajectory by adopting a composite curve of a quartic polynomial mathematical model and a quintic polynomial mathematical model, and calculating solutions of the corresponding mathematical models according to a linear constraint equation; next selecting a trajectory optimization target according to the principles of shortest motion time, minimum spatial motion distance and less than or equal to maximum set joint torque of the mobile mechanical arm; and finally globally optimizing the optimization target by utilizing a genetic algorithm to obtain an optimal trajectory curve of an end actuator of the mechanical arm. According to the method, the trajectory planning efficiency and the tracking accuracy of the mechanical arm are improved, and the problems of real-time trajectory planning of the mobile mechanical arm and trajectory planning optimization and control of the mechanical arm in an uncertain environment are also solved; and the trajectory planning optimization method for the mobile mechanical arm is effective.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods for precise sub-lane vehicle positioning
ActiveCN102529975AInstruments for road network navigationExternal condition input parametersOn boardCurve fitting
The invention relates to systems and methods for precise sub-lane vehicle positioning. A vehicle having an on-board computer, vehicle sensors, a satellite-positioning unit, a database storing a lane-level map performs a method to determine a new pose of the vehicle using map matching. The method includes the on-board computer of the vehicle receiving new data from at least one of the vehicle sensors and collecting measurements from the vehicle sensors. The method also includes the on-board computer of the vehicle computing propagation of vehicle pose with respect to consecutive time instances and performing a curve-fitting process. The method further includes the on-board computer of the vehicle performing a sub-routine of updating at least one observation model based on results of the curve-fitting process, performing a tracking sub-routine including using a probability distribution to update the vehicle pose in terms of data particles, and performing a particle filtering sub-routine based on the data particles to compute the new vehicle pose.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
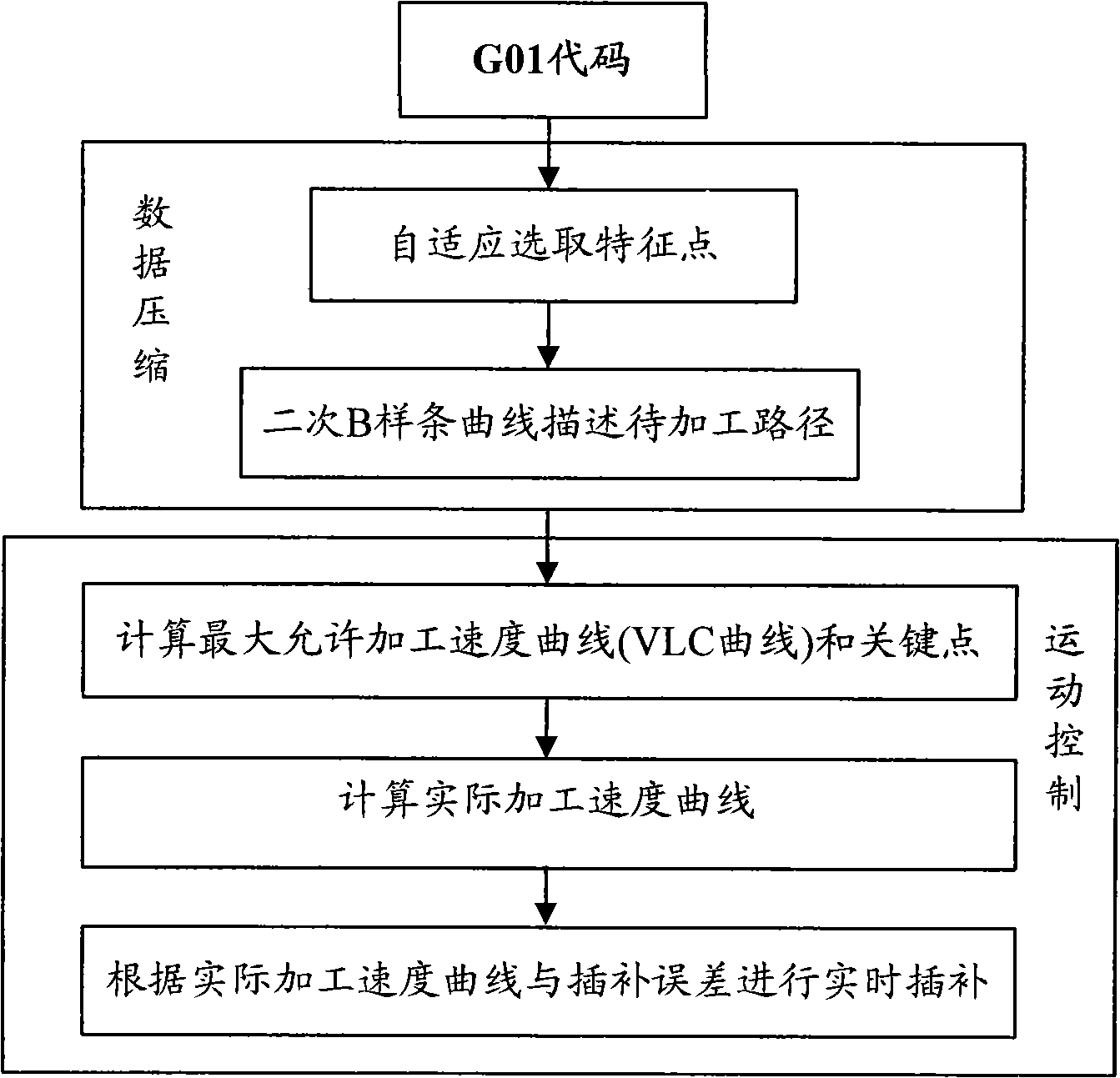
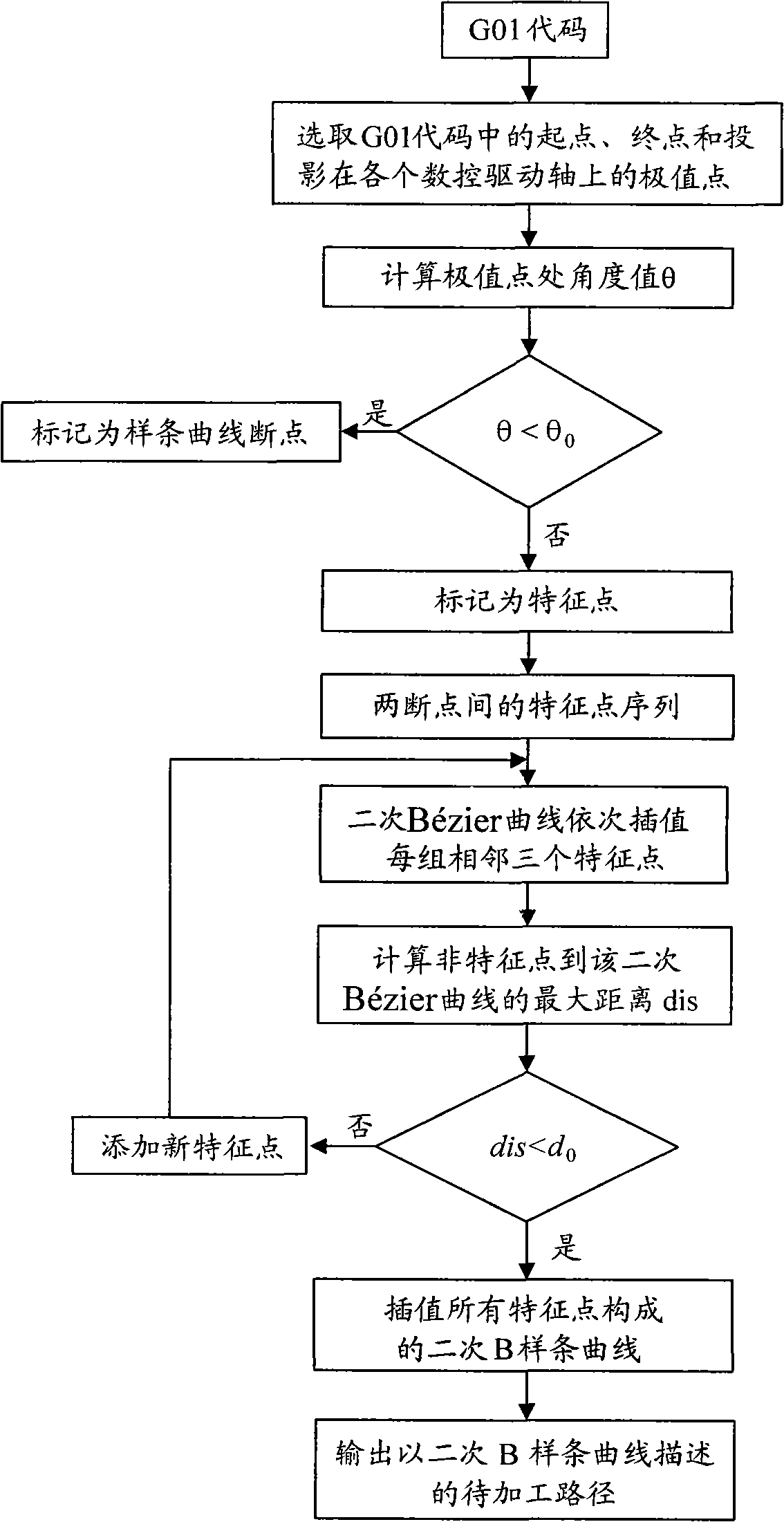
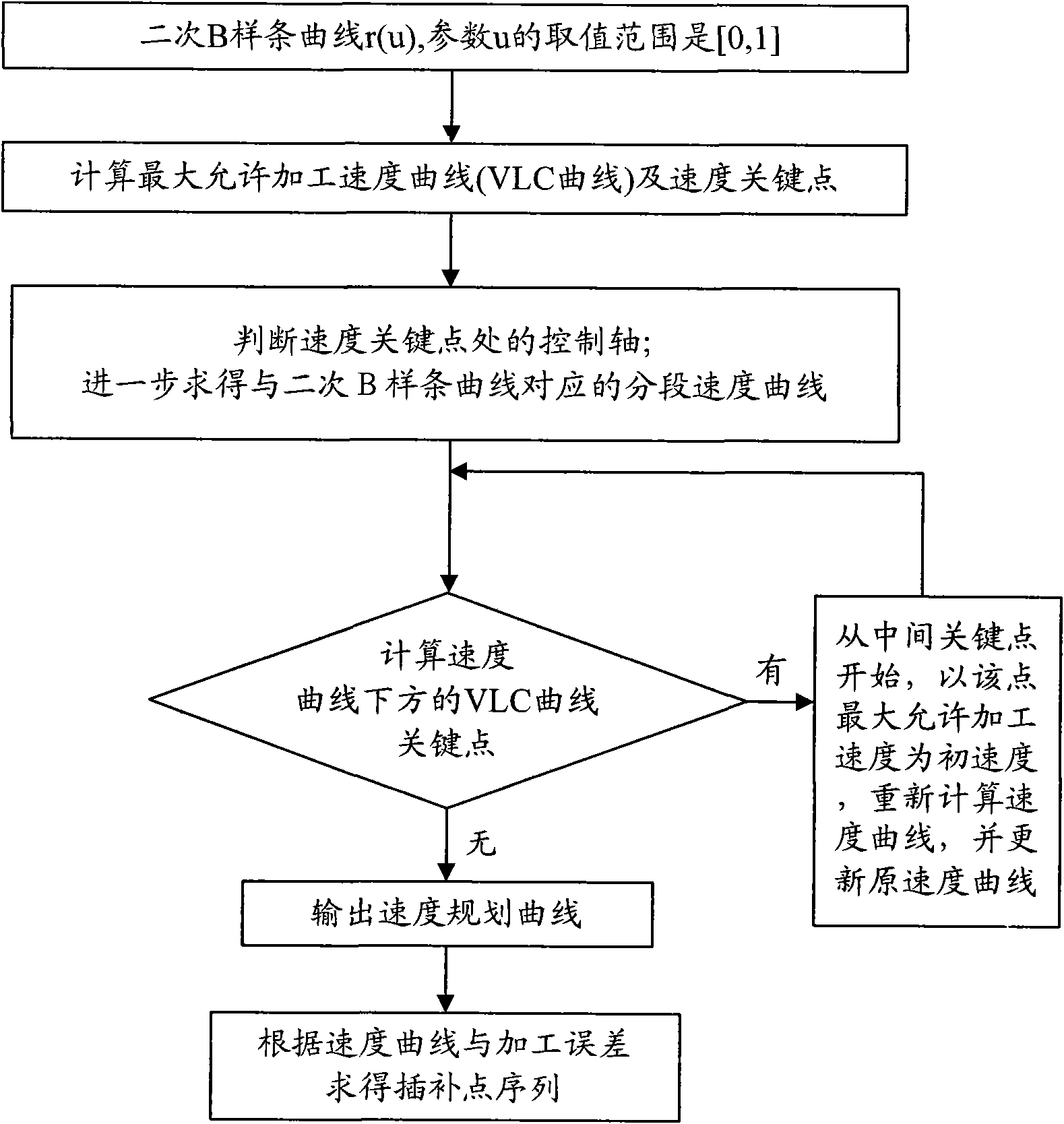
Method for fitting and interpolating G01 code based on quadratic B spline curve
InactiveCN101539769AAccurate descriptionMeet the precision requirementsProgramme controlAutomatic control devicesNumerical controlApplicability domain
The invention discloses a method for fitting and interpolating a G01 code based on a quadratic B spline curve, comprising the following steps of: by an adaptive approach selecting each characteristic point of each group of small line segment which is described by the G01 code; fitting a route which is to be processed with the quadratic B spline curve of all the characteristic points; according to the characteristic of the quadratic B spline curve and the limit of the acceleration of each driving shaft of the numerical control machine, simultaneously obtaining the maximum permissible machining velocity curve (VLC curve) of the quadratic B spline curve and the each speed key point on the VLC curve; according to the each speed key point, the control axis of the each key point, the maximum permissible machining velocity and the VLC curve, computing real machining velocity; according the real machining velocity curve and a interpolating error computing interpolating point and completing real-time interpolation. The invention has fast computing velocity, high machining precision, stable working performance and wide application range, can complete the interpolating computation of the spline curve in real time and meet digital control processing requirement of fast velocity and high precision under a premise that the preset precision of the system is met.
Owner:ACAD OF MATHEMATICS & SYSTEMS SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for adaptive segment refinement in optical proximity correction
InactiveUS20050055658A1Increase computational costAccurate representationOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designPattern recognitionCurve fitting
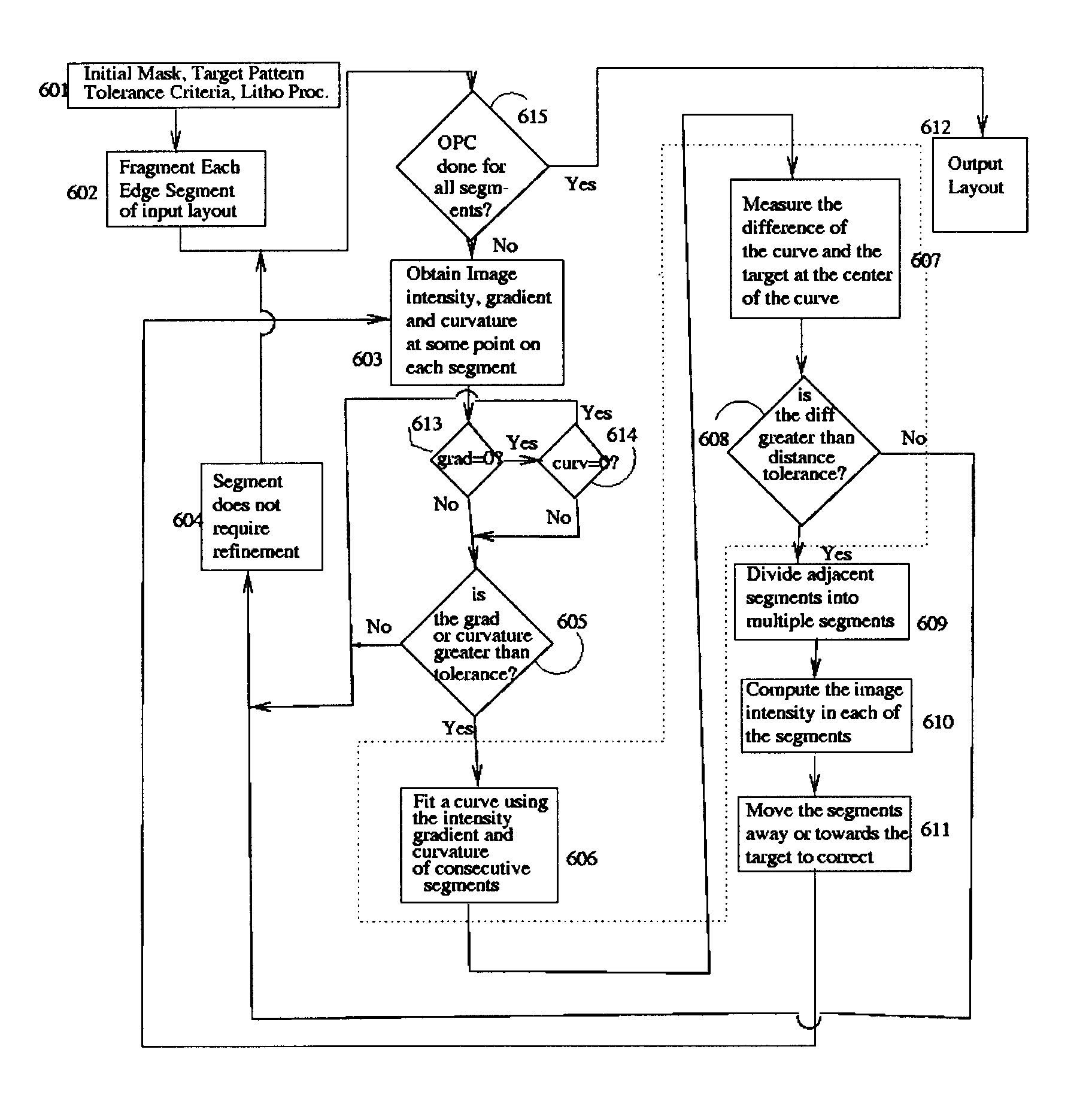
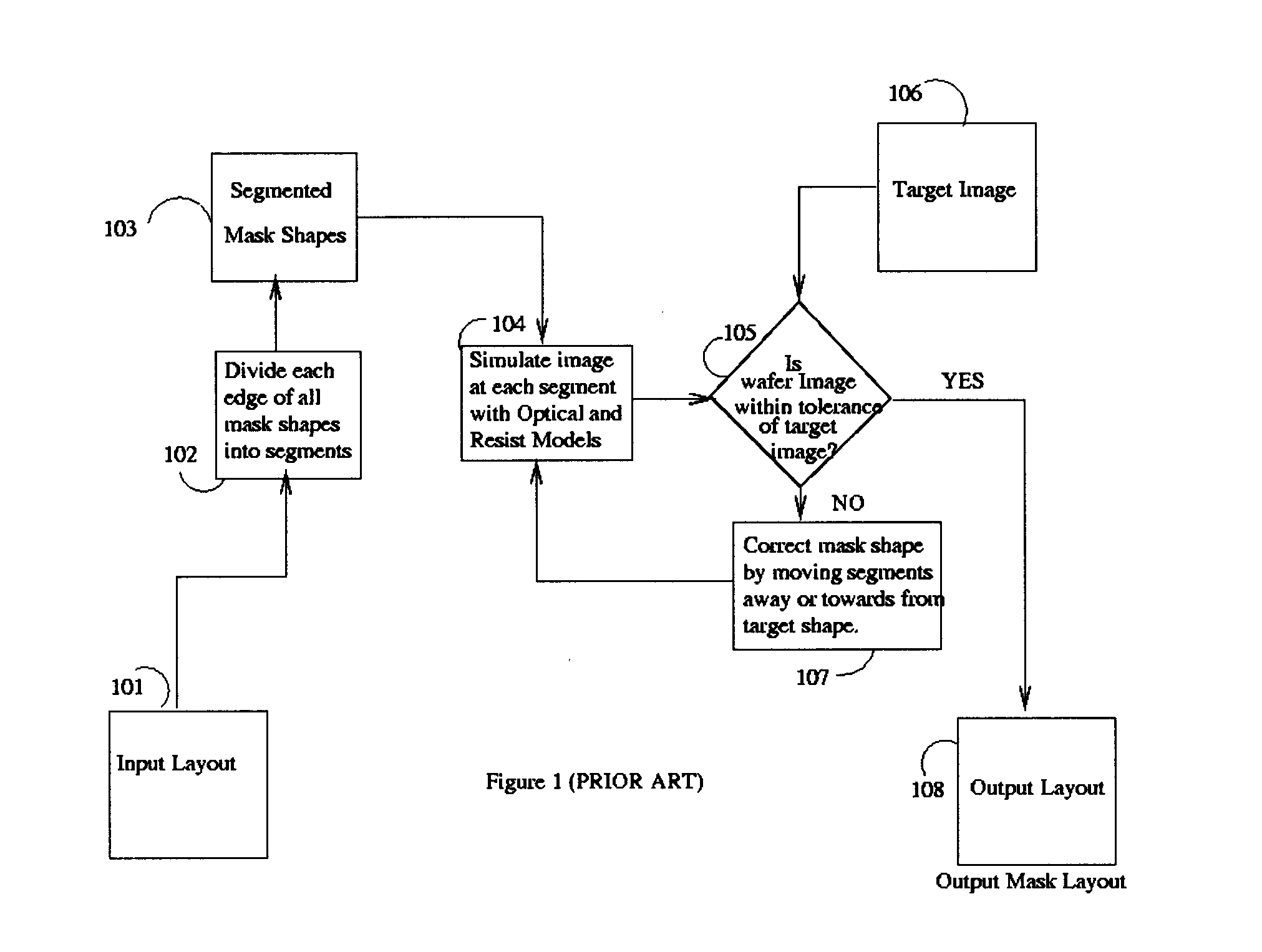
A method of designing lithographic masks is provided where mask segments used in a model-based optical proximity correction (MBOPC) scheme are adaptively refined based on local image information, such as image intensity, gradient and curvature. The values of intensity, gradient and curvature are evaluated locally at predetermined evaluation points associated with each segment. An estimate of the image intensity between the local evaluation points is preferably obtained by curve fitting based only on values at the evaluation points. The decision to refine a segment is based on the deviation of the simulated image threshold contour from the target image threshold contour. The output mask layout will provide an image having improved fit to the target image, without a significant increase in computation cost.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for pasting image to human face based on affine transformation
ActiveCN104778712ASolve the robustness problemNatural effectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCurve fittingAdaptive matching
The invention discloses a method and system for pasting an image to a human face based on affine transformation. Characteristic point locating and characteristic point extraction are carried out on a standard human face image, curve fitting is carried out on extracted characteristic points of the standard human face image through a Lagrange's interpolation method, standard grain coordinates are obtained, then characteristic point locating is carried out on the human face image to be processed, self-adaption matching is carried out on the standard grain coordinates and the corresponding characteristic points of the human face image to be processed through affine transformation according to the actual characteristic points of the human face image to be processed, and transformation grain coordinates are obtained; finally, image pasting materials are drawn on the corresponding characteristic points of the human face image to be processed through the transformation grain coordinates, and an effect human face image is obtained. Therefore, the method and system can adapt to human face portions in various shapes by itself, the processed effect human face image is more natural, and the problem of robustness of automatic decoration is solved.
Owner:XIAMEN MEITUZHIJIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com