Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100results about How to "Minimizing sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
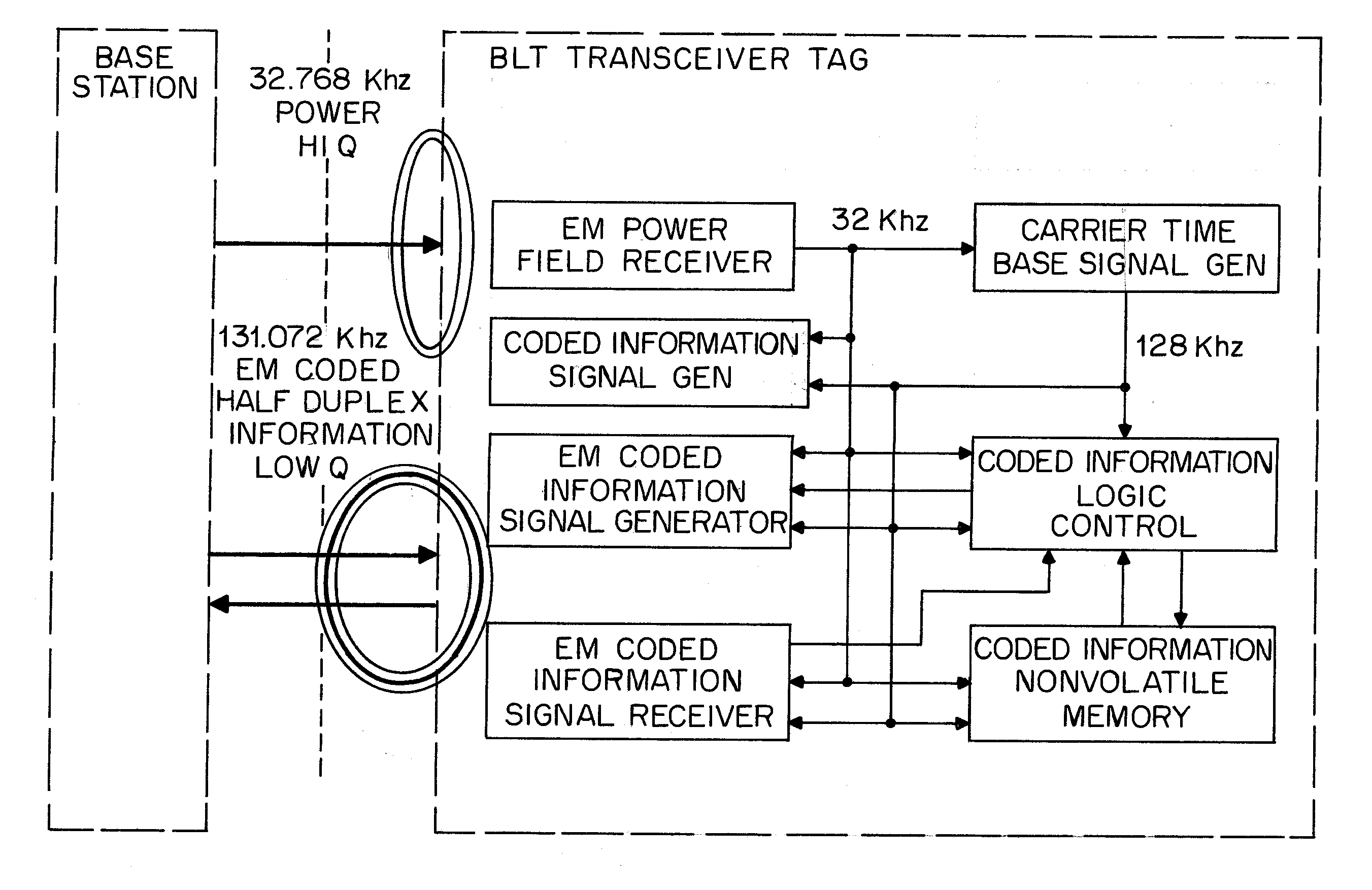
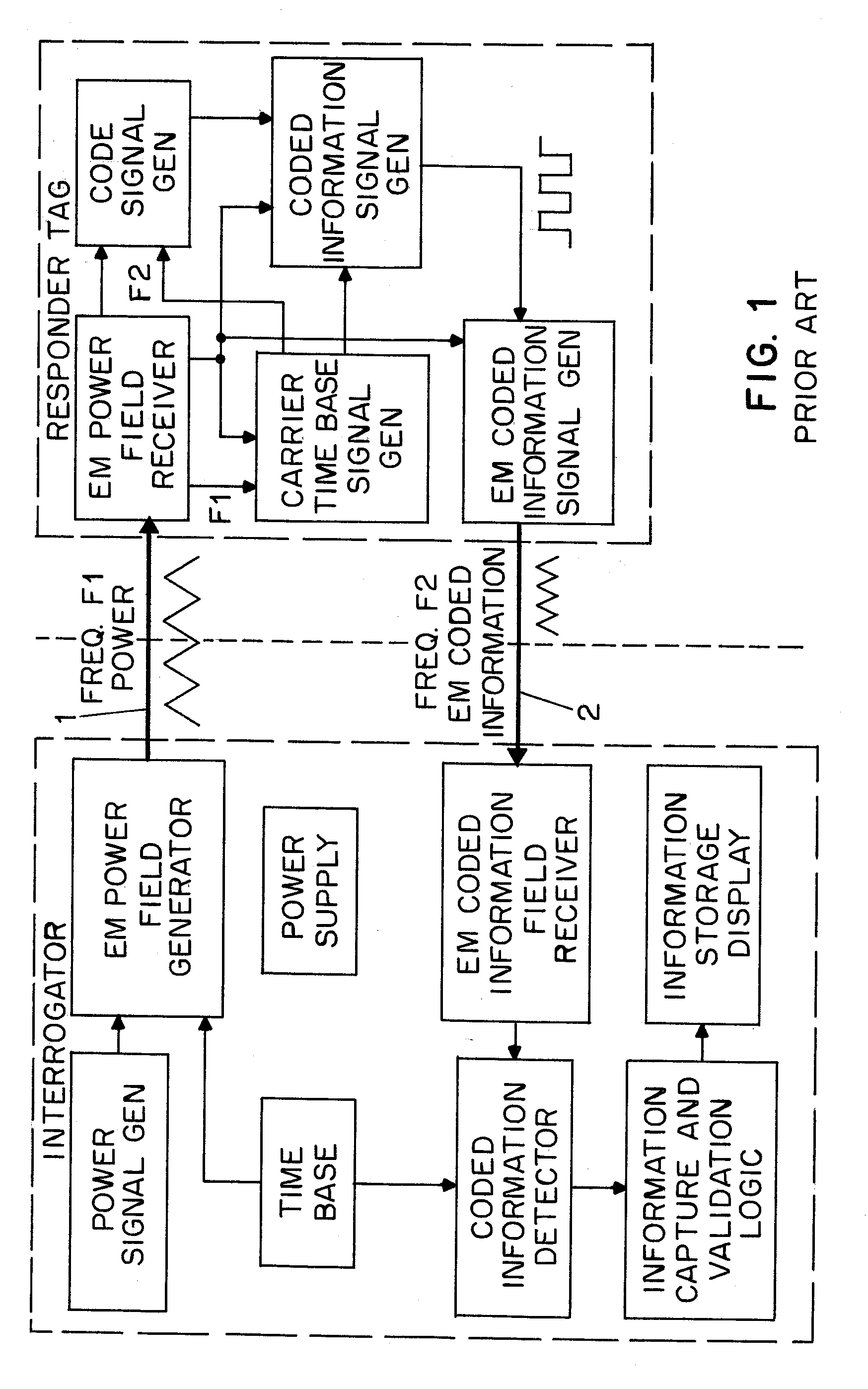
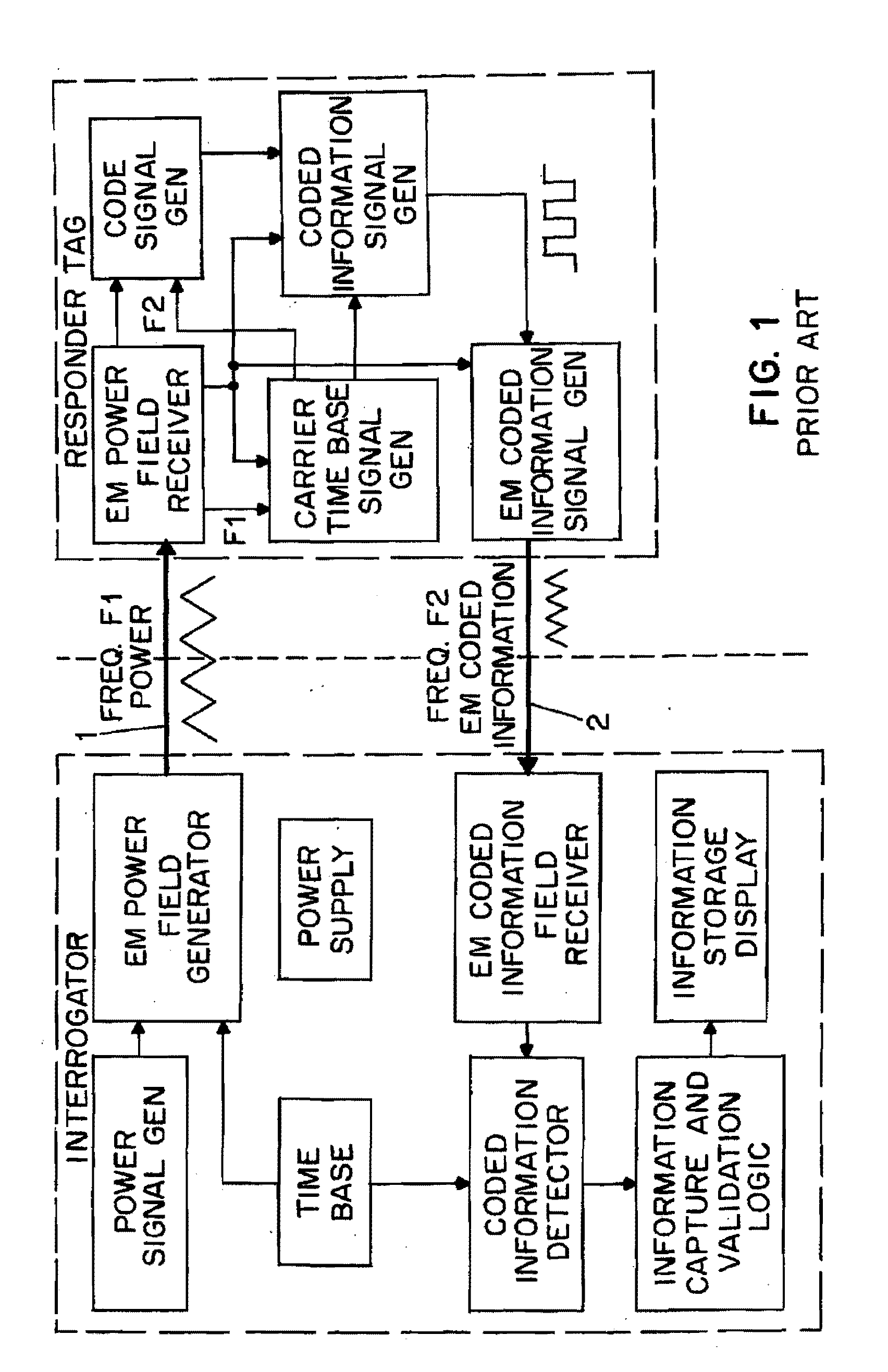
Radio tag and system
InactiveUS20070096875A1Double communication speedIncrease rangeSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesCouplingData signal
Passive tags use two antennas with only limited mutual coupling, one of which receives a power / clock field and the other of which receives a data signal. An area-reading antenna, or two or more antennas, are deployed to generate the power / clock field, from a base station. The base station, or active tags, or both, generate the data signals from time to time. This topology together with the use of low frequencies permits area reads, and permits small and economical passive tags, and further permits localization of a particular passive tag as being nearby to a particular active tag.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
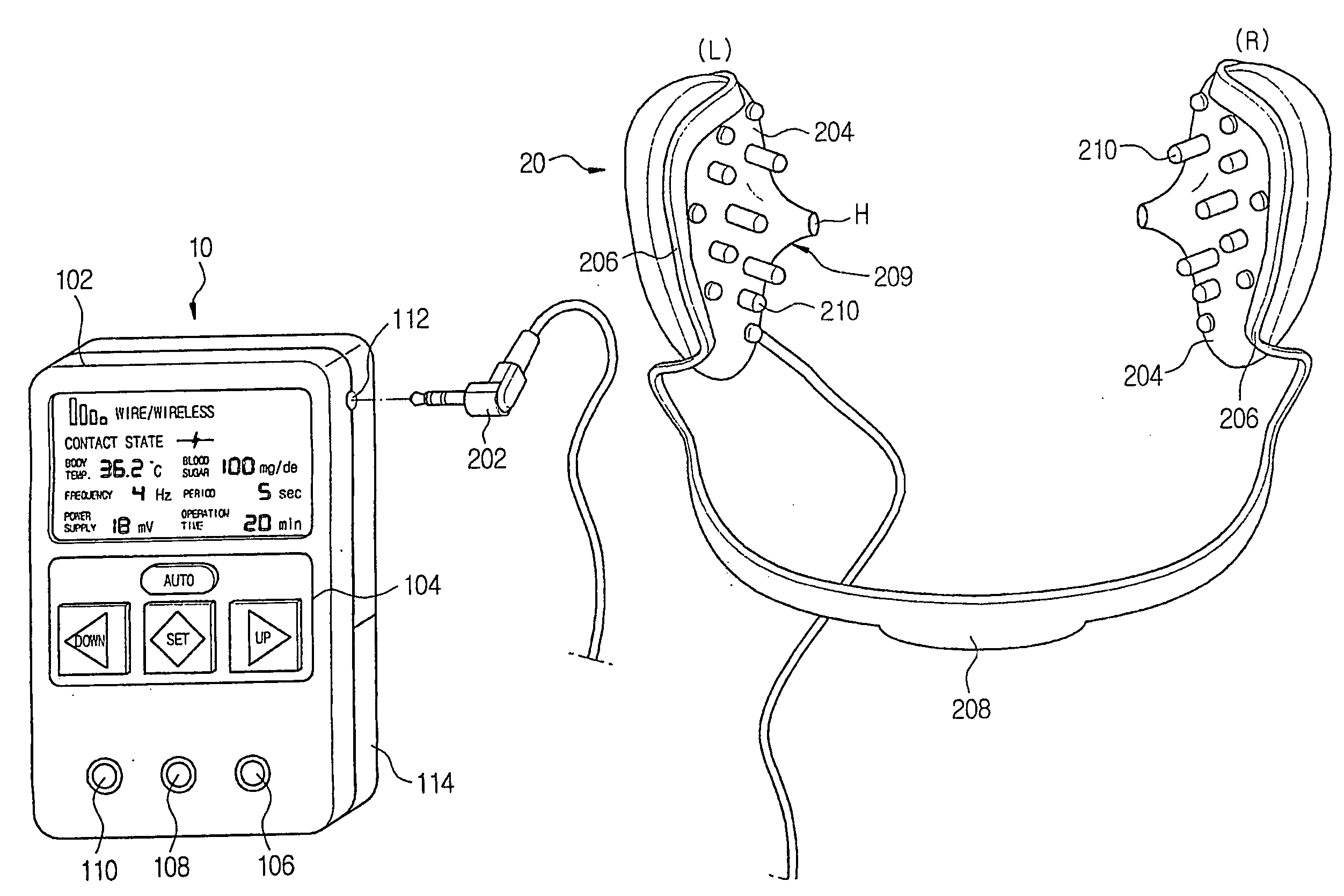
Electric stimilator for alpha-wave derivation
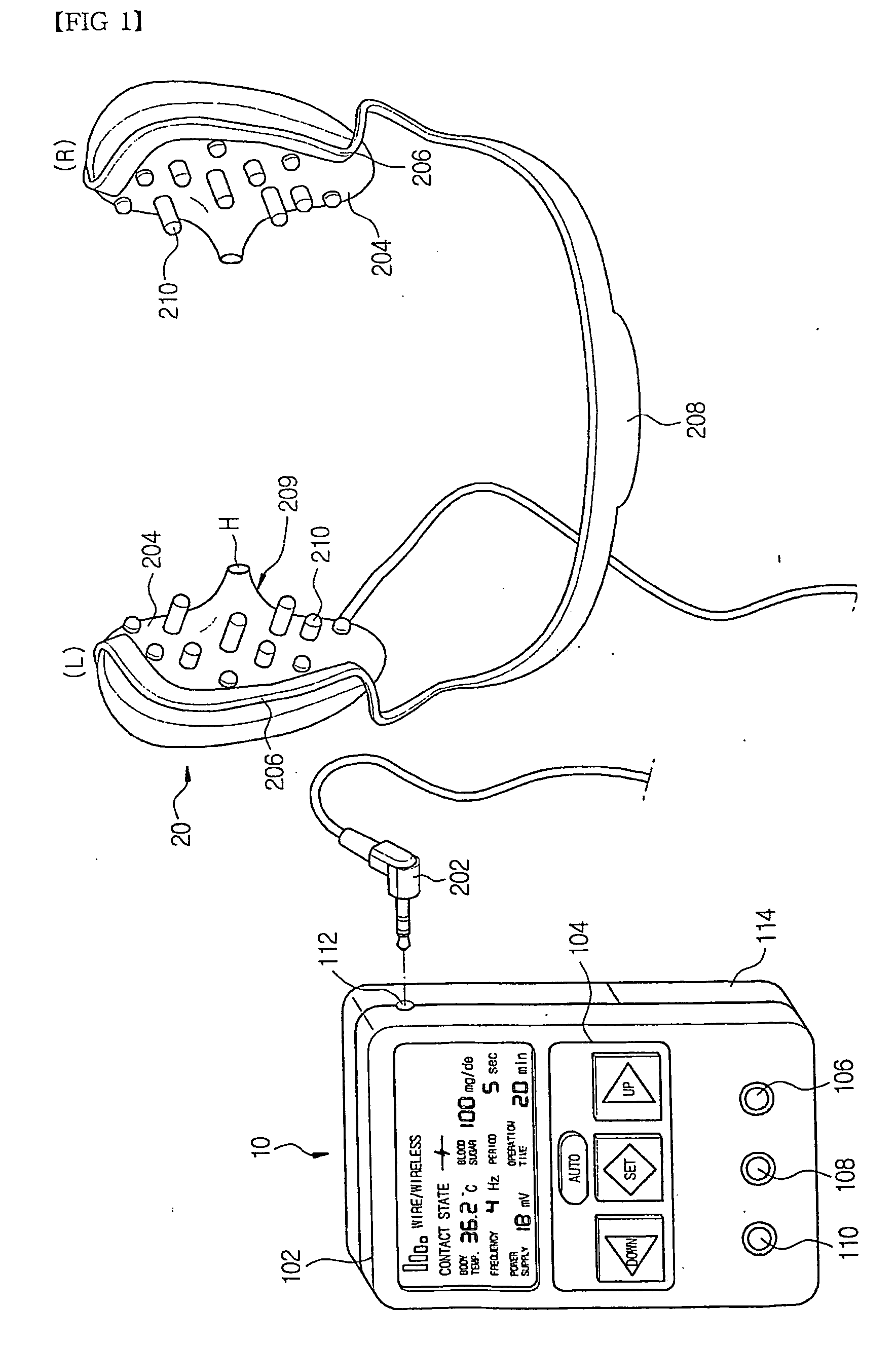
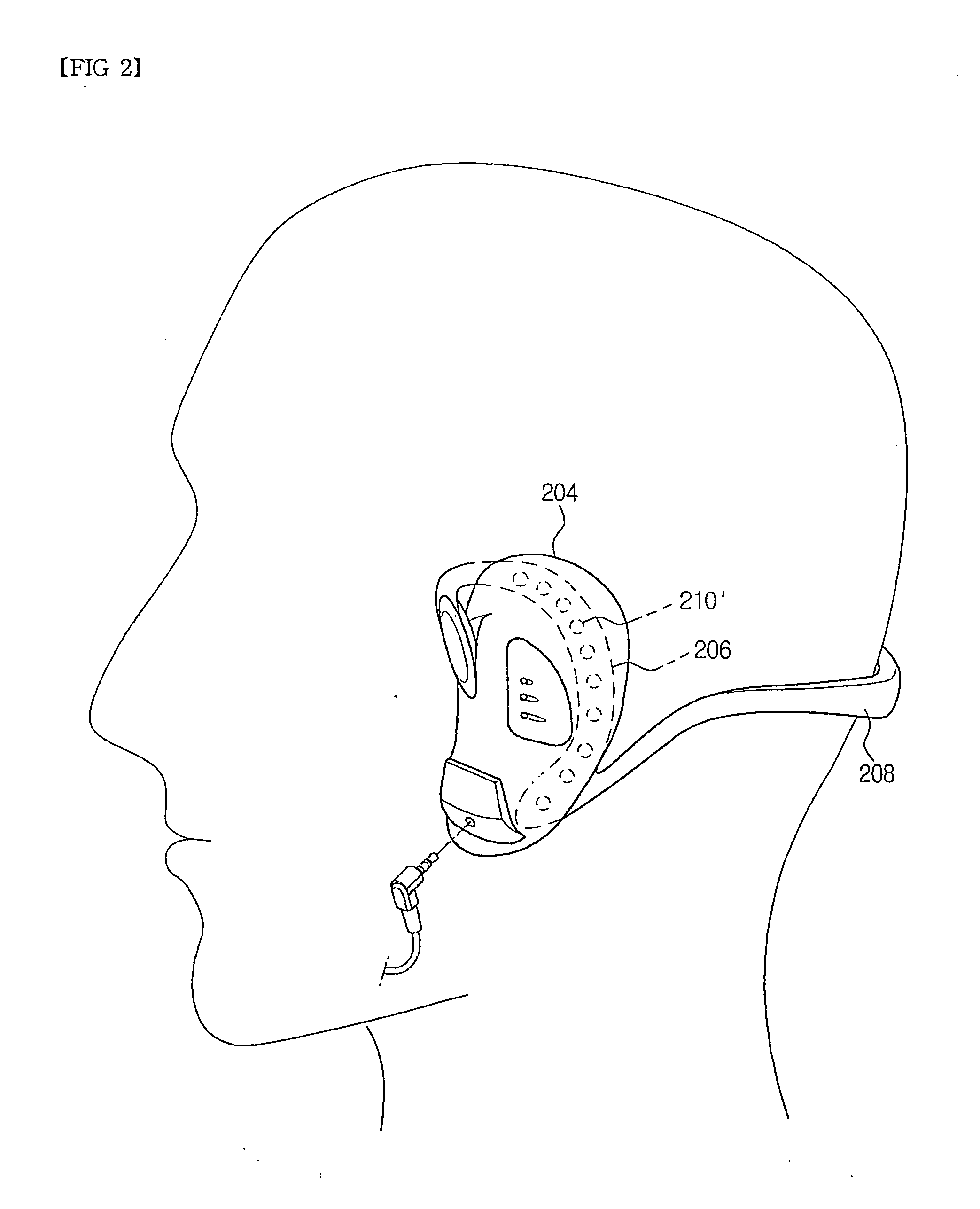
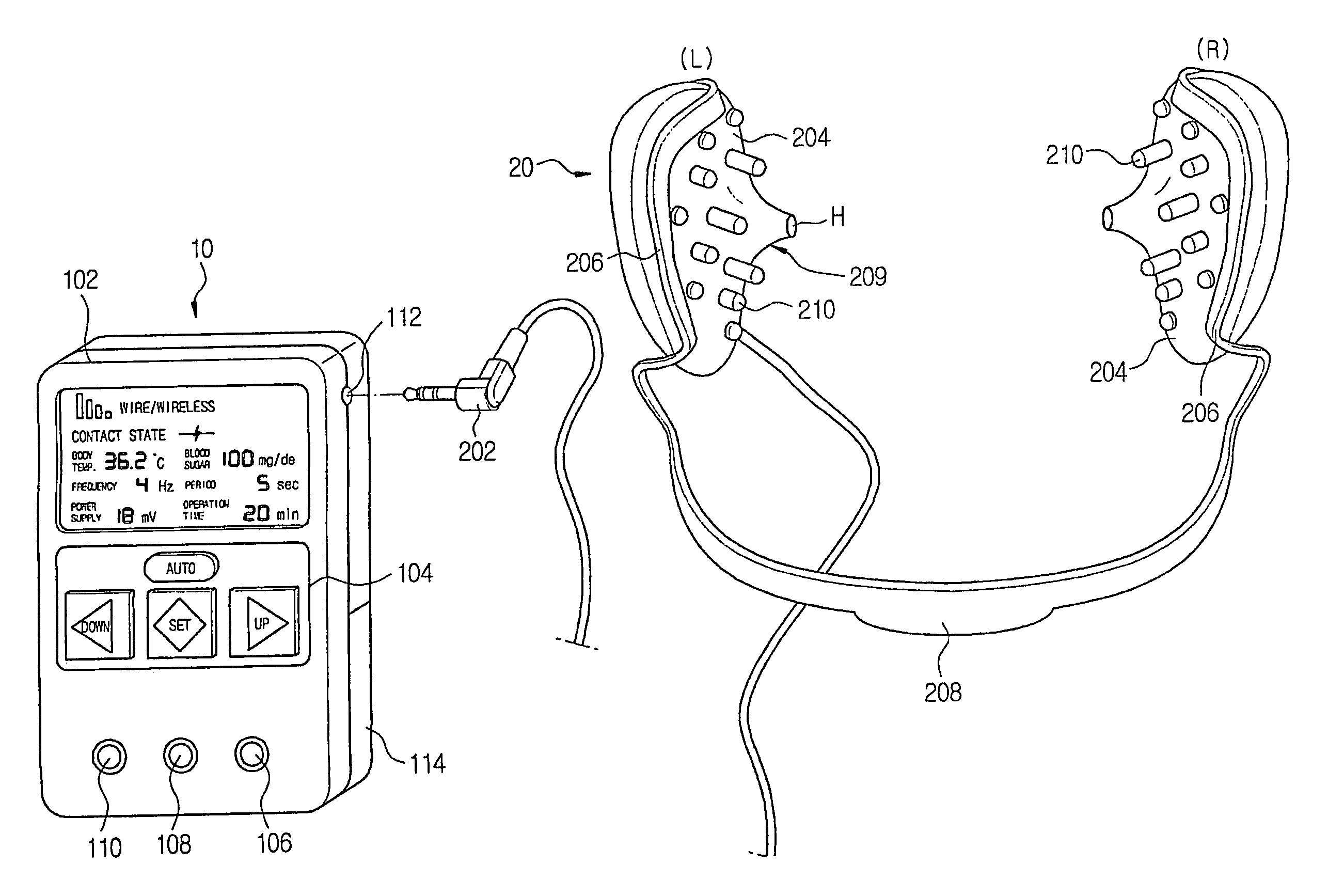
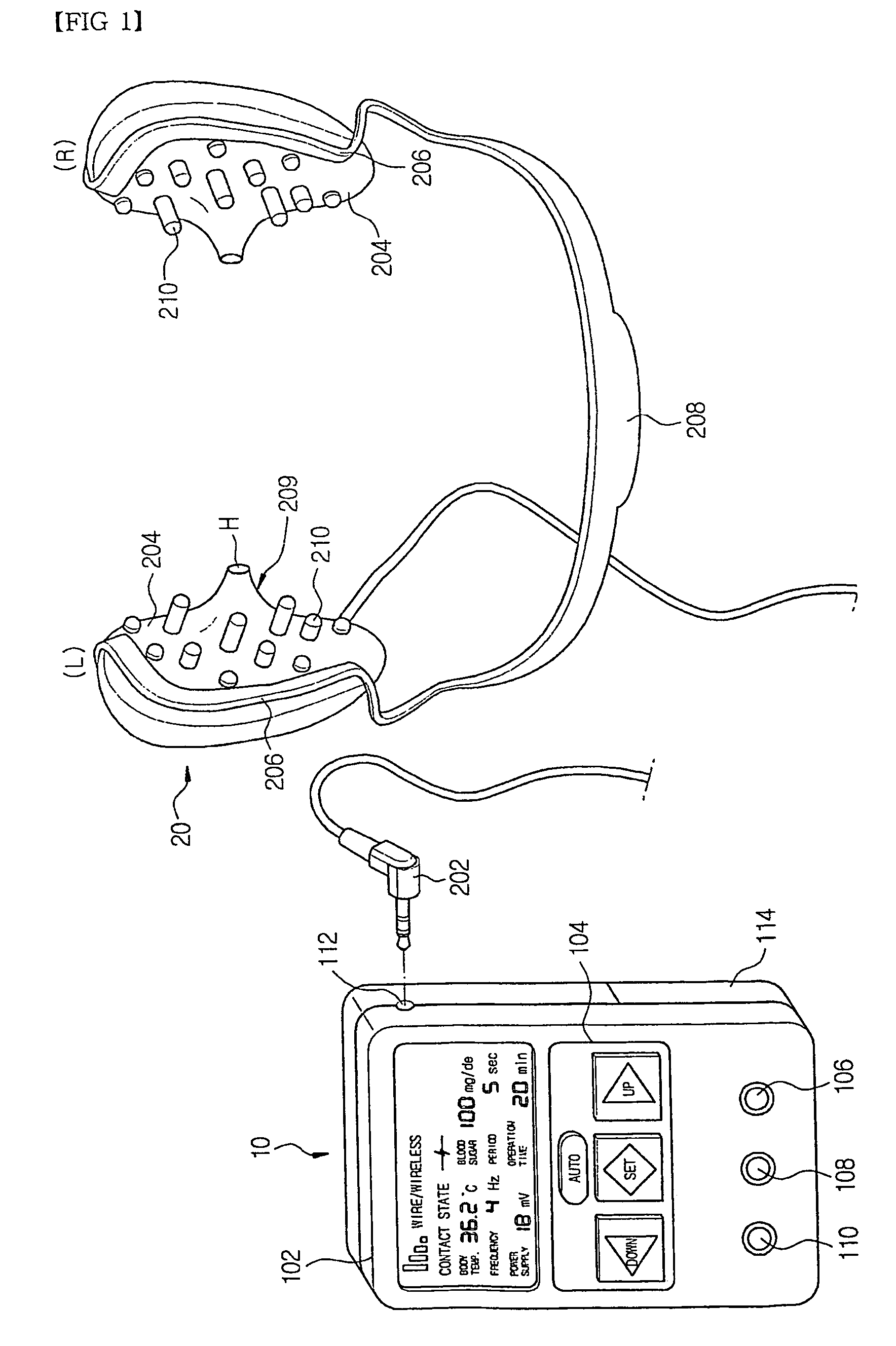
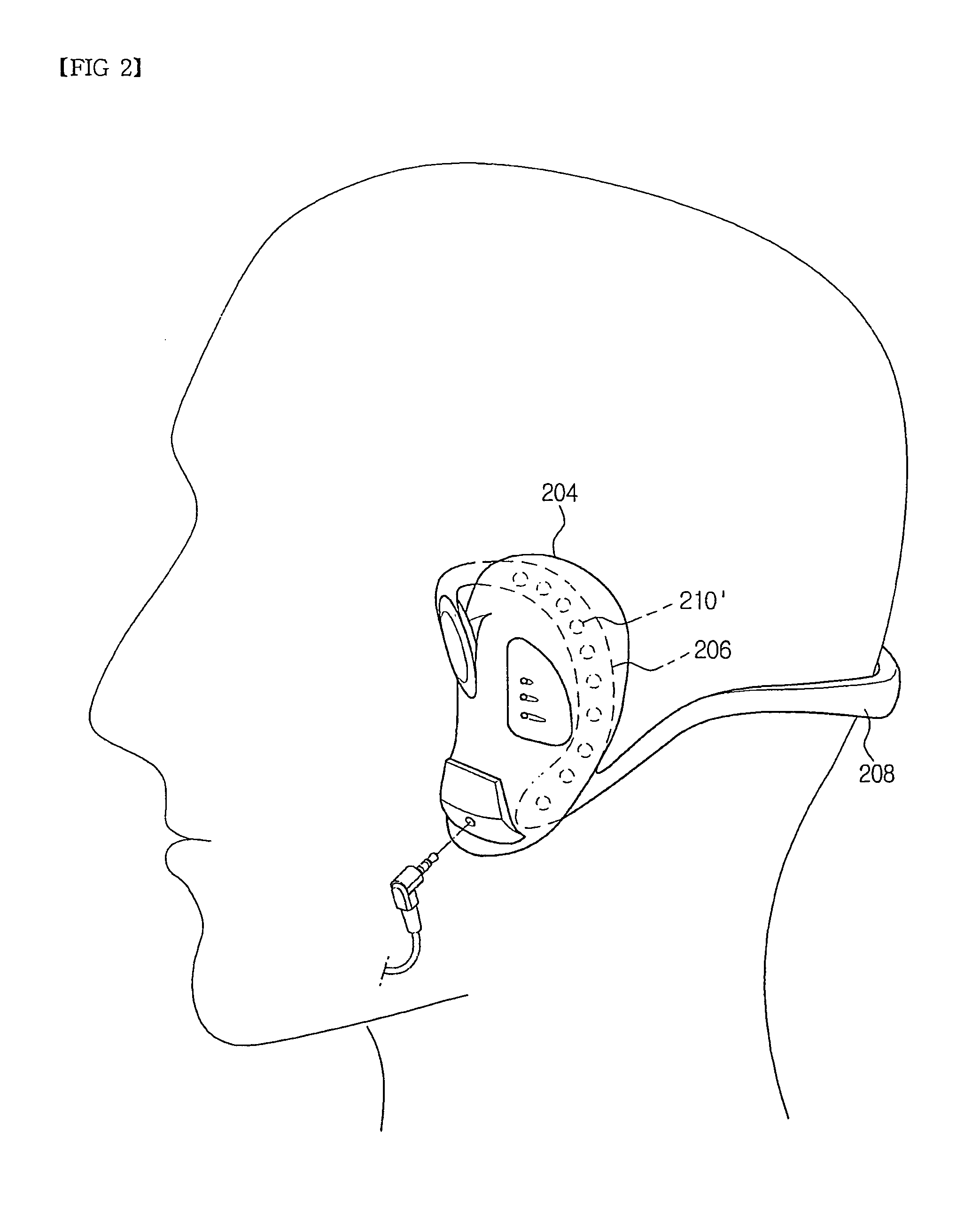
InactiveUS20060064139A1Efficient implementationMaximize the effect of treatmentInternal electrodesMedical devicesHuman bodyDisease
An electric stimulator for alpha-wave derivation is characterized in that frequency selected from a range of 1 Hz to 50 Hz, preferably, 7 Hz to 14 Hz, and an output voltage are applied to auricle of a patient's ears to derive alpha-waves, and that cycle and intensity of stimulation are varied depending upon body temperature and blood sugar. Prompt reaction may be obtained by directly applying the voltage to the ears, and the reaction may continue when stimulation is extended. In addition, it is suitable to treat various diseases having common cause due to stress or arousal reaction in the human body.
Owner:CHUNG JONG PIL
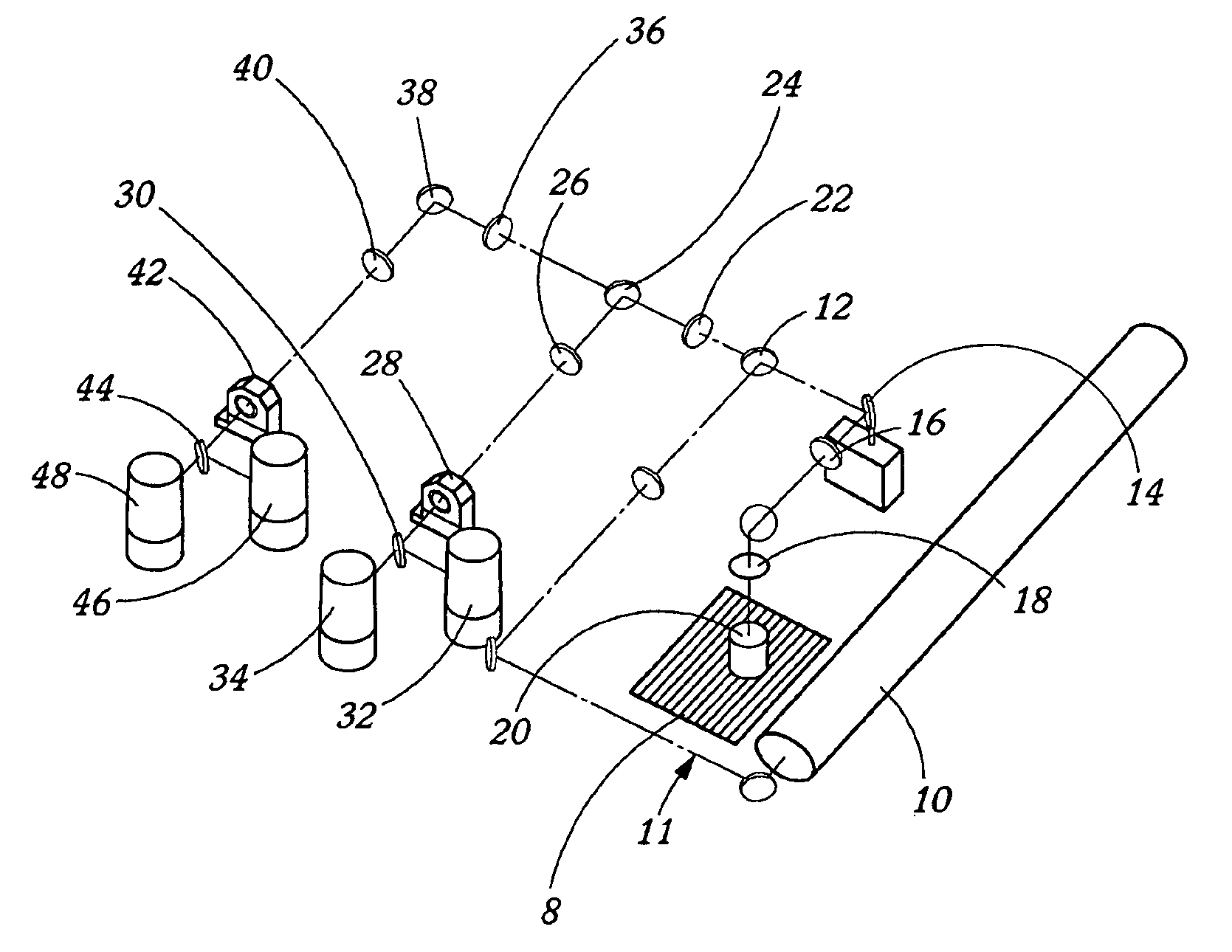
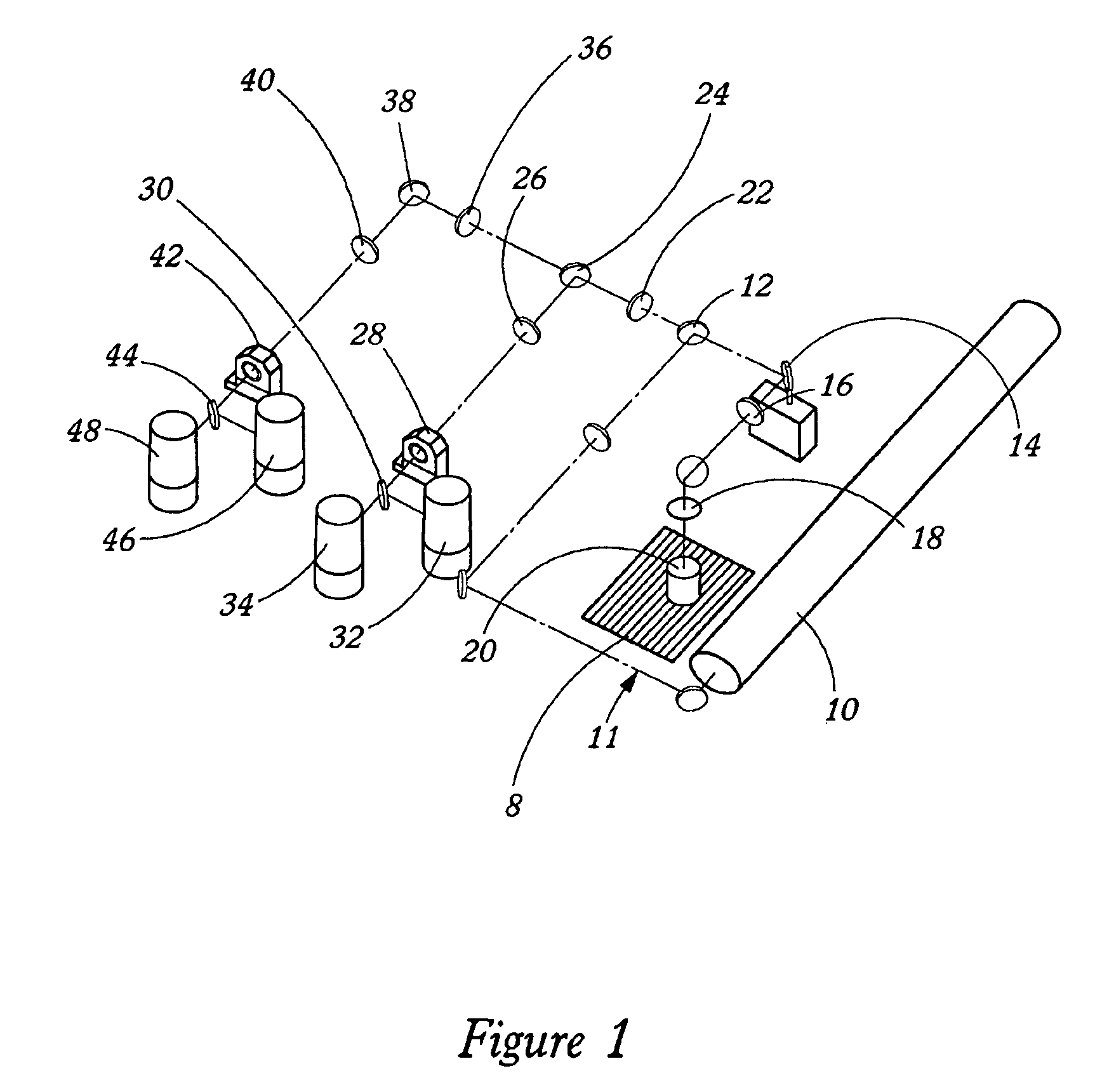
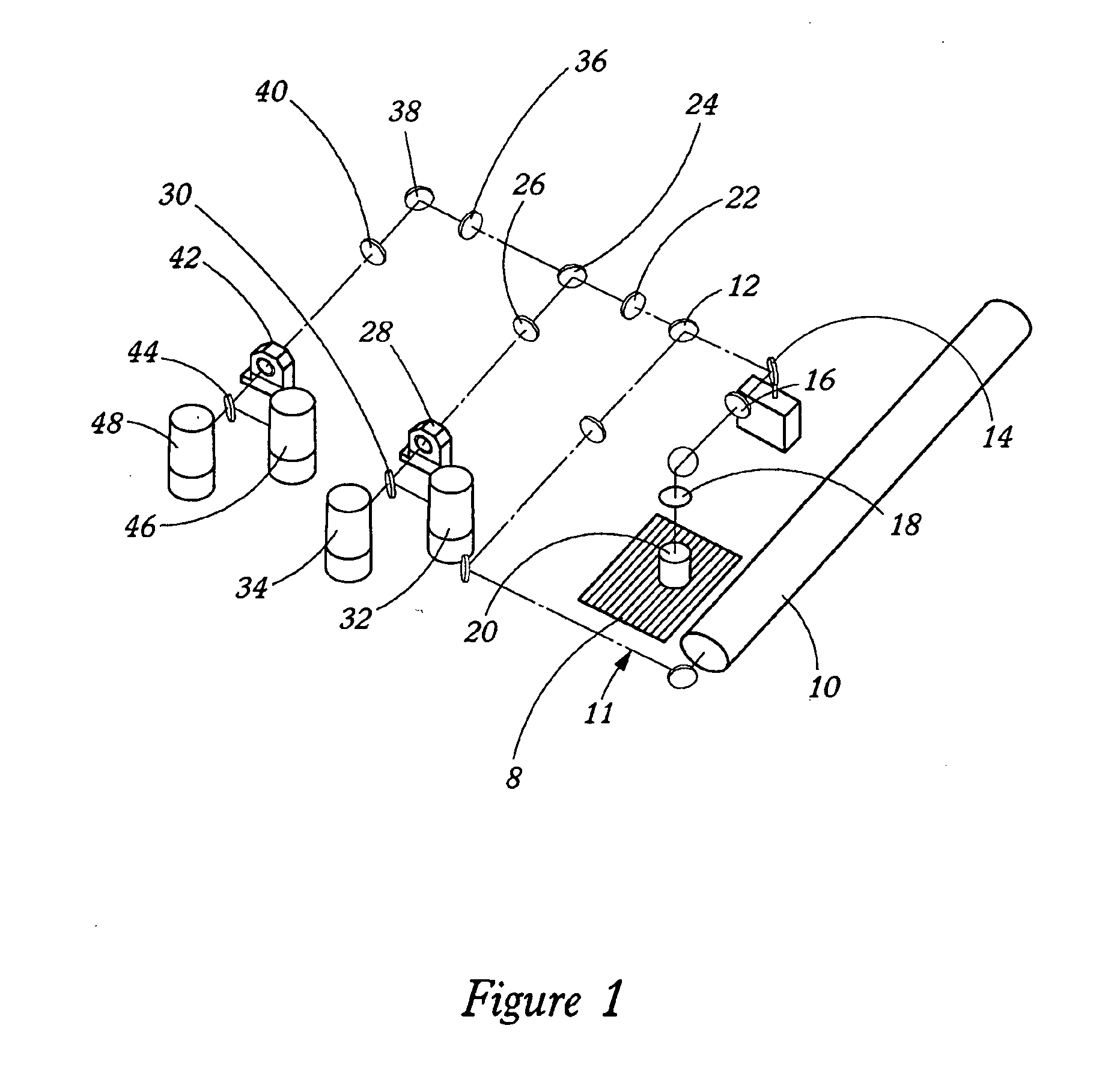
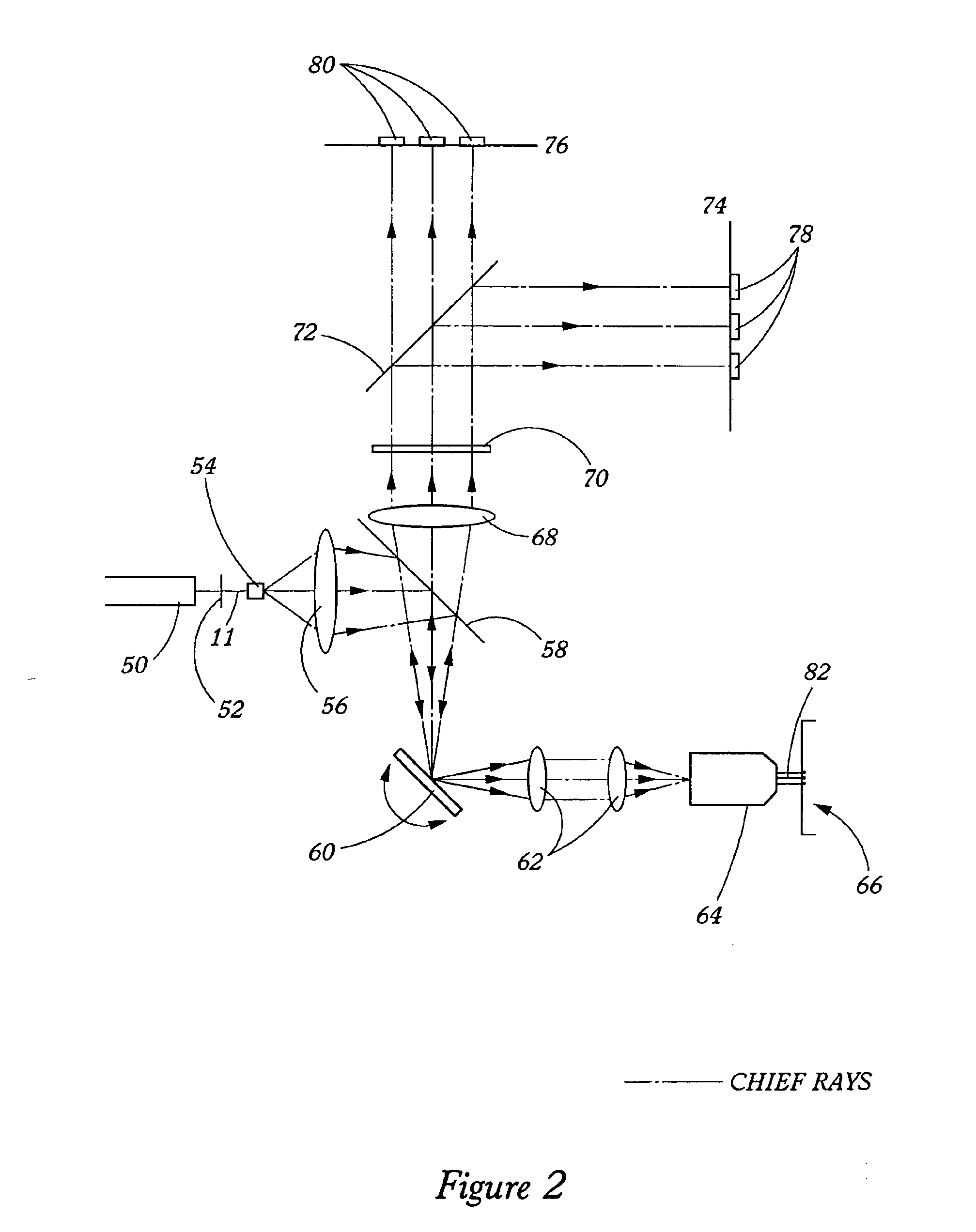
Optical architectures for microvolume laser-scanning cytometers
InactiveUS6979830B2Reduce power densityMinimizing limitationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSpectroscopyLaser scanning
Methods and instrumentation for performing charge coupled device (CCD)-based confocal spectroscopy with a laser spot array are provided. The methods and instruments of the invention are useful in any spectroscopic application, including, but not limited to, microscopy and microvolume laser scanning cytometry (MLSC).
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
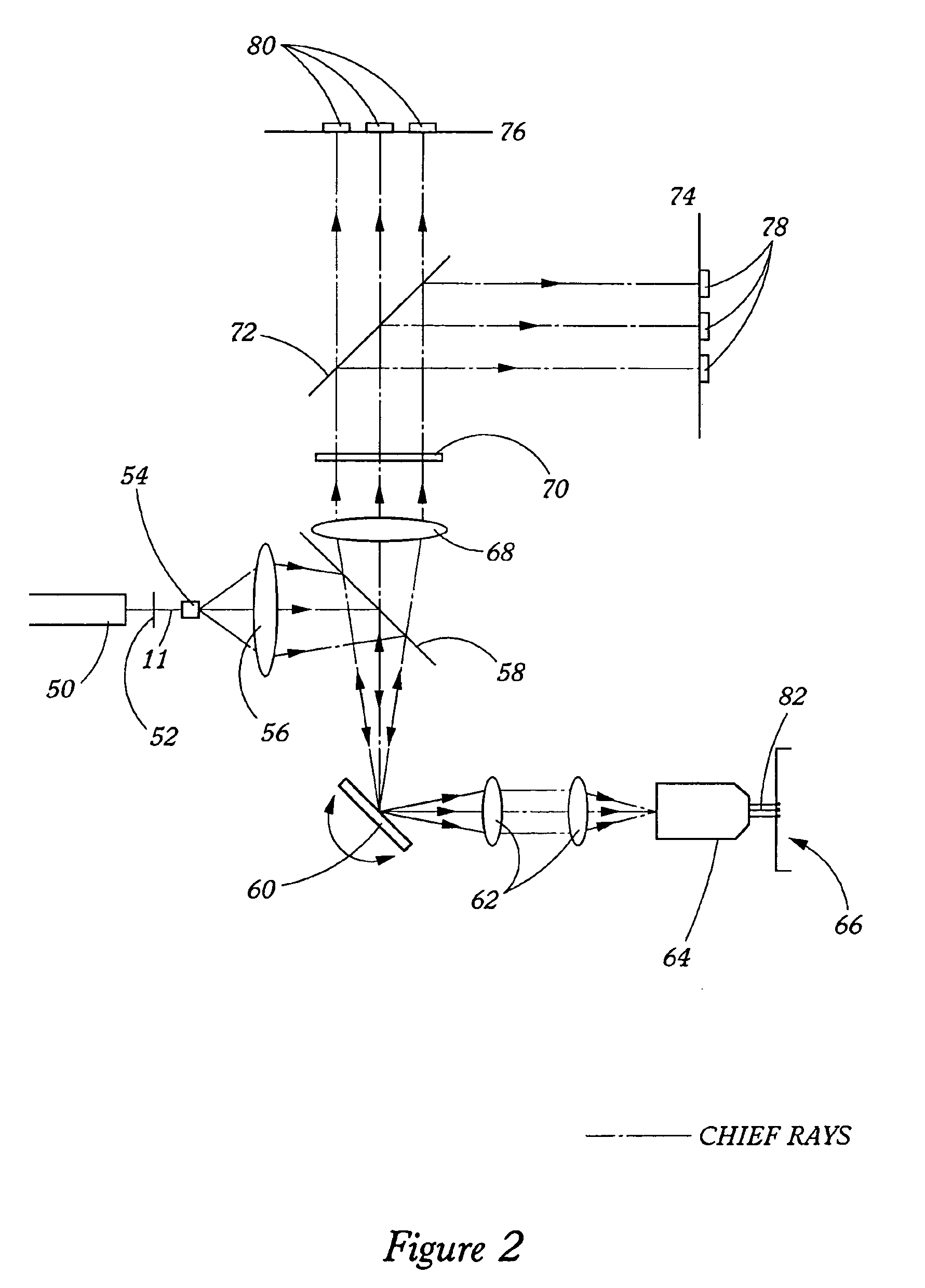
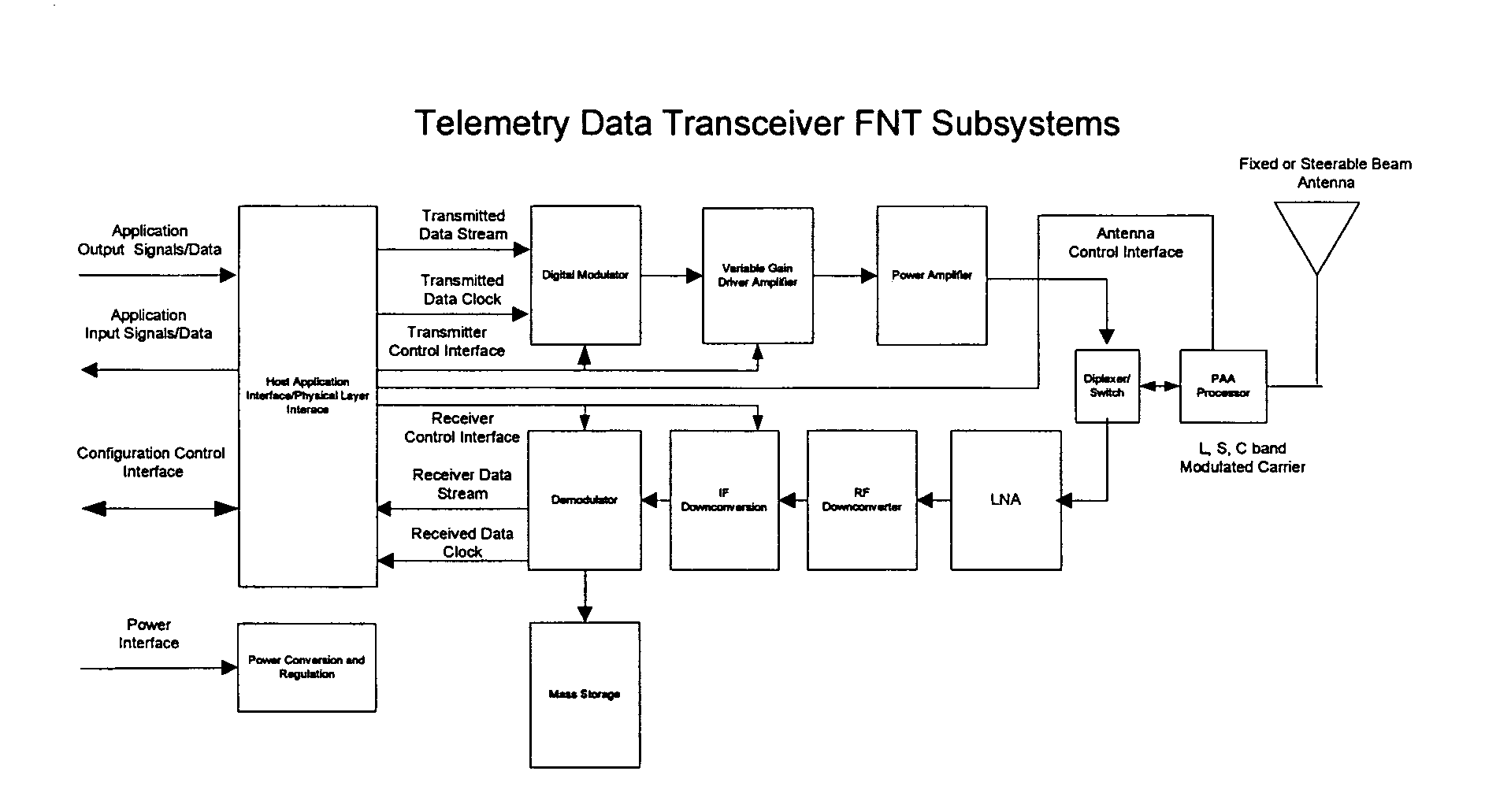
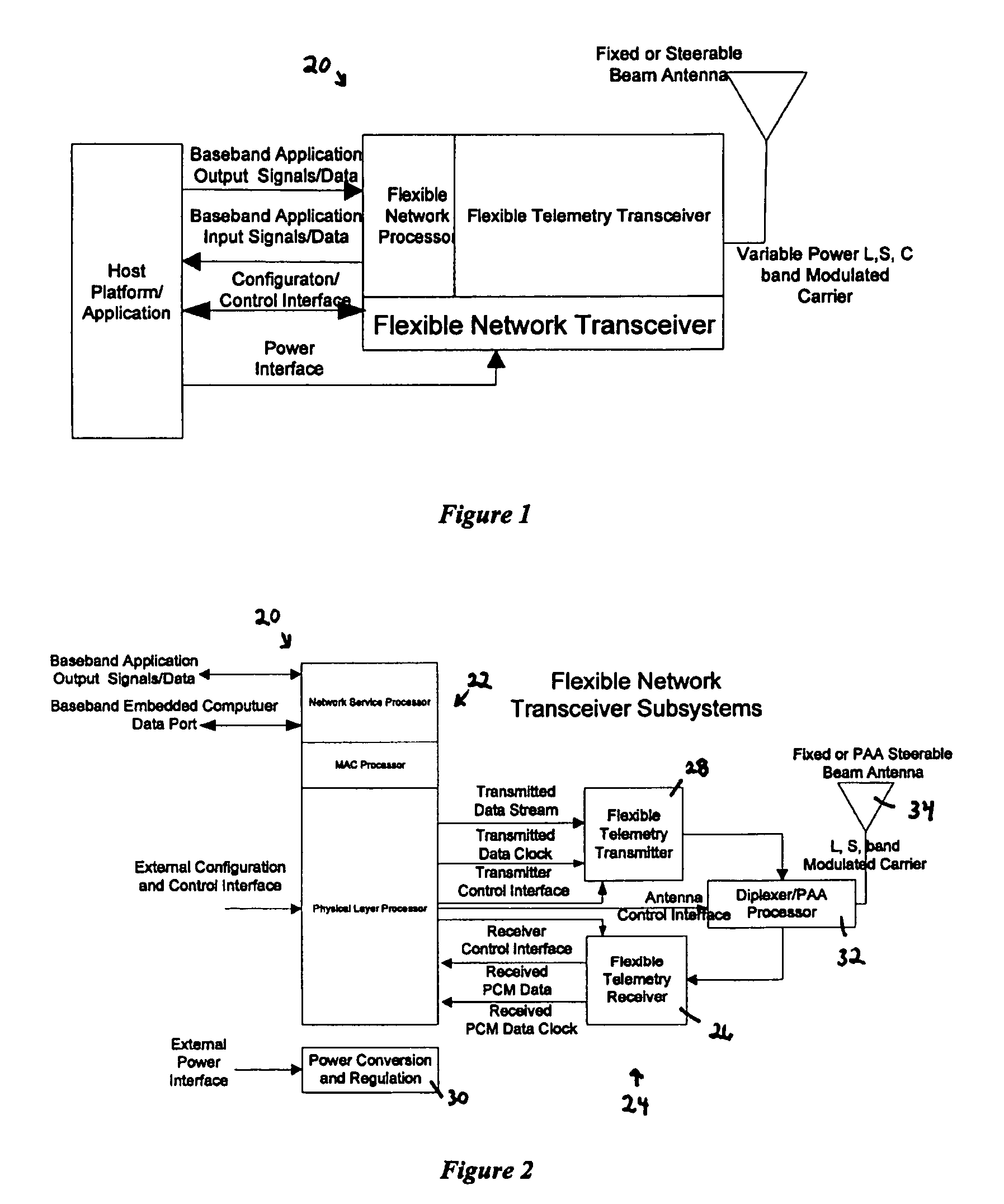
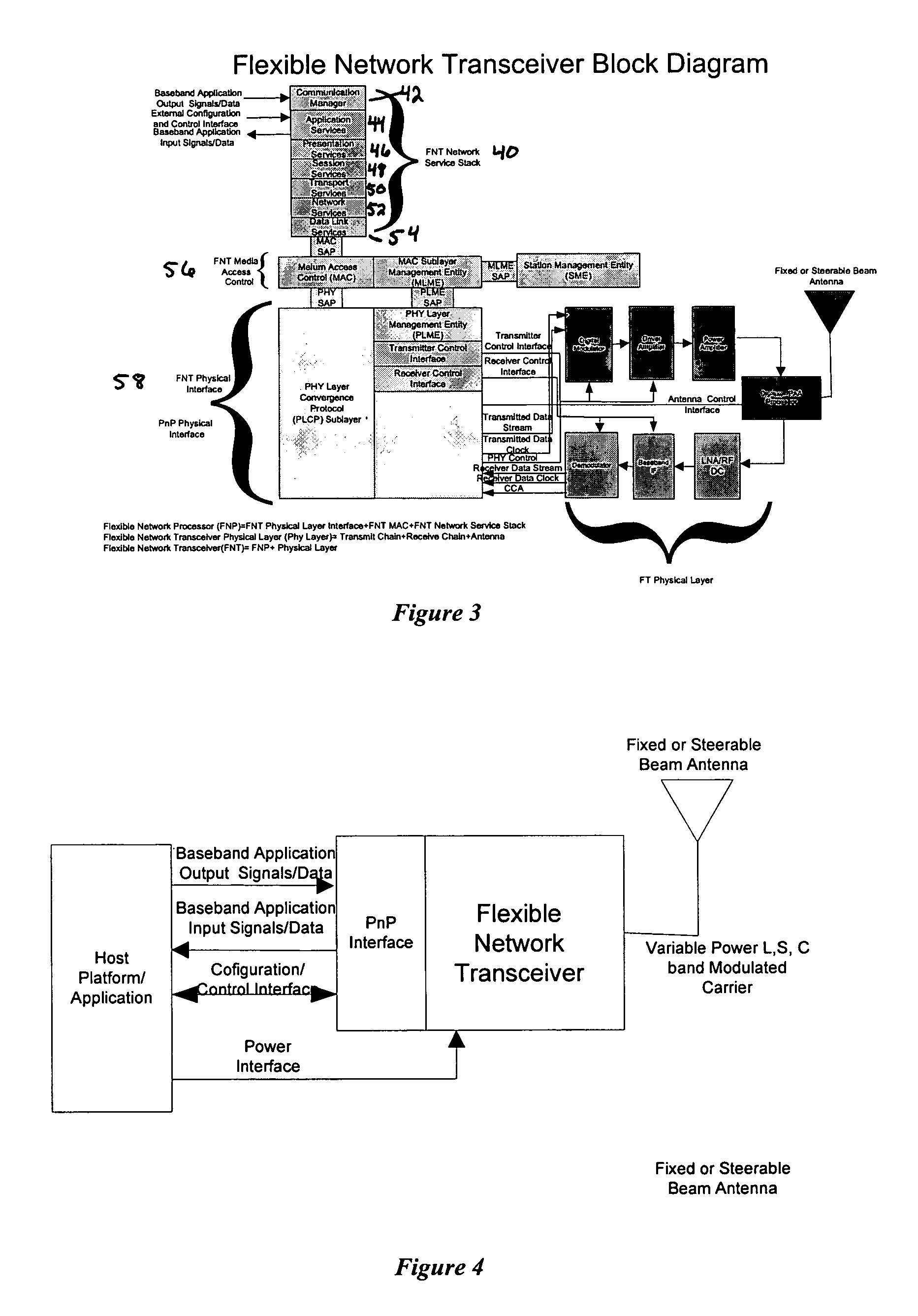
Flexible network wireless transceiver and flexible network telemetry transceiver
InactiveUS7408898B1Improve performanceIncrease data rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverGround vehicles
A transceiver for facilitating two-way wireless communication between a baseband application and other nodes in a wireless network, wherein the transceiver provides baseband communication networking and necessary configuration and control functions along with transmitter, receiver, and antenna functions to enable the wireless communication. More specifically, the transceiver provides a long-range wireless duplex communication node or channel between the baseband application, which is associated with a mobile or fixed space, air, water, or ground vehicle or other platform, and other nodes in the wireless network or grid. The transceiver broadly comprises a communication processor; a flexible telemetry transceiver including a receiver and a transmitter; a power conversion and regulation mechanism; a diplexer; and a phased array antenna system, wherein these various components and certain subcomponents thereof may be separately enclosed and distributable relative to the other components and subcomponents.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
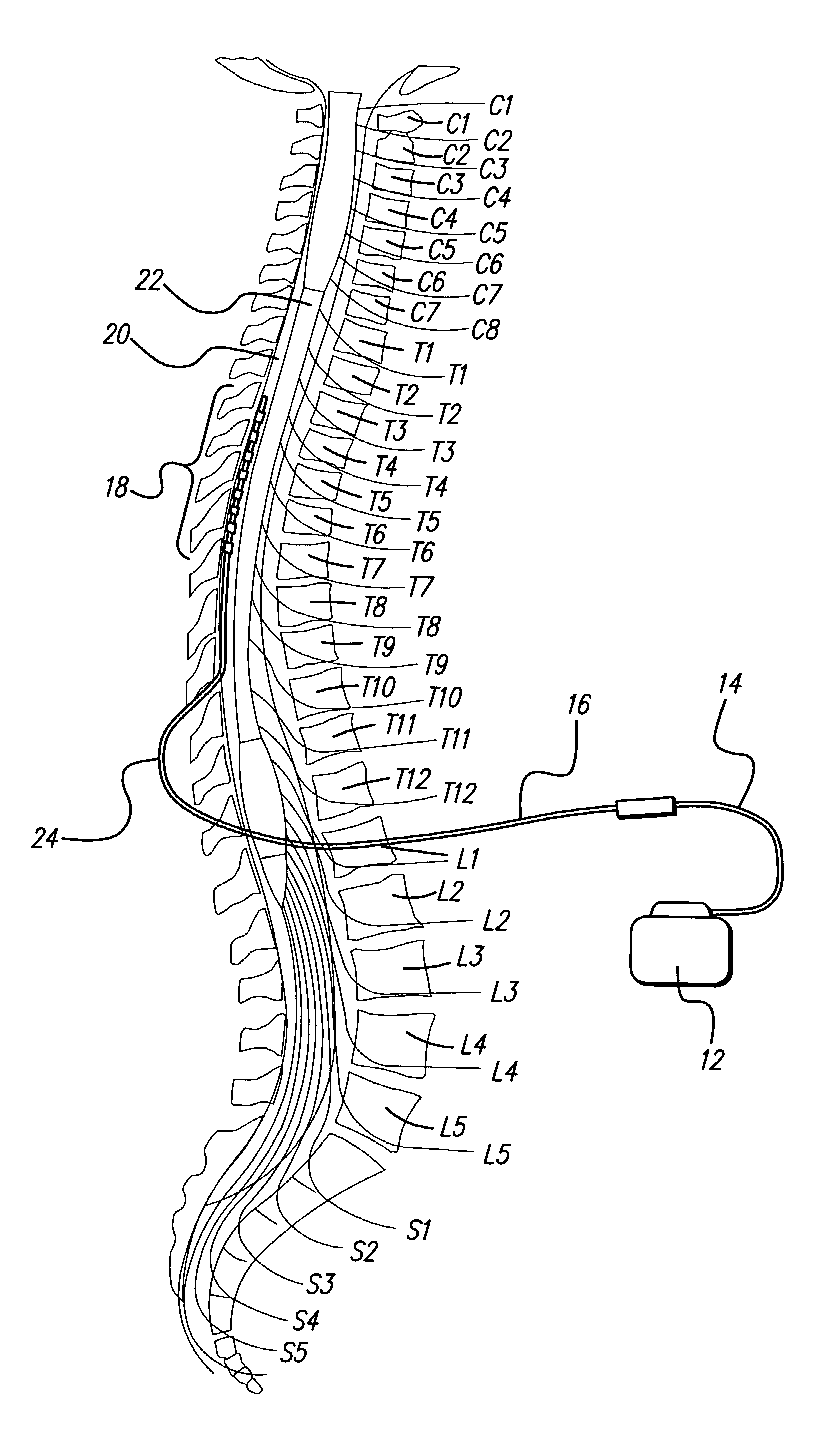
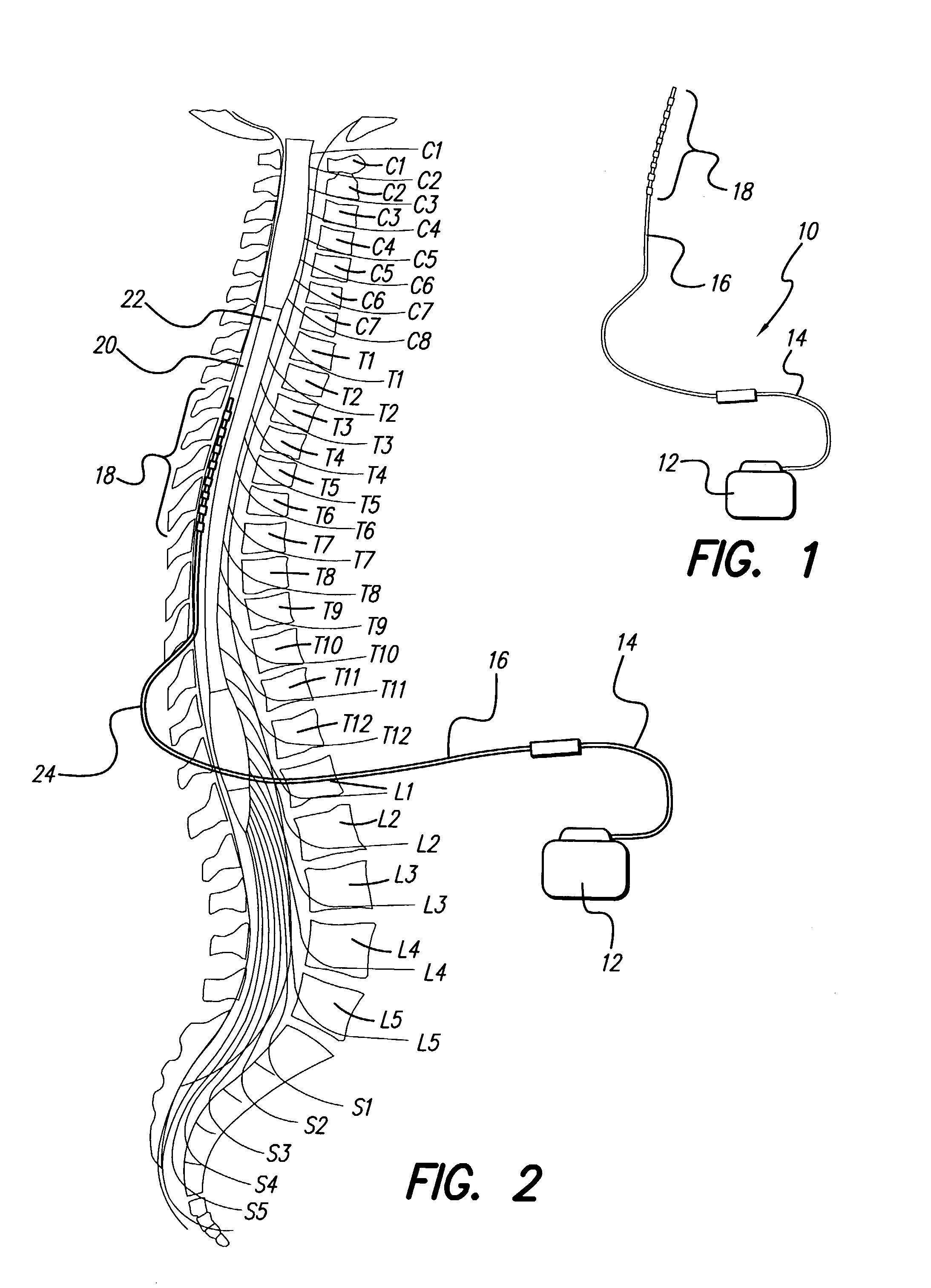
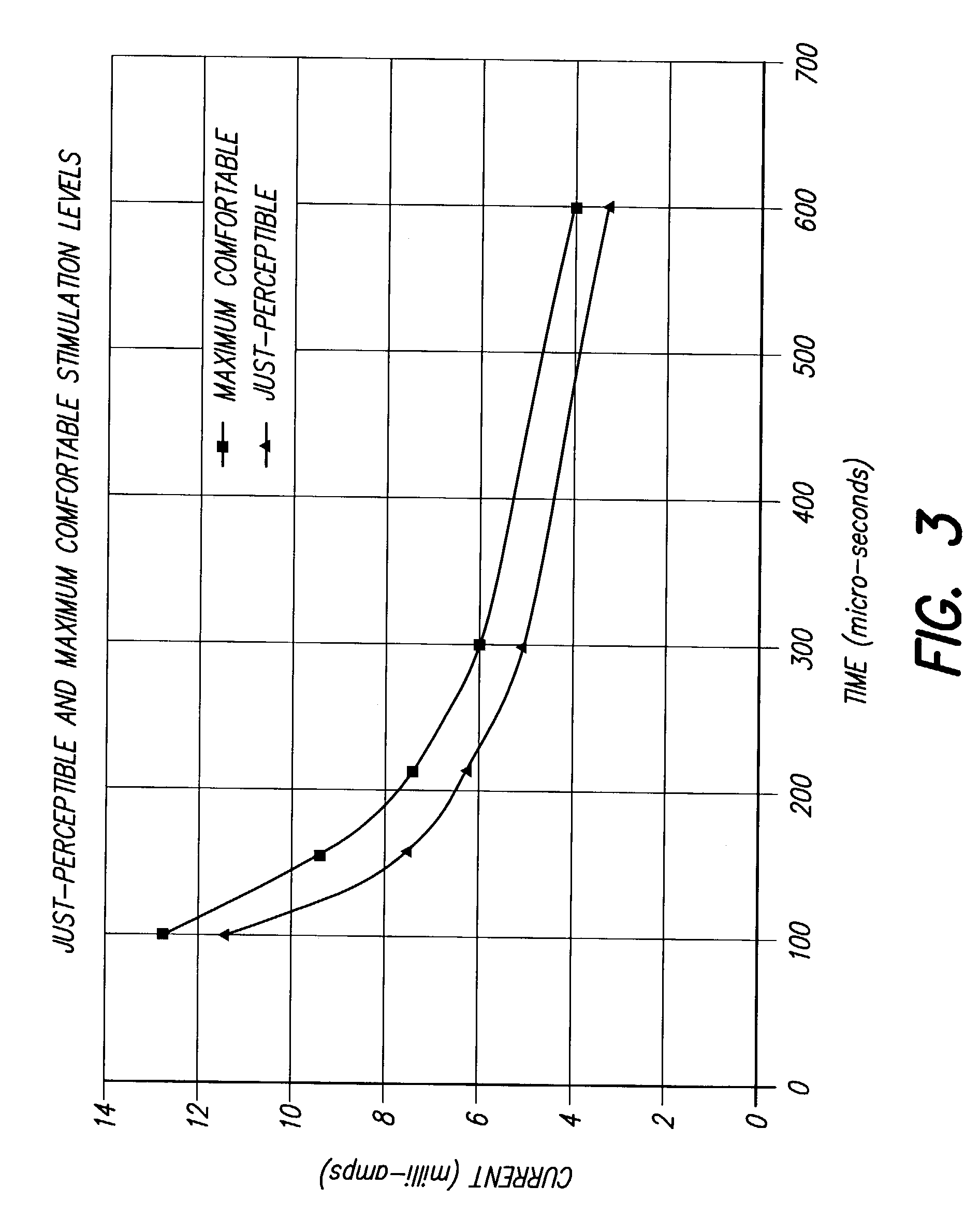
Method for increasing the therapeutic ratio/usage range in a neurostimulator
InactiveUS7127296B2Minimizing sensitivityExpand the scope of treatmentElectrotherapyCurve fittingIntensive care medicine
A system and method for patient control of the stimulation parameters of a Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) system, or other neurostimulation system, provides an increased Therapeutic Ratio (TR). Measurements of the just-perceptible stimulation level and the maximum-comfortable stimulation level are made for at least two values of pulse duration and two values of pulse amplitude. A Therapeutic Ratio is determined for stimulation level control strategies based on fixed pulse duration and variable pulse amplitude, and alternatively for fixed pulse amplitude and variable pulse duration. The control strategy providing the greatest therapeutic ratio is then selected for use by the patient. In an alternative embodiment, the pulse durations at the just-perceptible and maximum-comfortable stimulation levels are measured, and the pulse amplitudes at the just-perceptible and maximum-comfortable stimulation levels are determined using a curve-fitting process. Similarly, the pulse amplitudes may first be measured and the pulse widths determined using a curve-fitting process.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Novel optical architectures for microvolume laser-scanning cytometers
InactiveUS20050057749A1Reduce power densityMinimizing limitationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLaser scanningSpectroscopy
Methods and instrumentation for performing charge coupled device (CCD)-based confocal spectroscopy with a laser spot array are provided. The methods and instruments of the invention are useful in any spectroscopic application, including, but not limited to, microscopy and microvolume laser scanning cytometry (MLSC).
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
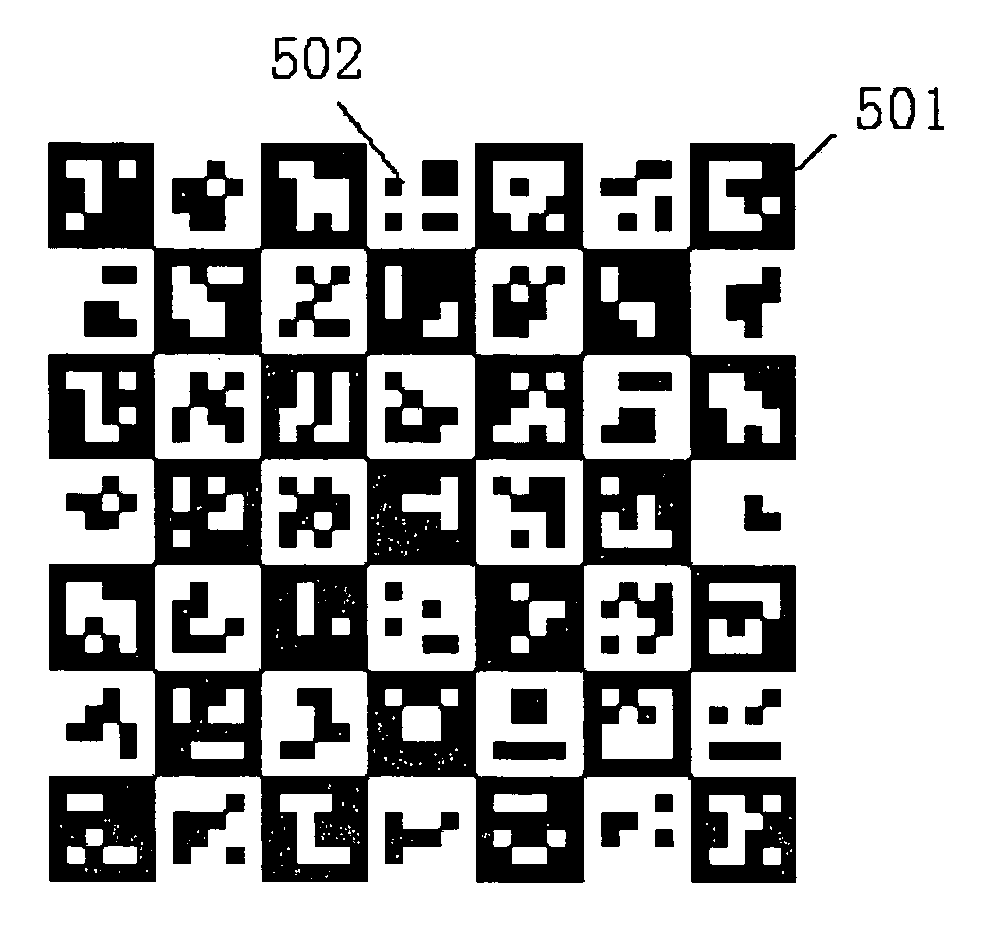
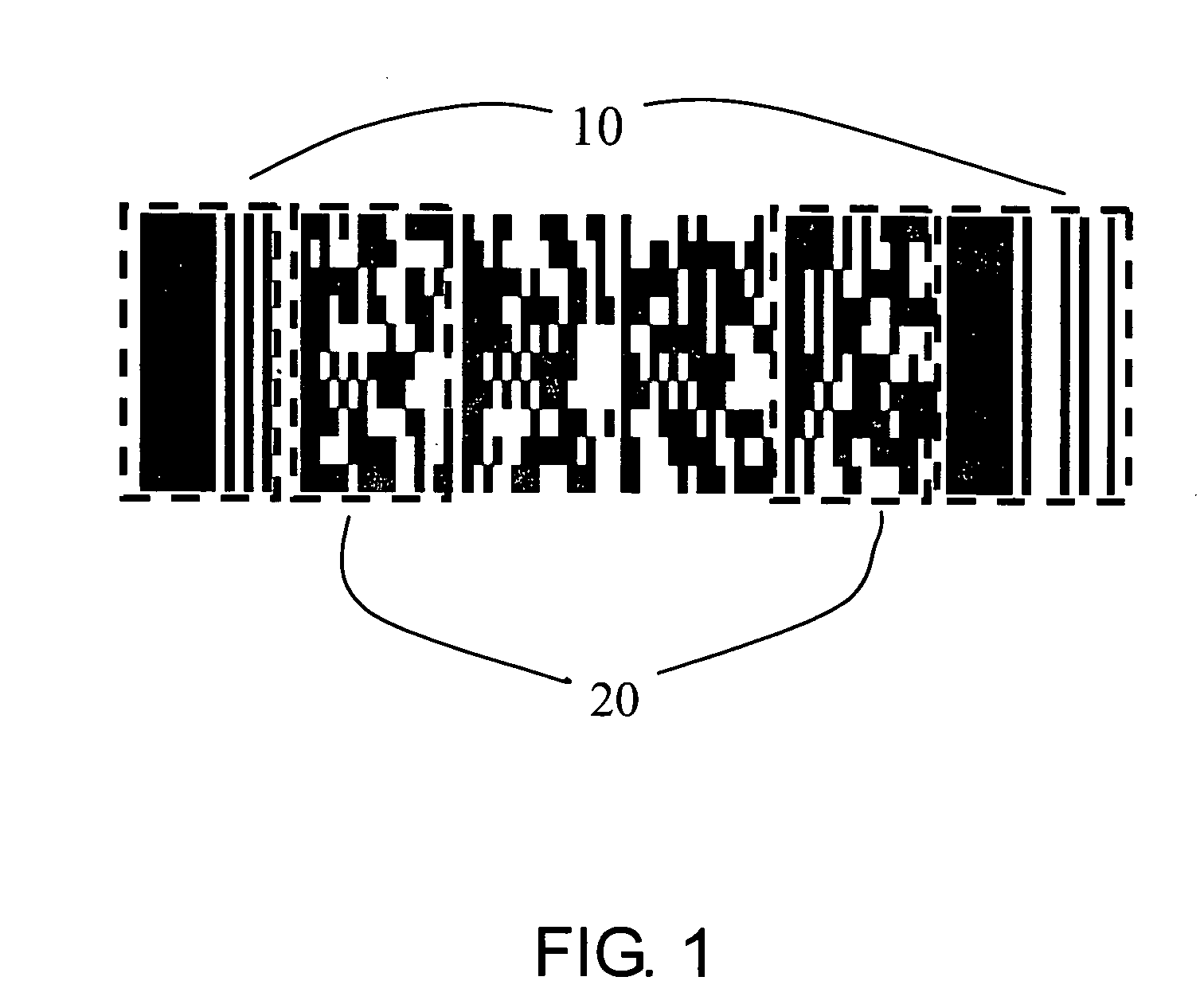
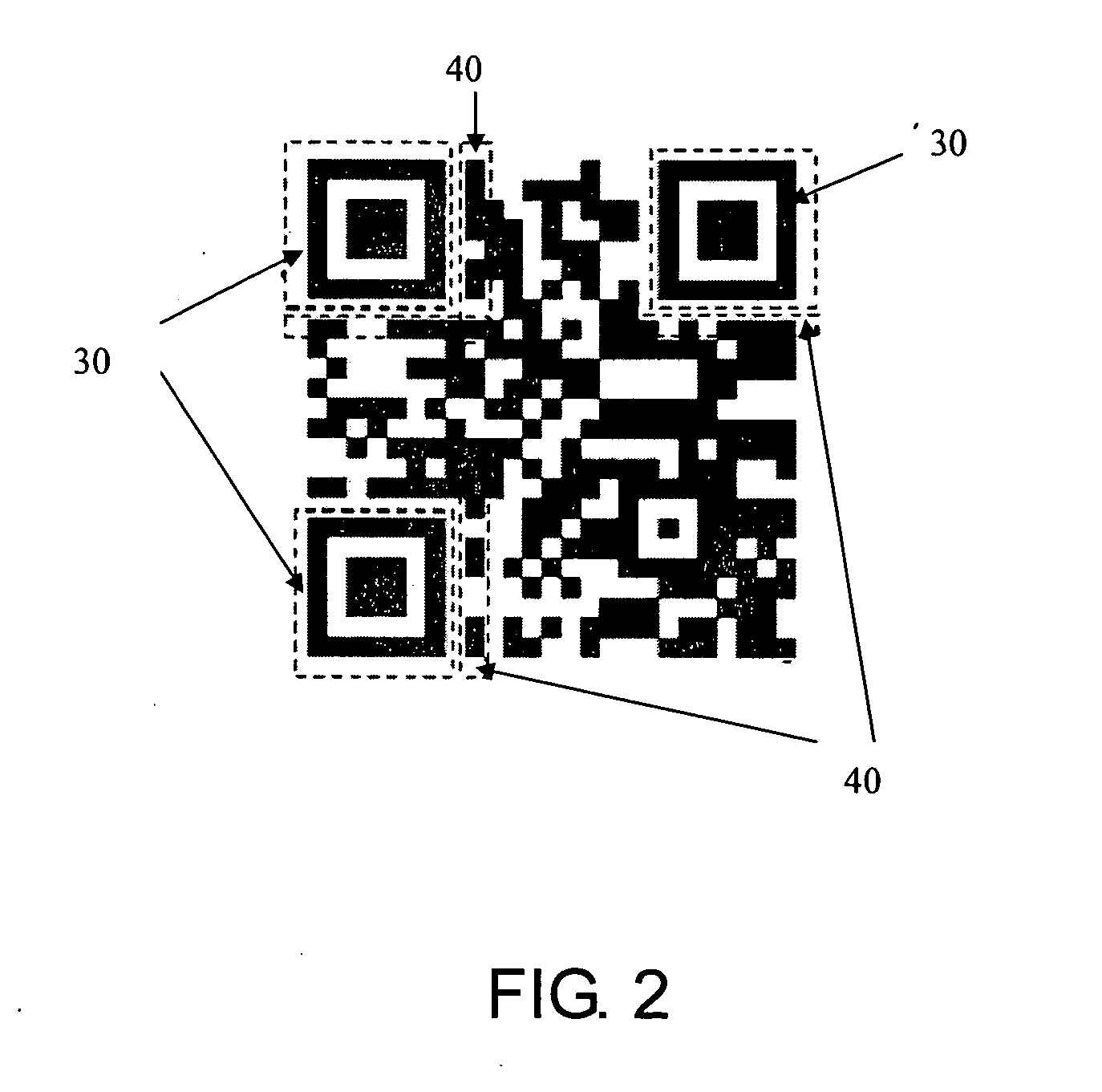
2D coding and decoding barcode and its method thereof
ActiveUS20050199721A1Improve reliabilityAccurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesBarcodeComputer science
A two-dimensional barcode includes a plurality of macro modules arranged in a two-dimensional array in a spiral sequence, each of macro modules includes a predetermined number of data unit modules for storing data codewords of a predetermined binary stream of bits, a predetermined number of cluster unit modules for storing a predetermined cluster number representing a location of the macro module, and a predetermined number of rim unit modules which possess a predetermined color to form a rim of the macro module. The rim unit modules of two adjacent macro modules are contrasting with each other to enhance identification of the respective macro module.
Owner:WUHAN SYSCAN TECH CO LTD +1
Combined microphone and receiver assembly for extended wear canal hearing devices
ActiveUS20090074220A1Place safeMinimize feedbackCompletely in canal hearing aidsEar supported setsCouplingHearing apparatus
An ultra miniature hearing device for extended wear entirely in the ear canal past the cartilaginous region is provided. The hearing device comprises a microphone and a speaker, each having a respective diaphragm. The speaker and microphone are placed parallel to each other in a single lateral assembly. The microphone and speaker can be arranged such that their diaphragms are orthogonal to one another so that cross coupling of vibrations is minimized, thus reducing internal feedback. Due to the parallel co-placement of the speaker and microphone in the single lateral assembly, the length of the device is substantially shorter than that of prior hearing aid devices. The hearing device is 12 mm or less in length to fit in the bony part of the ear canal for most individuals and is placed within approximately 3 mm from the eardrum.
Owner:INSOUND MEDICAL INC
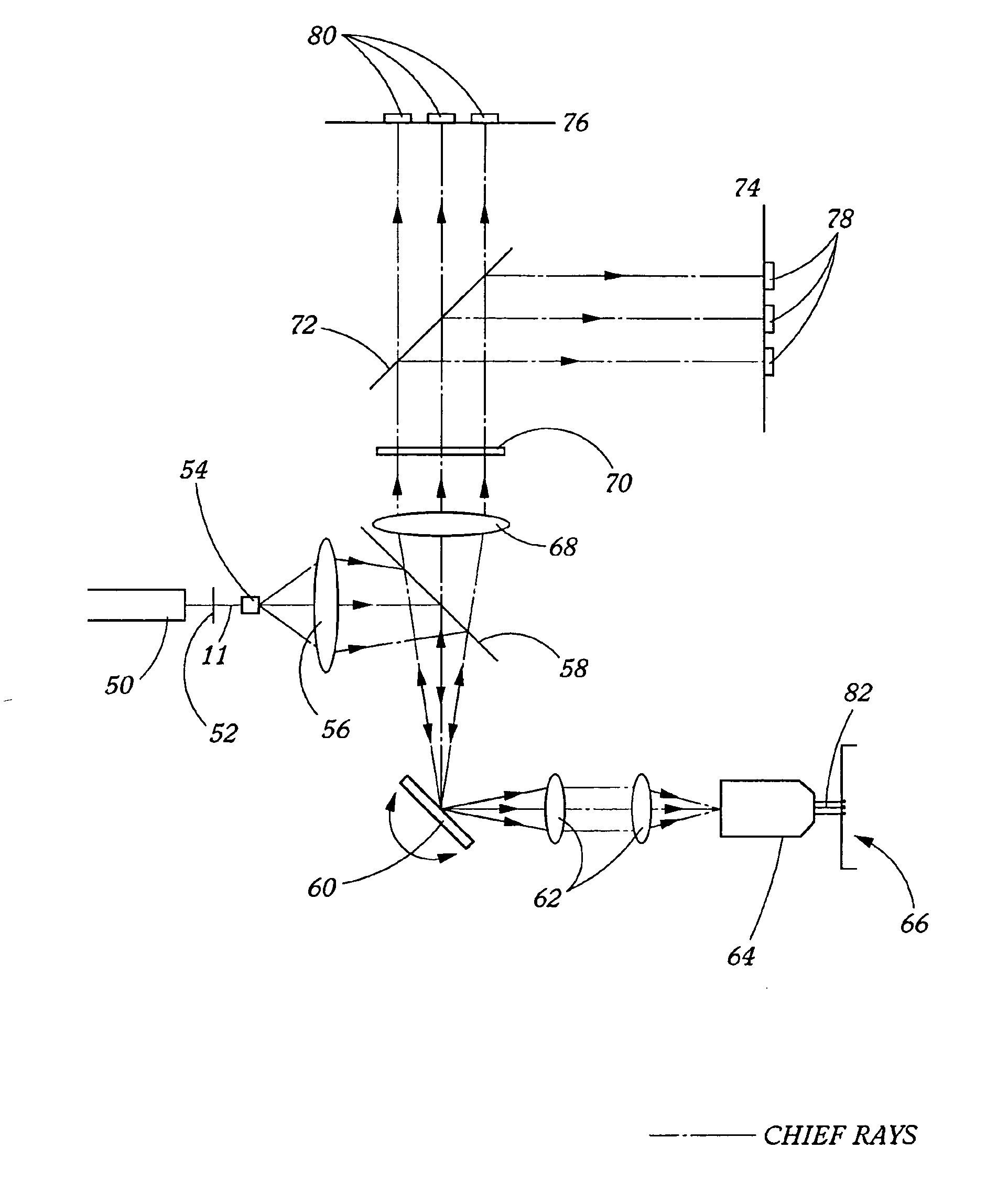
Optical reader for diffraction grating-based encoded optical identification elements
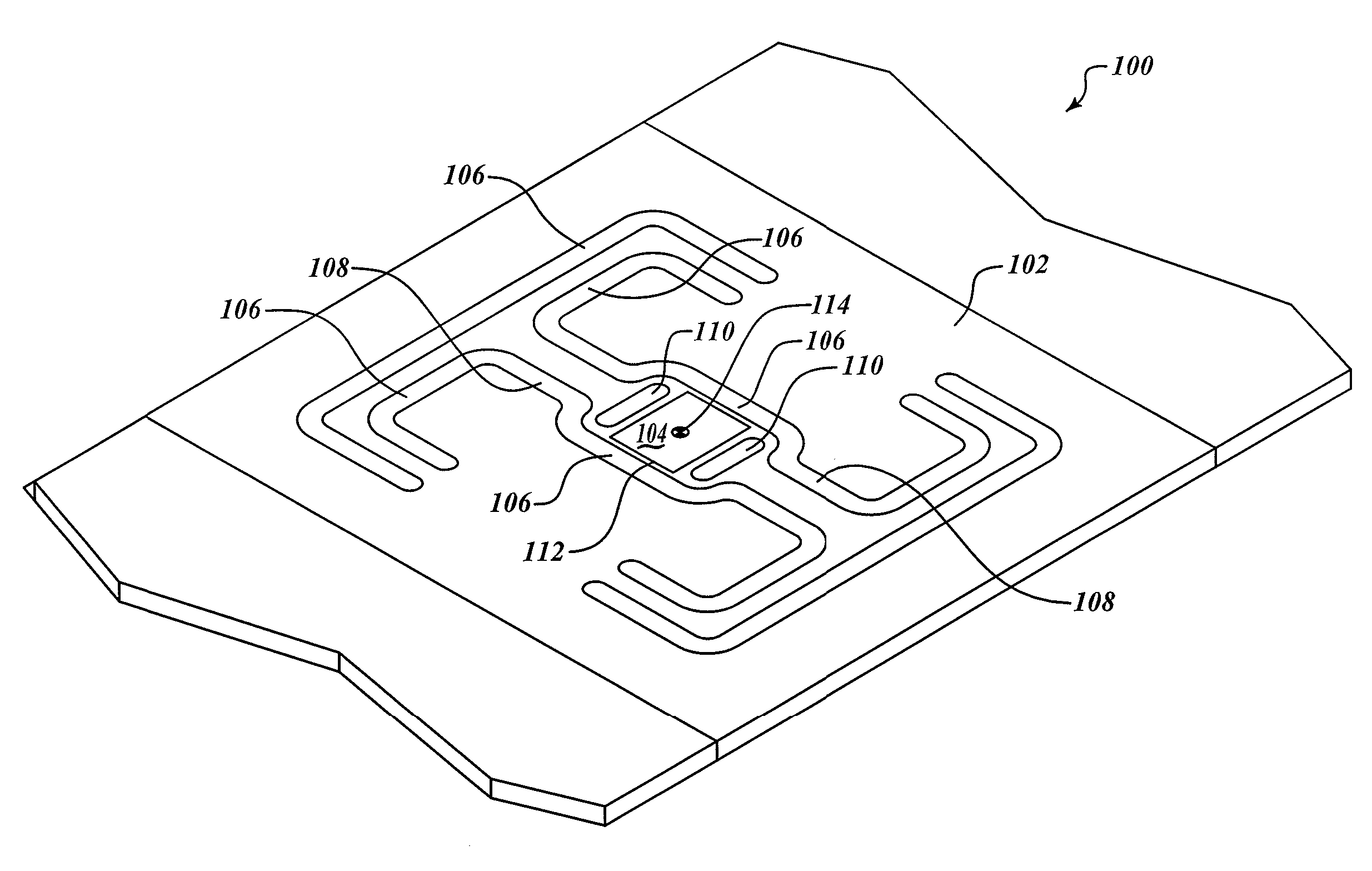
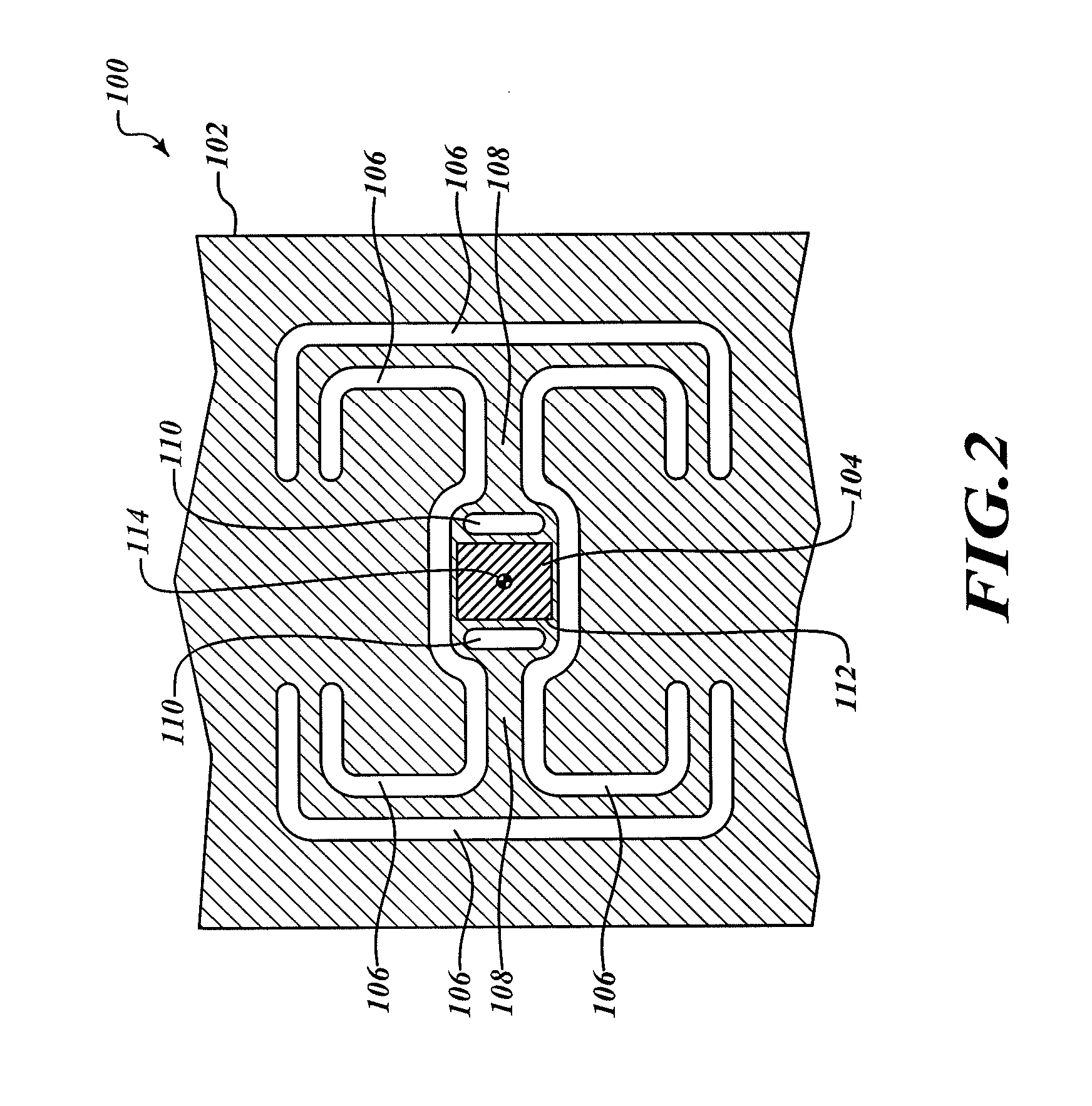
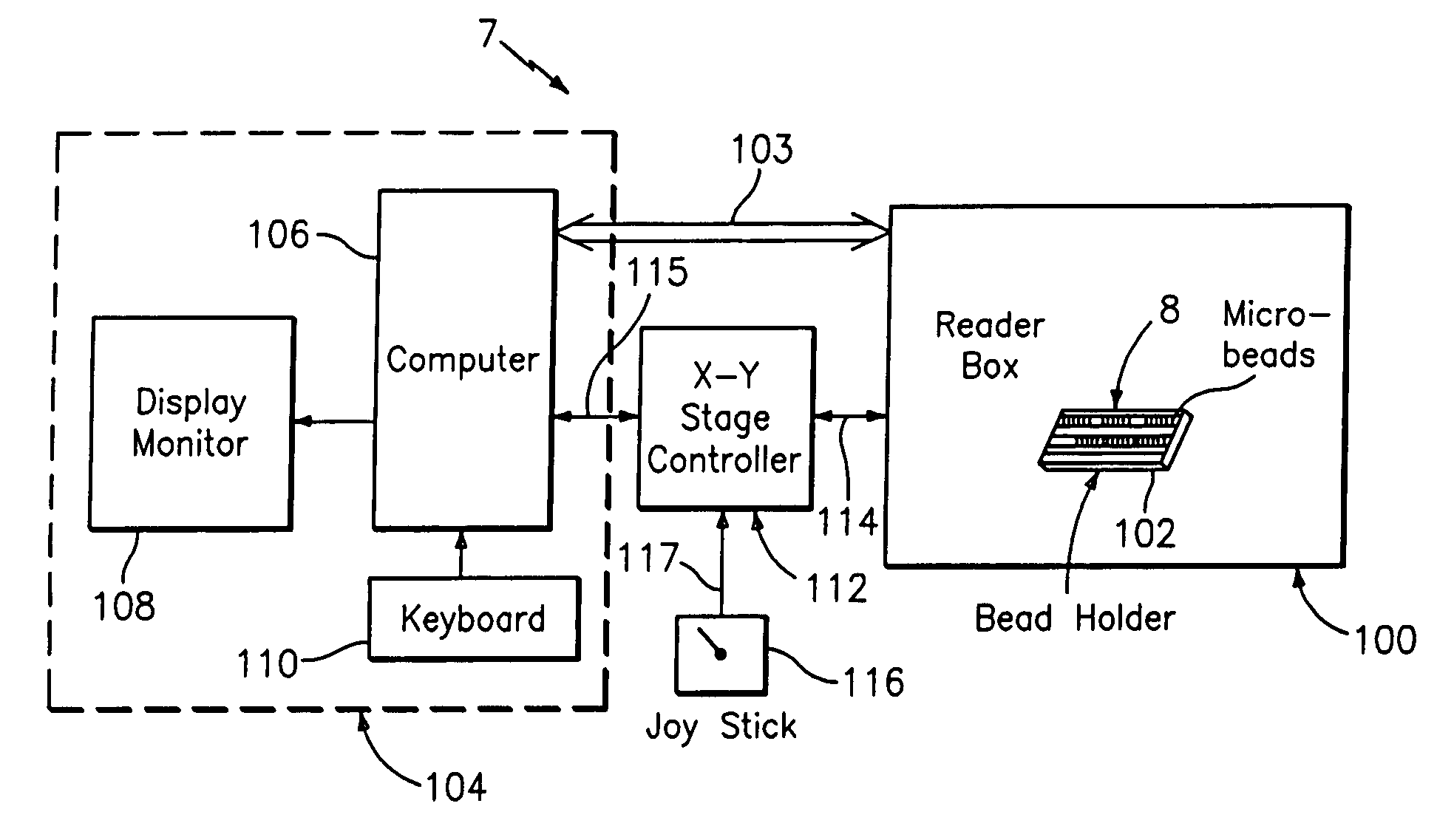
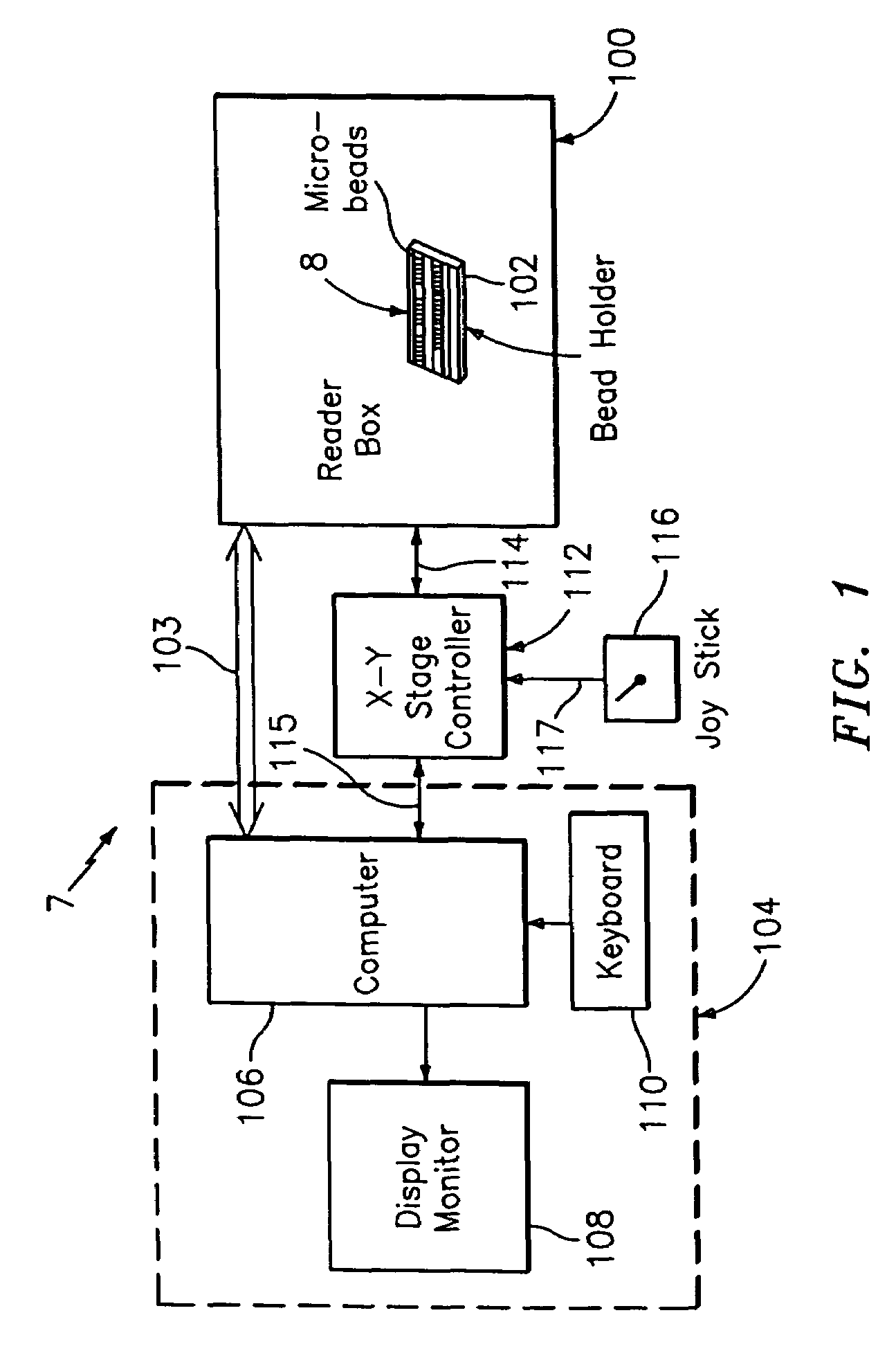
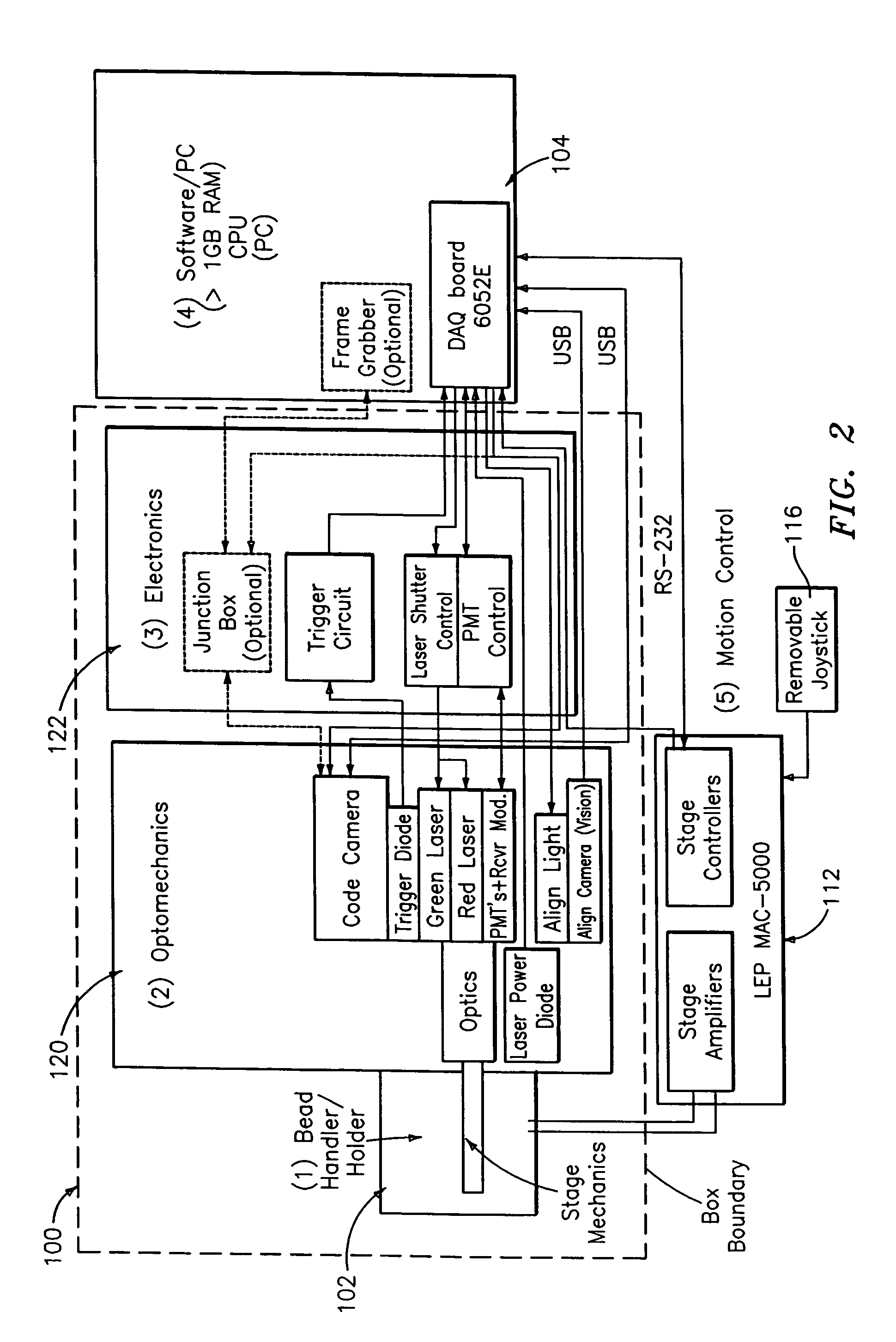
ActiveUS20060071075A1Increase the number ofMinimizing sensitivityPaper-money testing devicesRecord carriers used with machinesCuvetteFluorescence
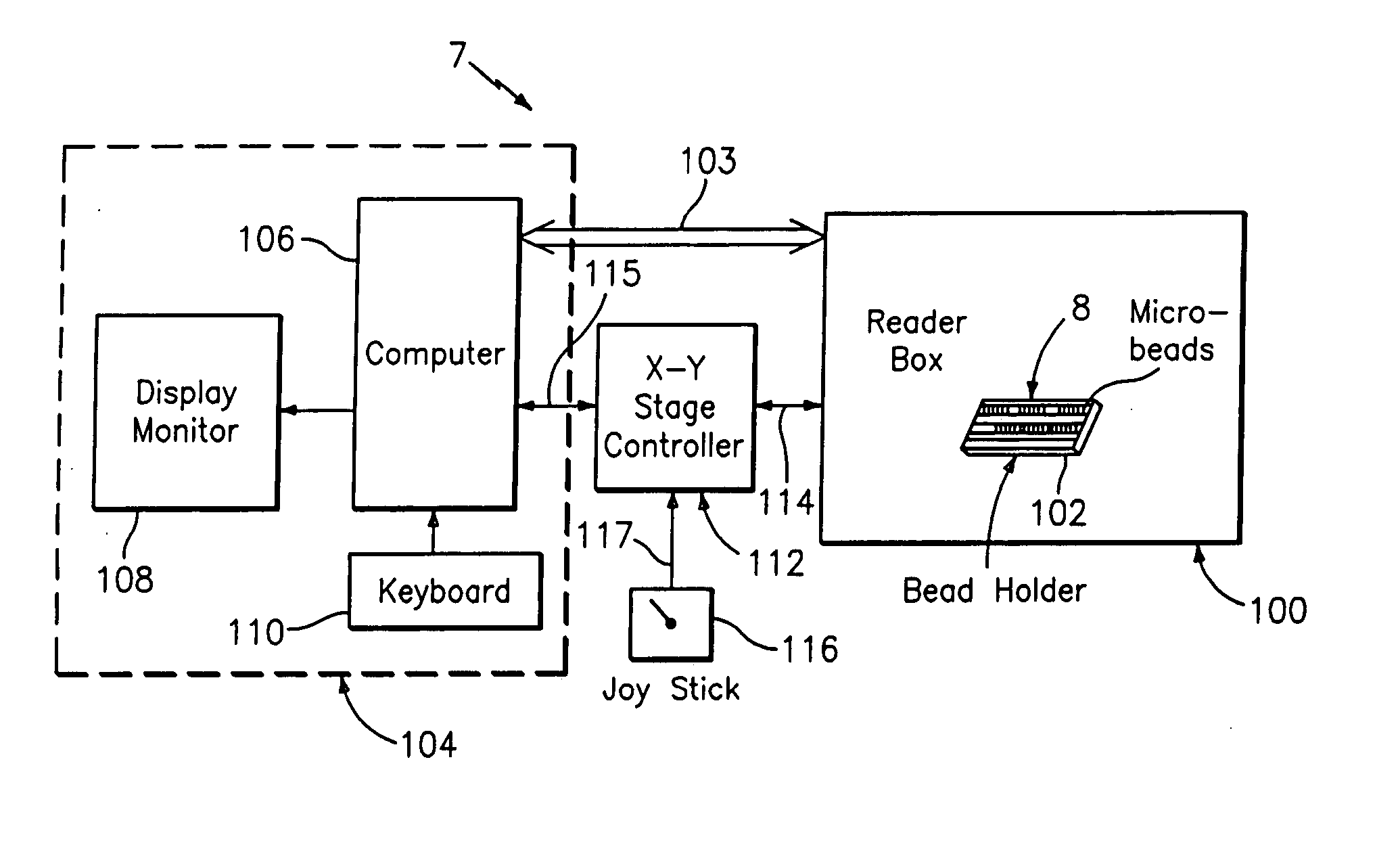
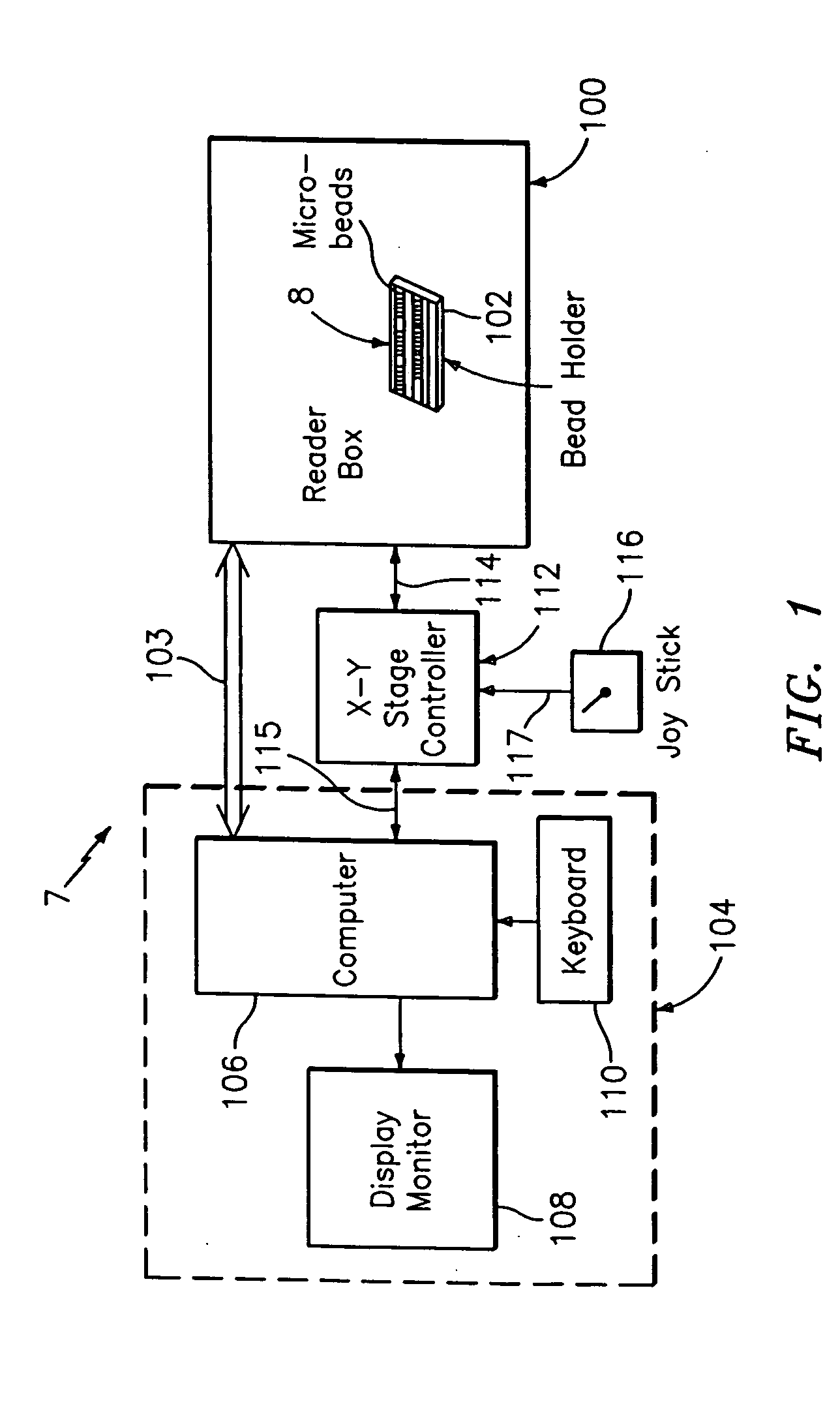
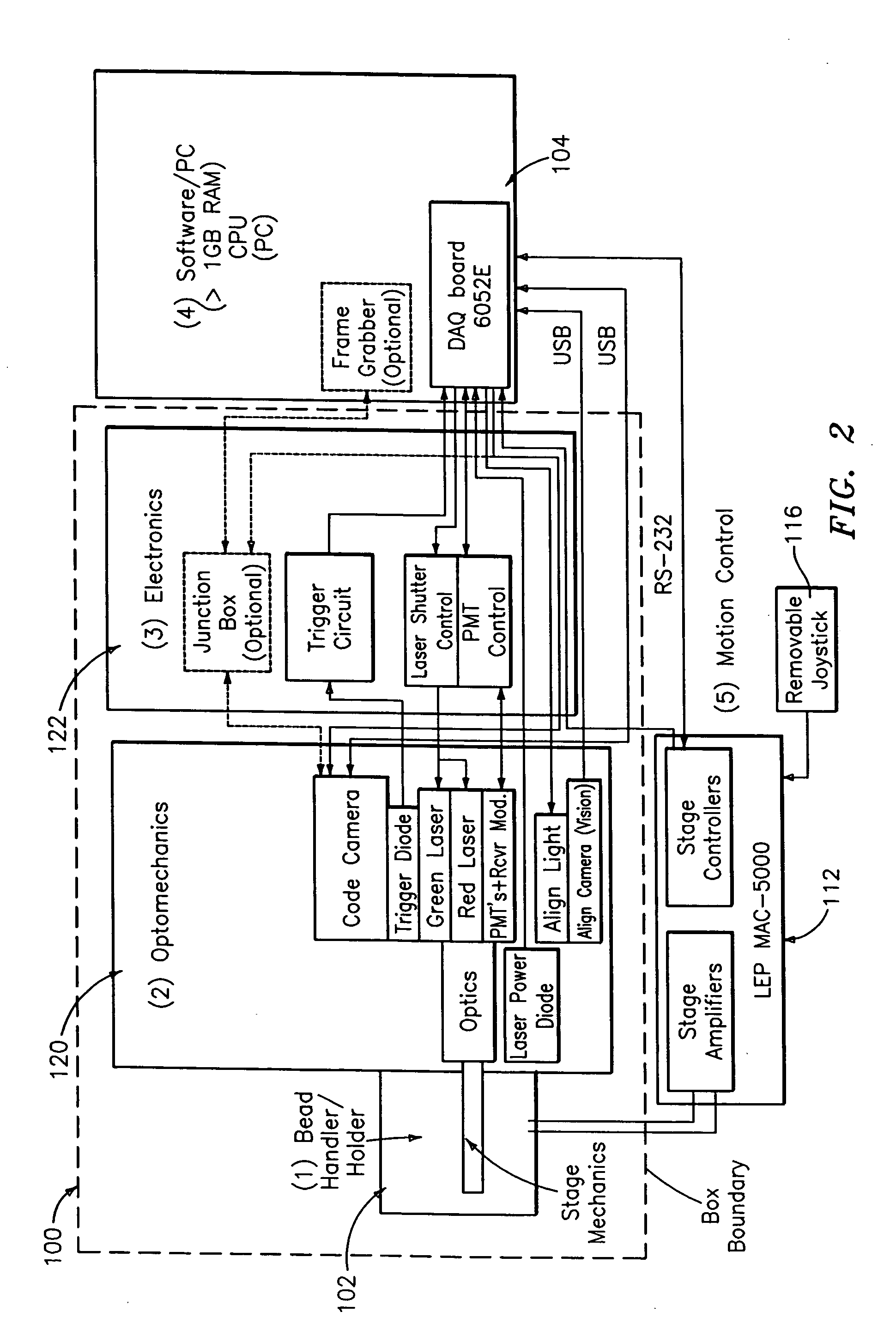
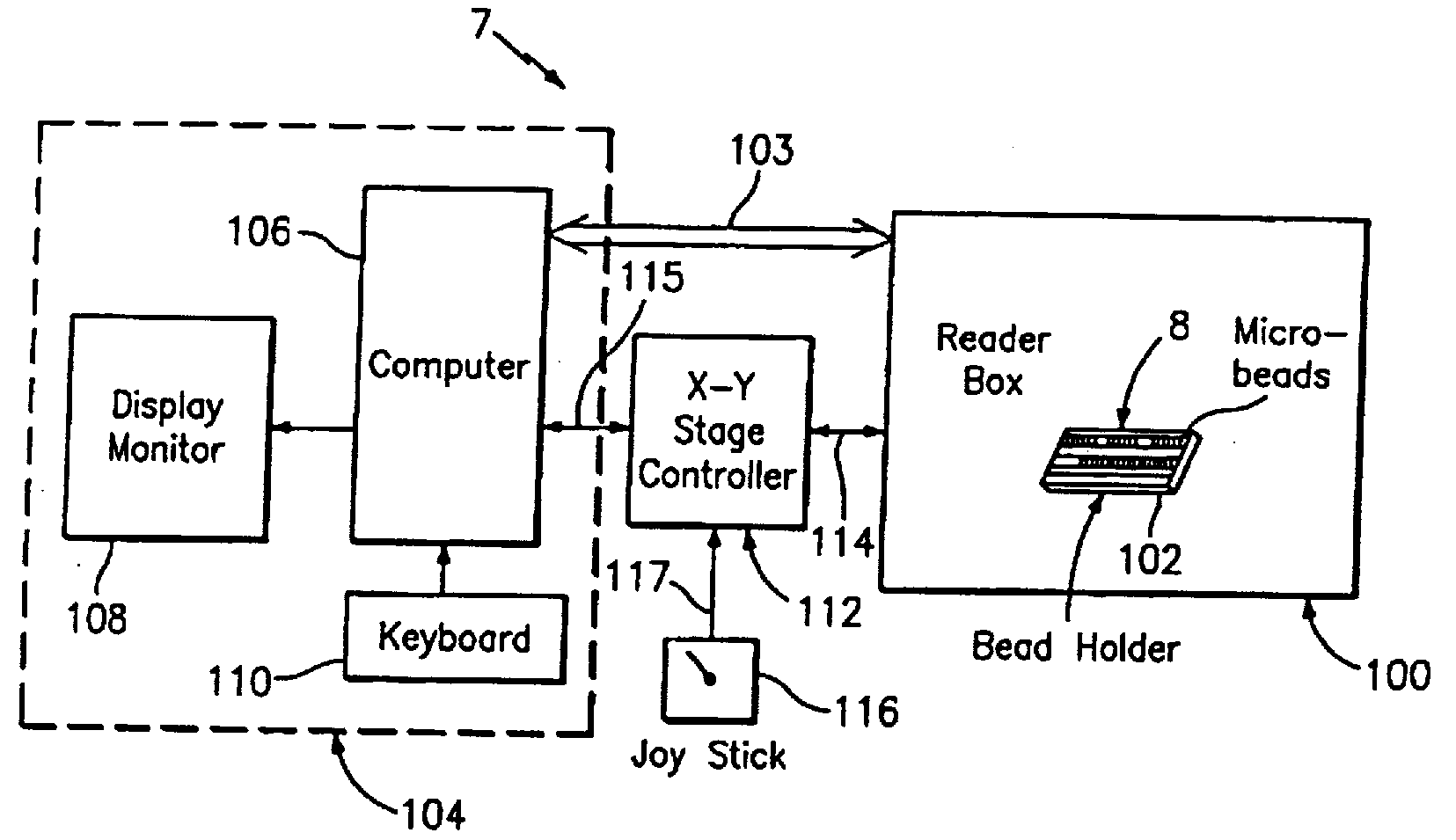
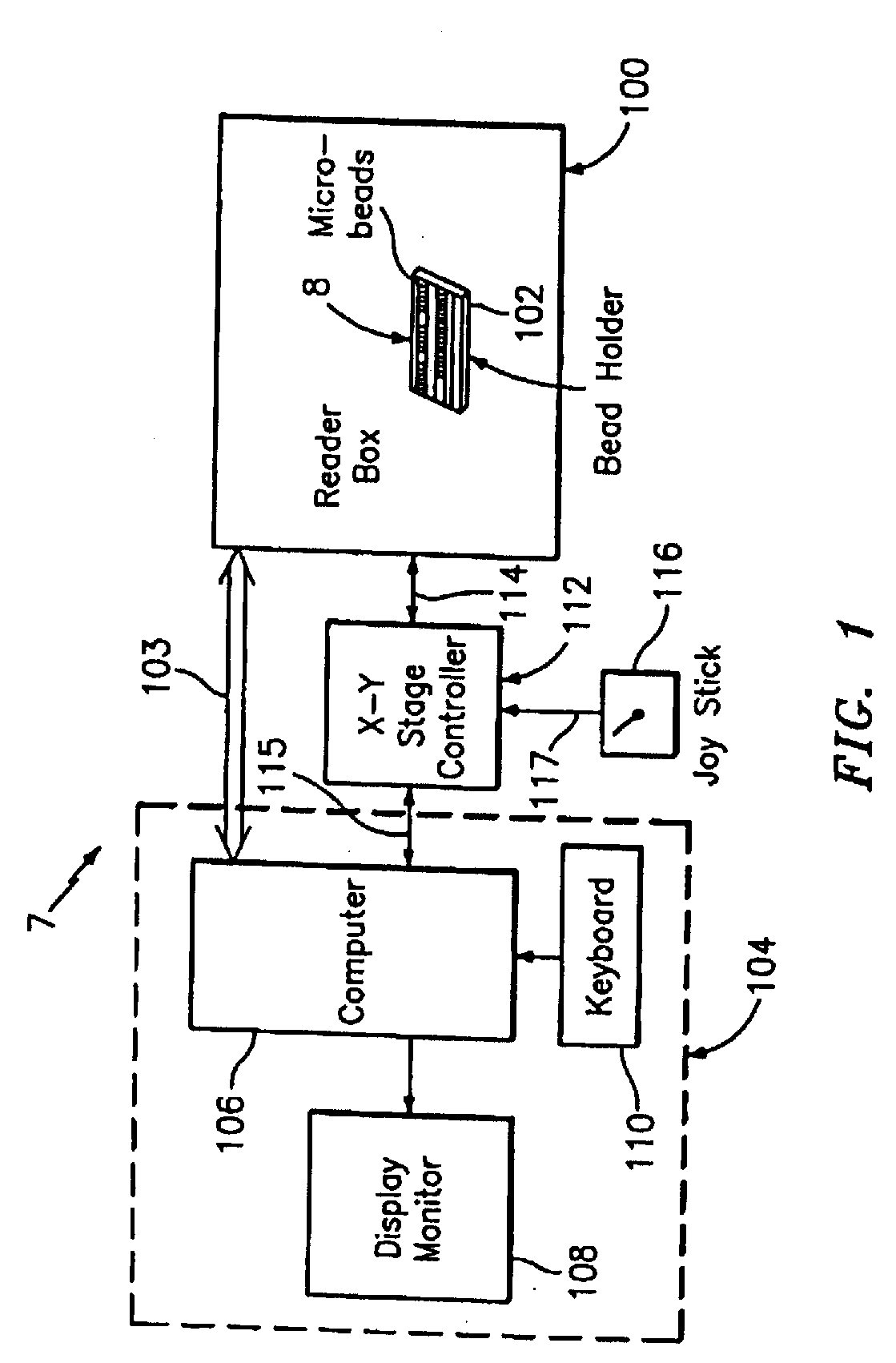
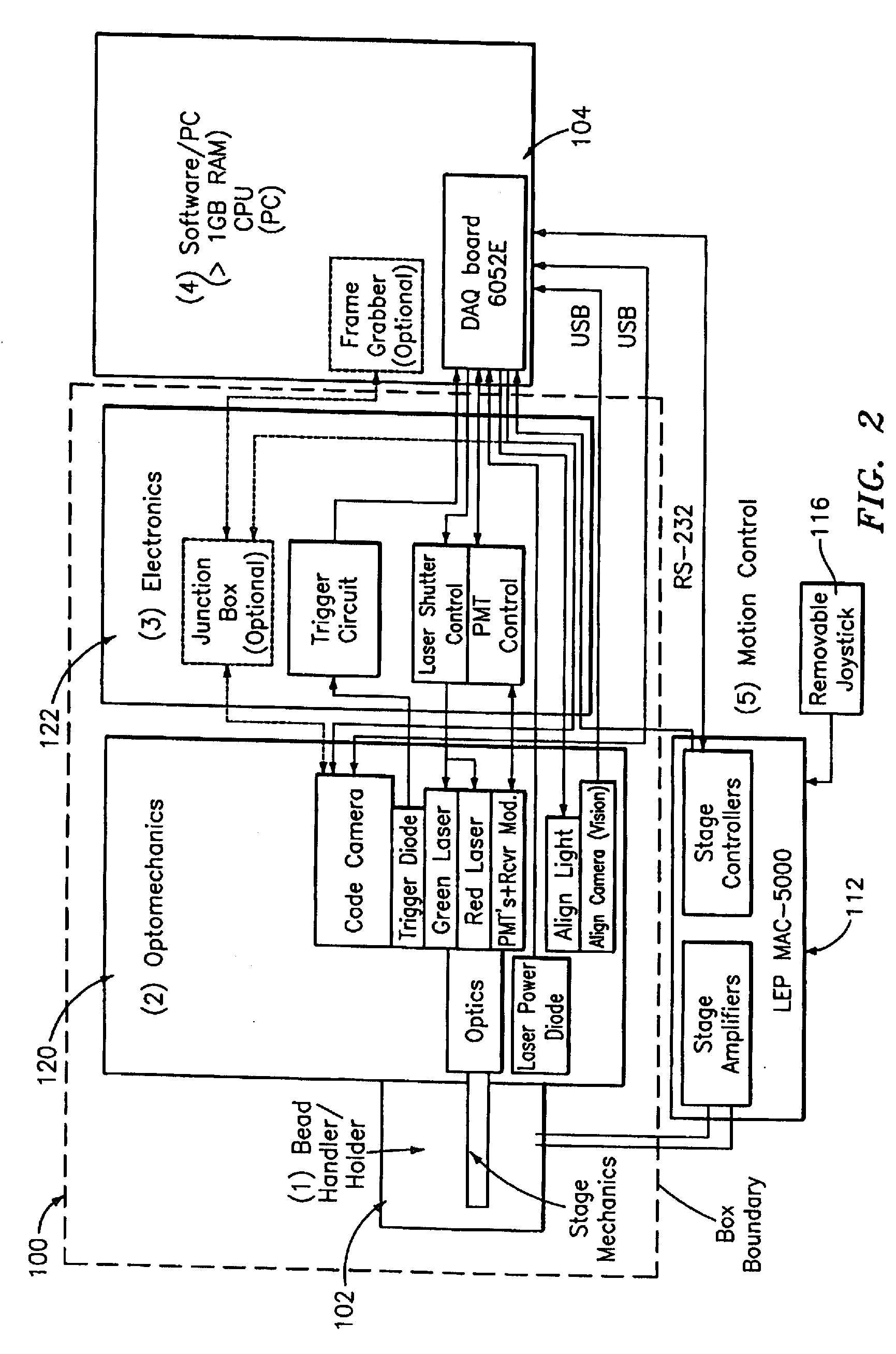
An optical reader system 7 for diffraction grating-based encoded microbeads (or bead reader system), comprises a reader box 100, which accepts a bead cell (or cuvette) 102 that holds the microbeads 8, having an embedded code therein. The reader box 100 interfaces along lines 103 with a known computer system 104. The reader box 100 interfaces with a stage position controller 112 and the controller 112 interfaces along a line 115 with the computer system 104 and a manual control device (or joy stick) 116 along a line 117. The reader interrogates the microbeads to determine the embedded code and / or the fluorescence level on the beads. The reader provides information similar to a bead flow cytometer but in a planar format, i.e., a virtual cytometer.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Apparatus and method for wafer surface defect inspection
InactiveUS20070182958A1The result is accurateImprove accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationForeign matterLight beam
A beam emitted from a first light source is shed on the surface of a rotating wafer to form a beam spot. Scattered light arising from foreign matter and other defects on the surface of the wafer is detected in a plurality of directions and output in the form of a signal. Vertical movement of the wafer surface is detected by using white light or broadband light from a second light source. The position of the beam spot on the wafer surface is corrected in accordance with the information on the detected vertical movement for the purpose of minimizing a coordinate error that may arise from the vertical movement of the wafer surface. Further, the emission direction and emission position of light generated from the first light source are corrected to minimize a coordinate error that may arise from variations of the first light source. These corrections are made to enhance the accuracy of the coordinates of detected foreign matter and other defects. Moreover, the illumination beam spot diameter is corrected to prevent the detection sensitivity and foreign matter coordinate detection error from varying from one apparatus to another.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Energy Harvesting for Low Frequency Inductive Tagging
InactiveUS20110163857A1Double communication speedIncrease rangeSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesTransceiverEngineering
A system for detection and tracking of objects which carry low radio frequency tags that comprise an inductive antenna and transceiver operable at a radio frequency below 1 megahertz, a transceiver operatively connected to that antenna, an ID data storage device, a microprocessor for handling data from the transceiver and data store, and an energy harvesting device to capture energy from an energy condition at said object. The system includes a field communication inductive antenna disposed, preferably at a distance of several feet from each object, and at an orientation that permits effective communication with the tag antennas at the aforesaid radio frequency, a data receiver, transmitter and reader data processor in operative communication with the field communication inductive antenna. The aforesaid tag communication inductive antenna may have a ferrite core to enhance data reception.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
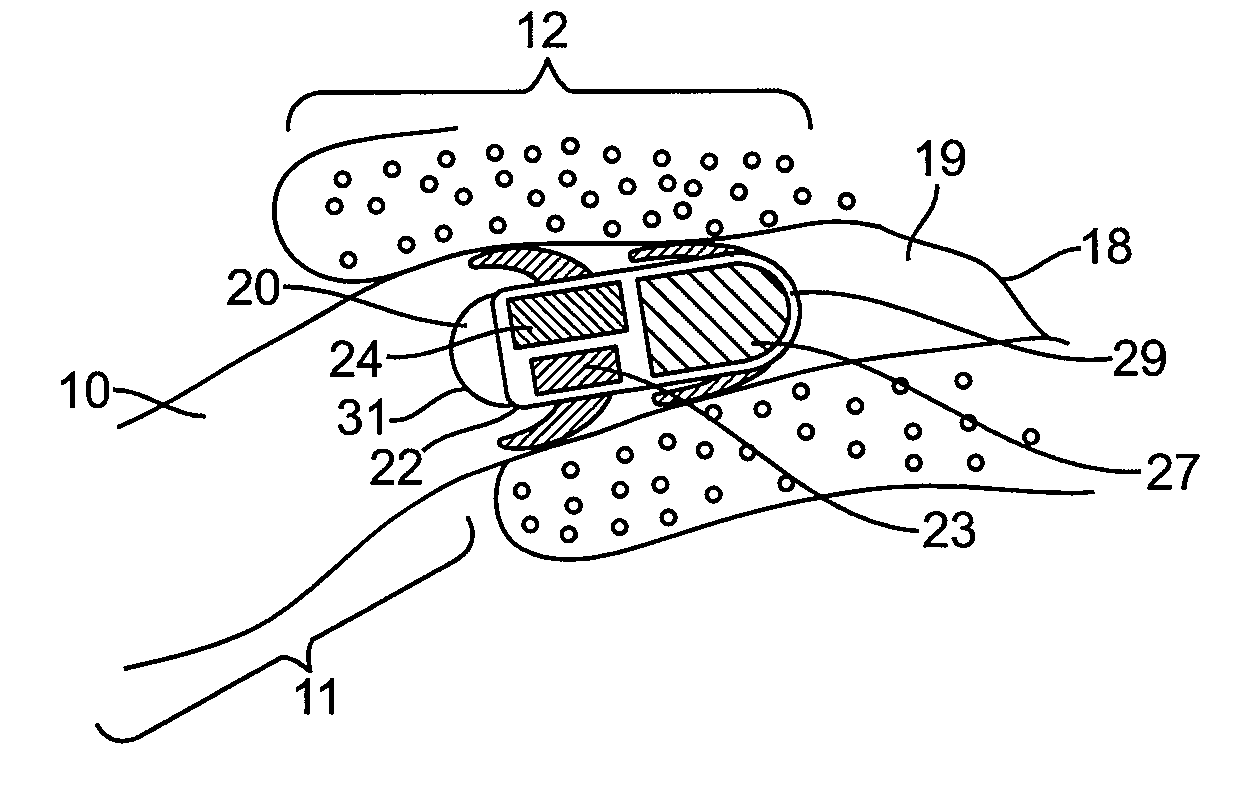
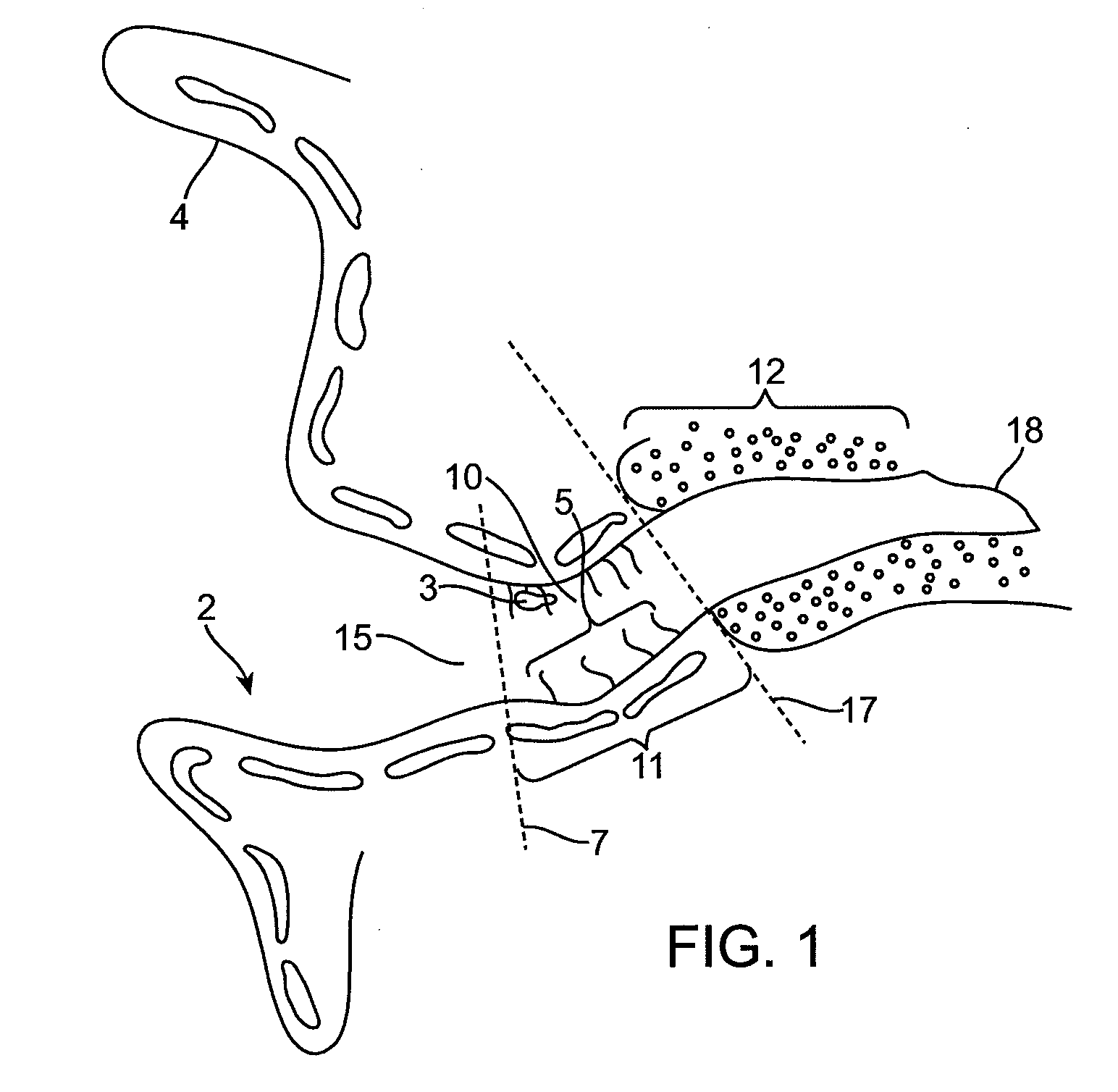
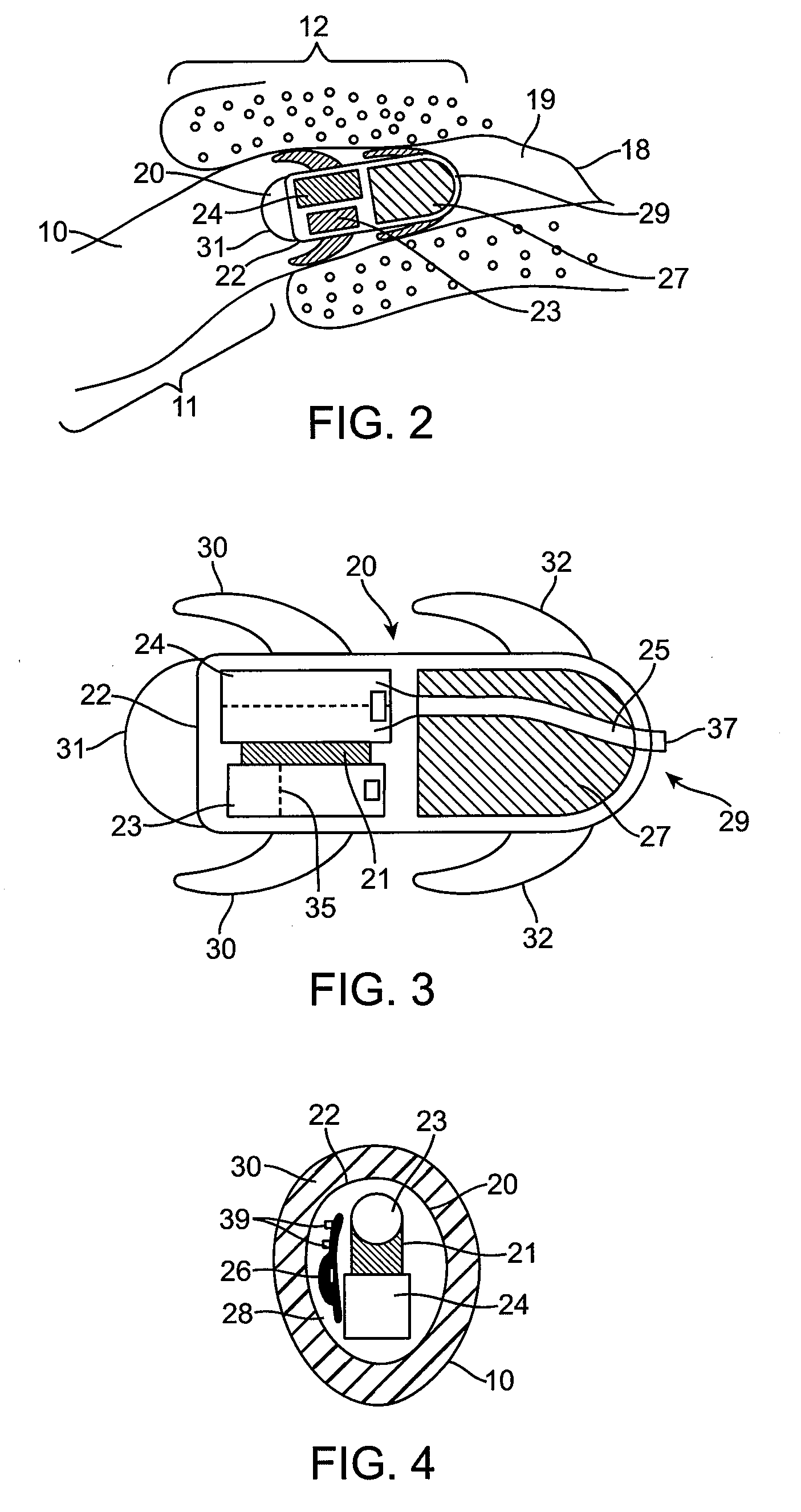
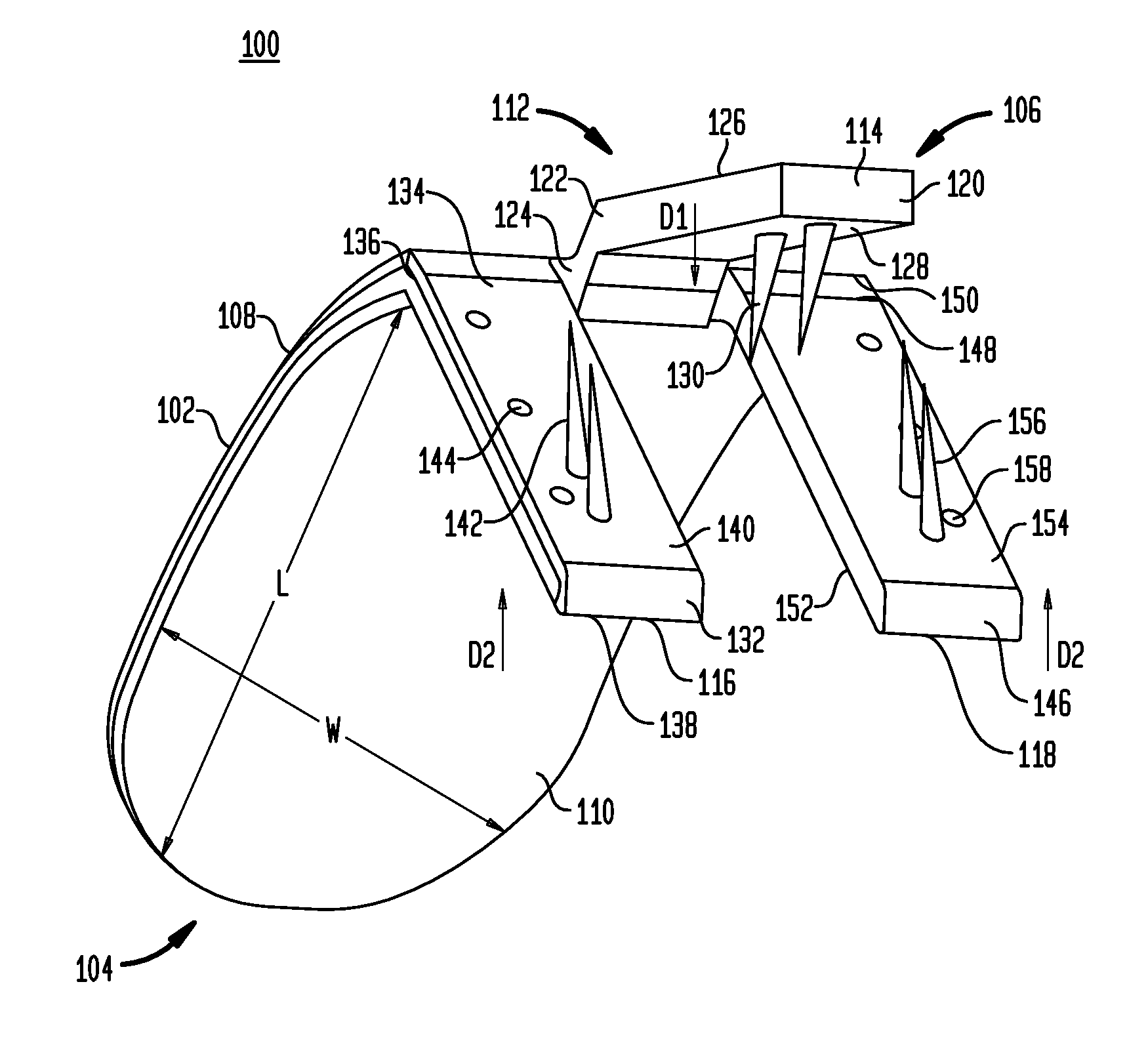
Implant systems and methods for treating obstructive sleep apnea
ActiveUS20100234946A1Increasing curveReducing curve and angleTeeth fillingSnoring preventionRight hard palateHard palate
A system for treating obstructive sleep apnea includes a body implantable in a soft palate, and a fastening element at a proximal end of the body for connecting the body with a hard palate. In one embodiment, the body is curved and has a convex top surface and a concave bottom surface. The curved body is adapted to support and / or change the shape of the soft palate for minimizing the likelihood of airway obstructions during sleep. The fastening element, secureable to the hard palate, includes at least one barb adapted to engage the hard palate for anchoring the body to the hard palate. In one embodiment, the body has a surface adapted to promote tissue in-growth. The implant body may be made of materials including nitinol, stainless steel, biocompatible polymers, temperature-sensitive materials, and shape memory materials.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Optical reader system for substrates having an optically readable code
ActiveUS20090194589A1Increase the number ofMinimizing sensitivityRecord carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationLight beamEngineering
An optical reader system that includes a plurality of substrates. The substrates have an optically readable code disposed therein and a source light assembly that is configured to illuminate the substrates with a code-reading beam and another beam for detecting another optically readable property of the substrate. The code-reading beam and the other beam form beam spots on the substrates that have different shapes. The system also includes a reader that is configured to receive output signals from the code-reading beam and the other beam when the substrates are illuminated. The output signals from the code-reading beam are indicative of the code.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Electric stimilator for alpha-wave derivation
InactiveUS7386347B2Efficient implementationMaximize the effect of treatmentInternal electrodesMedical devicesHuman bodyDisease
Owner:CHUNG JONG PIL
Method and apparatus for suppressing an acoustic interference signal in an incoming audio signal
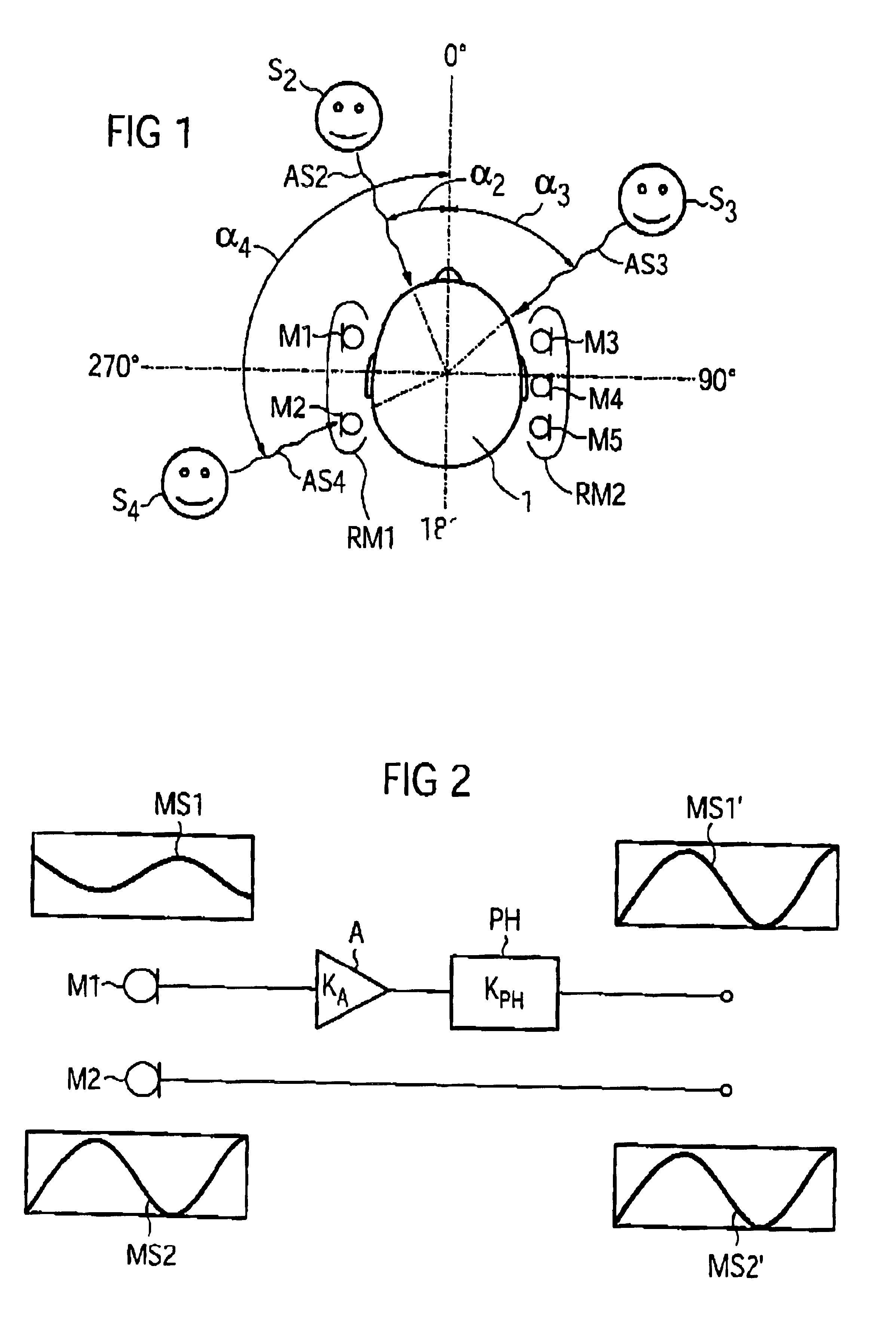
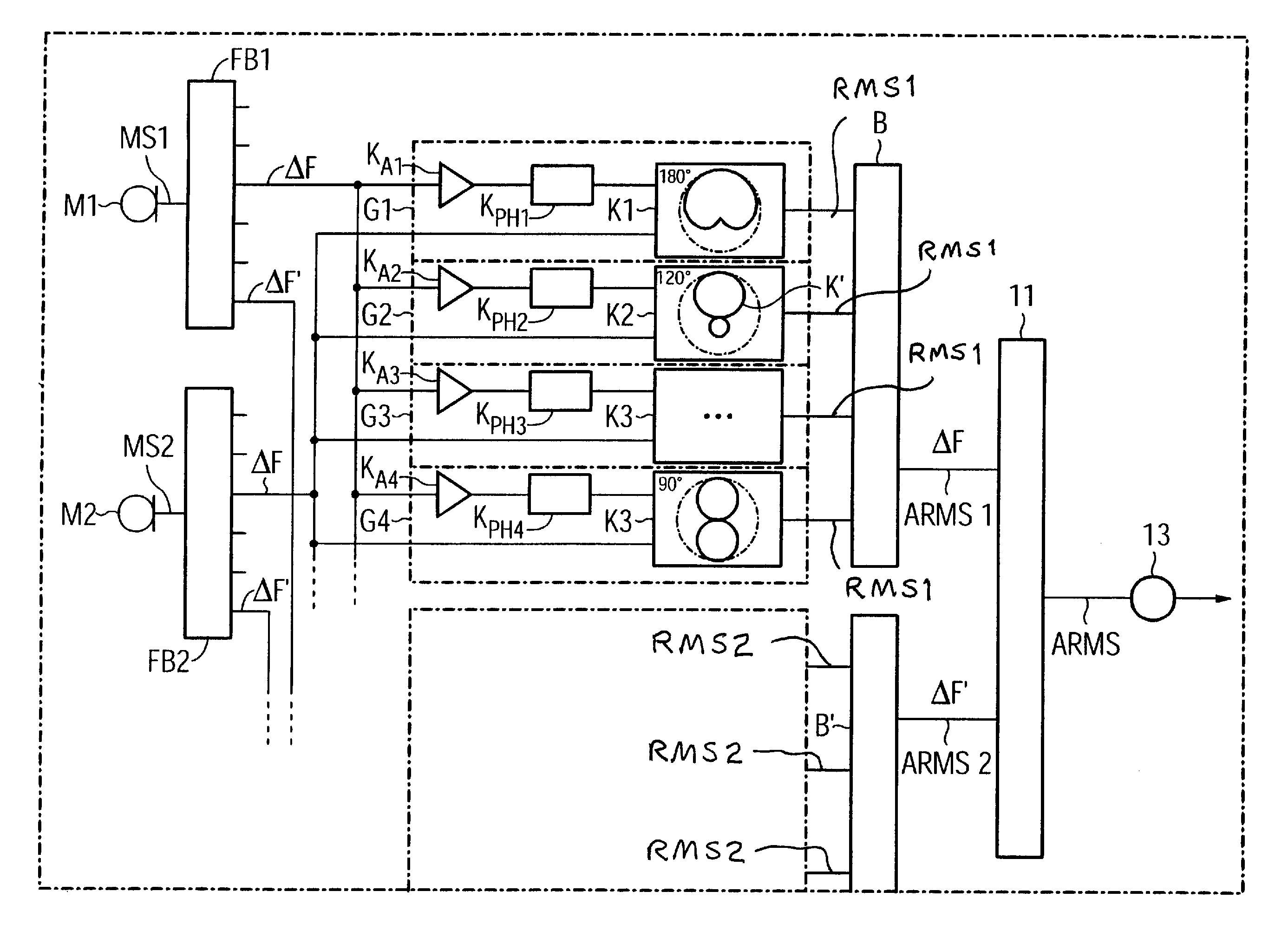
ActiveUS6950528B2Inhibition effectMinimal sensitivitySignal processingMicrophones signal combinationEngineeringAudio signal
In order to suppress at least one interference signal in an incoming audio signal using a directional microphone system having at least two microphones, that directional microphone signal which has the lowest interference signal component is selected from two or more directional microphone signals that have been produced by weighted combination from the signals of the microphones, with the weighting in each case determining a direction-dependent sensitivity. If a sensitivity distribution has a minimum in the direction of the interference signal source, then a low signal energy is detected, which characterizes a lower interference signal component.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Mounting system for torsional suspension of a MEMS device
ActiveUS20100089154A1Minimizing sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsEngineeringCentroid
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Optical reader for diffraction grating-based encoded optical identification elements
ActiveUS7441703B2Increase the number ofMinimizing sensitivityPaper-money testing devicesRecord carriers used with machinesCuvetteFluorescence
An optical reader system 7 for diffraction grating-based encoded microbeads (or bead reader system), comprises a reader box 100, which accepts a bead cell (or cuvette) 102 that holds the microbeads 8, having an embedded code therein. The reader box 100 interfaces along lines 103 with a known computer system 104. The reader box 100 interfaces with a stage position controller 112 and the controller 112 interfaces along a line 115 with the computer system 104 and a manual control device (or joy stick) 116 along a line 117. The reader interrogates the microbeads to determine the embedded code and / or the fluorescence level on the beads. The reader provides information similar to a bead flow cytometer but in a planar format, i.e., a virtual cytometer.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Stacked capacitor memory
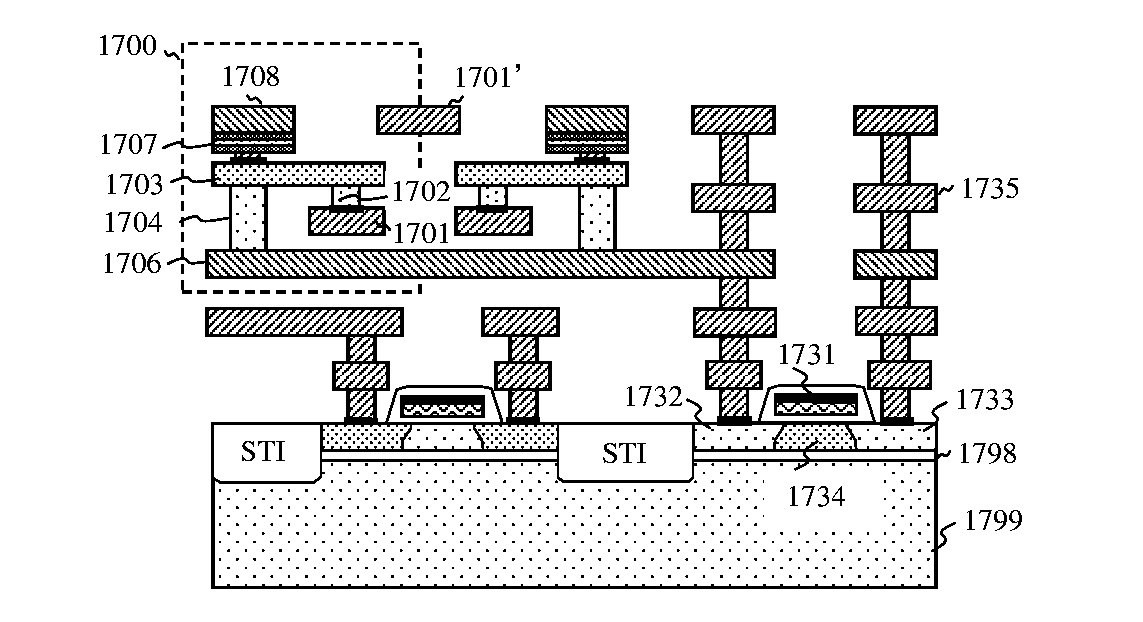
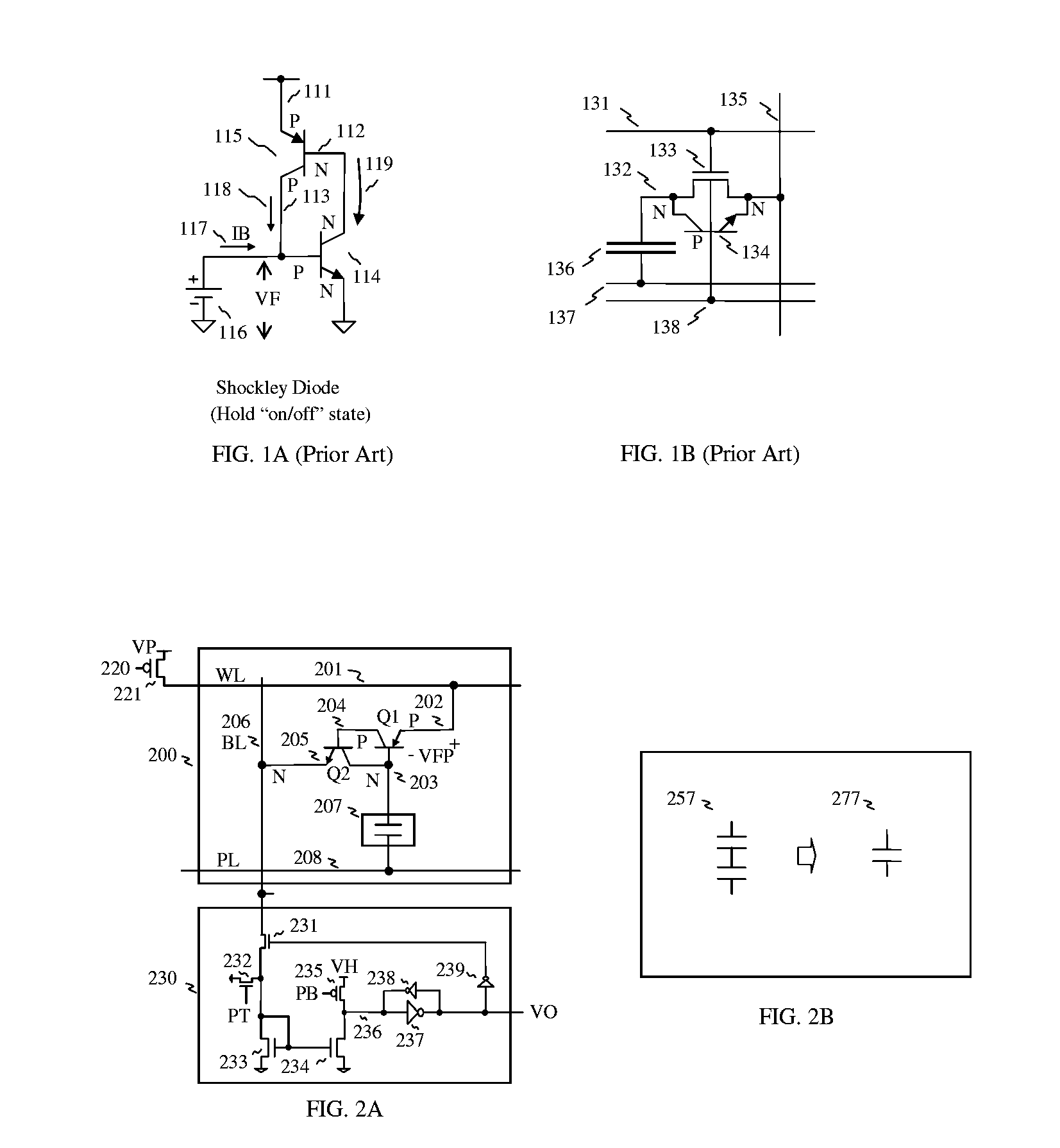
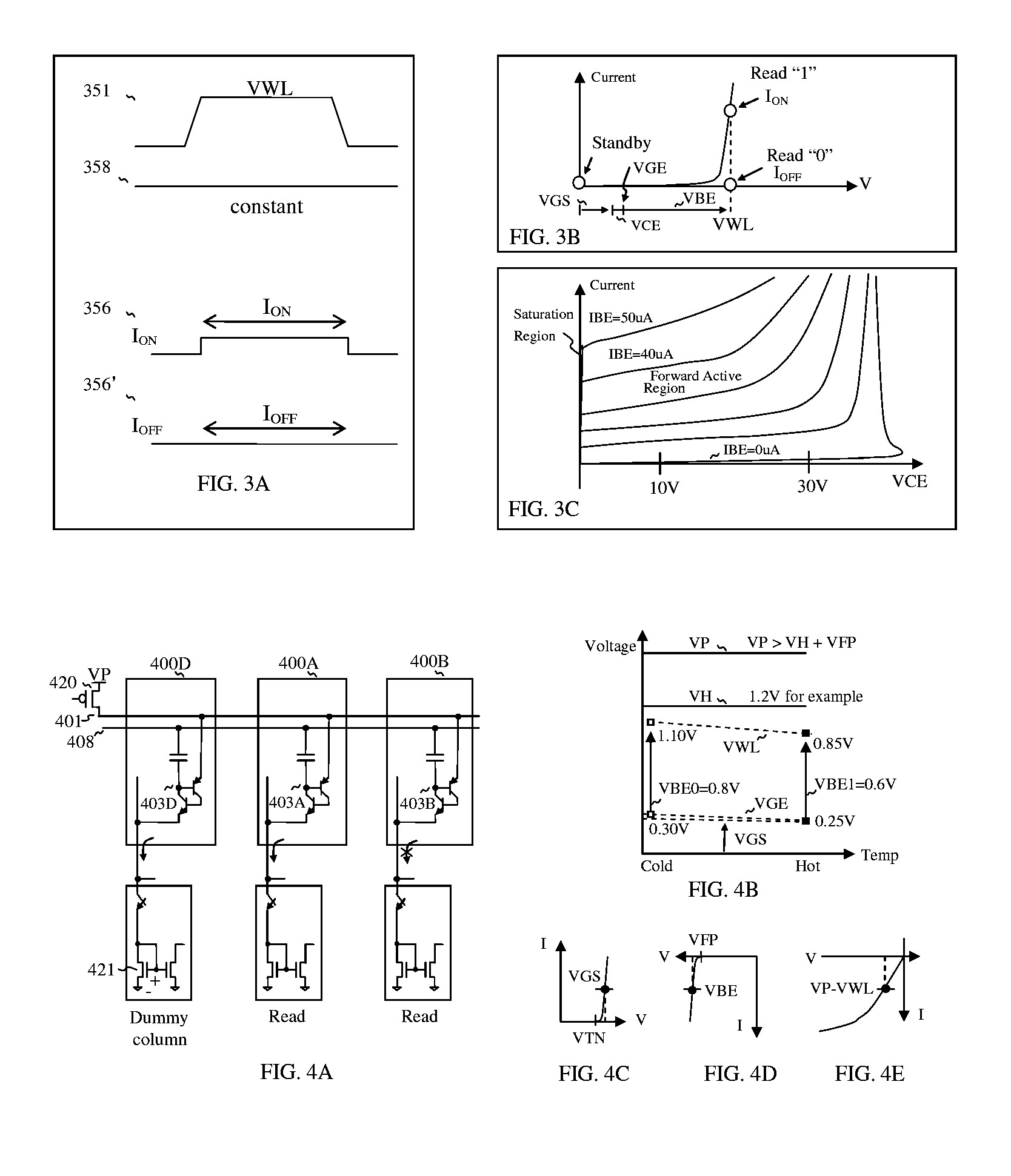
InactiveUS20070183191A1Reduce chip areaLess complicated to fabricateSolid-state devicesDiodeEngineeringMulti port
Stacked capacitor memory is realized, wherein a capacitor stores data and a diode serves as an access device instead of MOS transistor, the first terminal is connected to a word line, the second terminal is connected to the first electrode of the capacitor which serves as a storage node while the second electrode is connected to a plate line, the third terminal is floating, and the fourth terminal is connected to a bit line. When write, the storage node is charged or not, depending on the conducting state of the diode which is controlled by the bit line. When read, the diode also serves as a sense amplifier to detect whether the storage node is forward bias or not, and it sends binary data to a latch device wherein includes a current mirror and a feedback loop which cuts off the current path after latching, thus it reduces active current, minimizes data pattern sensitivity, and also rejects coupling noise. And dummy rows and columns generate replica delay signals which guarantee timing margin and reduce cycle time. And its applications are extended to single port, multi port and content addressable memory. In addition, the memory cells are formed in between the routing layers, which memory cells can be stacked over the transistor or another capacitor memory cell.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
Soft zero halogen flame retardant thermoplastic elastomers
InactiveUS20090124743A1Desirable vertical burn characteristicDesirable vertical burn characteristicsCoatingsPolyolefinPolymer chemistry
Soft flame retardant thermoplastic compositions that are preferably halogen free and include a styrenic block copolymer having a low modulus, one or more of a polyolefin polymer or copolymer and an acrylate containing polymer or copolymer, one or more of a softener and plasticizer, an inorganic phosphorous-containing flame retardant, and optionally but preferably, a platelet filler such as a nanoclay or an organic modified clay. In a preferred embodiment, the phosphorous-containing flame retardant has a surface coating thereon which reduces sensitivity of the flame retardant to water, and thus reduces the amount of the flame retardant that can leach out in the presence of water, thereby enabling the compositions of the present invention to be utilized outdoors or other environments where exposure to water or high humidity is possible. The hardness of the compositions according to the invention preferably ranges from about Shore A 40 to about Shore A 90. The compositions exhibit high char formation upon burning and also desirable vertical burn characteristics.
Owner:TEKNOR APEX
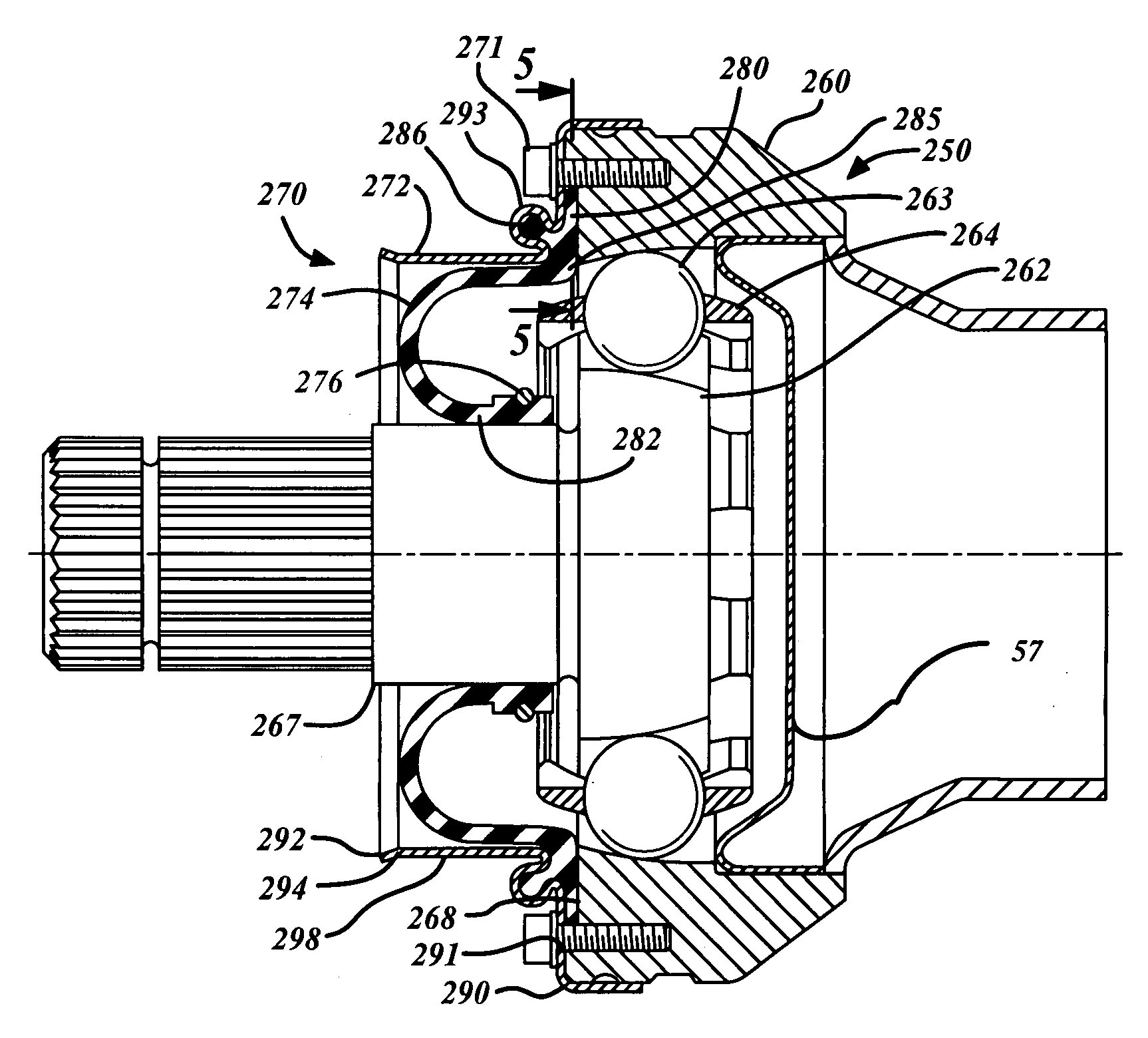
Rolling boot assembly
InactiveUS20070173337A1Minimizing sensitivityMinimizing bulging, kinking or binding of the bootYielding couplingShaftsEngineeringConstant-velocity joint
A rolling boot assembly includes a shroud having a first portion and a second portion, and a radial boot having a first section and a second section. The second portion of the shroud has a free end. The first section of the radial boot is connected to the first portion of the shroud advantageously allowing the radial boot to roll axially toward the second portion of the shroud when the second section of the radial boot is selectively attached to a shaft or an inner joint part and the first portion of the shroud is selectively connected to an outer joint part. The second portion of the shroud remains unconnected. Also provided is a constant velocity joint assembly.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
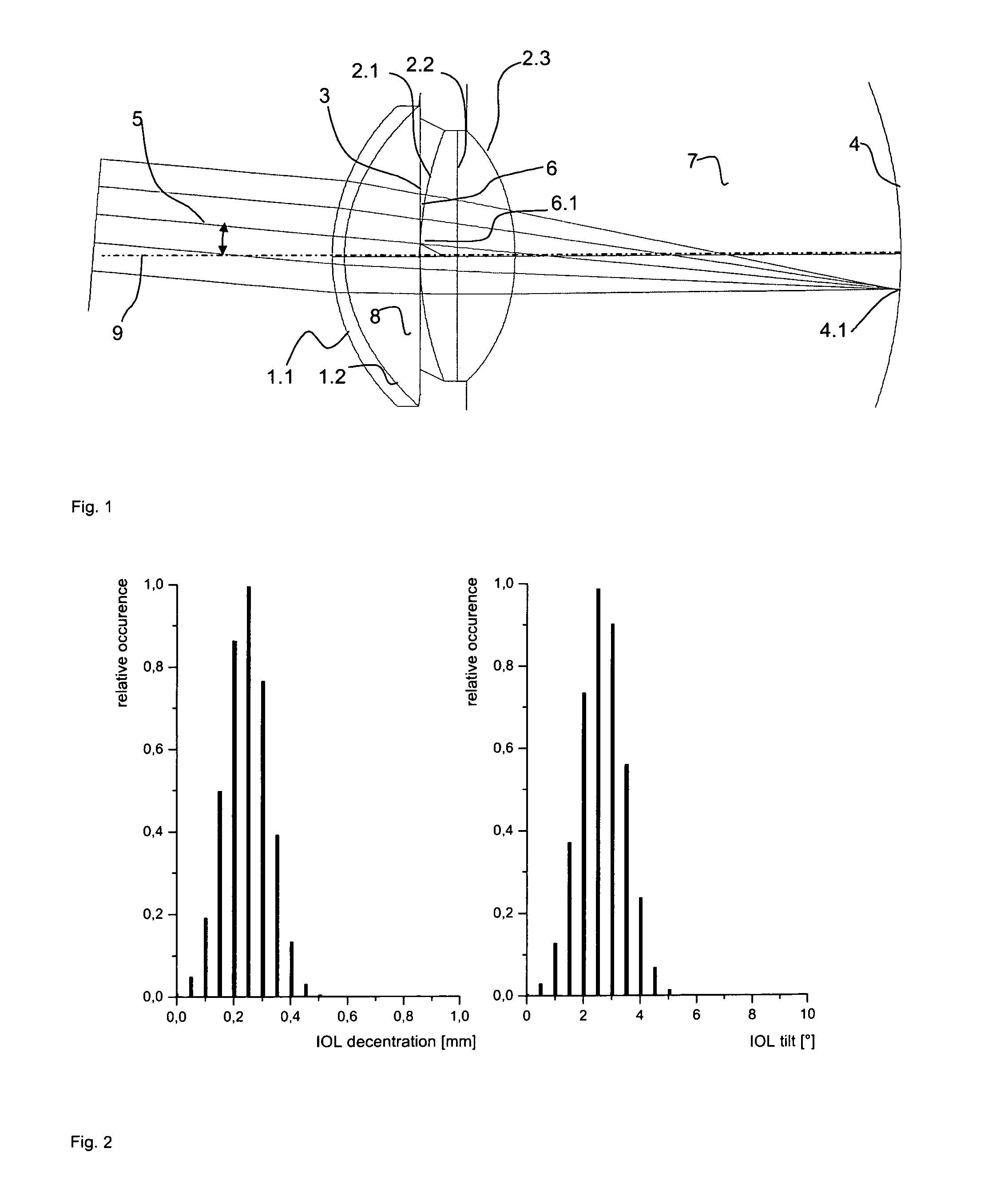
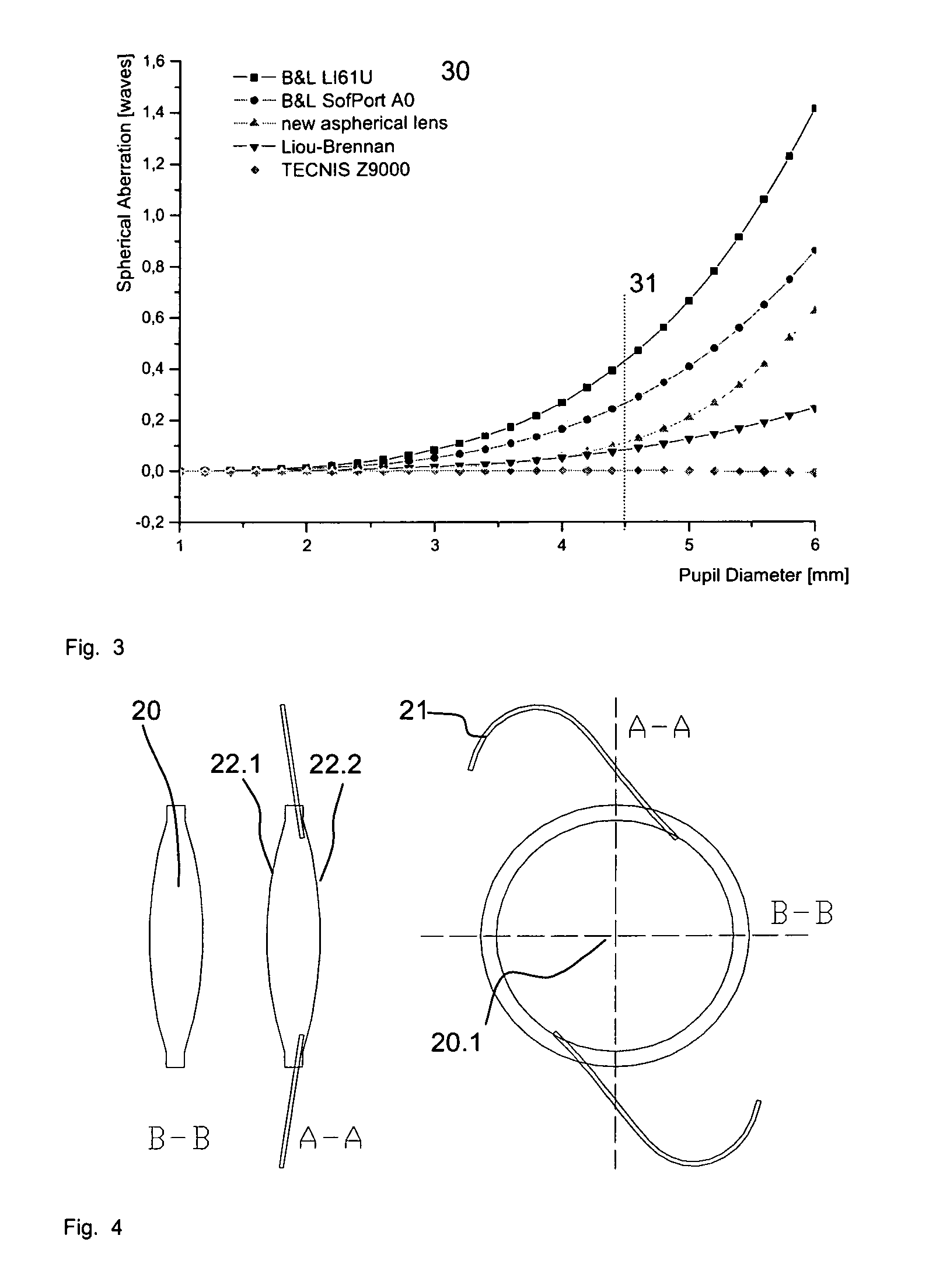
Method for making an aspheric intraocular lens
ActiveUS8235525B2Good optical performanceMinimizing sensitivitySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensSpherical shaped
The invention relates to a novel artificial intraocular lens (IOL) and a method for improving such a lens in the field of ophthalmology, with surface shape modifications that differ from perfect spherical geometries. The intraocular lens takes into account the natural optical configuration of the human vision apparatus, for example, visual axis tilt and pupil decentration. In addition, the method accounts for potential positioning errors caused by implantation and surgery effects.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Fluid borne particle analyzers
ActiveUS7436515B2Maximize their opportunityHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyChemical physicsImproved method
This invention describes an improved method and apparatus for the analysis of fluid borne particles and which is especially suitable for the detection of airborne biological particles. In one aspect of the invention provides an apparatus for the detection of fluid borne particles which comprises a zone through which a fluid to be analyzed flows in use, a source of illumination to illuminate / irradiate fluid borne particles present in said zone, and a detector to detect light from the particles as an indicator of the presence or characteristics of the particles, wherein the apparatus comprises an integrating sphere and the zone is within the integrating sphere. The apparatus is highly sensitive and can be used for detecting airborne particles even where the particles are present at very low particle concentrations in the air.
Owner:THE SEC OF STATE FOR DEFENCE IN HER BRITANNIC MAJESTYS GOVERNMENT OF THE UK OF GREAT BRITAIN & NORTHERN IRELAND
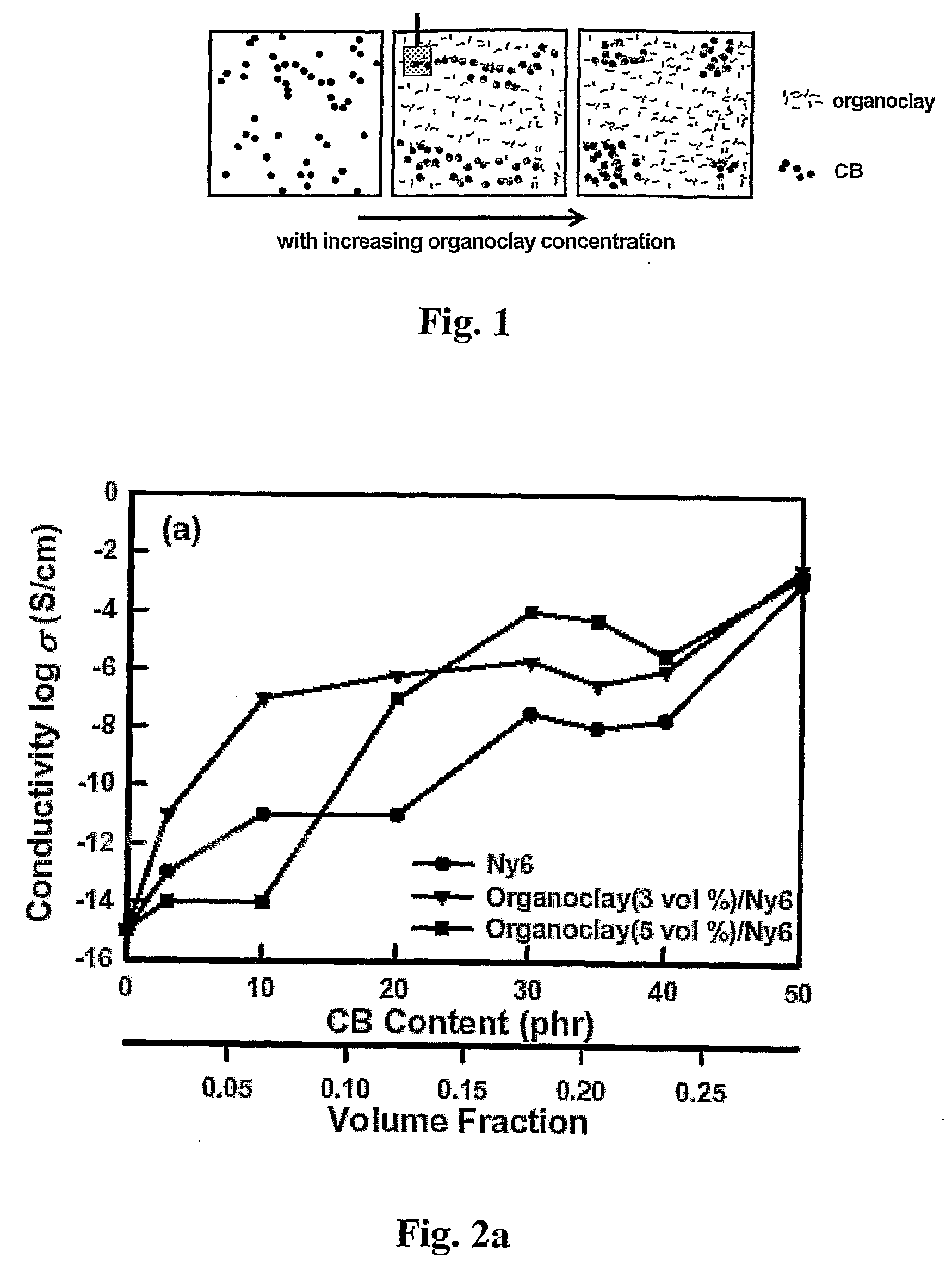
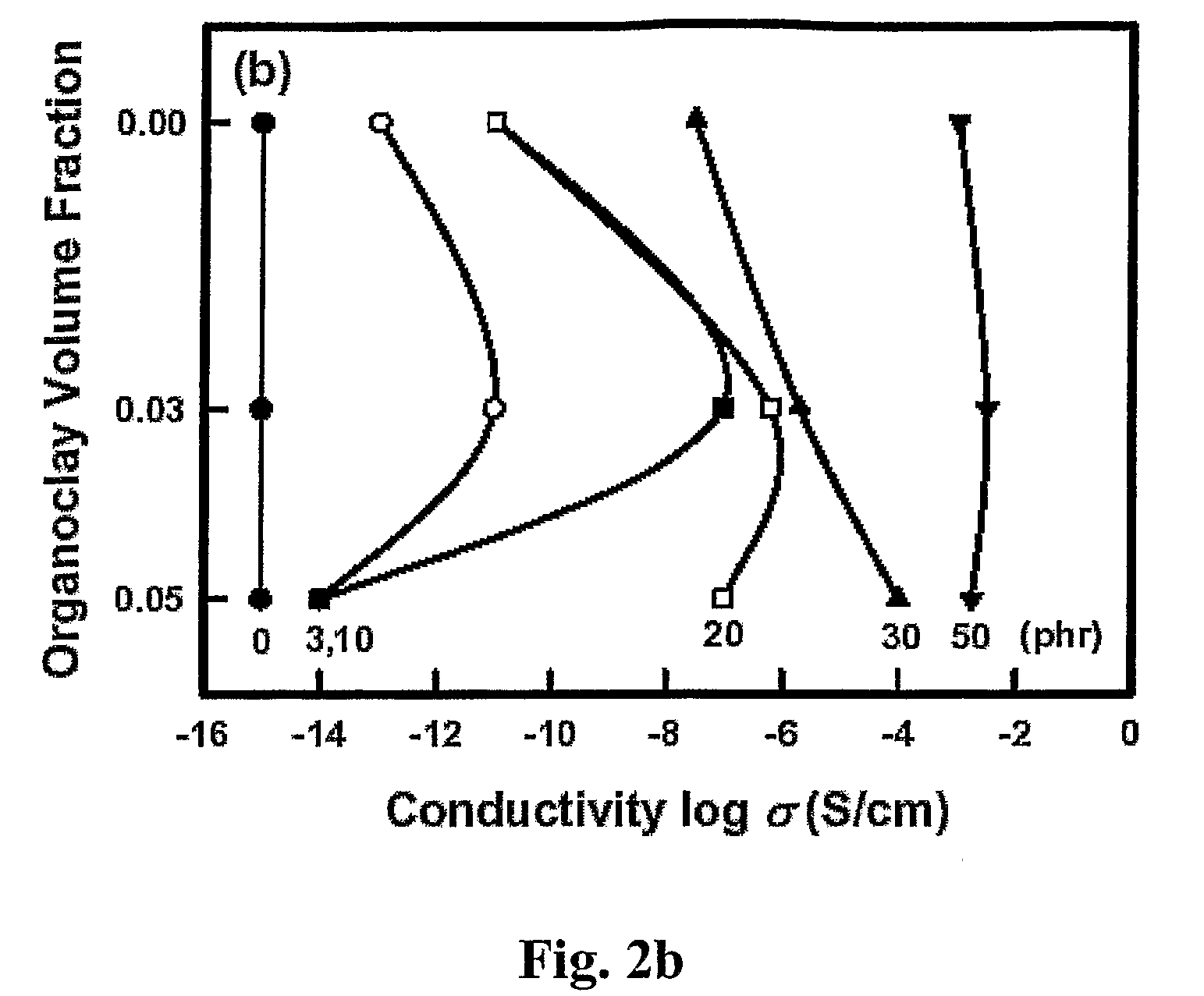
Electrically-Conducting Polymers, a Method for Preparing Electrically-Conducting Polymers, and a Method for Controlling Electrical Conductivity of Polymers
InactiveUS20080015284A1Minimize electrical conductivityMinimizing sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialPolymer resinConductive polymer
A method for controlling electrical conductivity of a polymeric composition and a polymeric composition including a polymeric resin, a conductive filler and an effective amount of a dispersion-control agent that promotes generally-uniform arrangement of the conductive filler throughout the polymeric composition. The polymeric composition is substantially devoid of polycyclic aromatic compounds.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
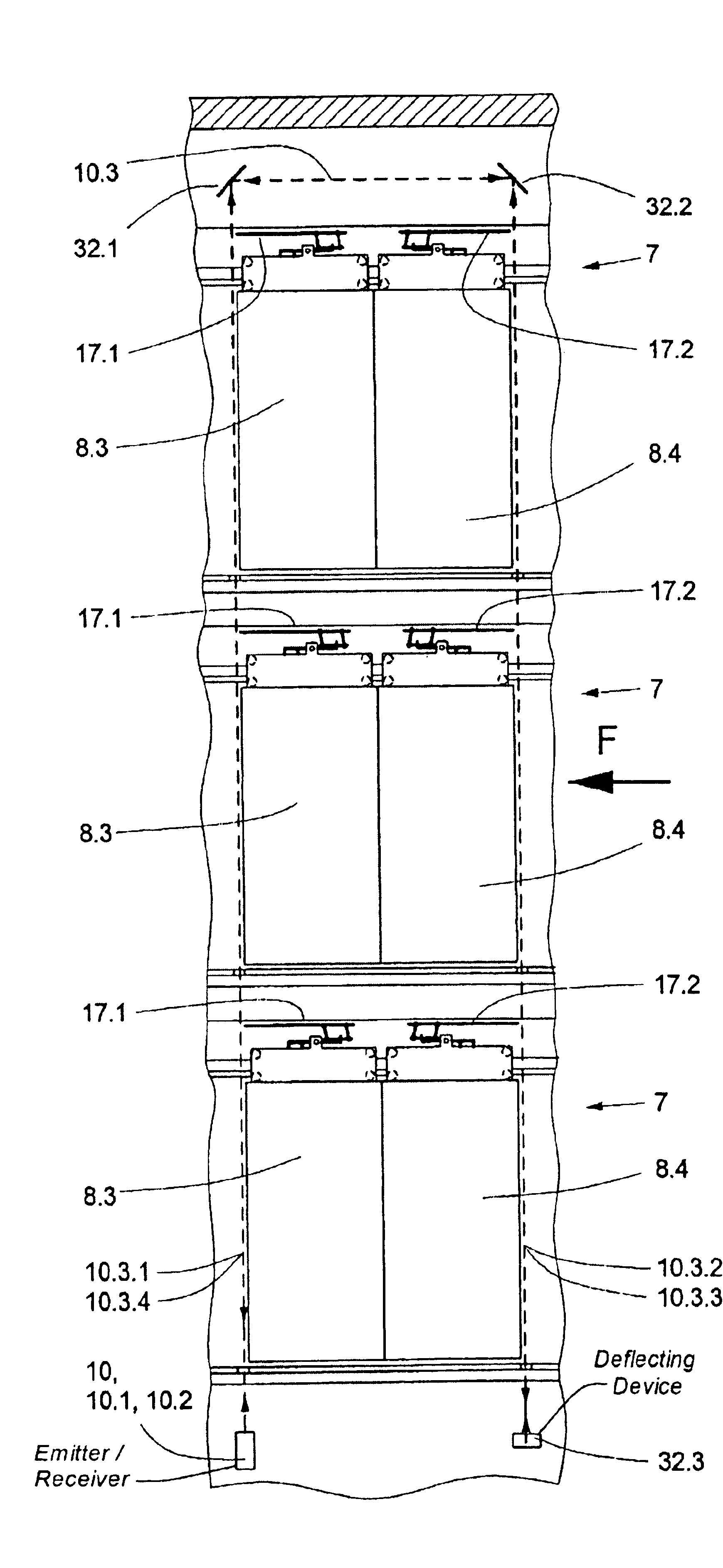
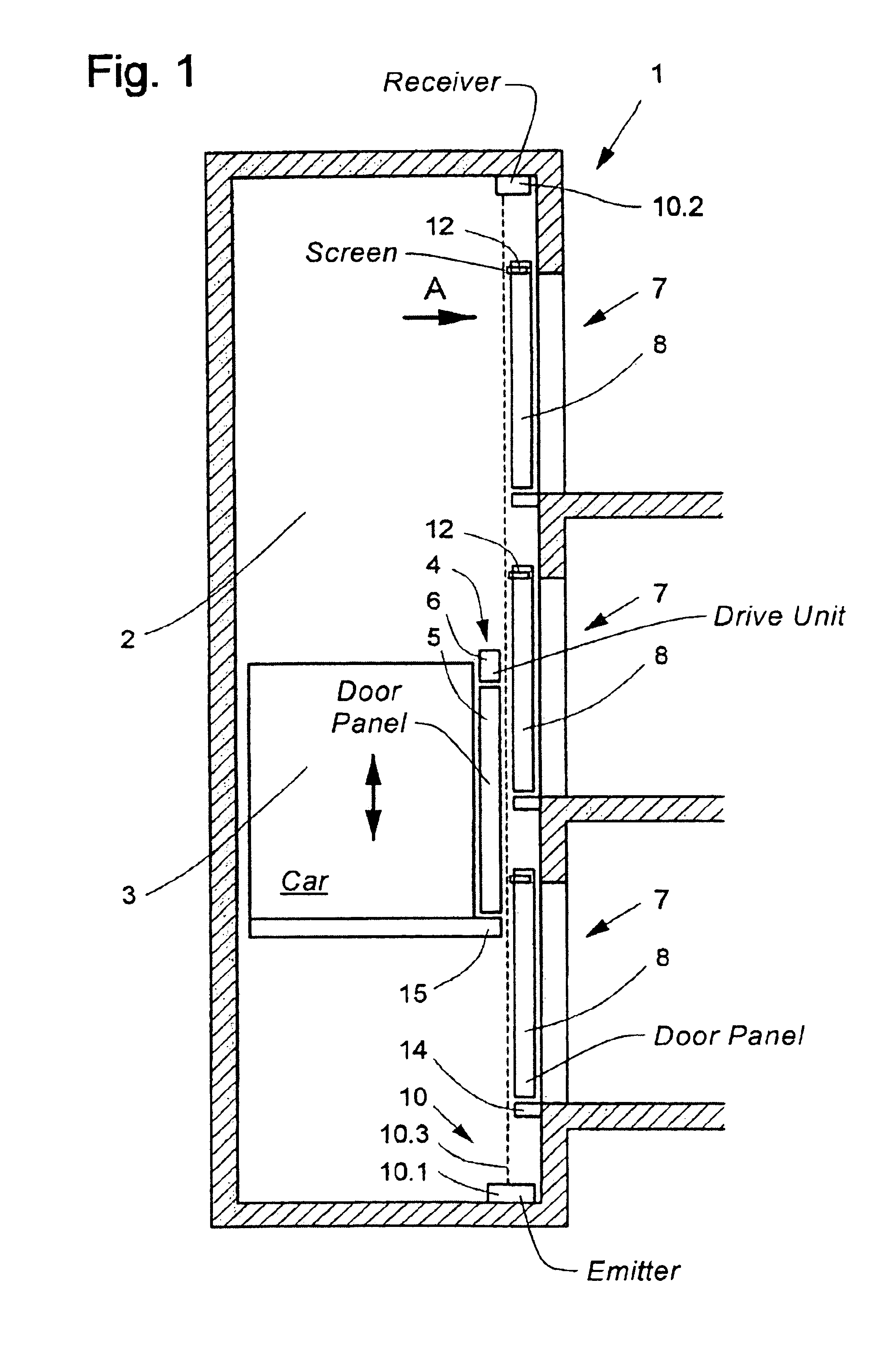
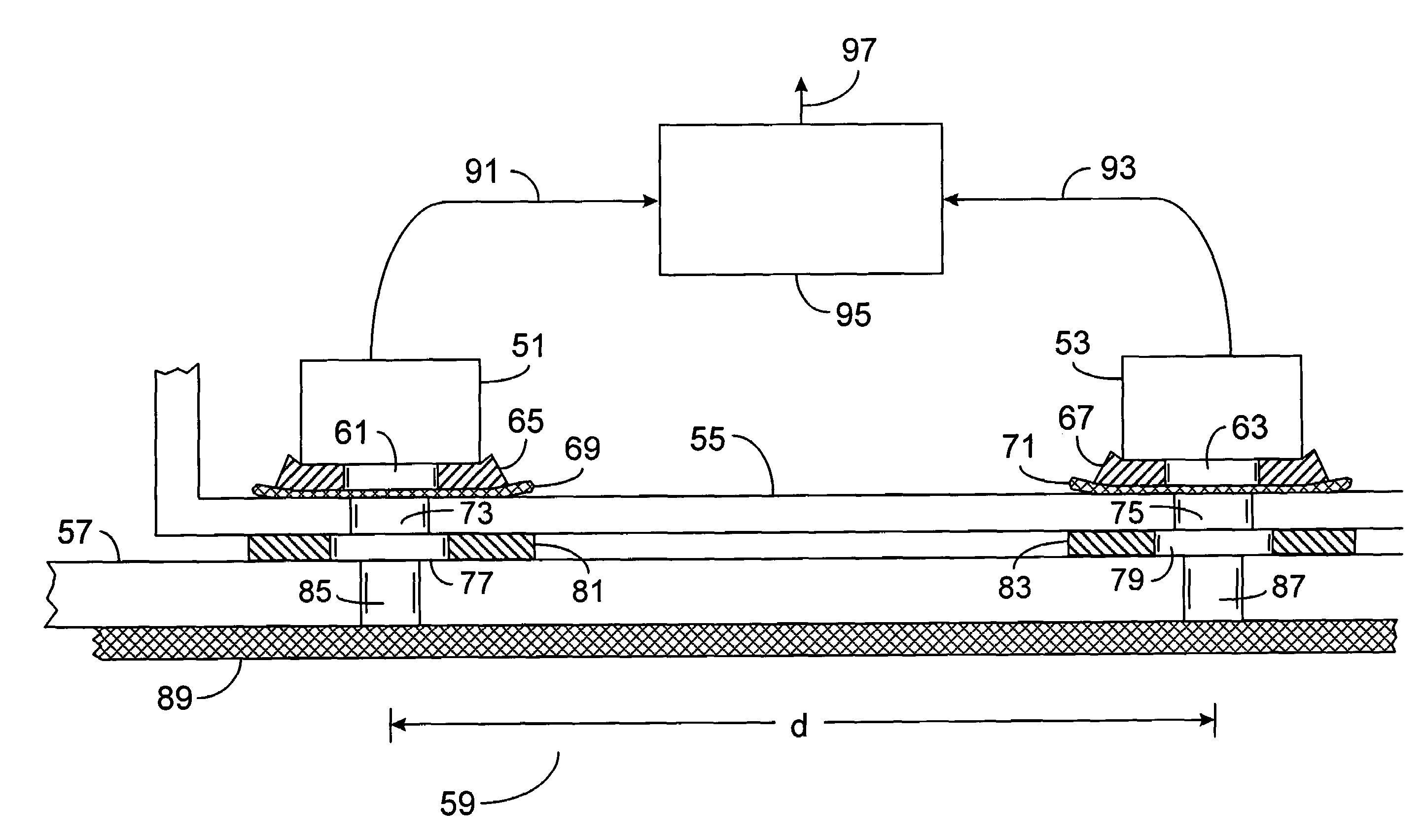
Method of contactlessly monitoring elevator shaft doors
ActiveUS6945363B2Simpler and economicMinimizing sensitivityElevatorsBuilding liftsSpecific detectionElevator control
A method for monitoring shaft doors of a elevator installation uses at least one contactlessly acting shaft door monitoring sensor to emit a beam of electromagnetic waves, wherein at least during specific detection phases the beam extends over several floors and is detected by a receiver. The beam is influenced by a shaft door panel not being completely closed and / or a shaft door lock not being disposed in the locking setting such that a disturbance signal is generated to the elevator control.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
2D coding and decoding barcode and its method thereof
InactiveUS20070114285A1Improve reliabilityMinimizing sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesComputer hardwareBarcode
Owner:WUHAN SYSCAN TECH CO LTD
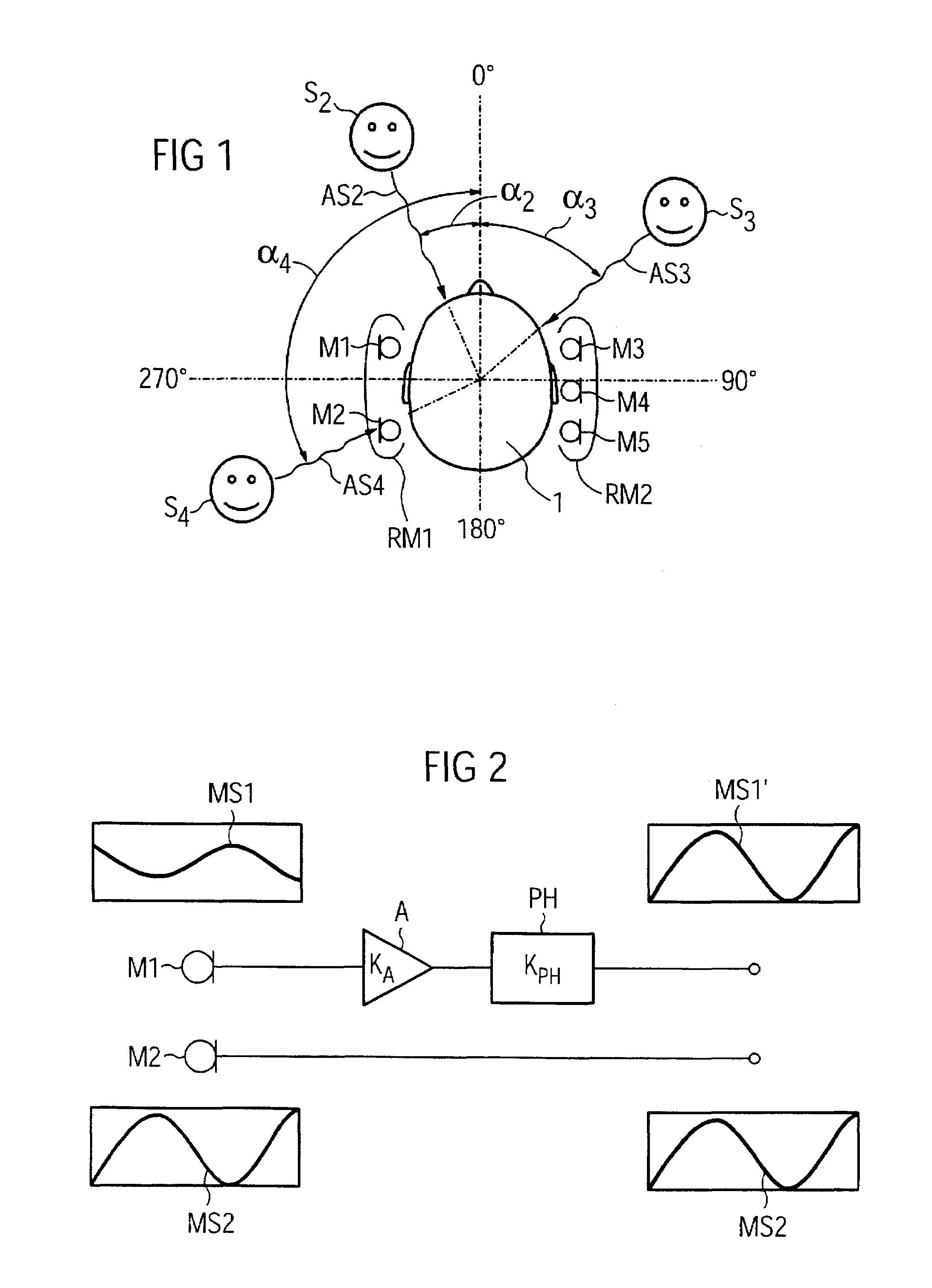
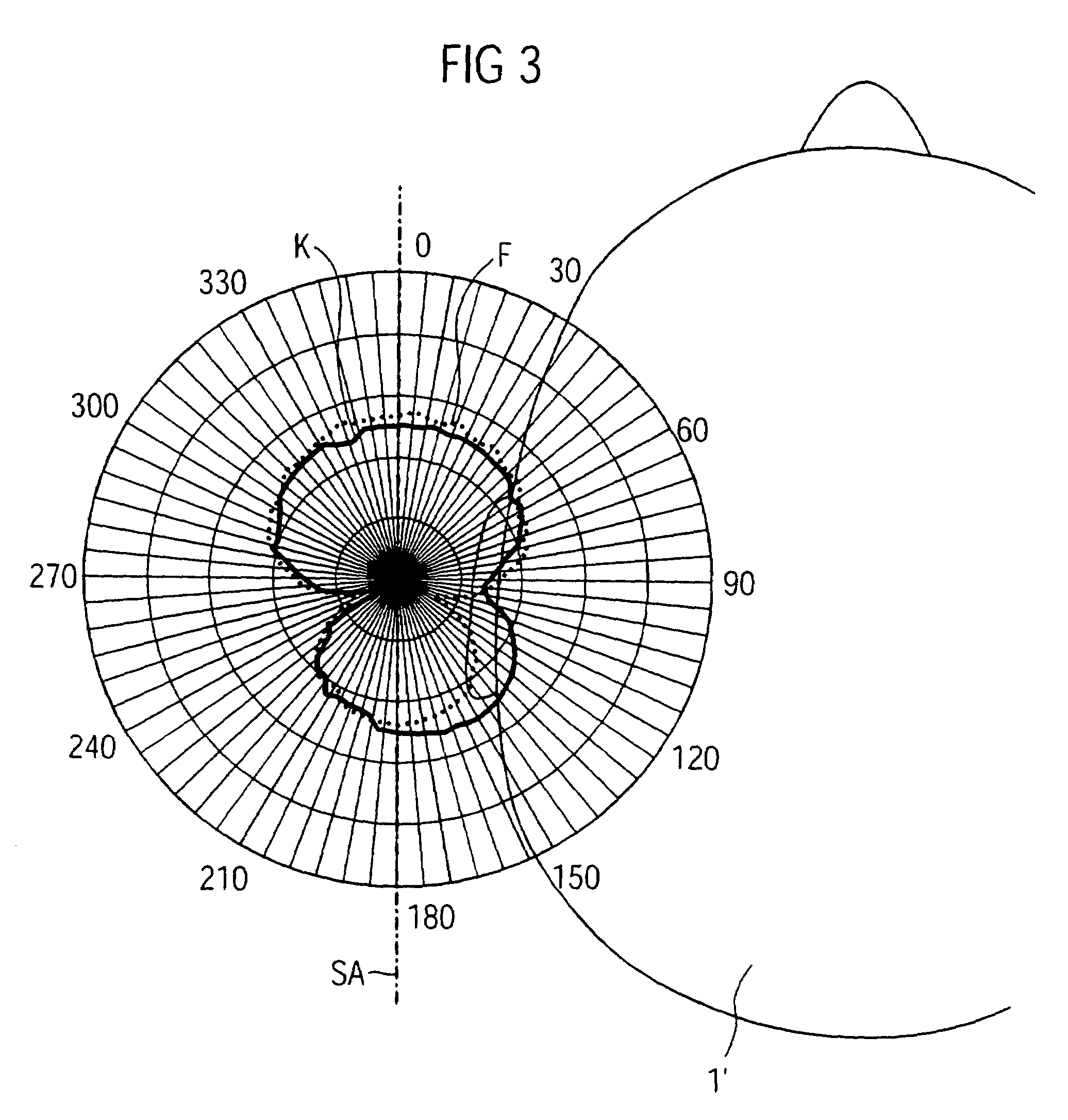
Method and apparatus for identifying the direction of incidence of an incoming audio signal
ActiveUS7561701B2Easy accessMinimizing sensitivityMicrophonesLoudspeakersSensitivity distributionSignal source
To determine the direction of incidence for a signal from an acoustic signal source using a directional microphone system, which has at least two microphones, two or more directional microphone signals are produced, each having a direction-dependent sensitivity distribution with a minimum in one direction. The directional microphone signals are assessed with regard to a quantity to determine the directional microphone signal which is most influenced by the associated direction dependent sensitivity distribution. The direction of incidence is determined as being the direction in which the minimum of the sensitivity distribution of this directional microphone signal is located.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Directional microphone assembly for mounting behind a surface
InactiveUS7110553B1Less sensitiveSimpler acoustic impedancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesElectrical polarityEngineering
A directional microphone assembly suitable for subsurface mounting. A directional pickup pattern is developed from the outputs of a plurality of omnidirectional microphone elements mounted in an assembly behind a surface such that their acoustic excitation comes from the opposite side of the surface through small openings in the surface. The openings may have varying dimensions and may be covered with acoustically semi-transparent material without significantly degrading the assembly frequency response or polar pattern. Precautions are taken to ensure design robustness considering practical microphone element characteristics and potential high levels of low-frequency excitation.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
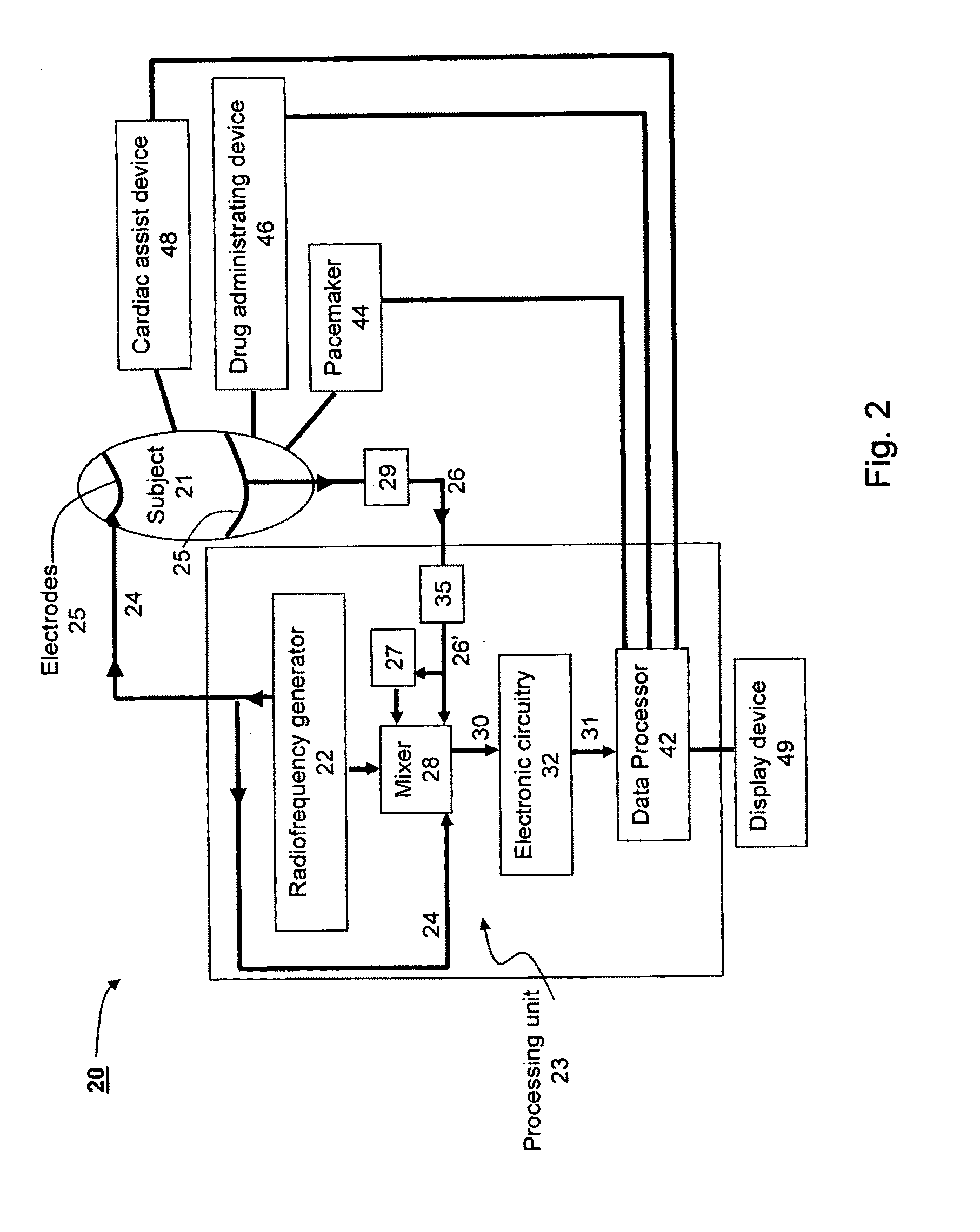
System, Method and Apparatus for Measuring Blood Flow and Blood Volume
ActiveUS20100069765A1Minimizing sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioCatheterSensorsPhase shiftedBlood stream
A method of calculating blood flow in an organ of a subject using output radiofrequency signals transmitted to the organ and input radiofrequency signals received from the organ, the method comprises determining a phase shift of the input radiofrequency signals relative to the output radiofrequency signals and using the phase shift to calculate the blood flow in the organ.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
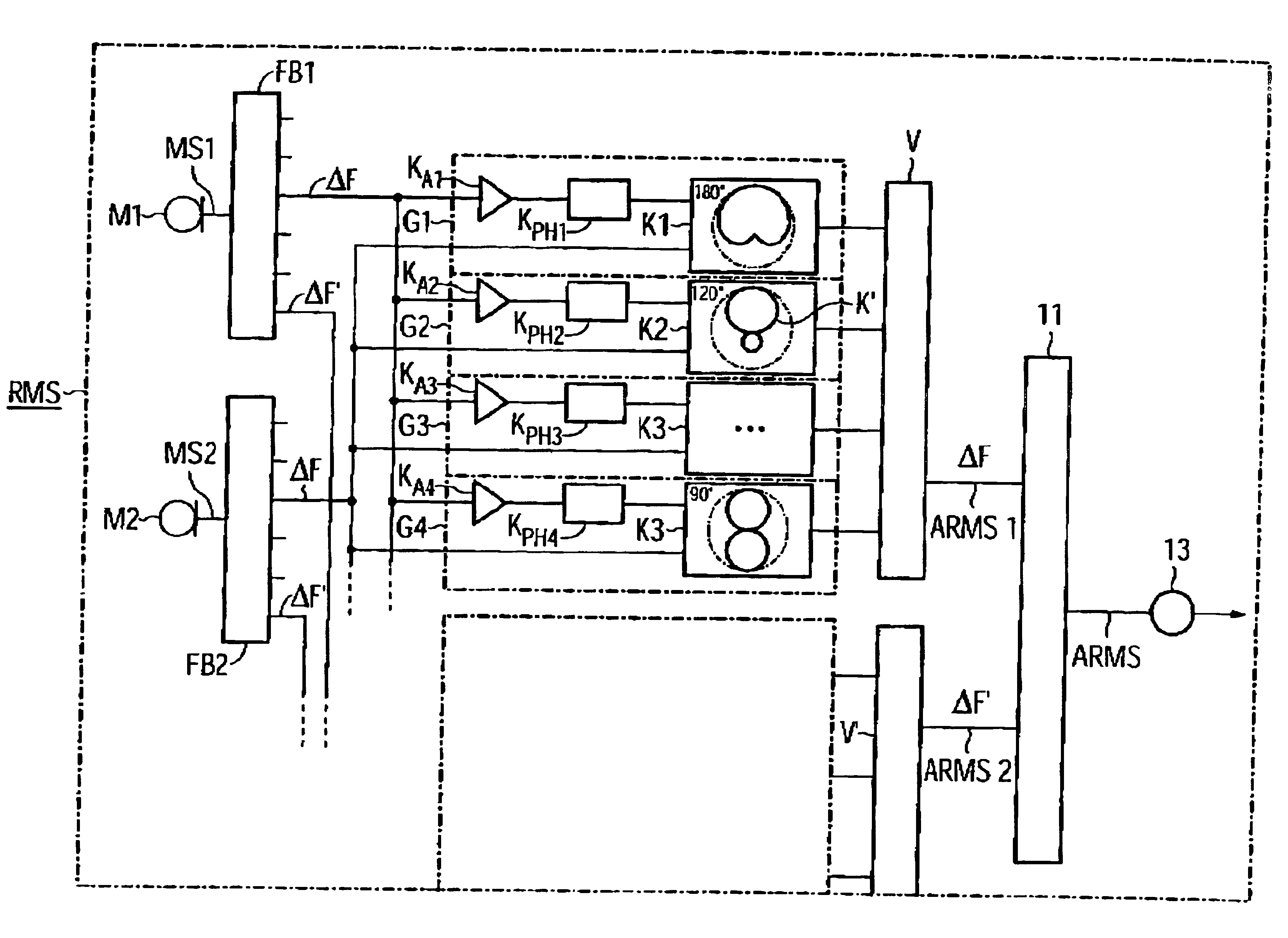
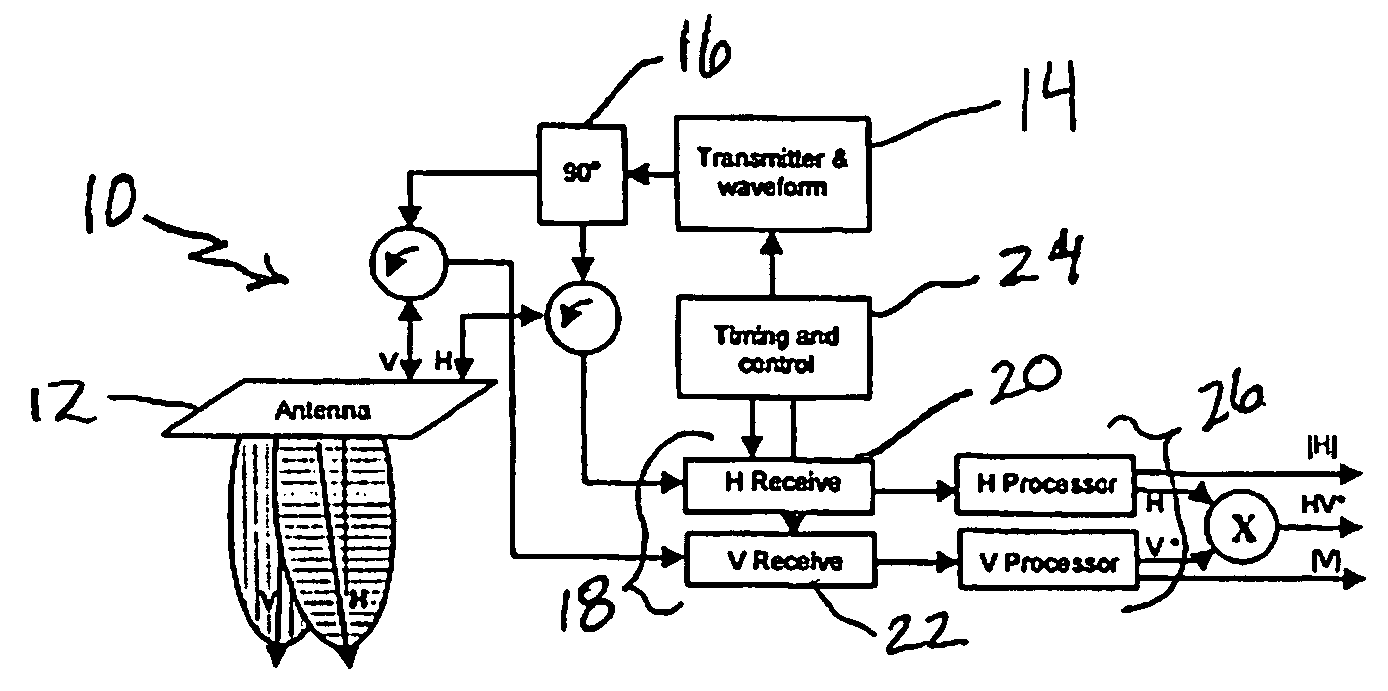
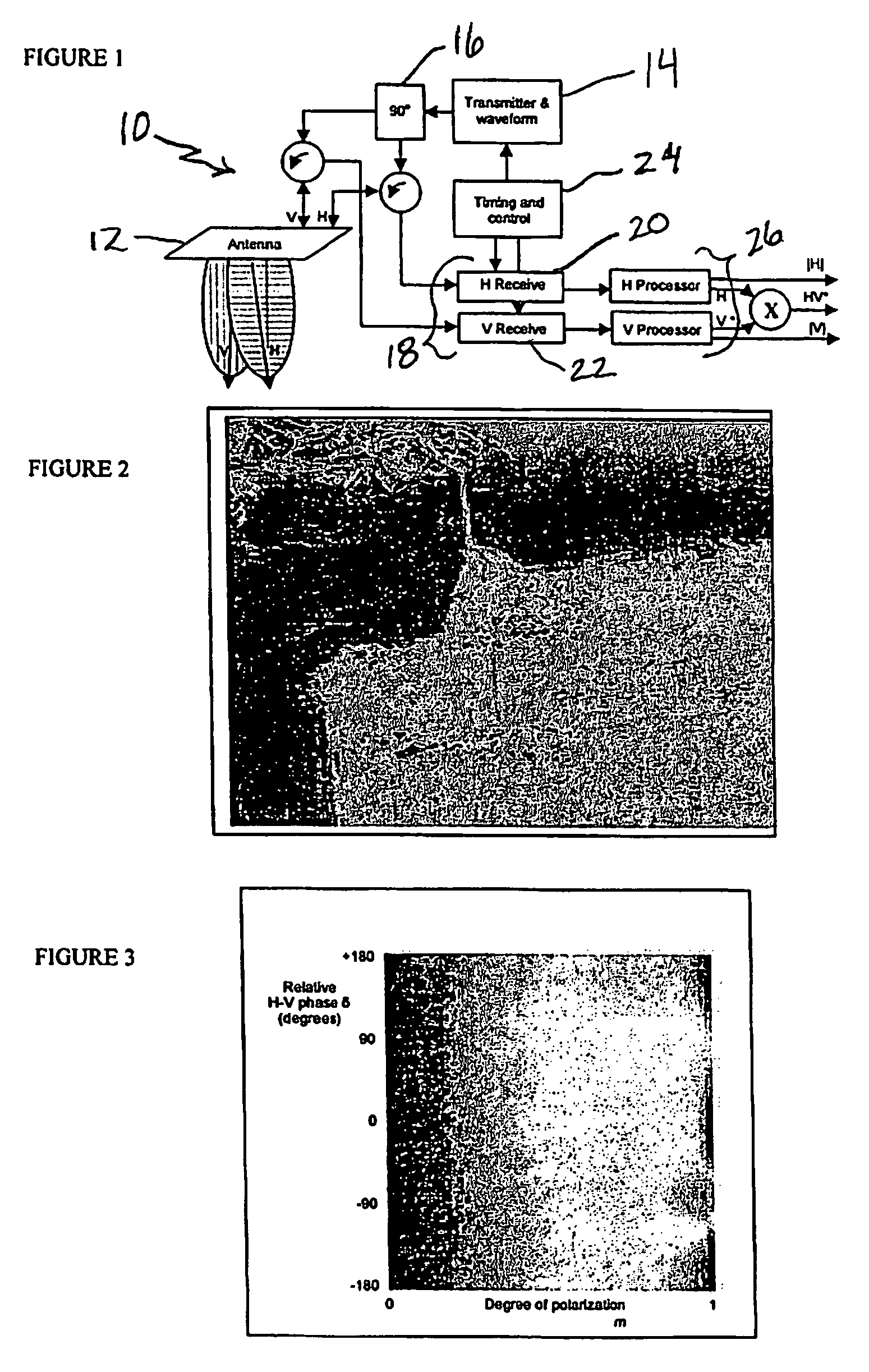
Synthetic aperture radar hybrid-polarity method and architecture for obtaining the stokes parameters of a backscattered field
ActiveUS7746267B2Minimizing sensitivitySimple systemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComplex amplitudeSynthetic aperture radar
A synthetic aperture radar hybrid-polarity method and architecture comprising transmitting circular polarization (by driving the orthogonal linear feeds simultaneously by two identical waveforms, 90° out of phase), and receiving horizontal (H) and vertical (V) linear polarizations, coherently. Once calibrated, the H and V single-look complex amplitude data are sufficient to form all four Stokes parameters, which fully characterize the observed backscattered field.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Implant systems and methods for treating obstructive sleep apnea
ActiveUS8307831B2Increasing curveReducing curve and angleTeeth fillingSnoring preventionSoft palateHard palate
Owner:ETHICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com