Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1208 results about "Constant-velocity joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
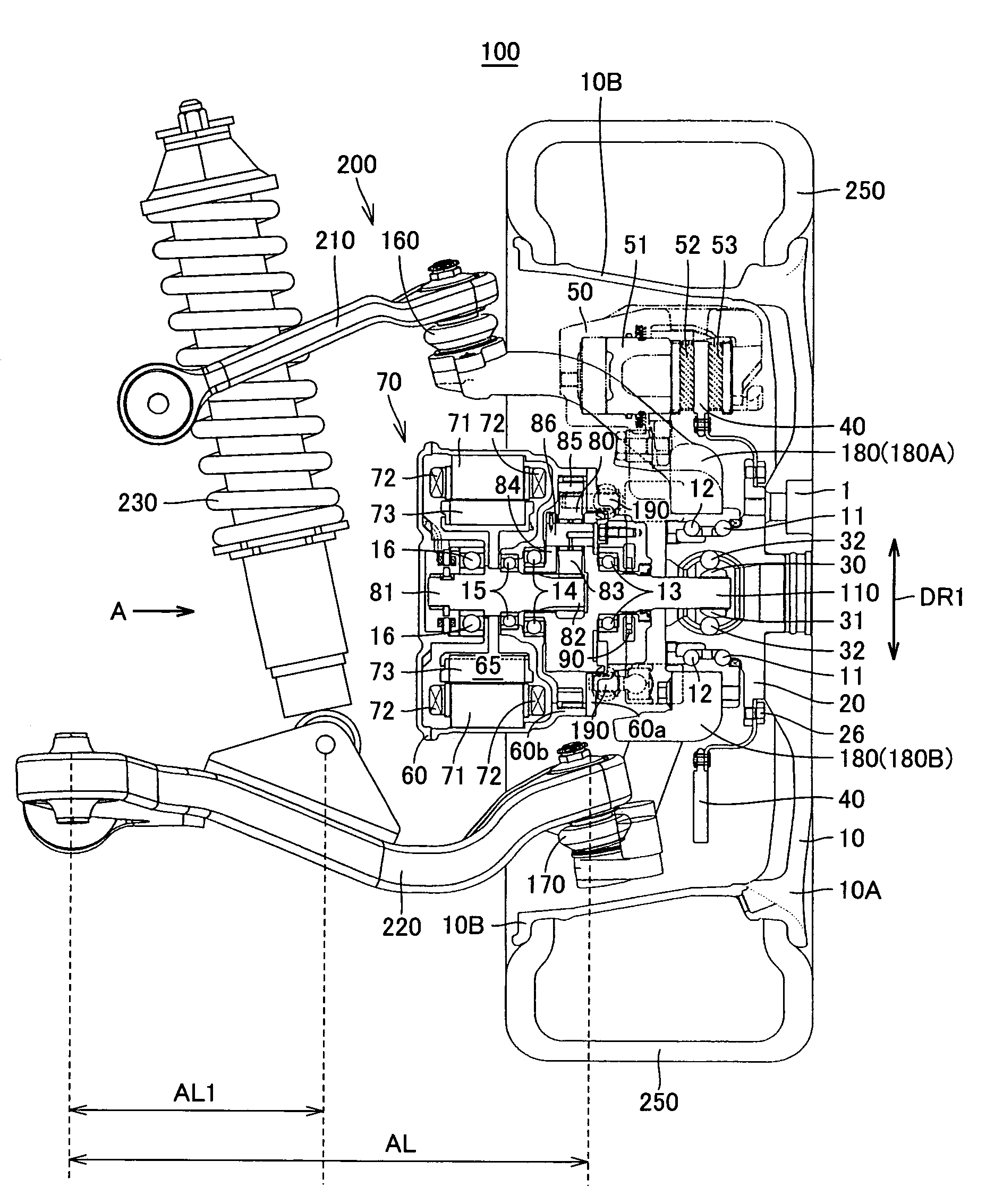
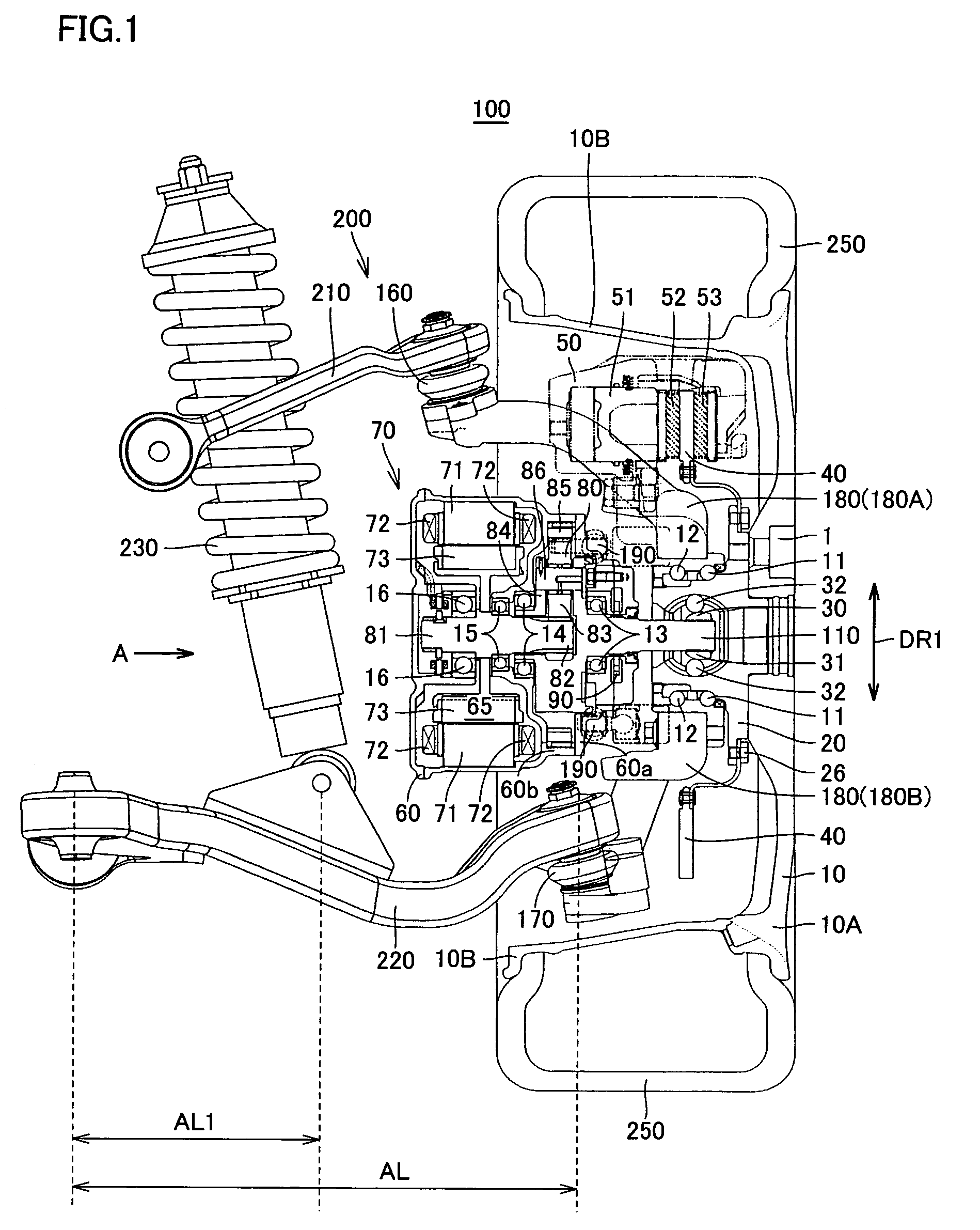
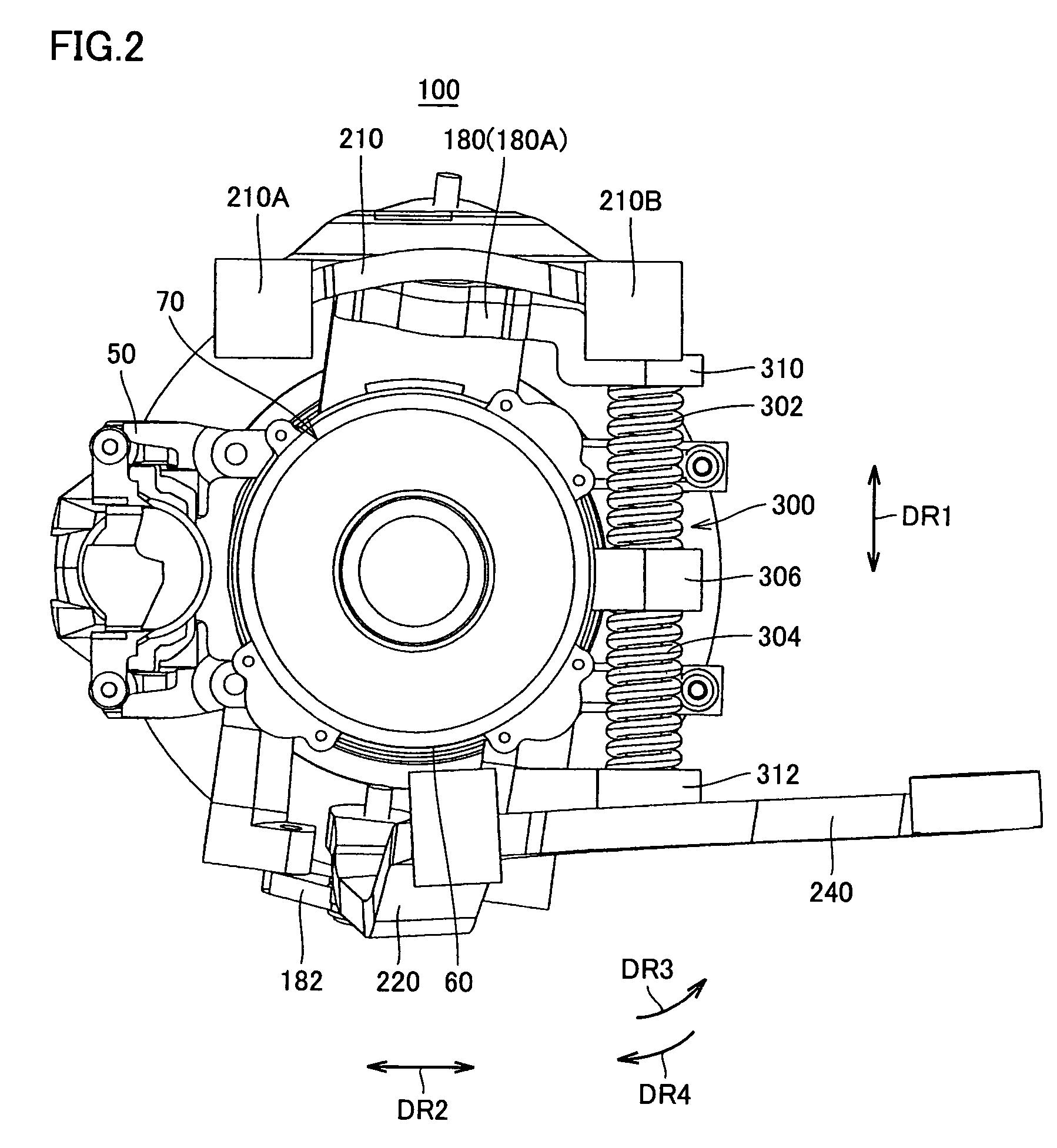
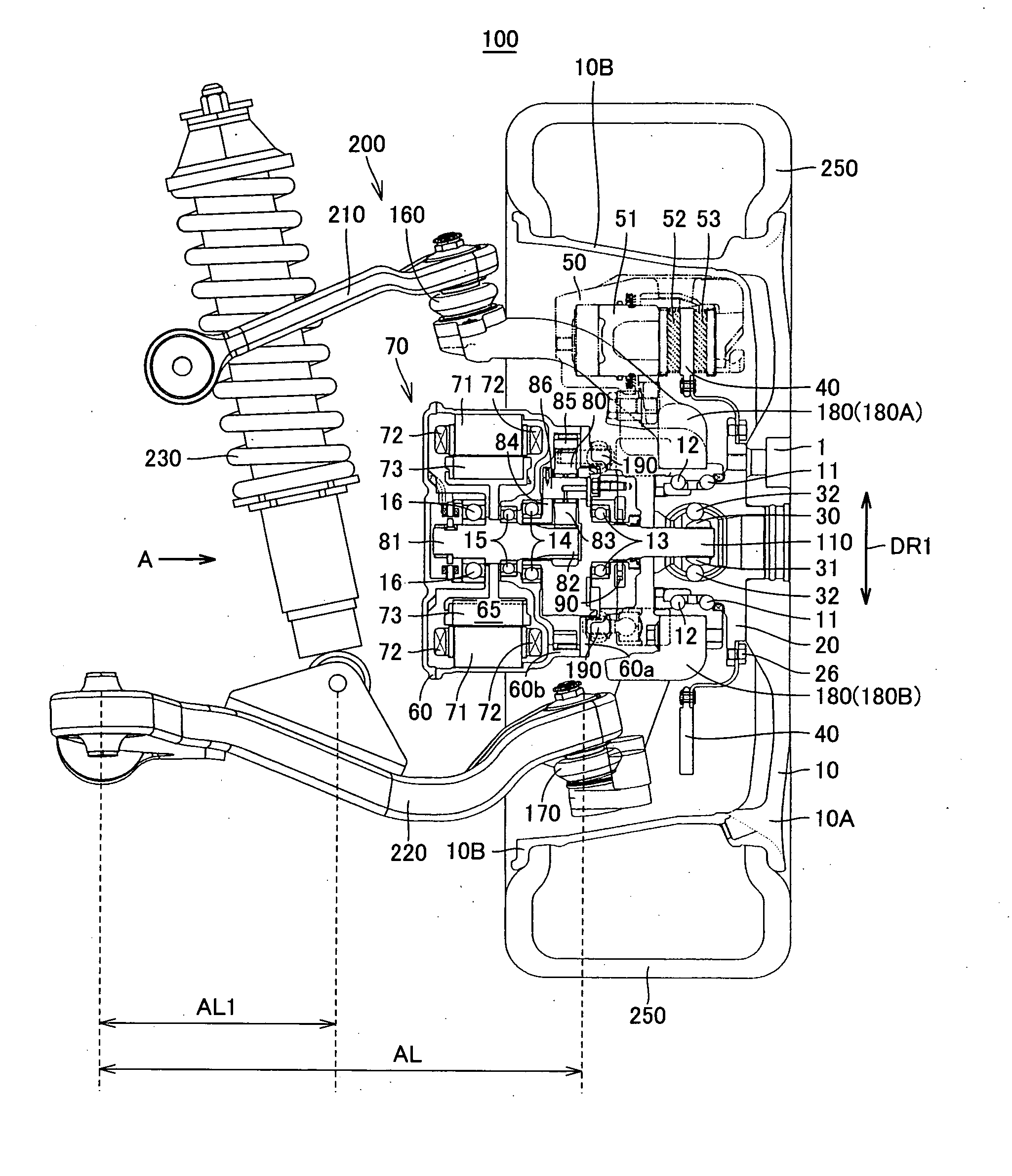
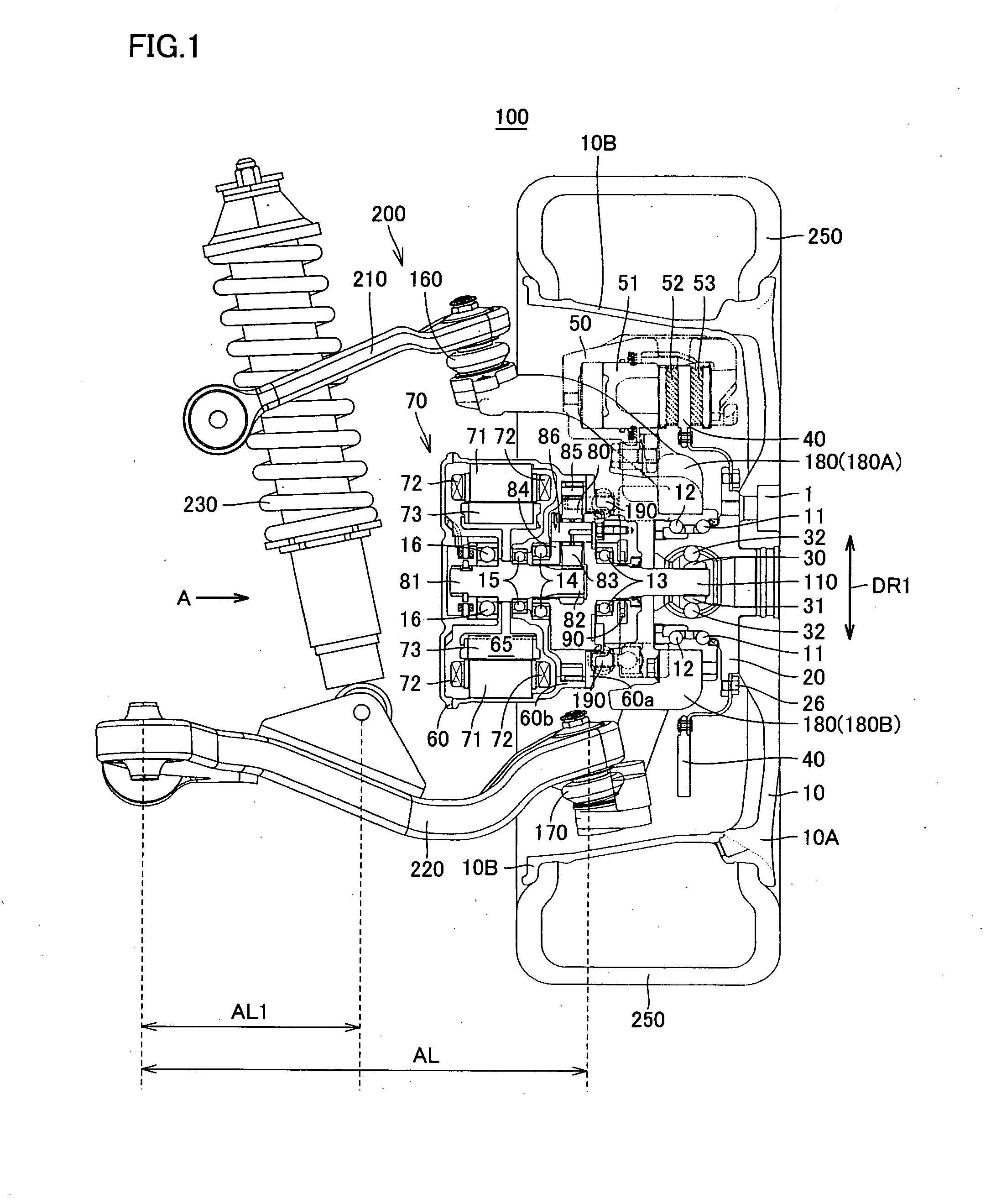
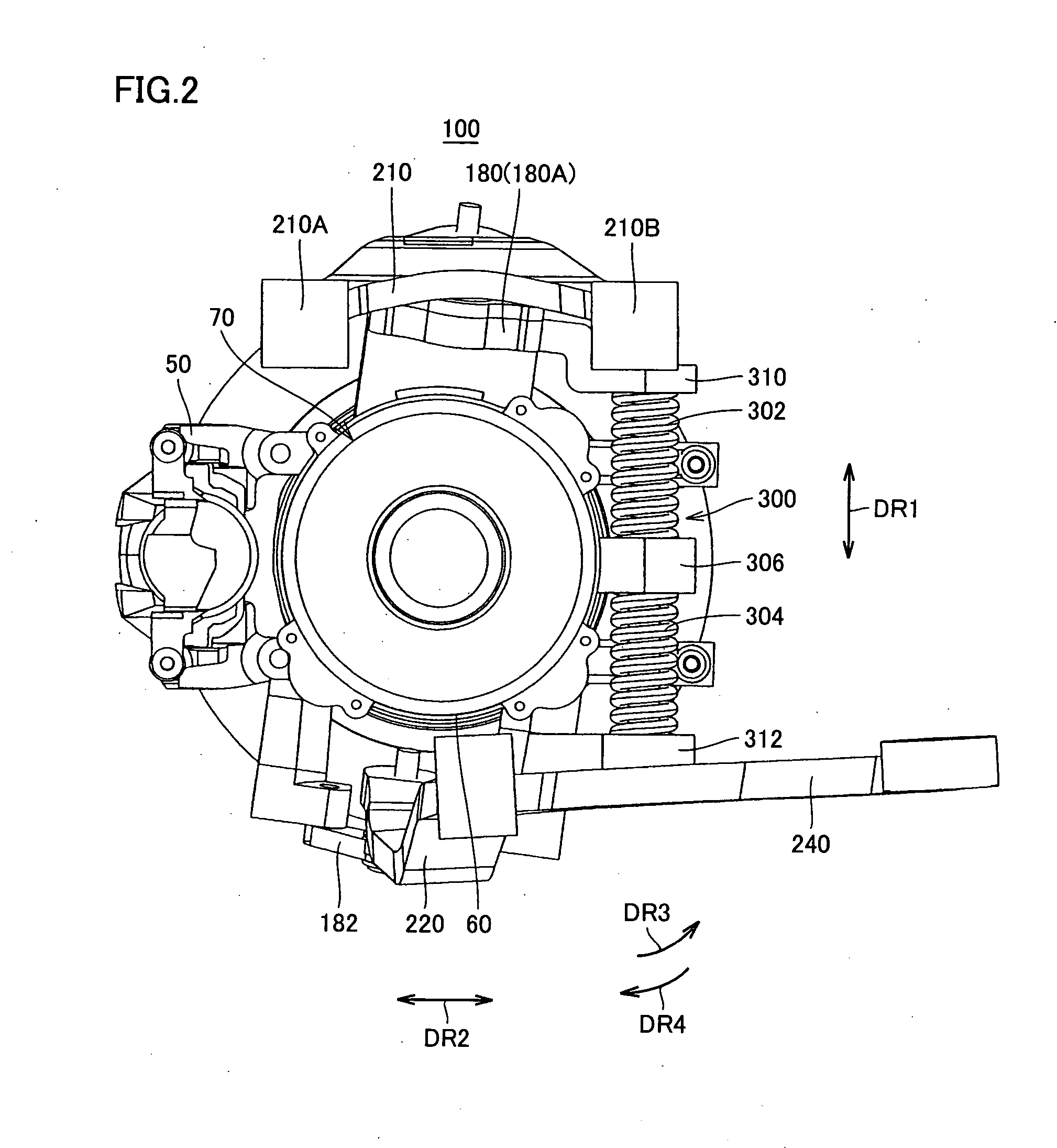
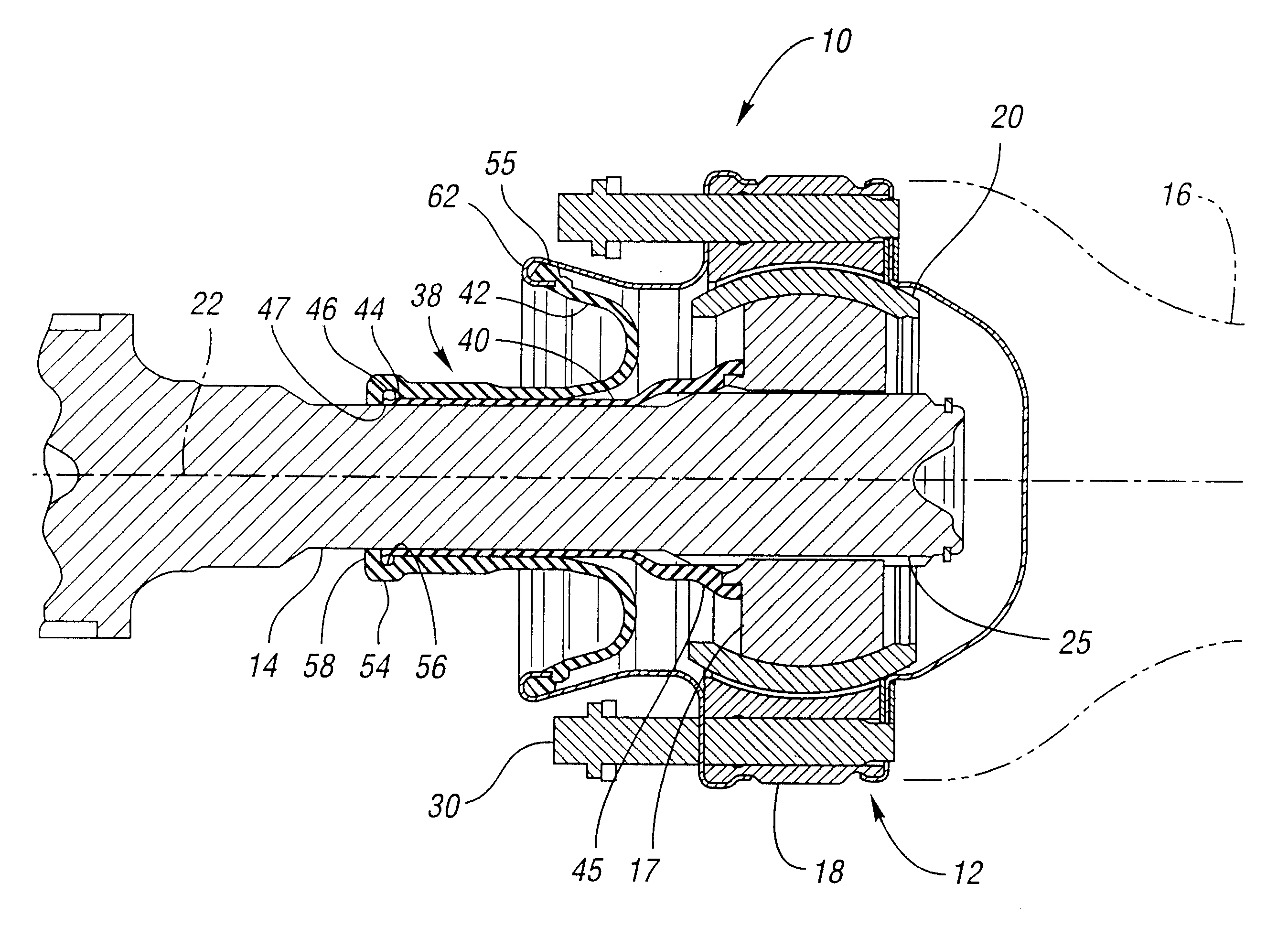
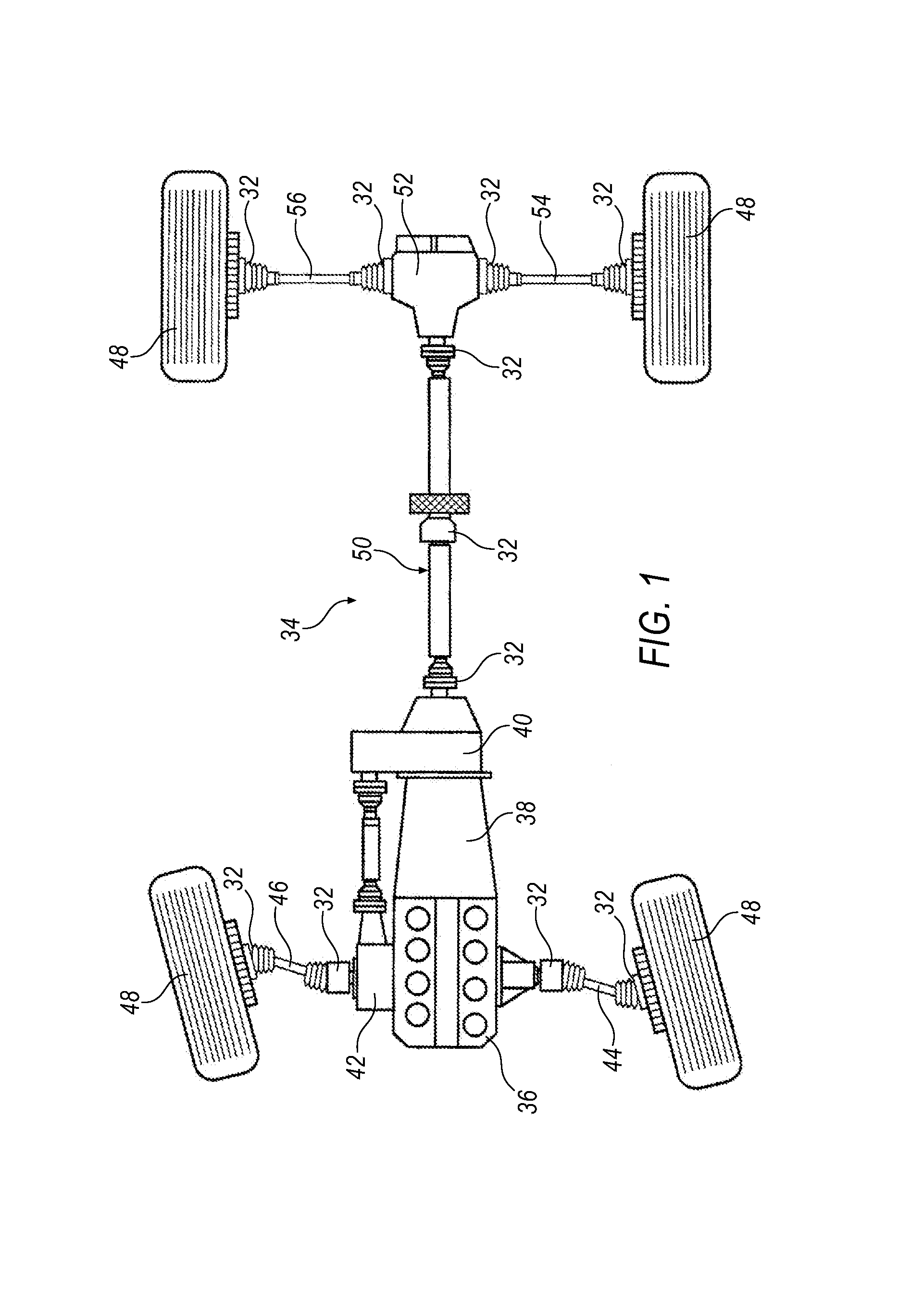
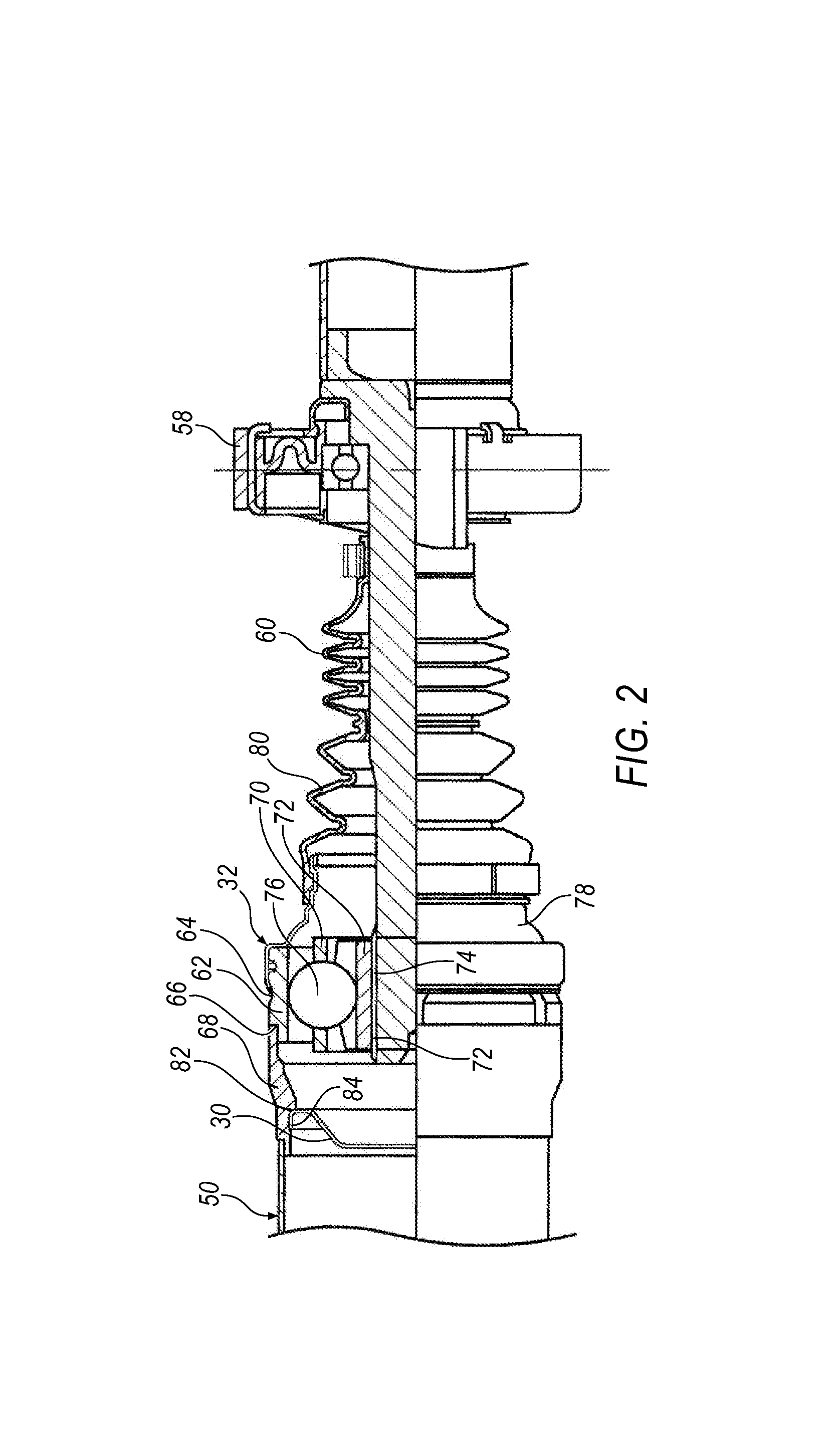
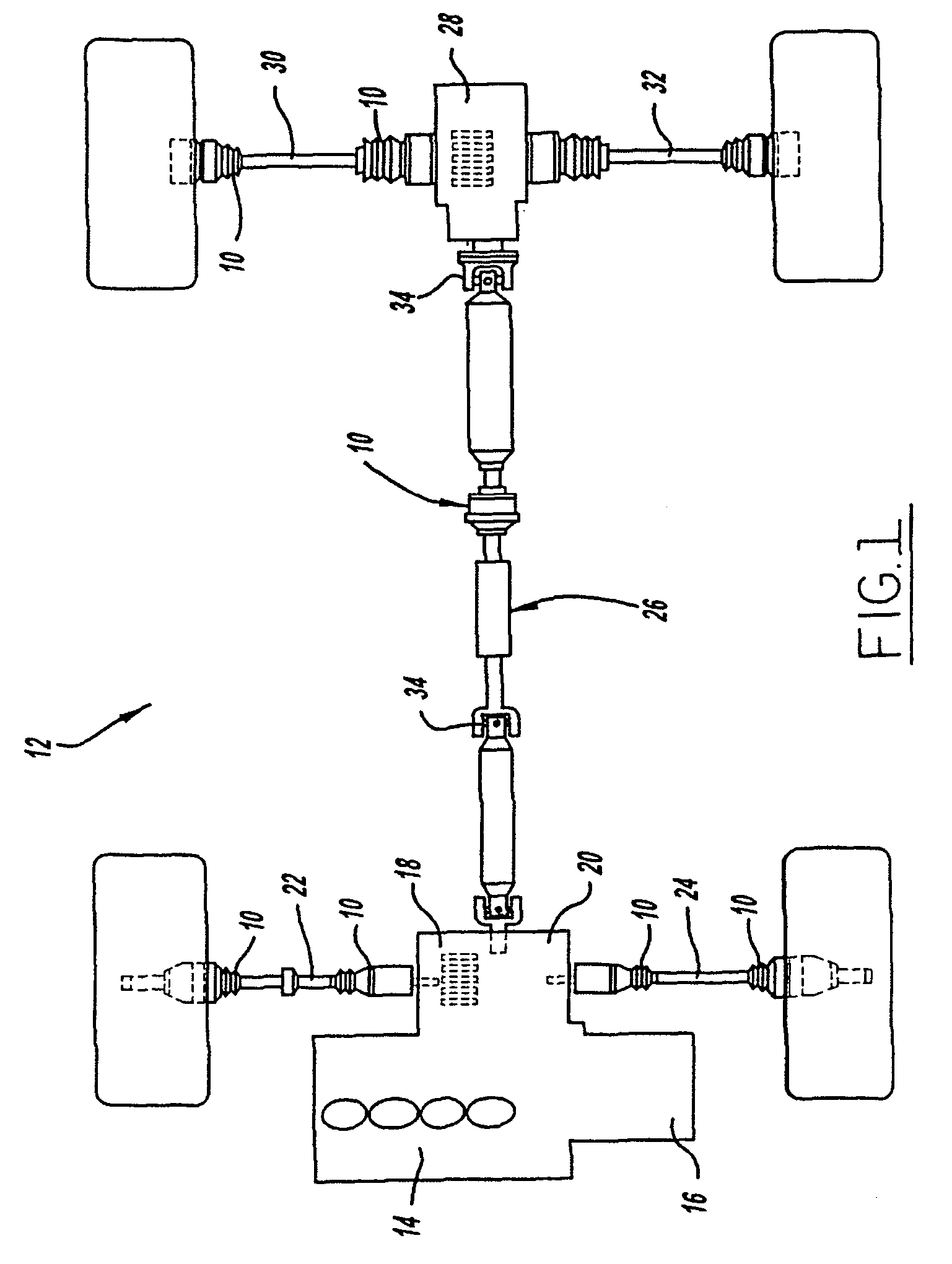
Constant-velocity joints (also known as homokinetic or CV joints) allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or play. They are mainly used in front wheel drive vehicles. Modern rear wheel drive cars with independent rear suspension typically use CV joints at the ends of the rear axle halfshafts and increasingly use them on the drive shafts.
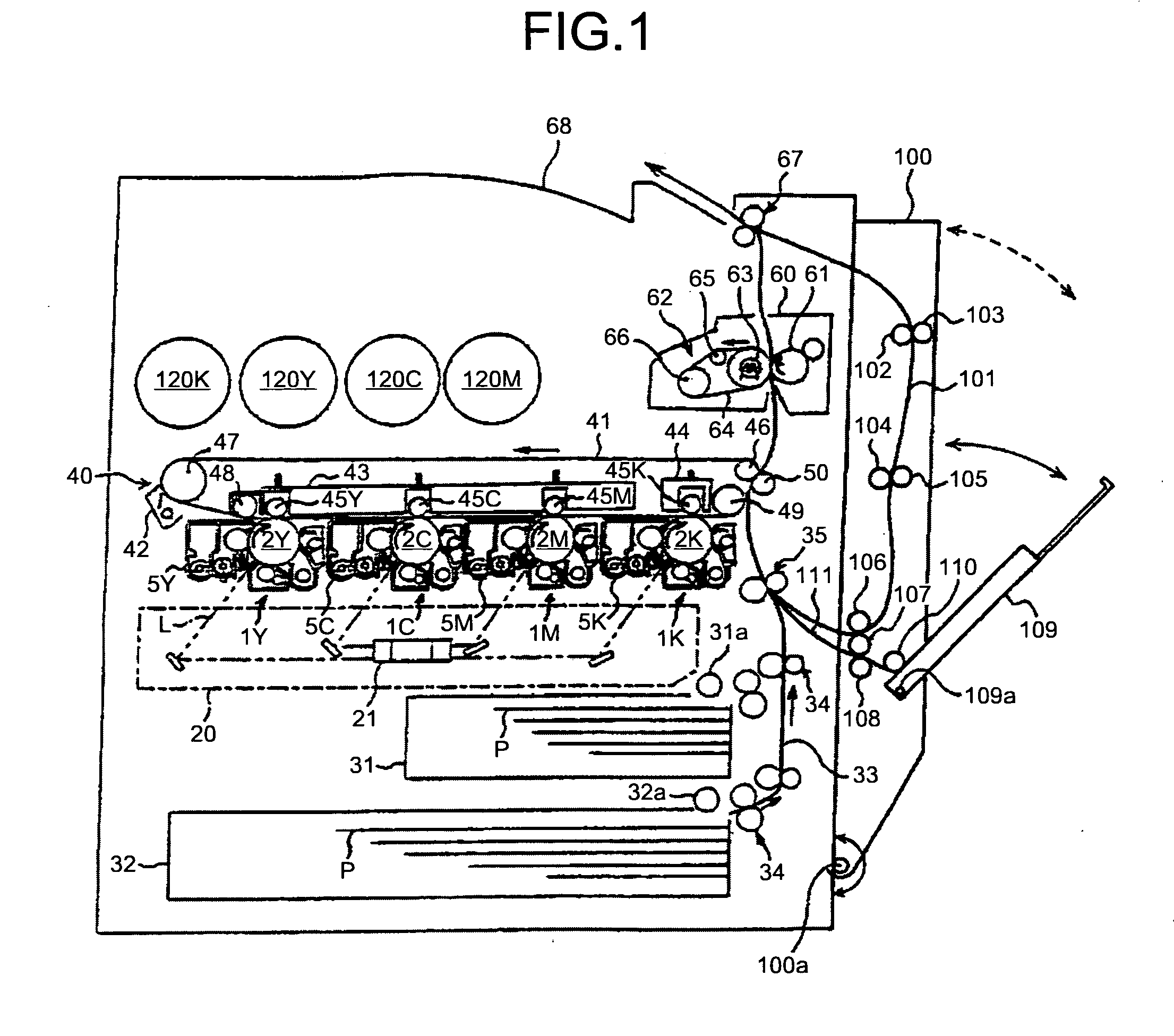
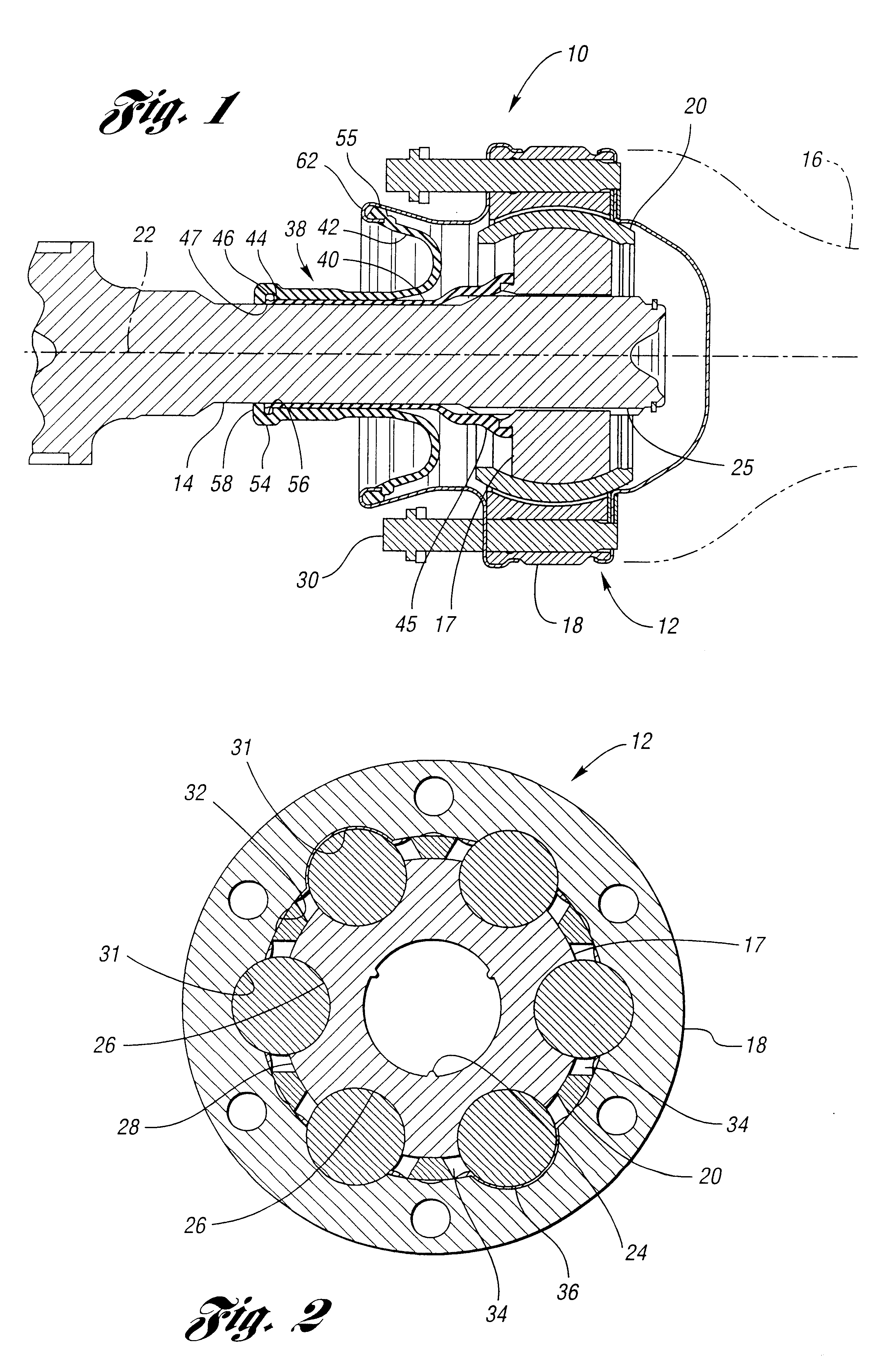
Constant-velocity joint and image forming device
InactiveUS20060240896A1Prevent leakageReduce noiseYielding couplingCouplings for rigid shaftsEngineeringSynthetic resin
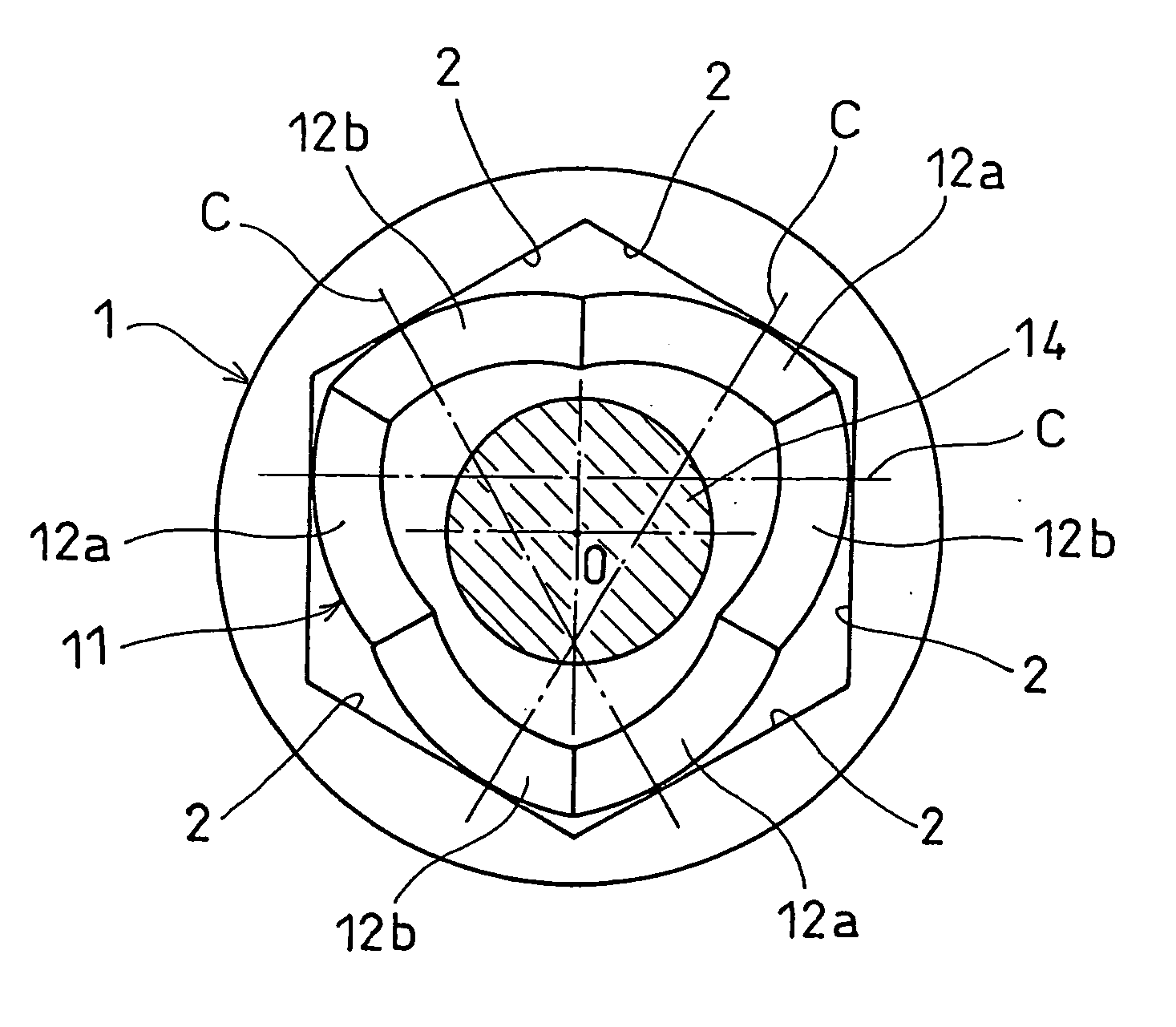
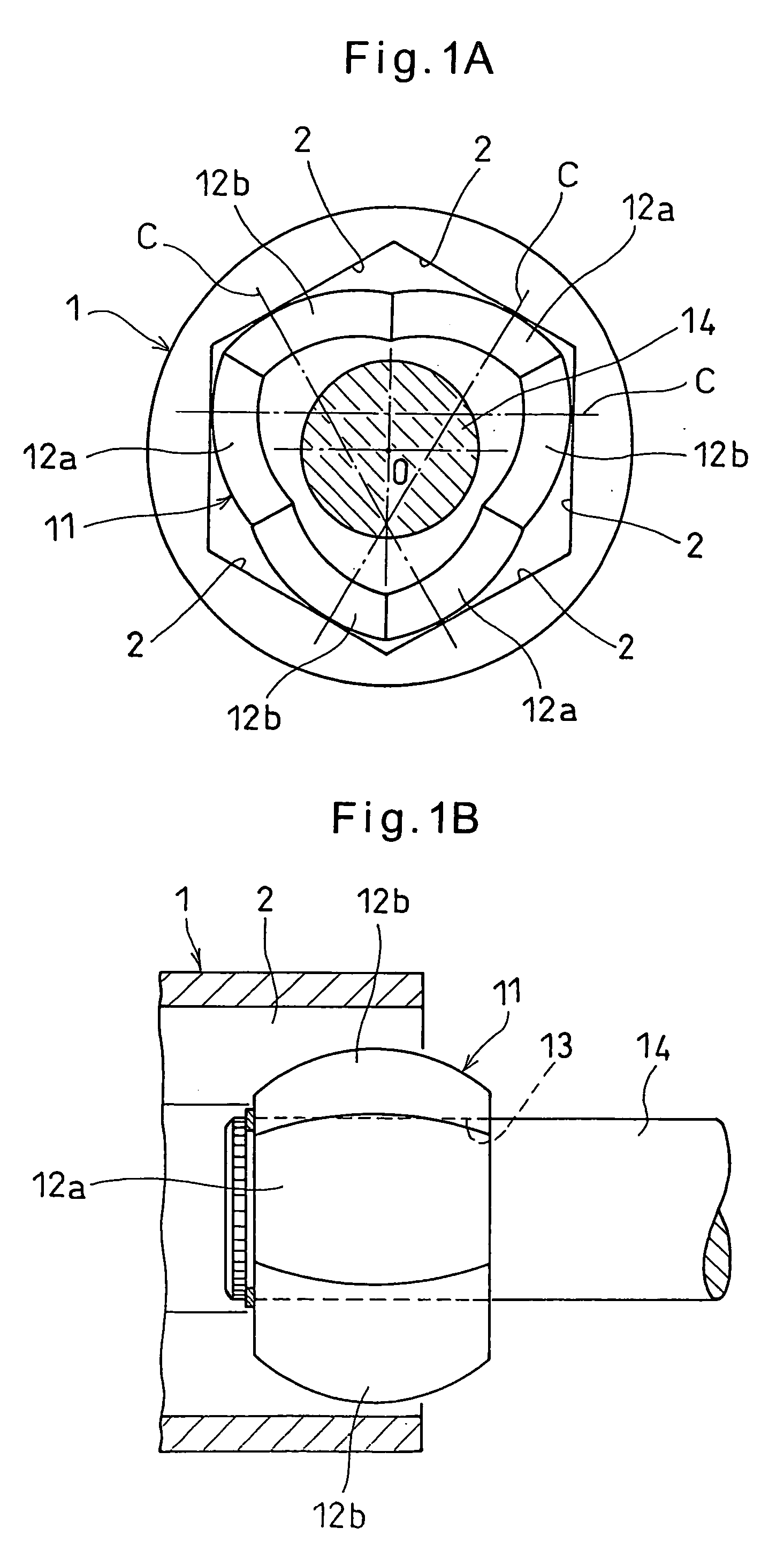
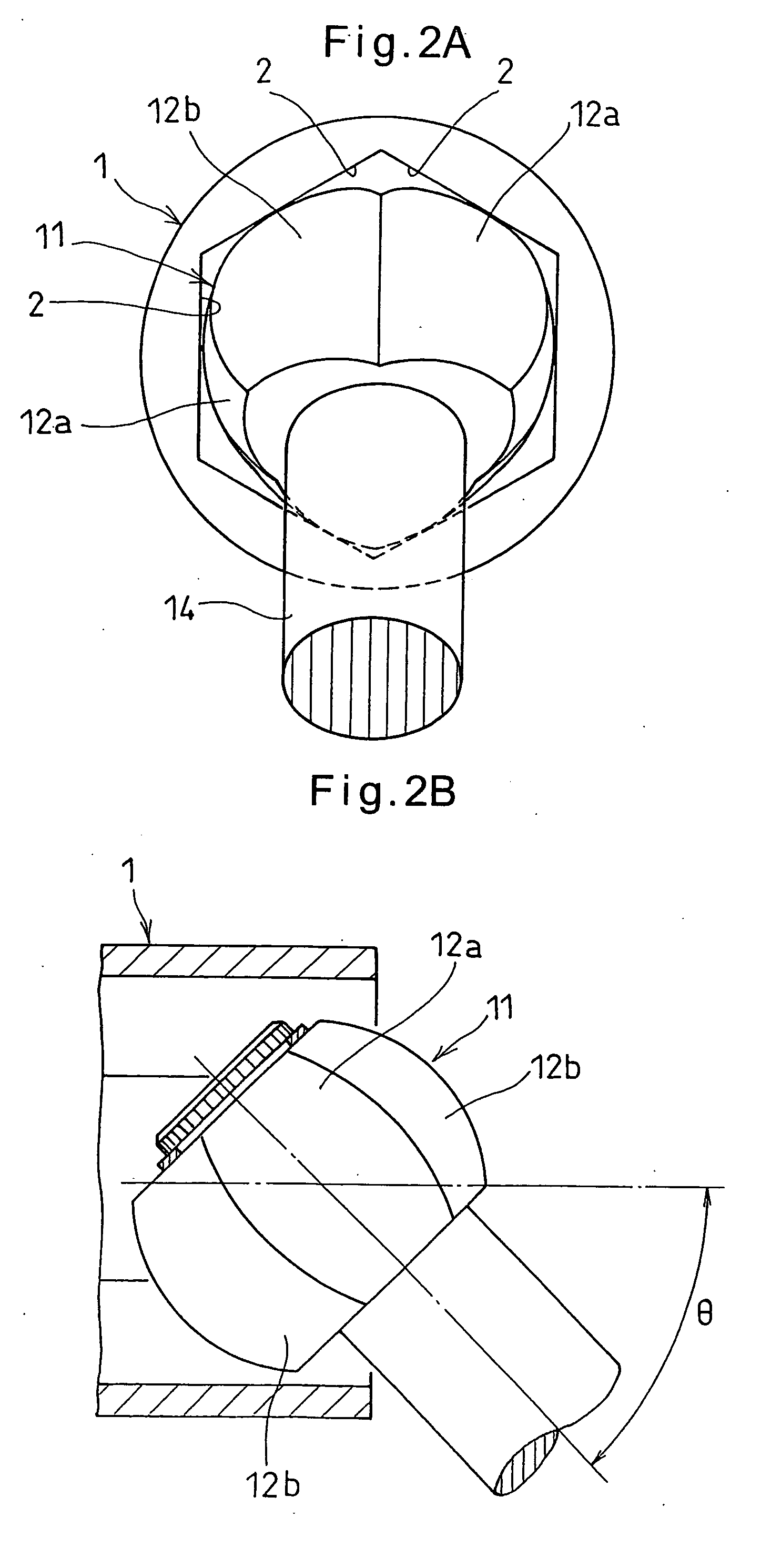
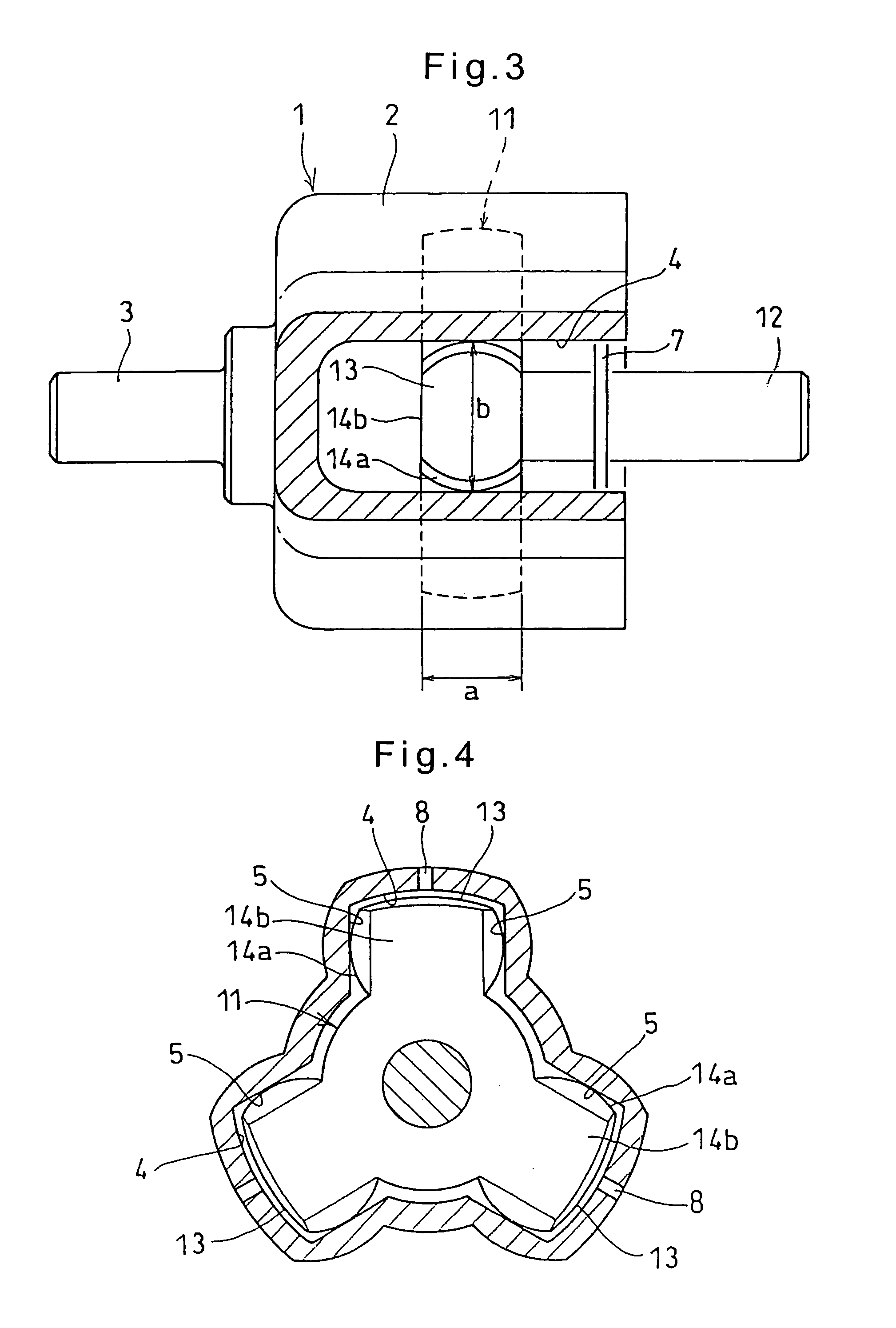
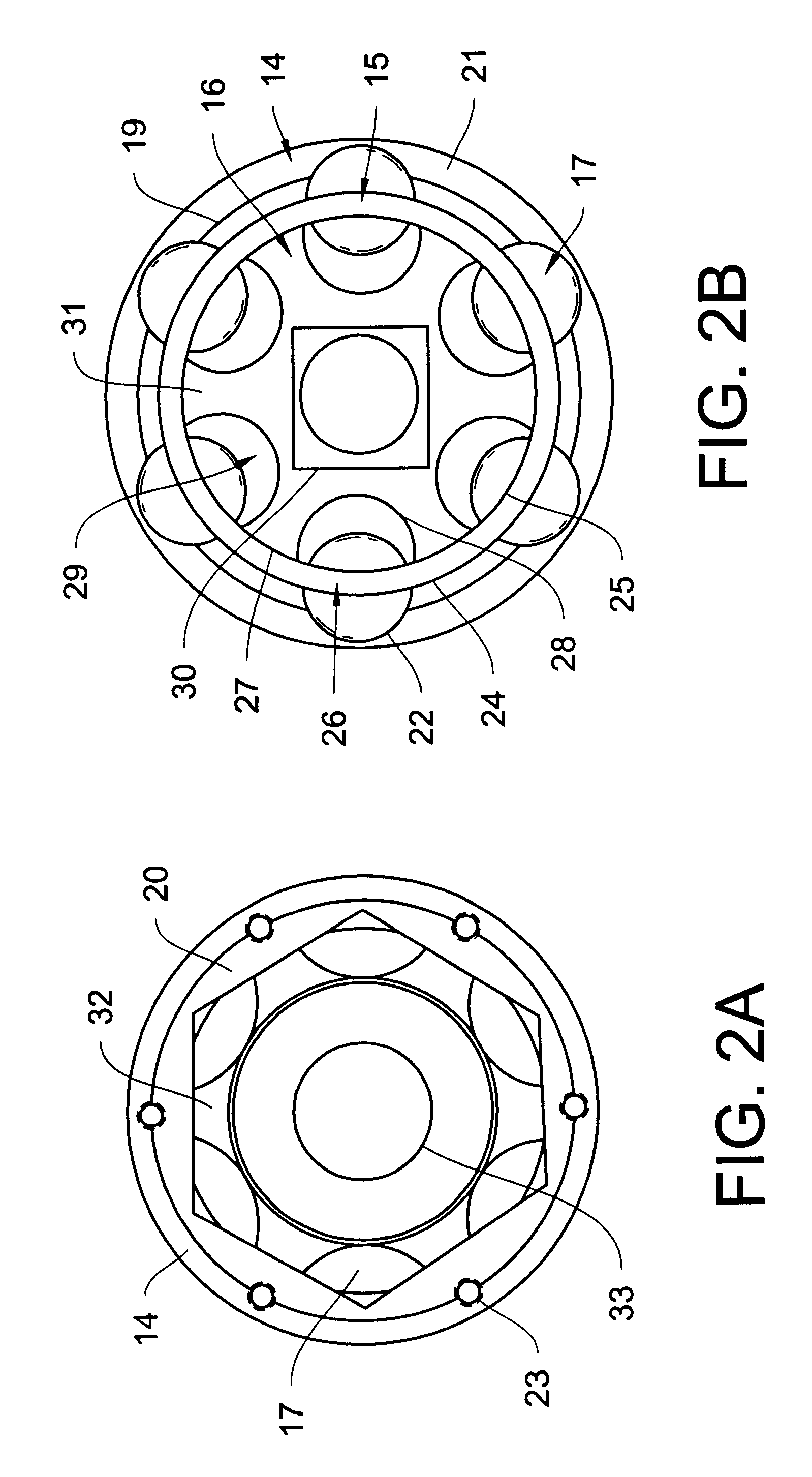
A constant-velocity joint includes an outer ring formed formed with a bore defined by six flat surfaces parallel to its axis, and a trunnion member received in the bore of the outer ring. The trunnion member has an outer periphery formed with three first spherical surfaces circumferentially spaced apart from each other and three second spherical surfaces circumferentially spaced apart from each other and each disposed between adjacent first spherical surfaces. Each first spherical surface is in contact with one of the flat surfaces at a point offset from the circumferential center of the flat surface in one circumferential direction. Each second spherical surface is in contact with another flat surface at a point offset from the circumferential center of the flat surface in the other circumferential direction. At least one of the outer ring and the trunnion member is made of a synthetic resin.
Owner:NTN CORP
Coupling device, and image forming apparatus
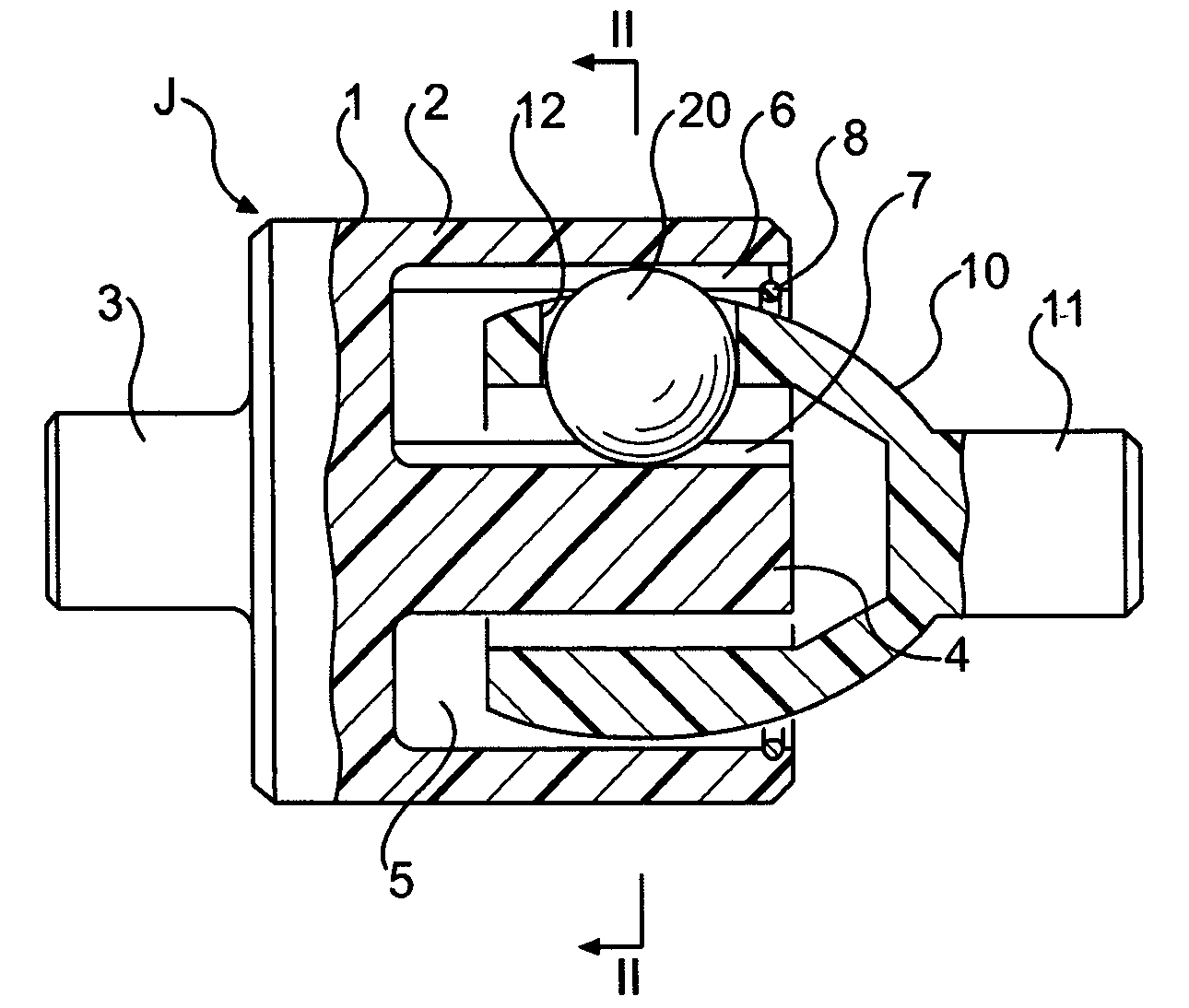
A coupling unit includes two constant velocity joints arranged in series in the shaft direction. The coupling unit couples a driven shaft and a drive shaft. Each constant velocity joint includes a ball non-retaining member and a ball retaining member. The ball non-retaining member has an annular space with one opened end and a plurality of track grooves extending in the shaft direction on an external wall surface of the annular space at a constant interval in a circumferential direction. The ball retaining member has a portion that engages with the annular space of the ball non-retaining member, and that retains a ball that slides along each of the track grooves formed in the ball non-retaining member.
Owner:RICOH KK
Constant-velocity joint and image-forming device
InactiveUS20050281586A1Minimizes operating noiseSimple structureYielding couplingElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringSynthetic resin
A constant-velocity joint includes an outer ring formed with an annular space therein having an opening at one end thereof. The annular space is defined by a radially outer wall and a radially inner wall. One of the radially inner and outer walls is formed with three axially extending track grooves circumferentially spaced apart from each other by 120 degrees. A cage is inserted in the annular space with one end thereof protruding from the opening of the annular space. A second shaft is provided on the one end of the cage. Balls are retained by the cage and adapted to roll in the track grooves. At least one of the outer ring and the cage is formed of a synthetic resin.
Owner:NTN CORP
Constant-velocity joint and image forming device
InactiveUS7529507B2Prevent leakageRule out the possibilityYielding couplingCouplings for rigid shaftsEngineeringSynthetic resin
A constant-velocity joint includes an outer ring formed with a bore defined by six flat surfaces parallel to its axis, and a trunnion member received in the bore of the outer ring. The trunnion member has an outer periphery formed with three first spherical surfaces circumferentially spaced apart from each other and three second spherical surfaces circumferentially spaced apart from each other and each disposed between adjacent first spherical surfaces. Each first spherical surface is in contact with one of the flat surfaces at a point offset from the circumferential center of the flat surface in one circumferential direction. Each second spherical surface is in contact with another flat surface at a point offset from the circumferential center of the flat surface in the other circumferential direction. At least one of the outer ring and the trunnion member is made of a synthetic resin.
Owner:NTN CORP
In-wheel motor with high durability
An in-wheel motor includes a motor generating motive power, a planetary gear arranged toward a wheel disc relative to the motor to reduce an output of the motor, and a shaft arranged toward the wheel disc relative to the planetary gear and connected to a planetary carrier. Shaft is connected to a constant velocity joint transmitting the motive power to wheel disc.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Constant-velocity joint and image forming device
InactiveCN1851282AReduce working noiseSimple structureYielding couplingTypewritersSynthetic resinWeight light
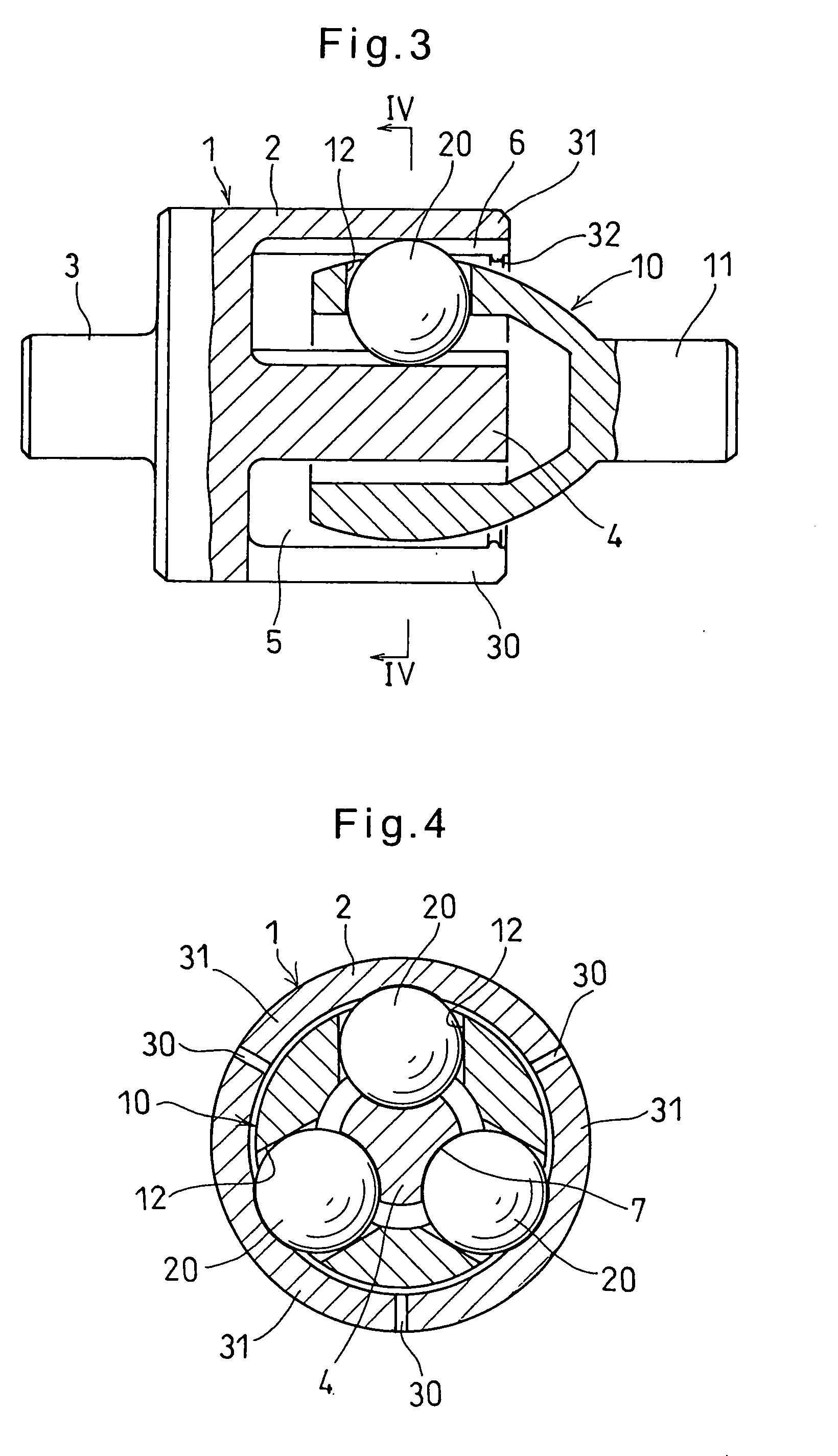
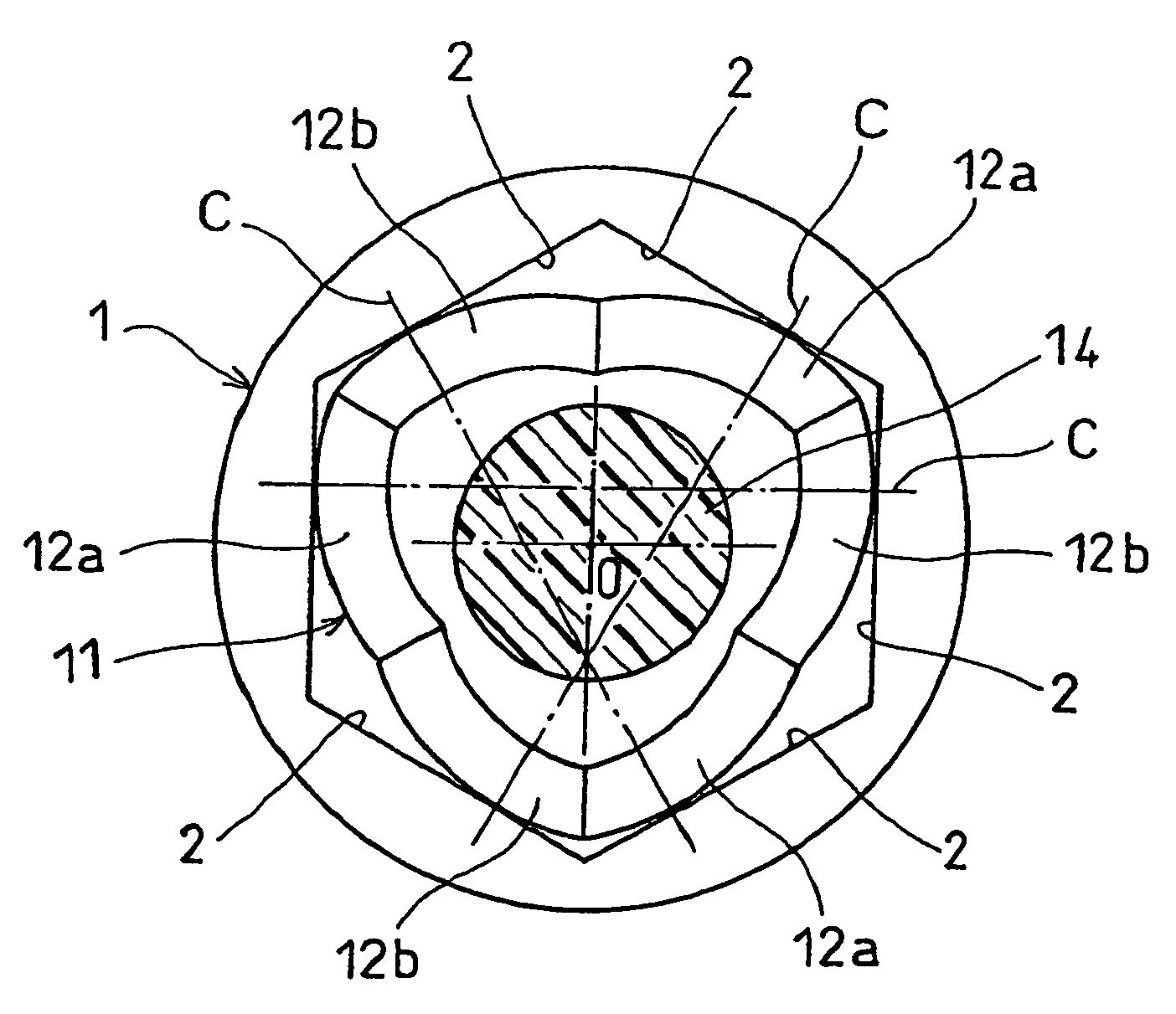
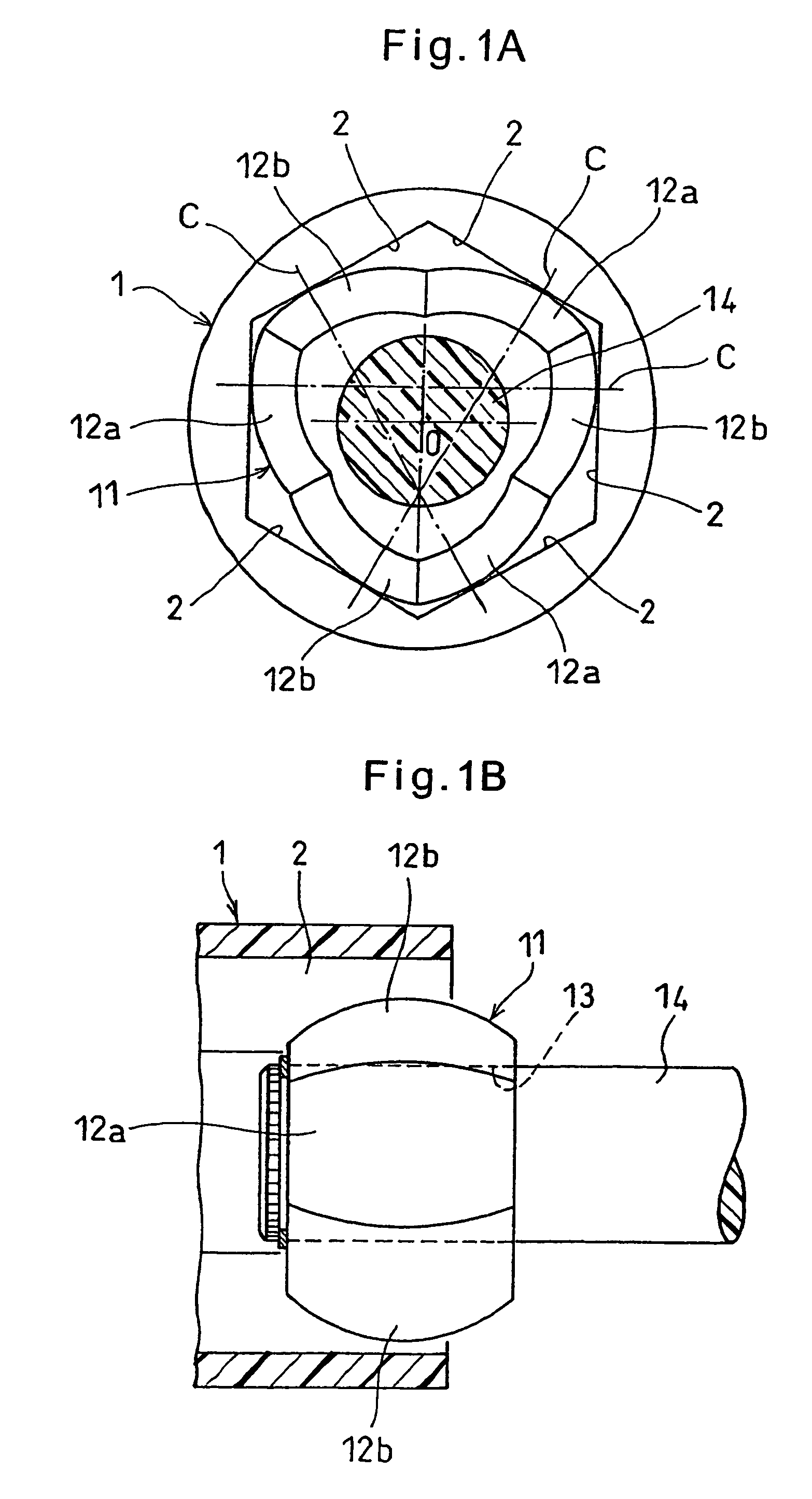
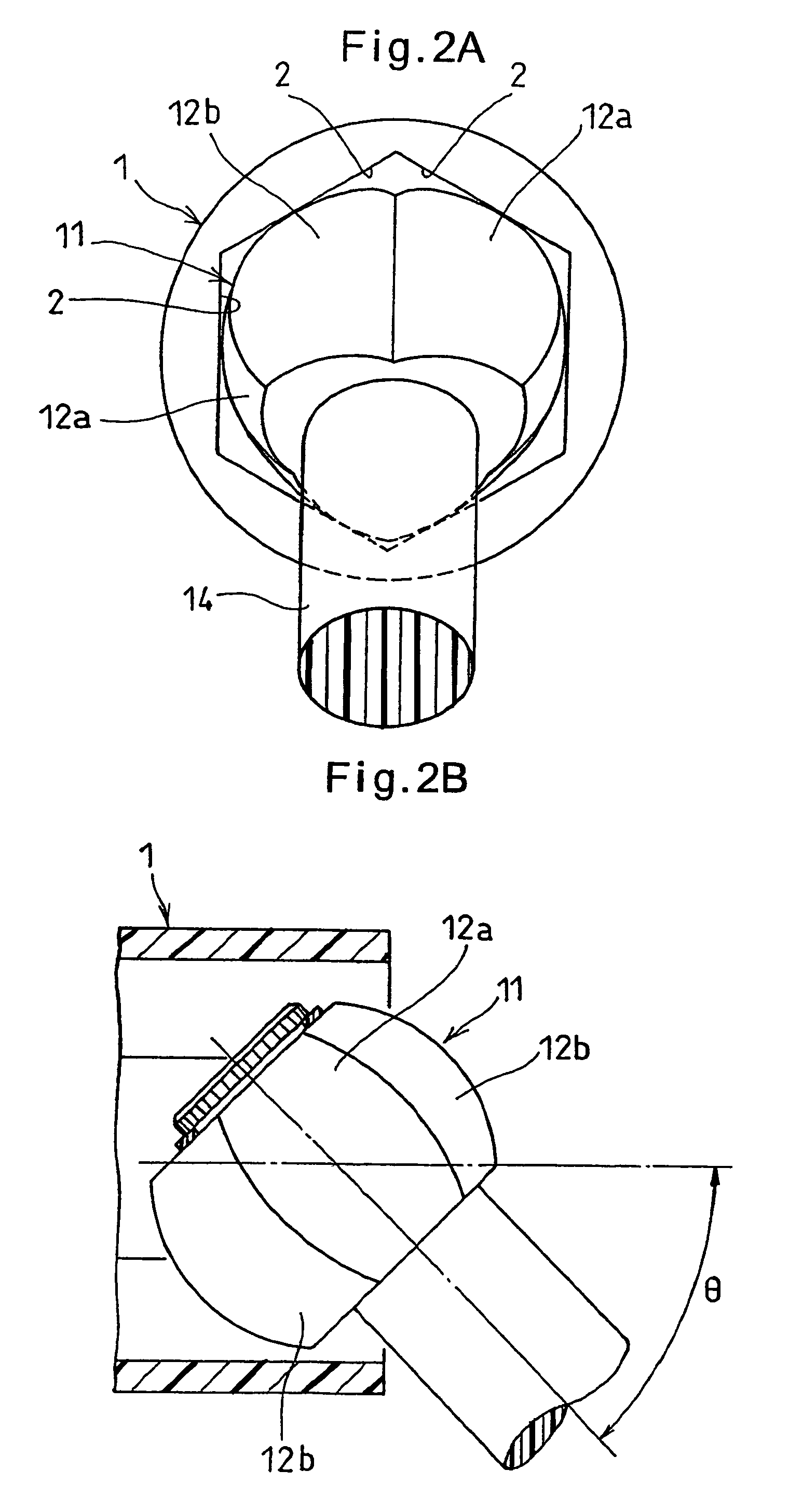
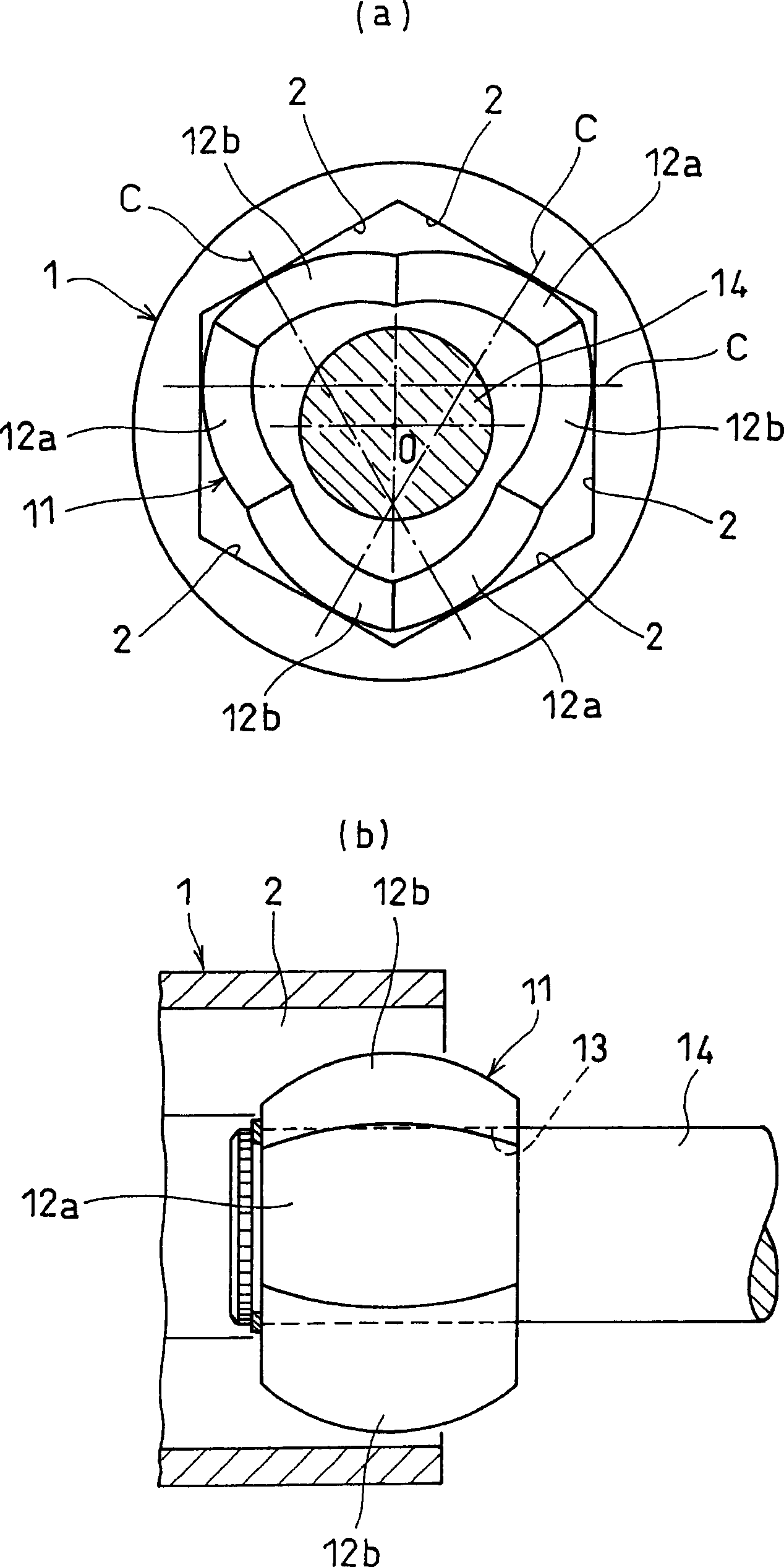
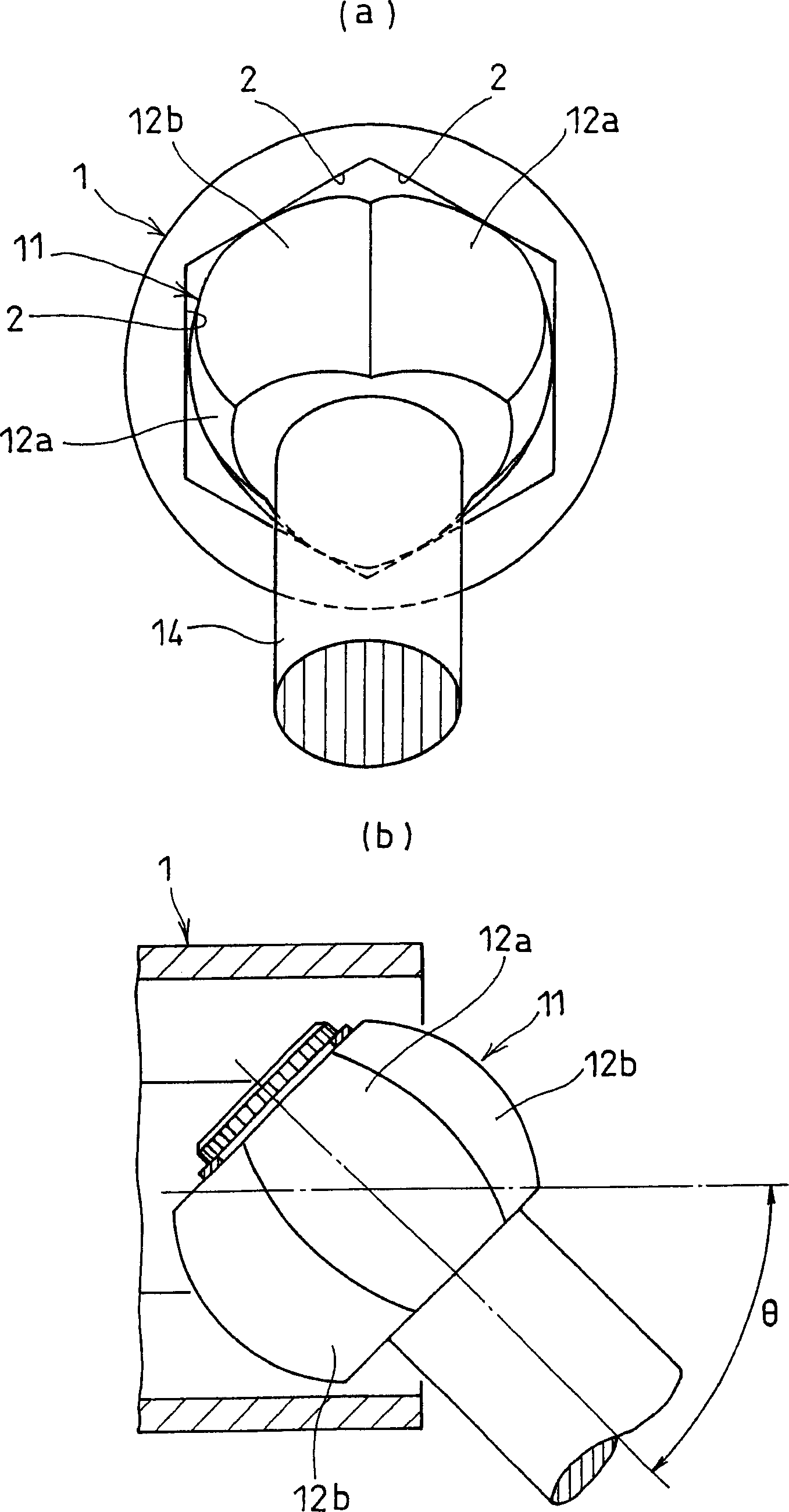
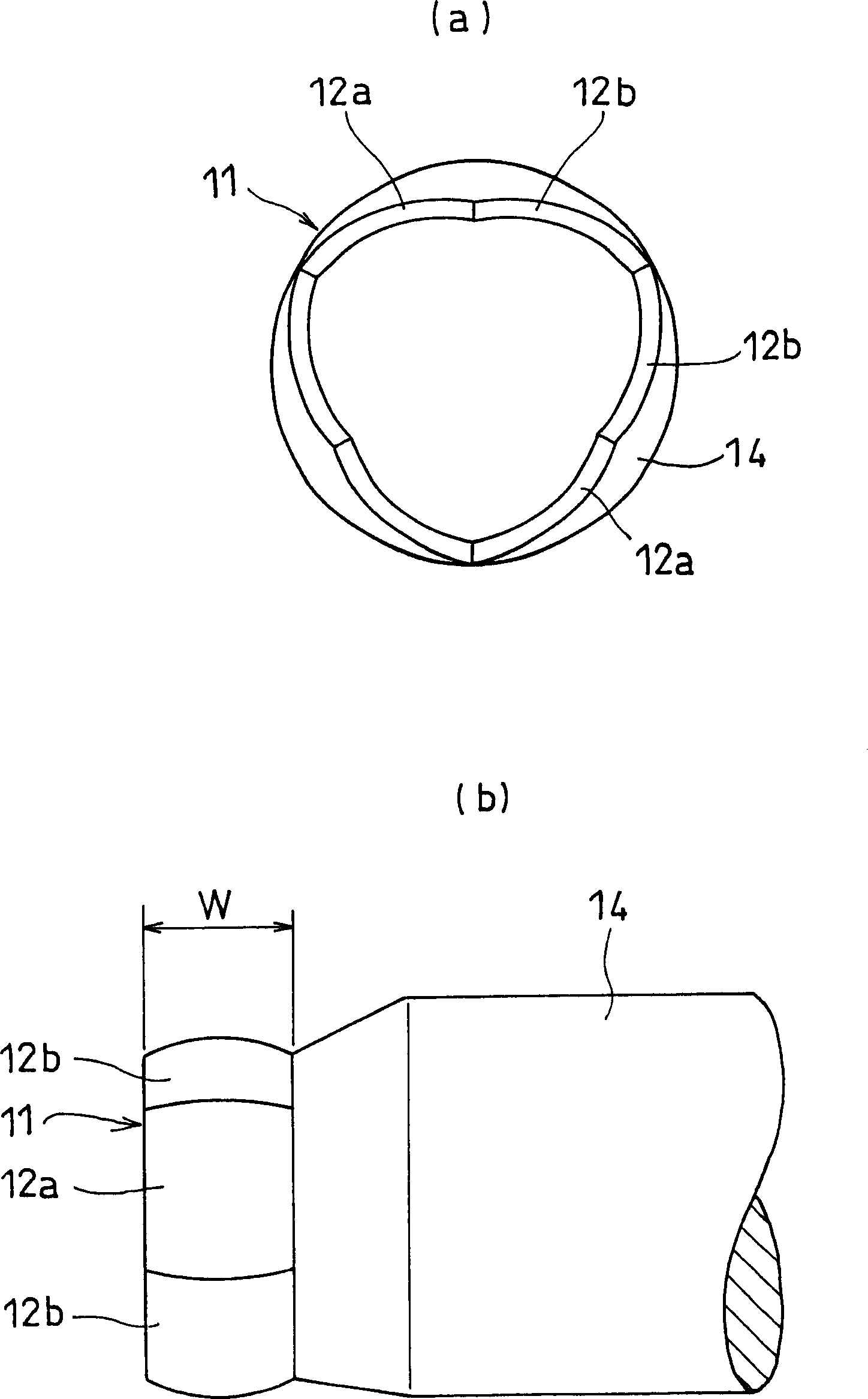
The present invention provides a lightweight constant velocity coupling that does not require grease lubrication. The pivot part (11) is assembled in the outer wheel (1), and the outer wheel (1) has a hexagonal hollow hole surrounded by 6 flat surfaces (2) parallel to the axis, and the pivot part (11 ), a first spherical surface (12a) and a second spherical surface (12b) are formed along the circumferential direction, and the first spherical surface (12a) is biased from the central position of the flat surface (2) in the circumferential direction to the circumferential direction The second spherical surface ( 12 b ) is in contact with the flat surface at a position offset from the central position to the other side in the circumferential direction. Since the outer ring 1 and the pivot member (11) are molded of synthetic resin, grease lubrication is not required, and the weight of the constant velocity coupling can be reduced.
Owner:NTN CORP
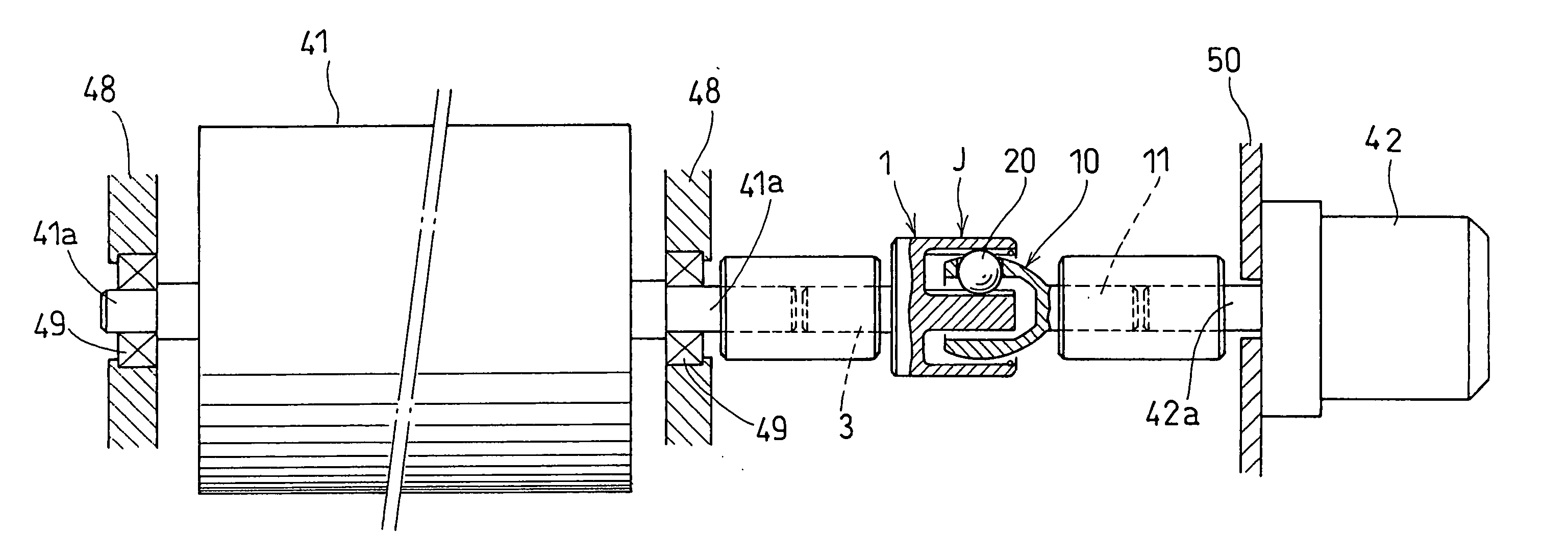
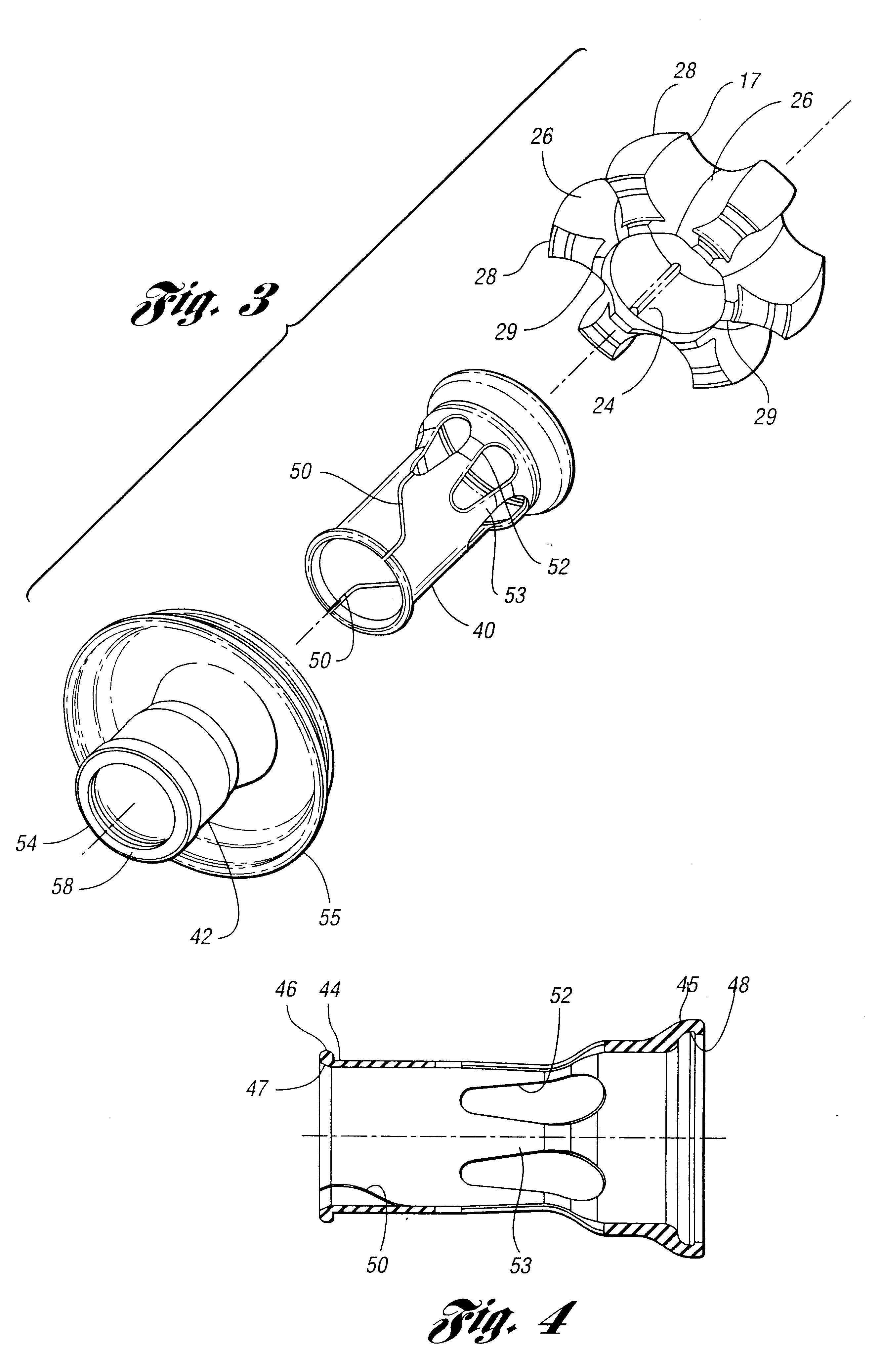
Tripod type constant-velocity joint and image-forming device
ActiveUS7289752B2Shorten the lengthReduce weightYielding couplingElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringSynthetic resin
A tripod type constant-velocity joint includes an outer ring formed with three axially extending track grooves circumferentially spaced apart from each other by 120 degrees. Each track groove has a pair of opposed, axially extending side faces. A tripod member is inserted in the outer ring. The tripod member includes three protrusions each slidably received in one of the track grooves and having a pair of circumferentially curved side faces each opposing one of the pair of side faces of each track groove. Torque is thus transmitted between the outer ring and the tripod member. At least the protrusions of the tripod member are formed of a synthetic resin.
Owner:NTN CORP
Constant-velocity joint and image-forming device
InactiveUS7366443B2Well formedEasy maintenanceYielding couplingElectrographic process apparatusImage formationSynthetic resin
A constant-velocity joint includes an outer ring formed with an annular space therein having an opening at one end thereof. The annular space is defined by a radially outer wall and a radially inner wall. One of the radially inner and outer walls is formed with three axially extending track grooves circumferentially spaced apart from each other by 120 degrees. A cage is inserted in the annular space with one end thereof protruding from the opening of the annular space. A second shaft is provided on the one end of the cage. Balls are retained by the cage and adapted to roll in the track grooves. At least one of the outer ring and the cage is formed of a synthetic resin.
Owner:NTN CORP
In-Wheel motor with high durability
InactiveUS20060144626A1Increased durabilityGearboxesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringMotive power
An in-wheel motor includes a motor generating motive power, a planetary gear arranged toward a wheel disc relative to the motor to reduce an output of the motor, and a shaft arranged toward the wheel disc relative to the planetary gear and connected to a planetary carrier. Shaft is connected to a constant velocity joint transmitting the motive power to wheel disc.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
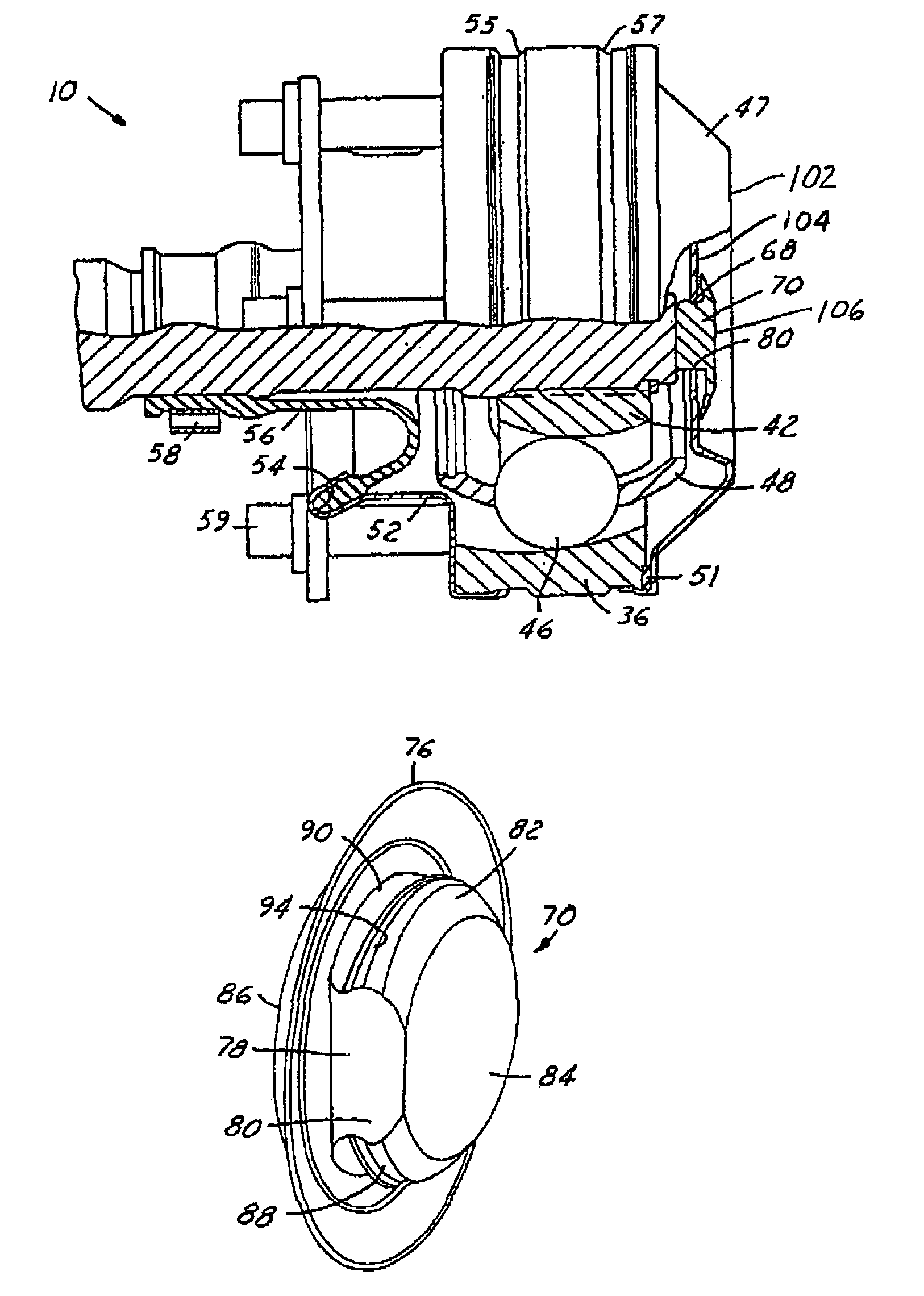
Boot arrangement for a constant velocity joint
InactiveUS6264568B1Avoid contactAxial deformation of the boot can be significantly reduced or eliminatedEngine sealsYielding couplingEngineeringConstant velocity
A boot arrangement is provided for use with a constant velocity joint and shaft assembly including a shaft, a first joint part slidably engageable with the shaft, and a second joint part cooperable with the first joint part to transmit torque therebetween. The boot arrangement includes a sleeve adapted to slidably engage the shaft and having first and second ends. The second end of the sleeve is adapted to be connected to the first joint part. The arrangement further includes a boot having a first end adapted to be connected to the sleeve proximate the first end of the sleeve, and a second end adapted to be operatively connected to the second joint part.
Owner:GKN AUTOMOTIVE INC
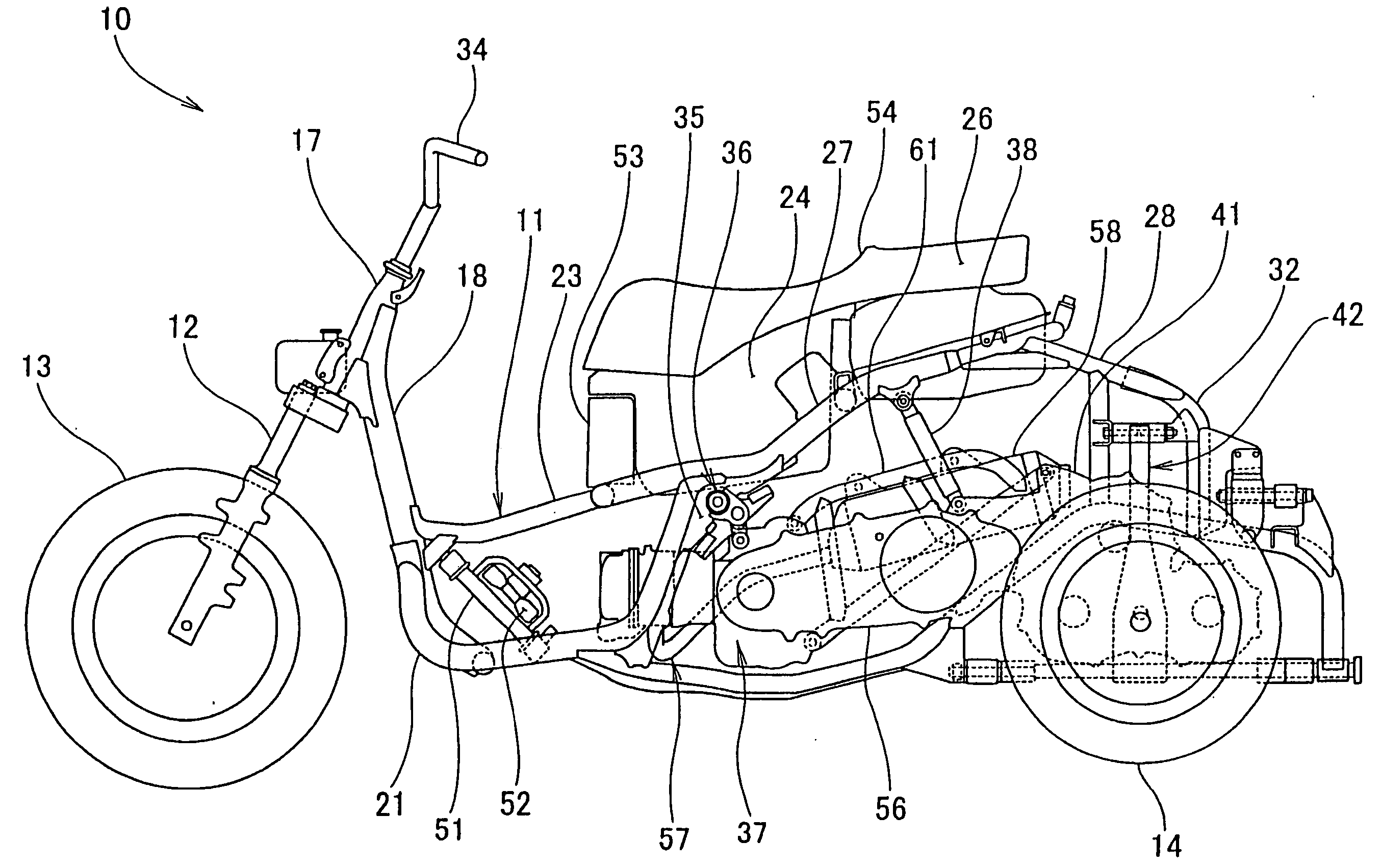
Swingable vehicle
InactiveUS7311167B2Increase freedomEnlarge the bend anglesCyclesVehicle body-frame connectionsDrive shaftEngineering
A left drive shaft and a right drive shaft each include an inside constant velocity joint and an outside constant velocity joint with a ball spline mechanism provided between the inside constant velocity joint and the outside constant velocity joint for enabling the distance between the inside constant velocity joint and the outside constant velocity joint to be contracted and extended. The ball spline mechanism includes a spline shaft having an outer circumferential surface provided with a plurality of axial grooves extending in the axial direction, a tubular portion surrounding the periphery of the spline shaft and having an inner circumferential surface provided with a plurality of axial grooves extending in the axial direction and a plurality of balls capable of rolling while being fitted in the axial grooves and in the axial grooves. In addition, a left lower arm and a right lower arm are formed into an A-shape and are supported by a lower part of a rising portion and a lower end of the downwardly extending portion via a lower supporting shaft.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
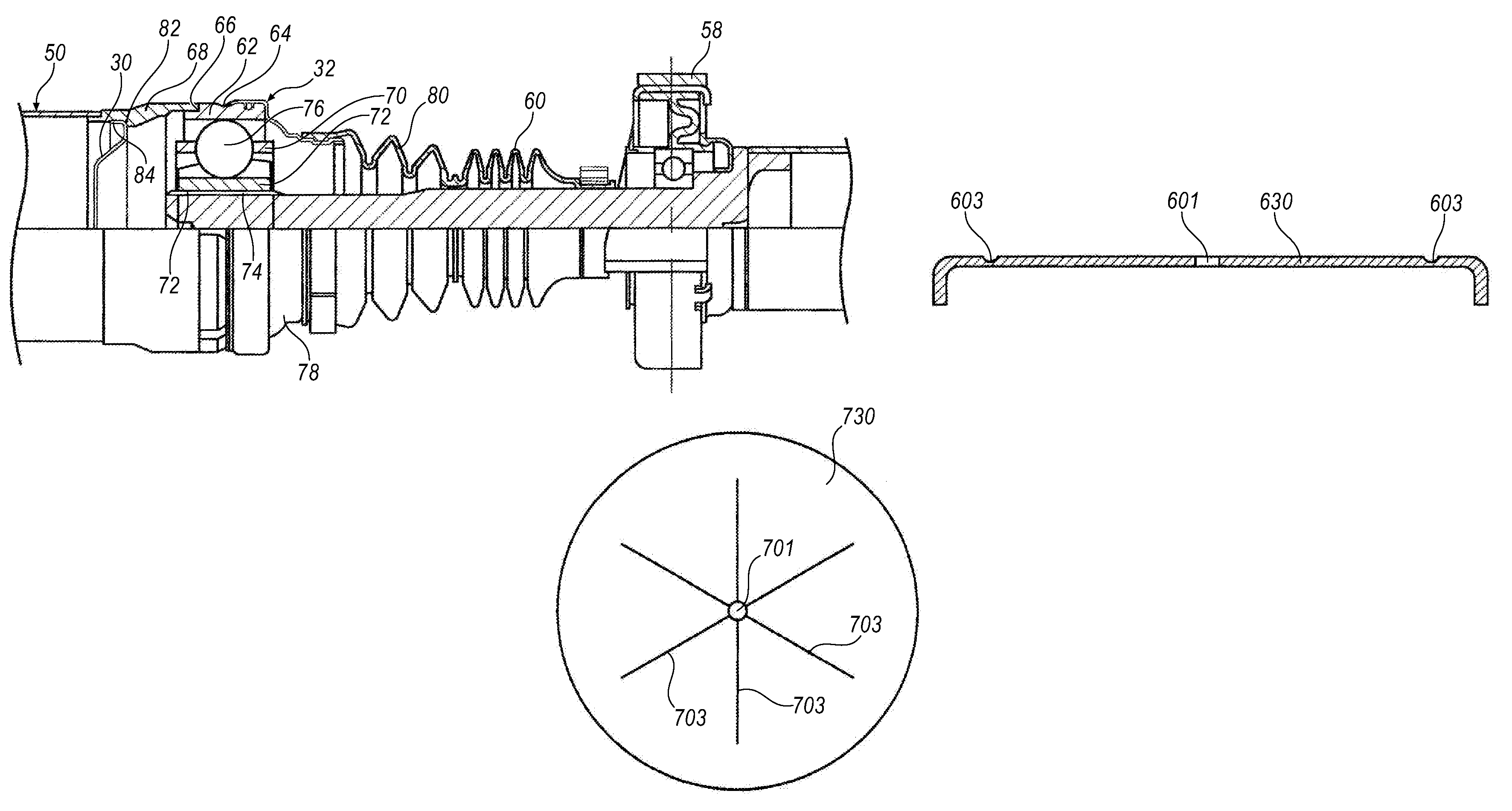
Crash optimized plunging CV joint
InactiveUS20030008716A1Minimize the number of componentsReduce the total massClutchesYielding couplingDrive shaftUniversal joint
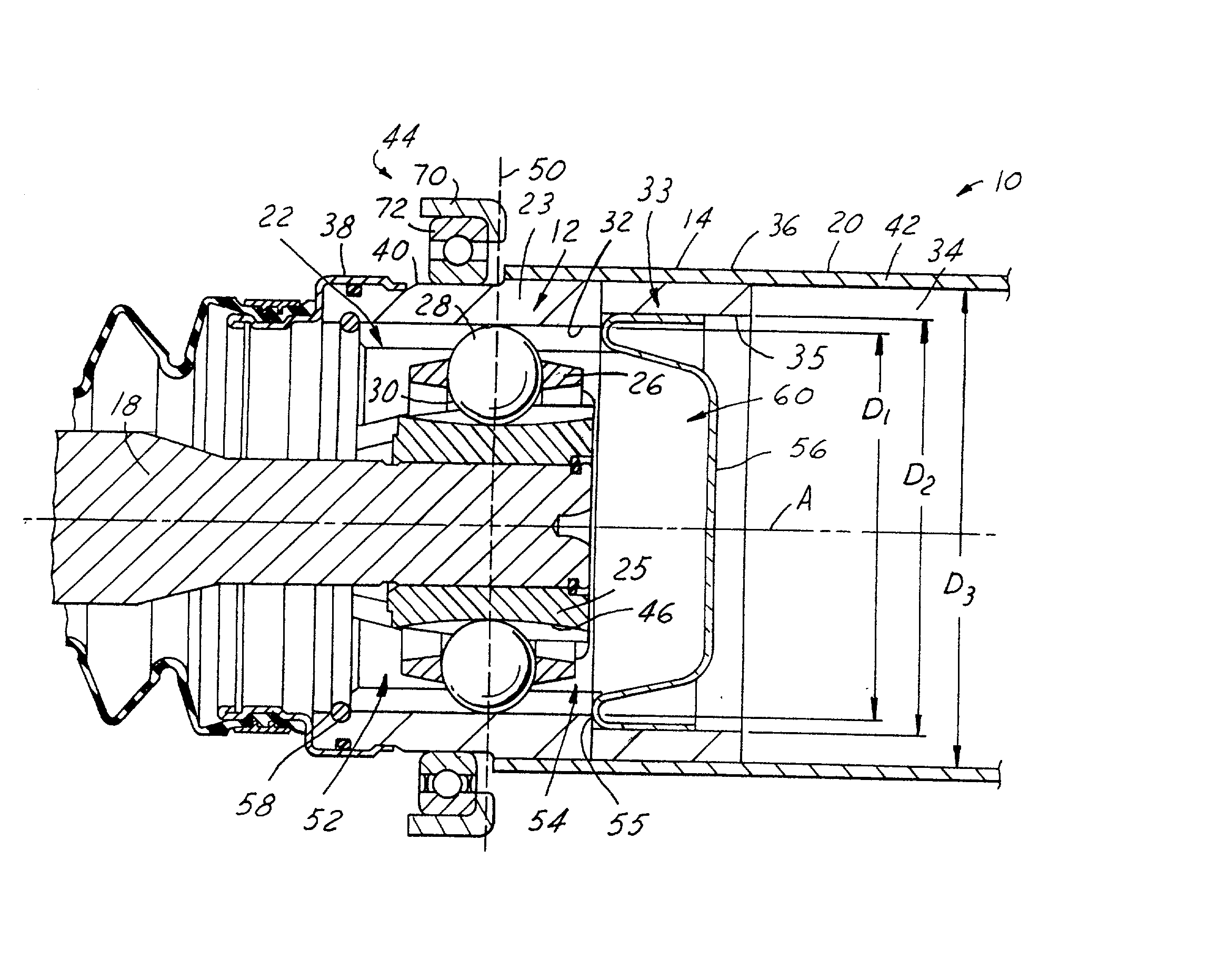
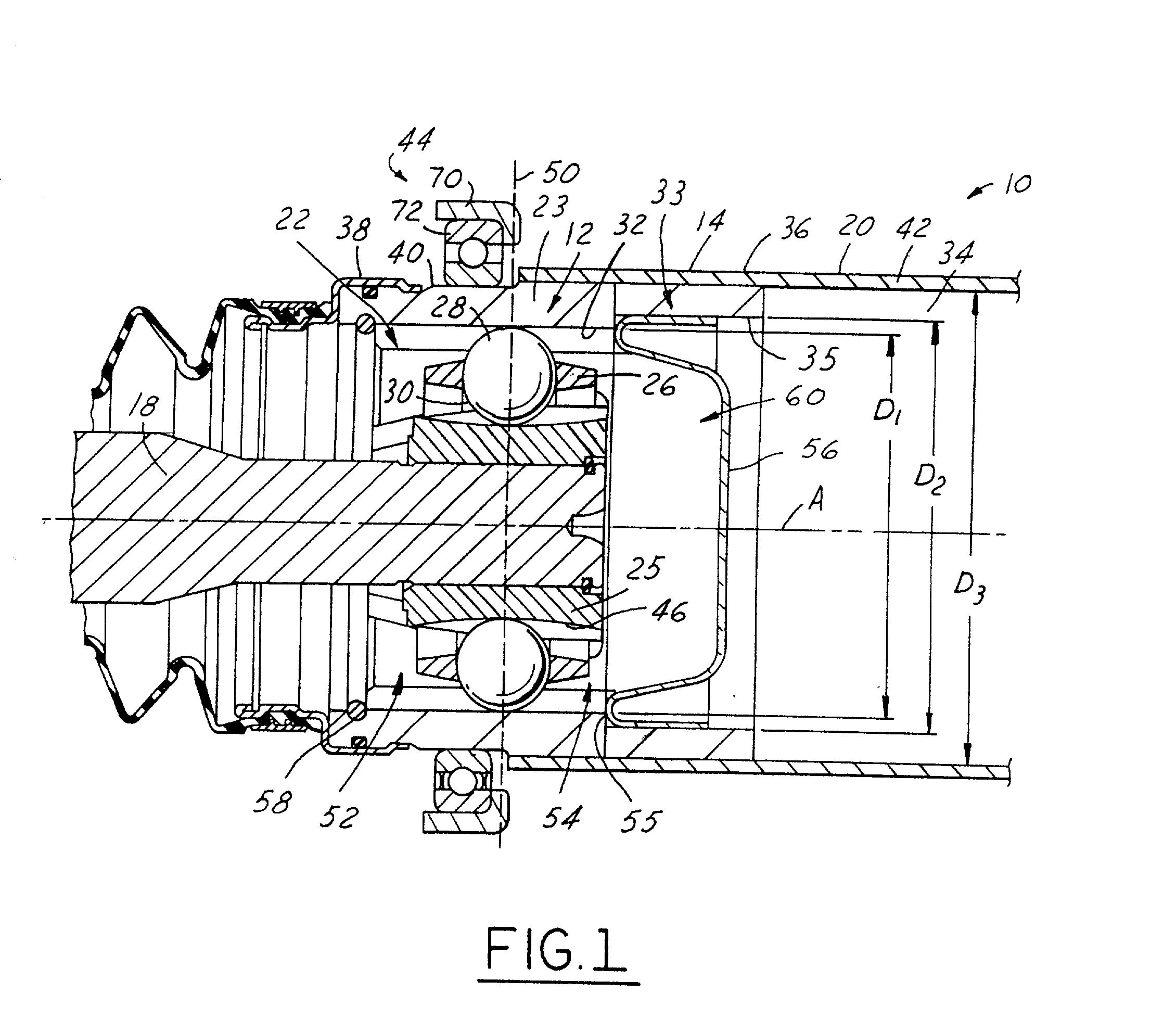
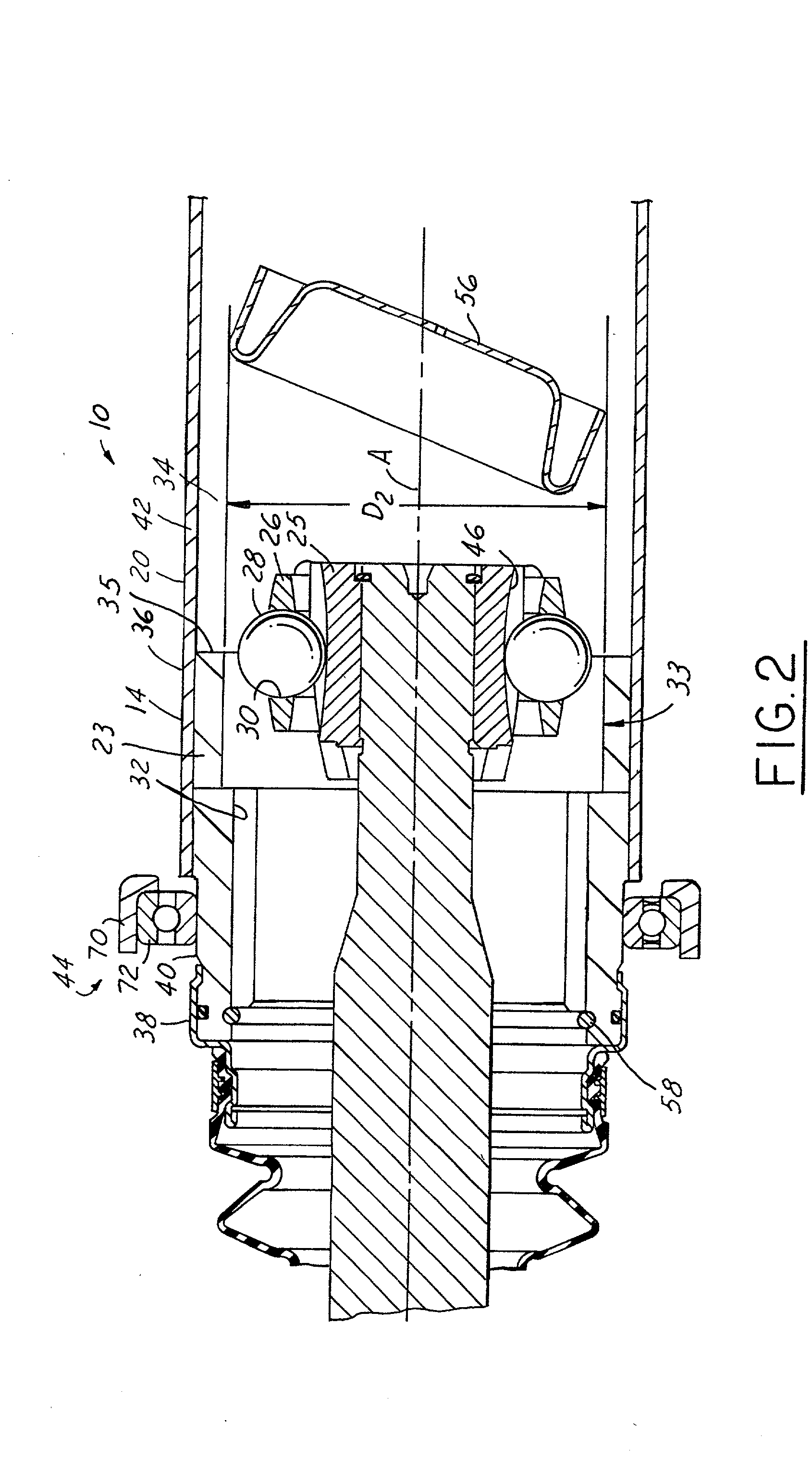
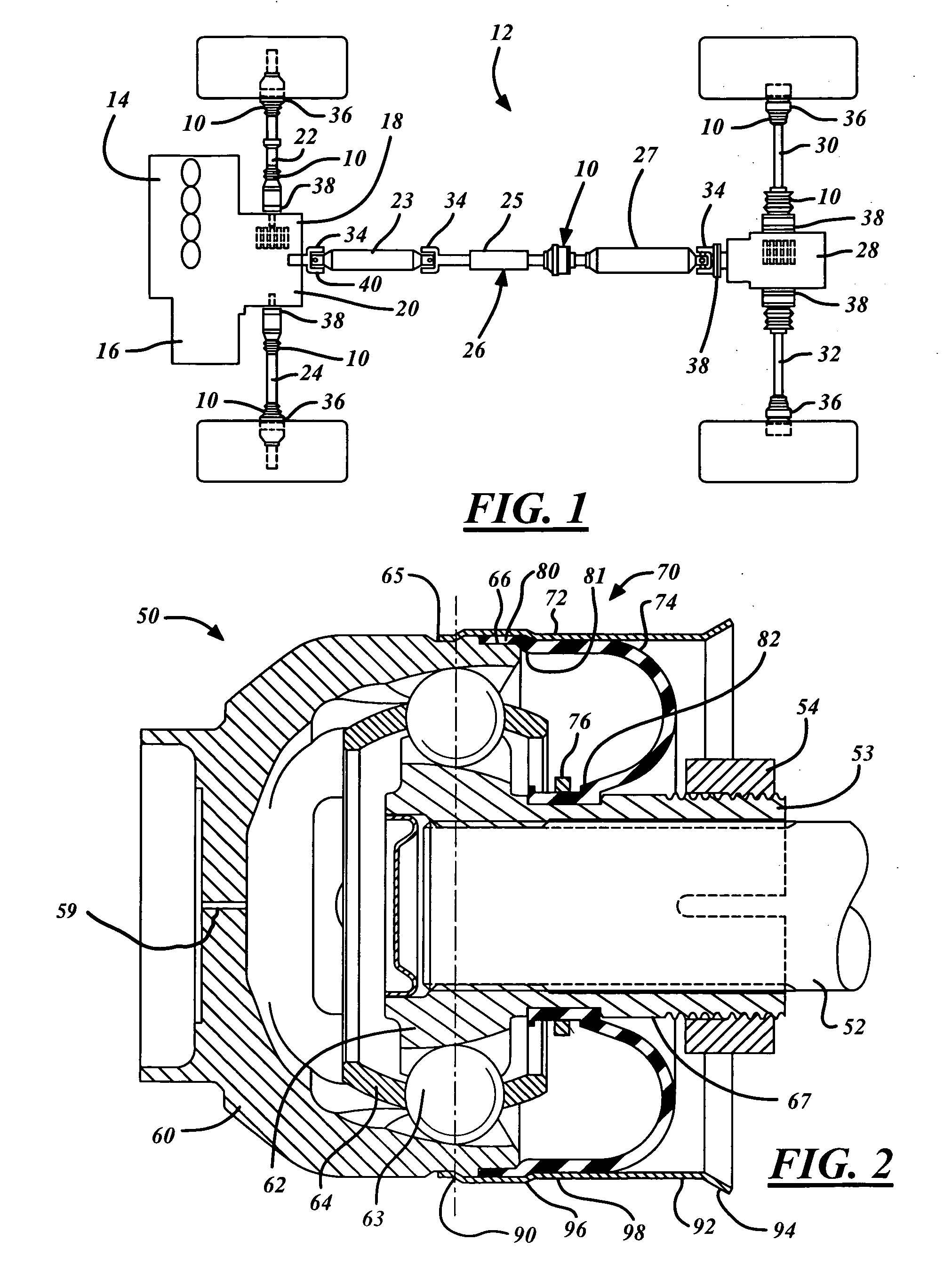
A propeller shaft assembly (10) comprising a constant velocity universal joint (12) including a hollow shaft (20) and a connecting shaft (18) is provided. The hollow shaft (20) includes an aft open area (34) and is connected to an outer joint part (23) that has outer ball tracks (32). The connecting shaft (18) is connected to an inner joint part (25) that has inner ball tracks (46). A ball cage (26) that has a plurality of balls (28) is included. A standard plunge (22) that has an aft plunge portion (54) is also included. The aft plunge portion (54) and the aft open area (34) having inner diameters that are greater then or equal to an inner diameter D.sub.1 of the outer joint part (23). A first stop (55) limits the ball movement of travel in the aft direction. The first stop (55) is forcibly dispensable such that the connecting shaft (18) may release the first stop (55) and intrude significantly within the aft open area (34) which is outside a normal operating range (24).
Owner:GKN AUTOMOTIVE INC
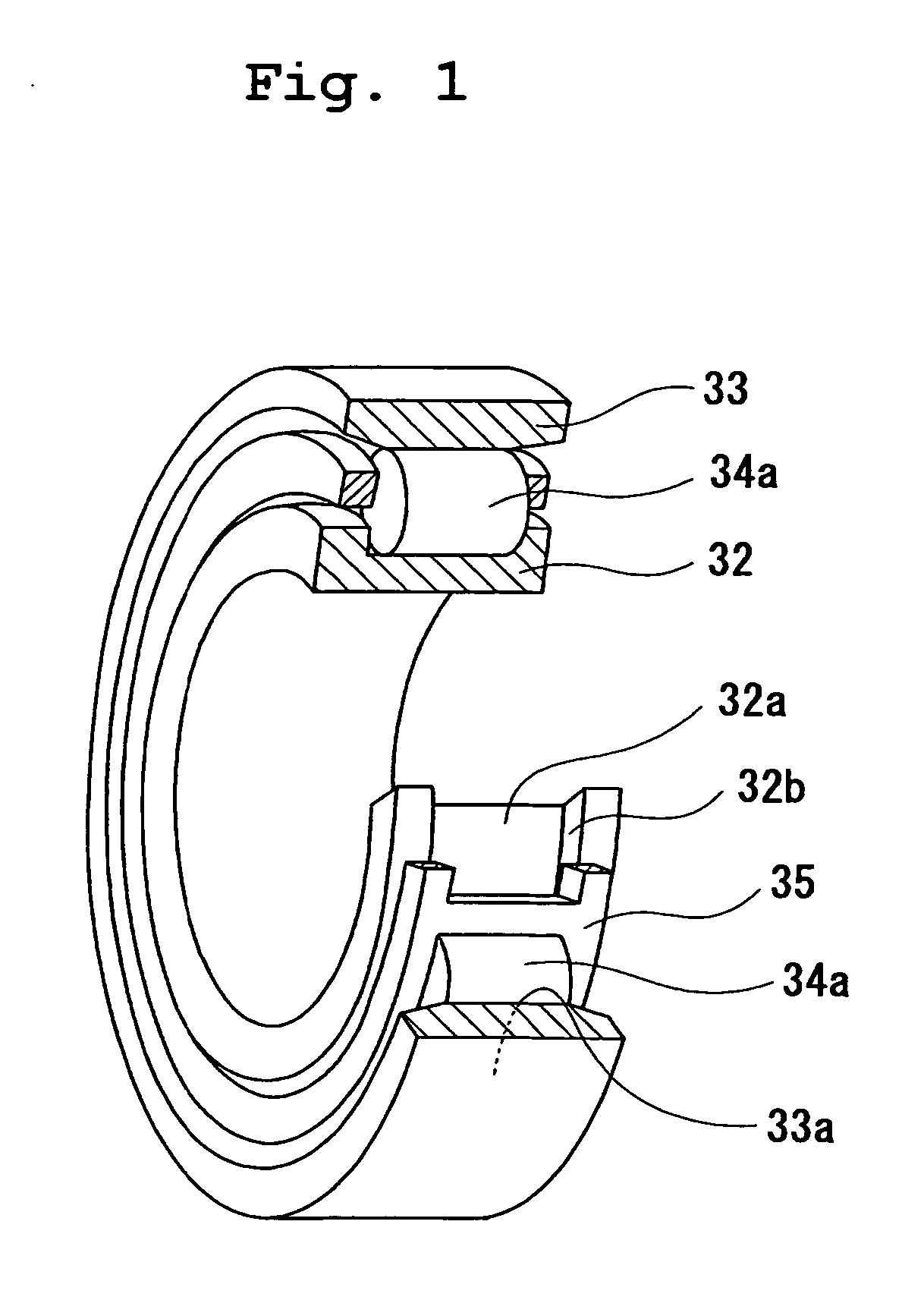
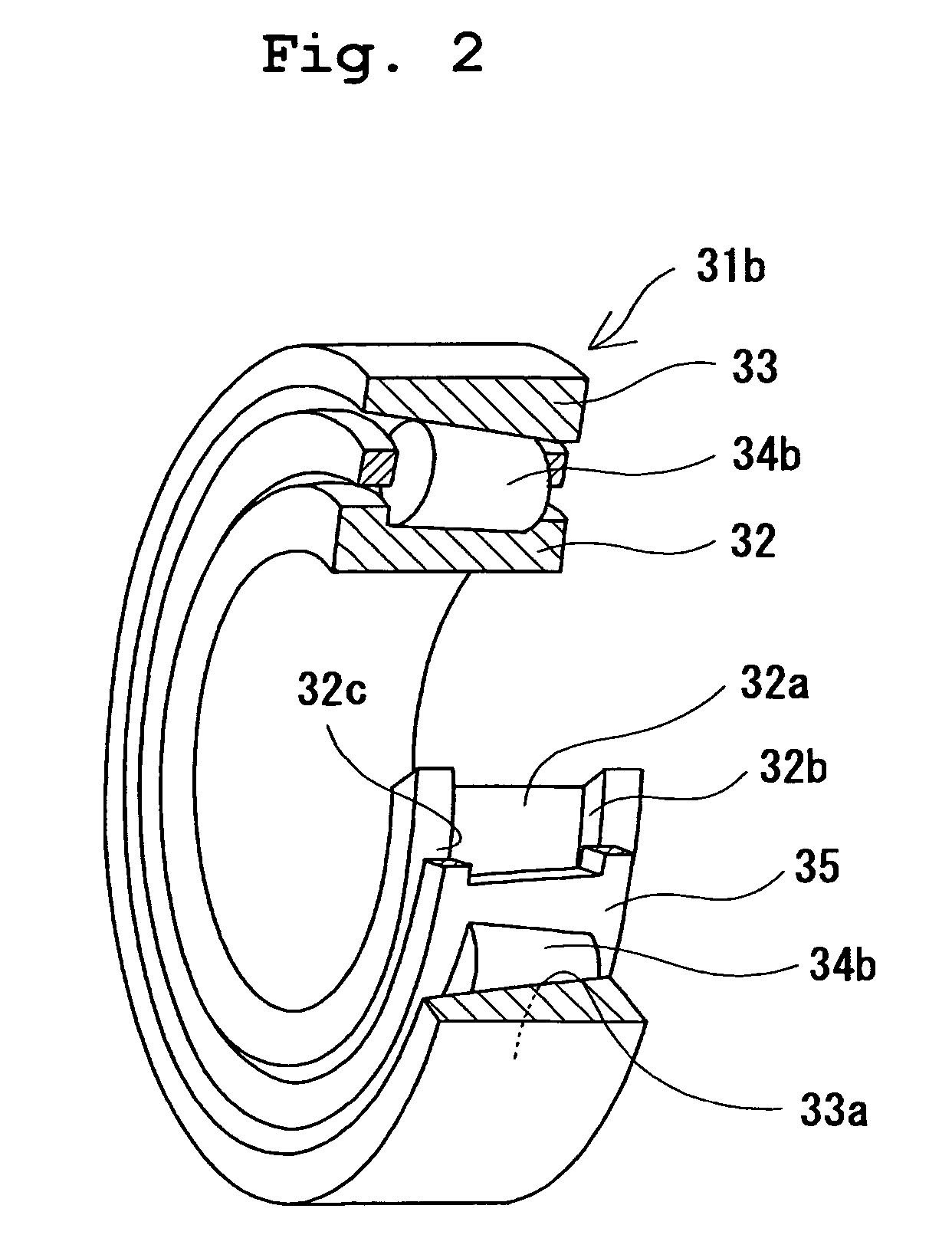
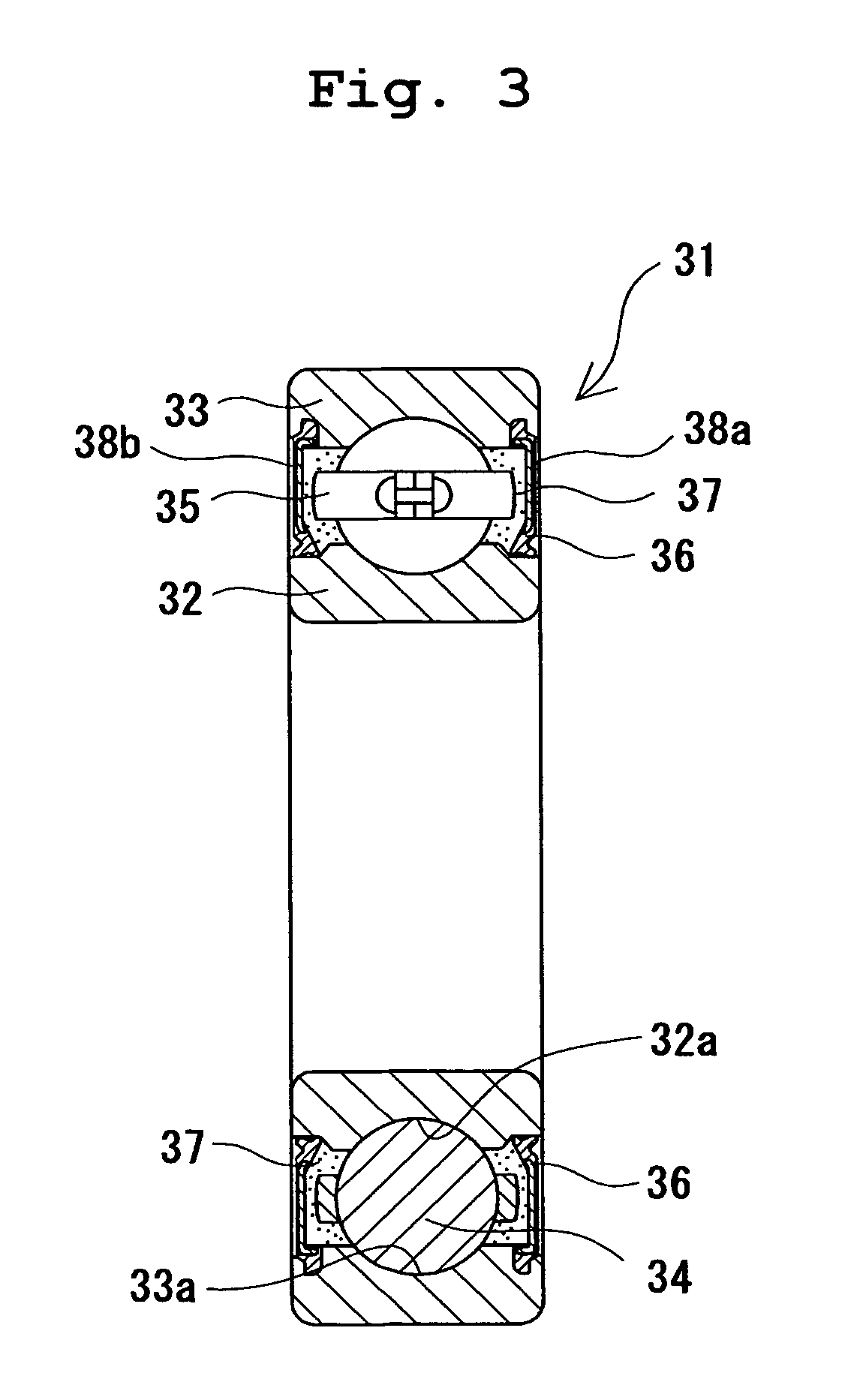
Constant velocity universal joint
InactiveUS20020077186A1Required machining timeMinimizing heat generationClutchesYielding couplingUniversal jointEngineering
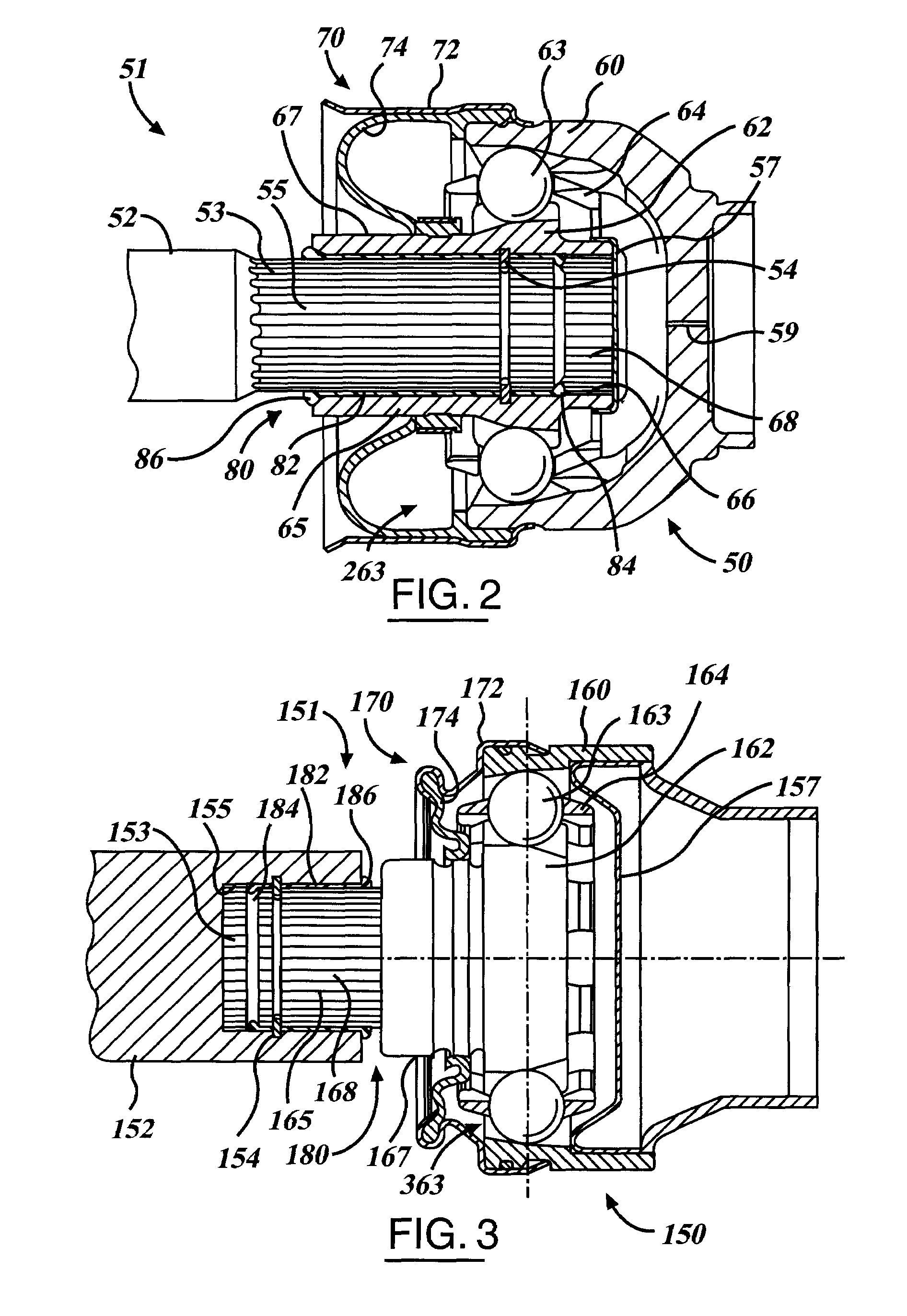
A spherical inner surface 5 of the outer race 1 and track grooves in the outer race 1 are each defined by a post-hardening cut surface. A spherical outer surface 6 of the inner race 2 and track grooves in the inner race 2 are also each defined by a post-hardening cut surface. A retainer 4 has a spherical outer surface 10, a spherical inner surface 11 and inner surfaces of the pockets 9, all of which are defined by a post-hardening cut surface. Respective surfaces of the retainer 4, the outer race 1 and the inner race 2 which contact with each other are formed with a surface treatment layer for reducing a frictional resistance.
Owner:NTN CORP
Grease cap for a constant velocity joint
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
Random ethylene/alkyl acrylate copolymers, compounds and elastomeric compositions thereof with improved low temperature properties
Disclosed are random copolymers derived from ethylene and at least two different alkyl acrylate comonomers, with or without an acid cure site-containing comonomer. In particular, disclosed are copolymers derived from copolymerization of (a) from 10 to 50 weight % of ethylene; (b) from 5 to 55 weight % of a first alkyl acrylate; (b) from 15 to 80 weight % of a second alkyl acrylate; and (d) from 0 to 7 weight % of a monoalkyl ester of 1,4-butene-dioic acid. Such copolymers exhibit lower glass transition temperatures (Tg) relative to previous ethylene copolymers comprising a single alkyl acrylate comonomer and maintain the good heat and fluid resistance when employed to produce cured elastomeric compositions as well as the improved low temperature properties. This invention also provides compounded compositions comprising these copolymers, and cured compositions (i.e., vulcanizates) as well as rubber articles formed from these compounded compositions, such as hoses, dampers, seals, gaskets, constant velocity joint (CVJ) boots and shaft boots.
Owner:DUPONT POLYMERS INC
Grease, rolling bearing, constant velocity joint and rolling parts
InactiveUS20070154128A1Resistance to durabilityHeat resistantClutchesMachines/enginesBismuth compoundSulfate
The present invention provides grease which prevents frictional wear on a lubricating surface and excellent in performance of preventing occurrence of flaking, heat-resistant performance, and long-term durability, a grease-enclosed rolling bearing, a constant velocity joint, and rolling parts. Grease is composed of base grease, essentially containing a thickener, to which at least 0.01 to 15 wt % of one substance selected from among bismuth and inorganic bismuth compounds is added. The inorganic bismuth compounds are at least one inorganic bismuth selected from among bismuth sulfate, bismuth trioxide, bismuth carbonate, and sodium bismuthate. The above-described grease is used for the rolling bearing and the constant velocity joint. A coating film of at least one substance selected from among the bismuth and the inorganic bismuth is formed on surfaces of the rolling parts.
Owner:NTN CORP
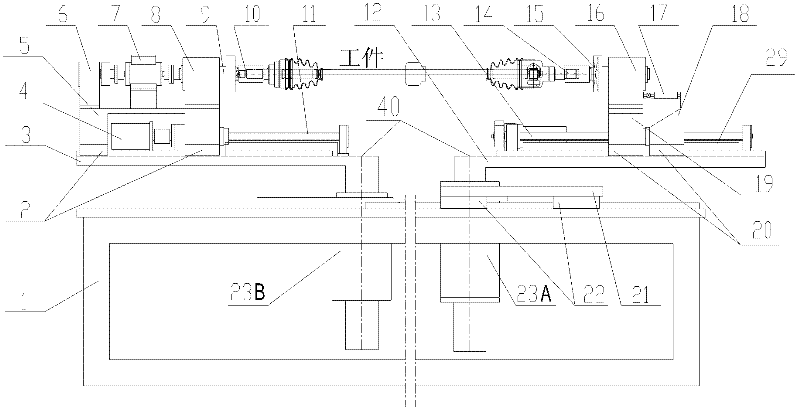
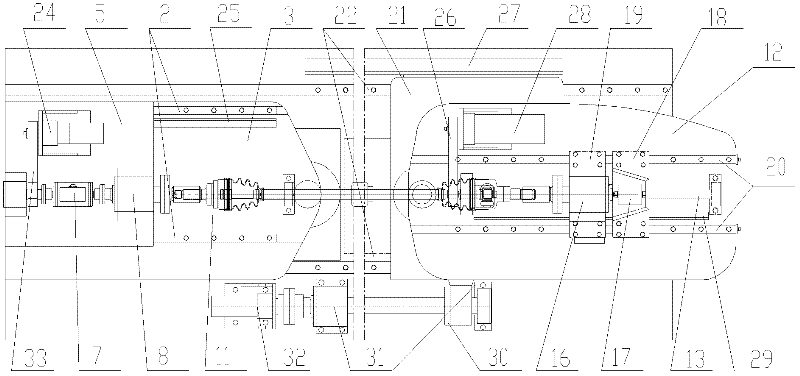
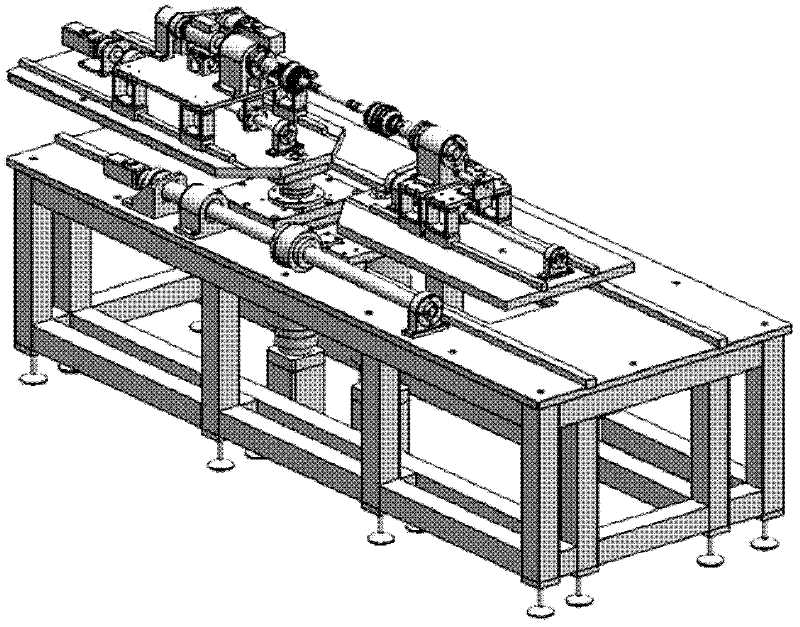
Test table for five-function test of driving shaft assembly of constant velocity universal joint
InactiveCN102654432AAchieve installationRealize functionMachine gearing/transmission testingUniversal jointDrive shaft
The invention relates to a test table for a five-function test of a driving shaft assembly of a constant velocity universal joint. The test table comprises a rack, a fixing end and a slippage end, wherein the fixing end and the slippage end are located on the rack; the fixing end comprises a guide rail and a sliding block, a swinging bedplate, a linear displacement driving assembly, a sliding bedplate, a torque rotating speed sensor, a spindle supporting base, a spindle, a clamp, a swinging and driving assembly, a spindle driving assembly, a linear displacement sensor and the like; the slippage end comprises a swinging bedplate, a clamp, a rotating shaft, a supporting base, a pull pressure sensor, a rear sliding board, a front sliding board, a guide rail and a sliding block, a swinging and driving assembly, a linear displacement sensor and the like; and the rack comprises a guide rail and a sliding block, a linear displacement sensor, a linear displacement driving assembly and the like. With regard to the driving shaft assemblies of the constant velocity universal joint with the different structures and sizes of the working pieces, the test table can test working pieces with various specifications and structures by replacing the clamps, and adjusting the position of the clamp at the fixing end and the position of the clamp at the slippage end, and the size of a rotary center distance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Swingable vehicle
InactiveUS20050077098A1Reduce length of driveIncrease freedomCyclesVehicle body-frame connectionsDrive shaftEngineering
A left drive shaft and a right drive shaft each include an inside constant velocity joint and an outside constant velocity joint with a ball spline mechanism provided between the inside constant velocity joint and the outside constant velocity joint for enabling the distance between the inside constant velocity joint and the outside constant velocity joint to be contracted and extended. The ball spline mechanism includes a spline shaft having an outer circumferential surface provided with a plurality of axial grooves extending in the axial direction, a tubular portion surrounding the periphery of the spline shaft and having an inner circumferential surface provided with a plurality of axial grooves extending in the axial direction and a plurality of balls capable of rolling while being fitted in the axial grooves and in the axial grooves. In addition, a left lower arm and a right lower arm are formed into an A-shape and are supported by a lower part of a rising portion and a lower end of the downwardly extending portion via a lower supporting shaft.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hub Unit for Driving Wheel
InactiveUS20070278851A1LengthReduce manufacturing costRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyDrive wheelUniversal joint
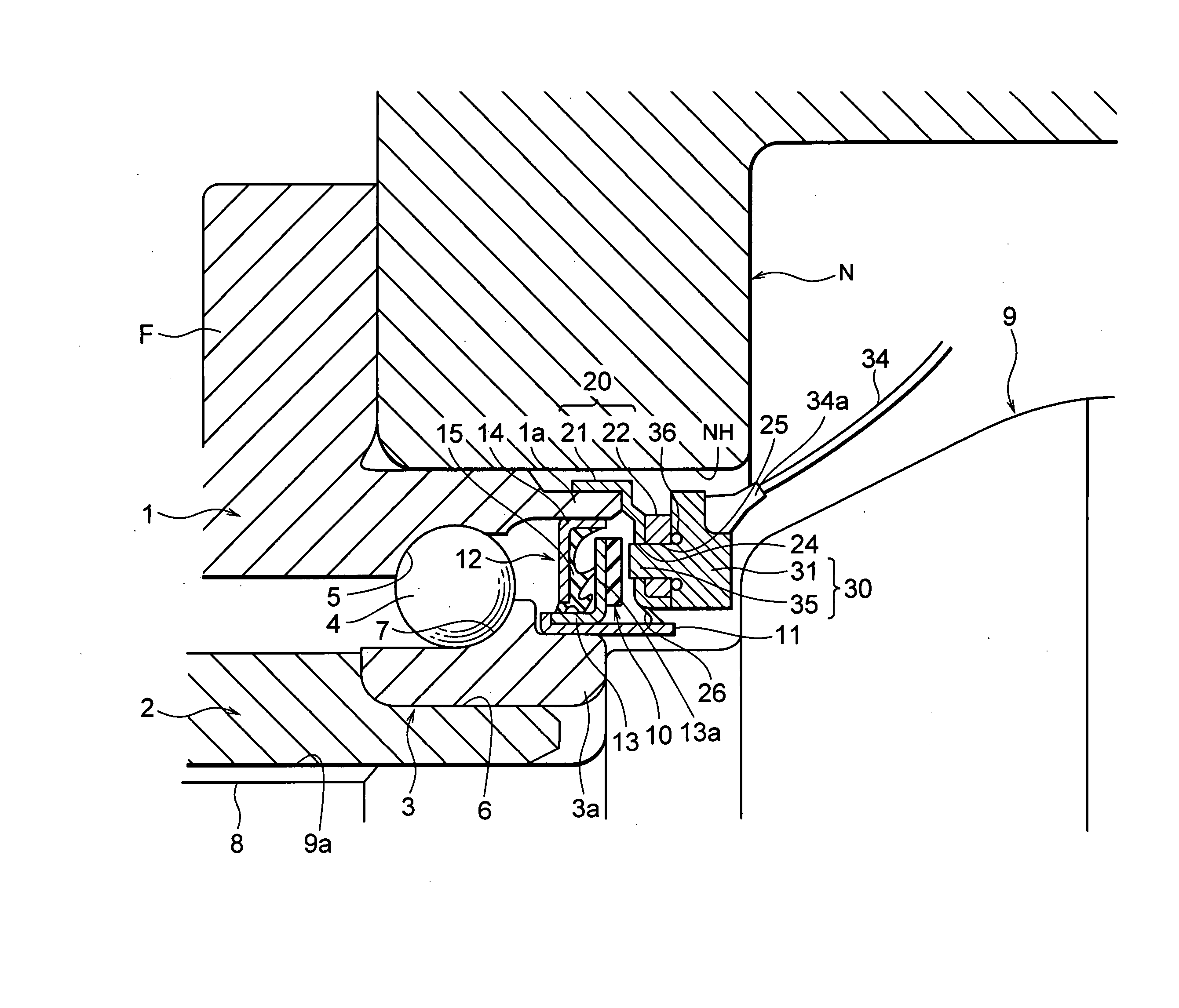
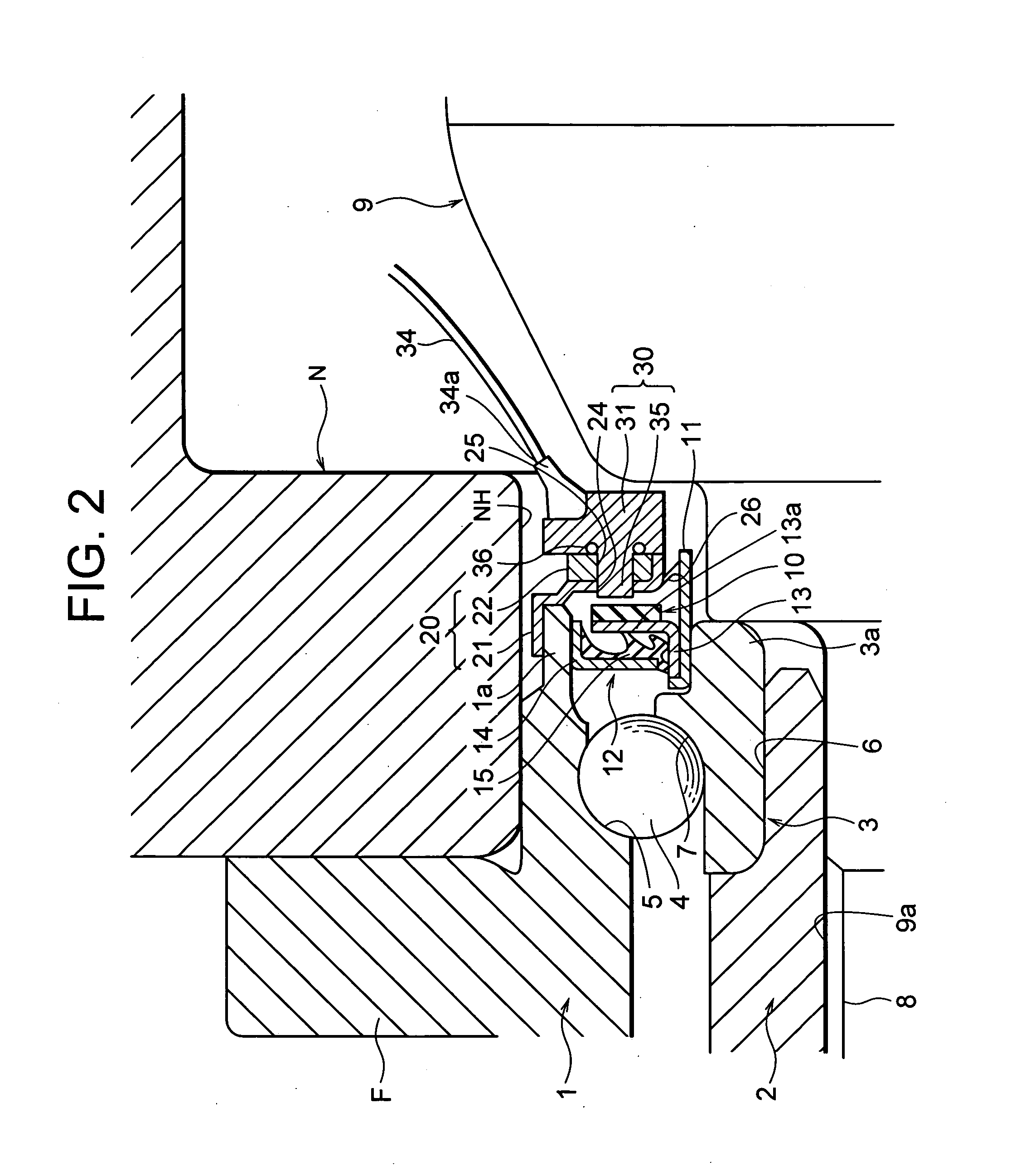
A sensor for detecting a speed of rotation is an active sensor, a sensing portion 35 of the sensor directly faces the magnetic encoder 10 without interposition between it and the encoder 10, and a harness 34 (or connector) of the sensor 30 for detecting the speed of rotation is taken out of a gap between a knuckle N and a constant velocity universal joint 9.
Owner:NSK LTD
Rolling boot assembly
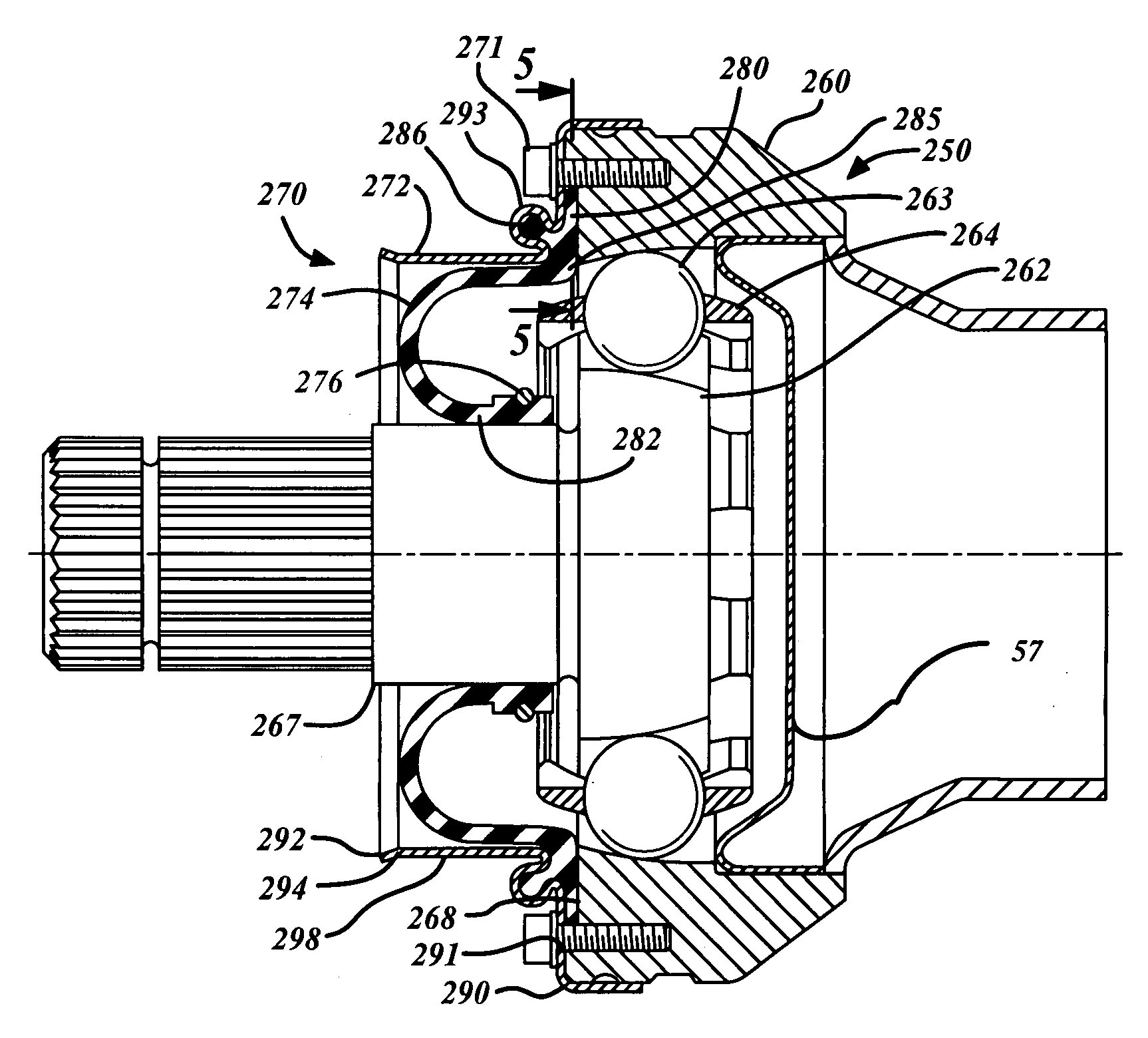
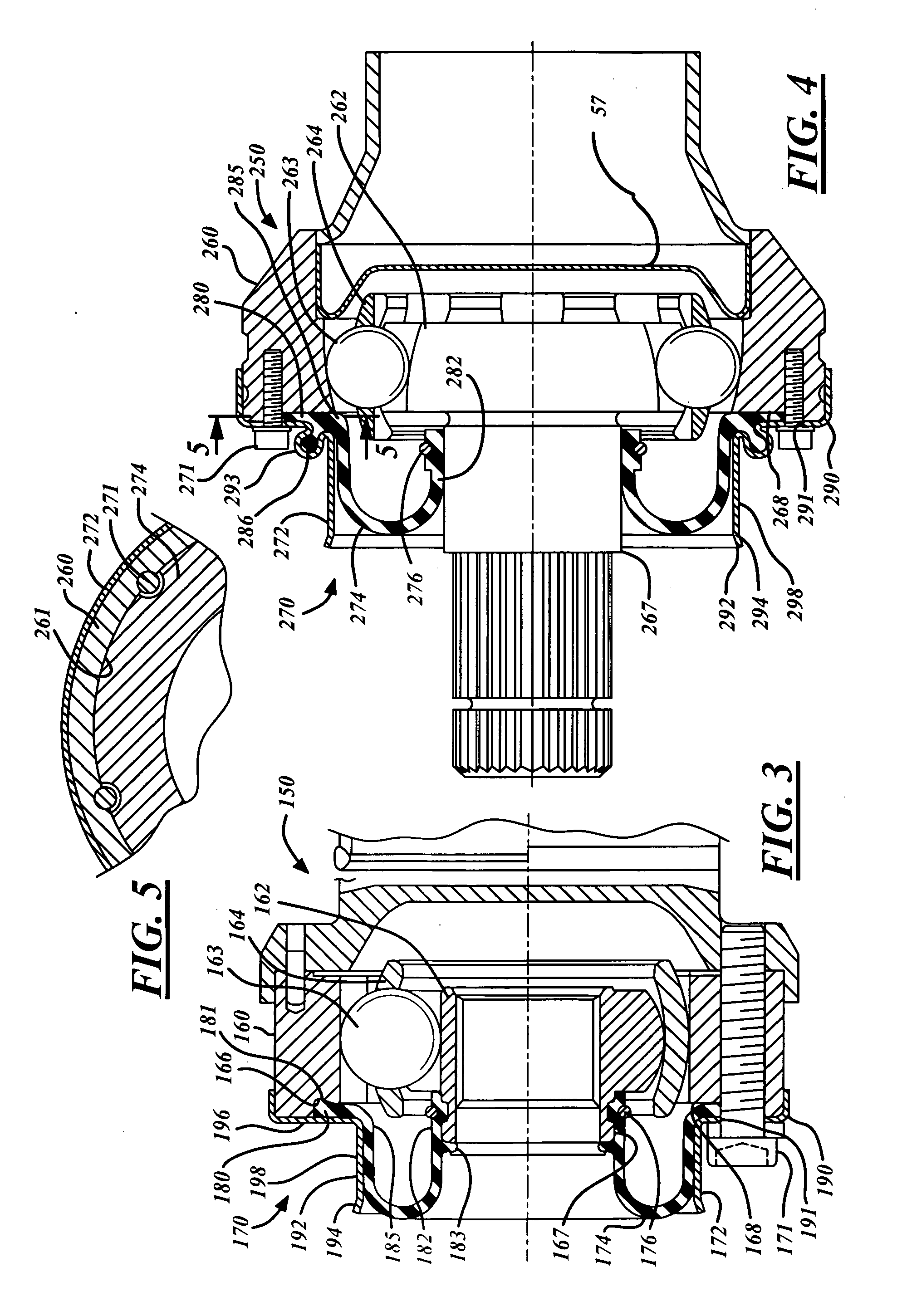
InactiveUS20070173337A1Minimizing sensitivityMinimizing bulging, kinking or binding of the bootYielding couplingShaftsEngineeringConstant-velocity joint
A rolling boot assembly includes a shroud having a first portion and a second portion, and a radial boot having a first section and a second section. The second portion of the shroud has a free end. The first section of the radial boot is connected to the first portion of the shroud advantageously allowing the radial boot to roll axially toward the second portion of the shroud when the second section of the radial boot is selectively attached to a shaft or an inner joint part and the first portion of the shroud is selectively connected to an outer joint part. The second portion of the shroud remains unconnected. Also provided is a constant velocity joint assembly.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
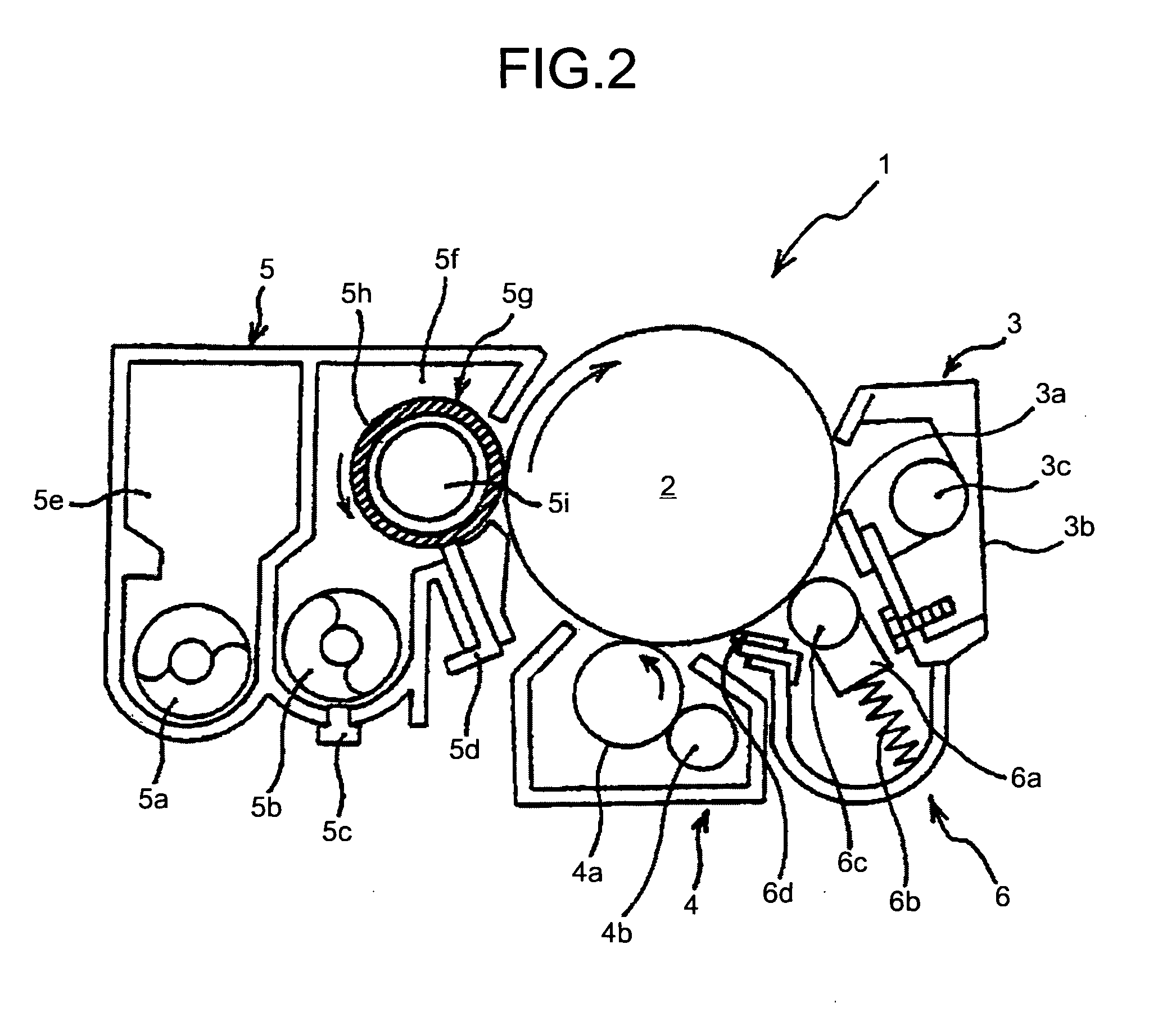
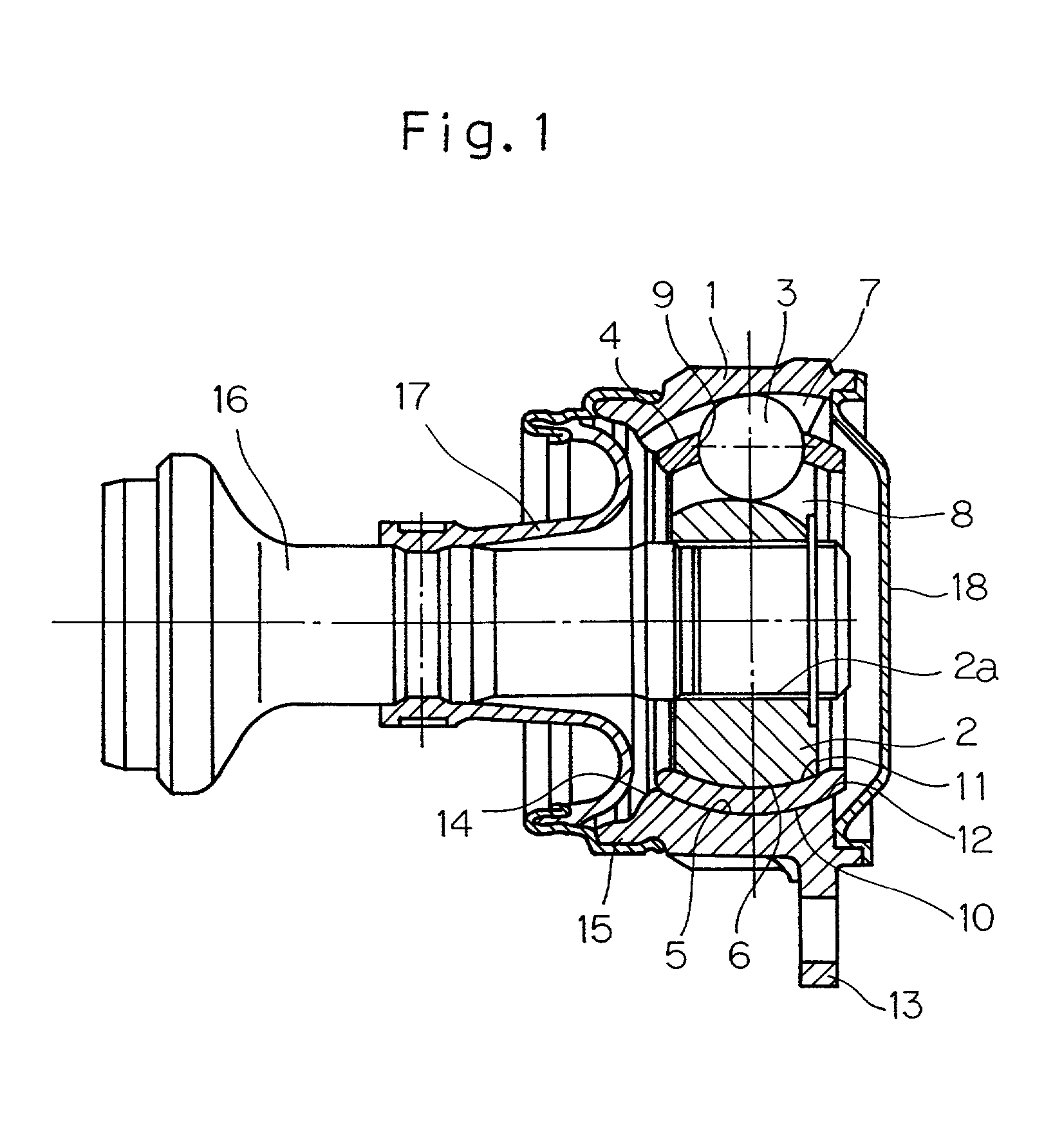
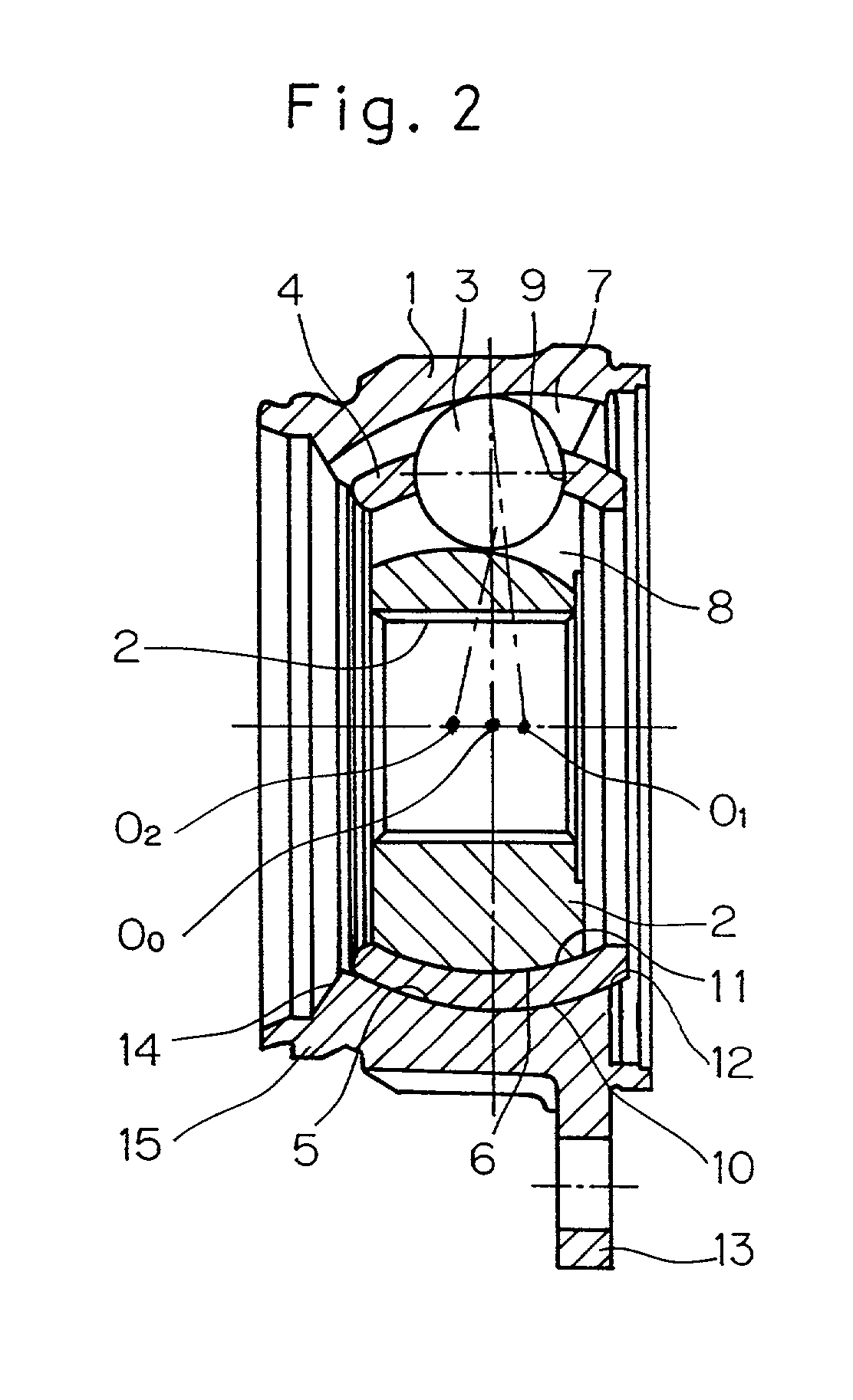
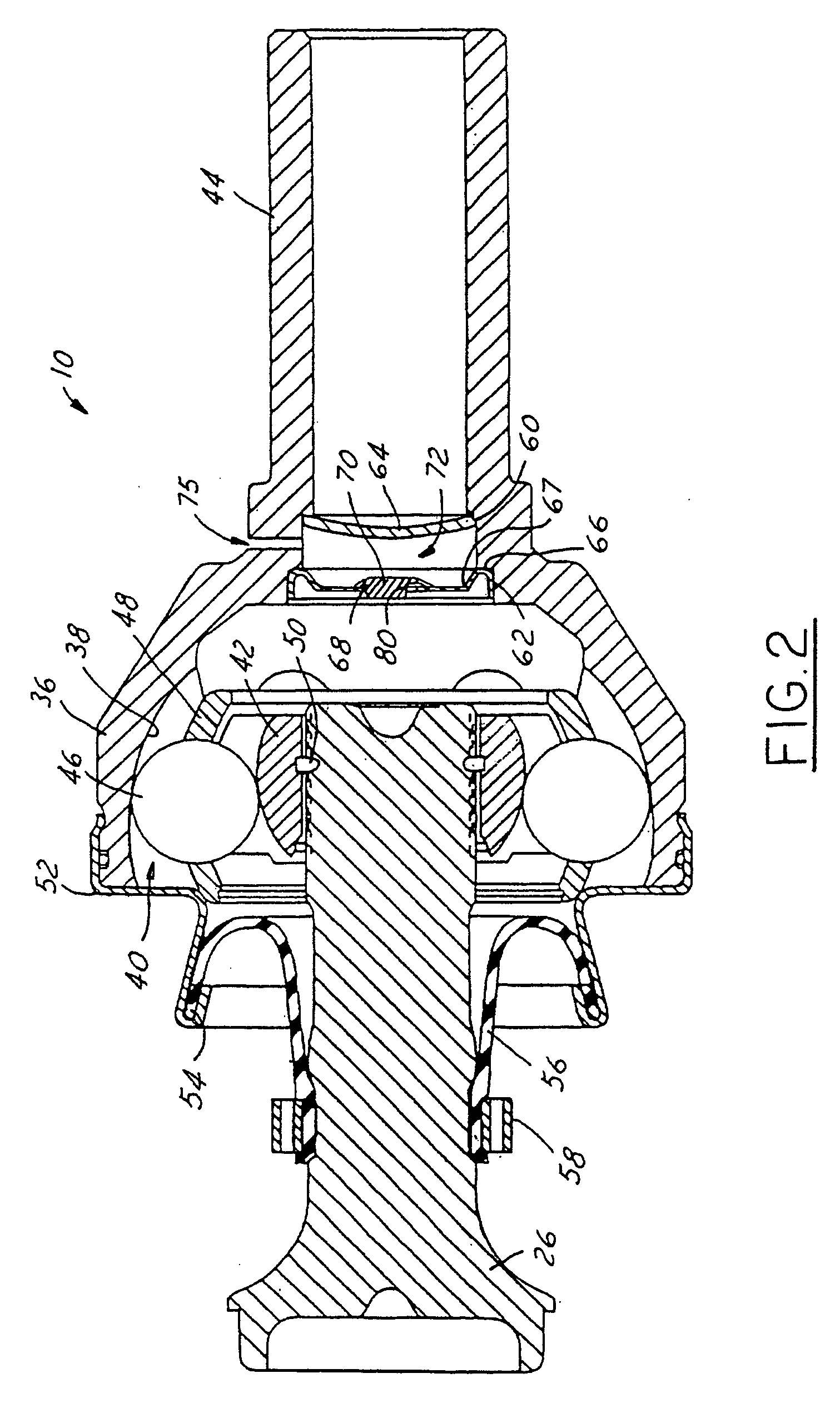
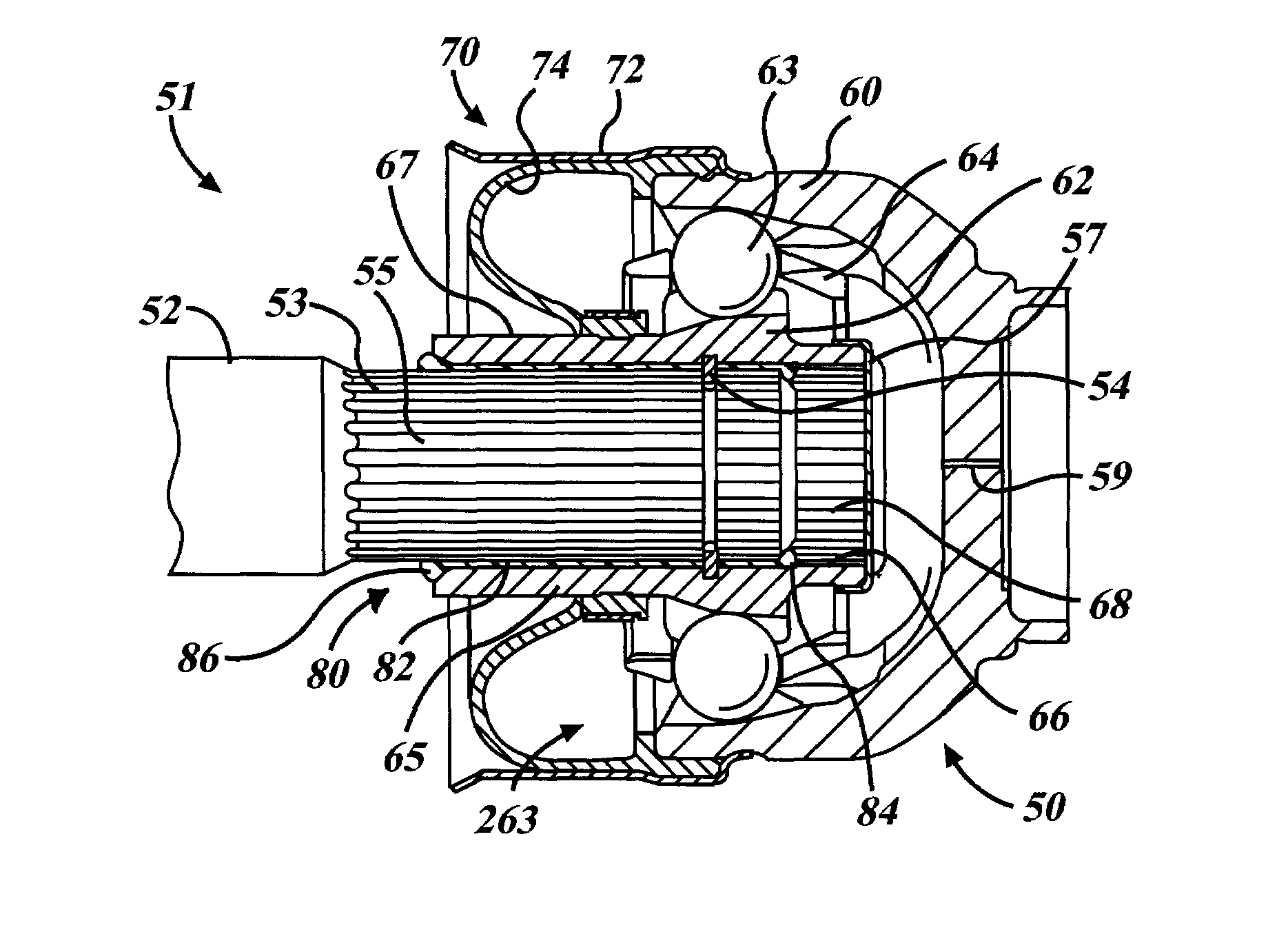
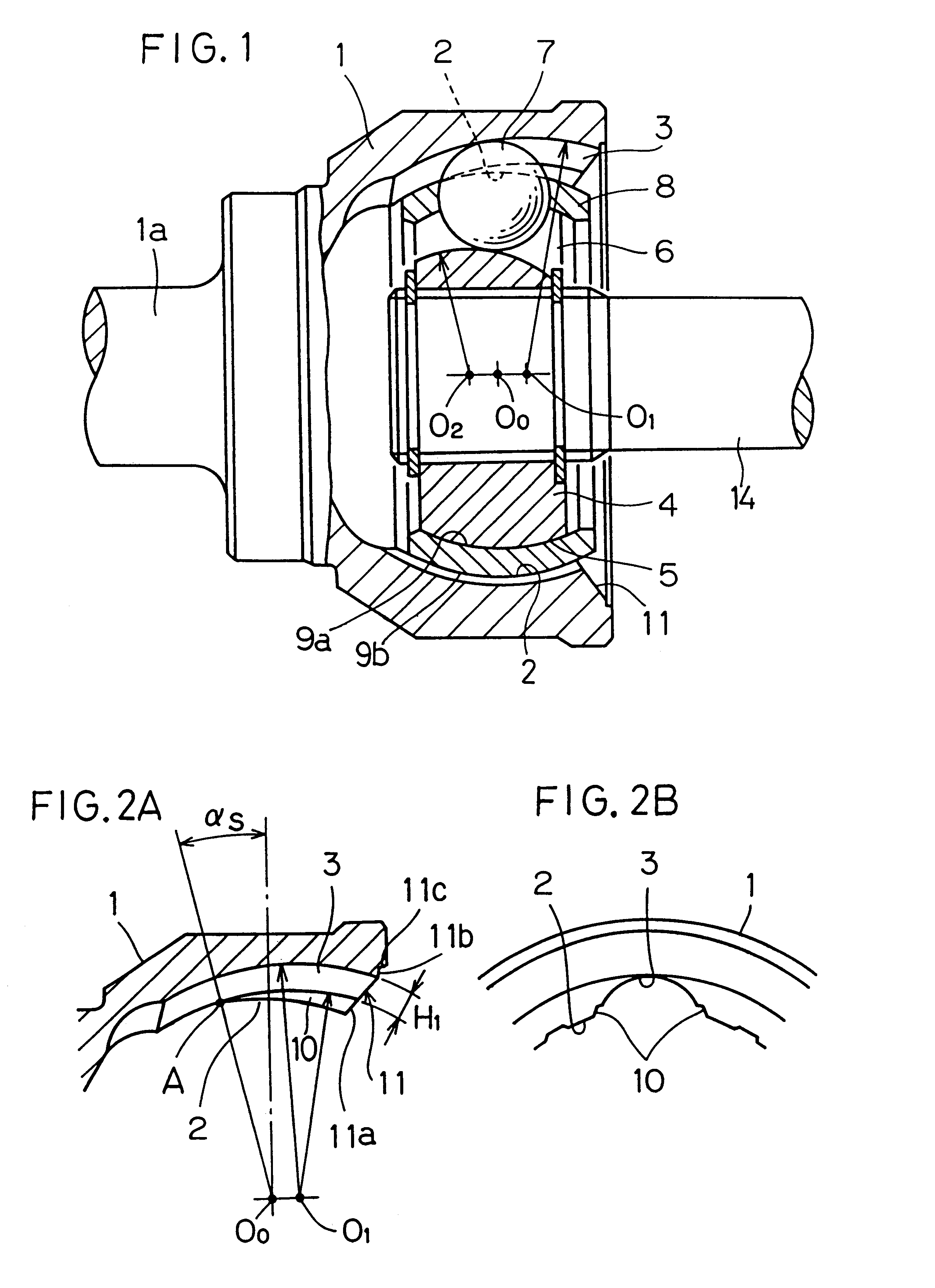
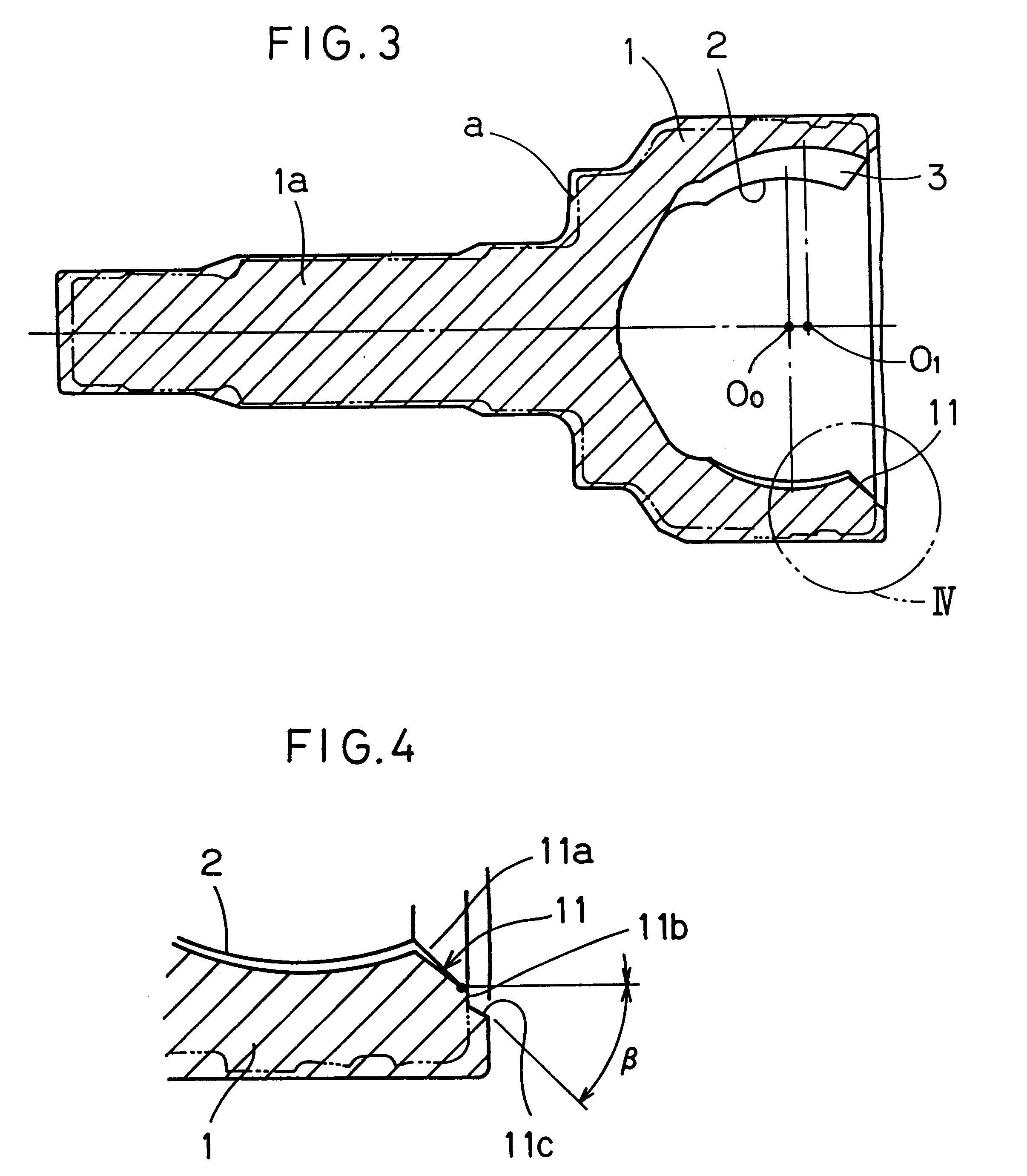
Constant velocity joint
ActiveUS20050272510A1Avoid wastingReduce weight and sizeYielding couplingRotary machine partsEngineeringControl theory
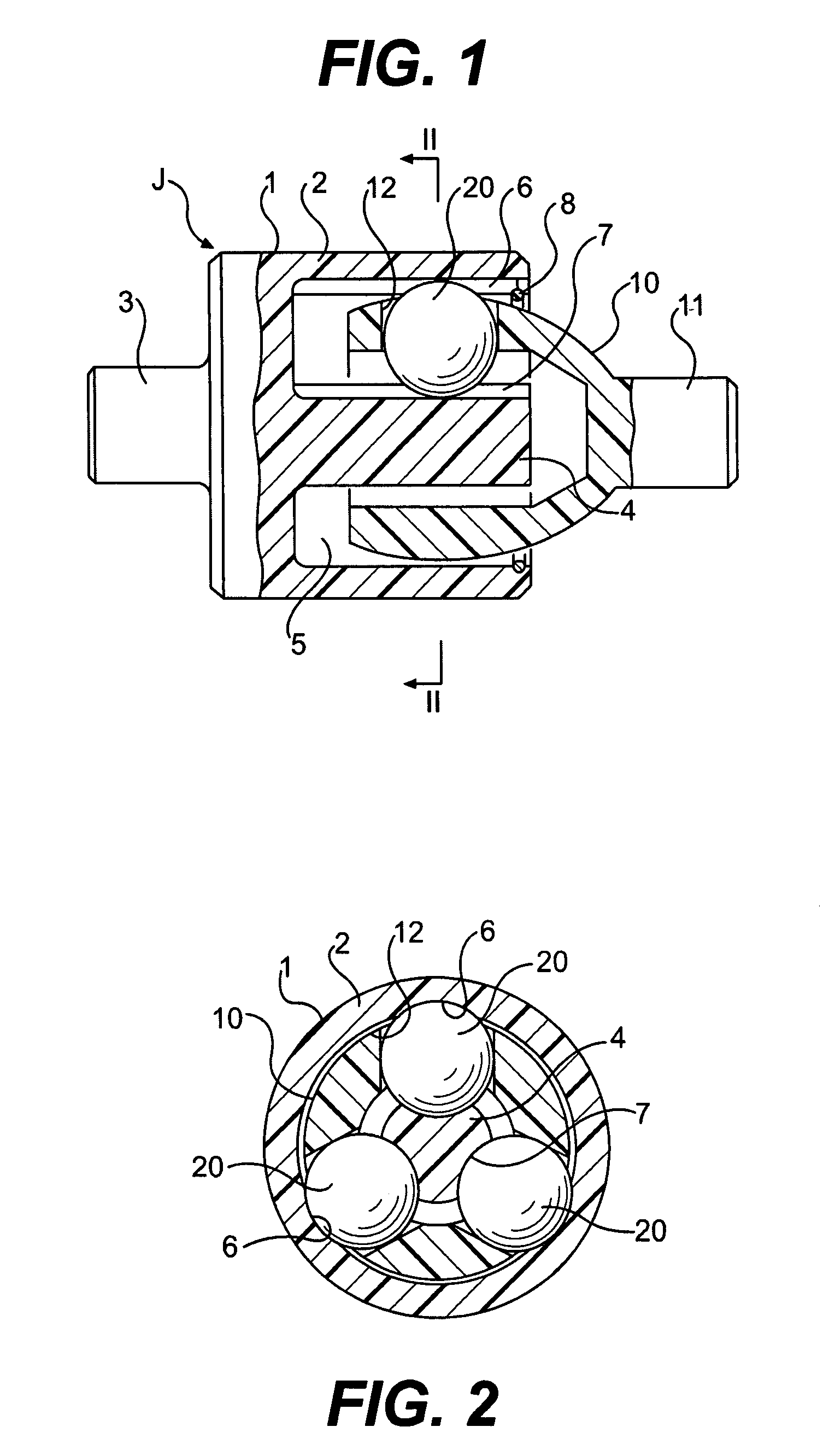
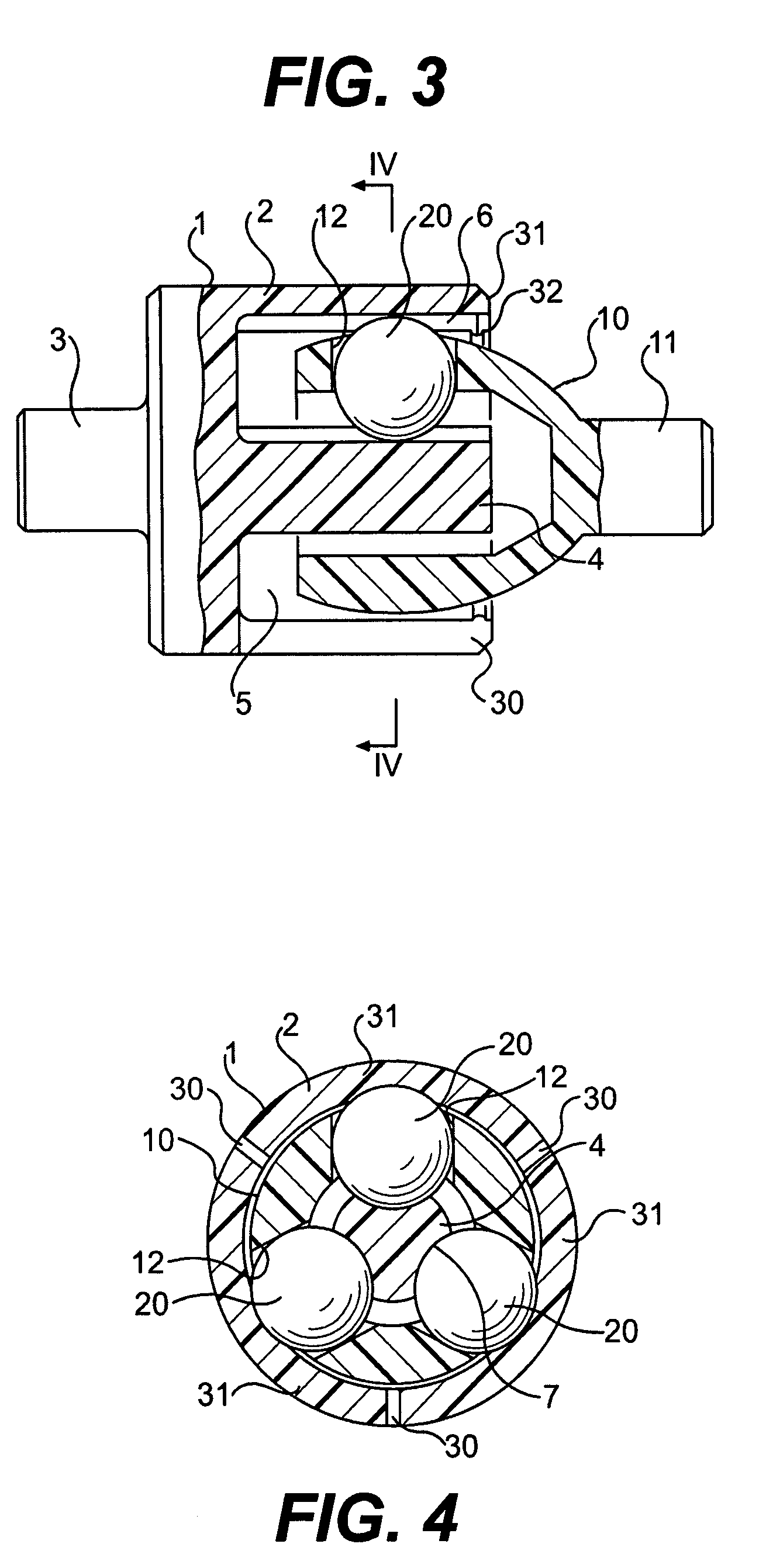
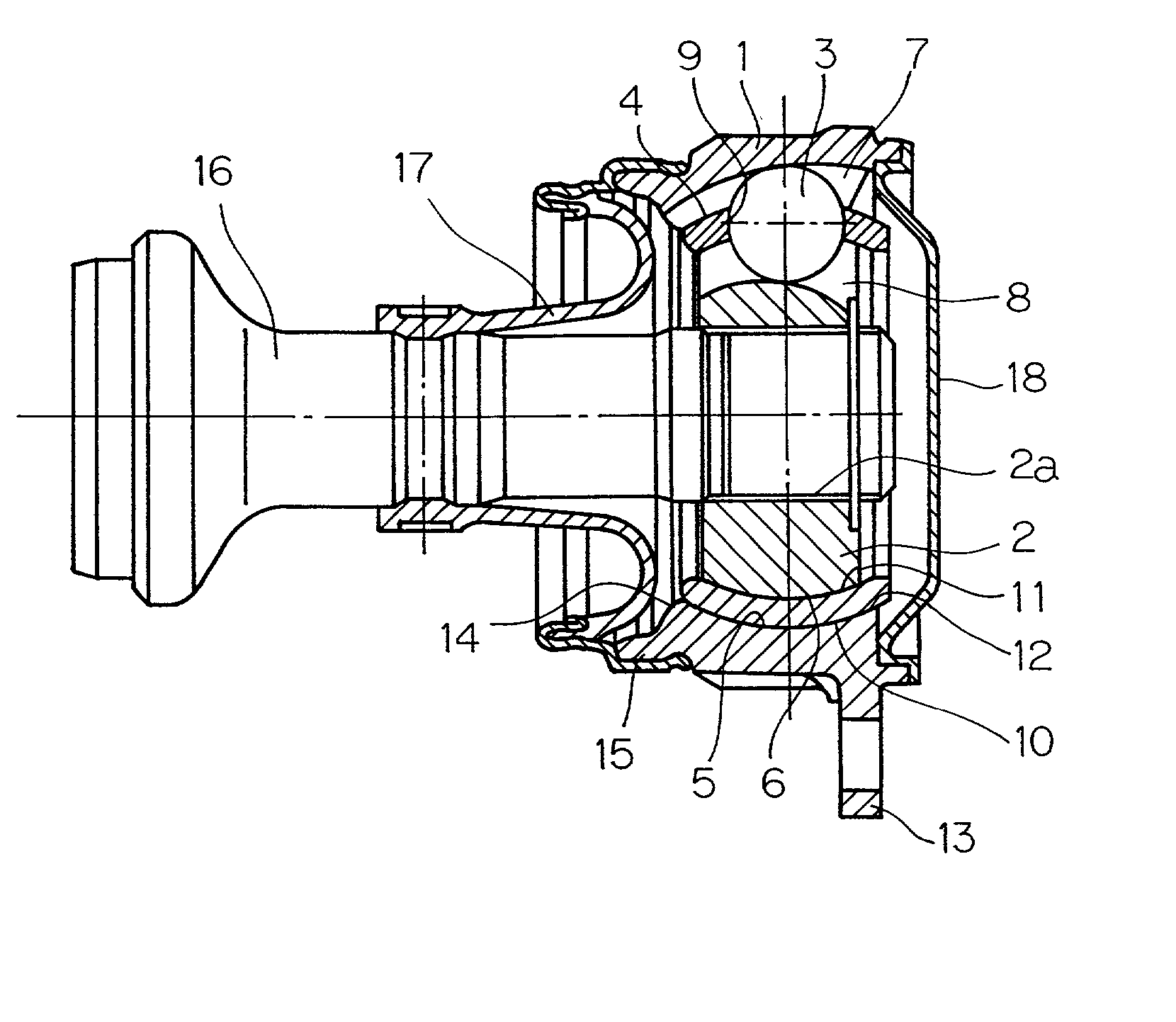
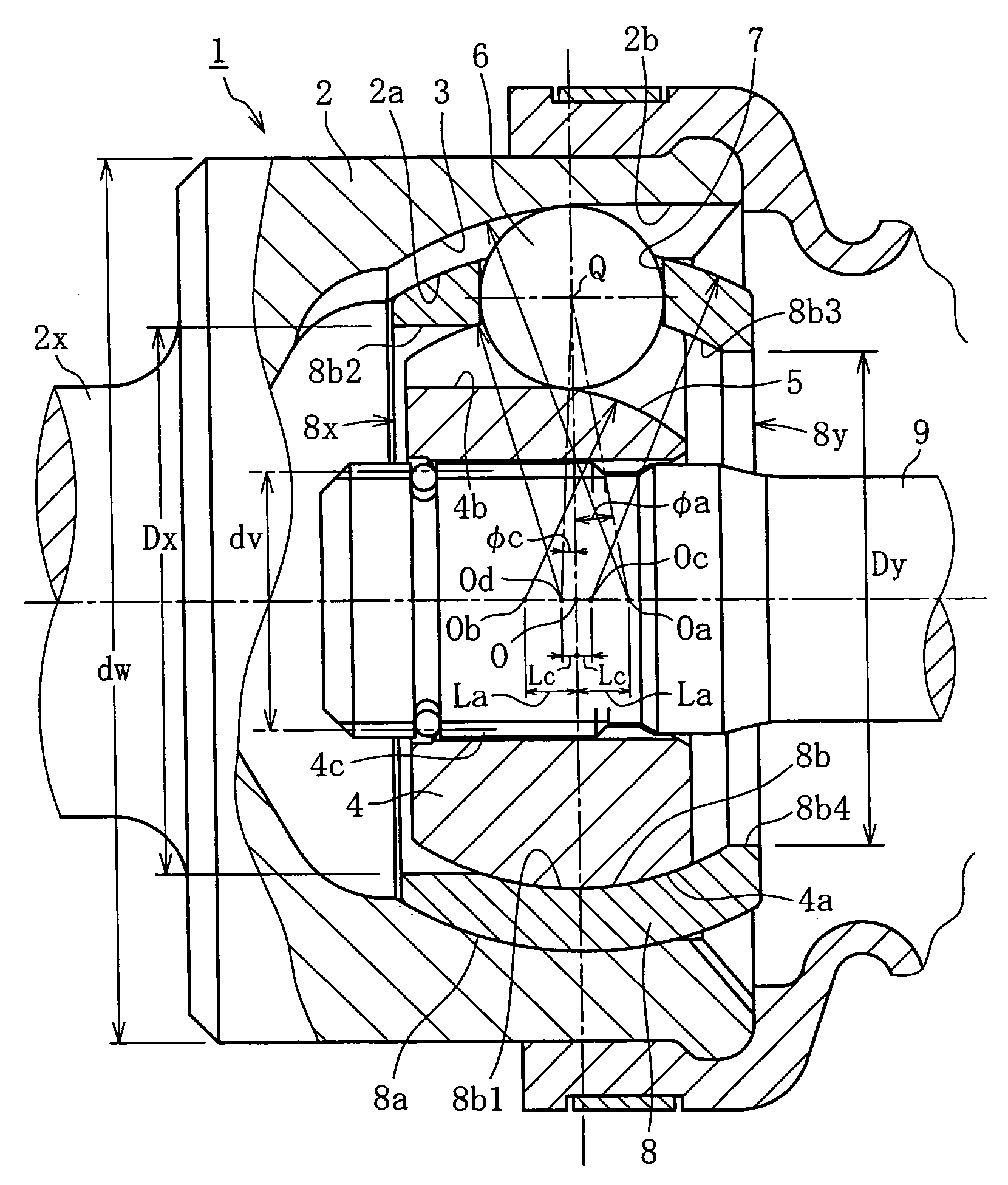
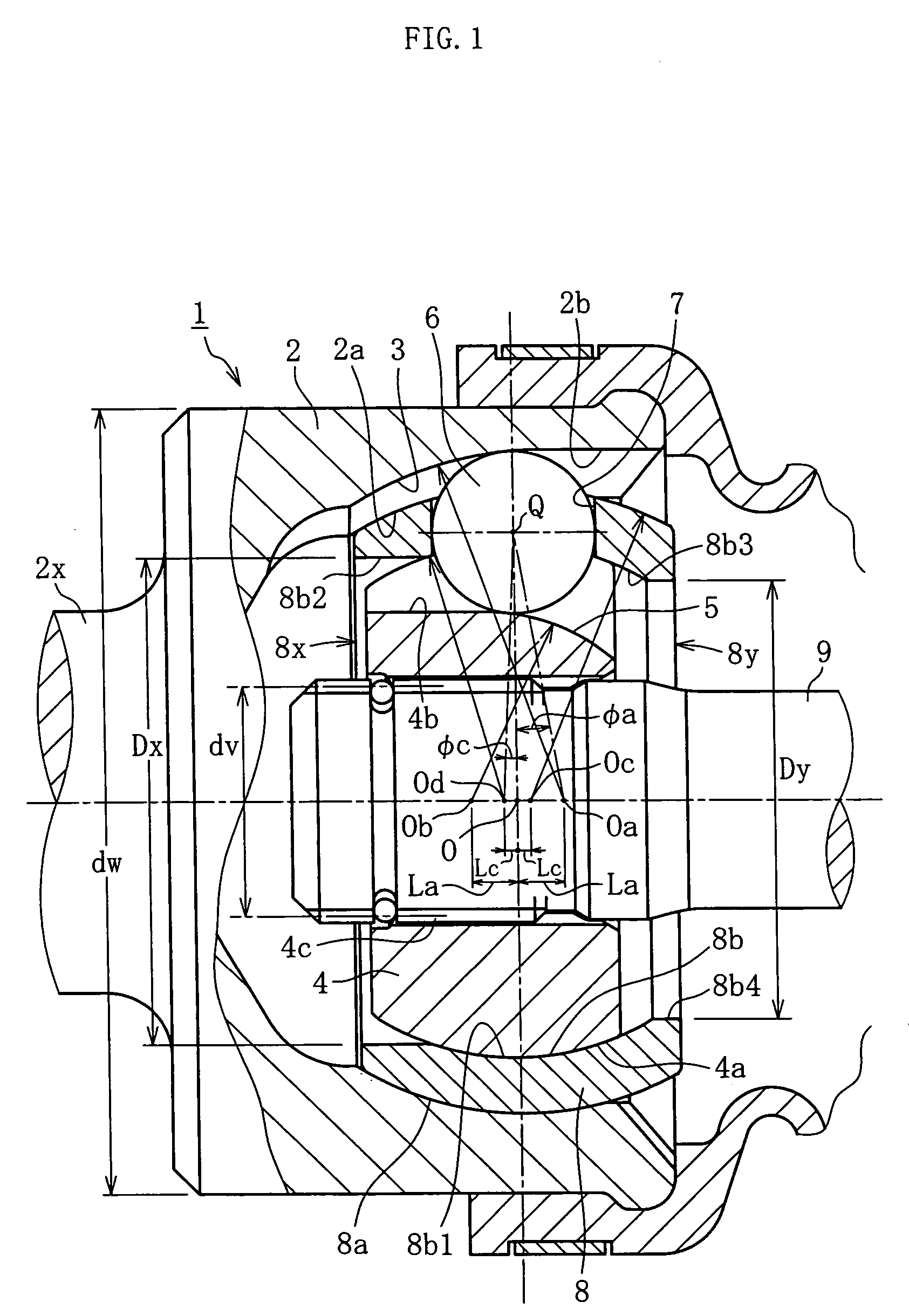
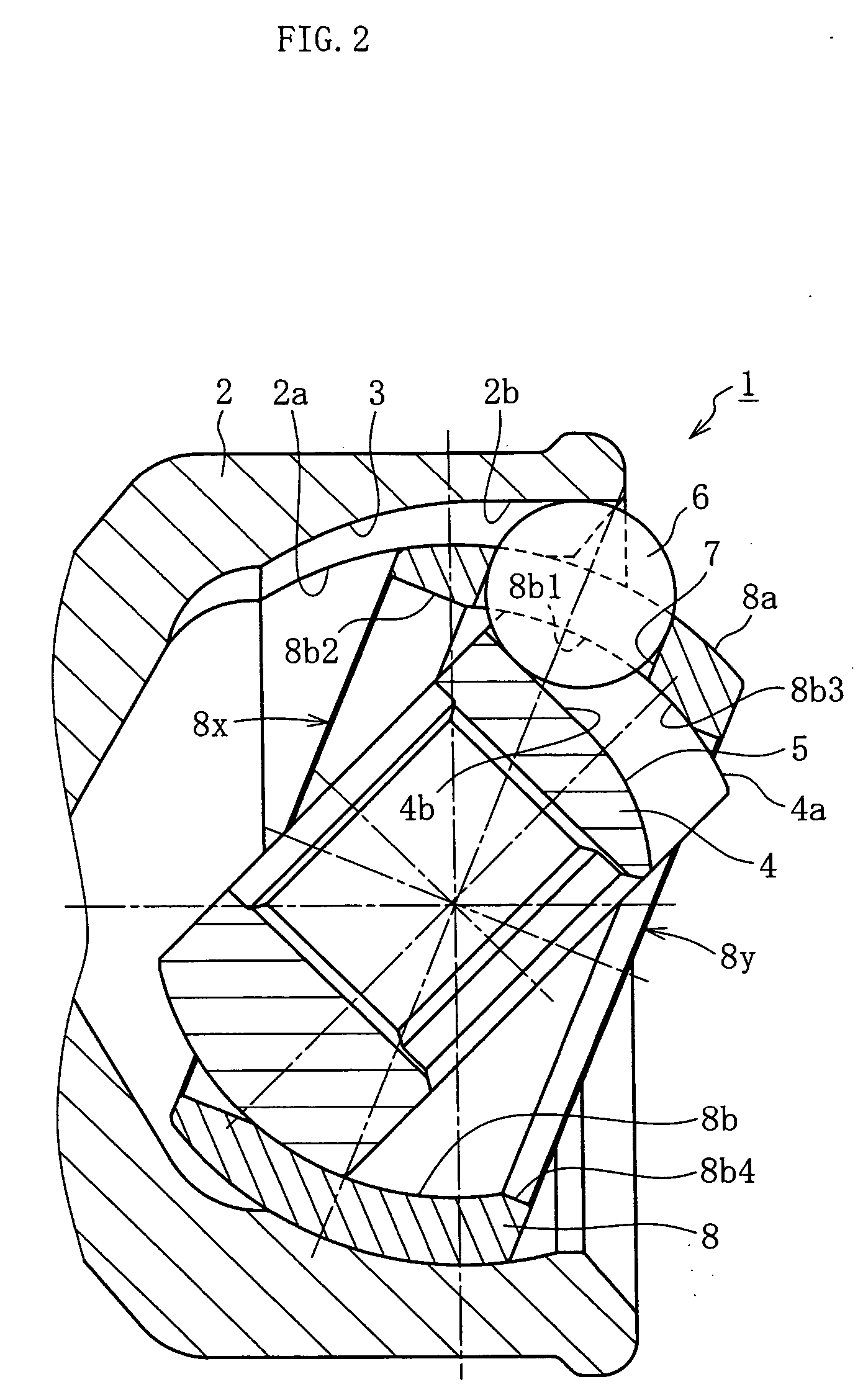
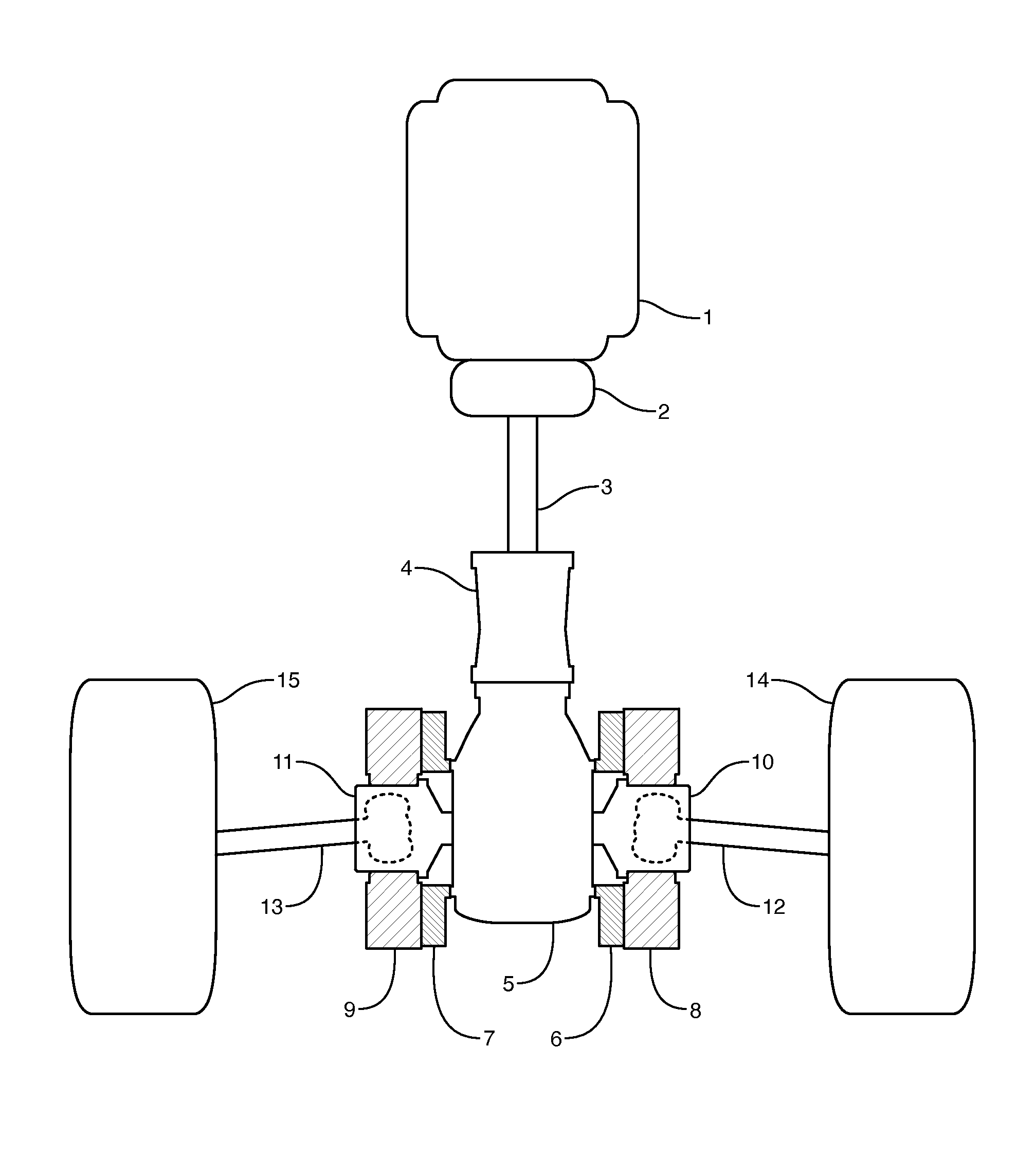
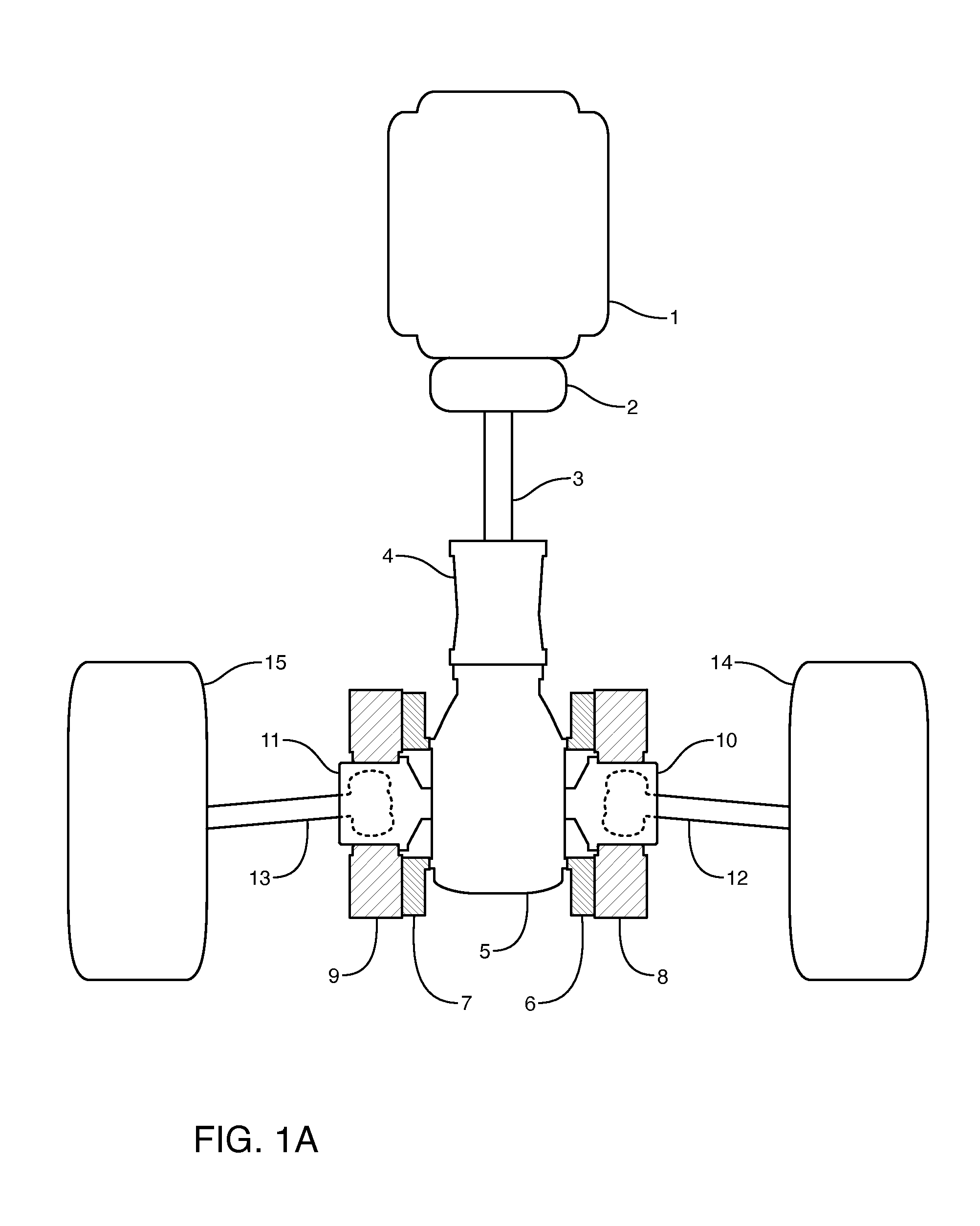
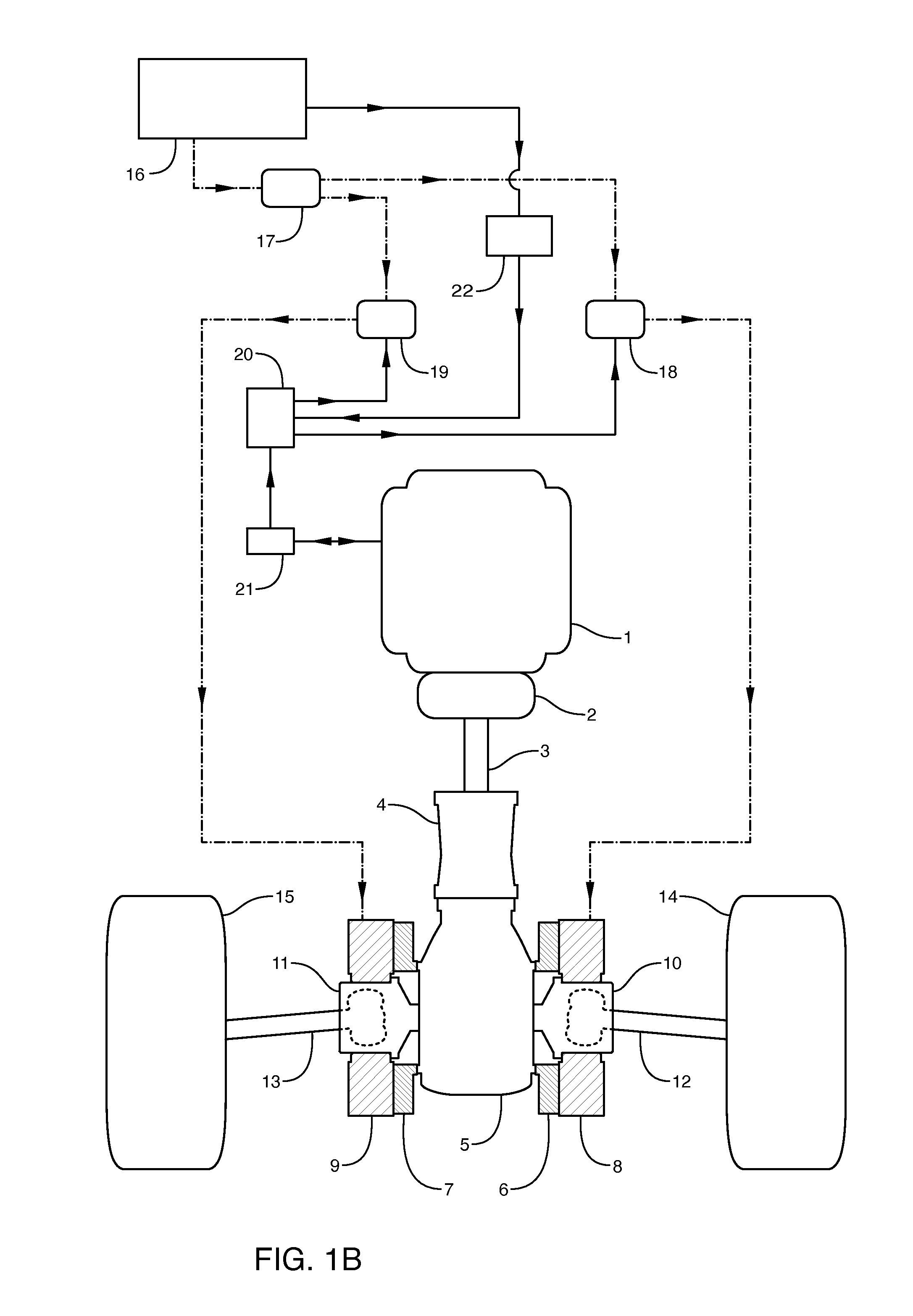
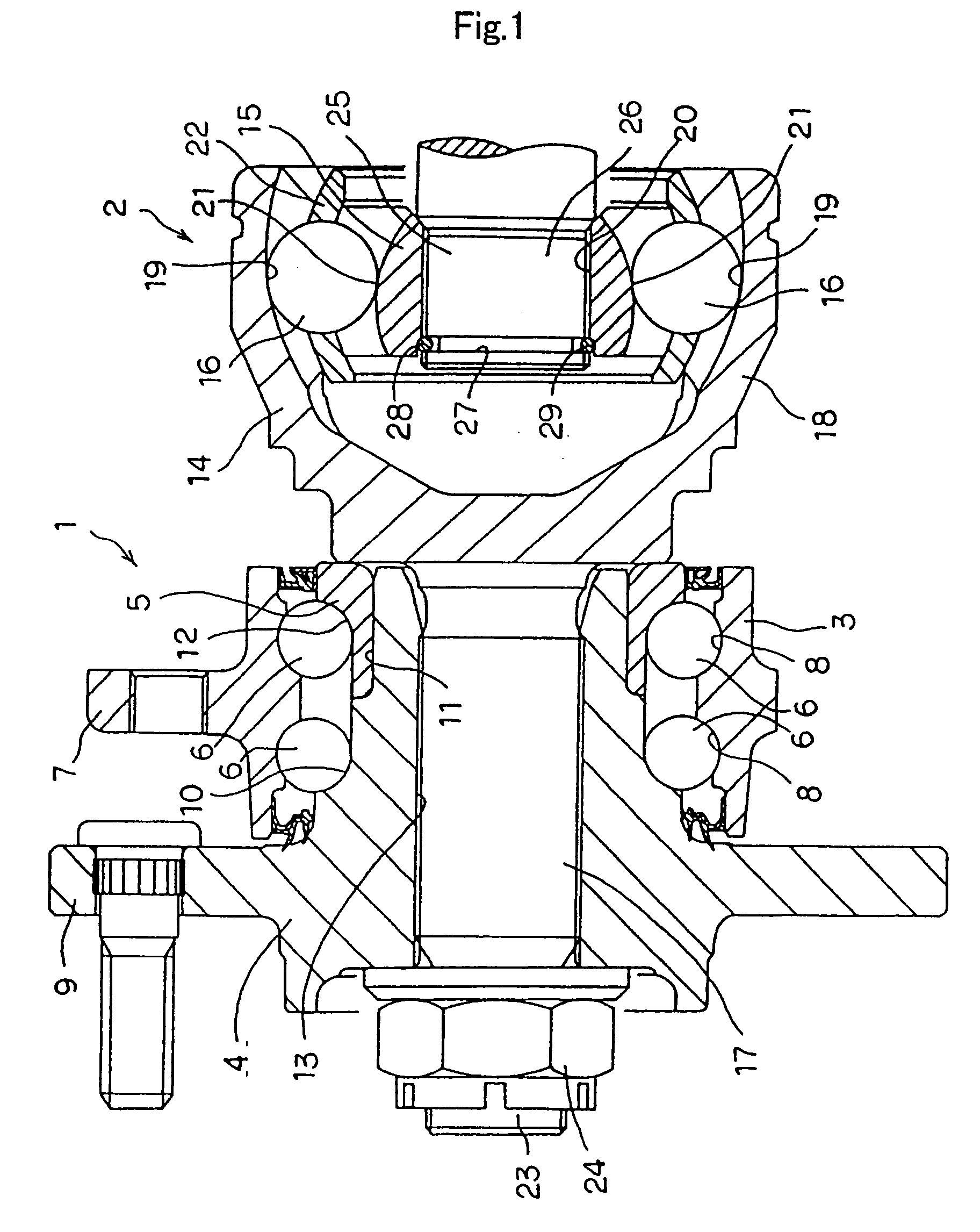
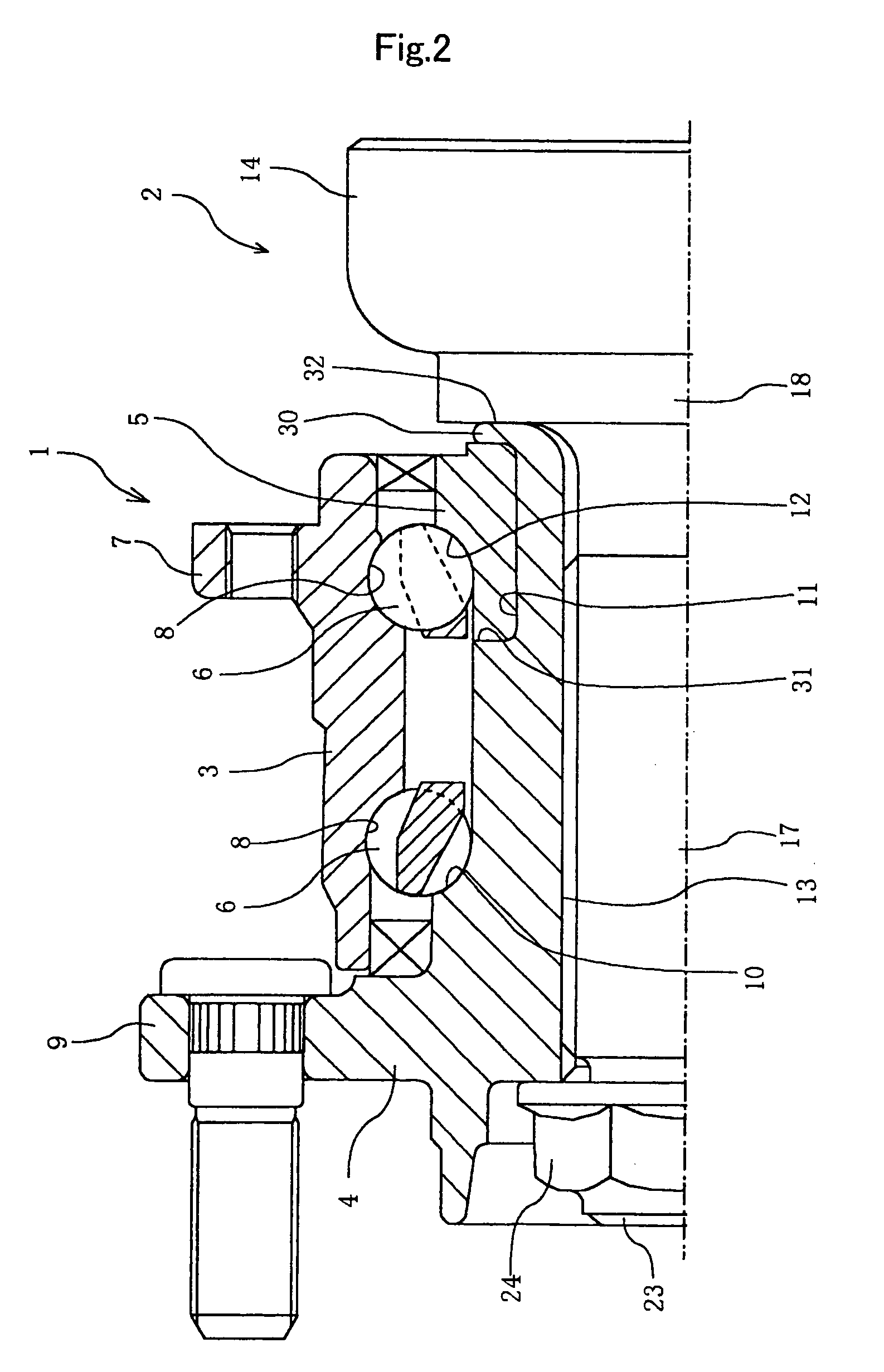
A constant velocity joint 1 disposed on the outboard side of a drive axle for transmitting drive power to a wheel, comprising an outer joint member 2 having a plurality of track grooves 3 on the spherical inner peripheral surface 2a, an inner joint member 4 having a plurality of track grooves 5 on the spherical outer peripheral surface 4a, torque transmitting balls 6 disposed in a plurality of ball tracks formed by the opposed track grooves 3 and 5 of both joint members 2 and 4, and a cage 8 interposed between both joint members 2 and 4 and receiving and holding the torque transmitting balls 6 in pockets 7, wherein the outboard-side end of the cage 8 is formed with an opening 8x for removably inserting the inner joint member 4 and the inboard-side end is formed with an opening 8y whose diameter is smaller than that of the outboard-side opening 8x.
Owner:NTN CORP
Constant velocity universal joint drive spindle assembly clearance test stand
InactiveCN101458061ASimple structureEasy to operateAngles/taper measurementsMechanical clearance measurementsDrive shaftUniversal joint
The invention relates to a clearance testing table for a uniform-speed universal joint driving shaft assembly in the technical field of automotive engineering. An angle sensor and a circumferential clearance testing collet are respectively arranged at the tail part and the head part of a circumferential clearance testing spindle; a circumferential clearance testing bearing seat, a clamp, a linear driving component, a torsion stress applying component and a guide way are fixed on a stand; one end of the torsion stress applying component is fixedly connected with the circumferential clearance testing spindle; a pull pressure sensor is positioned between a front skid and a tail skid and respectively connected with the front skid and the tail skid; the linear driving component is connected with the front skid; a motor is arranged at one end of the linear driving component; a displacement sensor is positioned on the stand at one side of the guide way and parallel to the guide way; an axial clearance testing collet is arranged on an axial clearance testing bracket, and, together with the axial clearance testing bracket, the axial clearance testing collet is fixed on the tail skid and parallel to the guide rail. The clearance testing table has a plurality of clearance testing functions, is suitable for a plurality of varieties and fully reflects the clearance of a tested component.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
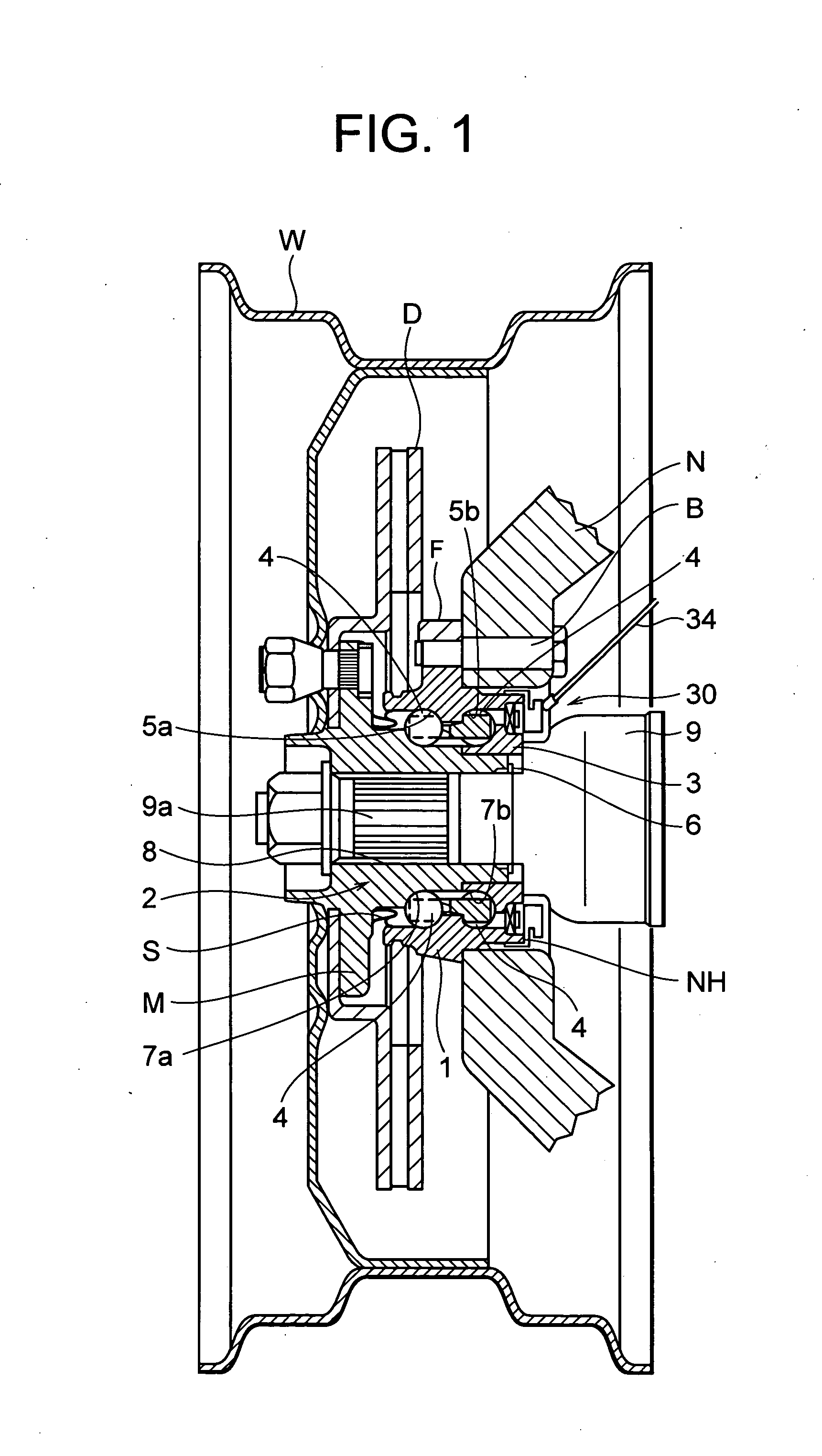
Wheel support bearing assembly with built-in load sensor
ActiveUS7604413B2Accurate detectionCompact installationRoller bearingsBearing assemblyUniversal jointEngineering
A wheel support bearing assembly comprises a stationary outer member and a rotatable inner member. The to-be-detected parts of angle detection sensors are fixed to the inner member and an outer race of a constant velocity joint connected to the inner member, respectively. Detecting parts of the angle detection sensors are fixed to the outer member in face-to-face relation with the to-be-detected parts. The bearing assembly also includes a load conversion unit detecting a relative angular difference between the inner member and the constant velocity universal joint by comparing the detection signals from the detecting parts to detect the load acting on the bearing assembly.
Owner:NTN CORP
Constant velocity joint vent valve
ActiveUS6988949B2Prevent escapeImprove ventilationClutchesYielding couplingMulti materialInternal pressure
A vent valve for use in a constant velocity joint having a vent aperture in communication with a joint chamber comprises a body having a first end and a second end and at least one flat extending therebetween; and an umbrella shaped flexible retention cap disposed adjacent the first end of the body and the at least one flat. The retention cap is operative in a normally closed position to cover the at least one flat and seal the joint from external contaminants, and in response to internal pressure created in the joint cavity, functions to bellow outward and expose the at least one flat to permit air to escape from the chamber. The at least one flat includes a straight-line vent to clean the grease off and away from the vent valve. The vent valve can be made from single or multiple materials, having porous and non-porous properties.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
Protected connection interface for direct torque flow constant velocity joint and method thereof
InactiveUS7677984B2Minimize exposureYielding couplingCouplings for rigid shaftsEngineeringControl theory
A direct torque flow constant velocity joint connection interface includes a drive unit, a direct torque flow constant velocity joint connector and a sealant. The drive unit includes a shaft having a second interface surface. The direct torque flow constant velocity joint connector includes a unitary inner joint part having a first interface surface, where the first interface surface is connected to the second interface surface of the drive unit. The sealant provides filling between the first and second interface surfaces. Also provided is a direct torque flow constant velocity joint connector having sealant on an interface portion of an inner joint part and a method thereof.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE NORTH AMERICA
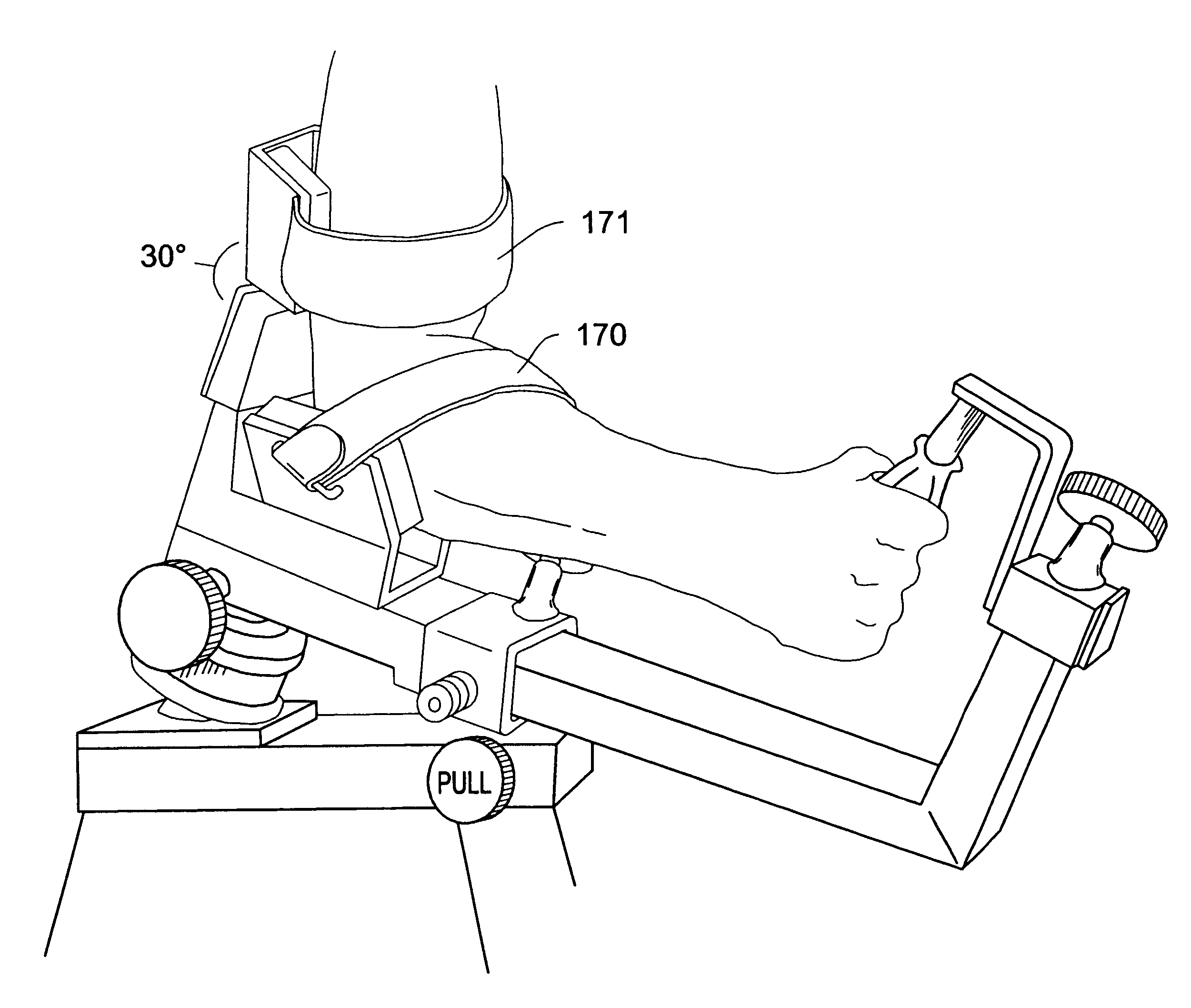
Constant velocity universal joint for therapy devices
The present invention relates to the use of universal joints, especially constant velocity universal joints, to provide multi-axial rotational freedom on exercise, rehabilitation and testing machines. The universal joints may be an integral part of the exercise, rehabilitation and testing machines, or they be provided as adapters for use on uni-axial machines. Furthermore, the adapters may function to act as converters such that attachments designed for machines using a receiver apparatus may be used on machines with an input shaft. Conversely, the adapters may function to act as converters such that attachments designed for machines using an input shaft may be used on machines using an attachment receiver. Additionally, an improved apparatus attachment is provided which uses an arm / joint stabilizer to further support the arm and joint position. The apparatus attachment primarily comprises a lever arm with a hand grip attached to a first end and the arm / joint stabilizer attached to a second end. The apparatus attachment is adapted to be used with any of the embodiments of the adapters described herein.
Owner:BROWN WILLIAM C
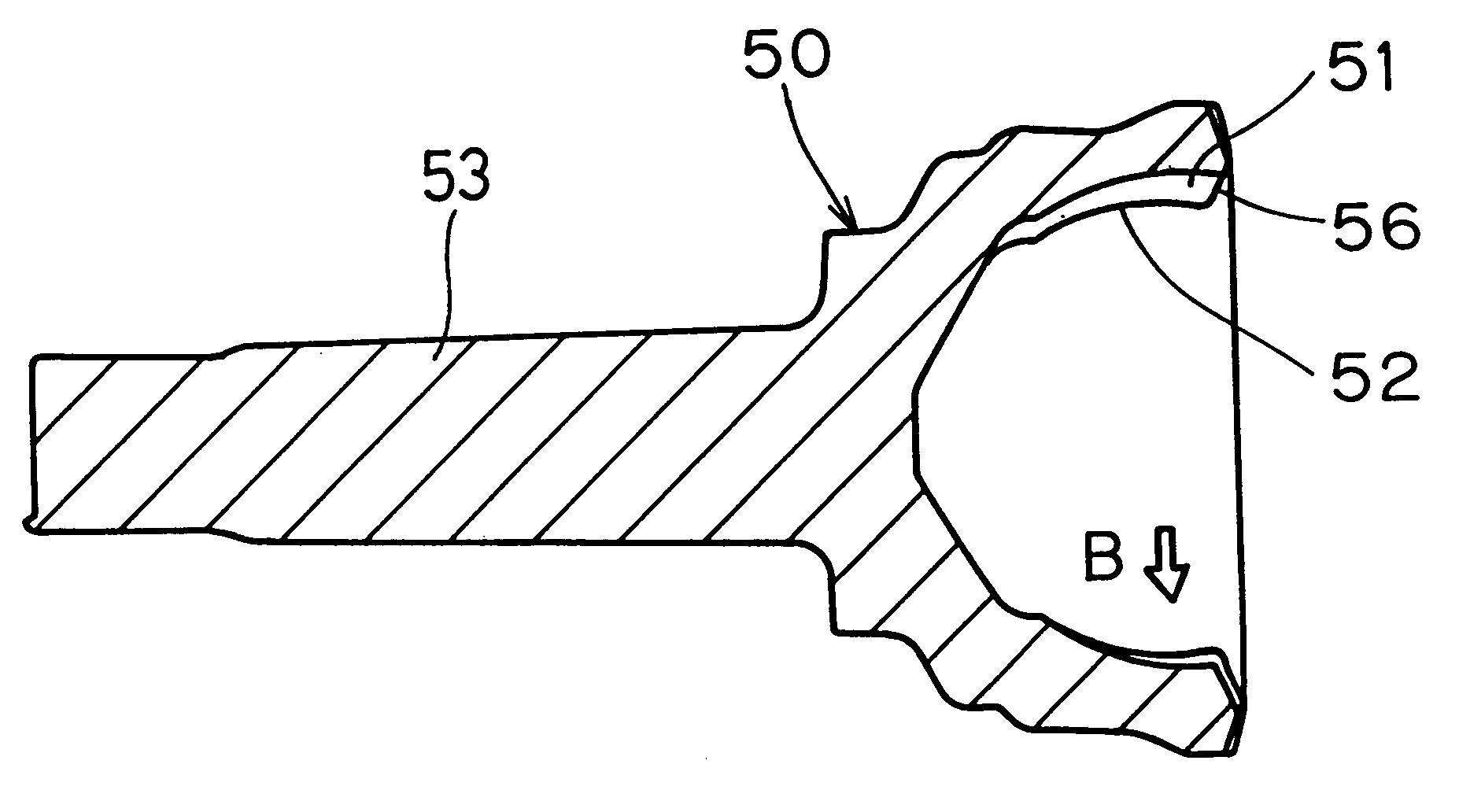
Constant velocity joint and method of making an outer race therefor
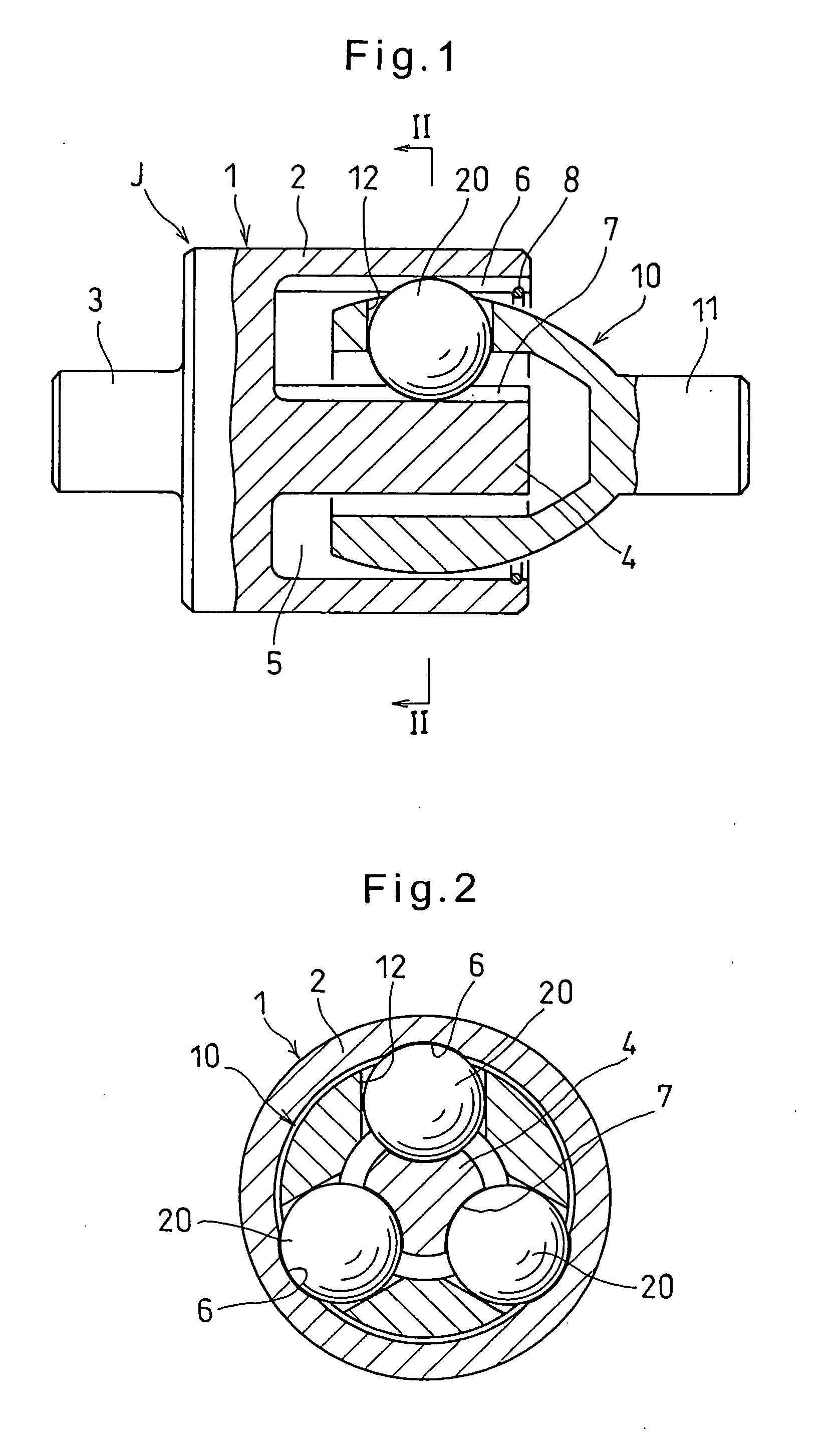
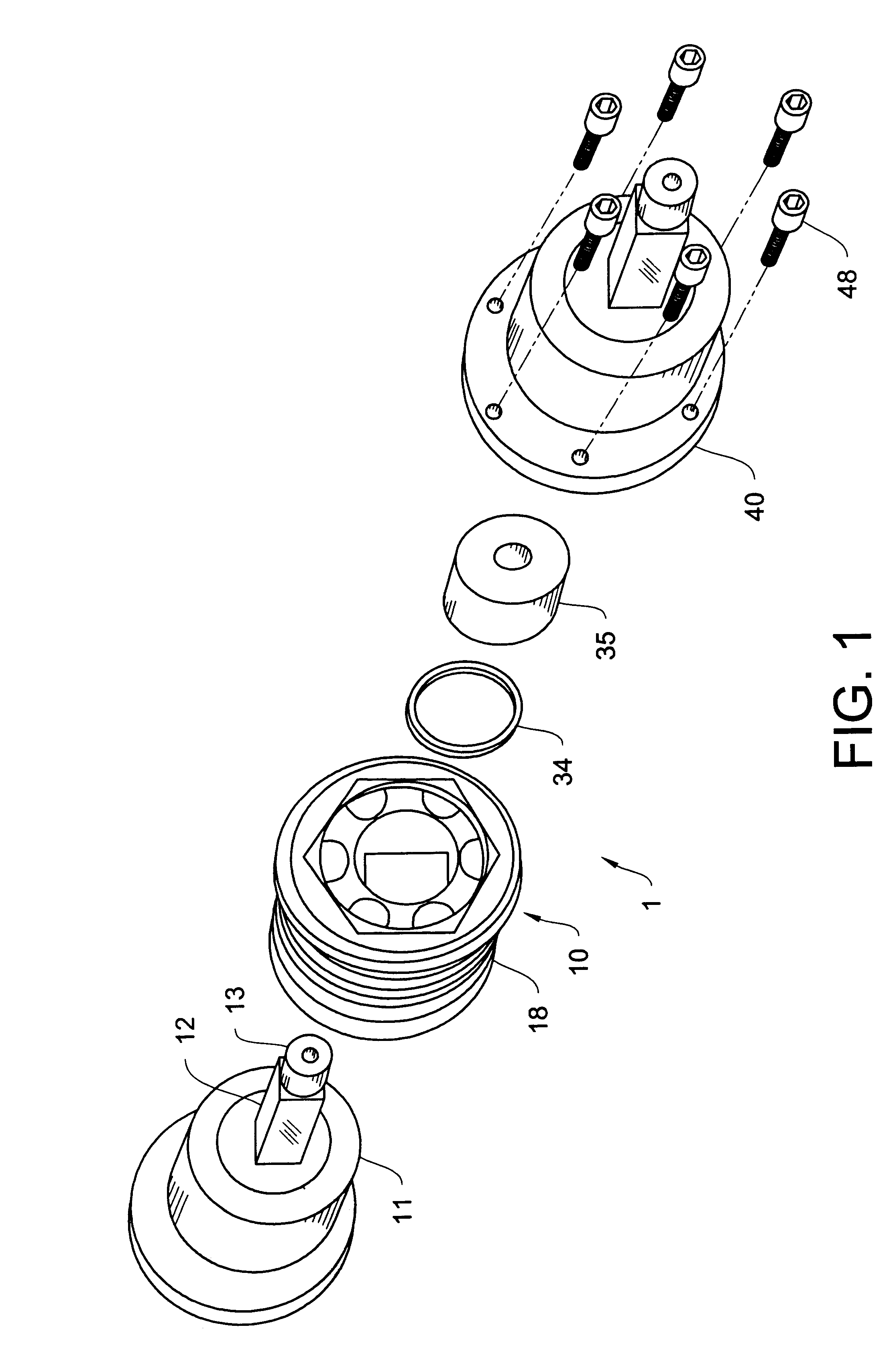
InactiveUS6224490B1High precisionReduce manufacturing stepsYielding couplingEngine componentsControl theoryConstant-velocity joint
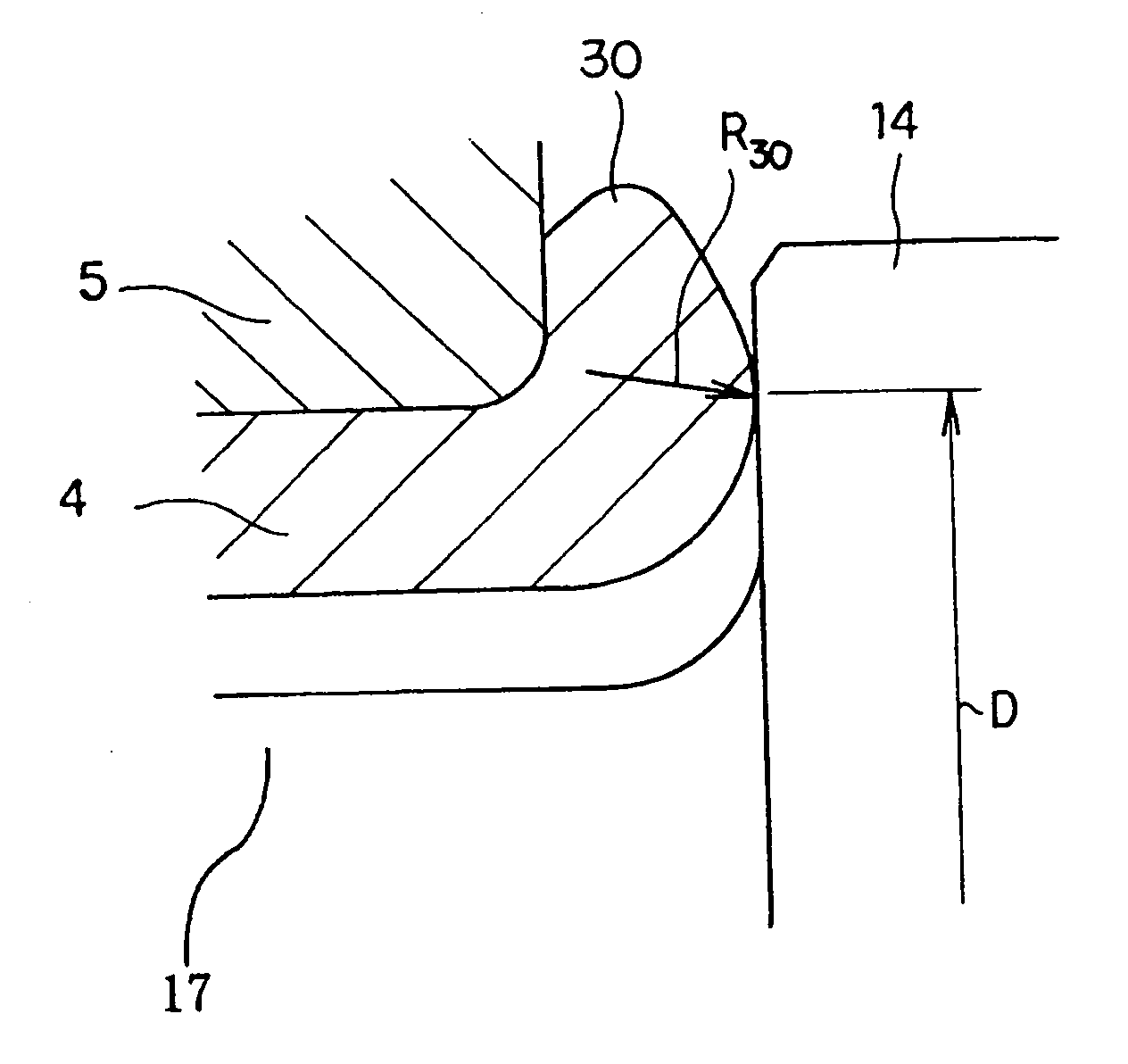
A constant velocity joint includes an outer race (1) having a spherical inner surface (2) with track grooves (3) each extending in an axial direction thereof, an inner race having a spherical outer surface (5) formed with track grooves (6) equal in number to the number of the track grooves (3) in the outer race (1), a plurality of torque transmitting balls (7) sandwiched between the inner race (4) and the outer race (1) and accommodated in part in the track grooves (6) in the inner race (4) and in part in the track grooves (3) in the outer race (1), and a cage (8) for retaining the torque transmitting balls (7) while being guided by and between the spherical inner surface (2) of the outer race (1) and the spherical outer surface (5) of the inner race (4). This constant velocity joint of the structure described above is featured in that at least the track grooves (3) in the outer race (1) and an entry chamfer (11) of the outer race (1) are formed by a plastic working process. A method of making the outer race (1) in the constant velocity joint is also provided.
Owner:NTN CORP
Vehicle hybrid drive arrangement
ActiveUS9387756B1Improve mobilityHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingDrive wheelElectric generator
A hybrid drive arrangement for a motor vehicle comprising two close-coupled electric traction motors / generators on the output of the vehicle differential. A constant velocity joint coupling device is incorporated into the central axis of the traction motors between the differential output shafts and the independent articulated axle shafts for the drive wheels. One embodiment comprises a kit for retrofitting an existing vehicle. The kit comprises two electric traction motors / generators incorporating the constant velocity joint coupling devices, two devices for mounting the traction motors to each side of the differential case between the differential and the independent, articulated axle shafts of the existing vehicle, a battery system electrically coupled to the traction motors, two traction motor controllers, and a vehicle sensing and control system. The arrangement provides for improved acceleration, deceleration, cornering, ease of parking, and fuel economy.
Owner:QUANTA PROD LLC
Bearing unit for wheel drive
An inner race 5 is retained by a crimped portion 30, so that a pre-load is applied to rolling elements 6. A bearing unit for wheel support 1 is connected to a constant velocity joint 2 through tightening of a nut 24. By regulating the tightening force of the nut 24, at the area of contact between the inside end of the crimped portion 30 and the outside end of the outer ring of the constant velocity joint 14, the load per unit length is controlled up to 125 N / mm, or the surface pressure is controlled up to 1.5x10<8 >Pa. Consequently, a bearing unit for wheel support is realized at a low cost with the pre-load securely applied, preventing unpleasant noise from occurring during operation, and preventing play due to plastic deformation.
Owner:NSK LTD
Constant velocity joint rear wheel suspension system for all-terrain vehicle
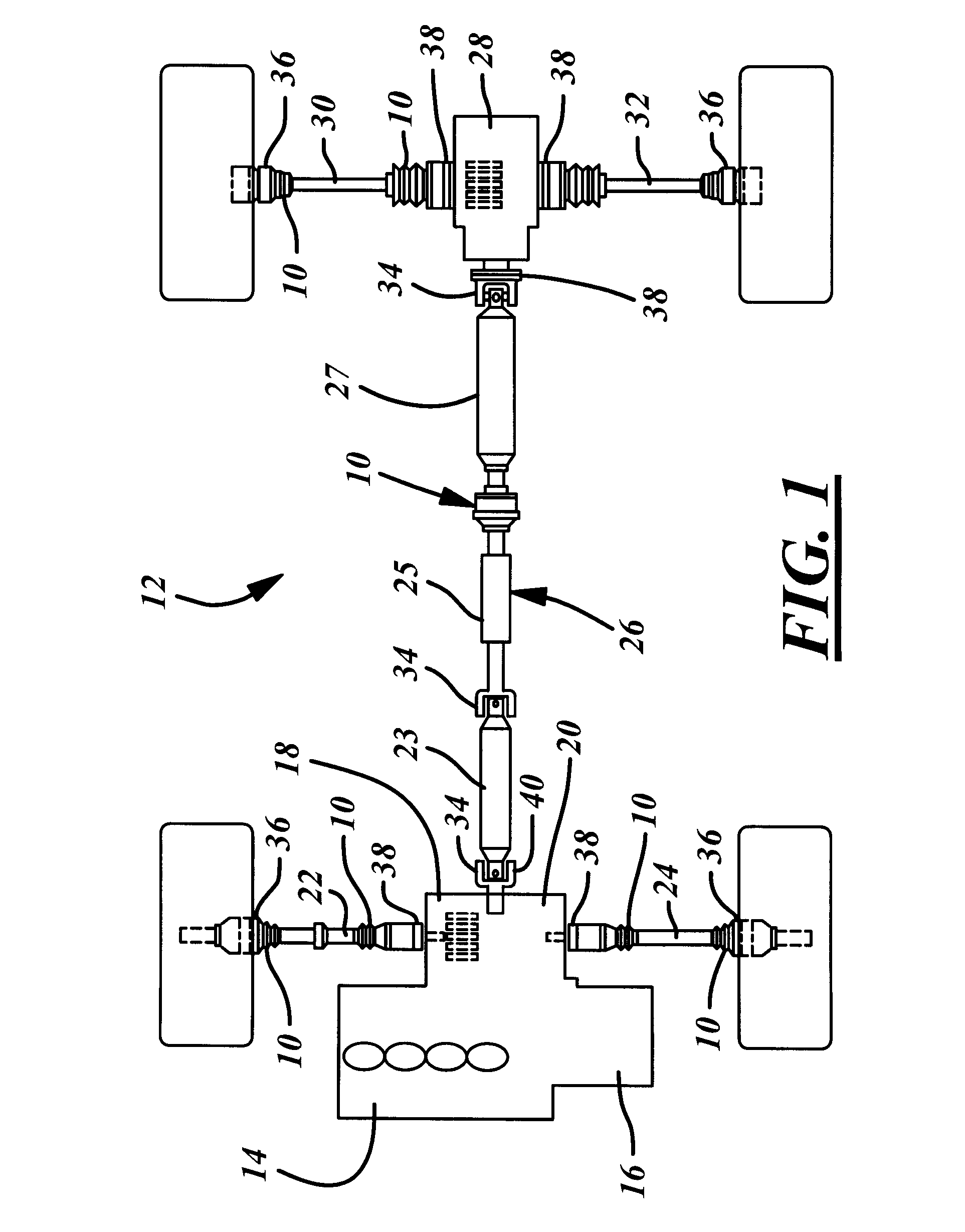
A rear suspension system for an all-terrain vehicle having a chassis and at least three wheels. Two trailing arms are pivotally connected to a chassis. Each of the trailing arms includes a drive shaft bearing. A CV joint pivot arm is pivotally connected to the chassis. A CV joint housing is connected to the CV joint pivot arm. The CV joint housing includes a CV joint bearing. A CV joint is housed inside the CV joint housing and is supported by the CV joint bearing. A drive shaft extends through the CV joint and rigidly connected to the CV joint. The drive shaft is further supported by each of the drive shaft bearings attached to the trailing arms. A shock absorption system is connected between the drive shaft and the chassis. In a preferred embodiment, a cross bar is connected between the trailing arms for stability. Also, preferably, the rear suspension system includes a sway bar and linear shock absorbers acting in combination to provide optimum suspension.
Owner:STEWART CRAIG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com