Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6956 results about "Thermoplastic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
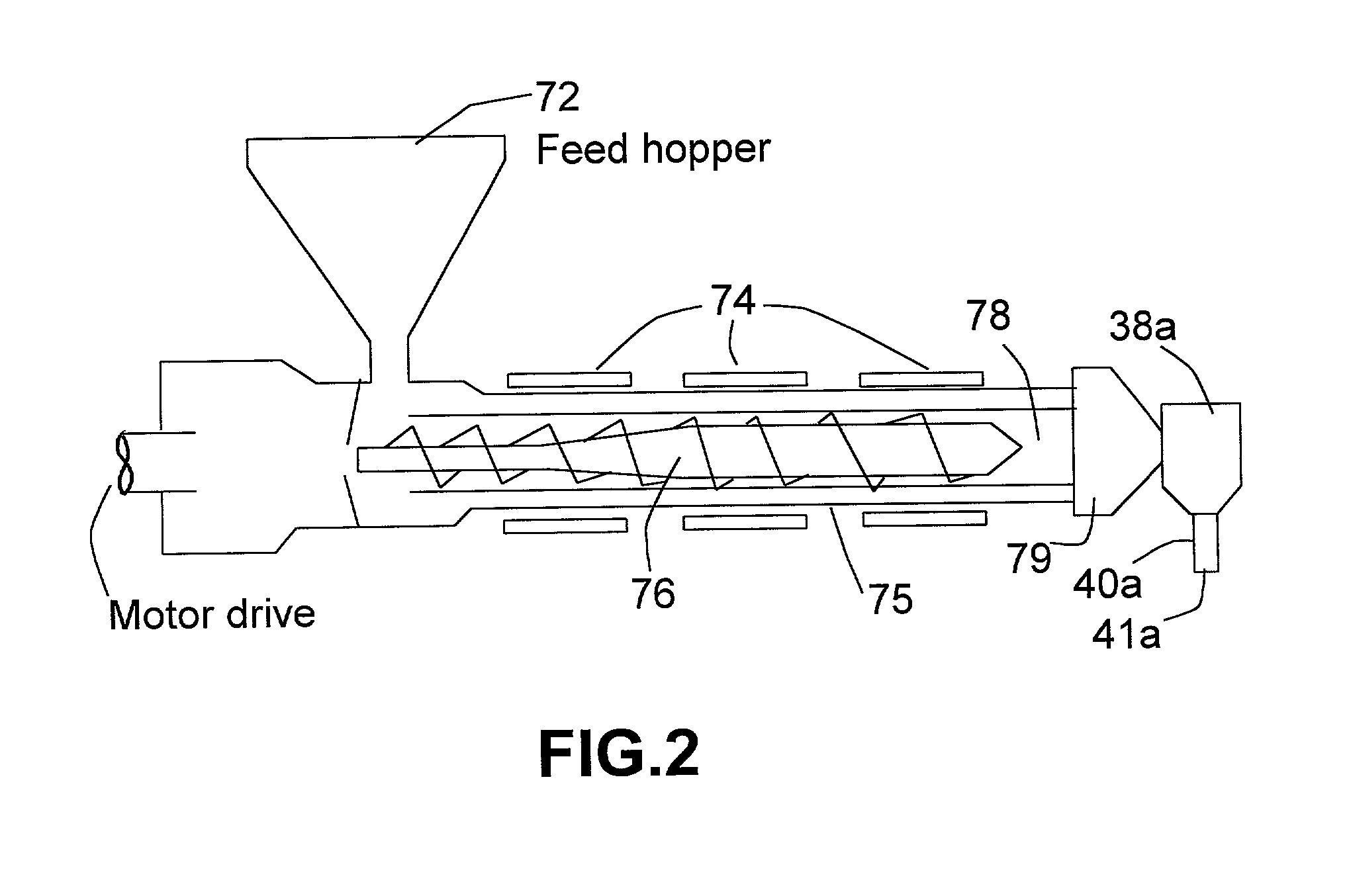
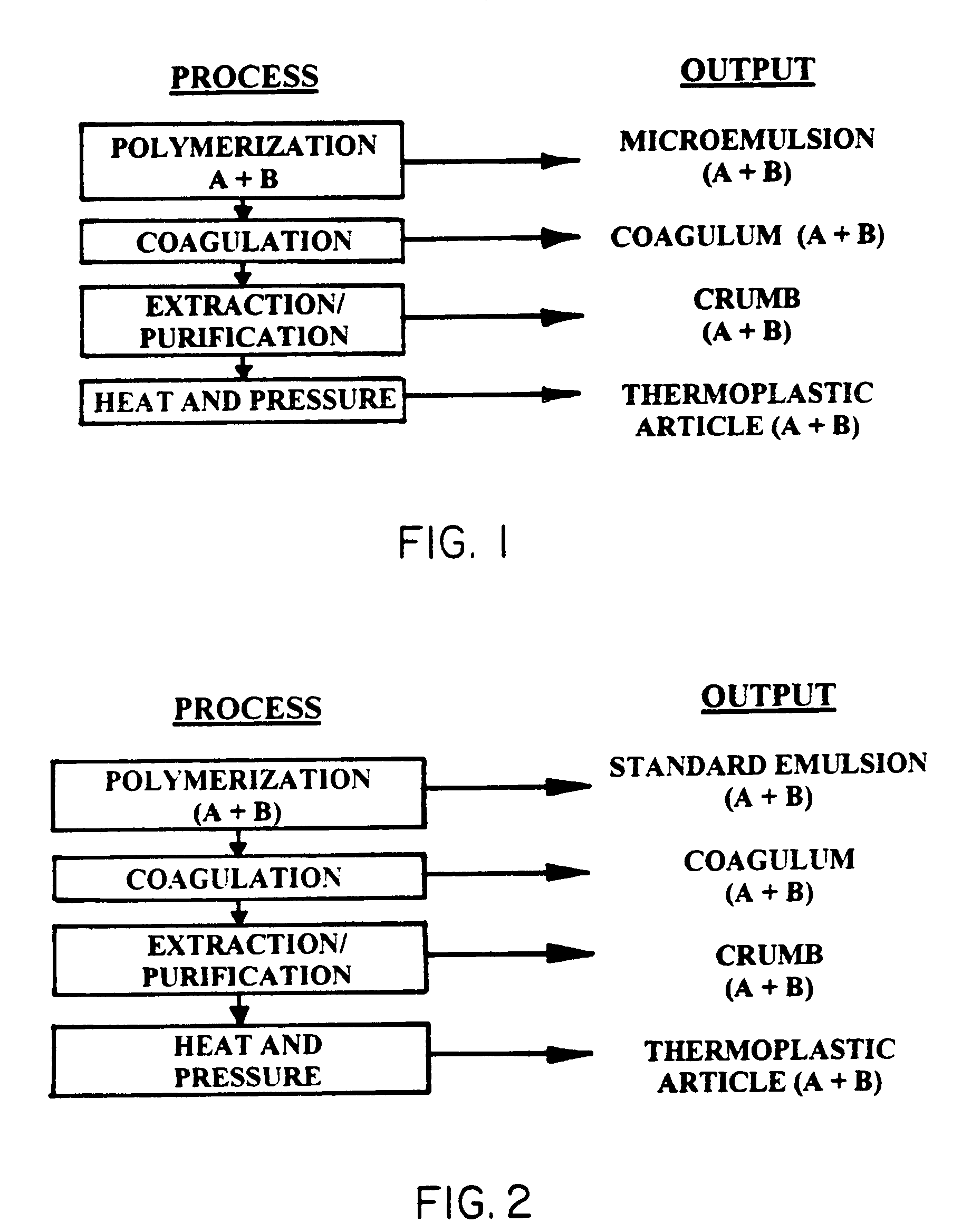
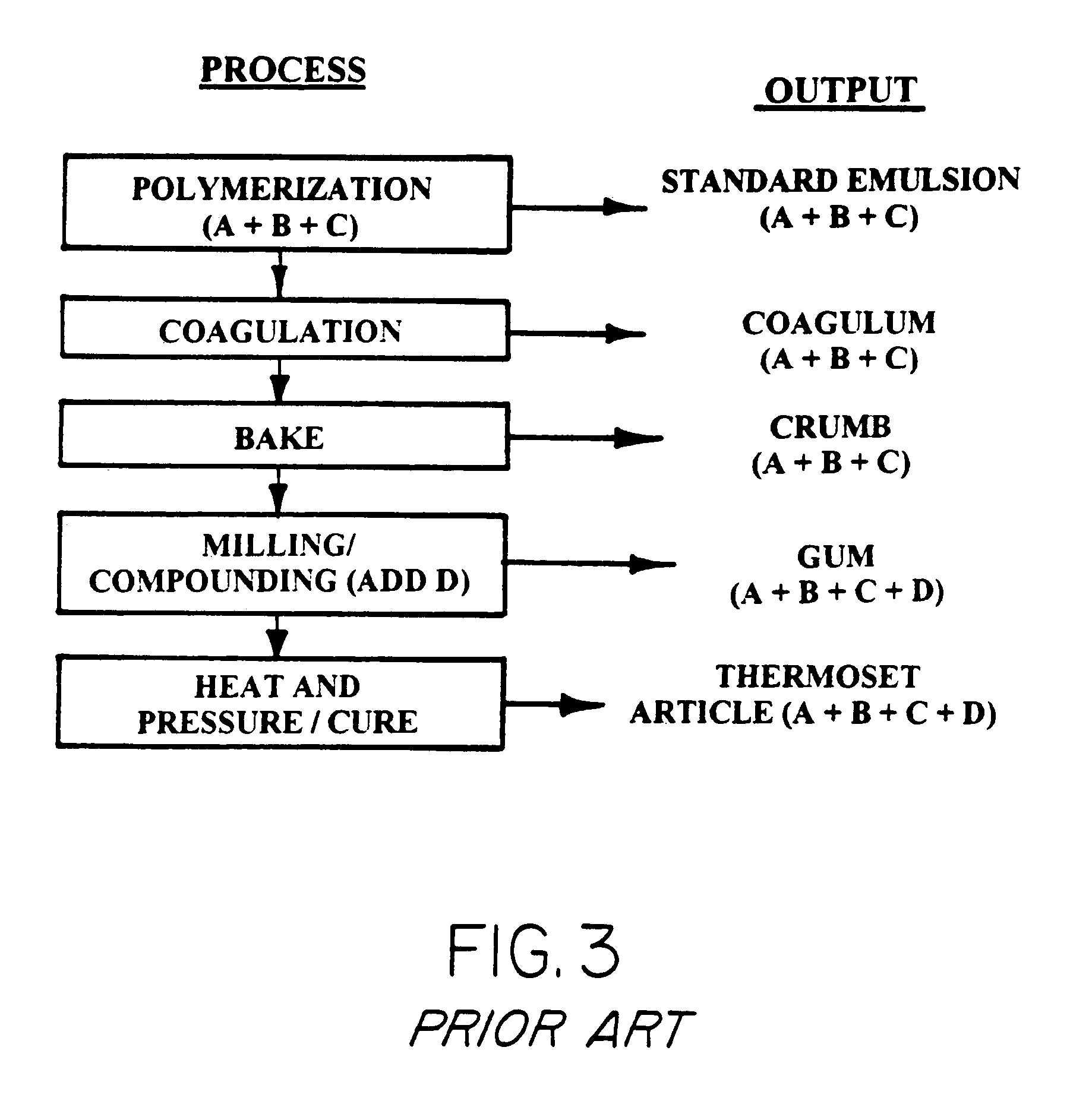
A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is a plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling.
End effector coatings for electrosurgical instruments
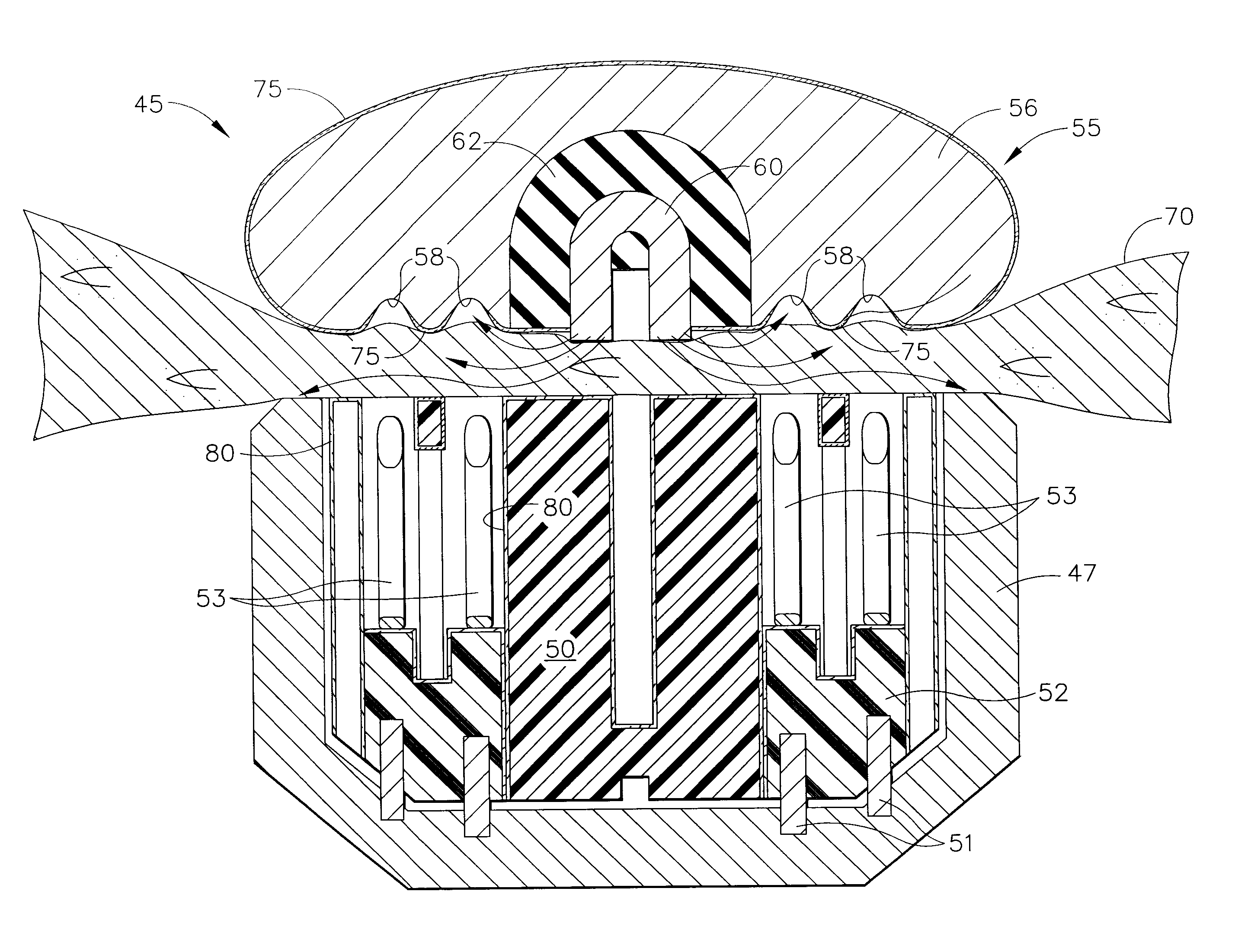
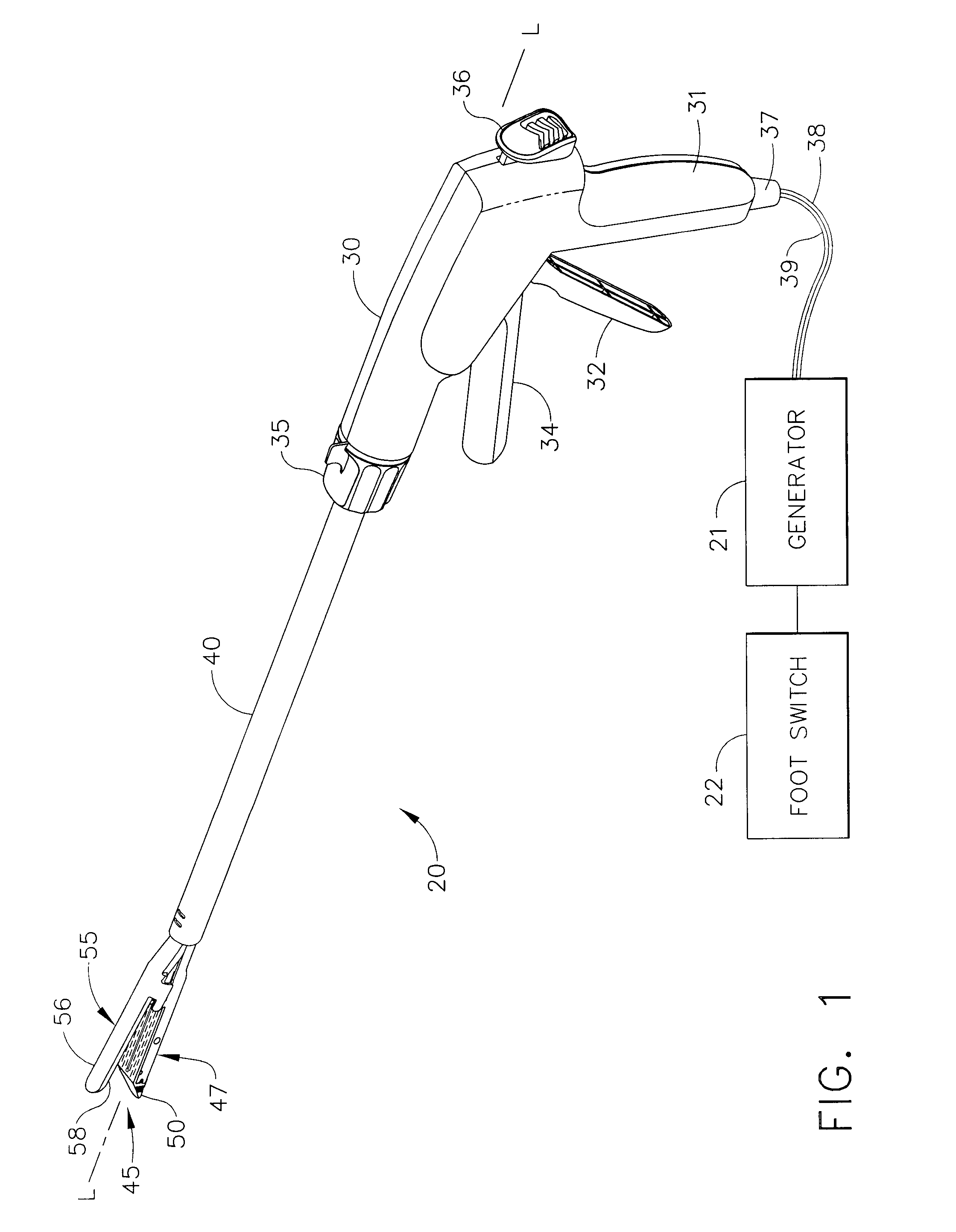
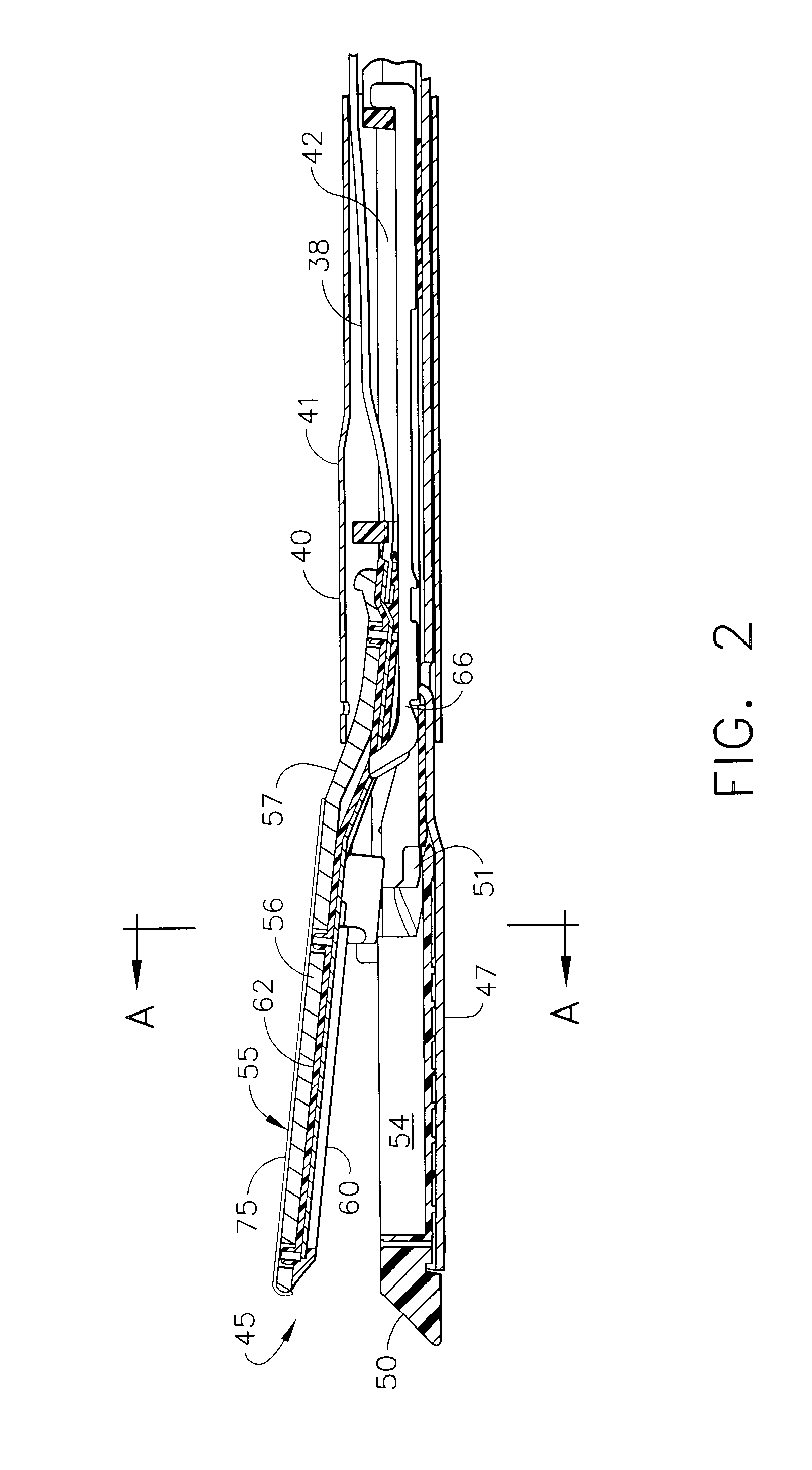
An electrosurgical stapling instrument includes an end effector capable of applying bipolar RF energy into tissue. The end effector has a first pole electrode and a second pole electrode for forming an RF contact circuit with tissue. At least one of the electrodes may have a dielectric coating thereon to create a RF circuit with tissue. The dielectric coating can cover one of the electrodes to create a capacitive coupling circuit with tissue, or can have at least one open passageway extending through the dielectric coating to enable tissue contact with the electrode and the passage of RF energy therethrough. The dielectric coating on the electrode can be masked to create passageways through the dielectric, or the dielectric coating can be locally removed with a variety of techniques to form passageways. The dielectric coating may provide a barrier to prevent shorting between the dielectrically coated electrode and a conductive fastener embedded within tissue. Alternately, a cartridge coating can be used to reduce an electric surface sheet charge on the cartridge thermoplastic that can occur during the application of RF energy to tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Method of forming a hybrid polymer film
InactiveUS6214422B1Fine surfaceLow costFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticCross-link
A hybrid film, comprising a first polymer film having a plasma-treated surface and a second polymer film having first and second surfaces, with the first surface of the second polymer film being disposed along the first plasma-treated surface of the first polymer film, has superior thermal and mechanical properties that improve performance in a number of applications, including food packaging, thin film metallized and foil capacitors, metal evaporated magnetic tapes, flexible electrical cables, and decorative and optically variable films. One or more metal layers may be deposited on either the plasma-treated surface of the substrate and / or the radiation-cured acrylate polymer A ceramic layer may be deposited on the radiation-cured acrylate polymer to provide an oxygen and moisture barrier film. The hybrid film is produced using a high speed, vacuum polymer deposition process that is capable of forming thin, uniform, high temperature, cross-liked acrylate polymers on specific thermoplastic or thermoset films. Radiation curing is employed to cross-link the acrylate monomer. The hybrid film can be produced in-line with the metallization or ceramic coating process, in the same vacuum chamber and with minimal additional cost.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Water-dispersable materials
InactiveUS6211309B1Increase flexibilityGood dispersionMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentThermoplasticFiber
The present invention relates to water-dispersible materials (e.g. fibers or films) and to a method of producing same. The materials of the invention comprise a water soluble component, for example, a sulfonated polycondensate thermoplastic, and a modifying auxiliary component, for example, a low melt temperature thermoplastic.
Owner:BASF CORP
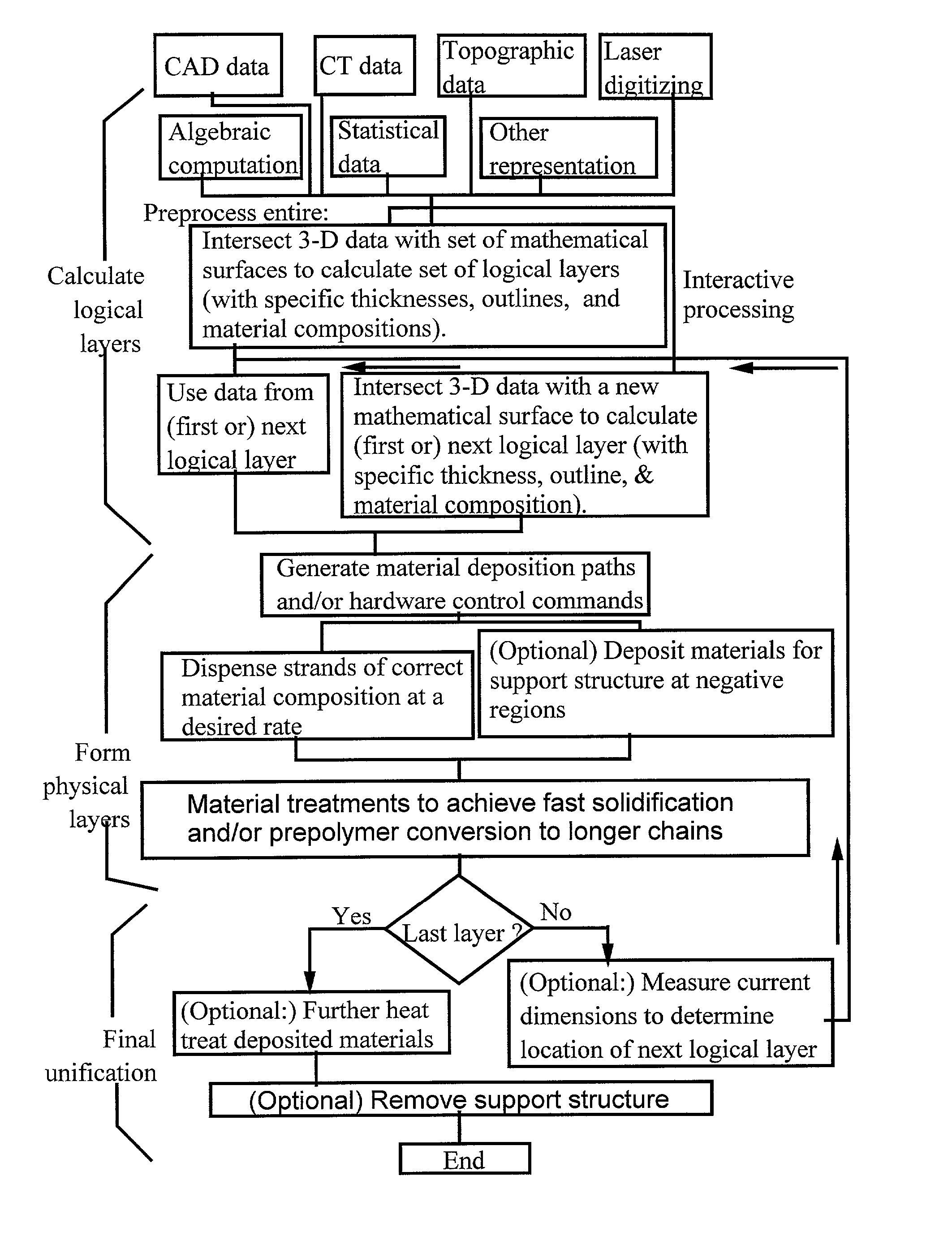
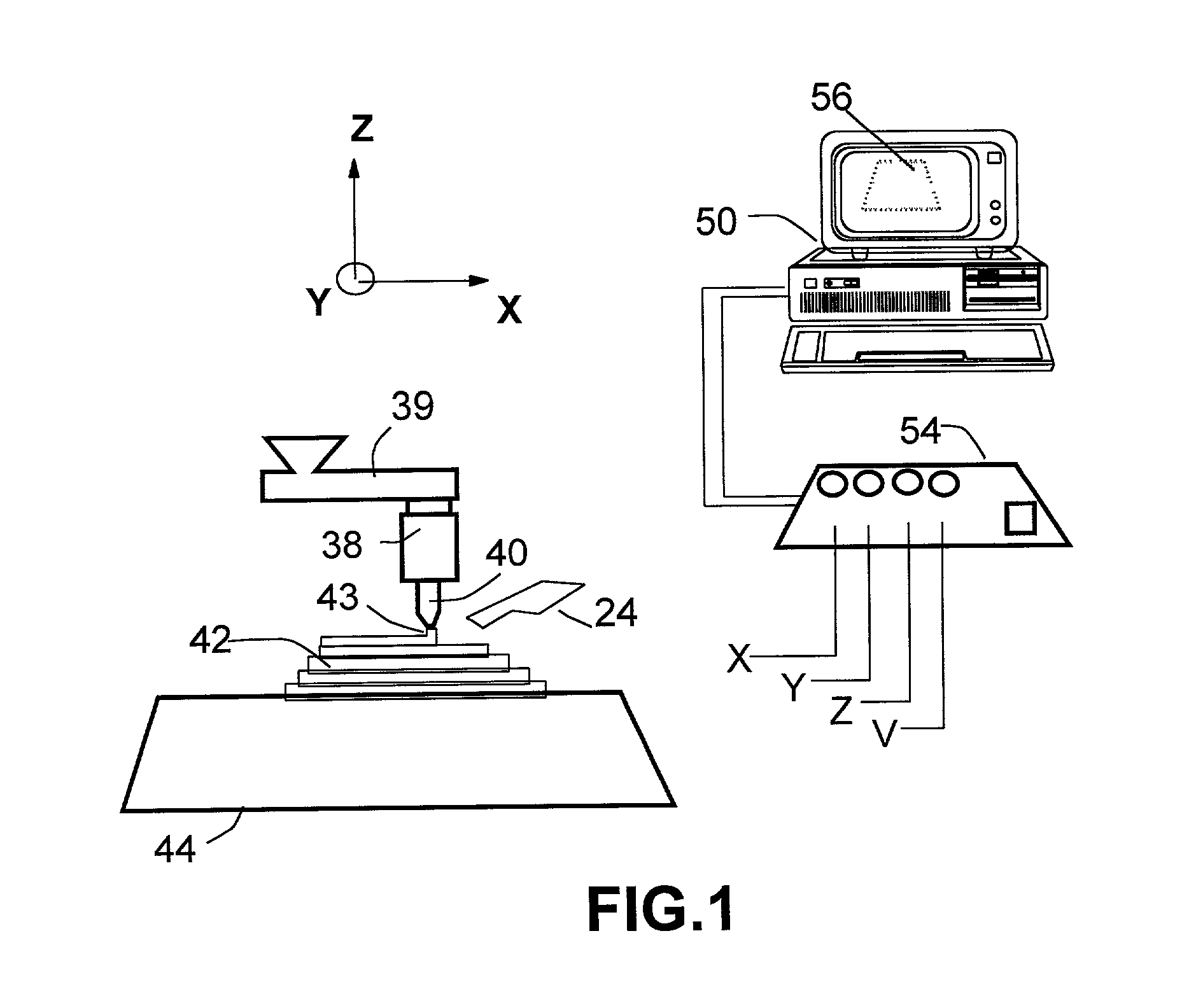
Freeform fabrication method using extrusion of non-cross-linking reactive prepolymers
InactiveUS20020113331A1Fast formingDifficult to prepareProgramme controlComputer controlCross-linkThermoplastic
An extrusion-based freeform fabrication method for making a three-dimensional object from a design created on a computer, including (a) providing a support member; (b) operating a dispensing head having at least one dispensing nozzle with a discharge orifice for dispensing continuous strands of a material composition in a fluent state at a first temperature onto the support member, the material composition including a reactive prepolymer with a melting point above 23° C. and the first temperature being greater than the prepolymer melting point; (c) operating material treatment devices for causing the dispensed strands of material composition to rapidly achieve a rigid state in which the material composition is substantially solidified to build up the 3-D object, the material treatment devices also working to convert the reactive prepolymer to a higher molecular weight thermoplastic resin; and (d) operating control devices for generating control signals in response to coordinates of the object design to control the movement of the dispensing nozzle relative to the support member and for controlling the strand dispensing of the material composition to construct the 3-D object.
Owner:ZHANG TAN +3
Polymer binders for flexible and transparent conductive coatings containing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050209392A1Decrease in optical transparencyDecrease in surface conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresThermoplasticCarbon nanotube
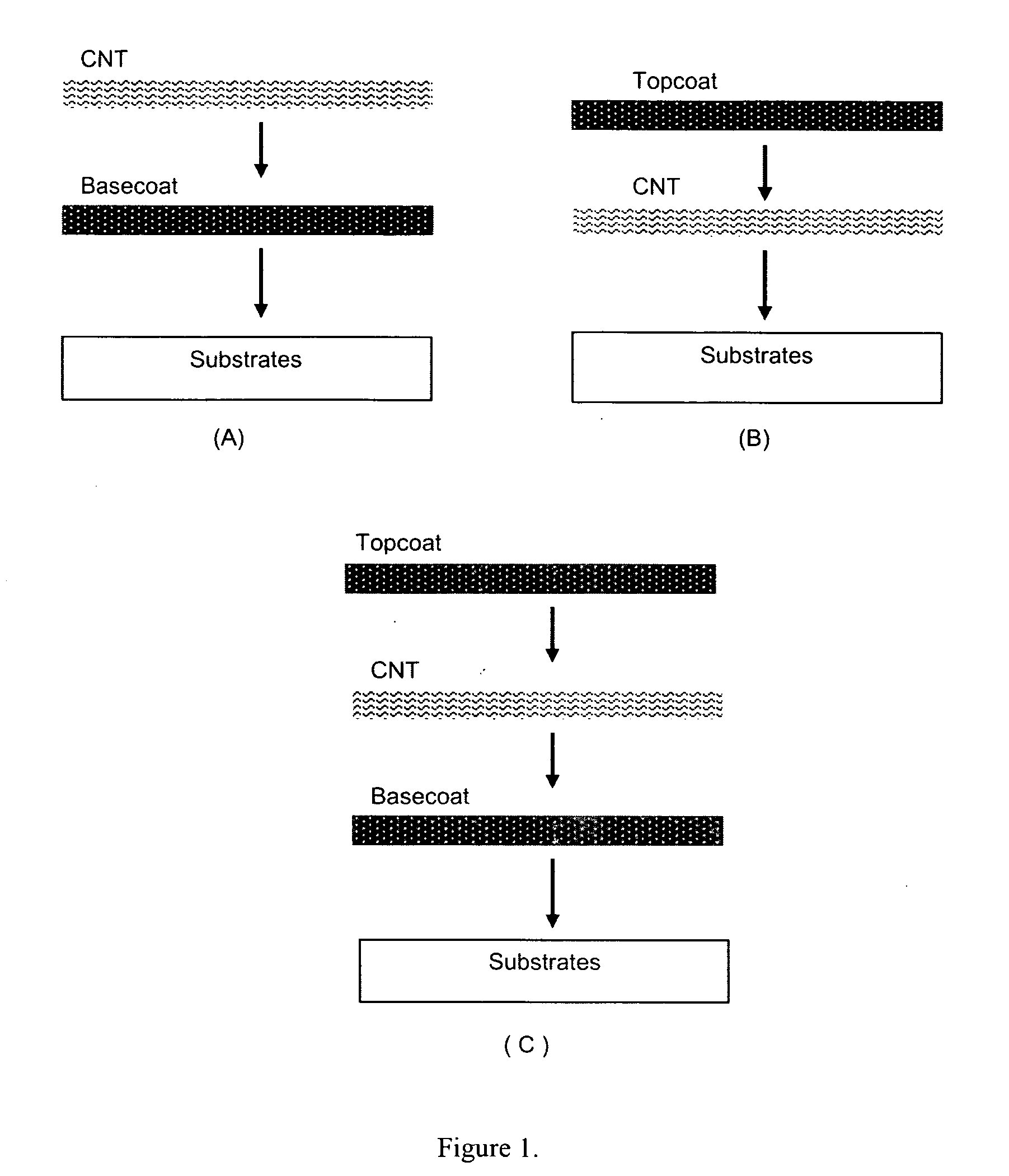
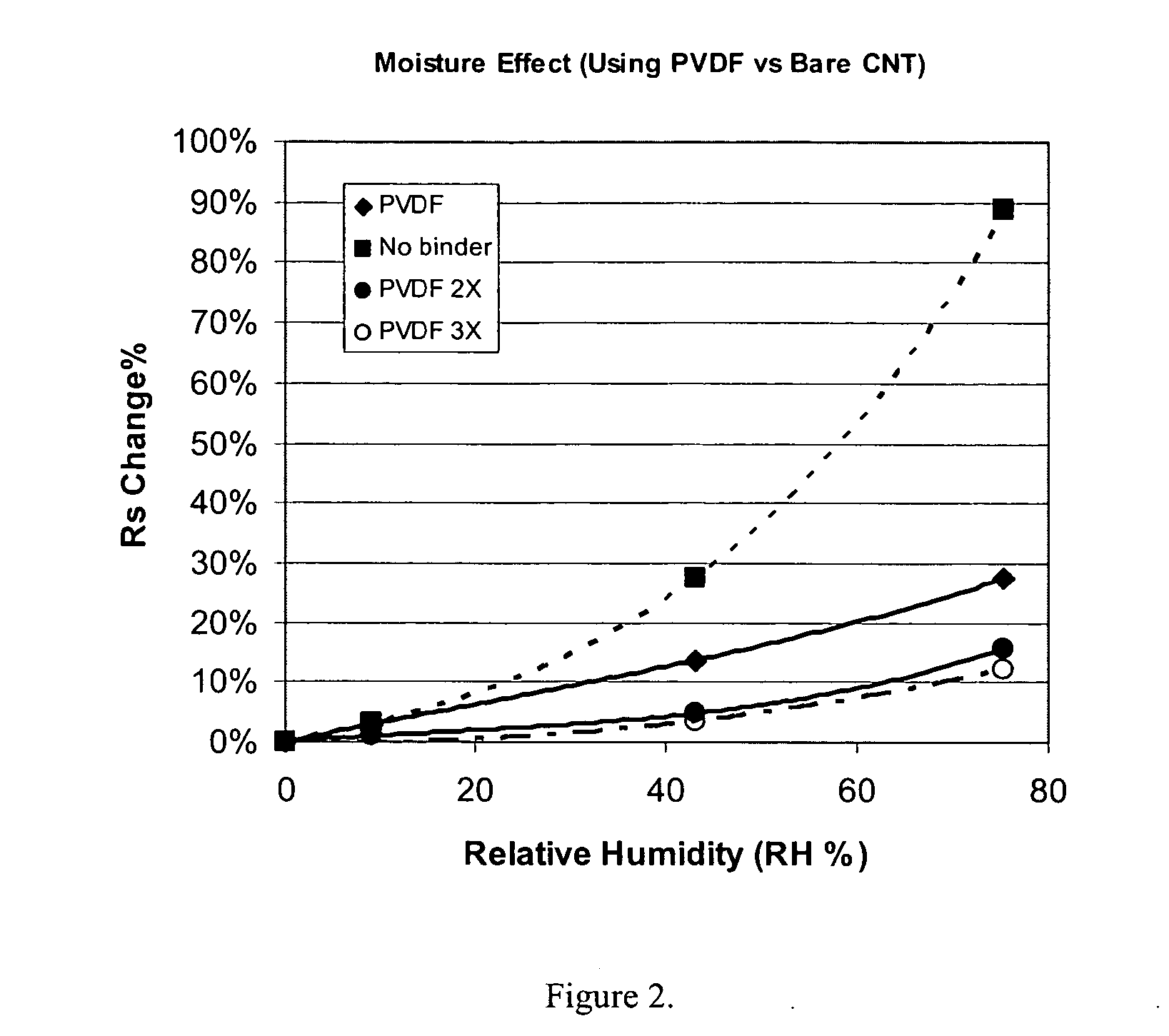
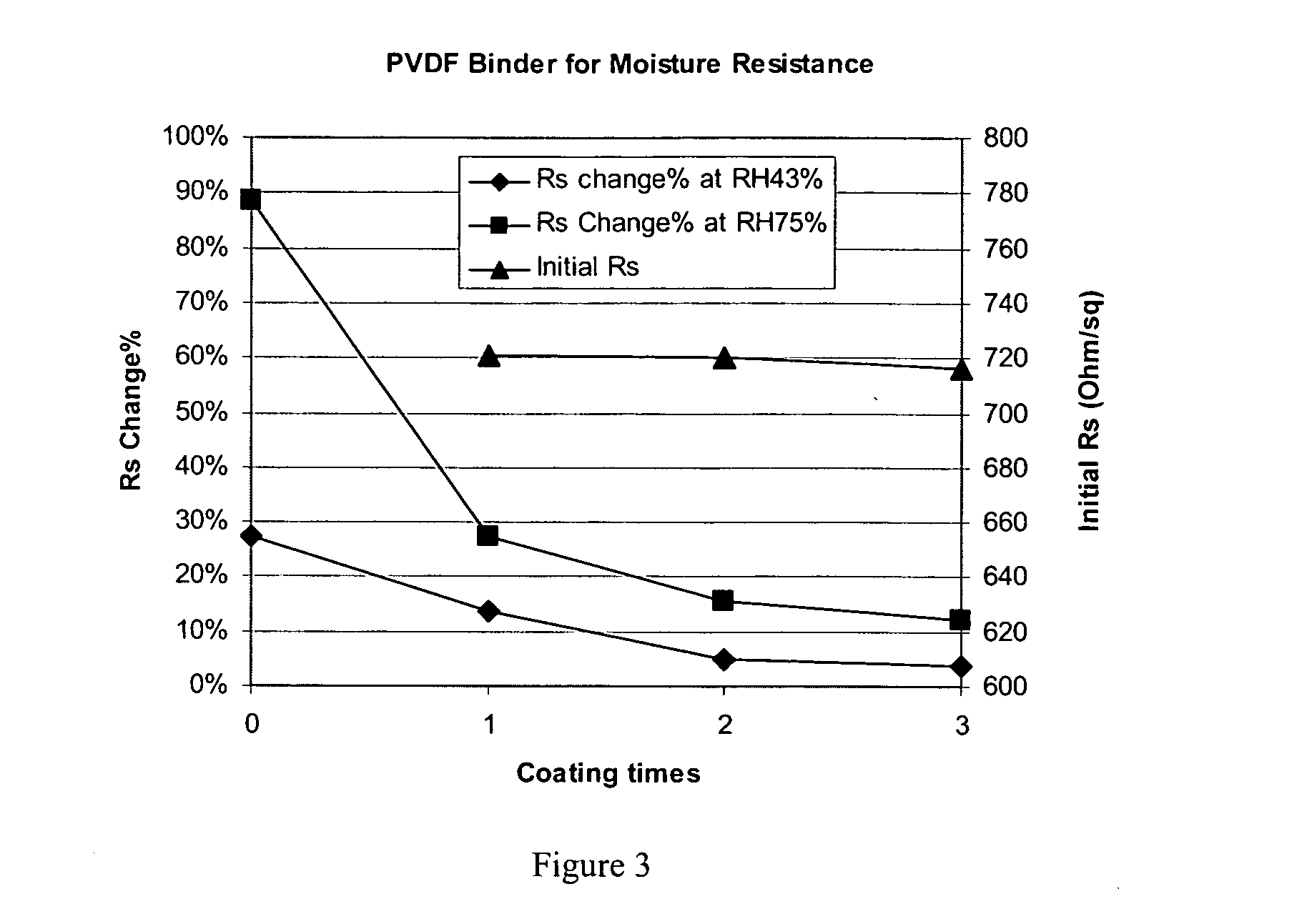
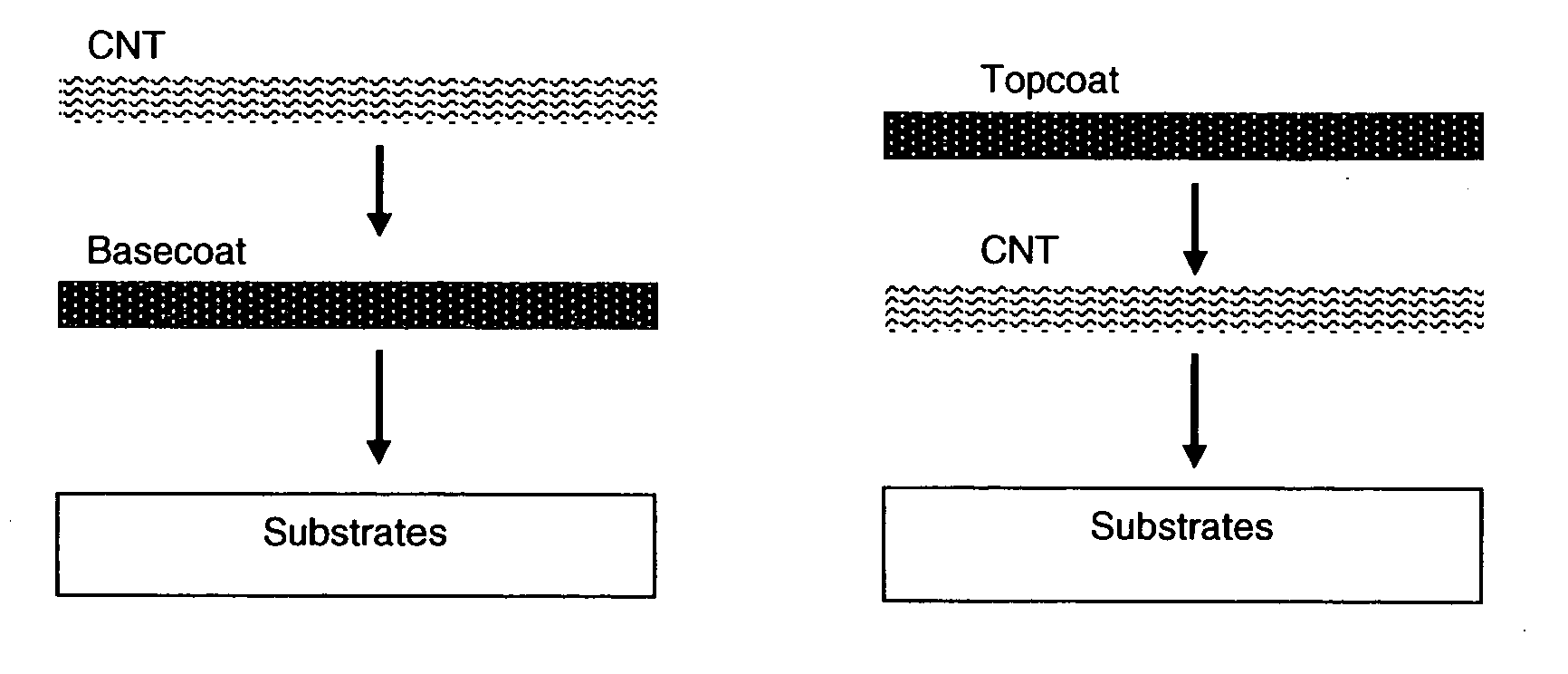
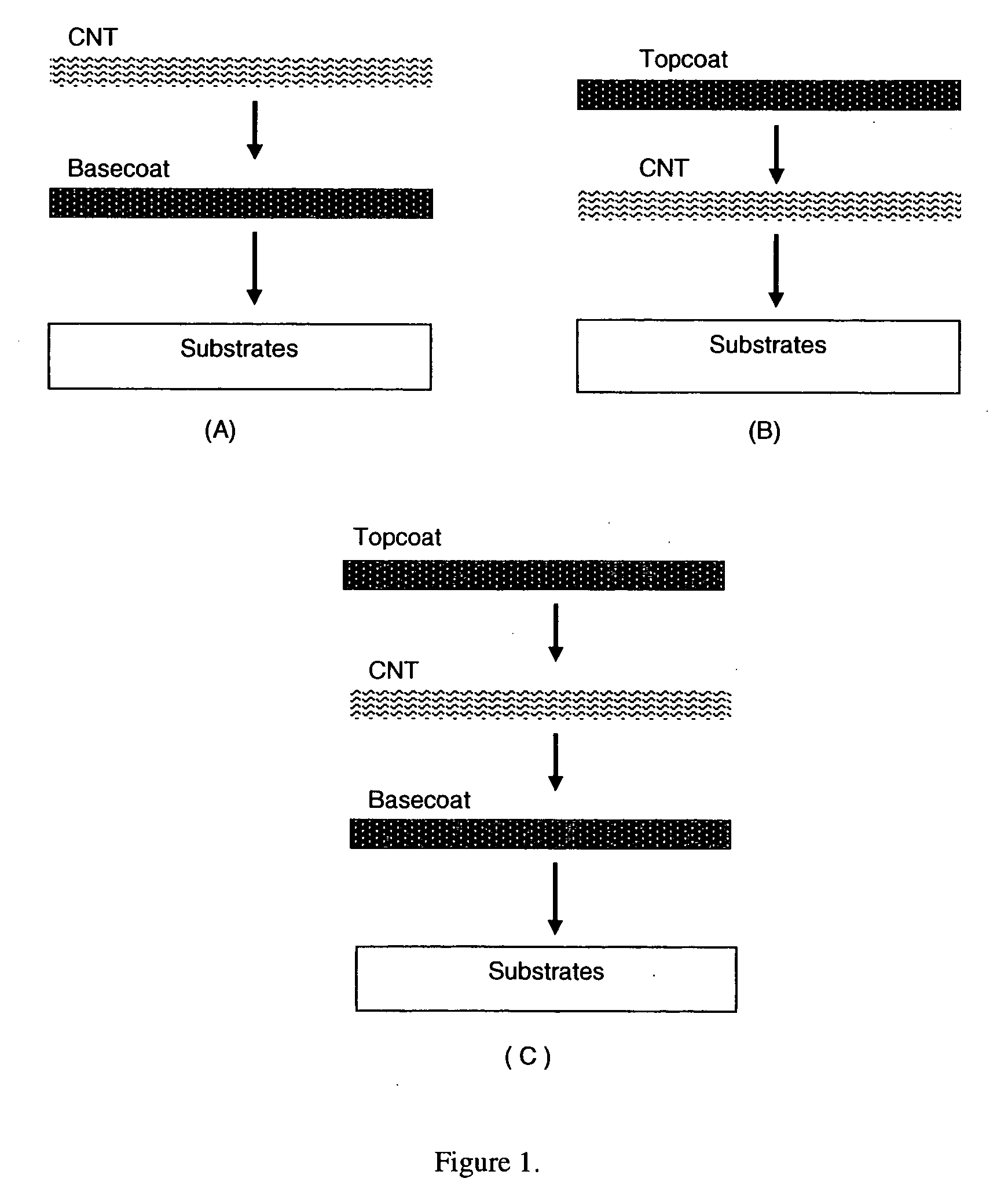
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using single wall carbon nanotubes and polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes (CNT) applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for the enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or any combination of both. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. Resulting films and articles can be used as transparent conductors for flat panel display, touch screen and other electronic devices.
Owner:EIKOS
Hybrid polymer film
InactiveUS6083628AFine surfaceLow costFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticCross-link
A hybrid film, comprising a first polymer film having a plasma-treated surface and a second polymer film having first and second surfaces, with the first surface of the second polymer film being disposed along the first plasma-treated surface of the first polymer film, has superior thermal and mechanical properties that improve performance in a number of applications, including food packaging, thin film metallized and foil capacitors, metal evaporated magnetic tapes, flexible electrical cables, and decorative and optically variable films. One or more metal layers may be deposited on either the plasma-treated surface of the substrate and / or the radiation-cured acrylate polymer. A ceramic layer may be deposited on the radiation-cured acrylate polymer to provide an oxygen and moisture barrier film. The hybrid film is produced using a high speed, vacuum polymer deposition process that is capable of forming thin, uniform, high temperature, cross-linked acrylate polymers on specific thermoplastic or thermoset films. Radiation curing is employed to cross-link the acrylate monomer. The hybrid film can be produced in-line with the metallization or ceramic coating process, in the same vacuum chamber and with minimal additional cost.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Particulate material containing thermoplastics and methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20050019574A1Retain and enhance proppant propertyReducing dust formationPretreated surfacesDrilling compositionThermoplasticPolymer chemistry
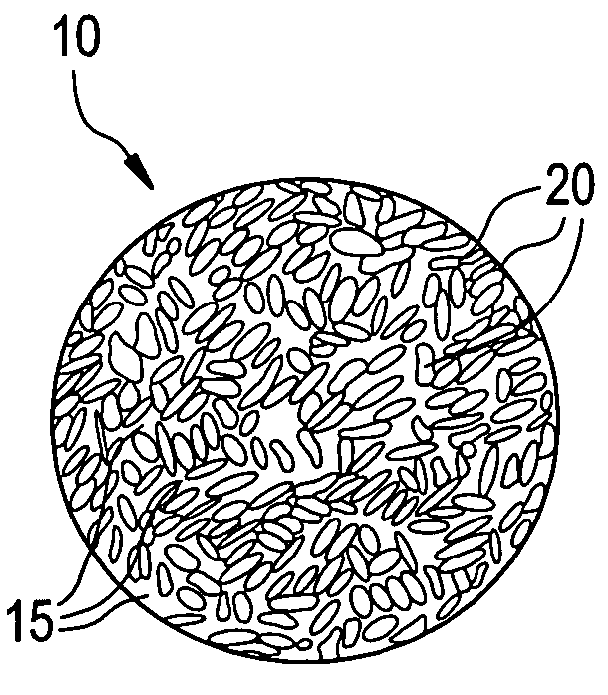
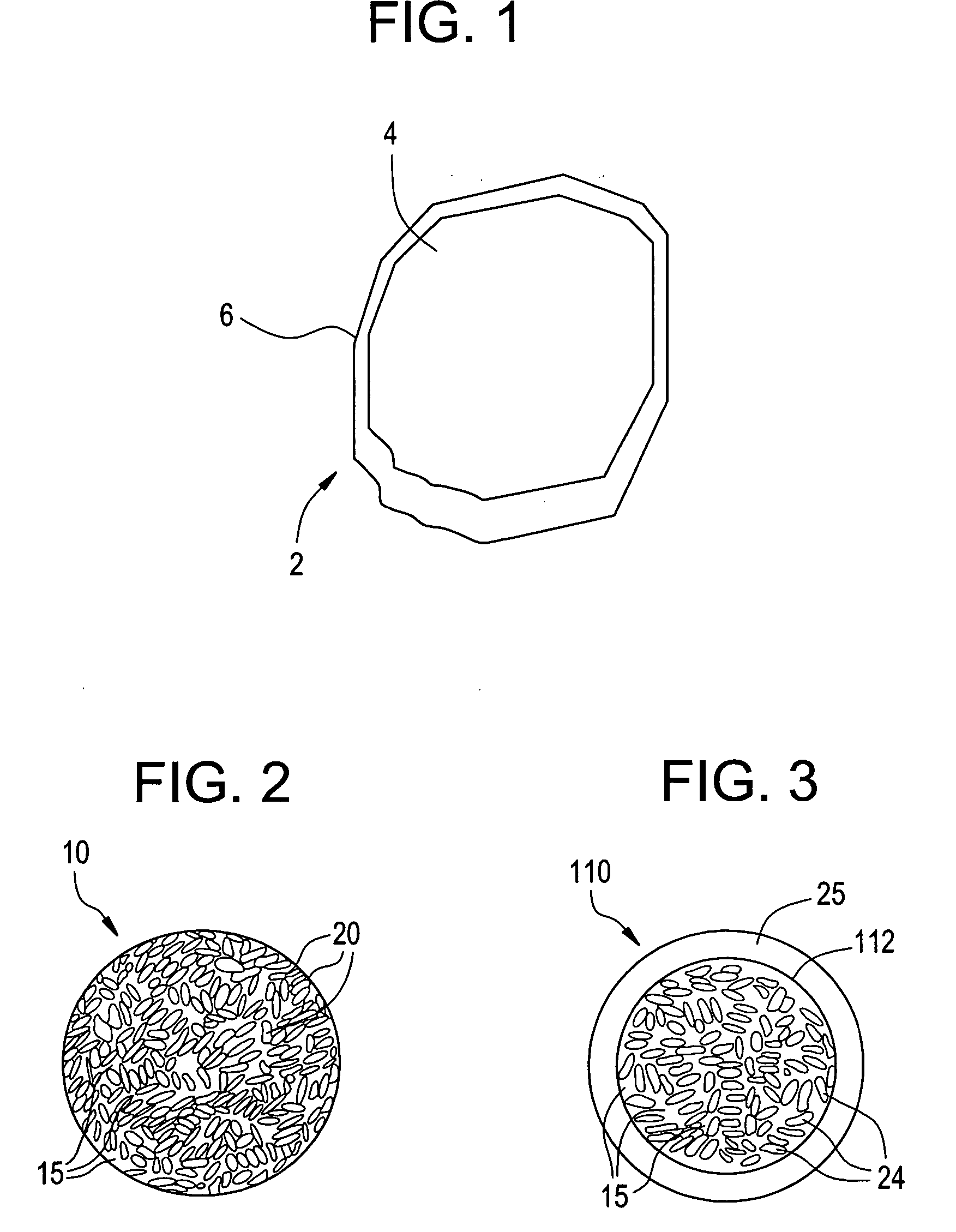
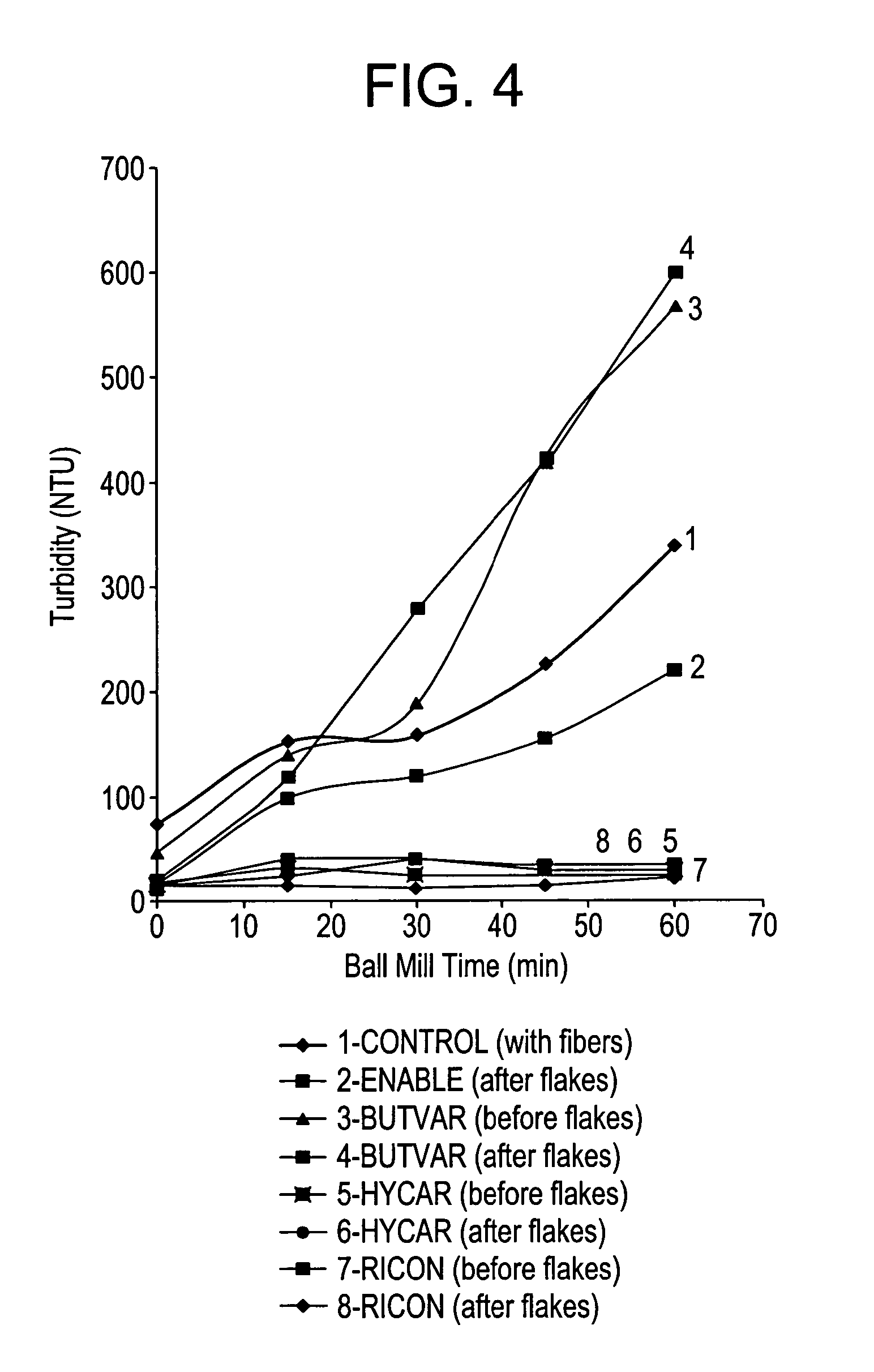
Disclosed herein is a particle comprising a particulate substrate; and a thermoplastic elastomer present on or in the substrate as an amount sufficient to improve the dust suppression of the particle above that which would occur if the thermoplastic elastomer was absent. Disclosed herein is a particle comprising a particulate substrate; and a thermoplastic elastomer, wherein the particle has a compressive strength retention of greater than about 50% as measured by a UCS test and a turbidity of about 10 to 200 NTU after a one hour ball mill test.
Owner:HEXION INC
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
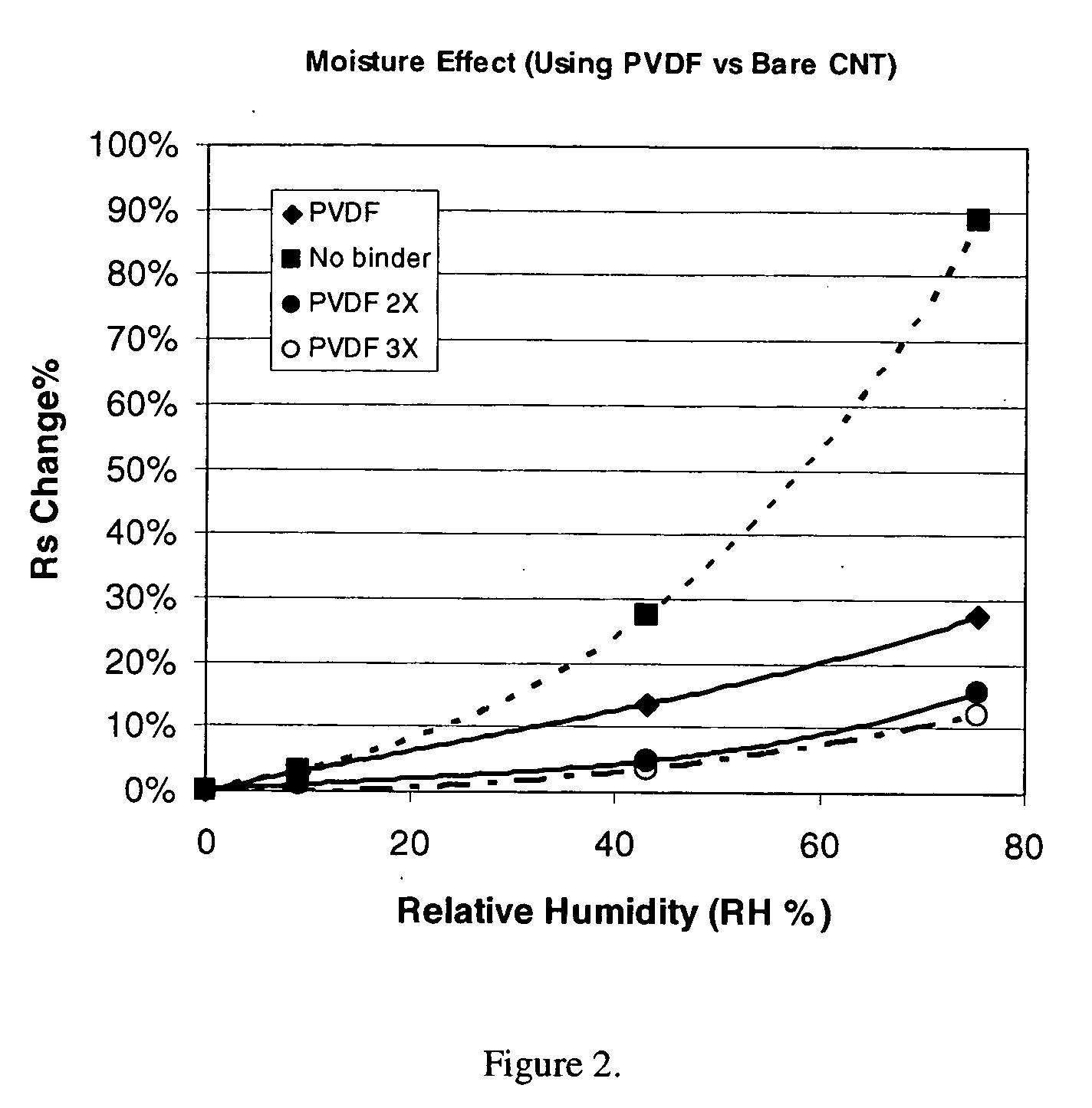
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
Edible thermoplastic and nutritious pet chew
The present invention relates to an edible thermoplastic made from about 30 to 50 wt. % protein comprising a mixture of plant and animal derived protein, about 20 to 50 wt. % starch about 10 to 20 wt. % water, about 1 to 10 wt. % edible fiber, and about 0.5 to 3 wt. % metallic salt hydrate. When molded, the thermoplastic has good strength and stiffness and other physical properties. The edible thermoplastic may be molded in a variety of shapes including a segmented nutritional pet chew with a plurality of segments separated by a plurality of scores. The scores serve to structurally weaken the pet chew so that it may be broken into smaller pieces. When molded the edible thermoplastic has a density of about 1.2 to 1.5 g / cubic centimeters.
Owner:BISMUTH INVESTMENTS
Thermoplastic copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether and medical devices employing the copolymer
An improved elastomeric material is described comprising an essentially noncross-linkable amorphous copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) and perfluoromethyl vinyl ether (PMVE) which is both a thermoplastic and exhibits exceptional mechanical properties. This material is particularly suitable for use in ultra-clean environments, and particularly for use in an implantable device, since it does not contain contaminants that previous thermoset TFE / PMVE copolymers have required. Among the improved properties of the present invention are excellent biocompatibility, high matrix tensile strength, high clarity, high abrasion resistance, high purity, adequate elasticity, and ease of processing due to the thermoplastic, and noncross-linkable structure of the copolymer. The material of the present invention is also a high strength bonding agent particularly suited for bonding porous PTFE to itself or to other porous substances at room or elevated temperatures.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Golf ball with vapor barrier layer and method of making same
A golf ball comprising a core, a barrier layer enveloping the core, and a cover enveloping the barrier layer, wherein the barrier layer has a moisture vapor transmission rate less than that of the cover, and the barrier layer comprises a thermoplastic or thermoset composition of microparticles dispersed in a binder.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
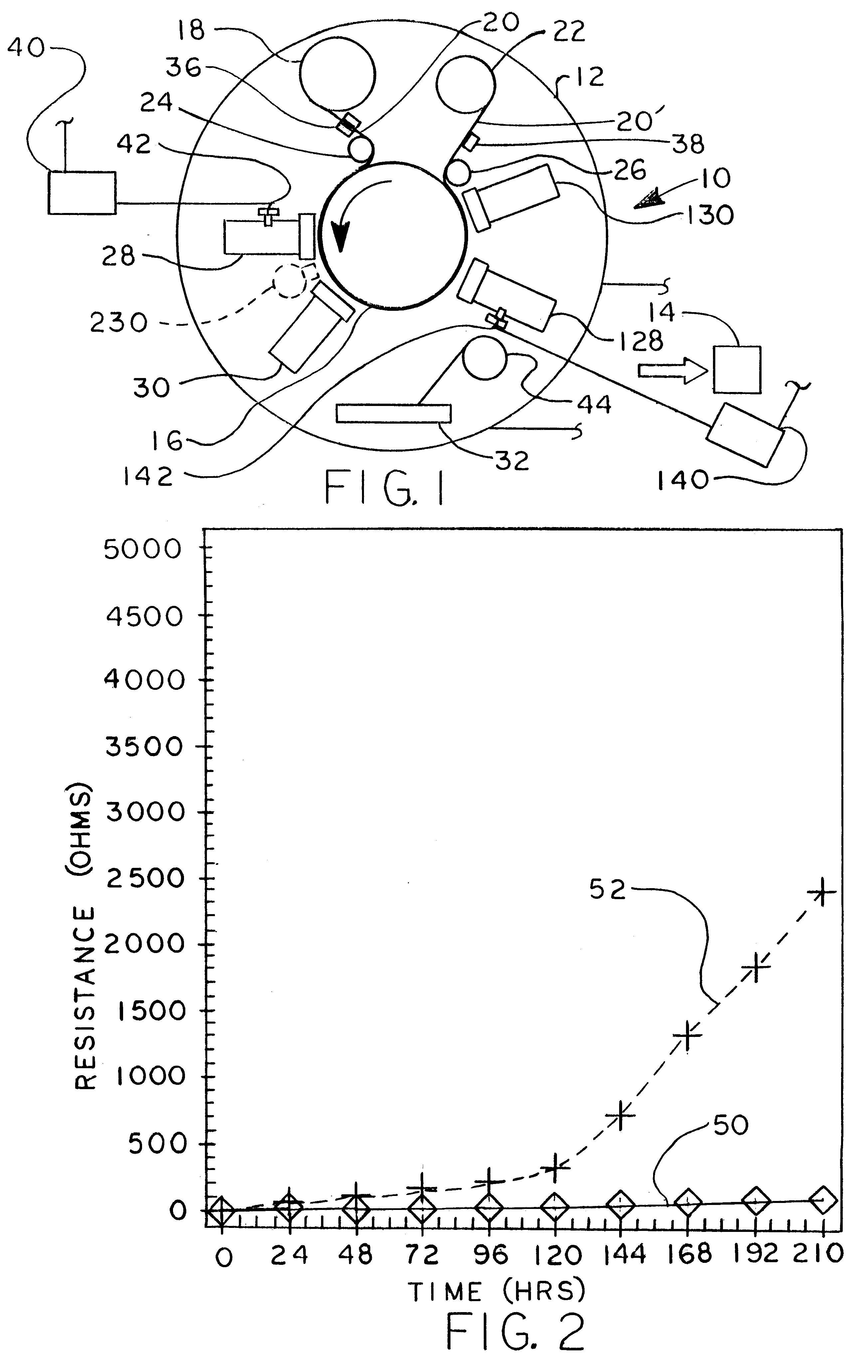
Droplet deposition method for rapid formation of 3-D objects from non-cross-linking reactive polymers
InactiveUS20020111707A13D object support structuresSpecial data processing applicationsThermoplasticControl signal
A droplet deposition-based freeform fabrication method for making a three-dimensional object from a design created on a computer, including (a) providing a support member; (b) operating a droplet dispensing head for dispensing droplets of a material composition in a fluent state at a first temperature onto the support member, the material composition including a reactive prepolymer with a melting point above 23° C. and the first temperature being greater than the prepolymer melting point; (c) operating material treatment devices for causing the material composition to rapidly achieve a rigid state in which the material composition is substantially solidified to build up the 3-D object, the material treatment devices also working to convert the reactive prepolymer to a higher molecular weight thermoplastic resin; and (d) operating control devices for generating control signals in response to coordinates of the object design to control the movement of the dispensing head relative to the support member and for controlling the droplet dispensing of the material composition to construct the 3-D object.
Owner:LI ZHIMIN +3
Carpet Construction and Carpet Backings for Same
Owner:PROPEX OPERATING
Apparatus for large area chemical vapor deposition using multiple expanding thermal plasma generators
InactiveUS6397776B1Efficient coatingDesirable propertyElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingThermoplasticGas phase
Chemical vapor deposition is performed using a plurality of expanding thermal plasma generating means to produce a coating on a substrate, such as a thermoplastic and especially a polycarbonate substrate. The substrate is preferably moved past the generating means. Included are methods which coat both sides of the substrate or which employ multiple sets of generating means, either in a single deposition chamber or in a plurality of chambers for deposition of successive coatings. The substrate surfaces spaced from the axes of the generating means are preferably heated to promote coating uniformity.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Thermally conductive thermoplastic
InactiveUS6162849AImprove thermal conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsMixingThermoplasticPolymer science
This invention relates to a thermally conductive moldable polymer blend comprising a thermoplastic polymer having a tensile at yield of at least 10,000 psi; at least 60% by weight of a mixture of boron nitride powders having an average particle size of at least 50 microns; and a coupling agent. The composition displays a thermal conductivity of at least about 15 W / m DEG K and it is capable of being molded using high speed molding techniques such as injection molding.
Owner:FERRO CORP
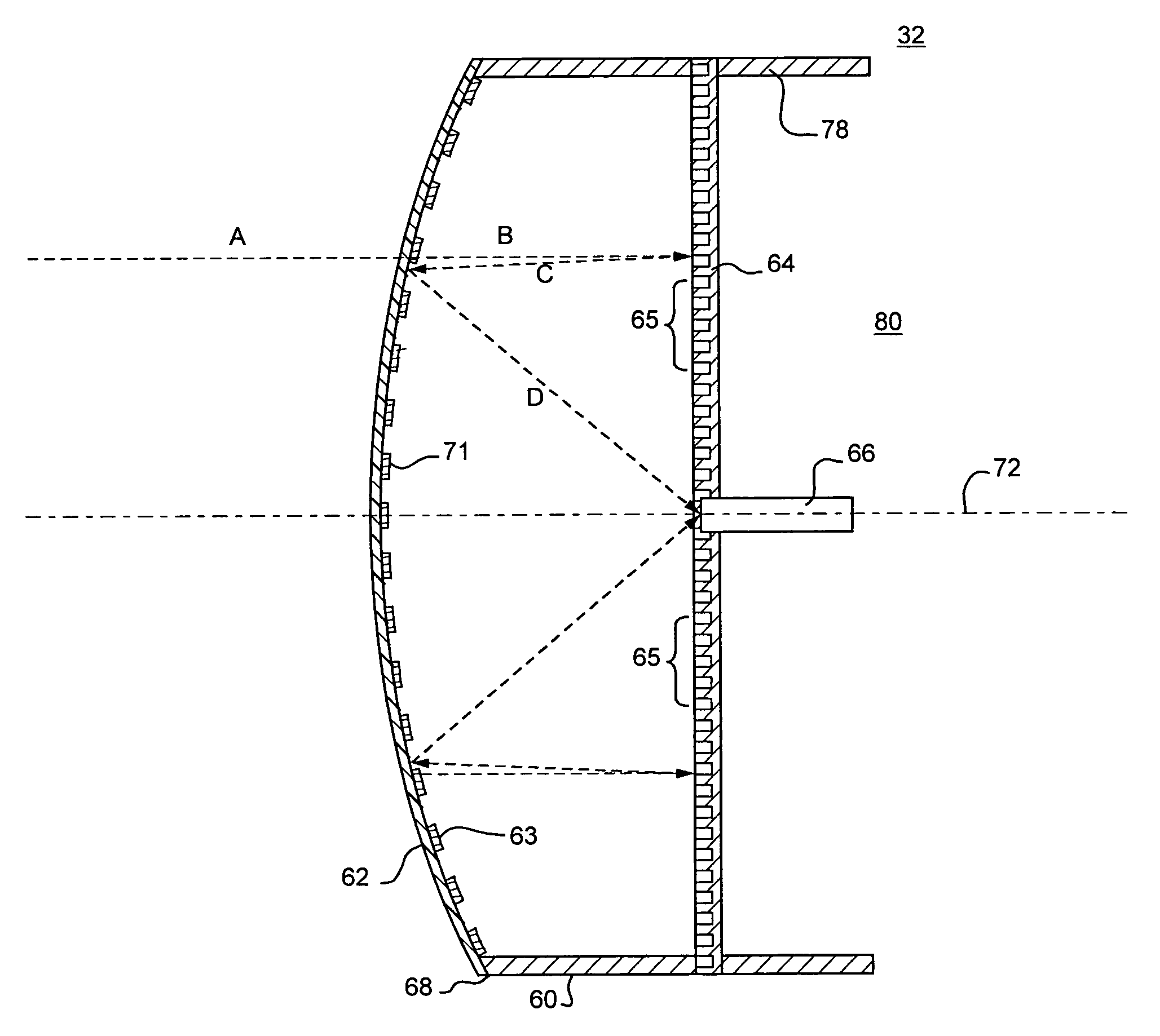
Transreflector antenna for wireless communication system
InactiveUS6965784B2Easy to controlLow profileBroadcast transmission systemsRadiating element housingsThermoplasticGrating
A compact lightweight antenna for receiving microwave direct line of sight wireless data signals used in services such as Local Multipoint Distribution Services (LMDS). The antenna provides for precise control over isolation of polarized signals. The antenna consists of an external parabolically shaped dome formed of a suitably resilient material such as thermoplastic. A polarizing conductive grating is formed on the interior surface of the dome and serves as a transreflector for initially passing received radiation having a vertical polarization. A twist reflector disposed at a point along an axis defined by the conductive grating reflects the received radiation, back in the direction of the transreflector with a different polarization. The now differently polarized energy is reflected by the parabolically shaped conductive grating at a feed point located in the center of the twist plate. The transreflecting element may be manufactured by providing a substrate that has been printed and etched and / or a film nonconductive substrate which has been silk screened with a conductive ink. In each of these cases in a preferred embodiment, the substrate or carrier film becomes an integral part of the mold in the resulting article.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Thermoplastic elastomers having improved processing and physical property balance
InactiveUS6451915B1Without deleteriously sacrificing mechanical propertyEasy to processThermoplasticPolymer science
A thermoplastic elastomer formed by a process comprising the steps of dynamically vulcanizing a rubber within a mixture that includes the rubber, from about 10 to about 80 percent by weight of a thermoplastic resin based upon the total weight of the rubber and the thermoplastic combined, and from about 1 to about 25 percent by weight of a polymeric processing additive based upon the total weight of the rubber and the thermoplastic combined, where the polymeric processing additive is a linear polyolefin resin that has an melt flow rate that is greater than about 1,000 dg / min, a diene-modified polyolefin polymer that has an melt flow rate that is greater than about 1,000 dg / min, from about 0.005 to about 2.00 mole percent polymeric units deriving from dienes, and a viscosity average branching index that is from about 0.4 to about 0.95, or a mixture of the linear polyolefin resin and the diene-modified polyolefin polymer, where the step of dynamically vulcanizing the rubber results in vulcanized rubber having a crosslink density of about 40 to about 180 mole per milliliter of rubber.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Foamed thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber profile and member
InactiveUS6054207AHigh compressive strengthImproved fastener retentionConstruction materialLoad-supporting elementsComposite constructionThermoplastic
Advanced structural components comprising a foamed thermoplastic that can be used in virtually any application where wooden components have a use. Such structural components can comprise sized lumber, shaped trim, posts, beams or shaped structural members. An advanced profile composite structural component comprising an exterior capping layer with an interior comprising a foamed thermoplastic can be used in the assembly of fenestration units adapted to residential and commercial structures. Preferably the profile structural component can be used in a window or door assembly. The profile member is adapted for ease of construction of the fenestration units, can be easily installed in a rough opening to framing members, and can be trimmed and adjusted on site. The profile is structurally strong, thermally stable, shrink resistant and will accept and retain the insertion of fasteners such as staples, nails and screws permanently with substantial retention and little or no damage to the units. The profile structural components possess strength that permits the manufacture of a structurally sound fenestration unit from two or more foamed profile members or other conventional members.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Metal salts of hexahydrophthalic acid as nucleating additives for crystalline thermoplastics
InactiveUS6599971B2Excellent calcium stearate compatibilityExcellent high peak crystallization temperatureOrganic compound preparationFibre treatmentThermoplasticScavenger
Compounds and compositions comprising specific metal salts of hexahydrophthalic acid (HHPA) in order to provide highly desirable properties within thermoplastic articles are provided. The inventive HHPA derivatives are useful as nucleating and / or clarifying agents for such thermoplastics, are practical and easy to handle. Such compounds provide excellent crystallization temperatures, stiffness, and acid scavenger compatibility within target polyolefins. Also, such compounds exhibit very low hygroscopicity and therefore excellent shelf stability as powdered or granular formulations. Thermoplastic additive compositions and methods of producing polymers with such compounds are also contemplated within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Wood-plastic composite material and prepration method thereof
The invention discloses a wood-plastic composite material and a preparation method thereof, and the wood-plastic composite material comprises the following raw materials according to the mixing ratio by parts by weight: 30-80 parts of modified fiber powder; 15-80 parts of plastics; 2-10 parts of phase solvent; 2-10 parts of lubricant; 0-10 parts of stabilizer; 0.2-1.0 part of antioxidant; 5-15 parts of filler; and 2-20 parts of flame retardant. Lignin is utilized for modifying fiber powder, then composition with the plastics is carried out, and a finished-product material is formed by extrusion. The preparation method can solve the problems of the compatibility of wood fibers with the thermoplastic plastics, the surface treatment technology of the raw materials by utilizing the lignin and the like, realize the comprehensive utilization of the lignin and the waste plastics, be capable of replacing wood, increase the additional value of the lignin and solve the utilization problem of the lignin wastes. The manufactured wood-plastic composite material can significantly improve the mechanical performance, the tensile strength, the flexural strength and the impact resistance, and realize the industrial production of high-performance products, such as construction materials.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
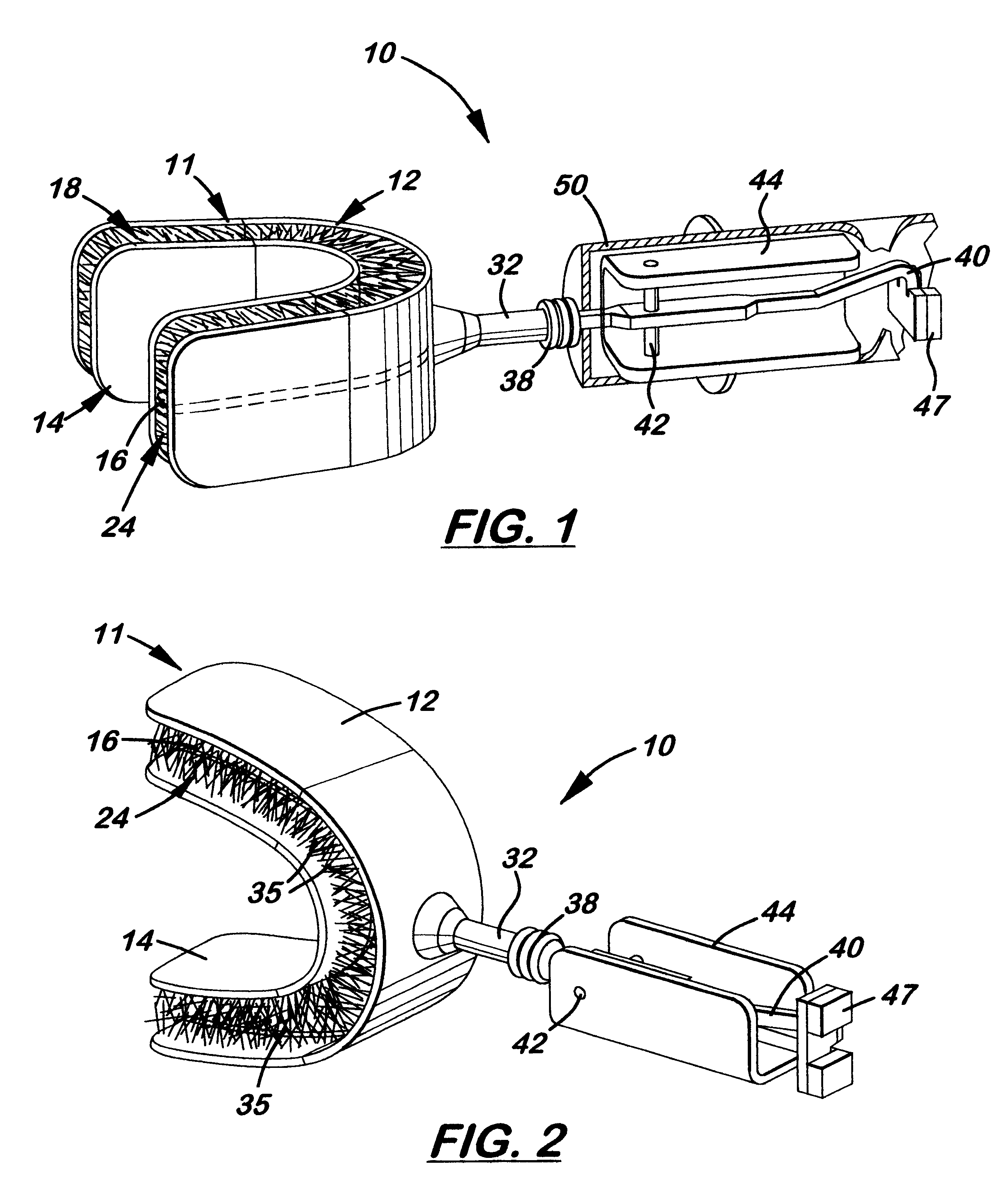
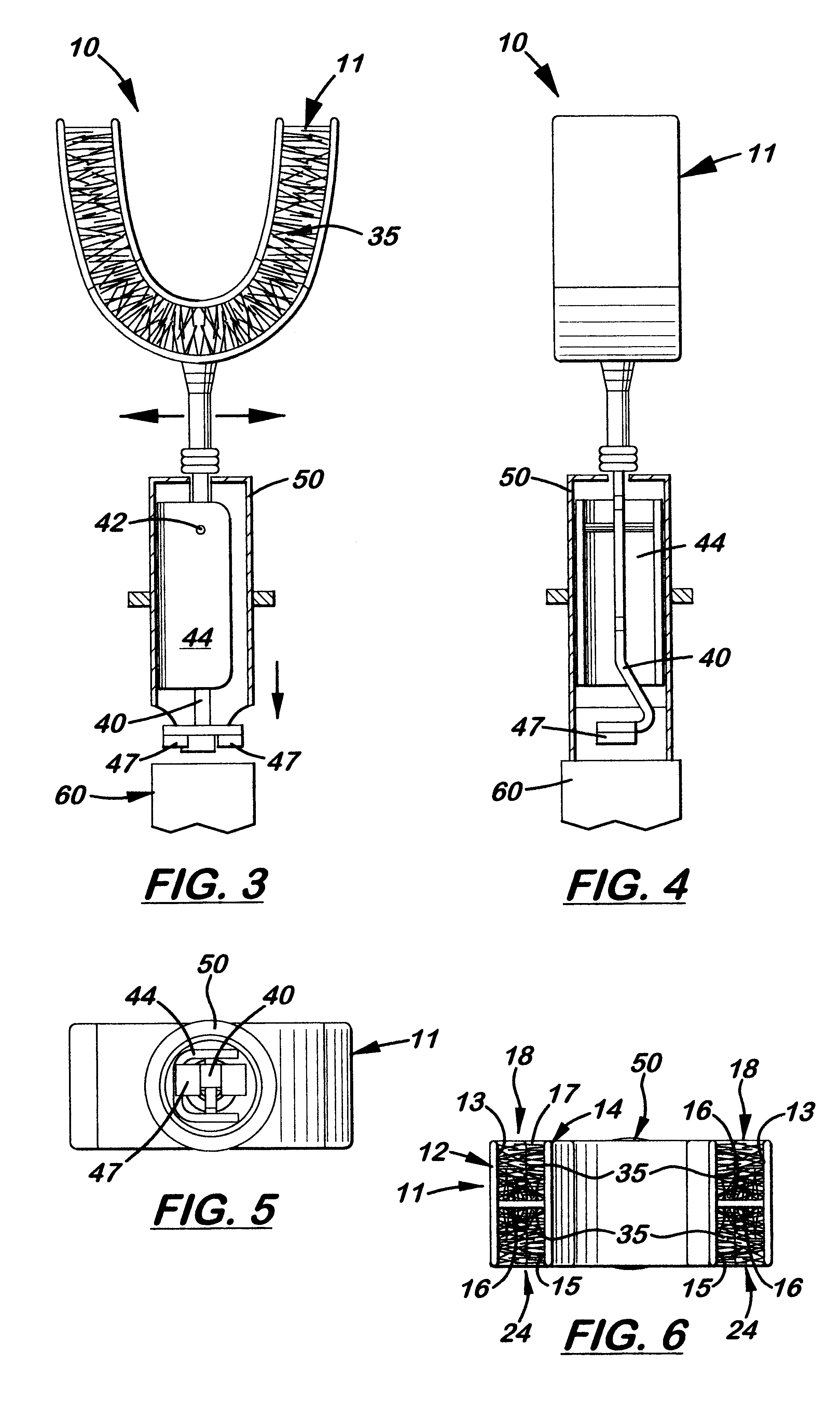
Combined ultrasonic toothbrush module
A U-shaped, ultrasonic toothbrush module to be used with currently available ultrasonic toothbrush hand pieces made of soft thermoplastic, silicone, or latex material with upper and lower bridge receiving spaces formed on opposite sides. The receiving spaces are designed to receive a user's upper and lower bridges when placed into the user's mouth. Disposed on the three inside surfaces of each receiving space are a plurality of bristles which completely contact the exposed surfaces of every tooth when the device is used. The module includes a housing with a pivoting T-shaped member and magnets attached at one end that connects to a standard ultrasonic toothbrush hand piece. Motion generated by the hand piece is transmitted through the T-shaped member and to the U-shaped member. The movement of the U-shaped member generates ultrasonic waves that are transmitted to the surfaces of the teeth and move the brushes when teeth are placed into the upper and lower bridge receiving spaces.
Owner:BERGE JASON
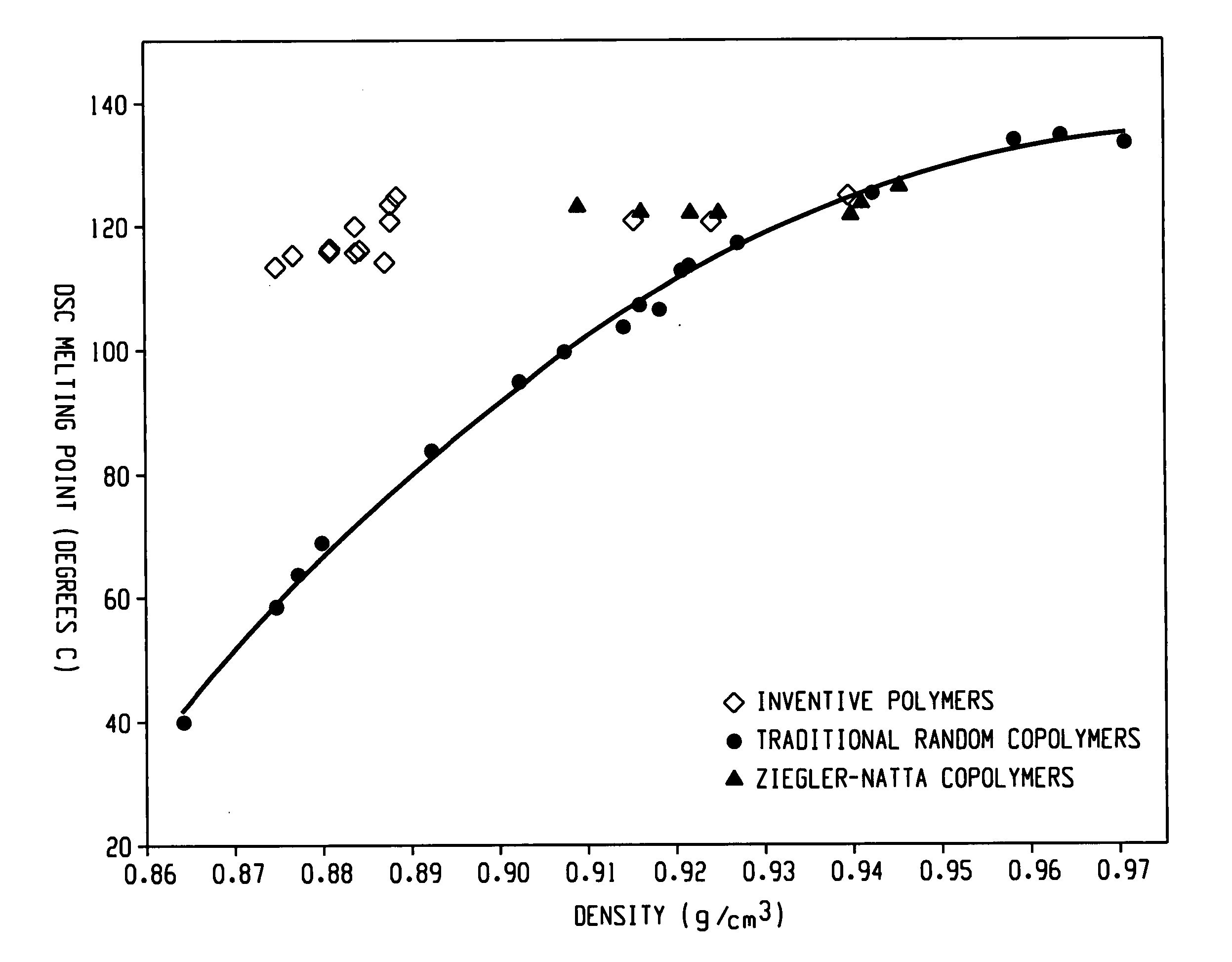
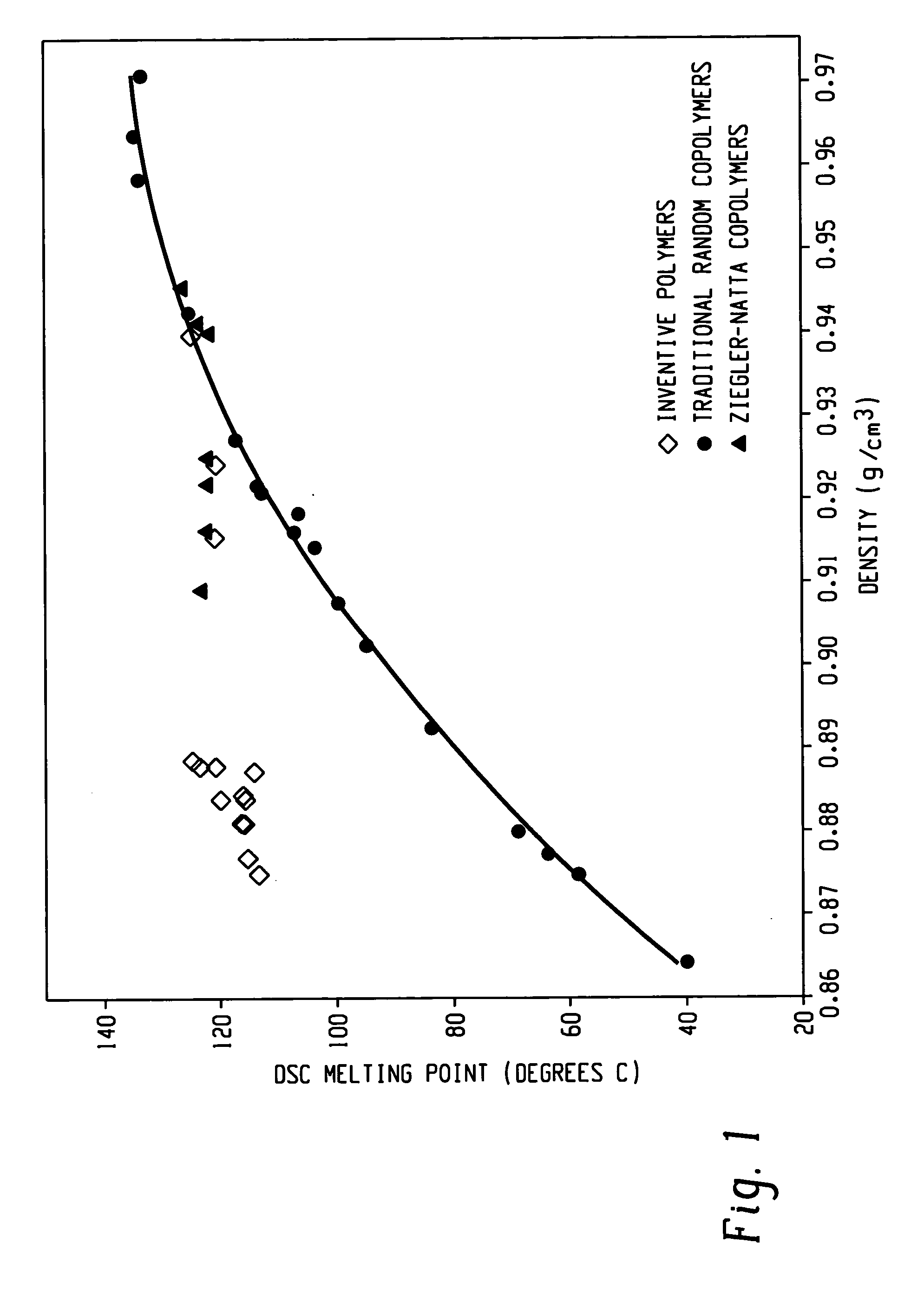
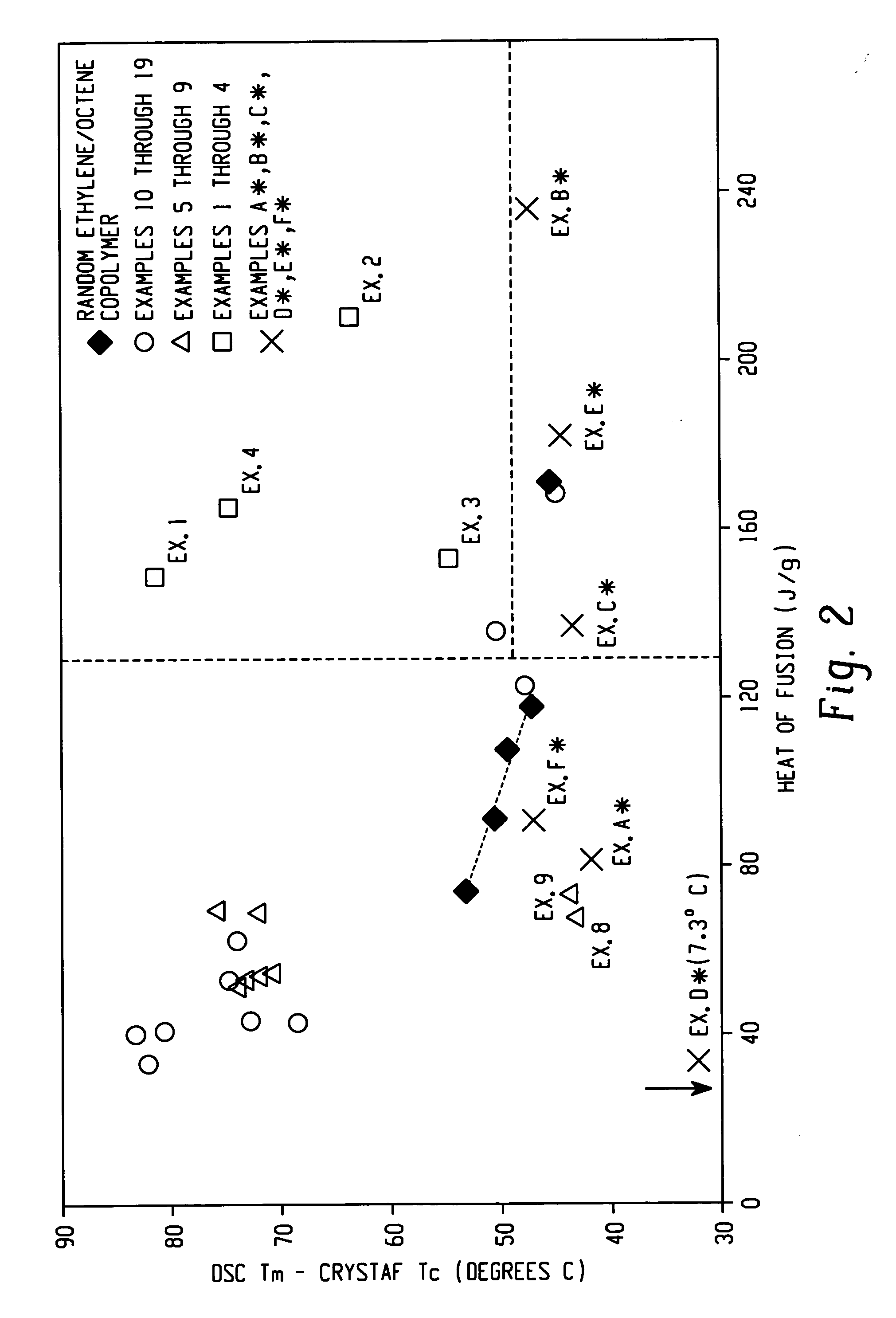
Impact modification of thermoplastics with ethylene/alpha-olefin interpolymers
ActiveUS20070010616A1Improve and maintain and impact performanceImprove and maintain modulusThermoplasticPolymer science
Compositions having good impact performance can be made from a thermoplastic (e.g., a polyolefin such as polypropylene or HDPE) and an ethylene multi-block copolymer. The compositions are easily molded and often have particular utility in making, for example, automotive facia, parts and other household articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015612AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthWood working apparatusRecord information storageFiberThermoplastic
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
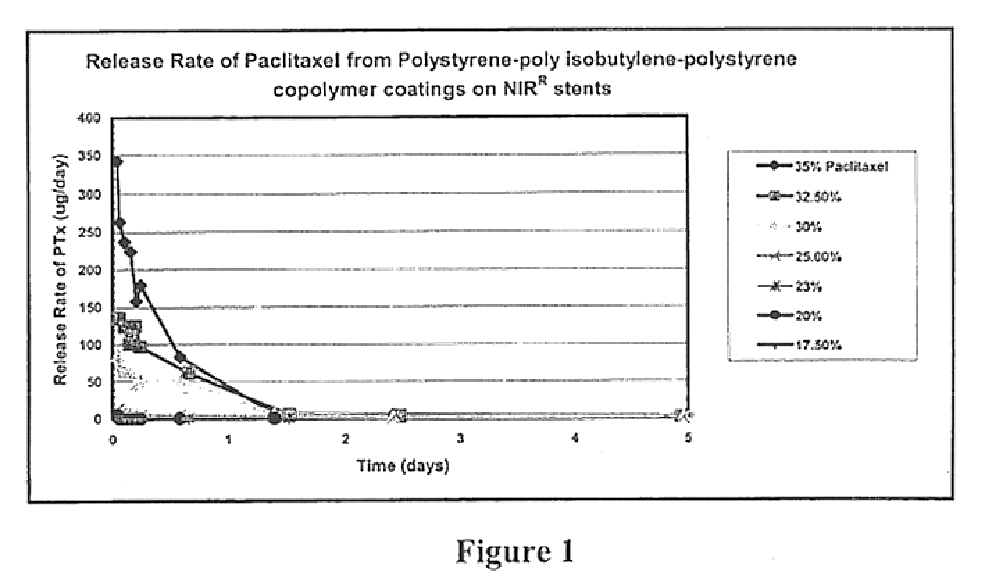
Drug delivery compositions and medical devices containing block copolymer
InactiveUS6855770B2Good mechanical integrityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsThermoplasticMethacrylate
A composition for delivery of a therapeutic agent is provided. The composition comprises: (a) a biocompatible block copolymer comprising one or more elastomeric blocks and one or more thermoplastic blocks and (b) a therapeutic agent, wherein the block copolymer is loaded with the therapeutic agent. The block copolymer is preferably of the formula X—(AB)n, where A is an elastomeric block, B is a thermoplastic block, n is a positive whole number and X is a seed molecule. The elastomeric blocks are preferably polyolefin blocks, and the thermoplastic blocks are preferably selected from vinyl aromatic blocks and methacrylate blocks. According to another aspect of the invention, a medical device is provided, at least a portion of which is insertable or implantable into the body of a patient. The medical device comprises (a) the above biocompatible block copolymer and (b) a therapeutic agent, wherein the block copolymer is loaded with the therapeutic agent. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method of treatment is provided in which the above device is implanted or inserted into a patient, resulting in the release of therapeutic agent in the patient over an extended period. According to yet another aspect of the invention, a coated medical device is provided which comprises: (a) an intravascular or intervascular medical device and (b) a coating over at least a portion of the intravascular or intervascular a medical device, wherein the coating comprises the above biocompatible block copolymer.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Advanced compatible polymer wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6210792B1Improve compatibilityGood material compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsThermoplasticFiber
The invention relates to a composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer, the fiber or both can be modified to increase compatibility. The wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Thermoplastic interface and shield assembly for separable insulated connector system
InactiveUS7494355B2Couplings bases/casesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsThermoplasticEngineering
A separable insulated connector assembly provided with a thermoplastic interface formed on a surface of a shield.
Owner:COOPER TECH CO
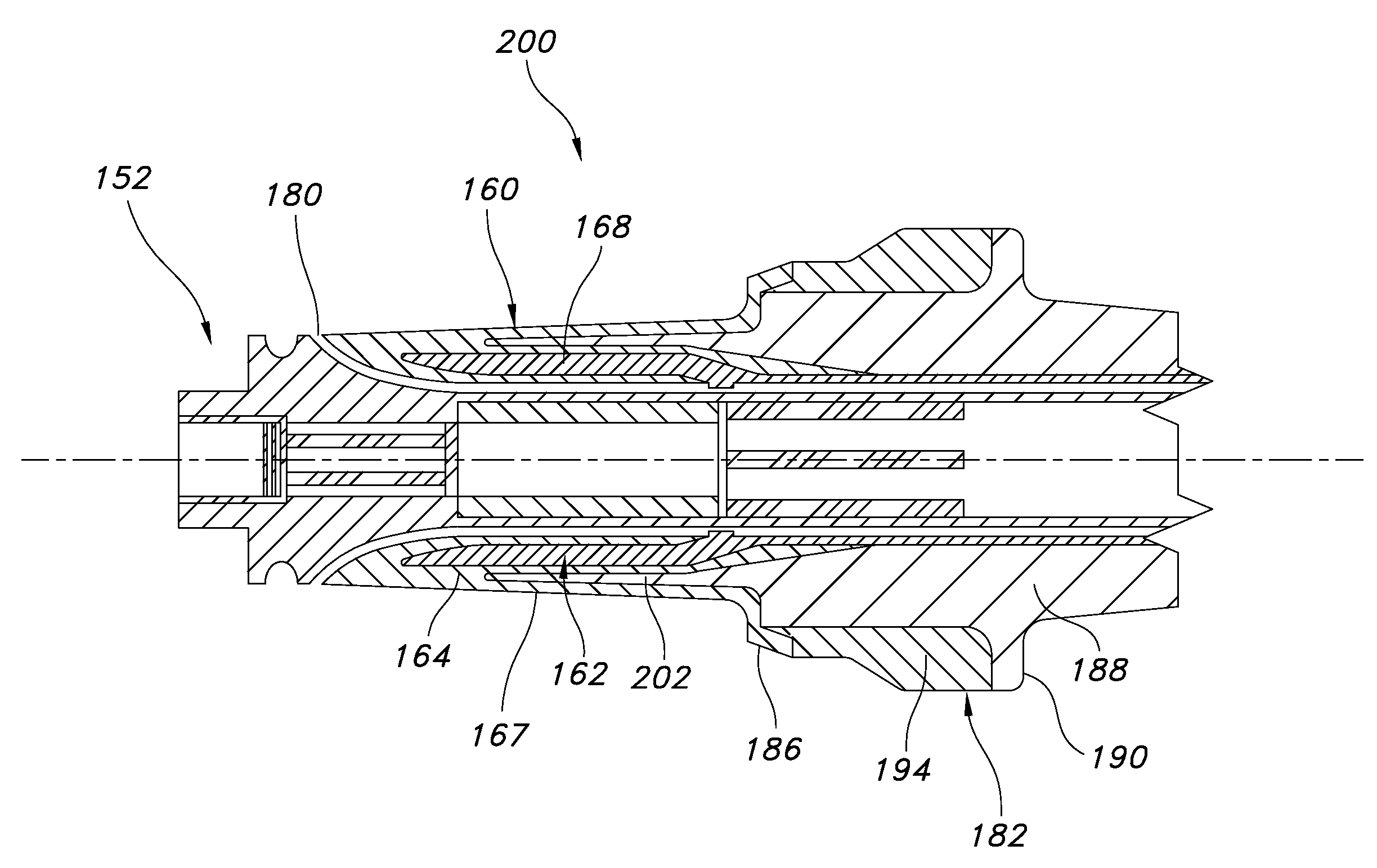
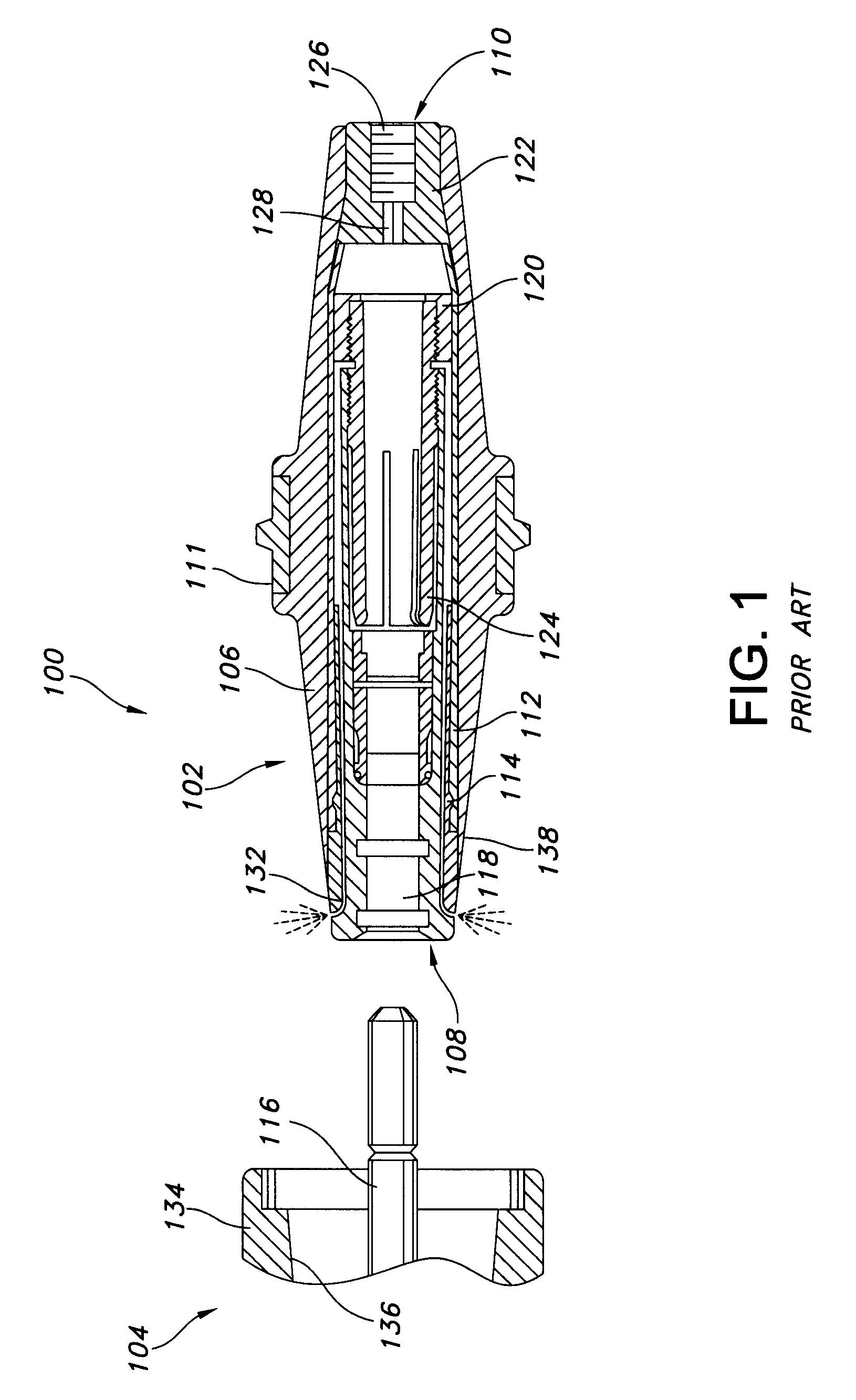
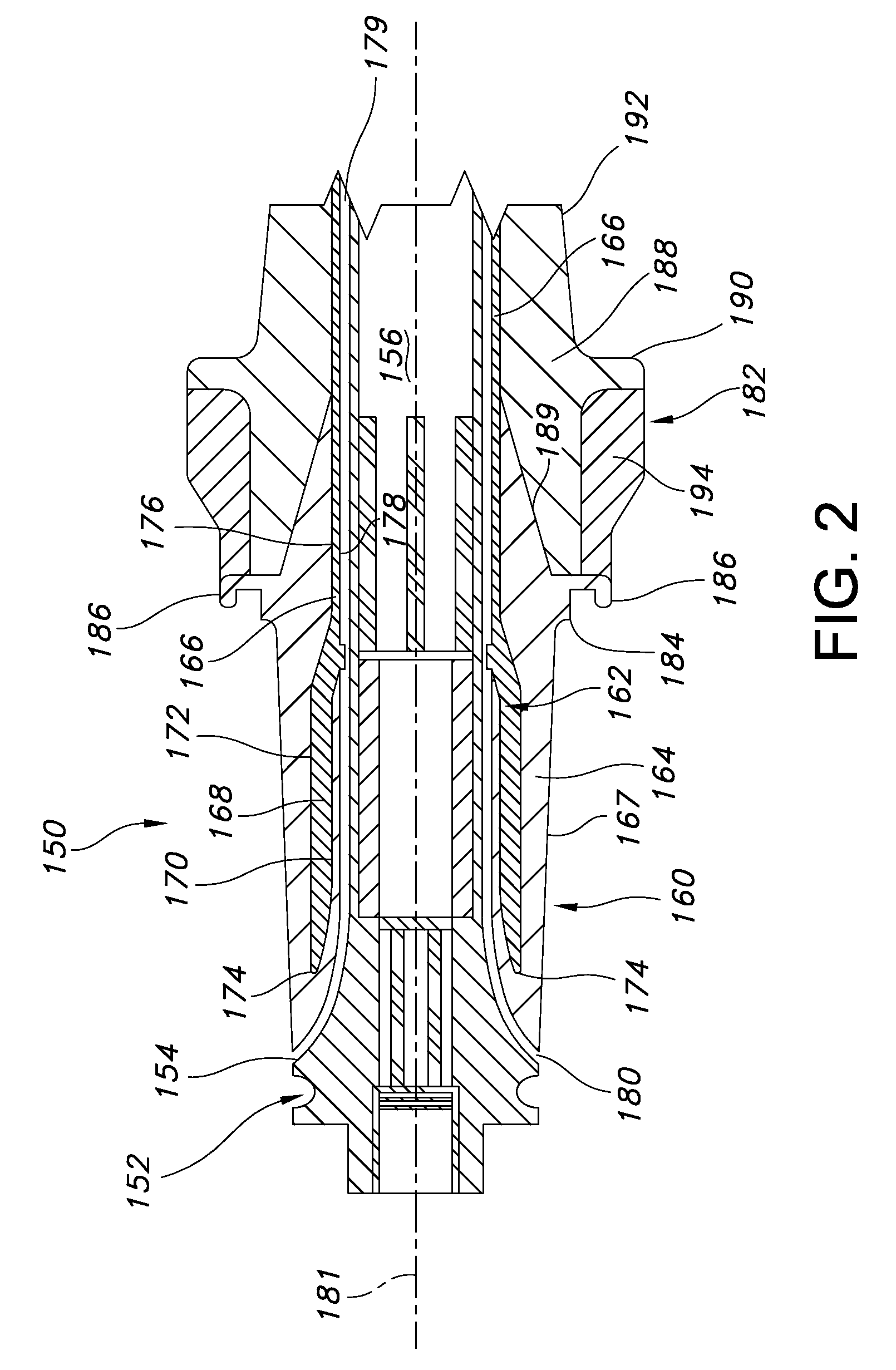
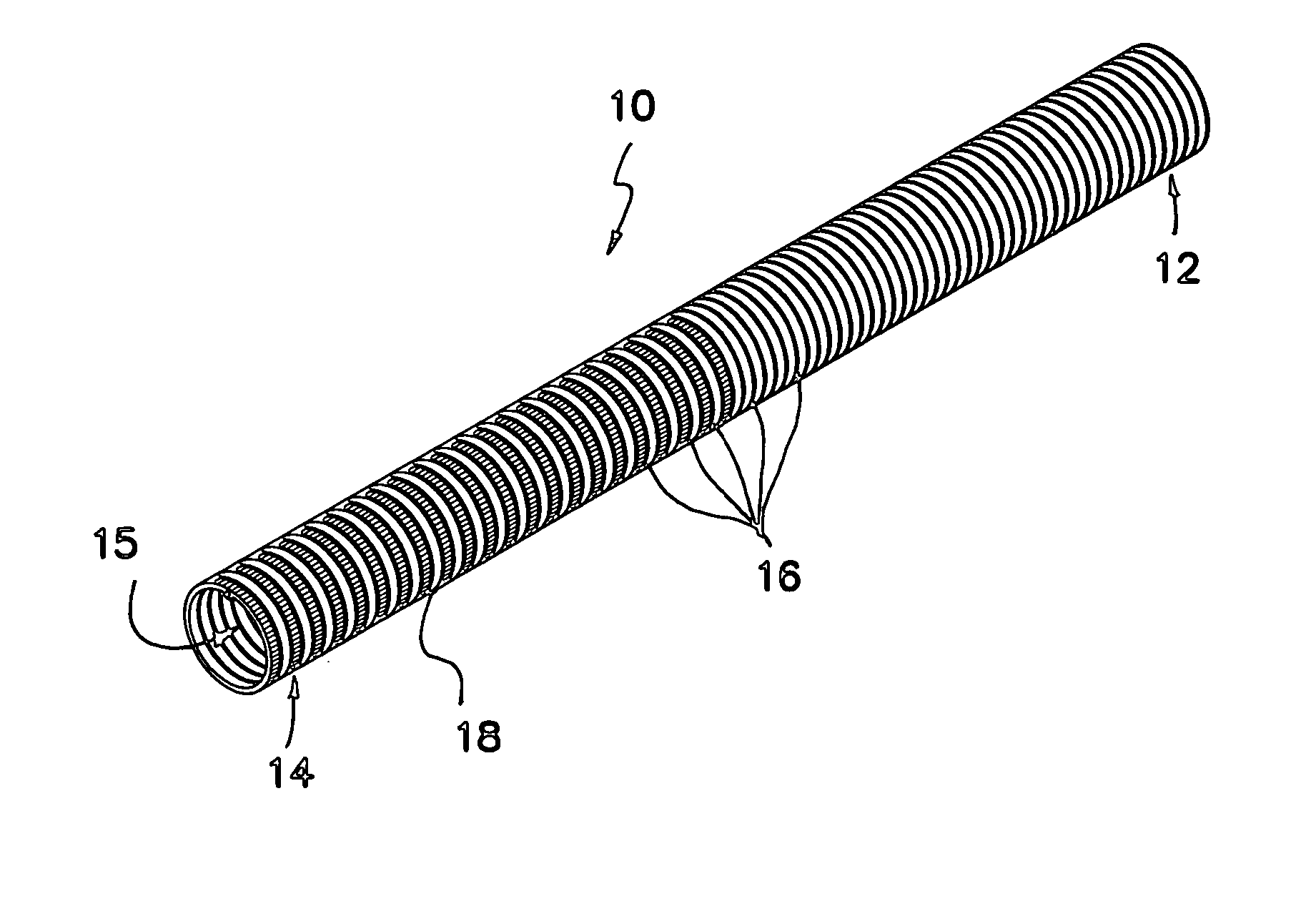
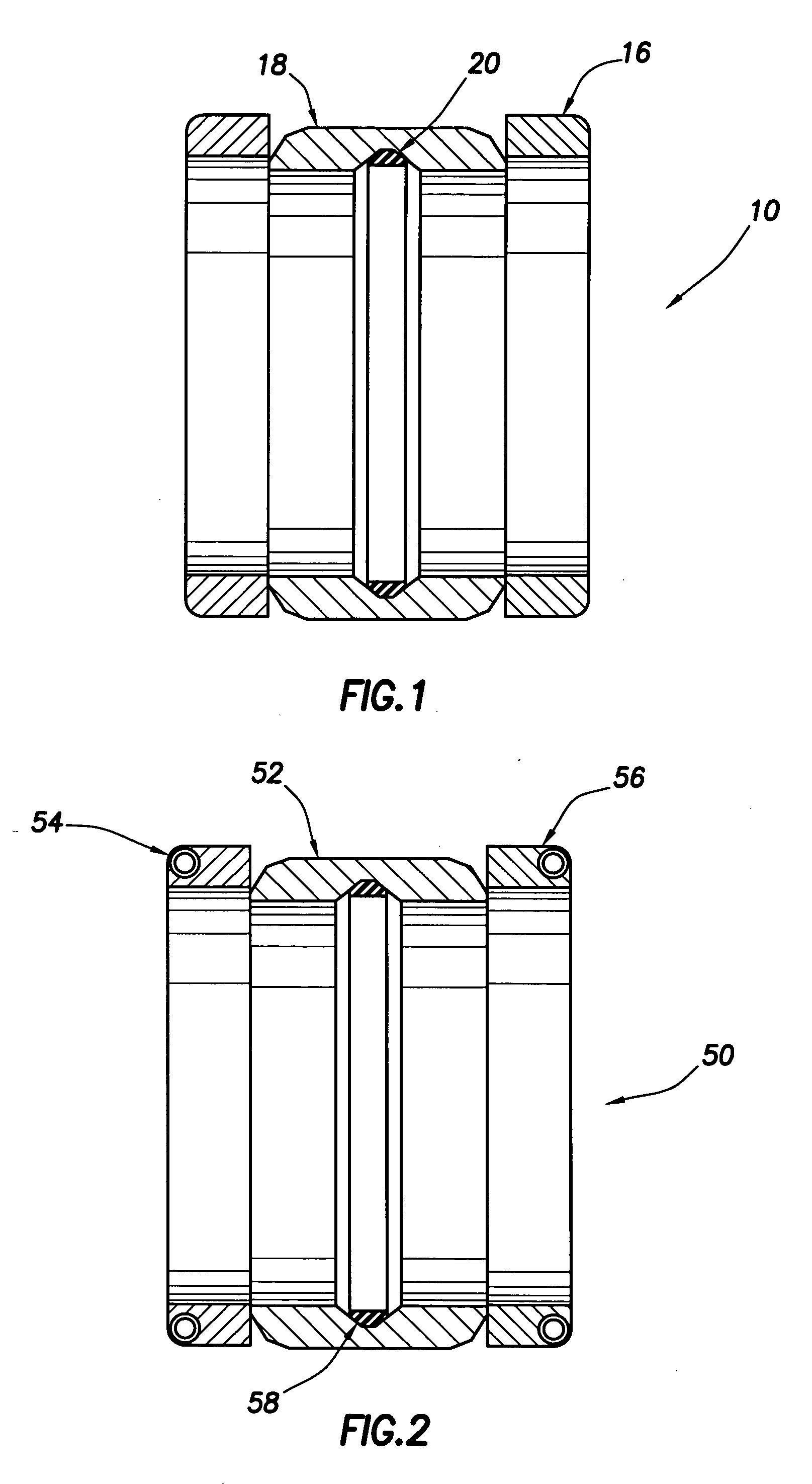
Medical tubing having variable characteristics and method of making same
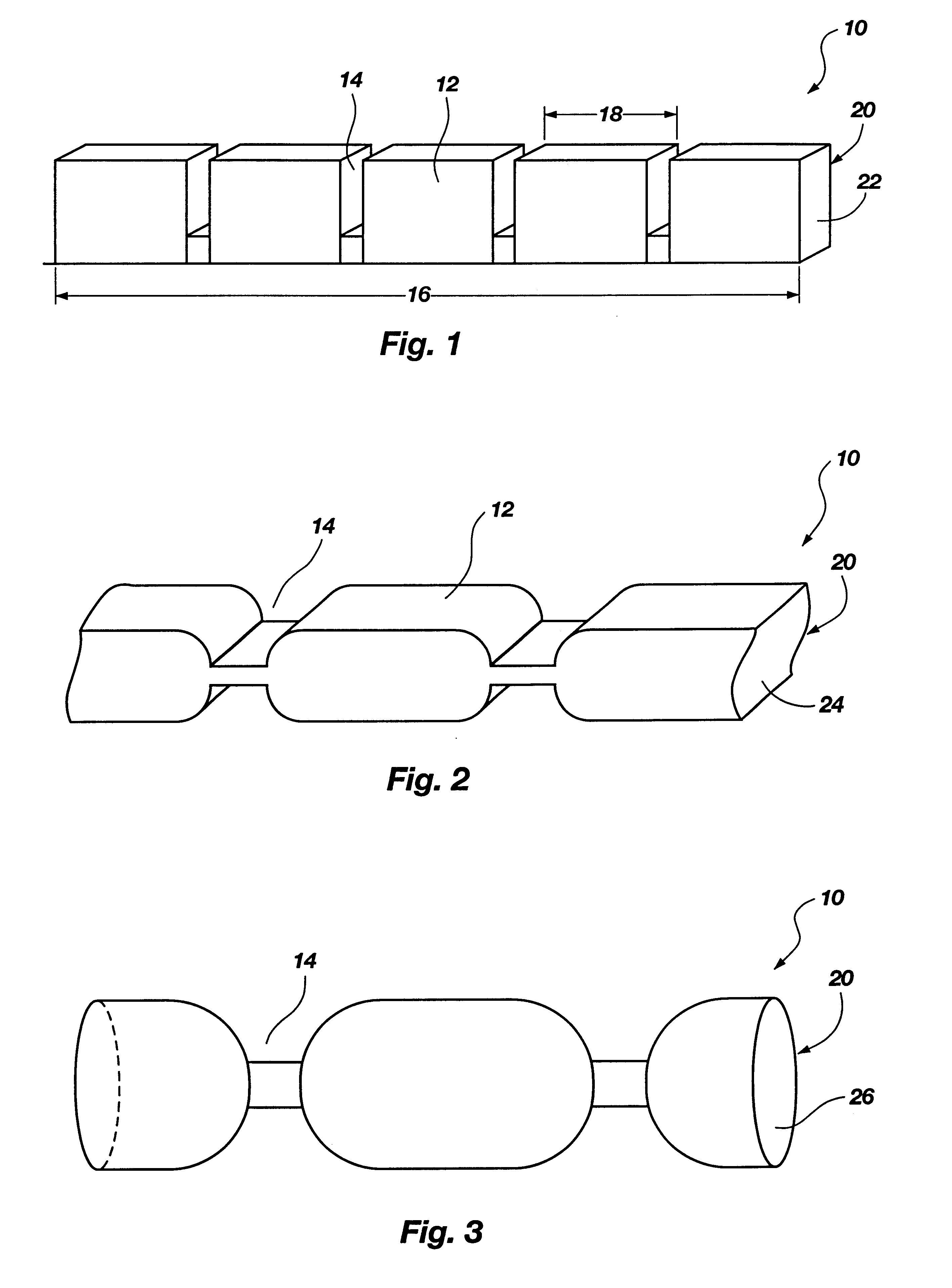
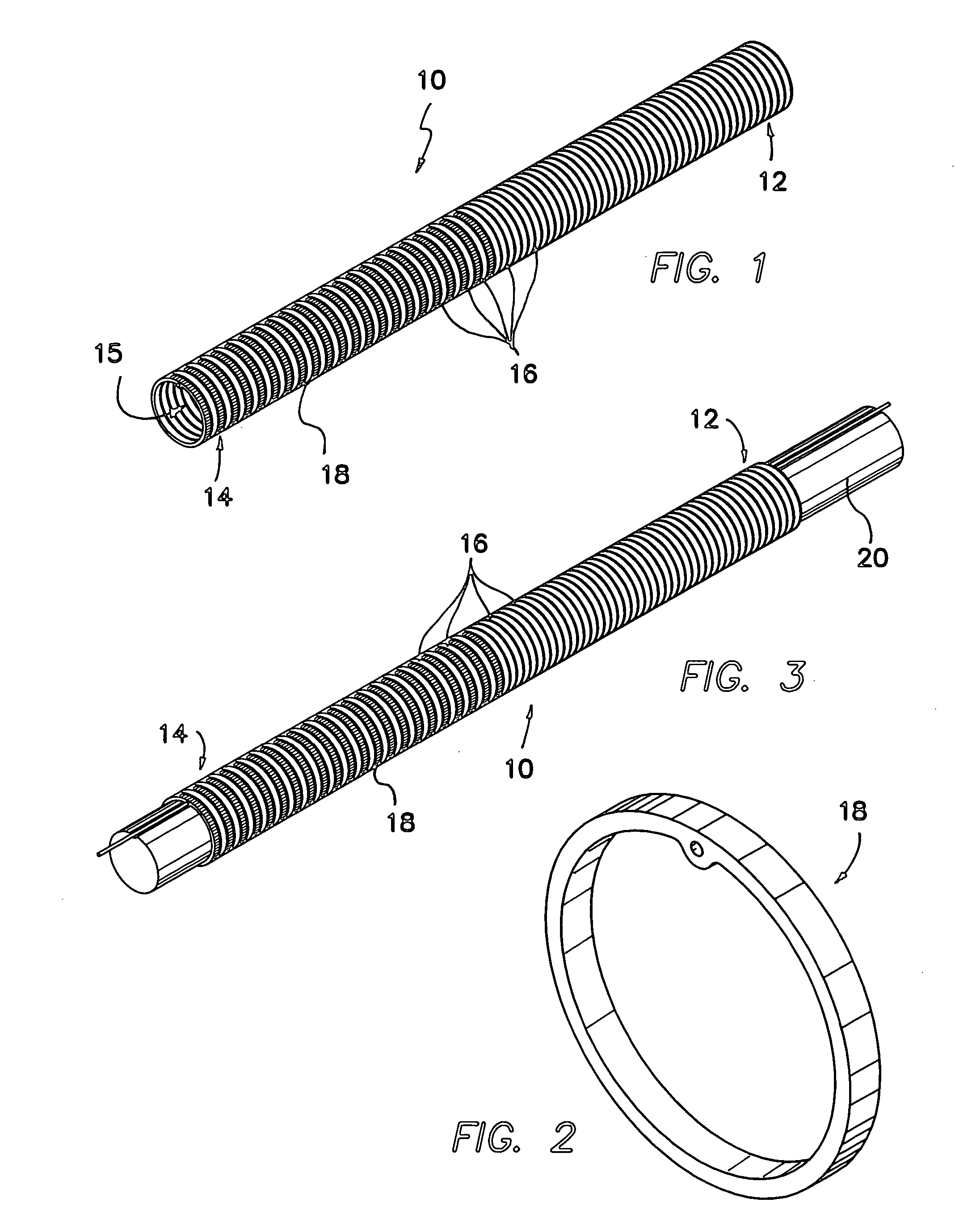
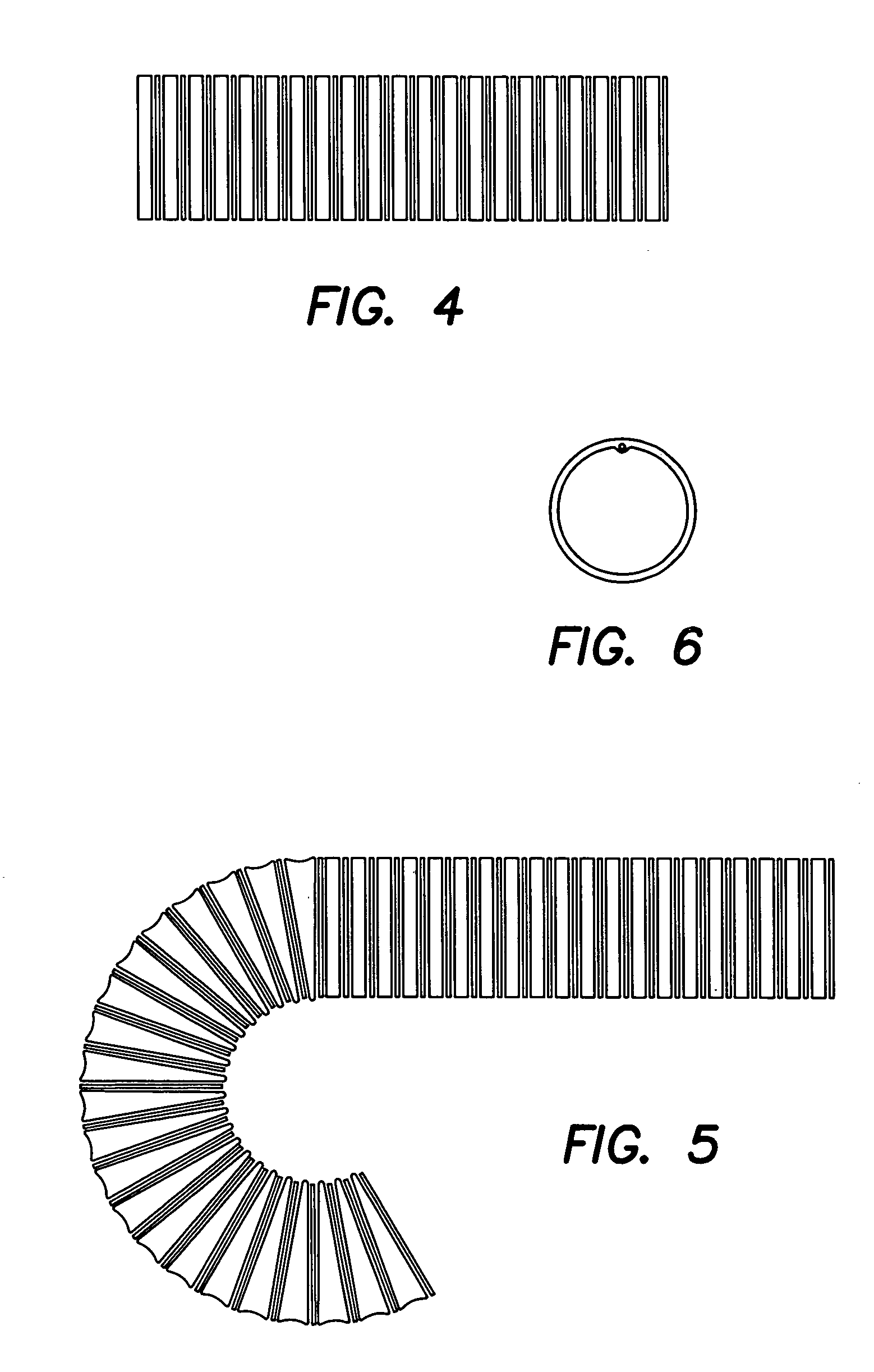
The invention primarily is directed to a medical tubing adapted for insertion into a body tissue or cavity and method of manufacturing different variations of the tubing along a length of the tubing. The tubing comprises a plurality of individual, discrete, generally ring-shaped elements arranged in series and fused or bonded together forming a continuous tubular structure. The ring-shaped elements may be formed of a thermoplastic or a thermoset material. The ring-shaped elements may include plastic rings, metallic rings, un-reinforced plastic rings and / or metal reinforced plastic rings assembled along the length of the tubular structure to provide variable flexibility and kink-resistance. The tubular structure may have a cross-section of any geometric shape and it may be bent, twisted or curved without kinking. The ring-shaped elements may have different flexural modulus. The ring-shaped elements may include a combination of flexible and rigid ring-shaped elements assembled along different portions or sections of the tubular structure. The ring-shaped elements may be metallic and may be bonded with a resilient, flexible elastomeric adhesive, wherein the ring-shaped elements may have different lengths and may be fused closer or further apart to one another depending on the characteristics of a portion or section of the tubing. In another aspect of the invention, the medical tubing may further comprise a secondary lumen and a pull wire to control the tubular structure. The ring-shaped elements may be truncated to provide a bending bias. In another aspect of the invention, the ring-shaped elements may vary in diameter and / or composition in different portions or sections of the tubular structure. In yet another aspect of the invention, some of the ring-shaped elements may be radiopaque, or the ring-shaped elements may comprise of different colors to operate as indicators along the tubular structure.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
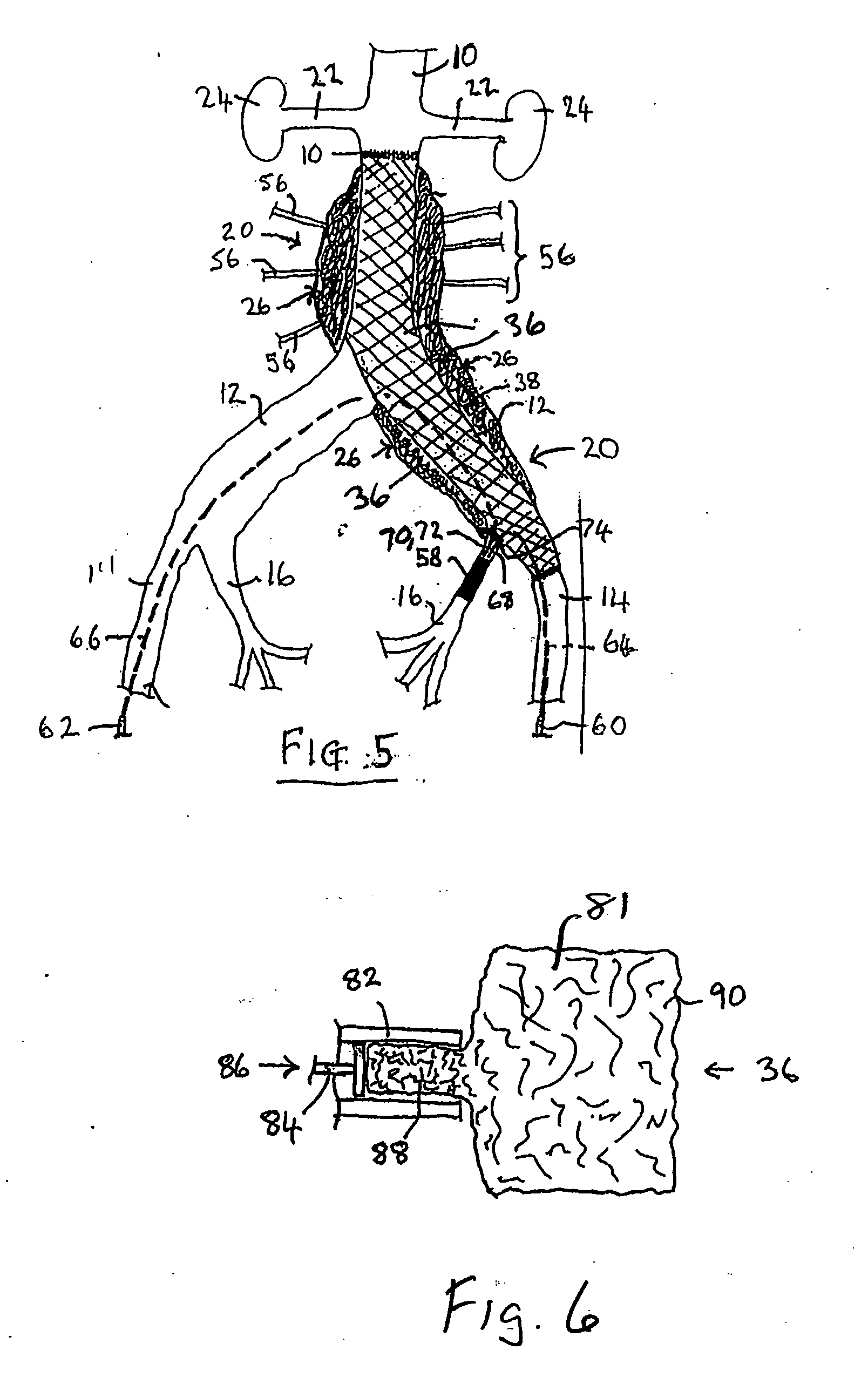
Endovascular treatment devices and methods
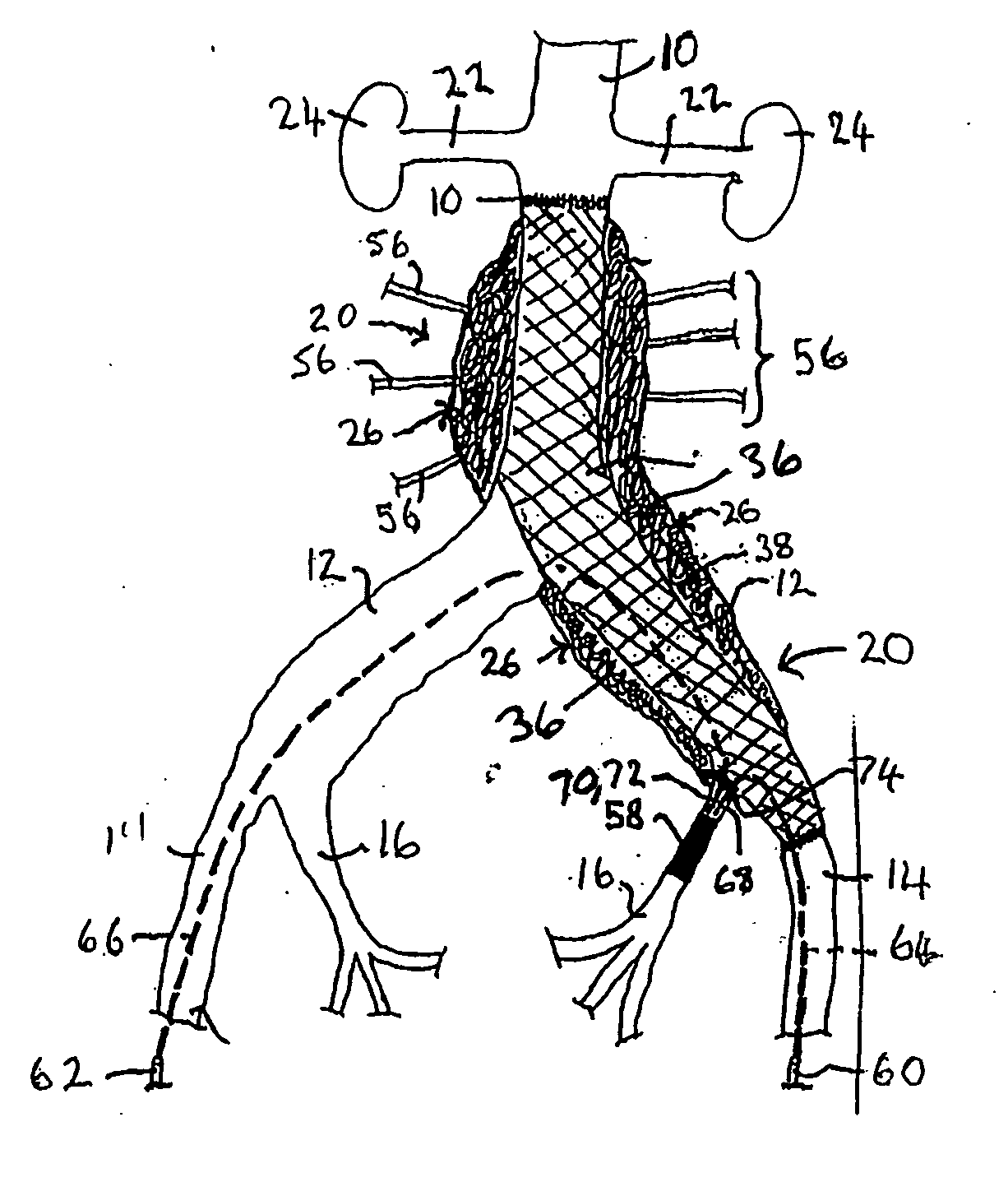
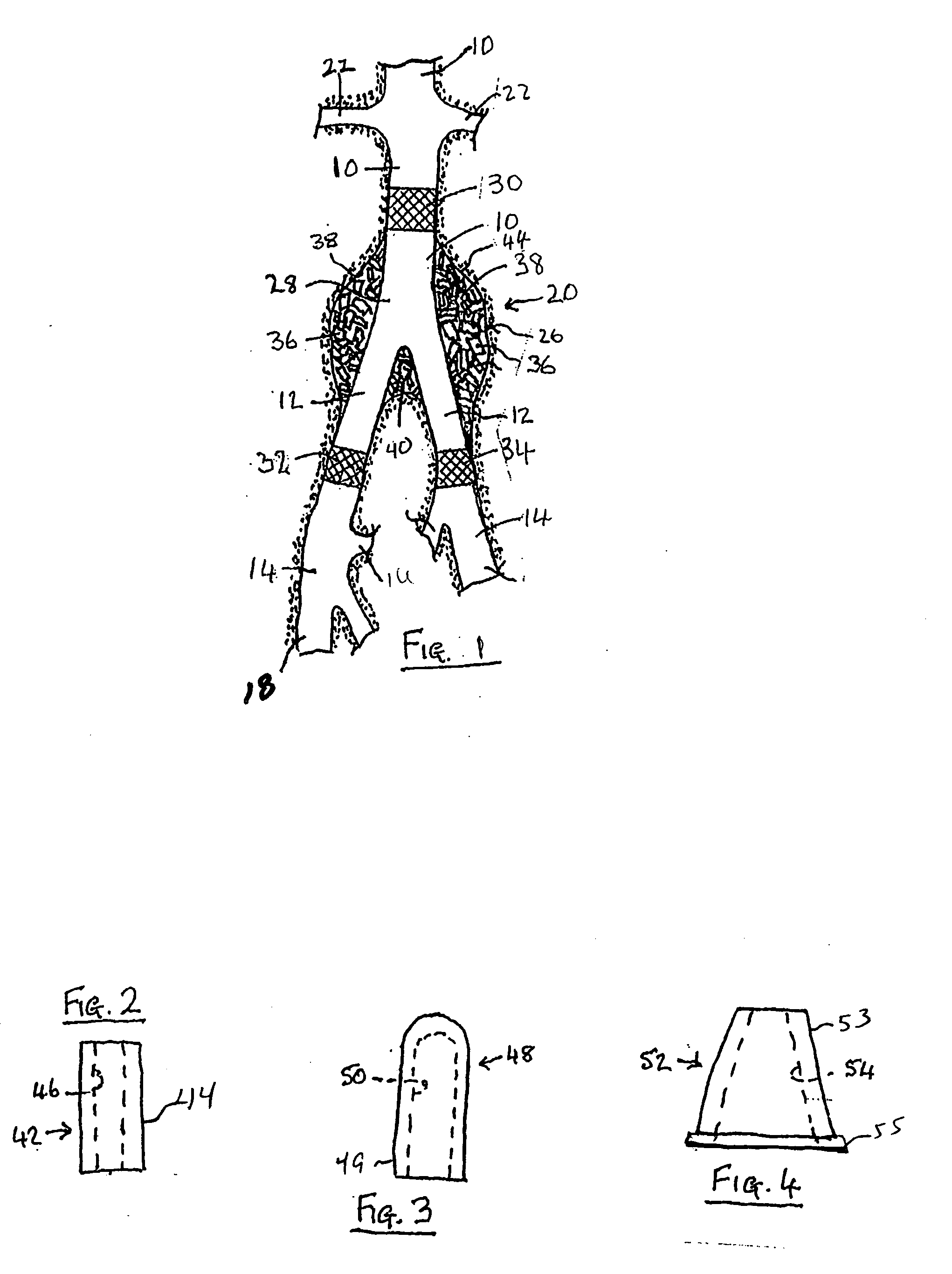
InactiveUS20050165480A1Simple and potentially effective treatmentTreating and preventing endoleakageTracheaeOcculdersEndovascular treatmentElastomer
A device for treating or preventing a vascular condition at a mammalian vascular site, comprises an implant formed from a compressible, reticulated elastomeric matrix in a shape conducive to delivery through a delivery instrument. One or more implants are delivered in a compressed state to the mammmalian vascular site where each implant recovers substantially to its uncompressed state following deployment from a delivery instrument. In a preferred embodiment the matrix comprises cross-linked polycarbonate polyurethane-urea or cross-linked polycarbonate polyurea-urethane. In another preferred embodiment the matrix comprises a cross-linked polycarbonate polyurethane. In a yet further embodiment, the matrix comprises thermoplastic polycarbonate polyurethane or thermoplastic polycarbonate polyurethane-urea.
Owner:THE BIOMERIX CORP
Thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene-base open-ring polymers, hydrogenated derivatives thereof, and processes for the preparation of both
InactiveUS6511756B1Improve efficiencyGood moldabilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticDouble bond
A thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene ring-opening polymer obtained by ring-opening polymerization of a monomer component containing a dicyclopentadiene monomer, characterized in that polycyclic rings which are repeating units of the polymer are bonded in cis-position relative to the carbon-carbon double bond of the main chain of the polymer in 50 mol % or more of the repeating units based on the total repeating units and the content of a low-molecular weight component of 2,000 or less in molecular weight is 10% by weight or less based on the total polymer components, and a hydrogenation product obtained by hydrogenating the carbon-carbon unsaturated bond of the thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene ring-opening polymer.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Hydrogel for use in downhole seal applications
InactiveUS20050171248A1Increase expansionAvoid seal failureOther chemical processesVehicle sealing arrangementsElastomerThermoplastic
The present invention is a composition for forming seals. The composition includes a base material and a hydrogel. The base materials is preferably an elastomer or a thermoplastic. Seals formed with the composition are particularly suited for use in a wellbore environment. The inclusion of hydrogel in the seals allows the seals to be manipulated or altered through certain environmental factors. For instance, temperature, oil / water ratio, pH and the electronic field may all be used to alter the characteristics of the hydrogel. In this way, the seal may be caused to swell in response to a specific stimulus, thereby preventing or sealing a leak without requiring additional work or input from the operator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com