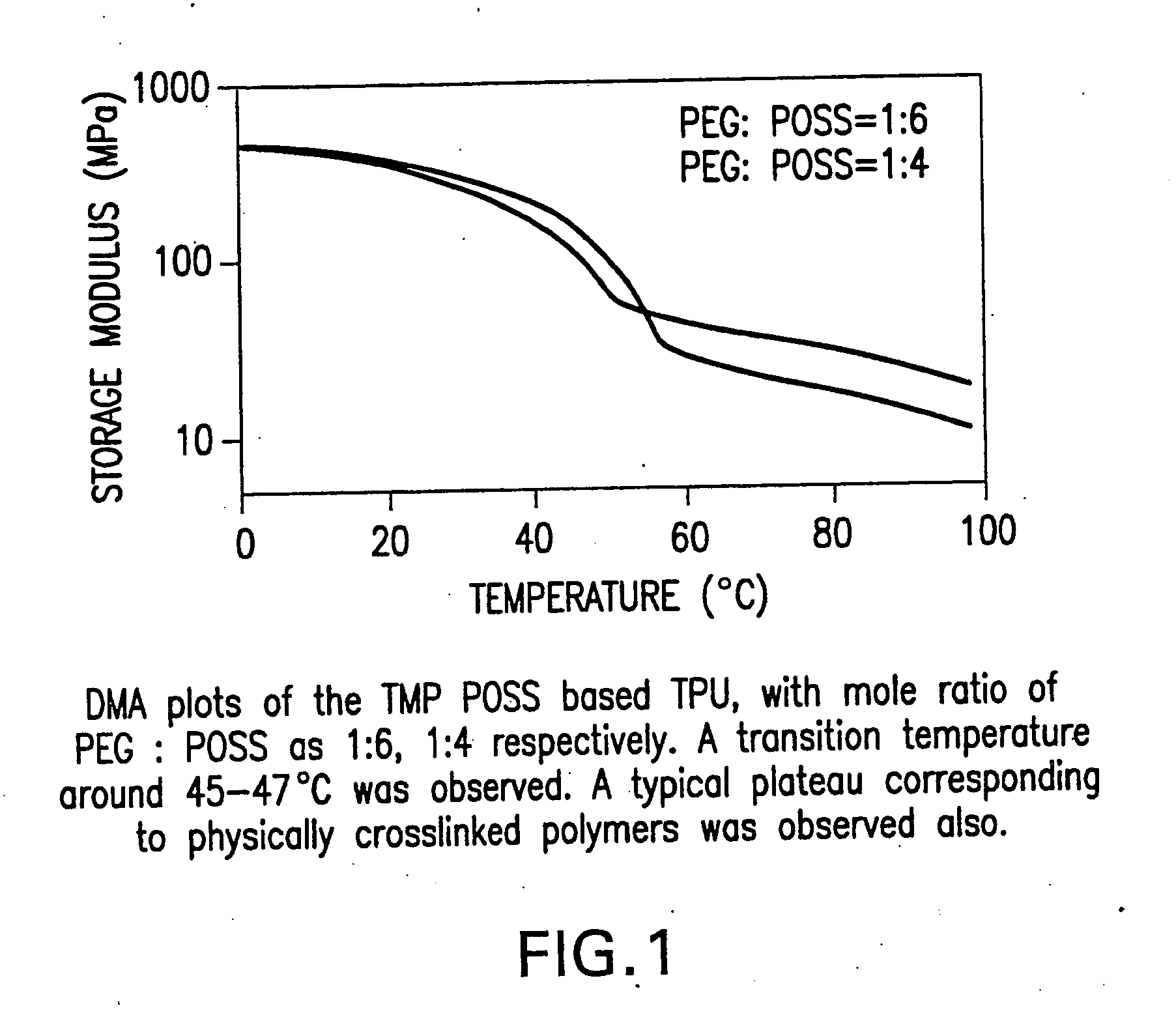
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4339results about How to "High modulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
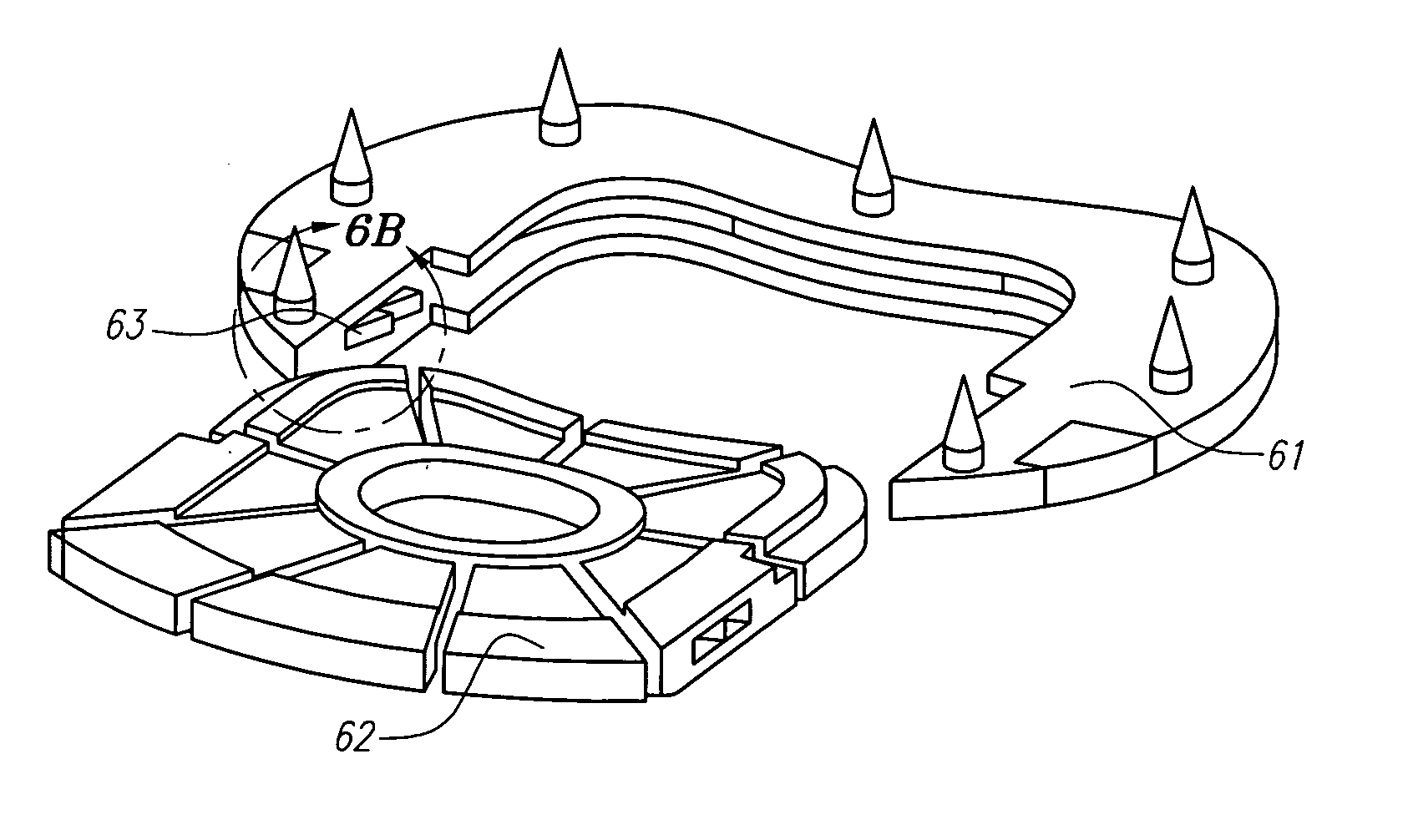
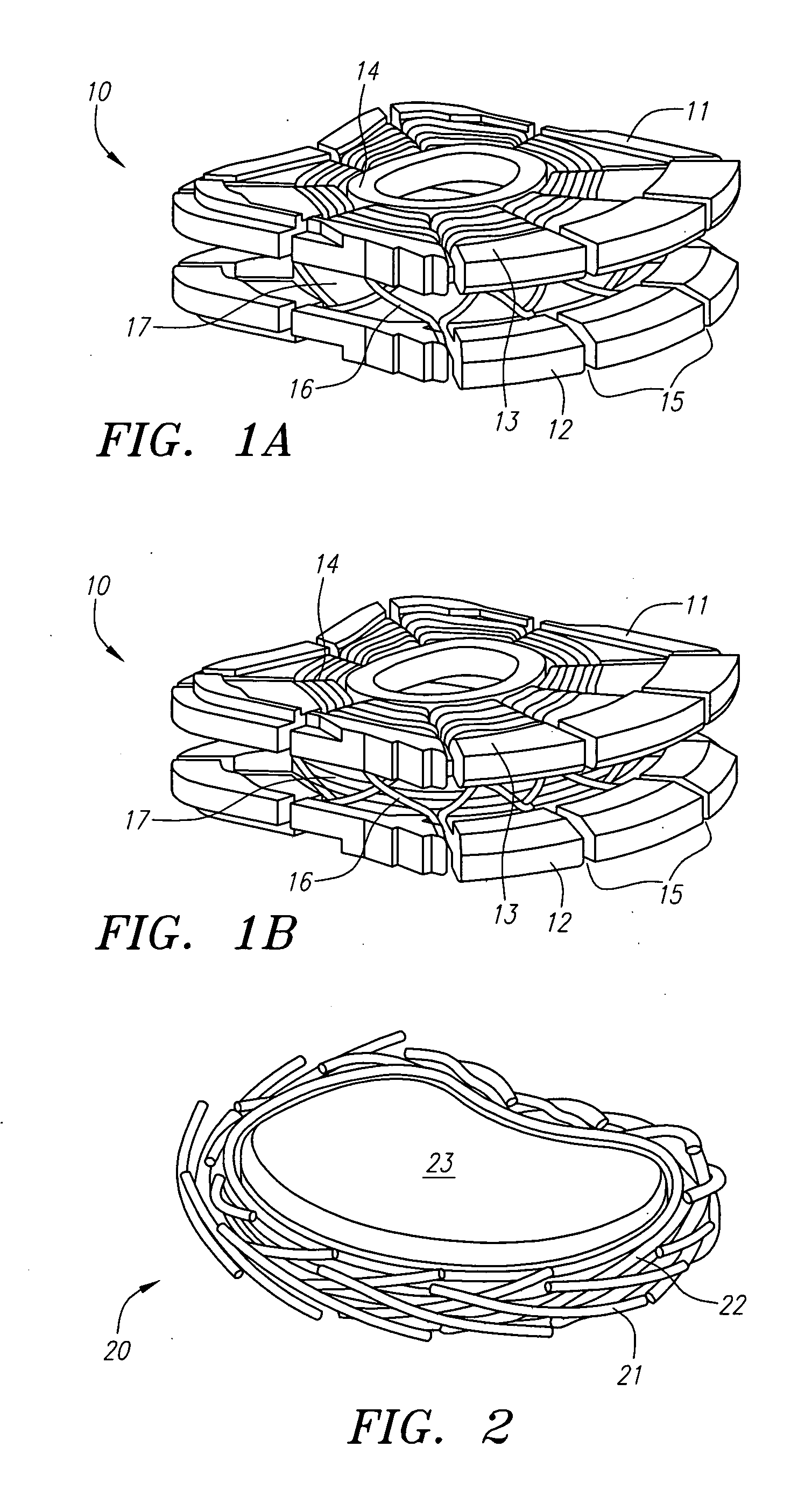
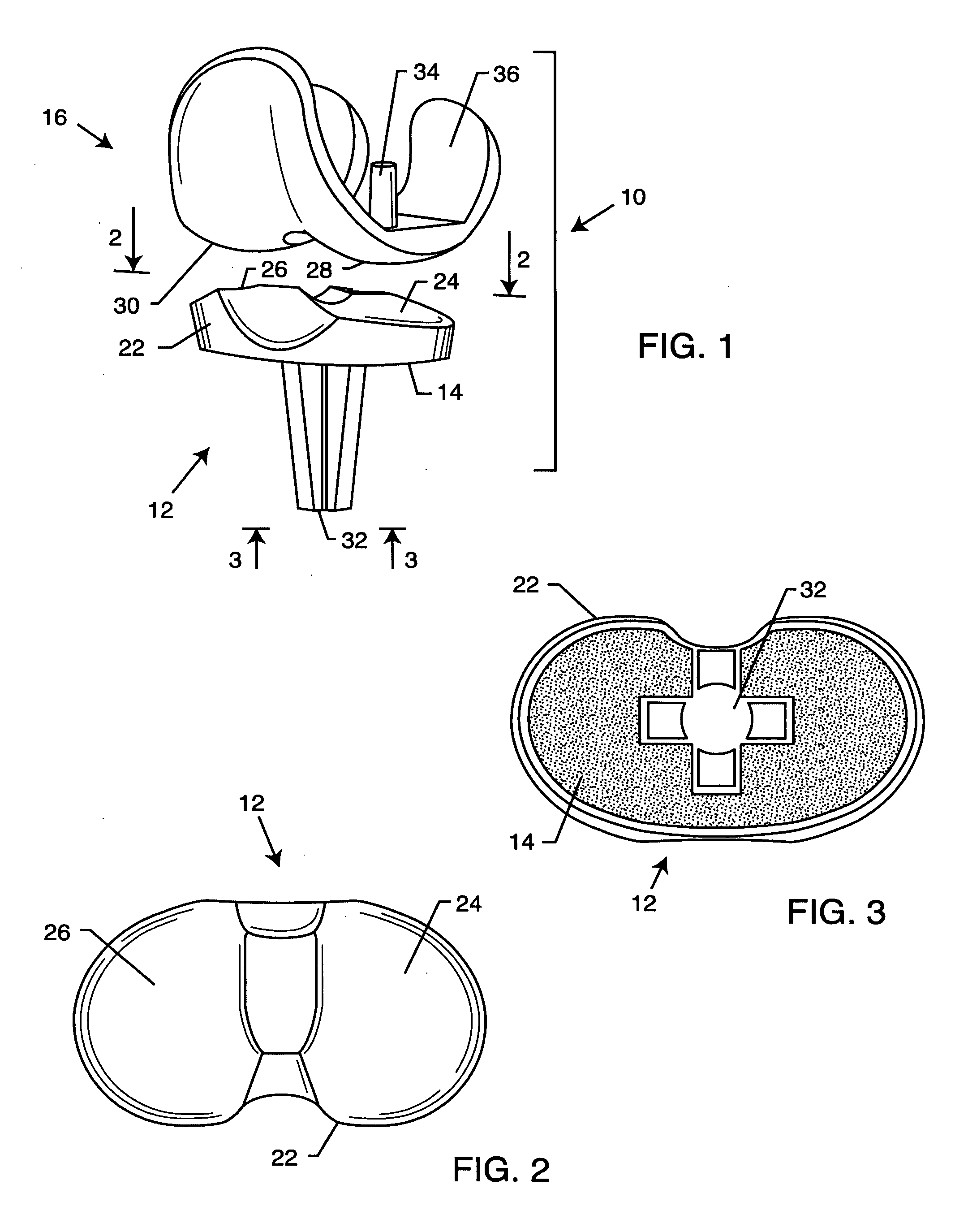
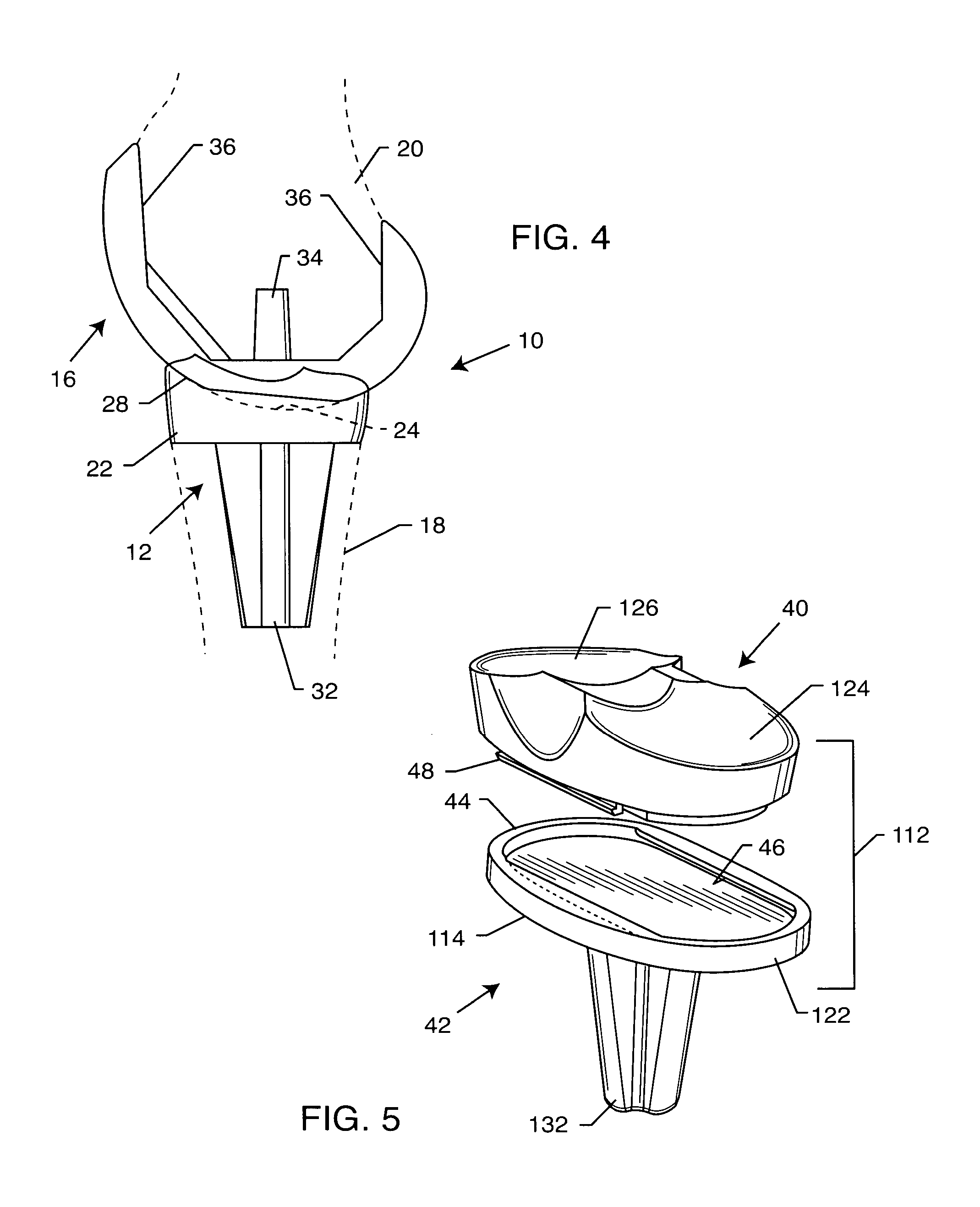
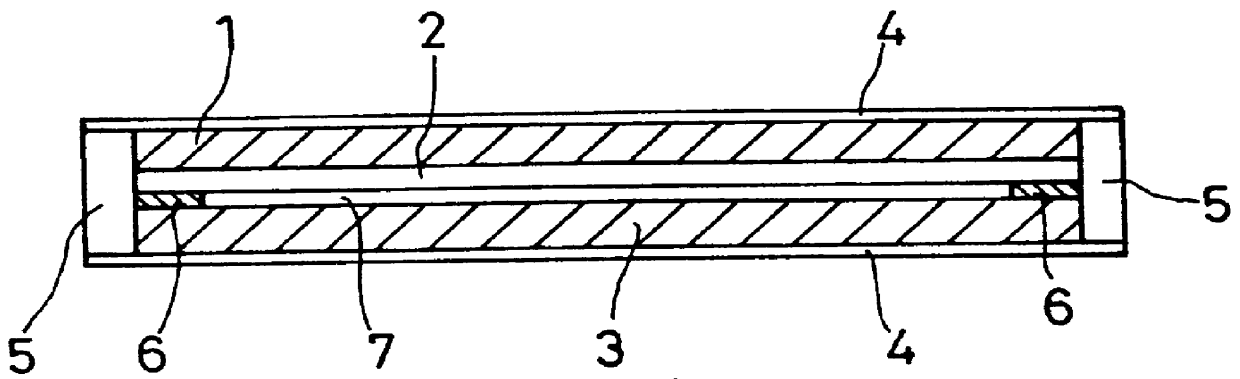
Prosthetic intervertebral disc and methods for using same
InactiveUS20050228500A1Improve toughnessHigh modulusJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical operationIntervertebral disc
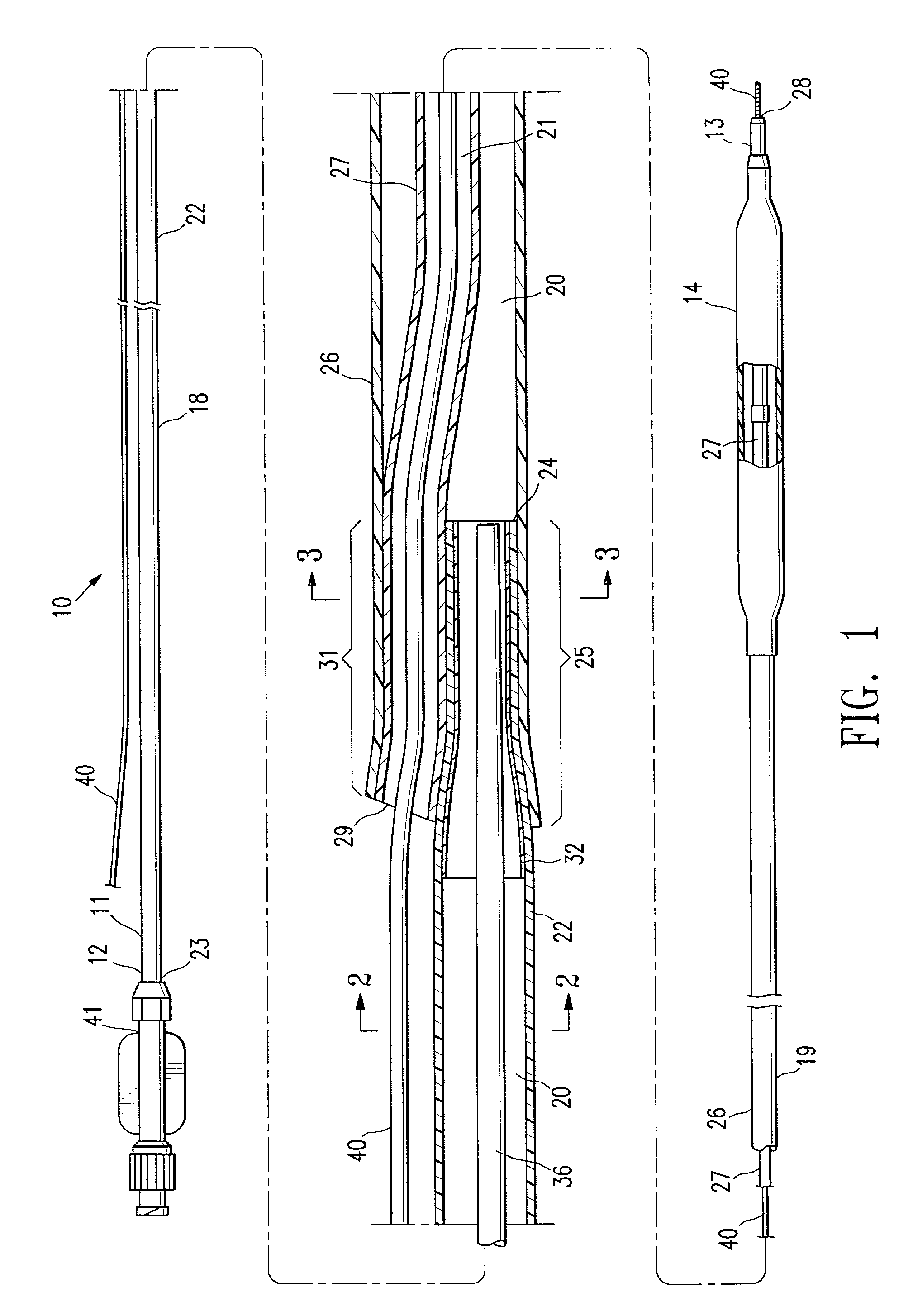
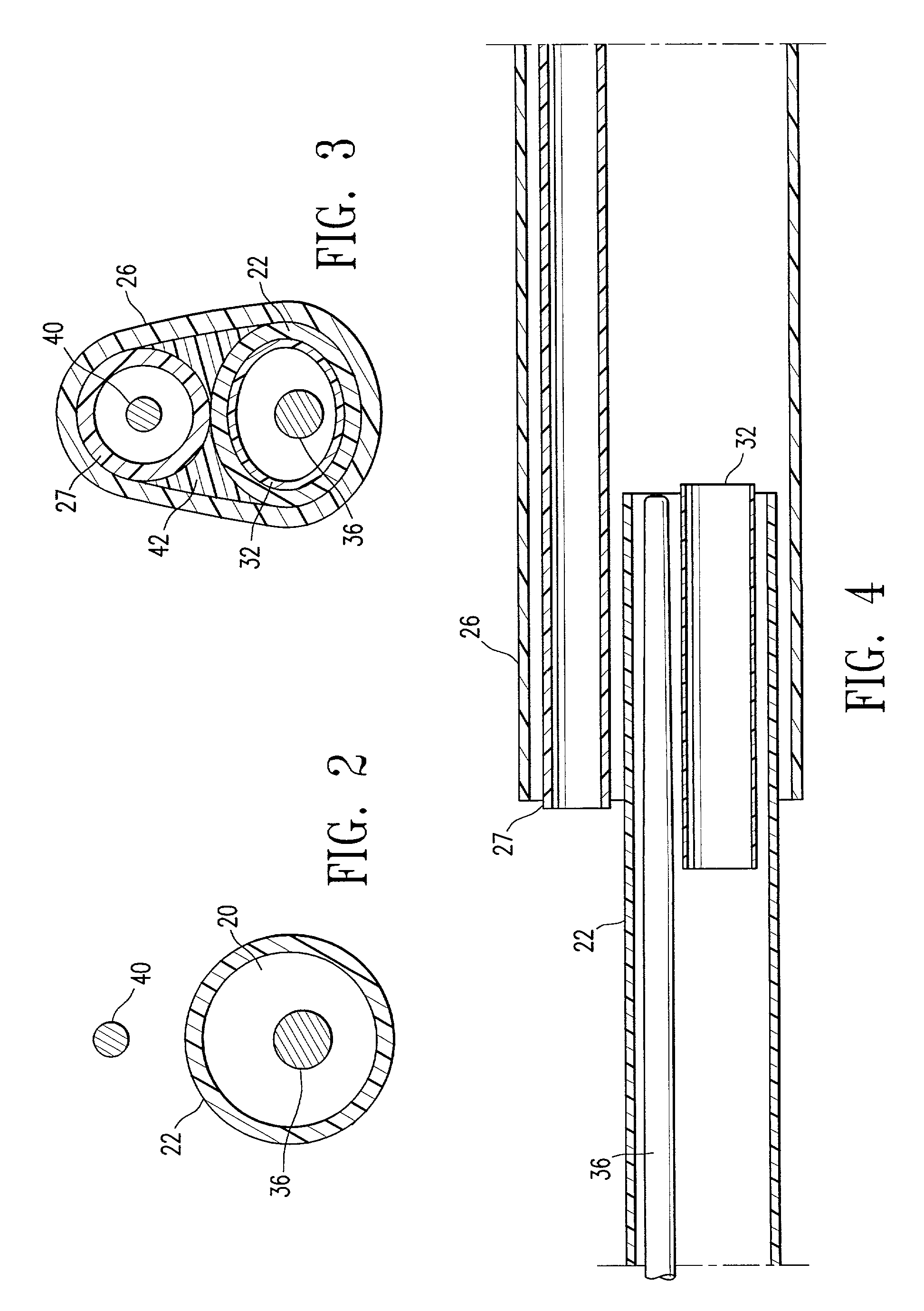
Prosthetic intervertebral discs and methods for using the same are described. The subject prosthetic discs include upper and lower endplates separated by a compressible core member. The prosthetic discs described herein include one-piece, two-piece, three-piece, and four-piece structures. The subject prosthetic discs exhibit stiffness in the vertical direction, torsional stiffness, bending stiffness in the saggital plane, and bending stiffness in the front plane, where the degree of these features can be controlled independently by adjusting the components of the discs. The interface mechanism between the endplates and the core members of several embodiments of the described prosthetic discs enables a very easy surgical operation for implantation.
Owner:SPINAL KINETICS
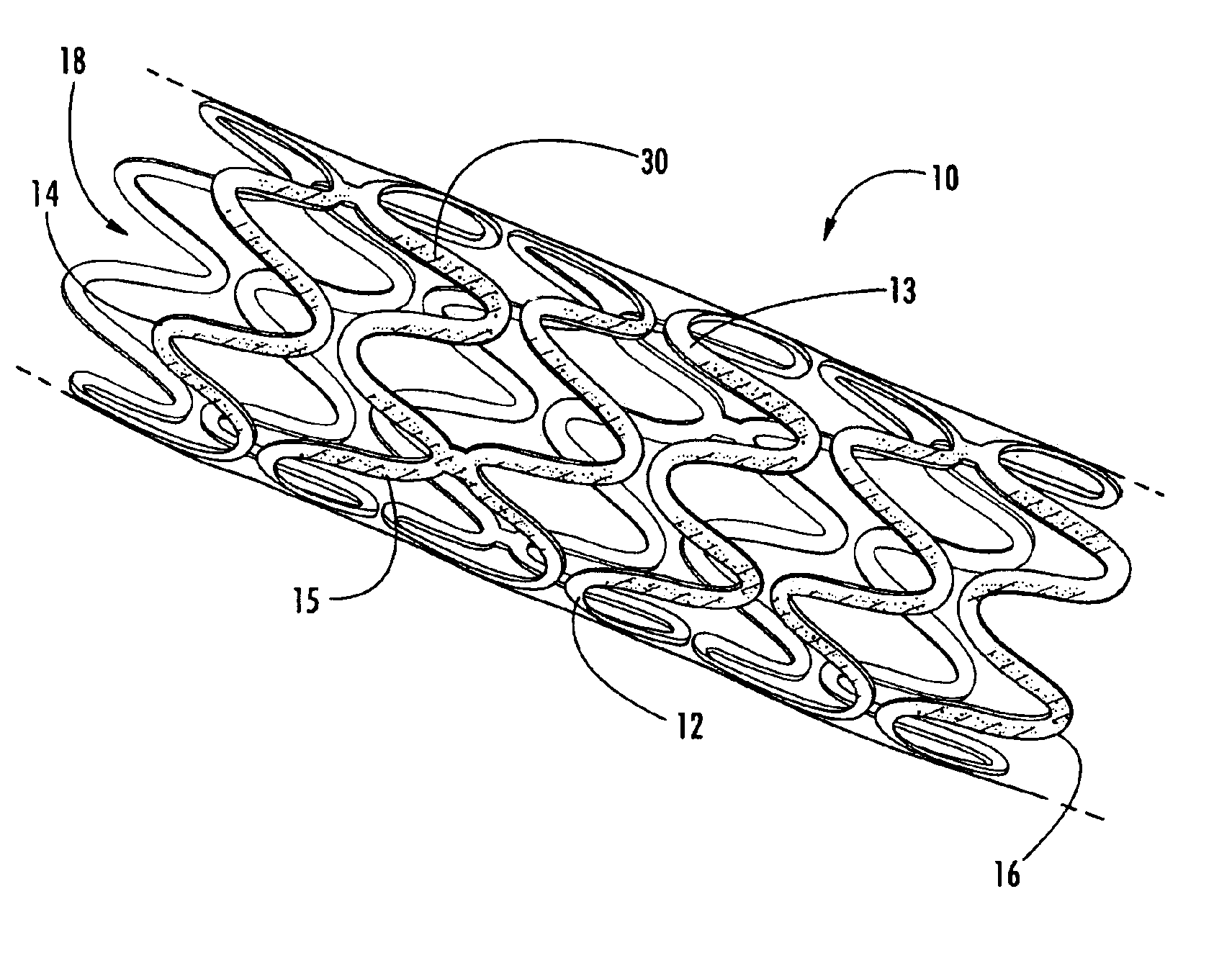
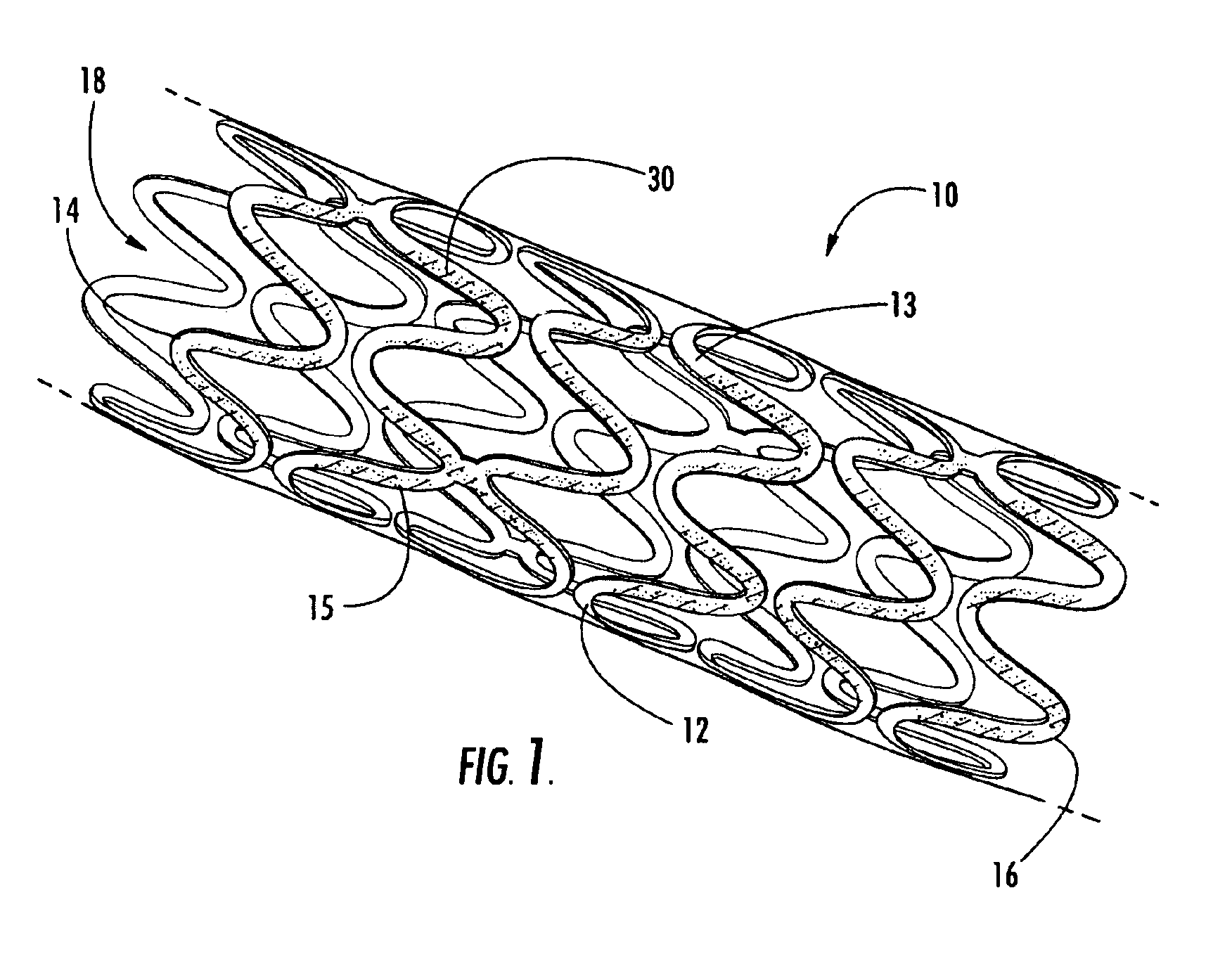
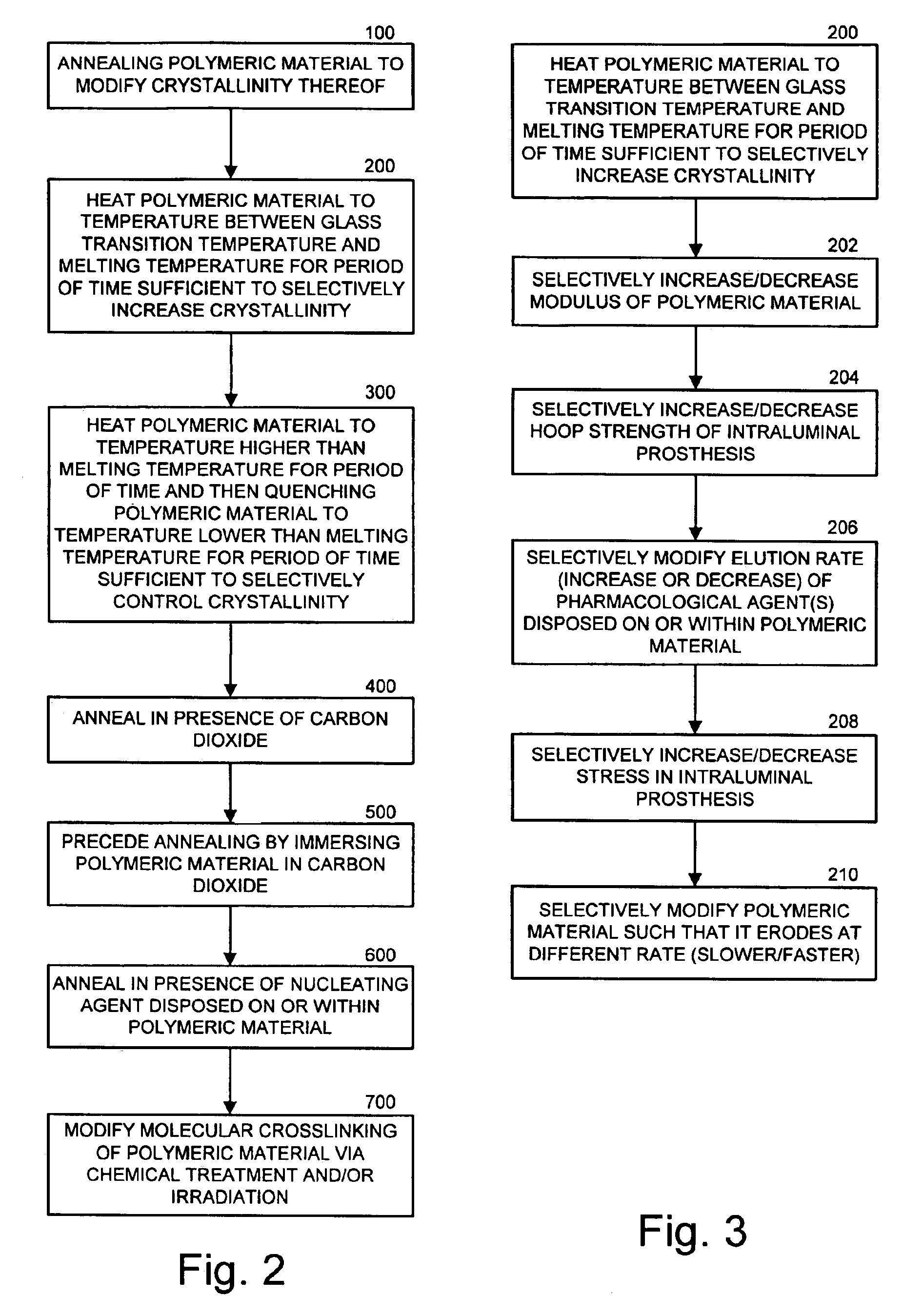
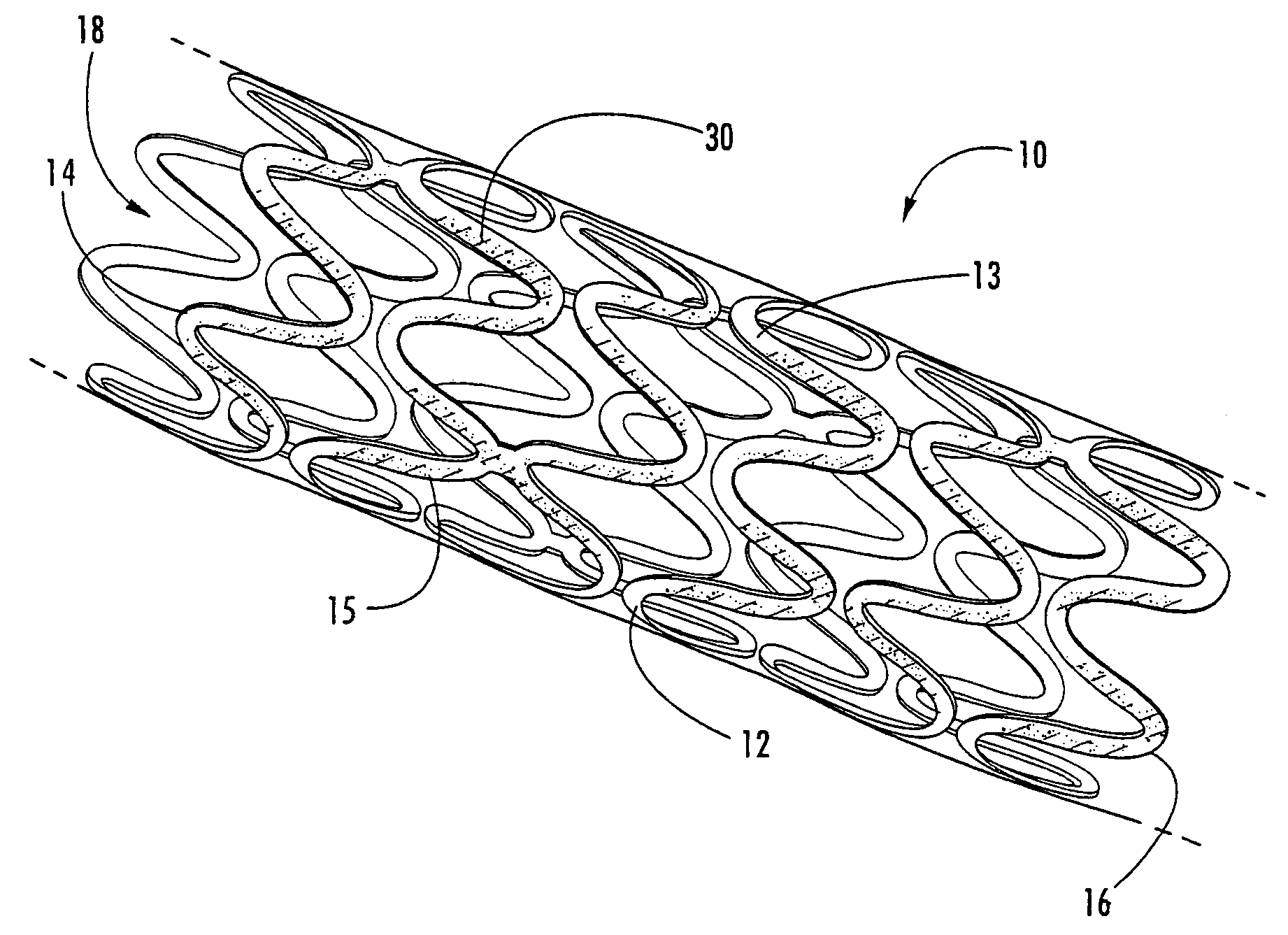
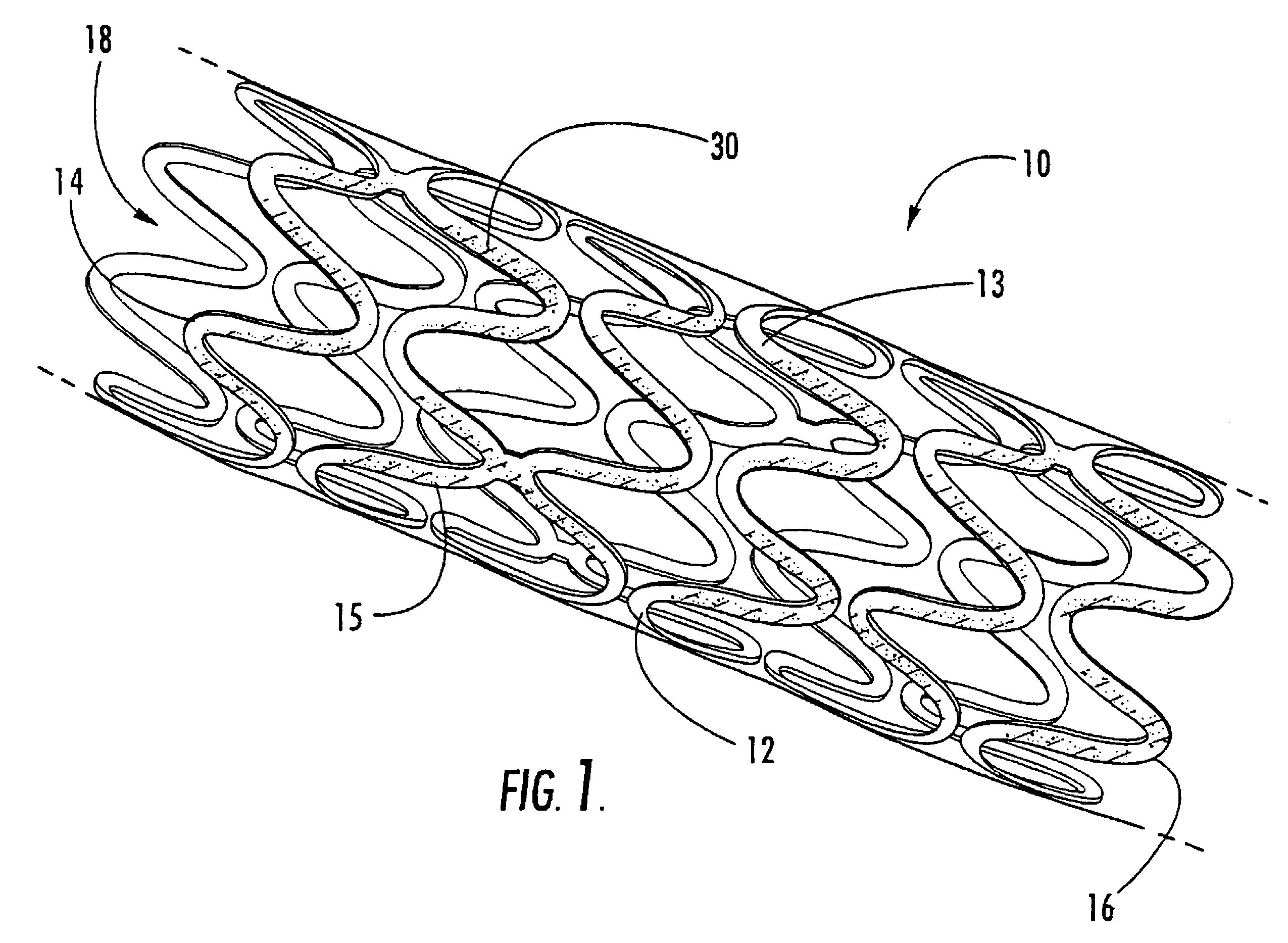
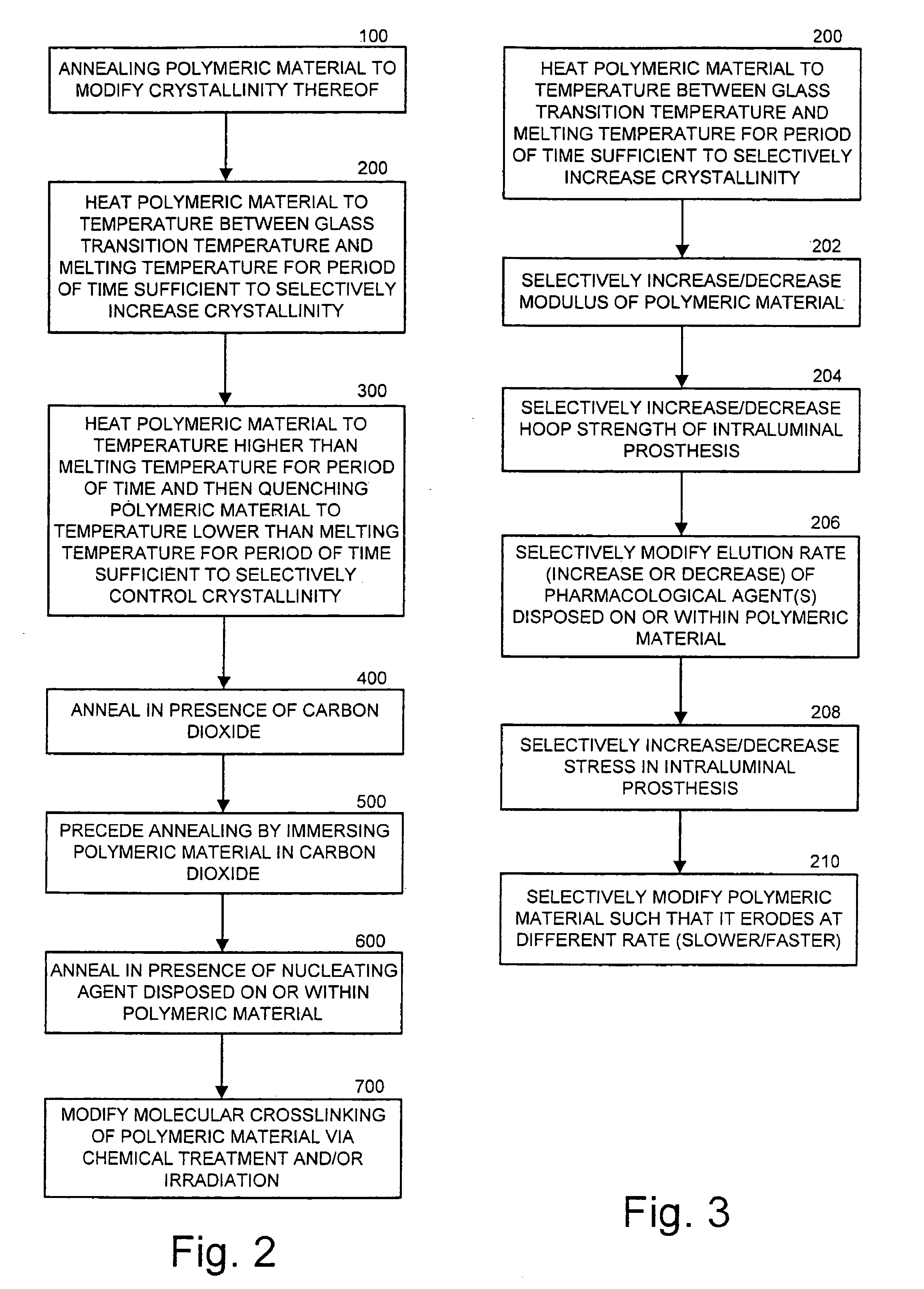
Intraluminal prostheses having polymeric material with selectively modified crystallinity and methods of making same
Methods of manufacturing polymeric intraluminal prostheses include annealing the polymeric material to selectively modify the crystallinity thereof. Annealing may be utilized to selectively modify various properties of the polymeric material of an intraluminal prosthesis, including: selectively increasing the modulus of the polymeric material; selectively increasing the hoop strength of the intraluminal prosthesis; selectively modifying the elution rate (increase or decrease) of a pharmacological agent subsequently disposed on or within the annealed polymeric material; selectively increasing / decreasing stress in the intraluminal prosthesis; and selectively modifying the polymeric material such that it erodes at a different rate.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
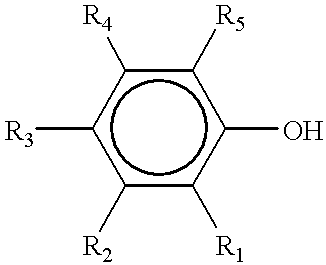
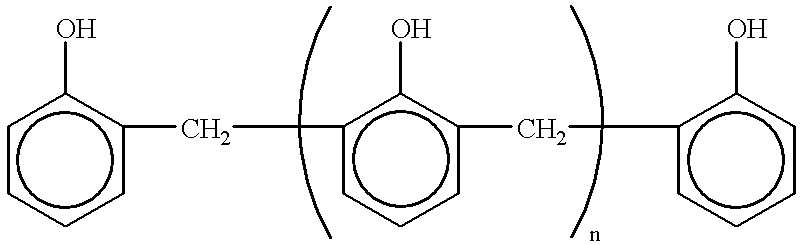
Ternary systems of benzoxazine, epoxy, and phenolic resins
Low viscosity ternary mixtures of benzoxazine, epoxy and phenolic resins have been developed. The blends render homogeneous and void free cured specimen with a wide range of properties. Melt viscosity values as low as 0.3 Pa.s at 100° C. can be achieved. The phenolic resin acts as a cure accelerator to the system, besides its typical function as a hardener of epoxy resin. Glass transition temperatures Tg as high as 170° C. can also be obtained.
Owner:EDISON POLYMER INNOVATION EPIC
Knee prosthesis with ceramic tibial component
InactiveUS20060052875A1Reduce wearHigh strengthHeart valvesJoint implantsArticular surfacesTibial bone
An improved knee prosthesis includes a ceramic tibial component for articulation with natural or prosthetic (re-surfaced) femoral surfaces. The ceramic tibial component is provided in the form of a ceramic monoblock adapted for fixation relative to the patient's tibial bone, or alternately in the form of a ceramic bearing insert component carried by a tibial baseplate member which is adapted in turn for fixation relative to tibial bone. In either form, the ceramic tibial component includes at least one upwardly concave articulation surface for movable bearing engagement by a generally convex or condylar shaped femoral articulation surface. The ceramic tibial component provides improved wear characteristics with extended service life.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
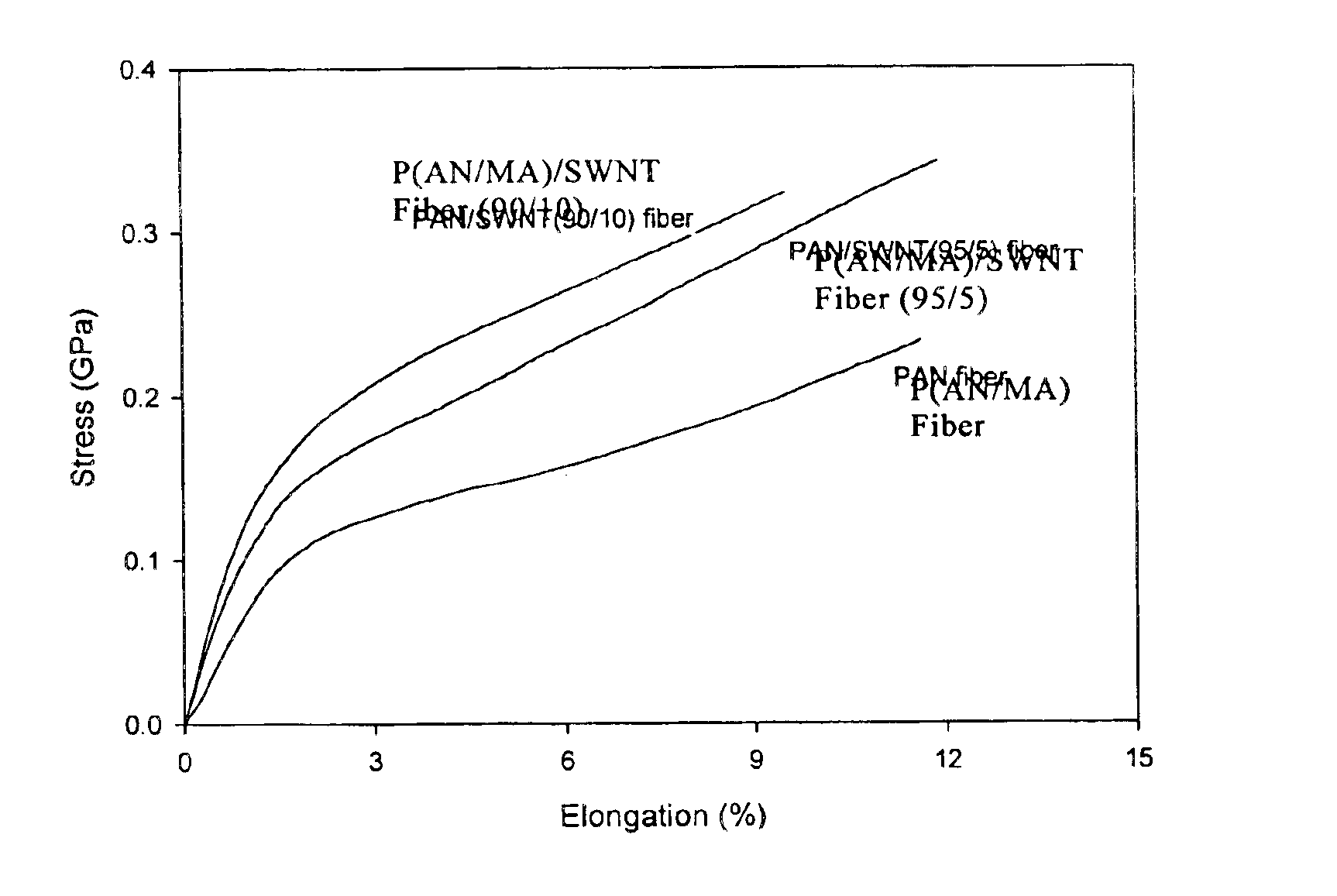
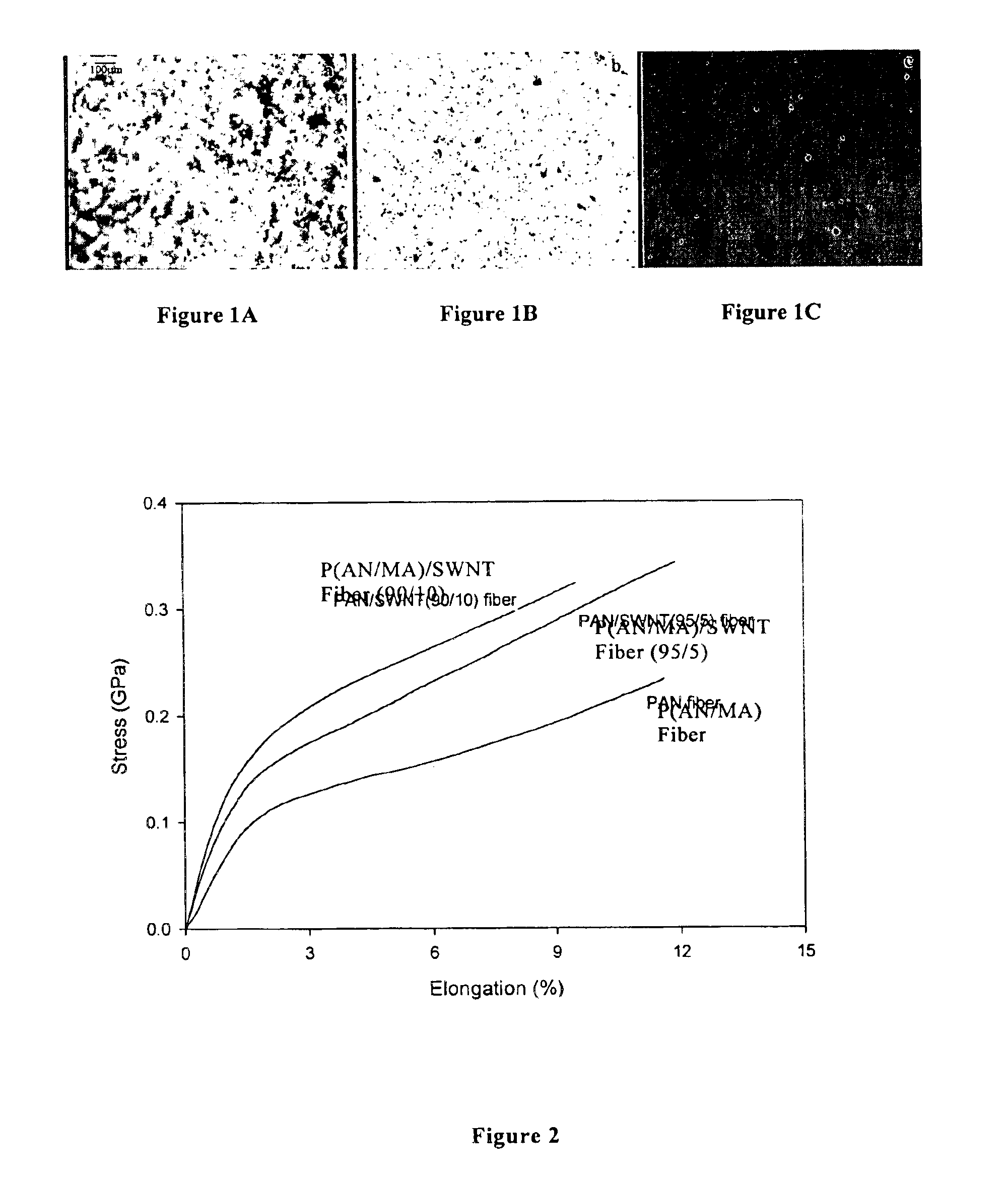
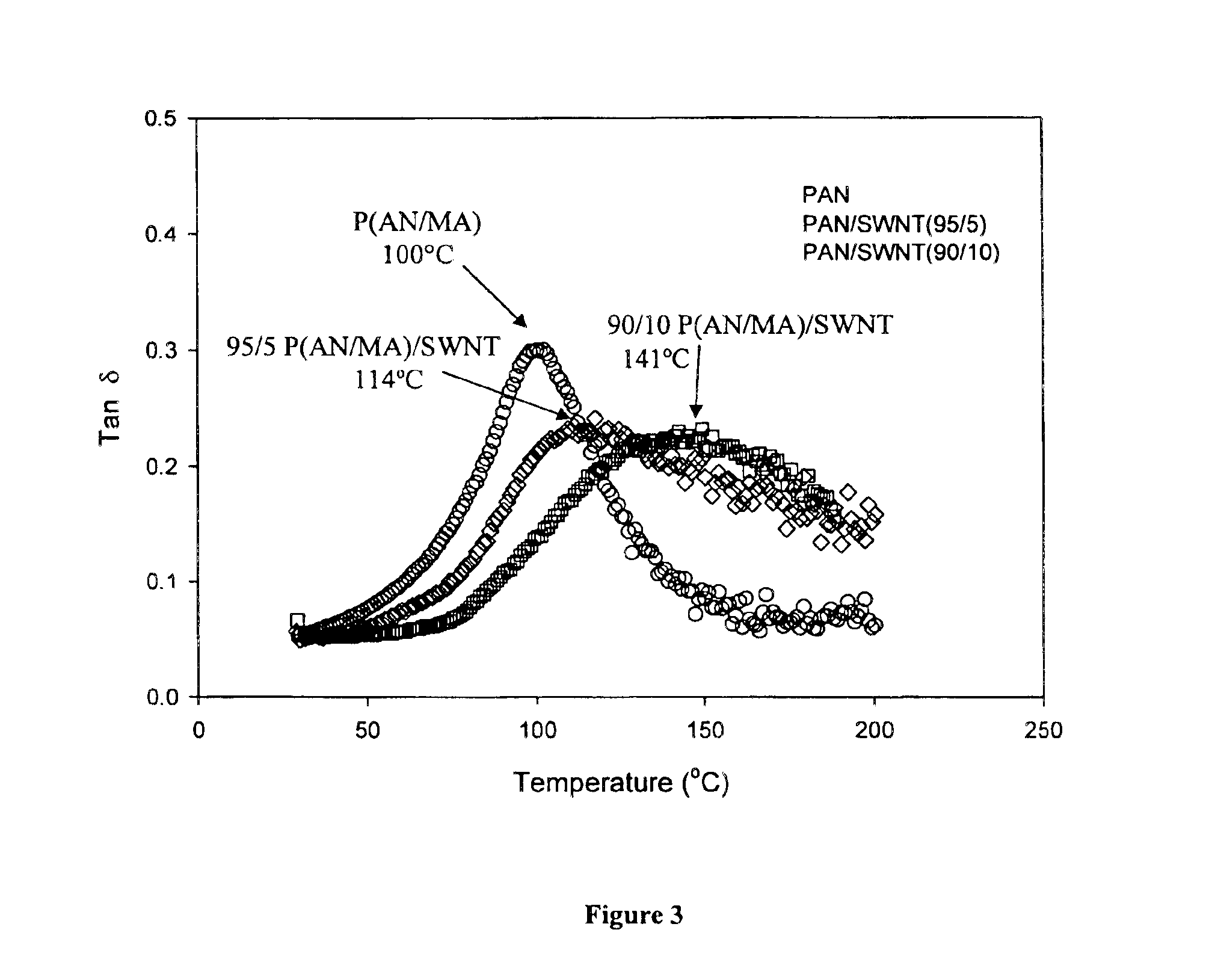
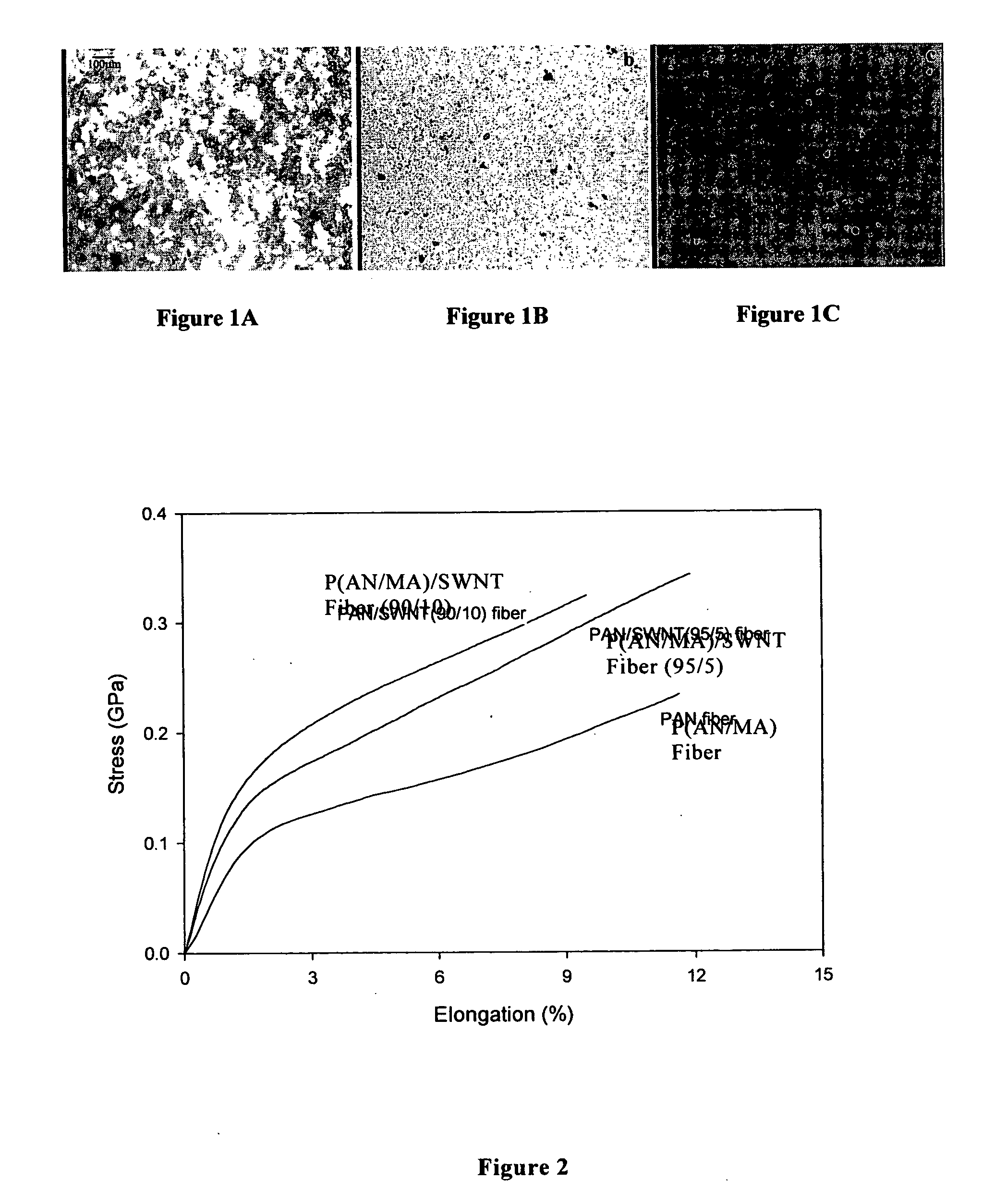
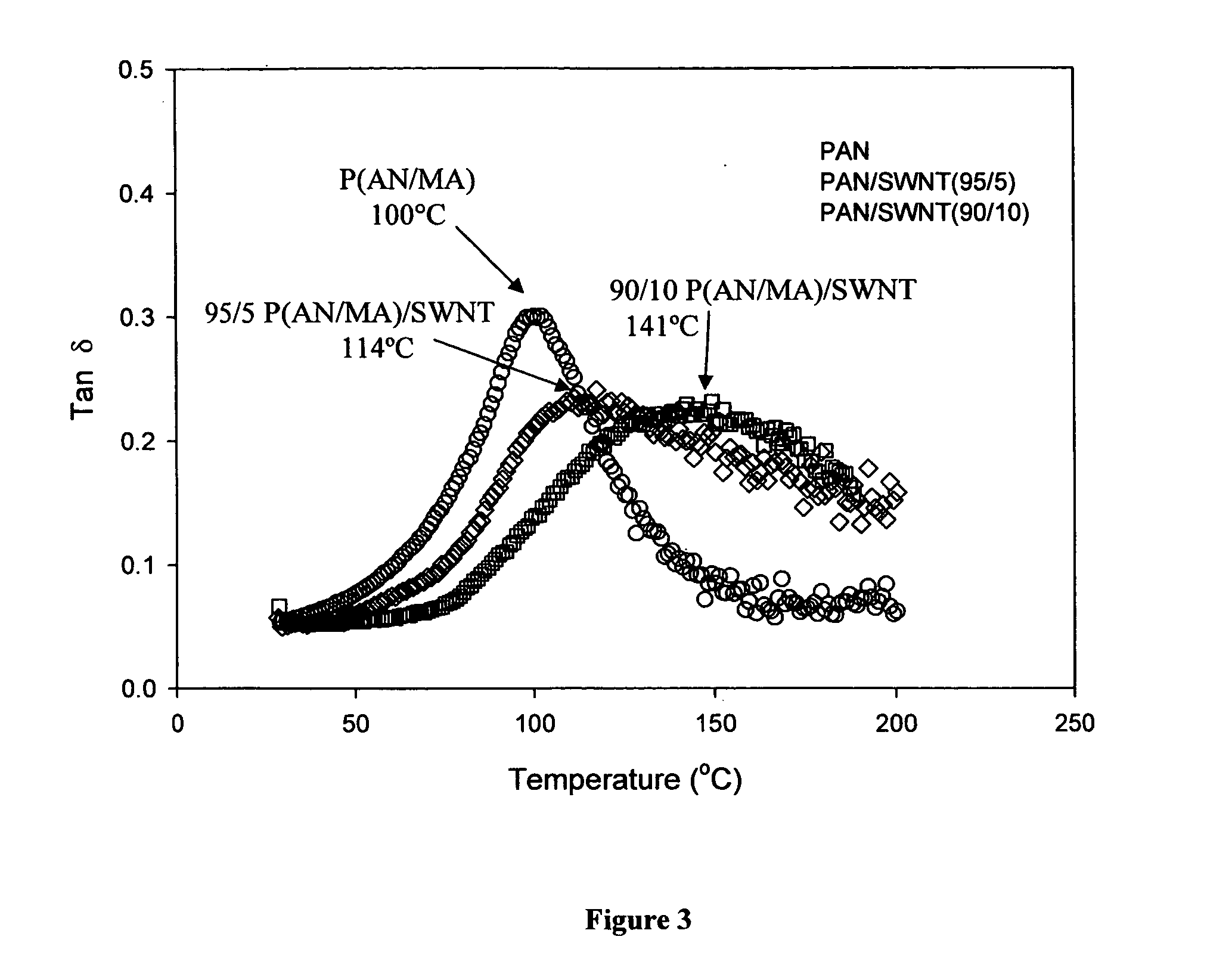
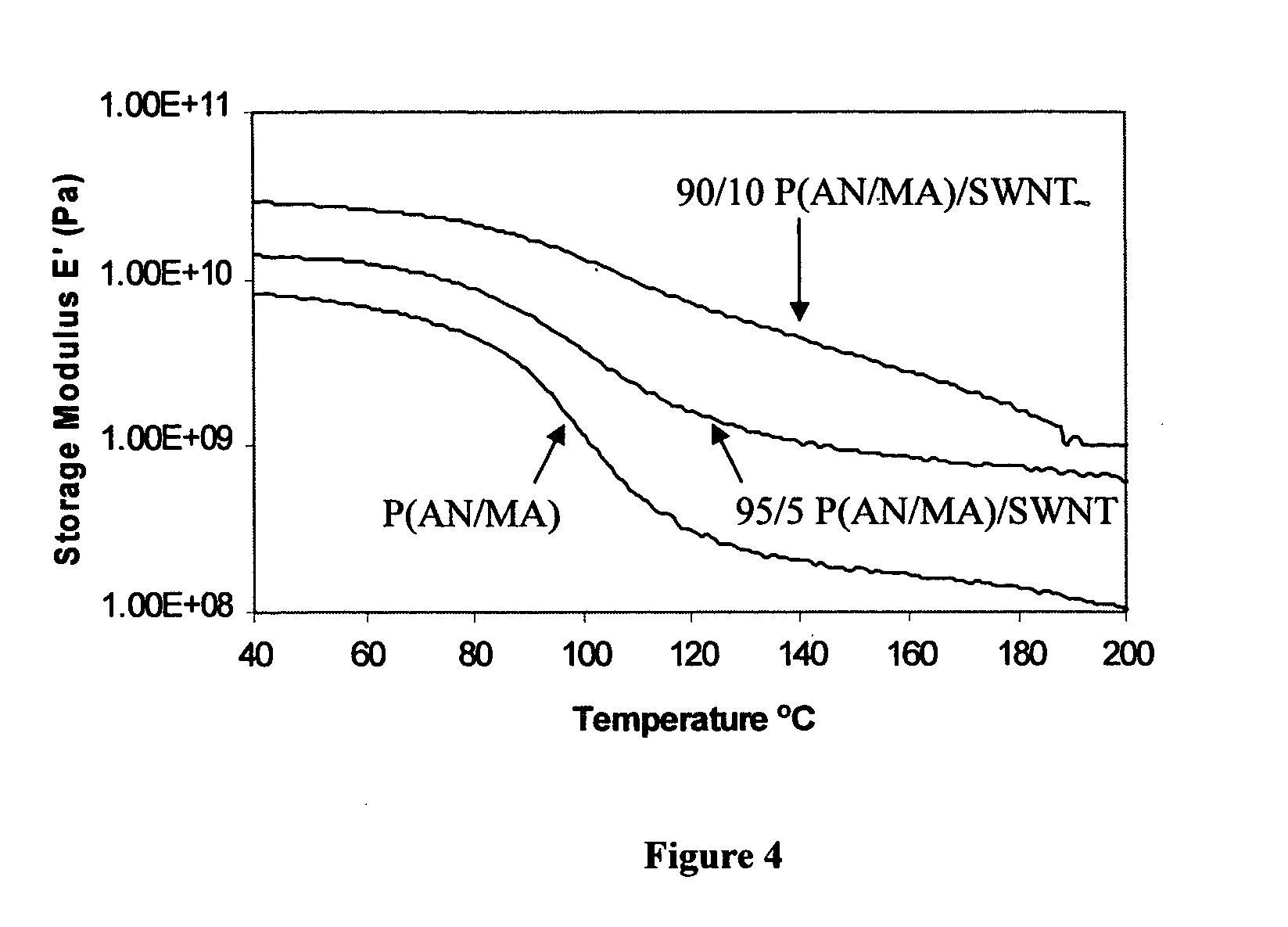
Macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and acrylonitrile-based polymer and process for making the same
InactiveUS6852410B2Increased tensile modulusReduced thermal shrinkageMaterial nanotechnologyElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureVitrificationPolymer science
The present invention relates to a high modulus macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) and an acrylonitrile-containing polymer. In one embodiment, the macroscopic fiber is a drawn fiber having a cross-sectional dimension of at least 1 micron. In another embodiment, the acrylonitrile polymer-SWNT composite fiber is made by dispersing SWNT in a solvent, such as dimethyl formamide or dimethyl acetamide, admixing an acrylonitrile-based polymer to form a generally optically homogeneous polyacrylonitrile polymer-SWNT dope, spinning the dope into a fiber, drawing and drying the fiber. Polyacrylonitrile / SWNT composite macroscopic fibers have substantially higher modulus and reduced shrinkage versus a polymer fiber without SWNT. A polyacrylonitrile / SWNT fiber containing 10 wt % SWNT showed over 100% increase in tensile modulus and significantly reduced thermal shrinkage compared to a control fiber without SWNT. With 10 wt % SWNT, the glass transition temperature of the polymer increased by more than 40° C.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
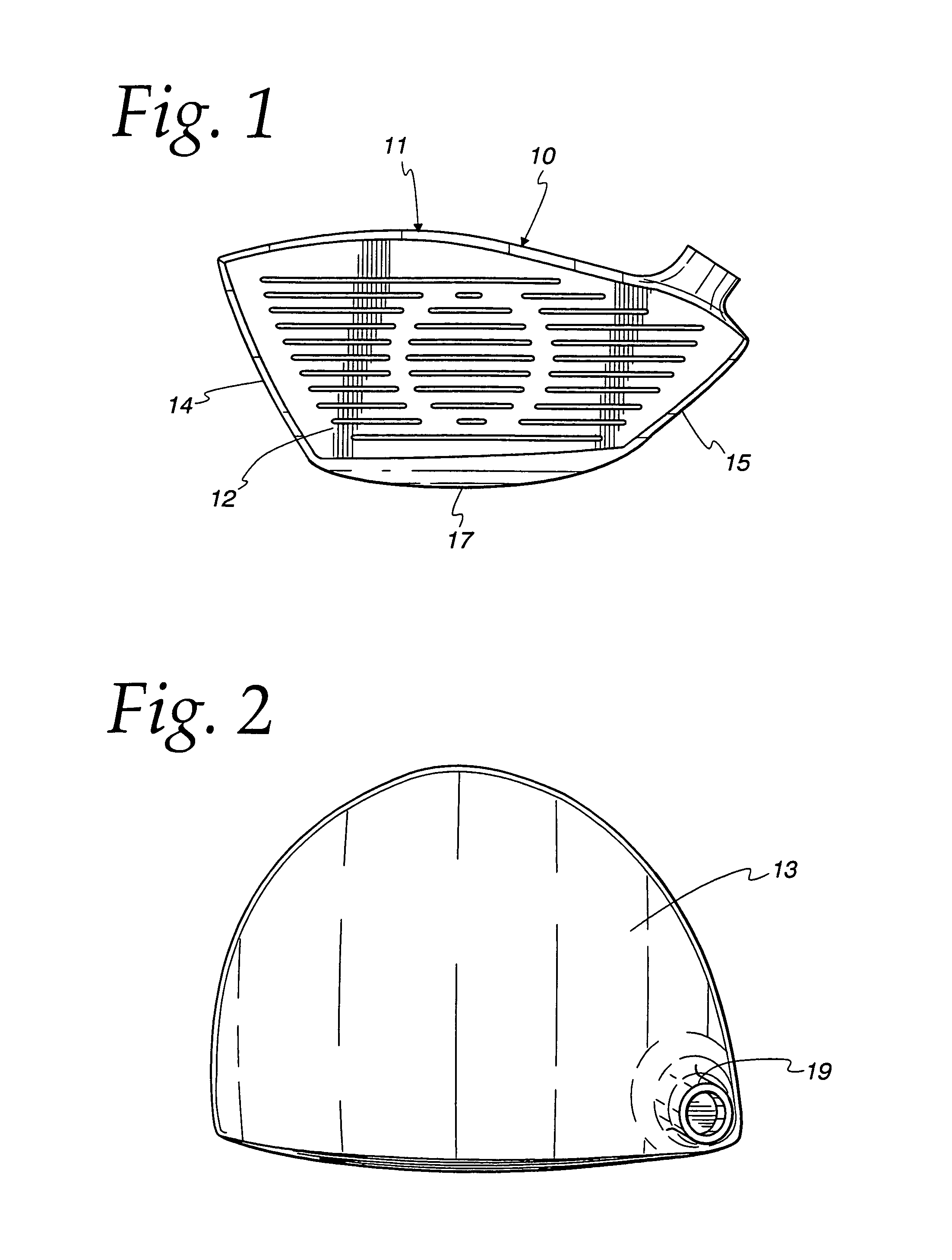
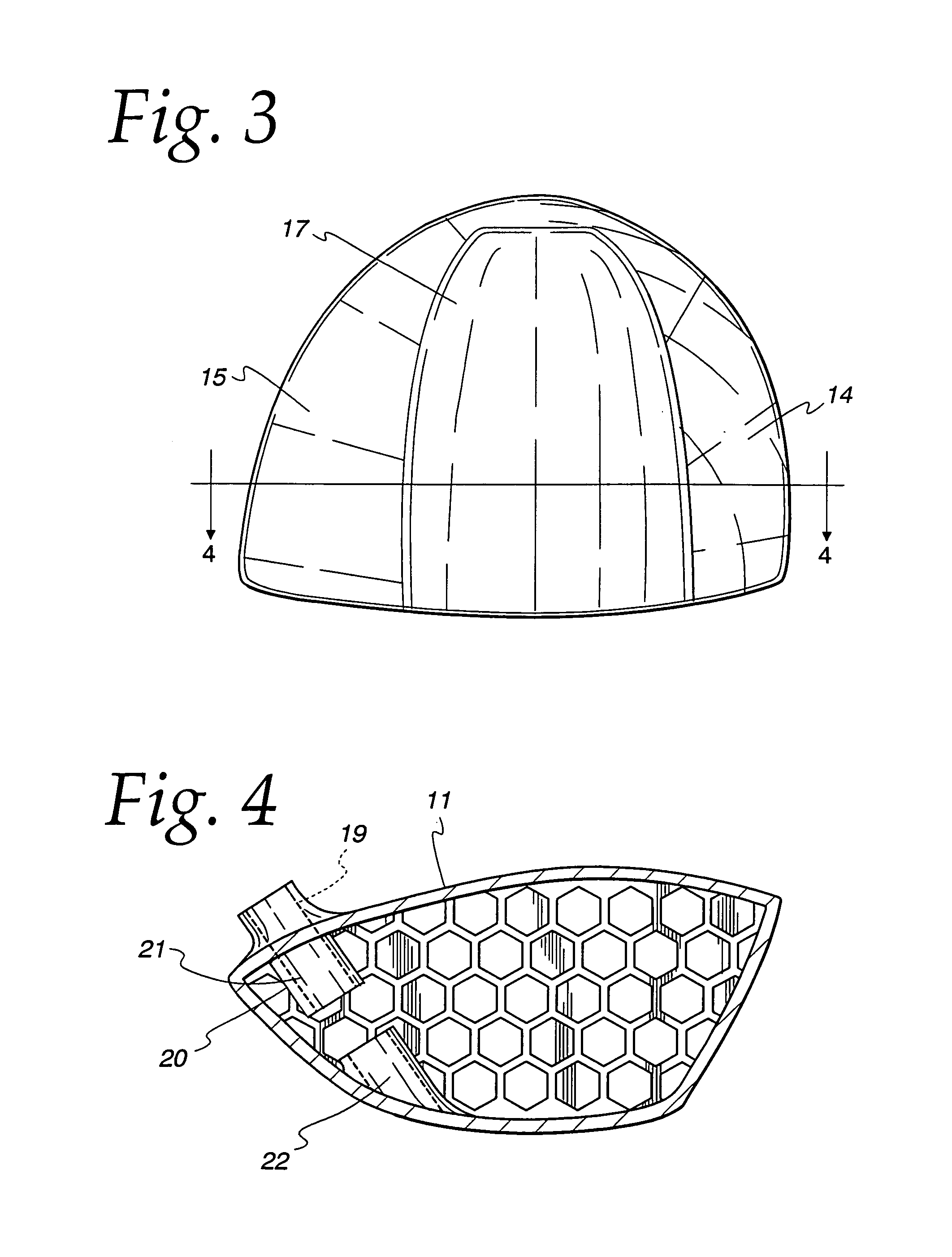
Golf club face flexure control system
InactiveUS6979270B1High modulusImprove energy transferGolf clubsRacket sportsControl systemGolf Ball
An improved line of golf clubs tailored to the golfer. The face wall firstly is designed so that the face wall modulus of elasticity increases from a low modulus for the low swing speed range to progressively higher modula for the higher swing speed ranges. Face modulus can be altered by a variety of techniques including face wall thinning, material selection and heat treatment or a combination thereof. In each of the swing speed range clubs, the face has a first modulus of elasticity determined by the face itself and after the face deflects to a predetermined value, the face modulus is significantly increased by a secondary wall parallel to and closely spaced behind the face wall.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
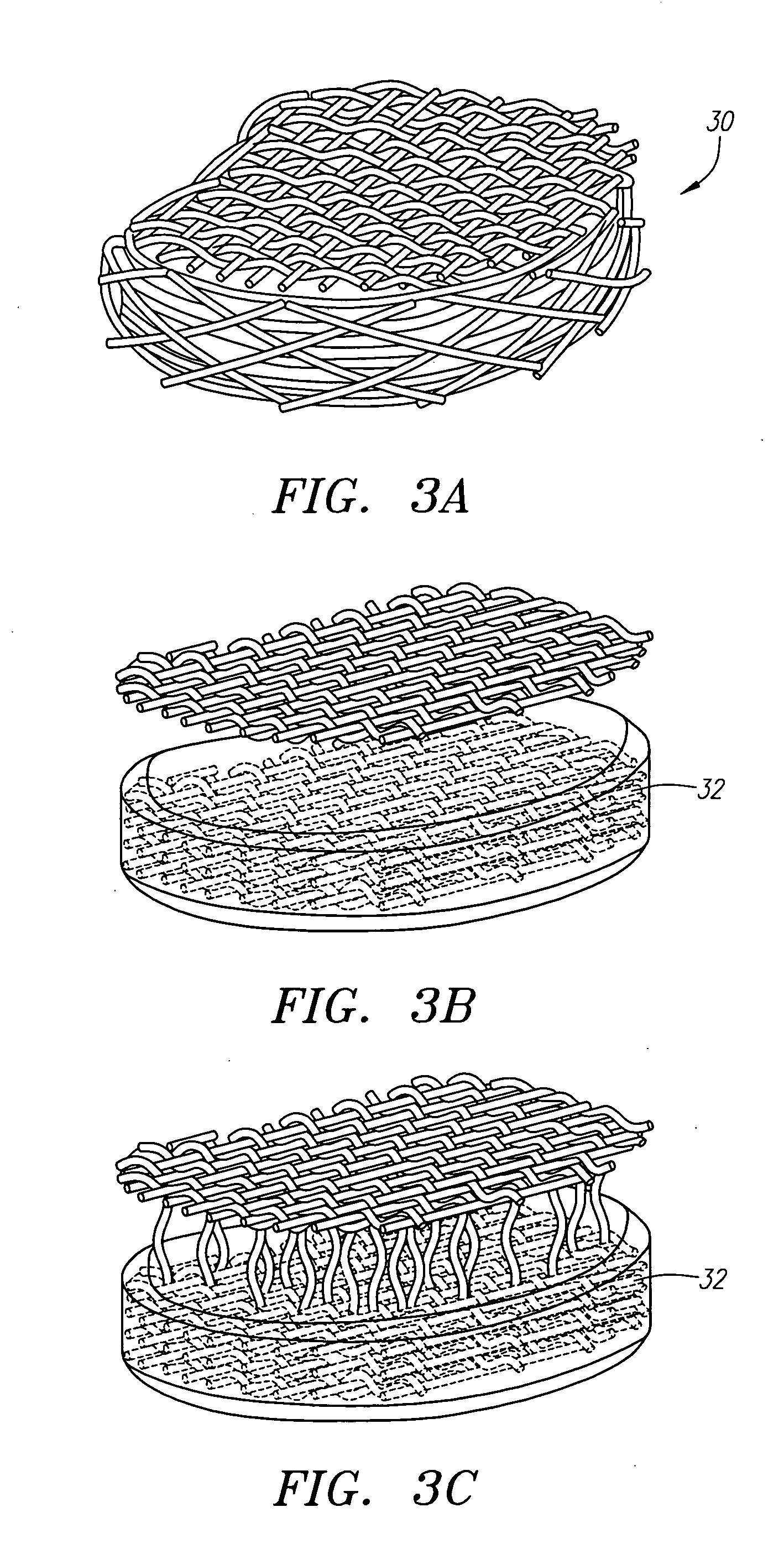
Vascular thrombectomby apparatus and method of use
InactiveUS20070288054A1Modulus of elasticityStay flexibleSurgeryDilatorsMembrane configurationBlood vessel
An apparatus is provided for removing matter from within a conduit. The apparatus generally comprises a separation edge attached to a wire at its proximal end, a frame attached to the distal end of the separation edge, and a membrane attached to the wire and disposed over the frame enclosing its interior. The membrane generally comprises a net constructed from a vaporized metal deposited on a mandrel. Alternatively, the membrane may comprise a braided tube constructed from wire. The apparatus may be employed as a filter or as a means for actively dislodging matter from the wall of a conduit. When employed as a filter, the apparatus is positioned downstream of the matter where it ensures that matter does not escape downstream as it is being removed. When employed to actively remover matter from a conduit, the apparatus is positioned downstream of the matter. The apparatus is then pulled proximally whereby it engages the matter and dislodges it from the wall of the conduit
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015612AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthWood working apparatusRecord information storageFiberThermoplastic
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
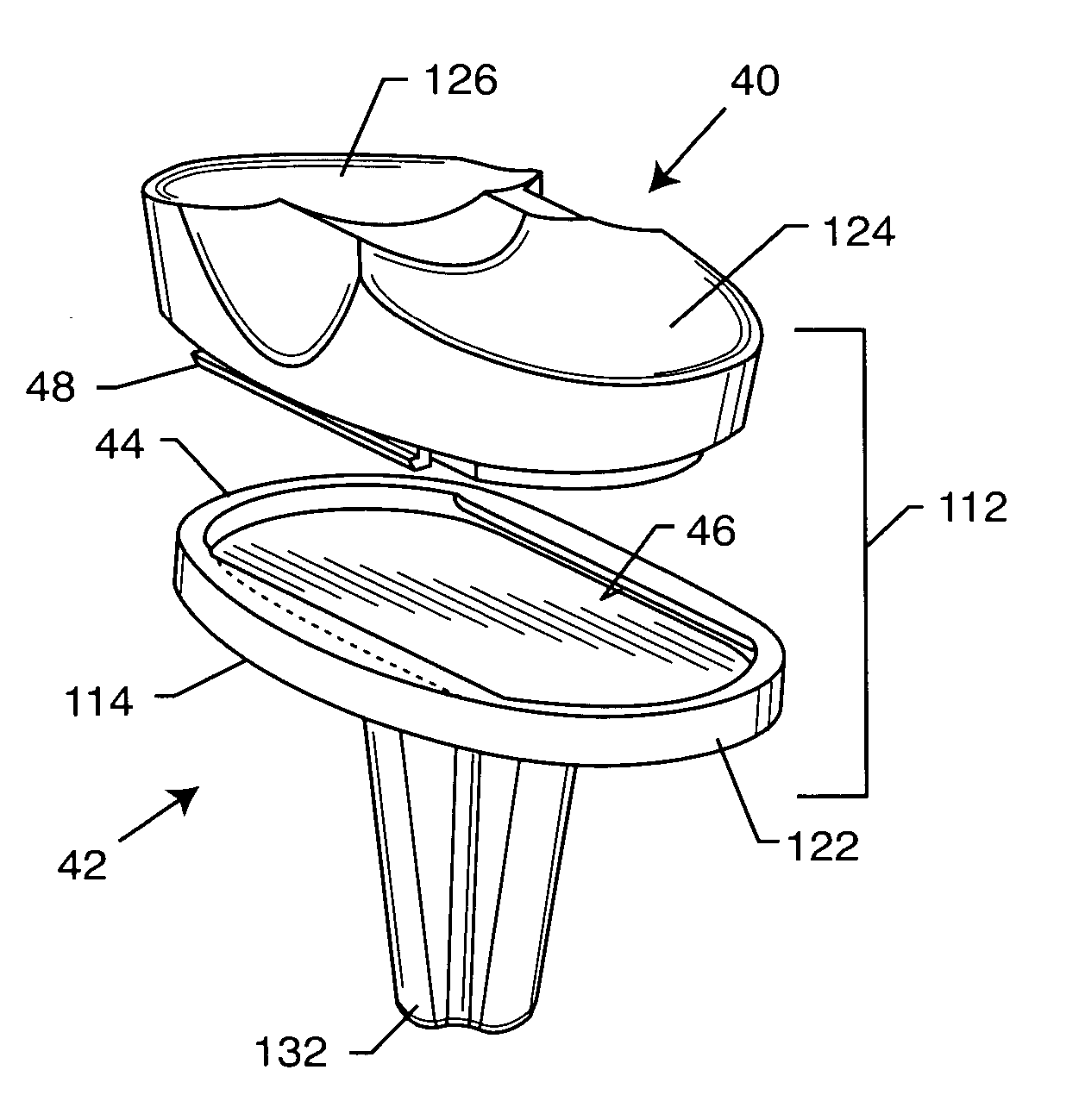
Methods and devices for intervertebral augmentation
InactiveUS20070150064A1Promote tissue growthHigh modulusBone implantLigamentsFilling materialsSmall intestine
Devices and methods for treating diseased or damaged portions of an intervertebral region are provided. In particular, intervertebral implants that can include use of a tissue regeneration structure having small intestine submucosa are described. The intervertebral implants can be utilized with any combination of load bearing structures for supporting loading on the implant, shaping structures for biasing the configuration of the implant, collapsible support structures for shaping the implant, and other features. Implants can also be formed with an enclosure to contain a filling material, such as an injectable small intestine submucosa formulation. Methods of delivering and utilizing the various implants are also discussed.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
Intraluminal prostheses having polymeric material with selectively modified crystallinity and methods of making same
InactiveUS7919162B2High modulusEnhanced hoop strengthStentsSynthetic resin layered productsProsthesisCrystallinity
Methods of manufacturing polymeric intraluminal prostheses include annealing the polymeric material to selectively modify the crystallinity thereof. Annealing may be utilized to selectively modify various properties of the polymeric material of an intraluminal prosthesis, including: selectively increasing the modulus of the polymeric material; selectively increasing the hoop strength of the intraluminal prosthesis; selectively modifying the elution rate (increase or decrease) of a pharmacological agent subsequently disposed on or within the annealed polymeric material; selectively increasing / decreasing stress in the intraluminal prosthesis; and selectively modifying the polymeric material such that it erodes at a different rate.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
Film for a separator of electrochemical apparatus, and production method and use thereof
InactiveUS6096456AHigh film strengthEasily and uniformly processedElectrolytic capacitorsSolid electrolyte cellsElectrolytic agentCarbamate
This invention provides a film comprising a cross-linked polymer having an oxyalkylene group or a cross-linked polymer having an oxyalkylene group through a urethane bond, as a constituent component, a production method of the film, and an electrochemical apparatus using the film as a separator. The film for separator of an electrochemical apparatus can be easily and uniformly processed, can include an electrolytic solution, exhibits good film thickness and ensures excellent safety and reliability. The electrochemical apparatus is free of leakage of the solution.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
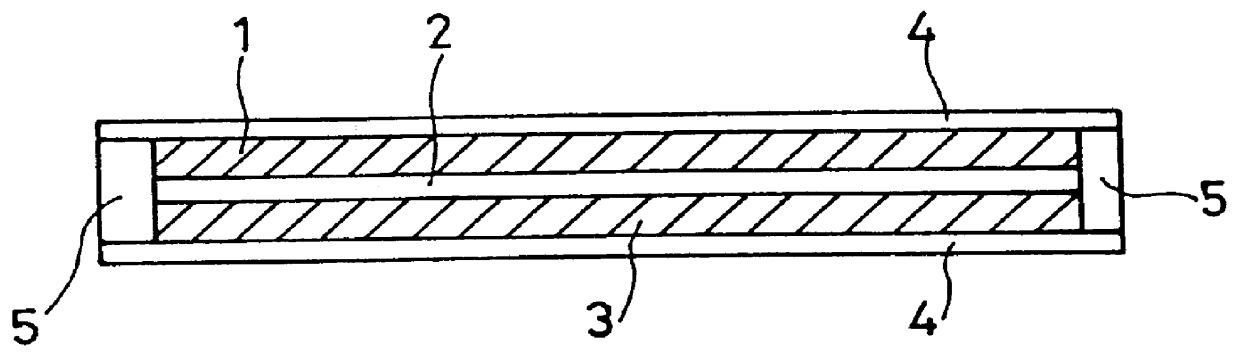
Prosthetic intervertebral discs
ActiveUS20070050033A1Improve wear resistanceHigh modulusInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsIntervertebral discProsthesis
Prosthetic intervertebral discs, systems including such prosthetic intervertebral discs, and methods for using the same are described. The subject prosthetic discs include upper and lower endplates separated by a compressible core member. The subject prosthetic discs exhibit stiffness in the vertical direction, torsional stiffness, bending stiffness in the saggital plane, and bending stiffness in the front plane, where the degree of these features can be controlled independently by adjusting the components, construction, and other features of the discs.
Owner:SPINAL KINETICS
Advanced polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015611AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthSynthetic resin layered productsPlastic recyclingWater basedThermoplastic
A composition in the form of pellets comprising a thermoplastic and wood fiber composite material suitable for forming structural members as a replacement for wood in the manufacture of doors and windows. The composite has less than about 10 wt % water based on pellet weight and a Young's modulus of at least about 500,000. Structural members are typically formed from the composite in an extrusion or an injection molding process.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Aliphatic polyester microfibers, microfibrillated articles and use thereof
InactiveUS6890649B2Increase surface areaUseful applicationEngine sealsFilament/thread formingPolyesterParticulates
The present invention relates to aliphatic polyester microfibers, films having a microfibrillated surface, and methods of making the same. Microfibers of the invention can be prepared by imparting fluid energy, typically in the form of high-pressure water jets, to a highly oriented, highly crystalline, aliphatic polyester film to liberate microfibers therefrom. Microfibrillated films of the invention find use as tape backings, filters for particulate contaminants, such as face masks and water or air filters, fibrous mats, such as those used for removal of oil from water and those used as wipes, and thermal and acoustical insulation. Microfibers of the invention, when removed from the film matrix may be used in the preparation of woven or nonwoven articles and used as wipes for the removal of debris or dust from a surface. The microfibers and microfibrillated articles of the invention may be biodegradable, rendering them useful for geotextiles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High-strength laminated sheet for optical applications
InactiveUS7514149B2Increase stiffnessHigh modulusGlass forming apparatusRecord information storageSurface layerHigh intensity
A laminated sheet includes a surface layer having an optical surface that is of fire-polished quality and a core layer having a higher modulus than the surface layer to increase an overall stiffness or fracture toughness of the laminated sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
Thermoplastic resin composition, molding material, and molded article thereof
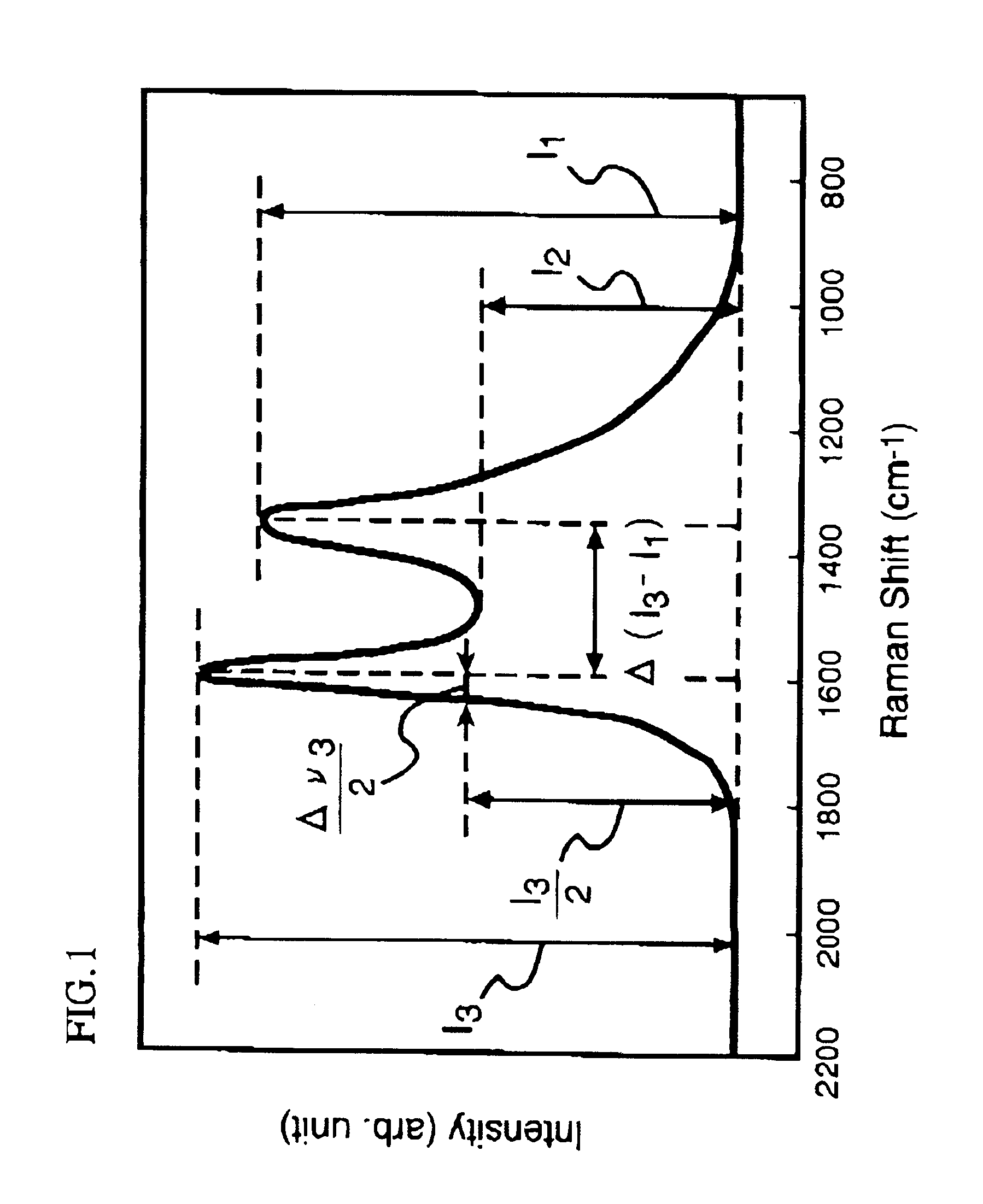
A thermoplastic resin composition capable of providing a thin walled molded article whose flame retardancy with a thickness of 1.6 mm ({fraction (1 / 16)} inch) in accordance with an UL 94 standard is V-0 or better, and which comprises the following components [A], [B] and [C], wherein the component [B] satisfies the following conditions (B1) and / or (B2):[A]: an electrically conductive fiber;[B]: a carbon powder;[C]: a thermoplastic resin;(B1): Raman scattering intensity ratio I2 / I1 is 0.55-0.8;(B2): Raman scattering intensity ratio I2 / I3 is 0.54-0.8; whereI1: local maximum value of Raman scattering intensity appearing near a Raman shift of 1360 cm-1;I2: local minimum value of the Raman scattering intensity appearing near a Raman shift of 1480 cm-1;I3: local maximum value of the Raman scattering intensity appearing neat a Raman shift of 1600 cm-1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Resin compositions with fluoropolymer filler combinations
InactiveUS20050143508A1Improve propertiesImprove mechanical propertiesSpecial tyresOrganic dyesDuctilityPolymer chemistry
A thermoplastic resin composition is disclosed which comprises a matrix polymer, and a combination of a fluoropolymer that can be at least partially encapsulated by an encapsulating polymer, and a filler. Methods for making the thermoplastic resin composition and articles made of such compositions are also disclosed. The composition and article can have improved tensile modulus, ductility and impact properties.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods using vasoconstriction for improved thermal treatment of tissues
InactiveUS6840954B2Improve the effectiveness of treatmentEnhance such thermal treatmentAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical instruments for heatingArteriolar VasoconstrictionTreatment effect
The present invention enhances the effectiveness of treatment of support tissue structures. Generally, such tissue structures support organs and hold the organs in their proper position for appropriate functioning. When such tissue structures become weak, hyper-elastic, and / or excessively lengthy, the organs of are no longer supported in their proper position. This often leads to physical manifestations such as incontinence, hernias, and the like. Remedies often involve thermal treatment of the support tissue structures, such as thermally inducted controlled shrinkage, contraction, or stiffening of the support tissue structure. To enhance such thermal treatment and diminish the possibility of undesirable heating and damage to nearby tissue surfaces, vasoconstrictive agents are used.
Owner:ASTORA WOMENS HEALTH
Downhole seal element formed from a nanocomposite material
ActiveUS20080121436A1Minimize impactMinimizes critical pressure and flaw sizeMaterial nanotechnologyDrill bitsPolymer scienceHost material
A seal element (70) for providing a static or dynamic seal between two components (74, 78) in a downhole tool includes a polymer host material (212) and a plurality of nanostructures (220) forming a nanocomposite material (210). The polymer host material (212) has a plurality of regions of free volume (222) that receive the nanostructures (220). The nanostructures (220) and the polymer host material (212) form interfacial interactions that improve the useful life of the seal element (70) by minimizing seal failures associated with explosive decompression, extrusion, spiral failure, abrasion, temperature degradation and the like.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Downhole seal element formed from a nanocomposite material
InactiveUS20050109502A1Minimize impactHigh shear modulusMaterial nanotechnologyFluid removalPolymer scienceHost material
A seal element (70) for providing a static or dynamic seal between two components (74, 78) in a downhole tool includes a polymer host material (212) and a plurality of nanostructures (220) forming a nanocomposite material (210). The polymer host material (212) has a plurality of regions of free volume (222) that receive the nanostructures (220). The nanostructures (220) and the polymer host material (212) form interfacial interactions that improve the useful life of the seal element (70) by minimizing seal failures associated with explosive decompression, extrusion, spiral failure, abrasion, temperature degradation and the like.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Extruded fiber reinforced cementitious products having wood-like properties and ultrahigh strength and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20100136269A1High yield stressImmediate form stabilityLayered productsPlastic recyclingPorosityFlexural strength
A method of manufacturing a cementitious composite including: (1) mixing an extrudable cementitious composition by first forming a fibrous mixture comprising fibers, water and a rheology modifying agent and then adding hydraulic cement; (2) extruding the extrudable cementitious composition into a green extrudate, wherein the green extrudate is characterized by being form-stable and retaining substantially a predefined cross-sectional shape; (3) removing a portion of the water by evaporation to reduce density and increase porosity; and (4) heating the green extrudate at a temperature from greater than 65° C. to less than 99° C. is disclosed. Such a process yields a cementitious composite that is suitable for use as a wood substitute. Particularly, by using higher curing temperatures for preparing the cementitious building products, the building products have a lower bulk density and a higher flexural strength as compared to conventional products. The wood-like building products can be sawed, nailed and screwed like ordinary wood.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
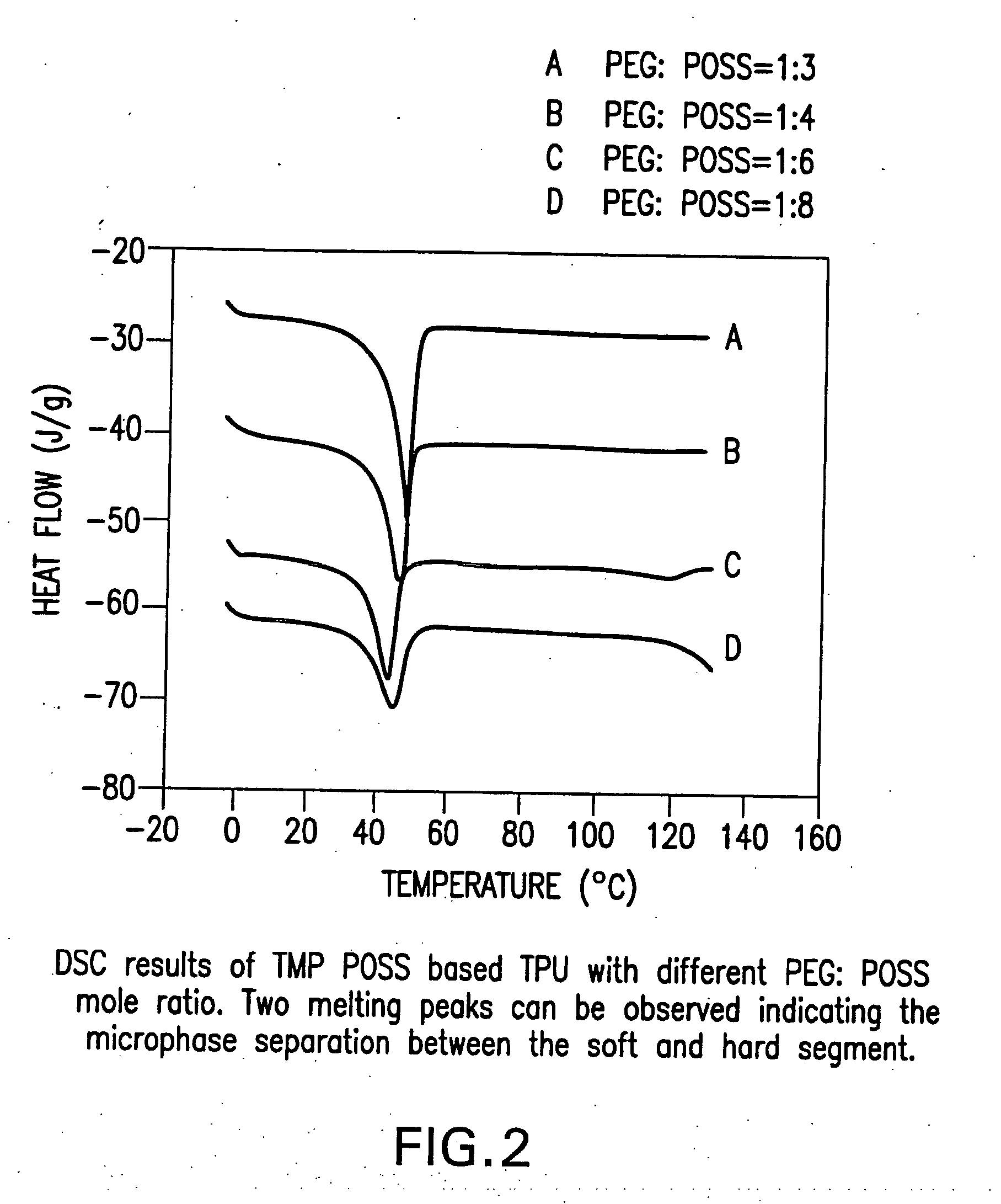
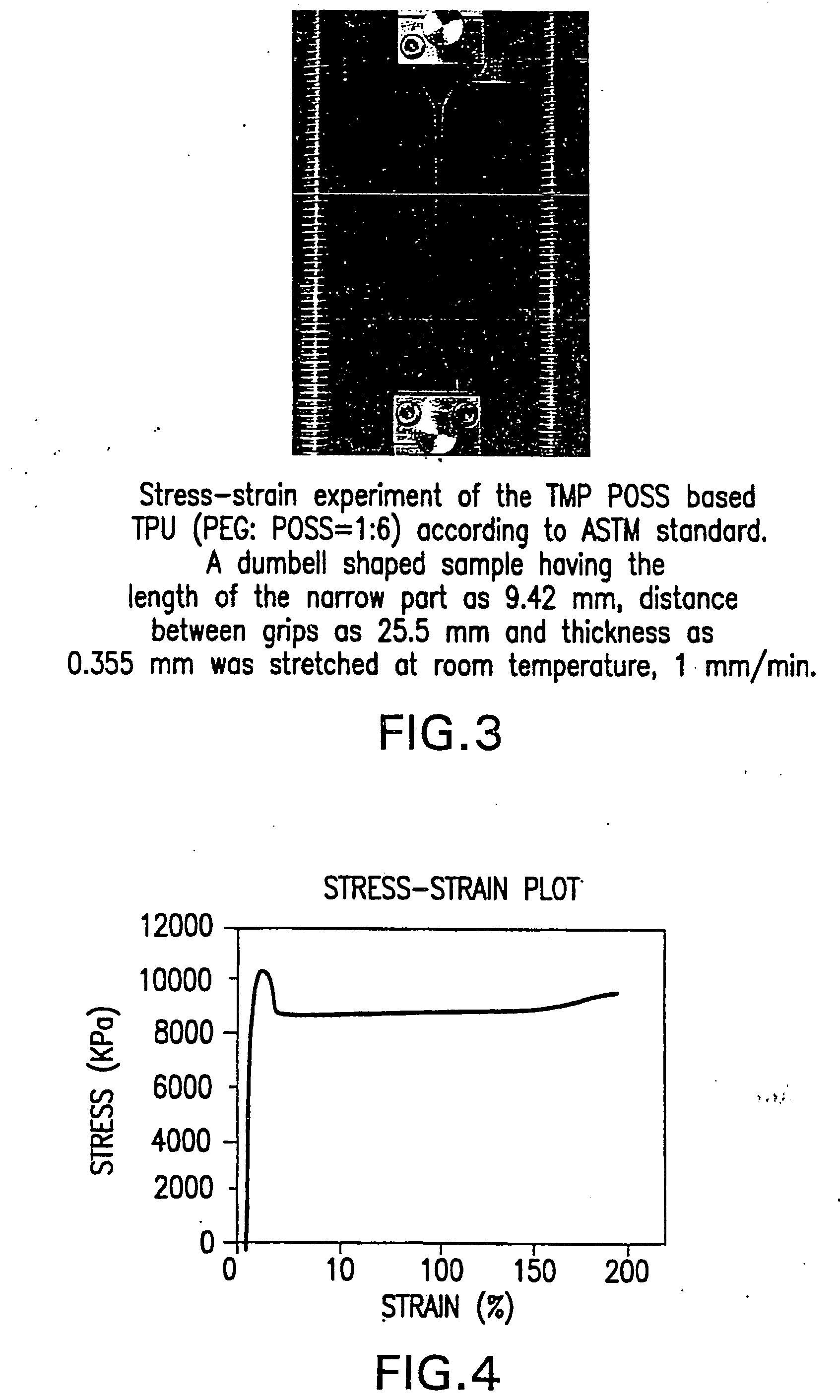
Shape memory polymers based on semicrystalline thermoplastic polyurethanes bearing nanostructured hard segments
InactiveUS20050245719A1Sharp and tunable transition temperatureAbove melting pointPolymer scienceAdhesive
Thermoplastic polyurethanes having an alternating sequence of hard and soft segments in which a nanostructured polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane diol is used as a chain extender to form a crystalline hard segment constituting SMPs. The polyurethanes are formed by reacting a polyol, a chain extender dihydroxyl-terminated polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane and a diisocyanate. The polyurethanes have multiple applications including for example, implants for human health care, drug delivery matrices, superabsorbant hydrogels, coatings, adhesives, temperature and moisture sensors, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and acrylonitrile-based polymer and process for making the same
InactiveUS20050100501A1Good orientationIncrease modulusMaterial nanotechnologyElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureVitrificationPolymer science
The present invention relates to a high modulus macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) and an acrylonitrile-containing polymer. In one embodiment, the macroscopic fiber is a drawn fiber having a cross-sectional dimension of at least 1 micron. In another embodiment, the acrylonitrile polymer-SWNT composite fiber is made by dispersing SWNT in a solvent, such as dimethyl formamide or dimethyl acetamide, admixing an acrylonitrile-based polymer to form a generally optically homogeneous polyacrylonitrile polymer-SWNT dope, spinning the dope into a fiber, drawing and drying the fiber. Polyacrylonitrile / SWNT composite macroscopic fibers have substantially higher modulus and reduced shrinkage versus a polymer fiber without SWNT. A polyacrylonitrile / SWNT fiber containing 10 wt % SWNT showed over 100% increase in tensile modulus and significantly reduced thermal shrinkage compared to a control fiber without SWNT. With 10 wt % SWNT, the glass transition temperature of the polymer increased by more than 40° C.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Coated optical fibers having strippable primary coatings and processes for making and using same
InactiveUS6014488ACleanly strippableHigh modulusGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusFiberSilicon dioxide
PCT No. PCT / US98 / 01289 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 1, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 1, 1998 PCT Filed Jan. 23, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 33081 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 30, 1998The invention relates to coated optical fibers which are coated with a particular radiation-cured primary coating layer composition. The fibers which are coated comprises a glass core and a glass cladding layer. The core, for example may comprises silica doped with oxides of germanium or phosphorous and the cladding, a pure or doped silicate such as fluorosilicate. Alternatively, the fibers may comprises a polymerclad silica glass core. Examples of such claddings include organosiloxanes such as polydimethylsiloxane or a fluorinated acrylic polymer.
Owner:HEXION INC
Semiconductor device
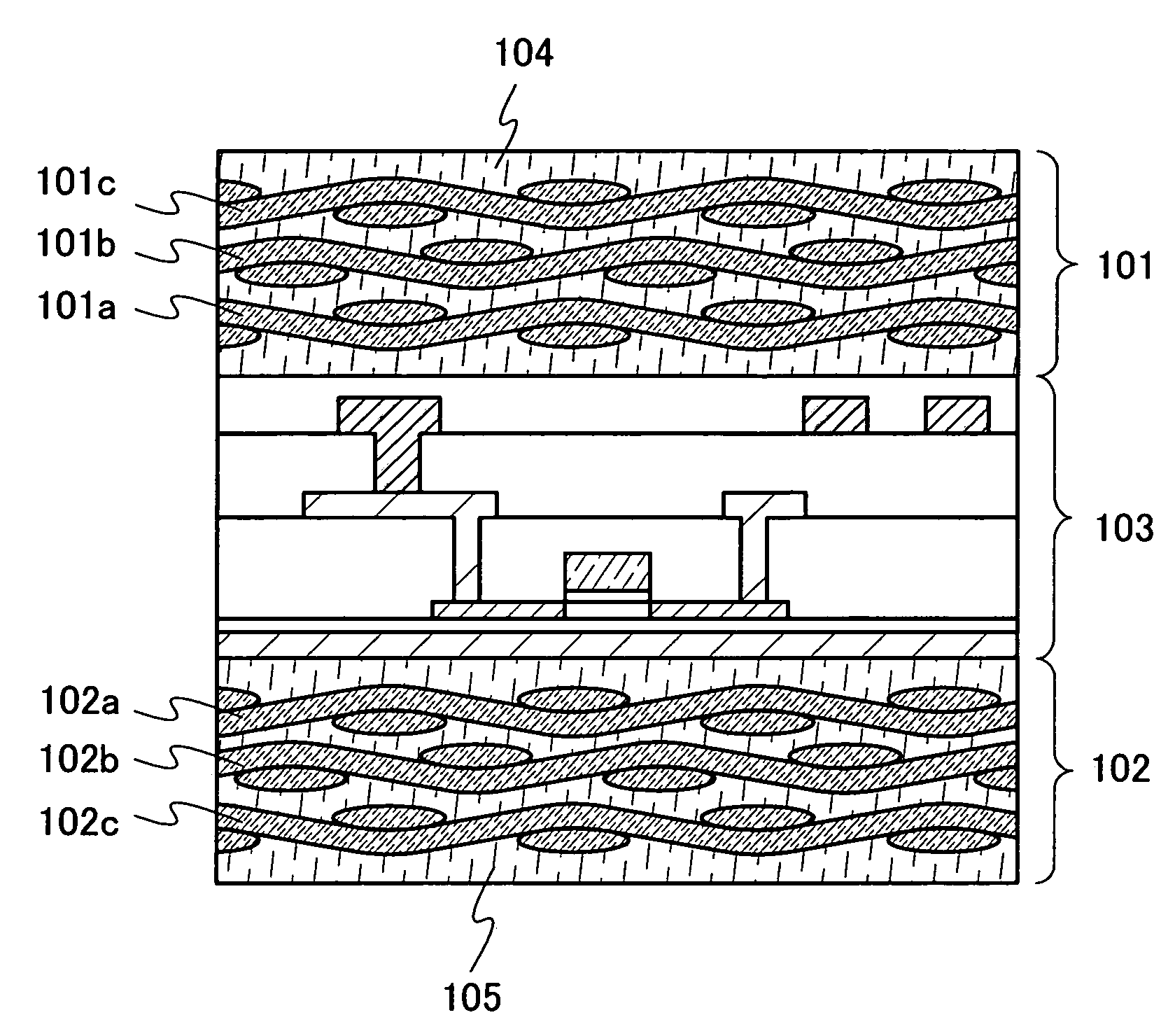
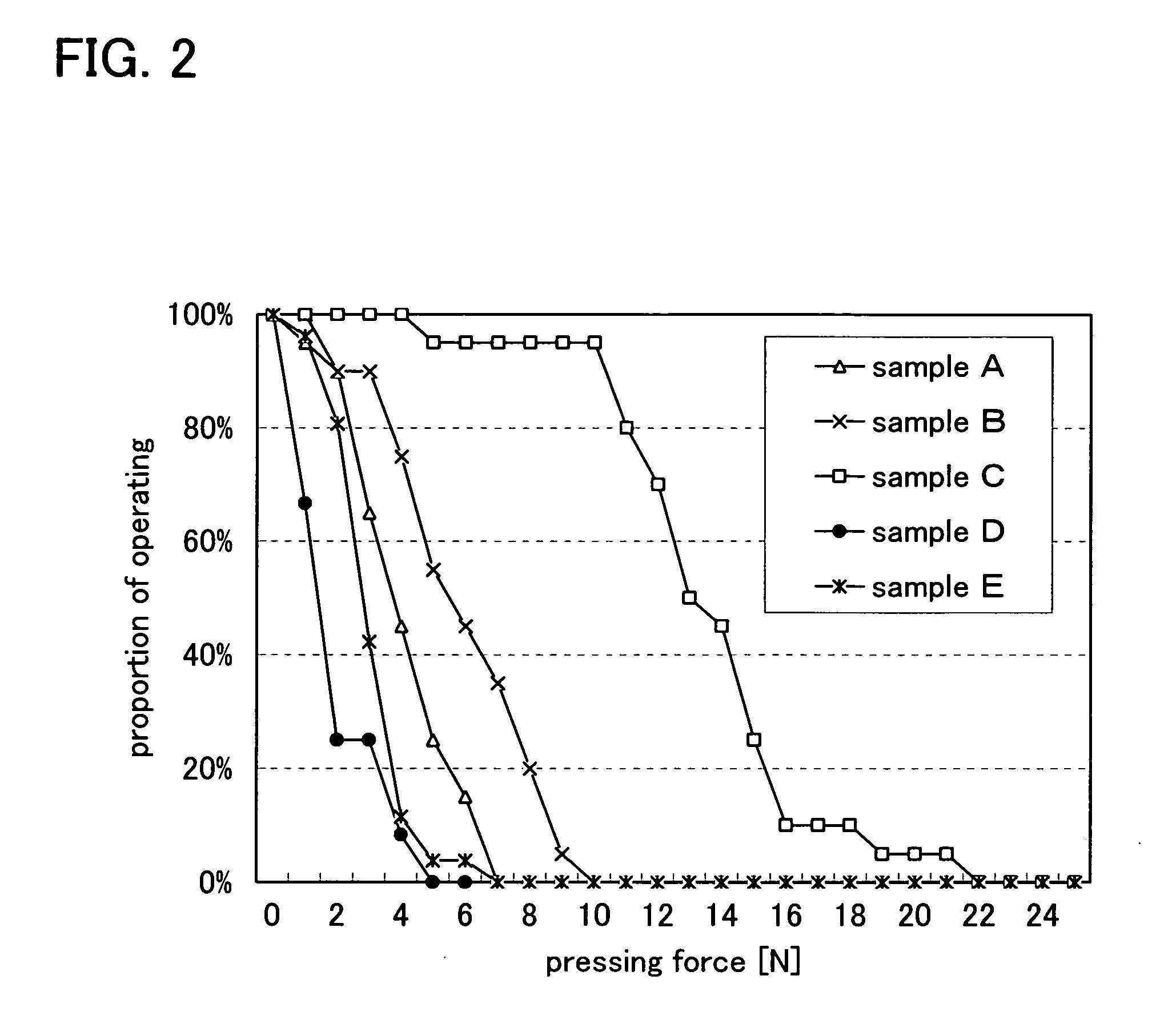
InactiveUS20080303140A1Improve reliabilityHigh modulusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInorganic compoundFibrous body
To provide a semiconductor device which can increase reliability with respect to external force, especially pressing force, while the circuit size or the capacity of memory is maintained. A pair of structure bodies each having a stack of fibrous bodies of an organic compound or an inorganic compound, which includes a plurality of layers, especially three or more layers, is impregnated with an organic resin, and an element layer provided between the pair of structure bodies are included. The element layer and the structure body can be fixed to each other by heating and pressure bonding. Further, a layer for fixing the element layer and the structure body may be provided. Alternatively, the structure body fixed to an element layer can be formed in such a way that after a plurality of fibrous bodies is stacked over the element layer, the fibrous bodies are impregnated with an organic resin.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
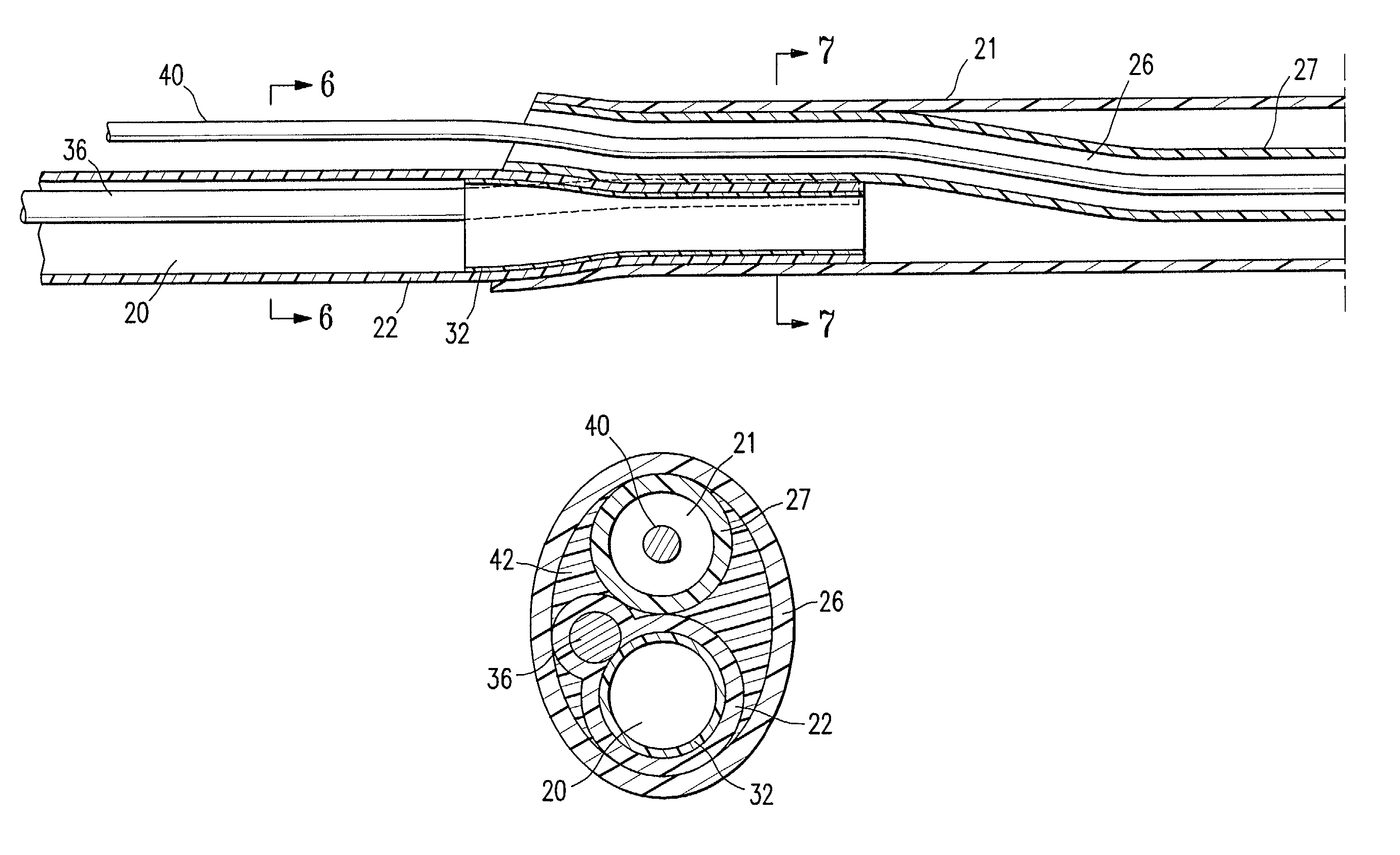
Catheter shaft junction having a polymeric reinforcing member with a high glass transition temperature
A catheter having a polymeric reinforcing member at a junction between shaft sections such as a rapid exchange catheter junction. The polymeric reinforcing member is around or within the tubular member defining the inflation lumen or the tubular member defining the guidewire lumen at the rapid exchange junction to prevent or inhibit damage to the tubular members defining the inflation lumen and / or guidewire lumen during assembly or use of a balloon catheter. In one embodiment, the polymeric reinforcing member is formed of a first polymeric material having a glass transition temperature greater than a glass transition temperature of a second polymeric material forming the distal portion of the proximal tubular member or the proximal portion of the inner tubular member. The first polymeric material forming the polymeric reinforcing member is preferably a high temperature, high modulus material, such as polyimide, and most preferably a thermoset polyimide.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Container closure
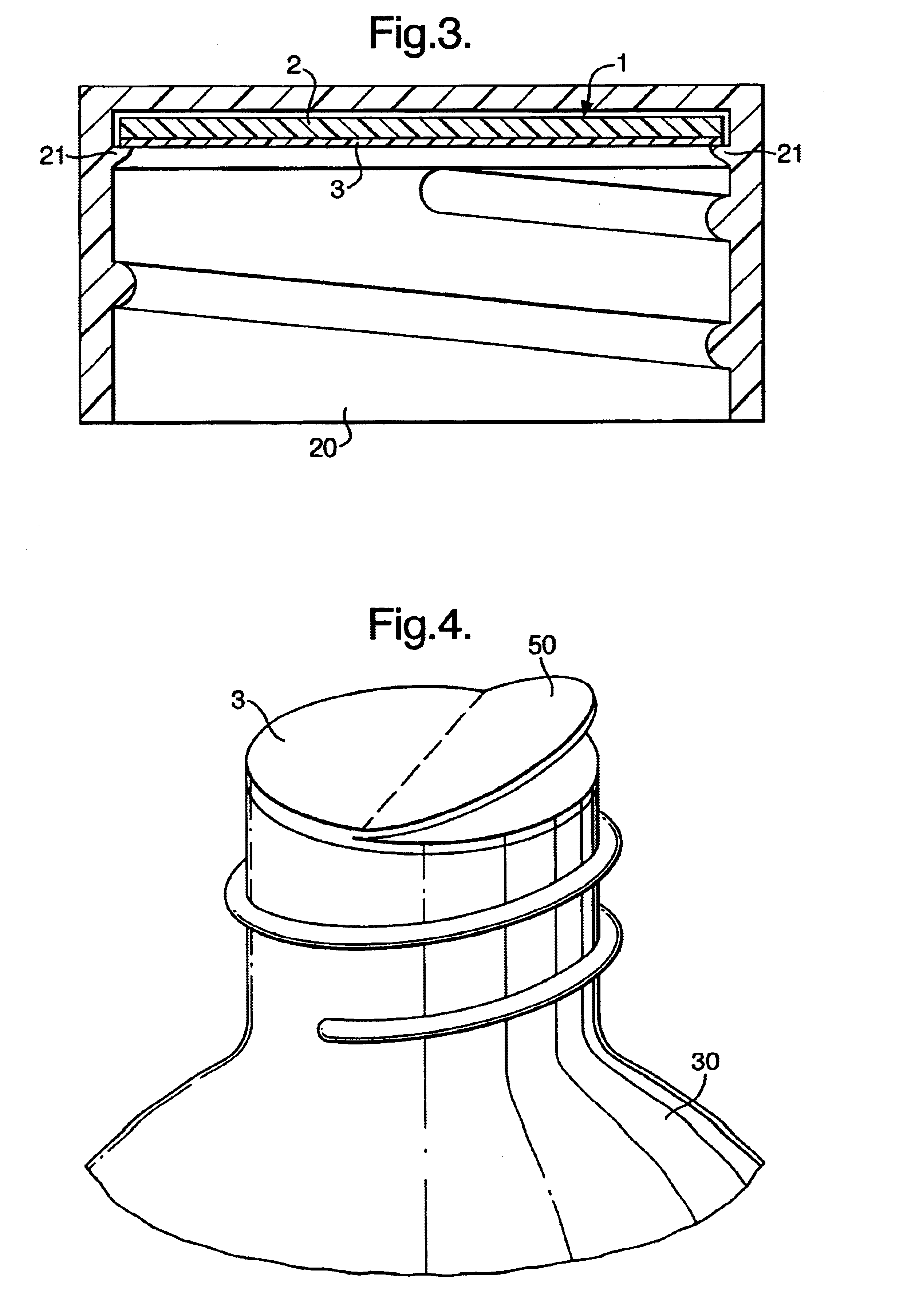
InactiveUS6902075B2Achieve stabilizationHigh elongationCapsThreaded caps applicationWaddingEngineering
A one-component seal and wadding system (1) for a screw-cap includes a seal (3) having lower layers (4,5) forming an induction heating sealable system for attaching the seal (3) to the neck of a container, a seal substrate (6) including a free tab (50) lying wholly within the circumference of the seal, a layer of liner (2), and an attachment element (10,11,12) including a release layer (11) for attaching the seal substrate (7) including the tab (50) to the wadding (2).
Owner:SELIG SEALING PROD INC
Thermoplastic monofilament fibers exhibiting low-shrink, high tenacity, and extremely high modulus levels
InactiveUS6759124B2High tensile strengthLow shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingThermoplasticYarn
Unique thermoplastic monofilament fibers and yarns that exhibit heretofore unattained physical properties are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the extrusion of thermoplastic resins that include a certain class of nucleating agent therein, and are able to be drawn at high ratios with such nucleating agents present that the tenacity and modulus strength are much higher than any other previously produced thermoplastic fibers, particularly those that also simultaneously exhibit extremely low shrinkage rates. Thus, such fibers require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target thermoplastic (for example, polypropylene), particularly after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target thermoplastic after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and allowing such an oriented polymer to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target thermoplastic without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for thermoplastic crystal growth. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as [2.2.1]heptane-bicyclodicarboxylic acid, otherwise known as HPN-68, sodium benzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts [such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11]. Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive thermoplastic fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Highly crystalline polypropylene with low xylene solubles
ActiveUS20040122196A1Narrow molecular weight distributionLow melt flow rateFlexural modulusPolypropylene
The invention is directed to a polypropylene resin which has a Mw / Mn of less than 5, a melt flow rate of less than 7 g / 10 min., a 1% secant flexural modulus of greater than 300,000 psi and less than 2 wt. % xylene solubles.
Owner:BRASKEM AMERICA
Nanocrystalline aluminum alloy metal matrix composites, and production methods
InactiveUS7097807B1Increase in flexure in flexure strengthIncrease modulusTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusParticulatesMetal matrix composite
Owner:CERACON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com