Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Submucosa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
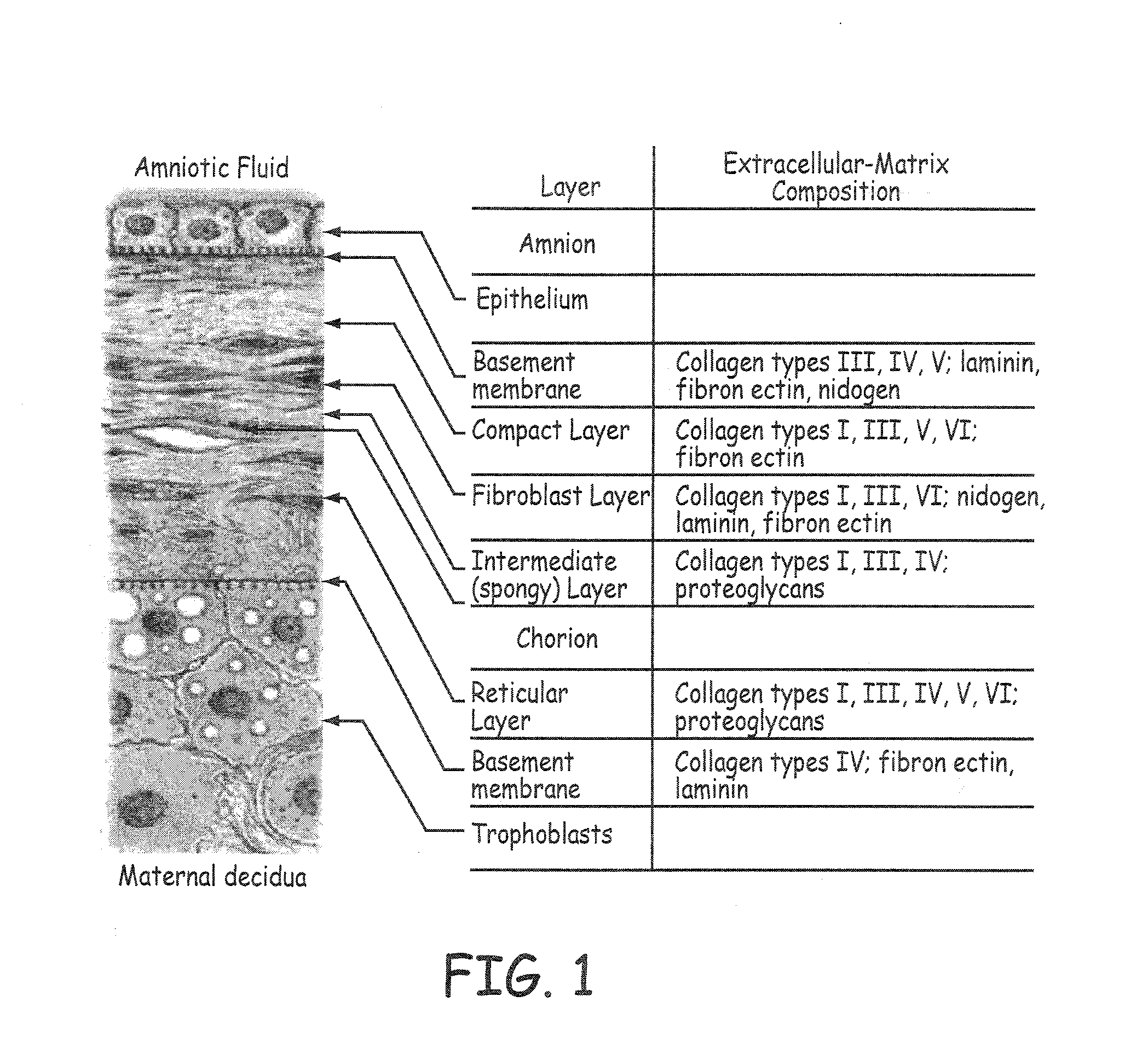
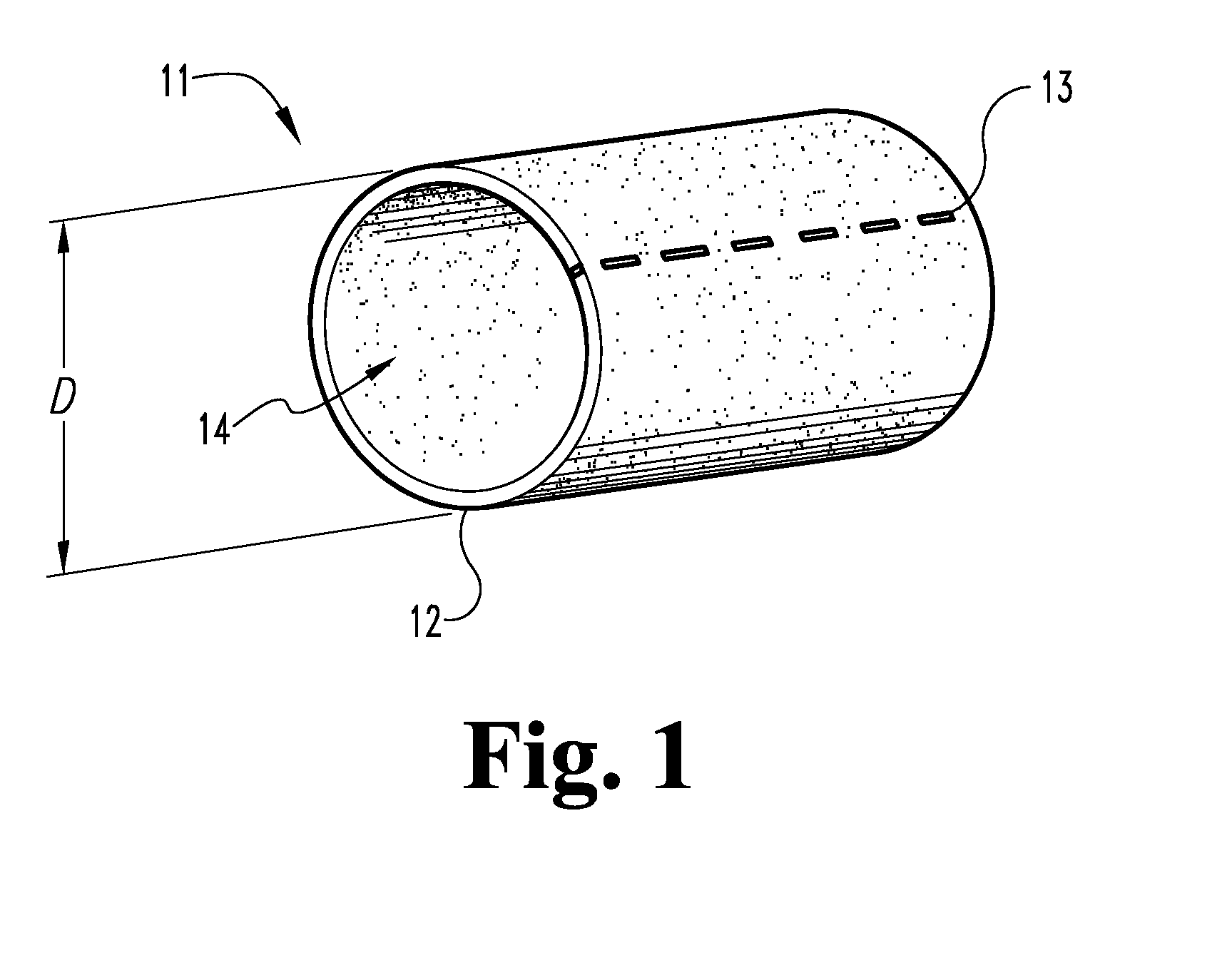
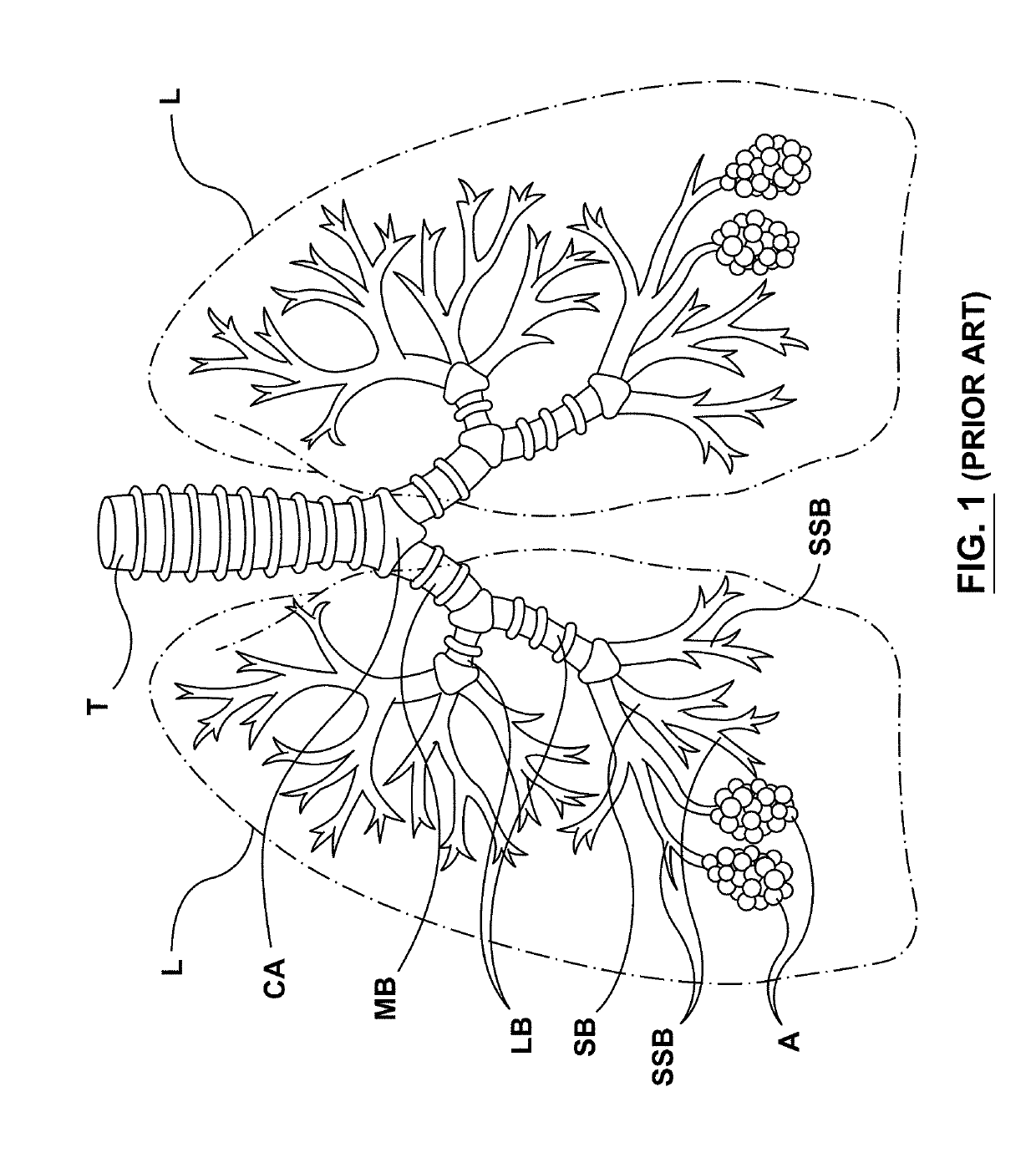
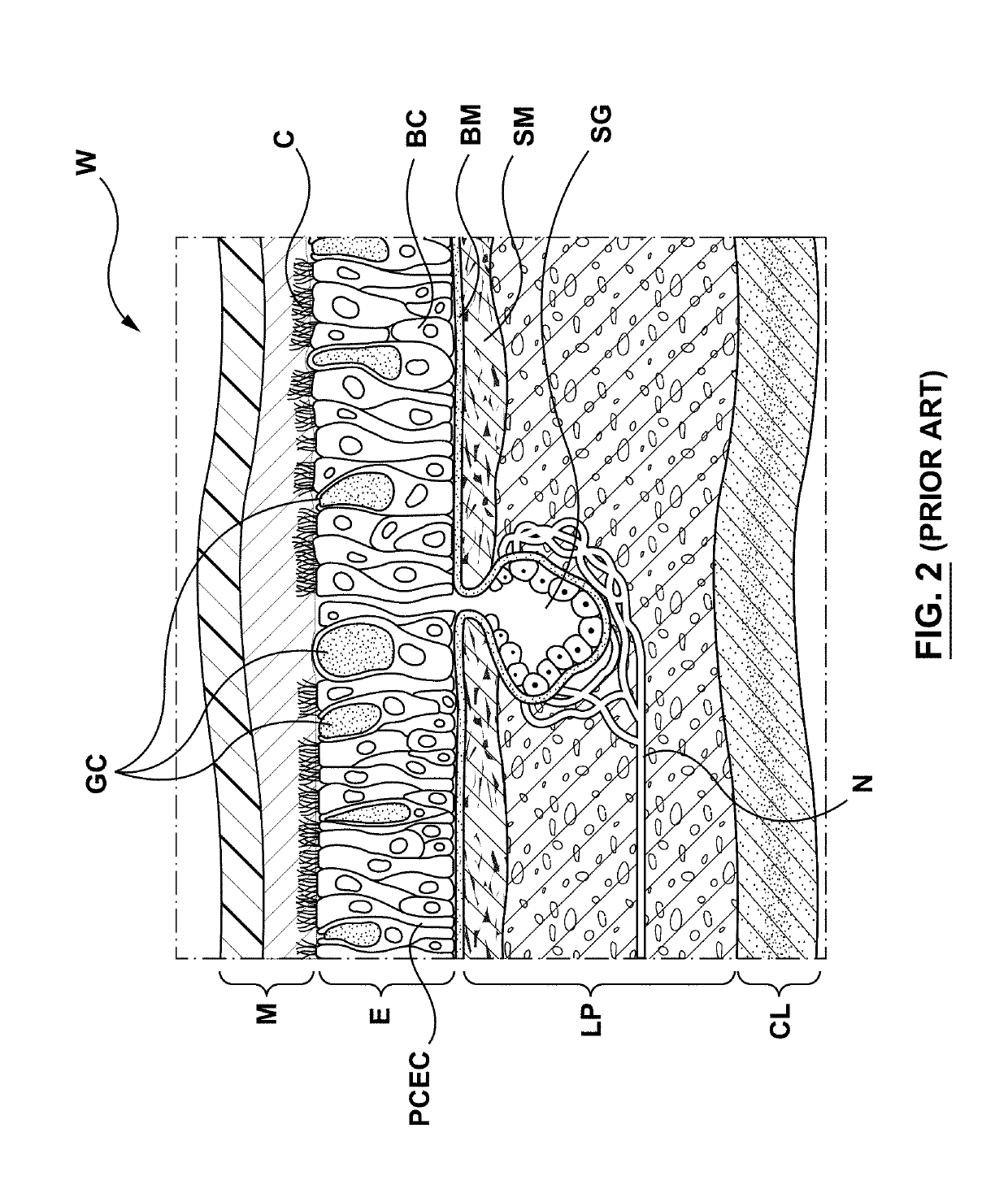
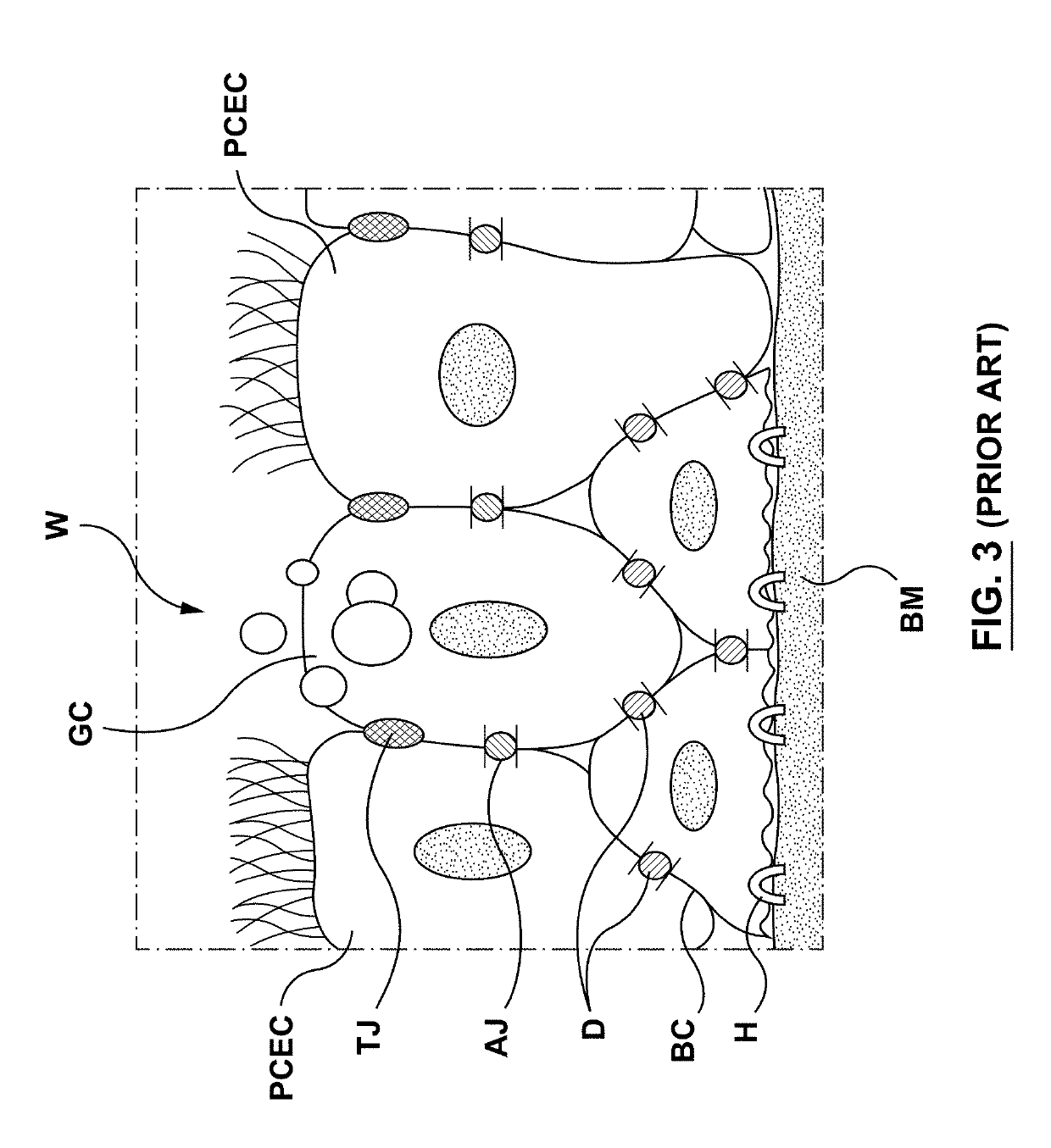
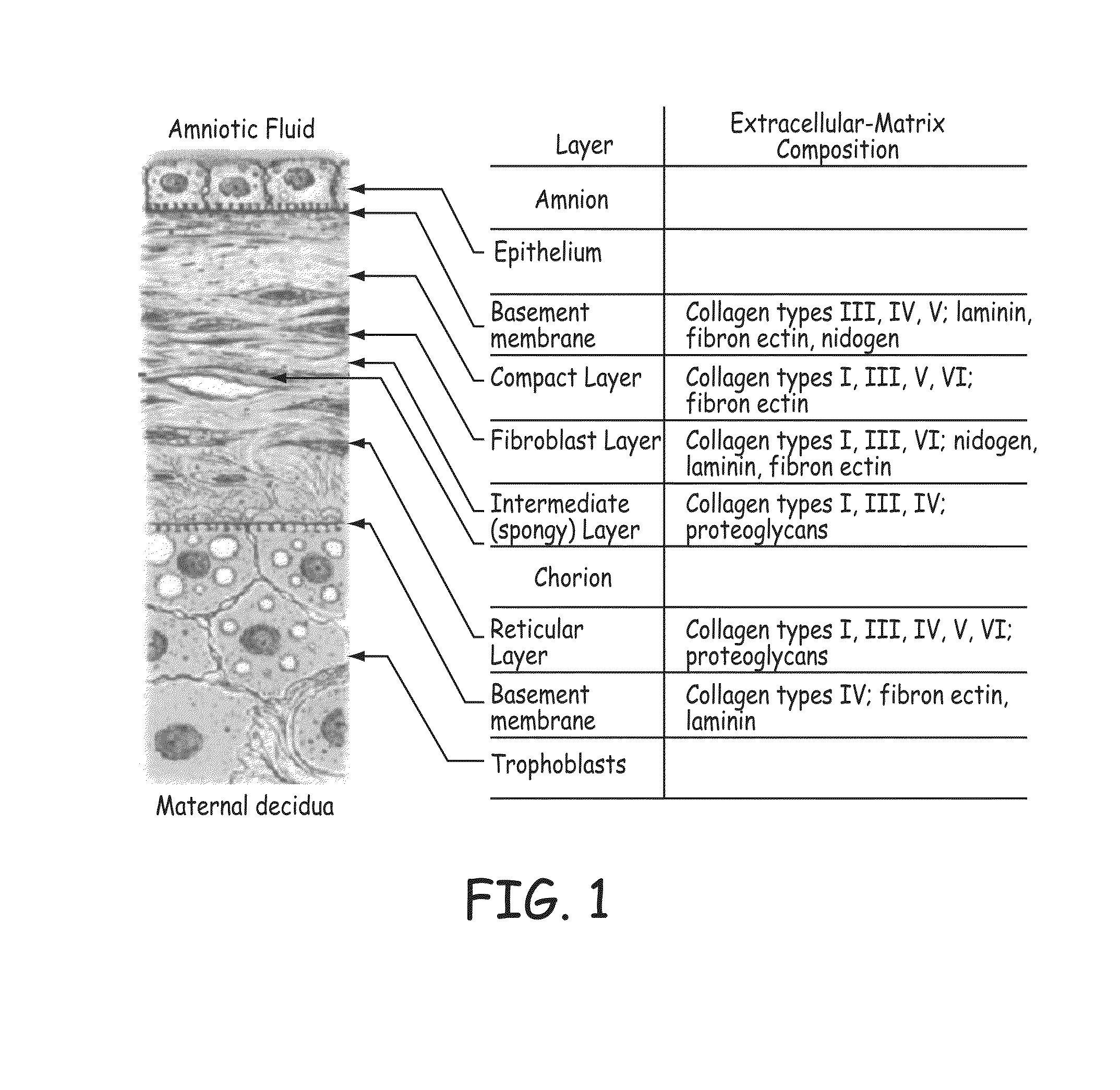
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) and joins it to the muscular layer, the bulk of overlying smooth muscle (fibers running circularly within layer of longitudinal muscle).
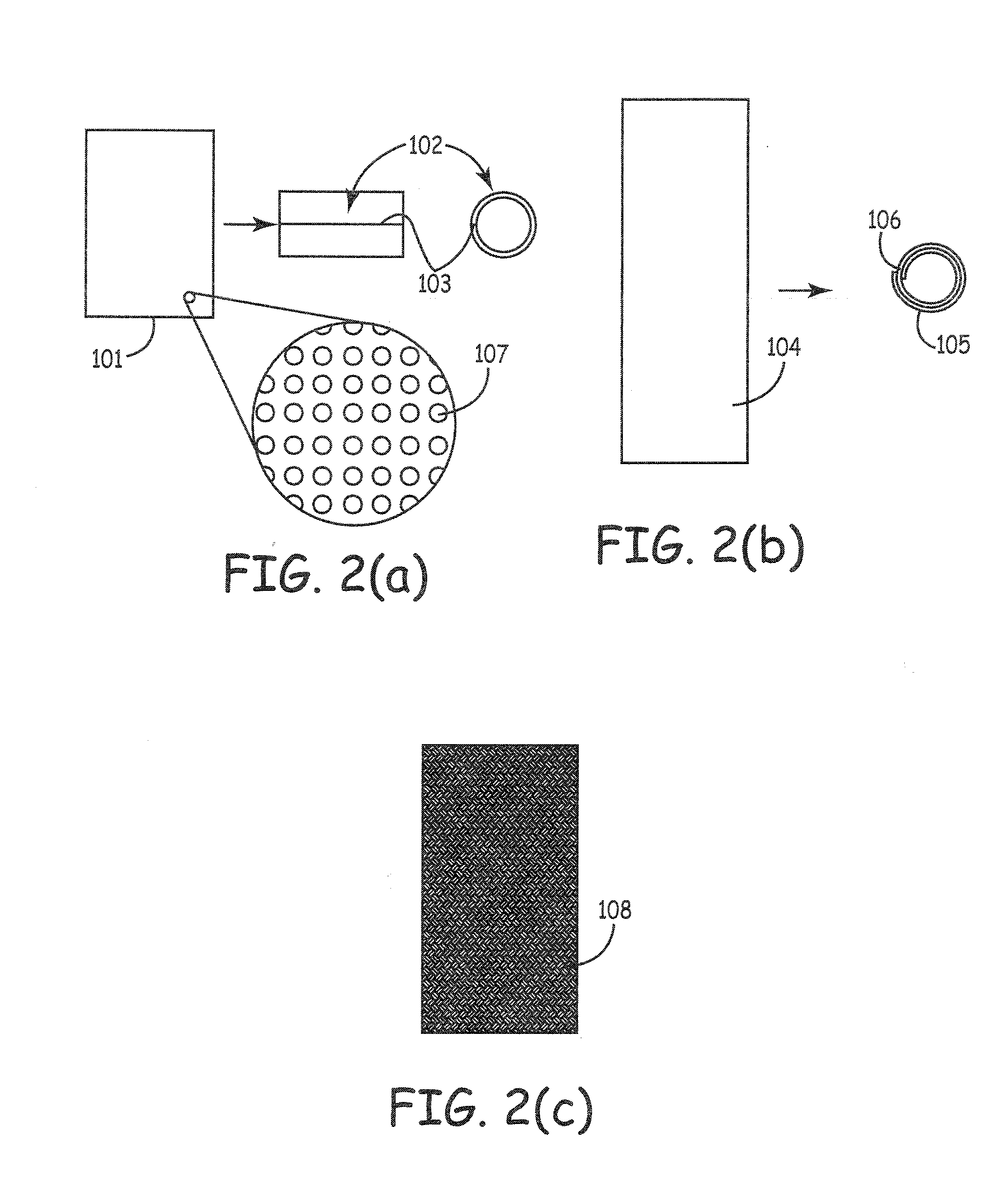
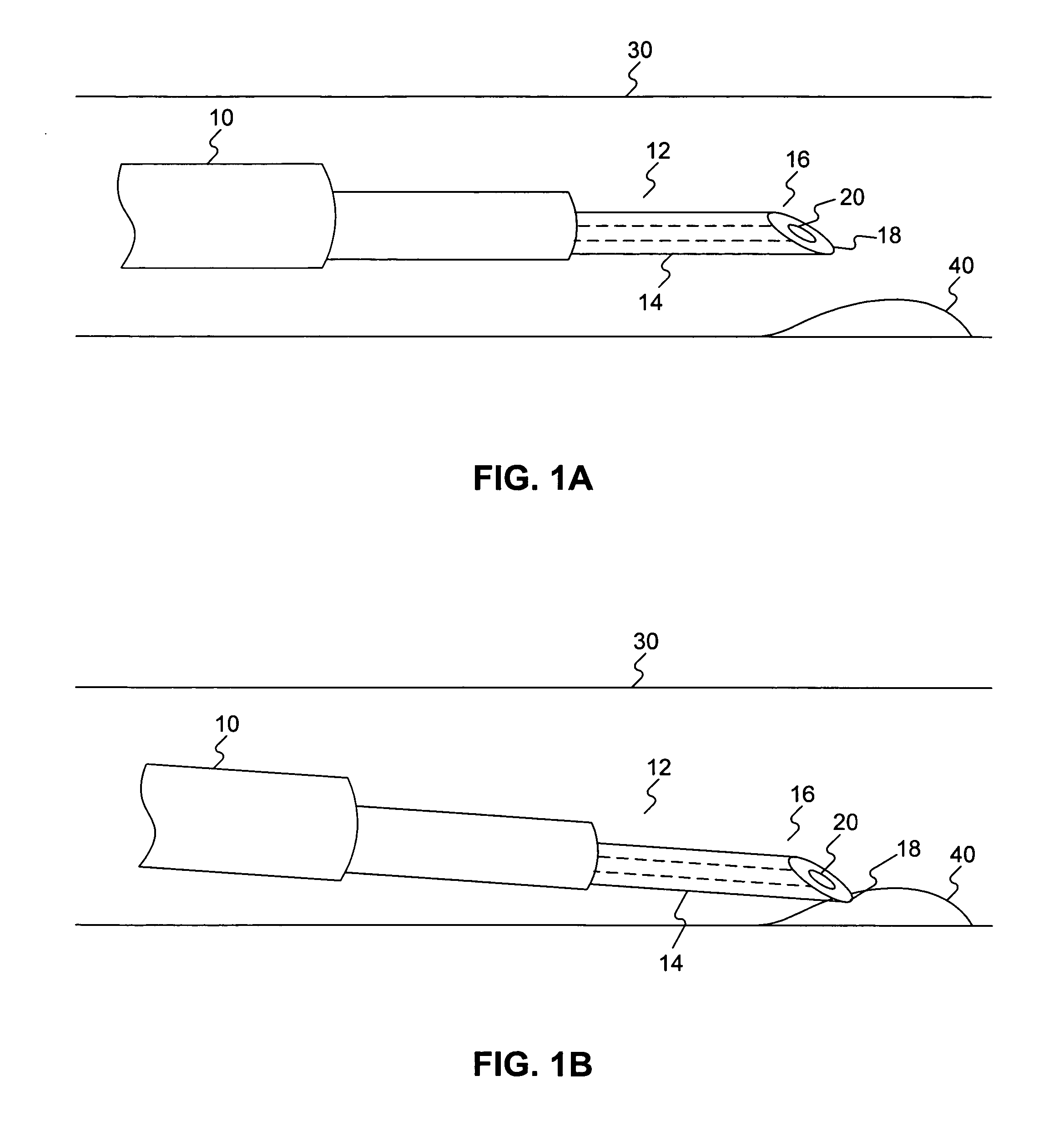
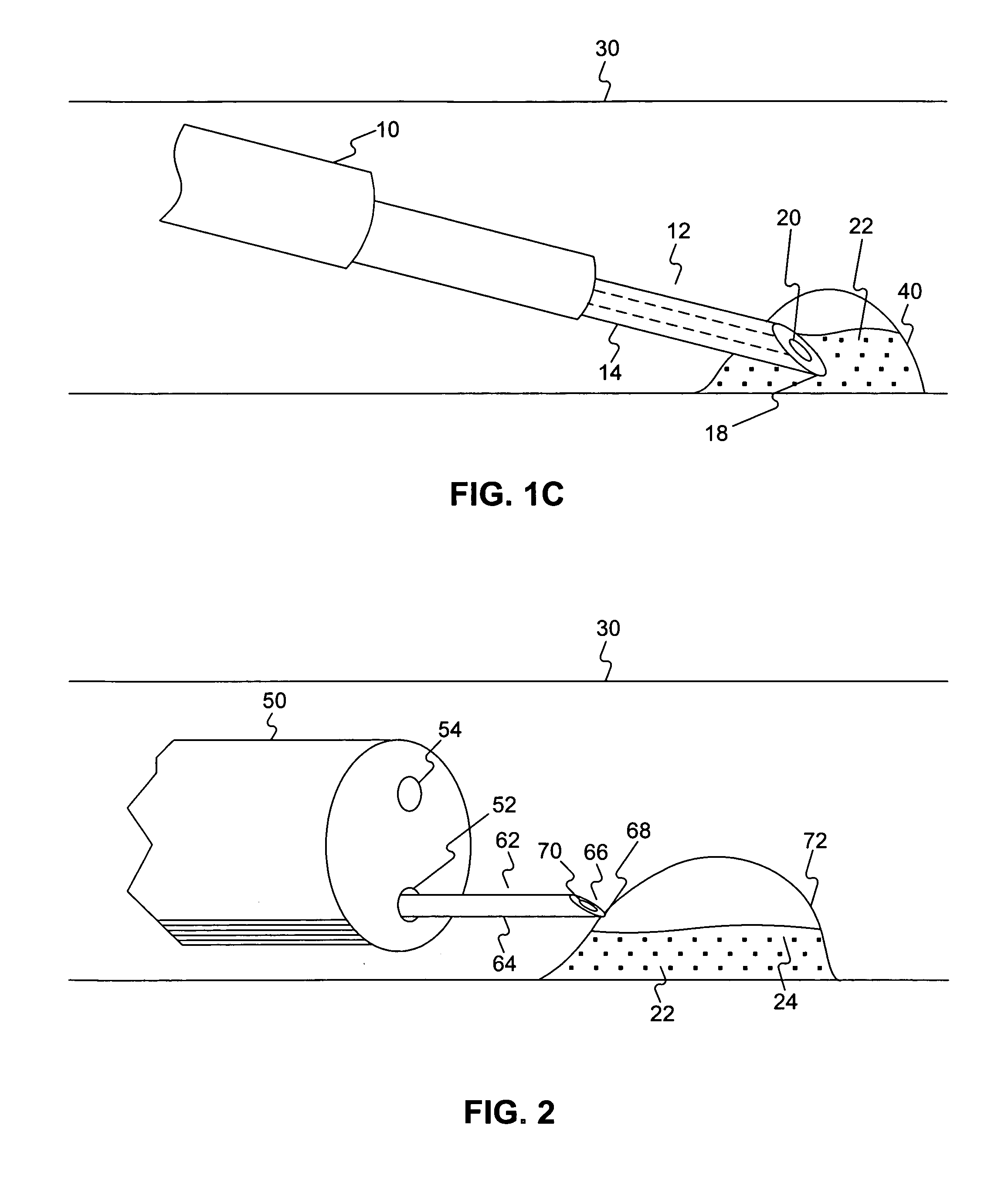
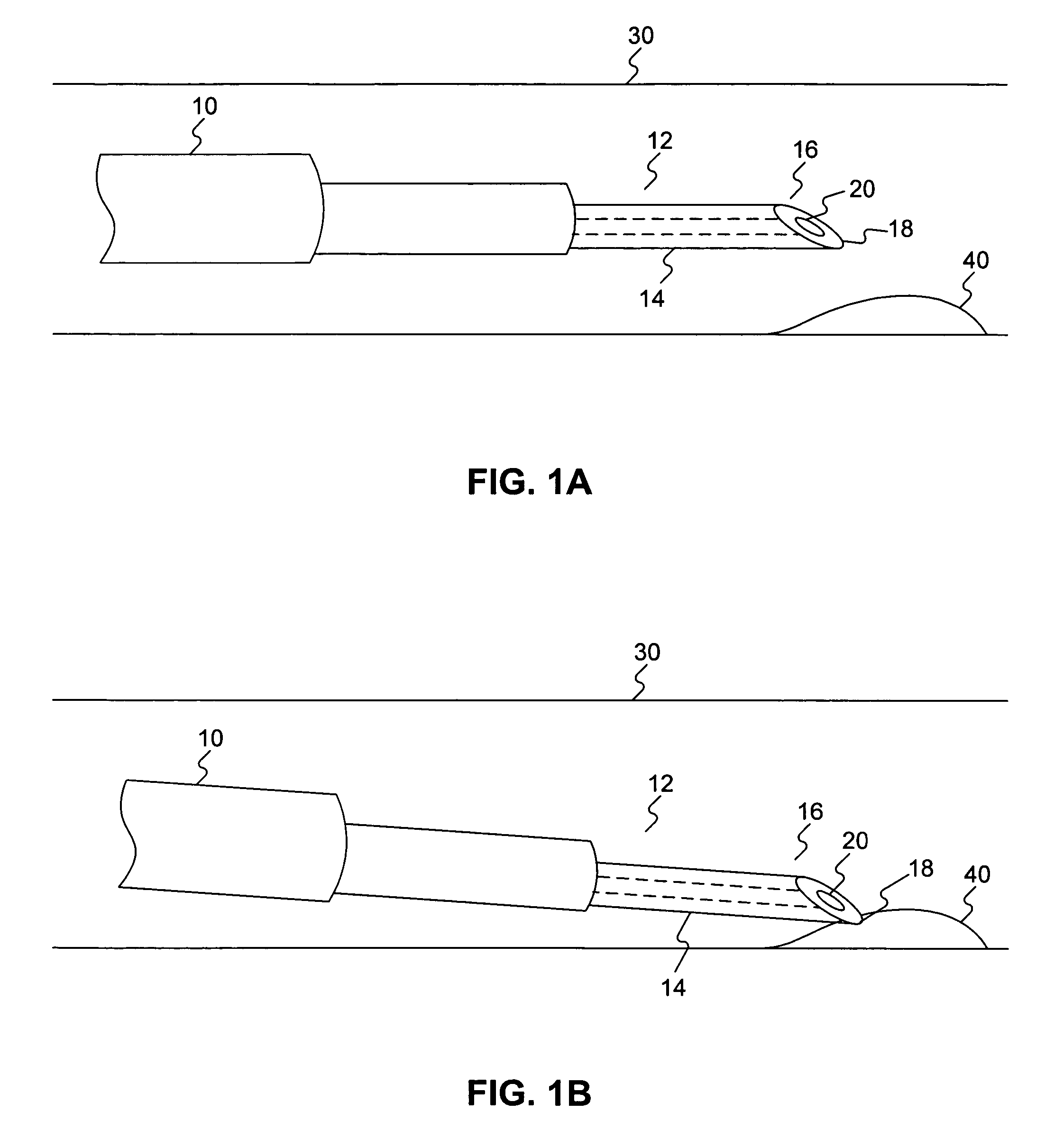
Biasing stretch receptors in stomach wall to treat obesity
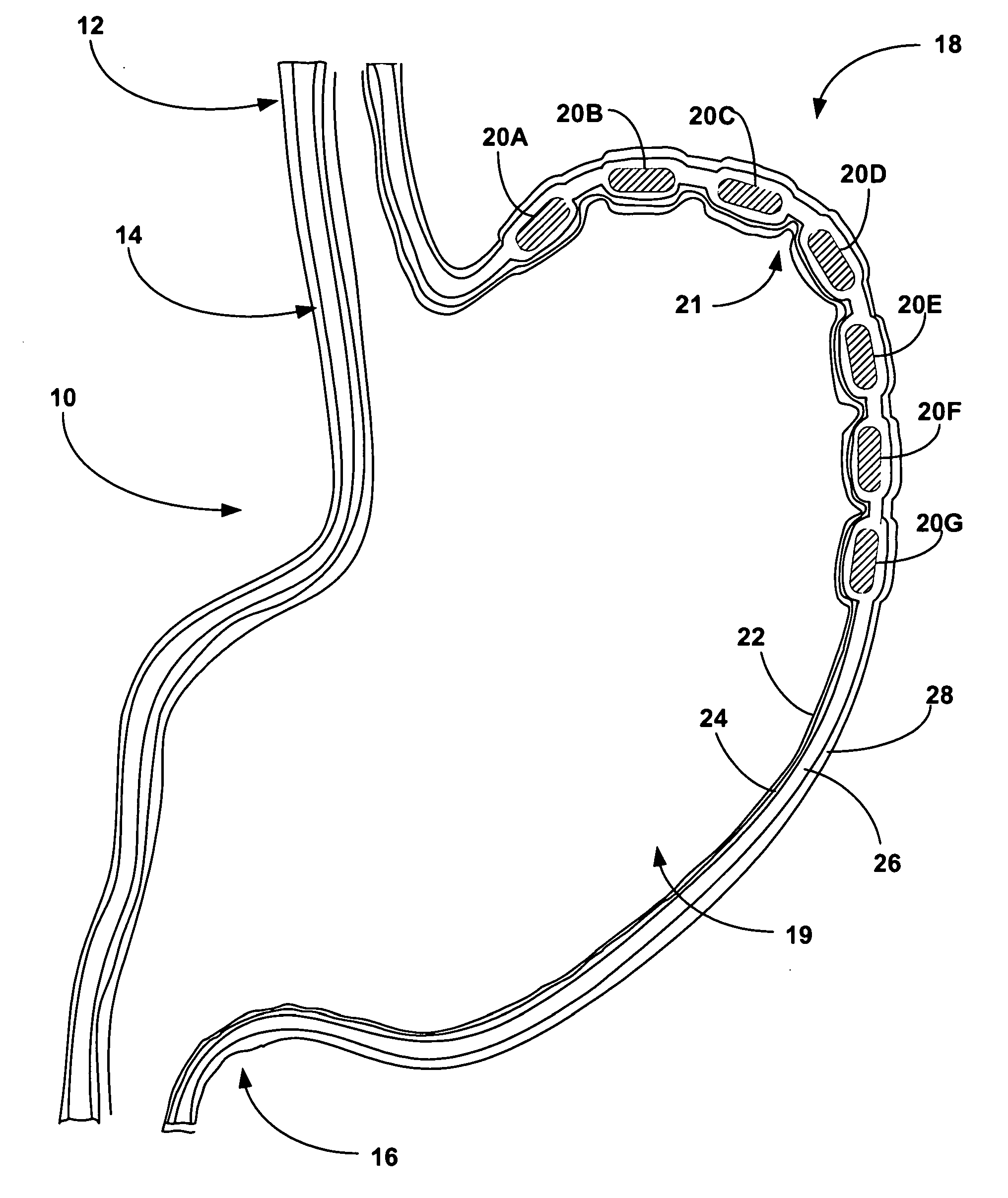
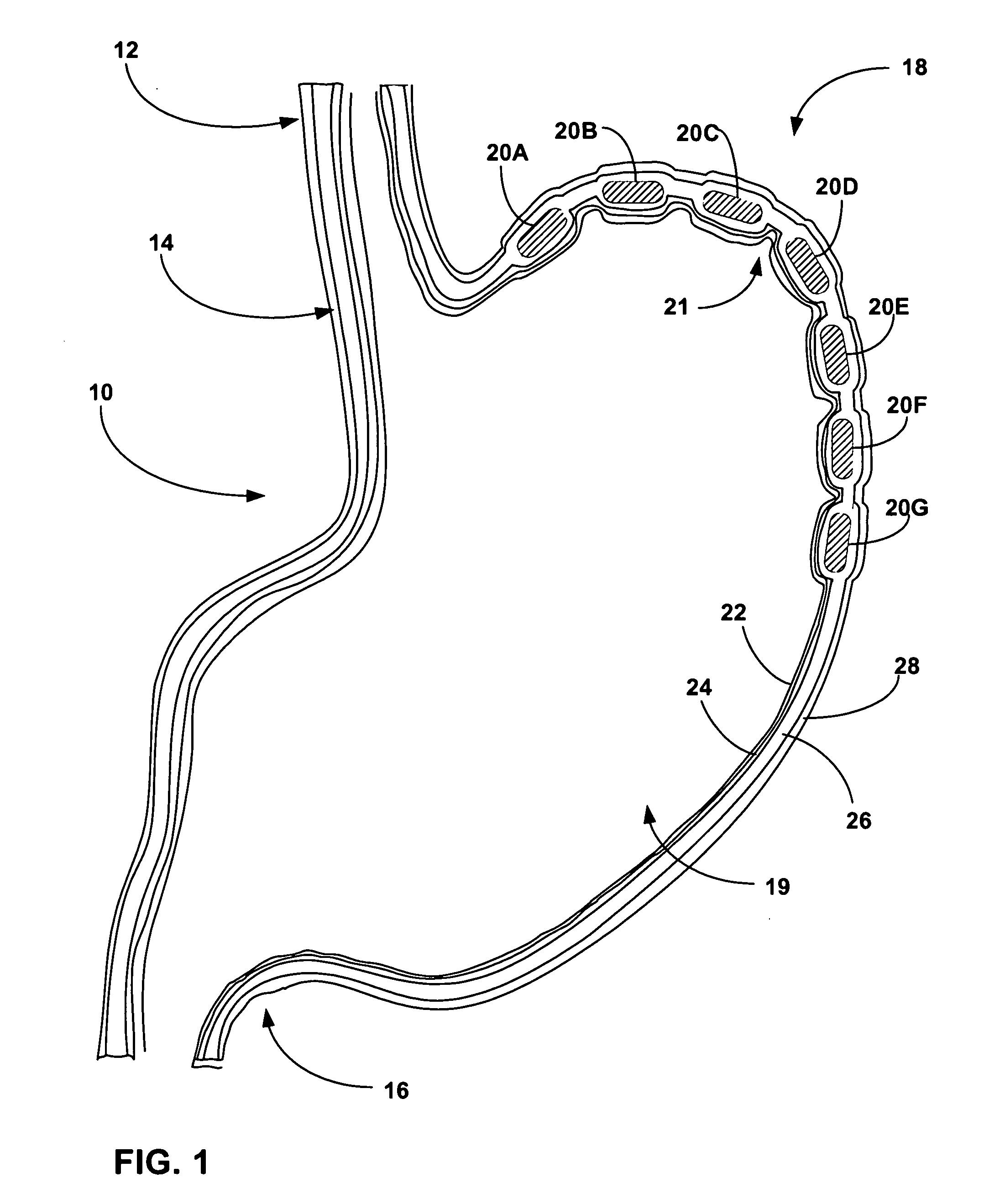
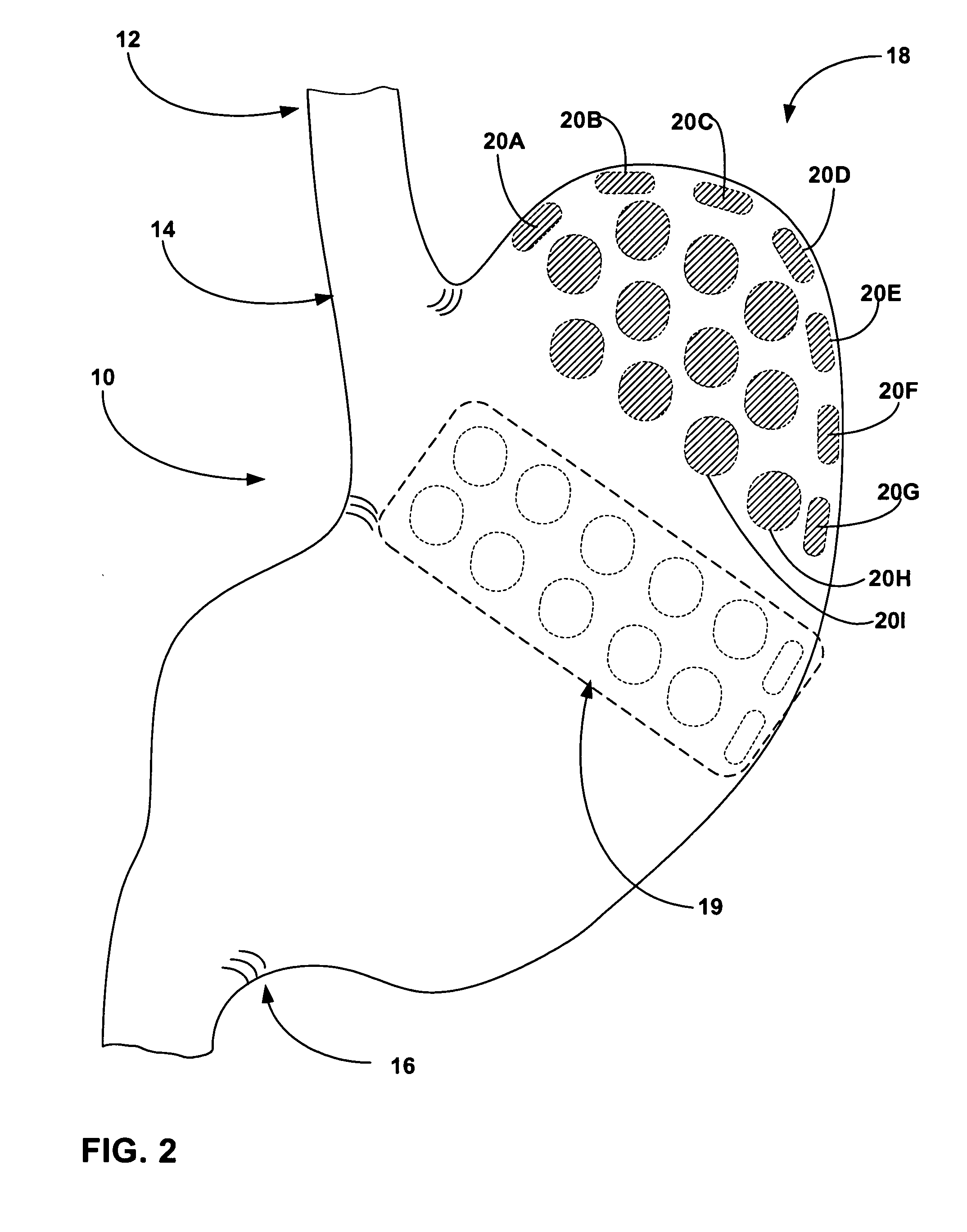
Medical devices and methods are designed to bias stretch receptors in the stomach wall of a patient to treat obesity. Biasing of the stretch receptors by pre-stretching induces an early sensation of satiety, causing the patient to consume less food. Biasing of the stretch receptors can be achieved by the placement of bulking devices within the wall of the stomach, e.g., in the mucosa, submucosa or muscle layer. The bulking devices may be expandable and, in some embodiments, may take the form of a hydrogel prosthesis that expands following implantation in a wall of the stomach.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
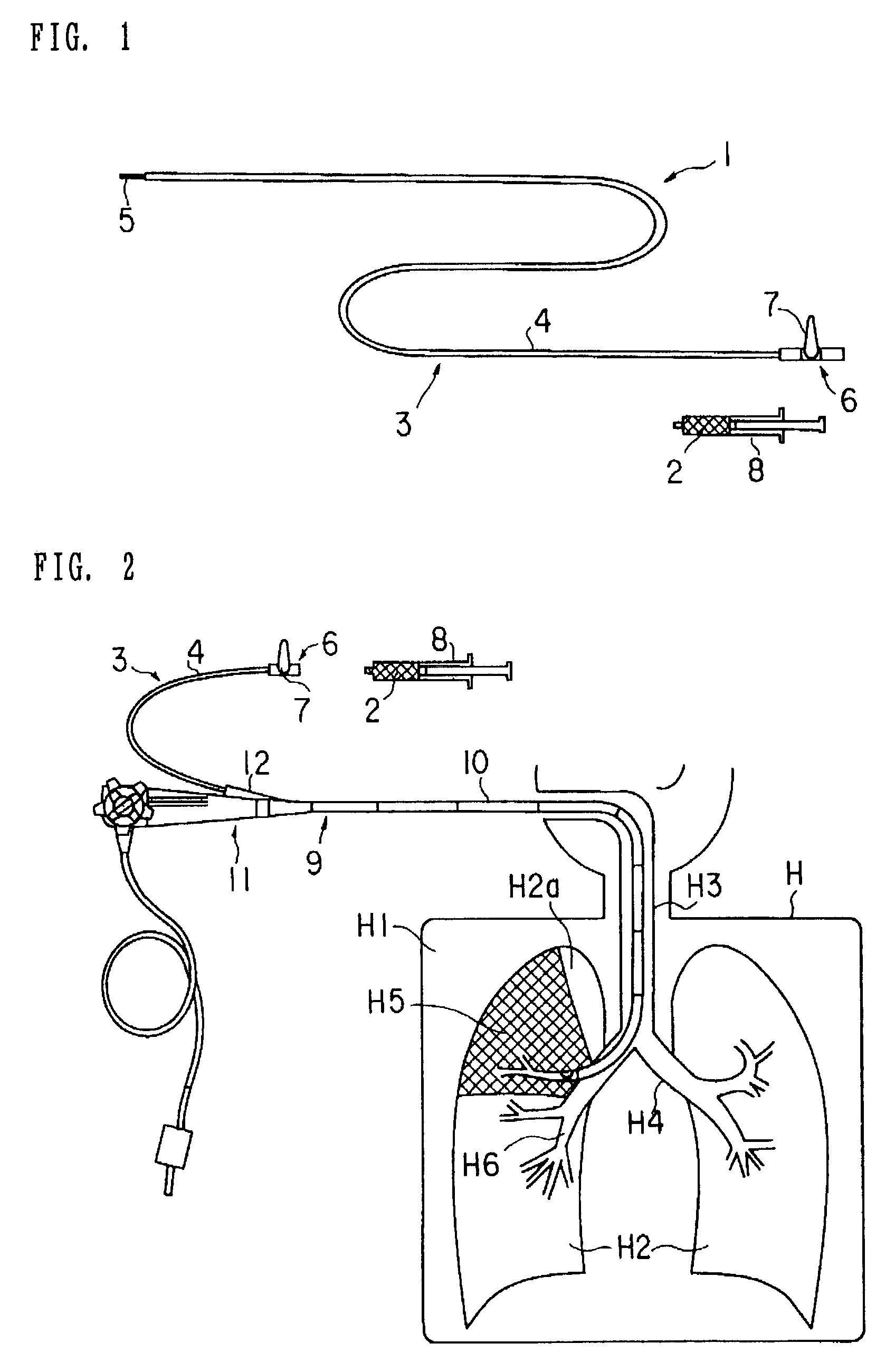
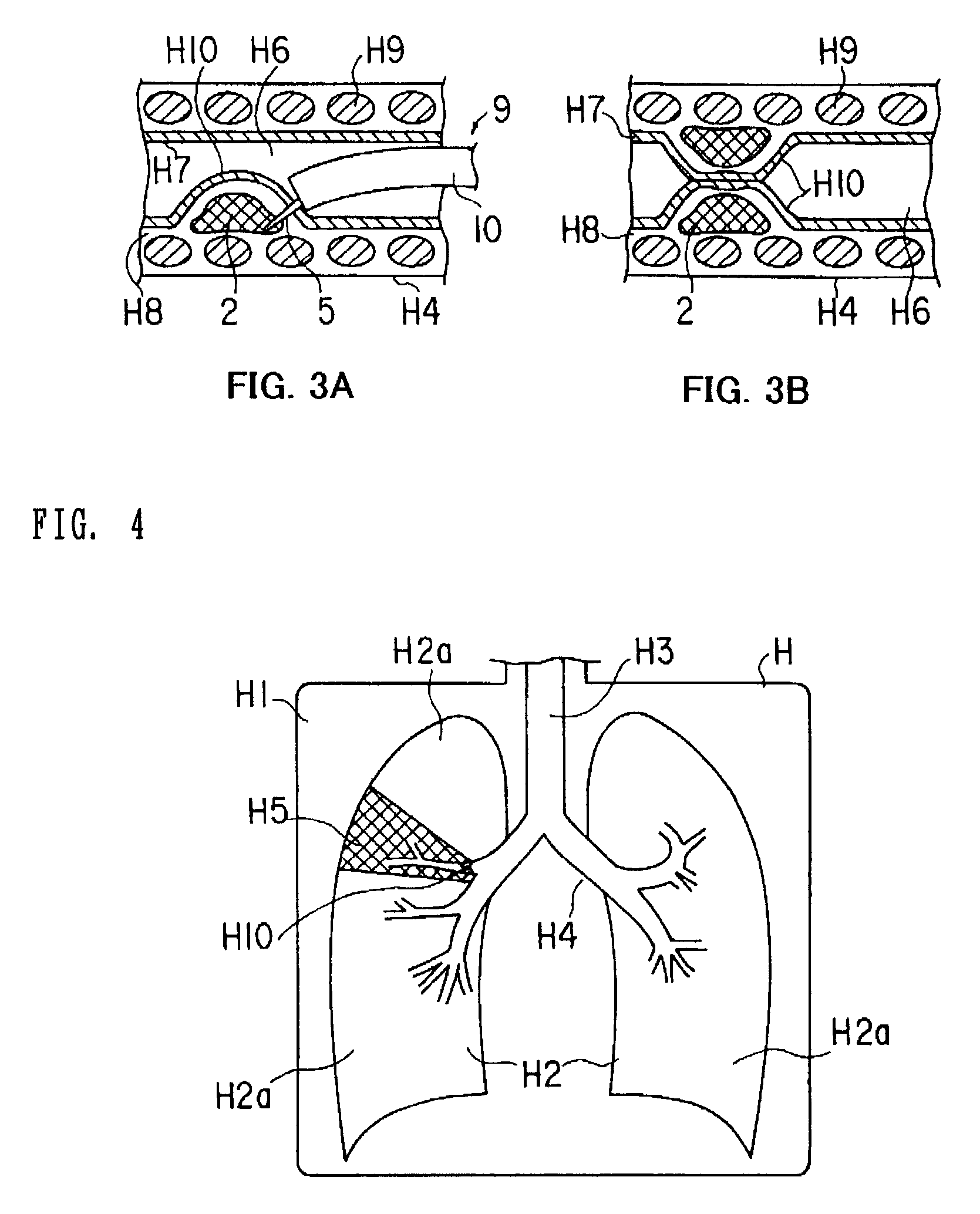
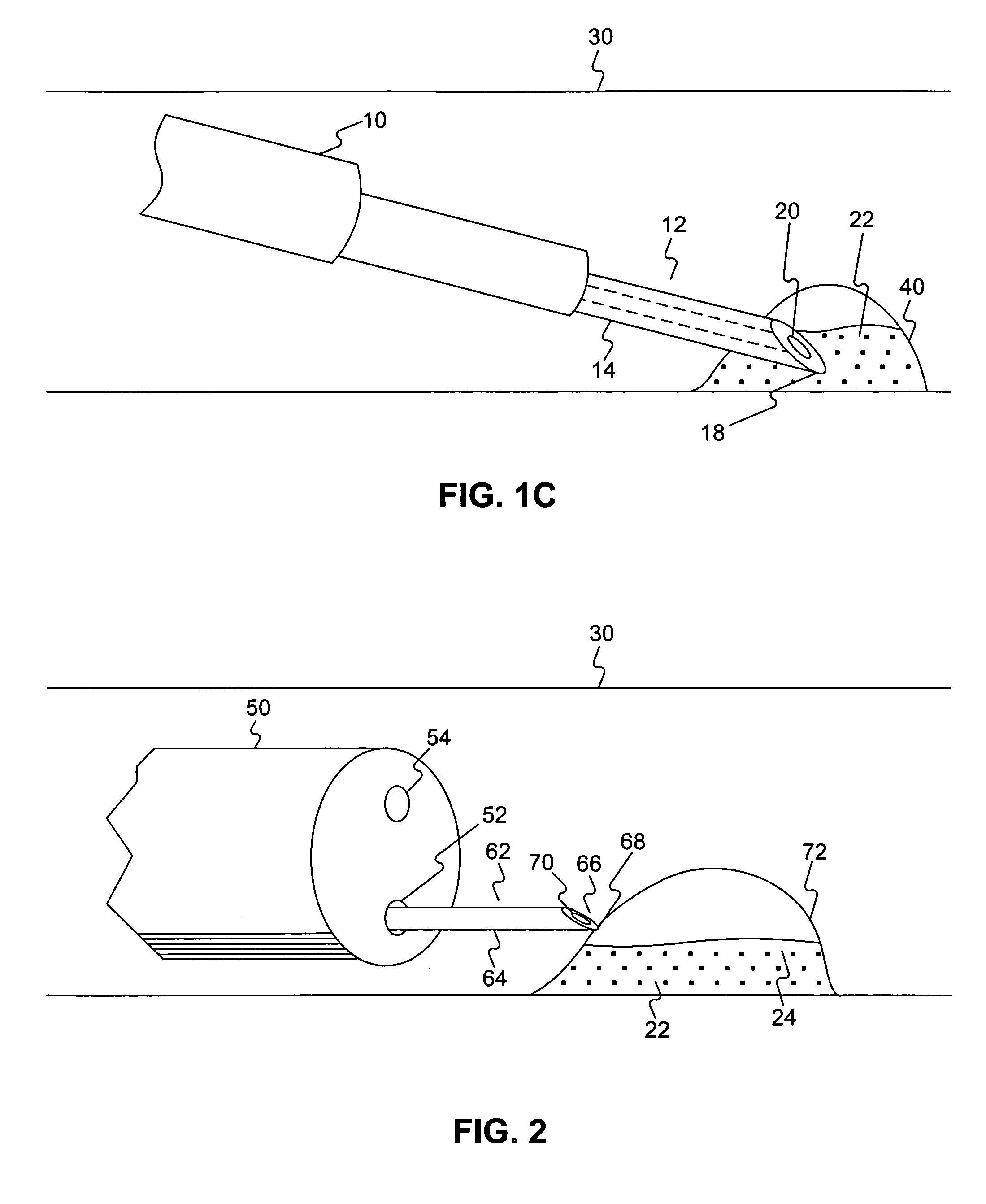
Medical device and method of embolizing bronchus or bronchiole
ActiveUS7357795B2Maintaining swellingGood biocompatibilityDiagnosticsDilatorsSurgical treatmentBronchial submucosa
To provide a medical device and a method both of which can suitably embolize a bronchus in a target part by embolizing the bronchus with (at least a part of) a living tissue during surgical treatment of lung emphysema. For example, an injection material is injected into a submucosa by the use of a syringe, and in the injected part, a swelling swollen into the internal cavity of the bronchus is formed to tightly seal the living tissue of the bronchus or a bronchiole, thereby embolizing a target bronchus.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
Preparation method for cellfree intestinum tenue submucosa biological material
ActiveCN101366975ARepair defectRepair membranous defectsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingIntestinal submucosa
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biomaterial of acellular small intestinal submucosa, which comprises the steps of preposition treatment, acellular treatment, enzyme treatment, preparations of membranous products and particle products. Compared with the prior art, the biomaterial has higher bioactivity and biocompatibility, no obvious immune rejection and no toxic effect on cells; besides, the biomaterial has a certain mechanical strength and toughness, and variable shape, size and thickness, thereby being convenient for clinical suturing and fixing. At the same time, the preparation method has the advantages of unlimited raw material source, cell-free residues, no ethical issues and being capable of effectively inactivating virus. The prepared products are applicable to the biomedical engineering fields, such as repairing defections of body tissue, serving as tissue filling materials, repairing facial depression deformity, serving as tissue reinforcements to replace fascia, repairing membranous defections and malnourished and infected surfaces of wound, serving as materials for biodegradable stents, and serving as injectable filling materials.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Endoscopic resection method
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Graft materials containing ECM components, and methods for their manufacture
ActiveUS20080107750A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Described are packaged, sterile medical graft products containing controlled levels of a growth factor such as Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 (FGF-2). Also described are methods of manufacturing medical graft products wherein processing, including sterilization, is controlled and monitored to provide medical graft products having modulated, known levels of a extracellular matrix factor, such as a growth factor, e.g. FGF-2. Preferred graft materials are extracellular matrix materials isolated from human or animal donors, particularly submucosa-containing extracellular matrix materials. Further described are ECM compositions that are or are useful for preparing gels, and related methods for preparation and use.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH +1
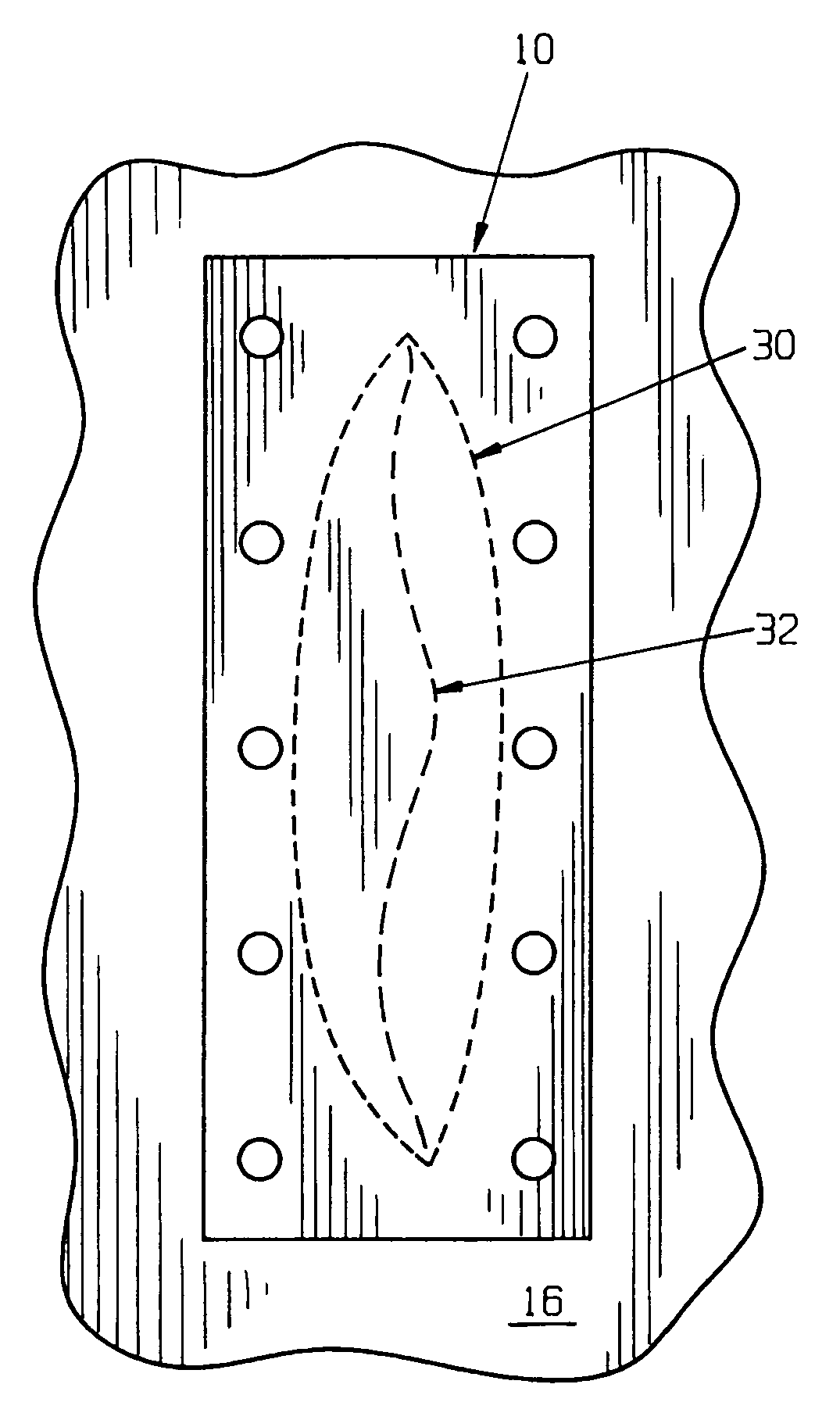
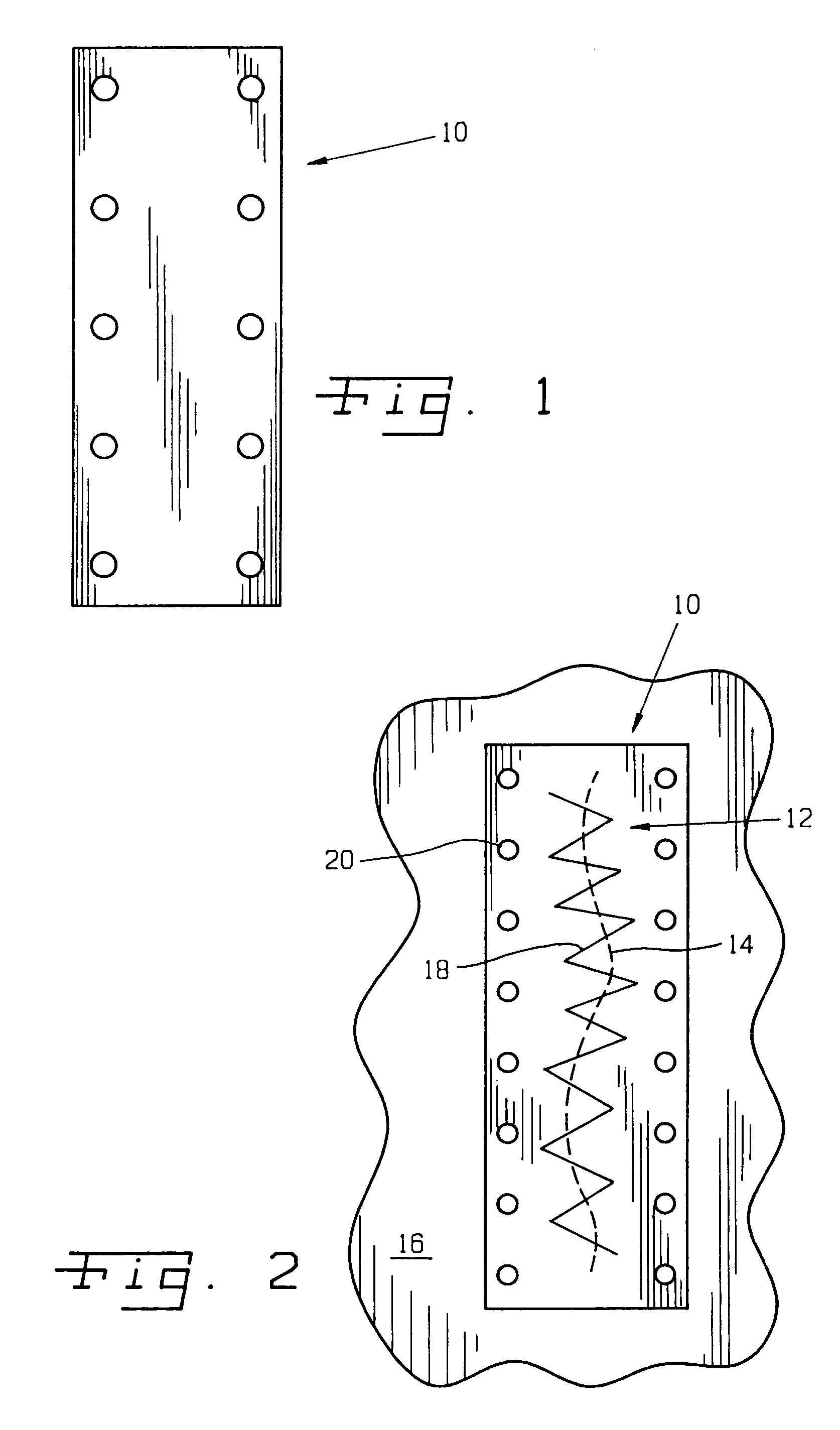
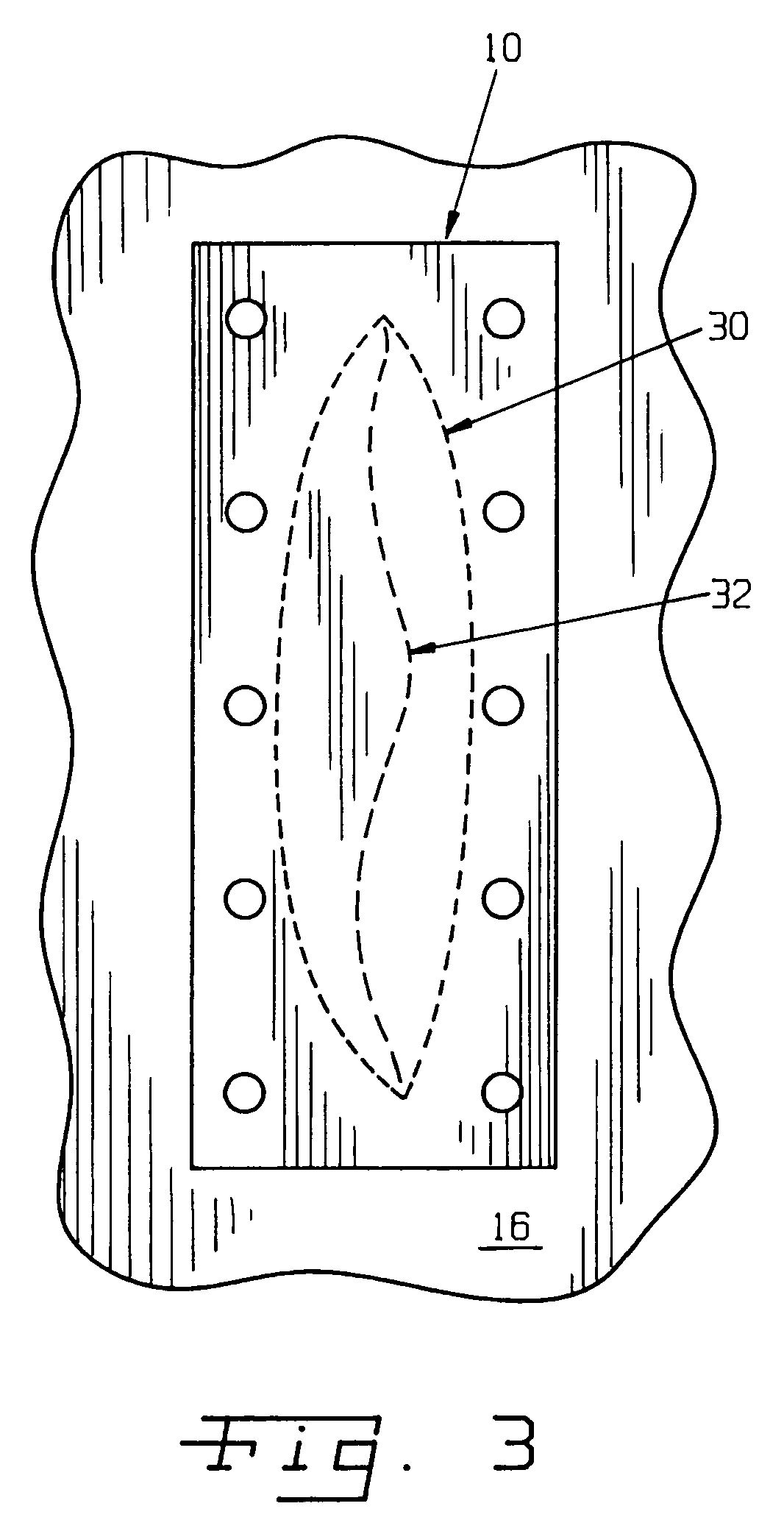
Surgical method and composition utilizing submucosal tissue to prevent incisional hernias
InactiveUS7105001B2Easy to adaptEliminate requirementsSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresAbdominal wall closure
A small intestine submucosa mesh is adapted for use in surgical abdominal closure routines. The submucosa mesh is incorporated into the normal surgical protocol for abdominal closure procedures. The submucosa mesh is applied to the abdominal incision area and maintains and enhances the stability and integrity of the abdominal wall closure, thereby preventing the onset or occurrence of incisional hernias. The submucosa mesh can also be applied to surgical closure procedures involving treatment of a hernia defect, such as an incisional hernia or other non-incisional hernia. The submucosa construct can also be adapted for use as a suturing component or bioretention suture. The submucosa construct can be adapted for use as part of a surgical strategy to facilitate wound healing, regeneration, reconstruction, and replacement of anatomical structures, such as tissues and organs.
Owner:MANDELBAUM JON A
Method for vocal cord reconstruction
A method for surgical repair of damaged or diseased head and neck tissues is described. In one aspect of the invention tissue graft constructs comprising vertebrate submucosa or vertebrate basement membrane materials are used to repair and promote growth of endogenous vocal cord tissue.
Owner:CLARIAN HEALTH PARTNERS
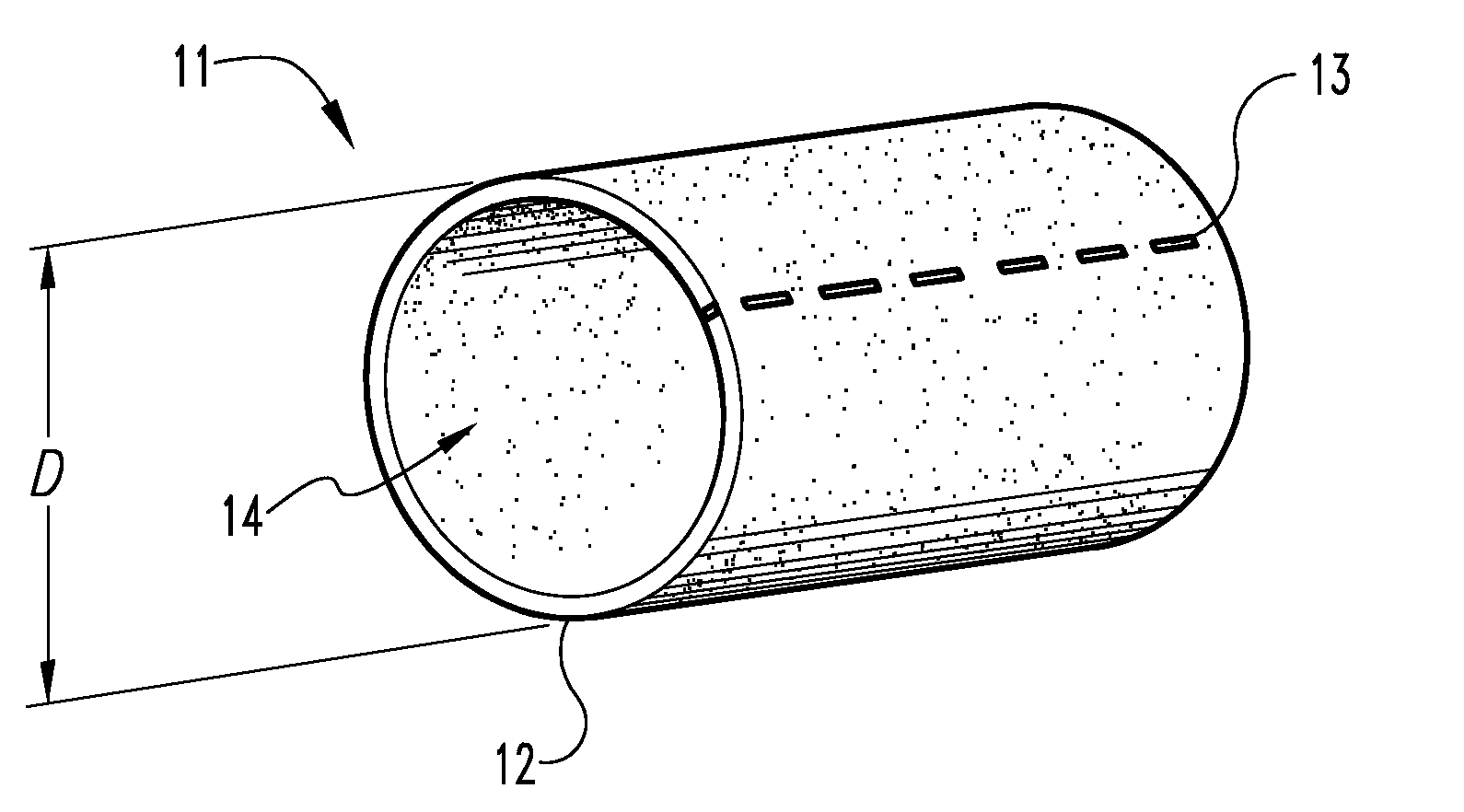
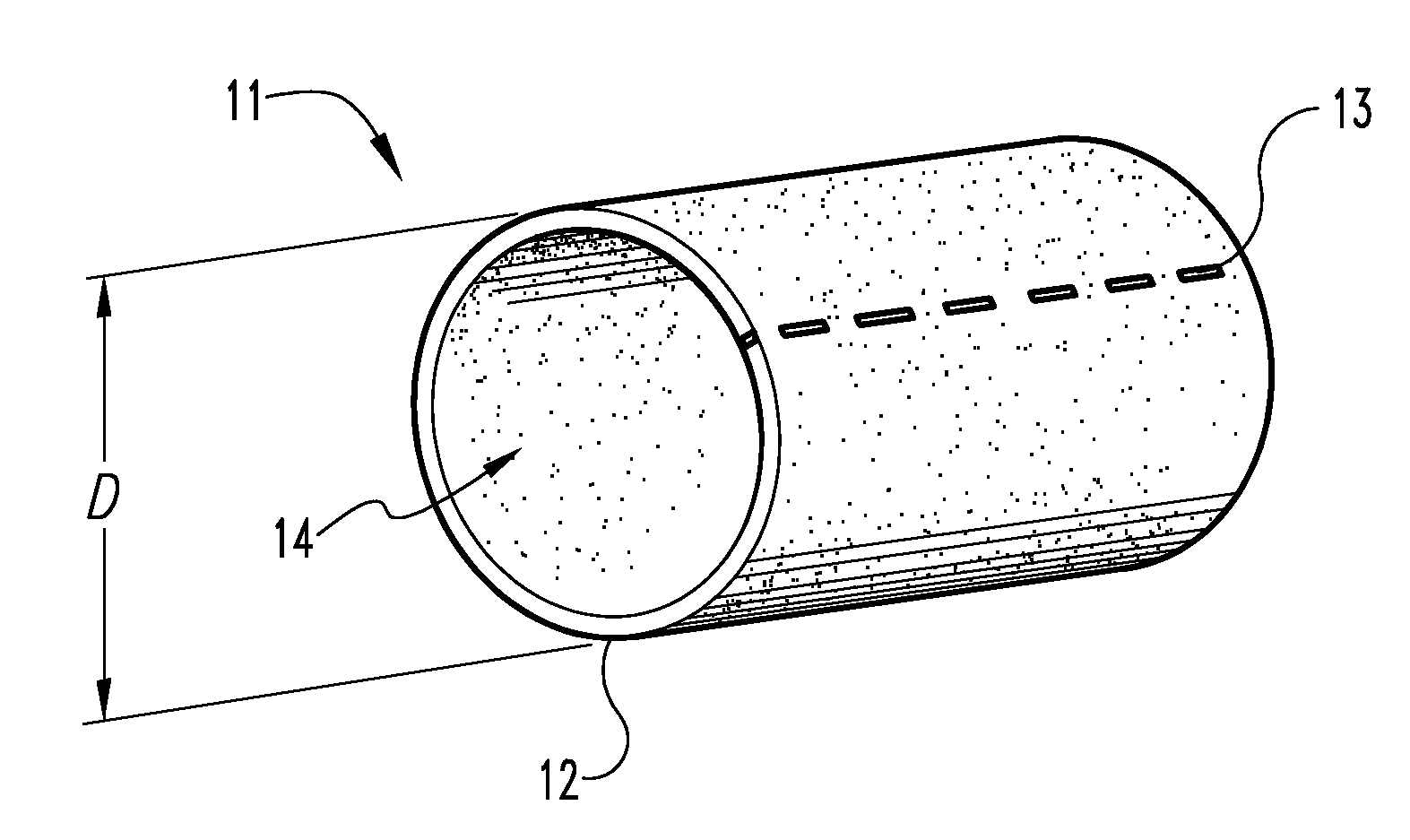
Graft prosthesis, materials and methods
A graft prostheses (11), materials and method for implanting, transplanting, replacing, or repairing a part of a patient. The graft prosthesis includes a purified, collagen-based matrix structure removed from a submucosa tissue source. The submucosa tissue source is purified by disinfection and removal steps to deactivate and remove contaminants, thereby making the purified structure biocompatible and suitable for grafting on and / or in a patient.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +2
Submucosa gel compositions
A composition comprising enzymatically digested submucosa of a warm-blooded vertebrate and a method of making that composition is described. More particularly the submucosa is enzymatically digested and gelled to form a shape retaining gel matrix suitable for inducing cell proliferation and growth both in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for the treatment of pulmonary disorders
ActiveUS20190231425A1Reduce in quantityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingDiseaseAcute bronchitis
Apparatuses, systems and methods are provided for treating pulmonary tissues via delivery of energy, generally characterized by high voltage pulses, to target tissue using a pulmonary tissue modification system (e.g., an energy delivery catheter system). Example pulmonary tissues include, without limitation, the epithelium (the goblet cells, ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells, and basal cells), lamina propria, submucosa, submucosal glands, basement membrane, smooth muscle, cartilage, nerves, pathogens resident near or within the tissue, or a combination of any of these. The system may be used to treat a variety of pulmonary diseases or disorders such as or associated with COPD (e.g., chronic bronchitis, emphysema), asthma, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), acute bronchitis and / or other pulmonary diseases or disorders.
Owner:GALVANIZE THERAPEUTICS INC
Graft prosthesis, materials and methods
A graft prostheses (11), materials and method for implanting, transplanting, replacing, or repairing a part of a patient. The graft prosthesis includes a purified, collagen-based matrix structure removed from a submucosa tissue source. The submucosa tissue source is purified by disinfection and removal steps to deactivate and remove contaminants, thereby making the purified structure biocompatible and suitable for grafting on and / or in a patient.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +2
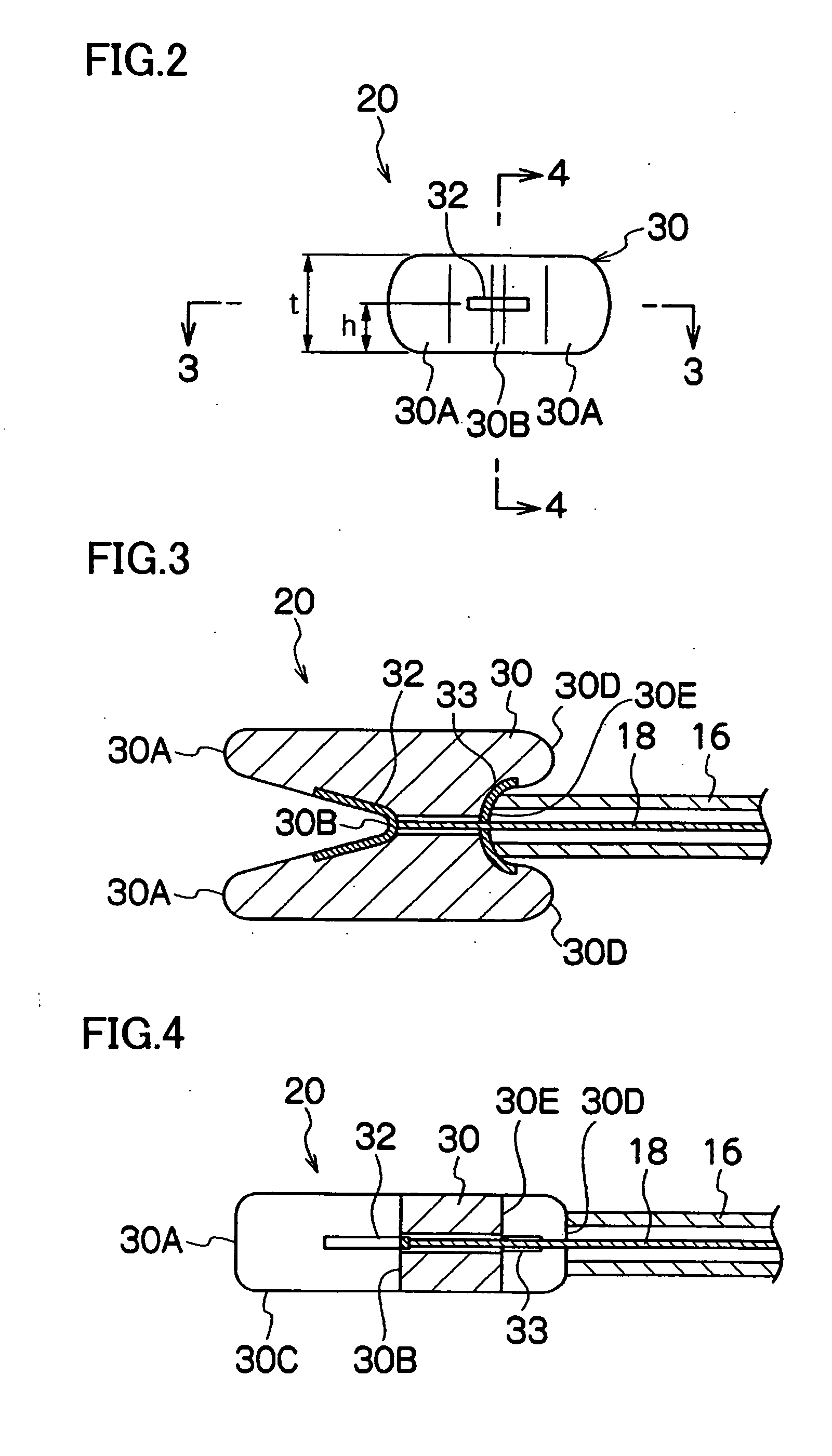
Instrument for Endoscopic Treatment
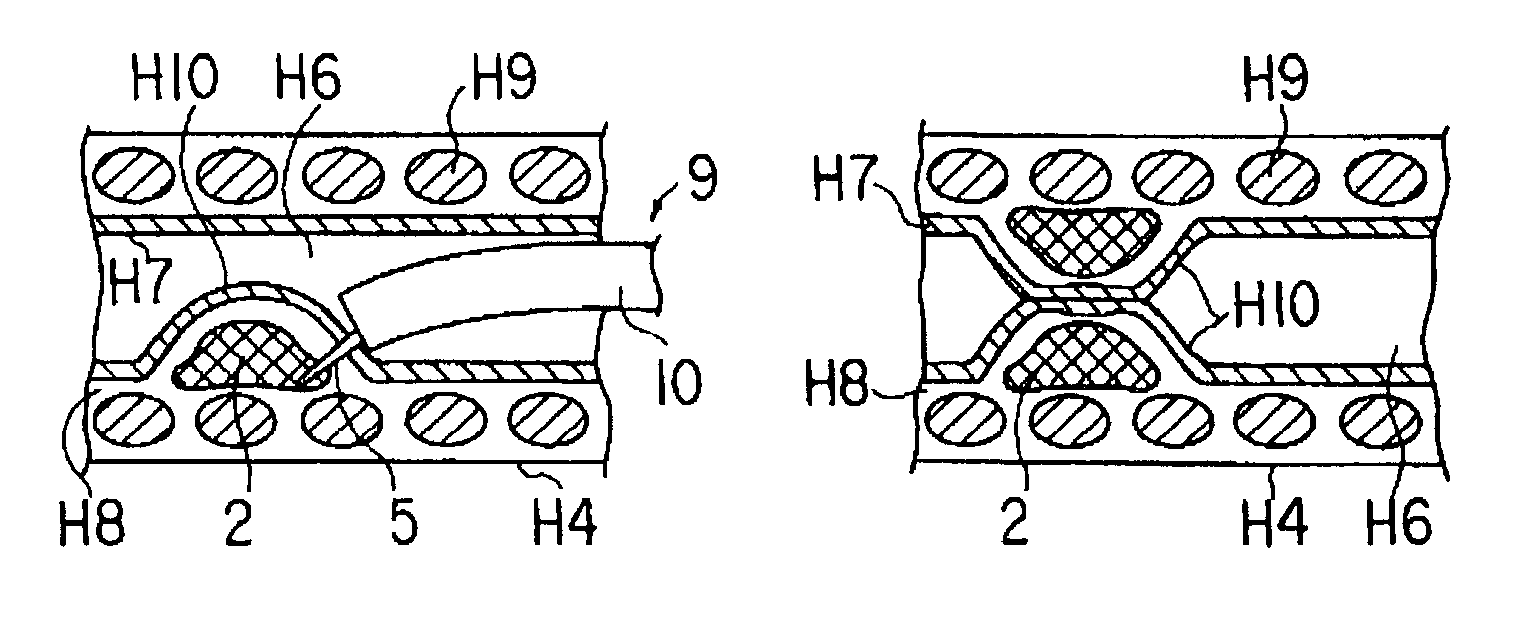
ActiveUS20090247823A1Carry-out quicklySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEndoscopic treatmentSubmucosa
A treatment instrument for an endoscope is provided that is suitable for cutting submucosa in endoscopic submucosal dissection. The treatment instrument for an endoscope includes a treatment portion having a cutting unit at a tip of an insertion portion that is to be inserted into the body. The main unit of the treatment portion is formed in a sawtooth shape having a peak portion and a valley portion. An electrode plate serving as the cutting unit is provided in the valley portion.
Owner:JICHI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
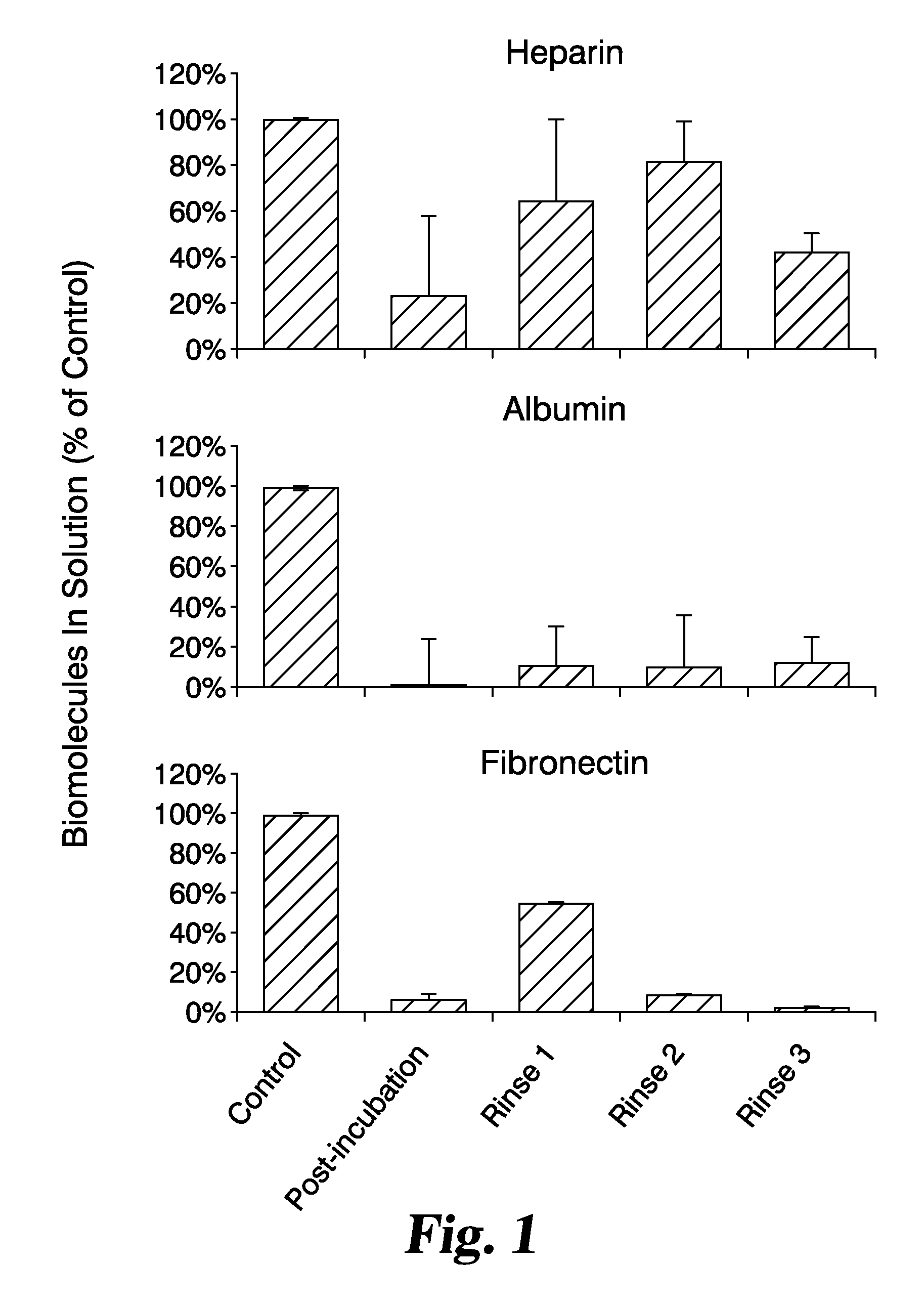
Fibronectin-modified ecm tissue graft constructs and methods for preparation and use thereof
InactiveUS20070184122A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixFibronectin binding
Described are modified submucosa and other extracellular matrix materials incorporating an amount of bound, exogenous fibronectin. Further described are such materials also having an amount of exogenous heparin bound to the exogenous fibronectin, and also potentially an amount of an exogenous bioactive material, such as a growth factor, bound to the exogenous heparin. Such materials may be used in methods for the treatment of wounds in patients.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Graft prosthesis, materials and methods
A graft prostheses (11), materials and method for implanting, transplanting, replacing, or repairing a part of a patient. The graft prosthesis includes a purified, collagen-based matrix structure removed from a submucosa tissue source. The submucosa tissue source is purified by disinfection and removal steps to deactivate and remove contaminants, thereby making the purified structure biocompatible and suitable for grafting on and / or in a patient.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +2
Dried collagenous biomaterial medical device prepared from a urinary tissue source
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Endoscopic resection method
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method of excising tissue including injecting fluid into the submucosa to raise targeted tissue. A first electrode is positioned below the targeted tissue within the injected fluid and a second electrode is positioned adjacent a surface of the raised targeted tissue opposite the first electrode. Electrical current is applied between the first and second electrodes and the targeted tissue is excised with the second electrode.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
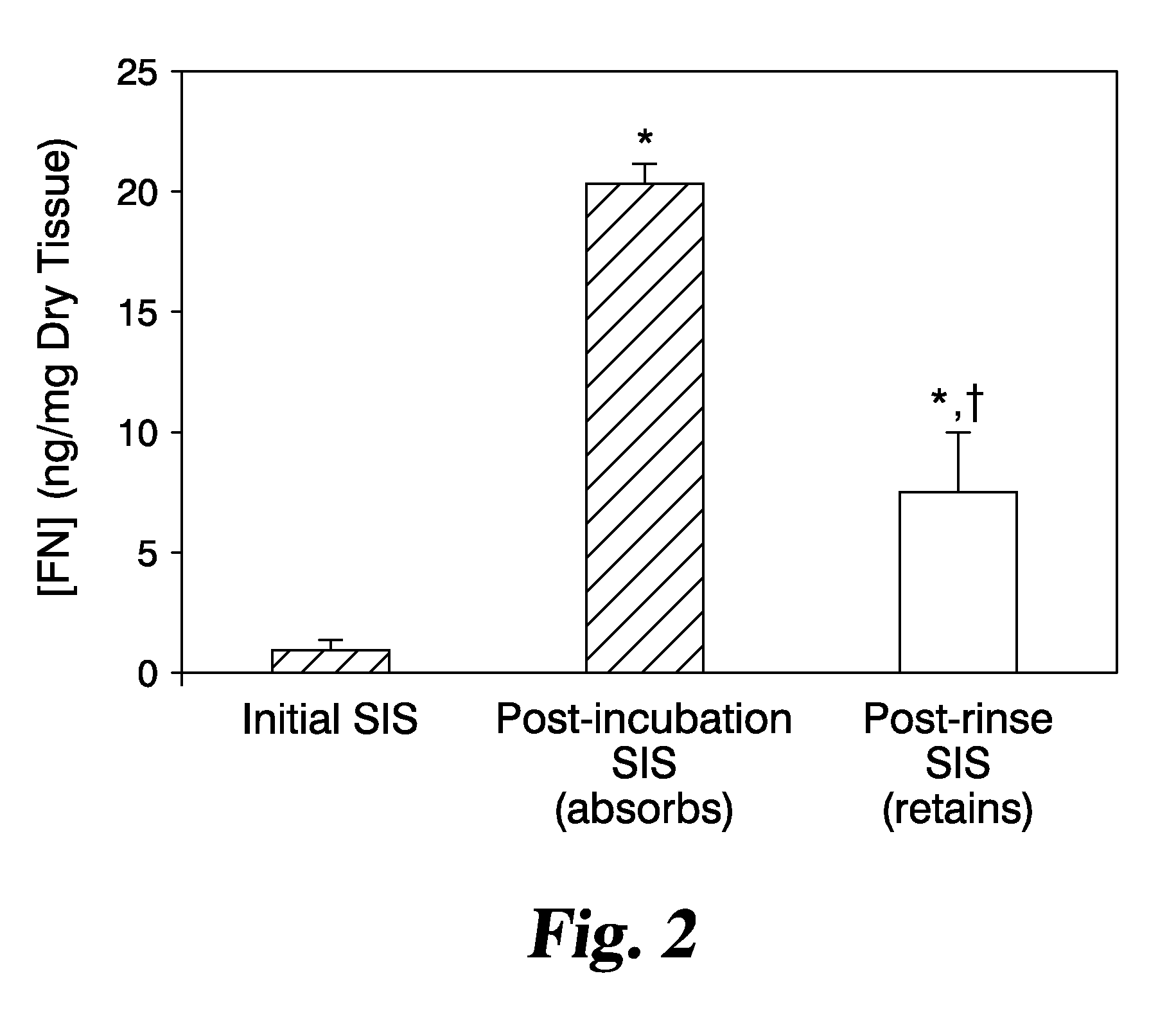
Graft materials and methods for staged delivery of bioactive components
Described, in certain aspects of the invention, are multilaminate medical graft products, as well as methods for preparing and using the same. An illustrative multilaminate medical graft product of the invention comprises a first layer of remodelable extracellular matrix (ECM) material bonded to a second layer of remodelable ECM material, wherein the first material layer is enriched with a growth factor relative to the second material layer. Such a remodelable ECM material may be comprised of submucosa from a warm-blooded vertebrate, for example, porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS).
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
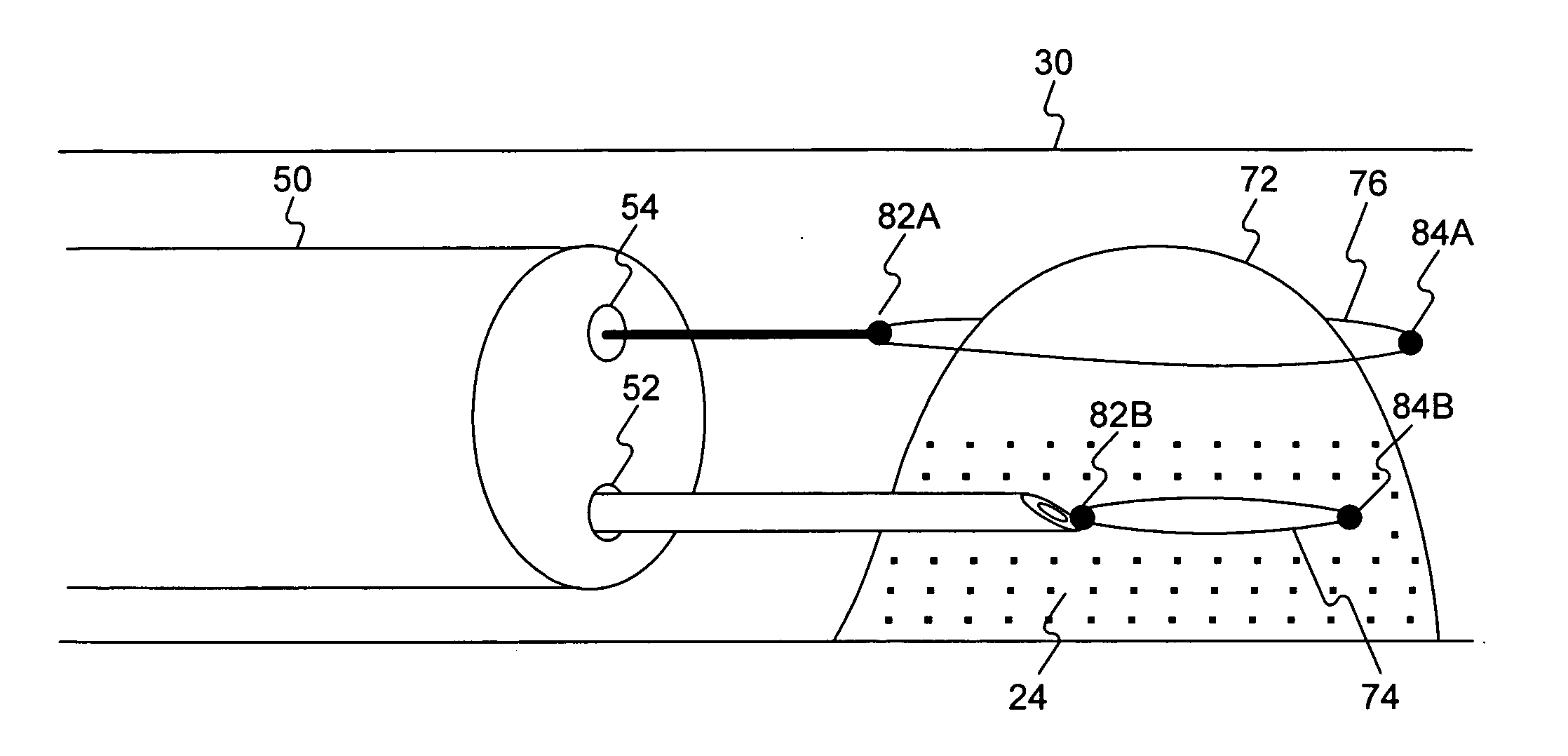
Maintenance of Bronchial Patency by Local Delivery of Cytotoxic, Cytostatic, or Anti-Neoplastic Agent
InactiveUS20150119850A1Keep openLimit recurrent bronchial occlusionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCytotoxicitySubmucosa
Methods for maintaining patency in a bronchus of a patient are presented. A catheter is positioned within the bronchus. A target region of one or more of a bronchial wall, submucosa, media, and adventitia is punctured at or adjacent a location of a debulked bronchial carcinoma with an injection needle disposed on a distal end of the catheter. Such puncturing is achieved by expanding a balloon disposed on the distal end of the catheter. The balloon is comprised of at least two materials of different elastic modulus, which allows for a flexible but relatively non-distensible, unfolding component of the balloon as well as an elastomeric, inflatable component of the balloon. Through the injection needle, an amount of cytotoxic, cytostatic, or anti-neoplastic agent is delivered to the target region. The delivered amount is effective to limit by a therapeutically beneficial amount recurrent bronchial occlusion due to recurrence of the bronchial carcinoma.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
Growth factor modified extracellular matrix material and methods for preparation and use thereof
ActiveUS20080299171A1Promote wound repairPromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Described are tissue graft constructs that include submucosa and other extracellular matrix materials that incorporate a number of exogenous proteins. Further described are methods for making tissue graft constructs that include stripping endogenous heparin binding proteins from a porcine graft material and thereafter binding one or more human growth factors to the native heparin molecules that are retained within the graft material. Such graft materials may be used in methods for the treatment of wounds in patients.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Reagent for detecting clostridium symbiosum and application thereof
InactiveCN105803061AEasy to judgeIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesFeces
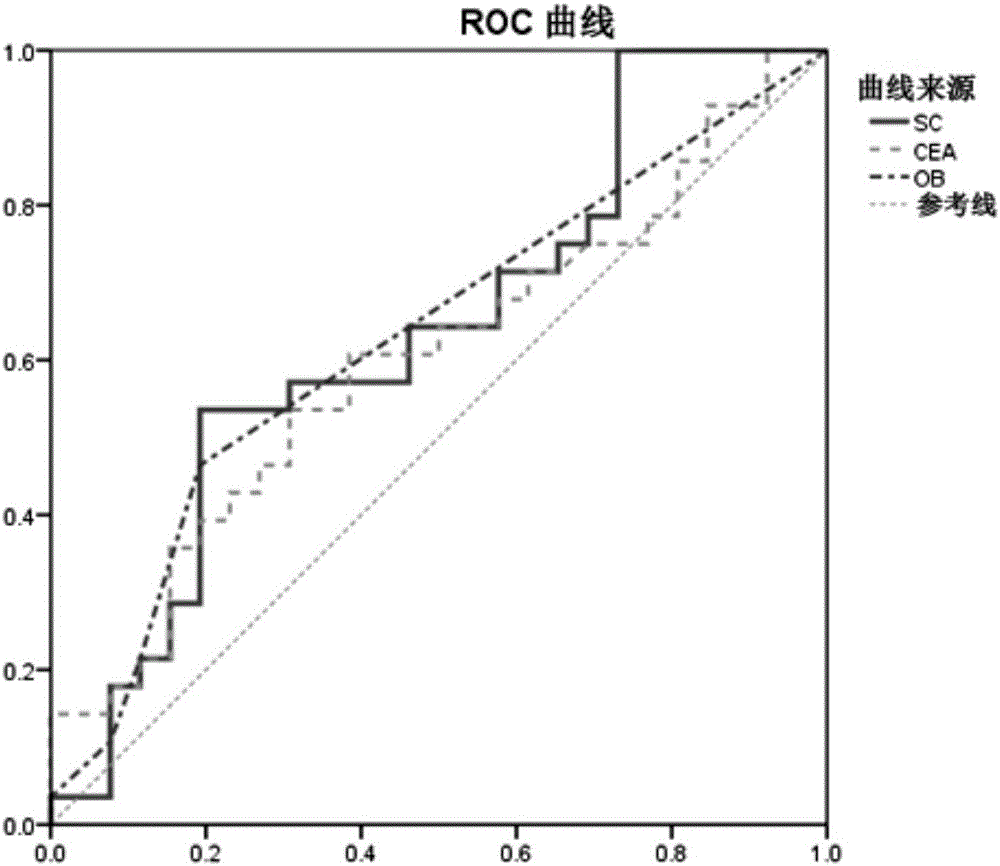
The invention discloses an application of the reagent for detecting clostridium symbiosum in preparing an early colorectal cancer diagnostic kit. According to the diagnostic kit, DNA of bacteria in excrement is extracted and a quantitative polymerase chain reaction is conducted so that the feature of relative abundance of the clostridium symbiosum can be acquired, and diagnosis of early colorectal cancers (limited to the colon cancer and the rectal cancer of submucosa) is conducted with the feature as a basis. Compared with noninvasive colorectal cancer screening methods applied to clinics at present and applied for a patent, the regent is completely noninvasive, operation is relatively easy and low in price, the colorectal cancers can be predicted more accurately, and the area under curve (AUC value) of an ROC curve is 0.70 or above.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Systems and methods of treating malacia by local delivery of hydrogel to augment tissue
ActiveUS20160243333A1Keep openLimit recurrent bronchial occlusionOrganic active ingredientsBalloon catheterSubmucosaBronchial cartilage
Systems, devices, and methods for maintaining patency in a bronchus of a patient are presented. A catheter is positioned within the bronchus. A target region of one or more of a bronchial wall, submucosa, media, and adventitia is punctured with an injection needle disposed on a distal end of the catheter. Such puncturing is achieved by expanding a balloon disposed on the distal end of the catheter. The balloon may be comprised of at least two materials of different elastic modulus, which allows for a flexible but relatively non-distensible, unfolding component of the balloon as well as an elastomeric, inflatable component of the balloon. Through the injection needle, an amount of one or more crosslinking agents is delivered to the target region. The delivered amount is effective to provide structural support for the bronchial wall, substituting for the bronchial cartilage thereby treating bronchomalacia.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
Traditional Chinese medicinal enema for treating chronic colitis
ActiveCN102727622AEnhance immune functionPromote local blood circulationDigestive systemPlant ingredientsToxic materialLicorice roots
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal enema for treating chronic colitis. According to the traditional Chinese medicinal science, the pathogenesis of chronic colitis is mainly due to syndromes of dampness-heat due to spleen deficiency and qi depression to blood stasis, especially develops in colonic mucosa and submucosa inflammation and ulcer changes, and is characterized by stomachache, diarrhea, mucous bloody stool and tenesmus in clinic. Therefore, traditional Chinese medicines, which have effects of clearing heat, drying damp, diminishing swelling, promoting granulation,removing pattogenic heat from the blood and toxic material from the body, relieving diarrhea, diminishing inflammation, resolving tetany and relieving pain, including traditional Chinese medicinal Swamp Mahogany Leaf, champion dutchmanspipe root, mongolian oak bark, Scutellaria baicalensis, cortex fraxini, Cape jasmine, Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae, licorice root, Codonopsis pilosula, cortex albiziae, fruits of Litsea rubescens, cortex cinnamomi and hurricane lamp, are selected to be made into the enema. Through clinical tests of our public health centre, the total effective rate of theenema reaches 96.3% and it is obviously better than a control group. In addition, patients have no adverse reaction after taking the medicine. Therefore, the medicine is worth of clinical popularization and application.
Owner:南通东湖国际商务服务有限公司
Multi-formed collagenous biomaterial medical device
InactiveUS8882850B2Improve welfareMore remodelingPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySubmucosaMedical device
A collagenous biomaterial medical device comprising a molded sponge material formed from comminuted submucosa fragments that have not been cross-linked with a cross-linking agent, wherein said submucosa has at least one biotropic agent, and wherein said biotropic agent is a growth factor is disclosed.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
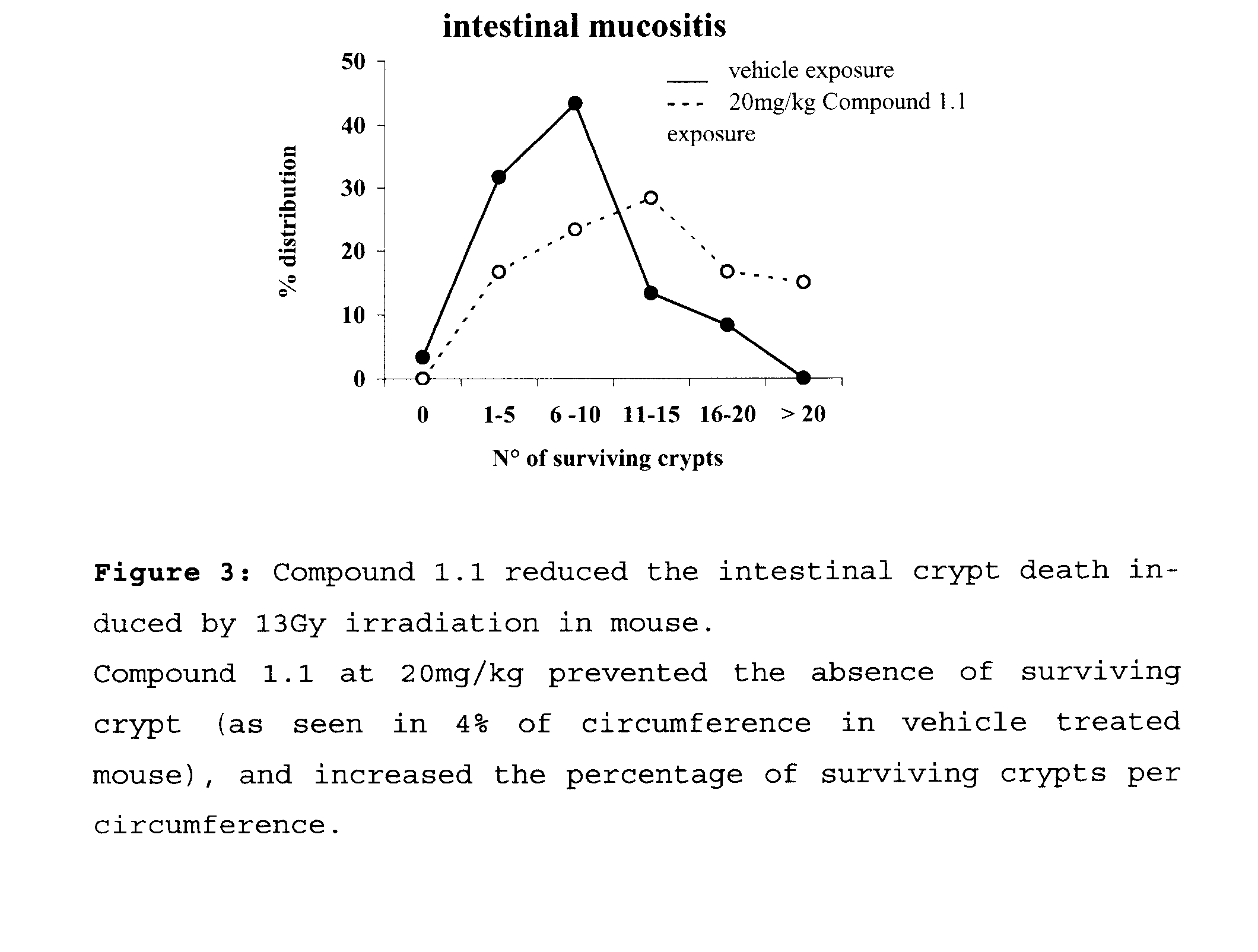
Benzamidine Derivatives for Treatment and Prevention of Cancer Therapy Induced Mucositis
InactiveUS20080194877A1Isocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCancer preventionSide effect
Mucositis is the result of a complex process of interactive biologic phenomena that take place in both the epitelium and the submucosa, often leading to severe pain and increased risk of dangerous syste f48 mic infections. Mucositis is often a side effect during chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The benzamidine derivatives herein described are particularly effective for treating and preventing mucositis since they are acting simultaneously at the several phases that characterize this disease. Data supplied from the esp@cenet database
Owner:ROTTAPHARM SPA
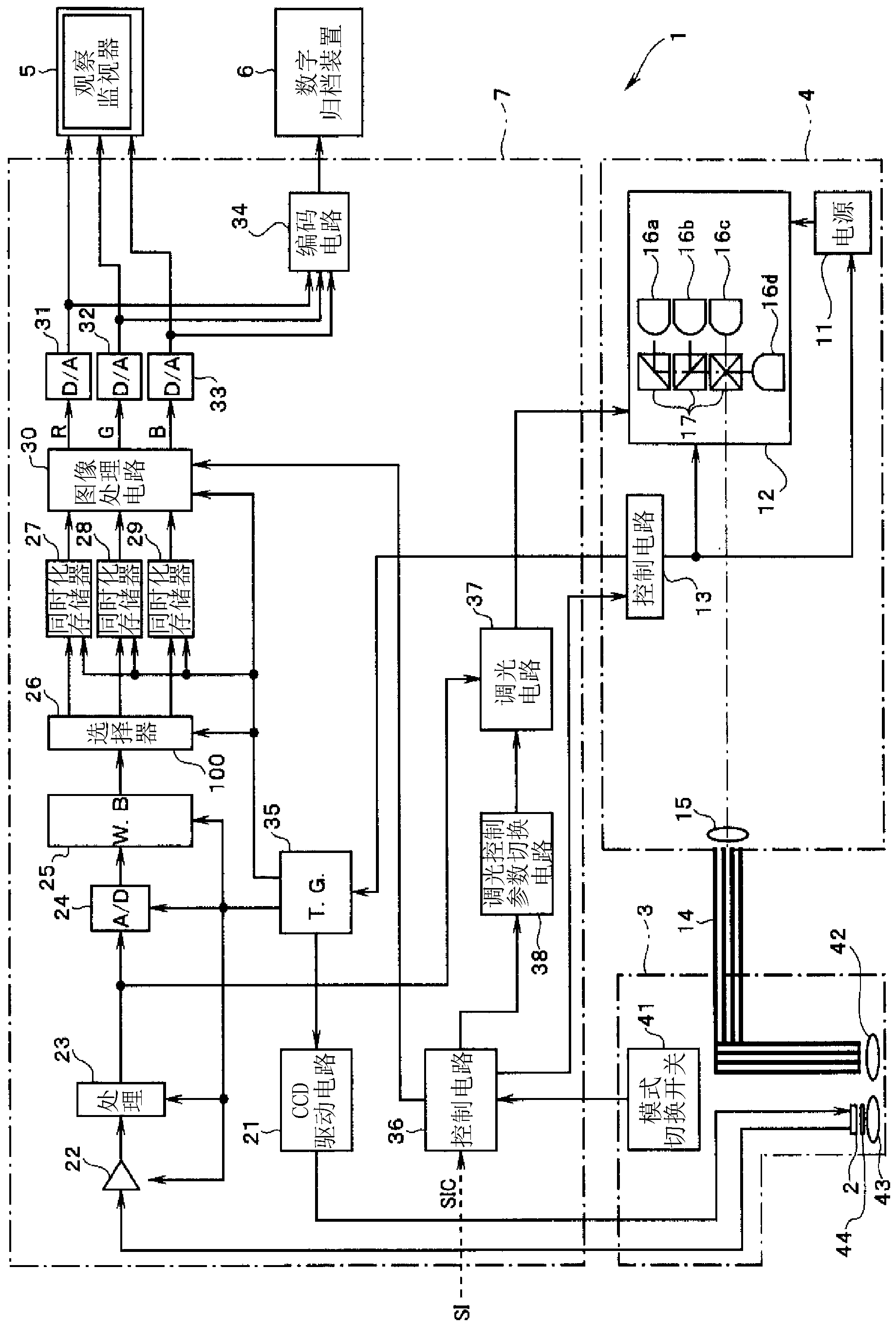
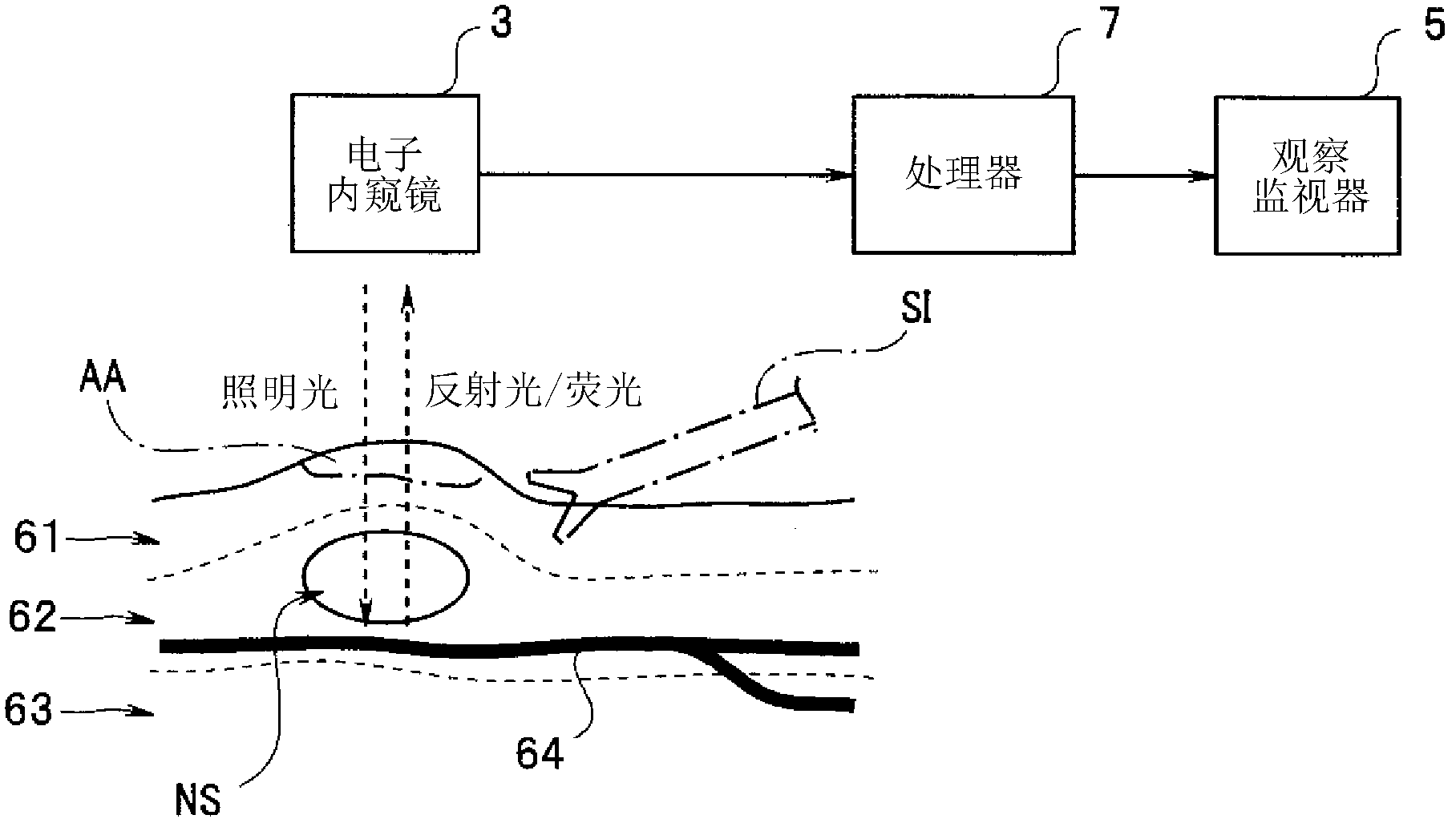
Endoscope device
An endoscope device (1), which comprises a light source (4), an endoscope (3), a processor (7) and a viewing monitor (5). The light source (4) switches the illumination light from an excitation light (EX) for exciting a connective tissue in the submucosa of a tissue within a body cavity to a narrowband light (NBa) that is absorbed by a blood vessel (64) running through the submucosa (62) or muscularis propria (63) and a narrowband light (NBb) that is absorbed by a substance topically injected into the submucosa (62). The processor (7) generates multiple image signals, said image signals having been obtained by taking images with CCD2 of the endoscope (3), and the viewing monitor (5) synthesizes and displays multiple images.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Biological sponge based on acellular small intestinal submucosa and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110051884AGood effectPromote ingrowthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationSubmucosaPepsin
The invention discloses a biological sponge based on the acellular small intestinal submucosa and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the acellular porcine small intestinal submucosa, pepsin enzymatic hydrolysis, washing, lyophilization, pulverization and cross-linking. According to the preparation method, the porcine small intestinal submucosa istaken as a source; after the decellularization treatment, the immunological rejection is extremely small. At the same time, the cross-linking treatment is carried out by using a non-toxic cross-linking agent to ensure the biosafety of the obtained product. The product can be used not only for wound repair, but also as an excellent tissue engineering skin scaffold material. The product is sufficient in source, safe and reliable, cheap and easy to obtain. The composition and structure are similar to the humans. No ethical problems exist, and scale industrial preparation can be facilitated.
Owner:上海仁康科技有限公司
Uterine cavity implant as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a uterine cavity implant as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The uterine cavity implant is characterized by having a bagged structure. The uterine cavity implant comprises a substrate material of animal small intestine submucosa subjected to decellularization treatment. An implantable medical device for preventing and treating intrauterine adhesion comprises a biological tissue substrate material. The present decellularization technology for a biological repairing material is improved; compared with the present product, the biological tissue substrate material provided by the invention has the advantages of lower DNA residual quantity, lower immunogenicity, higher anti-infection capacity and higher repairing capacity; and the uterine cavity implant is beneficial to the recovering of tissues, such as, uterine cavity base layer, submucosa and mucous layer. Besides, the invention prepares the biological repairing material into the uterine cavity built-in structure which is used for isolating wound surfaces, repairing uterine cavity tissues and reducing scar forming, so that the intrauterine adhesion problem is solved, and the accordingly generated sterility problem also can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSIS HEALING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Traditional Chinese medicine naristillae for treating migraine
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine naristillae for treating migraine. Traditional Chinese medical science considers that migraine is caused by external infection of six evils, infection of bump top and interference of lucid yang or improper diet, causes internal injury of spleen and kidney, and causes viscera disorder, qi and blood disorder and obstruction of meridians. Therefore, in the invention, traditional Chinese medicines such as flower bud of lily magnolia, radix angelicae, fructus viticis, corydalis tuber, pinellia cordata, ligusticum sinense, tuber fleeceflower stem, fructus piperis longi and borneol for dredging qi and dispelling wind and removing obstruction in the meridians are selected to prepare the naristillae. Clinical experiments in our hospital show that the total effective rate achieves 97.5 percent which is obviously better than that of a control group, and the time for headache remission is shorter than that of the control group. Clinical observation shows that treating migraine using the naristillae sufficiently utilizes the characteristic that the nasal cavity submucosa has abundant blood capillary and is poriferous and the advantage that medicine easily penetrates into blood and issue. The traditional Chinese medicine naristillae has the advantages of high curative effect, low dosage, convenience in use, no adverse reaction and the like.
Owner:任永强
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com