Patents
Literature
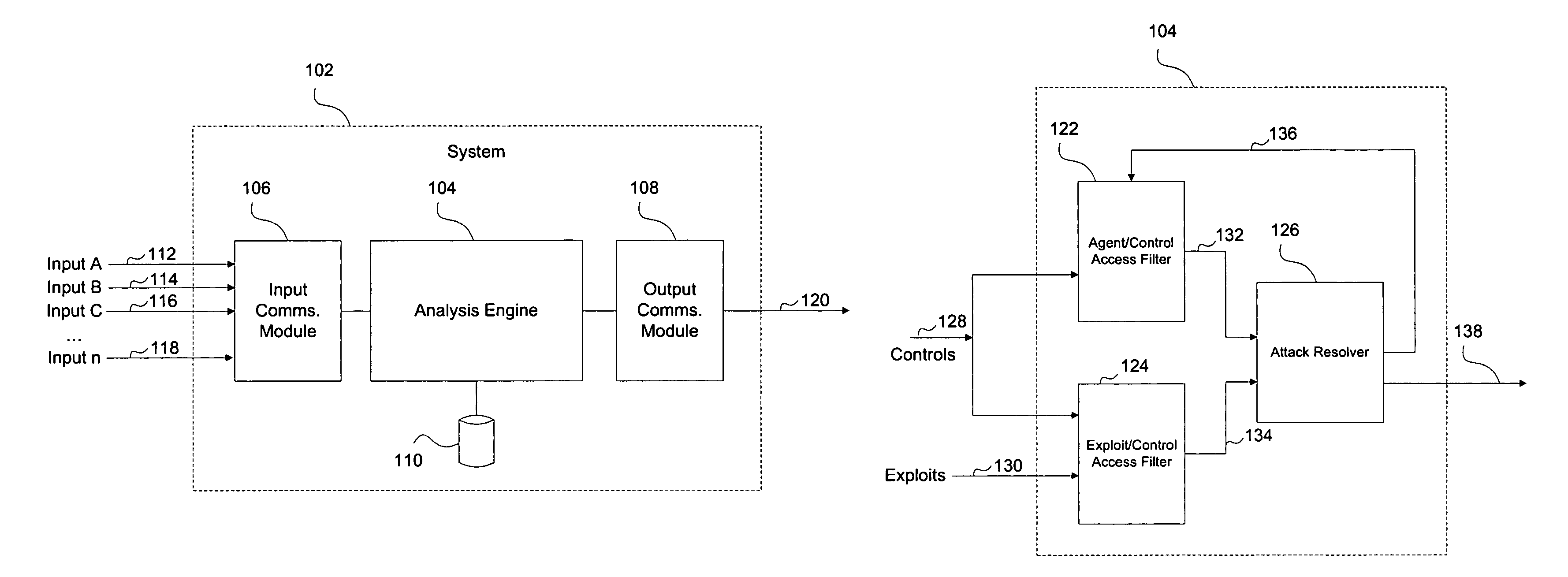
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1201 results about "Chain reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events.
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
InactiveUS20050164241A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionComponent separationOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains ≦500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of <500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising ≦500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Threat analysis
InactiveUS7530104B1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionChain reactionPenetration test
Virtual penetration testing using threat analysis is disclosed. Threat analysis may be achieved by evaluating attack paths and chain reactions of compromised assets created by threats, threat agents, or threat mechanisms. A threat agent having an existing access level is identified. The existing access level is used to analyze an attack path between the threat agent and an asset. The existing access level is updated if the analysis of the attack path between the threat agent and the asset indicates that an attack along the path would be successful.
Owner:GEN DIGITAL INC
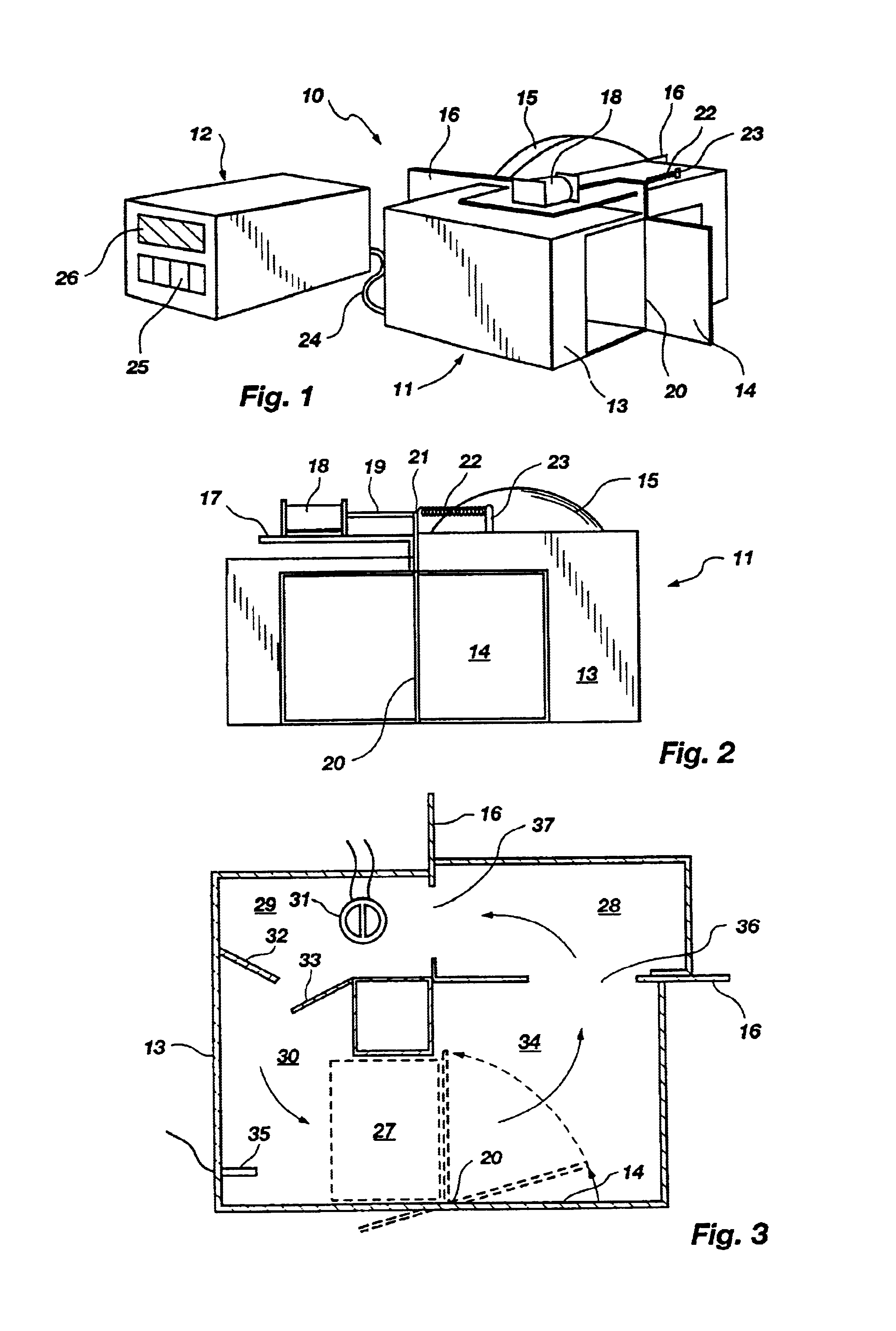
Devices and methods for the performance of miniaturized in vitro amplification assays
InactiveUS6706519B1Optimize thermal cycling parametersEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCentripetal forcePolymerase chain reaction
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The invention specifically provides devices and methods for performing miniaturized in vitro amplification assays such as the polymerase chain reaction. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing PCR are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG +1
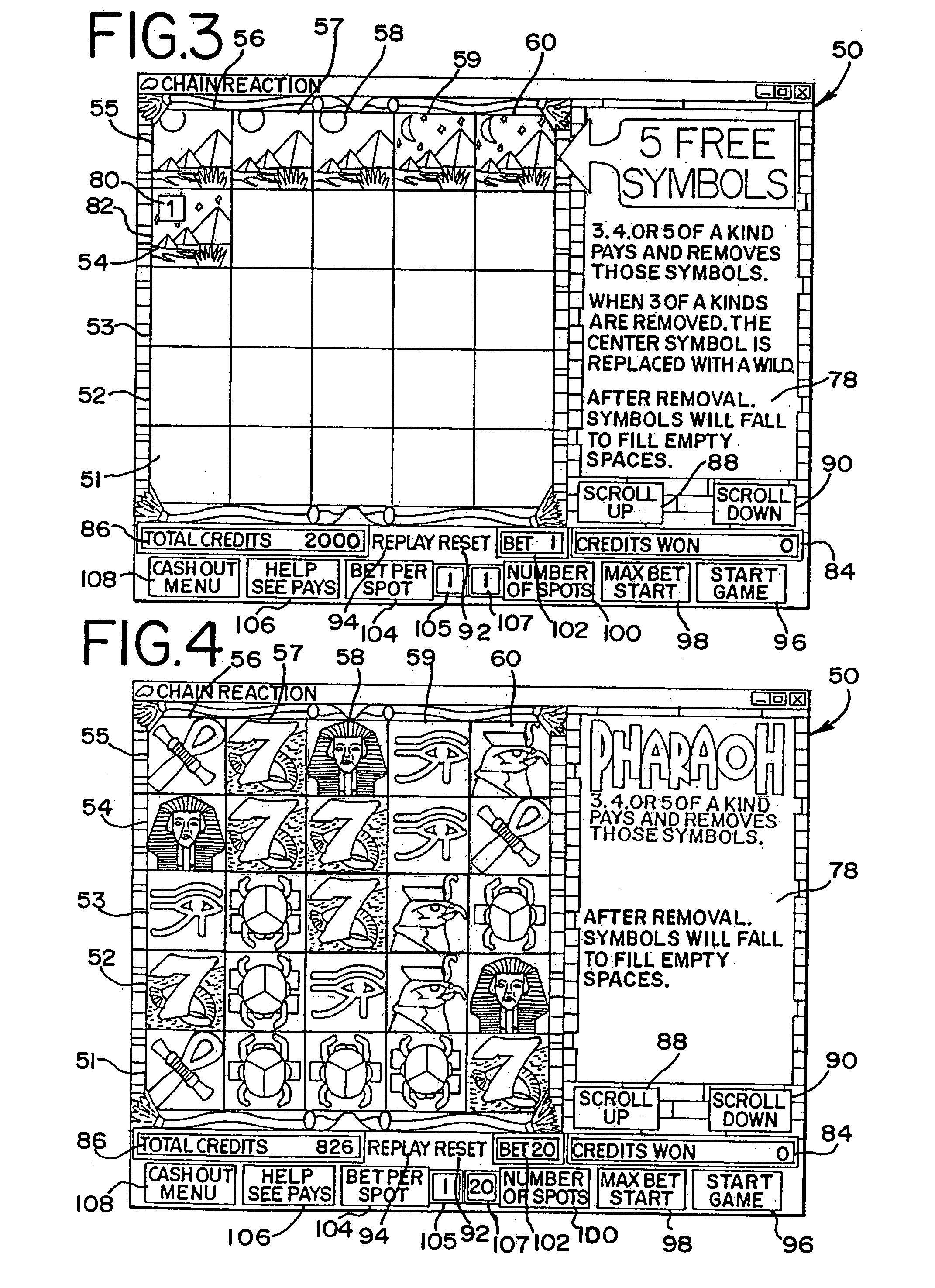
Chain reaction game
A game, gaming machine apparatus and game method wherein game elements are assigned to a matrix of game element locations. Play is initiated by evaluating the game elements for predetermined transformative conditions, such as a match of game elements. If a transformative condition is found, the game element(s) are transformed with at least one being removed from the matrix. The remaining game elements are moved, if permitted, according to a movement methodology. The steps of evaluating, transforming, removing, and moving the remaining game elements are repeated so long as a transformation is subsequently available for continued gameplay.
Owner:CASE VENTURE MANAGEMENT
LED or laser enabled real-time PCR system and spectrophotometer
InactiveUS7122799B2Easy to useReduce entirely avoid costRadiation pyrometryHeating or cooling apparatusPhotodetectorUltraviolet
A system for conducting a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay upon a collection of samples is disclosed. The PCR assay is performed by absorption detection. The system includes a multi-well plate which is adapted to retain a collection of sample wells. This system includes a thermal cycler for the multi-well plate. The system additionally includes a collection of photodetectors, and a corresponding number of light sources. The light sources are positioned such that light emitted from each of the respective light sources passes through a corresponding well retained in the multi-well plate and to a corresponding photodetector. The system also includes a processor or other means for analyzing the output signals from the photodetectors. In certain versions of the system, ultra-violet light is used.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
ActiveUS20080071076A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionSugar derivativesOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains .Itoreq.500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of .Itoreq.500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising .Itoreq.500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
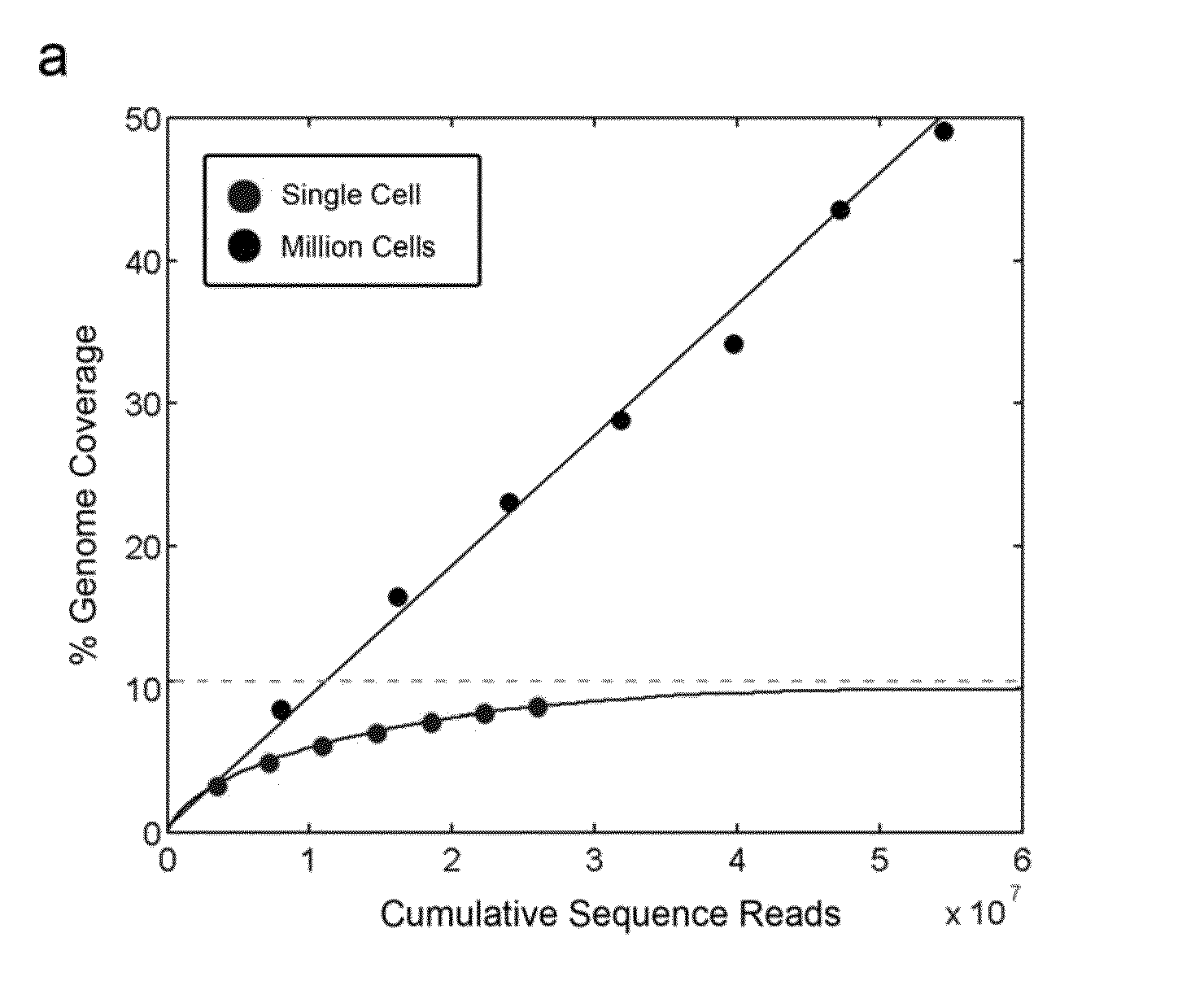
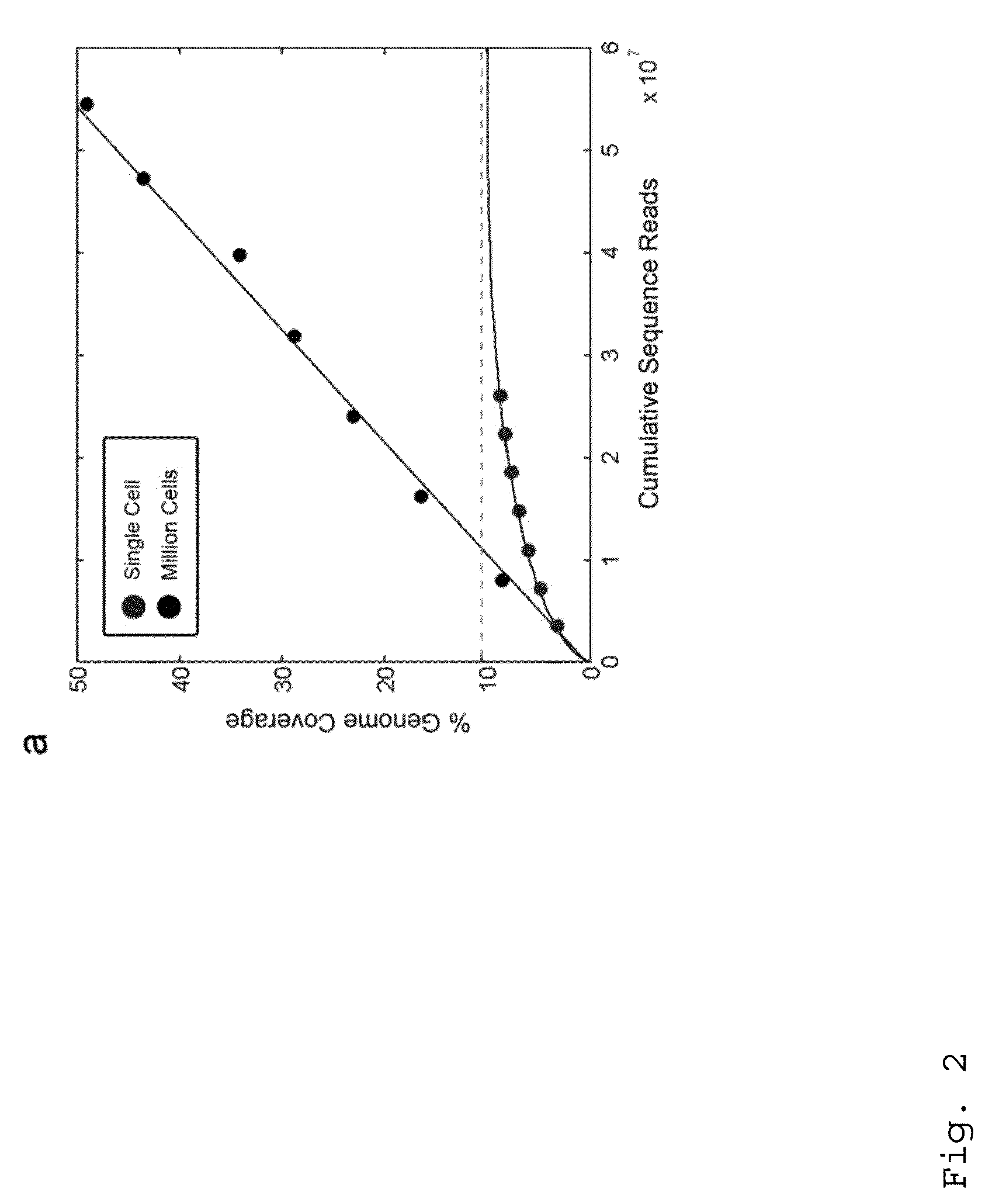
Varietal counting of nucleic acids for obtaining genomic copy number information
A method for obtaining from genomic material genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion, comprising obtaining segments of the genomic material, tagging the segments with substantially unique tags to generate tagged nucleic acid molecules, such that each tagged nucleic acid molecule comprises one segment of the genomic material and a tag, subjecting the tagged nucleic acid molecules to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, generating tag associated sequence reads by sequencing the product of the PCR reaction, assigning each tagged nucleic acid molecule to a location on a genome associated with the genomic material by mapping the subsequence of each tag associated sequence read corresponding to a segment of the genomic material to a location on the genome, and counting the number of tagged nucleic acid molecules assigned to the same location on the genome having a different tag, thereby obtaining genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
System and method for fluorescence monitoring
InactiveUS7081226B1Easy to controlHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDna amplification
A thermal cycling method and device is disclosed. The device comprises a sample chamber whose temperature can be rapidly and accurately modulated over a range of temperatures needed to carry out a number of biological procedures, such as the DNA polymerase chain reaction. Biological samples are placed in glass micro capillary tubes and then located inside the sample chamber. A programmable controller regulates the temperature of the sample inside the sample chamber. Monitoring of the DNA amplification is monitored by fluorescence once per cycle or many times per cycle. The present invention provides that fluorescence monitoring of PCR is a powerful tool for DNA quantification.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
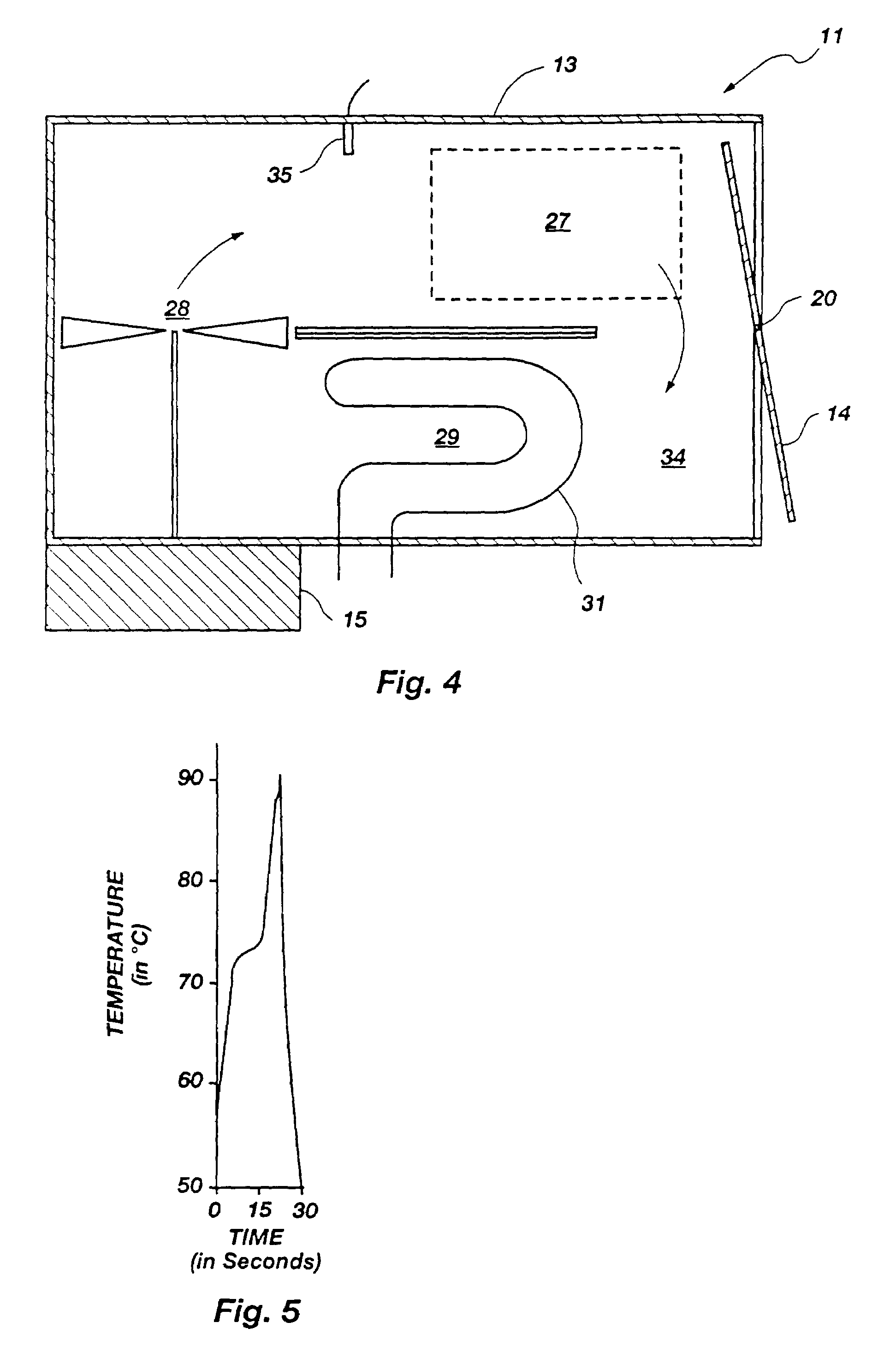
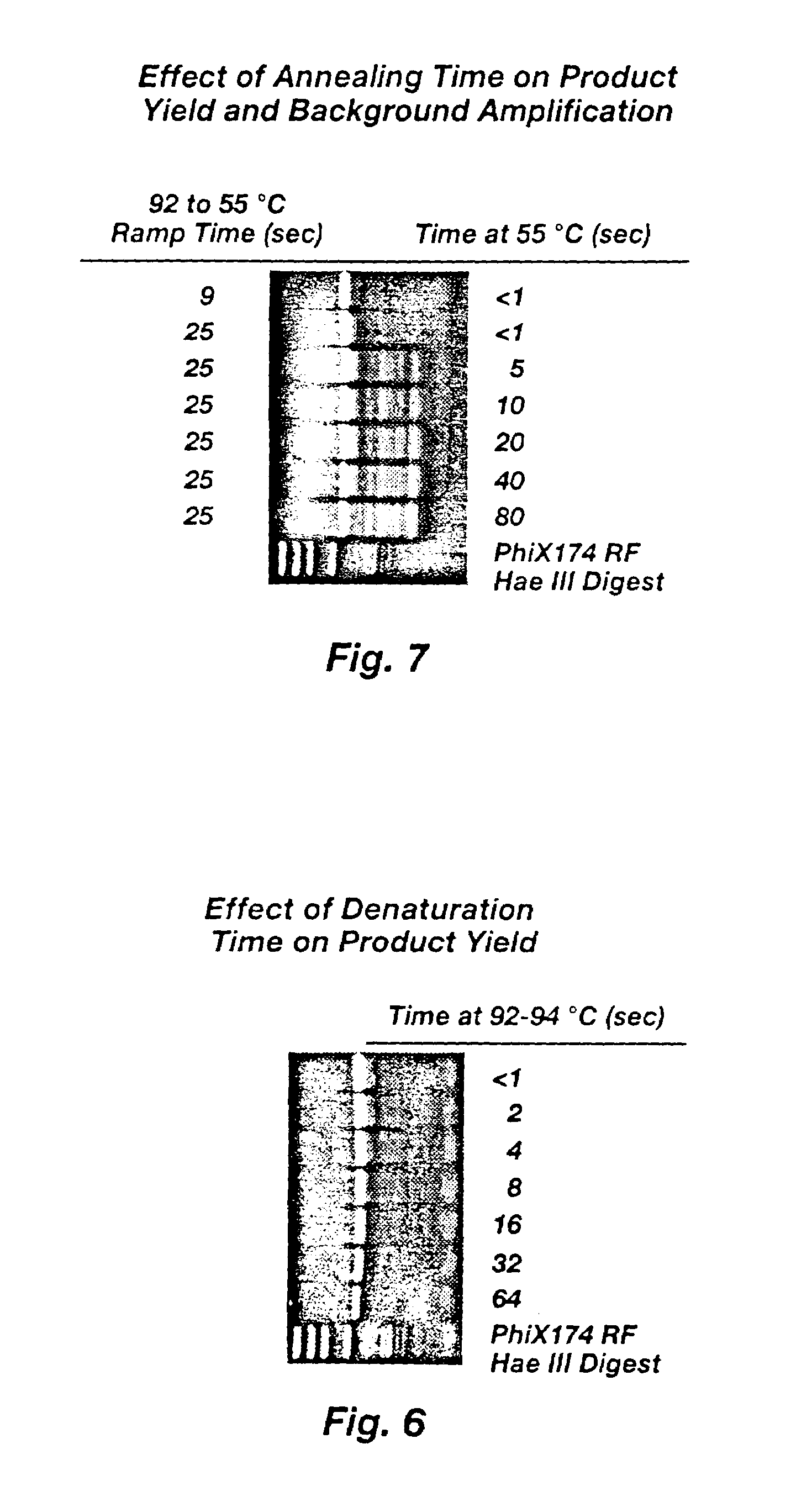
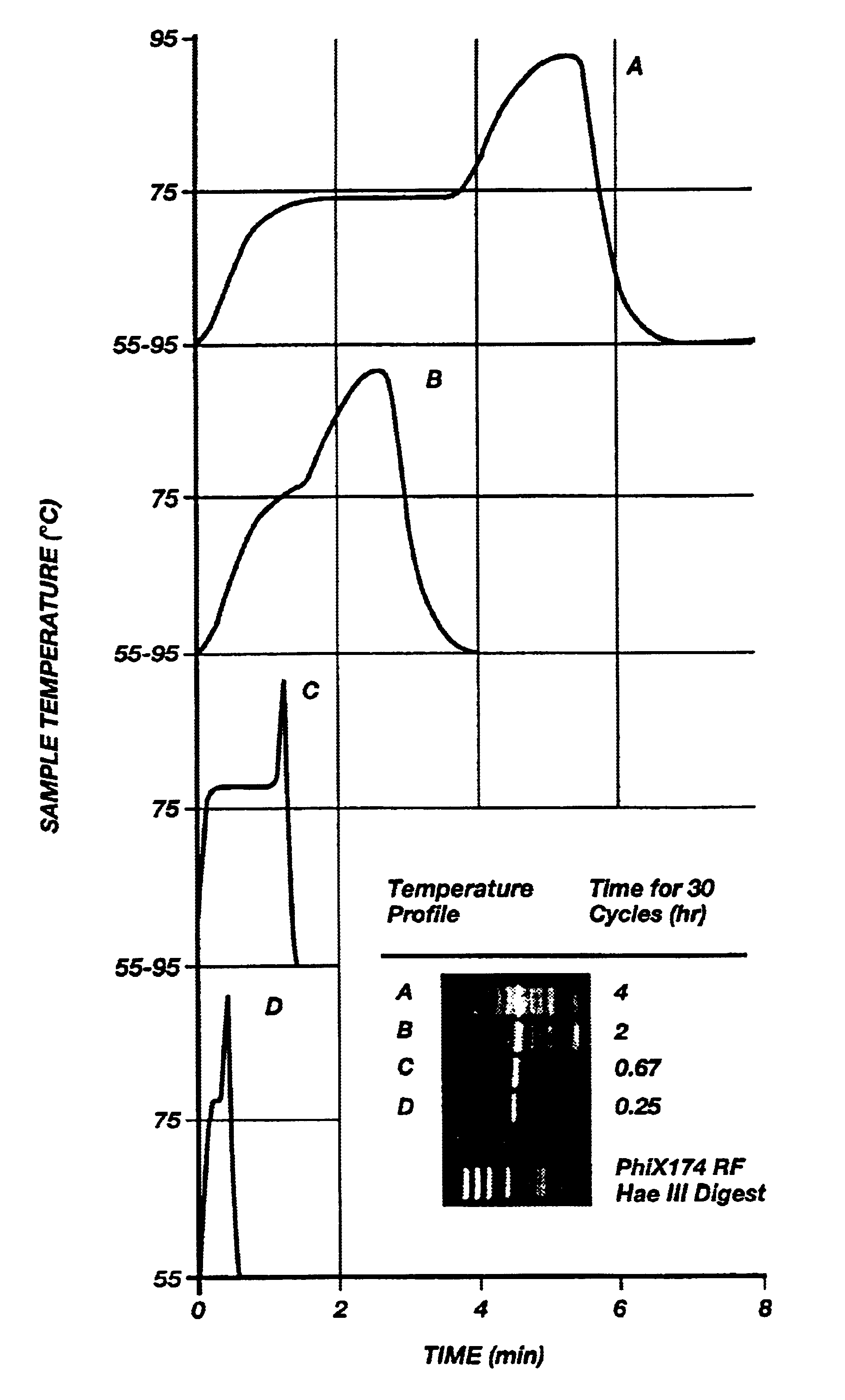
Method for rapid thermal cycling of biological samples
InactiveUS6787338B2Thermal massHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTime profileAmplification dna
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
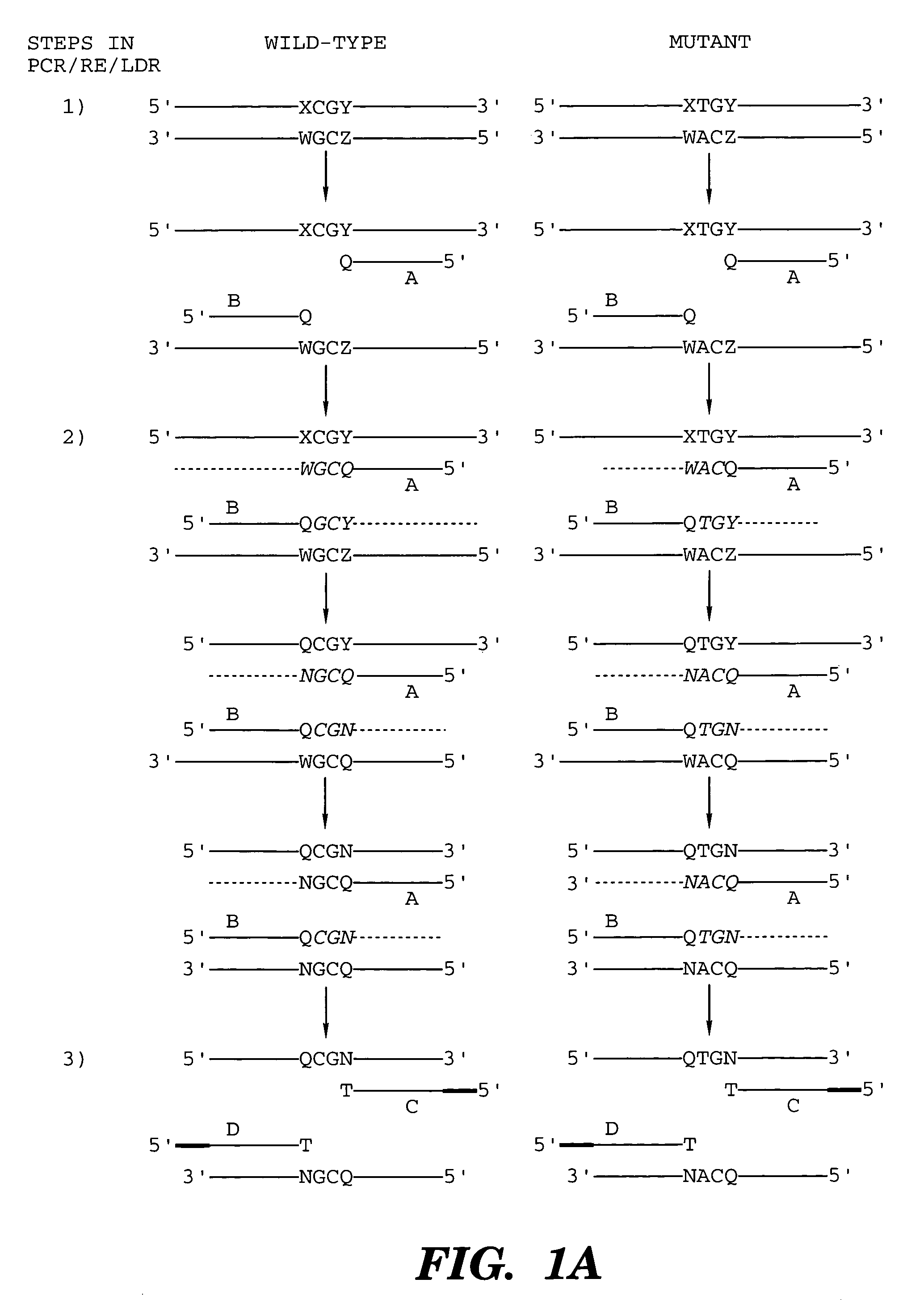
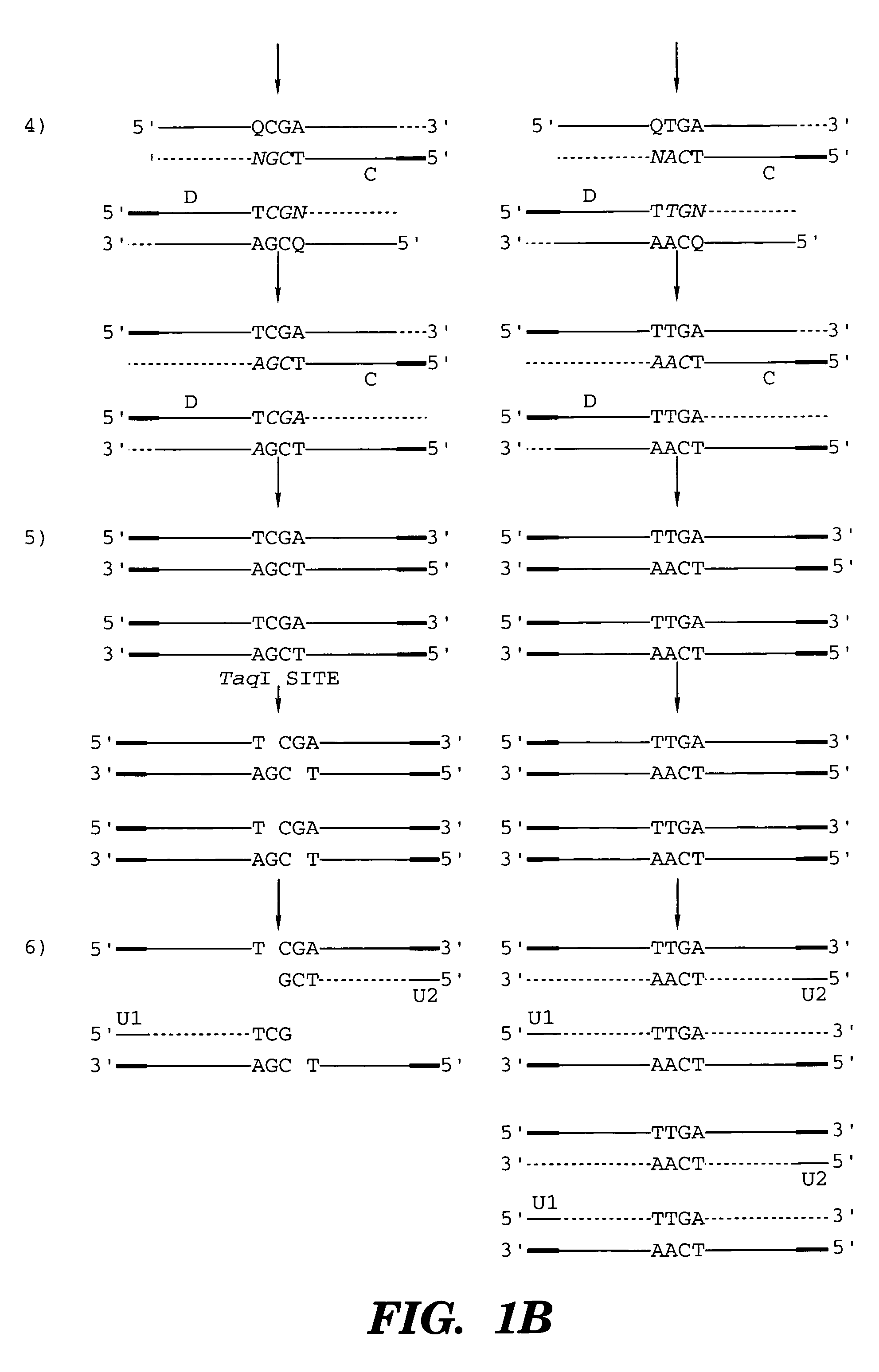
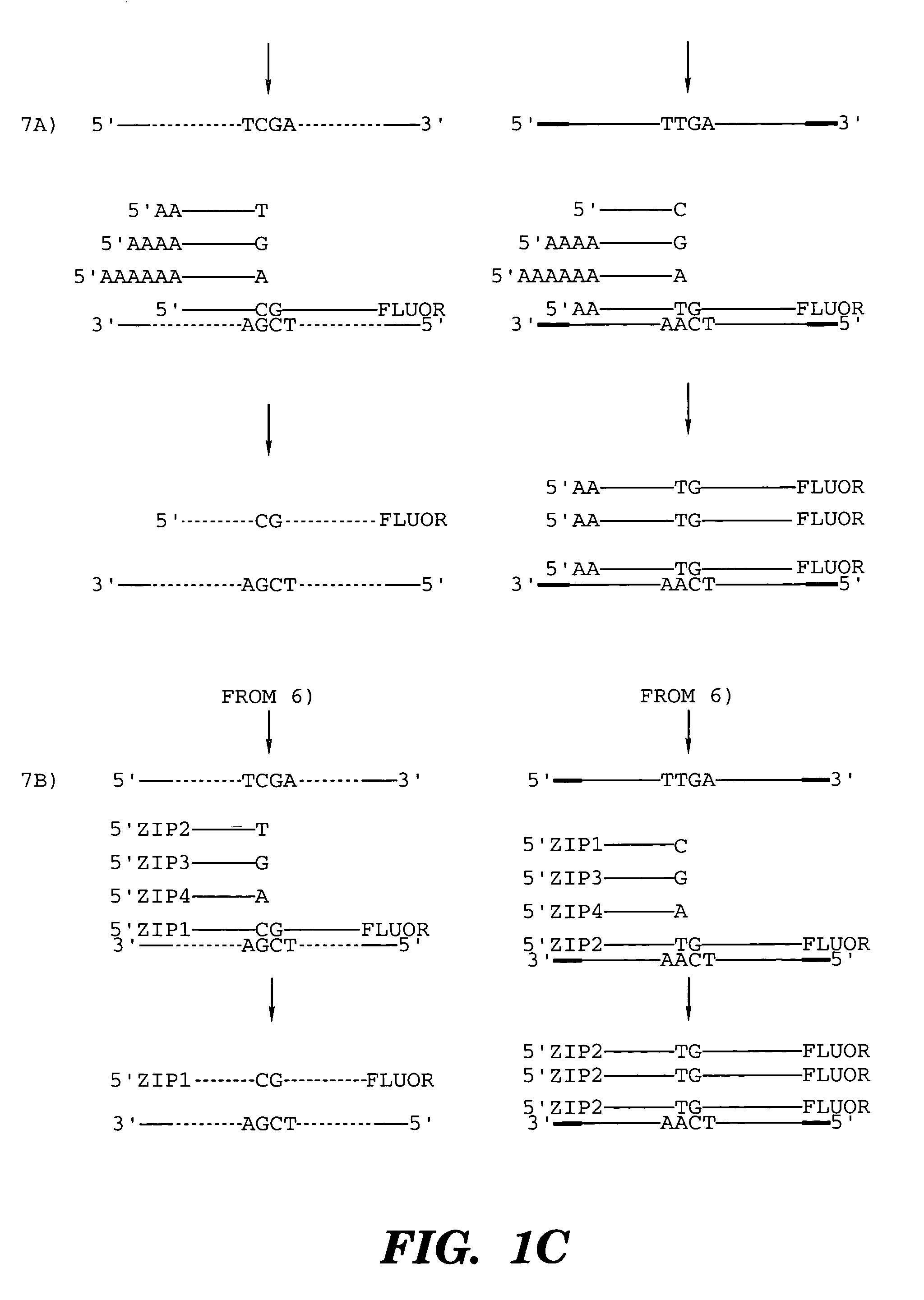
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
Devices and methods for the performance of miniaturized in vitro amplification assays
InactiveUS20040259237A1Temperature controlEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The invention specifically provides devices and methods for performing miniaturized in vitro amplification assays such as the polymerase chain reaction. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing PCR are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Methods and compositions for universal detection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110212846A1Increase distanceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolymerase chain reactionClinical settings
Provided are methods and compositions for detecting the presence or amount of one or more target nucleic acids in a sample. Methods of the present invention include linking universal nucleic acid segments into a single molecule in a linking reaction dependent on a target nucleic acid of interest. A variety of universal segment linking strategies are provided, including preamplification by polymerase chain reaction, ligation-based strategies, reverse transcription and linear polymerase extension. Linking the universal segments into a single molecule generates a tagged target nucleic acid which is detected in a manner dependent on an intramolecular interaction between one universal segment and a second portion of the tagged target nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, the intramolecular interaction includes the formation of a hairpin having a stem between a universal segment at one end of the tagged target nucleic acid and a second universal segment at the opposite end of the tagged target nucleic acid. A variety of detection formats are provided, including solution-phase and surface-based formats. The methods and compositions are well-suited for highly multiplexed nucleic acid detection, and are applicable for the detection of any target nucleic acid of interest in both research and clinical settings.
Owner:UNITAQ BIO
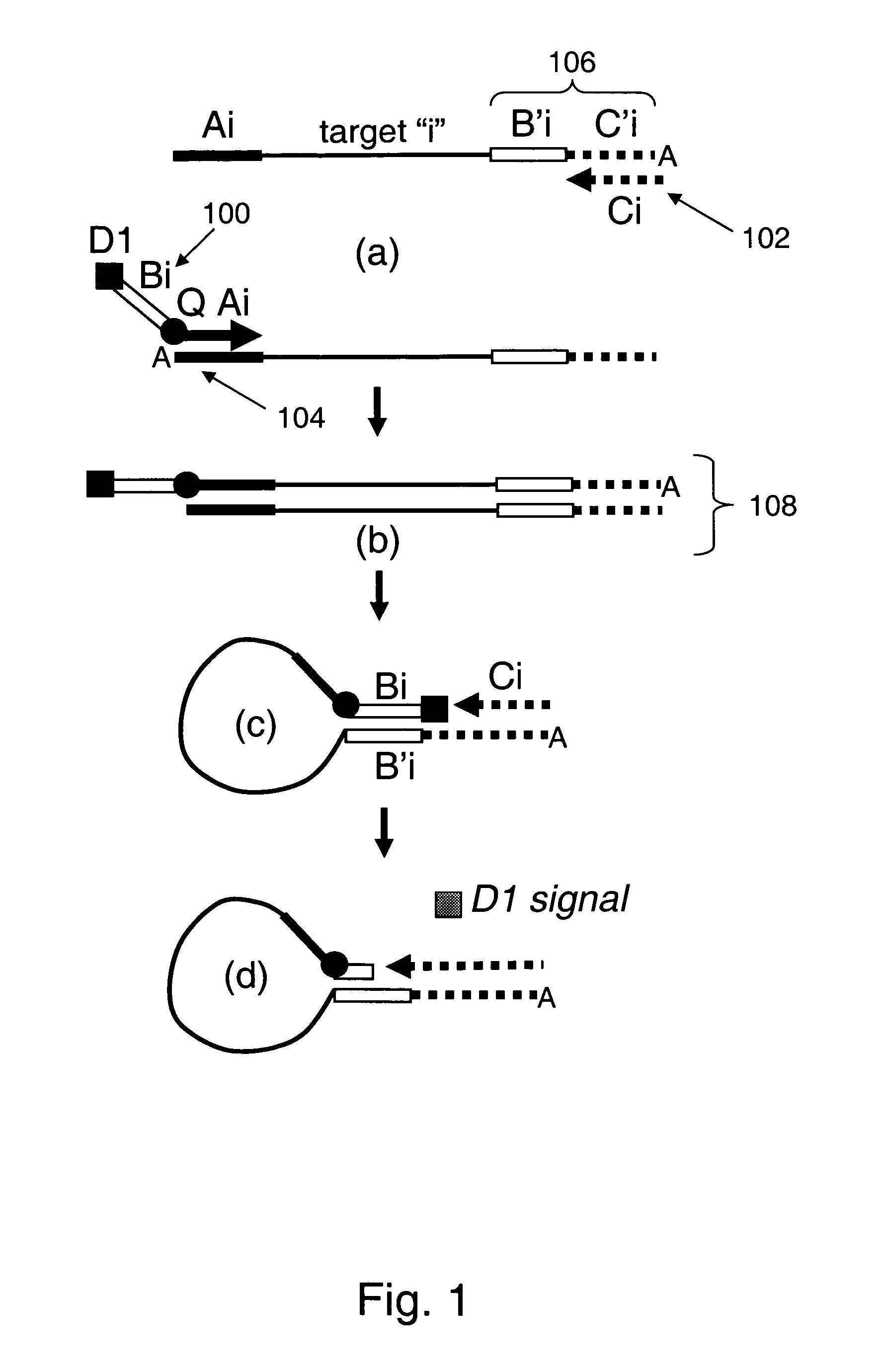
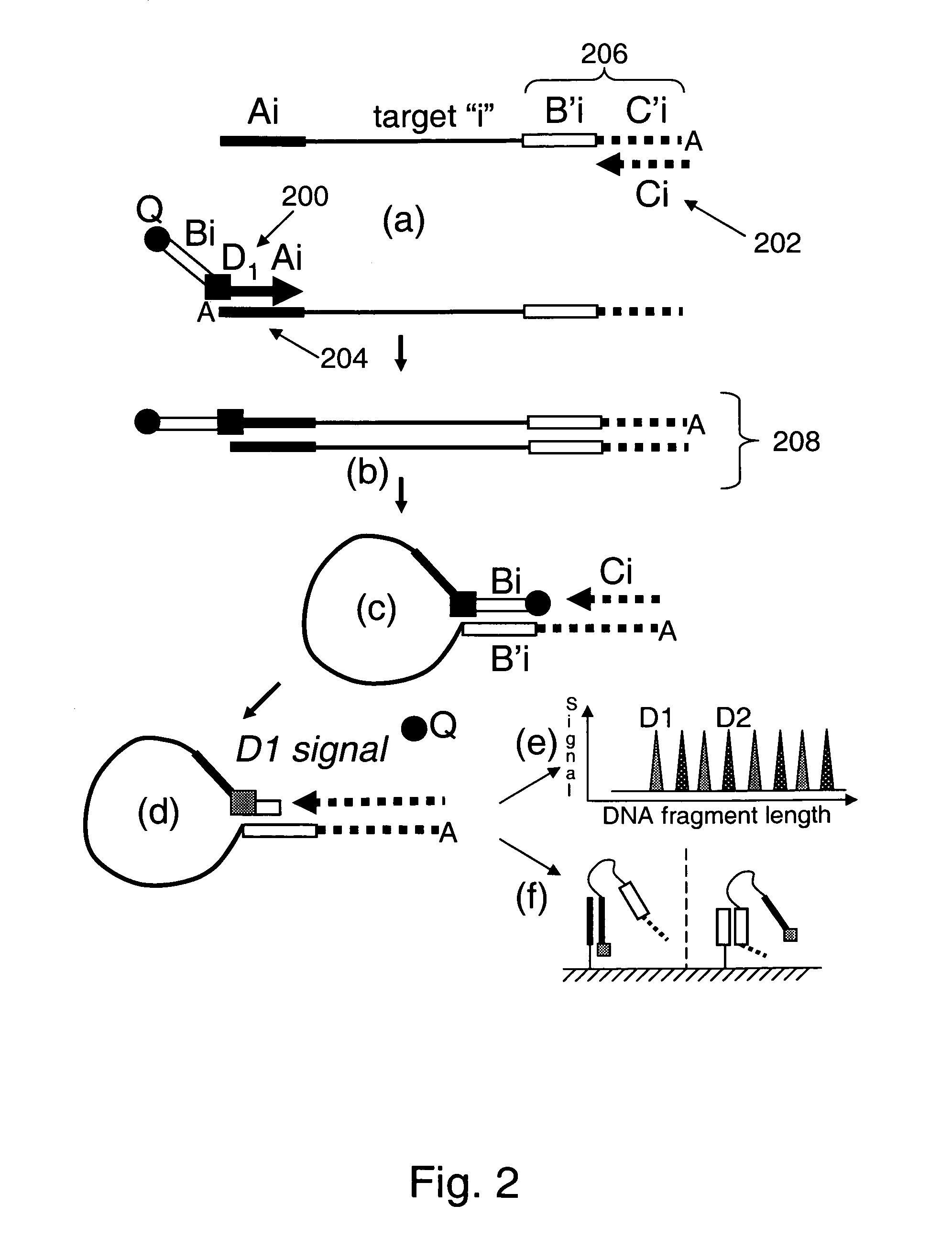
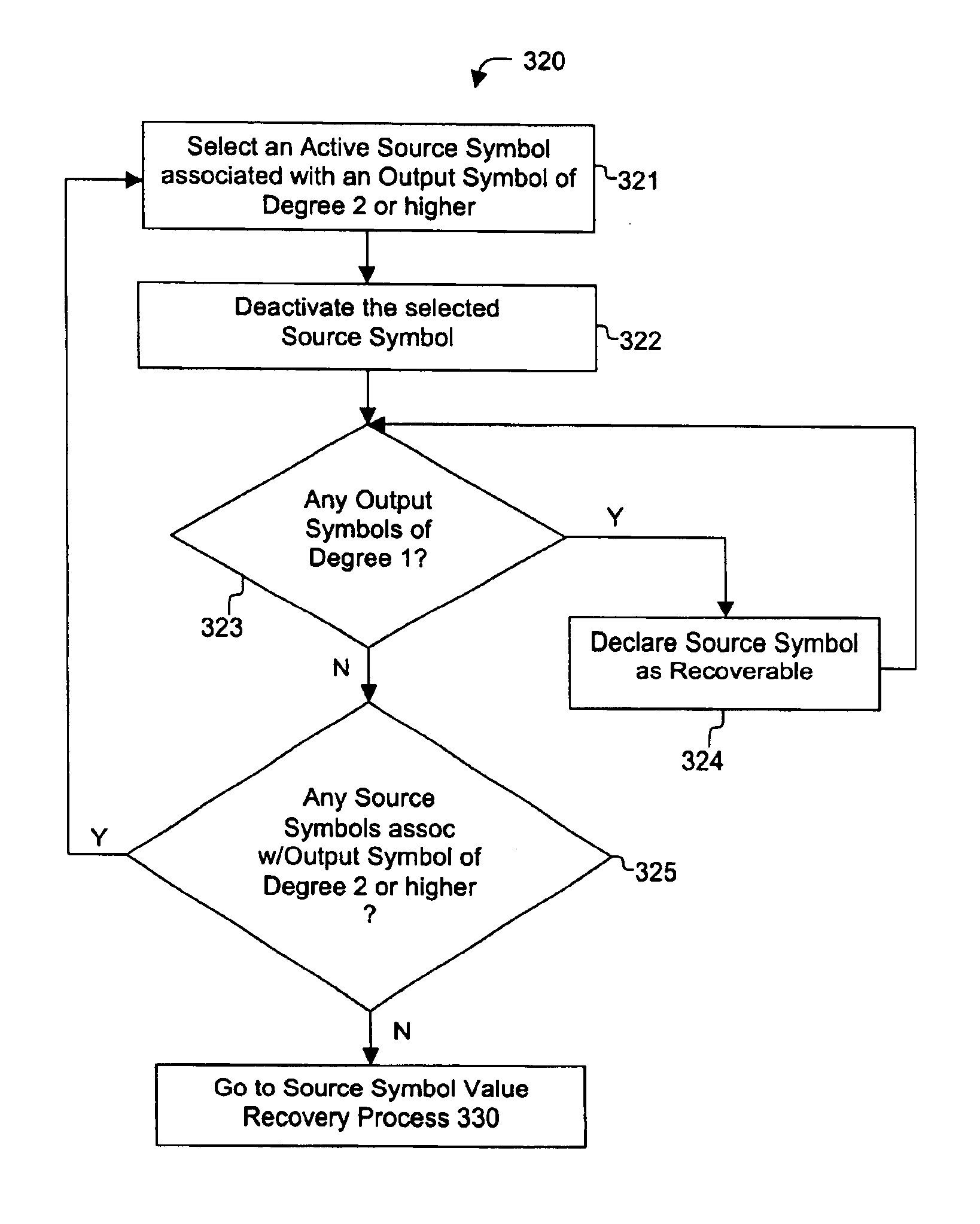
Systems and processes for decoding chain reaction codes through inactivation
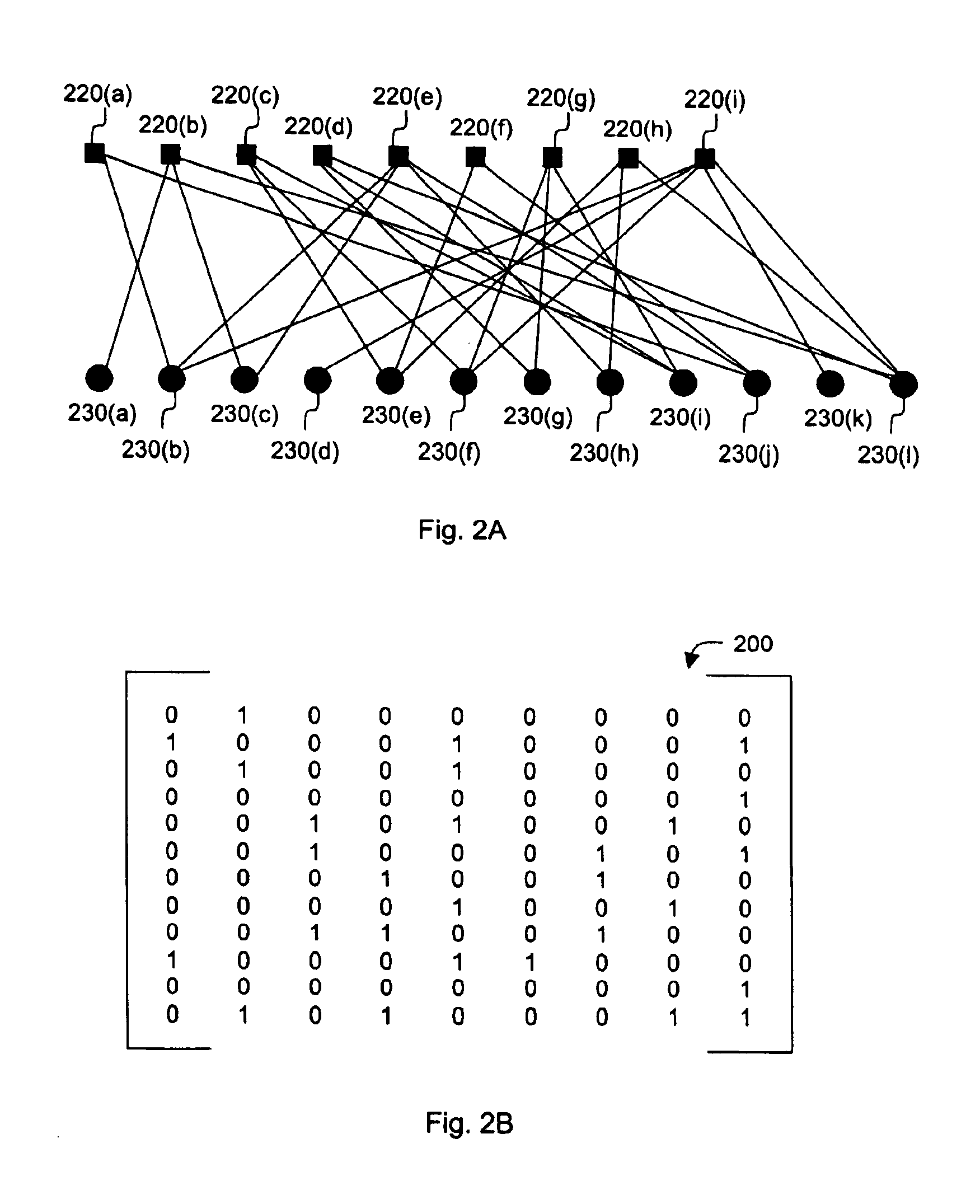
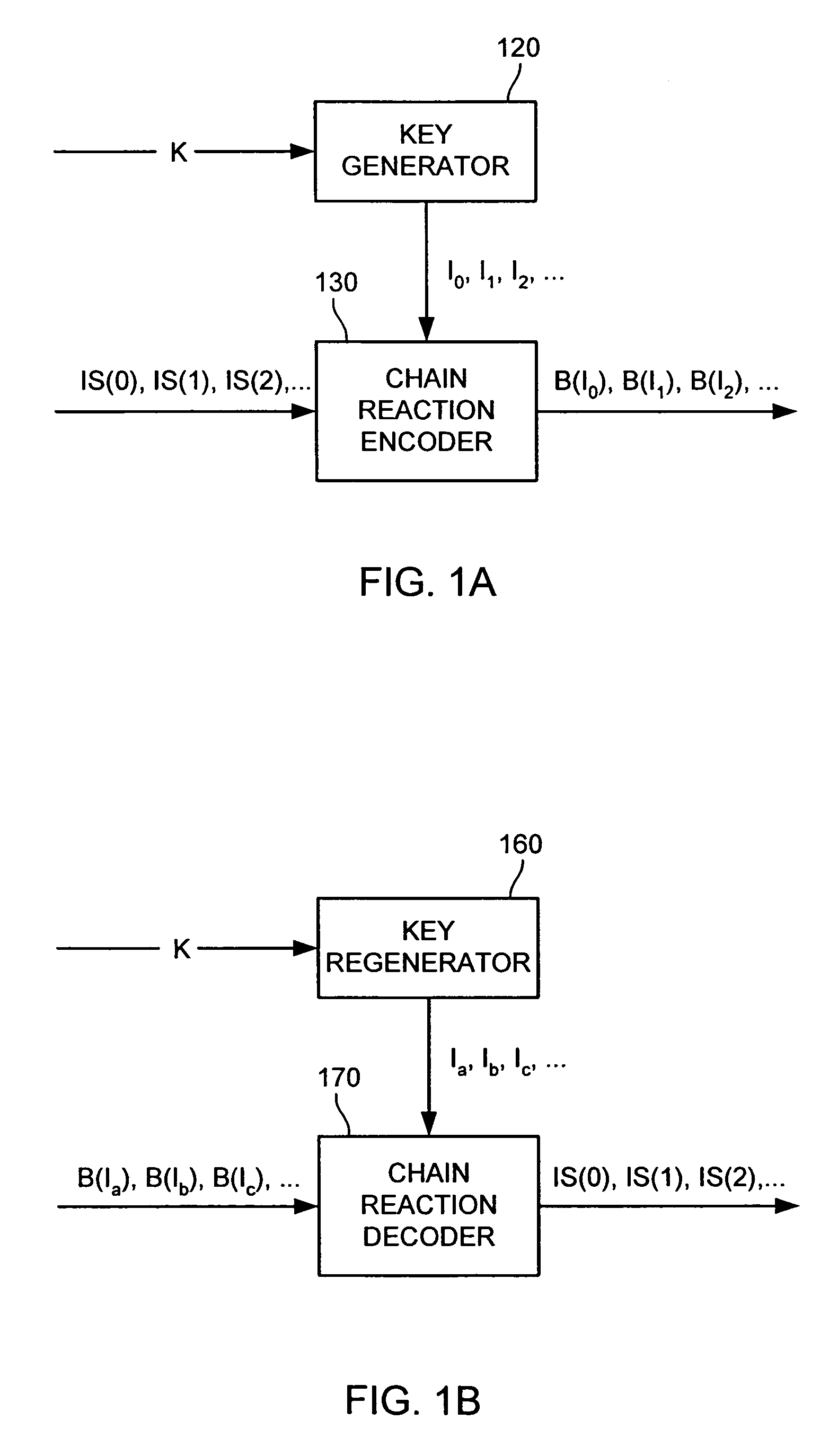
InactiveUS6856263B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesAlgorithmChain reaction
A method for processing a chain reaction codes includes first selecting a source symbol which is associated an output symbol of degree two or higher (i.e., an output symbol which is itself associated with two or more input symbols), and subsequently deactivating the selected source symbol in an attempt to produce an output symbol of degree one. The inactivation process can be repeated either successively until an output symbol of degree one is identified, and / or whenever the decoding process is unable to locate an output symbol of degree one.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Thermal cycler for automatic performance of the polymerase chain reaction with close temperature control
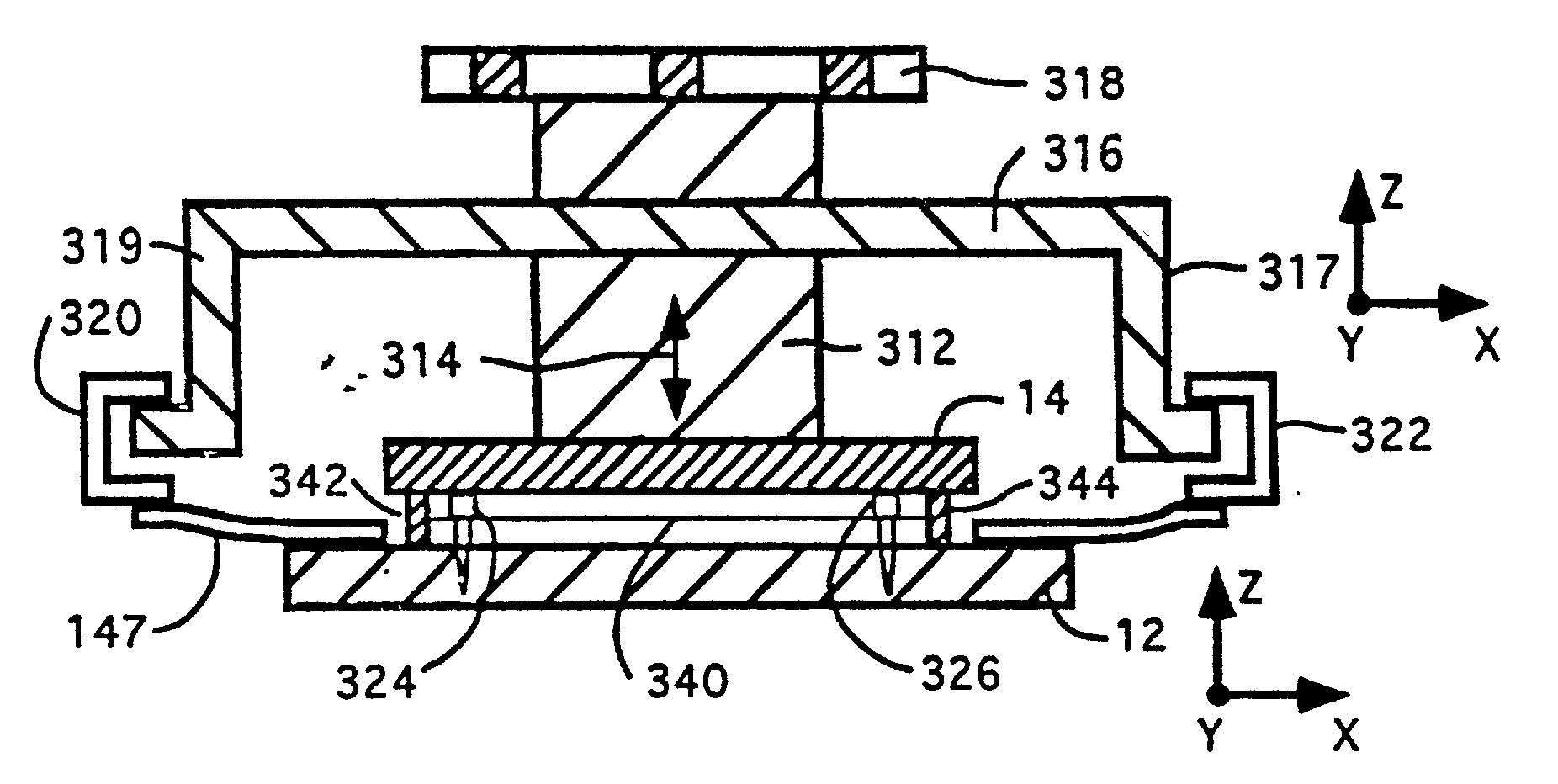
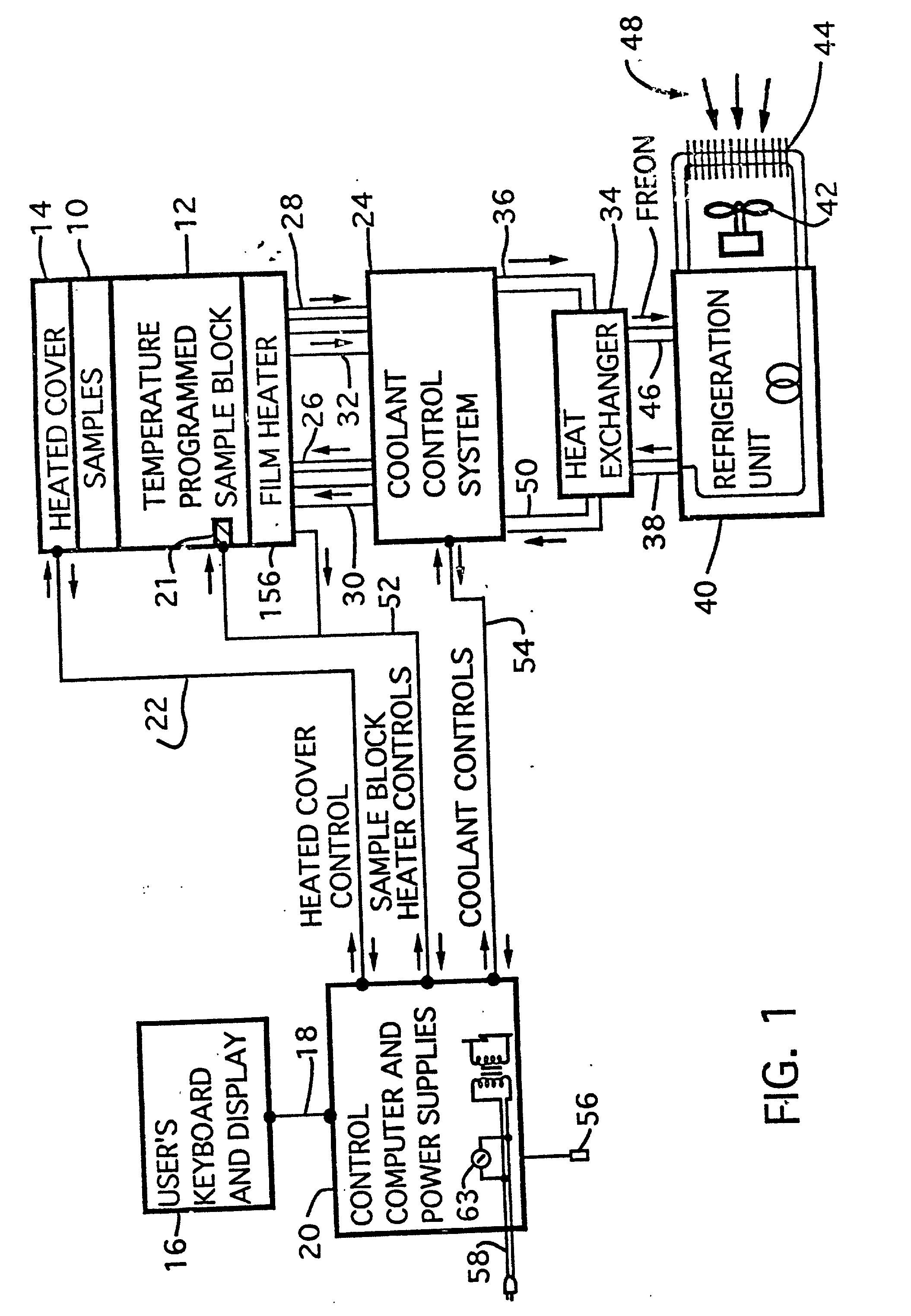
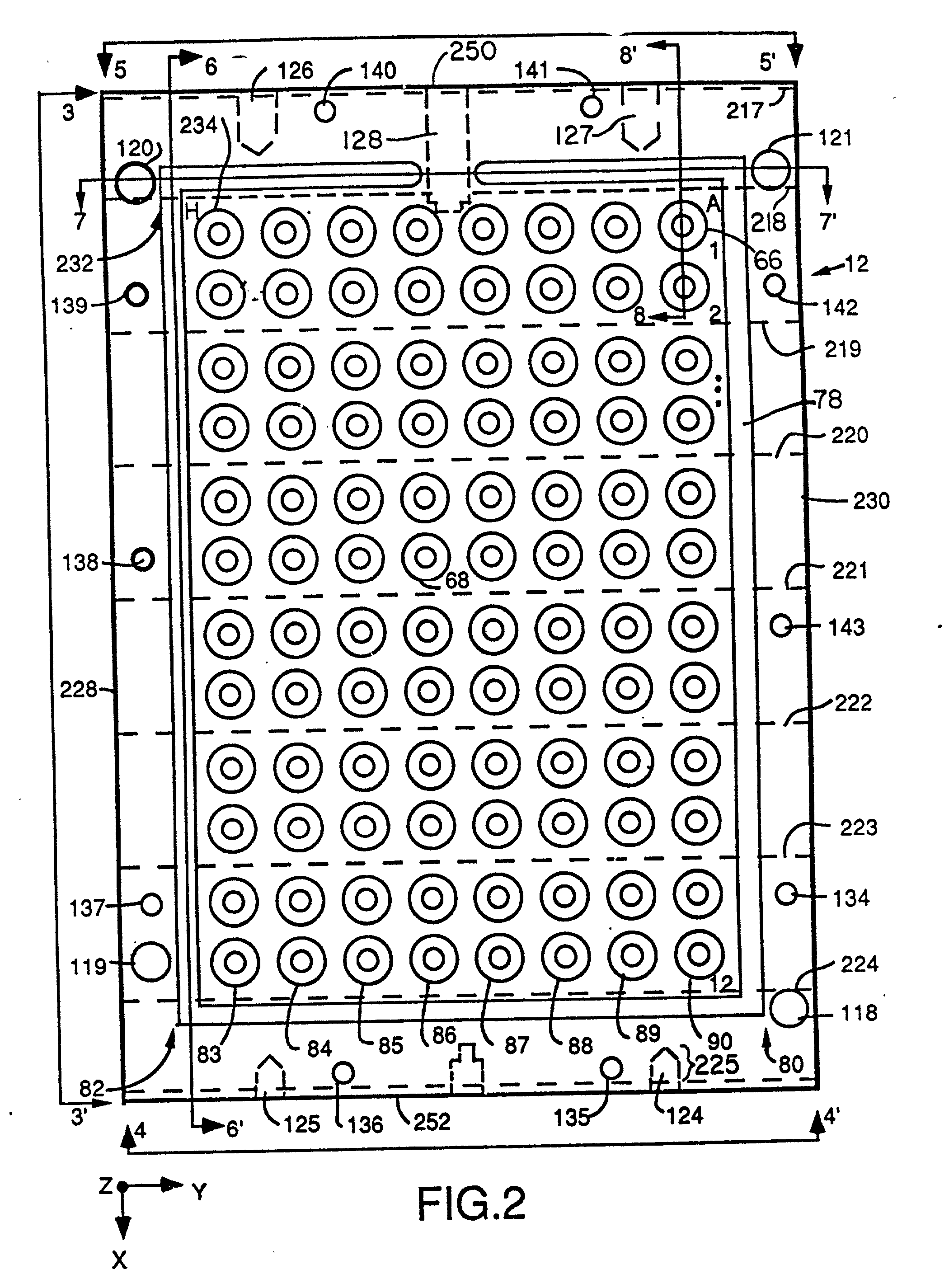
InactiveUS20020072112A1Shorten cycle timeLow cost of reagentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlSolenoid valve
An instrument for performing highly accurate PCR employing a sample block in microtiter tray format. The sample block has local balance and local symmetry. A three zone film heater controlled by a computer and ramp cooling solenoid valves also controlled by the computer for gating coolant flow through the block controls the block temperature. Constant bias cooling is used for small changes. Sample temperature is calculated instead of measured. A platen deforms plastic caps to apply a minimum acceptable threshold force for seating the tubes and thermally isolates them. A cover isolates the block. The control software includes diagnostics. An install program tests and characterizes the instrument. A new user interface is used. Disposable, multipiece plastic microtiter trays to give individual freedom to sample tubes are taught.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
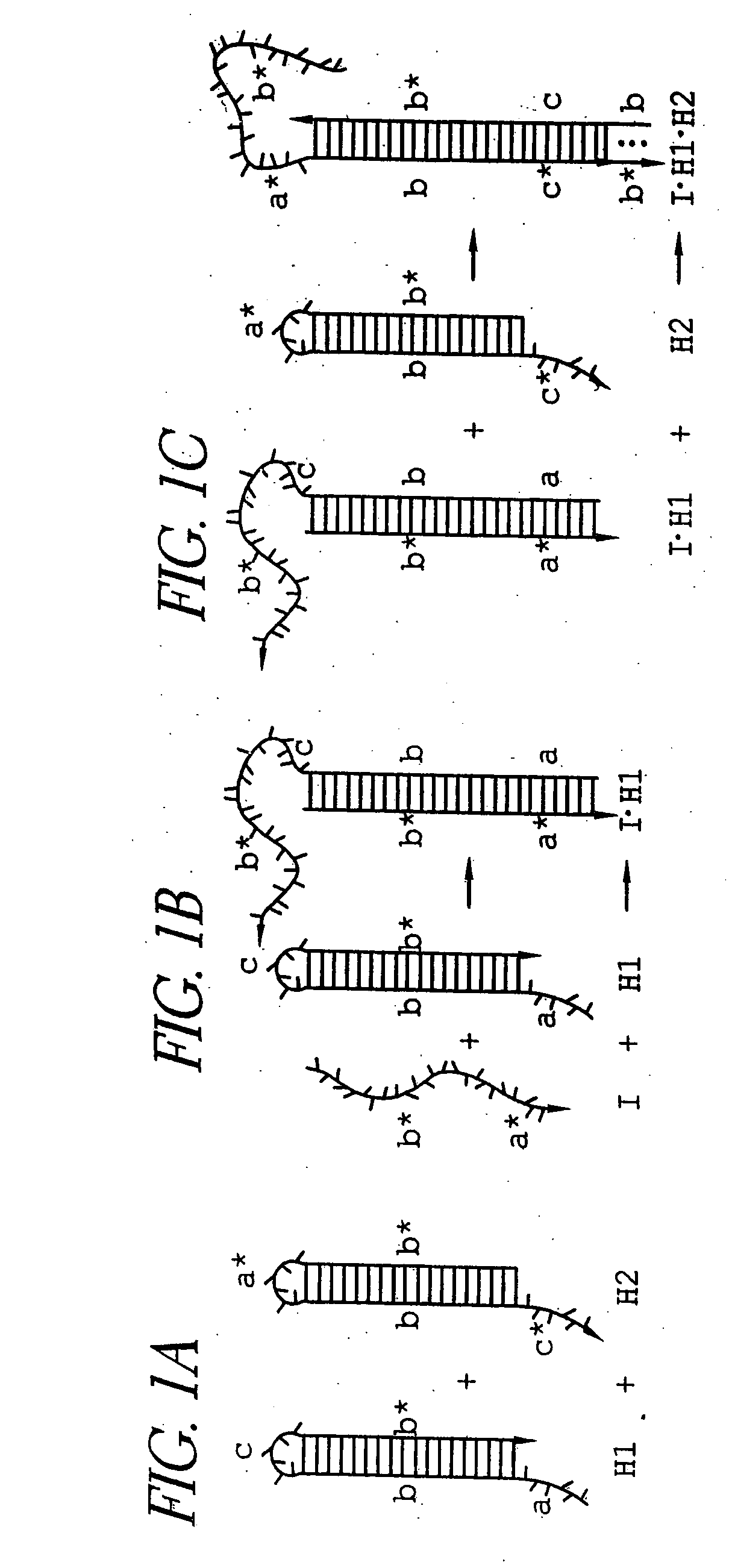
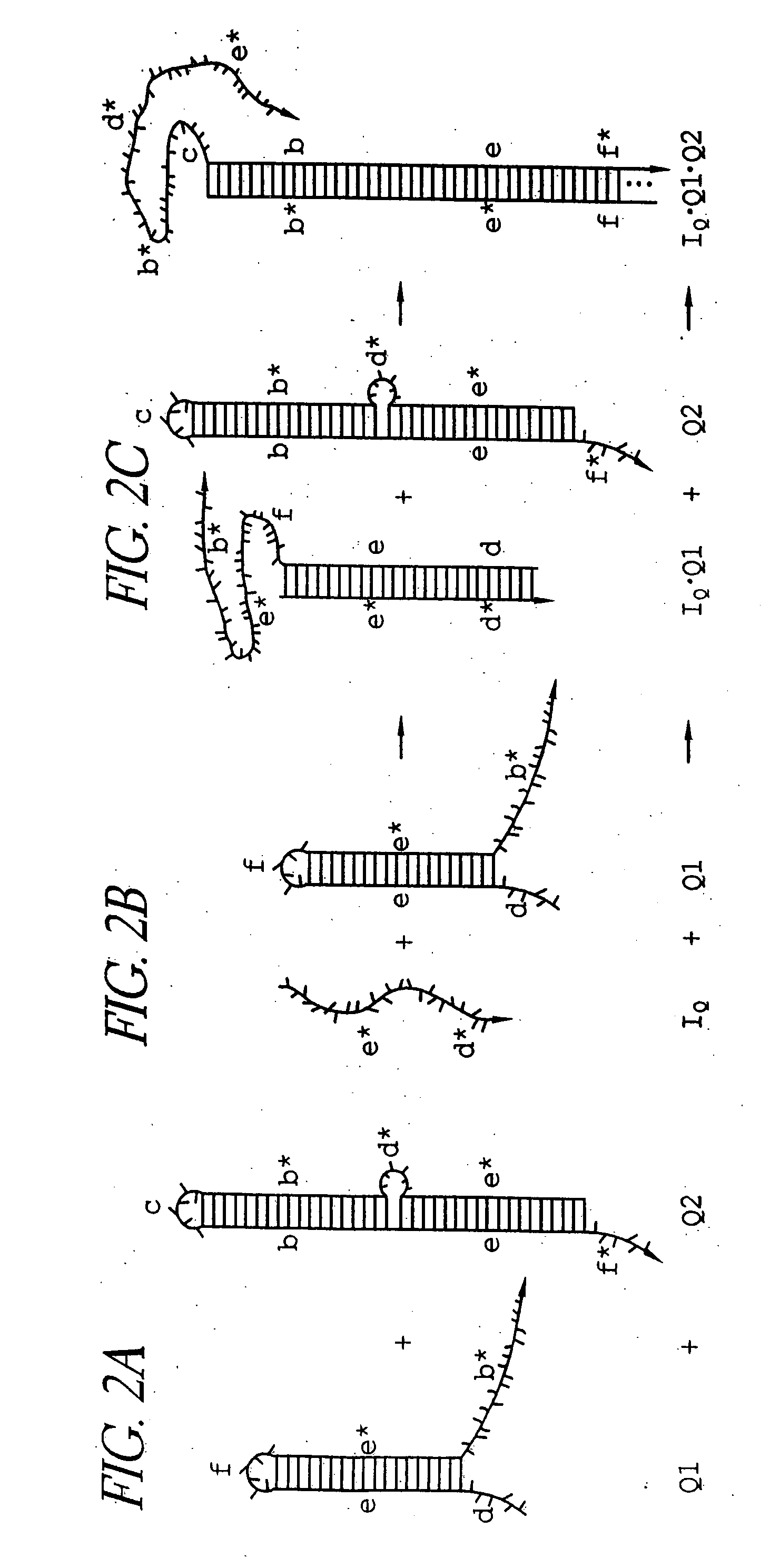
Hybridization chain reaction amplification for in situ imaging
ActiveUS20060228733A1Rapidly amplifyLow backgroundSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteNucleic Acid Probes
The present invention relates to the use of fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes to identify and image analytes in a biological sample. In the preferred embodiments, a probe is provided that comprises a target region able to specifically bind an analyte of interest and an initiator region that is able to initiate polymerization of nucleic acid monomers. After contacting a sample with the probe, labeled monomers are provided that form a tethered polymer. Triggered probes and self-quenching monomers can be used to provide active background suppression.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Apparatus for high throughput chemical reactions
ActiveUS20080176290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction temperature
Apparatus, systems, chips, and methods of performing a large number of simultaneous chemical reactions are provided herein. The chips of the invention comprise addressable units that can be addressed according to the temperature of the reaction to be run. The subject apparatus, systems, and chips are particularly suited for performing polymerase chain reactions on thousands of nucleic acid sequences, up to and including sequences of an entire genome of an organism of interest.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20120052560A1Rapid serial processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHandling systemData store
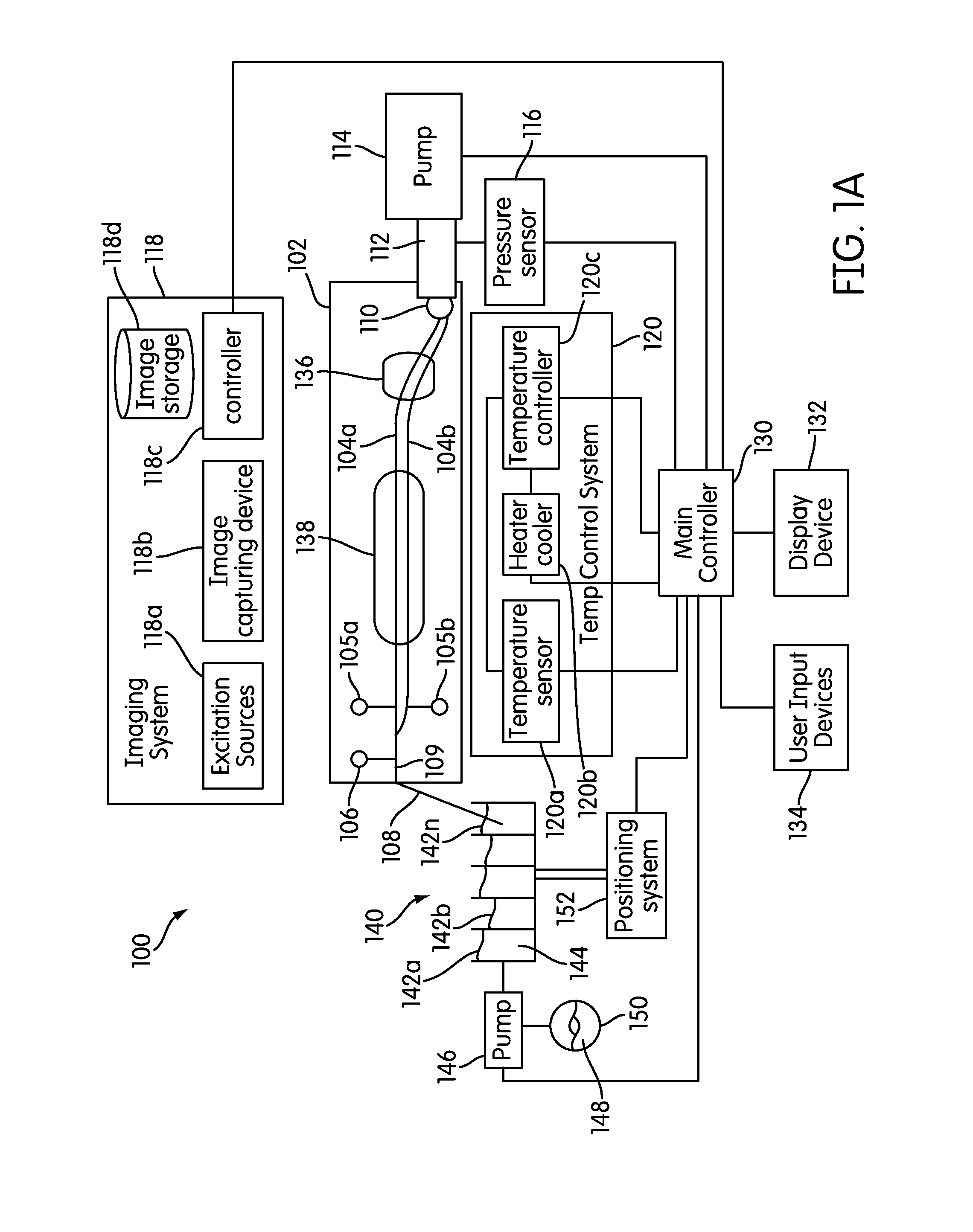
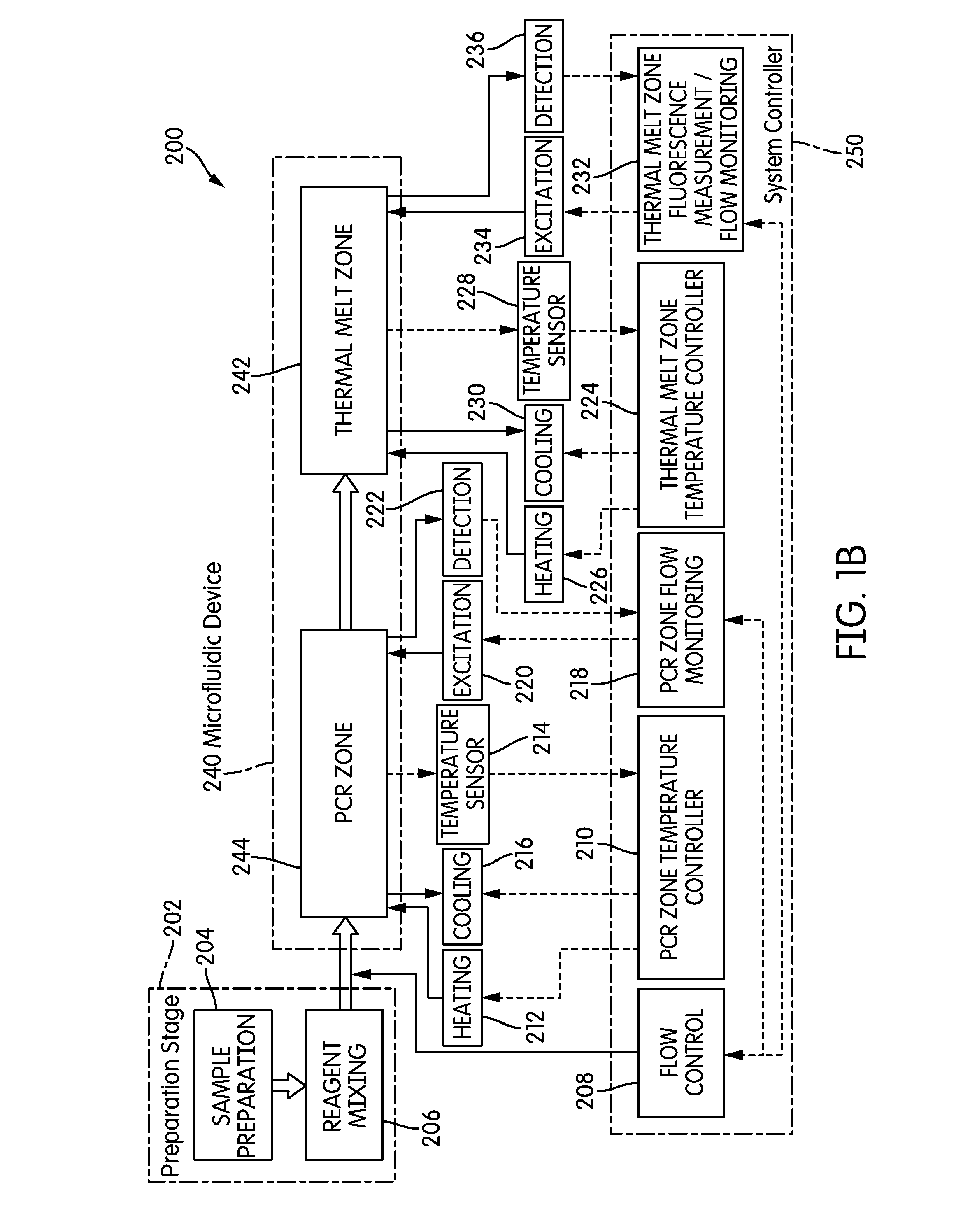
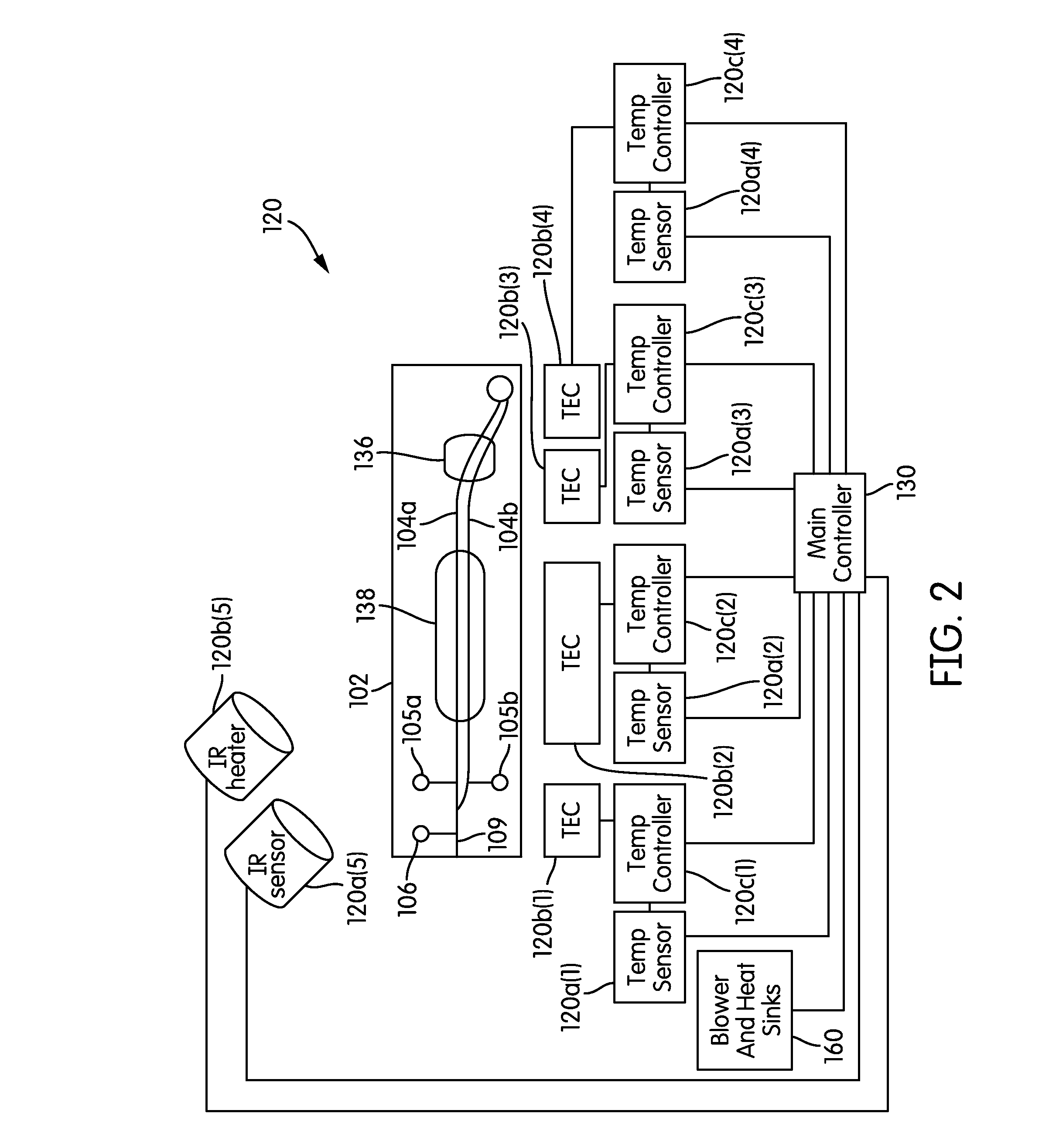
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays. More particularly, the present invention provides for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
Method and apparatus for identifying classifying or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS6141657ARapid and economical and quantitative and precise determination and classificationSufficient discrimination and resolutionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSequence databaseDNA Sequence Databases
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Container for carrying out and monitoring biological processes
InactiveUS20050064582A1Easy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceDna amplification
A thermal cycling method and device is disclosed. The device comprises a sample chamber whose temperature can be rapidly and accurately modulated over a range of temperatures needed to carry out a number of biological procedures, such as the DNA polymerase chain reaction. Biological samples are placed in containers each comprising a reservoir and a reaction portion, wherein the reaction portion has a small volume. The small volume reaction portion permits the rapid and accurate temperature modulation. With an optically transmissible reaction portion, DNA amplification may be monitored by fluorescence during PCR.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for a continuous rapid thermal cycle system
ActiveUS20090325234A1Easy to adaptLow production costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusTemperature controlChiller
A thermal cycle system and method suitable for mass production of DNA comprising a temperature control body having at least two sectors. Each sector has at least one heater, cooler, or other means for changing temperature. A path traverses the sectors in a cyclical fashion. In use, a piece of tubing or other means for conveying is placed along the path and a reaction mixture is pumped or otherwise moved along the path such that the reaction mixture is repetitively heated or cooled to varying temperatures as the reaction mixture cyclically traverses the sectors. The reaction mixture thereby reacts to form a product. In particular, polymerase chain reaction reactants may continuously be pumped through the tubing to amplify DNA. The temperature control body is preferably a single aluminum cylinder with a grooved channel circling around its exterior surface, and preferably has wedge-shaped or pie-shaped sectors separated by a thermal barrier.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
Container for carrying out and monitoring biological processes
InactiveUS7273749B1Easy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusFluorescenceDna amplification
A thermal cycling method and device is disclosed. The device comprises a sample chamber whose temperature can be rapidly and accurately modulated over a range of temperatures needed to carry out a number of biological procedures, such as the DNA polymerase chain reaction. Biological samples are placed in containers each comprising a reservoir and a reaction portion, wherein the reaction portion has a small volume. The small volume reaction portion permits the rapid and accurate temperature modulation. With an optically transmissible reaction portion, DNA amplification may be monitored by fluorescence during PCR.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
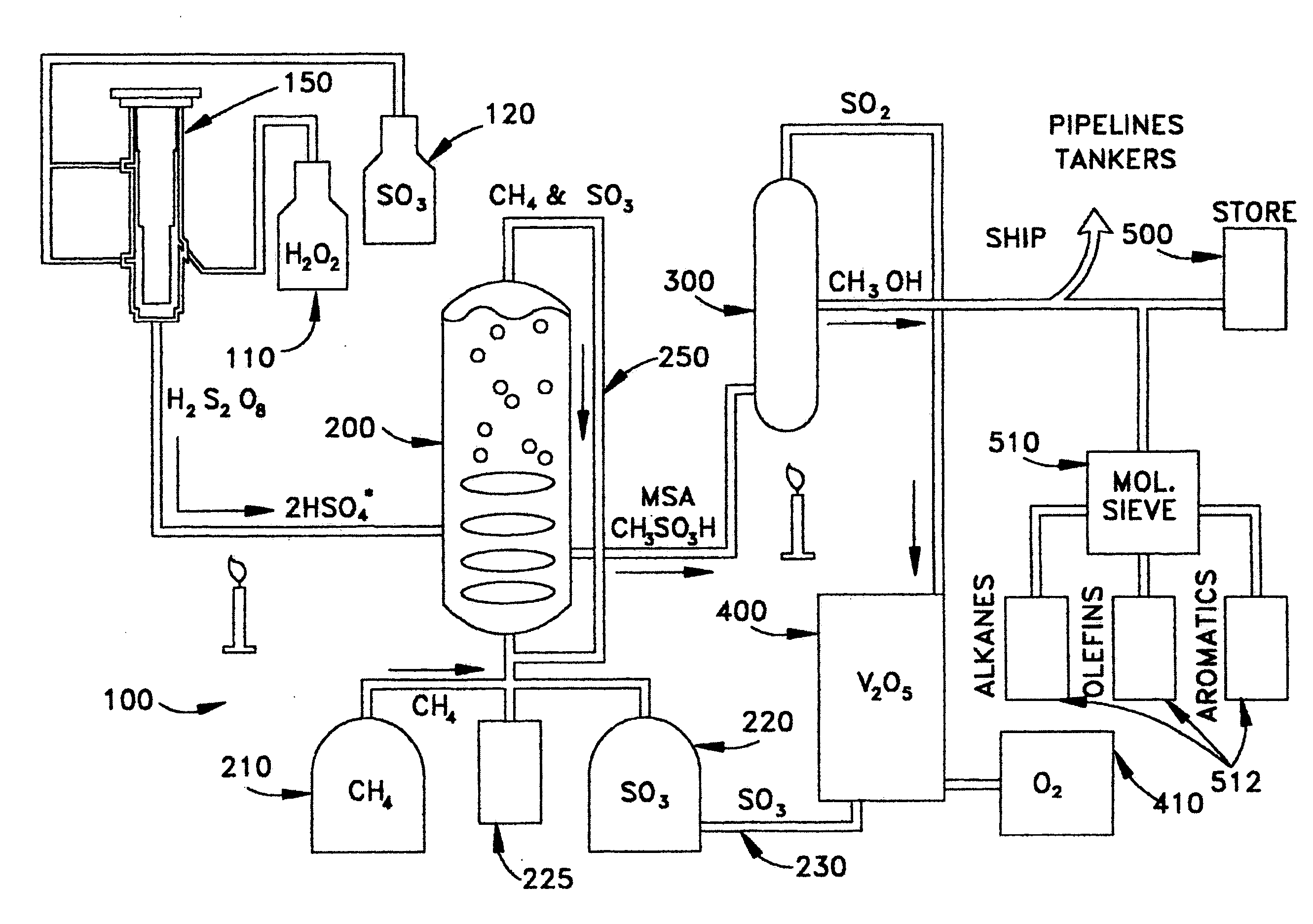
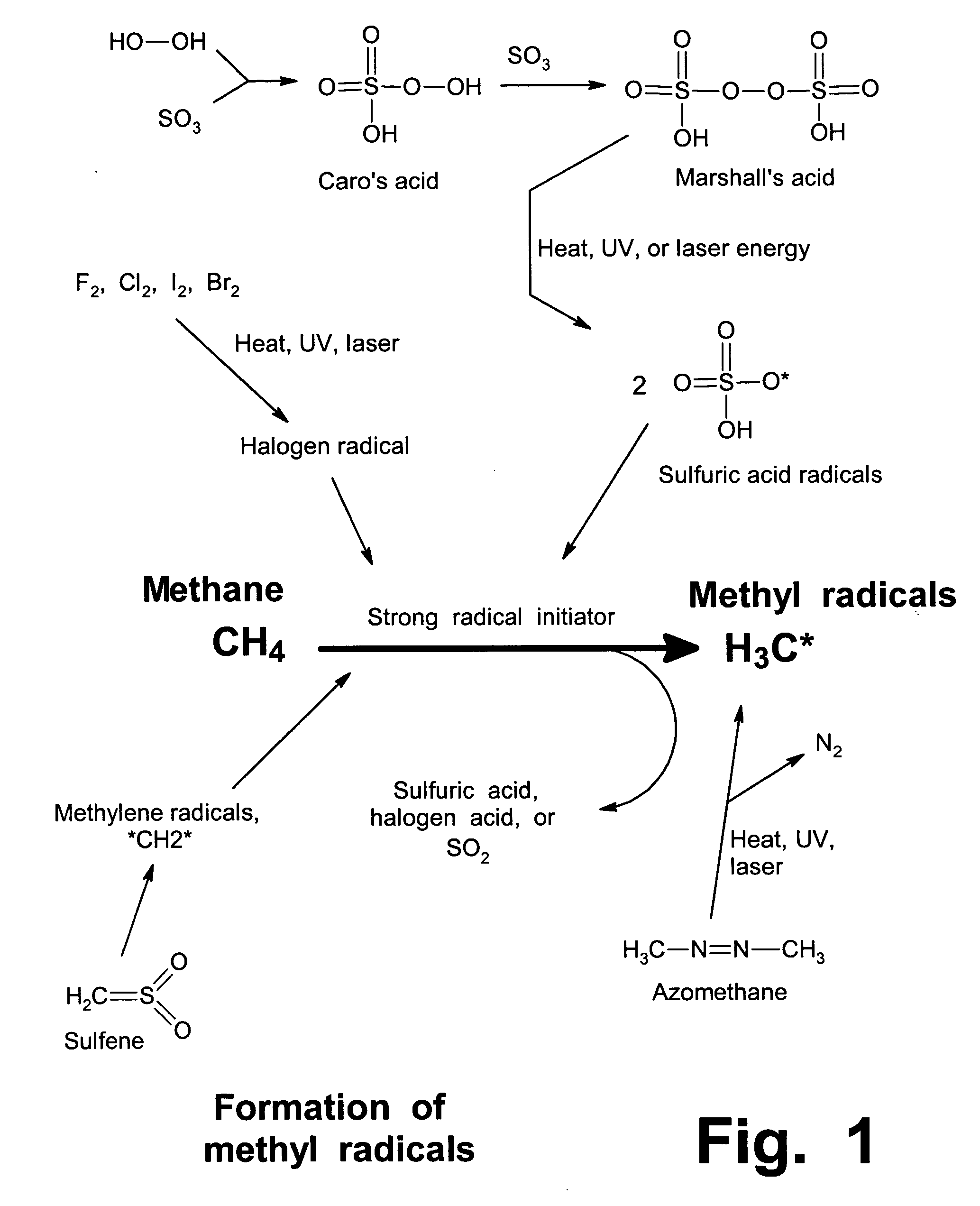
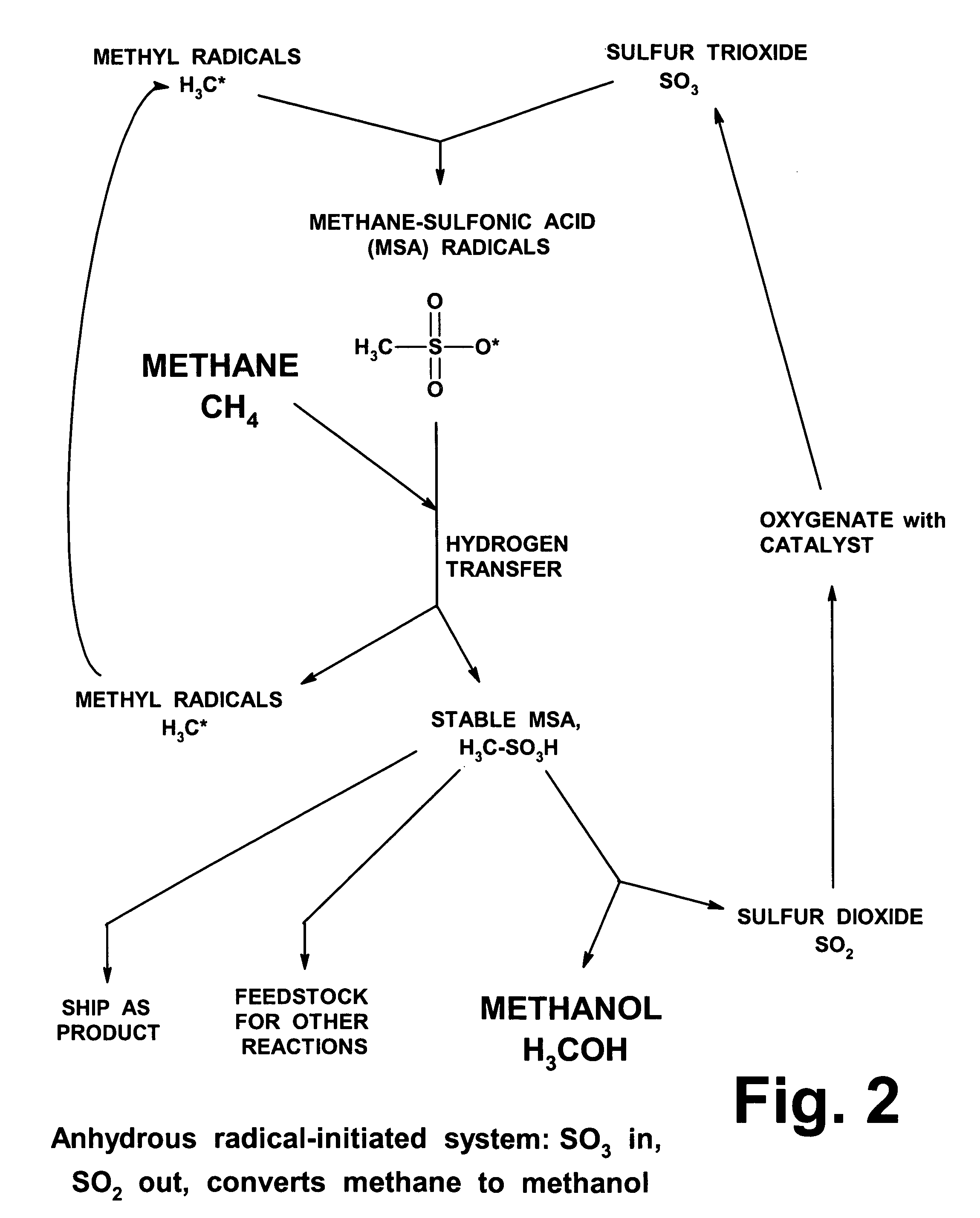
Anhydrous processing of methane into methane-sulfonic acid, methanol, and other compounds
ActiveUS20050070614A1Increases solubility and reaction rateEfficient removalHydrogenOrganic compound preparationLiquid fuelOxygen compound
Anhydrous processing to convert methane into oxygenates (such as methanol), liquid fuels, or olefins uses an initiator to create methyl radicals. These radicals combine with sulfur trioxide to form methyl-sulfonate radicals. These radicals attack fresh methane, forming stable methane-sulfonic acid (MSA) while creating new methyl radicals to sustain a chain reaction. This system avoids the use or creation of water, and liquid MSA is an amphoteric solvent that increasing the solubility and reactivity of methane and SO3. MSA from this process can be sold or used as a valuable chemical with no mercaptan or halogen impurities, or it can be heated and cracked to release methanol (a clean fuel, gasoline additive, and chemical feedstock) and sulfur dioxide (which can be oxidized to SO3 and recycled back into the reactor). MSA also can be converted into gasoline, olefins, or other valuable chemicals.
Owner:VEOLIA NORTH AMERICA REGENERATION SERVICES LLC
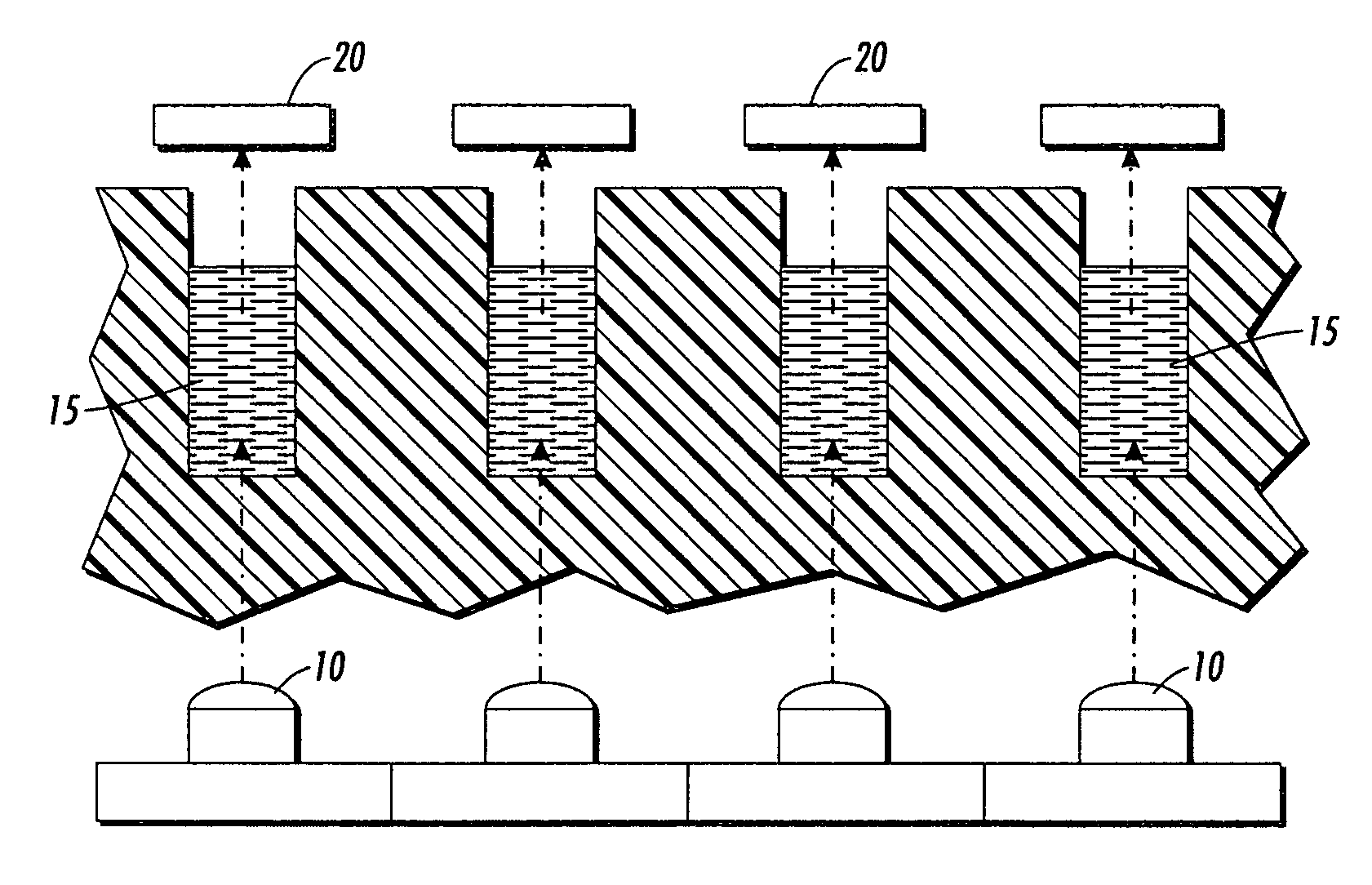
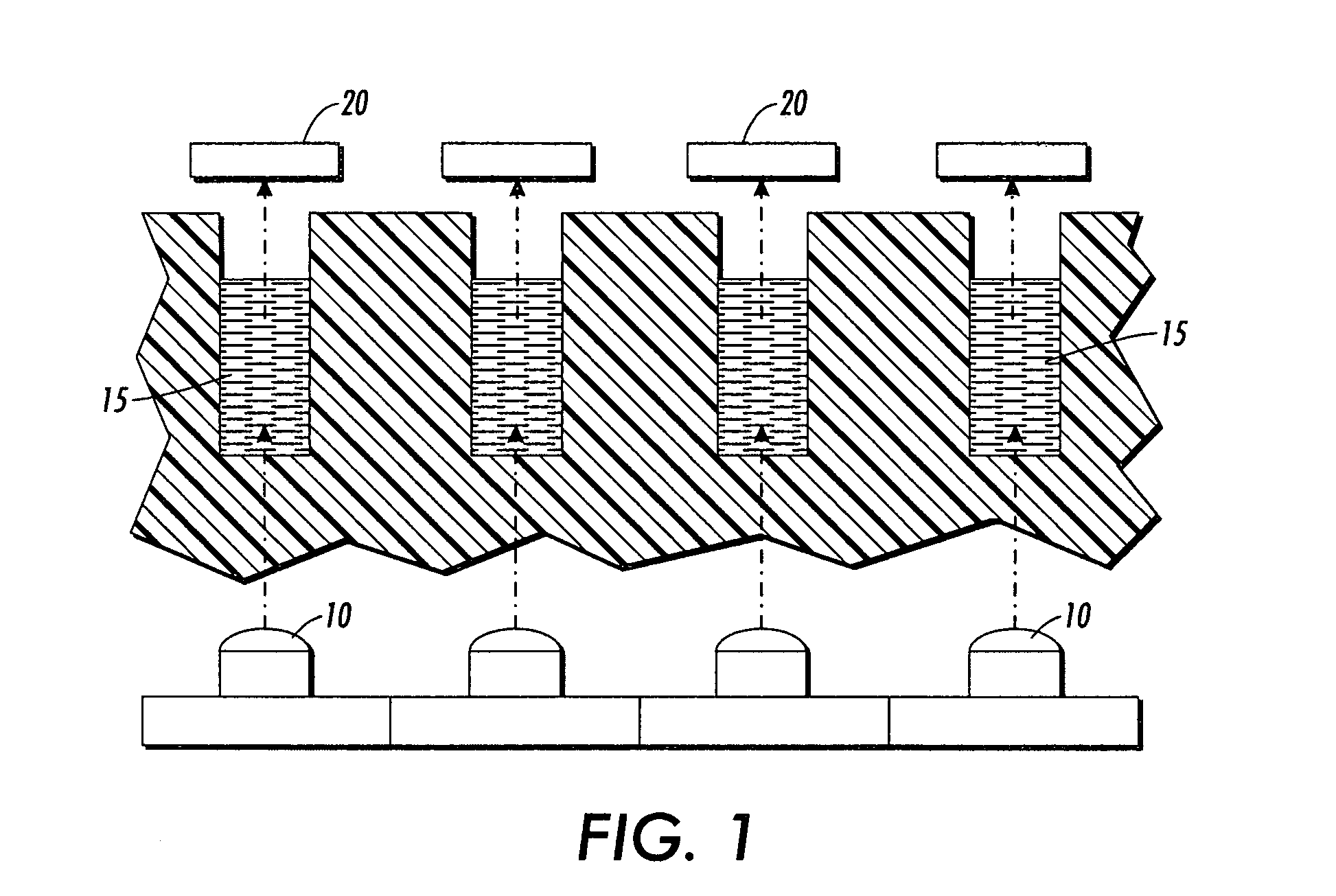
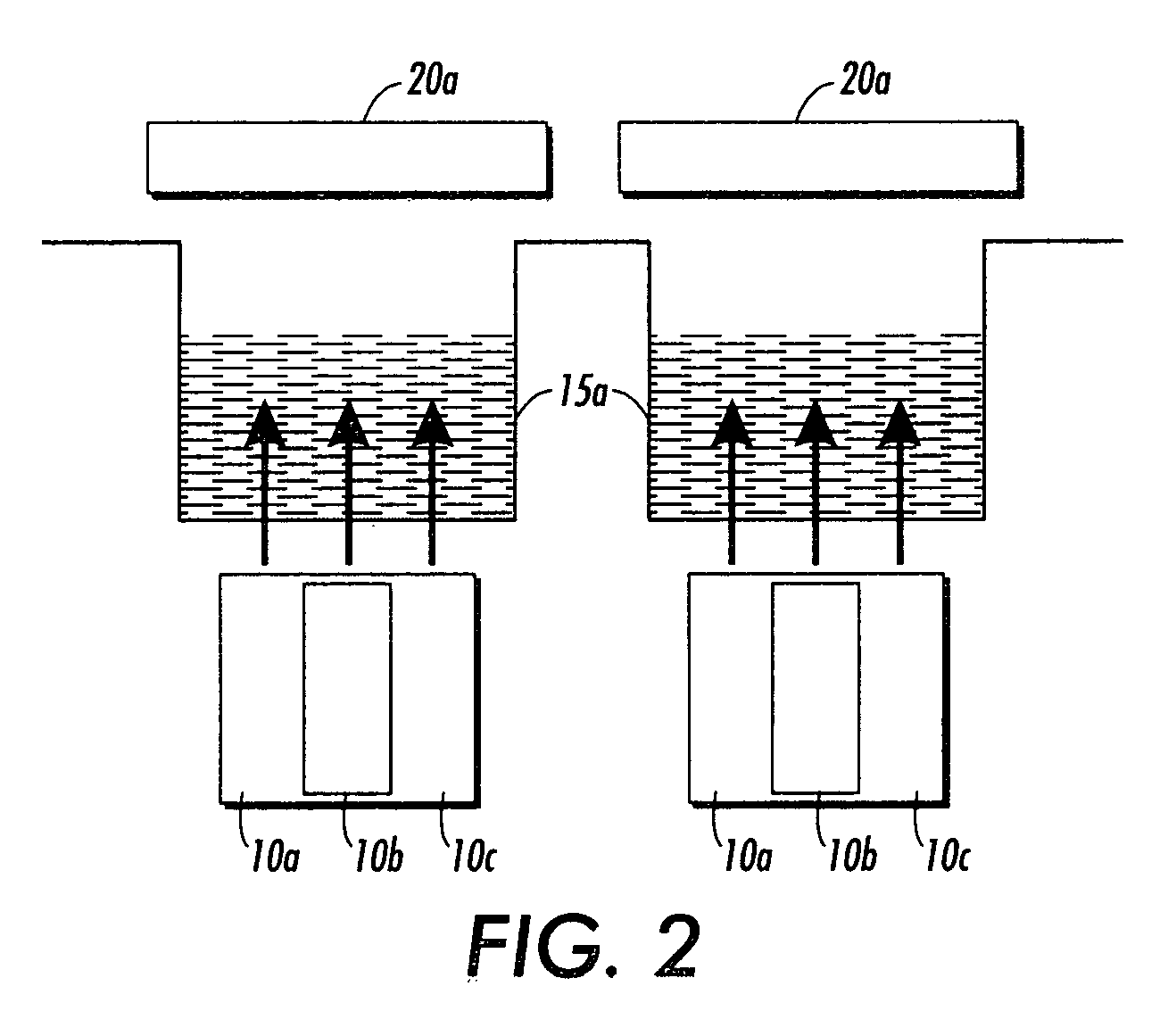
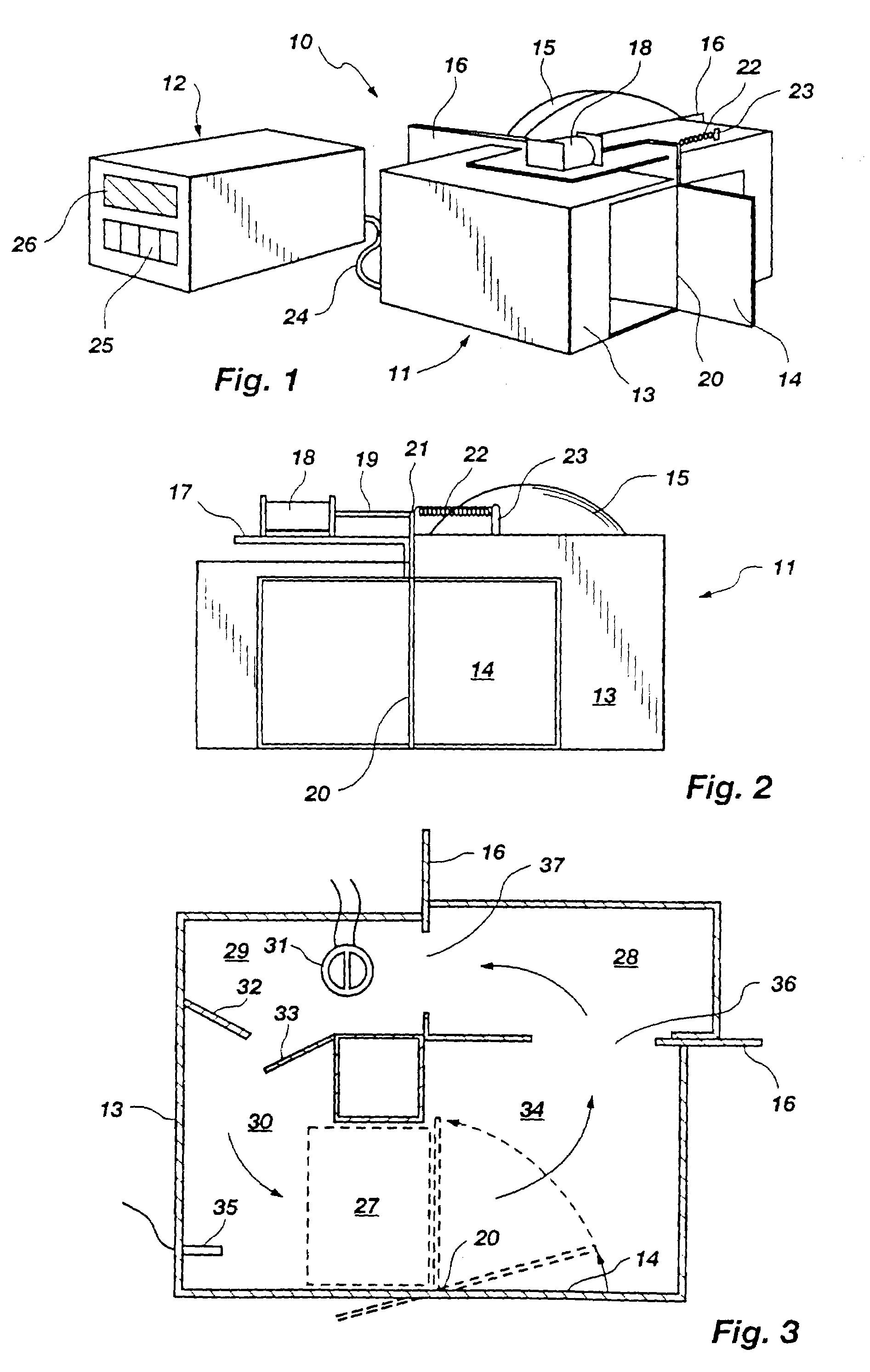
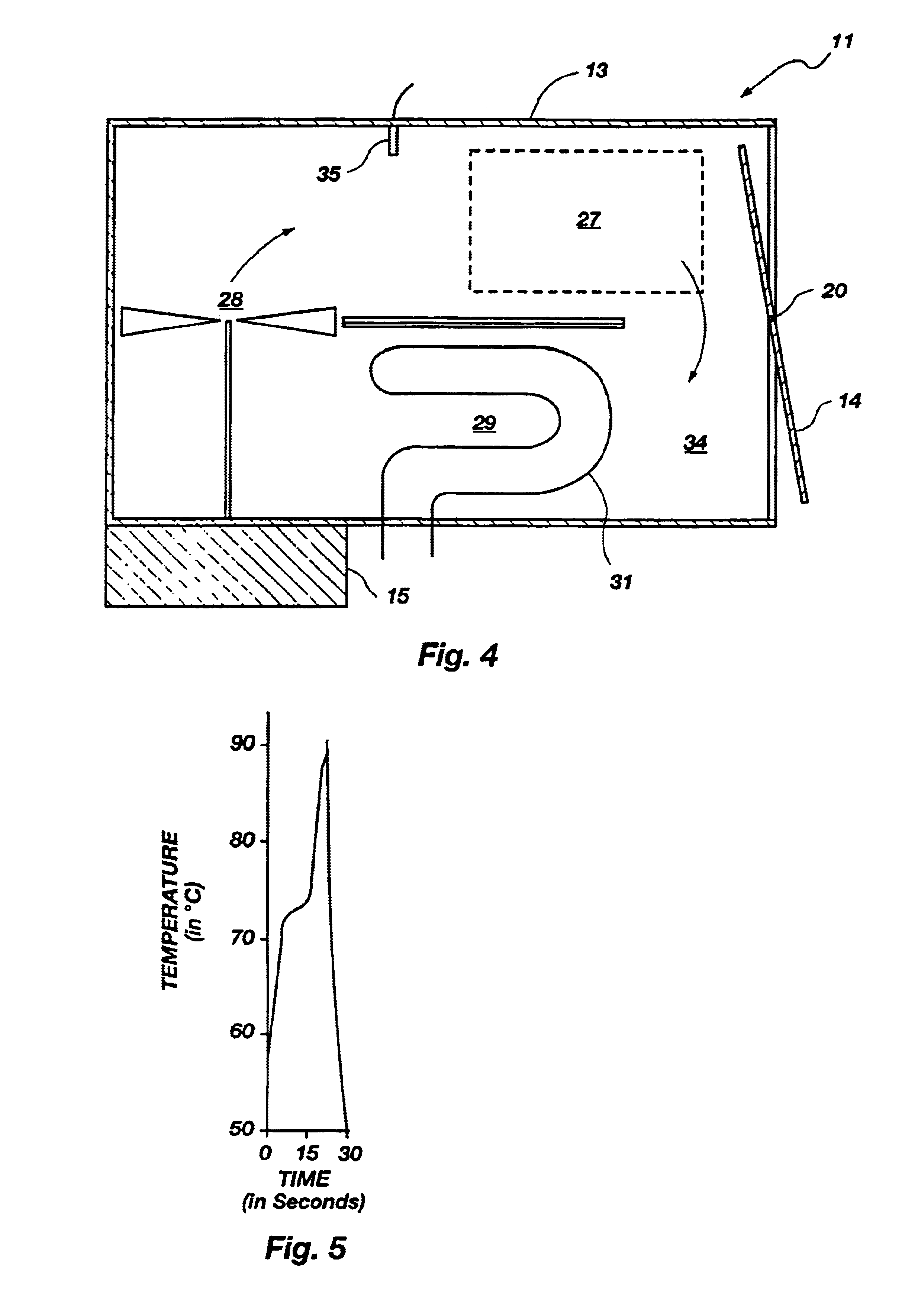
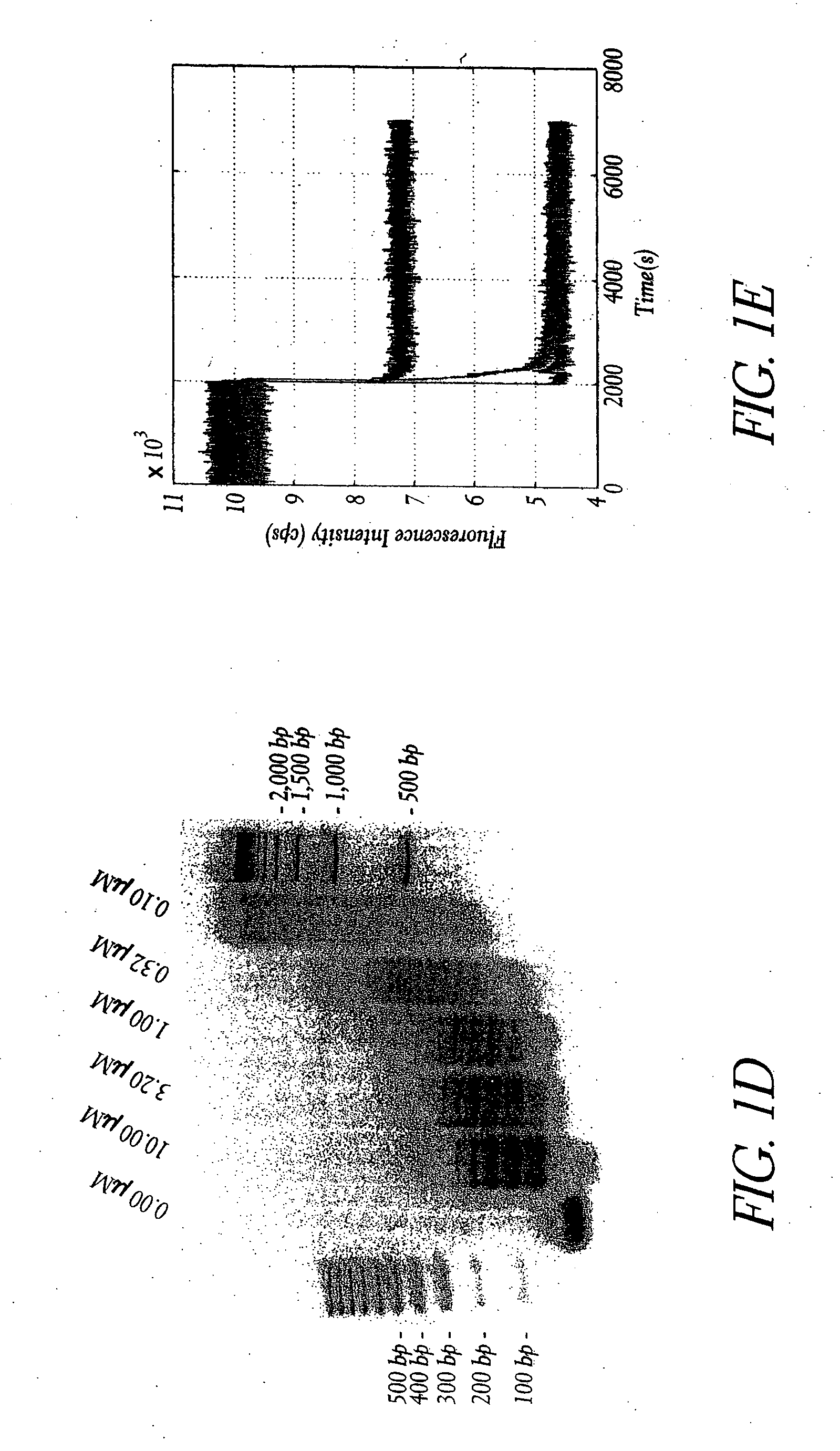
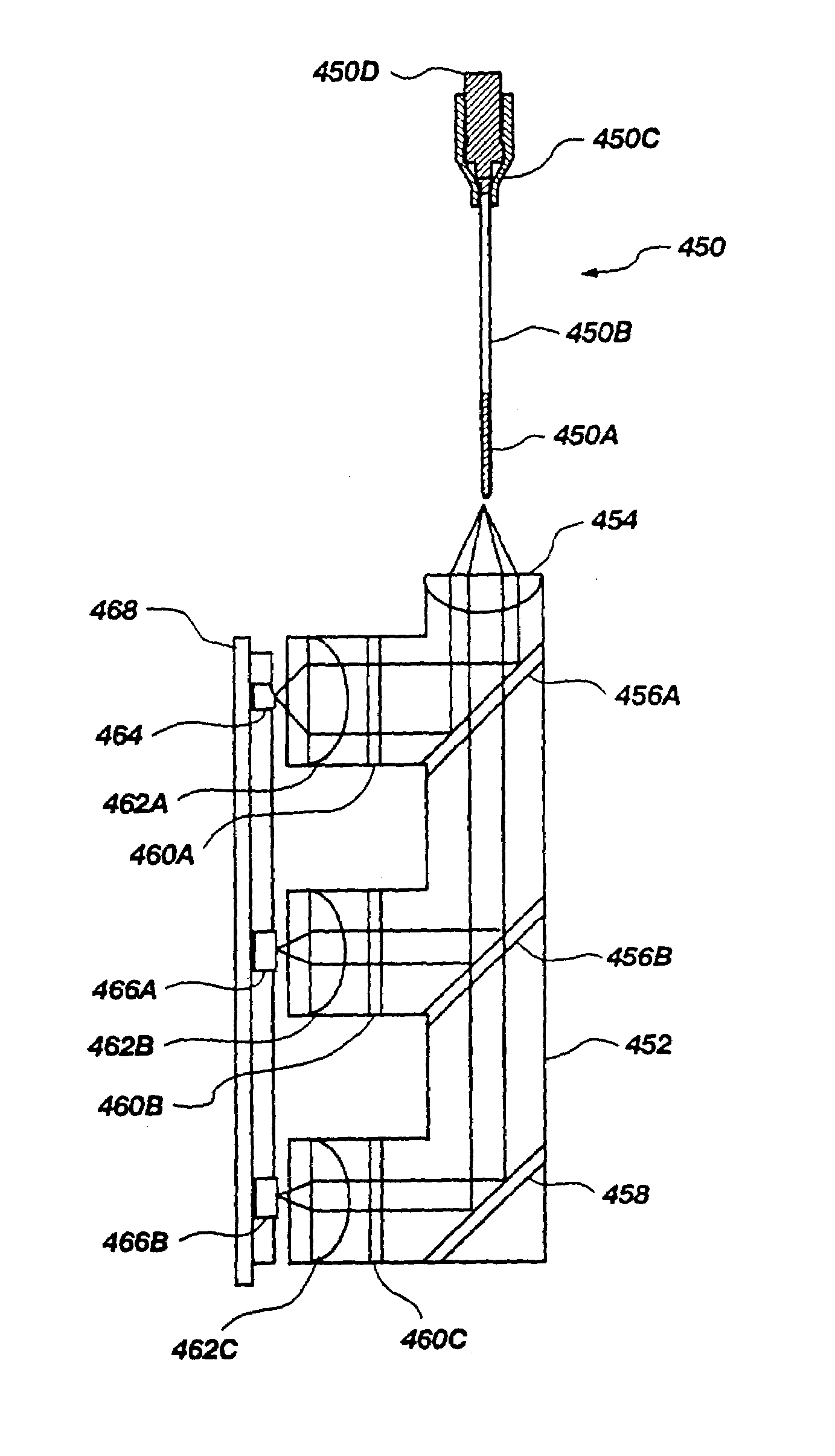
Device for thermo-dependent chain reaction amplification of target nucleic acid sequences, measured in real-time
InactiveUS6821771B2Readily be miniaturisedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingBiology
Owner:PALL GENESYST
Bamboo leaf antioxide and use thereof
InactiveCN1528197AWide variety of sourcesMild flavorAntibacterial agentsFood ingredient as antioxidantNitriteWater soluble
The present invention discloses a bamboo leaf antioxidant material (AOB) and its application. AOB is a yellow or brownish yellow powder or granules obtained from bamboo leaf, its main antioxidant component includes flavone, lactone and phenolic acid compound, the total flavone glucoside content determined by colourimetry is greater than or equal to 30%, total lactone content is greater than or equal to 15% and phenolic acid content is greater than or equal to 7.5%. It not only can be block the chain reaction of automatic oxidation of fat, but also can chelate trasition state metal ion, at the same time can be used as first-grade and second-grade antioxidant to produce action, and can effectively remove nitrite and can block synthesis of nitrosamine, and has the actions of resisting bacteria, inhibiting fungi, deodorization and increasing perfume, so that it has extensive application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU LEAF BIO TECH
Enzymatic antioxidant of allene oxide for lipid peroxidation in biological systems
InactiveUS6132711ABeneficial antioxidativeExtend effective lifeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationFatty acid
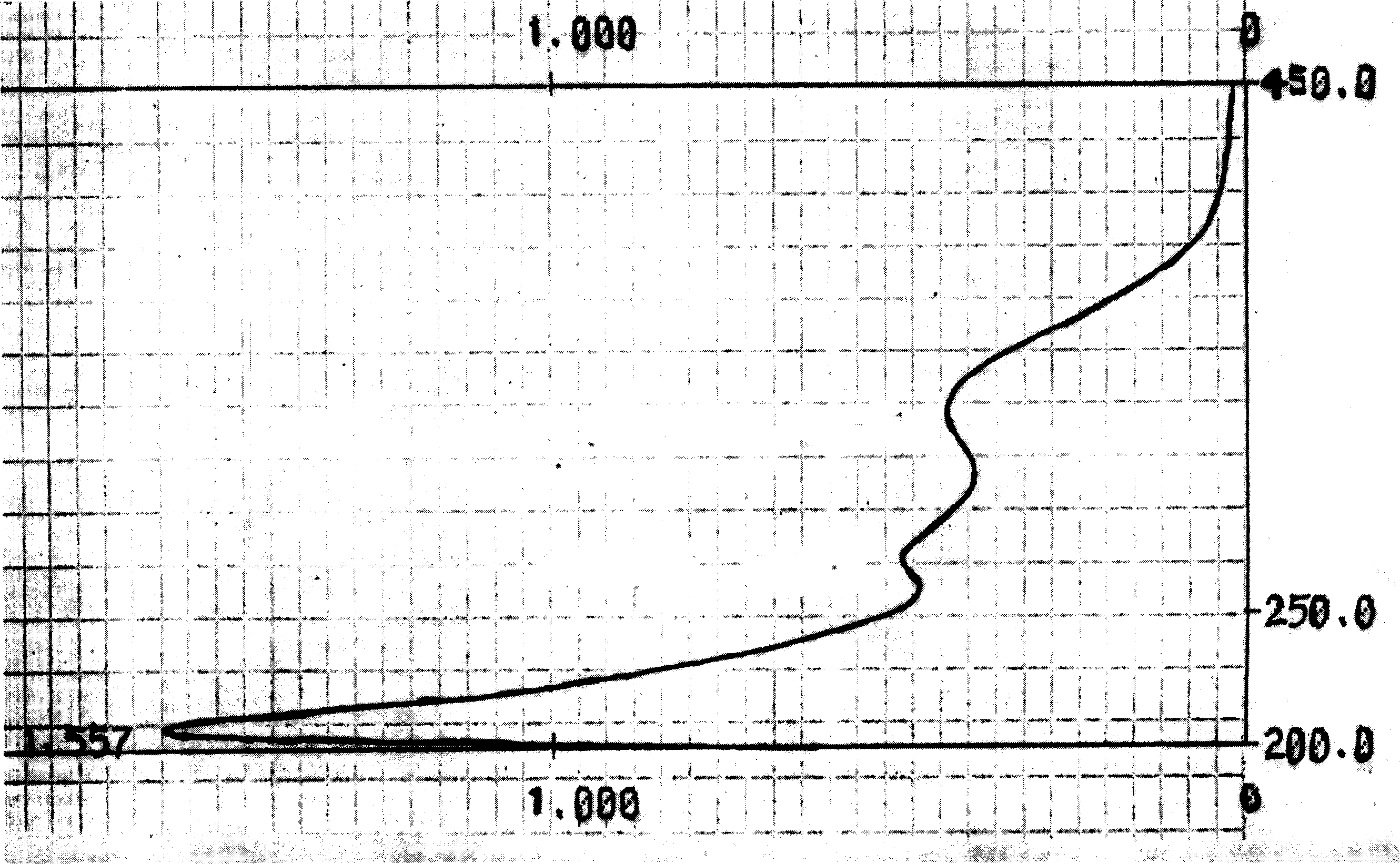
The present invention relates to the isolation and use of an allene oxide synthase enzyme as an antioxidant of lipid peroxides in biological systems. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that antioxidation is accomplished enzymatically by RPP, a species of allene oxide synthase, in guayule, and on the discovery that the allene oxide synthase RPP disrupts the chain reaction and propagation steps of lipid peroxidation. The present further invention relates to the use of an allene oxide synthase to result in a time-dependent disappearance of conjugated dienes (i.e. lipid hydroperoxides). The allene oxide synthase rapidly converts free or esterified fatty acid peroxides or hydroperoxides into their corresponding epoxides, which, in turn are converted to ketols. The lipid peroxide and hydroperoxide substrates for this enzyme are known to be toxic to biological organisms and can generate additional peroxides by chain propagation reactions. In the presence of an allene oxide synthase these compounds are rapidly and effectively converted to allene oxides (the epoxide), thus breaking the chain reaction.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
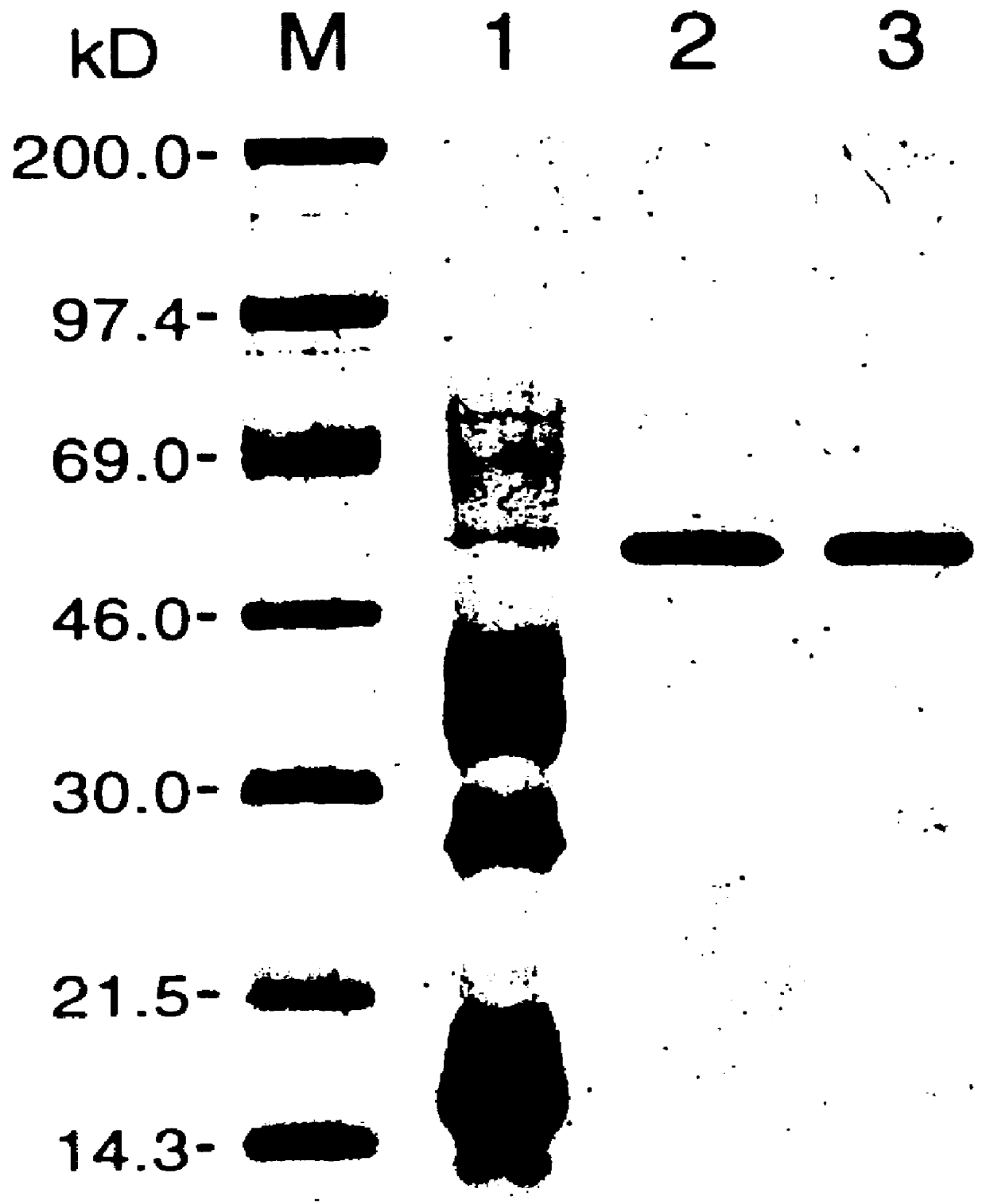
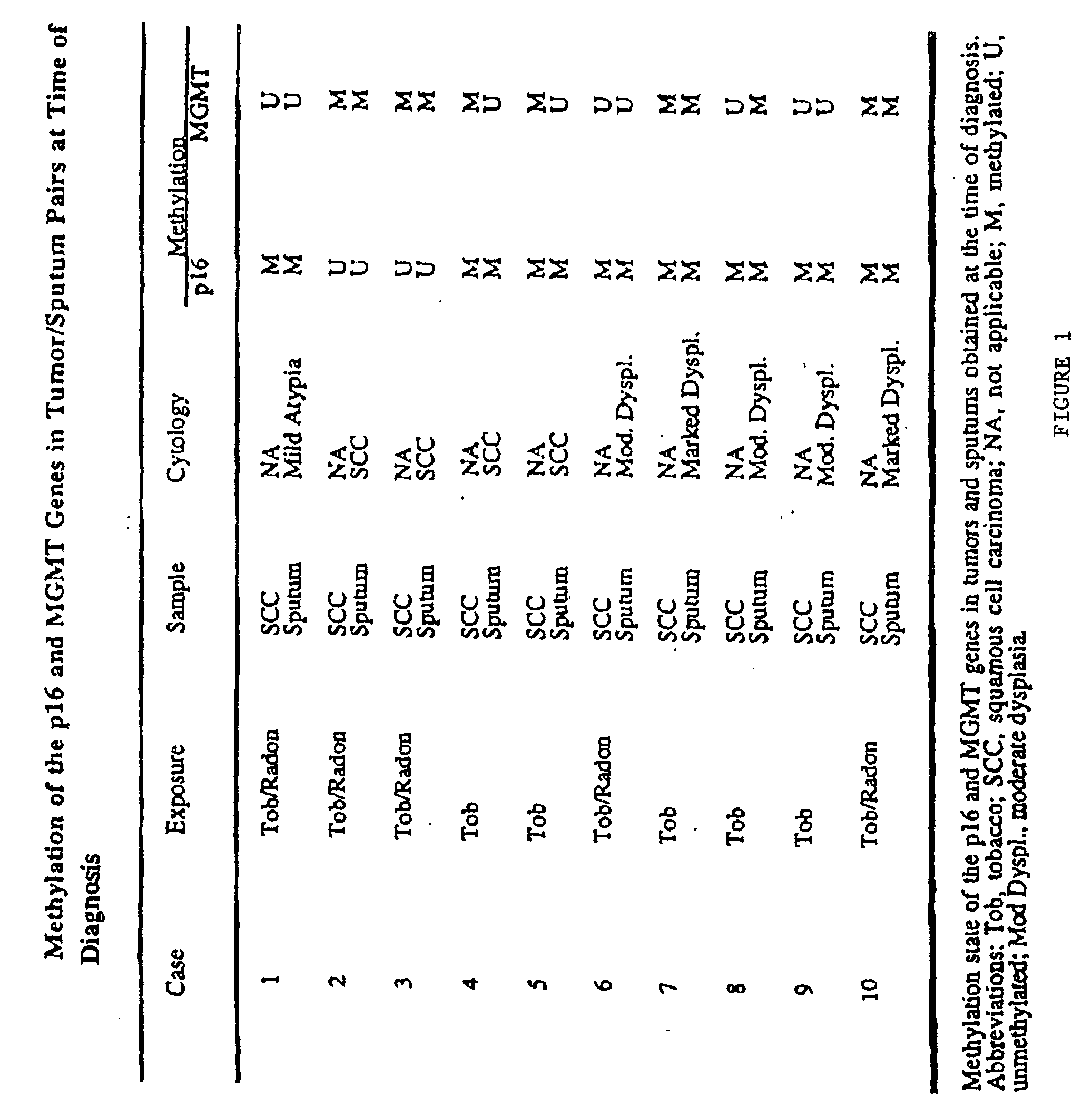
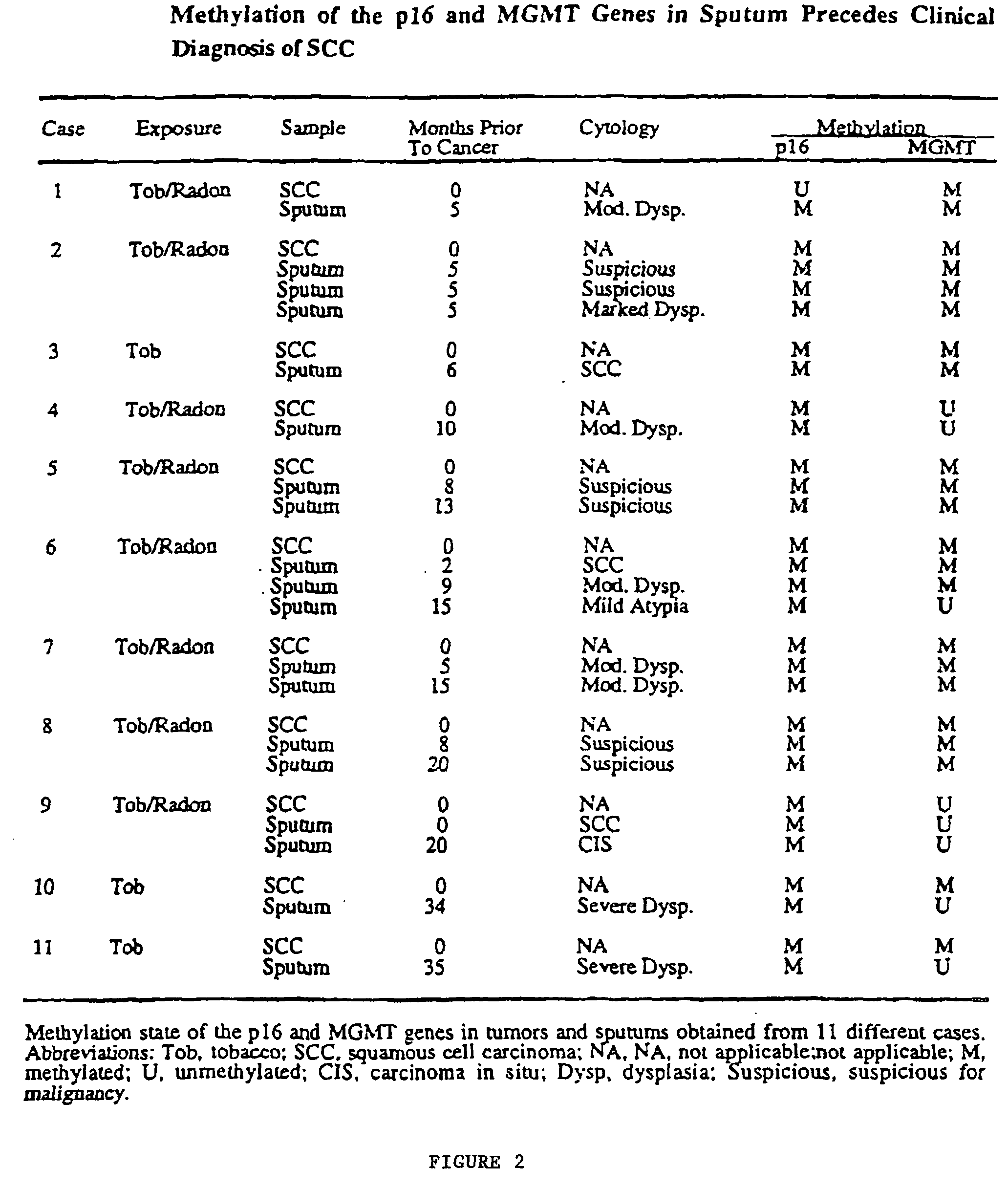
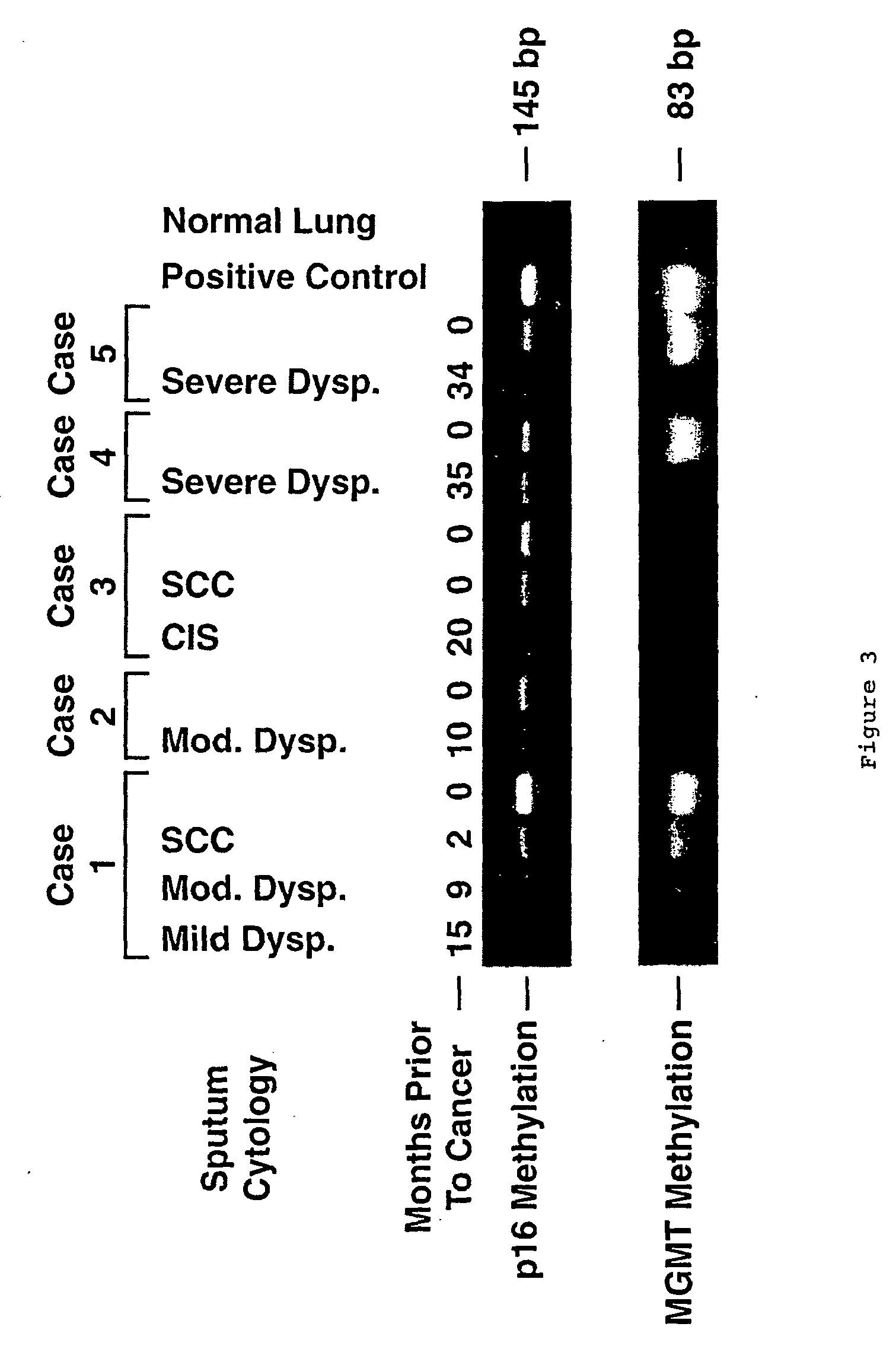
Nested methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction cancer detection method
A molecular marker-based method for monitoring and detecting cancer in humans. Aberrant methylation of gene promoters is a marker for cancer risk in humans. A two-stage, or "nested" polymerase chain reaction method is disclosed for detecting methylated DNA sequences at sufficiently high levels of sensitivity to permit cancer screening in biological fluid samples, such as sputum, obtained non-invasively. The method is for detecting the aberrant methylation of the p16 gene, O 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene, Death-associated protein kinase gene, RAS-associated family 1 gene, or other gene promoters. The method offers a potentially powerful approach to population-based screening for the detection of lung and other cancers.
Owner:LOVELACE RESPIRATORY RES INST
Methods for obtaining thermostable enzymes, DNA polymerase I variants from Thermus aquaticus having new catalytic activities, methods for obtaining the same, and applications of the same
The present invention provides a method for obtaining thermostable enzymes. The present invention also provides variants of DNA polymerase I from Thermus aquaticus. The present invention further provides methods of identifying mutant DNA polymerases having enhanced catalytic activity. The present invention also provides polynucleotides, expression systems, and host cells encoding the mutant DNA polymerases. Still further, the present invention provides a method to carry out reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and kits to facilitate the same.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
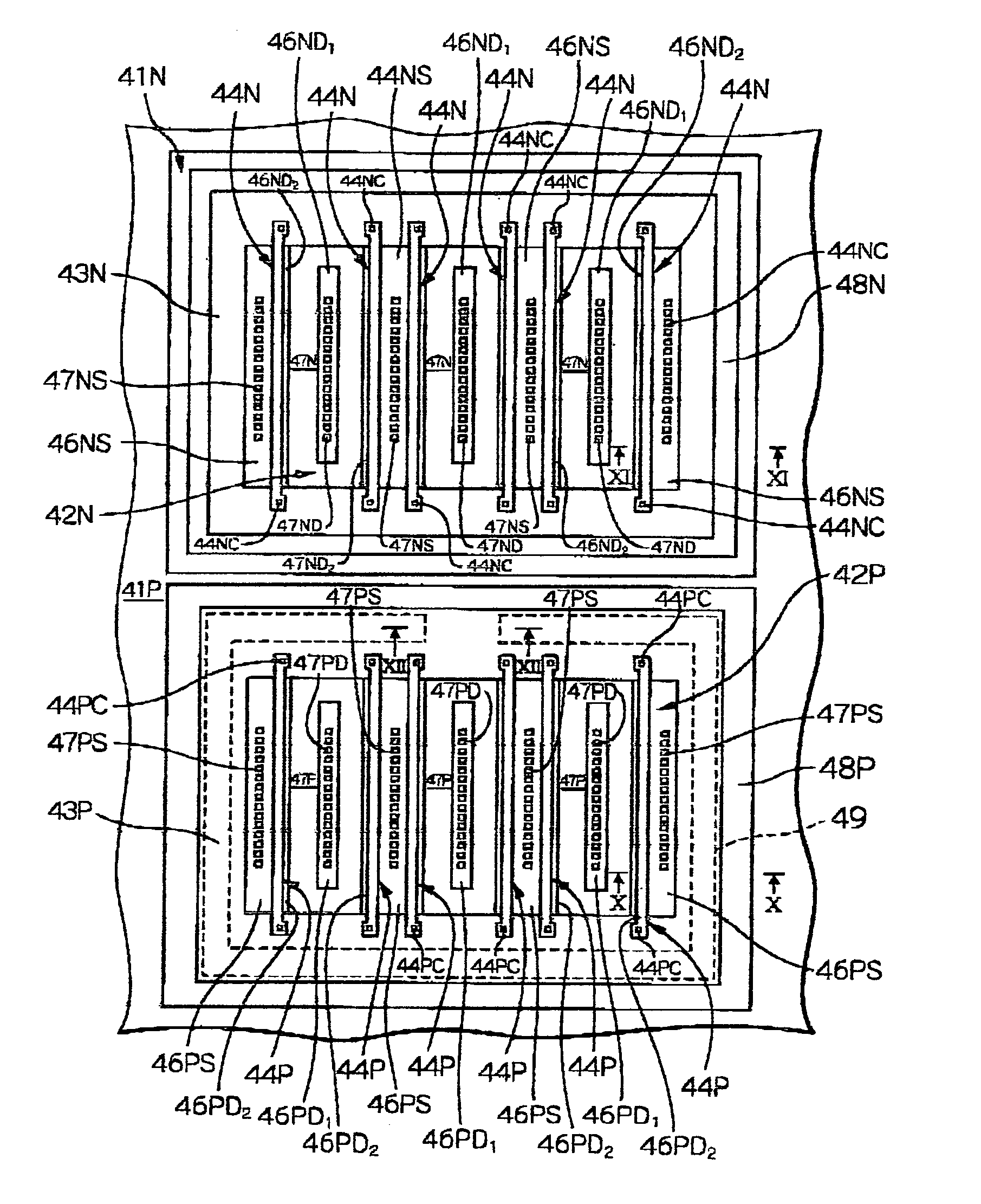
MOS type semiconductor device having electrostatic discharge protection arrangement
InactiveUS20050275032A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFinger structureEngineering
In a semiconductor device, a well region is formed in a semiconductor substrate, a transistor-formation region is defined in the well region. An electrostatic discharge protection device is produced in the transistor-formation region, and features a multi-finger structure including a plurality of fingers. A guard-ring is formed in the well region so as to surround the transistor-formation region, and a well blocking region is formed in the well region between the transistor-formation area and the guard-ring. A substrate resistance determination system is associated with the electrostatic discharge protection device to determine a substrate resistance distribution at the transistor-formation area such that snapbacks occur in all the fingers in a chain-reaction manner, and such that occurrence of a latch-up state is suppressed
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
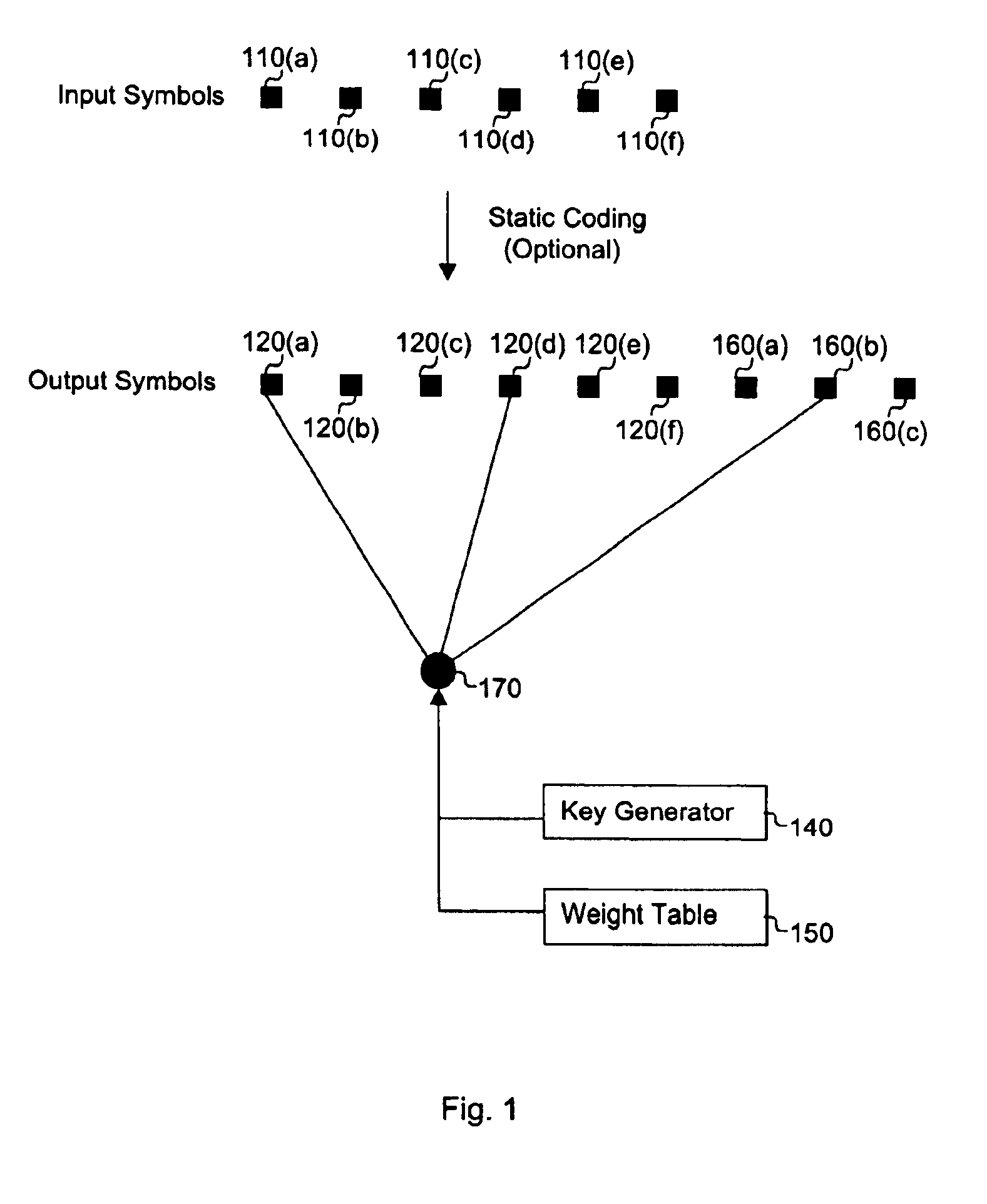
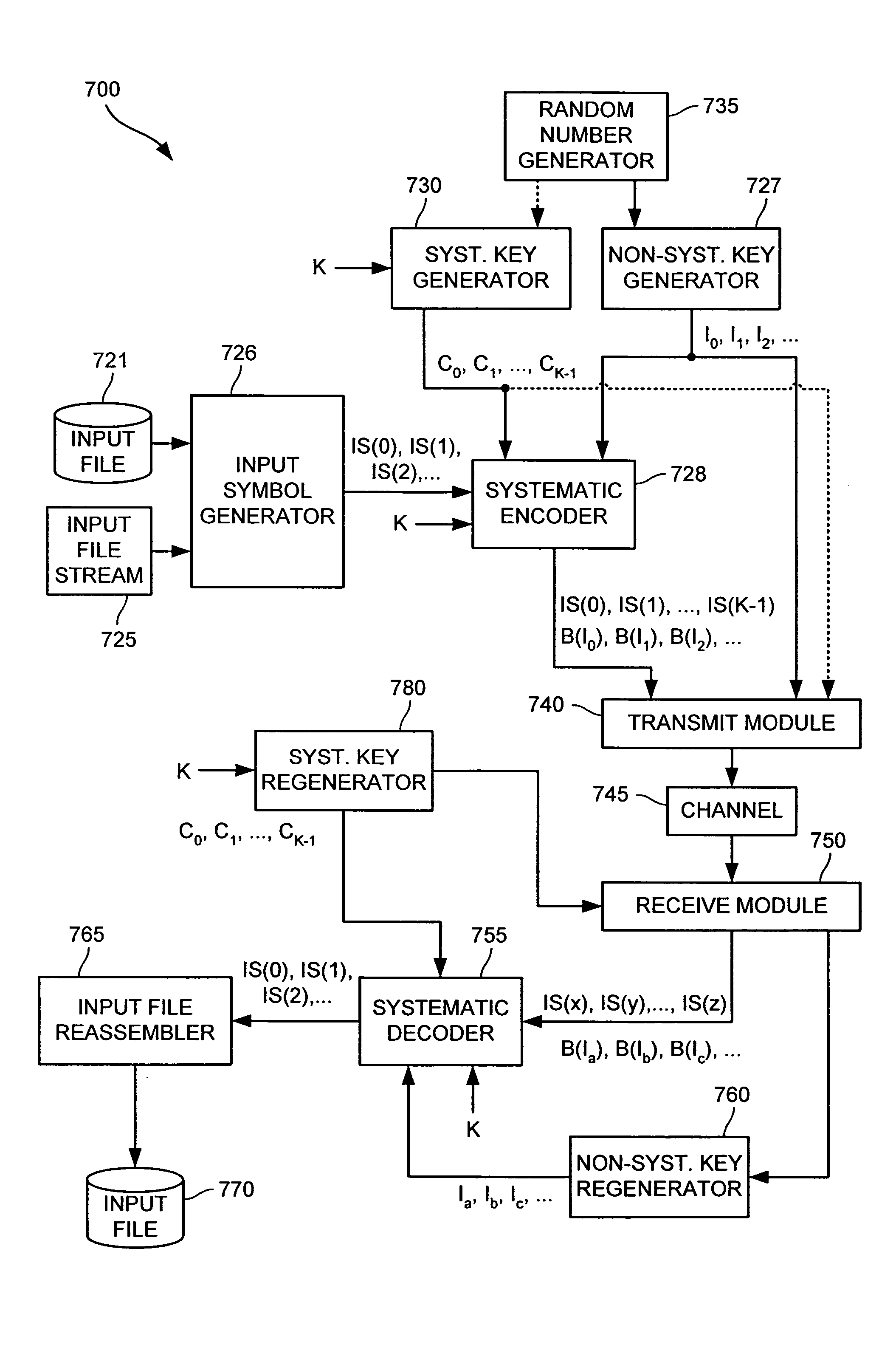
Systematic encoding and decoding of chain reaction codes
InactiveUS7394407B2Communicated faster, more reliablyLess computational expenseError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceData encoding
A method of encoding data into a chain reaction code includes generating a set of input symbols from input data. Subsequently, one or more non-systematic output symbols is generated from the set of input symbols, each of the one or more non-systematic output symbols being selected from an alphabet of non-systematic output symbols, and each non-systematic output symbol generated as a function of one or more of the input symbols. As a result of this encoding process, any subset of the set of input symbols is recoverable from (i) a predetermined number of non-systematic output symbols, or (ii) a combination of (a) input symbols which are not included in the subset of input symbols that are to be recovered, and (b) one or more of the non-systematic output symbols.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Listeria monocytogenes nucleic acid chromatography detection kit, its detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN102520172AGuaranteed SensitivityGuaranteed FeaturesMaterial analysisDNA extractionMicrobiology
The invention discloses a listeria monocytogenes nucleic acid chromatography detection kit, its detection method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and immunology. According to the invention, with the combination of a polymerase chain reaction technology in molecular biology and an immunochromatography technology, rapid detection of listeria monocytogenes in food is accomplished. The kit provided by the invention includes three parts of DNA extraction, PCR amplification and strip detection. The combination of the molecular biology technology and the immunochromatography technology is accomplished by modification of primers and selection of corresponding coatings and markers in strip preparation so as to achieve specific amplification product detection of listeria monocytogenes in food. Compared with a traditional biochemistry method, the method provided by the invention is used to greatly save detection time and simplify operation steps, has characteristics of accuracy, rapidity, convenience and safety, and is suitable for detection of a large number of samples.
Owner:北京陆桥技术股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com