Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4973 results about "Electrostatic discharge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
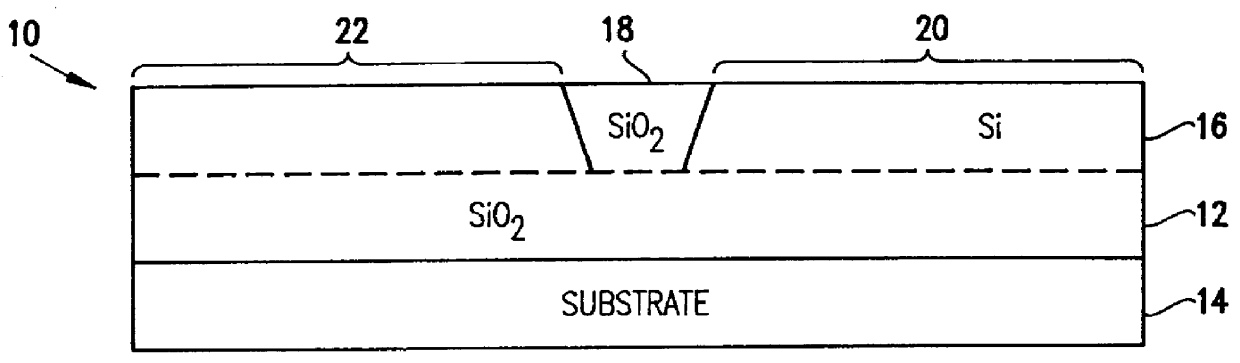
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short, or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused by tribocharging or by electrostatic induction. The ESD occurs when differently-charged objects are brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible spark.
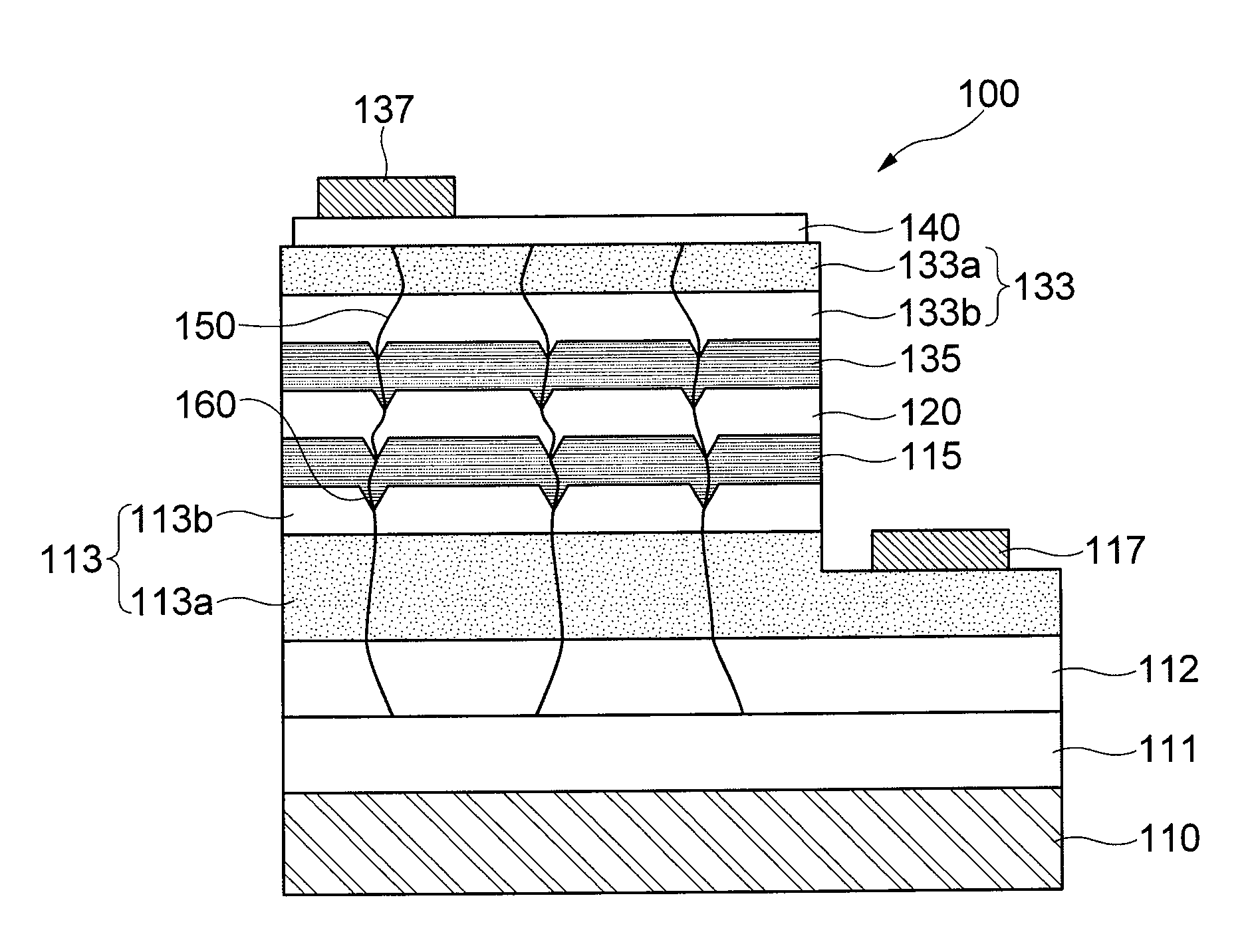
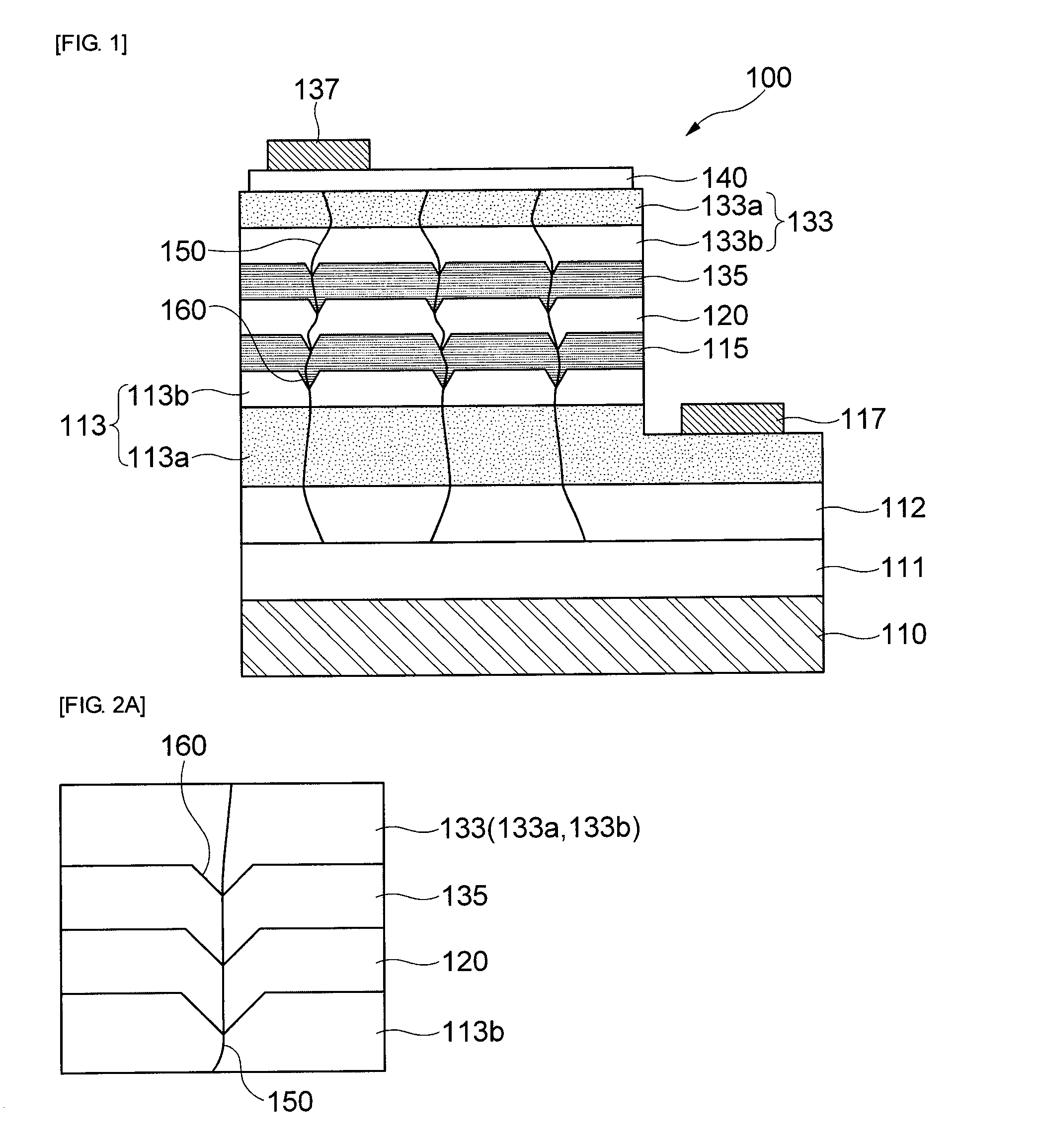
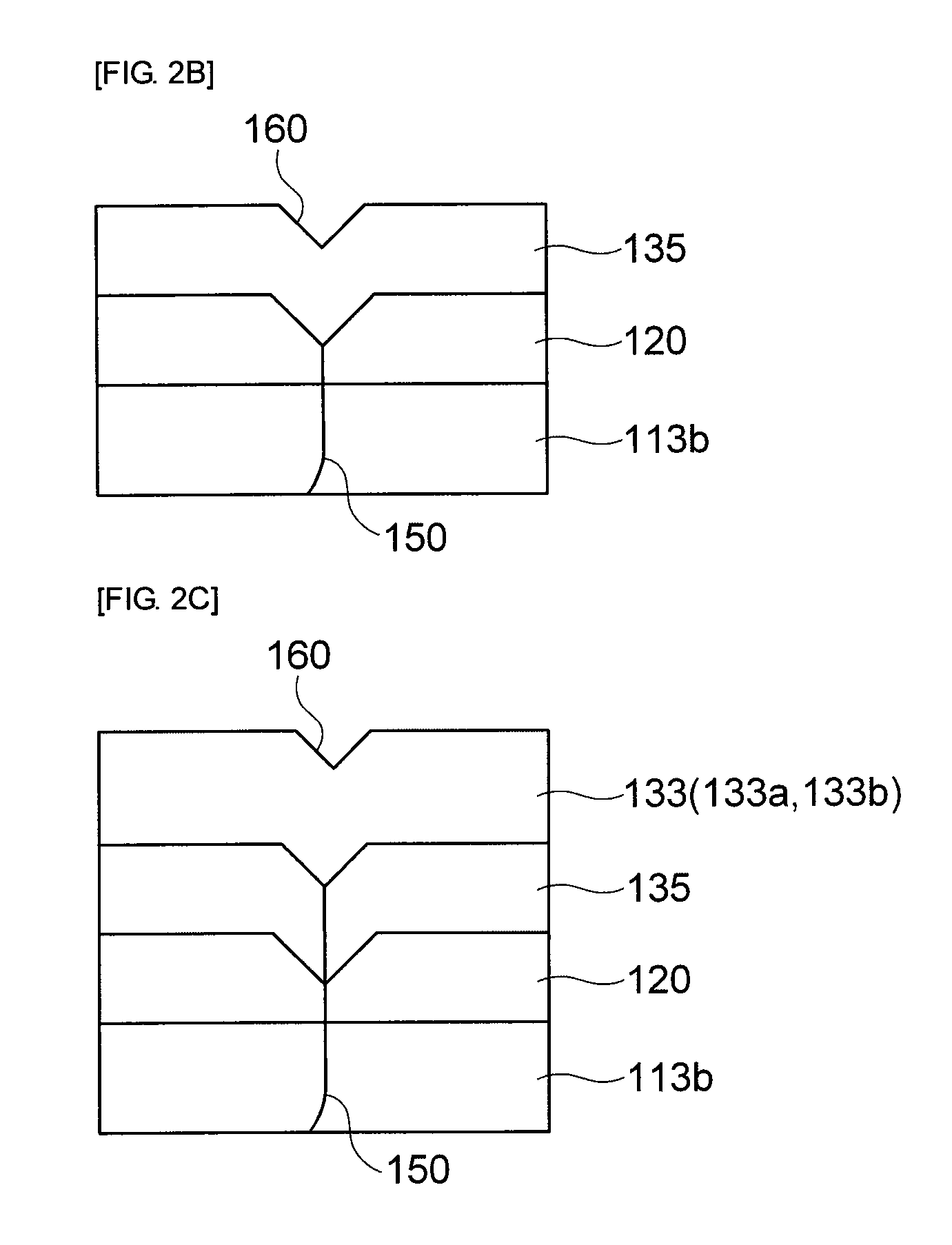
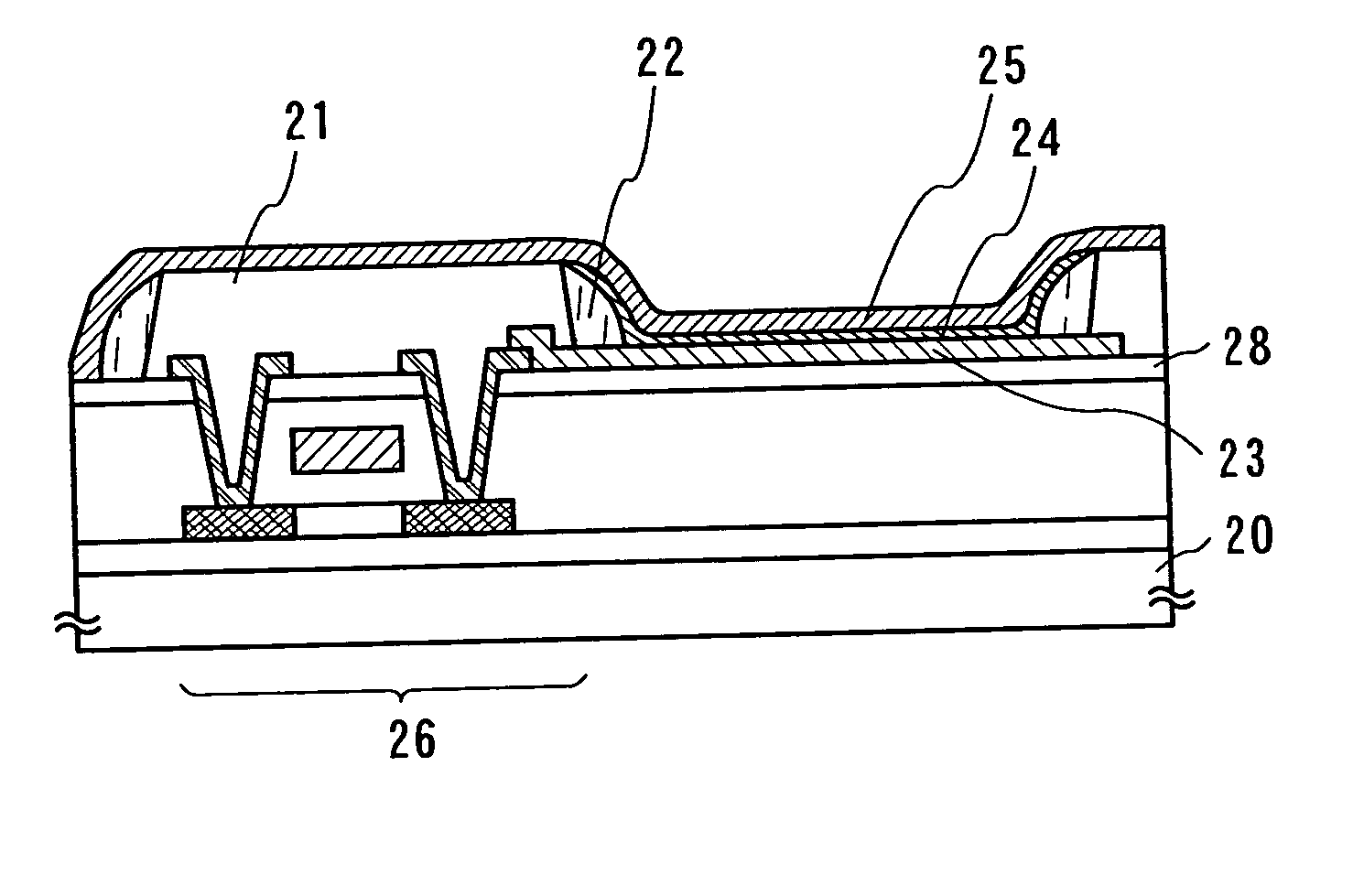
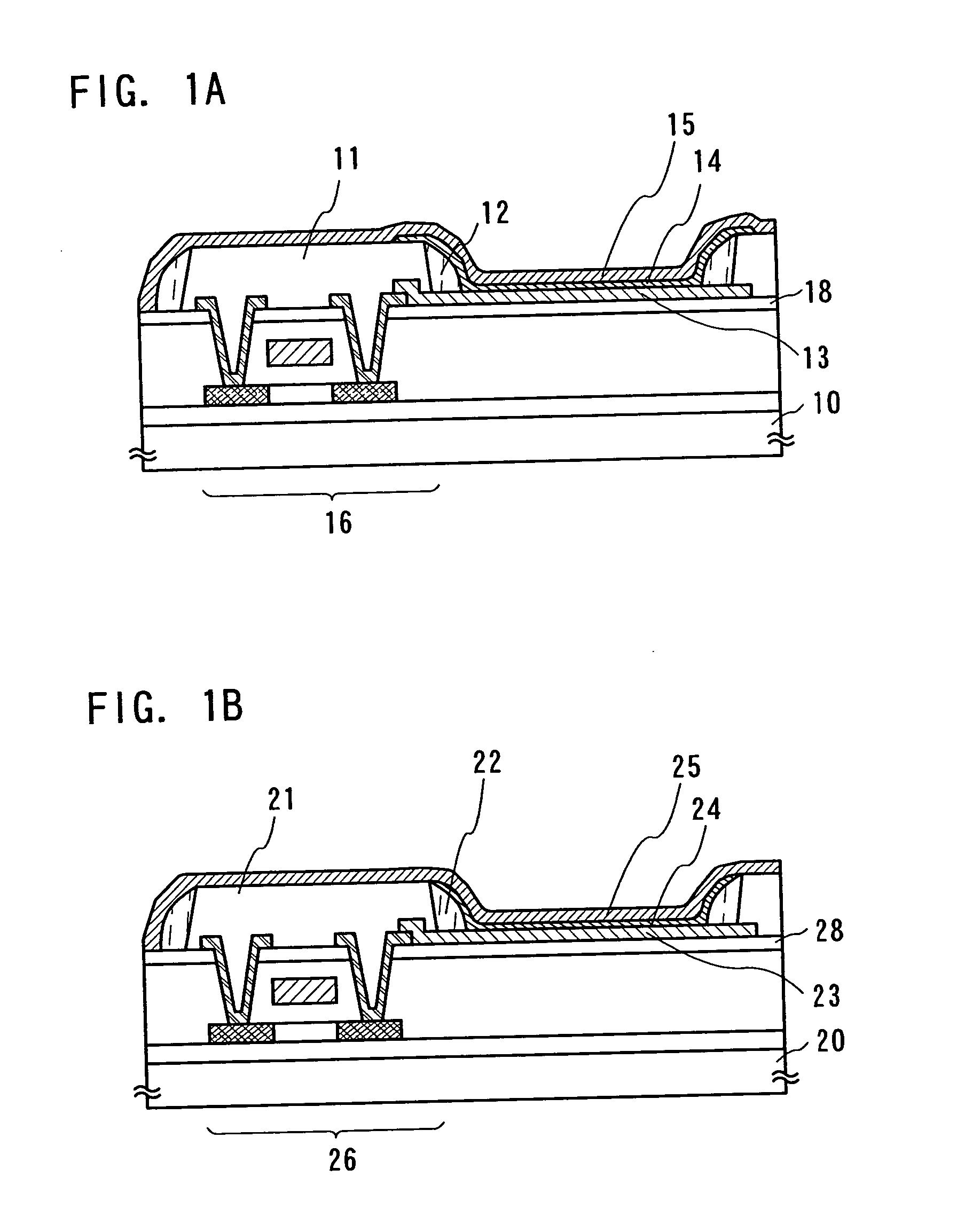
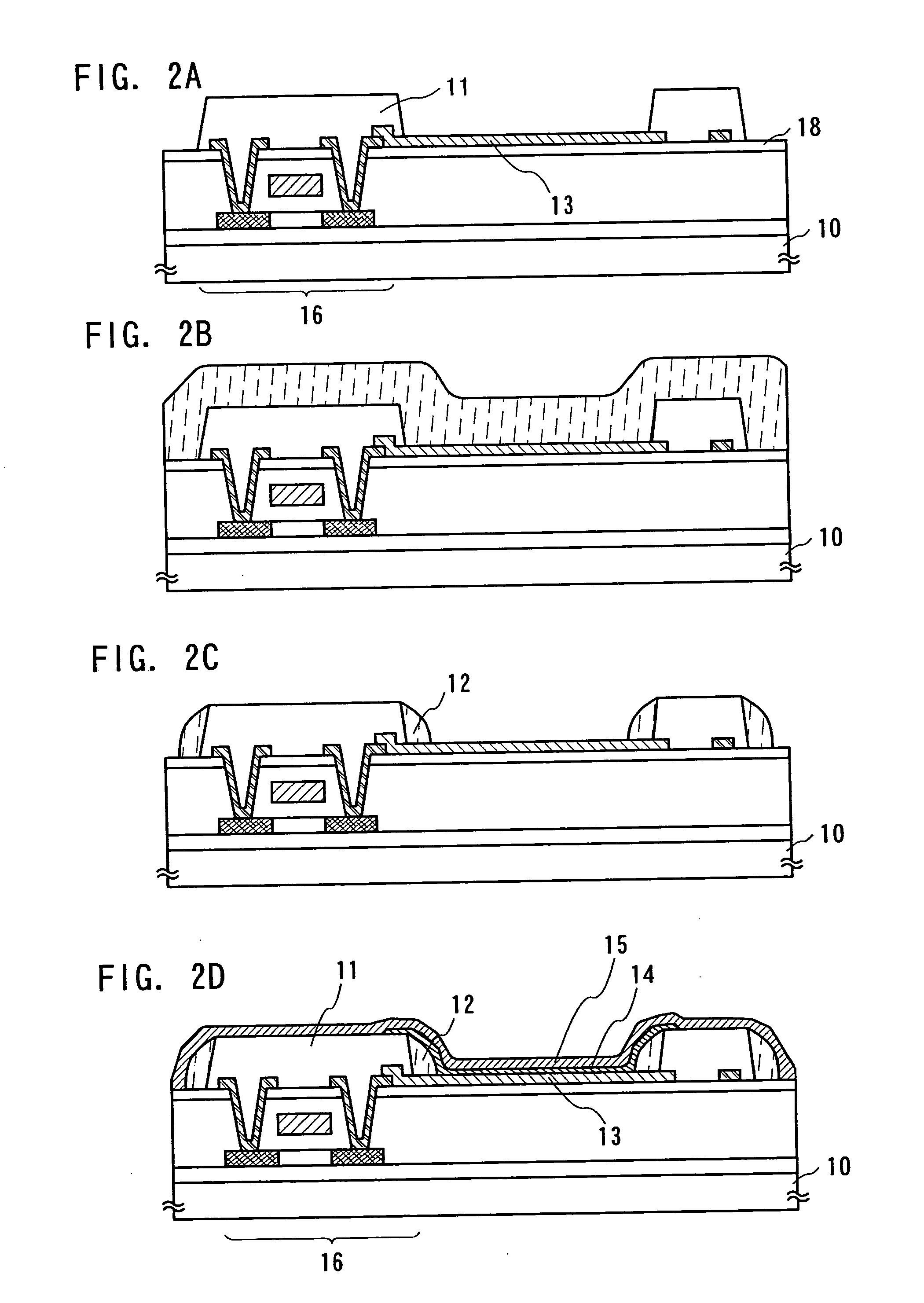
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS8129711B2Good effectReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight emitting device
The present invention relates to a GaN based nitride based light emitting device improved in Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) tolerance (withstanding property) and a method for fabricating the same including a substrate and a V-shaped distortion structure made of an n-type nitride semiconductor layer, an active layer and a p-type nitride semiconductor layer on the substrate and formed with reference to the n-type nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Package structure
ActiveUS20080142831A1Improve luminous efficiencyDesirable luminance efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSealantLight emitting device
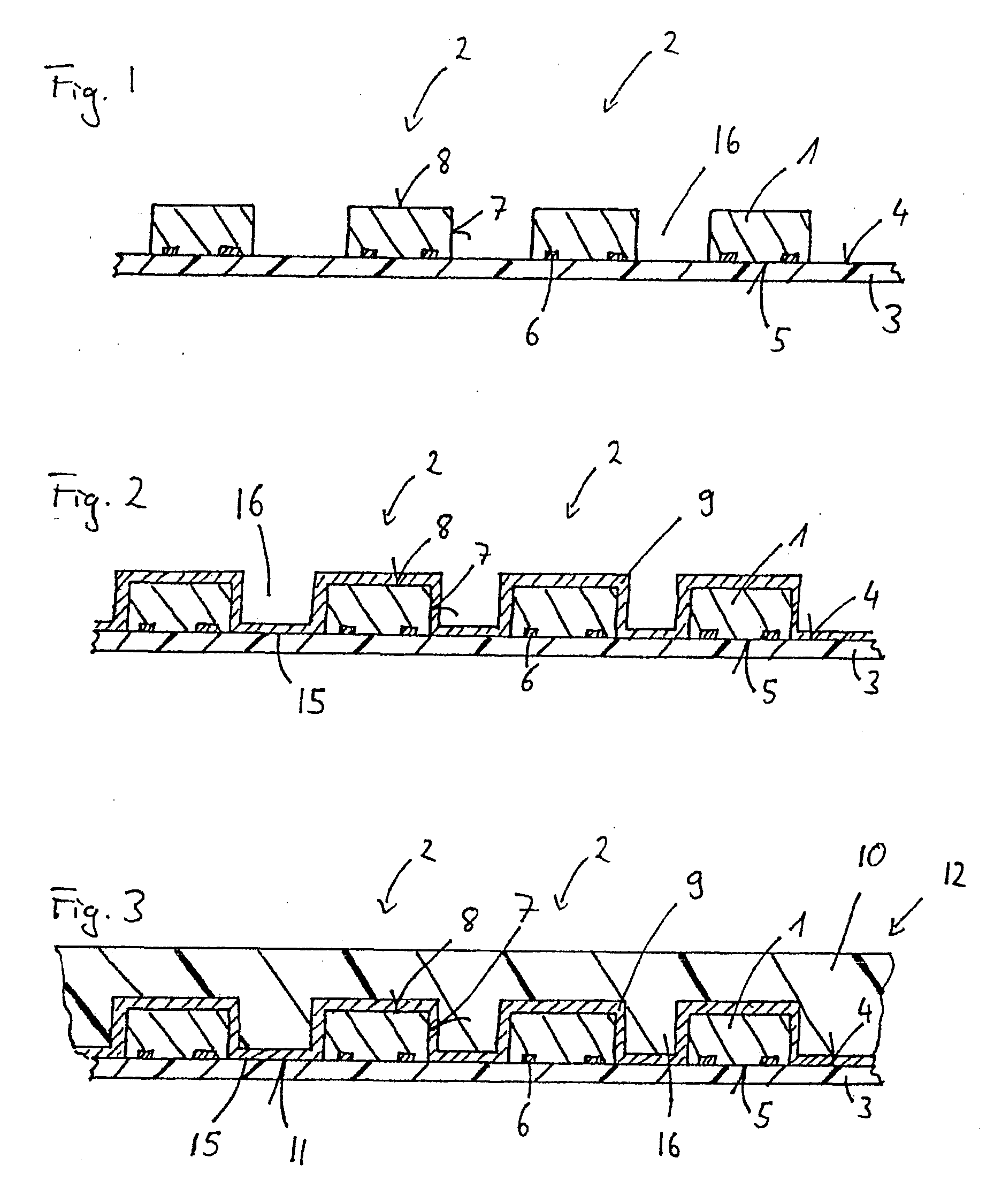
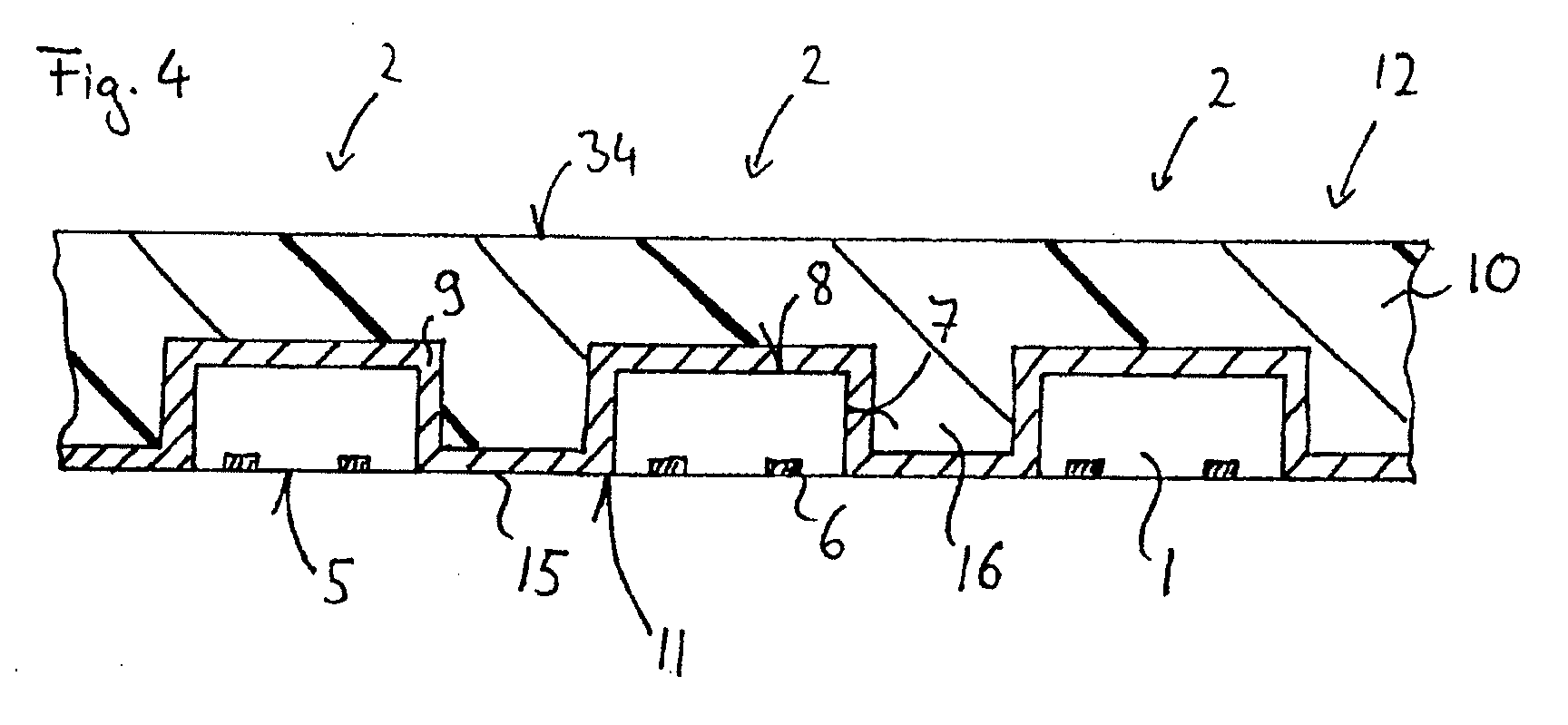
A package structure including a first lead, a second lead, an encapsulant, a light-emitting device and an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device is provided. The second lead is disposed beside the first lead, and parts of the first lead and the second lead are encapsulated by the encapsulant. The encapsulant has a first cavity and a second cavity. Parts of the first lead and the second lead are exposed by the first cavity and the other parts of the first lead and the second lead are exposed by the second cavity. The light-emitting device is disposed inside the first cavity and electrically connected to the first lead and the second lead. The ESD protection device is disposed inside the second cavity and electrically connected to the first lead and the second lead.
Owner:LEXTAR ELECTRONICS CORP
Solid state lighting device with improved thermal management, improved power management, adjustable intensity, and interchangable lenses
InactiveUS20060098440A1Easy to mass produceEasily adjustable light emission patternPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingLuminous intensityEngineering
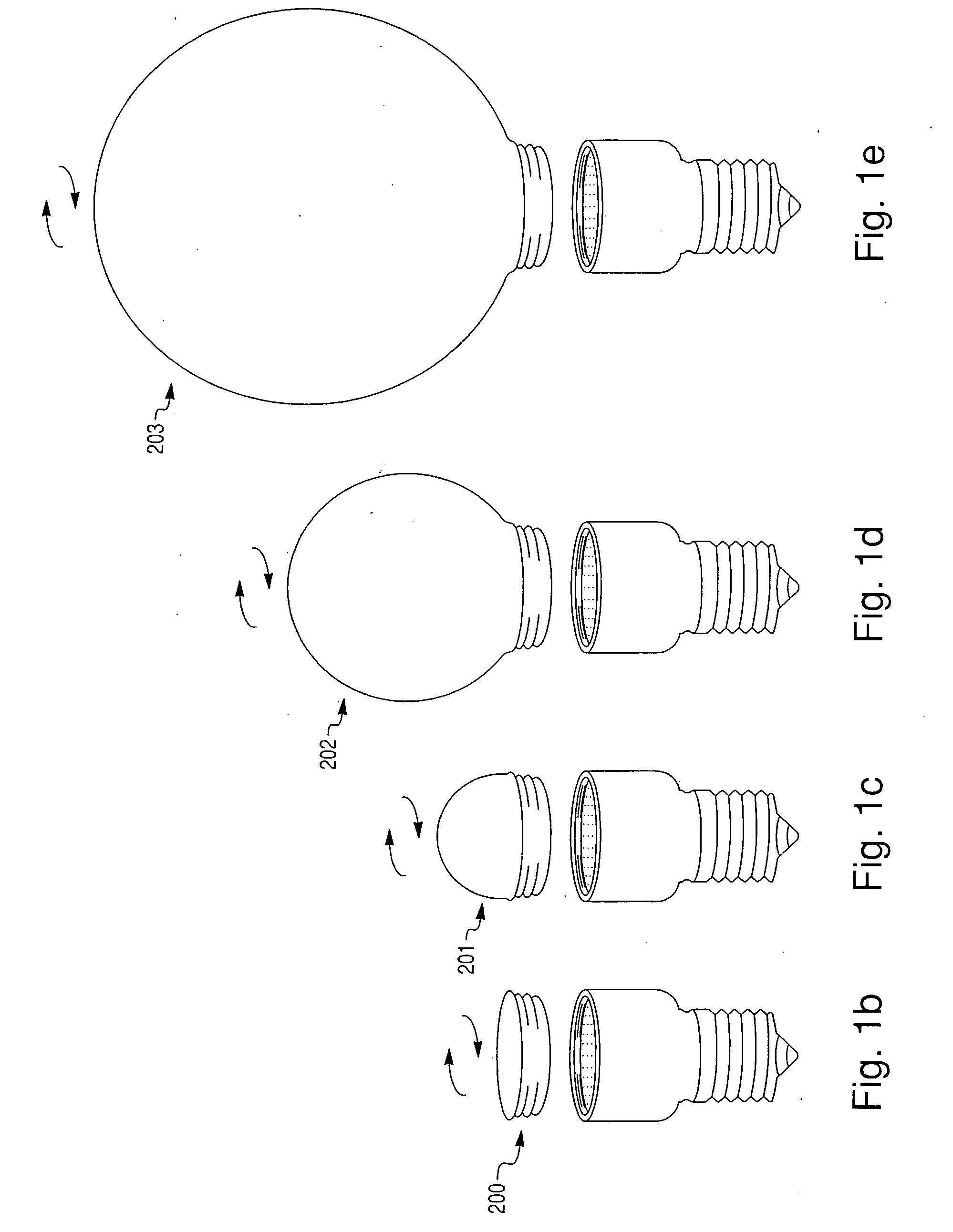
A solid state (light emitting diode) lamp in numerous configurations have improved thermal management by providing a direct thermal pathway from the plurality of LED chips to the threaded screw base (standard 100˜240 VAC lamp socket), or power coupling. The control circuitry is disposed opposite the printed circuit board and LED chips with respect to the heat sink so that the heat sink is interposed between the printed circuit board and the control circuitry. The LED chips are powered using a high voltage / high current configuration. The light radiation pattern is infinitely adjustable (very wide through very narrow) via a system of easily interchangeable lenses. The solid state lamps can be mass produced rapidly at significantly lower cost with very high luminous intensity. ESD protection may be included to protect the LED chips from electrostatic discharge damage.
Owner:NXGEN TECH
Method and devices for providing magnetoresistive heads with protection from electrostatic discharge and electric overstress events
InactiveUS6891702B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storageDisk packClassical mechanics
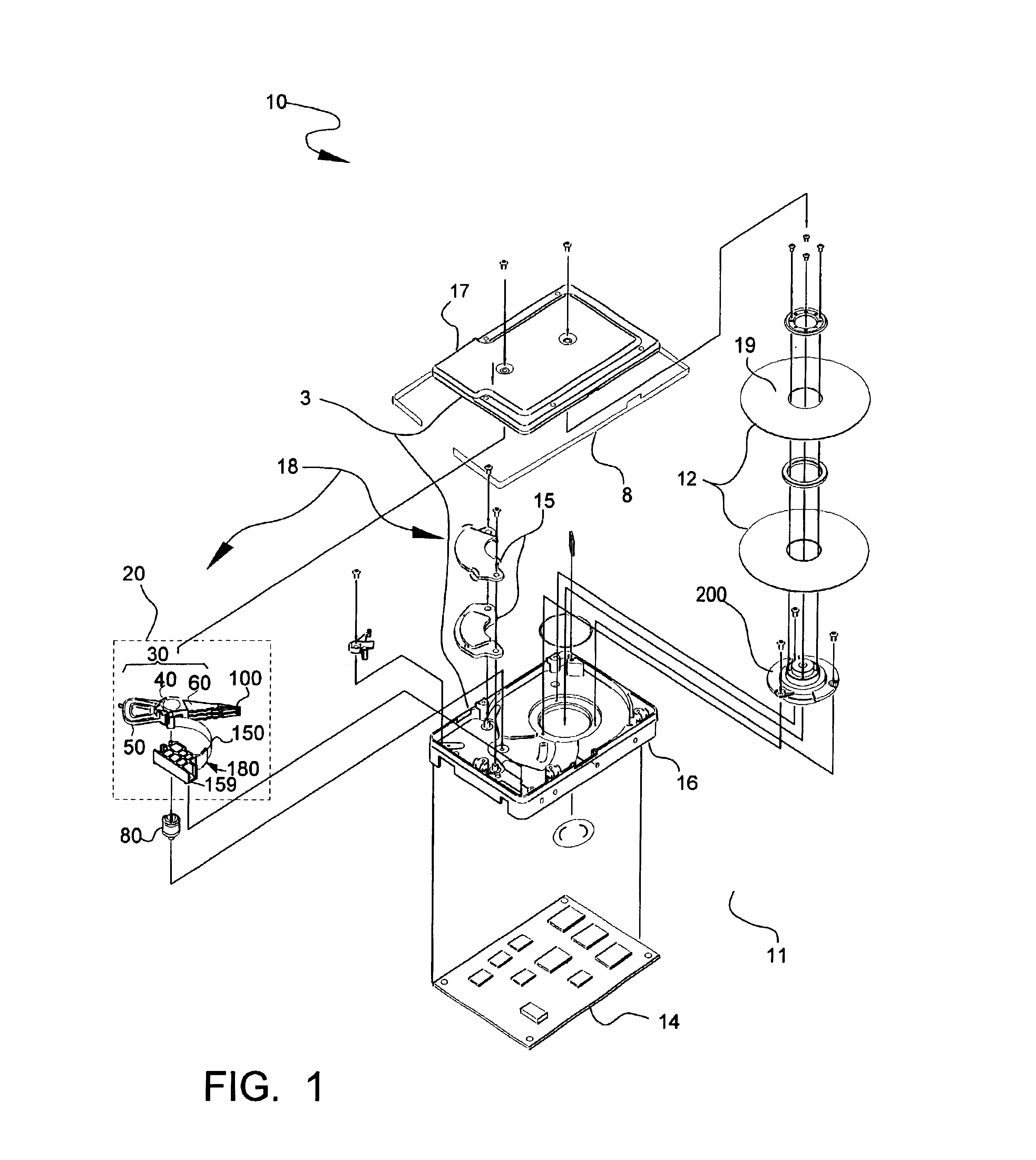
A disk drive includes a disk having a recording surface, a head stack assembly that includes a body portion, an actuator arm cantilevered from the body portion and a head gimbal assembly supported at the actuator arm. The head gimbal assembly includes a suspension having a first end and a second end, the first end being attached to the actuator arm, a slider coupled to the second end of the suspension, the slider comprising a transducer for reading from and writing to the recording surface. A gimbal is coupled to the second end of the suspension and to the slider. An array of diodes is attached to the suspension to protect the transducer from electrostatic discharge or electrical overstress events.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Electrostatic chuck and device of manufacturing organic light emitting diode having the same
ActiveUS20100188794A1Stable controlEasy to implementElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLight-emitting diode
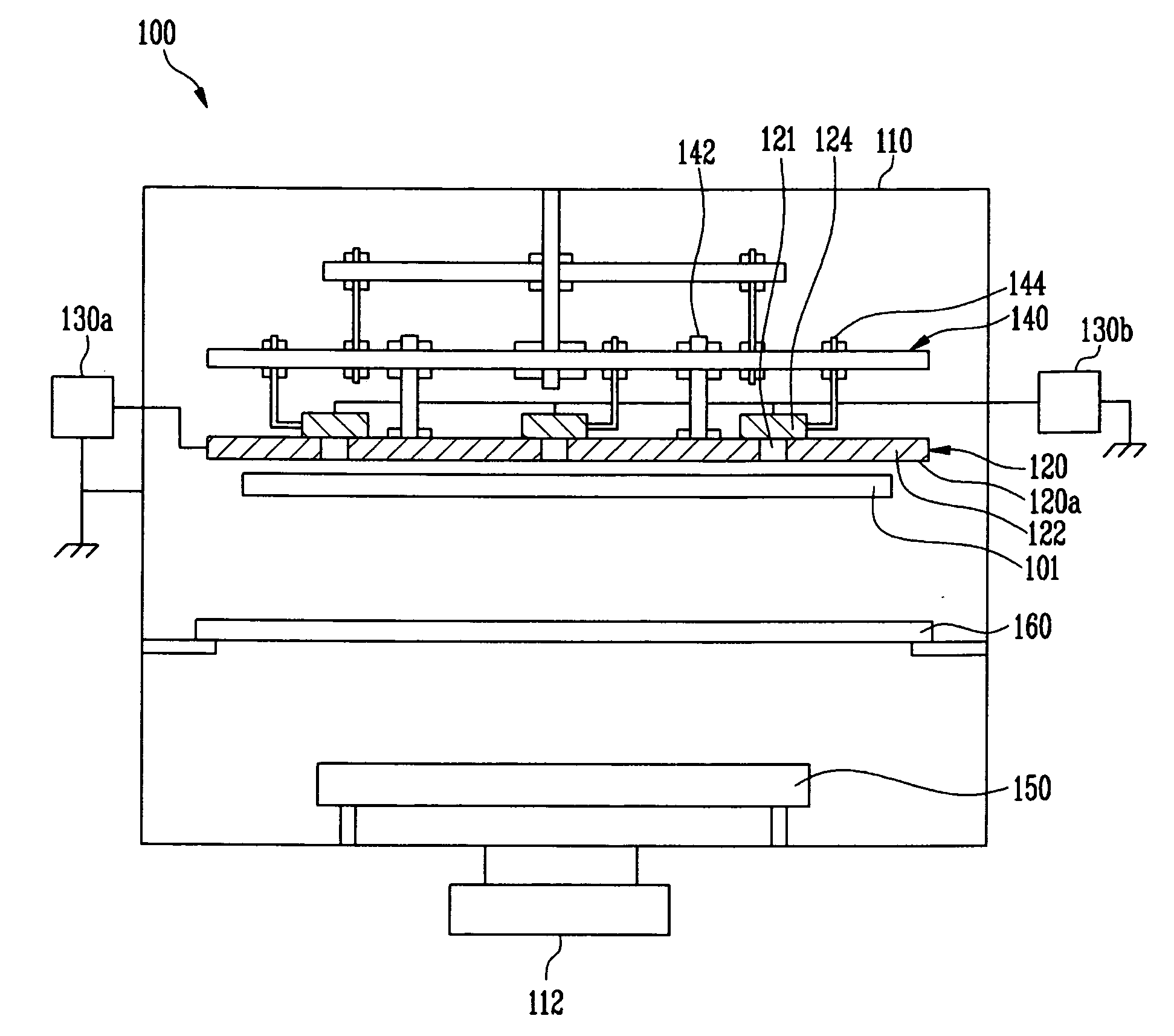
The present invention discloses an electrostatic chuck sucking and supporting a substrate with an electrostatic force and an OLED manufacturing apparatus having the same. The electrostatic chuck includes an insulating plate having at least one opening penetrating a center thereof, a pair of electrodes mounted on the insulating plate, a first controller applying a voltage to the pair of electrodes, and an electrostatic charge removing unit disposed near the insulating plate and emitting ions into the at least one opening to remove electrostatic charges distributed around a side of the insulating plate.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Disk drive comprising depletion mode MOSFETs for protecting a head from electrostatic discharge
InactiveUS7009820B1ESD protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETEngineering
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a head actuated over the disk. The head comprising a first head terminal and a second head terminal. The disk drive further comprises an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit comprising a first depletion mode metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) and a second depletion mode MOSFET. A first transistor terminal of the depletion mode MOSFETs are coupled to respective head terminals, and a second transistor terminal of the depletion mode MOSFETs are coupled to ground. The gate terminals of the first and second depletion mode MOSFETs are biased to turn on the depletion mode MOSFETs while the disk drive is powered down, thereby grounding the first and second head terminals to protect the head from ESD.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Substrate supporting rod and substrate cassette using the same
InactiveUS20050023231A1Improve rigiditySave materialLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
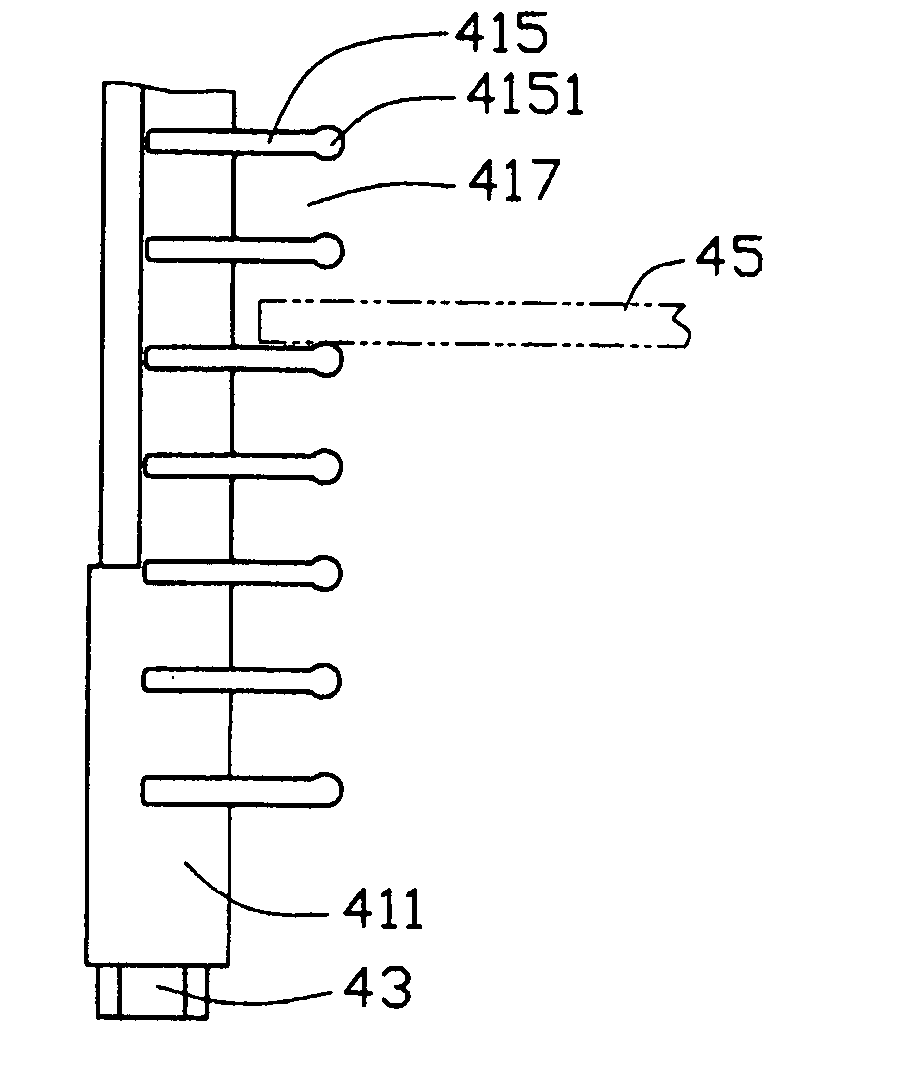
A substrate-supporting rod (4) comprises a resin body (41) and a metal rod (43). The resin body (41) includes a body portion (411) being cylinder-shaped and having a first through hole (413) in a direction of the axis thereof and a number of shelves (415, 415′) arising from said body portion (411) and extending in parallel and inwardly of a cassette (5) at a predetermined pitch. The metal rod (43) is received in the first through hole (413) of the body portion (411) so as to increase the rigidity of the substrate-supporting rob (4). A projection (4151) is defined on the end of each shelf (415, 415′) to support a substrate (45). Further, the body portion (411) is molded from an electrically conductive resin so that not only the cassette (5) can be protected against static discharge but also resin material is saved and cost is decreased.
Owner:FOXSEMICON INTEGRATED TECH INC
Disk drive comprising depletion mode MOSFET for protecting a head from electrostatic discharge
InactiveUS7046488B1ESD protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETField-effect transistor
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a head actuated over the disk. The head comprising a first head terminal and a second head terminal. The disk drive further comprises an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit comprising a first depletion mode metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) comprising a gate terminal and a first and second transistor terminals. The first transistor terminal of the first depletion mode MOSFET is coupled to the first head terminal, and the second transistor terminal of the first depletion mode MOSFET is coupled to the second head terminal. The gate terminal is biased to turn on the first depletion mode MOSFET while the disk drive is powered down, thereby shorting the first and second head terminals to protect the head from ESD.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Reduced Susceptibility To Electrostatic Discharge During 3D Semiconductor Device Bonding and Assembly
InactiveUS20100258949A1Reduce electrostatic dischargePotential damagePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrostatic dischargeGround plane
A method to reduce electrostatic discharge susceptibility when assembling a stacked IC device. The method includes coupling a ground plane of a first semiconductor device and a ground plane of a second semiconductor device to substantially a same electrical potential. Active circuitry on the first semiconductor device and active circuitry on the second semiconductor device are electrically coupled after the ground planes are coupled. Electrically coupling the ground planes of the first and the second semiconductor device creates a preferred electrostatic discharge path to ground, thus minimizing potential damage to sensitive circuit elements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Shielding For Stacked ICs
InactiveUS20100091475A1Magnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrostatic dischargeElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20090014713A1Good effectReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight emitting device
The present invention relates to a GaN based nitride based light emitting device improved in Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) tolerance (withstanding property) and a method for fabricating the same including a substrate and a V-shaped distortion structure made of an n-type nitride semiconductor layer, an active layer and a p-type nitride semiconductor layer on the substrate and formed with reference to the n-type nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
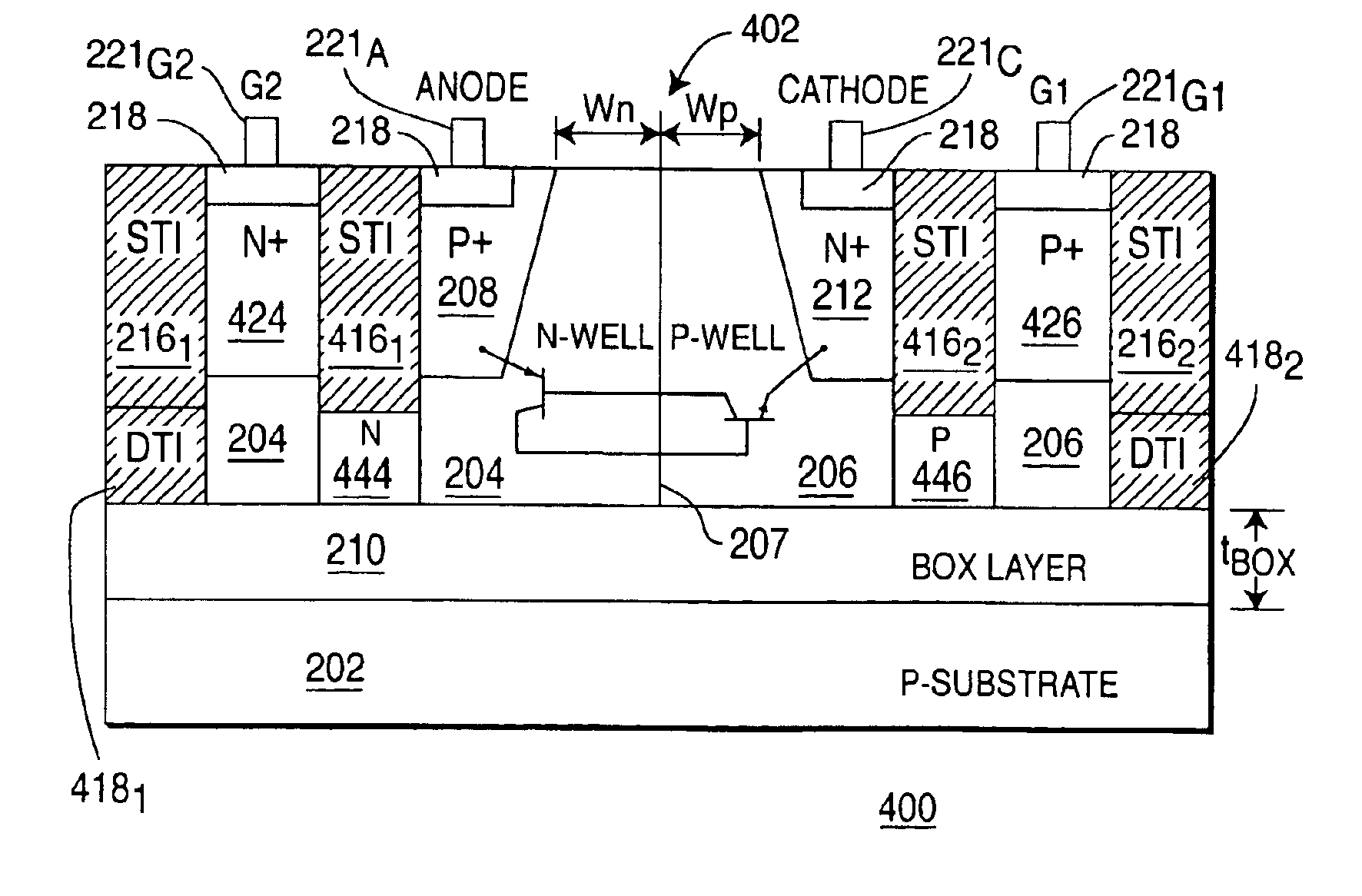
Low voltage silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) for electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection of silicon-on-insulator technologies
InactiveUS20050212051A1Low triggeringLow holding voltageTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Light-emitting apparatus and fabrication method of the same
InactiveUS20050057151A1Prevents electrostatic discharge damageAddressing Insufficient CoverageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLight emitting deviceAperture ratio
Conventionally, there are problems that high resolution is difficult to be achieved since an extreme narrow width bank can not be formed and an aperture ratio as a light-emitting device is low. In addition, there is a threat of electrostatic discharge damage or adhesion of dust during the transportation of a substrate provided with an anode into the equipment for depositing EL material. In view of the foregoing, a first bank formed of an inorganic insulating film is formed, and an insulating film is formed thereon, then, a second bank in contact with a side face of the first bank by carrying out etch back, and then, a side wall bank is formed. For preventing electrostatic discharge damage, an antistatic layer is formed, and the substrate is transported, then, the antistatic layer is removed to form the second bank.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low voltage silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) for electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection of silicon-on-insulator technologies
ActiveUS6909149B2Low triggeringLow holding voltageTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device that can protect very sensitive thin gate oxides by limiting the power dissipation during the ESD event, which is best achieved by reducing the voltage drop across the active (protection) device during an ESD event. In one embodiment, the invention provides very low triggering and holding voltages. Furthermore, the SOI protection device of the present invention has low impedance and low power dissipation characteristics that reduce voltage build-up, and accordingly, enable designers to fabricate more area efficient protection device
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Touch panel
ActiveUS20110057887A1Improve abilitiesImprove protectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTouch panelElectrostatic discharge
A touch panel including a substrate, a plurality of first sensing series, and a plurality of second sensing series is provided. The first sensing series and the second sensing series are disposed on the substrate. The first sensing series extend along a first direction and are electrically insulated from each other. Each of the first sensing series includes a plurality of first sensing pads and a plurality of first bridge portions connected between the first sensing pads. The second sensing series extend along a second direction and are electrically insulated from each other. Each of the second sensing series includes a plurality of second sensing pads and a plurality of second bridge portions connected between the second sensing pads. Each of the first bridge portions and one of the second bridge portions are intersected, and at least one of the second bridge portions has at least one electrostatic discharge tip.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Finger sensor including enhanced ESD protection and associated methods
InactiveUS20070086634A1Enhanced ESD protectionCost effectiveSolid-state devicesPerson identificationLine sensorFlexible circuits
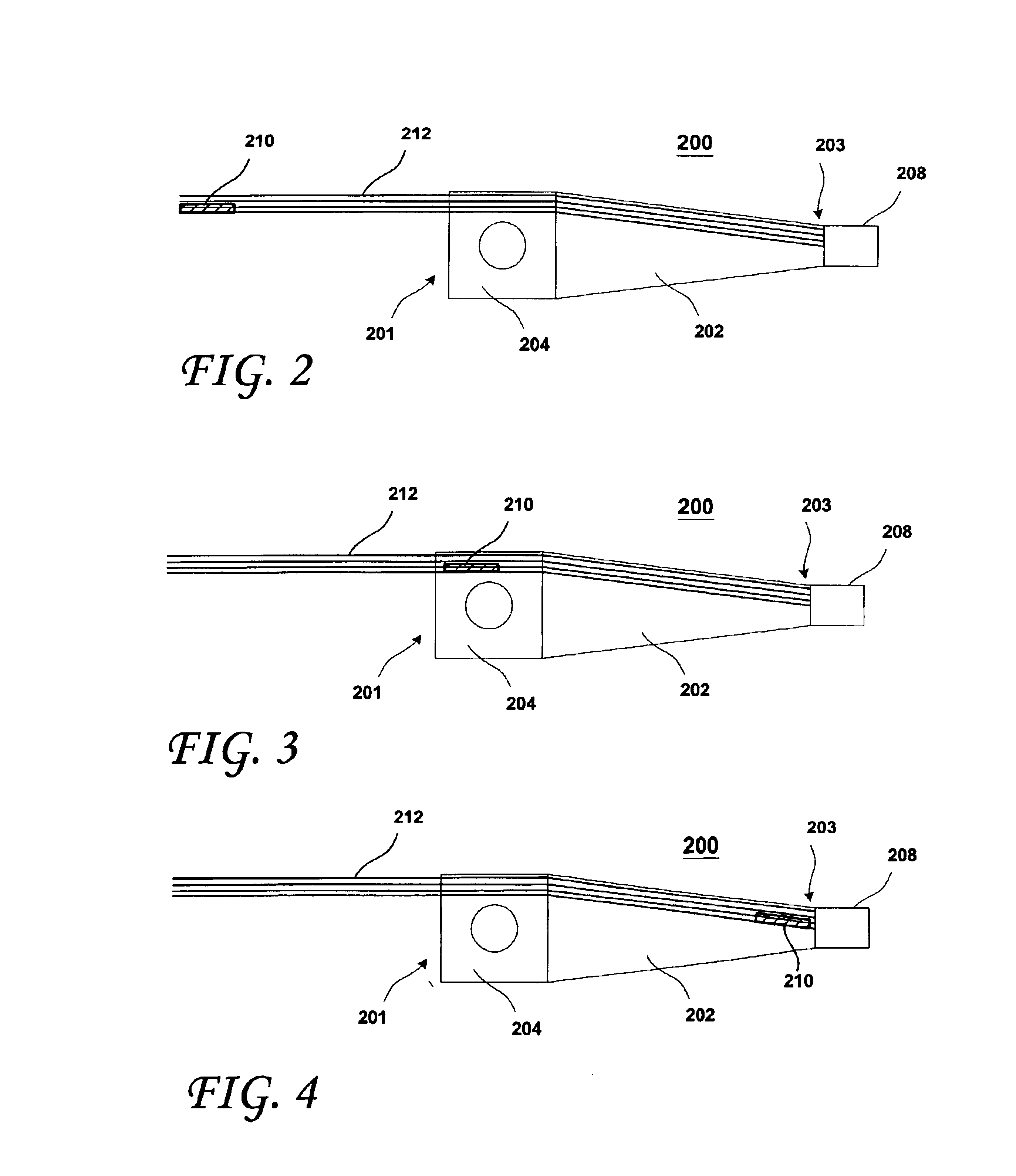
A finger sensor may include a finger sensing integrated circuit (IC) having a finger sensing area and at least one bond pad adjacent thereto, and a flexible circuit coupled to the IC finger sensor. More particularly, the flexible circuit may include a flexible layer, and at least one conductive trace carried thereby and coupled to the at least one bond pad. The sensor may also include at least one Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) electrode carried by the flexible layer. The ESD electrode may be positioned adjacent a beveled edge, for example, of an IC carrier and thereby exposed through a small gap between an adjacent portion of a frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of cleaning glass substrates
InactiveUS9561982B2Low levelEnhance electrostatic interactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible article cleaningThin glassElectrostatic discharge
A method of cleaning thin glass substrates comprises applying a sequence of chemical washing steps as the thin glass substrate is being conveyed in a conveyance direction. In addition, surfaces of the glass substrate may be treated to enhance electrostatic discharge properties of the glass substrates.
Owner:CORNING INC
Silicon-on-insulator and CMOS-on-SOI double film fabrication process with a coplanar silicon and isolation layer and adding a second silicon layer on one region
InactiveUS6096584AHigher power-to-failure thresholdImprove protectionTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerElectronic component
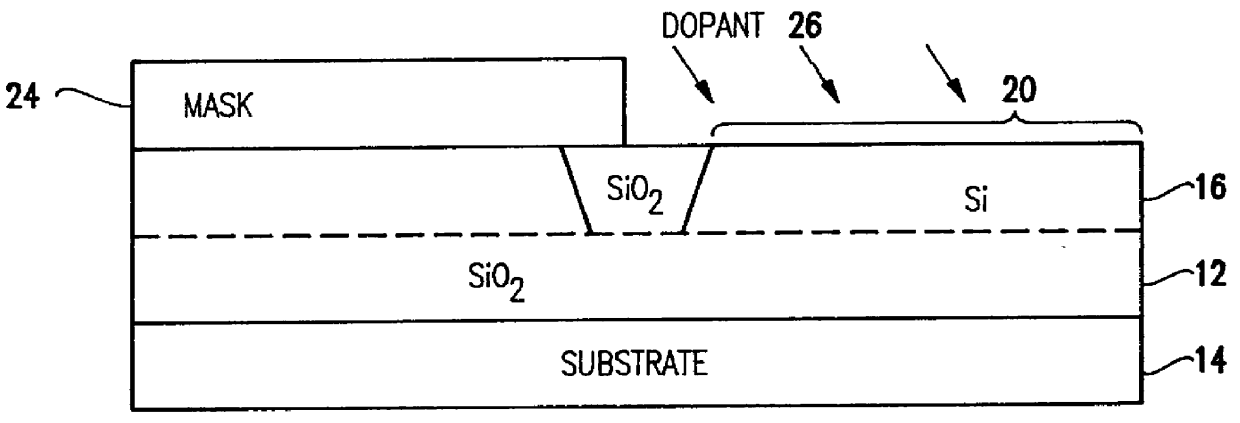
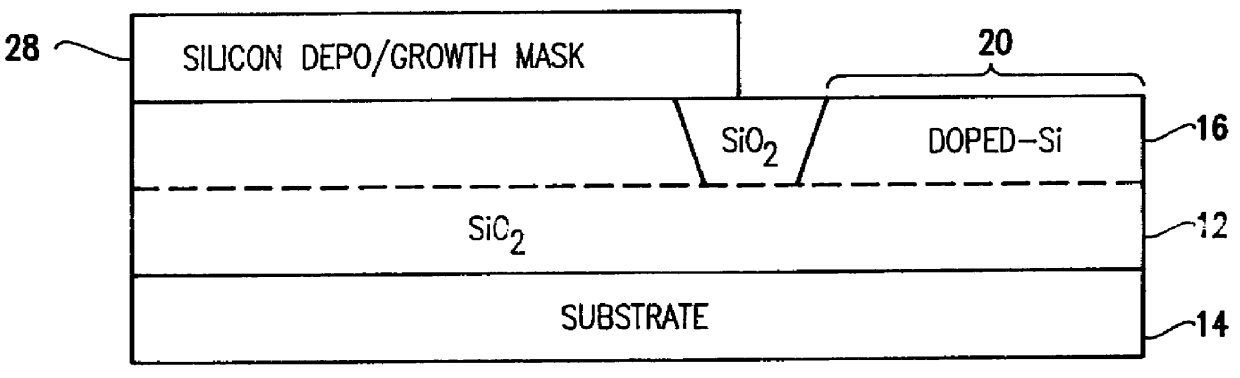
Silicon is formed at selected locations on a silicon-insulator (SOI) substrate during fabrication of selected electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and diodes. The silicon location is defined using a patterned, removable mask, and the silicon may be applied by deposition or growth and may take the form of polysilicon or crystalline silicon. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) characteristics of the SOI device is significantly improved by having a thick double layer of silicon in selected regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
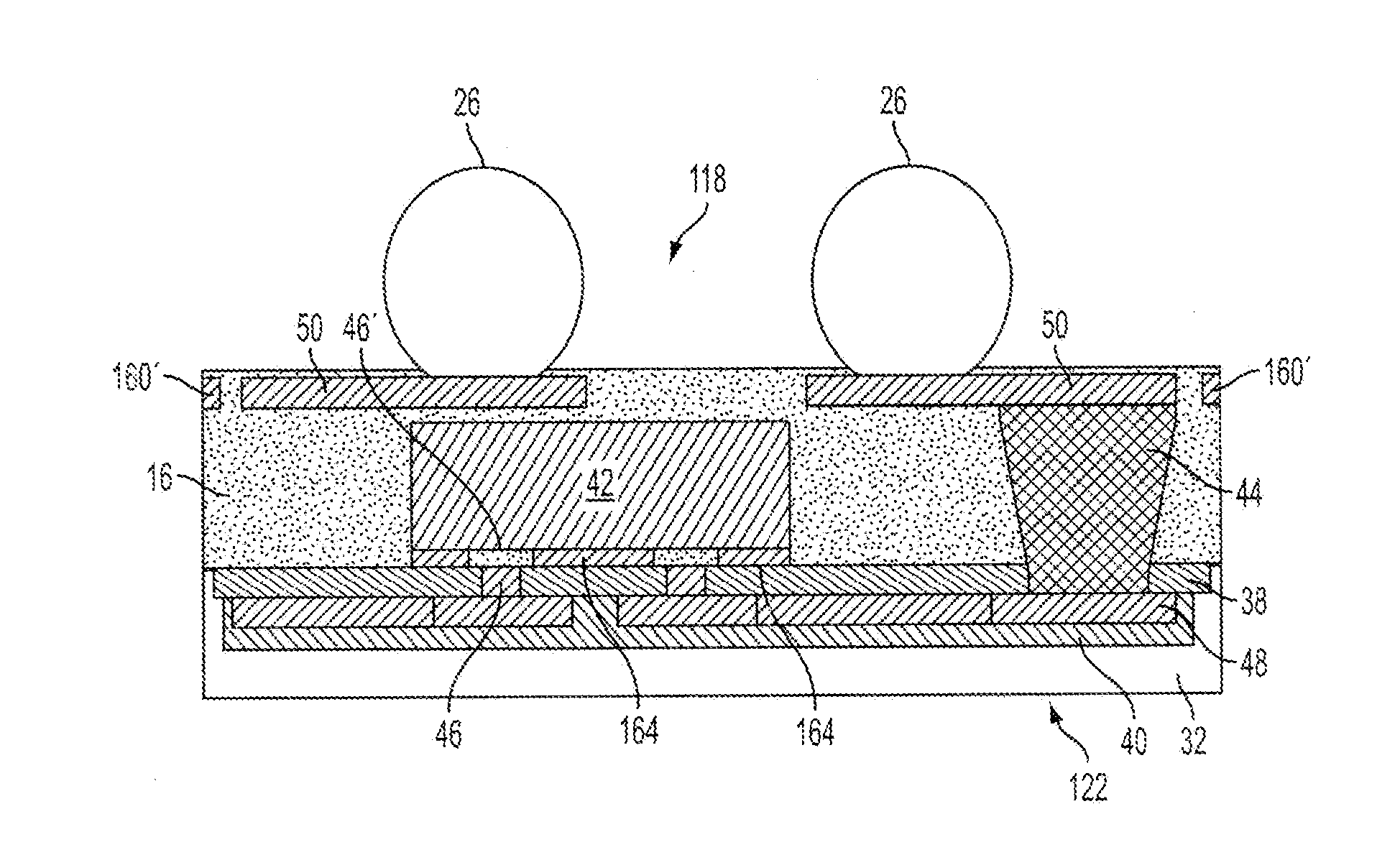
Structure for Electrostatic Discharge in Embedded Wafer Level Packages
ActiveUS20080265421A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A workpiece has at least two semiconductor chips, each semiconductor chip having a first main surface, which is at least partially exposed, and a second main surface. The workpiece also comprises an electrically conducting layer, arranged on the at least two semiconductor chips, the electrically conducting layer being arranged at least on regions of the second main surface, and a molding compound, arranged on the electrically conducting layer.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Transcutaneous implant
ActiveUS20050283203A1Protect from harmAvoid injuryHead electrodesMedical devicesElectrostatic dischargeReduced risk
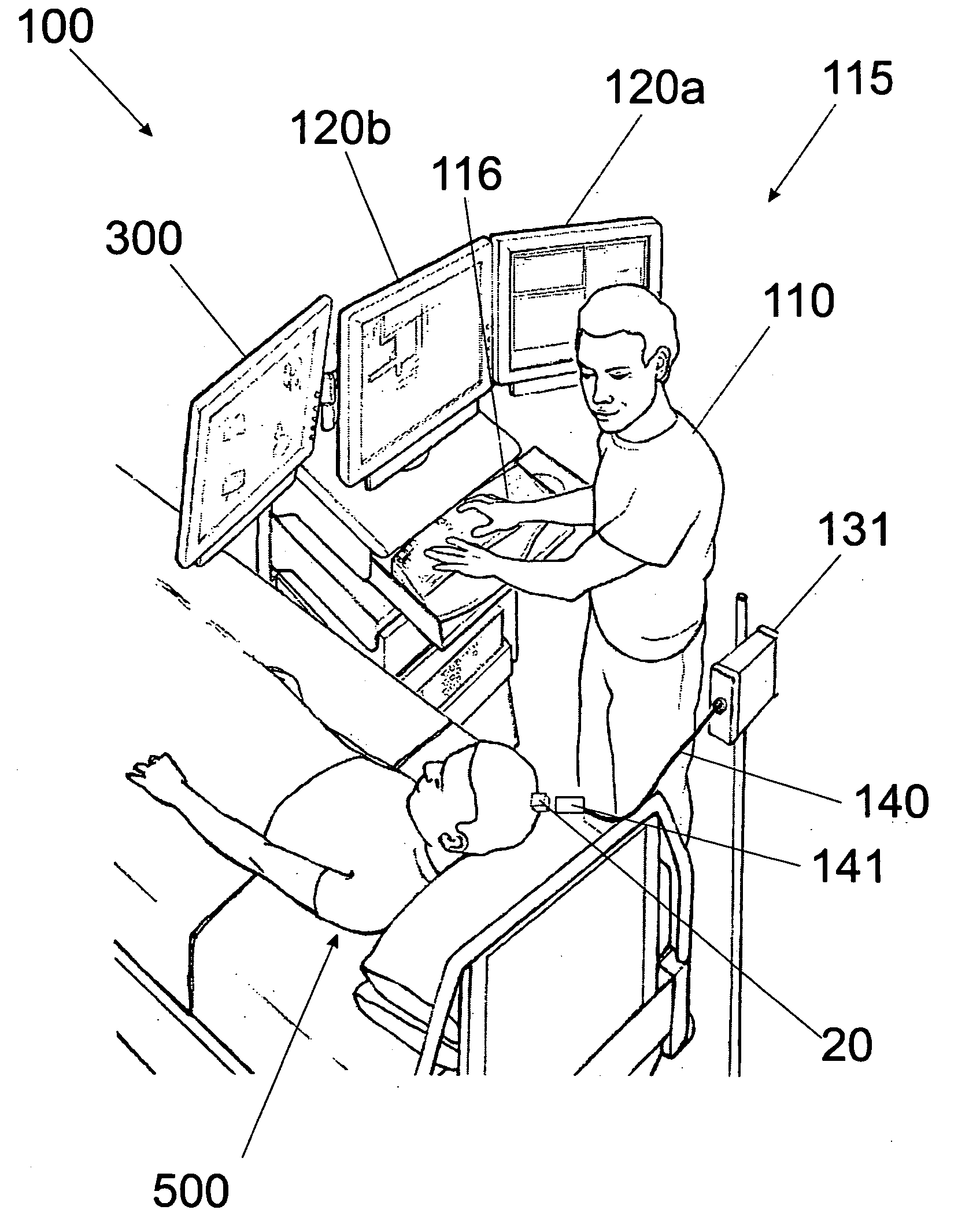
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for a neural access device that includes an implant which transcutaneously exits the skin of a patient and provides transport of signals between a sensor implanted in a patient and an external device. The transcutaneous implant has integrated features to provide reduced risk of injury due to mechanical forces as well as electrostatic discharge energy applied to the external portion of the device. Transcutaneous devices which provide wireless communication between a sensor and an external device are also disclosed.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Input/output electrostatic discharge device with reduced junction breakdown voltage
InactiveUS20110037121A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
An I / O electrostatic discharge (ESD) device having a gate electrode over a substrate, a gate dielectric layer between the gate electrode and the substrate, a pair of sidewall spacers respectively disposed on two opposite sidewalls of the gate electrode, a first lightly doped drain (LDD) region disposed under one of the sidewall spacers, a source region disposed next to the first LDD region, a second LDD region disposed under the other sidewall spacer, and a drain region disposed next to the second LDD region, wherein a doping concentration of the second LDD region is larger than a doping concentration of the first LDD region.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Packaging for fingerprint sensors and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20120256280A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityRedistribution layer
A fingerprint sensor package, including a sensing side for sensing fingerprint information and a separate connection side for electrically connecting the fingerprint sensor package to a host device, is disclosed. The fingerprint sensor package can also include a sensor integrated circuit facing the sensing side and substantially surrounded by a fill material. The fill material includes vias at peripheral locations around the sensor integrated circuit. The fingerprint sensor package can further include a redistribution layer on the sensing side which redistributes connections of the sensor integrated circuit to the vias. The connections can further be directed through the vias to a ball grid array on the connection side. Some aspects also include electrostatic discharge traces positioned at least partially around a perimeter of the connection side. Methods of manufacturing arc also disclosed.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for protecting fingerprint sensing circuitry from electrostatic discharge
A fingerprint sensor in accordance with the invention includes a non-conductive substrate providing a first surface onto which a user can apply a fingerprint to be sensed. A sensor circuit is applied to a second surface of the non-conductive substrate opposite the first surface to sense a fingerprint when juxtaposed proximally thereto. An electrostatic discharge conductor is applied to the non-conductive surface and is located between an area where a fingerprint is swiped and the sensor circuit. The electrostatic discharge conductor discharges electrostatic charge resulting from a user swiping a fingerprint across the first surface.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Vertical gate-all-around TFET
ActiveUS9385195B1Reduce contact resistanceImprove reliabilityTransistorNanoinformaticsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A vertical tunneling FET (TFET) provides low-power, high-speed switching performance for transistors having critical dimensions below 7 nm. The vertical TFET uses a gate-all-around (GAA) device architecture having a cylindrical structure that extends above the surface of a doped well formed in a silicon substrate. The cylindrical structure includes a lower drain region, a channel, and an upper source region, which are grown epitaxially from the doped well. The channel is made of intrinsic silicon, while the source and drain regions are doped in-situ. An annular gate surrounds the channel, capacitively controlling current flow through the channel from all sides. The source is electrically accessible via a front side contact, while the drain is accessed via a backside contact that provides low contact resistance and also serves as a heat sink. Reliability of vertical TFET integrated circuits is enhanced by coupling the vertical TFETs to electrostatic discharge (ESD) diodes.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Gallium nitride-based light emitting device having light emitting diode for protecting electrostatic discharge, and melthod for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060163604A1Improve the immunityReduce in quantityWriting connectorsSolid-state devicesGallium nitrideLight-emitting diode
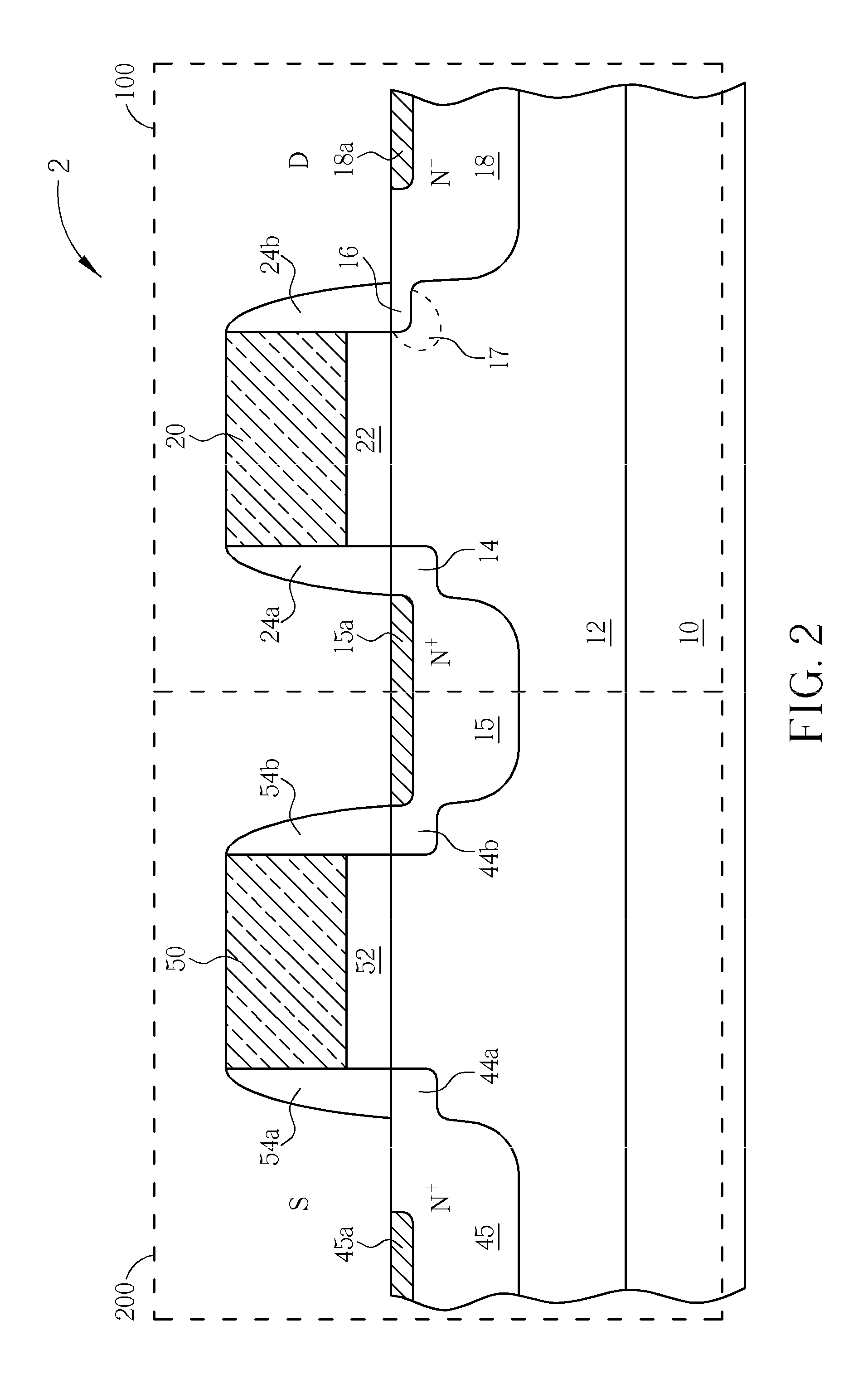
A gallium nitride-based light emitting device, and a method for manufacturing the same are provided. The light emitting device comprises a substrate; a main GaN-based LED including a first p-side electrode and a first n-side electrode, the main GaN-based LED formed in a first region on the substrate; and an ESD protecting GaN-based LED including a second p-side electrode and a second n-side electrode, the ESD protecting GaN-based LED formed in a second region on the substrate. The first region is separated from the second region by a device isolation region. The first p-side and n-side electrodes are electrically connected to the second n-side and p-side electrodes, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
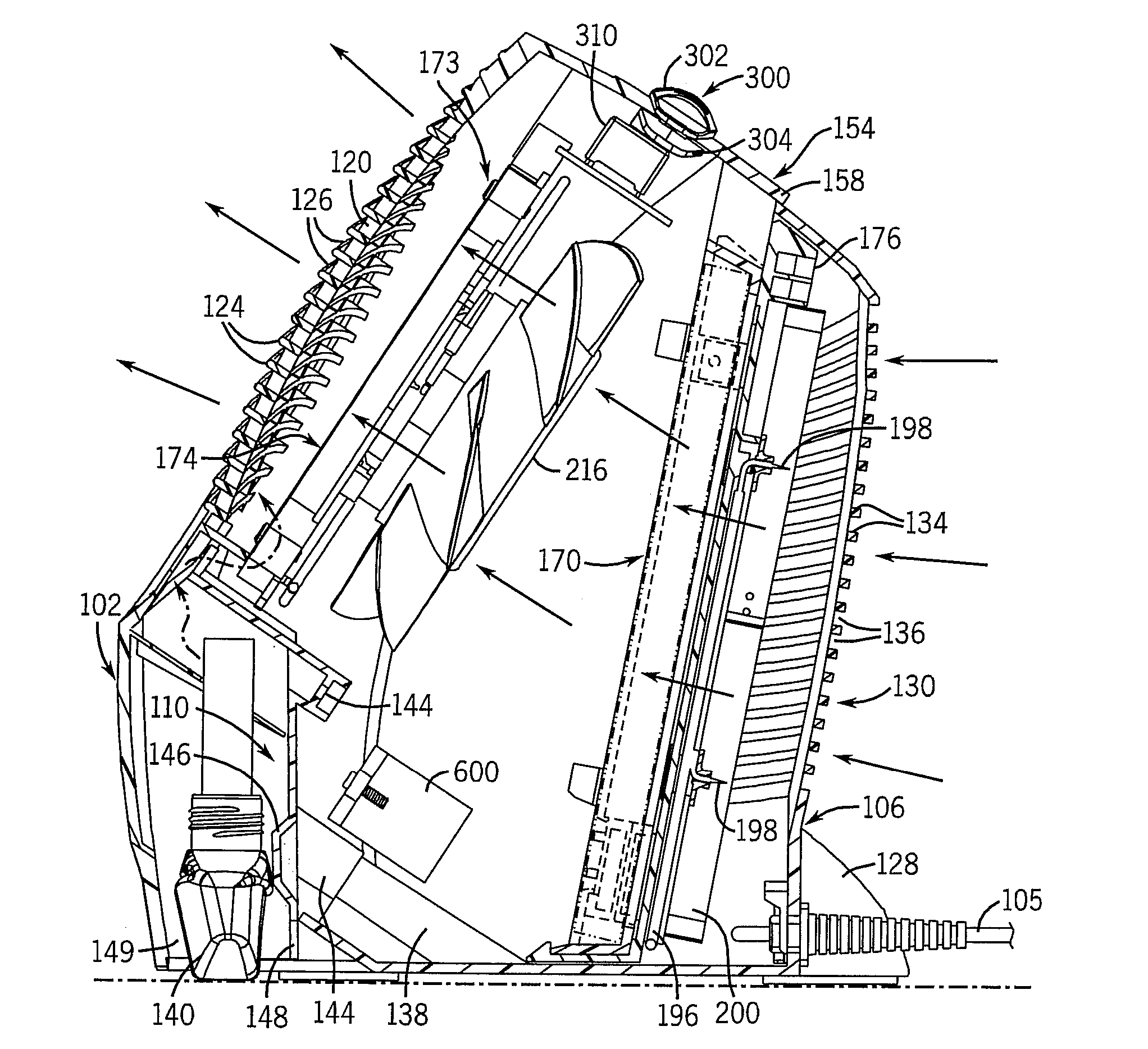
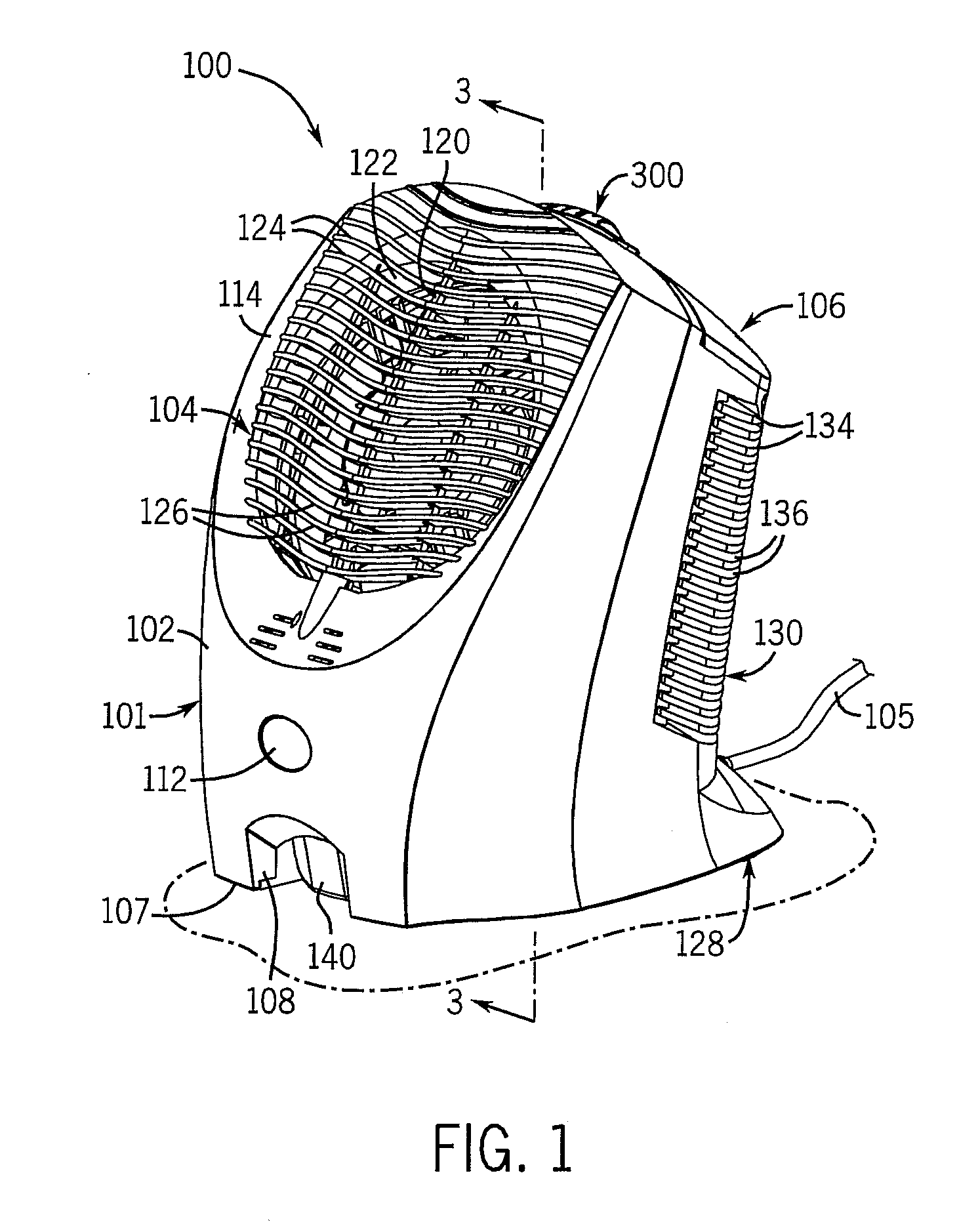
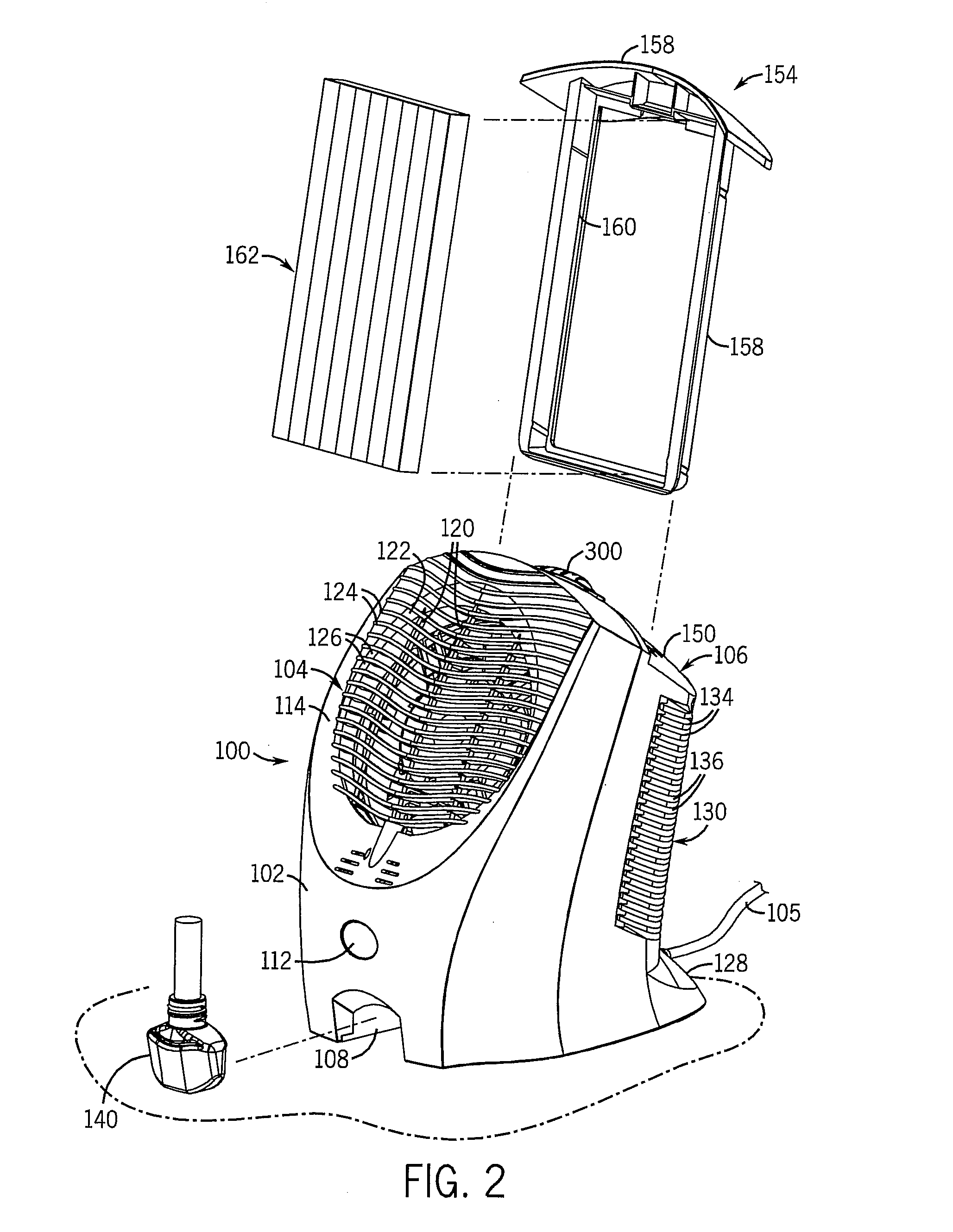
Air purifier
InactiveUS20070034082A1Maximize generationEfficient chargingCombination devicesMechanical apparatusEngineeringAir purifier
The present invention is an air purifier including an ionizing assembly that operates to charge particulate material in an air flow passing through the purifier. The charged particulate material is attracted to and retained by a filter element disposed downstream of the ionization assembly and having an electrical charge opposite to the charged particulate material. The purified air passing through the filter is directed out of the device, optionally in conjunction with a fragrance that is added to the purified air flow. The ionizing assembly is formed with a ground member disposed adjacent the ionizing member to keep the electrons generated by the ionizing assembly within the purifier, and thus prevent static discharges from occurring outside of the purifier. The air flow is directed by a fan through the purifier in an angular and substantially laminar manner, such that the efficiency of the purifier is increased.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
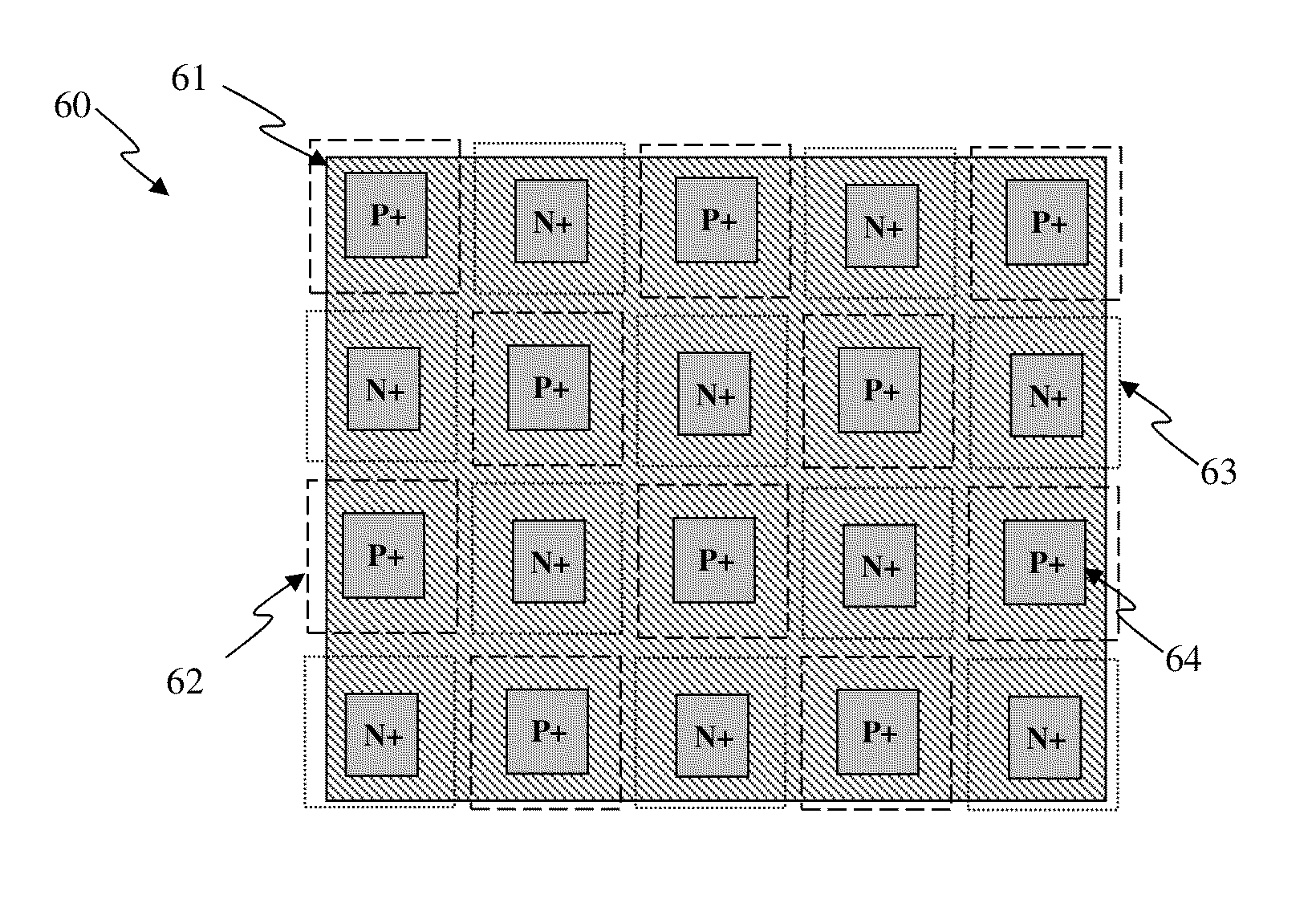
Structures and techniques for using mesh-structure diodes for electro-static discharge (ESD) protection
ActiveUS20130200488A1Improve immunityReduce input capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSBlocking layer
An Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) protection using at least one I / O pad with at least one mesh structure of diodes provided on a semiconductor body is disclosed. The mesh structure has a plurality of cells. At least one cell can have a first type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a second type of implant in at least one side of the cell, and at least cell can have a second type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a first type of implant in at least one side of the cell. The two types of implant regions can be separated with a gap. A silicide block layer (SBL) can cover the gap and overlap into the both implant regions to construct P / N junctions on the polysilicon or active-region body on an insulated substrate. Alternatively, the two types of implant regions can be isolated by LOCOS, STI, dummy gate, or SBL on silicon substrate. The regions with the first and the second type of implants can be coupled to serve as the first and second terminal of a diode, respectively. The mesh structure can have a first terminal coupled to the I / O pad and a first terminal coupled to a first supply voltage.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Low triggering voltage SOI silicon-control-rectifier (SCR) structure
A low triggering voltage PD-SOI (Partially-Depleted Silicon-on-Insulator) electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection structure is disclosed. In one embodiment, the protection structure includes: A semiconductor substrate; a thin film layer separated from a bulk silicon substrate by an insulator inside the semiconductor substrate; a first isolation region formed in the thin film layer; a second isolation region formed in the thin film layer; a first region having a first conductivity type formed in between the first and second isolation region; a second region formed in between the first region and the second isolation region, the second region being of a second conductivity type; a third region formed in between the first isolation region and the first region, the third region being of the first conductivity type; a fourth region formed in between the second isolation region and the second region, the fourth region being of the first conductivity type; a fifth region having an exposed upper surface formed in the first region, the fifth region being of the second conductivity type; a sixth region having an exposed surface formed in the second region, the sixth region being of the second conductivity type; and a seventh region having an exposed upper surface formed in the second region and overlapping the first region, moreover, the seventh region being between the fifth and sixth region and the seventh region being of the first conductivity type. Another embodiment of the present invention is very similar to the previous one, which is also extracted in the present specification.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
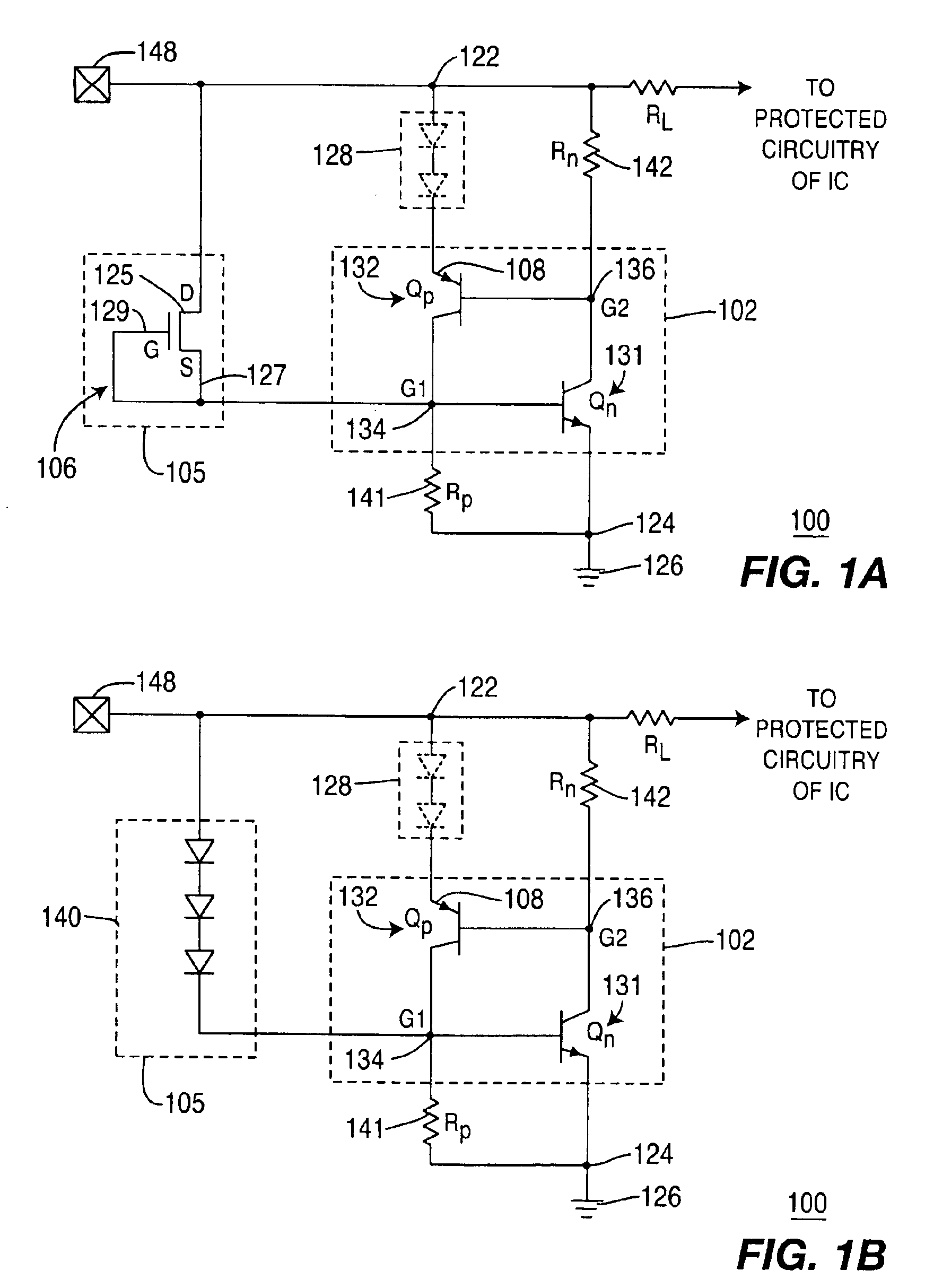
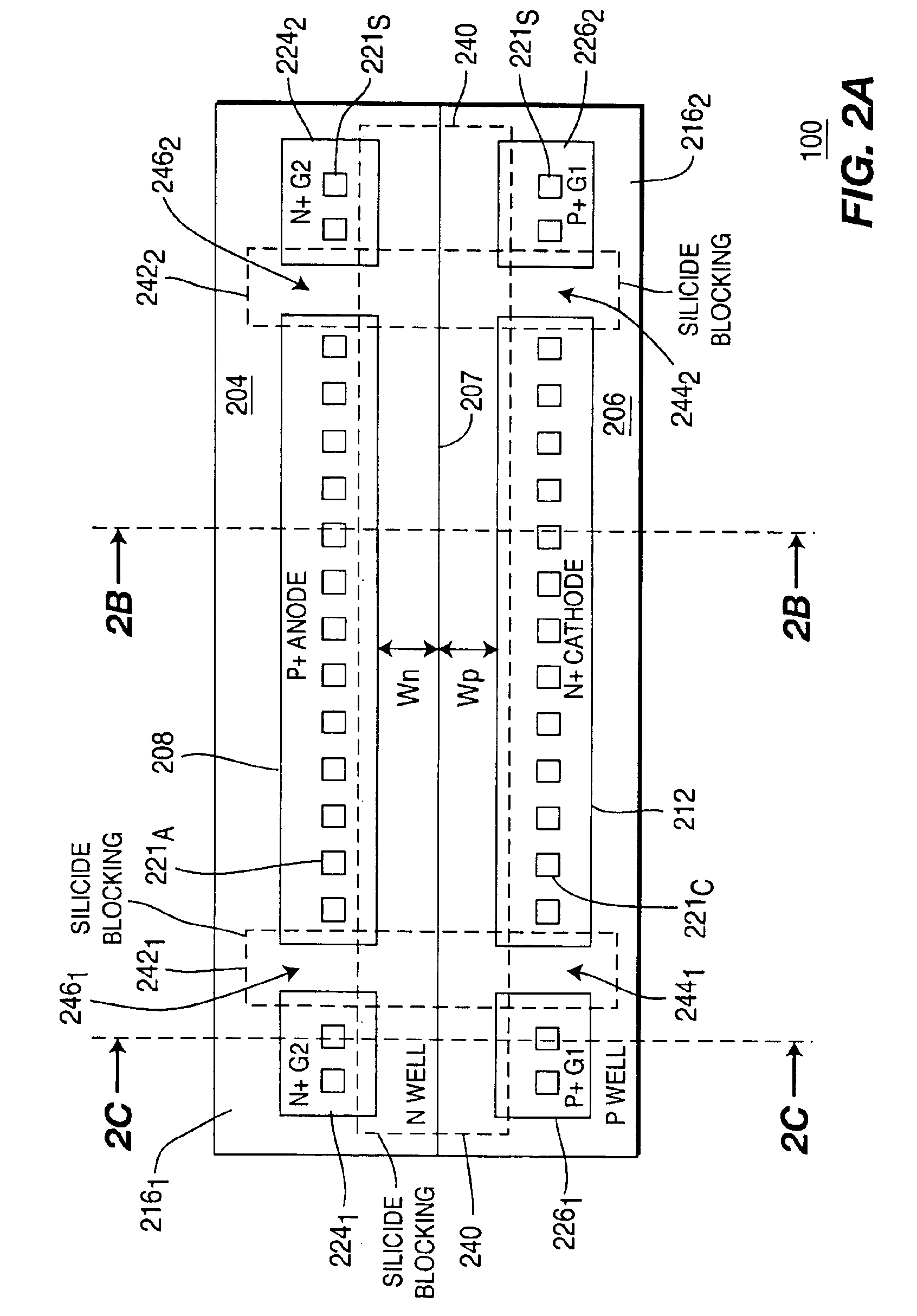
Complementary zener triggered bipolar ESD protection
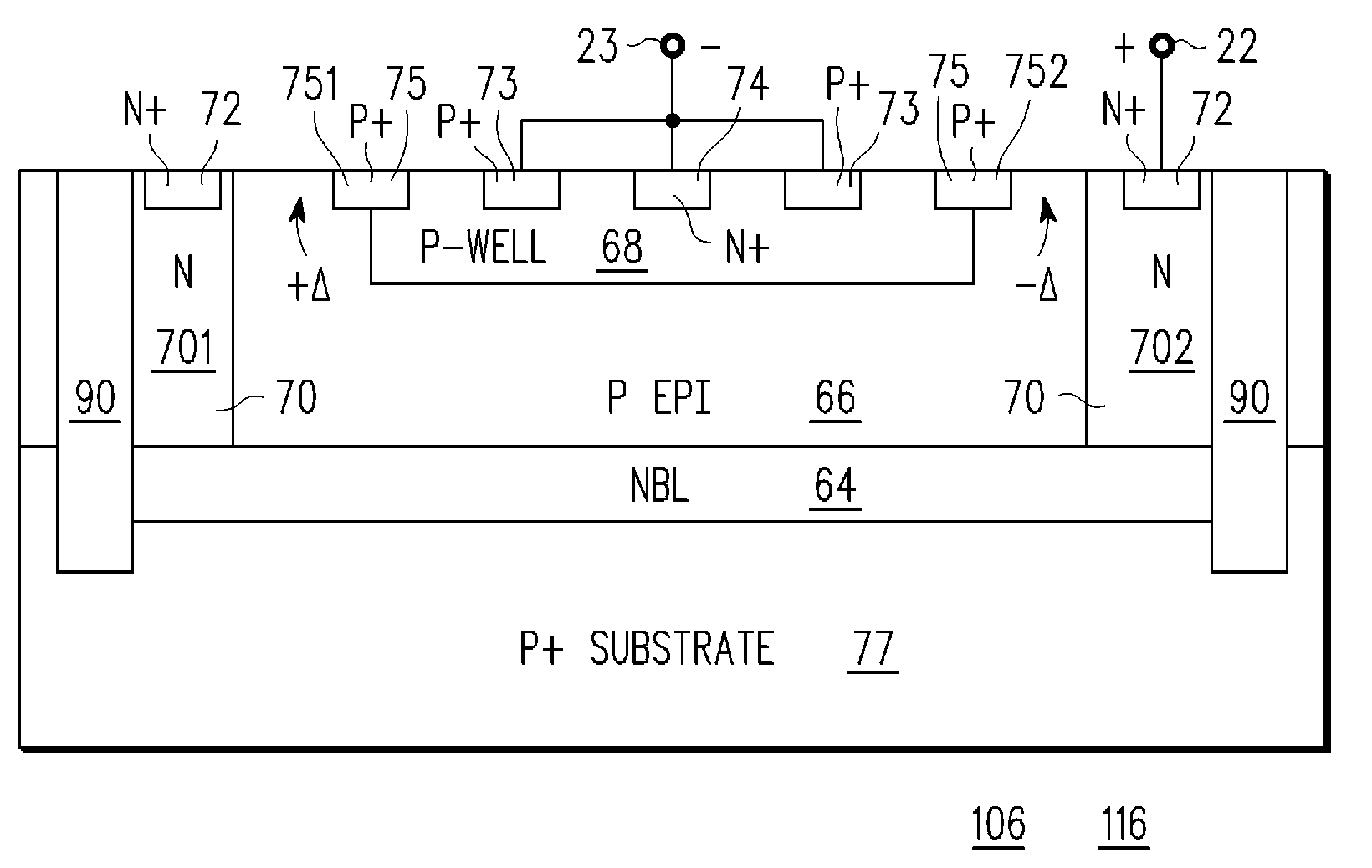
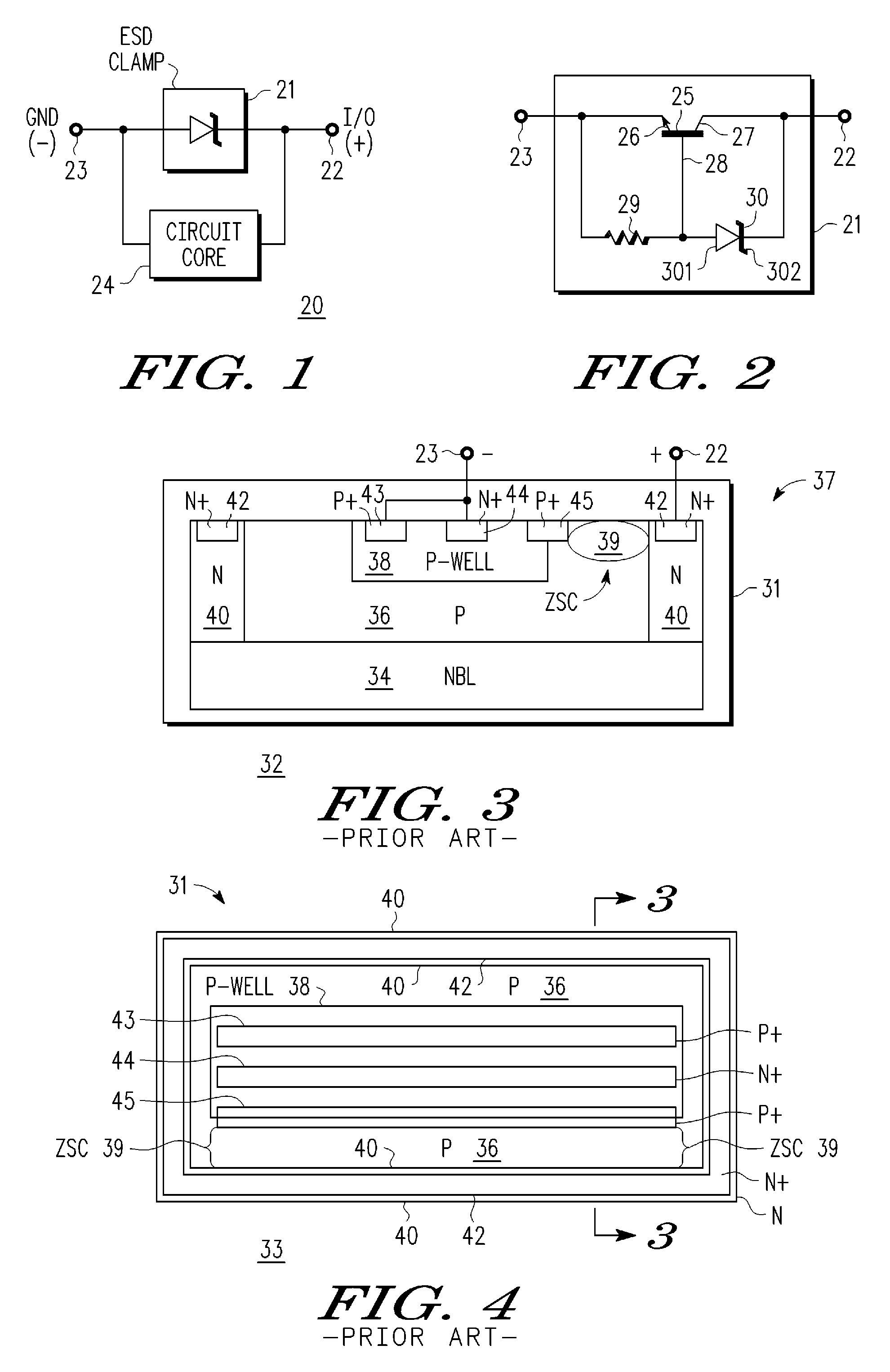
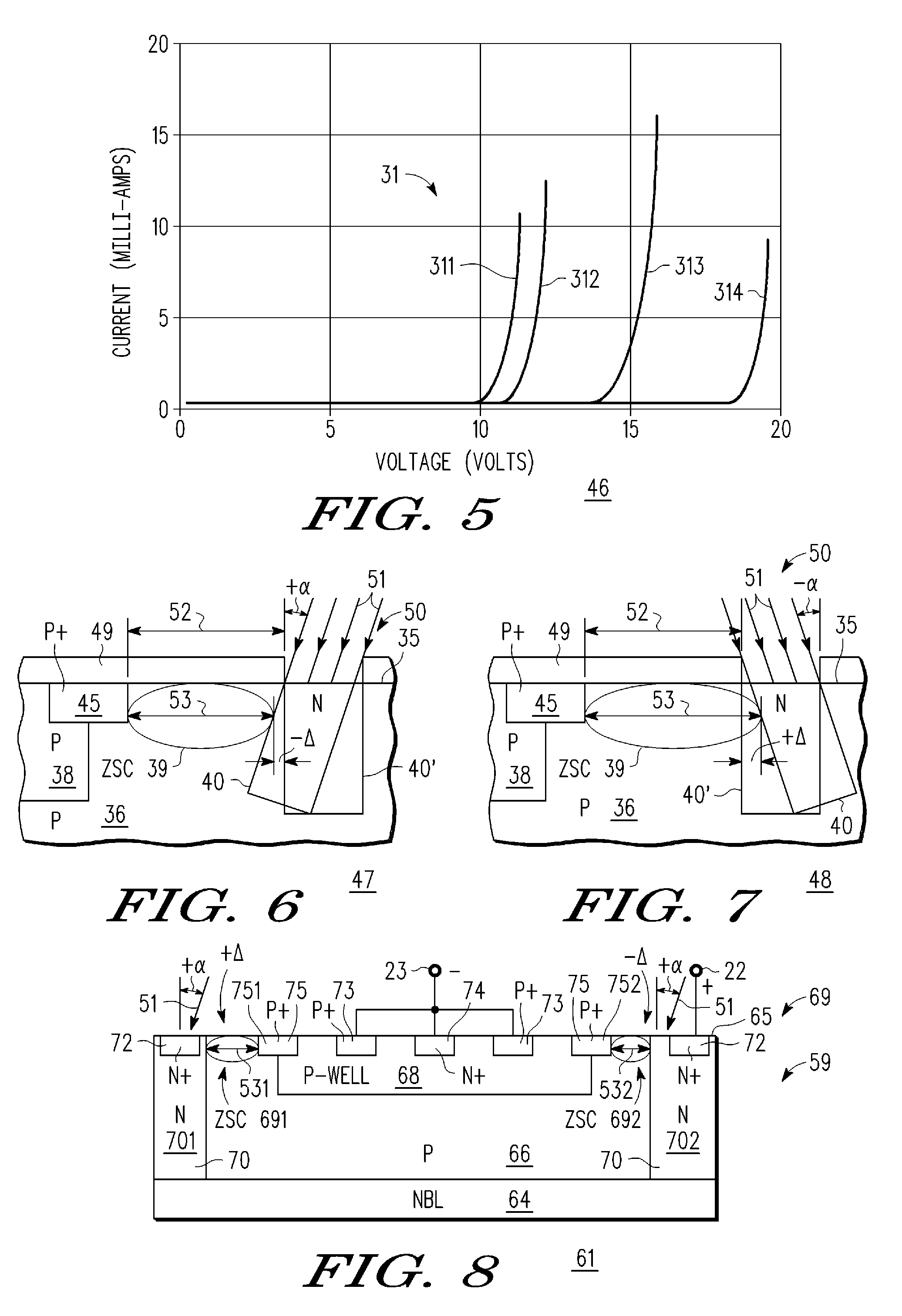
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection clamp (61) for I / O terminals (22, 23) of integrated circuits (ICs) (24) comprises an NPN bipolar transistor (25) coupled to an integrated Zener diode (30). Variations in the break-down current-voltage characteristics (311, 312, 313, 314) of multiple prior art ESD clamps (31) in different parts of the same IC chip is avoided by forming the anode (301) of the Zener (30) in the shape of a base-coupled P+ annular ring (75) surrounded by a spaced-apart N+ annular collector ring (70) for the cathode (302) of the Zener (30). Even though an angled implant (51, 86, 98) used to form the N+ annular collector ring (70) causes location dependent variations in the width (53) of the Zener space charge (ZSC) region (69), the improved annular shaped clamp (61) always has a portion that initiates break-down at the design voltage so that variations in the width (53) of the ZSC region (69) do not cause significant variations in the clamp's current-voltage characteristics (611, 612, 613, 614).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Anti-ESD photomask blank
ActiveUS20060154153A1Quality improvementShorten the timeGlass/slag layered productsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentOptoelectronicsPhotomask
An anti-electrostatic discharge photomask blank for fabrication of an anti-electrostatic discharge photomask is disclosed. The anti-electrostatic discharge photomask blank includes a mask substrate, a conductive layer provided on the mask substrate and an opaque patterning layer provided on the conductive layer. The conductive layer prevents charges of opposite polarity from accumulating on a photomask fabricated from the photomask blank, thus preventing electrostatic discharges on the photomask.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com