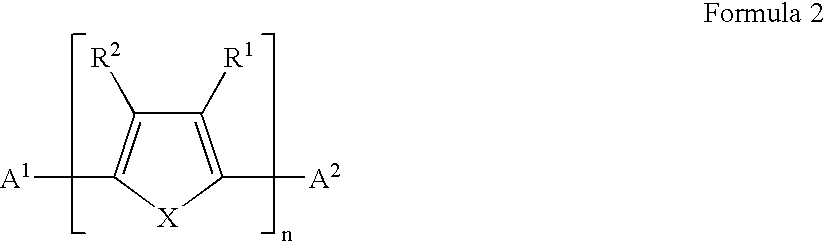Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
16224 results about "Field-effect transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
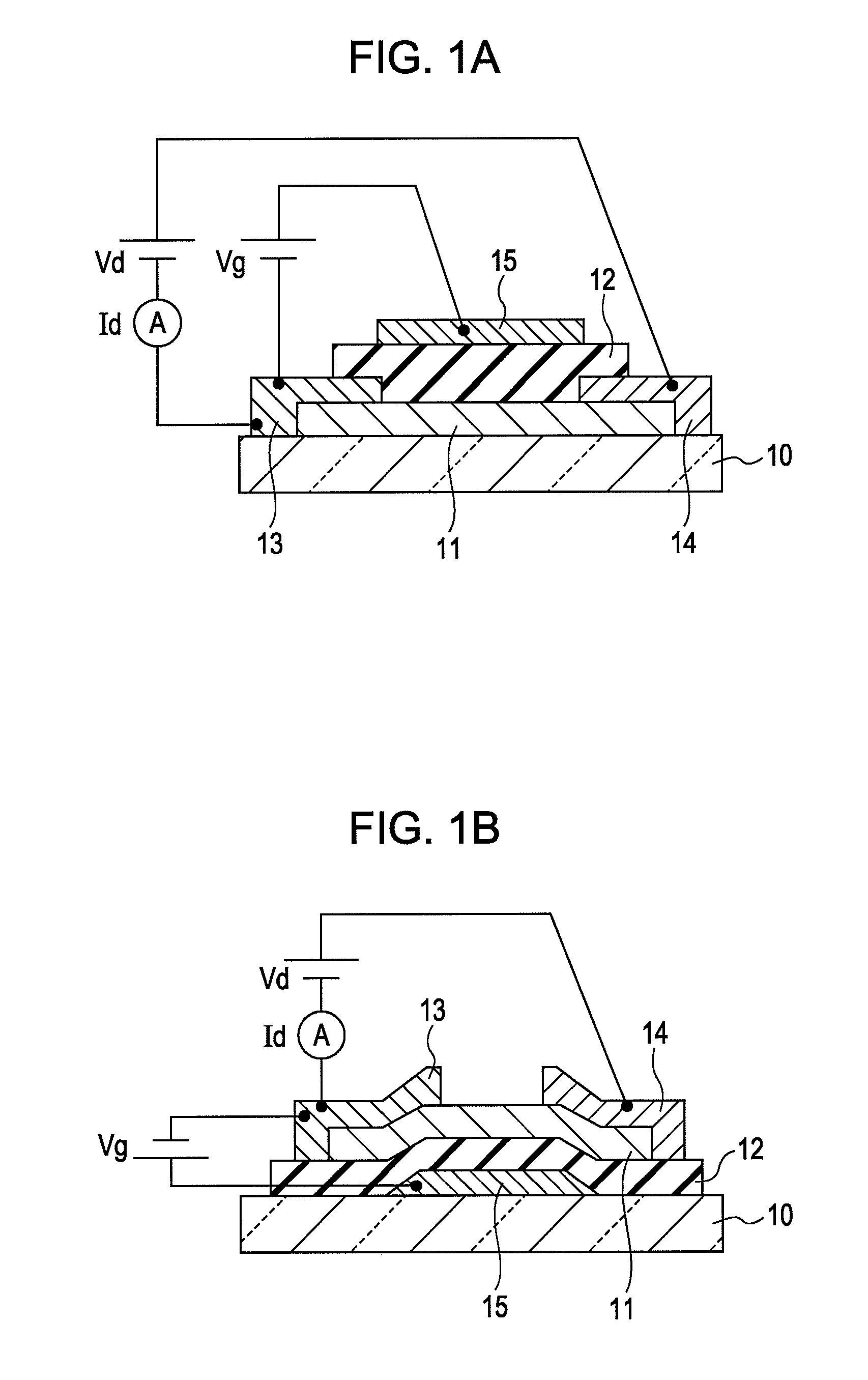
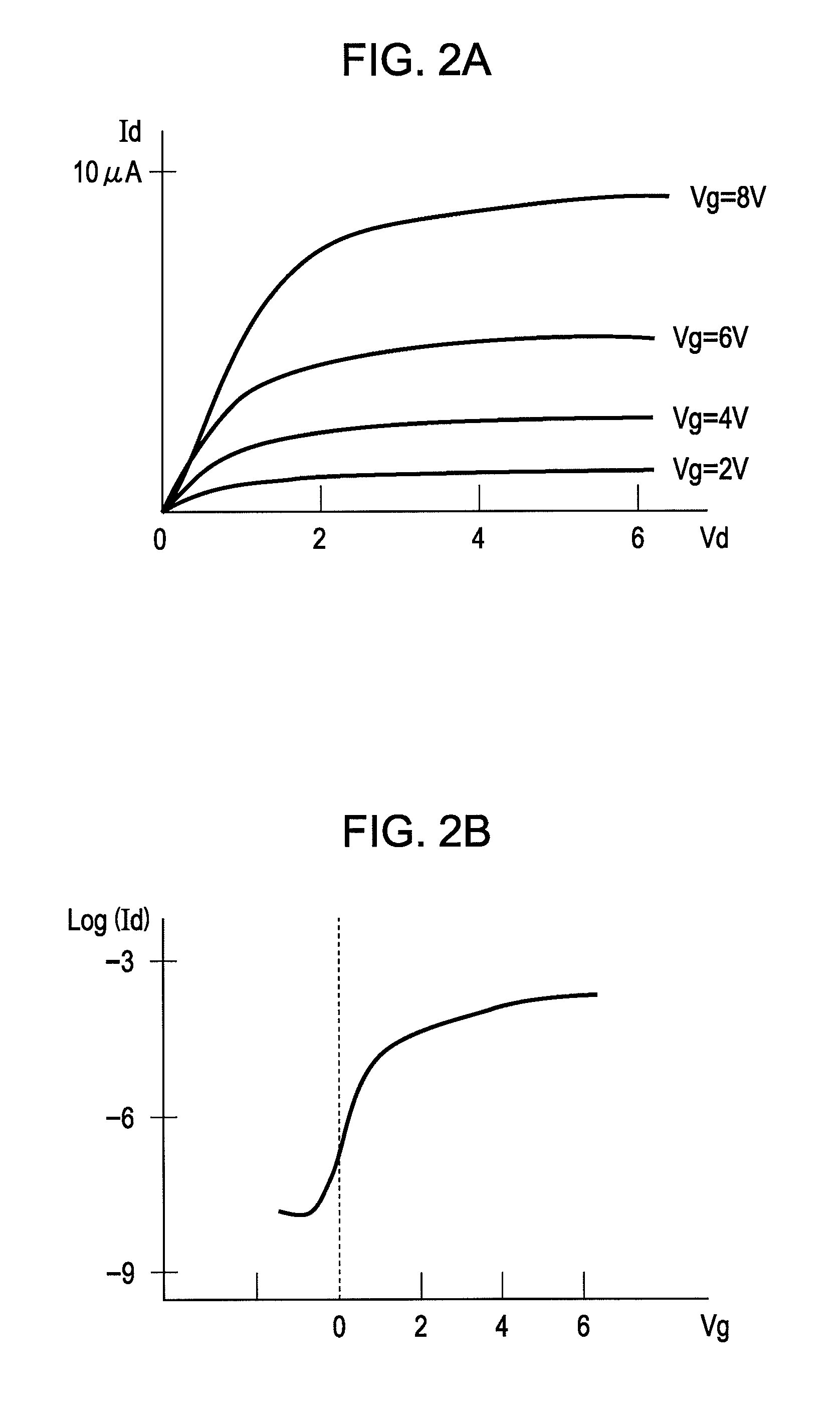
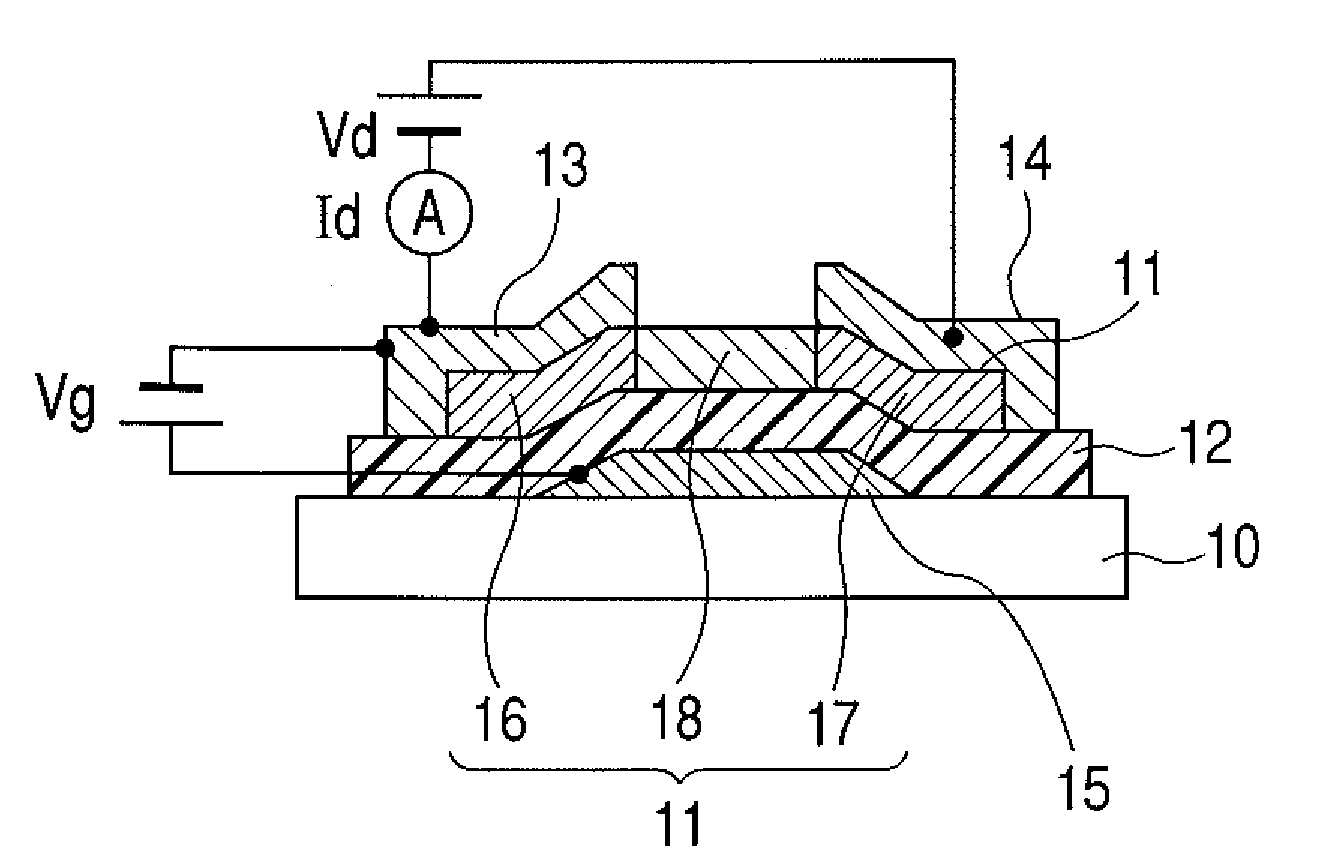
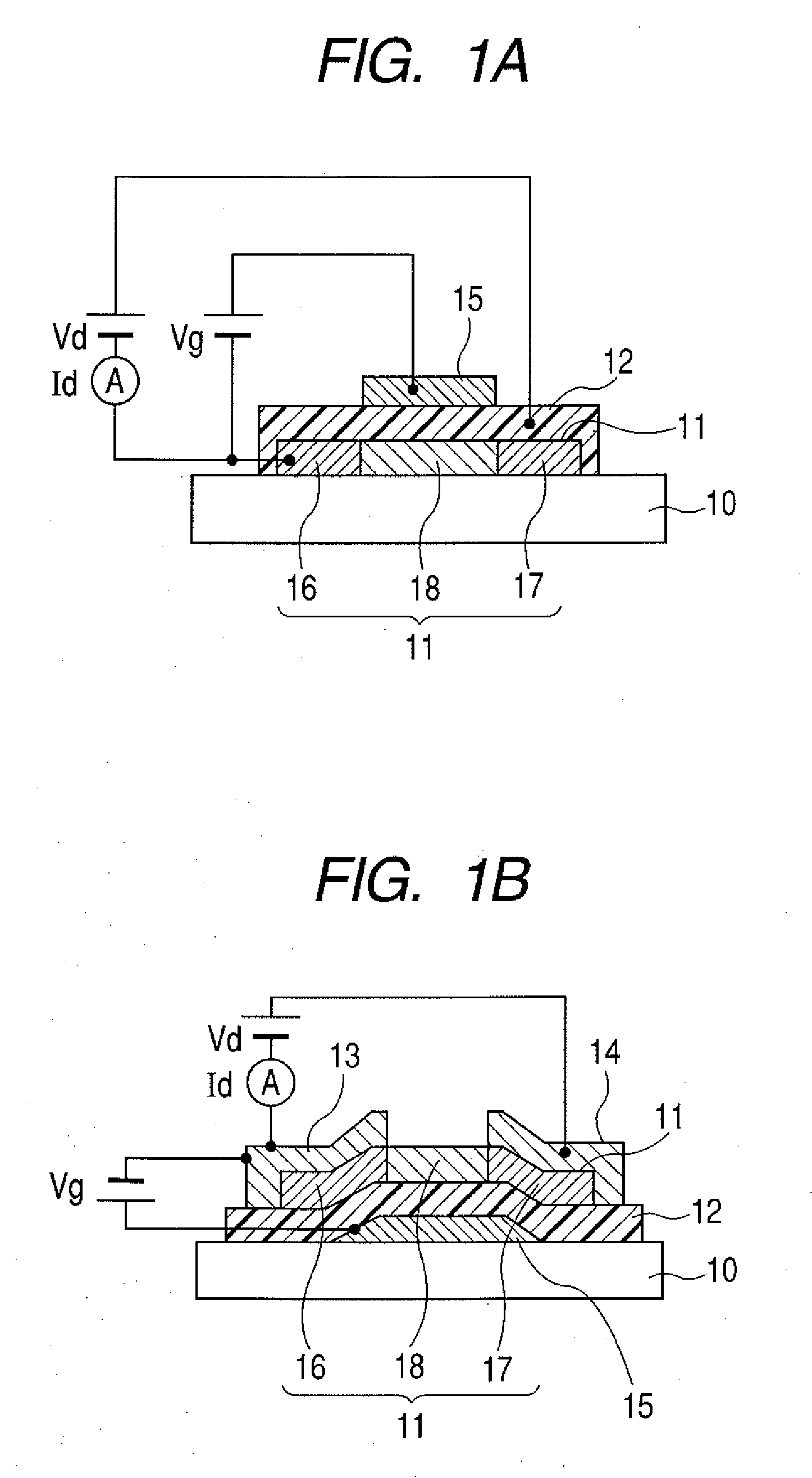
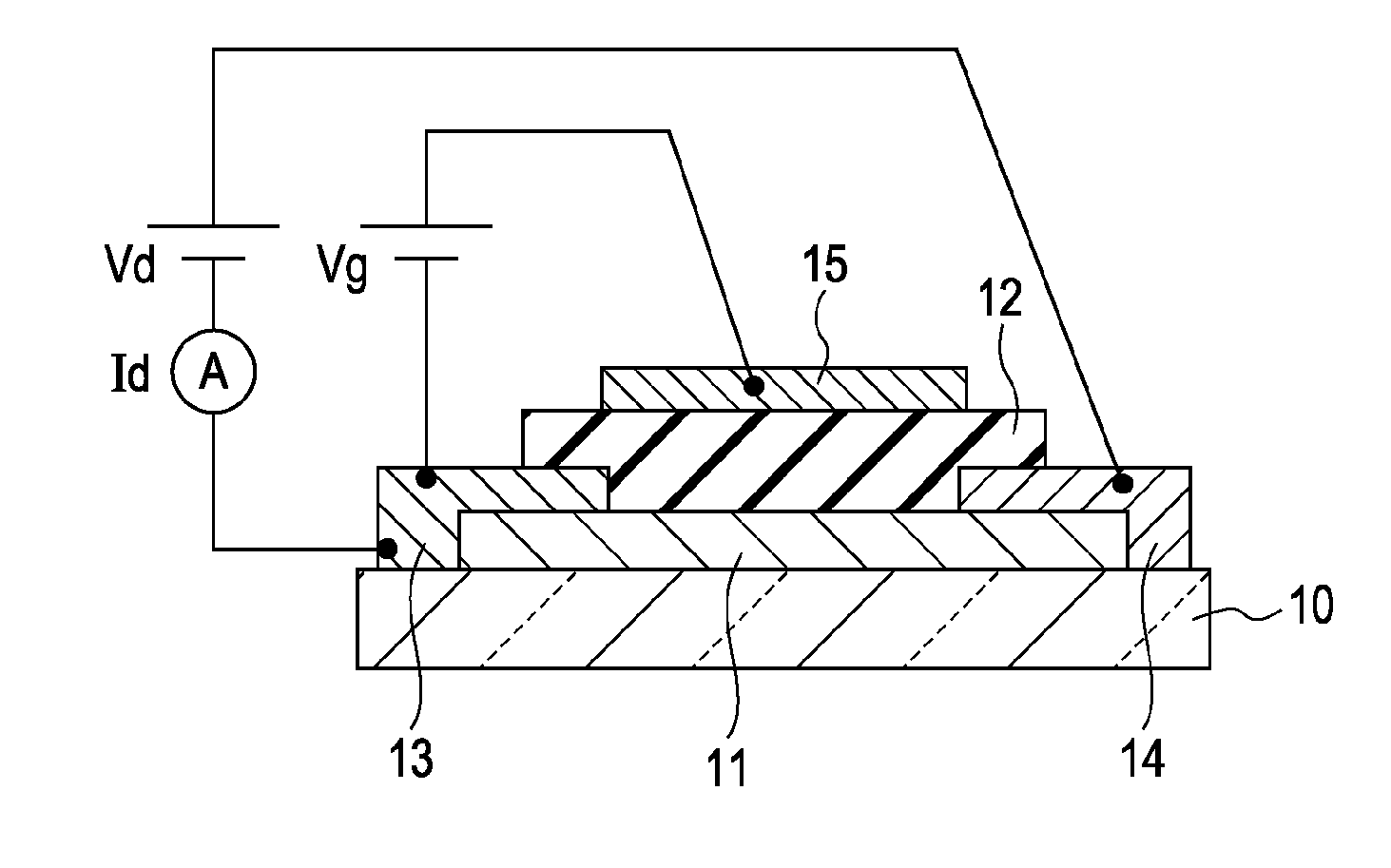
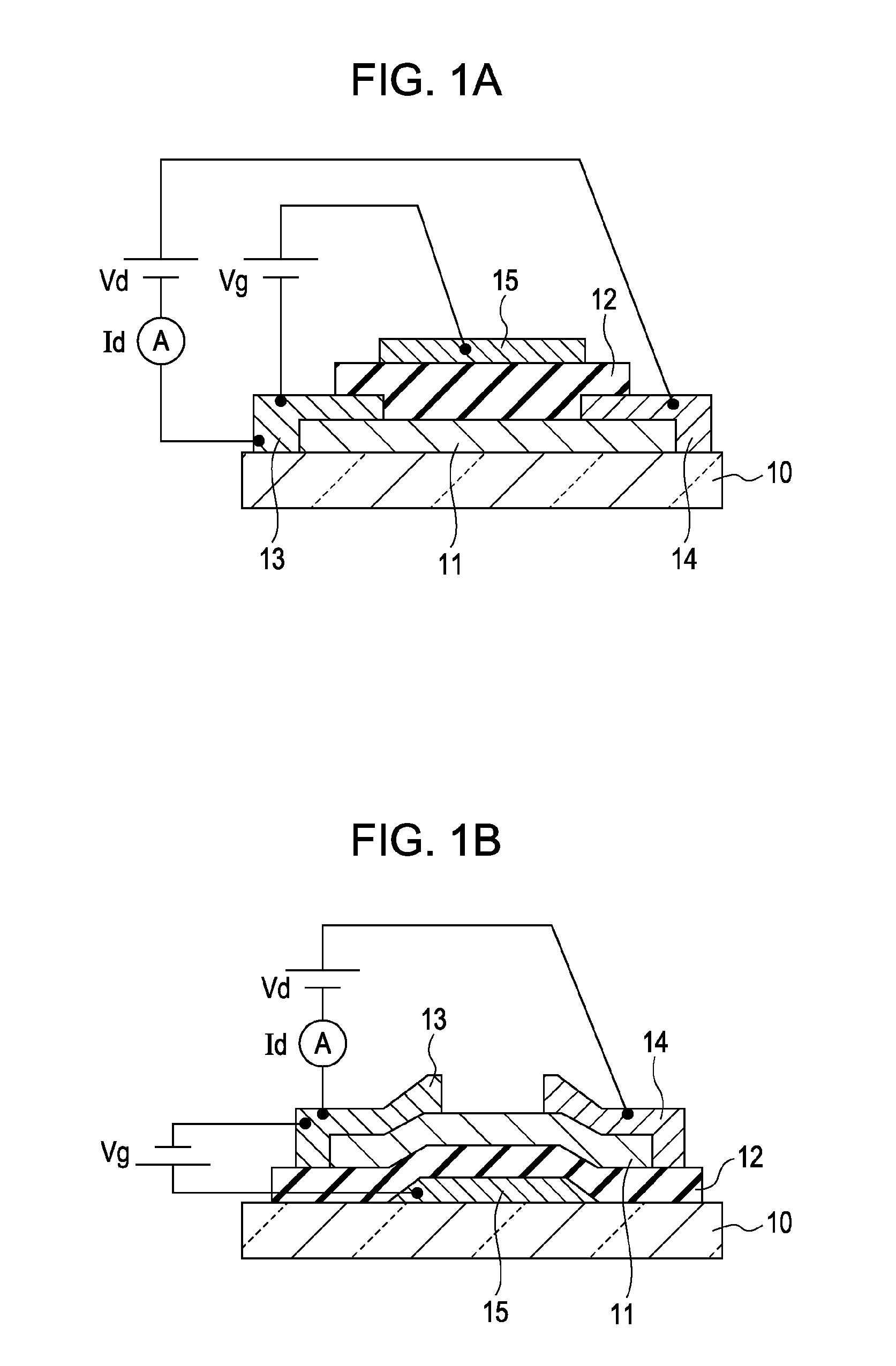
The field-effect transistor (FET) is an electronic device which uses an electric field to control the flow of current. FETs are devices with three terminals: source, gate, and drain. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source.
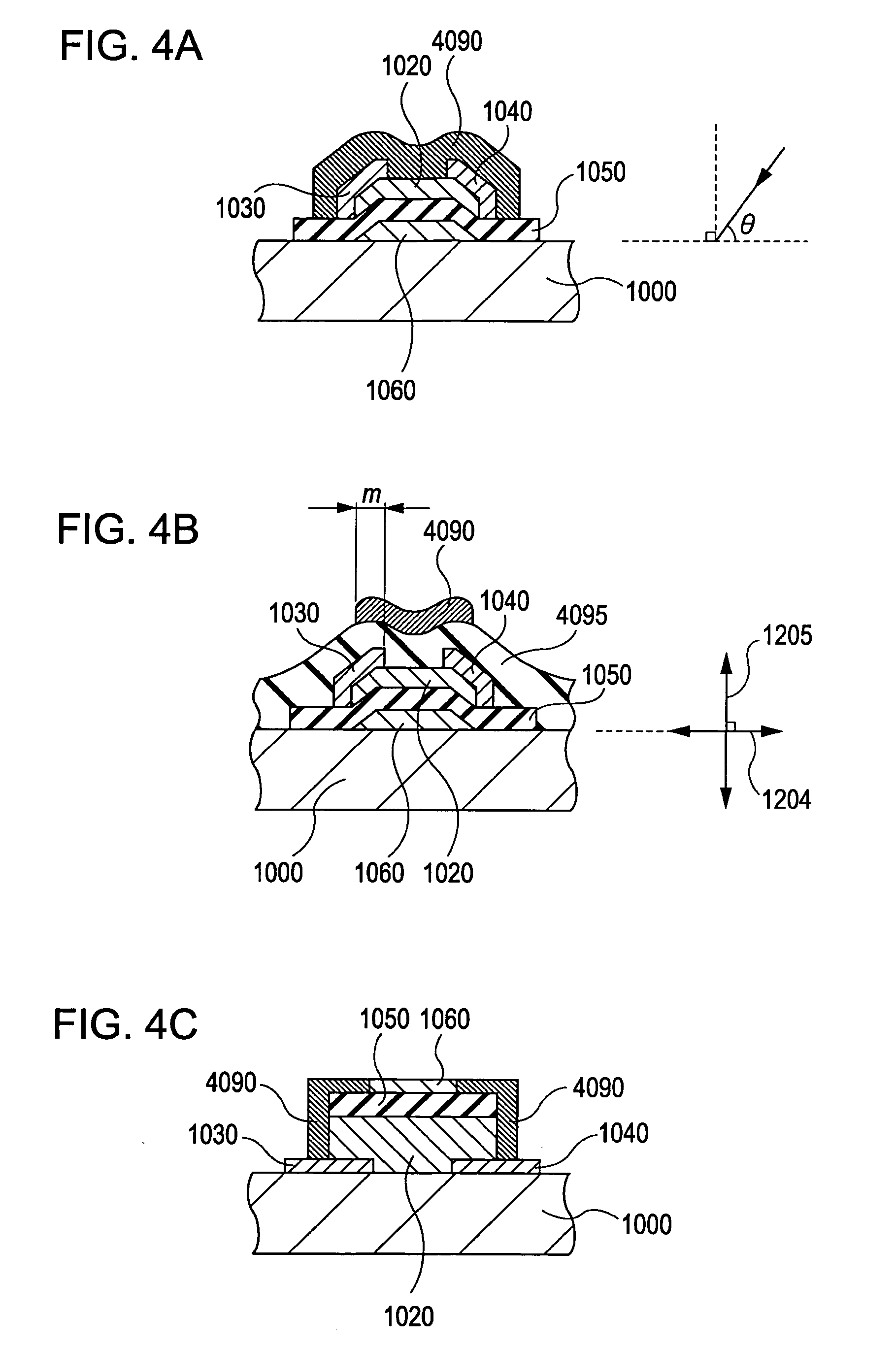
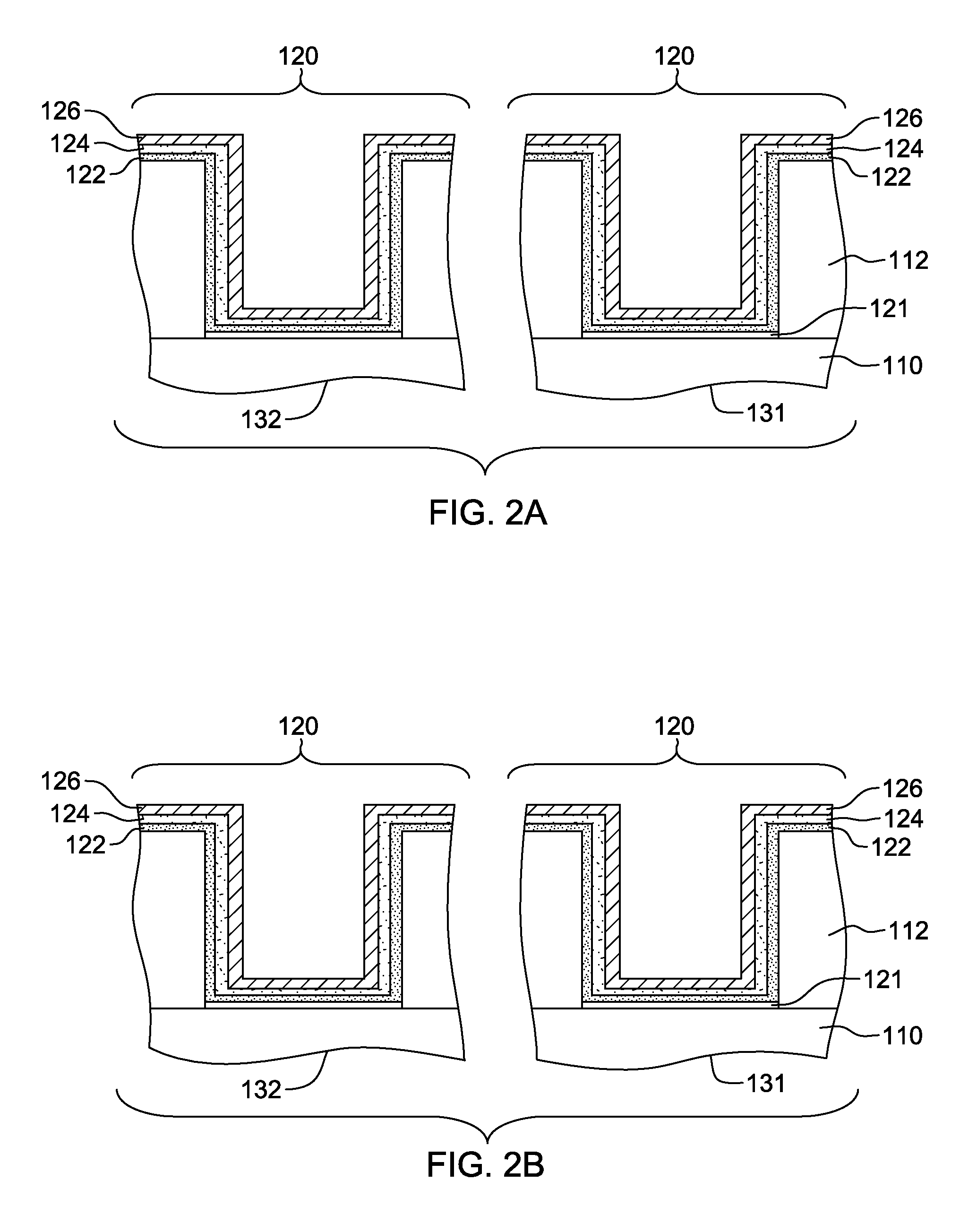
Amorphous oxide and field effect transistor
ActiveUS20060108636A1Reduced electron mobilityLow conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorActive layer
A novel amorphous oxide applicable, for example, to an active layer of a TFT is provided. The amorphous oxide comprises microcrystals.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Field effect transistor
ActiveUS20060113539A1Inhibit currentMaintain good propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorElectron
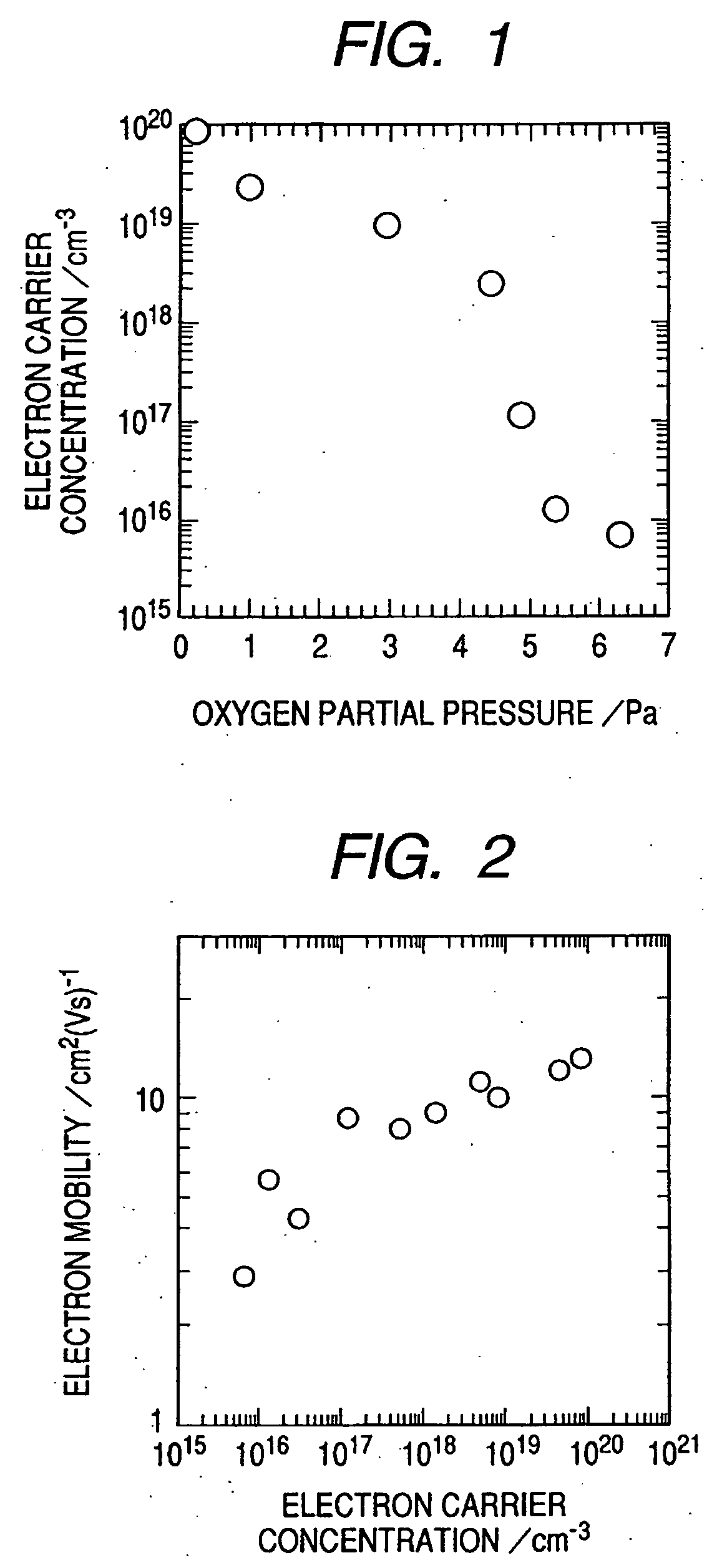
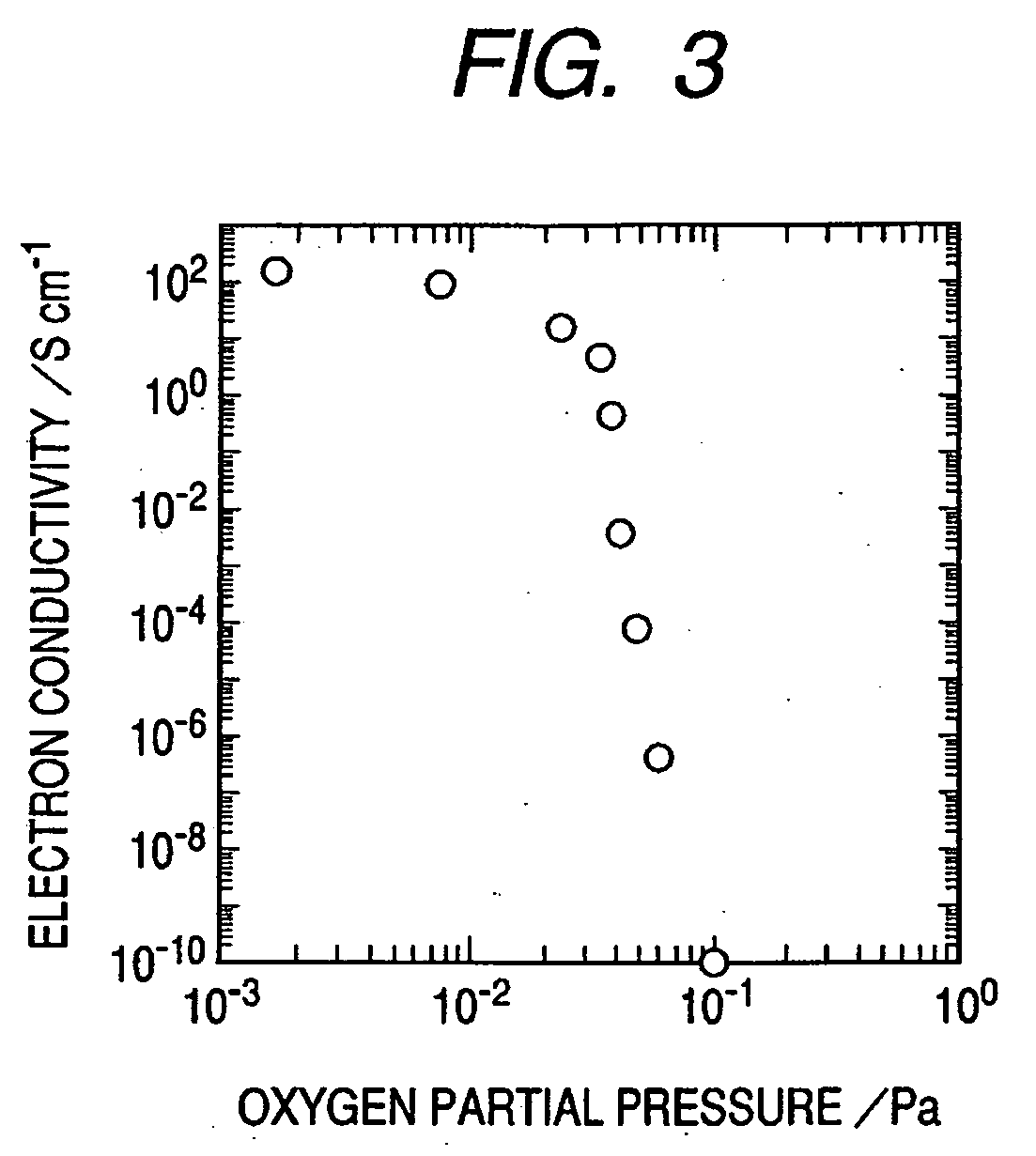
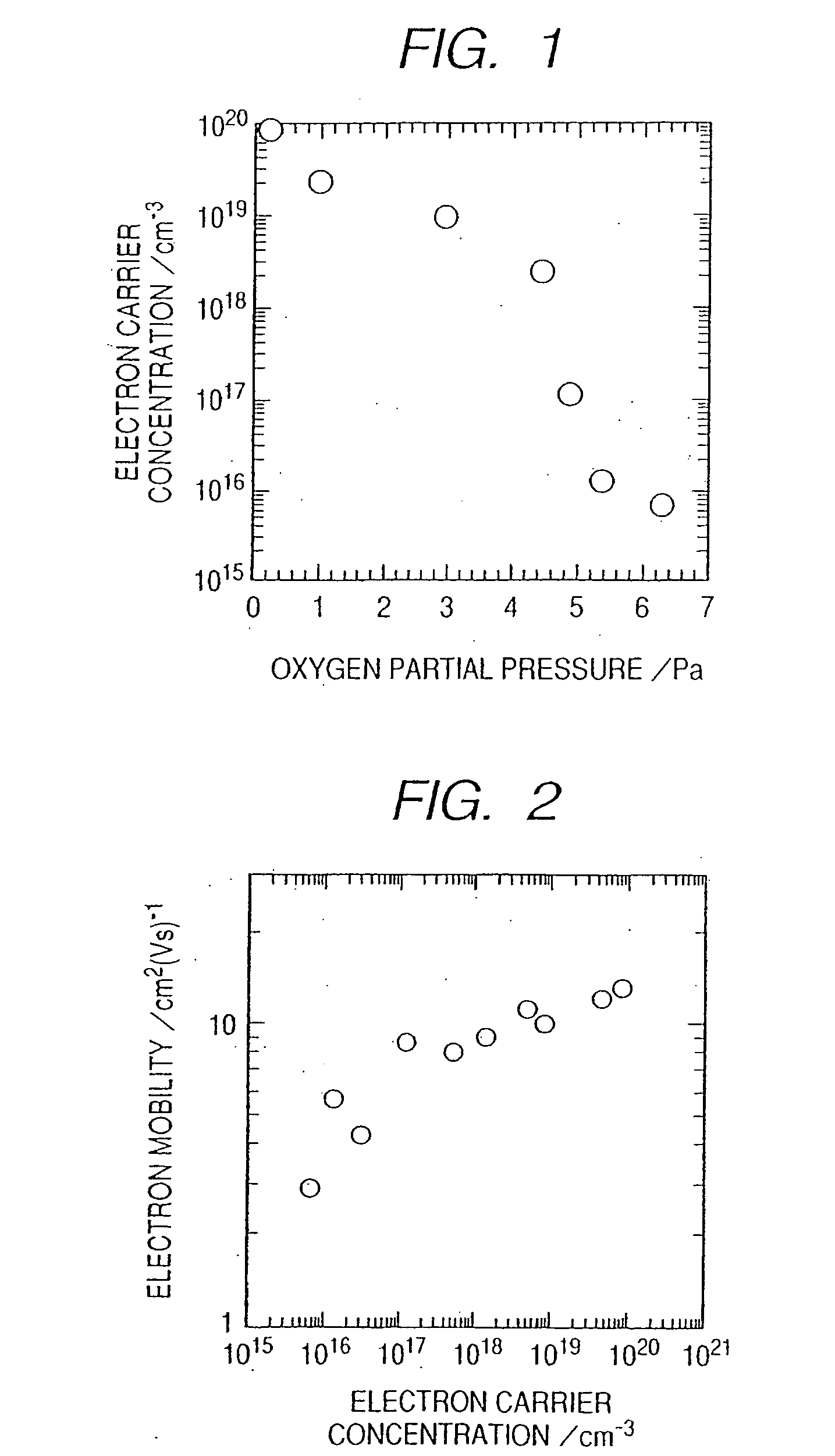
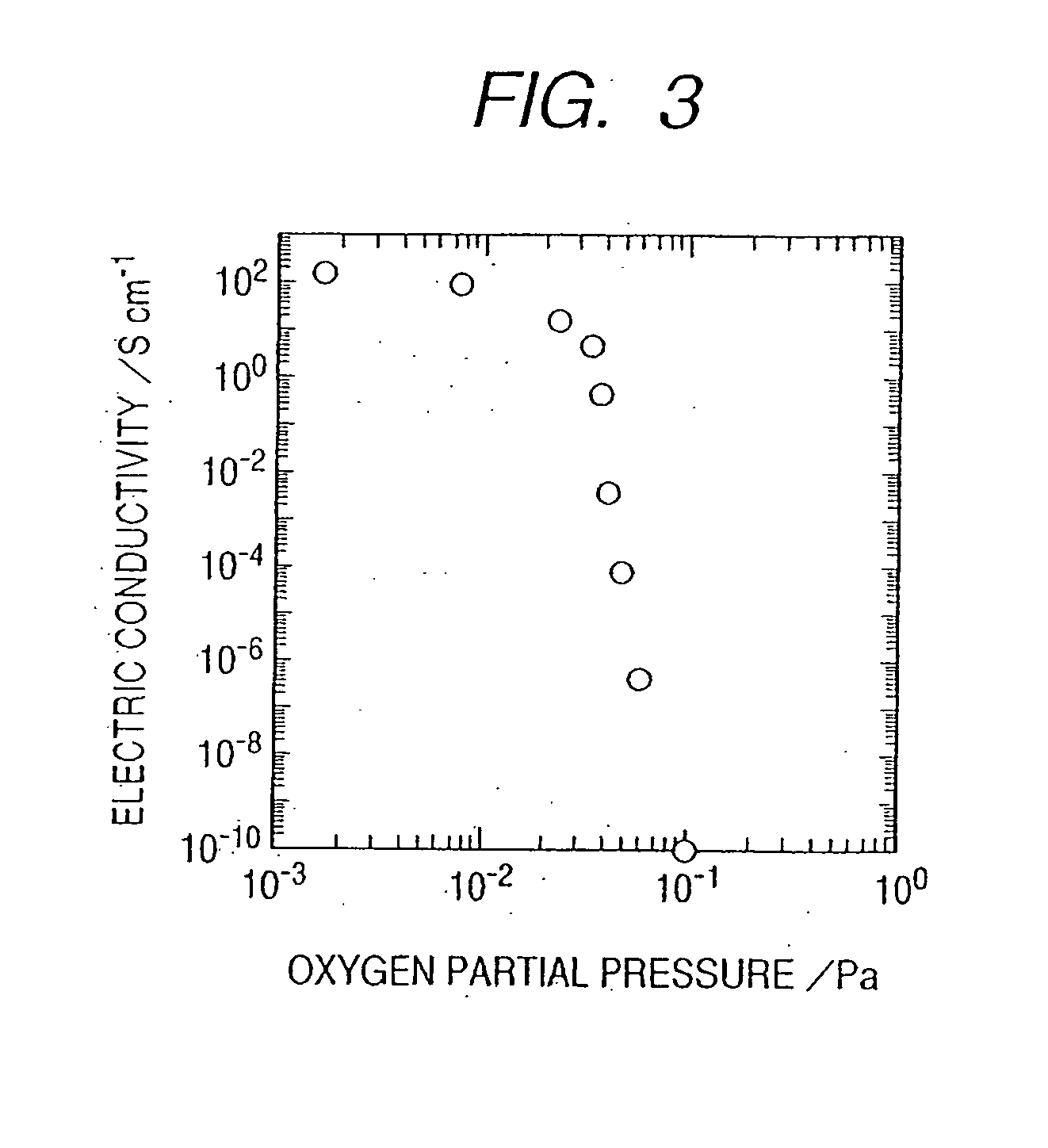
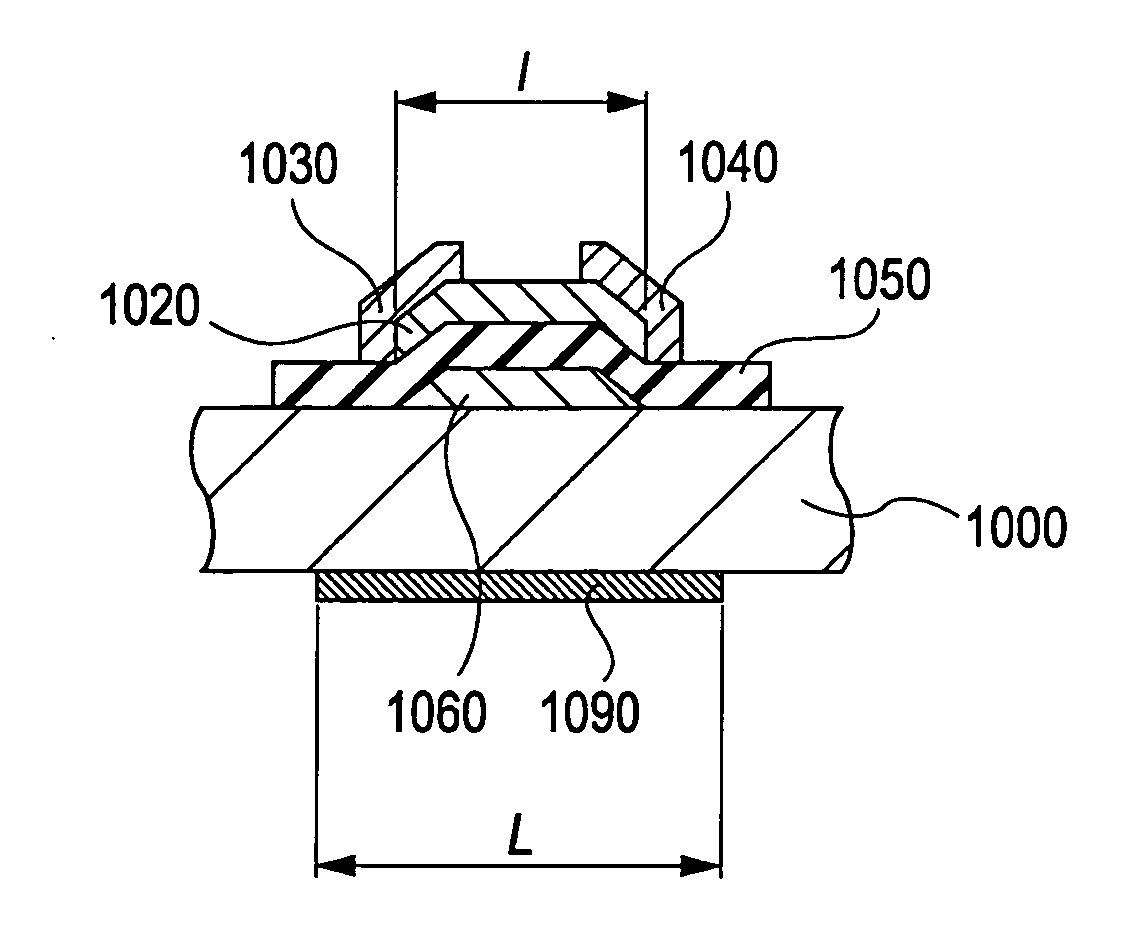
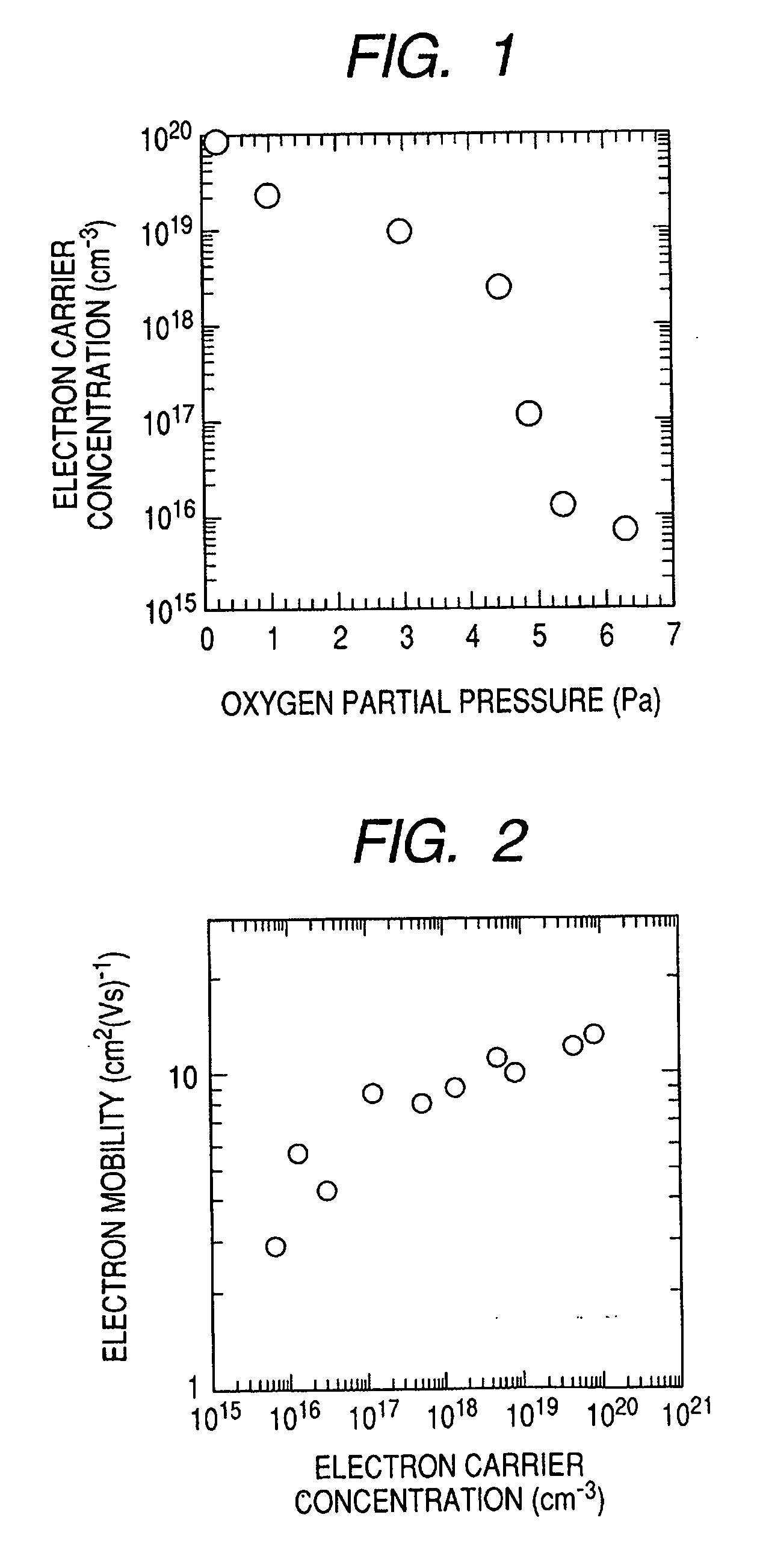
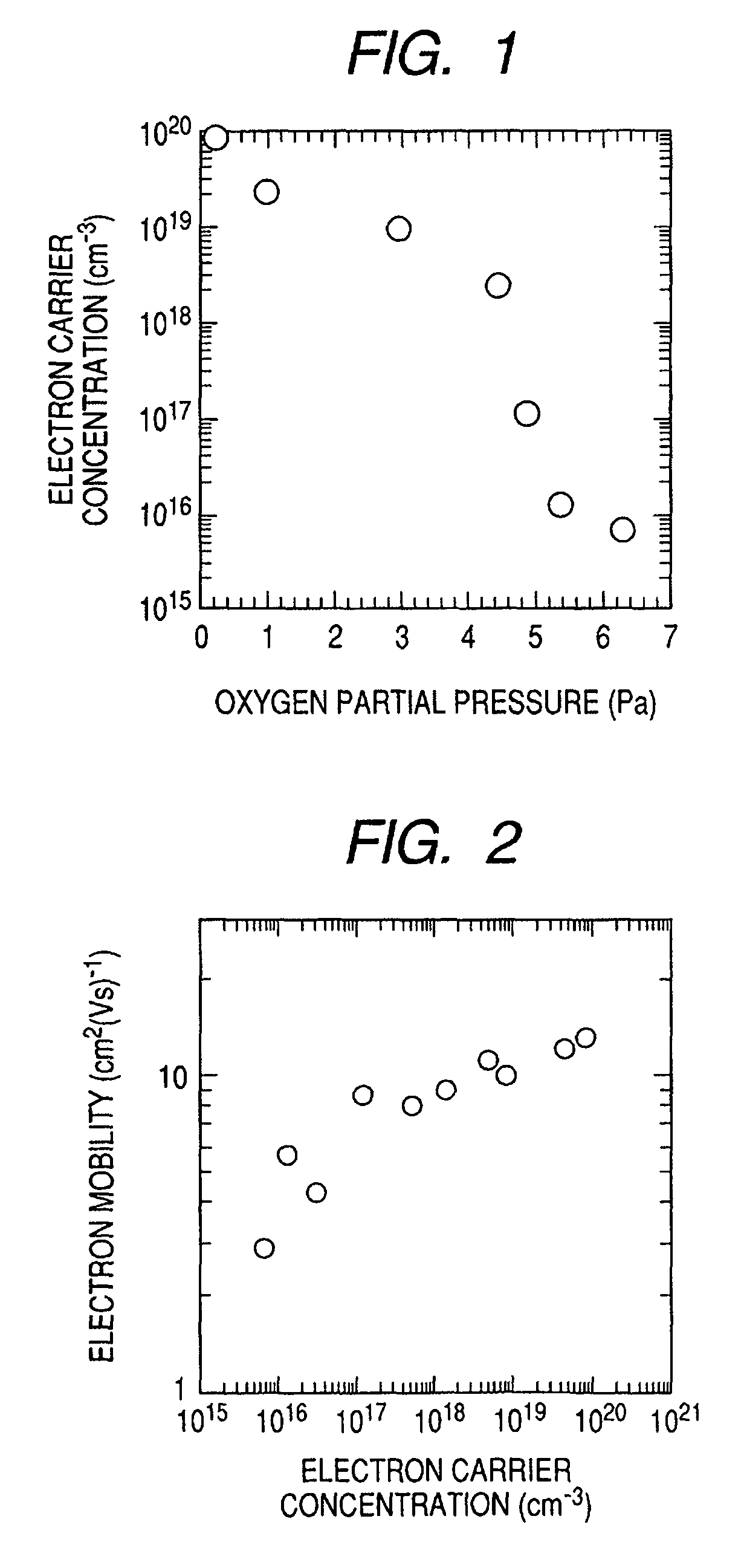
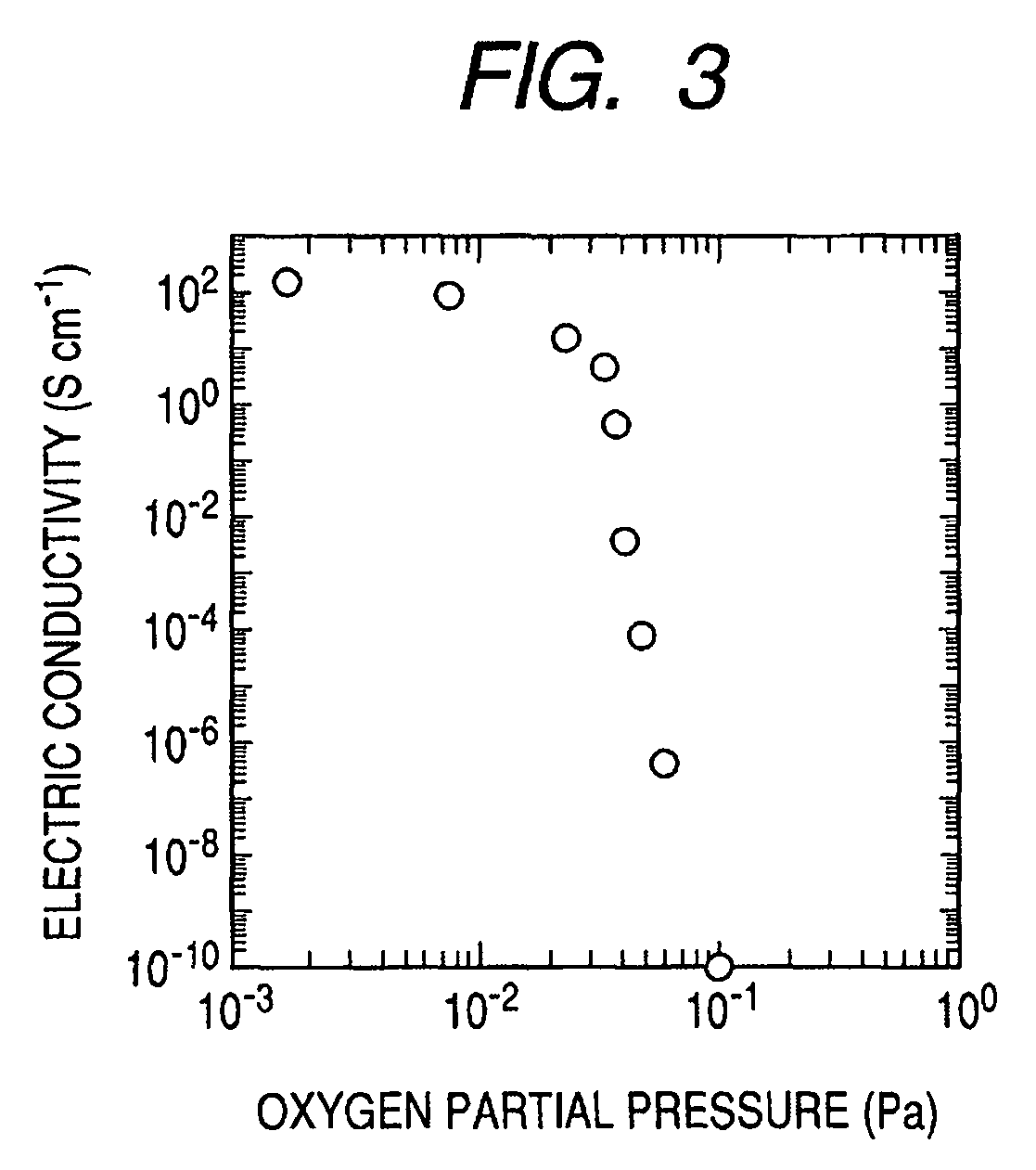
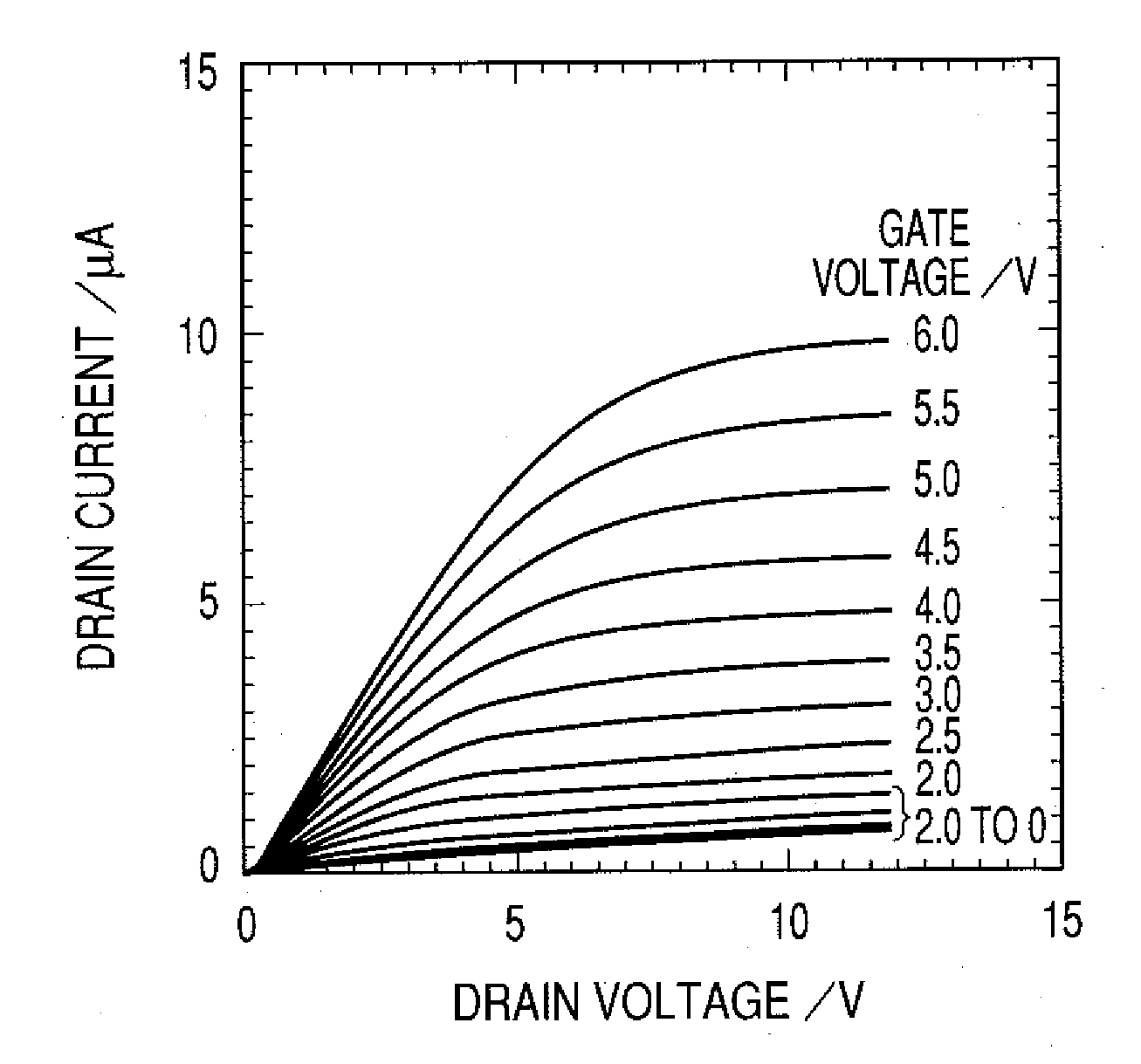
A novel field-effect transistor is provided which employs an amorphous oxide. In an embodiment of the present invention, the transistor comprises an amorphous oxide layer containing electron carrier at a concentration less than 1×10−18 / cm3, and the gate-insulating layer is comprised of a first layer being in contact with the amorphous oxide and a second layer different from the first layer.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Field-effect transistor including transparent oxide and light-shielding member, and display utilizing the transistor
A field-effect transistor includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode, a gate-insulating film, and an active layer. The active layer contains an oxide having a transmittance of 70% or more in the wavelength range of 400 to 800 nm. A light-shielding member is provided as a light-shielding structure for the active layer, for example, on the bottom face of the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Display
An active matrix display comprising a light control device and a field effect transistor for driving the light control device. The active layer of the field effect transistor comprises an amorphous.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Field-effect transistor and method for manufacturing the same
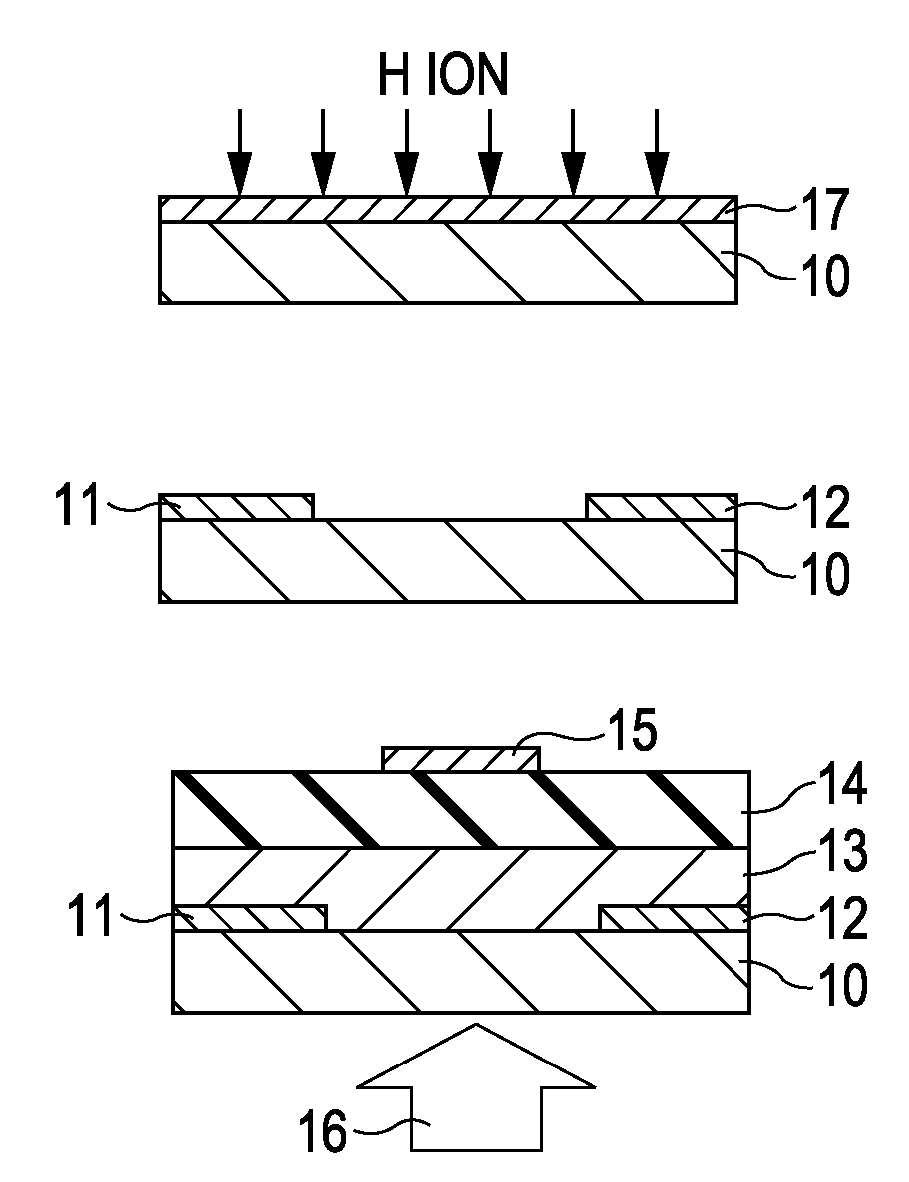
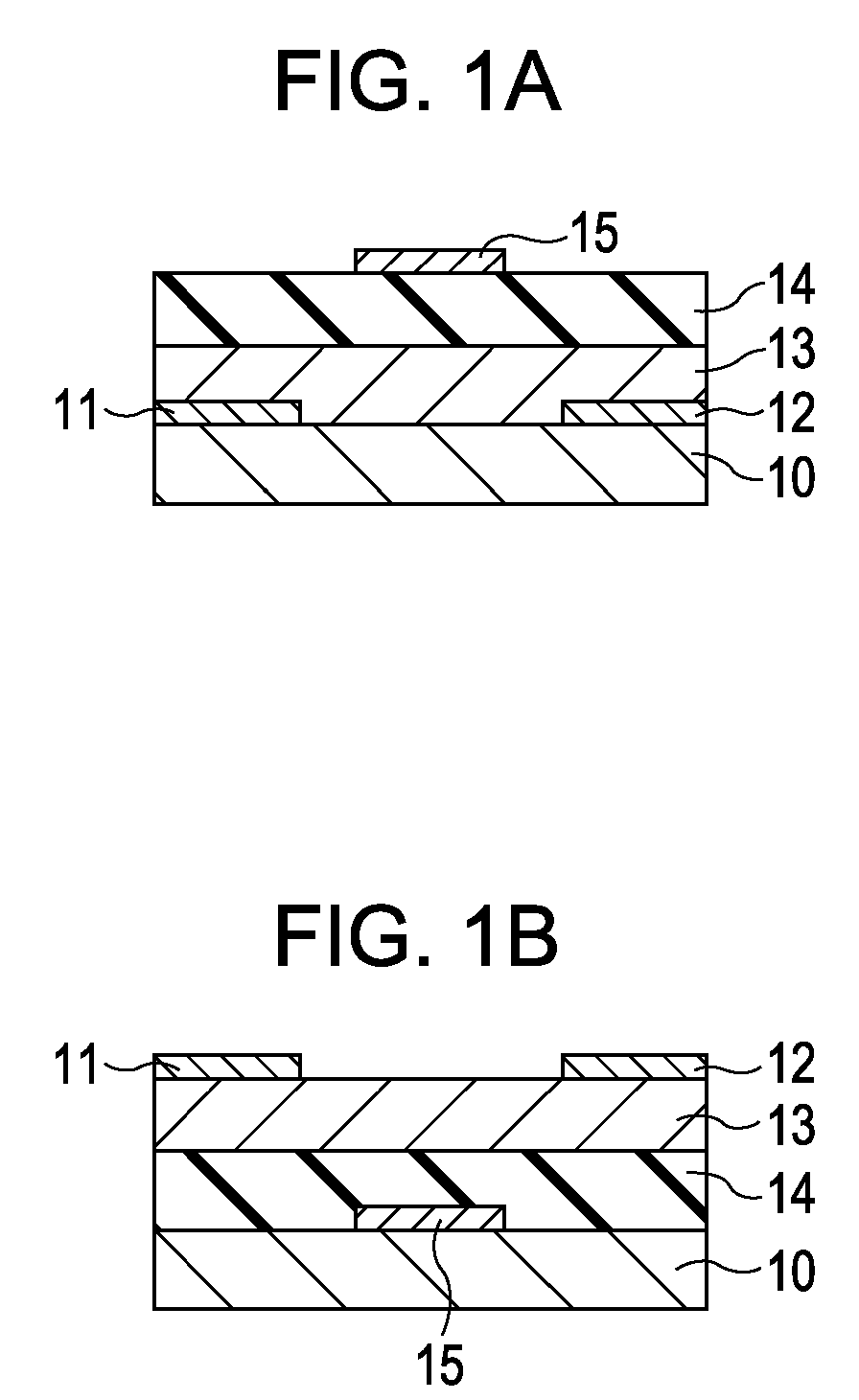
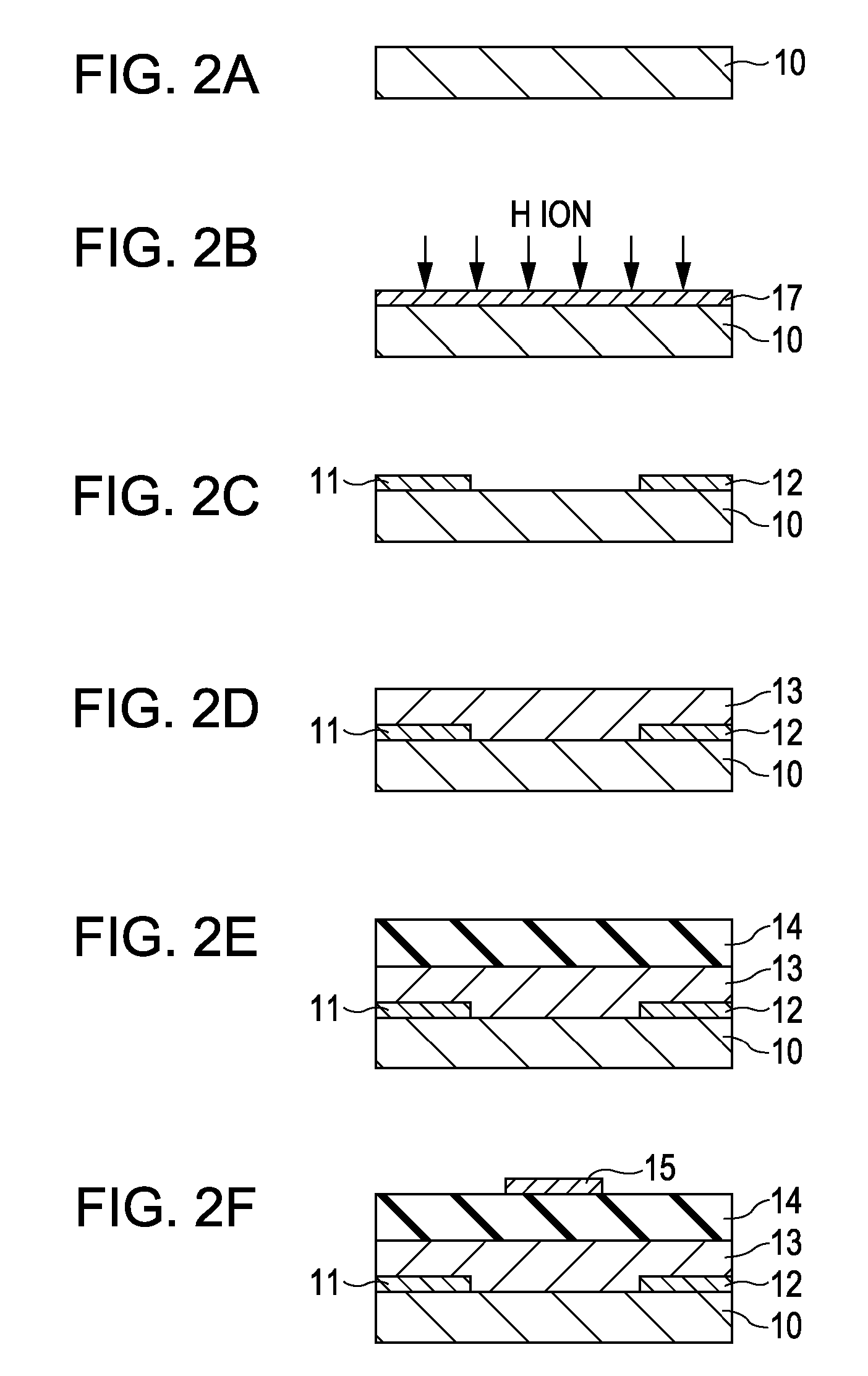
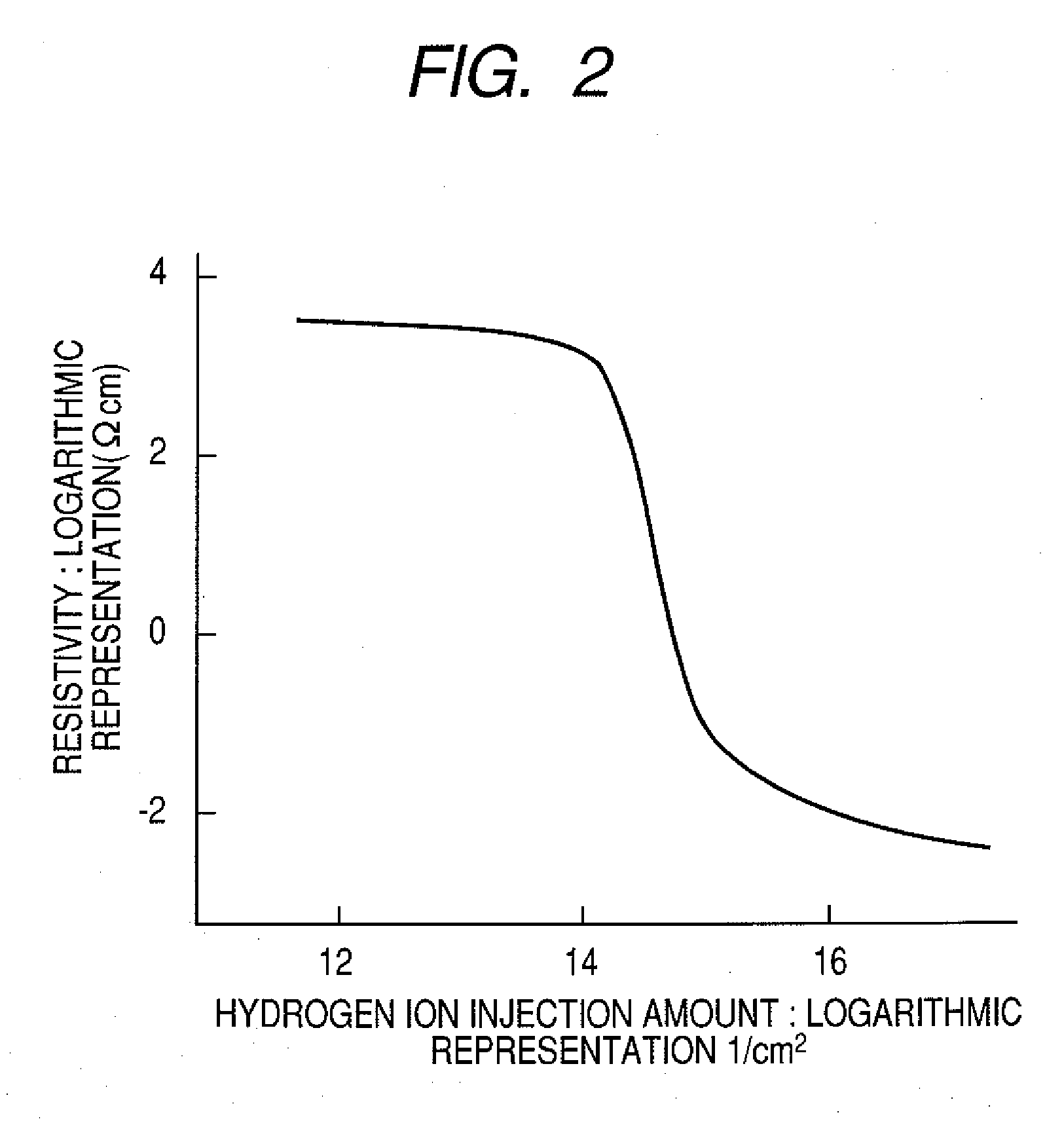
InactiveUS7411209B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenField-effect transistor
A method for manufacturing a field-effect transistor includes the steps of forming a source electrode and a drain electrode each containing hydrogen or deuterium; forming an oxide semiconductor layer in which the electrical resistance is decreased if hydrogen or deuterium is added; and, causing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse from the source electrode and the drain electrode to the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS20060113549A1Desired characteristicTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesField-effect transistorActive layer
An object of the present invention is to provide a new light-emitting device with the use of an amorphous oxide. The light-emitting device has a light-emitting layer existing between first and second electrodes and a field effect transistor, of which the active layer is an amorphous.
Owner:CANON KK +2
High-electron mobility transistor with zinc oxide
InactiveUS7105868B2Increase heightHigh electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierField-effect transistor
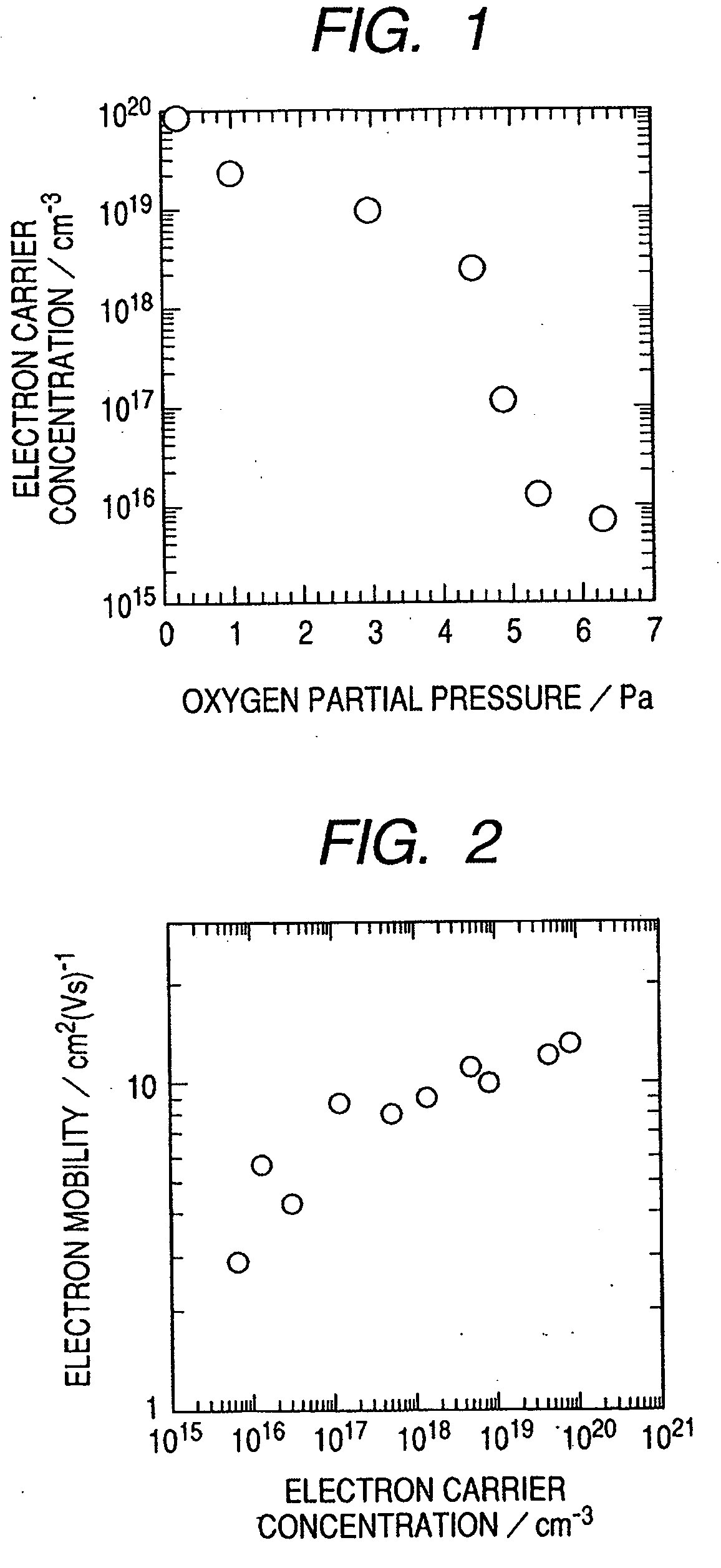
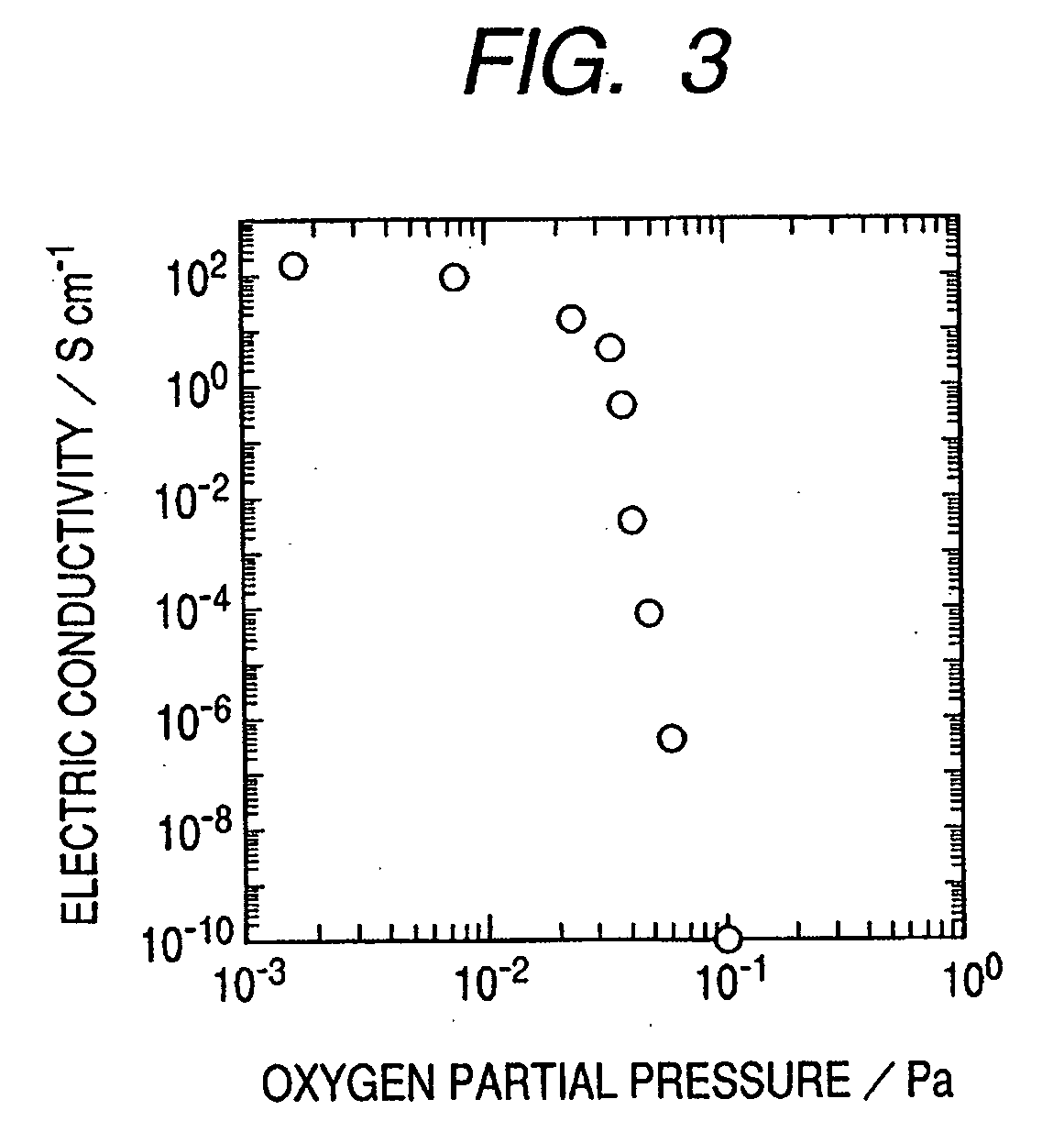
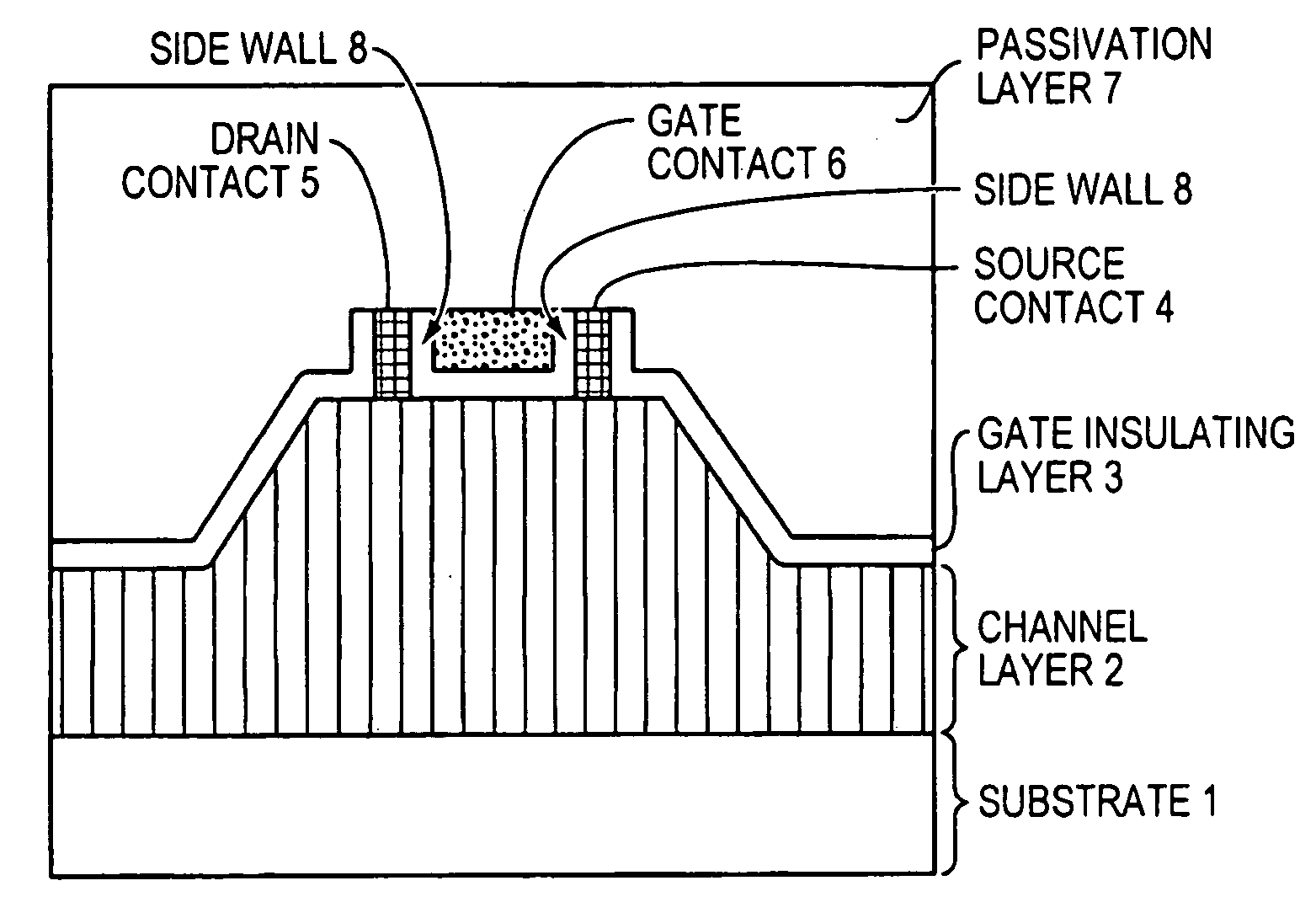
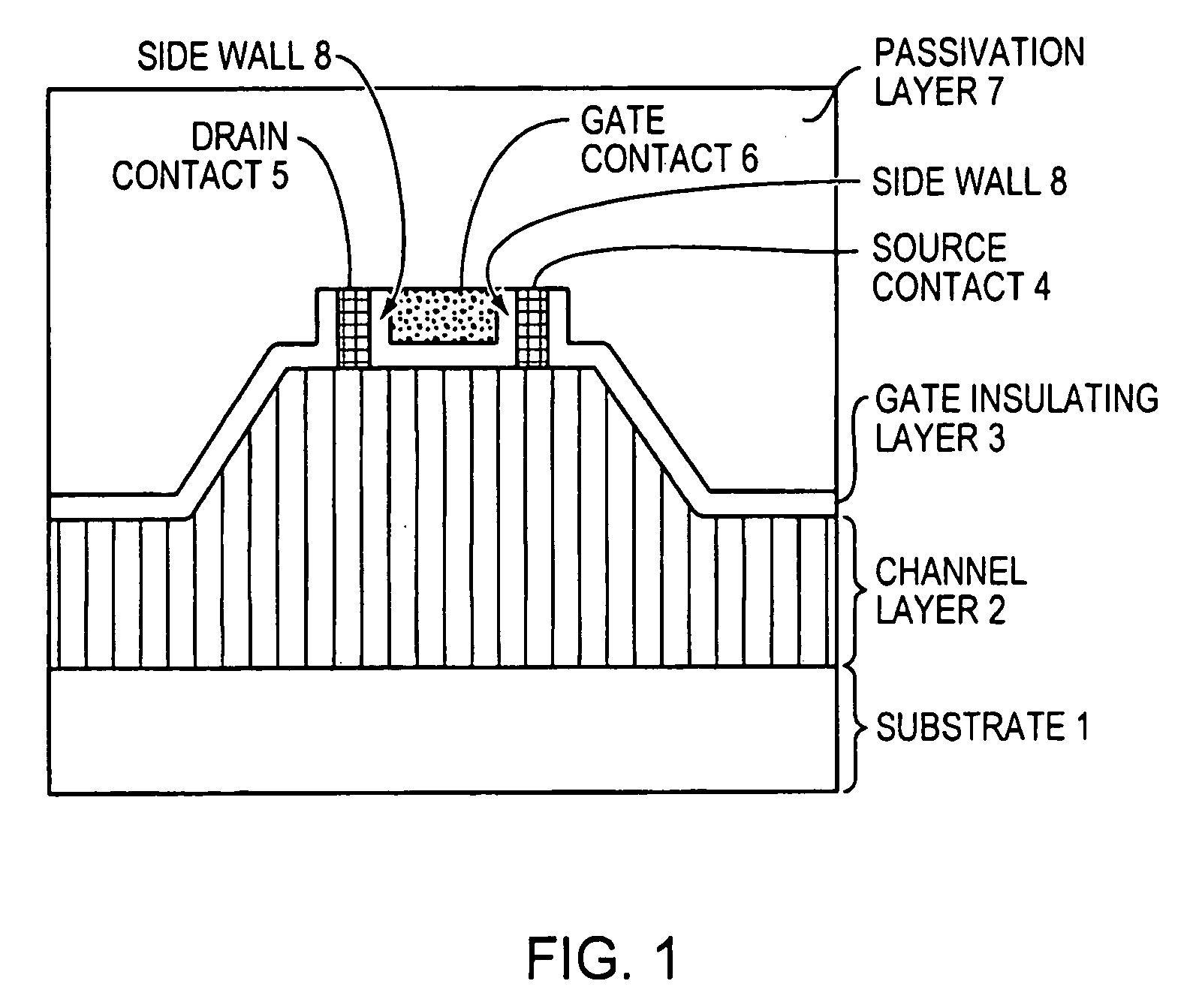
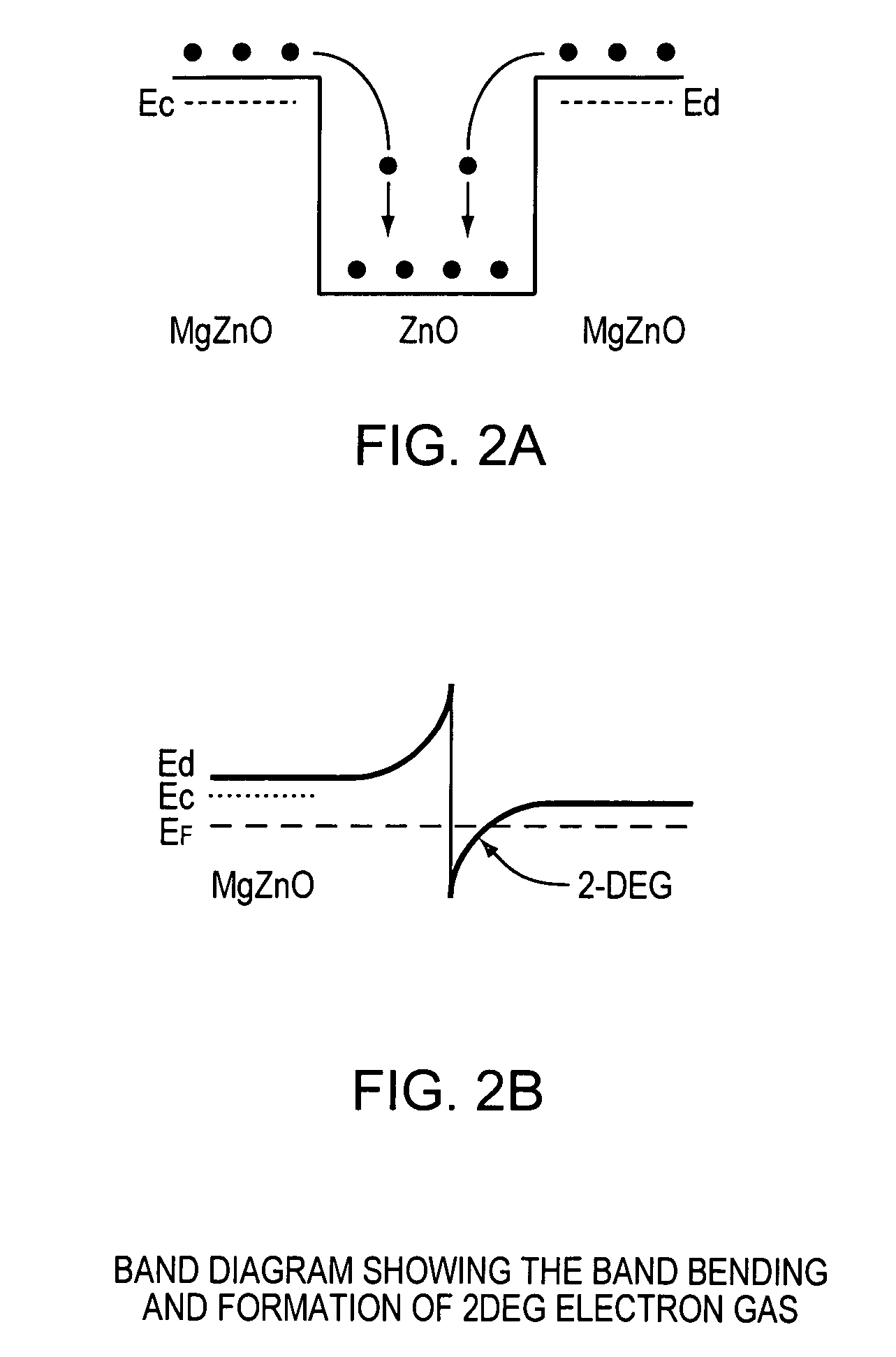
A zinc oxide (ZnO) field effect transistor exhibits large input amplitude by using a gate insulating layer. A channel layer and the gate insulating layer are sequentially laminated on a substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the gate insulating layer. A source contact and a drain contact are disposed at the both sides of the gate contact and are electrically connected to the channel layer via openings. The channel layer is formed from n-type ZnO. The gate insulating layer is made from aluminum nitride / aluminum gallium nitride (AlN / AlGaN) or magnesium zinc oxide (MgZnO), which exhibits excellent insulation characteristics, thus increasing the Schottky barrier and achieving large input amplitude. If the FET is operated in the enhancement mode, it is operable in a manner similar to a silicon metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (Si-MOS-type FET), resulting in the formation of an inversion layer.
Owner:NAUSE CATHERINE D
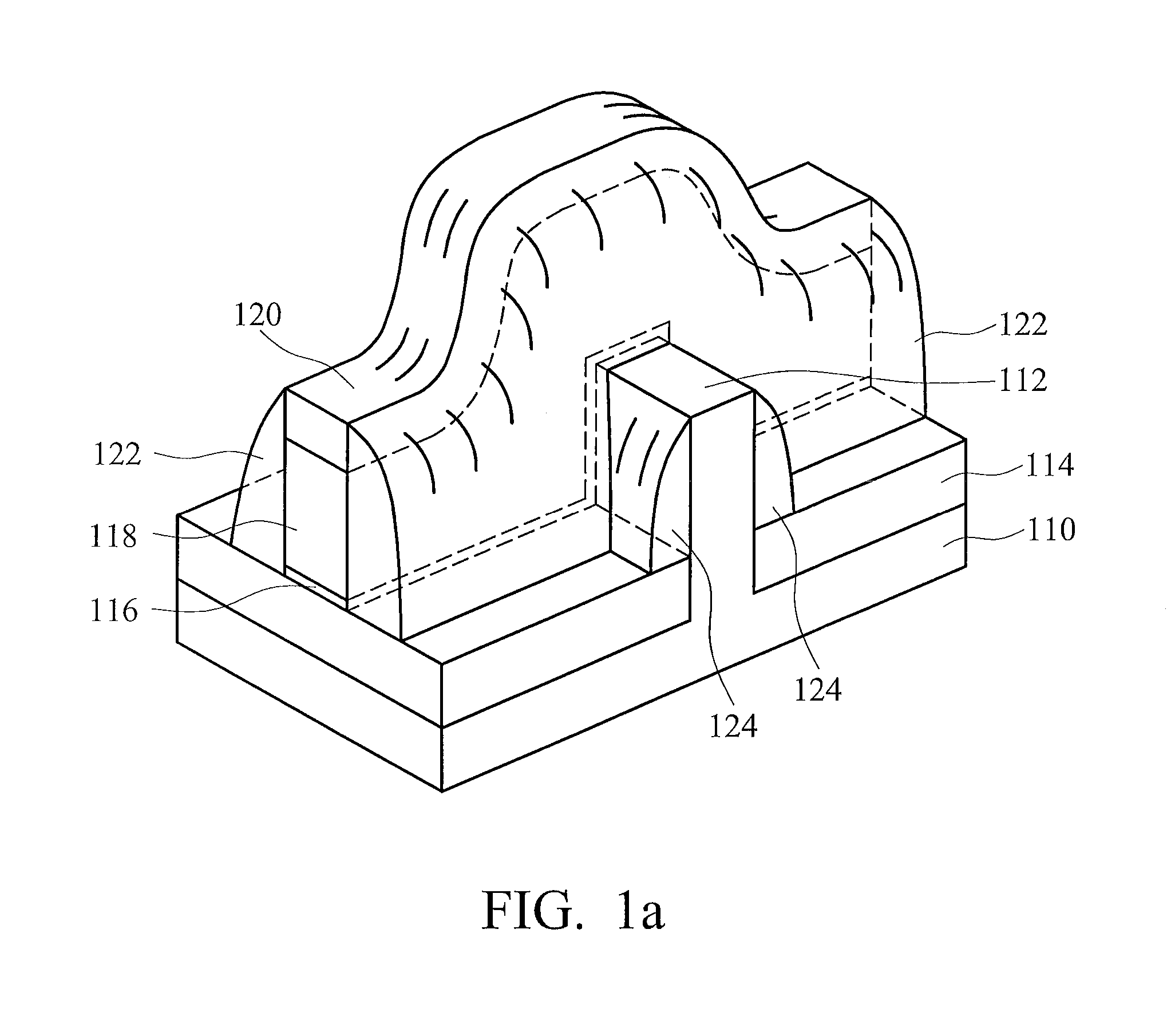
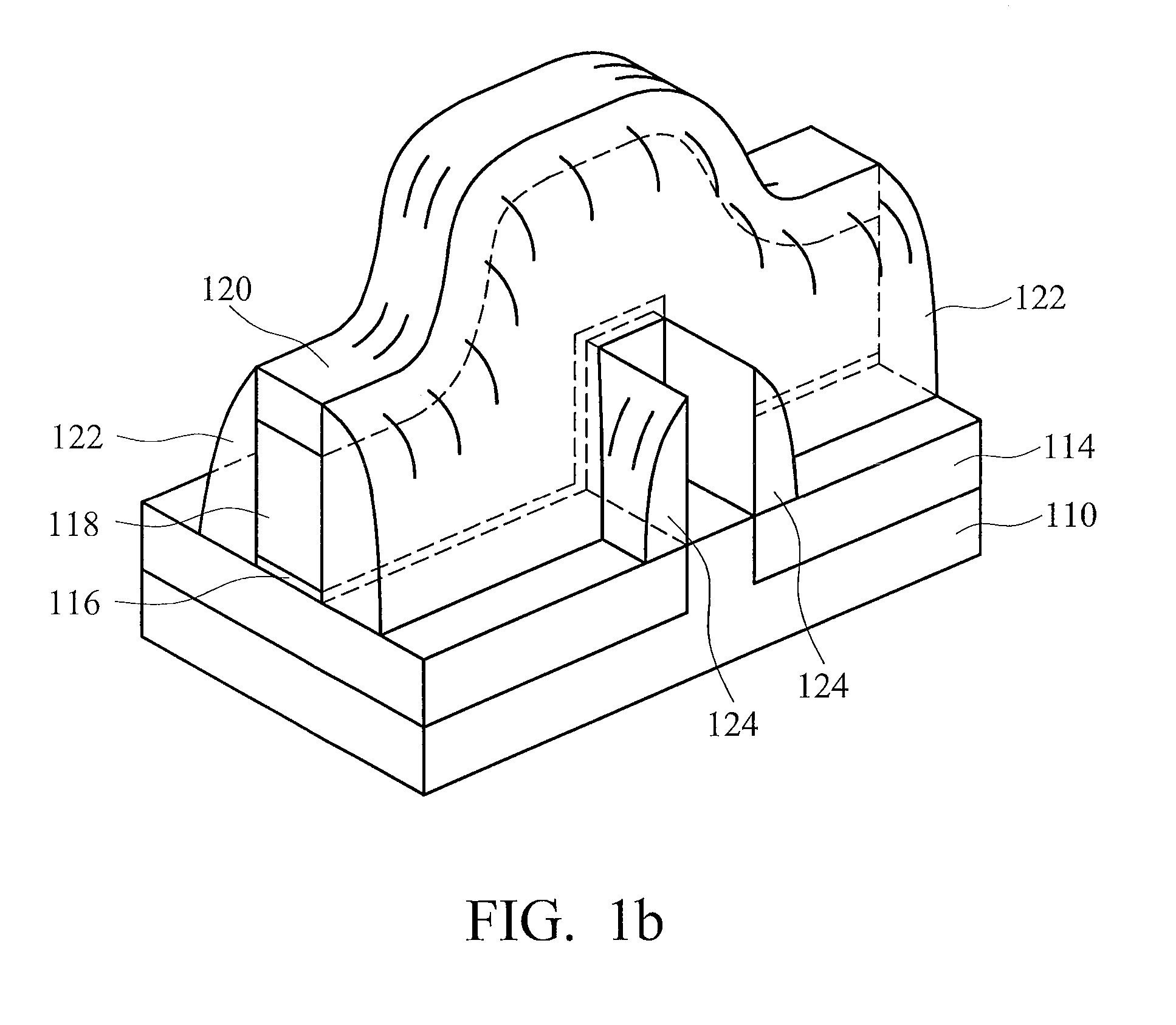
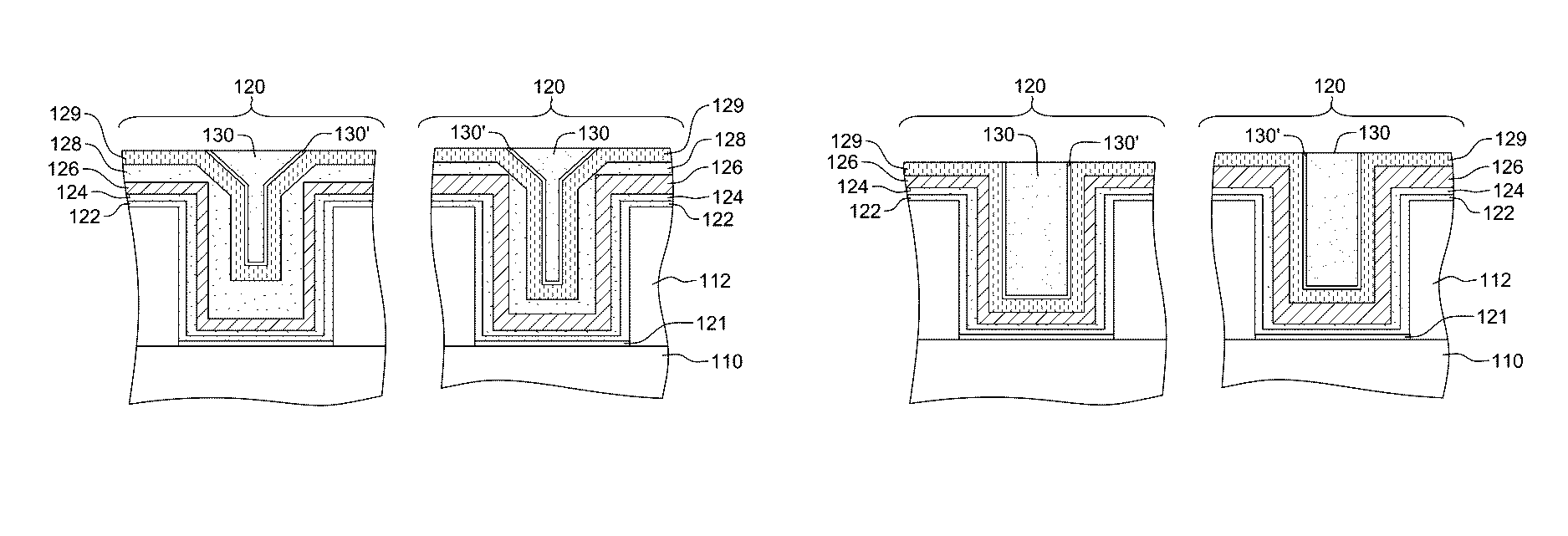
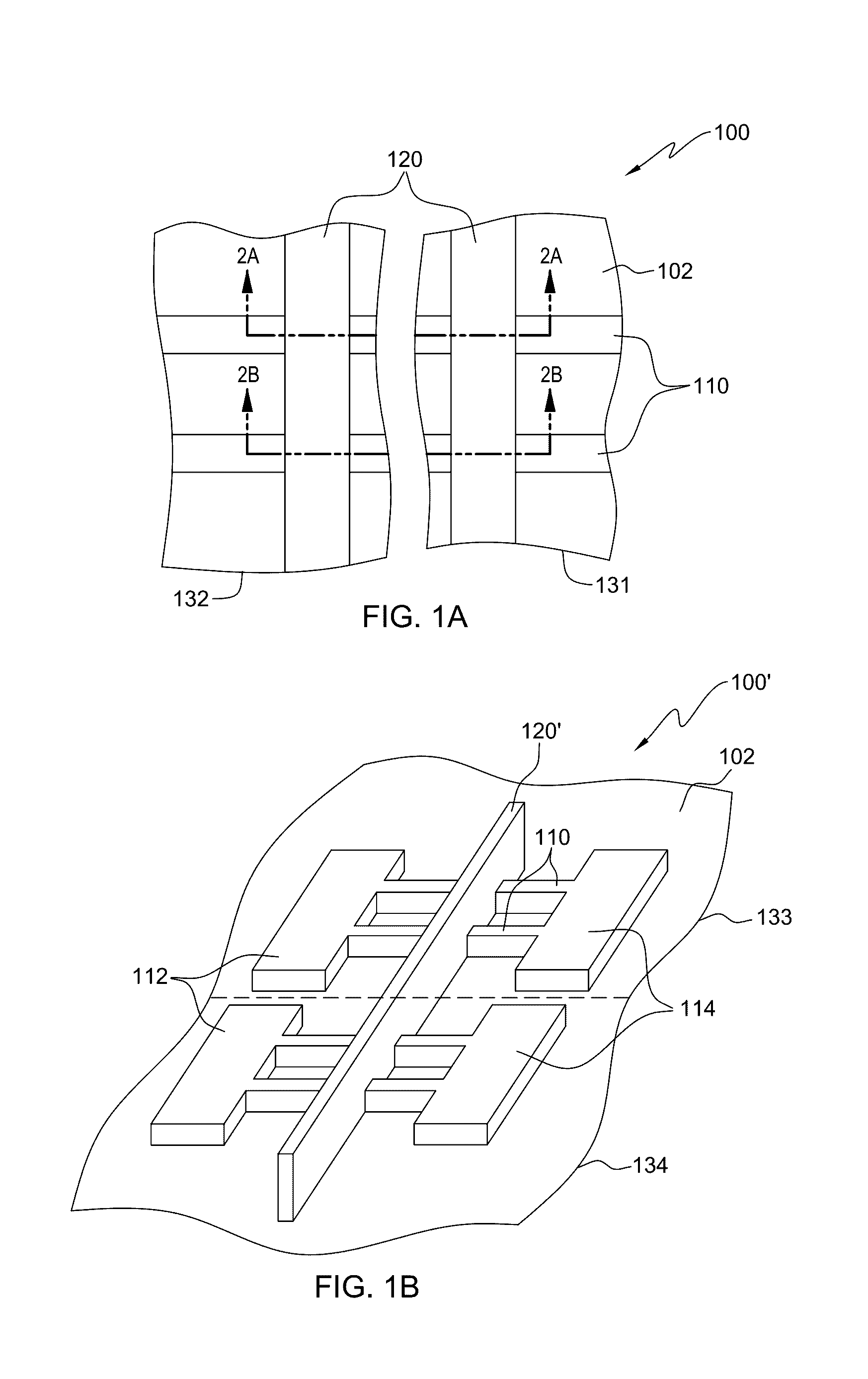
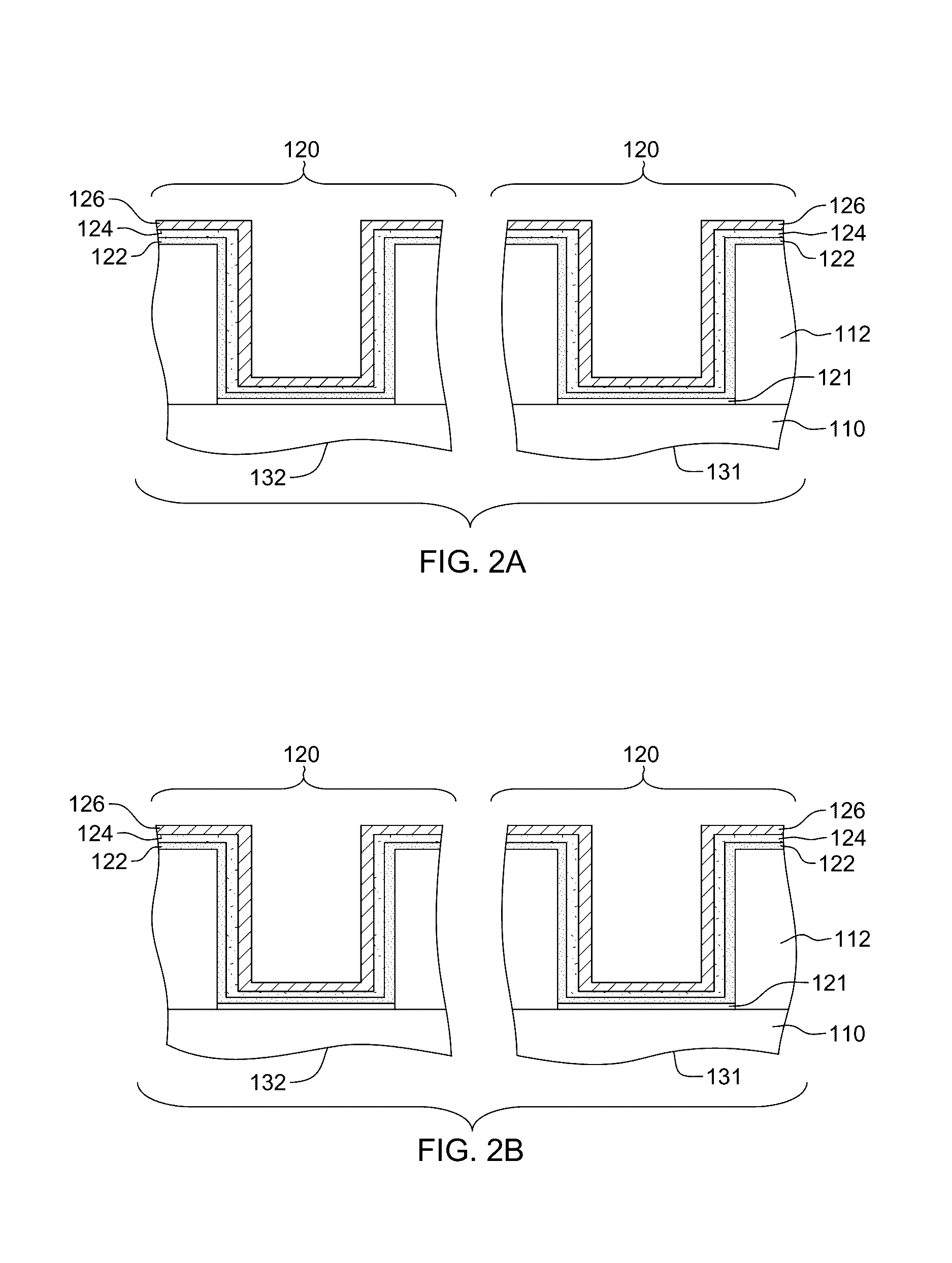
Cut-mask patterning process for fin-like field effect transistor (FinFET) device
ActiveUS9236267B2Liquid surface applicatorsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionField-effect transistor
A method for patterning a plurality of features in a non-rectangular pattern, such as on an integrated circuit device, includes providing a substrate including a surface with a plurality of elongated protrusions, the elongated protrusions extending in a first direction. A first layer is formed above the surface and above the plurality of elongated protrusions, and patterned with an end cutting mask. The end cutting mask includes two nearly-adjacent patterns with a sub-resolution feature positioned and configured such that when the resulting pattern on the first layer includes the two nearly adjacent patterns and a connection there between. The method further includes cutting ends of the elongated protrusions using the pattern on the first layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Display
Owner:CANON KK +2
Field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, manufacturing method of field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, and manufacturing method of amorphous oxide film
InactiveUS7791074B2Easy to controlSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHysteresisHydrogen
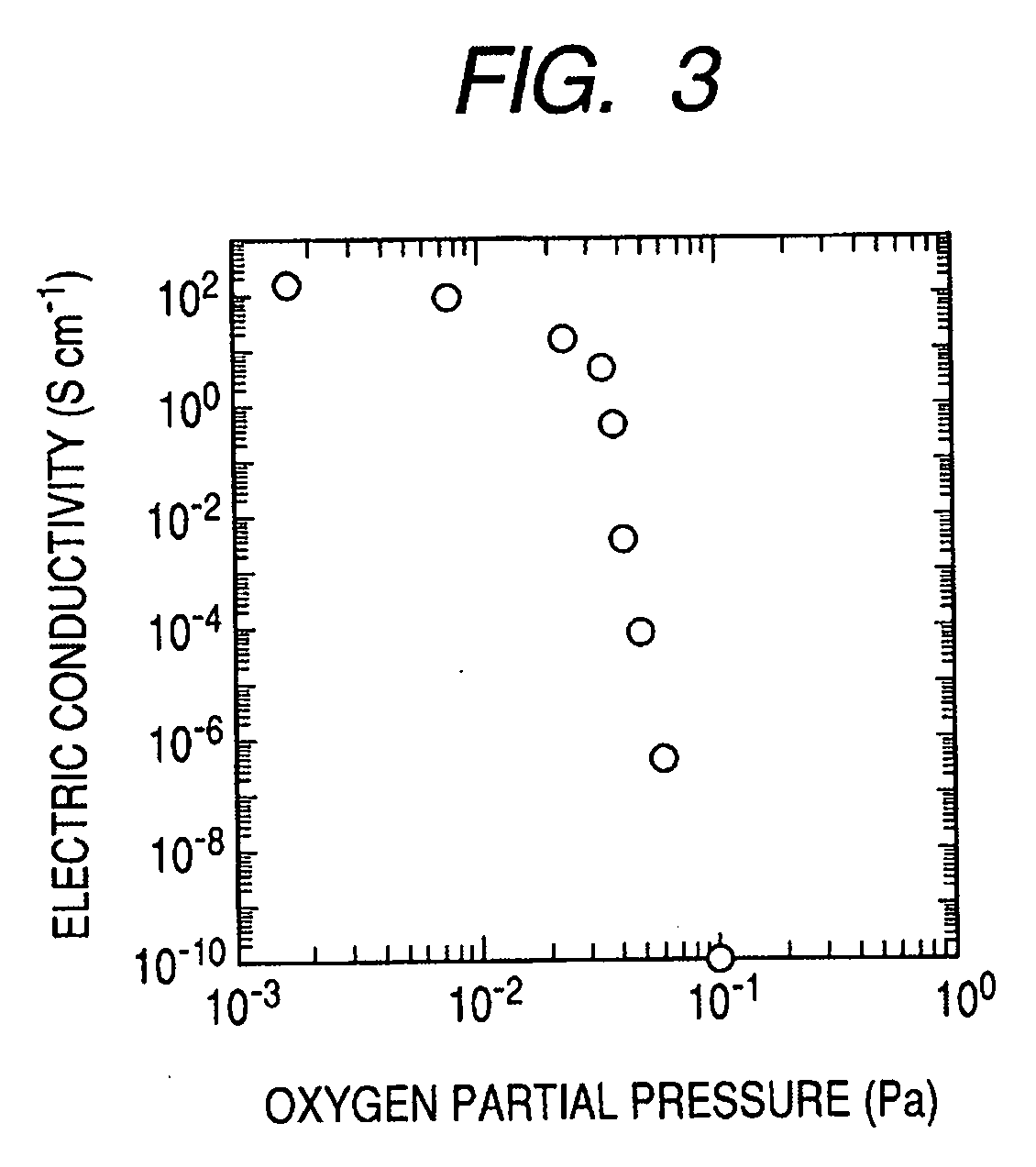
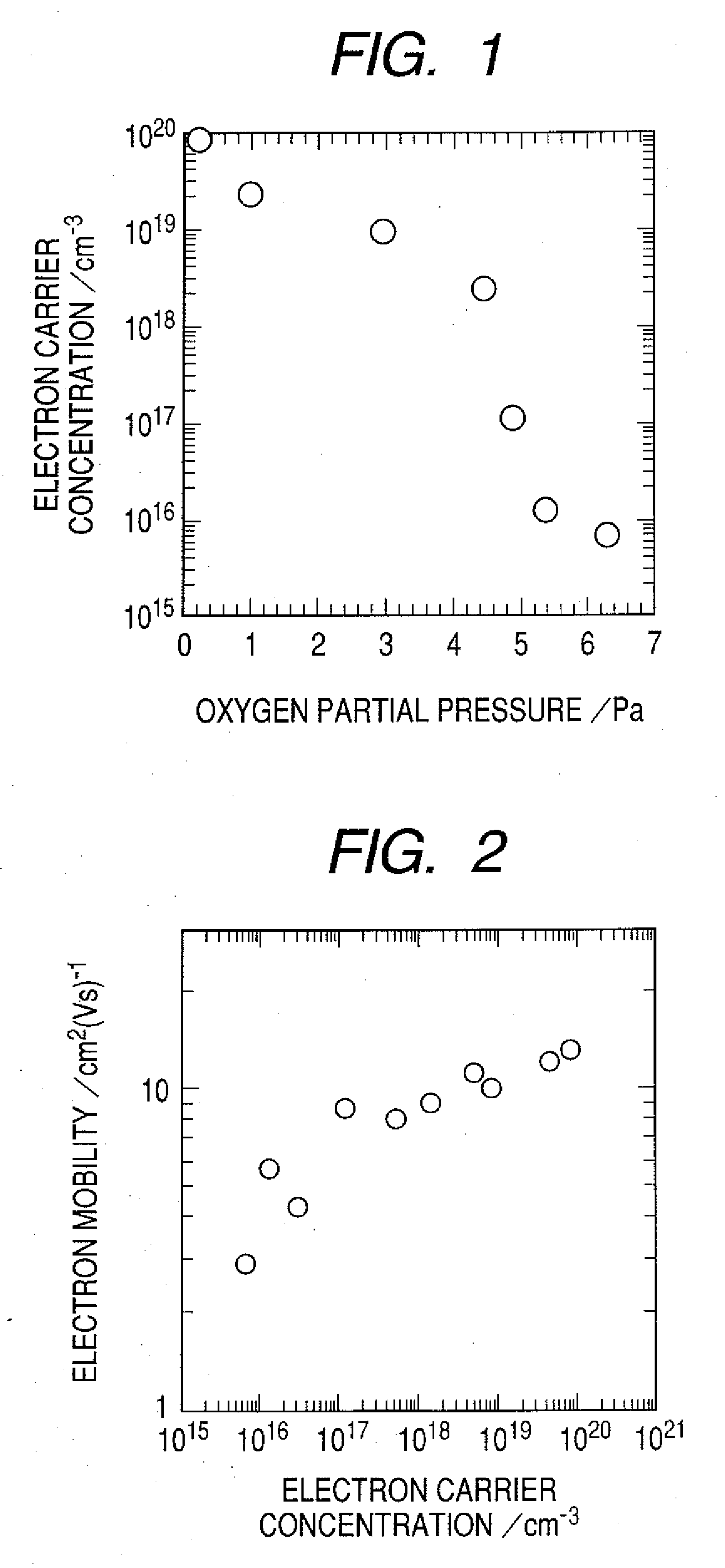
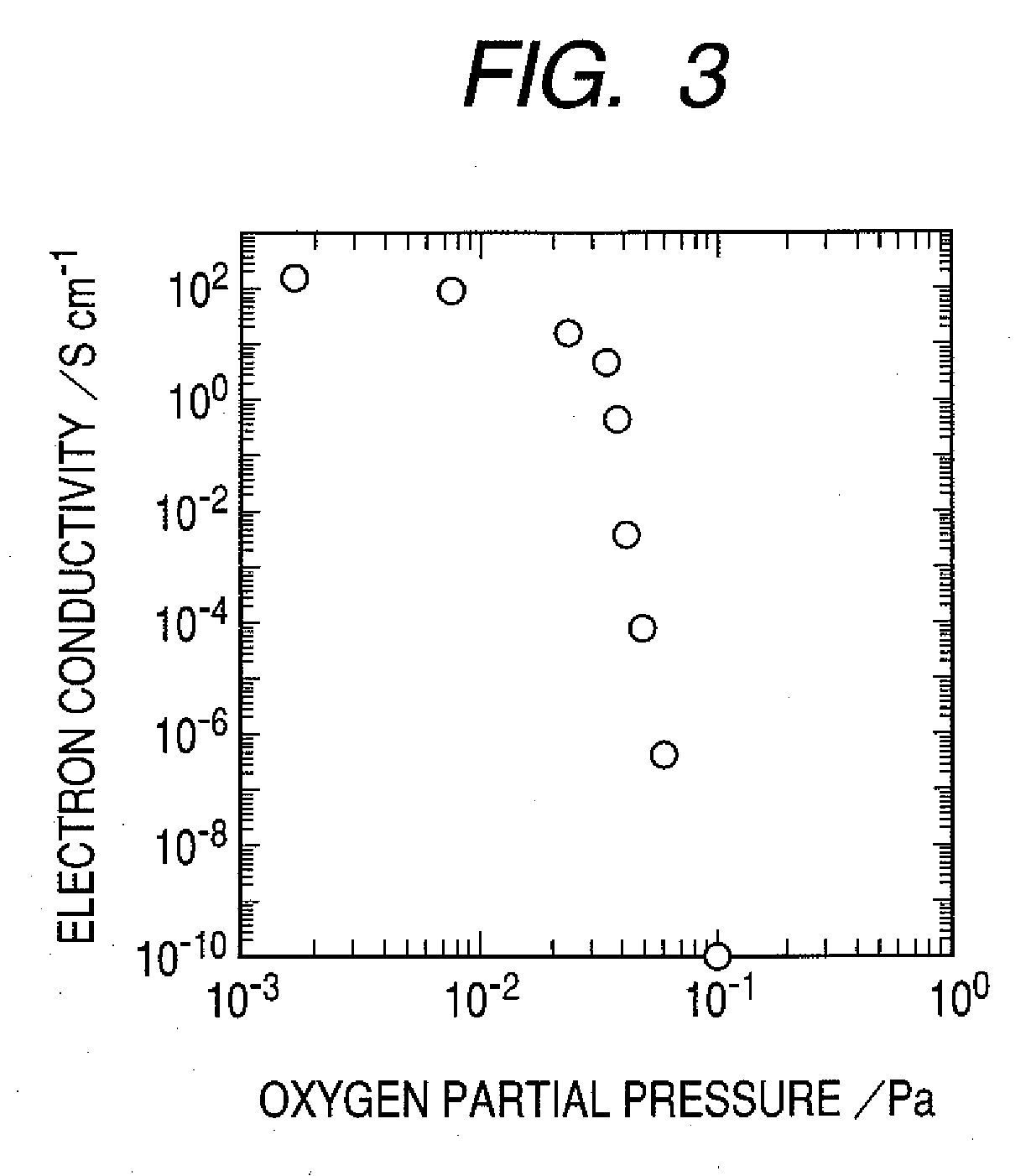
An amorphous oxide containing hydrogen (or deuterium) is applied to a channel layer of a transistor. Accordingly, a thin film transistor having superior TFT properties can be realized, the superior TFT properties including a small hysteresis, normally OFF operation, a high ON / OFF ratio, a high saturated current, and the like. Furthermore, as a method for manufacturing a channel layer made of an amorphous oxide, film formation is performed in an atmosphere containing a hydrogen gas and an oxygen gas, so that the carrier concentration of the amorphous oxide can be controlled.
Owner:CANON KK
Field effect transistor using oxide film for channel and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090065771A1Reduce variationImprove accuracyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenField-effect transistor
Owner:CANON KK
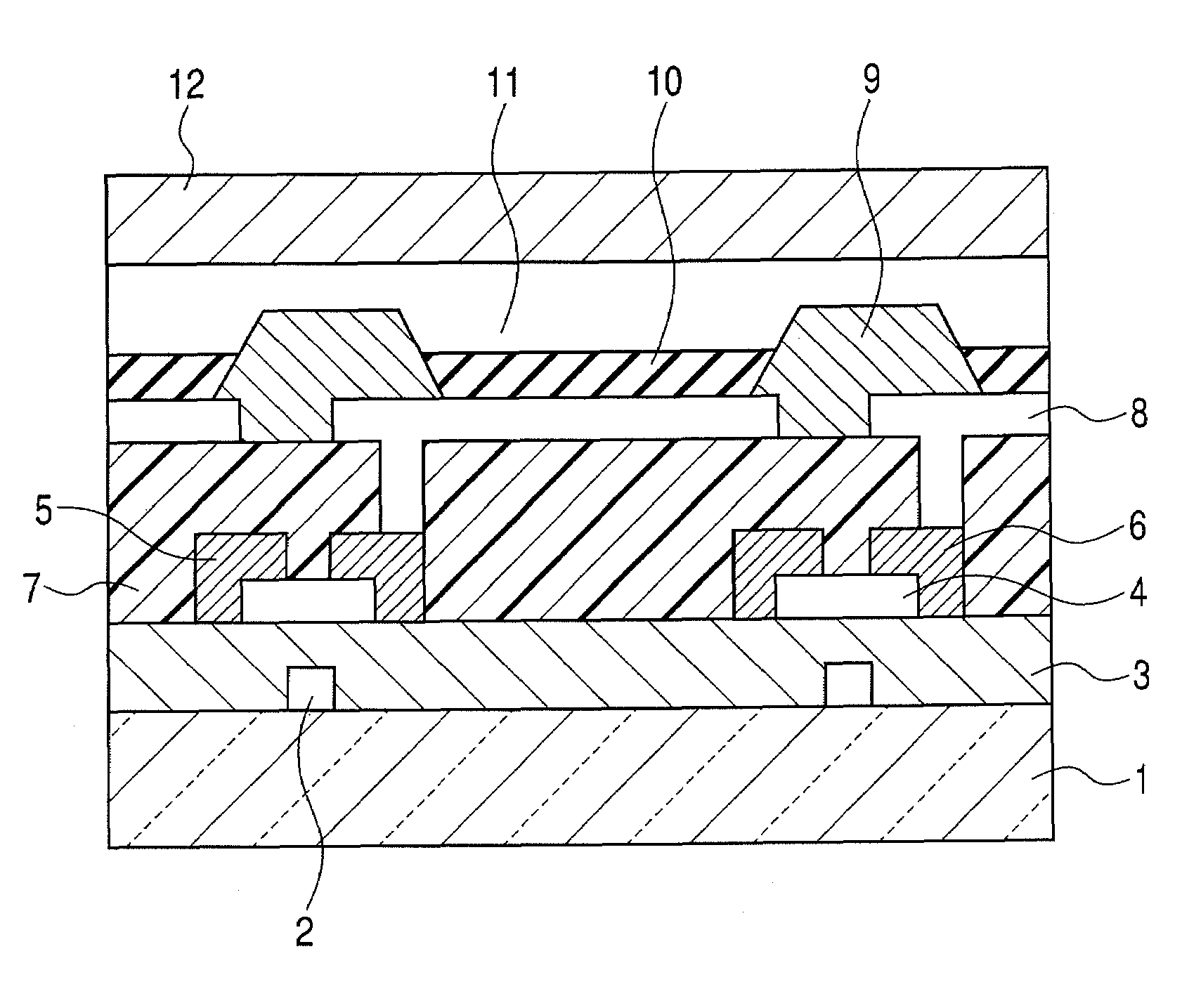
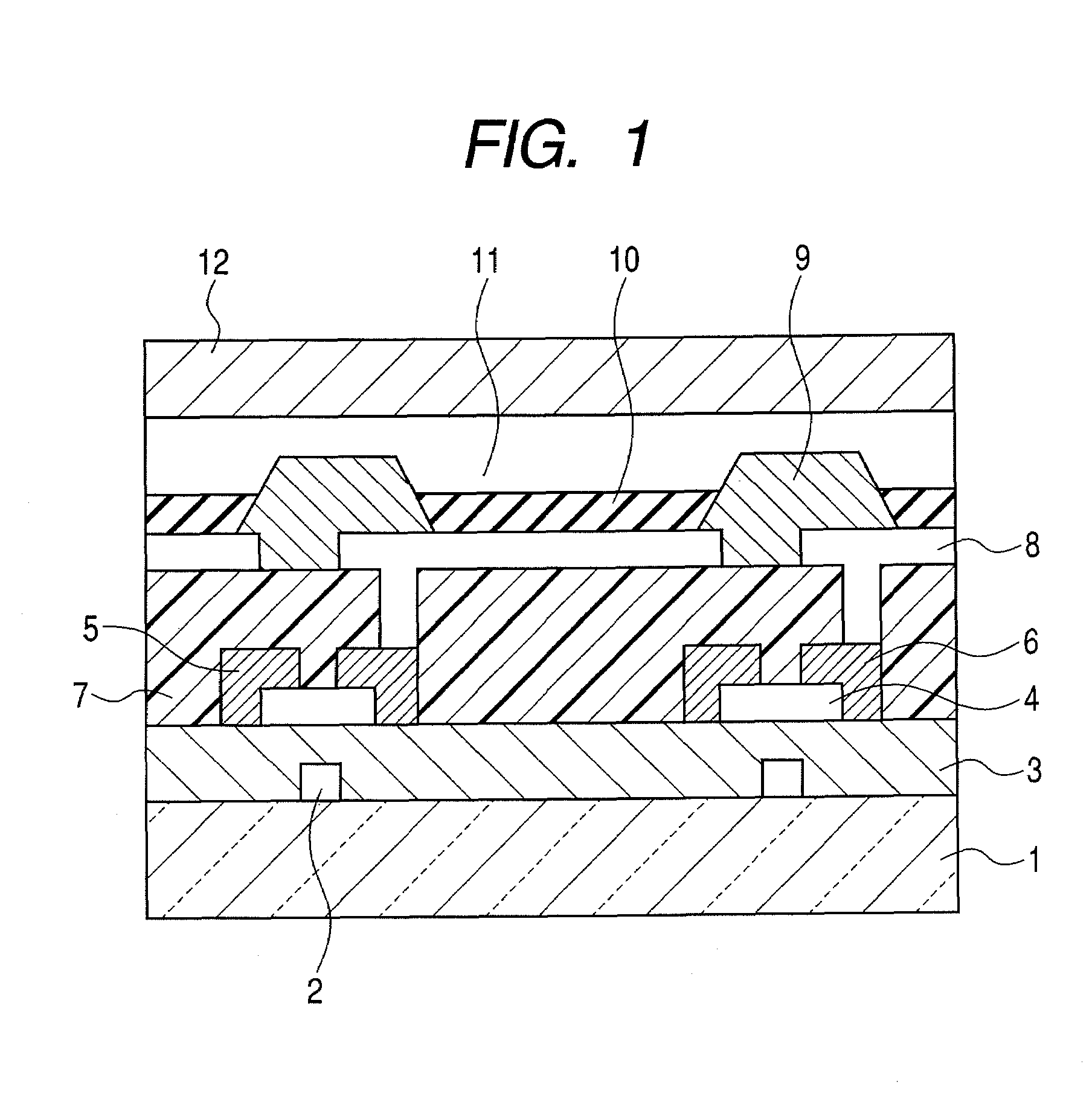
Thin film field effect transistor
ActiveUS8203143B2Increased durabilityImprove stabilitySemiconductor devicesInterface layerField-effect transistor
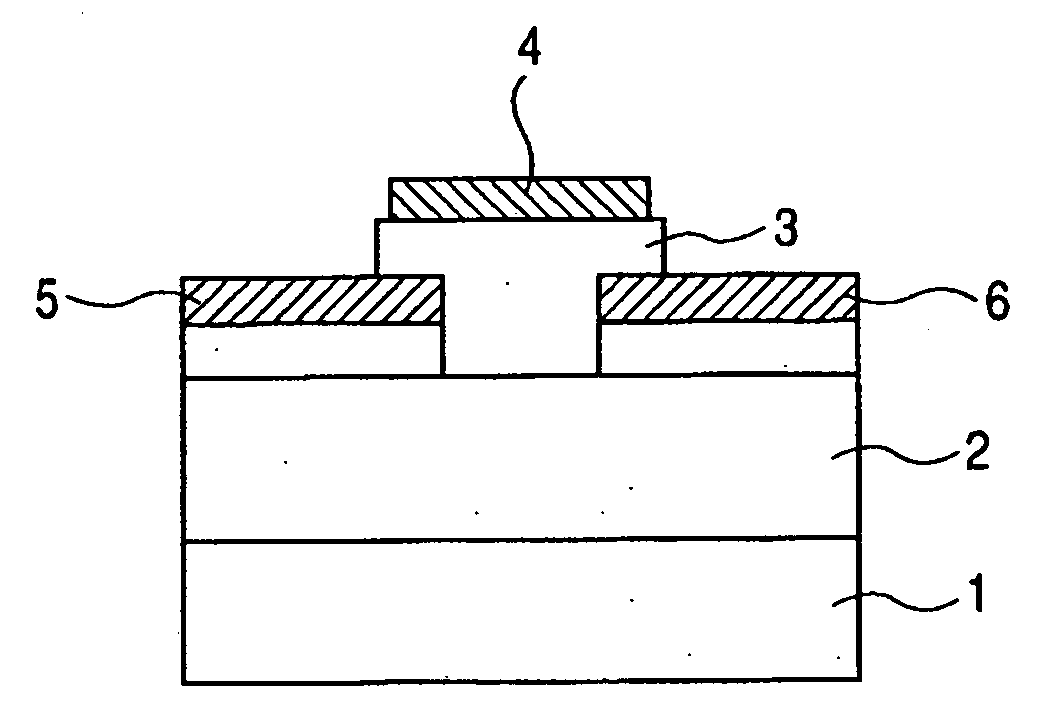
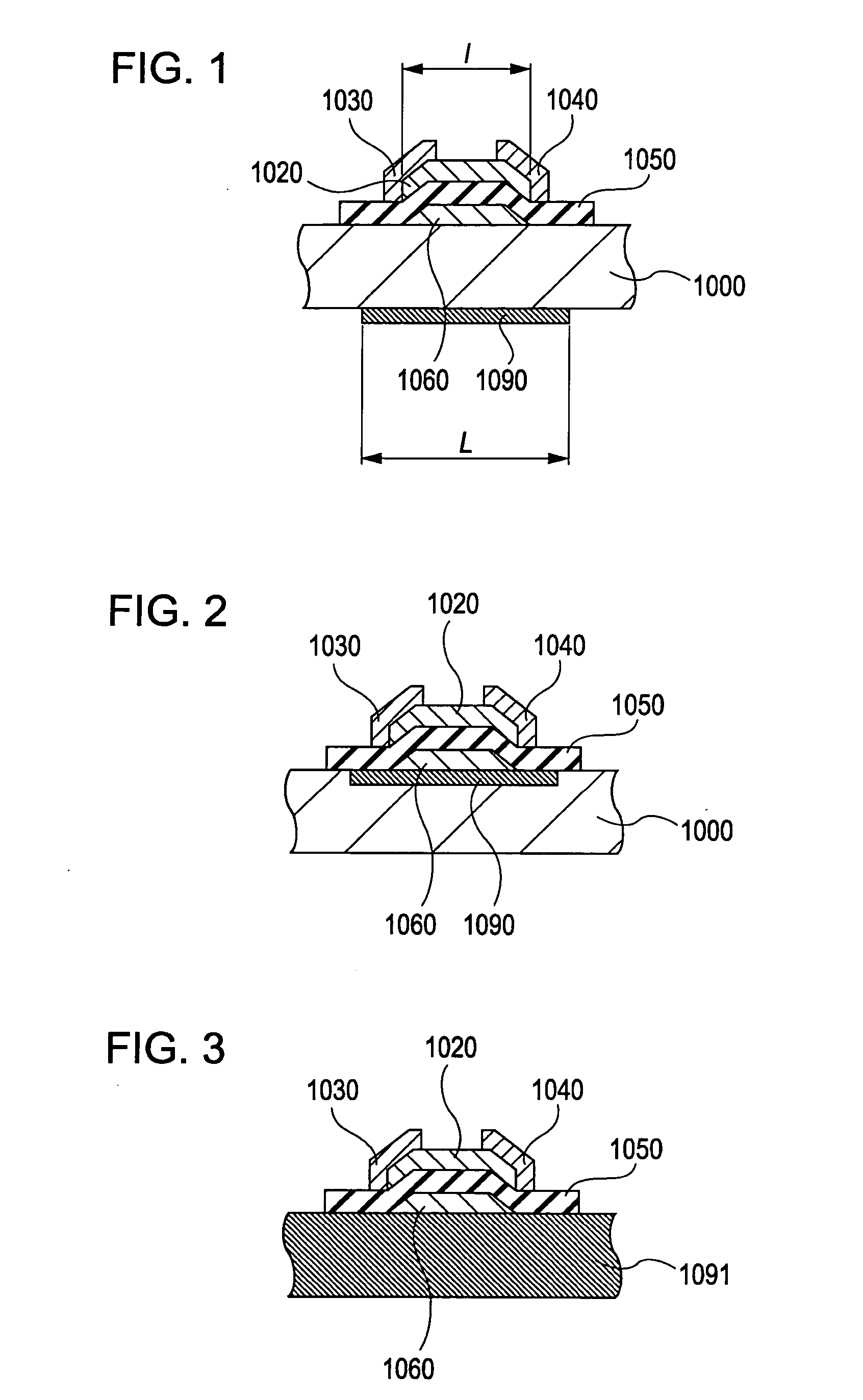
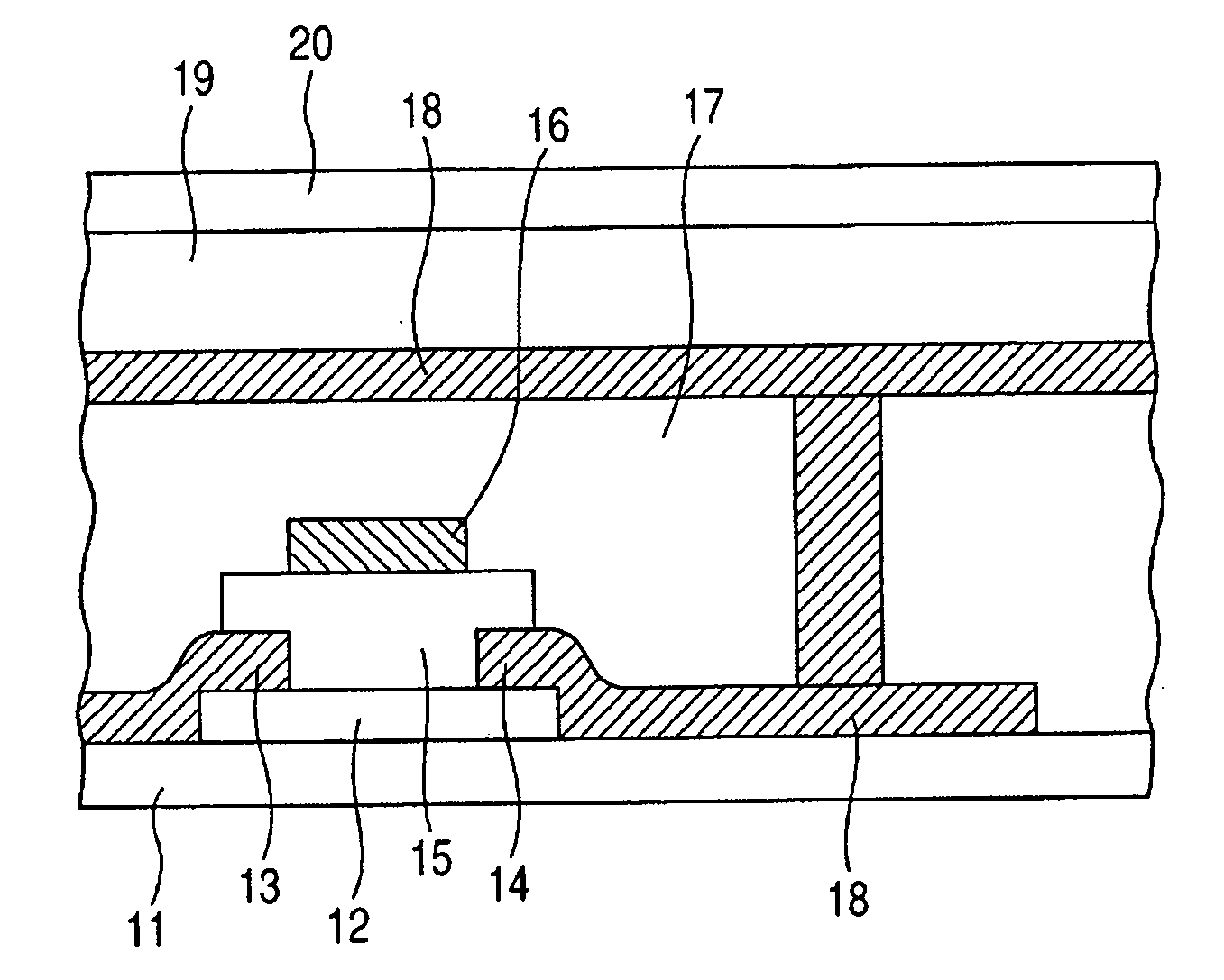
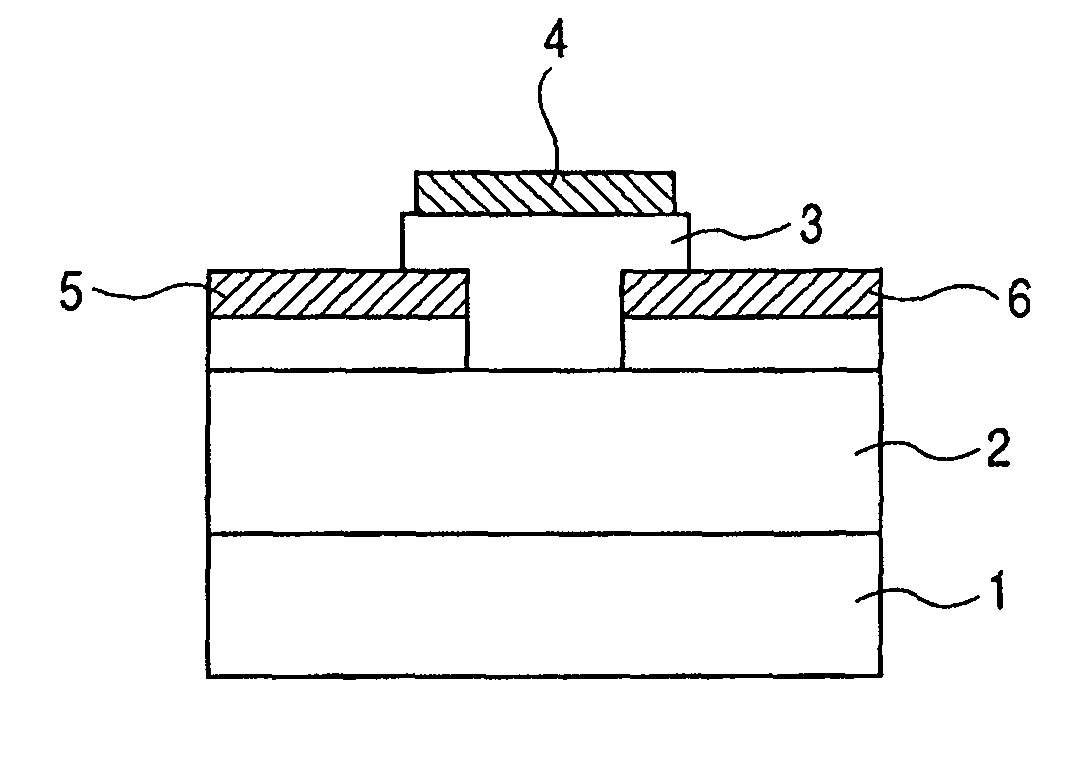
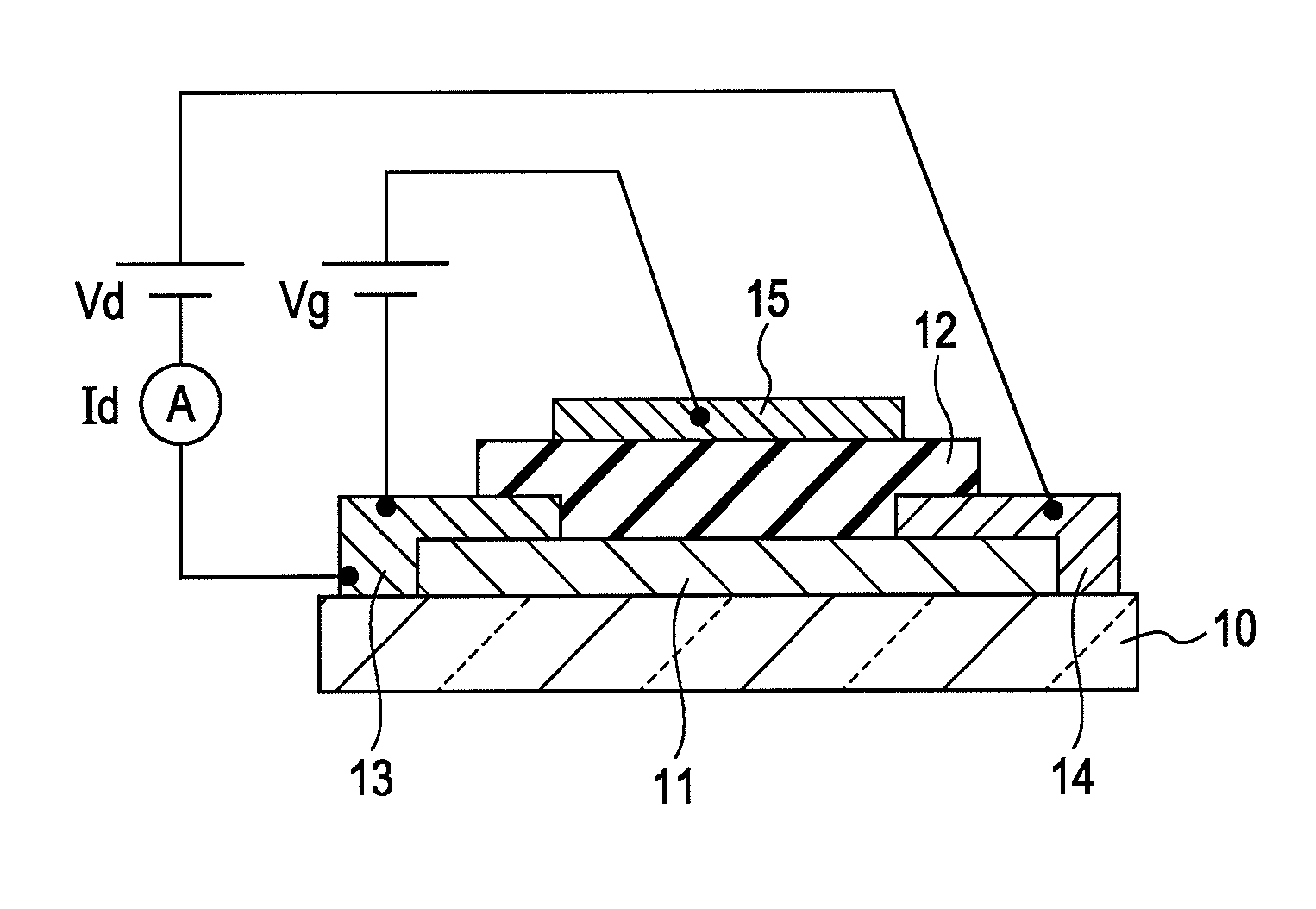
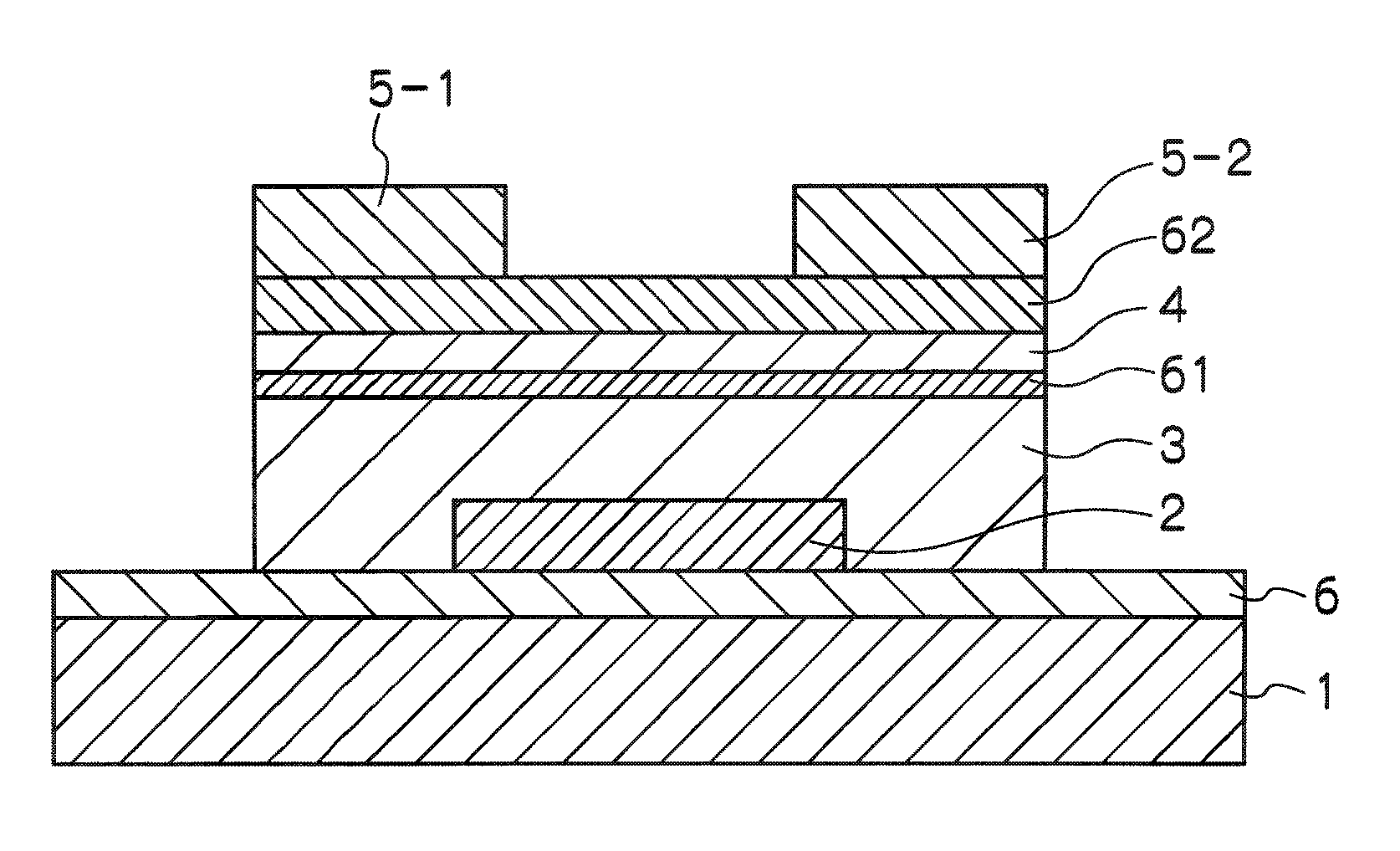
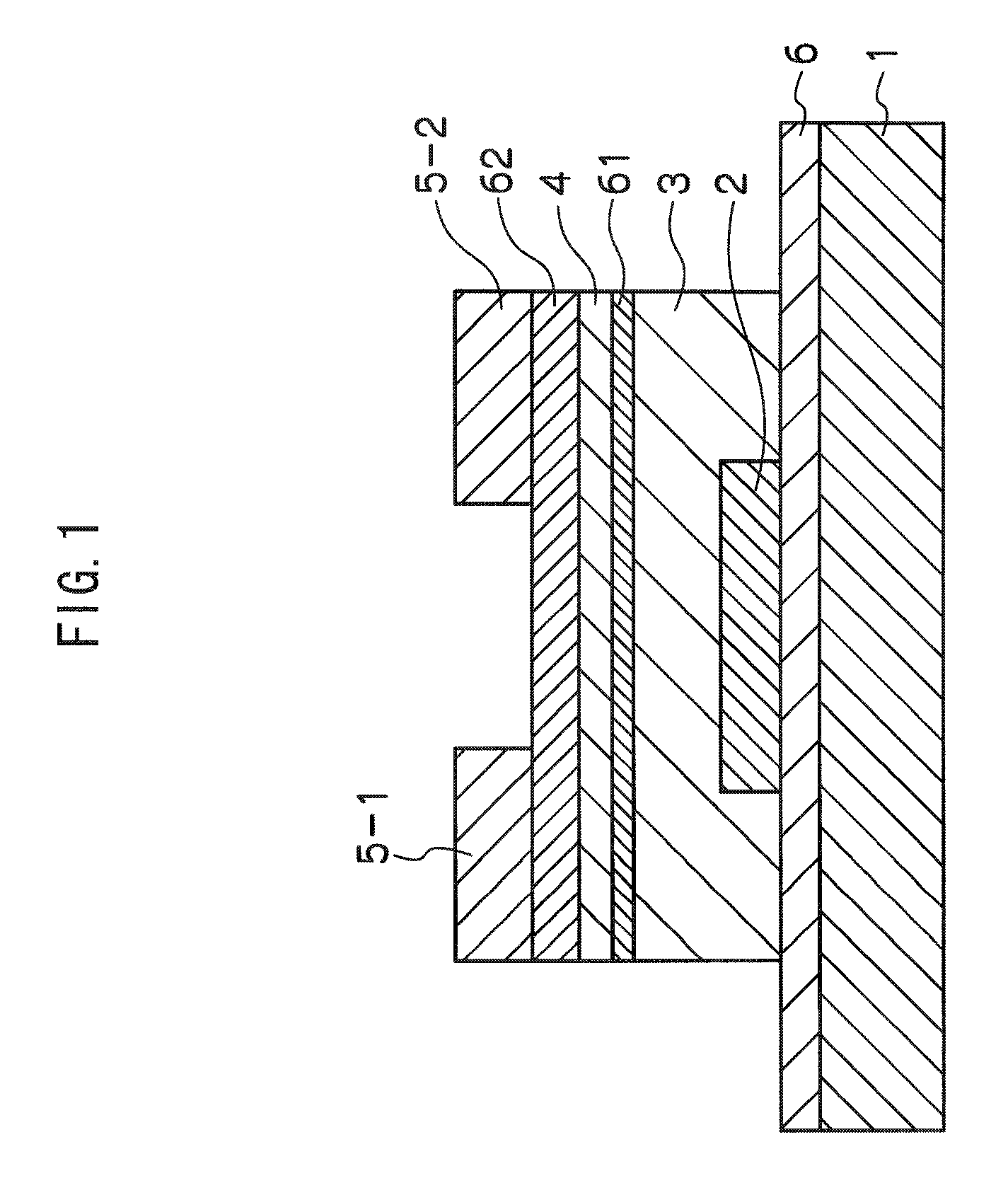
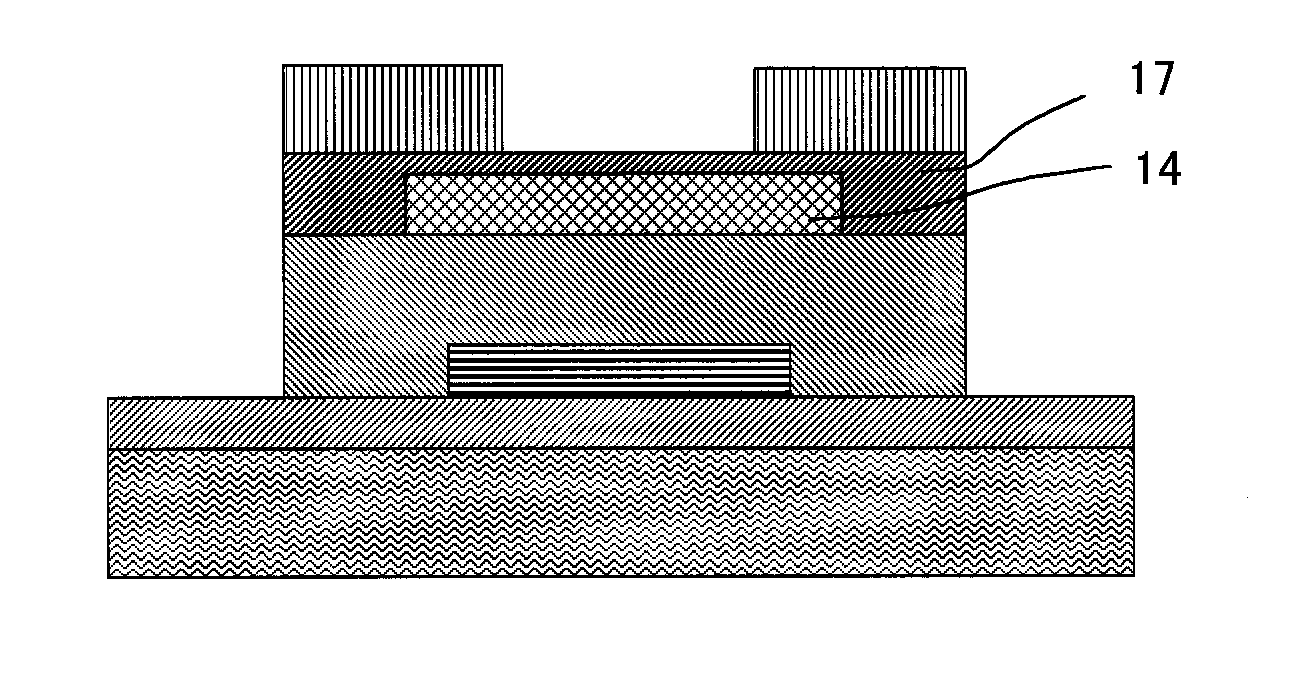
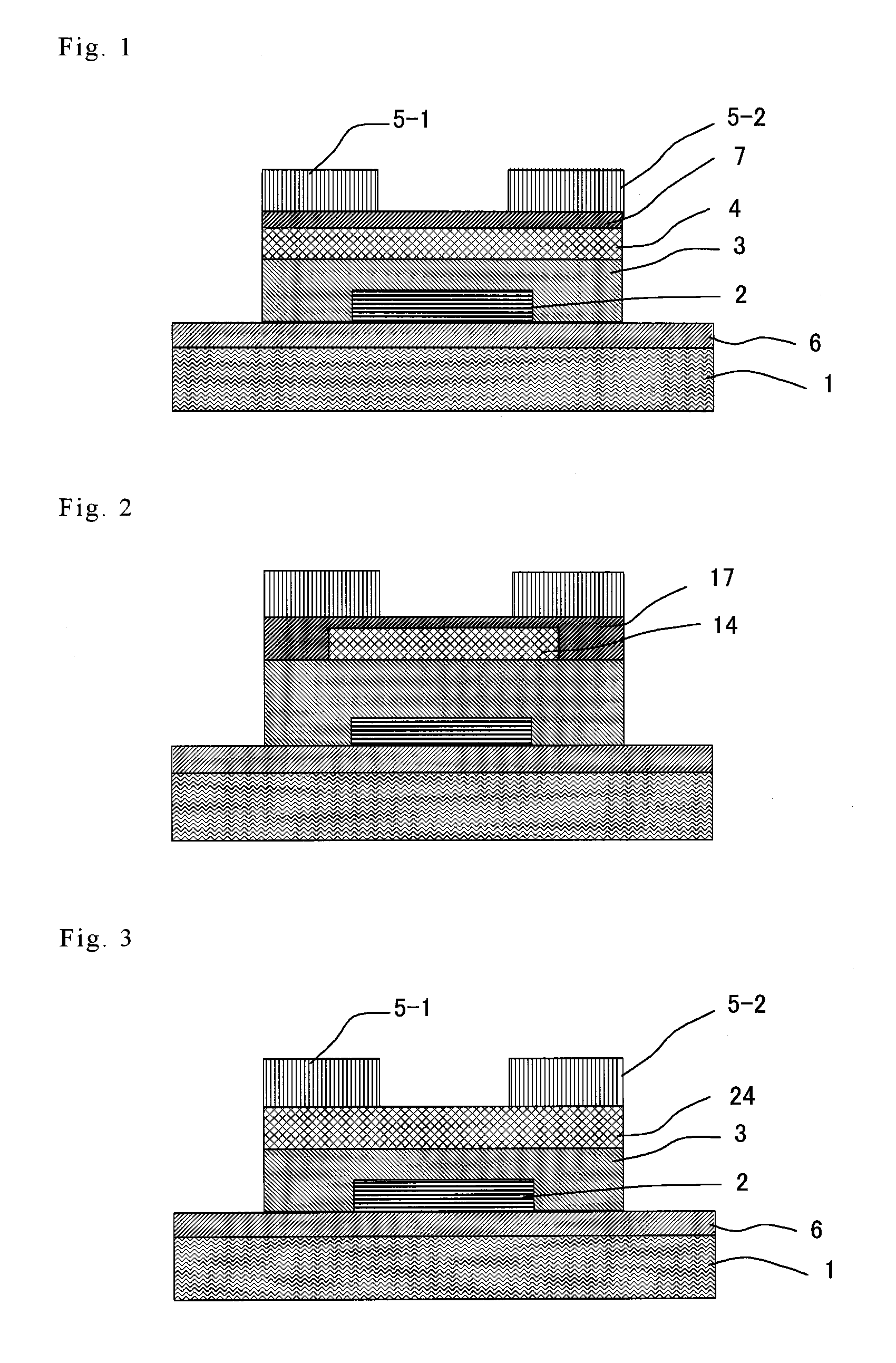
A thin film field effect transistor has at least a gate electrode 2, a gate insulating layer 3, an active layer 4, a source electrode 5-1 and a drain electrode 5-2 on a substrate 1. The active layer includes an amorphous oxide semiconductor including at least In and Zn, a first interface layer 61 is disposed between the gate insulating layer and the active layer such that it is adjacent to at least the active layer, and a second interface layer is disposed on the opposite side of the active layer with respect to the first interface layer such that it is adjacent to the active layer. A content of Ga or Al in the amorphous oxide semiconductor of each of the first interface layer and the second interface layer is higher than a content of Ga or Al in the amorphous oxide semiconductor of the active layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Thin film field effect transistor and display
ActiveUS8188480B2High concentrationElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceField-effect transistor
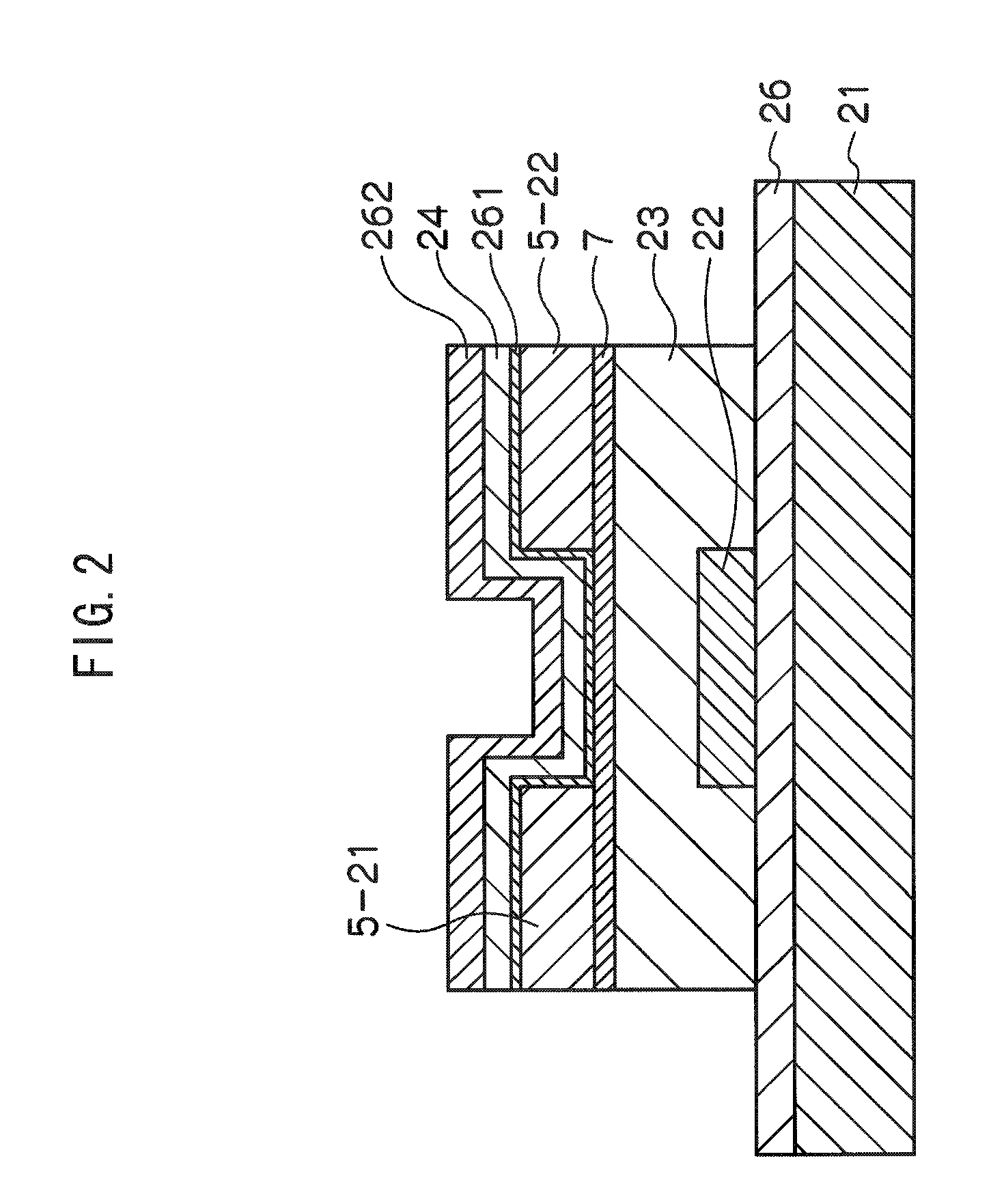
A TFT is provided which includes, on a substrate, at least a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer, an active layer containing an amorphous oxide semiconductor, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein a resistance layer containing an amorphous oxide and having a thickness of more than 3 nm is disposed between the active layer and at least one of the source electrode or the drain electrode, and a band gap of the active layer is smaller than a band gap of the resistance layer. Also, a display using the TFT is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Fin field-effect transistors
InactiveUS7667271B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringField-effect transistor
A fin field-effect transistor (finFET) with improved source / drain regions is provided. In an embodiment, the source / drain regions of the fin are removed while spacers adjacent to the fin remain. An angled implant is used to implant the source / drain regions near a gate electrode, thereby allowing for a more uniform lightly doped drain. The fin may be re-formed by either epitaxial growth or a metallization process. In another embodiment, the spacers adjacent the fin in the source / drain regions are removed and the fin is silicided along the sides and the top of the fin. In yet another embodiment, the fin and the spacers are removed in the source / drain regions. The fins are then re-formed via an epitaxial growth process or a metallization process. Combinations of these embodiments may also be used.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Light-emitting apparatus and production method thereof
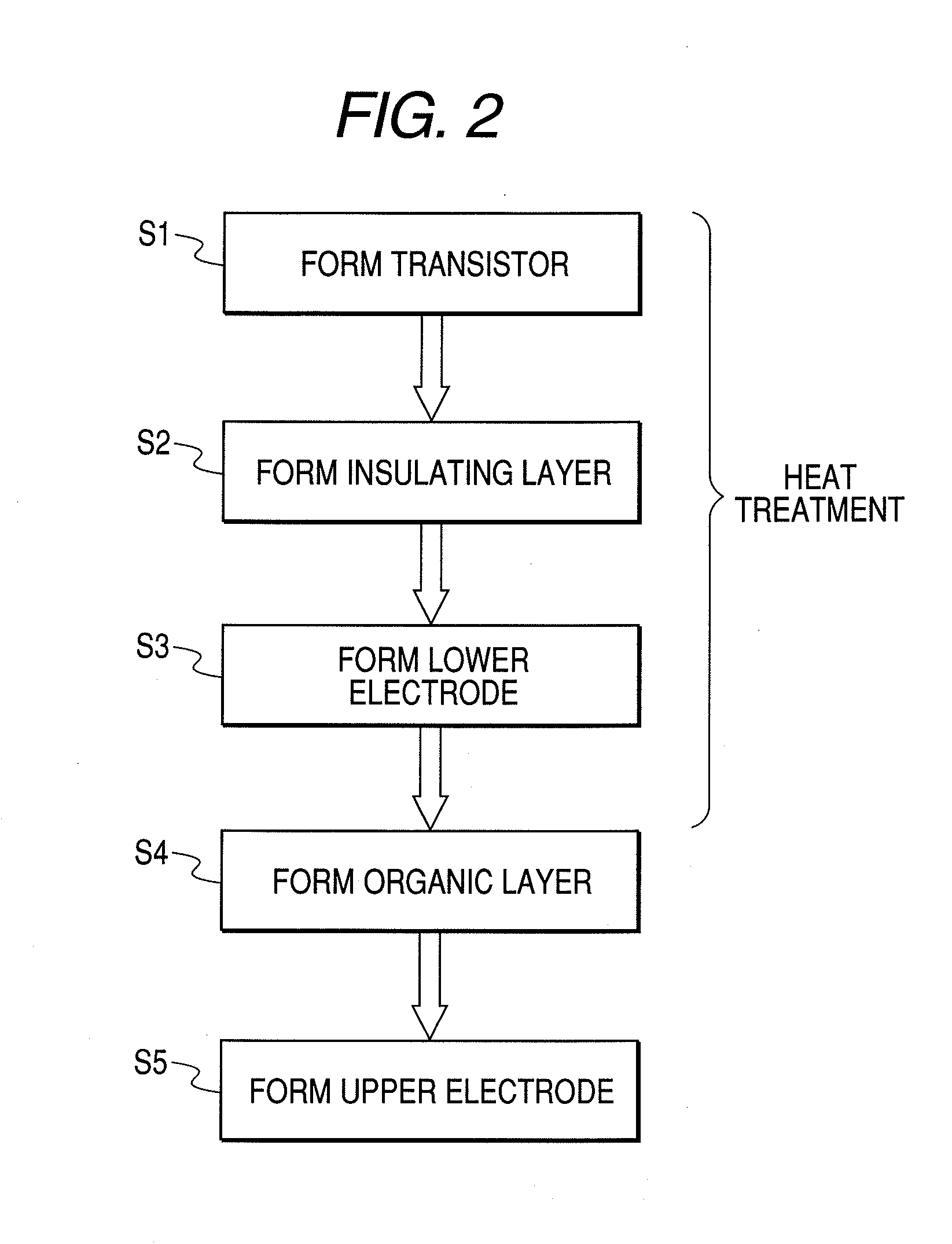
Provided is a method of producing a light-emitting apparatus having a field effect transistor for driving an organic EL device, the field effect transistor including an oxide semiconductor containing at least one element selected from In and Zn, the method including the steps of: forming a field effect transistor on a substrate; forming an insulating layer; forming a lower electrode on the insulating layer; forming an organic layer for constituting an organic EL device on the lower electrode; forming an upper electrode on the organic layer; and after the step of forming the semiconductor layer of the field effect transistor and before the step of forming the organic layer, performing heat treatment such that an amount of a component that is desorbable as H2O from the field effect transistor during the step of forming the organic layer is less than 10−5 g / m2.
Owner:CANON KK
Opto-thermal annealing methods for forming metal gate and fully silicided gate field effect transistors
ActiveUS20070249131A1Avoid opto-thermal annealing damageAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideGate dielectric
An opto-thermal annealing method for forming a field effect transistor uses a reflective metal gate so that electrical properties of the metal gate and also interface between the metal gate and a gate dielectric are not compromised when opto-thermal annealing a source / drain region adjacent the metal gate. Another opto-thermal annealing method may be used for simultaneously opto-thermally annealing: (1) a silicon layer and a silicide forming metal layer to form a fully silicided gate; and (2) a source / drain region to form an annealed source / drain region. An additional opto-thermal annealing method may use a thermal insulator layer in conjunction with a thermal absorber layer to selectively opto-thermally anneal a silicon layer and a silicide forming metal layer to form a fully silicide gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Phosphorus Containing Si Epitaxial Layers in N-Type Source/Drain Junctions
ActiveUS20080182075A1Keep the pressureLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETHigh concentration
Methods for formation of epitaxial layers containing n-doped silicon are disclosed. Specific embodiments pertain to the formation and treatment of epitaxial layers in semiconductor devices, for example, Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) devices. In specific embodiments, the formation of the n-doped epitaxial layer involves exposing a substrate in a process chamber to deposition gases including a silicon source, a carbon source and an n-dopant source. An epitaxial layer may have considerable tensile stress which may be created in a significant amount by a high concentration of n-dopant. A layer having n-dopant may also have substitutional carbon. Phosphorus as an n-dopant with a high concentration is provided. A substrate having an epitaxial layer with a high level of n-dopant is also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Field effect transistor having an interlayer dielectric material having increased intrinsic stress
InactiveUS20080203487A1Optimization mechanismImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentField-effect transistor
By providing a highly stressed interlayer dielectric material, the performance of at least one type of transistor may be increased due to an enhanced strain-inducing mechanism. For instance, by providing a highly compressive silicon dioxide of approximately 400 Mega Pascal and more as an interlayer dielectric material, the drive current of the P-channel transistors may be increased by 2% and more while not unduly affecting the performance of the N-channel transistors.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Integrated circuits with varying gate structures and fabrication methods
ActiveUS20150243658A1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageTransistorSolid-state devicesGate stackField-effect transistor
Integrated circuits and fabrication methods are provided. The integrated circuit includes: a varying gate structure disposed over a substrate structure, the varying gate structure including a first gate stack in a first region of the substrate structure, and a second gate stack in a second region of the substrate structure; a first field-effect transistor in the first region, the first field-effect transistor including the first gate stack and having a first threshold voltage; and a second field-effect transistor in the second region, the second field-effect transistor including the second gate stack and having a second threshold voltage, where the first threshold voltage is different from the second threshold voltage. The methods include providing the varying gate structure, the providing including: sizing layer(s) of the varying gate structure with different thickness(es) in different region(s).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Field effect transistor with amorphous oxide layer containing microcrystals
InactiveUS20090179199A1Reduced electron mobilityLow conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorActive layer
A novel amorphous oxide applicable, for example, to an active layer of a TFT is provided. The amorphous oxide comprises microcrystals.
Owner:CANON KK +1
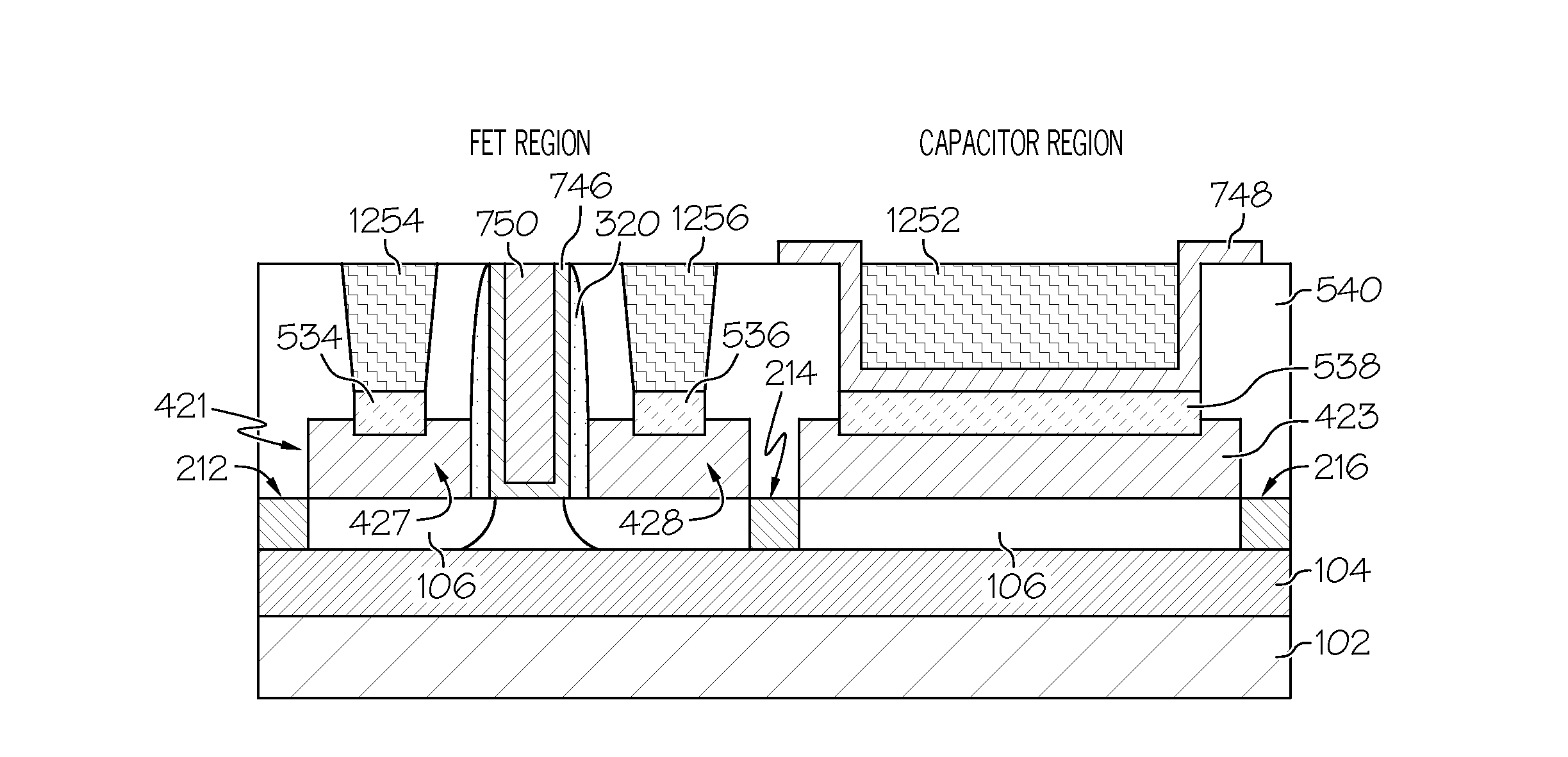
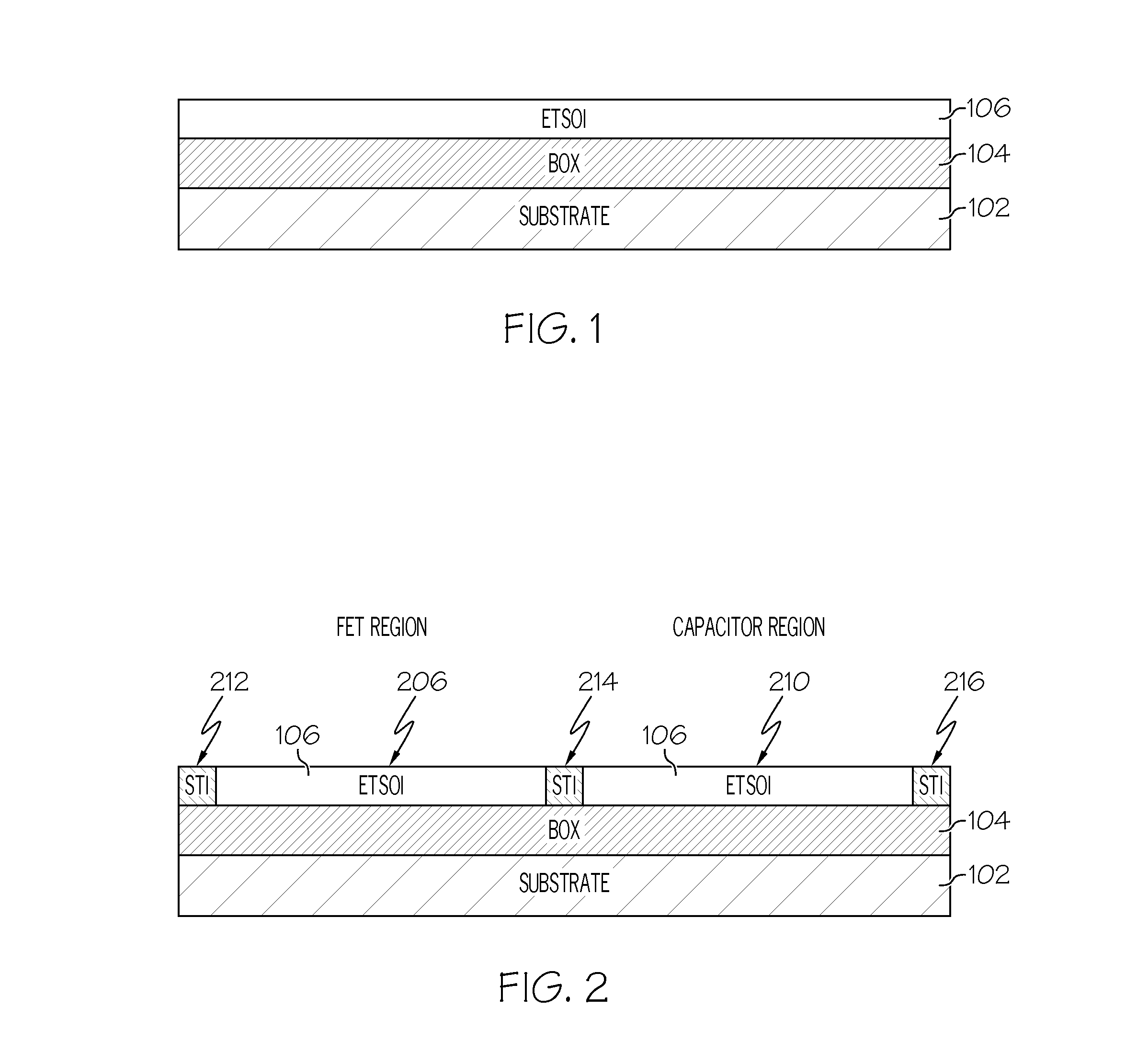
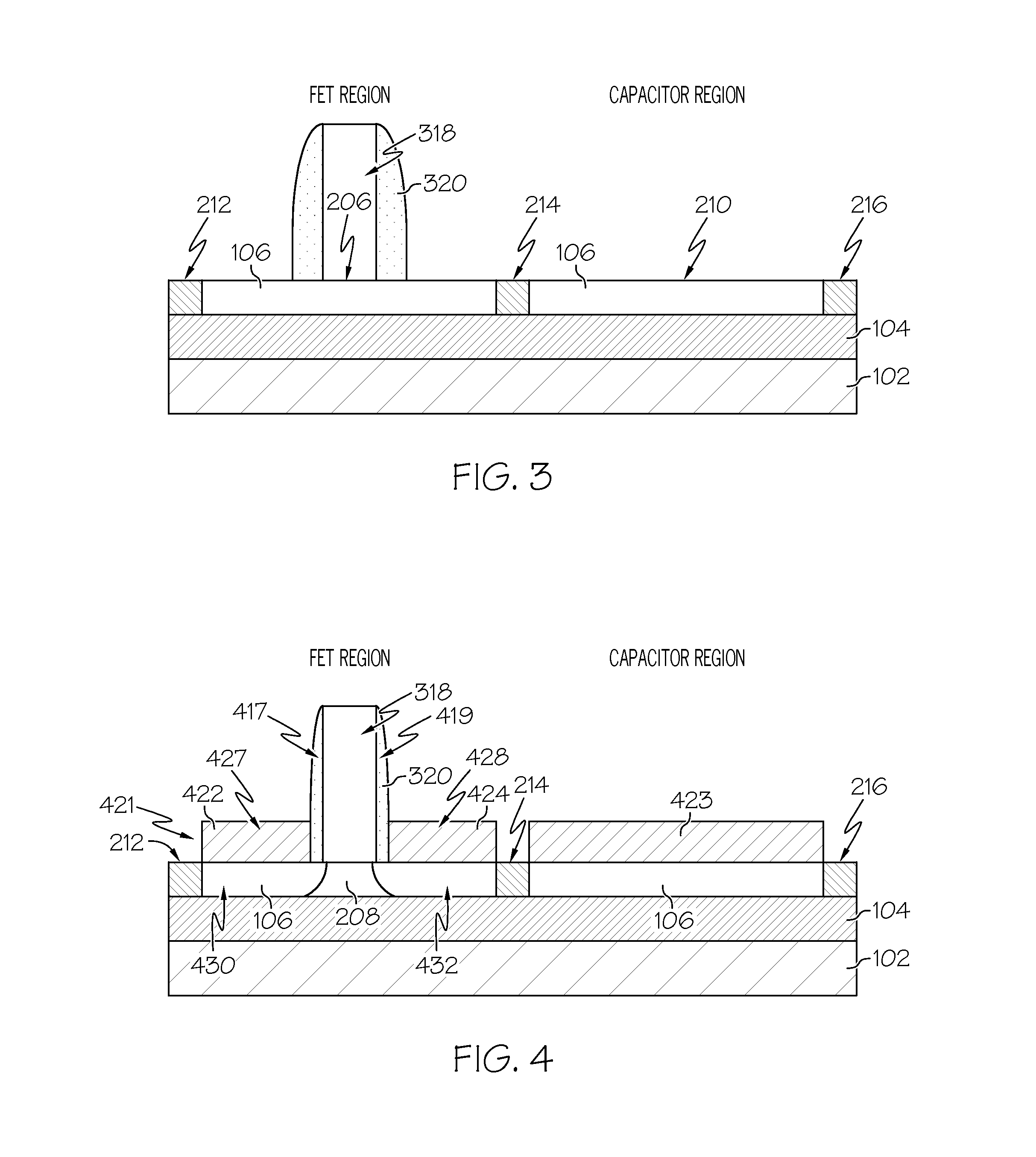
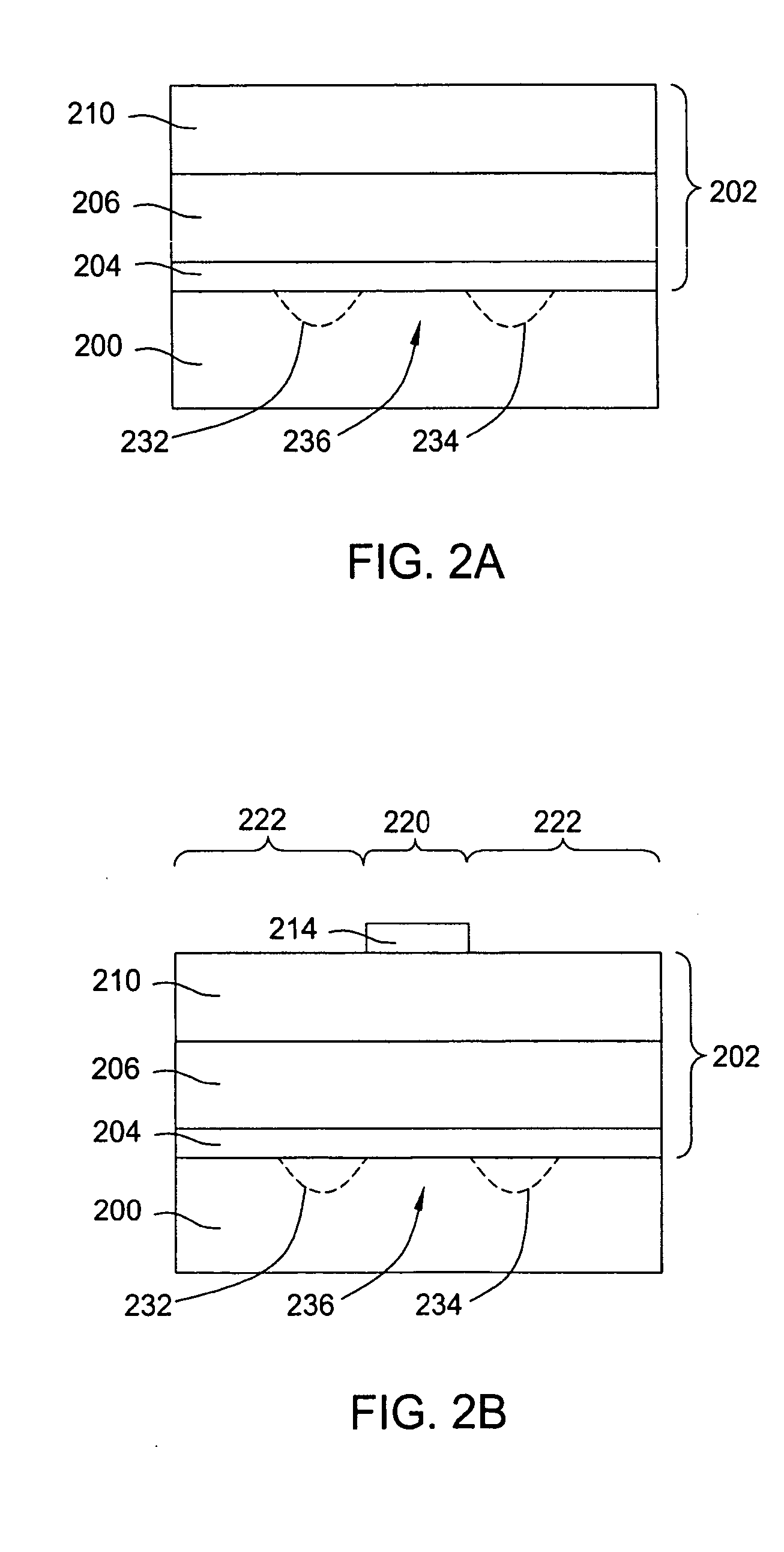
Integrated circuit with a thin body field effect transistor and capacitor
An integrated circuit includes a transistor and a capacitor. The transistor includes a first semiconductor layer and a gate stack located on the first semiconductor layer. The gate stack includes a metal layer and a first high-k dielectric layer. A gate spacer is located on sidewalls of the gate stack. The first high-k dielectric layer is located between the first semiconductor layer and the metal layer and between the gate spacer and sidewalls of the metal layer. A first silicide region is located on a first source / drain region. A second silicide region is located on a second source / drain region. The capacitor includes a first terminal that comprises a third silicide region located on a portion of the second semiconductor. A second high-k dielectric layer is located on the silicide region. A second terminal comprises a metal layer that is located on the second high-k dielectric layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Field effect transistors and materials and methods for their manufacture
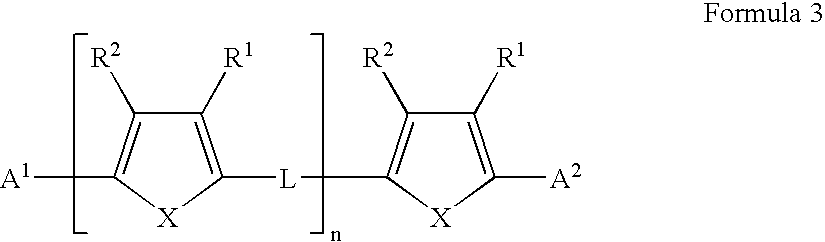
A field effect transistor in which a continuous semiconductor layer comprises:a) an organic semiconductor; and,b) an organic binder which has an inherent conductivity of less than 10−6Scm−1 and a permittivity at 1,000 Hz of less than 3.3and a process for its production comprising:coating a substrate with a liquid layer which comprises the organic semiconductor and a material capable of reacting to form the binder; and,converting the liquid layer to a solid layer comprising the semiconductor and the binder by reacting the material to form the binder.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, manufacturing method of field effect transistor using amorphous oxide film as channel layer, and manufacturing method of amorphous oxide film
An amorphous oxide containing hydrogen (or deuterium) is applied to a channel layer of a transistor. Accordingly, a thin film transistor having superior TFT properties can be realized, the superior TFT properties including a small hysteresis, normally OFF operation, a high ON / OFF ratio, a high saturated current, and the like. Furthermore, as a method for manufacturing a channel layer made of an amorphous oxide, film formation is performed in an atmosphere containing a hydrogen gas and an oxygen gas, so that the carrier concentration of the amorphous oxide can be controlled.
Owner:CANON KK
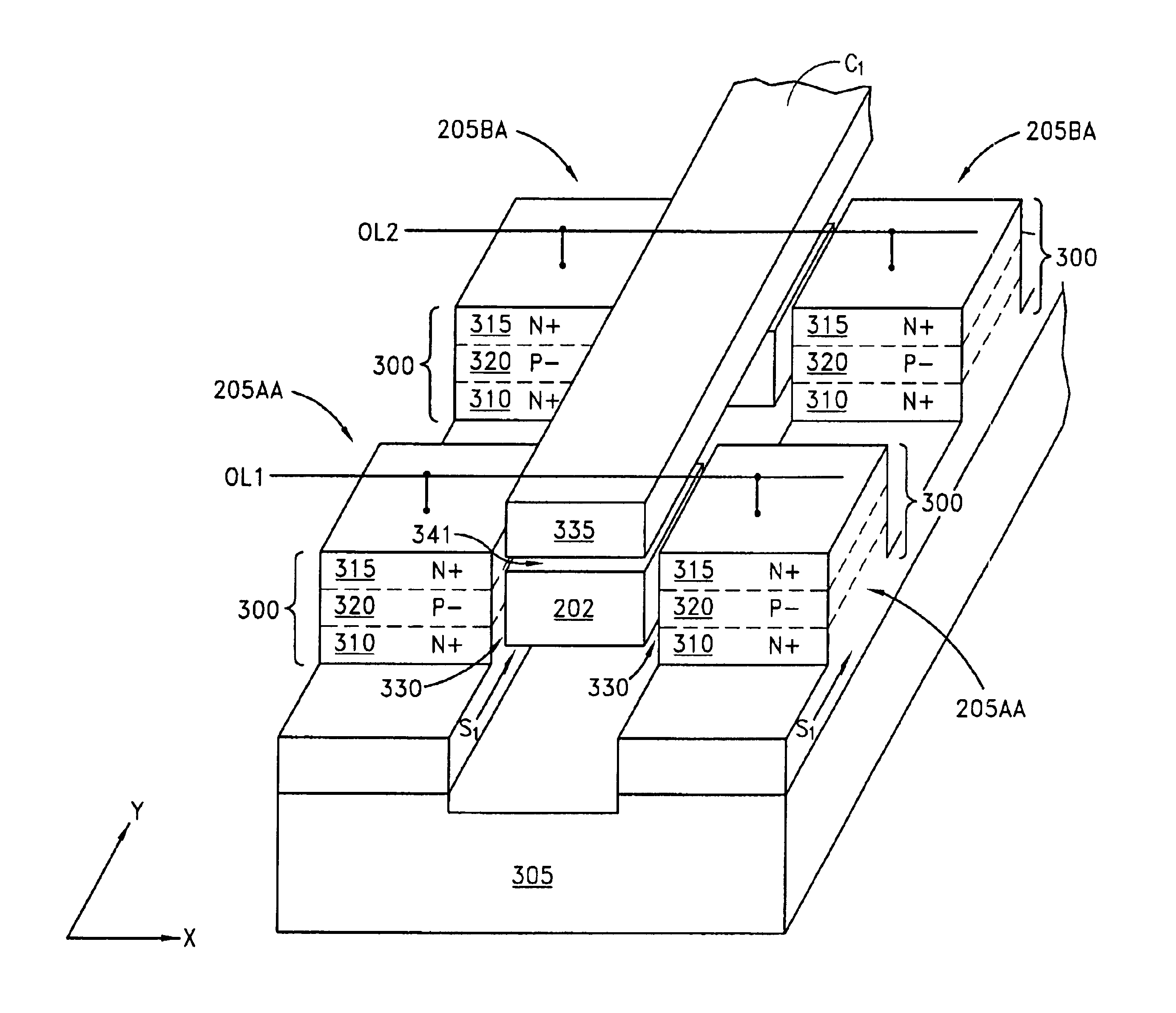
Floating gate transistor with horizontal gate layers stacked next to vertical body
Vertical body transistors with adjacent horizontal gate layers are used to form a memory array in a high density flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) or a logic array in a high density field programmable logic array (FPLA). The transistor is a field-effect transistor (FET) having an electrically isolated (floating) gate that controls electrical conduction between source regions and drain regions. If a particular floating gate is charged with stored electrons, then the transistor will not turn on and will provide an indication of the stored data at this location in the memory array within the EEPROM or will act as the absence of a transistor at this location in the logic array within the FPLA. The memory array or the logic array includes densely packed cells, each cell having a semiconductor pillar providing shared source and drain regions for two vertical body transistors that have control gates overlaying floating gates distributed on opposing sides of the semiconductor pillar. Both bulk semiconductor and silicon-on-insulator embodiments are provided. If a floating gate transistor is used to store a single bit of data or to represent a logic function, an area of only 2F<2 >is needed per respective bit of data or bit of logic, where F is the minimum lithographic feature size.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
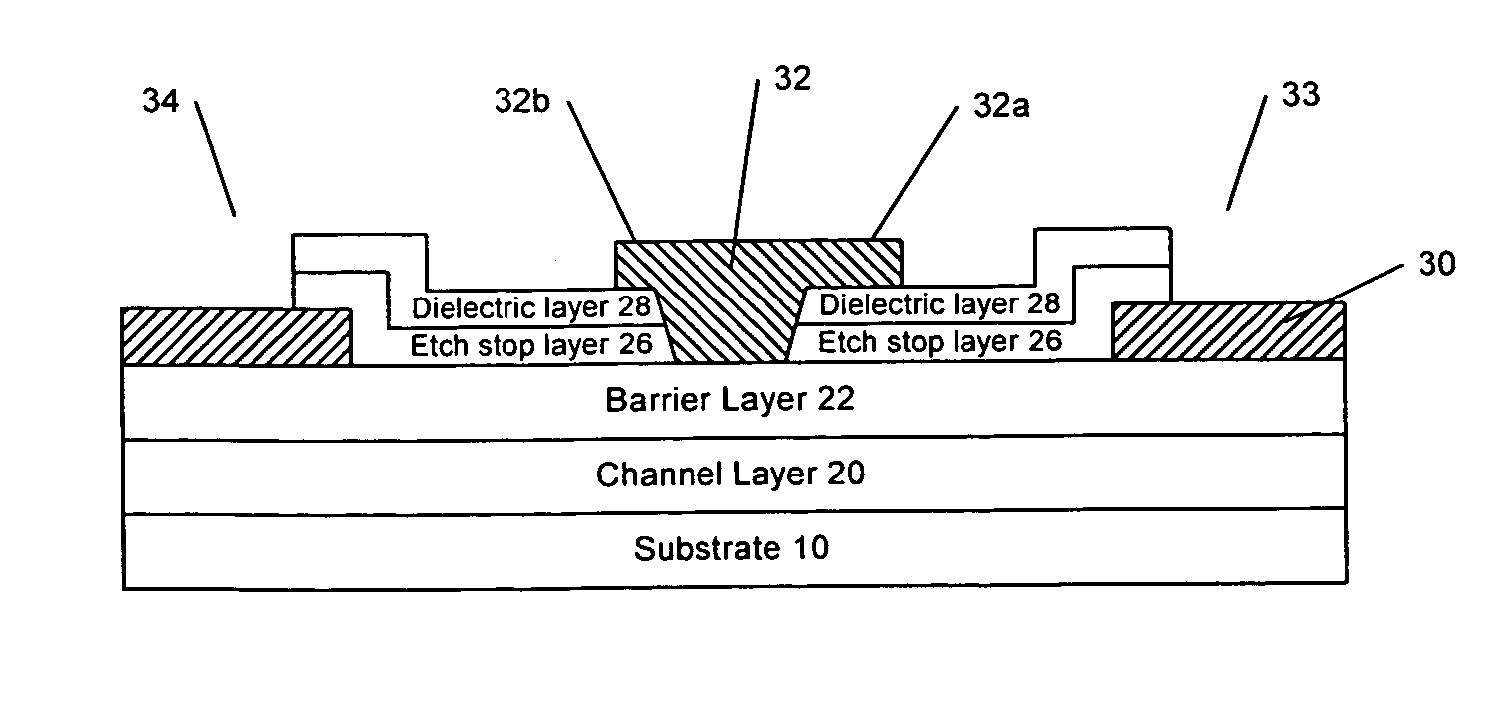
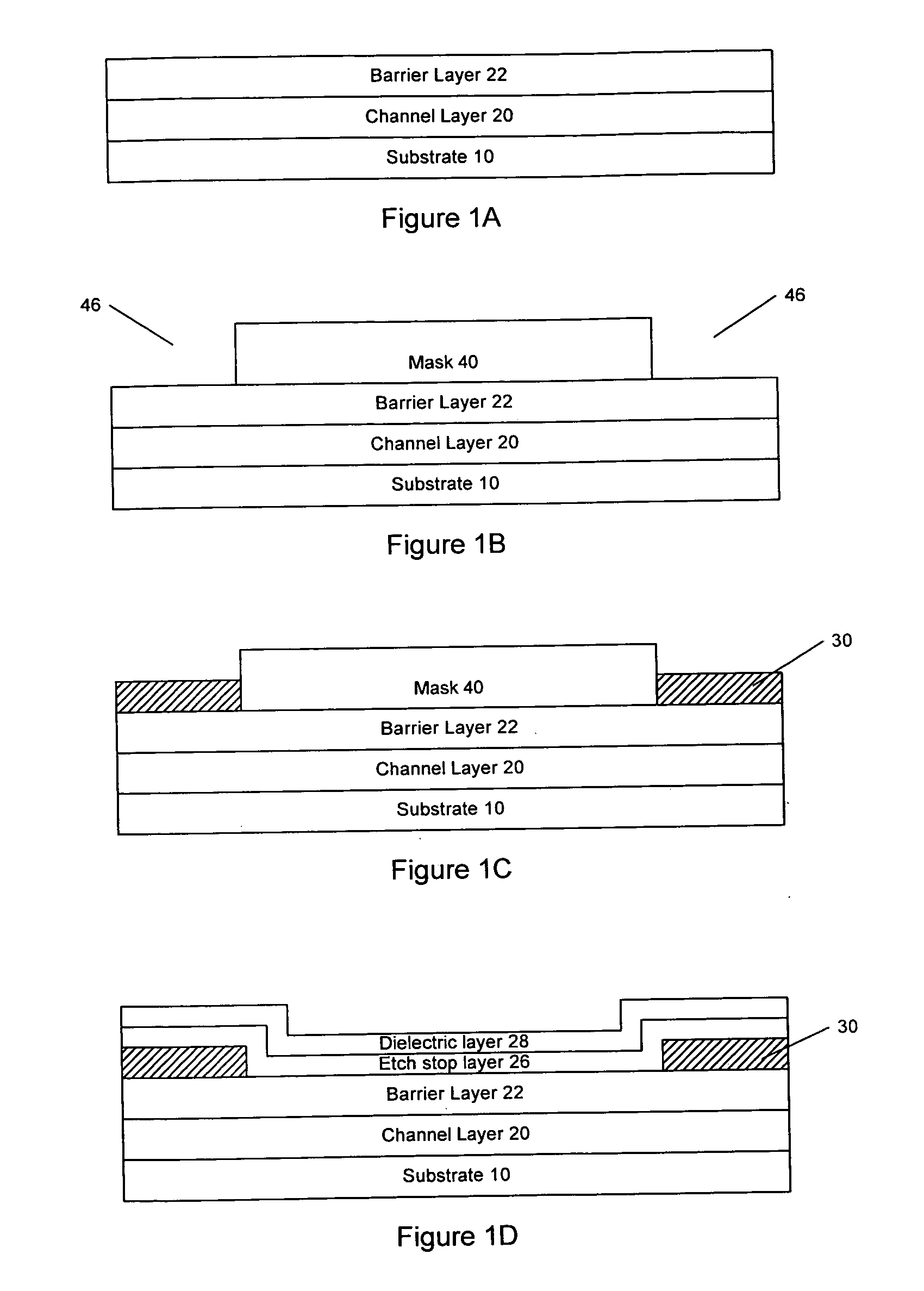
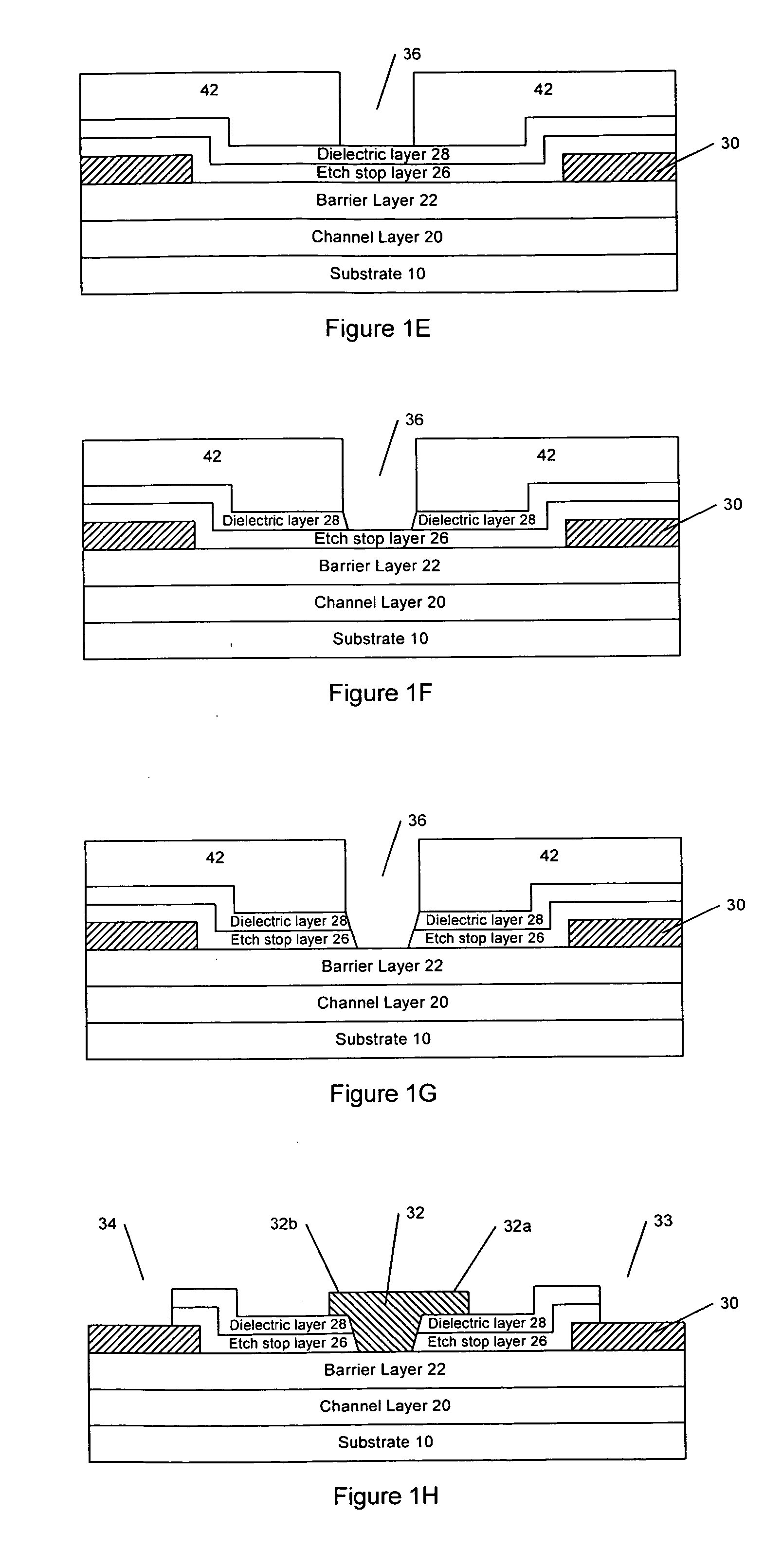
Nitride-based transistors and fabrication methods with an etch stop layer
InactiveUS20070018199A1Reduce harmSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField-effect transistor
A III-Nitride field-effect transistor, specifically a HEMT, comprises a channel layer, a barrier layer on the channel layer, an etch stop layer on the cap layer, a dielectric layer on the etch stop layer, a gate recess that extends to the barrier layer, and a gate contact in the gate recess. The etch stop layer may reduce damage associated with forming the recessed gate by not exposing the barrier layer to dry etching. The etch stop layer in the recess is removed and the remaining etch stop layer serves as a passivation layer.
Owner:CREE INC
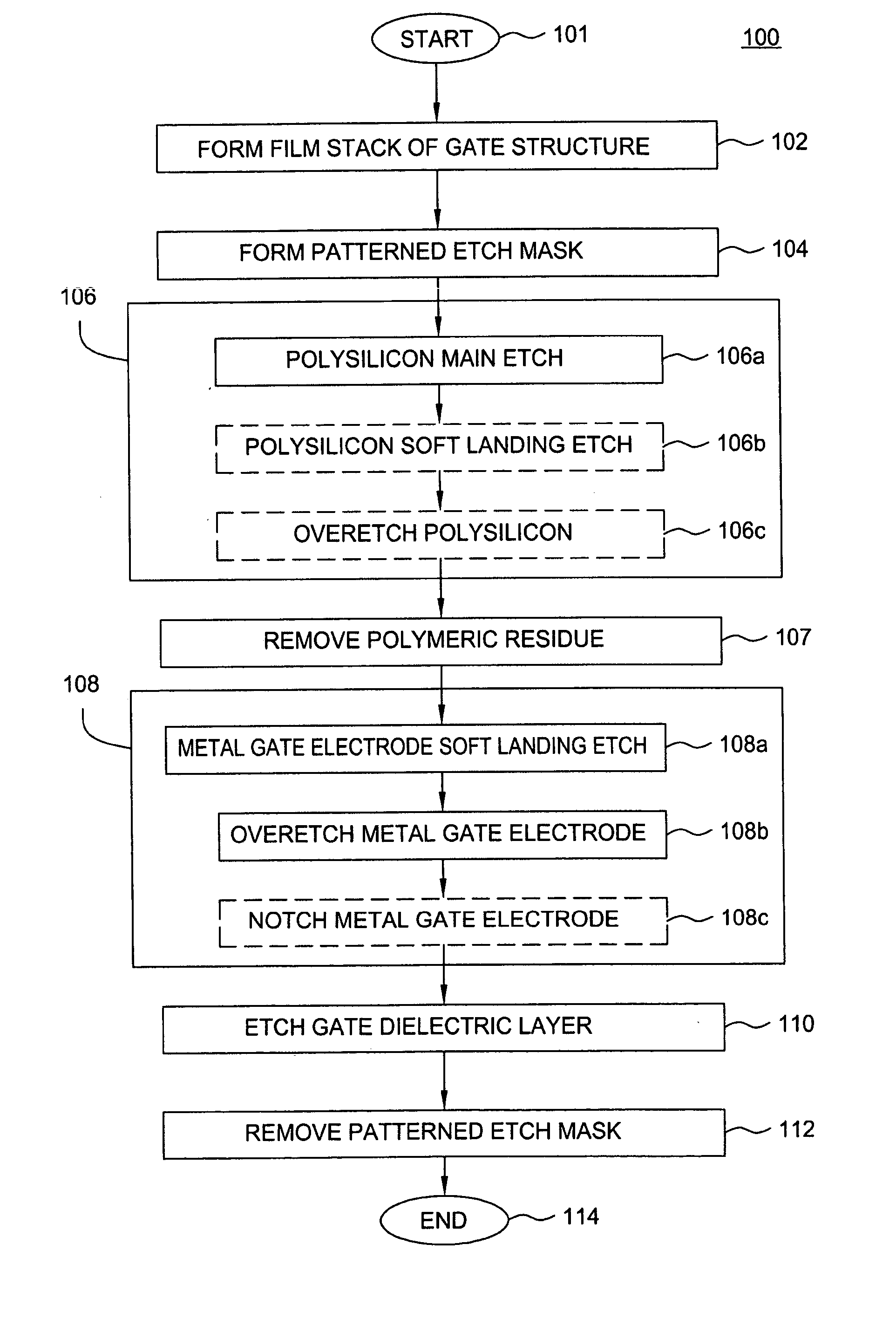
Method of fabricating a gate structure of a field effect transistor having a metal-containing gate electrode
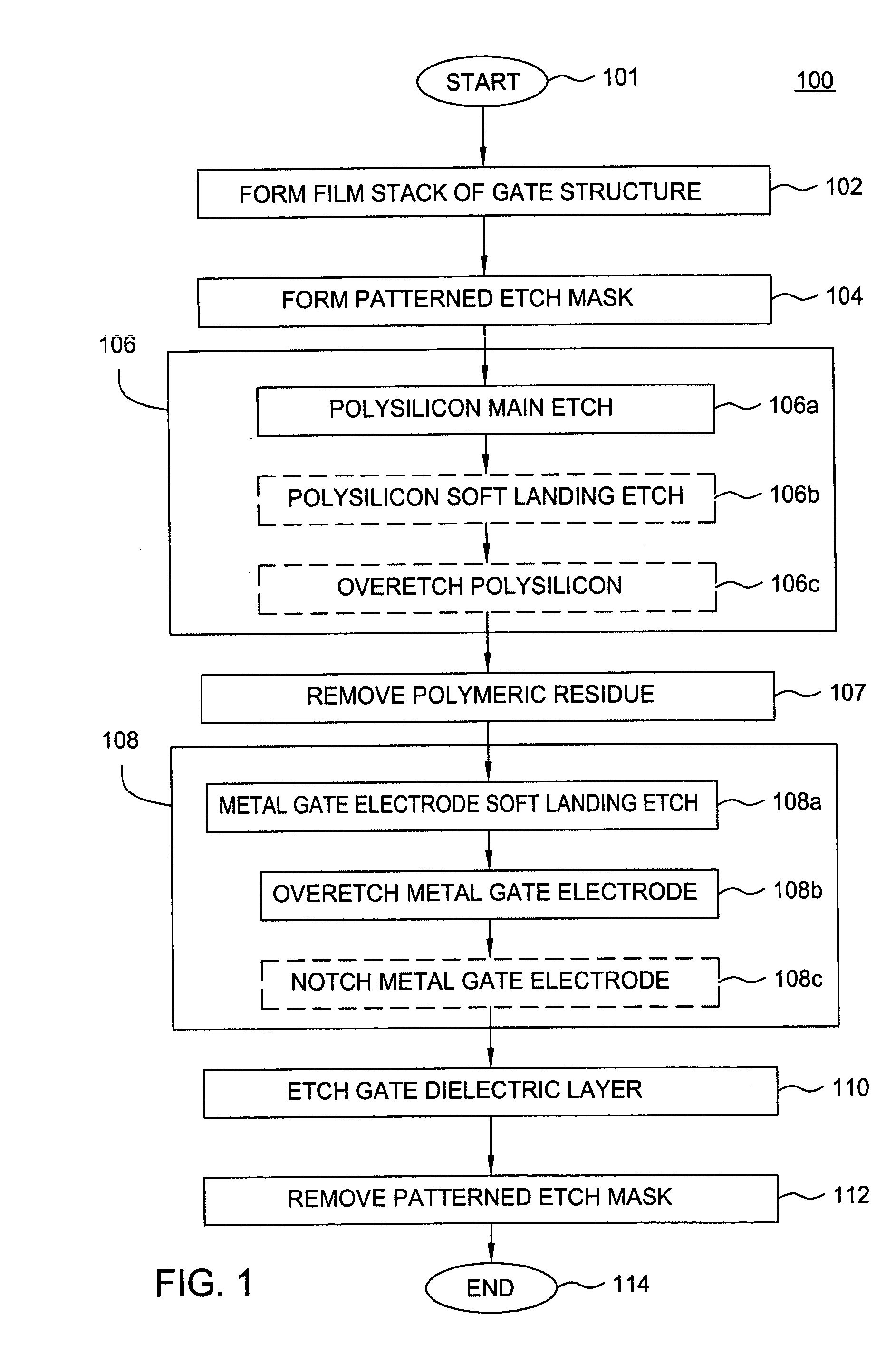
InactiveUS20050009358A1High selectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBromineTitanium nitride
A method of etching metals and / or metal-containing compounds using a plasma comprising a bromine-containing gas. In one embodiment, the method is used during fabrication of a gate structure of a field effect transistor having a titanium nitride gate electrode, an ultra-thin (about 10 to 20 Angstroms) silicon dioxide gate dielectric, and a polysilicon upper contact. In a further embodiment, the gate electrode is selectively notched to a pre-determined width.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
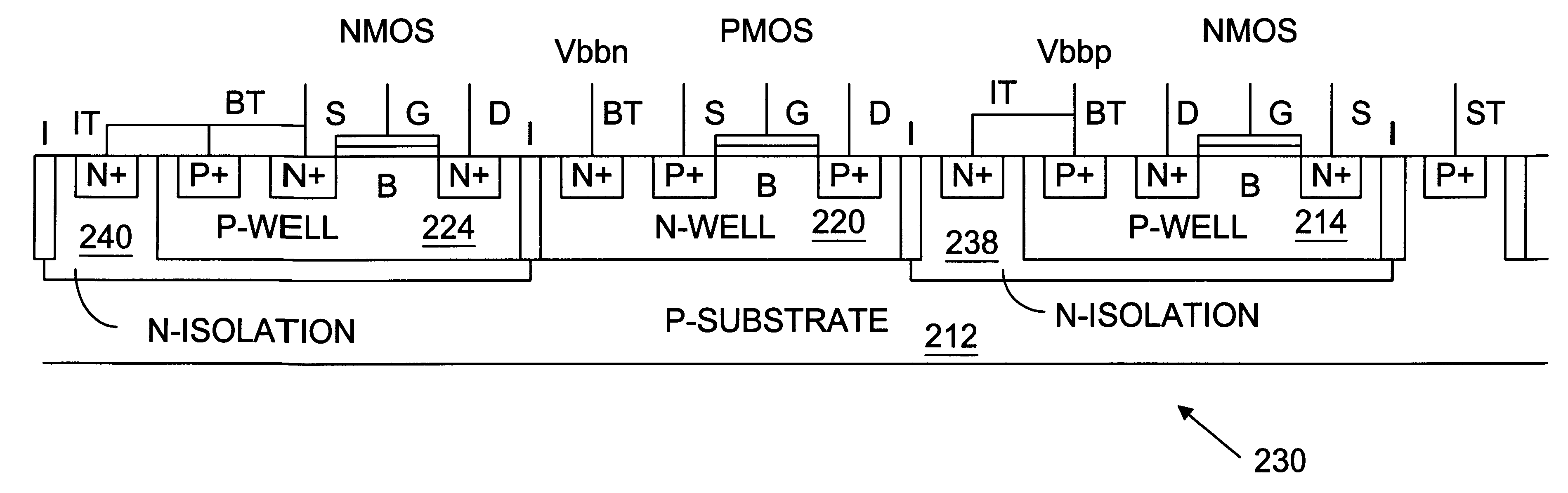
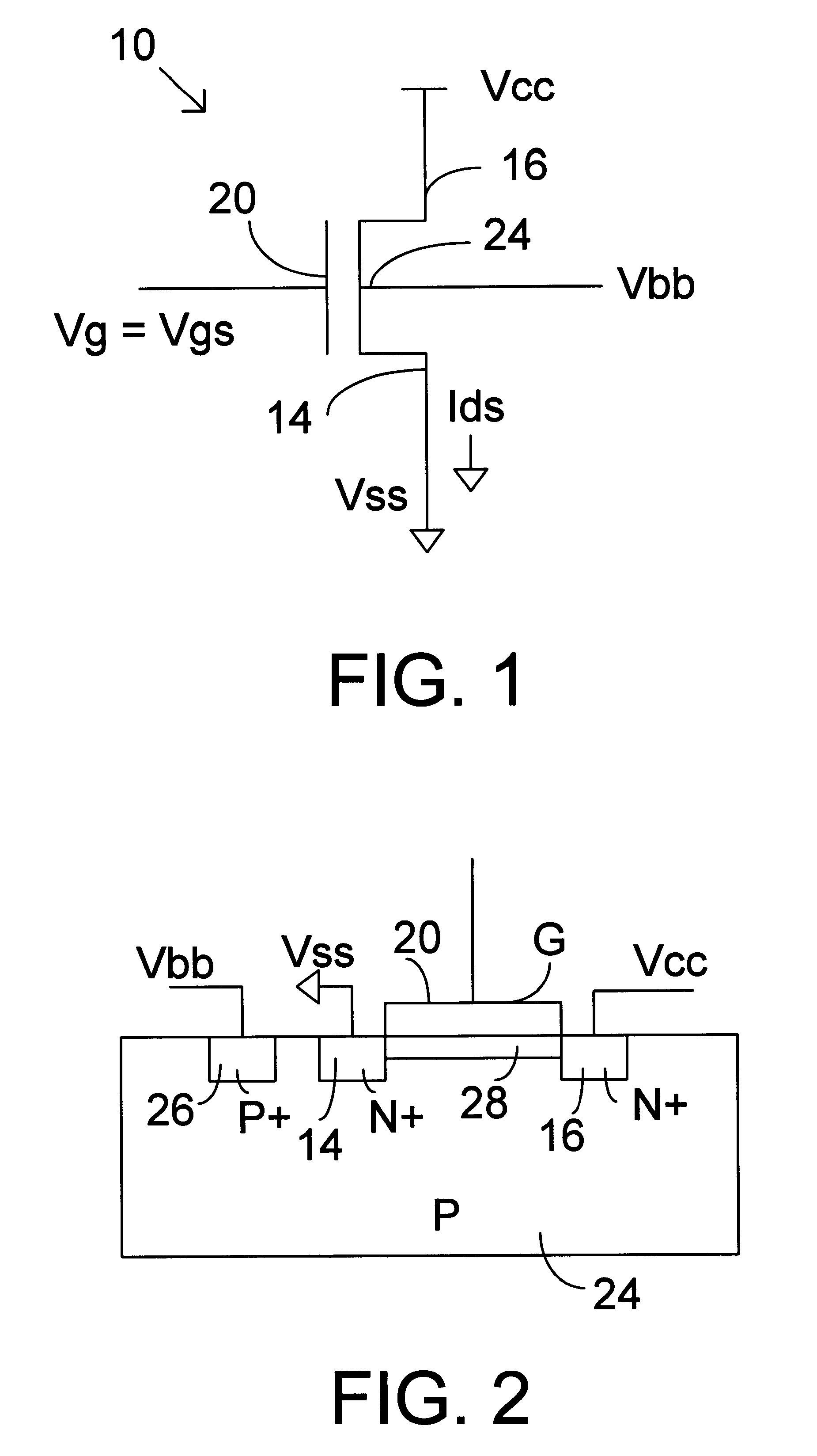
Multiple well transistor circuits having forward body bias
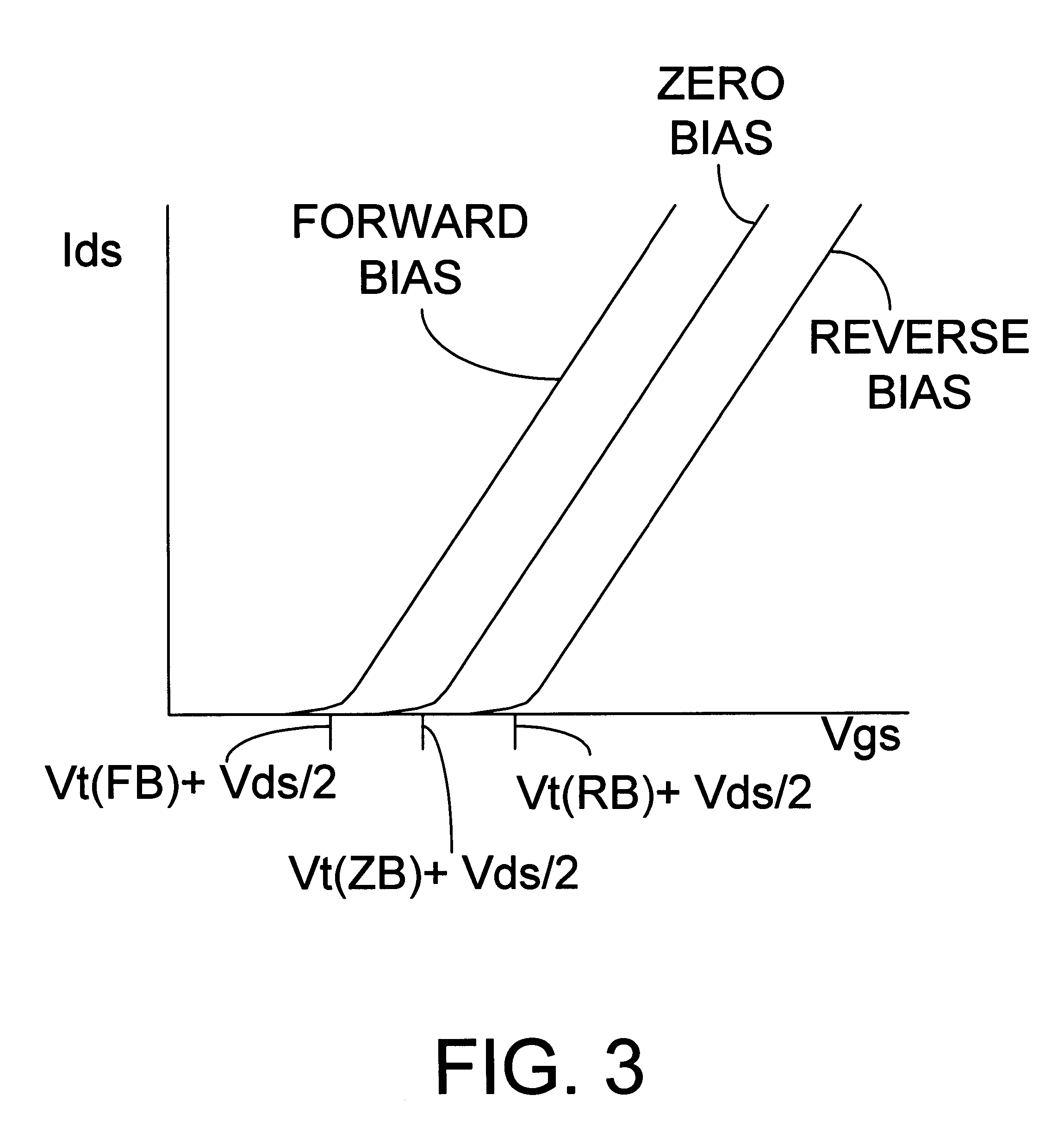
In one embodiment to the invention, a semiconductor circuit includes a substrate and a first well formed in the substrate. A first group of field effect transistors is formed in the first well and has a first body. The circuit includes a first body voltage to the first body to forward body bias the first group of field effect transistors. The circuit includes a first isolation structure to contain the first body voltage in the first well. In another embodiment, the circuit further includes a second group of field effect transistors having a non-forward body bias and the first isolation structure prevents the first body voltage from influencing a voltage of a body of the second group of field effect transistors. In yet another embodiment, a second isolation structure adjacent to the second well contain a second body voltage in a second well holding the second group of field effect transistors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Integrated circuit having multiple threshold voltages
In one aspect there is set forth herein an integrated circuit having a first plurality of field effect transistors and a second plurality of field effect transistor, wherein field effect transistors of the first plurality of field effect transistors each have a first gate stack and wherein field effect transistors of the second plurality of field effect transistors each have a second gate stack, the second gate stack being different from the first gate stack by having a metal layer common to the first gate stack and the second gate stack that includes a first thickness at the first gate stack and a second thickness at the second gate stack.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Integrated circuits with varying gate structures and fabrication methods
Integrated circuits and fabrication methods are provided. The integrated circuit includes: a varying gate structure disposed over a substrate structure, the varying gate structure including a first gate stack in a first region of the substrate structure, and a second gate stack in a second region of the substrate structure; a first field-effect transistor in the first region, the first field-effect transistor including the first gate stack and having a first threshold voltage; and a second field-effect transistor in the second region, the second field-effect transistor including the second gate stack and having a second threshold voltage, where the first threshold voltage is different from the second threshold voltage. The methods include providing the varying gate structure, the providing including: sizing layer(s) of the varying gate structure with different thickness(es) in different region(s).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
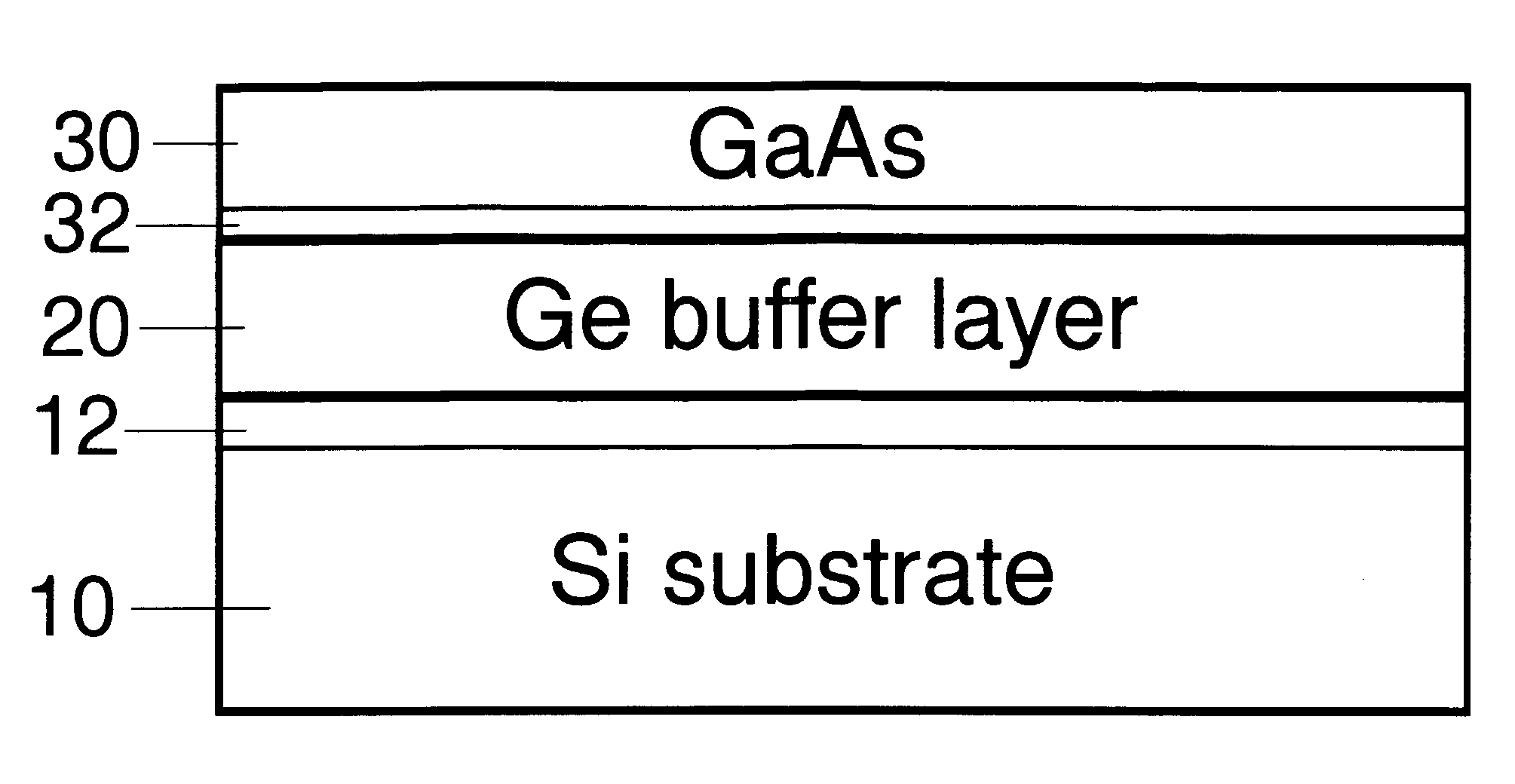
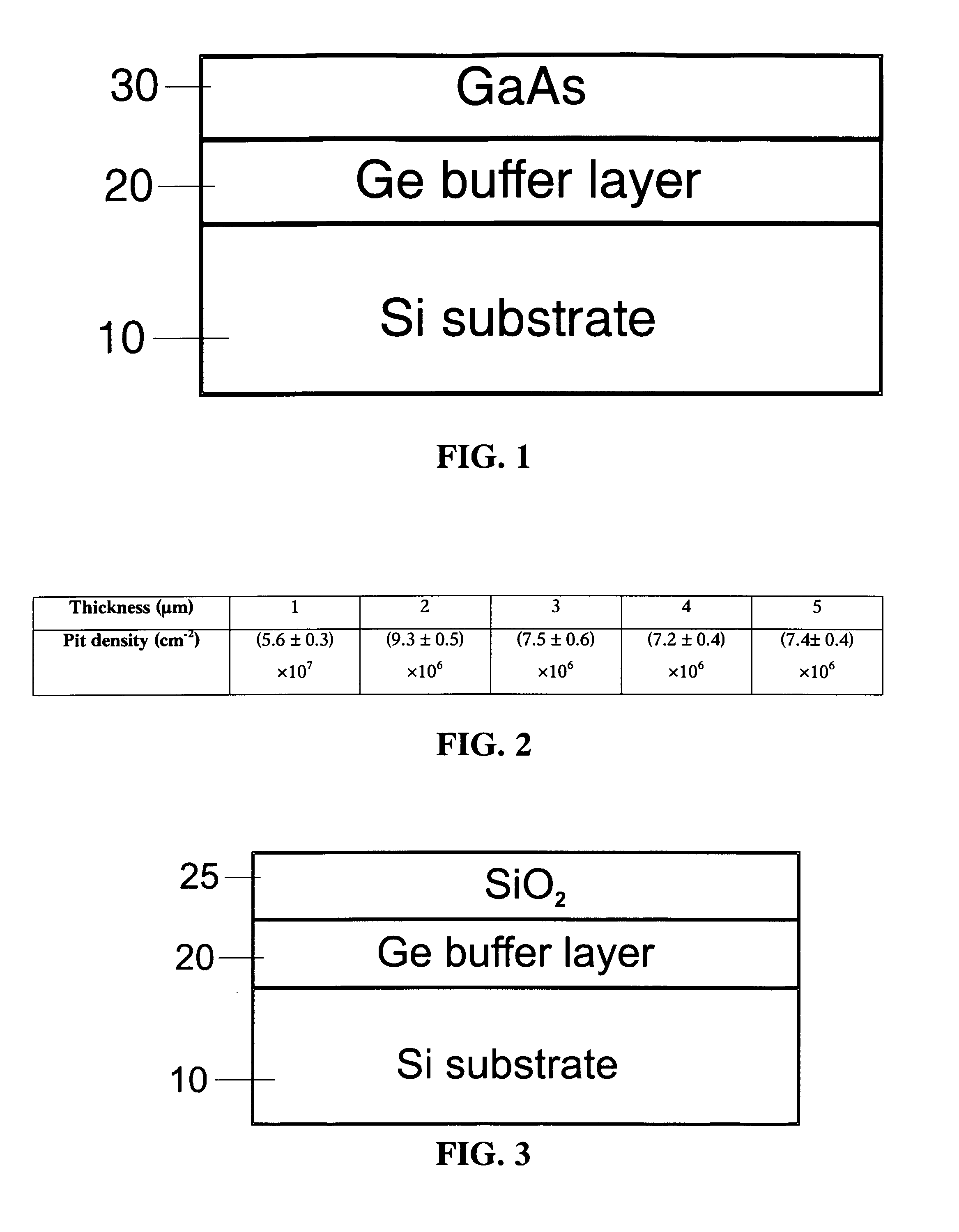
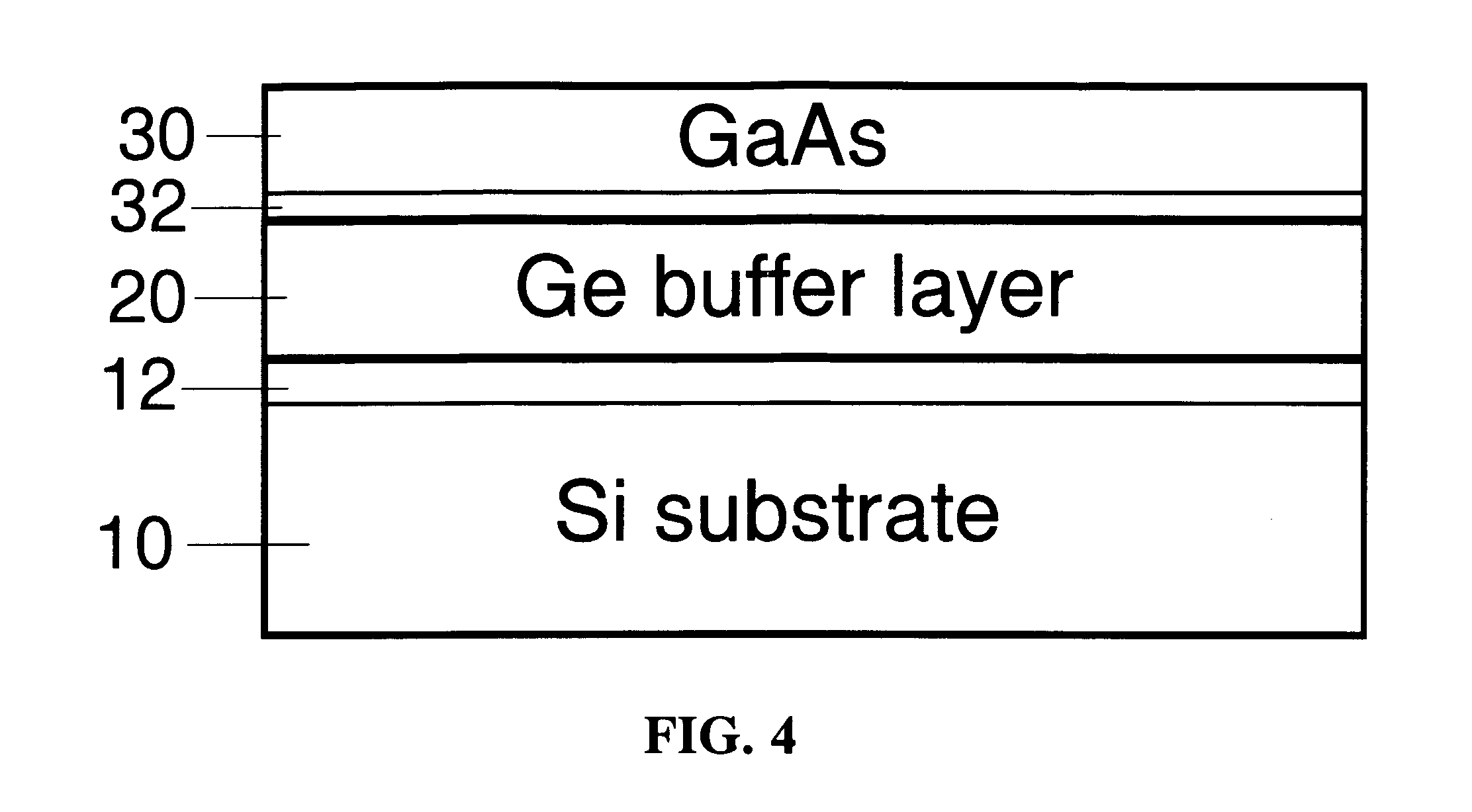
Method for Producing Virtual Ge Substrates for III/V-Integration on Si(001)
InactiveUS20070231488A1Fast epitaxial growthCheap methodSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSolar cell
Relaxed germanium buffer layers can be grown economically on misoriented silicon wafers by low-energy plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, in conjunction with thermal annealing and / or patterning, the buffer layers can serve as high-quality virtual substrates for the growth of crack-free GaAs layers suitable for high-efficiency solar cells, lasers and field effect transistors.
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com