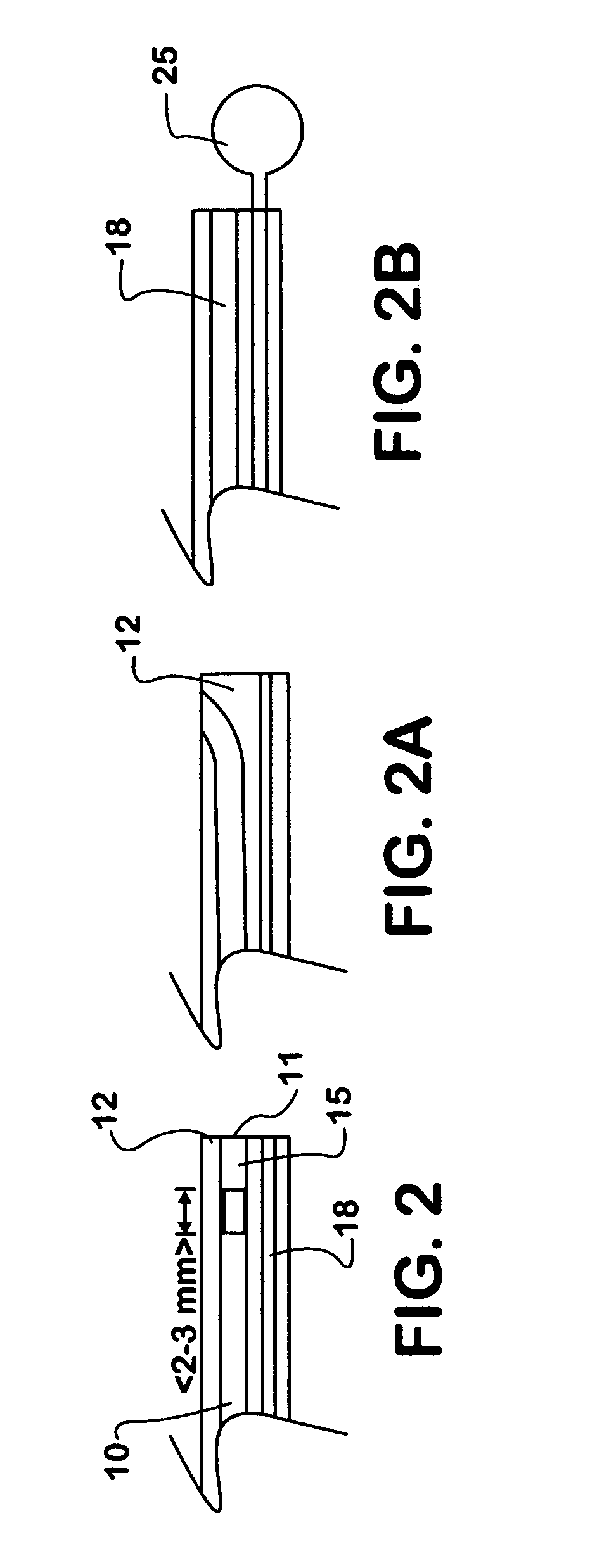
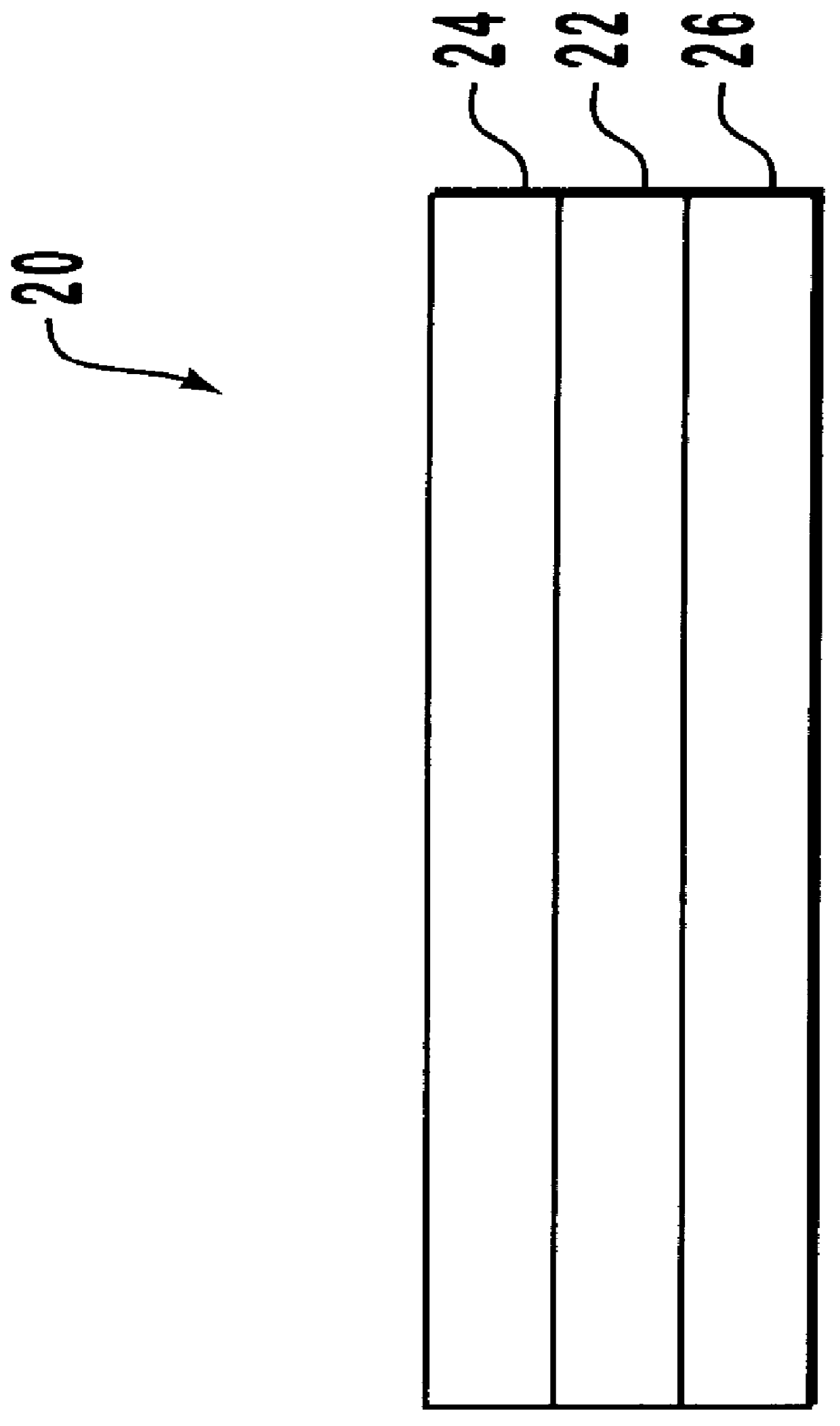
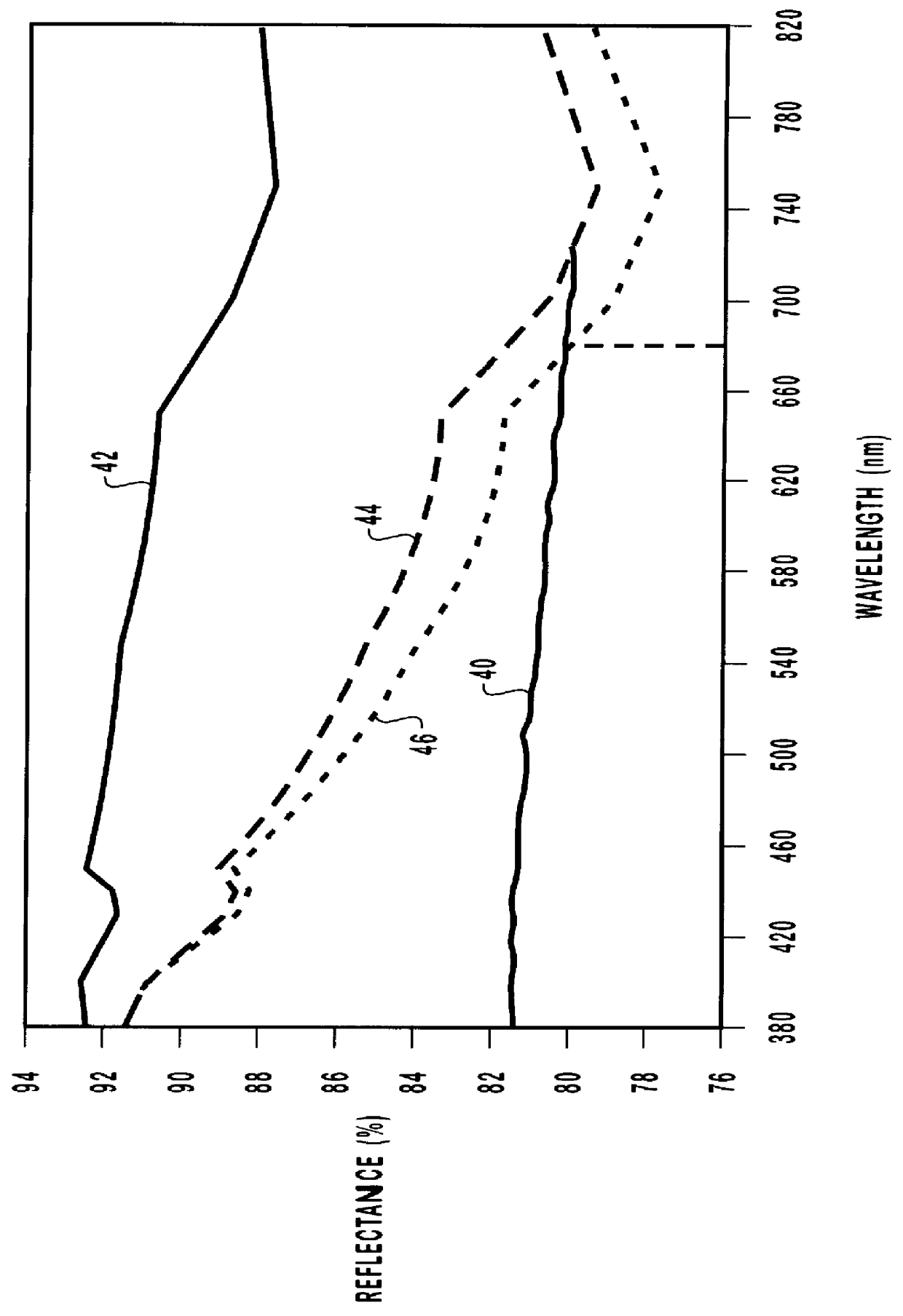
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9621 results about "Wavelength range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
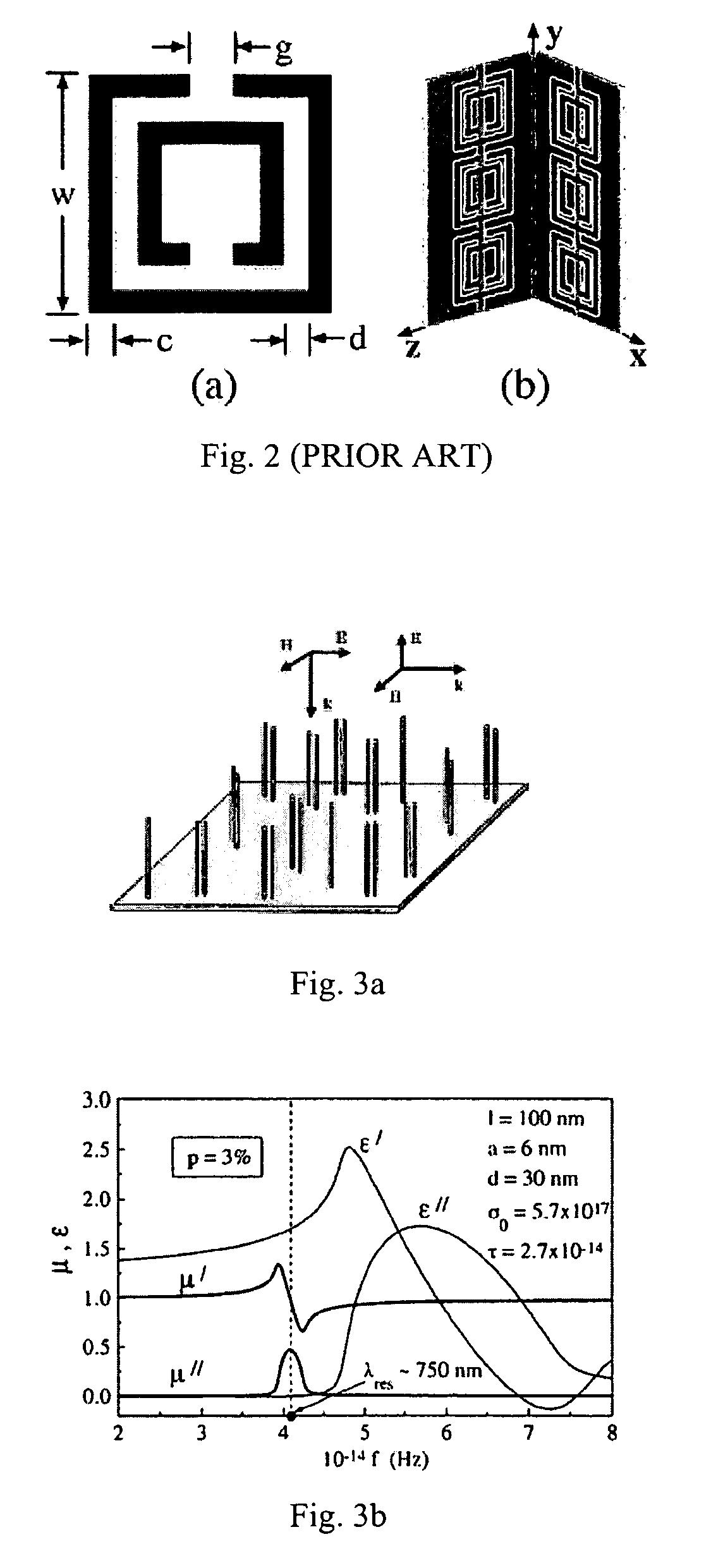
The wavelength range is from about 1 millimeter down to 750 nm. The range adjacent to the visible spectrum is called the "near infrared" and the longer wavelength part is called "far infrared".
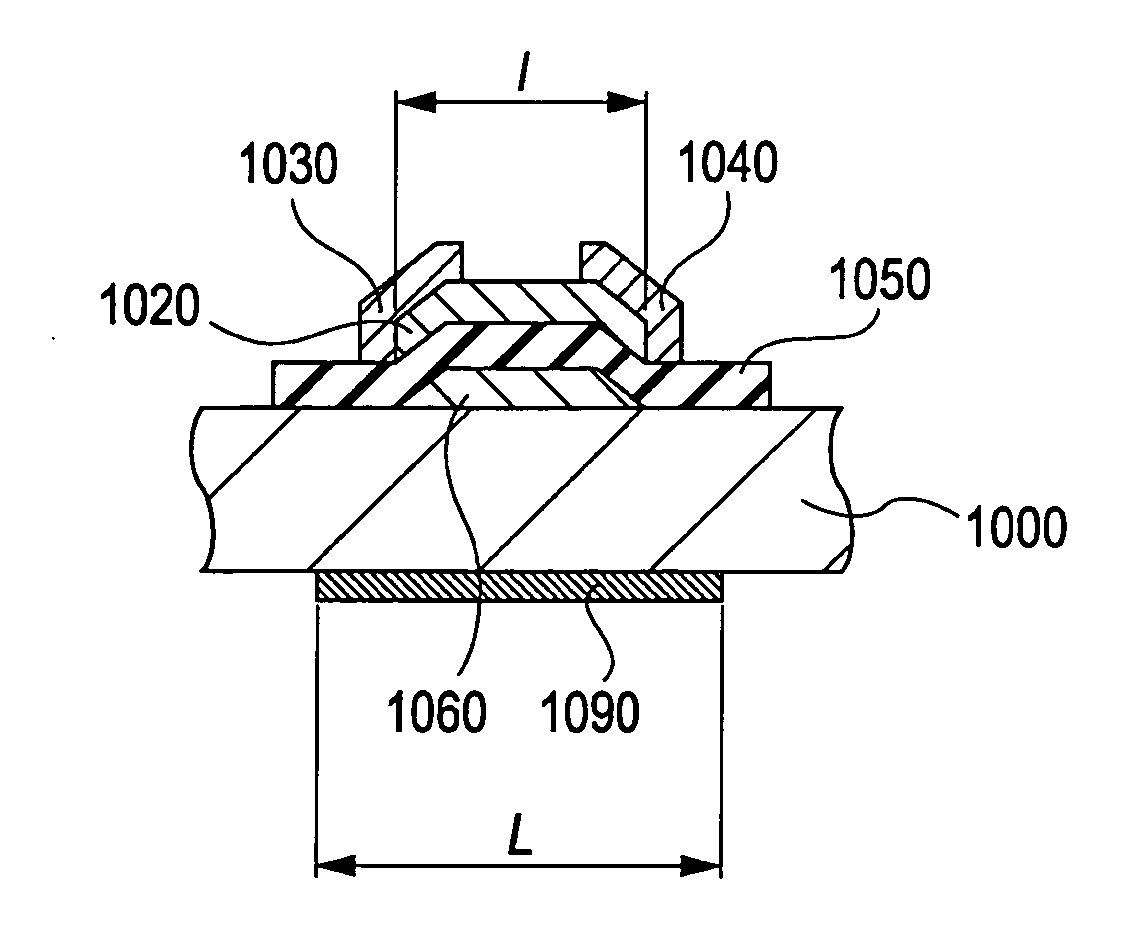
Field-effect transistor including transparent oxide and light-shielding member, and display utilizing the transistor
A field-effect transistor includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode, a gate-insulating film, and an active layer. The active layer contains an oxide having a transmittance of 70% or more in the wavelength range of 400 to 800 nm. A light-shielding member is provided as a light-shielding structure for the active layer, for example, on the bottom face of the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
UV-Curing Apparatus Provided With Wavelength-Tuned Excimer Lamp and Method of Processing Semiconductor Substrate Using Same
InactiveUS20140099798A1Prevents unnecessary riseLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceUltraviolet
A UV irradiation apparatus for processing a semiconductor substrate includes: a UV lamp unit having at least one dielectric barrier discharge excimer lamp which is constituted by a luminous tube containing a rare gas wherein an inner surface of the luminous tube is coated with a fluorescent substance having a peak emission spectrum in a wavelength range of 190 nm to 350 nm; and a reaction chamber disposed under the UV lamp unit and connected thereto via a transmission window.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Fiber optic illumination and detection patterns, shapes, and locations for use in spectroscopic analysis
InactiveUS6411373B1Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberMonochromator
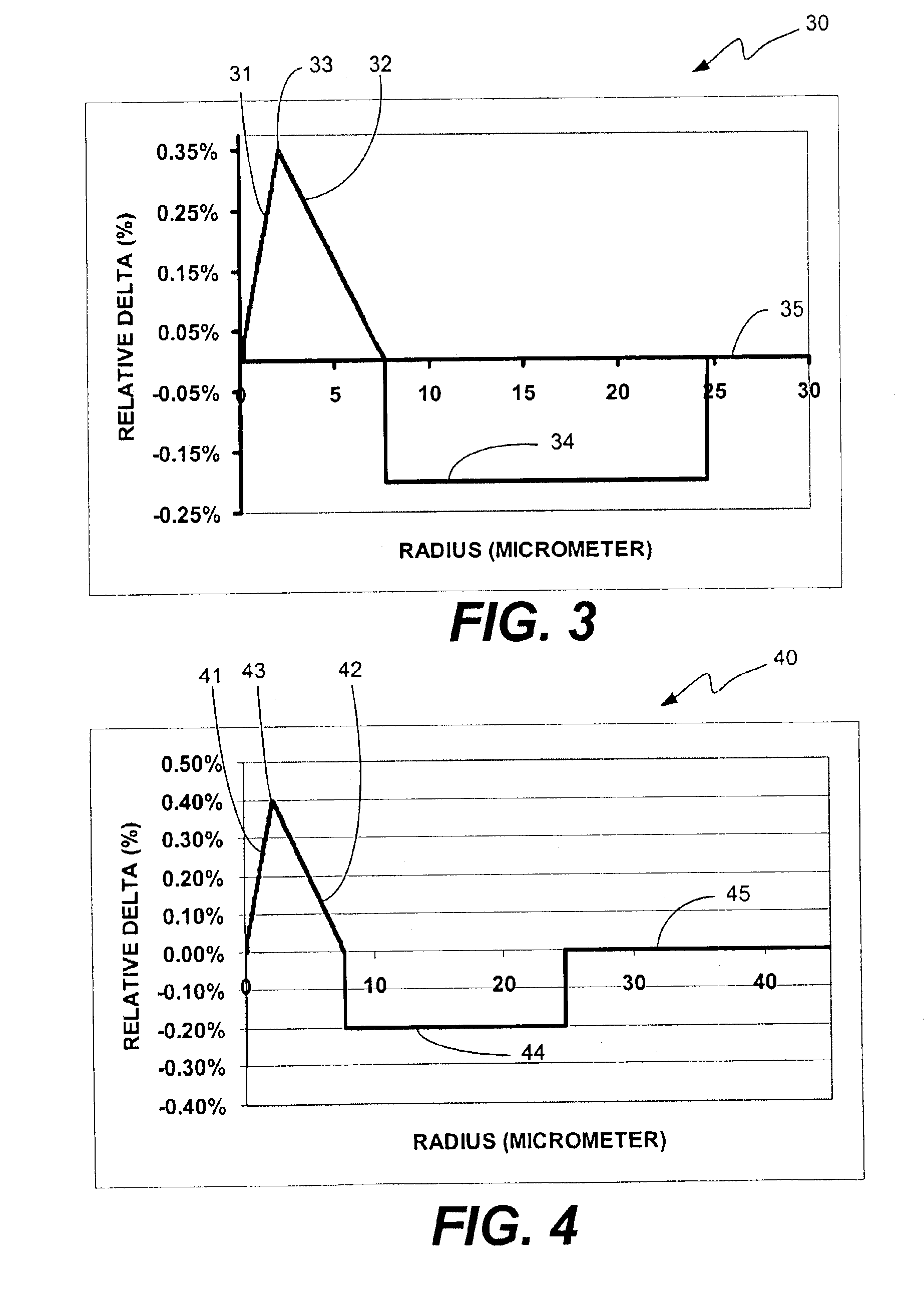
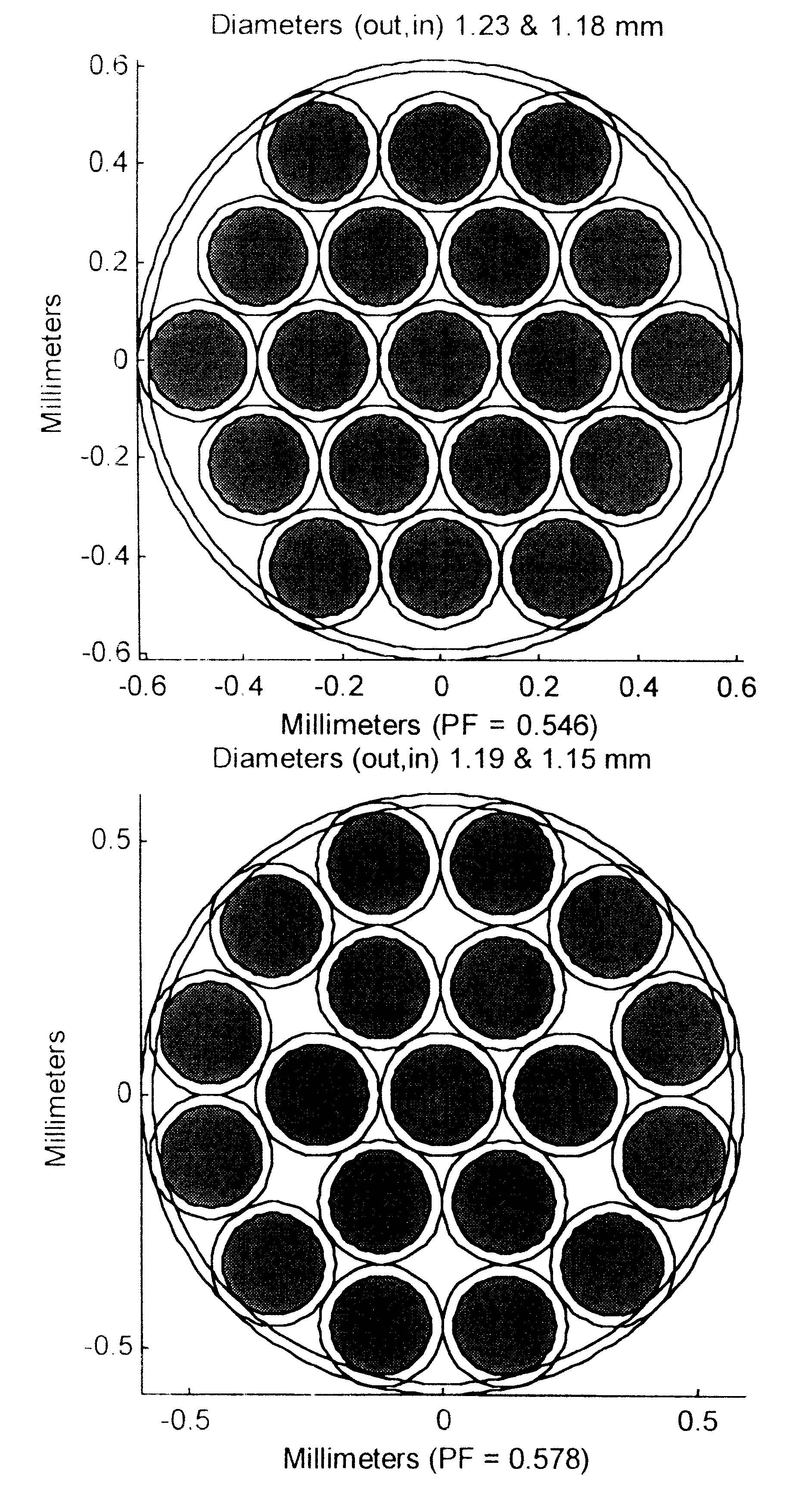
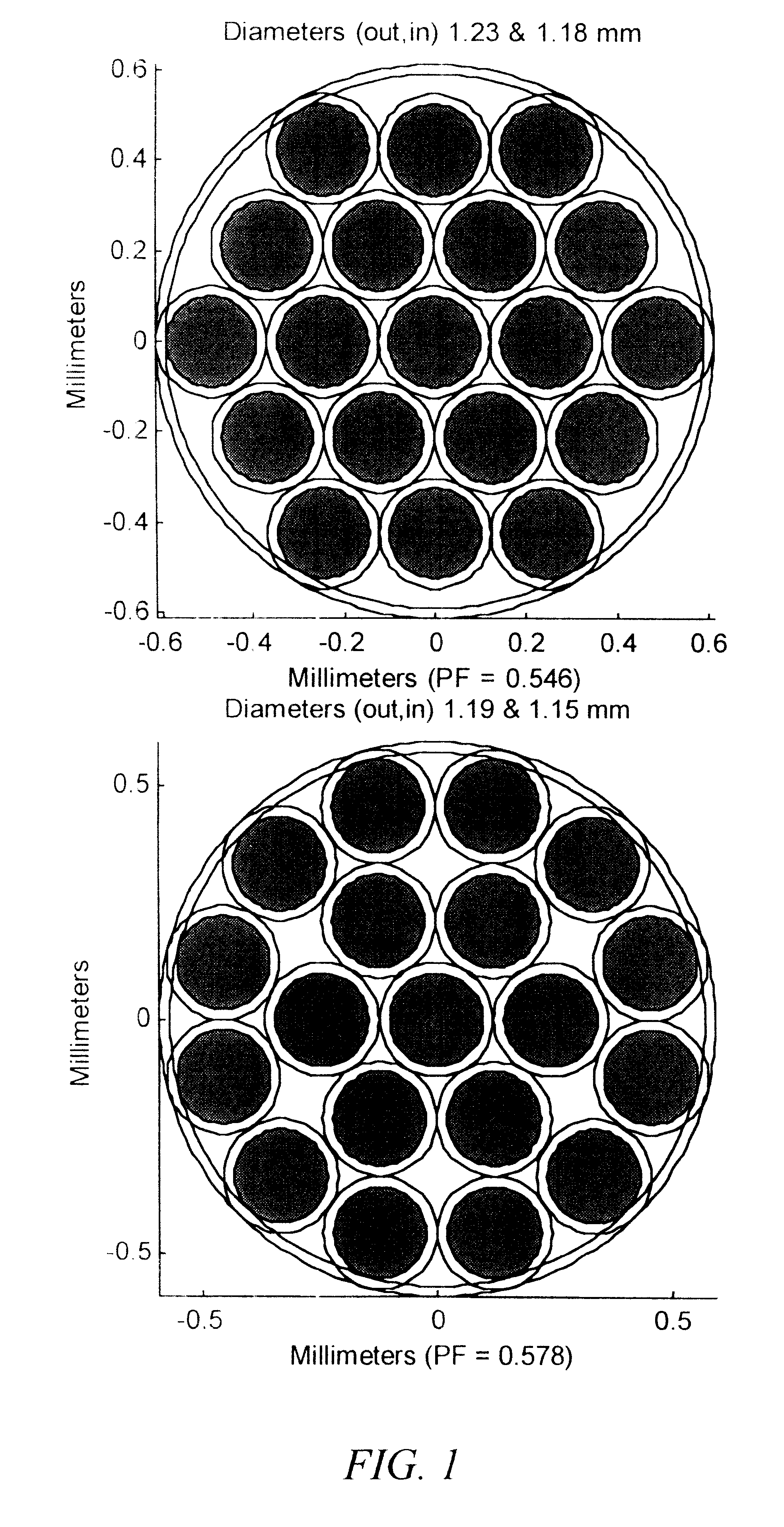
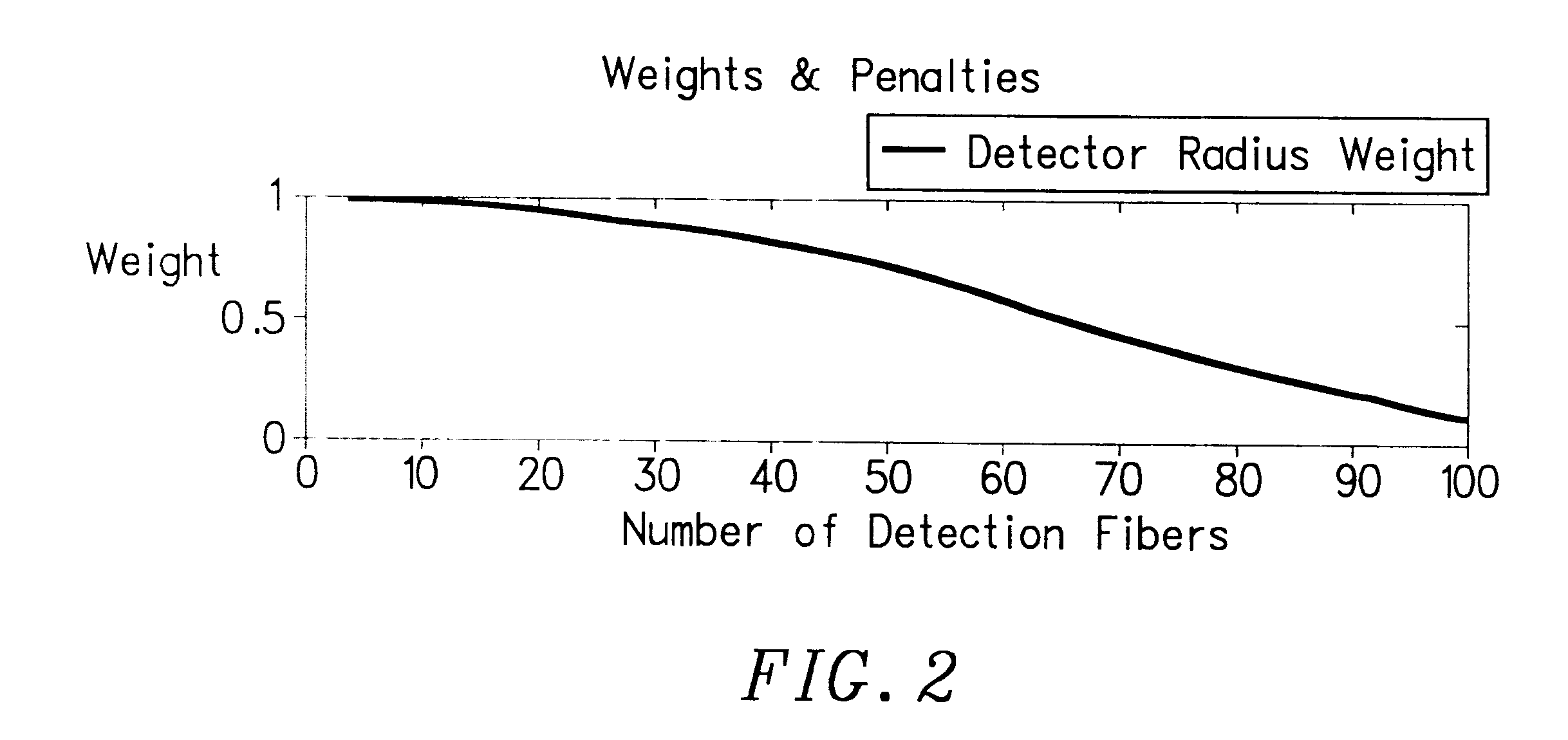
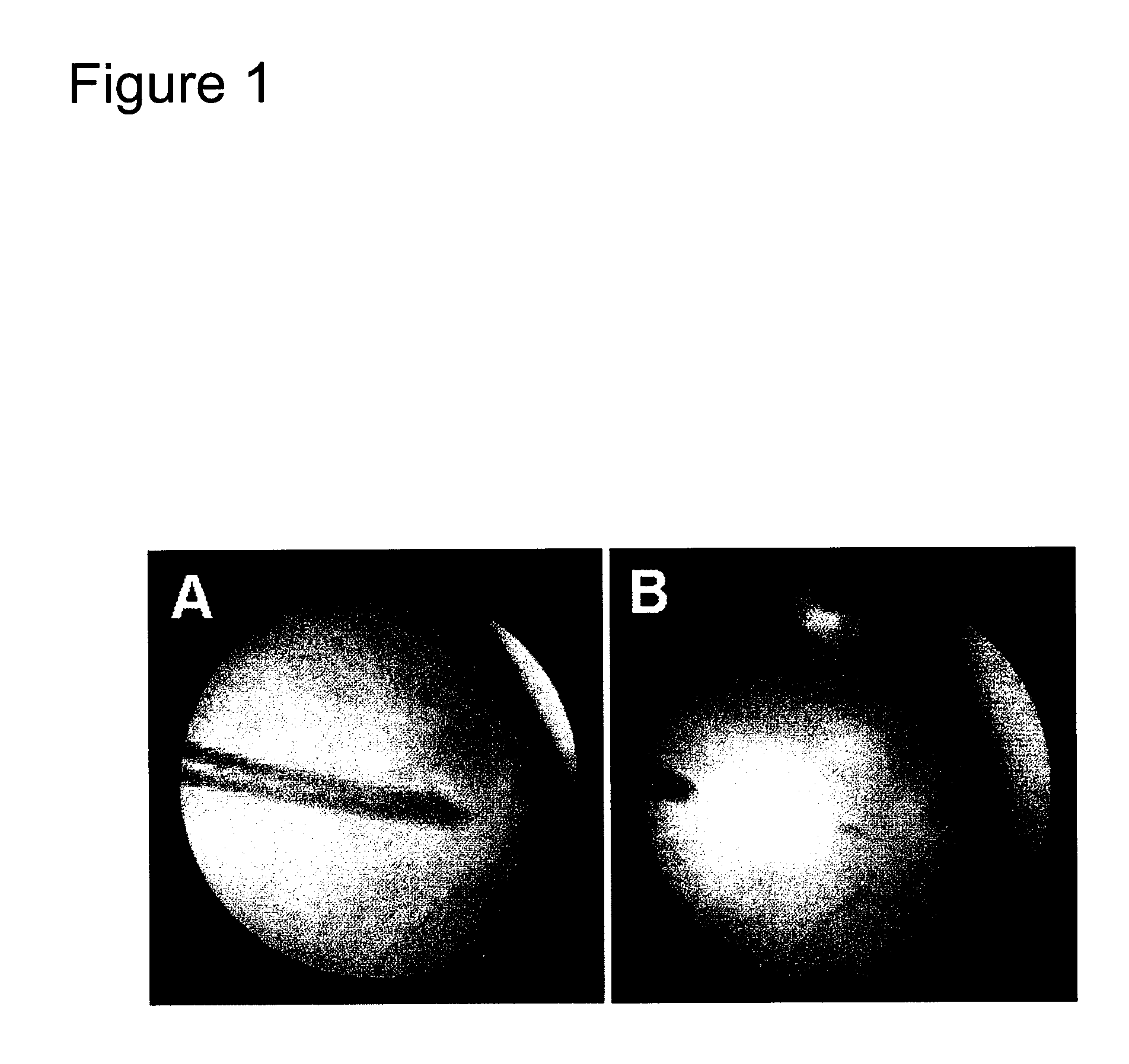
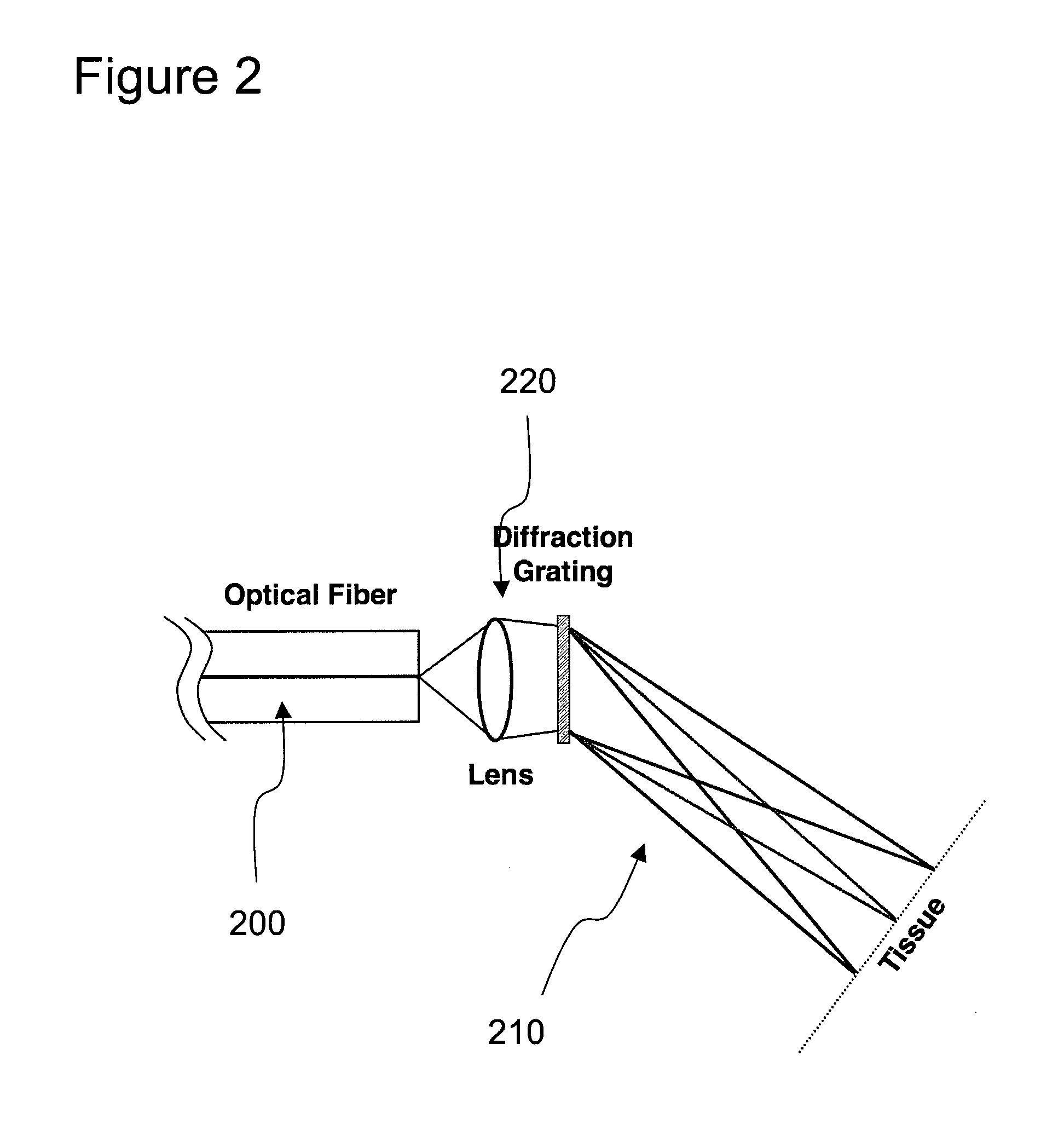
The invention provides a design process that is used in the determination of the pattern of detector and illumination optical fibers at the sampling area of a subject. Information about the system, specifically a monochromator (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at an output slit) and the bundle termination at a detector optics stack (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at the bundle termination), is of critical importance to this design. It is those numbers that determine the ratio and number of illumination to detection fibers, significantly limiting and constraining the solution space. Additional information about the estimated signal and noise in the skin is necessary to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the wavelength range of interest. Constraining the fibers to a hexagonal perimeter and prescribing a hex-packed pattern, such that alternating columns contain illumination and detection fibers, yields optimal results. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, two detectors share the totality of the detection fibers at the sampling interface. A third group of detection fibers is used for classification purposes.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
High stability optical encapsulation and packaging for light-emitting diodes in the green, blue, and near UV range
InactiveUS6204523B1Advantageously stable optical transmission propertyGreat freedomDischarge tube luminescnet screensSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
An LED component is provided, with light emission in the green-to-near UV wavelength range. The light-emitting semiconductor die is encapsulated with one or more silicone compounds, including a hard outer shell, an interior gel or resilient layer, or both. The silicone material is stable over temperature and humidity ranges, and over exposure to ambient UV radiation. As a consequence, the LED component has an advantageously long lifetime, in which it is free of "yellowing" attenuation which would reduce the green-to-near UV light output.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Materials, components, and methods for use with extreme ultraviolet radiation in lithography and other applications
ActiveUS20160085003A1Improve reflectivitySpread the wordMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhotonicsUltraviolet
Nanostructured photonic materials, and associated components for use in devices and systems operating at ultraviolet (UV), extreme ultraviolet (EUV), and / or soft Xray wavelengths are described. Such a material may be fabricated with nanoscale features tailored for a selected wavelength range, such as at particular UV, EUV, or soft Xray wavelengths or wavelength ranges. Such a material may be used to make components such as mirrors, lenses or other optics, panels, lightsources, masks, photoresists, or other components for use in applications such as lithography, wafer patterning, astronomical and space applications, biomedical applications, biotech or other applications.
Owner:JAISWAL SUPRIYA
White light emitting device comprising a plurality of light emitting diodes with different peak emission wavelengths and a wavelength converter
ActiveUS8071988B2Improve emission efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEffect lightUltraviolet
Disclosed herein is a light emitting device including one or more light emitting diodes to primarily emit light having different wavelengths in the wavelength range of ultraviolet rays and / or blue light, and a wavelength-conversion means to convert the primary light into secondary light in the visible light wavelength range. The light emitting device of the current invention has a high color temperature of 2000 to 8000 K or 10000 K and a high color rendering index of 90 or more, thus easily realizing desired emission on the color coordinate system. Therefore, the lighting emitting device is applicable to mobile phones, notebook computers, and keypads or backlight units for various electronic products, and, in particular, automobiles and exterior and interior lighting fixtures.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Illumination systems utilizing multiple wavelength light recycling
An illumination system has a light source and a wavelength conversion layer within a light-recycling envelope. The light source is a light-emitting diode or a semiconductor laser. The light source will emit light of a first wavelength range that is transmitted through the wavelength conversion layer in order to convert a portion of the light of a first wavelength range into light of a second wavelength range. Light of both the first and second wavelength ranges will exit the light-recycling envelope through an aperture. The recycling of the light by the light-recycling envelope will enhance the output radiance and luminance of the light exiting the illumination system.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Plasma etching method and apparatus therefor
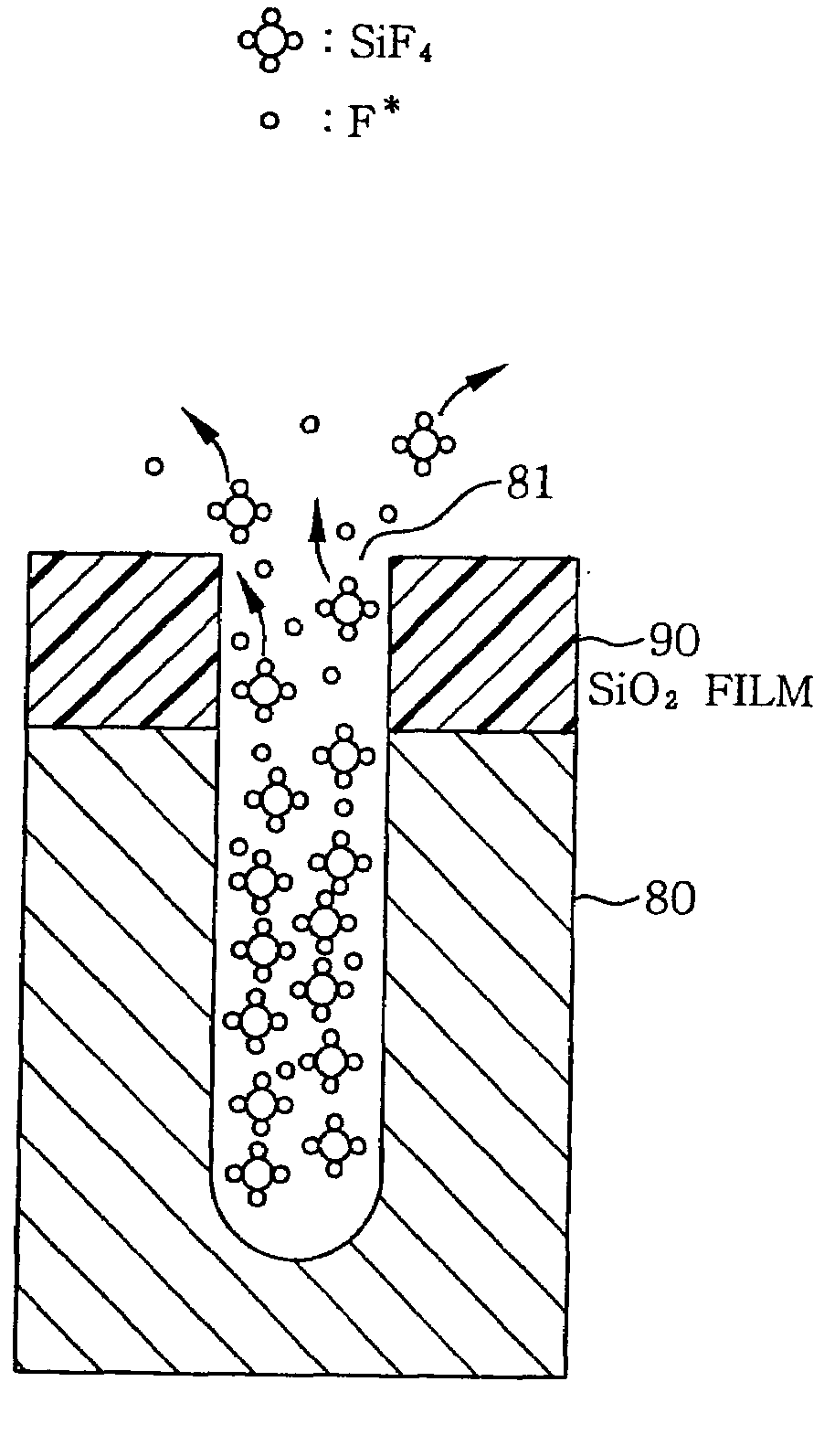
InactiveUS20090045167A1Increase chanceIncrease etch rateElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsPeak intensityFluorine containing
A fluorine-containing compound gas, e.g., SF6 gas, is converted into a plasma and a silicon portion of an object to be processed is etched by the plasma. At the same time, using a light source having a peak intensity of light in a wavelength range of light absorption of a reaction product, e.g., SiF4, for which, to be more precise, ranges from 9 μm to 10 μm, the light is irradiated onto a surface of an object to be processed from the light source. The SiF4 molecules absorb the light, become activated and gain kinetic energy to be used in gaining an easy escape from a hole. As a consequence, an amount (a partial pressure) of fluorine radicals (F*) used as an etchant is increased and an etching rate of a silicon is increased.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
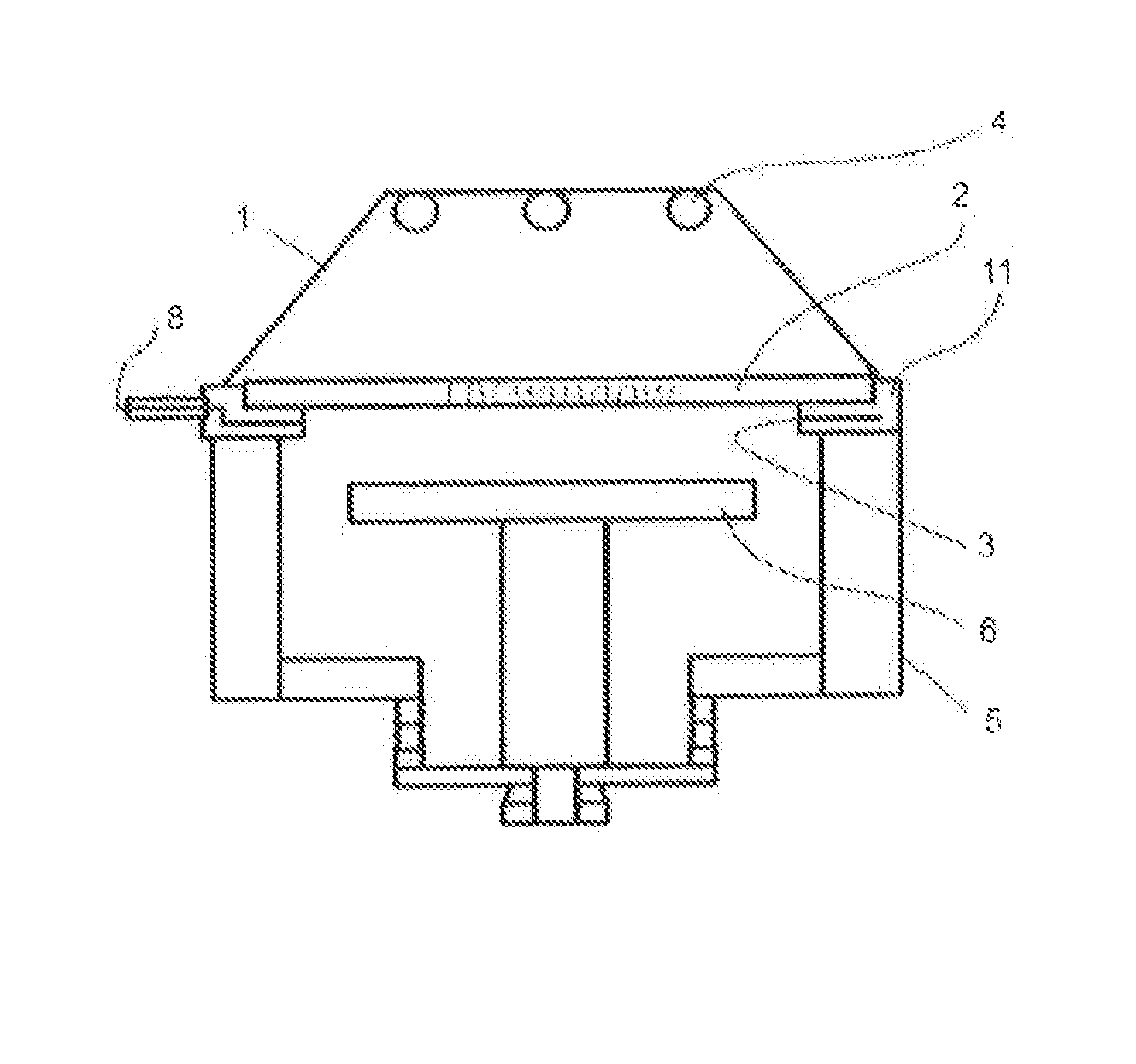
Light-emitting semiconductor device, light-emitting system and method for fabricating light-emitting semiconductor device
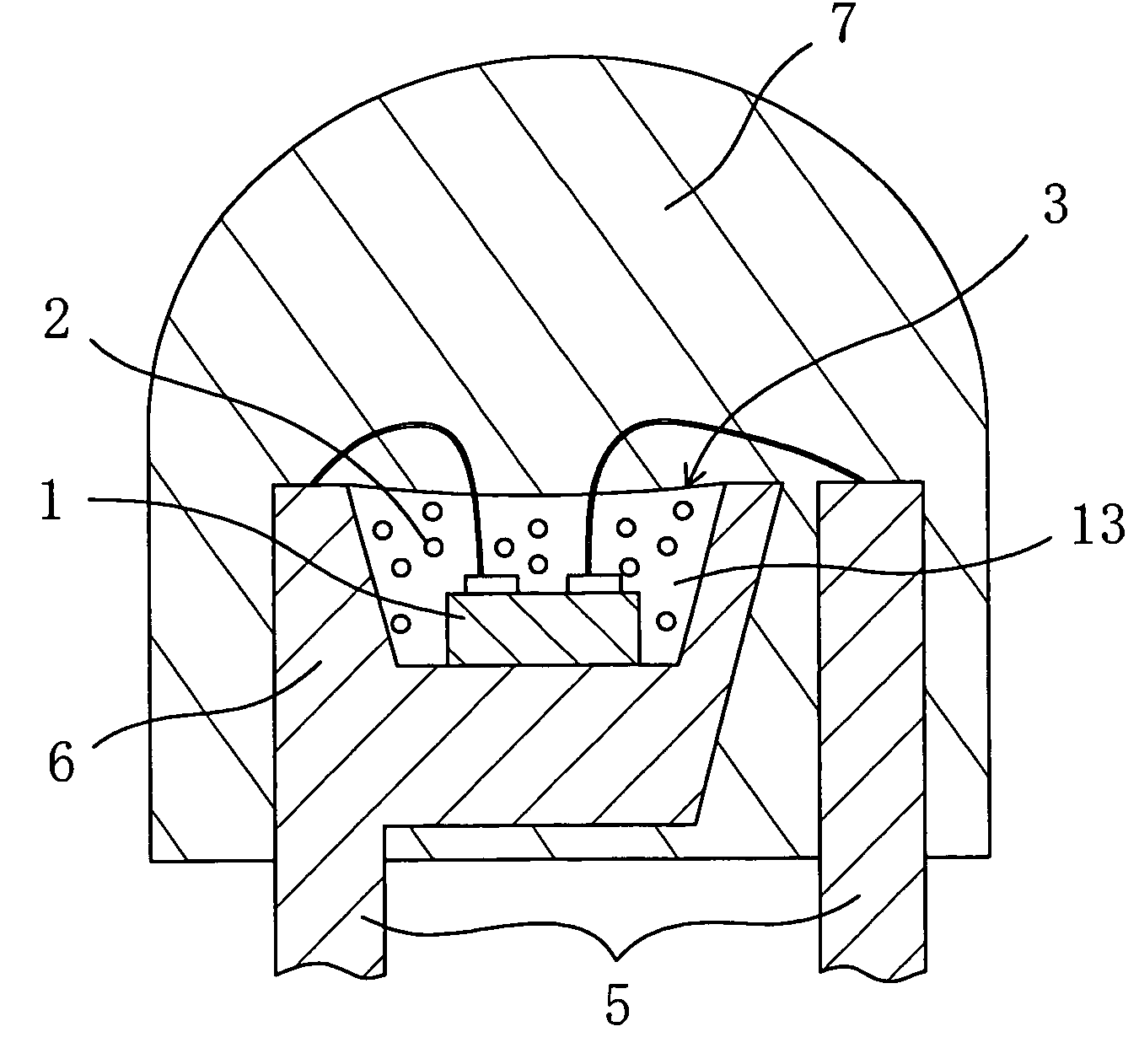
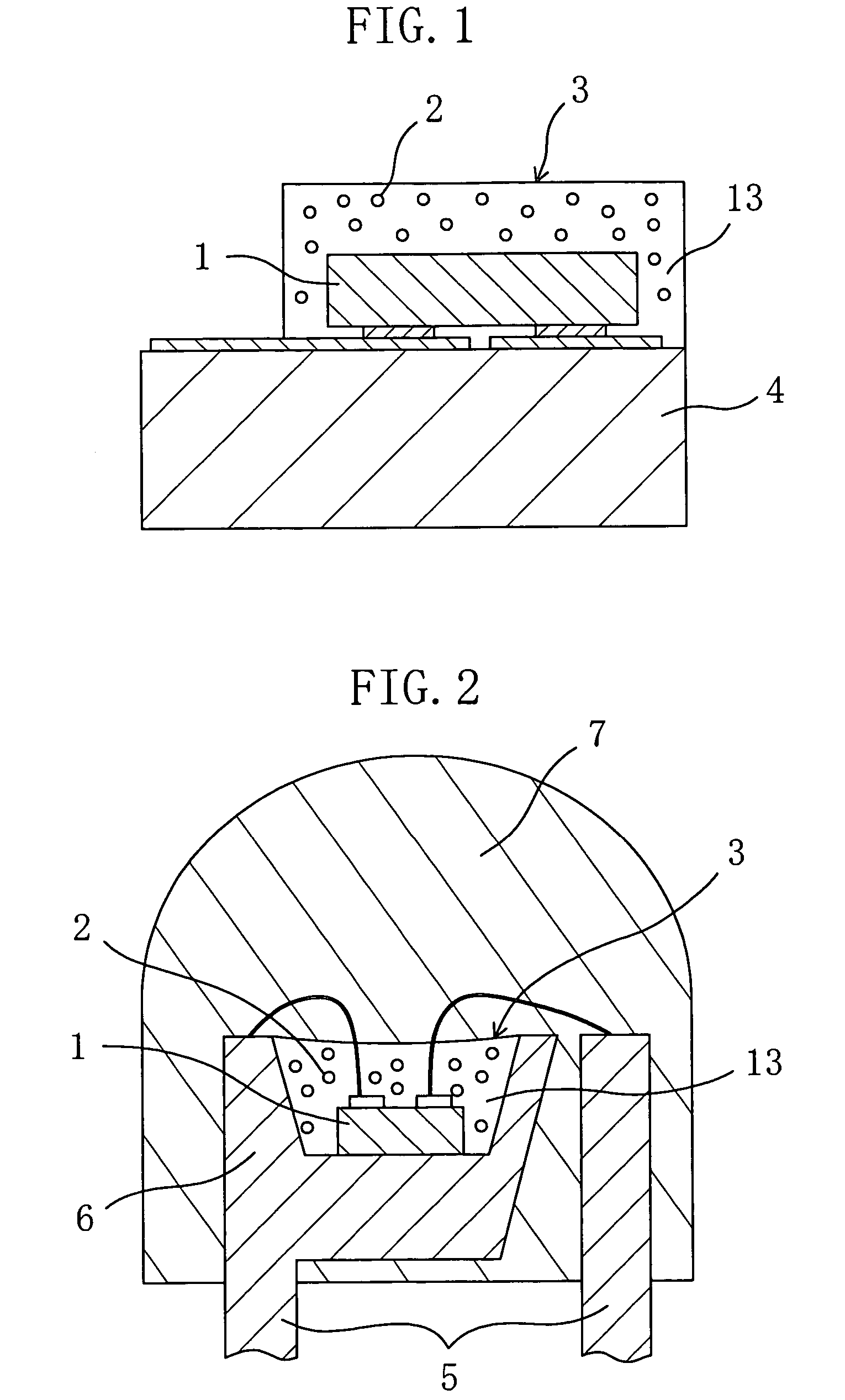
InactiveUS7023019B2Suppress color unevennessLittle color unevennessDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceDevice material
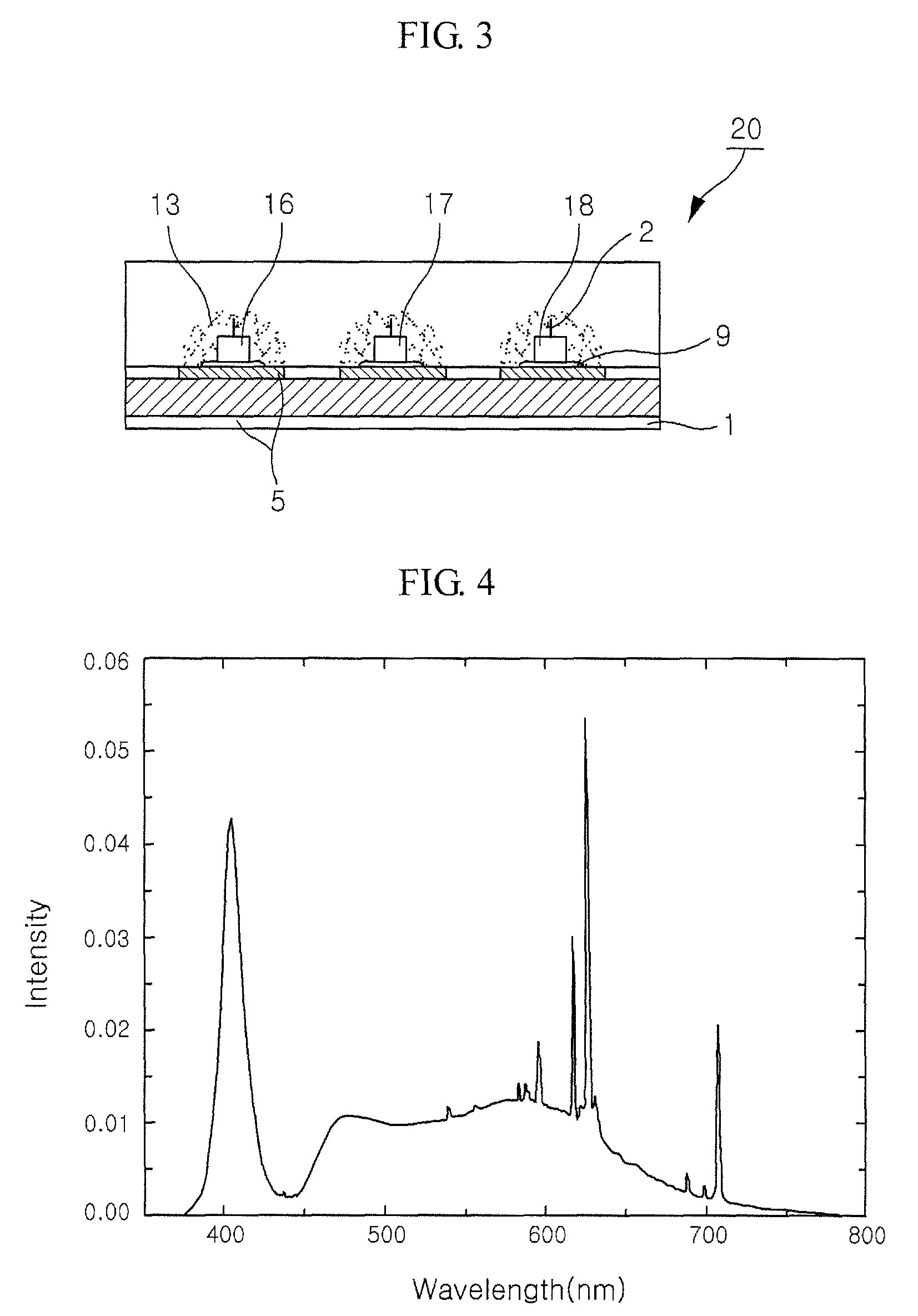
A chip-type light-emitting semiconductor device includes: a substrate 4 ; a blue LED 1 mounted on the substrate 4 ; and a luminescent layer 3 made of a mixture of yellow / yellowish phosphor particles 2 and a base material 13 (translucent resin). The yellow / yellowish phosphor particles 2 is a silicate phosphor which absorbs blue light emitted by the blue LED 1 to emit a fluorescence having a main emission peak in the wavelength range from 550 nm to 600 nm, inclusive, and which contains, as a main component, a compound expressed by the chemical formula: (Sr1-a1-b1-xBaa1Cab1Eux)2SiO4 (0<=a1<=0.3, 0<=b1<=0.8 and 0<x<1). The silicate phosphor particles disperse substantially evenly in the resin easily. As a result, excellent white light is obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
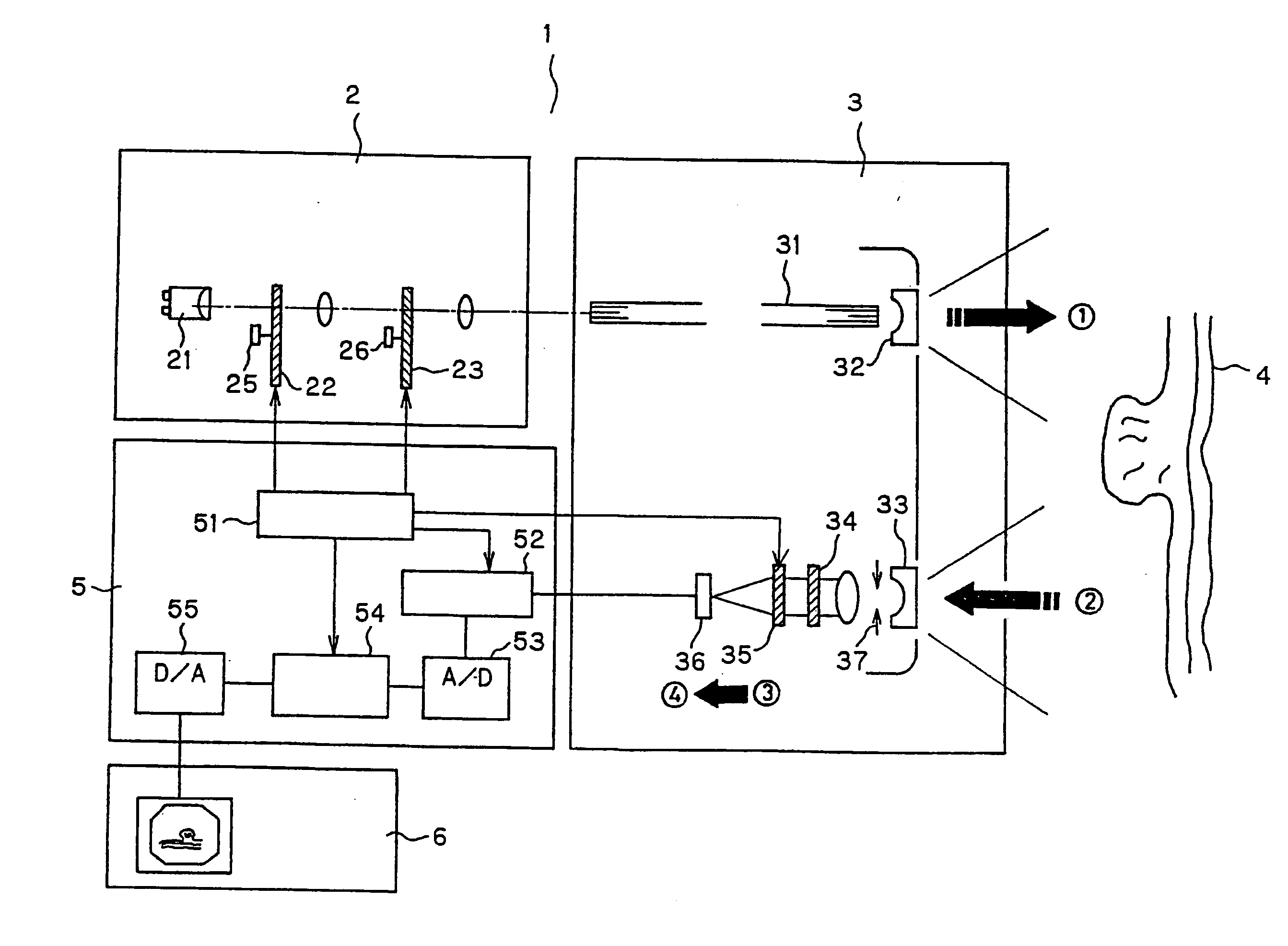
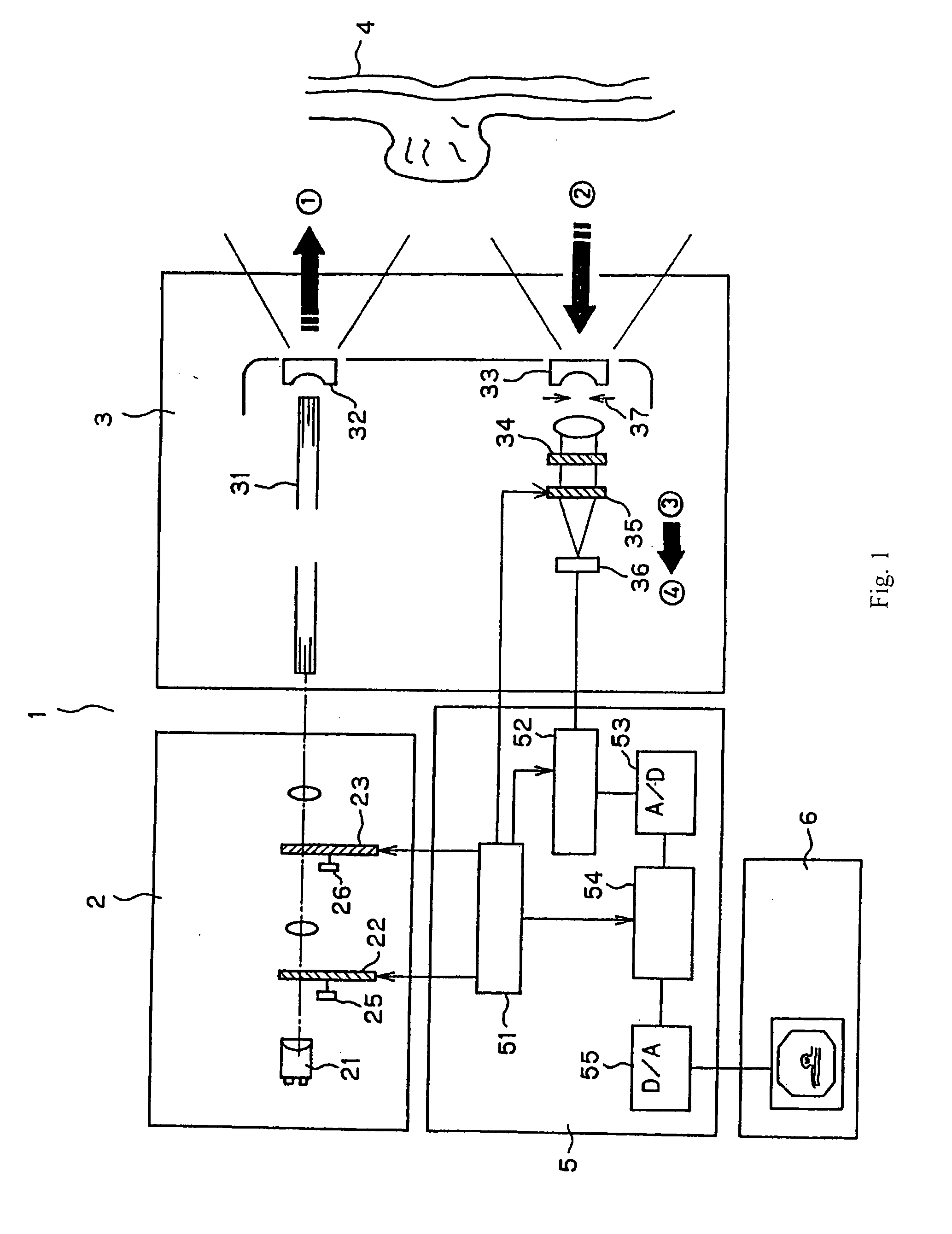
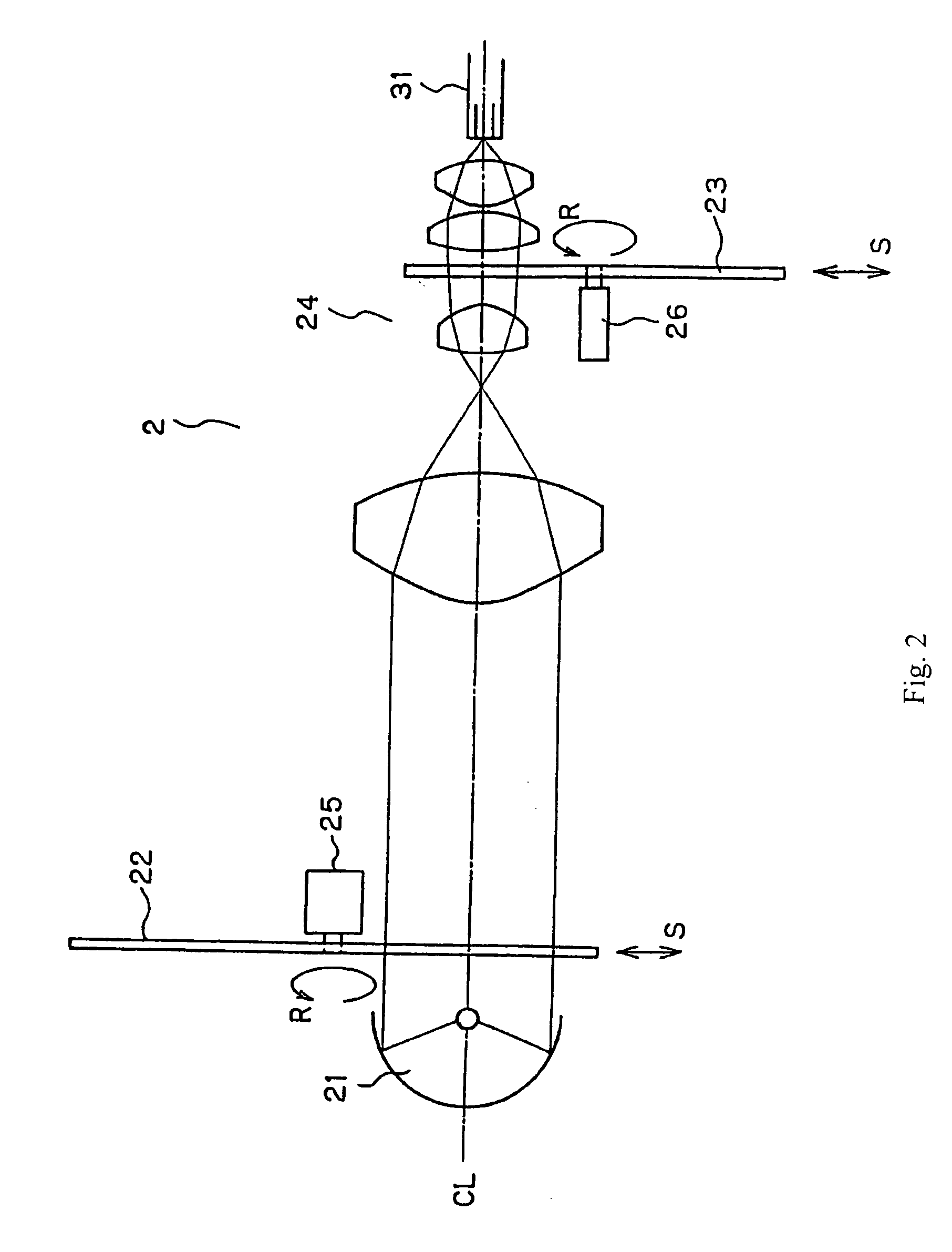
Apparatus and method for obtaining and providing imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample, and effecting such portion(s)
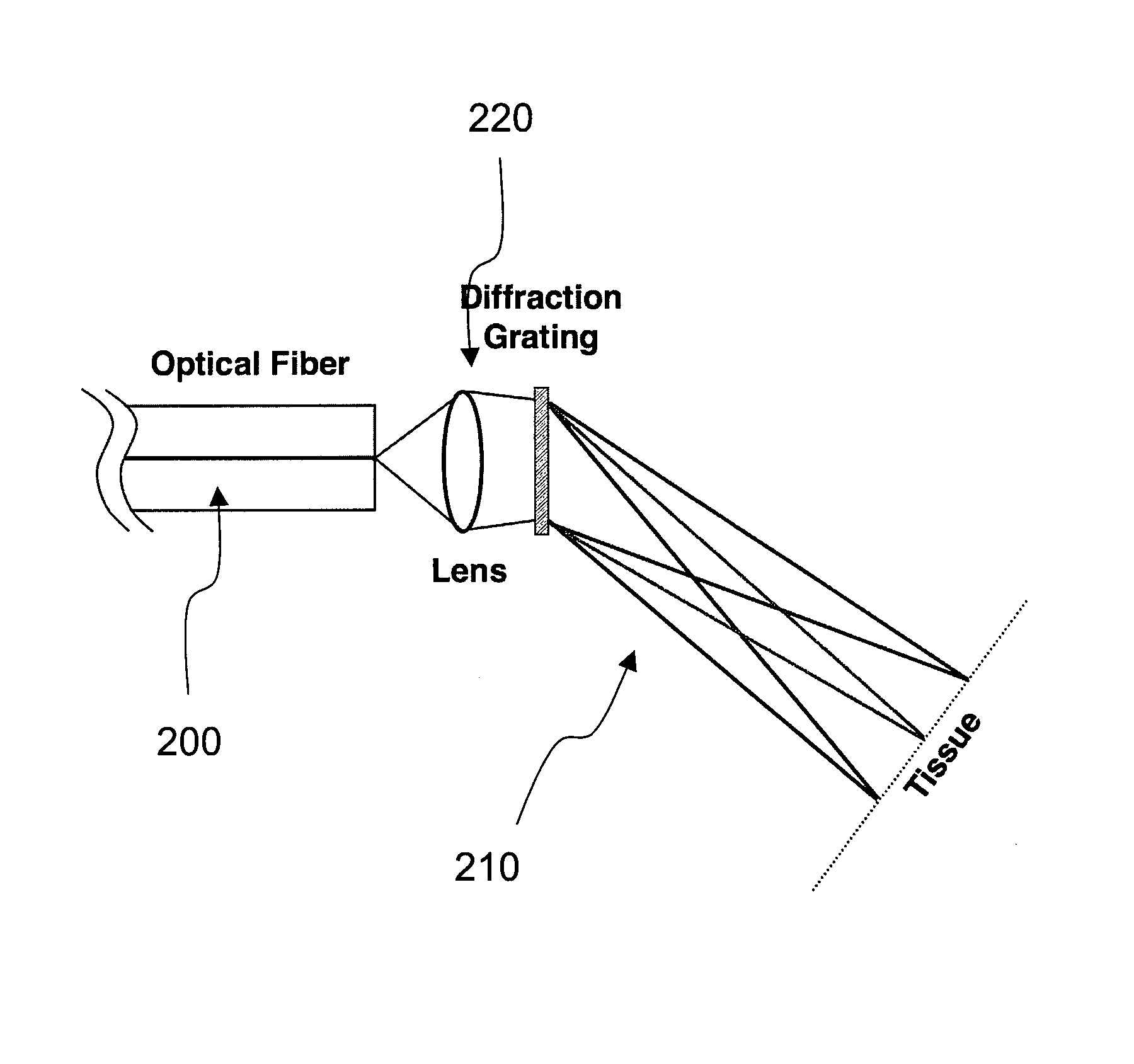
ActiveUS20080097225A1Treatment safetyImprove image qualityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightRelative phaseElectromagnetic radiation
Exemplary apparatus and process can be provided for imaging information associated with at least one portion of a sample. For example, (i) at least two first different wavelengths of at least one first electro-magnetic radiation can be provided within a first wavelength range provided on the portion of the sample so as to determine at least one first transverse location of the portion, and (ii) at least two second different wavelengths of at least one second electro-magnetic radiation are provided within a second wavelength range provided on the portion so as to determine at least one second transverse location of the portion. The first and second ranges can east partially overlap on the portion. Further, a relative phase between at least one third electro-magnetic radiation electro-magnetic radiation being returned from the sample and at least one fourth electro-magnetic radiation returned from a reference can be obtained to determine a relative depth location of the portion. First information of the portion based on the first transverse location and the relative depth location, and second information of the portion based on the second transverse location and the relative depth location can be obtained. The imaging information may include the first and second information.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
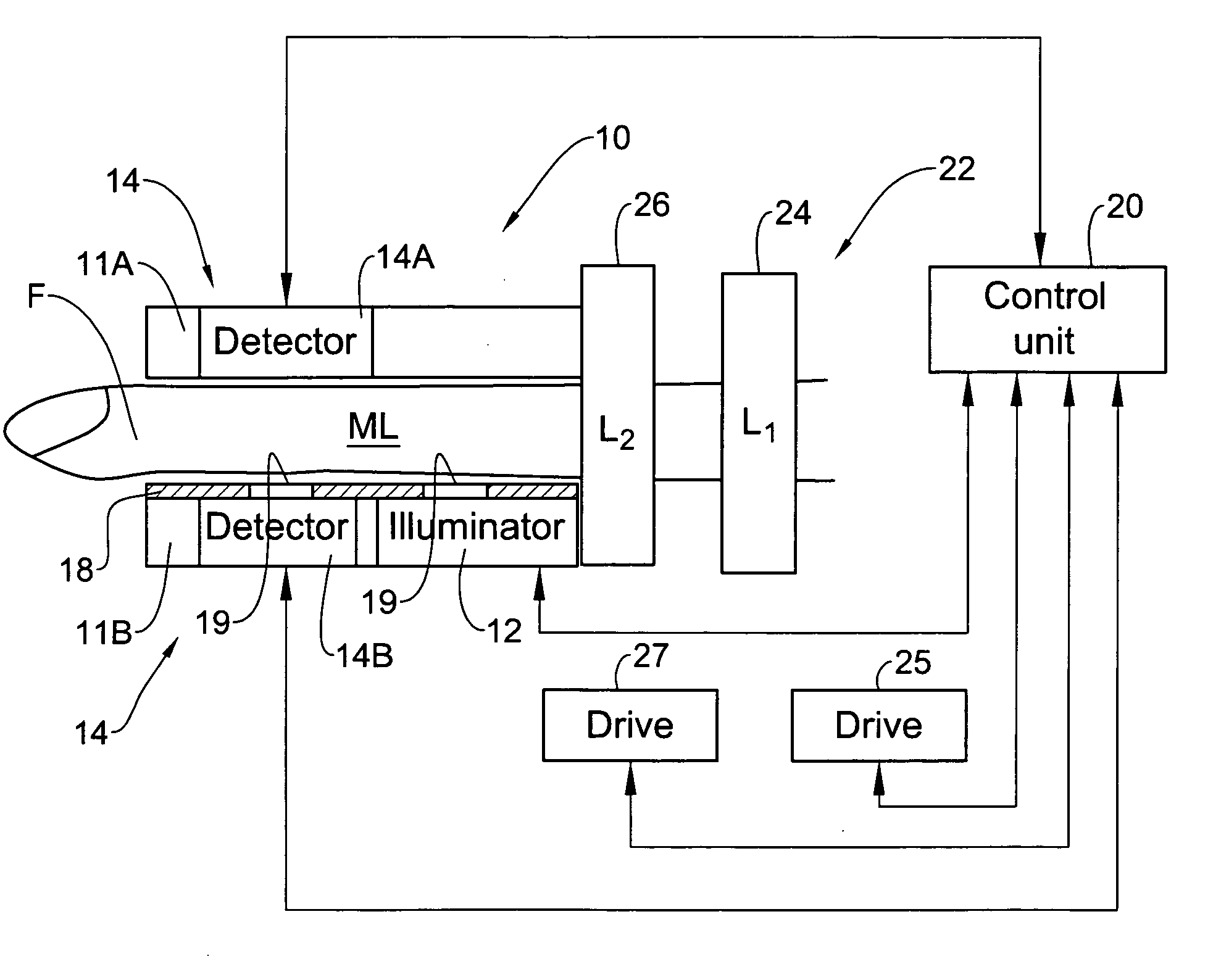
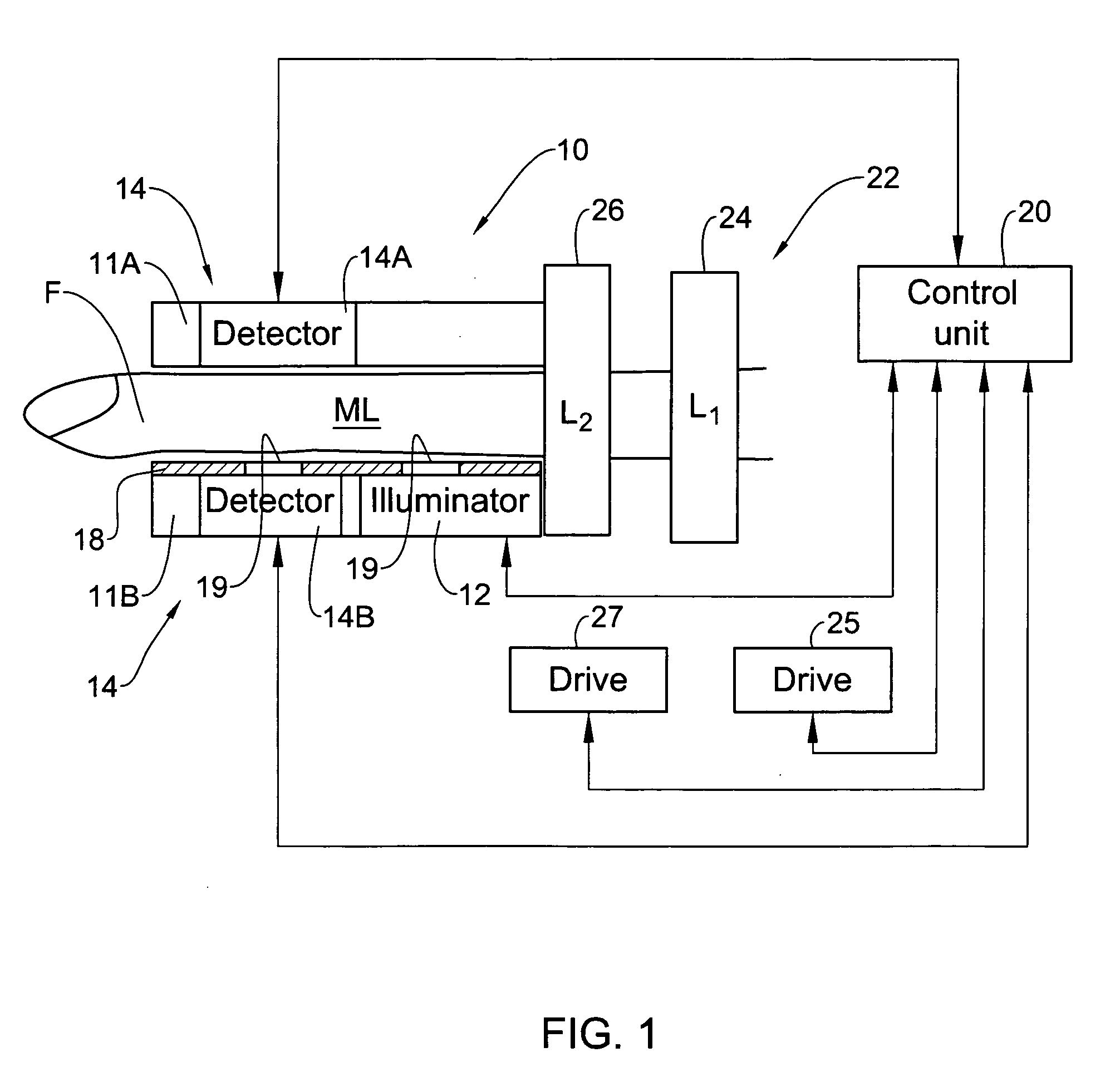
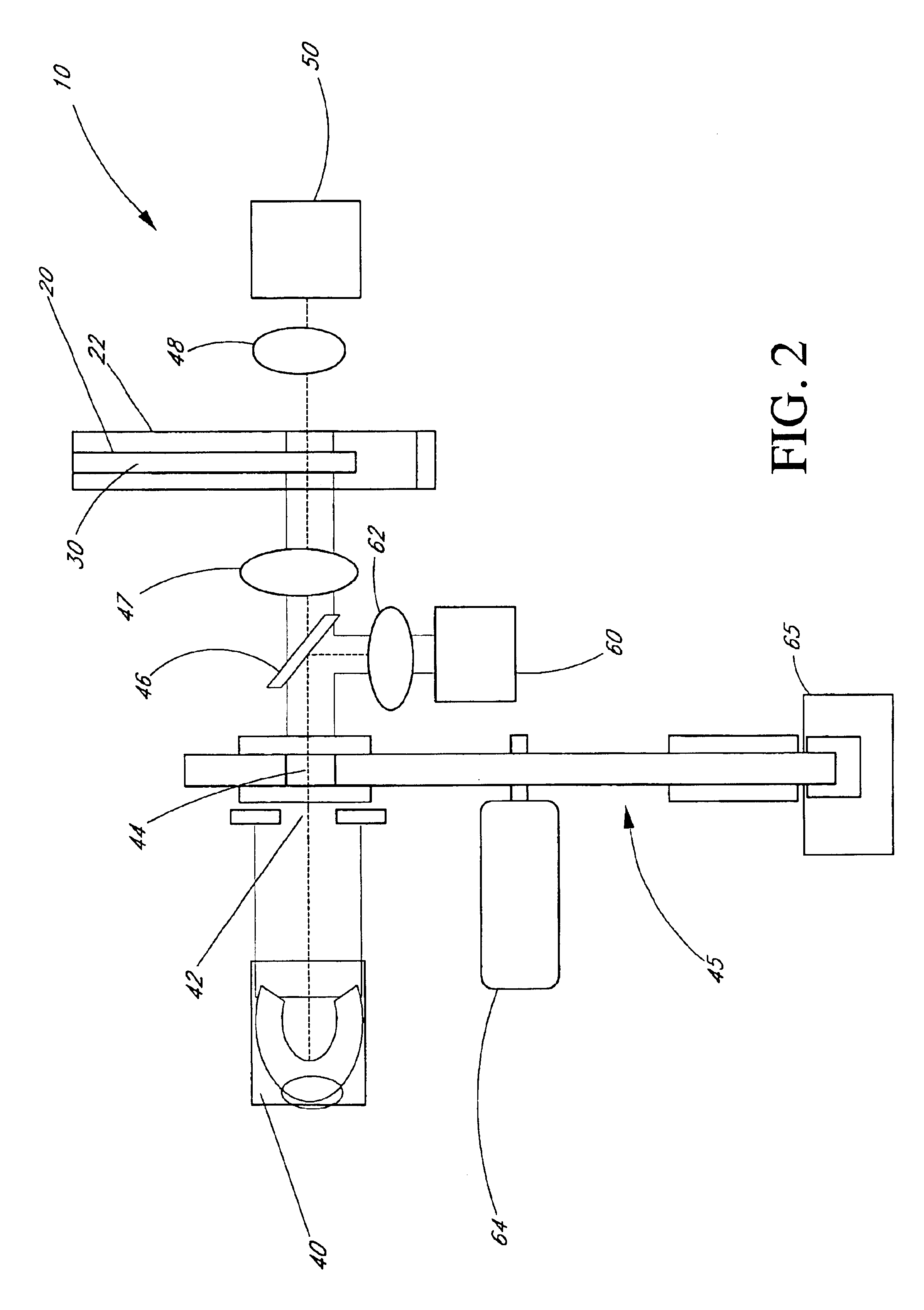
Device and method for non-invasive optical measurements
ActiveUS7313425B2Facilitate non-invasive optical measurementStable responseDiagnostics using pressureSensorsOptical measurementsNon invasive
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
Bright metal flake based pigments
InactiveUS6150022AGood specular reflectance characteristicPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsSynthetic resin layered productsDielectricReflectivity
A flake-based pigment is provided having improved specular reflectance characteristics in the visible wavelength range. The flake-based pigment has a plurality of core flake sections each formed of a central reflector layer and dielectric support layers on opposing sides of the reflector layer. The resulting core flake section is a very thin three-layered structure that exhibits a uniaxial compressive strength much greater than a corresponding uniaxial tensile strength. This structure provides the benefits of rigidity and brittle fracture during manufacturing and application processes, which ultimately provides favorable planar and specular reflectance characteristics for the pigment in the visible wavelength range. A variety of outer coating layers can be formed around the core flake sections, such as various dielectric and absorber layers having thicknesses dependent upon the desired optical characteristics of the pigment.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
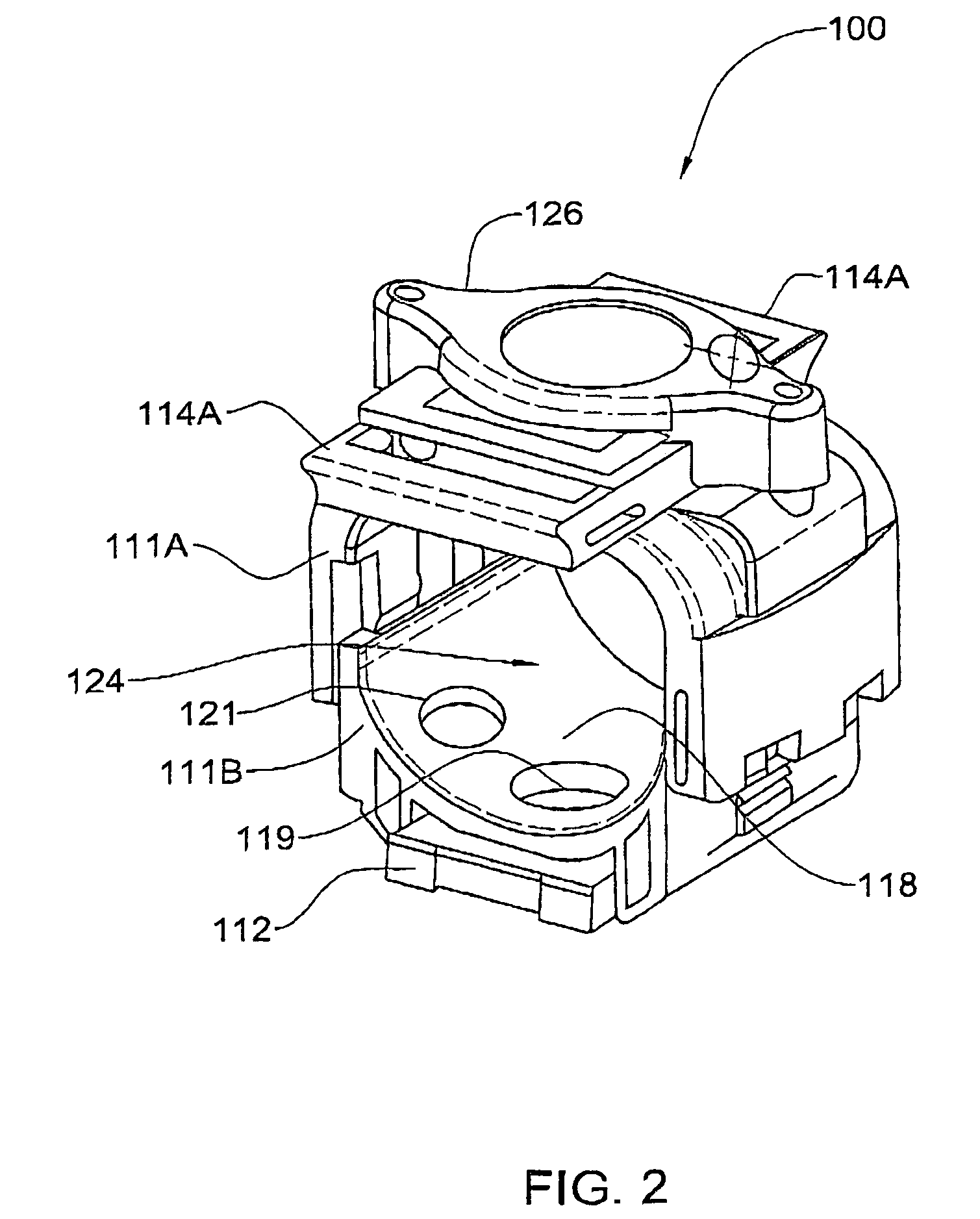
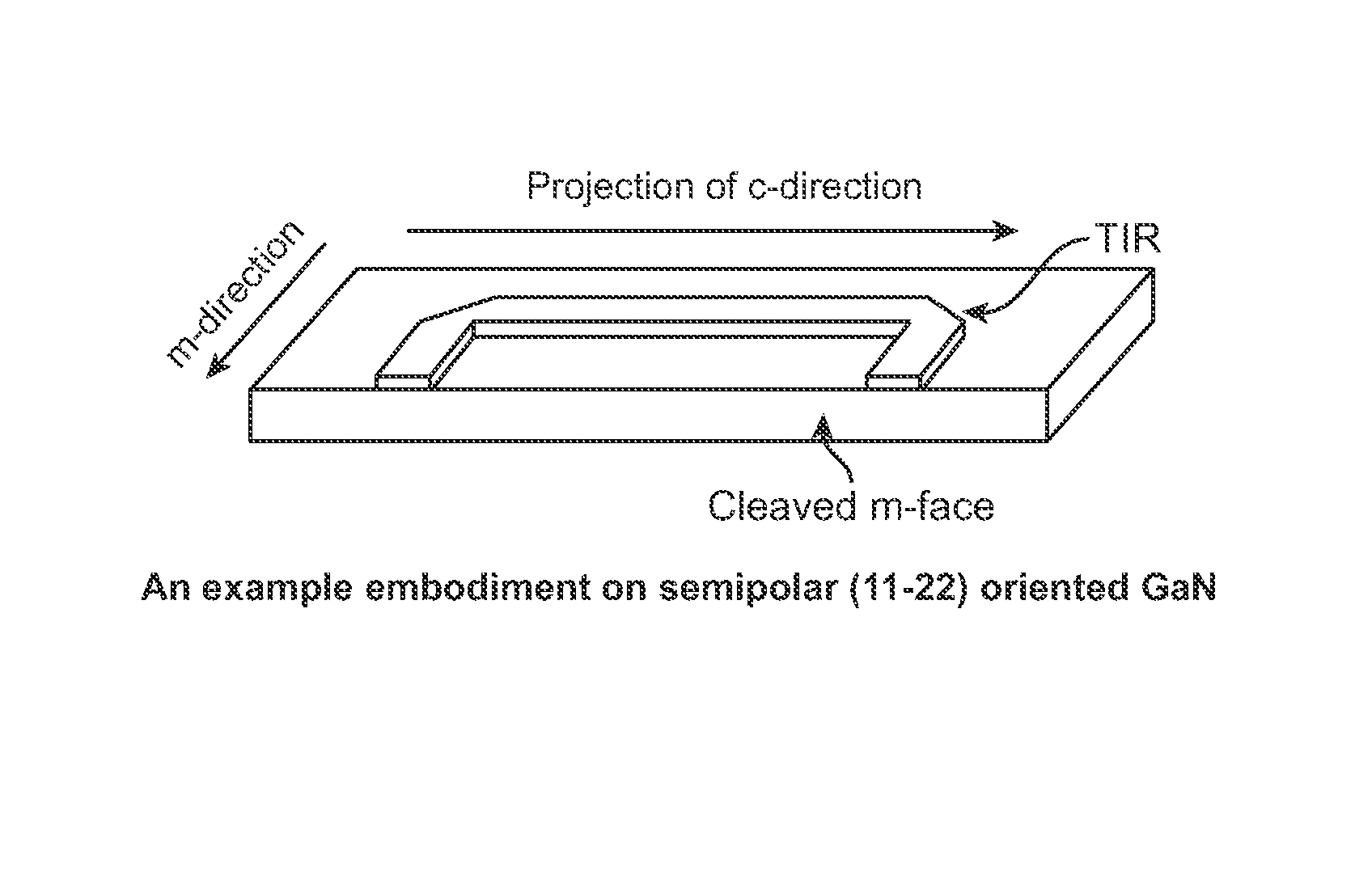
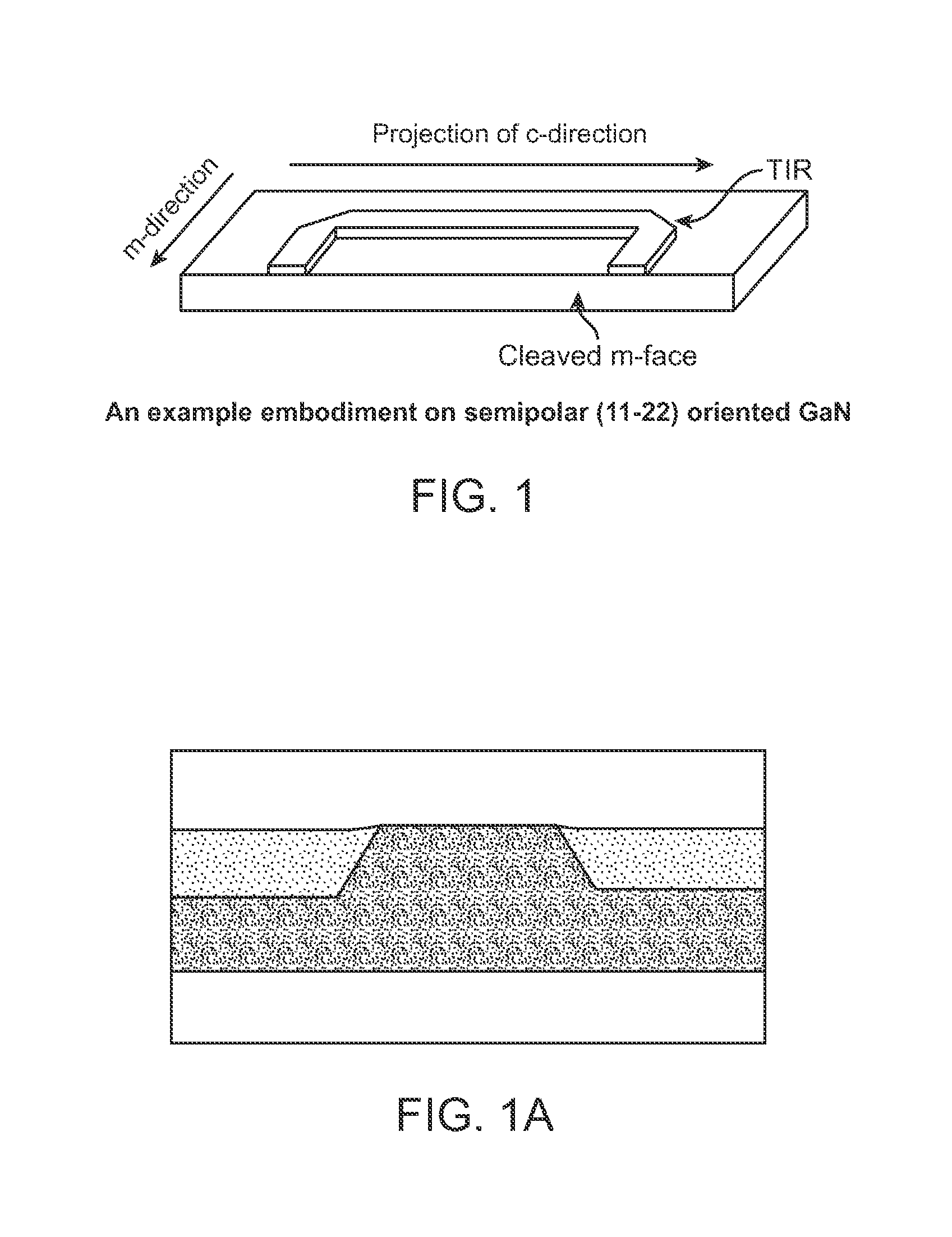
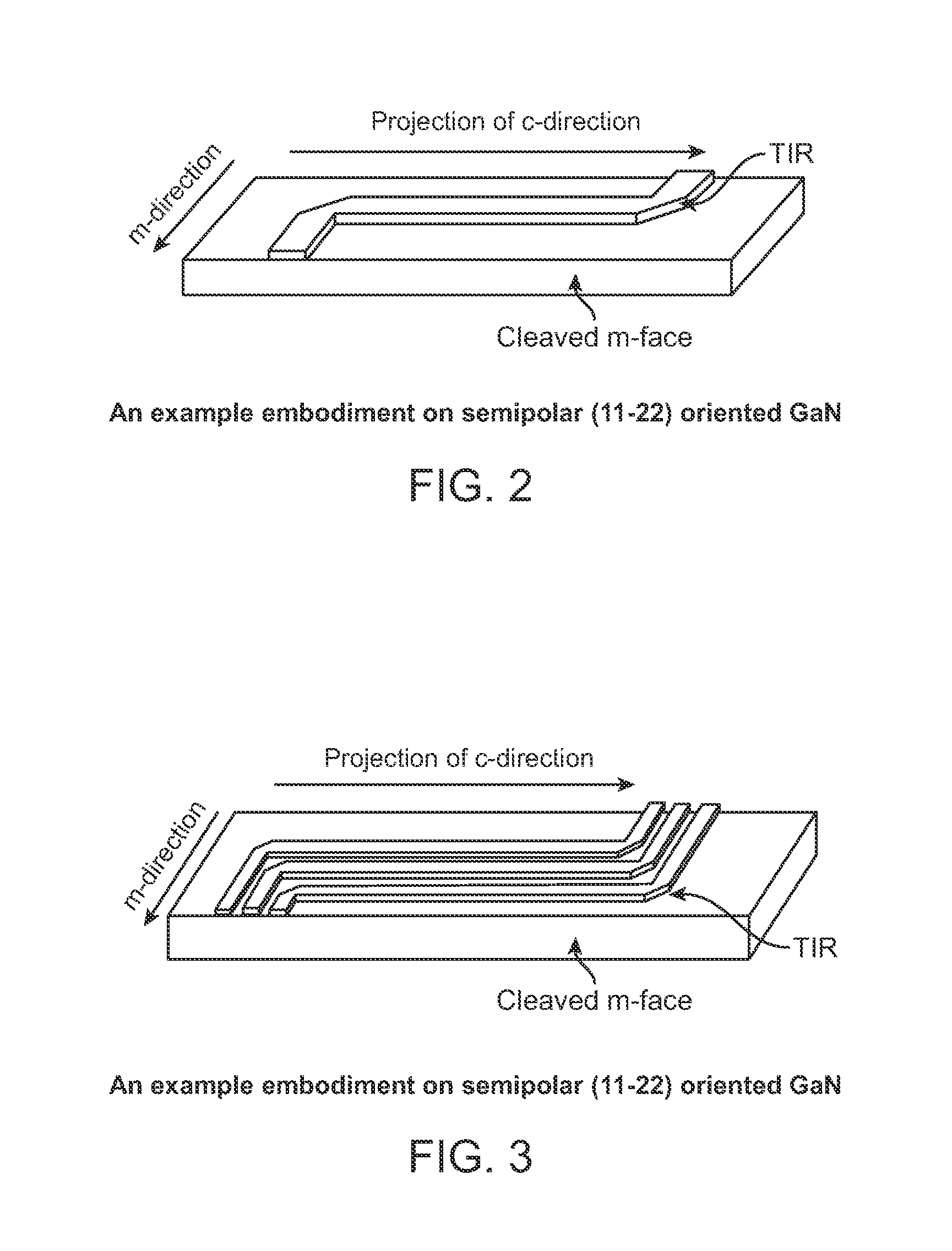
Integrated total internal reflectors for high-gain laser diodes with high quality cleaved facets on nonpolar/semipolar GaN substrates
ActiveUS8259769B1High yieldWell formedOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionTotal internal reflectionCrystal plane
A laser diode device operable at a one or more wavelength ranges. The device has a first waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first gain characteristic and a first direction. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first end and a second end and a first length defined between the first end and the second end. The device has a second waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a second gain characteristic and a second direction. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a first end, a second end, and a second length defined between the first end and the second end. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has the first end being coupled to the first end of the first waveguide. The second length is in a different direction from the second length. In a specific embodiment, the device has a cleaved region provided on the second end of the second waveguide, the cleaved region being perpendicular to the second direction of the second waveguide.
Owner:KAAI +1
Device and method for non-invasive optical measurements
ActiveUS20060009685A1Facilitate non-invasive optical measurementStabilizing optical responseDiagnostics using pressureSensorsOptical measurementsLight signal
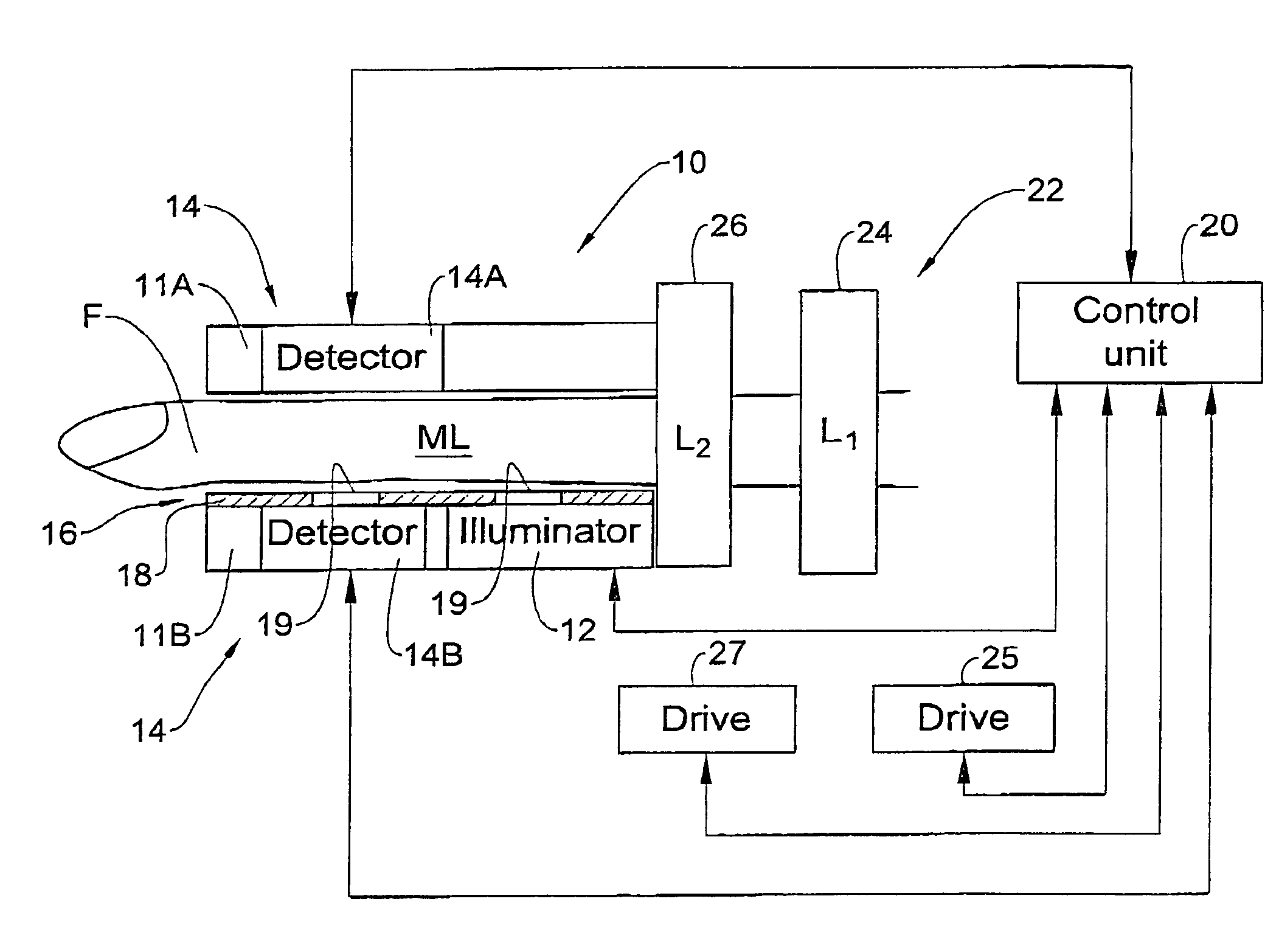
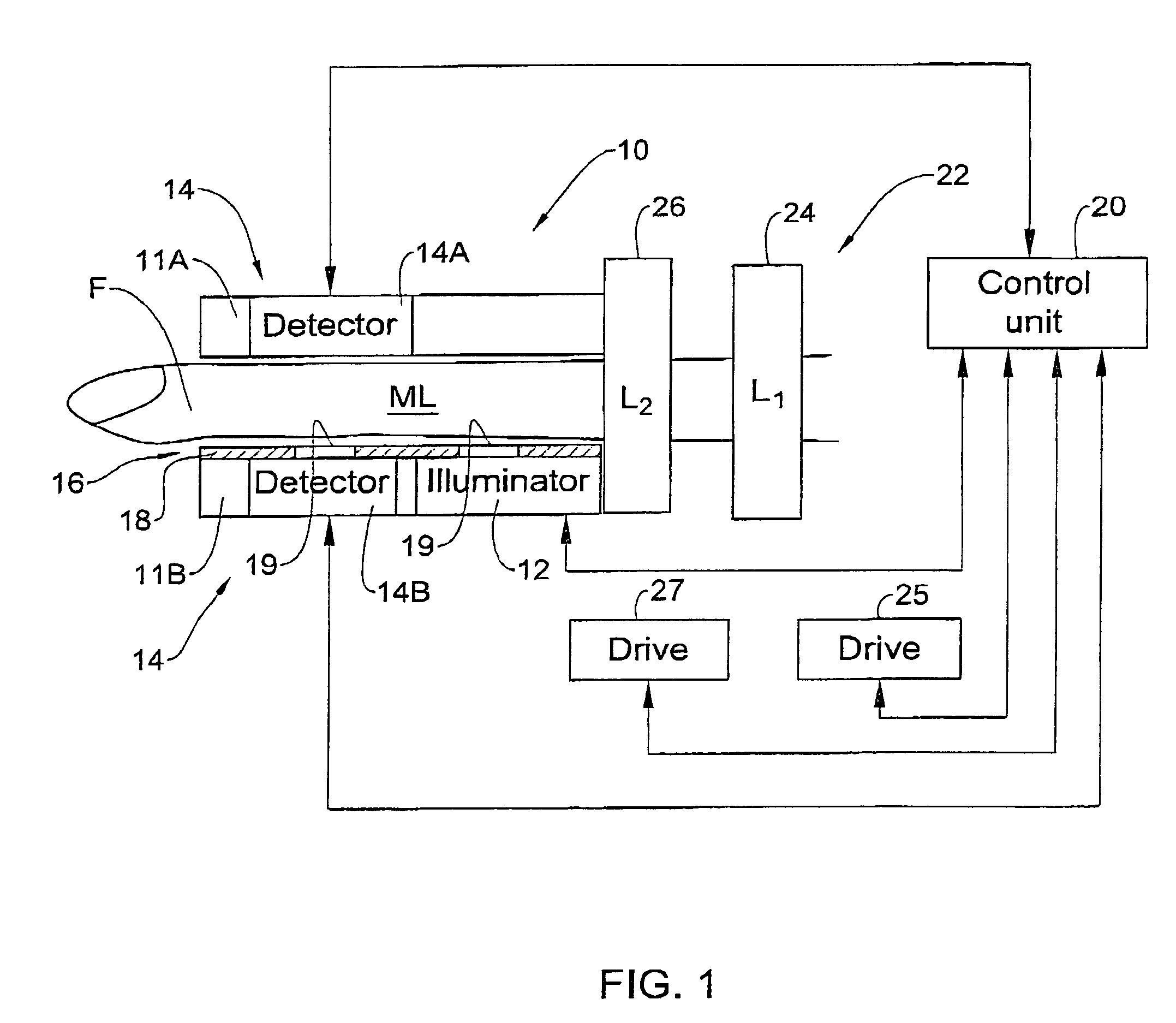
An optical measurement device and method are presented for use in non-invasive measurements on a patient's body. The device comprises an illumination assembly configured and operable to generate illuminating light of a predetermined wavelength range; a detection assembly; and a light directing assembly. The detection assembly comprises a first detector unit for detecting a first light signal transmitted through an illuminated body portion and generating first measured data indicative of the detected transmitted light, and a second detector unit for detecting a second light signal reflected from the illuminated body portion and generating second measured data indicative of the detected reflected light. The light directing assembly comprises a light diffuser for scattering back light incident thereto, to thereby direct the illuminating light or the light coming from the body portion back towards the body portion. This technique provides for increasing the amount of light reaching a region of interest inside the body portion and maximizing homogeneity of the first and second detected light signals.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
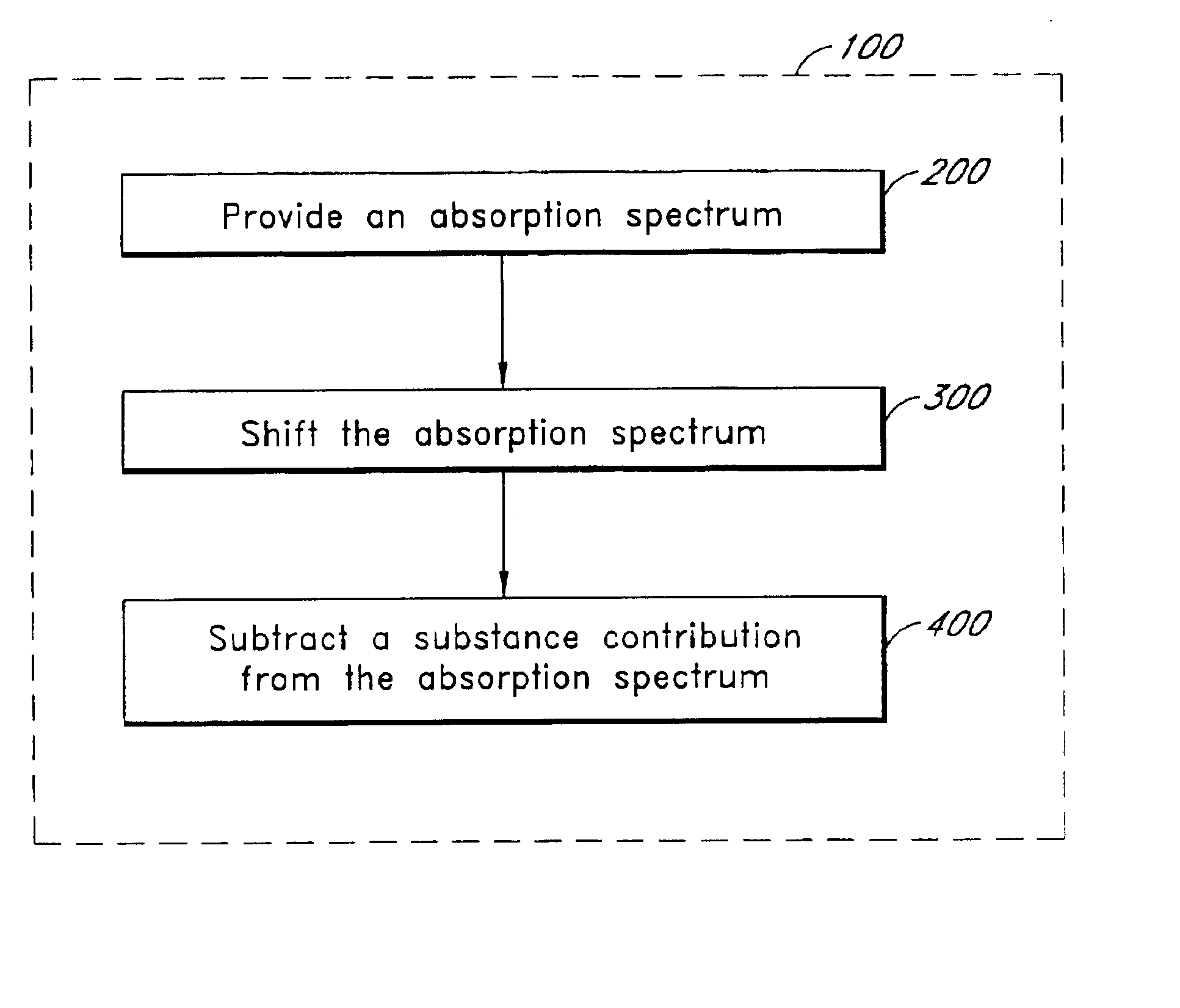
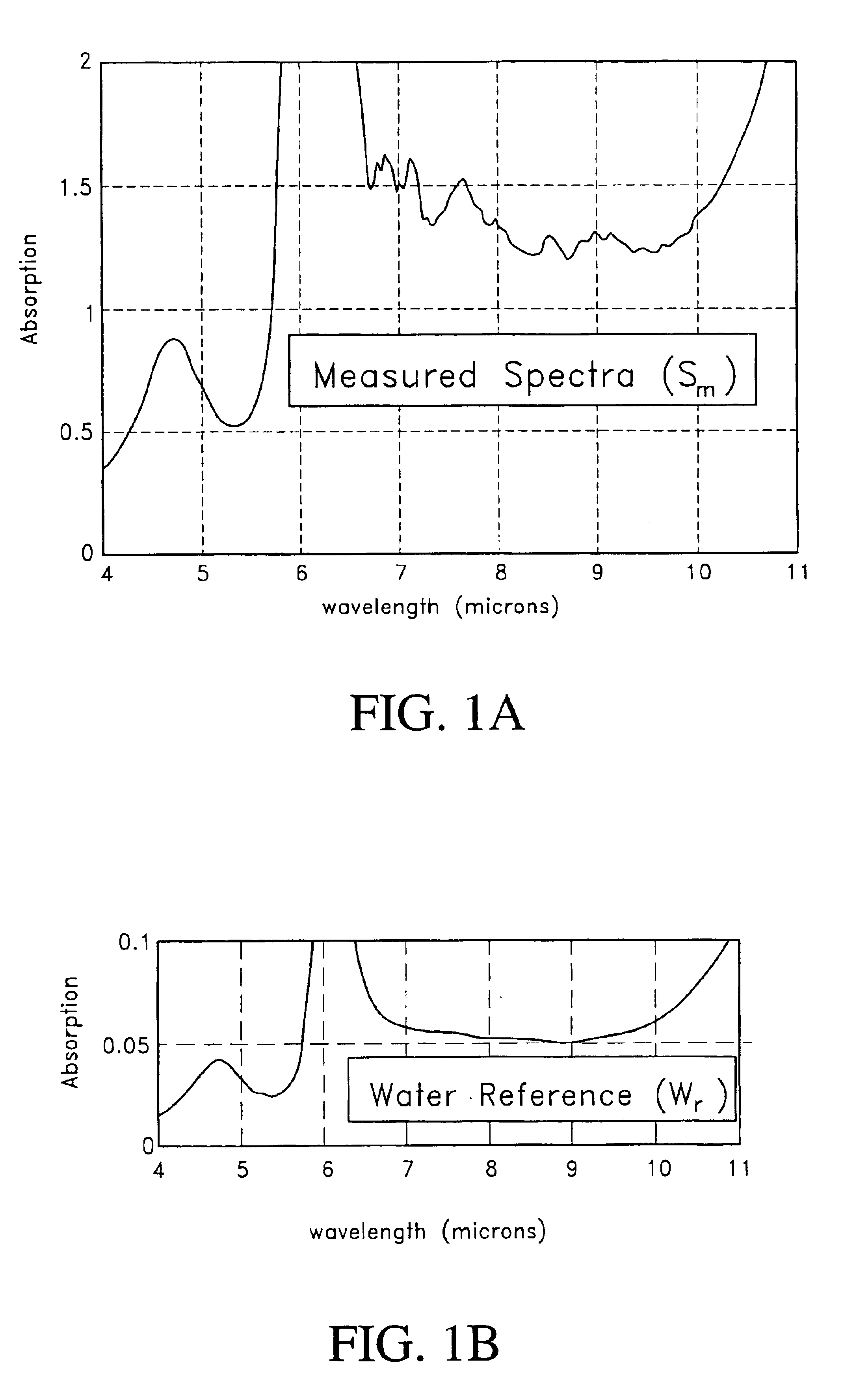
Method of determining an analyte concentration in a sample from an absorption spectrum
InactiveUS6862534B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAction spectrumAnalyte
A method determines an analyte concentration in a sample including the analyte and a substance. The method includes providing an absorption spectrum of the sample. The absorption spectrum has an absorption baseline. The method further includes shifting the absorption spectrum so that the absorption baseline approximately equals a selected absorption value in a selected absorption wavelength range. The method further includes subtracting a substance contribution from the absorption spectrum. Thus, the method provides a corrected absorption spectrum substantially free of a contribution from the substance.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
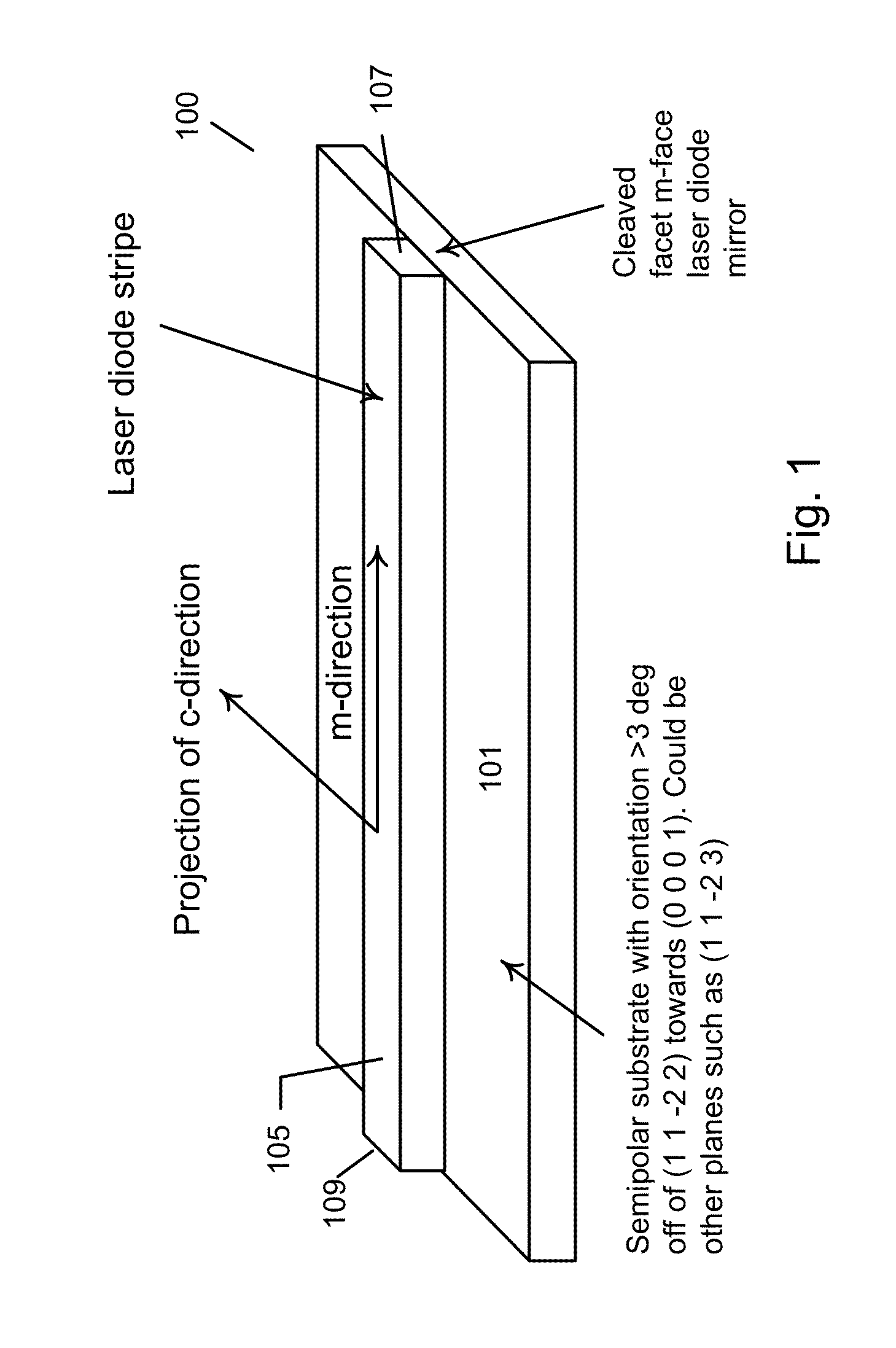
Optical device structure using miscut GaN substrates for laser applications
ActiveUS8422525B1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersLength waveGallium nitride
An optical device capable of emitting light having a wavelength ranging from about 490 to about 580 nanometers has a gallium nitride substrate with a semipolar crystalline surface region characterized by an orientation of greater than 3 degrees from (11-22) towards (0001) but less than about 50 degrees. A laser stripe formed on the substrate has a cavity orientation substantially parallel to the m-direction.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Light-Emitting Element and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20110215714A1Improve power efficiencyConsume less powerDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminosityLength wave
To provide a light-emitting element whose power efficiency is improved and which emits light of natural color like light bulb color. In the light-emitting element, at least three light-emitting units are stacked. The emission spectrum of the light-emitting element has two peaks. One of the two peaks is obtained by combining spectra of light emitted from two light-emitting units. The peak is in the yellow to orange wavelength range and has a wavelength greater than or equal to 560 nm and less than 580 nm. Thus, a wavelength range of high luminosity can be used and the power efficiency can be improved. The color of light emitted from the light-emitting element is close to a blackbody locus in a chromaticity diagram, and light of natural color like light bulb color can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Vehicle lamp using emitting device for suppressing color tone difference according to illumination conditions
InactiveUS7501749B2High light transmittanceVehicle headlampsDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorUltraviolet lights
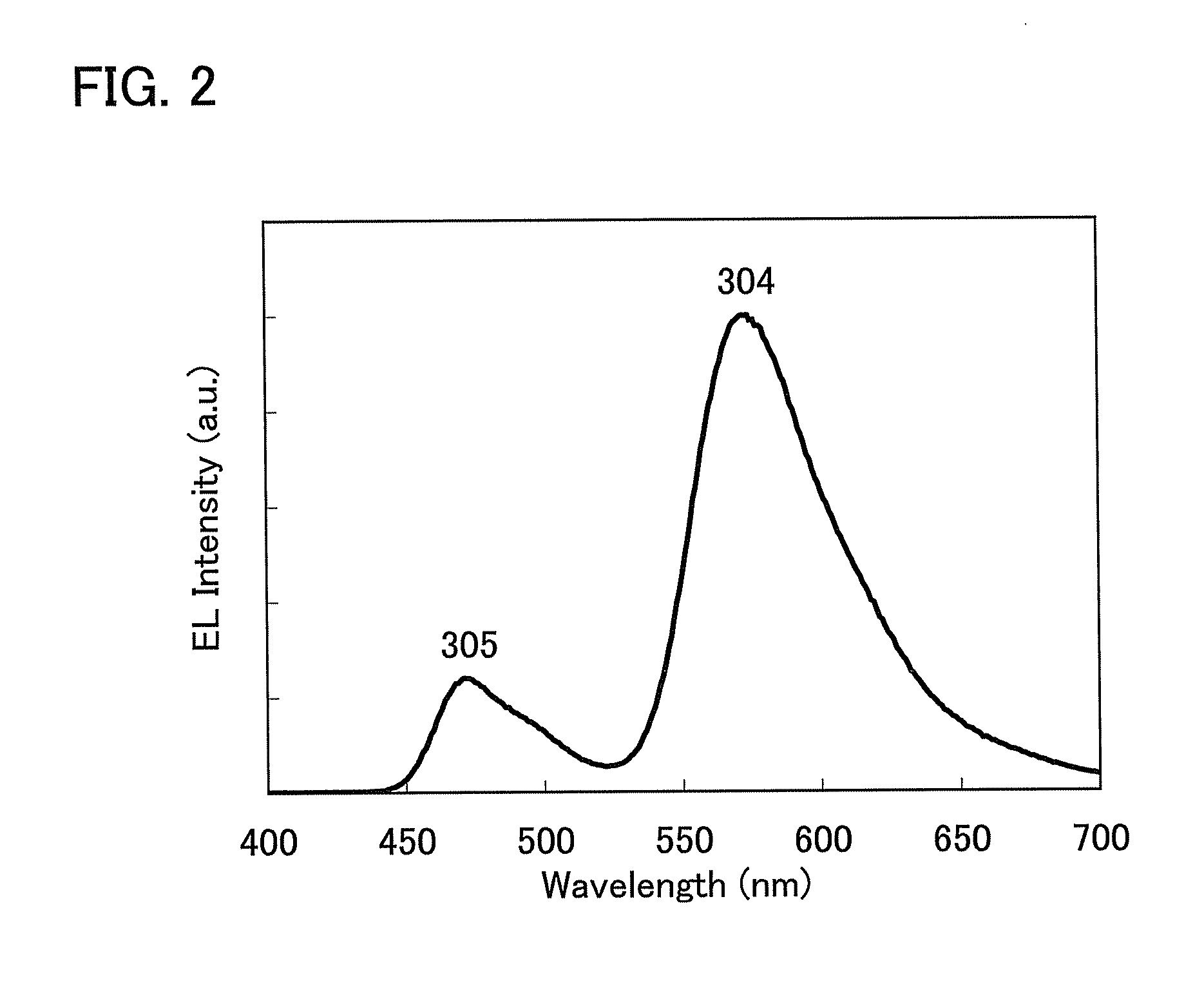
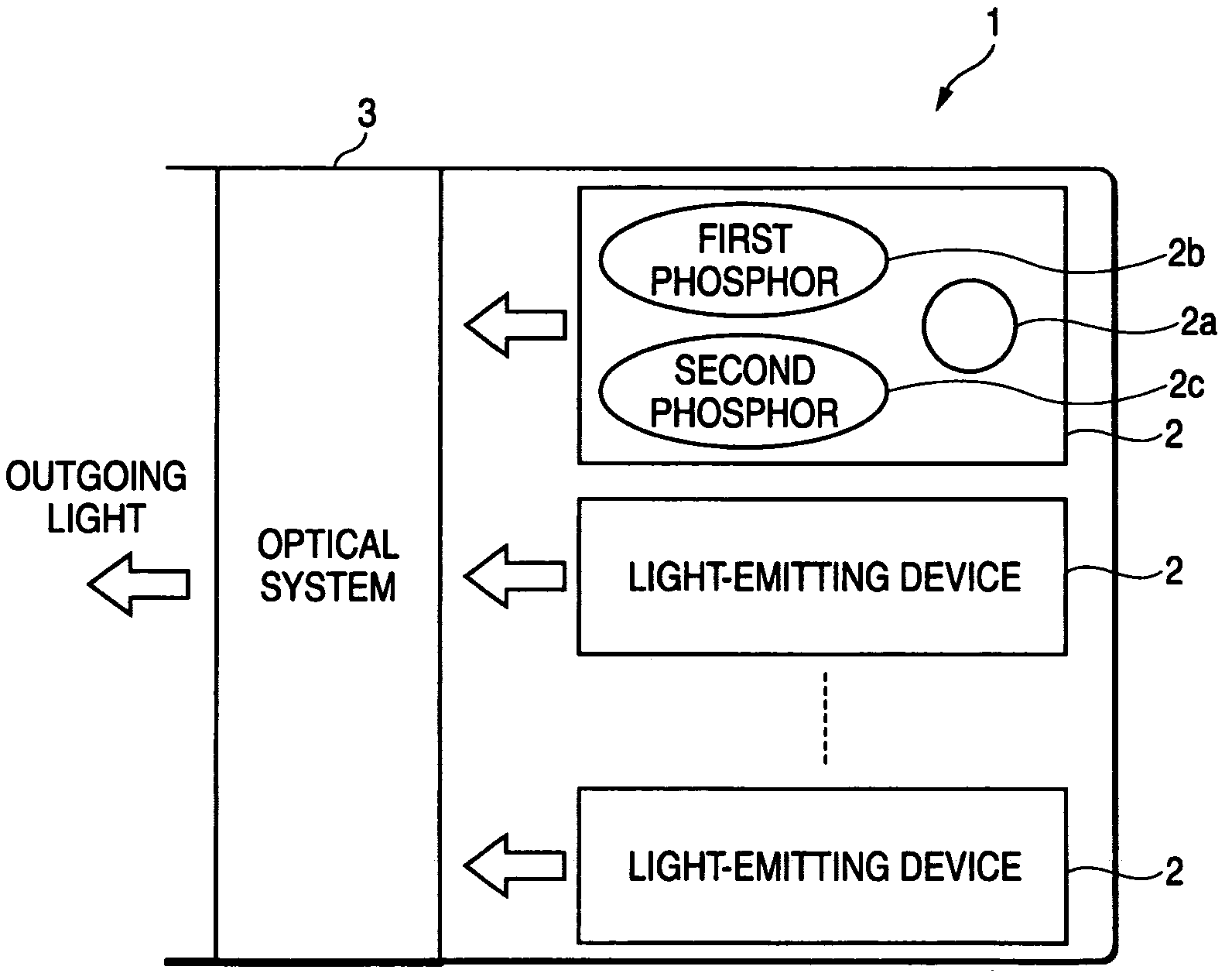
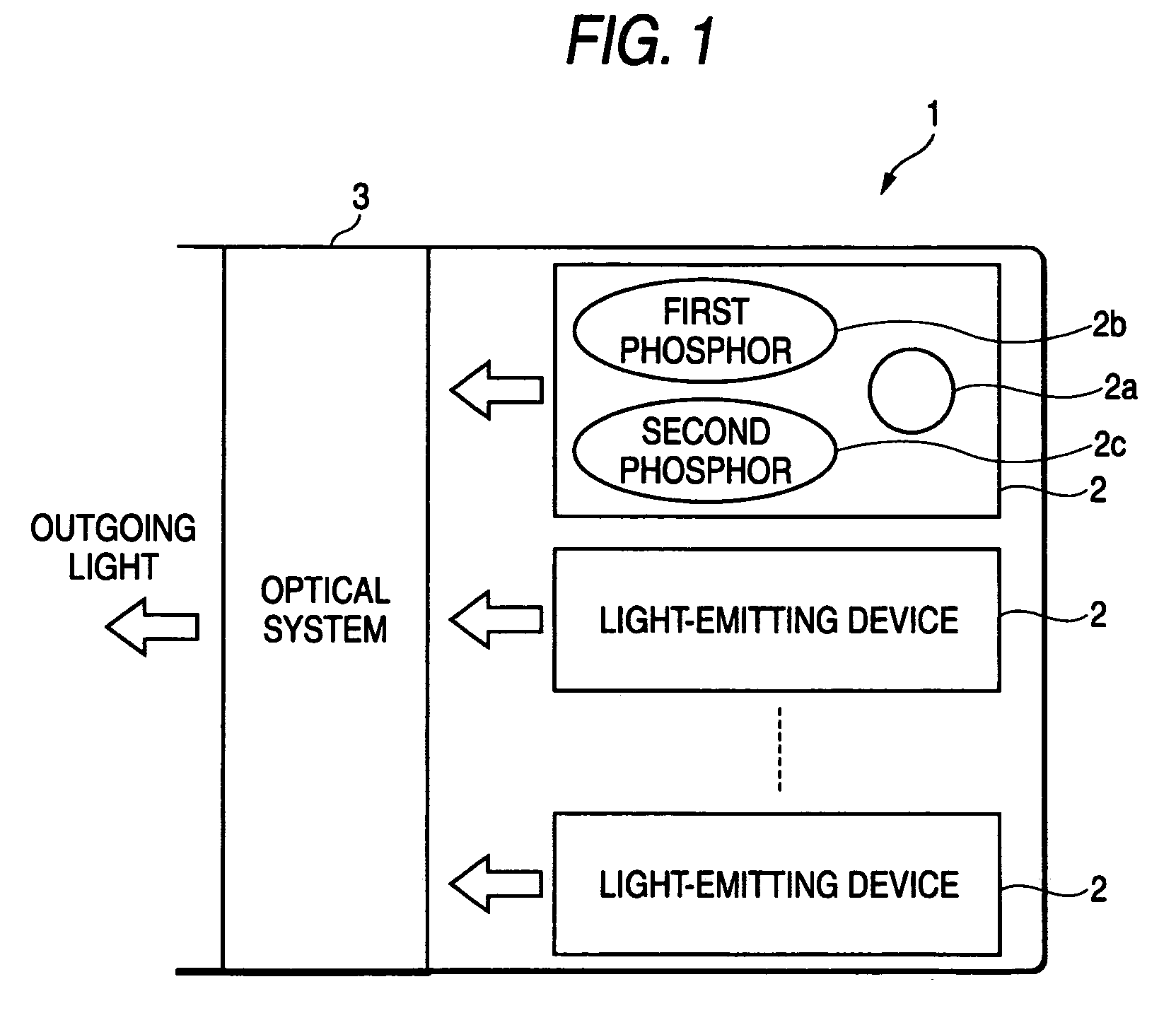
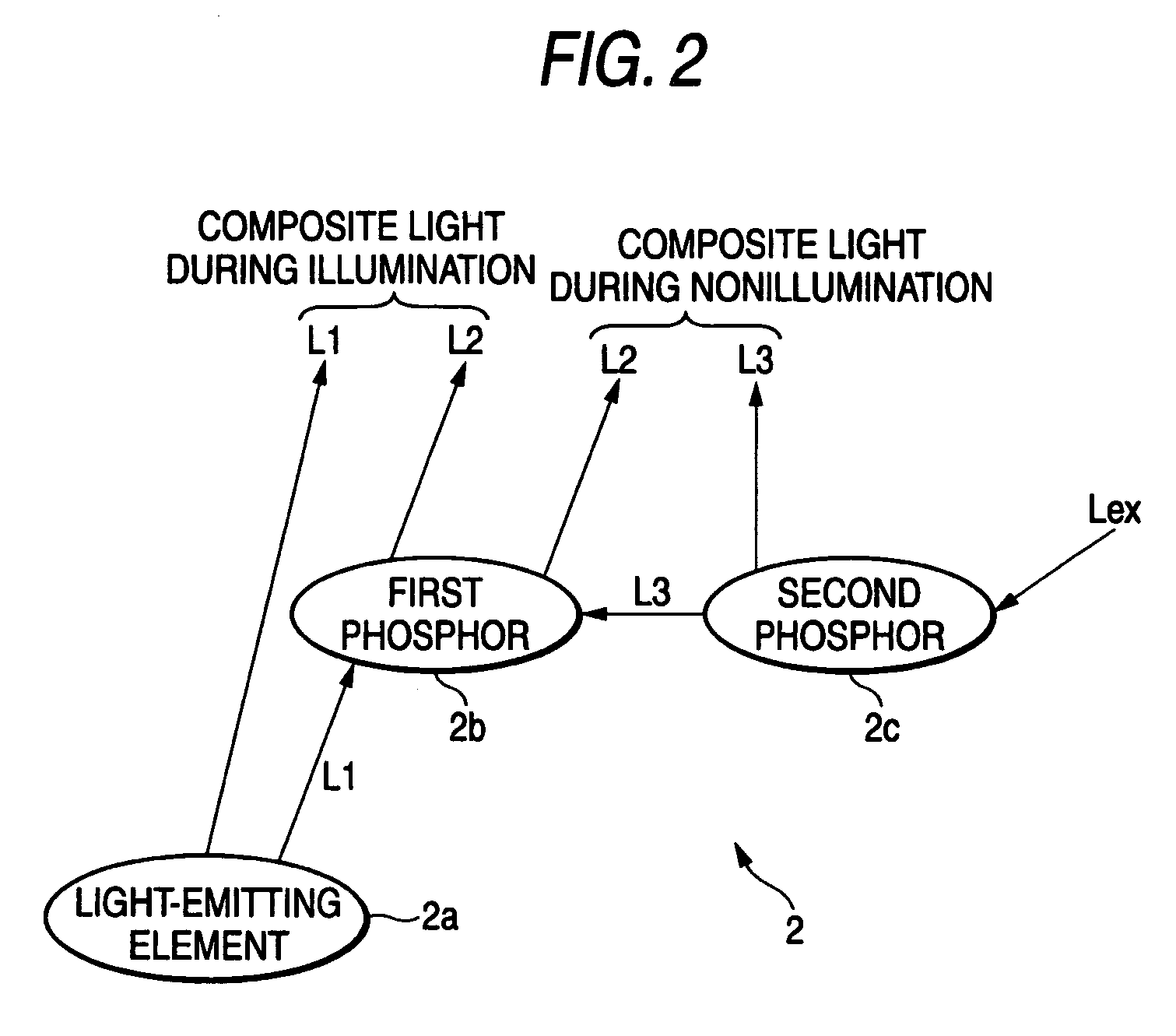
A light-emitting device (2) including a light-emitting element (2a), a first phosphor (2b), and a second phosphor (2c). The light-emitting element (2a) emits light L1 having a wavelength range within the visible region. Upon receipt of the light L1, or light L3 originating from the second phosphor (2c), the first phosphor (2b) emits light L2 having a wavelength range, which differs from that of the first light L1 and the third light L3, but falls within the visible region. Upon receipt of a specific wavelength component (ultraviolet light, or the like) included in external light, the second phosphor (2c) generates the light L3 whose wavelength range is substantially the same as that of the light L1, thereby radiating the first phosphor (2b) with the light L3.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
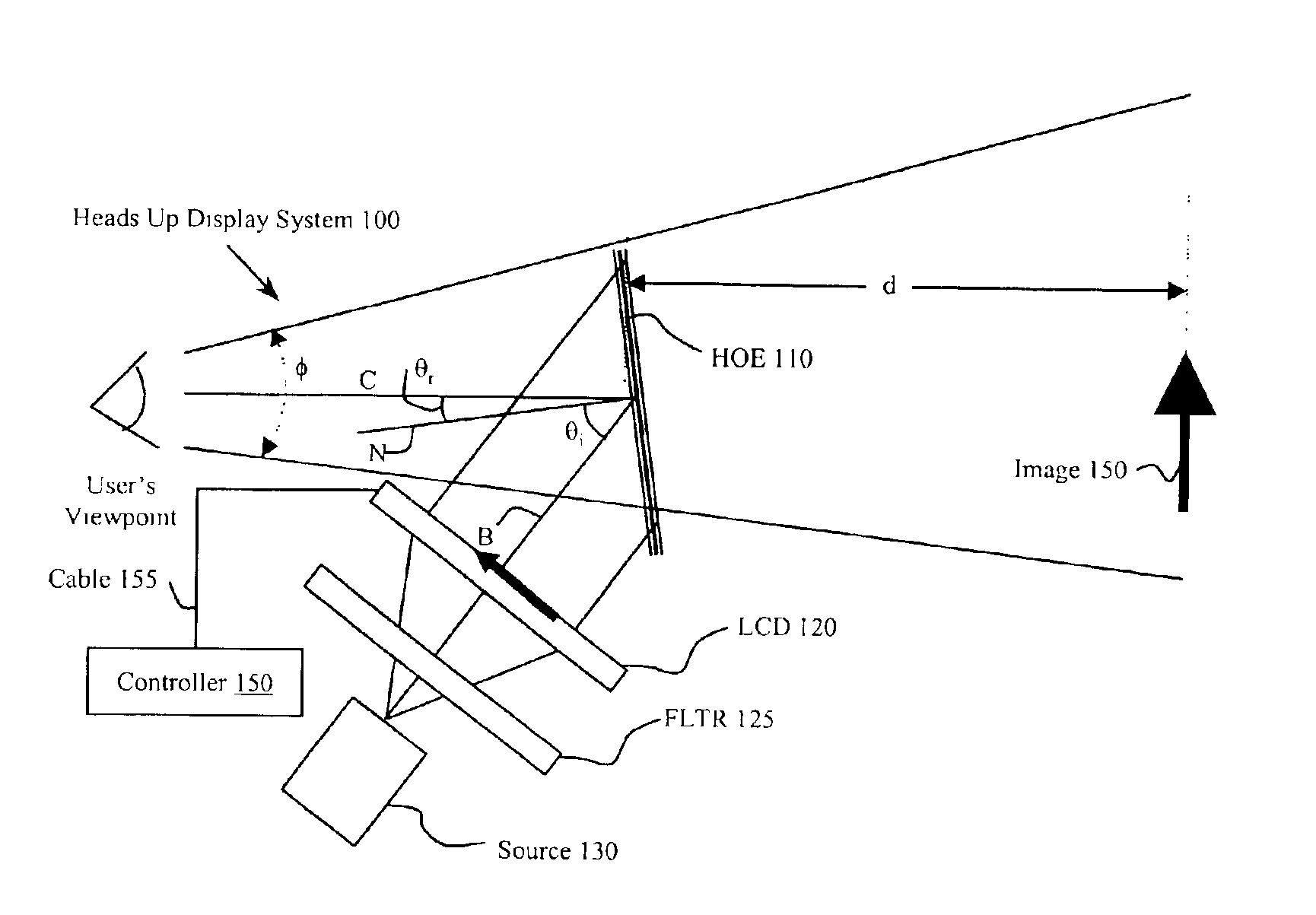
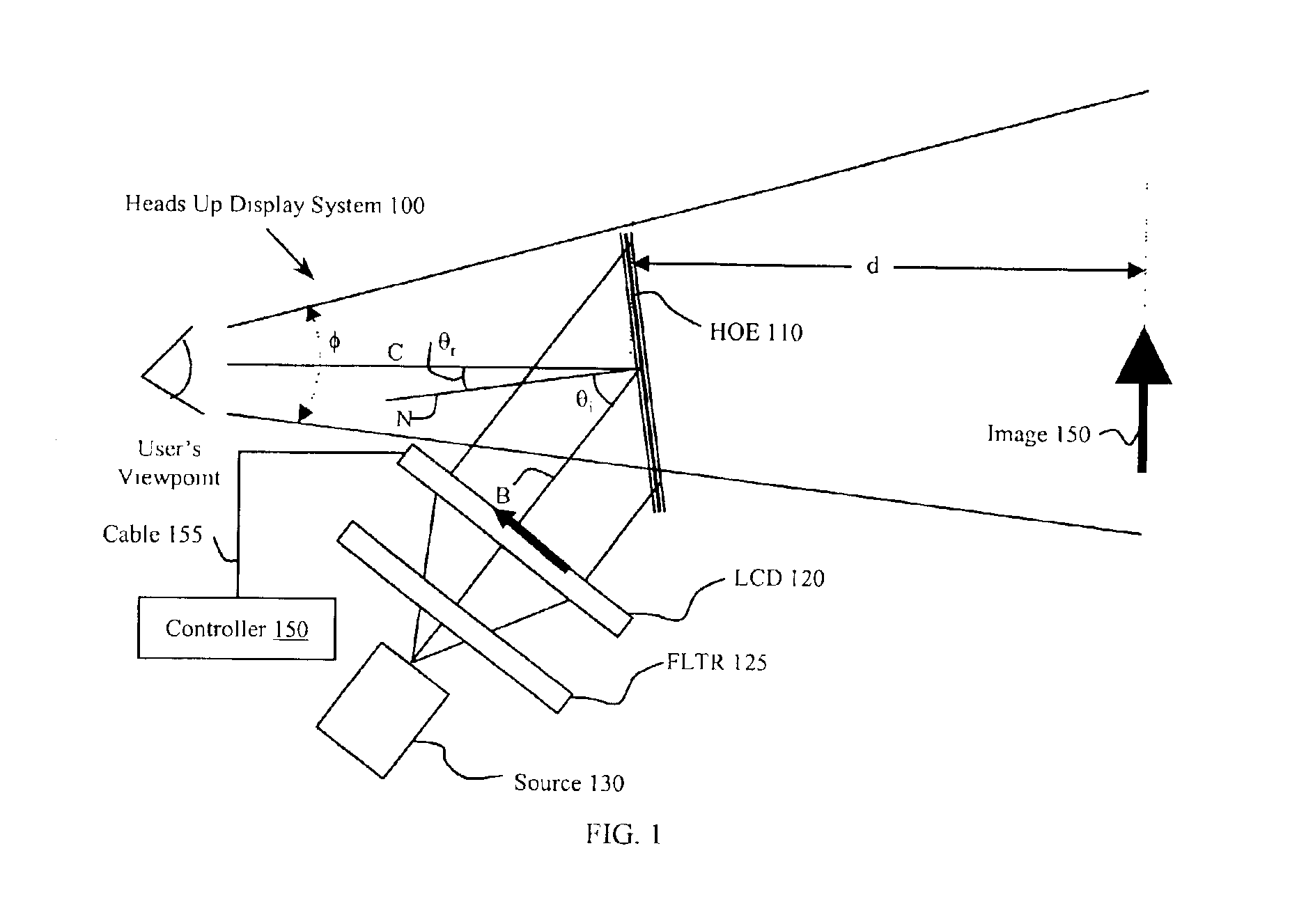
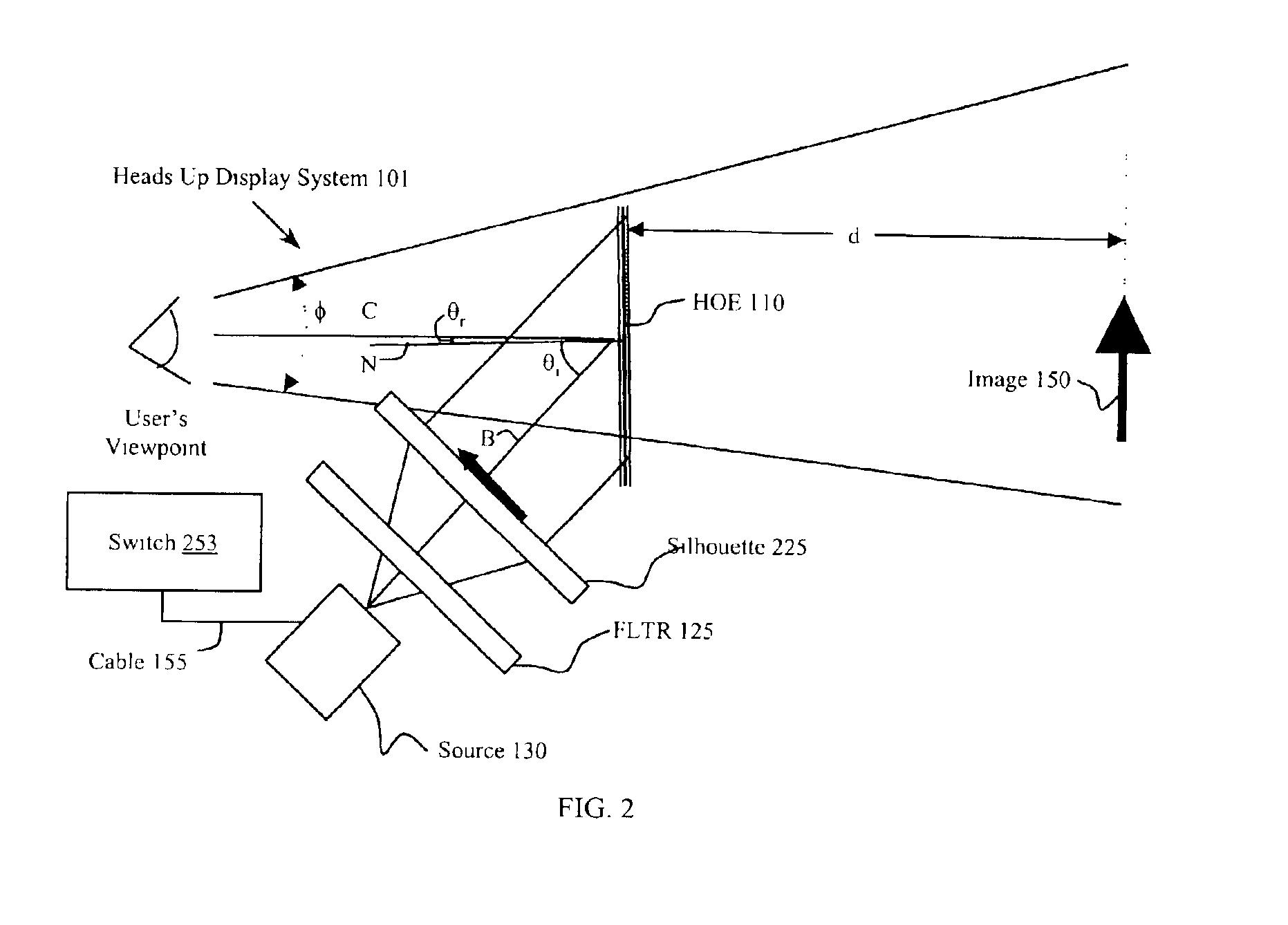
Full color holographic image combiner system
InactiveUS6906836B2High resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsHead-up displayGas-discharge lamp
A device, such as a heads up display, includes equipment for generating a virtual image in the field of view of an observer. The equipment includes at least one light source having a wavelength range less than 2 nm. The light source can be a low pressure gas discharge lamp. The device also includes a holographic optical element that provides a virtual image. The device also includes an image source, such as a mask or an LCD. In one embodiment the holographic optical element combines an image on a display with an ambient image. The holographic element provides multiple colors undistorted in a virtual image appearing to the observer as converging from the same distance.
Owner:MARSUPIAL HLDG
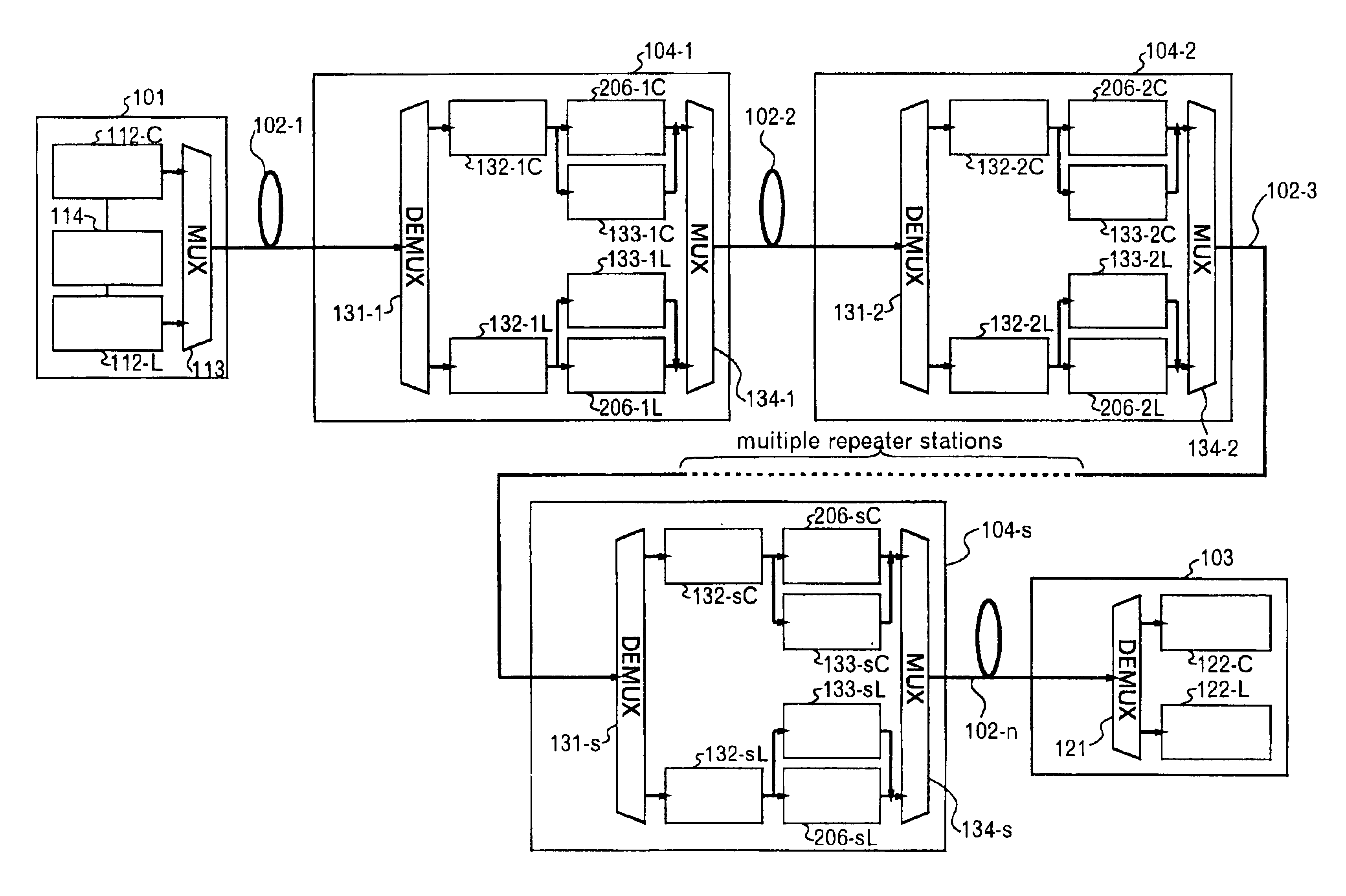
Method of activating optical communication system, channel increasing/decreasing method, and computer-readable recording medium
InactiveUS6839160B2Improve reliabilityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
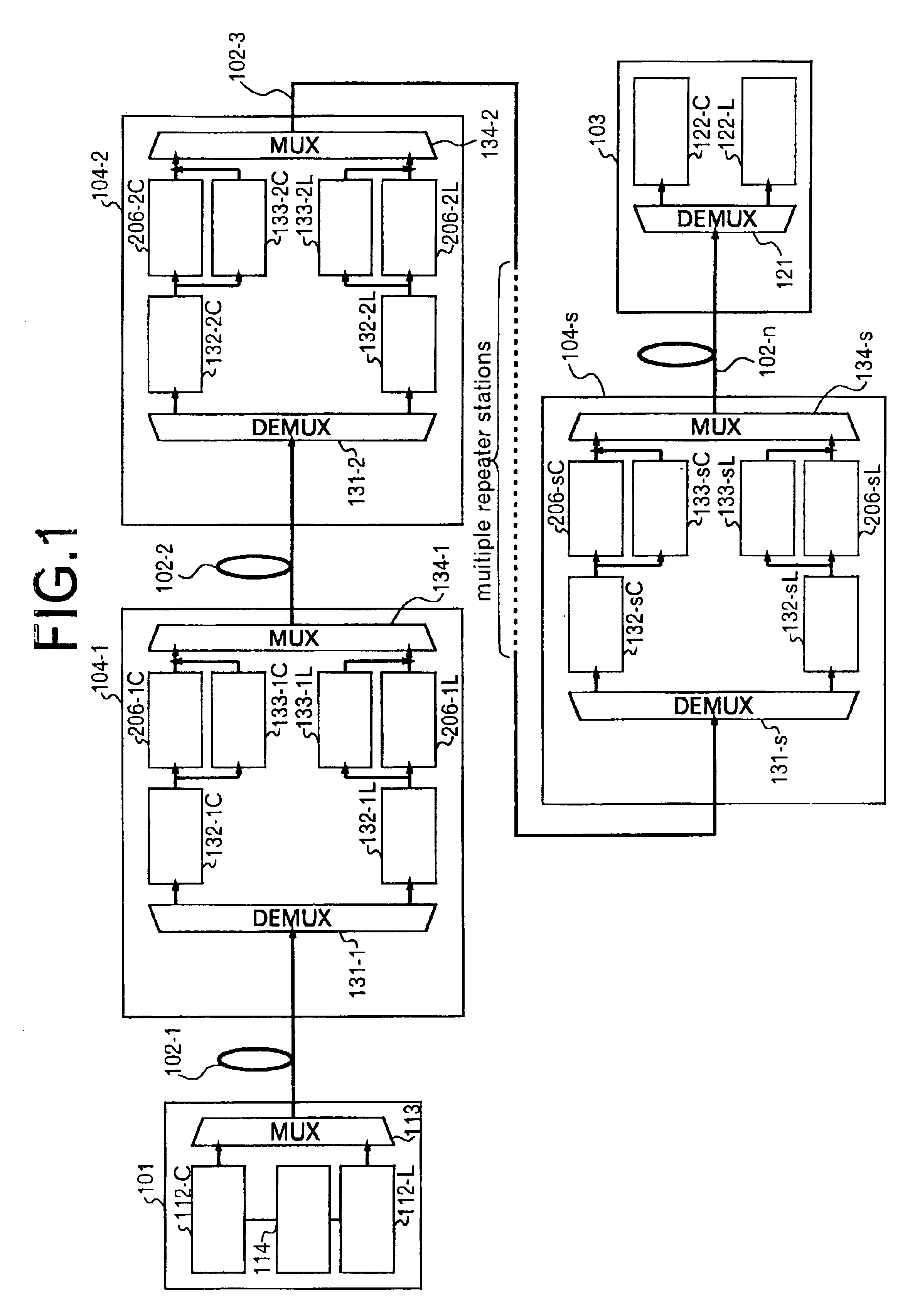
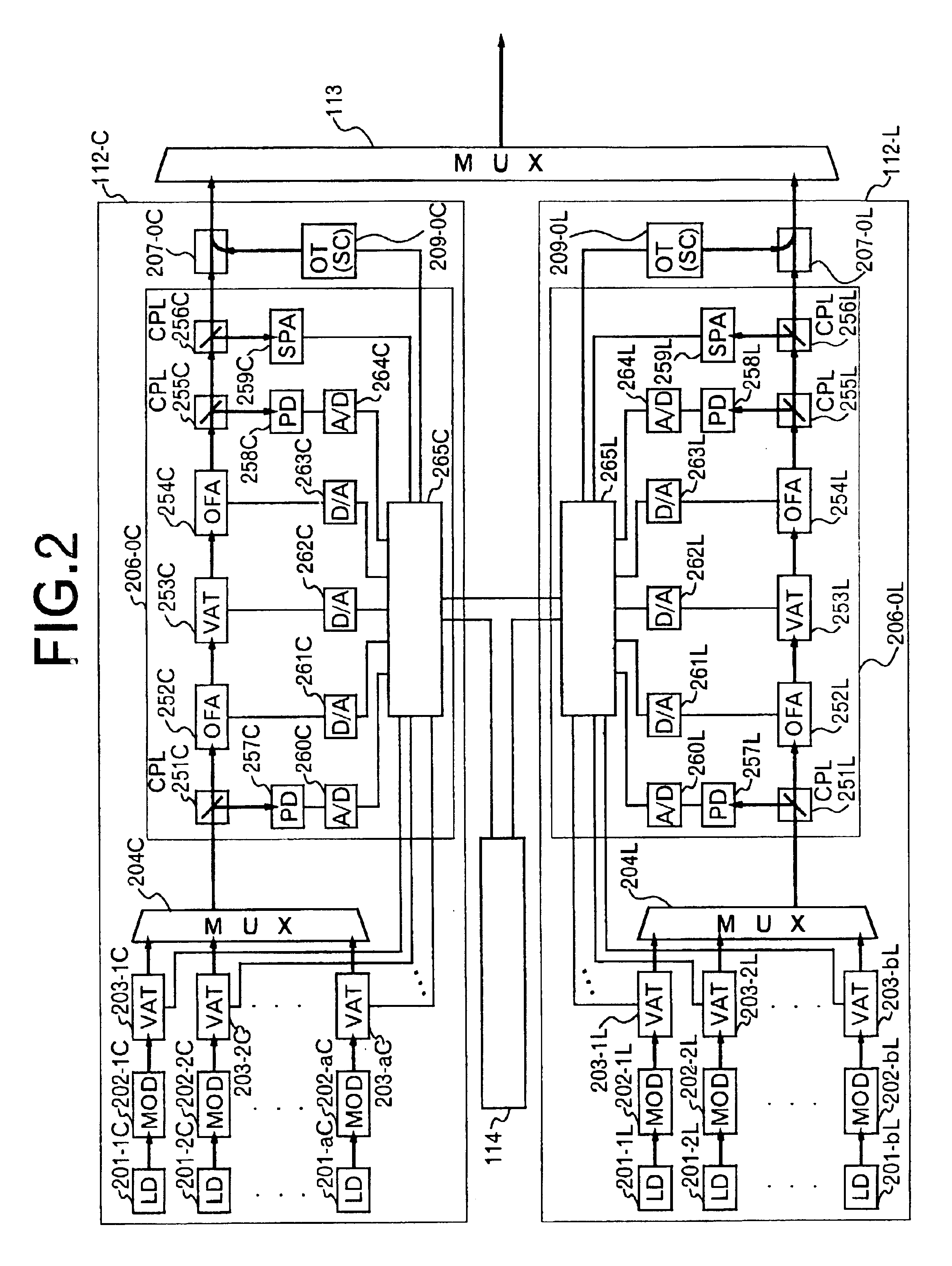
The invention relates to a method of activating an optical communication system comprising a plurality of optical amplifiers having an optical amplifier, between optical transmission lines in which wavelength-division multiplex optical signals are transmitted. The method comprises steps of: generating a desired slope in a desired wavelength range of a gain wavelength curve of the optical amplifier; adjusting an output of the optical amplifier to a desired output level; performing the above two steps in a plurality of optical repeater stations, the steps being carried out in sequence from the first to the last optical repeater stations; and adjusting a level in each optical signal in the wavelength-division multiplex optical signal so as to have substantially constant optical signal-to-noise ratios in the optical signals to be received. Activating the optical communication system according to this procedure allows proper execution of gain slope compensation, output control, and pre-emphasis control.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electromagnetic photonic catheter for reducing restenosis
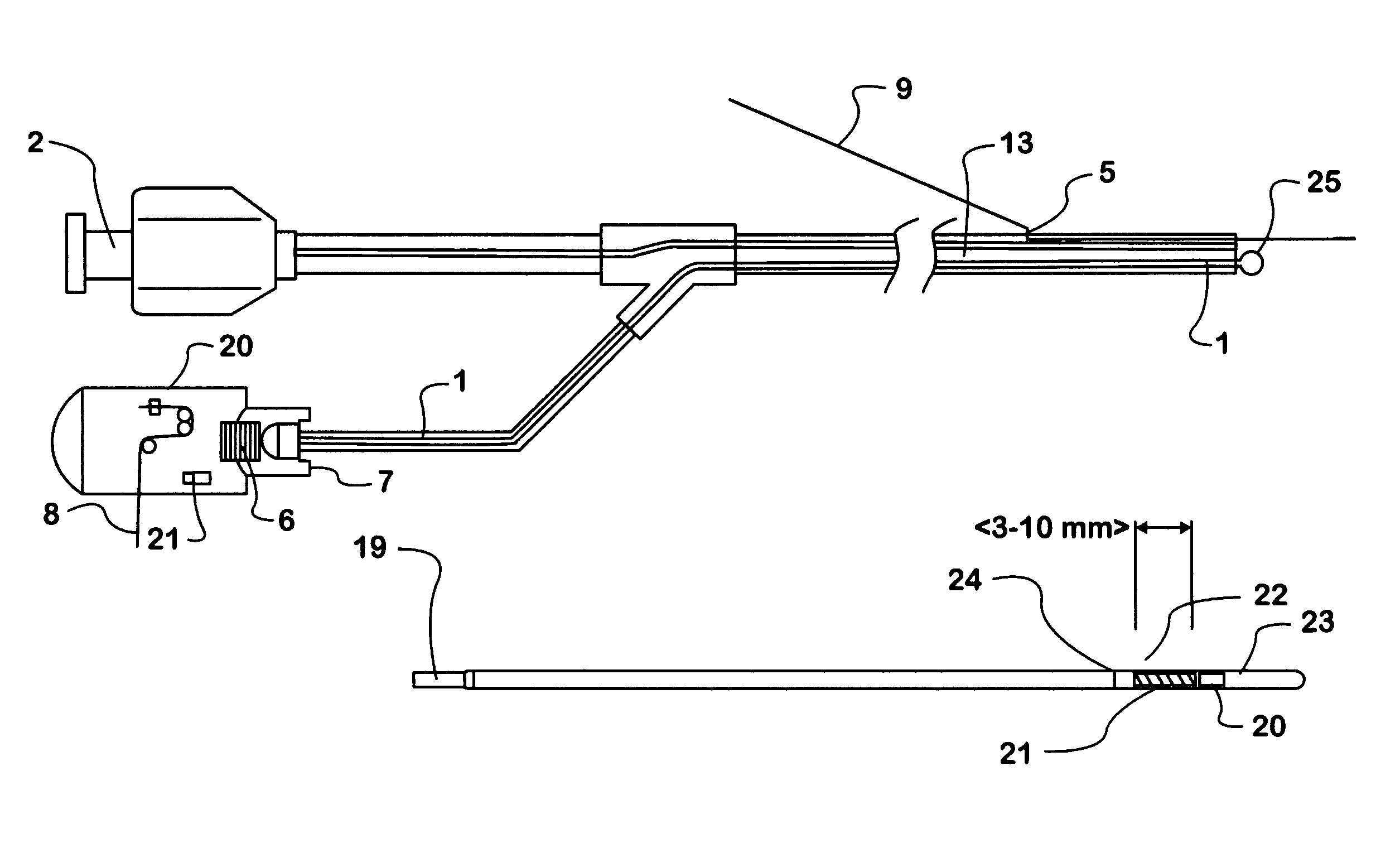
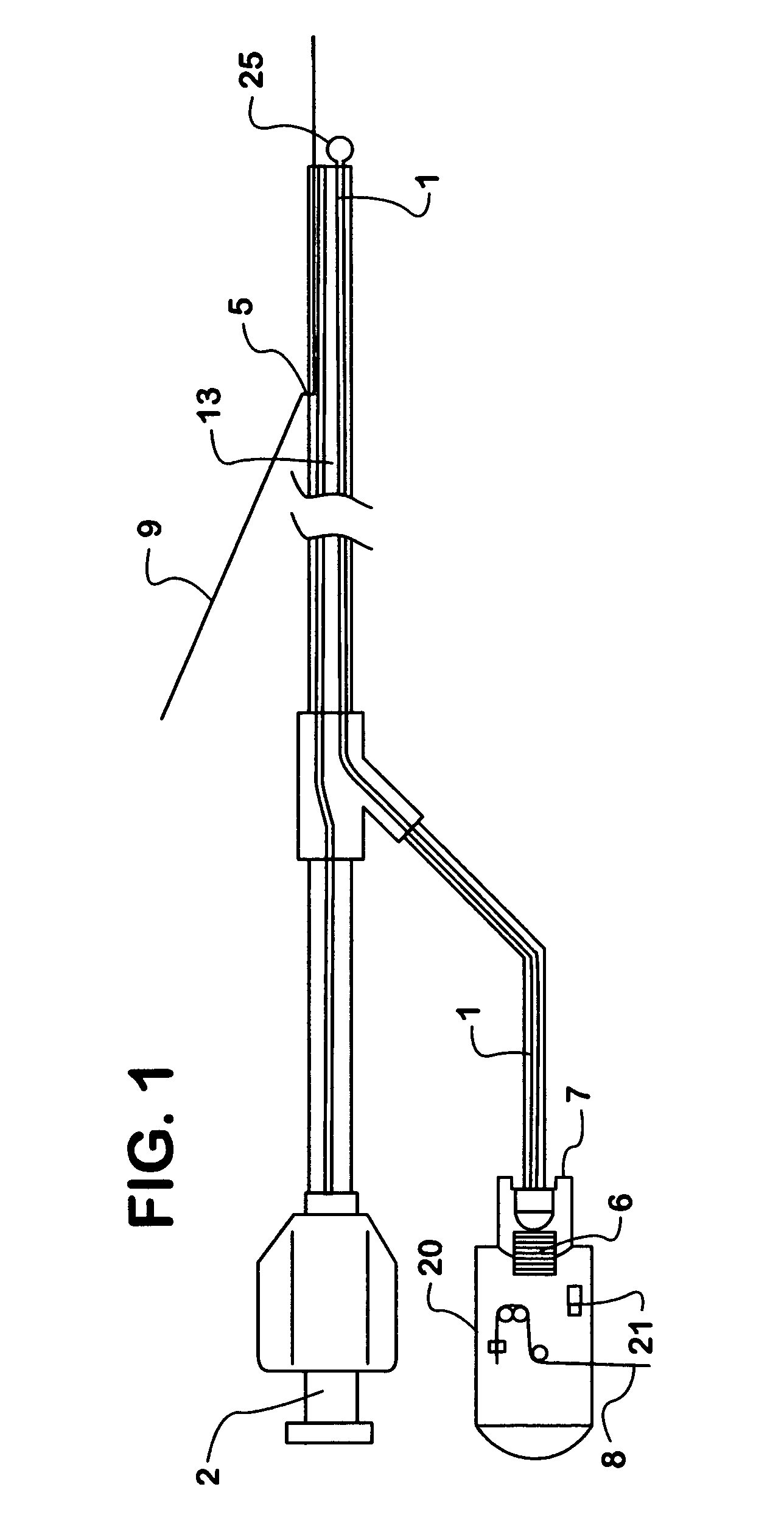
InactiveUS6962584B1Reduce spreadImprove scalabilitySurgical instrument detailsCatheterPhotonicsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The method of vascular treatment for restenosis or vulnerable plaque after an invasive procedure, such as for example angioplasty, stenting with or without drug coating, or drug delivery, comprises: inserting a catheter or hollow guide wire to the treatment location; delivering light through the catheter in the wavelength range of about 700–2500 nm; and moving the light to treat the affected region.
Owner:STONE GREGG W +5
Bright metal flake
InactiveUS6013370AGood specular reflectance characteristicHigh aspect ratioPigmenting treatmentRecord information storageSilicon dioxideReflectivity
A rigid and brittle bright metal flake is formed of a central layer of a reflective material supported on both sides by dielectric layers. In a preferred embodiment, the metal layer is aluminum having a thickness of about 100 nm and the dielectrics are either silicon dioxide or magnesium fluoride, each having a thickness of about 100 nm. The result is a very thin three-layered metal flake about 300 nm thick that exhibits a uniaxial compressive strength of about 8 times a corresponding uniaxial tensile strength. As a result, the metal flake is then afforded the benefits of rigidity and brittle fracture during the manufacturing and applicational processes which ultimately provides favorable planar and specular reflectance characteristics in the visible wavelength range.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
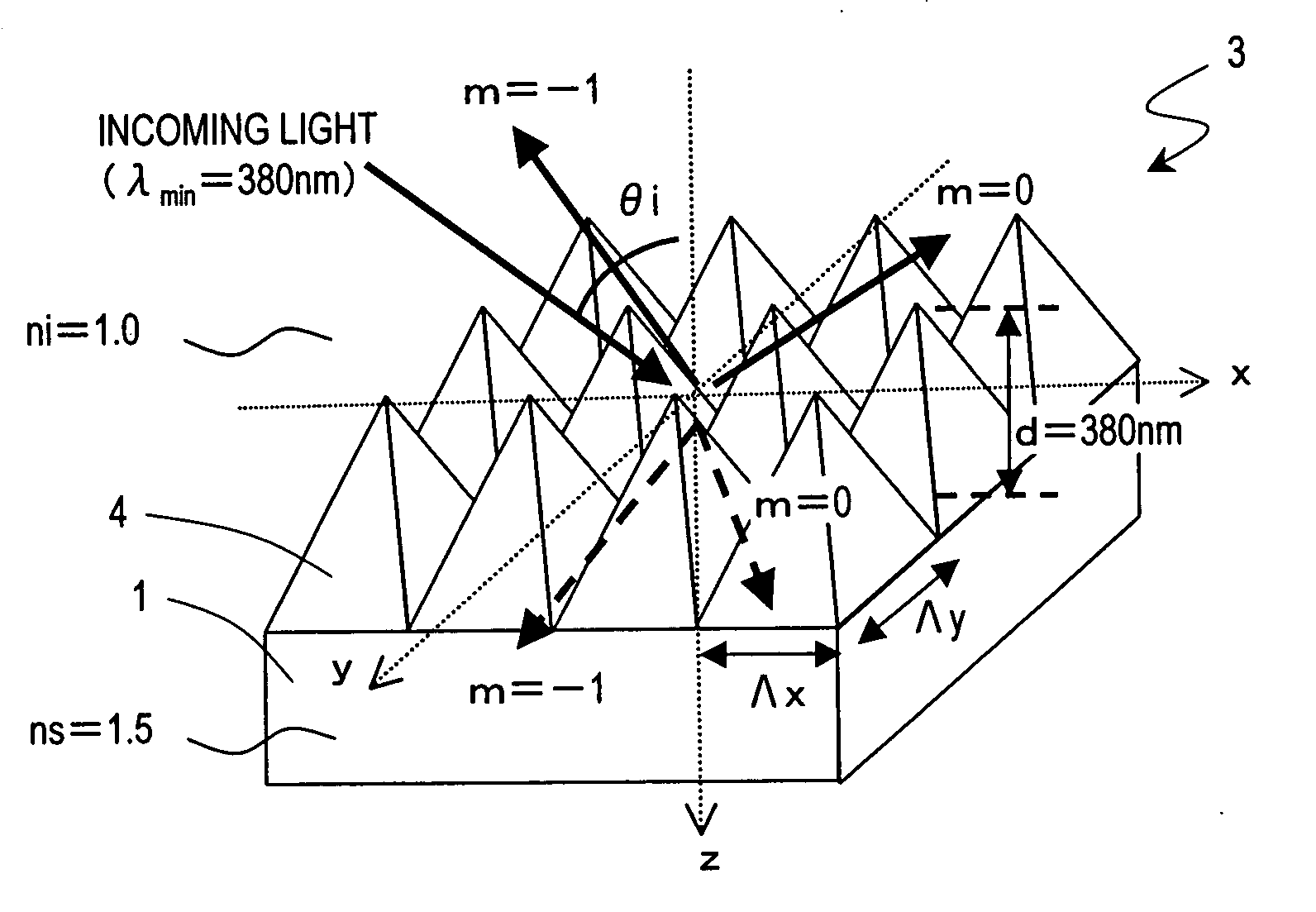
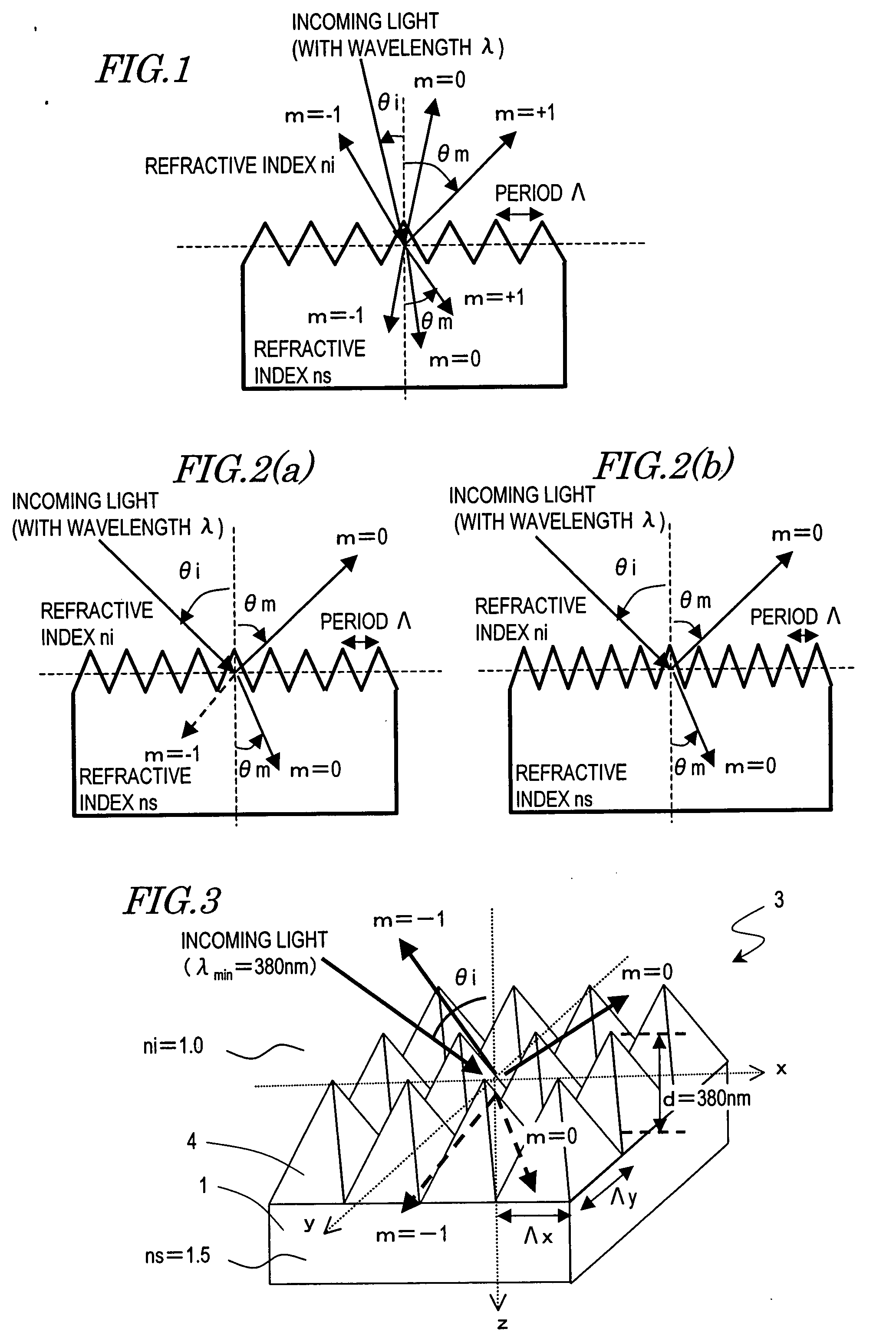
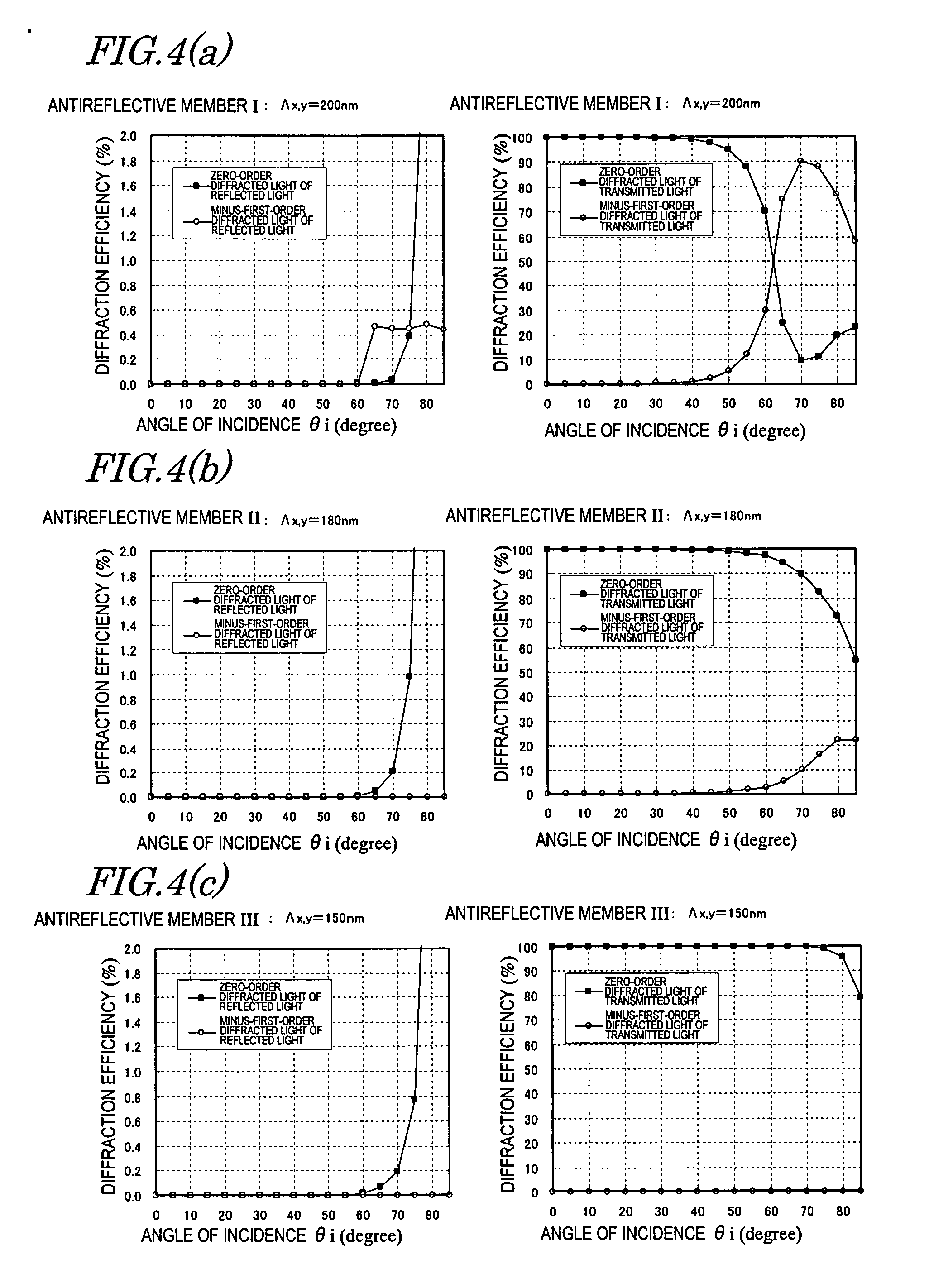
Antireflective member, optical element, display device, method of making stamper and method of making antireflective member using the stamper
ActiveUS20070159698A1Reduce regular reflectionLittle dependenceAnodisationElectric discharge tubesDisplay deviceRefractive index
An antireflective member according to the present invention has an uneven surface pattern, in which unit structures are arranged in x and y directions at respective periods that are both shorter than the shortest wavelength of an incoming light ray, on the surface of a substrate and satisfies the following Inequality (1): Λ x,yλmin<1ni+ni·sin θ imax(1)where λmin is the shortest wavelength of the incoming light ray, θimax is the largest angle of incidence of the incoming light ray, ni is the refractive index of an incidence medium, Λx is the period of the uneven surface pattern in the x direction, and Λy is the period of the pattern in the y direction. As a result, diffraction of short-wave light components can be reduced in a broad wavelength range.
Owner:SHARP KK
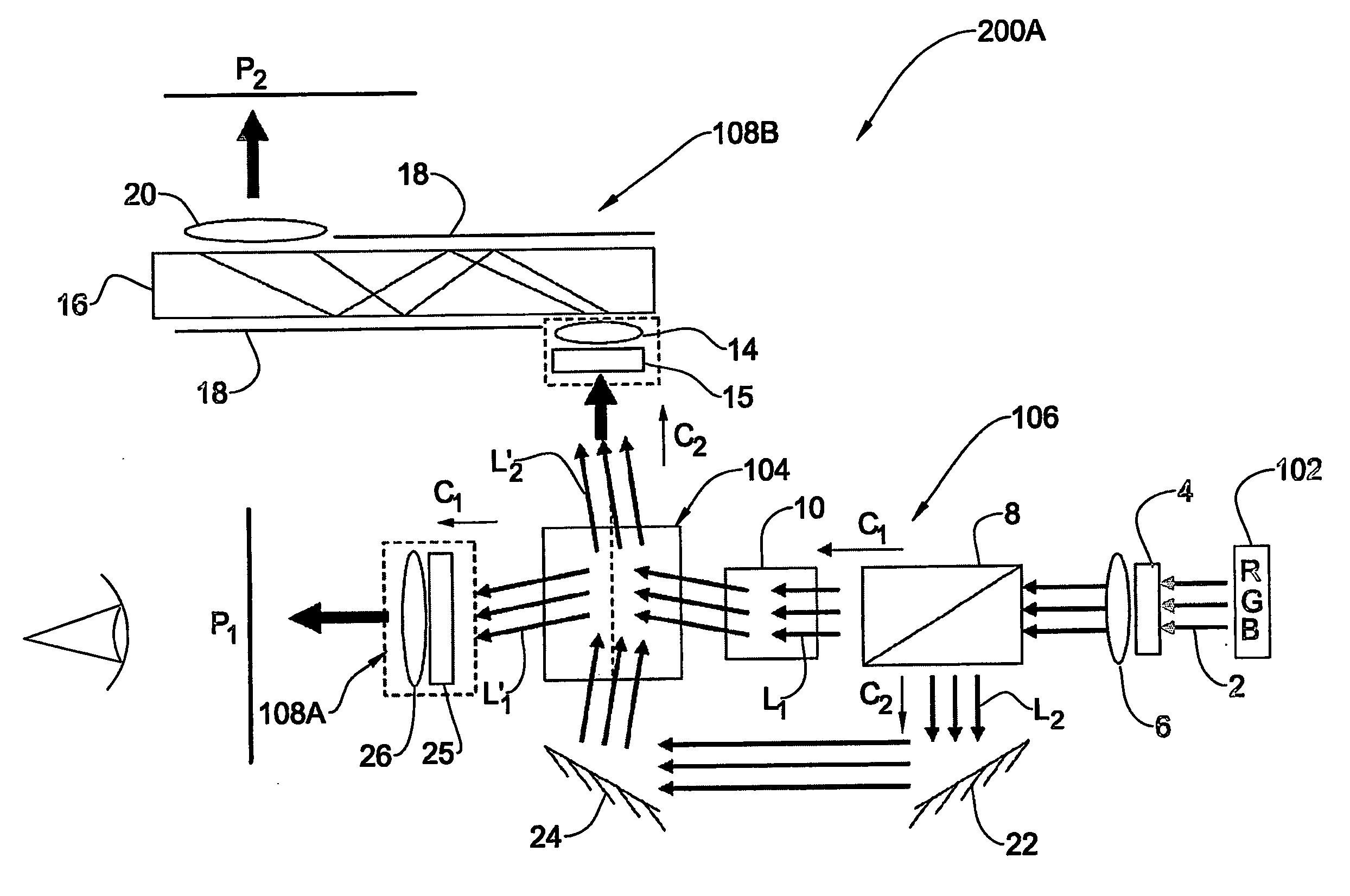
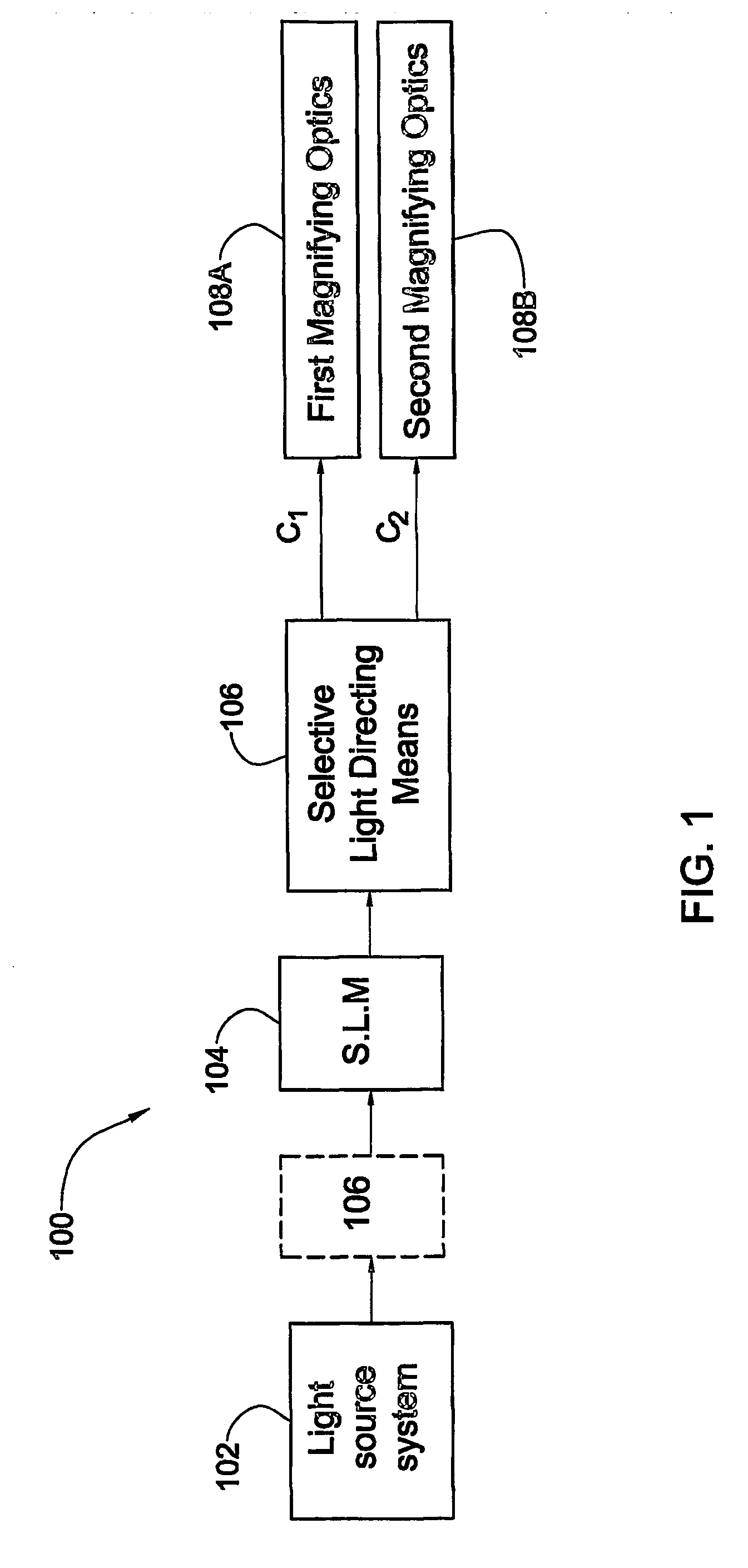
Projection system and method
InactiveUS20060279662A1Large and clear imageReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsProjectorsSpatial light modulatorMagnification
An image projection system and method are presented to project an image on at least one of first and second projection planes. The system comprises a light source system including one or more light source assemblies operable to generate light of one or more predetermined wavelength range; a spatial light modulator (SLM) system including one or more SLM units operable to spatially modulate input light in accordance with an image to be directly projected or viewed; and two optical assemblies associated with two spatially separated light propagation channels, respectively, to direct light to, respectively, the first and second projection planes with desired image magnification. The system is configured to selectively direct the input light propagating towards the SLM system or light modulated by the SLM system to propagate along at least one of the two channels associated with the first and second projection planes, respectively.
Owner:EXPLAY
Light recycling illumination systems with wavelength conversion
An illumination system has a light source and a wavelength conversion layer within a light-recycling envelope. The wavelength conversion layer is a solid phosphor layer. The light source is a light-emitting diode or a semiconductor laser. The light source will emit light of a first wavelength range that is transmitted through the wavelength conversion layer in order to convert a portion of the light of a first wavelength range into light of a second wavelength range. Light of both the first and second wavelength ranges will exit the light-recycling envelope through an aperture. The recycling of the light by the light-recycling envelope will enhance the output radiance and luminance of the light exiting the illumination system.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Endoscope system for fluorescent observation
An endoscope system is disclosed for detecting fluorescent light emitted in the near-infrared region by a plurality of fluorescent labeling materials introduced into a living tissue. An illumination system generates illumination light in the wavelength range 600 nm-2000 nm which serves as excitation light for the plurality of fluorescent labeling materials, and a detection system that can separately detect different ones of the plurality of fluorescent light emissions that are emitted at different wavelengths from among the plurality of fluorescent labeling materials is provided. The endoscope system may include a conventional-type endoscope having an insertion section, or a capsule endoscope that wirelessly transmits image data. By superimposing the image data obtained using reflected light in the visible region and fluorescent light emitted by the fluorescent labeling materials, improved diagnostic capabilities are provided.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
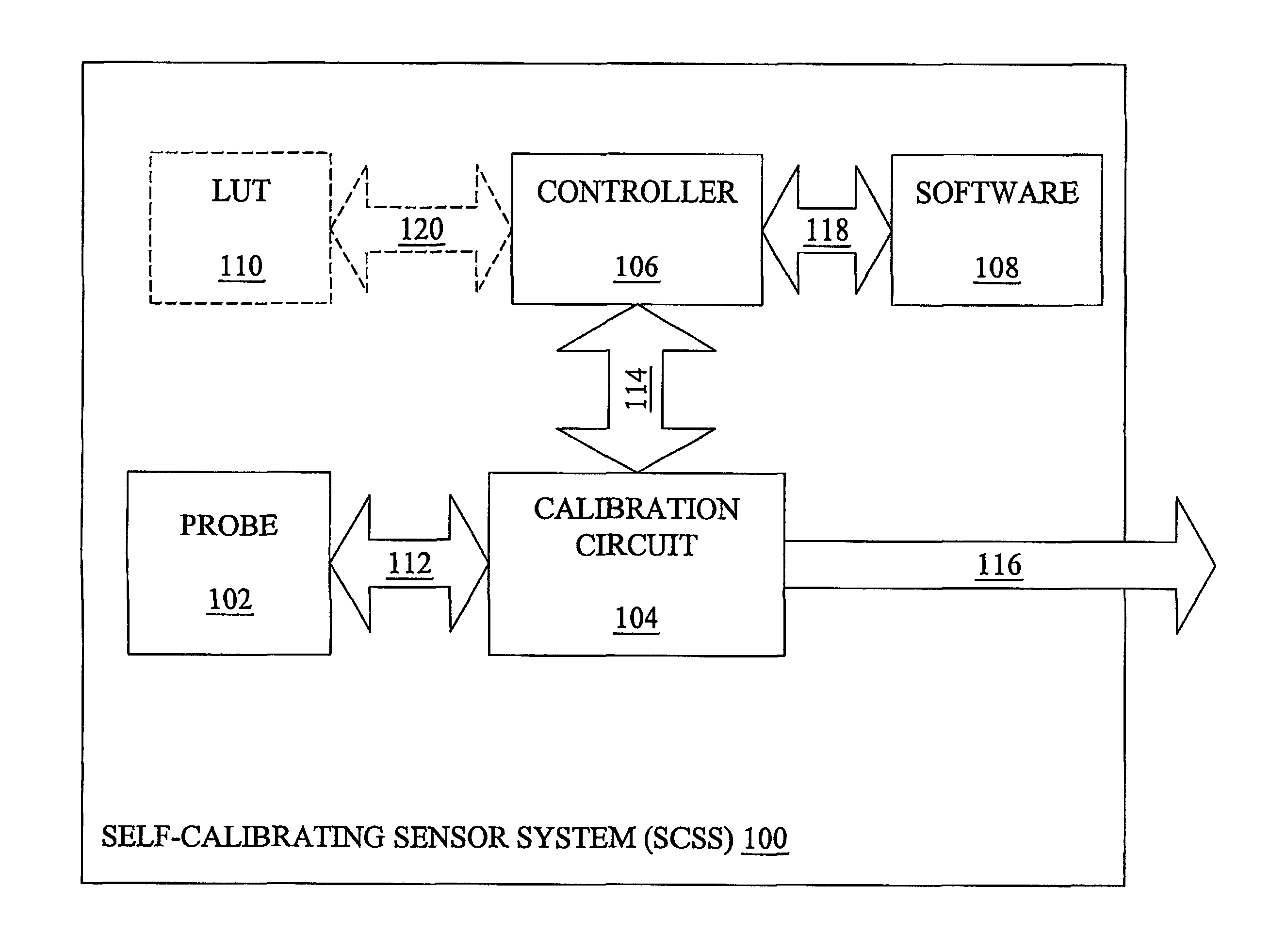
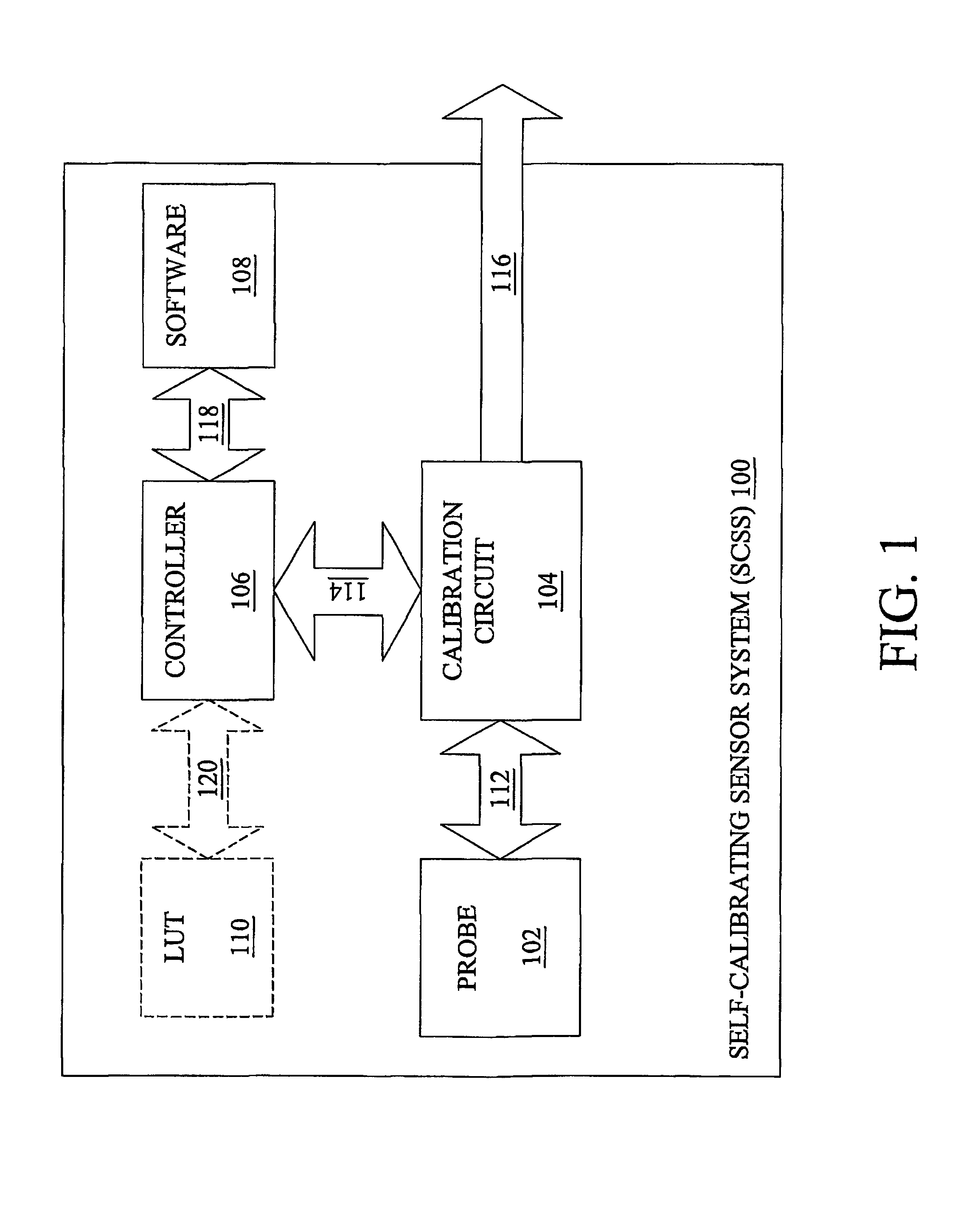
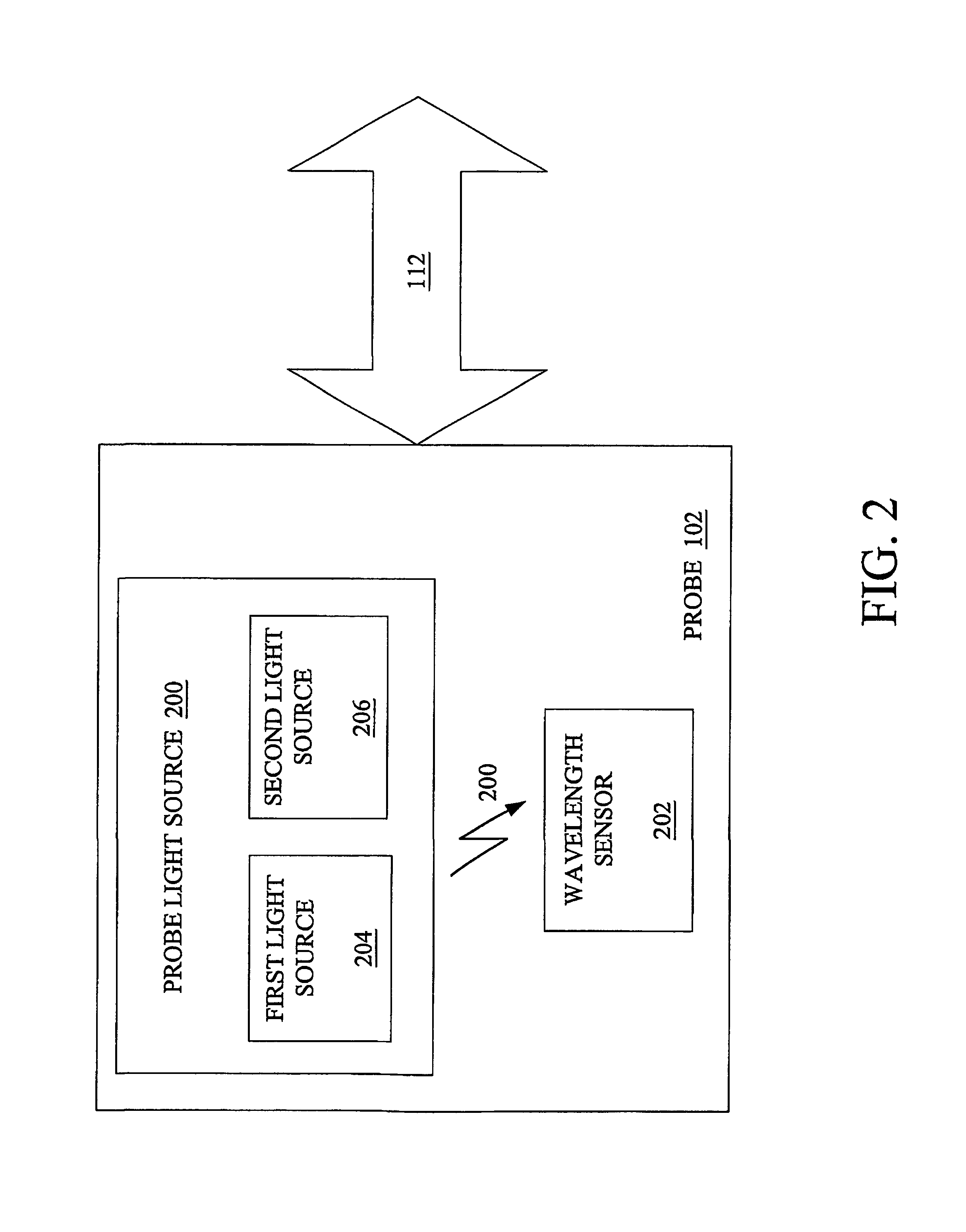
System and method for a self-calibrating non-invasive sensor
A non-invasive emitter-photodiode sensor which is able to provide a data-stream corresponding to the actual wavelength of light emitted thereby allowing calibration of the sensor signal processing equipment and resulting in accurate measurements over a wider variation in emitter wavelength ranges.
Owner:MEDTOR INC
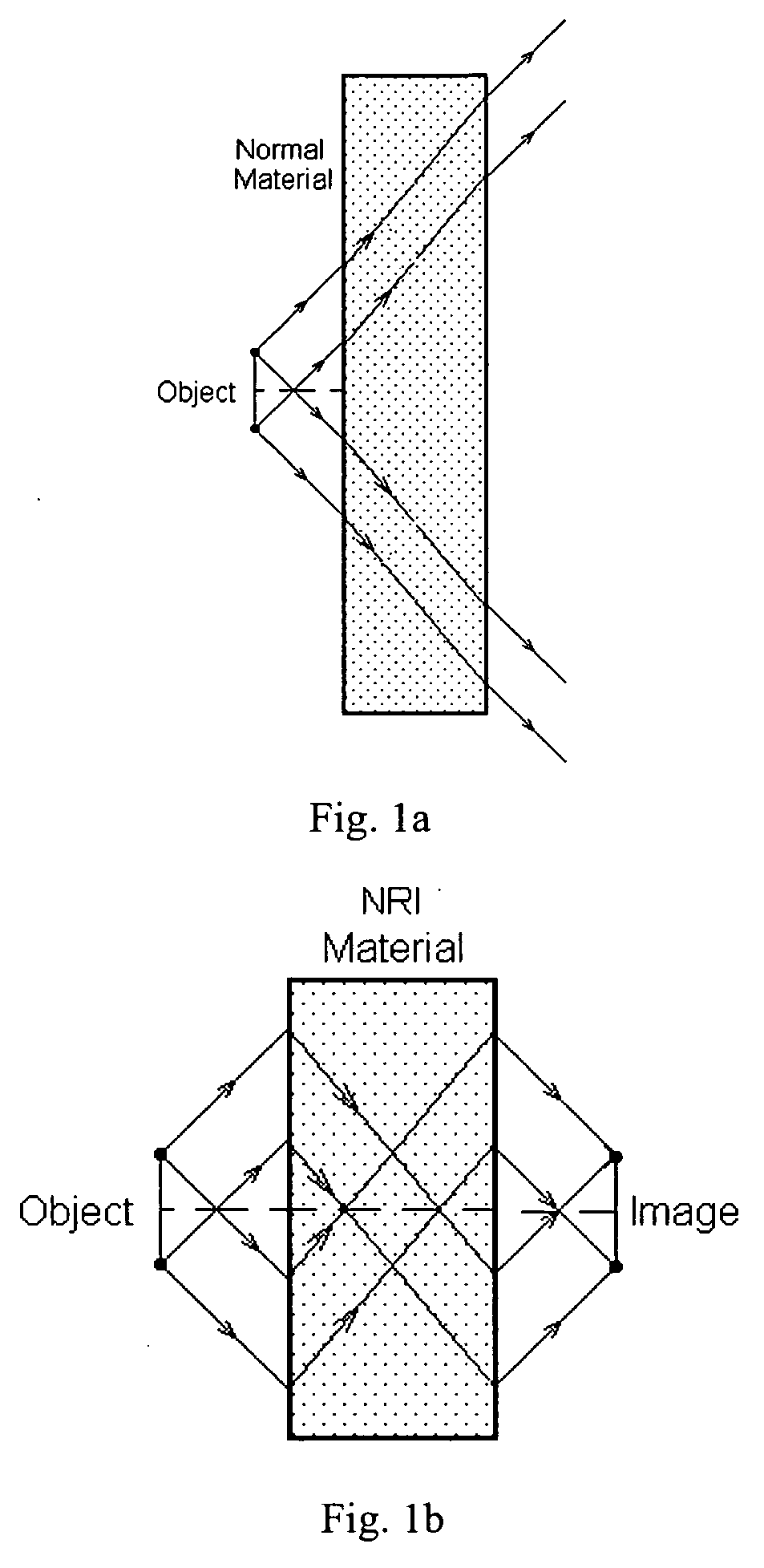
Negative refractive index and opto-magnetic materials and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20050221128A1Reduce processing timeLow chemical consumptionNanoopticsRecord information storageCost effectivenessOptical property
One-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional negative refractive index (NRI) and / or opto-magnetic materials operating in spectral ranges spanning from the visible to far IR wavelength ranges is disclosed. Said materials are comprised of metal or metal / dielectric wire pairs arranged in a number of sublattices (one for one dimensional material, two for two-dimensional and three or more for three dimensional material), such that in each lattice, said wire pairs are essentially parallel to each other. Such a materials are useful and practical in obtaining previously unachievable important optical functions in these spectral ranges. Such optical properties are highly desired for many applications. A practical means of manufacture that is compatible with cost-effective and large-scale production methods is also provided.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Wavelength conversion for producing white light from high power blue LED
InactiveUS20100289044A1Reduce energy consumptionElectroluminescent light sourcesGas discharge lamp usageFull width at half maximumJunction temperature
A white light LED is described that uses an LED die that emits visible blue light in a wavelength range of about 450-470 nm. A red phosphor or quantum dot material converts some of the blue light to a visible red light having a peak wavelength between about 605-625 nm with a full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) less than 80 nm. A green phosphor or quantum dot material converts some of the blue light to a green light having a FWHM greater than 40 nm, wherein the combination of the blue light, red light, and green light produces a white light providing a color rendering of Ra,8>90 and a color temperature of between 2500K-5000K. Preferably, the red and green converting material do not saturate with an LED die output of 100 W / cm2 and can reliably operate with an LED die junction temperature over 100 degrees C.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com