Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1120 results about "Surface pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A designer who specialises in creating patterns & repeats, surface pattern. Pattern has the ability to decorate a surface with the use of repetition. It creates rhythm energy & movement.
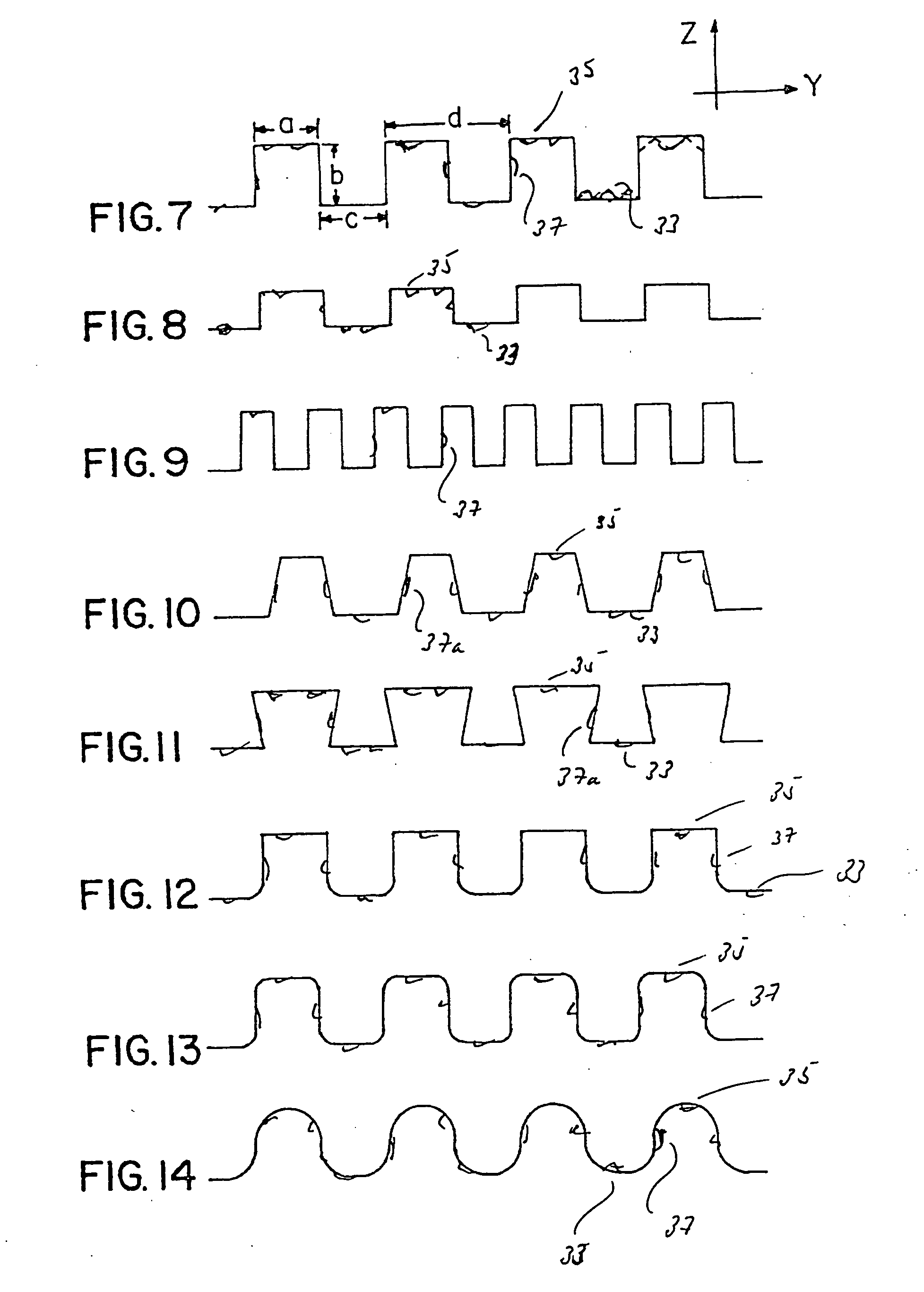
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS20170316940A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface patternSilanes
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
LED device for wide beam generation
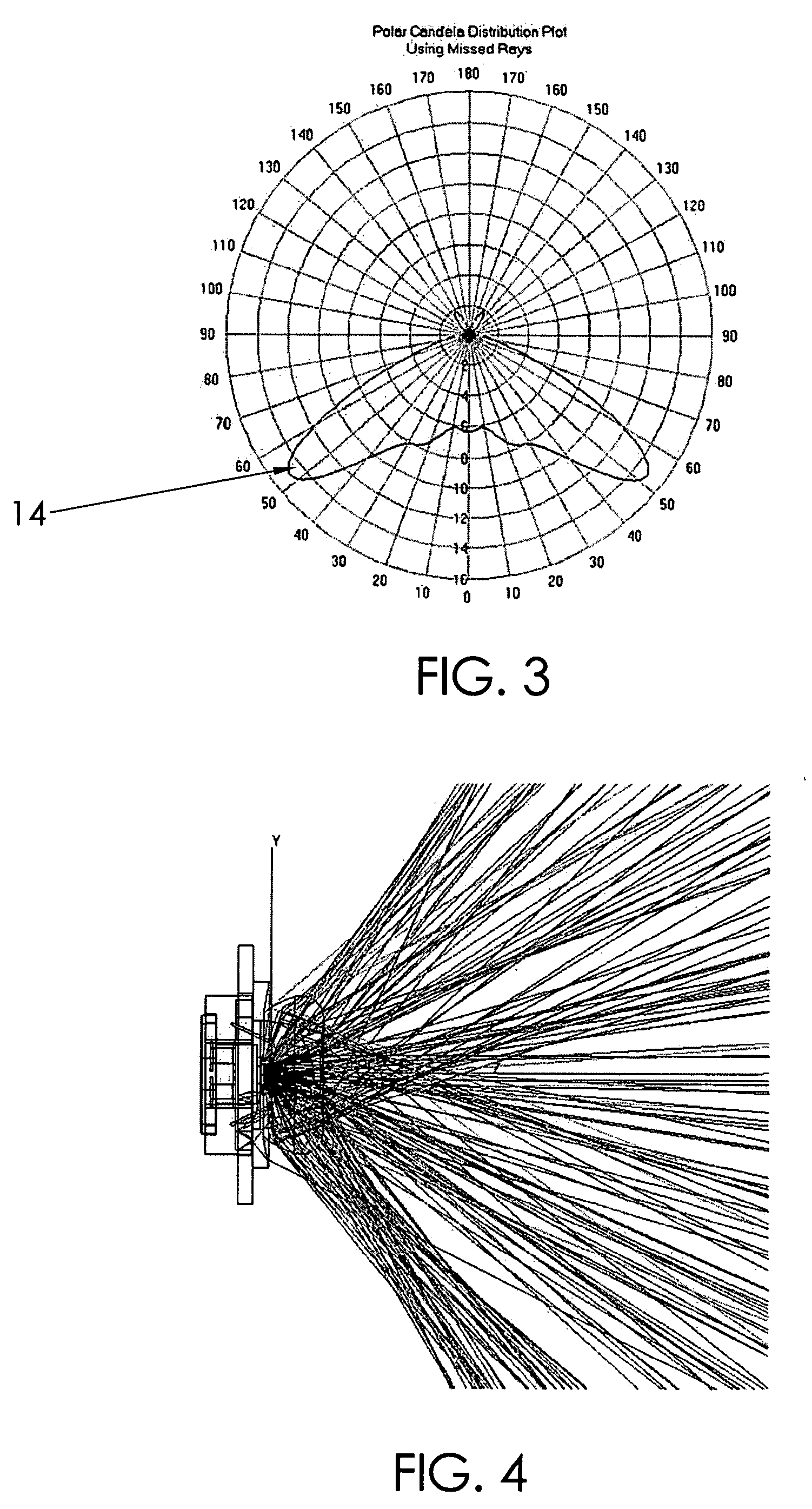
ActiveUS7674018B2Easy to combineReduce discontinuityPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusSurface patternWide beam
An apparatus and method is characterized by providing an optical transfer function between a predetermined illuminated surface pattern, such as a street light pattern, and a predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source, such as that from an LED. A lens is formed having a shape defined by the optical transfer function. The optical transfer function is derived by generating an energy distribution pattern using the predetermined energy distribution pattern of the light source. Then the projection of the energy distribution pattern onto the illuminated surface is generated. The projection is then compared to the predetermined illuminated surface pattern to determine if it acceptably matches. The process continues reiteratively until an acceptable match is achieved. Alternatively, the lens shape is numerically or analytically determined by a functional relationship between the shape and the predetermined illuminated surface pattern and predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source as inputs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method and Systems for Illuminating
InactiveUS20080055931A1Illumination system is relatively slimIncrease brightnessMechanical apparatusHollow light guidesSurface patternLight guide
Methods and systems are described for illumination in different applications. Real thin illumination systems ( 200 ) with good luminance uniformity, good efficiency and good colour mixing uniformity are obtained, even if different light sources emitting different colours are used. A plurality of light sources ( 102 ), emitting light from different colours, couple their light sideways, i.e. substantially parallel to the plane of light out-coupling, into a light guide ( 104 ) through recesses ( 108 ) distributed over the light guide ( 104 ). Providing a specially structured surface pattern ( 106 ), in combination with light in-coupling parallel to the plane of light out-coupling of the light guide ( 104 ) allows to obtain a good colour mixing of the differently coloured light originating from the plurality of light sources ( 102 ). The light then is only coupled out after it has been in the light guide ( 104 ) for a significant long time such that the light emanating from different light sources ( 102 ) is significantly mixed. The illumination system ( 200 ) has an important application in non-emissive displays.
Owner:BARCO NV
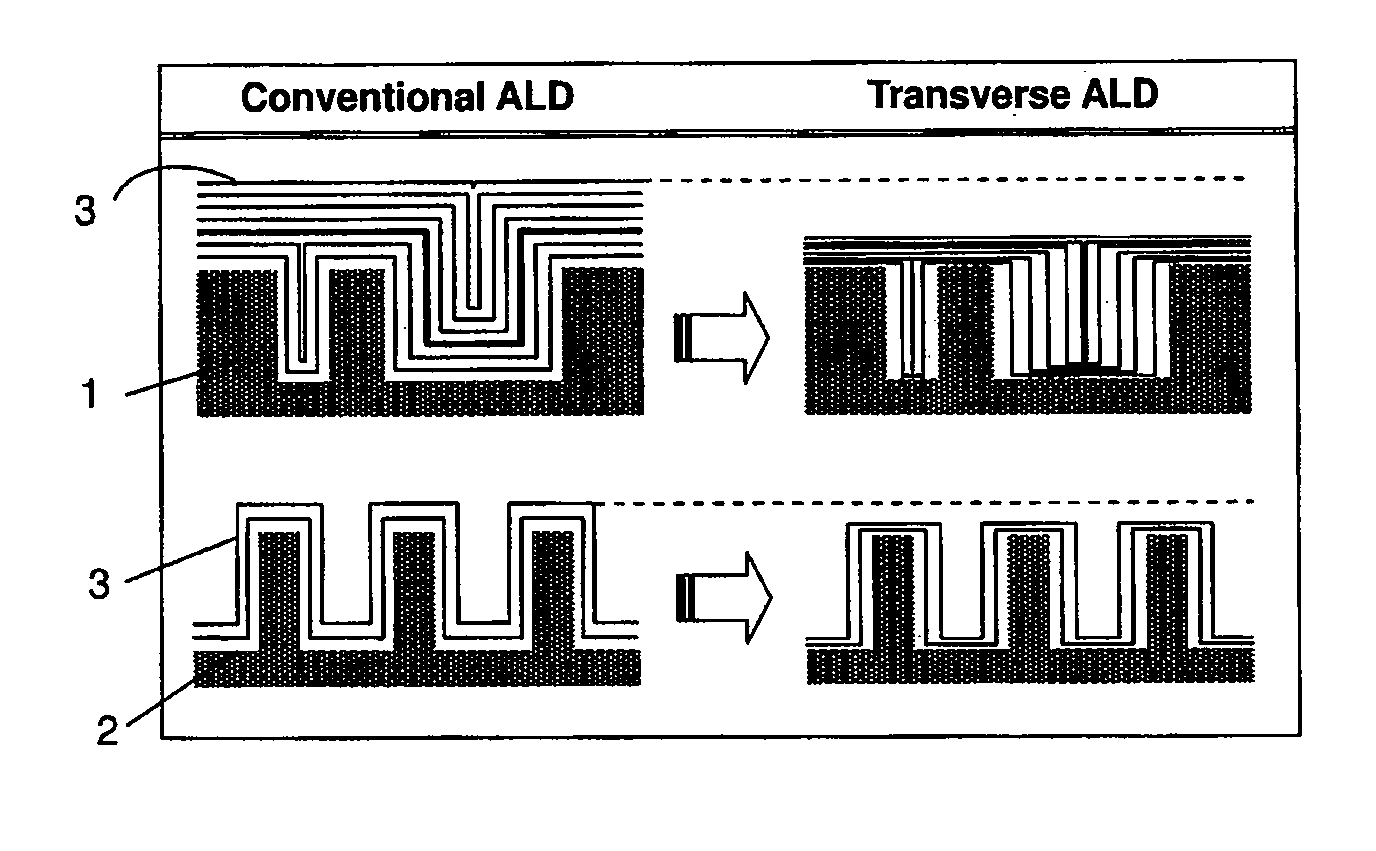
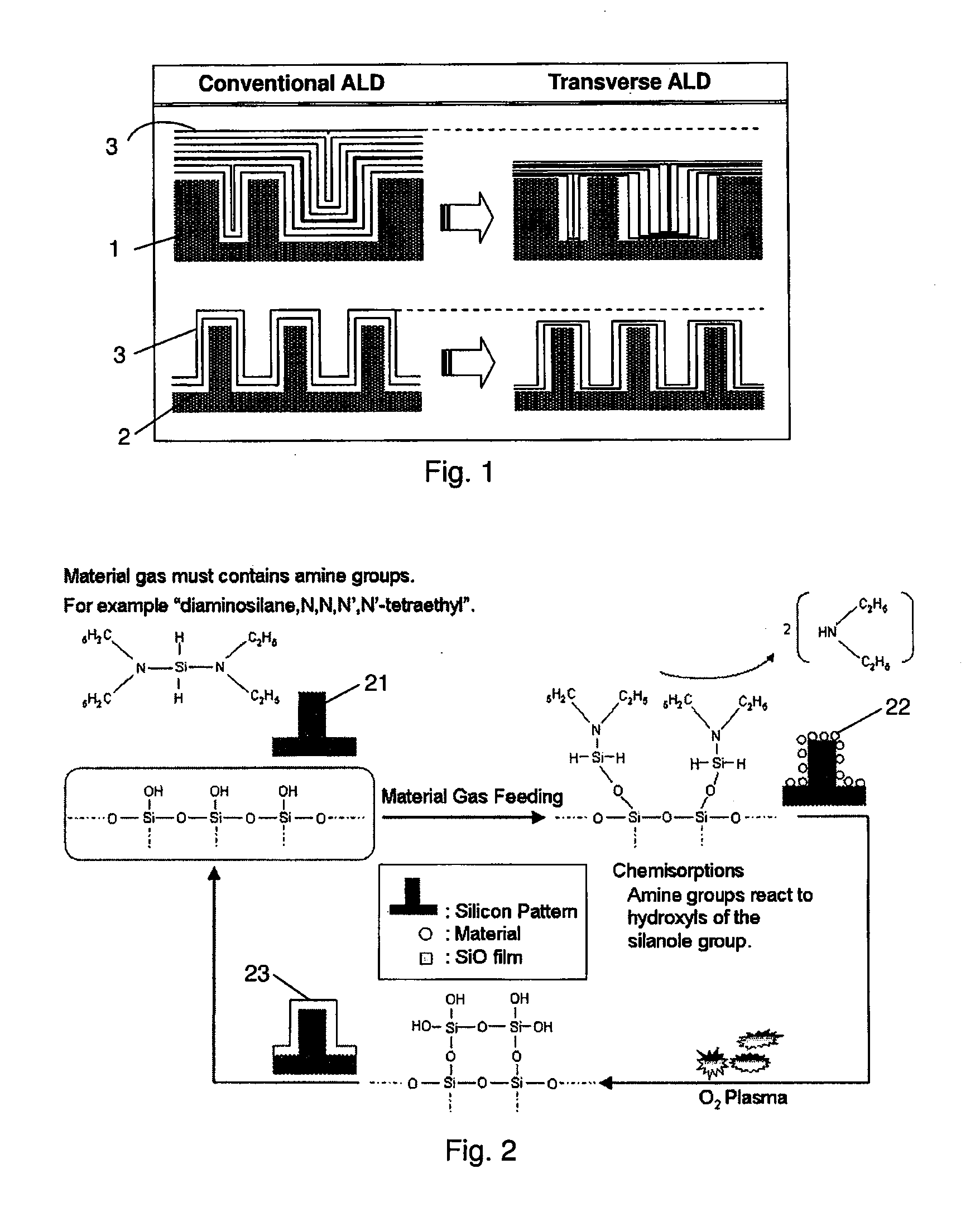
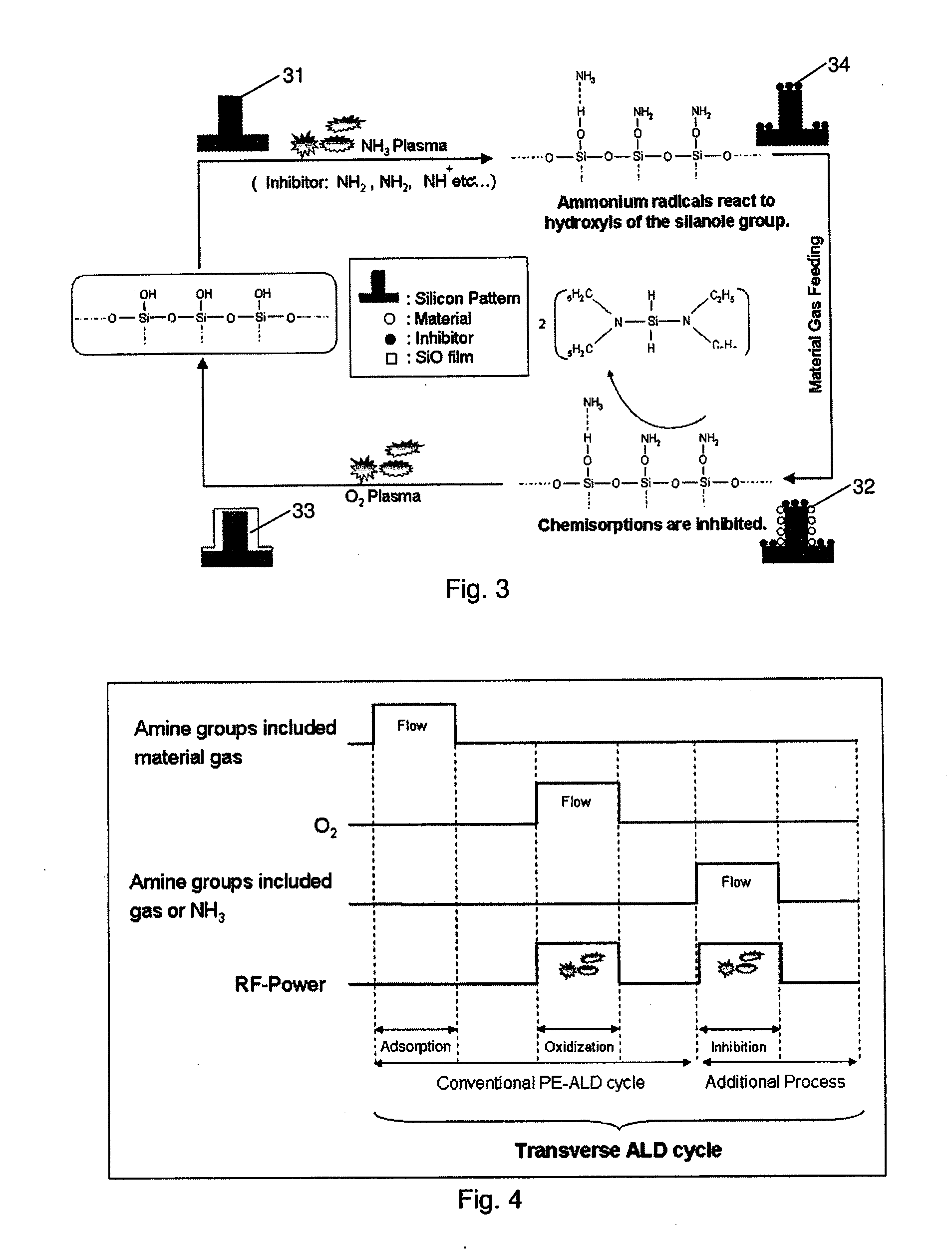
Atomic Layer Deposition For Controlling Vertical Film Growth
ActiveUS20120276306A1Improve directionLower film growth rateVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesSurface patternVertical growth
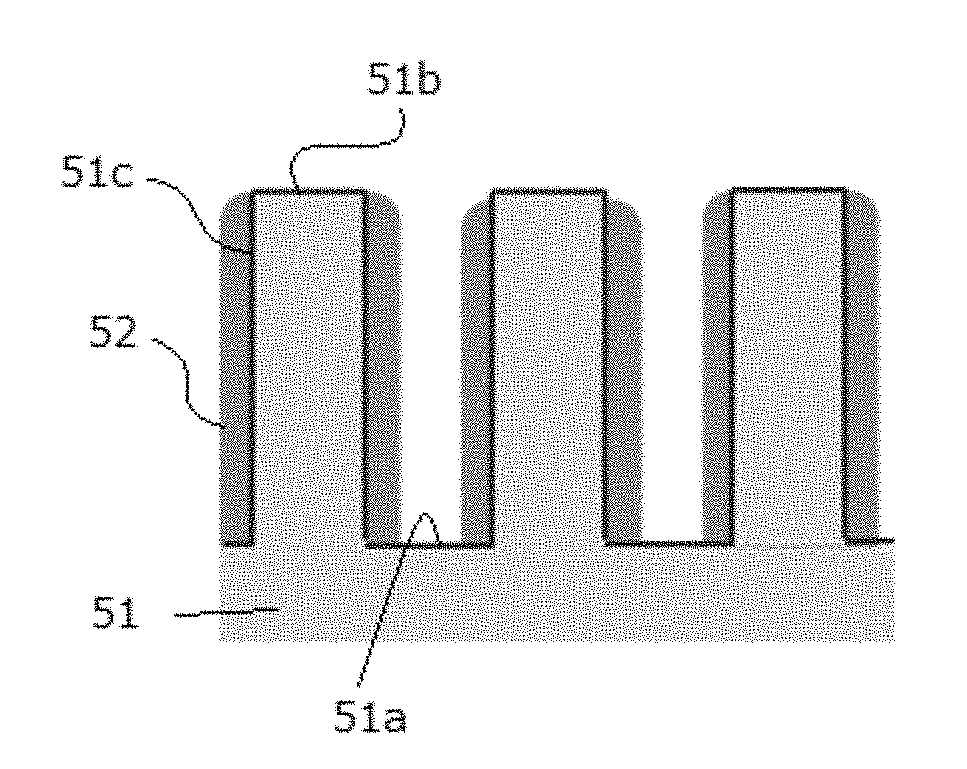
A method for forming a film by atomic layer deposition wherein vertical growth of a film is controlled, includes: (i) adsorbing a metal-containing precursor for film formation on a concave or convex surface pattern of a substrate; (ii) oxidizing the adsorbed precursor to form a metal oxide sub-layer; (iii) adsorbing a metal-free inhibitor on the metal oxide sub-layer more on a top / bottom portion than on side walls of the concave or convex surface pattern; and (iv) repeating steps (i) to (iii) to form a film constituted by multiple metal oxide sub-layers while controlling vertical growth of the film by step (iii). The adsorption of the inhibitor is antagonistic to next adsorption of the precursor on the metal oxide sub-layer
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Fused loop of filamentous material and apparatus for making same
InactiveUS7090111B2Maximize joint strengthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurface patternUltrasonic welding
A welding apparatus that includes a first member having a first suture-contacting surface, a second member having a second suture-contacting surface, and a device for moving the first member relative to the second member to define a gap between the respective suture-contacting surfaces. The first member is capable of vibrating and delivering mechanical energy at ultrasonic frequencies. The second member is stationary relative to the first member. A fixture element is adapted to receive and maintain two or more segments of a material to be welded in a predetermined alignment in the gap between the first and second surfaces of the first and second members during a welding operation. According to another aspect of the invention, an ultrasonic welding apparatus includes first and second members with patterned first and second suture-contacting surfaces. The patterned surfaces can be complementary or non-complementary and the surface patterns on each member may vary in either a periodic or a non-periodic manner.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Surgical implant for promotion of osseo-integration
InactiveUS20050119758A1Enhanced cell attachmentInhibit cell growthDental implantsInternal osteosythesisSurface patternSurgical implant
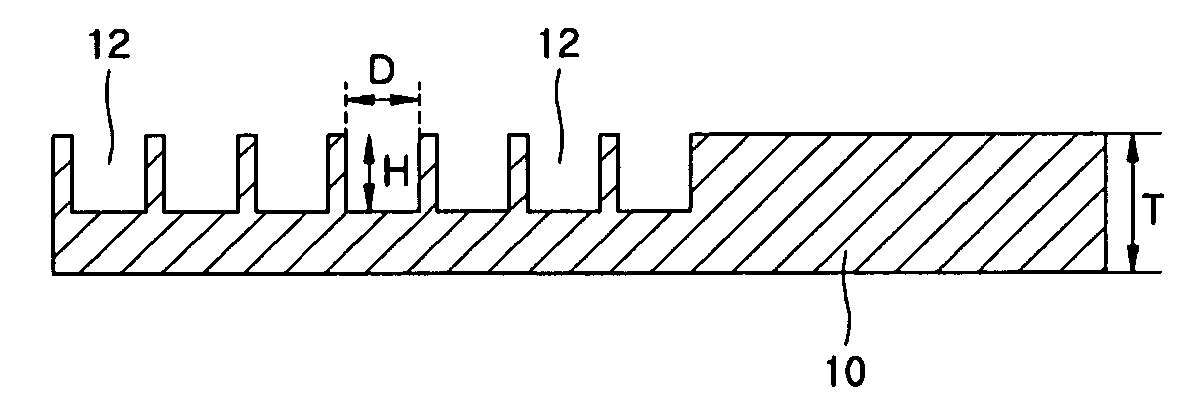
An implant for surgical insertion into tissue of a patient includes a microgeometric, repetitive pattern, in the form of a multiplicity of alternating ridges and grooves, each having an established width in a range of about 2 to about 25 microns, and an established depth in a range of about 2 to about 25 microns, each groove having a base and a wall; and a microgeometric random surface pattern, applied over the repetitive surface pattern, defining a multiplicity of micro-pits having dimensions in a range of about 0.1 to about 4 microns.
Owner:BIO LOK INT INC
Mechanically induced trapping of molecular interactions
InactiveUS20070224617A1Reduce pressureRapid lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurface patternChemical physics
The invention provides devices and methods for surface patterning the substrate of a microfluidic device, and for detection and analysis of interactions between molecules by mechanically trapping a molecular complex while substantially expelling solvent and unbound solute molecules. Examples of molecular complexes include protein-protein complexes and protein-nucleic acid complexes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Reduction of RF induced tissue heating using conductive surface pattern
InactiveUS20090099555A1Providing mechanical stabilityInteraction is limitedElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsSurface patternTissue heating
The present invention provides, among other things, means to suppress AC current propagation along elongated medical devices incorporating long conductive structures. AC currents in the frequency range from approximately 10 MHz to 3 GHz can be substantially suppressed without altering the low and DC frequency response of the medical device.
Owner:RENTENDO CORP
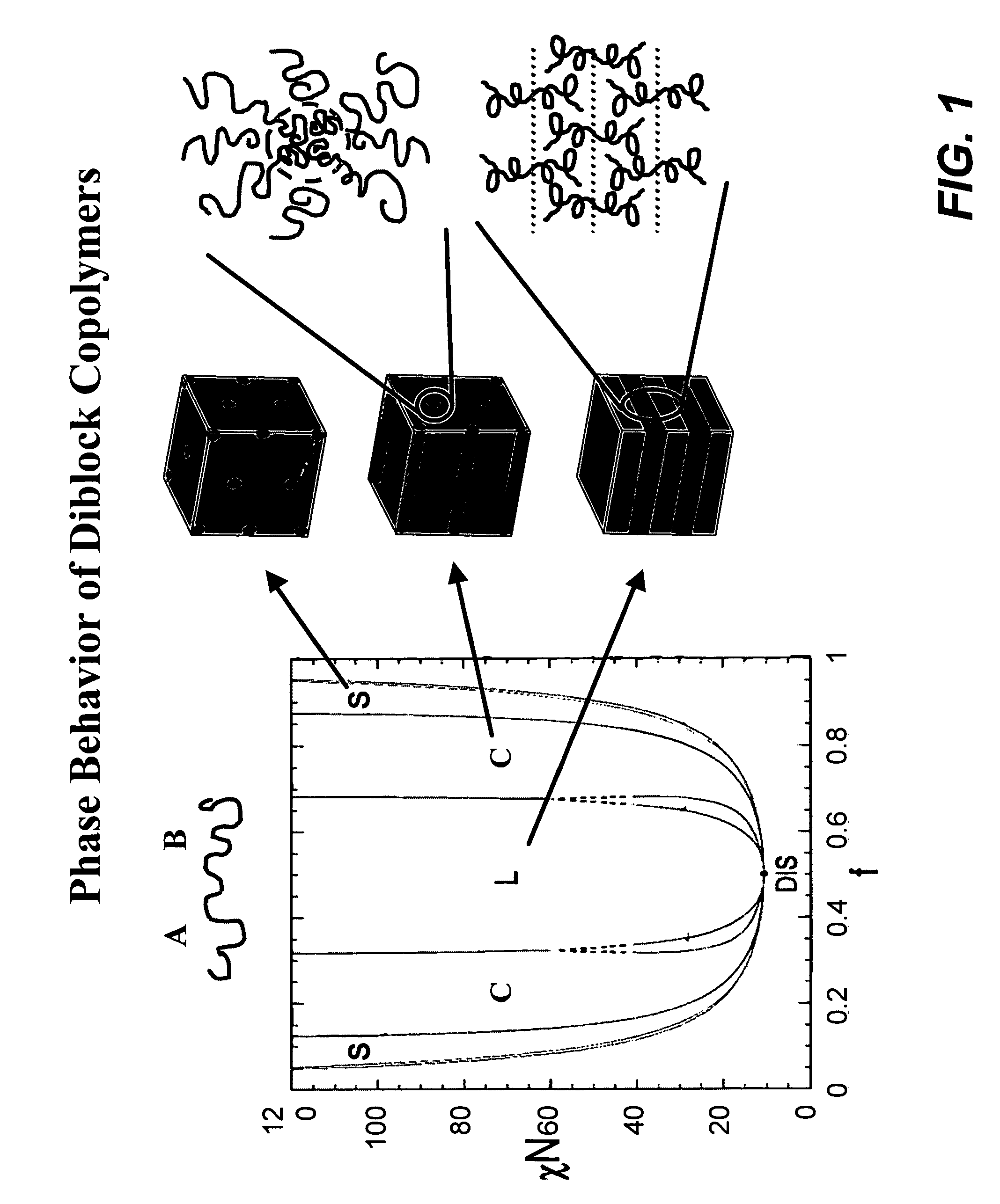
Directed assembly of triblock copolymers
Methods of directed self-assembly of multi-block (i.e., triblock and higher-order) copolymers on patterned substrates and related compositions are provided. According to various embodiments, the methods involve depositing copolymer materials on substrates configured to drive the assembly of micro-phase separated films that exhibit the same morphology as that copolymer materials in the bulk. In certain embodiments, binary patterns are used to drive the triblock copolymer films. The binary two-dimensional surface patterns are transformed into three-component and three-dimensional structures throughout the thickness of the overlying copolymer films.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Polishing pad, method of manufacturing the polishing pad, and cushion layer for polishing pad
InactiveUS20040055223A1Easy to processHigh thickness accuracyOther chemical processesAbrasion apparatusSurface patternEngineering
The polishing pad of this invention is a polishing pad effecting stable planarizing processing, at high polishing rate, materials requiring surface flatness at high level, such as a silicon wafer for semiconductor devices, a magnetic disk, an optical lens etc. This invention provides a polishing pad which can be subjected to surface processing to form a sheet or grooves, is excellent in thickness accuracy, attains a high polishing rate, achieves a uniform polishing rate, and also provides a polishing pad which is free of quality variations resulting from an individual variation, easily enables a change the surface patterns, enables fine surface pattern, is compatible with various materials to be polished, is free of burrs upon forming the pattern. This invention provides a polishing pad which can have abrasive grains mixed at very high density without using slurry, and generates few scratches by preventing aggregation of abrasive grains dispersed therein. The polishing pad of this invention has a polishing layer formed from a curing composition to be cured with energy rays, the polishing layer being formed surface pattern thereon by photolithography. The polishing pad of this invention comprises a polishing layer resin having abrasive grains dispersed therein, the resin containing ionic groups in the range of 20 to 1500 eq / ton.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Image reading apparatus for feature image of live body
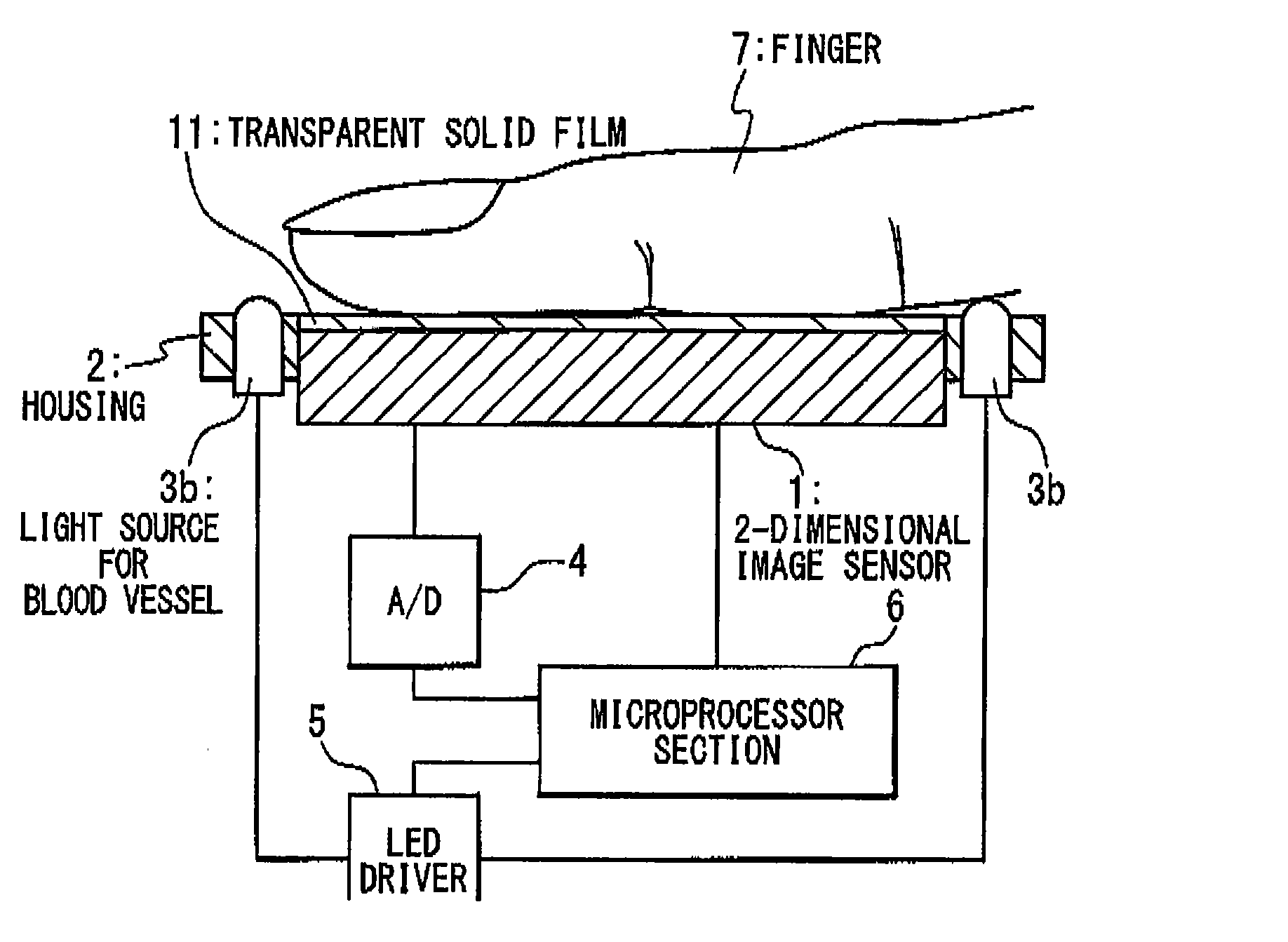
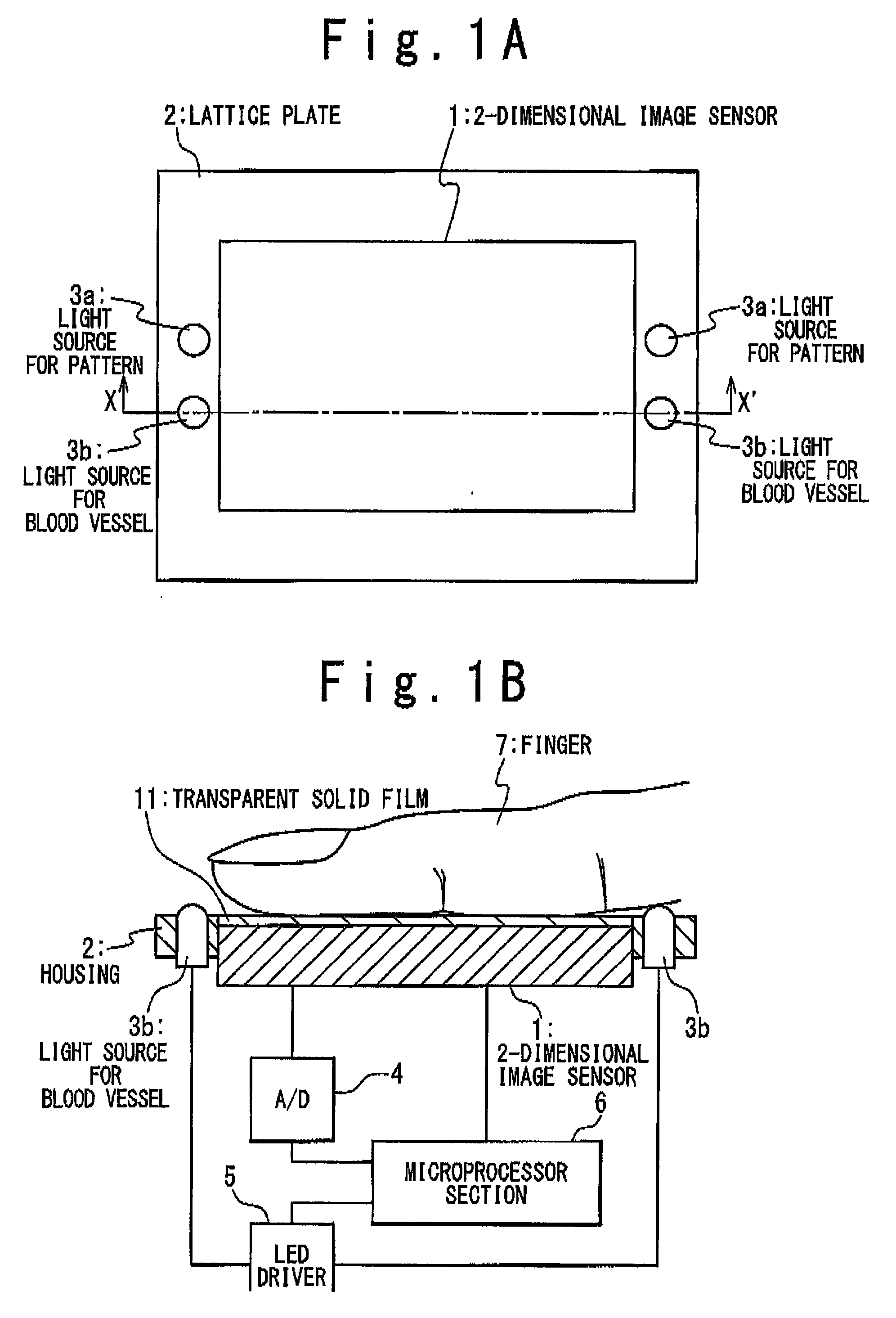
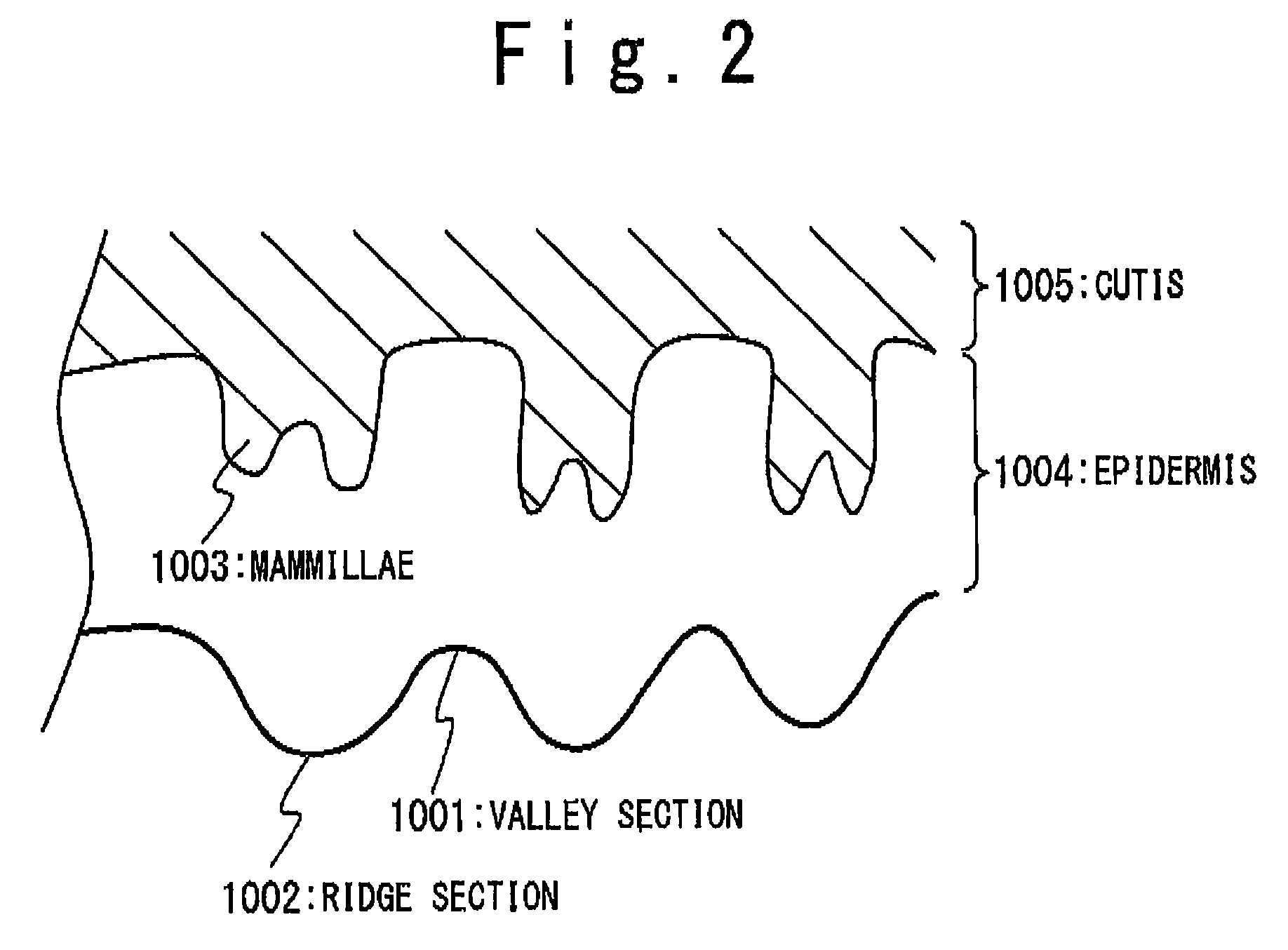
InactiveUS20070253607A1Avoid lossImprove accuracyDetecting live finger characterSubcutaneous biometric featuresSurface patternProcessing element
An image reading apparatus includes first and second light sources configured to emit first and second lights into a detection target, respectively, a 2-dimensional image sensor and a processing unit. The 2-dimensional image sensor has light receiving elements arranged in a matrix, and picks up a light emitted from the detection target through the emission of the first light from the first light source to generate a first image indicating a first pattern corresponding to an internal structure of the detection target, and picks up a light emitted from the detection target through the emission of the second light from the second light source to generate a second image indicating a second pattern corresponding to a surface pattern of the detection target. The processing unit drives the first and second light sources while switching the first and second light sources, and performs a predetermined process on the first and second images.
Owner:NEC CORP
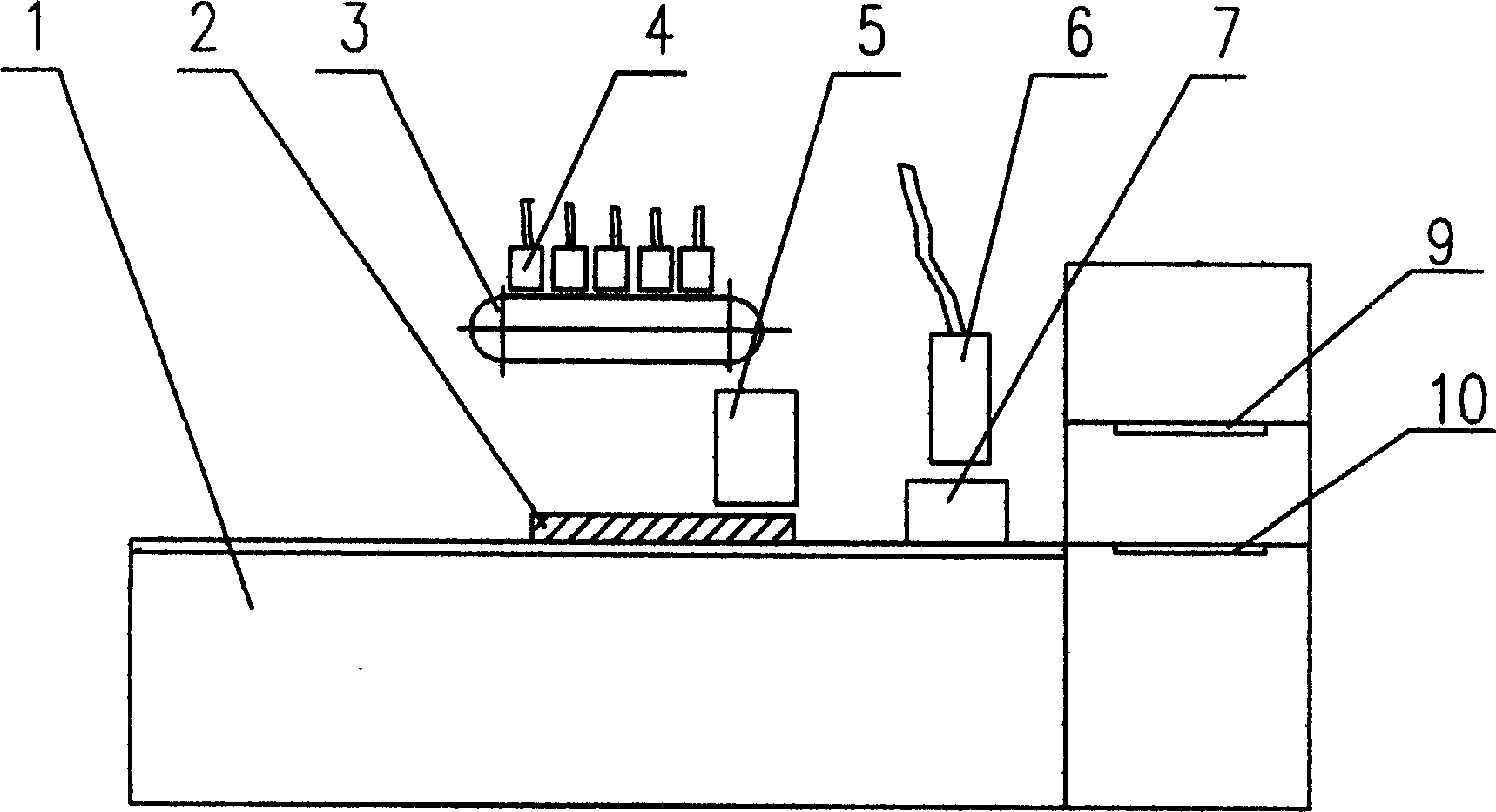
Method for constructing anti-reflection microstructure using single layer nanometer particle as etching blocking layer
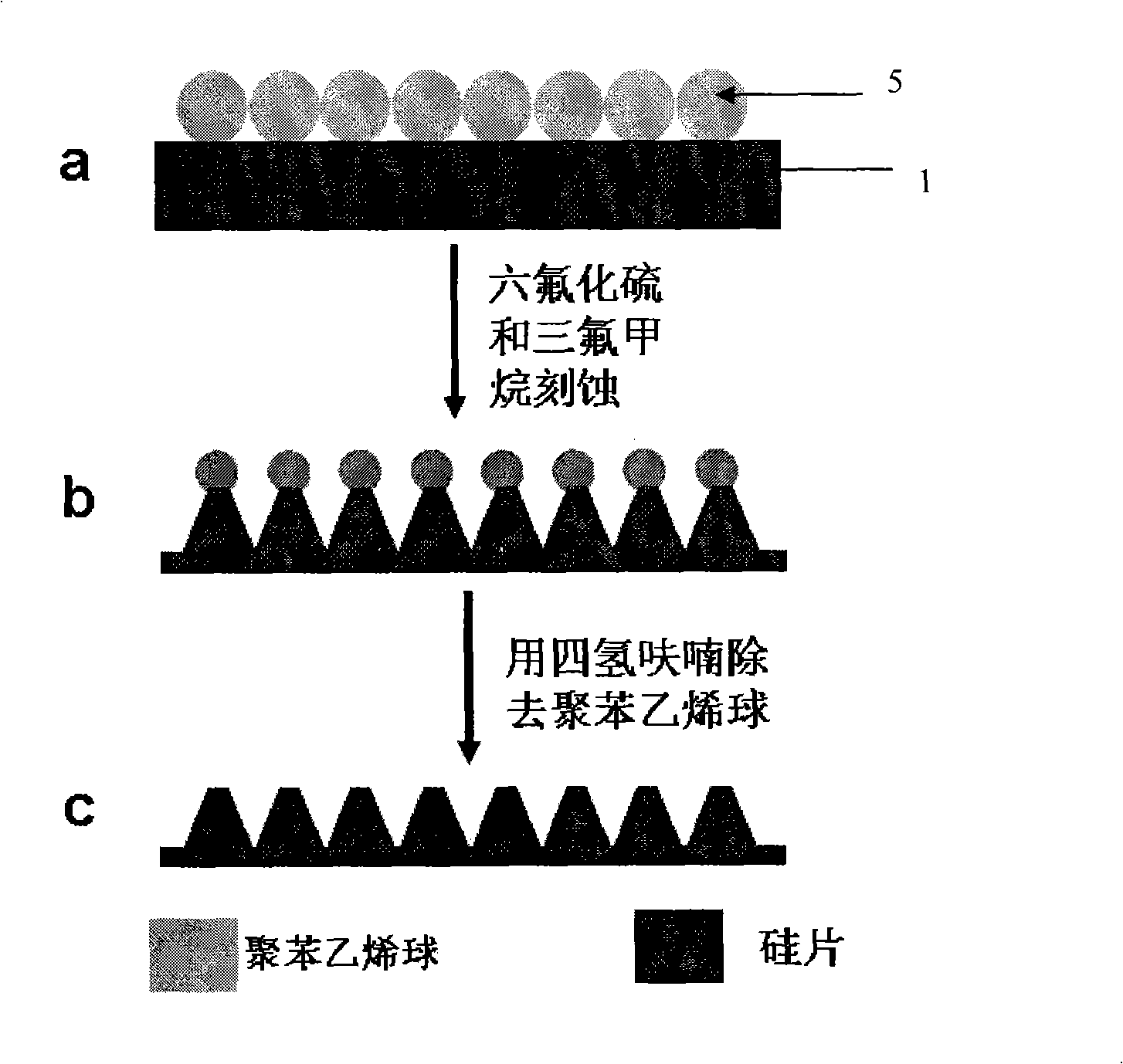
InactiveCN101308219ASimple methodBase variableSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsSurface patternLight energy
The invention belongs to the surface patterning microstructure construction technique, which relates to a method for constructing a microstructure with anti-reflection performance on a foundation base by combining the self-assembly technique with the reactive ion beam etching technique. The method is to take monolayer polymeric micro-spheres, silicon dioxide micro-spheres and nano-particles of metal or metal oxides as a barrier layer and implement the RIE etching to the foundation base, then an approximate cone-shaped microstructure is constructed on the foundation base, and the structure has extreme high anti-reflection performance, thereby effectively improving the light energy utilization rate, reducing the interference of veiling glare in an optical system, increasing the optical transmittance, and further improving the sensitivity and stability of the optical system, and the method can be used for constructing large-area anti-reflection structures. The method of the invention has advantages of simple operation, changeable foundation base, strong applicability, good repeatability, low cost, high efficiency, adjustable anti-reflective applied wavelength and conformity to industrialized standards, and can be used for making photoelectric devices such as solar batteries and white light sensors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
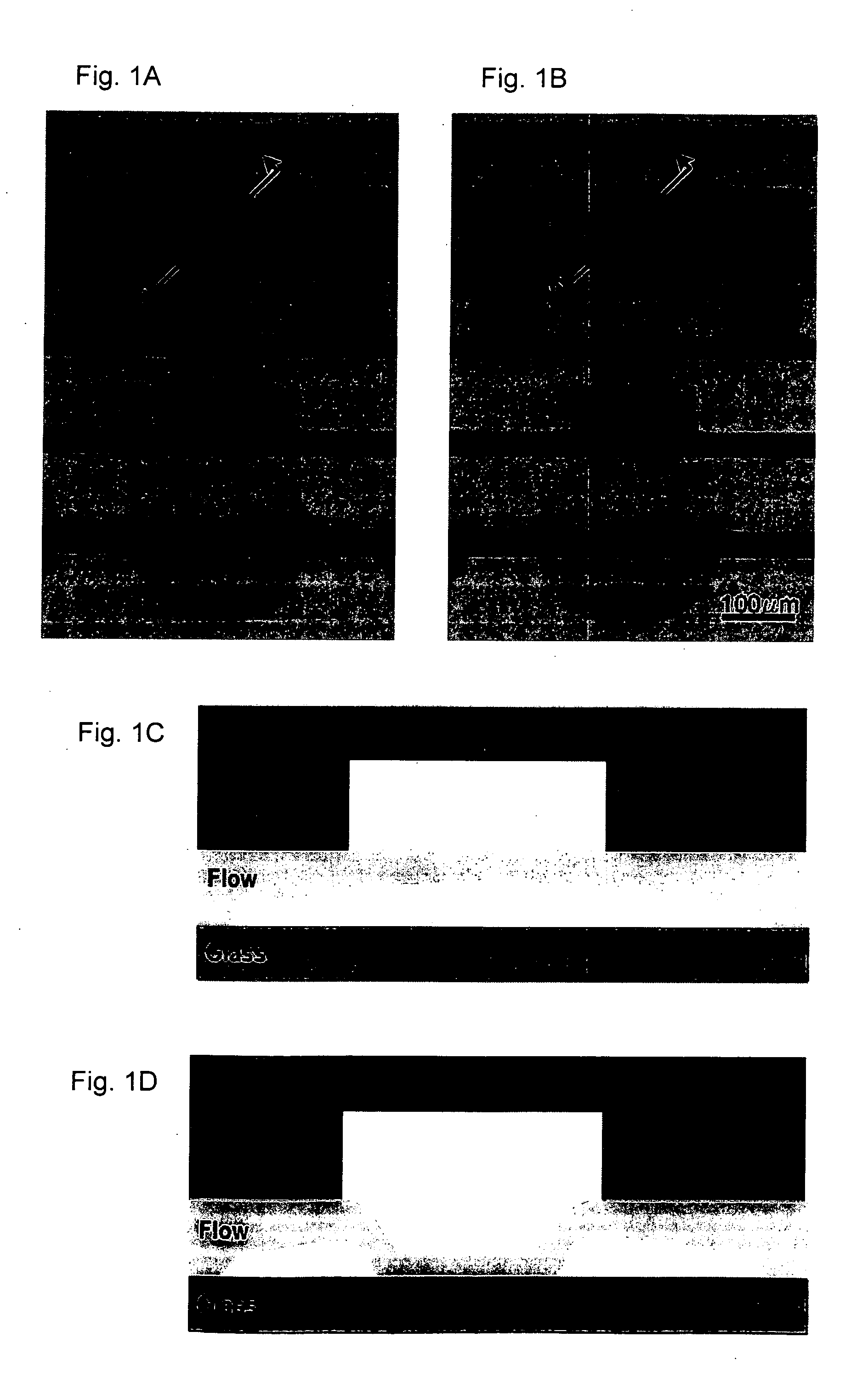
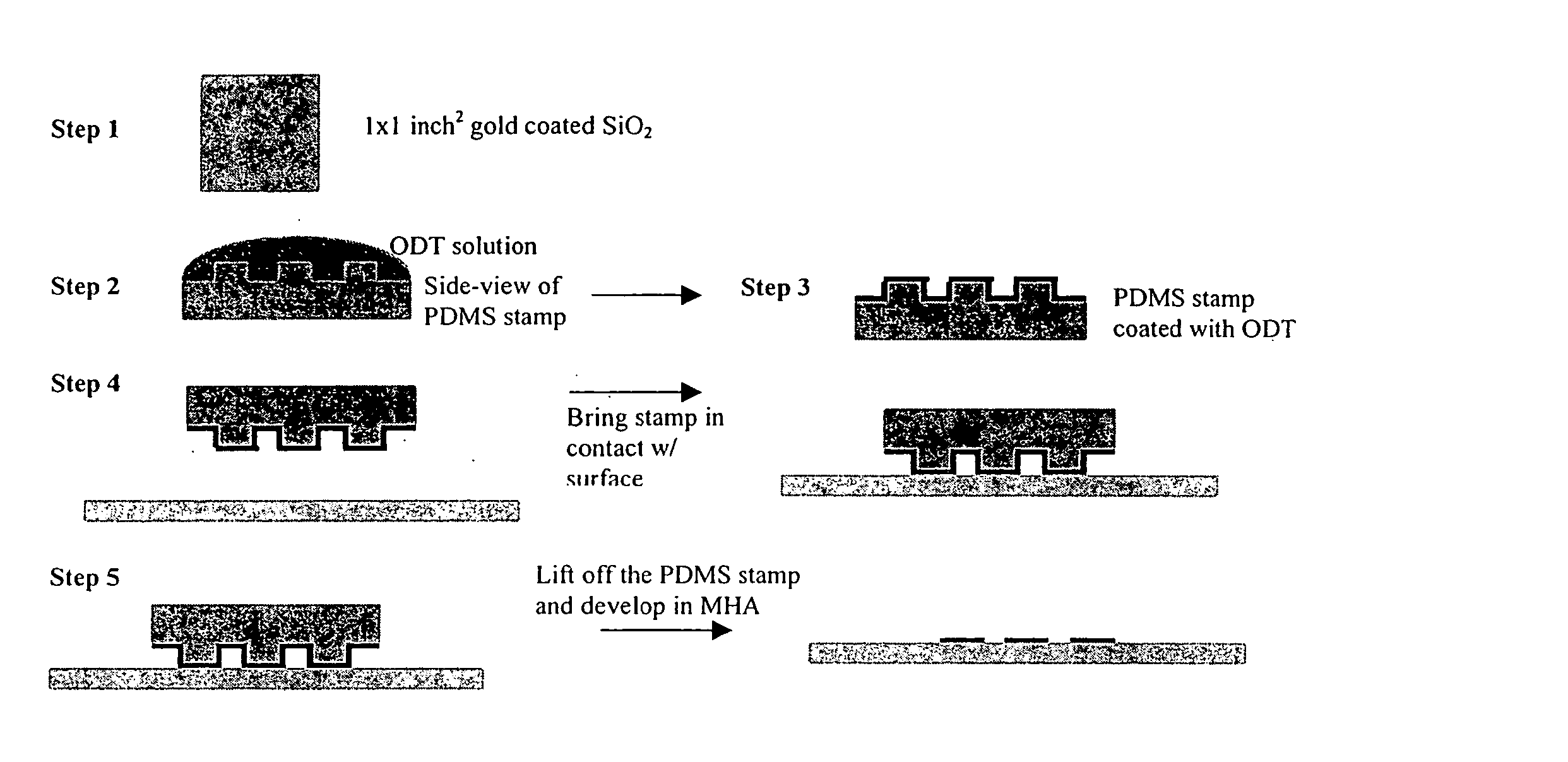
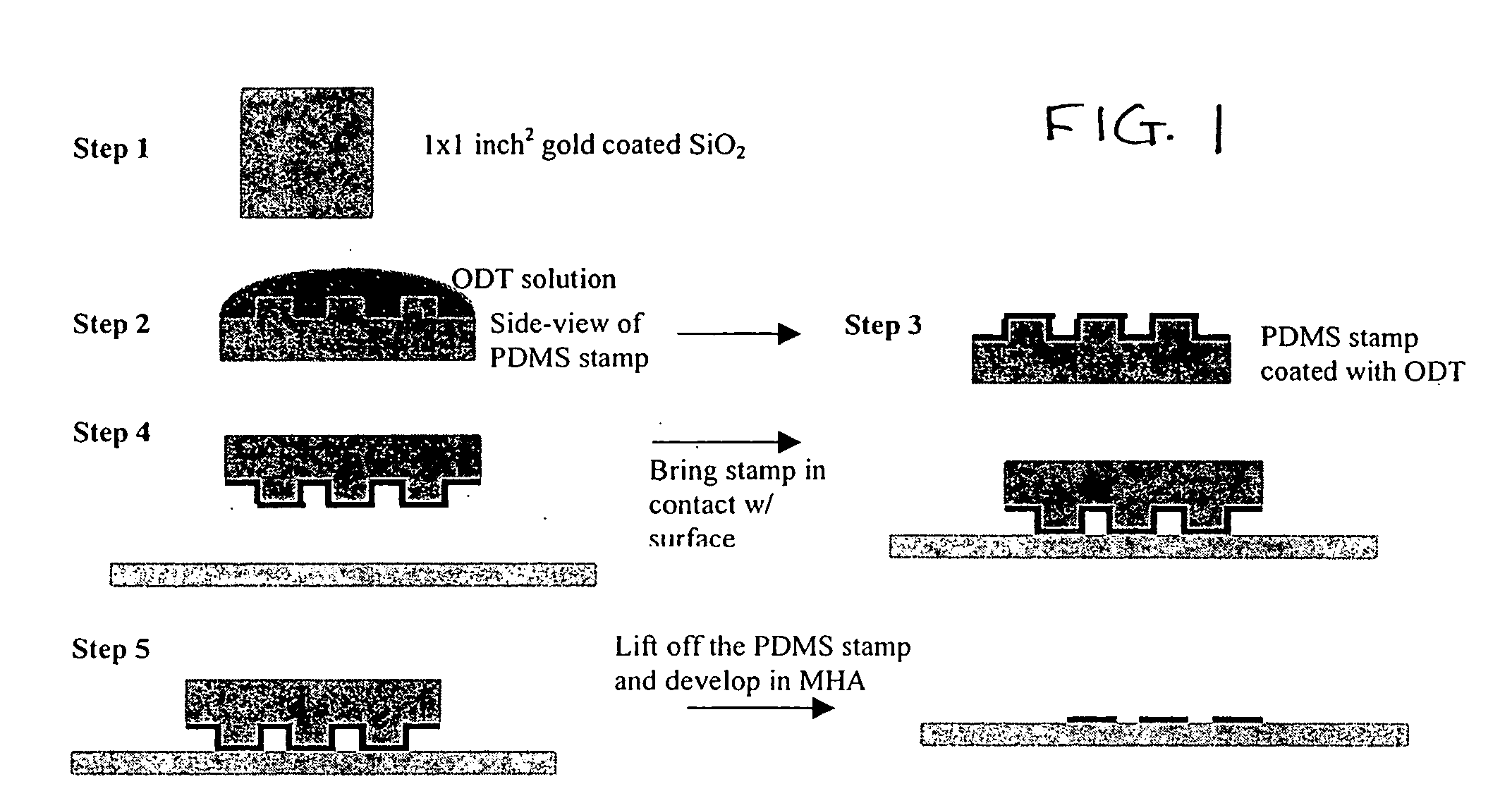
Patterning of surfaces utilizing microfluidic stamps including three-dimensionally arrayed channel networks
InactiveUS7267938B2Conveniently routedEasy stampingImmobilised enzymesFixed microstructural devicesSurface patternChannel network
The present invention describes improved microfluidic systems and procedures for fabricating improved microfluidic systems, which contain one or more levels of microfluidic channels. The methods for fabrication the systems disclosed can provide a convenient route to topologically complex and improved microfluidic systems. The microfluidic systems can include three-dimensionally arrayed networks of fluid flow paths therein including channels that cross over or under other channels of the network without physical intersection at the points of cross over. The microfluidic networks can be fabricated via replica molding processes utilizing mold masters including surfaces having topological features formed by photolithography. The present invention also involves microfluidic systems and methods for fabricating complex patterns of materials, such as biological materials and cells, on surfaces utilizing the microfluidic systems. Specifically, the invention provides microfluidic surface patterning systems and methods for fabricating complex, discontinuous patterns on surfaces that can incorporate or deposit multiple materials onto the surfaces. The present invention also provides improved microfluidic stamps or applicators for microcontact surface patterning, which are able to pattern onto a surface arbitrary two-dimensional patterns, and which are able to pattern multiple substances onto a surface without the need for multiple steps of registration or stamping during patterning and without the need to selectively “ink” different regions of the stamp with different materials.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
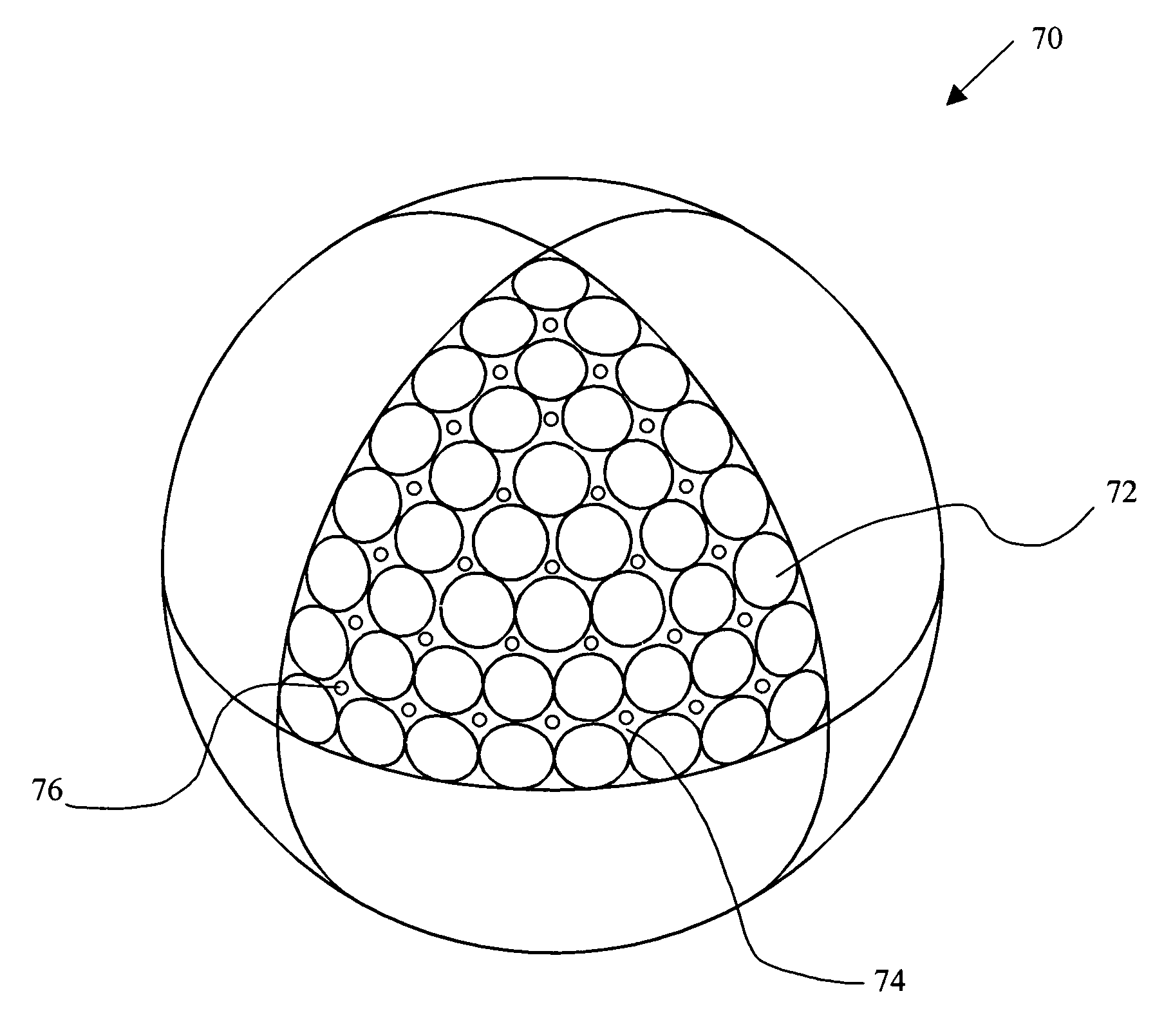
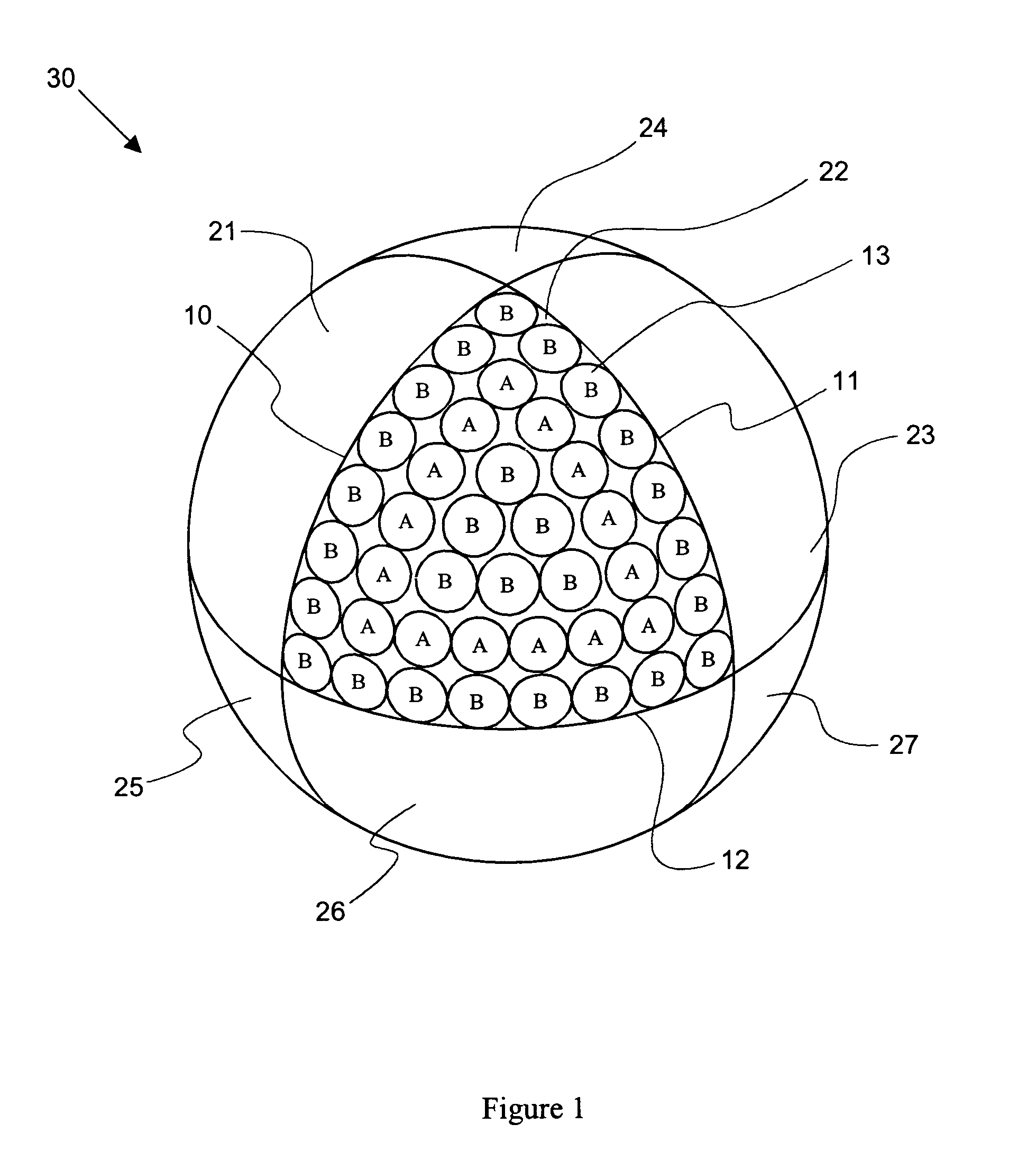
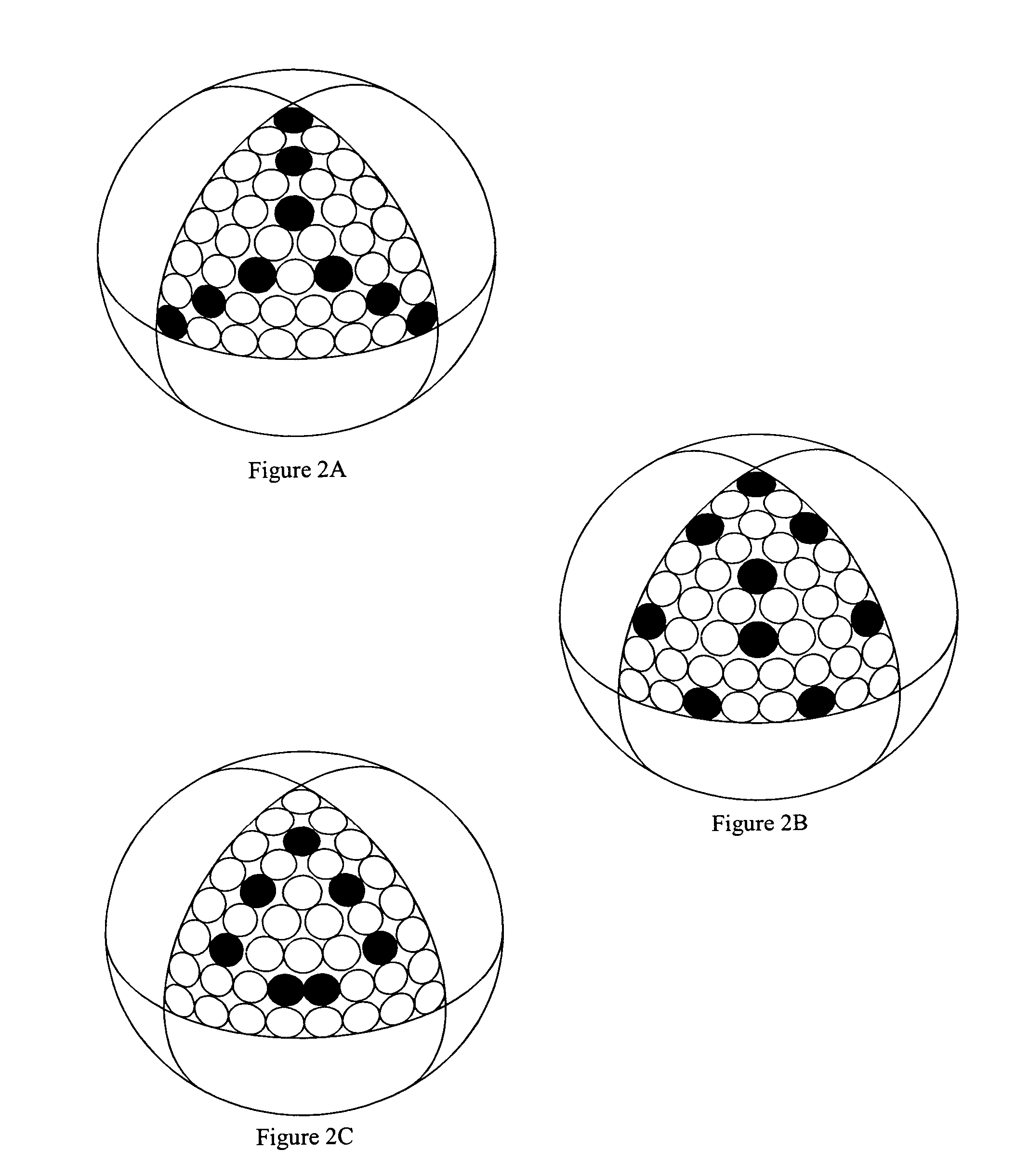
Surface pattern for golf balls
A golf ball surface pattern including depressions and protrusions is disclosed and claimed. In one embodiment, the depressions and protrusions are positioned on the ball according to a known dimple pattern, with some of the dimples being replaced with protrusions. In another embodiment, the depressions are positioned on the ball according to a known dimple pattern, and protrusions are positioned on the land areas. Alternatively, protrusions can be positioned on the ball according to a known dimple pattern, and depressions positioned on the land areas. The turbulence generators (dimples and protrusions) that are positioned on the land areas can be positioned manually or with a distribution scheme. In another embodiment, the turbulence generators are positioned according to a scheme based on the principles of electromagnetic theory.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Anode for lithium metal polymer secondary battery comprising surface patterned anodic current collector and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20060110661A1Cyclic stabilityExtend your lifeElectrode carriers/collectorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesSurface patternLithium metal
There are provided an anode for a lithium metal polymer secondary battery comprising an anodic current collector having a surface on which a plurality of recesses having a predetermined shape are formed and a method of preparing the same. The plurality of recesses are formed on a surface of the anodic current collector using a physical method or a chemical method. In a lithium metal polymer secondary battery employing the anode, oxidation / reduction of lithium and the formation of dendrite occur only in the recesses formed by surface patterning of the anodic current collector. Thus, expanding and shrinking of a battery due to a change in the thickness of the lithium anode can be prevented and cycling stability and the lifespan of a battery can be improved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Materials and methods for creating imaging layers
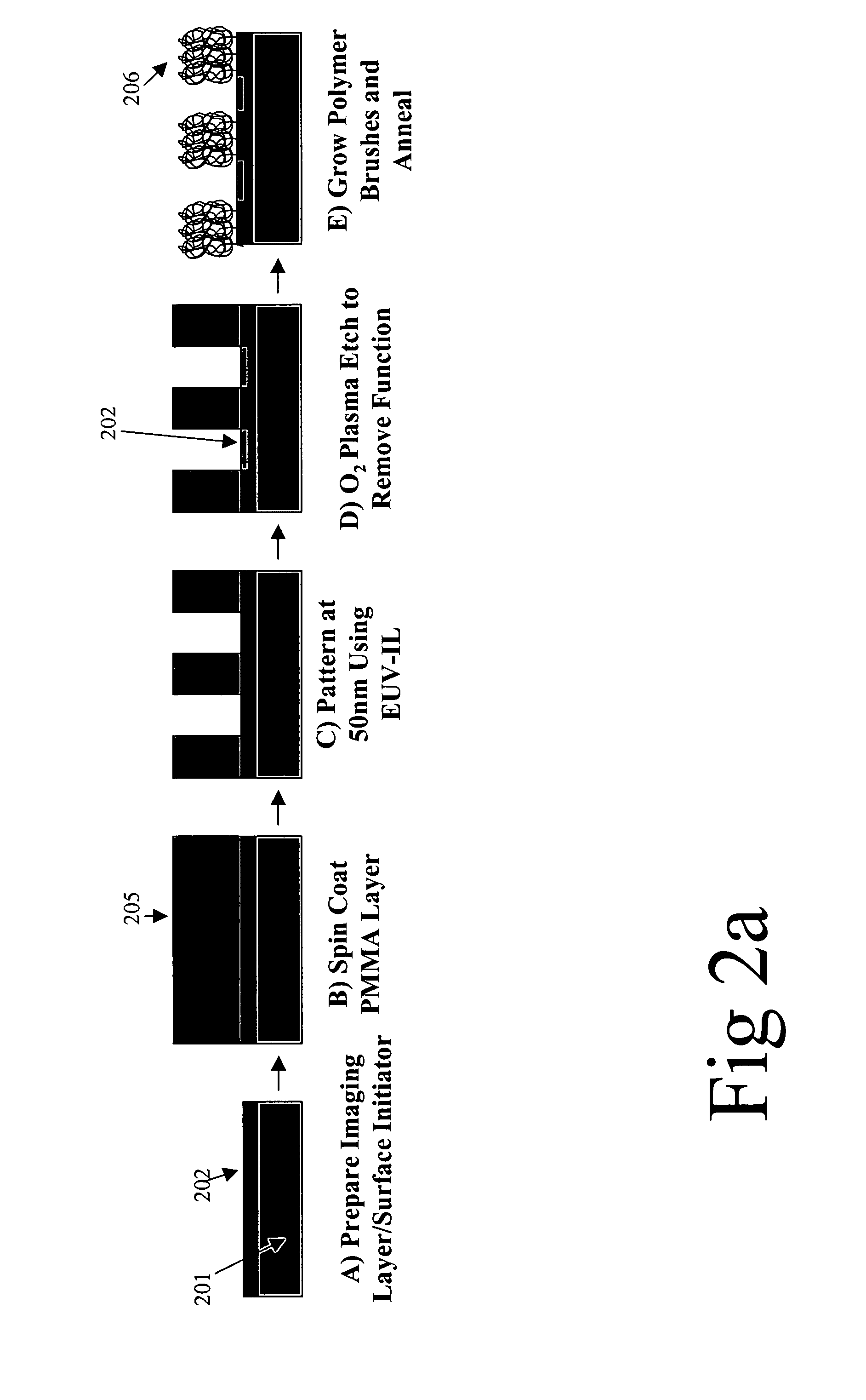
ActiveUS20070020749A1High aspect ratioMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSmooth surfaceAspect ratio
The present invention provides patterned features of dimensions of less than 50 nm on a substrate. According to various embodiments, the features may be “Manhattan” style structures, have high aspect ratios, and / or have atomically smooth surfaces. The patterned features are made from polymer brushes grafted to a substrate. In some embodiments, the dimensions of the features may be determined by adjusting the grafting density and / or the molecular weight of the brushes. Once the brushes are patterned, the features can be shaped and reshaped with thermal or solvent treatments to achieve the desired profiles. The chemical nature of the polymer brush is thus independent of the patterning process, which allows for optimization of the polymer brush used for specific applications. Applications include masks for pattern transfer techniques such as reactive ion etching.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Process for producing thin film-like material having decorative surface
Thin film-like material that has printability, that can have unique surface patterns of various kinds, and that can have a design having an effect that has been never produced, and process of producing it are provided. The thin film-like material has a laminated structure in which an adhesive layer and a metal thin layer are laid in this order on the entire surface or parts of the surface of one or each of opposite sides of a base material A surface of the metal thin layer is formed by transfer process as a smooth surface having a mirror pattern, a surface having a mat pattern, a surface having a hairline pattern, a surface having an embossed pattern, a surface having a hologram pattern or a surface having two or more of those patterns combined appropriately.
Owner:TOPPAN PROSPRINT
Interlayers for laminated safety glass with superior de-airing and laminating properties and process for making the same
This invention relates to thermoplastic interlayers for laminated safety glass with superior vacuum de-airing at elevated temperatures and superior tacking and edge sealing properties. The sheeting has surface pattern on at least one of the surfaces characterized by flat surfaces with substantially uninterrupted channels for airflow in at least two non-parallel directions. The channels allow for rapid de-airing while the area roughness parameter ratio ARp / ARt in the range of 0.52 to 0.62, ARt being less than 32 μm, and area kurtosis less than 2.5, allow for ease of tacking of the interlayer onto glass and edge sealing after de-airing has been completed. Said surface pattern may also be superimposed onto a pattern which is generated by melt fracture or other means on at least one side to enhance de-airing and aid edge sealing.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Implants with integration surfaces having regular repeating surface patterns
ActiveUS20130006363A1Increase frictionImplant stabilityBone implantSpinal implantsSurface patternBone structure
An interbody spinal implant, such as a solid-body or composite implant. The implant has at least one integration surface with a roughened surface topography including a repeating pattern, without sharp teeth that risk damage to bone structures, adapted to grip bone through friction generated when the implant is placed between two vertebral endplates and to inhibit migration of the implant. The repeating pattern is formed of at least three at least partially overlapping repeating patterns. The repeating patterns may radiate at a fixed distance from at least one point and may include recesses having a slope of thirty degrees or less relative to the integration surface. Also disclosed are processes of fabricating the integration surfaces.
Owner:TITAN SPINE
LED device for wide beam generation
ActiveUS20100172135A1Easy to combineReduce discontinuityMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceSurface patternWide beam
An apparatus and method is characterized by providing an optical transfer function between a predetermined illuminated surface pattern, such as a street light pattern, and a predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source, such as that from an LED. A lens is formed having a shape defined by the optical transfer function. The optical transfer function is derived by generating an energy distribution pattern using the predetermined energy distribution pattern of the light source. Then the projection of the energy distribution pattern onto the illuminated surface is generated. The projection is then compared to the predetermined illuminated surface pattern to determine if it acceptably matches. The process continues reiteratively until an acceptable match is achieved. Alternatively, the lens shape is numerically or analytically determined by a functional relationship between the shape and the predetermined illuminated surface pattern and predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source as inputs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
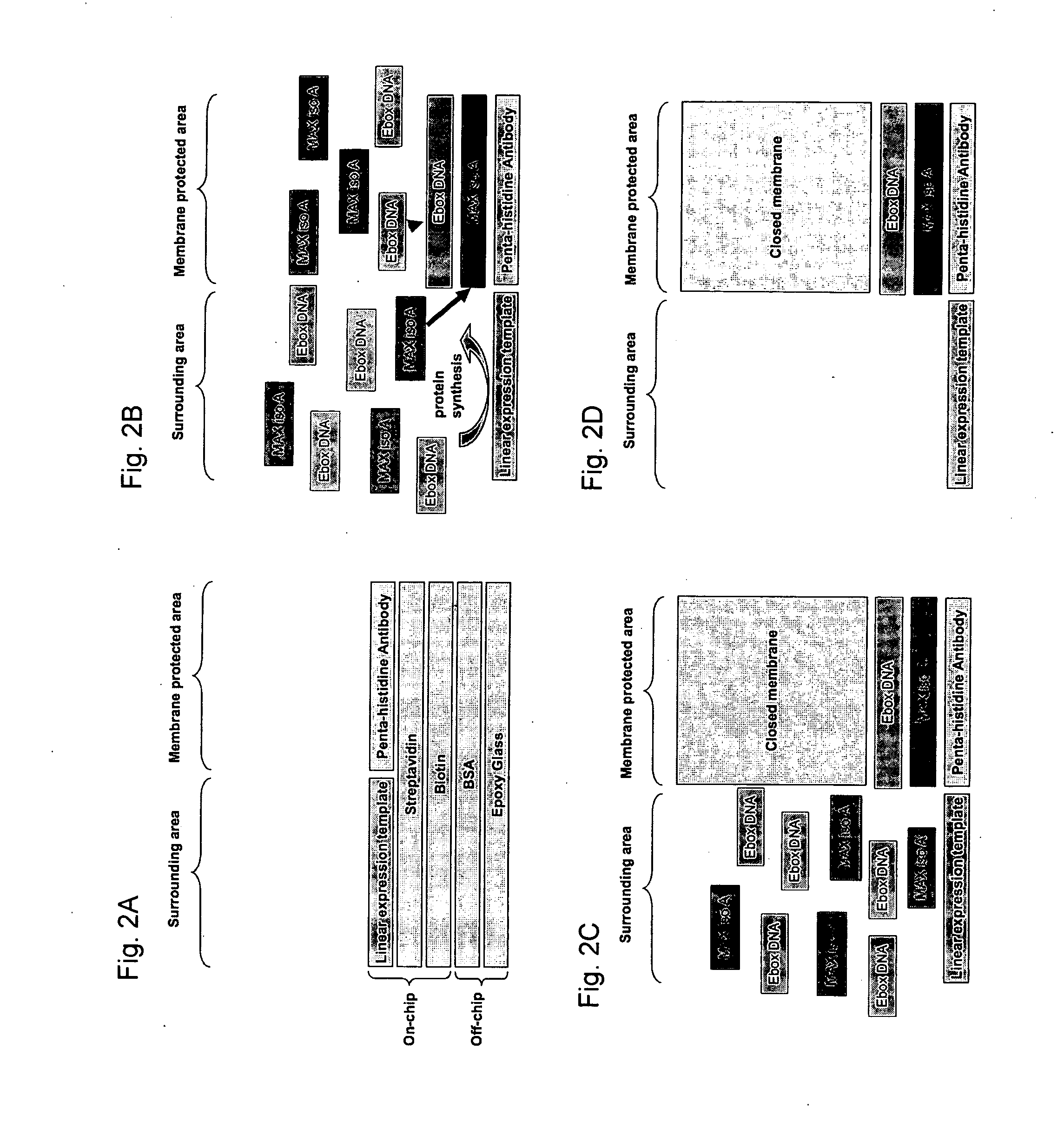
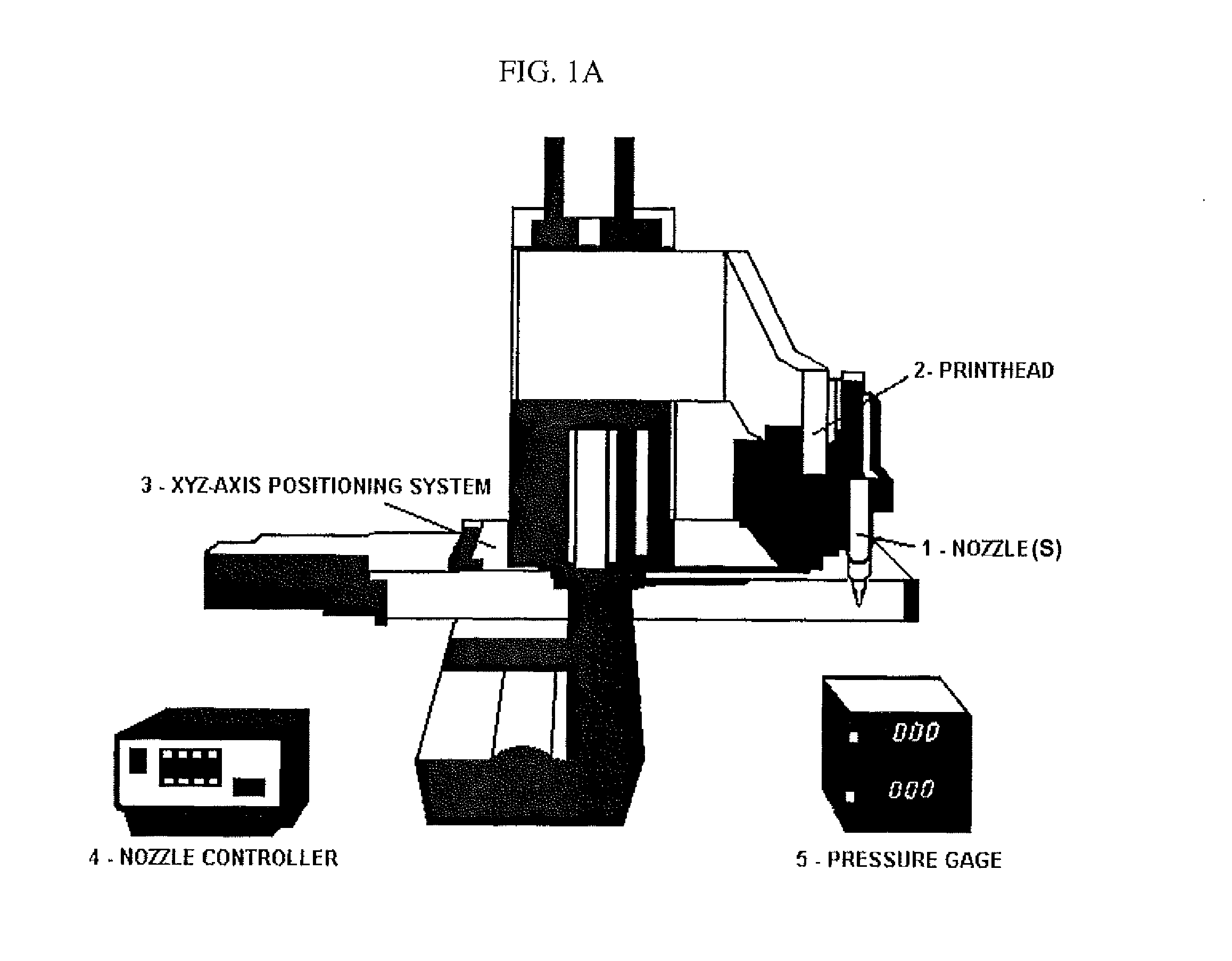
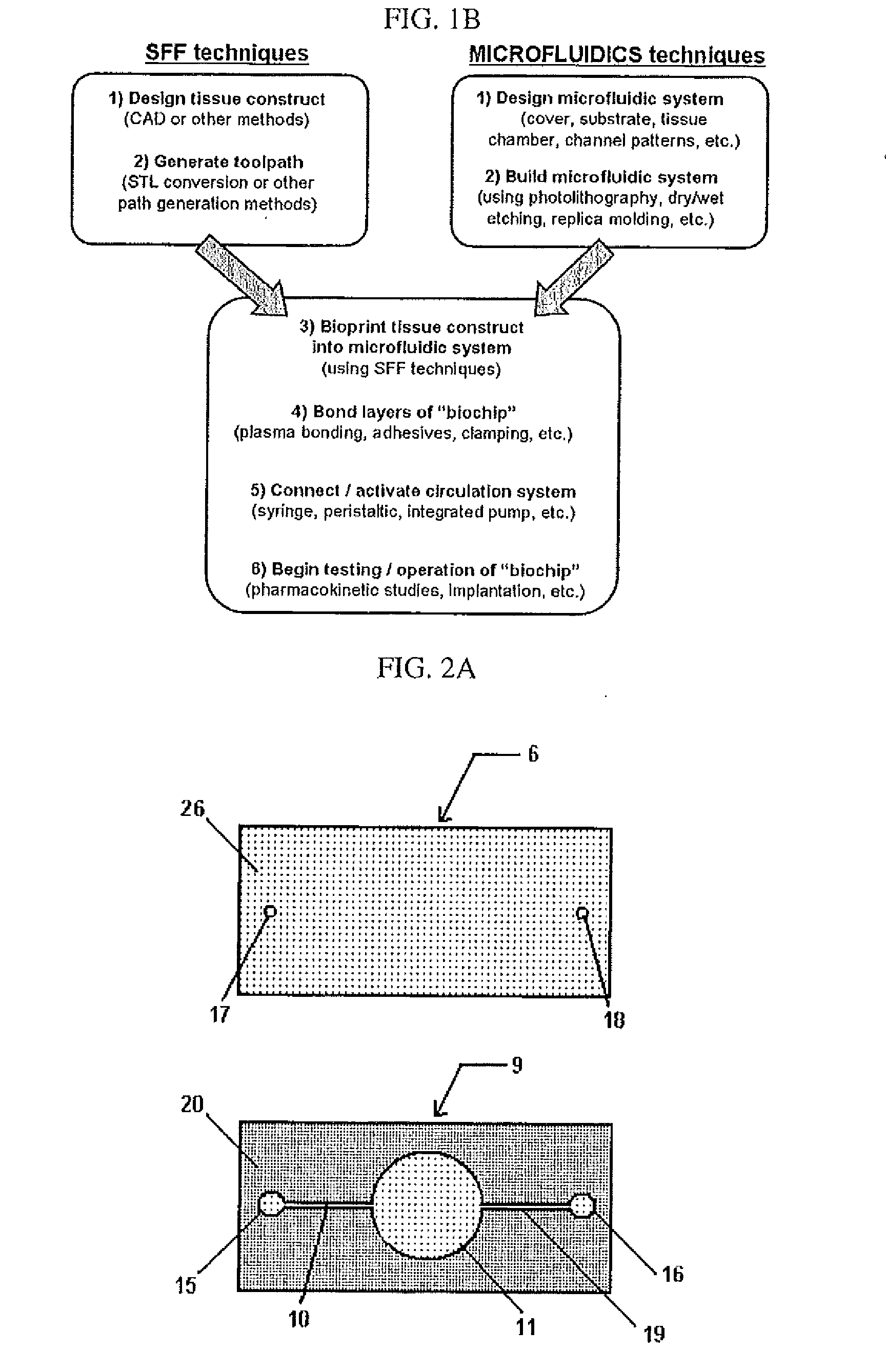
Compositions and Methods for Functionalized Patterning of Tissue Engineering Substrates Including Bioprinting Cell-Laden Constructs for Multicompartment Tissue Chambers
InactiveUS20110136162A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentDrug metabolism
The present invention relates to microfluidic systems and methods for monitoring or detecting a change in a characteristic of an input substance. Specifically, the invention relates to a model for in vitro pharmacokinetic study and other pharmaceutical applications, as well as other uses including computing, sensing, filtration, detoxification, production of chemicals and biomolecules, testing cell / tissue behavior, toxicology, drug metabolism, drug screening, drug discovery, and implantation into a subject. The present invention also relates to systems and methods of a microplasm functionalized surface patterning of a substrate. The present invention represents an improvement over existing plasma systems used to modify the surface of a substrate, as the present invention creates surface patterning without the use of a mask, stamp or a chemical treatment.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Surface projection device for augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR) is the process of overlaying or projecting computer generated images over a user's real world view of the physical world. The present invention allows for gameplay and / or training to contain augmented special effects. It is used to create surface patterns which are incorporated into augmented reality systems. It also allows for gesture control of AR elements during use.
Owner:SULON TECH
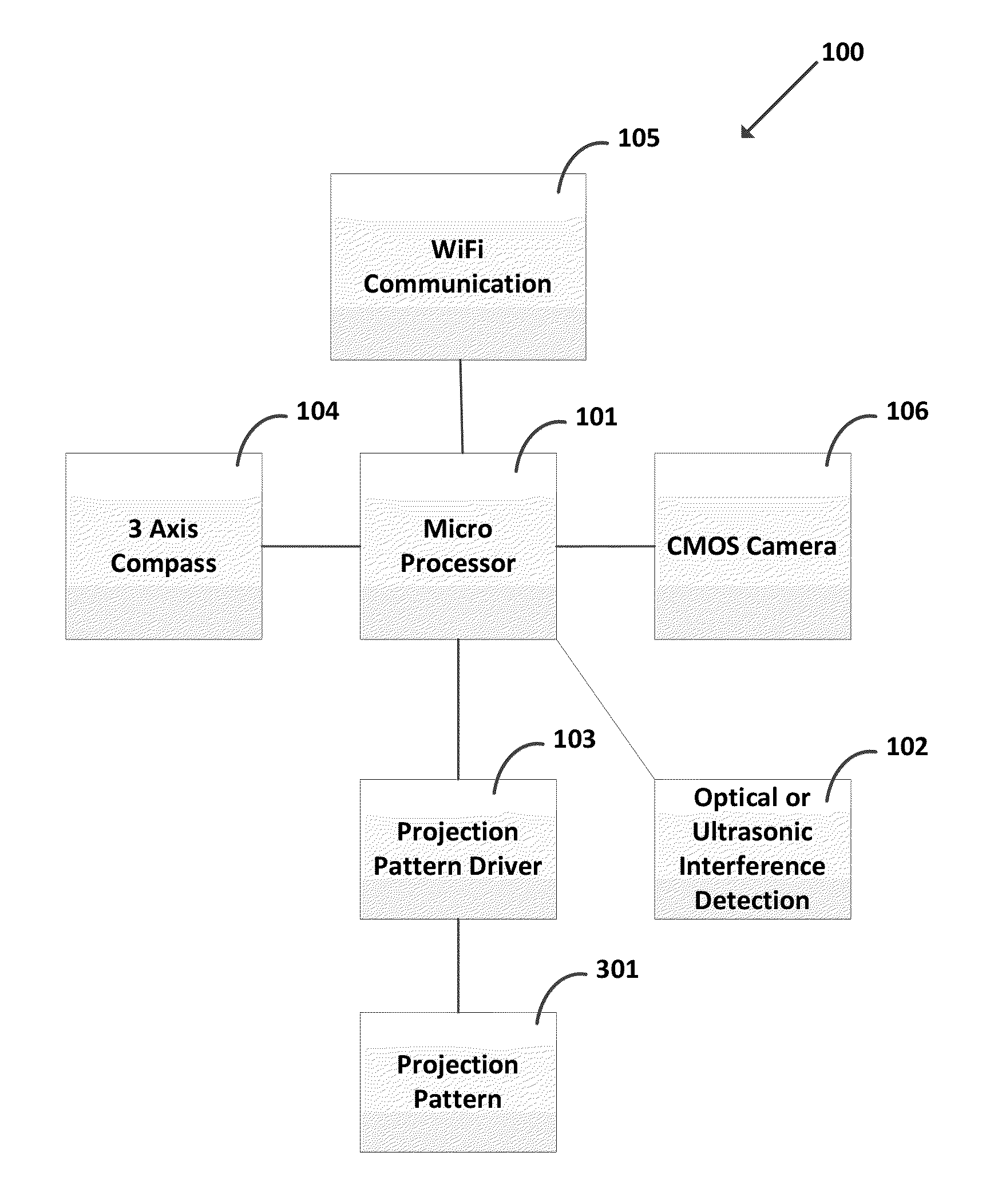
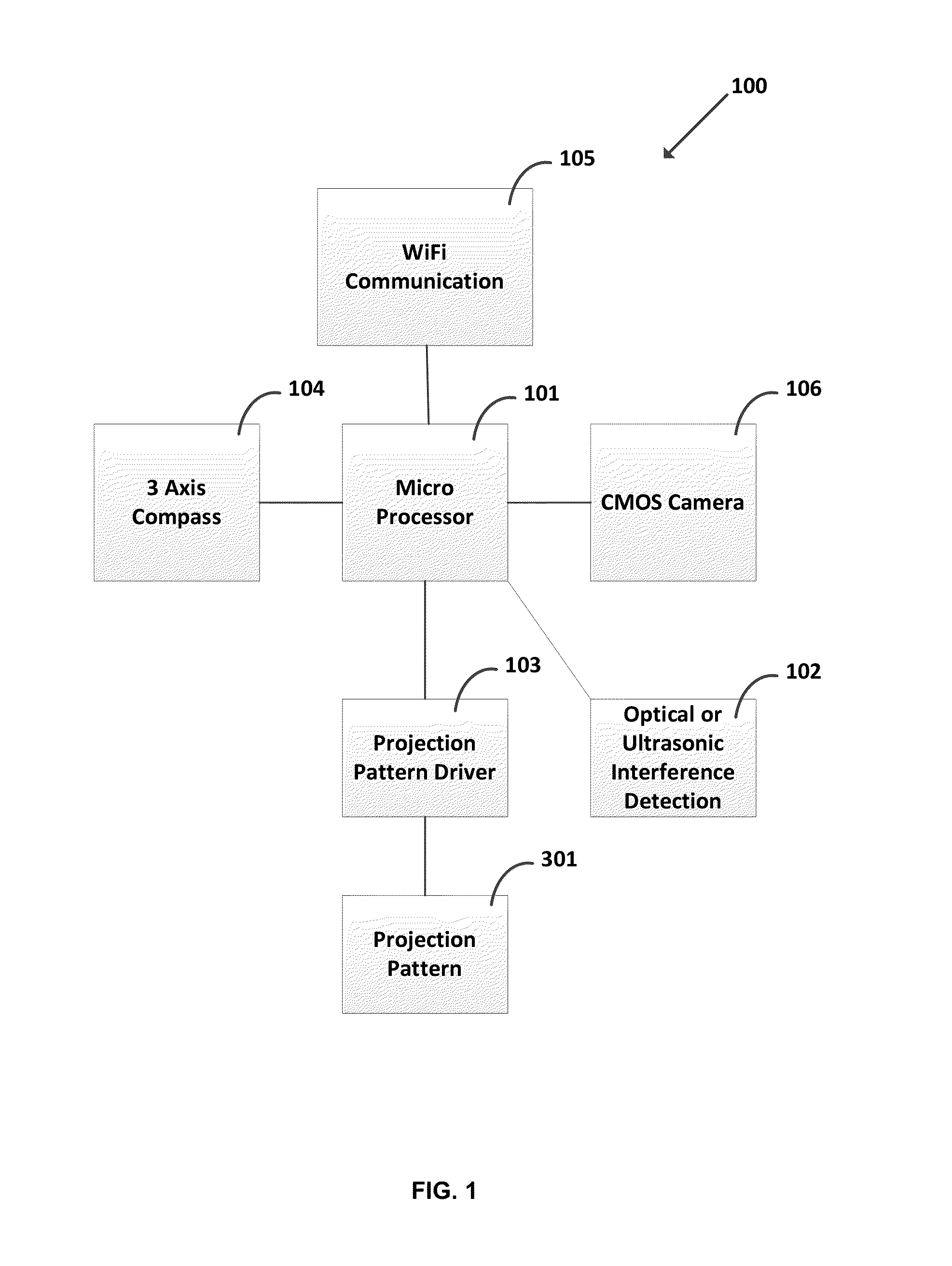
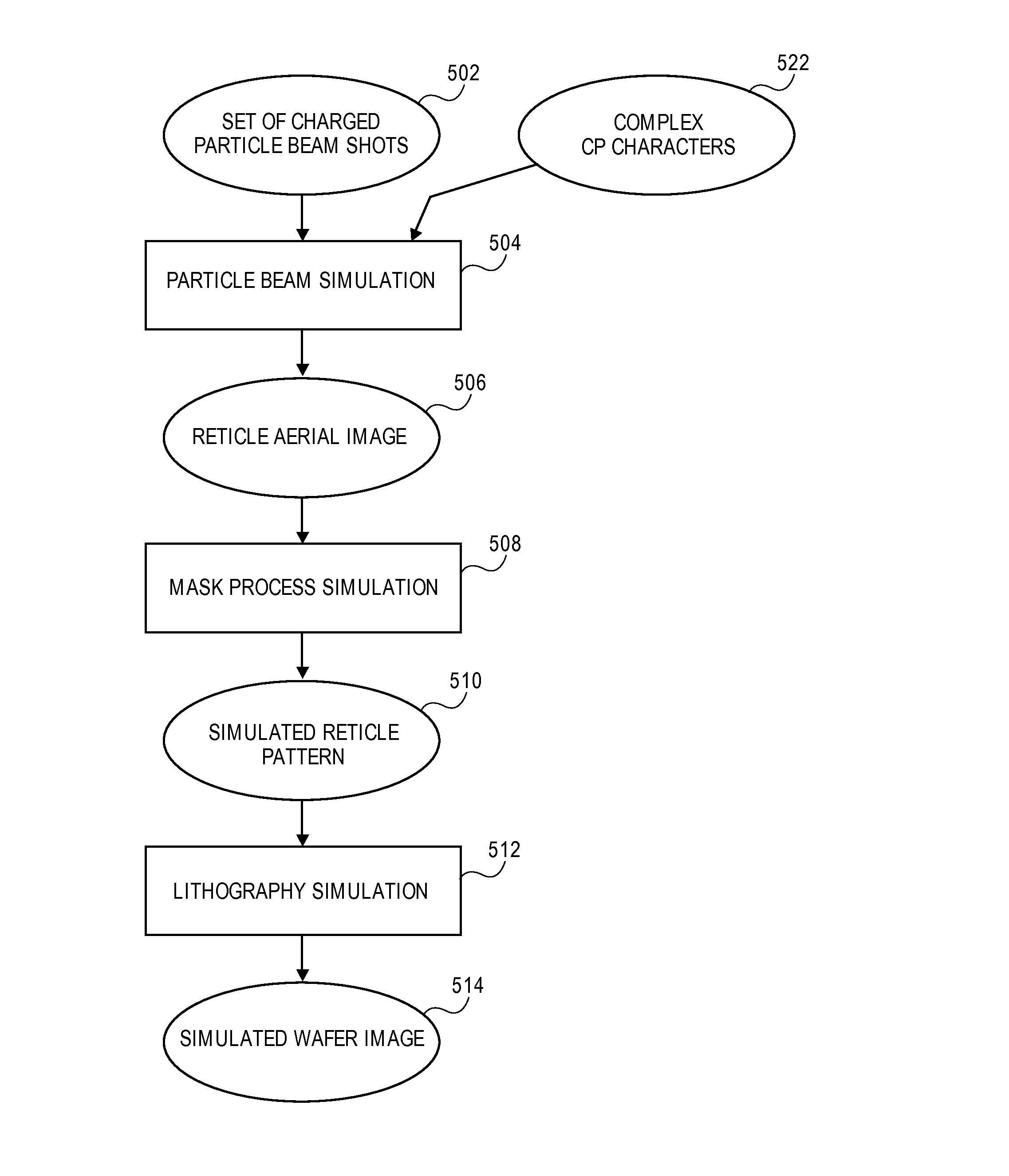
Method and System for Optimization of an Image on a Substrate to be Manufactured Using Optical Lithography
InactiveUS20130070222A1Improve calculated substrate imageElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusSurface patternLithographic artist
A method and system for optimization of an image to be printed on a substrate using optical lithography is disclosed in which a set of charged particle beam shots, some of which overlap, is determined so as to form a target pattern on a surface such as a reticle. The charged particle beam shots are simulated to determine the pattern that would be formed on the surface. Next, a substrate image is calculated from the simulated surface pattern. One or more shots in the set of shots are then modified to improve the calculated substrate image.
Owner:D2S
Silicon-Based Light Emitting Diode for Enhancing Light Extraction Efficiency and Method of Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20080303018A1Efficient integrationReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface patternNanodot
Due to the indirect transition characteristic of silicon semiconductors, the light extraction efficiency of a silicon-based light emitting diode is lower than that of a compound semiconductor-based light emitting diode. For this reason, there are difficulties in practically using and commercializing silicon-based light emitting diodes developed so far. Provided is a silicon-based light emitting including: a substrate with a lower electrode layer on a lower surface thereof; a lower doped layer that is formed on an upper surface of the substrate and supplies carriers to an emitting layer; the emitting layer that is a silicon semiconductor layer including silicon quantum dots or nanodots formed on the lower doped layer and has a light-emitting characteristic; an upper doped layer that is formed on the emitting layer and supplies carriers to the emitting layer; an upper electrode layer formed on the upper doped layer; and a surface structure including a surface pattern formed on the upper electrode layer, a surface structure including an upper electrode pattern and an upper doped pattern formed by patterning the upper electrode layer and the upper doped layer, or a surface structure including the surface pattern, the upper electrode pattern, and upper doped pattern, wherein the surface structure enhances the light extraction efficiency of light emitted from the emitting layer according to geometric optics.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Antireflective member, optical element, display device, method of making stamper and method of making antireflective member using the stamper
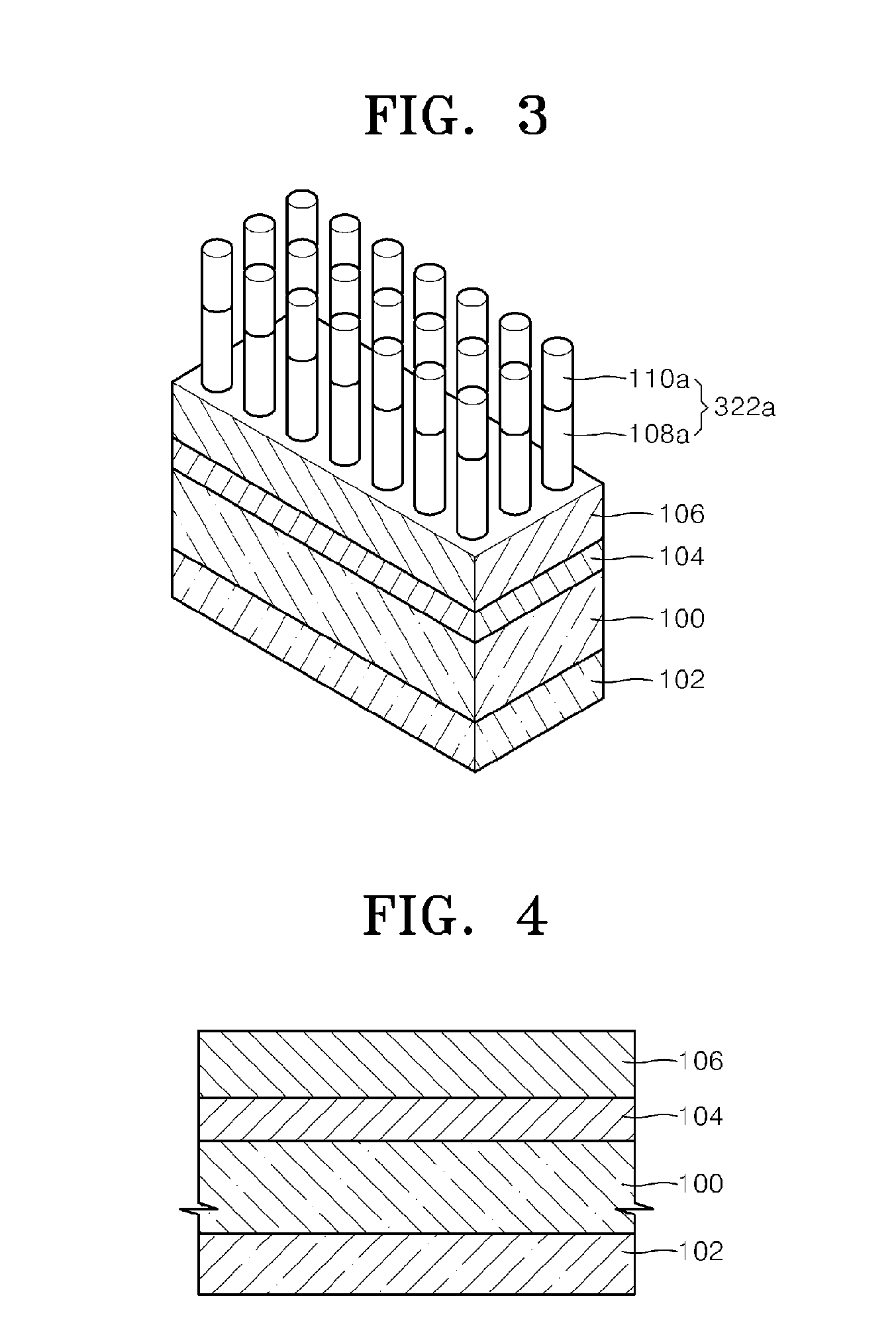
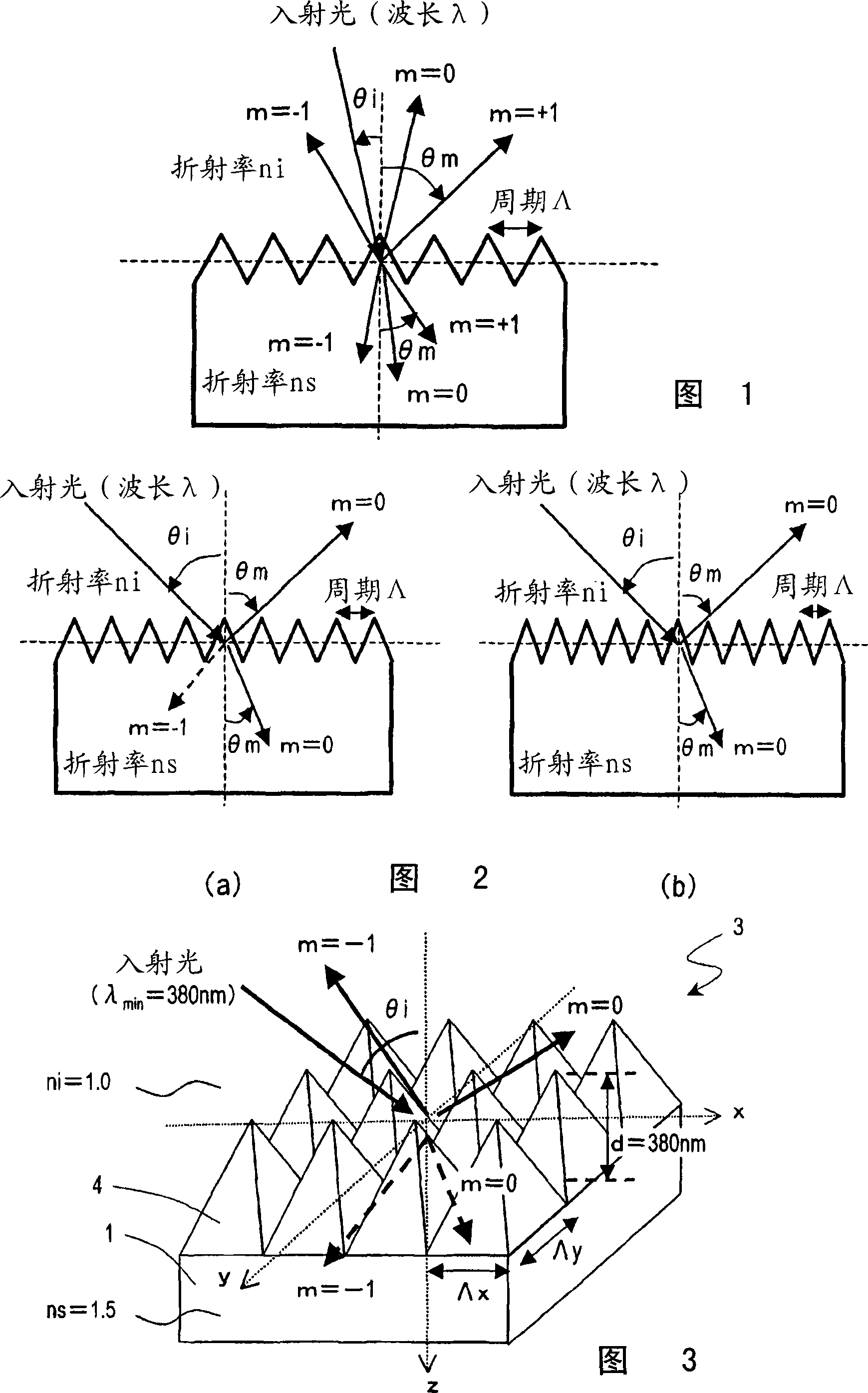
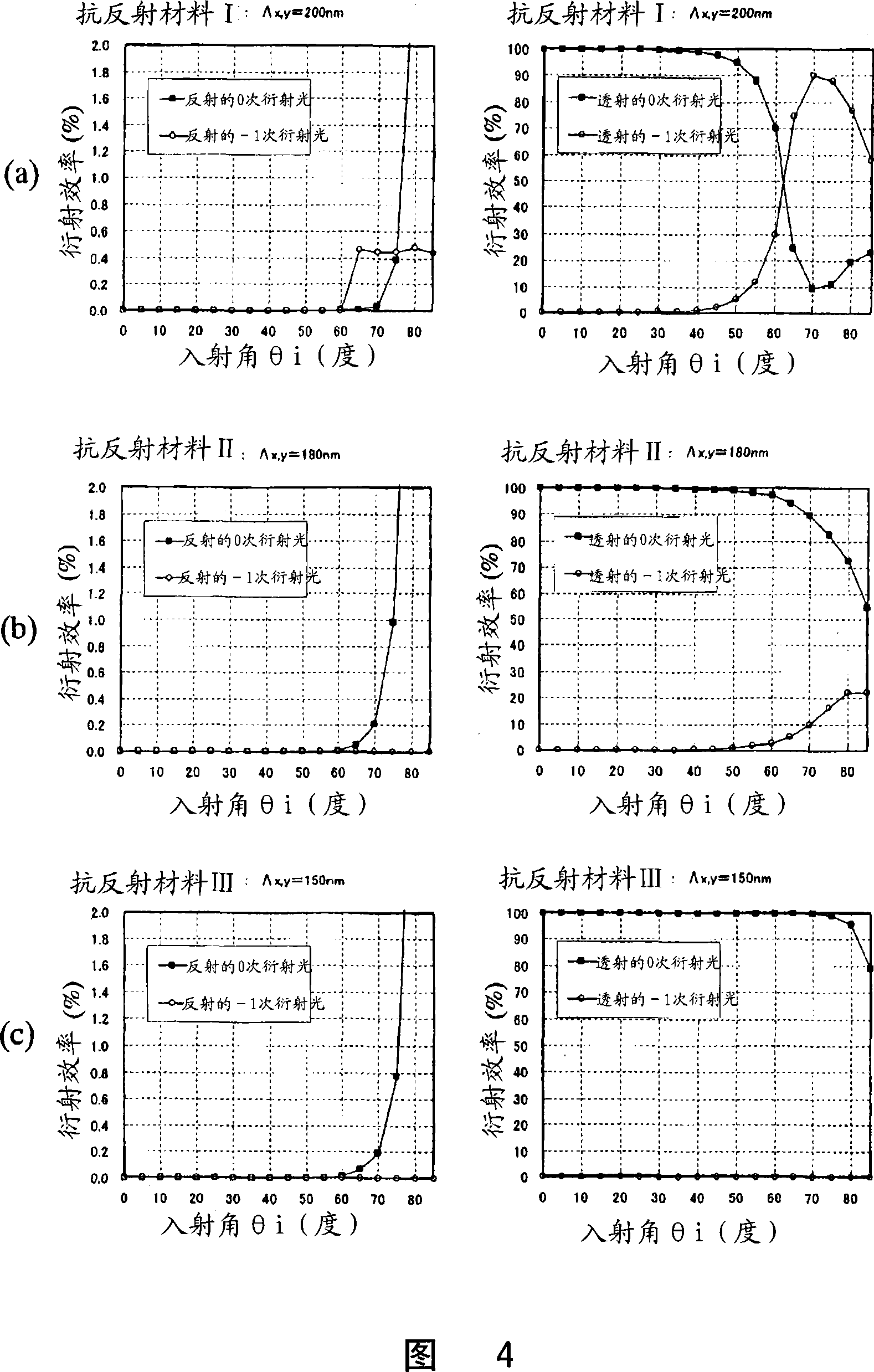
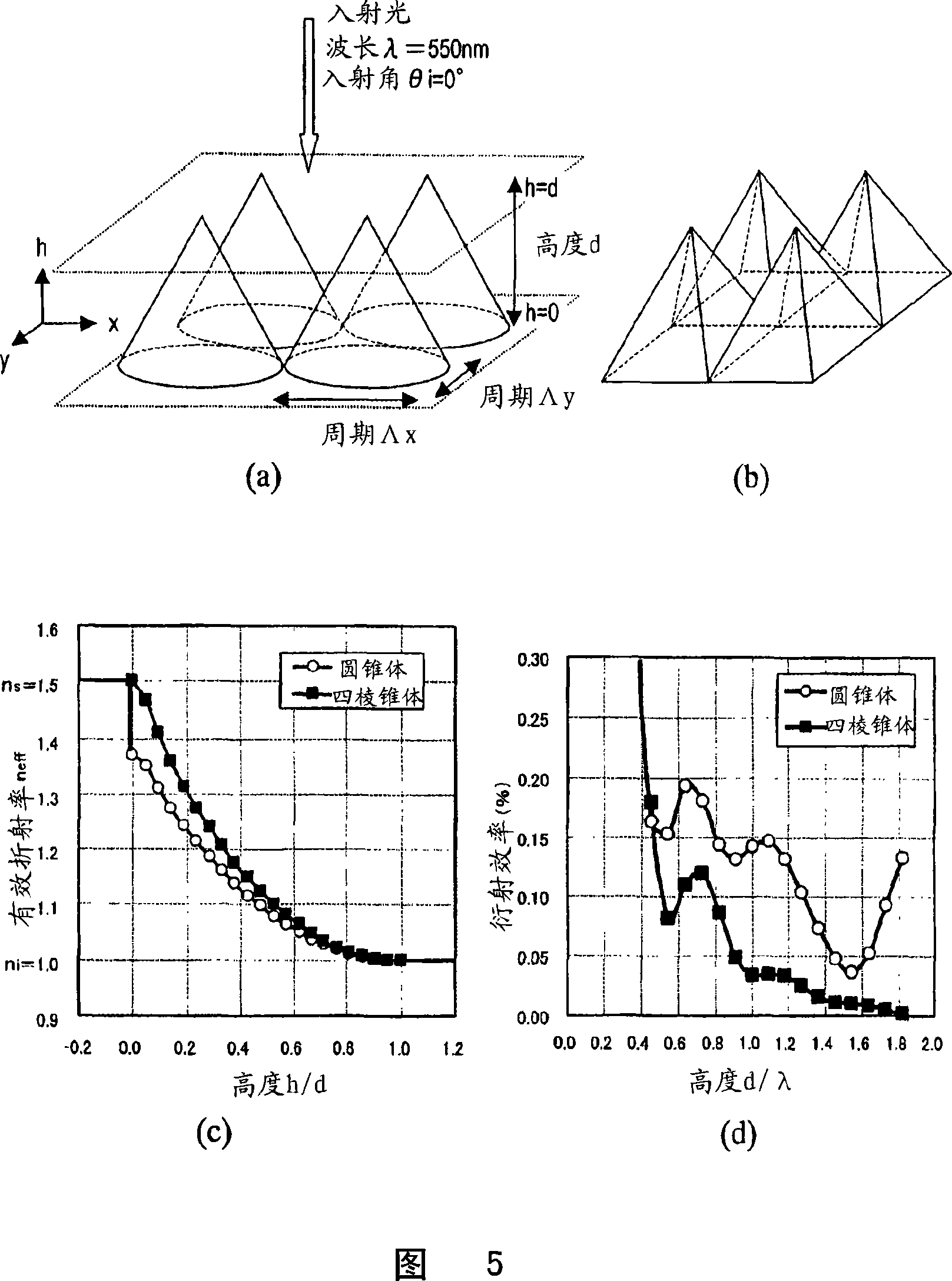
ActiveCN101088030ASuppression of regular reflectionImprove anti-reflection effectLayered productsCoatingsSurface patternAngle of incidence
An antireflective member according to the present invention has an uneven surface pattern, in which unit structures are arranged in x and y directions at respective periods that are both shorter than the shortest wavelength of an incoming light ray, on the surface of a substrate and satisfies the following inequality (1): lambda, / lambda ) . . ., where lambda is the shortest wavelength of the incoming light ray, theta i is the largest angle of incidence of the incoming light ray, ni is the refractive index of an incidence medium, lambda is the period of the uneven surface pattern in the x direction, and lambda is the period of the pattern in the y direction. As a result, diffraction of short-wave light components can be reduced in a broad wavelength range.
Owner:SHARP KK
Planar plasmonic device for light reflection, diffusion and guiding
A planar plasmonic device includes a first material layer having a surface configured to receive at least one photon of incident light. A patterned plasmonic nanostructured layer is disposed adjacent and optically coupled to the first material layer. The patterned plasmonic nanostructured layer includes a selected one of: a) at least a portion of a surface of the patterned plasmonic nanostructured layer includes a textured surface, and b) at least one compound nanofeature including a first material disposed adjacent to a second material within the compound nanofeature.
Owner:LIGHTWAVE POWER
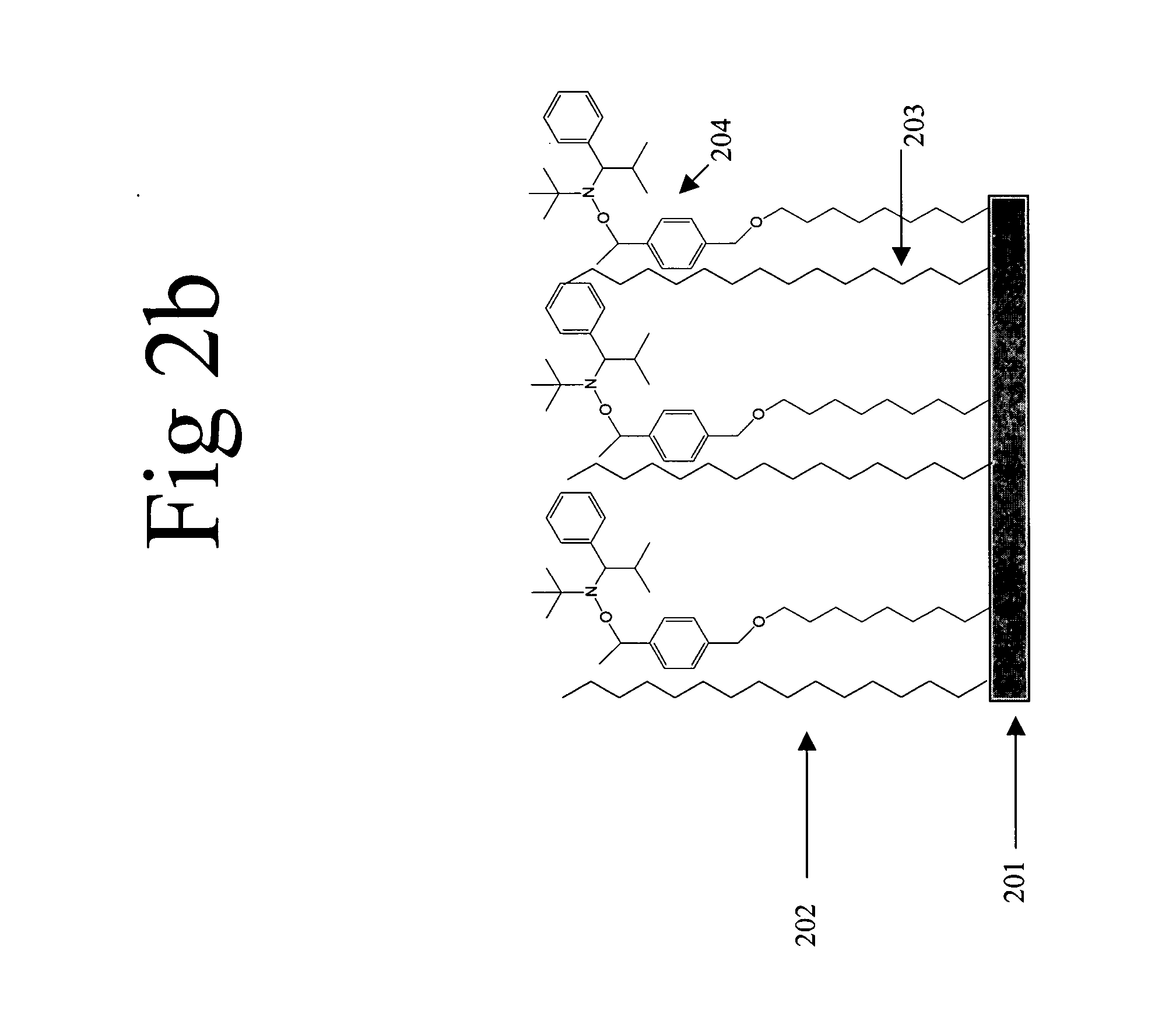
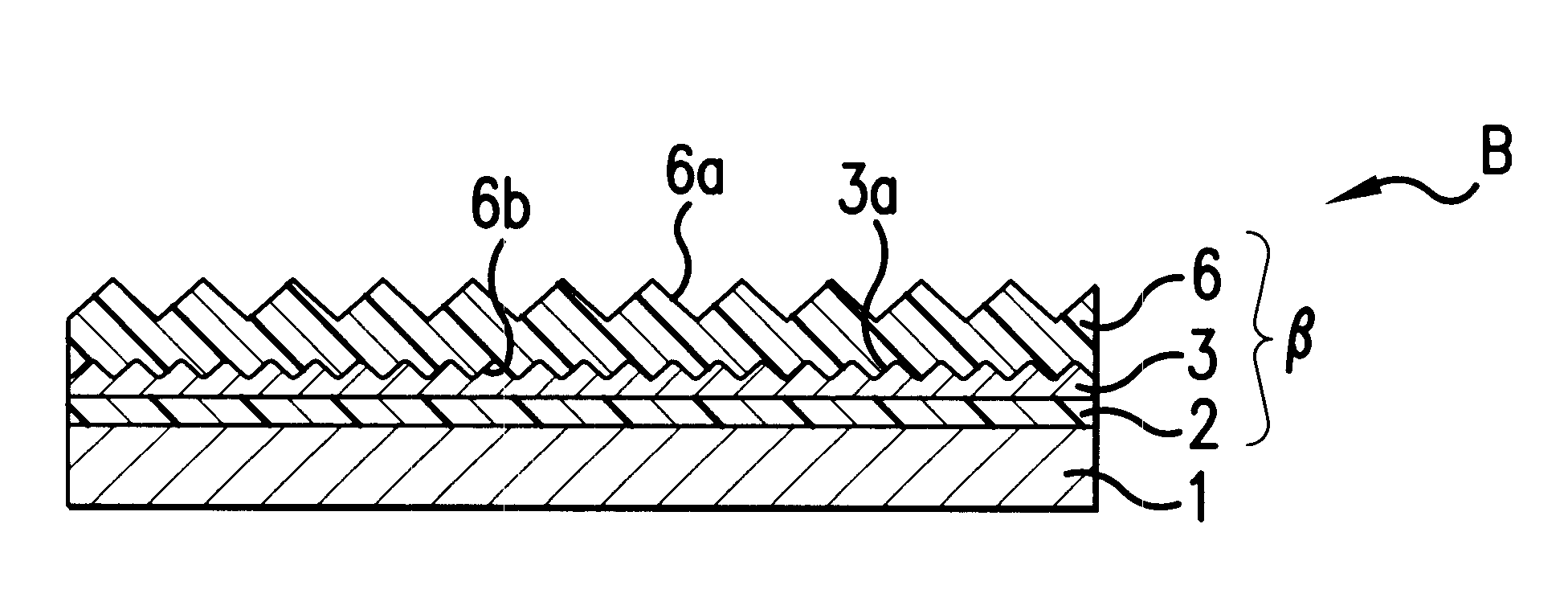
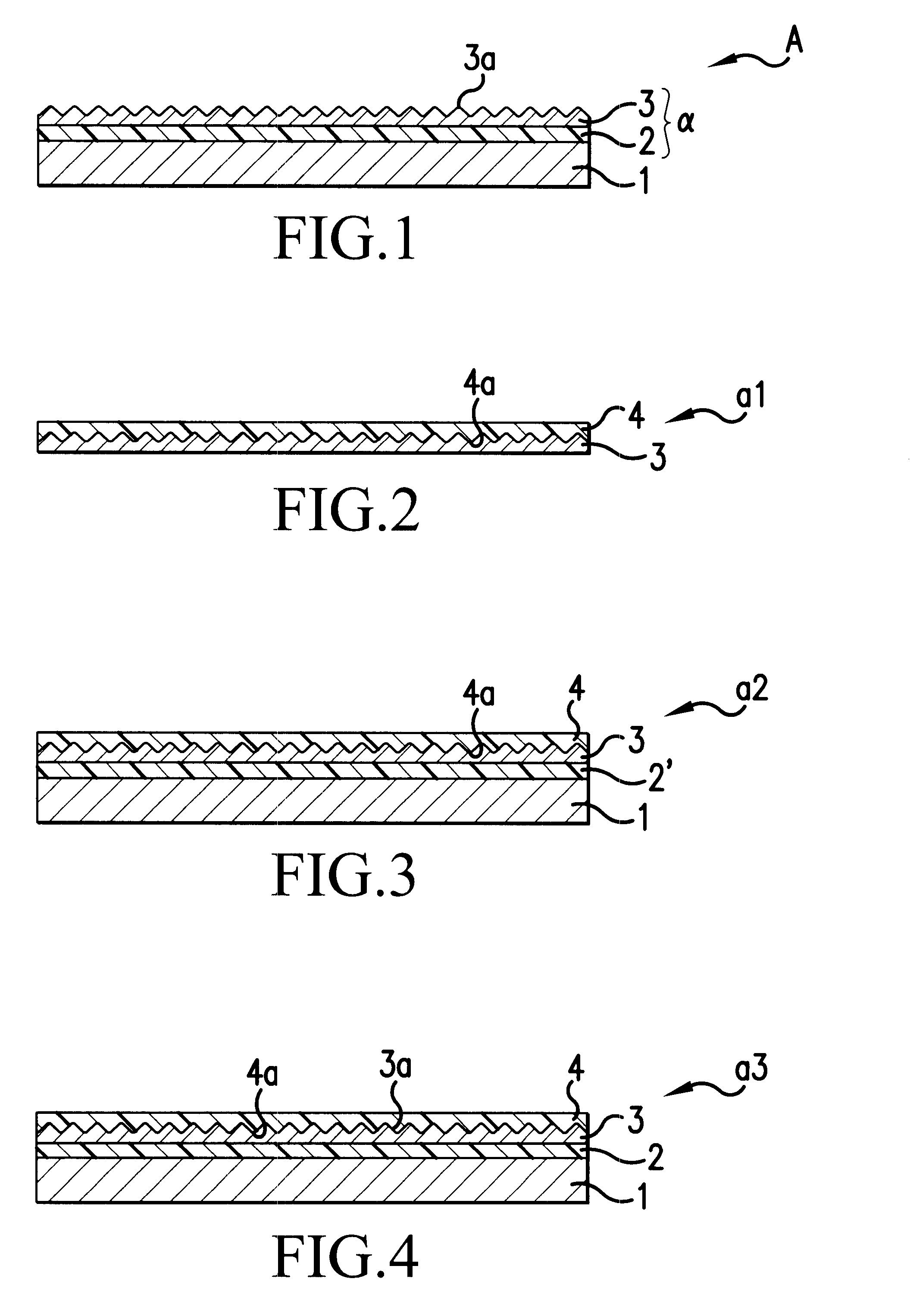
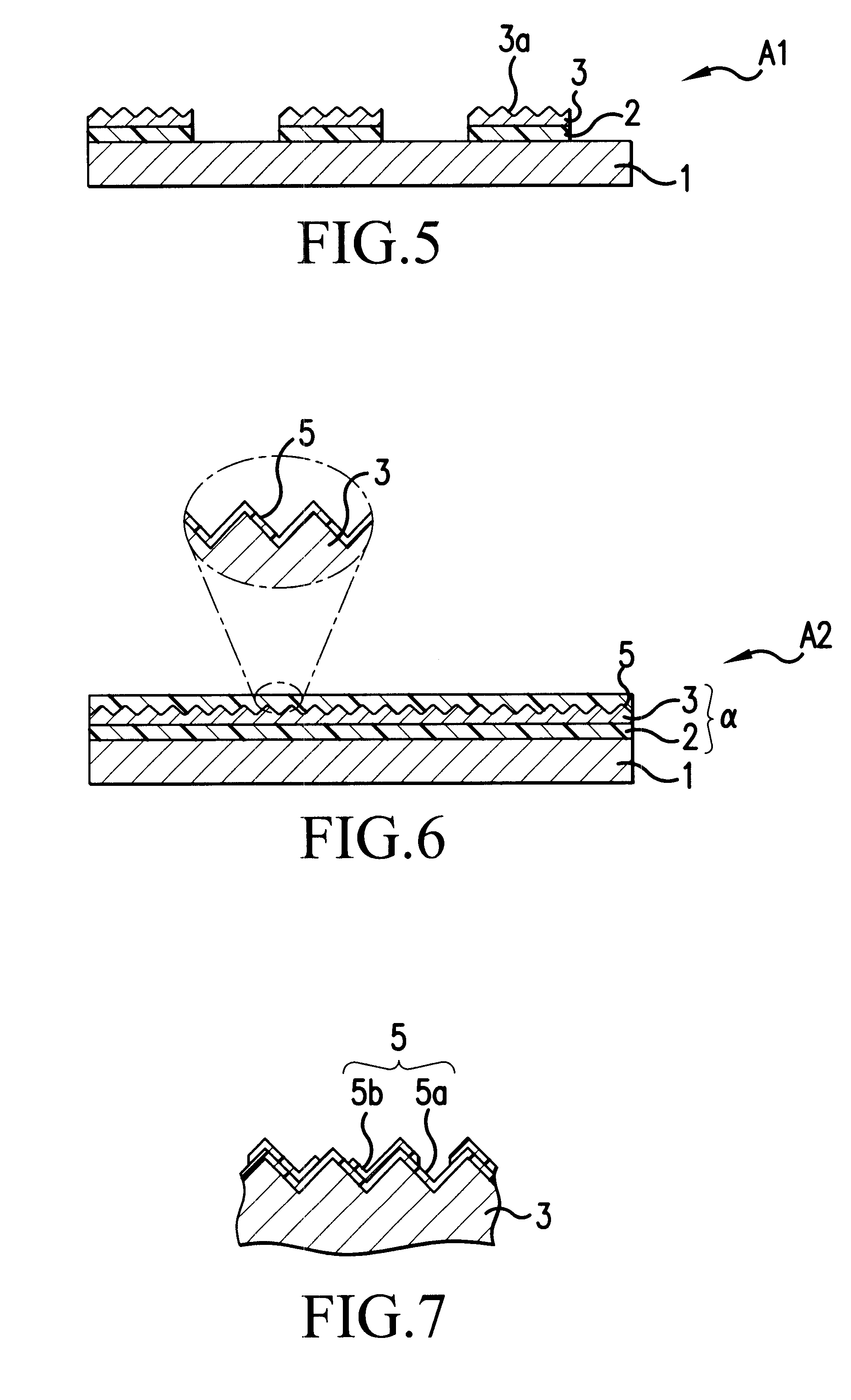
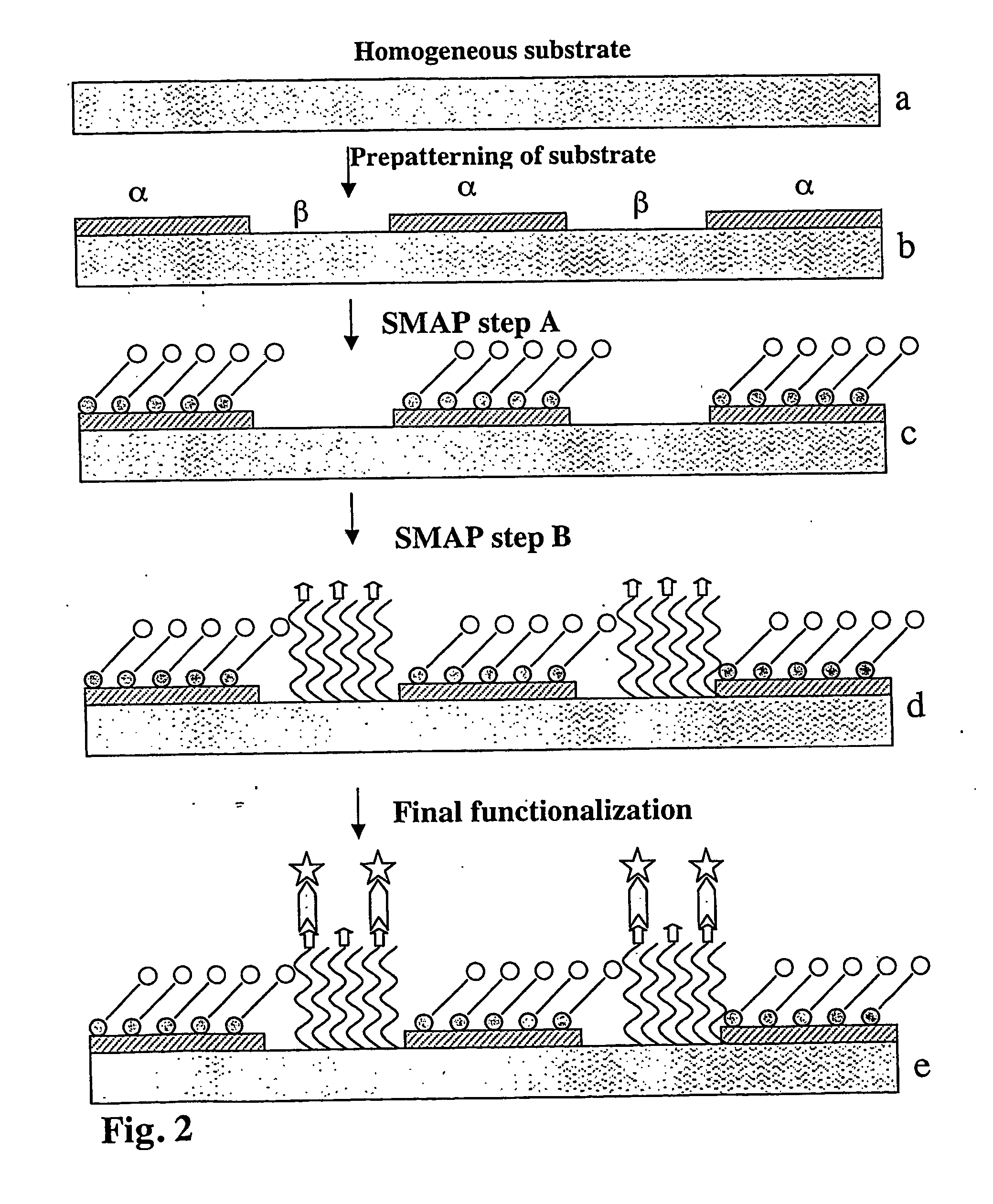
Device with chemical surface patterns
InactiveUS20050014151A1Retarded and prevented reactionSustained inflammationMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSurface patternChemical composition
A device with chemical surface patterns (defined surface areas of at least two different chemical compositions) with biochemical or biological relevance on substrates with prefabricated patterns of at least two different types of regions (α, β, . . . ), whereas at least two different, consecutively applied molecular self-assembly systems (A, B, . . . ) are used in a way that at least one of the applied assembly systems (A or B or . . . ) is specific to one type of the prefabricated patterns (α or β or . . . ).
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Shoes with interchangeable strap covers
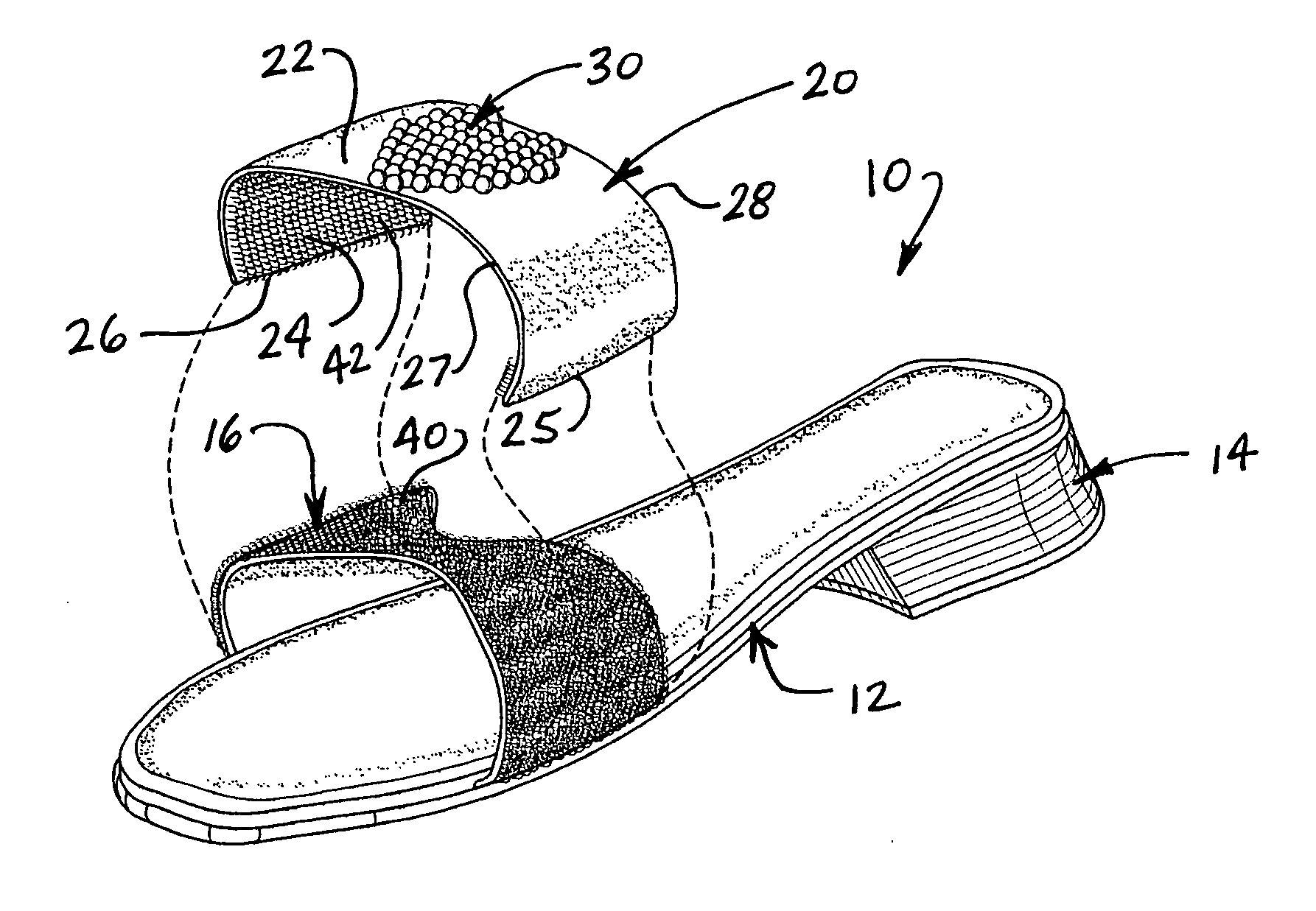
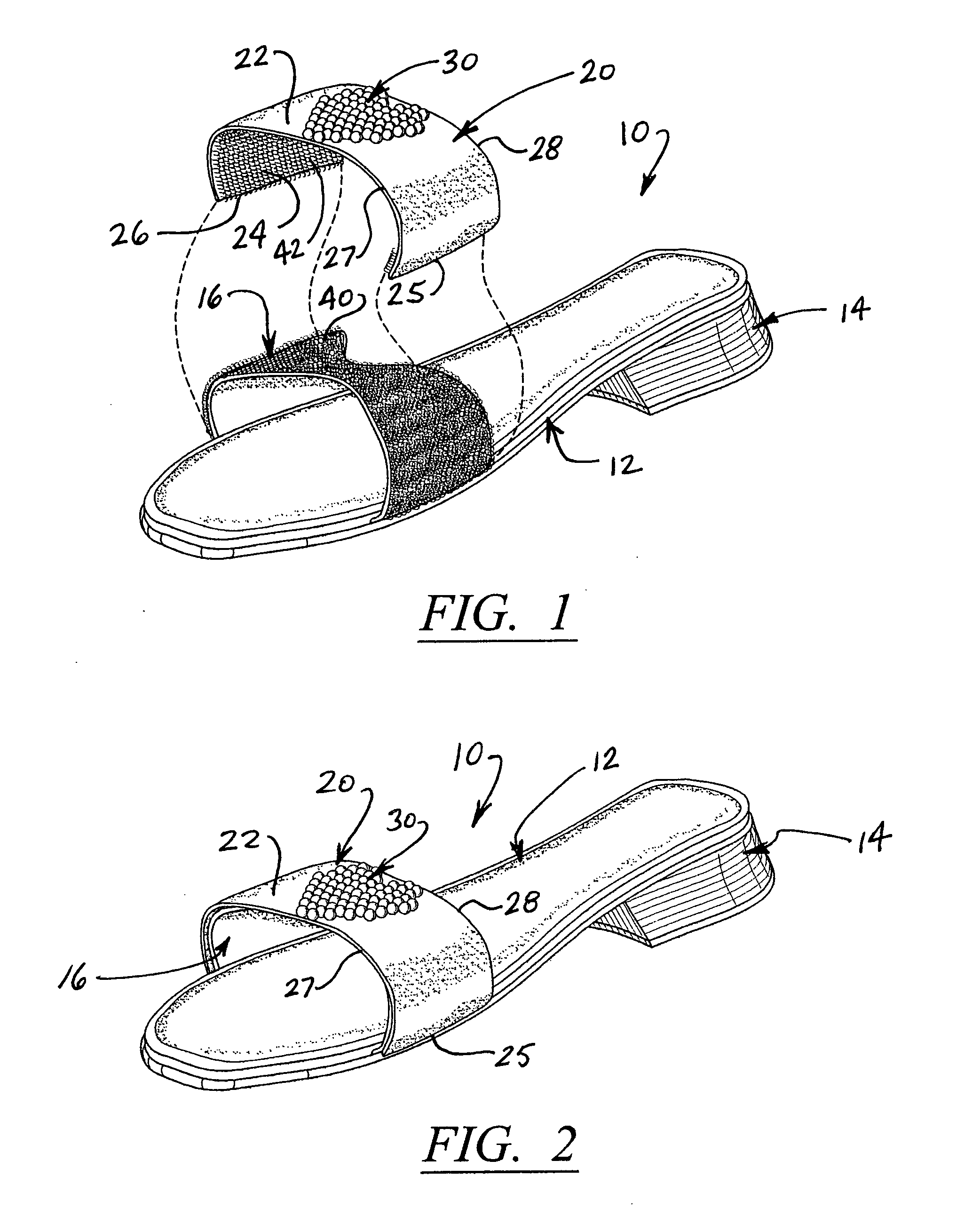
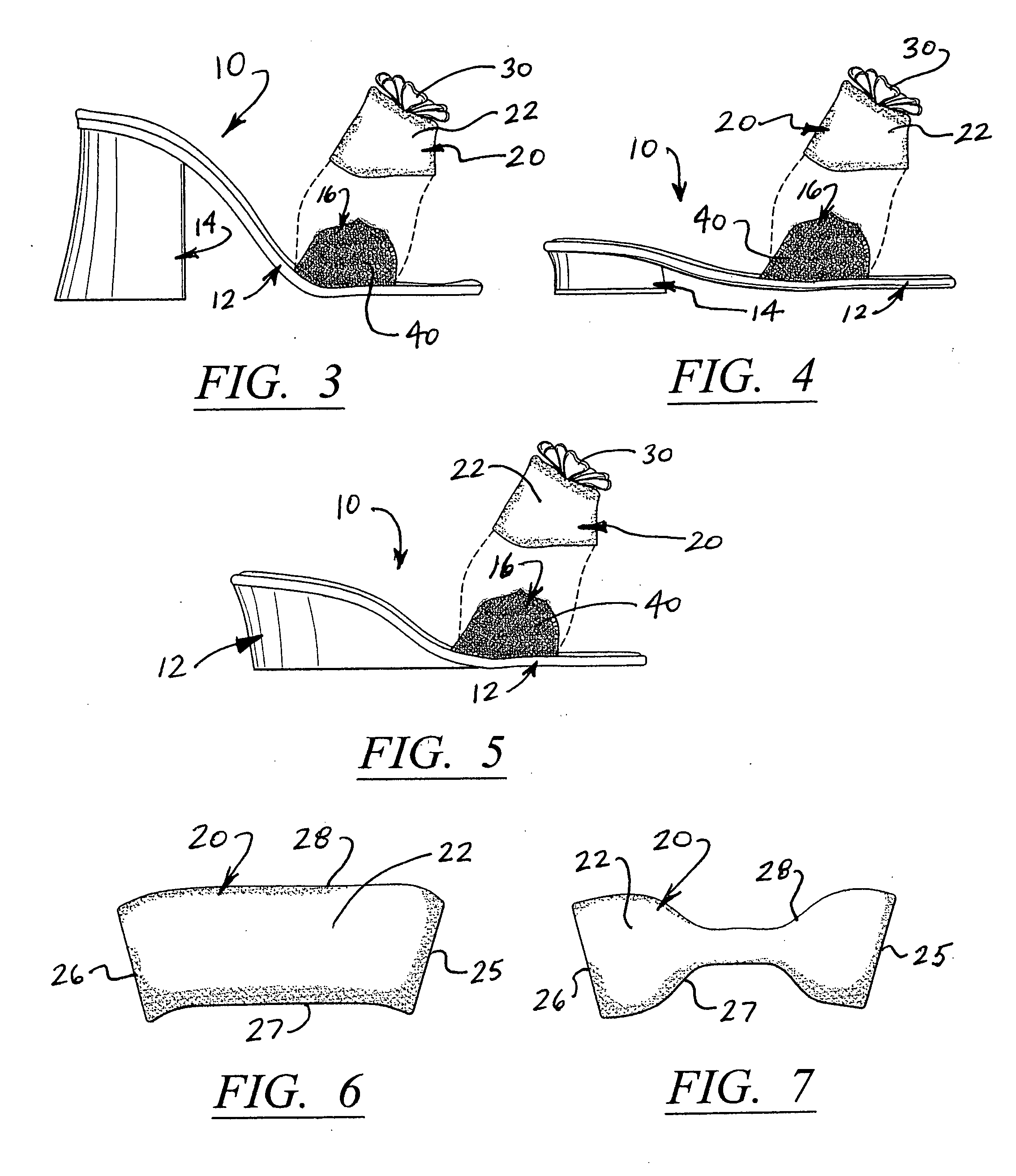
A women's shoe includes a sole, a heel and a base strap secured to opposite sides of the shoe and positioned to extend across of the wearer's foot. Strap covers are provided in various colors, materials, shapes and decorative surface patterns. The strap covers are each removably attachable to the base straps, in covering relation thereto, and are selectively interchangeable to provide a variety of different styles and appearances, thereby allowing the same shoe to be worn with many different outfits. The shoes are provided in different sizes, heel shapes and heights to further enhance the versatility of style and appearance, ranging from formal to casual.
Owner:LIU NANCY J
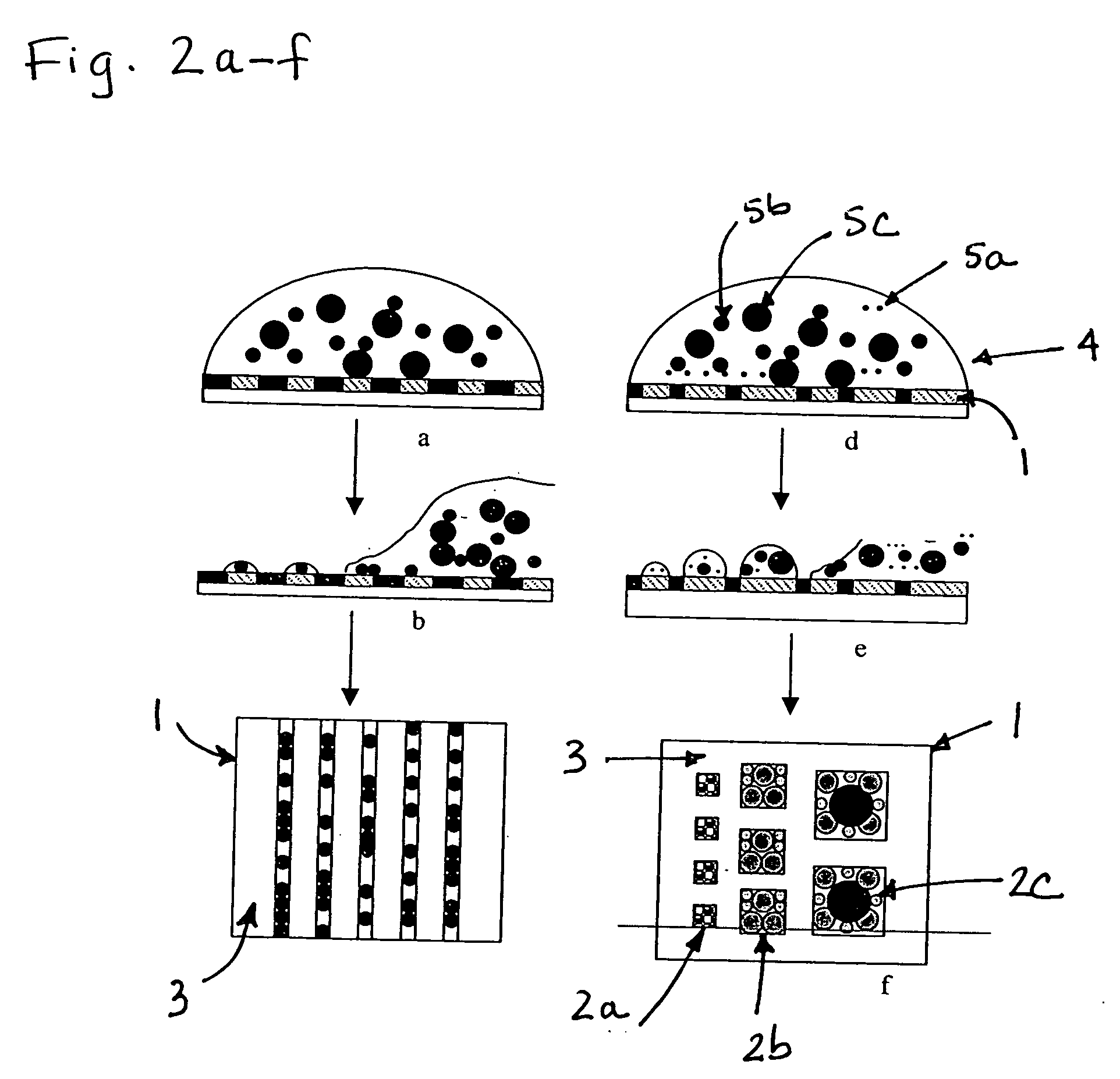
Control of the spatial distribution and sorting of micro-or nano-meter or molecular scale objects on patterned surfaces
InactiveUS20050118338A1Wide applicabilityEasy to classifyMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsSurface patternCrystallography
A method of depositing and sorting micro-scale, nano-scale and molecular-scale objects onto a surface. In particular, the methods can be used to produce arrays of micro- and nanoscale objects on a surface by use of fluidic alignment with surface patterning techniques. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the objects are sorted and / or spatially distributed and arrayed into micro- or nanometer scale geometries with periodicity on a larger area by evaporation (or other means of selective removal of solvent) of liquid containing molecular scale solutes, nanowires, metallic particles, polymeric particles, inorganic particles or composite particles formed from such materials or preferably, such particles may be sorted and deposited from suspensions by continuously creating and evaporating films of the suspension on patterned substrates.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Distributing method for ceramic tile
InactiveCN1586851ADelicate and rich colorsThe pattern is natural and smoothFeeding arrangmentsSurface patternBrick
The material distributing method for ceramic tile is one back side forming process including first distributing powder material and then distributing base material. Fine powder, granular material and their mixture are loaded one layer by one layer onto the conveying belt, added into specially designed lattice via bin to complete the first material distribution; and the base material then falls from the movable bin to fill the mold cavity to complete the second material distribution. During the twice material distribution, the lattice is filled with the fine powder or the mixture of fine powder and the granular material. The present invention has the features of multiple tube material distribution and lattice material distribution, and can form natural and fluent patterns and grains similar to that of natural stone material. The present invention has raised material distribution speed and the back side formation process has no influence on the surface pattern of the returned lattice.
Owner:TEDI CERAMIC FOSHAN CITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com