Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3398 results about "Reticle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A reticle, or reticule (from Latin reticulum, meaning 'net'), also known as a graticule (from Latin craticula, meaning 'gridiron'), is a pattern of fine lines or markings built into the eyepiece of a sighting device, such as a telescopic sight in a telescope, a microscope, or the screen of an oscilloscope, to provide measurement references during visual examination. Today, engraved lines or embedded fibers may be replaced by a computer-generated image superimposed on a screen or eyepiece. Both terms may be used to describe any set of lines used for optical measurement, but in modern use reticle is most commonly used for gunsights and such, while graticule is more widely used for the oscilloscope display, microscope slides, and similar roles.
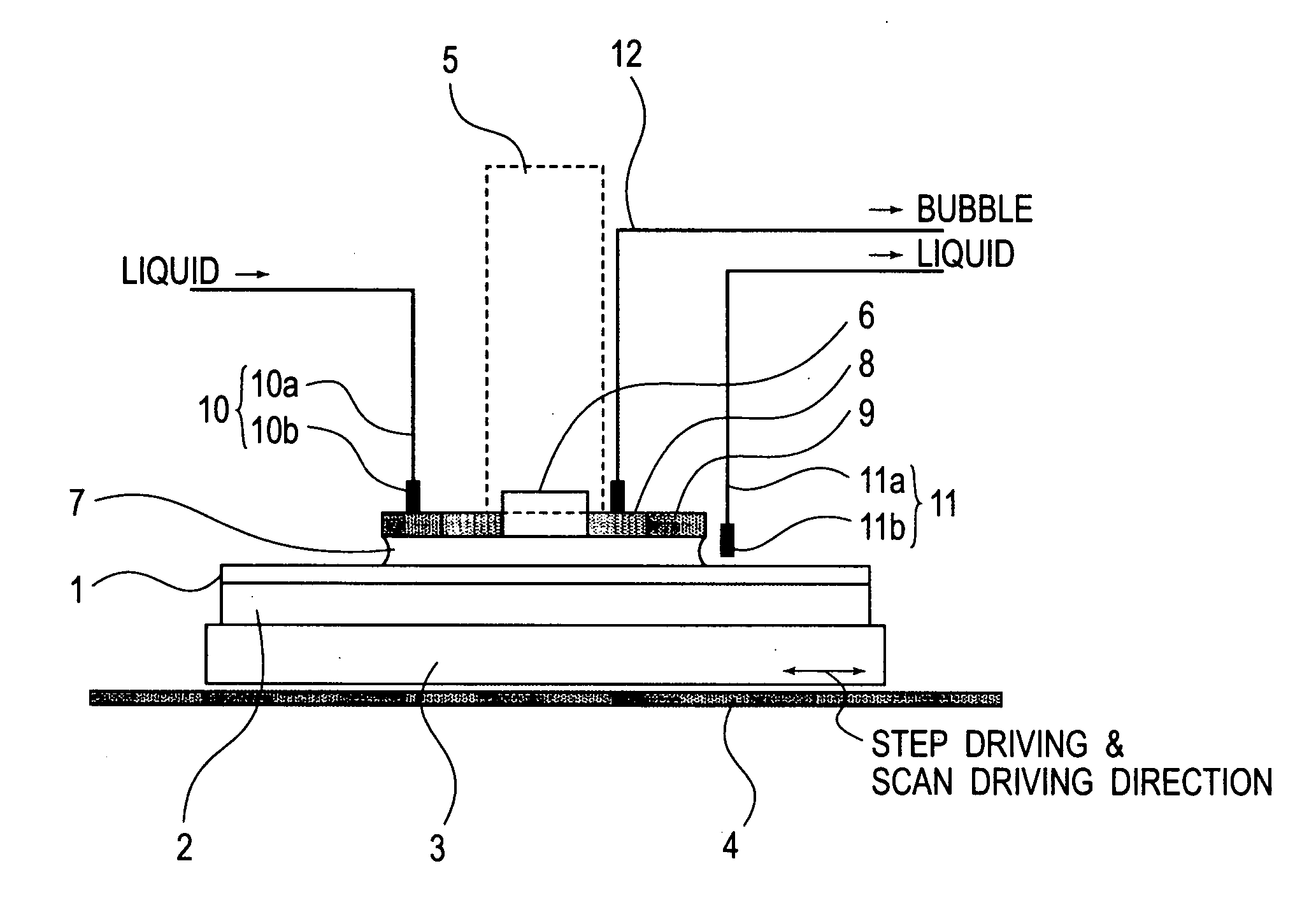
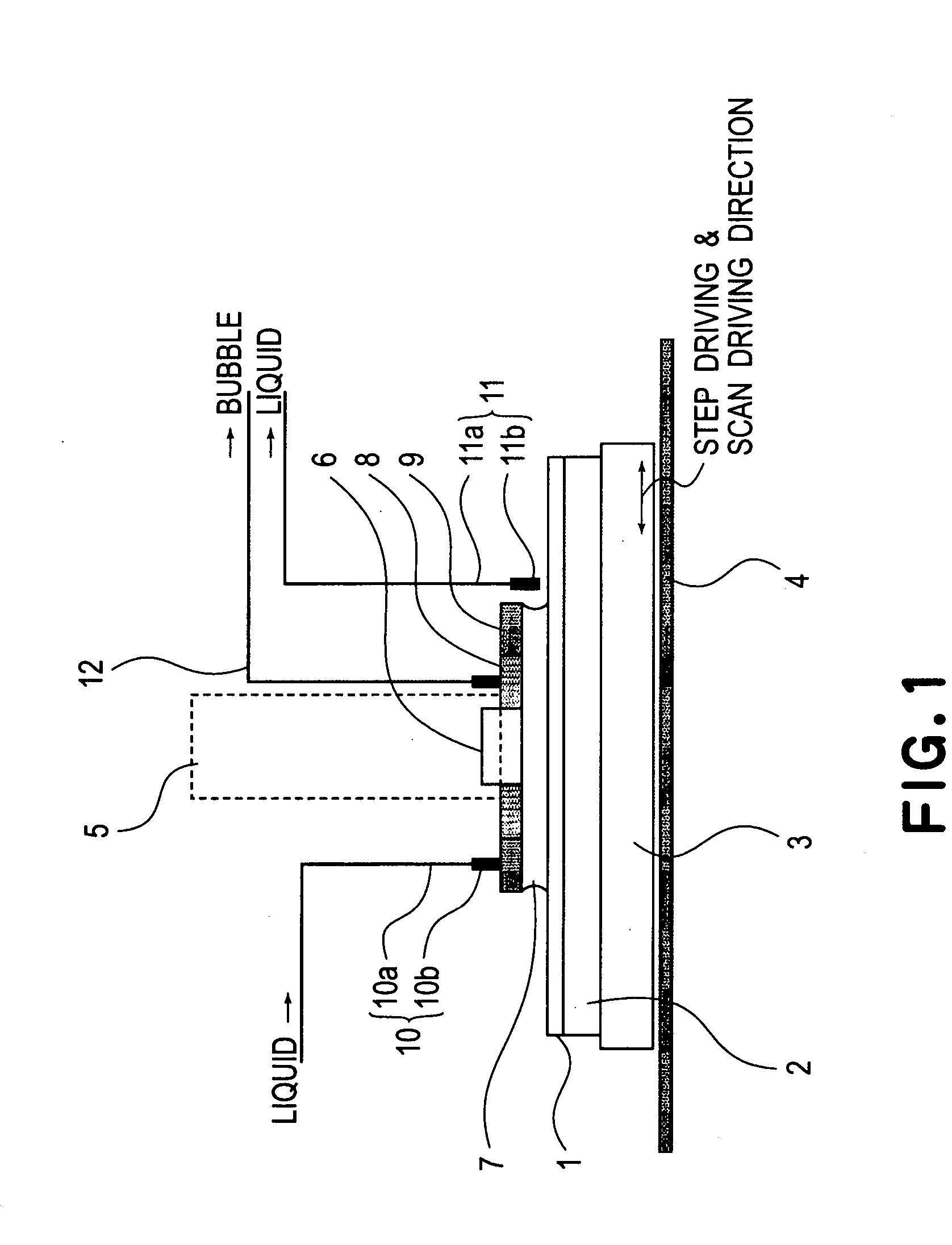
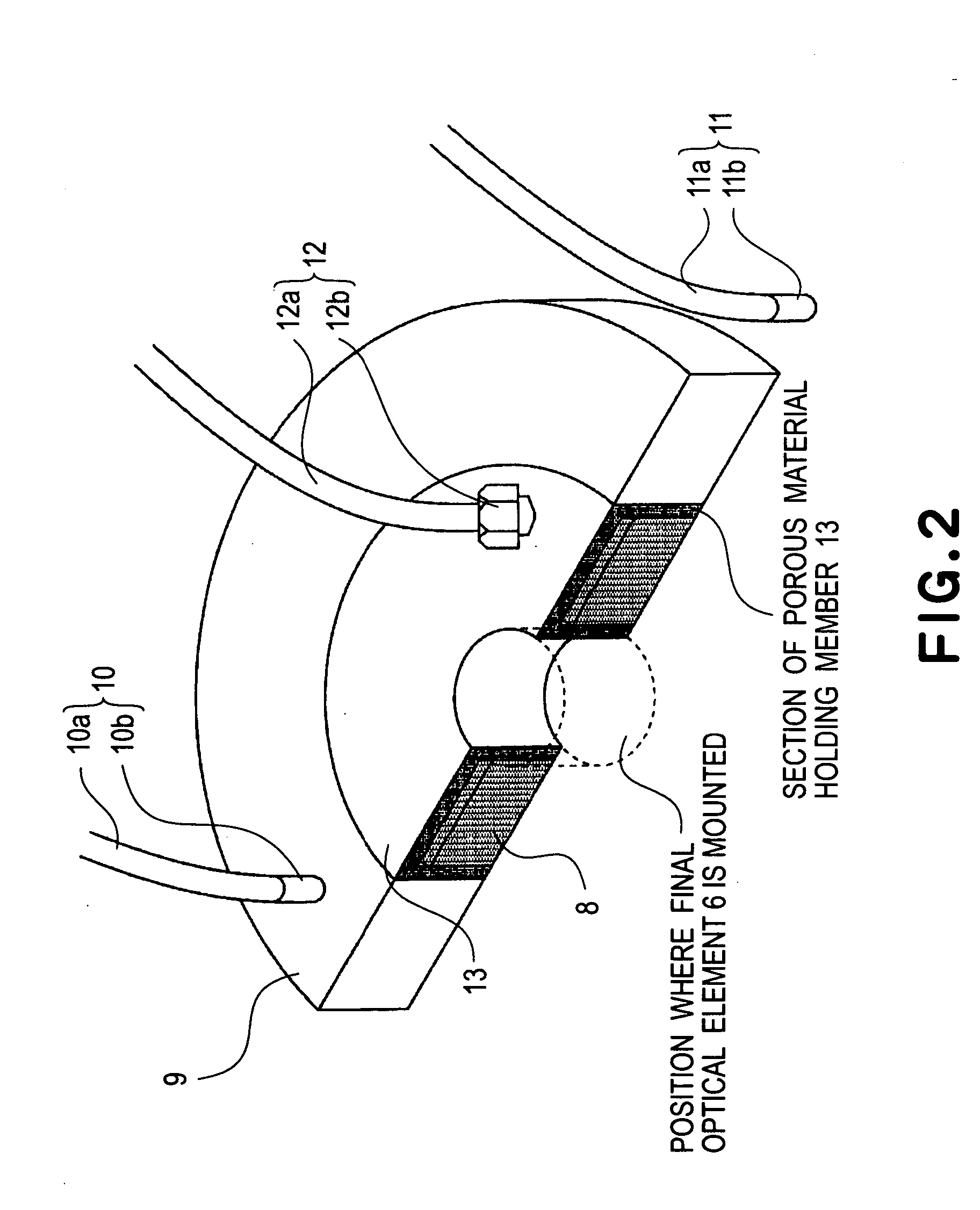
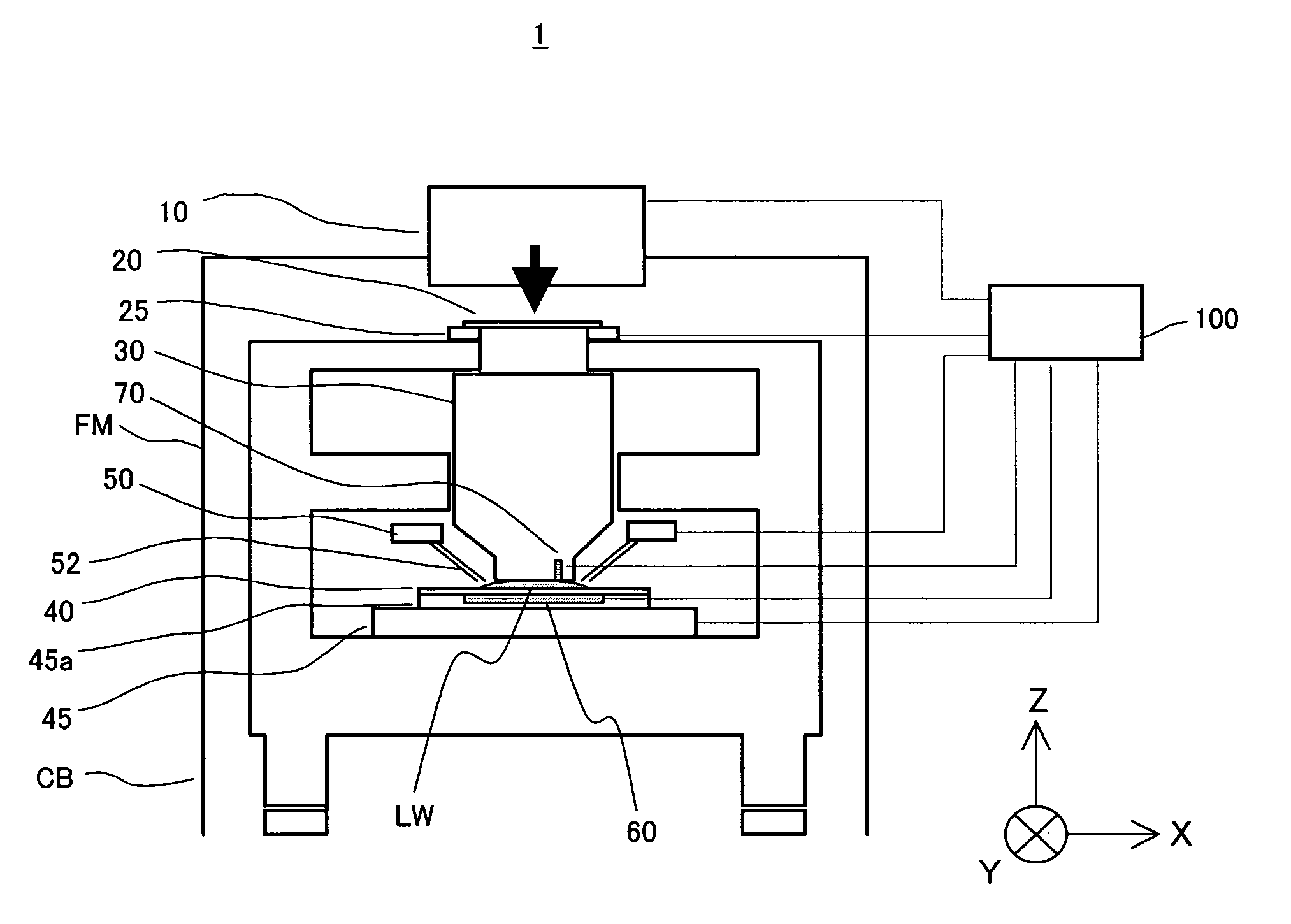
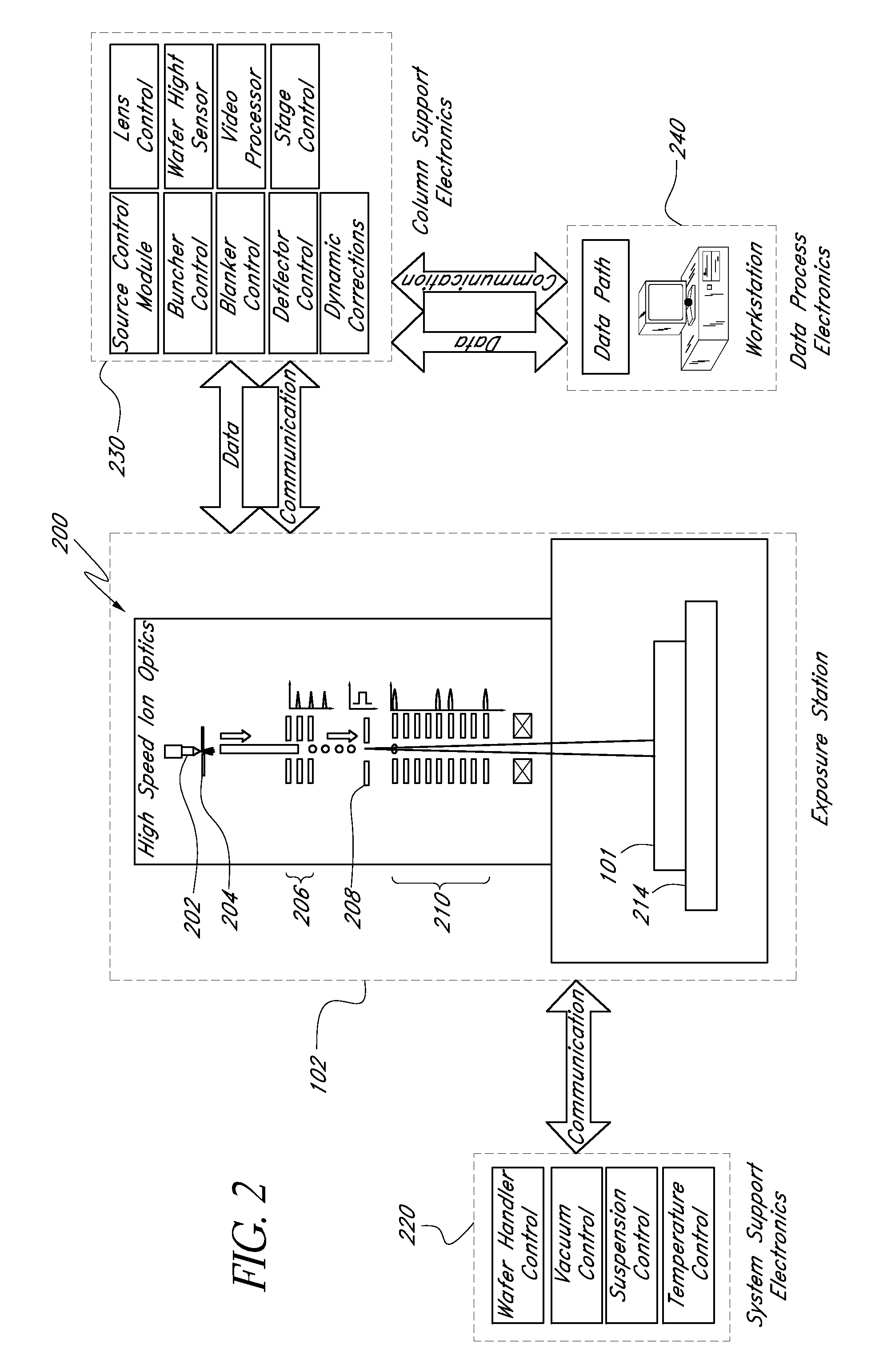
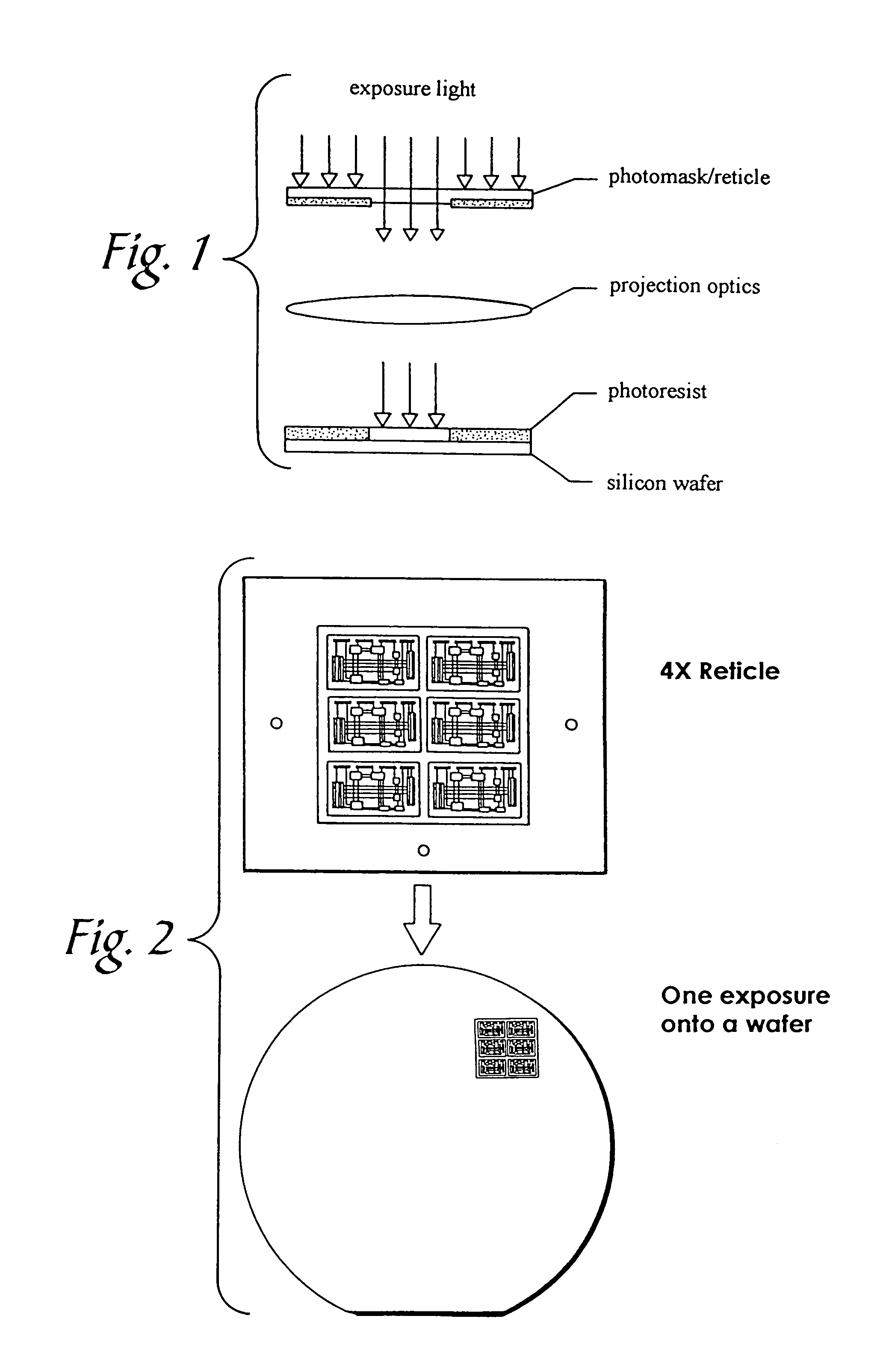
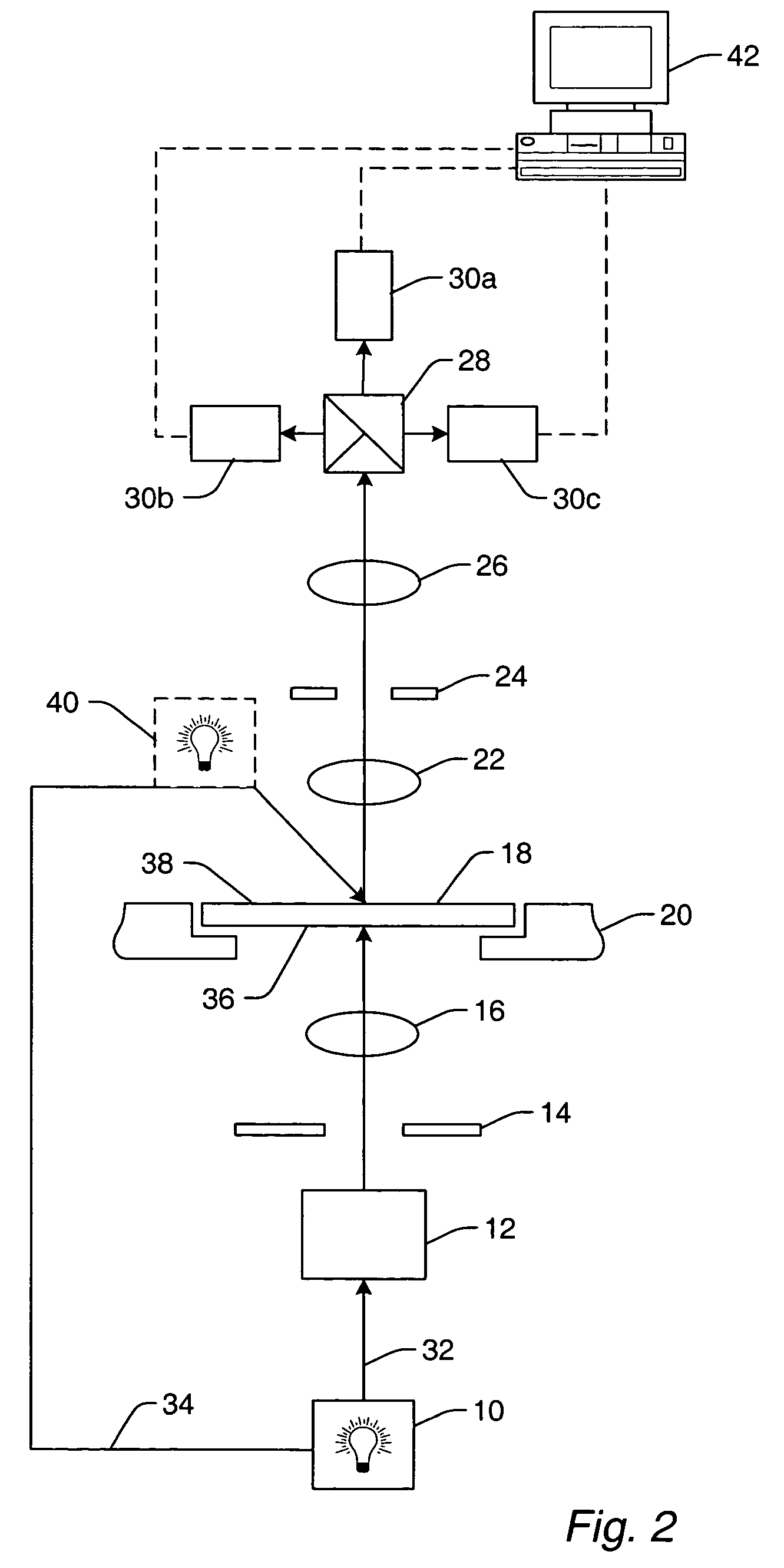
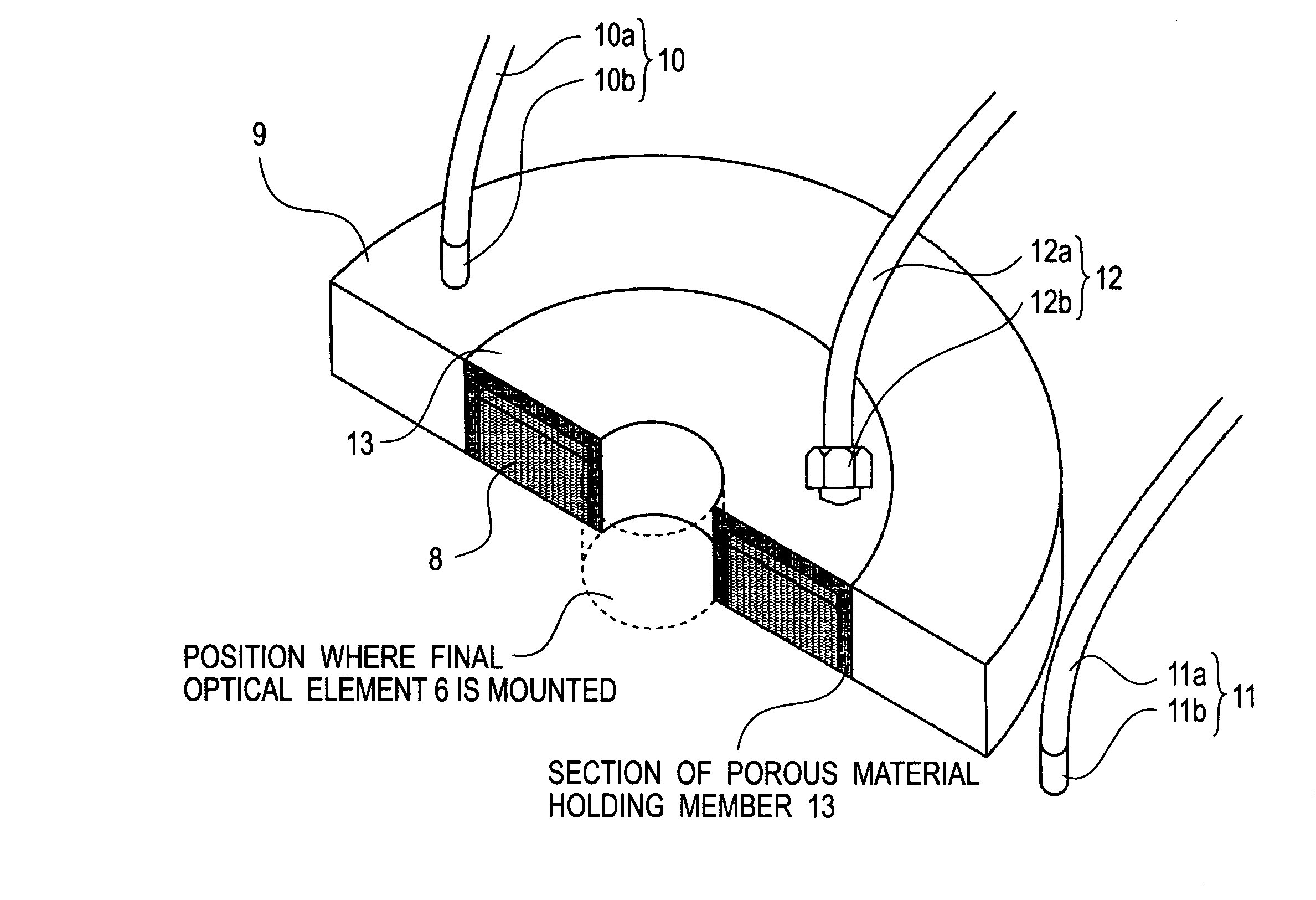
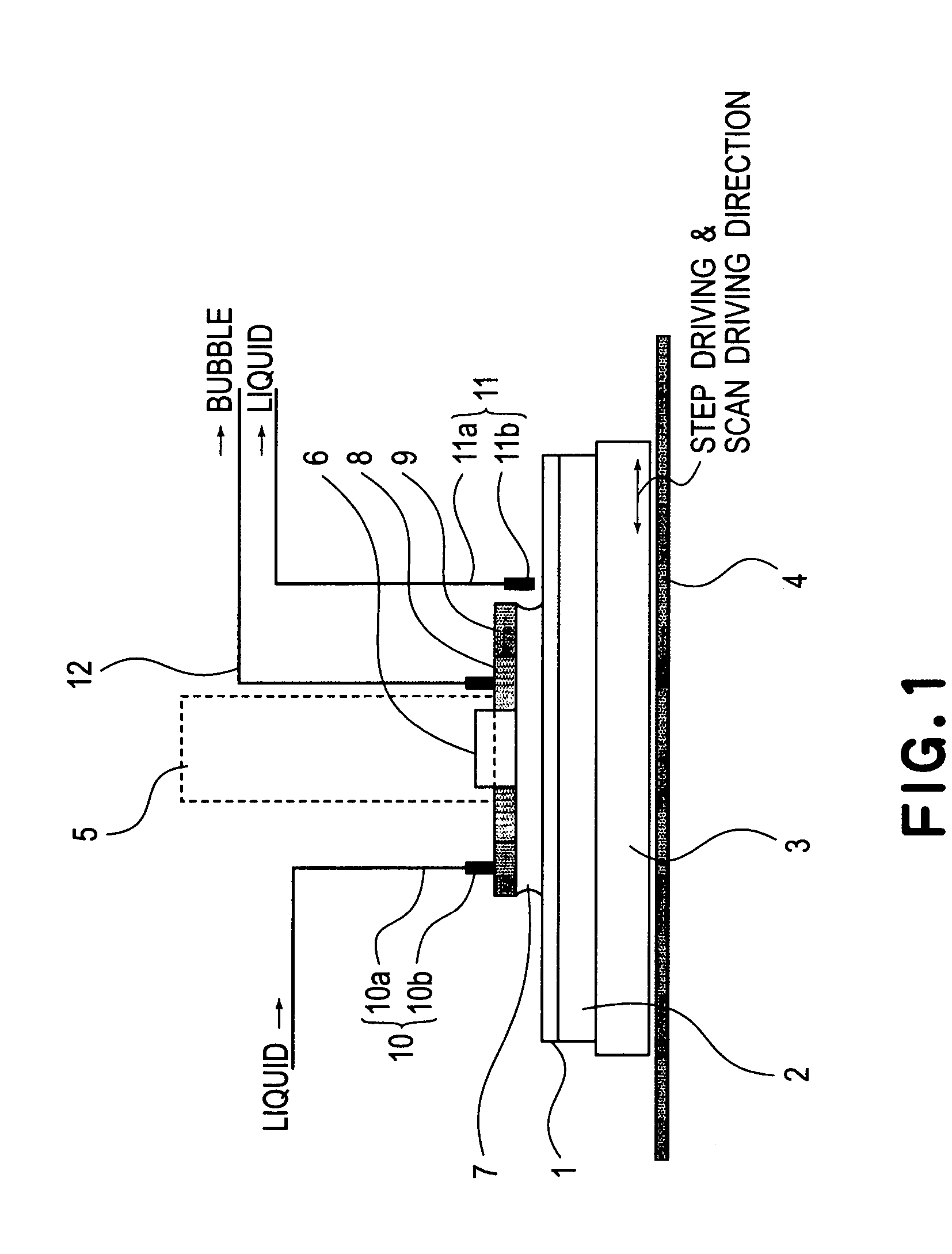
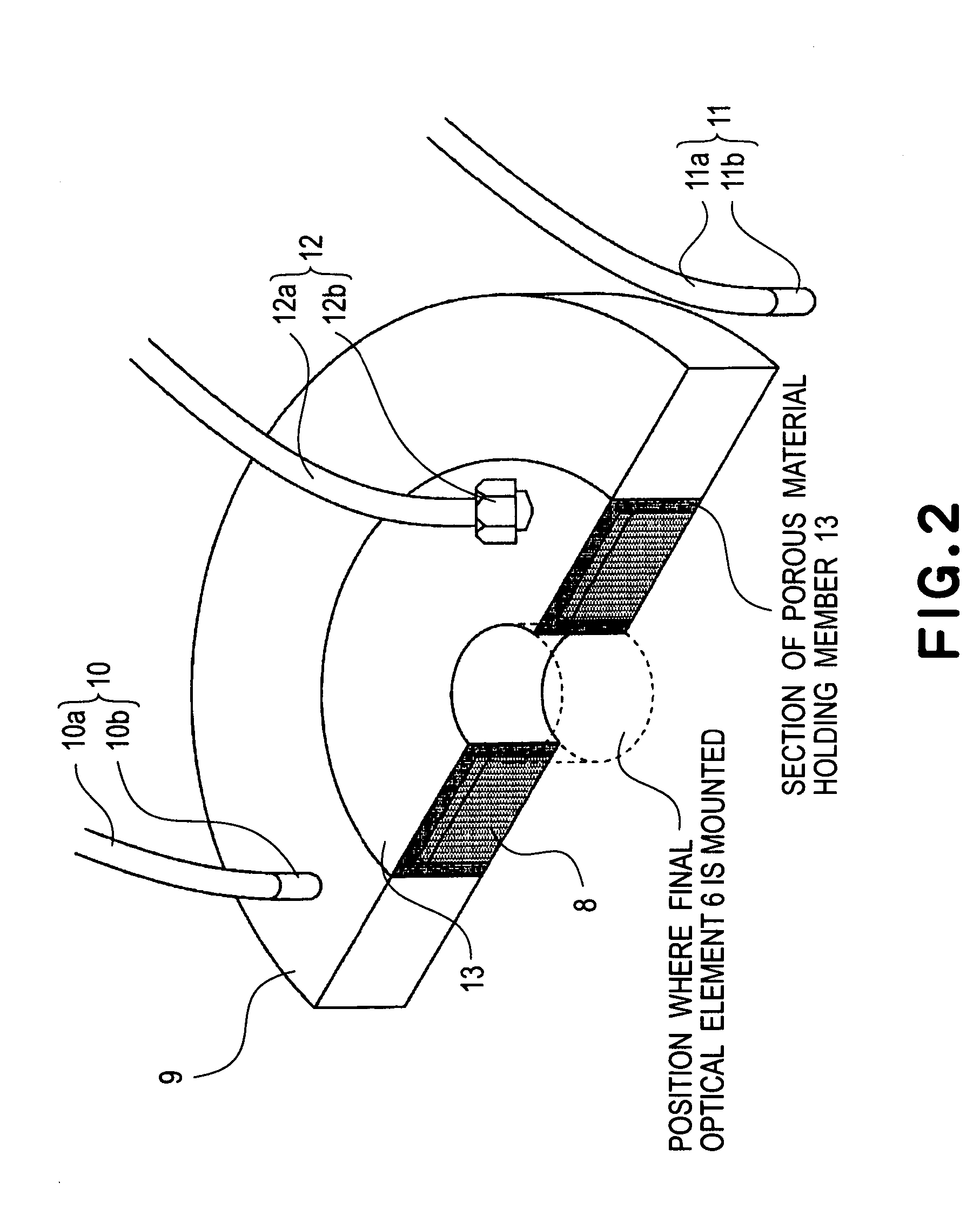
Liquid immersion type exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20050233081A1High resolutionLow refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid mediumCollection system
Disclosed is an exposure apparatus which includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern of a reticle onto a substrate, wherein the substrate is exposed through a liquid medium kept at least in a portion between the substrate and an optical element of the projection optical system which optical element is nearest to the substrate, a supplying system for supplying a liquid medium, a collecting system for collecting a liquid medium, and an exhausting system for removing a bubble in the liquid medium through a bubble removing material having such property that it passes a gas but it does not pass a liquid.
Owner:CANON KK
Exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20050146693A1Accurate exposureLarge numerical apertureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRefractive indexReticle
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern on a reticle onto an object to be exposed, a reference mark that serves as a reference for an alignment between the reticle and the object, a first fluid that has a refractive index of 1 or greater, and fills a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the object and a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the reference mark, and an alignment mechanism for aligning the object by using the projection optical system and the first fluid.
Owner:CANON KK
Etching of nano-imprint templates using an etch reactor
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
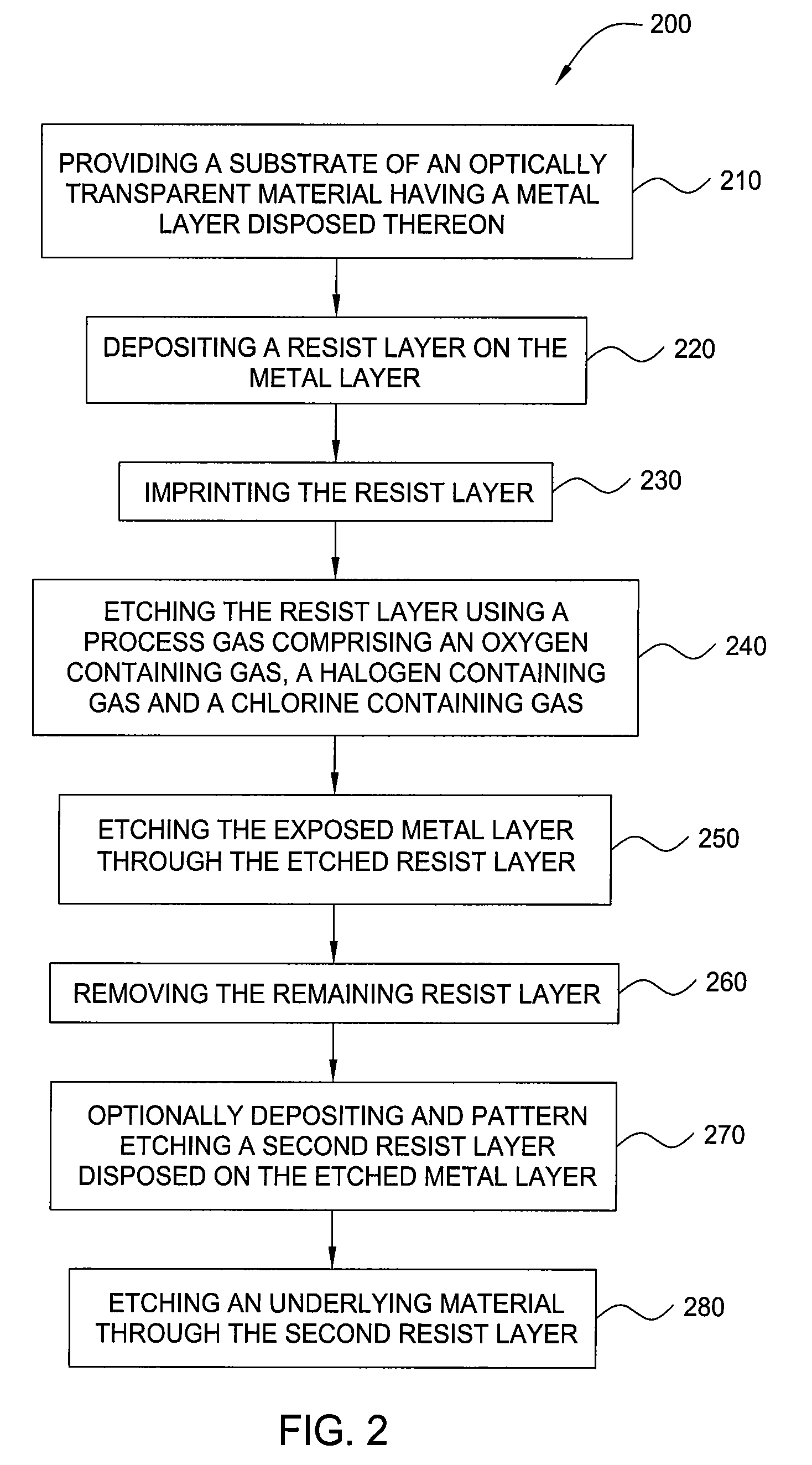
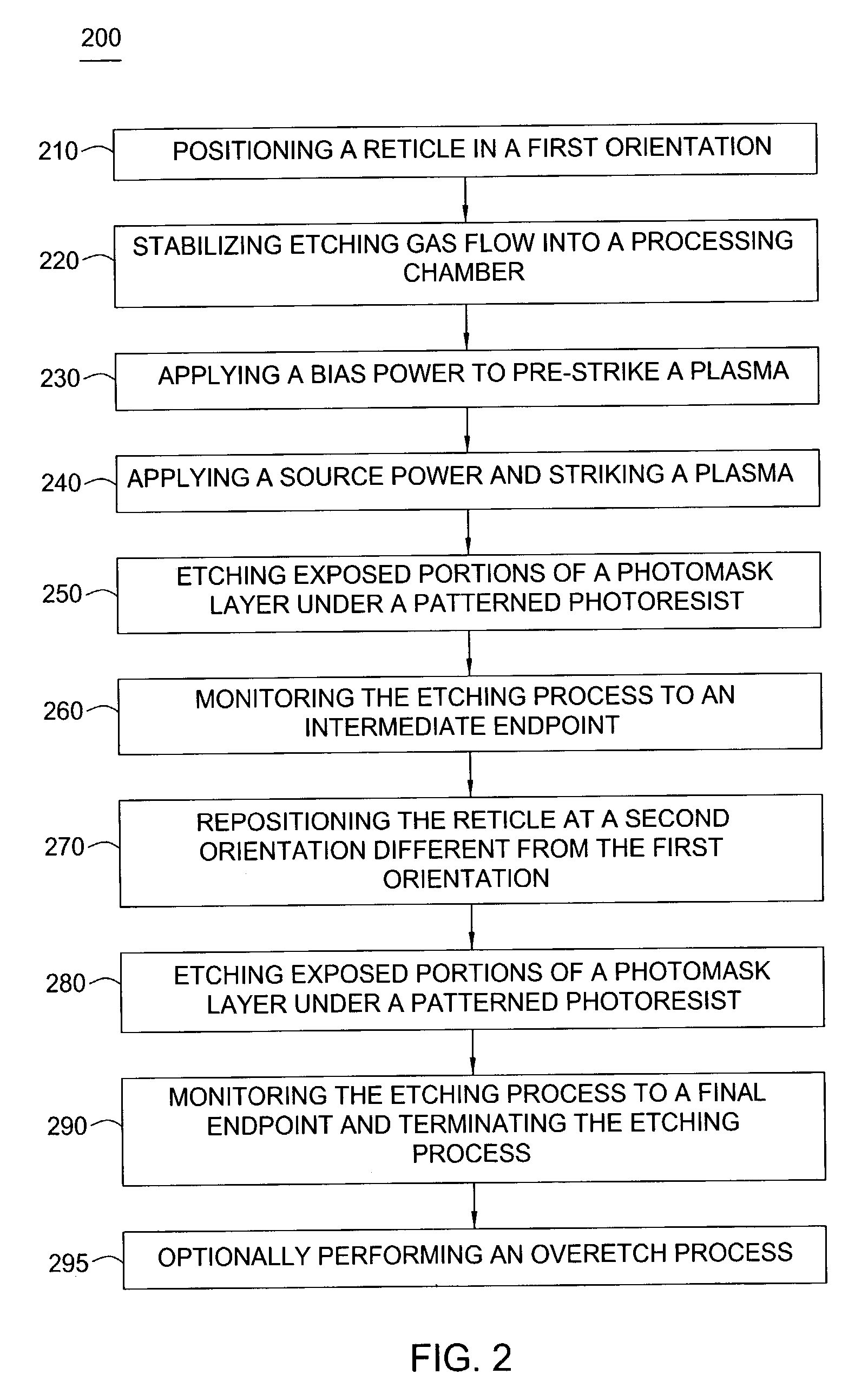
Methods for substrate orientation
Method and apparatus for etching a metal layer disposed on a substrate, such as a photolithographic reticle, are provided. In one aspect, a method is provided for processing a photolithographic reticle including positioning the reticle in a first orientation on a reticle support in a processing chamber, wherein the reticle comprises a metal photomask layer formed on an optically transparent substrate, and a patterned resist material deposited on the metal photomask layer, etching the metal photomask layer in the first orientation, positioning the reticle in at least a second orientation, and etching the metal photomask layer in the at least second orientation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
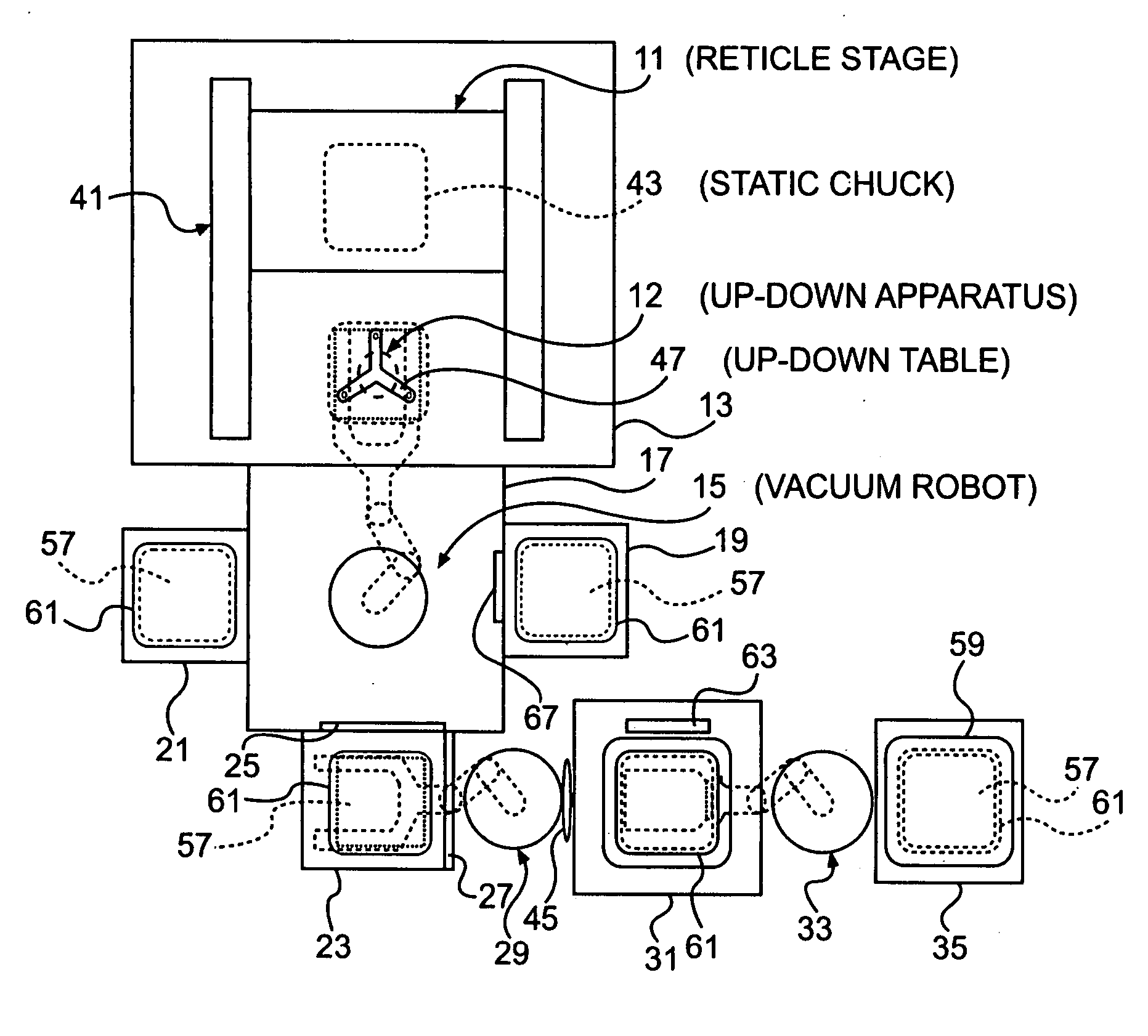
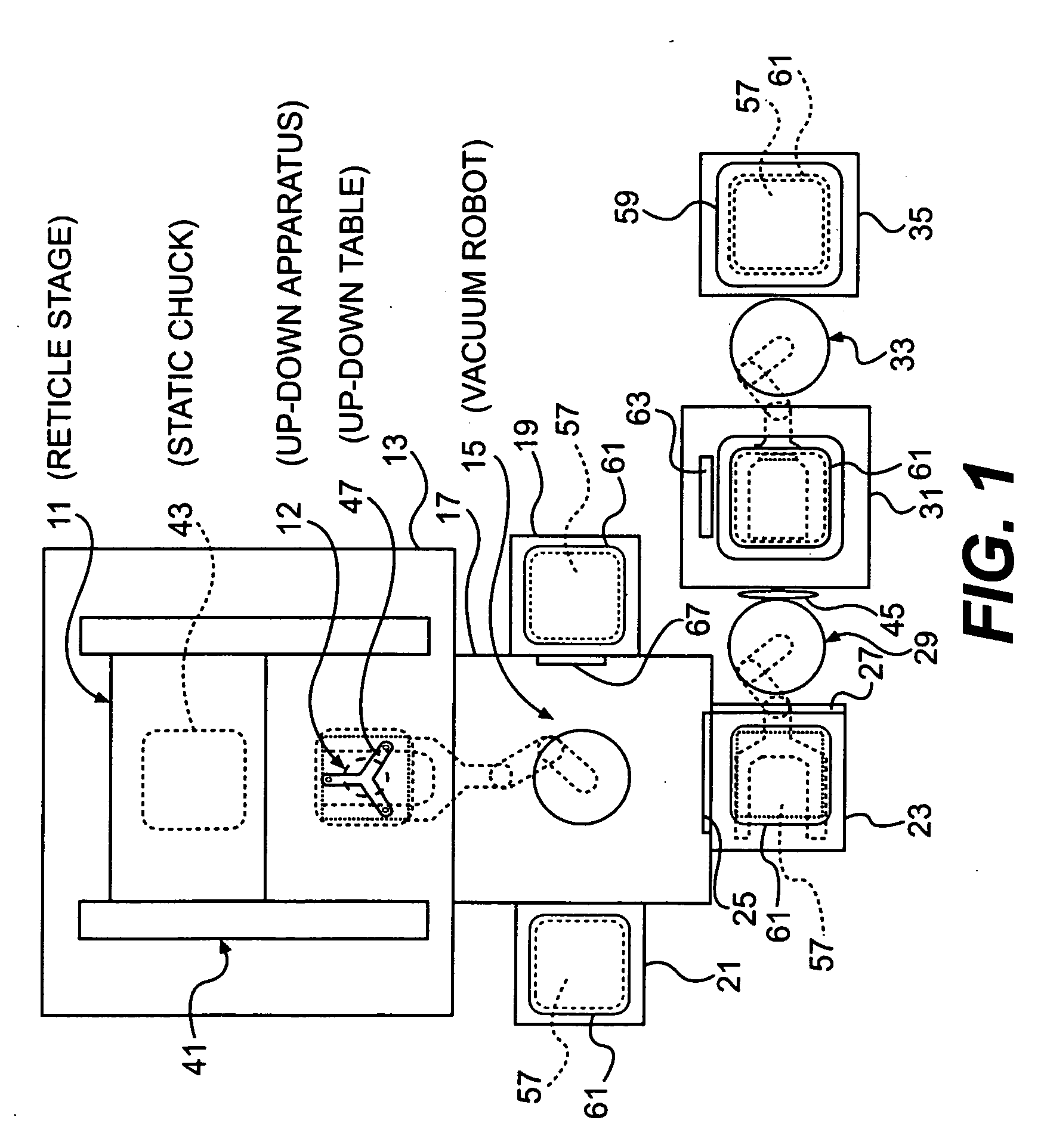
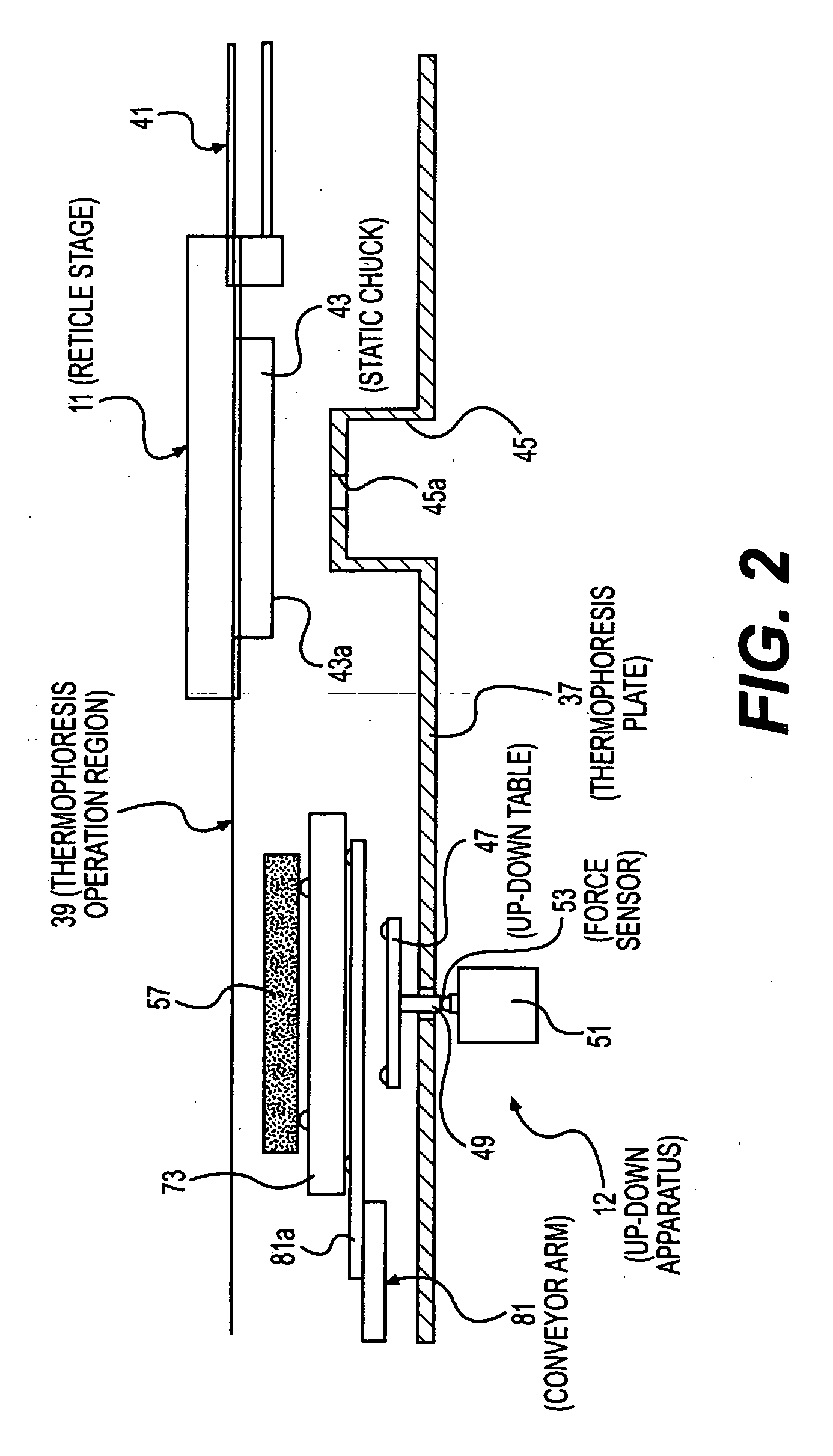
Substrate conveyor apparatus, substrate conveyance method and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS20060291982A1Improve reliabilityStrong adhesionPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringReticle
The present invention pertains to a substrate conveyor apparatus that carries a substrate such as a reticle, a substrate conveyance method and an exposure apparatus, with the object of reliably adhering a substrate to the lower surface of a chuck. The present invention is characterized by having a movable stage that can move in the horizontal direction and that is equipped with a chuck having an adhesion surface that faces down for adhering a substrate, an up-down means equipped with an up-down table that is positionable in a position below the substrate and within the movement range of the movable stage, and a conveyance means equipped with a conveyor arm that carries the substrate to the up-down means.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20050213066A1Facilitating liquid controlReduce solubilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusReticleLight source
An exposure apparatus includes a illumination optical system for illuminating a reticle with light from a light source, and a projection optical system for projecting a pattern of the reticle onto an object, said projection optical system includes a lens closest to the object, wherein a surface on the object side of the lens is smaller than an effective area of a surface on the reticle side of the lens, and wherein said exposure apparatus exposes the object via a liquid that is filled in a space between the lens and the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Exposure apparatus and method
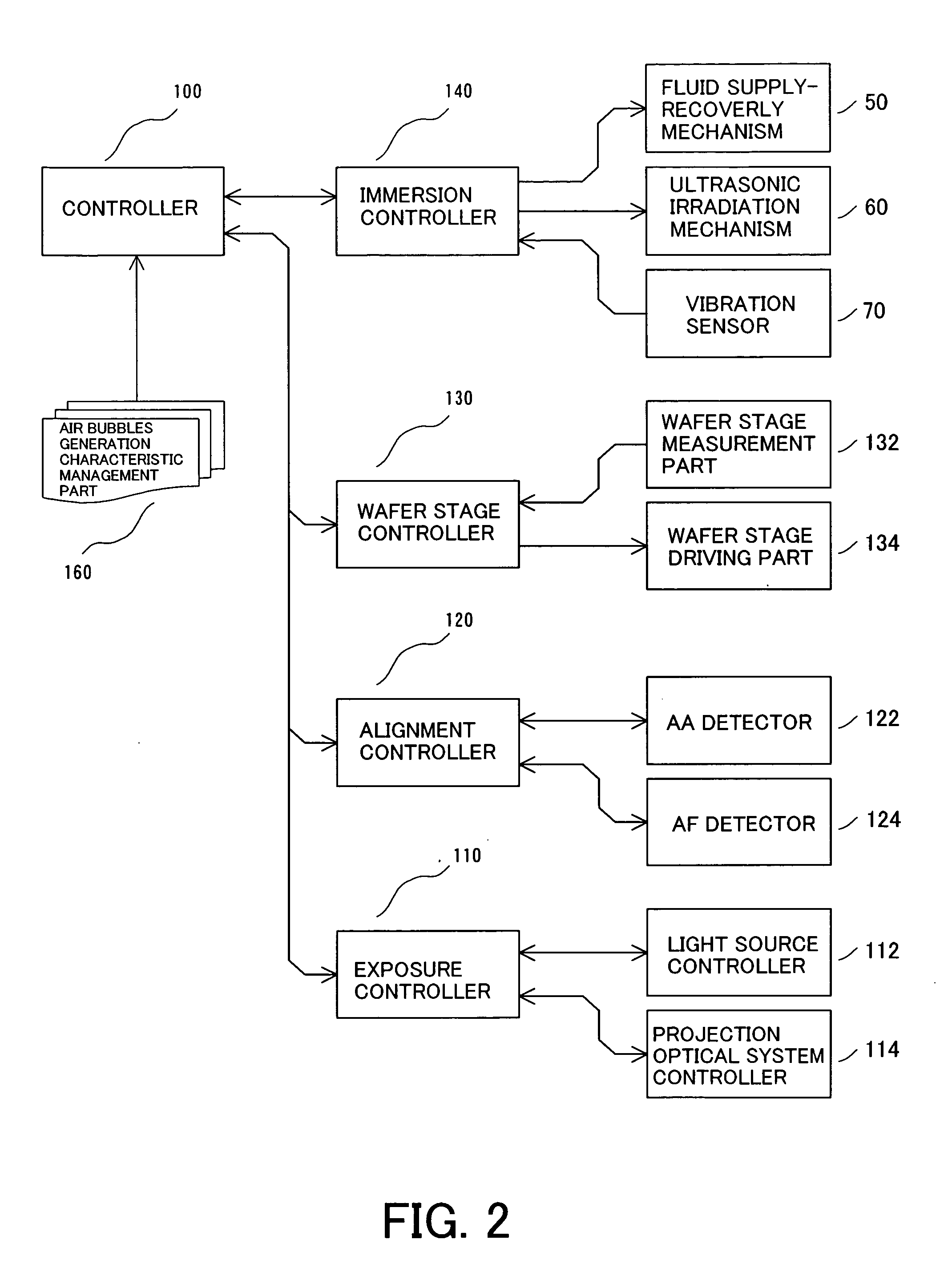
InactiveUS20050213065A1Efficient removalInhibit deteriorationRailway vehiclesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReticleOptics
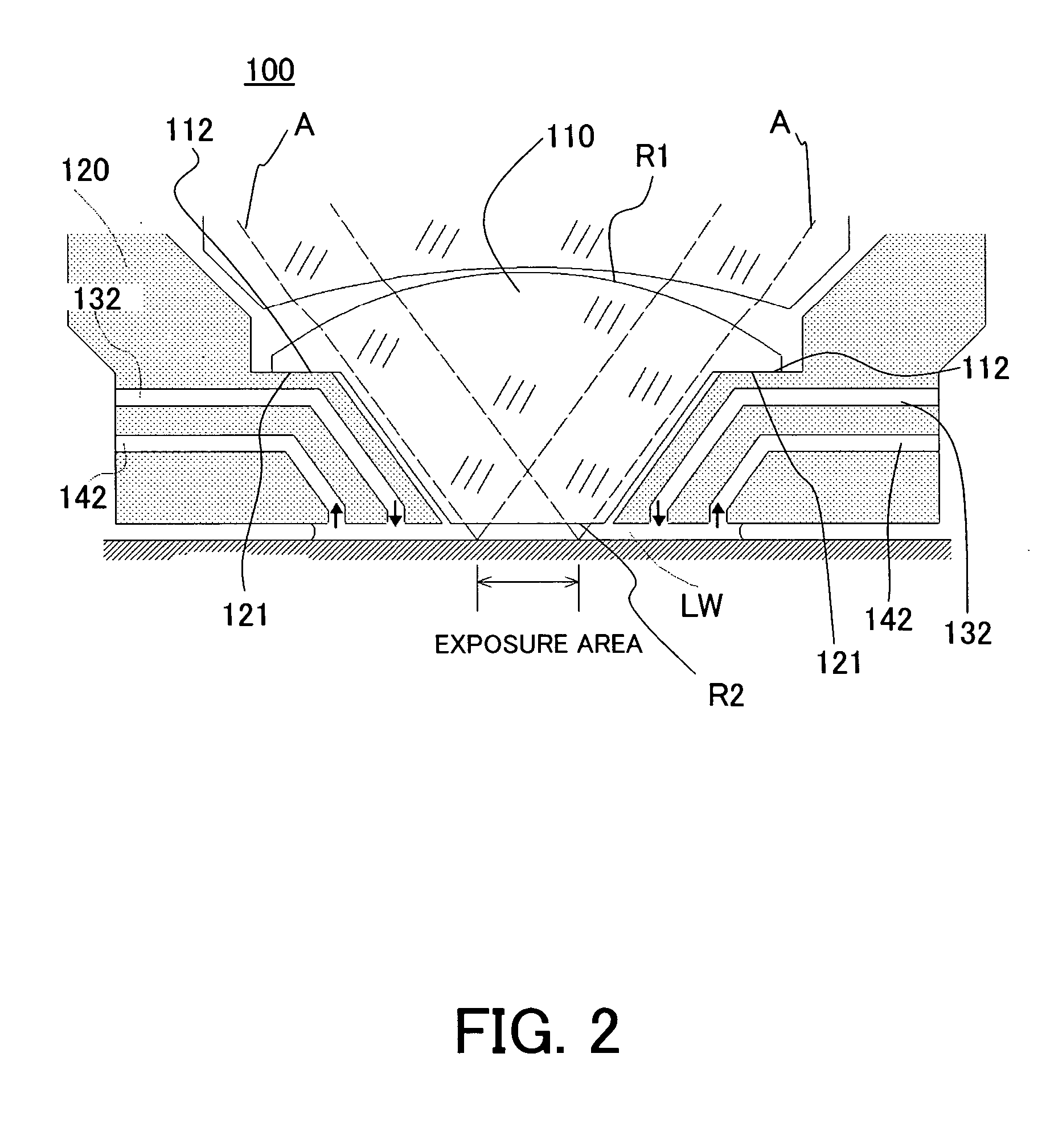
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting an image of a pattern of a reticle onto an object, via a fluid that is filled in a space between said projection optical system and the object, a vibrator part for vibrating at least one of the fluid, the object, and the projection optical system, and a controller for controlling the vibrator part so that the vibration of at least one of the fluid, the object, and the projection optical system becomes a tolerance during a processing of the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Illumination system particularly for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6198793B1Etendu can be effectively increasedAvoid blurringsNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionCamera lensGrating
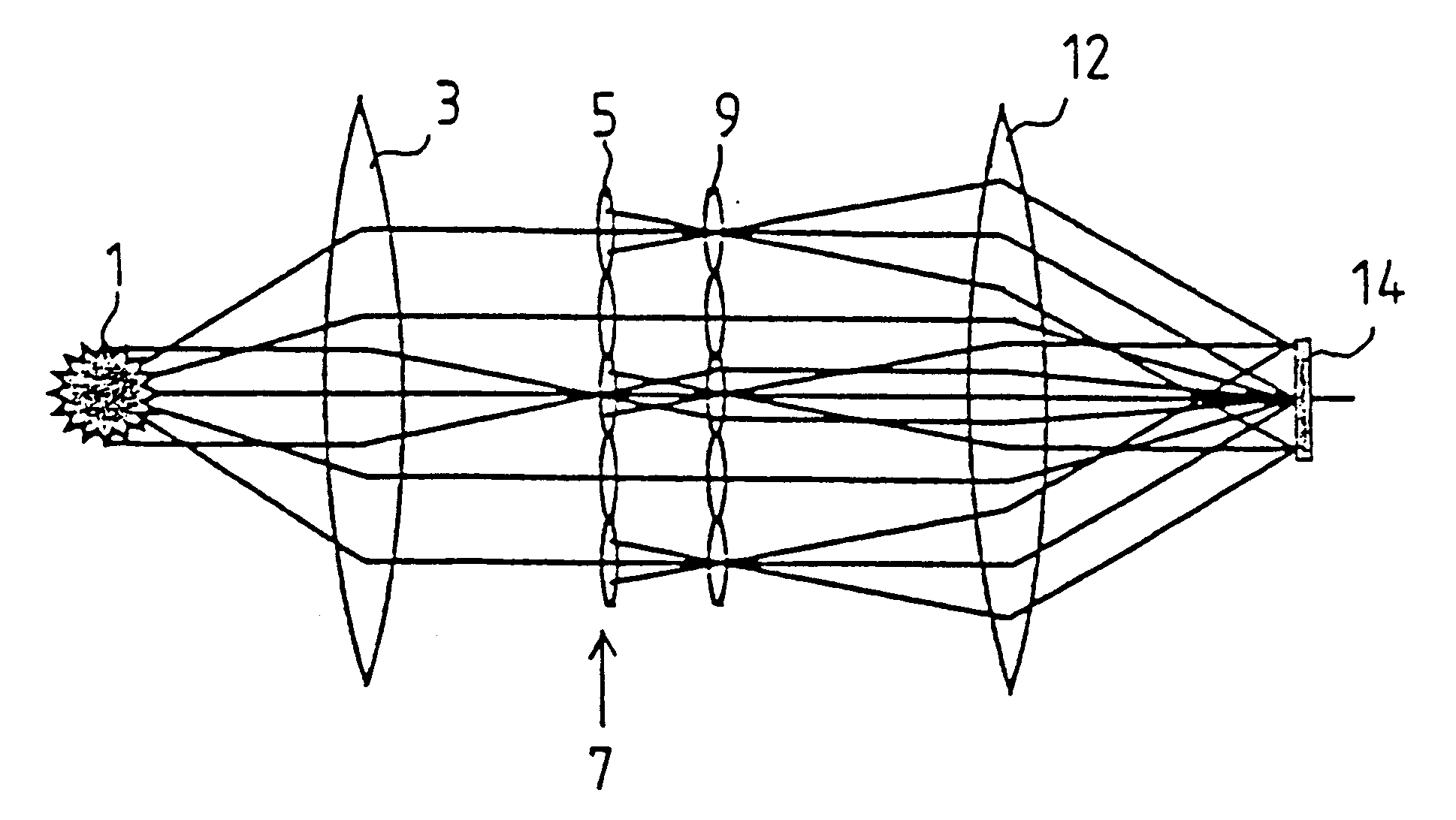
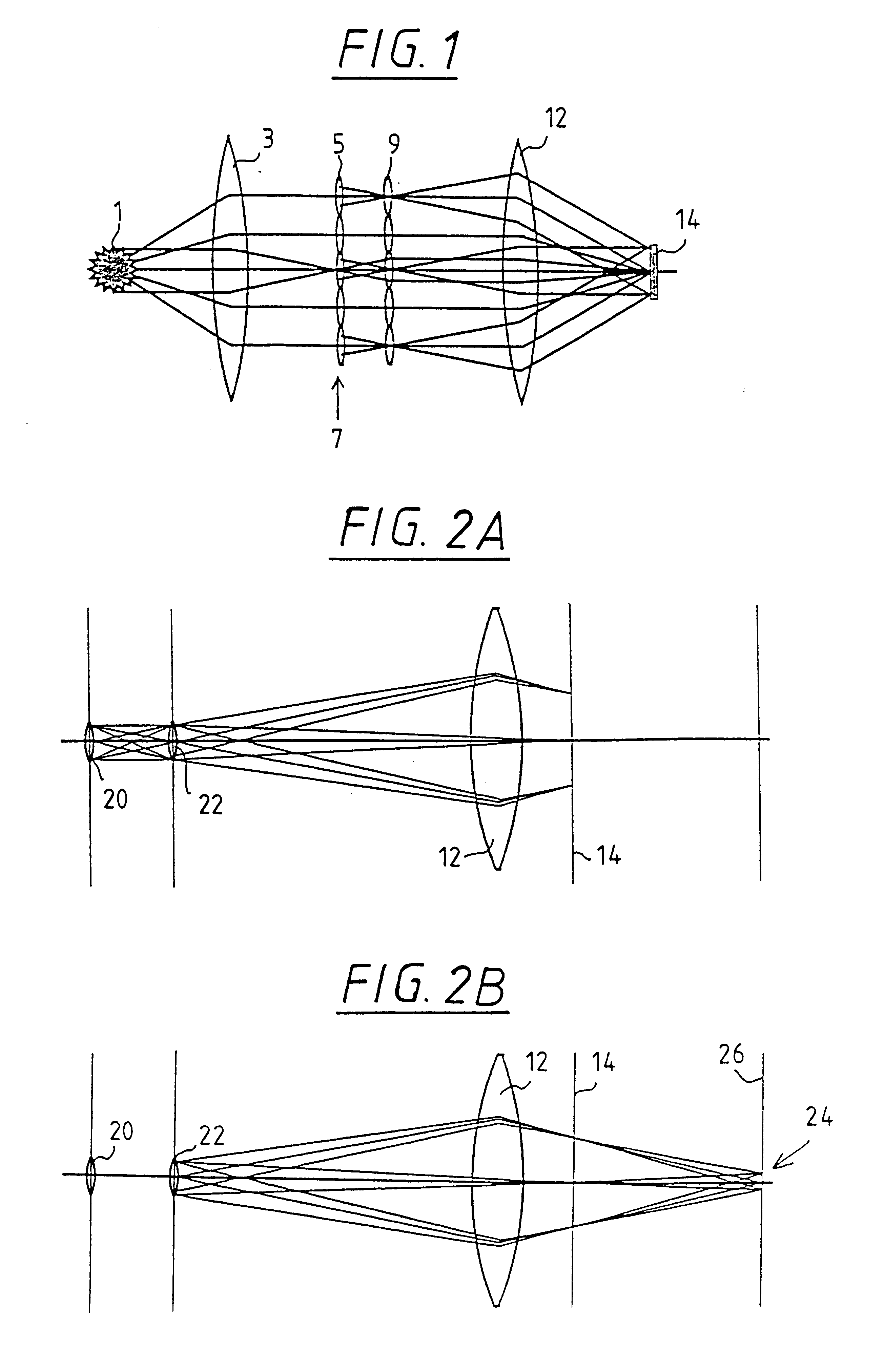
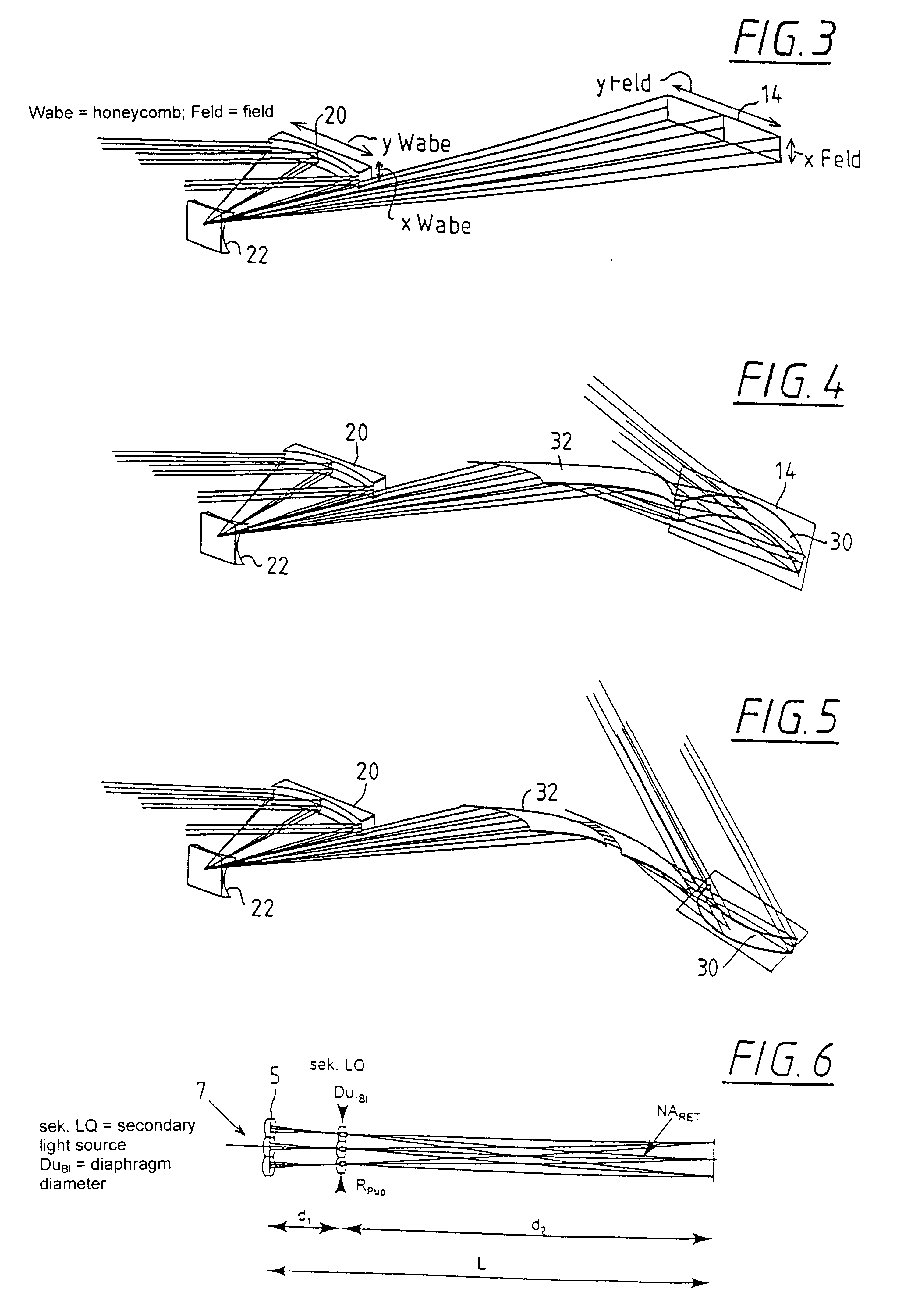
The invention concerns an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, particularly for EUV lithography, with at least one light source, which has an illumination A in a predetermined surface; at least one device for producing secondary light sources; at least one mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements; one or more optical elements, which are arranged between the mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements and the reticle plane, whereby the optical elements image the secondary light sources in the exit pupil of the illumination system.The illumination system is characterized by the fact that the raster elements of the one or more mirror or lenses are shaped and arranged in such a way that the images of the raster elements cover by means of the optical elements the major portion of the reticle plane and that the exit pupil defined by aperture and filling degree is illuminated.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Apparatus and method for conformal mask manufacturing
ActiveUS20080160431A1Electric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsComputational physicsIrradiation
A manufacturing process technology creates a pattern on a first layer using a focused ion beam process. The pattern is transferred to a second layer, which may act as a traditional etch stop layer. The pattern can be formed on the second layer without irradiation by light through a reticle and without wet chemical developing, thereby enabling conformal coverage and very fine critical feature control. Both dark field patterns and light field patterns are disclosed, which may enable reduced or minimal exposure by the focused ion beam.
Owner:NEXGENSEMI HLDG INC
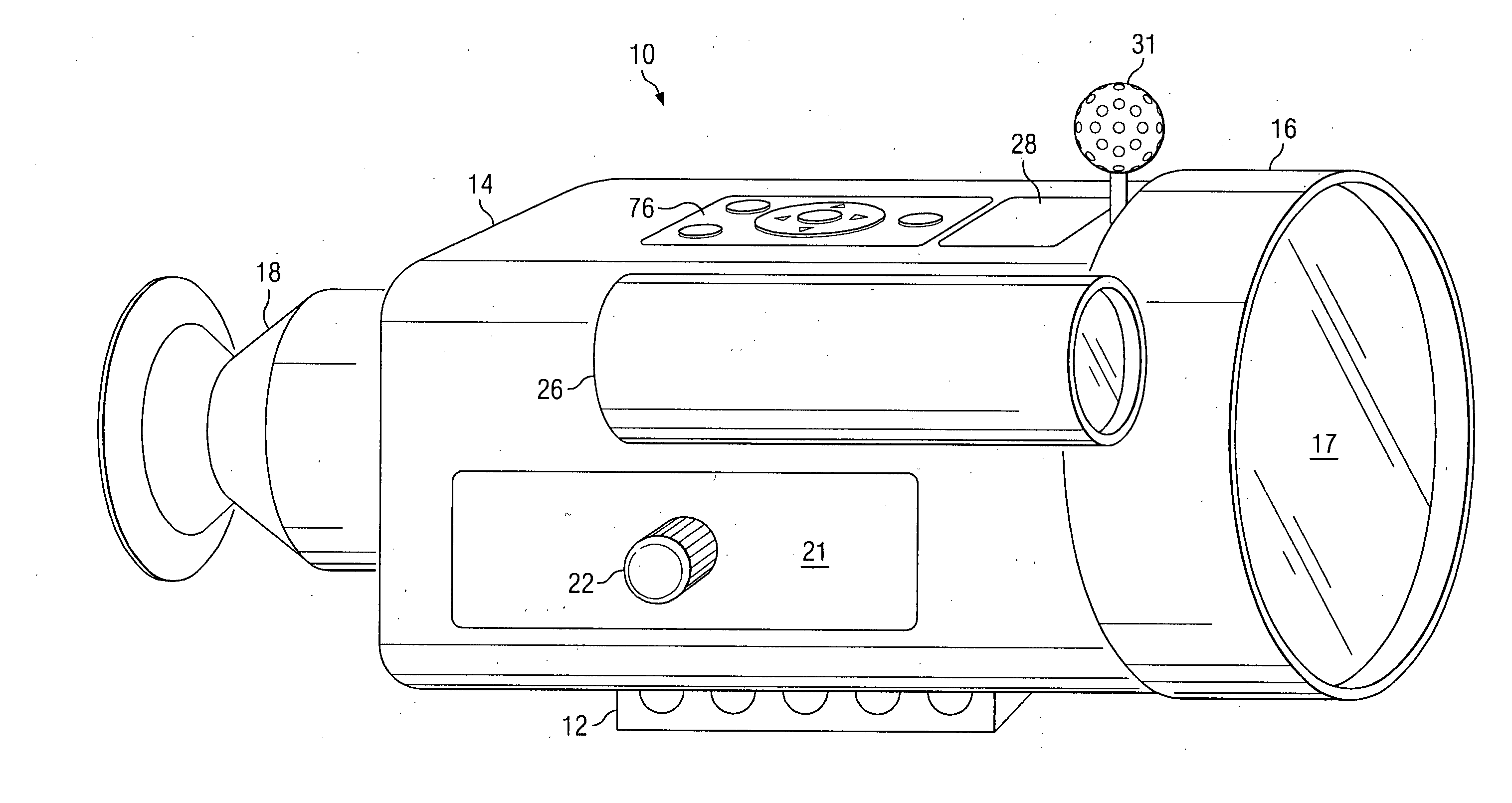
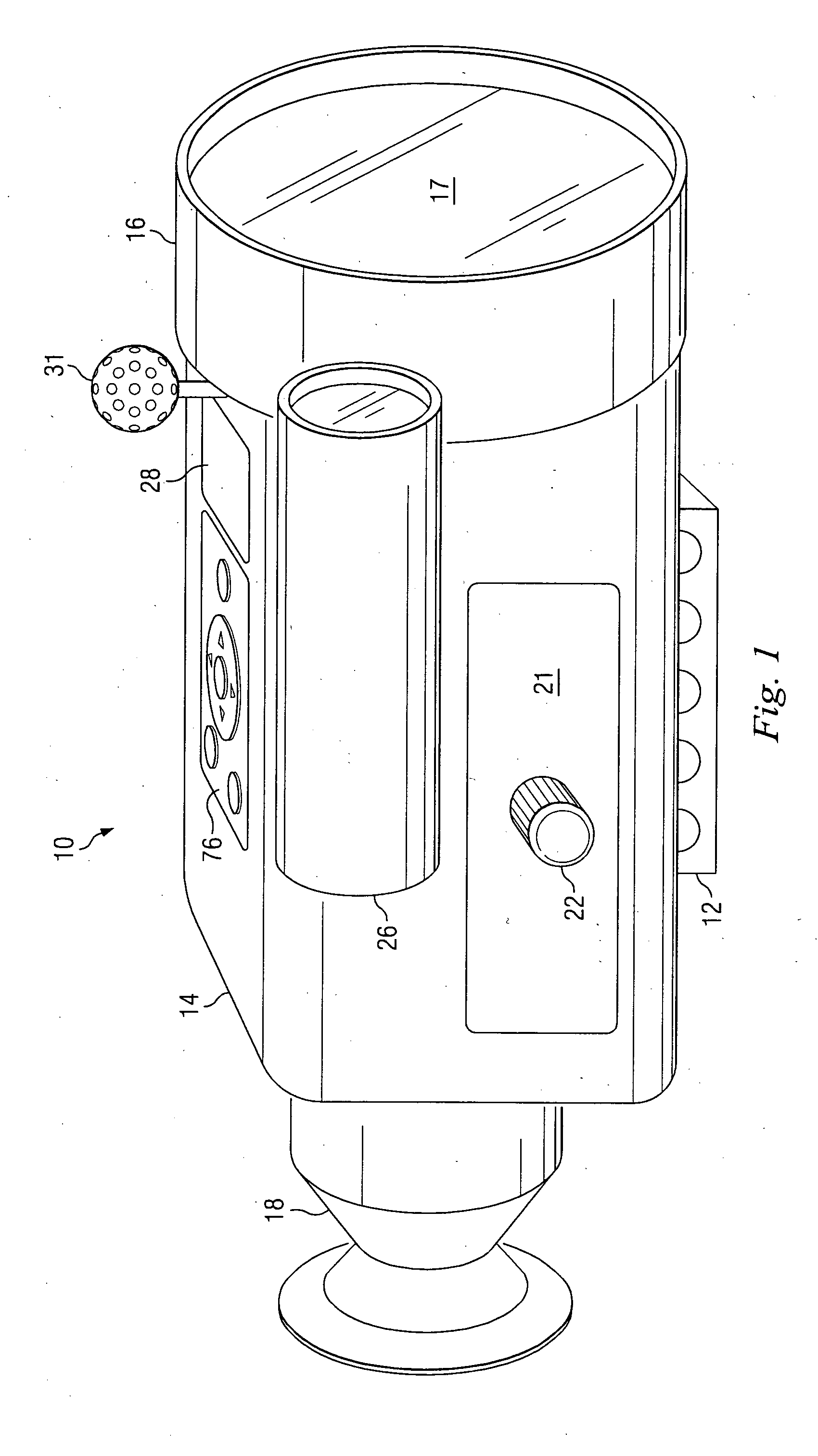
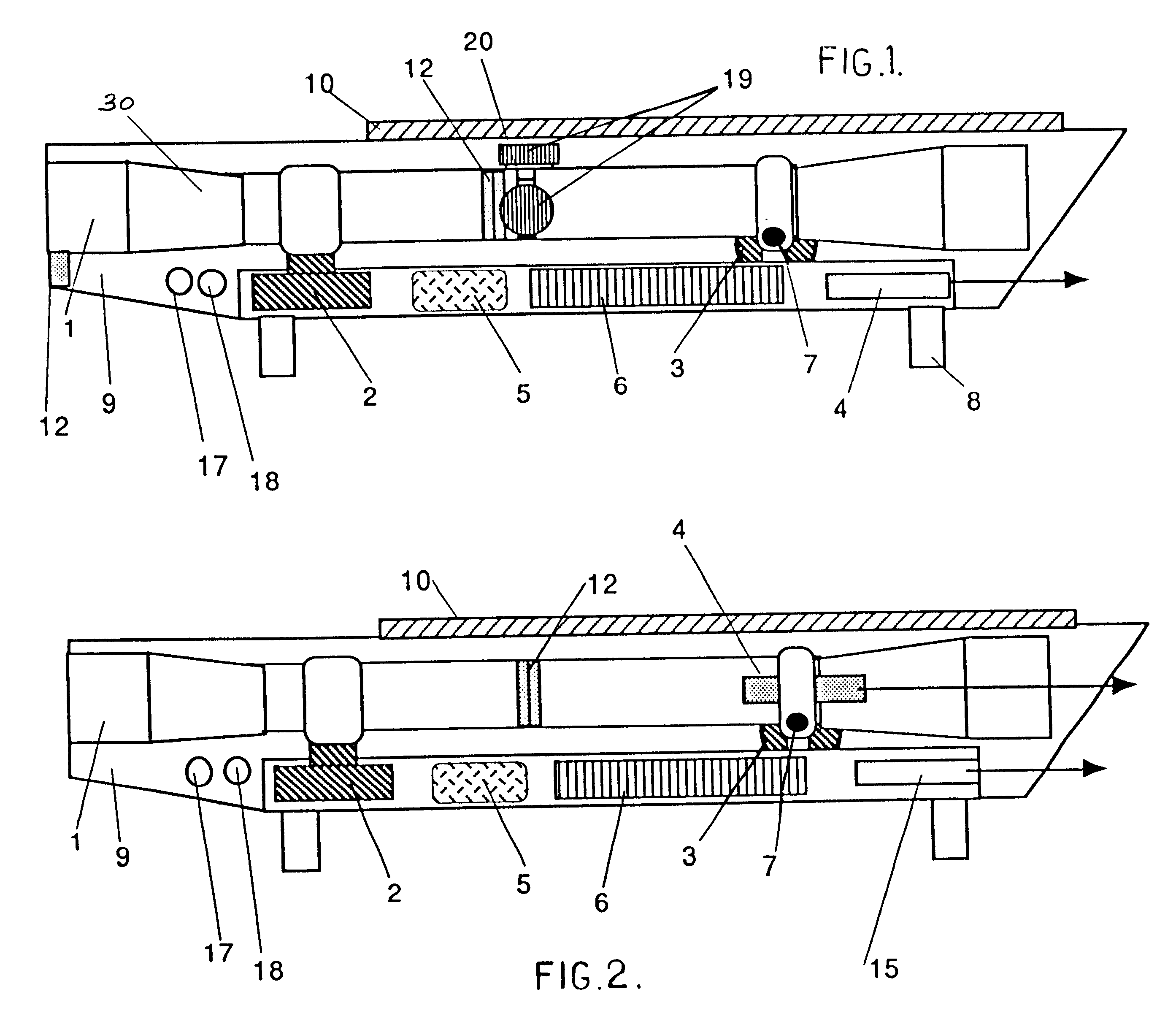
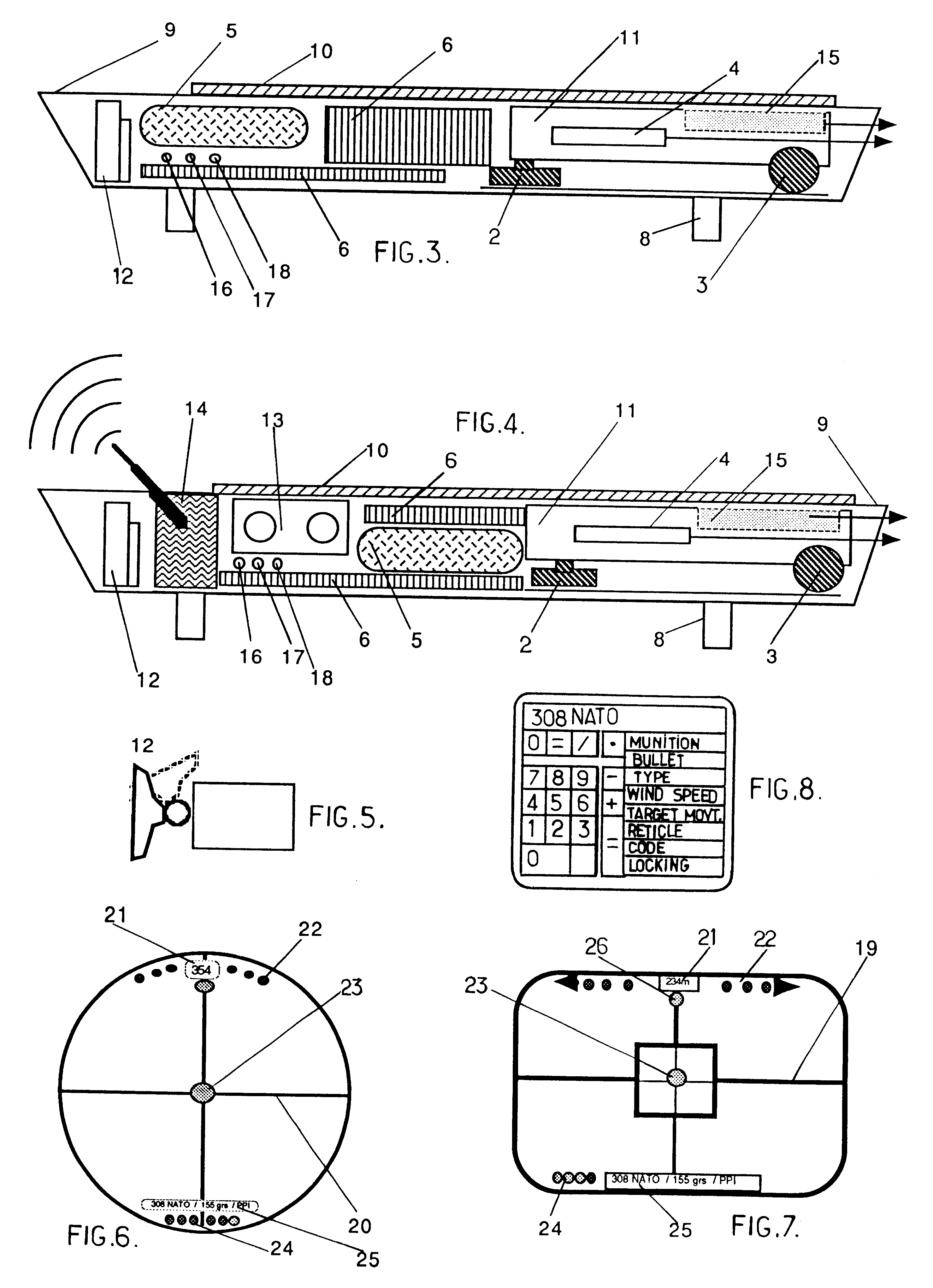
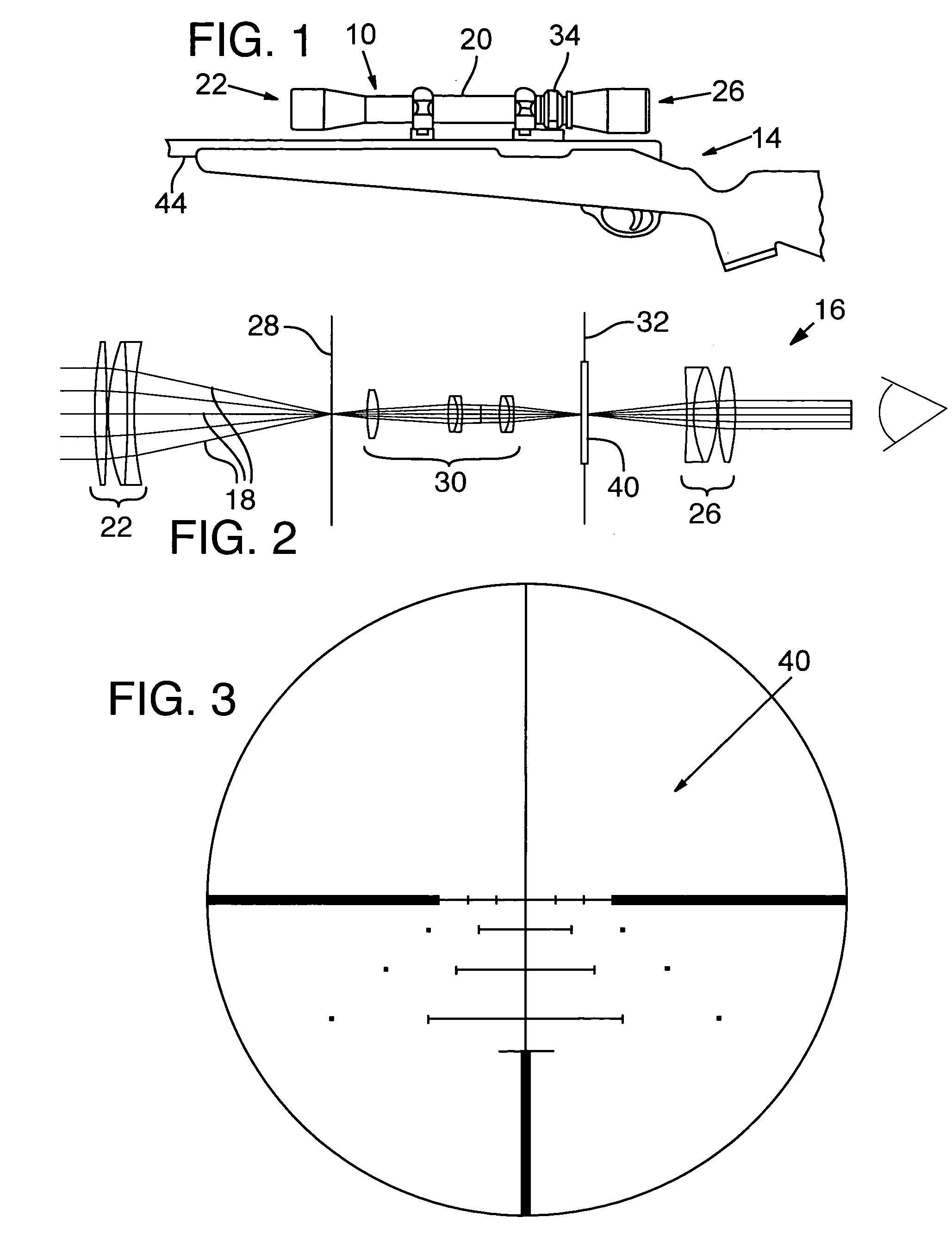
Electronic sight for firearm, and method of operating same
A firearm sight receives information regarding a factor, and then automatically adjusts the relative positions of a digital reticle and an image on a viewing section to compensate for the influence of the factor on a projectile trajectory. A different feature involves automatically adjusting a characteristic of the reticle based on the image. Another feature involves automatically adjusting the digital image to distinguish a portion thereof aligned with the reticle from an adjacent portion thereof. Yet another feature involves causing the firearm sight to generate an audible sound. Still another feature involves presenting information on the viewing section which represents the position of the firearm sight on the surface of the earth.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
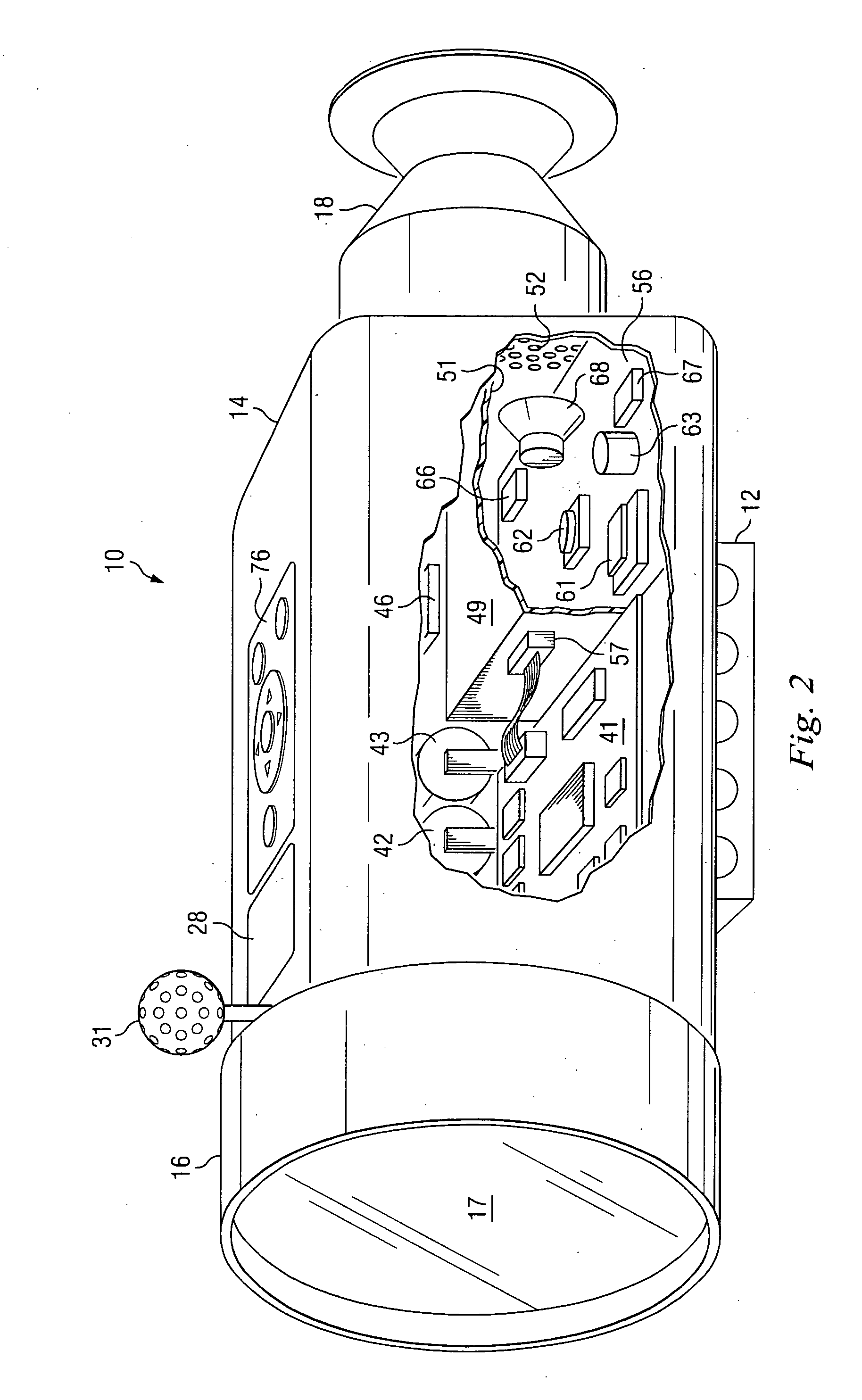
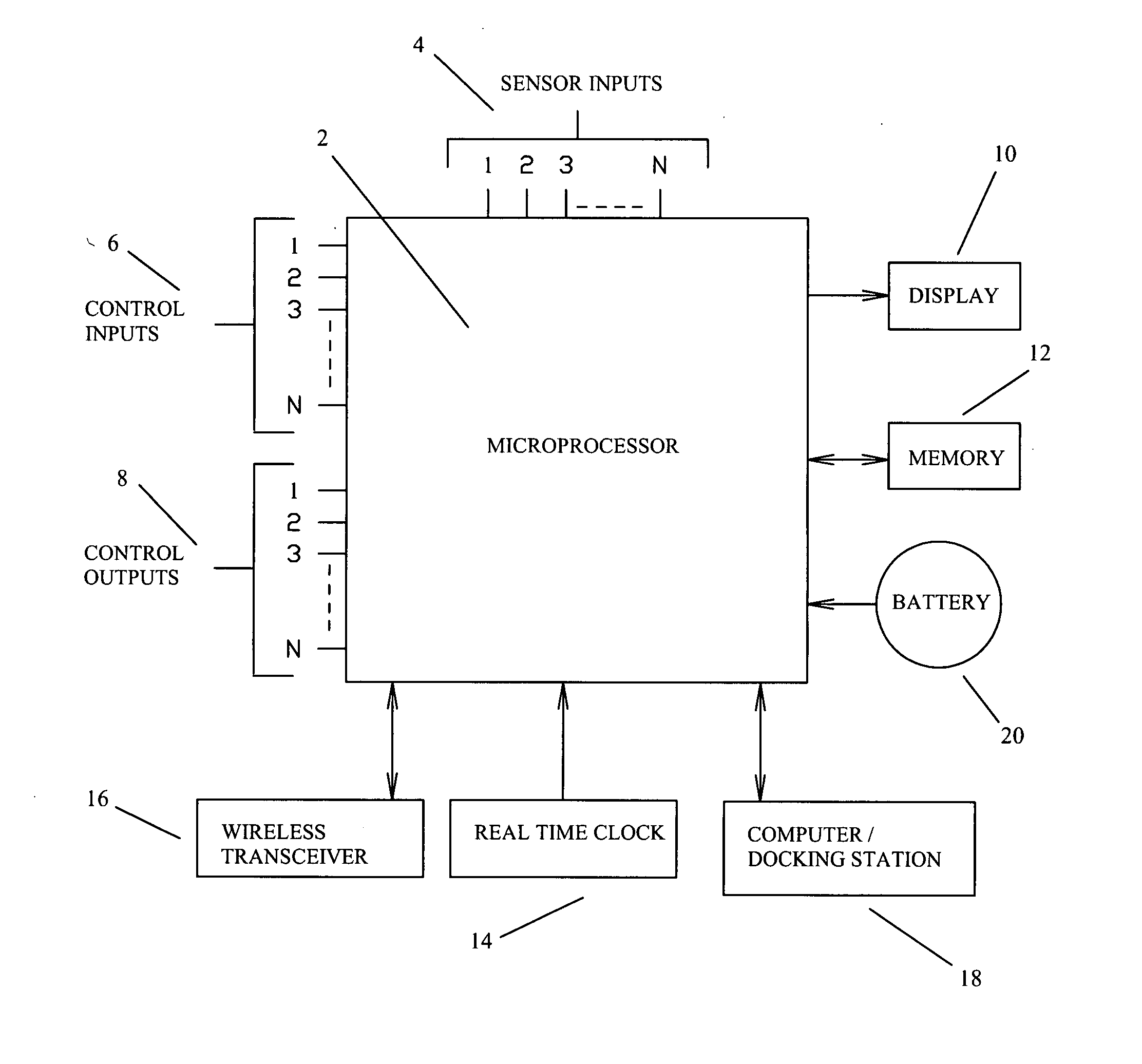
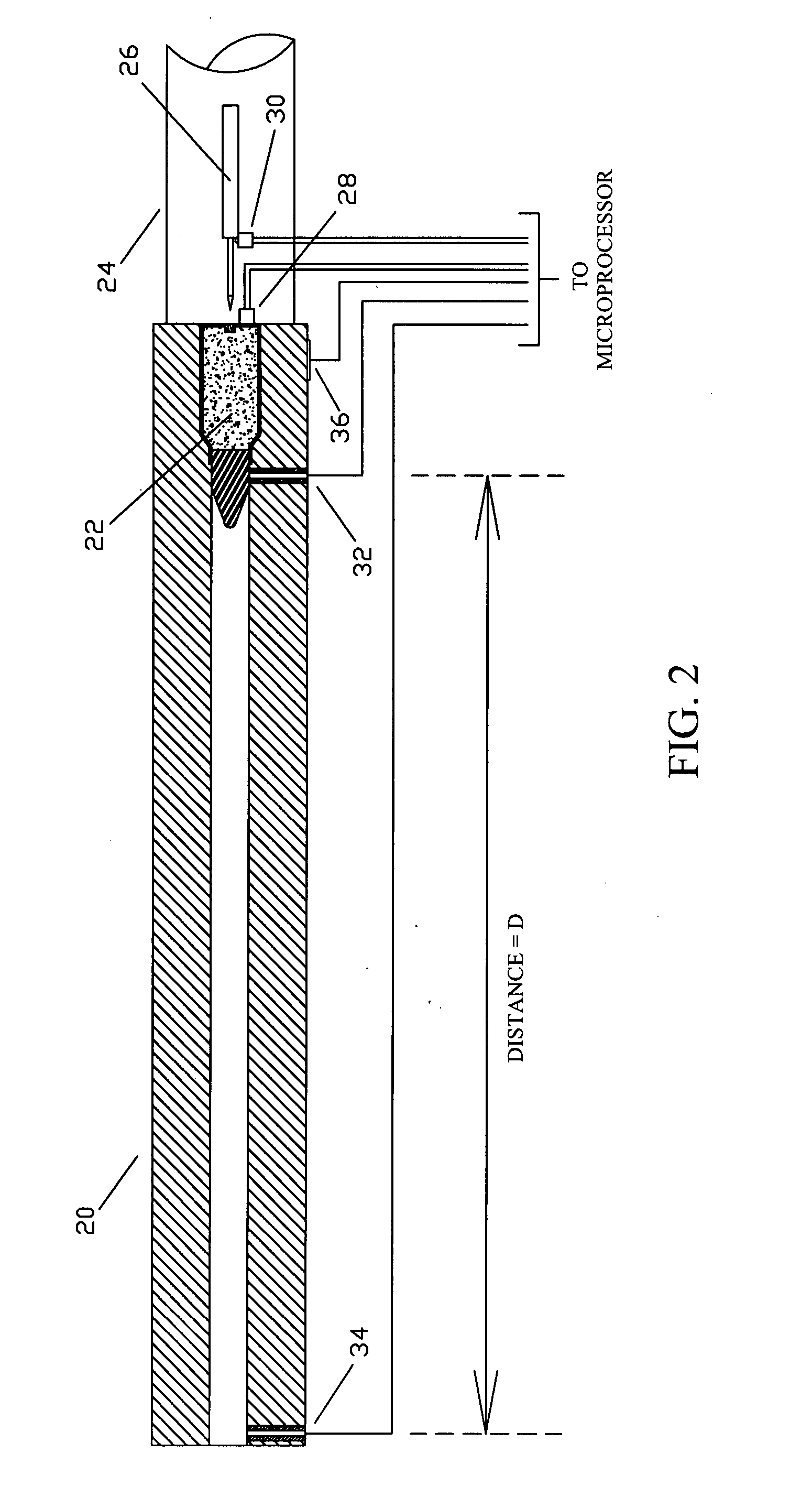
Firearm system for data acquisition and control
InactiveUS20080039962A1Input/output for user-computer interactionSafety arrangementDocking stationData acquisition
A microprocessor circuit that is used to monitor and control a firearm. The microprocessor circuit accomplishes this by monitoring various sensor & control inputs, and acting on these inputs to execute user defined functions. The microprocessor circuit can use the sensory input to determine firearm statistics. These statistics can include the number of times the firearm has been shot, the efficiency of the firearm automatic action, range-to-target, and et cetera. The firearm system can also use a combination of sensors to fabricate a bullet chronograph whereby the muzzle velocity of a cartridge can be determined. These statistics can be date-stamped and recorded into memory. Statistics from Law Enforcement firearms can be used for courtroom evidence and police reporting. These statistics can also be used for firearm maintenance and warranty repair. The microprocessor circuit can display the statistical data to the user via simple light emitting diodes, or sophisticated liquid crystal displays. Data can also be downloaded to a computer docking station as well. The microprocessor circuit can also display the information within the optics of a riflescope. When used in conjunction with a laser range finder sensor, the microprocessor circuit can adjust the electronic cross-hairs (reticle) to compensate for the bullet trajectory.
Owner:MCRAE MICHAEL WILLIAM
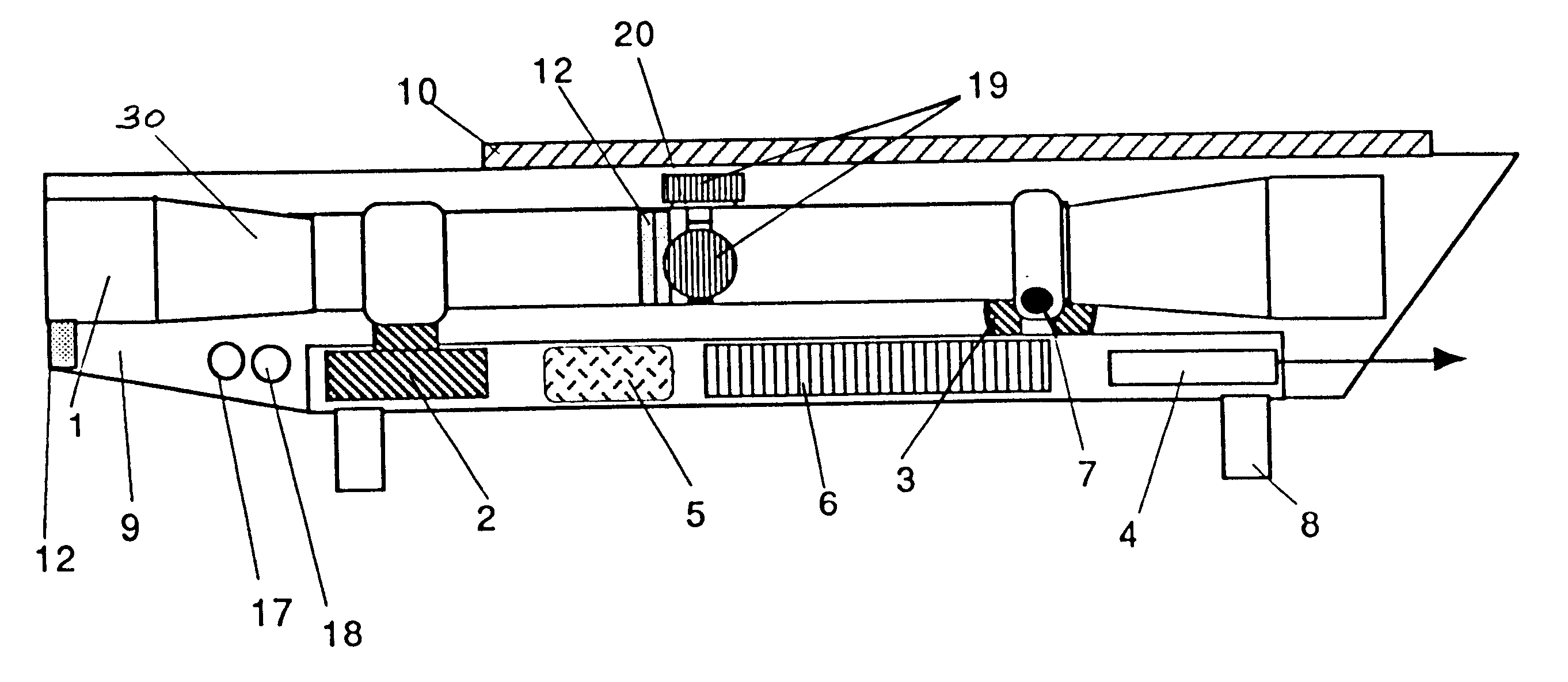
Telescopic sight for individual weapon with automatic aiming and adjustment
The invention concerns a telescopic rifle sight for individual weapon equipped with at least one step micro-motor designed to vary the angle of the sight relative to the axis of the weapon and the initial axis of aim, thereby adequately varying the whole sight assembly and thus varying the original position of the sight reticle from the original point of aim to the required point of aim.
Owner:GUARY GABRIEL +1
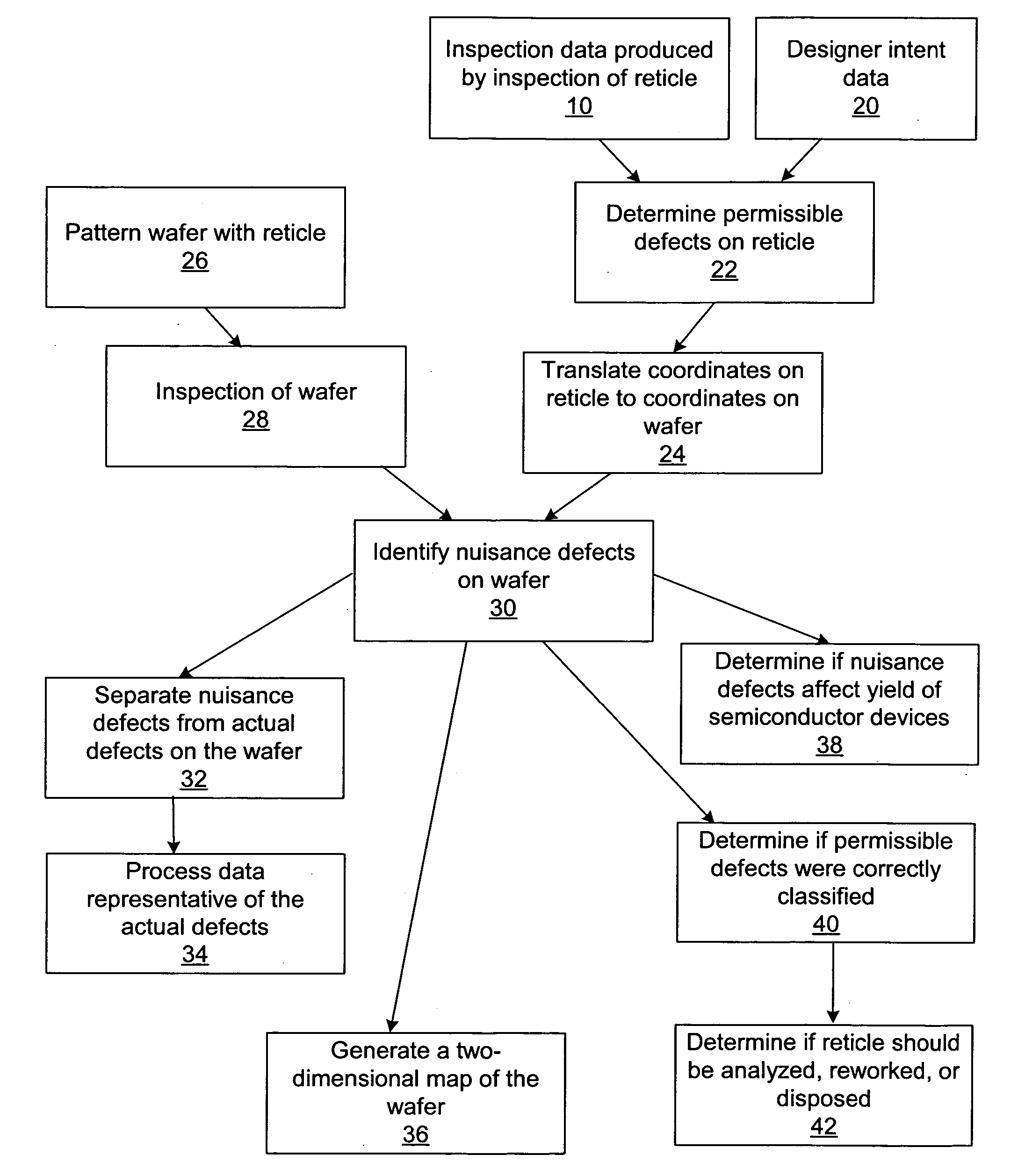
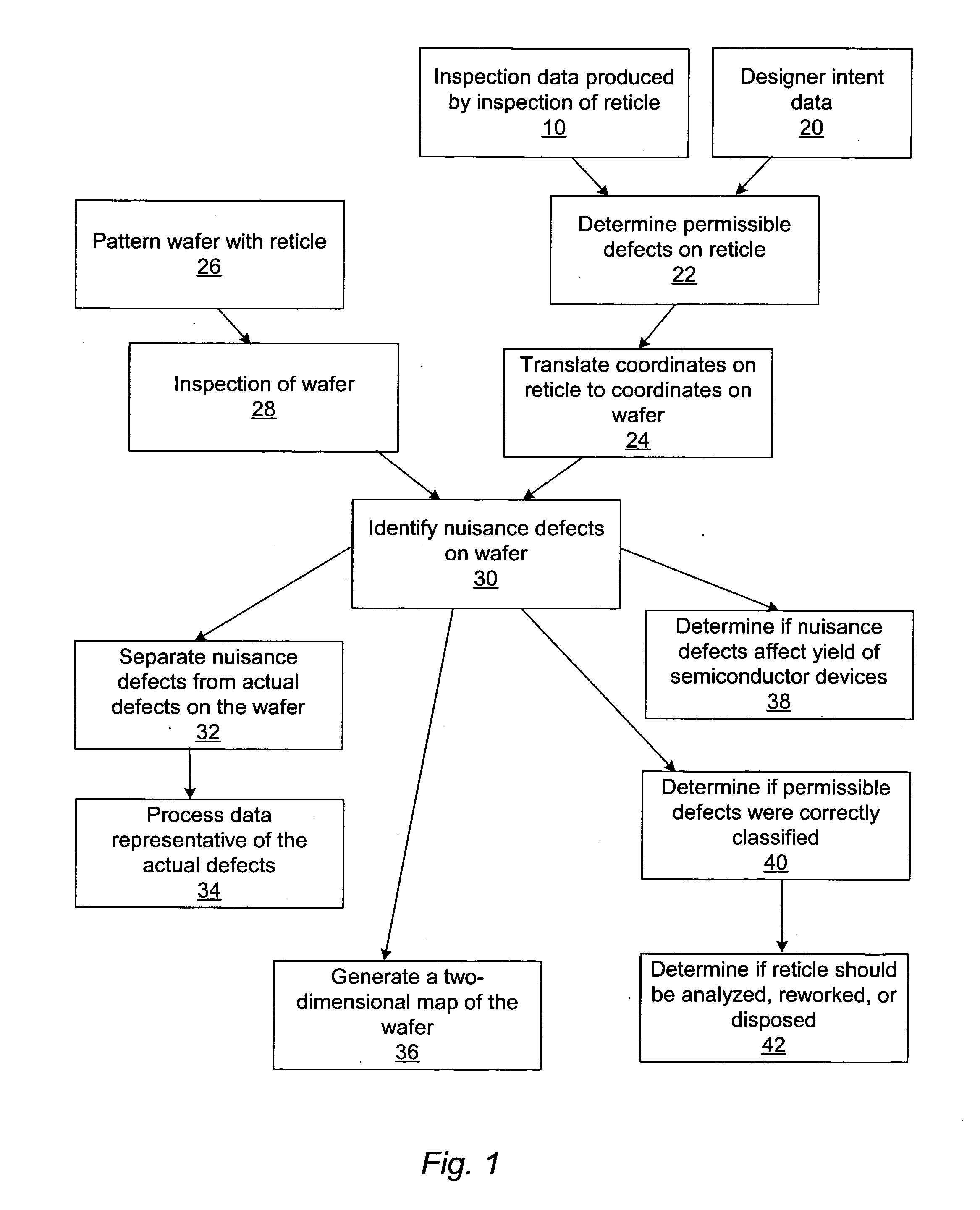
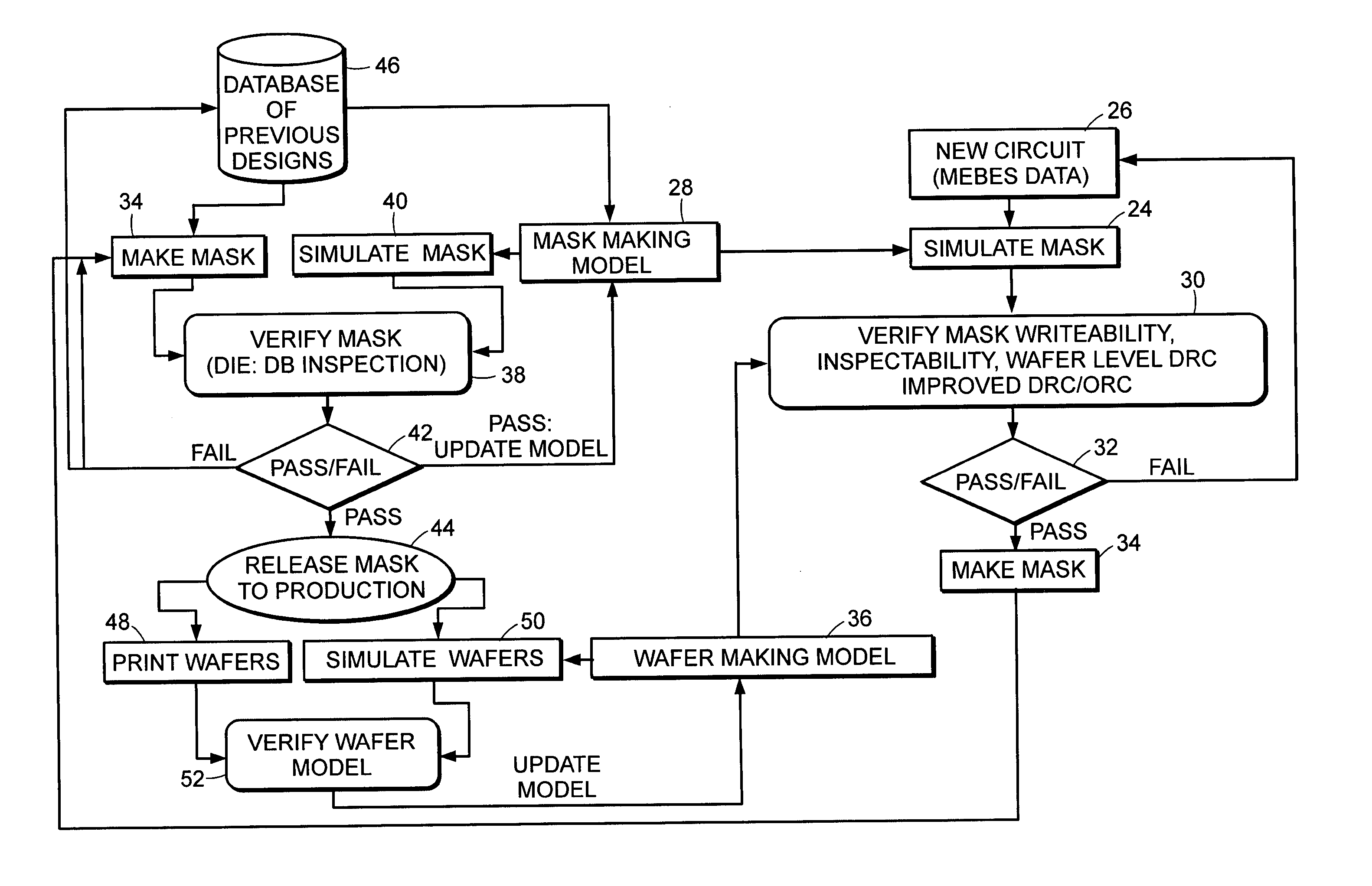
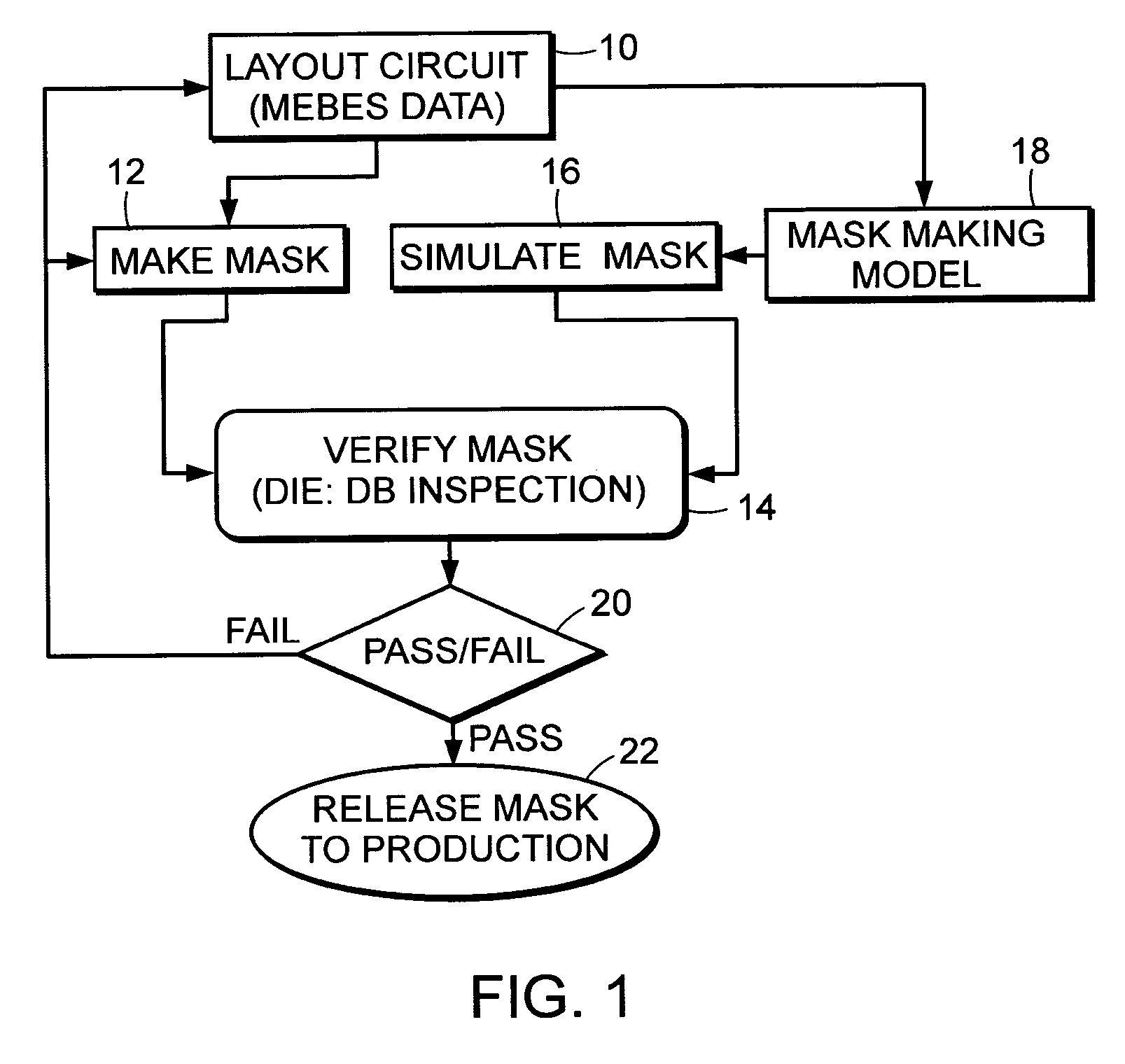
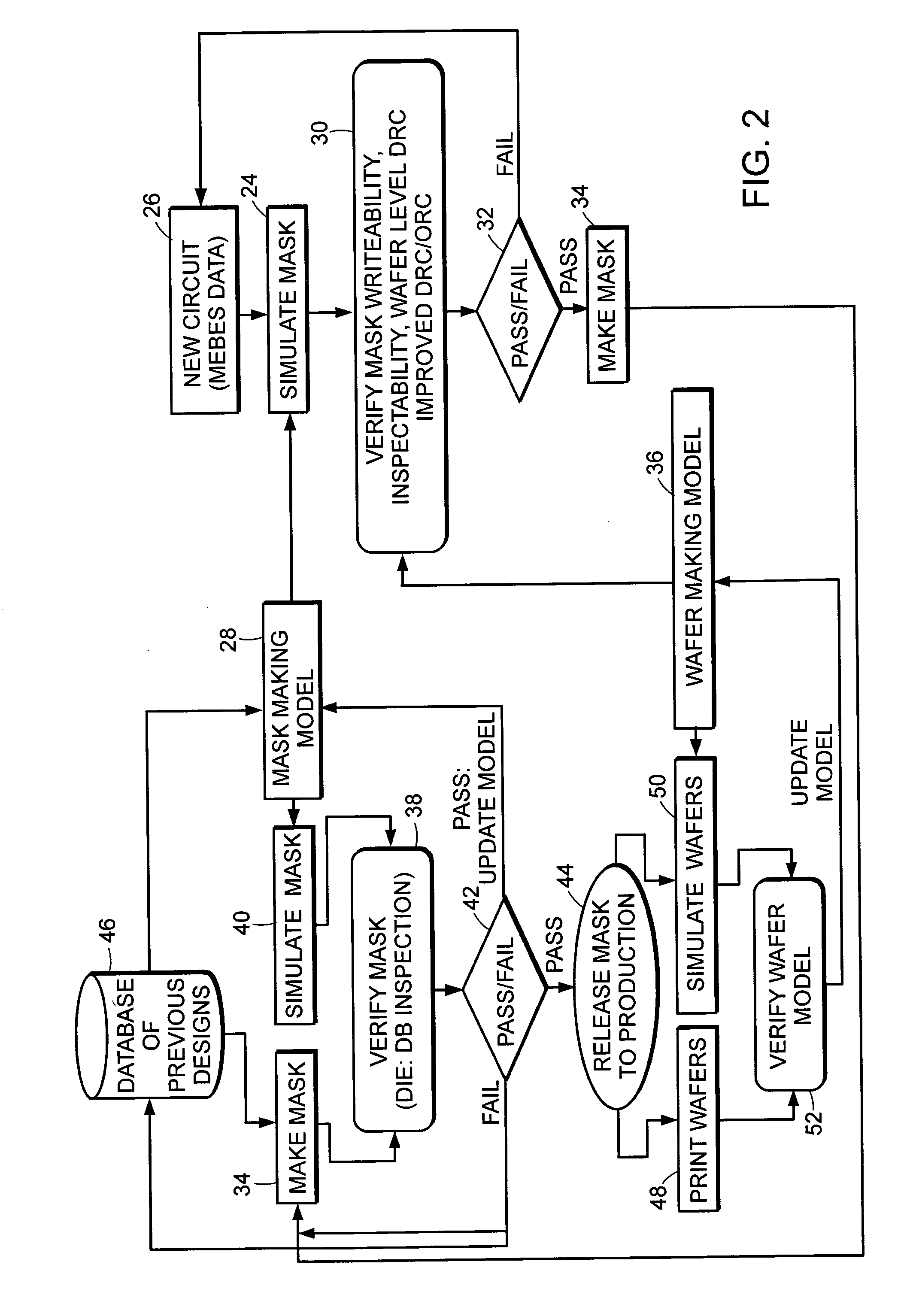
Methods and systems for inspection of wafers and reticles using designer intent data
Methods and systems for inspection of wafers and reticles using designer intent data are provided. One computer-implemented method includes identifying nuisance defects on a wafer based on inspection data produced by inspection of a reticle, which is used to form a pattern on the wafer prior to inspection of the wafer. Another computer-implemented method includes detecting defects on a wafer by analyzing data generated by inspection of the wafer in combination with data representative of a reticle, which includes designations identifying different types of portions of the reticle. An additional computer-implemented method includes determining a property of a manufacturing process used to process a wafer based on defects that alter a characteristic of a device formed on the wafer. Further computer-implemented methods include altering or simulating one or more characteristics of a design of an integrated circuit based on data generated by inspection of a wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method of locating sub-resolution assist feature(s)
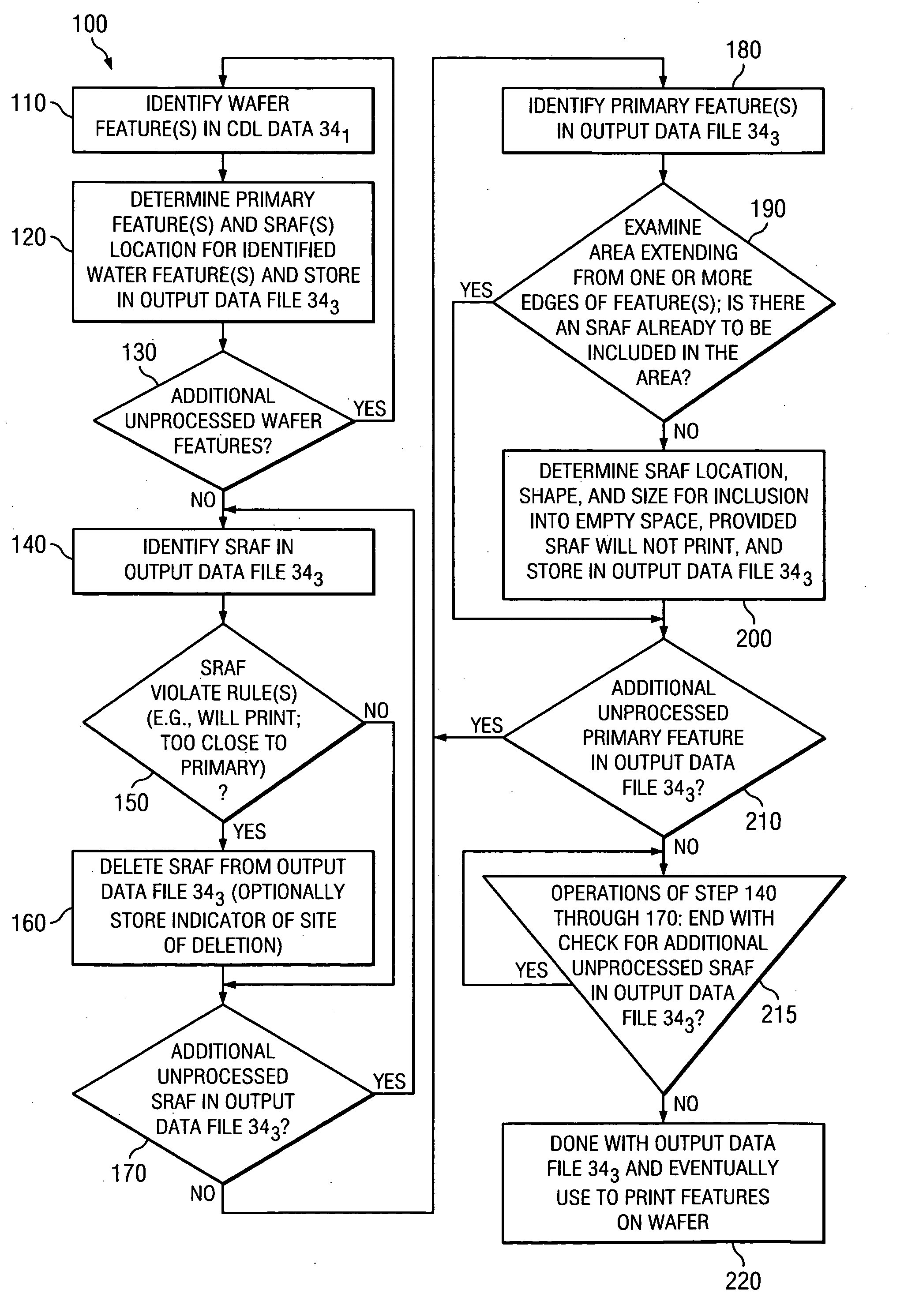
ActiveUS7200835B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsData fileComputing systems
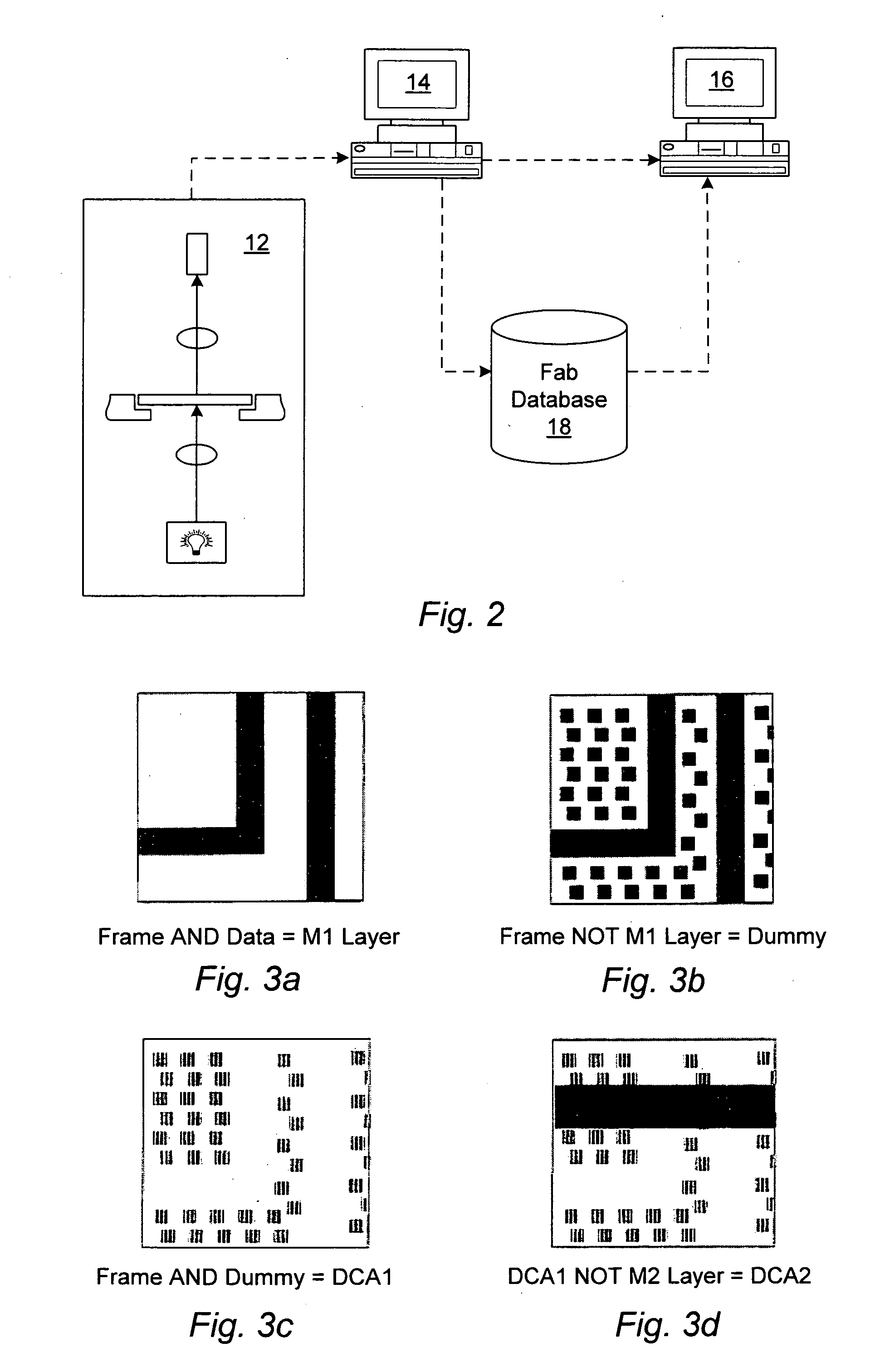
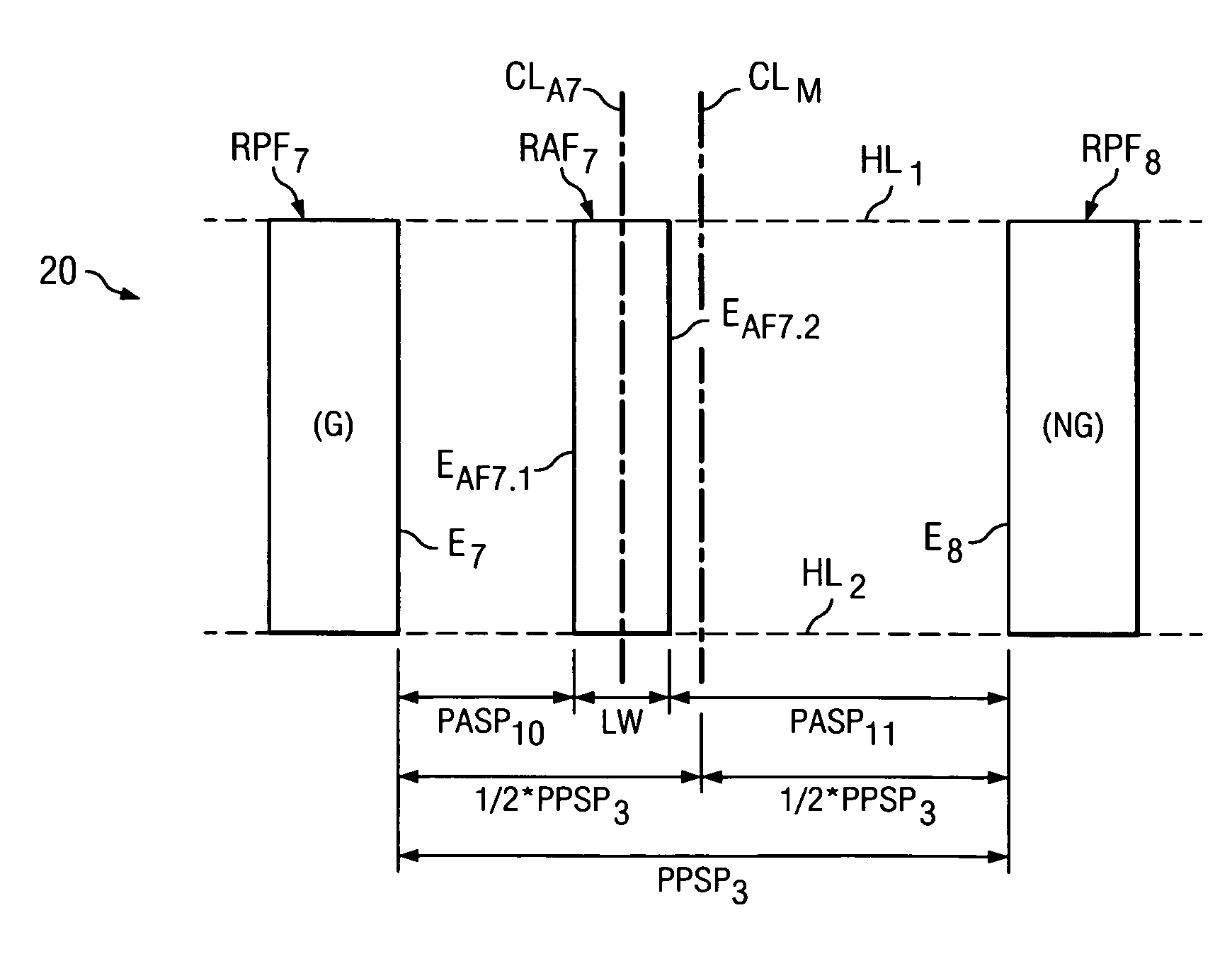
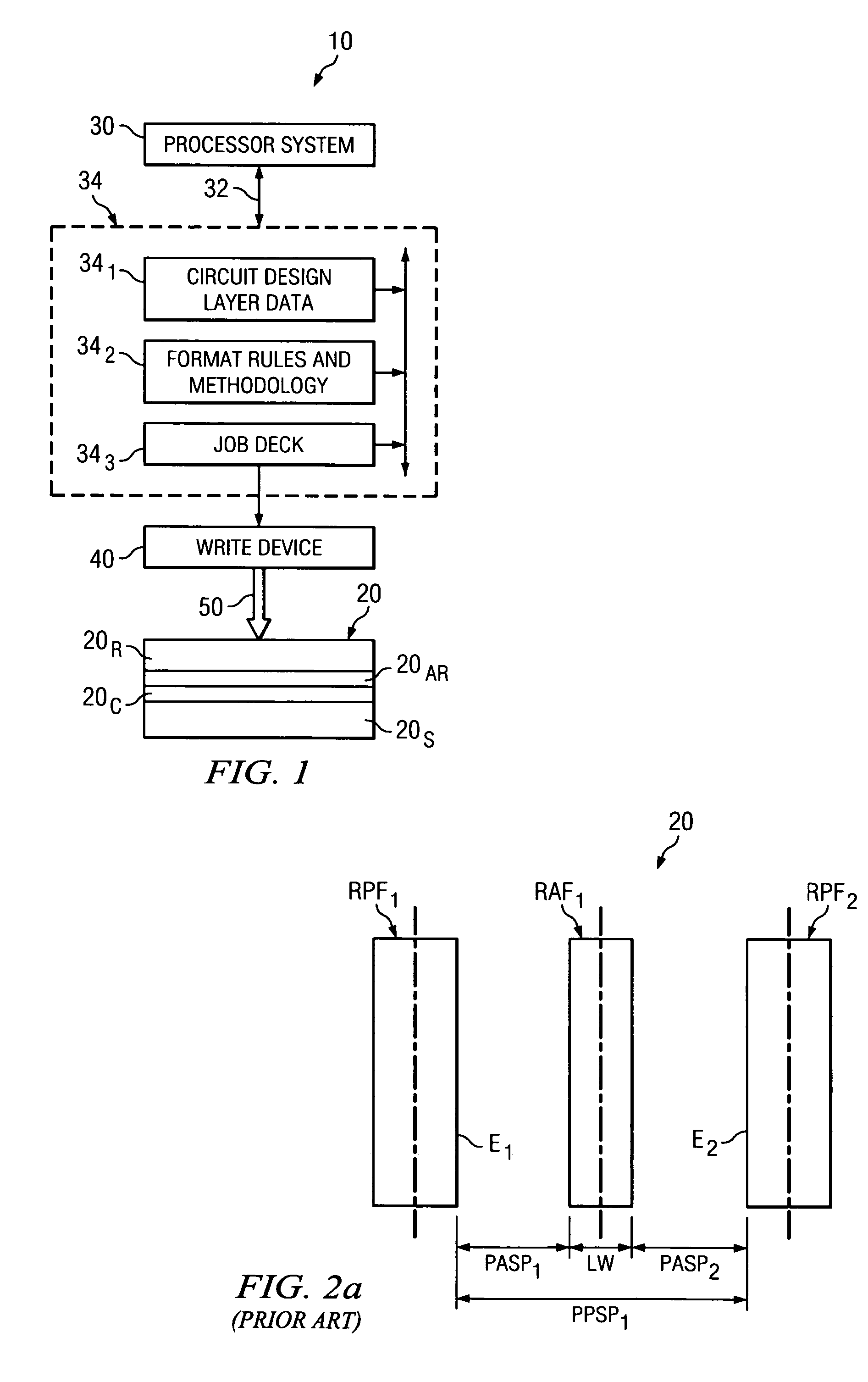
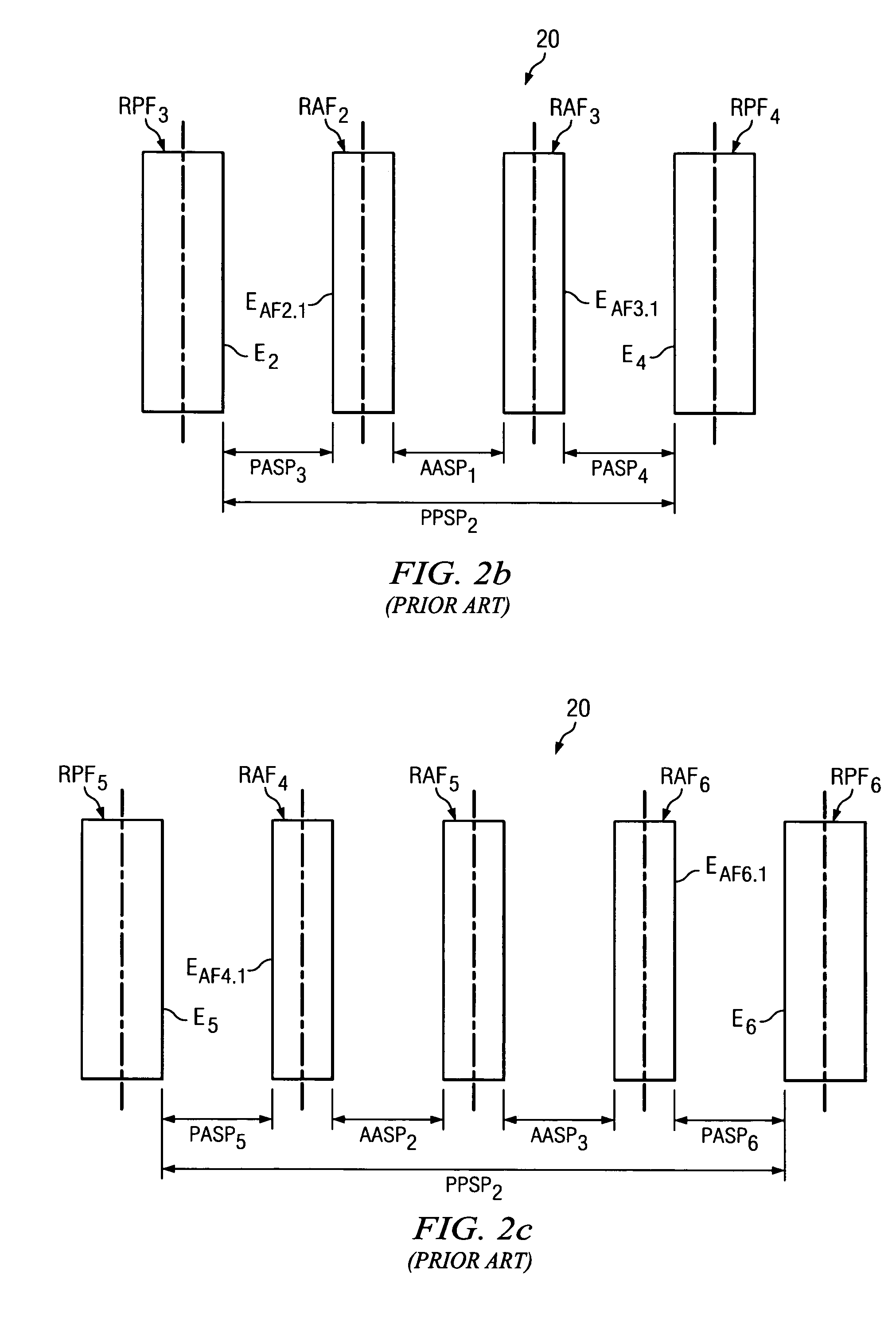
A method of operating a computing system to determine reticle data. The reticle data is for completing a reticle for use in projecting an image to a semiconductor wafer. The method receives circuit design layer data comprising a desired circuit layer layout, and the layout comprises a plurality of lines. The method also identifies in the plurality of lines a first line portion for use as a first circuit function and a second line portion for use as a second circuit function that differs from the first circuit function. The first line portion is parallel and adjacent to the second line portion. The method also provides the reticle data in an output data file for use in forming features on the reticle. The method also indicates parameters for forming first and second primary features as well as at least one assist feature on the reticle having an area between the first primary feature and the second primary feature, wherein in use of the reticle for use in projecting the image to the semiconductor wafer the area will favor greater assistance to the first primary feature as compared to the second primary feature.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of inclusion of sub-resolution assist feature(s)
InactiveUS20080082952A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsData fileComputer science
A method of operating a computing system to determine reticle data. The reticle data is for completing a reticle for use in projecting an image to a semiconductor wafer. The method comprises receiving circuit design layer data comprising a desired circuit layer layout, the layout comprising a plurality of circuit features. The method further comprises providing the reticle data for inclusion in an output data file for use in forming reticle features on the reticle. This providing step comprises a first iteration and a second iteration. In a first iteration, the method indicates parameters for forming a plurality of primary features and a first plurality of assist features on the reticle and it selectively removes the parameters of selected ones of the first plurality assist features. In a second iteration, the method indicates parameters for forming a second plurality of assist features on the reticle.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
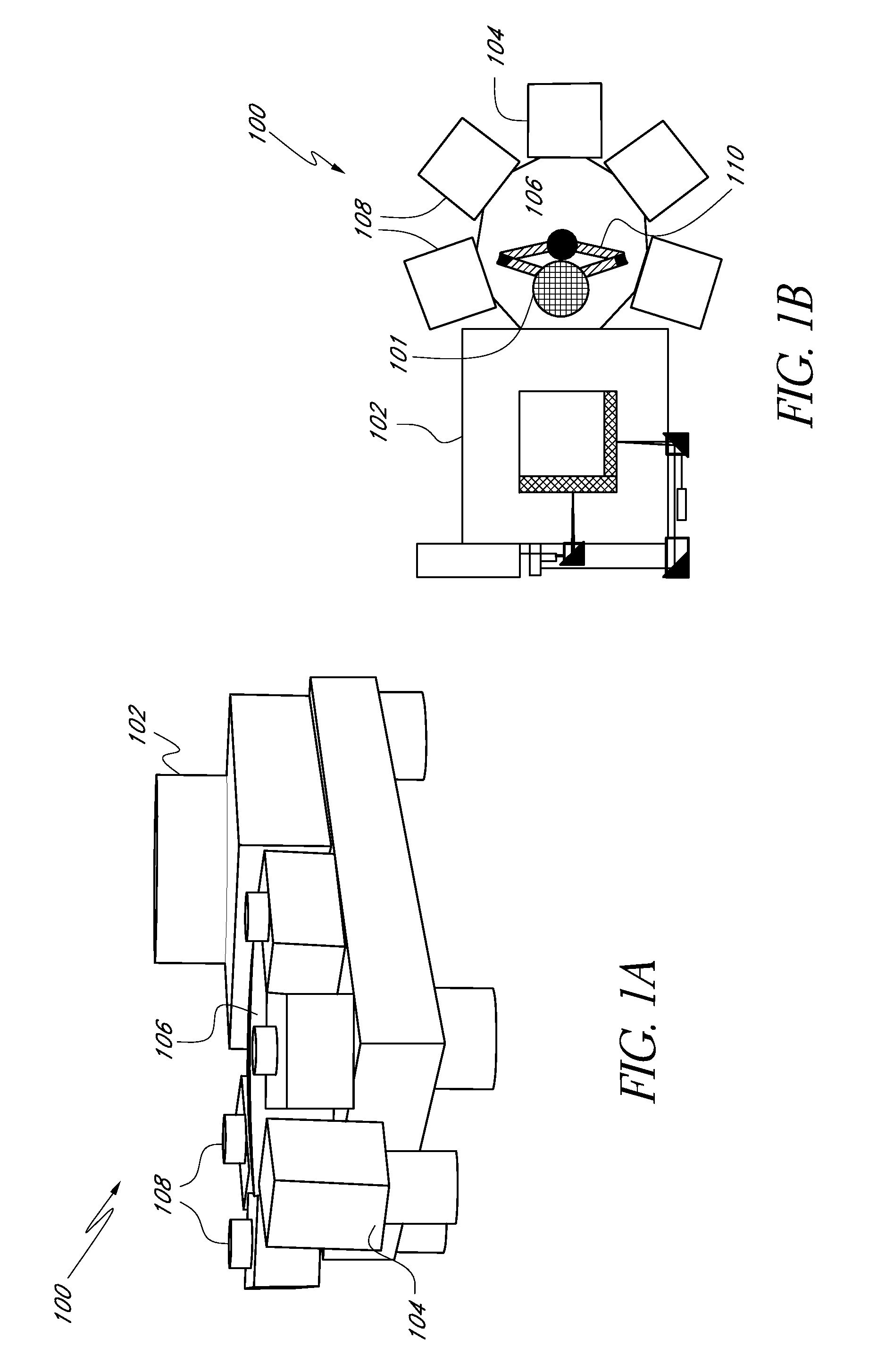
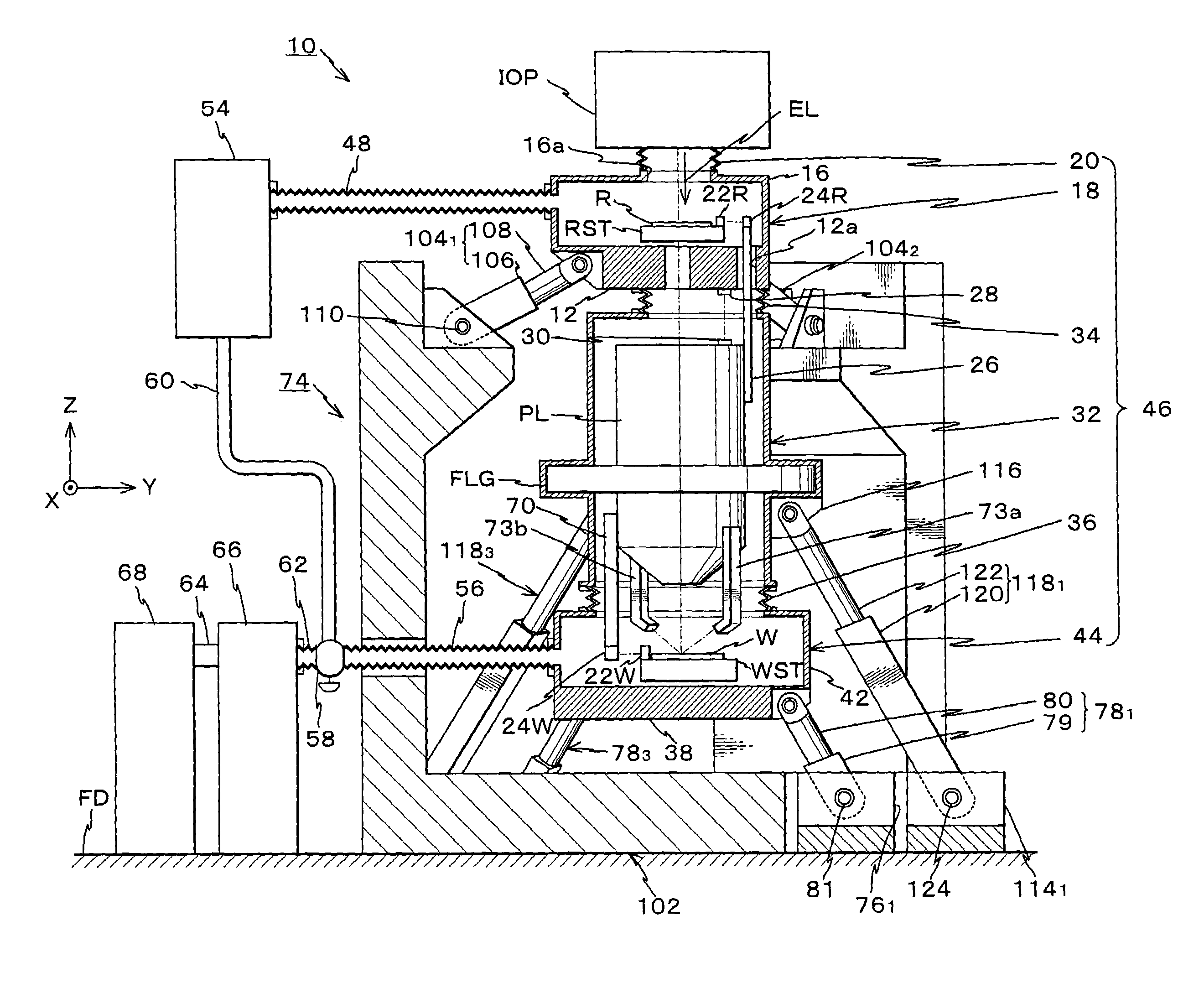
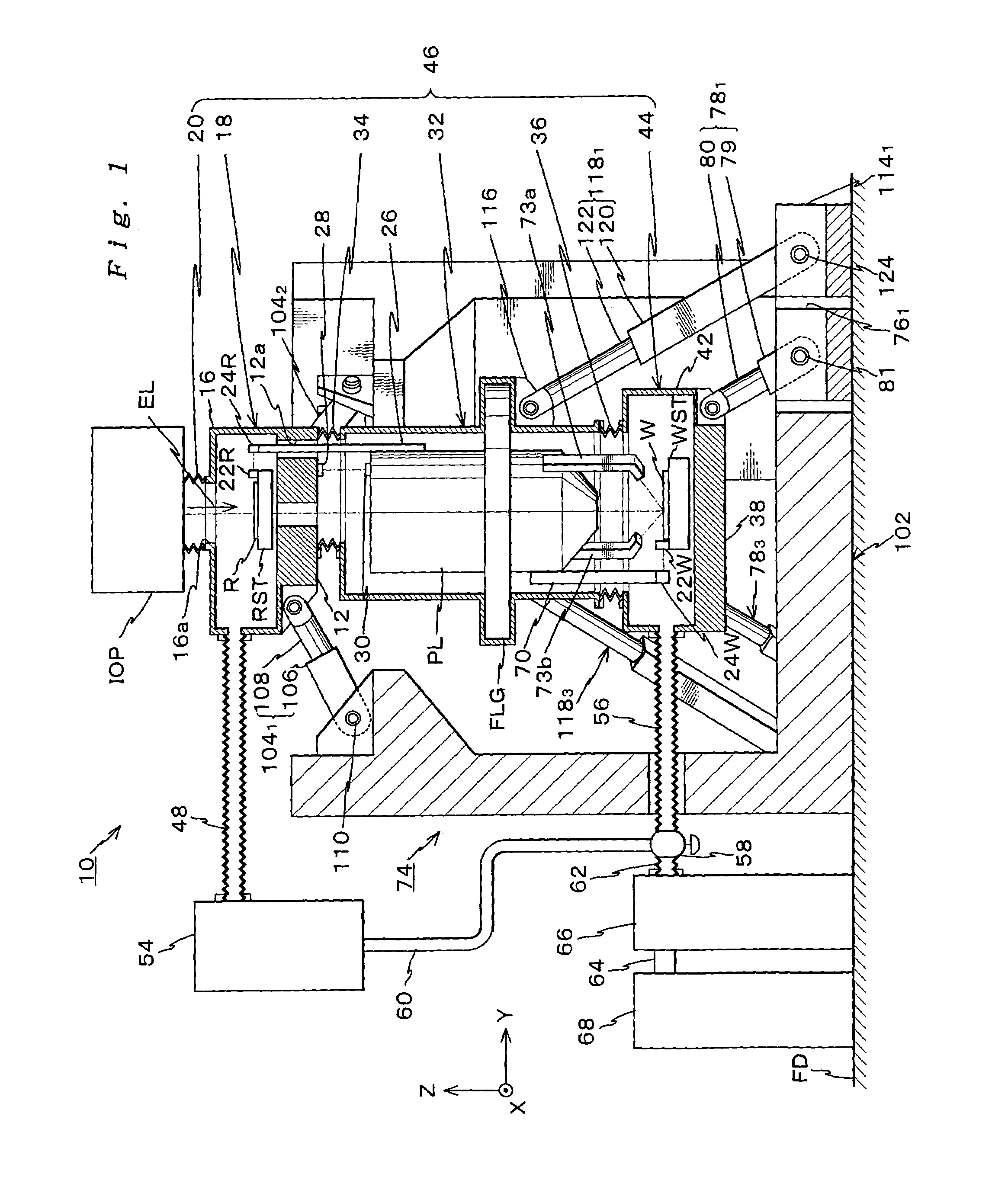
Parallel link mechanism, exposure system and method of manufacturing the same, and method of manufacturing devices
InactiveUS6940582B1Precision of superpositionEasy to integrateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringProjection system
A reticle base level block to support a reticle stage for holding a reticle, a wafer base level block to support a wafer stage for holding a wafer, and the like are supported to be independent of other portions and be controllable in their attitudes by parallel link mechanisms each including at least three expandable rods. Therefore, the portions supported by the parallel link mechanism can be made lightweight using the advantages of the parallel link mechanism, and the attitudes of those can be precisely controlled with excellent operational-characteristics and high rigidity. In addition, transmission of vibrations and the like between the reticle base level block, the wafer base level block and other portions, e.g. an optical projection system, can be prevented. Therefore, a fine pattern formed on the reticle can be precisely transferred onto the wafer.
Owner:NIKON CORP
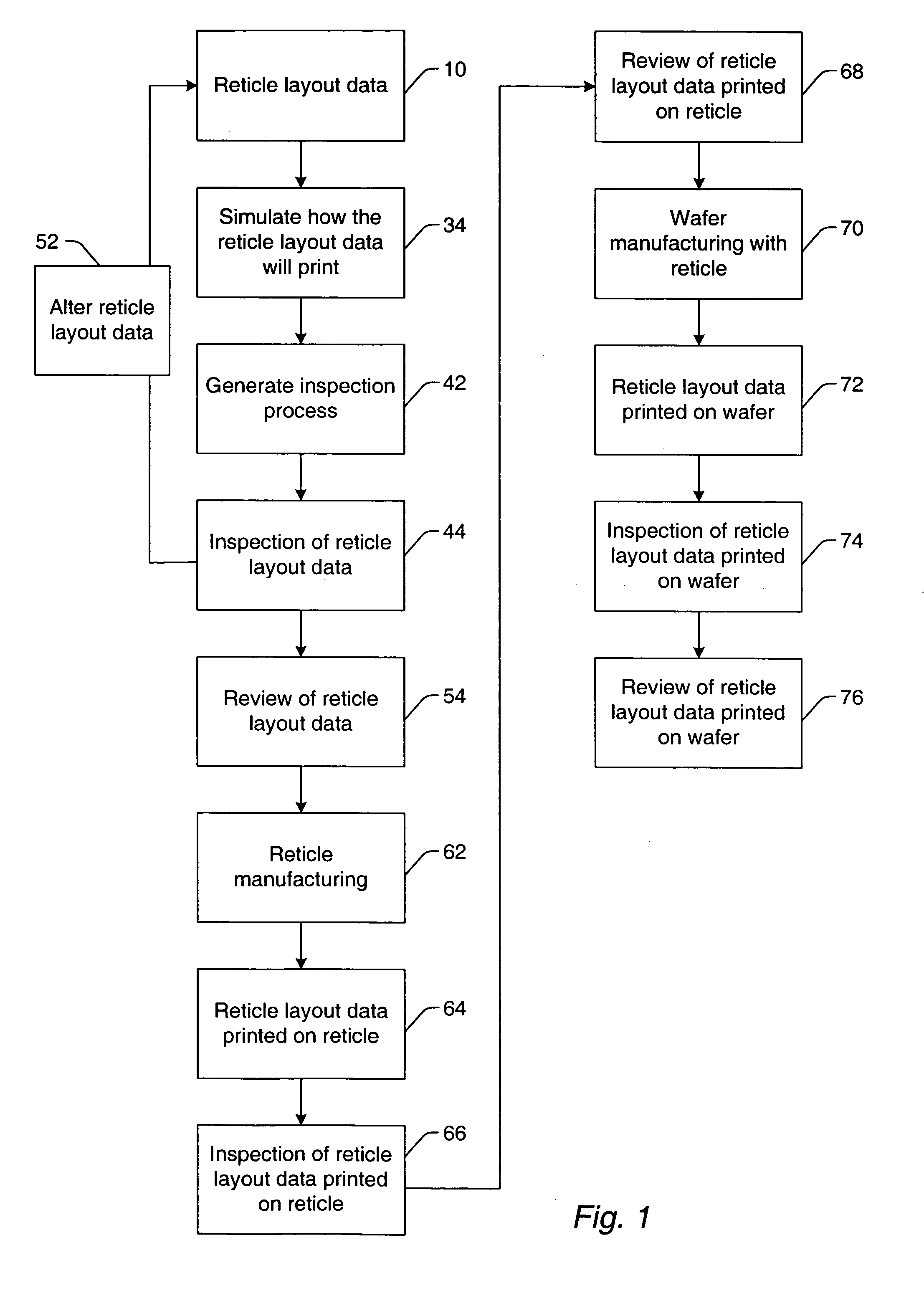
Methods, systems, and carrier media for evaluating reticle layout data
ActiveUS20060062445A1Forming accuratelyCharacter and pattern recognitionCAD circuit designProgram instructionComputer science
Various computer-implemented methods are provided. One method for evaluating reticle layout data includes generating a simulated image using the reticle layout data as input to a model of a reticle manufacturing process. The simulated image illustrates how features of the reticle layout data will be formed on a reticle by the reticle manufacturing process. The method also includes determining manufacturability of the reticle layout data using the simulated image. The manufacturability is a measure of how accurately the features will be formed on the reticle. Also provided are various carrier media that include program instructions executable on a computer system for performing a method for evaluating reticle layout data as described herein. In addition, systems configured to evaluate reticle layout data are provided. The systems include a computer system and a carrier medium that includes program instructions executable on the computer system for performing method(s) described herein.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
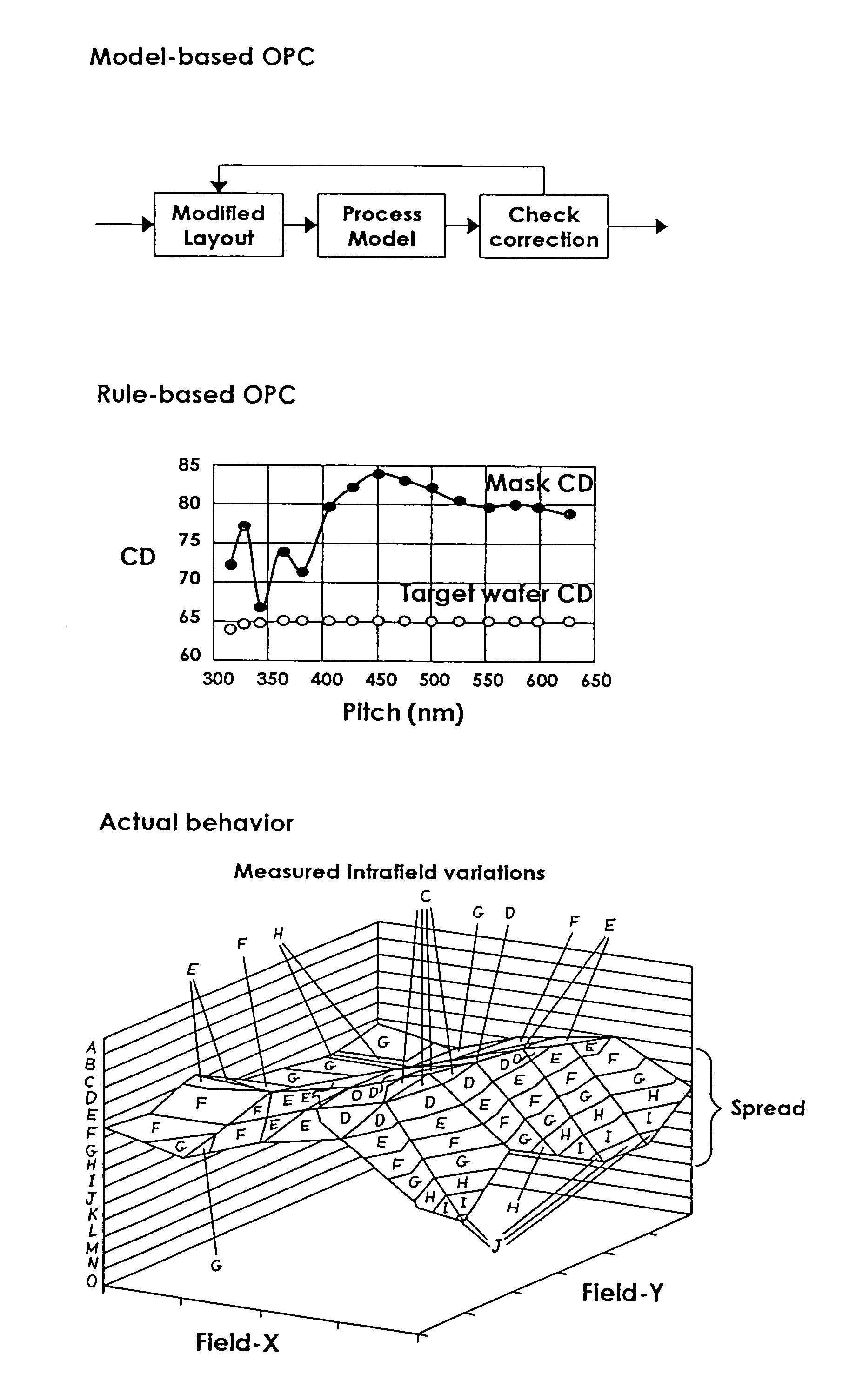
System and method for reducing patterning variability in integrated circuit manufacturing through mask layout corrections
ActiveUS7318214B1Improve accuracyImprove fidelityPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method of modifying the mask layout shapes of an integrated circuit layout design to compensate for reticle field location-specific systematic CD variations resulting from mask writing process variations, lens imperfections in lithographic patterning, and photoresist process variations. Called PLC (Process-optimized Layout Compensation), each set of compensation rules according to the present invention is specifically tailored for a particular mask-writer-patterning-tools-and-resist-process combination, and are performed on a reticle-wide basis. Furthermore, for each geometric shape in the mask layout, the amount of modification is determined based on a categorization of the type of the shape, the specific location in the reticle field the particular shape falls in, its context (i.e., surrounding patterns, orientation, etc.), as well as certain photoresist parameters to be used in the patterning process.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
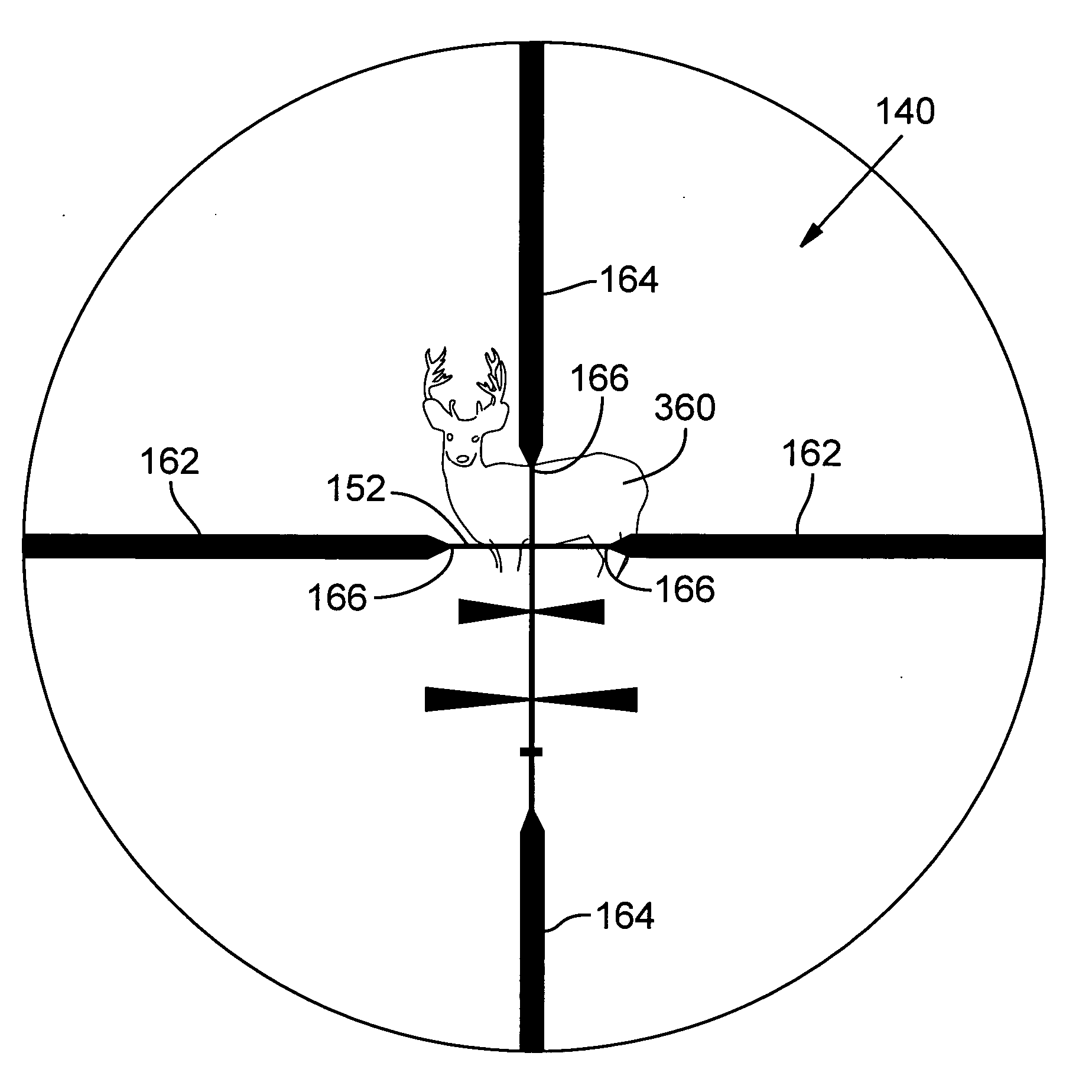
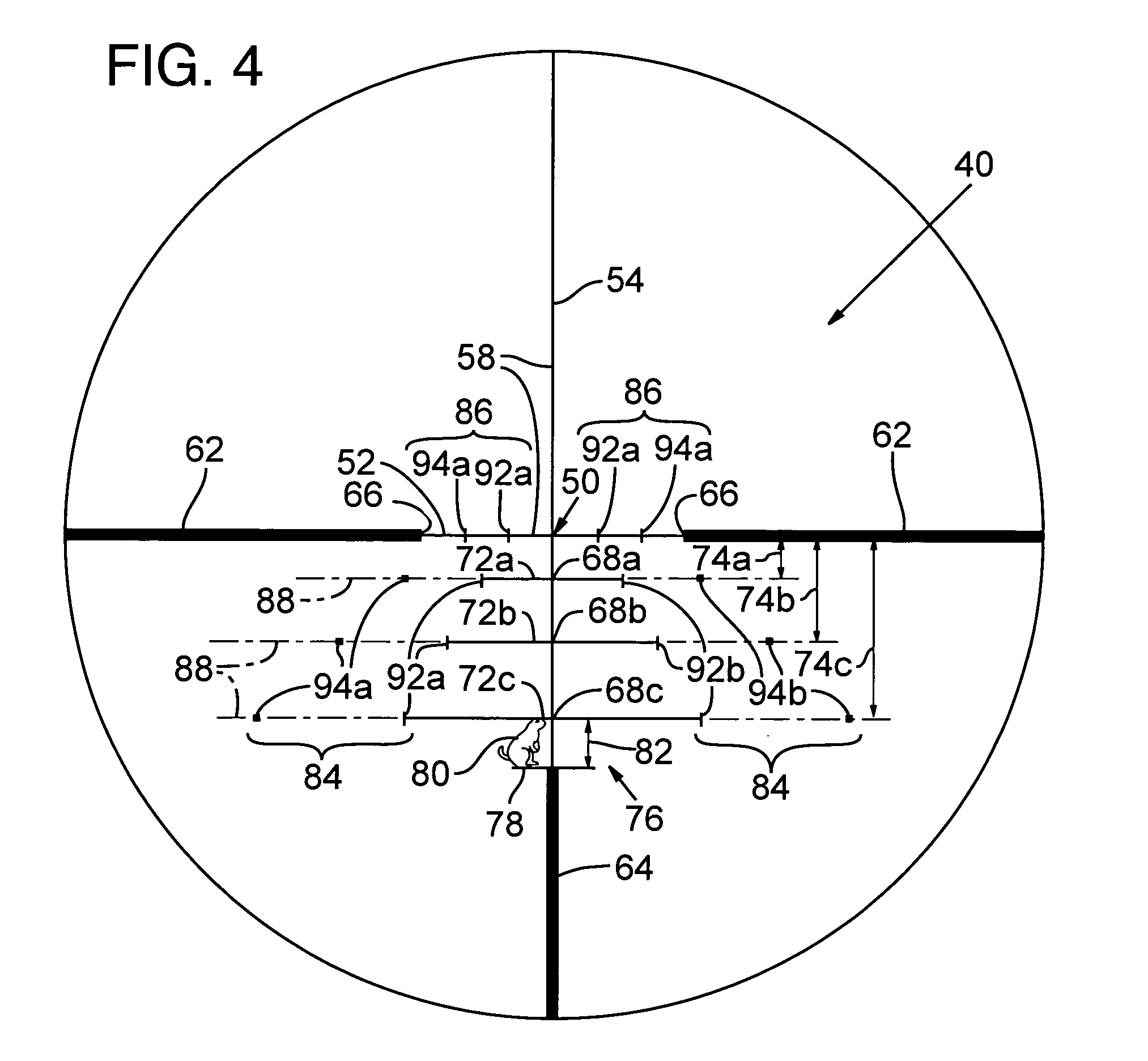
Ballistic reticle for projectile weapon aiming systems and method of aiming
ActiveUS20050229468A1Good compensationCompensation effectSighting devicesHorizontal axisOptical power
A reticle of a projectile weapon aiming system such as a riflescope includes a primary aiming mark adapted to be sighted-in at a first selected range and further includes a plurality of secondary aiming marks spaced apart below the primary aiming mark. The secondary aiming marks are positioned to compensate for ballistic drop at preselected incremental ranges beyond the first selected range, for a selected group of ammunition having similar ballistic characteristics. Angles subtended by adjacent aiming marks of the reticle can be adjusted by changing the optical power of the riflescope, to thereby compensate for ballistic characteristics of different ammunition. In some embodiments, the reticle includes a set of windage aiming marks spaced apart along at least one secondary horizontal axis intersecting a selected one of the secondary aiming marks, to facilitate compensation for the effect of crosswinds on the trajectory of the projectile.
Owner:LEUPOLD & STEVENS
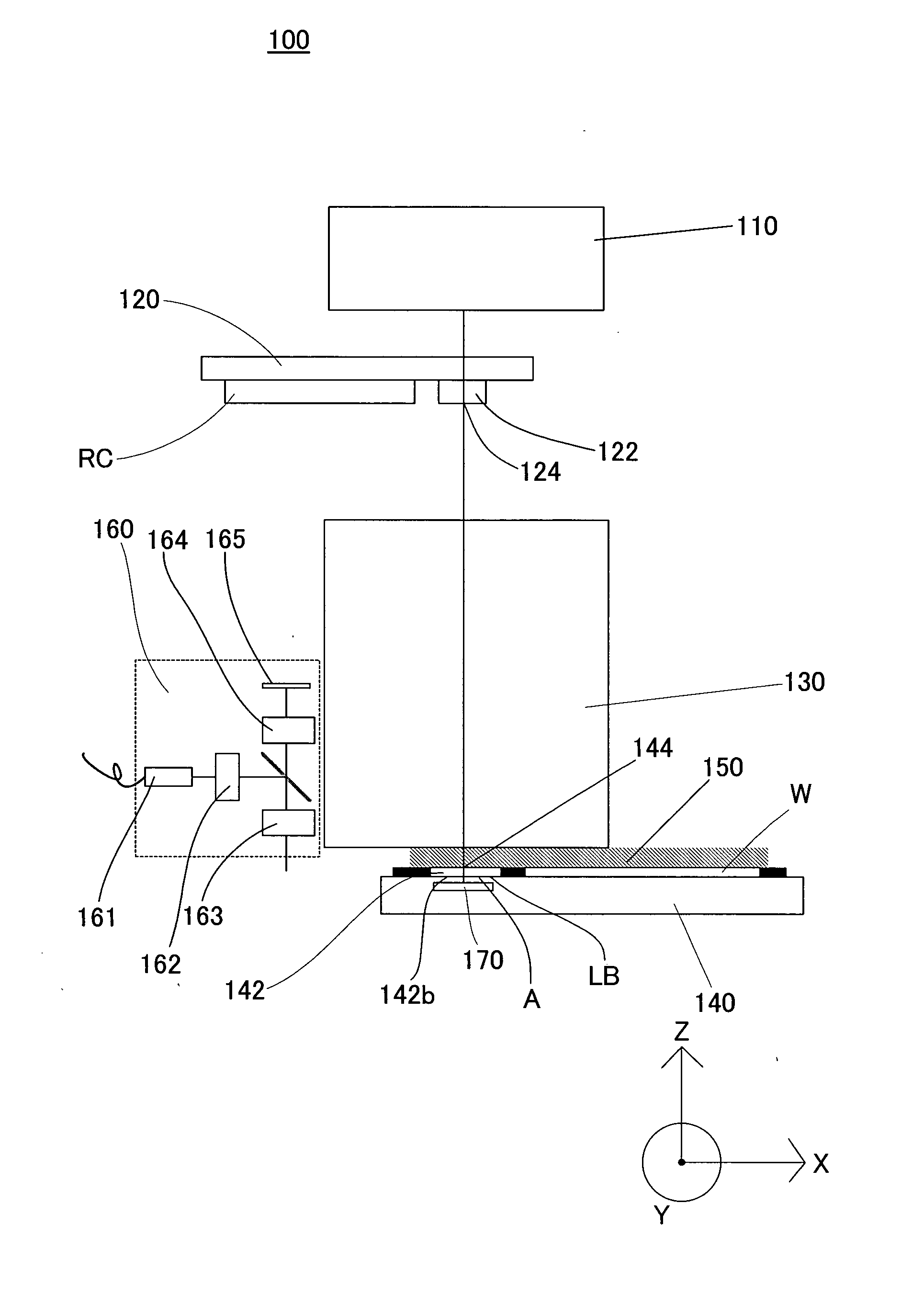
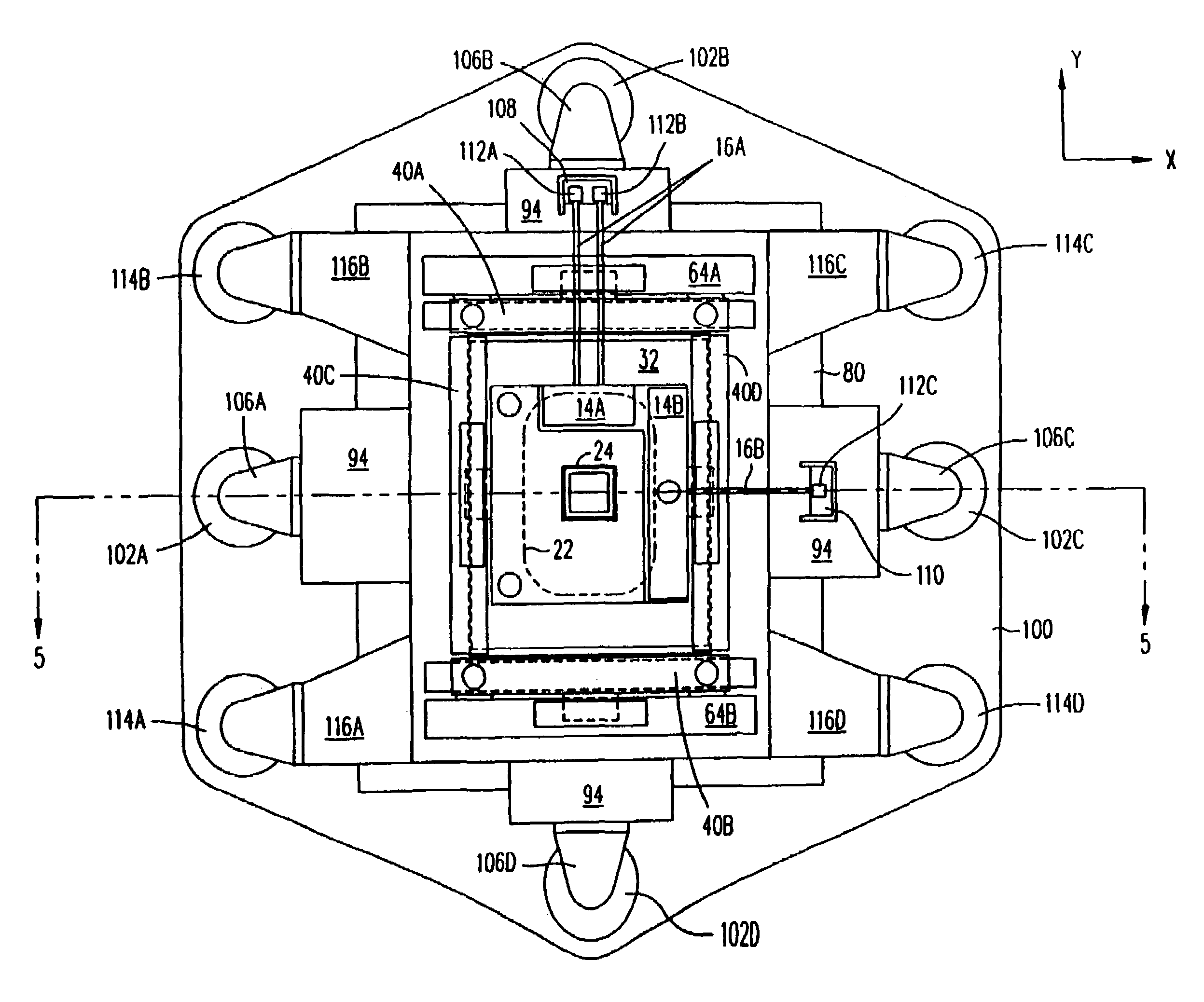
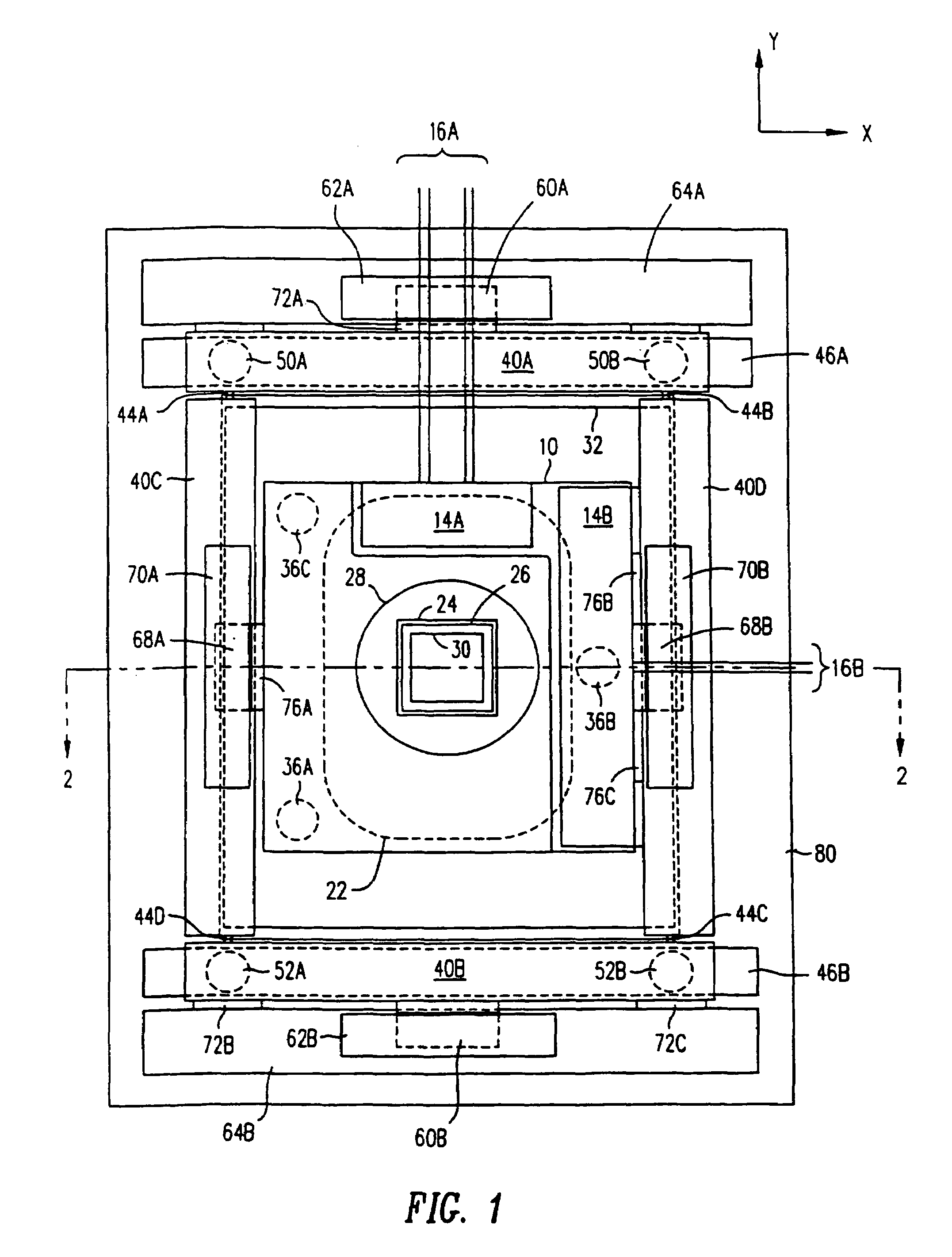
Positioning device having dynamically isolated frame, and lithographic device provided with such a positioning device
InactiveUS6989647B1Small distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDrive motorEngineering
A guided stage mechanism suitable for supporting a reticle in a photolithography machine includes a stage movable in the X-Y directions on a base. Laterally surrounding the stage is a rectangular window frame guide which is driven in the X-axis direction on two fixed guides by means of motor coils on the window frame guide cooperating with magnetic tracks fixed on the base. The stage is driven inside the window frame guide in the Y-axis direction by motor coils located on the stage cooperating with magnetic tracks located on the window frame guide. Forces from the drive motors of both the window frame guide and the stage are transmitted through the center of gravity of the stage, thereby eliminating unwanted moments of inertia. Additionally, reaction forces caused by the drive motors are isolated from the projection lens and the alignment portions of the photolithography machine. This isolation is accomplished by providing a mechanical support for the stage independent of the support for its window frame guide. The window frame guide is a hinged structure capable of a slight yawing (rotational) motion due to hinged flexures which connect the window frame guide members.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Reticle and optical proximity correction method
ActiveUS20070105023A1Low costIncrease flexibilityOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsOptical transmittanceReticle
An OPC method includes providing a primary mask having a primary pattern, forming an assist mask having a correction pattern substantially complementary to the primary pattern, and forming a reticle by overlapping the primary mask and the assist mask. The light transmittance of the correction pattern is adjustable so as to equalize the light intensity distribution of the primary mask.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Reticle and optical proximity correction method
ActiveUS7527900B2Increase flexibilityLow costOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsOptical transmittanceReticle
An OPC method includes providing a primary mask having a primary pattern, forming an assist mask having a correction pattern substantially complementary to the primary pattern, and forming a reticle by overlapping the primary mask and the assist mask. The light transmittance of the correction pattern is adjustable so as to equalize the light intensity distribution of the primary mask.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Methods and systems for inspecting reticles using aerial imaging and die-to-database detection
ActiveUS7123356B1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionReference imageAerial imaging
Methods and systems for inspecting a reticle are provided. In an embodiment, a method may include forming an aerial image of the reticle using a set of exposure conditions. The reticle may include optical proximity correction (OPC) features. The method may also include detecting defects on the reticle by comparing the aerial image to a reference image stored in a database. The reference image may be substantially optically equivalent to an image of the reticle that would be printed on a specimen by an exposure system under the set of exposure conditions. The reference image may not include images of the OPC features. Therefore, a substantial portion of the defects include defects that would be printed onto the specimen by the exposure system using the reticle under the set of exposure conditions. The method may also include indicating the defects that are detected in critical regions of the reticle.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Liquid immersion type exposure apparatus
InactiveUS7053983B2High resolutionSlow changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid mediumEngineering
Disclosed is an exposure apparatus which includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern of a reticle onto a substrate, wherein the substrate is exposed through a liquid medium kept at least in a portion between the substrate and an optical element of the projection optical system which optical element is nearest to the substrate, a supplying system for supplying a liquid medium, a collecting system for collecting a liquid medium, and an exhausting system for removing a bubble in the liquid medium through a bubble removing material having such property that it passes a gas but it does not pass a liquid.
Owner:CANON KK
Computer-implemented methods for detecting defects in reticle design data
ActiveUS20060236294A1Market predictionsDetecting faulty computer hardwareManufacturing technologyImage detection
Computer-implemented methods for detecting defects in reticle design data are provided. One method includes generating a first simulated image illustrating how the reticle design data will be printed on a reticle using a reticle manufacturing process. The method also includes generating second simulated images using the first simulated image. The second simulated images illustrate how the reticle will be printed on a wafer at different values of one or more parameters of a wafer printing process. The method further includes detecting defects in the reticle design data using the second simulated images. Another method includes the generating steps described above in addition to determining a rate of change in a characteristic of the second simulated images as a function of the different values. This method also includes detecting defects in the reticle design data based on the rate of change.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Semiconductor device and a manufacturing method of the same
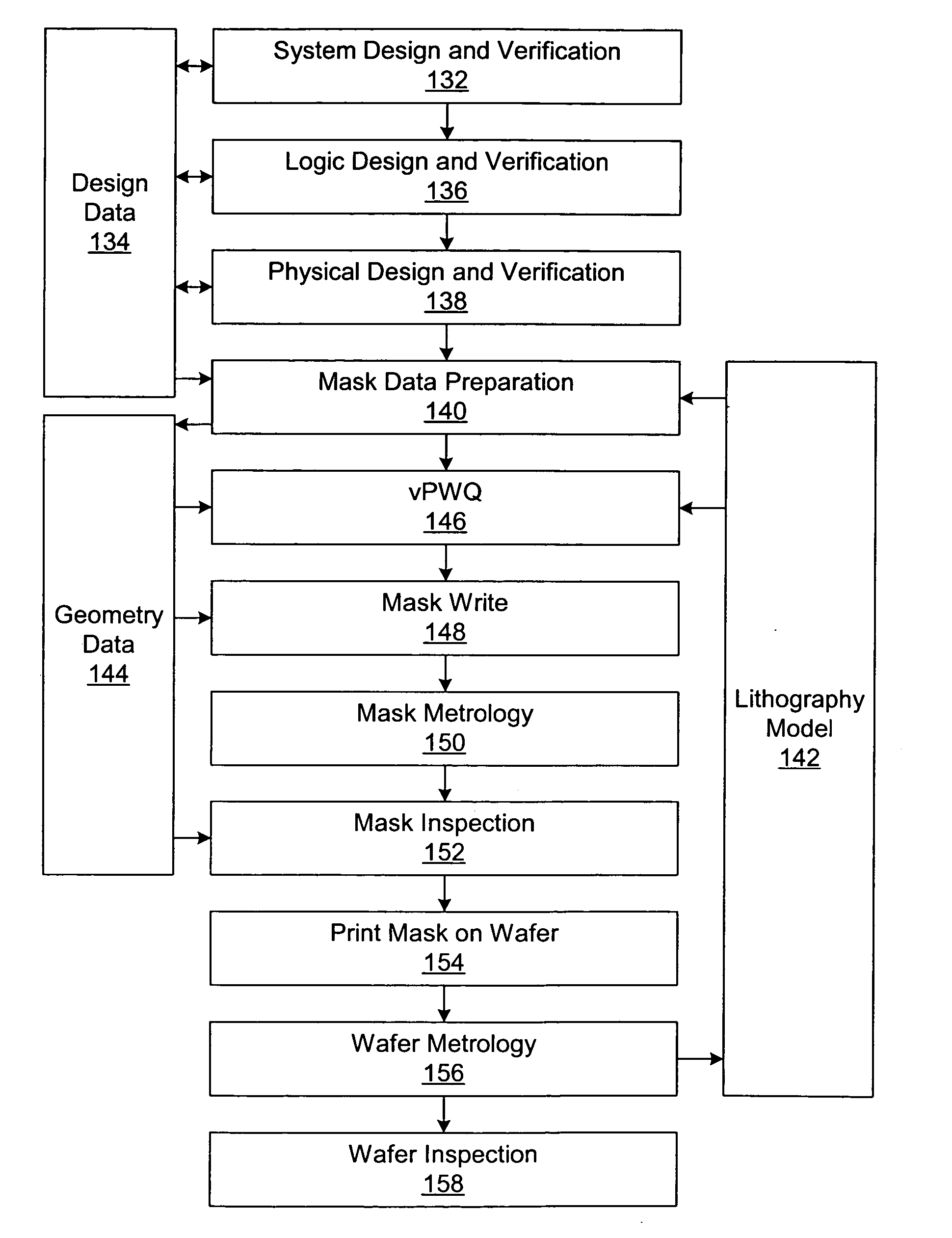
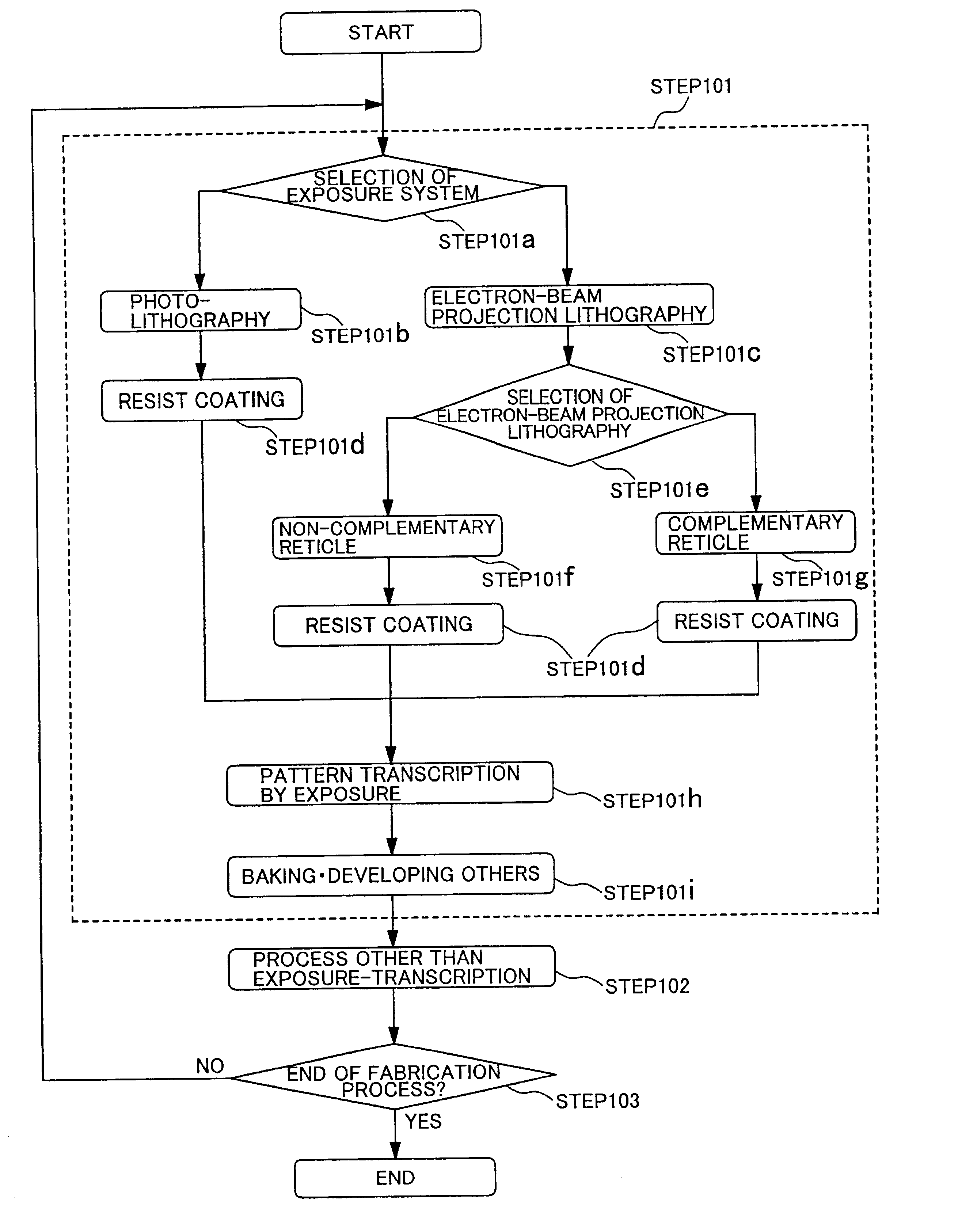
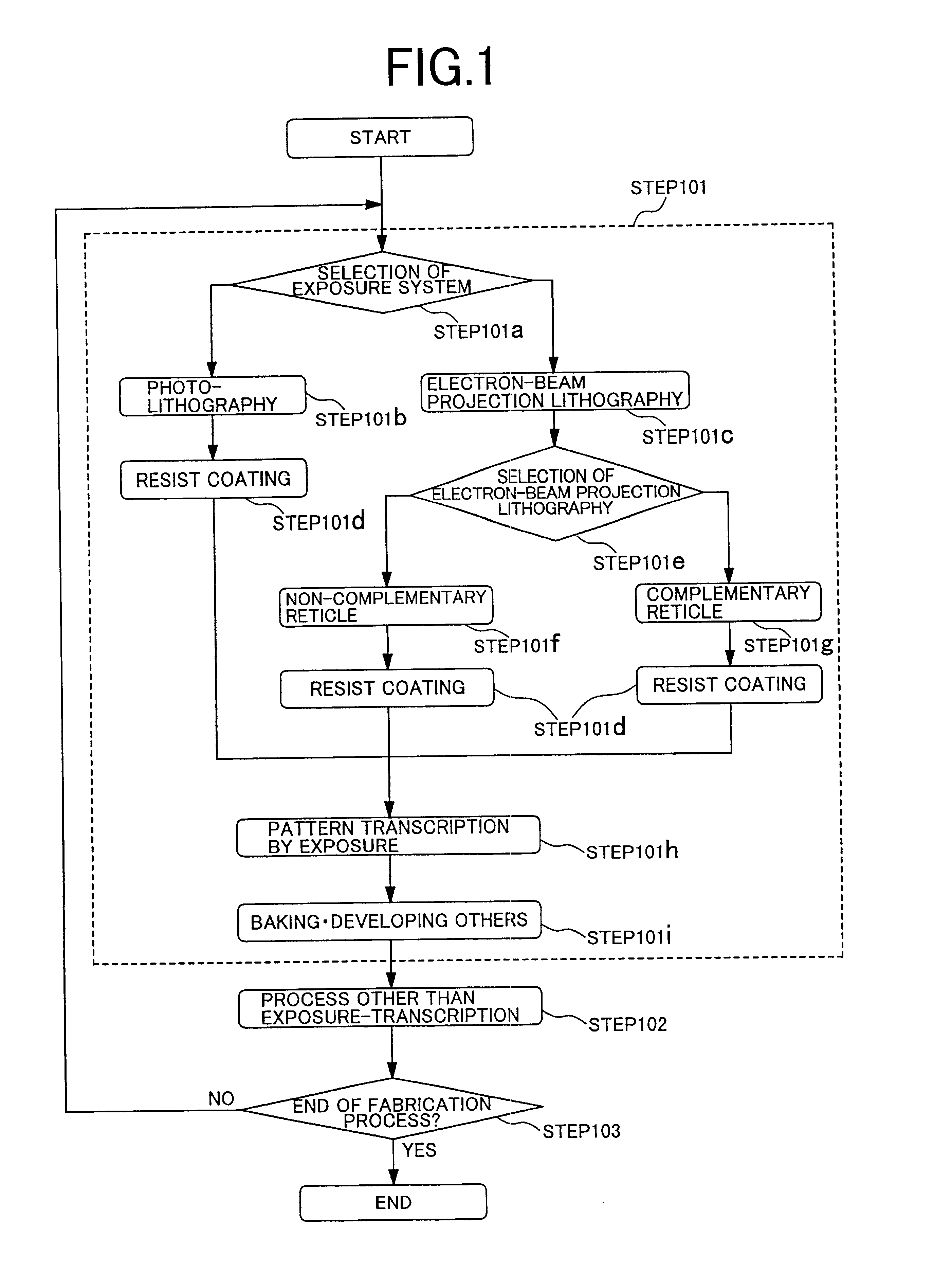
There is disclosed a method for forming micro patterns in a semiconductor integrated circuit device with high productivity and high accuracy. A photolithography having high throughput and electron beam lithography using a reticle and having relatively high throughput and high resolution are selectively used so as to obtain highest throughput while satisfying accuracy and resolution required for each product / layer. In the case of using the electron beam lithography, a non-complementary reticle and a complementary reticle are selectively used so as to obtain highest throughput while satisfying required accuracy and resolution. Thus, productivity and integration can be improved for the semiconductor integrated circuit device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
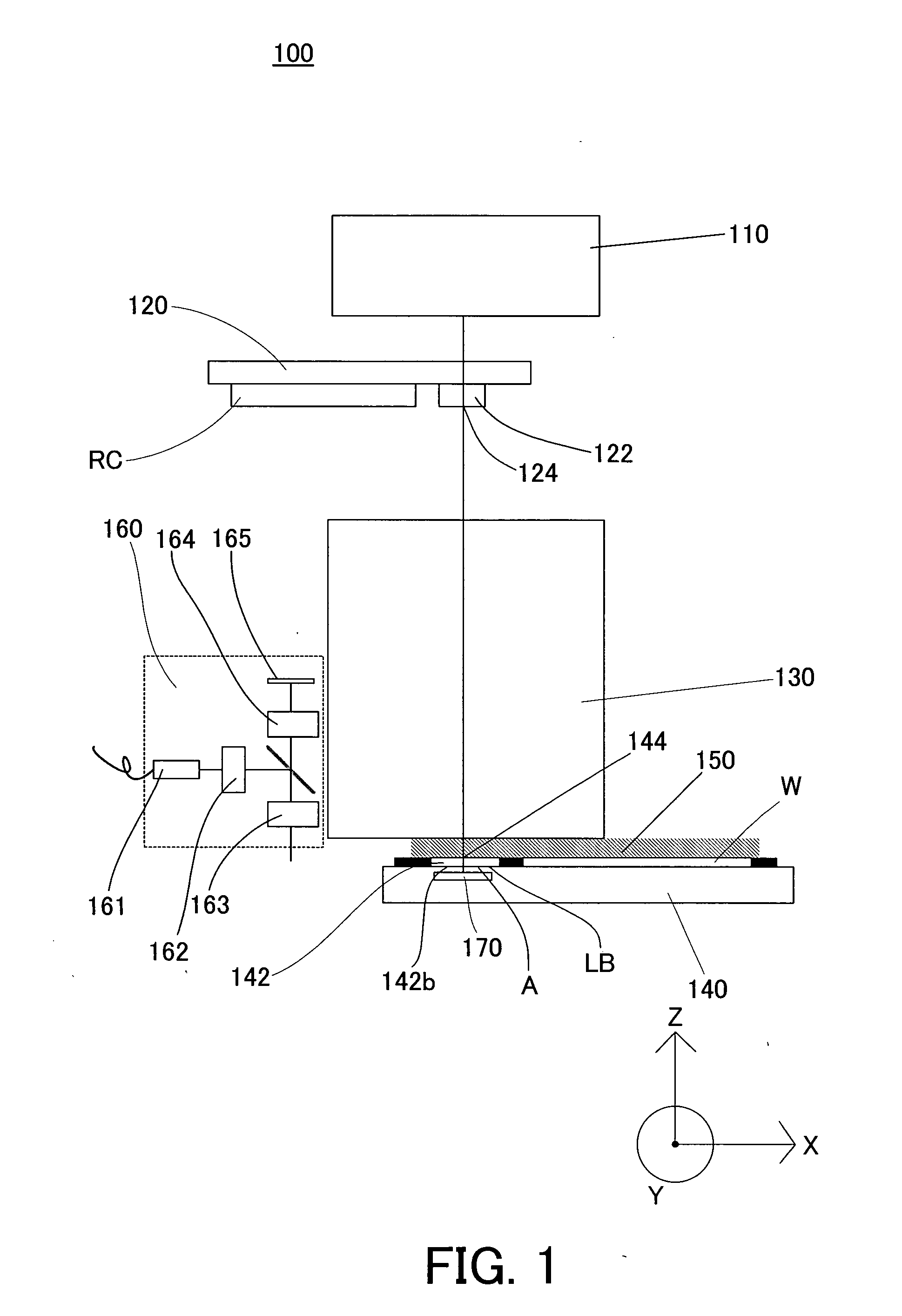
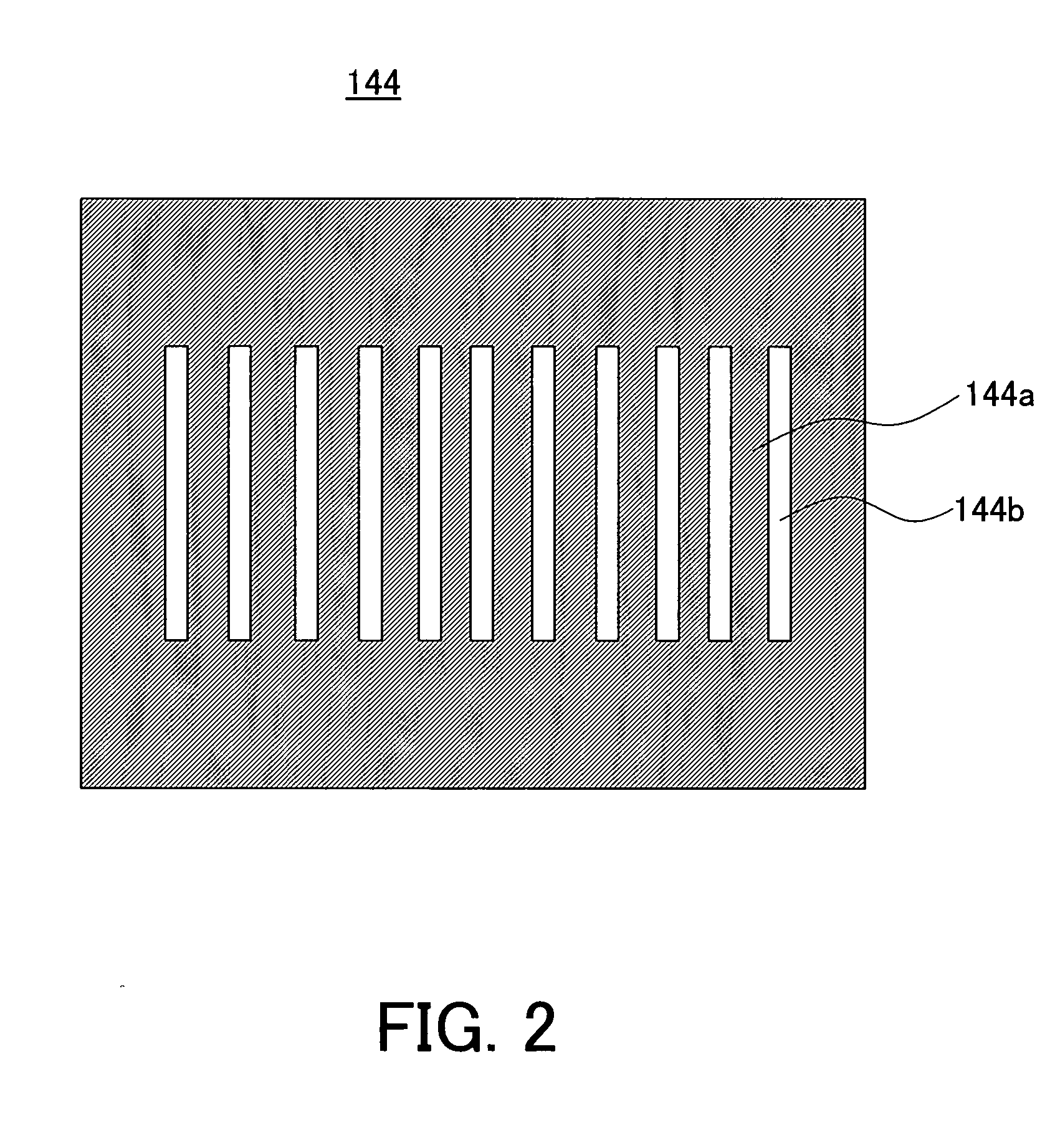
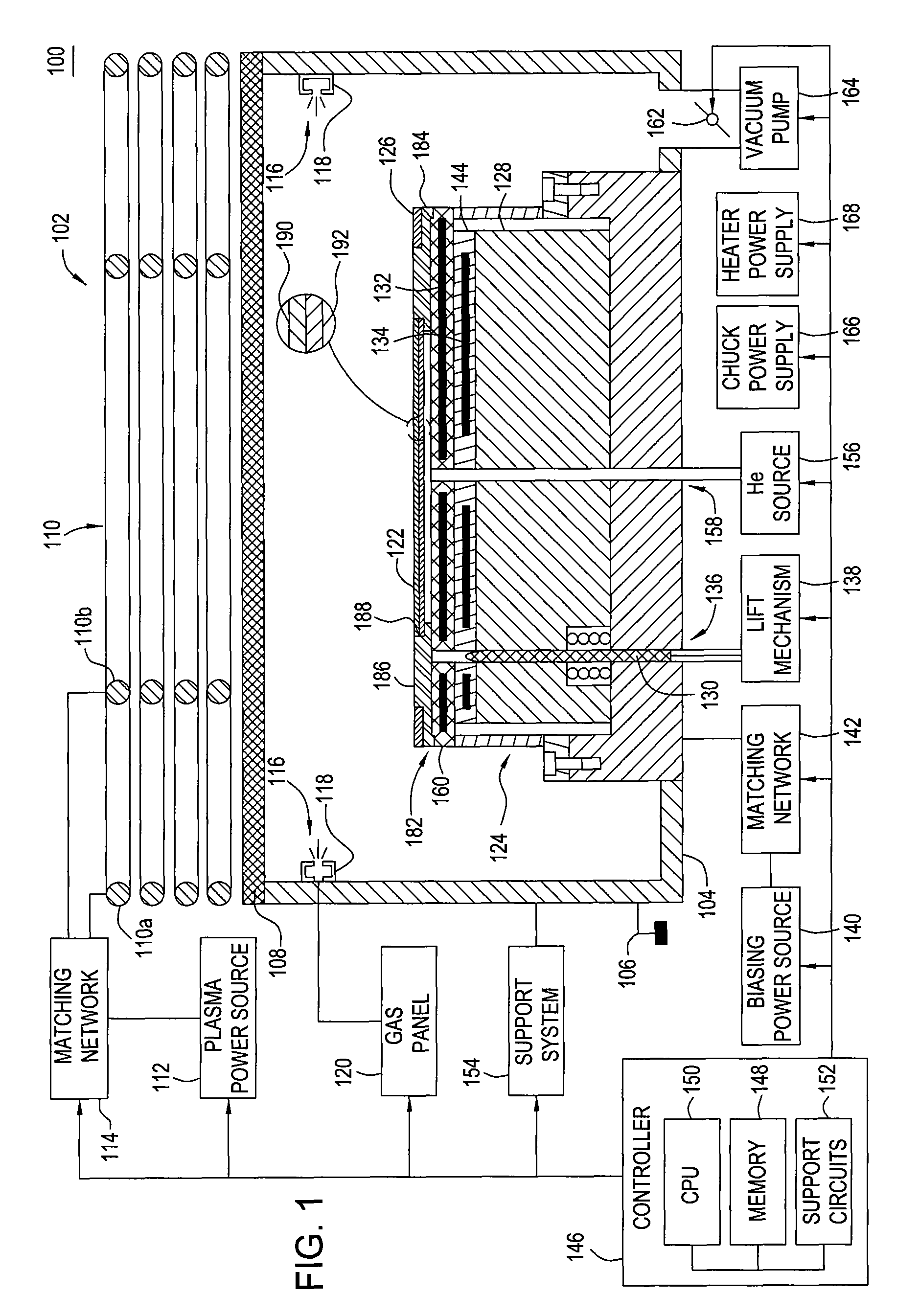
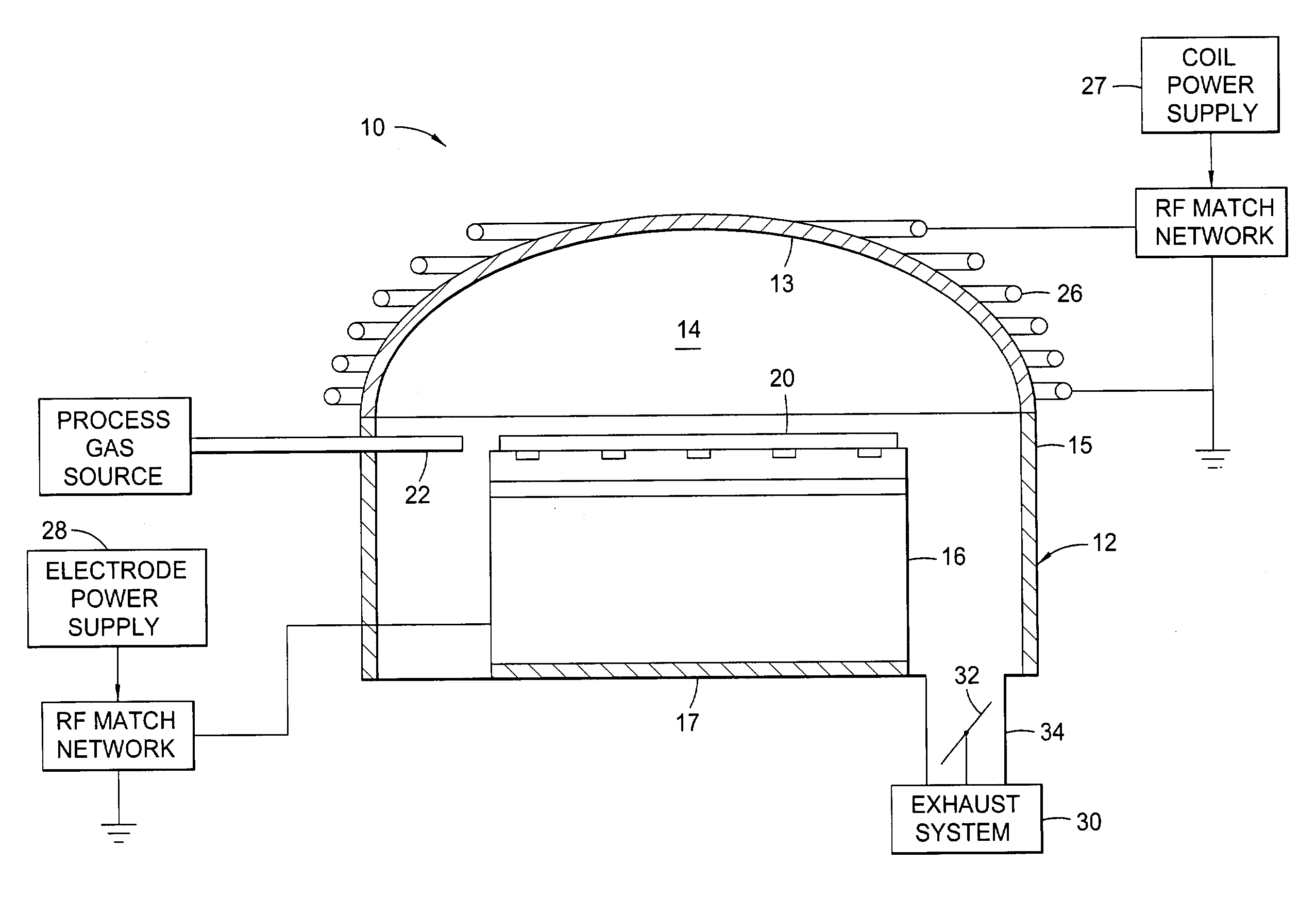
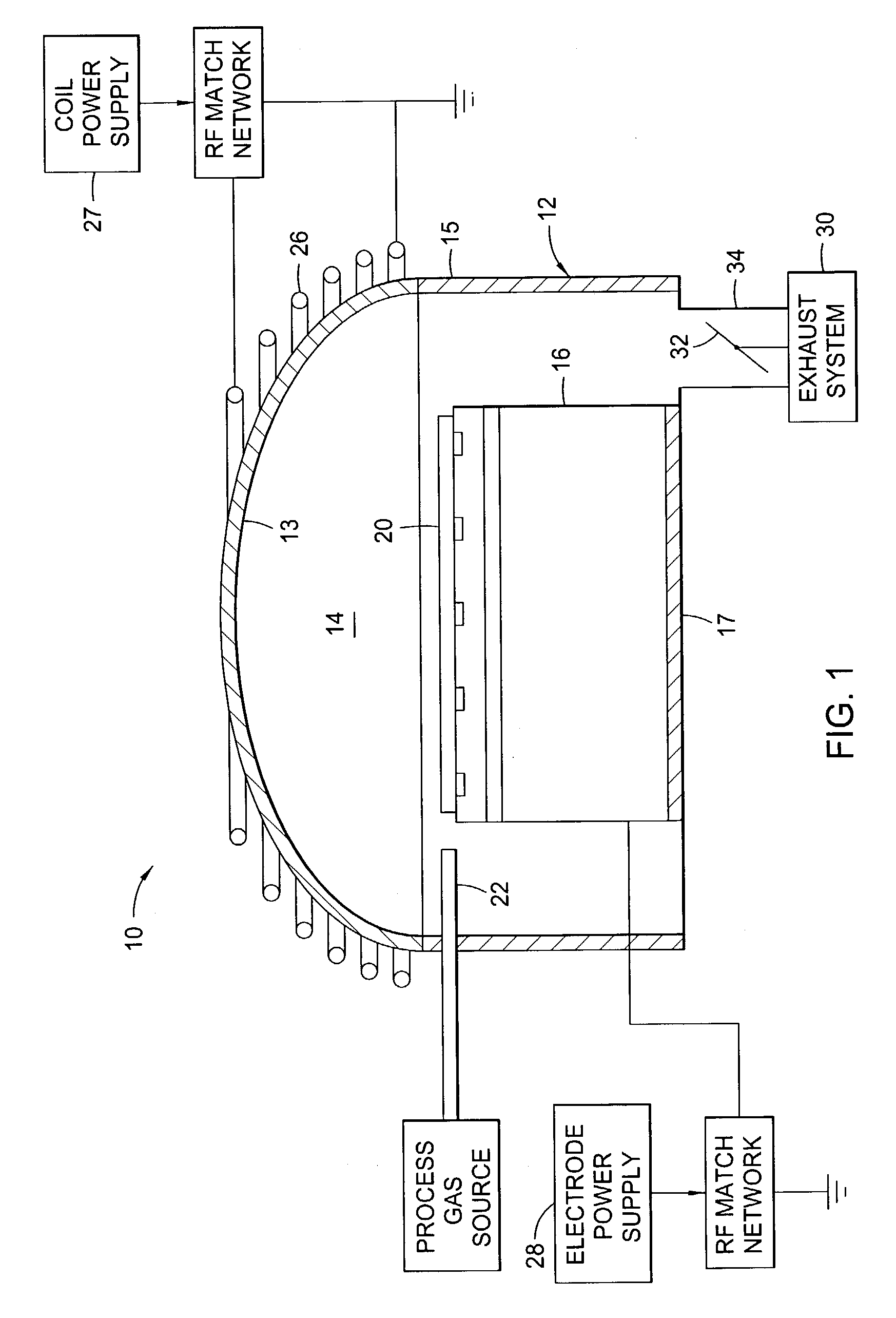
Tuned potential pedestal for mask etch processing apparatus
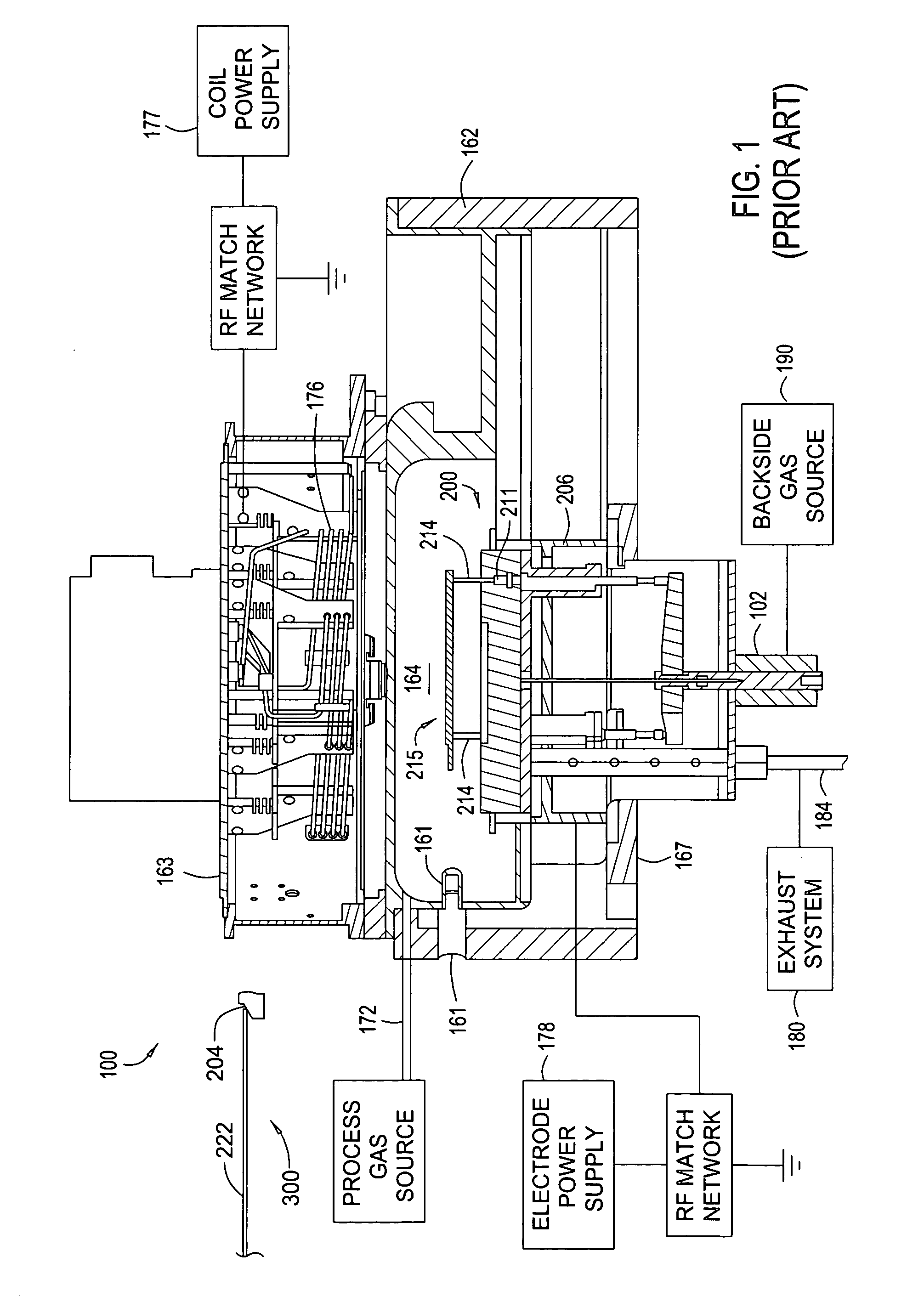
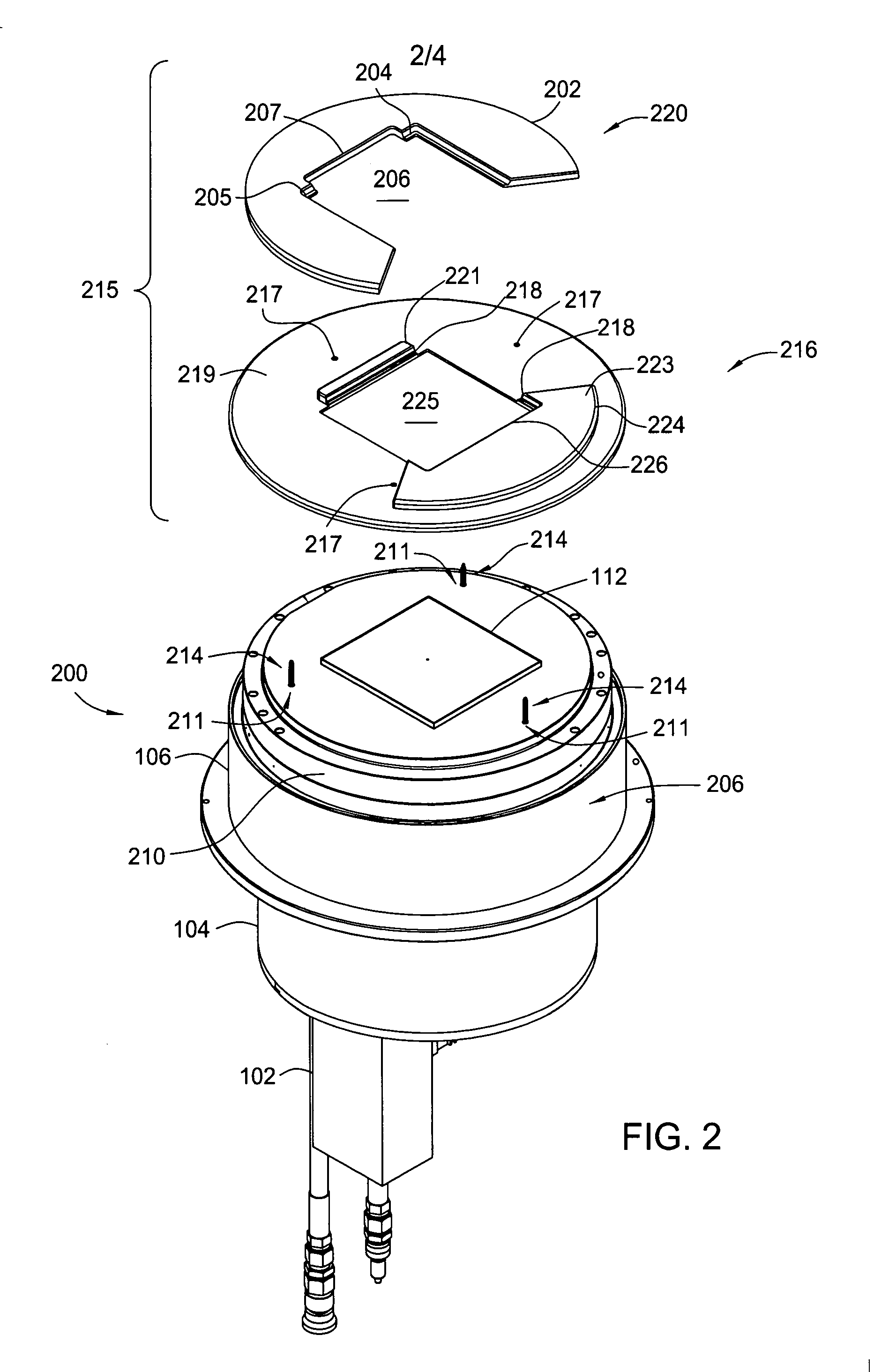
InactiveUS20050133166A1Great RF powerEnhancing plasma etching processElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringReticle
The present invention generally provides an improved pedestal for supporting a substrate. The pedestal has greatest application during a plasma etching process, such as for a quartz photomask, or “reticle.” The pedestal defines a body, and a substrate support base along an upper surface of the body. The substrate support base has an outer edge, and an intermediate substrate support ridge for receiving and supporting the substrate. At least a portion of the substrate support base outside of the intermediate substrate support ridge is fabricated from a dielectric material. The purpose is to couple greater RF power through the reticle in order to enhance the plasma etching process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Computer-implemented methods, processors, and systems for creating a wafer fabrication process
InactiveUS20060161452A1Market predictionsDetecting faulty computer hardwareWafer fabricationEngineering
Computer-implemented methods, processors, and systems for creating a wafer fabrication process are provided. One computer-implemented method includes determining individual error budgets for different parameters of the wafer fabrication process based on an overall error budget for the wafer fabrication process and simulated images that illustrate how reticle design data will be printed on a wafer at different values of the different parameters. The method also includes creating the wafer fabrication process based on the overall error budget and the individual error budgets.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for error reduction in lithography
InactiveUS6883158B1High precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusError reductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for predicting and correcting geometrical errors in lithography using masks, such as large-area photomasks or reticles, and exposure stations, such as wafer steppers or projection aligners, printing the pattern of said masks on a workpiece, such as a display panel or a semi-conductor wafer. The method according to the invention comprises the steps of collecting information about a mask substrate, a mask writer, an exposure stati n, and / or about behavior of a processing step that will occur after the writing of the mask. Further the method comprises predicting from the combined information distorsions occuring in the pattern, when it is subsequently printed on the workpiece; calculating from said prediction a correction to diminish said predicted distorsion, and exposing said pattern onto said mask substrate while applying said correction for said distorsions.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
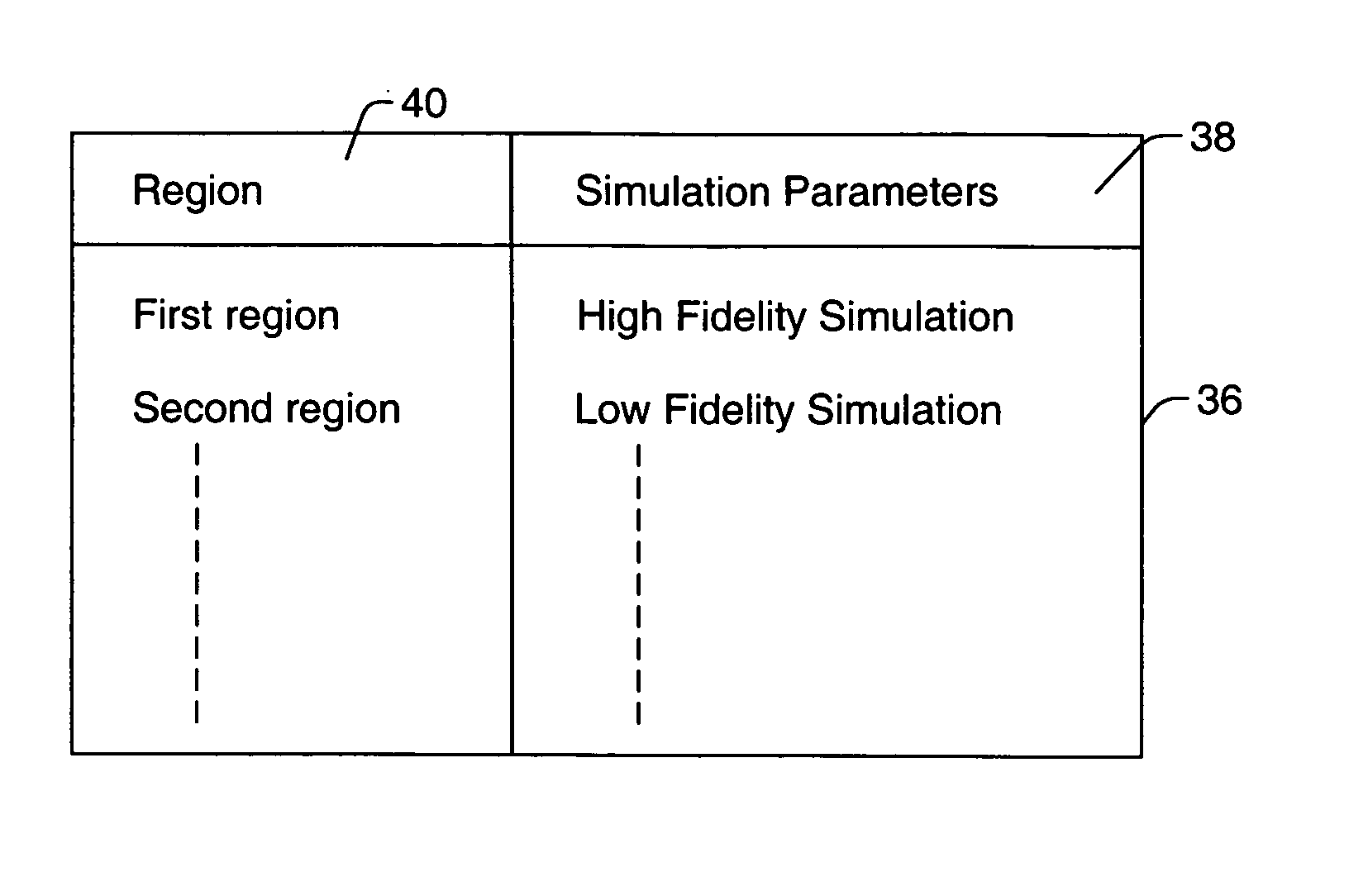
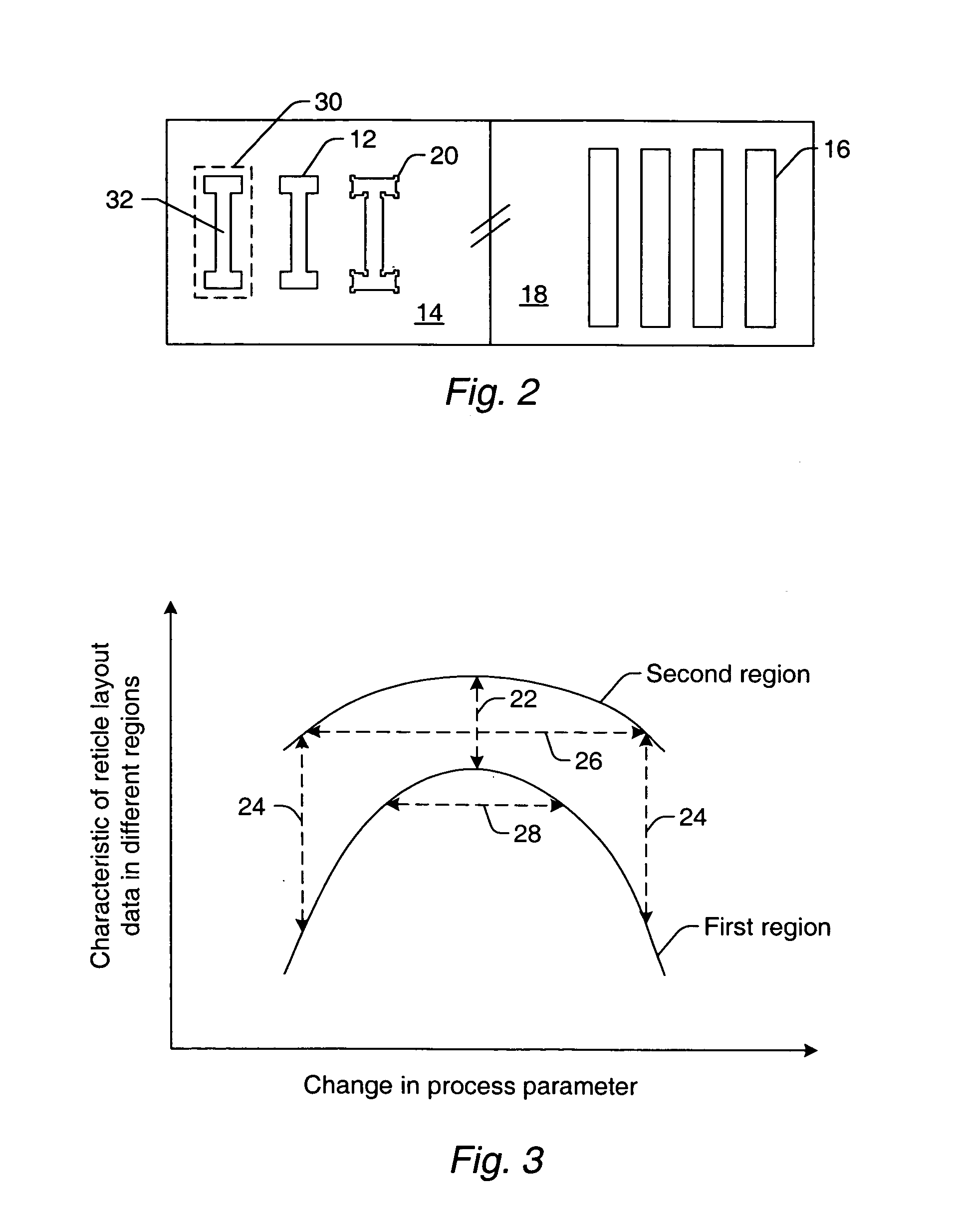
Methods for simulating reticle layout data, inspecting reticle layout data, and generating a process for inspecting reticle layout data
ActiveUS20060051682A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareOriginals for photomechanical treatmentEngineeringReticle
Various computer-implemented methods are provided. One method for generating a process for inspecting reticle layout data includes identifying a first region in the reticle layout data. A printability of the first region is more sensitive to changes in process parameters than a printability of a second region in the reticle layout data. The method also includes assigning one or more inspection parameters to the first region and the second region such that the first region will be inspected during the process with a higher sensitivity than the second region. Another method includes inspecting the first region with a higher sensitivity than the second region. An additional method includes simulating how the reticle layout data will print. Simulation of the first and second regions is performed with one or more different simulation parameters such that the first region is simulated with a higher fidelity than the second region.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com