Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
22206 results about "Manufacturing technology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
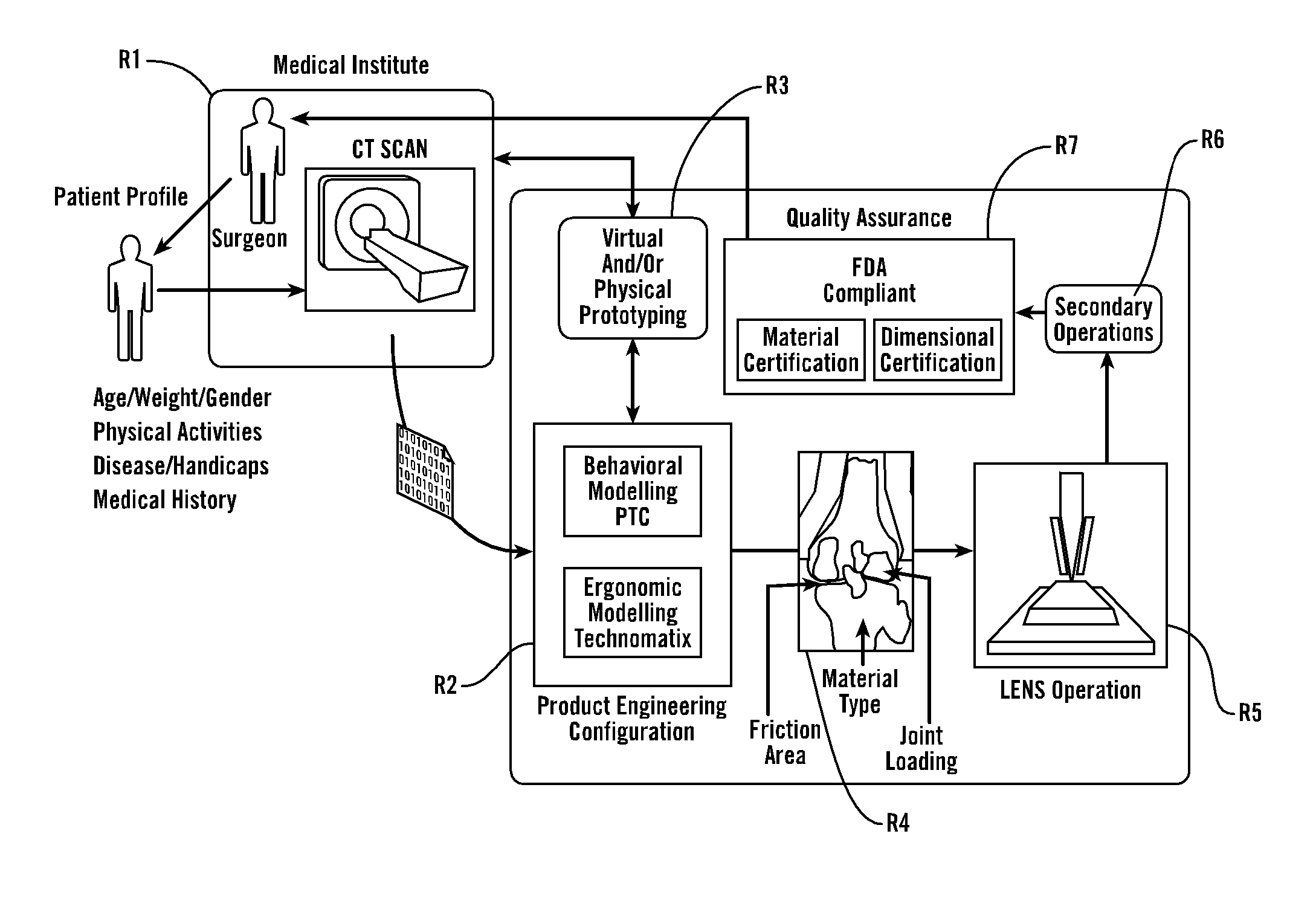
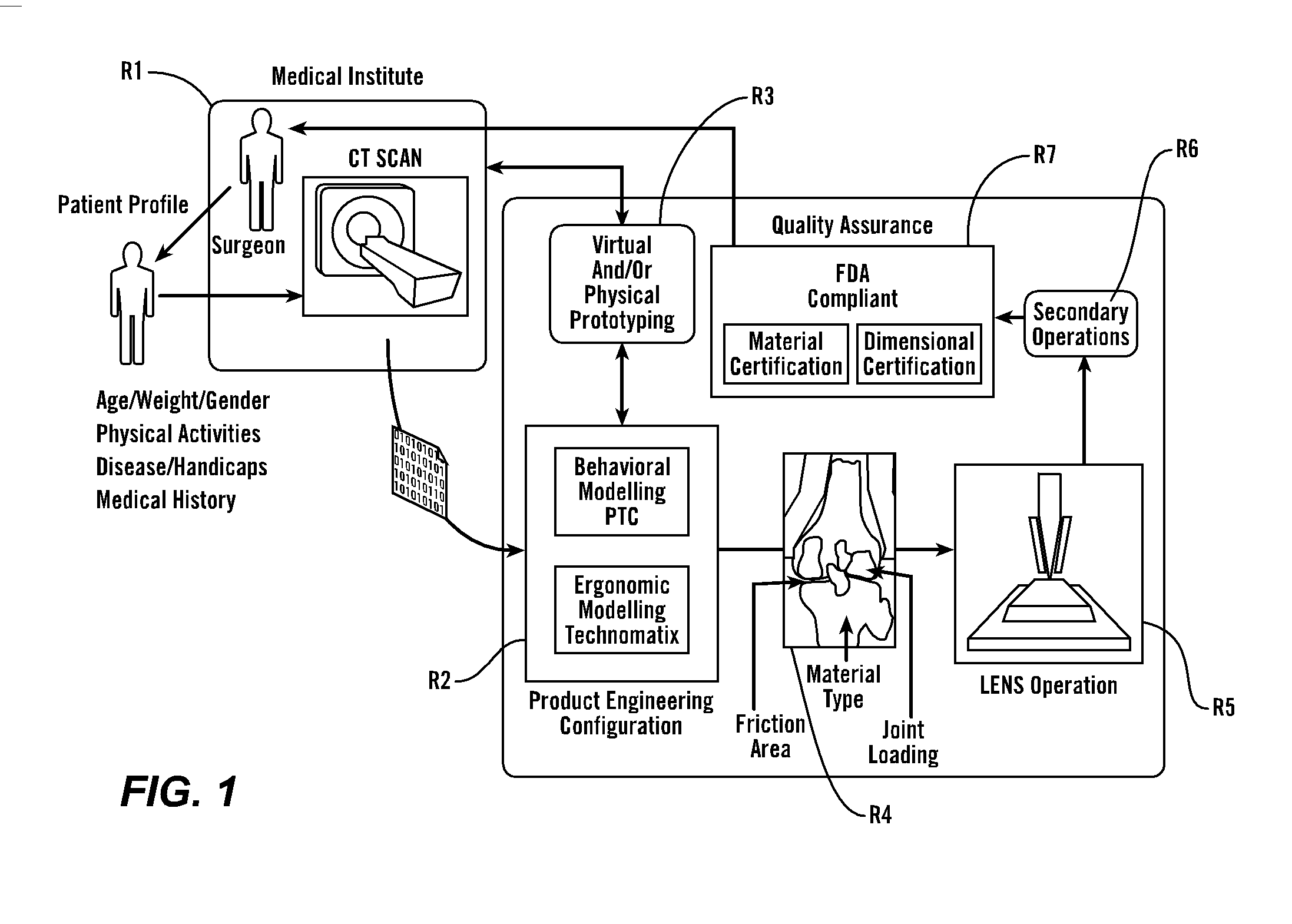
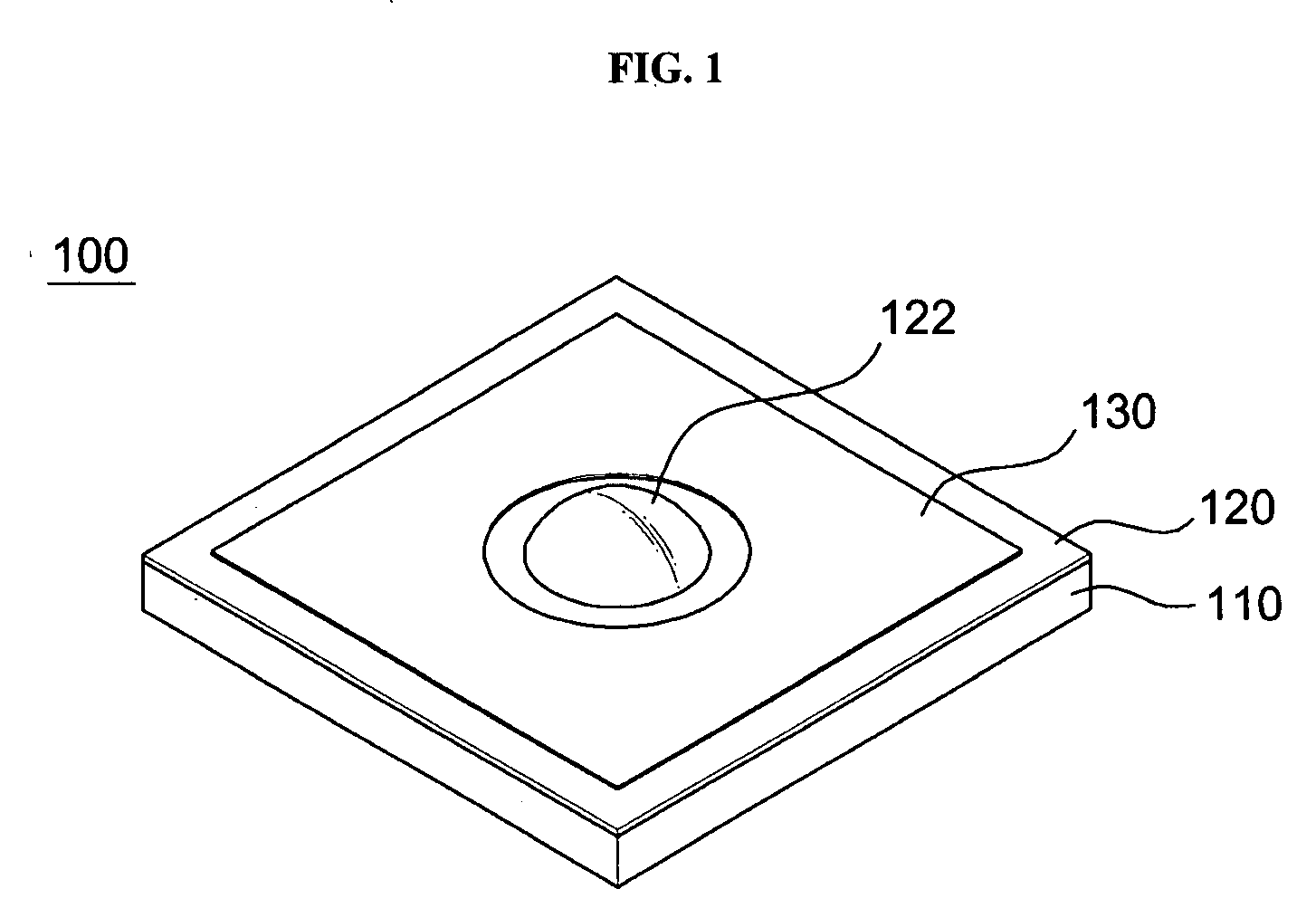
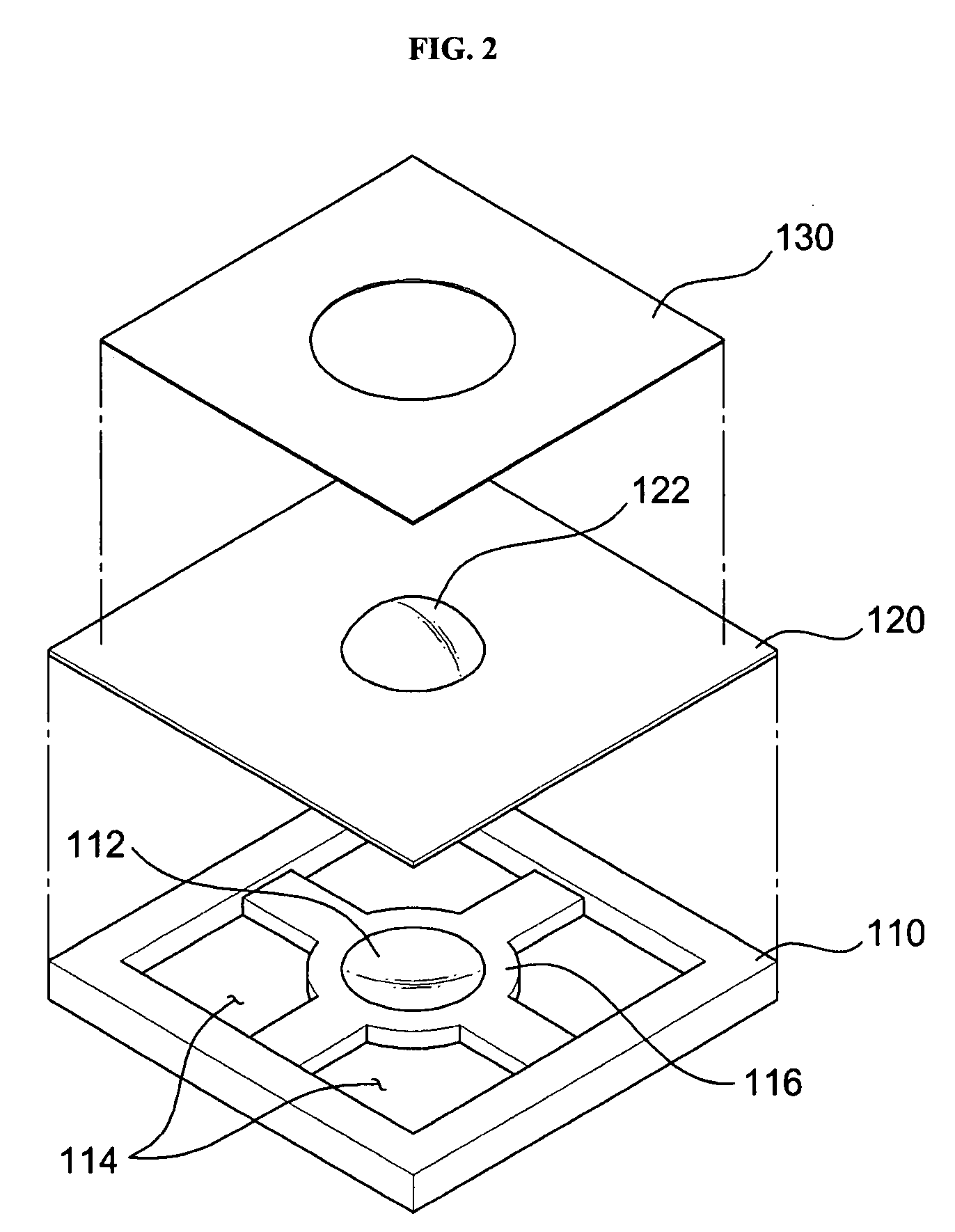
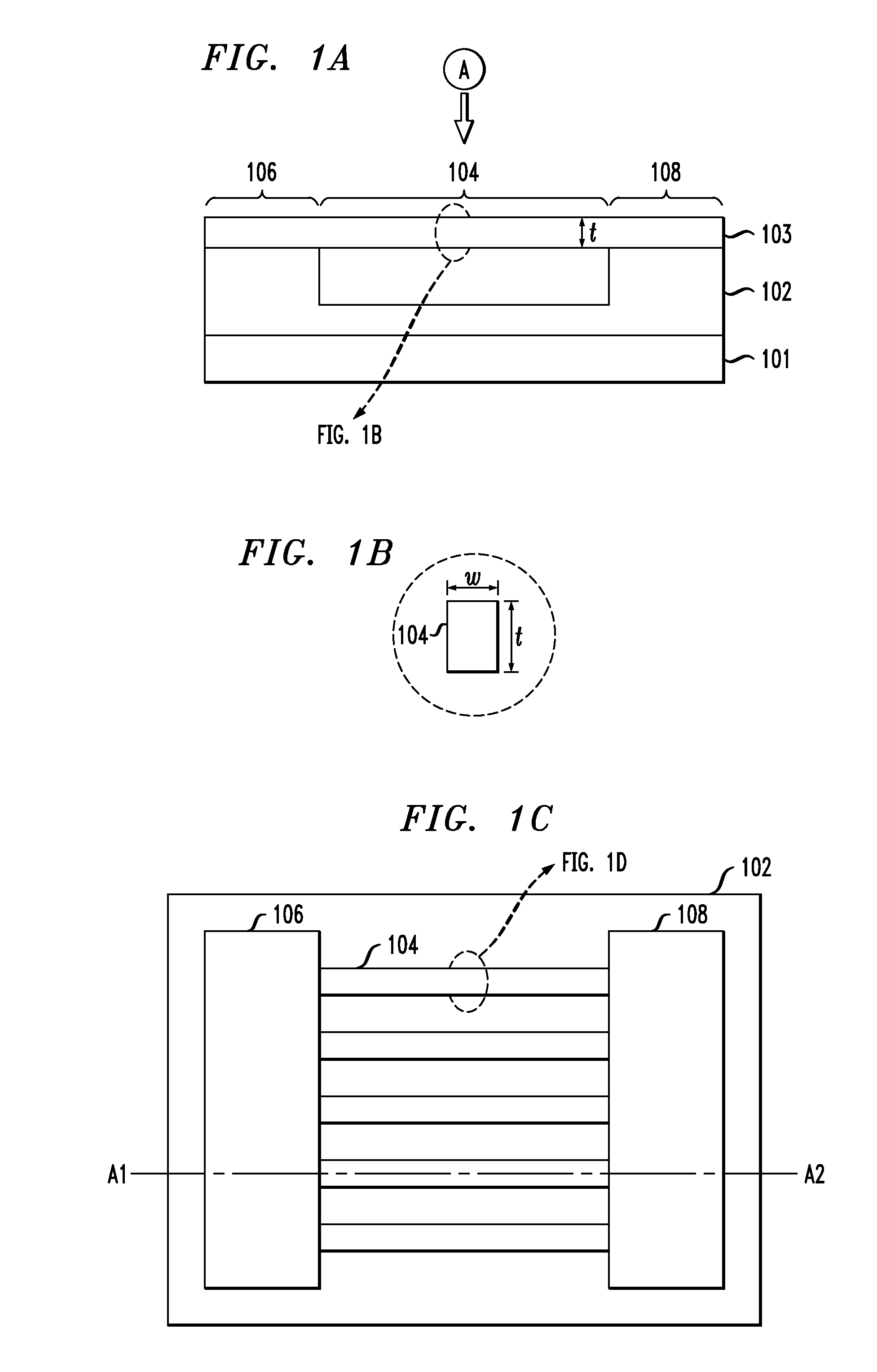
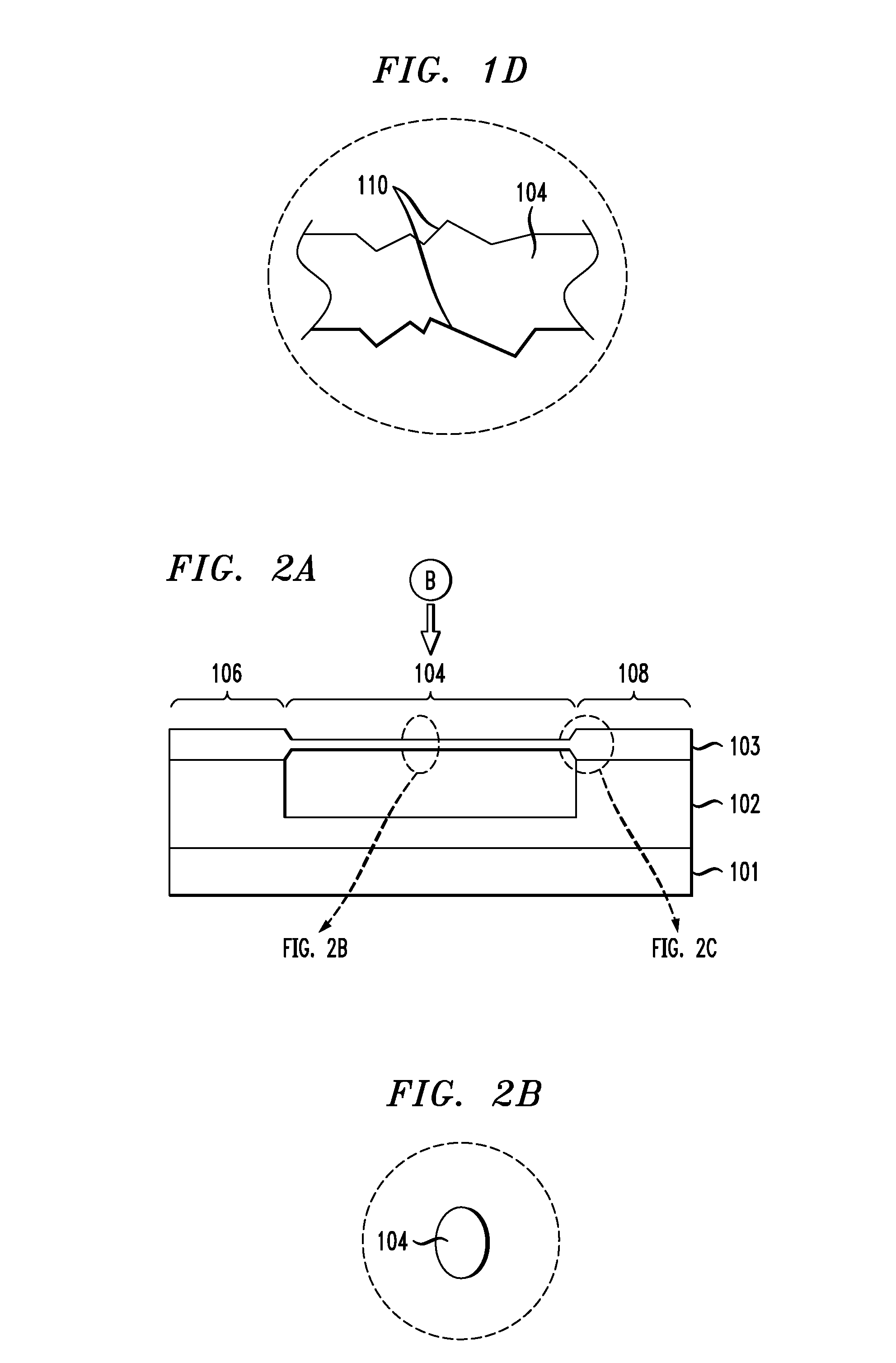
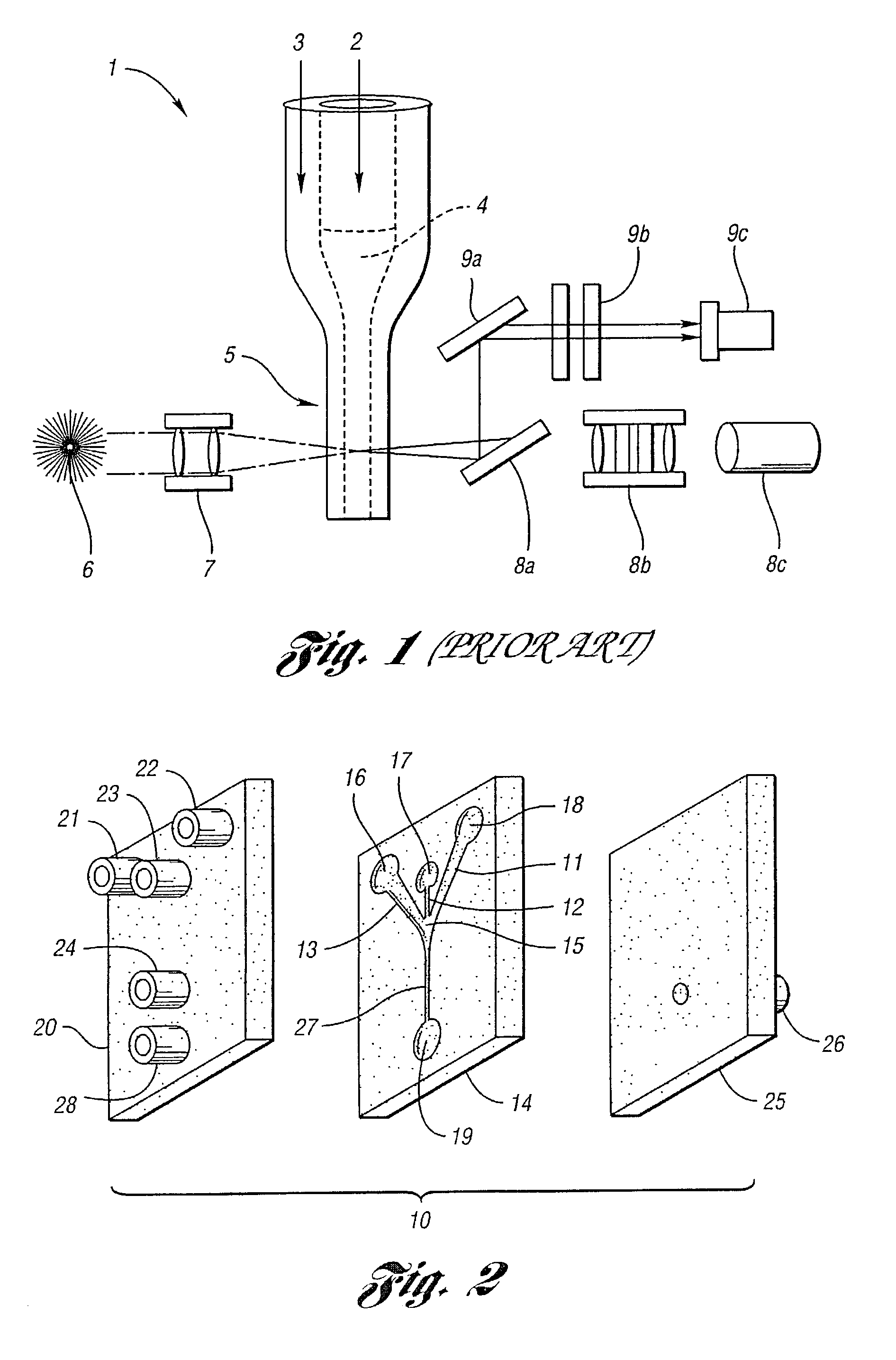
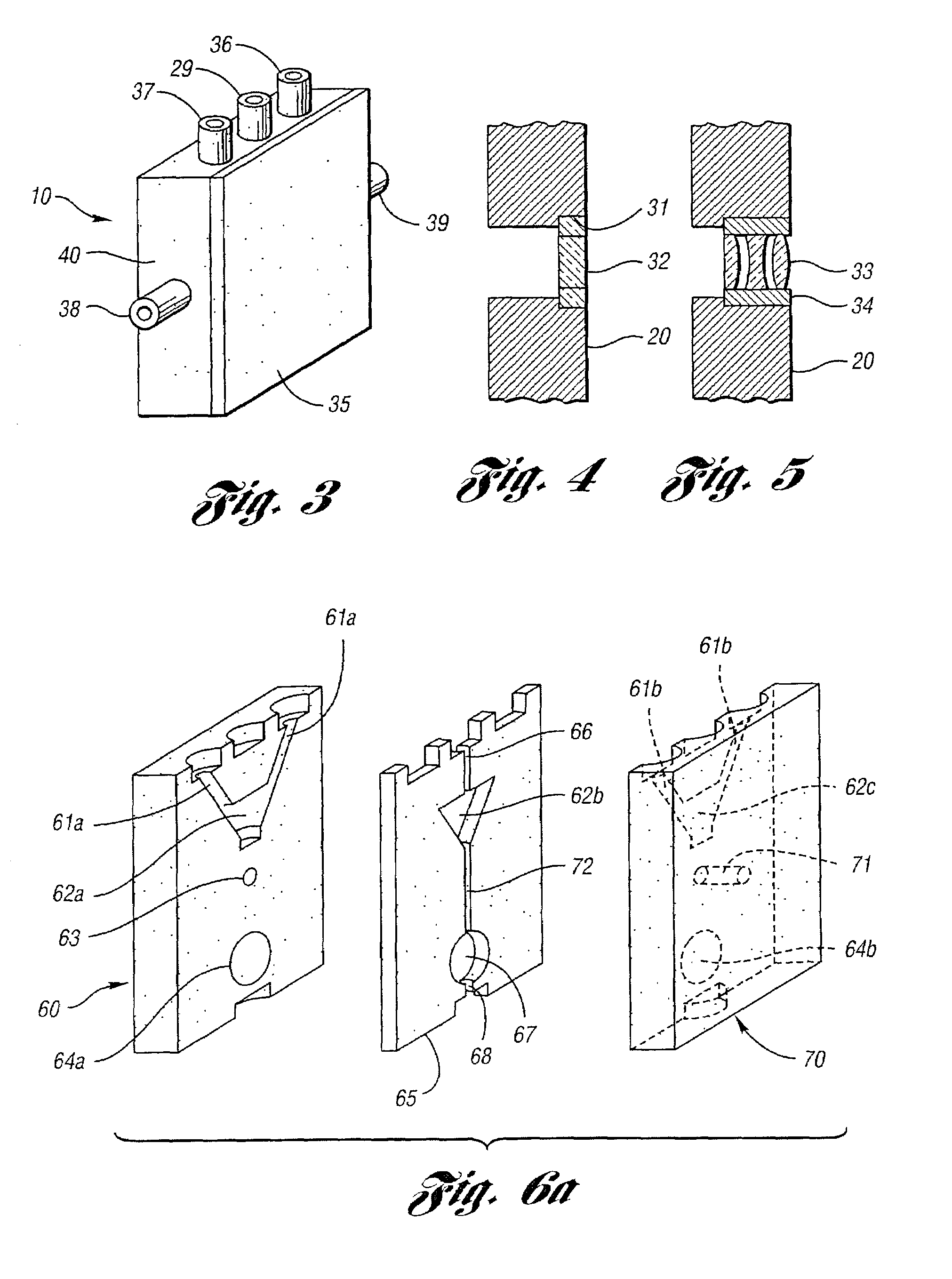
Personal fit medical implants and orthopedic surgical instruments and methods for making
InactiveUS20070118243A1Minimizing Ni toxicityImprove visualizationElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPersonalizationManufacturing technology
The present invention provides methods, techniques, materials and devices and uses thereof for custom-fitting biocompatible implants, prosthetics and interventional tools for use on medical and veterinary applications. The devices produced according to the invention are created using additive manufacturing techniques based on a computer generated model such that every prosthesis or interventional device is personalized for the user having the appropriate metallic alloy composition and virtual validation of functional design for each use.
Owner:VANTUS TECH CORP
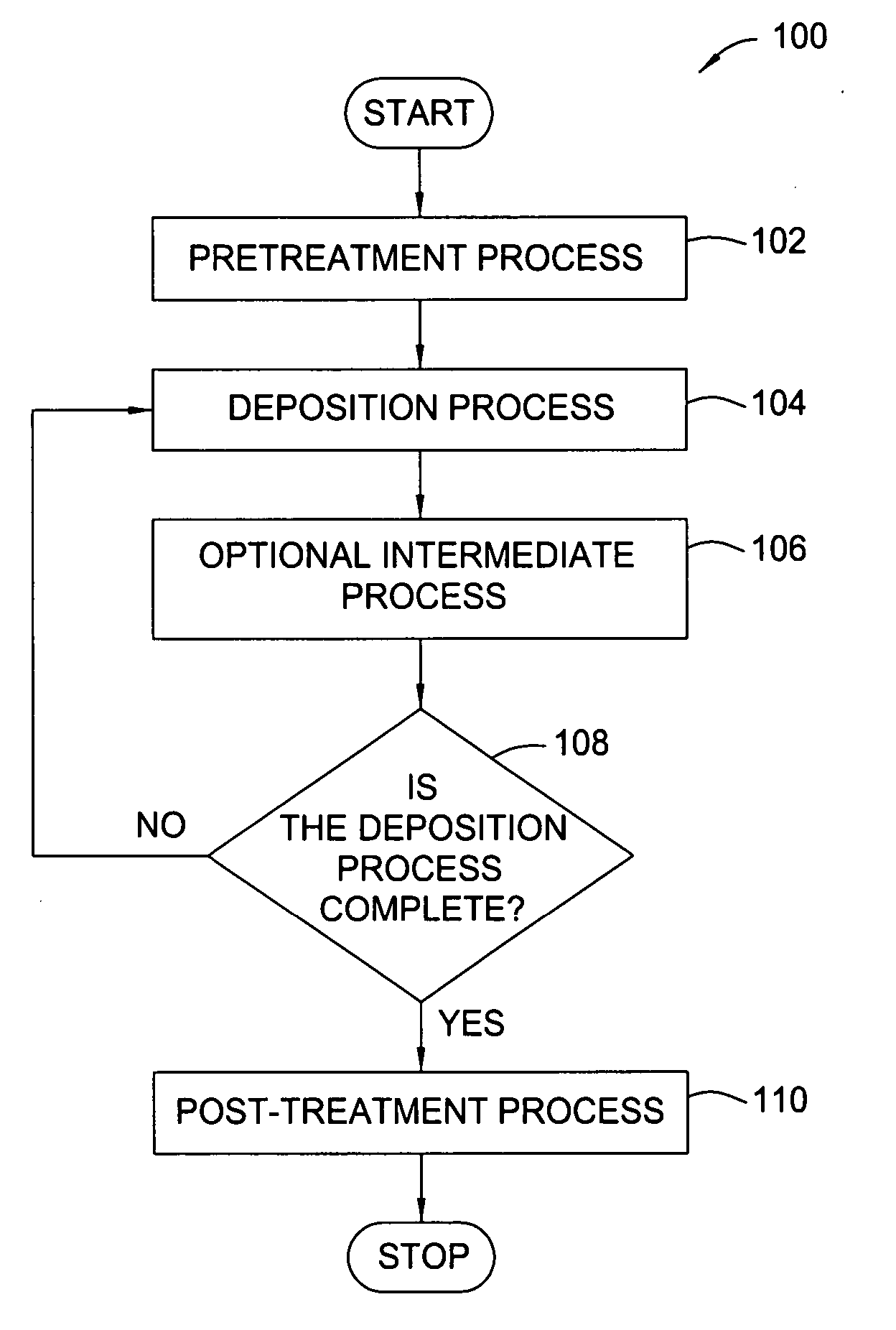
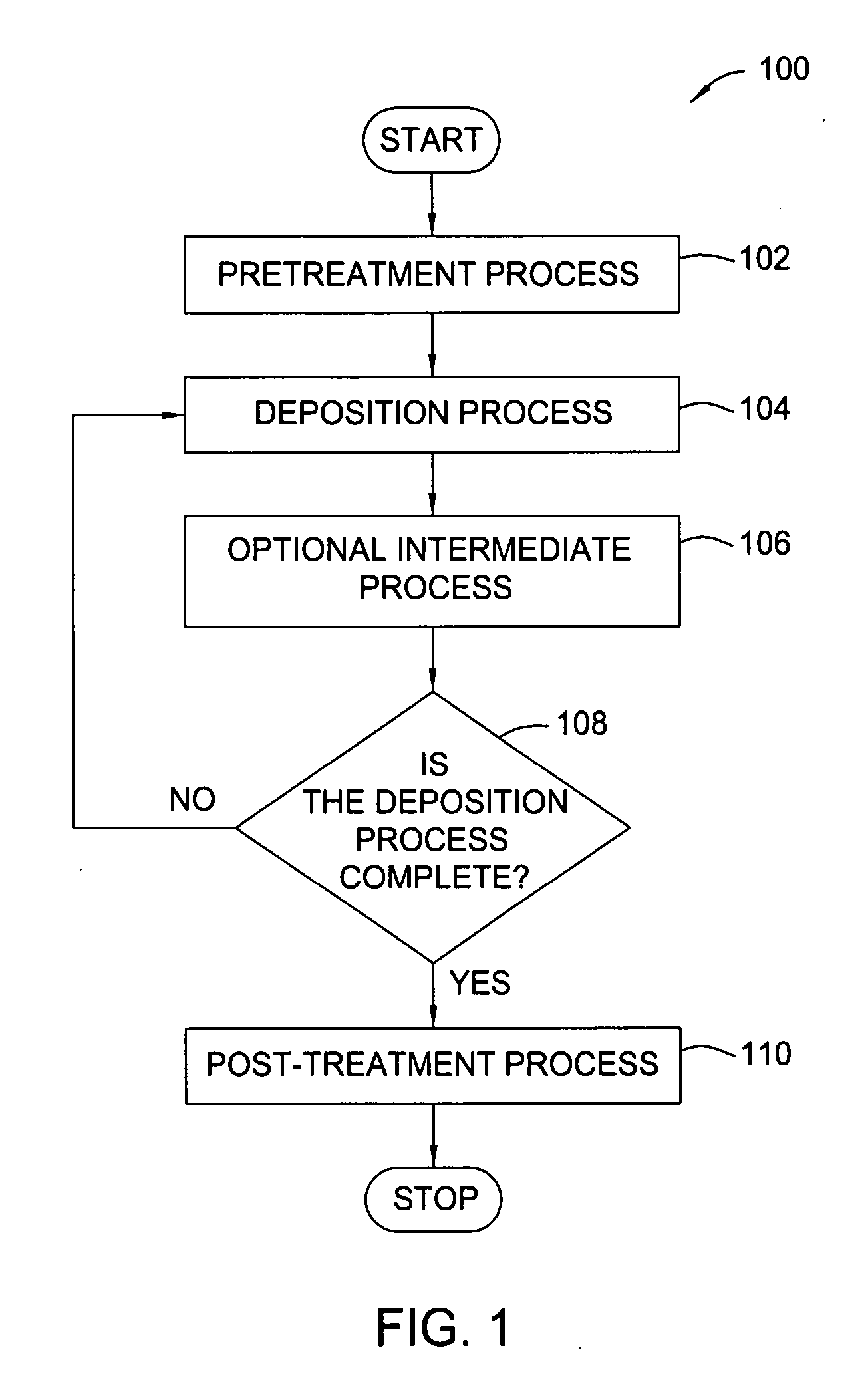
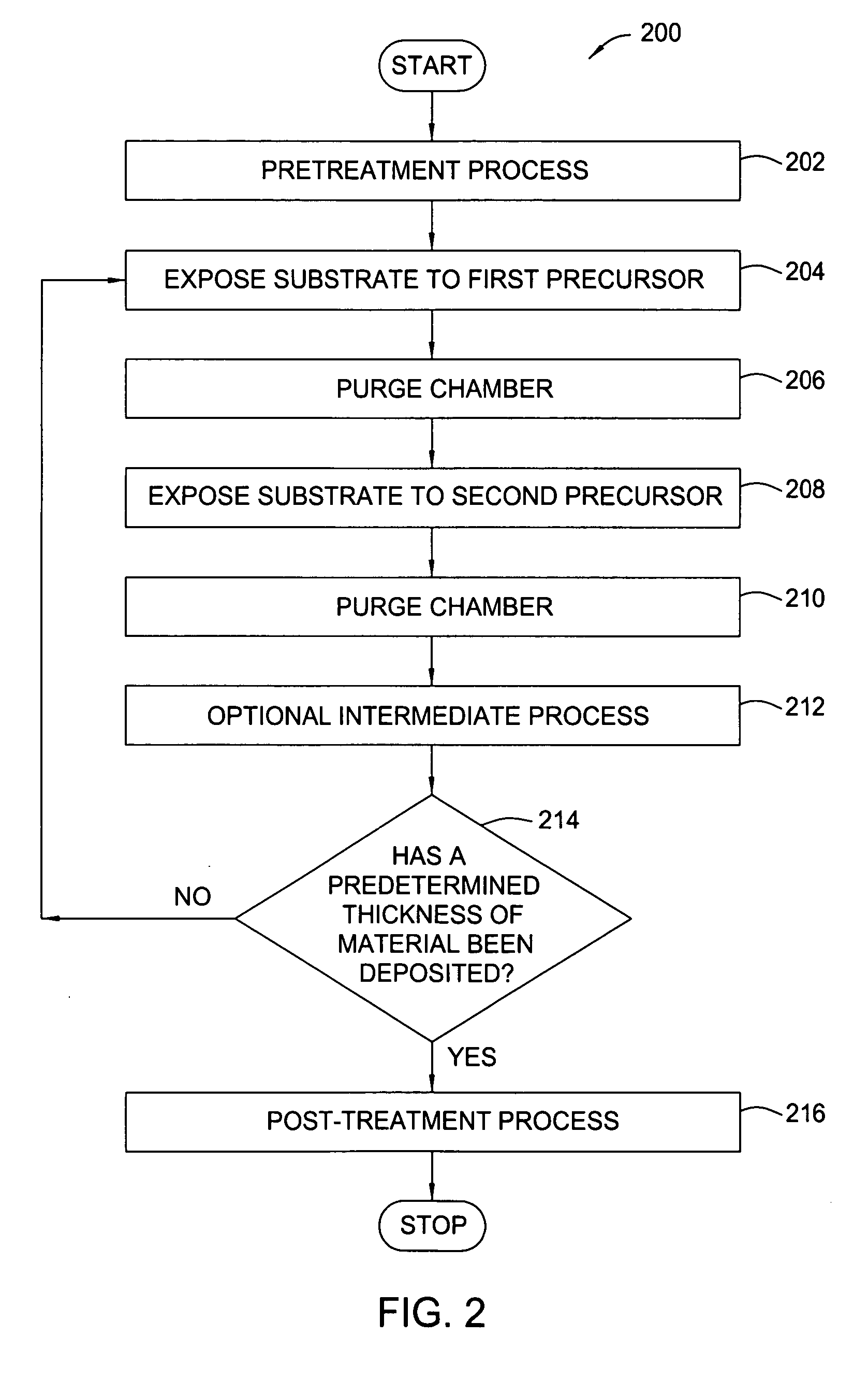
Treatment processes for a batch ALD reactor
Embodiments of the invention provide treatment processes to reduce substrate contamination during a fabrication process within a vapor deposition chamber. A treatment process may be conducted before, during or after a vapor deposition process, such as an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. In one example of an ALD process, a process cycle, containing an intermediate treatment step and a predetermined number of ALD cycles, is repeated until the deposited material has a desired thickness. The chamber and substrates may be exposed to an inert gas, an oxidizing gas, a nitriding gas, a reducing gas or plasmas thereof during the treatment processes. In some examples, the treatment gas contains ozone, water, ammonia, nitrogen, argon or hydrogen. In one example, a process for depositing a hafnium oxide material within a batch process chamber includes a pretreatment step, an intermediate step during an ALD process and a post-treatment step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
PVC nanocomposite manufacturing technology and applications
InactiveUS20080194736A1Material nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPolymer scienceManufacturing technology
The present invention relates to a process and a product of forming polymer (especially PVC) nanocomposites with a variety of nanofillers. The present invention provides a method for forming a polymer nanocomposite, comprising powder mixing a composition comprising polymer resin, a nanofiller, and a coupling agent for a residence time of about 4 to about 8 minutes to form a dry blend and extruding the dry blend in an extrusion process. Additionally, the present invention relates to a polymer nanocomposite formed by a process, comprising powder mixing a polymer resin, a nanofiller, and a coupling agent for a residence time of about 4 to about 8 minutes to form a dry blend and extruding the dry blend in an extrusion process to achieve homogeneous dispersion of nanofillers in the polymer matrix.
Owner:FORMOSA PLASTICCS CORP
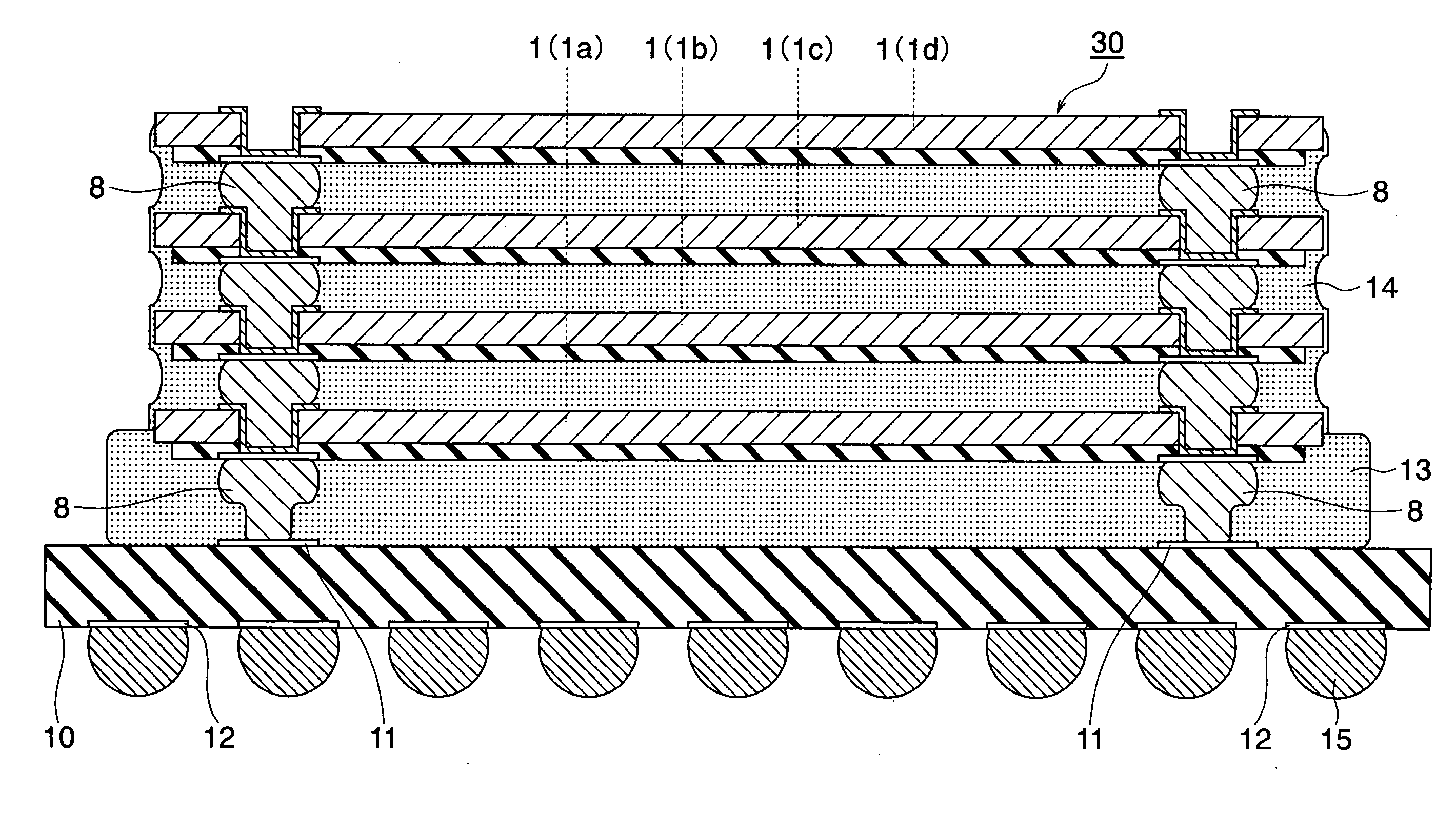
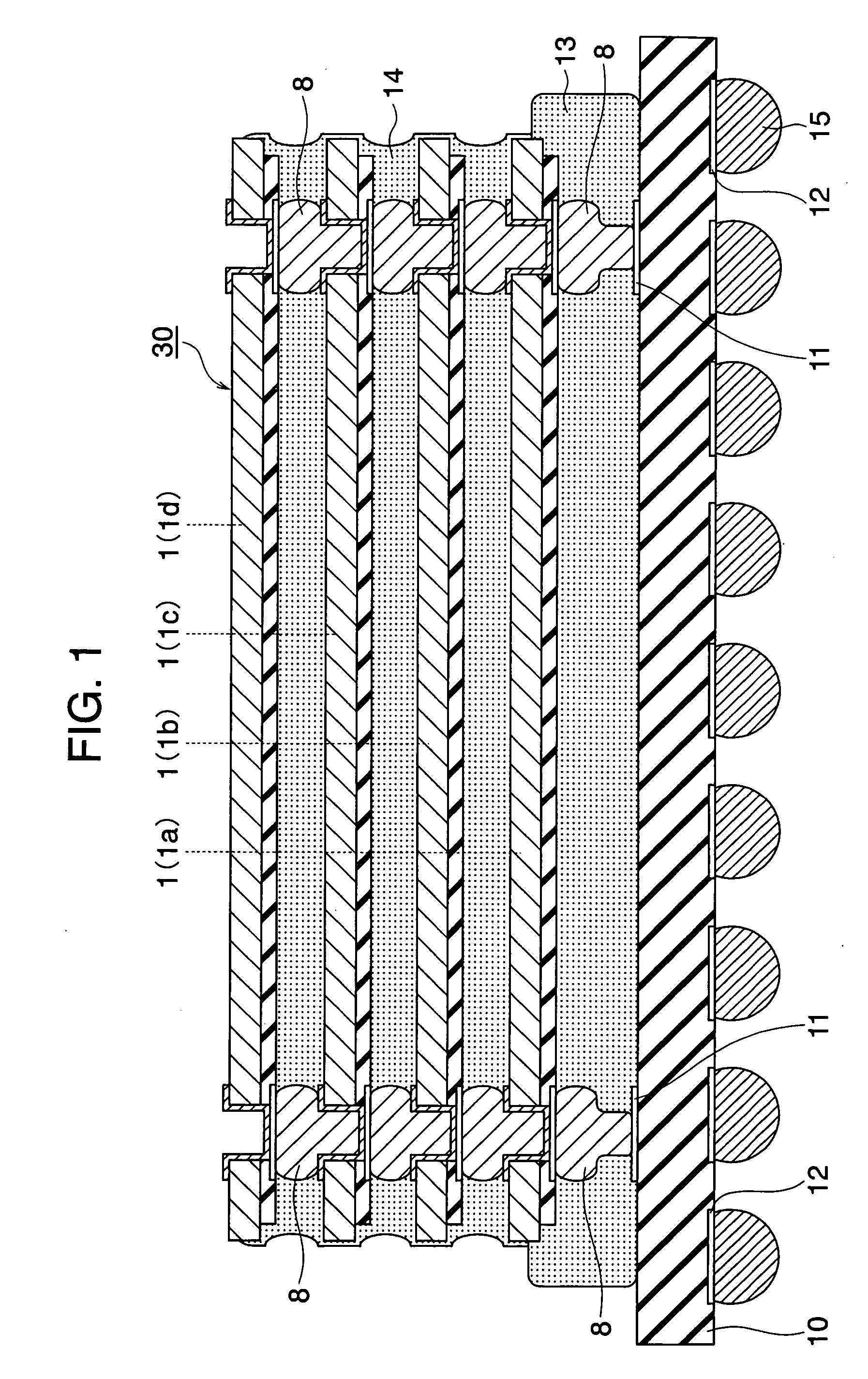
Semiconductor device and manufacturing process therefor
InactiveUS20050263869A1Improve reliabilityHigh practicabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologySurface layer
To provide a very-low-cost and short-TAT connection structure superior in connection reliability in accordance with a method for three-dimensionally connecting a plurality of semiconductor chips at a shortest wiring length by using a through-hole electrode in order to realize a compact, high-density, and high-function semiconductor system. The back of a semiconductor chip is decreased in thickness up to a predetermined thickness through back-grinding, a hole reaching a surface-layer electrode is formed at a back position corresponding to a device-side external electrode portion through dry etching, a metallic deposit is applied to the sidewall of the hole and the circumference of the back of the hole, a metallic bump (protruded electrode) of another semiconductor chip laminated on the upper side is deformation-injected into the through-hole by compression bonding, and the metallic bump is geometrically caulked and electrically connected to the inside of a through-hole formed in an LSI chip. It is possible to realize a unique connection structure having a high reliability in accordance with the caulking action using the plastic flow of a metallic bump in a very-low-cost short-TAT process and provide a three-dimensional inter-chip connection structure having a high practicability.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Manufacturing method of thin film integrated circuit device and manufacturing method of non-contact type thin film integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050148121A1Easy to disassembleEfficient use ofSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyContact type
With non-contact and contact IC chips becoming common, it is necessary to mass-produce enormous amount of IC chips, which are utilizable for human beings, animals and plants, commercial products, banknotes, and the like, at low cost. For example, it is necessary to manufacture IC chips to be applied to commercial products, banknotes, and the like at a cost of 1 to several yen per IC chip, preferably, at a cost less than 1 yen, and it is desired to realize a structure of an IC chip that can be mass-produced at low cost and a manufacturing process of the IC chip. A method of-manufacturing a thin film integrated circuit device according to the present invention includes steps of forming a peel-off layer over a thermally oxidized silicon substrate, forming a plurality of thin film integrated circuit devices over the peel-off layer with a base film interposed therebetween, forming a groove between the plurality of thin film integrated circuit devices, and separating the plurality of thin film integrated circuit devices by introducing one of a gas and a liquid including halogen fluoride into the groove to remove the peel-off layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
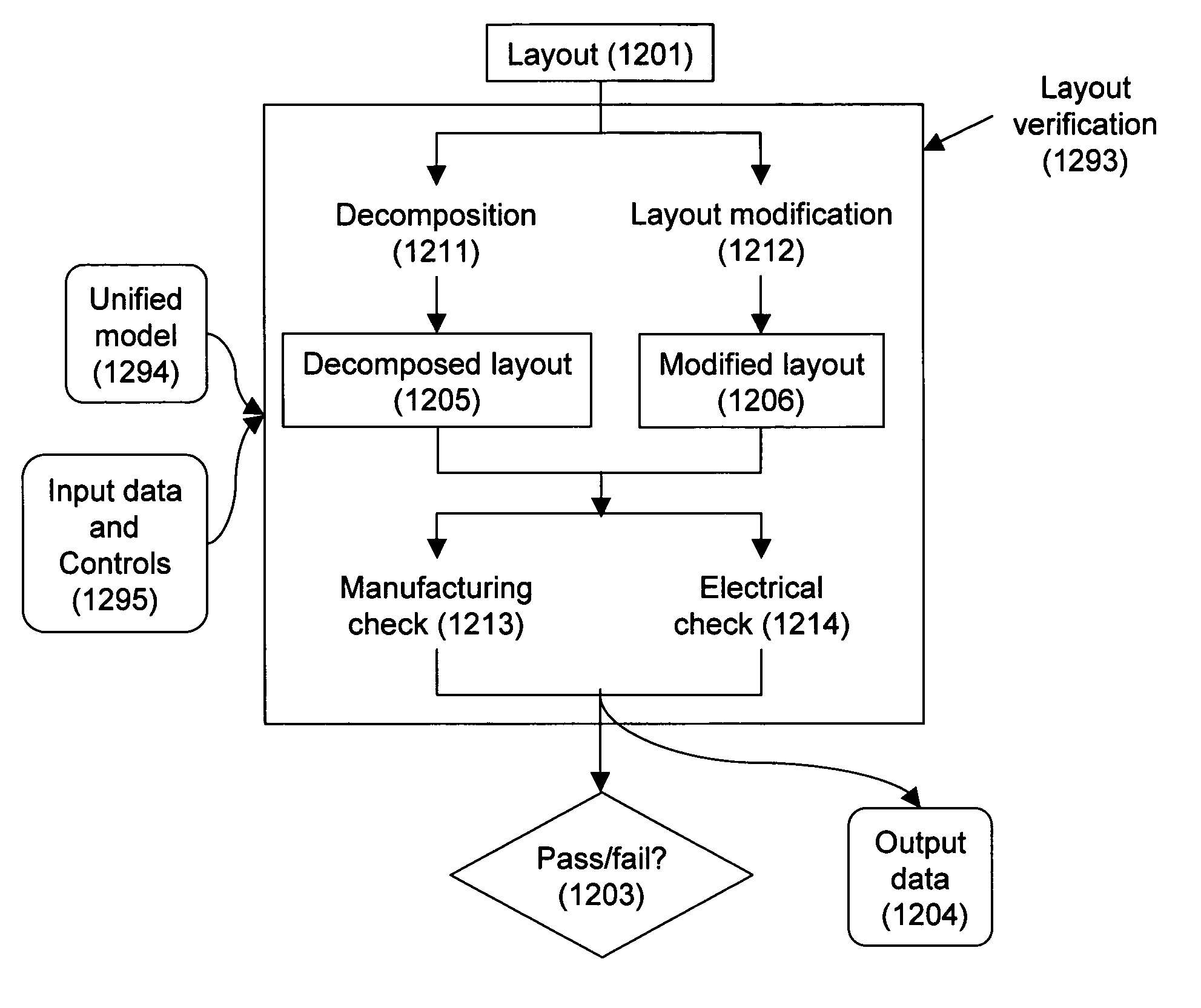
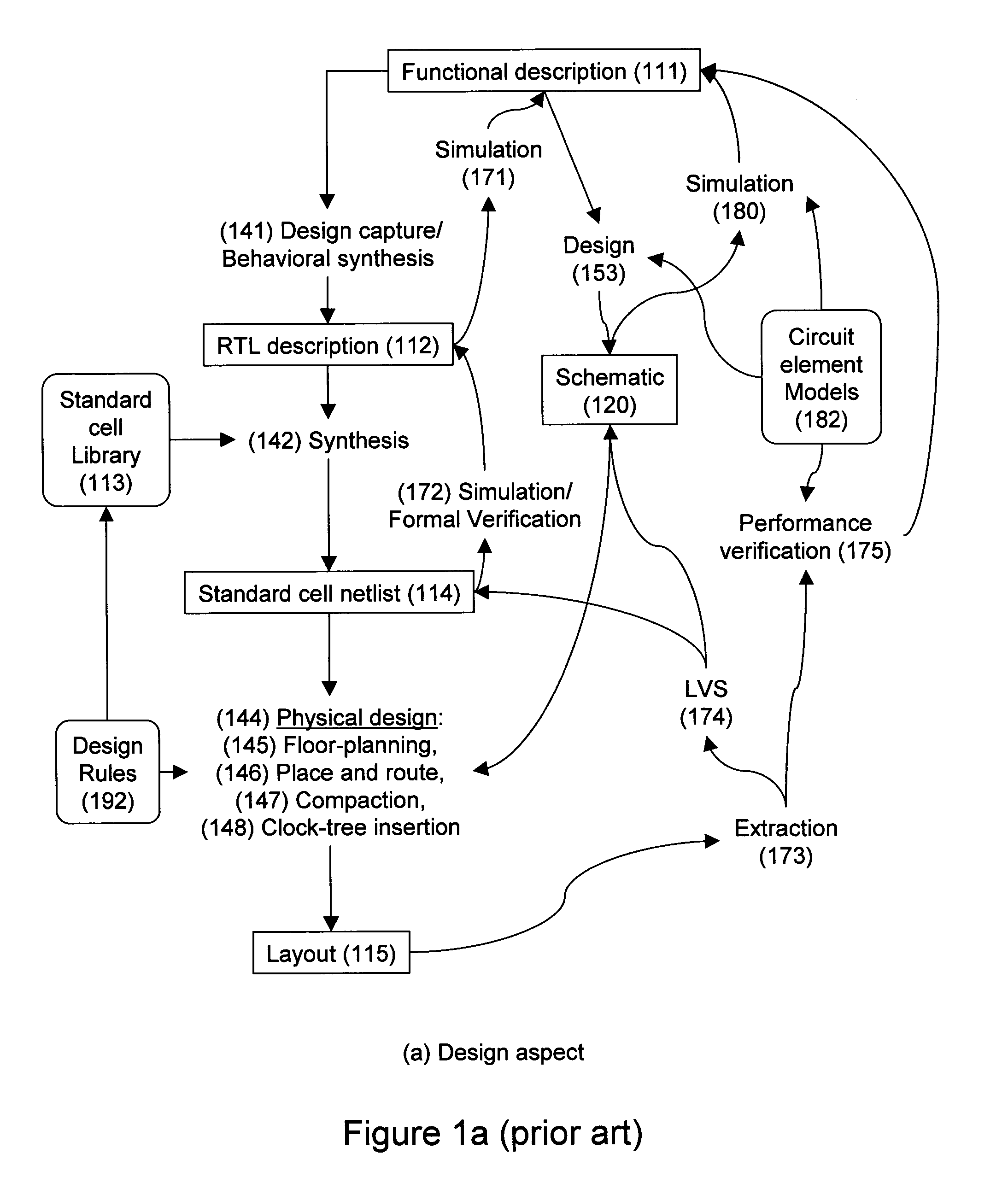
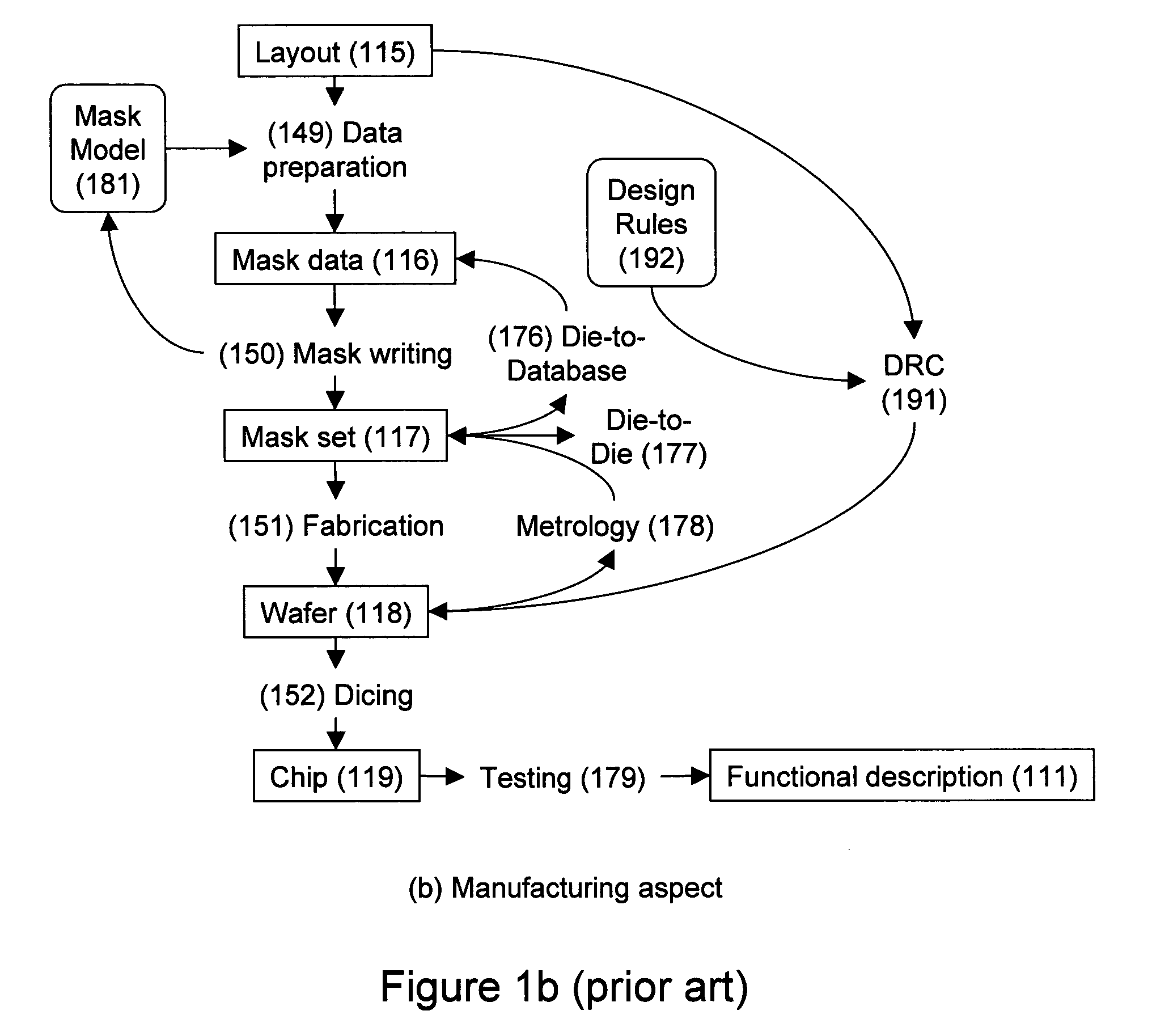
Design-manufacturing interface via a unified model
ActiveUS20050076316A1Create additionalImprove accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationManufacturing technologyMiniaturization
Subtleties of advanced fabrication processes and nano-scale phenomena associated with integrated circuit miniaturization have exposed the insufficiencies of design rules. Such inadequacies have adverse impact on all parts of the integrated circuit creation flow where design rules are used. In addition, segregation of the various layout data modification steps required for deep sub-micrometer manufacturing are resulting in slack and inefficiencies. This invention describes methods to improve integrated circuit creation via the use of a unified model of fabrication processes and circuit elements that can complement or replace design rules. By capturing the interdependence among fabrication processes and circuit elements, the unified model enables efficient layout generation, resulting in better integrated circuits.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Circuit layout methodology using a shape processing application
InactiveUS7188322B2Low costSmall sizeCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsManufacturing technologySoftware engineering
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Complex Coil And Manufacturing Techniques
Owner:TERUMO KK
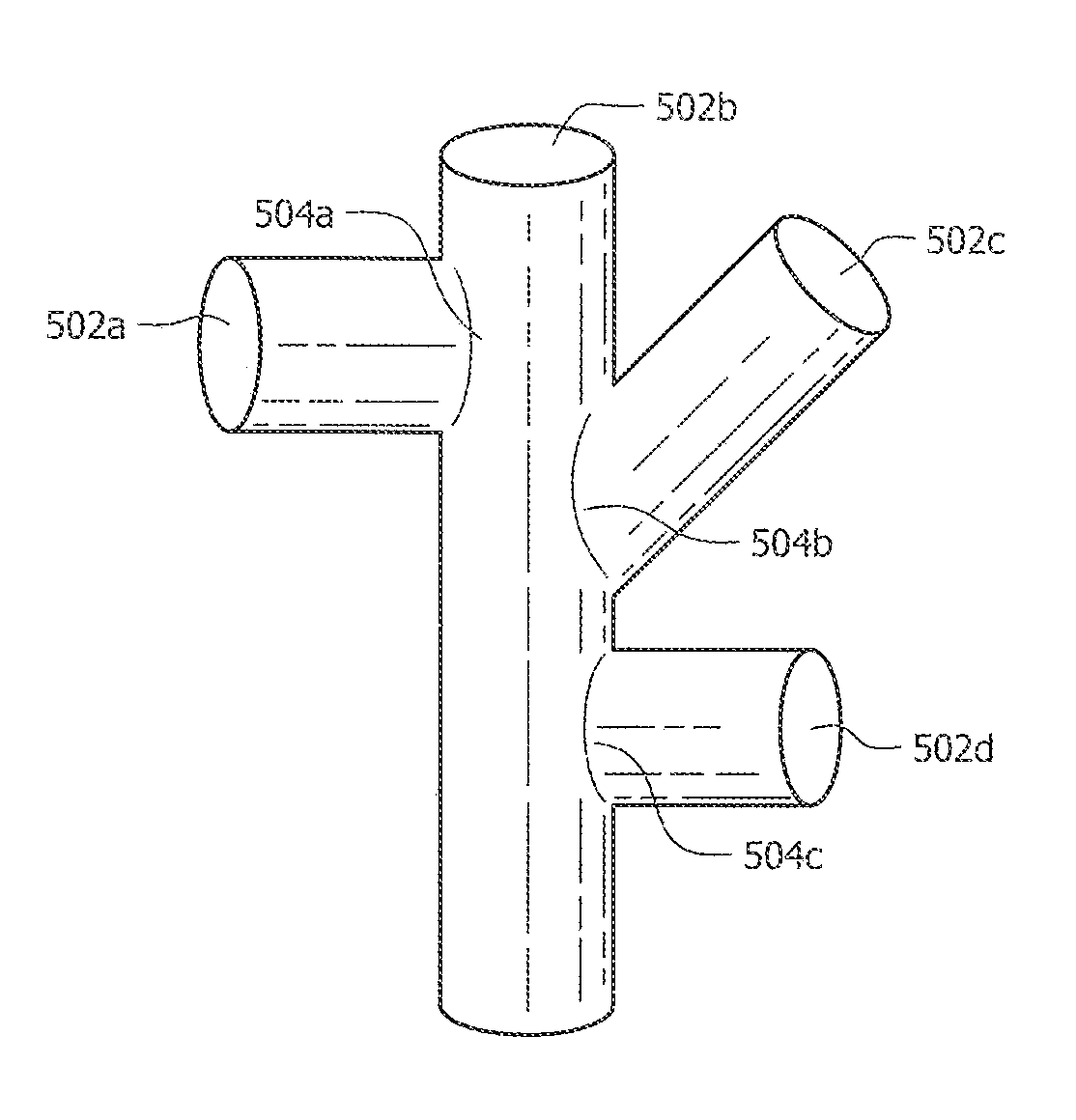
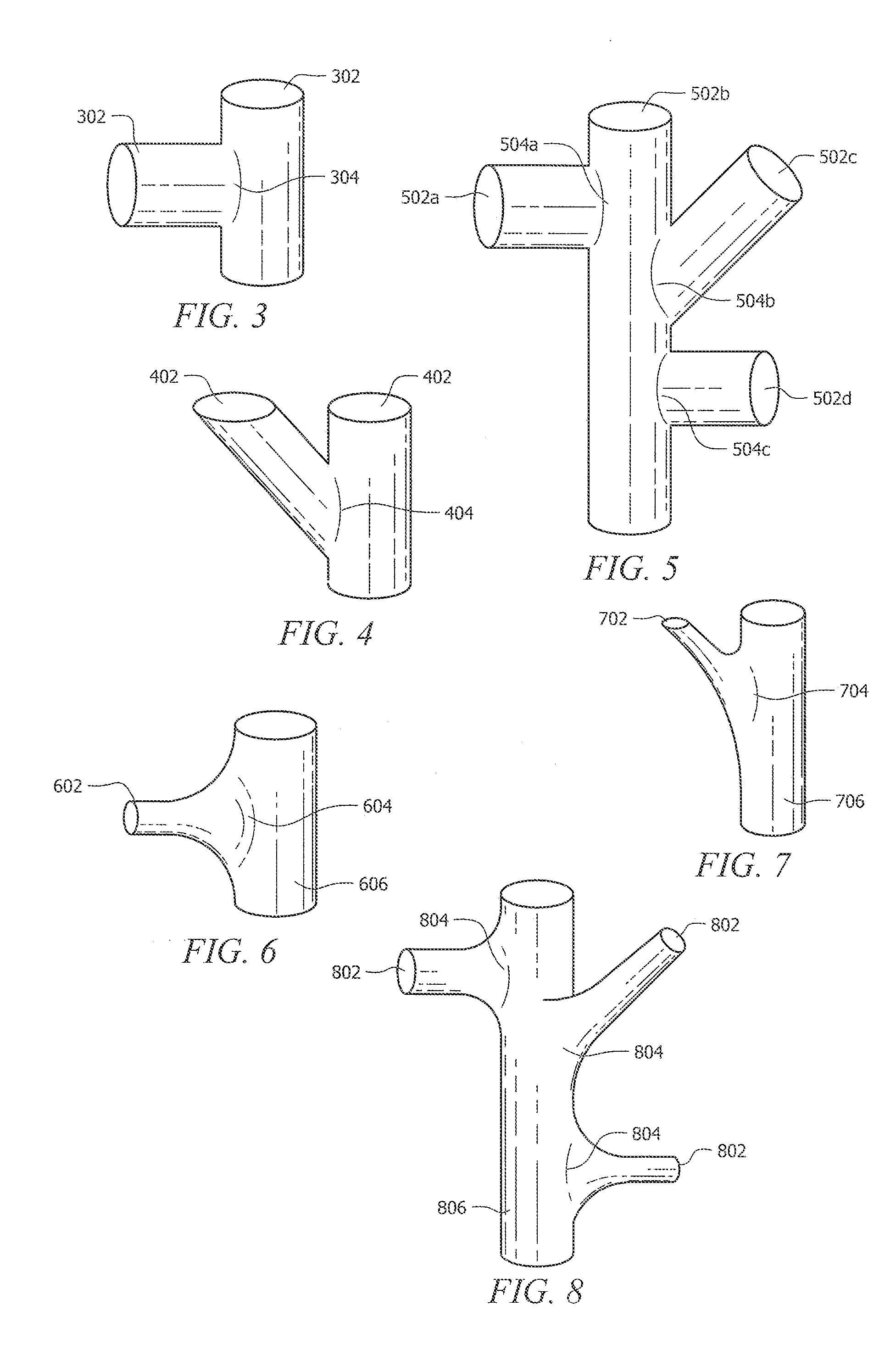
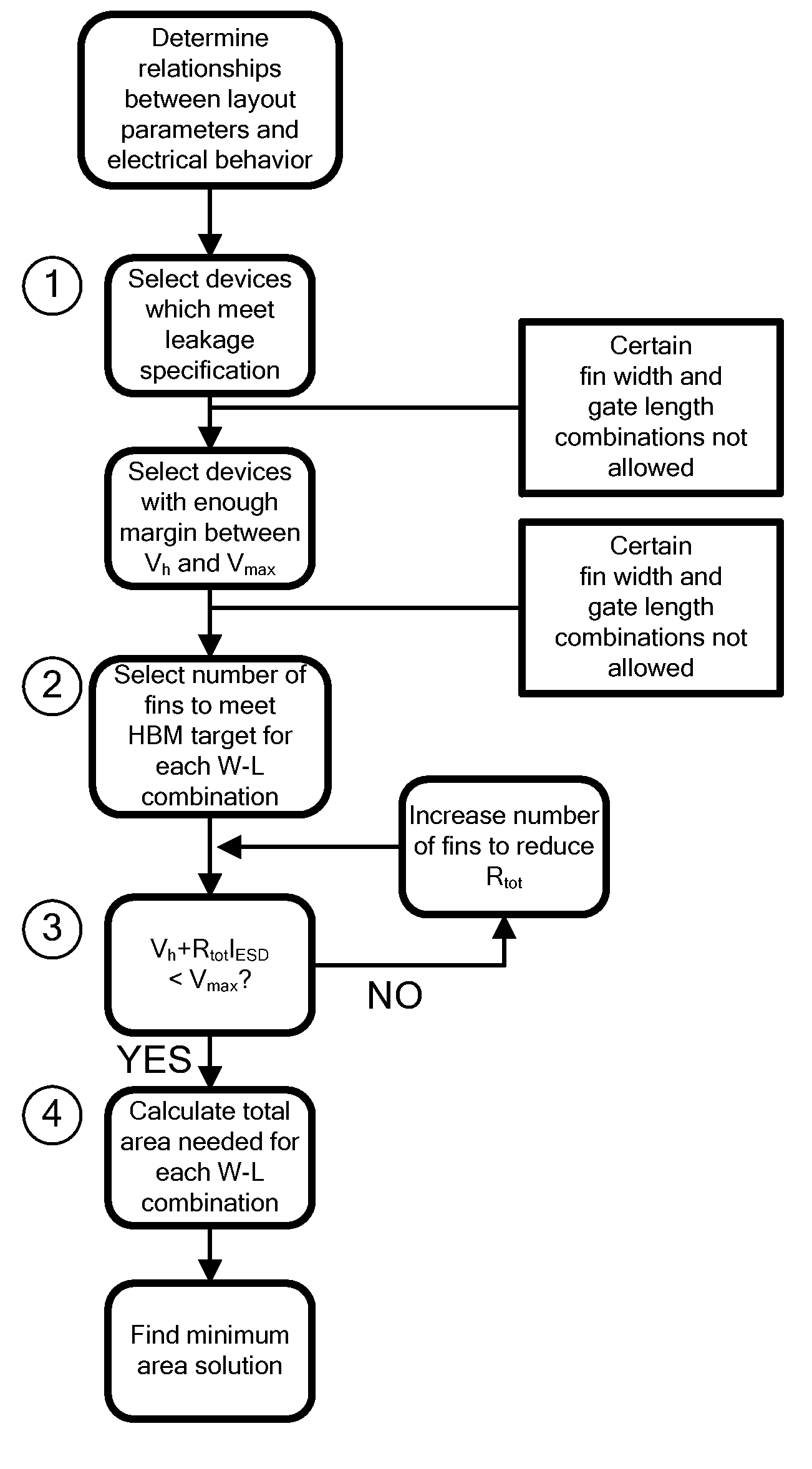
Design Methodology for MuGFET ESD Protection Devices
InactiveUS20090280582A1Easy to optimizePromote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
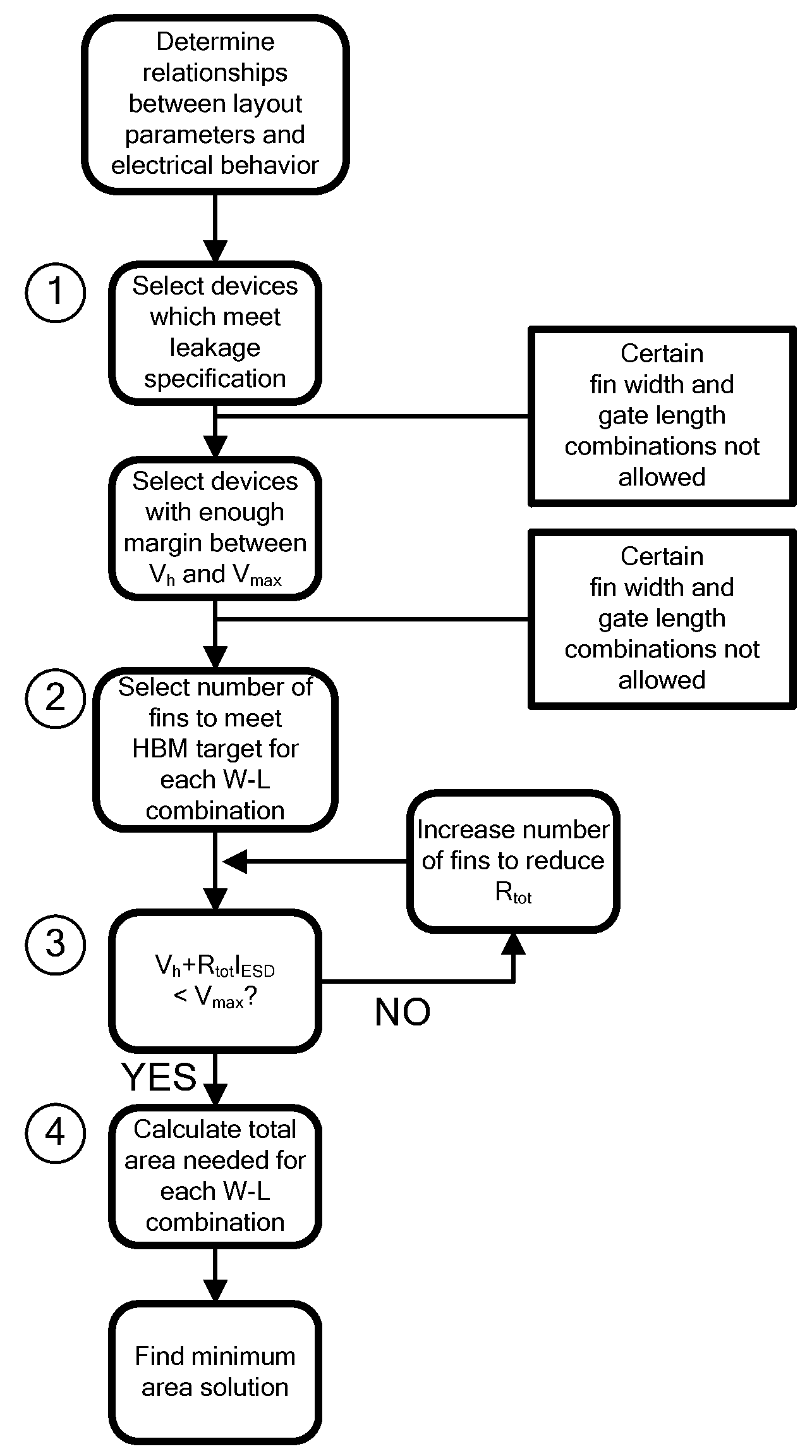
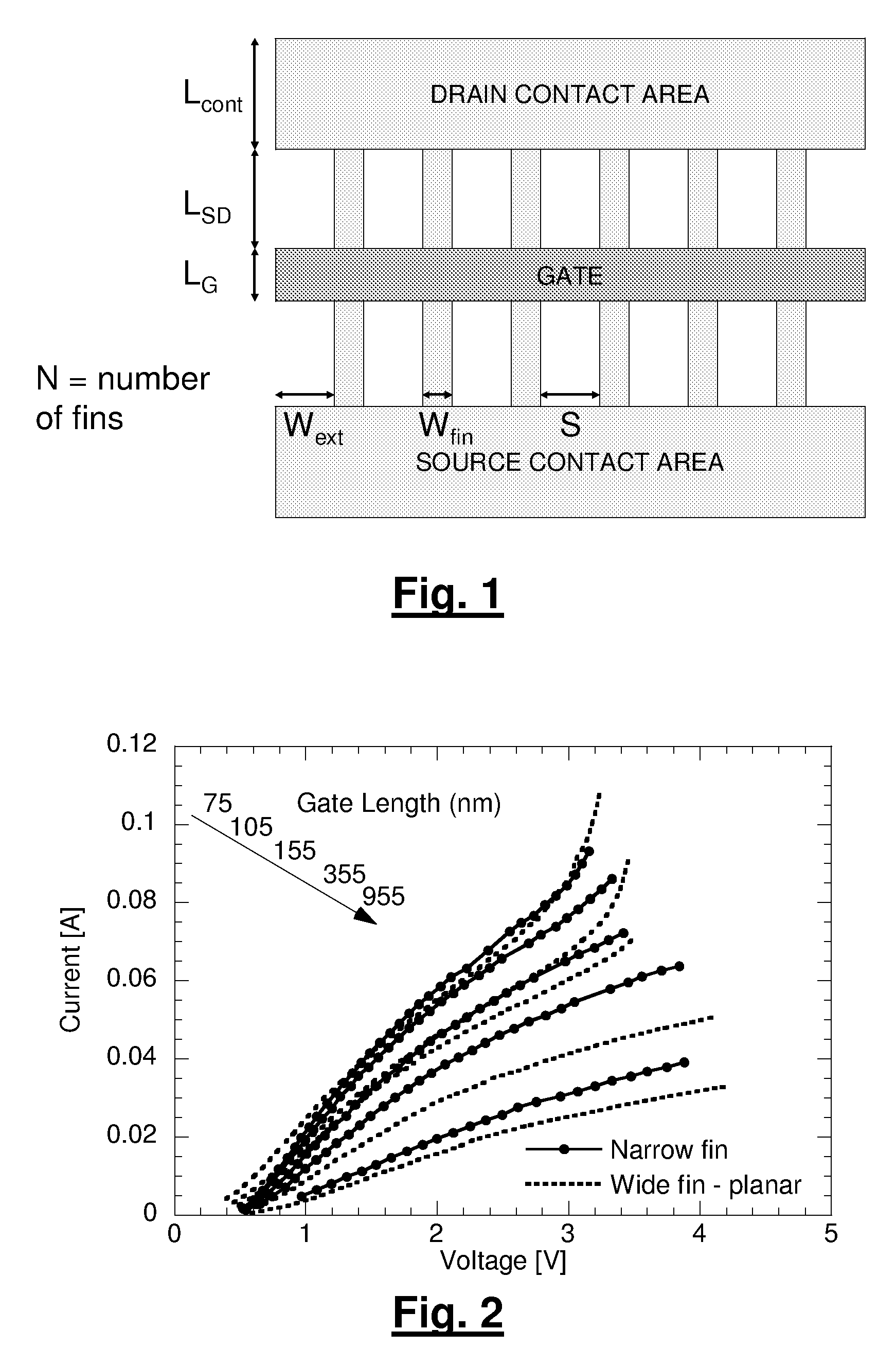
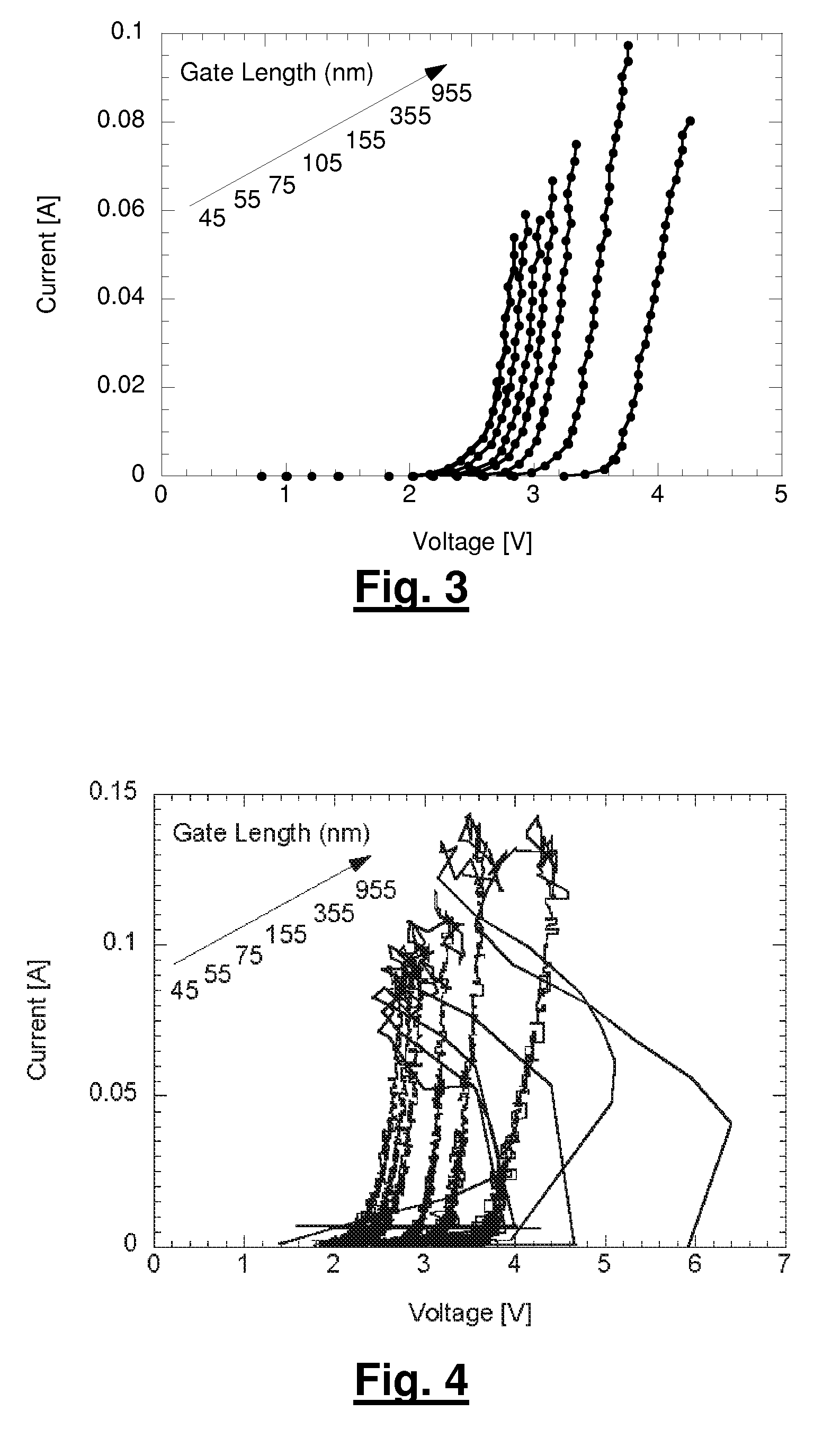
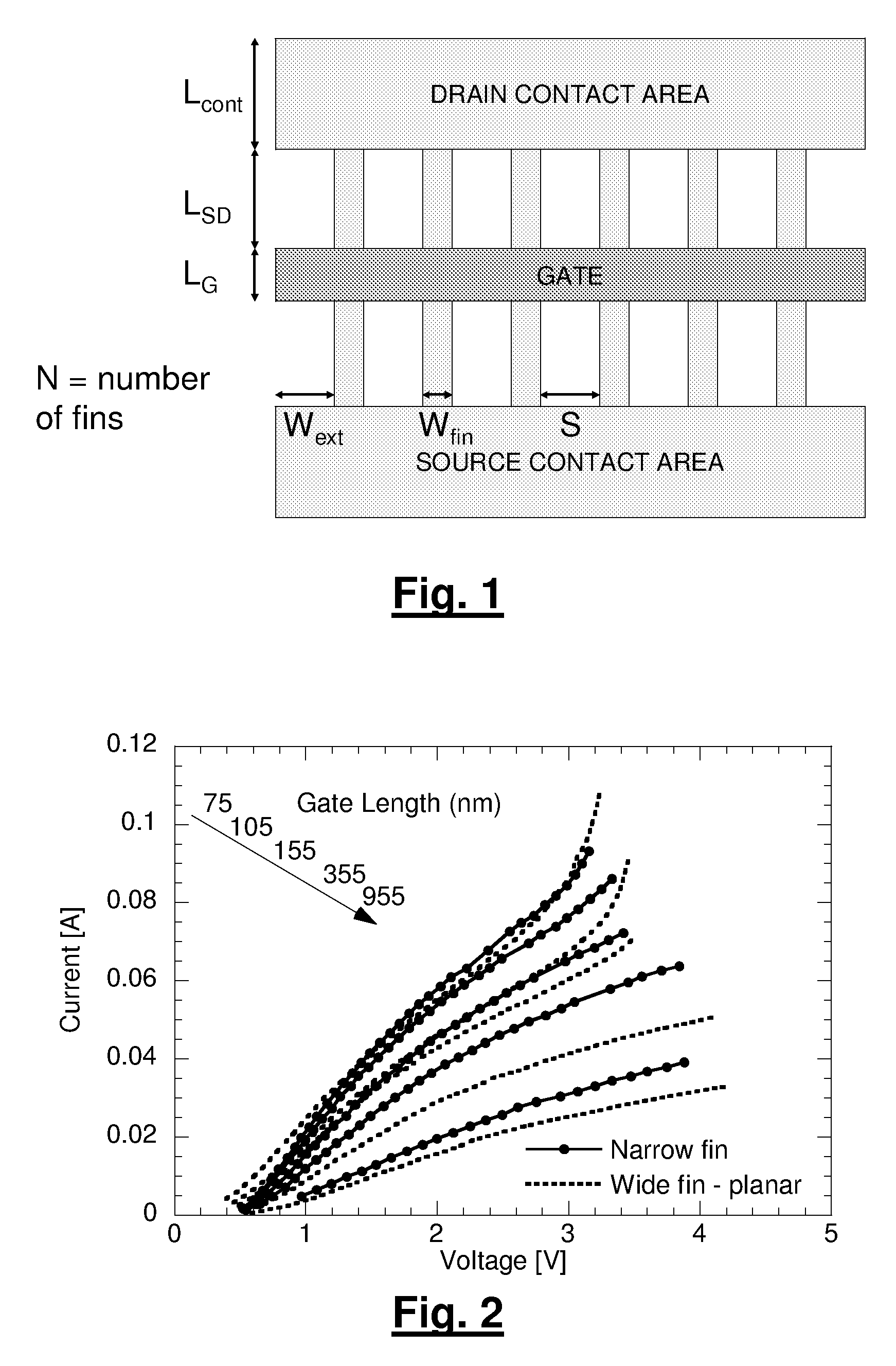
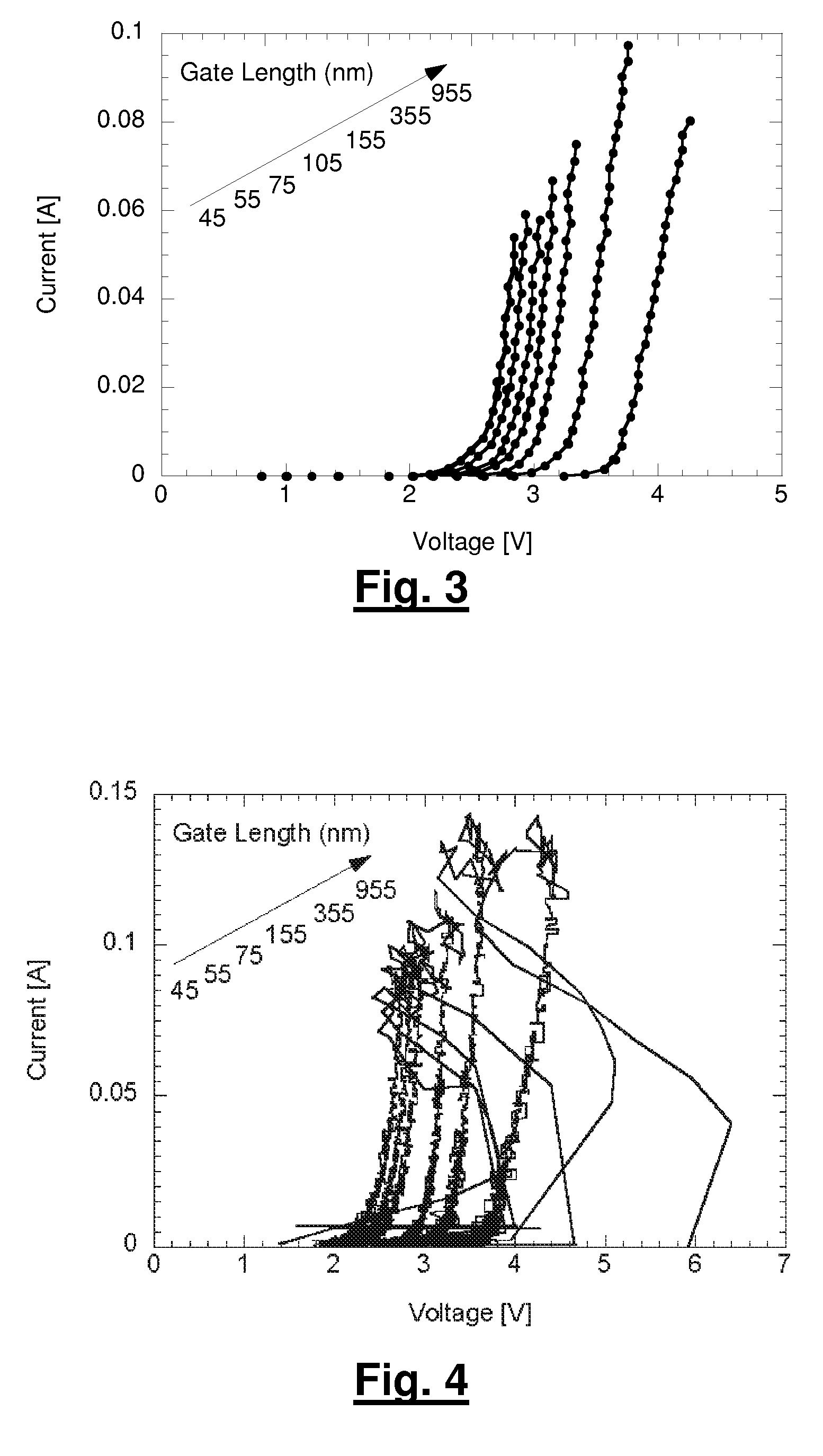
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
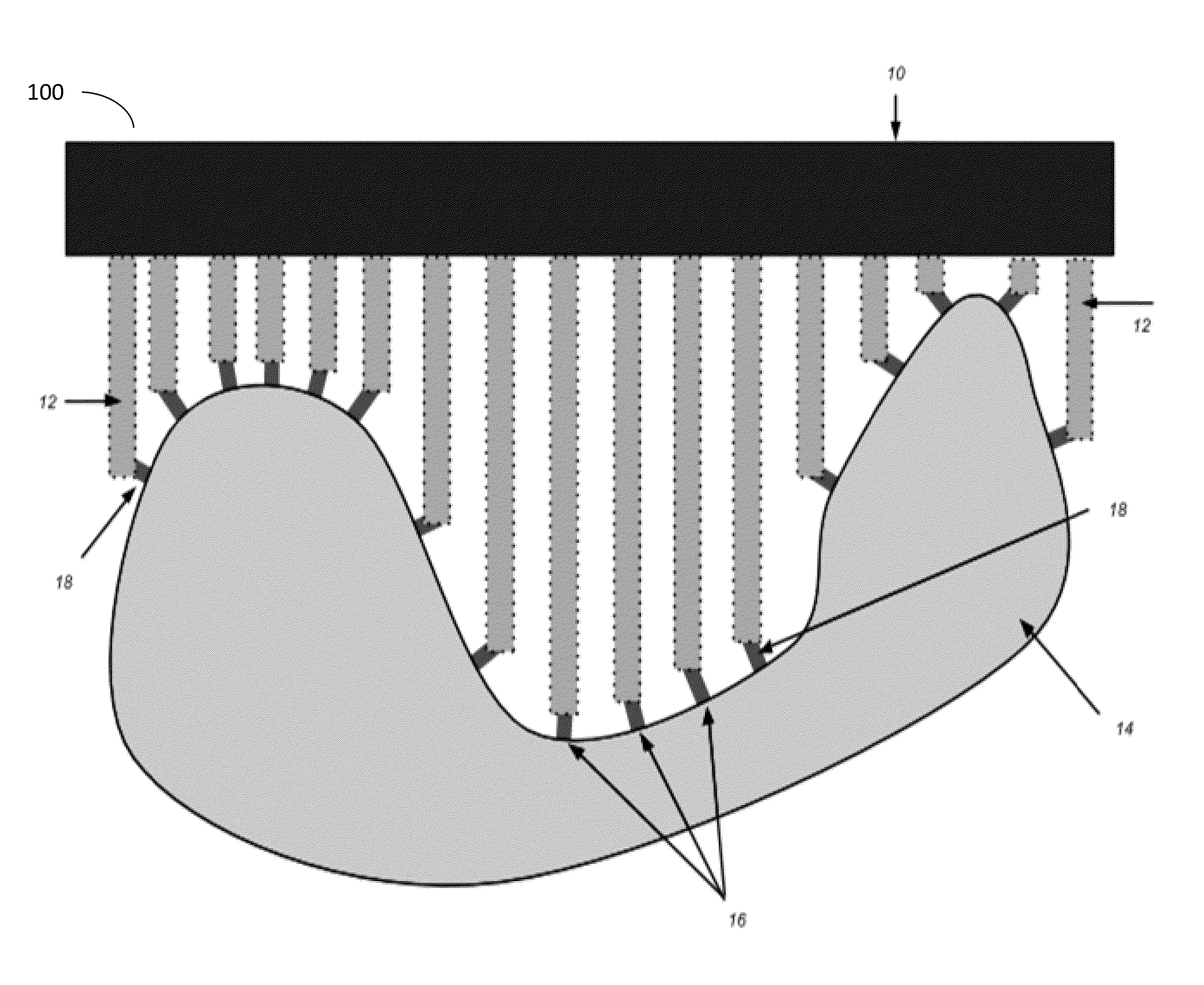
Porous implant structures
InactiveUS20120215310A1High porosityHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical adhesivesNODALManufacturing technology
Porous biocompatible structures suitable for use as medical implants and methods for fabricating such structures are disclosed. The disclosed structures may be fabricated using rapid manufacturing techniques. The disclosed porous structures has a plurality of struts and nodes where no more than two struts intersect one another to form a node. Further, the nodes can be straight, curved, portions that are curved and / or straight. The struts and nodes can form cells which can be fused or sintered to at least one other cell to form a continuous reticulated structure for improved strength while providing the porosity needed for tissue and cell in-growth.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Design methodology for MuGFET ESD protection devices
InactiveUS7923266B2Promote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Partially patterned lead frames and methods of making and using the same in semiconductor packaging
InactiveUS20080258278A1Reduce thicknessImprove structural rigiditySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingBonding process
A method of making a lead frame and a partially patterned lead frame package with near-chip scale packaging lead-count, wherein the method lends itself to better automation of the manufacturing line and improved quality and reliability of the packages produced therefrom. A major portion of the manufacturing process steps is performed with a partially patterned strip of metal formed into a web-like lead frame on one side so that the web-like lead frame is also rigid mechanically and robust thermally to perform without distortion or deformation during the chip-attach and wire bond processes, both at the chip level and the package level. The bottom side of the metal lead frame is patterned to isolate the chip-pad and the wire bond contacts only after the front side, including the chip and wires, is hermetically sealed with an encapsulant. The resultant package being electrically isolated enables strip testing and reliable singulation.
Owner:UNISEM M BERHAD
Solar Cell Module and Manufacturing Process Thereof
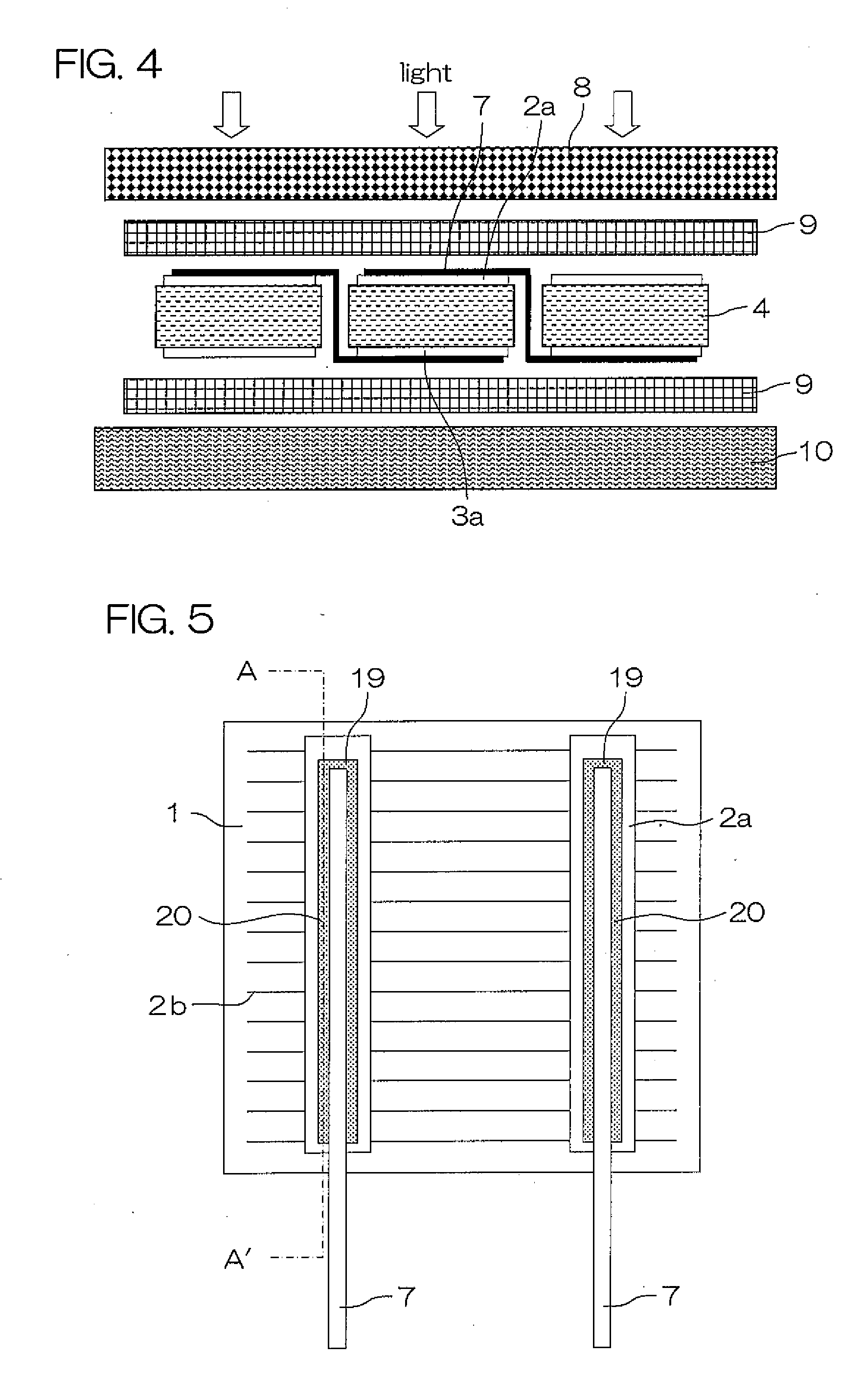
InactiveUS20070235077A1Final product manufactureGlass/slag layered productsPrincipal stressManufacturing technology
In a solar cell module, a solder fillet 19 is formed on an end surface on the shorter length side of a connection tab to be connected to a bus bar electrode 2a, 3a up to the height of the connection tab. The geometry of the solder fillet 19 is adjusted so that an indentation amount is 0-54% of the height or a bulge amount is 0-10% of the height, by which the maximum principal stress generated during the manufacturing process of a solar cell element 4 can be reduced, and therefore occurrences of cracks can be reduced. Also during a laminating process, breaking of the solar cell element or crack generation can be eliminated.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Multi-material stereolithography
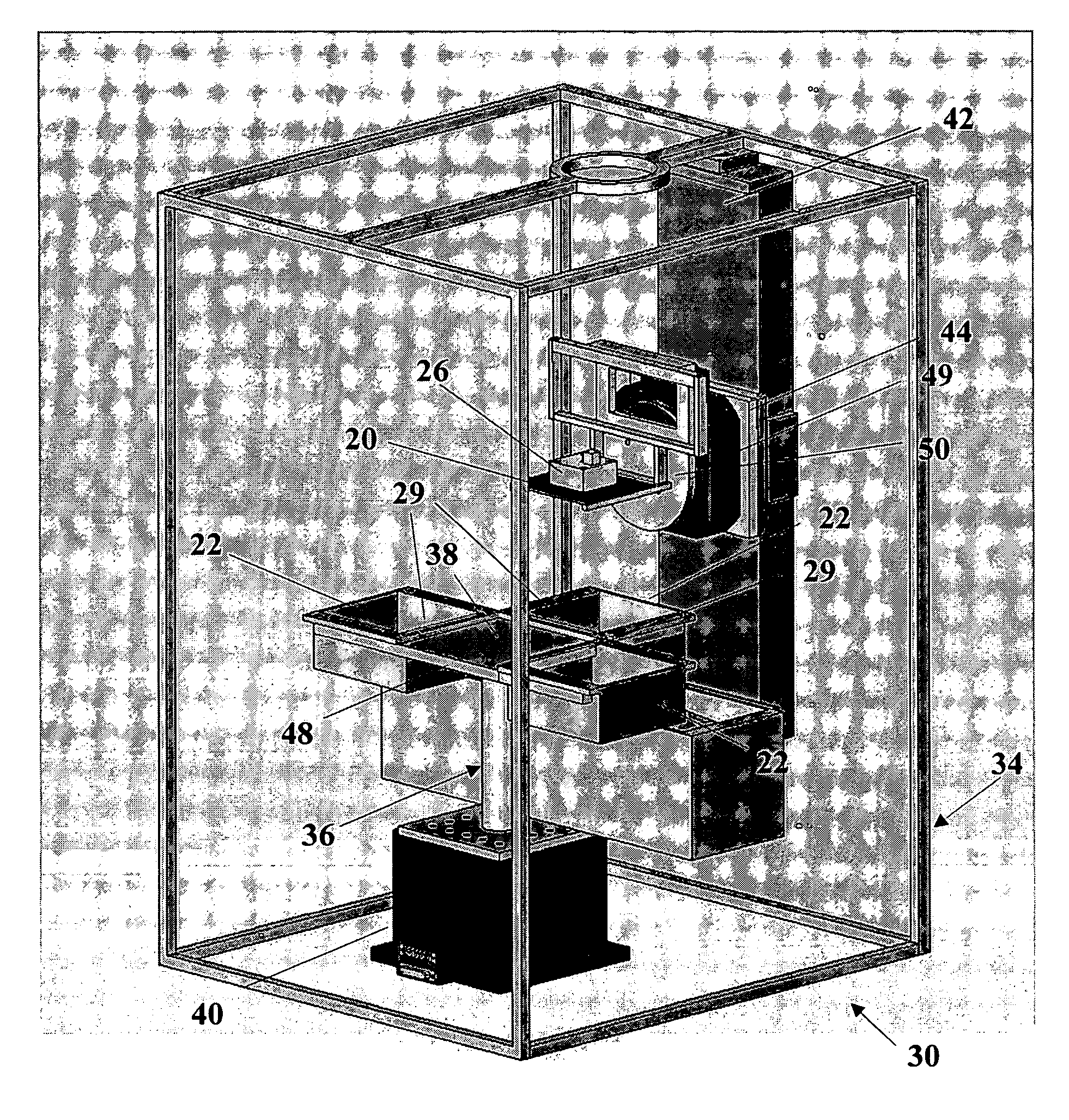
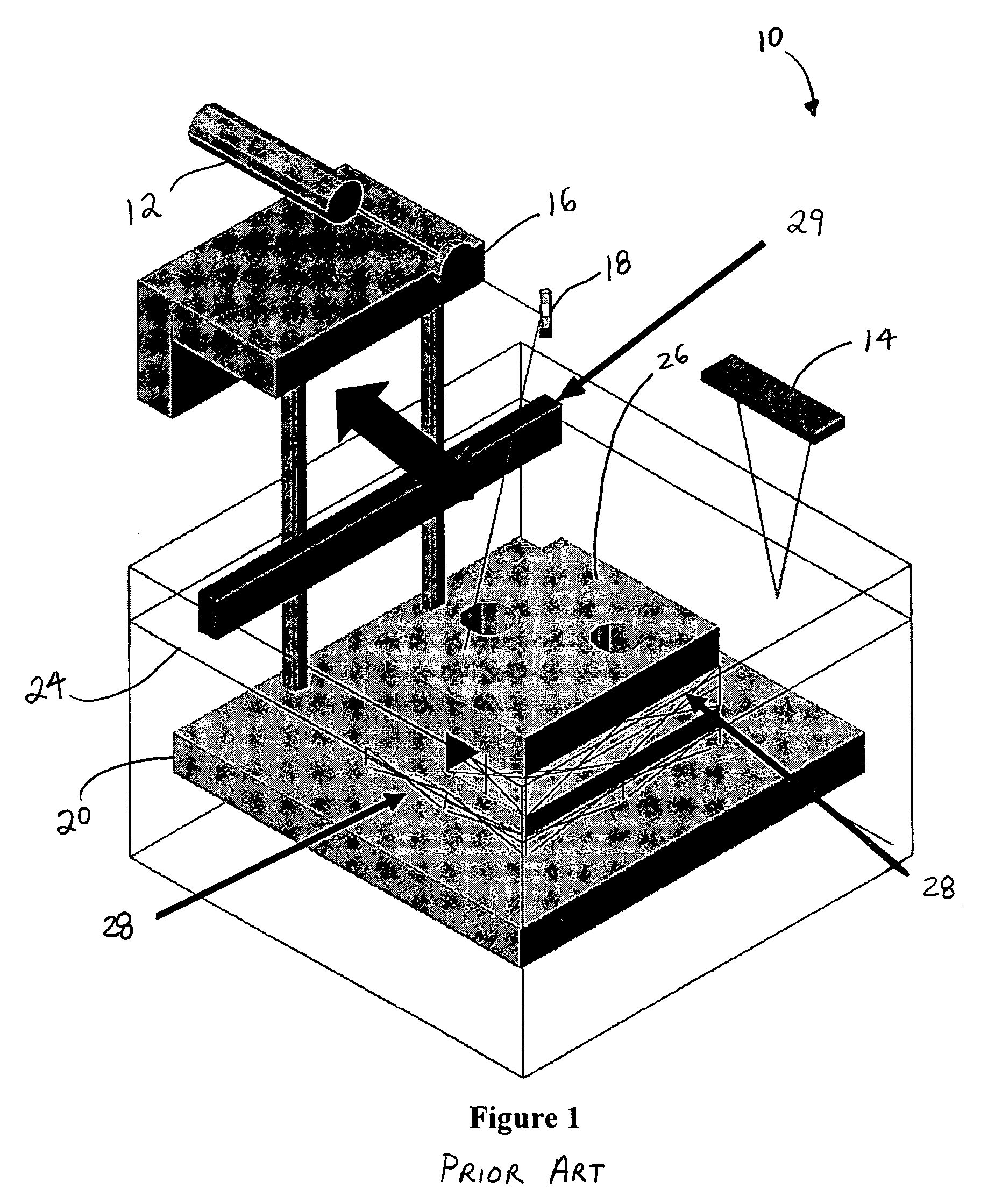
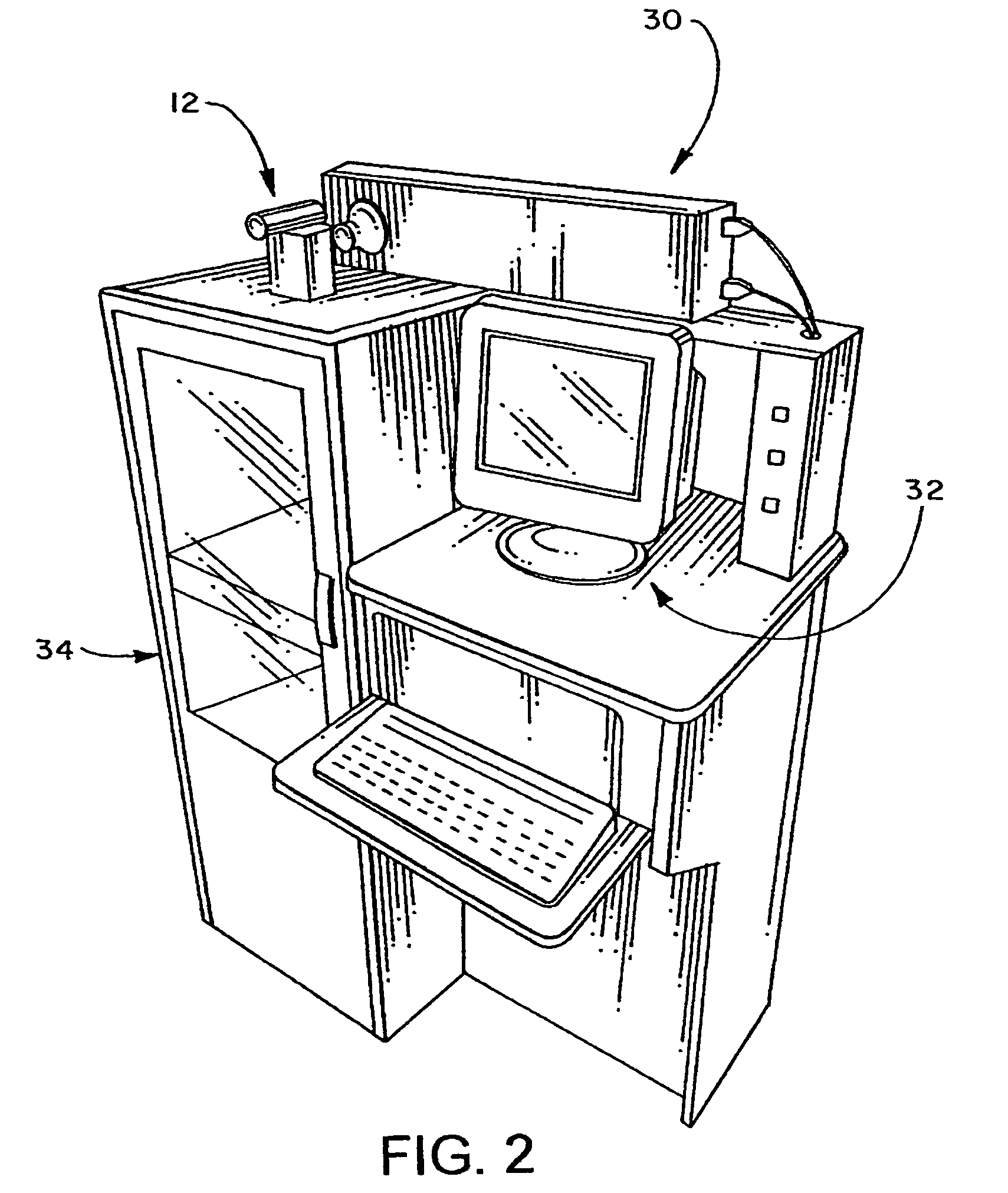
Methods and systems of stereolithography for building cost-efficient and time-saving multi-material, multi-functional and multi-colored prototypes, models and devices configured for intermediate washing and curing / drying is disclosed including: laser(s), liquid and / or platform level sensing system(s), controllable optical system(s), moveable platform(s), elevator platform(s), recoating system(s) and at least one polymer retaining receptacle. Multiple polymer retaining receptacles may be arranged in a moveable apparatus, wherein each receptacle is adapted to actively / passively maintain a uniform, desired level of polymer by including a recoating device and a material fill / remove system. The platform is movably accessible to the polymer retaining receptacle(s), elevator mechanism(s) and washing and curing / drying area(s) which may be housed in a shielded enclosure(s). The elevator mechanism is configured to vertically traverse and rotate the platform, thus providing angled building, washing and curing / drying capabilities. A horizontal traversing mechanism may be included to facilitate manufacturing between components of SL cabinet(s) and / or alternative manufacturing technologies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
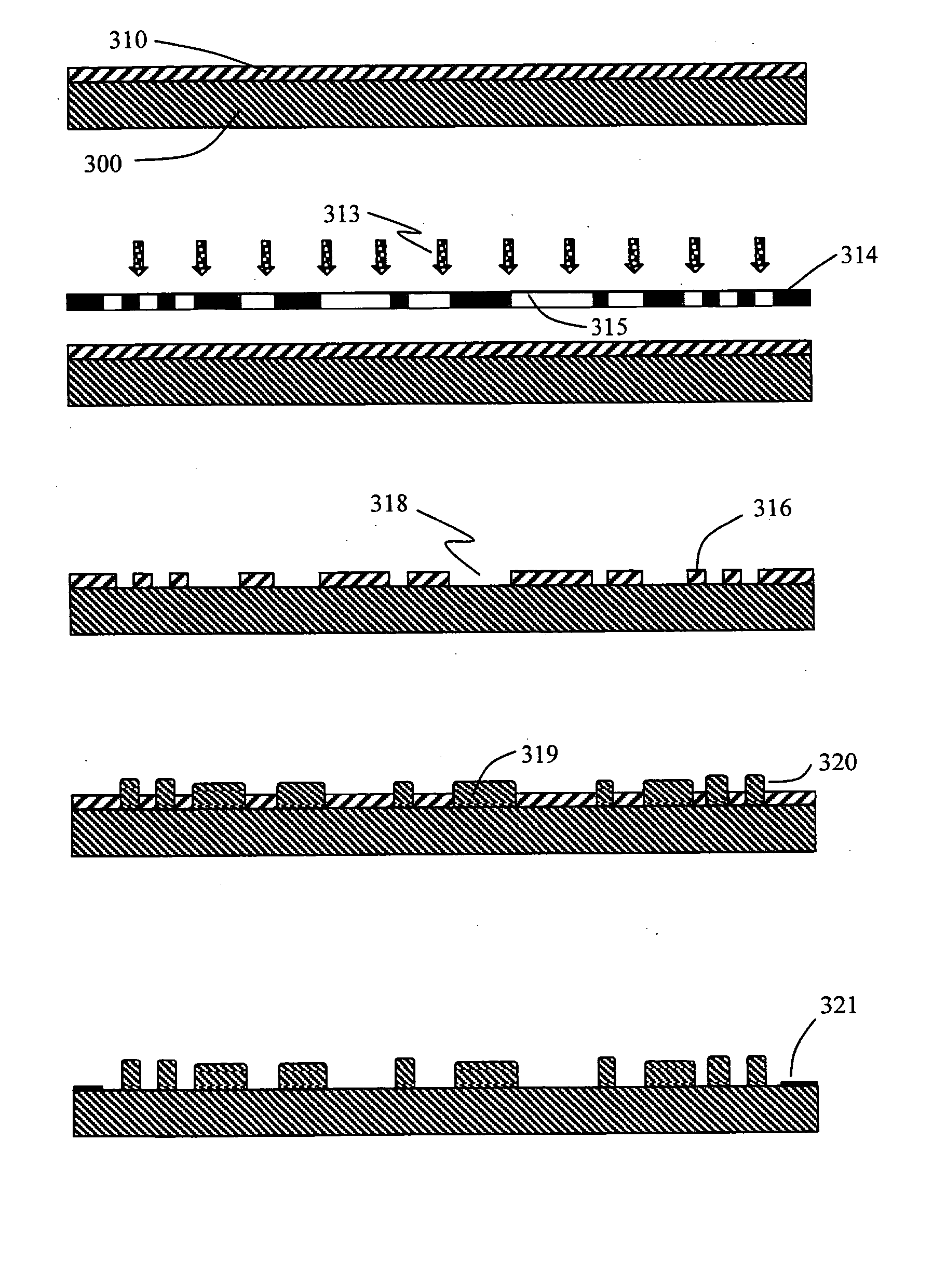
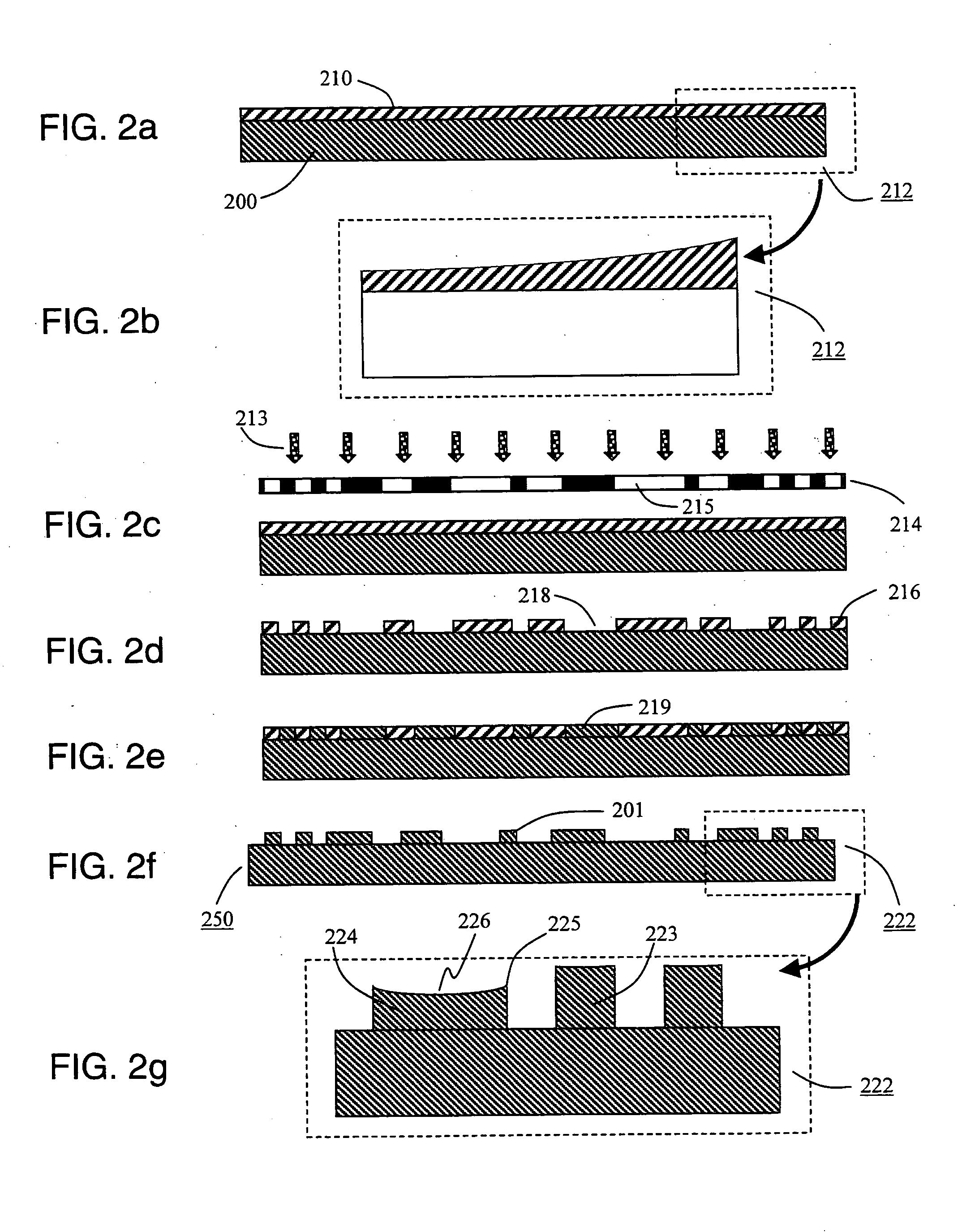
Microfabricated structures and processes for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050067286A1Minimize surface roughnessEasy to controlElectroforming processesMicroelectromechanical systemsManufacturing technologyCompound (substance)
Various techniques for the fabrication of highly accurate master molds with precisely defined microstructures for use in plastic replication using injection molding, hot embossing, or casting techniques are disclosed herein. Three different fabrication processes used for master mold fabrication are disclosed wherein one of the processes is a combination of the other two processes. In an embodiment of the first process, a two-step electroplating approach is used wherein one of the metals forms the microstructures and the second metal is used as a sacrificial support layer. Following electroplating, the exact height of the microstructures is defined using a chemical mechanical polishing process. In an embodiment of the second process, a modified electroforming process is used for master mold fabrication. The specific modifications include the use of Nickel-Iron (80:20) as a structural component of the master mold, and the use of a higher saccharin concentration in the electroplating bath to reduce tensile stress during plating and electroforming on the top as well as sides of the dummy substrate to prevent peel off of the electroform. The electroforming process is also well suited towards the fabrication of microstructures with non-rectangular cross sectional profiles. Also disclosed is an embodiment of a simple fabrication process using direct deposition of a curable liquid molding material combined with the electroforming process. Finally, an embodiment of a third fabrication process combines the meritorious features of the first two approaches and is used to fabricate a master mold using a combination of the two-step electroplating plus chemical mechanical polishing approach and the electroforming approach to fabricate highly accurate master molds with precisely defined microstructures. The microstructures are an integral part of the master mold and hence the master mold is more robust and well suited for high volume production of plastic MEMS devices through replication techniques such as injection molding.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIVERISITY OF THE
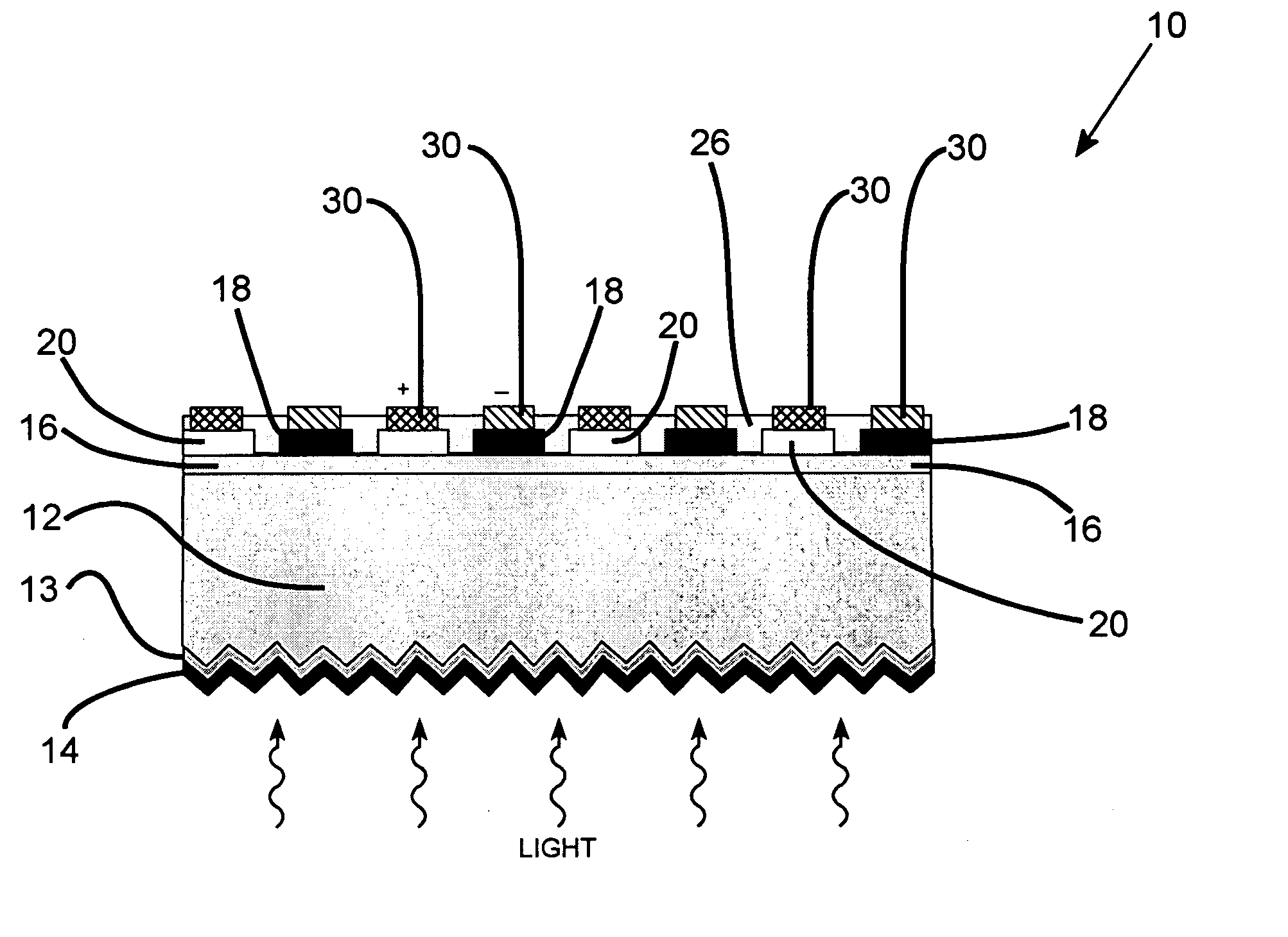
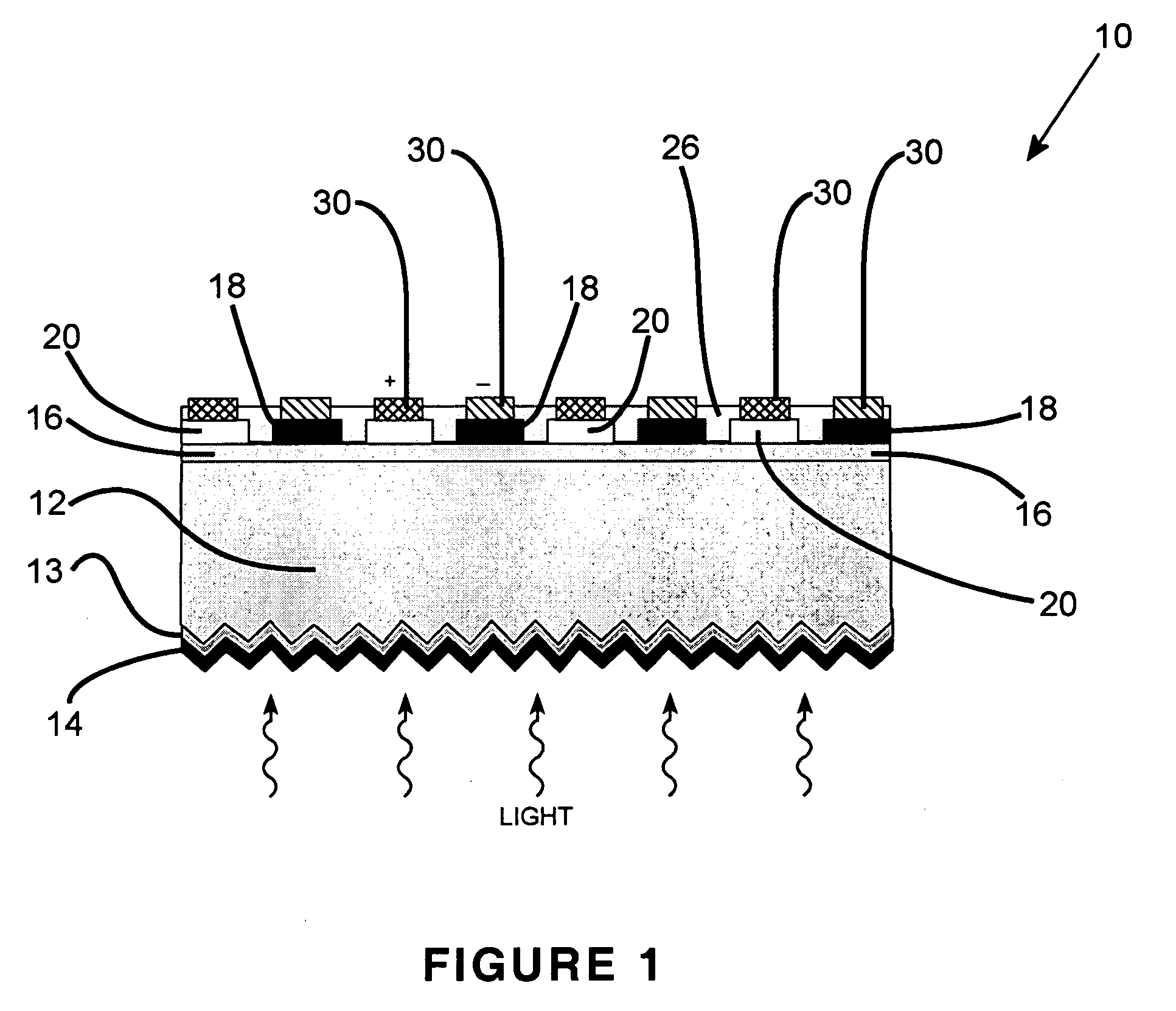
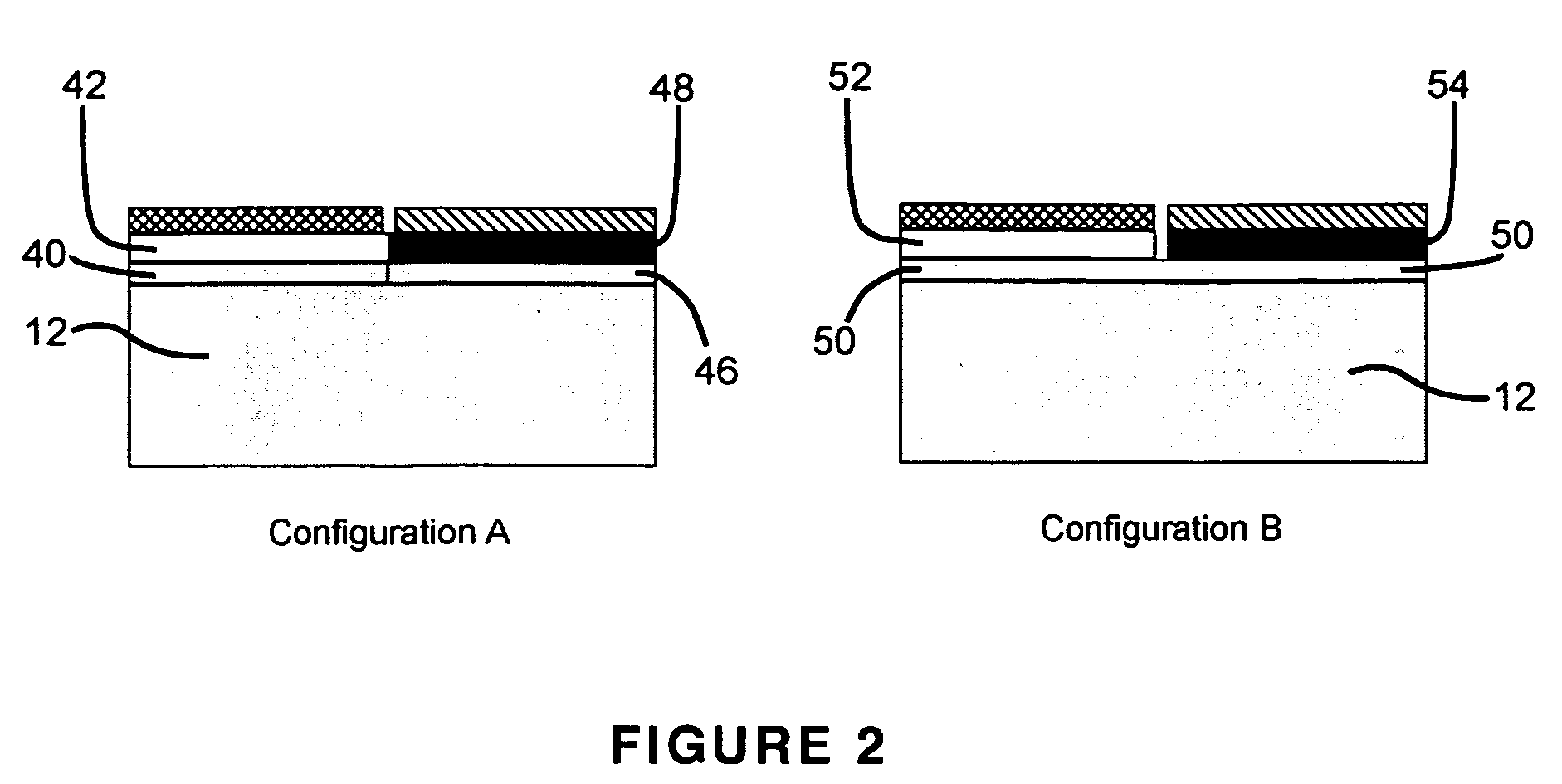
Solar cell
InactiveUS20070169808A1Low costEasy to usePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionManufacturing technology
The present invention provides a thin film amorphous silicon-crystalline silicon back heterojunction and back surface field device configuration for a heterojunction solar cell. The configuration is attained by the formation of heterojunctions on the back surface of crystalline silicon at low temperatures. Low temperature fabrication allows for the application of low resolution lithography and / or shadow masking processes to produce the structures. The heterojunctions and interface passivation can be formed through a variety of material compositions and deposition processes, including appropriate surface restructing techniques. The configuration achieves separation of optimization requirements for light absorption and carrier generation at the front surface on which the light is incident, and in the bulk, and charge carrier collection at the back of the device. The shadowing losses are eliminated by positioning the electrical contacts at the back thereby removing them from the path of the incident light. Back contacts need optimization only for maximum charge carrier collection without bothering about shading losses. A range of elements / alloys may be used to effect band-bending. All of the above features result in a very high efficiency solar cell. The open circuit voltage of the back heterojunction device is higher than that of an all-crystalline device. The solar cell configurations are equally amenable to crystalline silicon wafer absorber as well as thin silicon layers formed by using a variety of fabrication processes. The configurations can be used for radiovoltaic and electron-voltaic energy conversion devices.
Owner:KHERANI NAZIR P +1
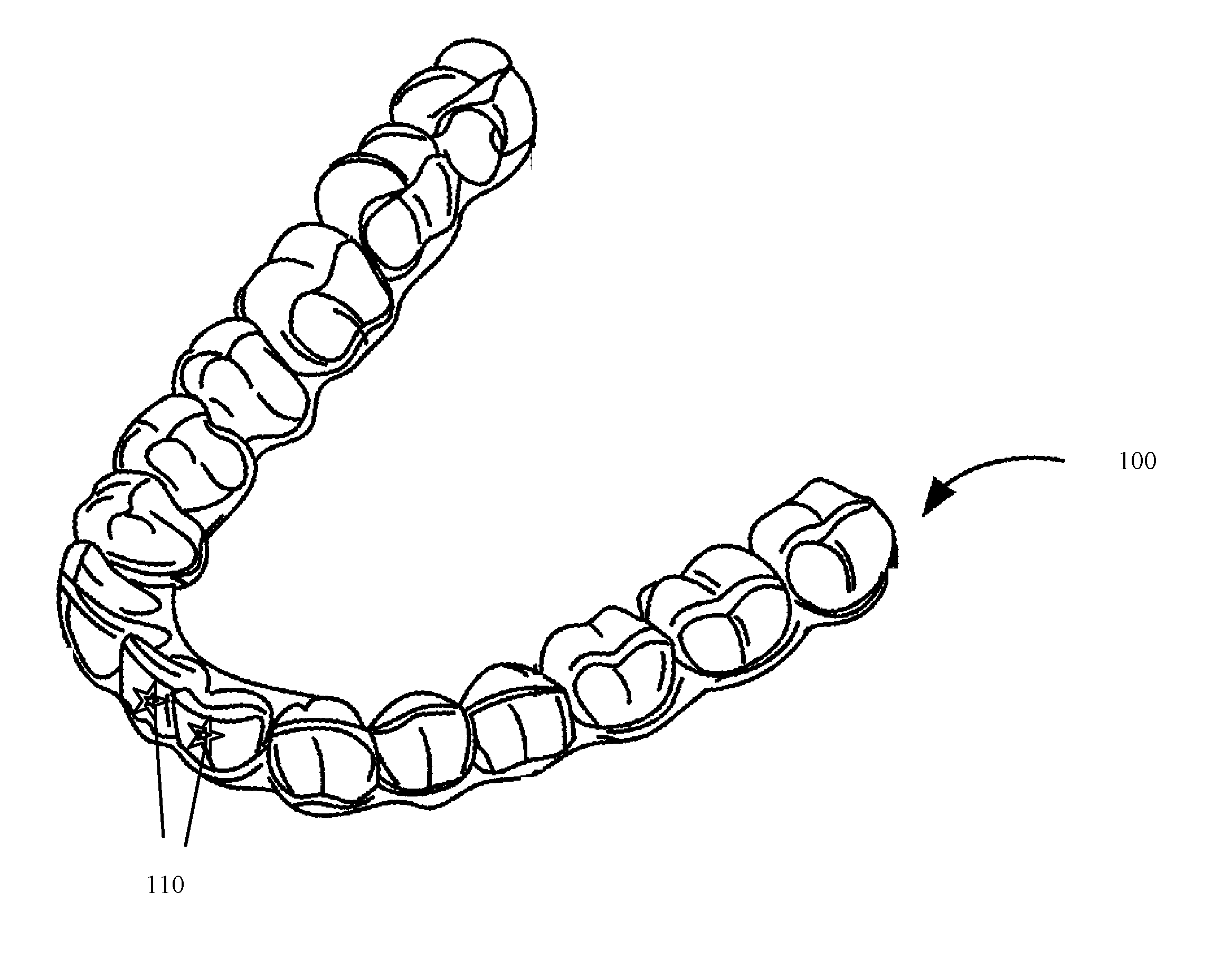
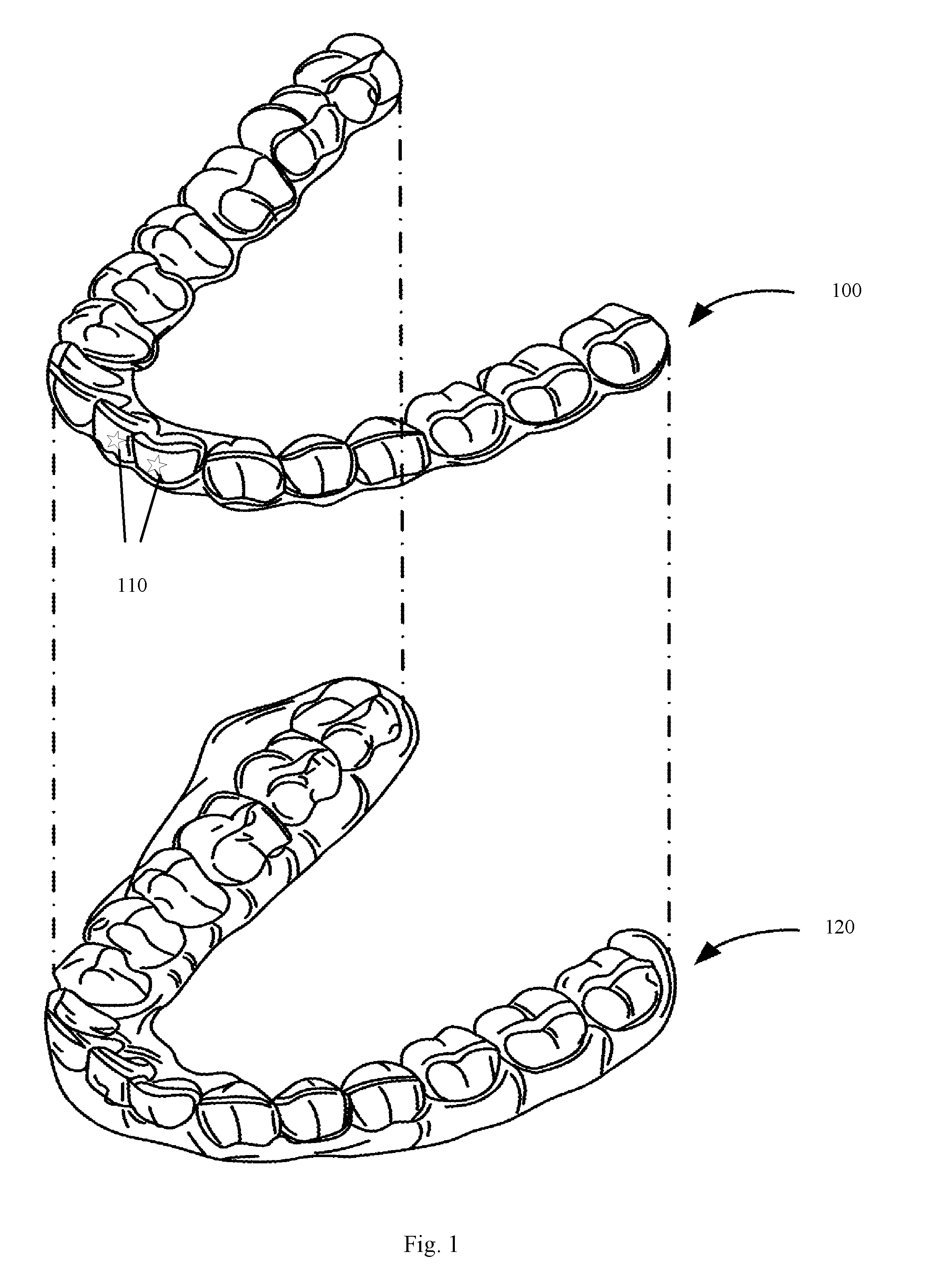
Systems, apparatuses and methods for substance delivery from dental appliance
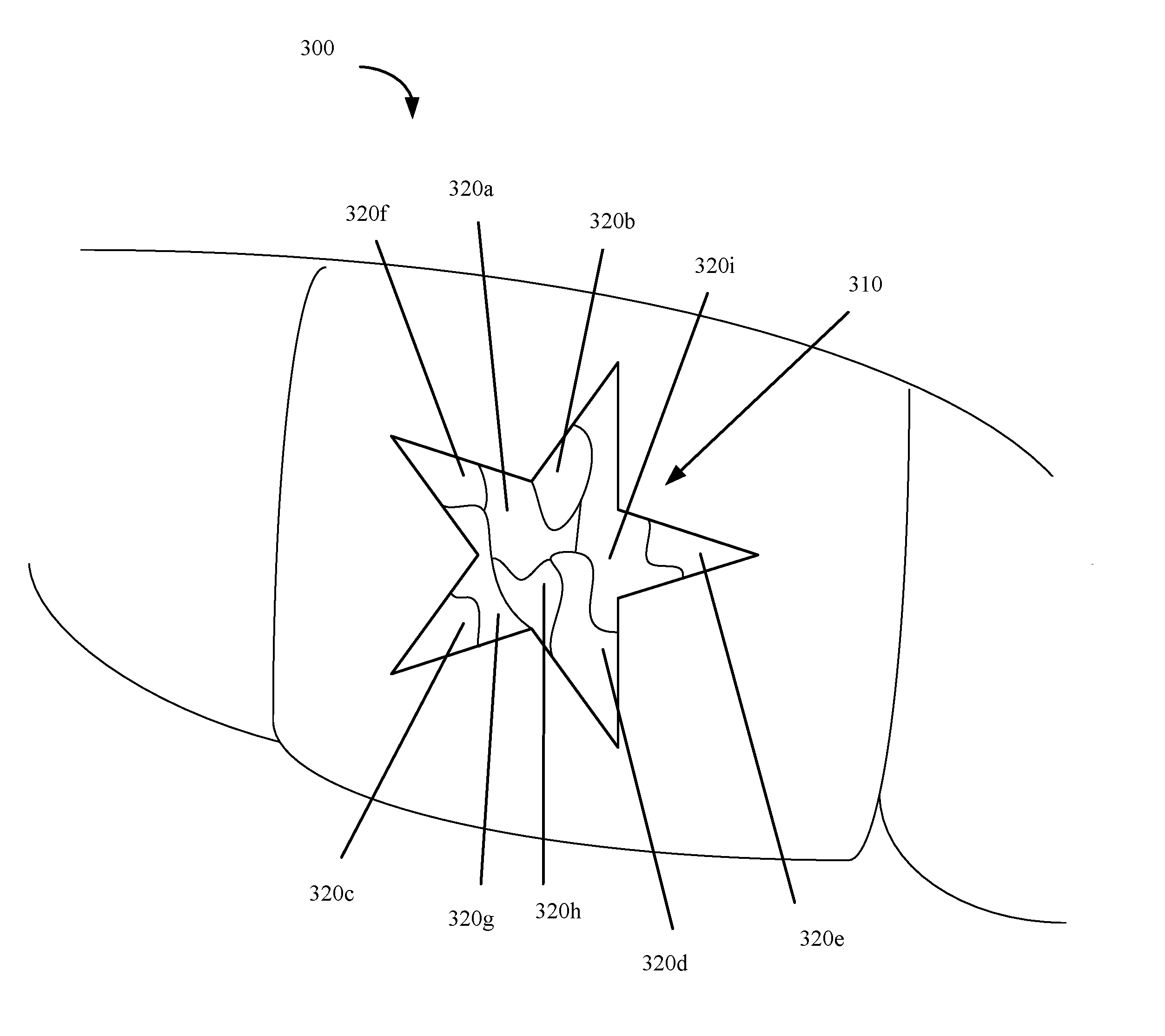
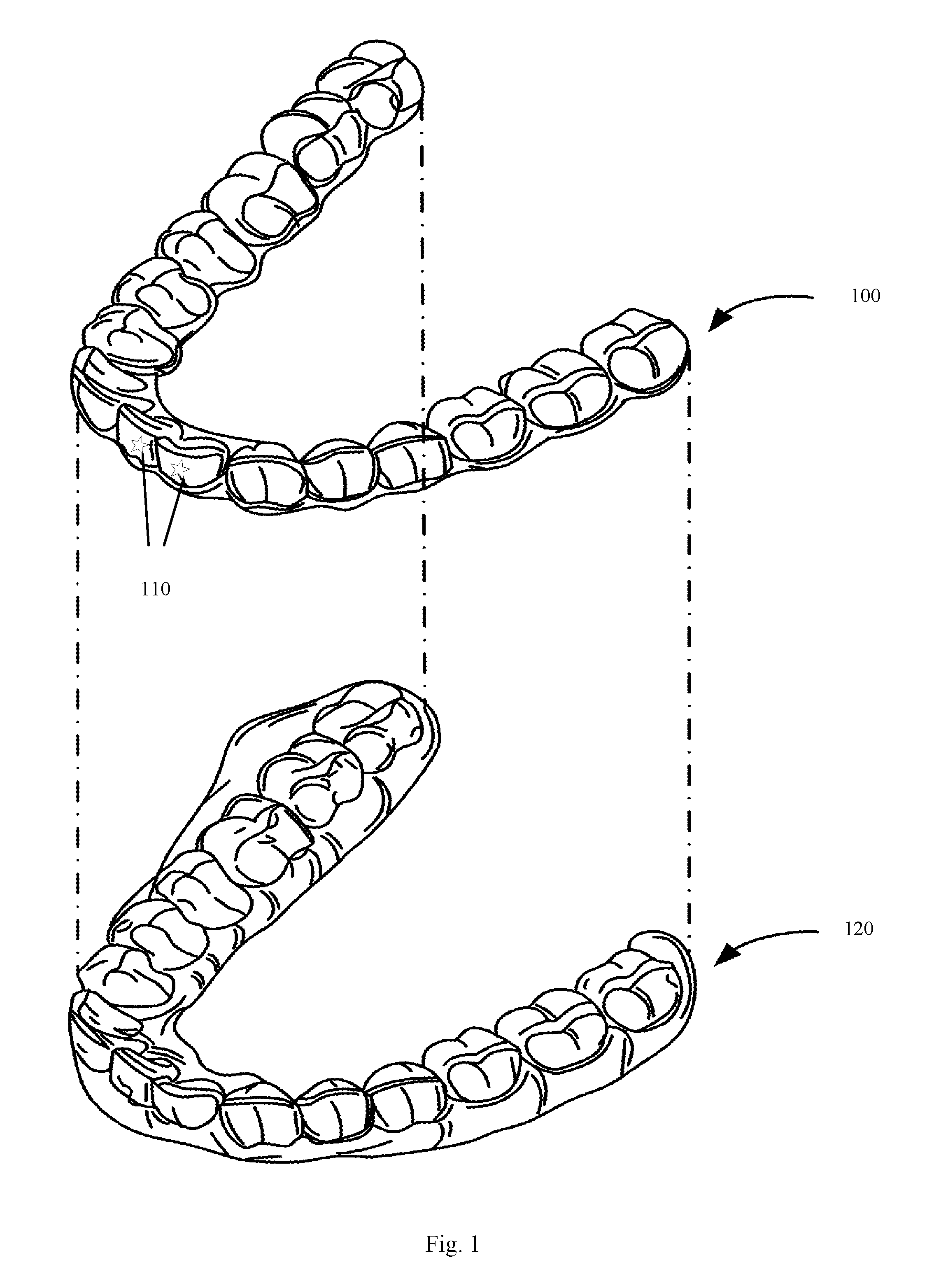
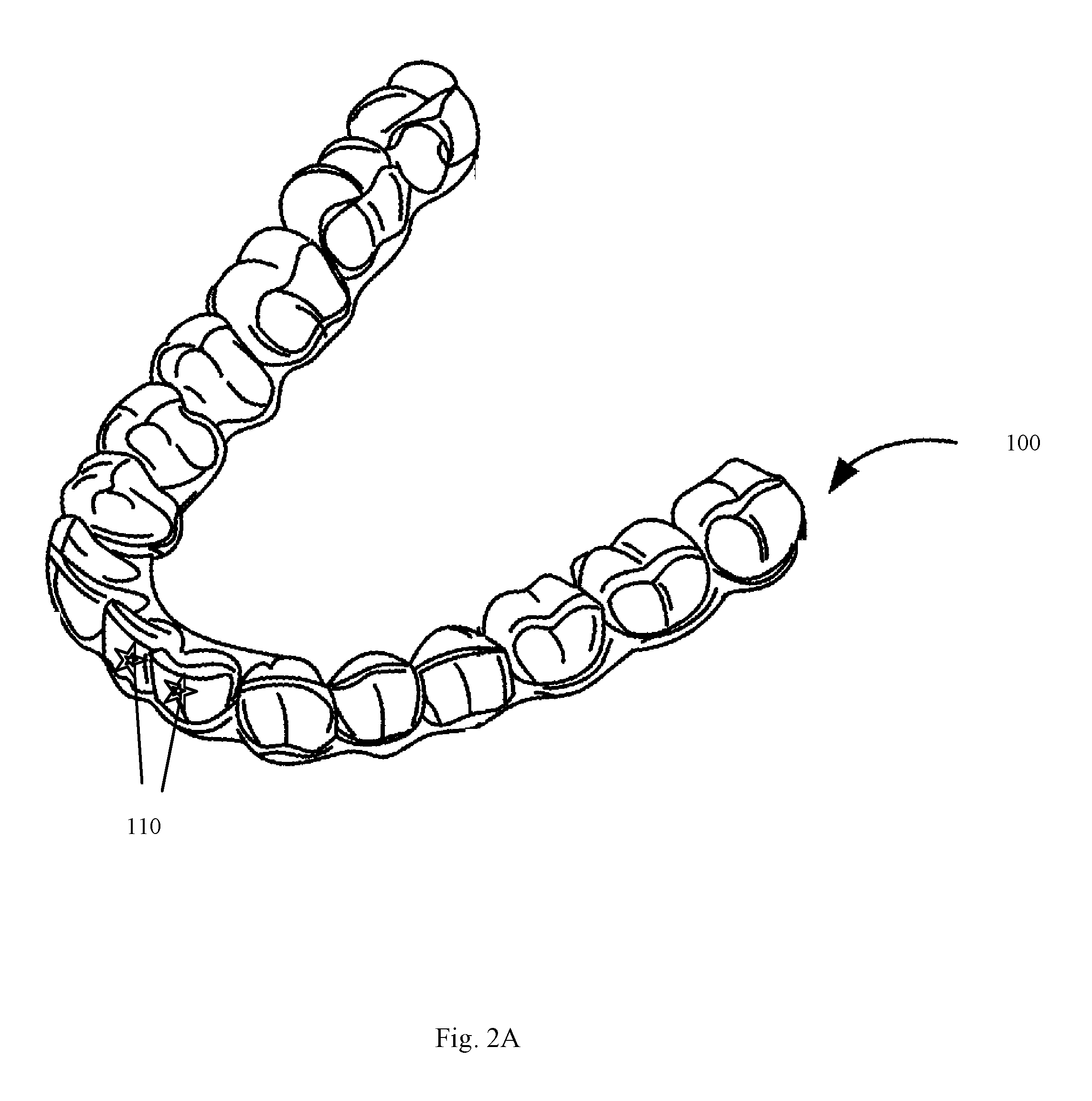
ActiveUS20170007386A1Additive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsManufacturing technologyEngineering
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Optical lens and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080112059A1Improve efficiencyLower performance requirementsOptical articlesMountingsProduction rateManufacturing technology
An optical lens is provided. The optical lens provides miniaturization and thin size, and reduces the cost and improves productivity by simplifying the structure and manufacturing process. The optical lens includes a light-transmitting substrate with a lens chamber and a fluidic chamber that are connected with each other. The optical lens also includes a light-transmitting elastic film which seals the lens chamber, a buffer elastic film which seals the fluidic chamber, and an actuator on the buffer elastic film which corresponds to the fluidic chamber, and varies the volume of the fluidic chamber to vary a pressure acting on the light-transmitting elastic film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dental appliance having ornamental design
ActiveUS20170008333A1Additive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsManufacturing technologyEngineering
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Rice whole genome SNP chip and application thereof
ActiveCN102747138AImprove throughputGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementManufacturing technologyGermplasm
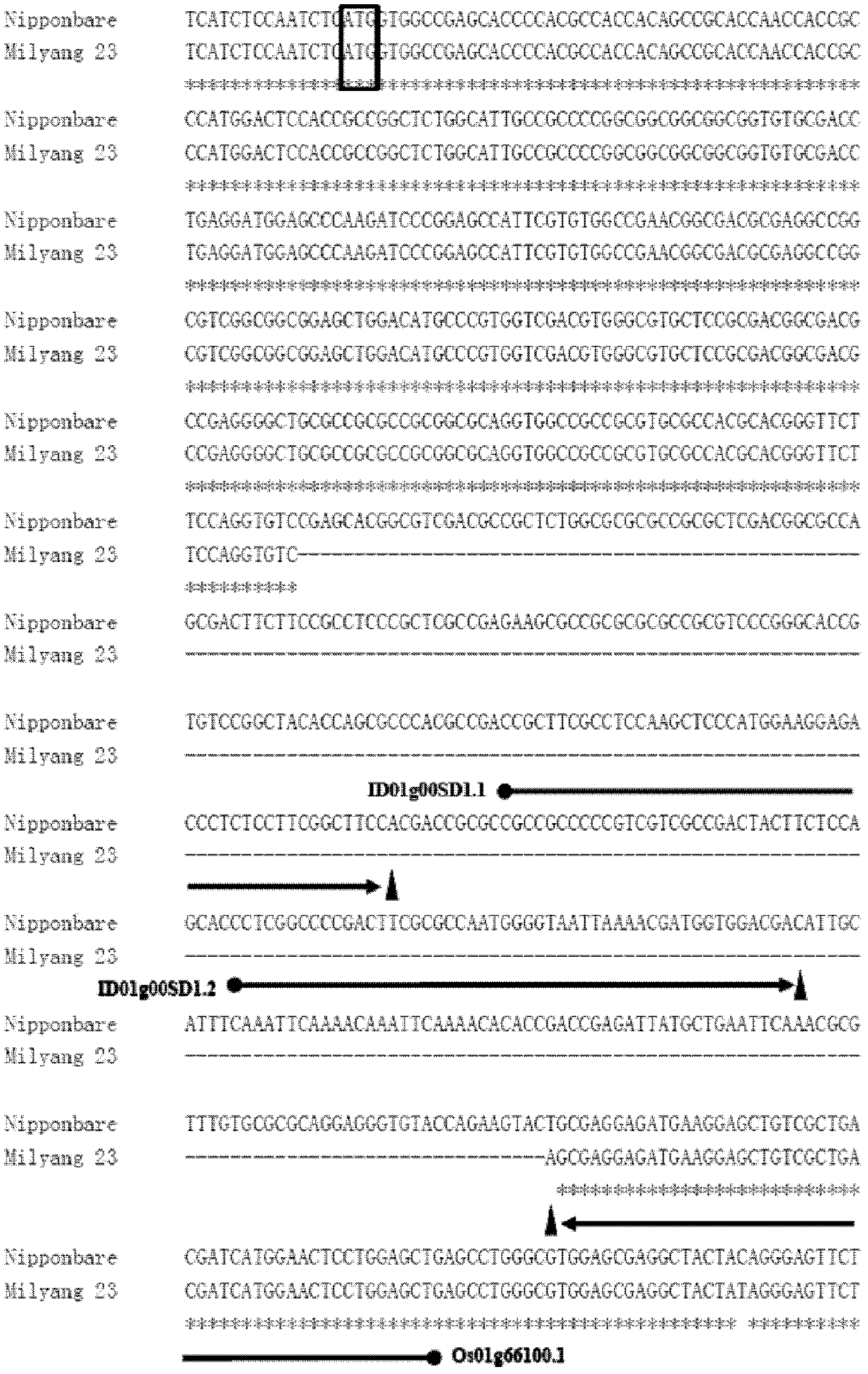
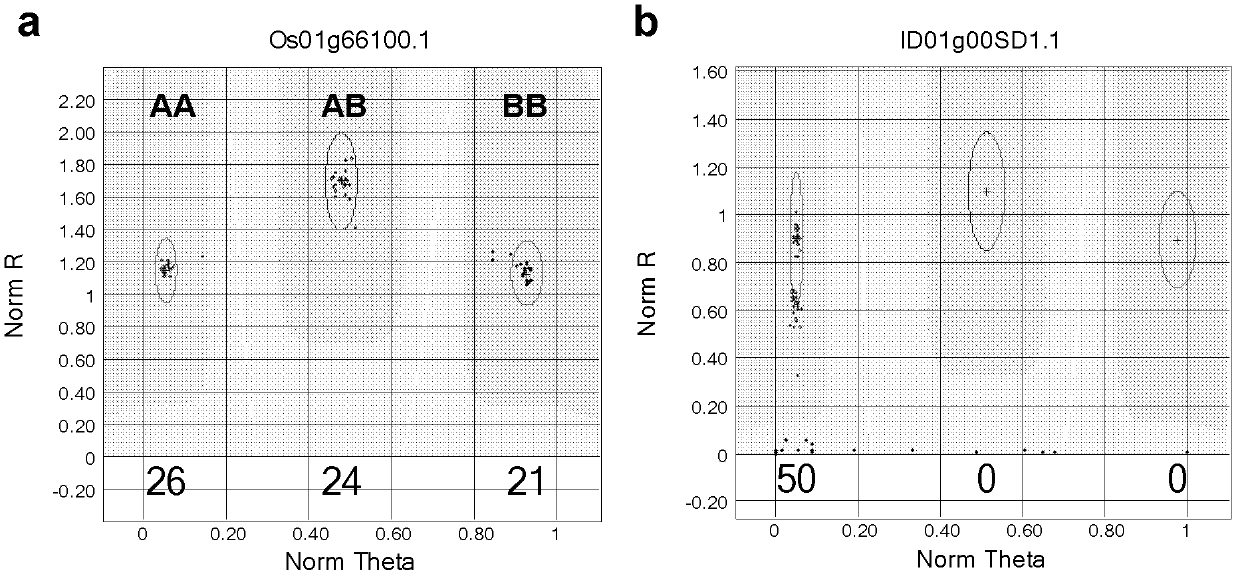
The present invention discloses a rice whole genome SNP chip and an application thereof. A method for preparing the chip comprises: (1) obtaining a first class of probes on a chip, wherein sequencing is performed to obtain a parental genome sequence, resequencing data of other rice varieties in a public database are combined, a Nipponbare genome is adopted as a reference sequence, a MAQ software is adopted to match and analyze all the sequencing data, and finally a SNP marker is screened; (2) obtaining a second class of probes on the chip, wherein a rice function gene is obtained from the public database, sequence difference reflecting gene function is searched, and a SNP / INDEL probe is designed according to the sequence difference; (3) adopting an infinium chip manufacturing technology to produce a SNP chip; and (4) testing accuracy and application efficiency of the chip. The chip of the present invention can be applicable for rice germplasm resource molecule marker fingerprint analysis, seed authenticity detection, filial generation genotyping, and other related researches.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
Device manufacturing process utilizing a double patterning process
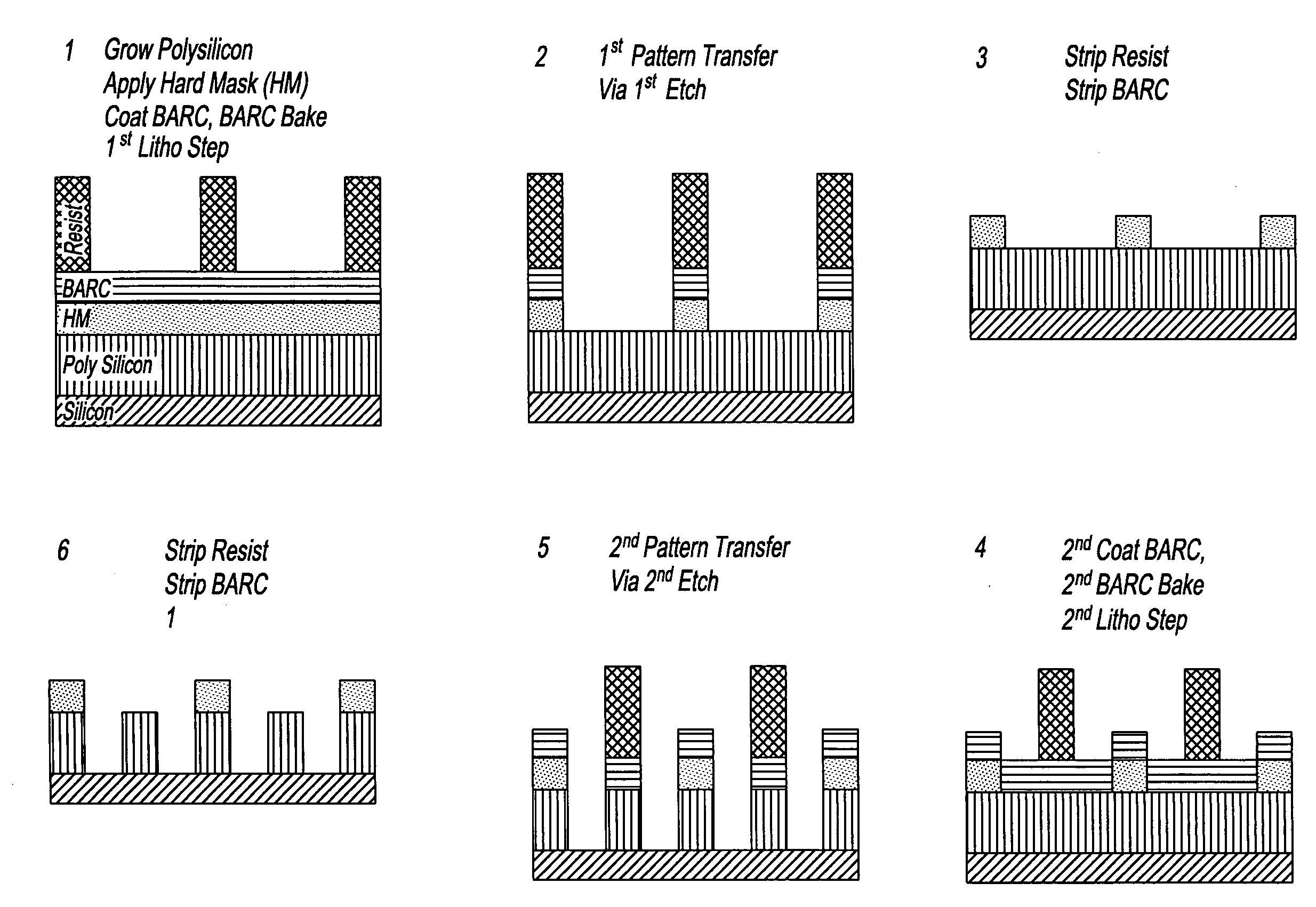
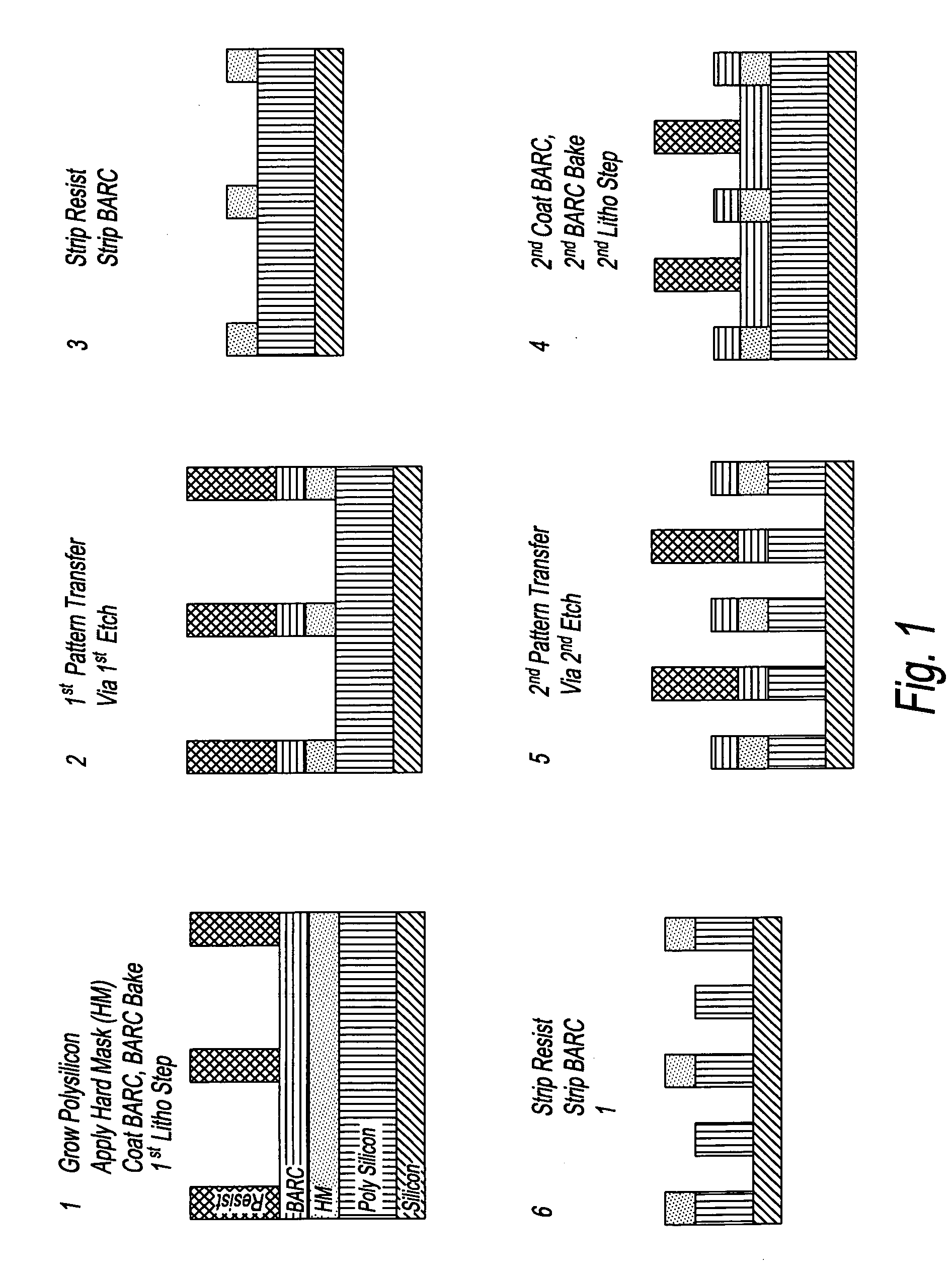
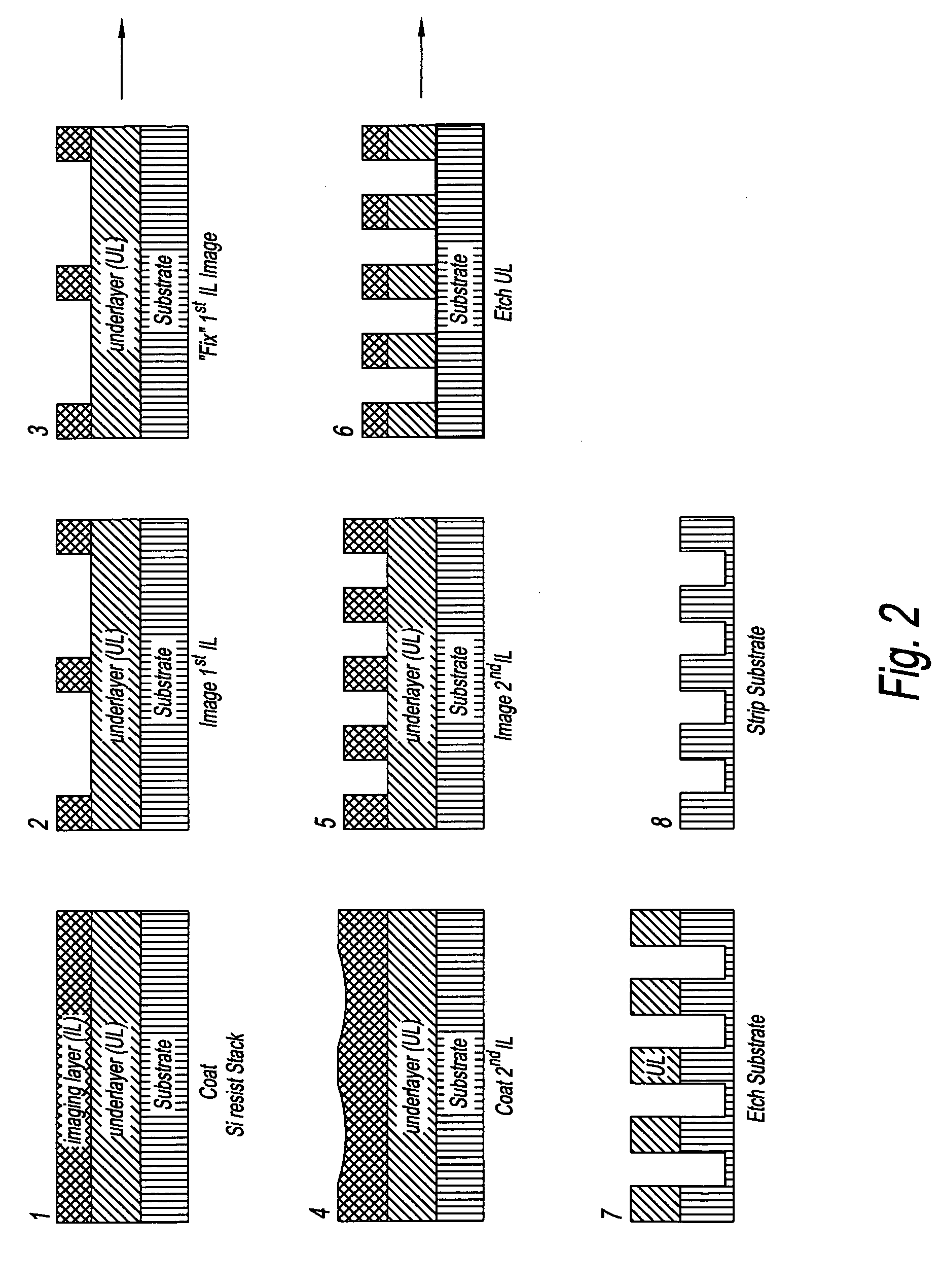
InactiveUS20080199814A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityAnti-reflective coating
Manufacturing semiconductor device by steps of:a) providing substrate with antireflective coating or underlayer,b) applying first photosensitive composition over substrate,c) exposing first composition to radiation to produce first pattern,d) developing exposed first composition to produce an imaged bilayer stack,e) rinsing the stack,f) applying fixer to the stack,g) applying optional bake,h) rinsing the stack,i) applying second optional bake,j) applying second photosensitive composition onto the stack to produce multilayer stack,k) exposing second composition to produce second pattern offset from first pattern,l) developing exposed second composition to produce multilayer stack, andm) rinsing multilayer stack;the photosensitive compositions have photoacid generator and substantially aqueous base insoluble polymer whose solubility increases upon treatment with acid and further comprises an anchor group, and the fixer is a polyfunctional compound reactive with anchor group, but does not contain silicon and the substrate stays within a lithographic cell from at least first coating step until at least after final exposure.
Owner:FUJIFILM ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US
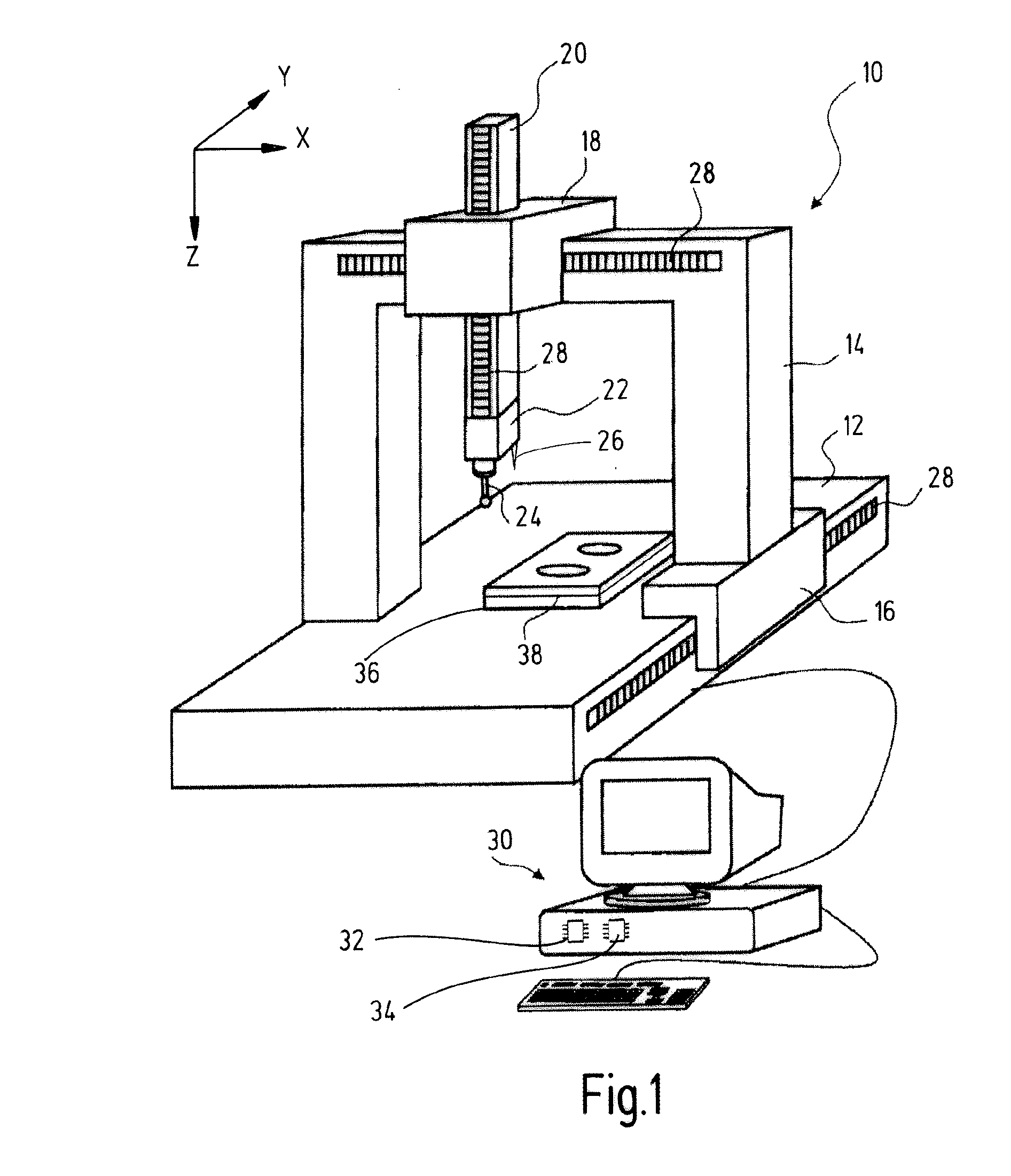
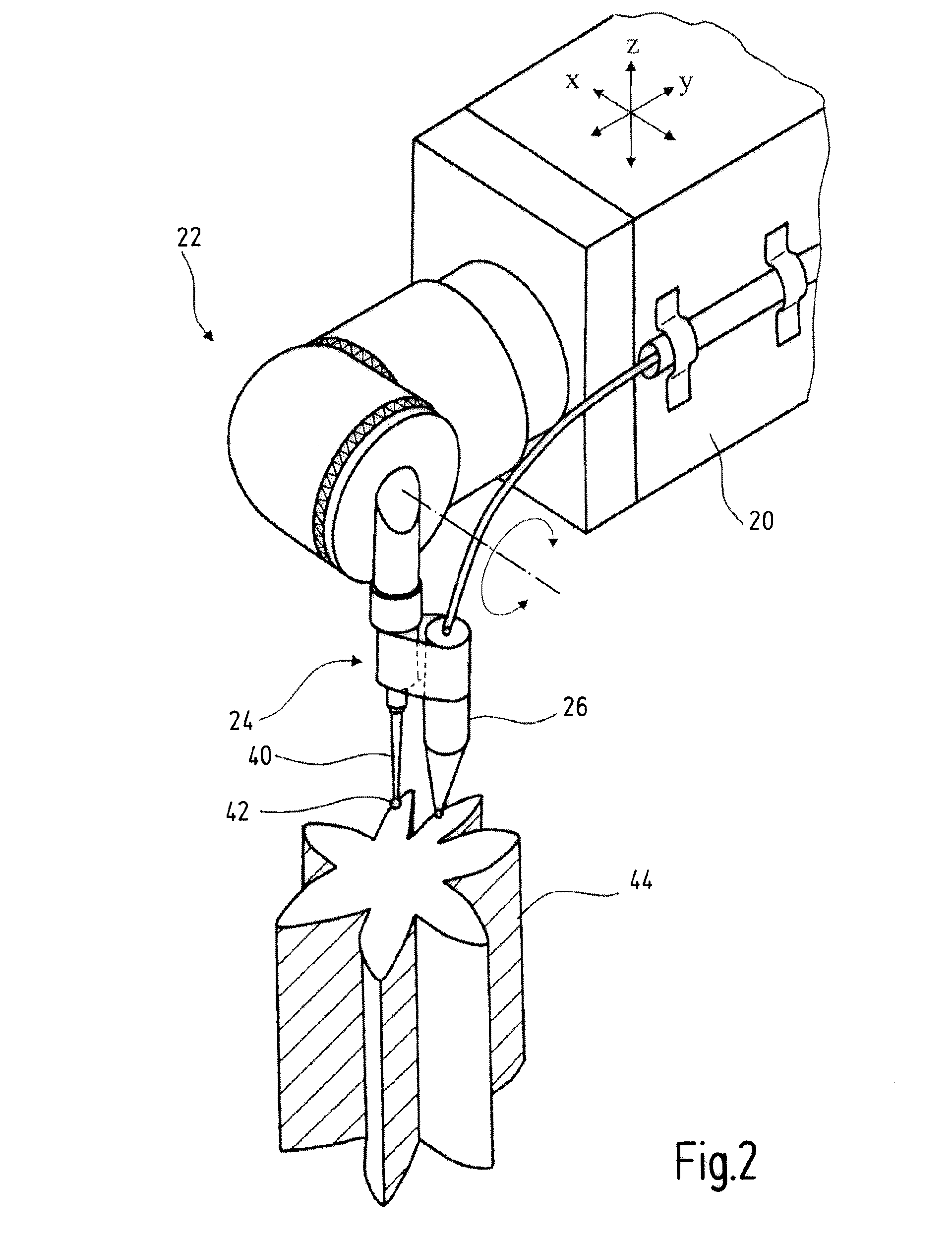
Method and arrangement for producing a workpiece by using additive manufacturing techniques
ActiveUS20150061170A1Cost-efficient productionAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusManufacturing technologyProcess measurement
A method and an arrangement for producing a workpiece using additive manufacturing techniques involve in-process measurement in order to determine individual characteristics of one or more workpiece layers. In particular, dimensional and / or geometrical characteristics of a workpiece layer are measured before the next workpiece layer is produced. Advantageously, the measurement results are fed back into the production process in order to increase accuracy and precision of the production process.
Owner:CARL ZEISS IND MESSTECHN GMBH +1
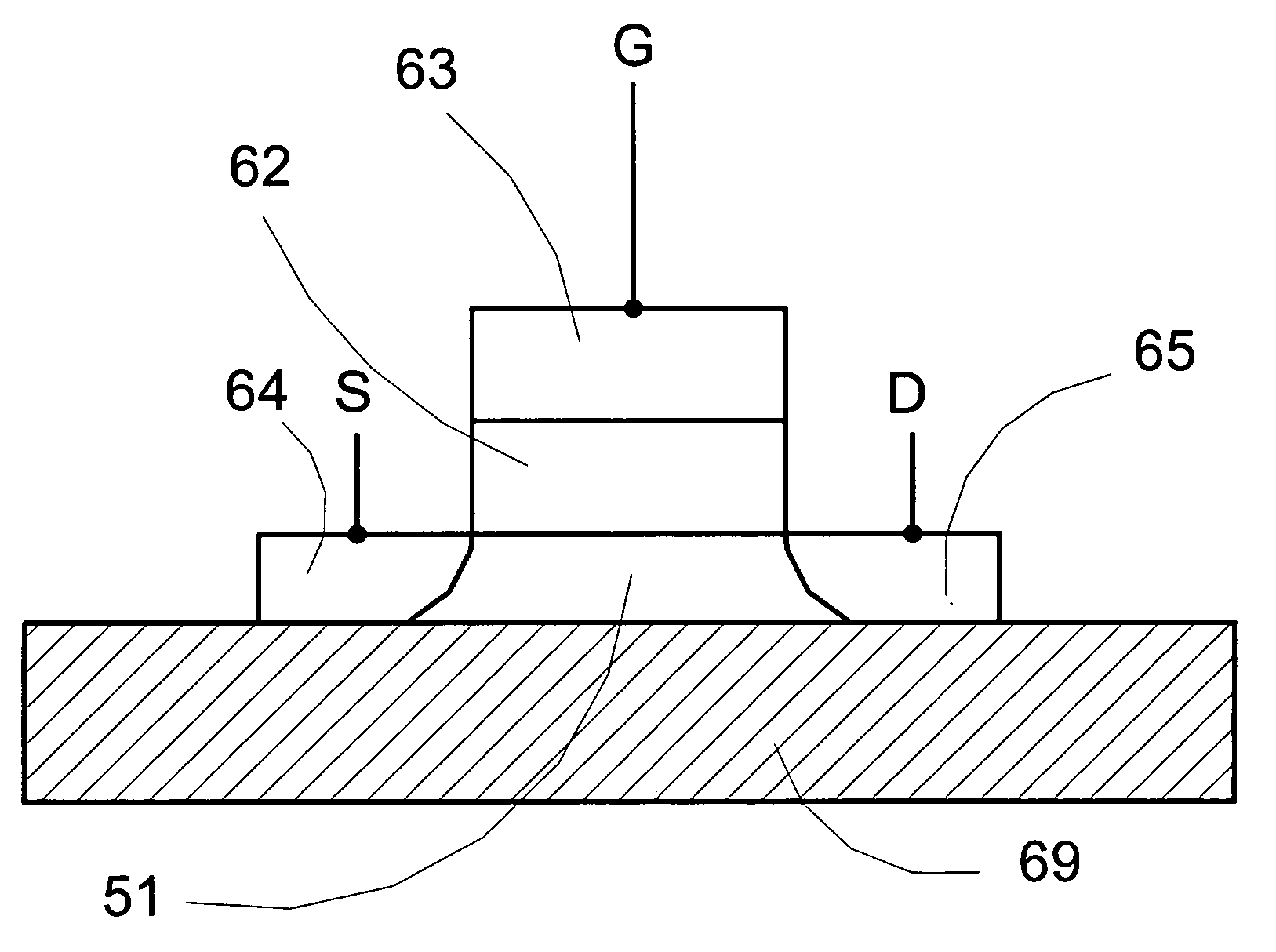
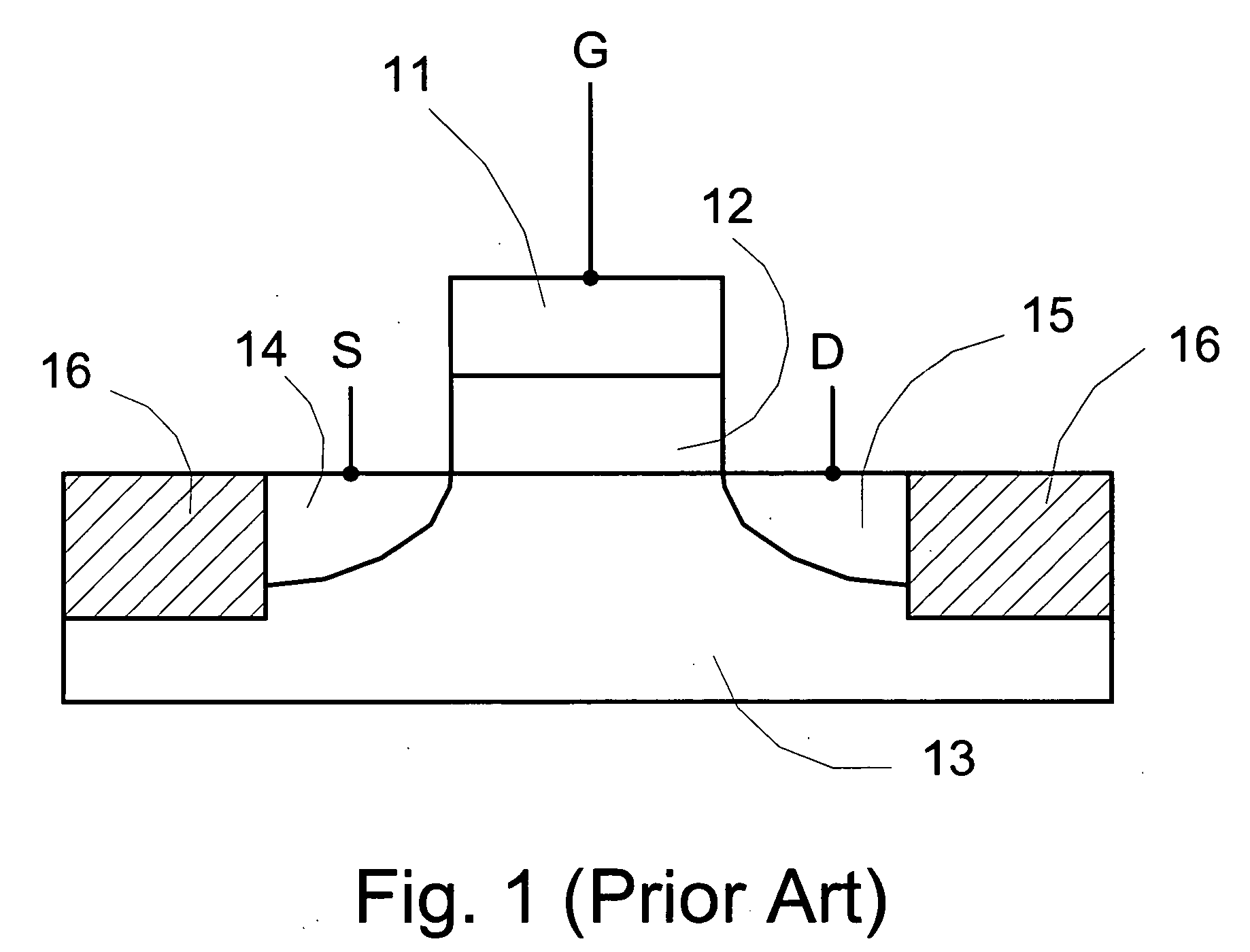
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS20060038242A1Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Multi-material stereolithography
ActiveUS20060022379A1Improves SL functionalityEliminate pollutionMouldsConfectioneryMulti materialManufacturing technology
Methods and systems of stereolithography for building cost-efficient and time-saving multi-material, multi-functional and multi-colored prototypes, models and devices configured for intermediate washing and curing / drying is disclosed including: laser(s), liquid and / or platform level sensing system(s), controllable optical system(s), moveable platform(s), elevator platform(s), recoating system(s) and at least one polymer retaining receptacle. Multiple polymer retaining receptacles may be arranged in a moveable apparatus, wherein each receptacle is adapted to actively / passively maintain a uniform, desired level of polymer by including a recoating device and a material fill / remove system. The platform is movably accessible to the polymer retaining receptacle(s), elevator mechanism(s) and washing and curing / drying area(s) which may be housed in a shielded enclosure(s). The elevator mechanism is configured to vertically traverse and rotate the platform, thus providing angled building, washing and curing / drying capabilities. A horizontal traversing mechanism may be included to facilitate manufacturing between components of SL cabinet(s) and / or alternative manufacturing technologies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
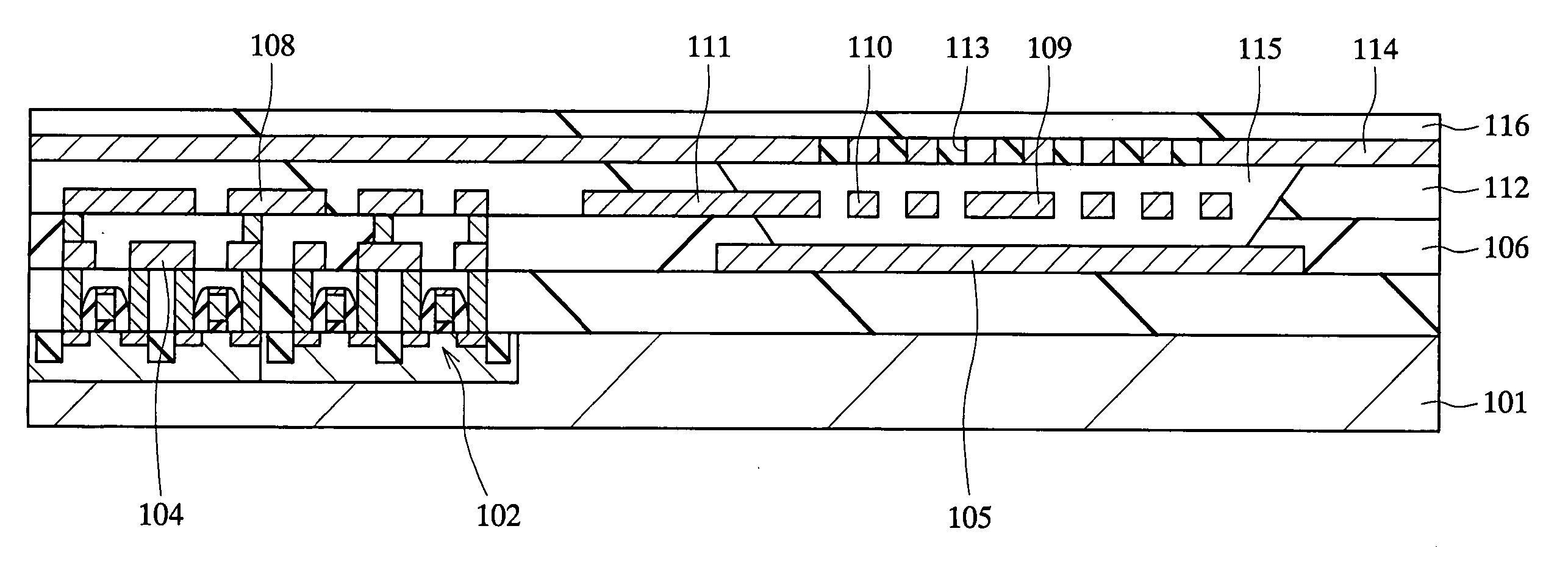
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Process Therefor
ActiveUS20070241414A1Less dislocation and defectControlled amount of strainTransistorSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyDevice material
This invention relates to a semiconductor device having a beam made of a semiconductor to which strain is introduced by deflection, and a current is permitted to flow in the beam.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Maskless Process for Suspending and Thinning Nanowires
ActiveUS20100193770A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireManufacturing technology
Semiconductor-based electronic devices and techniques for fabrication thereof are provided. In one aspect, a device is provided comprising a first pad; a second pad and a plurality of nanowires connecting the first pad and the second pad in a ladder-like configuration formed in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) layer over a buried oxide (BOX) layer, the nanowires having one or more dimensions defined by a re-distribution of silicon from the nanowires to the pads. The device can comprise a field-effect transistor (FET) having a gate surrounding the nanowires wherein portions of the nanowires surrounded by the gate form channels of the FET, the first pad and portions of the nanowires extending out from the gate adjacent to the first pad form a source region of the FET and the second pad and portions of the nanowires extending out from the gate adjacent to the second pad form a drain region of the FET.
Owner:IBM CORP
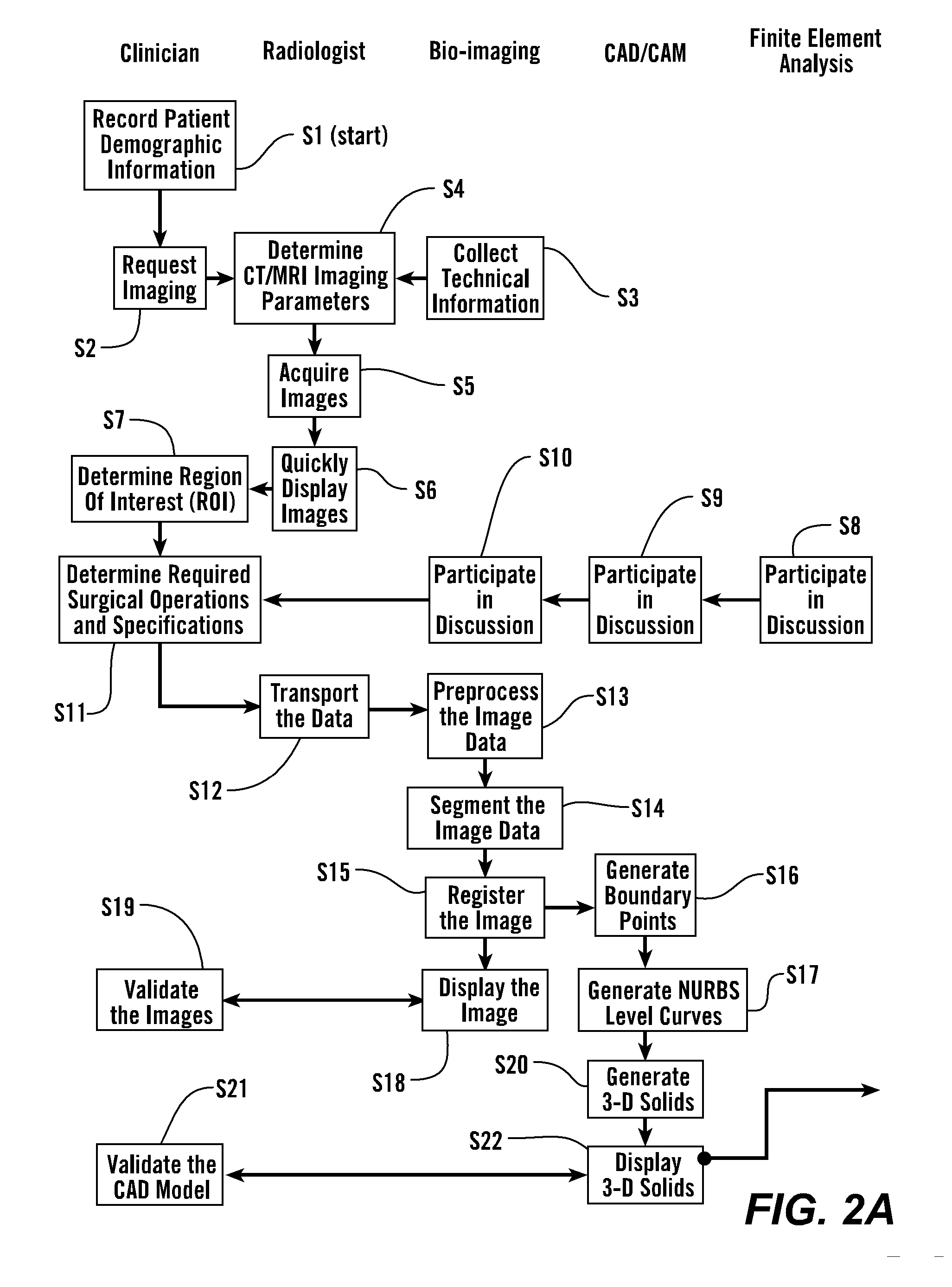
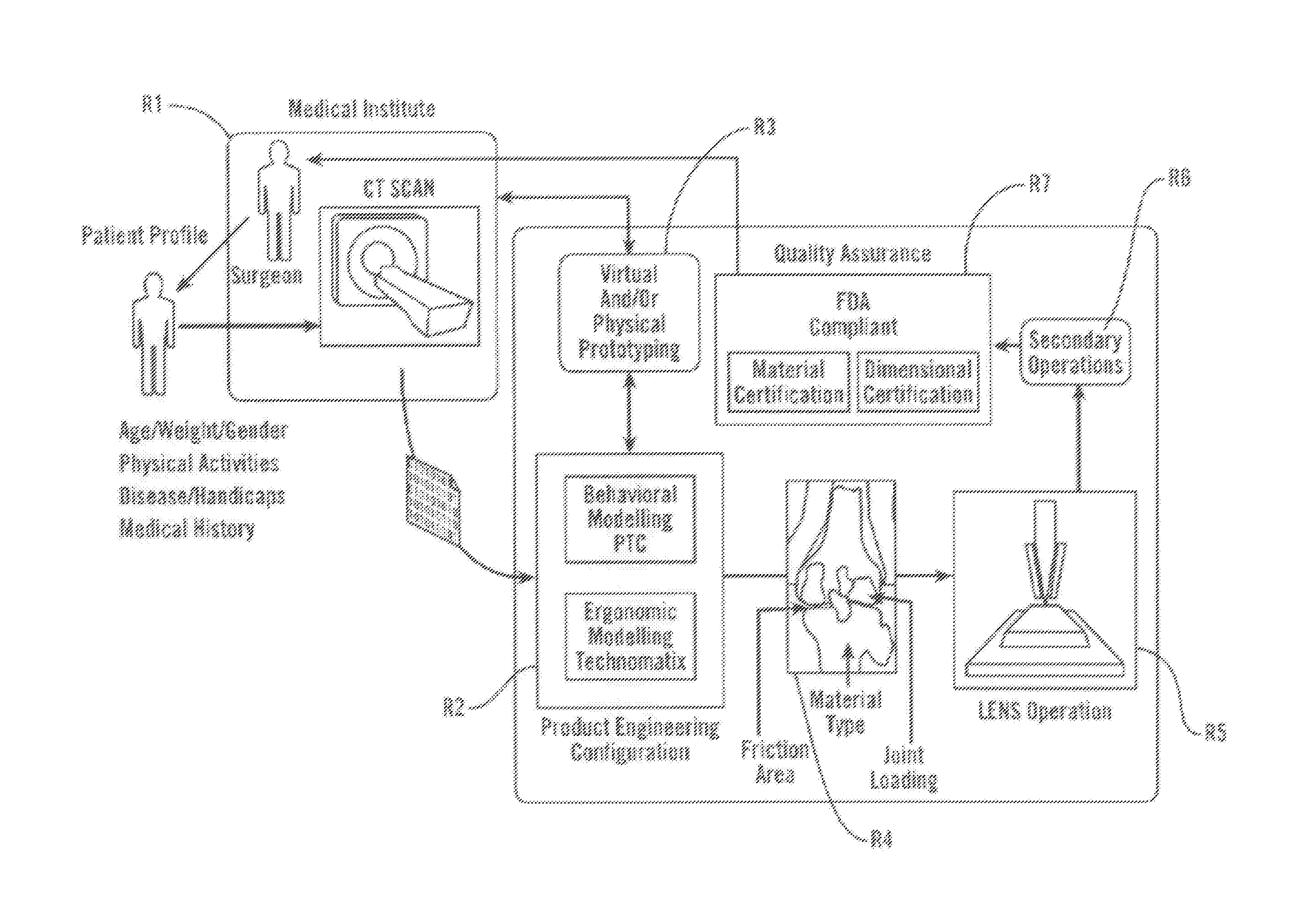
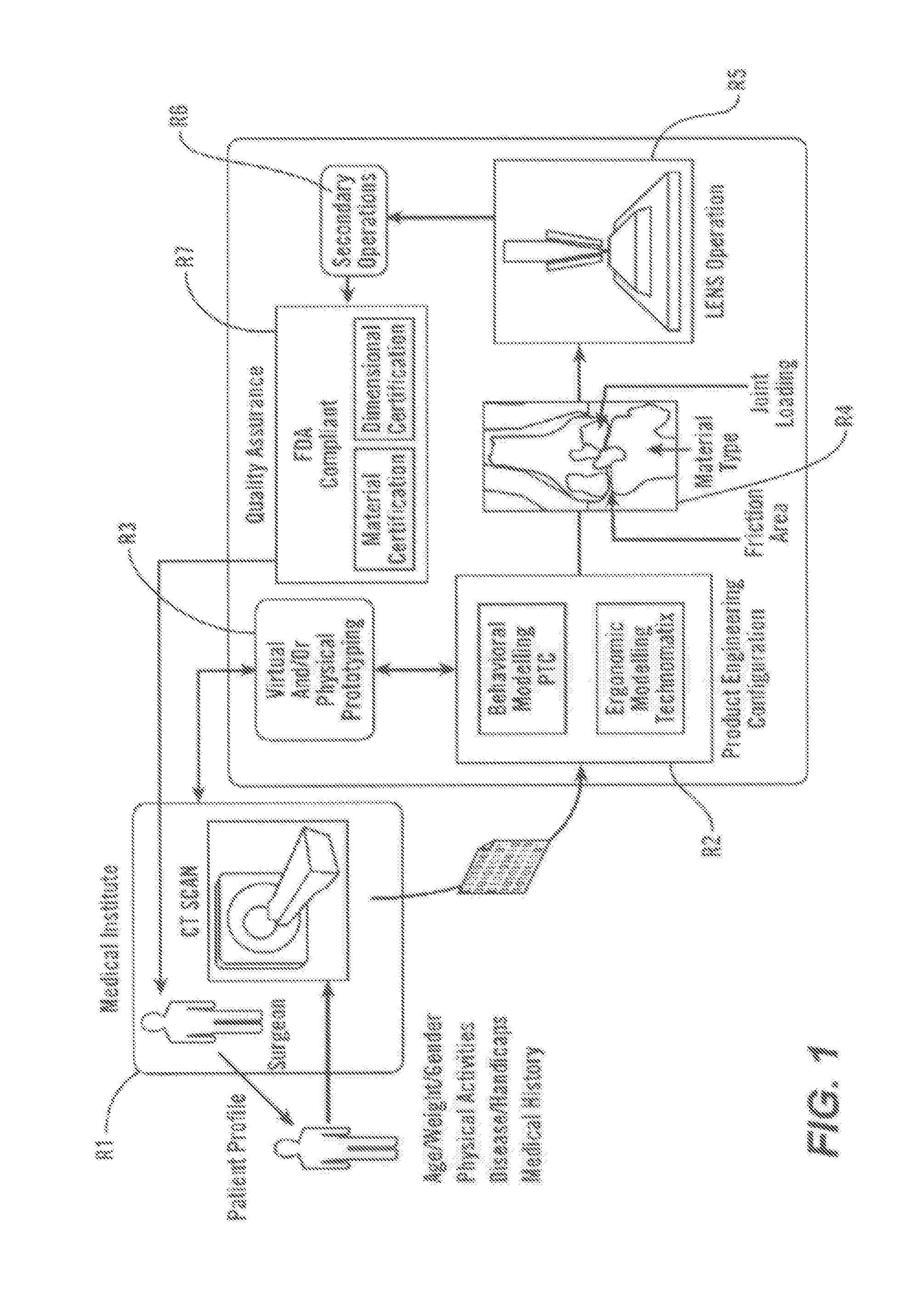
Personalized Fit and Functional Designed Medical Prostheses and Surgical Instruments and Methods for Making
ActiveUS20130245801A1Simple designFast learningMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusPersonalizationManufacturing technology
Methods, devices and systems for virtual, remote and real-time collaboration between surgeons and engineers using system learning and intelligent and timely disbursement of design and performance information to engineering teams embarking on the preliminary design event of a personalized orthopedic implant or personalize surgical instrument utilizing a case-based reasoning expert system. Additive manufacturing technology and statistically controlled advanced manufacturing processes quickly produce personalized medical devices worldwide.
Owner:SCHROEDER JAMES
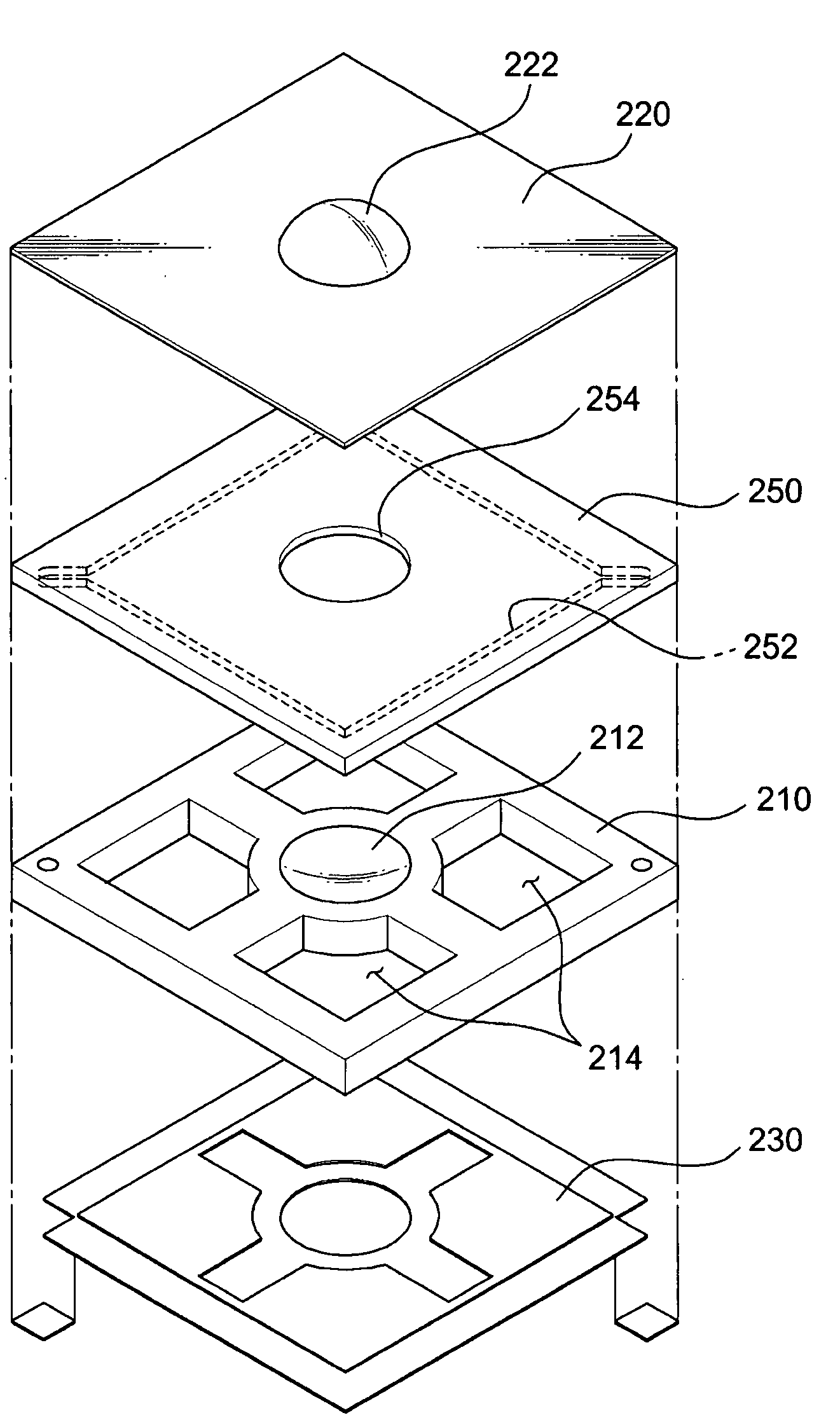
Integrated micro electro-mechanical system and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060205106A1Accurate representationHigh dimensional accuracyTelevision system detailsInflated body pressure measurementDielectricEtching
In the manufacturing technology of an integrated MEMS in which a semiconductor integrated circuit (CMOS or the like) and a micro machine are monolithically integrated on a semiconductor substrate, a technology capable of manufacturing the integrated MEMS without using a special process different from the normal manufacturing technology of a semiconductor integrated circuit is provided. A MEMS structure is formed together with an integrated circuit by using the CMOS integrated circuit process. For example, when forming an acceleration sensor, a structure composed of a movable mass, an elastic beam and a fixed beam is formed by using the CMOS interconnect technology. Thereafter, an interlayer dielectric and the like are etched by using the CMOS process to form a cavity. Then, fine holes used in the etching are sealed with a dielectric.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Flow cytometers and detection system of lesser size
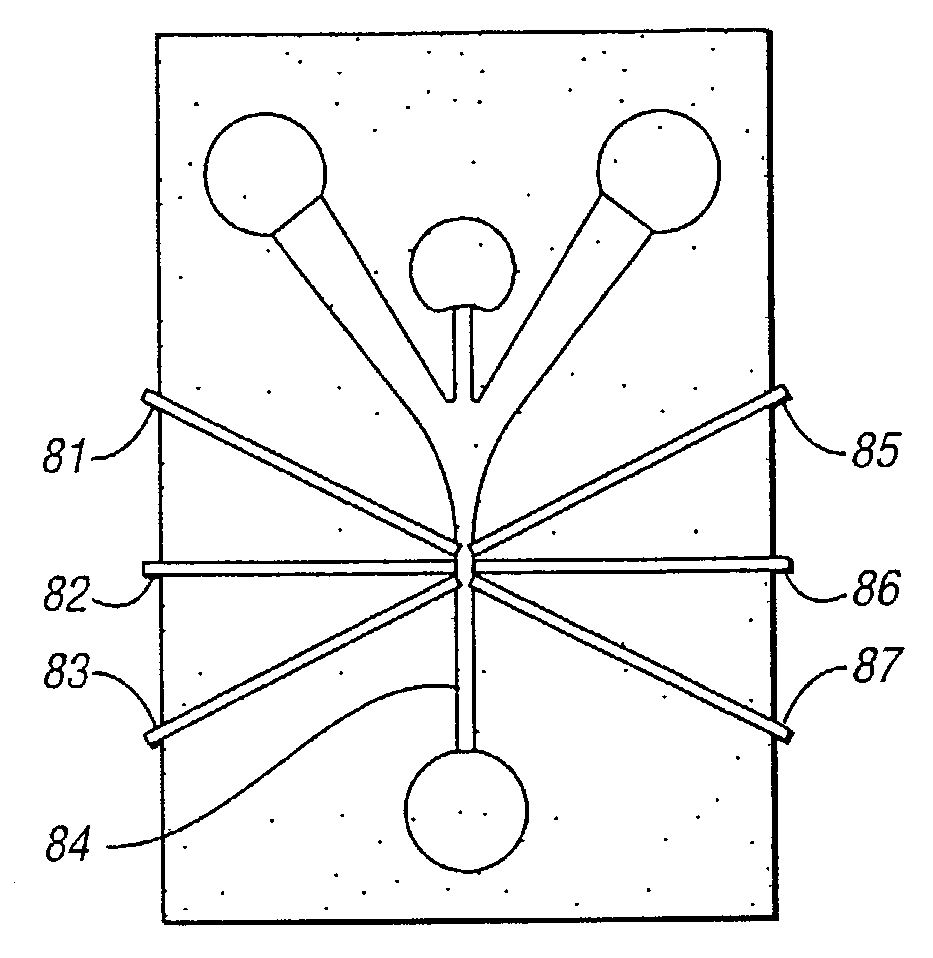
InactiveUS7105355B2Increase the number ofMaximize signal to noiseWithdrawing sample devicesAnalysis by material excitationFiberManufacturing technology
Gas focusing flow cytometers are fabricatable employing simple and inexpensive manufacturing techniques. When such cytometers or conventional cytometers are combined with fiber optical light paths and laser diode and semiconductor photodetectors, light weight and handheld, optionally disposable devices which maintain high performance are possible.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Additive fabrication support structures
ActiveUS20140300017A1Minimize contactProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
Some aspects provide a method of generating a support structure for an object, the support structure and the object to be fabricated via one or more additive fabrication techniques, comprising identifying one or more regions of the object as one or more regions to which mechanical support is to be provided, identifying one or more support points within at least a first region of the one or more regions, and generating the support structure for the object, the support structure comprising one or more support tips coupled to the object at the one or more support points, the support tips being generated based at least in part on a direction normal to the surface of the object at the respective support point.
Owner:FORMLABS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com