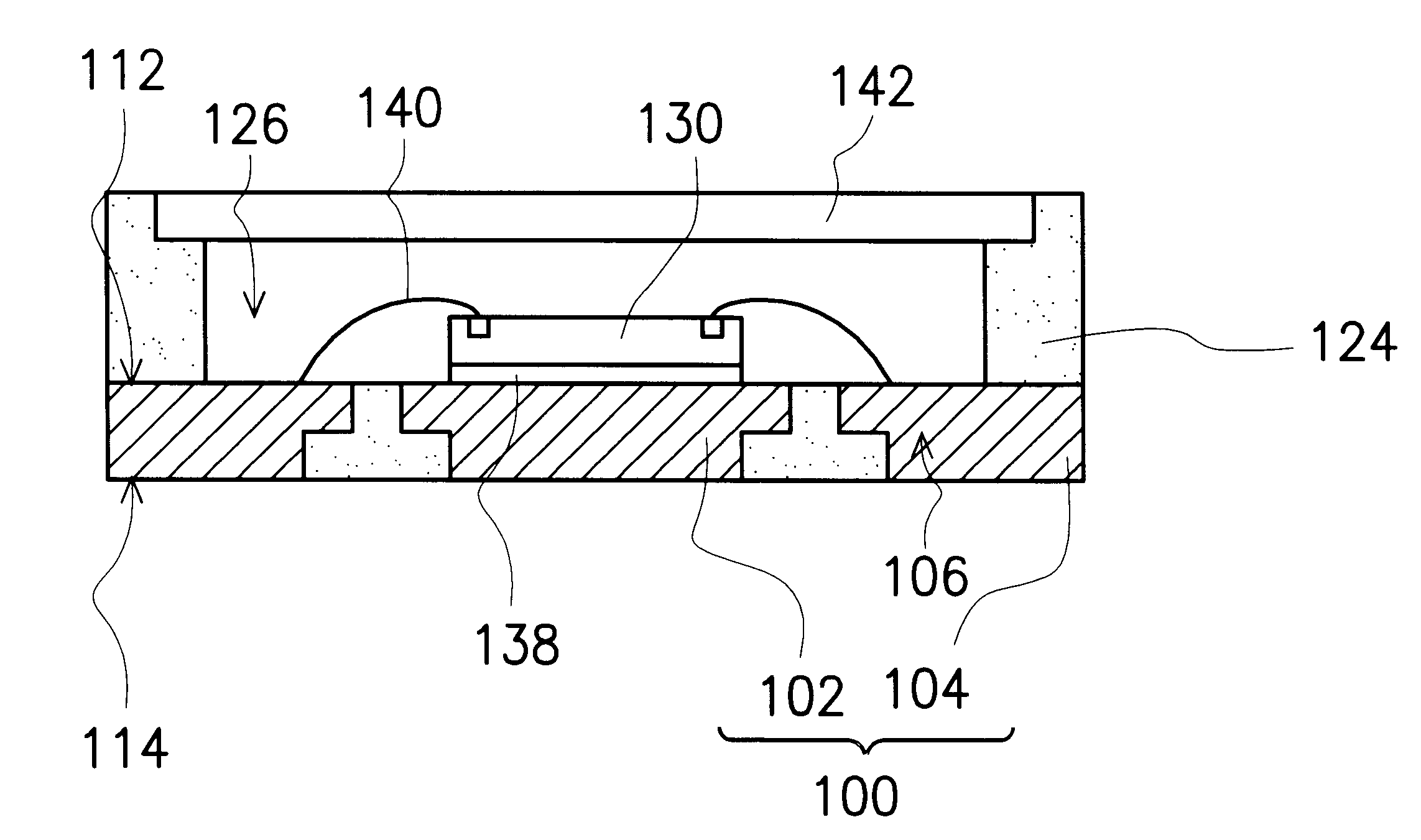
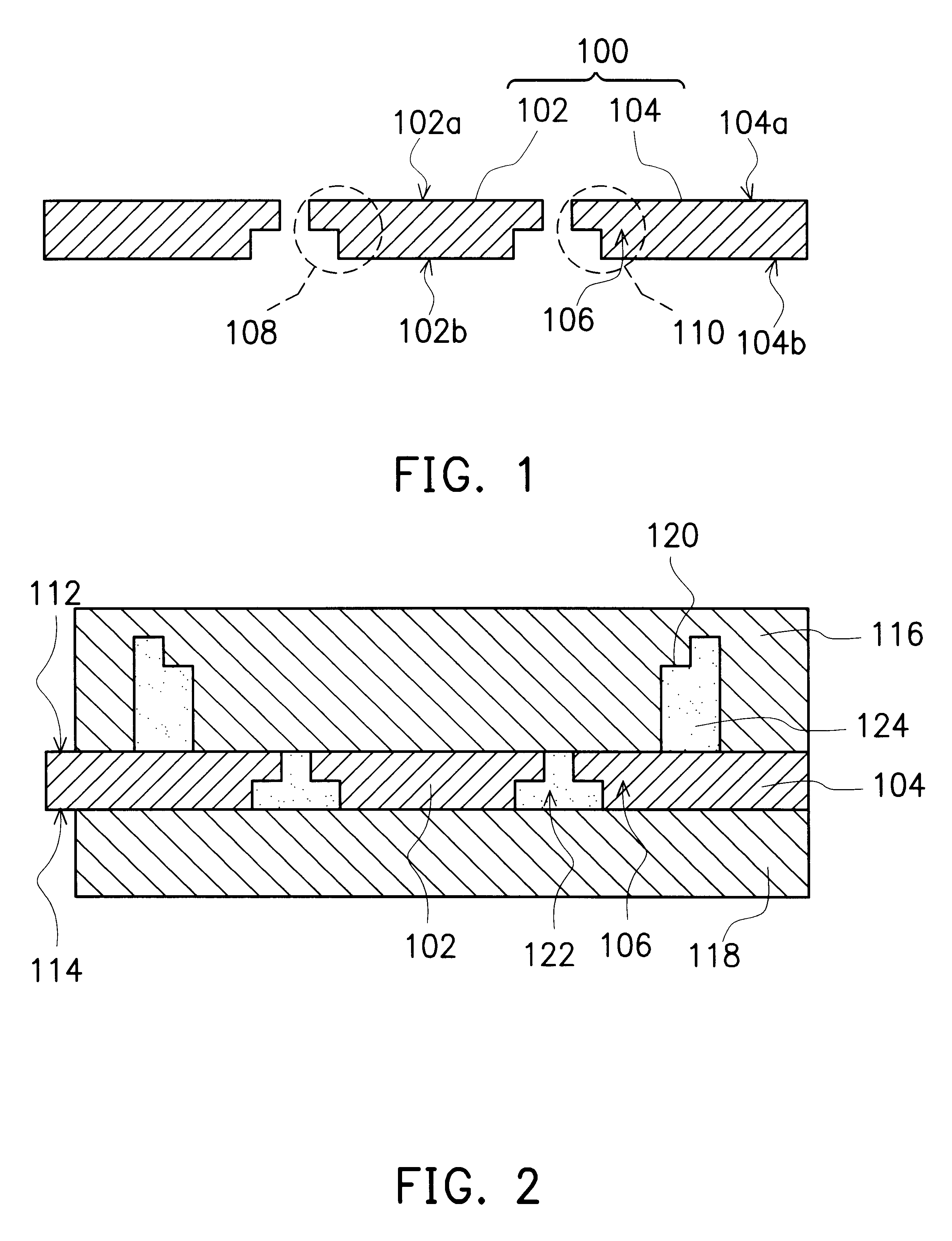
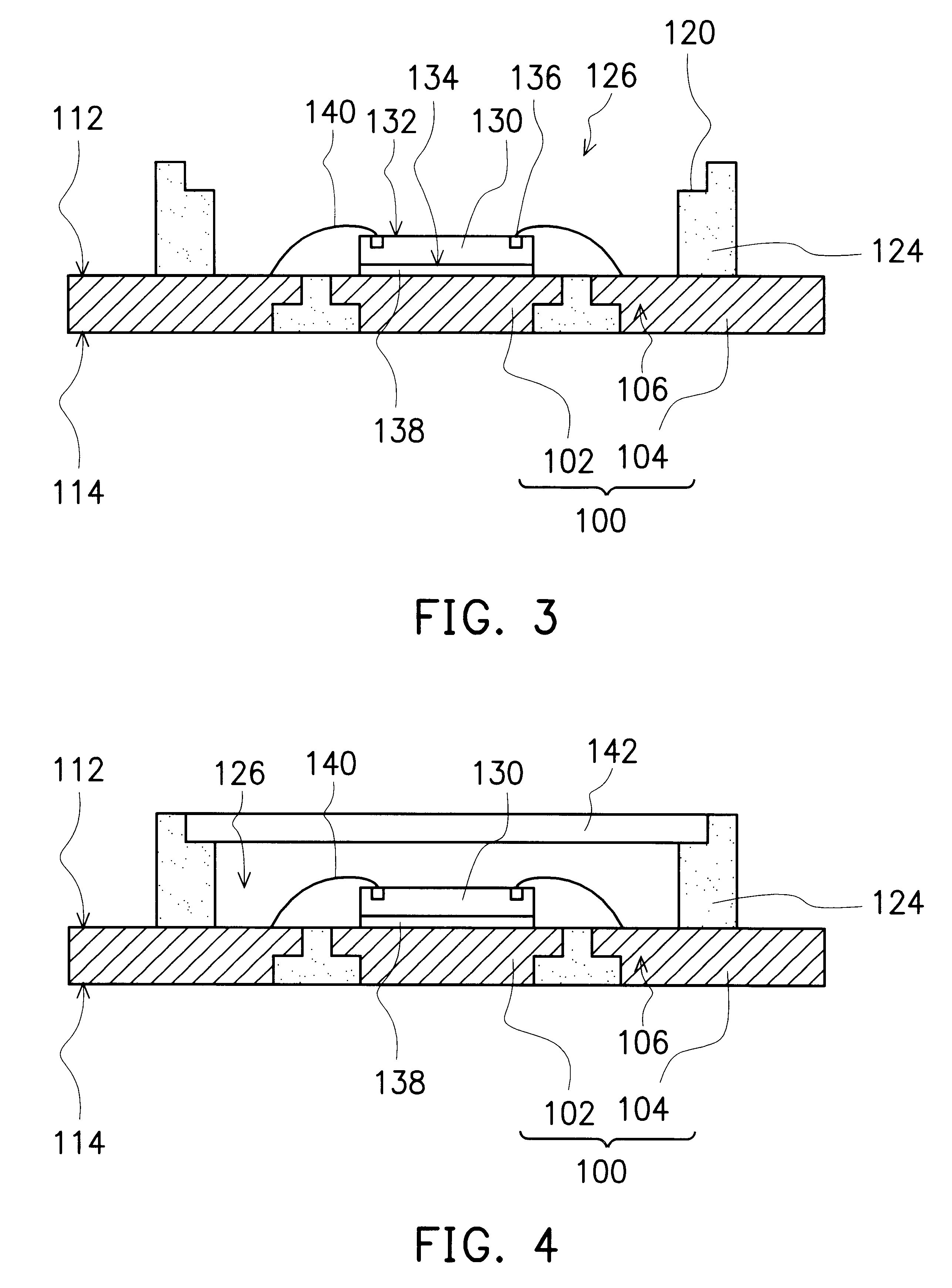
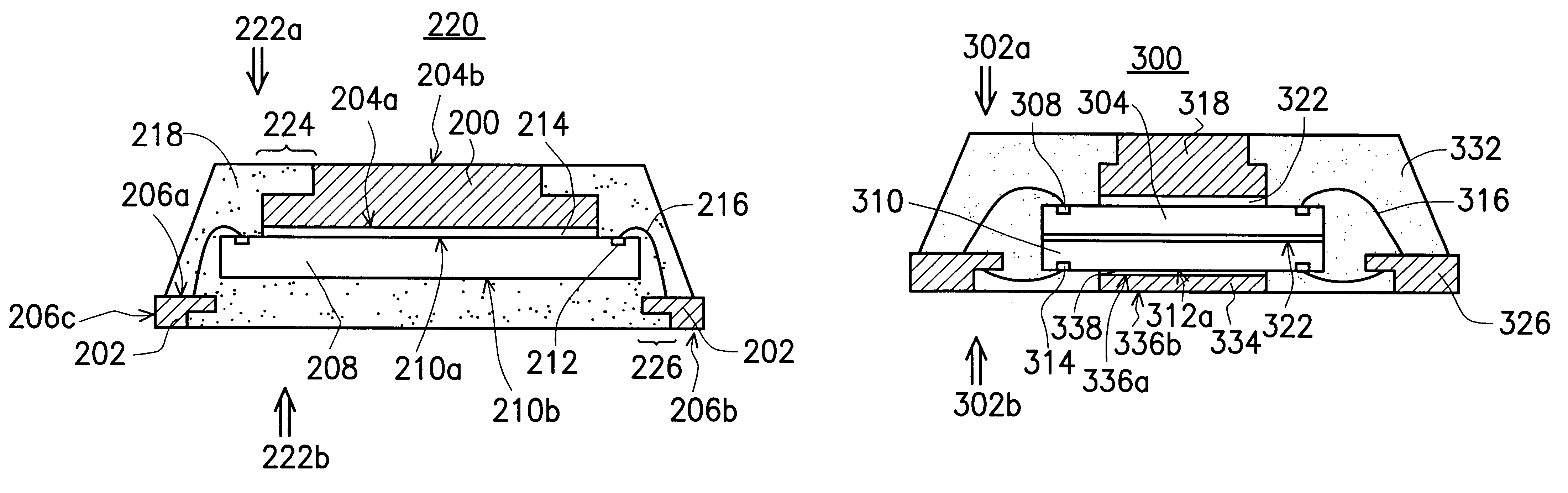
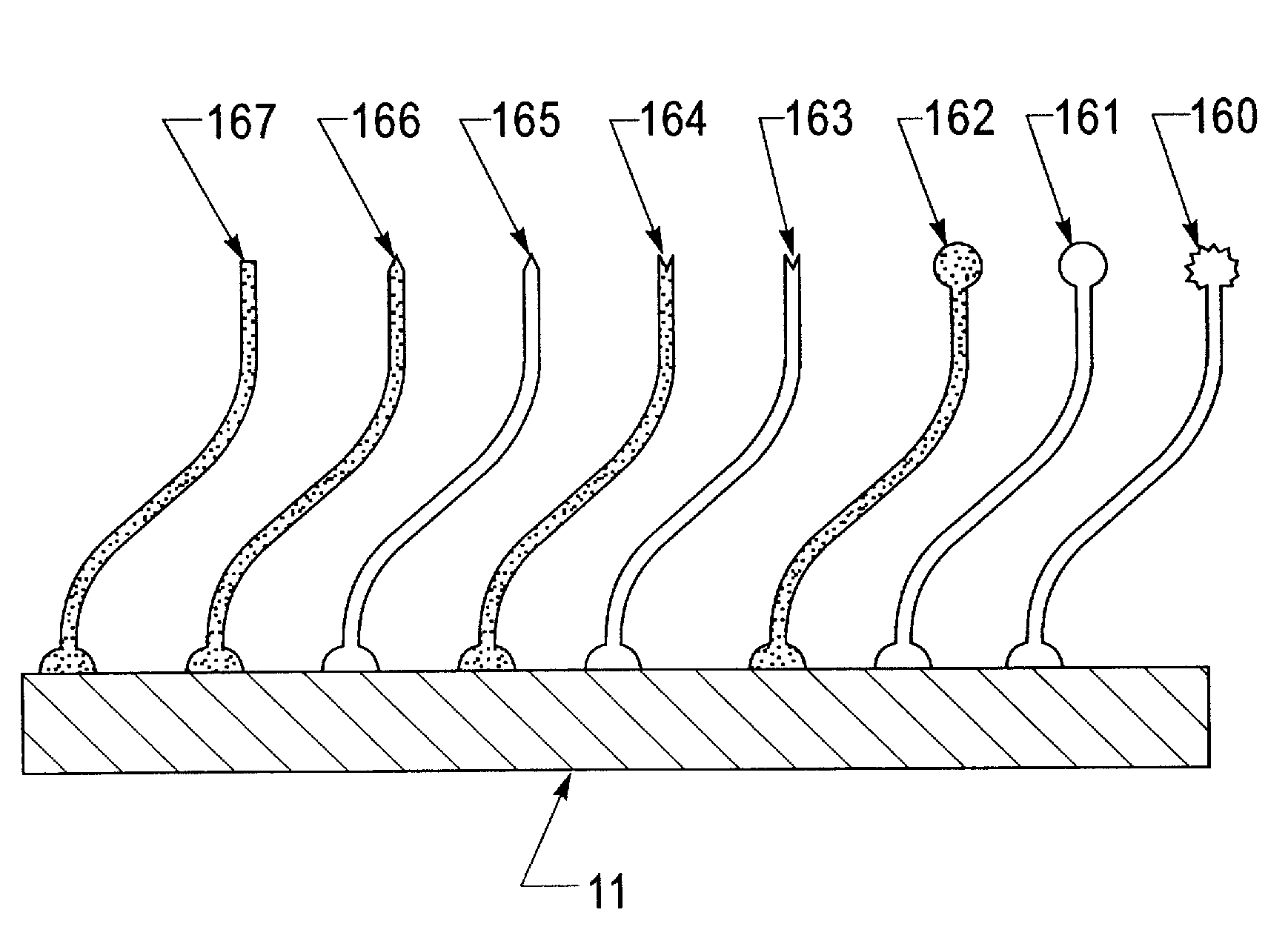
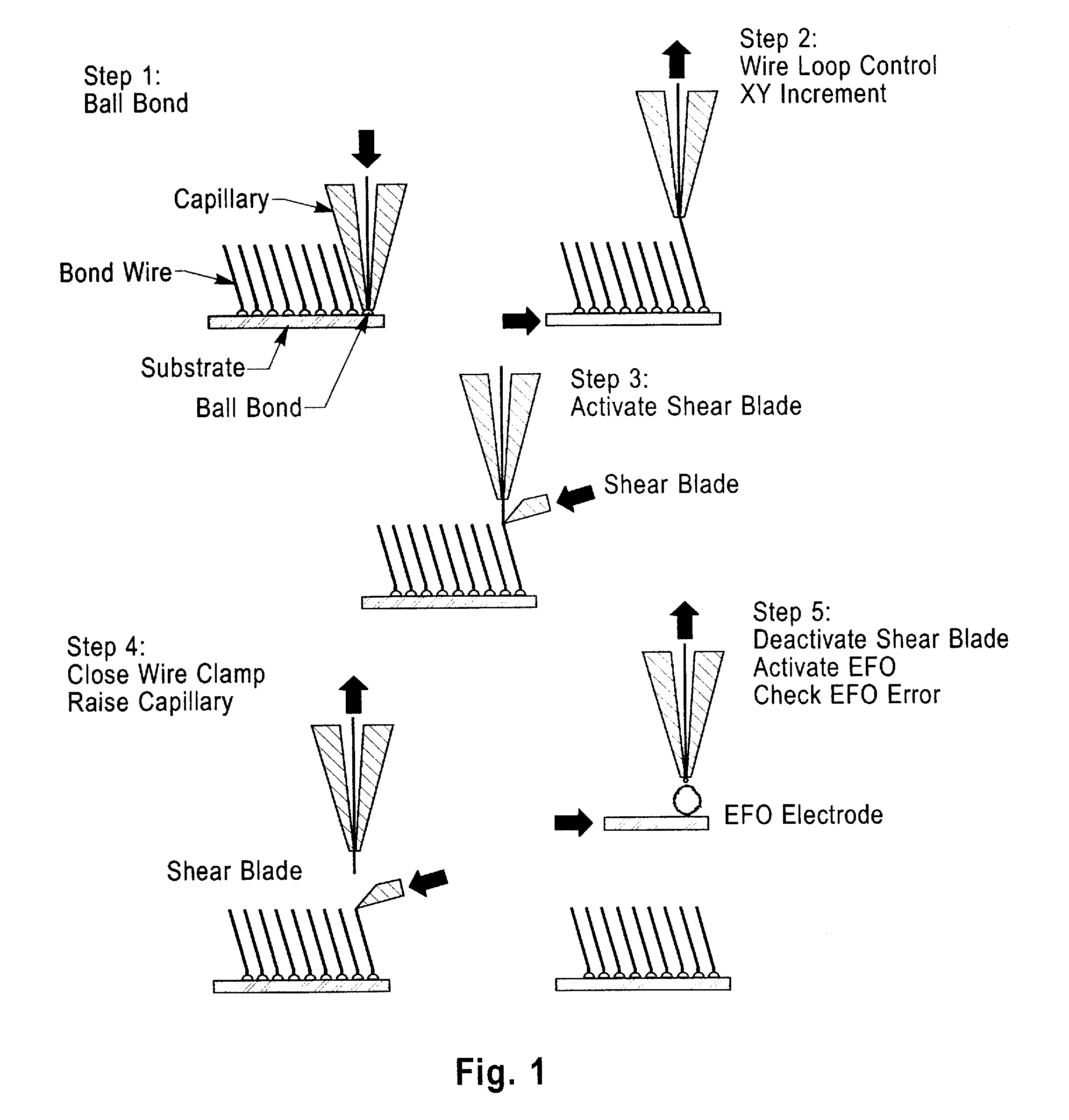
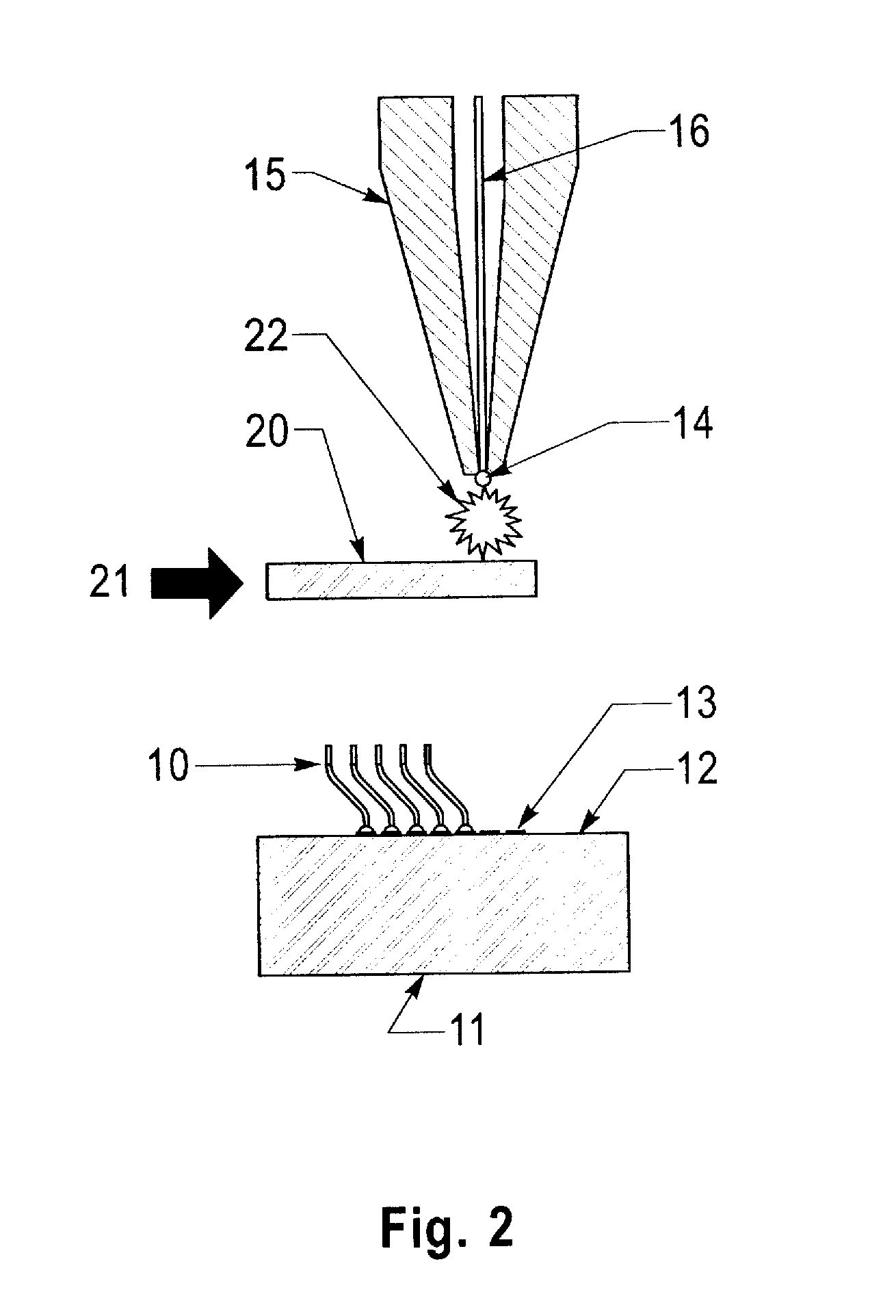
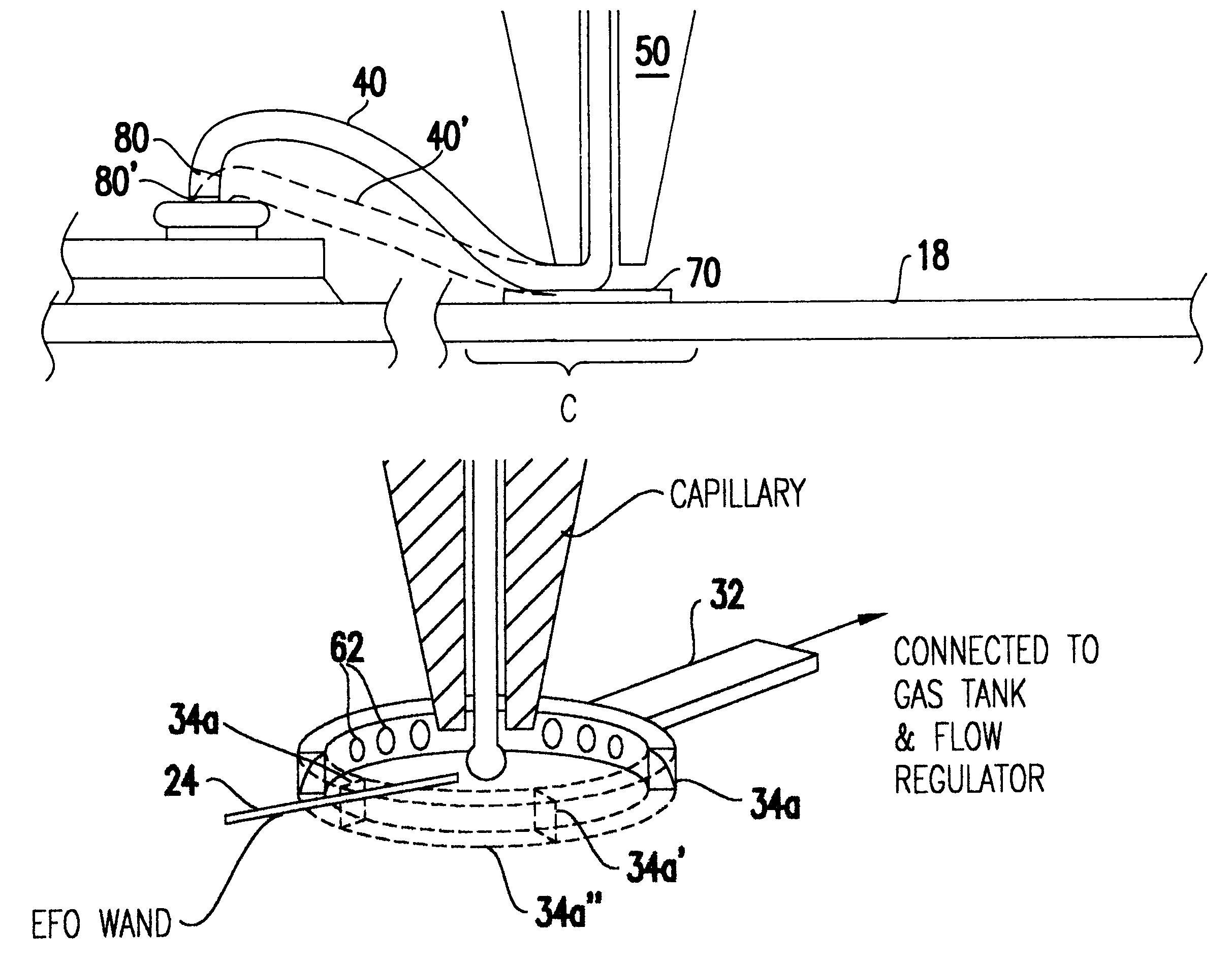
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1704 results about "Lead bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
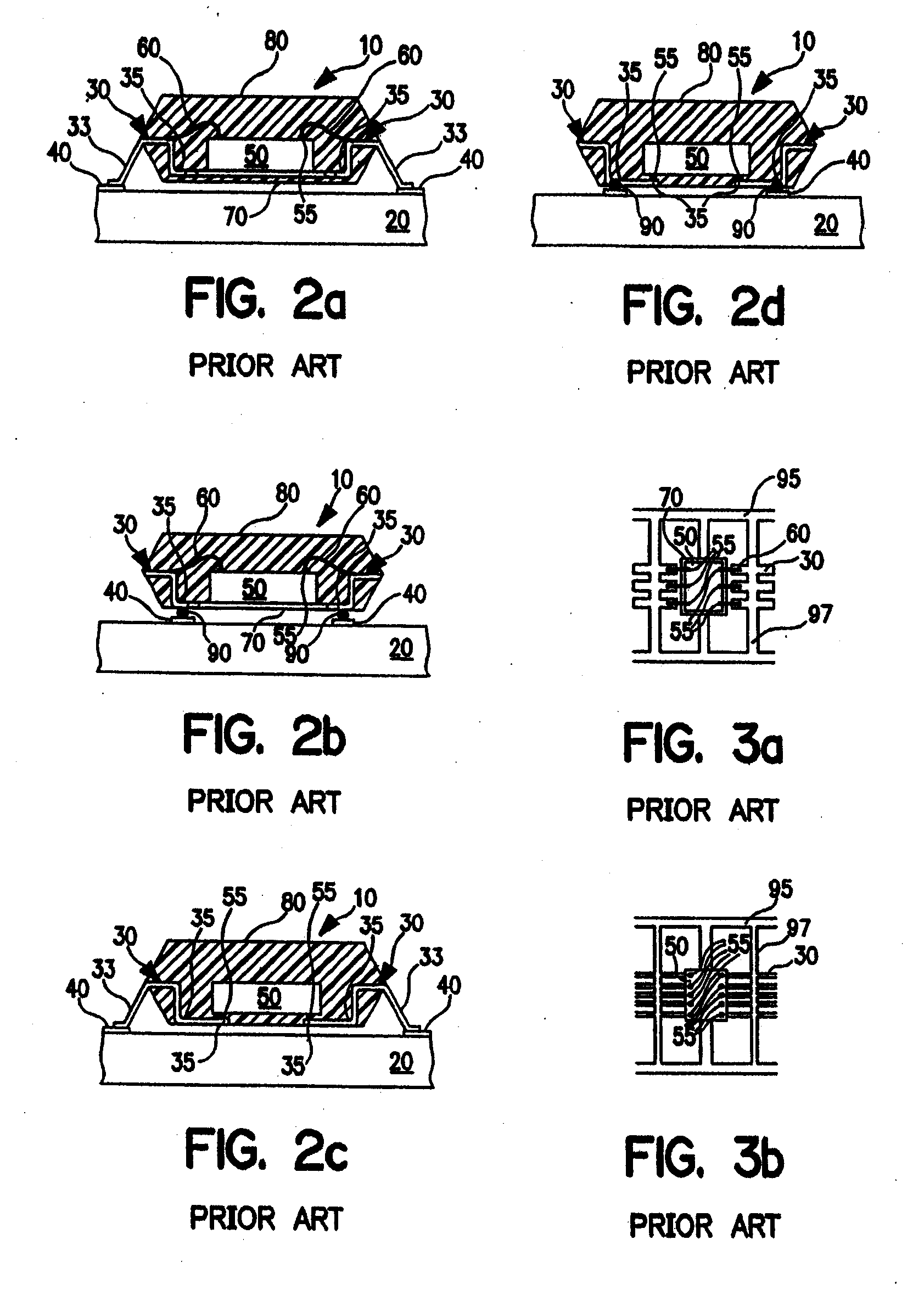
Lead Bonding. Lead Bonding as it is known is when the manufacturer bond the two pieces of wood together with industrial glue.
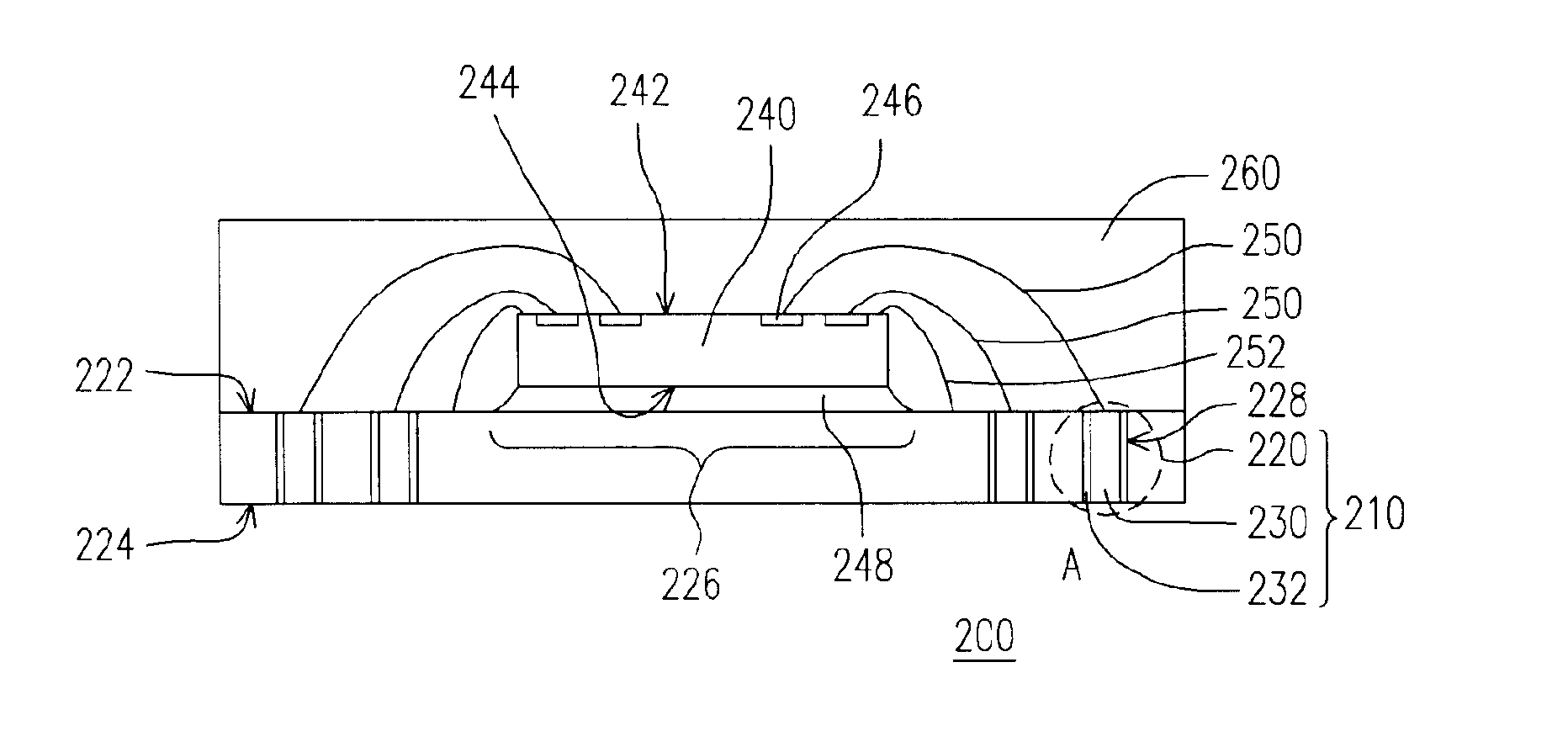
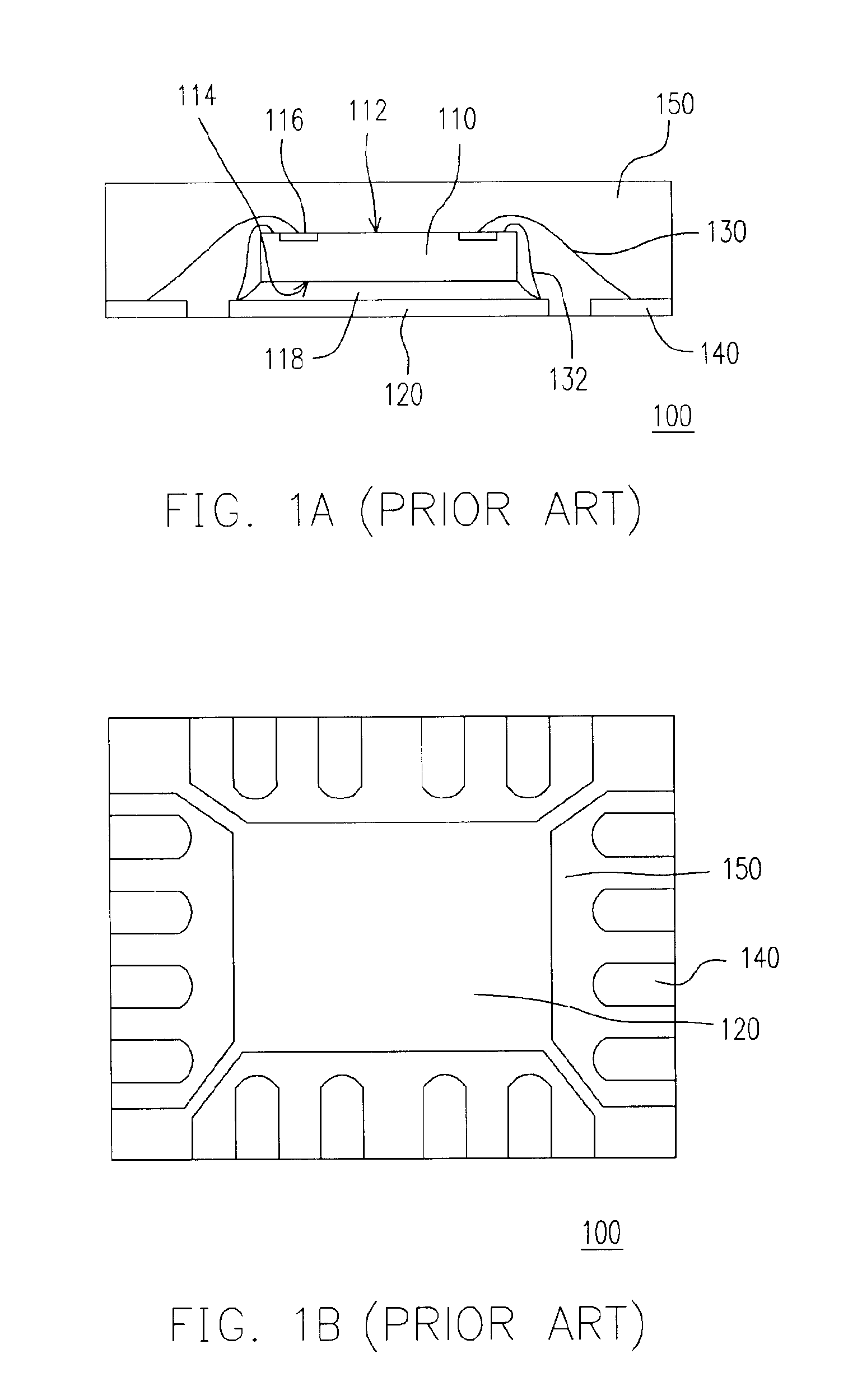
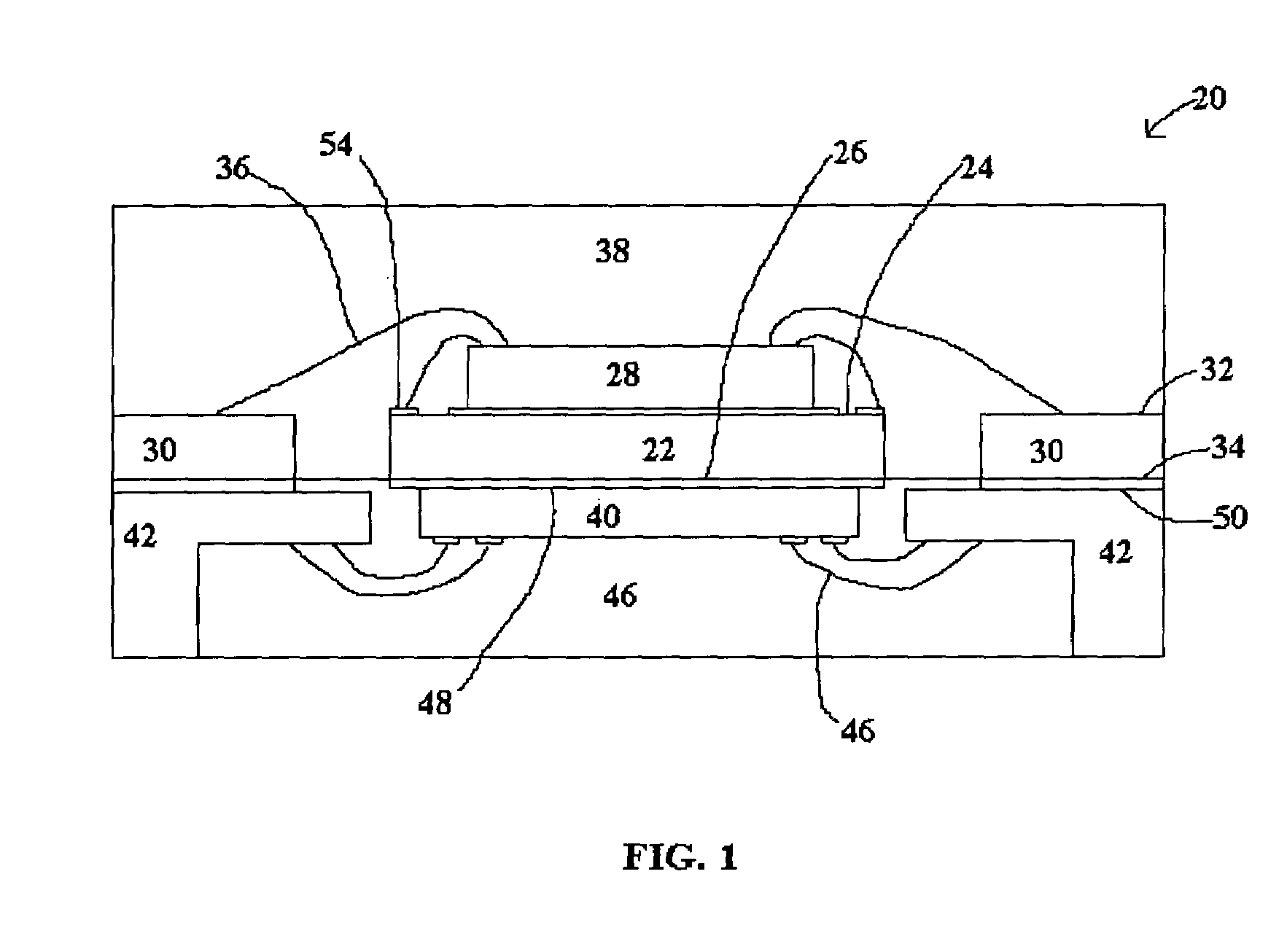
Leadless image sensor package structure and method for making the same
InactiveUS6384472B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
A leadless image sensor package constructed on a lead frame includes a die pad and a plurality of leads disposed at the periphery of the die pad. A molding compound, disposed on the top surface of the lead frame and being surrounding the die pad on the periphery of the lead frame, fills the clearance between the die pad and the leads and exposes, on the top surface, the die pad and the wire-bonding portion of the leads. Moreover, the lead frame and the molding compound constitute a "chip containing space" with chip set therein. Further, the chip with its back surface attached to the top surface of the die pad makes use of the wires to electrically connect to the bonding pad and the top surface of the wire-bonding portion, thereafter, a transparent lid is used to cap and seal the "chip containing space".
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
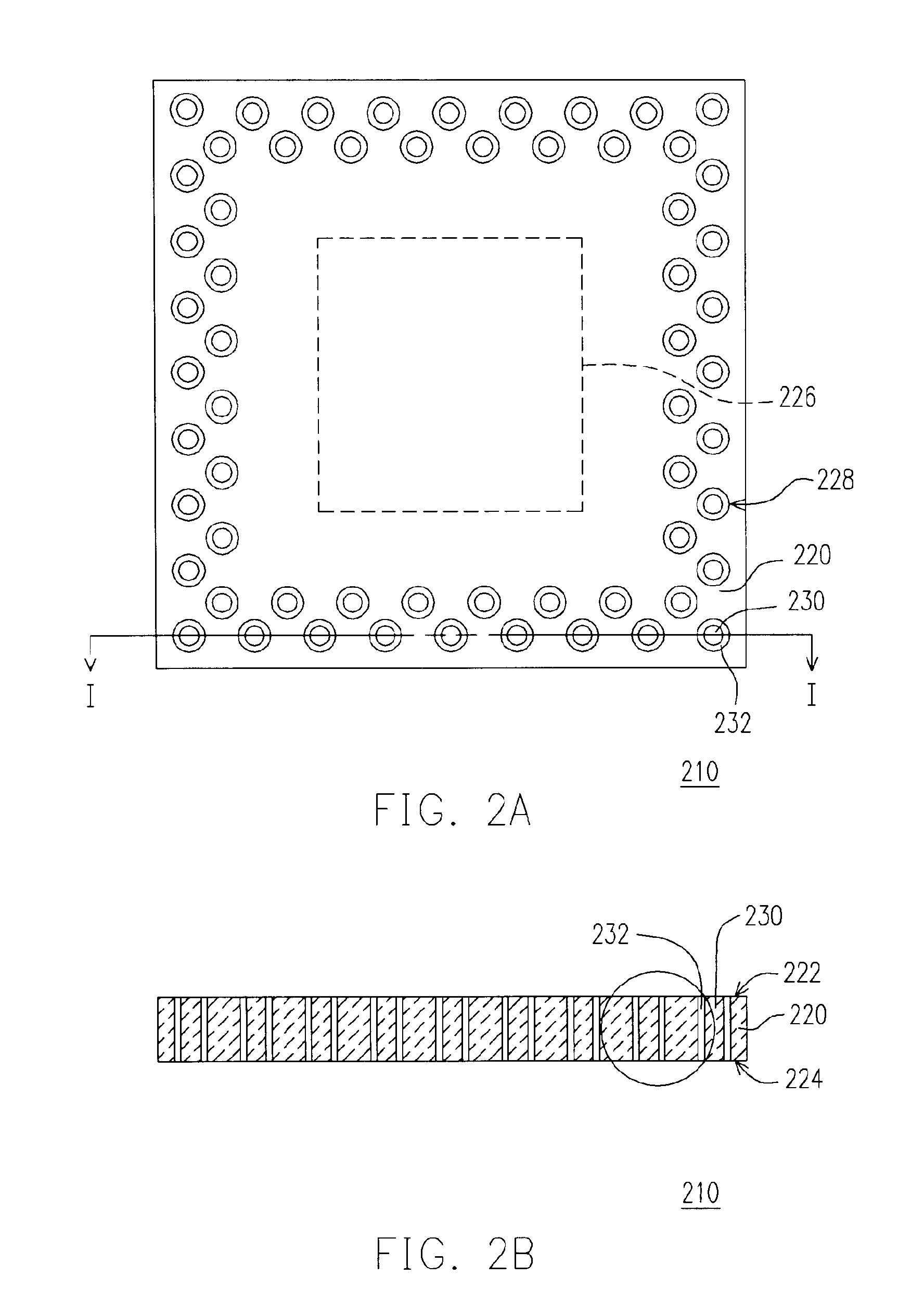
Quad flat non-lead package of semiconductor
InactiveUS6414385B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingSemiconductor package
A Quad Flat Non-Lead package of semiconductor comprises a chip, a plurality of leads, and a molding compound. The chip has its active surface bonded to the die pad, and the area of the die pad is smaller than that of the chip in order to expose the bonding pad on the active surface of the chip. The leads are disposed at the periphery of the die pad. A plurality of bonding wires is used to electrically connect the top surface of the leads to the bonding pads. The molding compound encapsulates the chip, the die pad, the bonding wires, and a portion of the surface of the leads. In this way, the encapsulating process make the side surface of the lead, and the portion excluding the wire-bonding protruded zone of the bottom surface of the lead exposed in order to make the leads become the external connections of the package structure.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
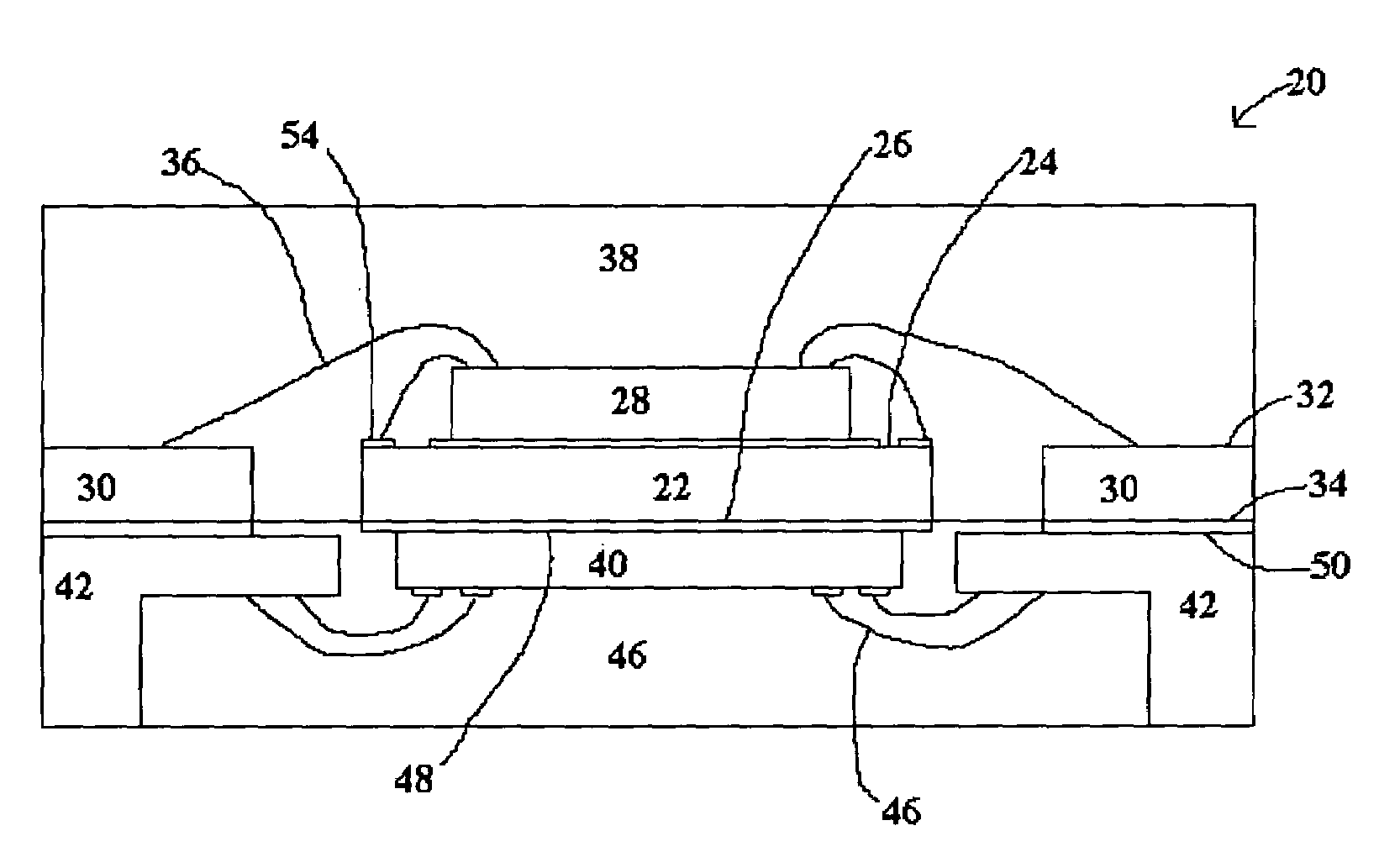
Method and apparatus for a semiconductor package for vertical surface mounting
InactiveUS6291894B1Electrically conductive connectionsDigital data processing detailsDevice materialSurface mounting
A method for packaging a semiconductor device includes connecting a plurality of wire leads to a corresponding plurality of electrical connection pads on the semiconductor device, covering at least a portion of the semiconductor device and at least a portion of each of the wire leads with an encapsulating material, and removing a portion of the encapsulating material and a portion of each of the wire leads to form a packaged semiconductor device wherein each of the wire leads has an exposed portion only at an end. The invention also includes a packaged semiconductor device having an integrated circuit device with a plurality of electrical connection pads, a plurality of wire leads coupled to the plurality of electrical connection pads, and a covering of encapsulating material covering at least a portion of the integrated circuit device and covering each of the wire leads, wherein each of the wire leads has an exposed end. The present invention contemplates wire bonding and encapsulation of individual die as well as multiple die on a single wafer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Multi-chip stacked devices
InactiveUSRE36613E1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
A multiple stacked die device is disclosed that contains up to four dies and does not exceed the height of current single die packages. Close-tolerance stacking is made possible by a low-loop-profile wire-bonding operation and thin-adhesive layer between the stacked dies.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method of stacking thin substrates by transfer bonding
InactiveUS20060057836A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCost effectivenessAdhesive
This invention describes a method of stacking, bonding, and electrically interconnecting a plurality of thin integrated circuit wafers to form an interconnected stack of integrated circuit layers. The first integrated circuit layer is formed by conventional processing on a silicon wafer to the stage where bond pads are patterned on a wiring layer interconnecting the subjacent semiconductive devices. The remaining integrated circuit layers are formed by first processing a standard wafer to form integrated circuit devices and wiring levels up to but not including bond pads. Each of these wafers is mounted onto a handler wafer by its upper face with a sacrificial bonding agent. The wafer is thinned, permanently fastened to the top surface of the first base wafer by a non-conductive adhesive applied to the thinned under face, and dismounted from the handler. Vertical openings are etched through the thinned layer to the bond pads on the subjacent wafer. Robust conductive pass-through plugs with integrated upper bond pads are formed in the openings. Additional thinned integrated circuit layers may be prepared, thinned, cemented onto the stack. Wiring interconnections can be made between any two or more layers. The process is unique in that it can be used to further stack and interconnect any number of thinned wafer layers to form a three dimensional integrated circuits, including MEMS devices. This approach provides a low temperature wafer bonding method using an adhesive which results in process simplicity and cost effectiveness by eliminating an additional masking and patterning process for under bump metal thereby enabling standard wafers to be integrated into a 3D stack with existing wire bonded wafers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Semiconductor multi-package module having wire bond interconnect between stacked packages and having electrical shield
ActiveUS6838761B2Low production costOverall design flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
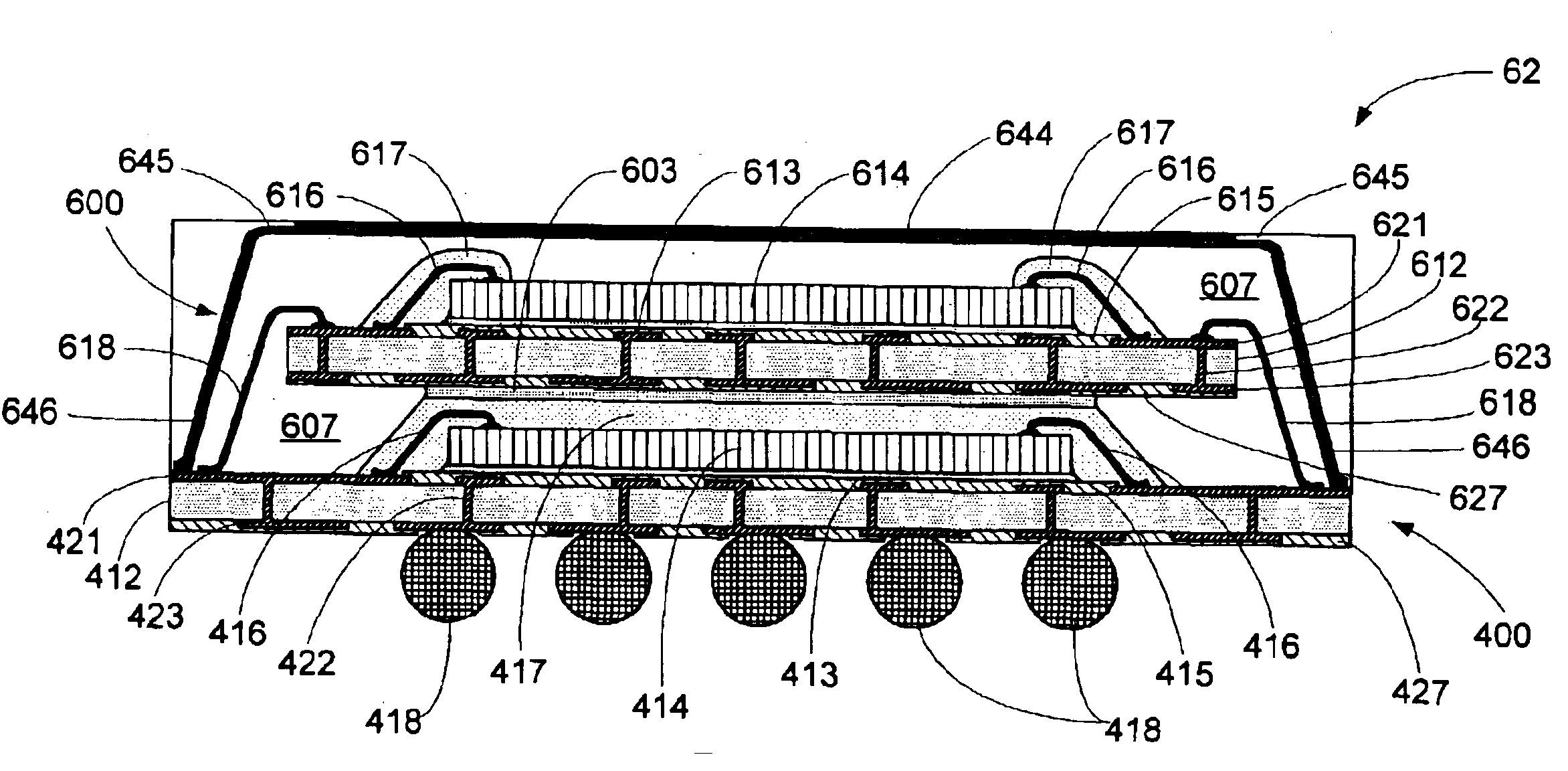
A semiconductor multi-package module having stacked lower and upper packages, each package including a die attached to a substrate, in which the upper and lower substrates are interconnected by wire bonding. Also, a method for making a semiconductor multi-package module, by providing a lower molded package including a lower substrate and a die, affixing an upper molded package including an upper substrate onto the upper surface of the lower package, and forming wire bond z-interconnects between the upper and lower substrates.
Owner:STATS CHIPPAC LTD
Chip package and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070205520A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnisotropic conductive filmLead bonding
A chip package includes a semiconductor substrate, a first metal pad over the semiconductor substrate, and a second metal pad over the semiconductor substrate. In a case, the first metal pad is tape automated bonded thereto, and the second metal pad is solder bonded thereto. In another case, the first metal pad is tape automated bonded thereto, and the second metal pad is wirebonded thereto. In another case, the first metal pad is solder bonded thereto, and the second metal pad is wirebonded thereto. In another case, the first metal pad is bonded to an external circuitry using an anisotropic conductive film, and the second metal pad is solder bonded thereto. In another case, the first metal pad is bonded to an external circuitry using an anisotropic conductive film, and the second metal pad is wirebonded thereto.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
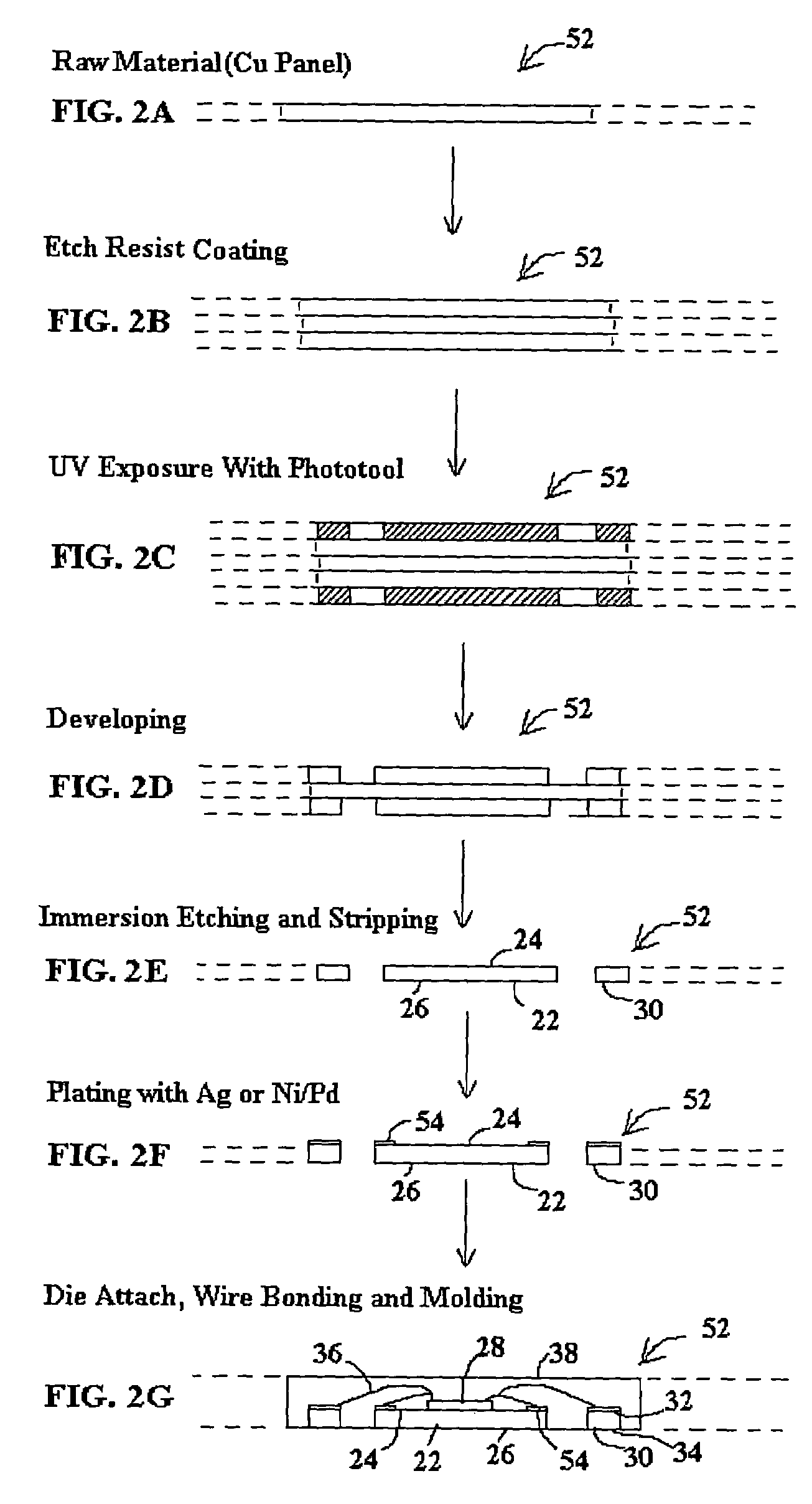
Partially patterned lead frames and methods of making and using the same in semiconductor packaging
InactiveUS20080258278A1Reduce thicknessImprove structural rigiditySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingBonding process
A method of making a lead frame and a partially patterned lead frame package with near-chip scale packaging lead-count, wherein the method lends itself to better automation of the manufacturing line and improved quality and reliability of the packages produced therefrom. A major portion of the manufacturing process steps is performed with a partially patterned strip of metal formed into a web-like lead frame on one side so that the web-like lead frame is also rigid mechanically and robust thermally to perform without distortion or deformation during the chip-attach and wire bond processes, both at the chip level and the package level. The bottom side of the metal lead frame is patterned to isolate the chip-pad and the wire bond contacts only after the front side, including the chip and wires, is hermetically sealed with an encapsulant. The resultant package being electrically isolated enables strip testing and reliable singulation.
Owner:UNISEM M BERHAD
Through-wafer interconnects for photoimager and memory wafers
InactiveUS7300857B2High densityImprove functionalitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPath lengthLead bonding
A through-wafer interconnect for imager, memory and other integrated circuit applications is disclosed, thereby eliminating the need for wire bonding, making devices incorporating such interconnects stackable and enabling wafer level packaging for imager devices. Further, a smaller and more reliable die package is achieved and circuit parasitics (e.g., L and R) are reduced due to the reduced signal path lengths.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
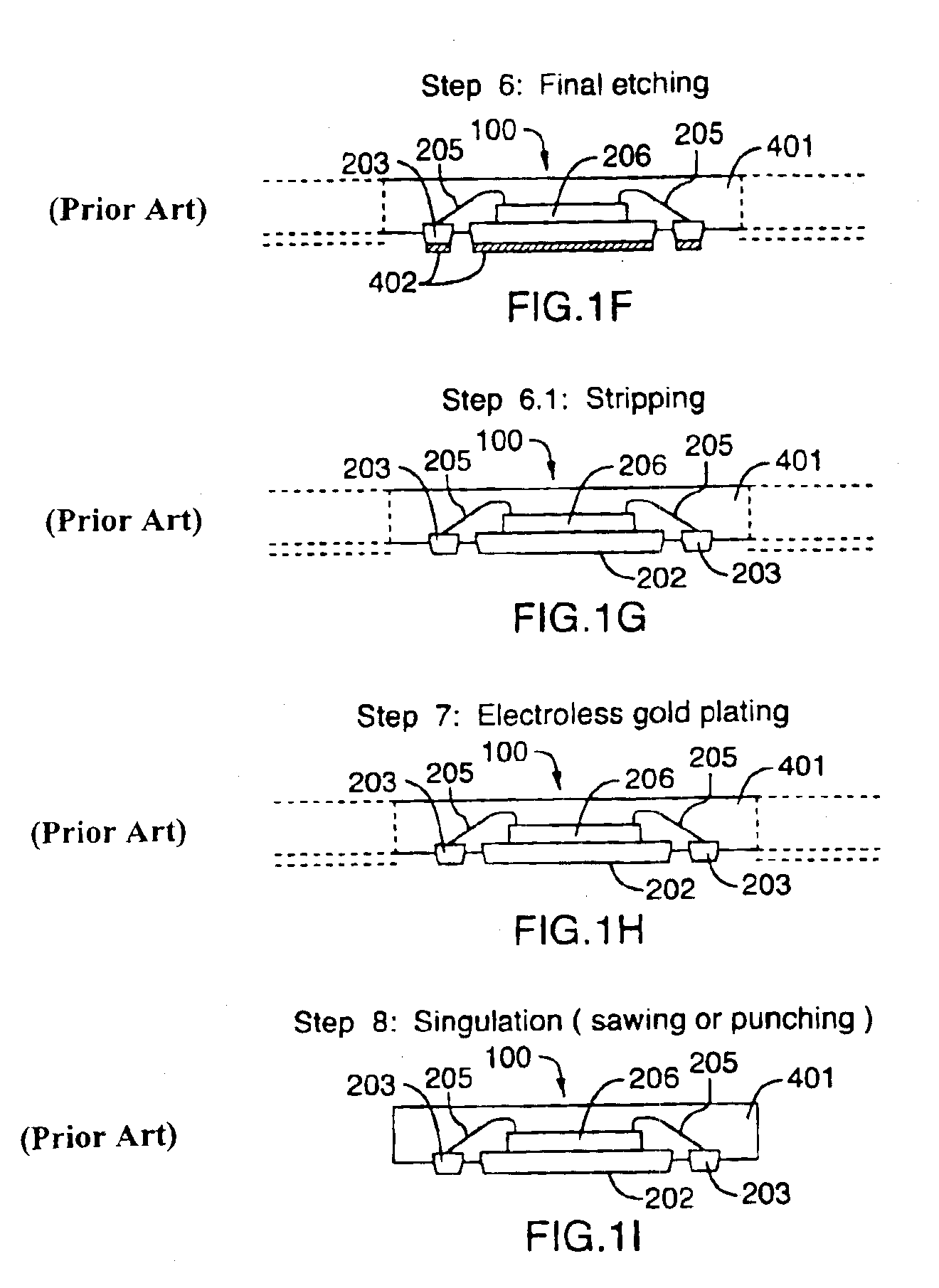
Leadless plastic chip carrier with etch back pad singulation
InactiveUS6933594B2Improve interlockEasy alignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingPunching
A leadless plastic chip carrier is constructed by half etching one or both sides of the package design onto a leadframe strip so as to create unique design features such as power and / or ground ring surrounding the die attach pad, interlocking rivet head construction for the contact pads, and an interlocking pattern for the die attach pad. After wire bonding and molding, a further etching is performed to isolate and expose contact pads. Singulation of individual chip packages from the leadframe strip is then performed by saw singulation or die punching.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
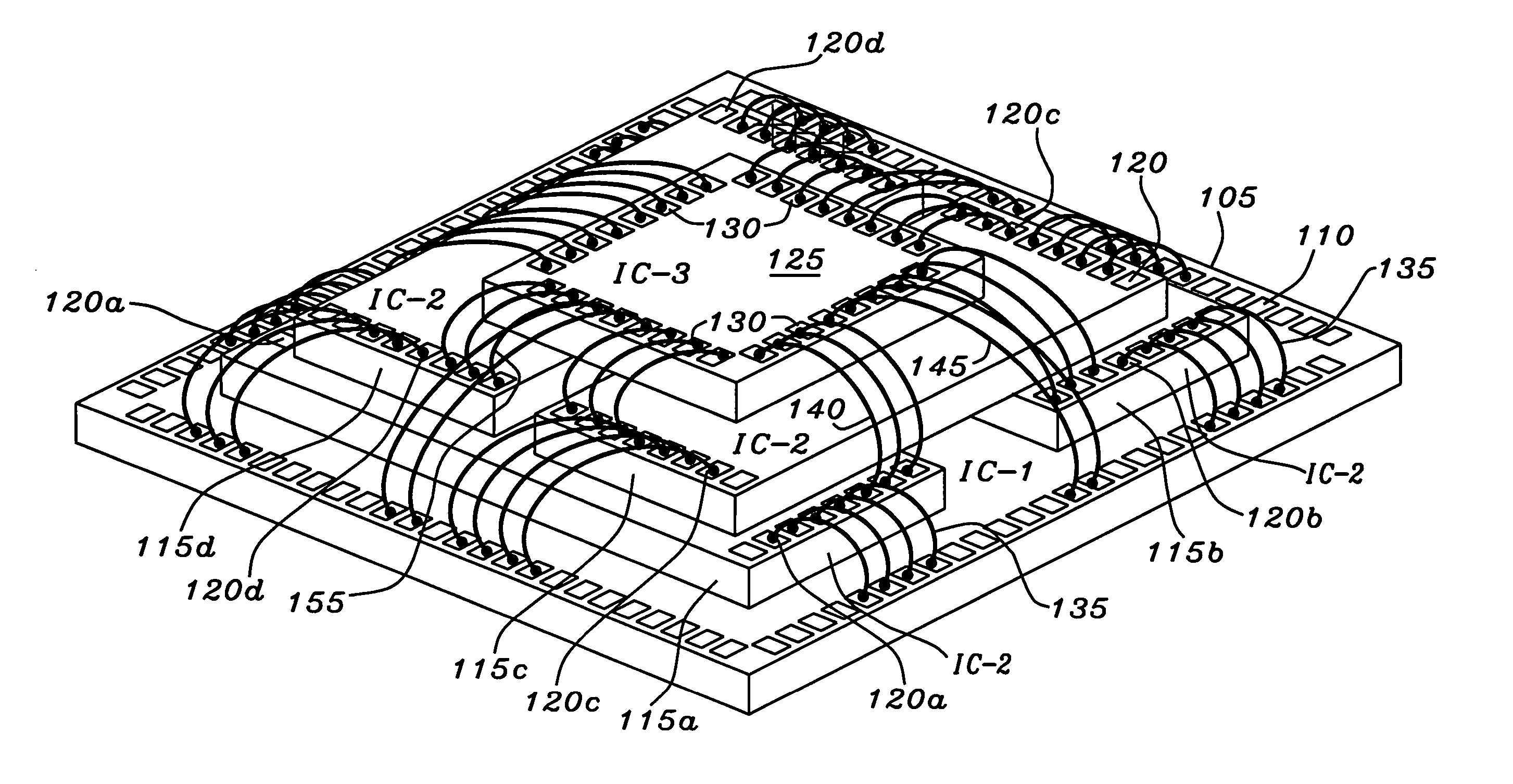
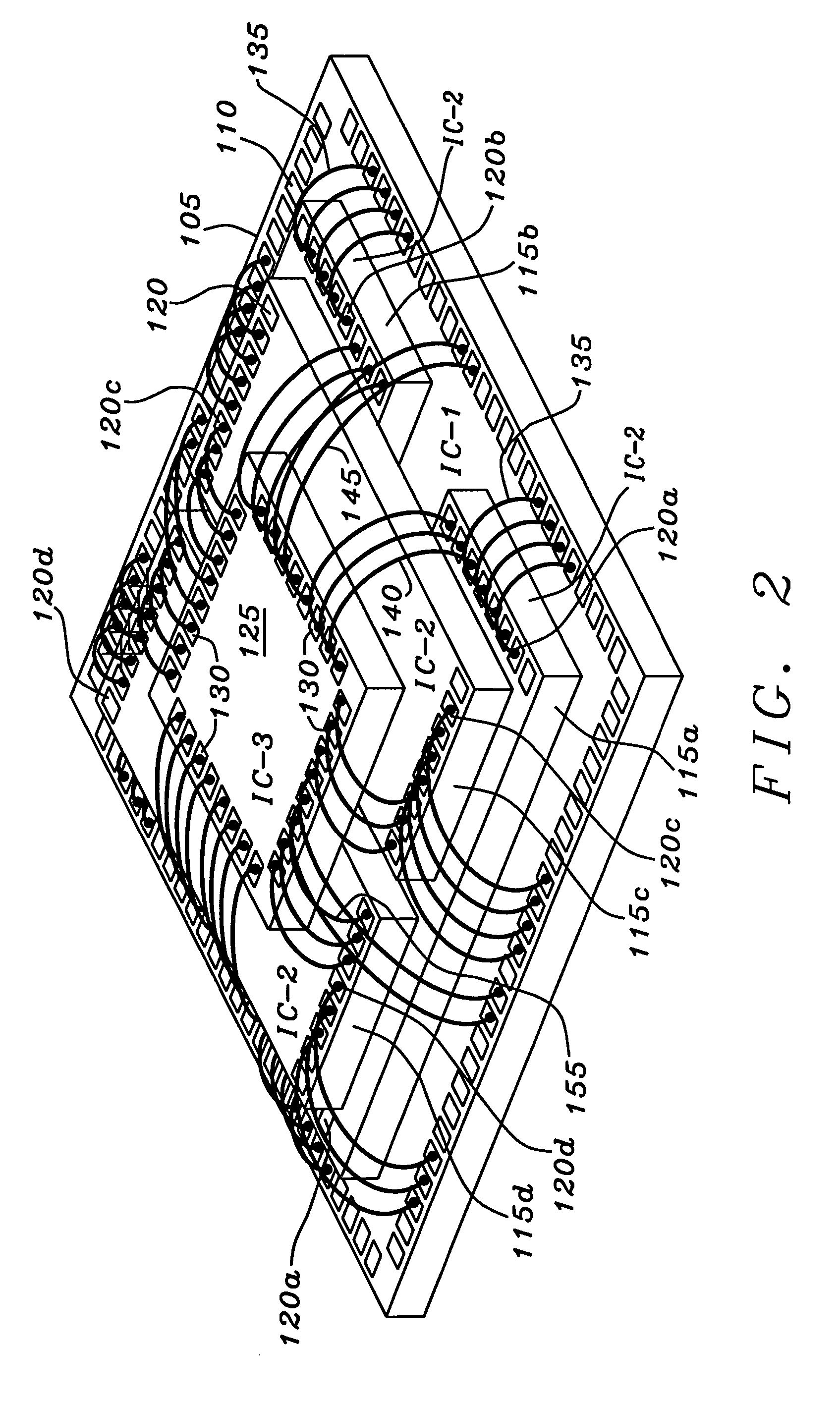
Stacked multiple integrated circuit die package assembly
InactiveUS20060087013A1Interference be notSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
An electronic package assembly is formed with a plurality of integrated circuit dies stacked in layers. At least one first die is placed on a substrate. Each subsequent layer of the stack contains at least one die. Each die on each layer has a size and shape such that, when placed on the dies on a lower layer, it is offset from the edges of the dies on the lower layer to allow affixing of wirebonds to input / output pads of the dies on the lower layer. Each die on each layer with more than one die has input / output pads placed on two sides of the die. Each die on an upper layer is placed orthogonally to each die of a lower each layer such that wirebonds are affixed without interference.
Owner:ETRON TECH INC
Wire bond free wafer level LED
ActiveUS20090121241A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLead bondingPhosphor
A wire-bond free semiconductor device with two electrodes both of which are accessible from the bottom side of the device. The device is fabricated with two electrodes that are electrically connected to the oppositely doped epitaxial layers, each of these electrodes having leads with bottom-side access points. This structure allows the device to be biased with an external voltage / current source, obviating the need for wire-bonds or other such connection mechanisms that must be formed at the packaging level. Thus, features that are traditionally added to the device at the packaging level (e.g., phosphor layers or encapsulants) may be included in the wafer level fabrication process. Additionally, the bottom-side electrodes are thick enough to provide primary structural support to the device, eliminating the need to leave the growth substrate as part of the finished device.
Owner:CREELED INC
Method of forming vias in silicon carbide and resulting devices and circuits
InactiveUS6515303B2Promote differentiationErosion is goodSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingInductance
A method of fabricating an integrated circuit on a silicon carbide substrate is disclosed that eliminates wire bonding that can otherwise cause undesired inductance. The method includes fabricating a semiconductor device on a first surface of a silicon carbide substrate and with at least one metal contact for the device on the first surface of the substrate. The opposite, second surface of the substrate is then ground and polished until it is substantially transparent. The method then includes masking the polished second surface of the silicon carbide substrate to define a predetermined location for a via that is opposite the device metal contact on the first surface; etching the desired via through the desired masked location until the etch reaches the metal contact on the first surface; and metallizing the via to provide an electrical contact from the second surface of the substrate to the metal contact and to the device on the first surface of the substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface
ActiveUS8618659B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEdge surfaceLead bonding
A microelectronic assembly includes a substrate having a first surface and a second surface remote from the first surface. A microelectronic element overlies the first surface and first electrically conductive elements are exposed at one of the first surface and the second surface. Some of the first conductive elements are electrically connected to the microelectronic element. Wire bonds have bases joined to the conductive elements and end surfaces remote from the substrate and the bases, each wire bond defining an edge surface extending between the base and the end surface. An encapsulation layer extends from the first surface and fills spaces between the wire bonds such that the wire bonds are separated by the encapsulation layer. Unencapsulated portions of the wire bonds are defined by at least portions of the end surfaces of the wire bonds that are uncovered by the encapsulation layer.
Owner:TESSERA LLC
Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface
ActiveUS20120280386A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEdge surfaceLead bonding
A microelectronic assembly includes a substrate having a first surface and a second surface remote from the first surface. A microelectronic element overlies the first surface and first electrically conductive elements are exposed at one of the first surface and the second surface. Some of the first conductive elements are electrically connected to the microelectronic element. Wire bonds have bases joined to the conductive elements and end surfaces remote from the substrate and the bases, each wire bond defining an edge surface extending between the base and the end surface. An encapsulation layer extends from the first surface and fills spaces between the wire bonds such that the wire bonds are separated by the encapsulation layer. Unencapsulated portions of the wire bonds are defined by at least portions of the end surfaces of the wire bonds that are uncovered by the encapsulation layer.
Owner:TESSERA LLC
Semiconductor device having semiconductor chips stacked and mounted thereon and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060175697A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingSemiconductor chip
Chips are stacked and mounted on a circuit board having external connection electrodes and mounted thereon by wire bonding. At least one of the chips stacked on the chip includes overhung portions each of which has a start point inside bonding pads, is made thinner in a direction towards the outer periphery to an end point reaching the side wall and forms a space used to accommodate ball bonding portions between the overhung portion and the main surface of the chip arranged in the lower stage on a backside corresponding in position to the bonding pads, and insulating members formed to cover the overhung portions and prevent bonding wires of the chip arranged in the lower stage from being brought into contact with the upper-stage chip.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Array-processed stacked semiconductor packages
ActiveUS7892889B2Raise countLow contour devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingElectrical connection
One embodiment of the invention is a semiconductor system (1400) of arrays (1401, 1402, etc.) of packaged devices. Each array includes a sheet-like substrate (1411, 1412, etc.) made of insulating material integral with conductive horizontal lines and vertical vias, and terminals on the surfaces. Semiconductor components, which may include more than one active or passive chips, or chips of different sizes, are attached to the substrate; the electrical connections may include flip-chip, wire bond, or combination techniques. Encapsulation compound (1412, 1422, etc.), which adheres to the substrate, embeds the connected components. Metal posts (1431, 1432, etc.) traverse the encapsulation compound vertically, connecting the substrate vias with pads on the encapsulation surface. The pads are covered with solder bodies used to connect to the next-level device array so that a 3-dimensional system of packaged devices is formed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
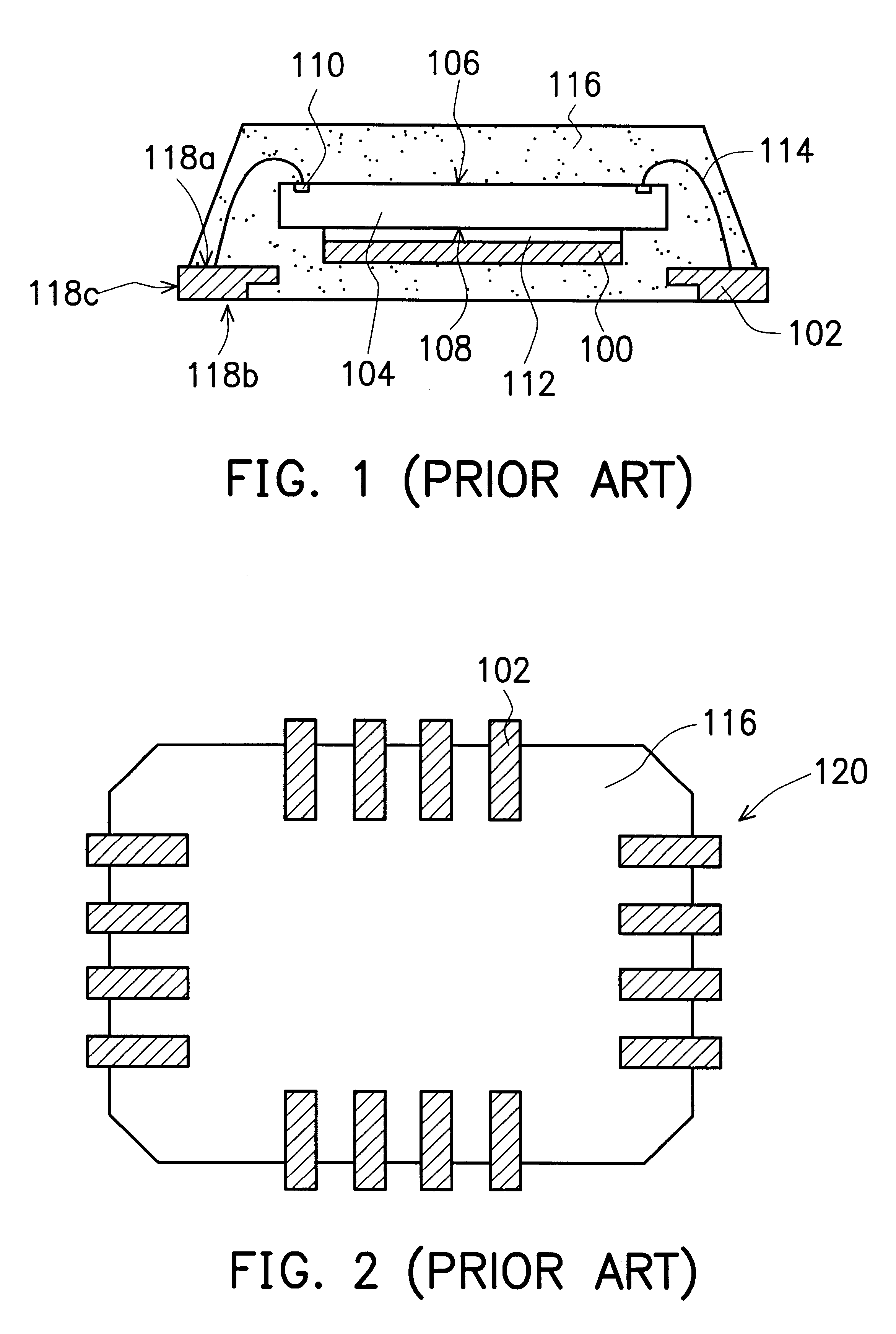
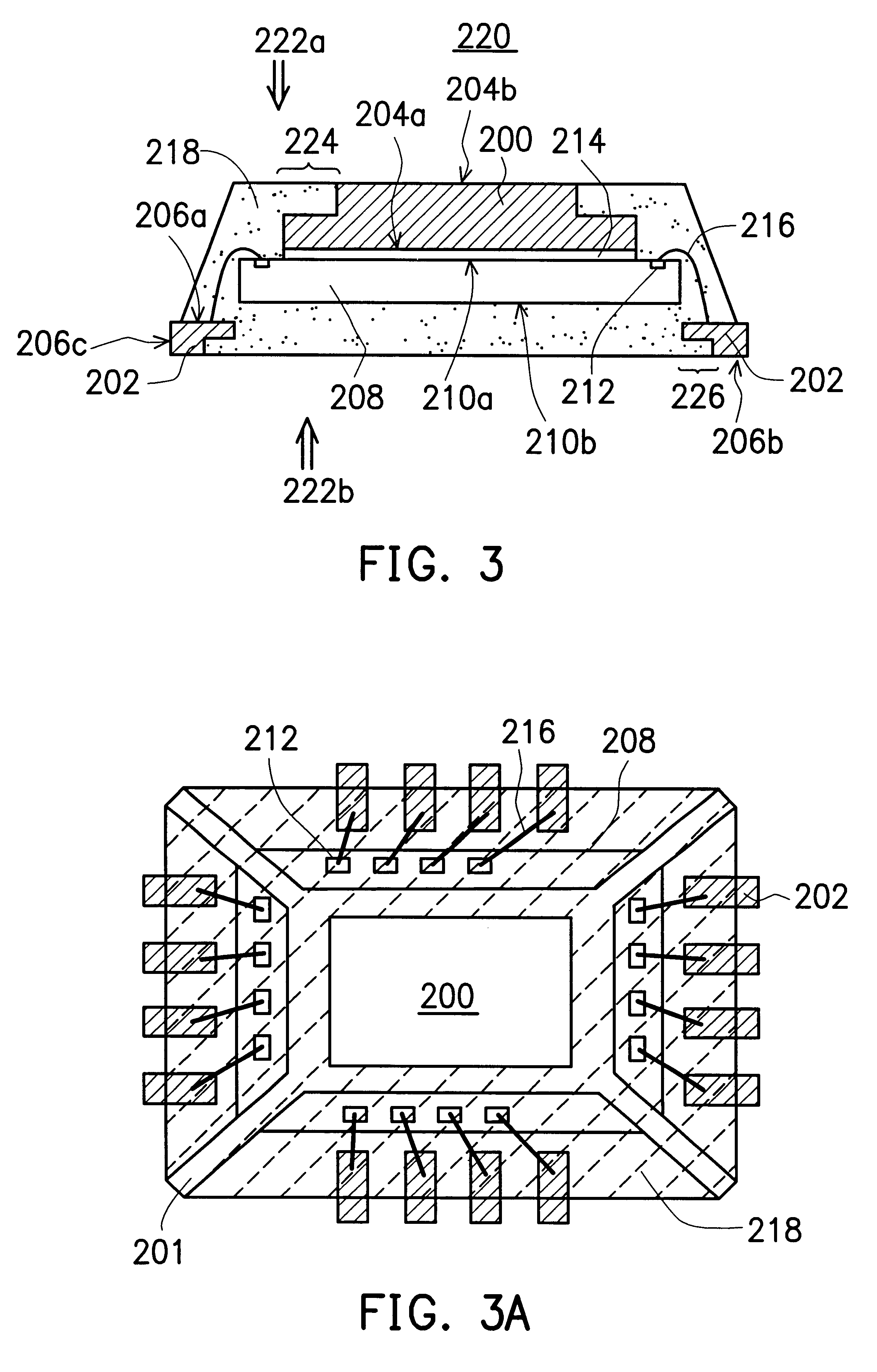
Bi-level multilayered microelectronic device package with an integral window
InactiveUS6495895B1Reduce pollutionMinimize timePrinted circuit detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHermetic sealLead bonding
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method of forming vias in silicon carbide and resulting devices and circuits
InactiveUS7125786B2Eliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLead bondingInductance
A method of fabricating an integrated circuit on a silicon carbide substrate is disclosed that eliminates wire bonding that can otherwise cause undesired inductance. The method includes fabricating a semiconductor device in epitaxial layers on a surface of a silicon carbide substrate and with at least one metal contact for the device on the uppermost surface of the epitaxial layer. The opposite surface of the substrate is then ground and polished until it is substantially transparent. The method then includes masking the polished surface of the silicon carbide substrate to define a predetermined location for at least one via that is opposite the device metal contact on the uppermost surface of the epitaxial layer and etching the desired via in steps. The first etching step etches through the silicon carbide substrate at the desired masked location until the etch reaches the epitaxial layer. The second etching step etches through the epitaxial layer to the device contacts. Finally, metallizing the via provides an electrical path from the first surface of the substrate to the metal contact and to the device on the second surface of the substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
System for providing an open-cavity low profile encapsulated semiconductor package
InactiveUS6962282B2Small possible sizeReduce the overall heightPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsSensor arrayLead bonding
System for providing an open-cavity semiconductor package. The system includes a method for wire bonding a finger sensor die to an external circuit. The finger sensor die includes a sensor array having one or more die contacts that are wire bonded to one or more external contacts of the external circuit so that a usable portion of the sensor array is maximized. The method comprises steps of forming a ball at a first end of a bonding wire, forming an electrically conductive connection between the ball and a selected external contact of the external circuit, extending the bonding wire to a selected die contact so as to form a wire loop having a low loop height, and forming an electrically conductive stitch connection between a second end of the bonding wire and the selected die contact.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Semiconductor components having through wire interconnects (TWI)
ActiveUS20070126091A1Reduce capacitanceReduce noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
A semiconductor component includes a semiconductor substrate having a substrate contact, and a through wire interconnect (TWI) bonded to the substrate contact. The through wire interconnect (TWI) includes a via through the substrate contact and the substrate, a wire in the via bonded to the substrate contact, and a contact on the wire. A stacked semiconductor component includes the semiconductor substrate, and a second semiconductor substrate stacked on the substrate and bonded to a through wire interconnect on the substrate. A method for fabricating a semiconductor component with a through wire interconnect includes the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate with a substrate contact, forming a via through the substrate contact and part way through the substrate, placing the wire in the via, bonding the wire to the substrate contact, and then thinning the substrate from a second side to expose a contact on the wire. A system for fabricating the semiconductor component includes a bonding capillary configured to place the wire in the via, and to form a bonded connection between the wire and the substrate contact.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
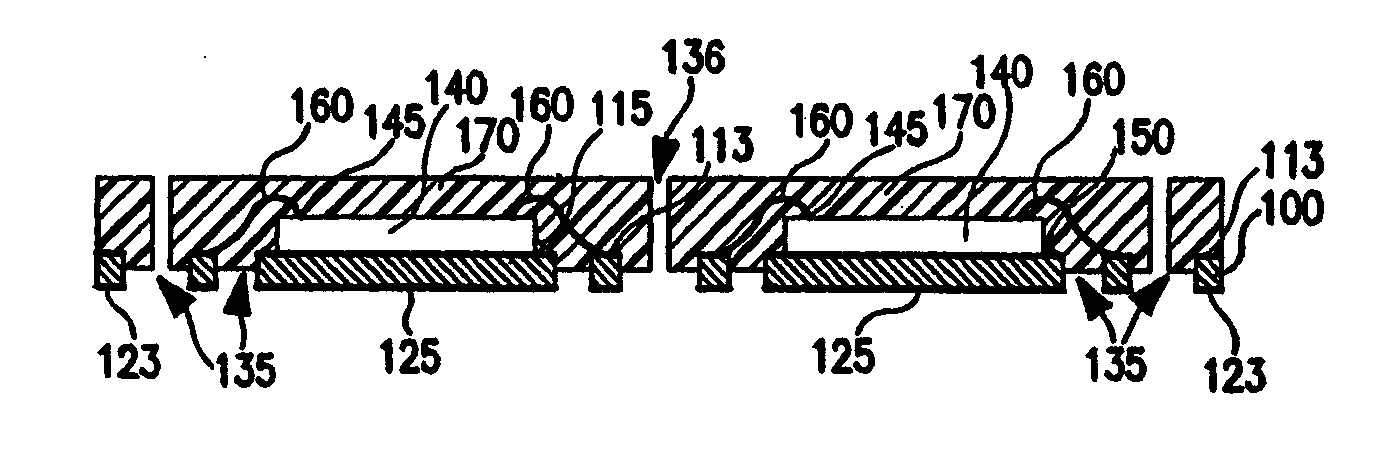
Integrated circuit package and process for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7091581B1Improve thermal characteristicsReduce generationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padLead bonding
A process for fabricating an integrated circuit package includes: selectively etching a leadframe strip to define a die attach pad and at least one row of contact pads; mounting a semiconductor die to one side of the leadframe strip, on the die attach pad; wire bonding the semiconductor die to ones of the contact pads; releasably clamping the leadframe strip in a mold by releasably clamping the contact pads; molding in a molding compound to cover the semiconductor die, the wire bonds and a portion of the contact pads not covered by the clamping; releasing the leadframe strip from the mold; depositing a plurality of external contacts on the one side of the leadframe strip, on the contact pads, such that the external contacts protrude from the molding compound; and singulating to provide the integrated circuit package.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Semiconductor device and method of fabrication thereof, circuit board, and electronic equipment
InactiveUS6335568B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialLead bonding
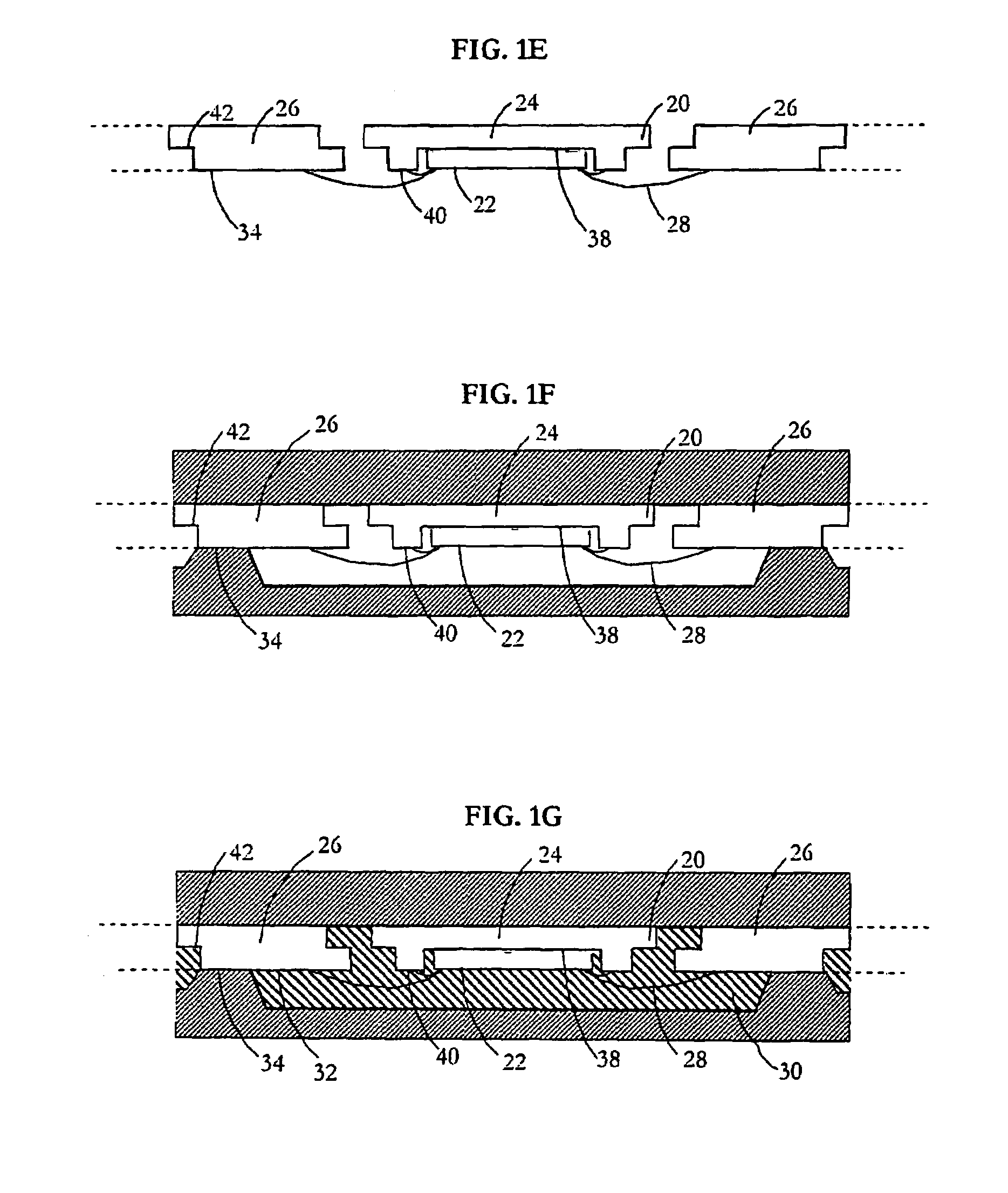
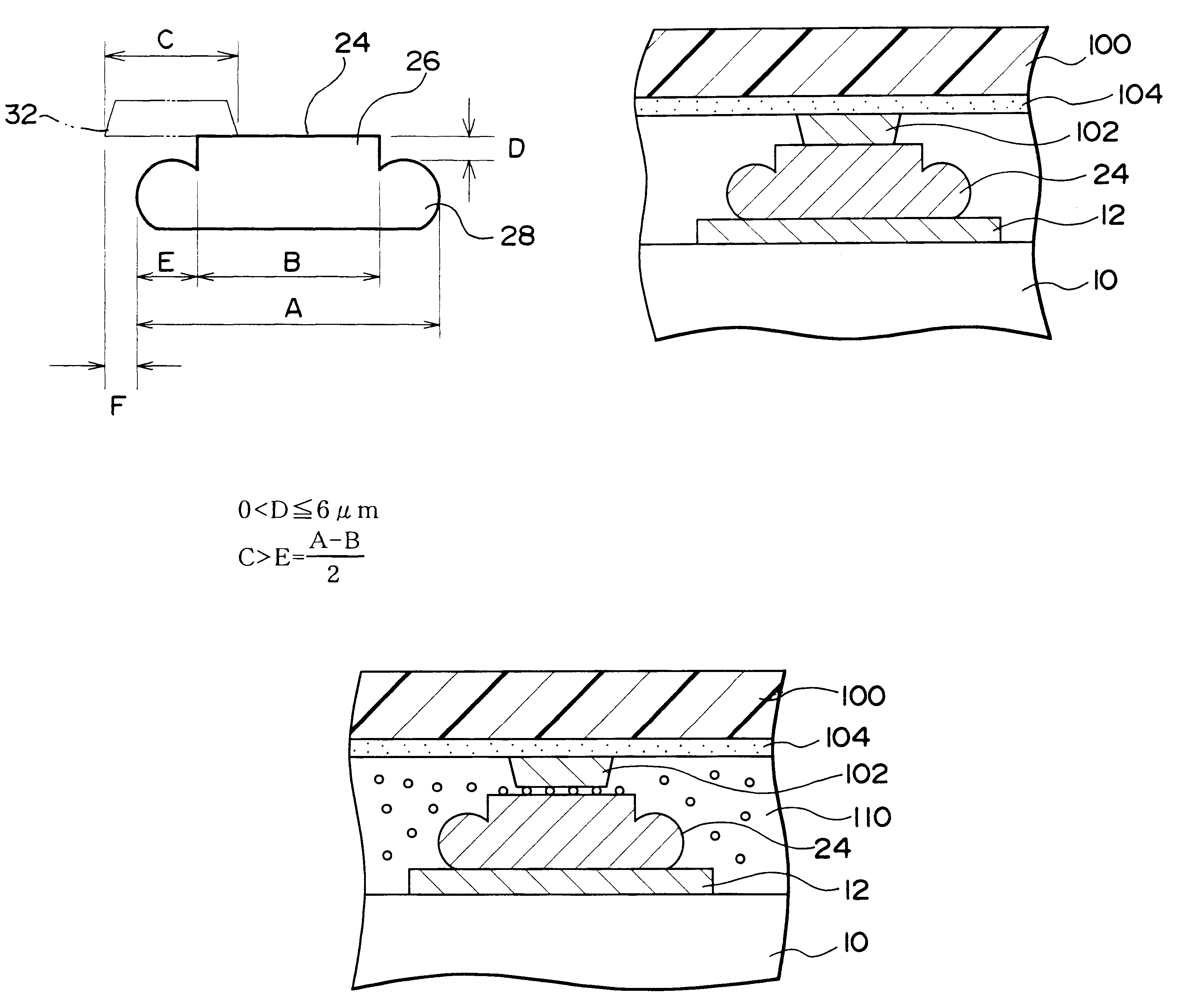
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device including: a first step of bonding a conductive wire to any one of a plurality of electrodes of a semiconductor chip; a second step of tearing off the bonded conductive wire in such a manner that a part remains on one of the electrodes; a third step of pressing the part of the conductive wire remaining on the one of the electrodes, to form a bump having a head portion and a base portion; and, a fourth step of bonding a lead to the bump; wherein a distance D between an upper surface of the base portion of the bump and an upper surface of the head portion is such that: 0<D<=6 mum.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
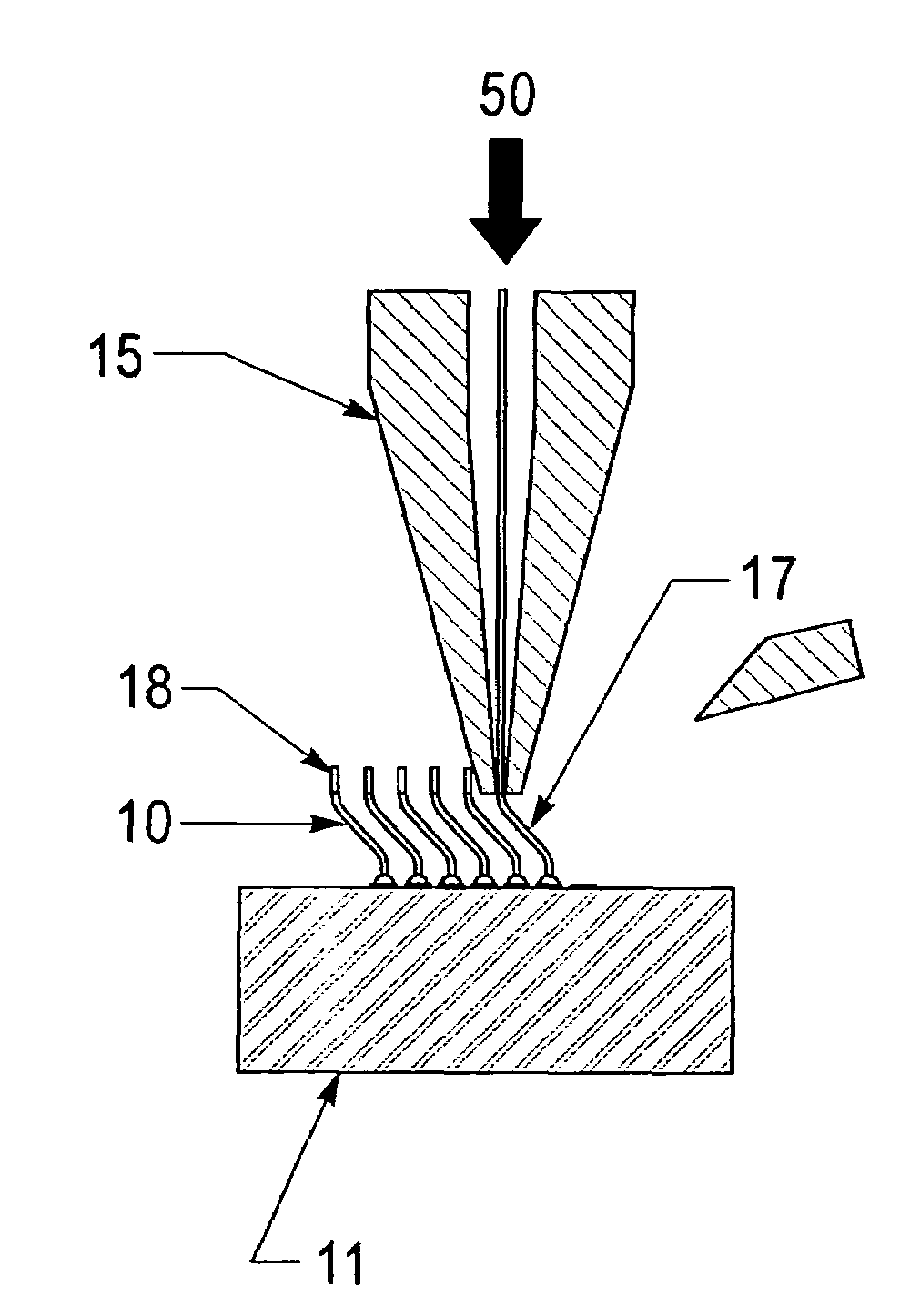
Angled flying lead wire bonding process
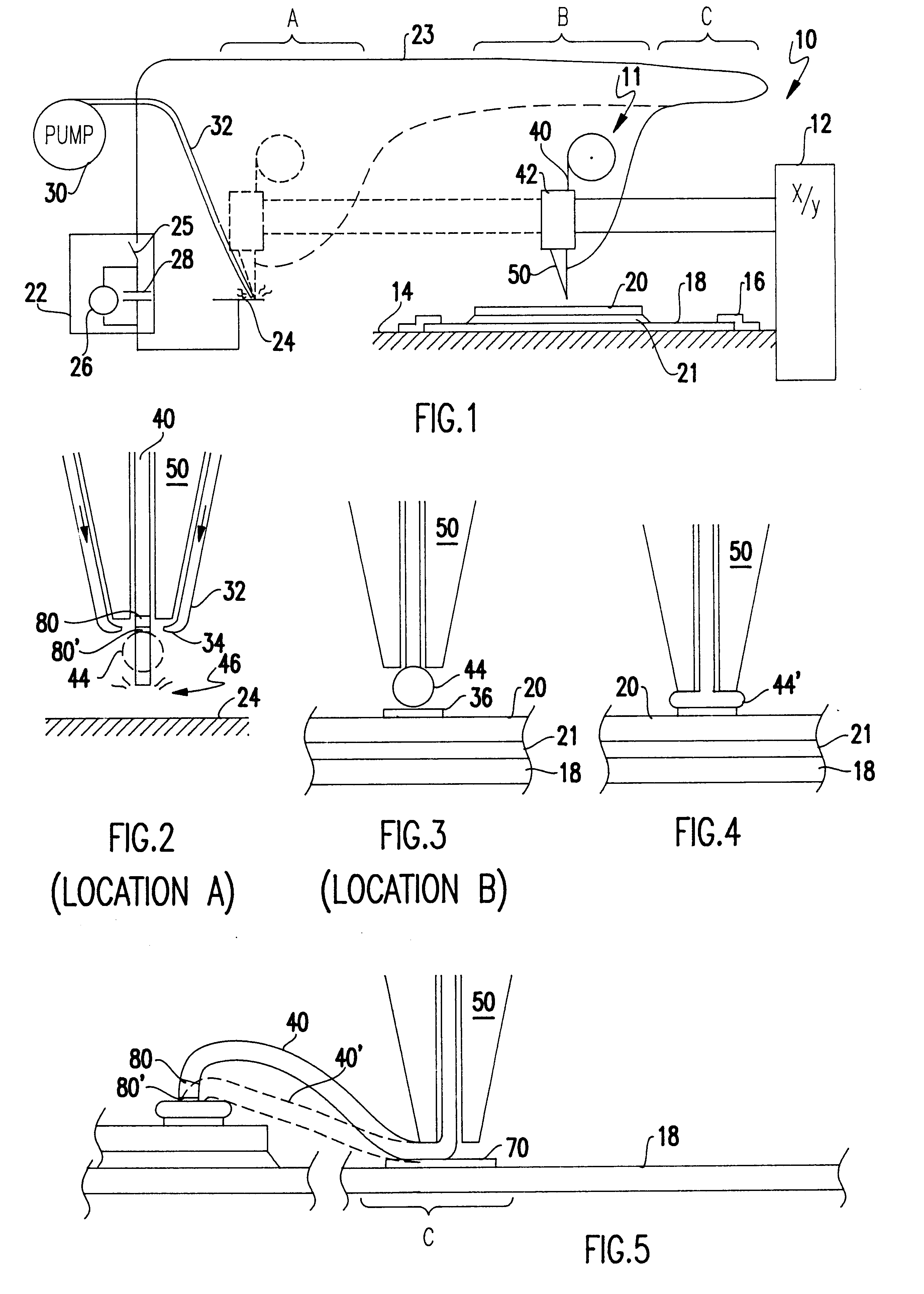
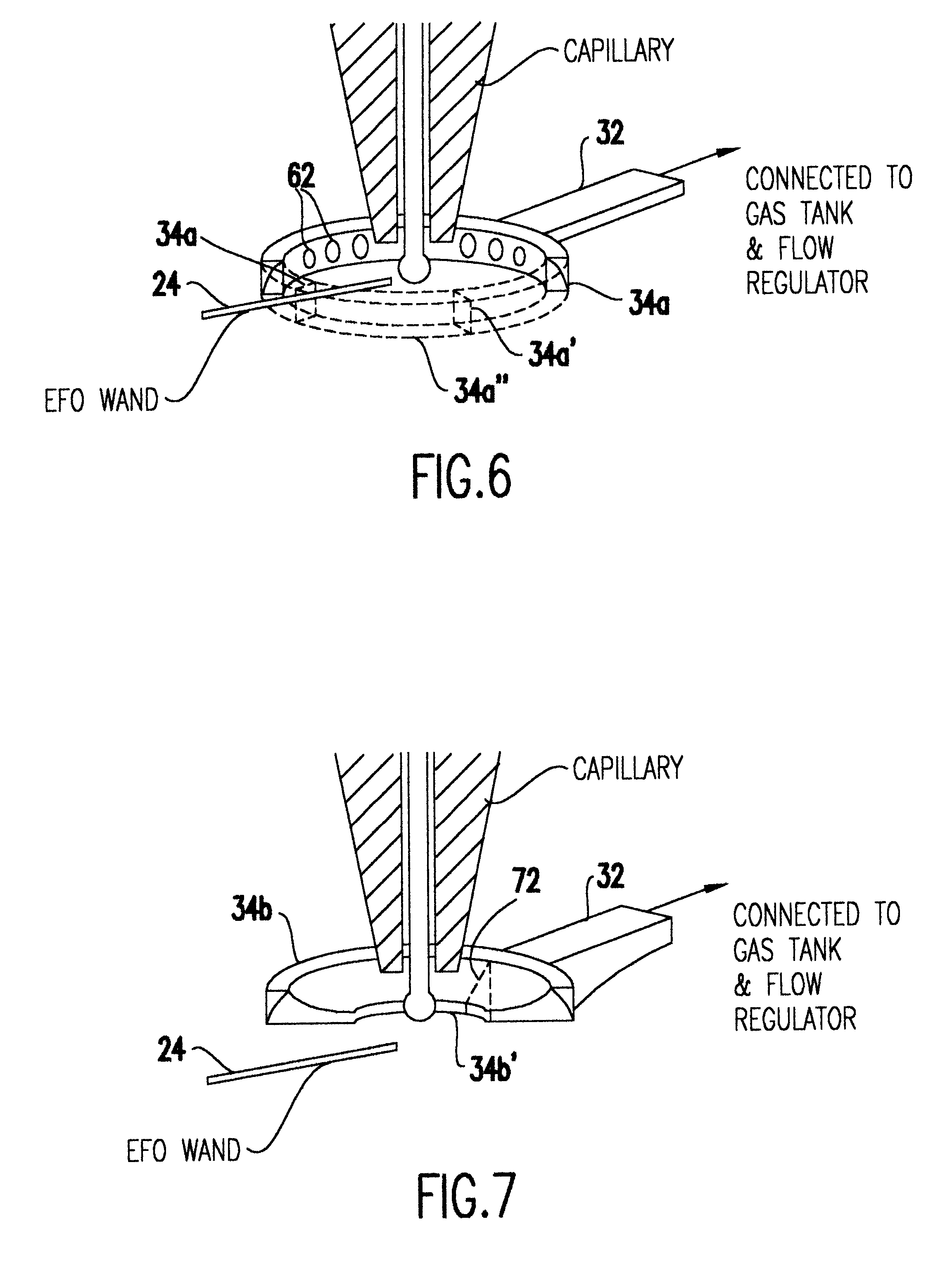
InactiveUS20090189288A1Line/current collector detailsElectrical measurement instrument detailsLead bondingEngineering
A method is described having the steps of providing a surface having a plurality of wire bondable locations; wire bonding a wire to each of the wire bondable locations using a wire capillary tool; controlling the position of the capillary tool with respect to the substrate; after forming a wire bond of the wire to the wire bondable location moving the capillary tool relative to the surface as the capillary tool is moved away from the surface to form a wire having a predetermined shape.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
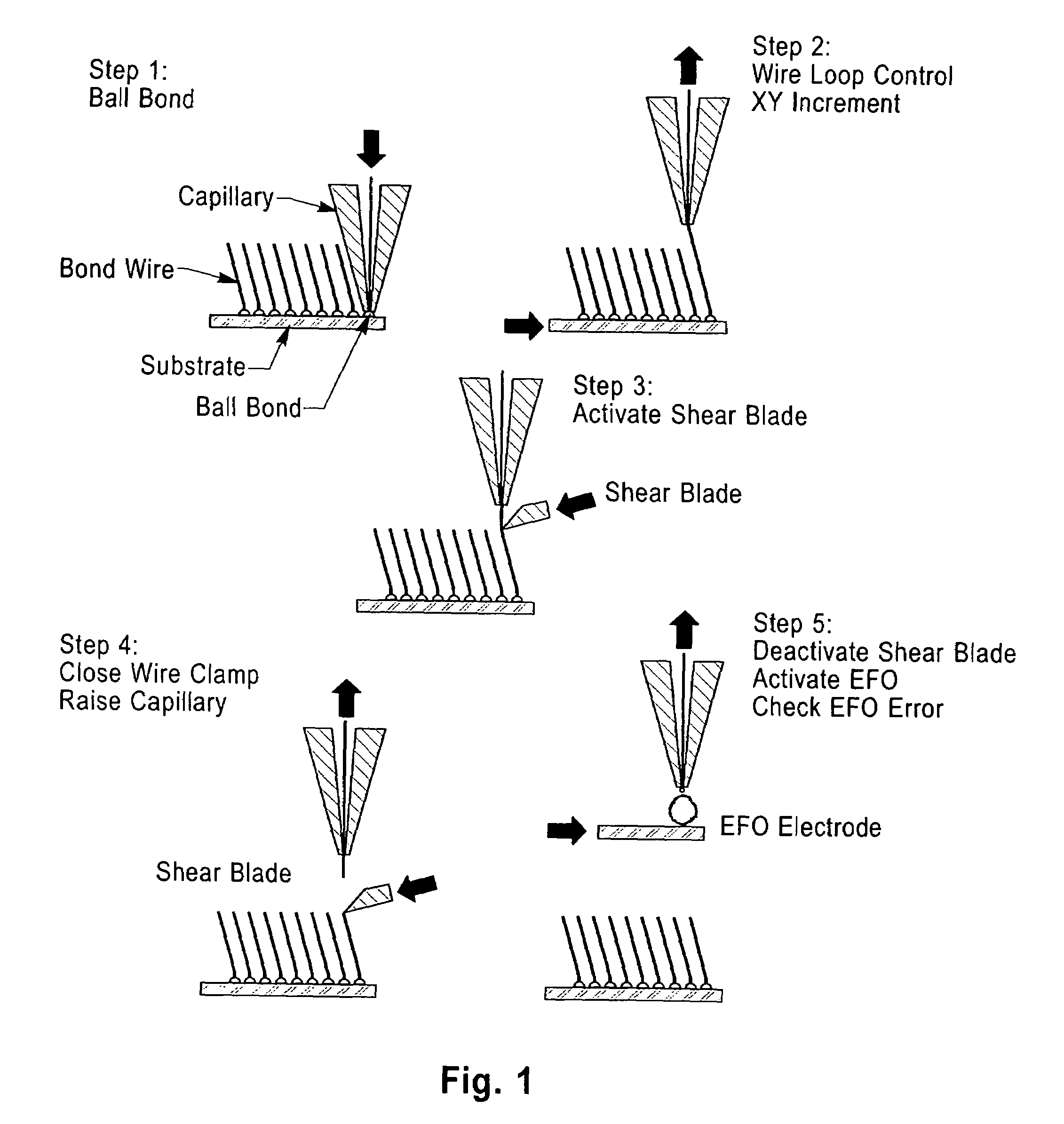
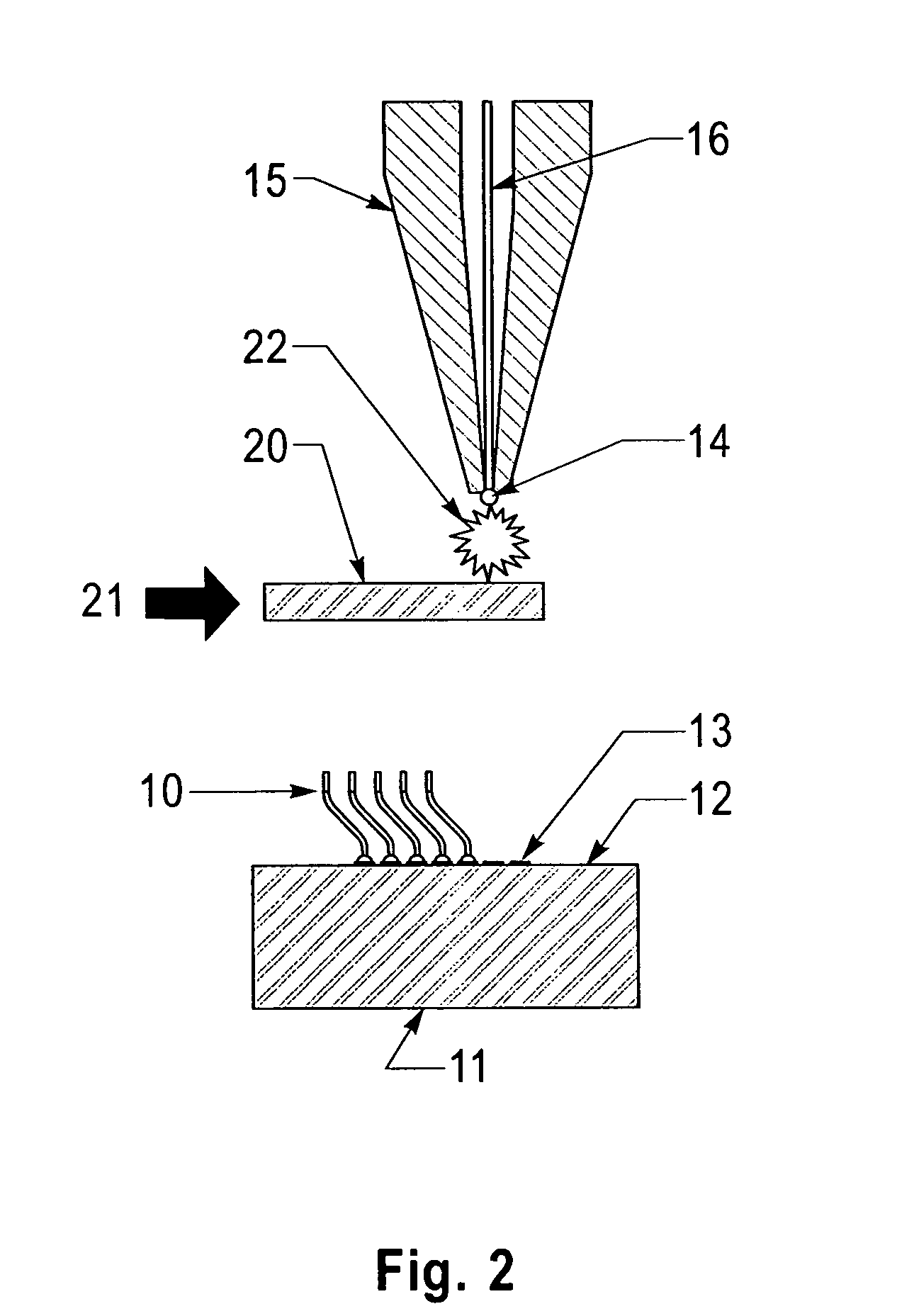
Control of size and heat affected zone for fine pitch wire bonding
InactiveUS6180891B1Electrically conductive connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat-affected zoneLead bonding
The amount of melting of the bonding wire is closely regulated, and reduction of size and improvement of uniformity of the free air ball is obtained for ball bonding at pitches of less than ninety mils even when bonding wire of reduced diameter is employed. Quenching of the bonding wire adjacent to the free air ball also limits the temperature rise in the bonding wire and the extent of a heat affected zone having less tensile strength and stiffness to less than one micron and with reduced grain enlargement. The present invention provides such a bond for electronic packaging of increased reliability, potential functionality, increased manufacturing yield and reduced process complexity.
Owner:IBM CORP
Partially Patterned Lead Frames and Methods of Making and Using the Same in Semiconductor Packaging
ActiveUS20070052076A1Increase surface areaImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyLead bonding
A method of making a lead frame and a partially patterned lead frame package with near-chip scale packaging (CSP) lead-counts is disclosed, wherein the method lends itself to better automation of the manufacturing line as well as to improving the quality and reliability of the packages produced therefrom. This is accomplished by performing a major portion of the manufacturing process steps with a partially patterned strip of metal formed into a web-like lead frame on one side, in contrast with the conventional fully etched stencil-like lead frames, so that the web-like lead frame, which is solid and flat on the other side is also rigid mechanically and robust thermally to perform without distortion or deformation during the chip-attach and wire bond processes, both at the chip level and the package level. The bottom side of the metal lead frame is patterned to isolate the chip-pad and the wire bond contacts only after the front side, including the chip and wires, is hermetically sealed with an encapsulant. The resultant package being electrically isolated enables strip testing and reliable singulation without having to cut into any additional metal. The use of the instant partially patterned lead frame in making ELP, ELPF and ELGA-type CSPs is also disclosed.
Owner:UNISEM M BERHAD
Angled flying lead wire bonding process
InactiveUS7495342B2Line/current collector detailsElectrical measurement instrument detailsWire rodLead bonding
A method is described having the steps of providing a surface having a plurality of wire bondable locations, wire bonding a wire to each of the wire bondable locations using a wire capillary tool; controlling the position of the capillary tool with respect to the substrate; after forming a wire bond of the wire to the wire bondable location moving the capillary tool relative to the surface as the capillary tool is moved away from the surface to form a wire having a predetermined shape.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Quad flat no-lead chip carrier
ActiveUS6882057B2High I/O densityImprove chip qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingEngineering
A quad flat no-lead chip carrier for a wire-bonded chip package is provided. The chip carrier comprises a conductive plate, a plurality of conductive columns and a plurality of dielectric walls. A chip is attached to the conductive plate. The conductive plate furthermore has a plurality of columnar through holes distributed around a chip-bonding region. The conductive columns are set up within the columnar through holes. The dielectric walls are set up between the sidewall of the conductive columns and the inner surface of the columnar through holes. The chip is electrically connected to the conductive columns via conductive wires. The bottom end of the conductive columns serves as input / output contacts for connecting with external contacts. The chip carrier is able to increase overall density of the input / output contacts and improve the electrical performance of the chip package.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Shielded integrated circuit package
InactiveUS7071545B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padLead bonding
An integrated circuit package is provided. The package includes a die attach pad having a first side and a second side. A first semiconductor die is mounted to the first side of the die attach pad, a plurality of contact pads disposed in close proximity to the first semiconductor die. A first plurality of wire bonds connect the first semiconductor die and ones of the contact pads. An overmold encapsulates the first plurality of wire bonds and the first semiconductor die, the die attach pad and the contact pads being embedded in the overmold. A plurality of leads are disposed proximal the second side of the die attach pad. A second semiconductor die is mounted to one of the second side of the die attach pad and ones of the plurality of leads such that the ones of the plurality of leads are electrically connected to the second semiconductor die. The second semiconductor die and the leads are embedded in an encapsulant. The die attach pad shields the second semiconductor die.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for non-conductively interconnecting integrated circuits
InactiveUS6916719B1Increased signal noiseIncrease speedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead bondingComputer module
Methods and apparatus are described for capacitively signaling between different semiconductor chips and modules without the use of connectors, solder bumps, wire-bond interconnections or the like. Preferably, pairs of half-capacitor plates, one half located on each chip, module or substrate are used to capacitively couple signals from one chip, module or substrate to another. The use of plates relaxes the need for high precision alignment as well as reduces the area needed to effect signaling, and reduces or eliminates the requirements for exotic metallurgy.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com