Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3511results about "Electroforming processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
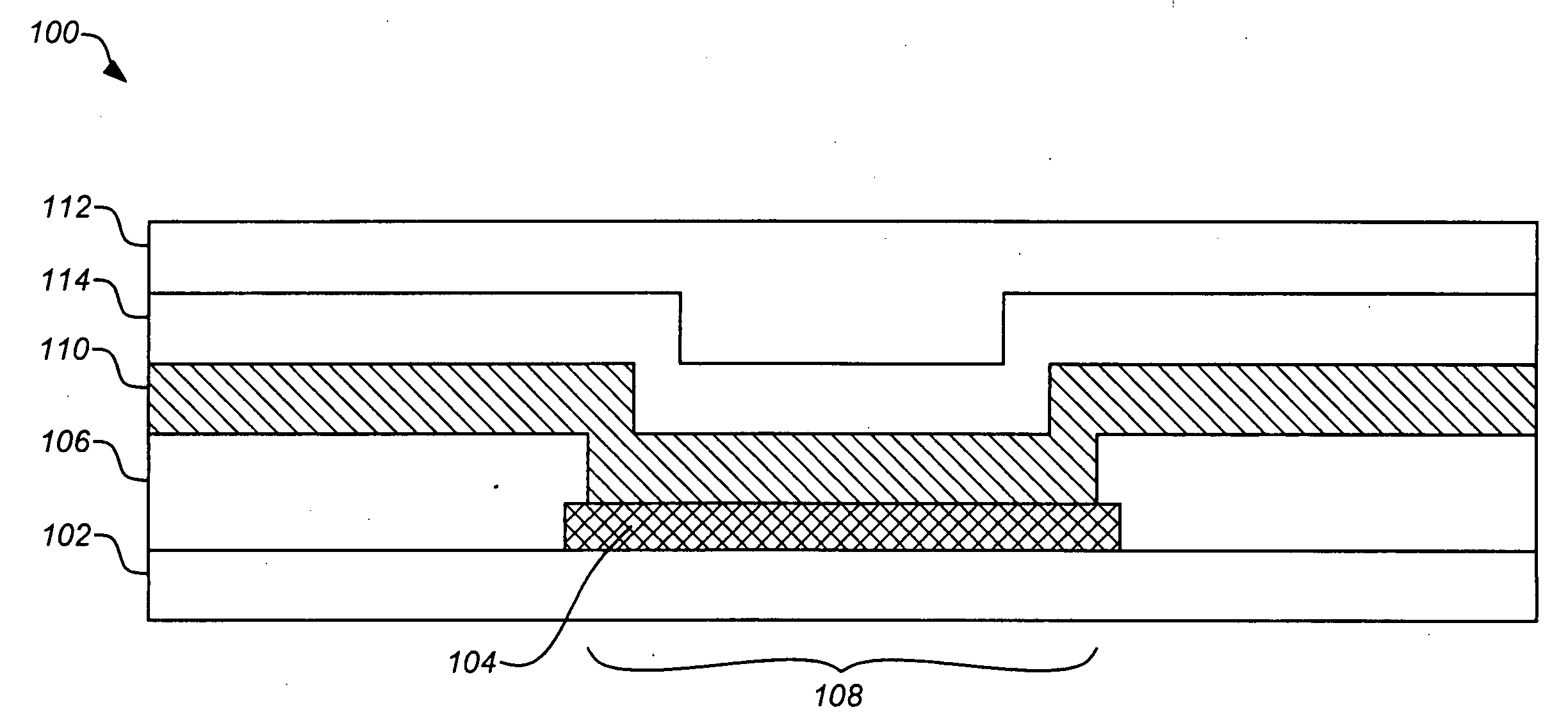
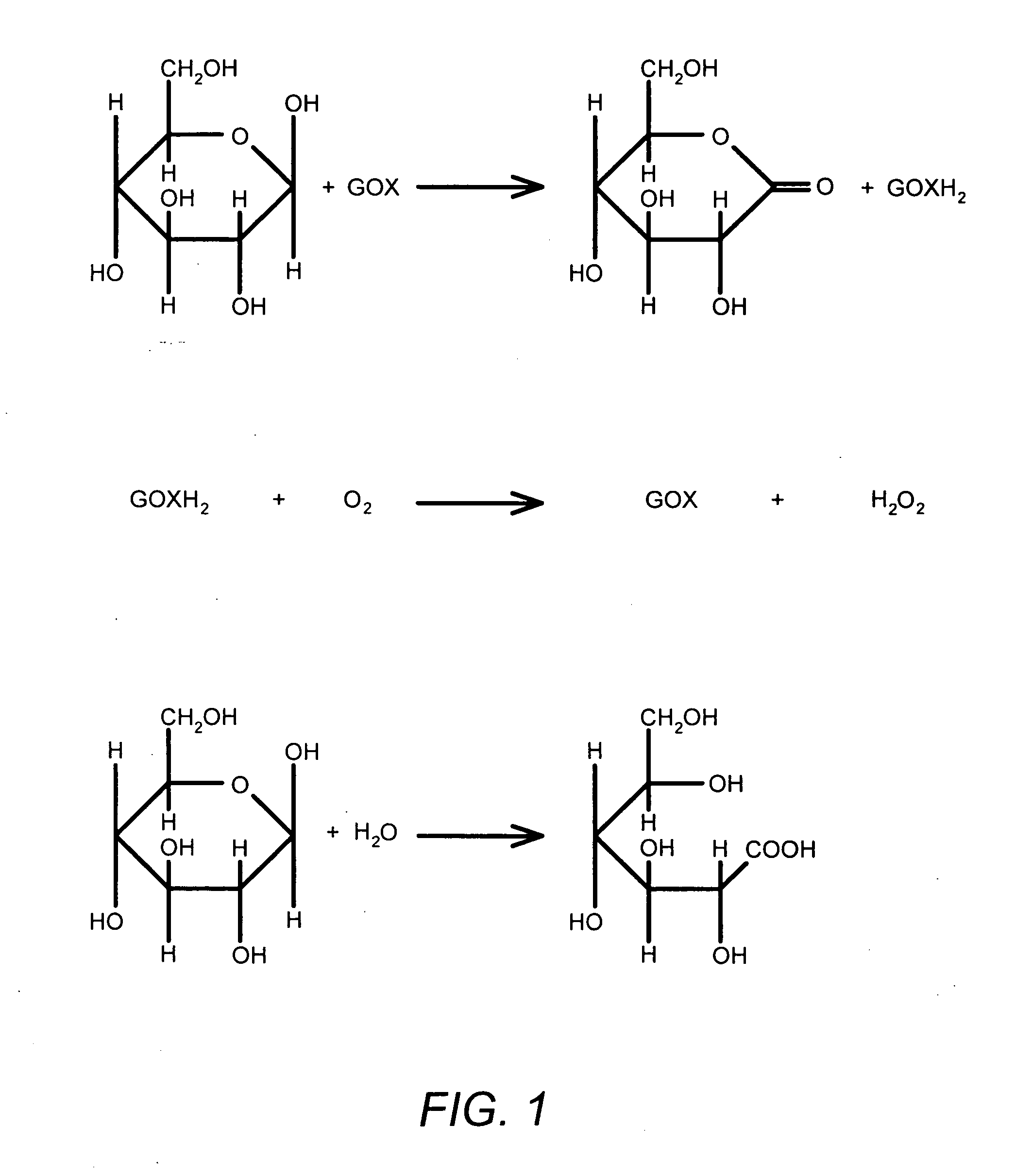
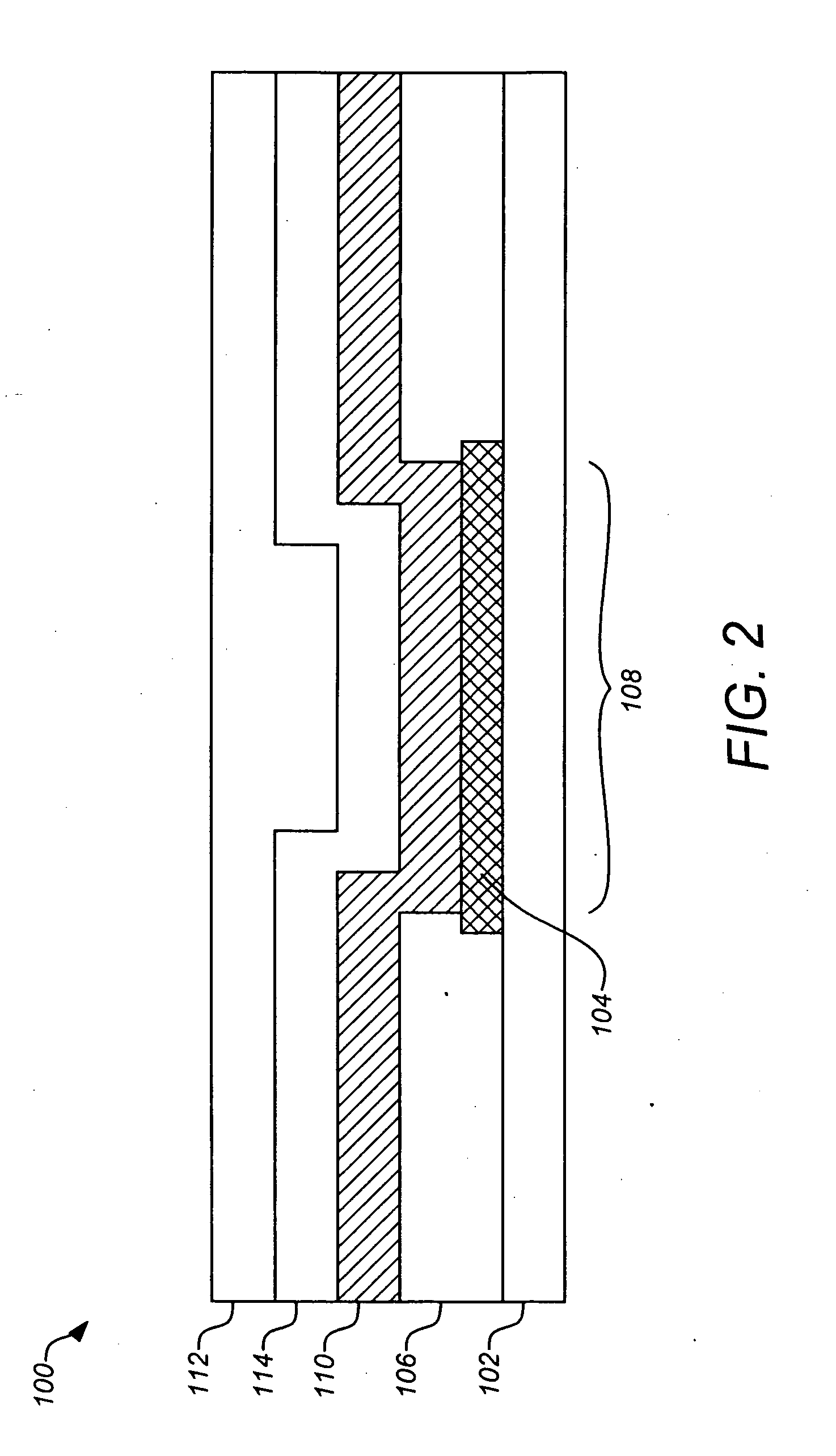
Methods and materials for controlling the electrochemistry of analyte sensors
InactiveUS20070227907A1Increase surface areaImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseAnalyte
Embodiments of the invention provide electrochemical analyte sensors having elements designed to modulate their electrochemical reactions as well as methods for making and using such sensors.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
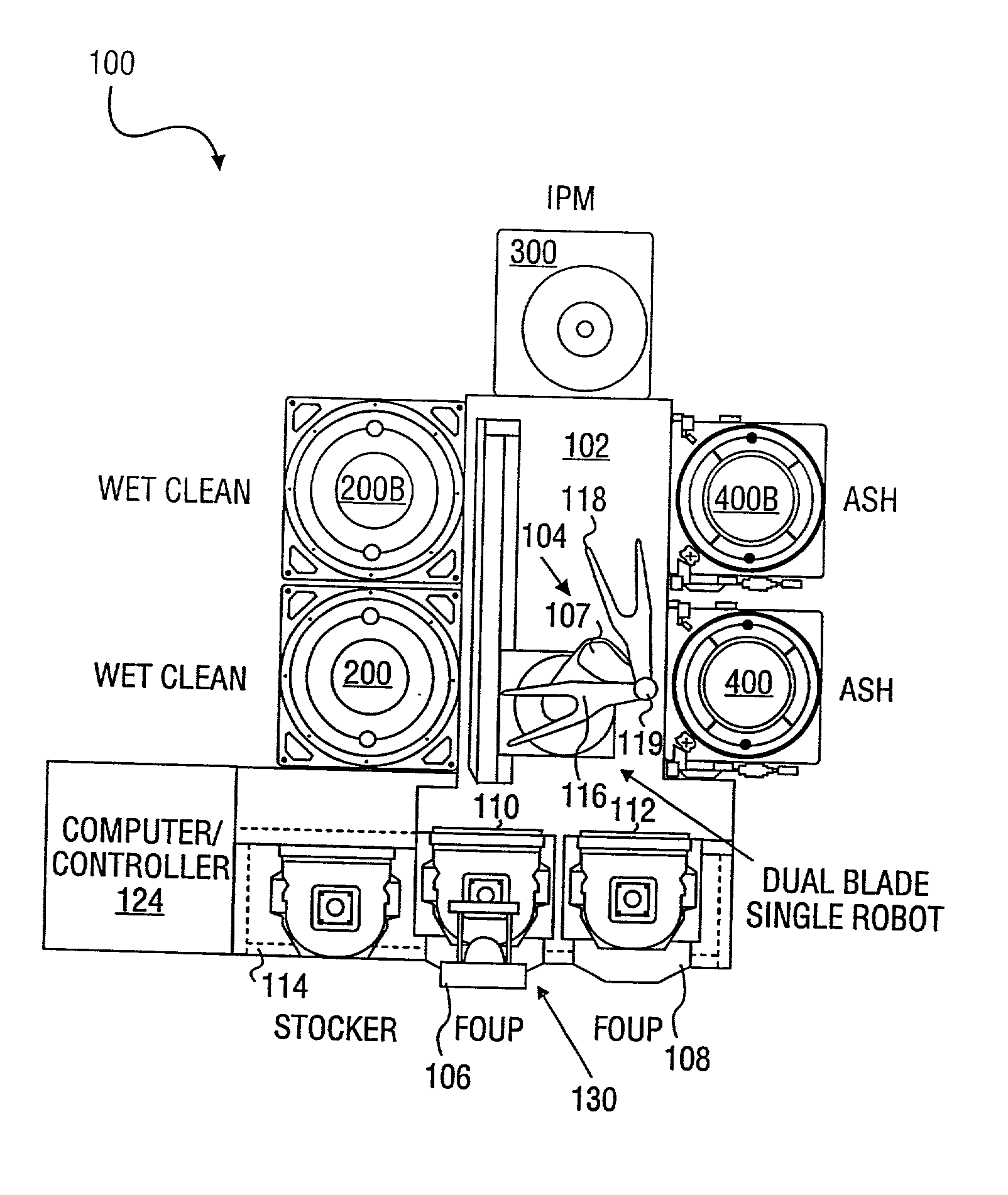
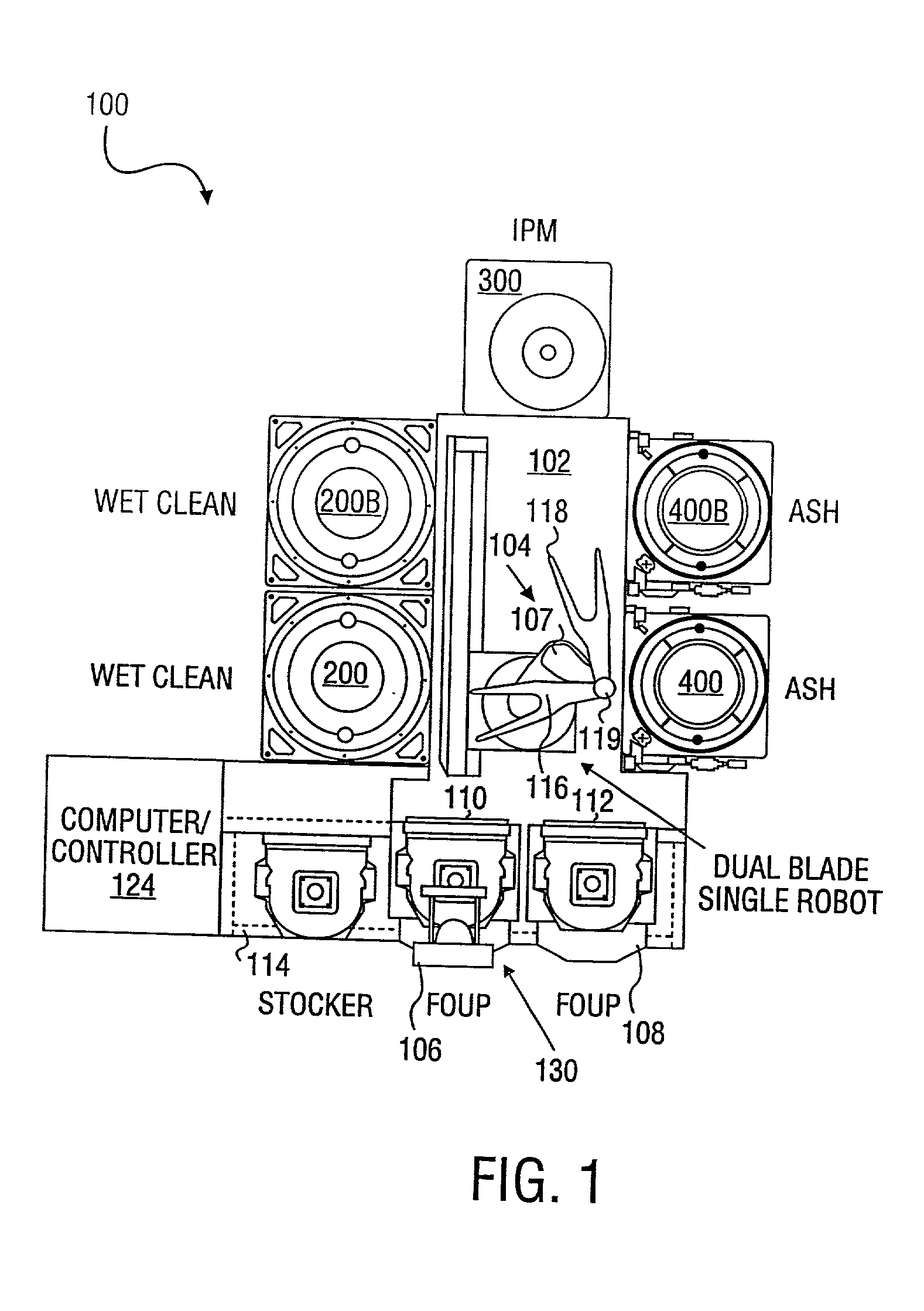
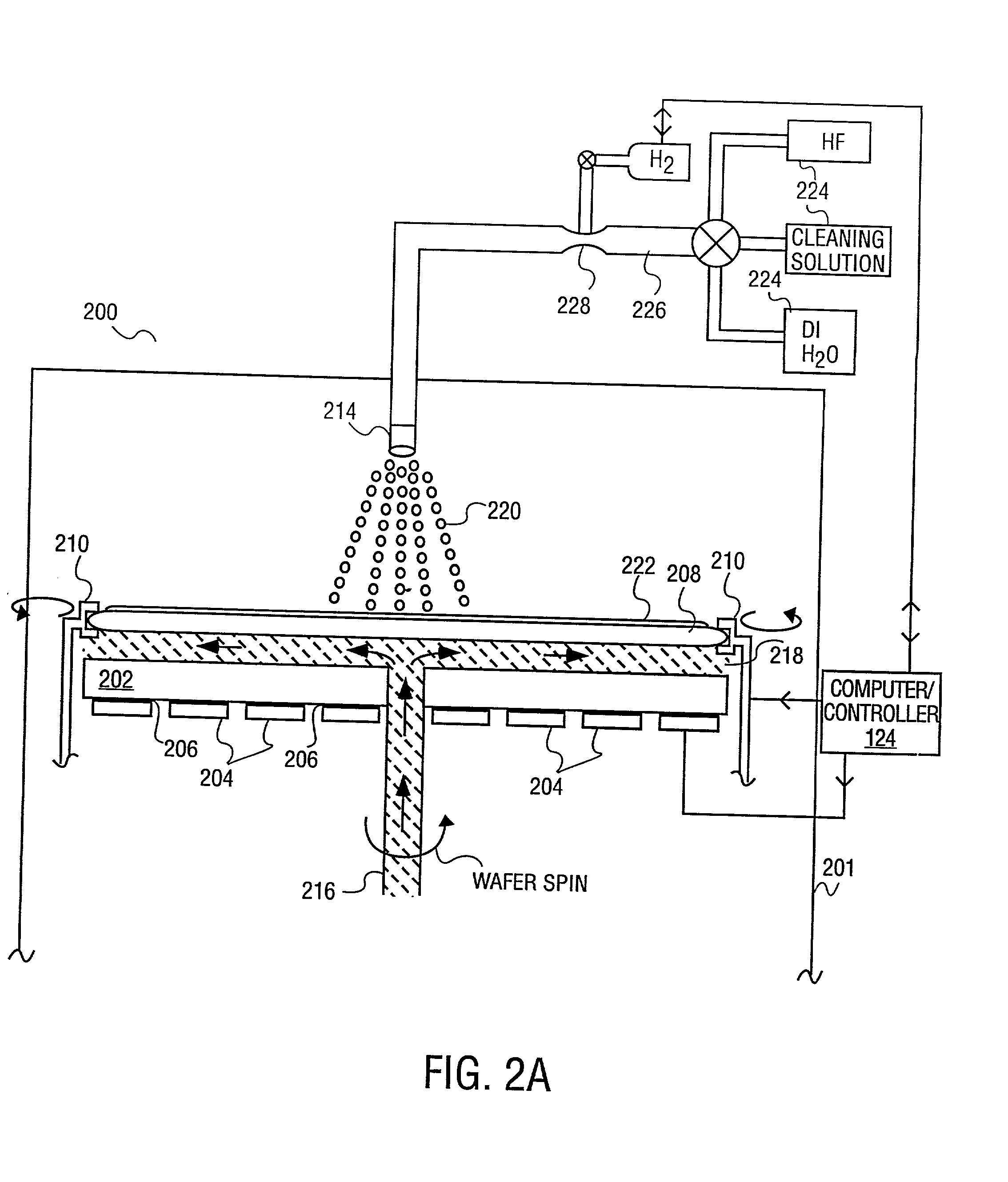
Method and apparatus for processing a wafer
InactiveUS20030045098A1Vacuum evaporation coatingPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method of a single wafer wet / dry cleaning apparatus comprising: a transfer chamber having a wafer handler contained therein; a first single wafer wet cleaning chamber directly coupled to the transfer chamber; and a first single wafer ashing chamber directly coupled to the transfer chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
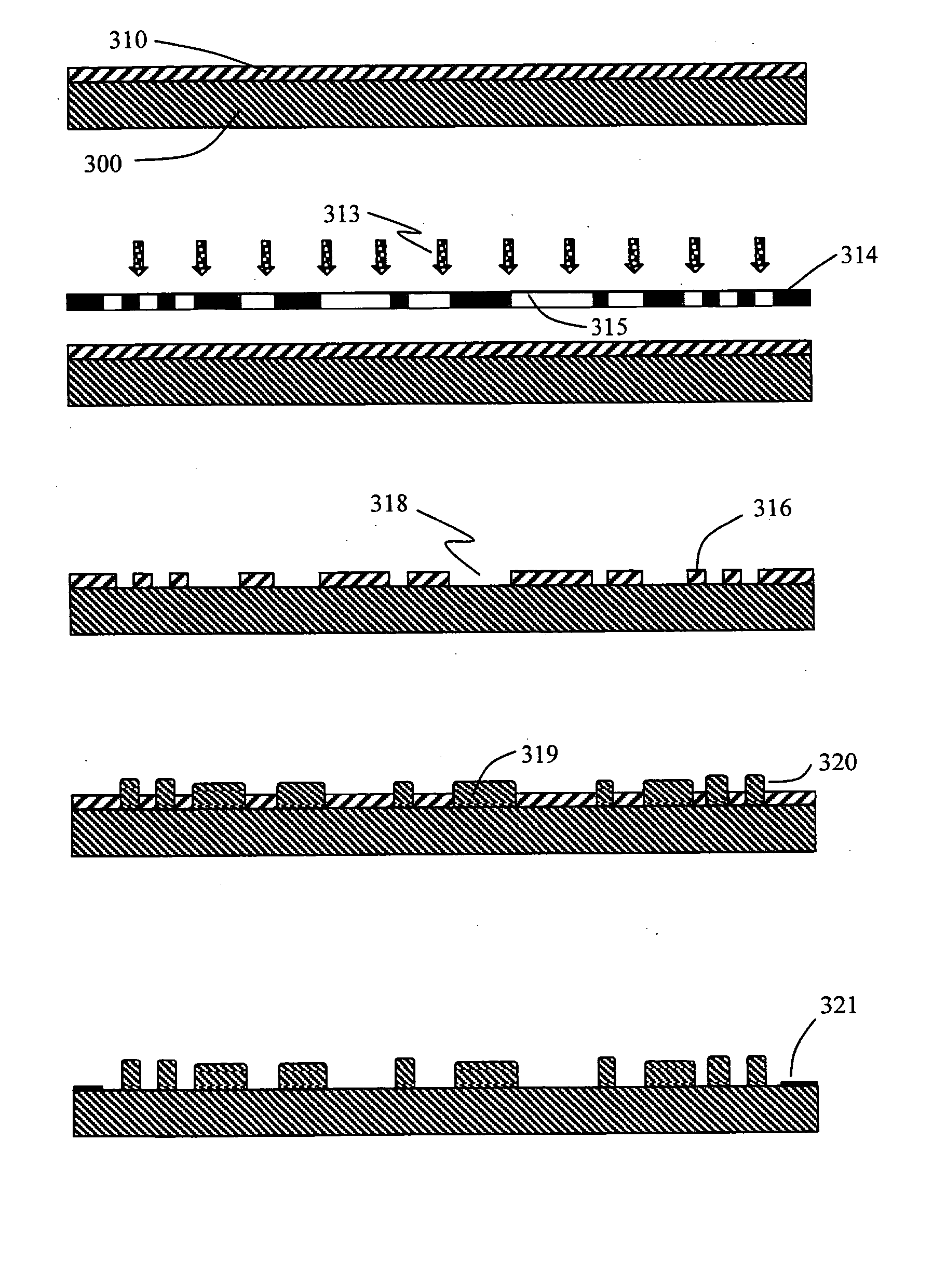
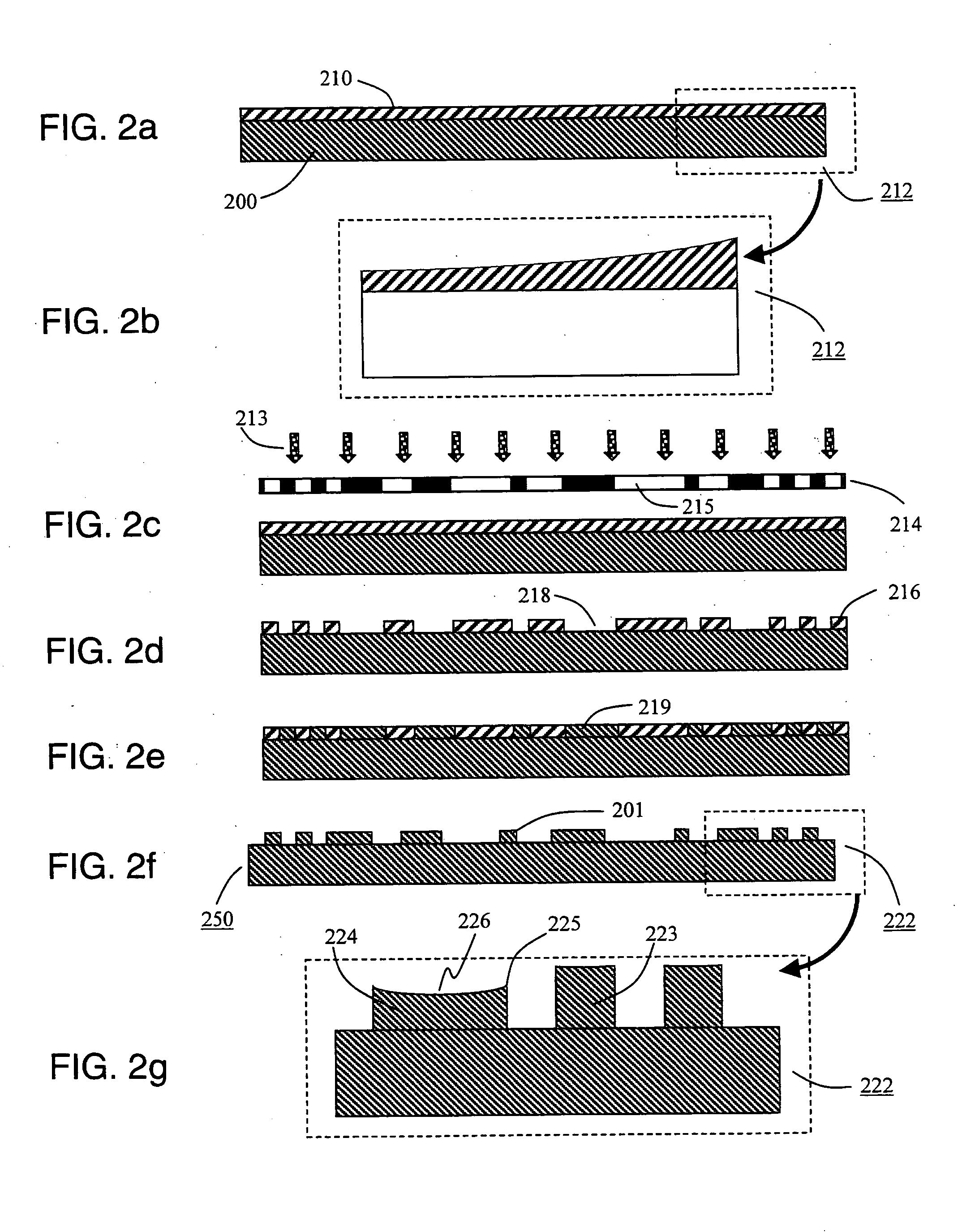
Microfabricated structures and processes for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050067286A1Minimize surface roughnessEasy to controlElectroforming processesMicroelectromechanical systemsManufacturing technologyCompound (substance)
Various techniques for the fabrication of highly accurate master molds with precisely defined microstructures for use in plastic replication using injection molding, hot embossing, or casting techniques are disclosed herein. Three different fabrication processes used for master mold fabrication are disclosed wherein one of the processes is a combination of the other two processes. In an embodiment of the first process, a two-step electroplating approach is used wherein one of the metals forms the microstructures and the second metal is used as a sacrificial support layer. Following electroplating, the exact height of the microstructures is defined using a chemical mechanical polishing process. In an embodiment of the second process, a modified electroforming process is used for master mold fabrication. The specific modifications include the use of Nickel-Iron (80:20) as a structural component of the master mold, and the use of a higher saccharin concentration in the electroplating bath to reduce tensile stress during plating and electroforming on the top as well as sides of the dummy substrate to prevent peel off of the electroform. The electroforming process is also well suited towards the fabrication of microstructures with non-rectangular cross sectional profiles. Also disclosed is an embodiment of a simple fabrication process using direct deposition of a curable liquid molding material combined with the electroforming process. Finally, an embodiment of a third fabrication process combines the meritorious features of the first two approaches and is used to fabricate a master mold using a combination of the two-step electroplating plus chemical mechanical polishing approach and the electroforming approach to fabricate highly accurate master molds with precisely defined microstructures. The microstructures are an integral part of the master mold and hence the master mold is more robust and well suited for high volume production of plastic MEMS devices through replication techniques such as injection molding.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIVERISITY OF THE
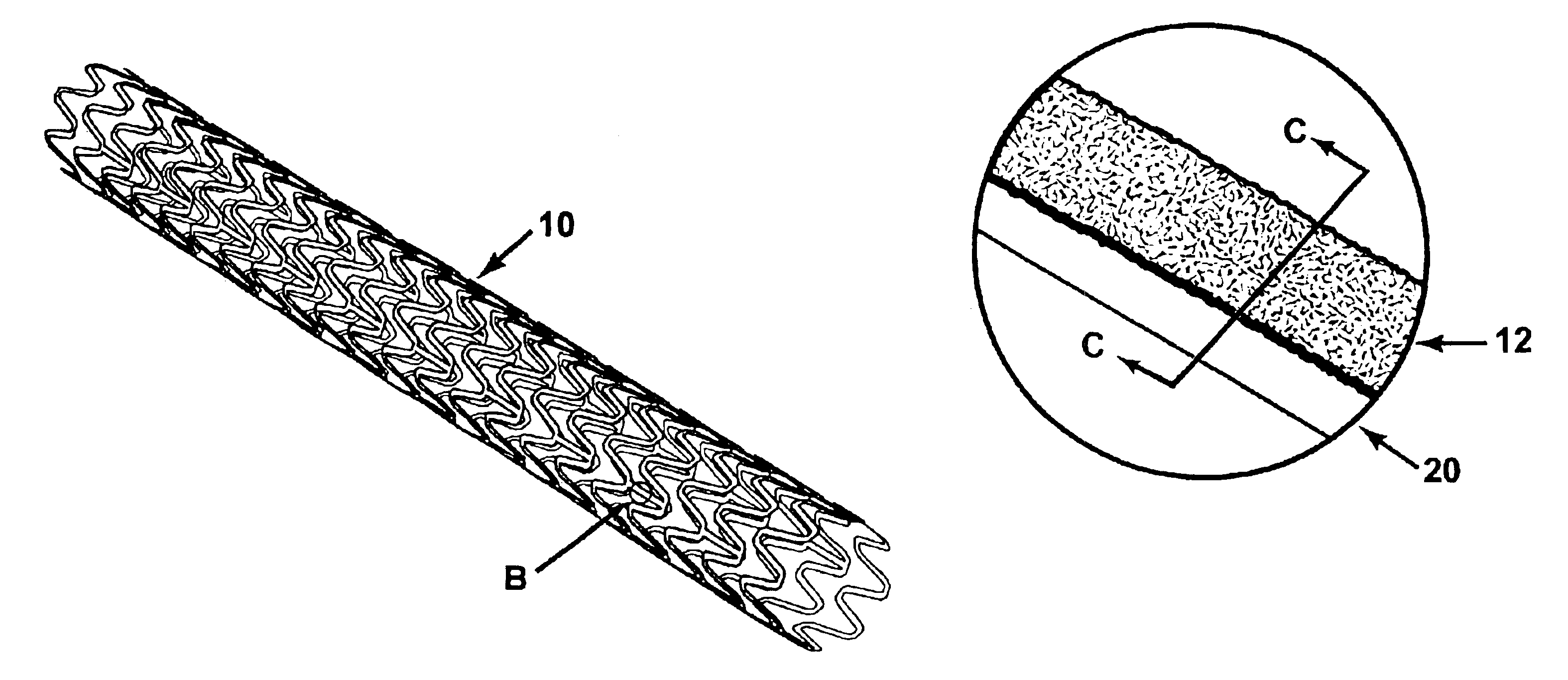
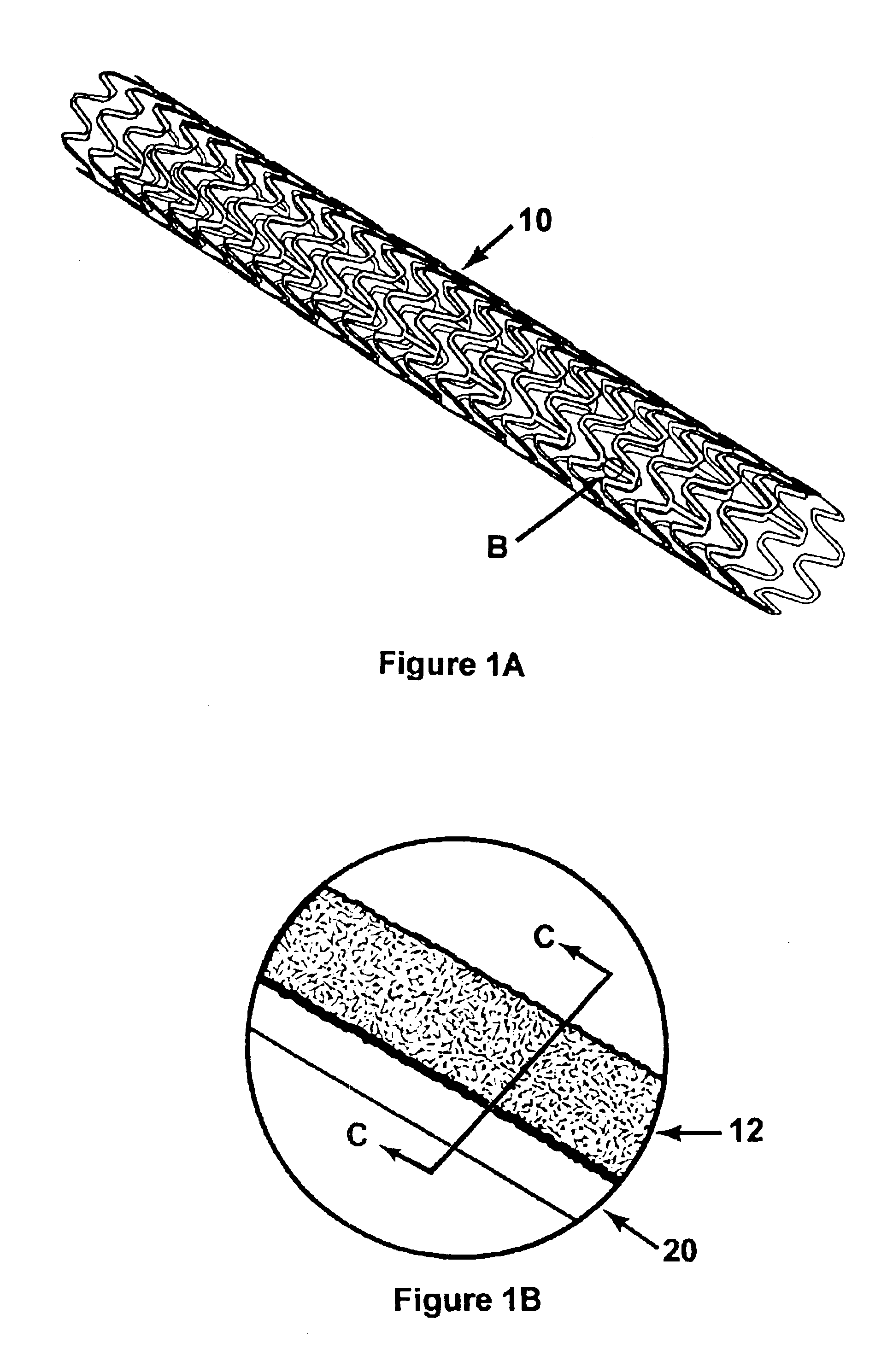
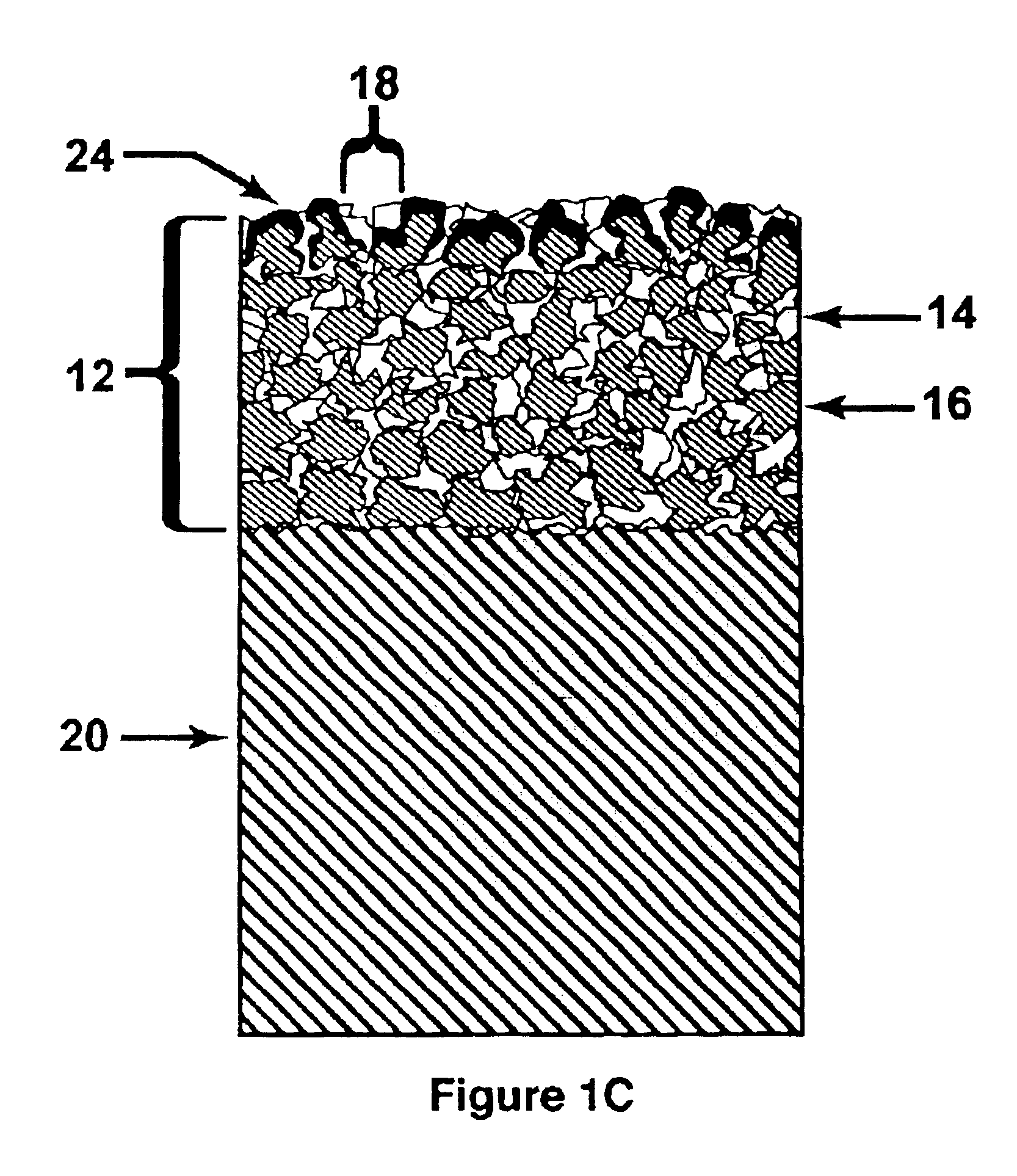
Method for manufacturing intraluminal device
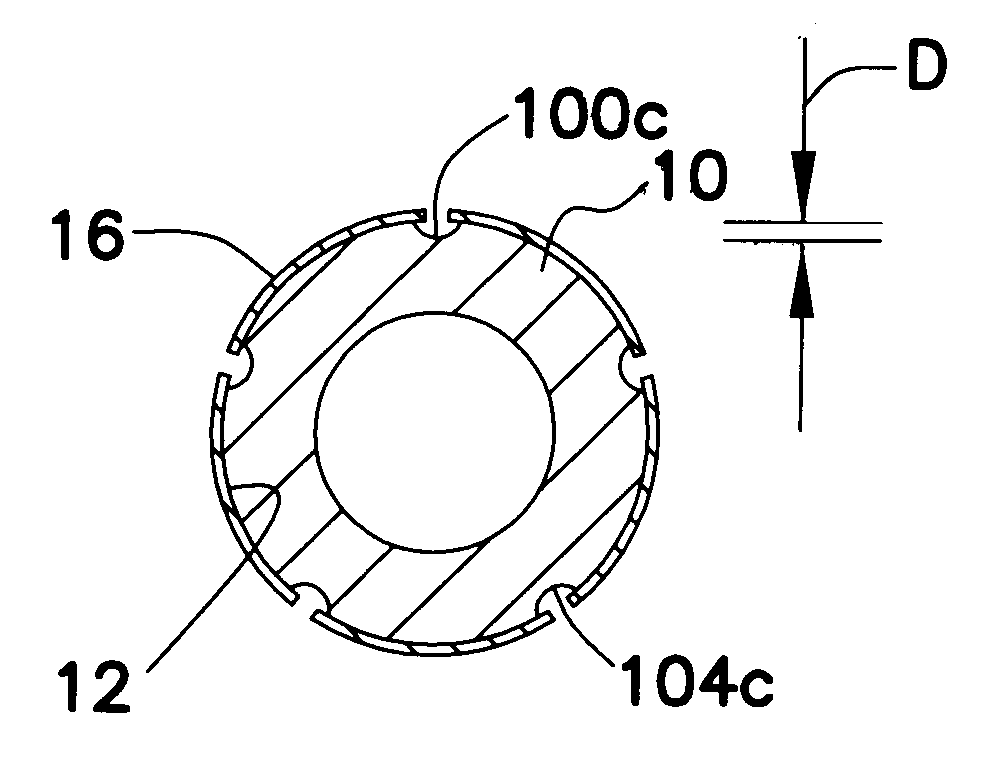
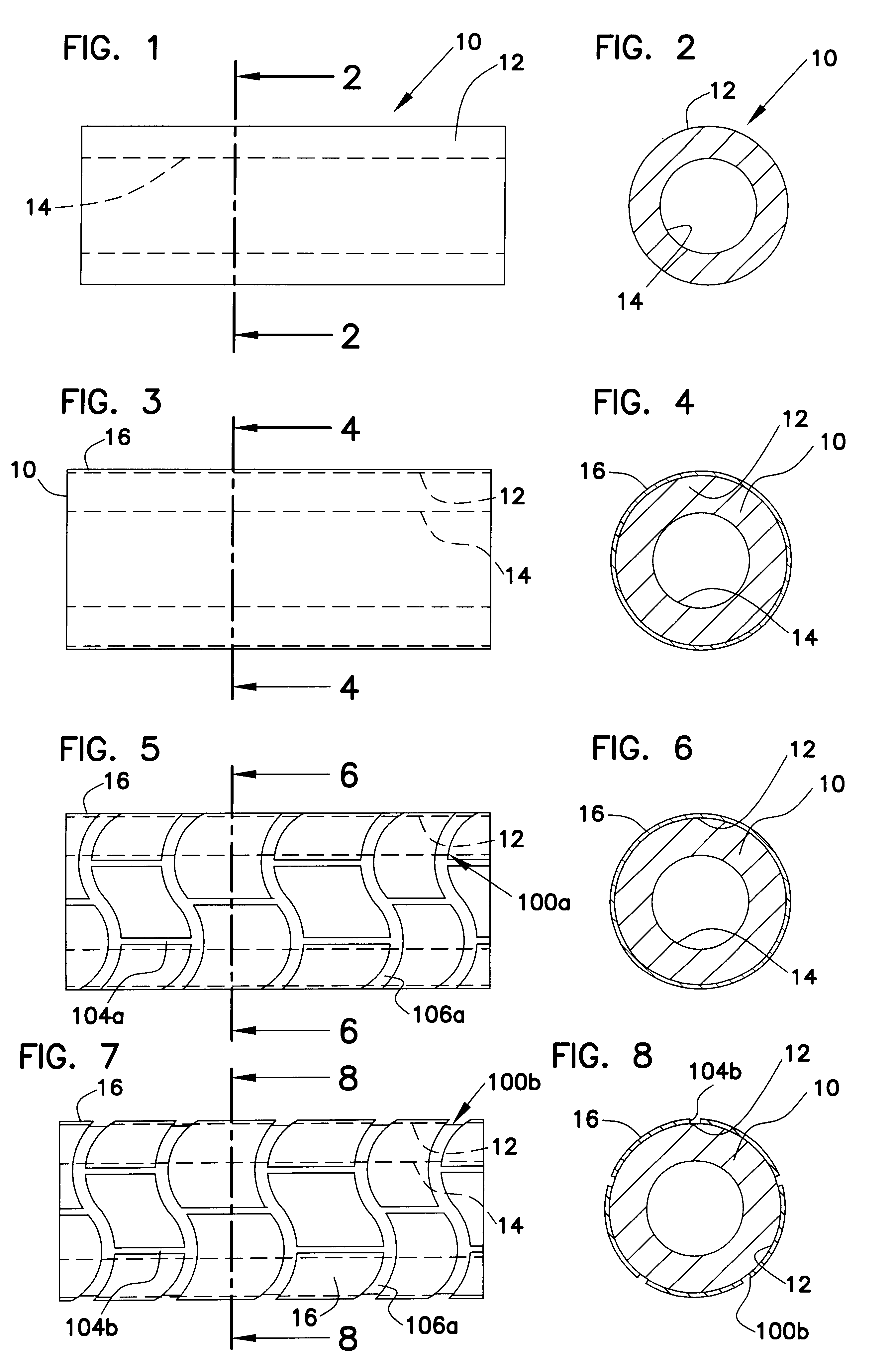
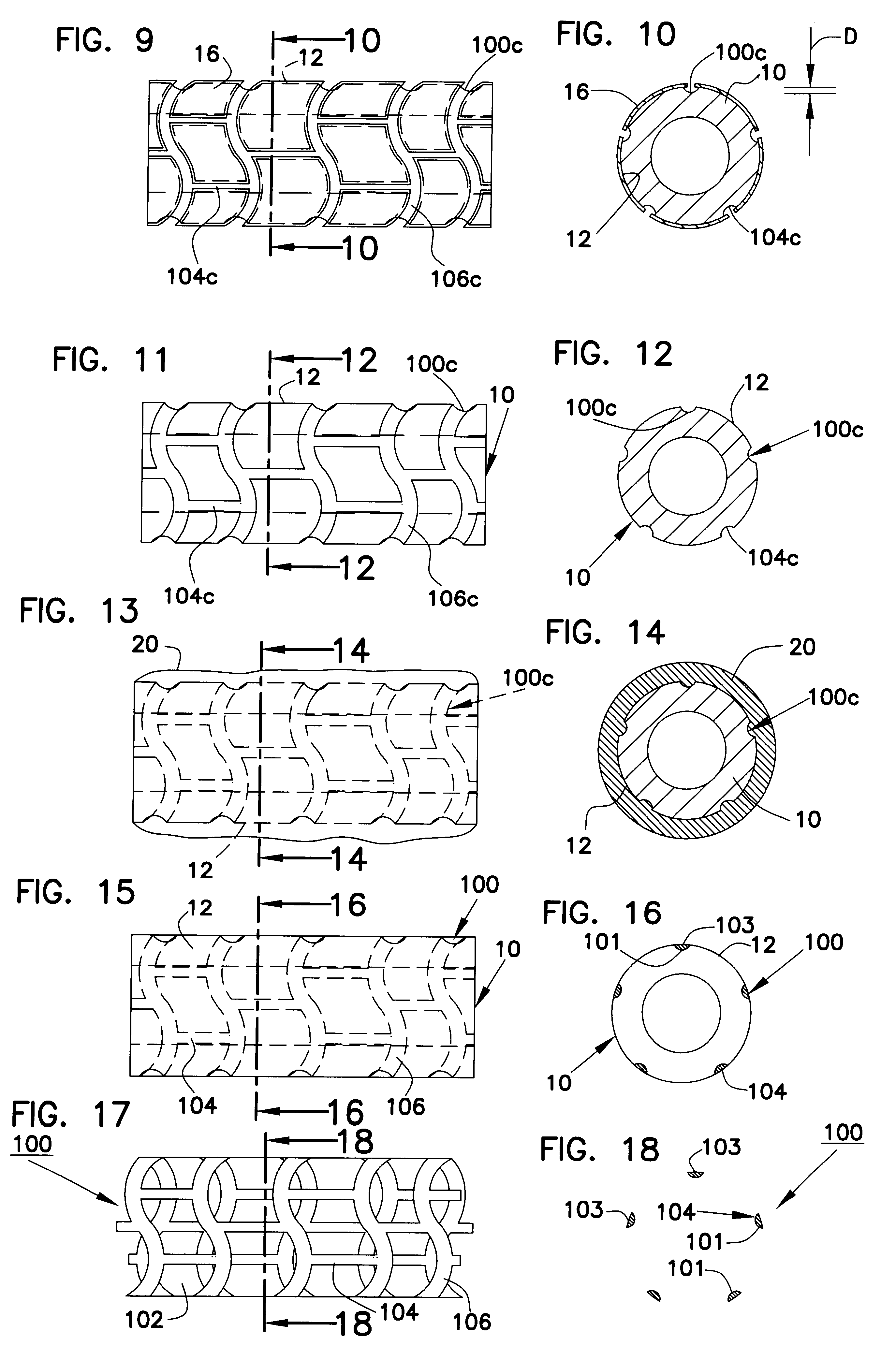
A generally tubular device (e.g., a stent or catheter) for placement in a lumen of a patient's body is made by forming a depressed pattern in an external surface of a mold. The depressed pattern corresponds to a desired shape of the generally tubular device. A material is deposited in the depressed pattern for the material to form the generally tubular device conforming to the depressed pattern. The generally tubular device is separated from the mold.
Owner:EV3 PERIPHERAL +1
Electrochemical microsensor package
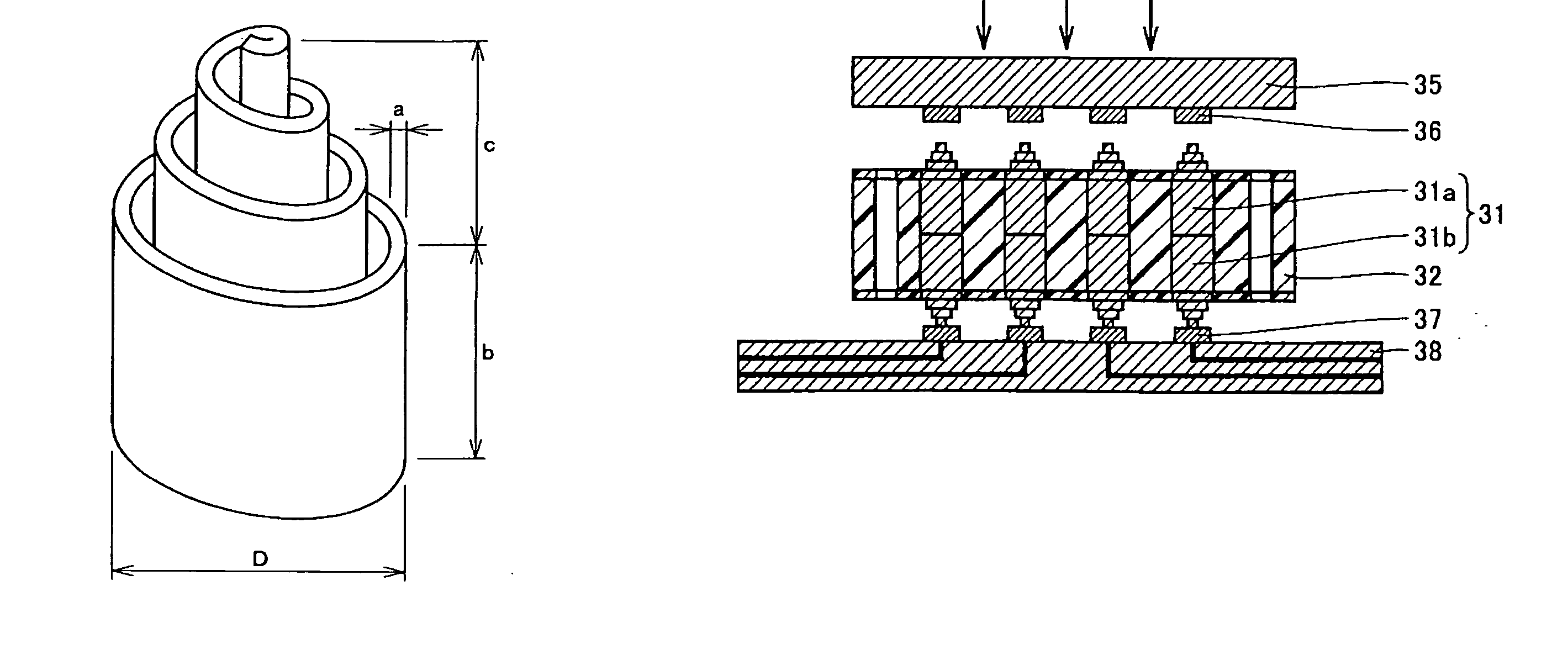
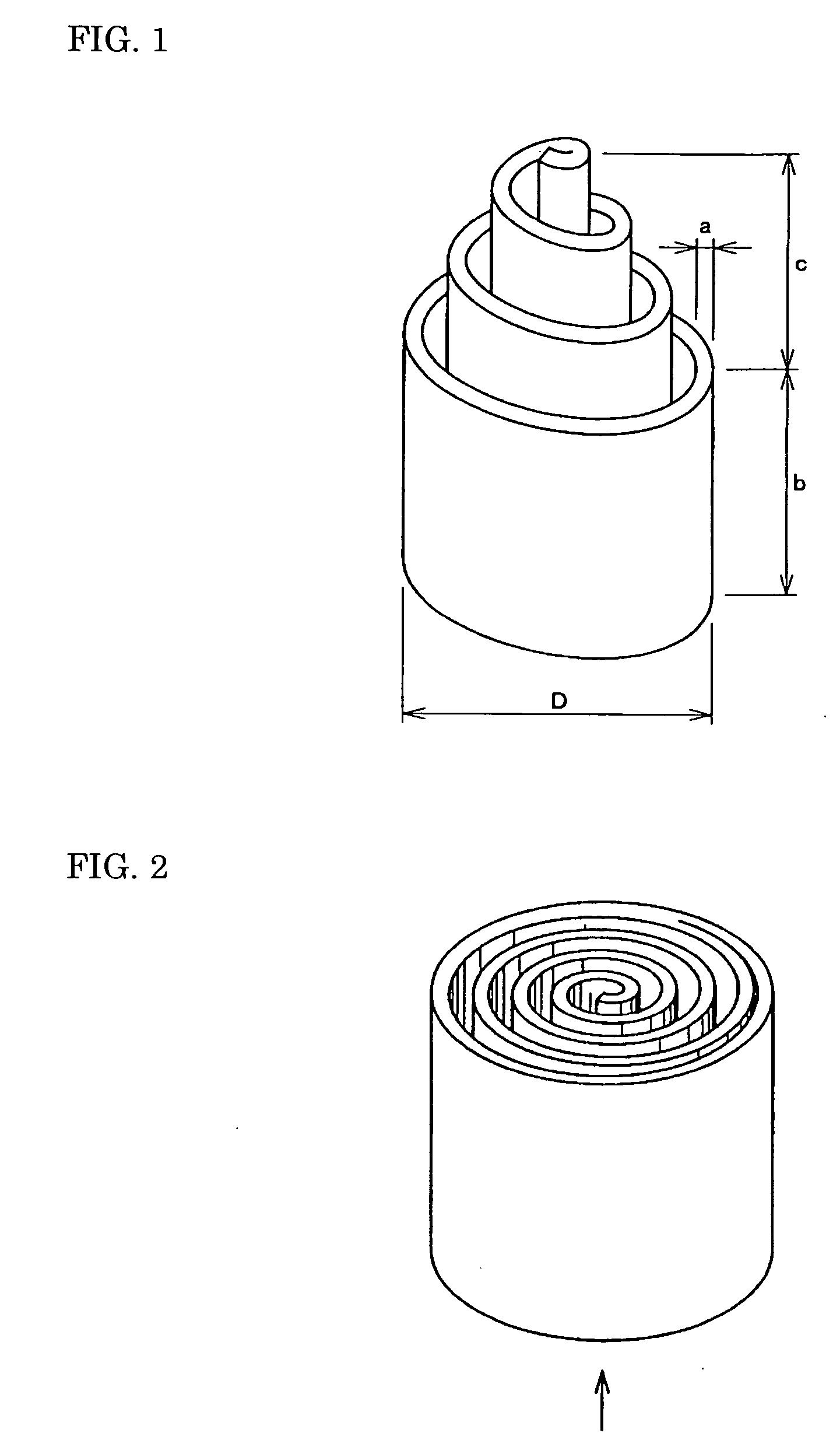
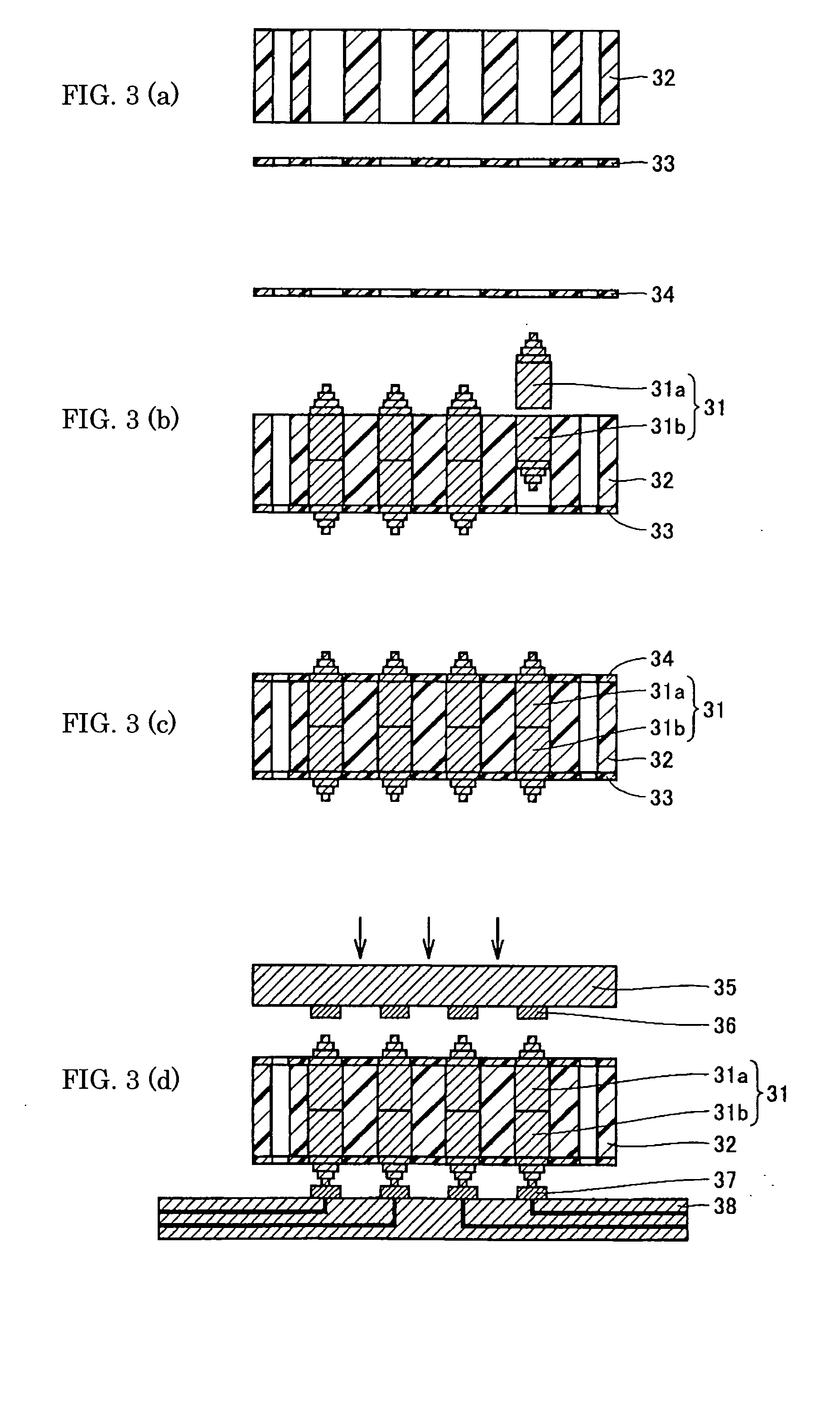
InactiveUS6849168B2Increase productionLamination ancillary operationsLaminationElectrolyteElectrical contacts
An electrochemical microsensor package comprises a substrate matrix having a upper non-conductive layer and an adjacent lower non-conductive layer with a conductive trace or pad extending over an area therebetween. The conductive pad has integral therewith a projecting contact button that projects through and below the second non-conductive for making contact with external electrical contacts. A sensor electrode is positioned on the surface of the conductive pad toward the upper non-conductive layer and in electrical contact therewith. A well extends through the upper non-conductive layer to the upper surface of the electrode. The microsensor packages may be produced by electrodeposition of the conductive pad onto a conductive mandrel having depressions to form the contact button.The microsensor package is fabricated into a microsensor by appropriate adaptation of the well of the microsensor package including applying an appropriate oxide or other layer over the electrode, introduction of an electrolyte or other sensing chemicals into the well and or applying a permeable or impermeable membrane over the top of the well.
Owner:MICROBIONICS
Medical device with extended or multiple reservoirs
An exemplary embodiment of a process can be provided for a manufacture of an implantable medical device or a part thereof. For example, at least one metallic layer can be deposited on a three-dimensional template of the device and at least partially removing the template. Implants can be produced, e.g., which may have relatively large reservoirs for including an active ingredient, such as a pharmacologically, therapeutically or biologically active agent, a diagnostically active agent, a marker, an absorptive agent, for eluting in-vivo.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
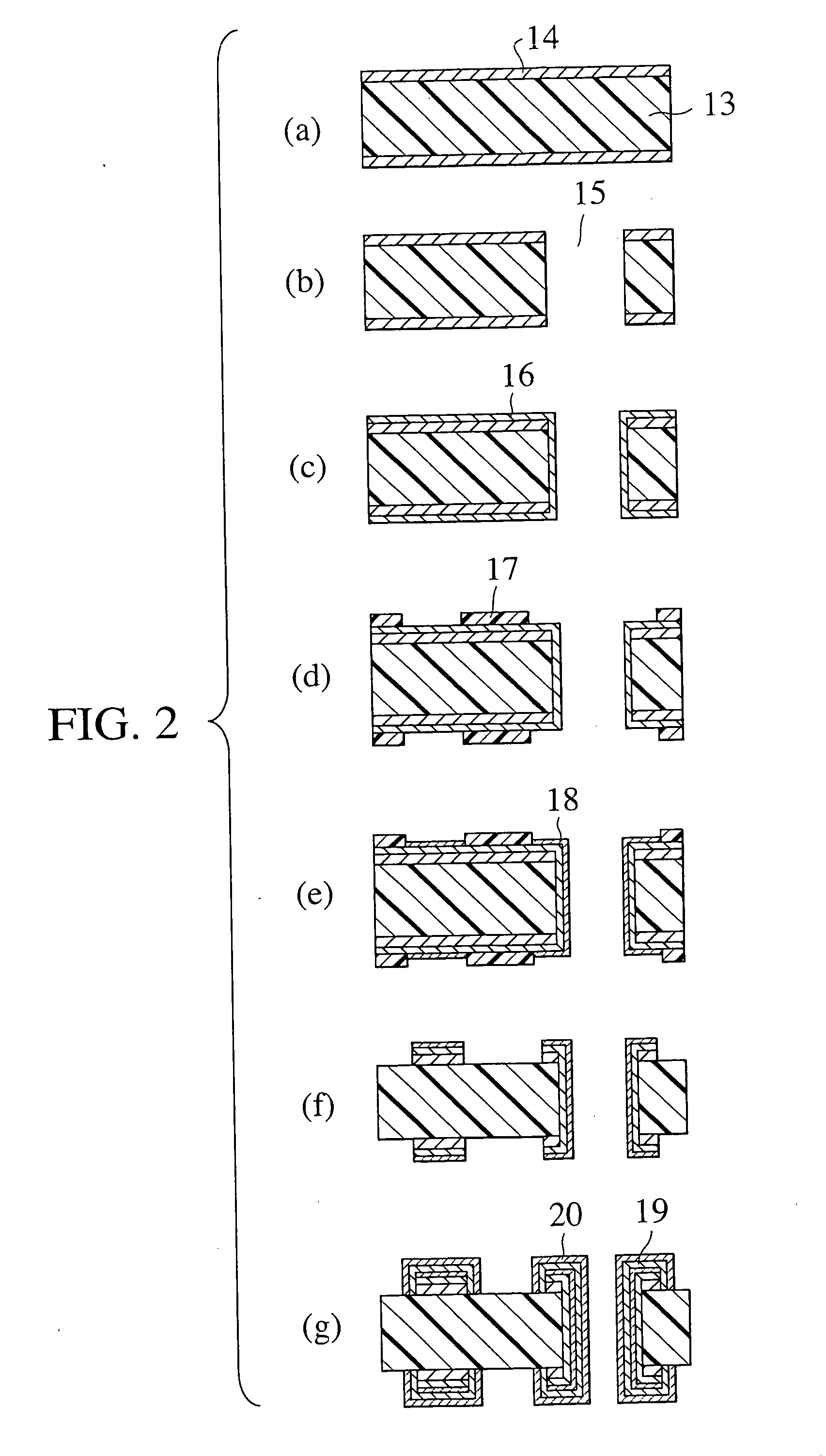
Metal foil with resin and metal-clad laminate, and printed wiring board using the same and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20050121229A1Cost efficiency and handlingCircuit formability highInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical conductorMetal foil
The present invention provides a metal clad laminate or a resin coated metal foil having a metal foil whose both surfaces are not substantially roughening-treated and an insulating resin composition layer using generally used insulating resin, and a printed wiring board and a manufacturing method thereof, in which the metal clad laminate or the resin coated metal foil is used, the reliability and circuit formability are high, and the conductor loss is extremely low.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
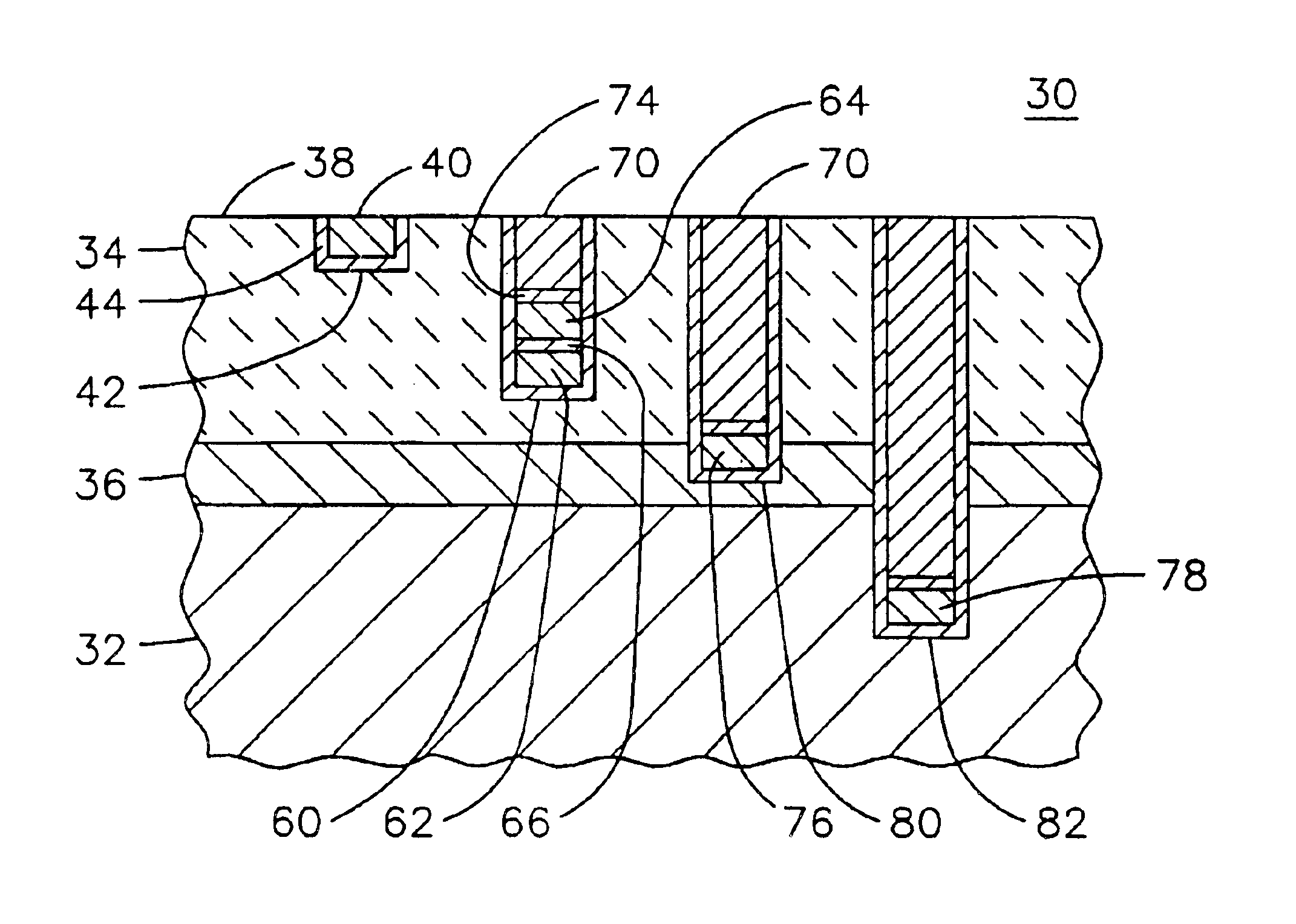
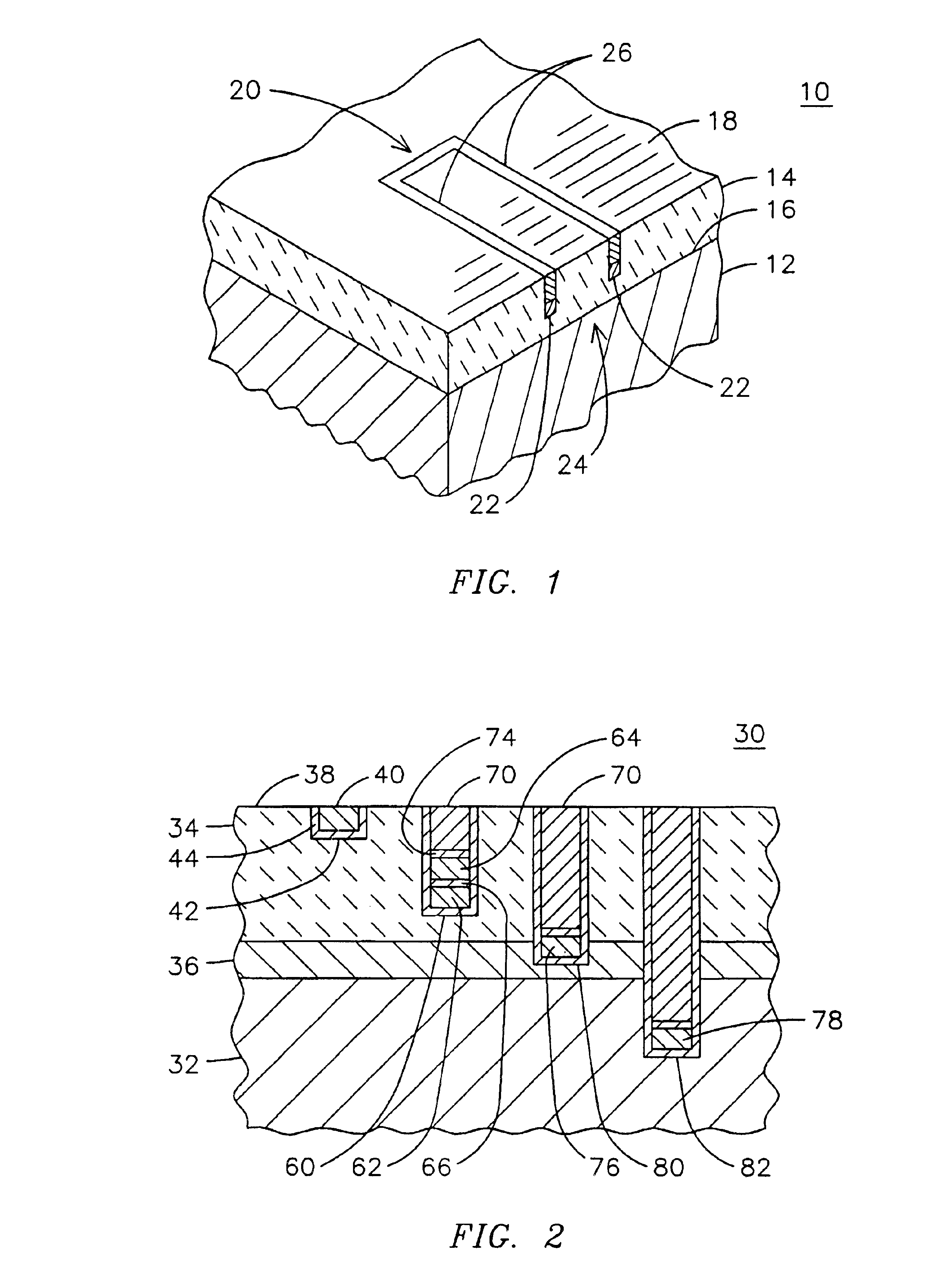
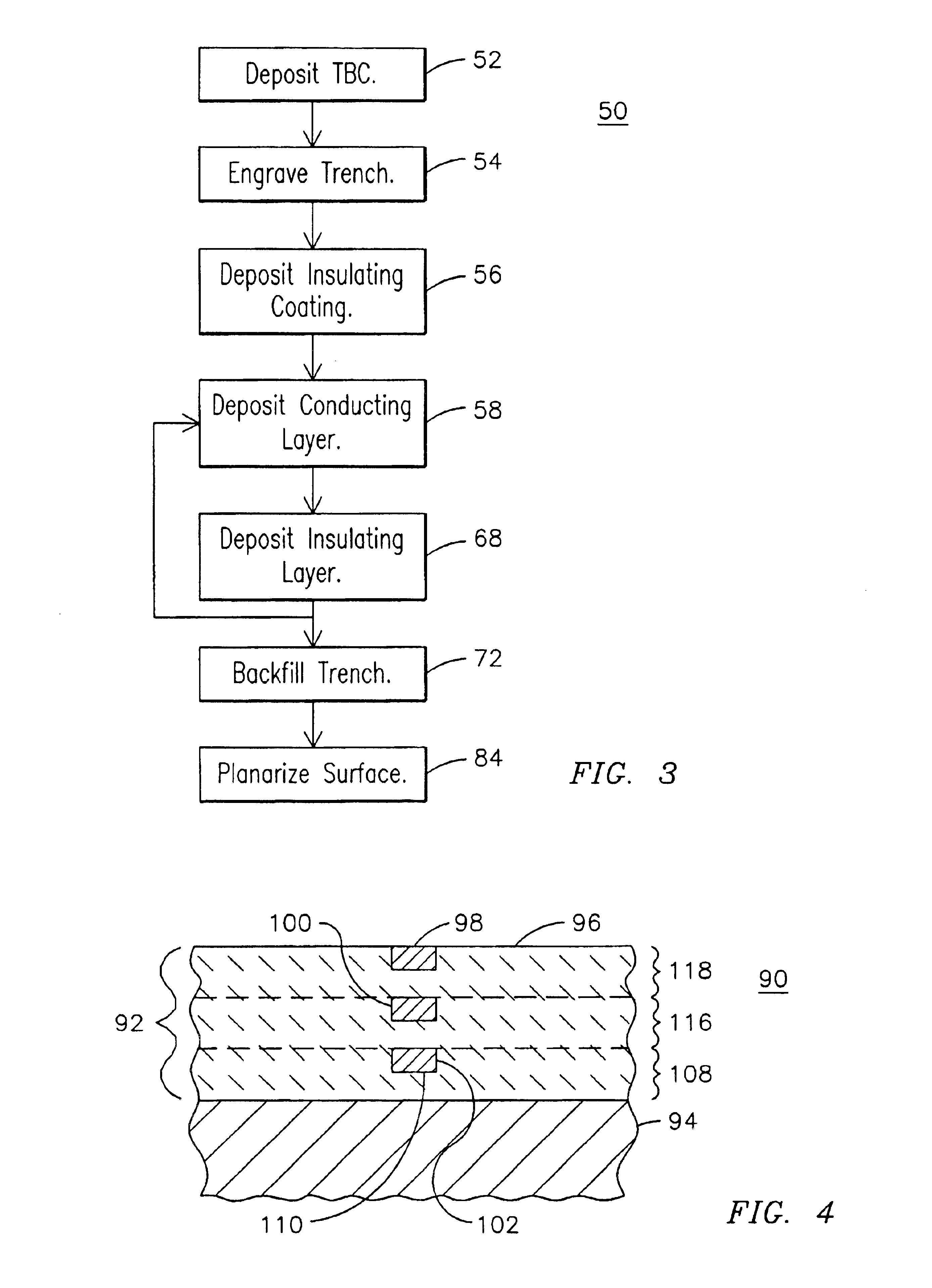
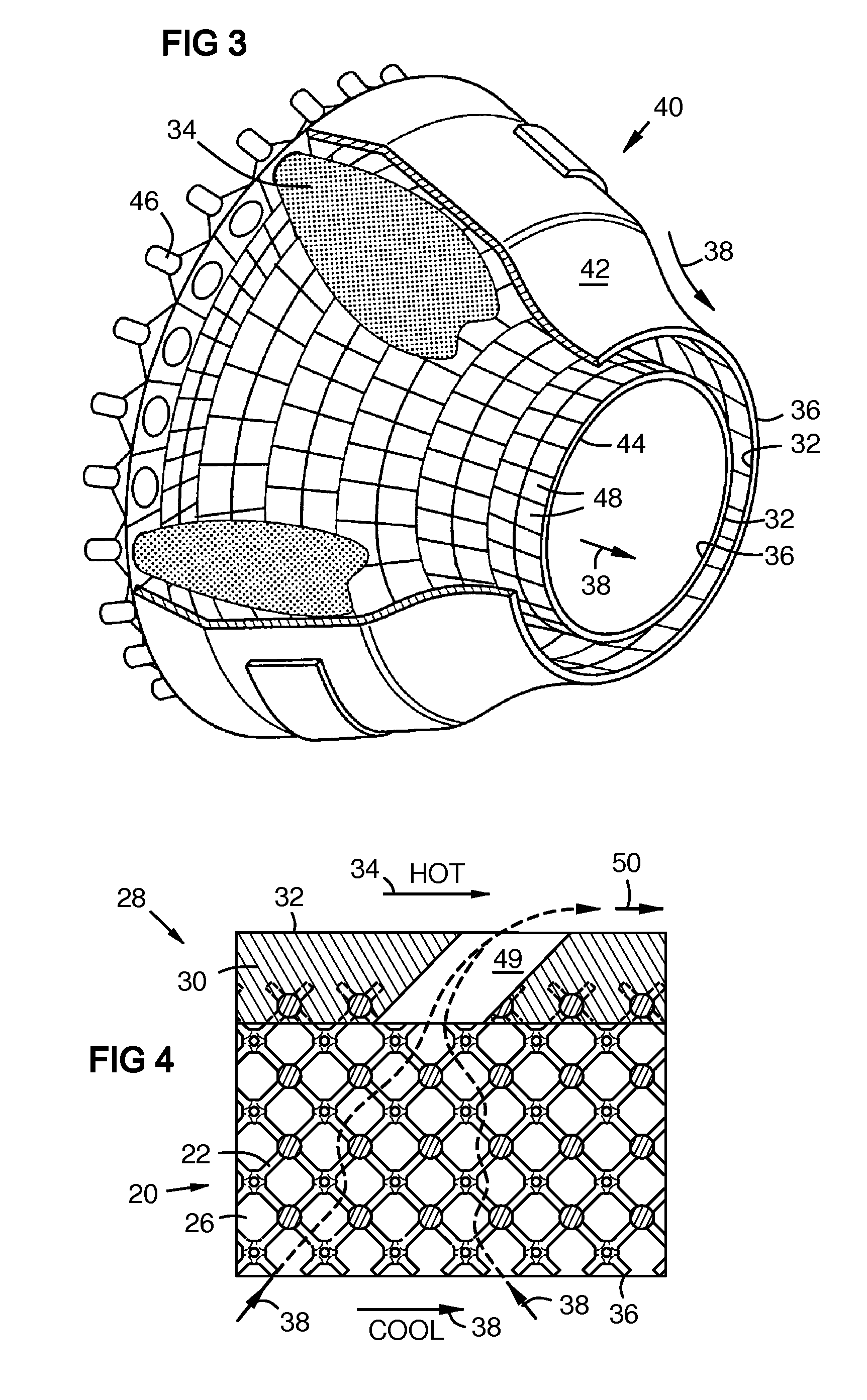
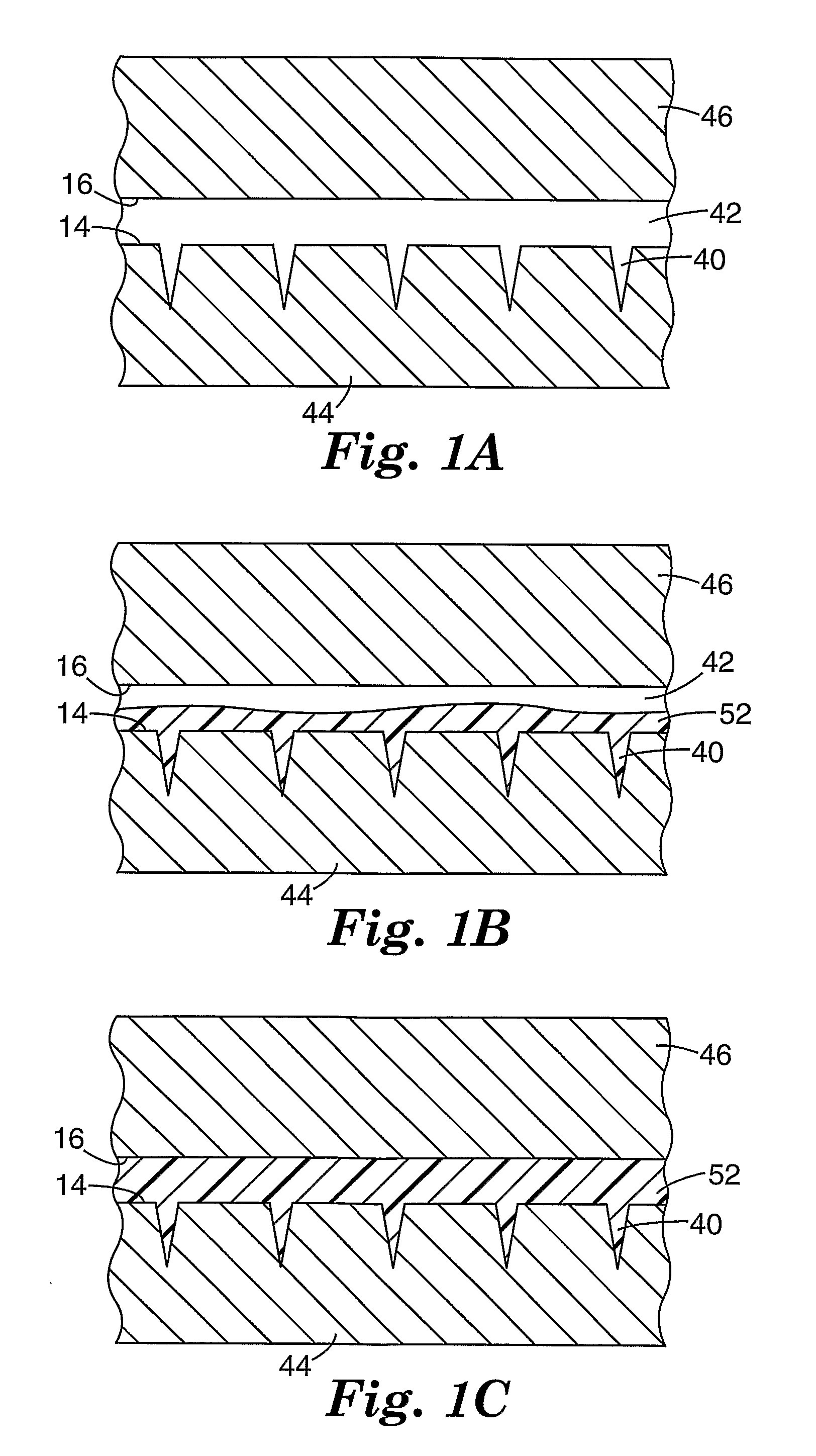
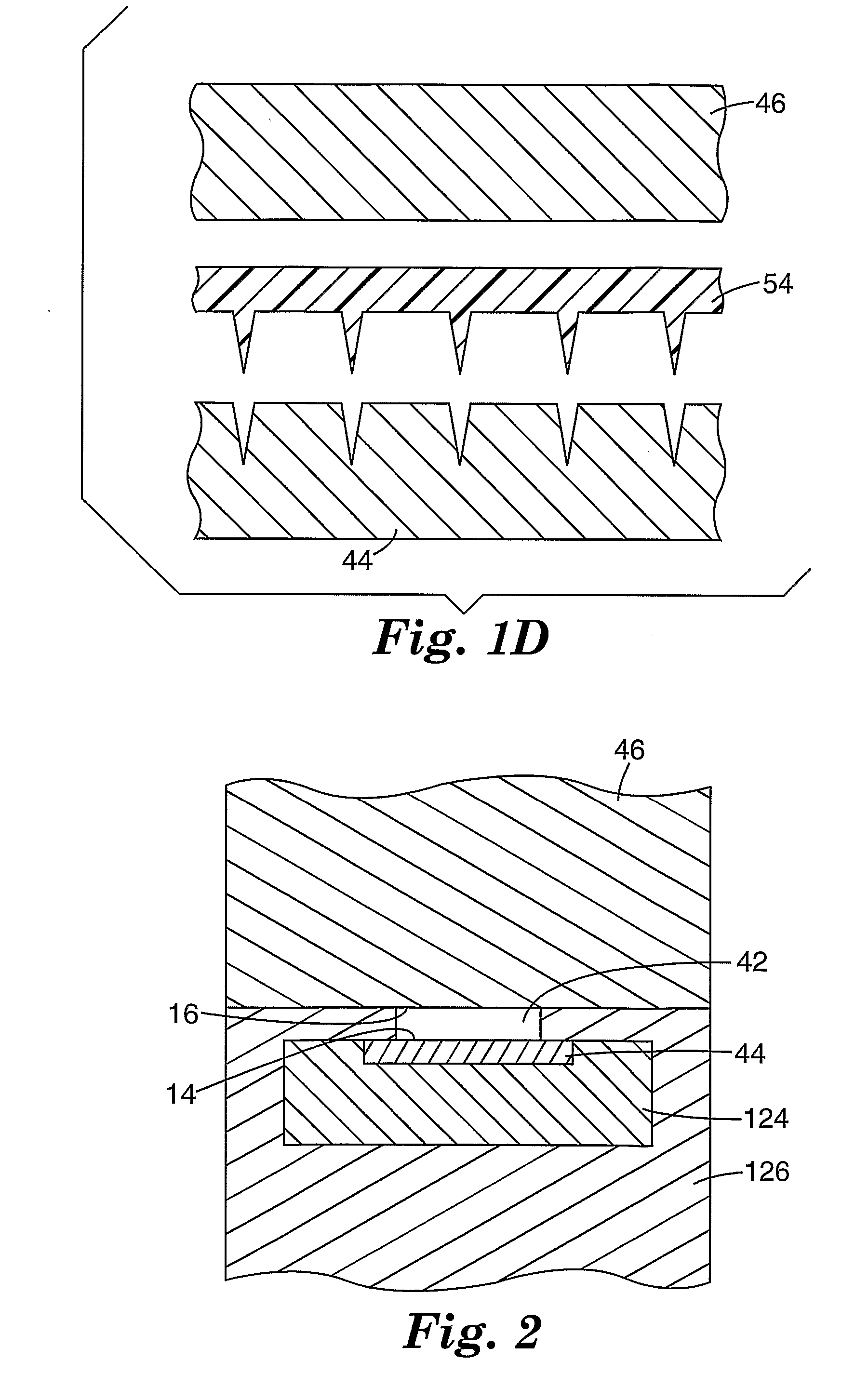
Method and apparatus for instrumenting a gas turbine component having a barrier coating
InactiveUS6838157B2Molten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingSelective laser meltingElectrical conductor
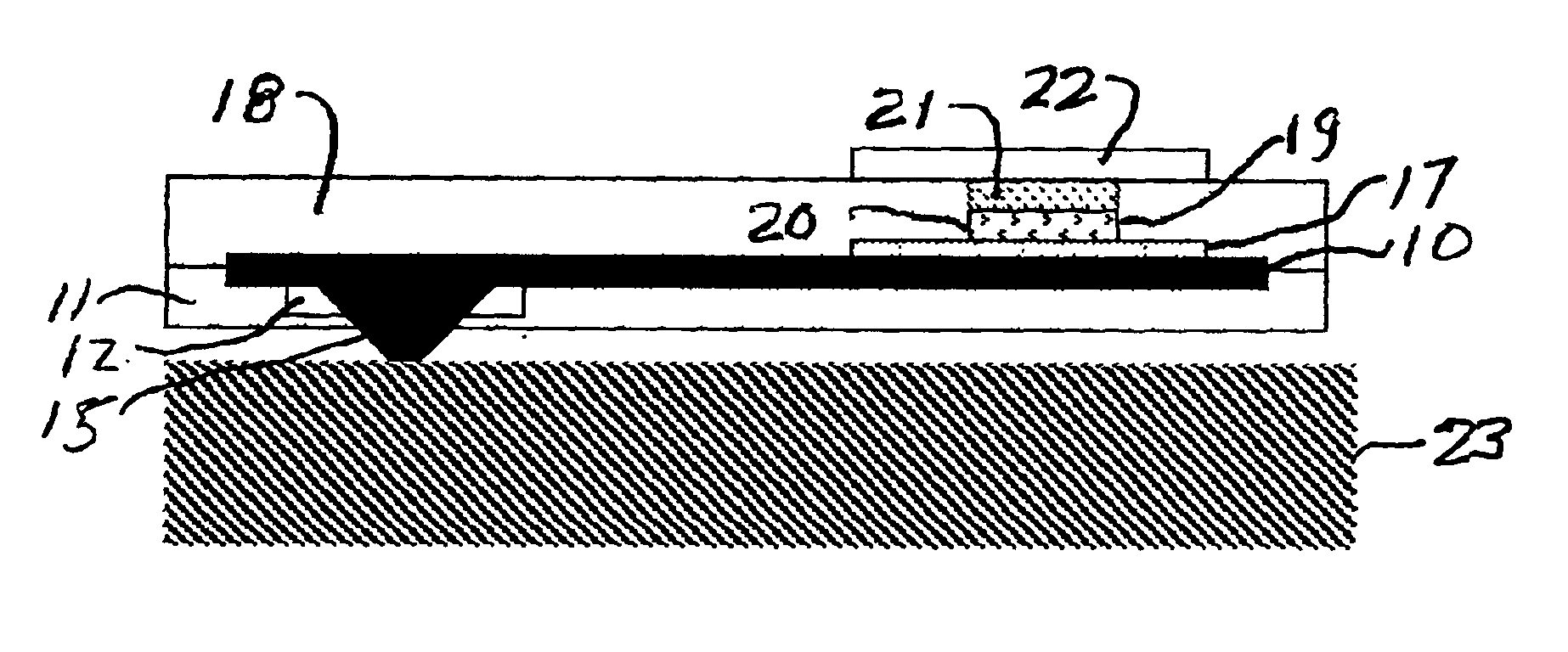
A method (50) of instrumenting a component (10) having a barrier coating (14). A sensor (76) is embedded within or below the coating. Material forming the sensor is deposited within a trench (80) formed into the barrier coating. The trench is then backfilled with material (70) to protect the sensor from the environment within which the component is operating. In this manner, the sensor may be embedded at any desired location and any desired depth within a barrier coating on a previously fabricated component. An array of sensors (98, 100, 102) may be embedded across the depth of the coating to provide signals indicative of operating conditions across the coating. The signals may be conducted to a connection location (24) by conductors (62, 64) that are deposited within the trench. The trench may be formed with a laser engraving process (54) and the material for the sensor and conductors may be deposited with a selective laser melting process (58).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Process for forming a porous drug delivery layer
InactiveUS6904658B2Increase drug retention timeImprove adhesionStentsMetal rolling stand detailsPorous layerVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention is directed to a process for forming a drug delivery device by electroplating onto a substrate a porous layer having pores of a controlled size and density and loading a drug into the pores. Preferably the drug delivery device is a gold stent plated with a gold porous layer.
Owner:ELECTROFORMED STENTS
Variable property electrodepositing of metallic structures
ActiveUS20090159451A1Increase floor spaceAdd equipmentCellsElectrolytic coatingsParticulatesMetallic materials
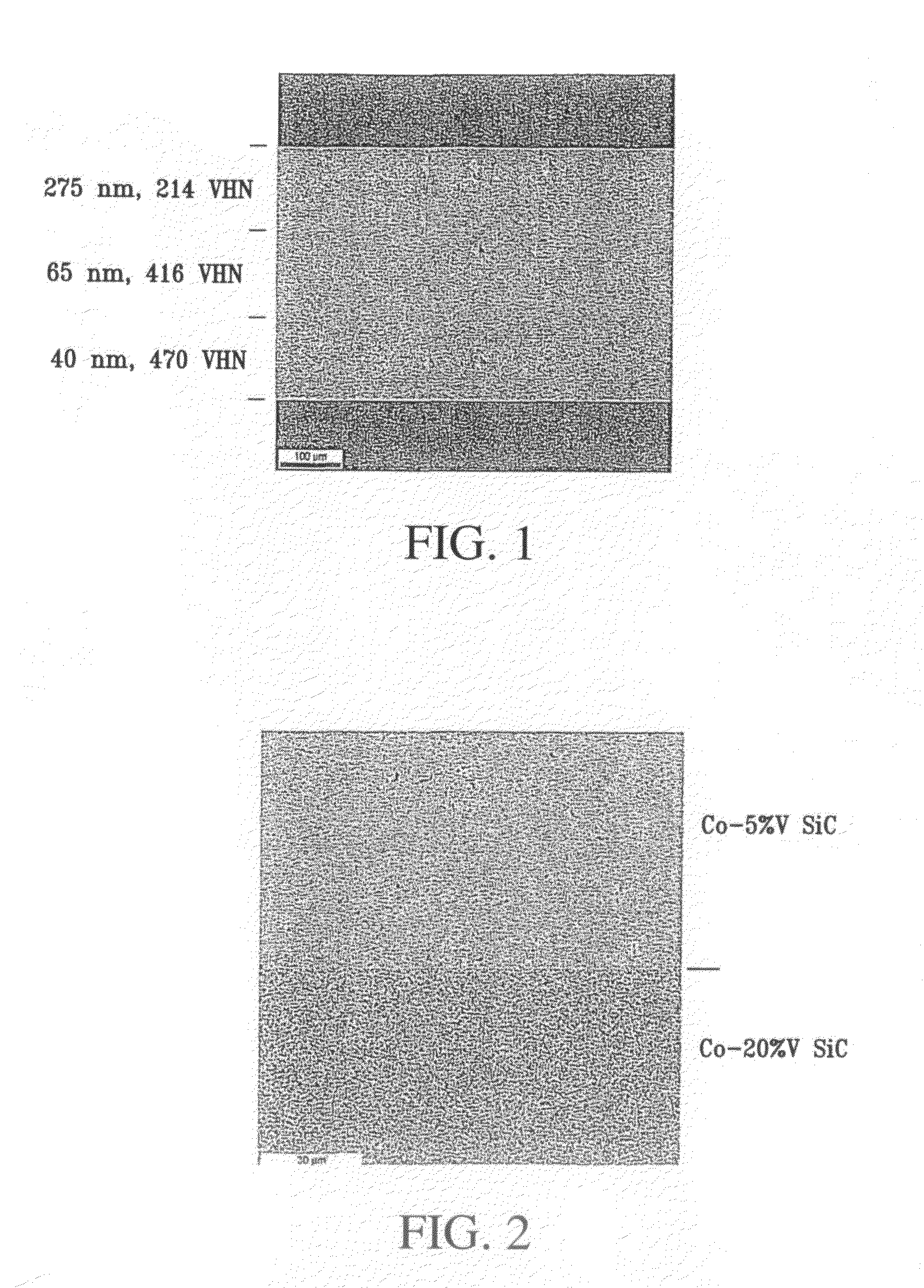
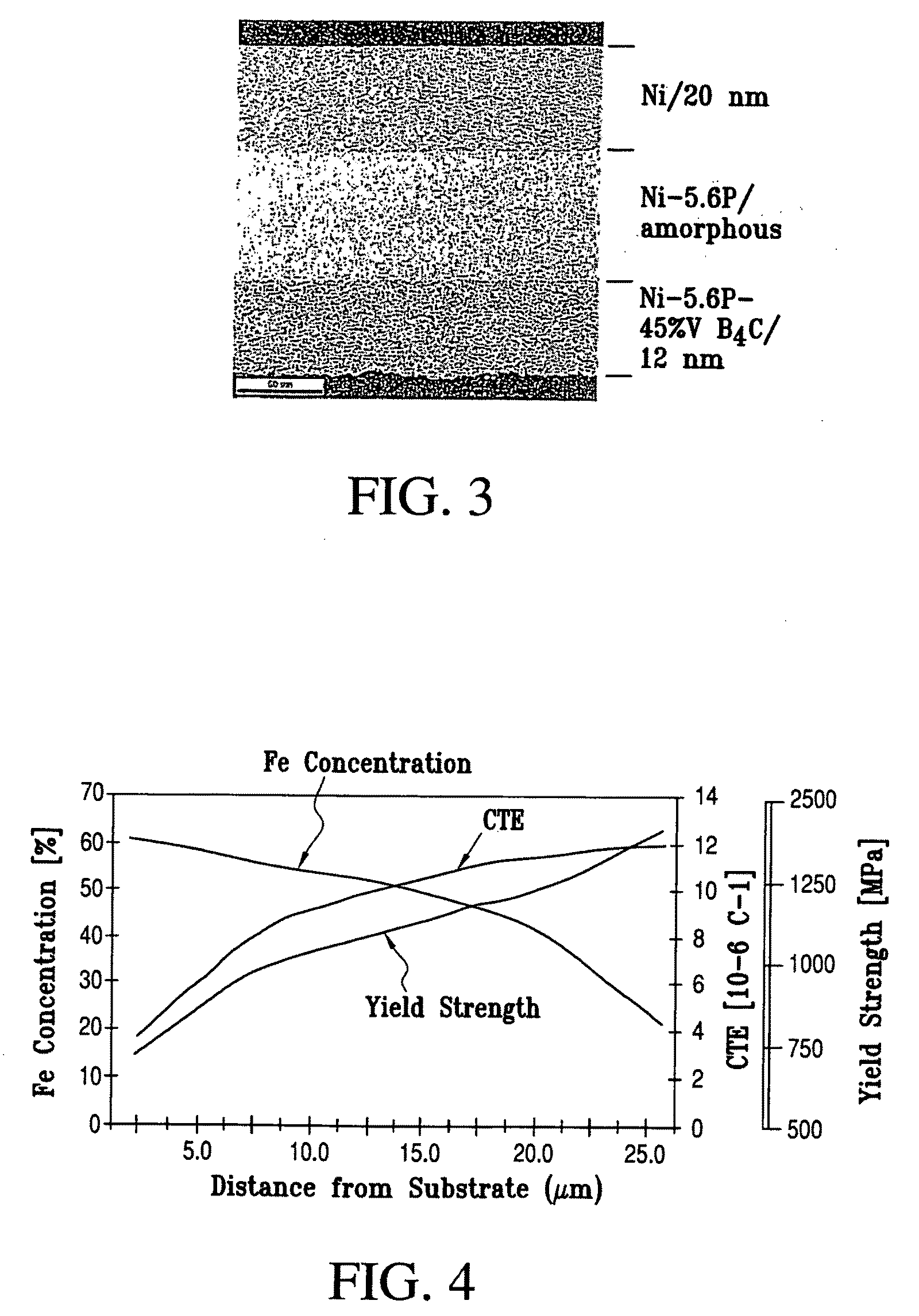
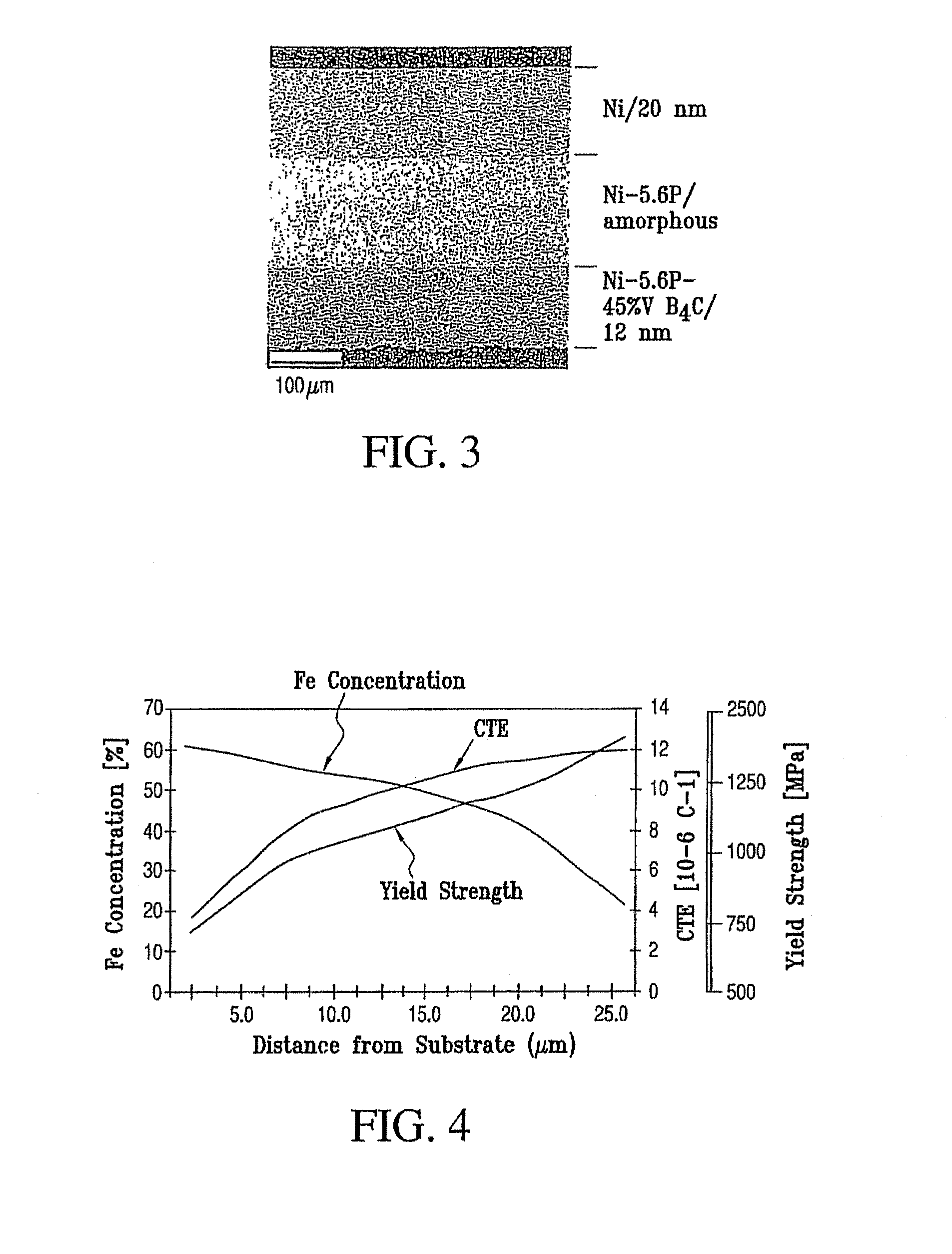
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: 2 nm-5 micron), entirely coarse-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Anode for nonaqueous secondary battery, process of producing the anode, and nonaqueous secondary battery
InactiveUS20060147802A1Simple materialRaise the ratioCellsElectrochemical processing of electrodesSurface layerLithium compound
A negative electrode for nonaqueous secondary batteries is disclosed. The negative electrode has a pair of current collecting surface layers of which the surfaces are adapted to be brought into contact with an electrolyte and at least one active material layer interposed between the surface layers. The active material layer contains particles of an active material having high capability of forming a lithium compound. The material constituting the surfaces is preferably present over the whole thickness of the active material layer to electrically connect the surfaces so that the electrode exhibits a current collecting function as a whole. The surface layers each preferably have a thickness of 0.3 to 10 μm.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Mask electro-forming method for vaporization coating of organic light-emitting display
ActiveCN1804138AUniform openingEasy transferVacuum evaporation coatingPhotomechanical apparatusPosition toleranceDisplay device
The mask electroforming method for OLED comprises: preparing module core, pre-treating the core; sticking mask; exposing; developing; deoiling; cleaning in water; activating / passivating; cleaning; electroforming mask; cleaning; removing mask; peeling mask; bonding with silk screen; detecting the product; packing. This invention can prepare the high-precise mask for OLED with thickness less than 0.5mm, and has opening tolerance up to í‚0.005mm; for example, for a 370mmí‡470mm mask plate, the crosshole position tolerance just is í‚0.008mm.
Owner:KUN SHAN POWER STENCIL
Ceramic substrate, ceramic package for housing light emitting element
InactiveUS20060147746A1Reduce smoothnessIncrease costExtrusion containersSolid-state devicesGold layerCeramic substrate
A ceramic substrate comprising a metallic layer on its surface, wherein said metallic layer includes: a silver layer containing silver; a gold layer containing gold; and a nickel layer containing nickel, in this order from an outermost layer of said metallic layer.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Process for making a wall with a porous element for component cooling
A structural layer (30) may be bi-cast onto ligaments (62) extending from a porous cooling construction (20). The material of the structural layer may be optimized for high-temperature strength, while the material of the porous construction may be optimized for high thermal conductivity. A fugitive material (56) such as wax may be formed on the ligaments of the porous construction. A second fugitive material (58) such as ceramic may fill the remaining part of the porous construction. An investment casting shell (60) may be disposed around the porous construction and the fugitive materials. The first fugitive material may then be replaced with the material of the structural layer (30), and the second fugitive material may be removed to provide coolant paths (26). A second structural layer (52) may be bi-cast onto further ligaments (62) on a second side of the porous construction.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
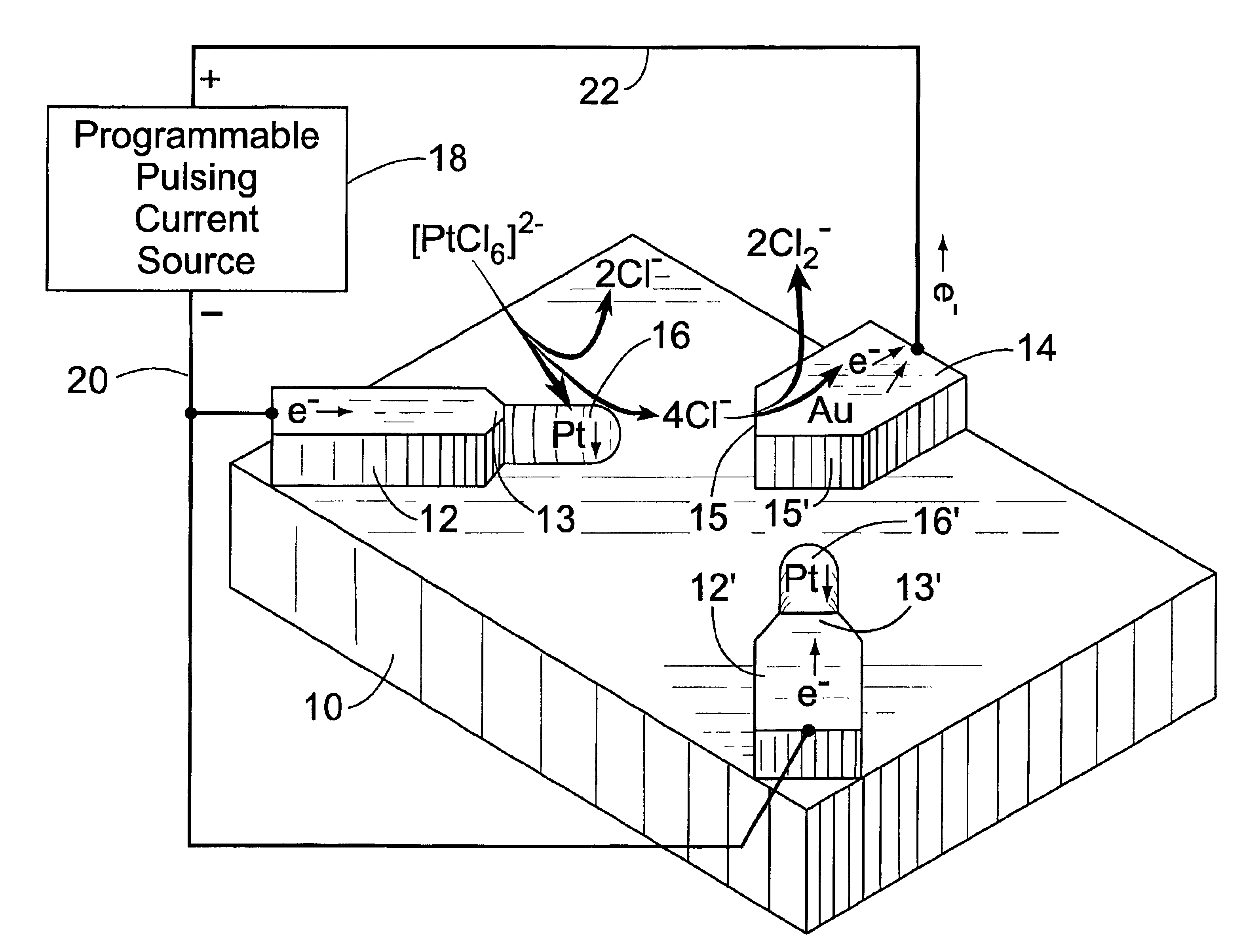
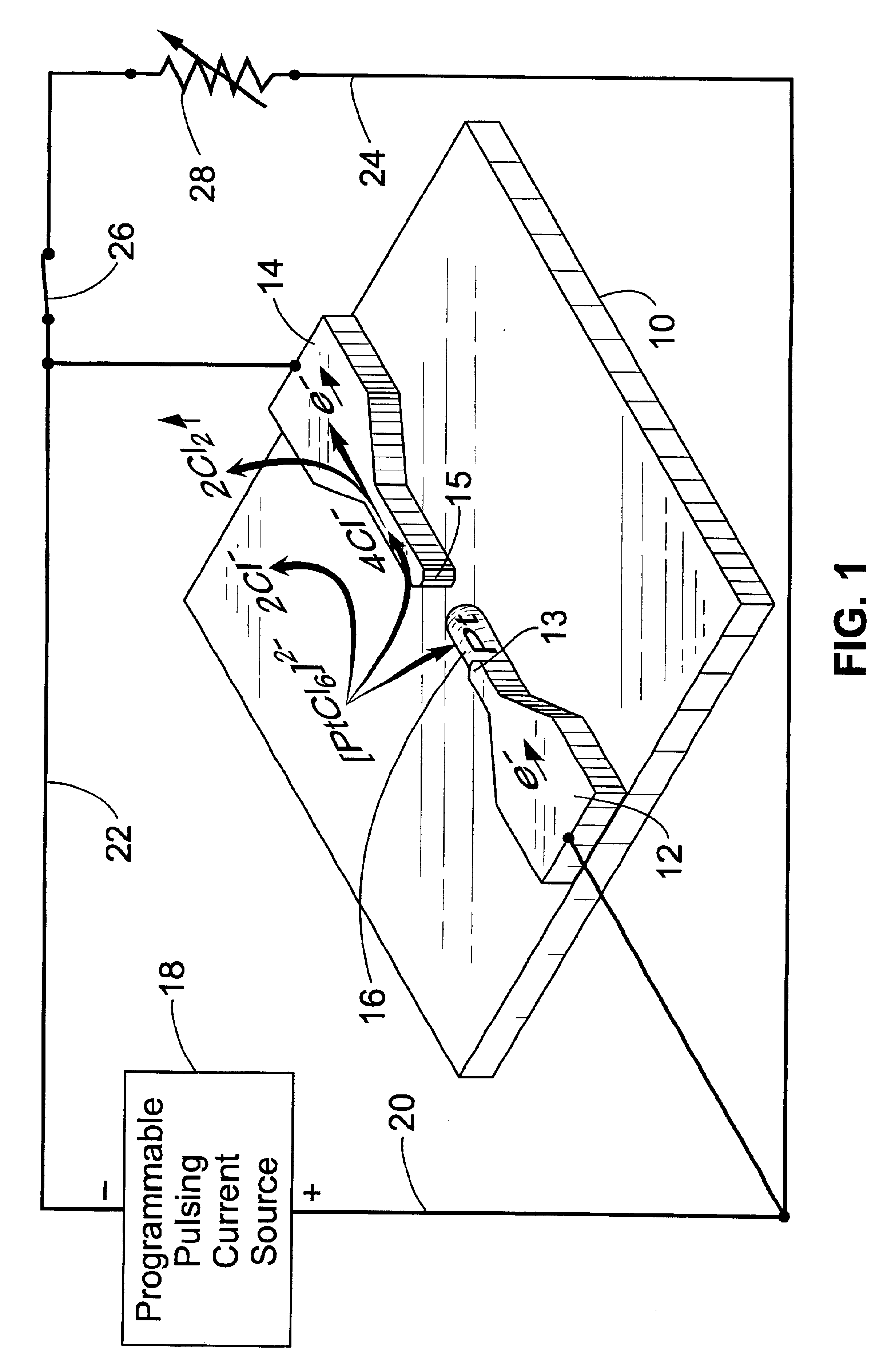
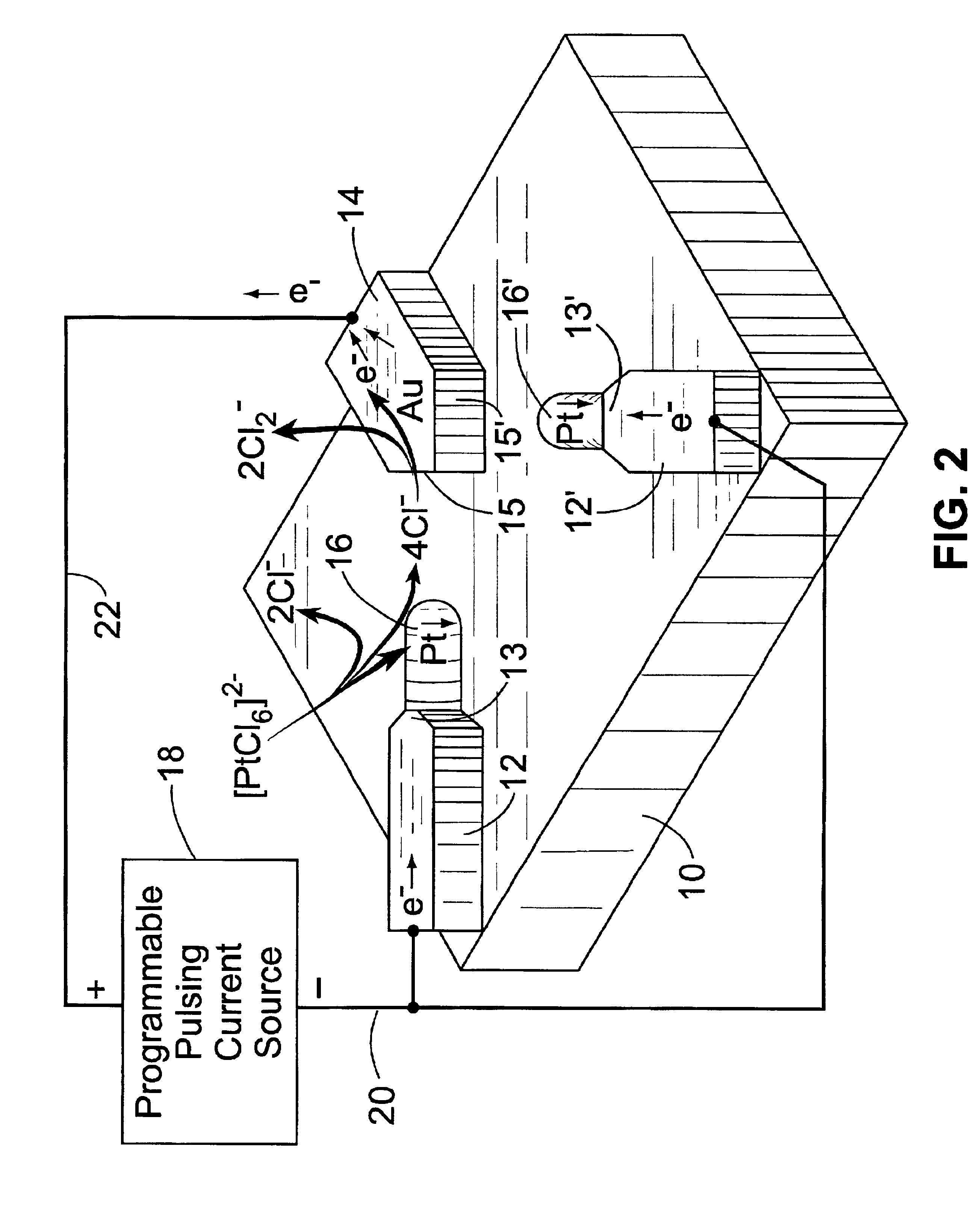
Catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes on tips of cantilevers and nanowires
InactiveUS6755956B2Improve performanceEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsFiberNanowire
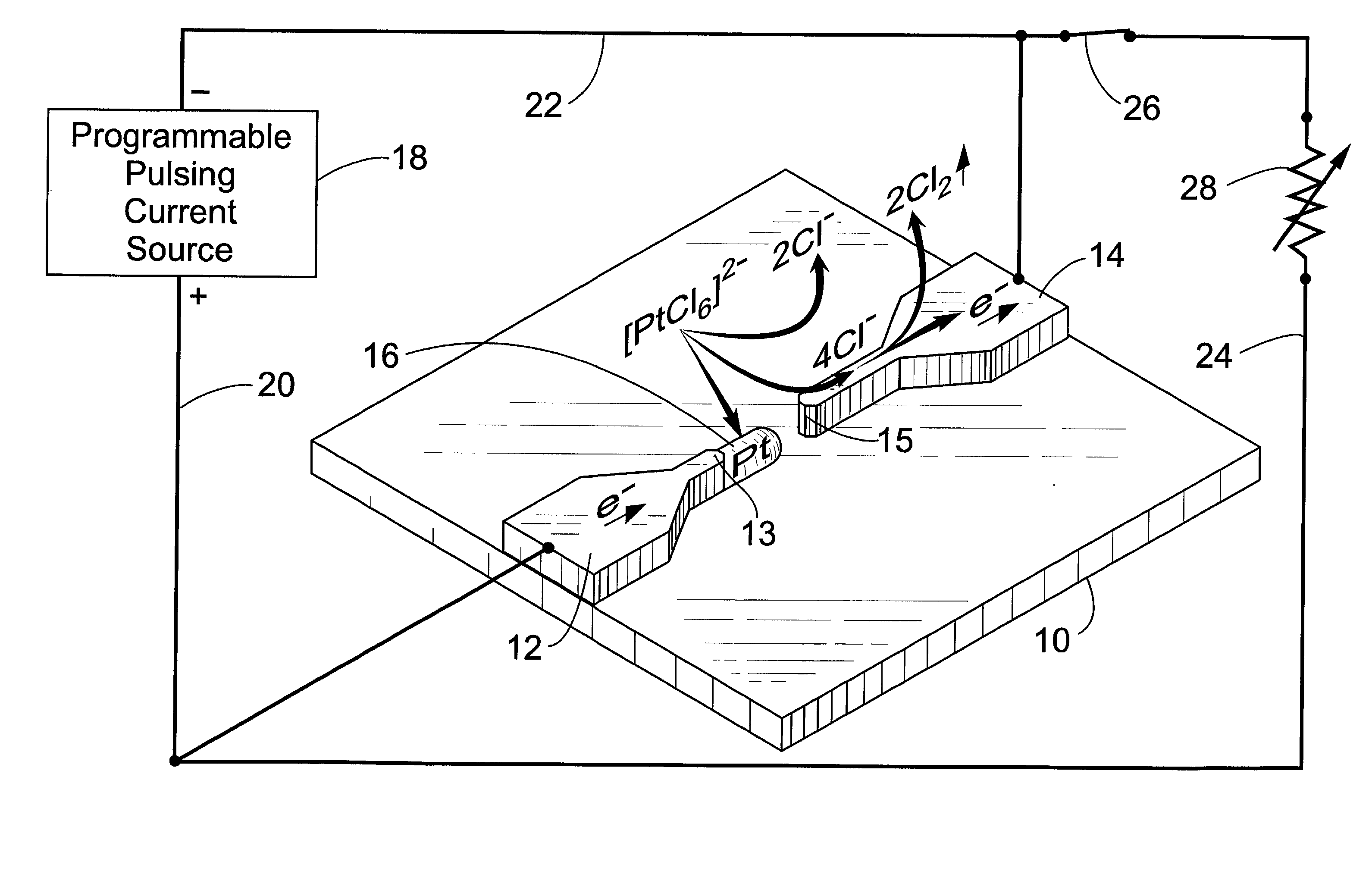
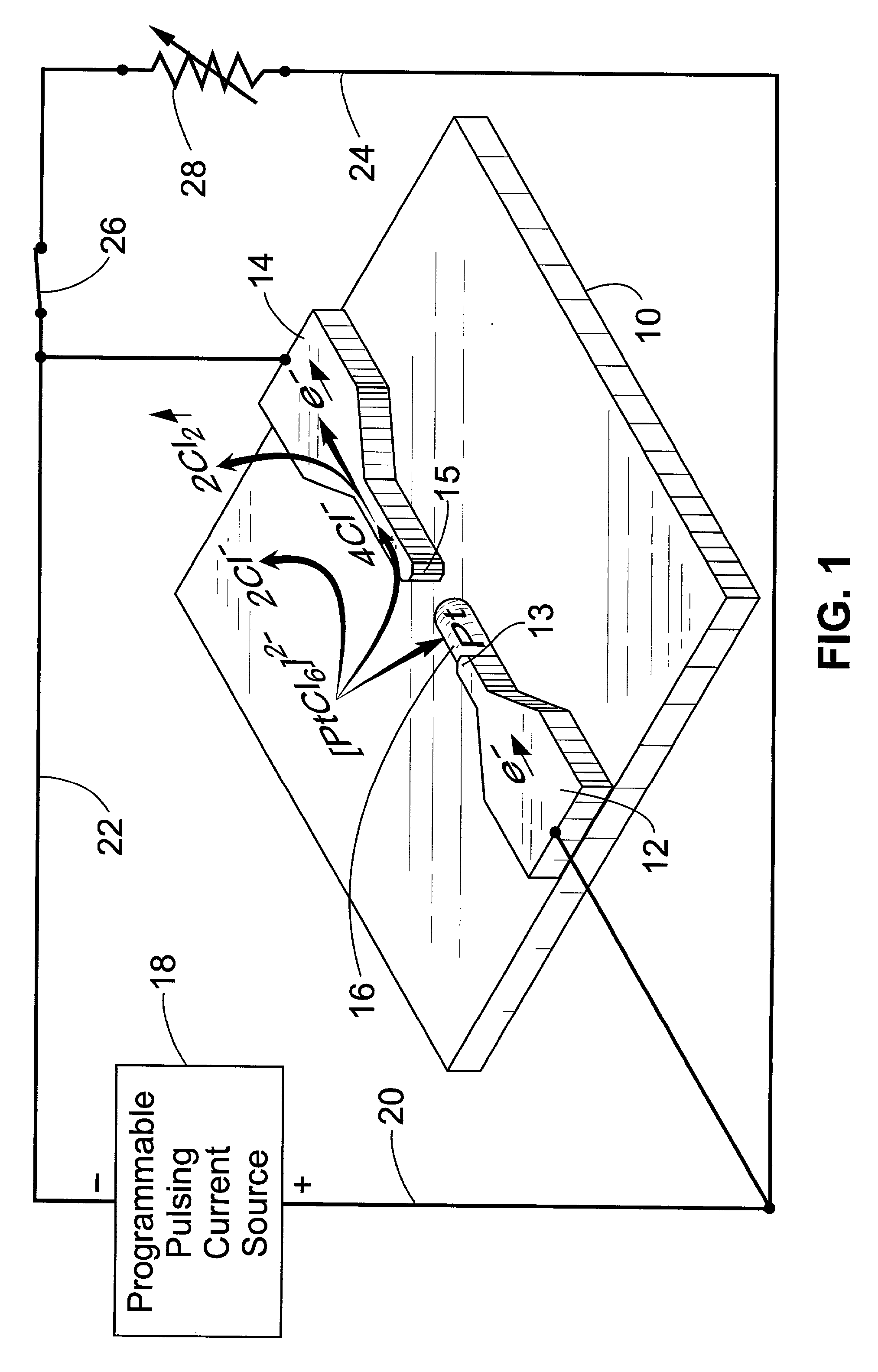
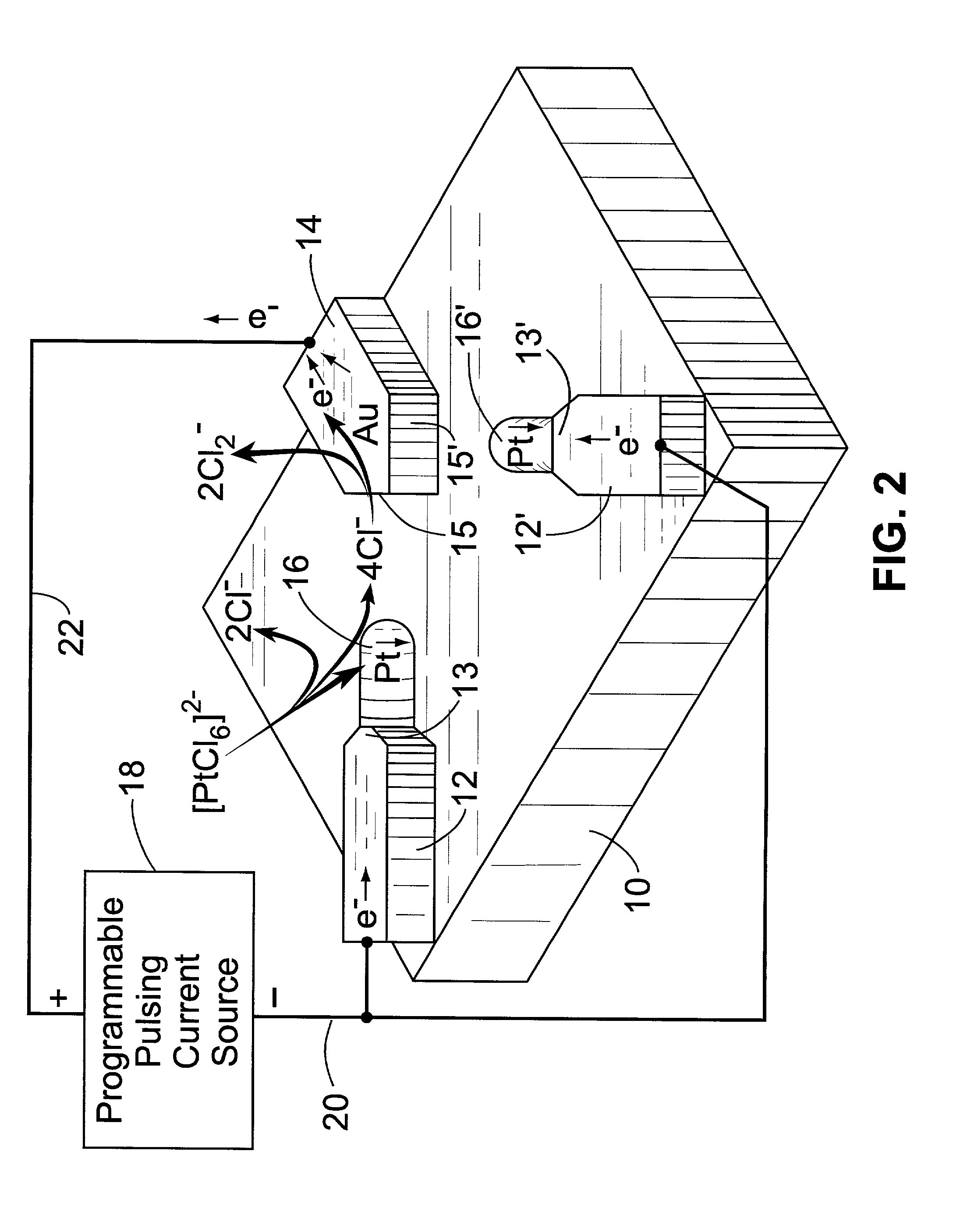
A method is described for catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes, nanofibers, and other nanostructures on the tips of nanowires, cantilevers, conductive micro / nanometer structures, wafers and the like. The method can be used for production of carbon nanotube-anchored cantilevers that can significantly improve the performance of scaning probe microscopy (AFM, EFM etc). The invention can also be used in many other processes of micro and / or nanofabrication with carbon nanotubes / fibers. Key elements of this invention include: (1) Proper selection of a metal catalyst and programmable pulsed electrolytic deposition of the desired specific catalyst precisely at the tip of a substrate, (2) Catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes / fibers at the catalyst-deposited tips, (3) Control of carbon nanotube / fiber growth pattern by manipulation of tip shape and growth conditions, and (4) Automation for mass production.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Method of molding for microneedle arrays
InactiveUS20070191761A1Meet needsDuplicating/marking methodsSurgical needlesMaterials scienceTissue skin
A method of manufacturing a moldable microneedle array (54) is described comprising providing a negative mold insert (44) characterized by a negative image of microneedle topography wherein at least one negative image of a microneedle is characterized by an aspect ratio of between about 2 to 1 and about 5 to 1. The negative mold insert (44) is used to define a structured surface of a negative mold cavity (42). Molten plastic material is injected into the heated negative mold cavity. The molten plastic material is subsequently cooled and detached from the mold insert to provide a molded microneedle array (54). One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue through the skin.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Wire grid polarizer and method for producing same
ActiveUS20050046943A1High light transmittanceLow costPolarising elementsOptical articlesWire gridLithographic artist
There are provided a thin wire grid polarizer having a high transmittance, a high quenching ratio and a high degree of polarization, and a method for producing the same at low costs. A fluoridated polyimide thin film 12, a hydrophilic thin film 13 and a hydrophobic thin film 14 are sequentially stacked on a glass substrate 11 to be pressed by a die 1 from the side of the hydrophobic thin film 14 to transfer the fine pattern of groove forming protrusions 3 of the die 1 to the hydrophobic thin film 14 and hydrophilic thin film 13 by the nano-imprinted lithography technique, and then, metal fine wires are caused to grow by plating.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Metallic Structures with Variable Properties
InactiveUS20110256356A1Increased durabilityIncrease floor spaceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesMetallic materials
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Methods and moulds for use in fabricating side-ported microneedles
Side-ported microneedles are produced from a suitably shaped microneedle mould (40). A microneedle mould base (32) is made with a number of microneedle mould recesses (30) in it. One surface of the microneedle mould base (32) is coated with a seed layer (34). The microneedle mould base (32) contains two microneedle mould sheets (24, 26), which are separated to gain access to an internal surface of one of the microneedle mould sheets (24, 26). Side-port forming channels (38) are formed on one of the internal surfaces, intersecting with the recesses (30) within the relevant microneedle mould sheet (24). The two microneedle mould sheets (24, 26) are placed back together and joined together as a unitary microneedle mould (40). The microneedles are formed in the recesses (30) by depositing a microneedle layer (44) therein and on the surface with the seed layer (34). The microneedle layer (44) fails to deposit at side-port forming holes (42) where the side-port forming channels (38) intersect the recesses (30), which result in side-ports (46) in the moulded microneedles (52).
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Bonded body of galvanized steel sheet and adherend, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110008644A1Firmly connectedGood adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsPolyolefinSheet steel
The invention is a technique for strongly integrating a galvanized steel sheet and a resin molded article. A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet “Z18” is immersed in an aqueous solution for aluminum degreasing at 75° C. for 7 minutes, to form roughness having an RSm of 0.8 to 2.3 μm and an Rz of 0.3 to 1.0 μm on the surface. The surface is covered with convex protrusions having a diameter of about 100 nm, and a chromate treatment layer appears in the surface. In other words, three conditions suitable for bonding are satisfied thereby. A resin composition comprising 70 to 97 wt % of polyphenylene sulfide and 3 to 30 wt % of a polyolefin resin is injected onto the surface. The resin composition penetrates into ultra-fine irregularities and is cured in that state, whereby a composite in which the galvanized steel sheet and the resin molded article are strongly integrated is obtained. The shear rupture strength of the composite is extremely high, in excess of 20 MPa.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
Catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes on tips of cantilevers and nanowires
InactiveUS20020046953A1Easy to controlImprove performanceAnodisationMaterial nanotechnologyFiberNanowire
A method is described for catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes, nanofibers, and other nanostructures on the tips of nanowires, cantilevers, conductive micro / nanometer structures, wafers and the like. The method can be used for production of carbon nanotube-anchored cantilevers that can significantly improve the performance of scaning probe microscopy (AFM, EFM etc). The invention can also be used in many other processes of micro and / or nanofabrication with carbon nanotubes / fibers. Key elements of this invention include: (1) Proper selection of a metal catalyst and programmable pulsed electrolytic deposition of the desired specific catalyst precisely at the tip of a substrate, (2) Catalyst-induced growth of carbon nanotubes / fibers at the catalyst-deposited tips, (3) Control of carbon nanotube / fiber growth pattern by manipulation of tip shape and growth conditions, and (4) Automation for mass production.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Method of fabricating microneedles
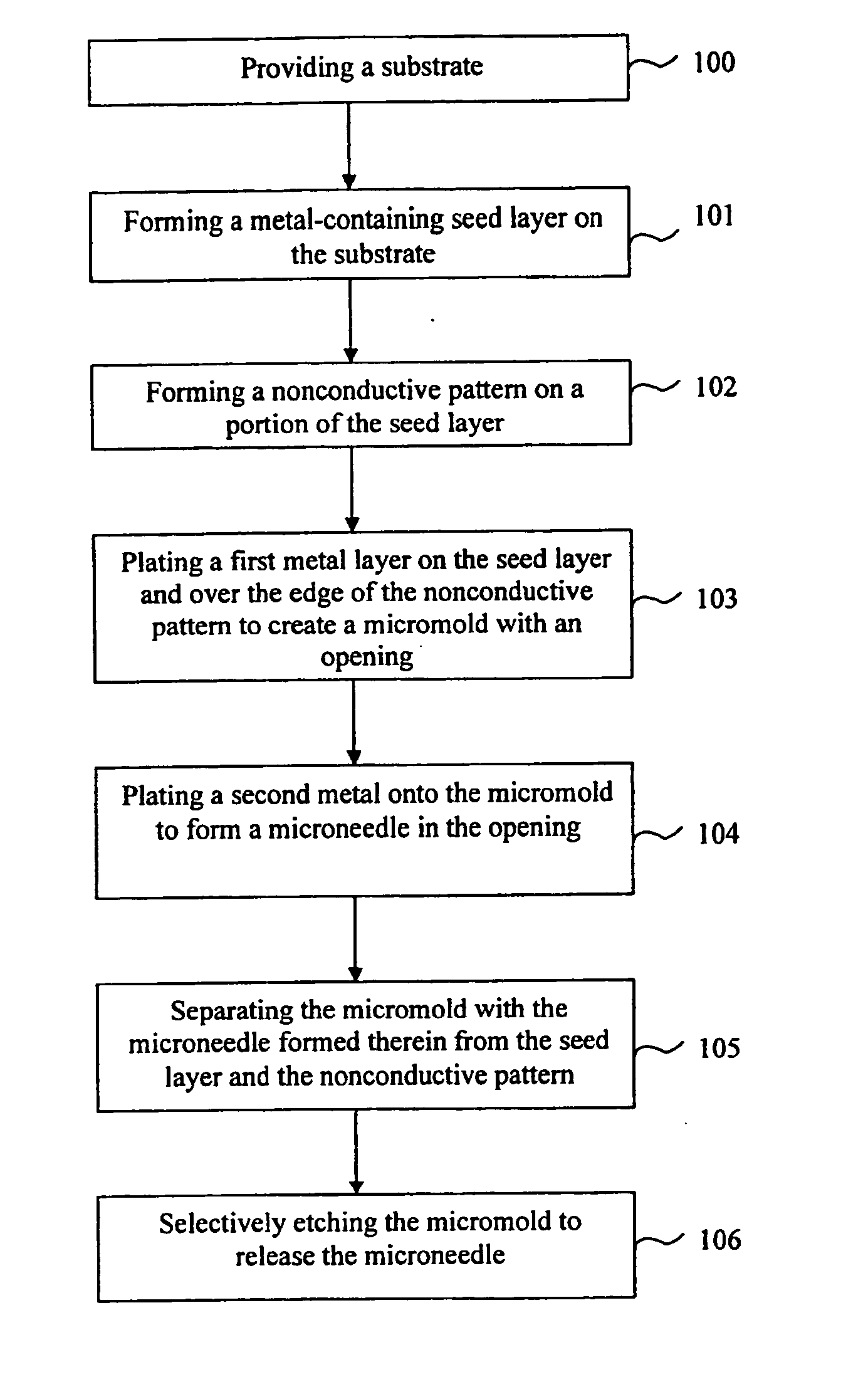
A low cost method for fabricating microneedles is provided. According to one embodiment, the fabrication method includes the steps of: providing a substrate; forming a metal-containing seed layer on the top surface of the substrate; forming a nonconductive pattern on a portion of the seed layer; plating a first metal on the seed layer and over the edge of the nonconductive pattern to create a micromold with an opening that exposes a portion of the nonconductive pattern, the opening having a tapered sidewall surface; plating a second metal onto the micromold to form a microneedle in the opening; separating the micromold with the microneedle formed therein from the seed layer and the nonconductive pattern; and selectively etching the micromold so as to release the microneedle.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Metal matrix composite casting and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6245442B1Well formedEasy to processHot-dipping/immersion processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal matrix compositeCompound s
A metal matrix composite casting comprises a metal matrix composite and a processed member inserted in the metal matrix composite by enveloped casting. By the processed member which is easier to process than the metal matrix composite, a processed portion of a predetermined shape can be formed in the metal matrix composite. That is, by a simple processing such that the processed member is removed from the metal matrix composite or the processed portion is formed in the processed member itself, the processed portion having a desired shape can be easily formed in the metal matrix composite.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Method of manufacturing protruding-volute contact, contact made by the method, and inspection equipment or electronic equipment having the contact
InactiveUS20050088193A1Low costImprove reliabilityContact member manufacturingManufacture of electrical instrumentsCouplingCoil spring
A method of manufacturing a protruding-volute contact for attaining electrical continuity with an electrode of electronic equipment or inspection equipment, the method comprising the steps of forming a plastic mold (resist structure) with a metal mold; forming a layer consisting of metallic material on the plastic mold (resist structure) by means of electroforming; and performing convex formation of a metal microstructure made from the layer consisting of metallic material so as to form a spiral spring that protrudes volutedly outward. With such method, an inspection contact or coupling contact having high reliability and capable of attaining electrical continuity of large electric current can be produced at low cost.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method of forming polymide coating containing dielectric filler on surface of metallic material process for producing copper clad laminate for formation of capacitor layer for printed wiring board and copper clad laminate obtained by the process
InactiveUS20050161149A1Avoid damageIncrease flexibilityInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetallic materialsMaterials science
A method of forming a dielectric layer containing dielectric filler, which is excellent in film thickness uniformity, from a polyimide electrodeposition liquid containing dielectric filler. In particular, a method of forming a polyimide coating container dielectric filler on a surface of metallic material according to the electrodeposition coating technique, characterized in that as the dielectric filler, use is made of dielectric powder of perovskite structure in approximately spherical form which has an average particle diameter (D1A) of 0.05 to 1.0 μm and a weight cumulative particle diameter (D50), measured in accordance with the laser diffraction scattering type particle size distribution measuring method, of 0.1 to 2.0 μm and further exhibits an aggregation degree, in terms of D50 / D1a wherein D50 and D1a represent a weight cumulative particle diameter and an average particle diameter obtained by image analysis, respectively, of 4.5 or less.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Method to plate C4 to copper stud
InactiveUS6251528B1Removing platingImprove productivitySolid-state devicesExtrusion containersCopper platingPhotoresist
A method for plating a second metal directly to a first metal without utilizing a mask. A semiconductor substrate is provided including at least one metal feature and at least one insulating layer covering the metal feature and the substrate. At least one recess is formed in the at least one insulating layer thereby exposing at least a portion of the metal feature. At least one conductive barrier layer is formed over the insulating layer and the exposed portion of the metal feature. A plating seed layer of a first metal is formed over the at least one barrier layer. A photoresist layer is deposited over the plating seed layer. Portions of the photoresist layer and of the plating seed layer outside of the at least one recess are removed. Photoresist remaining in the at least one recess is removed. A second metal is electroplated to the plating seed layer in the recess.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Sports articles formed using nanostructured materials
InactiveUS20060160636A1Increases weight of unitWeight increaseWalking sticksMaterial nanotechnologyMicrochiropteraSports equipment
A sports article includes a portion that includes a nanostructured material. The nanostructured material includes a metal, and the nanostructured material has an average grain size that is in the range of 2 nm to 5,000 nm, a yield strength that is in the range of 200 MPa to 2,750 MPa, and a hardness that is in the range of 100 Vickers to 2,000 Vickers. The sports article can be any of a variety of sports equipment and associated components, such as a golf club, a baseball bat, a softball bat, a lacrosse stick, or a hockey stick.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Producing method of flexible wired circuit board
InactiveUS20050067293A1Large thicknessAvoid it happening againPrinted circuit detailsDecorative surface effectsResistElectrolysis
A producing method of a flexible wired circuit board that can prevent the formation of a gap between an elongate substrate and a stiffener sheet bonded thereto to prevent contamination of the flexible wired circuit board obtained. In the process subsequent to the process of forming a conductive pattern 3 on a surface of the elongate substrate 1 by the semi-additive process using electrolysis plating and then annealing the elongate substrate 1 with the conductive pattern 3 in its wound up state, a stiffener sheet 9 having a width narrower than the elongate substrate 1 is bonded to the back side of the elongate substrate 1. Thereafter, an oxidized film formed on a surface of the conductive pattern 3 is removed and then a solder resist 11 is formed thereon. This prevents the strip of the stiffener sheet 9 from the elongate substrate 1 and in turn prevents etching solution or developing solution from entraining in a gap therebetween.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Electrodeposited copper foil with its surface prepared, process for producing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS6475638B1Eliminate deformationHigh peel strengthInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementLapping machinesSurface roughnessCopper foil
A process for producing an electrodeposited copper foil with its surface prepared, comprising the steps of: subjecting an electrodeposited copper foil having a shiny side and a matte side whose average surface roughness (Rz) is in the range of 2.5 to 10 mum to at least one mechanical polishing so that the average surface roughness (Rz) of the matte side becomes in the range of 1.5 to 3.0 mum; and subjecting the matte side having undergone the mechanical polishing to a selective chemical polishing so that the average surface roughness (Rz) of the matte side becomes in the range of 0.8 to 2.5 mum. The invention further provides an electrodeposited copper foil with its surface prepared, produced by the above process, and still further provides PWBs and a multilayer laminate of PWBs, produced with the use of the above electrodeposited copper foil with its surface prepared. The mechanical polishing followed by chemical polishing of the matte side enables obtaining an electrodeposited copper foil with its surface prepared, the matte side of which exhibits excellent properties, and hence enables obtaining PWBs and a multilayer PWBs which have excellent properties.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
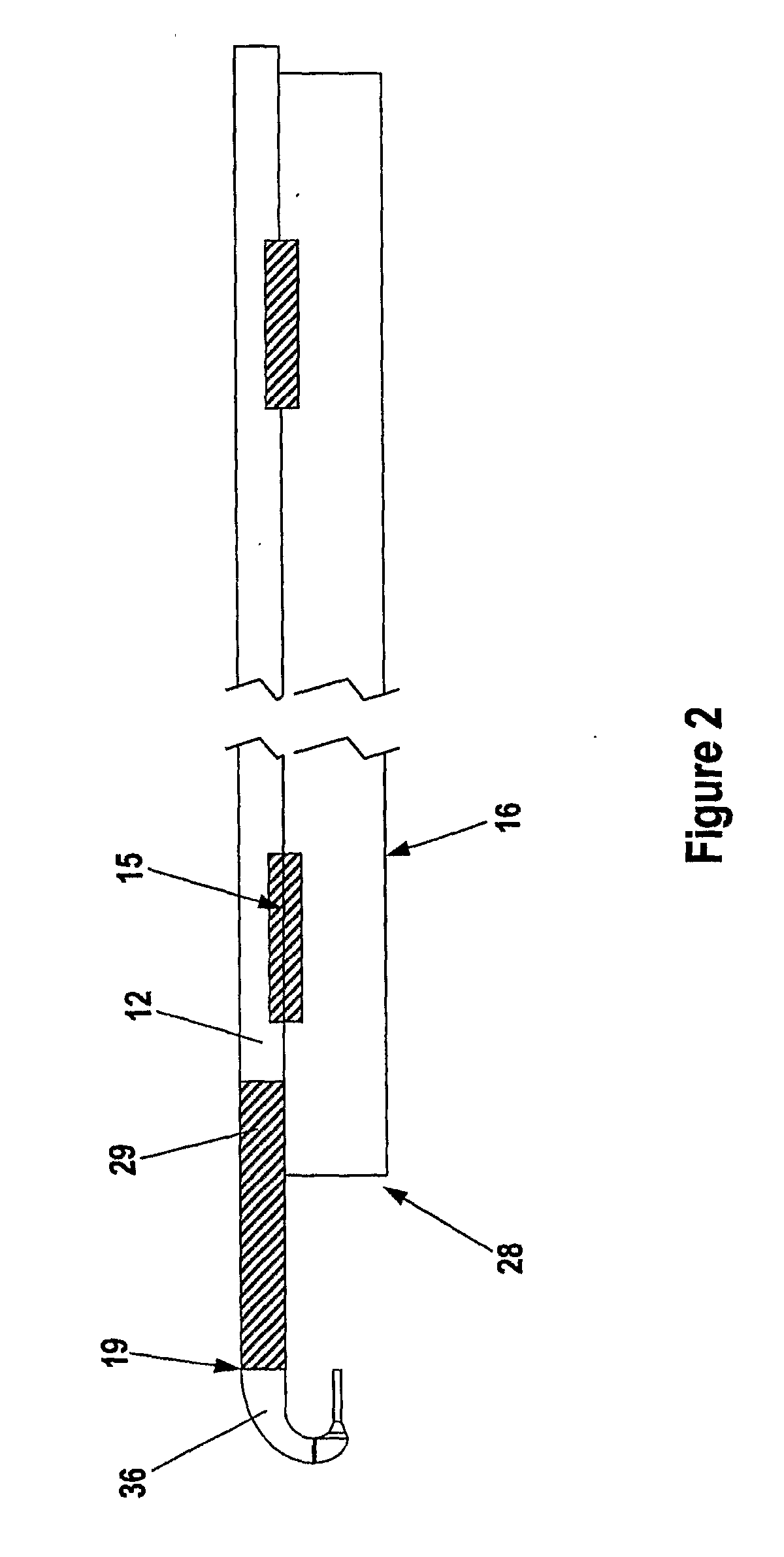
Electroformed liquid jet surgical instrument
InactiveUS20090306692A1Minimize the numberMinimize complexityMedical devicesSurgical instrument detailsLiquid jetEngineering
Certain embodiments of the invention provide a variety of methods of manufacturing a liquid jet-forming surgical instrument. According to these methods, a nozzle assembly of the instrument is electroformed on a mandrel. The nozzle assembly includes a nozzle providing a jet-opening, wherein the nozzle is shaped to form a liquid jet. In some embodiments, the mandrel includes a first mandrel portion and a second mandrel portion. Once the nozzle assembly is formed, the mandrel may be removed from the nozzle assembly. The nozzle assembly may in certain embodiments be coupled to an outlet of the pressure tube. In certain embodiments, an inlet of an evacuation tube is positioned such that a jet-receiving opening of the evacuation tube is positioned opposite the jet-opening of the nozzle.
Owner:HYDROCISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com