Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5653 results about "Lithographic artist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
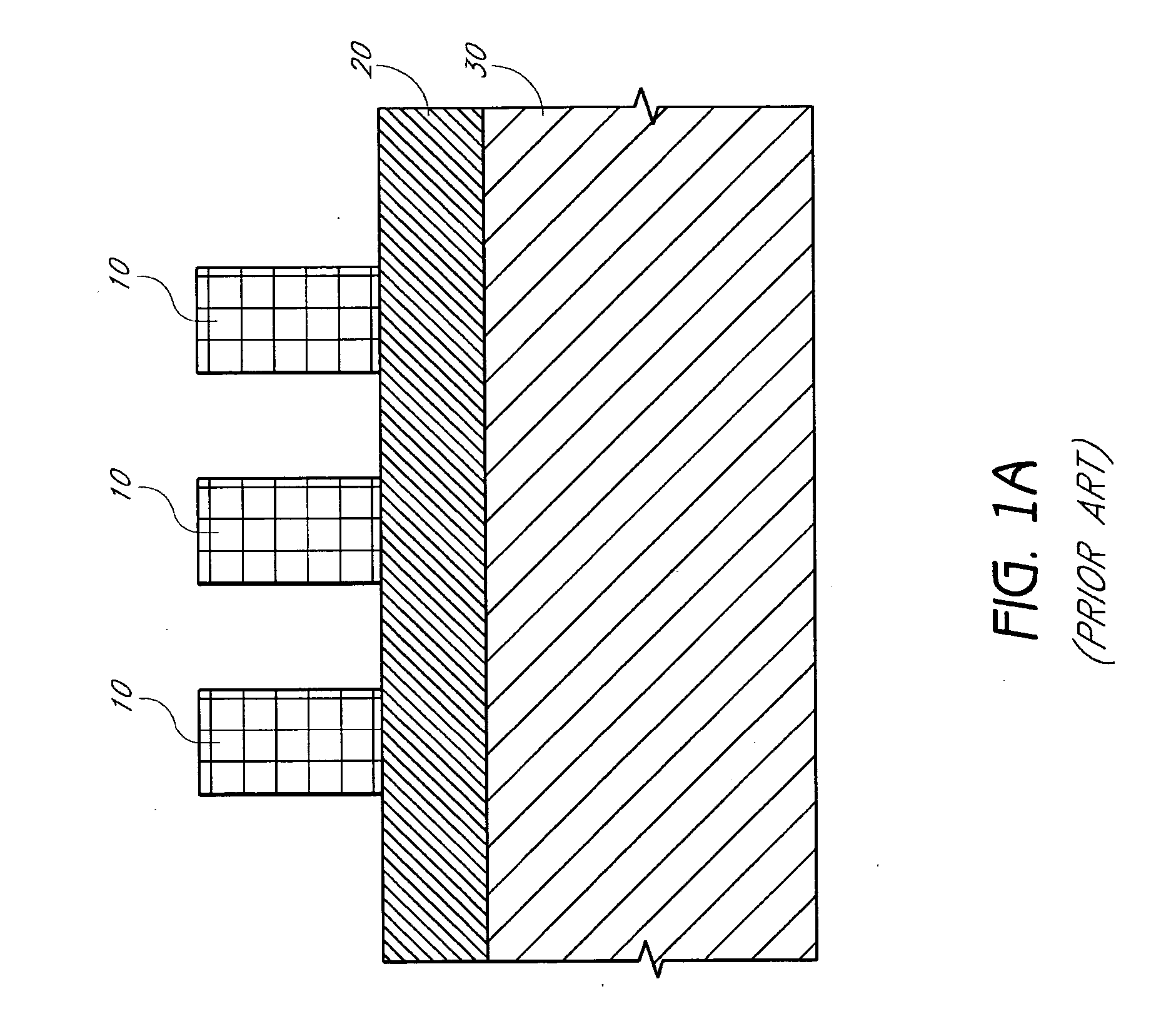
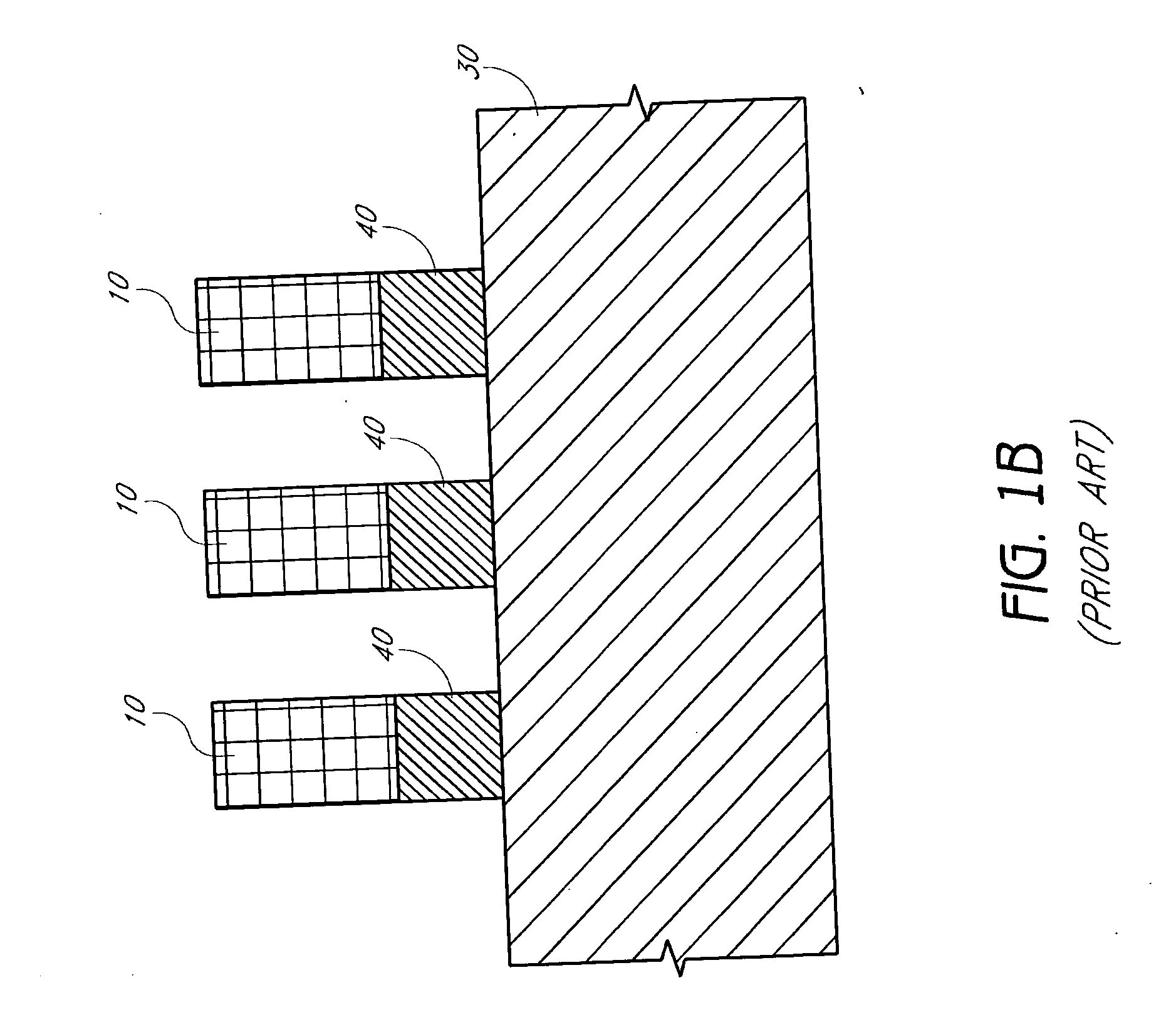
The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by German author and actor Alois Senefelder as a cheap method of publishing theatrical works. Lithography can be used to print text or artwork onto paper or other suitable material.
Projection exposure method and projection exposure system
InactiveUS20050030506A1Avoid defocusing errorProvides adequateNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansLithographic artistHigh numerical aperture
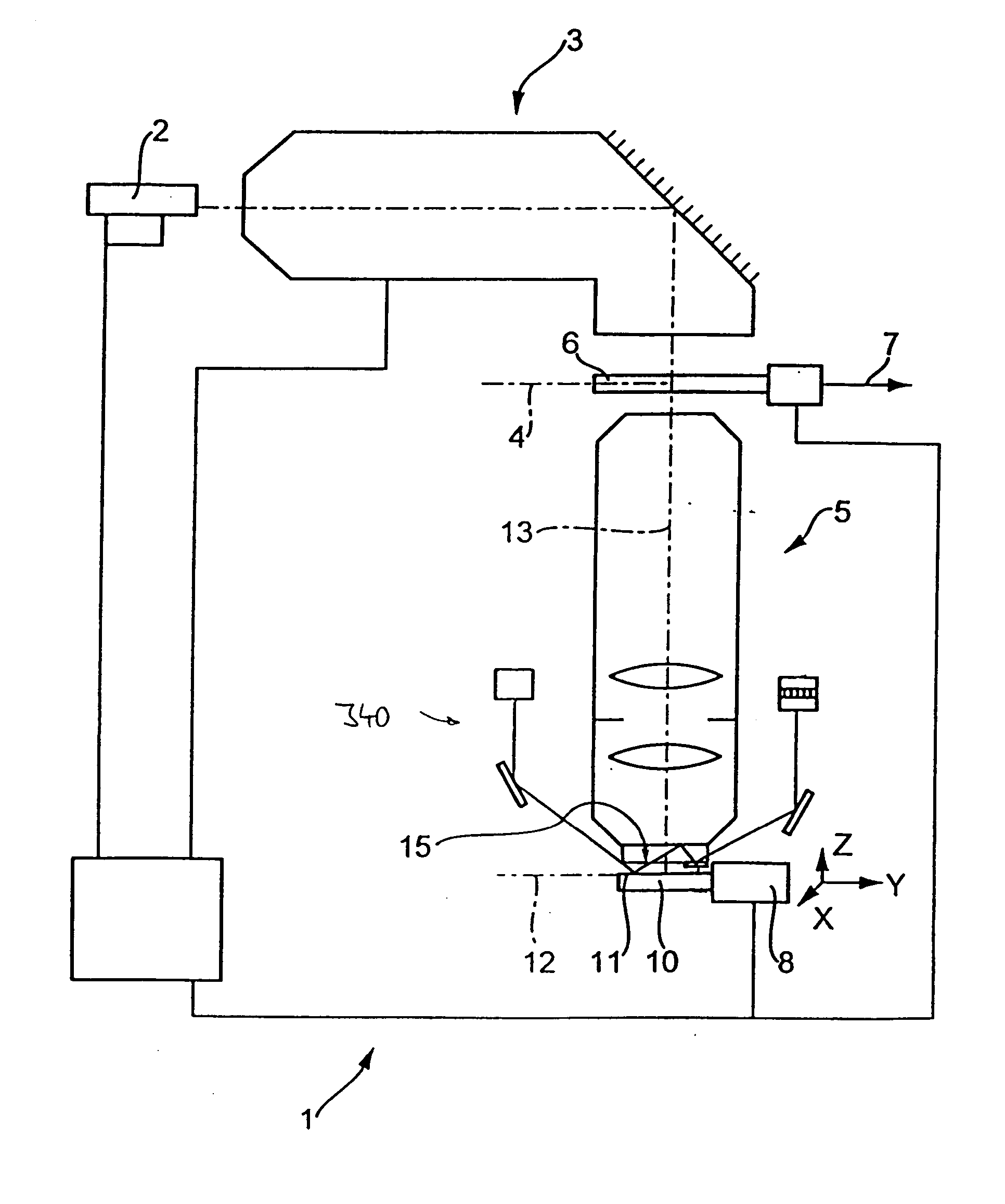
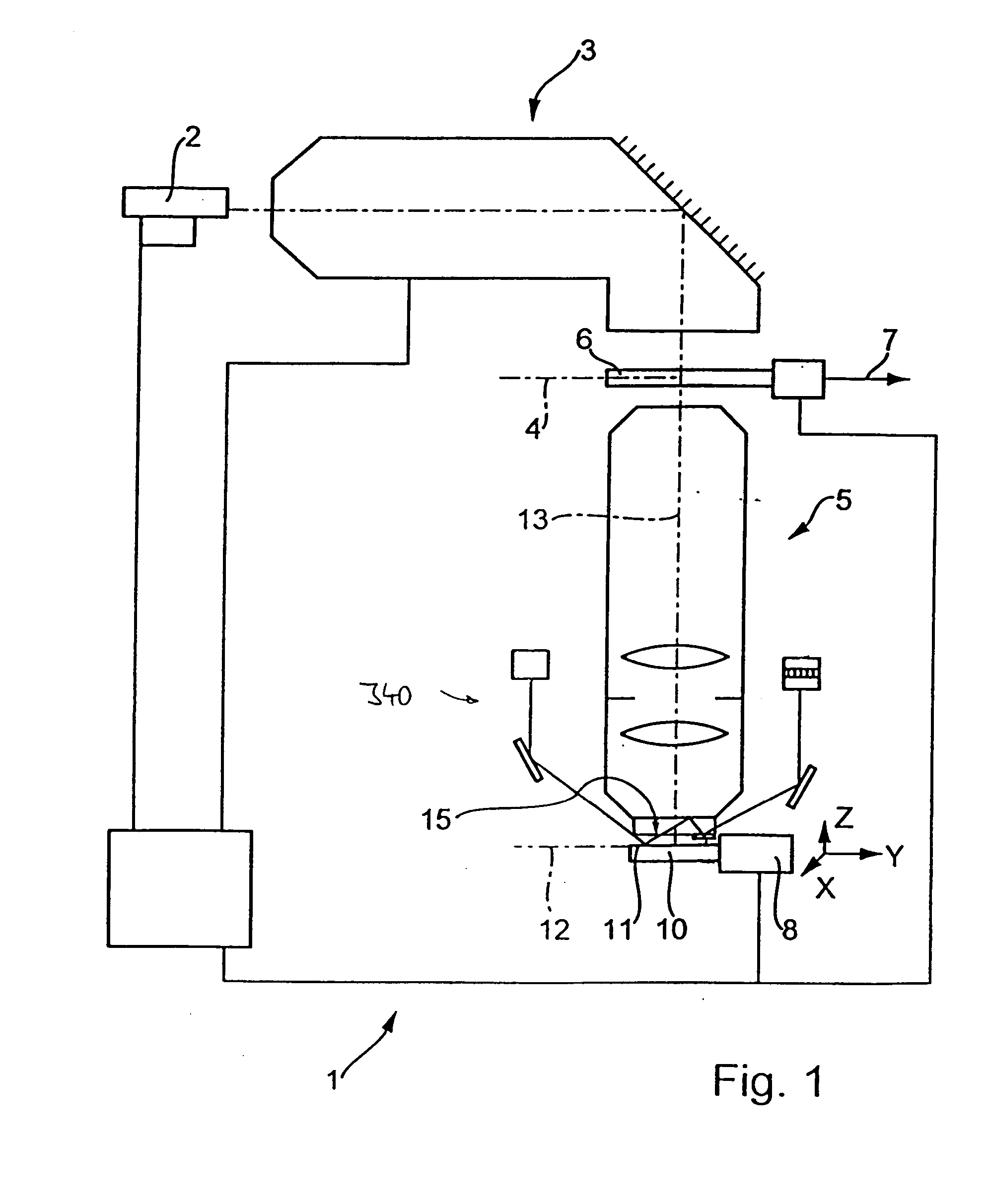
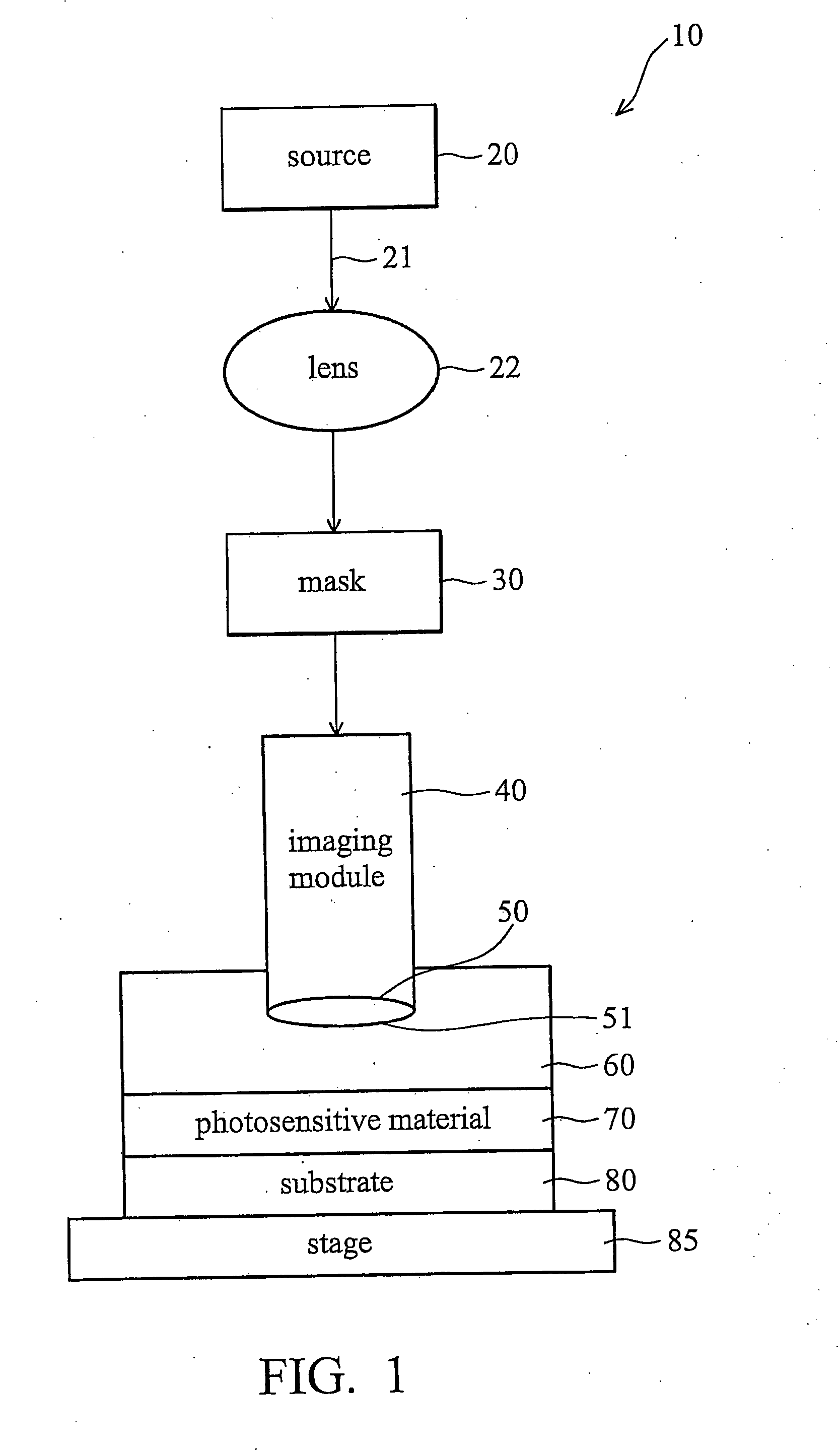
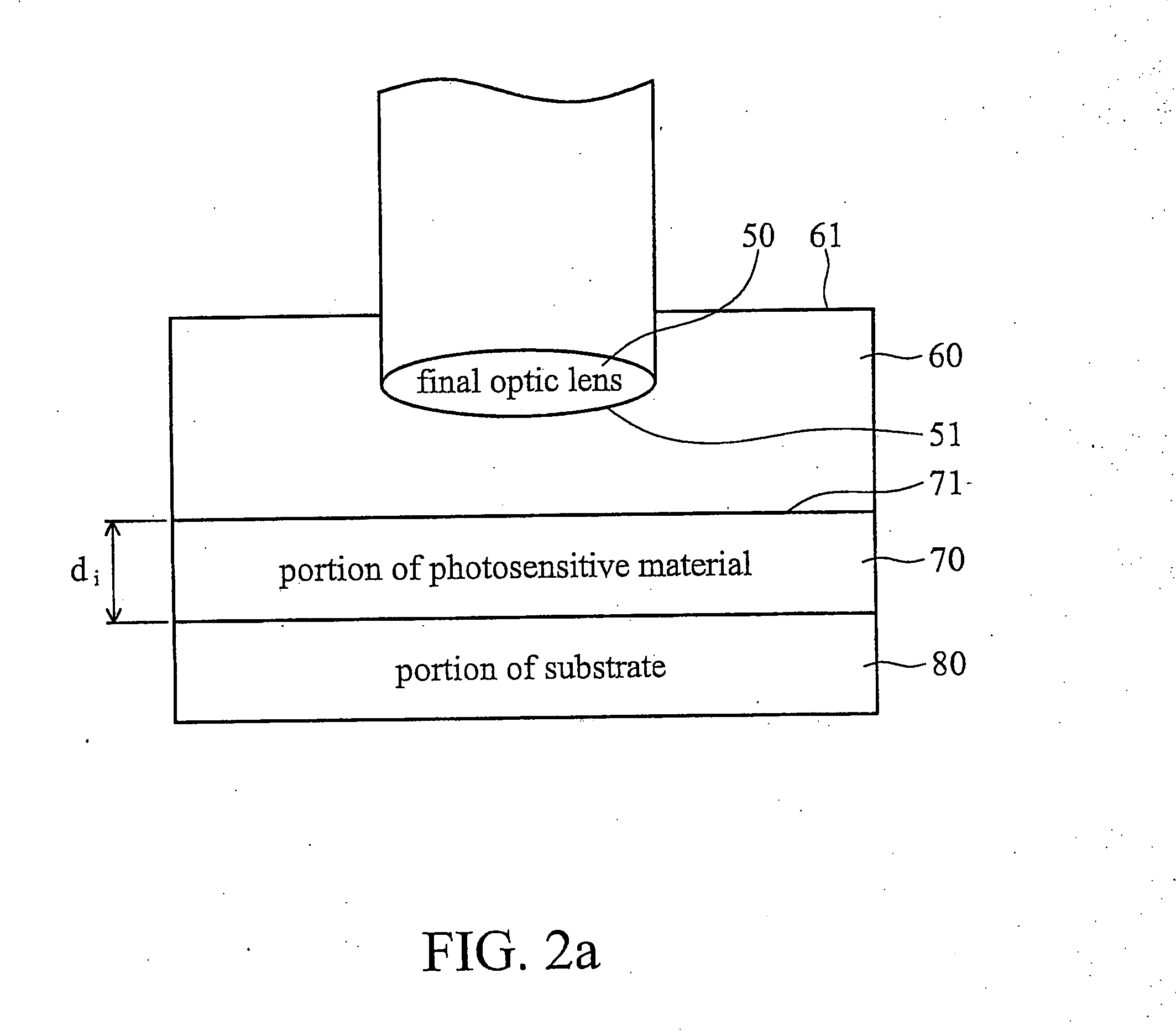
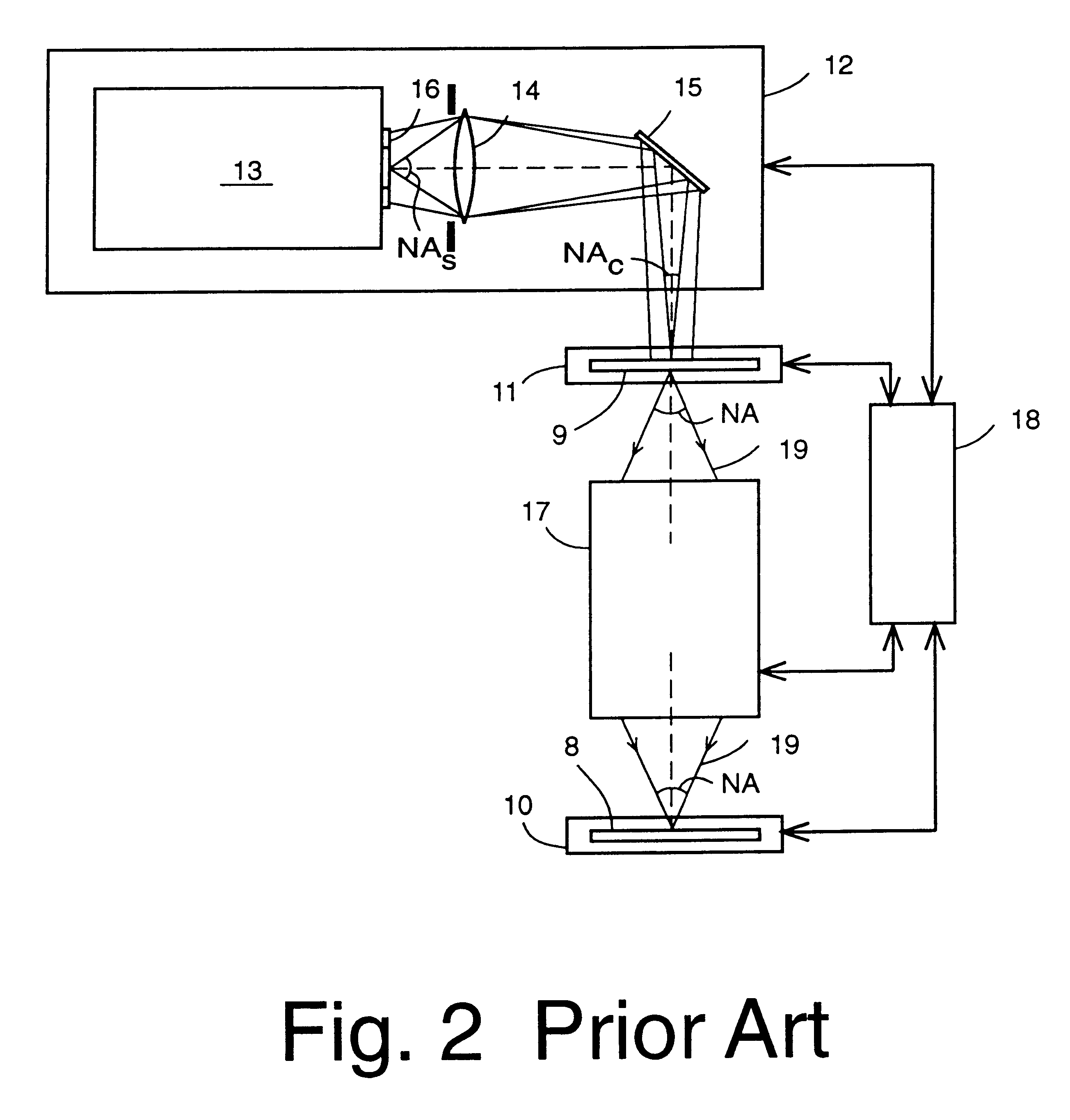
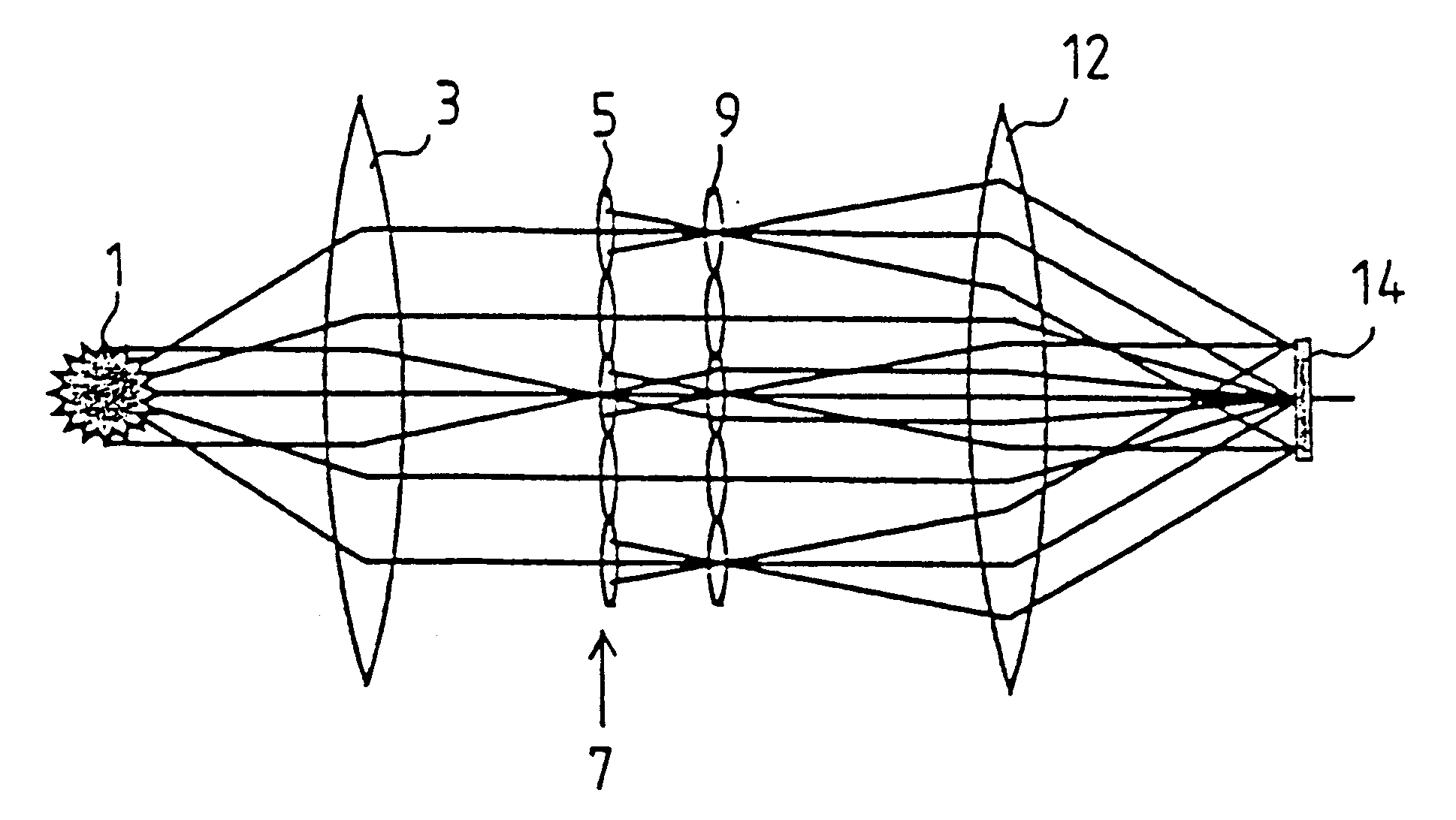
In a method for manufacturing semiconductor devices and other finely structured parts, a projection objective (5) is used in order to project the image of a pattern arranged in the object plane of the projection objective onto a photosensitive substrate which is arranged in the region of the image plane (12) of the projection objective. In this case, there is set between an exit surface (15), assigned to the projection objective, for exposing light and an incoupling surface (11), assigned to the substrate, for exposing light a small finite working distance (16) which is at least temporarily smaller in size and exposure time interval than a maximum extent of an optical near field of the light emerging from the exit surface. As a result, projection objectives with very high numerical apertures in the region of NA>0.8 or more can be rendered useful for contactless projection lithography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Lithography apparatus for manufacture of integrated circuits
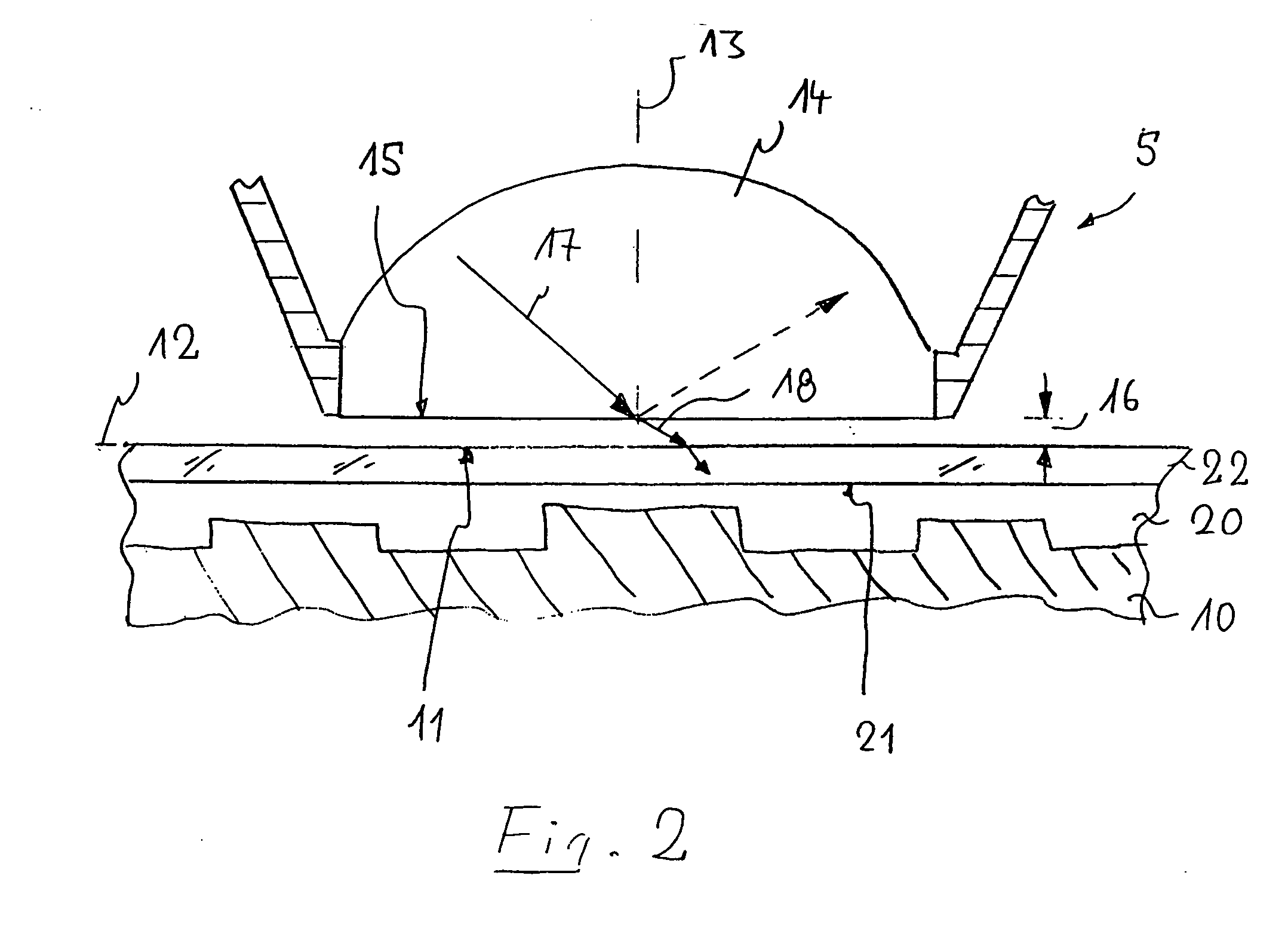
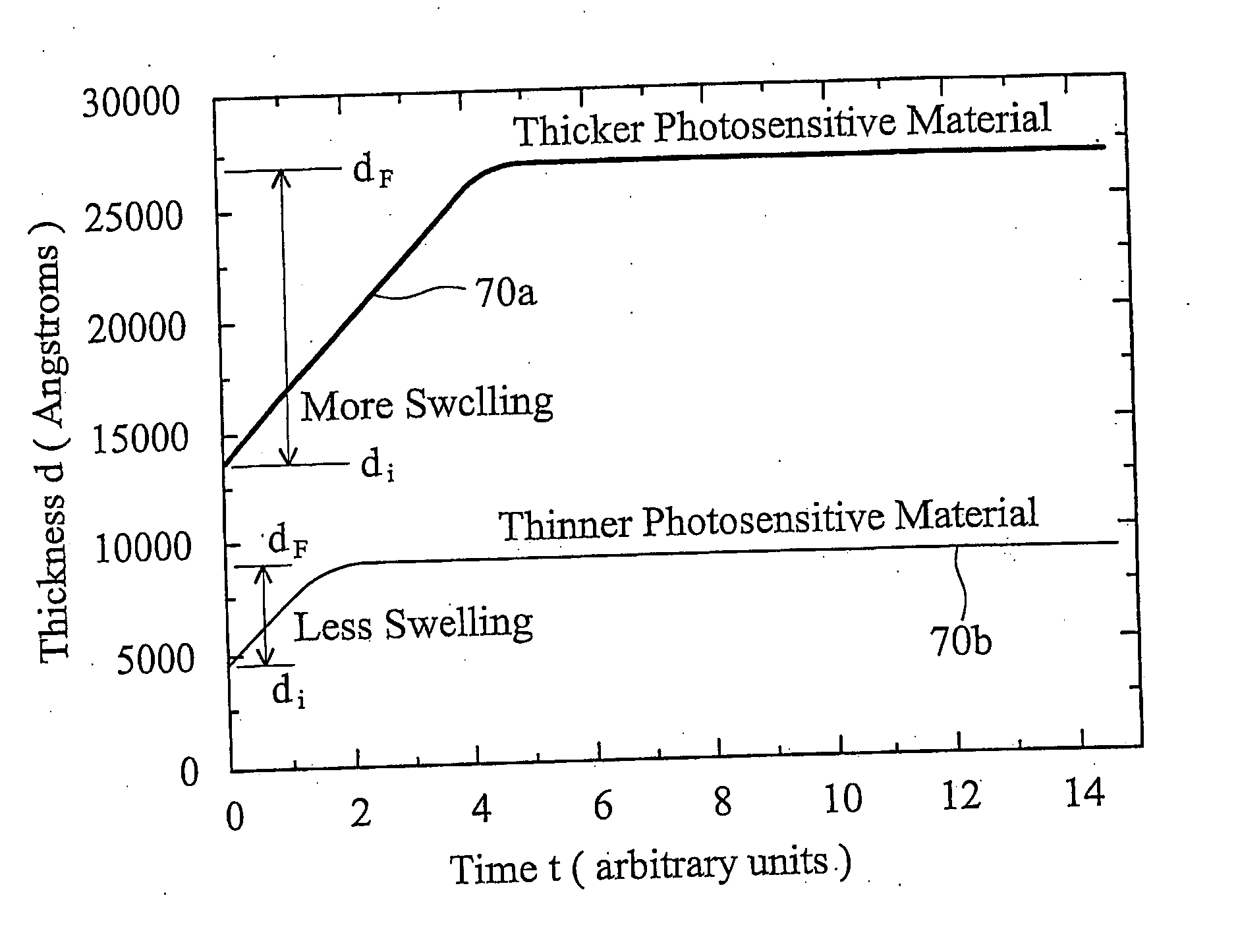
ActiveUS20050036184A1Limit amount of swellingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistSemiconductor structure
An immersion lithographic system 10 comprises an optical surface 51, an immersion fluid 60 contacting at least a portion of the optical surface, and a semiconductor structure 80 having a topmost photoresist layer 70 having a thickness of less than about 5000 angstroms, wherein a portion of the photoresist is in contact with the immersion fluid. Further, a method for illuminating a semiconductor structure 80 having a topmost photoresist layer 70 with a thickness of less than about 5000 angstroms, comprising introducing an immersion fluid 60 into a space between an optical surface 51 and the photoresist layer, and directing light preferably with a wavelength of less than about 450 nm through the immersion fluid and onto the photoresist.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Contact printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050068639A1Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusRefractive indexOff-axis illumination
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Moving lens for immersion optical lithography
InactiveUS20050145803A1Reduce turbulenceReduces air bubbleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotometryLithographic artistImage resolution
An apparatus for immersion optical lithography having a lens capable of relative movement in synchrony with a horizontal motion of a semiconductor wafer in a liquid environment where the synchronous motion of the lens apparatus and semiconductor wafer advantageously reduces the turbulence and air bubbles associated with a liquid environment. The relative motions of the lens and semiconductor wafer are substantially the same as the scanning process occurs resulting in optimal image resolution with minimal air bubbles, turbulence, and disruption of the liquid environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
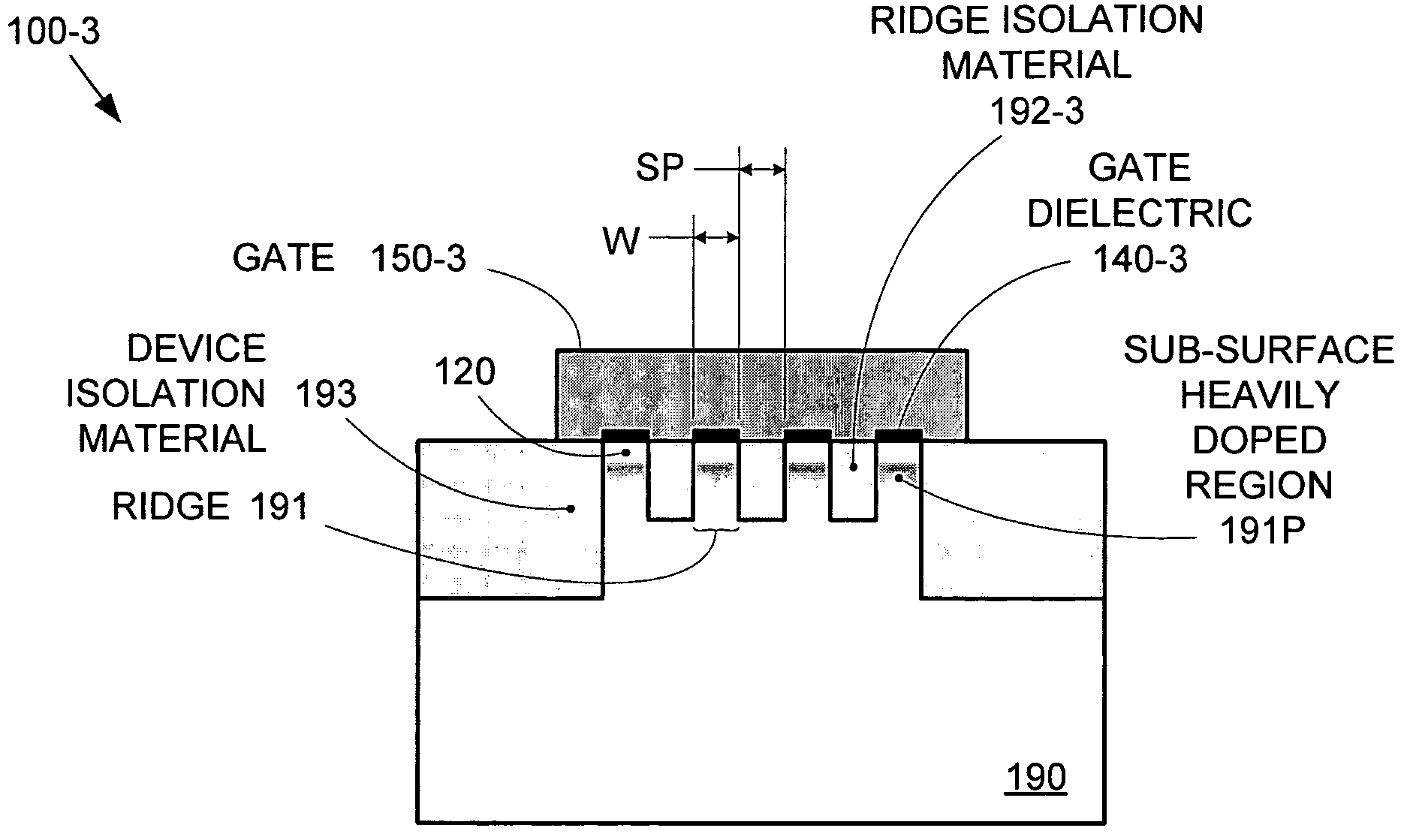
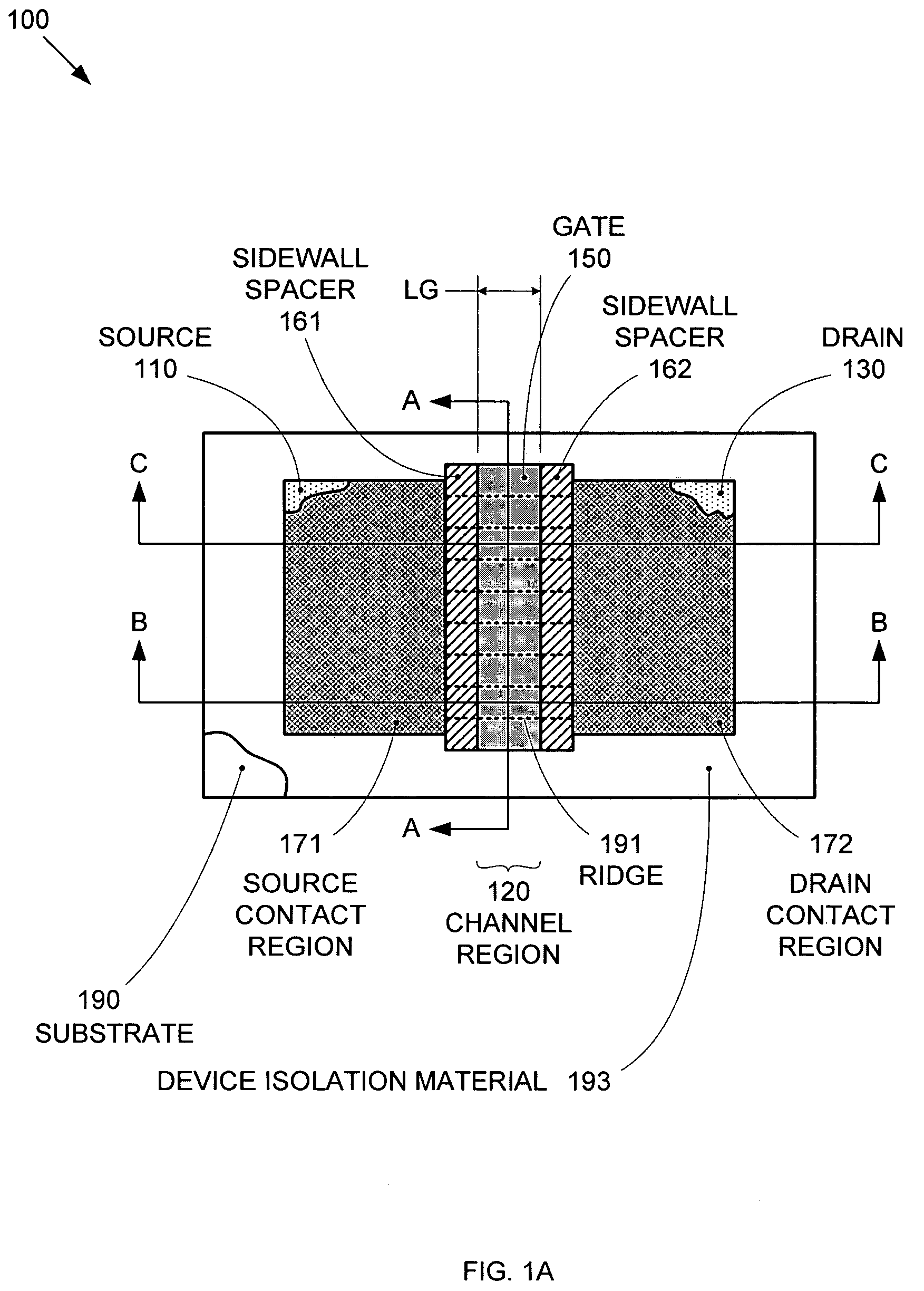
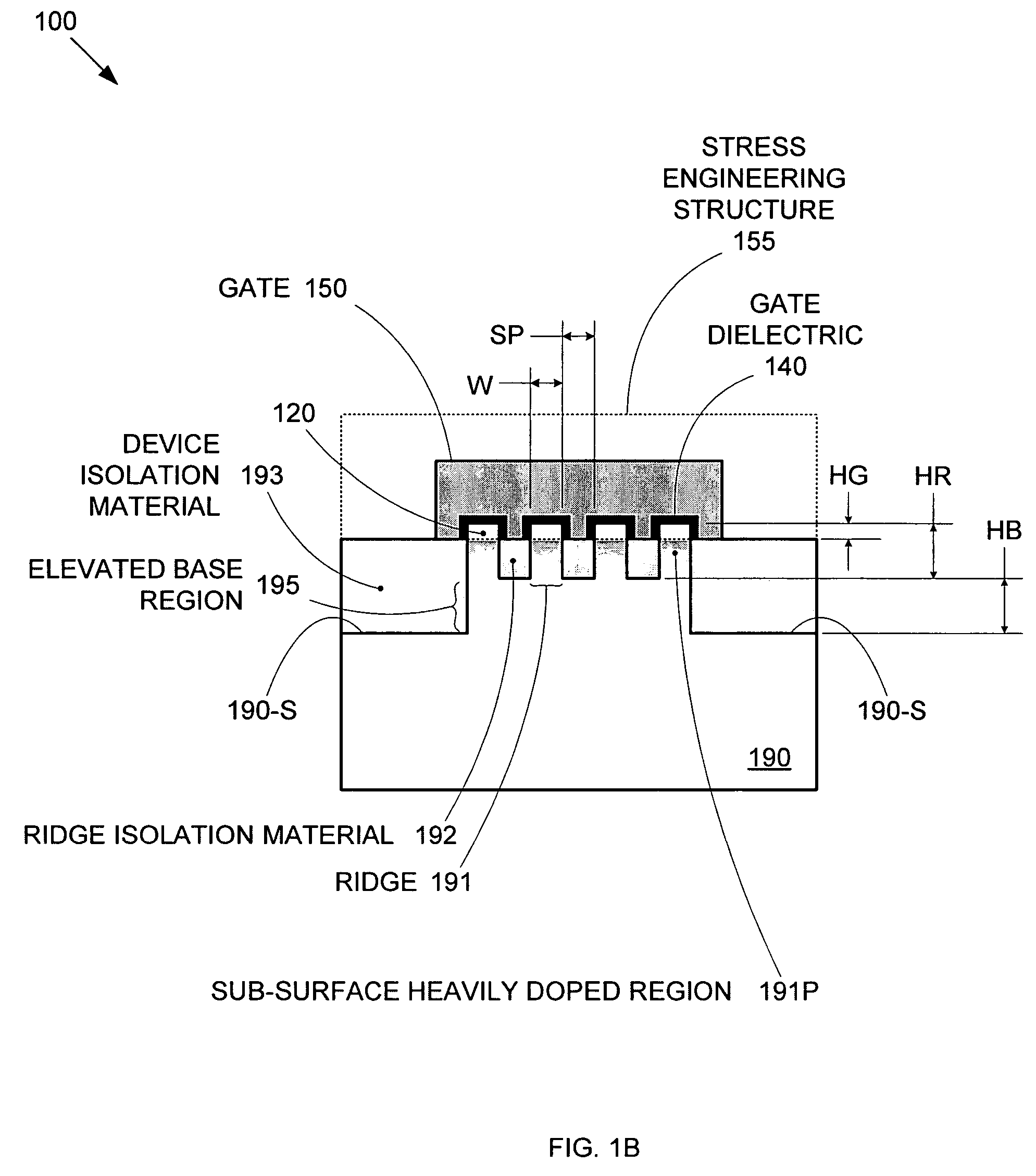
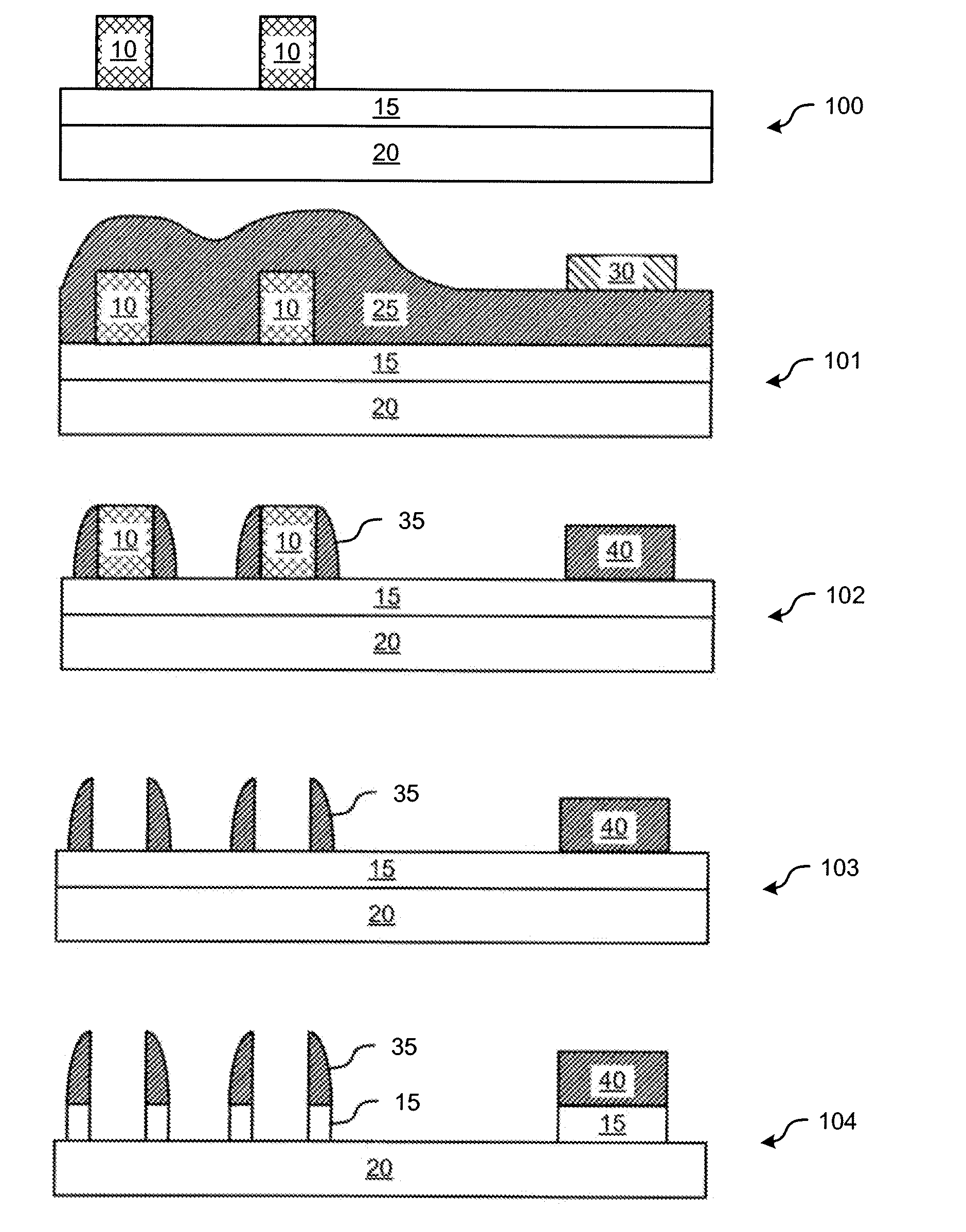
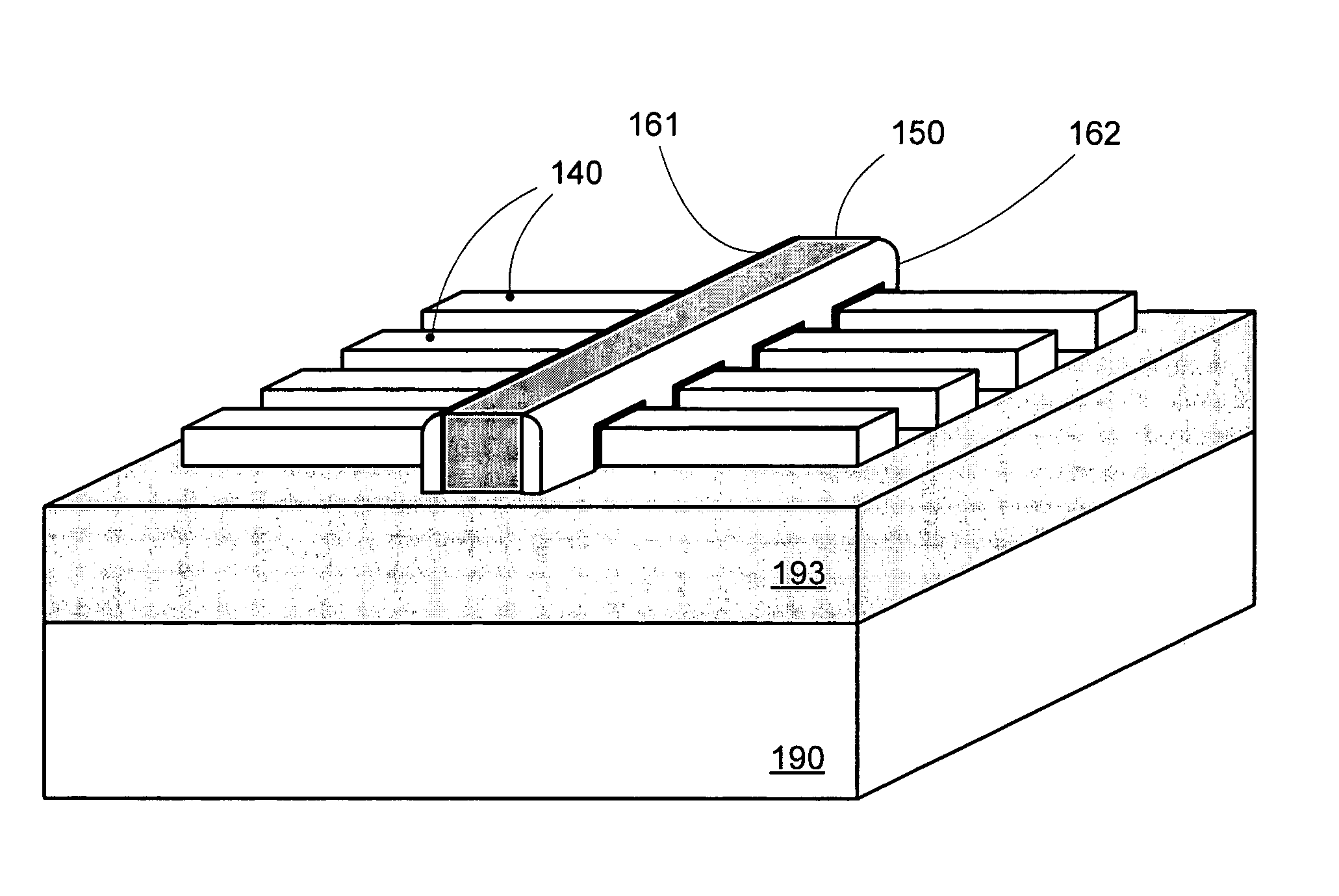
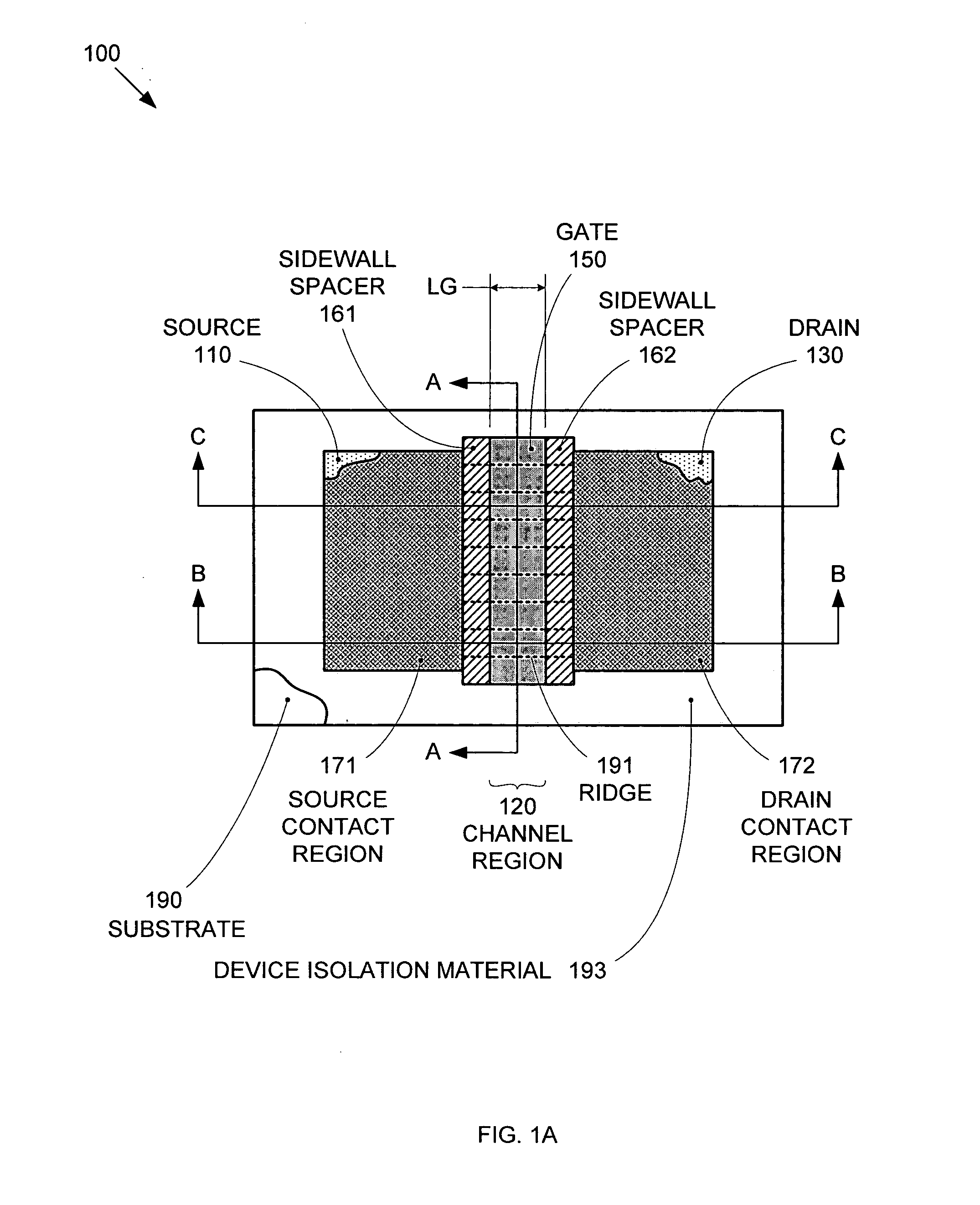
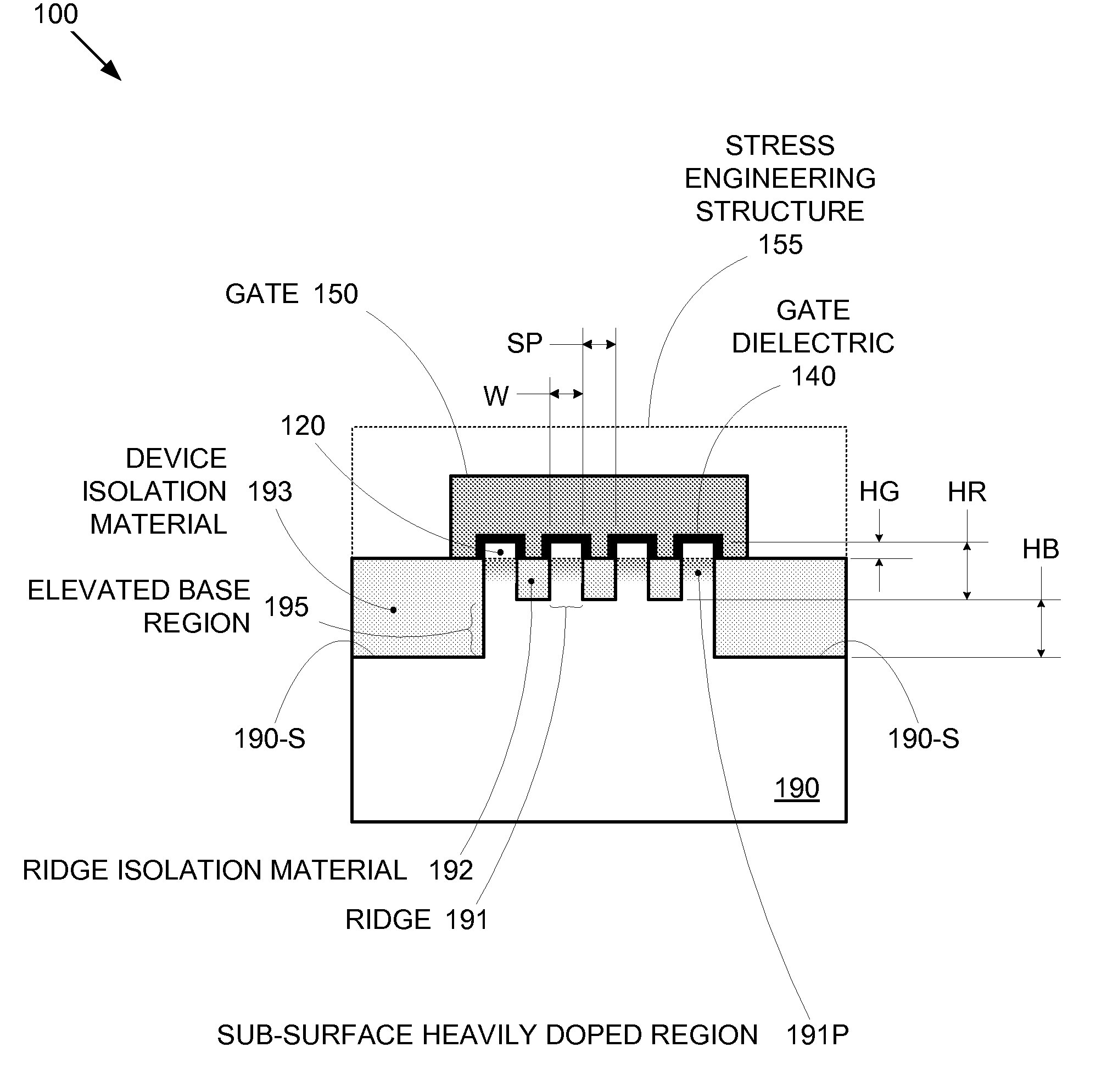
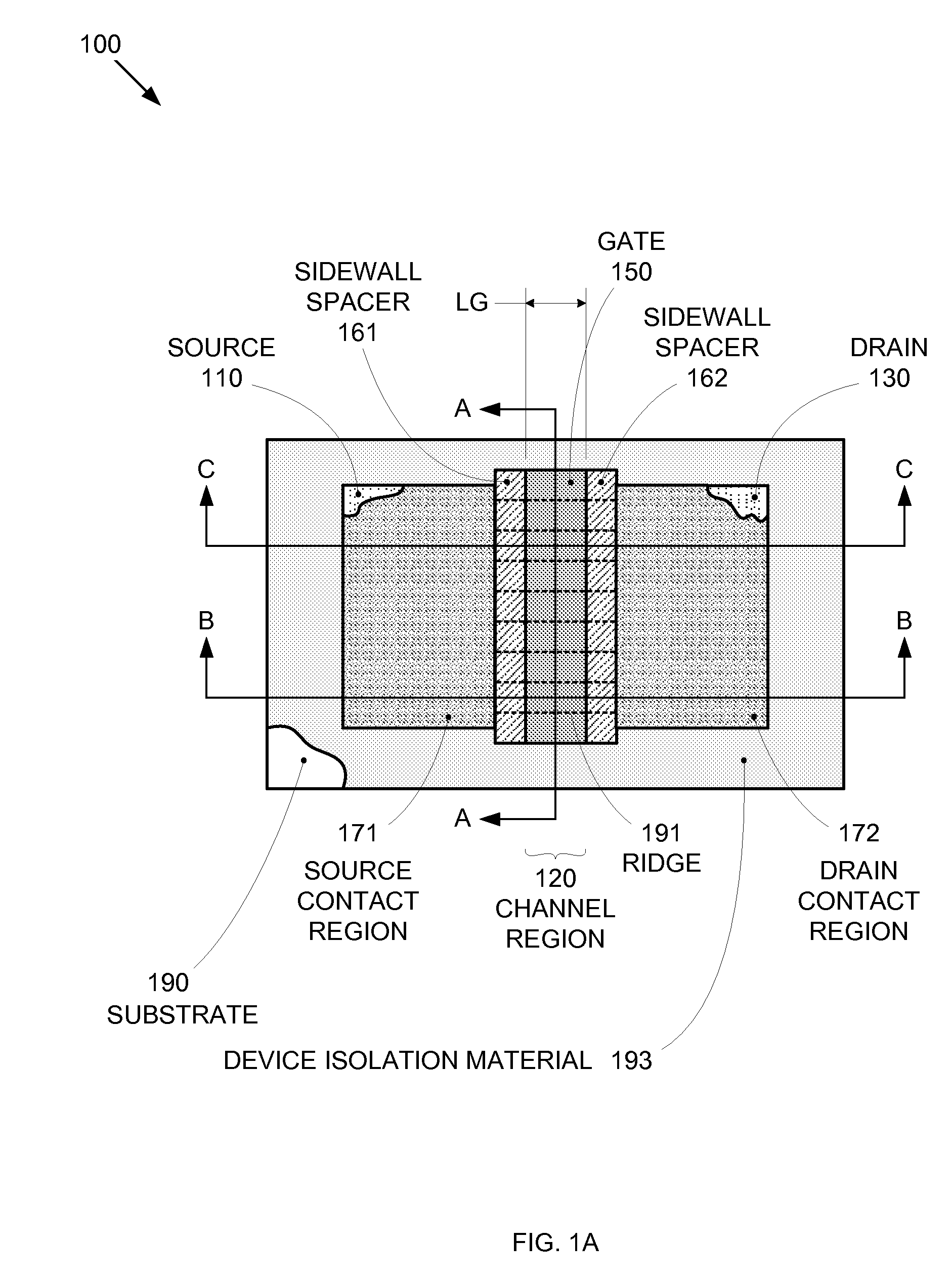
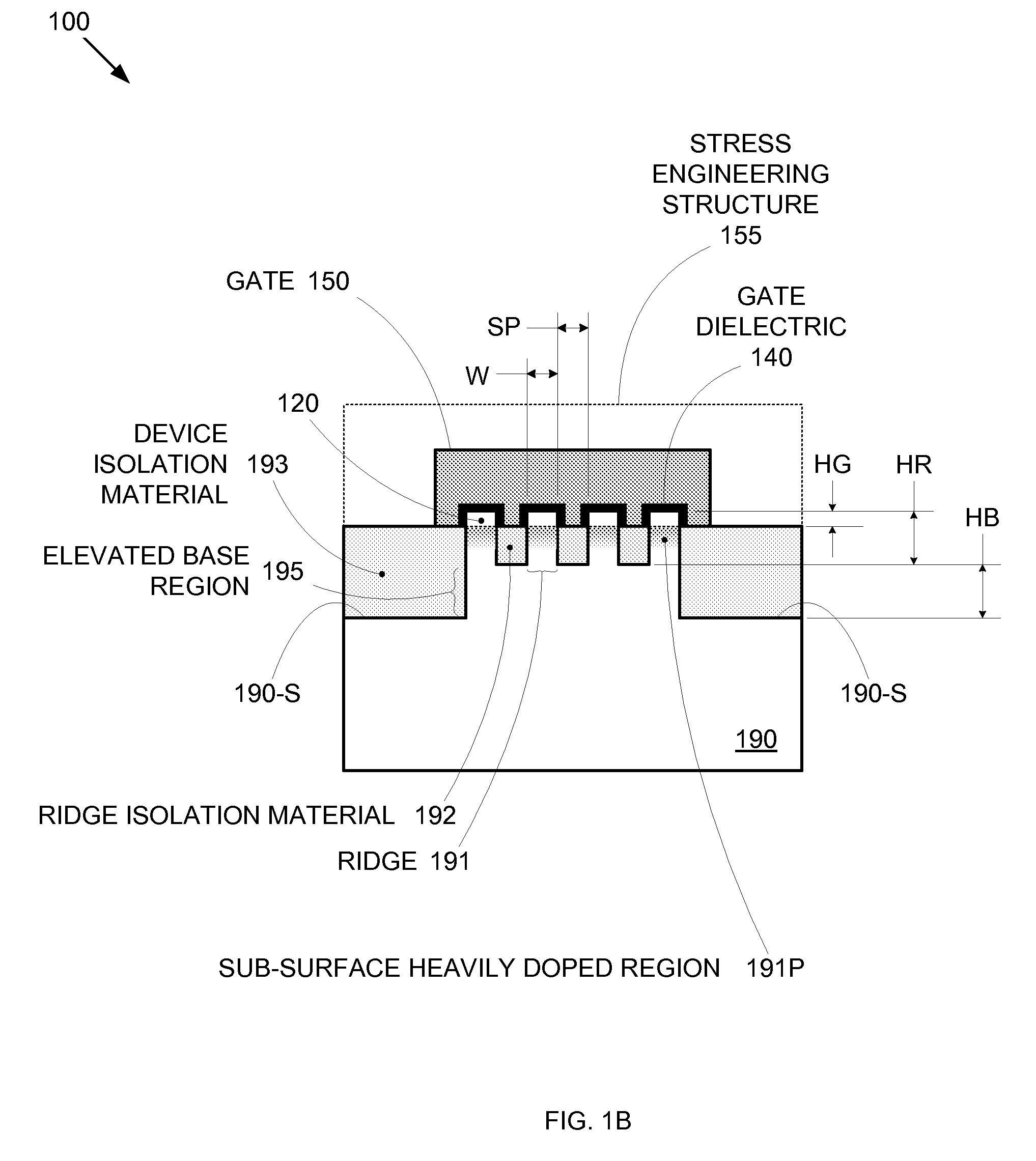
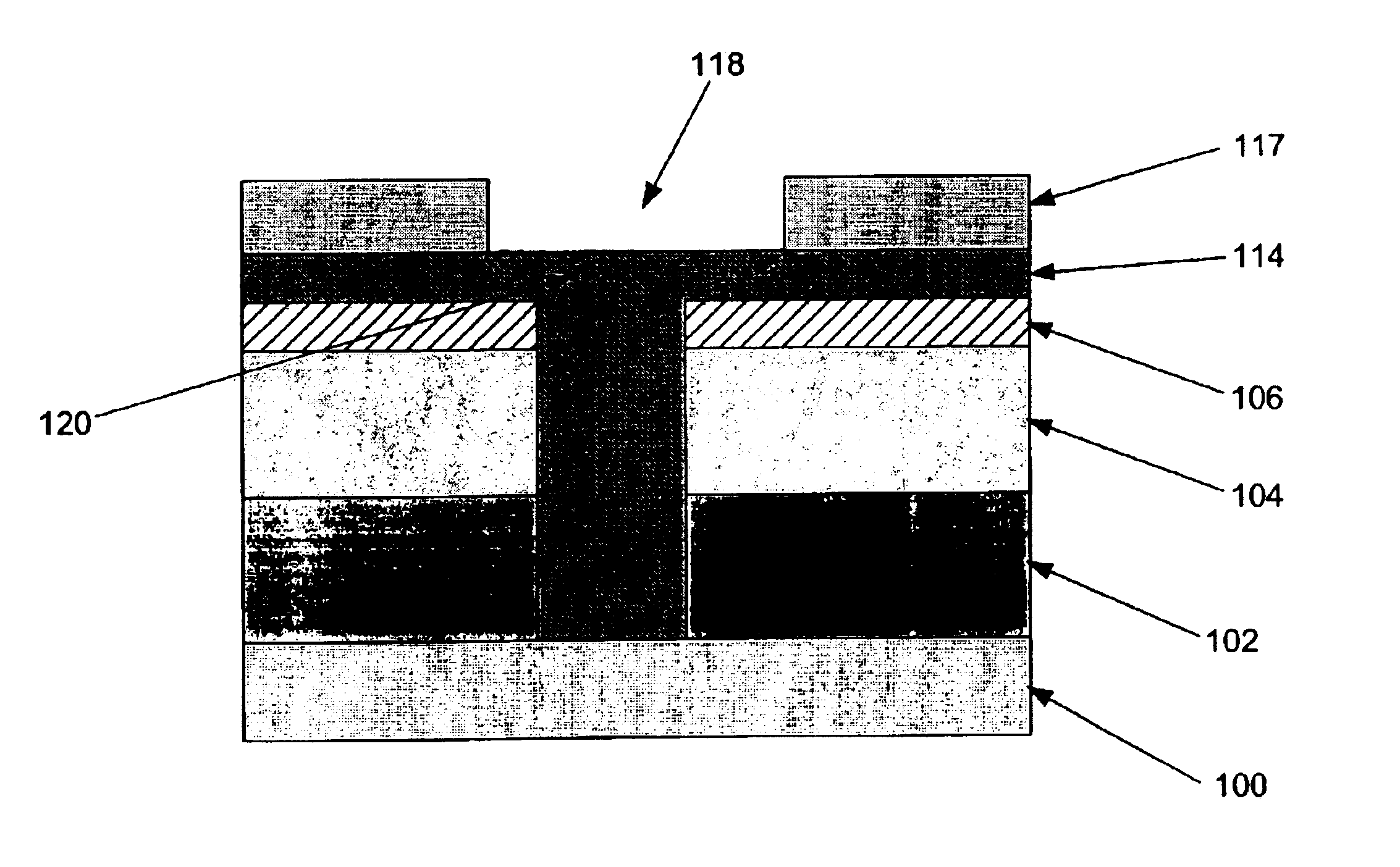
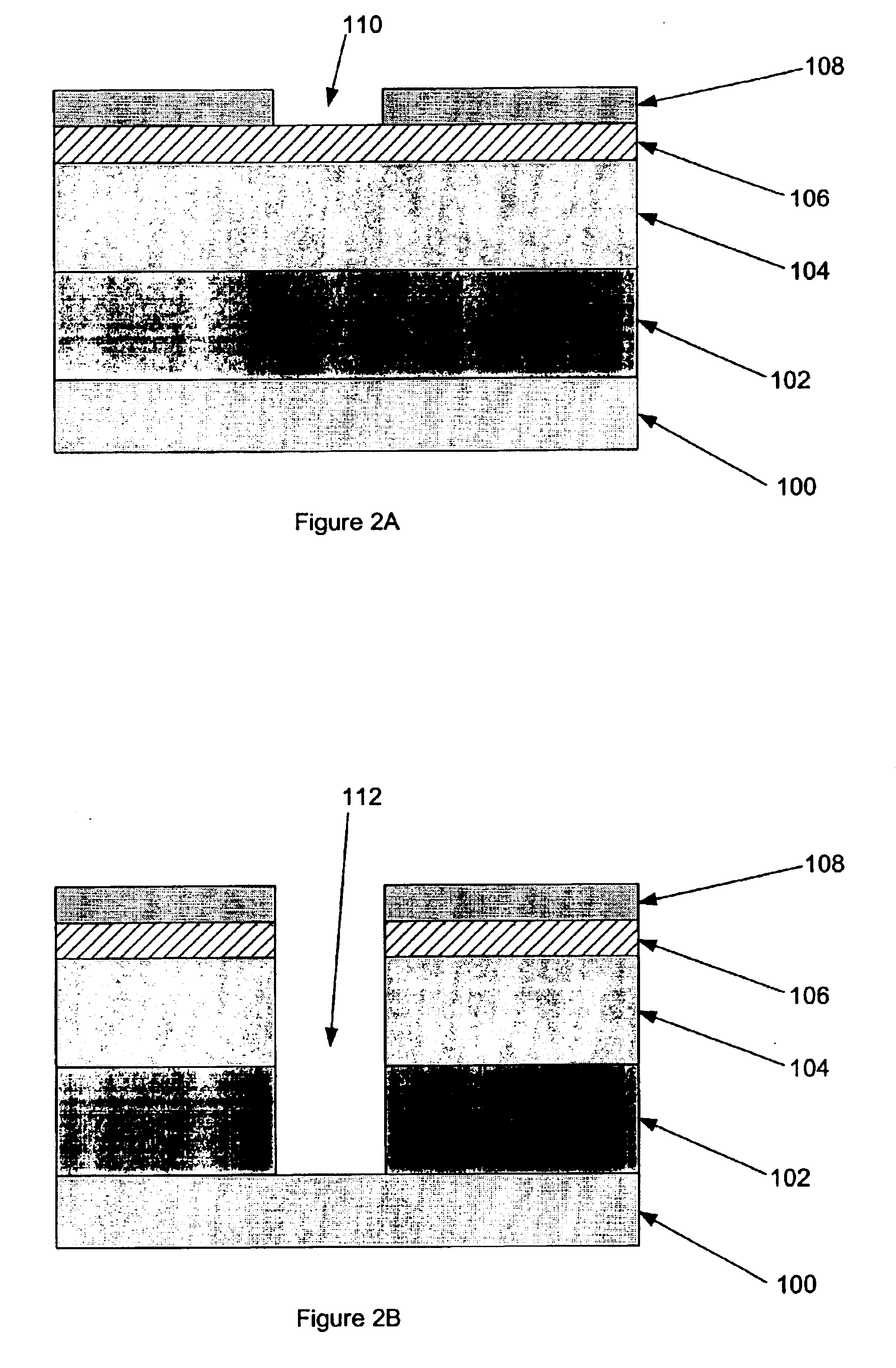
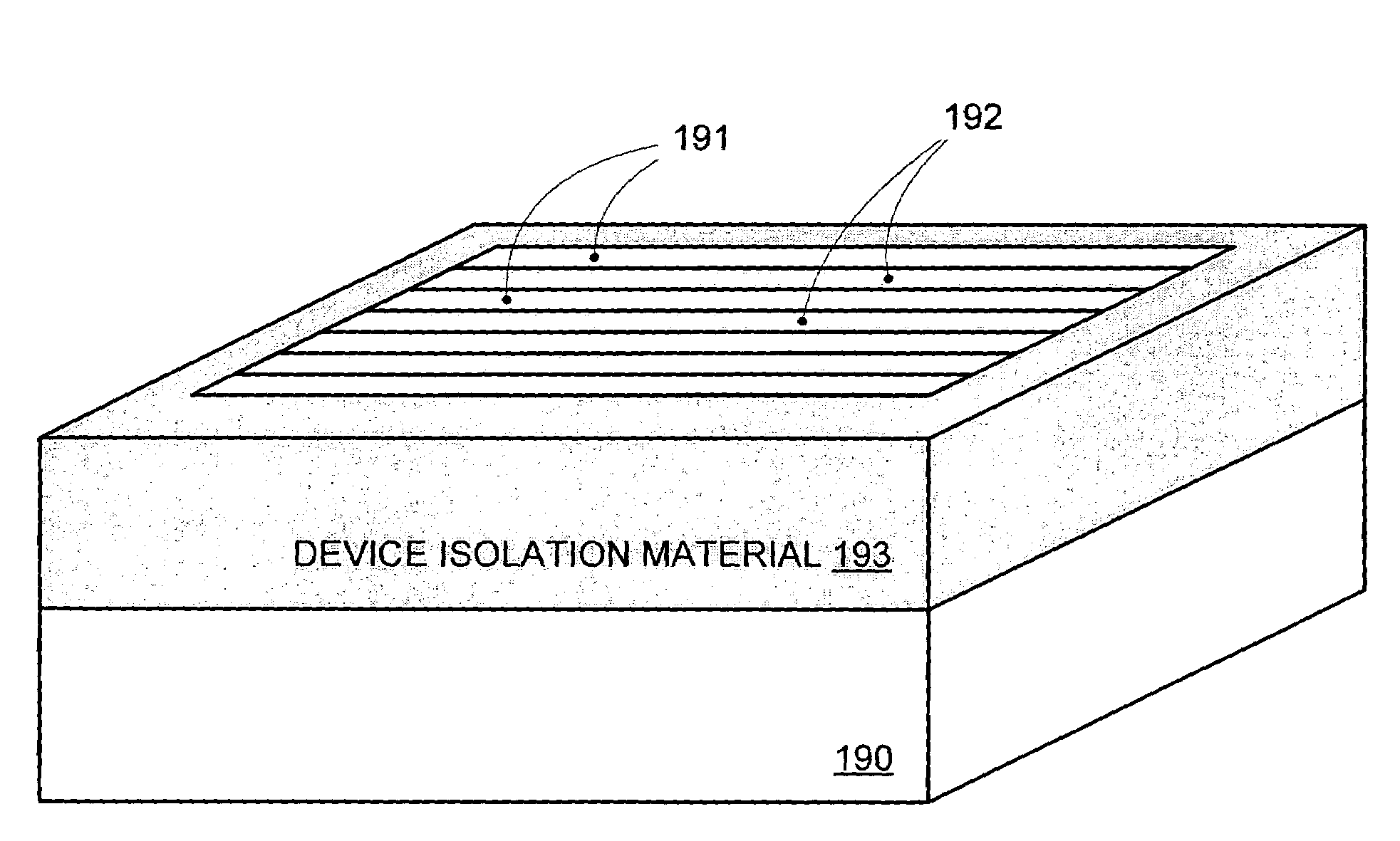
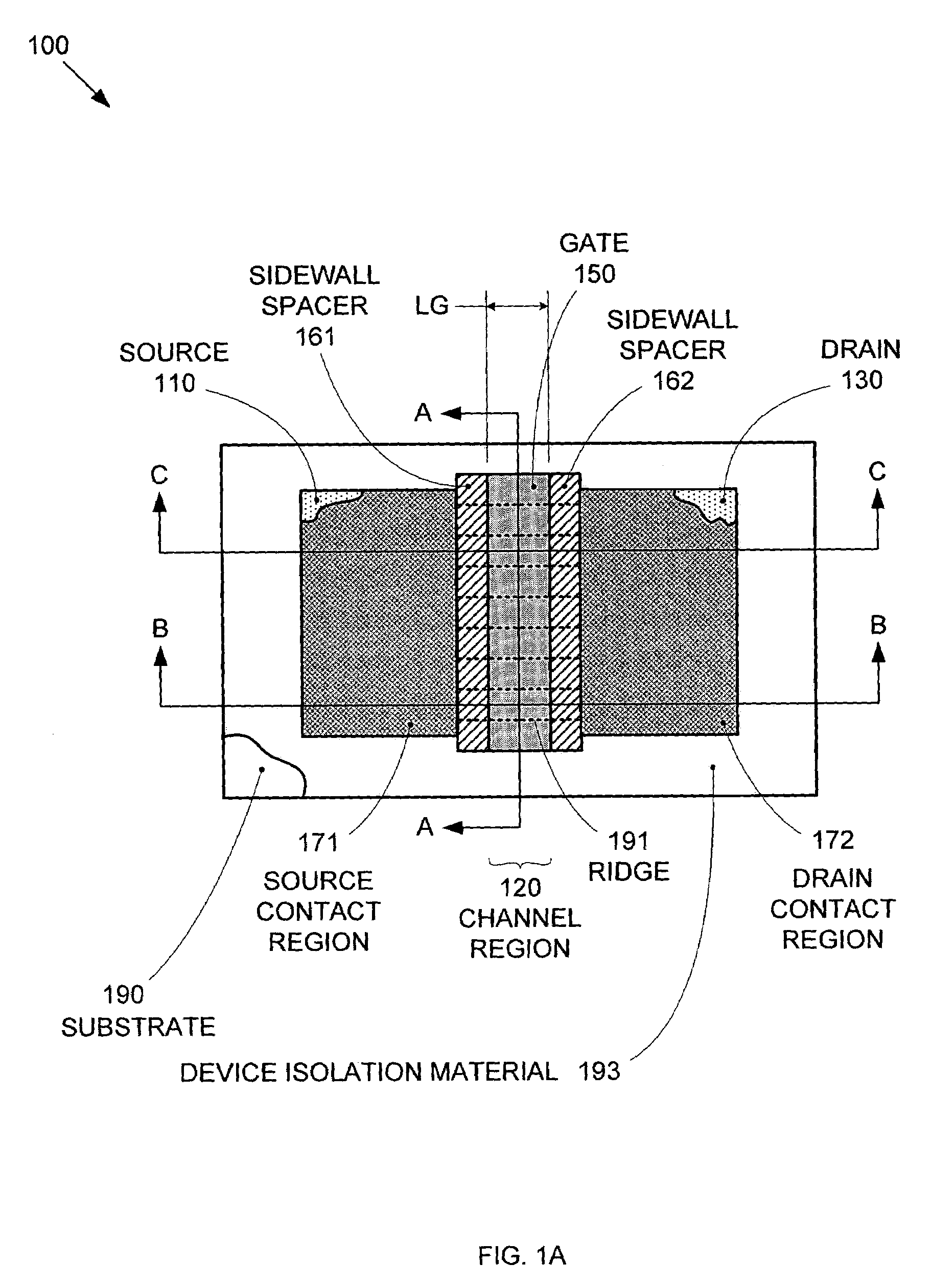
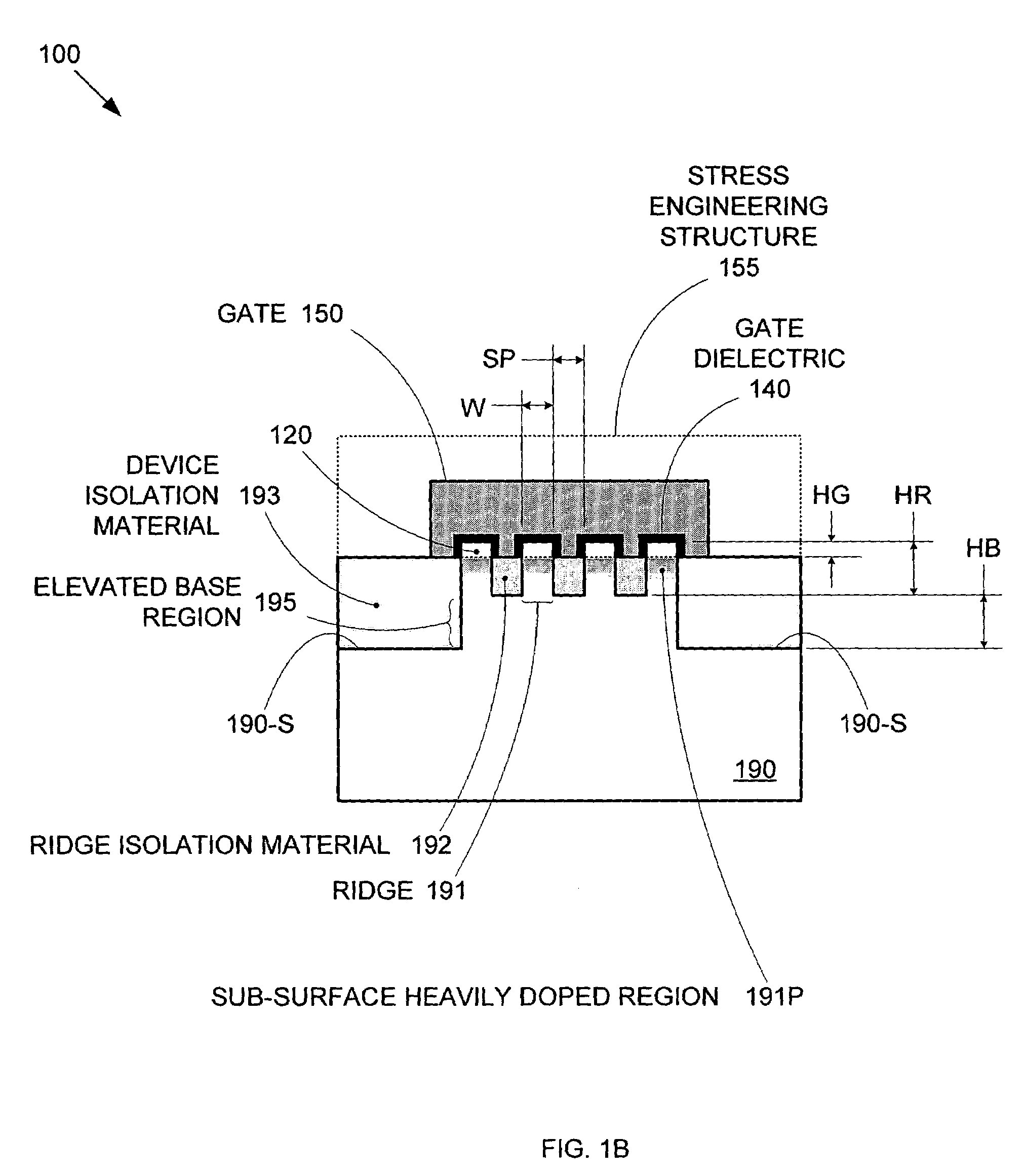
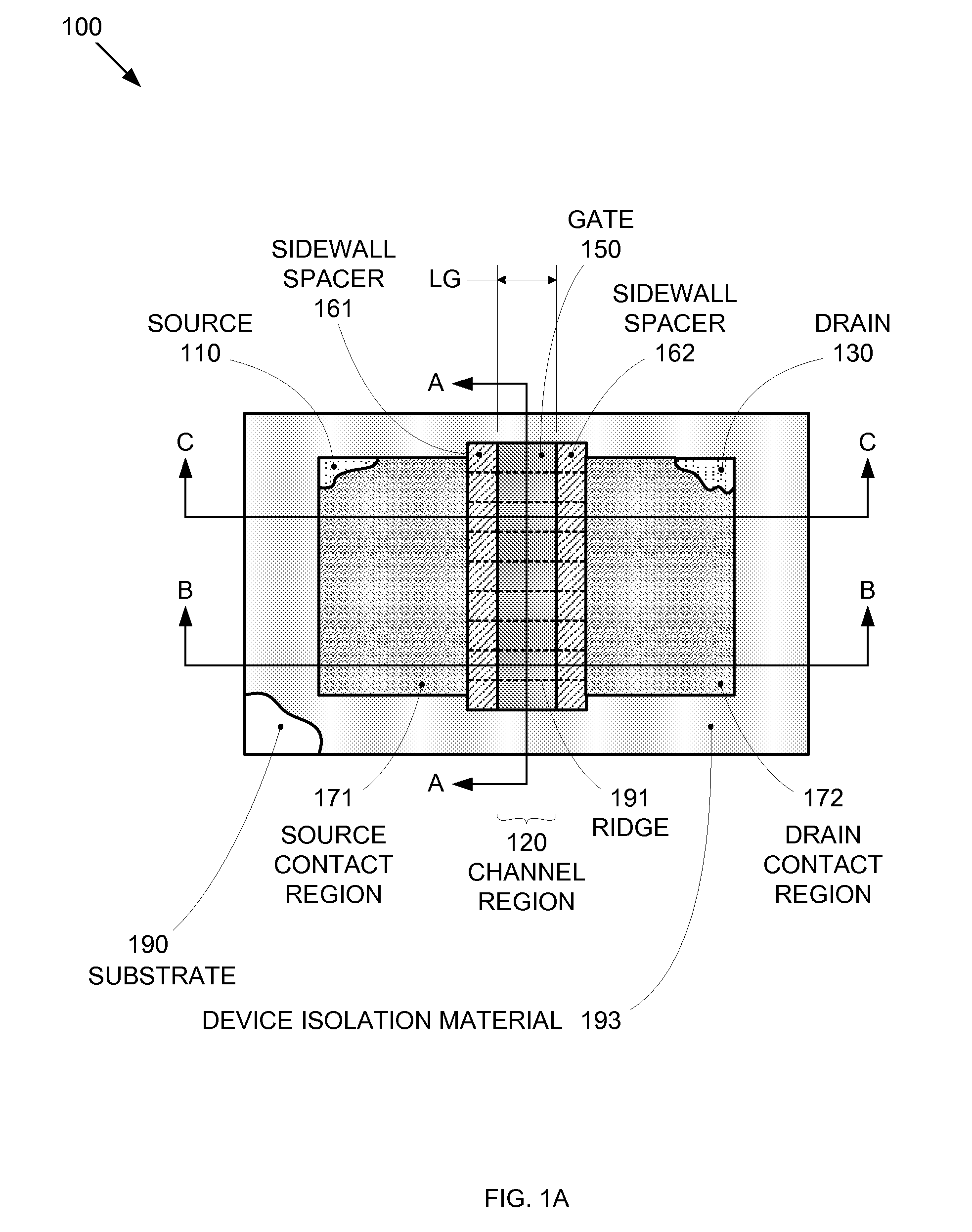
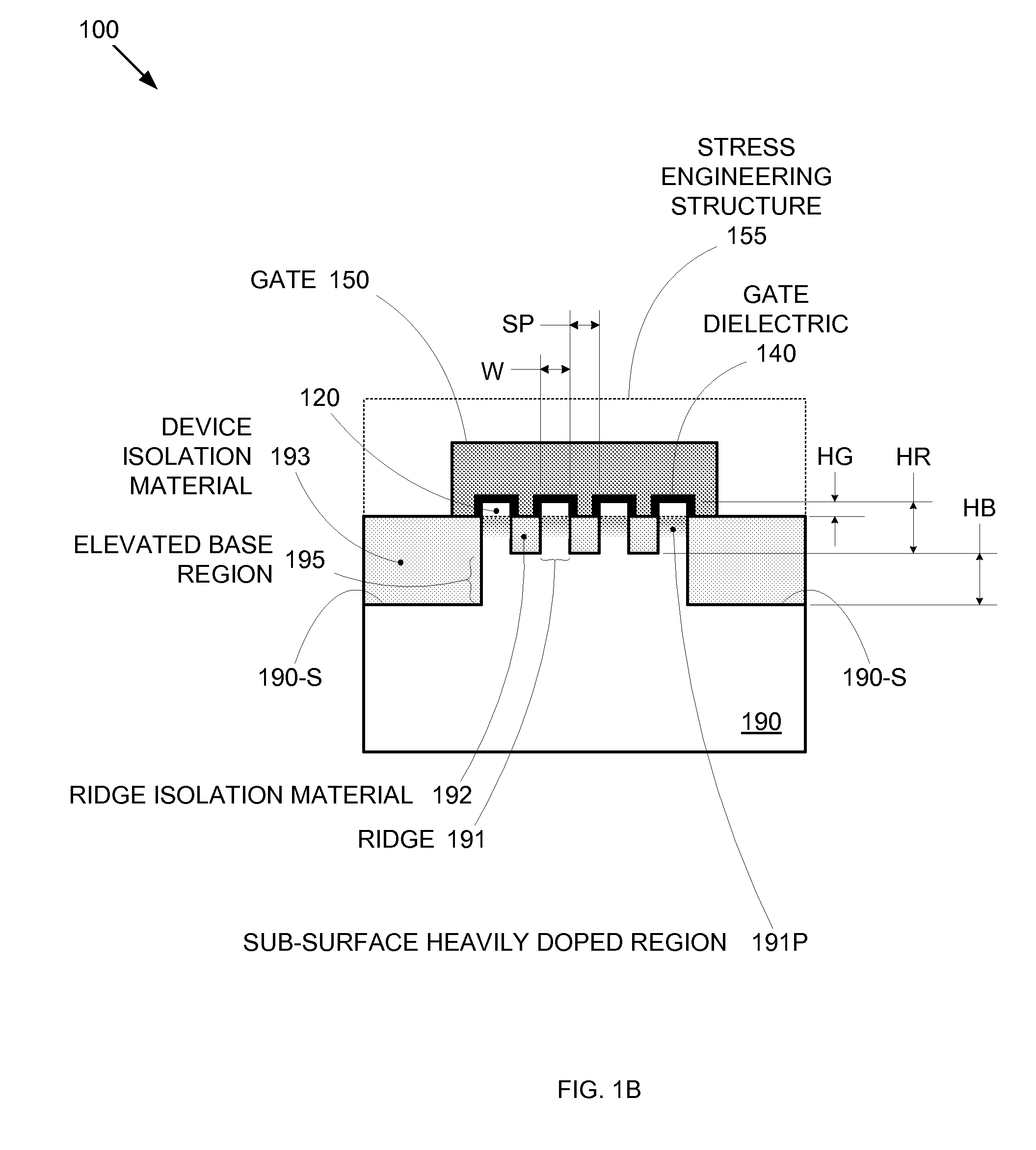
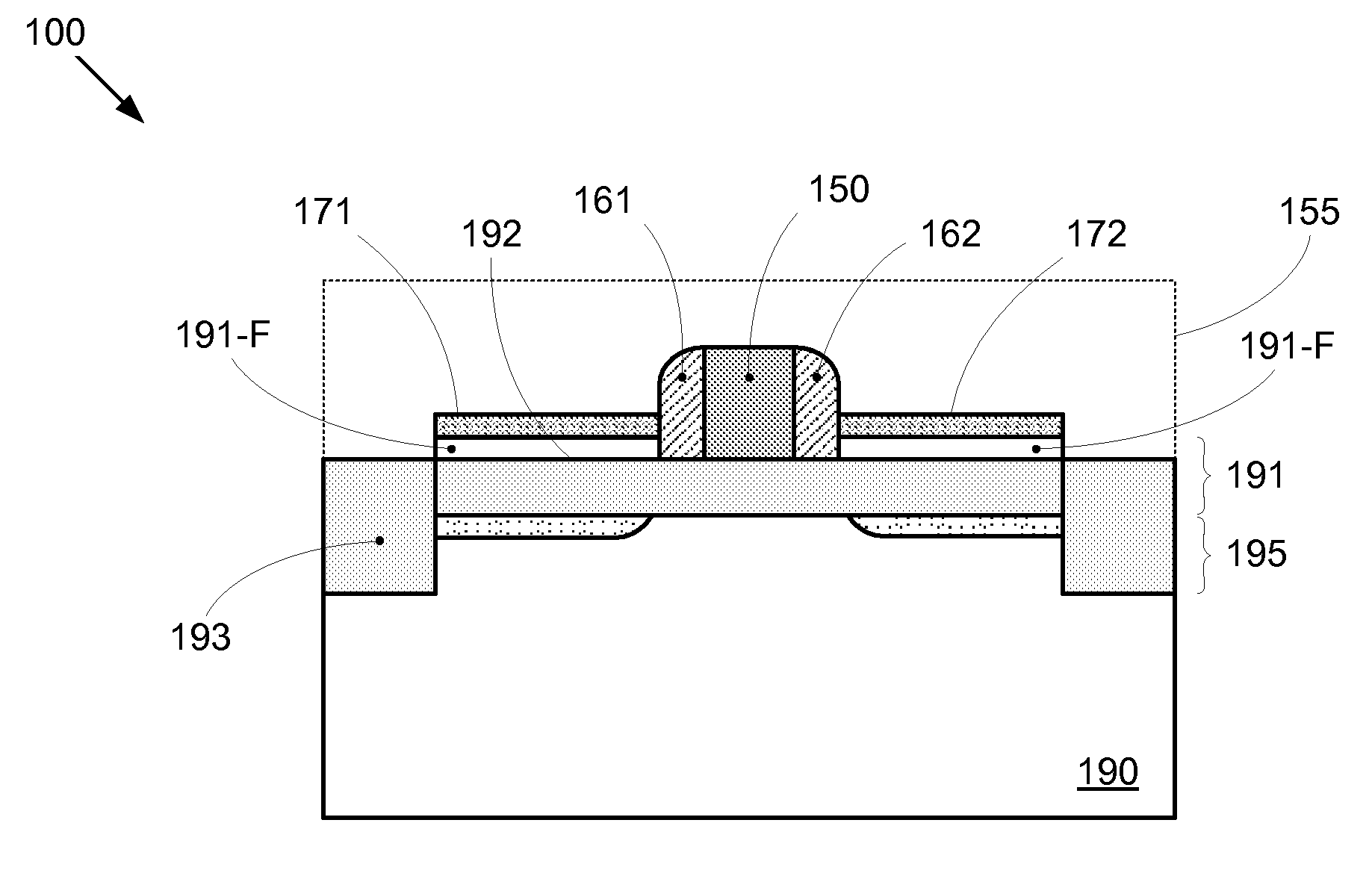
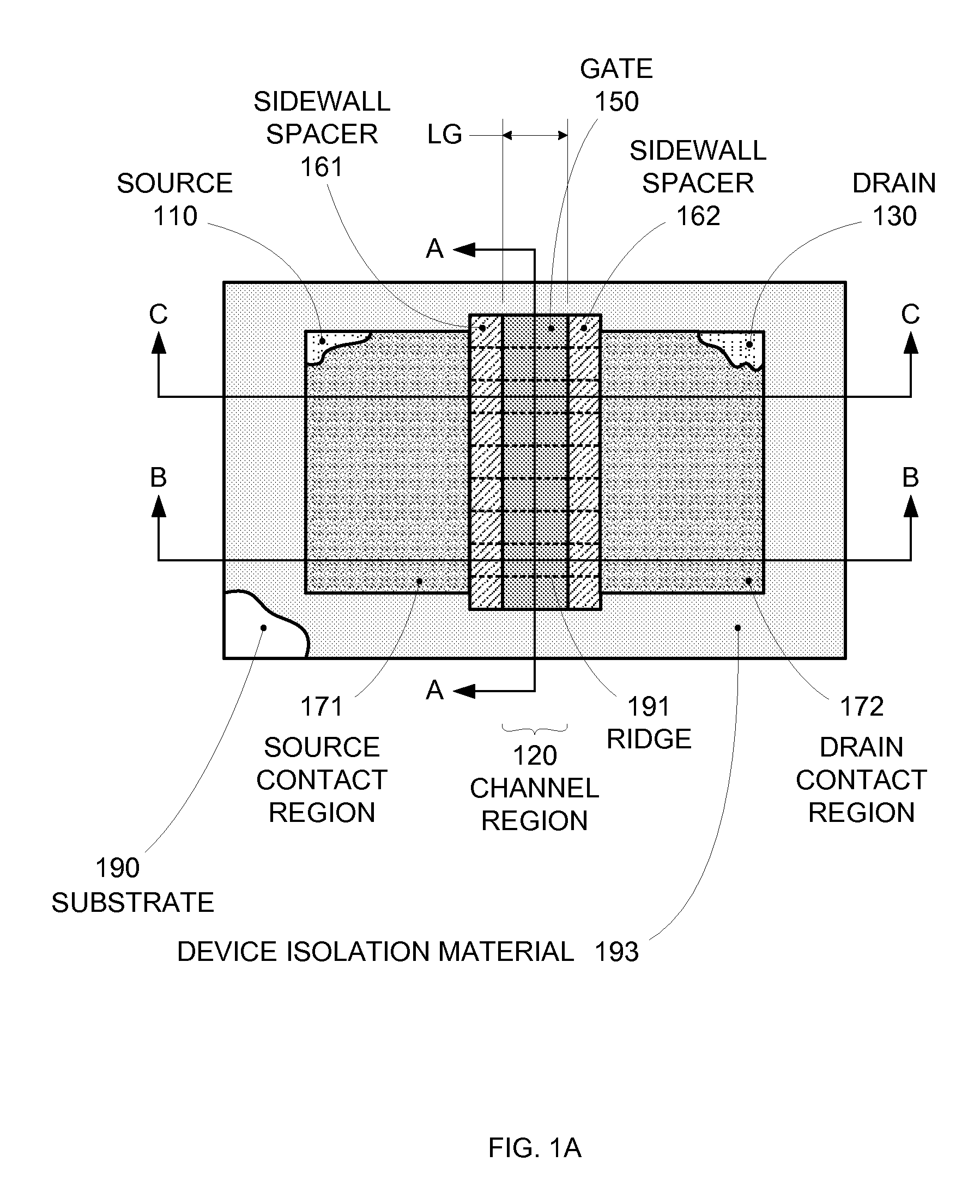
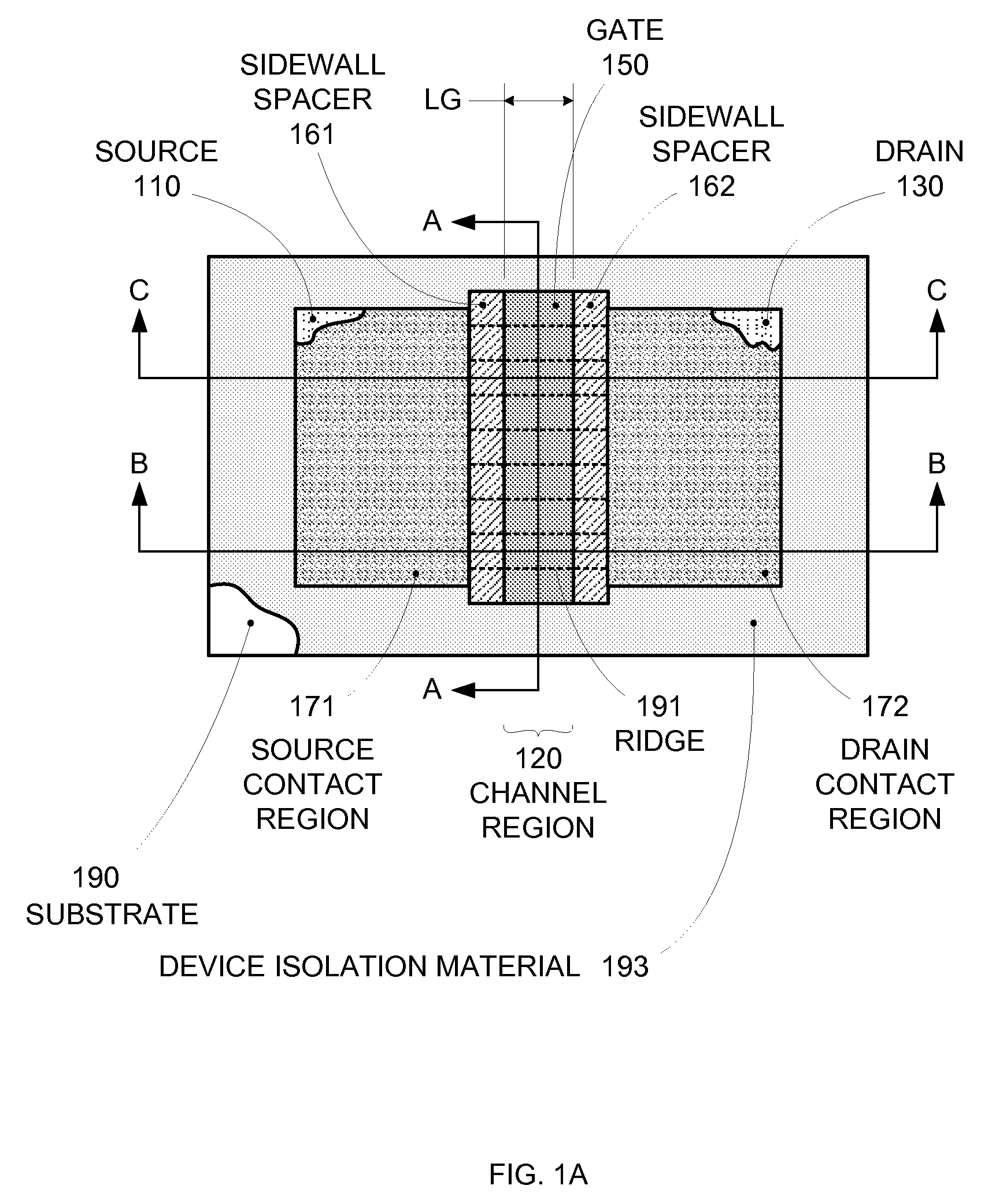
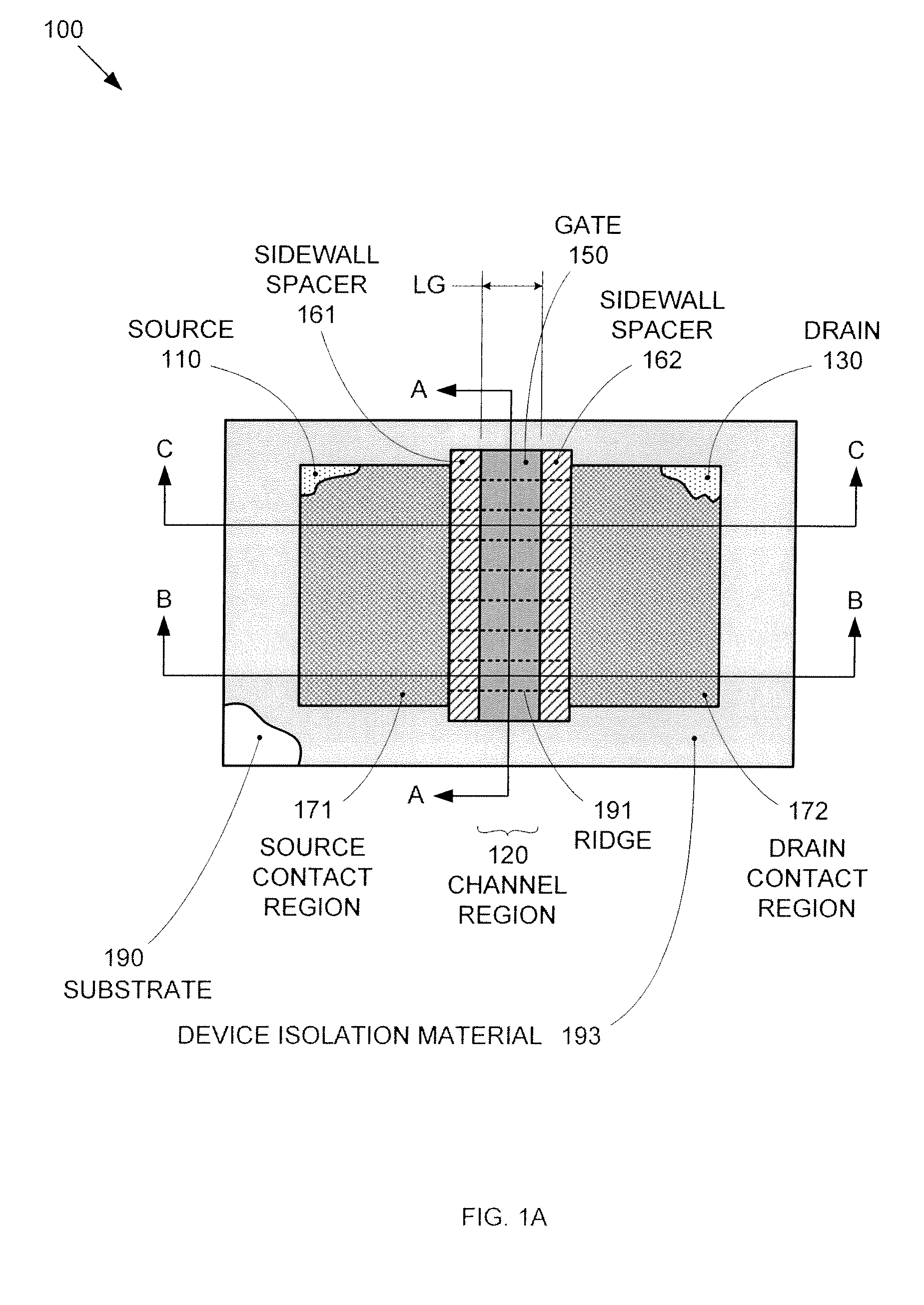
Segmented channel MOS transistor
ActiveUS7247887B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLithographic artist
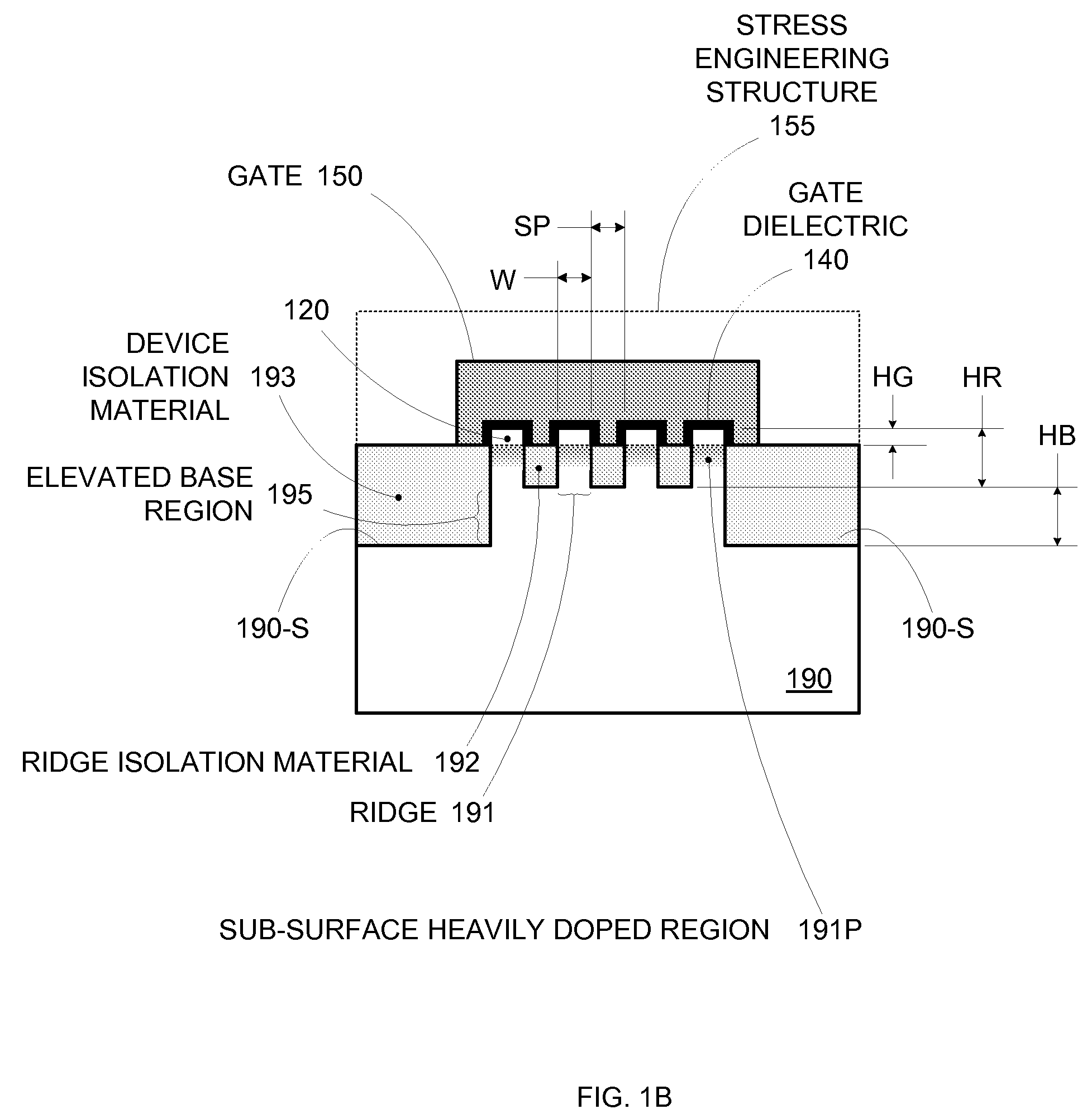
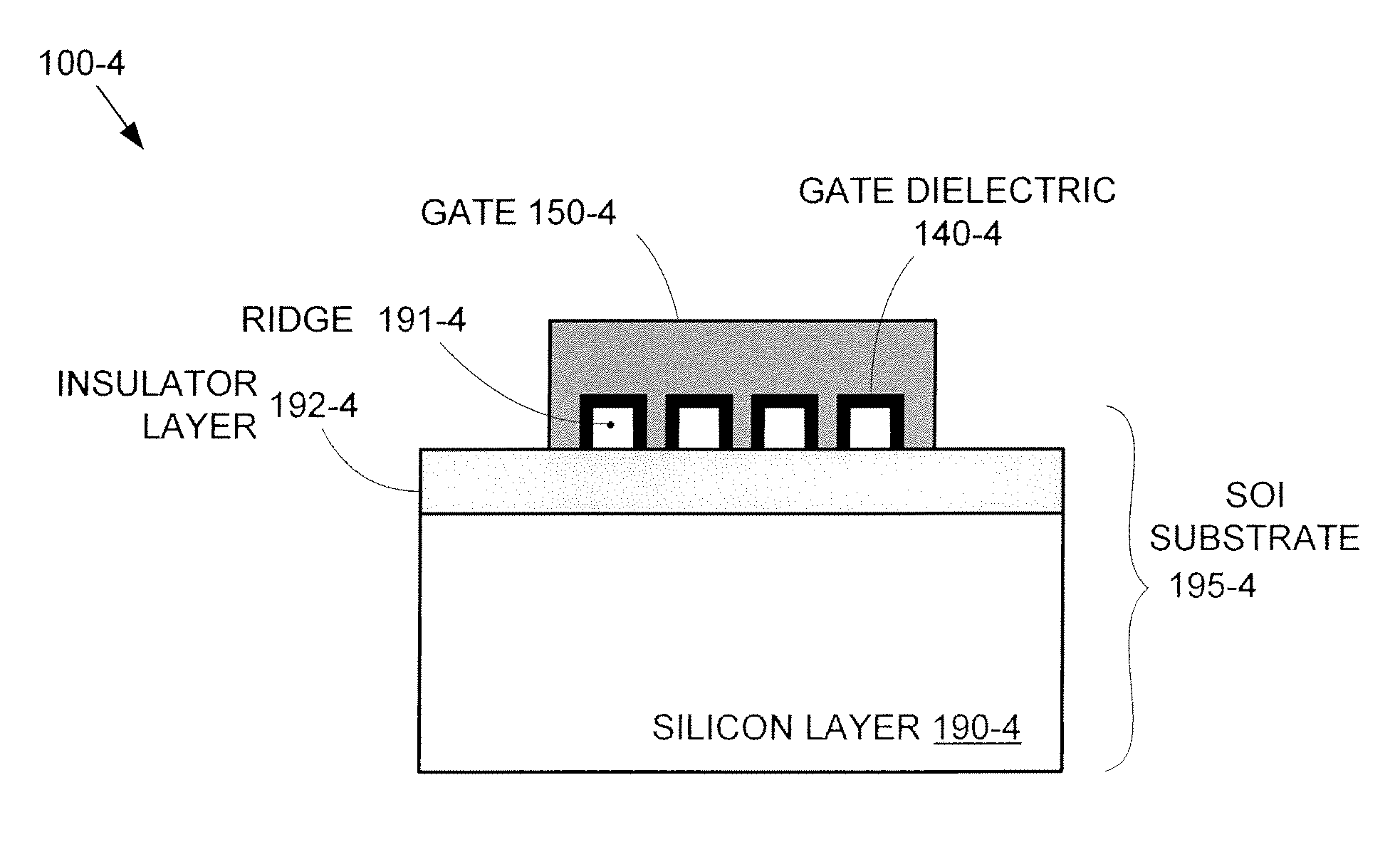
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method of eliminating a lithography operation
ActiveUS20090146322A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithographic artistEngineering
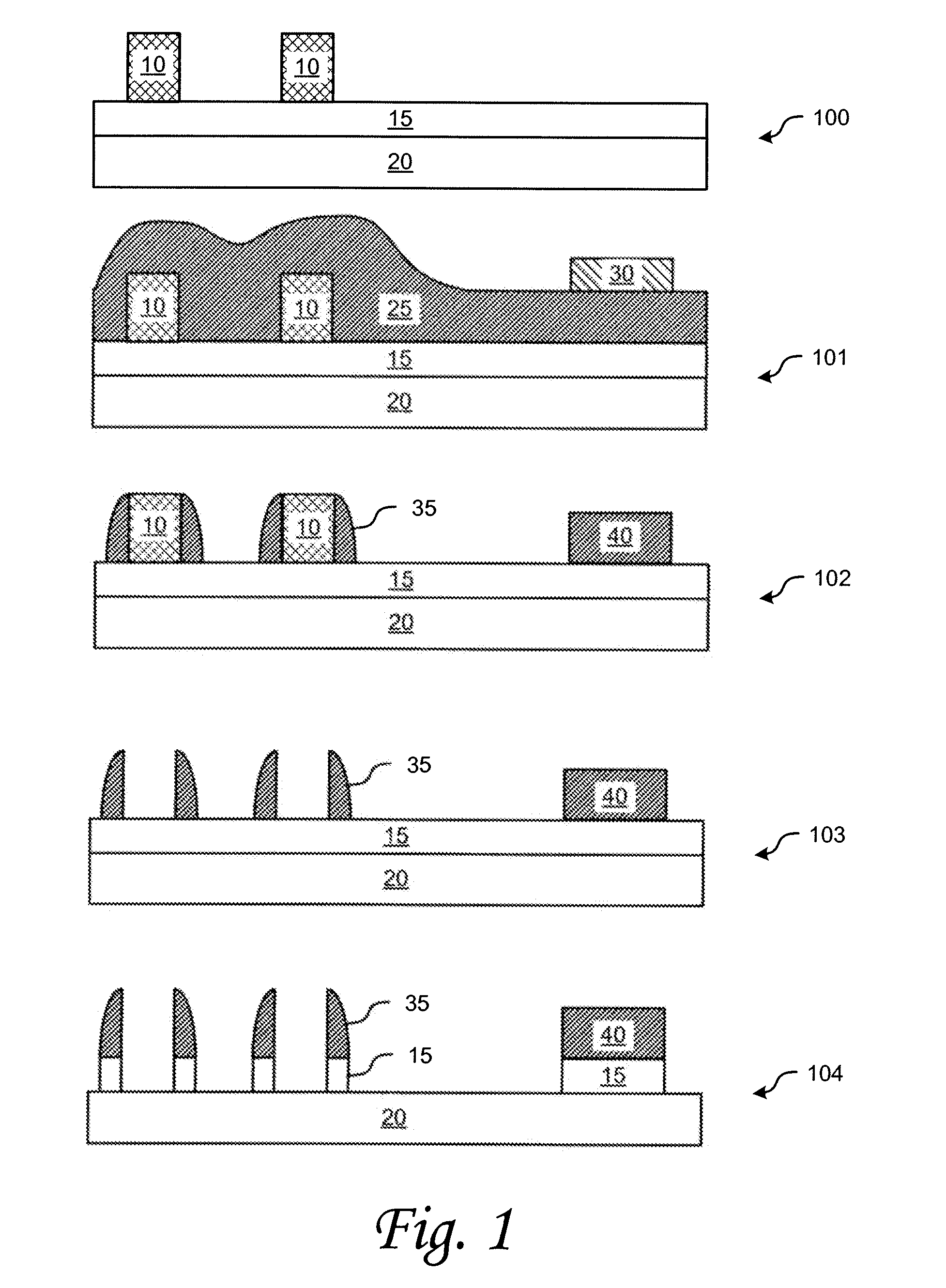
Methods of semiconductor device fabrication are disclosed. An exemplary method includes processes of depositing a first pattern on a semiconductor substrate, wherein the first pattern defines wide and narrow spaces; depositing spacer material over the first pattern on the substrate; etching the spacer material such that the spacer material is removed from horizontal surfaces of the substrate and the first pattern but remains adjacent to vertical surfaces of a wide space defined by the first pattern and remains within narrow a space defined by the first pattern; and removing the first pattern from the substrate. In one embodiment, the first pattern can comprise sacrificial material, which can include, for example, polysilicon material. The deposition can comprise physical vapor deposition, chemical vapor deposition, electrochemical deposition, molecular beam epitaxy, atomic layer deposition or other deposition techniques. According to another embodiment, features for lines and logic device components having a width greater than that of the lines are formed in the spacer material in the same mask layer.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Seamless, maskless lithography system using spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6312134B1Eliminate needImprove processing throughputMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiation DosagesSpatial light modulator
The invention is a seamless projection lithography system that eliminates the need for masks through the use of a programmable Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) with high parallel processing power. Illuminating the SLM with a radiation source (1), which while preferably a pulsed laser may be a shuttered lamp or multiple lasers with alternating synchronization, provides a patterning image of many pixels via a projection system (4) onto a substrate (5). The preferred SLM is a Deformable Micromirror Device (3) for reflective pixel selection using a synchronized pulse laser. An alternative SLM is a Liquid Crystal Light Valve (LCLV) (45) for pass-through pixel selection. Electronic programming enables pixel selection control for error correction of faulty pixel elements. Pixel selection control also provides for negative and positive imaging and for complementary overlapping polygon development for seamless uniform dosage. The invention provides seamless scanning by complementary overlapping scans to equalize radiation dosage, to expose a pattern on a large area substrate (5). The invention is suitable for rapid prototyping, flexible manufacturing, and even mask making.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
ActiveUS6932934B2Low viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processLithographic artist
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. An imprint lithography method includes placing a curable liquid on a substrate. A template may be contacted with the curable liquid. Surface forces at the interface of the curable liquid and the template cause the curable liquid to gather in an area defined by a lower surface of the template. Alternately, the curable liquid may fill one or more relatively shallow recesses in the template and the area under the template lower surface. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid to form a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Integrated circuit on corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7190050B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
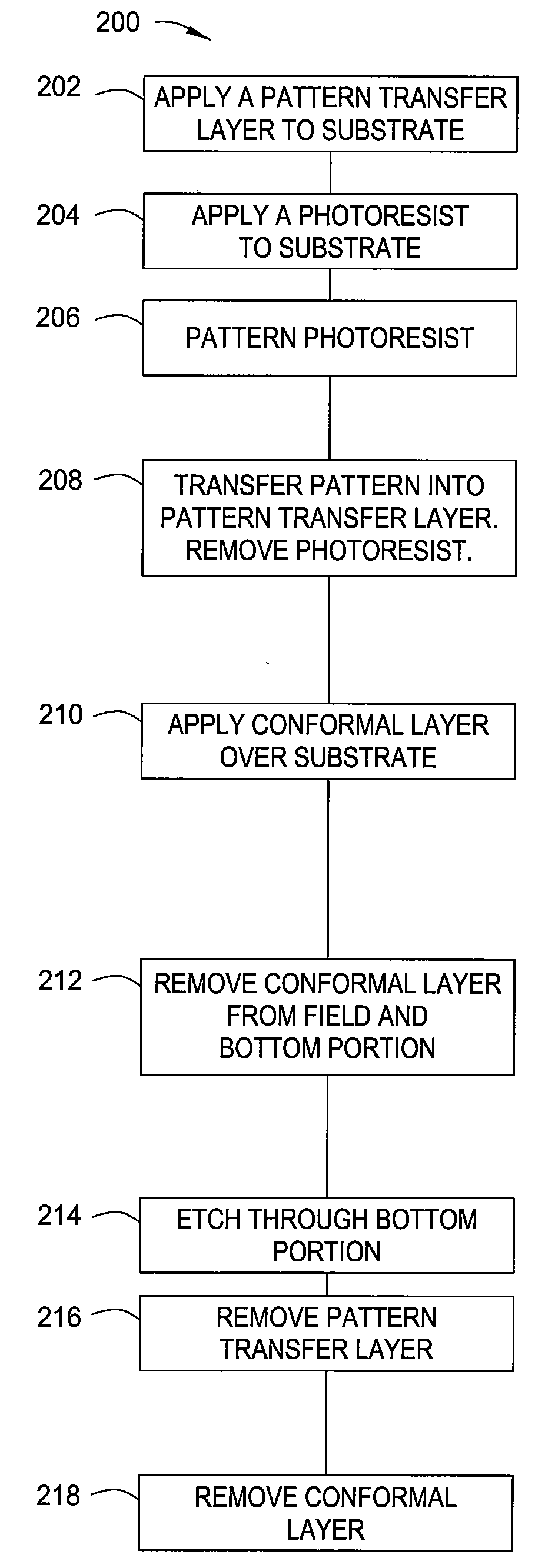
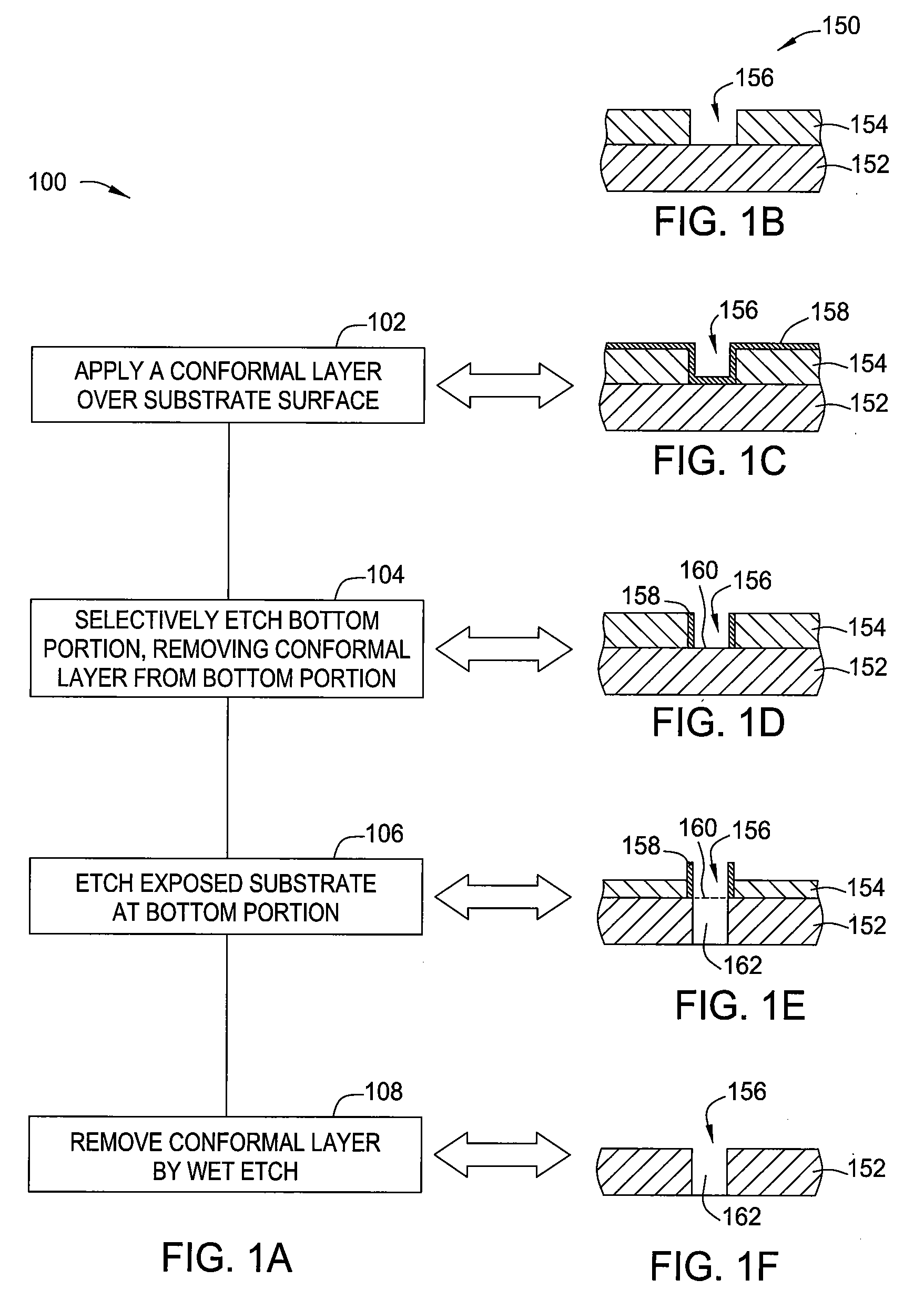
Method for critical dimension shrink using conformal pecvd films
InactiveUS20090286402A1Critical dimension reductionGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistAnisotropic etching
A method and apparatus for forming narrow vias in a substrate is provided. A pattern recess is etched into a substrate by conventional lithography. A thin conformal layer is formed over the surface of the substrate, including the sidewalls and bottom of the pattern recess. The thickness of the conformal layer reduces the effective width of the pattern recess. The conformal layer is removed from the bottom of the pattern recess by anisotropic etching to expose the substrate beneath. The substrate is then etched using the conformal layer covering the sidewalls of the pattern recess as a mask. The conformal layer is then removed using a wet etchant.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
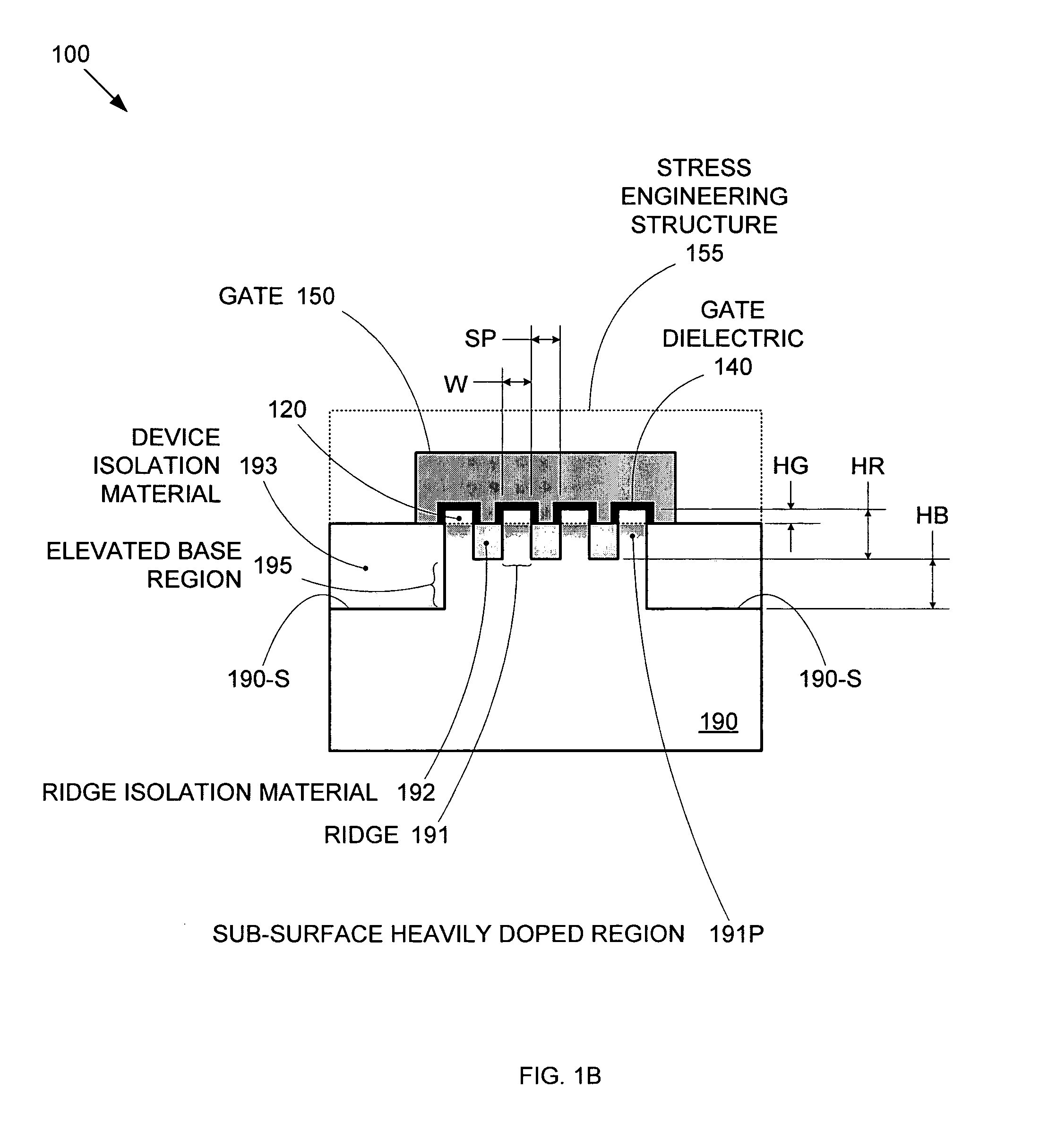
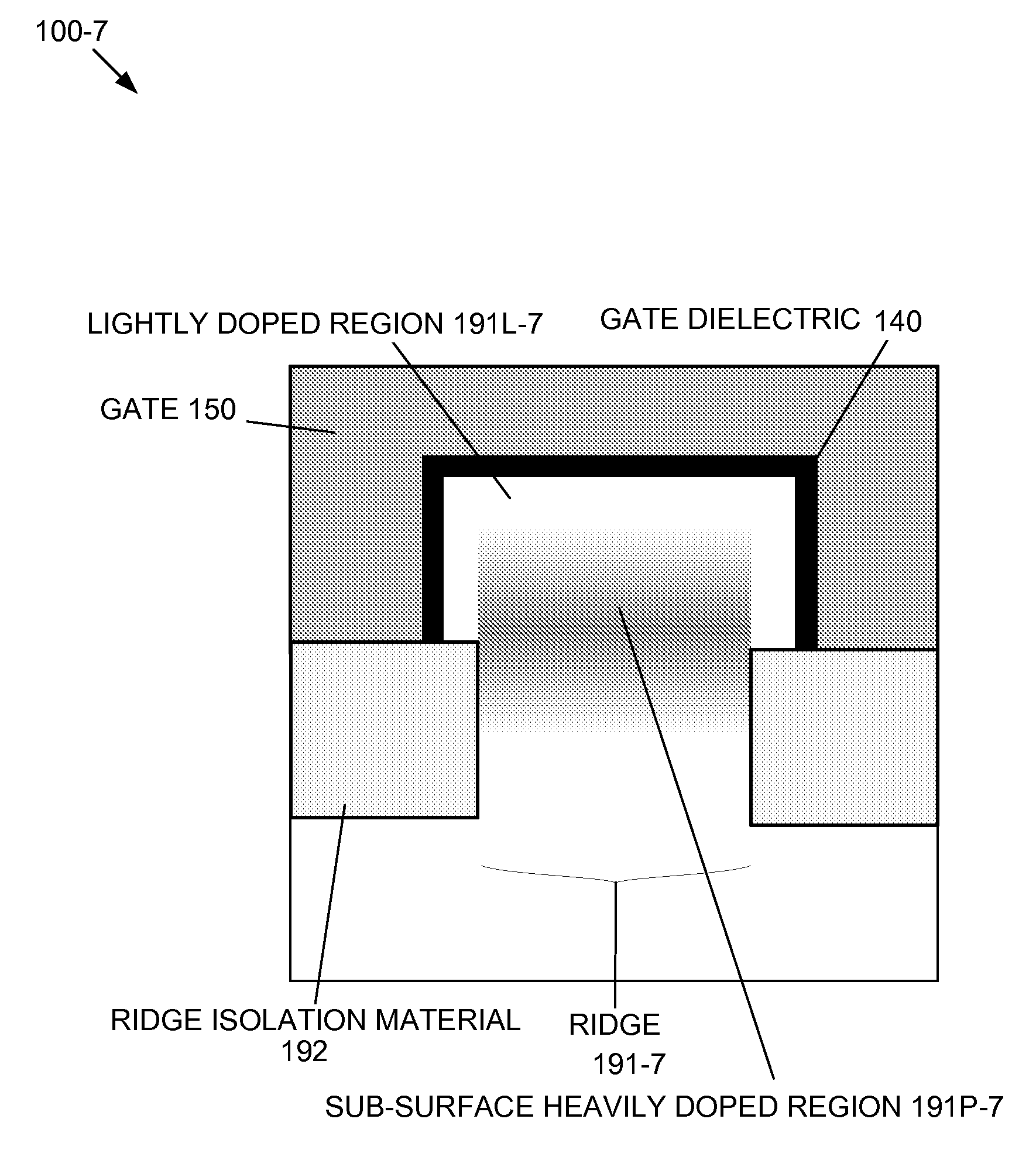
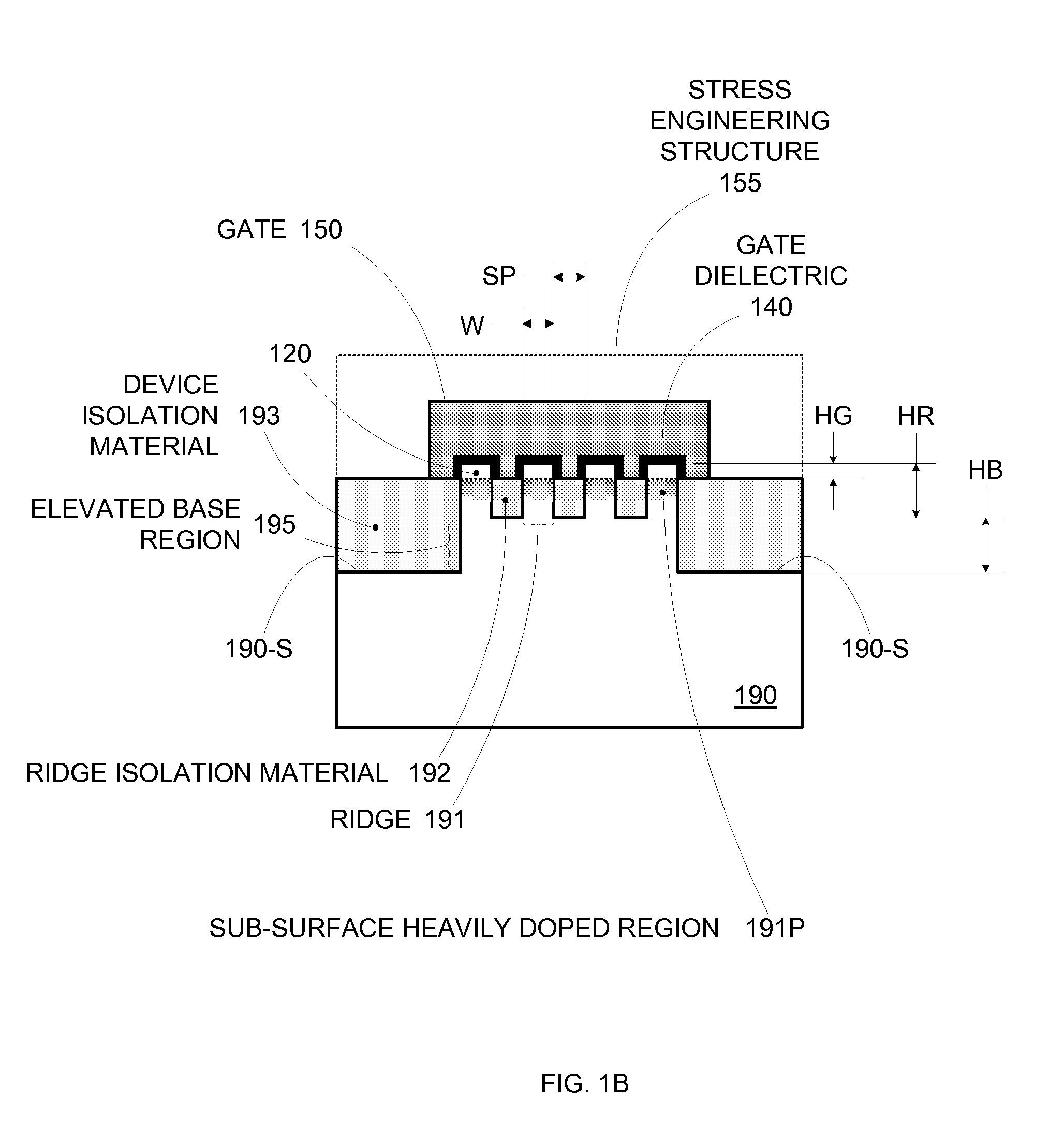
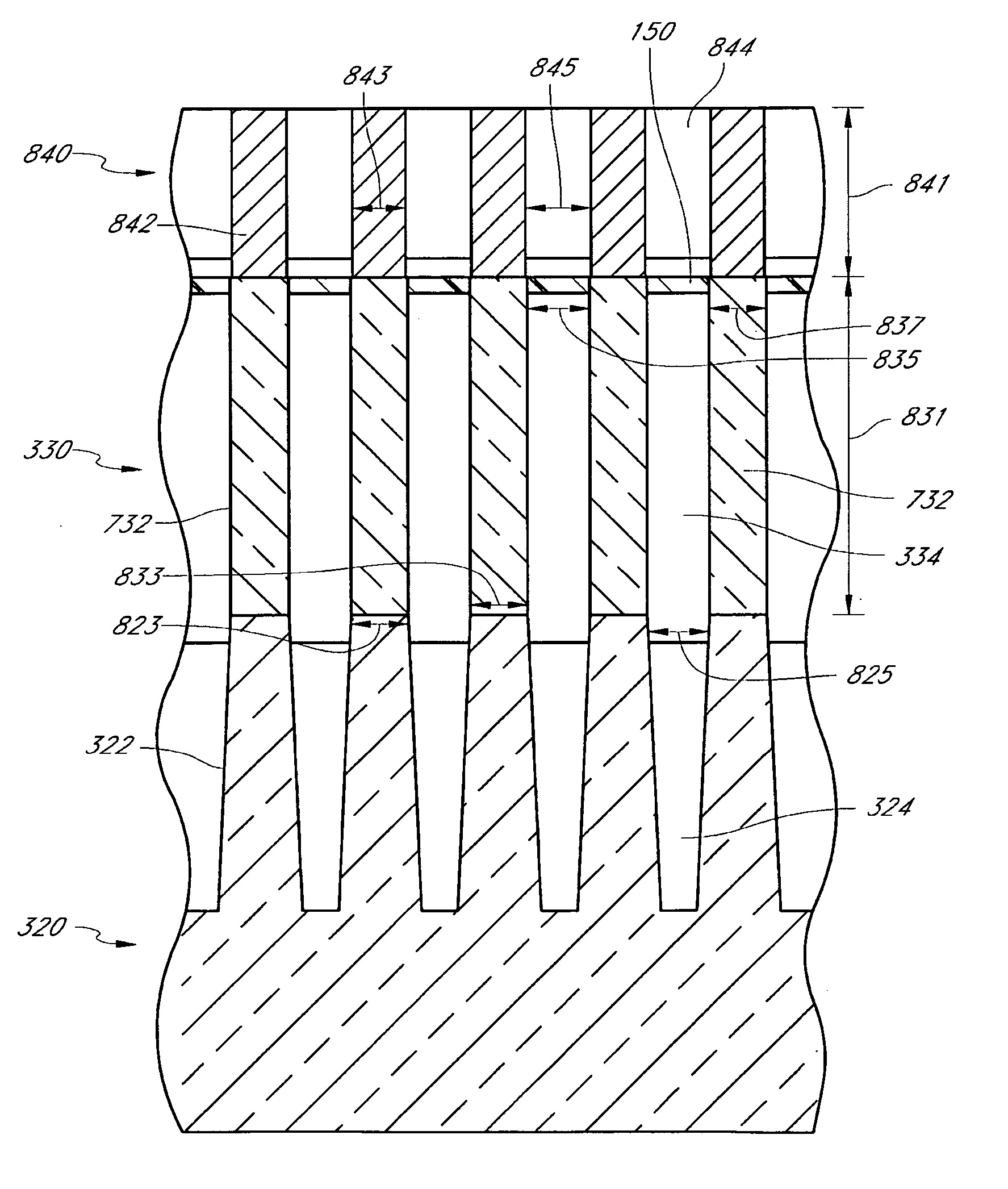
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Glass substrate-holding tool and method for producing an EUV mask blank by employing the same
InactiveUS8967608B2InhibitionAccurate placementWorkpiece holdersVacuum evaporation coatingLithographic artistMaterials science
A glass substrate-holding tool employed during the production of a reflective mask blank for EUV lithography includes an electrostatic chuck and a mechanical chuck. A caught and held portion of a glass substrate caught and held by the electrostatic chuck, and pressed portions of the glass substrate pressed by the mechanical chuck are located outside a quality-guaranteed region on each of a film deposition surface and a rear surface of the glass substrate. The sum of a catching and holding force applied to the glass substrate by the electrostatic chuck and a holding force applied to the glass substrate by the mechanical chuck is at least 200 kgf. A pressing force per unit area applied to the glass substrate by the mechanical chuck is at most 25 kgf / mm2.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Polymer sacrificial light absorbing structure and method
InactiveUS6876017B2From solid stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolubilityLithographic artist
Method and structure for optimizing dual damascene patterning with polymeric dielectric materials are disclosed. Certain embodiments of the invention comprise polymeric sacrificial light absorbing materials (“polymer SLAM”) functionalized to have a controllable solubility switch wherein such polymeric materials have substantially the same etch rate as conventionally utilized polymeric dielectric materials, and subsequent to chemical modification of solubility-modifying protecting groups comprising the SLAM materials by thermal treatment or in-situ generation of an acid, such SLAM materials become soluble in weak bases, such as those conventionally utilized to remove materials in lithography treatments.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7265008B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with narrowed base regions
ActiveUS7508031B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably produced. Ridges on the corrugated substrate can be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials, high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
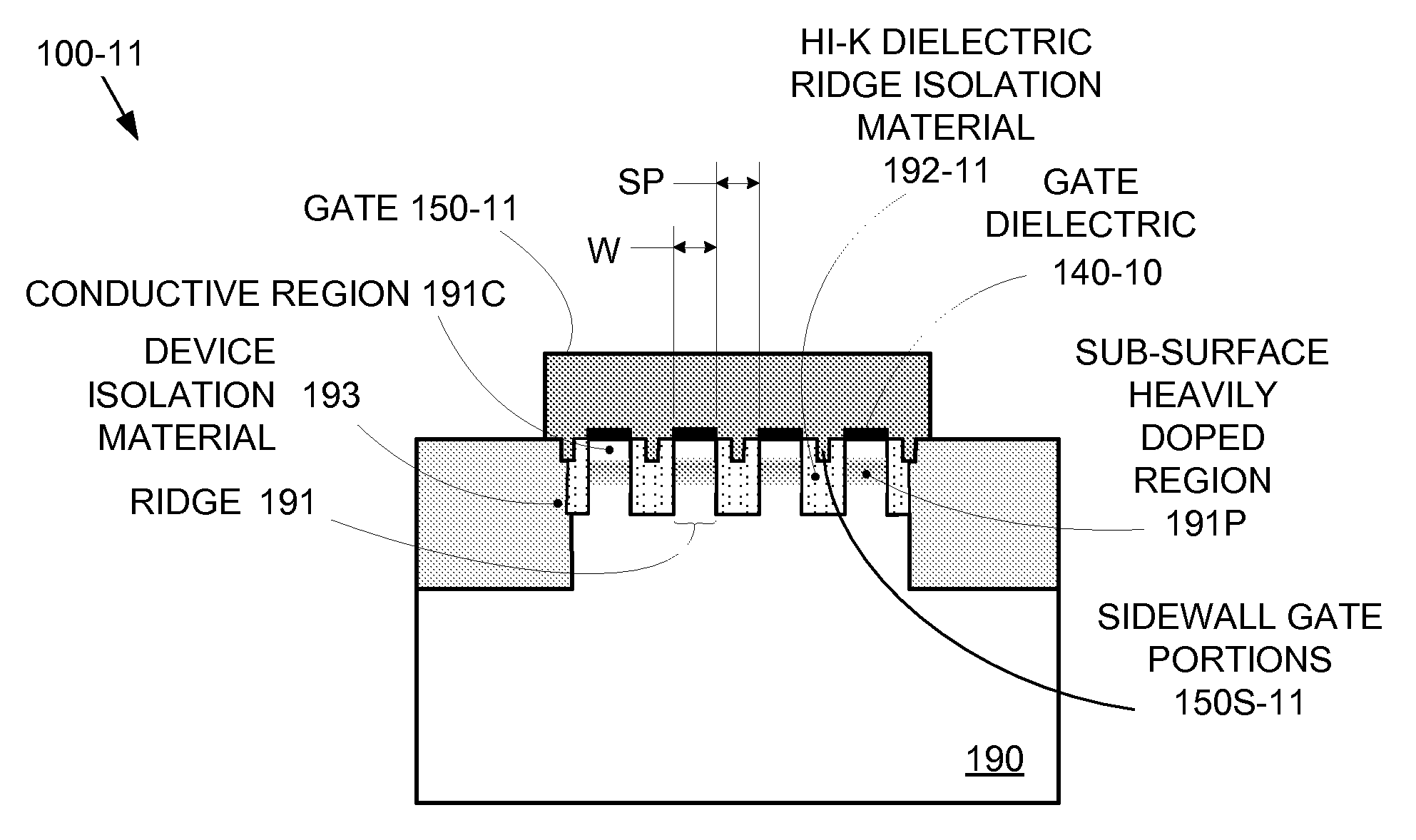
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with High-Permittivity Dielectric Isolation Material
ActiveUS20070122953A1Increase costImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
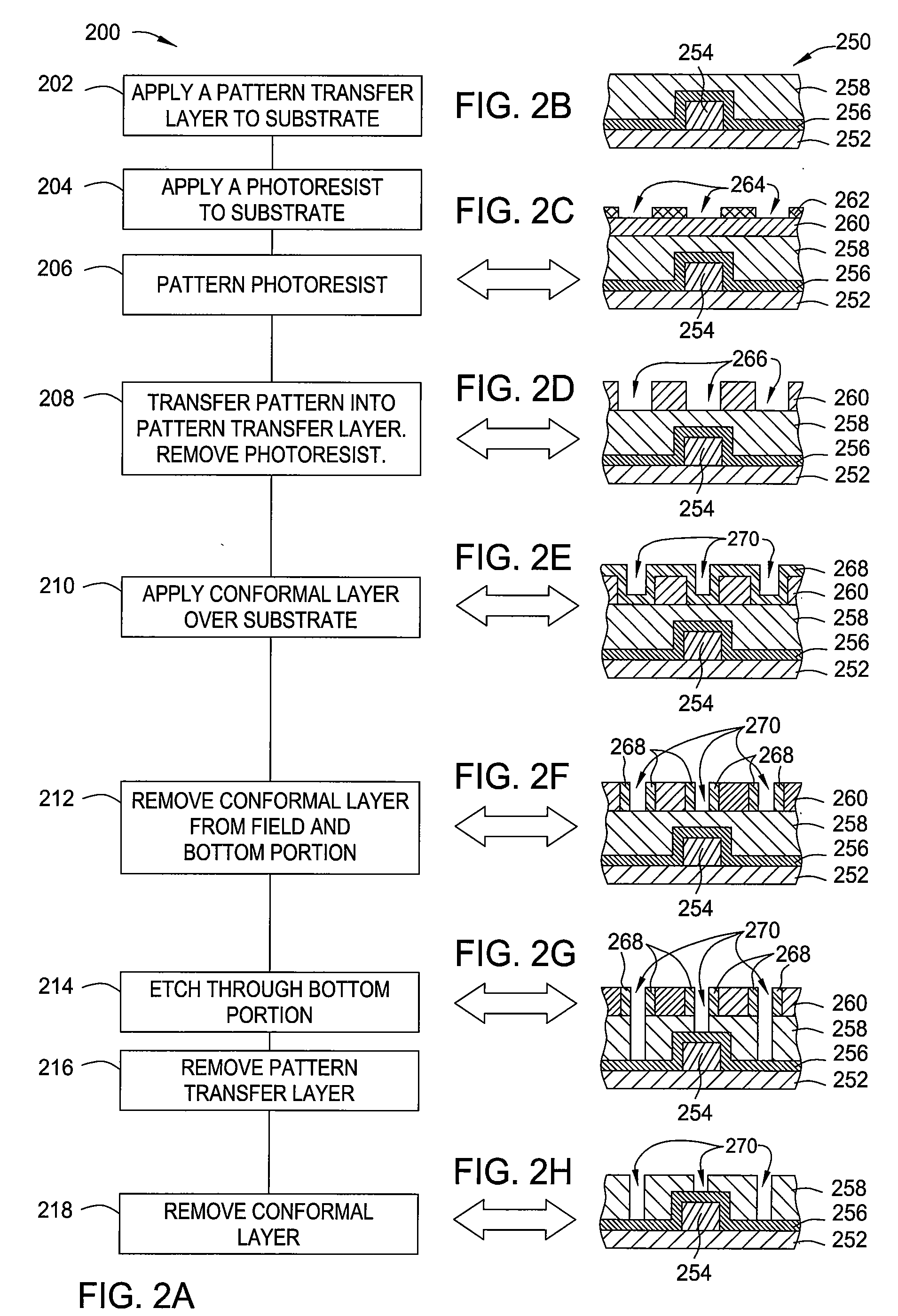
Method of forming pitch multipled contacts
ActiveUS20070049035A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineLithographic artist
Methods of forming electrically conductive and / or semiconductive features for use in integrated circuits are disclosed. Various pattern transfer and etching steps can be used, in combination with pitch-reduction techniques, to create densely-packed features. The features can have a reduced pitch in one direction and a wider pitch in another direction. Conventional photo-lithography steps can be used in combination with pitch-reduction techniques to form elongate, pitch-reduced features such as bit-line contacts, for example.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
Integrated Circuit On Corrugated Substrate
ActiveUS20070132053A1Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor materials
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
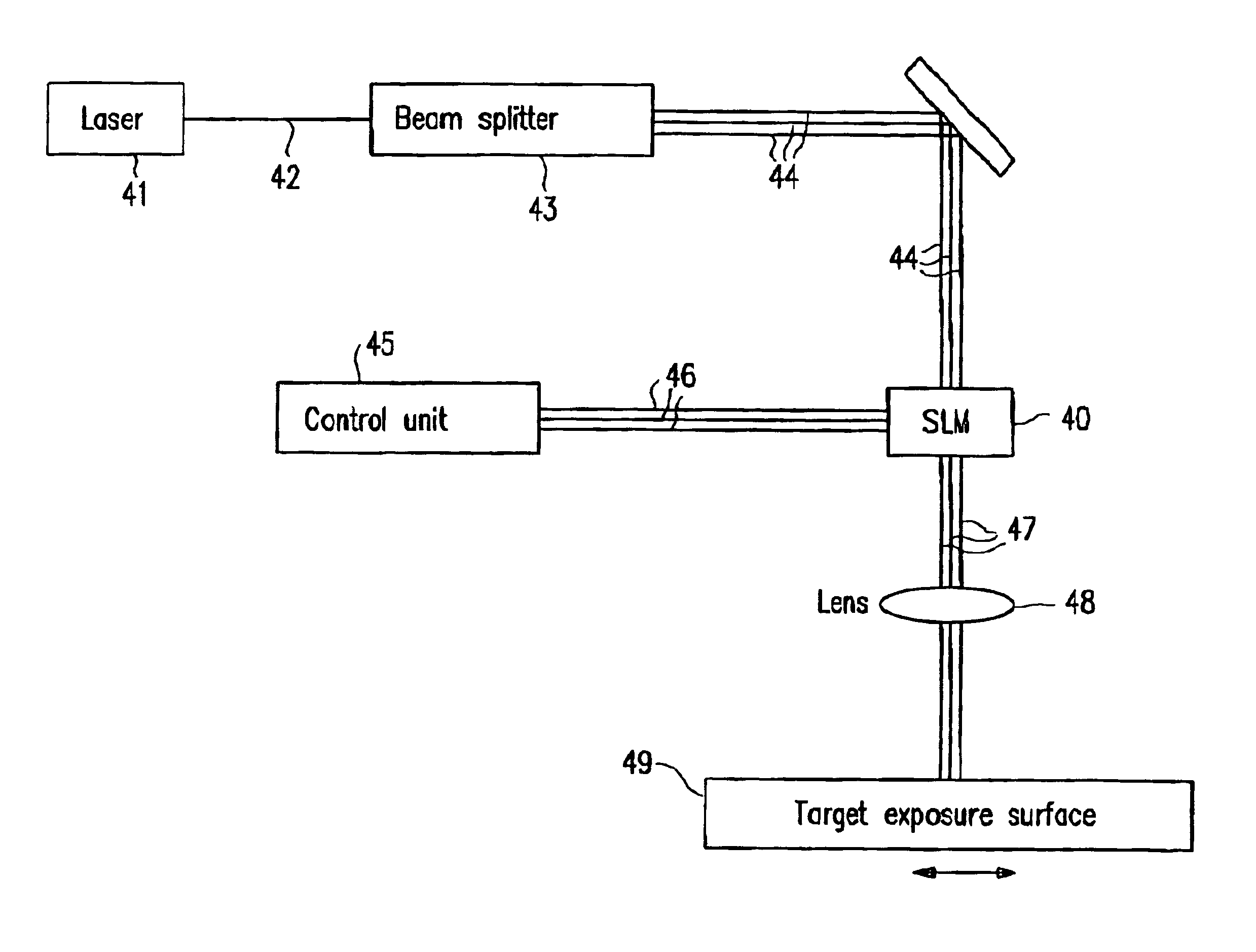
Lithography system
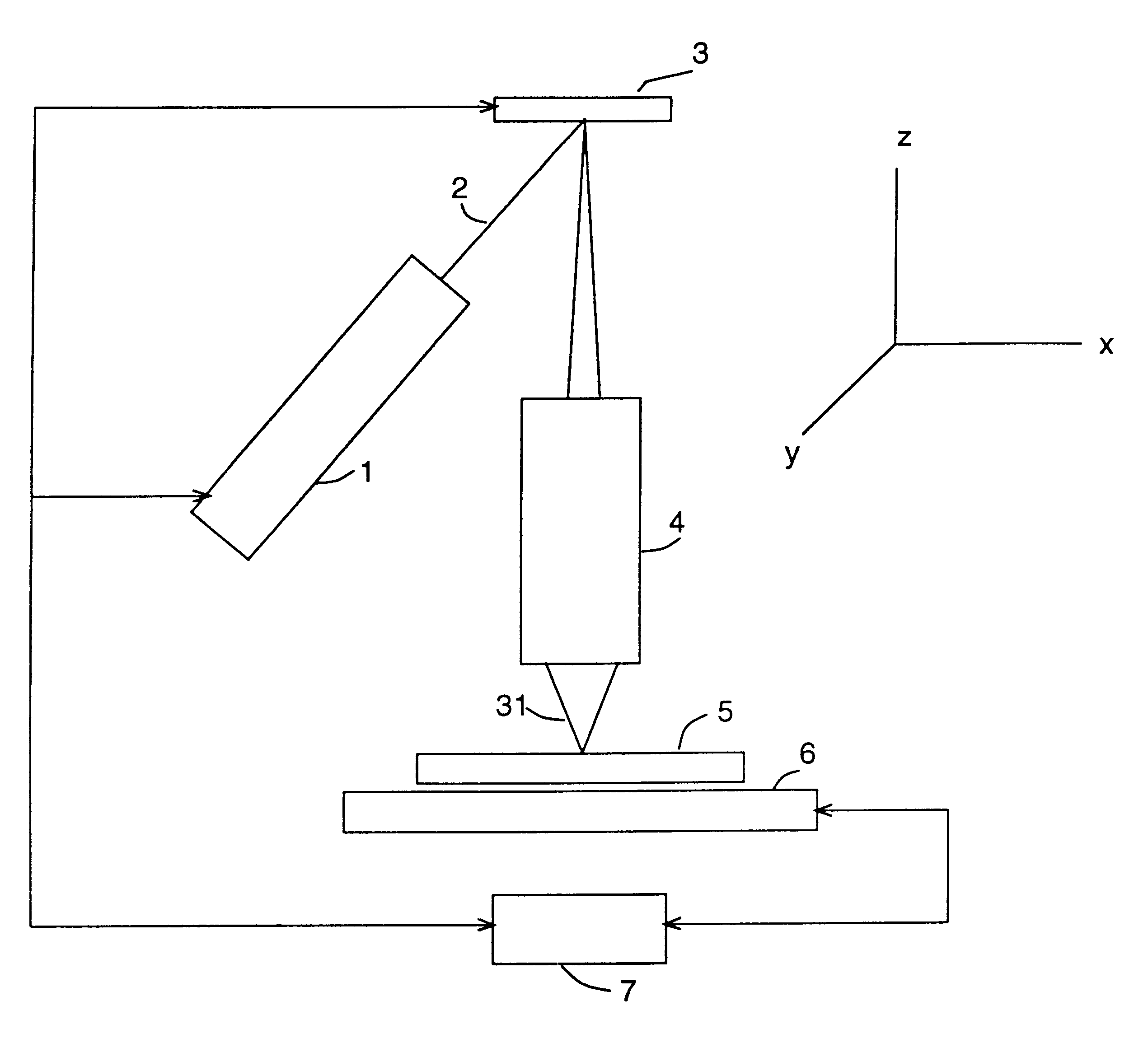
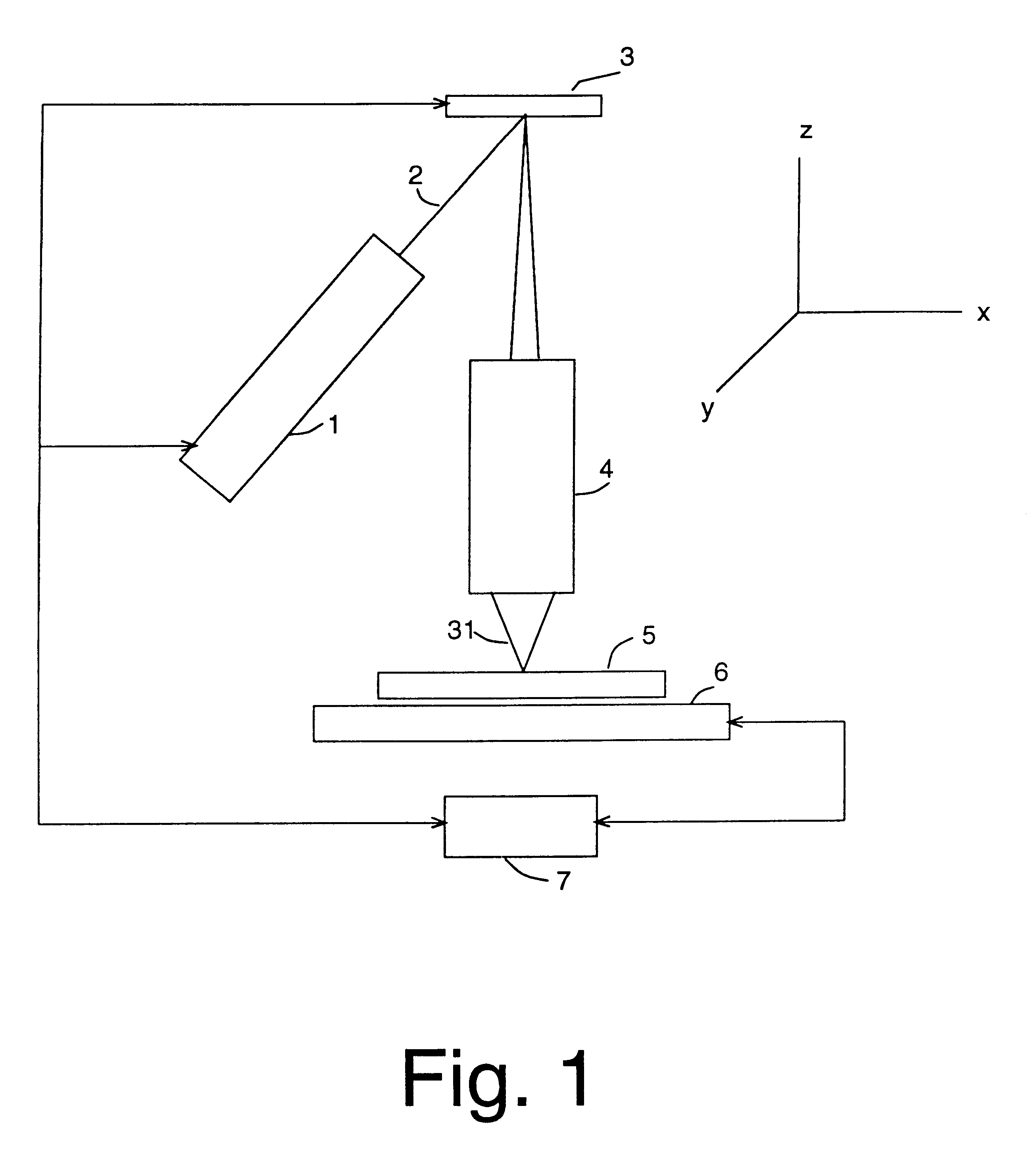
ActiveUS6958804B2Location somewhat remoteReduce transmission lossMirrorsElectric discharge tubesLithographic artistLight beam
A maskless lithography system for transferring a pattern onto the surface of a target. At least one beam generator for generating a plurality of beamlets. A plurality of modulators modulate the magnitude of a beamlet, and a control unit controls of the modulators. The control unit generates and delivers pattern data to the modulators for controlling the magnitude of each individual beamlet. The control unit includes at least one data storage for storing the pattern data, at least one readout unit for reading out the data from the data storage, at least one data converter for converting the data that is read out from the data storage into at least one modulated light beam, and at least one optical transmitter for transmitting the at least one modulated light beam to the modulation modulators.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Composition for forming resist overlayer film for EUV lithography
ActiveUS20130209940A1High resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoatingsLithographic artistLithography process
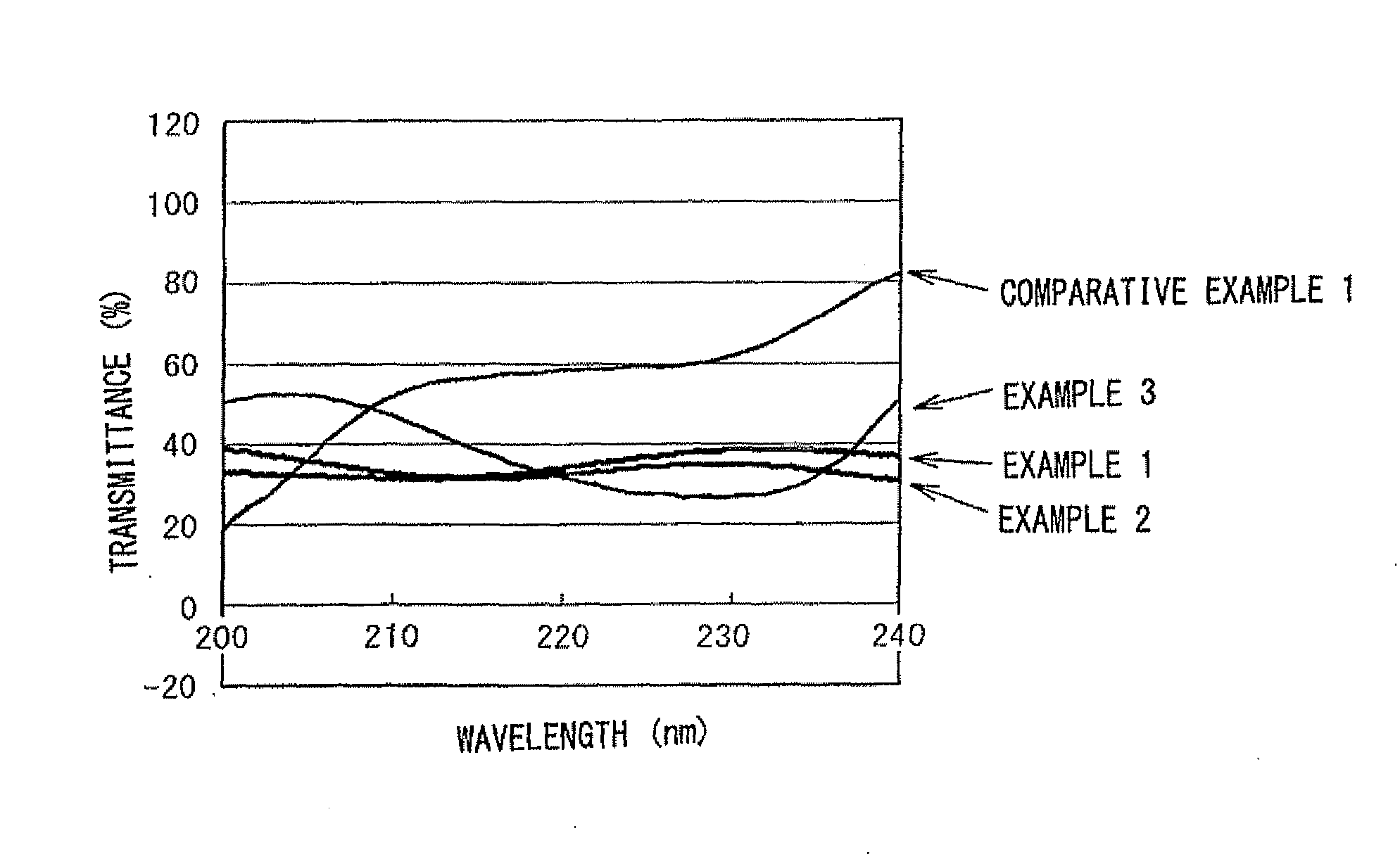
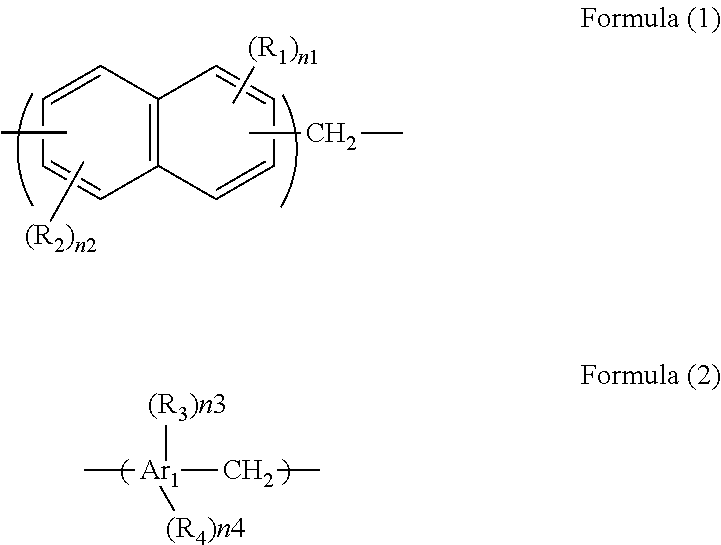
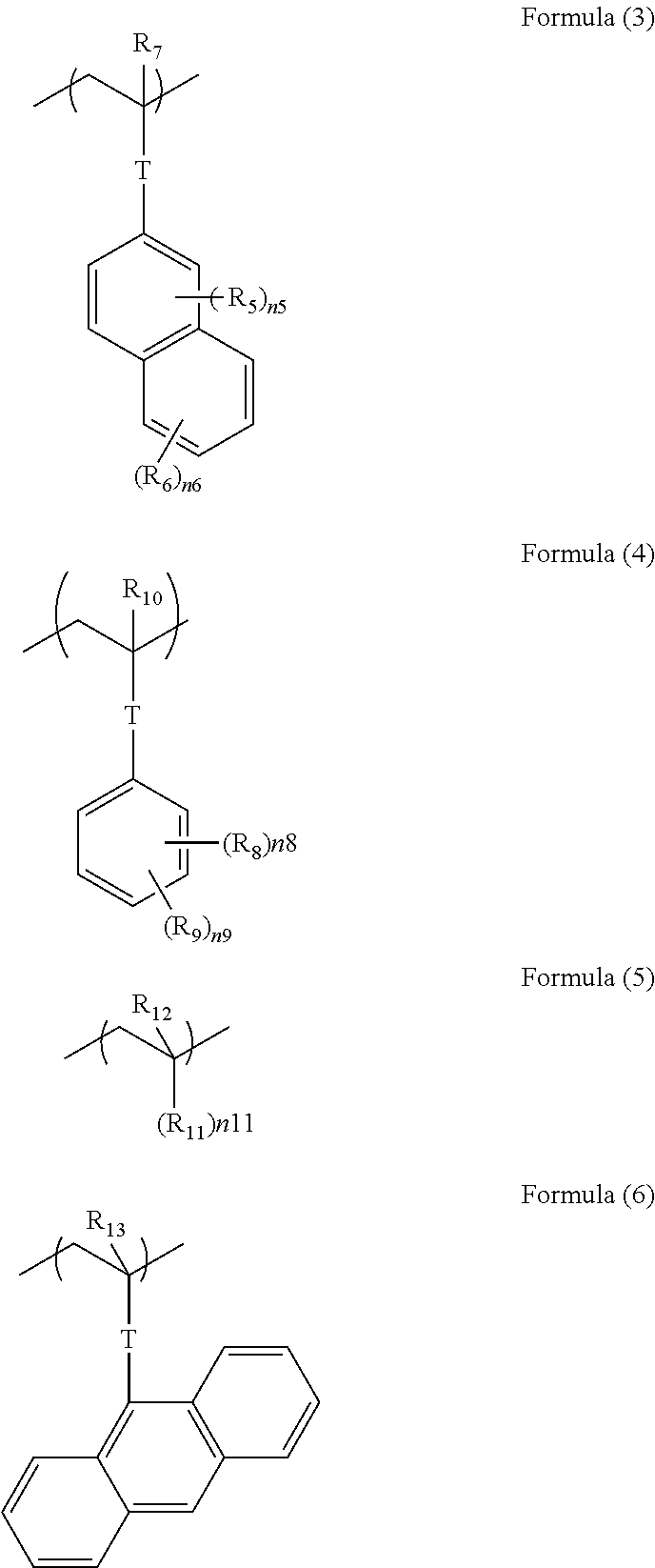
There is provided a composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film that is used in an EUV lithography process, that does not intermix with the EUV resist, that blocks unfavorable exposure light for EUV exposure, for example, UV light and DUV light and selectively transmits EUV light alone, and that can be developed with a developer after exposure. A composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film used in an EUV lithography process including a resin containing a naphthalene ring in a main chain or in a side chain and a solvent, in which the resin may include a hydroxy group, a carboxy group, a sulfo group, or a monovalent organic group having at least one of these groups as a hydrophilic group.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
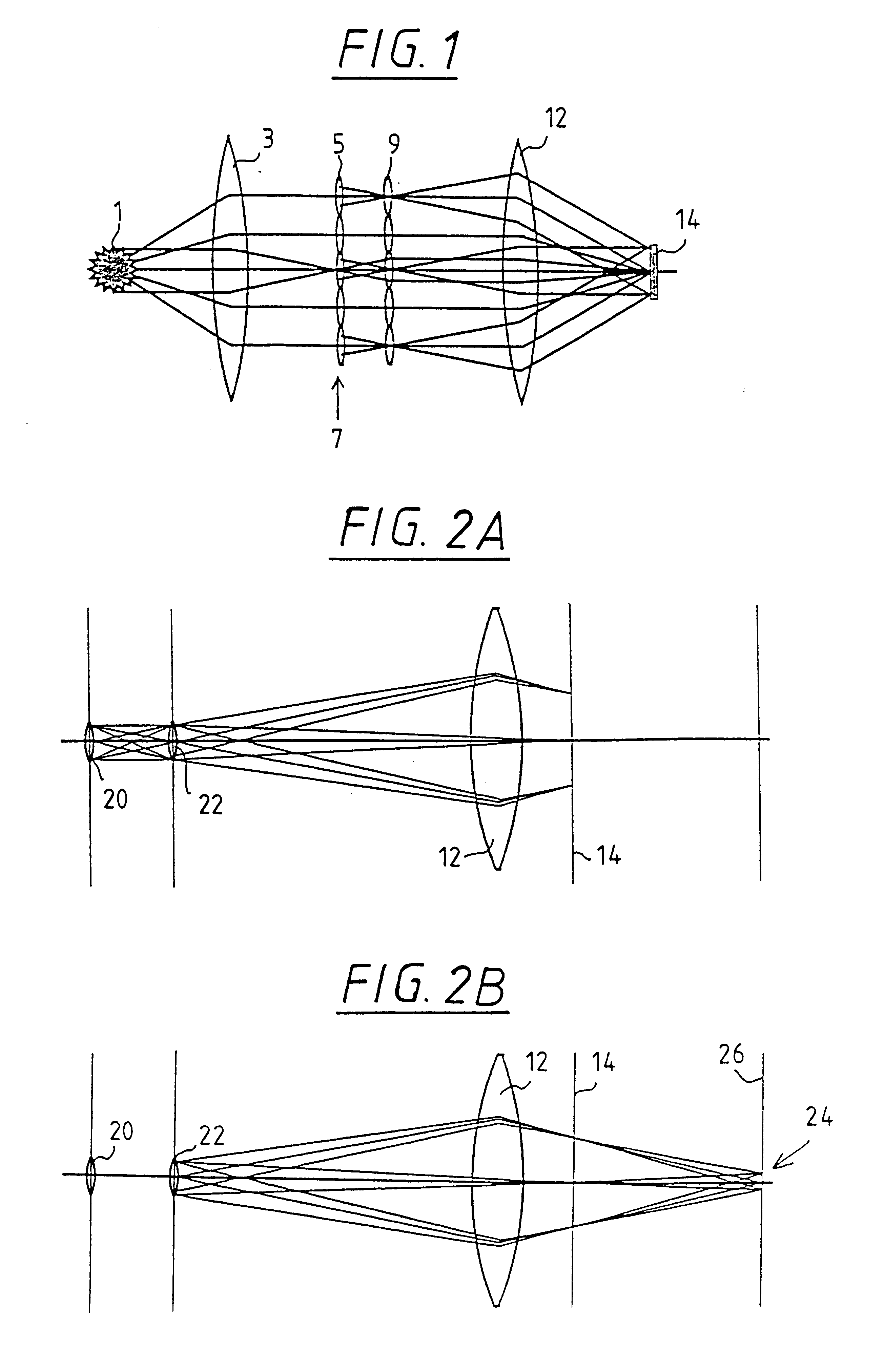
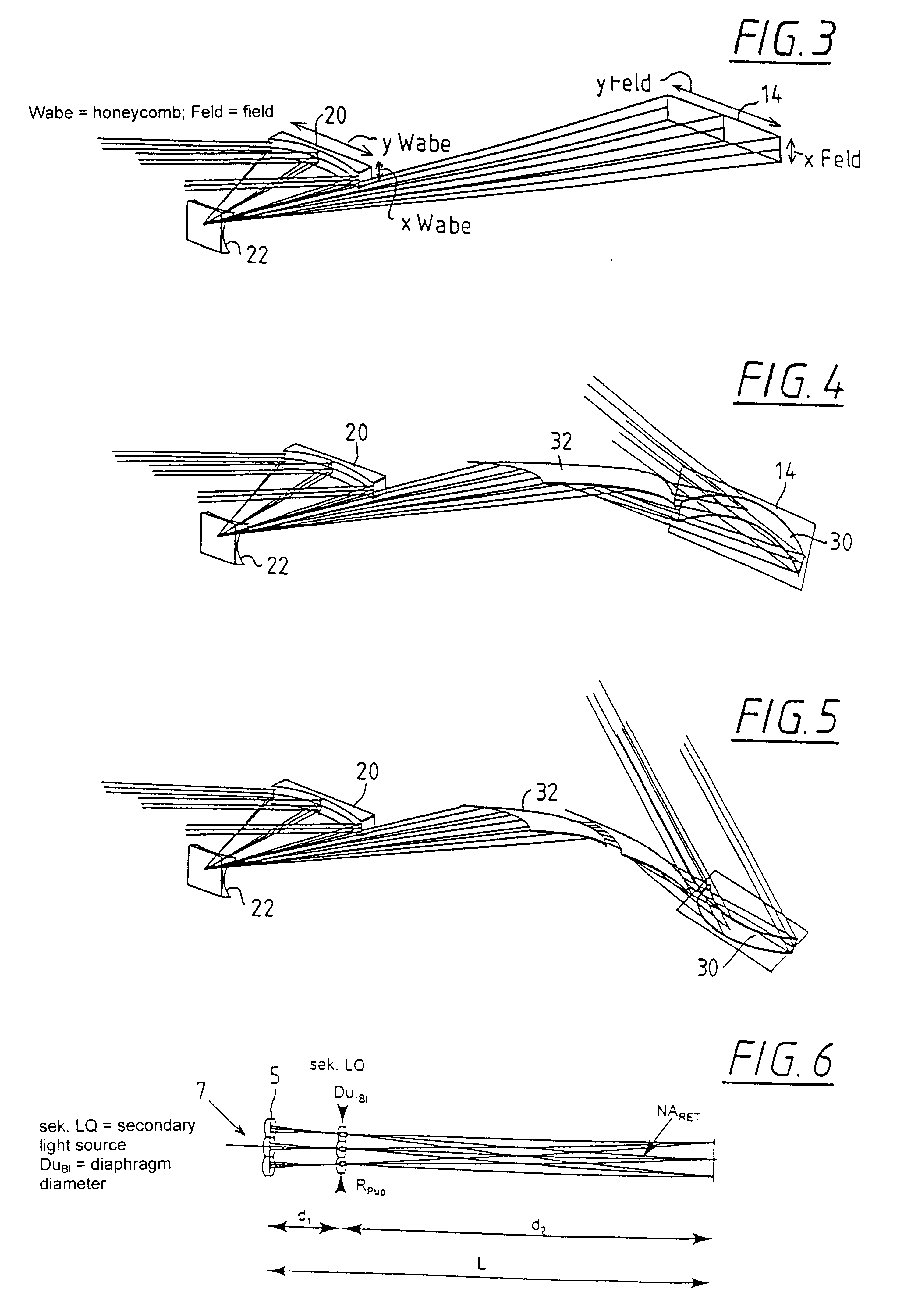
Illumination system particularly for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6198793B1Etendu can be effectively increasedAvoid blurringsNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionCamera lensGrating
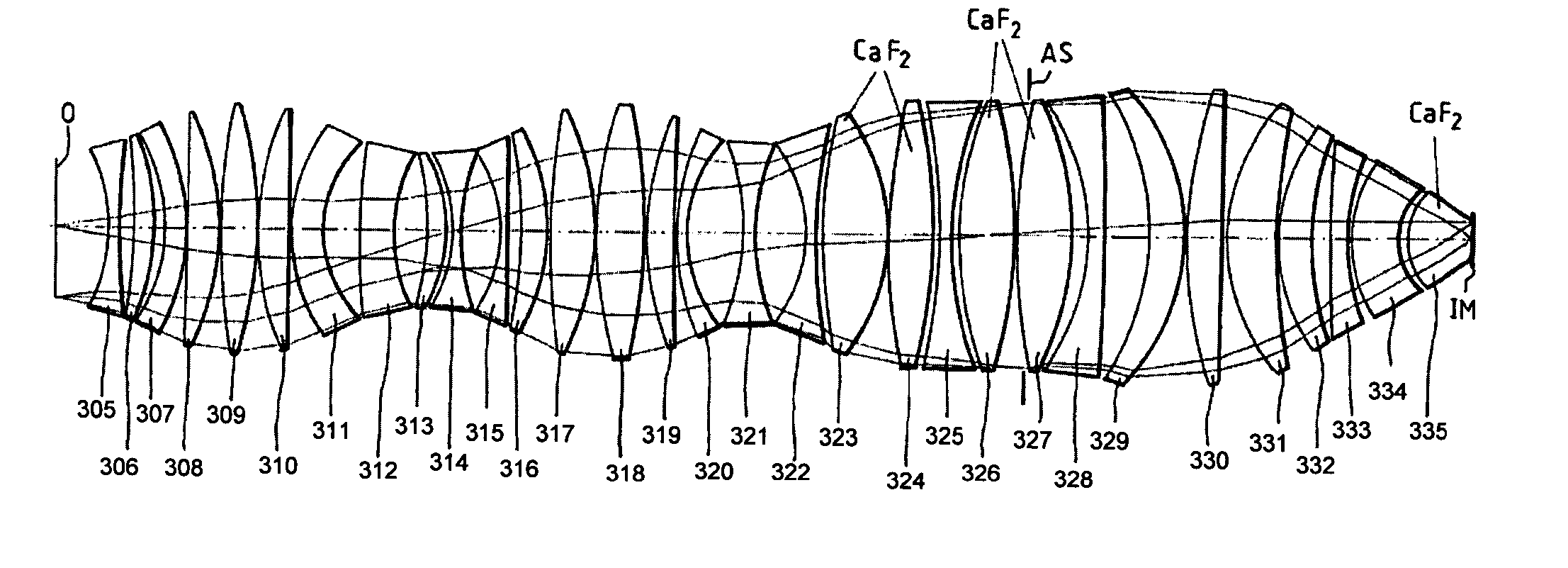
The invention concerns an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, particularly for EUV lithography, with at least one light source, which has an illumination A in a predetermined surface; at least one device for producing secondary light sources; at least one mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements; one or more optical elements, which are arranged between the mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements and the reticle plane, whereby the optical elements image the secondary light sources in the exit pupil of the illumination system.The illumination system is characterized by the fact that the raster elements of the one or more mirror or lenses are shaped and arranged in such a way that the images of the raster elements cover by means of the optical elements the major portion of the reticle plane and that the exit pupil defined by aperture and filling degree is illuminated.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
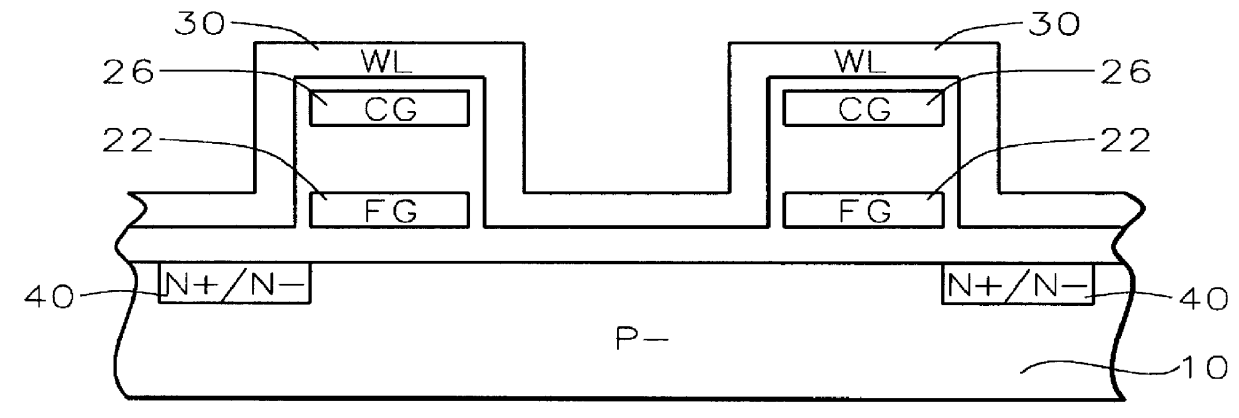
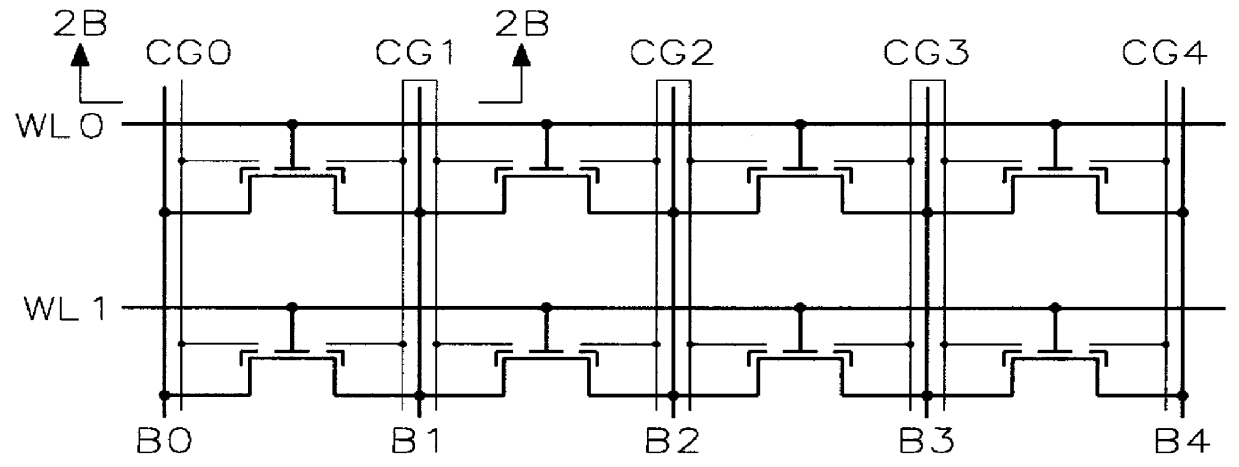
Process for making and programming and operating a dual-bit multi-level ballistic flash memory
An fast program, ultra-high density, dual-bit, multi-level flash memory process, which can be applied to a ballistic step split gate side wall transistor, or to a ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor, which enables program operation by low voltage requirement on the floating gate during program is described. Two side wall floating gates are paired with a single word line select gate, and word lines are arranged to be perpendicular both the bit lines and control gate lines. Two adjacent memory cells on the same word line do not require an isolation region. Also, the isolation region between adjacent memory cells sharing the same bitline is defined by the minimum lithography feature, utilizing a self align fill technique. Adjacent memory cells on the same word line share bitline diffusion as well as a third poly control gate. Control gates allow program and read access to the individual floating gate. In addition to the dual-bit nature of the cell, density can be even further improved by multi-level storage. In one embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic step split gate side wall transistor. In a second embodiment, the dual multi-level structure is applied to the ballistic planar split gate side wall transistor. Both types of ballistic transistors provide fast, low voltage programming. The control gates are used to override or suppress the various threshold voltages on associated floating gates, in order to program to and read from individual floating gates. The targets for this non-volatile memory array are to provide the capabilities of high speed, low voltage programming (band width) and high density storage.
Owner:HALO LSI DESIGN & DEVICE TECH
SLM Lithography: Printing to below K1=.30 without previous OPC processing
ActiveUS20070209029A1Quick calculationReduce usagePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistPaper document
Previously disclosed methods and devices are extended in this application by two-dimensional analysis of optical proximity interactions and by fashioning a computationally efficient kernel for rapid calculation of adjustments to be made. The computations can be made in realtime, whereby the use of OPC assist features can be reduced, with substantial savings in file size and computational requirements. Further aspects of the invention are disclosed in the descriptions, figures, claims and documents incorporated by reference.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
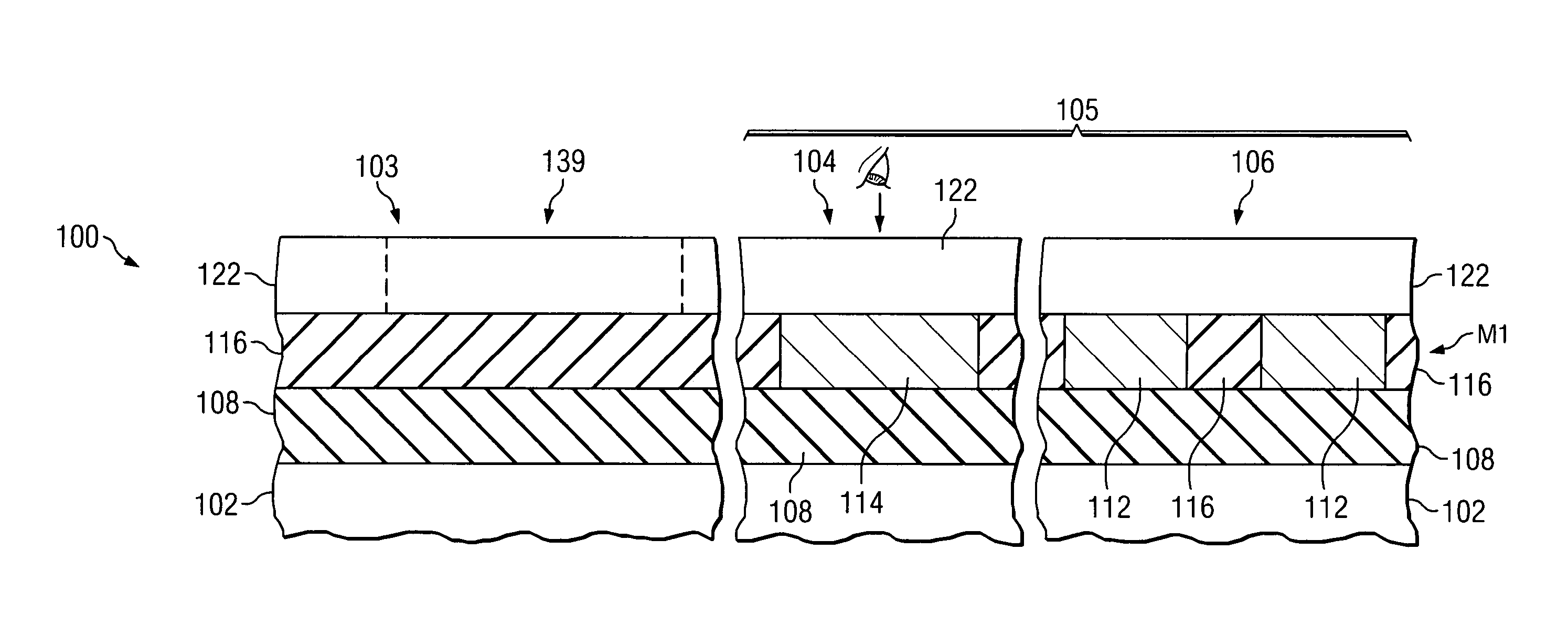
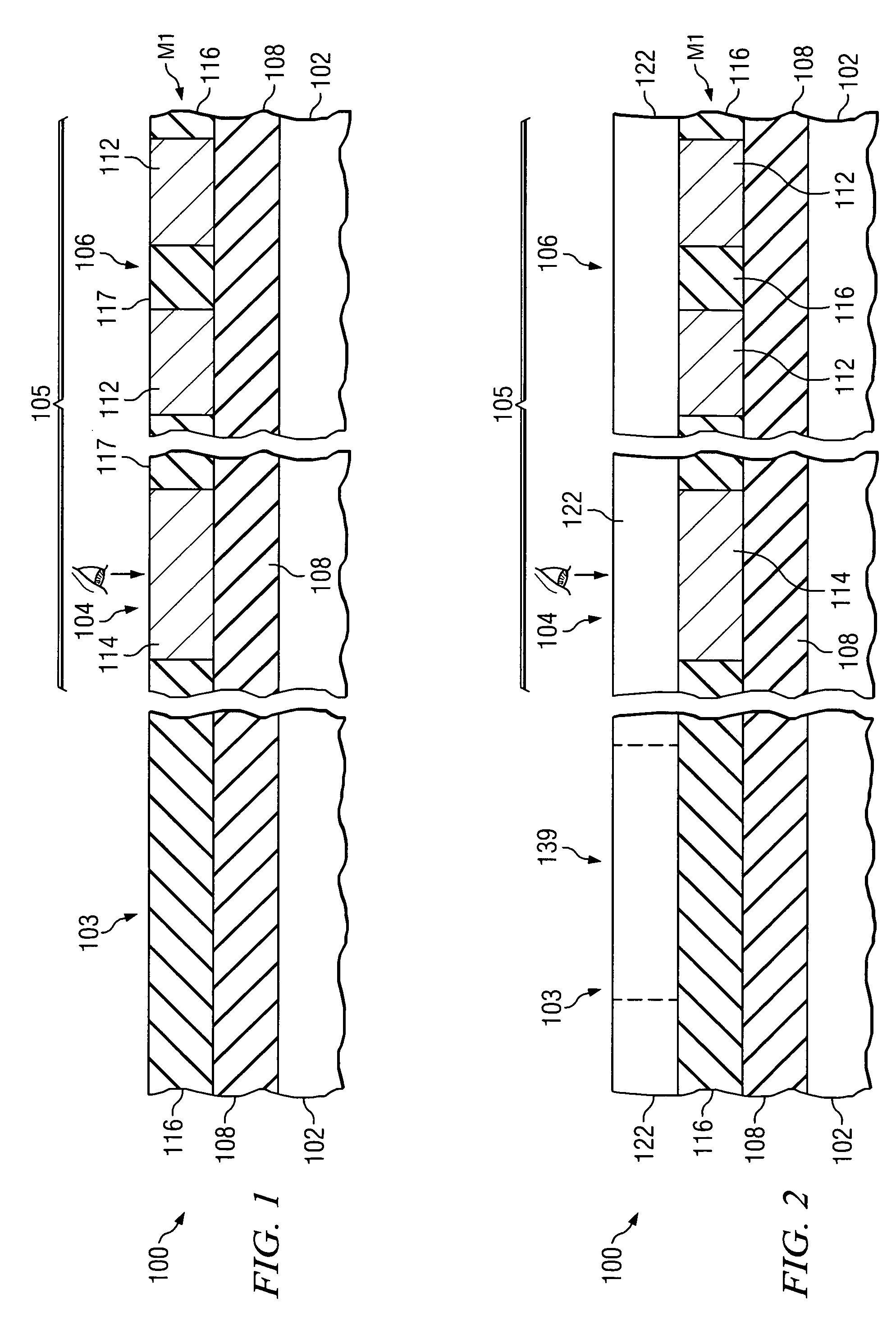
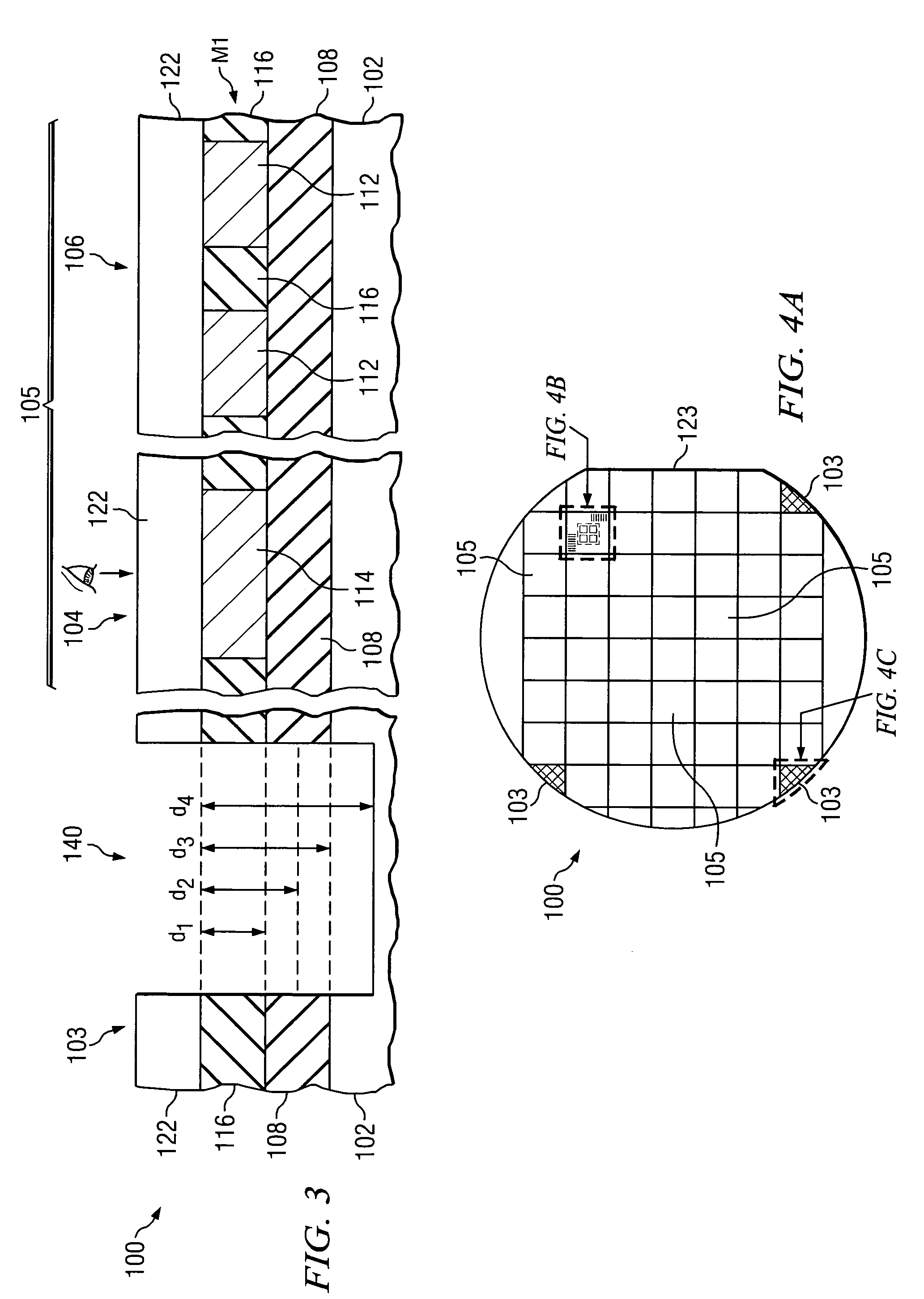
Deep alignment marks on edge chips for subsequent alignment of opaque layers
InactiveUS20060024923A1Easy alignmentIncrease patternSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithographic artistLithography process
A method of forming alignment marks on edge chips in a kerf region of a semiconductor workpiece. The alignment marks are formed in at least one material layer of the semiconductor device. The alignment marks are formed using a separate lithography mask, and may extend into lower layers, including the workpiece, of the semiconductor device. An opaque material layer is deposited, and depressions are formed in the opaque layer over the deep alignment mark trenches. The depressions in the opaque material layer are used to align a lithography process to open the opaque material layer over alignment marks in an underlying metallization layer. The alignment marks in the metallization layer are then used to align the lithography process used to pattern the opaque material layer.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Dual damascene fabrication with low k materials
The invention provides methods and apparatuses for fabricating a dual damascene structure on a substrate. First, trench lithography and trench patterning are performed on the surface of a substrate to etch a low-k dielectric material layer to a desired etch depth to form a trench prior to forming of a via. The trenches can be filled with an organic fill material and a dielectric hard mask layer can be deposited. Then, via lithography and via resist pattering are performed. Thereafter, the dielectric hard mask and the organic fill material are sequentially etched to form vias on the surface of the substrate, where the trenches are protected by the organic fill material from being etched. A bottom etch stop layer on the bottom of the vias is then etched and the organic fill material is striped. As a result, the invention provides good patterned profiles of the via and trench openings of a dual damascene structure.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
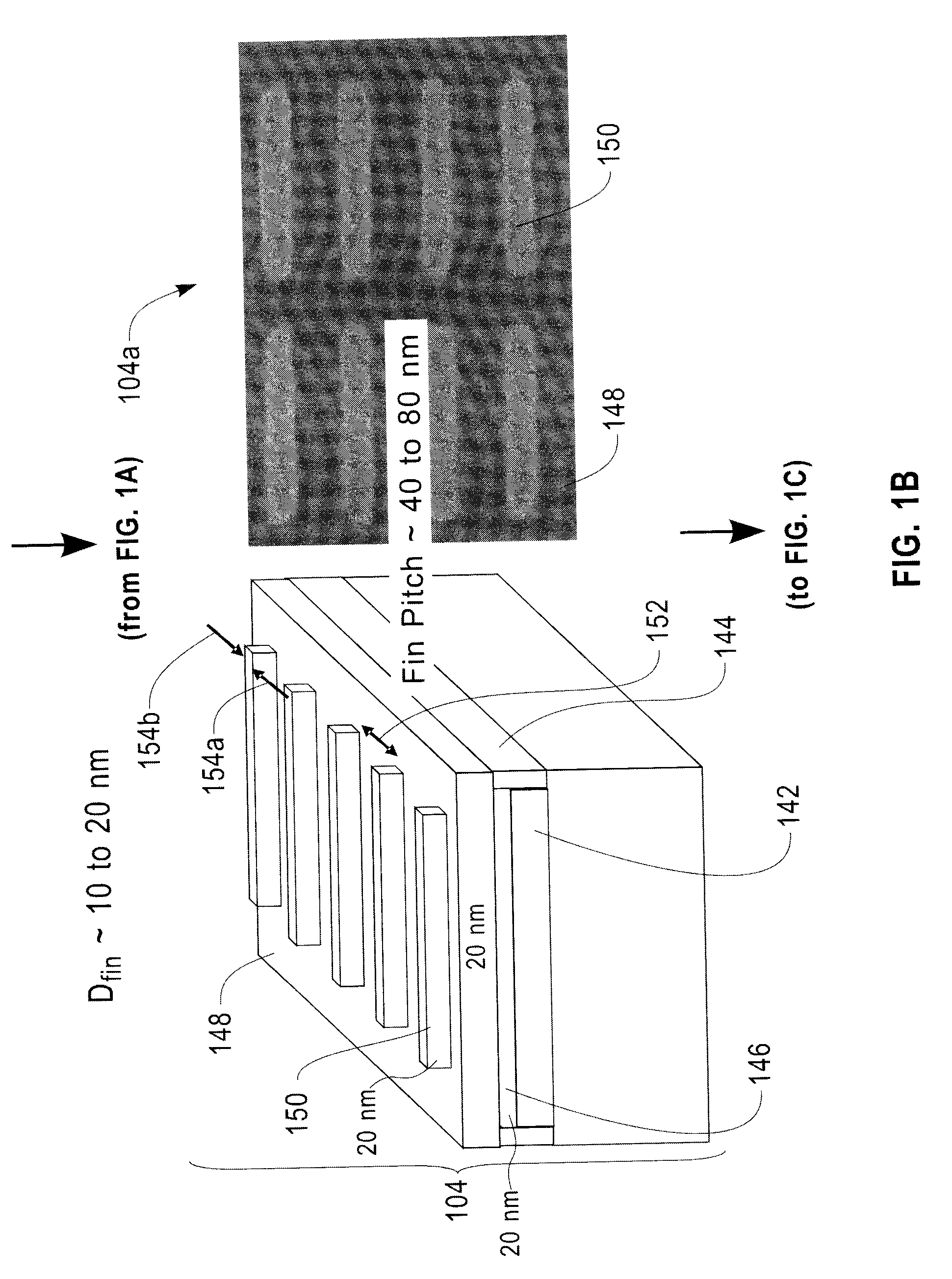
Fin Field Effect Transistor Devices with Self-Aligned Source and Drain Regions
Improved fin field effect transistor (FinFET) devices and methods for the fabrication thereof are provided. In one aspect, a method for fabricating a field effect transistor device comprises the following steps. A substrate is provided having a silicon layer thereon. A fin lithography hardmask is patterned on the silicon layer. A dummy gate structure is placed over a central portion of the fin lithography hardmask. A filler layer is deposited around the dummy gate structure. The dummy gate structure is removed to reveal a trench in the filler layer, centered over the central portion of the fin lithography hardmask, that distinguishes a fin region of the device from source and drain regions of the device. The fin lithography hardmask in the fin region is used to etch a plurality of fins in the silicon layer. The trench is filled with a gate material to form a gate stack over the fins. The filler layer is removed to reveal the source and drain regions of the device, wherein the source and drain regions are intact and self-aligned with the gate stack.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
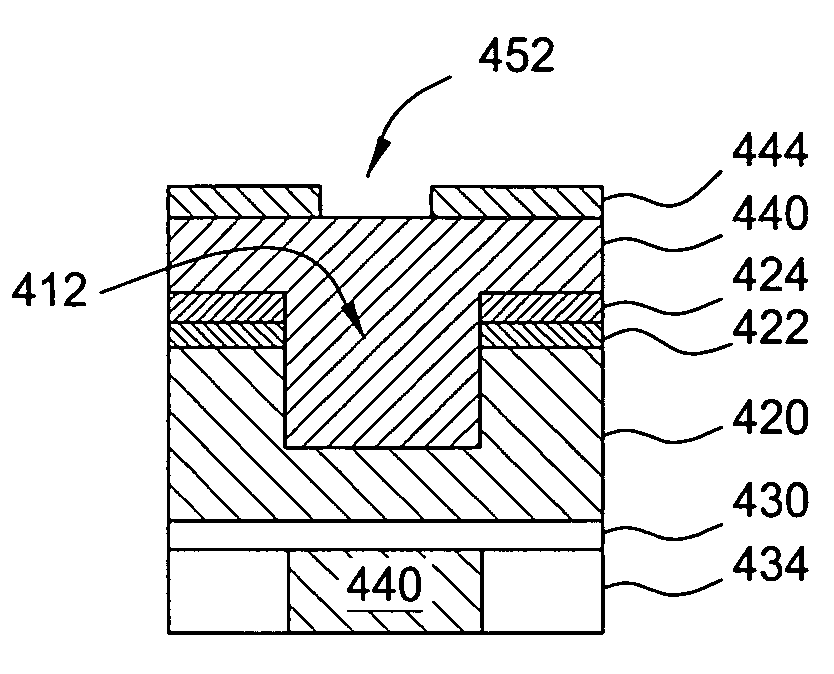
Alignment of MTJ stack to conductive lines in the absence of topography
InactiveUS7223612B2Convenient lengthIncrease patternSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithography processLithographic artist
A scheme for aligning opaque material layers of a semiconductor device. Alignment marks are formed in a via level of the semiconductor device. The alignment marks are formed using a separate lithography mask, and may have about the same length as vias formed in the via layer. The alignment marks comprise trenches that are not filled with material and are not exposed to a CMP process. An opaque material layer is deposited, and depressions are formed in the opaque material layer over the alignment mark trenches. The depressions in the opaque material layer are used to align a lithography process to open the opaque material layer over alignment marks in an underlying metallization layer. The alignment marks in the metallization layer are then used to align the lithography process used to pattern the opaque material layer.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
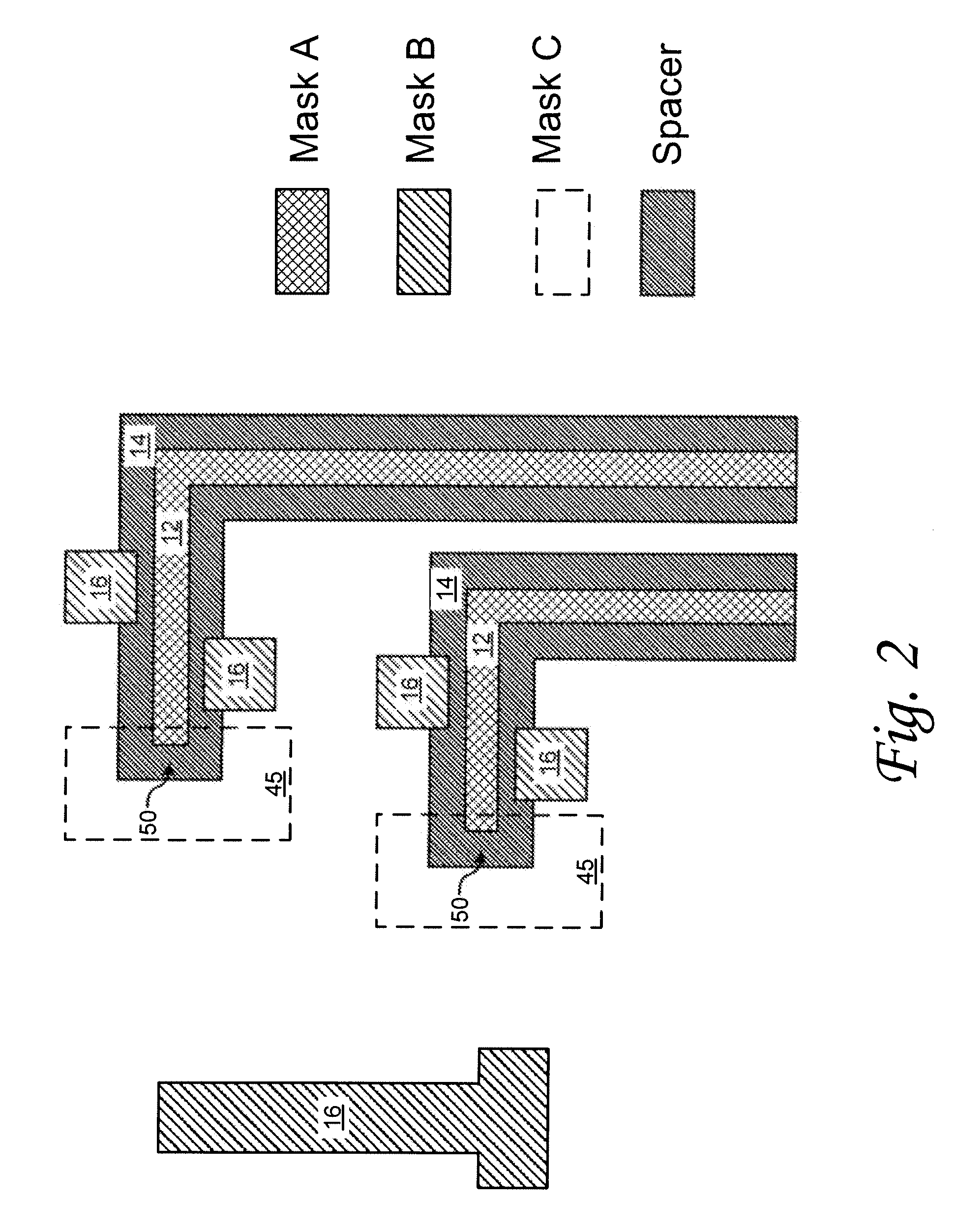
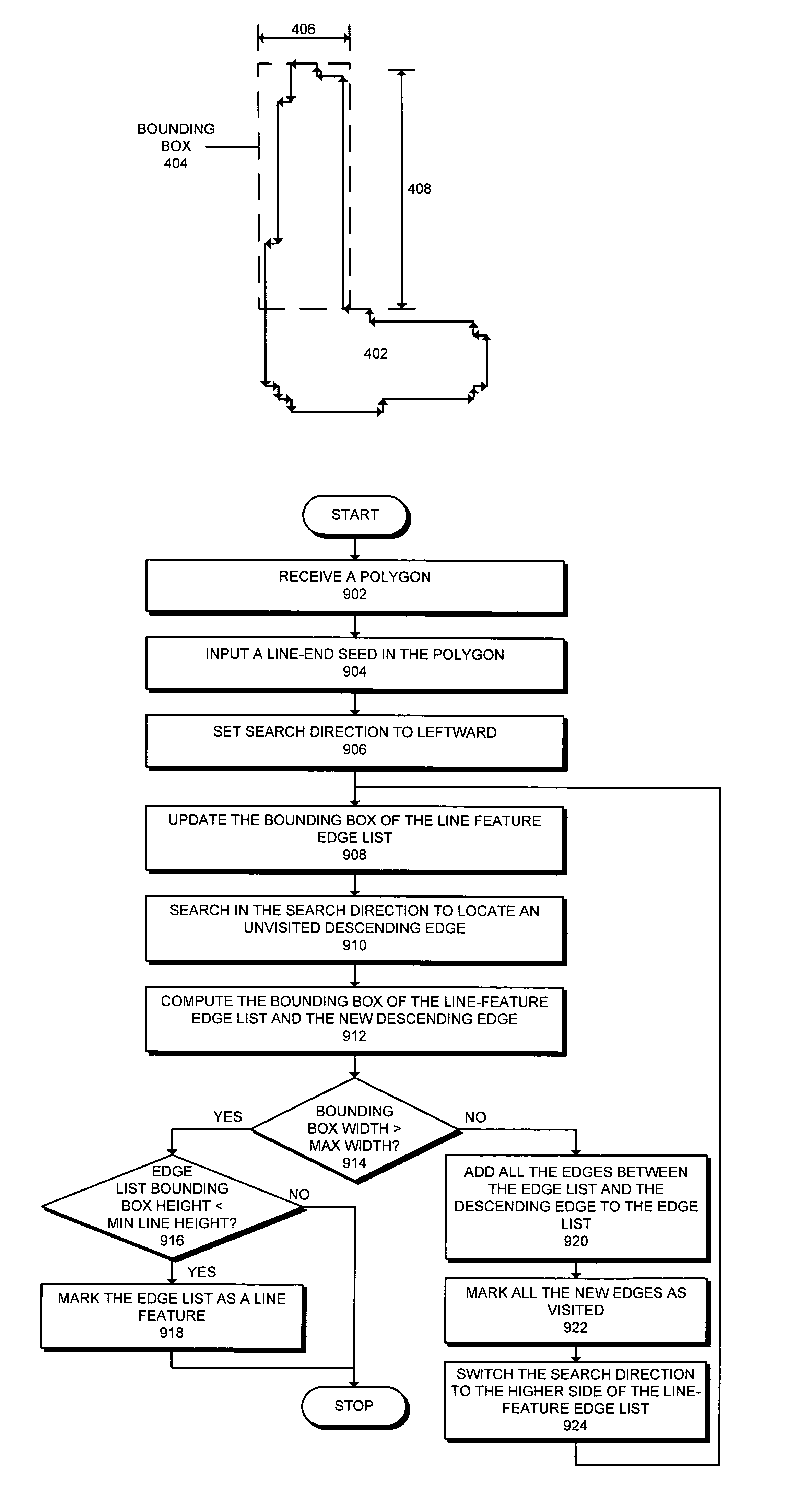
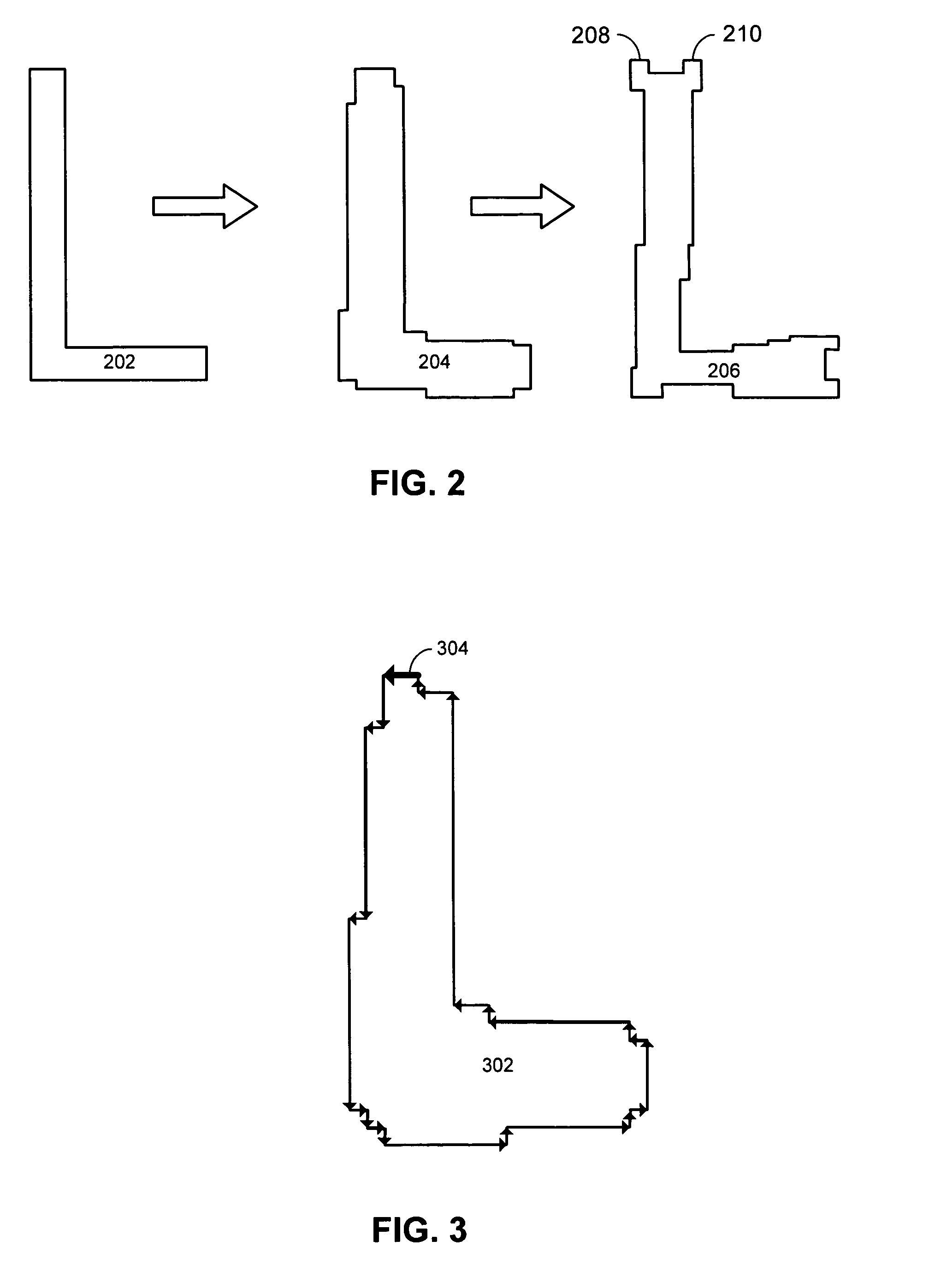
Method and apparatus for identifying line-end features for lithography verification
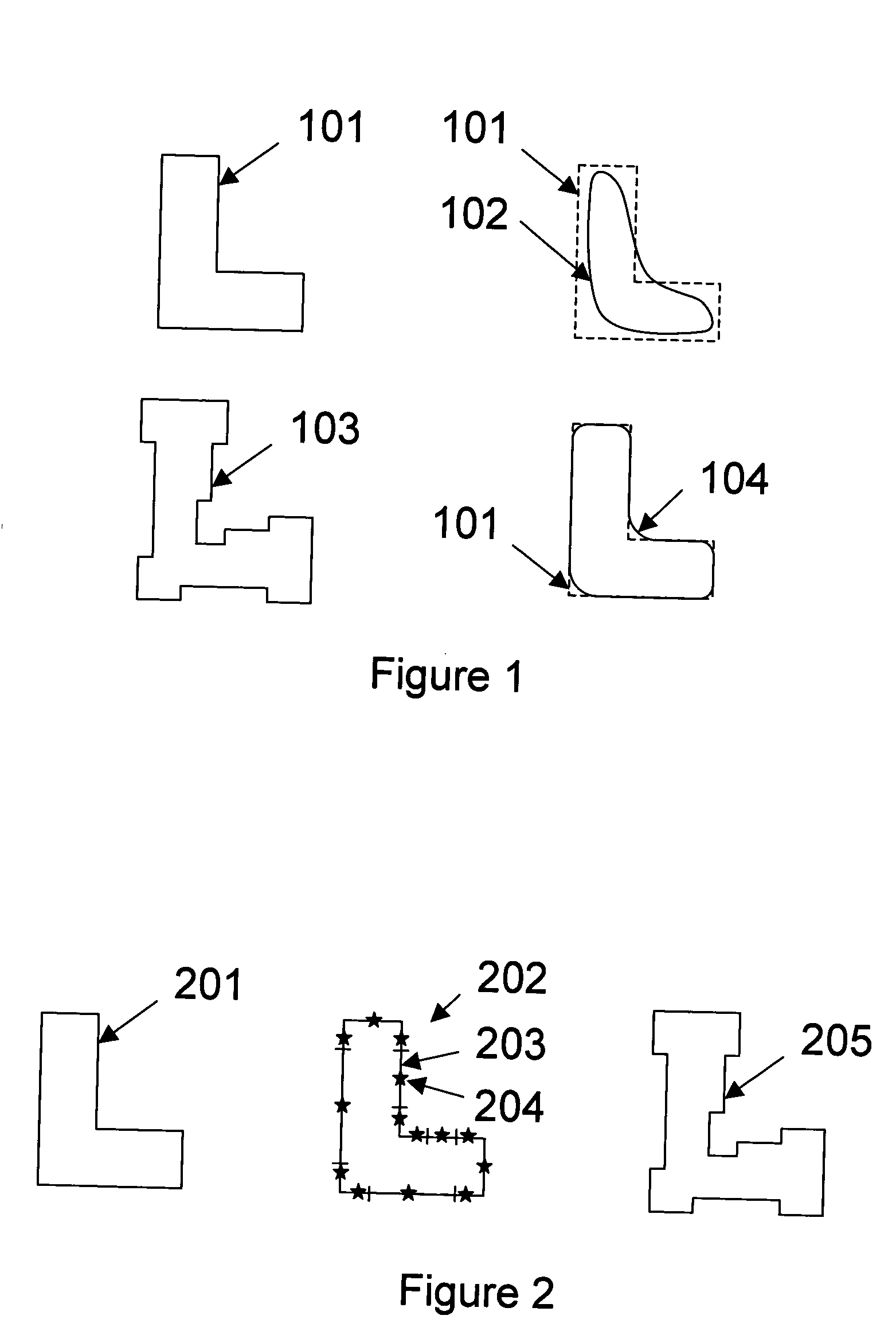
ActiveUS7194712B2Facilitates identifying line-end featureComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsLithographic artistEngineering
One embodiment of the invention provides a system that facilitates identifying line-end features in a layout for an integrated circuit. The system operates by first receiving the layout for the integrated circuit. Next, the system selects a polygon from the layout and marks a line-end seed on the polygon. The system then determines if the line-end seed is associated with a line feature, and if so, the system marks the line-end feature inside the line feature.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com