Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3742 results about "Pulsed laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
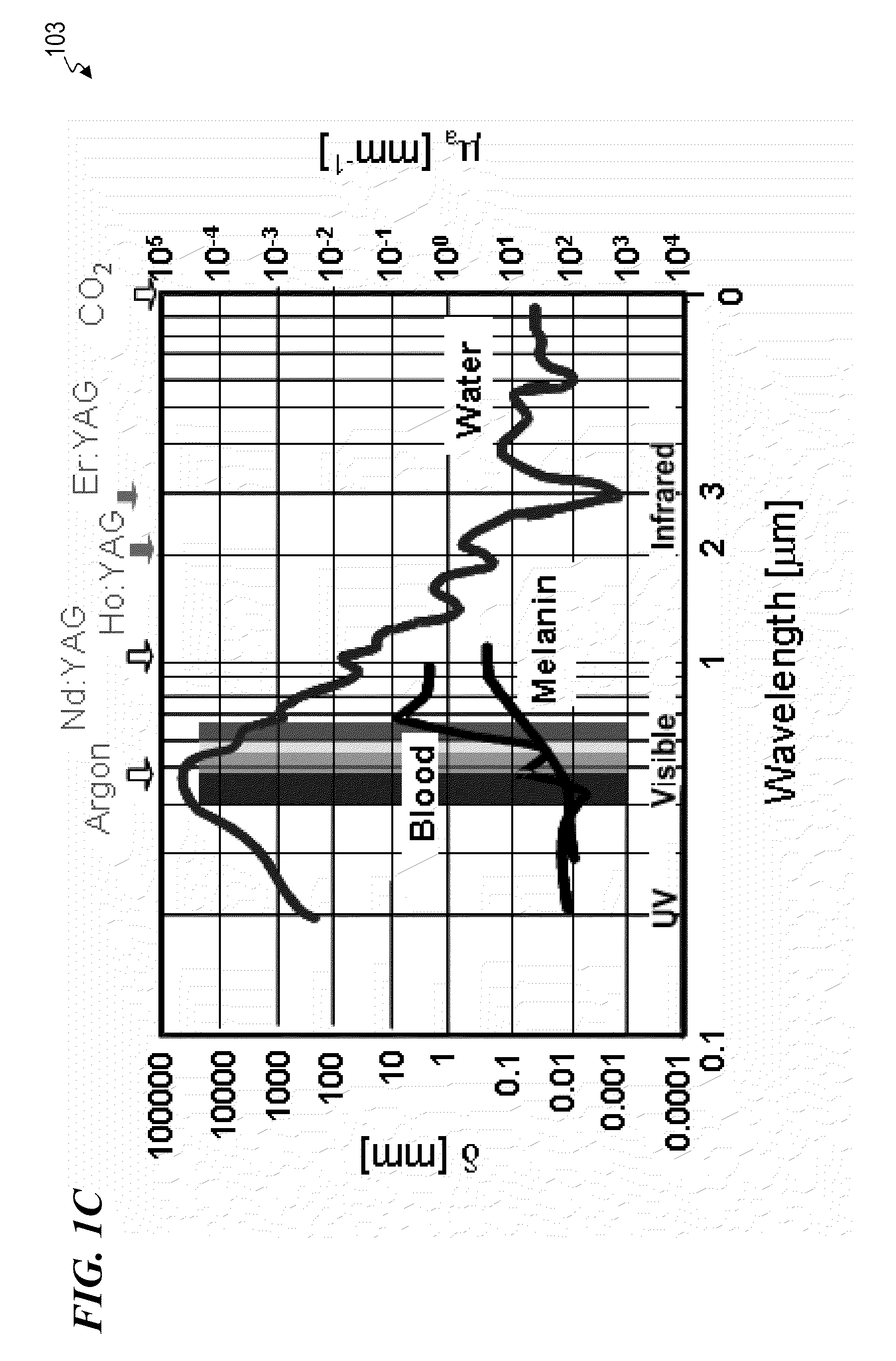
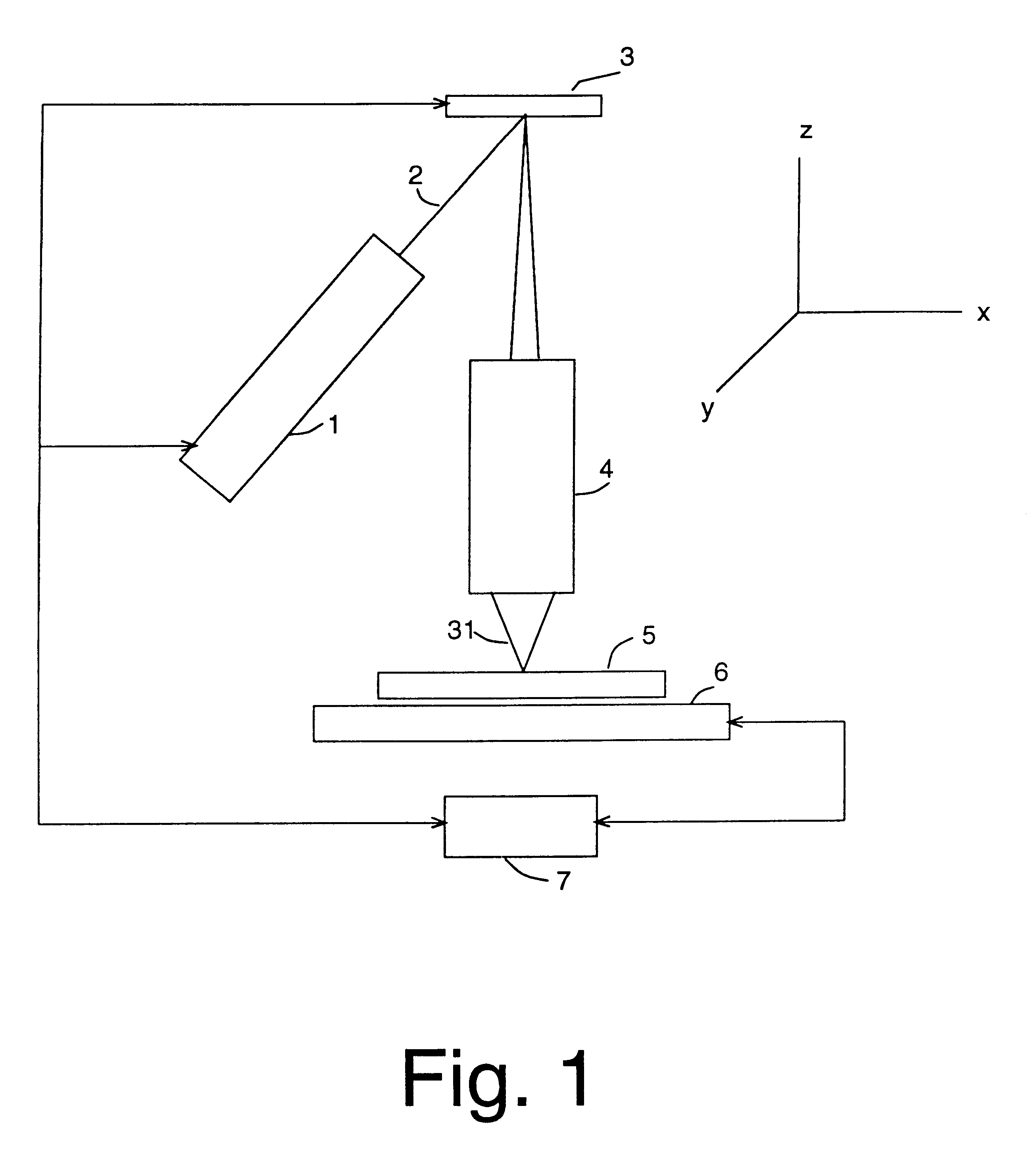
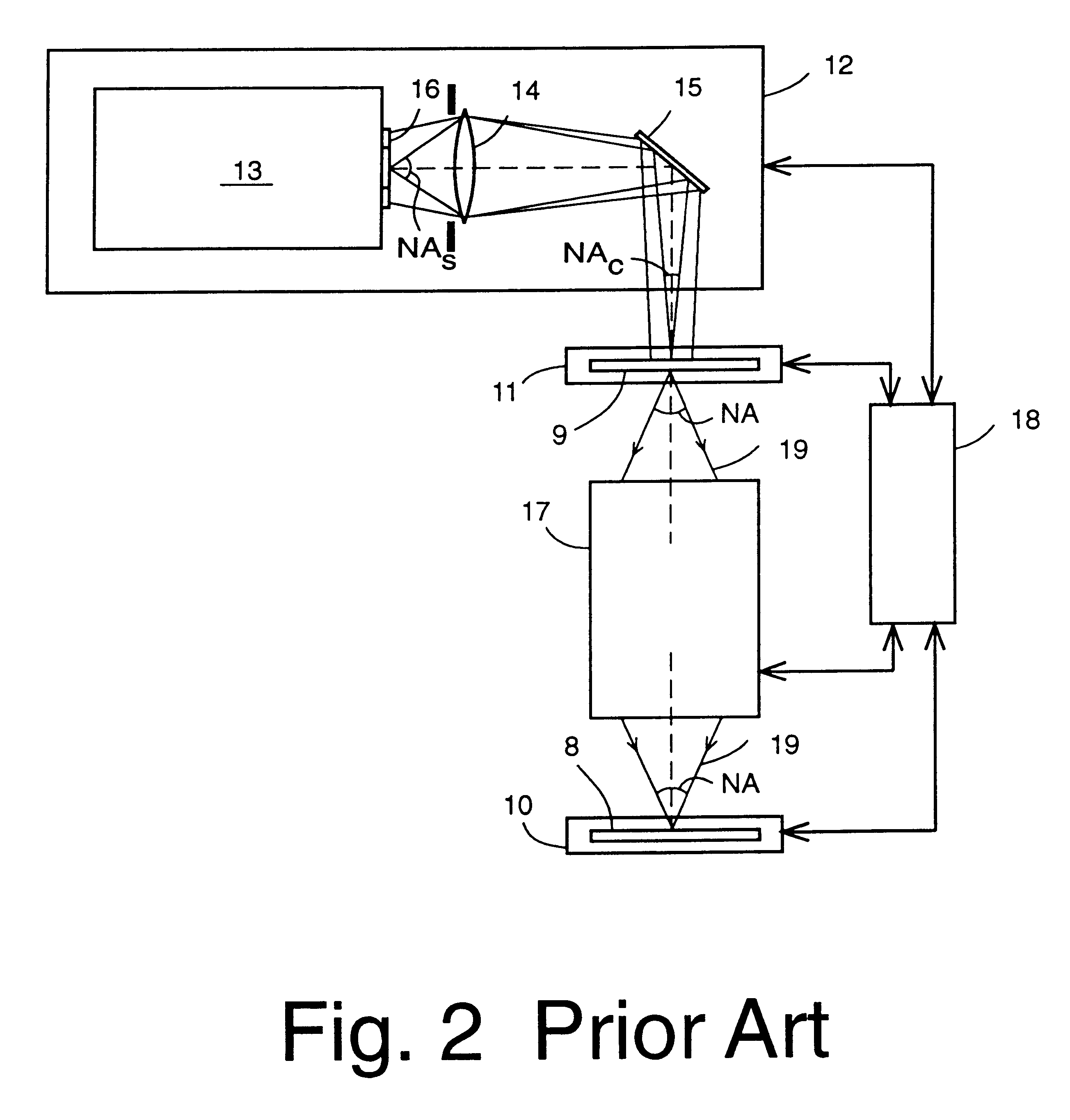
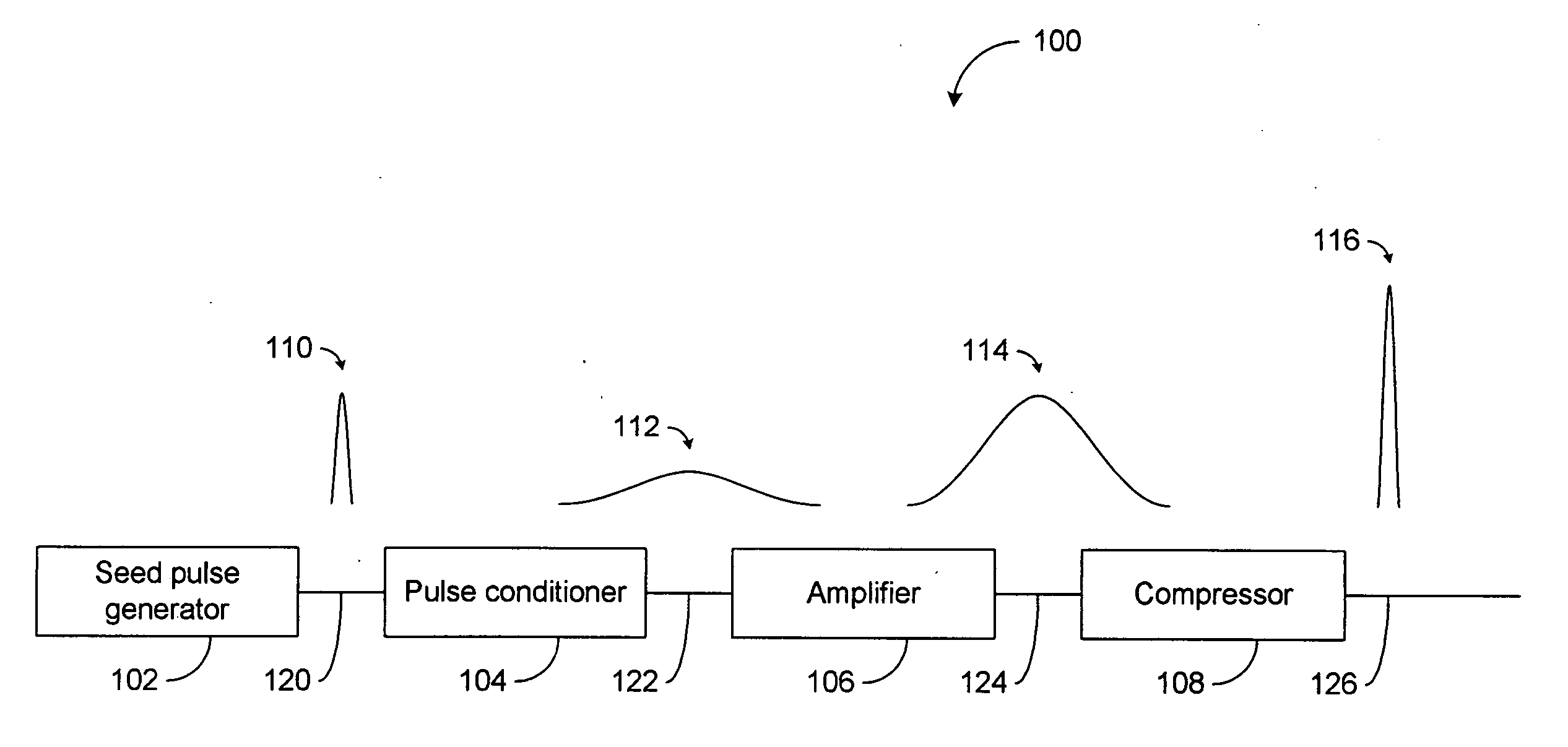
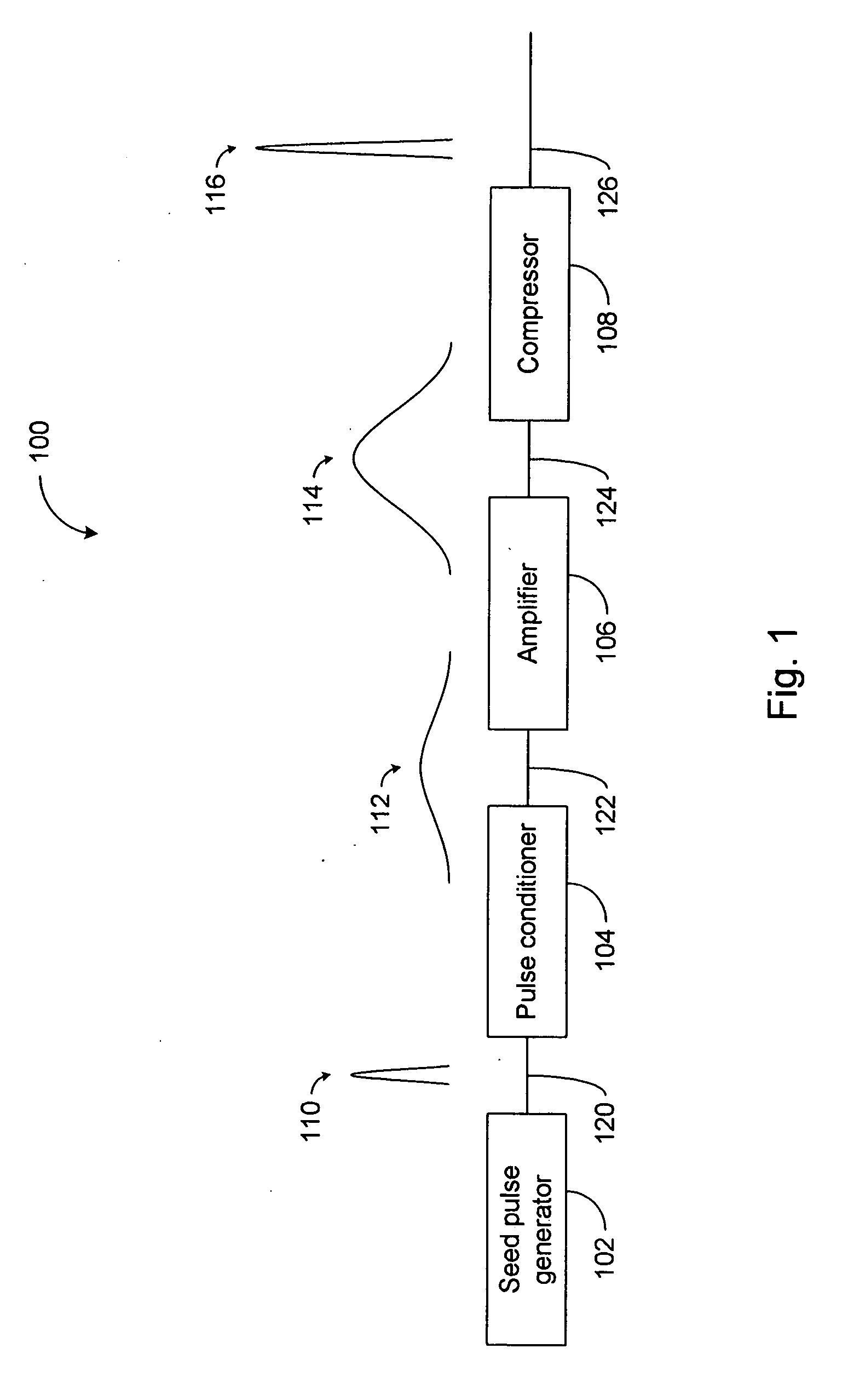
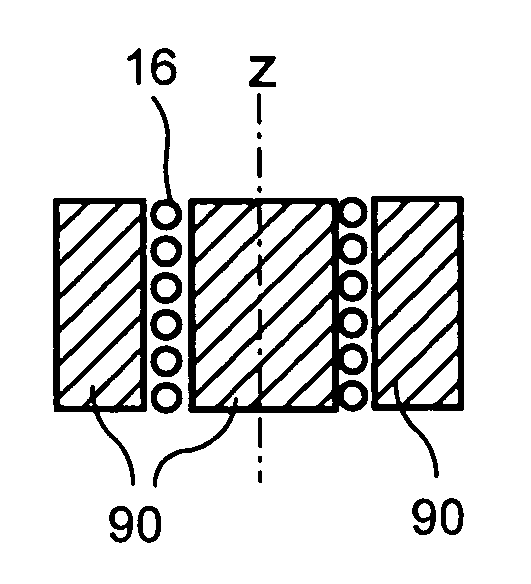
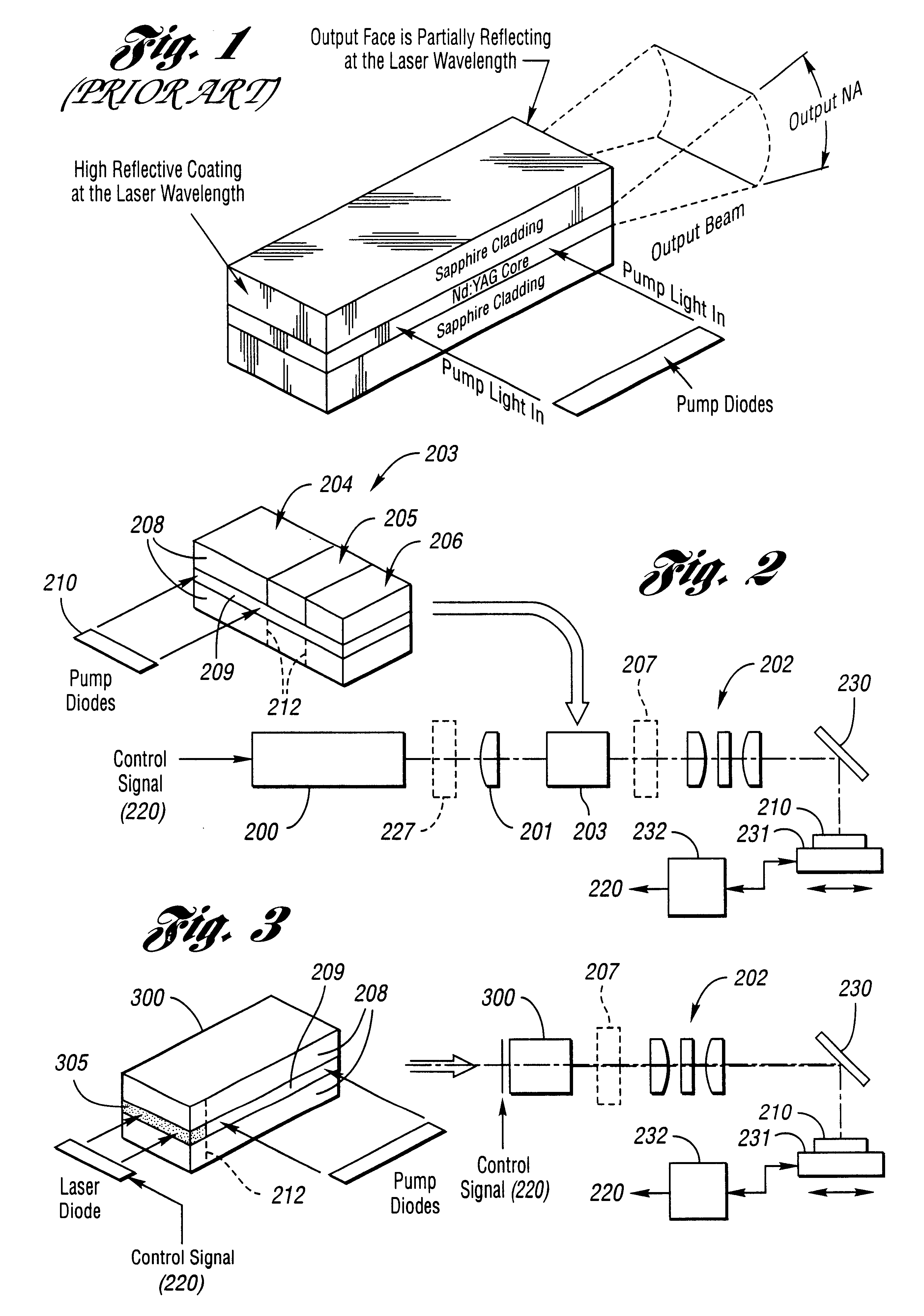
Pulsed operation of lasers refers to any laser not classified as continuous wave, so that the optical power appears in pulses of some duration at some repetition rate. This encompasses a wide range of technologies addressing a number of different motivations. Some lasers are pulsed simply because they cannot be run in continuous mode.
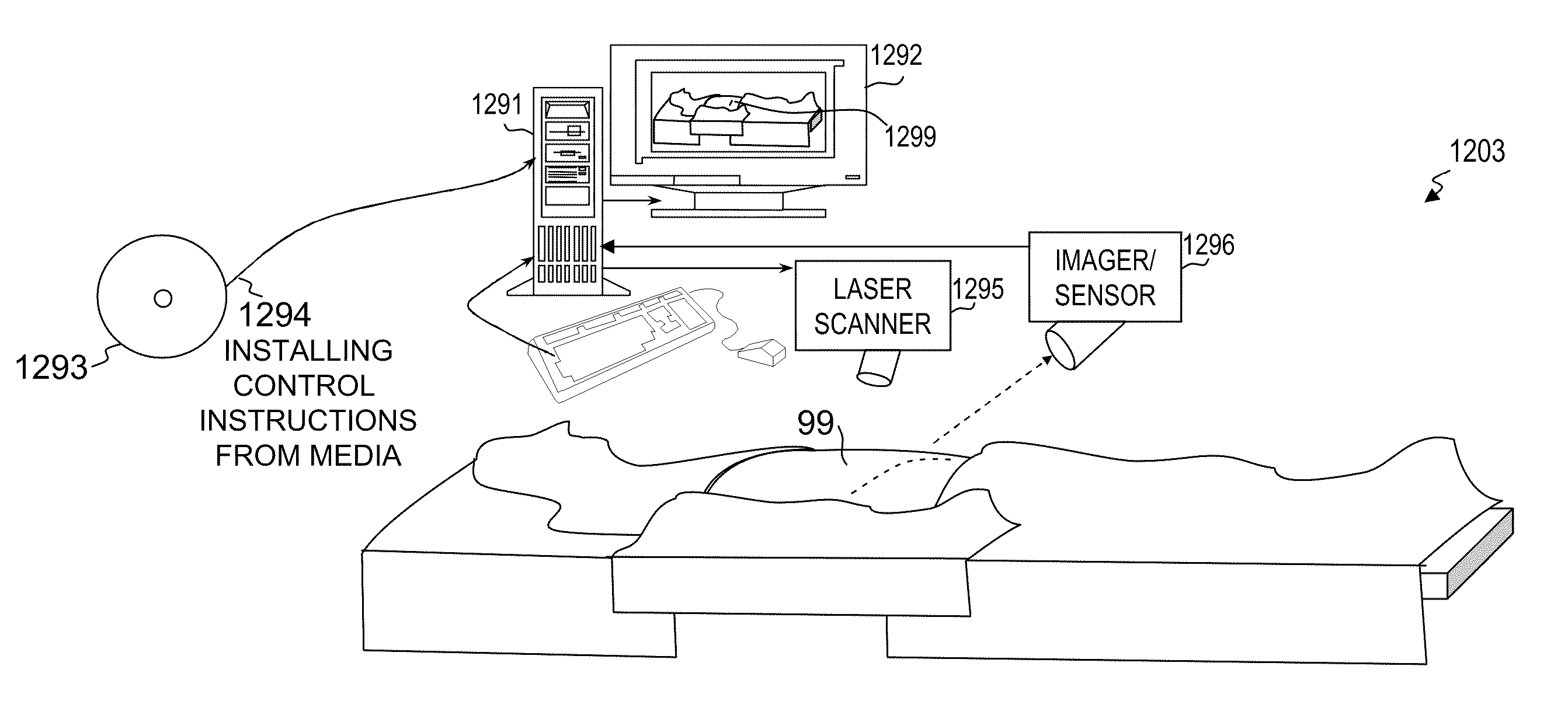
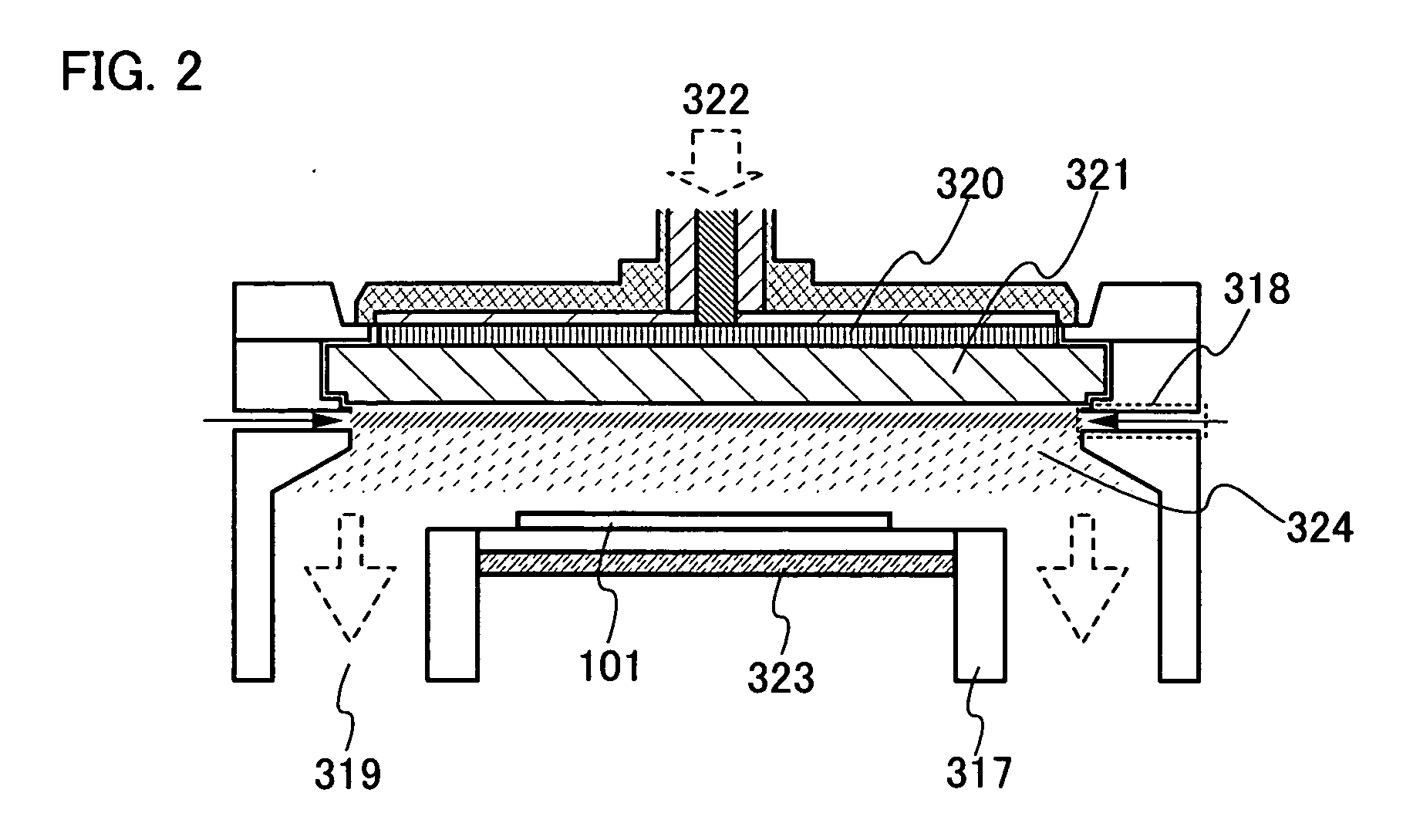
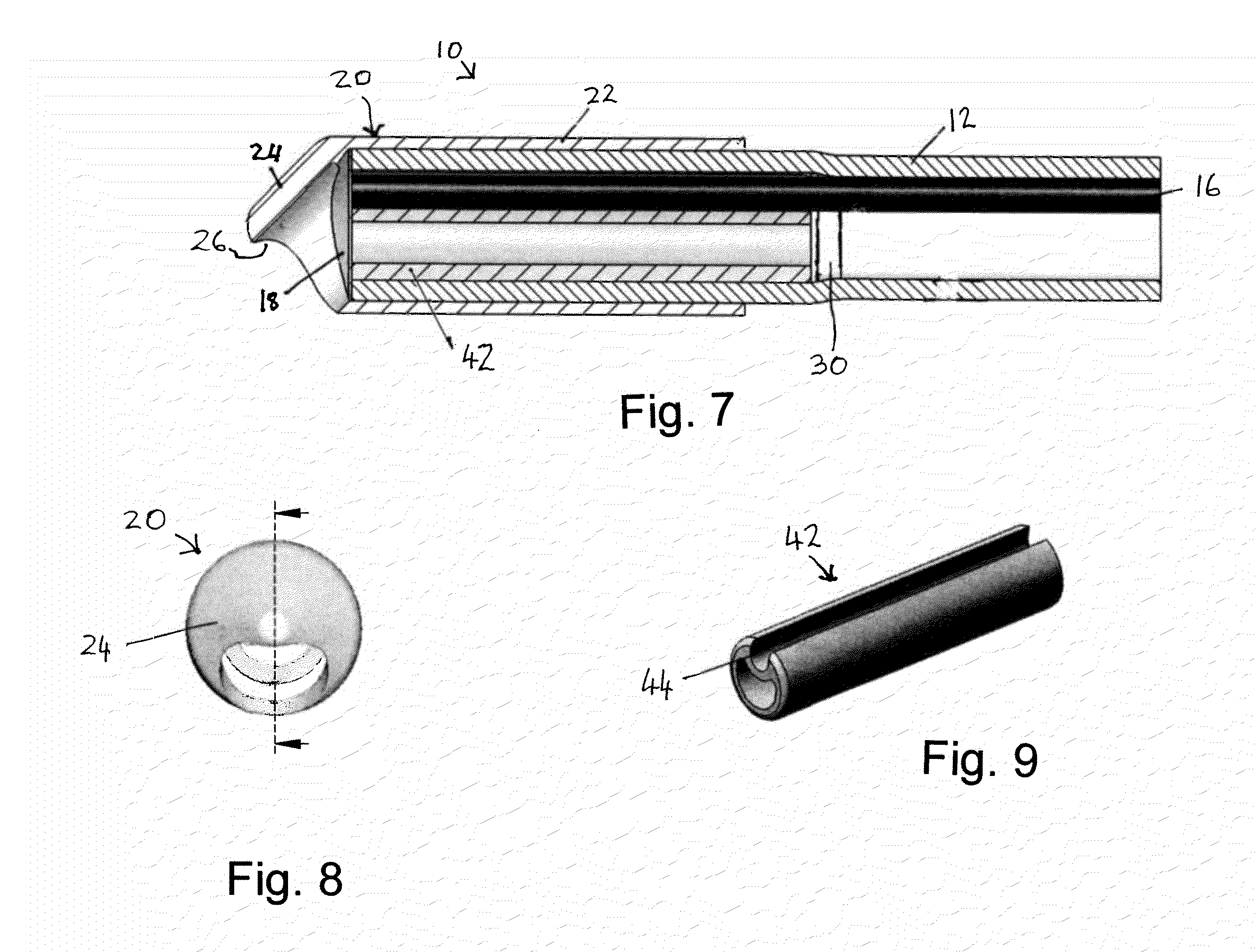
System and method for conditioning animal tissue using laser light
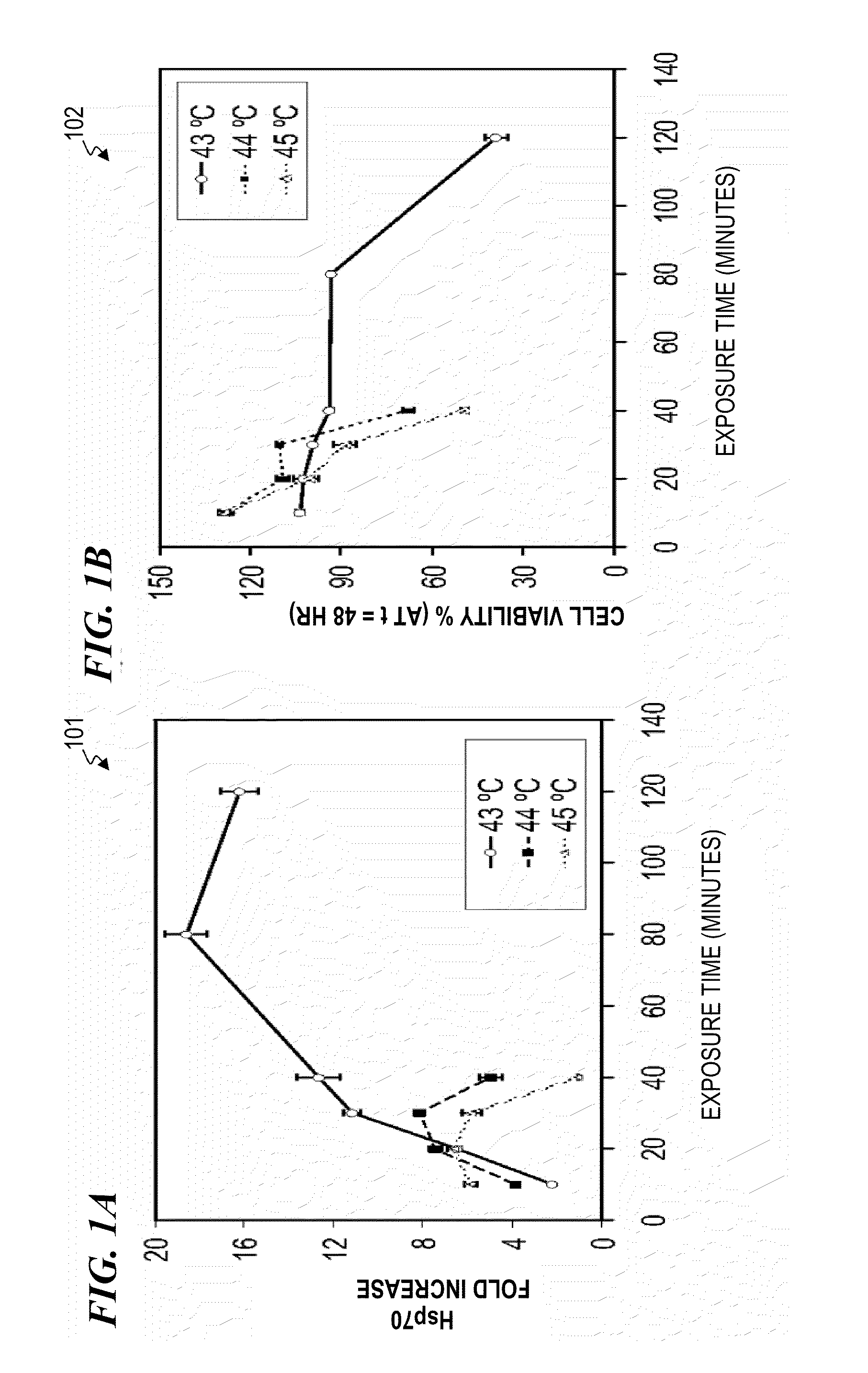
InactiveUS20100049180A1Promote wound repairEnhances surgical wound healingSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyLaser lightHsp70 expression
Systems and methods for prophylactic measures aimed at improving wound repair. In some embodiments, laser-mediated preconditioning would enhance surgical wound healing that was correlated with hsp70 expression. Using a pulsed laser (λ=1850 nm, Tp=2 ms, 50 Hz, H=7.64 mJ / cm2) the skin of transgenic mice that contain an hsp70 promoter-driven luciferase were preconditioned 12 hours before surgical incisions were made. Laser protocols were optimized using temperature, blood flow, and hsp70-mediated bioluminescence measurements as benchmarks. Bioluminescent imaging studies in vivo indicated that an optimized laser protocol increased hsp70 expression by 15-fold. Under these conditions, healed areas from incisions that were laser-preconditioned were two times stronger than those from control wounds. Our data suggest that these methods can provide effective and improved tissue-preconditioning protocols and that mild laser-induced heat shock that correlated with an expression of Hsp70 may be a useful therapeutic intervention prior to or after surgery.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP +2
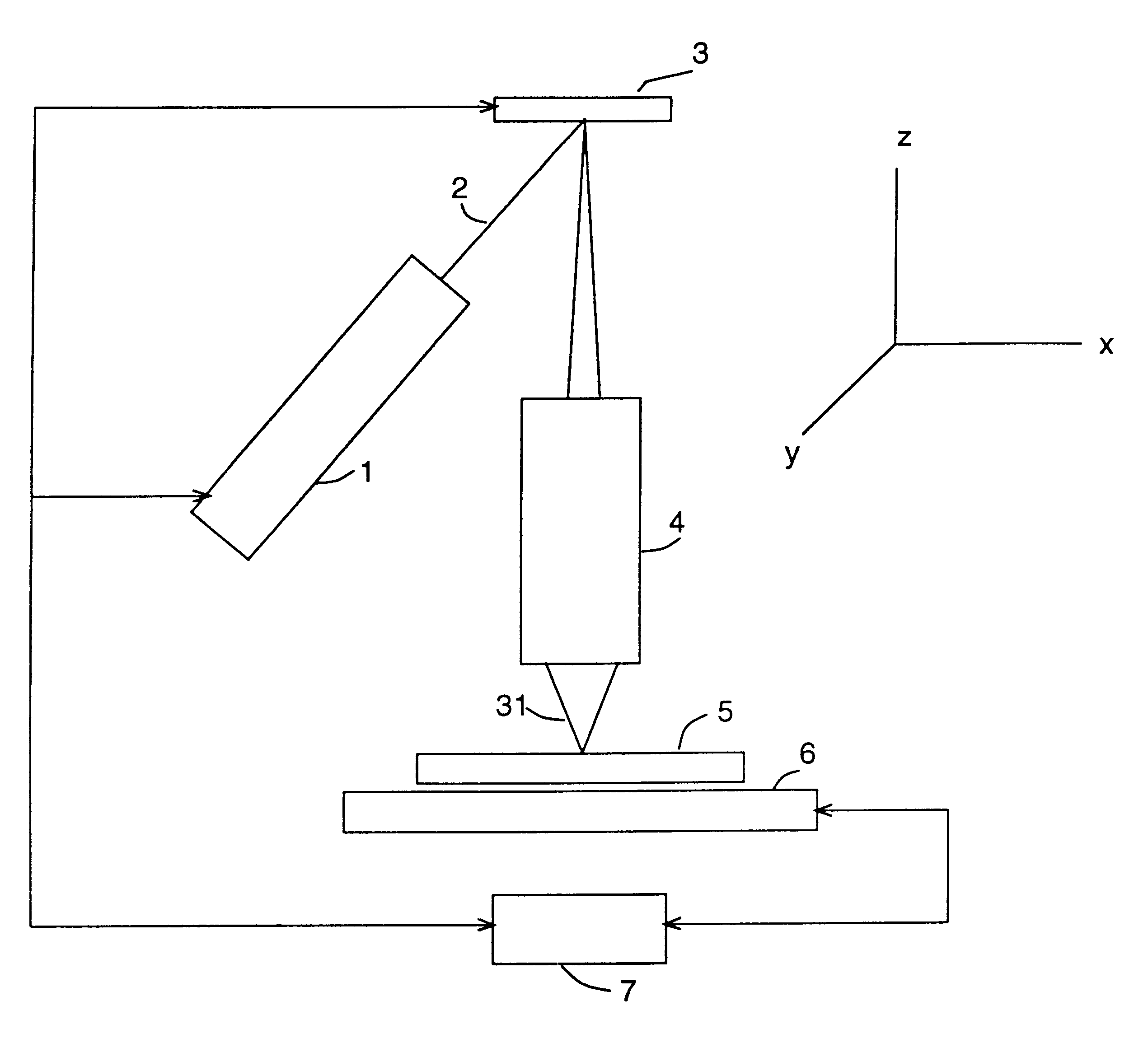
Seamless, maskless lithography system using spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6312134B1Eliminate needImprove processing throughputMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiation DosagesSpatial light modulator
The invention is a seamless projection lithography system that eliminates the need for masks through the use of a programmable Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) with high parallel processing power. Illuminating the SLM with a radiation source (1), which while preferably a pulsed laser may be a shuttered lamp or multiple lasers with alternating synchronization, provides a patterning image of many pixels via a projection system (4) onto a substrate (5). The preferred SLM is a Deformable Micromirror Device (3) for reflective pixel selection using a synchronized pulse laser. An alternative SLM is a Liquid Crystal Light Valve (LCLV) (45) for pass-through pixel selection. Electronic programming enables pixel selection control for error correction of faulty pixel elements. Pixel selection control also provides for negative and positive imaging and for complementary overlapping polygon development for seamless uniform dosage. The invention provides seamless scanning by complementary overlapping scans to equalize radiation dosage, to expose a pattern on a large area substrate (5). The invention is suitable for rapid prototyping, flexible manufacturing, and even mask making.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060275710A1Reduce light intensityImprove routing densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialContinuous wave laser beam
To provide a semiconductor device having a circuit with high operating performance and high reliability, and improve the reliability of the semiconductor device, thereby improving the reliability of an electronic device having the same. The aforementioned object is achieved by combining a step of crystallizing a semiconductor layer by irradiation with continuous wave laser beams or pulsed laser beams with a repetition rate of 10 MHz or more, while scanning in one direction; a step of photolithography with the use of a photomask or a leticle including an auxiliary pattern which is formed of a diffraction grating pattern or a semi-transmissive film having a function of reducing the light intensity; and a step of performing oxidation, nitridation, or surface-modification to the surface of the semiconductor film, an insulating film, or a conductive film, with high-density plasma with a low electron temperature.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Systems and methods for laser texturing of surfaces of a substrate
The present application is directed to a method of modifying a surface of an article and includes irradiating pulsed laser light output at repetition rates in excess of about 1kHz, directing the laser light to a spot on the surface, and producing micro-grooved surfaces having one or more grooves formed thereon, the grooves having groove depths in the range of about 1 μm to about 100 μm.
Owner:SPECTRA PHYSICS
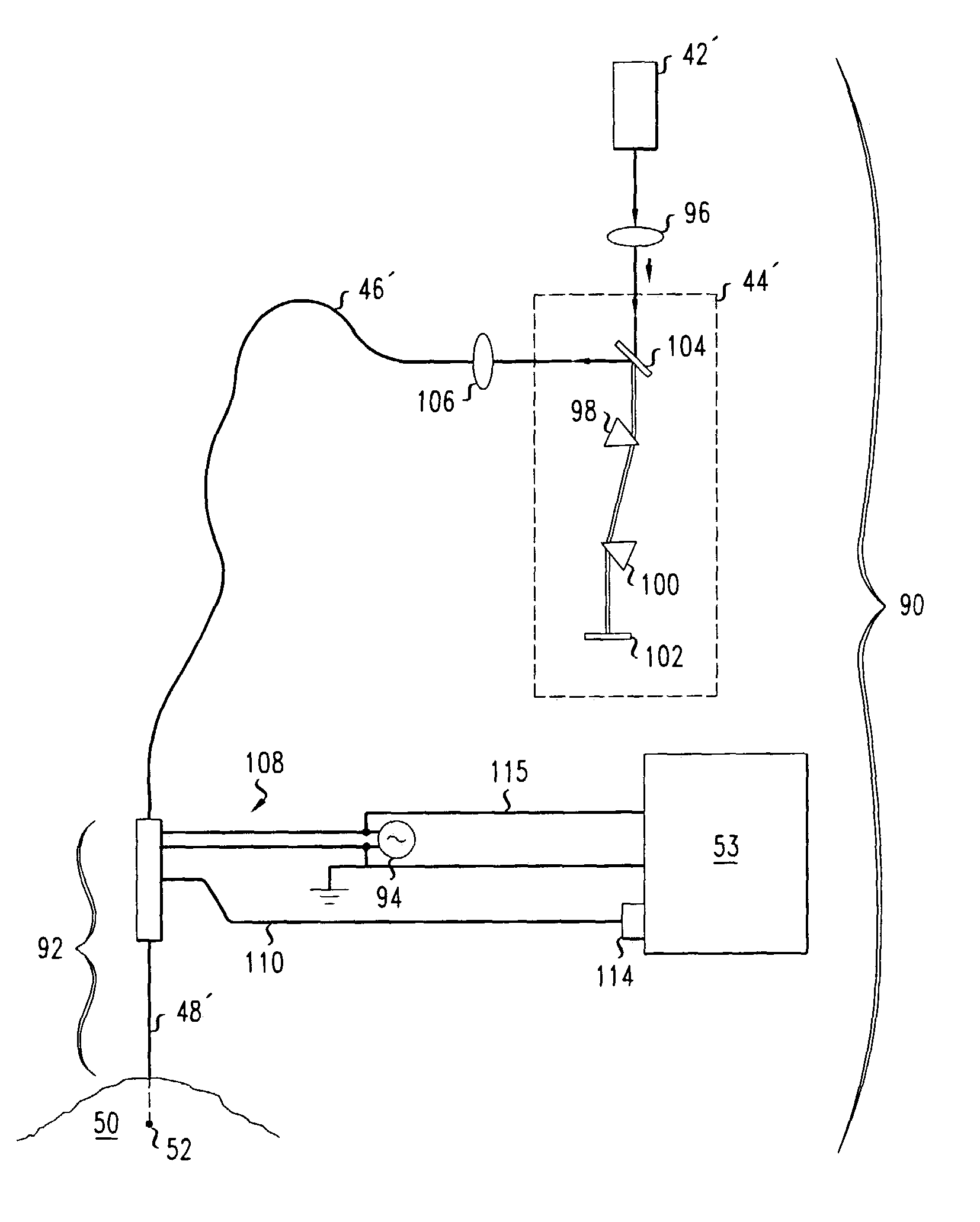
LADAR transmitting and receiving system and method
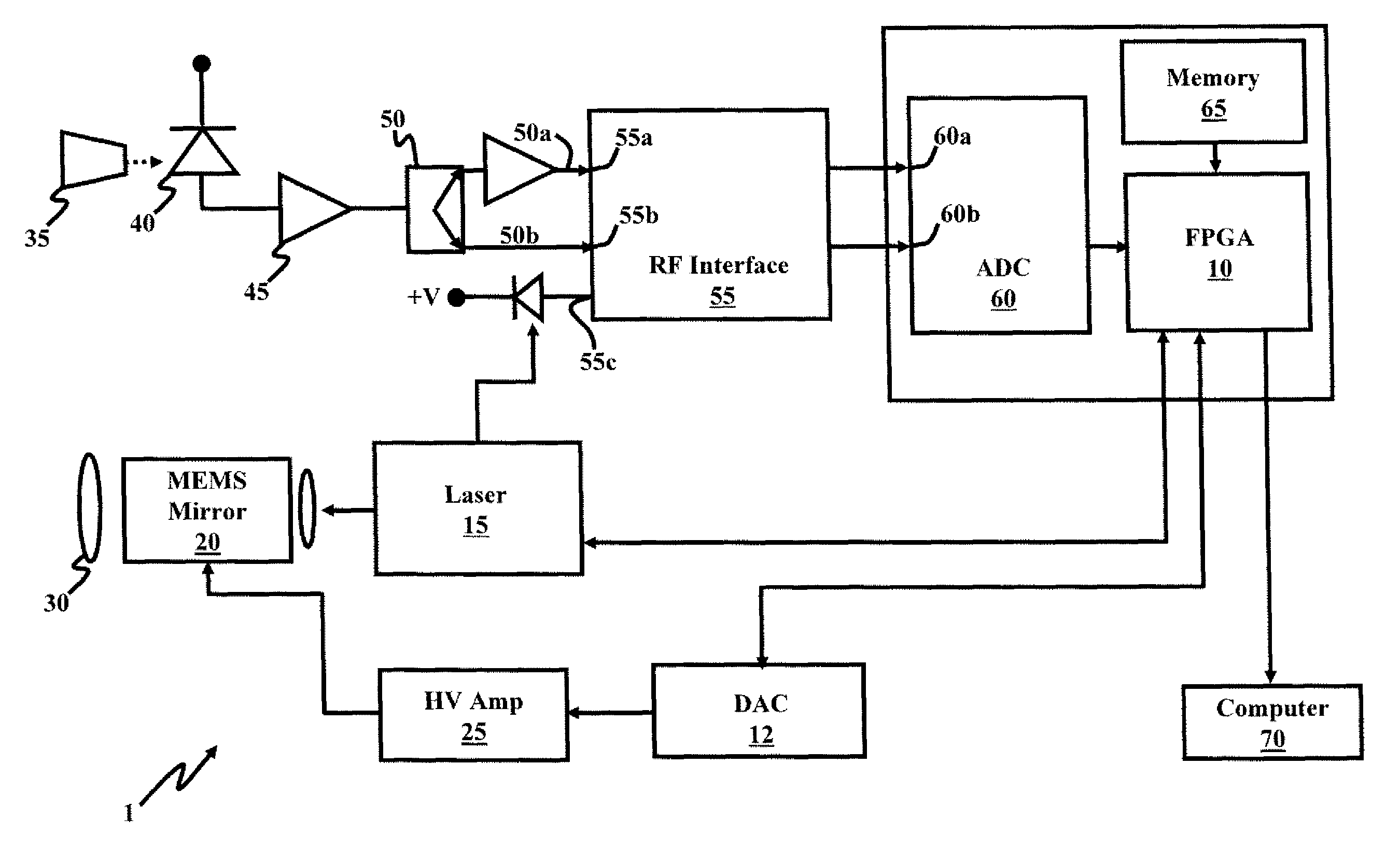
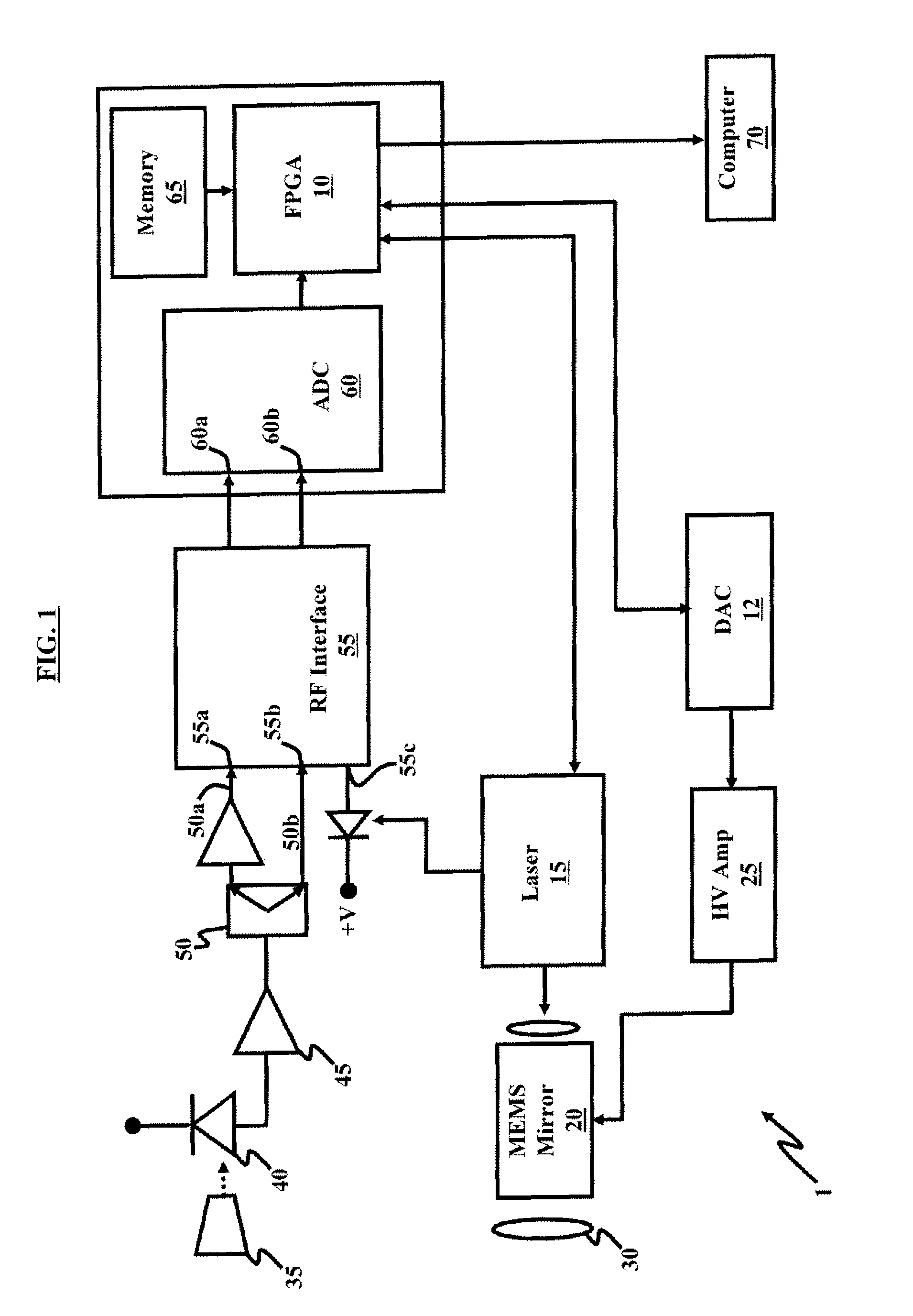
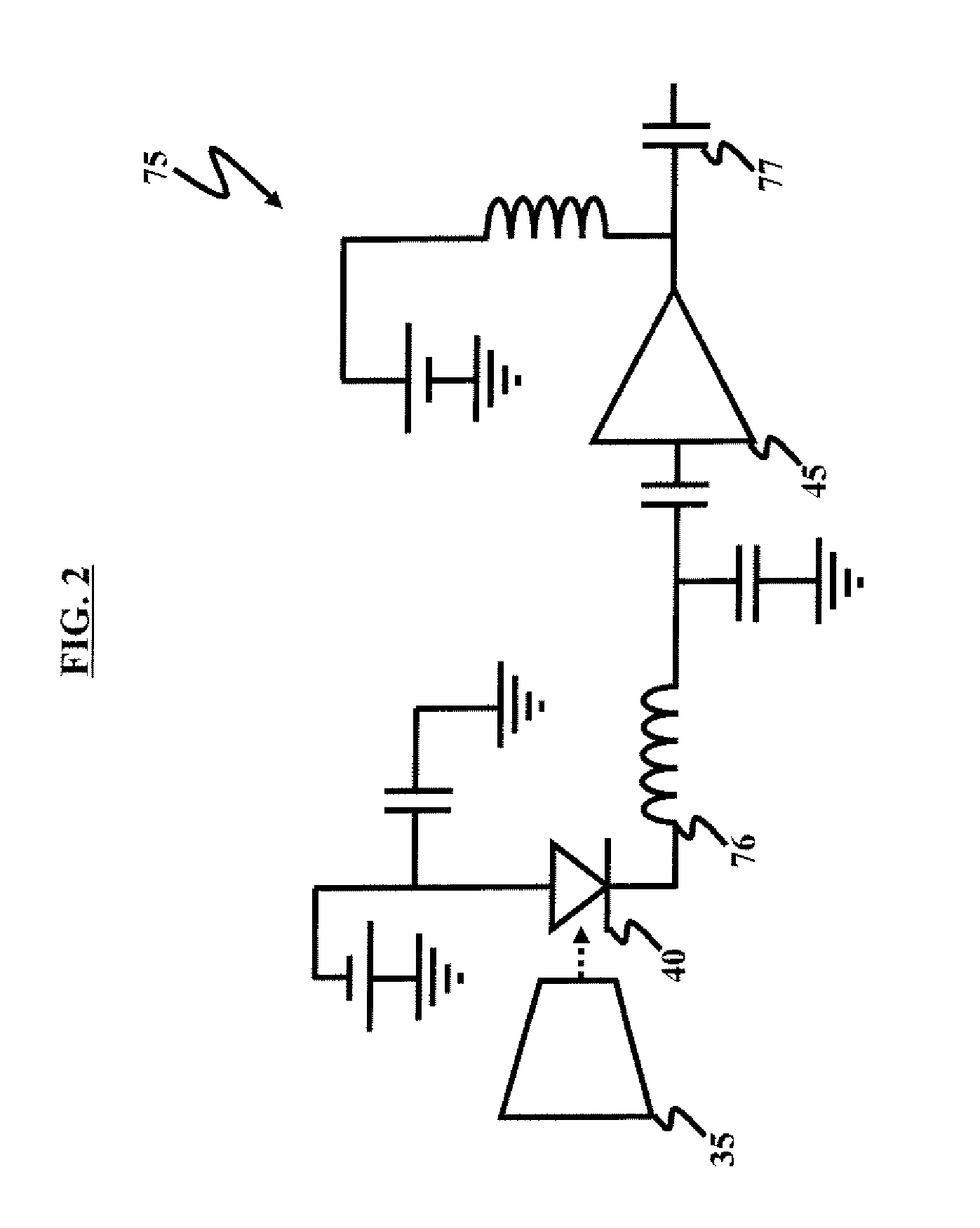
A compact LADAR transmitting and receiving apparatus includes a pulse laser generating pulses of light; a transmitter collimating and directing the pulses of light toward a target; a receiver collecting reflected pulses of light, the reflected pulses of light having been reflected from the target, the receiver comprising a tapered fiber bundle; a sensor operatively connected to the tapered fiber bundle, where the sensor comprises a photosensitive region and outputs a photocurrent; an amplifier amplifying the photocurrent; and a power divider splitting the amplified photocurrent between a high gain channel and a low gain channel; a RF interface accepting the high gain channel, the low gain channel, and an undelayed sample of a pulse of light generated from the pulse laser as input; a processing unit accepting output from the RF interface; and a display unit displaying output from the processing unit.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Program-controlled dicing of a substrate using a pulsed laser
InactiveUS7776720B2Facilitate dicing of the substrateControl damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureChemical reactionPulse rate
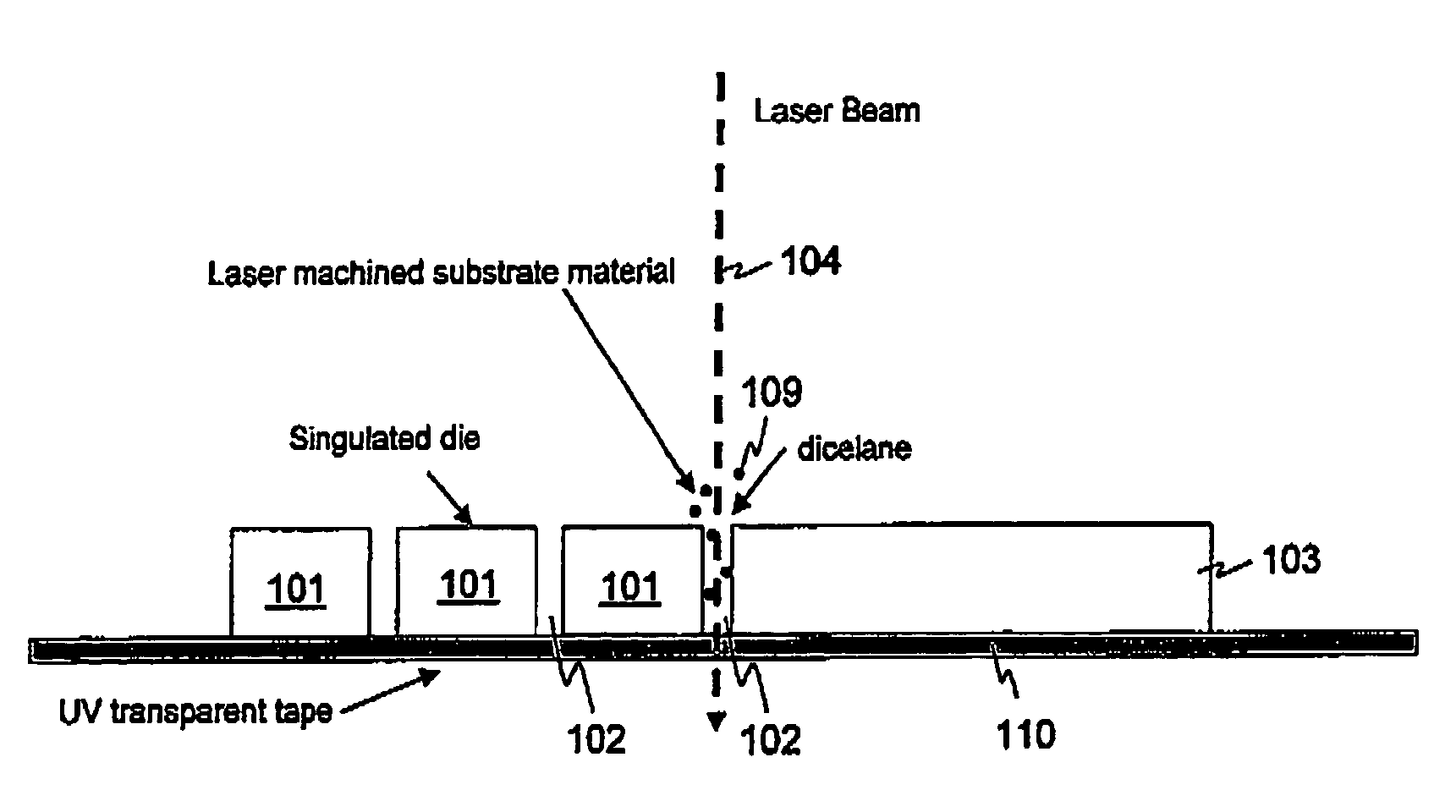
A substrate is diced using a program-controlled pulsed laser beam apparatus having an associated memory for storing a laser cutting strategy file. The file contains selected combinations of pulse rate Deltat, pulse energy density E and pulse spatial overlap to machine a single layer or different types of material in different layers of the substrate while restricting damage to the layers and maximising machining rate to produce die having predetermined die strength and yield. The file also contains data relating to the number of scans necessary using a selected combination to cut through a corresponding layer. The substrate is diced using the selected combinations. Gas handling equipment for inert or active gas may be provided for preventing or inducing chemical reactions at the substrate prior to, during or after dicing.
Owner:XSIL TECH
Method and a device for electro microsurgery in a physiological liquid environment
A method and device for electrical emulation of pulsed laser is disclosed. The device utilizes high voltage electrical discharges of sub-microsecond duration in a liquid medium to produce cavitation bubbles of sub-millimeter size for use in high speed precision cutting. Such bubbles are produced by a micro-electrode (1.6) having a central wire having a diameter of 1 microns to 100 microns embedded in an insulator. A coaxial electrode (1.9) surrounds the insulator, and may be spaced from the outer surface of the insulator to provide a path for removing tissue.
Owner:NANOPTICS
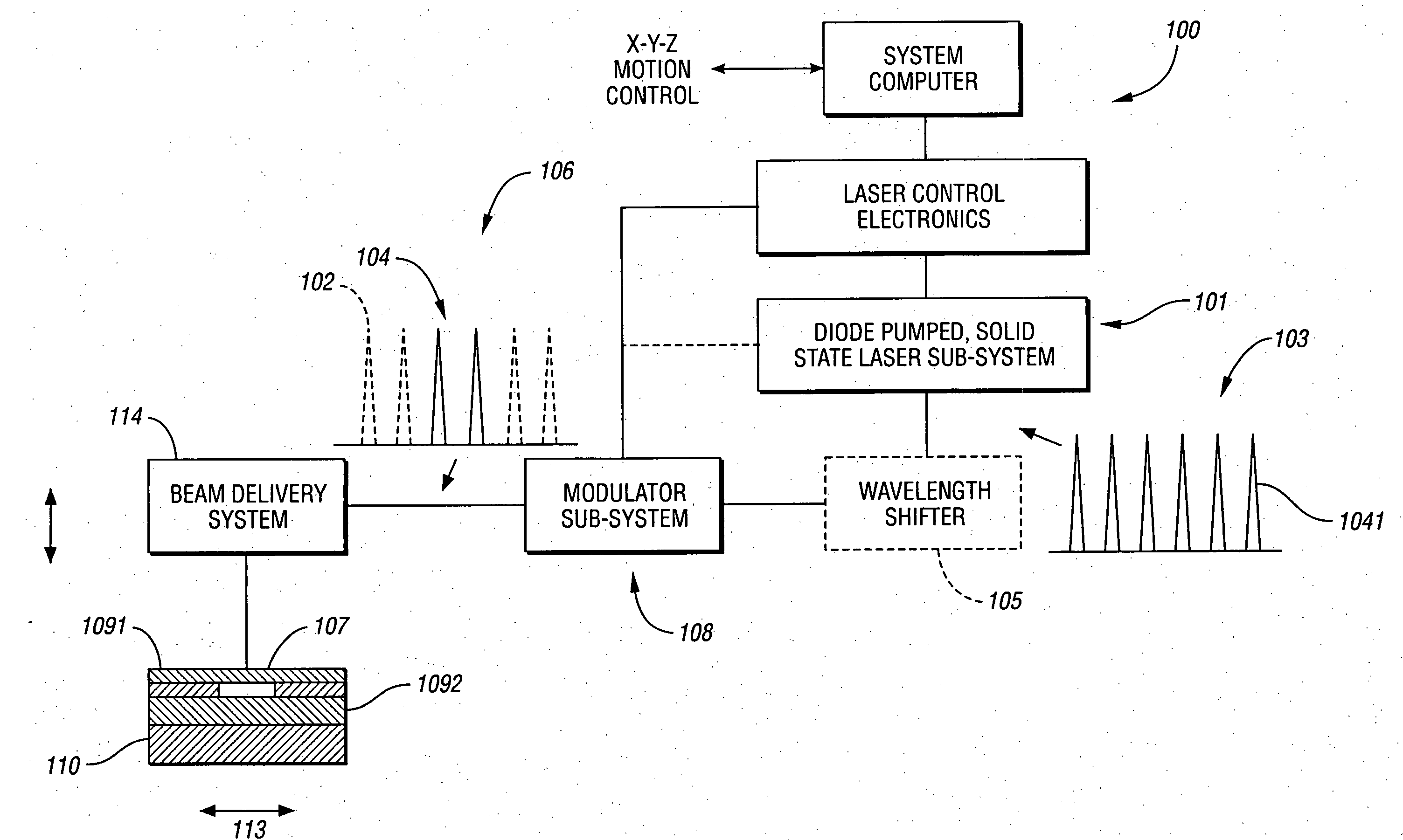
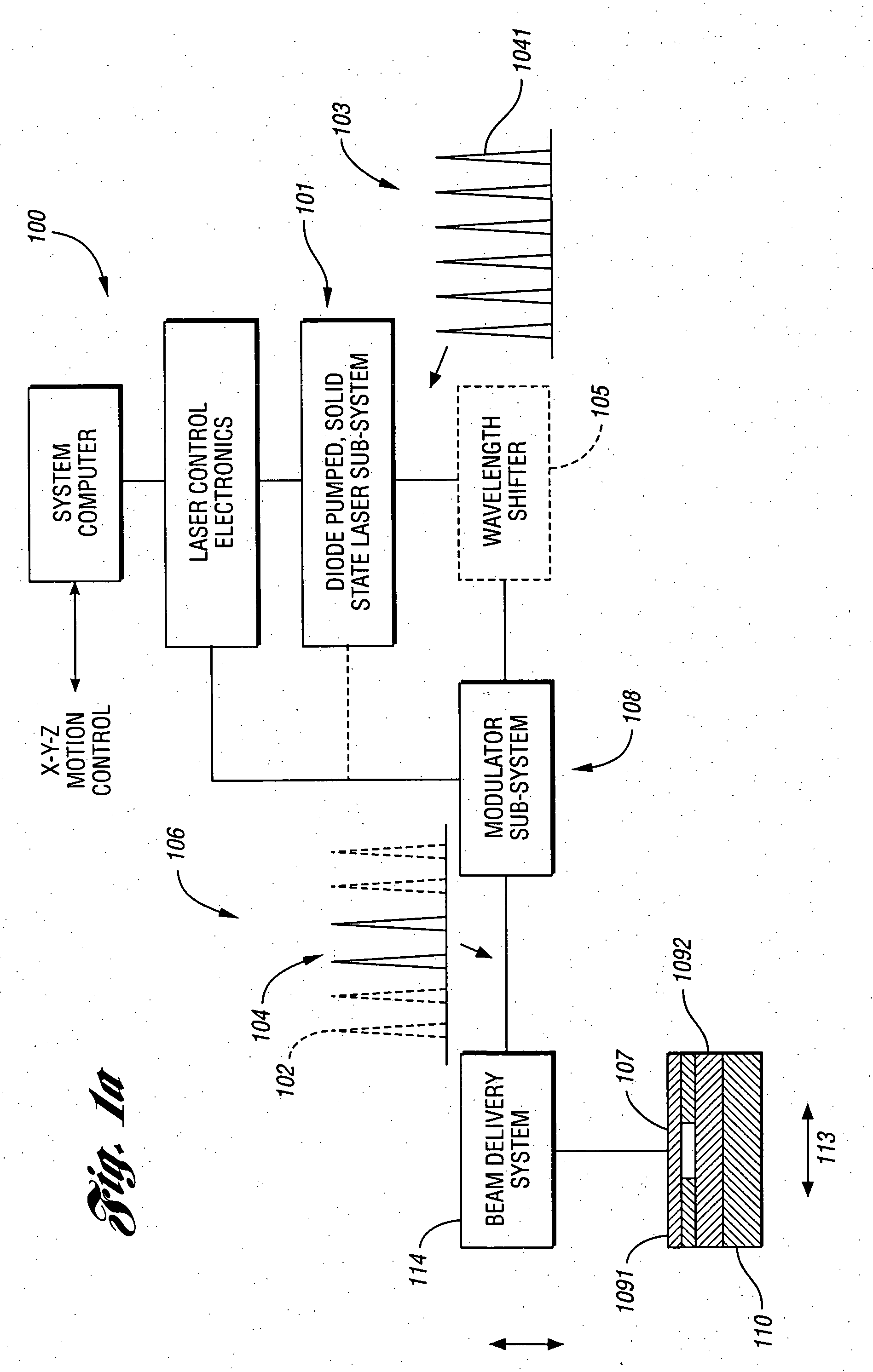
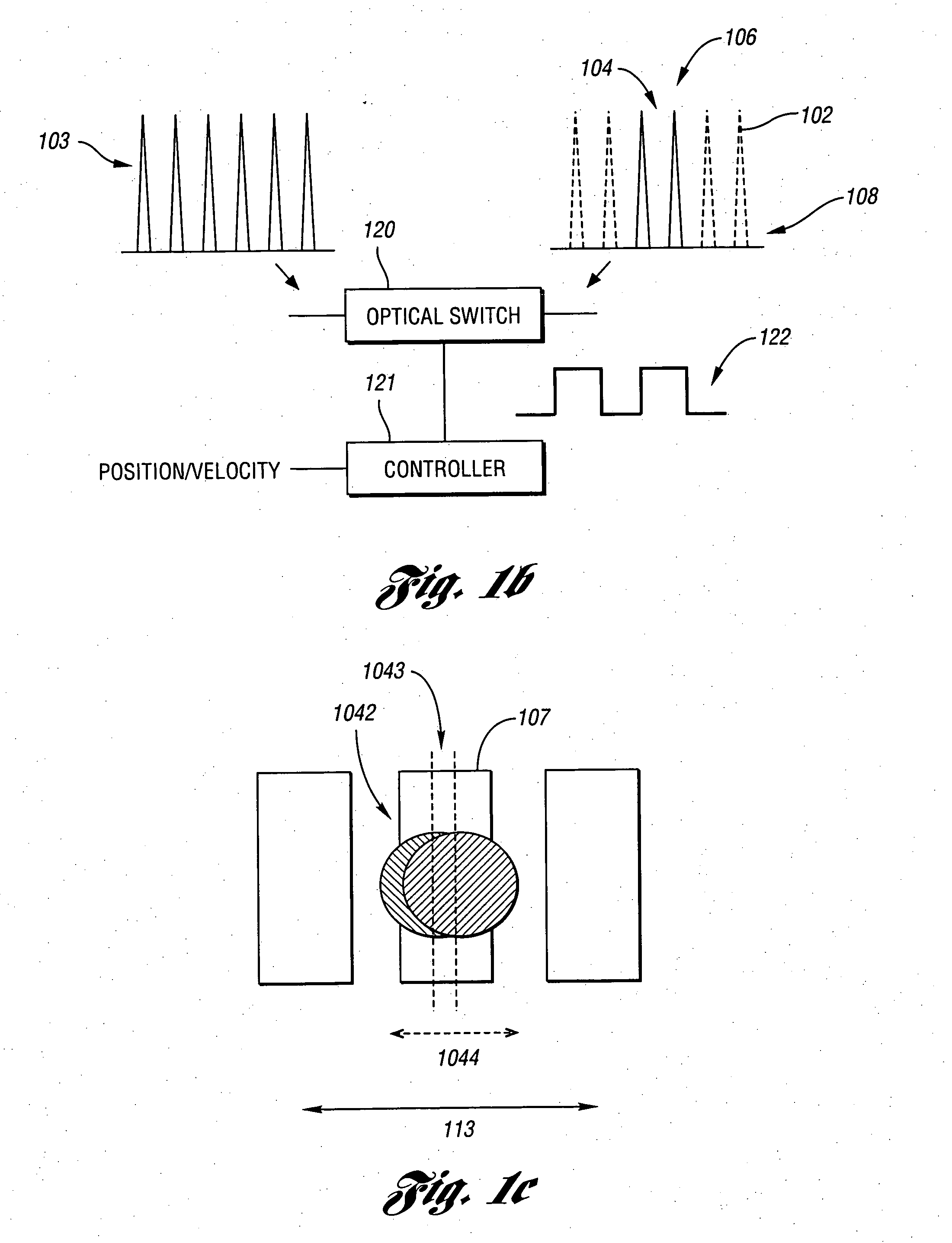
High repetition rate laser produced plasma EUV light source
An EUV light source apparatus and method are disclosed, which may comprise a pulsed laser providing laser pulses at a selected pulse repetition rate focused at a desired target ignition site; a target formation system providing discrete targets at a selected interval coordinated with the laser pulse repetition rate; a target steering system intermediate the target formation system and the desired target ignition site; and a target tracking system providing information about the movement of target between the target formation system and the target steering system, enabling the target steering system to direct the target to the desired target ignition site. The target tracking system may provide information enabling the creation of a laser firing control signal, and may comprise a droplet detector comprising a collimated light source directed to intersect a point on a projected delivery path of the target, having a respective oppositely disposed light detector detecting the passage of the target through the respective point, or a detector comprising a linear array of a plurality of photo-sensitive elements aligned to a coordinate axis, the light from the light source intersecting a projected delivery path of the target, at least one of the which may comprise a plane-intercept detection device. The droplet detectors may comprise a plurality of droplet detectors each operating at a different light frequency, or a camera having a field of view and a two dimensional array of pixels imaging the field of view. The apparatus and method may comprise an electrostatic plasma containment apparatus providing an electric plasma confinement field at or near a target ignition site at the time of ignition, with the target tracking system providing a signal enabling control of the electrostatic plasma containment apparatus. The apparatus and method may comprise a vessel having and intermediate wall with a low pressure trap allowing passage of EUV light and maintaining a differential pressure across the low pressure trap. The apparatus and method may comprise a magnetic plasma confinement mechanism creating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the target ignition site to confine the plasma to the target ignition site, which may be pulsed and may be controlled using outputs from the target tracking system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
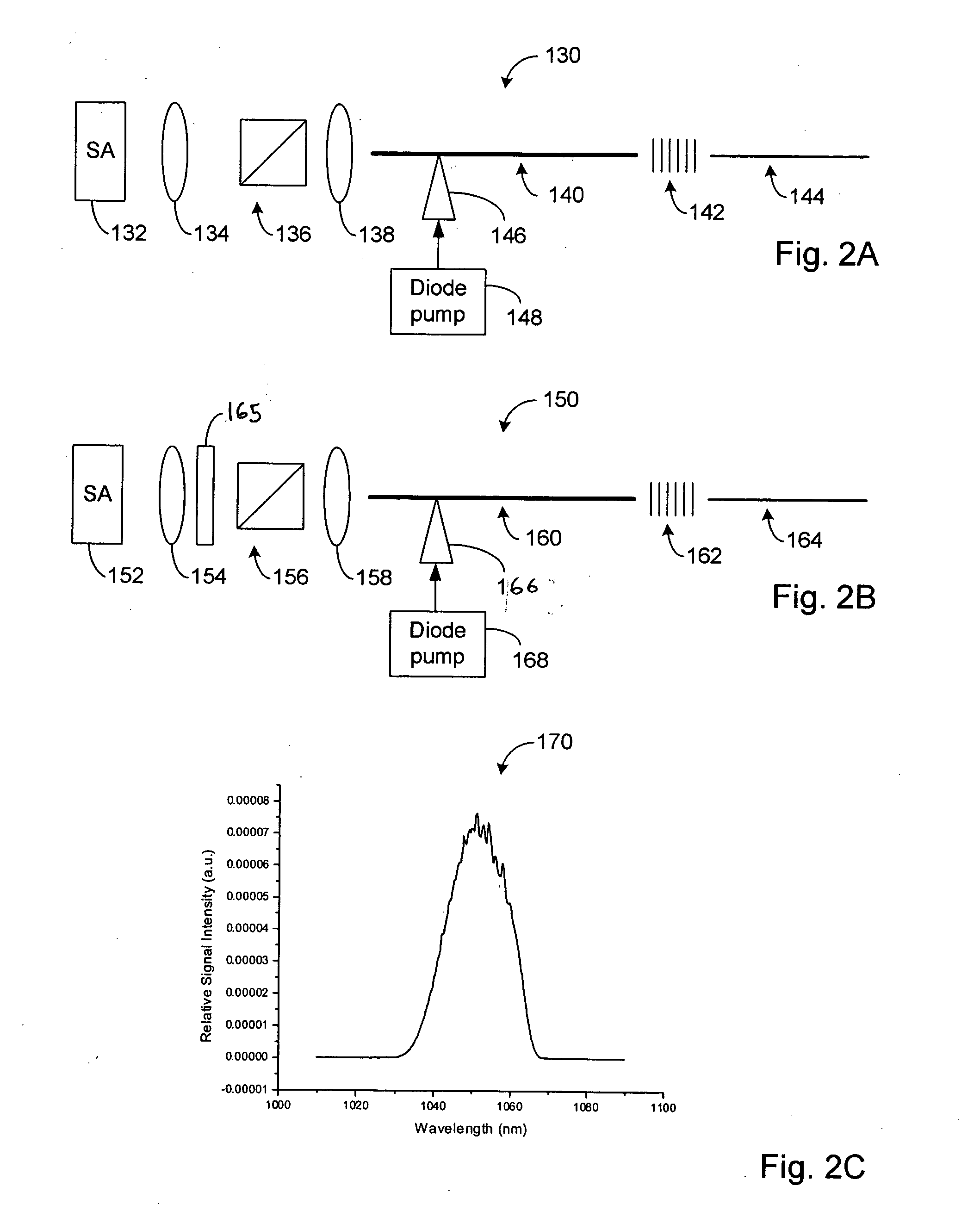
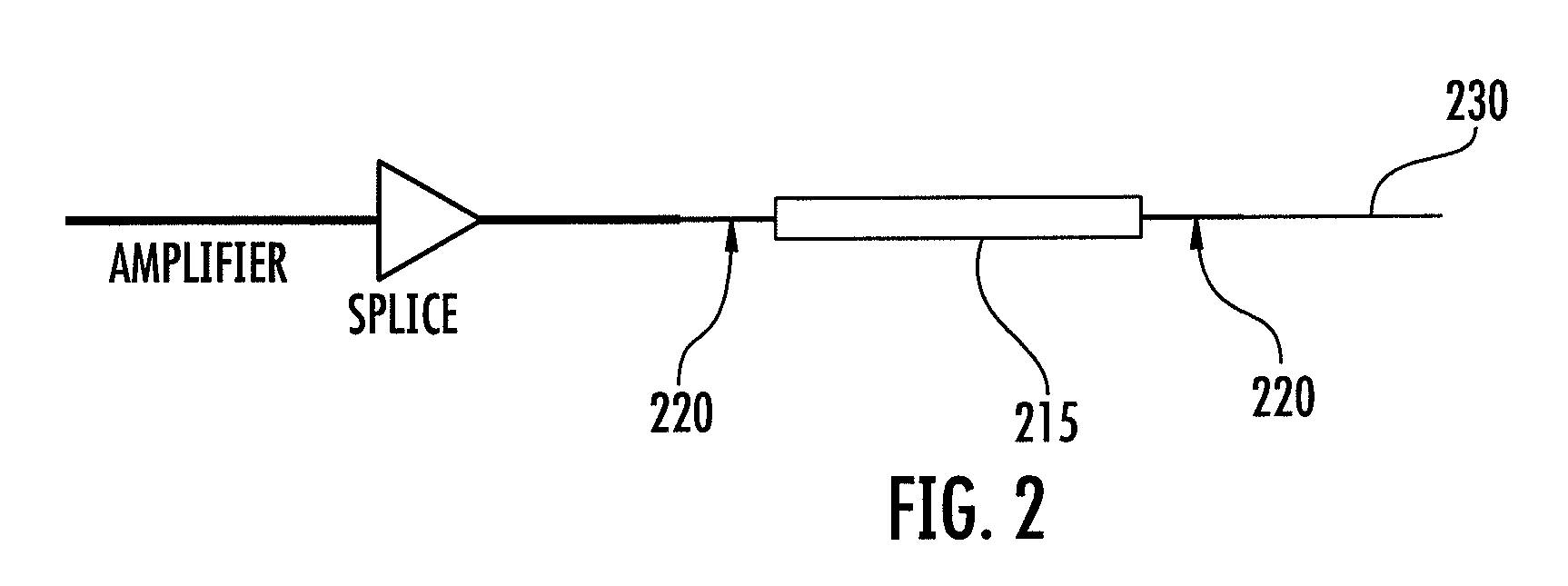
High power short pulse fiber laser
InactiveUS20050226278A1Reduce widthWeaken energyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsAudio power amplifierPigtail
A pulsed laser comprises an oscillator and amplifier. An attenuator and / or pre-compressor may be disposed between the oscillator and amplifier to improve performance and possibly the quality of pulses output from the laser. Such pre-compression may be implemented with spectral filters and / or dispersive elements between the oscillator and amplifier. The pulsed laser may have a modular design comprising modular devices that may have Telcordia-graded quality and reliability. Fiber pigtails extending from the device modules can be spliced together to form laser system. In one embodiment, a laser system operating at approximately 1050 nm comprises an oscillator having a spectral bandwidth of approximately 19 nm. This oscillator signal can be manipulated to generate a pulse having a width below approximately 90 fs.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
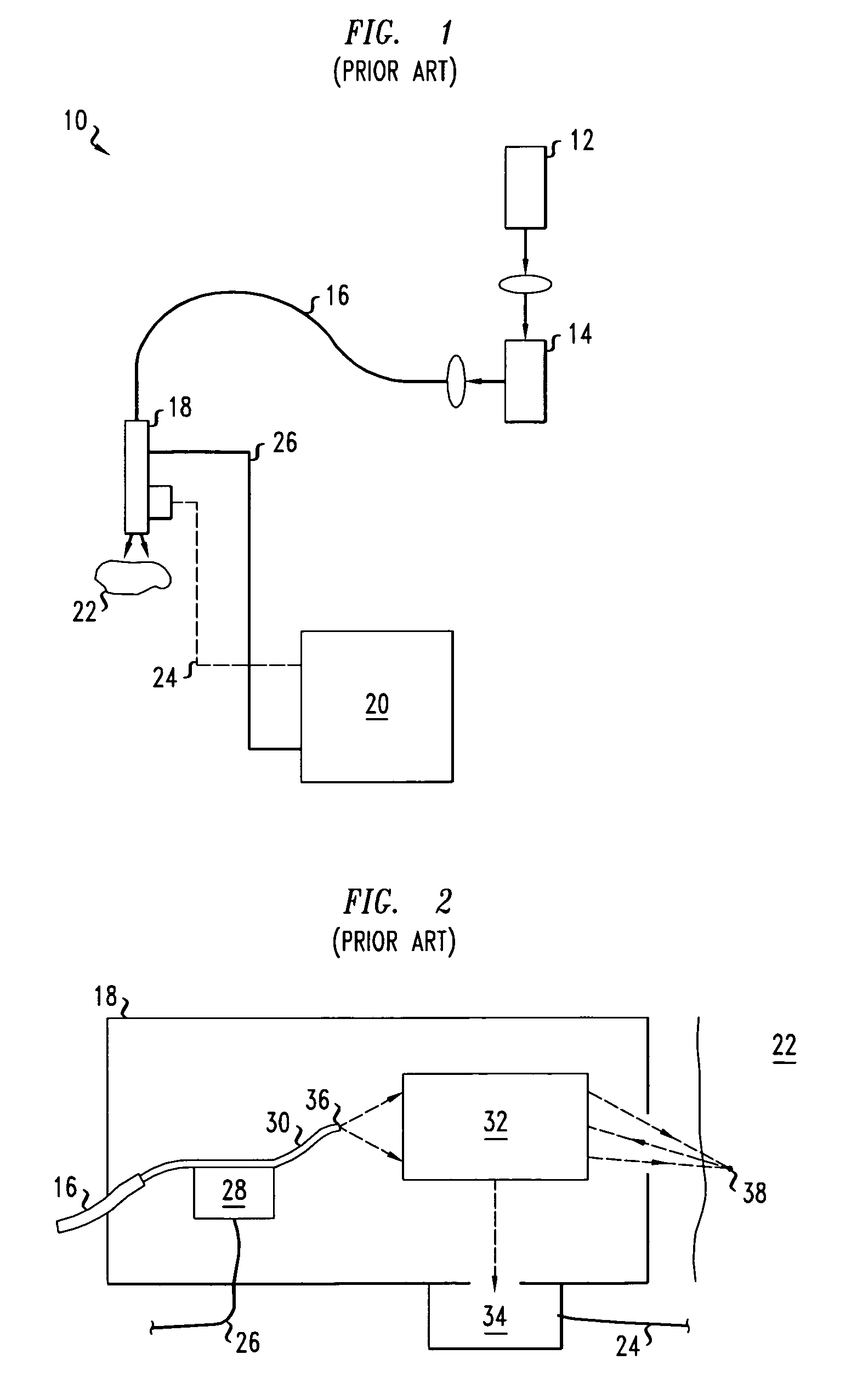
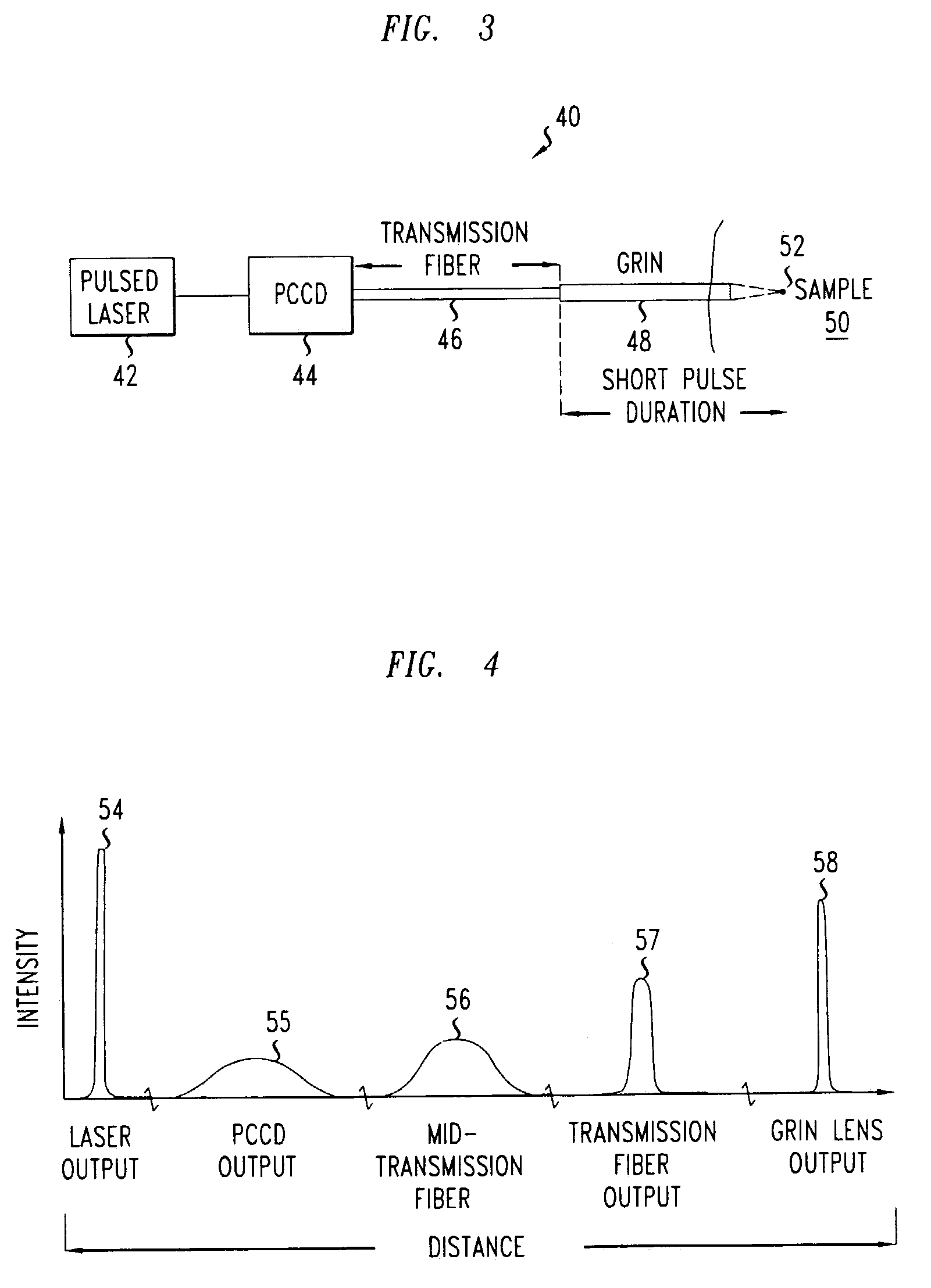
Multi-photon endoscopic imaging system
An imaging system includes a pulsed laser, a pre-compensator for chromatic dispersion, a transmission optical fiber, and a GRIN lens. The pre-compensator chirps optical pulses received from the laser. The transmission optical fiber transports the chirped optical pulses from the pre-compensator. The GRIN lens receives the transported optical pulses from the transmission optical fiber. The GRIN lens has a wider optical core than the transmission optical fiber and substantially narrows the transported optical pulses received from the transmission optical fiber.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby
InactiveUS20060000814A1Prevent unwanted changesSufficient total fluenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTarget surfaceSlag
A laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby are provided. The system processes the targeted surface material within a region of a workpiece while avoiding undesirable changes to adjacent non-targeted material. The system includes a primary laser subsystem including a primary laser source for generating a pulsed laser output including at least one pulse having a wavelength and a pulse width less than 1 ns. A delivery subsystem irradiates the targeted surface material of the workpiece with the pulsed laser output including the at least one pulse to texture the targeted surface material. The pulsed laser output has sufficient total fluence to initiate ablation within at least a portion of the targeted surface material and the pulse width is short enough such that the region and the non-targeted material surrounding the material are substantially free of slag.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser ablation method and apparatus having a feedback loop and control unit
InactiveUS20060084957A1Improve ablation effectImprove controllability and precisionControlling energy of instrumentLaser beamsEquipment use
A laser ablation method and apparatus uses a laser device to generate a pulsed laser using a laser device and to project the pulsed laser onto an ablation target to be ablated. A probe is then used to measure an indicative property of the ablation target or of the pulsed laser projected on the ablation target. A control loop is used to optimize ablation effect by generating a feedback signal according to the measured indicative property, sending the feedback signal to a control unit, and adjusting an output parameter of the pulsed laser according to the feedback signal. The measured indicative property may be a size of the laser beam spot or a material composition. The ablation, the feedback and the adjustment may be performed dynamically.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Method and apparatus for precision working of material
A method for precise working of material, particularly organic tissue, comprises the step of providing laser pulses with a pulse length between 50 fs and 1 ps and with a pulse frequency from 50 kHz to 1 MHz and with a wavelength between 600 and 2000 nm for acting on the material to be worked. Apparatus, in accordance with the invention, for precise working of material, particularly organic tissue comprising a pulsed laser, wherein the laser has a pulse length between 50 fs and 1 ps and with a pulse frequency of from 50 kHz to 1 MHz is also described.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
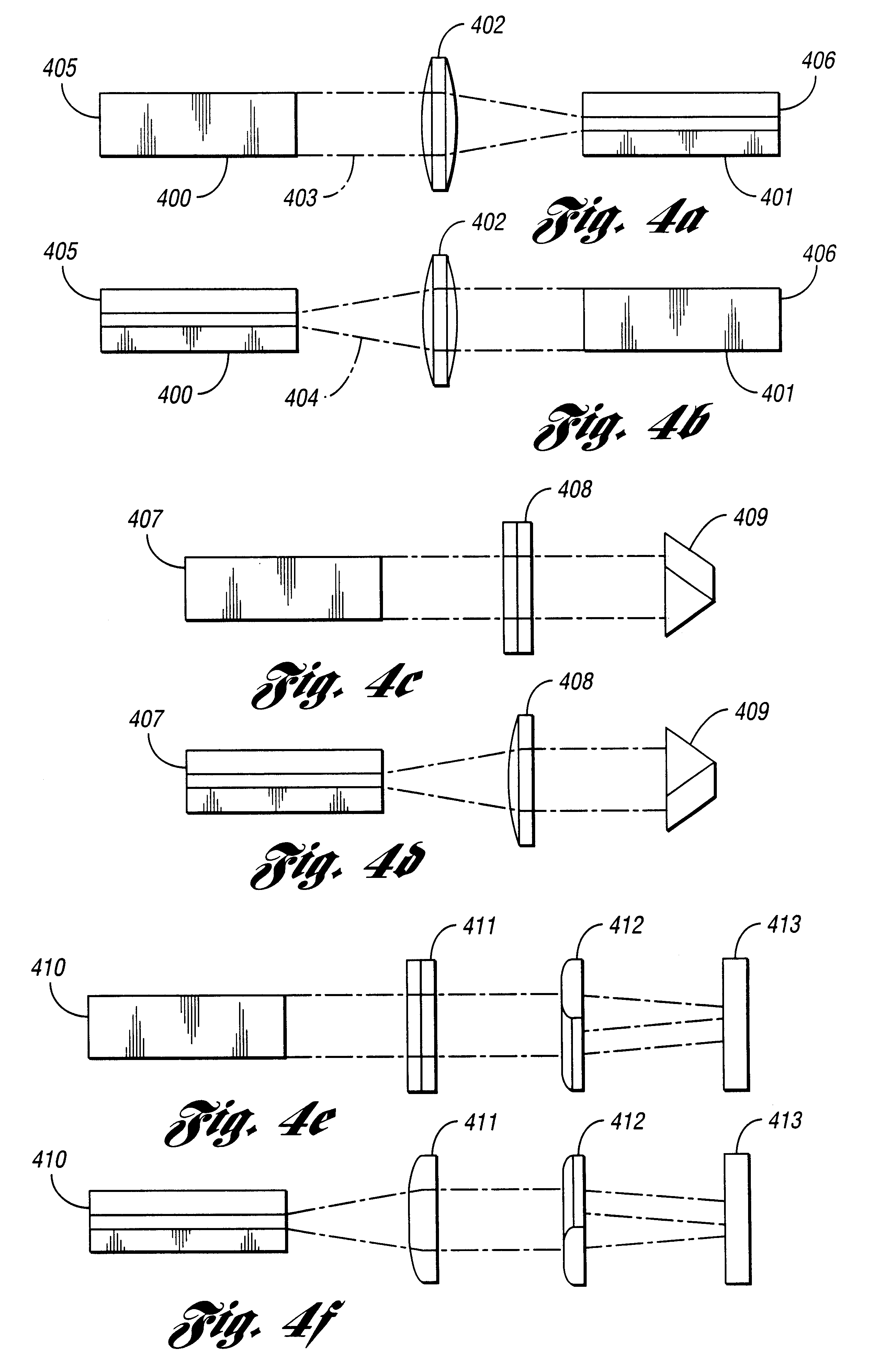
Waveguide architecture, waveguide devices for laser processing and beam control, and laser processing applications
InactiveUS20030161375A1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionEngineeringWaveguide
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
Process and system for treating a vascular occlusion or other endoluminal structure
A process and instruments for diminishing an undesired endoluminal structure present at a treatment site in a mammalian treatment subject. The endoluminal can be or include a vascular occlusion, a biofilm or another undesired biological structure. The process can include applying mechanical shockwaves to the endoluminal structure and the endoluminal structure absorbing the applied mechanical shockwaves and becoming diminished, dispersed or weakened. The shockwaves can be generated by pulsed laser energy delivered to an ionizable target via an optical fiber.
Owner:KRESPI YOSEF
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134896A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserNanosecond
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
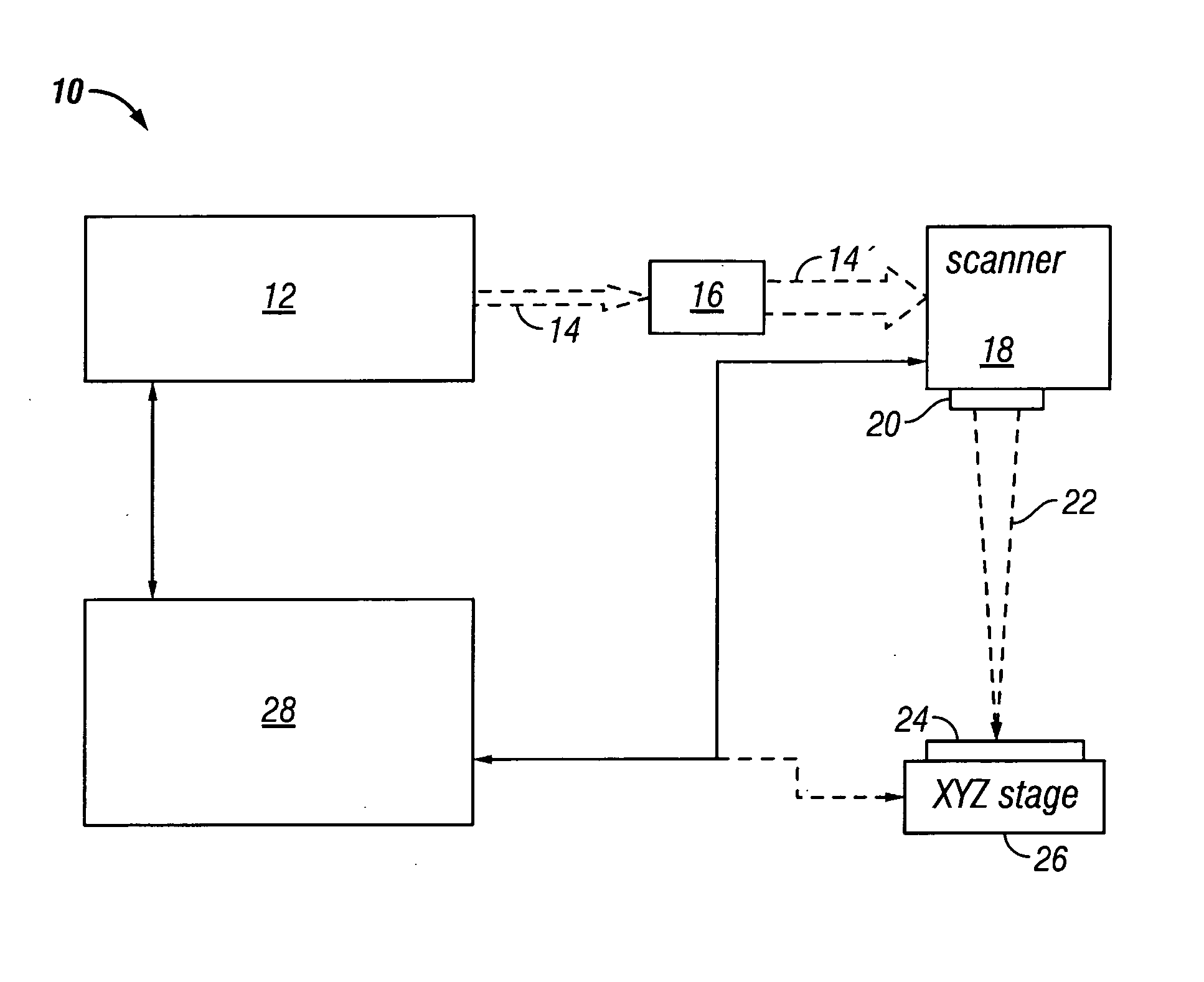
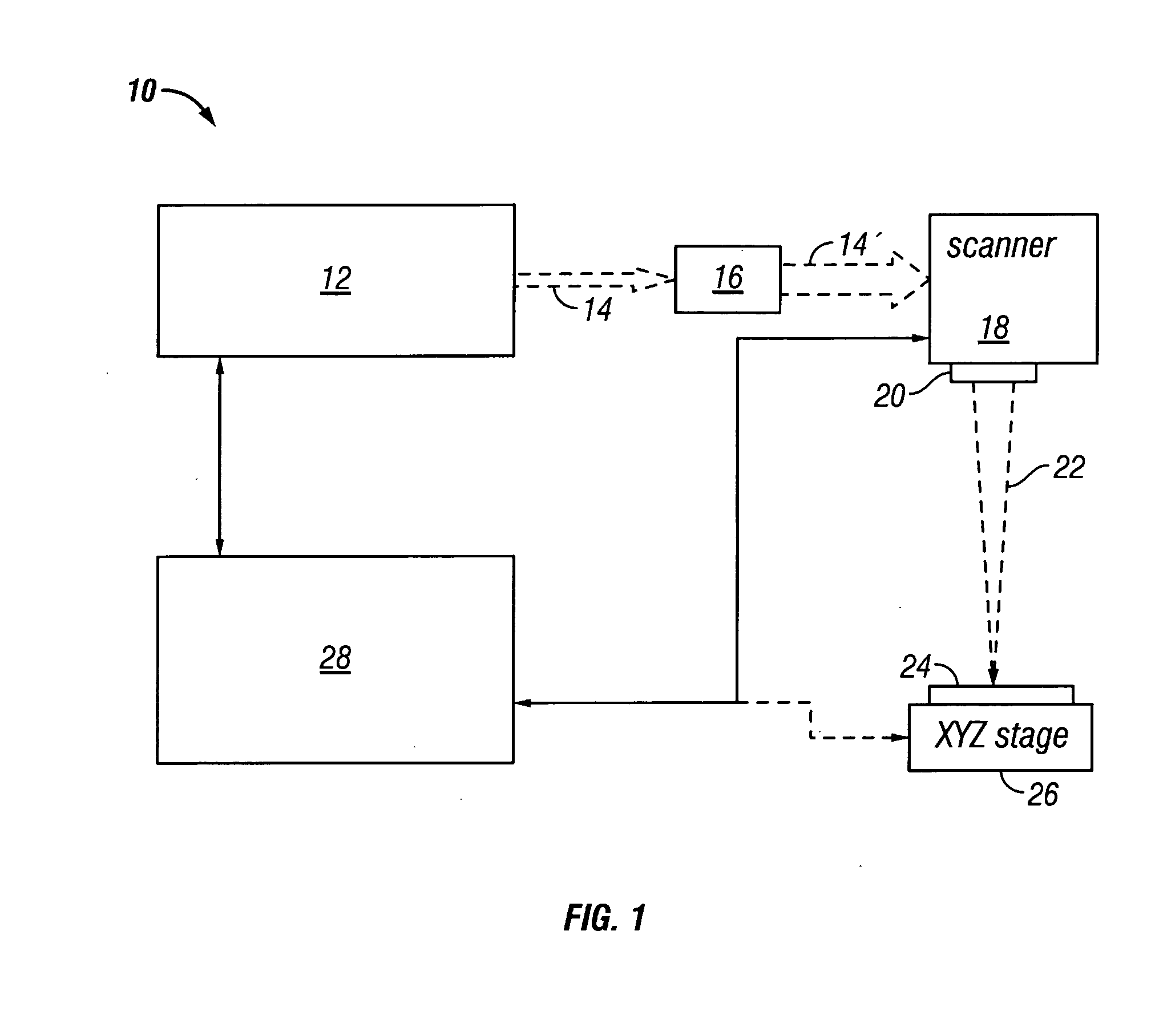
3D scanning system and method of obtaining 3D image
ActiveUS20140111812A1Solve the slow scanning speedSmall volumeUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloud3d image
Disclosed are a 3D laser scanning system and a method of obtaining a 3D image by using the system that detect, with a linear array type photo detector, a reflected light reflected from a target after rotation-emitting a line-shaped pulsed laser light through 360 degrees and obtain a 3D image through point cloud data obtained by measuring a distance to the target.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
Laser based material processing methods and scalable architecture for material processing
InactiveUS6738396B2Improve stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionPower applicationNanosecond
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
High repetition rate laser produced plasma EUV light source
An EUV light source apparatus and method are disclosed, which may comprise a pulsed laser providing laser pulses at a selected pulse repetition rate focused at a desired target ignition site; a target formation system providing discrete targets at a selected interval coordinated with the laser pulse repetition rate; a target steering system intermediate the target formation system and the desired target ignition site; and a target tracking system providing information about the movement of target between the target formation system and the target steering system, enabling the target steering system to direct the target to the desired target ignition site. The target tracking system may provide information enabling the creation of a laser firing control signal, and may comprise a droplet detector comprising a collimated light source directed to intersect a point on a projected delivery path of the target, having a respective oppositely disposed light detector detecting the passage of the target through the respective point, or a detector comprising a linear array of a plurality of photo-sensitive elements aligned to a coordinate axis, the light from the light source intersecting a projected delivery path of the target, at least one of the which may comprise a plane-intercept detection device. The droplet detectors may comprise a plurality of droplet detectors each operating at a different light frequency, or a camera having a field of view and a two dimensional array of pixels imaging the field of view. The apparatus and method may comprise an electrostatic plasma containment apparatus providing an electric plasma confinement field at or near a target ignition site at the time of ignition, with the target tracking system providing a signal enabling control of the electrostatic plasma containment apparatus. The apparatus and method may comprise a vessel having and intermediate wall with a low pressure trap allowing passage of EUV light and maintaining a differential pressure across the low pressure trap. The apparatus and method may comprise a magnetic plasma confinement mechanism creating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the target ignition site to confine the plasma to the target ignition site, which may be pulsed and may be controlled using outputs from the target tracking system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
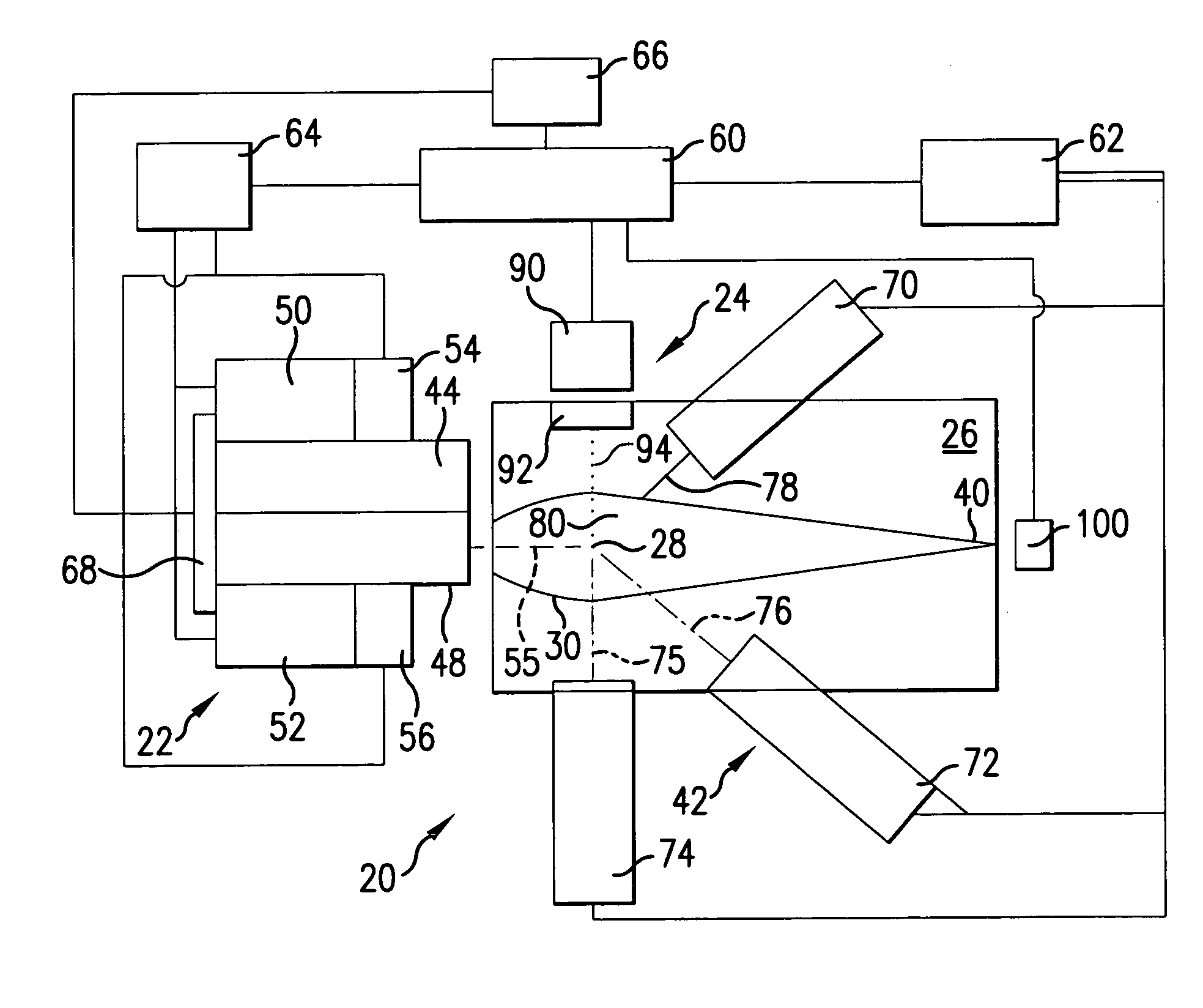
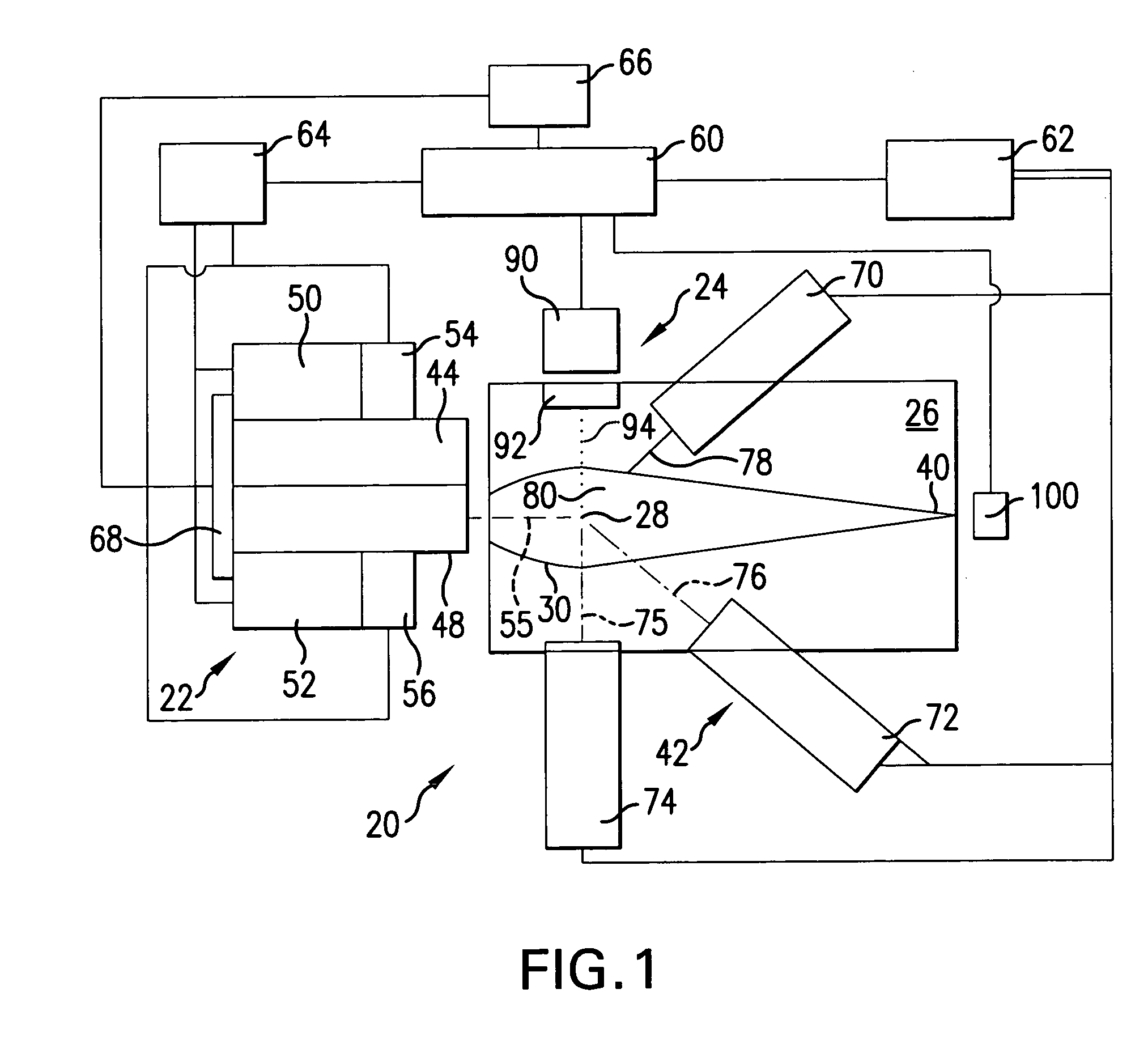
Laser radar projection with object feature detection and ranging
A 3D pulsed laser projection system scans an object to produce a dense 3D point cloud and projects a laser light beam onto an object as a glowing template. A high-sensitivity optical feedback system receives and detects a feedback beam of the output beam light diffusely reflected from the object. The feedback light and projected beam share the same beam path between steering mirrors and the object. A light suppression component controls stray scattered light, including ambient light, from being detected. A time-of-flight measurement subsystem provides a distance-to-object measurement for projected pulses. An acousto-optical modulator, variable gain detected signal amplification and variable photo-detector power together produce a dynamic range for detected reflected feedback signals of at least 100,000, and up to 500,000. Optical fiber cables spatially filter scattered light and isolate the photo-detectors thermally. The laser is preferably pulsed at least 50 kHz, with sampling of the projected and feedback reflected optical pulse signals at a sampling rate of up to 10 gigasamples per second.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Smart linear pulsed laser diode driver, and method
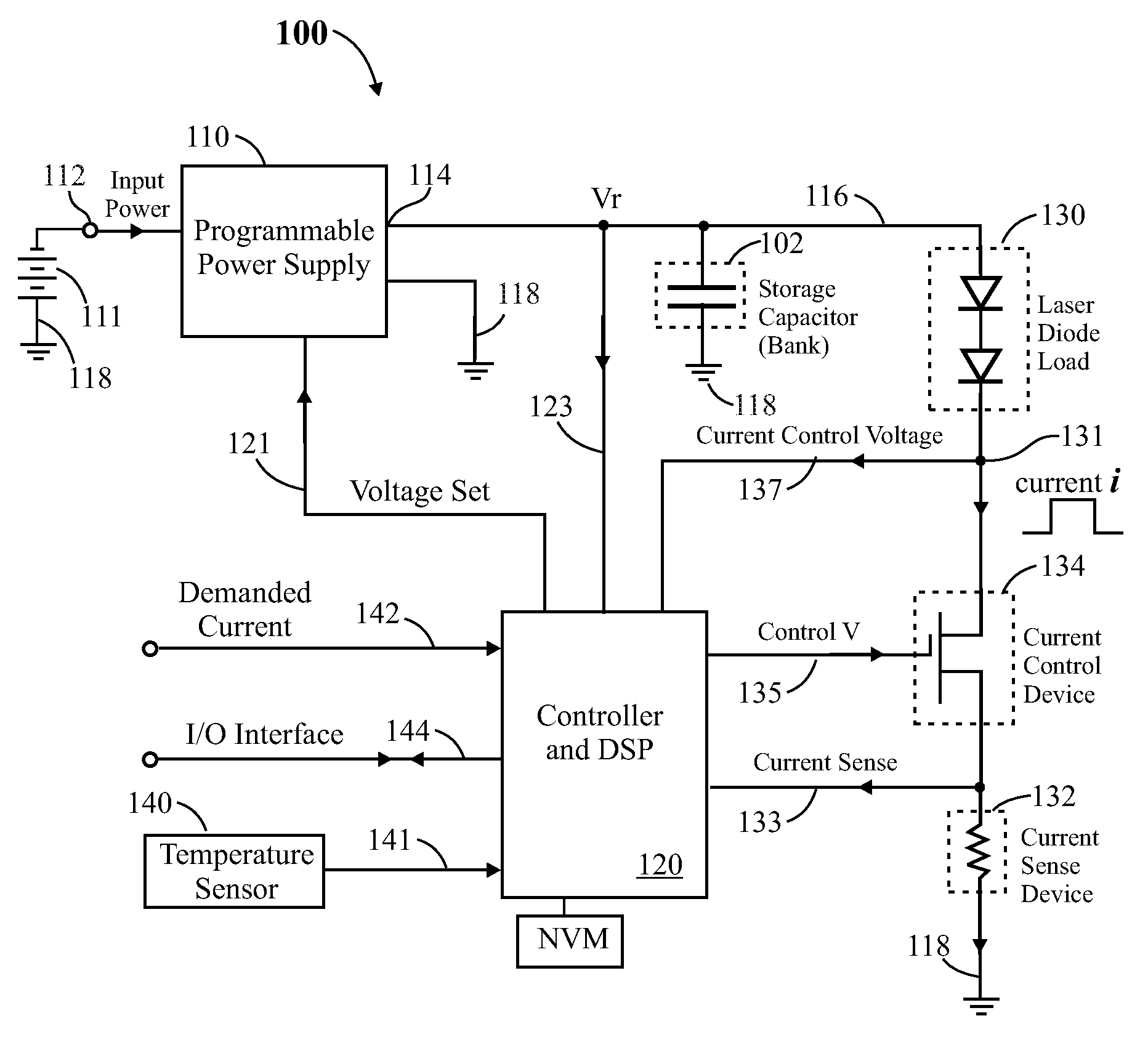
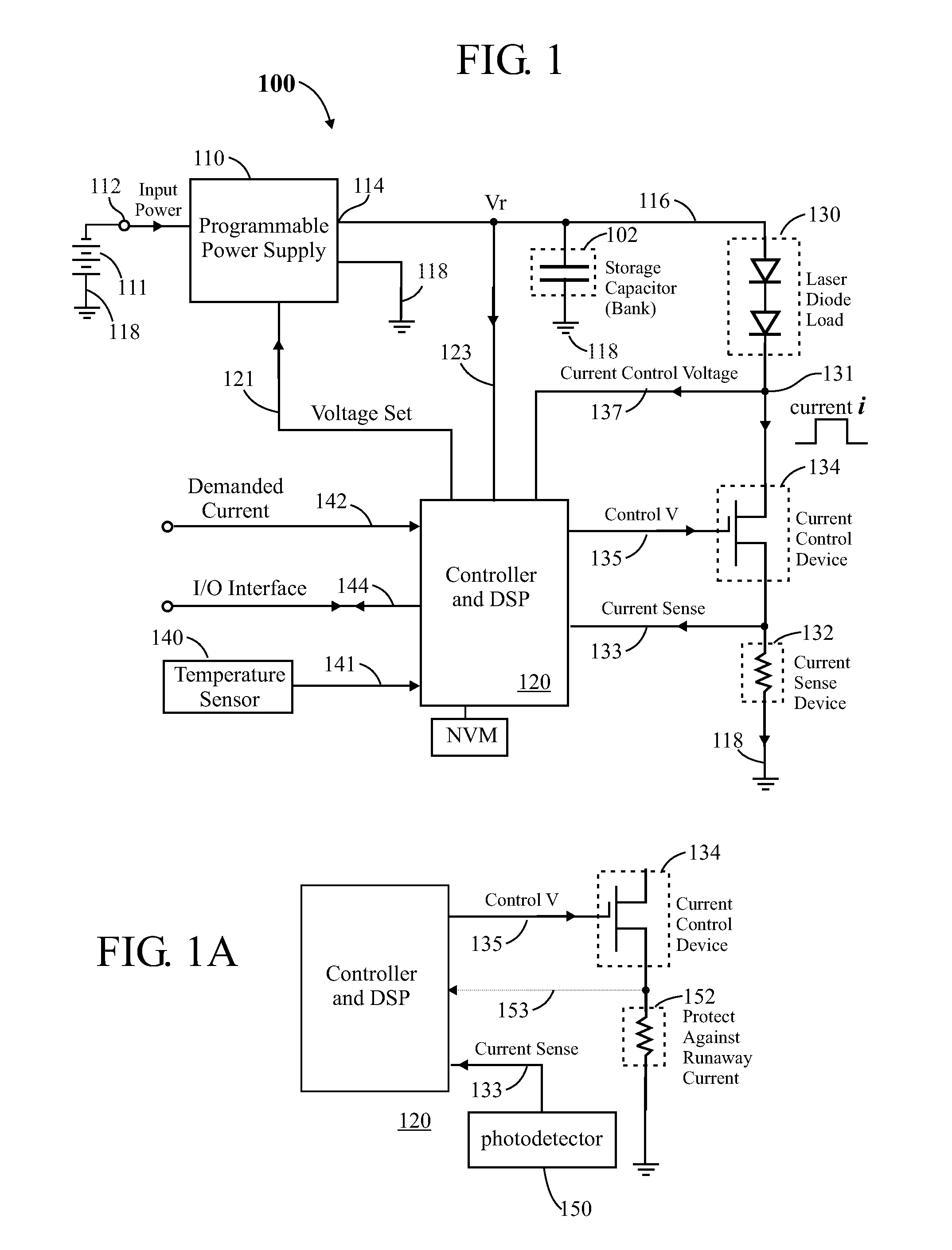
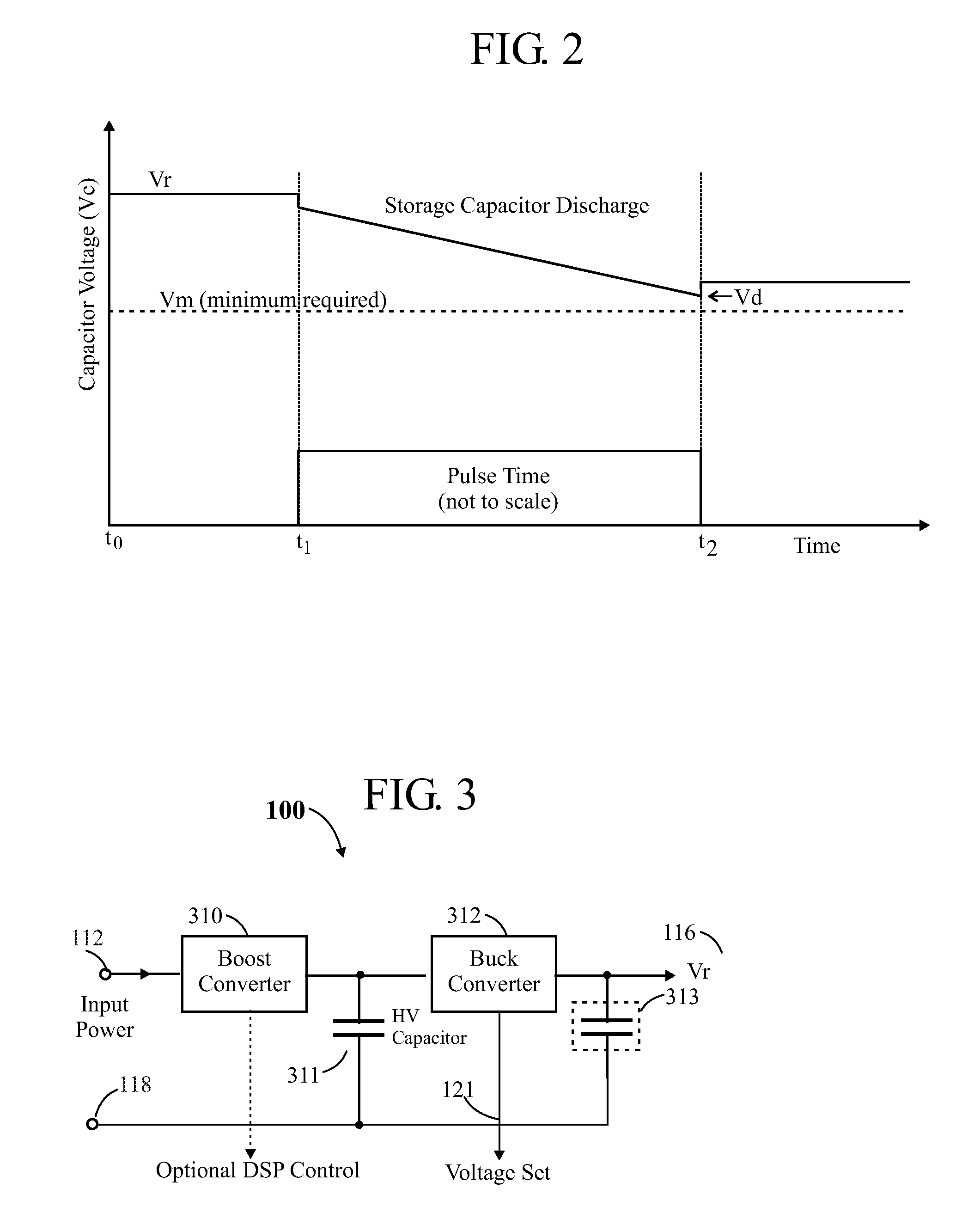
ActiveUS20110085576A1Improve efficiencySmall sizeLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitor voltageEngineering
In a pulsed laser diode driver an energy storage capacitor is continuously being charged to a supply voltage Vr. When a pulse is initiated, energy stored in the capacitor is delivered to the laser diode load. The capacitor voltage Vd at the end of a pulse is used to control Vr to ensure that Vd is maintained above a minimum voltage Vm required to ensure operation of a current control device (such as FET) just above saturation. Test pulses (such as with attenuated currents or reduced pulsewidth) may be fired to determine an initial optimum value for Vr. After a test pulse, a slightly high estimate for Vr may be used and may be iterated (incremented) down to an optimum value Vm during a firing burst. A digital processor may be used to calculate and store data to optimize the performance. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ANALOG MODULES
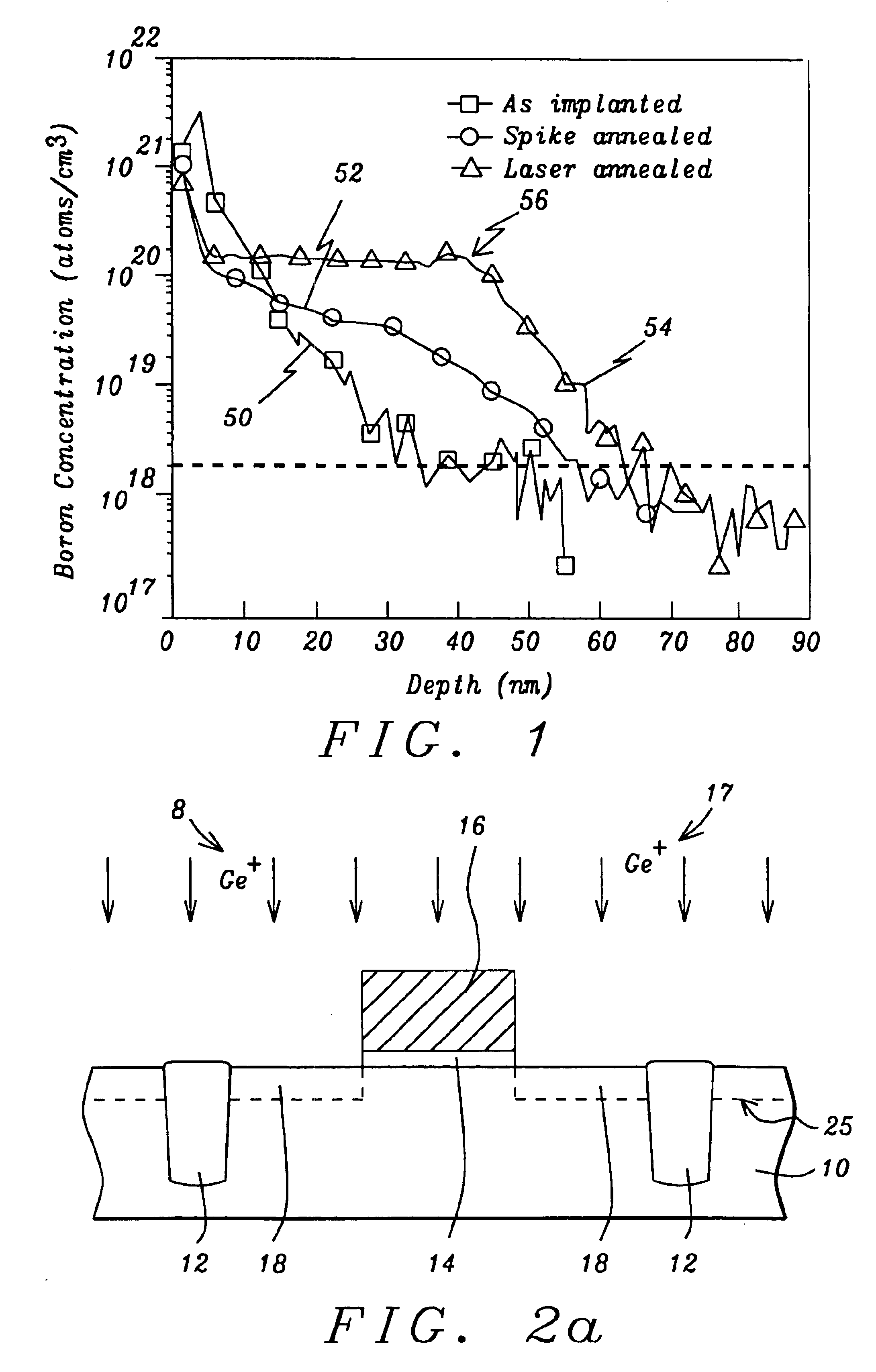
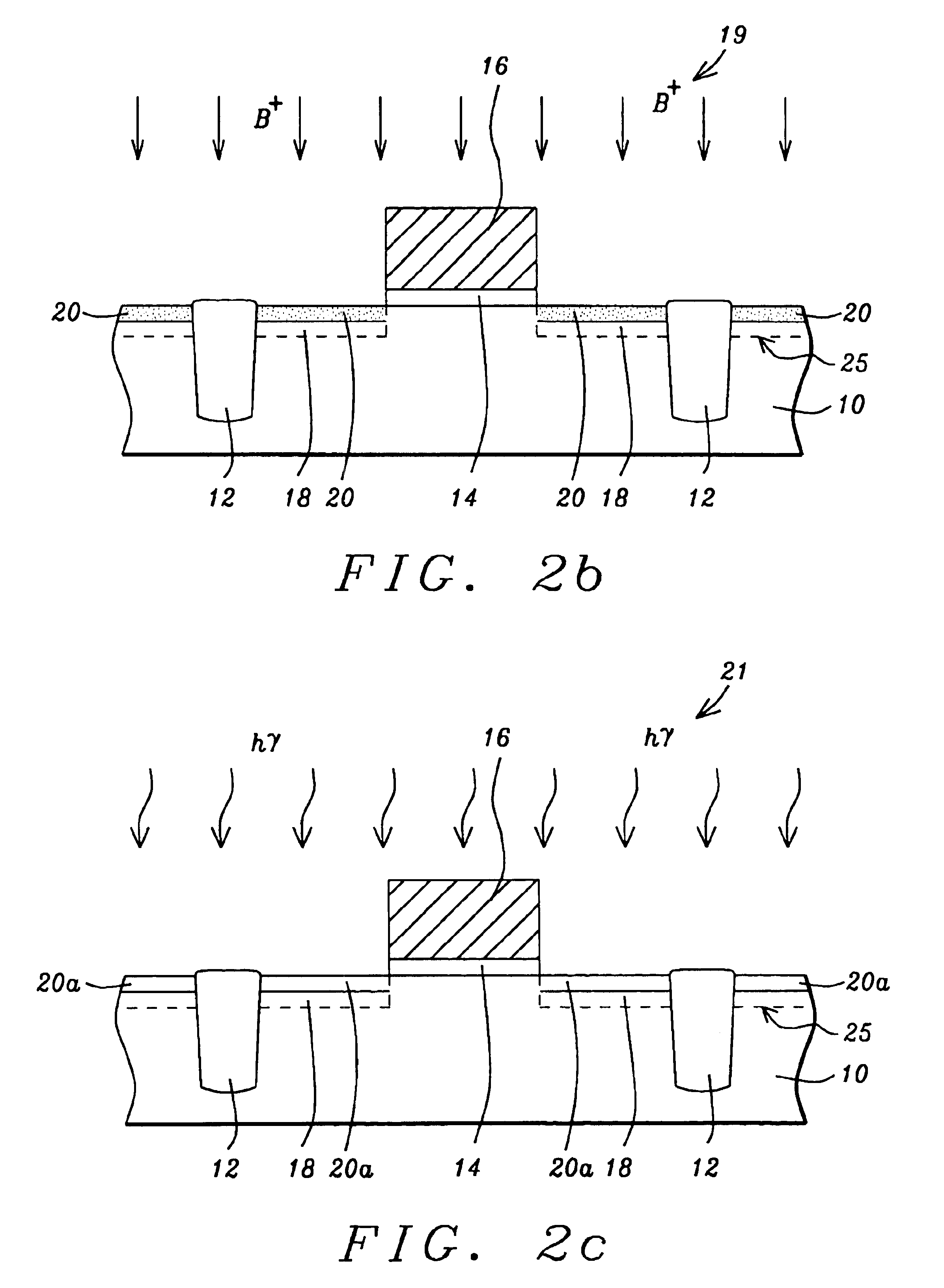
Method of multiple pulse laser annealing to activate ultra-shallow junctions
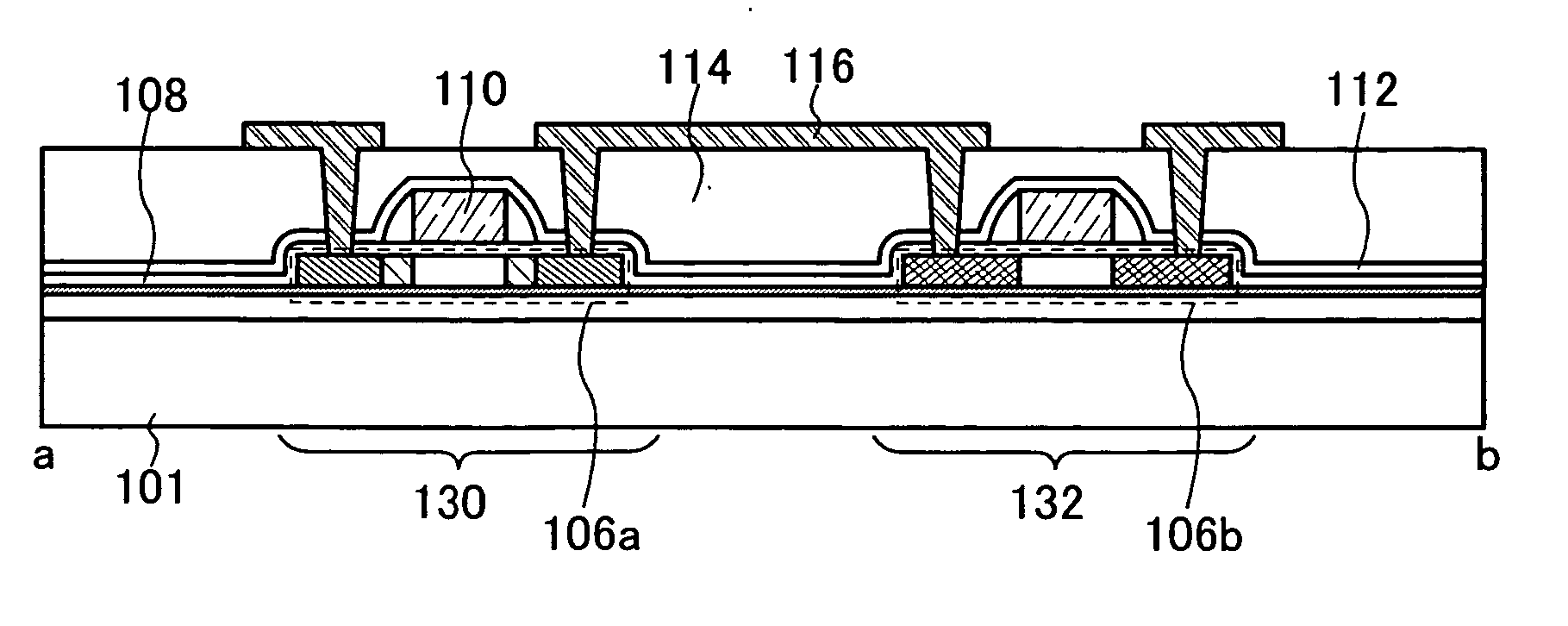
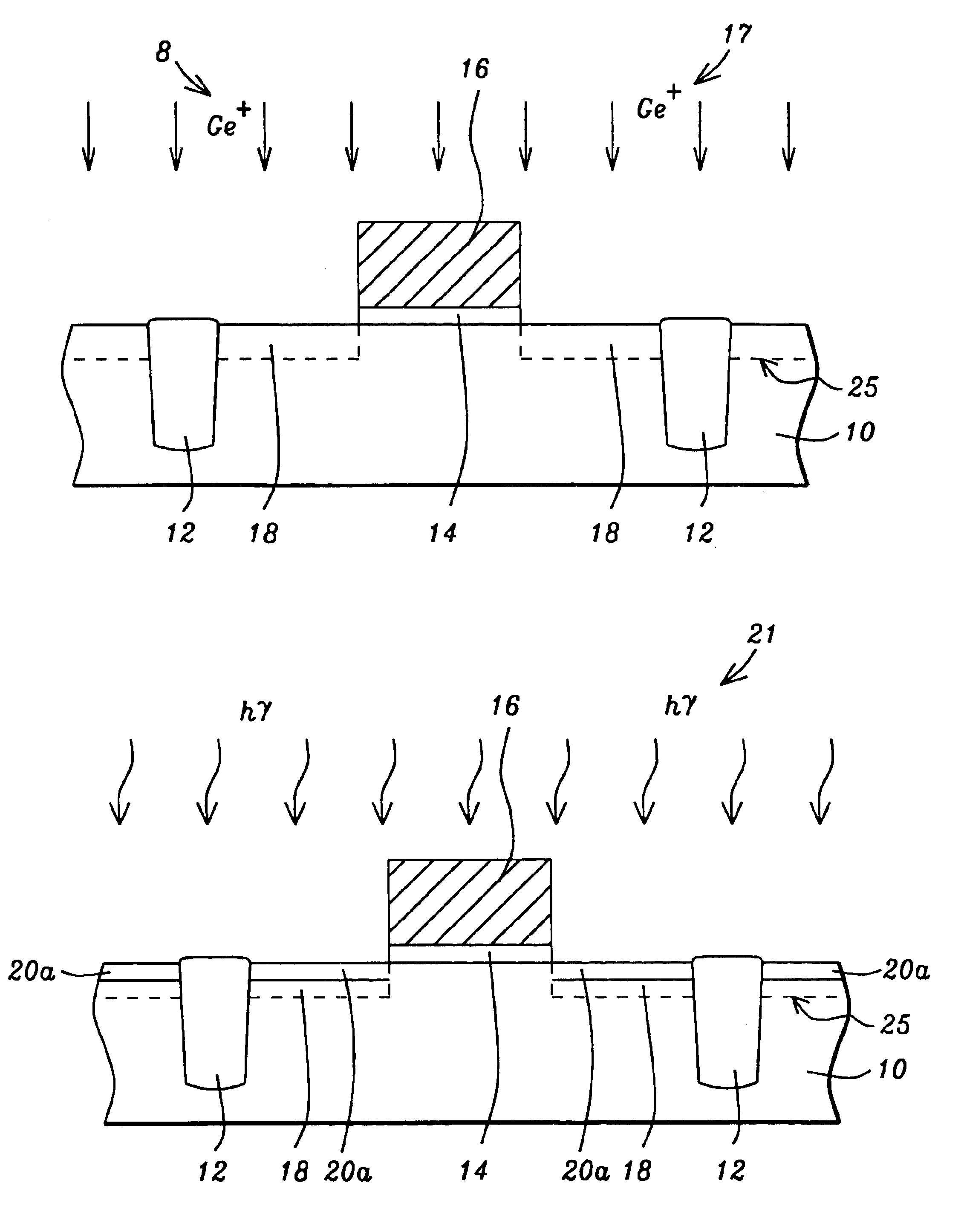
A method for forming a highly activated ultra shallow ion implanted semiconductive elements for use in sub-tenth micron MOSFET technology is described. A key feature of the method is the ability to activate the implanted impurity to a highly active state without permitting the dopant to diffuse further to deepen the junction. A selected single crystalline silicon active region is first amorphized by implanting a heavy ion such as silicon or germanium. A semiconductive impurity for example boron is then implanted and activated by pulsed laser annealing whereby the pulse fluence, frequency, and duration are chosen to maintain the amorphized region just below it's melting temperature. It is found that just below the melting temperature there is sufficient local ion mobility to secure the dopant into active positions within the silicon matrix to achieve a high degree of activation with essentially no change in concentration profile. The selection of the proper laser annealing parameters is optimized by observation of the reduction of sheet resistance and concentration profile as measured on a test site. Application of the method is applied to forming a MOS FET and a CMOS device. The additional processing steps required by the invention are applied simultaneously to both n-channel and p-channel devices of the CMOS device pair.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Method for real-time optical diagnostics in laser ablation and laser processing of layered and structured materials
ActiveUS20110100967A1Strong specificityImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingOptical diagnostics
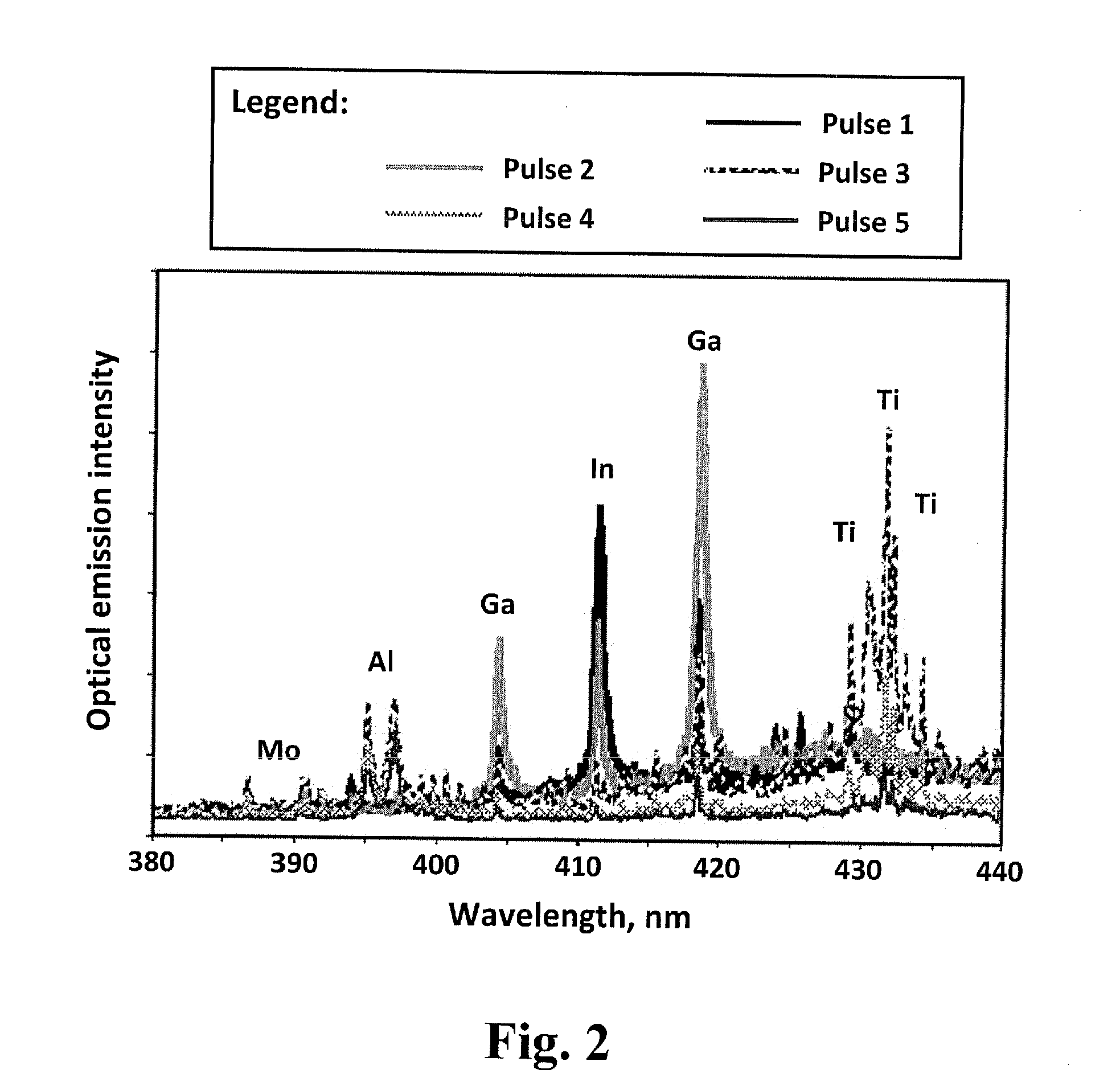
A method for real-time optical diagnostics in laser ablation and laser processing of layered or structured materials or material structures. Diagnostics is provided during laser ablation that is utilized regularly in laser processing and / or chemical analysis of structured materials, by means of measuring optical emission generated as a result of the pulsed laser-material interaction in real time. The method can involve a single-layer-film or a stack of multiple layers or a structure of different domains. The method is particularly beneficial in fabrication of thin-film structures, such as photovoltaic and electronic devices or circuits of devices.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRA
Contact Probe for the Delivery of Laser Energy
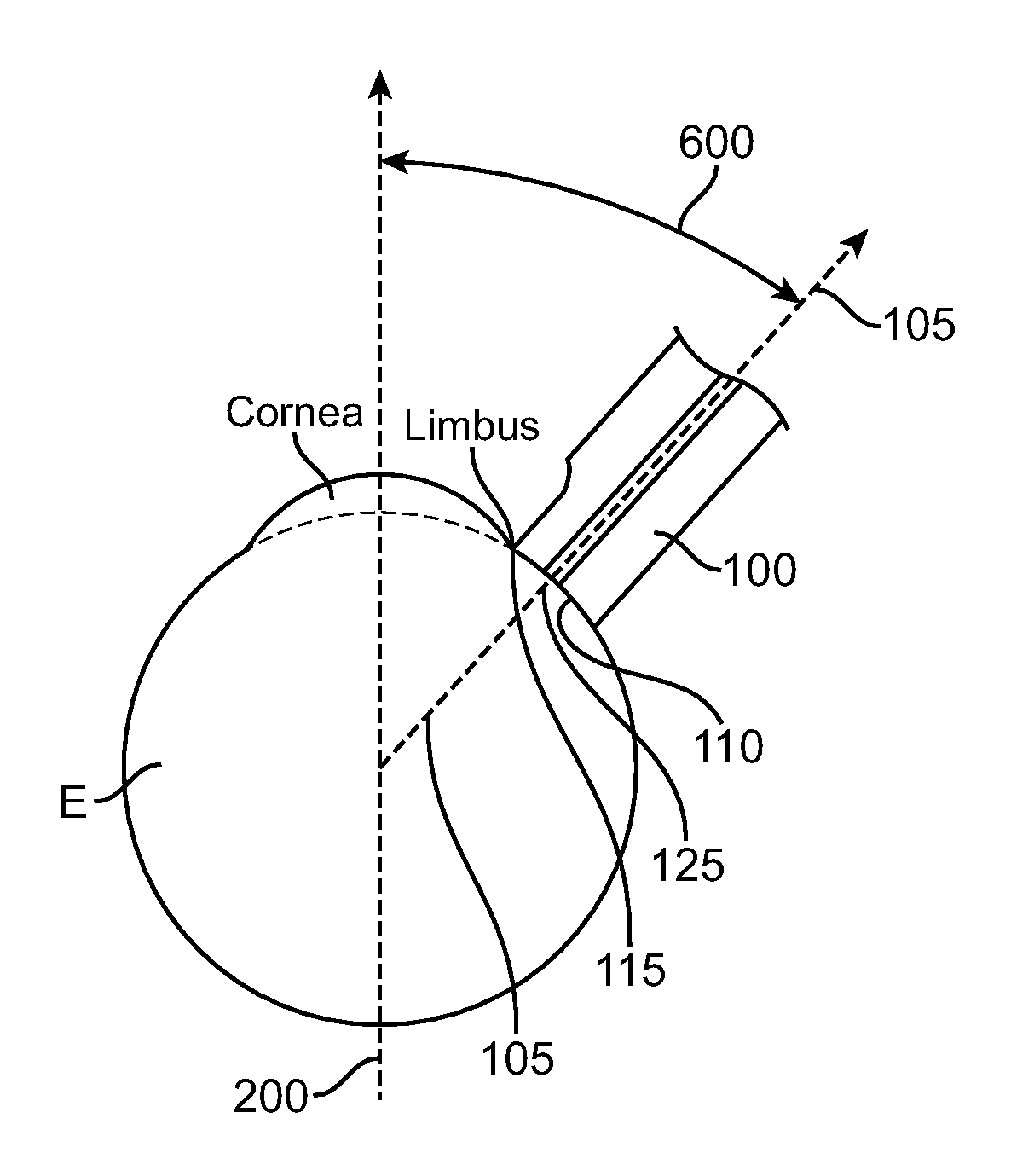
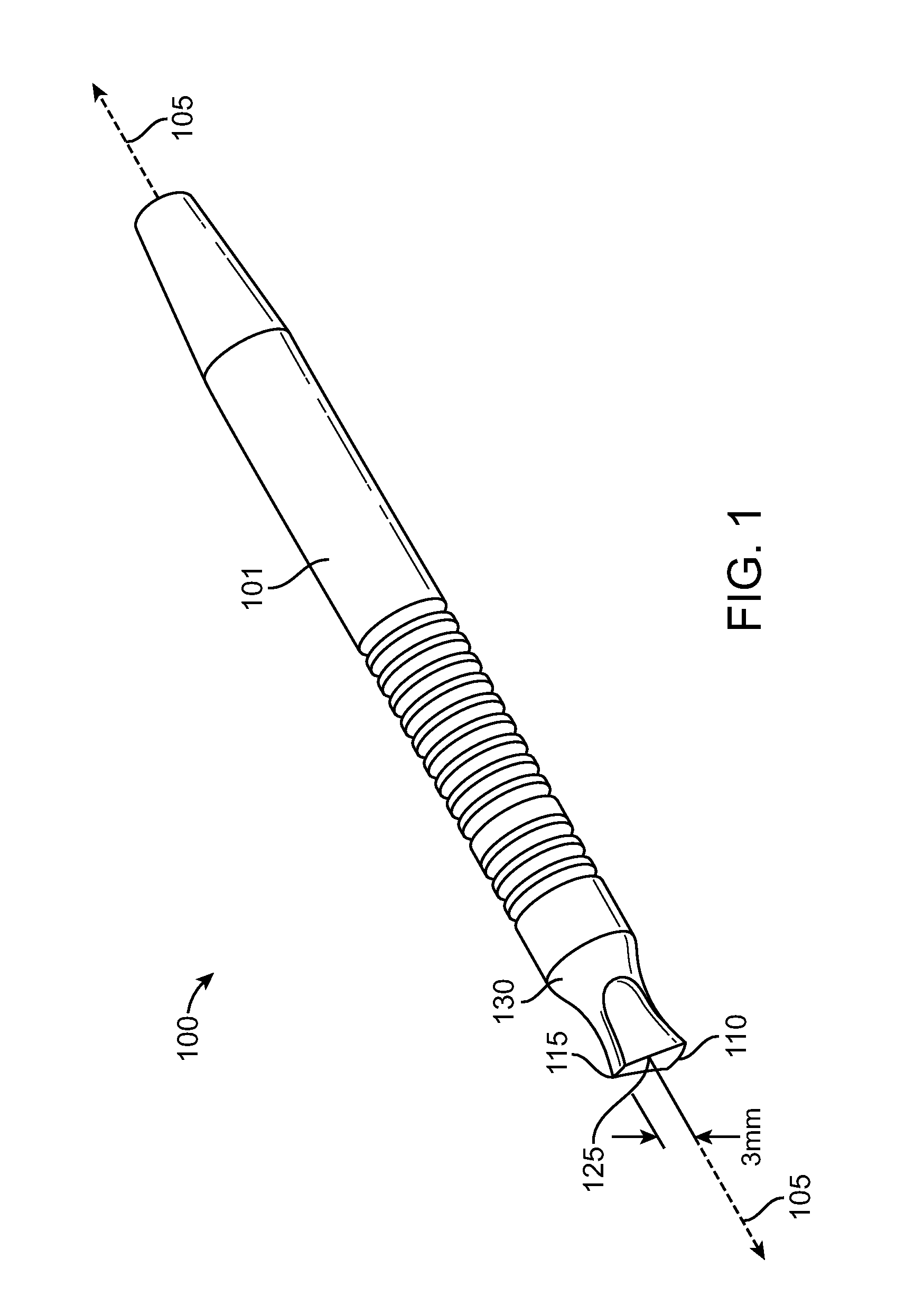
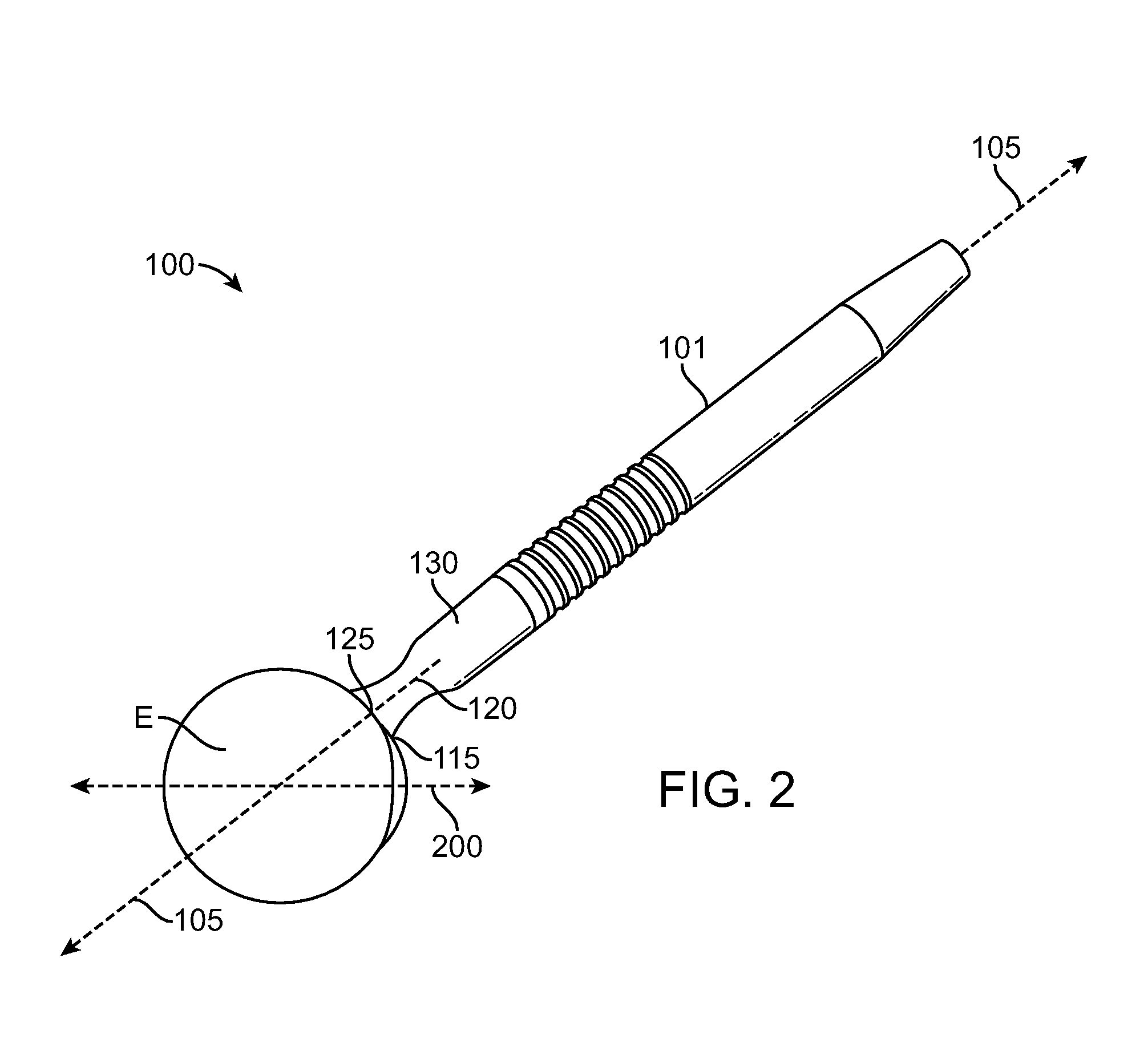
ActiveUS20100076419A1Avoiding and all photocoagulationLower eye pressureLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptical axisPars plana
Systems, devices, and methods for treating a glaucomatous eye are provided. An amount of pulsed laser energy is delivered to the pars plana of the eye by a hand-holdable device which comprises a hand-holdable elongate member and a contact member disposed on an end of the elongate member. A contact surface of the contact member is placed in direct contact with the eye so that a reference edge of the contact member aligns with the limbus and a treatment axis defined by the elongate member is angularly offset from the optical axis of the eye. The amount of pulsed laser energy delivered is insufficient to effect therapeutic photocoagulation but is sufficient to increase uveoscleral outflow so as to maintain a reduction from pre-laser treatment intraocular pressure. Amounts of pulsed laser energy will be transmitted to a circumferential series of tissue regions of the eye.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP +2
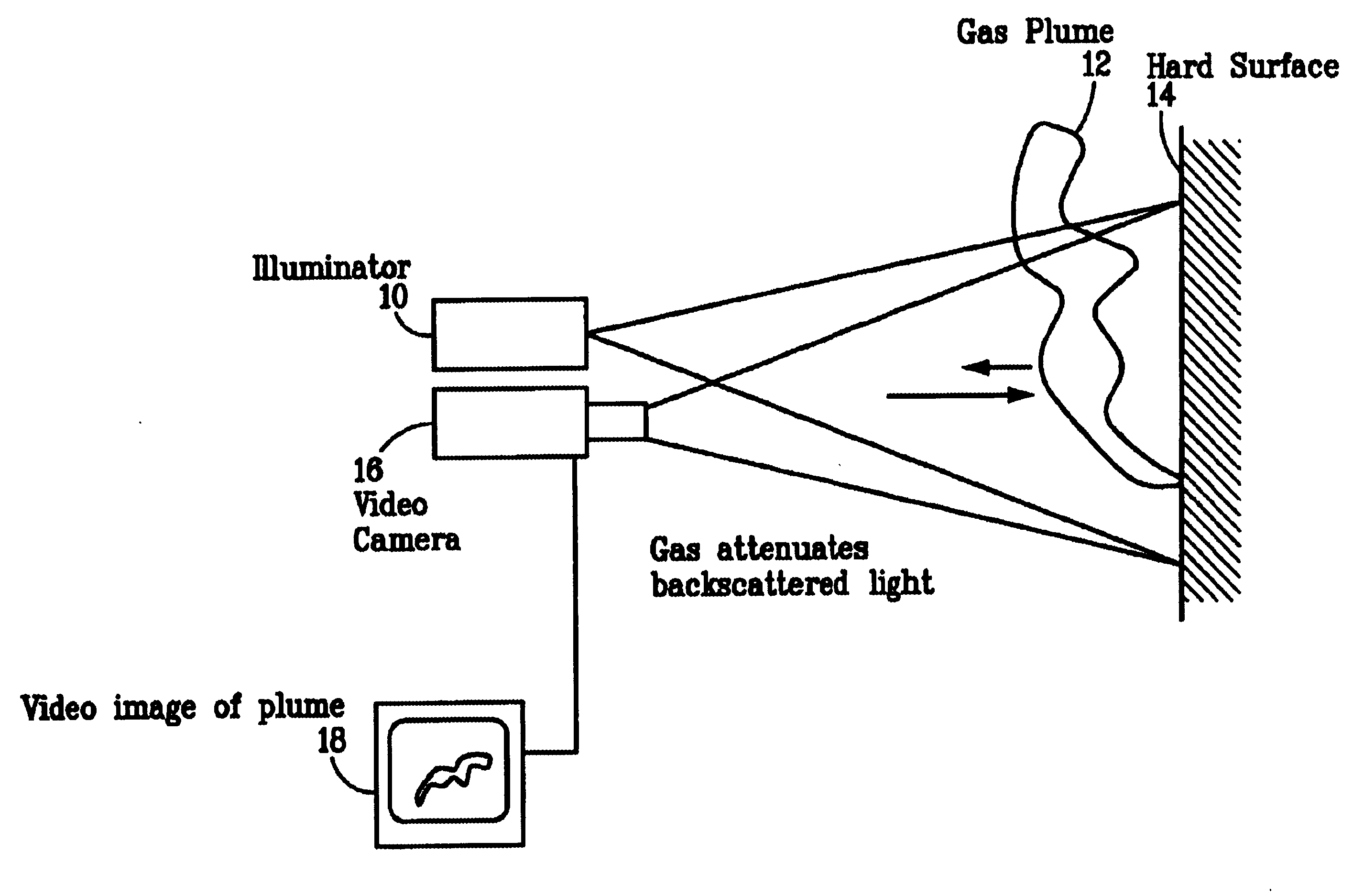
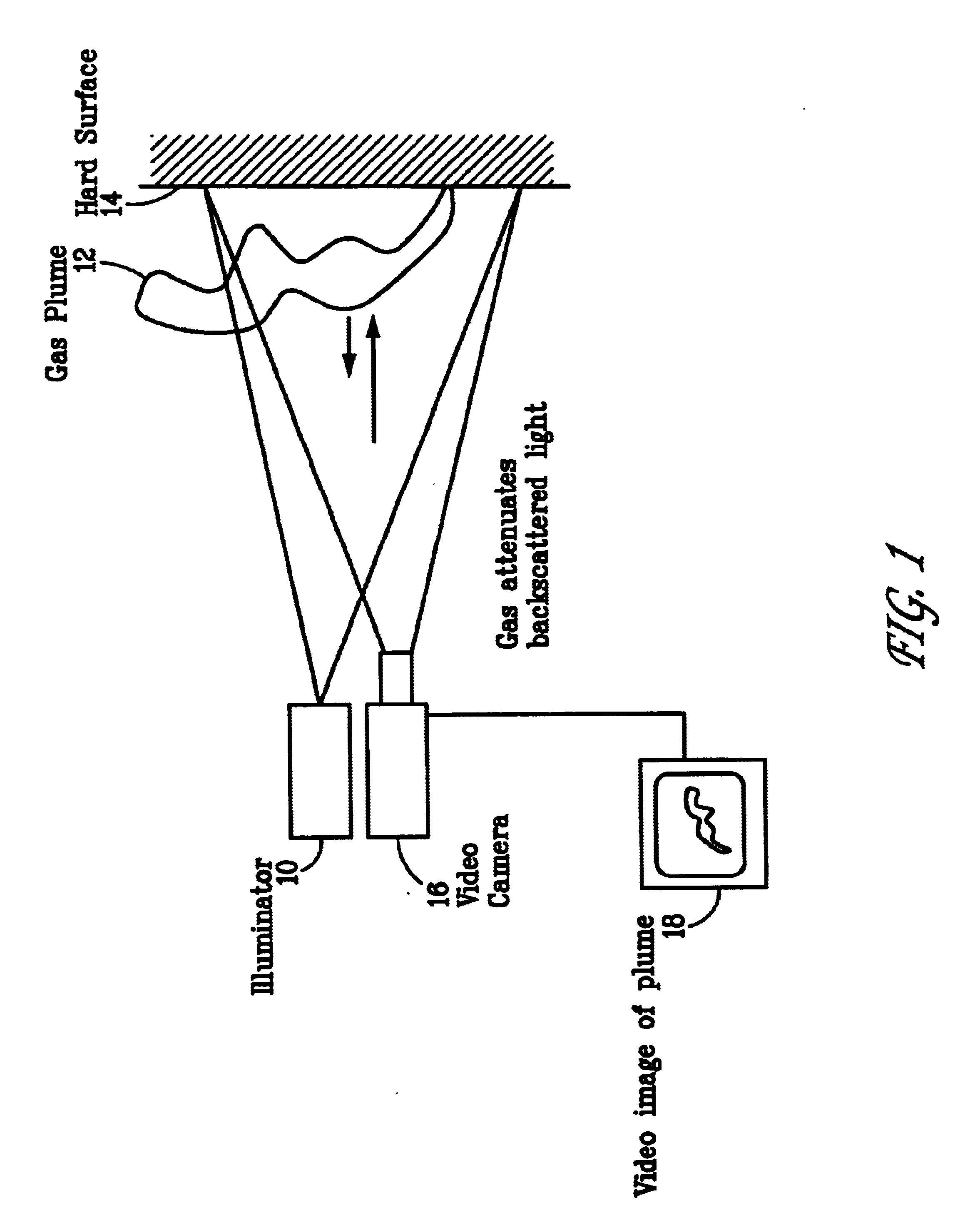
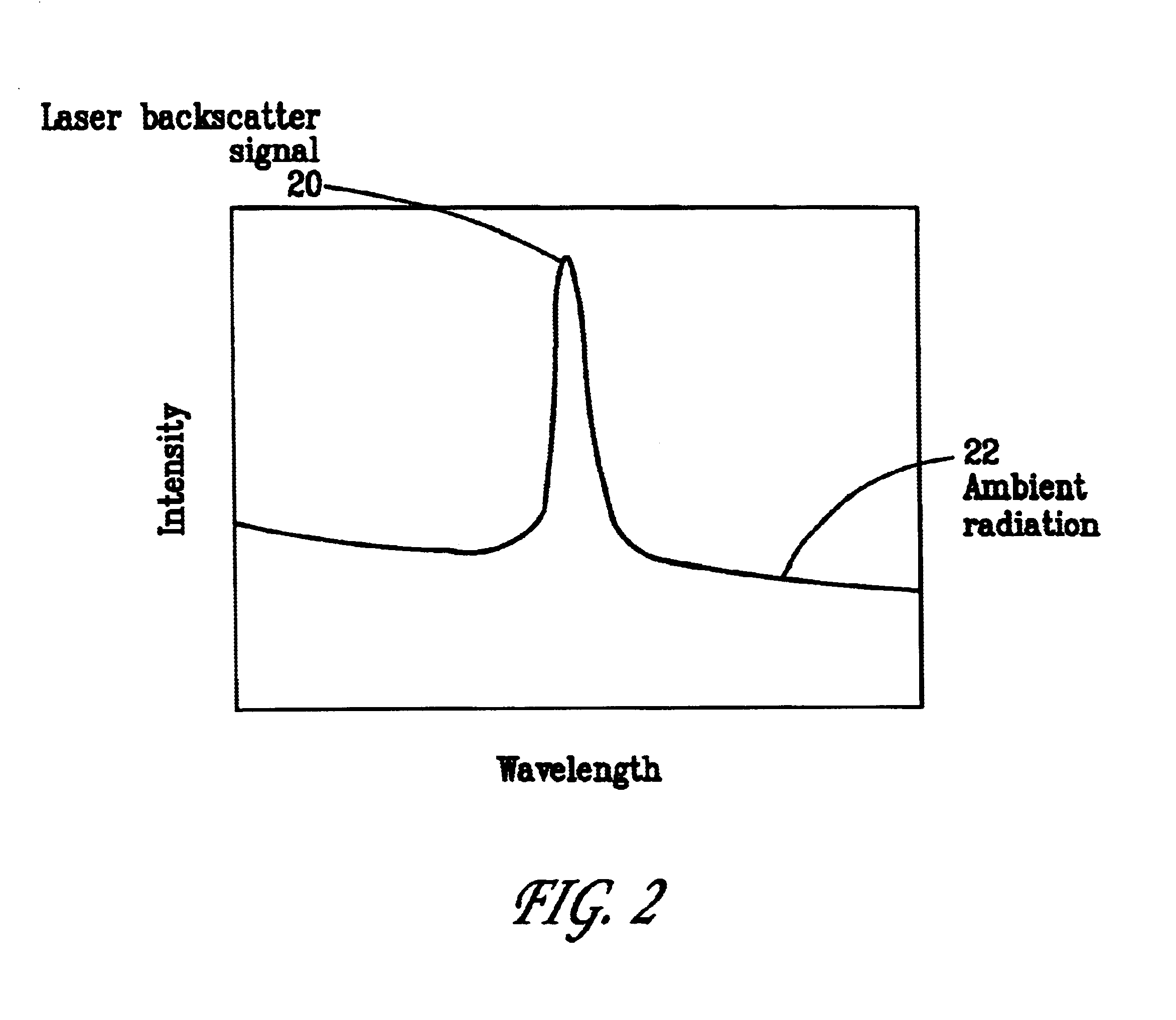
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS6690472B2Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMobile vehicleFluence
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
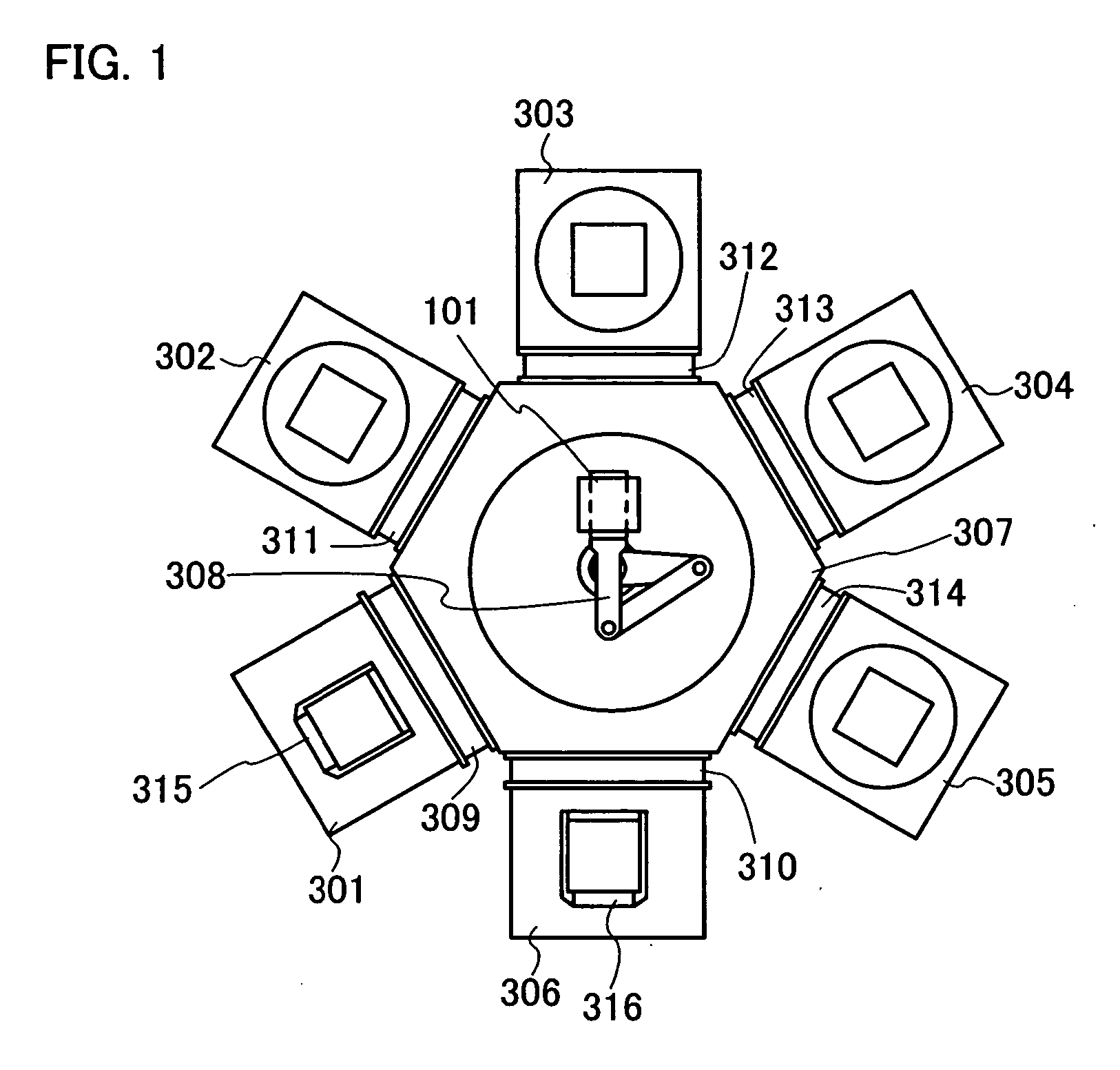
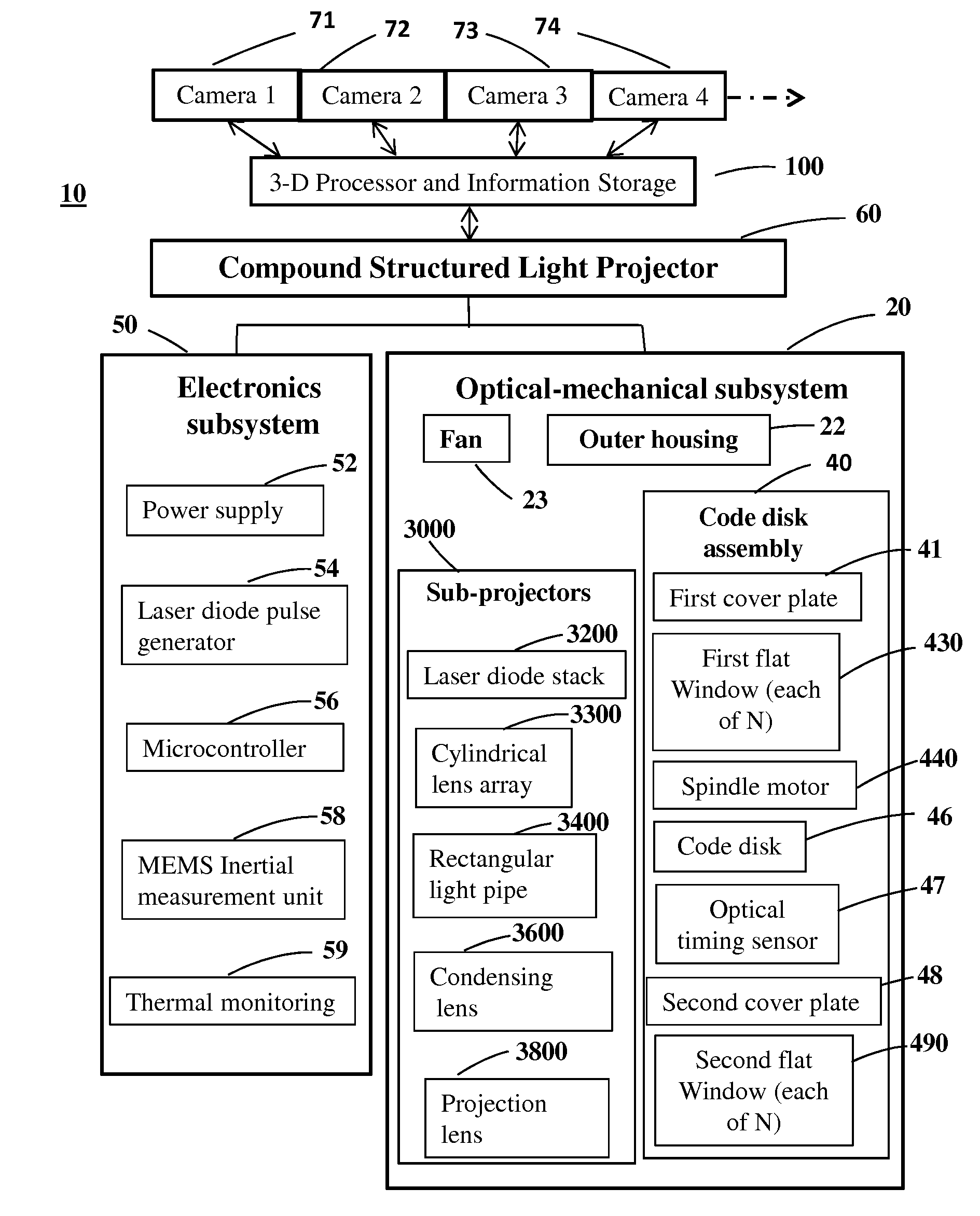
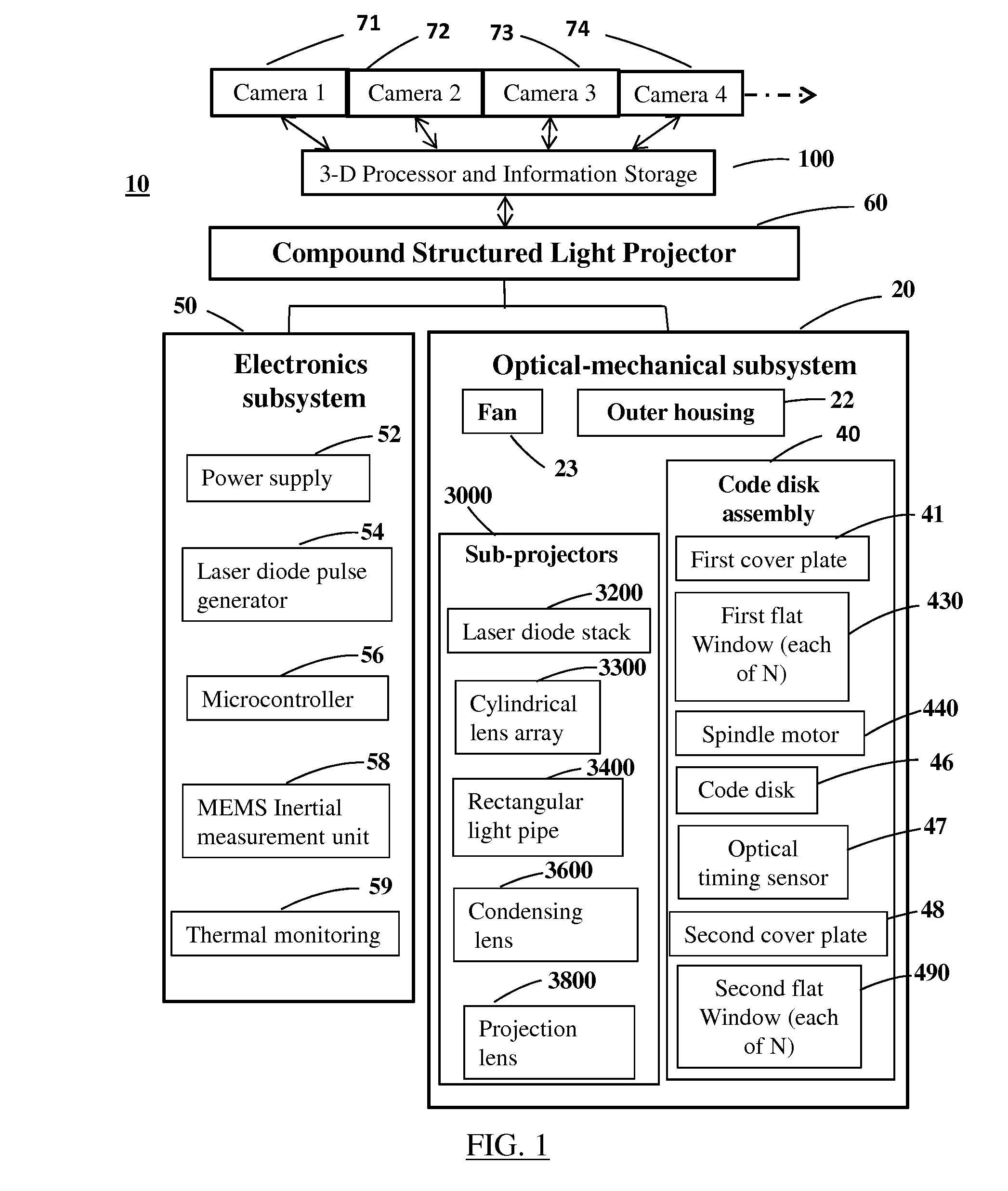
Compound structured light projection system for 3-D surface profiling
InactiveUS20140320605A1Increase powerImprove efficiencyUsing optical meansSteroscopic systemsHigh frame rateProjection system
A method and apparatus is provided for high speed, non-contact method of measuring the 3-D coordinates of a dense grid of points on a surface, including high accuracy interpolation between grid points. A plurality of pulsed laser sub-projectors sequentially illuminates a plurality of discrete Gray code bar pattern transparencies carried on a spinning circular code disk to project high frame rate structured light. The structured light is reflected by the surface and recorded at high signal-to-noise ratio by a plurality of high frame rate digital cameras, then decoded and interpolated by electronic signal processing. A numerical formula is derived for numbers of equally spaced discrete code patterns on the code disk that allow each camera to receive pulses from all sub-projectors and all patterns at a constant frame rate. Methods to derive an extended complementary Gray code pattern sequence and to normalize measured signal amplitudes are presented.
Owner:JOHNSON PHILIP MARTIN
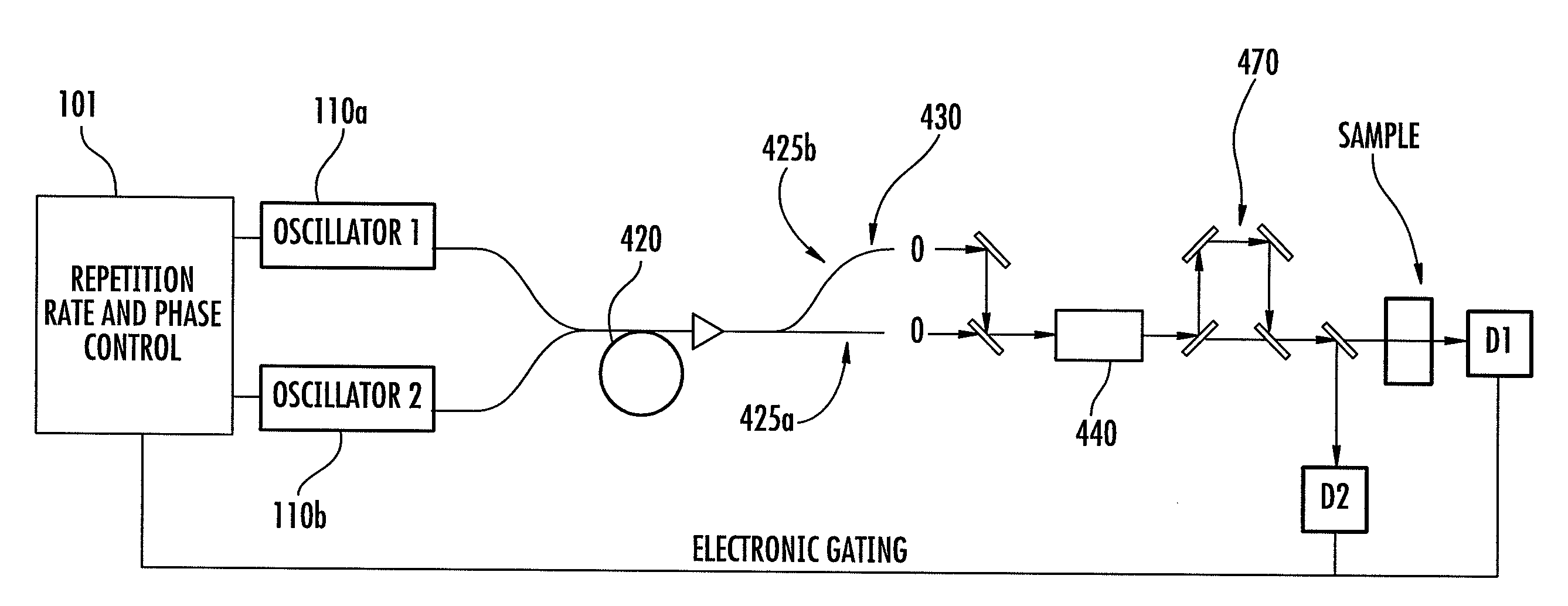
Optical signal processing with modelocked lasers
ActiveUS20110080580A1High resolutionMinimize fluctuationLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFiberTime delays
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. In some embodiments an effective CDSL is constructed with only one laser. At least one embodiment includes a coherent scanning laser system (CSL) for generating pulse pairs with a time varying time delay. A CDSL, effective CDSL, or CSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Silicon chip carrier with through-vias using laser assisted chemical vapor deposition of conductor
ActiveUS20050082676A1High aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesControl mannerGas phase
This disclosure teaches a method of filling deep vias or capping deep conducting paste filled vias in silicon or glass substrate using laser assisted chemical vapor deposition of metals. This method uses a continuous wave or pulsed laser to heat the via bottom and the growing metal fill selectively by selecting the laser wavelength such that silicon and / or glass do not absorb the energy of the laser in any appreciable manner to cause deposition in the field. Alternatively holographic mask or an array of micro lenses may be used to focus the laser beams to the vias to fill them with metal. The substrate is moved in a controlled manner in the z-direction away from the laser at about the rate of deposition thus causing the laser heating to be focused on the surface region of the growing metal fill.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
Laser three-dimensional imaging device based on single-photon detector
InactiveCN101776760AHigh sensitivityMiniaturizationElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsMeasurement pointFlight time
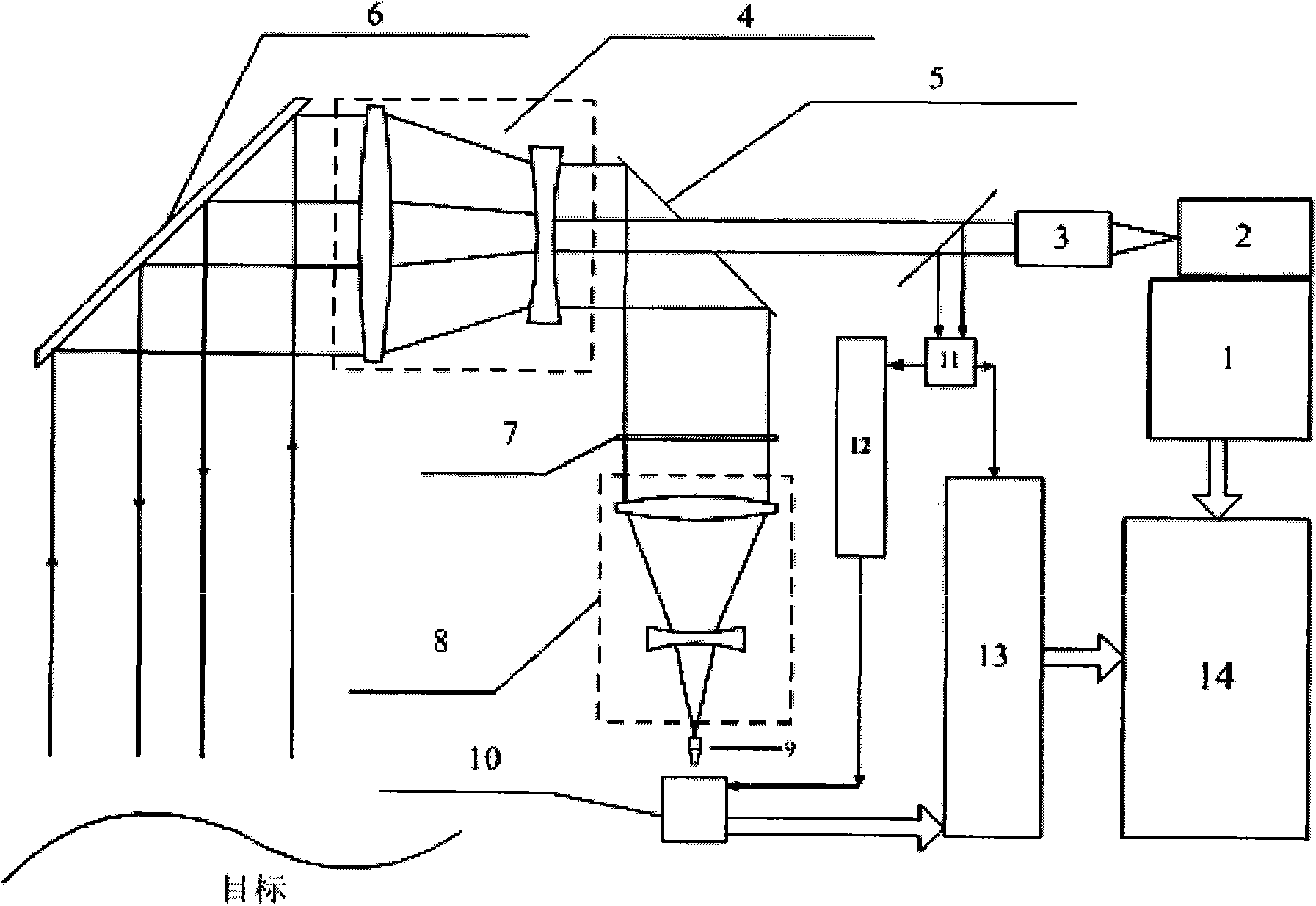
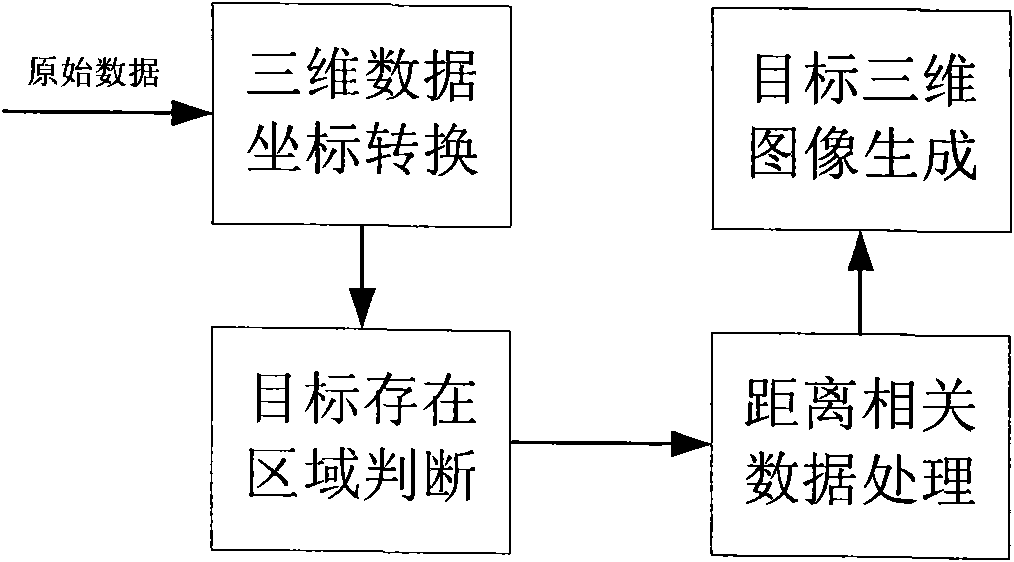
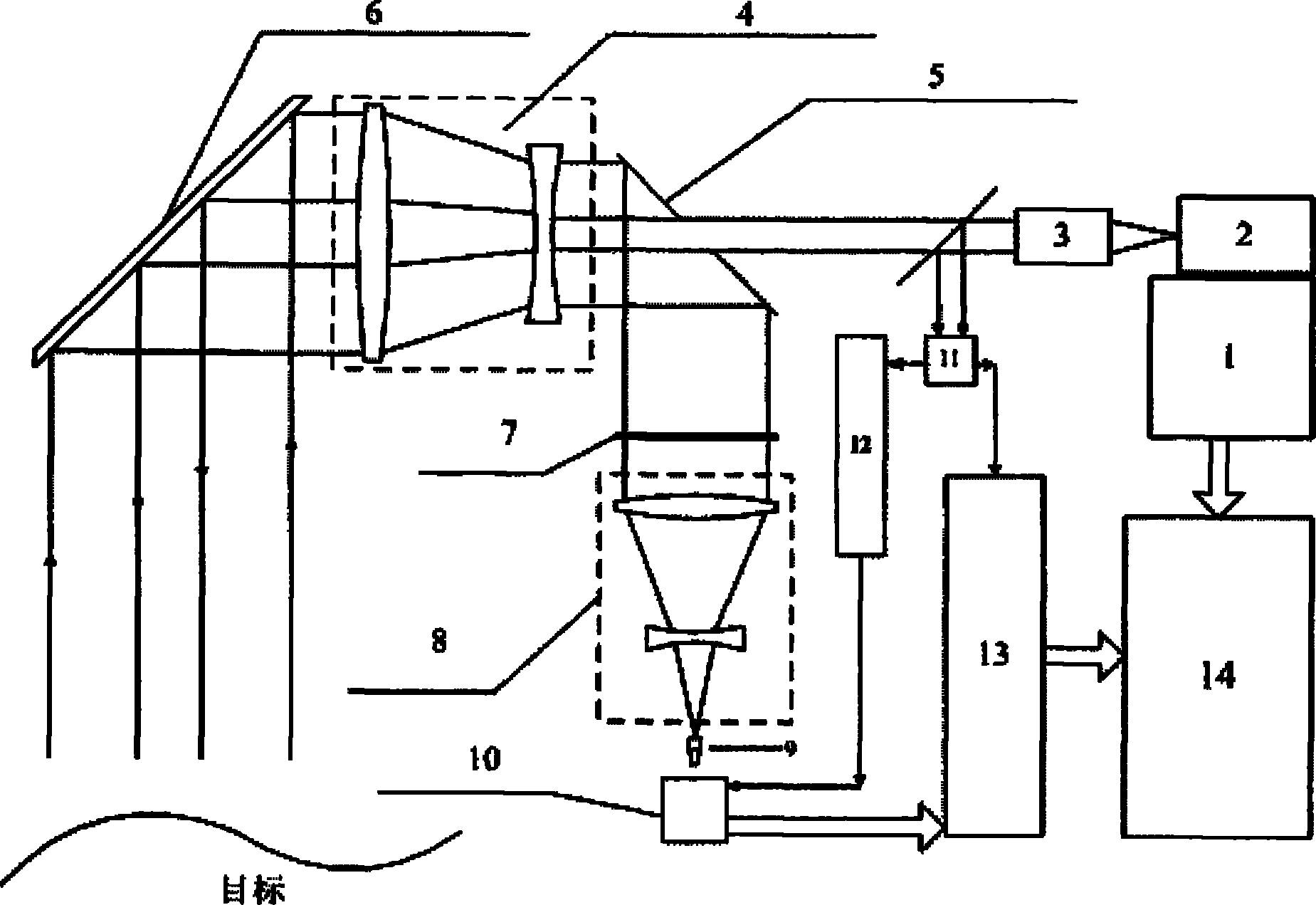
The invention discloses a laser three-dimensional imaging device based on a single-photon detector, belonging to the technical field of photoelectric instruments. A target to be detected is irradiated by the laser pulse emitted by a pulsed laser via a scanning system; the returning photons are received by a receiving / emitting co-axial optical system, i.e., the returning photons are received by a double-gating single-photon detecting module via a spectral filter and a spatial filter and an arriving pulse is outputted, so that the photon flight time of the target measuring point can be measured by combining the laser emission detection and the multi-photon arriving pulse time; and a data processing unit is used for carrying out the coordinate conversion based on the position and attitude data, scanning mirror targeting data, and photon flight time of the three-dimensional imaging device, de-noising and three-dimensional image construction and correction, so as to output the reliable target three-dimensional range image. The invention solves the problems that the existing laser three-dimensional imaging device is incapable of penetrating vegetation and camouflage and being miniaturized when conducting long-distance operations.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
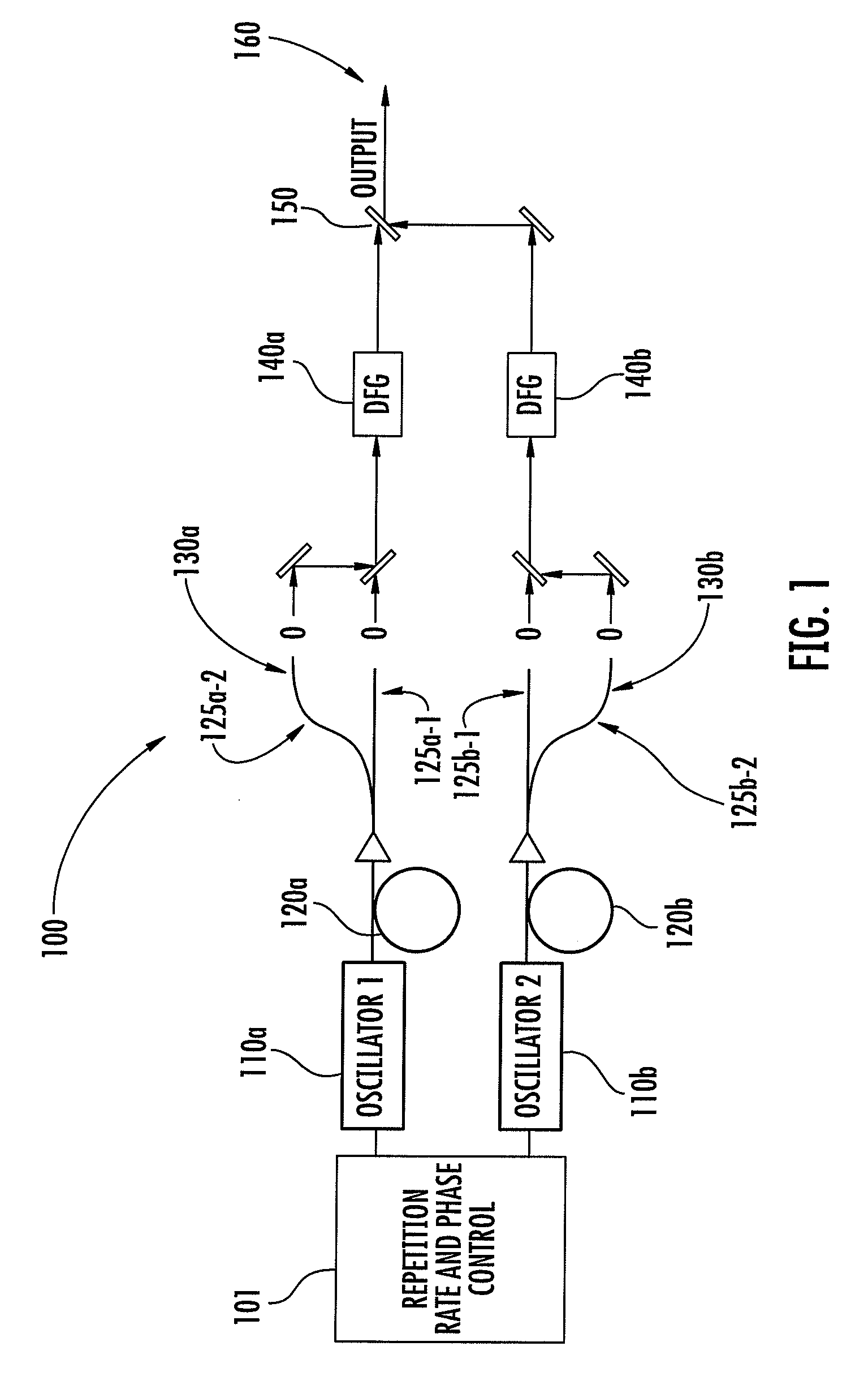
Optical scanning and imaging systems based on dual pulsed laser systems
ActiveUS20100225897A1Noise minimizationEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsFiberFrequency conversion
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated, including highly integrated configurations. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. The oscillators are configured to operate at slightly different repetition rates, such that a difference δfr in repetition rates is small compared to the values fr1 and fr2 of the repetition rates of the oscillators. The CDSL system also includes a non-linear frequency conversion section optically connected to each oscillator. The section includes a non-linear optical element generating a frequency converted spectral output having a spectral bandwidth and a frequency comb comprising harmonics of the oscillator repetition rates. A CDSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com