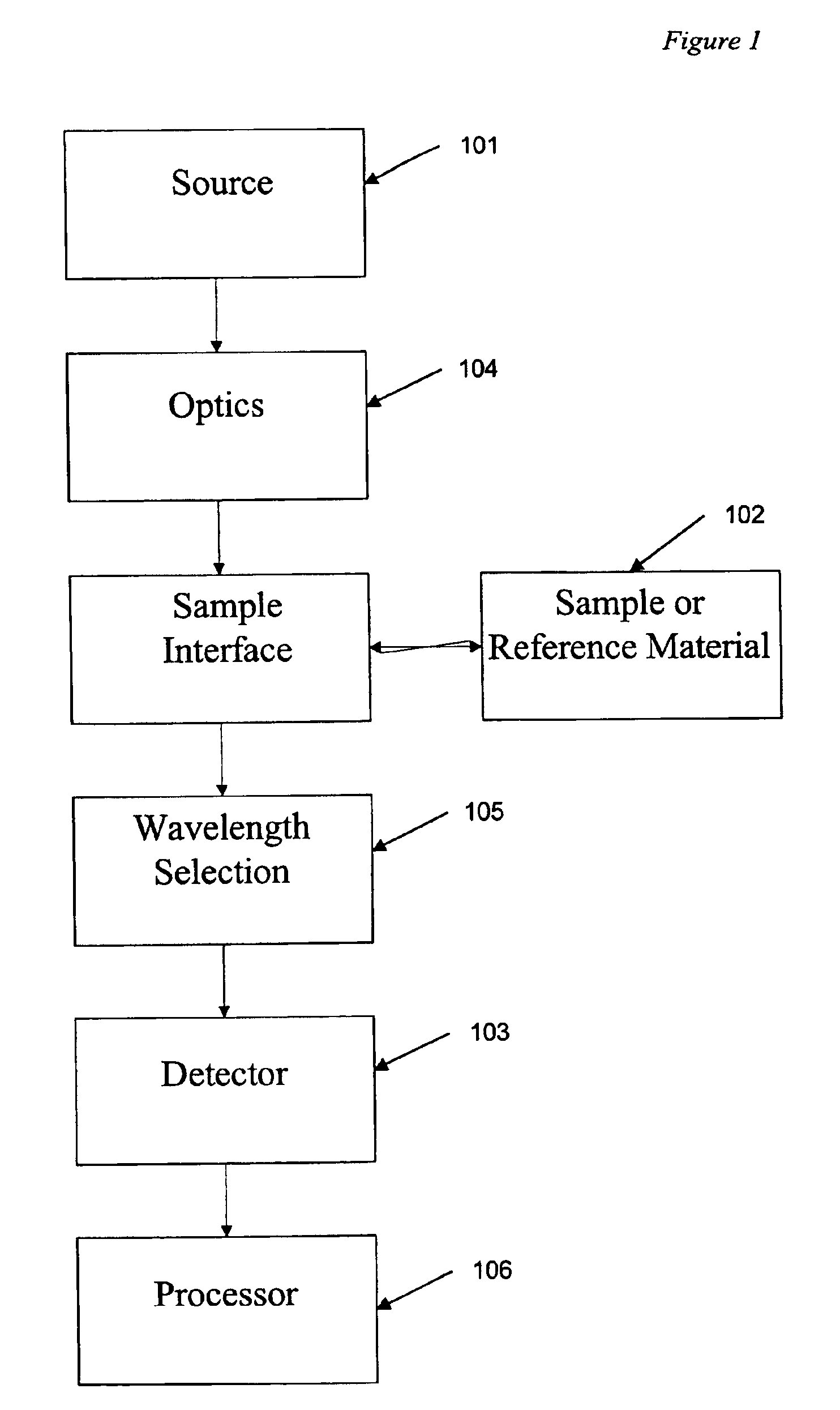
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13043 results about "Reflectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at an interface. The reflectance spectrum or spectral reflectance curve is the plot of the reflectance as a function of wavelength.
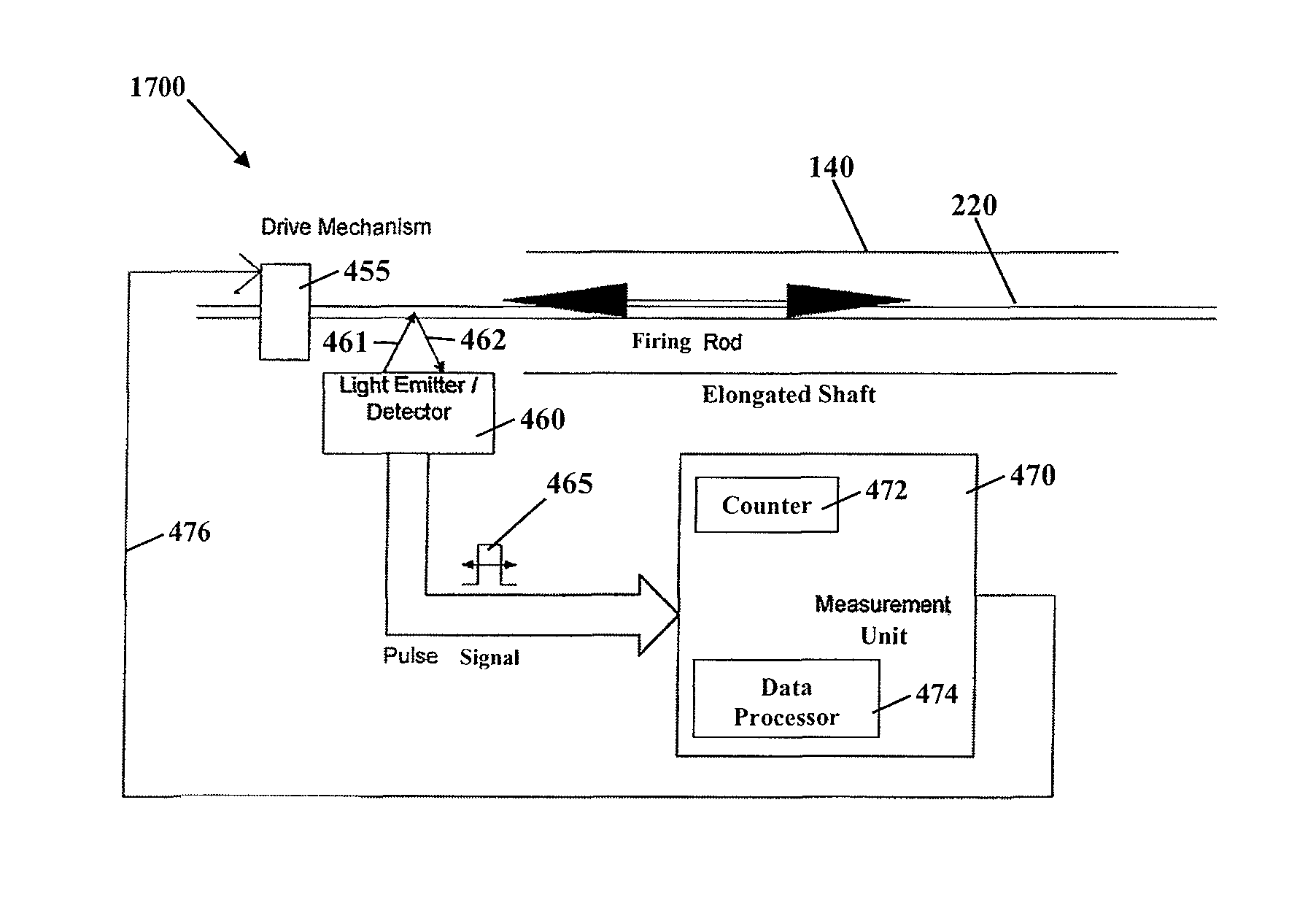
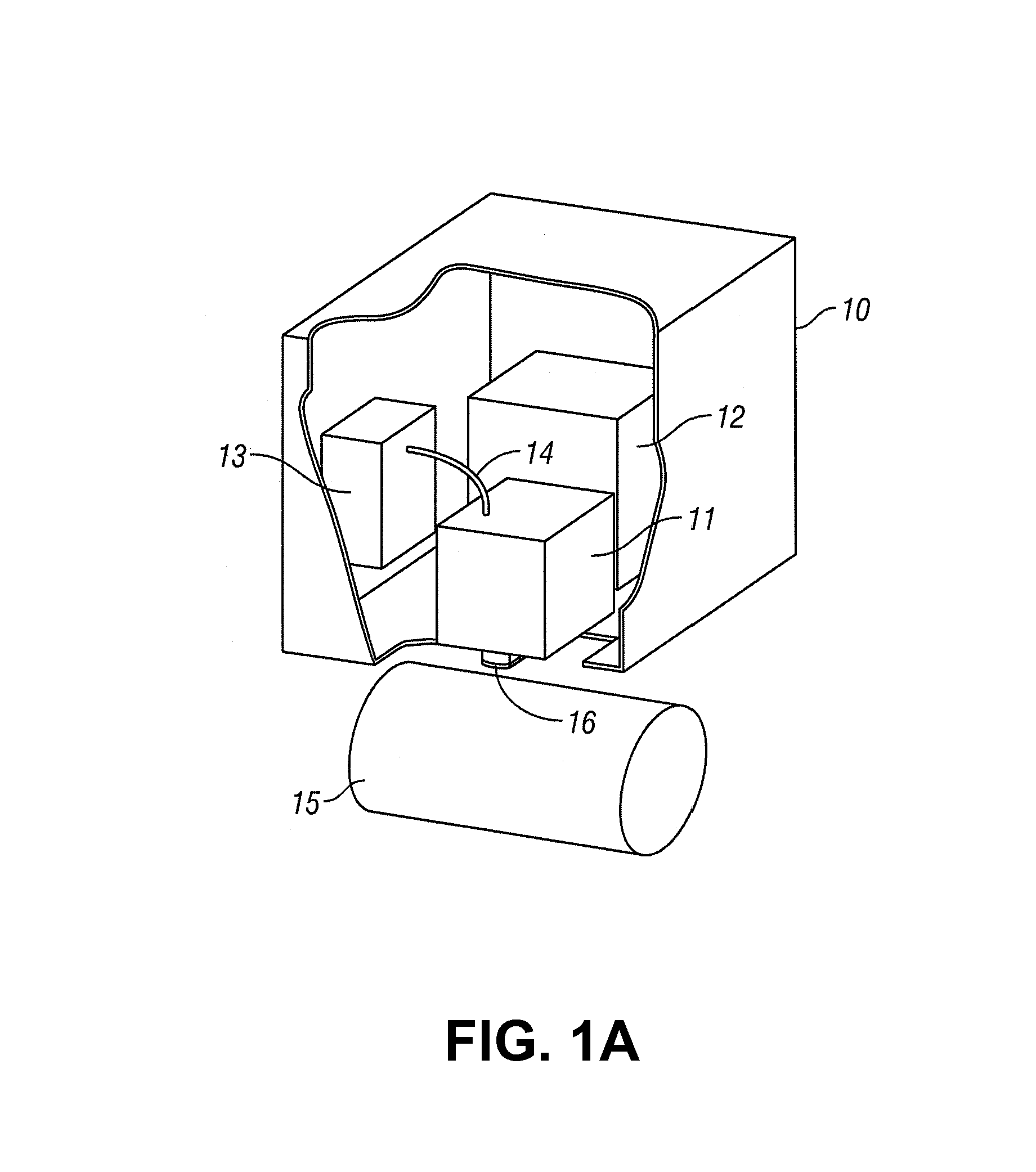
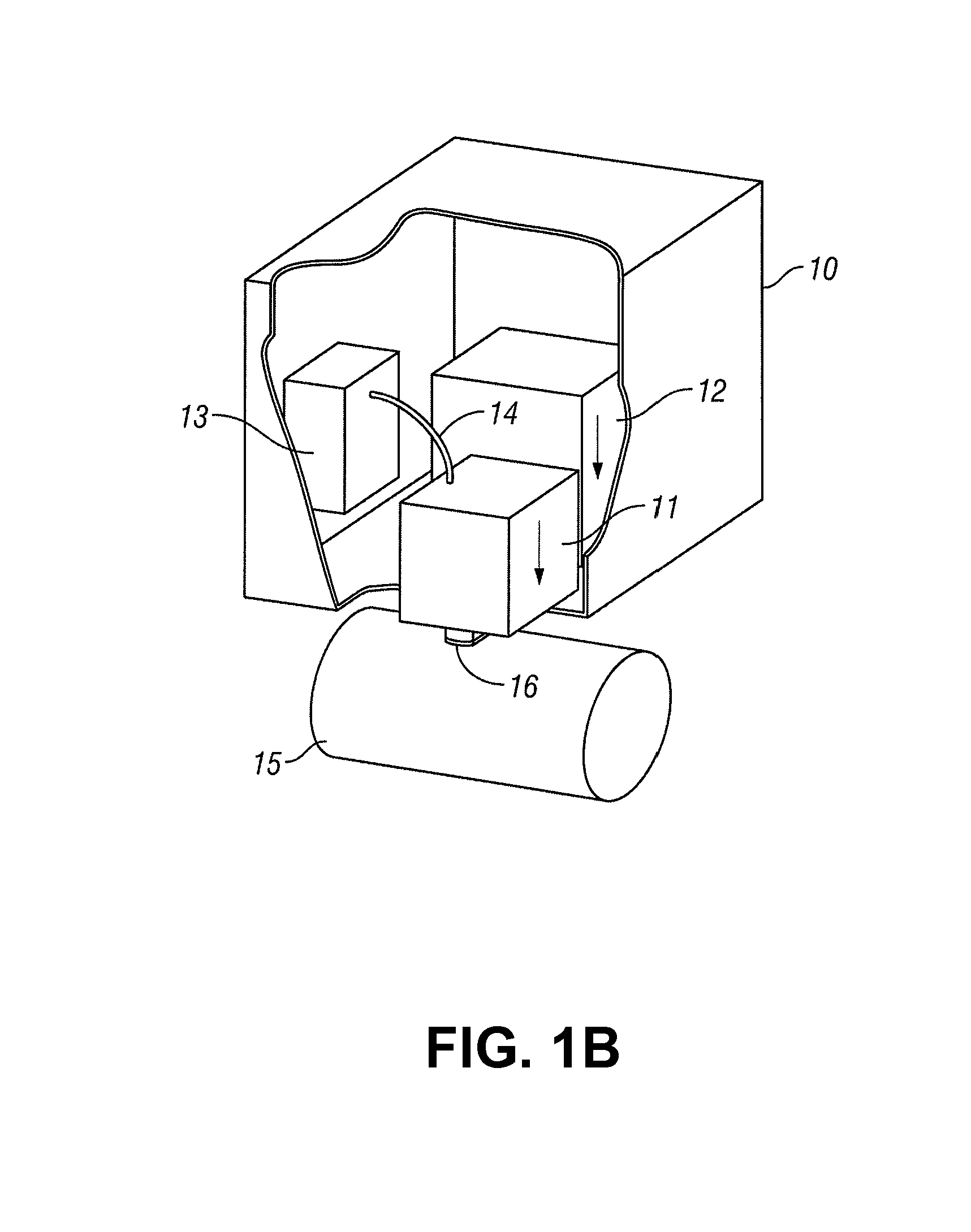
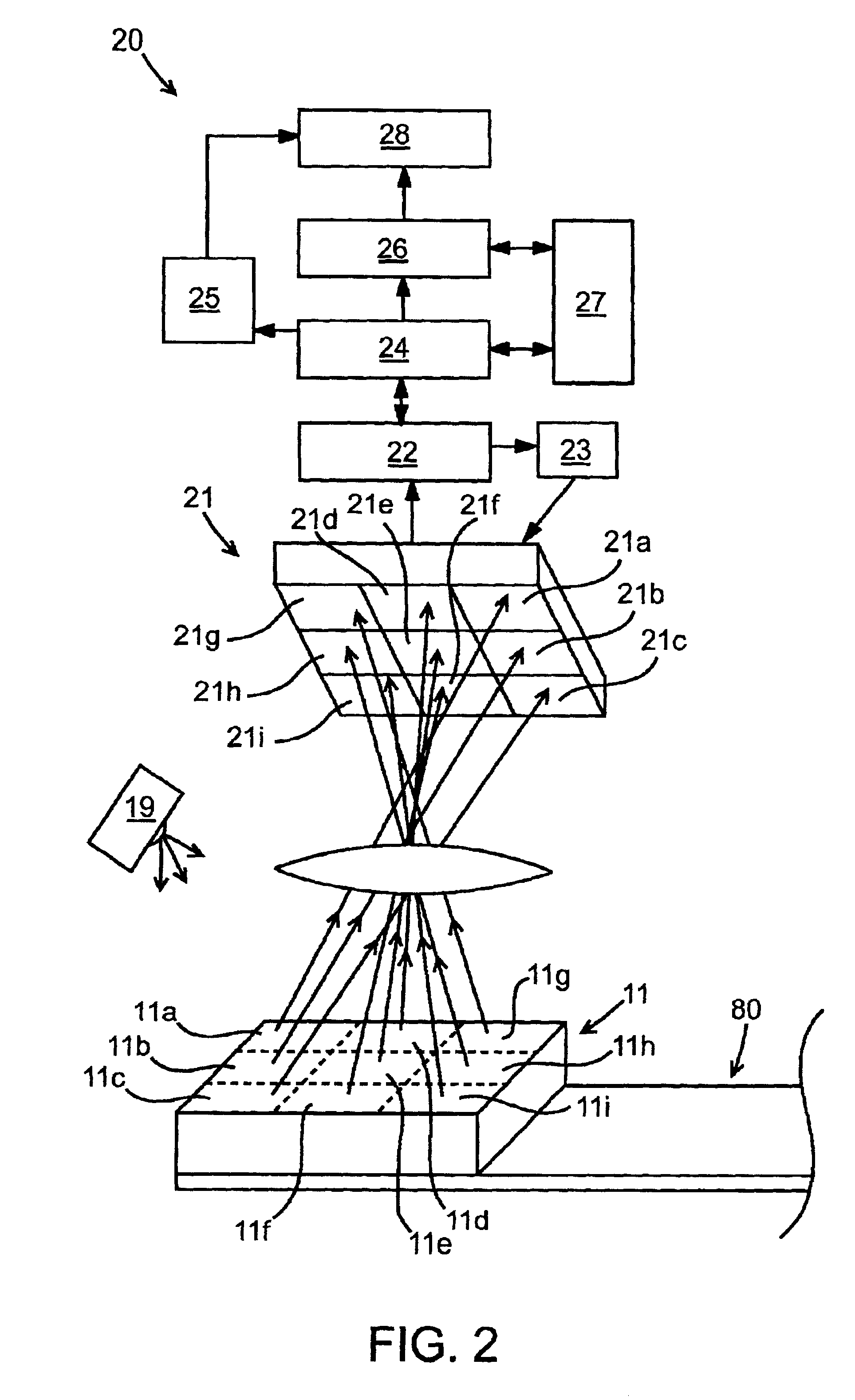
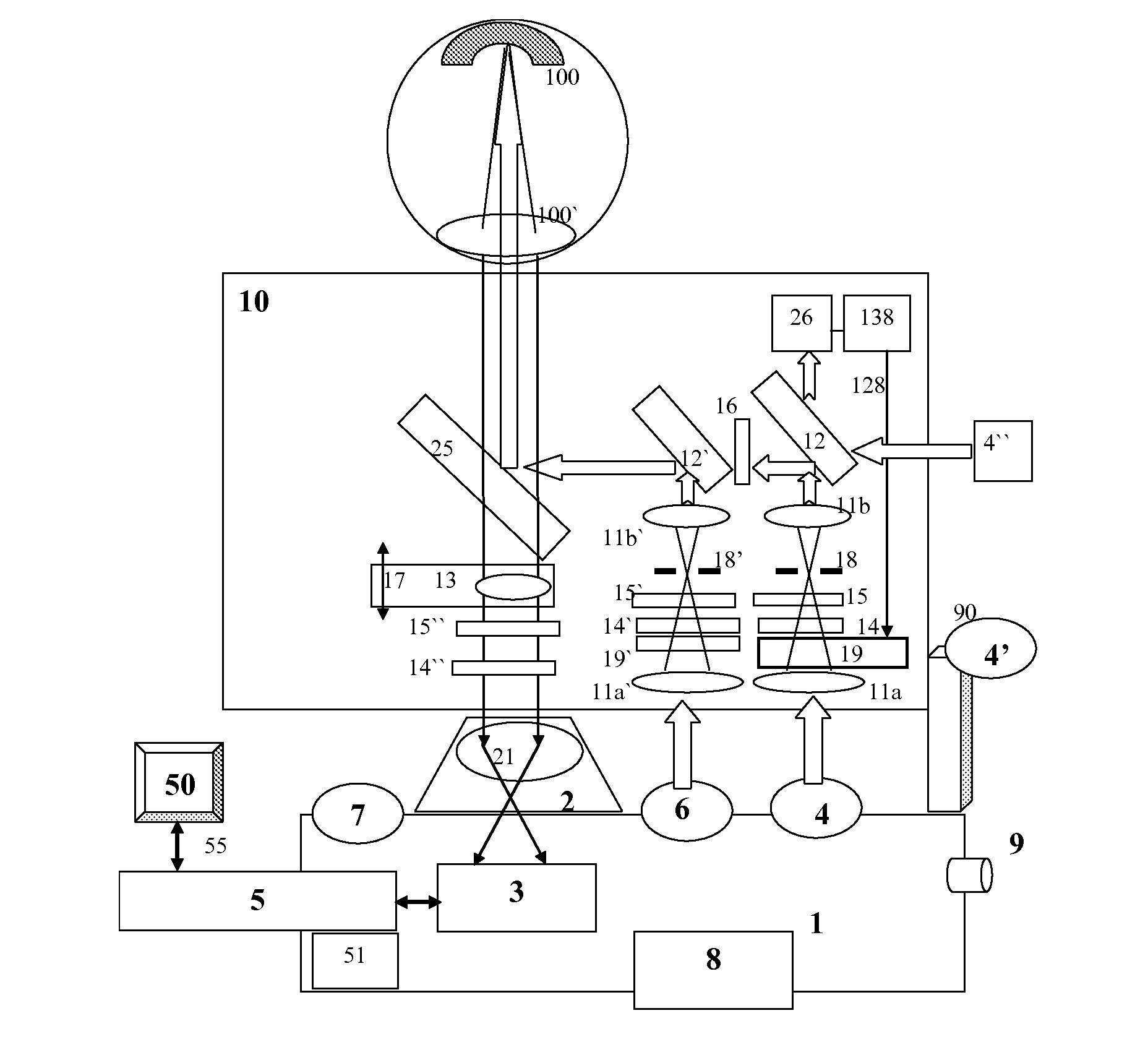
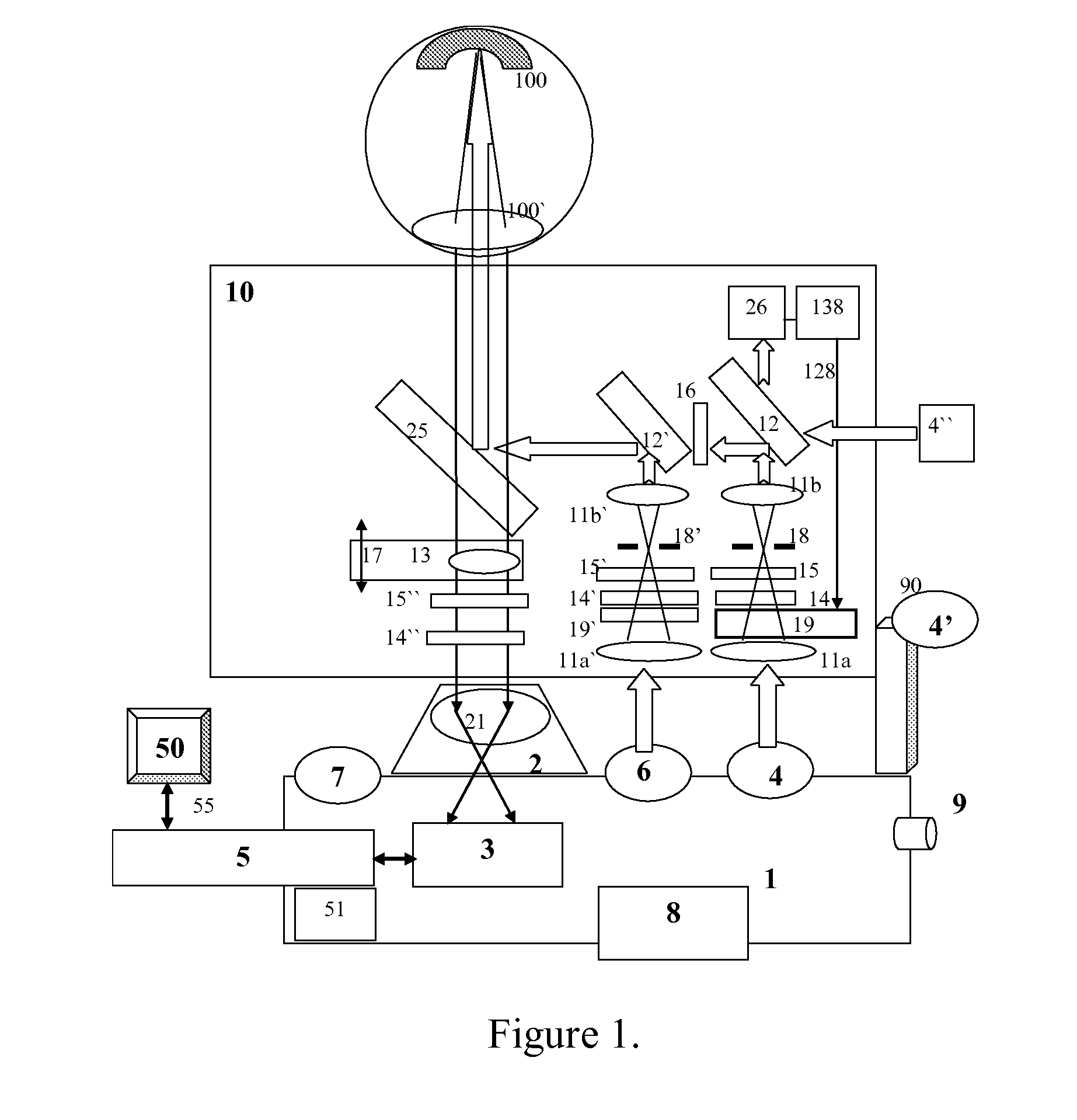
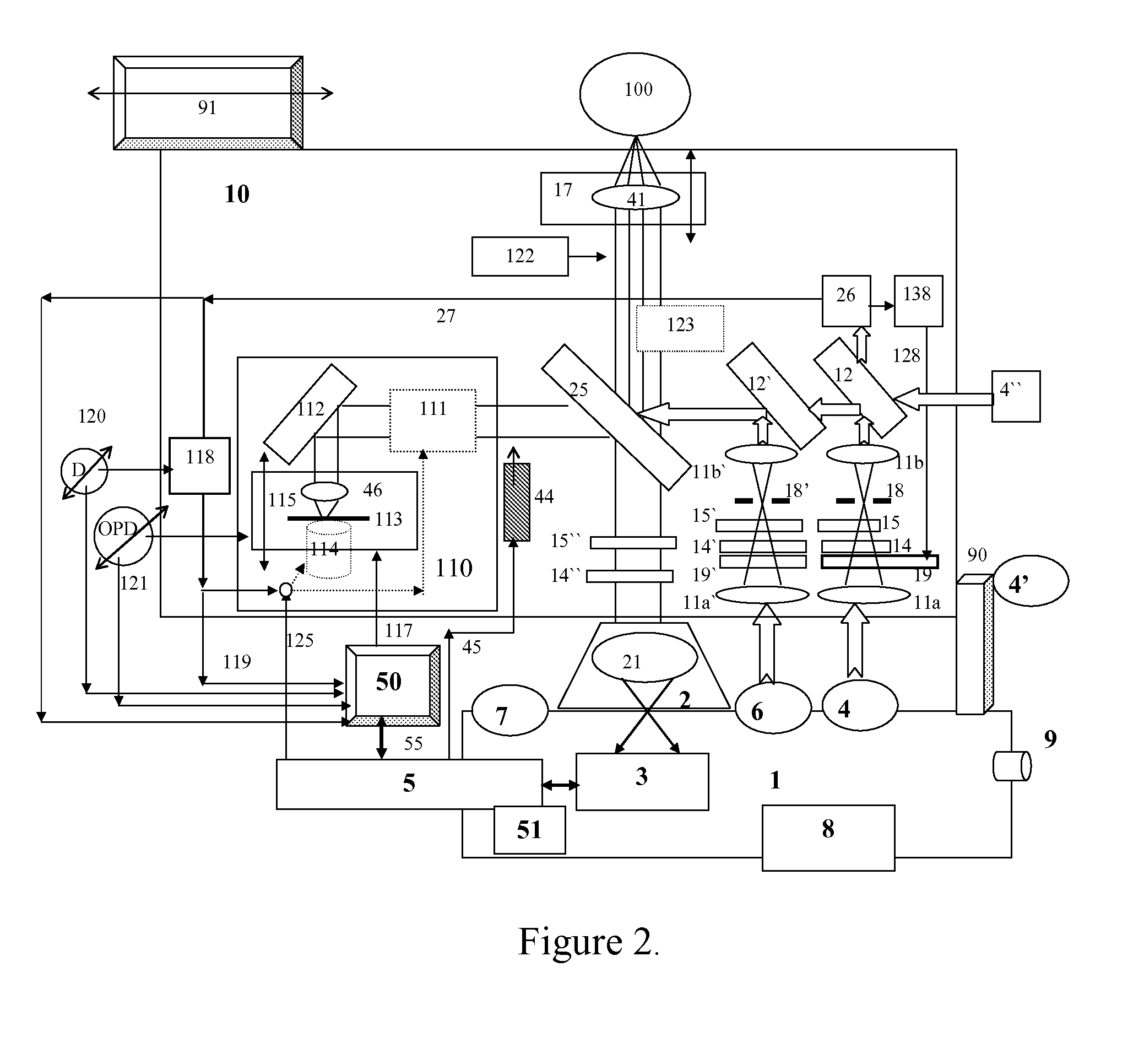
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS8967443B2Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionMotion parameter
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A sensor senses a parameter of light reflected from the surface of the firing rod, which includes markings that change the reflectivity of the firing rod. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position and speed of the firing rod, based on the sensed parameter of the light reflected from the surface of the firing rod.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Optical probe including predetermined emission wavelength based on patient type
ActiveUS7096052B2Reduce light energyCorrectly employDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLight energyPatient type
A reflectance sensor which can be applied to a patient in a manner which reduces the light energy reaching the detector without first being attenuated by the tissue at the measurement site. Moreover, the reflectance sensor includes emitting devices adapted for use in legacy patient monitoring systems.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Electro-optic mirror cell
ActiveUS7255451B2Limit and substantially precludes touching and harmingSimple preparation processMirrorsThin material handlingElectricityConductive coating
A reflective element assembly for a variable reflectance vehicular mirror includes a front substrate having a transparent conductive coating disposed on a second surface, and a rear substrate having a third surface conductive coating disposed on its third surface and preferably, a fourth surface conductive coating disposed on its fourth surface. At least a portion of the third surface conductive coating may wrap around an edge portion of the rear substrate and at least a portion of the fourth surface conductive coating may wrap around at least a second portion of the perimeter edge so as to establish electrical continuity between the fourth surface conductive coating on the fourth surface and the third surface conductive coating on the third surface. The rear substrate may have a smaller dimension than the front substrate so as to provide an overhang region, preferably at the wraparound region.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
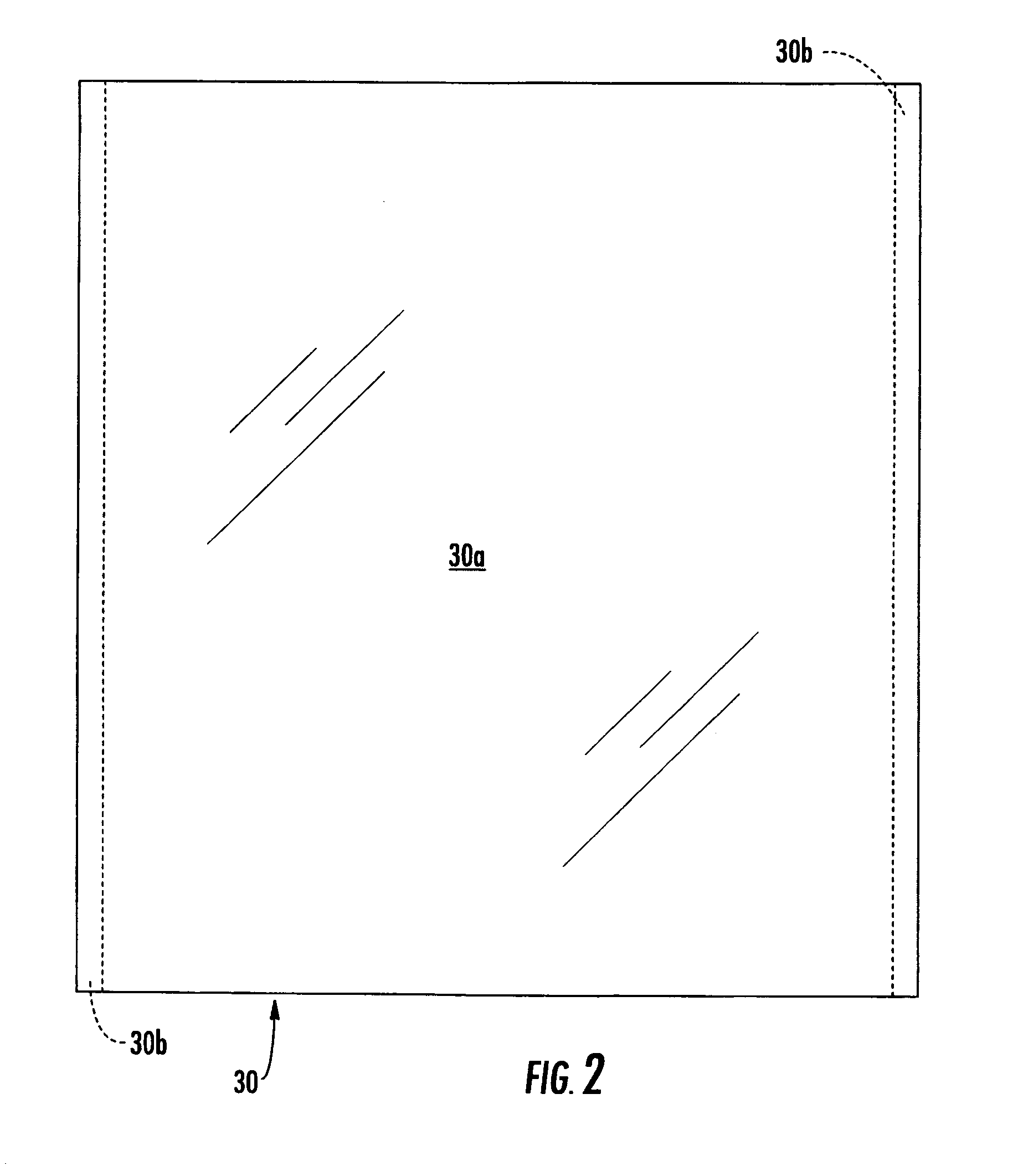
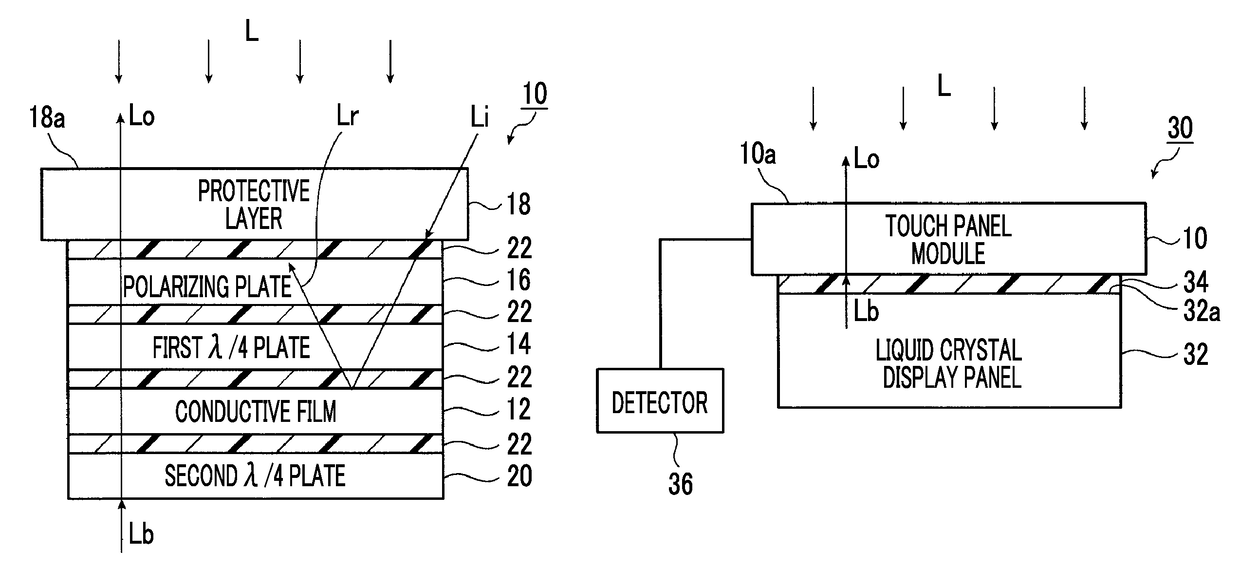
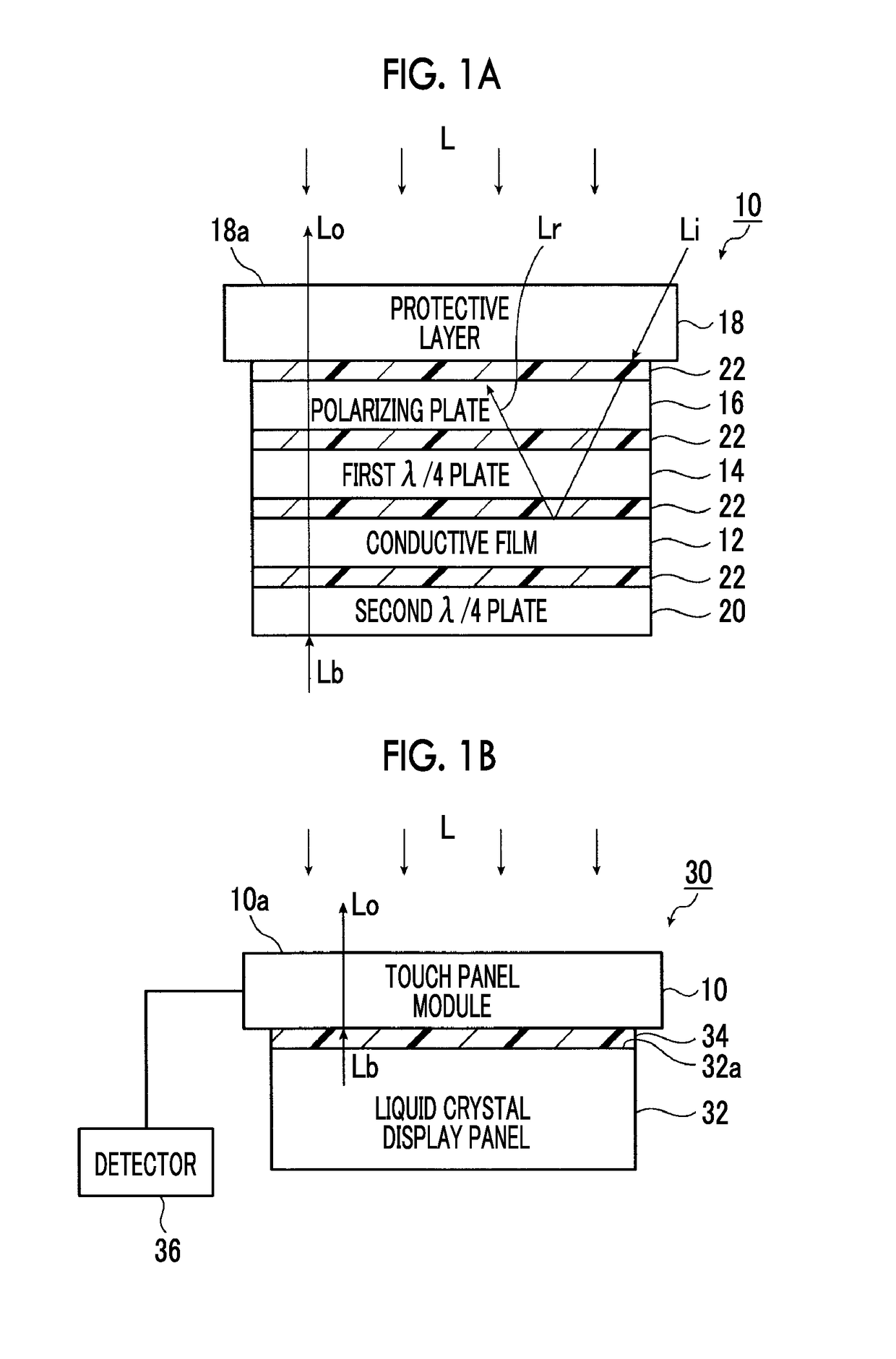
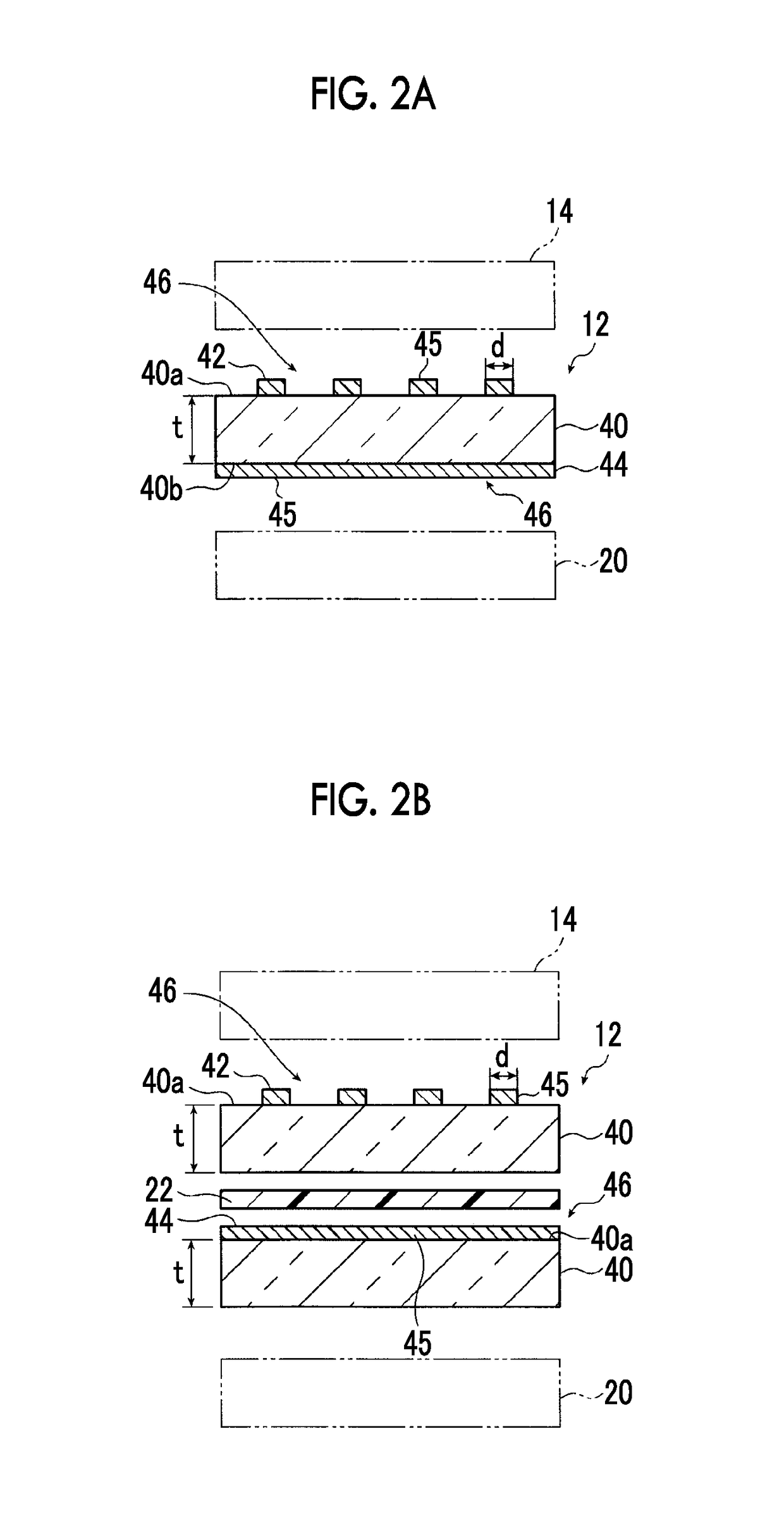
Touch panel module and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS10101861B2Improve visibilityLower resistanceInput/output processes for data processingMetal electrodesProtection layer
A touch panel module in which a conductive film in which a mesh conductive layer composed of a mesh-like metal electrode is formed on a support, a λ / 4 plate, a polarizing plate, and a protective layer are arranged in this order. A λ / 4 plate is further arranged on a side of the conductive film opposite to the protective layer. The touch panel module has a visible light diffuse reflectivity of 2% or less, which is measured from the protective layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
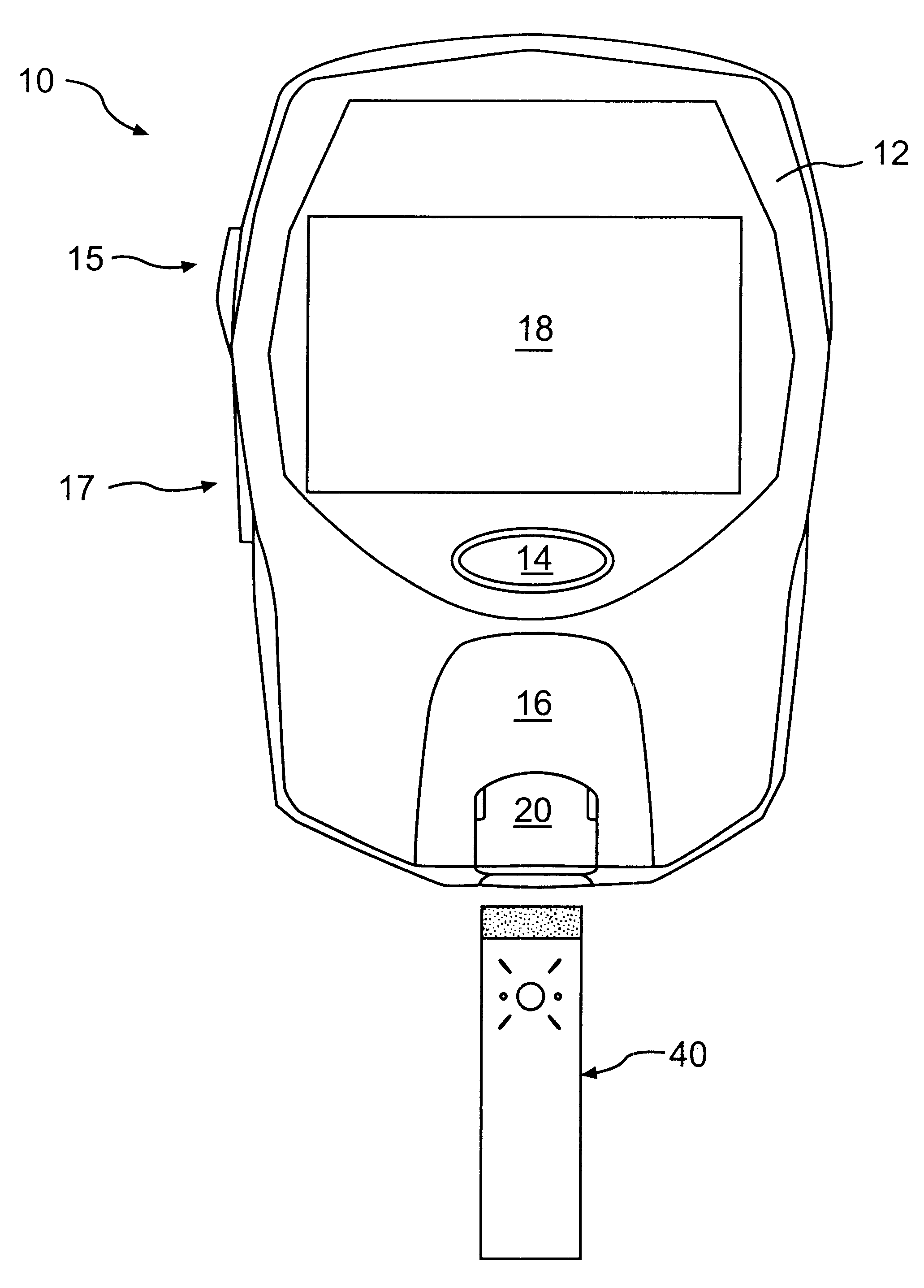
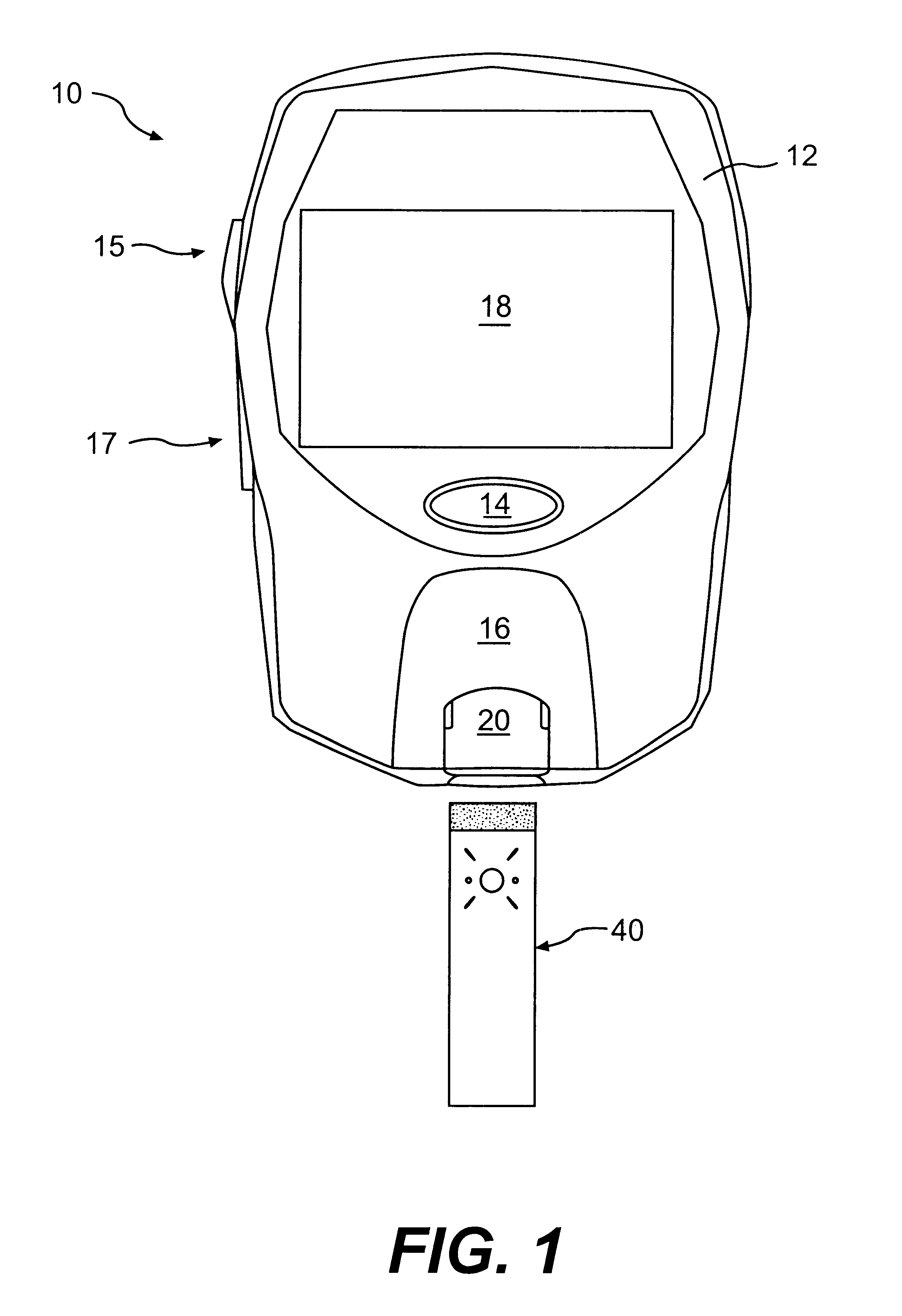
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
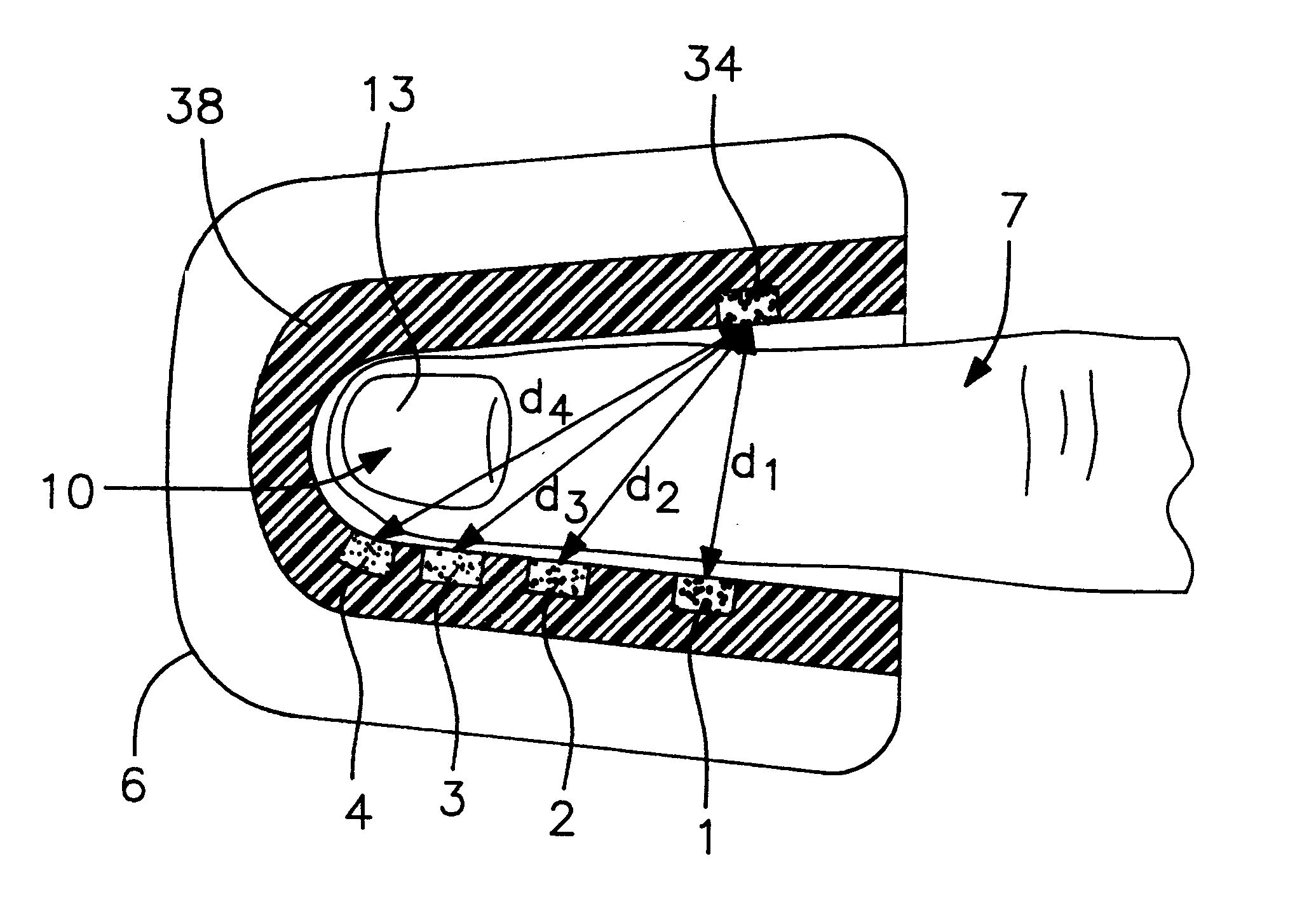
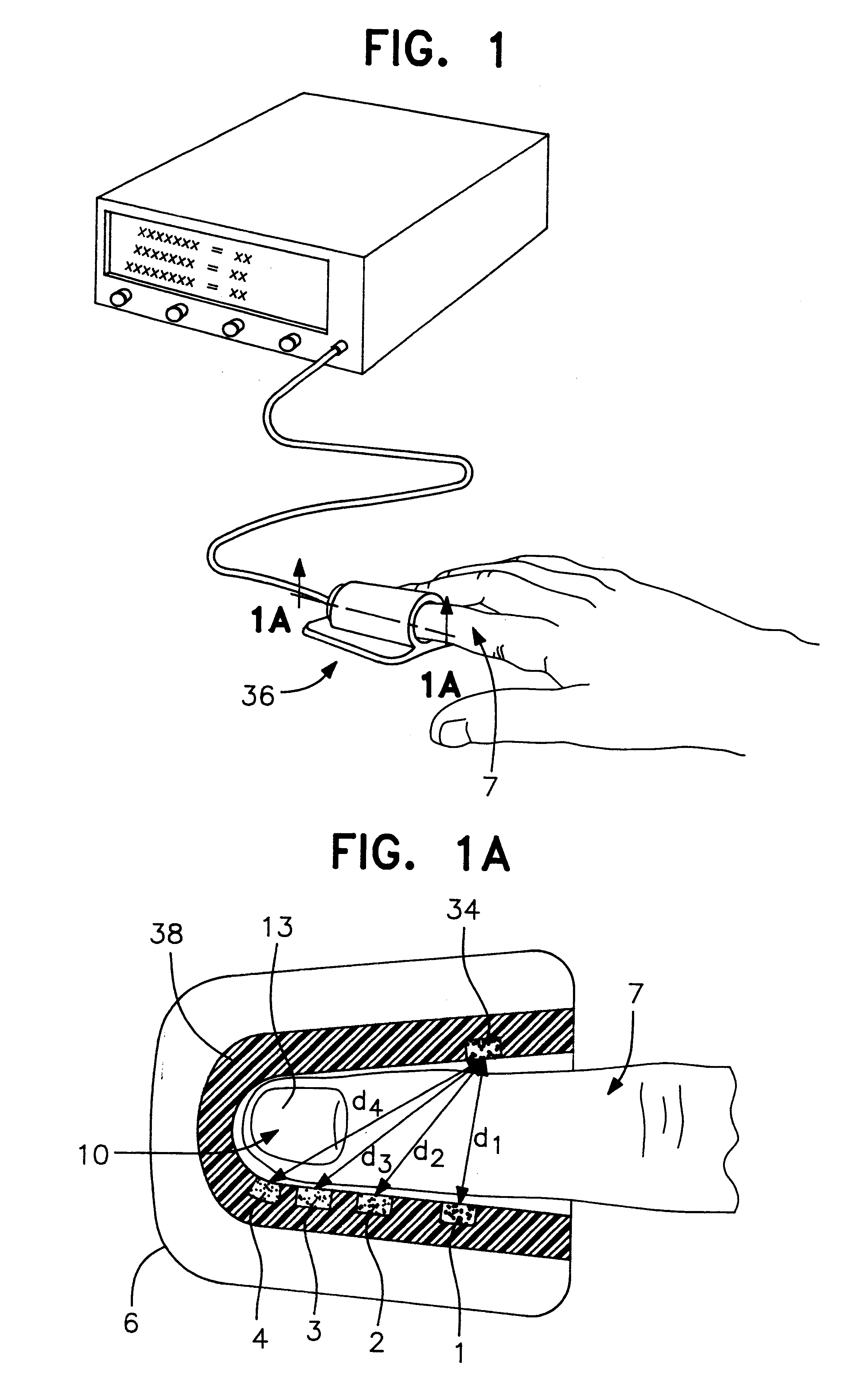
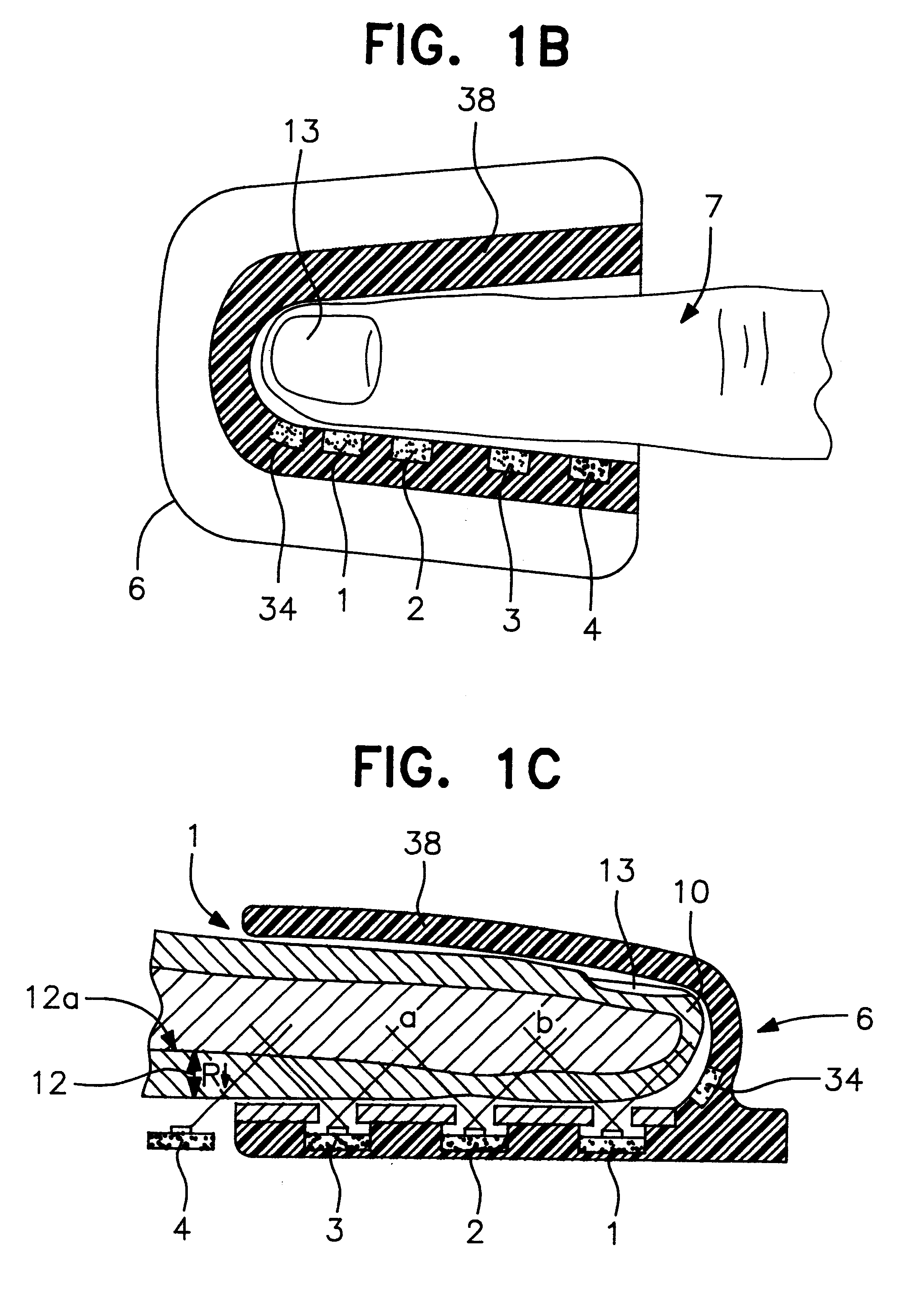
InactiveUS6181958B1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveHemoglobin G Szuhu
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Method and apparatus for coupling a sample probe with a sample site
ActiveUS8718738B2Diagnostics using spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansDelivery systemDistortion
The invention comprises method and apparatus for fluid delivery between a sample probe and a sample. The fluid delivery system includes: a fluid reservoir, a delivery channel, a manifold or plenum, a channel or moat, a groove, and / or a dendritic pathway to deliver a thin and distributed layer of a fluid to a sample probe head and / or to a sample site. The fluid delivery system reduces sampling errors due to mechanical tissue distortion, specular reflectance, probe placement, and / or mechanically induced sample site stress / strain associated with optical sampling of the sample.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
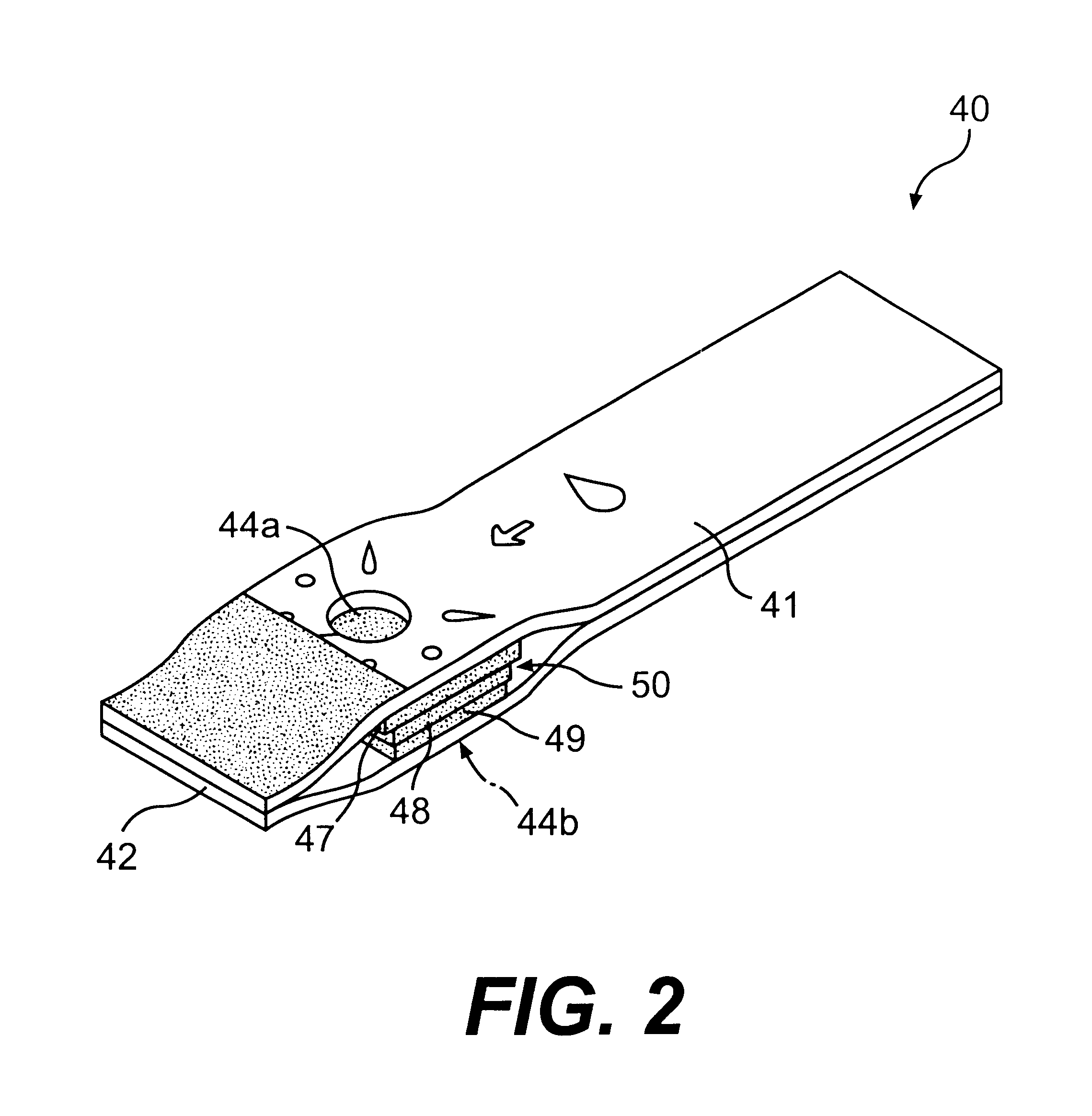
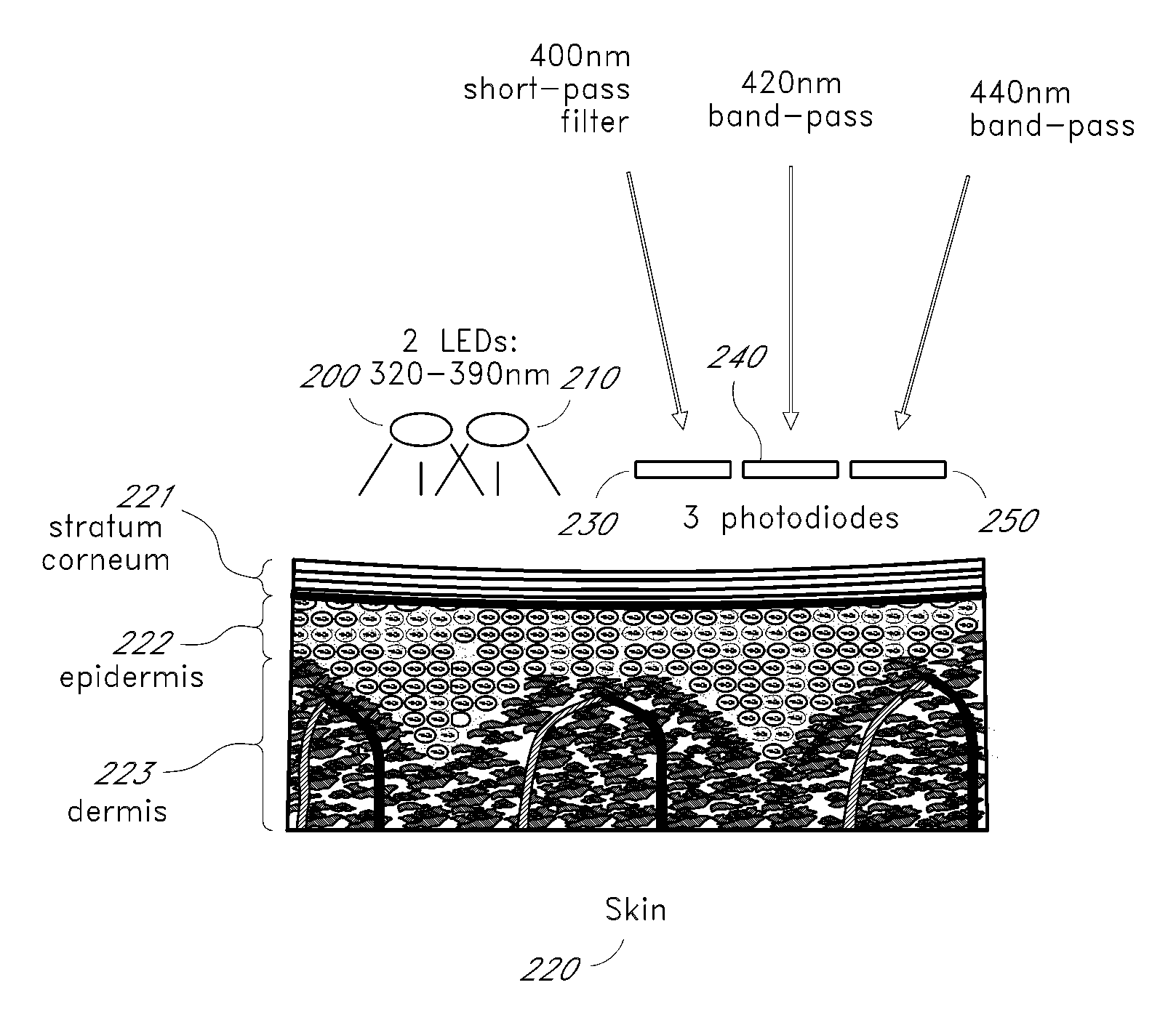
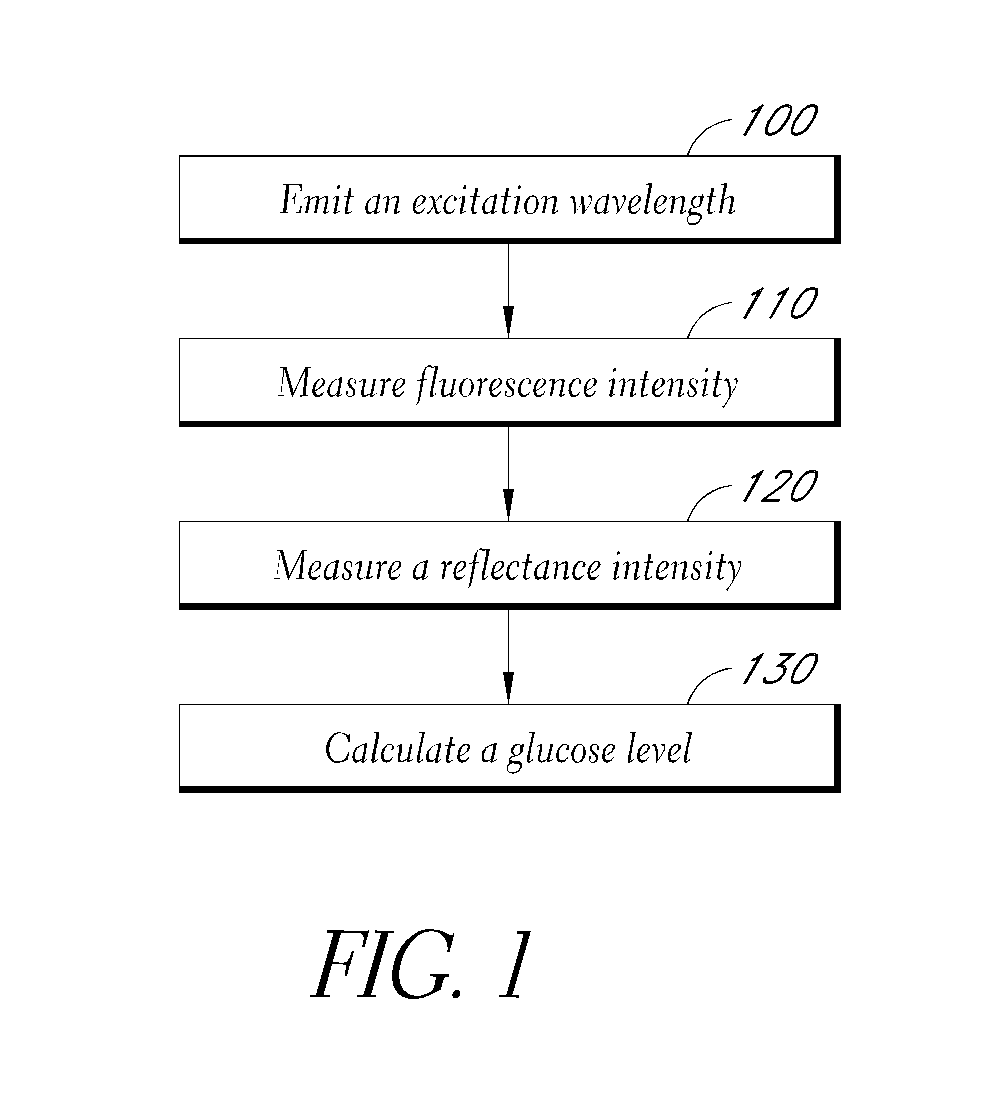
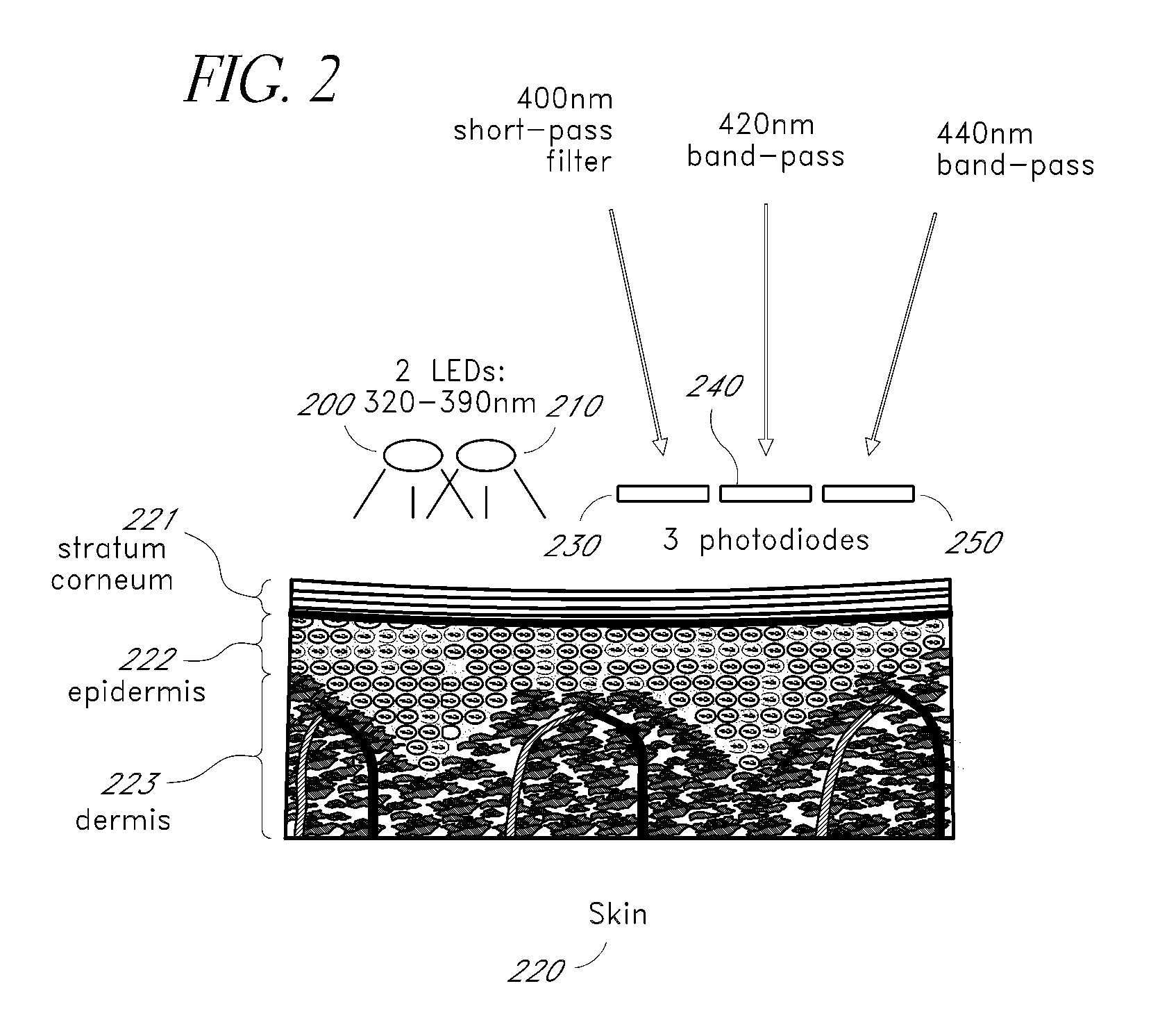
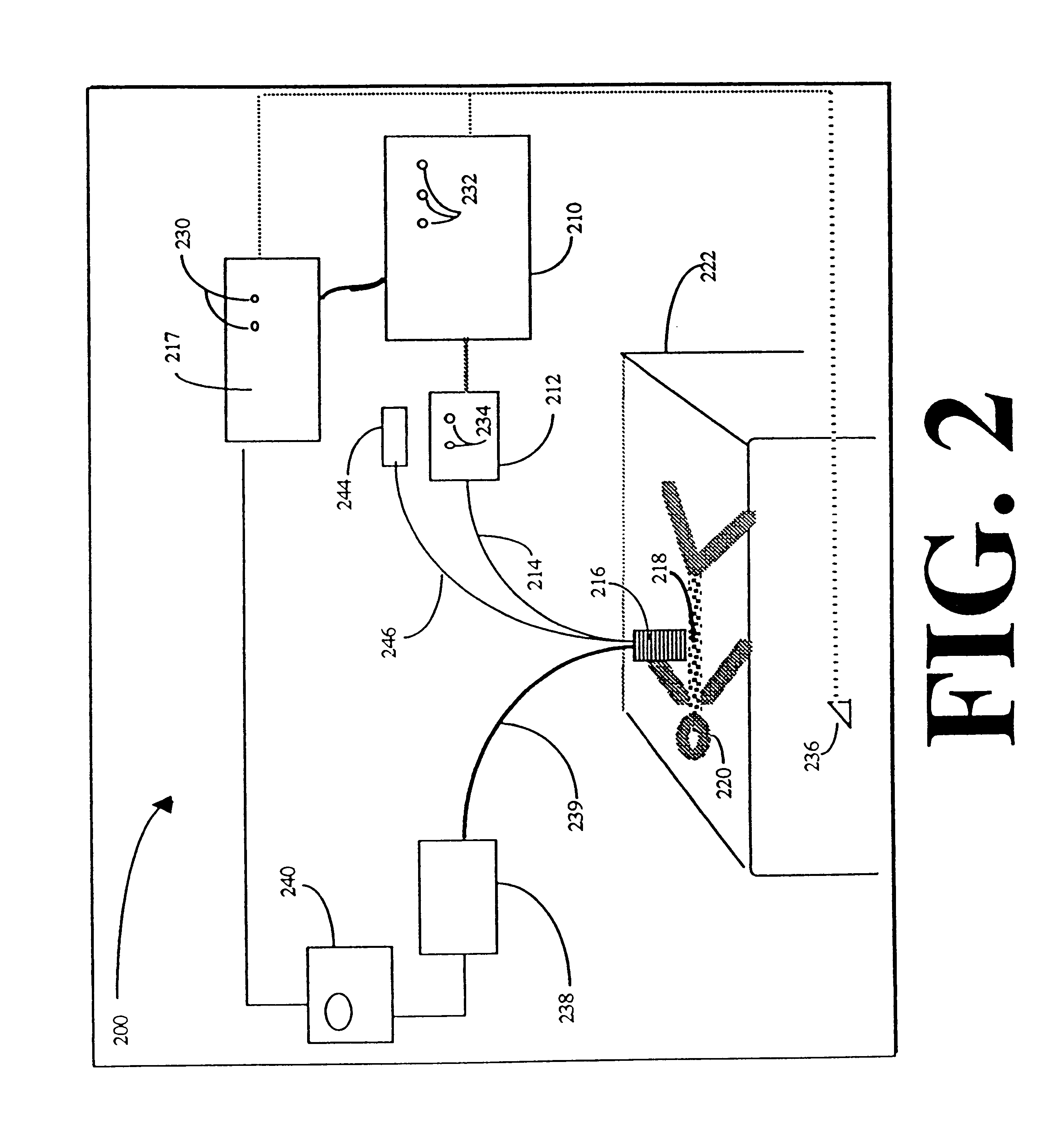
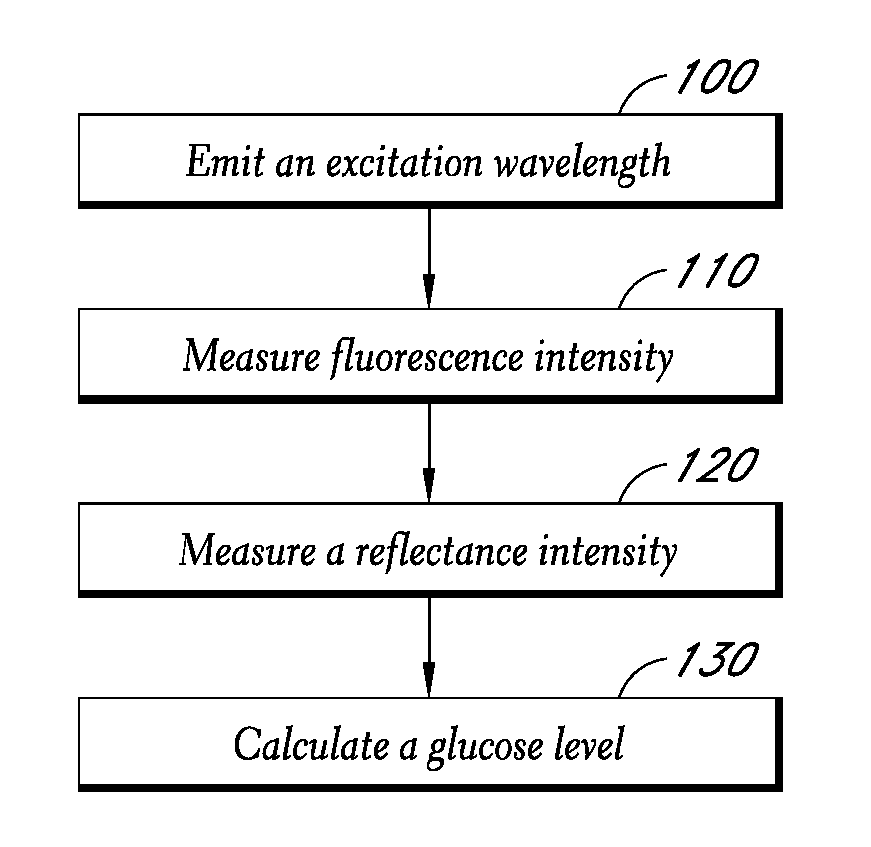
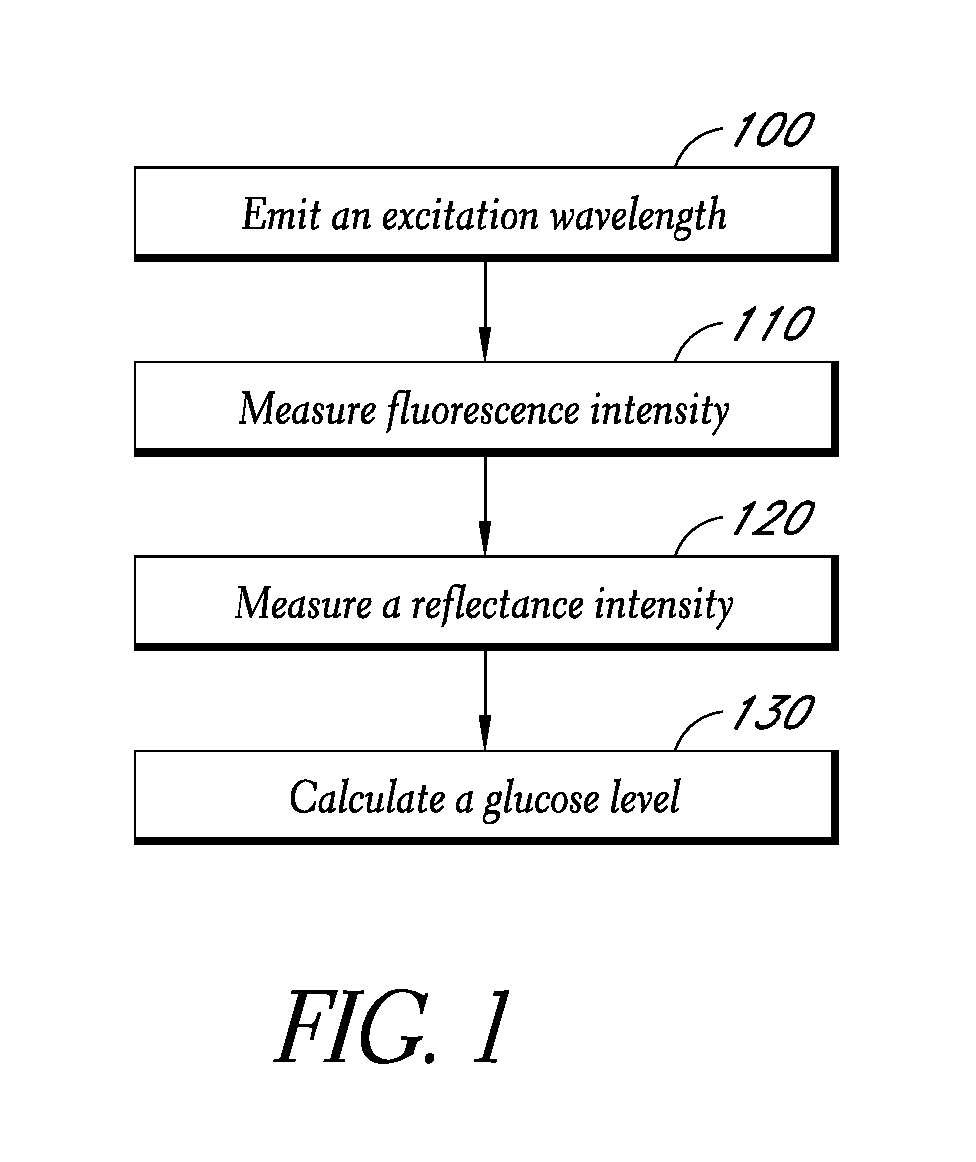
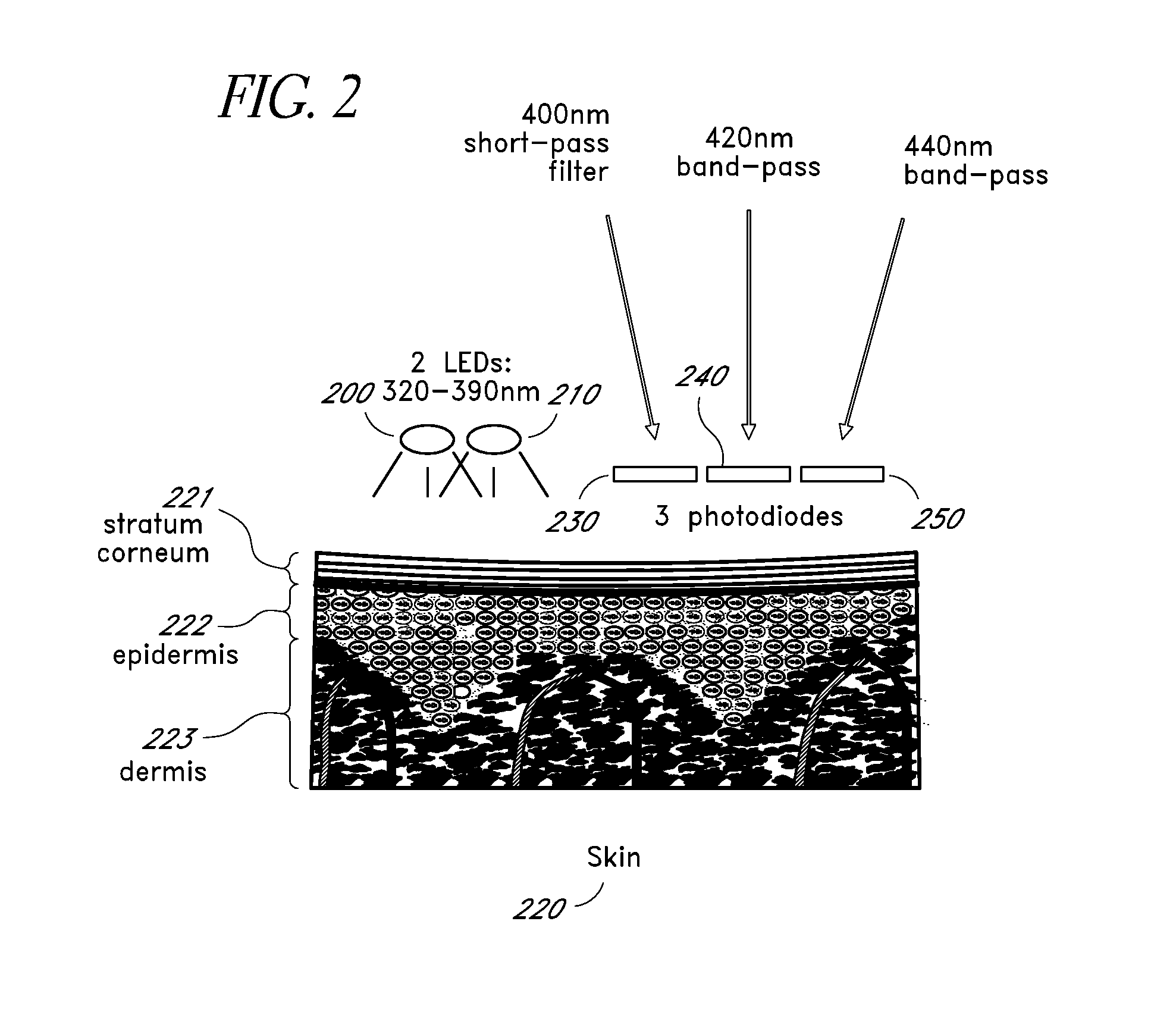
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20140330098A1Easy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteMedicine
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Electrochromic rearview mirror incorporating a third surface metal reflector
InactiveUS6064508AEconomical and reliableLow costMirrorsSolid-state devicesEpoxyElectrical conductor
An electrochromic variable reflectance mirror for a vehicle includes a reflector / electrode on the third surface of the mirror. This reflector / electrode forms an integral electrode in contact with the electrochromic media, and may be a single layer of a highly reflective material or may comprise a series of coatings. When a series of coatings is used for the reflector / electrode, there should be a base coating which bonds to the glass surface and resists any adverse interaction, e.g., corrosive action, with the constituents comprising the electrochromic media, an optional intermediate layer (or layers) which bonds well to the base coating and resists any adverse interaction with the electrochromic media, and at least one highly reflective layer which directly contacts the electrochromic media and which is chosen primarily for its high reflectance, stable behavior as an electrode, resistance to adverse interaction with the materials of the electrochromic media, resistance to atmospheric corrosion, resistance to electrical contact corrosion, the ability to adhere to the base or intermediate layer(s) (if present) and to the epoxy seal, and ease of cleaning. If a base layer is deposited it preferably covers the entire third surface; however, when this is done the highly reflective layer may optionally only coat the central portion of the third surface and not the perimeter edge portion. The third surface reflector / electrode provides of improved electrical interconnection techniques used to impart a voltage drive potential to a transparent conductor on the mirror's second surface.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
InactiveUS6819426B2Accurate measurementLimited space availableSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatuses and methods for analyte concentration determination
InactiveUS6847451B2Investigating moving sheetsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteInsufficient Sample
Apparatuses and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. The subject apparatuses include at least one light source, a detector array, means for determining whether a sufficient amount of sample is present on each of the plurality of different areas, and means for determining the concentration of the analyte based on the reflected light detected from those areas determined to have sufficient sample, where areas having insufficient sample are not used in analyte concentration determination. The subject methods include illuminating each area of a test strip, obtaining reflectance from each of the different areas, determining which areas have sufficient sample based on detected light therefrom and deriving analyte concentration from the areas determined to have sufficient sample, where areas determined not to have sufficient sample are not used in the derivation. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Camera Adapter Based Optical Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110043661A1Cancel noiseLow costTelevision system detailsInterferometersSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
The invention describes several embodiments of an adapter which can make use of the devices in any commercially available digital cameras to accomplish different functions, such as a fundus camera, as a microscope or as an en-face optical coherence tomography (OCT) to produce constant depth OCT images or as a Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography to produce a reflectivity profile in the depth of an object or cross section OCT images, or depth resolved volumes. The invention admits addition of confocal detection and provides simultaneous measurements or imaging in at least two channels, confocal and OCT, where the confocal channel provides an en-face image simultaneous with the acquisition of OCT cross sections, to guide the acquisition as well as to be used subsequently in the visualisation of OCT images. Different technical solutions are provided for the assembly of one or two digital cameras which together with such adapters lead to modular and portable high resolution imaging systems which can accomplish various functions with a minimum of extra components while adapting the elements in the digital camera. The cost of such adapters is comparable with that of commercial digital cameras, i.e. the total cost of such assemblies of commercially digital cameras and dedicated adapters to accomplish high resolution imaging are at a fraction of the cost of dedicated stand alone instruments. Embodiments and methods are presented to employ colour cameras and their associated optical sources to deliver simultaneous signals using their colour sensor parts to provide spectroscopic information, phase shifting inferometry in one step, depth range extension, polarisation, angular measurements and spectroscopic Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography in as many spectral bands simultaneously as the number of colour parts of the photodetector sensor in the digital camera. In conjunction with simultaneous acquistion of a confocal image, at least 4 channels can simultaneously be provided using the three color parts of conventional color cameras to deliver three OCT images in addition to the confocal image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
Electrophoretic display and novel process for its manufacture
ActiveUS7072095B2Improve contrast ratioImprove switching performanceStatic indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisElectrophoresisDisplay device
This invention relates to an electrophoretic display with improved contrast ratio, switching performance, reflectivity at the Dmin state and structural integrity, and methods for its manufacture.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
White Light Apparatus and Method
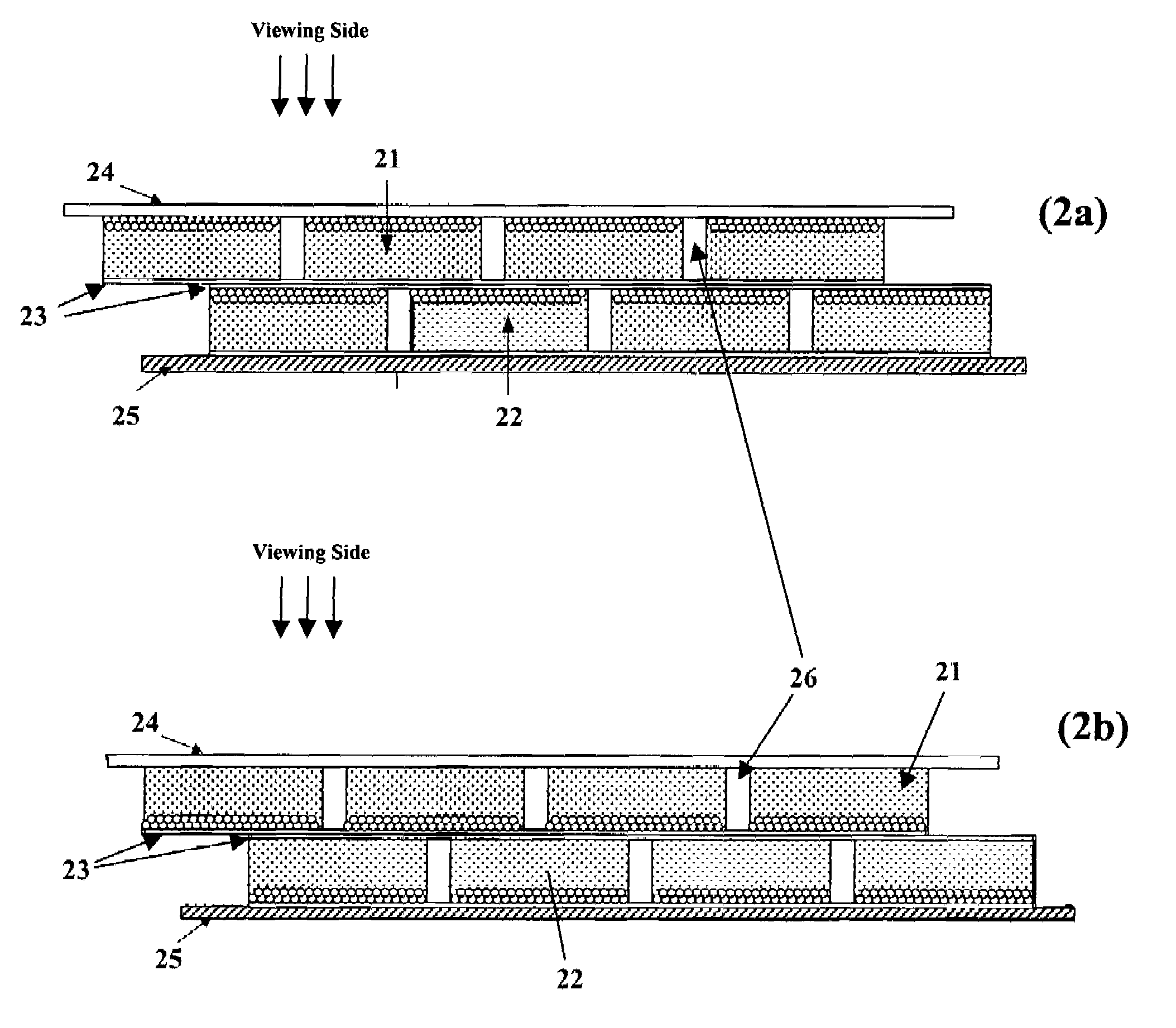
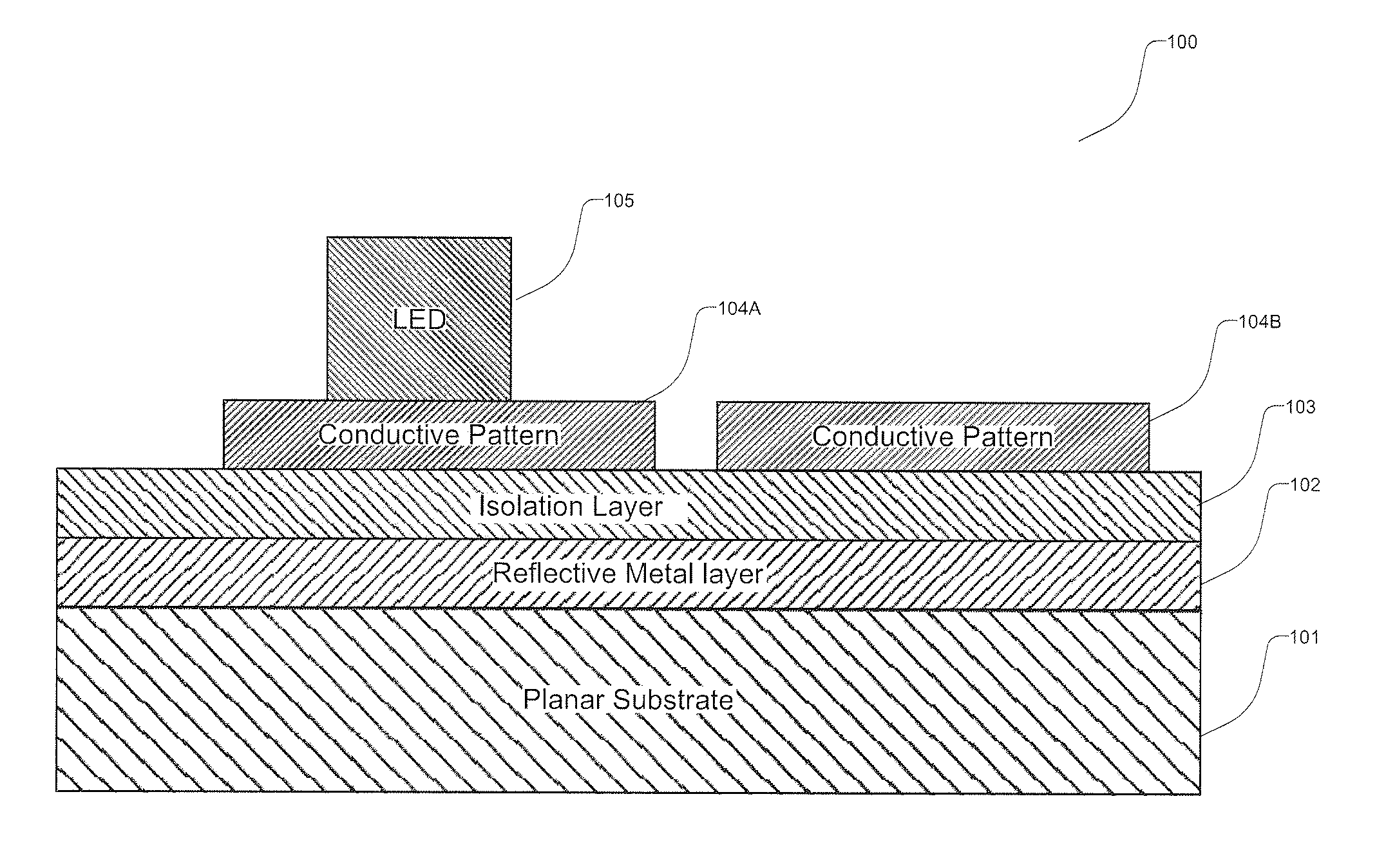
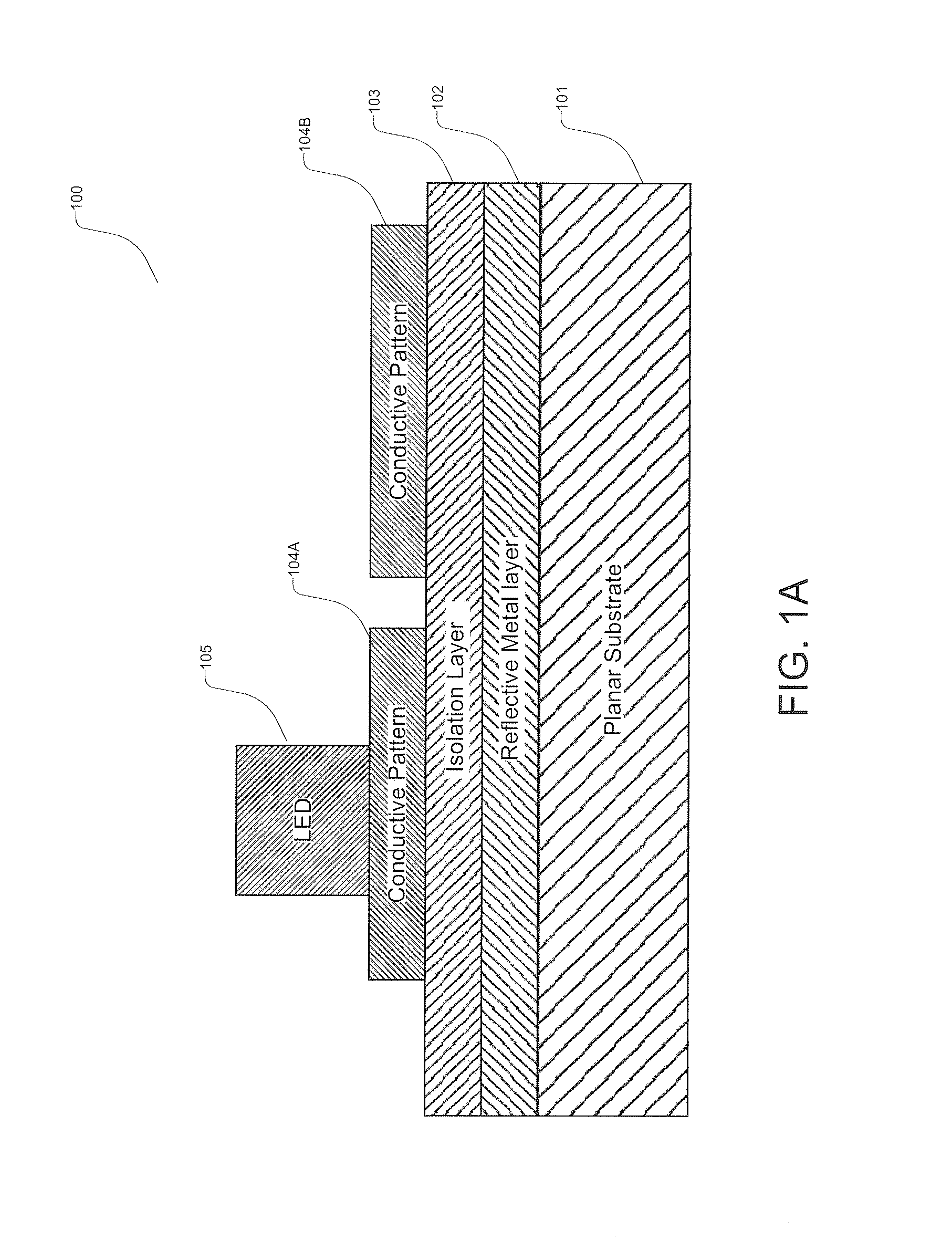
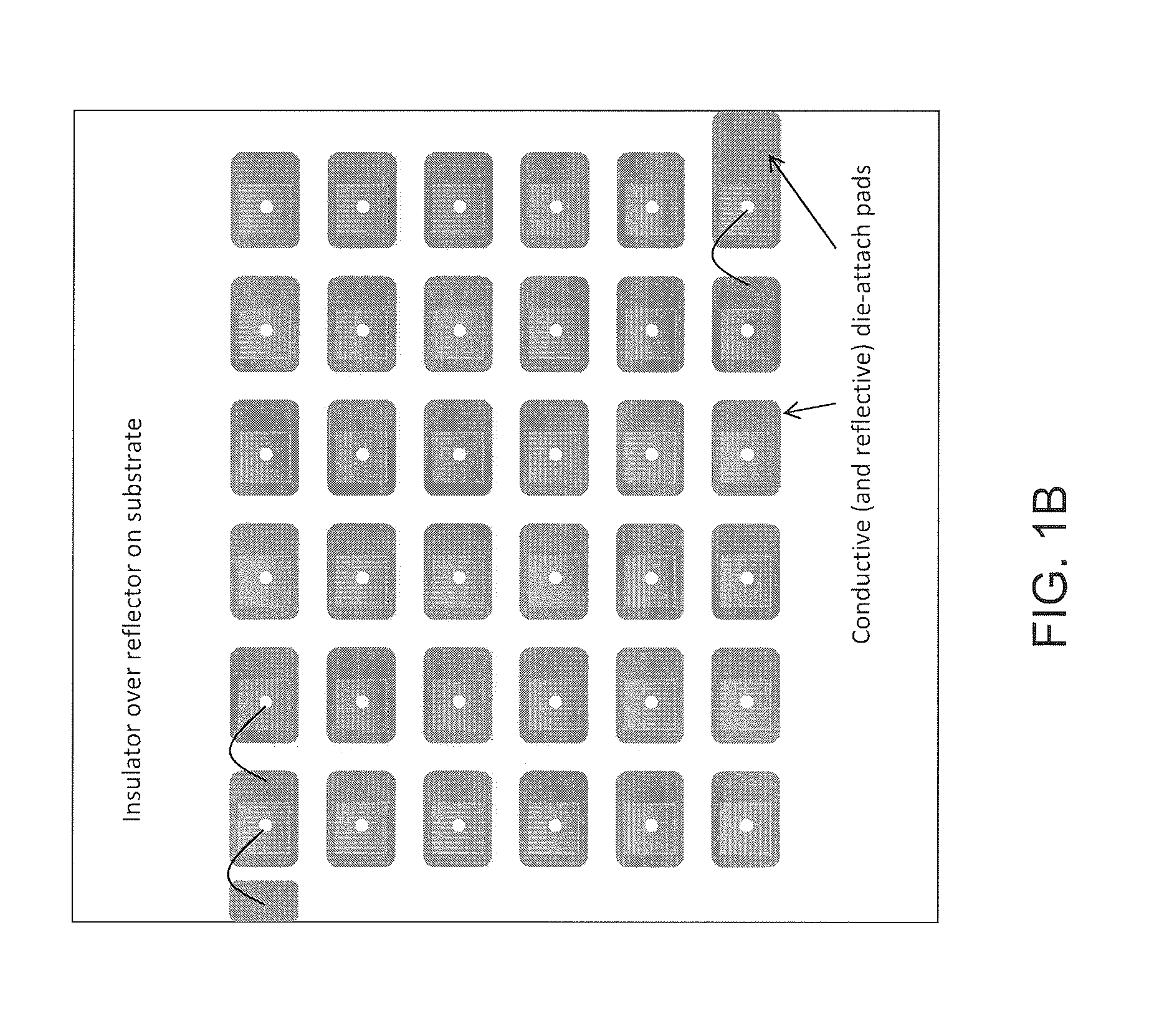
InactiveUS20110186874A1Easy to implementImprove efficiencyPoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesReflective layerWhite light
A method of manufacturing LED devices using substrate scale processing includes providing a substrate member having a surface region. A reflective layer is disposed on the surface region, the reflective surface having a reflectivity of at least 85%, An array of conductive regions is spatially disposed on the reflective surface. LED devices are affixed to each of the array regions.
Owner:SORAA
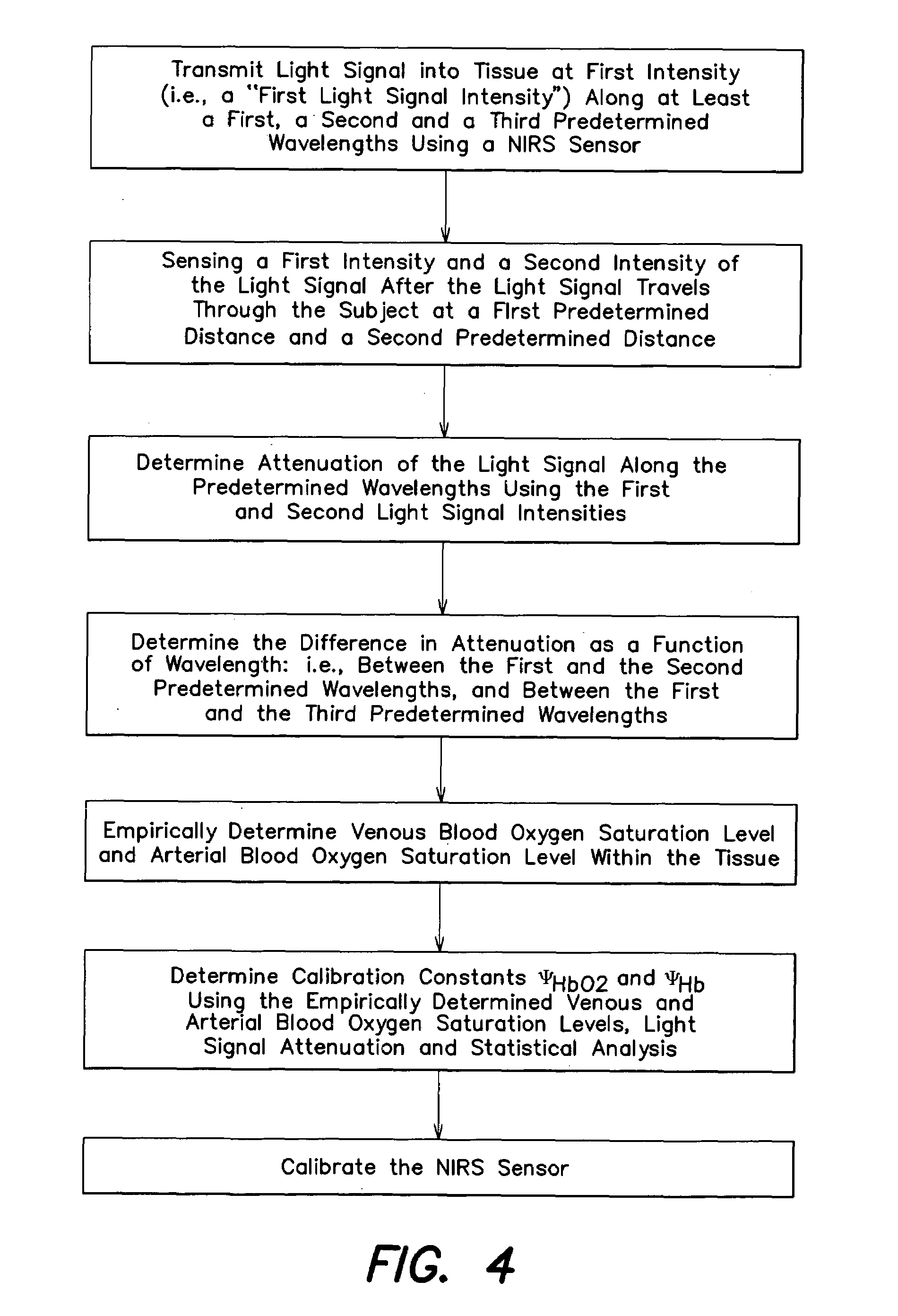
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
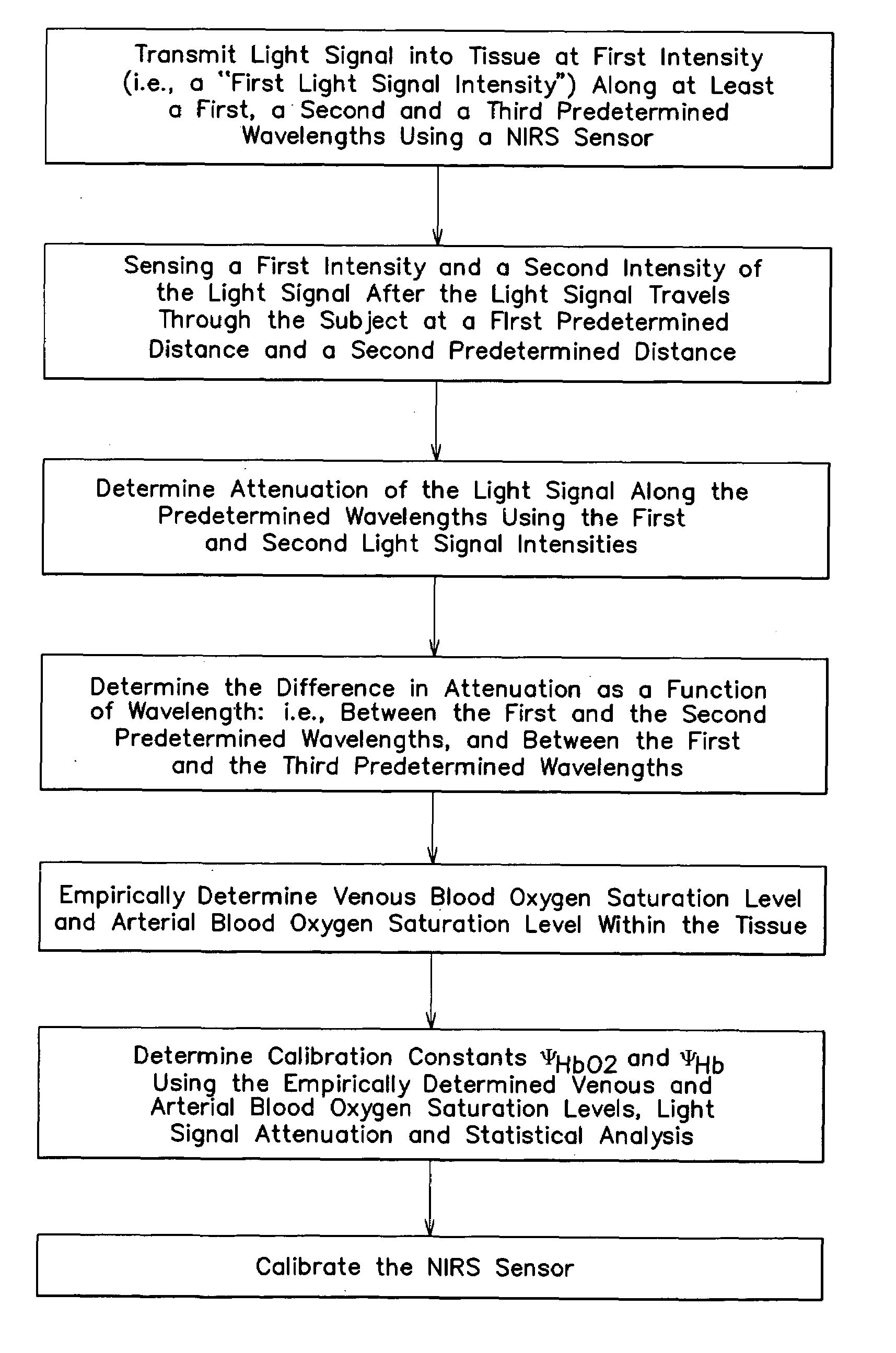
ActiveUS7072701B2Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationBlood oxygenation
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the tissue via transmittance or reflectance. The method includes the steps of: (1) transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
InactiveUS20020158193A1Limited space availableOvercome difficultiesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
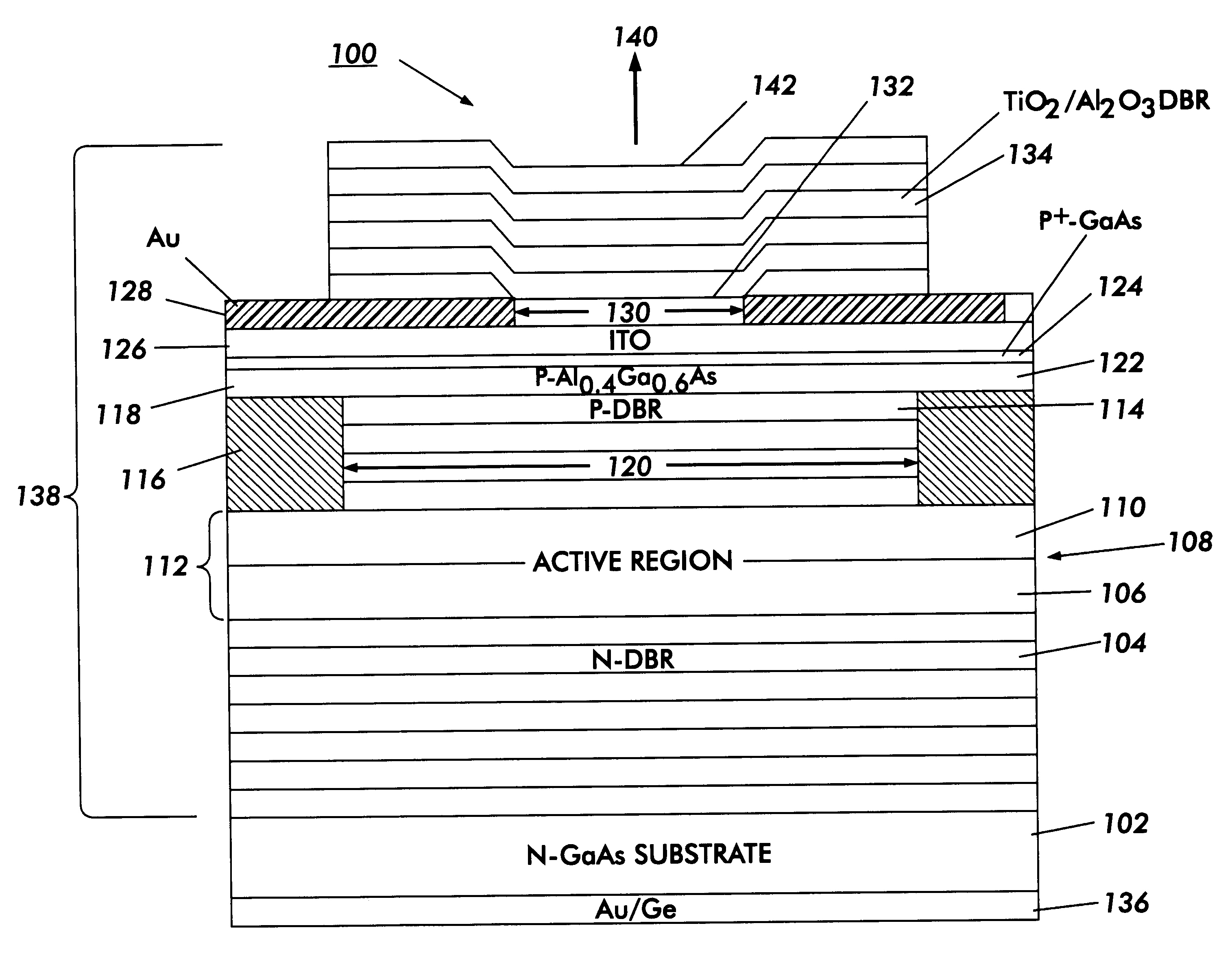
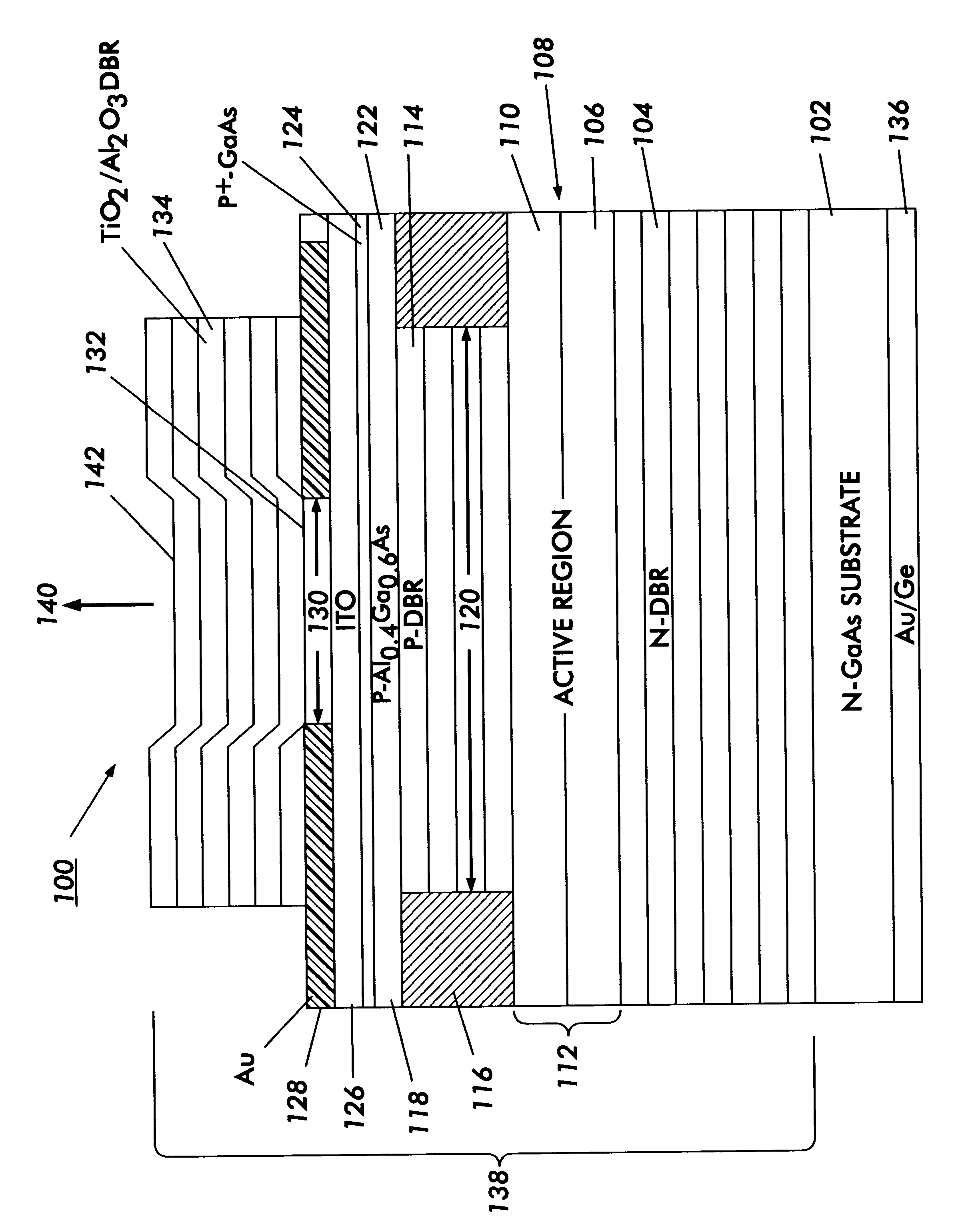
Metal spatial filter to enhance model reflectivity in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser
InactiveUS6185241B1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
An annular metal layer is provided between a conductive oxide layer and a dielectric mirror in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The annular metal layer defines the output window for the laser cavity which matches the TEM.sub.00 fundamental mode of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL. The metal layer outside the output window provides modal reflectivity discrimination against high order transverse modes of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL.
Owner:XEROX CORP
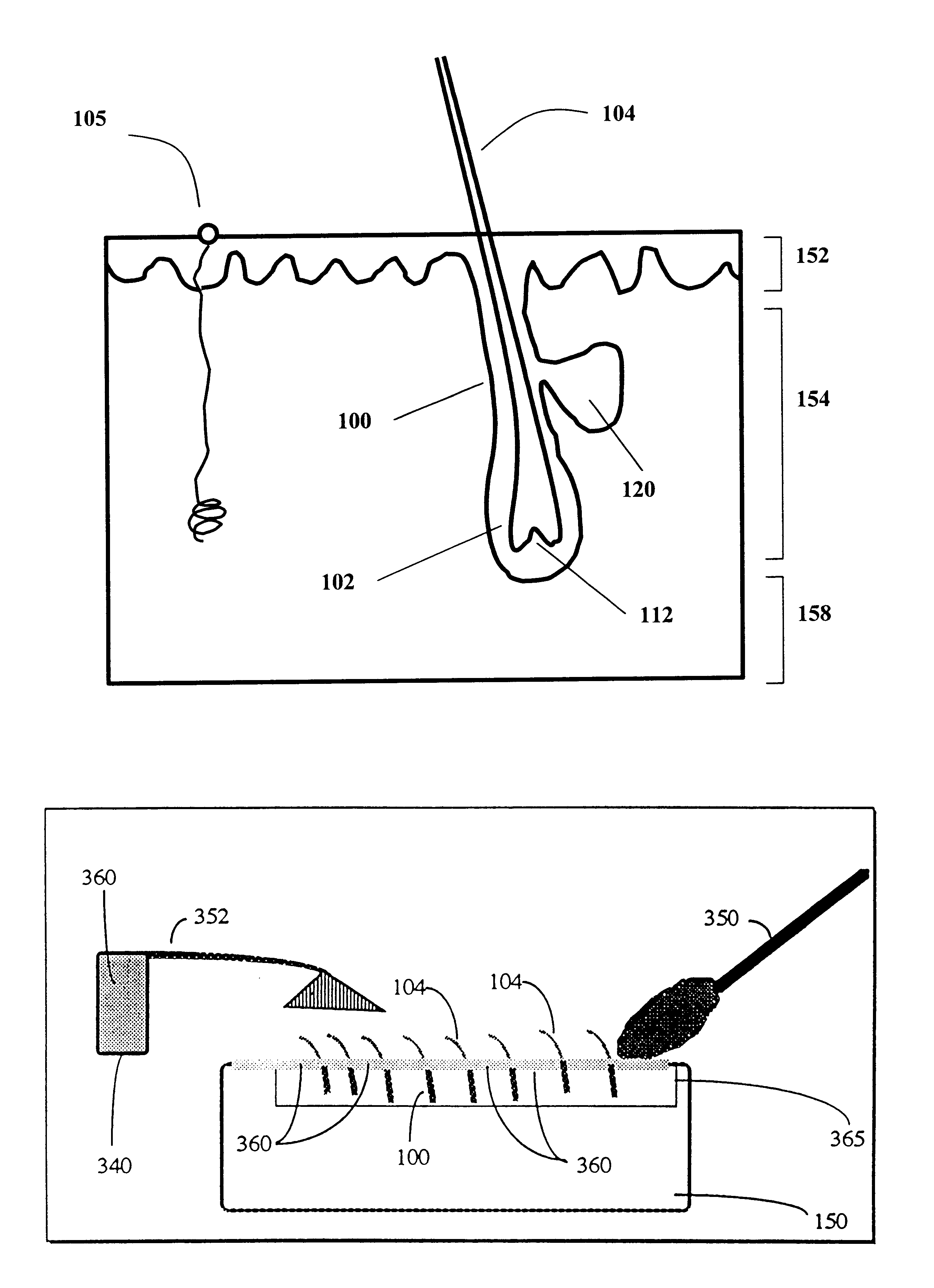
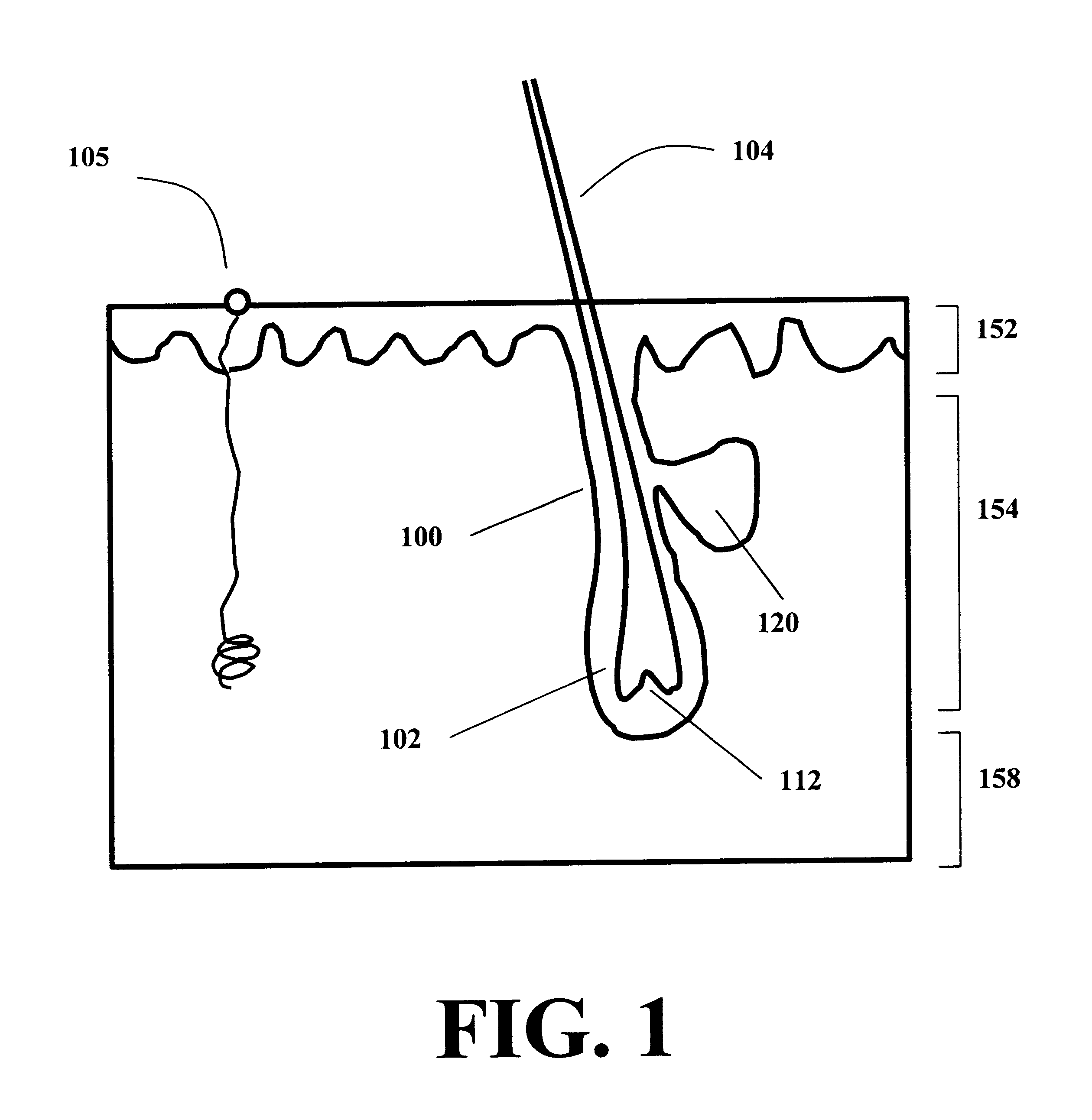
Method for permanent hair removal
InactiveUS6168590B1Reduce generationMinimize damageControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyHair growthHair follicle
A method for permanently removing hair utilizes the hair shaft and hair ducts to transmit light into the tissue sustaining the hair follicle, thereby permanently destroying or modifying the tissue in a manner which desirably mitigates hair growth. The method includes the steps of covering the patient's skin area with a high reflectance substance so as to substantially protect all skin components other than those sustaining the hair. The hair is optionally shaved or pulled out, and then the skin is illuminated with either a large-area electromagnetic radiation field for simultaneous destruction of multiple hair-follicles, or alternatively with a tightly-focused beam which destroys one hair at a time. Optionally, the beam may be rapidly scanned so as to destroy single hairs quickly in succession. The surrounding skin region is left substantially free of injury. This mitigates pain and enhances post hair removal healing.
Owner:Y BEAM TECH
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20110028806A1Easily detected fluorescenceEasy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteLight energy
A noninvasive or minimally invasive procedure and system for measuring blood glucose levels is disclosed. A set of photodiodes detects the fluorescence and reflectance of light energy emitted from one or more emitters, such as LEDs, into a patient's skin. In an embodiment, small molecule metabolite reporters (SMMRs) that bind to glucose are introduced to the measurement area to provide more easily detected fluorescence.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Virtual image display device
ActiveUS8587869B2Quality improvementSuppressing observationOptical light guidesSteroscopic systemsAngle of incidenceLight guide
A half mirror layer has an angle dependency in which when an angle of incidence becomes larger than the angle of incidence range of image light, reflectance increases, such that it is possible to prevent unintended light, which is emitted to a light transmitting member from a light guiding member and is reflected inside a light transmitting member, from being returned to a light emission portion of the light guiding member after passing through the half mirror layer as a reflective film at a relatively large angle of incidence. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the image light passed through the light transmitting member from becoming ghost light while mitigating the demand for increasing processing accuracy of the light transmitting member, and bonding accuracy between the light guiding member and the light transmitting member.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Apparatus and method of determining conditions of bank notes
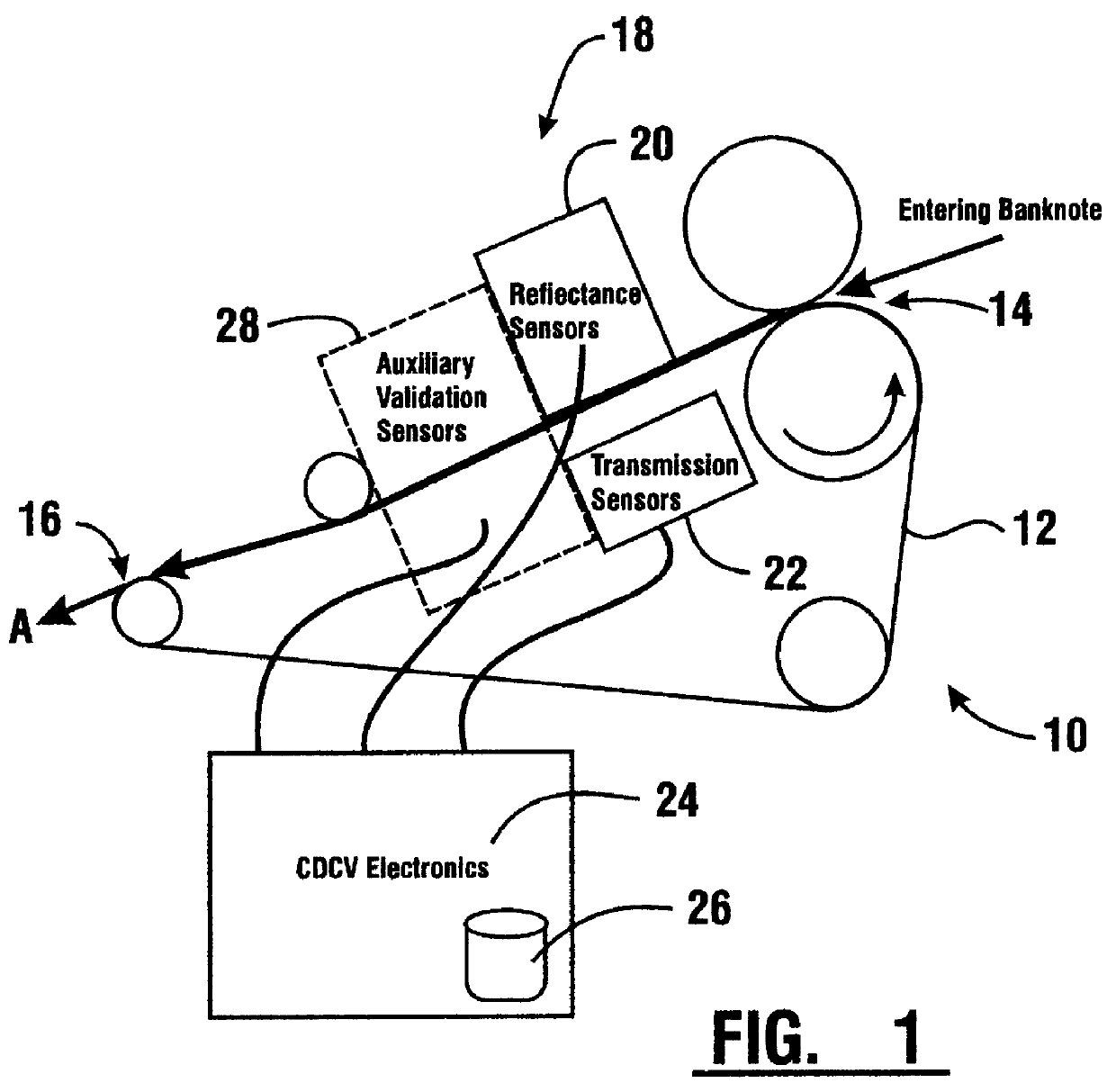
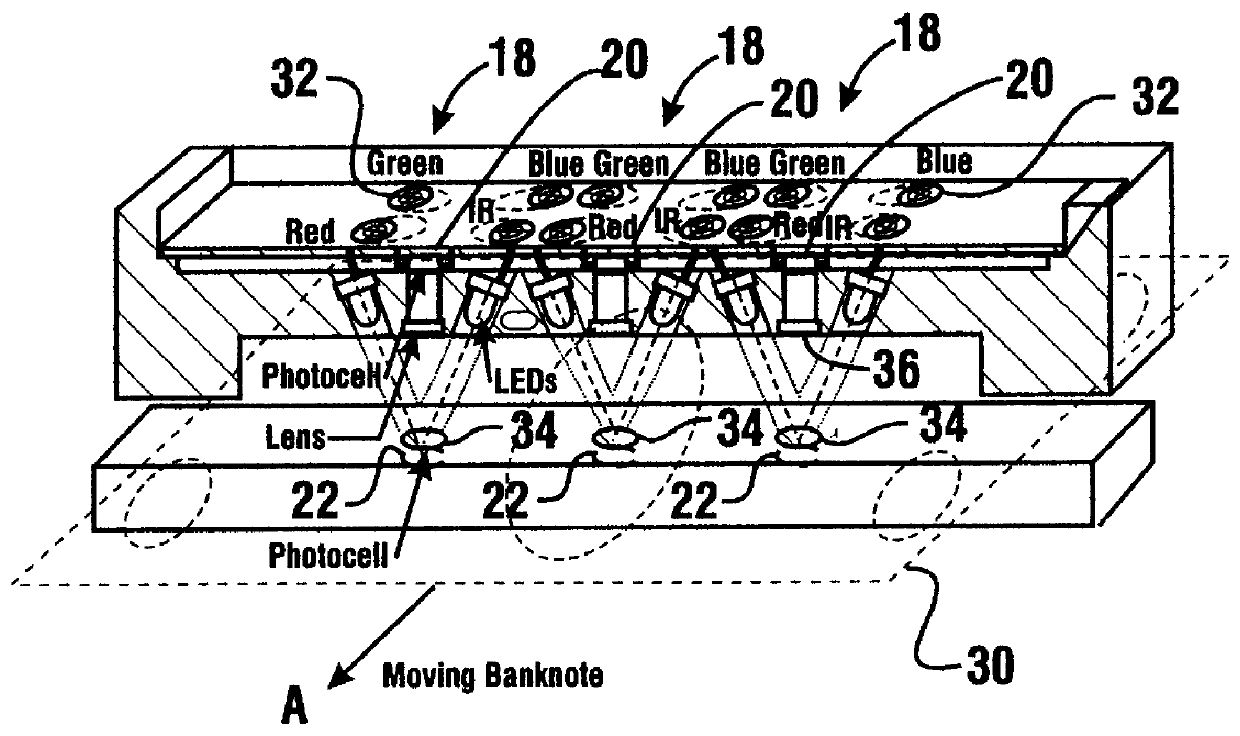
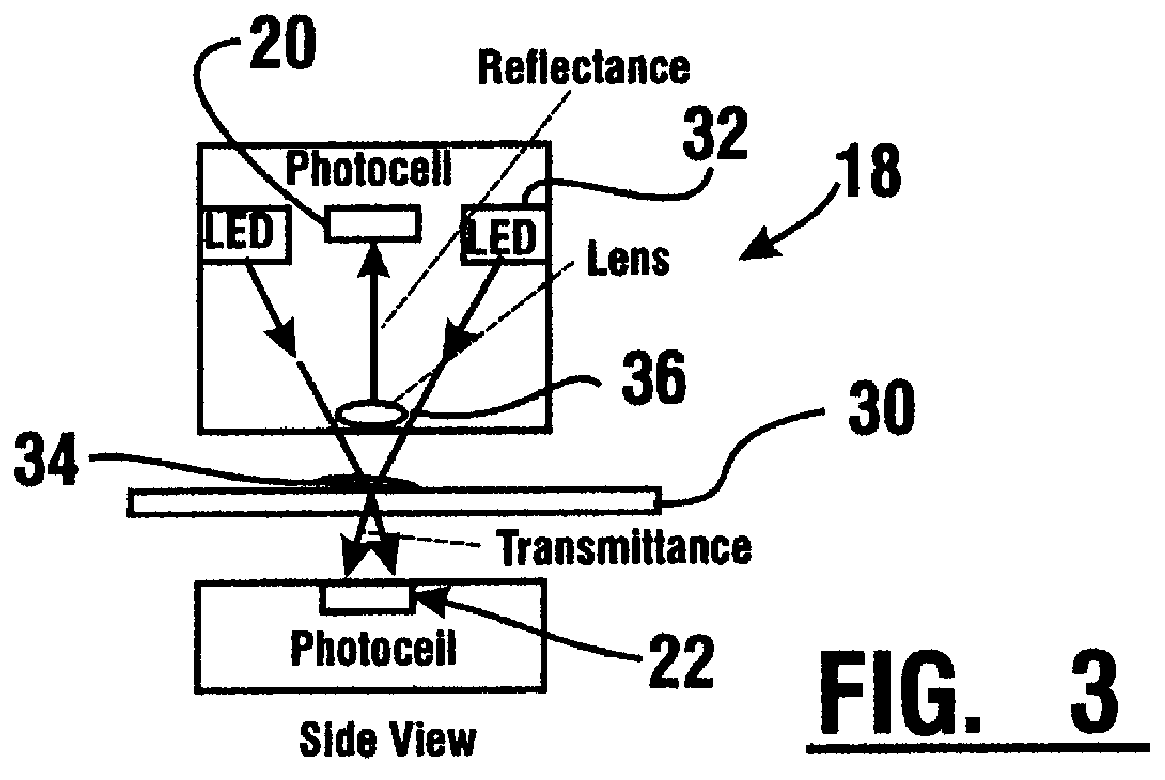
InactiveUS6101266AEconomical to useCheap manufacturingPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringData memory
An apparatus and method for providing an indication of a type and / or a condition of a note passing through the apparatus includes a note transport (12) which moves the note past transversely spaced spot sensing assemblies (18). Each spot sensing assembly includes four emitters (32). Each of the emitters produces radiation at different wavelengths. The spot sensing assemblies include a reflectance detector (20) and a transmission detector (22) which are disposed on opposed sides of the passing note. The emitters direct radiation onto test spots (34) on the passing note. Radiation reflected from and transmitted through the test spots is detected by the respective reflector and transmission detectors. A control circuit (24) produces sensed values that correspond to the detected radiation. A data store in operative connection with the control circuit comprises memories (138) that include stored data representative of transition and reflectance values for know note types. The control circuit calculates a level of correlation between the stored values and the sensed values. By comparing the correlated values to threshold values, the control circuit is operative to determine the type of note and other conditions such as if a note is worn, soiled, or a doubles note.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
Coated article having low-E coating with absorber layer(s)
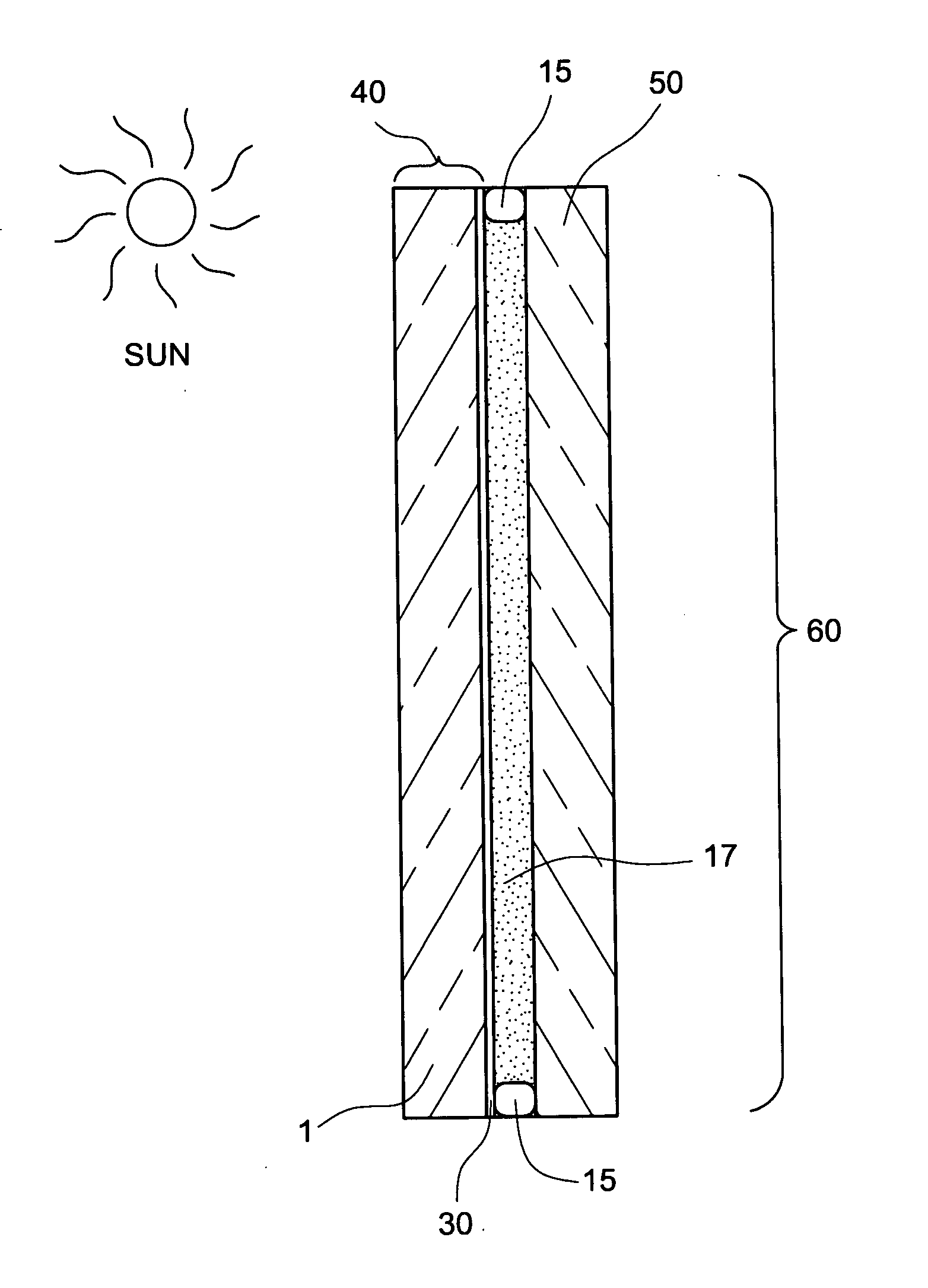
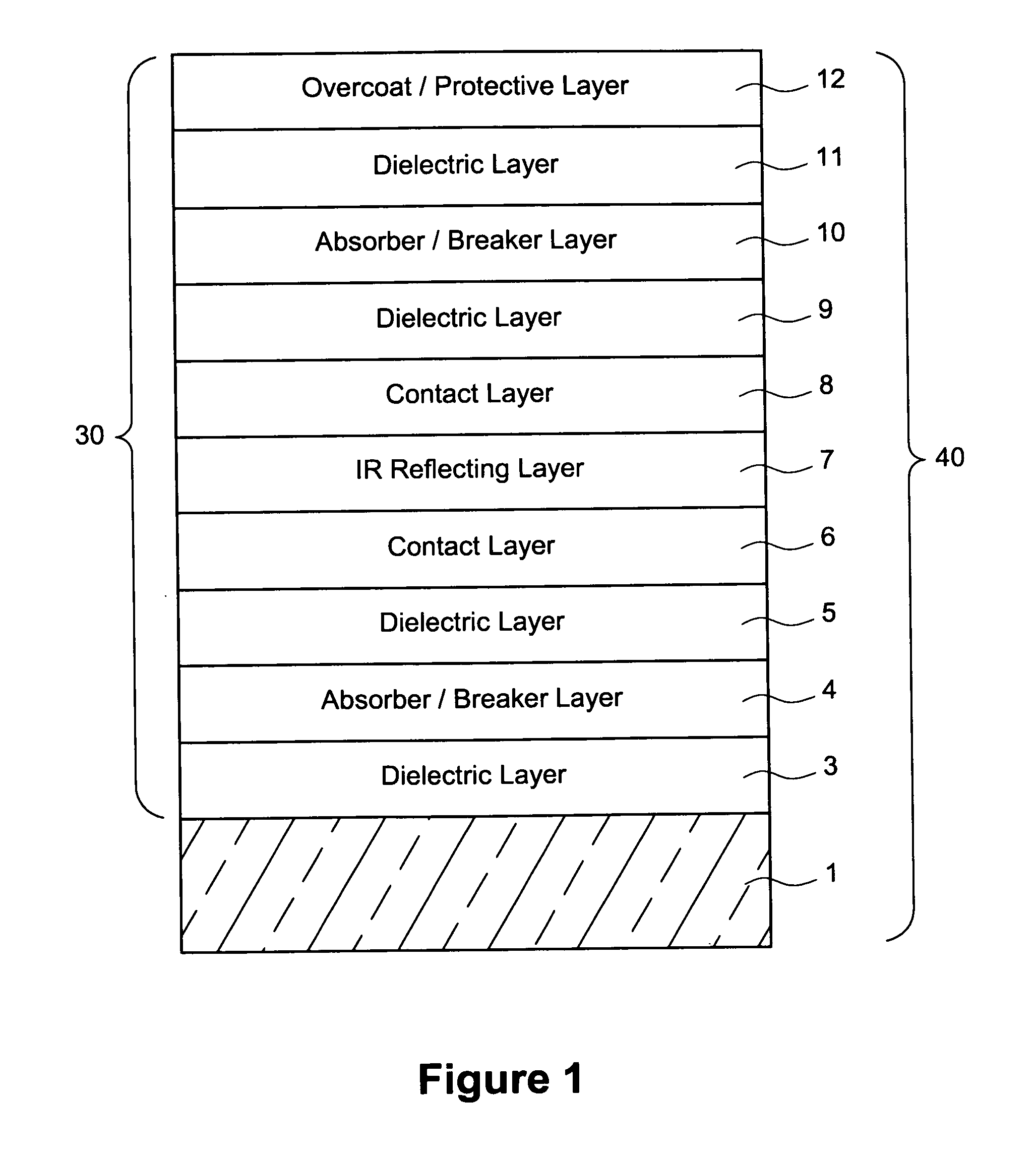
ActiveUS20110262726A1Low emissivityReduce sheet resistanceGlass/slag layered productsThin material handlingElectrical resistance and conductanceInsulated glazing
A coated article is provided, having a coating supported by a glass substrate where the coating includes at least one color and / or reflectivity-adjusting absorber layer. The absorber layer(s) allows color tuning, and reduces the glass side reflection of the coated article and / or allows sheet resistance of the coating to be reduced without degrading glass side reflection. In certain example embodiments the absorber layer is provided between first and second dielectric layers which may be of substantially the same material and / or composition. In certain example embodiments, the coated article is capable of achieving desirable transmission, together with desired color, low reflectivity, and low selectivity, when having only one infrared (IR) reflecting layer of silver and / or gold. Coated articles according to certain example embodiments of this invention may be used in the context of insulating glass (IG) window units, monolithic windows, or the like.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC +1
Bright metal flake based pigments
InactiveUS6150022AGood specular reflectance characteristicPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsSynthetic resin layered productsDielectricReflectivity
A flake-based pigment is provided having improved specular reflectance characteristics in the visible wavelength range. The flake-based pigment has a plurality of core flake sections each formed of a central reflector layer and dielectric support layers on opposing sides of the reflector layer. The resulting core flake section is a very thin three-layered structure that exhibits a uniaxial compressive strength much greater than a corresponding uniaxial tensile strength. This structure provides the benefits of rigidity and brittle fracture during manufacturing and application processes, which ultimately provides favorable planar and specular reflectance characteristics for the pigment in the visible wavelength range. A variety of outer coating layers can be formed around the core flake sections, such as various dielectric and absorber layers having thicknesses dependent upon the desired optical characteristics of the pigment.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Method for determination of analytes using NIR, adjacent visible spectrum and discrete NIR wavelenths
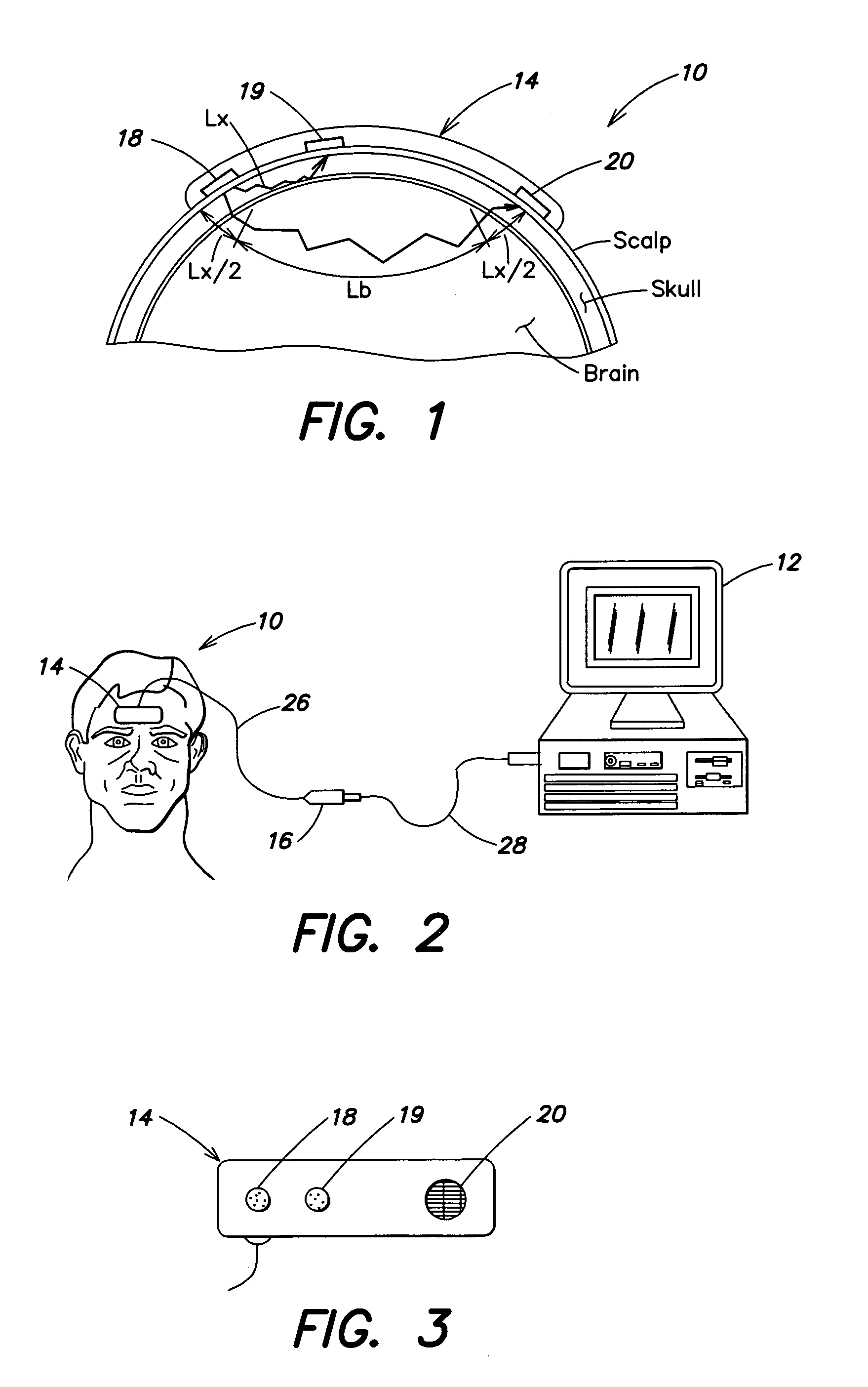
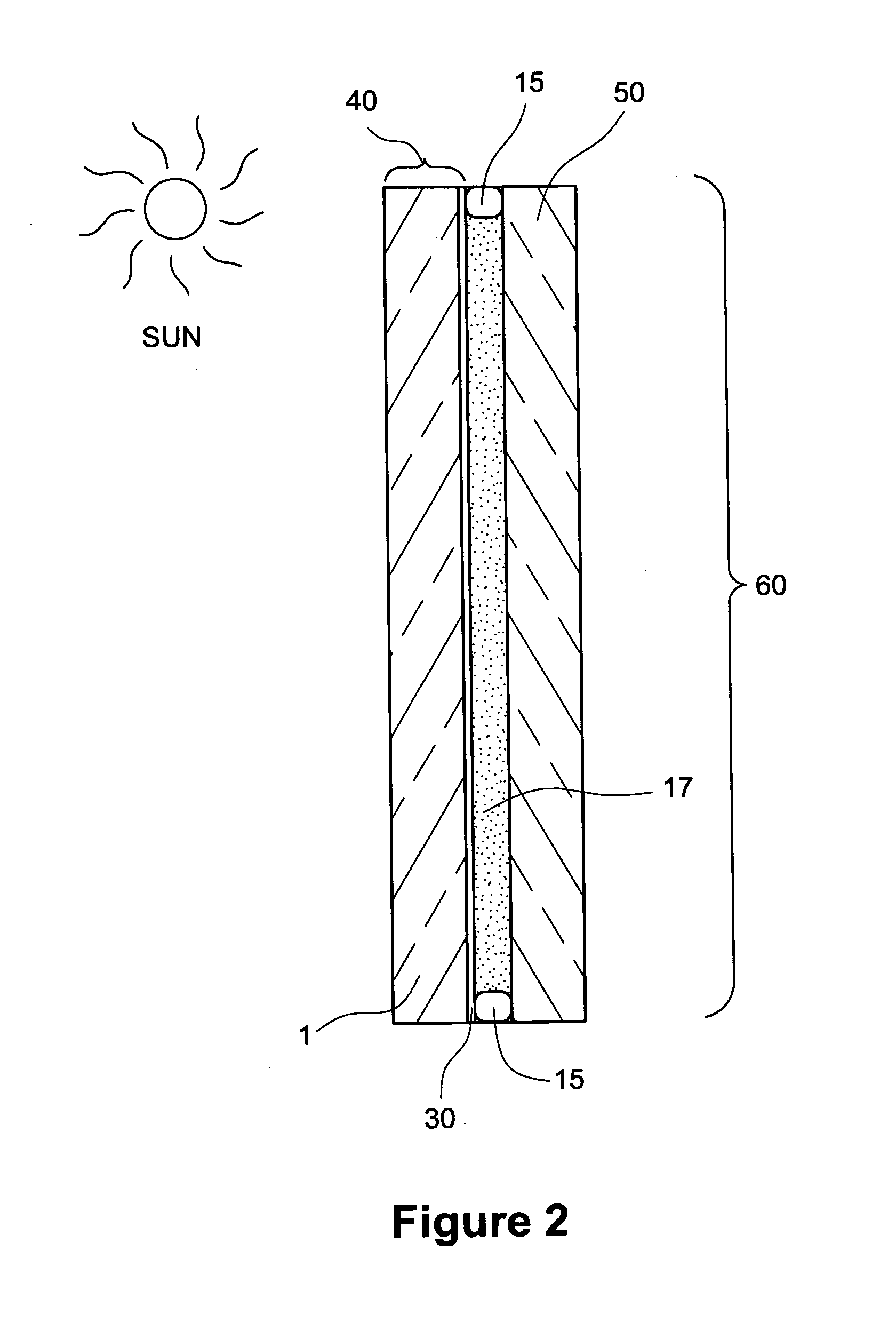
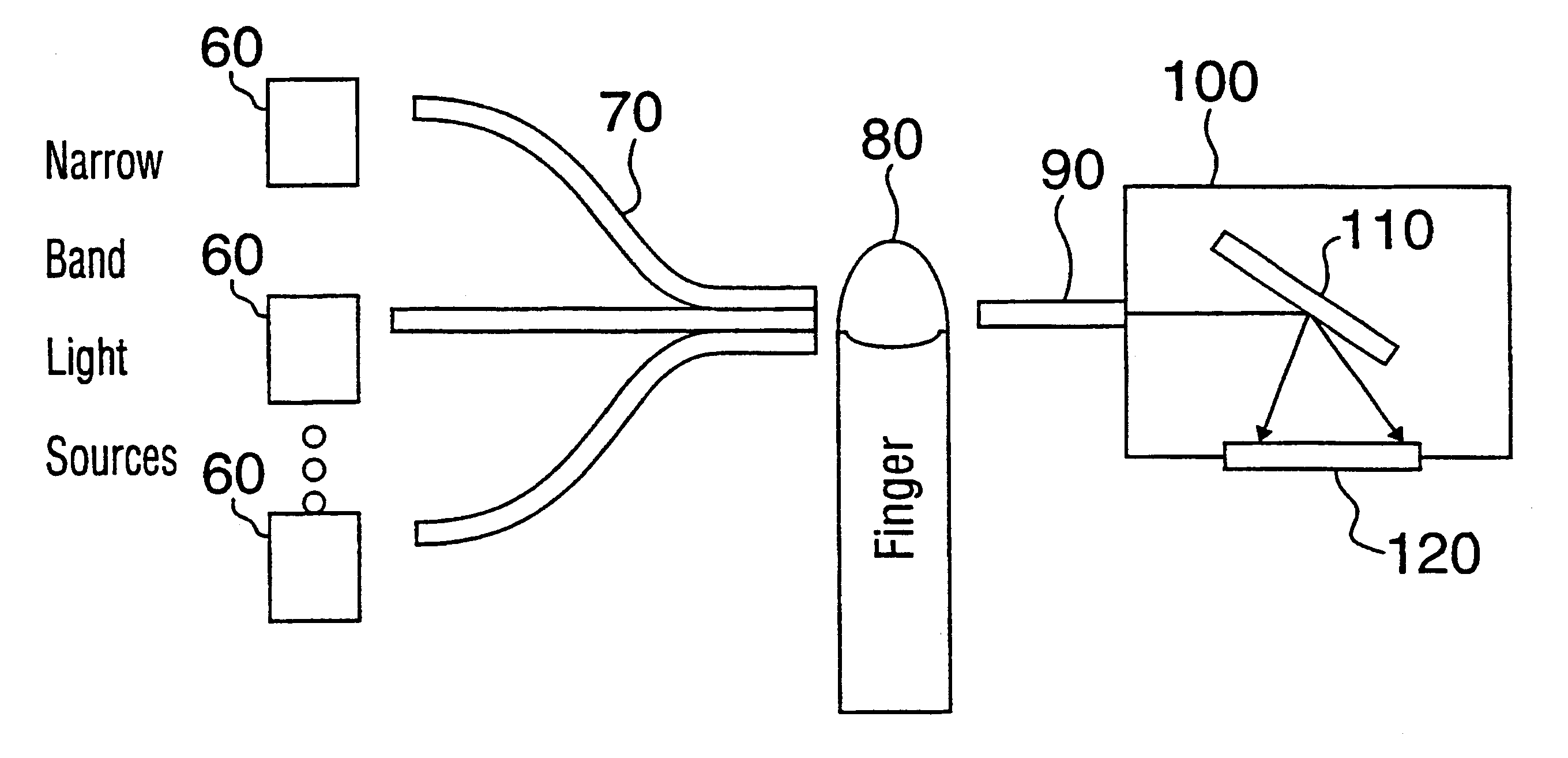
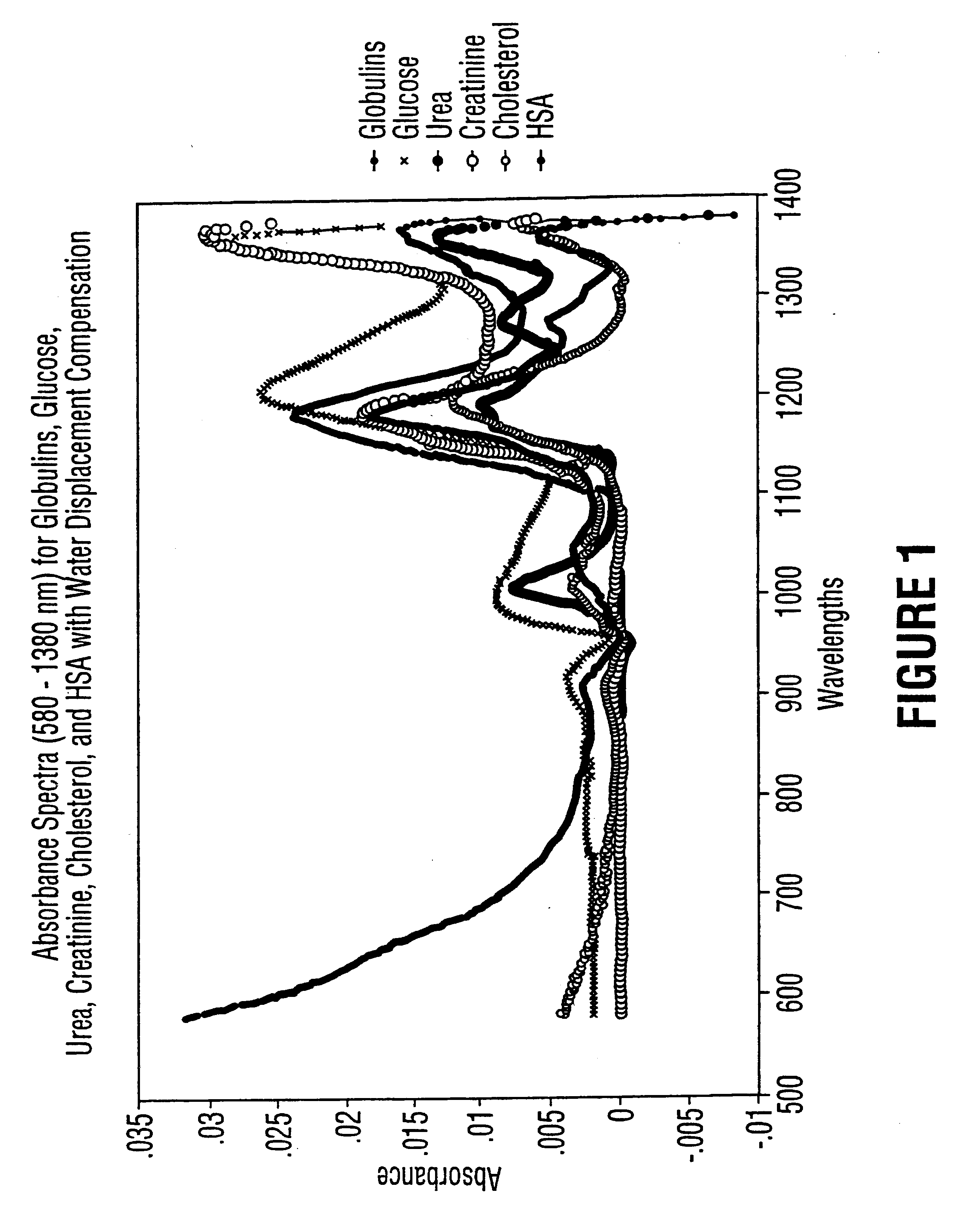
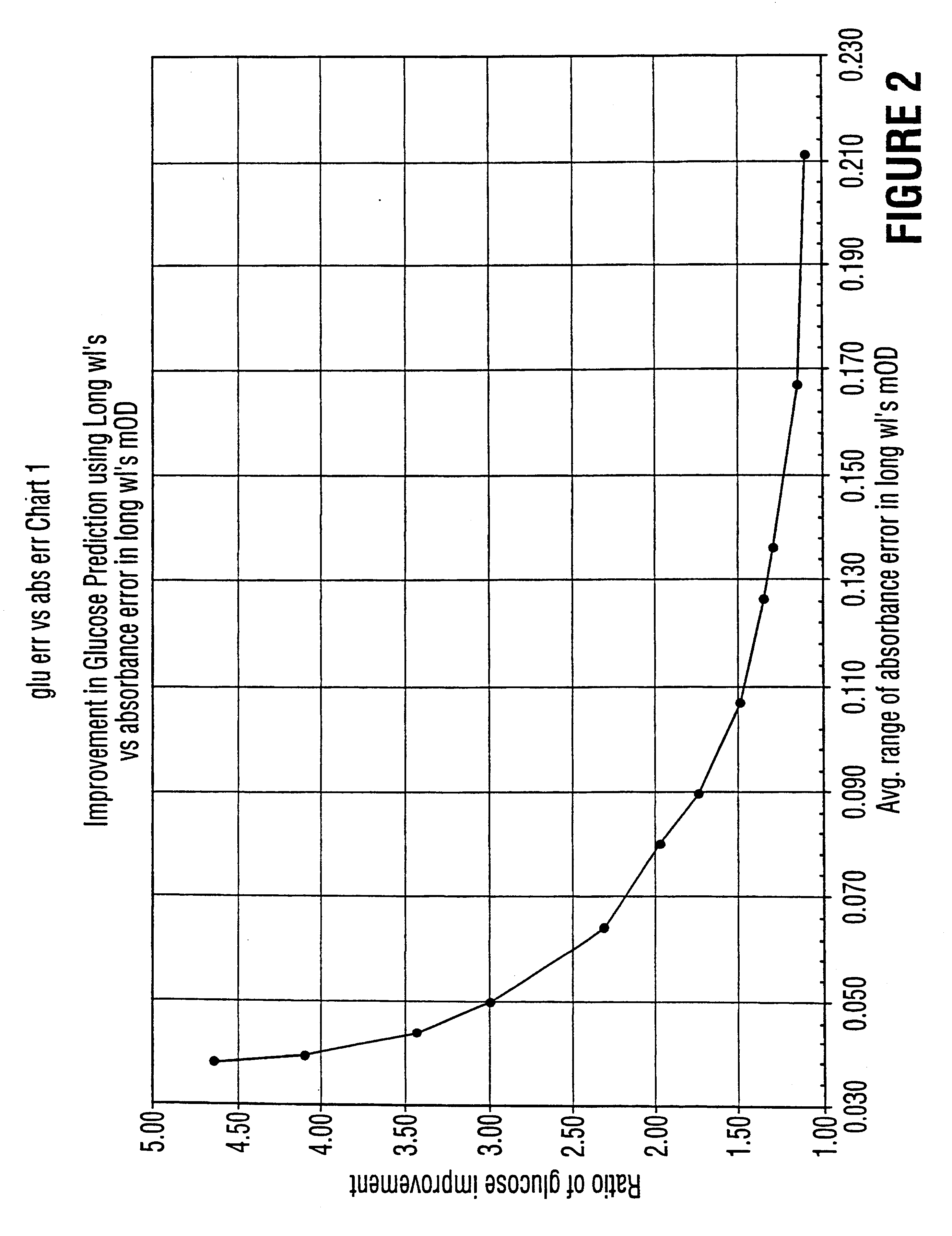
Described is a method for measuring the concentration of a blood constituent within a body part (80) of a living subject which comprises irradiating a body part of the subject with a continuum of a broad spectrum of radiation in adjacent and near infrared range of the electomagnetic spectrum; collecting the band of radiation after the radiation has been directed onto the part; dispersing the continuum of collected radiation into a dispersed spectrum of component wavelengths onto a detector (120) the detector taking measurements of at least one of transmitted or reflected radiation from the collected radiation; and transferring the measurements to a processor (300), and then measuring the same kind of absorbance or reflectance with respect to one or more a discrete wavelengths of radiation from the longer near infrared range and using the measurements to calculate the concentration of the constituent.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Side emitting illumination systems incorporating light emitting diodes
InactiveUS20070086211A1Increasing the effective brightness of the light emitting diodeIncrease brightnessNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight-emitting diodeBrightness perception
The invention is a side-emitting illumination system that incorporates a light emitting diode. The side-emitting illumination system recycles a portion of the light internally generated by a light emitting diode back to the light emitting diode as externally incident light. The light emitting diode reflects the recycled light, thereby increasing the effective brightness of the light emitting diode. The light reflected by the light emitting diode is directed though the output aperture of the side-emitting illumination system, thereby increasing the output brightness and efficiency of the side-emitting illumination system. The light emitting diode reflects externally incident light with a reflectivity greater than 40 percent.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
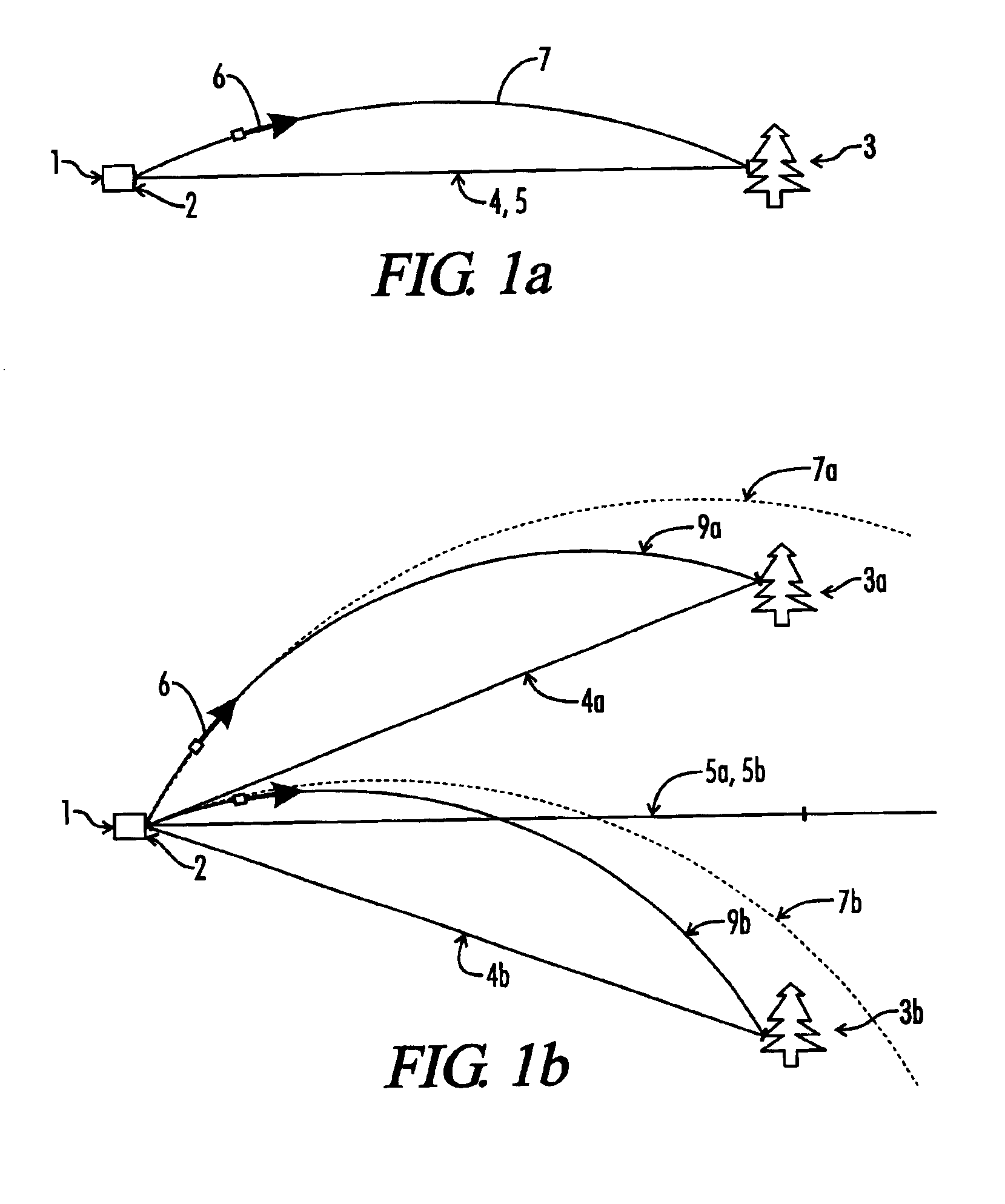
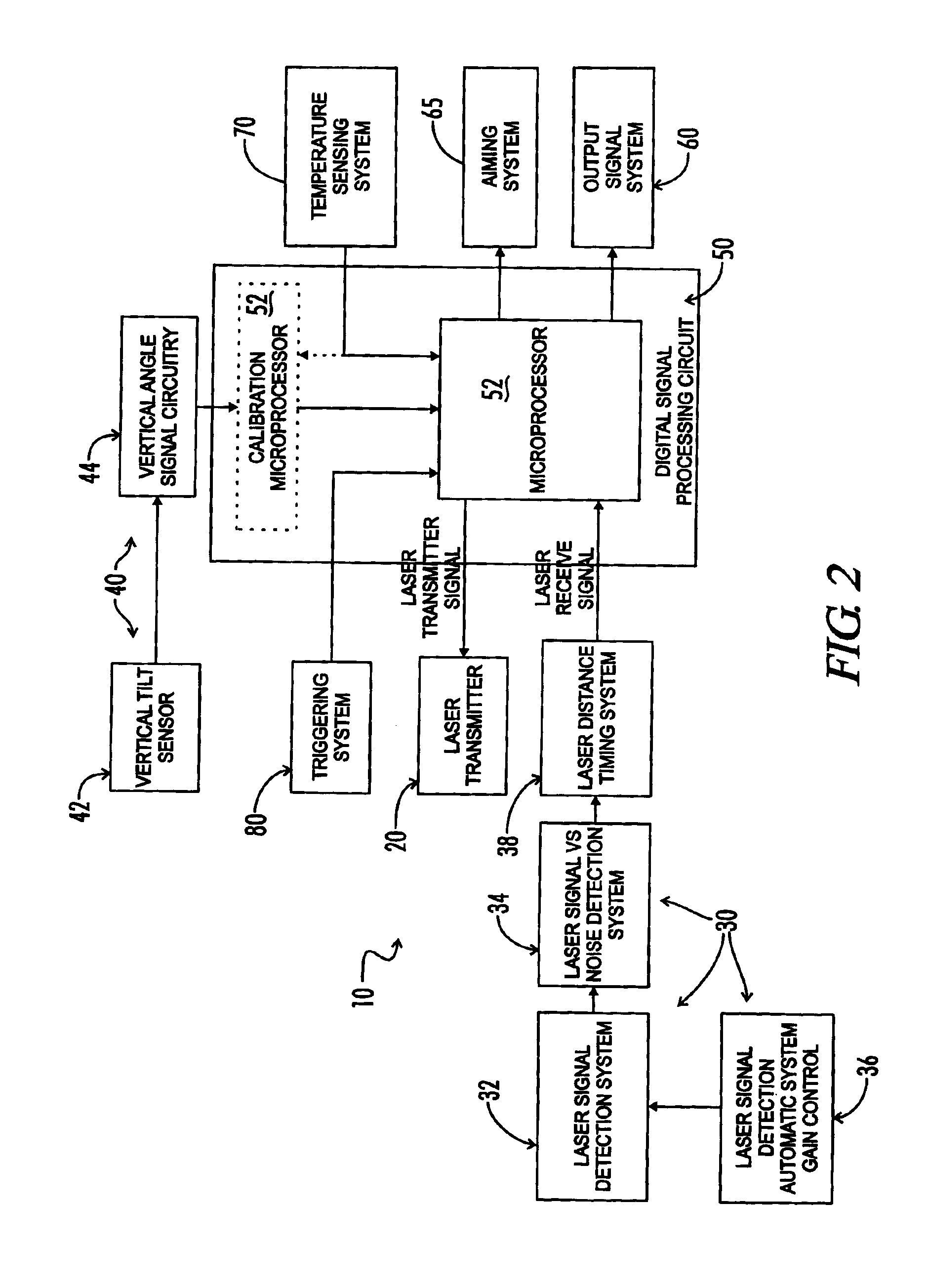
Tilt-compensated laser rangefinder
InactiveUS6873406B1Minimize impactError minimizationAngle measurementOptical rangefindersDigital signal processingInternal temperature
The present invention is a laser ranging device that incorporates an internal tilt sensor, an internal temperature sensor, and an internal pressure sensor. The tilt sensor is used to measure the target's vertical angle relative to the horizontal reference plane. Digital signal processing circuitry controls the firing of the laser pulse, calculation of time-of-flight range, measurement of the vertical angle of the tilt sensor, measurement of ambient temperature and storage of tilt sensor and temperature sensor calibration data. The digital signal processing circuitry then provides the user temperature corrected ballistic ranging information, including horizontal range. Additionally, an automatic gain control system minimizes the effects of target to target variance in reflectivity and its associated errors. It is also an object of this invention to electronically minimize errors in the measurement of a vertical angle caused by housing vibration and by temperature variance errors.
Owner:OPTI LOGIC CORP
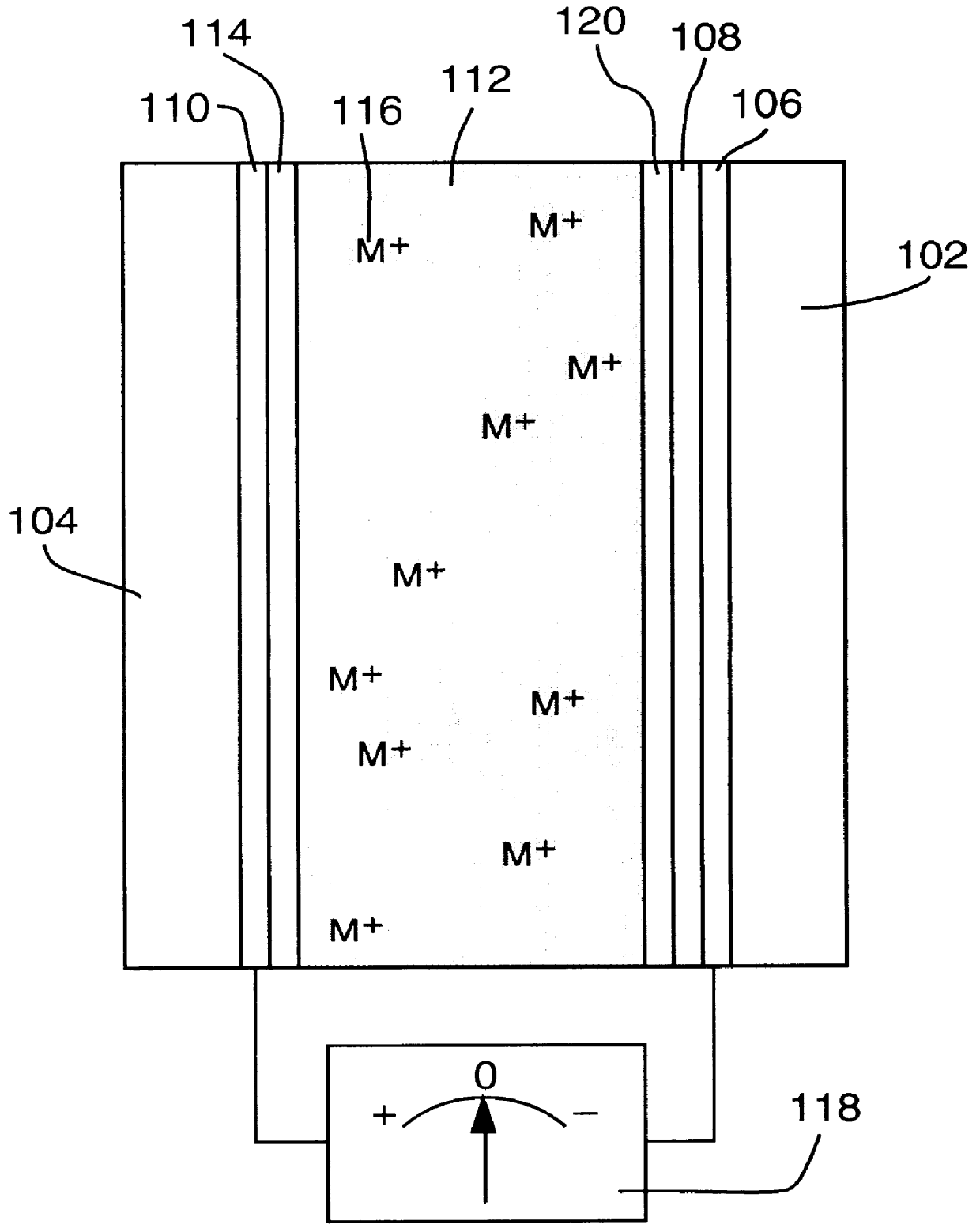
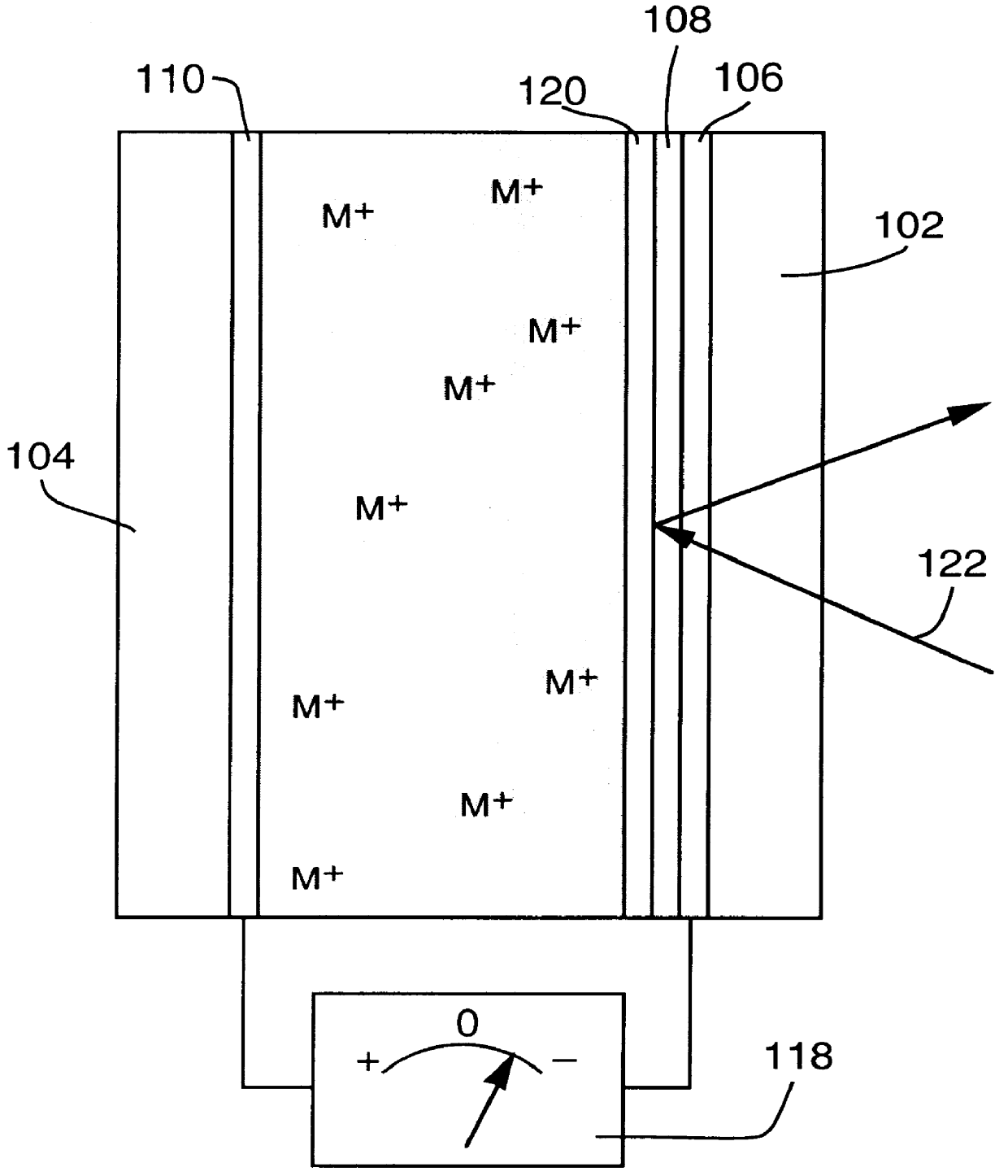
Reversible electrochemical mirror for modulation of reflected radiation
InactiveUS6166847APrecise and Efficient ControlUniform nucleationNon-linear opticsElectricityElectromagnetic radiation
An electrochemical mirror includes a transparent first electrode and a second electrode. An electrolytic solution, disposed between the first and second electrodes, contains ions of a metal which can electrodeposit on the electrodes. A negative electrical potential applied to the first electrode causes deposited metal to be dissolved from the second electrode into the electrolytic solution and to be electrodeposited from the solution onto the first electrode, thereby affecting the reflectivity of the mirror for electromagnetic radiation. A surface modification layer applied to the first electrode ensures that the electrodeposit is substantially uniform, resulting in a mirror layer which increases the reflectivity of the mirror. A positive electrical potential applied to the first electrode causes deposited metal to be dissolved from the first electrode and electrodeposited from the solution onto the second electrode, thereby decreasing the reflectivity of the mirror.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Copper damascene barrier and capping layer
InactiveUS20060024954A1Improve electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingEngineering
A method for forming a damascene with improved electrical properties and resulting structure thereof including providing at least one dielectric insulating layer overlying a first etch stop layer; forming an anti-reflectance coating (ARC) layer prior to a photolithographic patterning process; forming at least one opening extending through a thickness portion of the at least one dielectric insulating layer and first etch stop layer according to said photolithographic patterning and an etching process; blanket depositing a barrier layer including material selected from the group consisting of silicon carbide and silicon oxycarbide to line the at least one opening; blanket depositing a refractory metal liner over the barrier layer; blanket depositing at least one metal layer to fill the at least one opening; and, removing at least the at least one metal layer overlying the at least one opening level according to a chemical mechanical polish (CMP) process.
Owner:WU ZHEN CHENG +3
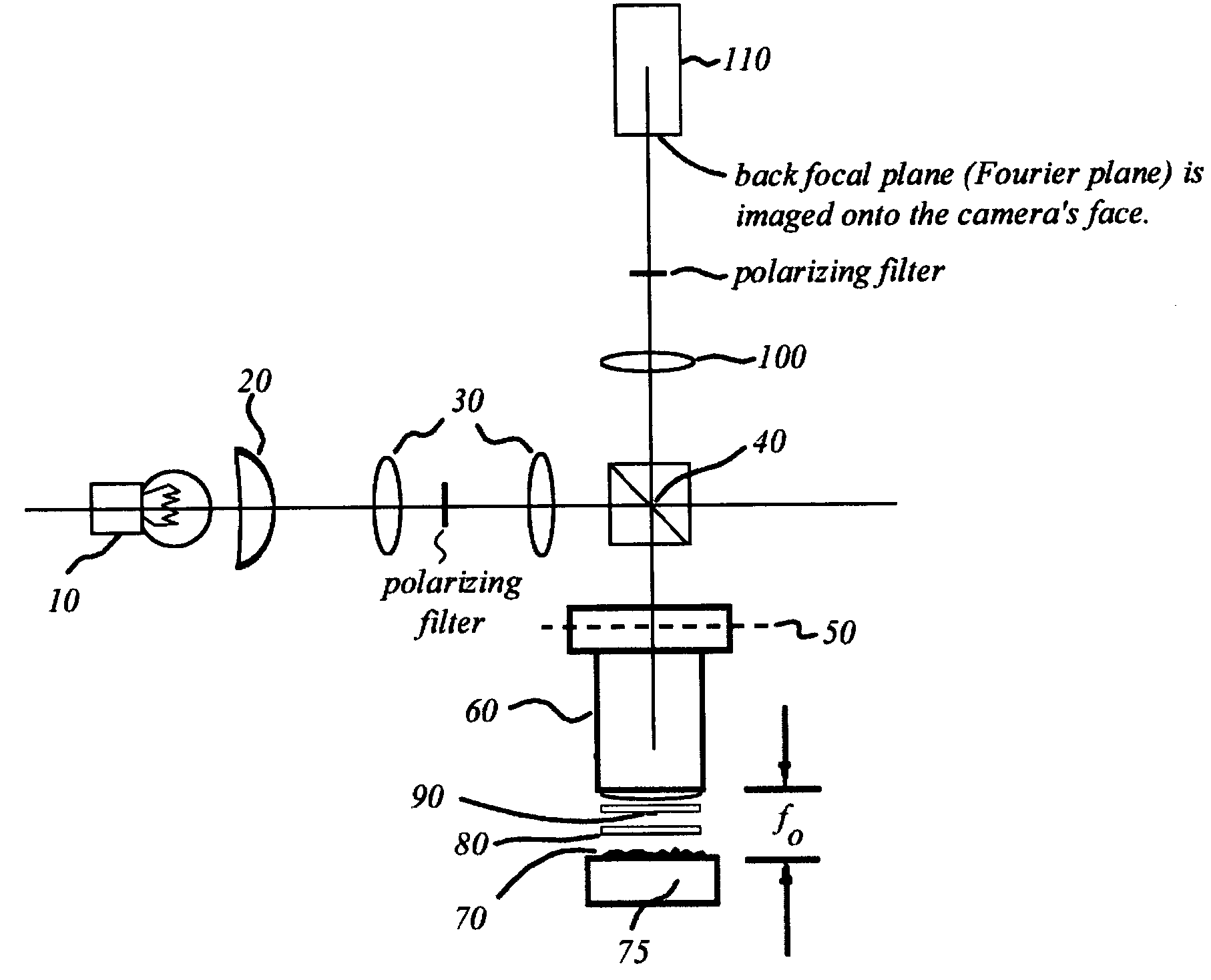
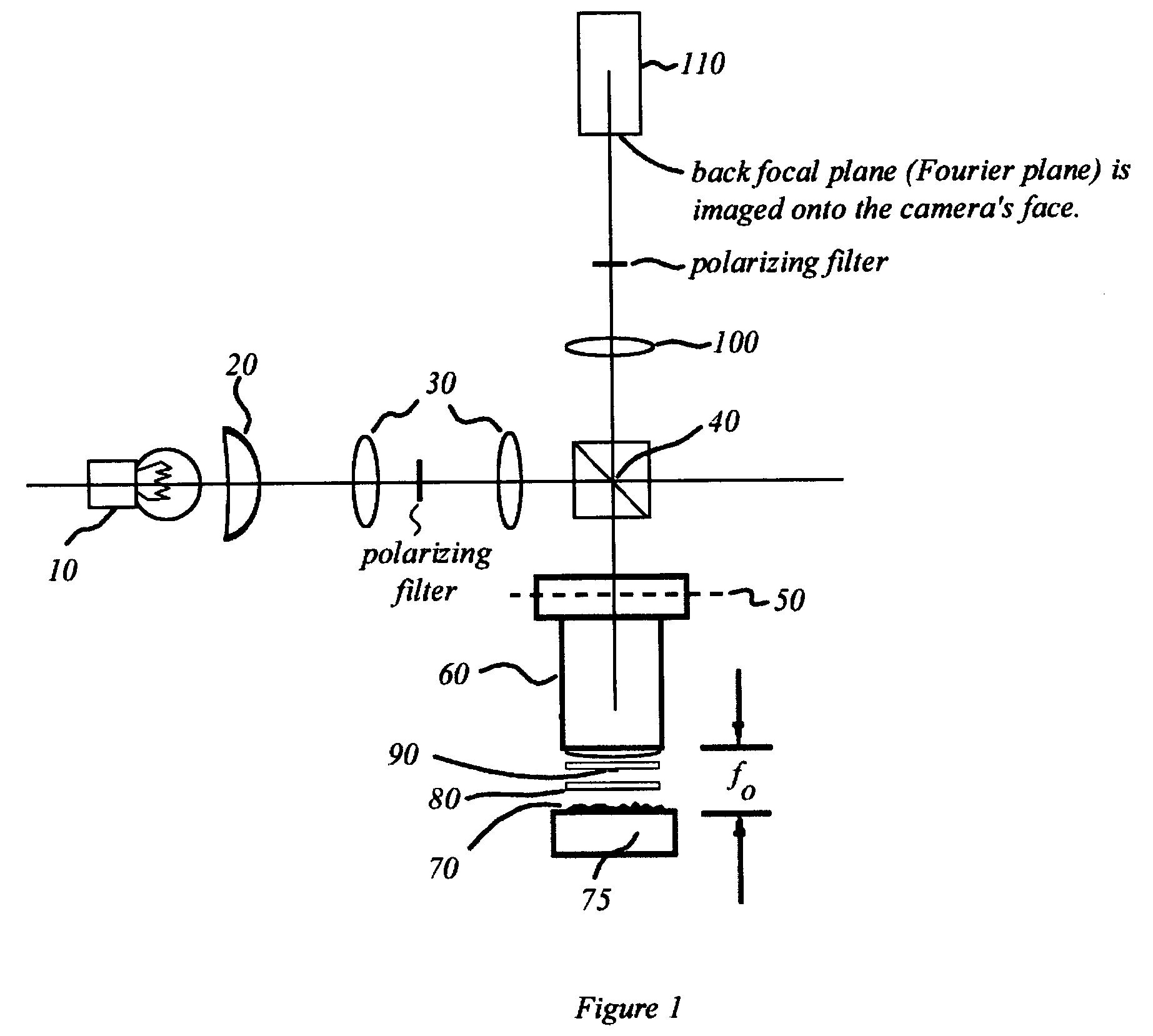
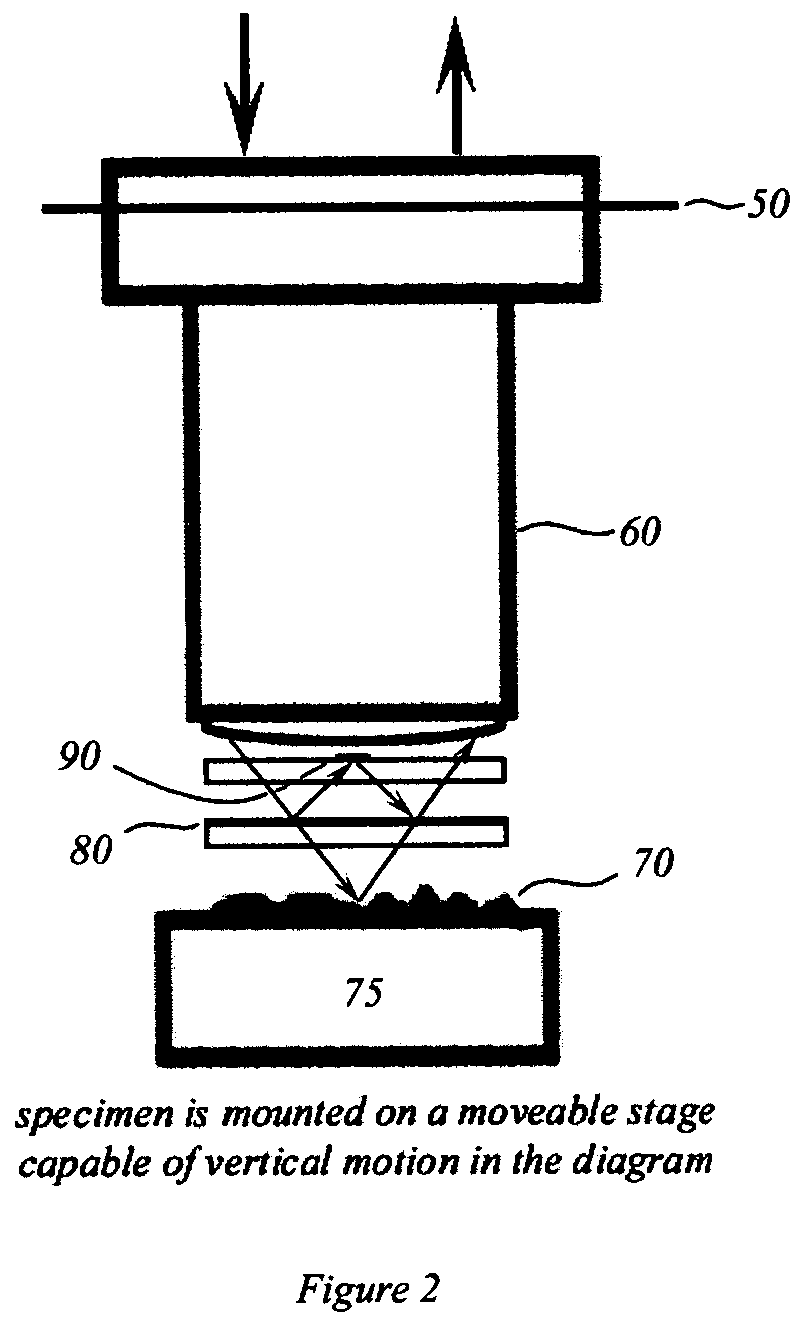
Interferometric back focal plane scatterometry with Koehler illumination
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
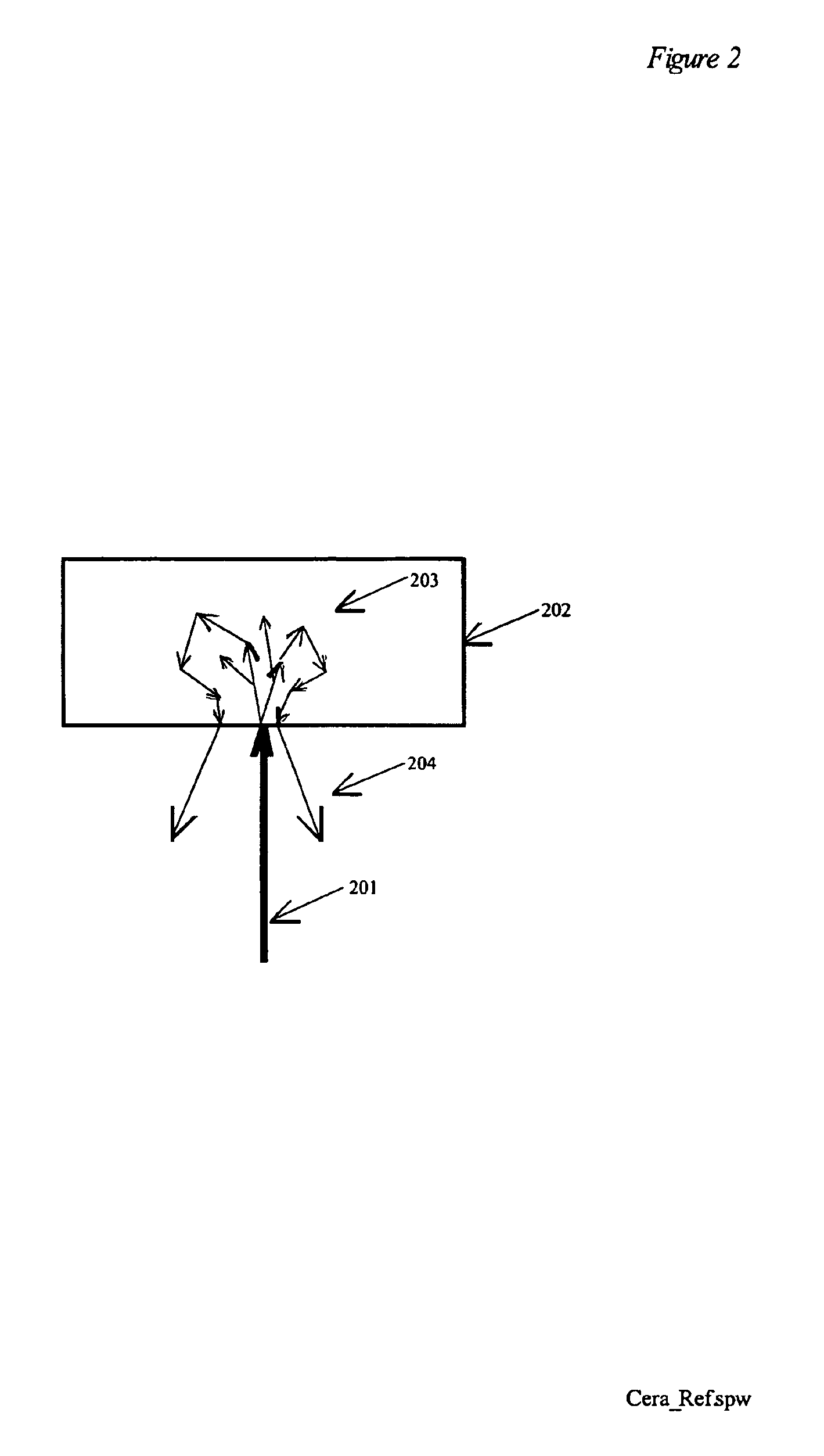
Spectroscopic system and method using a ceramic optical reference
A ceramic reference in conjunction with a spectrometer, a metallized ceramic material, and a method of utilizing a ceramic material as a reference in the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, or infrared spectral regions are presented. The preferred embodiments utilize a ceramic reference material to diffusely reflect incident source light toward a detector element for quantification in a reproducible fashion. Alternative embodiments metallize either the incident surface or back surface of to form a surface diffuse reflectance standard. Optional wavelength reference layers or protective layers may be added to the ceramic or to the metallized layer. The reference ceramic is used to provide a measure of optical signal of an analyzer as a function of the analyzers spatial, temporal, and environmental state.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com