Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7955 results about "Blood pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure is due to work done by the heart by pumping blood through the circulatory system. Used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the pressure in large arteries of the systemic circulation. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum in between two heartbeats) and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), above the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
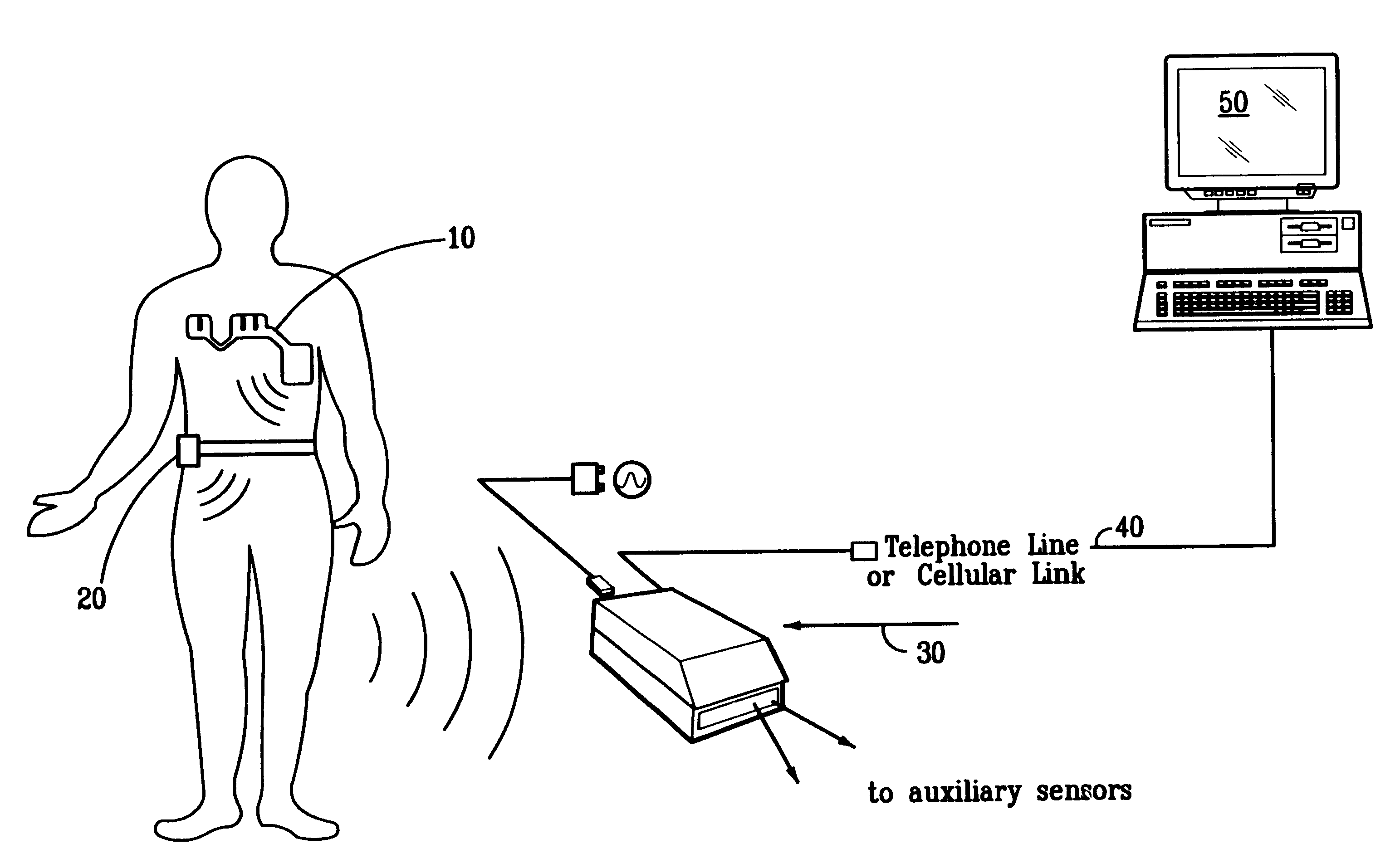
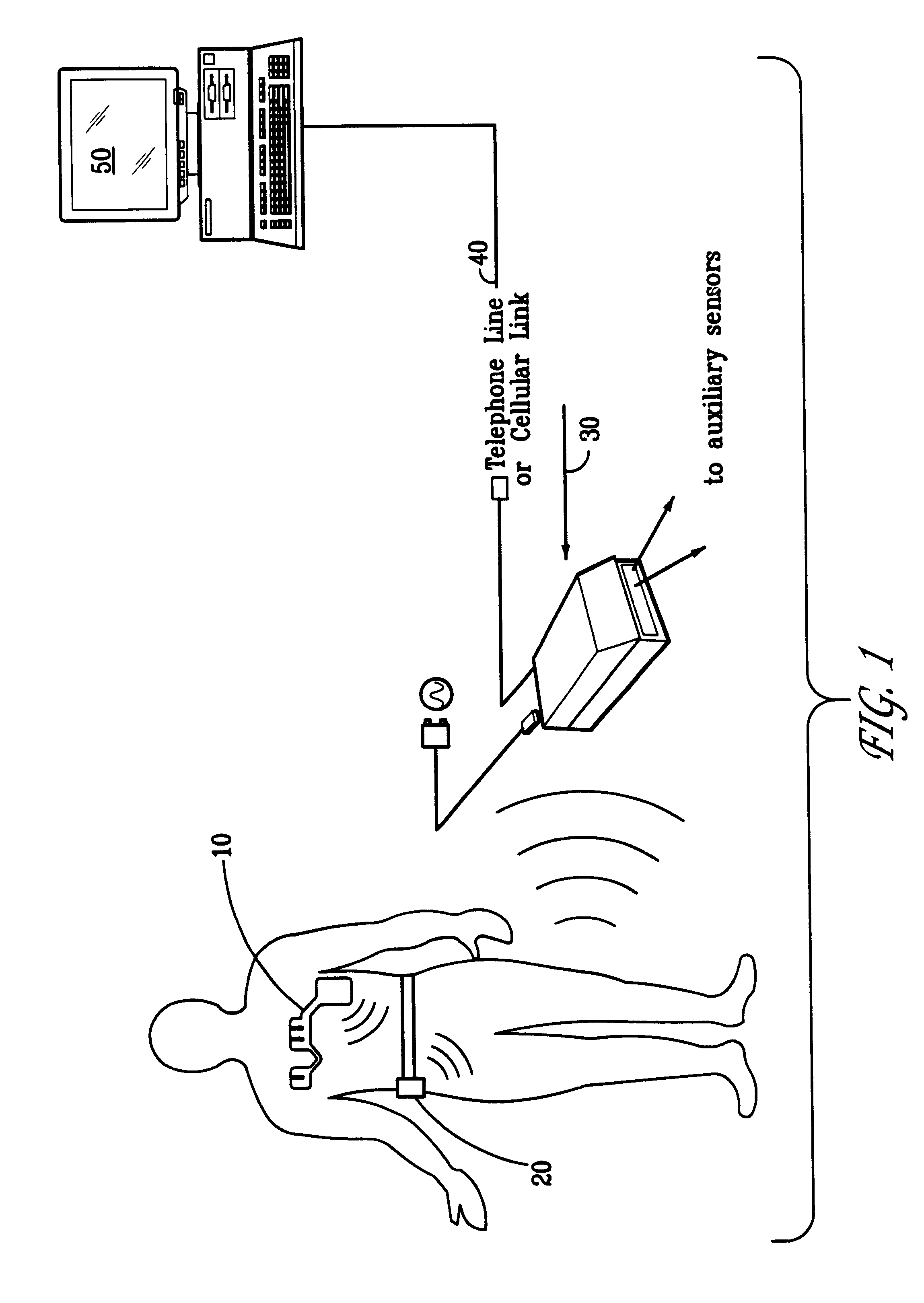
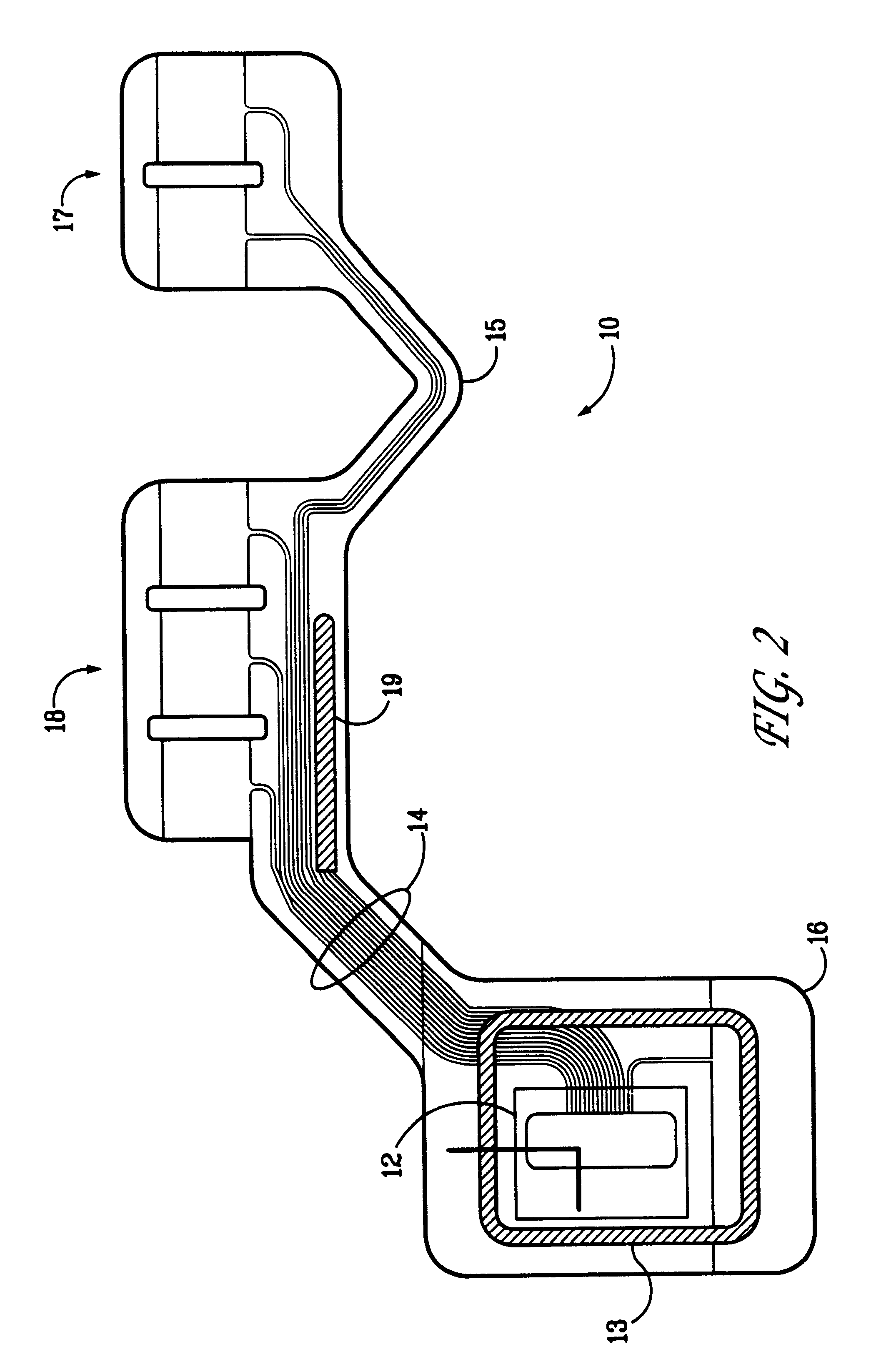
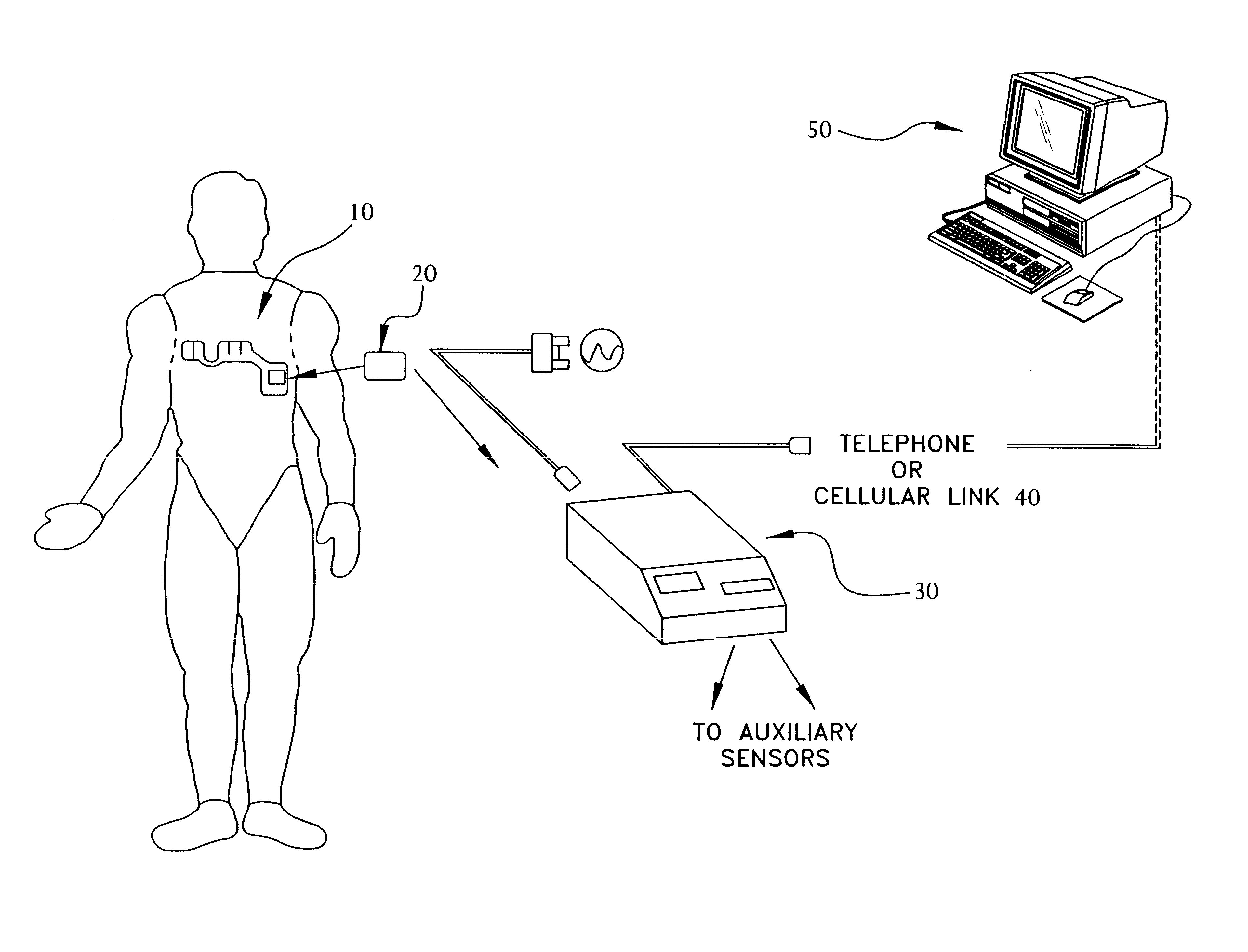
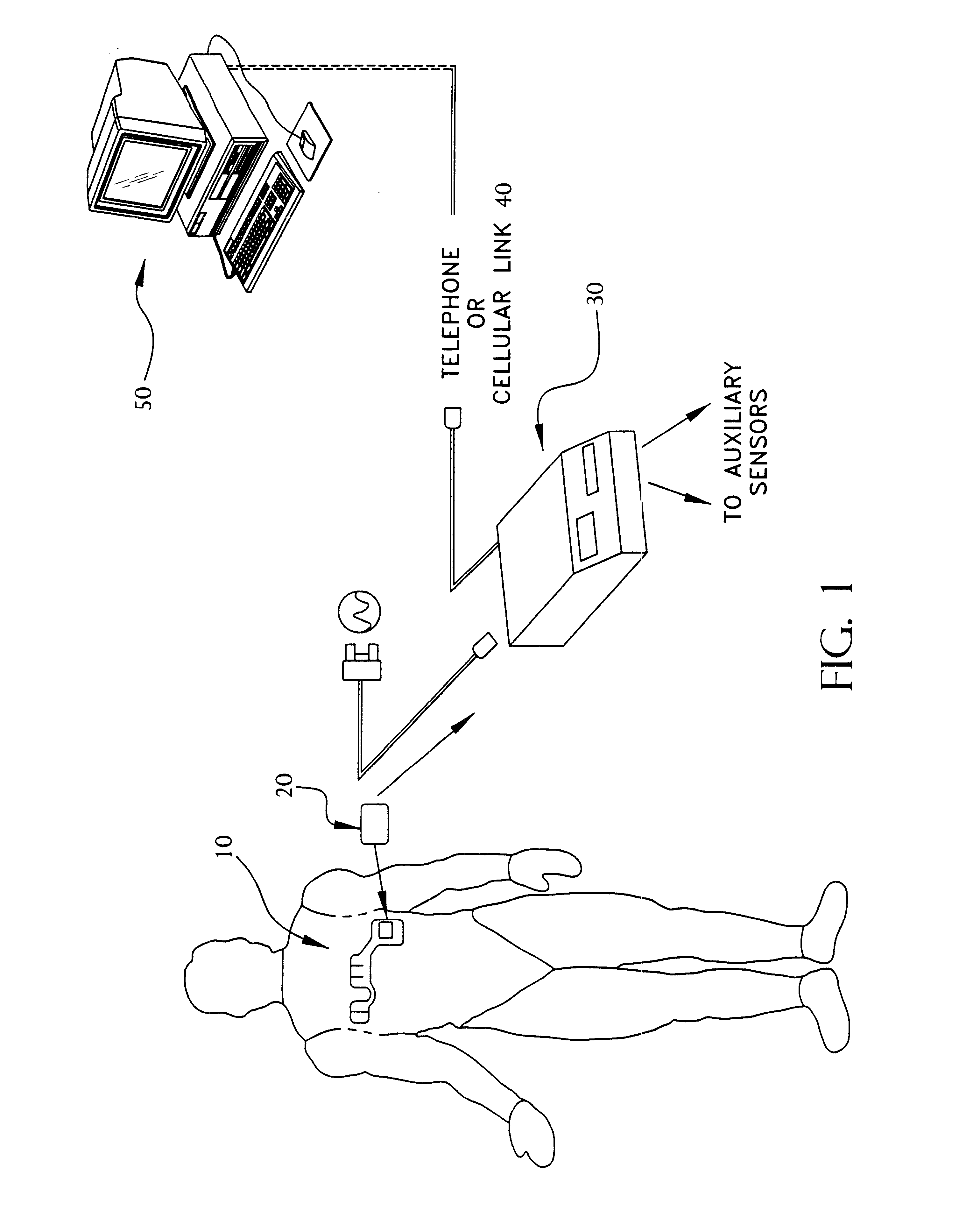
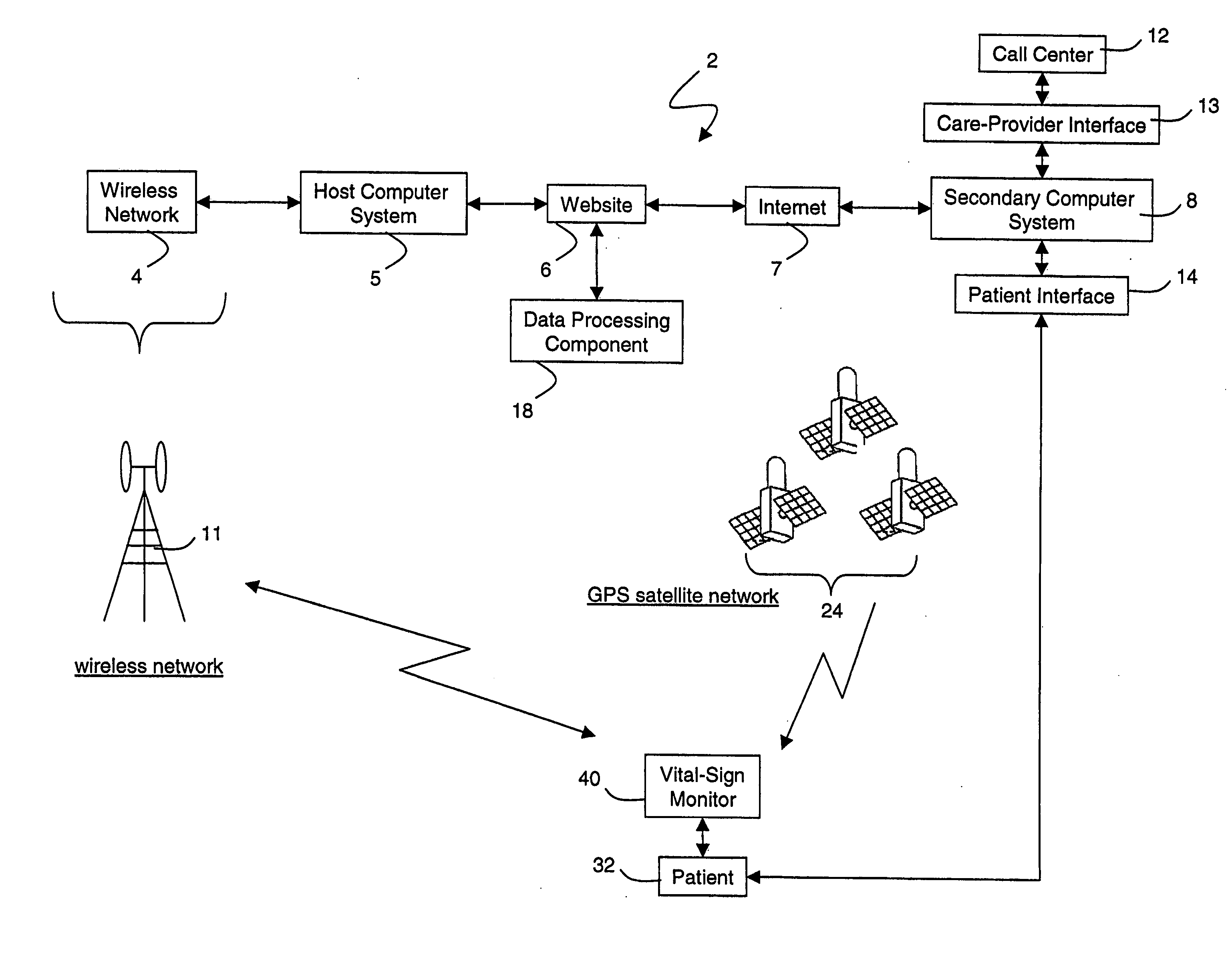
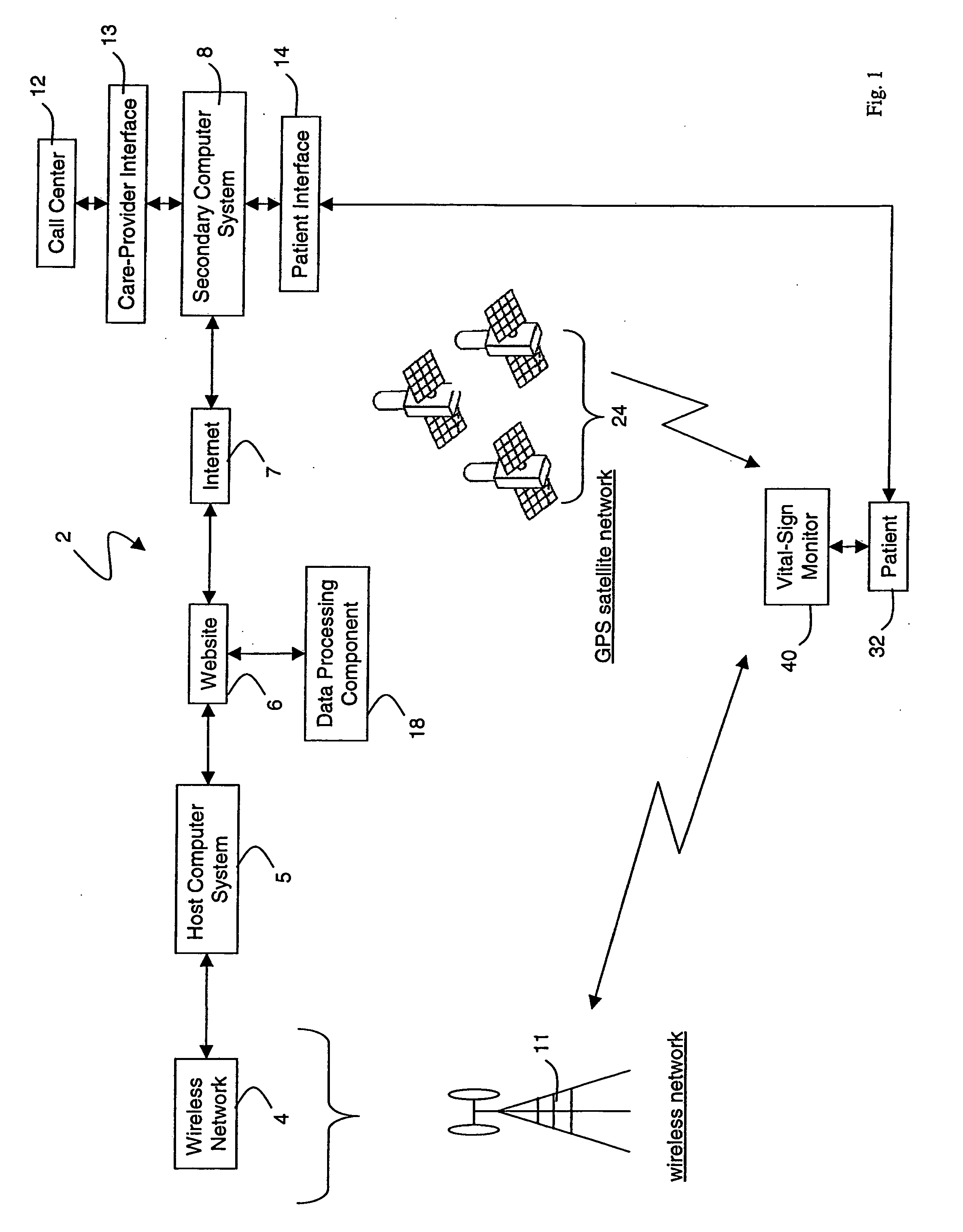
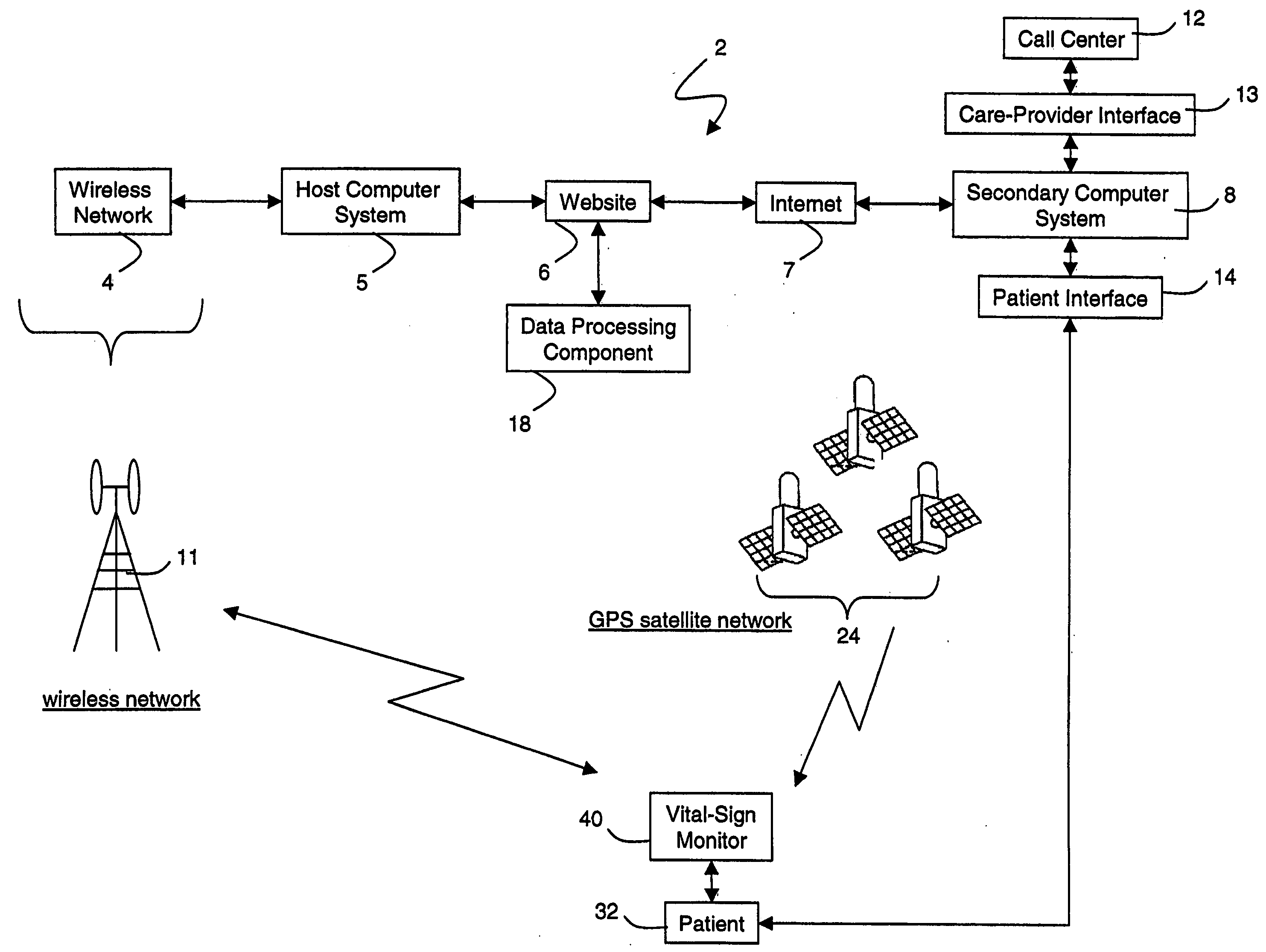
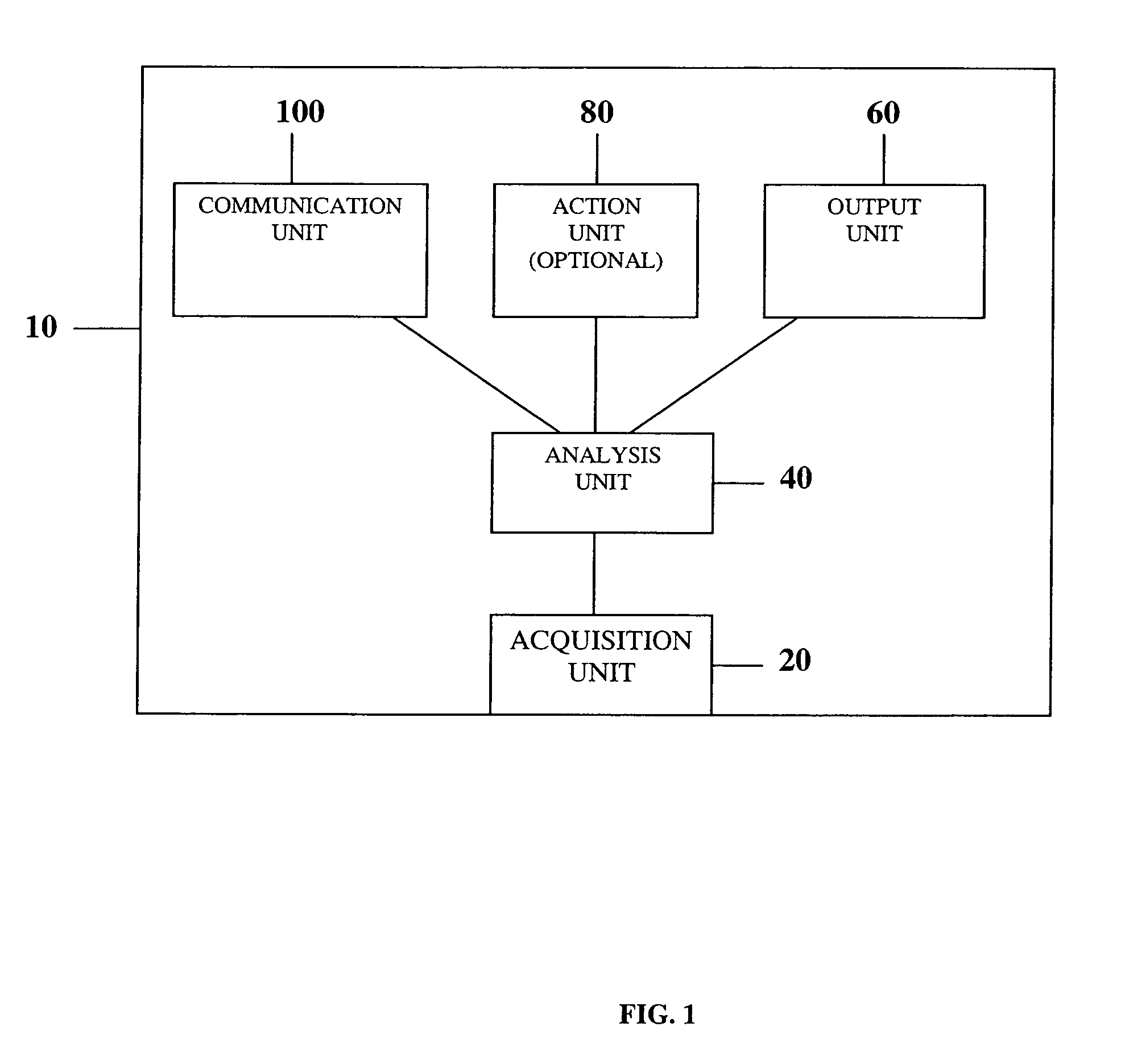
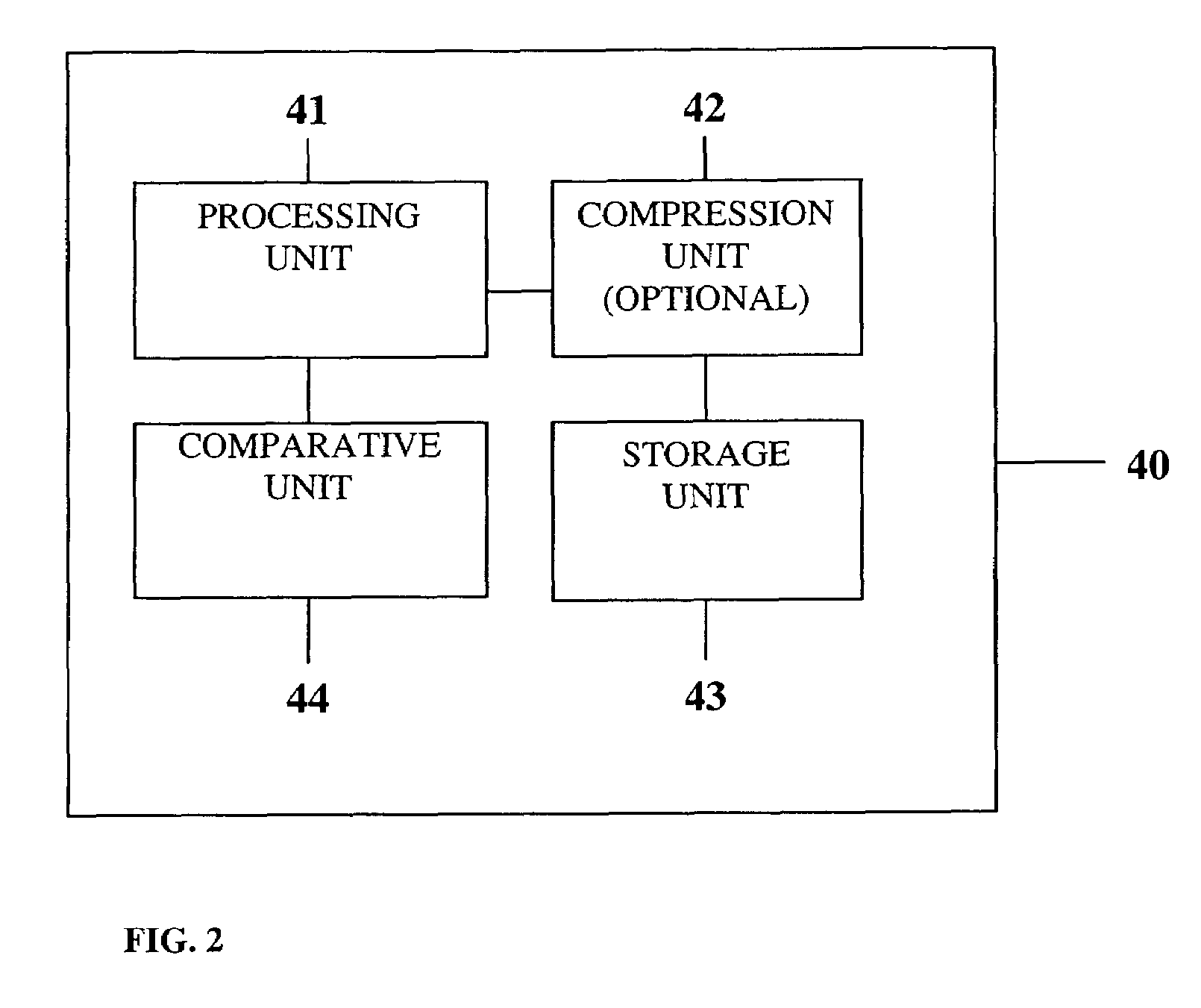
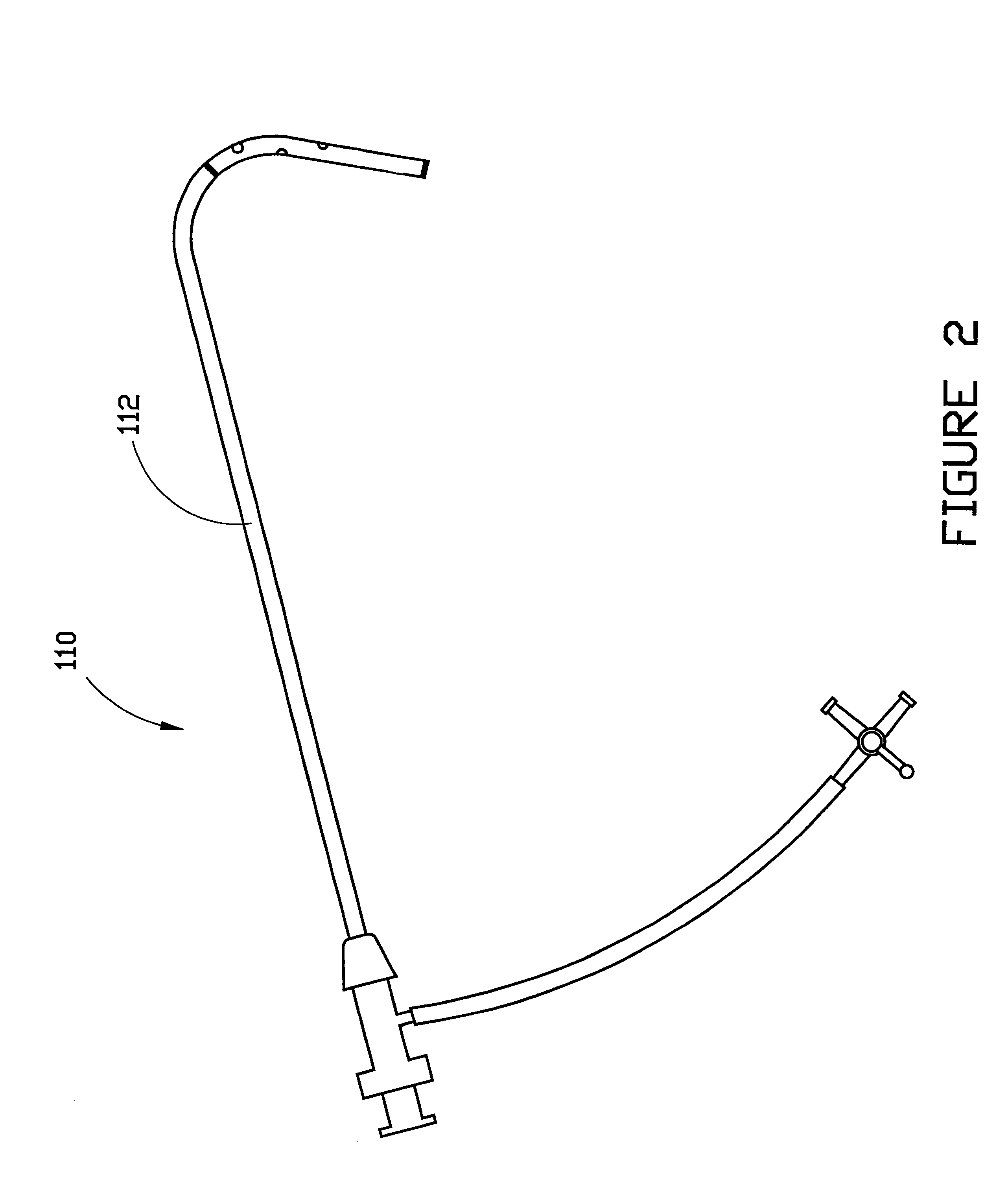
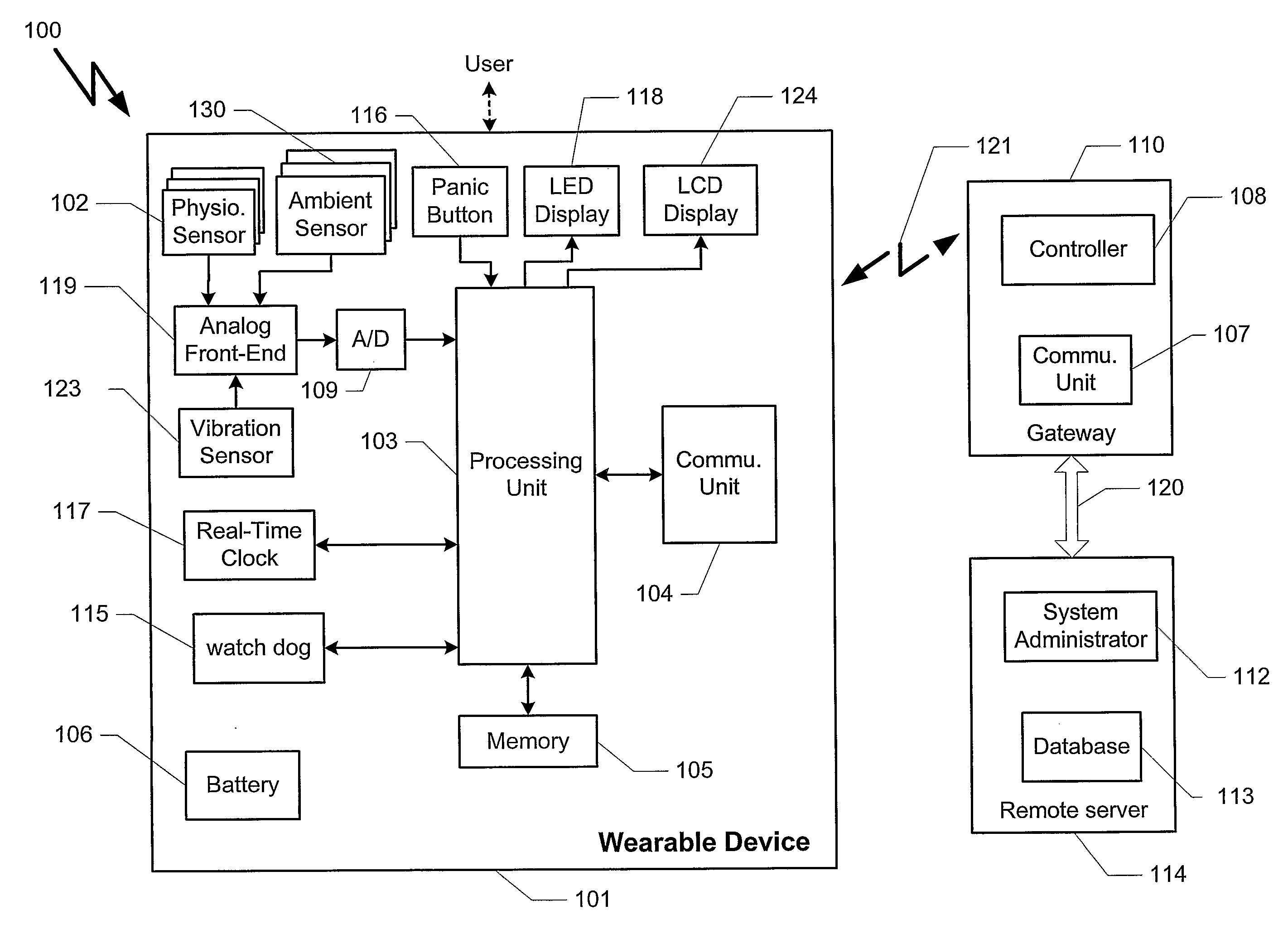
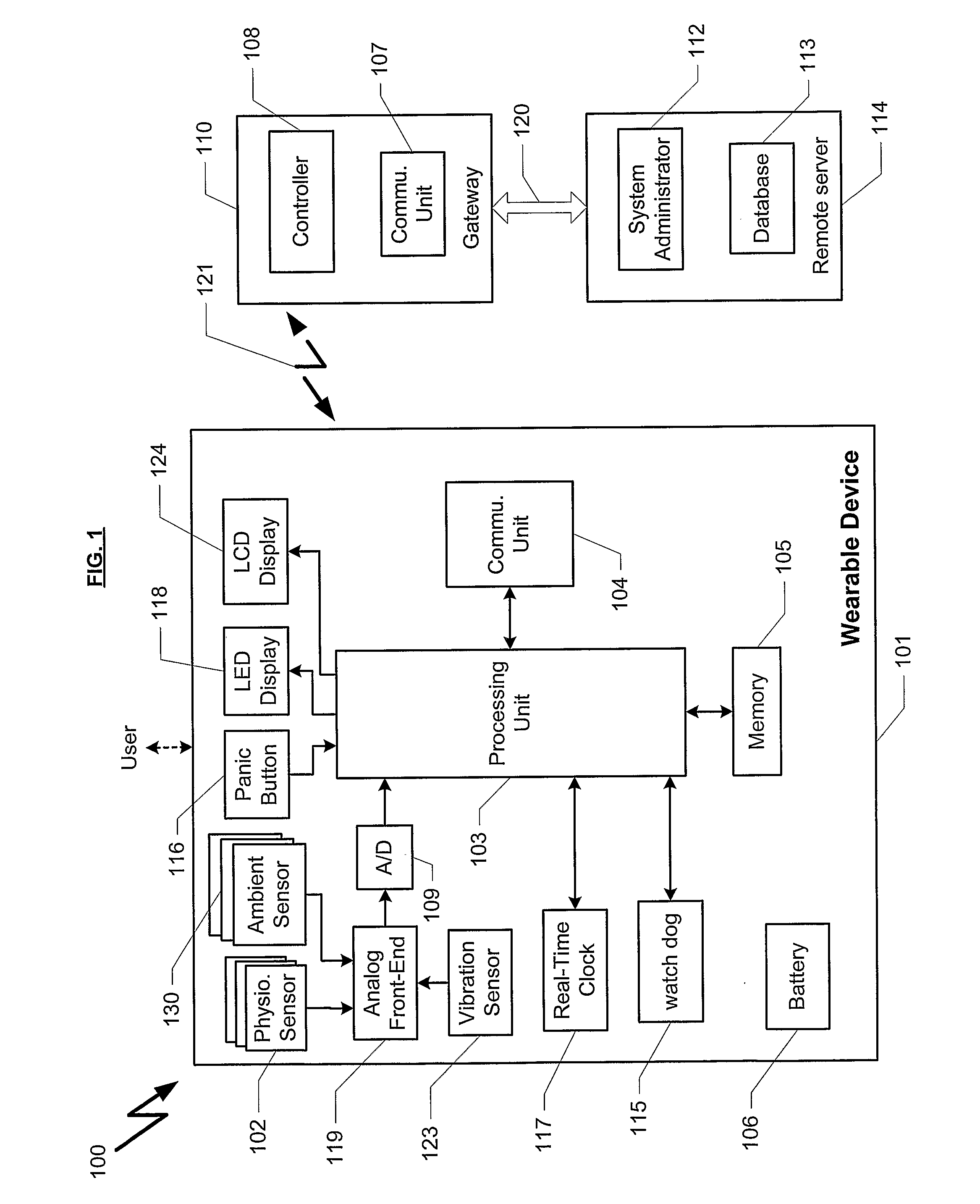
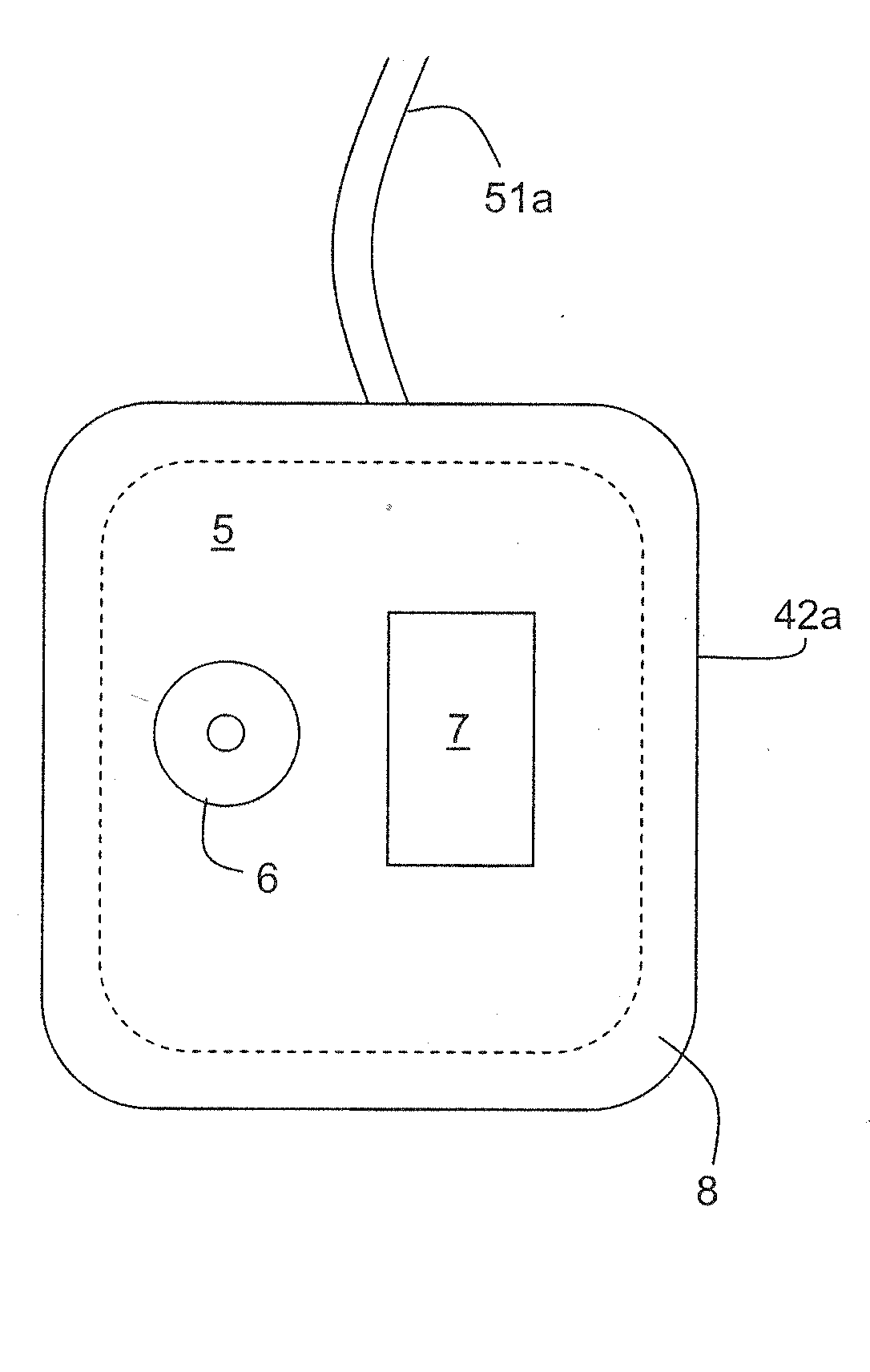
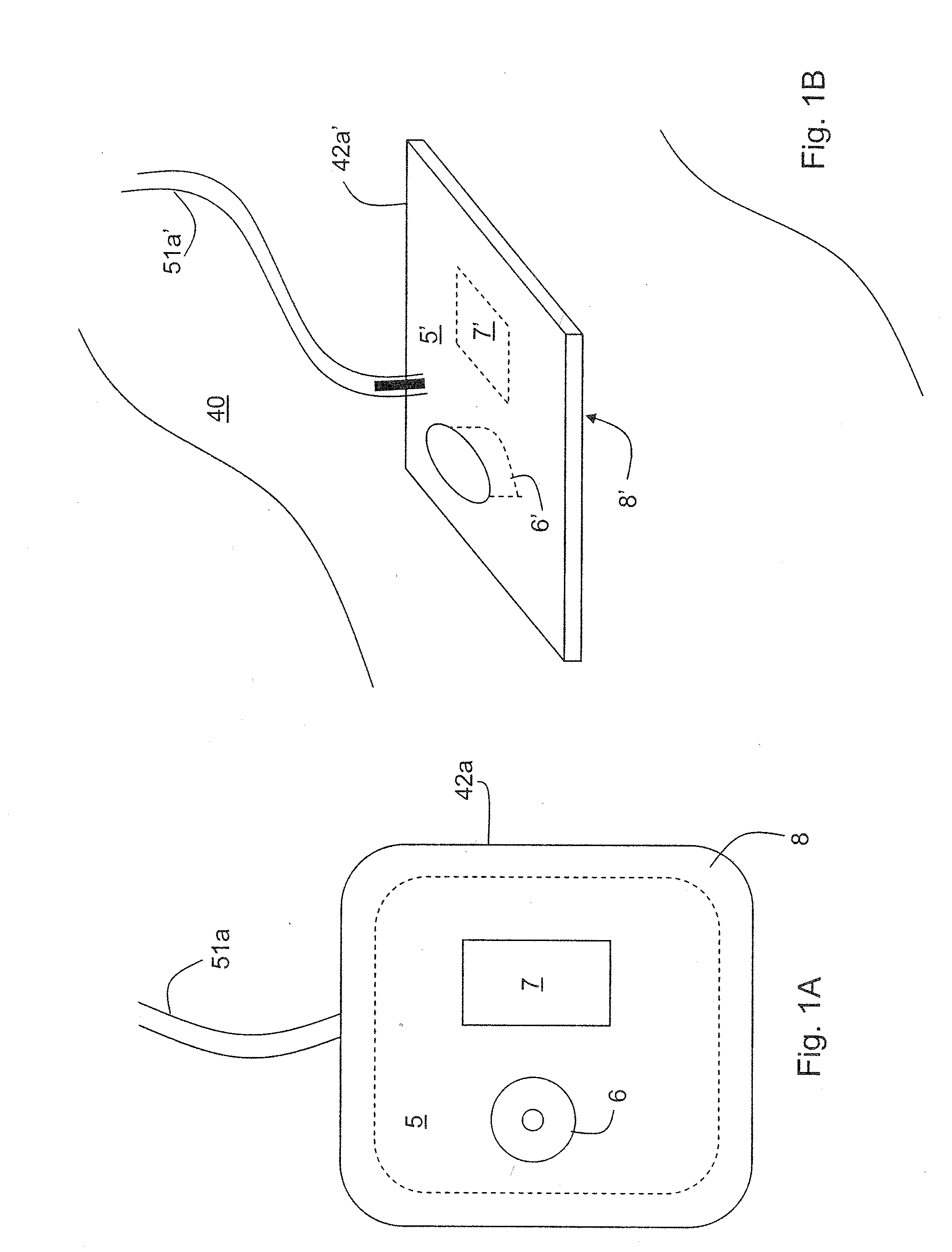
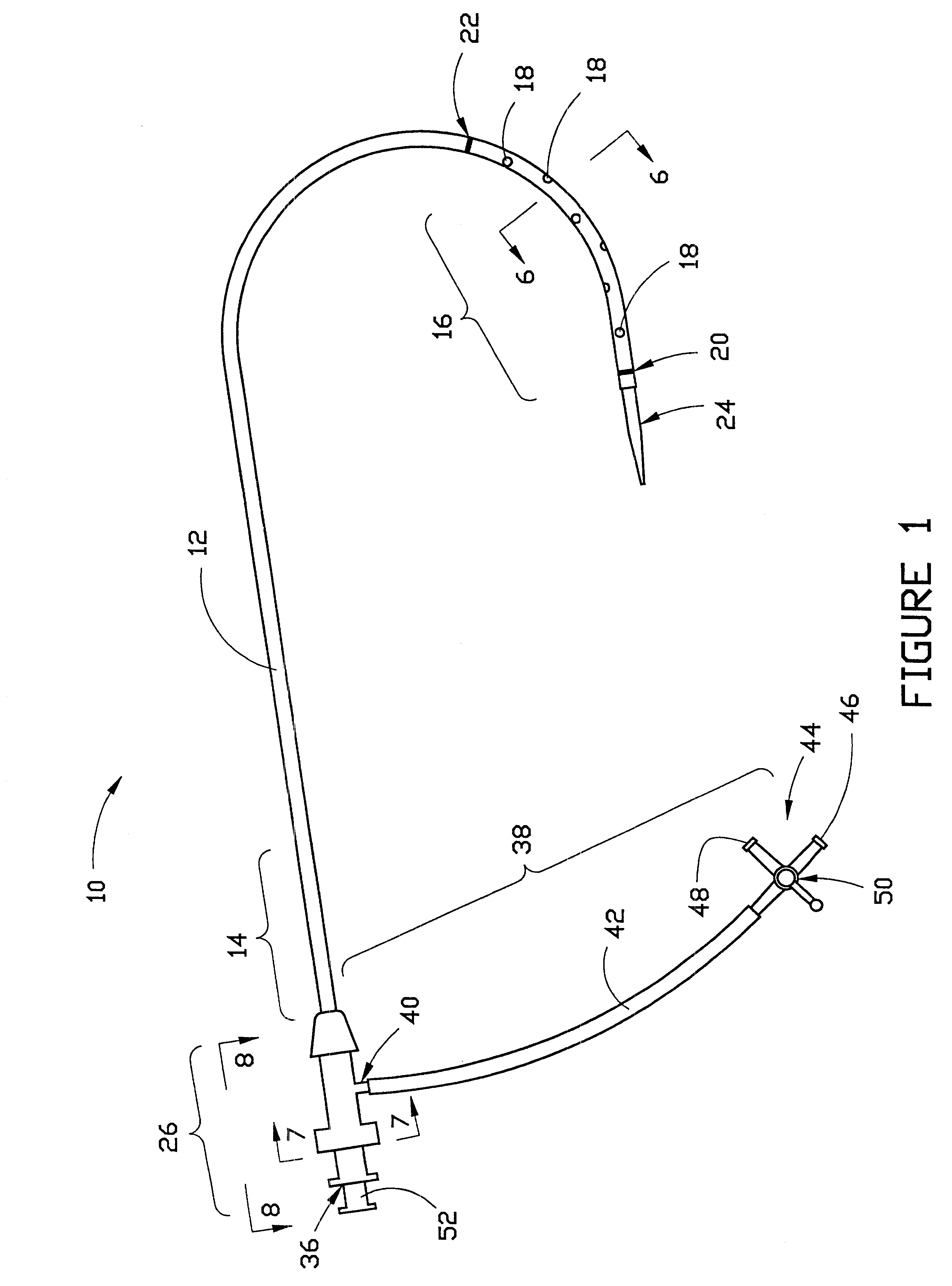
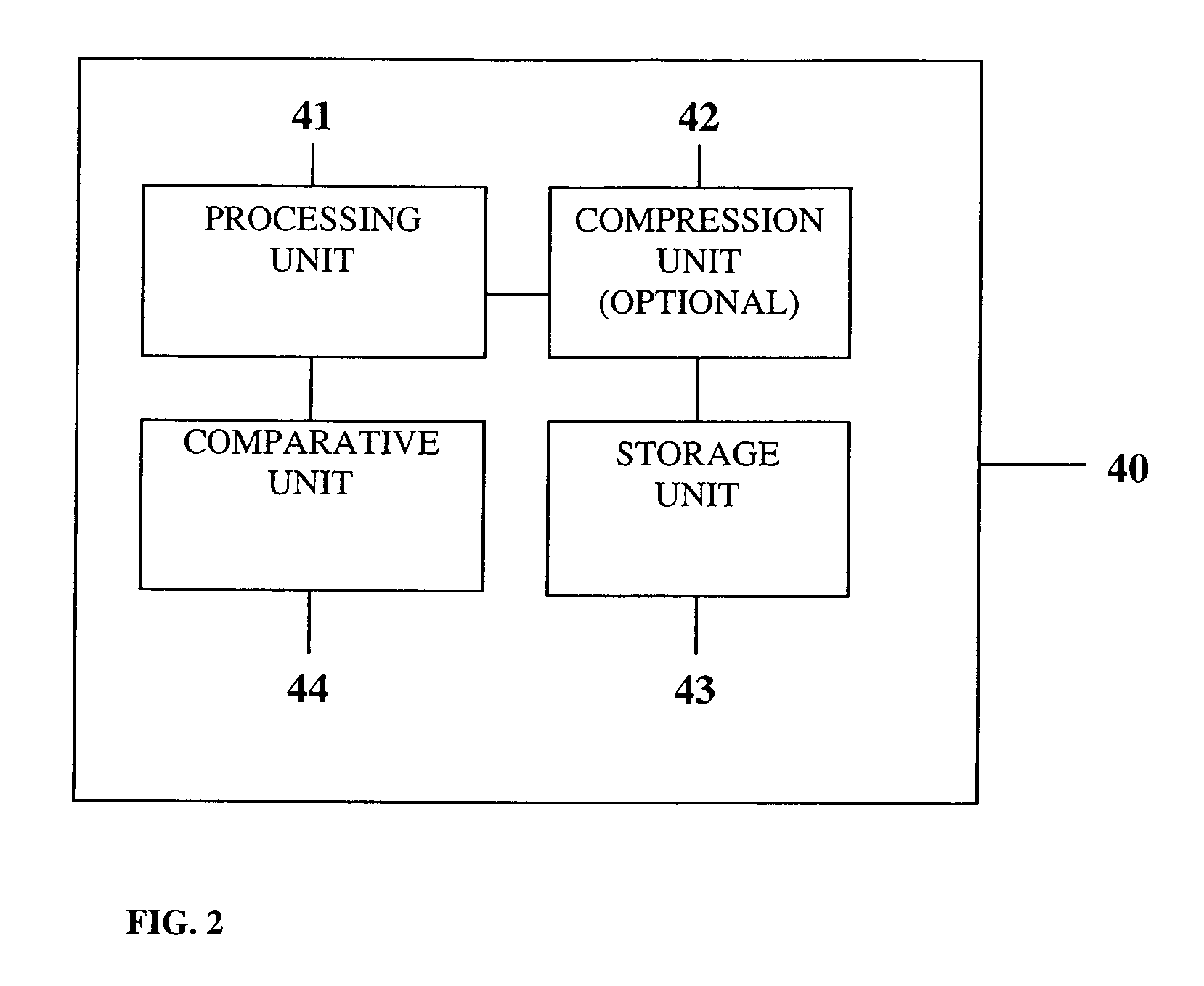
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system
A system and method for monitoring vital signs and capturing data from a patient remotely using radiotelemetry techniques. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors form measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and transmission circuitry for the detection and transmission of vital signs data of the patient. A small signal transfer unit that can either be worn by the patient, e.g., on his or her belt, or positioned nearby receives data from the sensor band, which it then forwards by e.g., radio transmission to a base station that can be located up to 60 meters away. The base station receives data transmissions from the signal transfer unit and is designed to connect to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Patient safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g., ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. Such events are indicated to the physician and could be indicated to the patient by reverse transmission to the signal transfer unit. A remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of patient clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
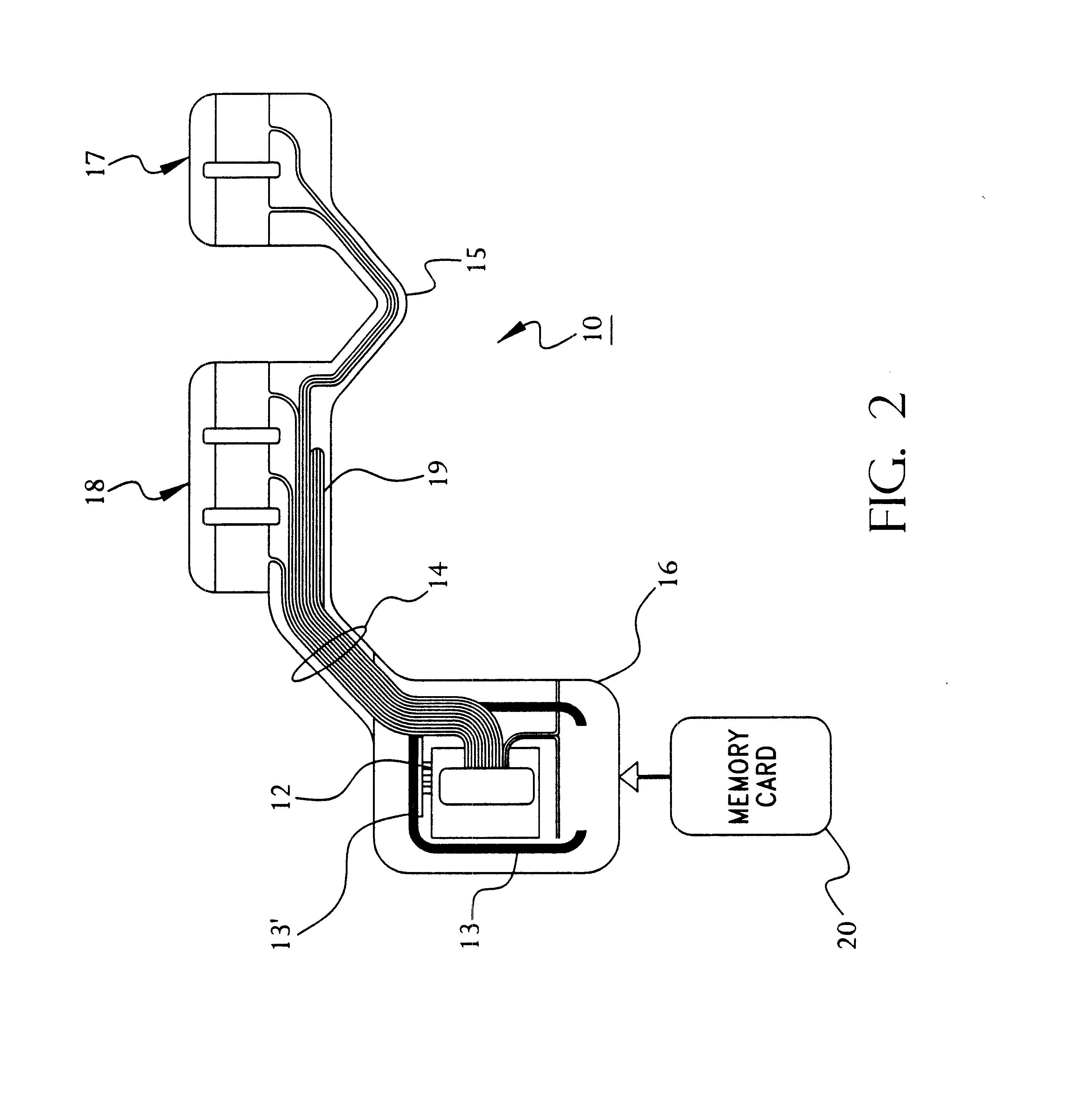
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system using a memory card or smart card
InactiveUS6454708B1Low costIncrease the number ofSurgeryRespiratory organ evaluationSmart cardFull waveform
A system and method for monitoring health parameters and capturing data from a subject. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors for measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and a connector which accepts a memory card or a smart card for storage of the measured data. After a predetermined period of time, such as when the sensor band is removed, the memory card or smart card is removed and inserted into a monitoring device which reads the stored health parameter data of the subject. The monitoring device includes a base station that includes a memory / smart card reader and is connected to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Subject safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g. ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. The remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. In alternative embodiments, a smart card includes the sensor band's electronics and / or signal transmission circuitry in conjunction with a portable data logger so that the electronics may be reused from one disposable sensor band to the next without limiting the patient's range of movement. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of subject clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of subjects with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
Non-invasive measurement of second heart sound components
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Signal processing apparatus
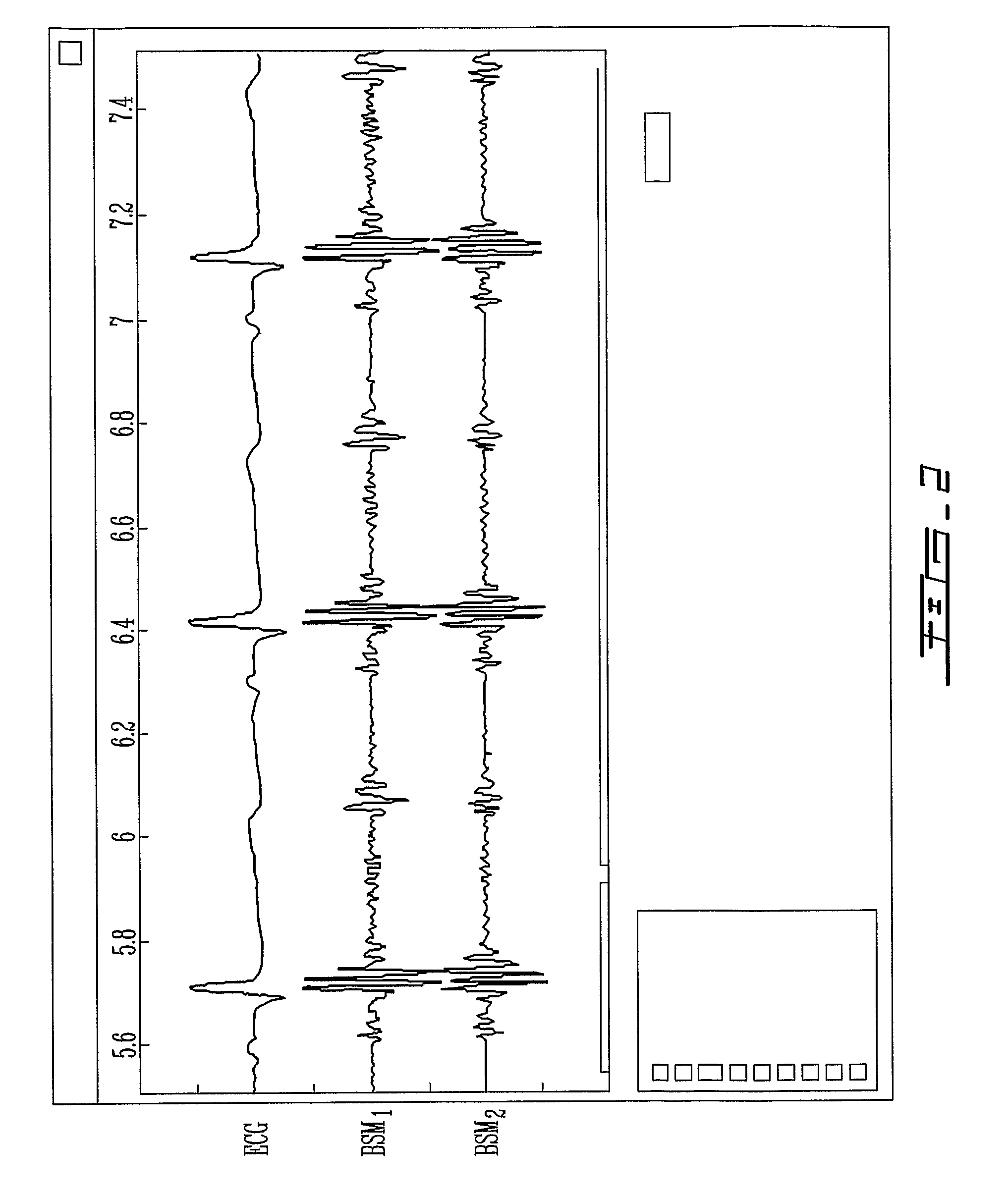
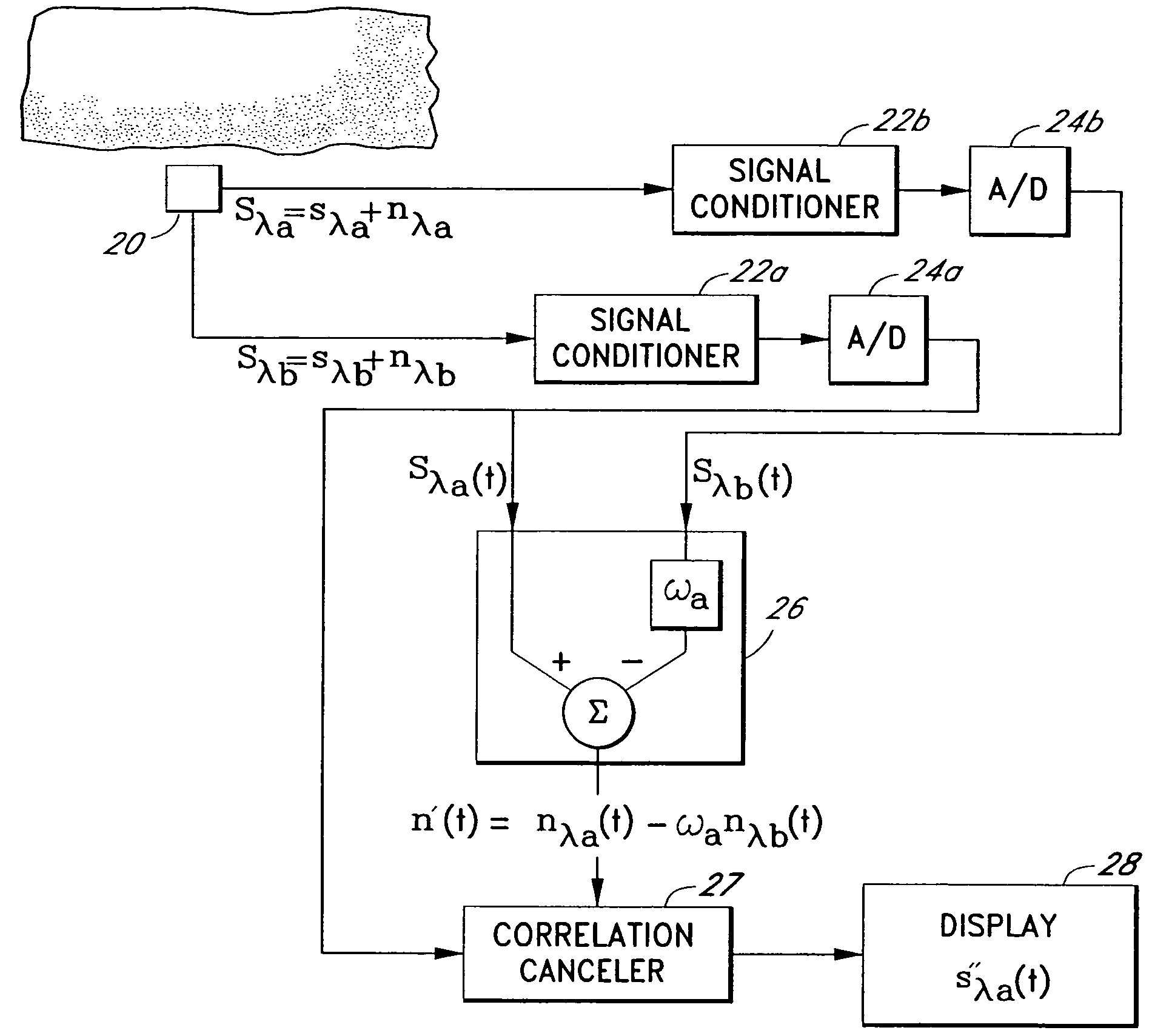
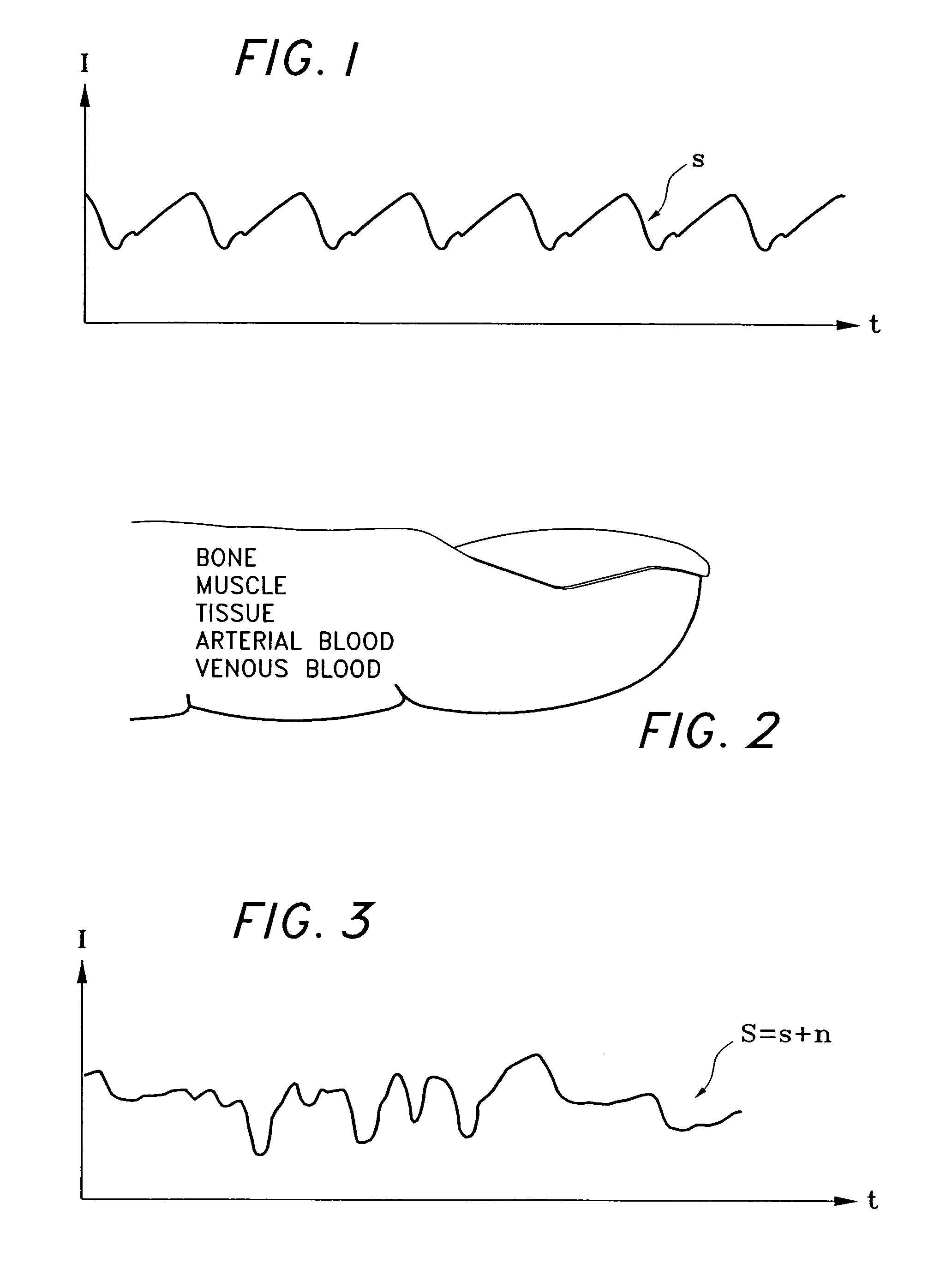
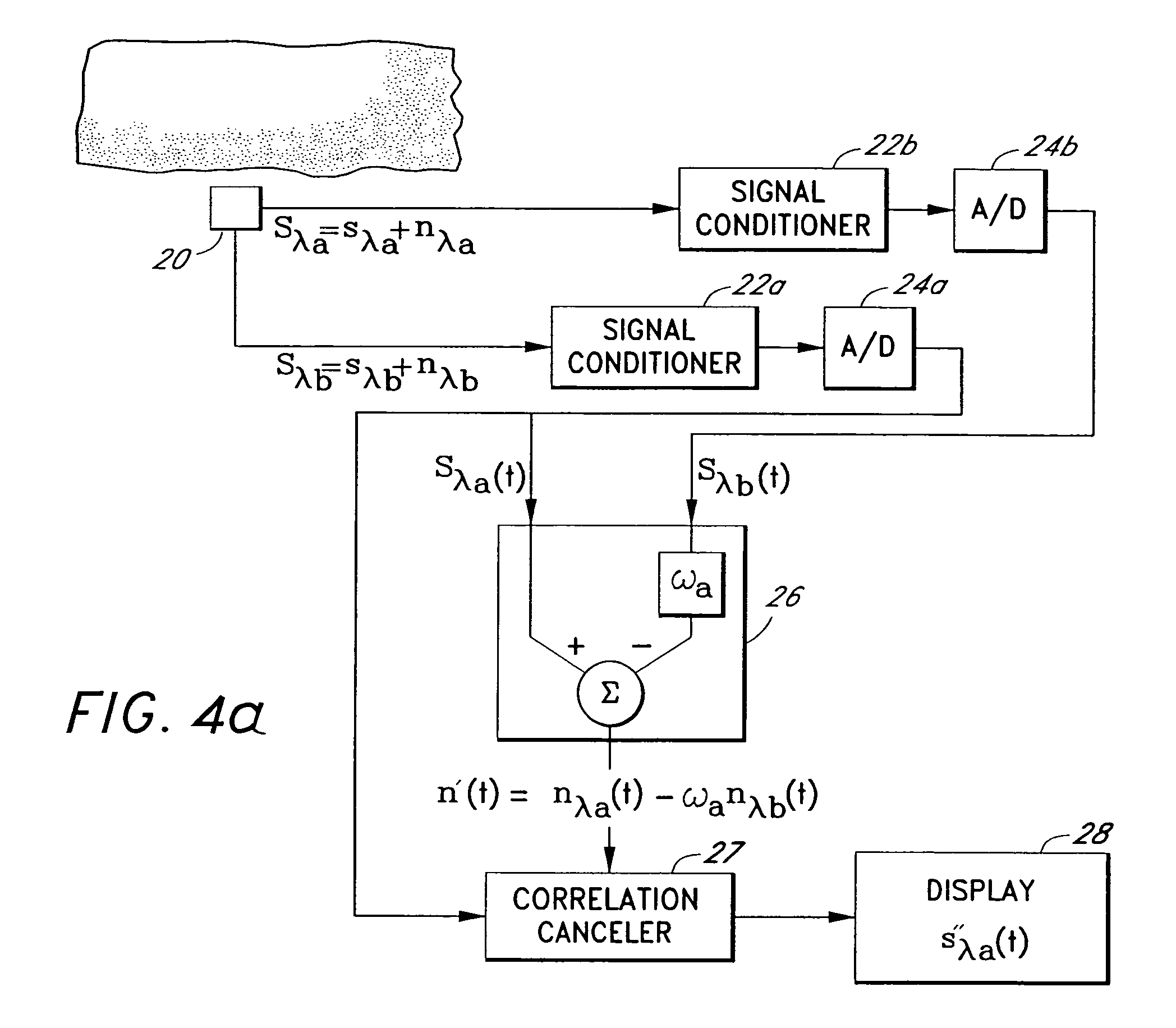
A signal processor which acquires a first signal, including a first primary signal portion and a first secondary signal portion, and a second signal, including a second primary signal portion and a second secondary signal portion, wherein the first and second primary signal portions are correlated. The signals may be acquired by propagating energy through a medium and measuring an attenuated signal after transmission or reflection. Alternatively, the signals may be acquired by measuring energy generated by the medium. A processor of the present invention generates a primary or secondary reference signal which is a combination, respectively, of only the primary or secondary signal portions. The secondary reference signal is then used to remove the secondary portion of each of the first and second measured signals via a correlation canceler, such as an adaptive noise canceler, preferably of the joint process estimator type. The primary reference signal is used to remove the primary portion of each of the first and second measured signals via a correlation canceler. The processor of the present invention may be employed in conjunction with a correlation canceler in physiological monitors wherein the known properties of energy attenuation through a medium are used to determine physiological characteristics of the medium. Many physiological conditions, such as the pulse, or blood pressure of a patient or the concentration of a constituent in a medium, can be determined from the primary or secondary portions of the signal after other signal portion is removed.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
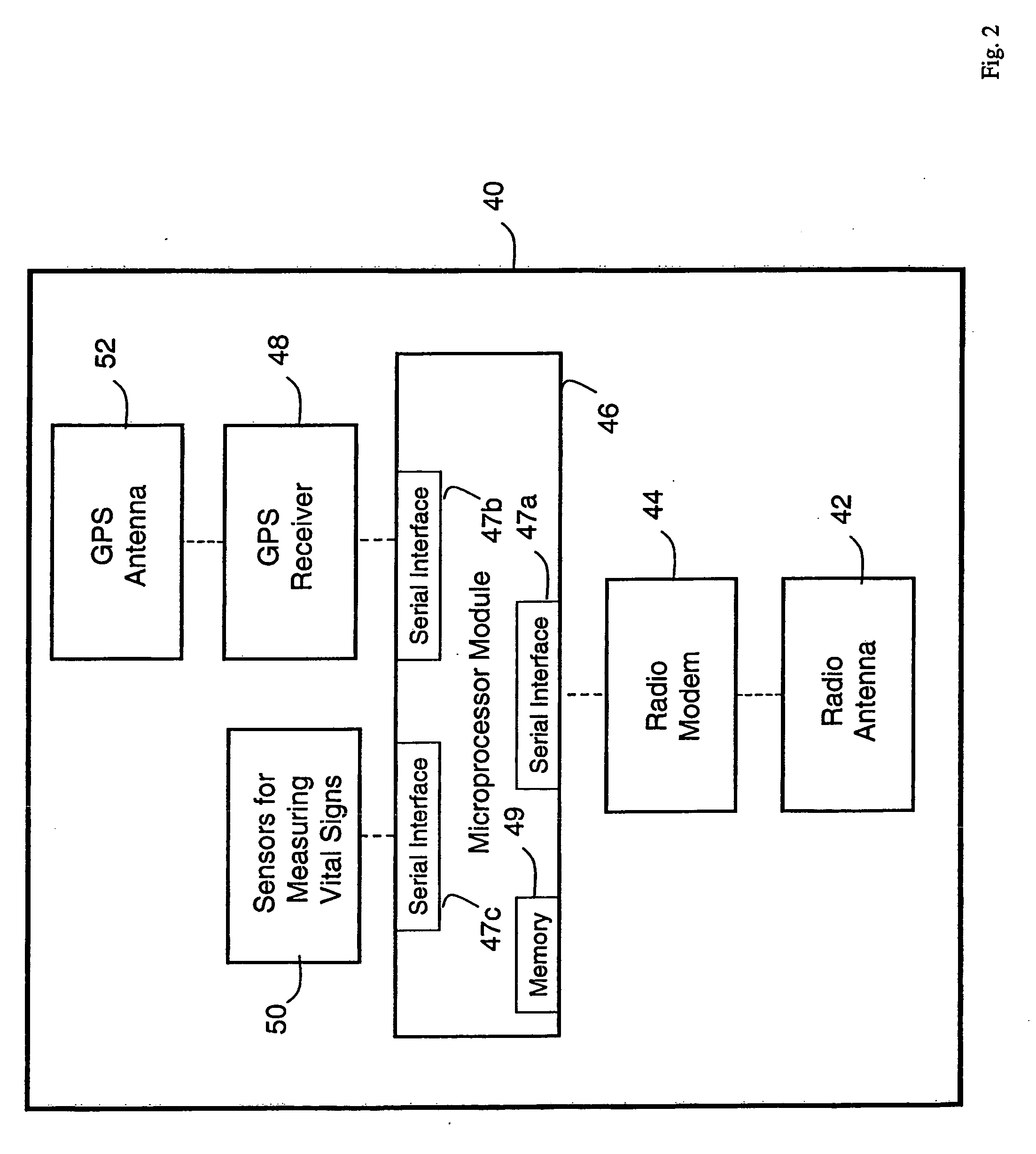
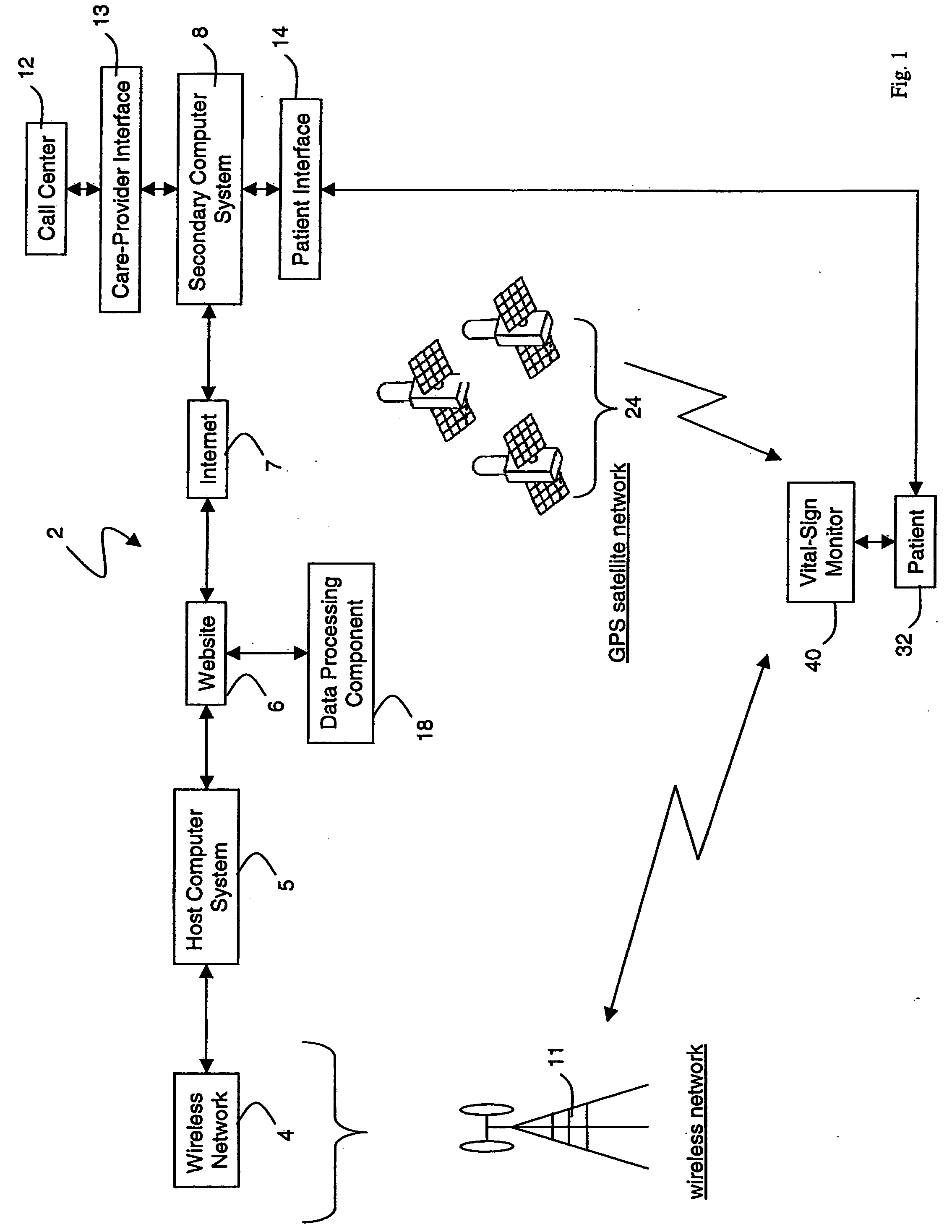
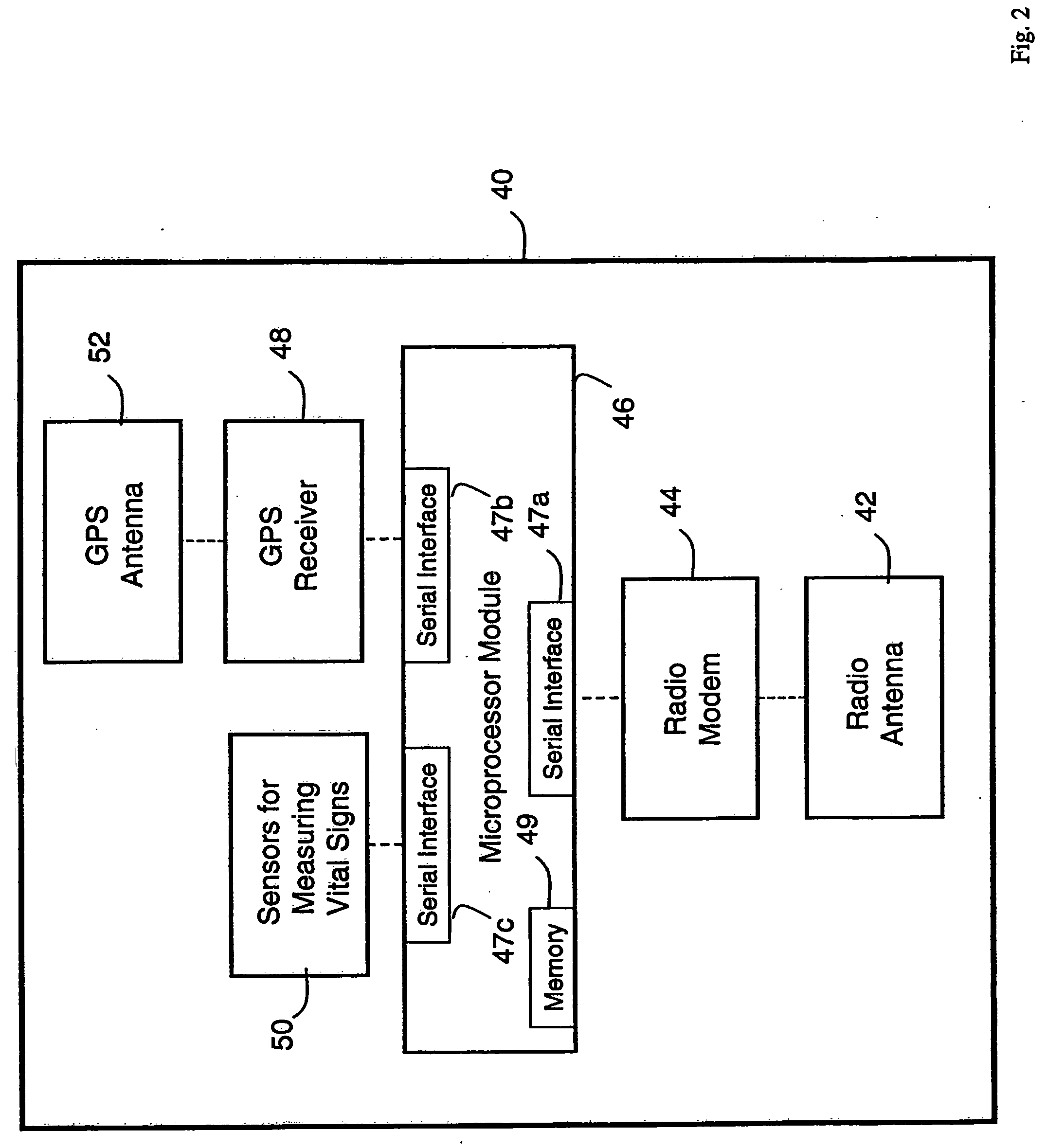
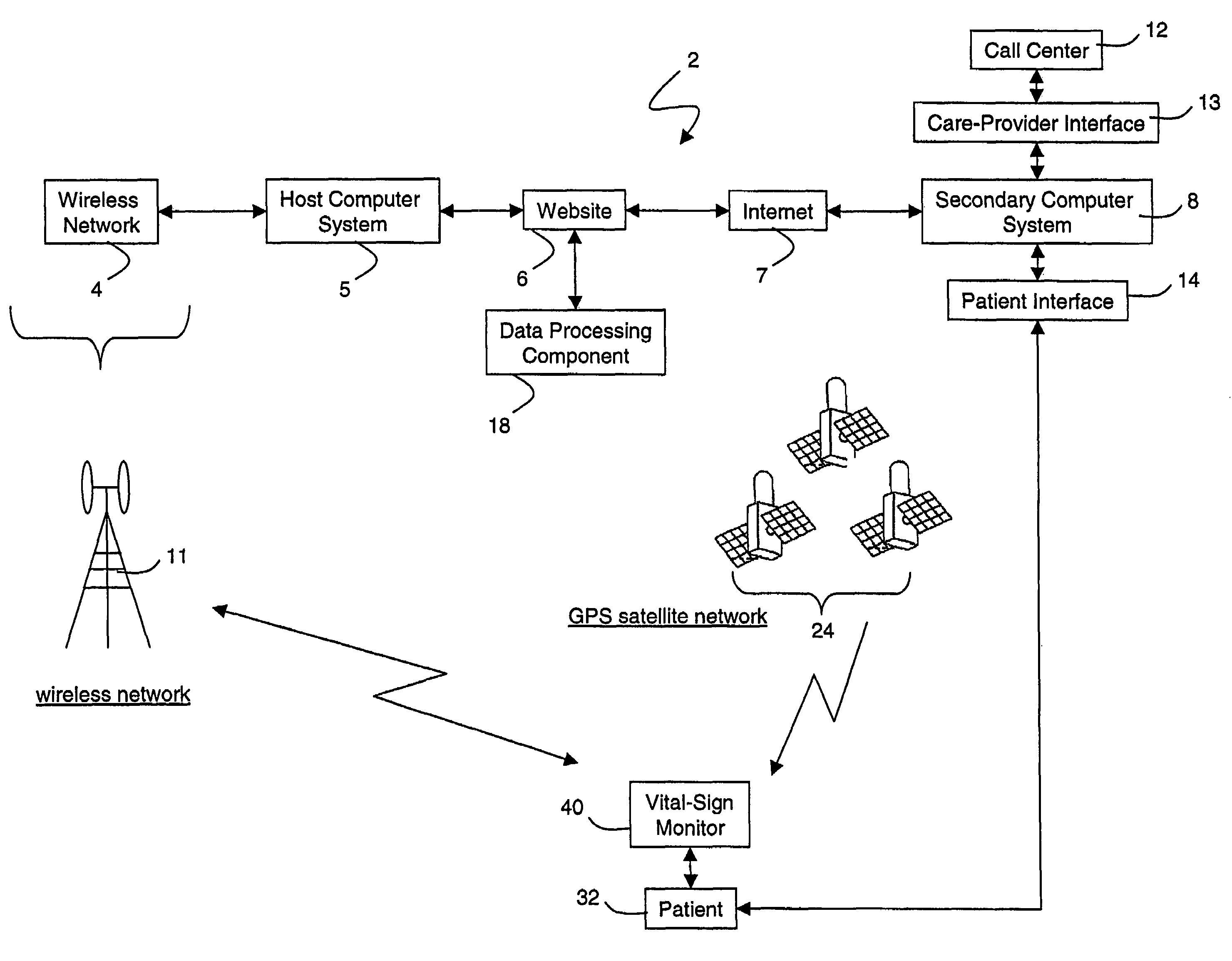
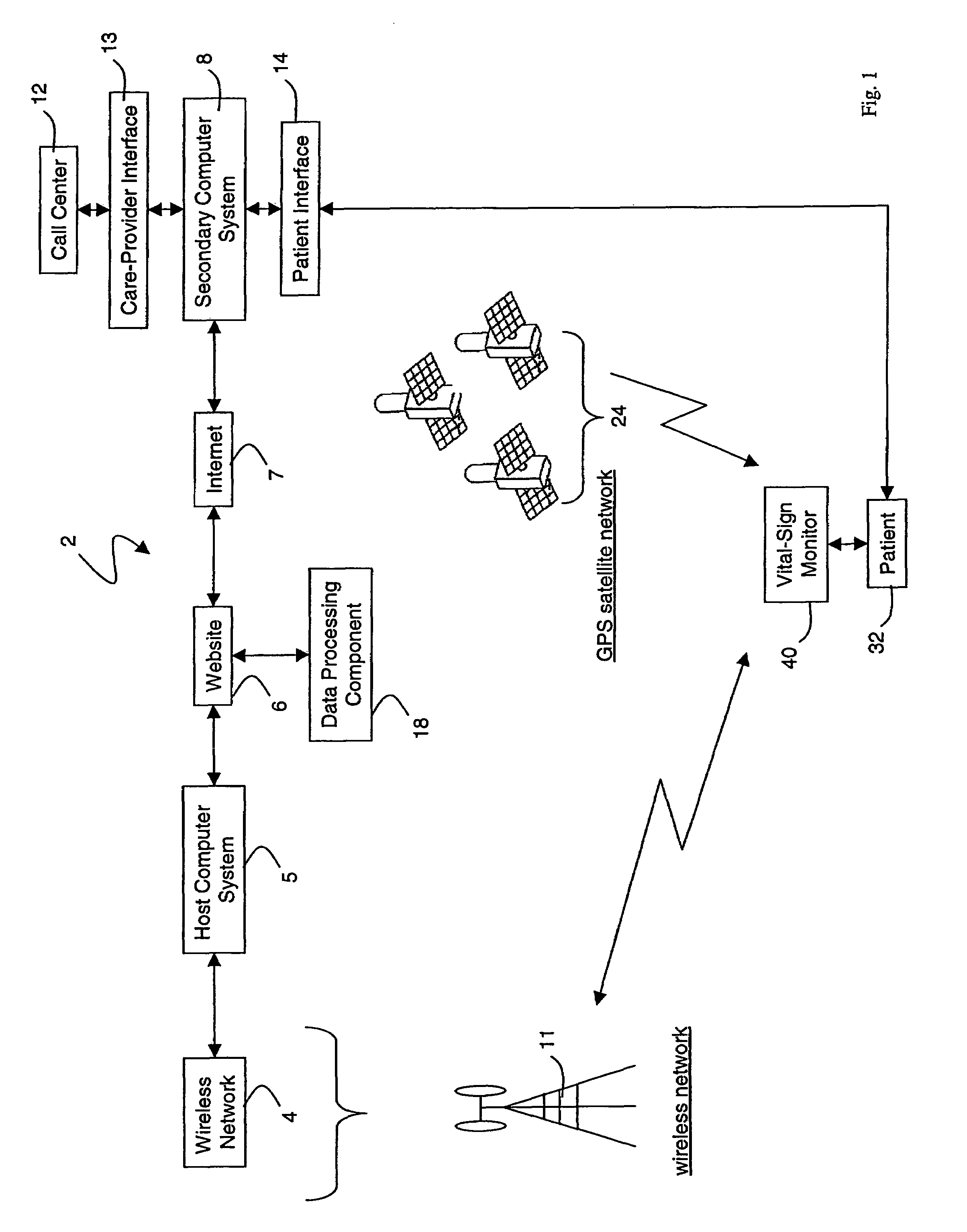
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS20050010087A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
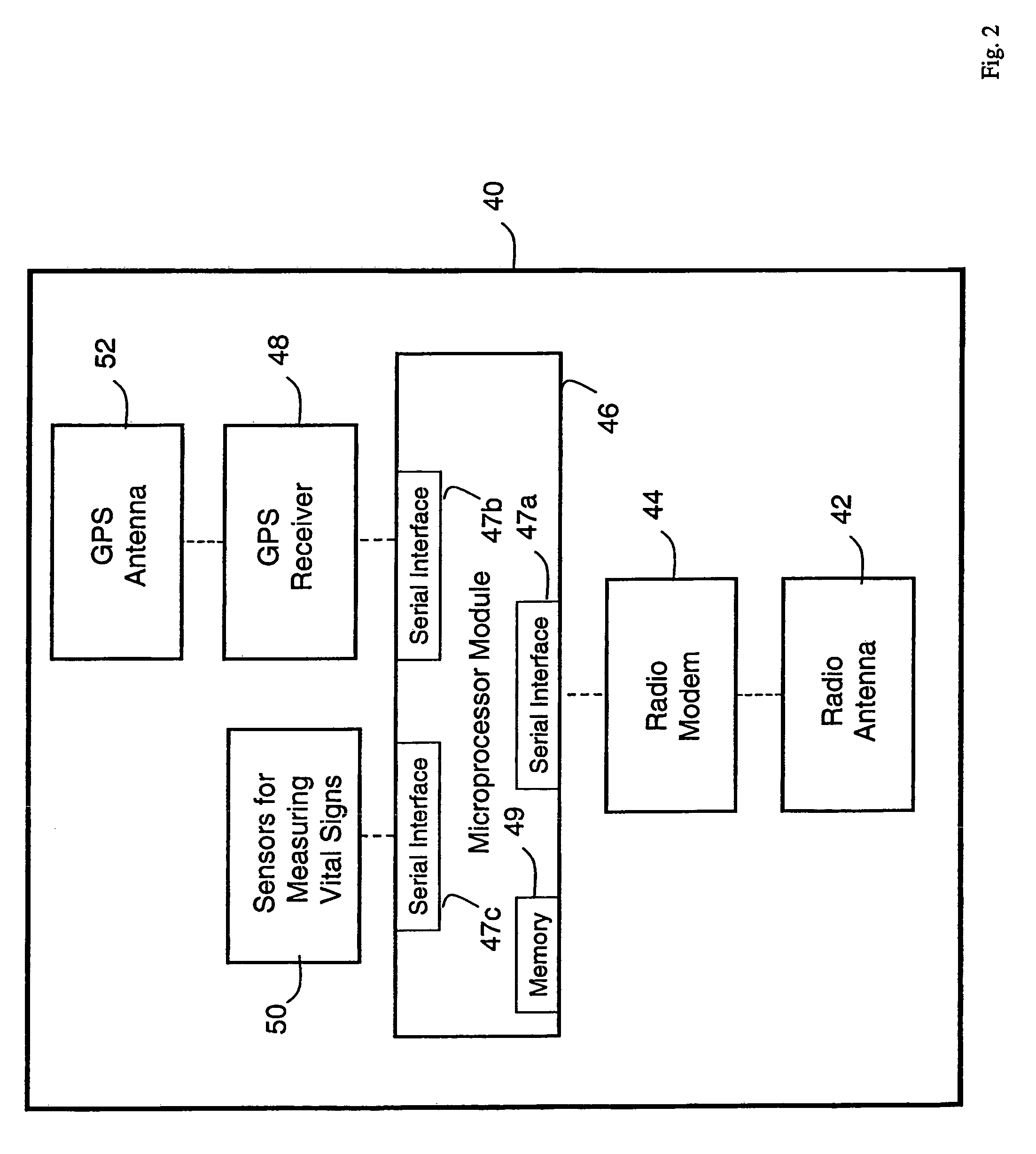
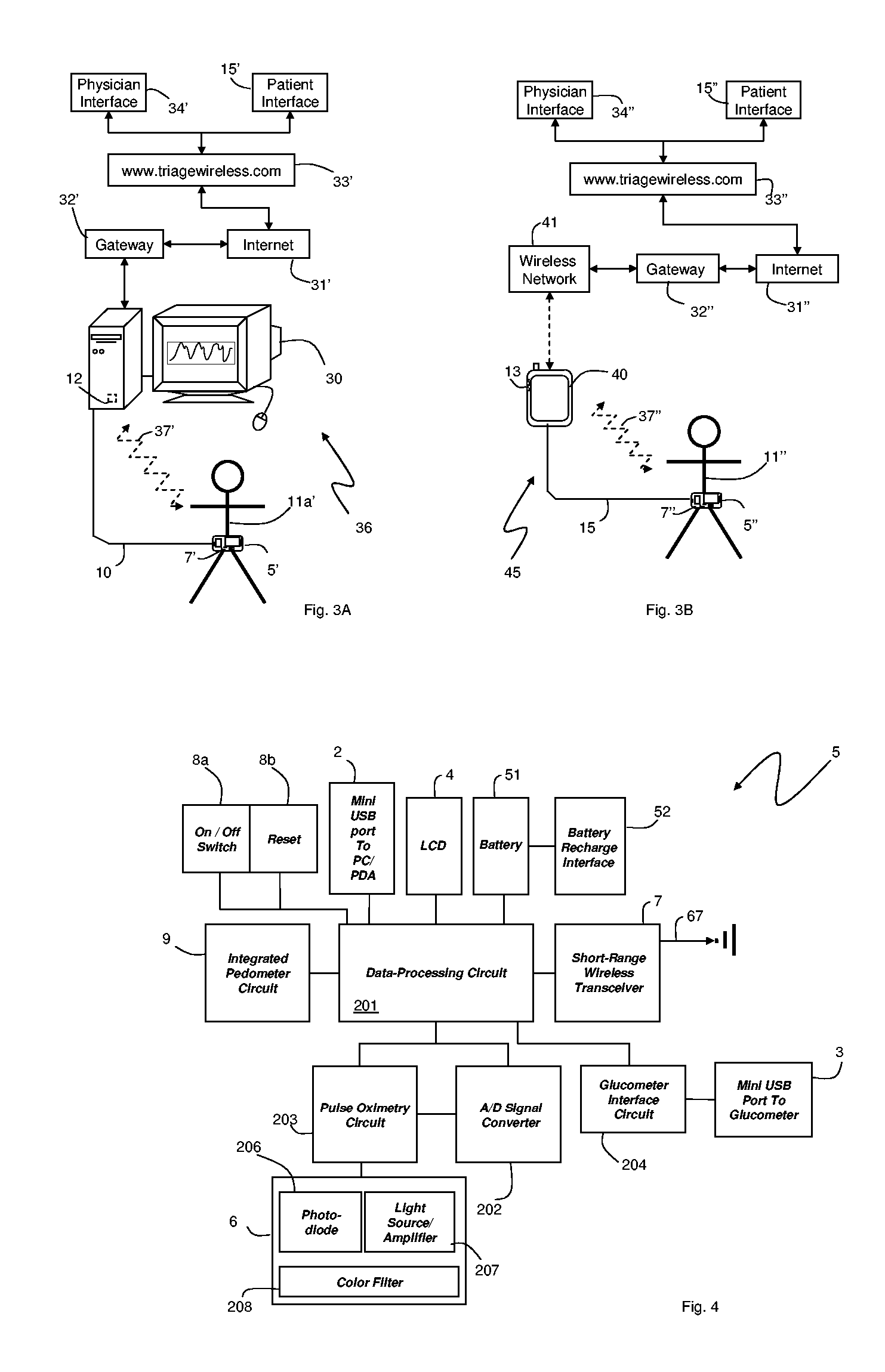
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Wireless, internet-based, medical diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060142648A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmergency medicineGlobal Positioning System
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:TRIAGE DATA NETWORKS
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS7396330B2Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
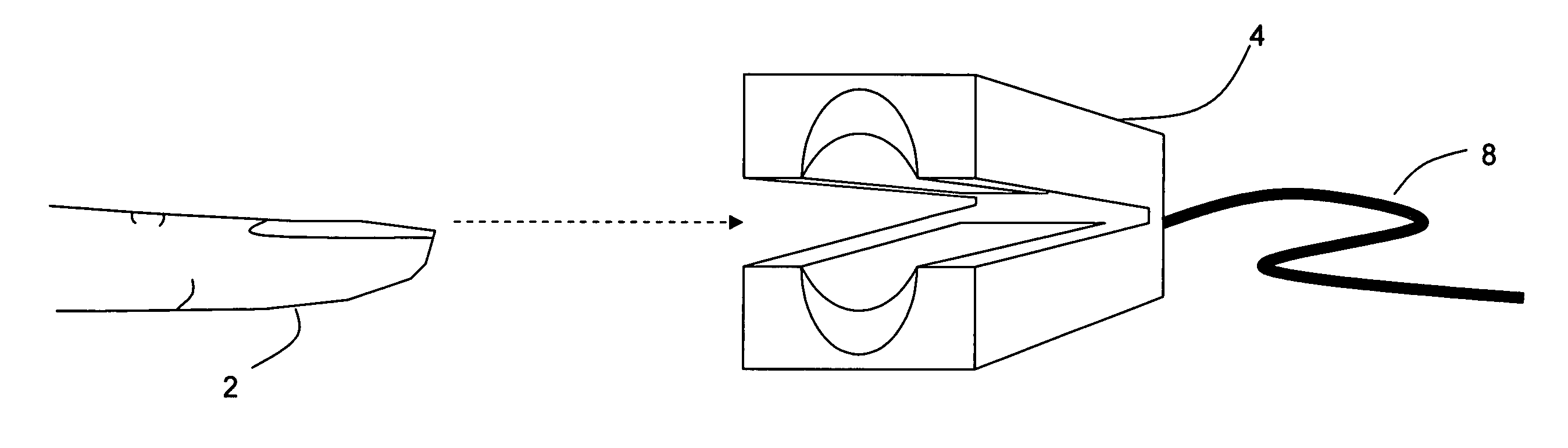
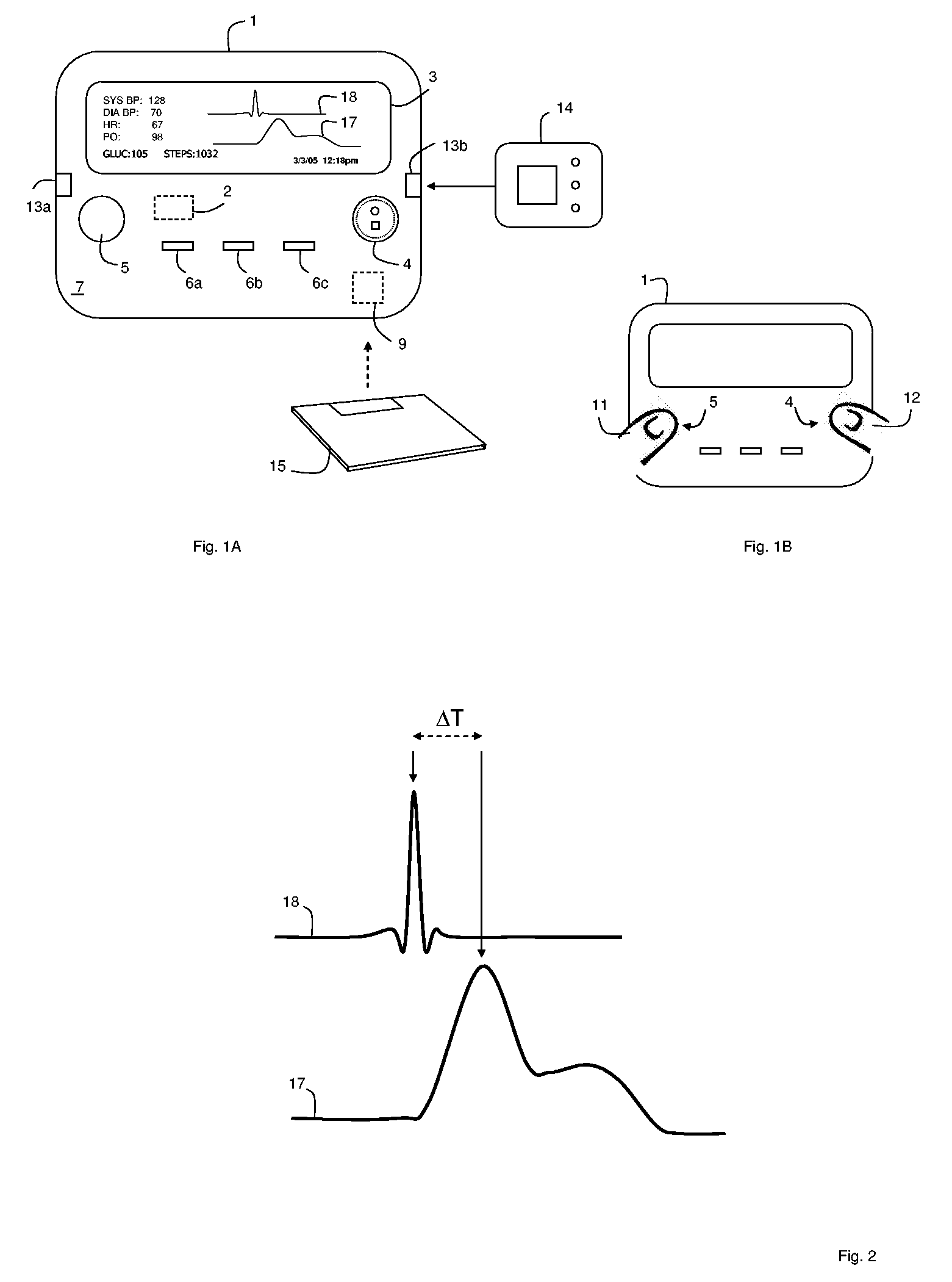
Small-scale, vital-signs monitoring device, system and method
InactiveUS20050228244A1Quick measurementLow costEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
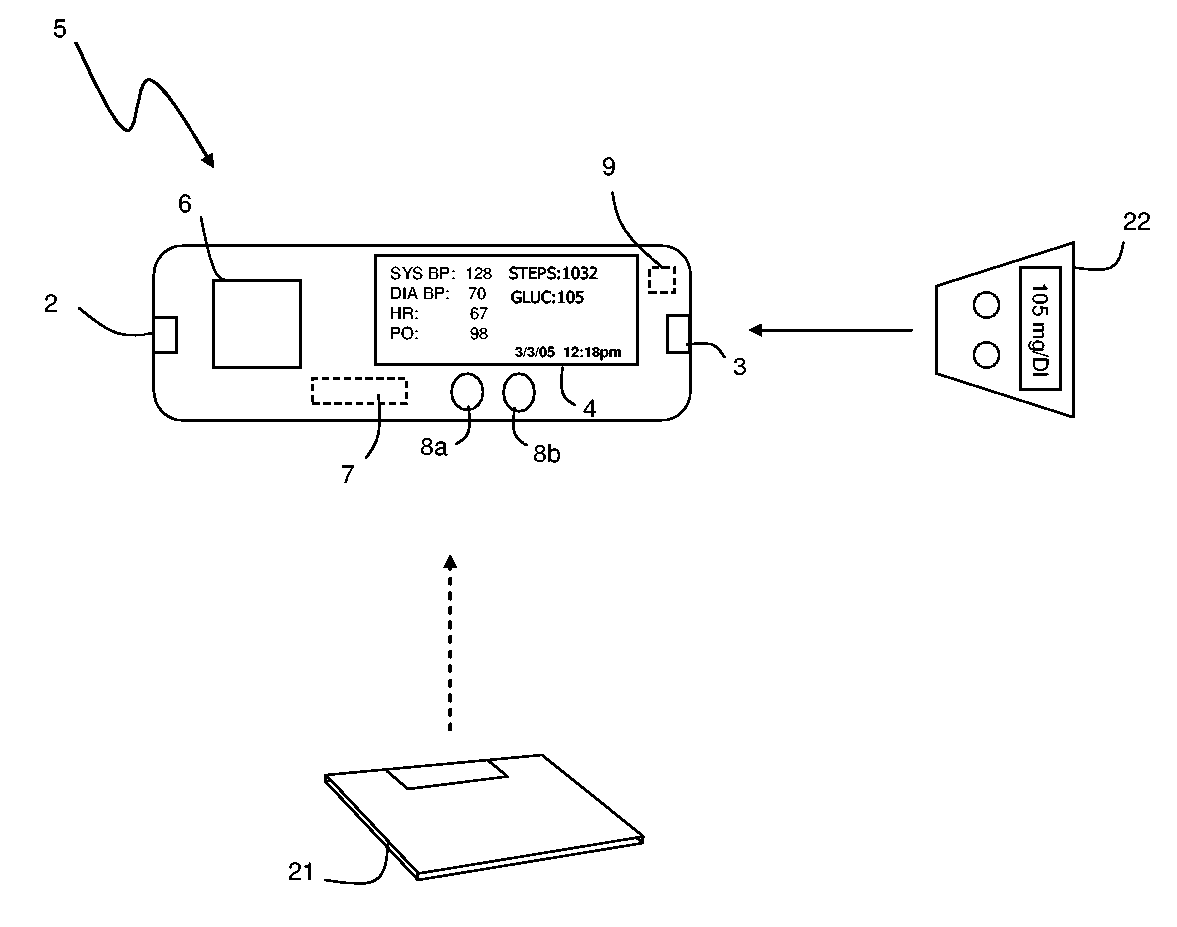
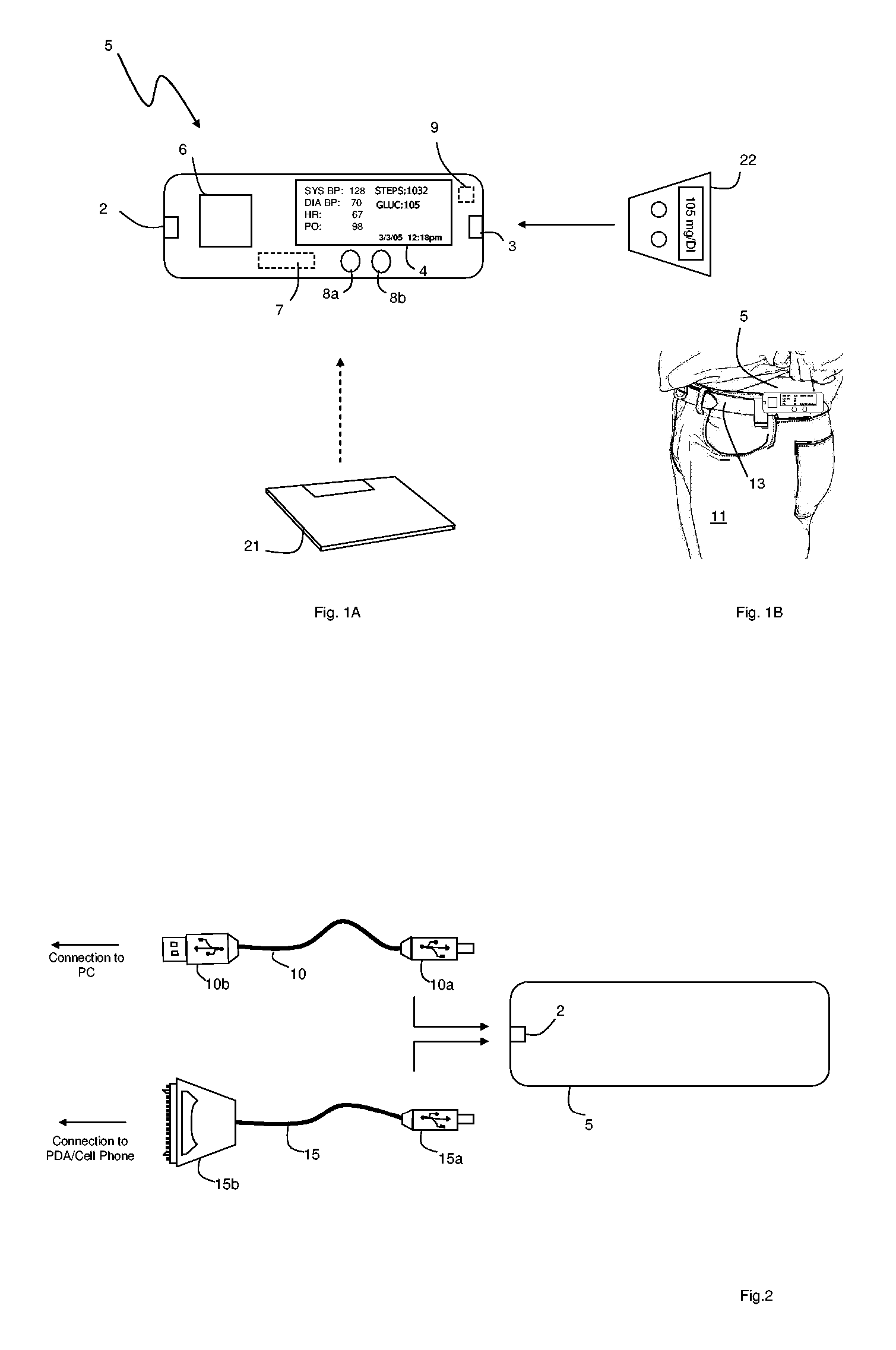
The invention provides a monitoring device featuring: 1) a housing having a first surface; 2) a sensor pad, positioned on the first surface, that includes a first LED emitting red light, a second LED emitting infrared light, and a photodetector; 3) a data-processing circuit that analyzes a signal from the photodetector to generate a blood pressure value; and 4) means for transmitting the blood pressure value to an external device.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
Vital signs probe
InactiveUS20050209516A1Improve performanceAccurate calculationEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPulse oximetryCore temperature
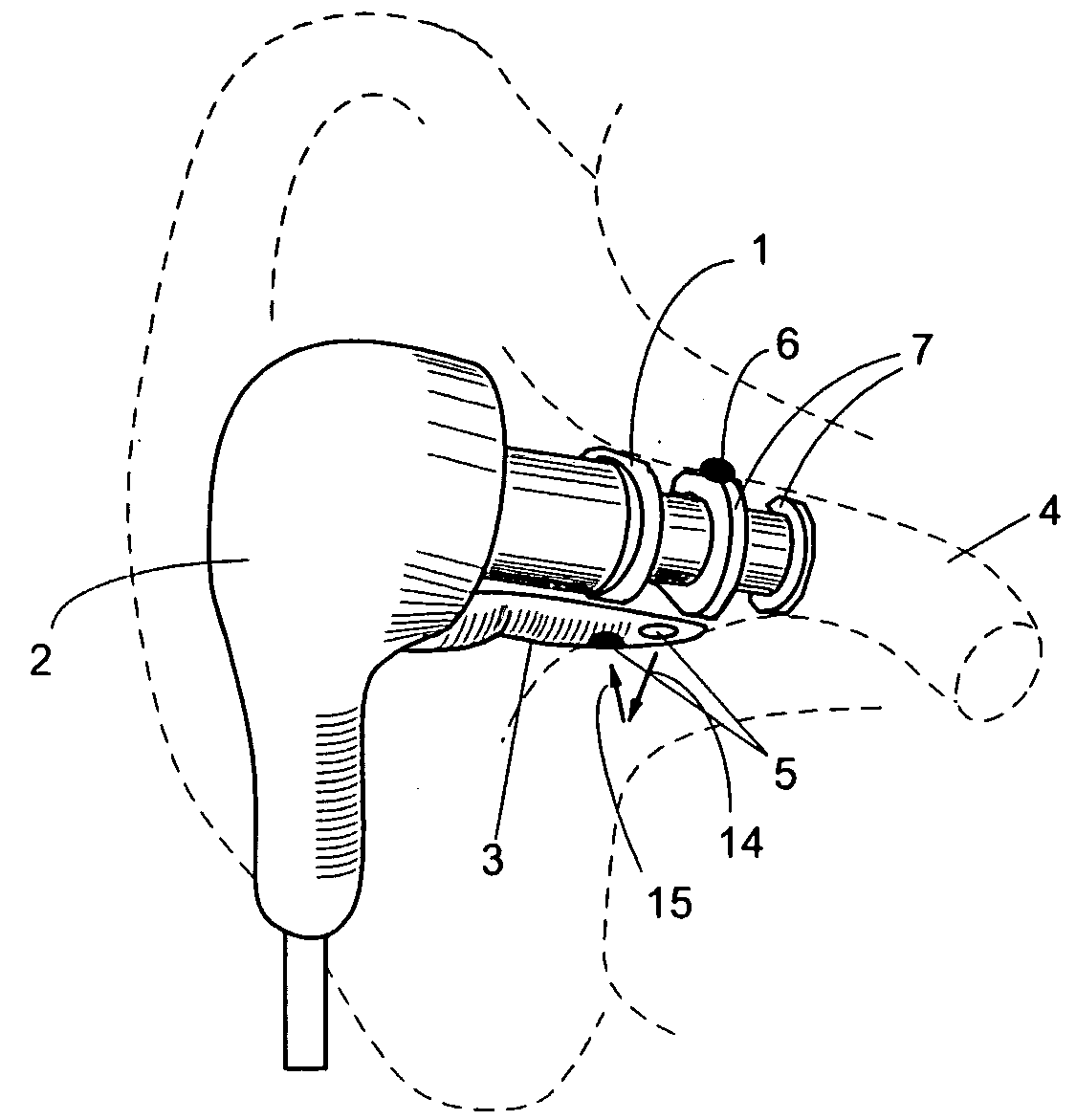
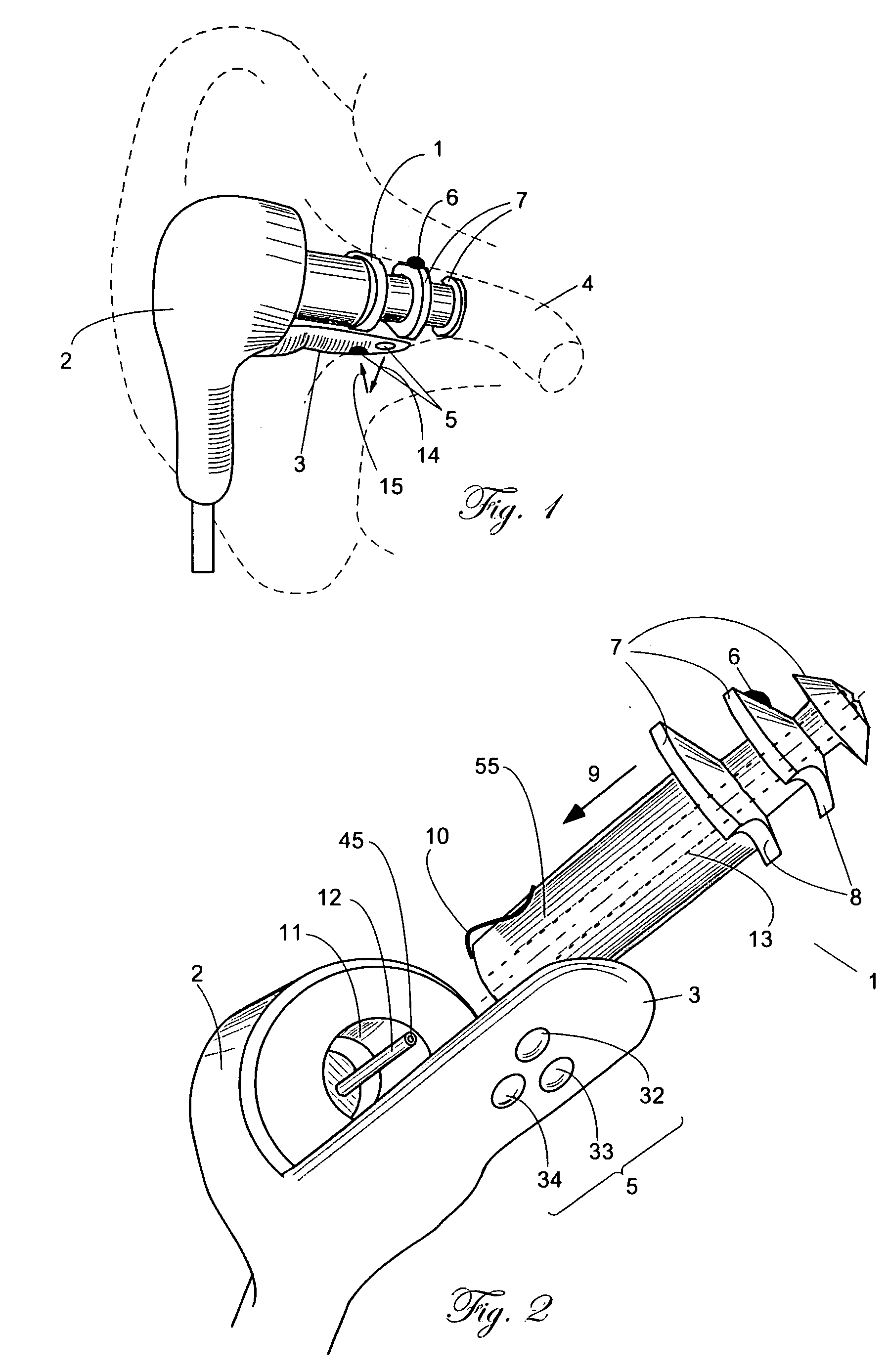
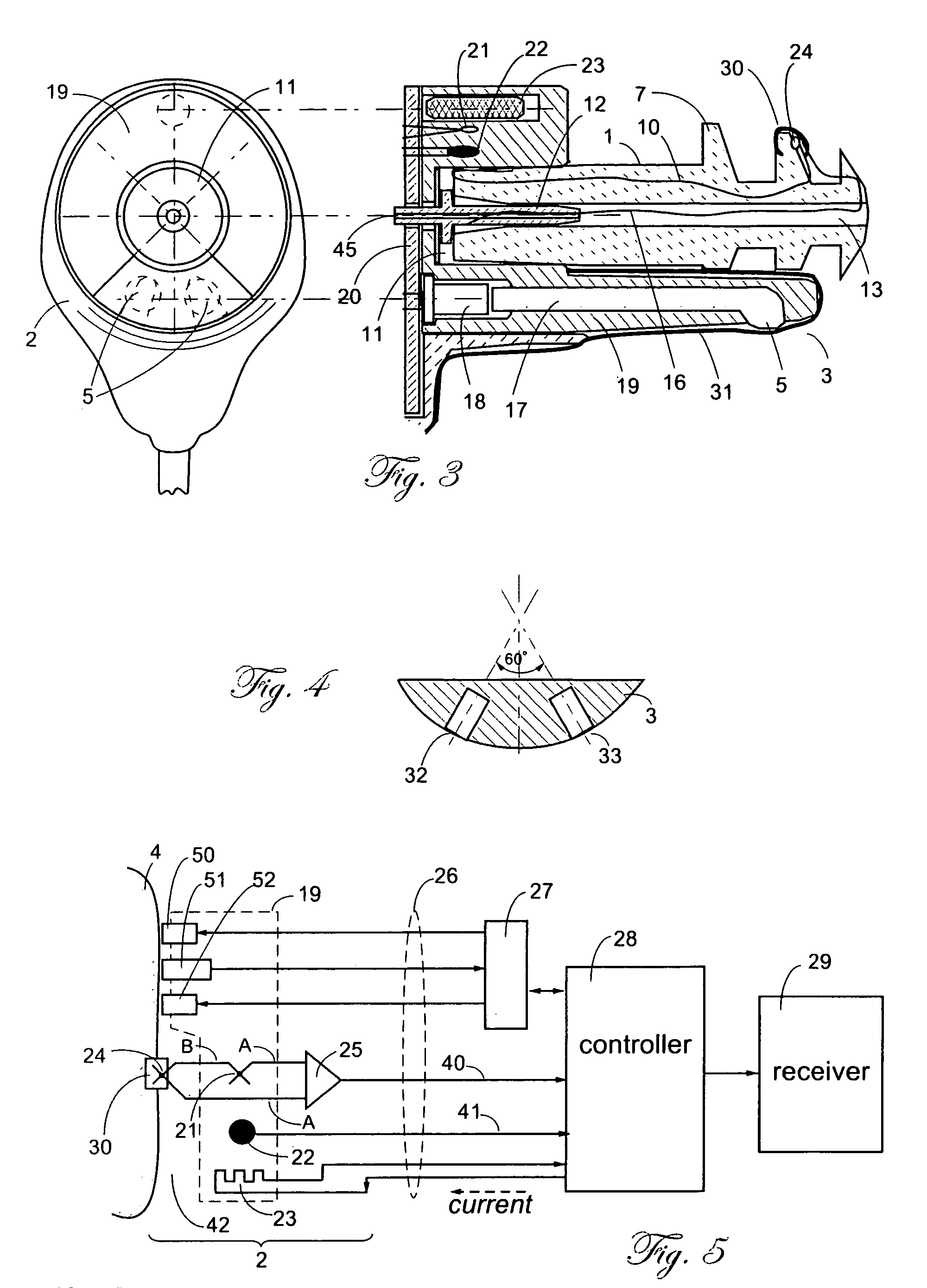
A combination of a patient core temperature sensor and the dual-wavelength optical sensors in an ear probe or a body surface probe improves performance and allows for accurate computation of various vital signs from the photo-plethysmographic signal, such as arterial blood oxygenation (pulse oximetry), blood pressure, and others. A core body temperature is measured by two sensors, where the first contact sensor positioned on a resilient ear plug and the second sensor is on the external portion of the probe. The ear plug changes it's geometry after being inserted into an ear canal and compress both the first temperature sensor and the optical assembly against ear canal walls. The second temperature sensor provides a reference signal to a heater that is warmed up close to the body core temperature. The heater is connected to a common heat equalizer for the temperature sensor and the pulse oximeter. Temperature of the heat equalizer enhances the tissue perfusion to improve the optical sensors response. A pilot light is conducted to the ear canal via a contact illuminator, while a light transparent ear plug conducts the reflected lights back to the light detector.
Owner:FRADEN JACOB
Telemetry method and apparatus using magnetically-driven MEMS resonant structure
InactiveUS20070236213A1High quality factorImprove reliabilityMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringIntraocular pressurePressure sense
A telemetry method and apparatus using pressure sensing elements remotely located from associated pick-up, and processing units for the sensing and monitoring of pressure within an environment. This includes remote pressure sensing apparatus incorporating a magnetically-driven resonator being hermetically-sealed within an encapsulating shell or diaphragm and associated new method of sensing pressure. The resonant structure of the magnetically-driven resonator is suitable for measuring quantities convertible to changes in mechanical stress or mass. The resonant structure can be integrated into pressure sensors, adsorbed mass sensors, strain sensors, and the like. The apparatus and method provide information by utilizing, or listening for, the residence frequency of the oscillating resonator. The resonant structure listening frequencies of greatest interest are those at the mechanical structure's fundamental or harmonic resonant frequency. The apparatus is operable within a wide range of environments for remote one-time, random, periodic, or continuous / on-going monitoring of a particular fluid environment. Applications include biomedical applications such as measuring intraocular pressure, blood pressure, and intracranial pressure sensing.
Owner:LAUNCHPOINT TECH
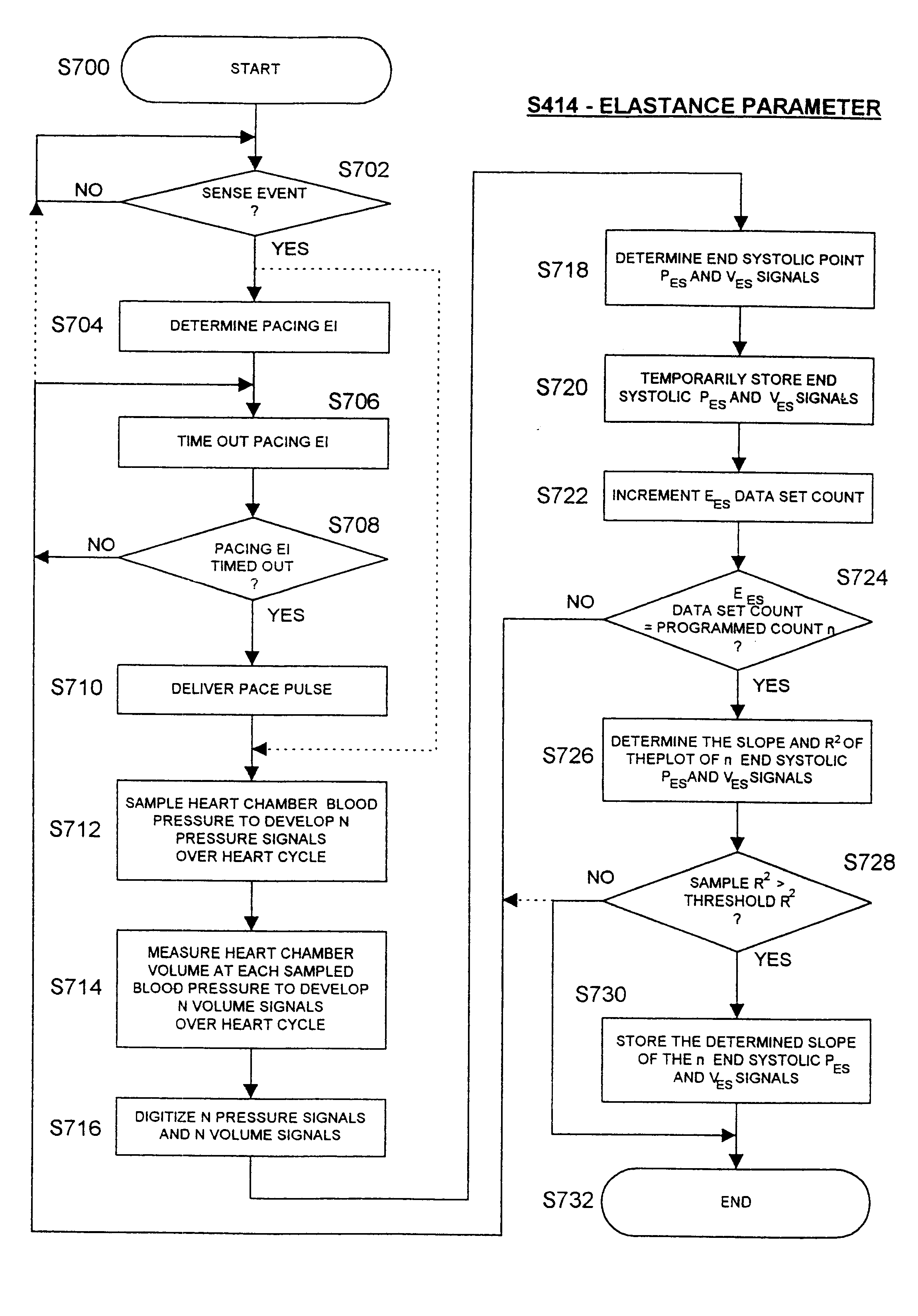
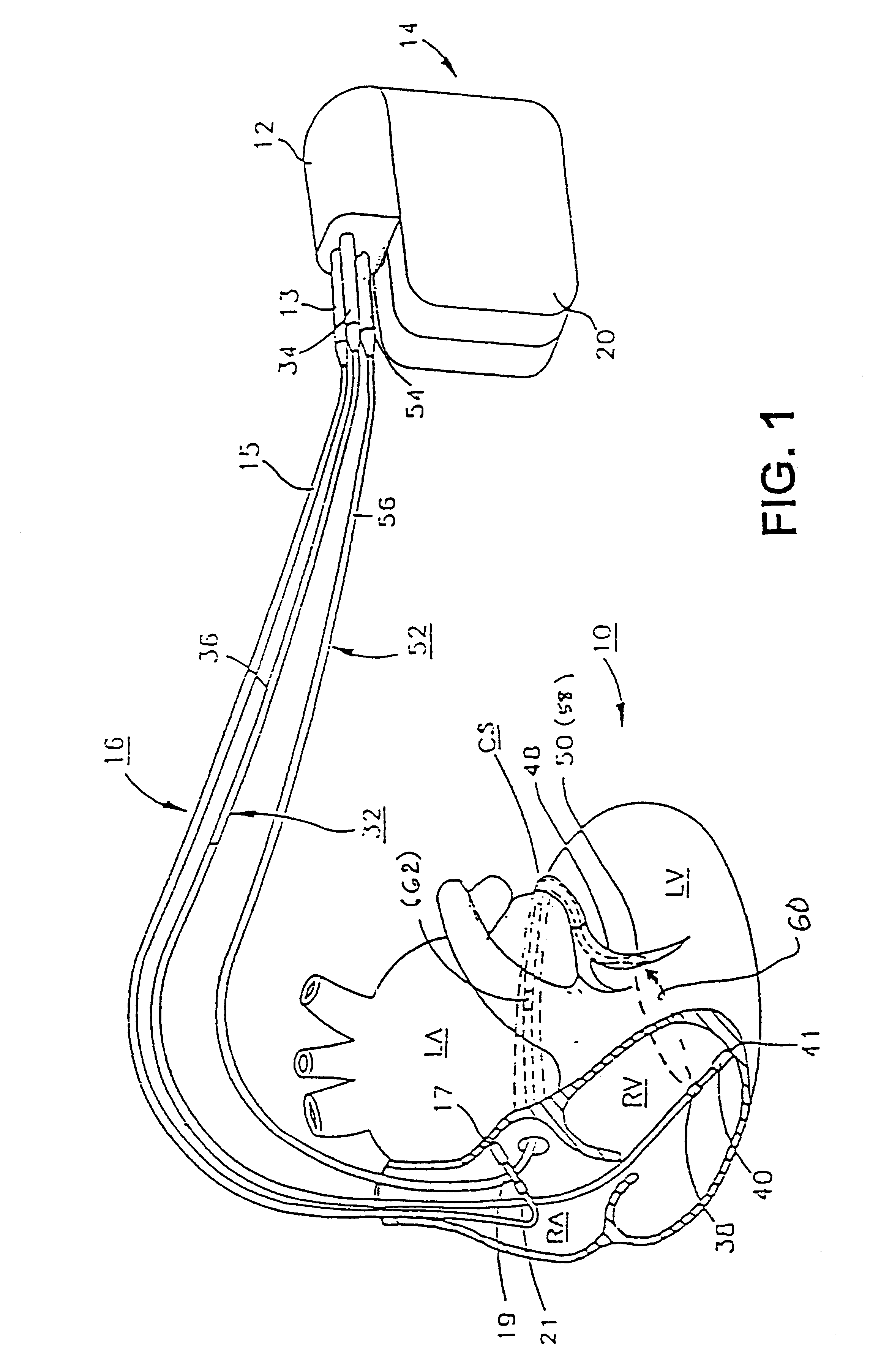
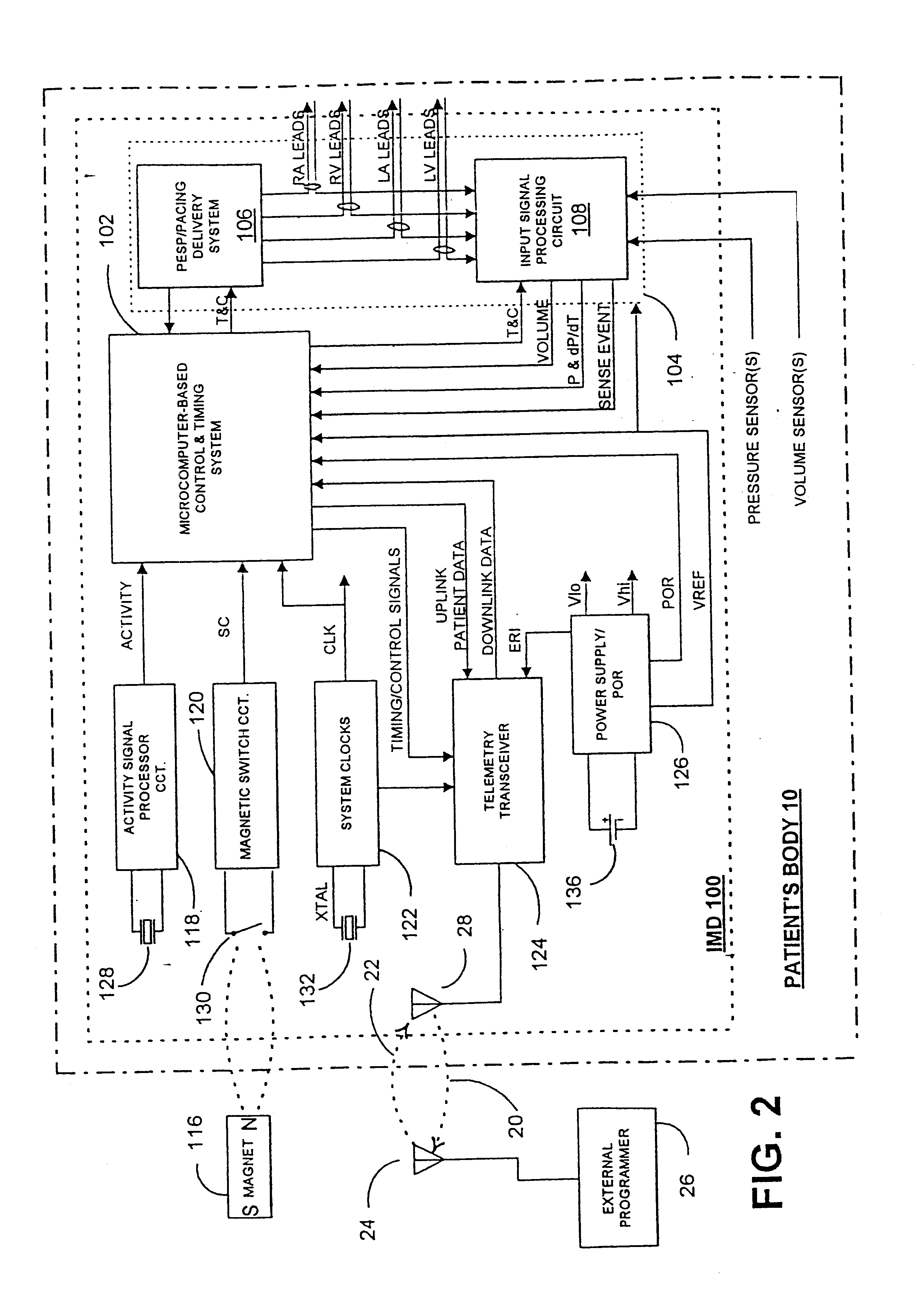
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS6738667B2Increase contractilityEasy to relaxCatheterHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleHeart chamber
An implantable stimulator and monitor measures a group of heart failure parameters indicative of the state of heart failure employing EGM signals, measures of blood pressure including absolute pressure P, developed pressure (DP=systolic P-diastolic P), and / or dP / dt, and measures of heart chamber volume (V) over one or more cardiac cycles. These parameters include: (1) relaxation or contraction time constant tau (.tau.); (2) mechanical restitution (MR), i.e., the mechanical response of a heart chamber to premature stimuli applied to the heart chamber; (3) recirculation fraction (RF), i.e., the rate of decay of PESP effects over a series of heart cycles; and (4) end systolic elastance (E.sub.ES), i.e., the ratios of end systolic blood pressure P to volume V. These heart failure parameters are determined periodically regardless of patient posture and activity level. The physician can determine whether a particular therapy is appropriate, prescribe the therapy for a period of time while again accumulating the stored patient data for a later review and assessment to determine whether the applied therapy is beneficial or not, thereby enabling periodic changes in therapy, if appropriate. Drug therapies and electrical stimulation therapies, including PESP stimulation, and pacing therapies including single chamber, dual chamber and multi-chamber (bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular) pacing can be delivered. In patient's prone to malignant tachyarrhythmias, the assessment of heart failure state can be taken into account in setting parameters of detection or classification of tachyarrhythmias and the therapies that are delivered.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
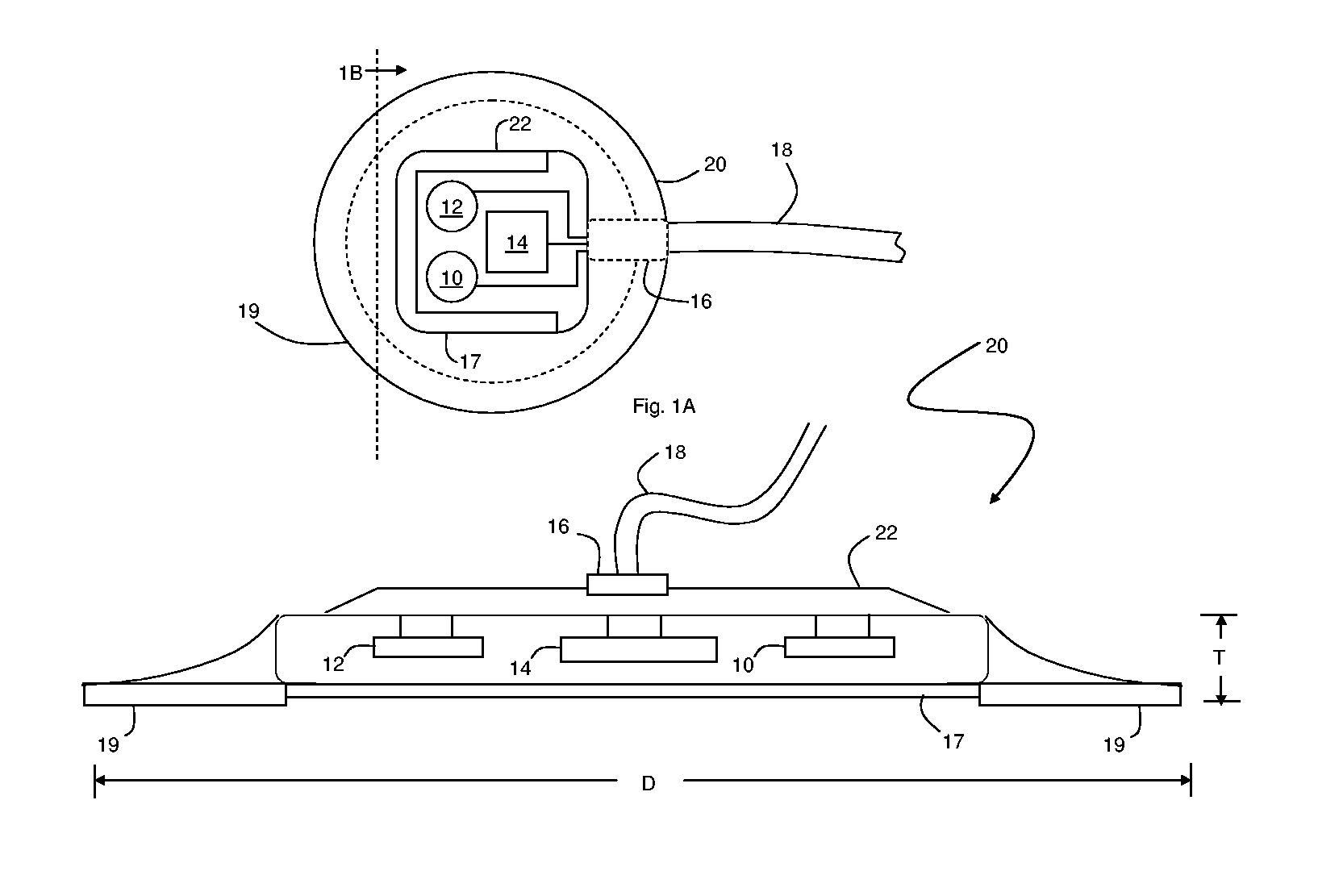
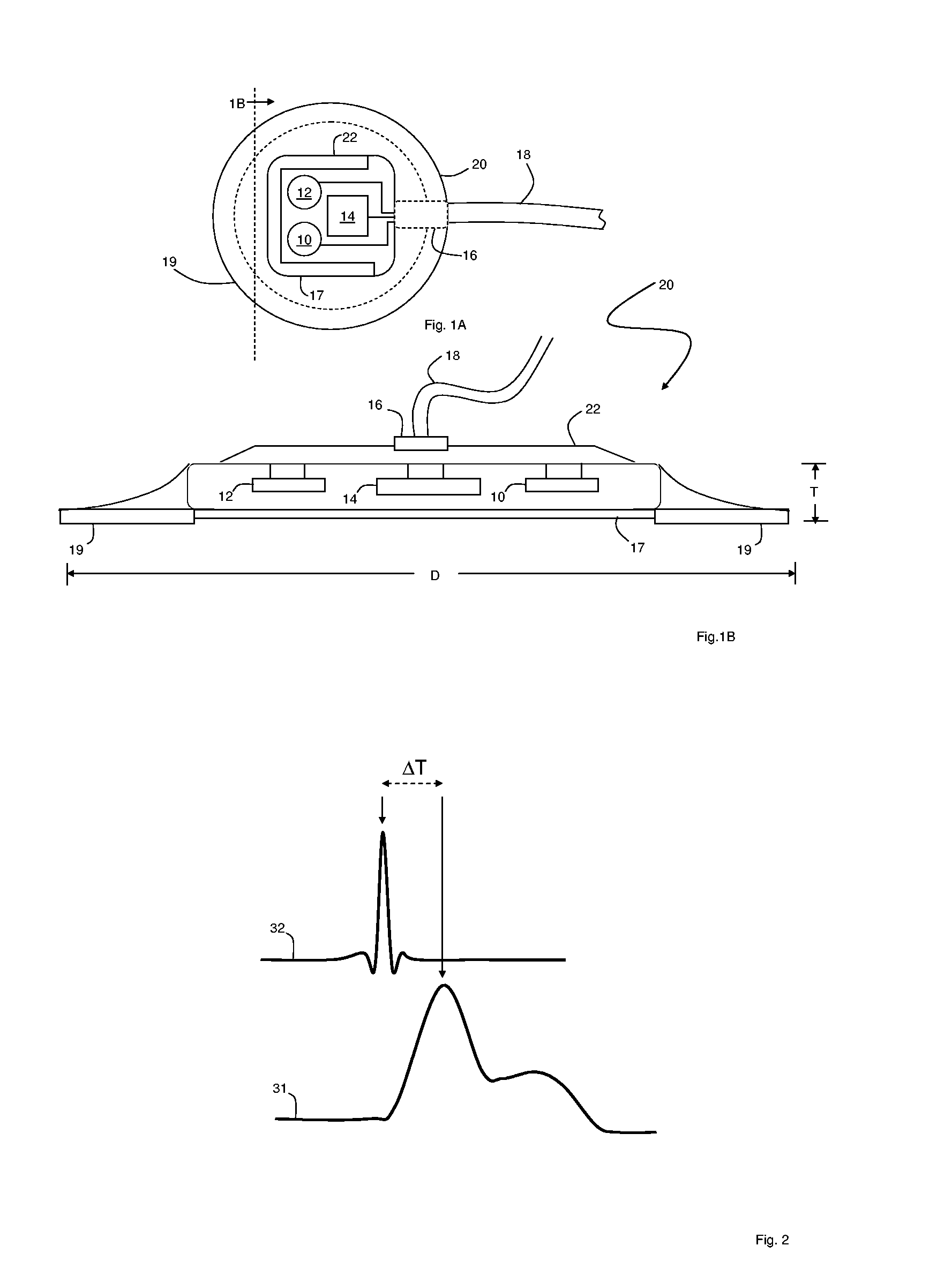
Patch sensor for measuring blood pressure without a cuff
InactiveUS20050228299A1Easy can be wornNon-invasive measurementElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressureEngineering
A monitoring device, method and system for monitoring vital signs of a patient over a wireless network are disclosed herein. The monitoring device includes an adhesive patch sensor, typically mounted on a patient's head, and a processing component. The adhesive patch sensor typically includes an optical system that generates an optical waveform, and an electrode that generates an electrical waveform. The processing component processes the optical and electrical waveforms, along with a calibration table, to determine the patient's vital signs.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
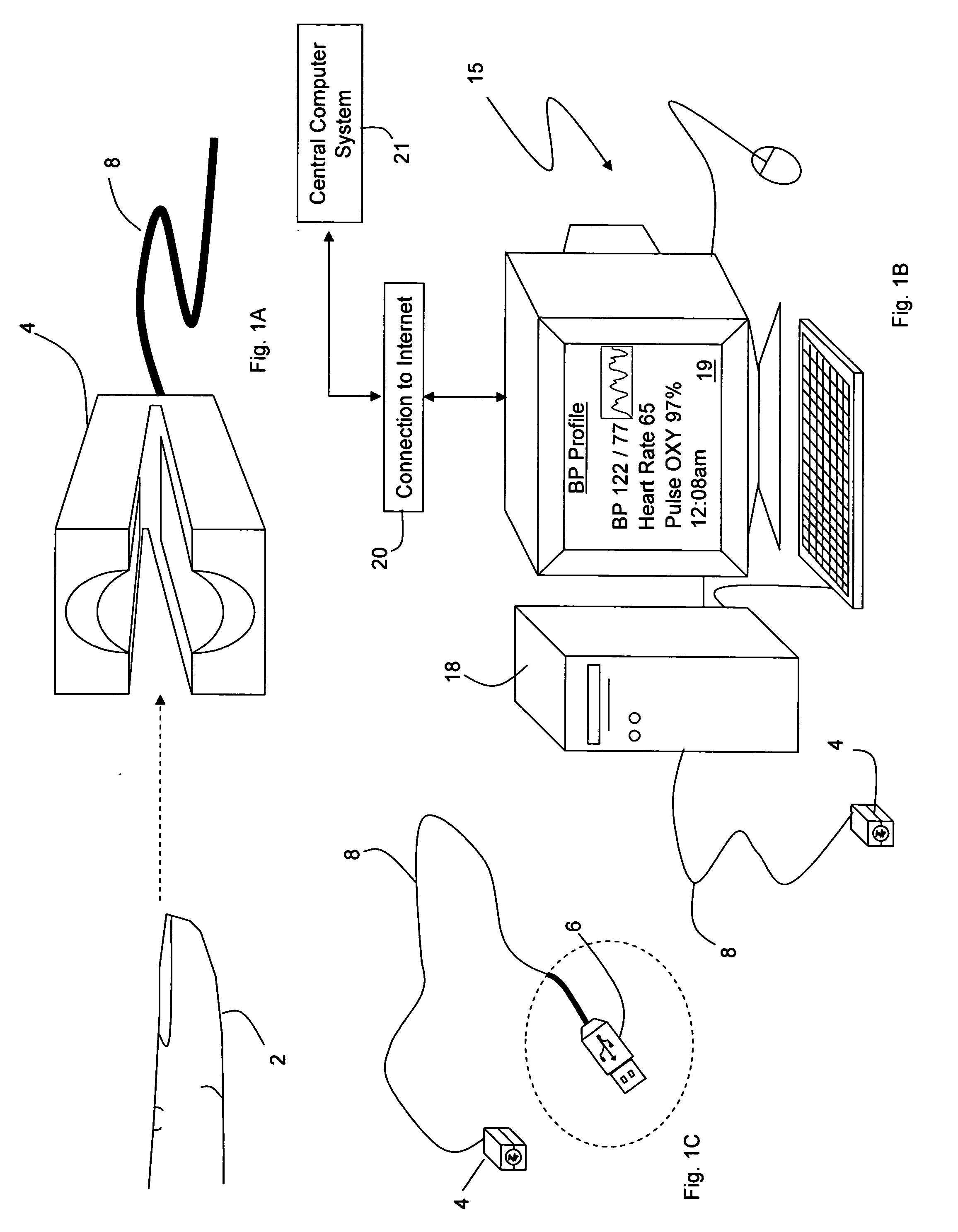
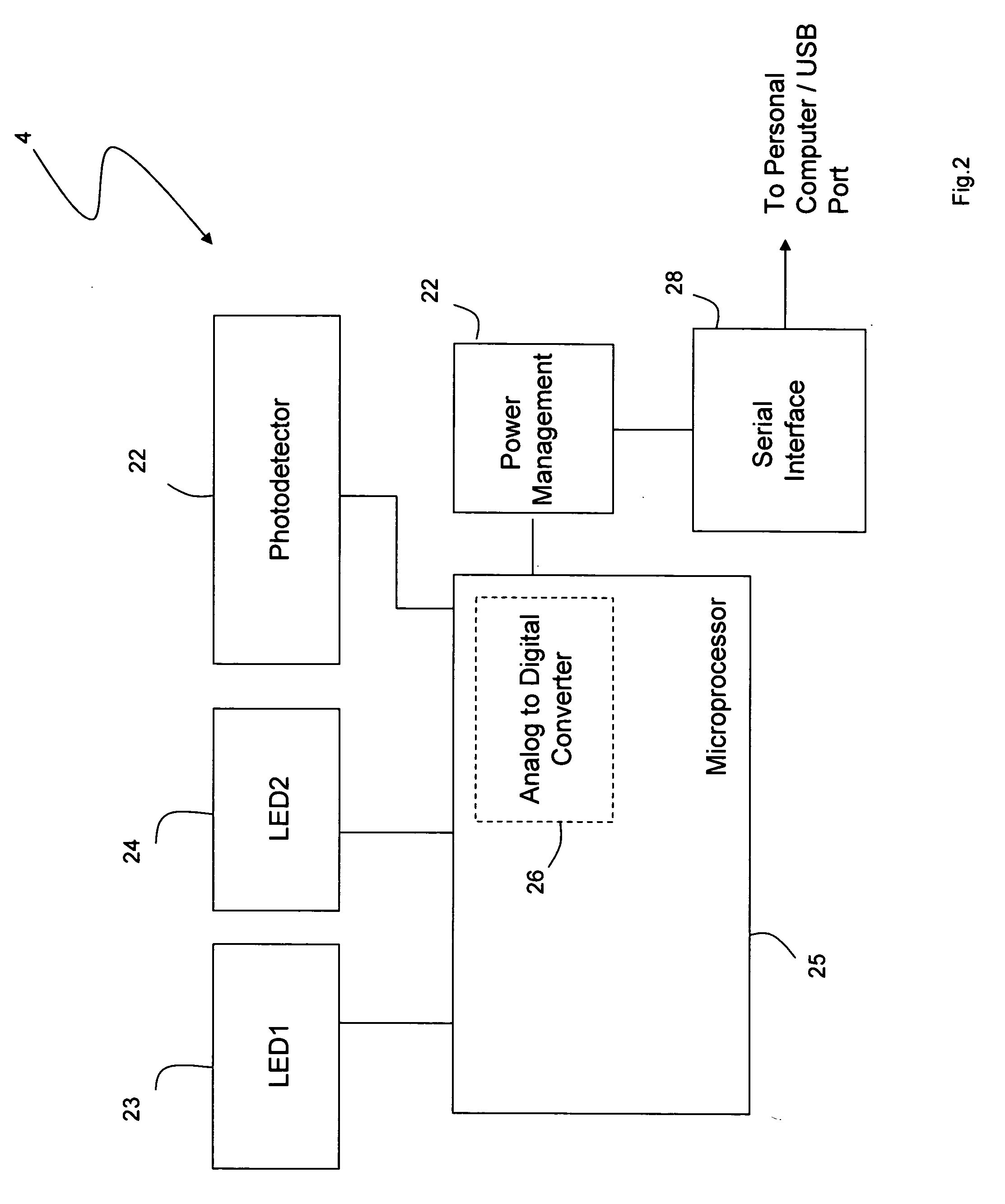
Personal computer-based vital signs monitor
InactiveUS20060084878A1Quickly and accurately measureSimple and low-cost systemCatheterSensorsOptical ModuleBlood pressure
The invention provides a system for measuring blood pressure from a patient that includes: 1) an optical module featuring systems for measuring signals from the patient, serial communication, and power management; 2) an external computing device configured to attach to the optical module, supply power to the optical module, and receive information from the optical module through the system for serial communication; and 3) an algorithm, operating on the external computing device, that processes information received through the system for serial communication to determine the patient's blood pressure.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
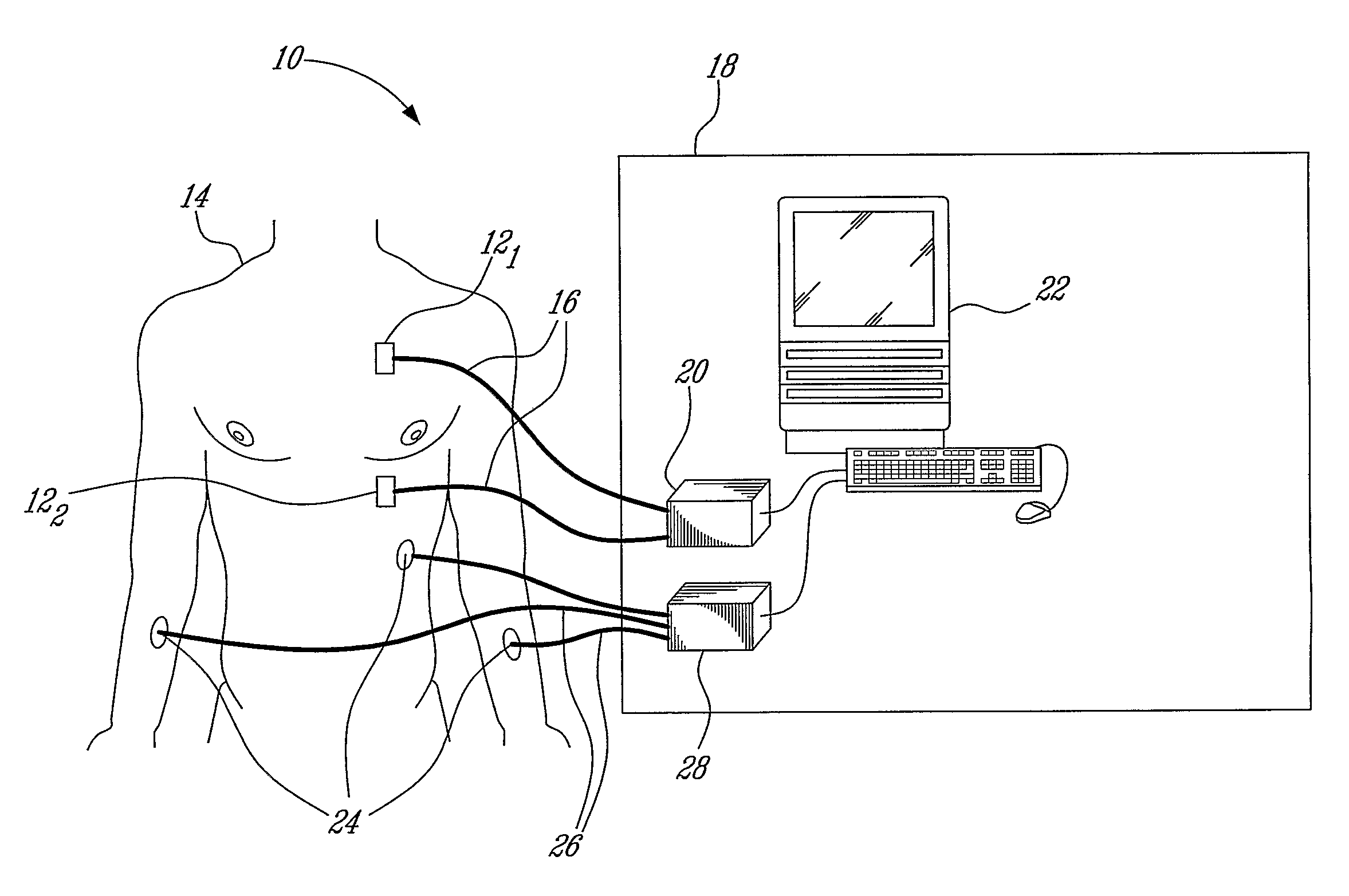
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
InactiveUS7485095B2Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
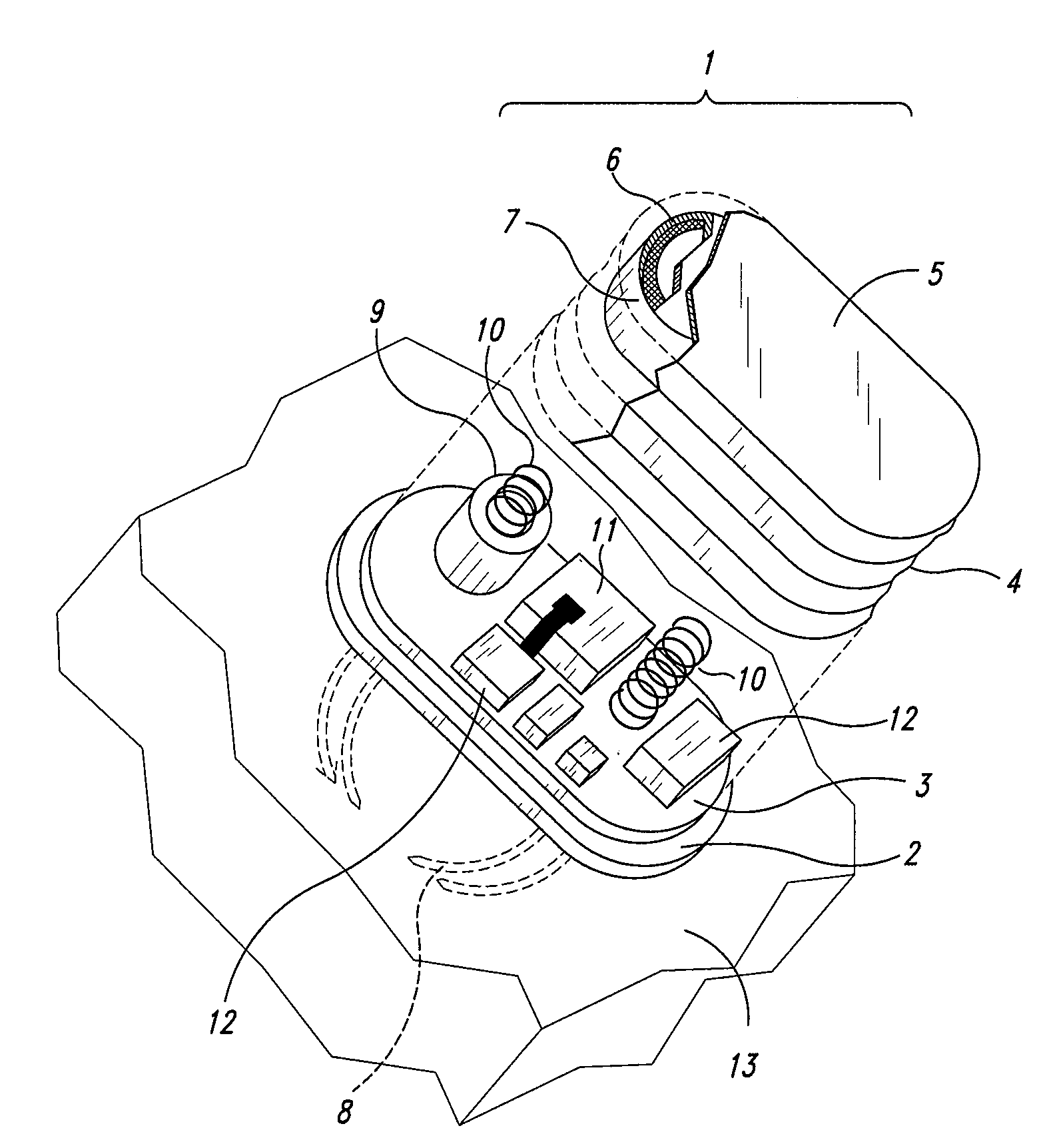
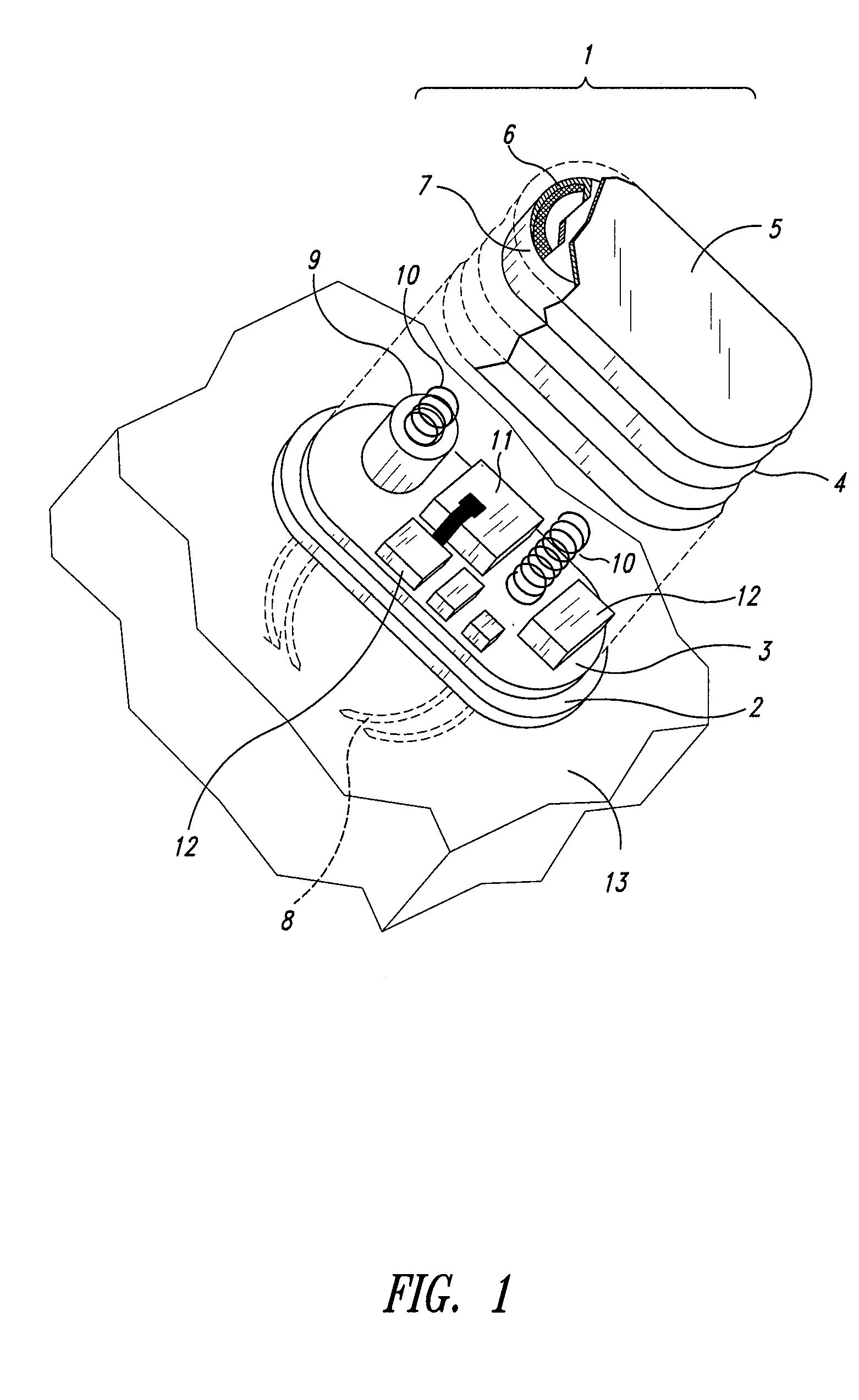
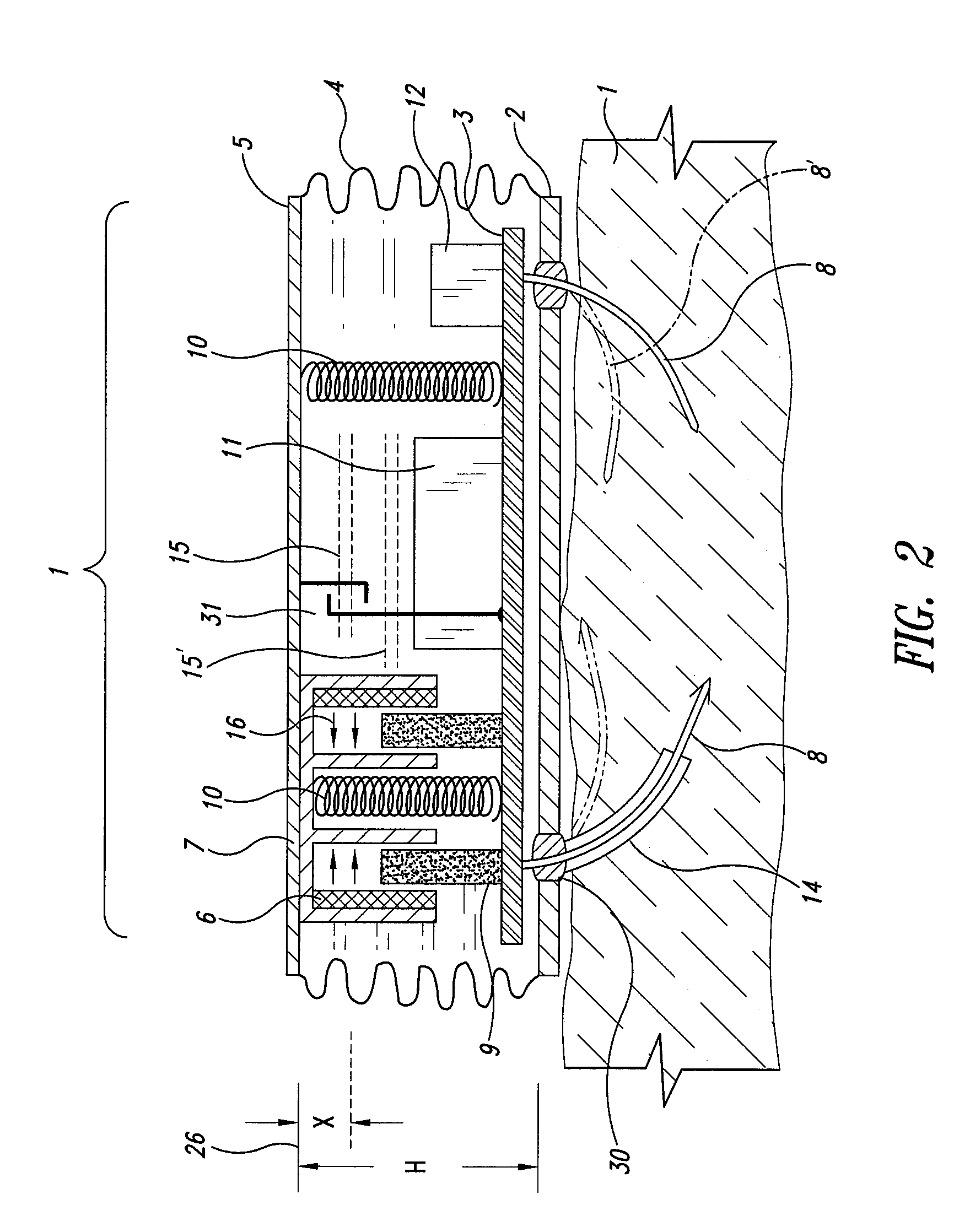
Self-powered resonant leadless pacemaker
InactiveUS20070293904A1Increases natural velocity and acceleration of heart muscleExtended durationElectrotherapyCardiac cycleCardiac pacemaker electrode
A self-powered medical device, for example a pacemaker uses the variations of blood pressure inside the heart or a major artery to create a mechanical resonance in an electromagnetic or piezoelectric generator. The resonance extends the time power is generated during the cardiac cycle. The pressure variations compress a bellows carrying the resonant generator. The inside of the bellows may be evacuated to a partial or full vacuum, and a spring restores the bellows to the desired equilibrium point, acting against the blood pressure. The current pulses are stored in a capacitor. Eliminating the battery allows dramatic miniaturization of the medical device to the point it can be implanted at the point of desired stimulation via a catheter.
Owner:LG RES PARTNERSHIP
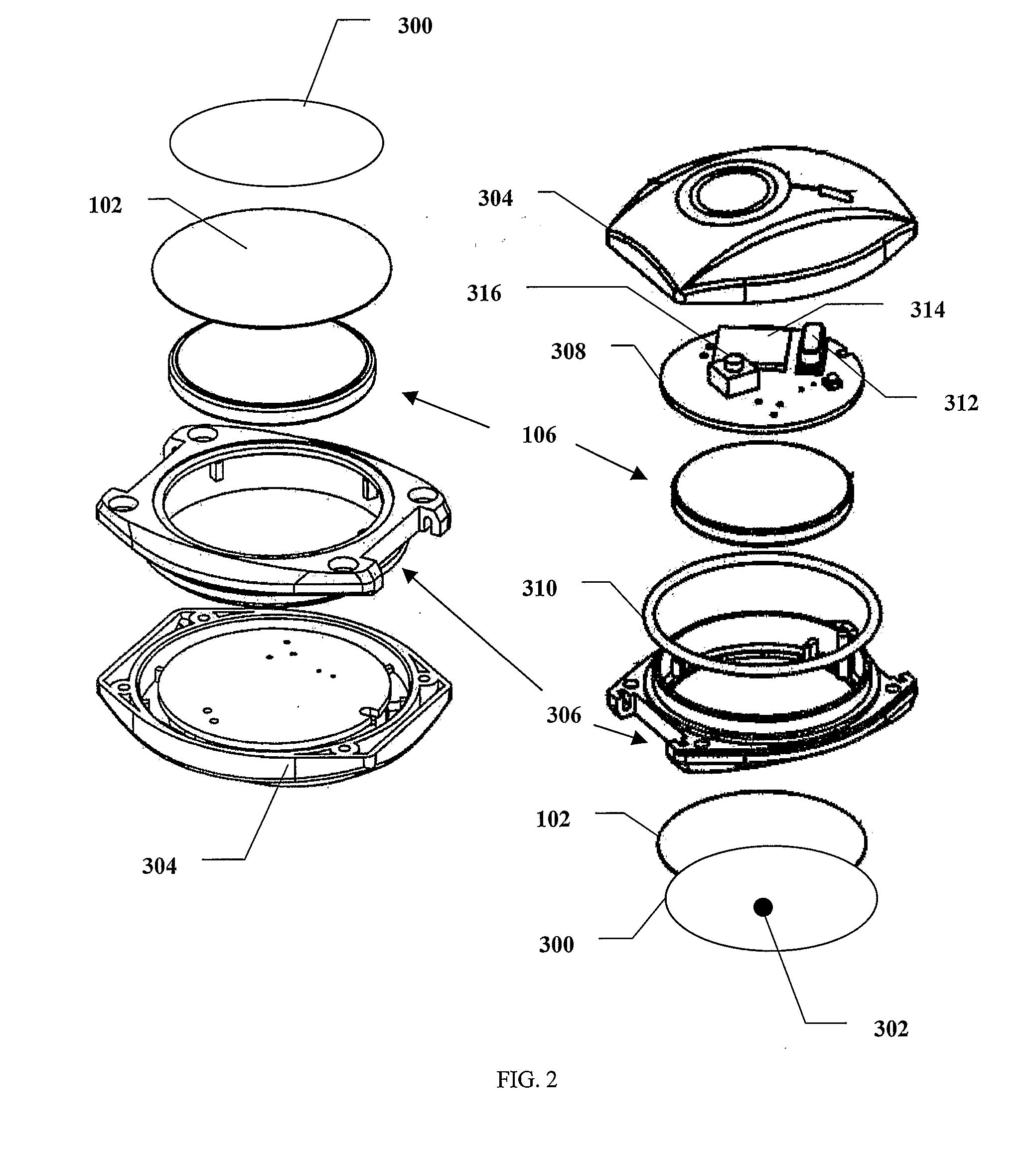
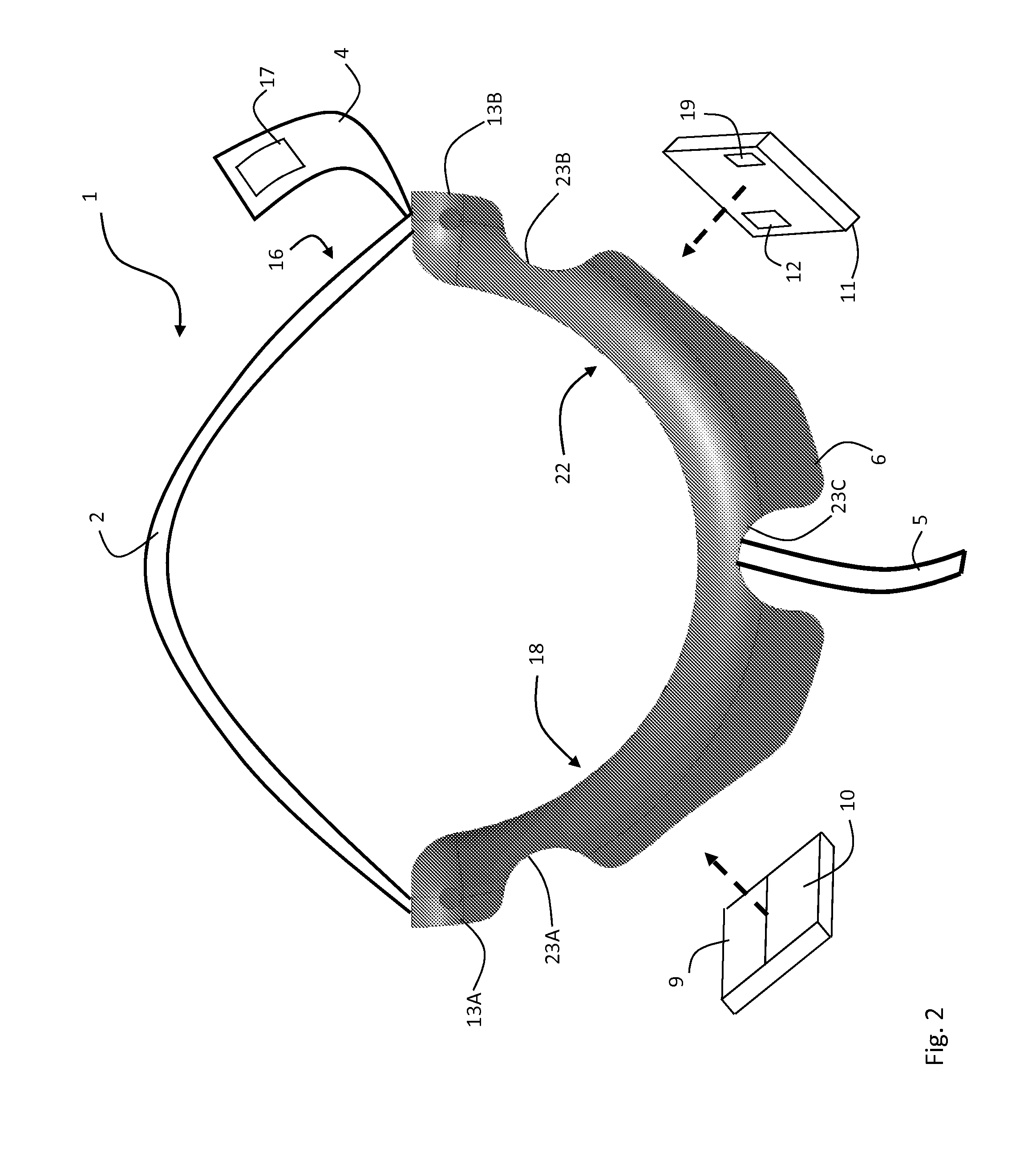
Wearable blood pressure sensor and method of calibration
Methods and apparatus for measuring arterial blood pressure at an extremity of a subject. Arterial blood pressure is derived from a circulatory measurement performed on an extremity of a subject and the circulatory measurement is normalized to account for the instantaneous vertical displacement of the extremity. The vertical displacement of the extremity relative to the heart of the subject is obtained using the angular orientation of the subject's extremity. An improved photoplethysmograph can discriminate light traversing the extremity from ambient light on the basis of differential response. The apparatus may have a conducting polymer actuator for applying pressure to the extremity of the subject. A pulsatile waveform from the photoplethysmographic signal may be obtained at a plurality of externally applied pressures to calibrate the photoplethysmograph.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
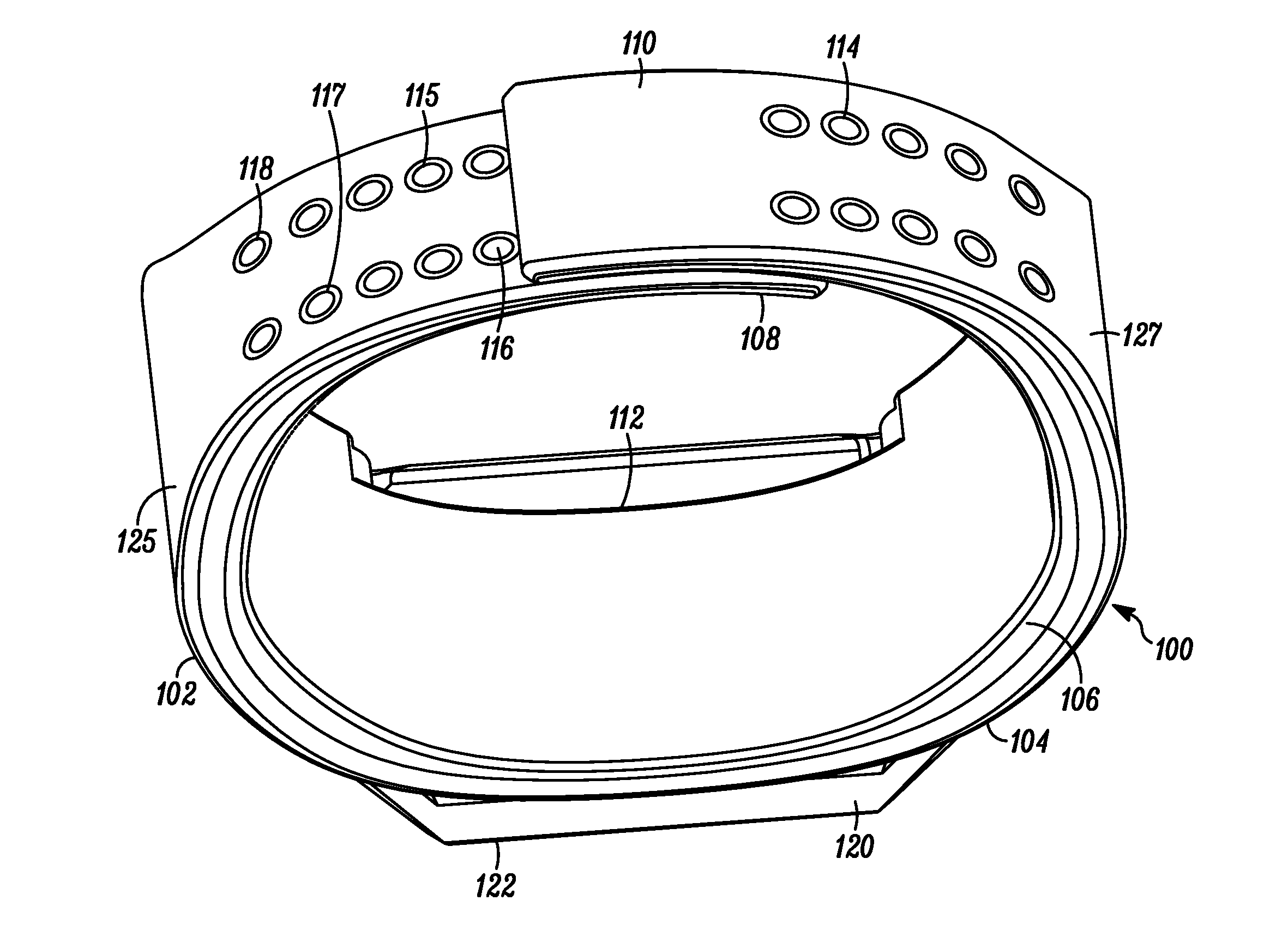
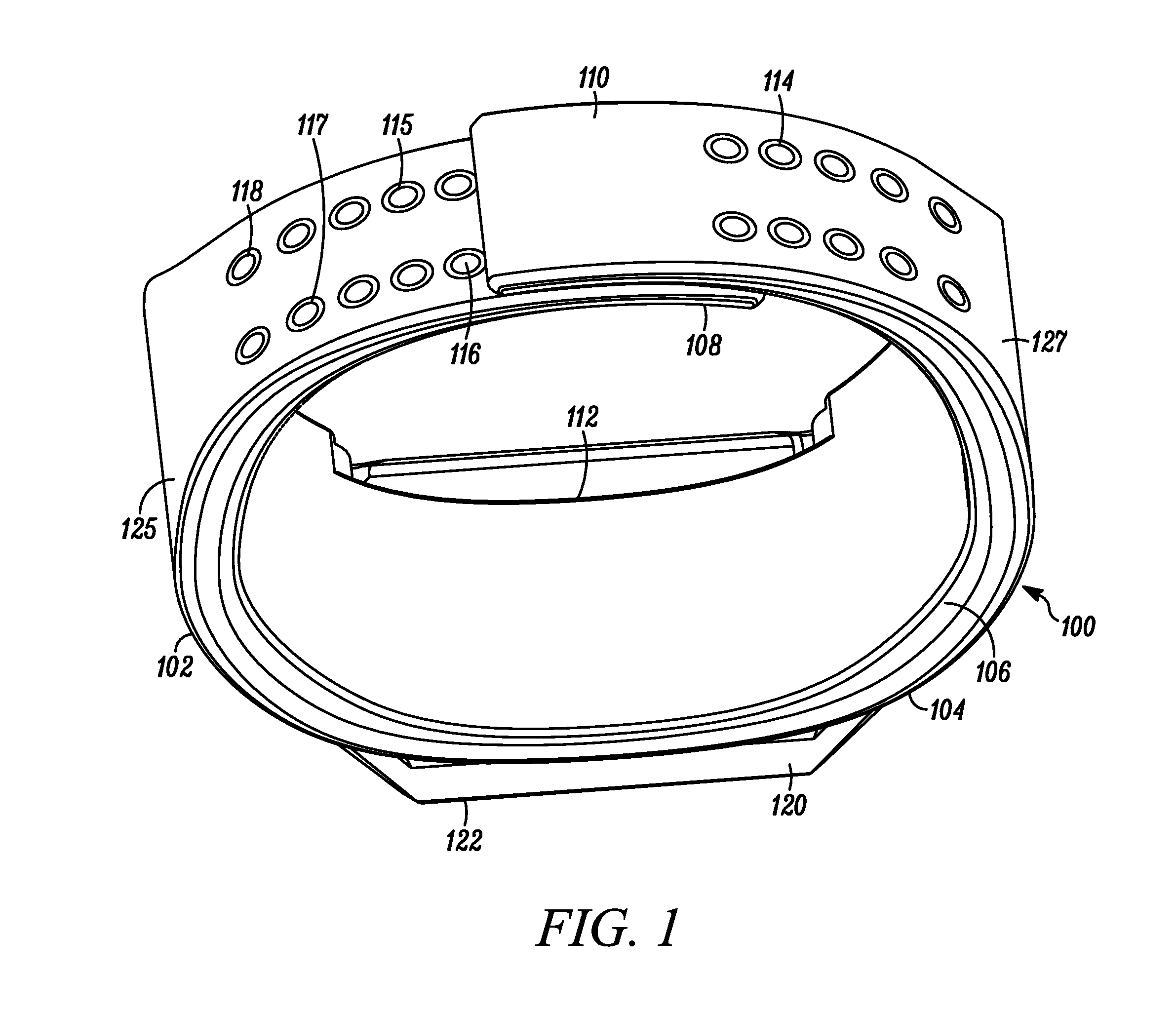
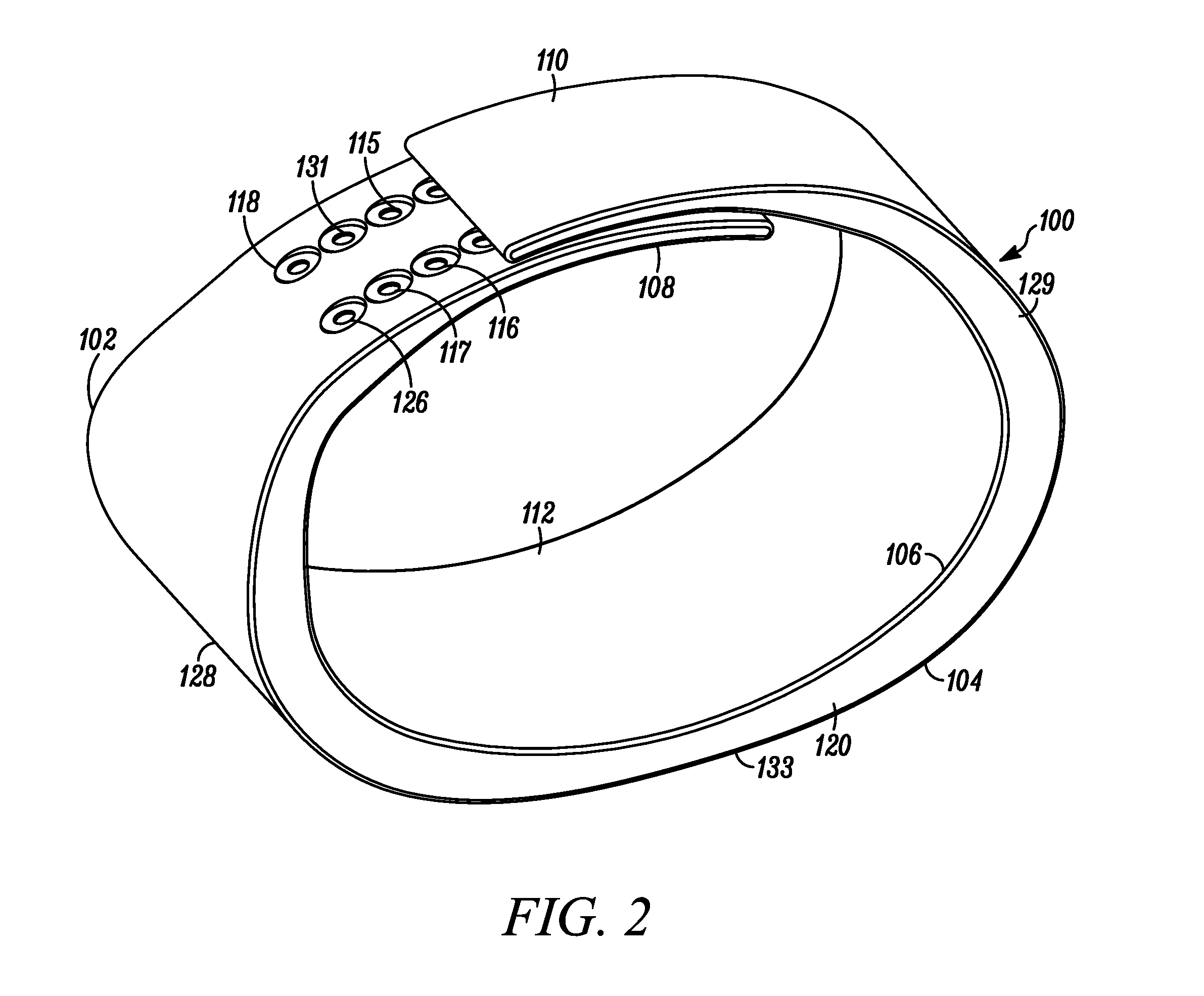
Wearable Band with Ease of Adjustment
An impact resistant wearable band assembly 10 which is particularly usefully and durable during physical exercise, fitness activities, sports, blood pressure measurements, and health care monitoring, can have a matrix, series or array of interlocking magnetic mechanisms 114 with matingly engageable portions 115 and 117 comprising magnets 116 and magnetically attractable portions 118 for detachably and magnetically securing end portions of a user friendly wearable band. In use, the versatile wearable band can be easily adjusted in a one handed movement from a locked position to a released position and vice versa. Advantageously, the wearable band assembly includes an electronic device 122 secured to an electronic device-supporting portion 120 of the wearable band.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
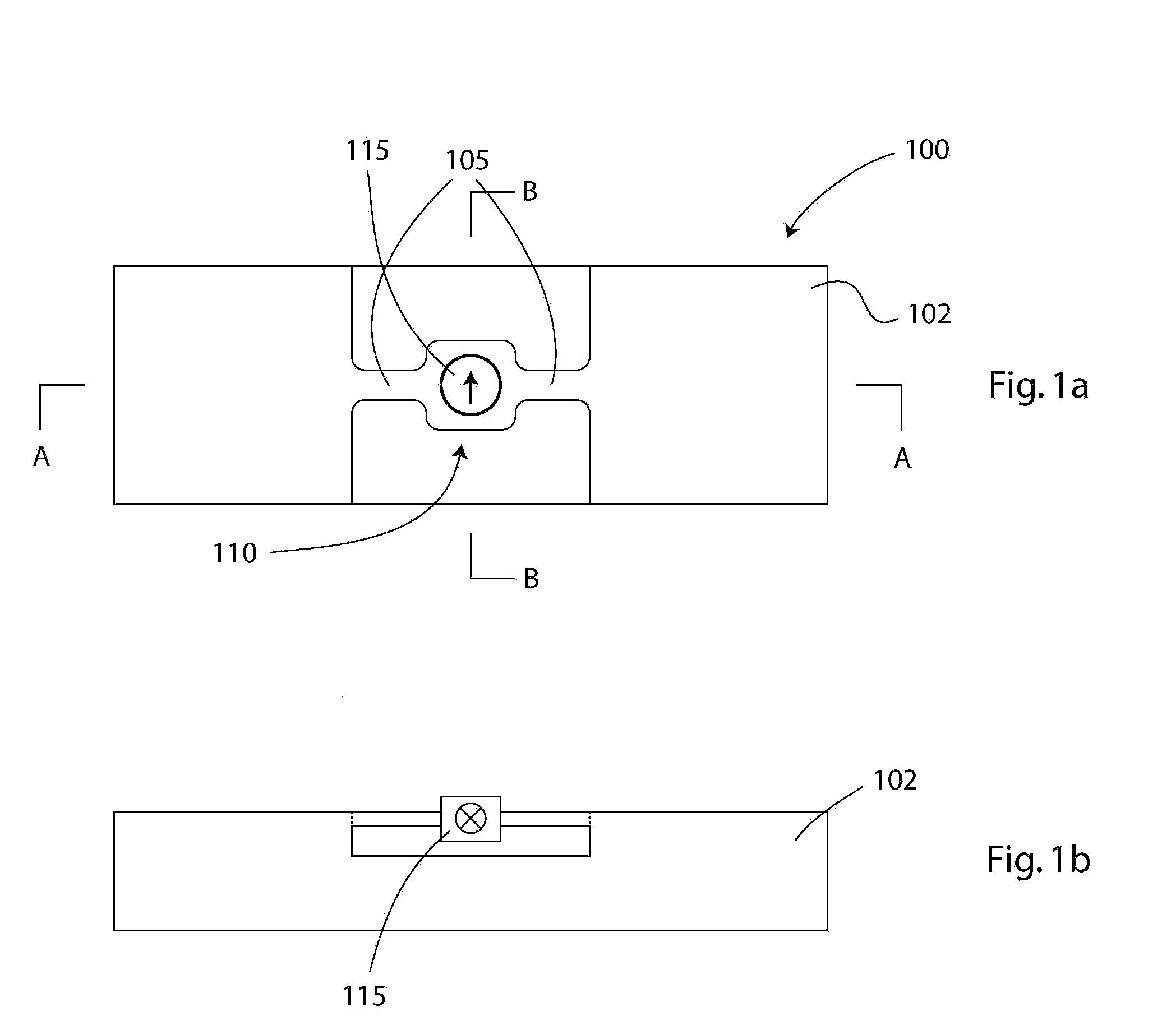
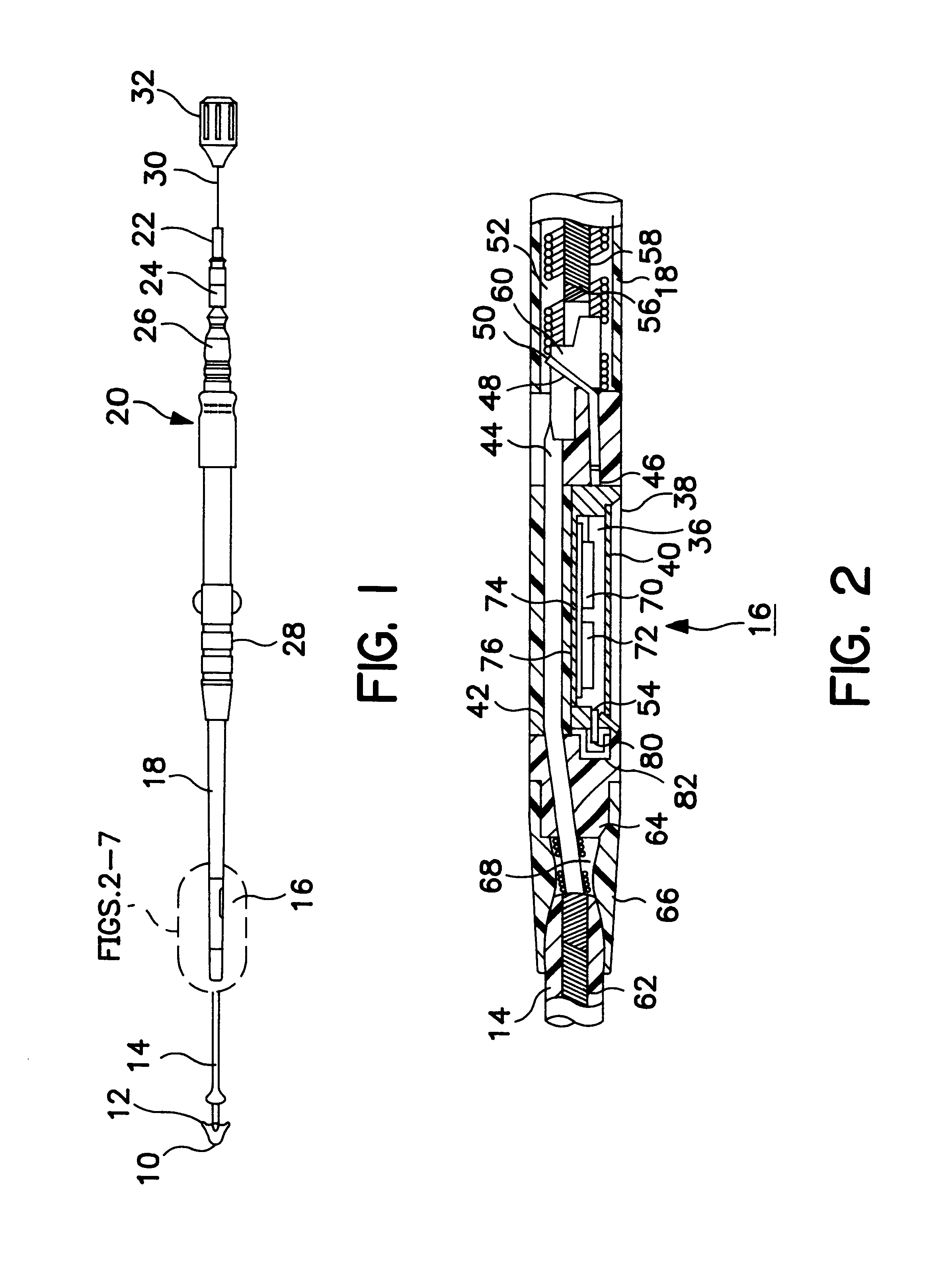
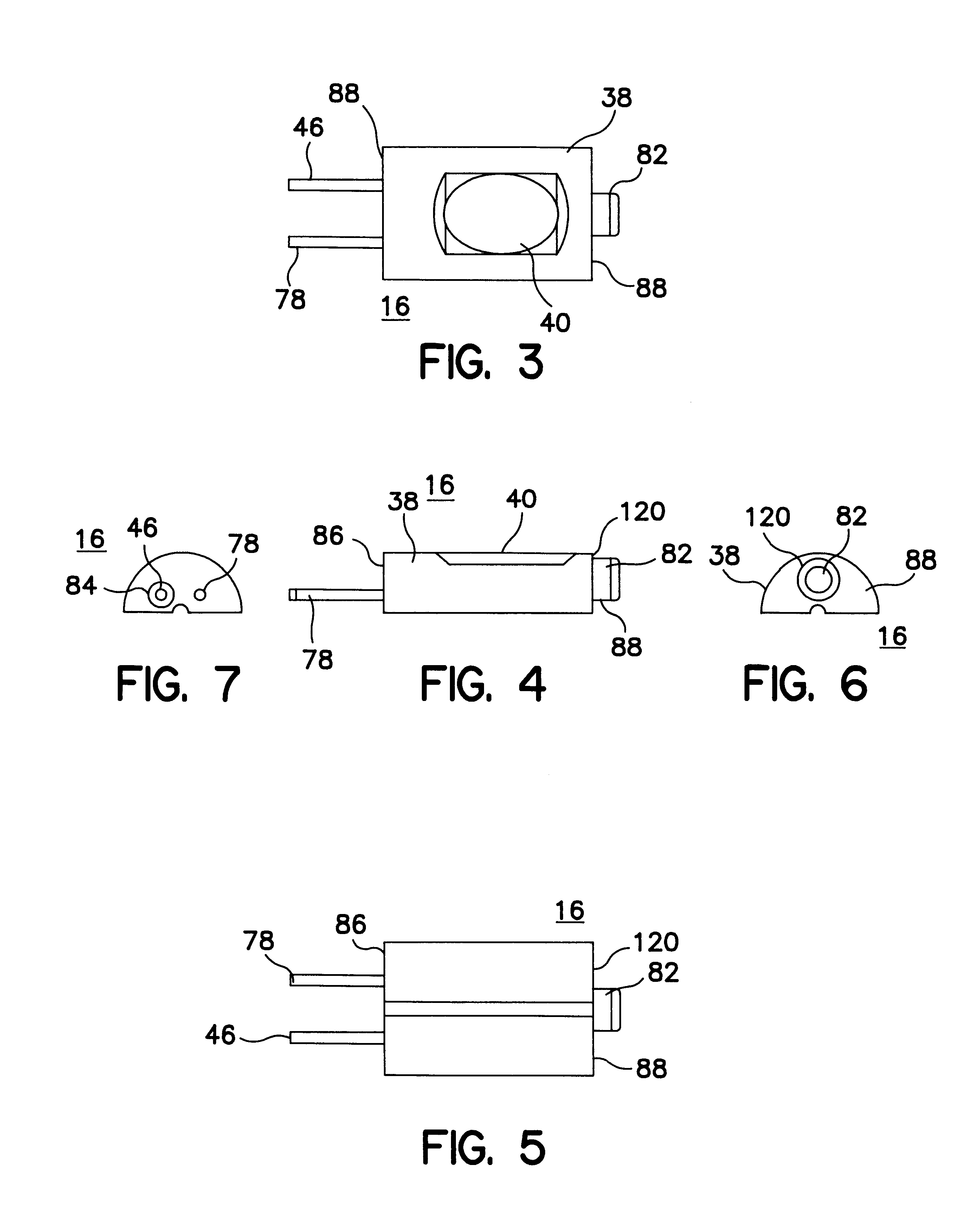
Implantable pressure sensor and method of fabrication
A body implantable pressure sensor attached to an endocardial lead for implantation in a heart chamber or cardiac blood vessel for sensing blood pressure and providing blood pressure signals to an implanted or external hemodynamic monitor and / or therapy delivery device and method of fabrication thereof. A pressure sensor module is formed of an elongated receptacle having an elongated receptacle cavity for receiving a calibrated, micro-machined pressure transducer having a pressure responsive element. The receptacle cavity is covered by a diaphragm disposed alongside the lead body and in parallel with the lead axis. The receptacle cavity is filled with a incompressible oil for transferring pressure forces that are applied to the diaphragm to the pressure transducer. The oil is introduced through a fill port, and the fill port is sealed after the oil is introduced to prevent leakage of the oil from the receptacle cavity and to complete the hermetic sealing of the receptacle cavity. The fill port further comprises a fill tube having a fill tube lumen extending outward of an end wall of the receptacle cavity to a fill tube end, and said sealing step further comprises the steps of crimping or otherwise obstructing the fill tube end to close the fill tube lumen, fitting a fill port cover having an abutting edge over the crimped fill tube end and against the end wall of the receptacle to enclose the sealed fill tube end within a fill port cover cavity, and sealing the abutting edge against the receptacle end wall to hermetically enclose the sealed fill tube end within the fill port cover cavity.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
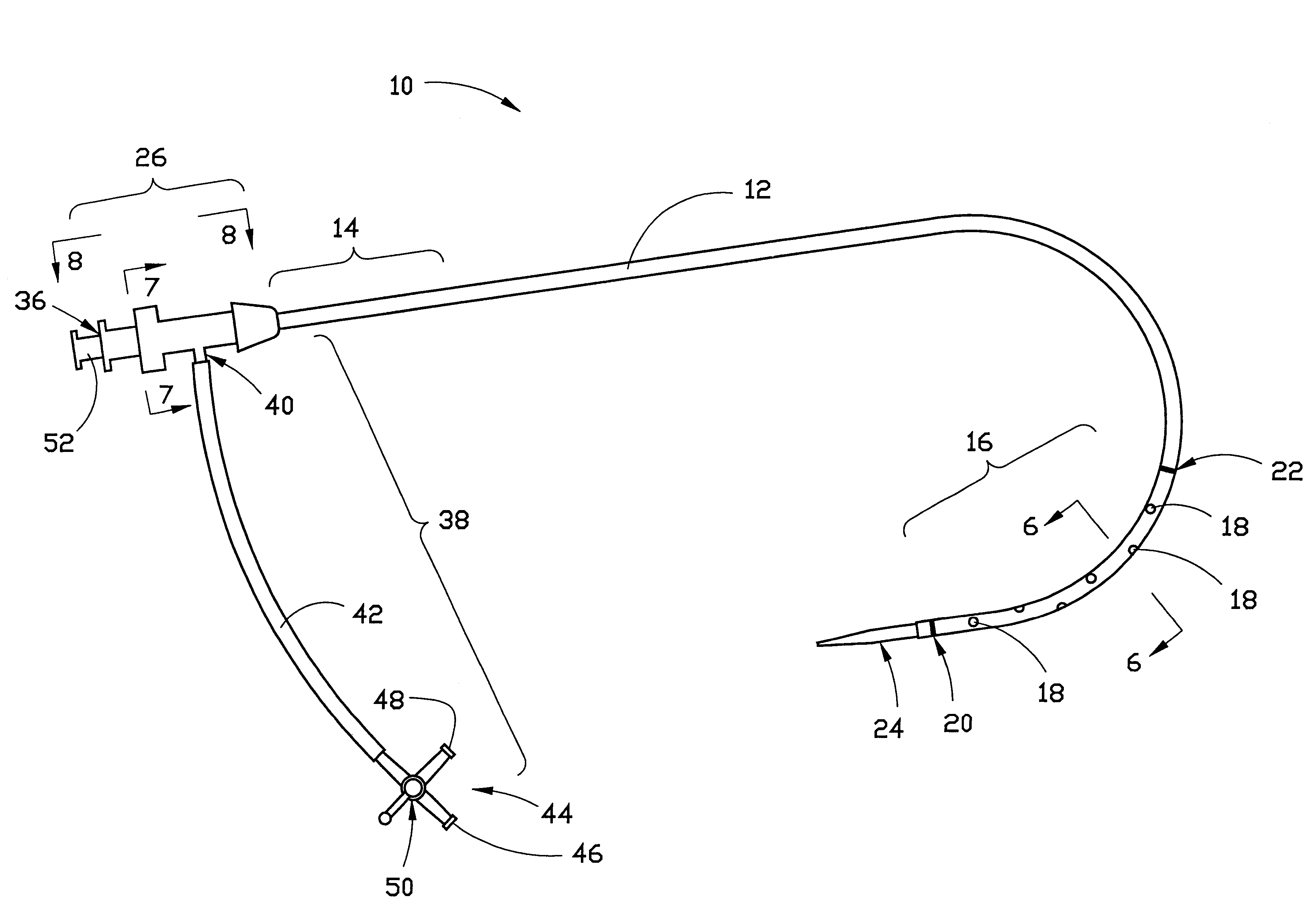
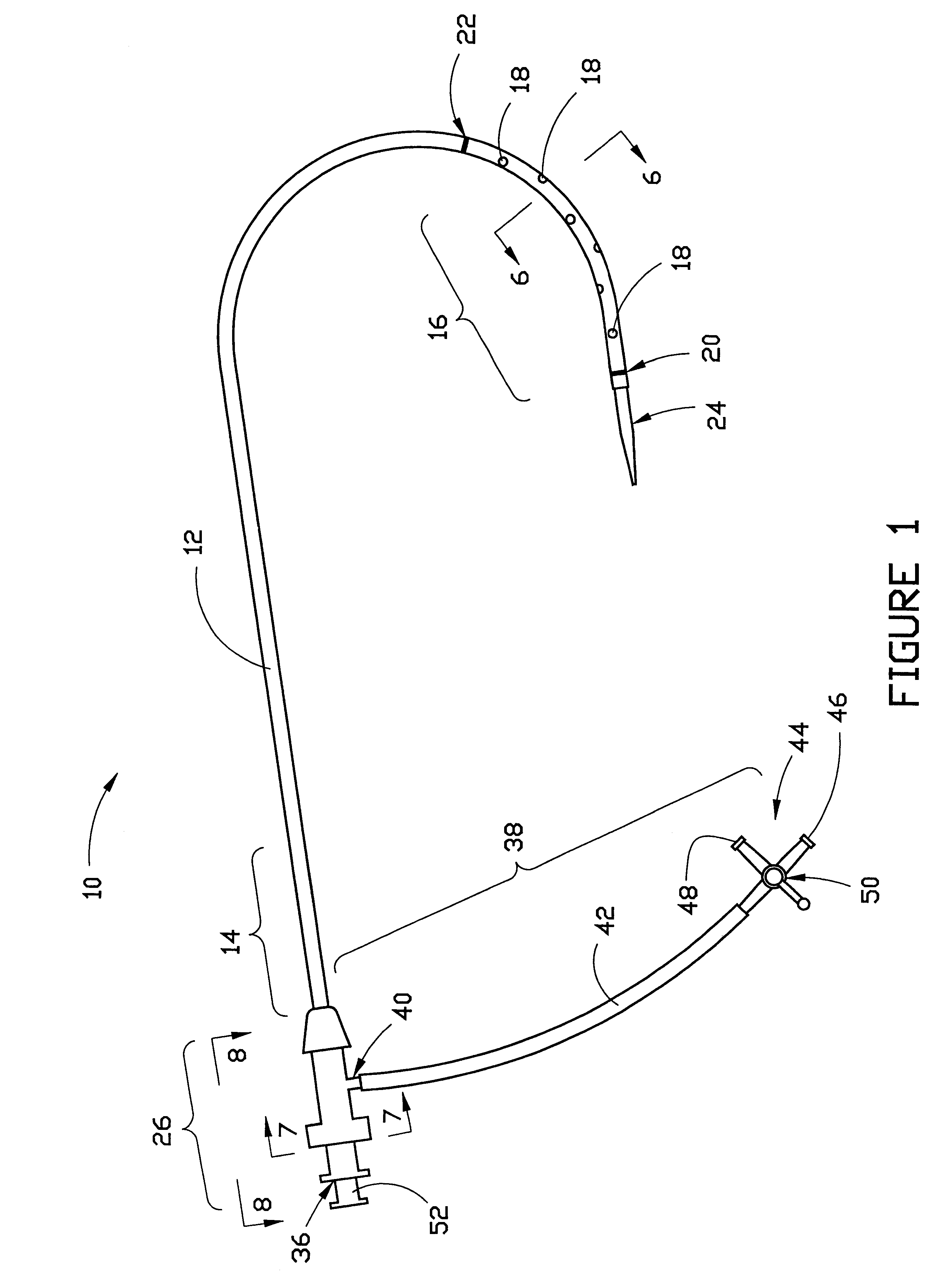
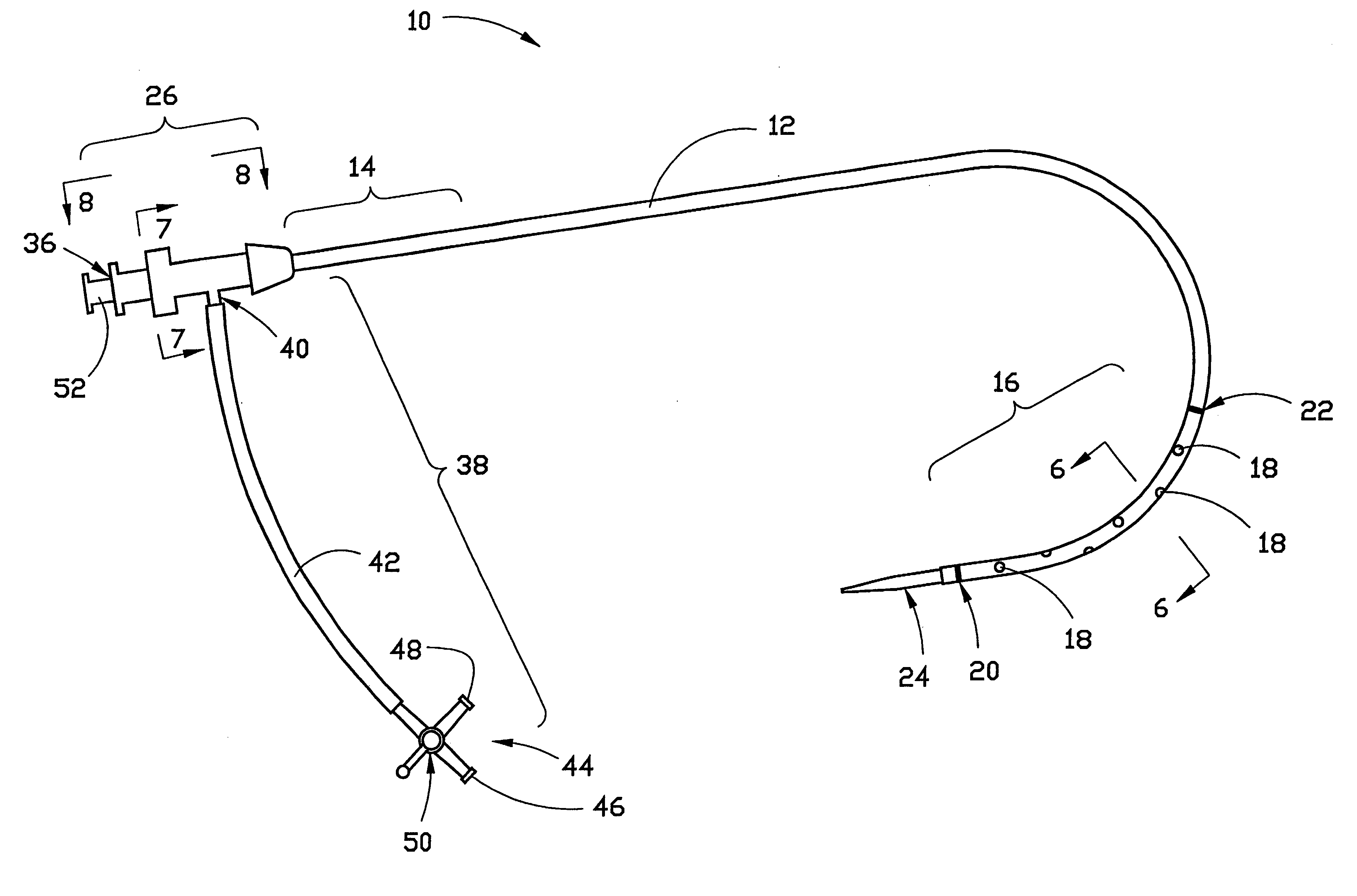
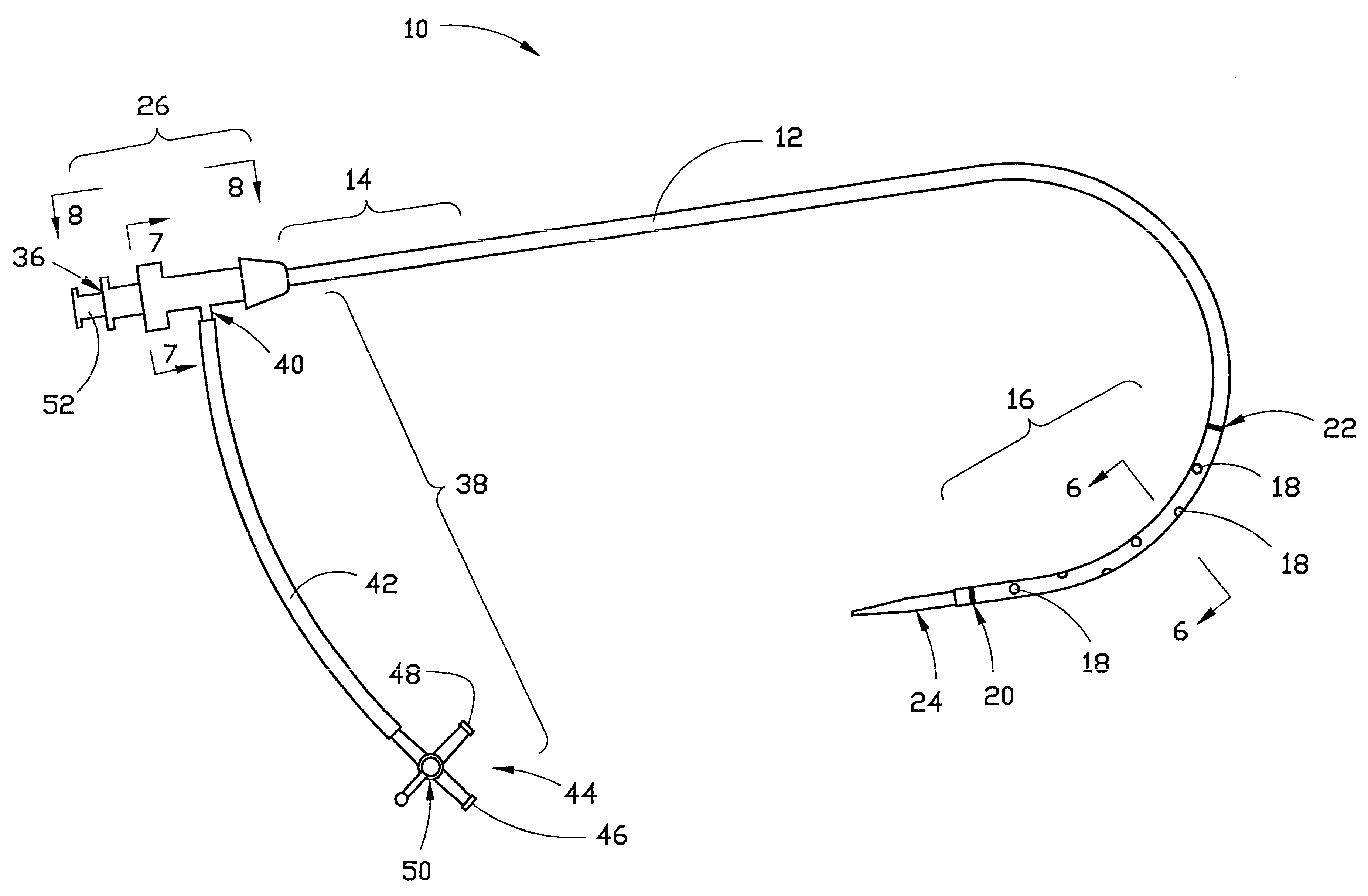
Combination sheath and catheter for cardiovascular use
InactiveUS6245045B1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureGuide needlesInfusion syringesVascular diseaseDilator
A vascular interventional device may be introduced over a guidewire into a vessel of the cardiovascular system of a patient. This device includes a hollow, flexible tube having a proximal end and a distal end that is adapted to selectively engage a target vessel of the cardiovascular system of the patient. This tube also includes a lumen that is continuous from the proximal to the distal end, and has an end hole in the distal end that is in fluid communication with the lumen. A plurality of side holes are provided near the distal end of the tube, each of which is in continuous fluid communication with the lumen. The device also includes a hollow vessel dilator that is adapted for insertion into and through the tube and over the guidewire. The dilator has an inside diameter that is slightly larger than the guidewire and an outside diameter that is slightly smaller than the diameter of the lumen of the tube. The distal end of the dilator is adapted to accommodate vascular entry over the guidewire, and the dilator is adapted to dilate the vessel to accept the tube. The device also includes a hub at the proximal end of the tube. The hub includes an end port through which a second interventional device having an outside diameter smaller than the diameter of the lumen may be introduced into the lumen of the tube. The hub also includes a side port through which a fluid agent may be injected for delivery through the lumen and out the end hole and side holes of the tube. A sealing mechanism is also provided in the hub to prevent air from entering the tube and blood and other fluids from leaking out of the tube through the hub. A pair of vascular interventional devices, at least one of which is constructed according to the invention, may be utilized to treat or study a cardiovascular condition, or to measure the blood pressure across a vascular segment.
Owner:STRATIENKO ALEXANDER ANDREW
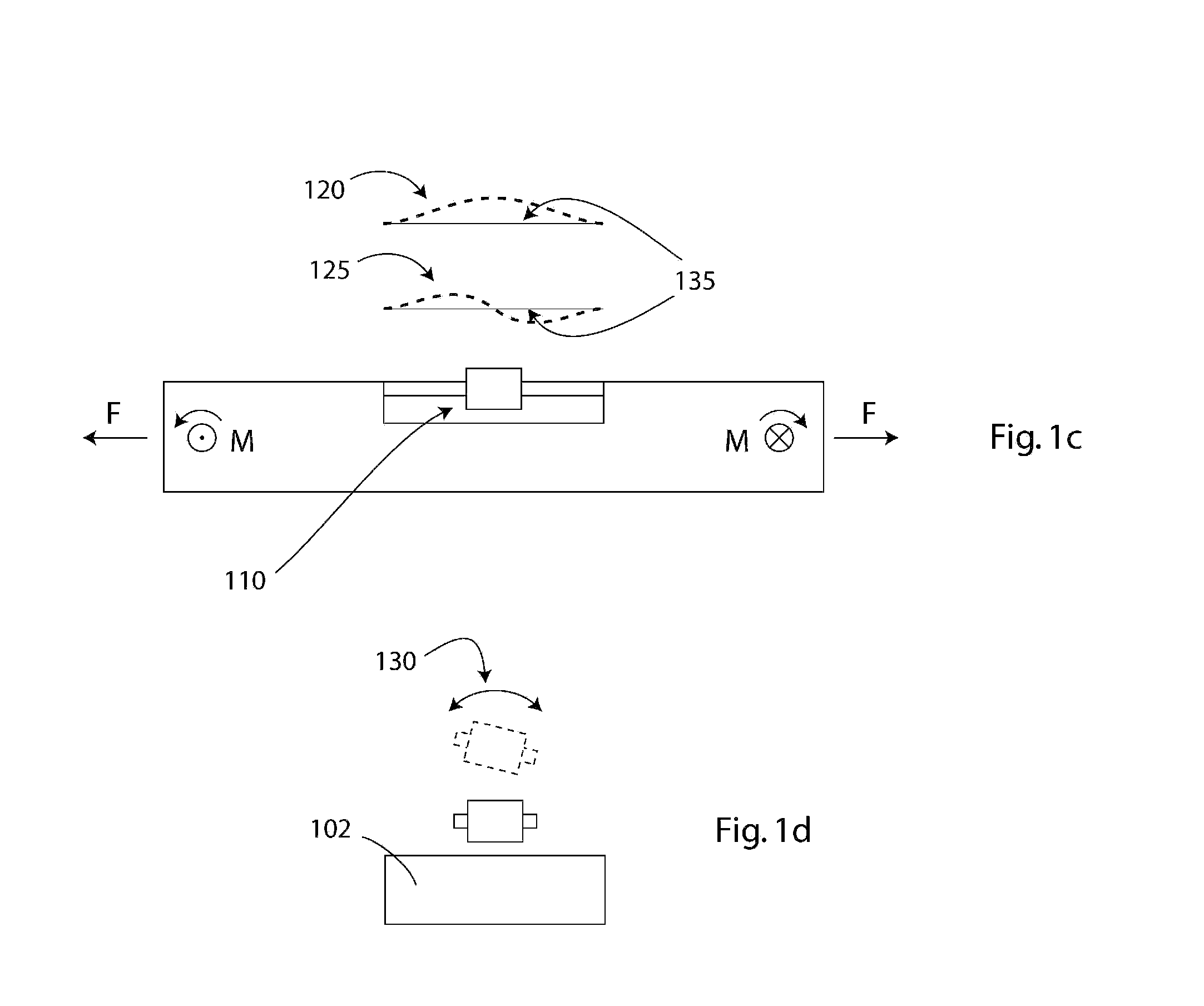
Self-powered leadless pacemaker
InactiveUS20070276444A1Minimize interferenceImprove compression performanceElectrotherapyCardiac pacemaker electrodeEngineering
A self-powered pacemaker uses the variations of blood pressure inside the heart or a major artery to create a periodic change in the magnetic flux inside a coil. The pressure variations compress a bellows carrying a magnet moving inside a coil. The inside of the bellows is evacuated to a partial or full vacuum, and a spring restores the bellows to the desired equilibrium point, acting against the blood pressure. The current pulses are stored in a capacitor. Eliminating the battery allows dramatic miniaturization of the pacemaker to the point it can be implanted at the point of desired stimulation via a catheter. The invention includes means of compensating for atmospheric pressure changes.
Owner:LG RES PARTNERSHIP
Method And Device For Measuring Physiological Parameters At The Hand
InactiveUS20080051667A1Easily enable the device to transmit the alarm signalLow and high blood pressureMedical communicationElectrocardiographyBlood pressureBiomedical engineering
A wrist-mounted device (100) for measuring at least one physiological parameter of the user. The present invention enables such a measurement to preferably be transformed into clinically useful information about the user. Such information may then optionally be sent to medical personnel, for example at a contact and / or monitoring center. The measuring parameters may include blood pressure, ECG, location. The present invention can perform a Holter process over more than one physiological parameter.
Owner:MEDICA4ALL AG
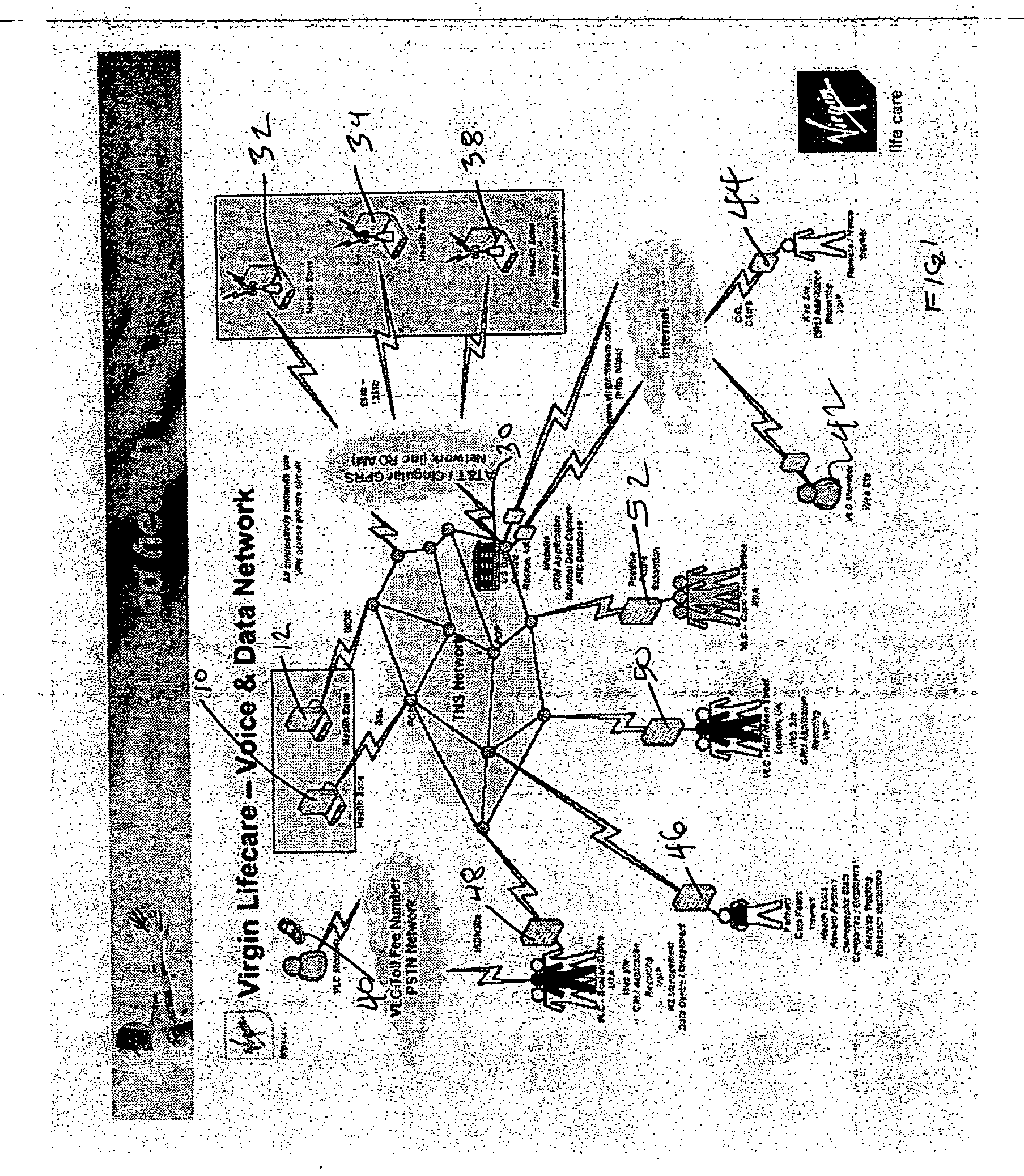
Interactive, internet supported health and fitness management system
A wellness system monitors the controlled progress of patients under surveillance and includes a server base station which is generally off-site, a web-site interface and a local station at the point-of-use, which is generally a health or fitness center. A unique data base is created for each user and goals and objectives may be set with progress monitored. Typically, the user will respond to a survey or questionnaire to populate his specific database. This is combined with a professional assessment and an automated measurement of vital statistics such as weight, blood pressure and body composition as measured at the local station. Other data may be entered manually such as height, age and the like. In a more comprehensive system the invention is designed to monitor other data such as cholesterol and blood glucose, as well. The locally input data may be updated at will by the user or on behalf of the user by professional personnel.
Owner:VIRGIN PULSE INC
Cardiovascular sheath/catheter
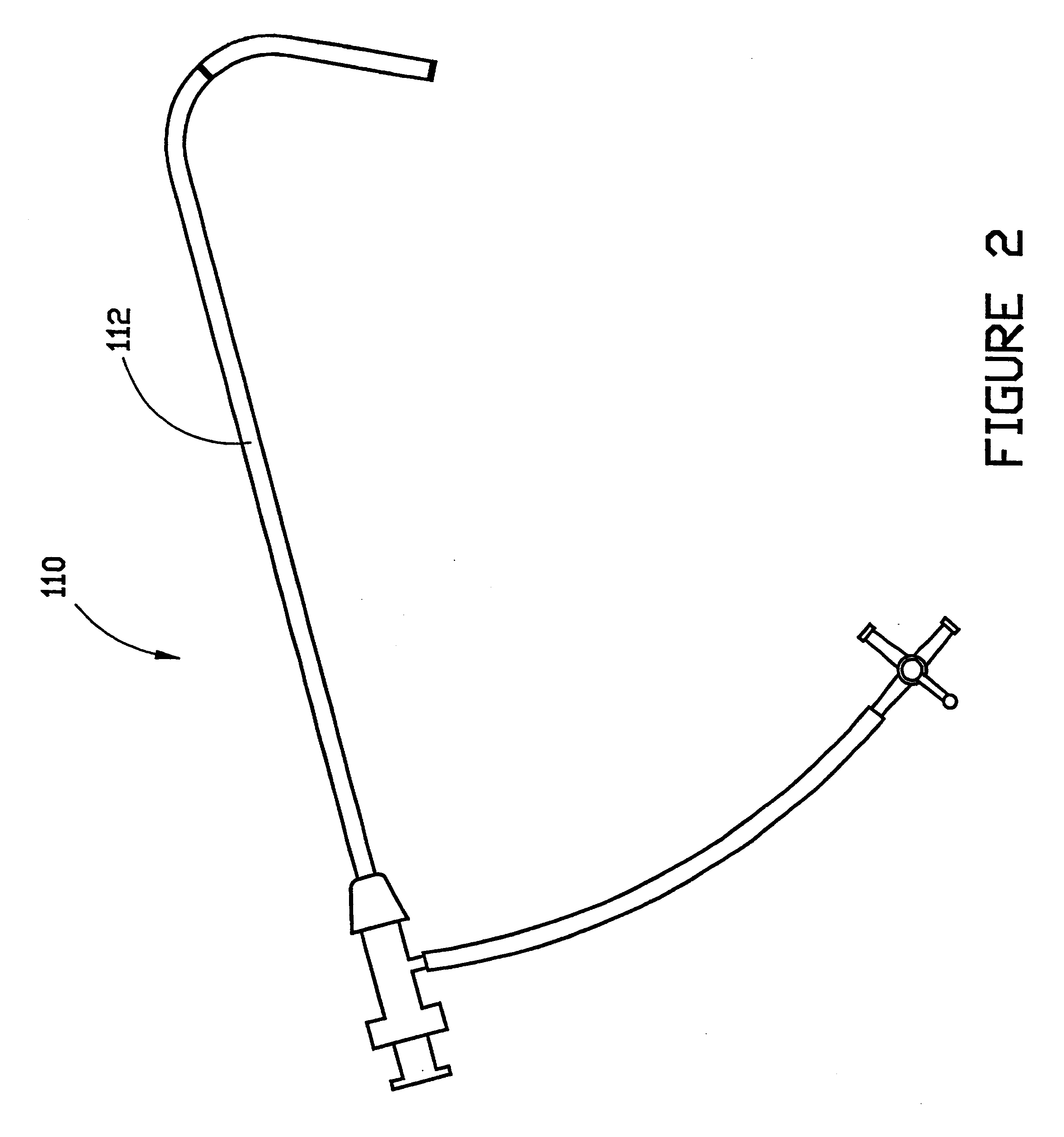
InactiveUS6595959B1Convenient treatmentFacilitate studyGuide needlesInfusion syringesVascular diseaseDilator
A vascular interventional device may be introduced over a guidewire into a vessel of the cardiovascular system of a patient. This device includes a hollow, flexible tube having a proximal end and a distal end that is adapted to selectively engage a target vessel of the cardiovascular system of the patient. This tube also includes a lumen that is continuous from the proximal to the distal end, and has an end hole in the distal end that is in fluid communication with the lumen. The device also includes a hollow vessel dilator that is adapted for insertion into and through the tube and over the guidewire. The dilator has an inside diameter that is slightly larger than the guidewire and an outside diameter that is slightly smaller than the diameter of the lumen of the tube. The distal end of the dilator is adapted to accommodate vascular entry over the guidewire, and the dilator is adapted to dilate the vessel to accept the tube. The device also includes a hub at the proximal end of the tube. The hub includes an end port through which a second interventional device having an outside diameter smaller than the diameter of the lumen may be introduced into the lumen of the tube. The hub also includes a side port through which a fluid agent may be injected for delivery through the lumen and out the end hole of the tube. A sealing mechanism is also provided in the hub to prevent air from entering the tube and blood and other fluids from leaking out of the tube through the hub. A pair of vascular interventional devices, at least one of which is constructed according to the invention, may be utilized to treat or study a cardiovascular condition, or to measure the blood pressure across a vascular segment.
Owner:STRATIENKO ALEXANDER A
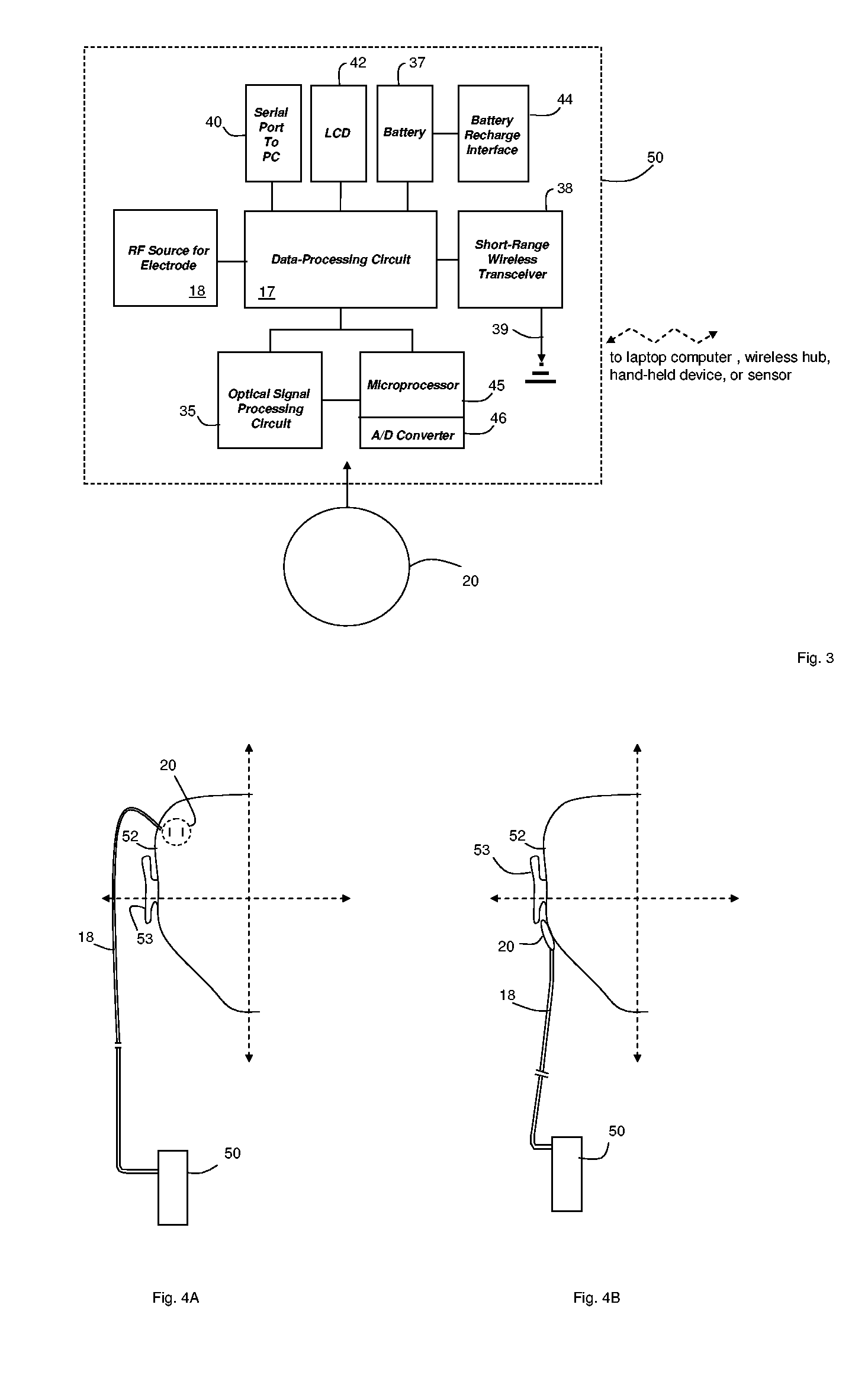
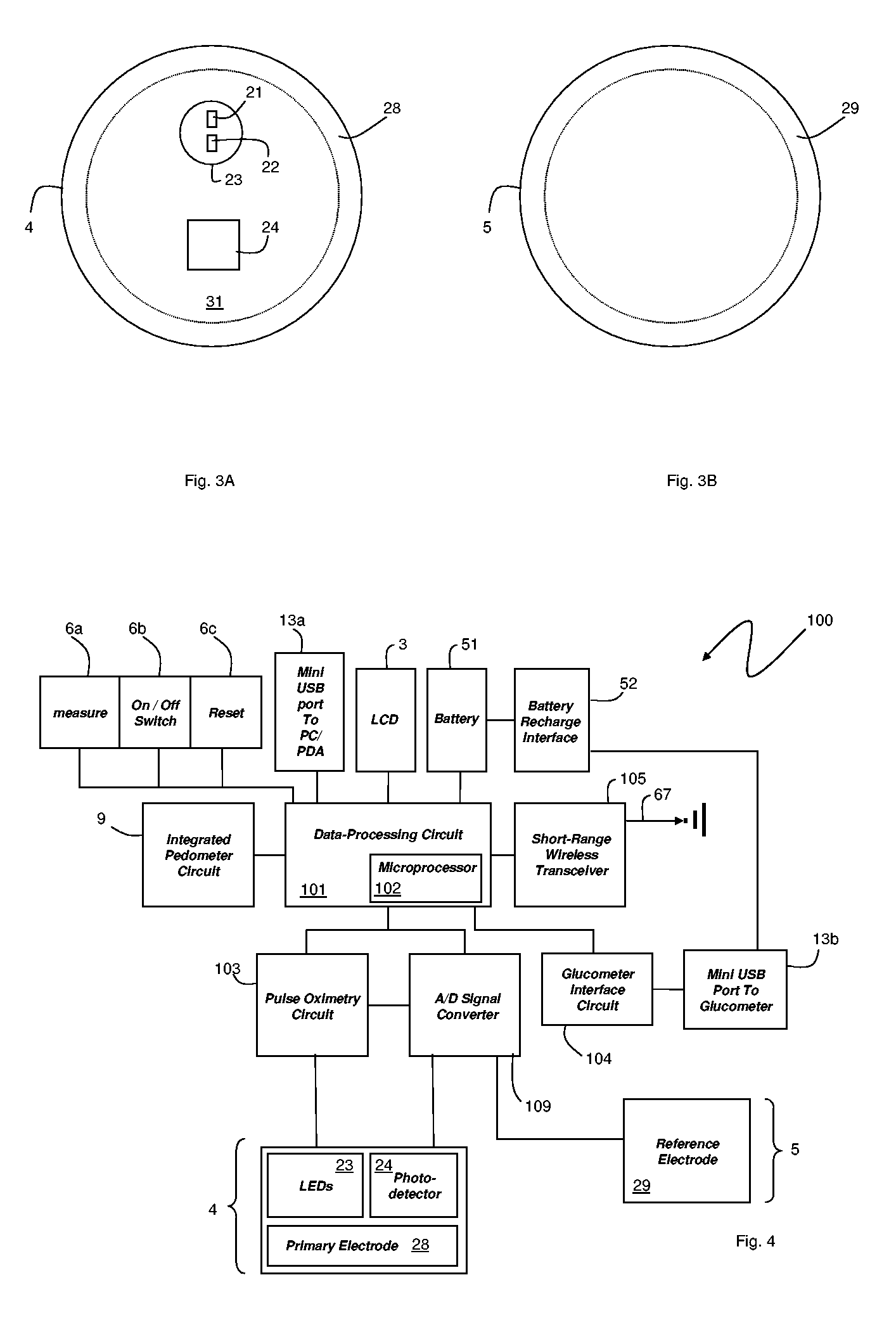
Hand-held monitor for measuring vital signs
InactiveUS20060009698A1Easily perform throughout dayGood blood pressureElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsOptical radiationPhotodetector
The invention provides a monitor for measuring blood pressure and other vital signs from a patient without using a cuff. The monitor features a housing with a first surface that, in turn, supports a first sensor. The first sensor features: i) an optical system with one or more light sources (e.g., LEDs or laser diodes) that generate optical radiation, and a photodetector oriented to collect radiation after it irradiates the patient and in response generate an optical signal; and ii) a first electrode. A second sensor features a second electrode paired with the first electrode that collects an electrical signal from the patient. A microprocessor in electrical communication with the first and second sensor receives the optical and electrical signals and processes them with an algorithm to determine systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
Optical sensors for use in vital sign monitoring
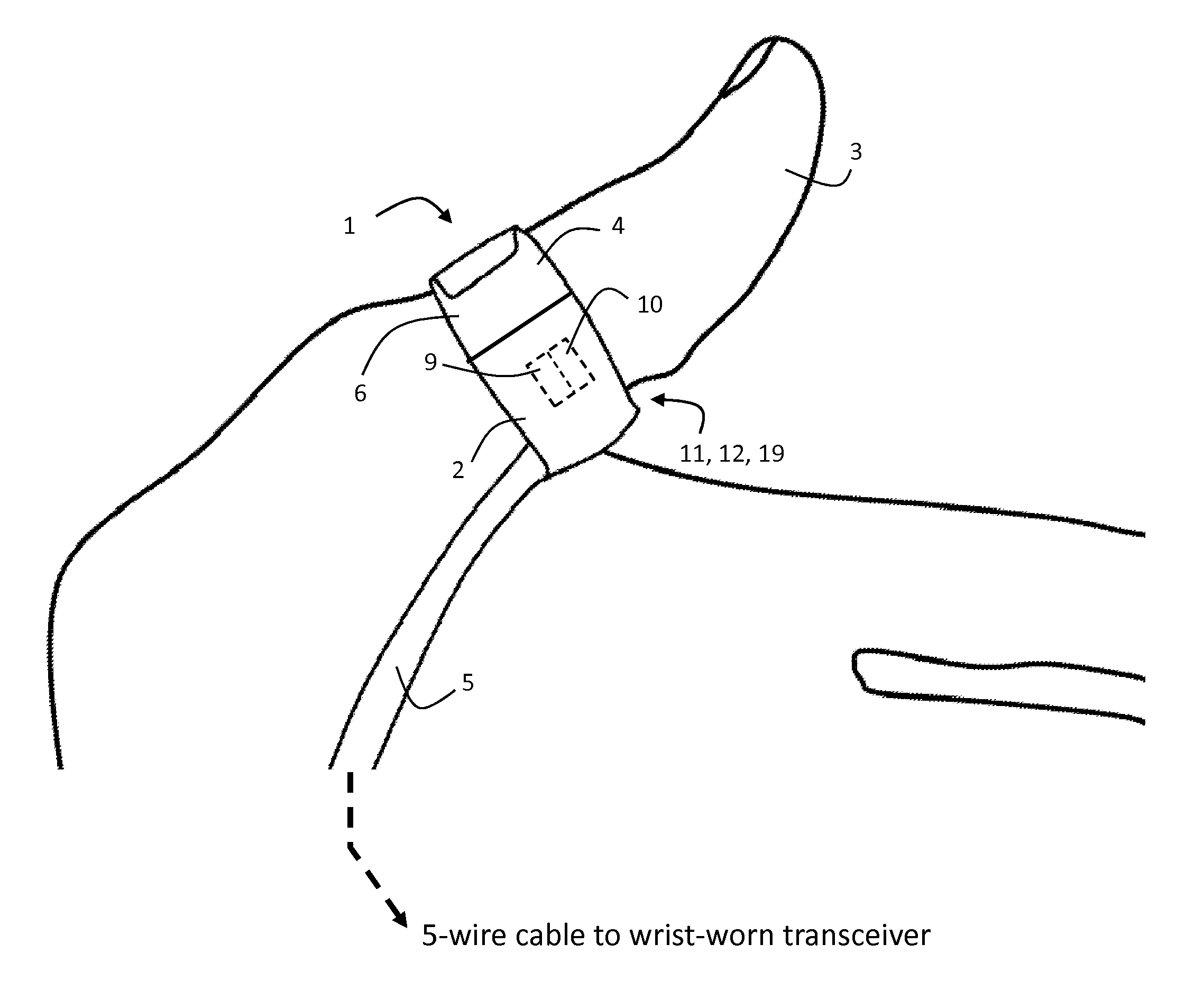
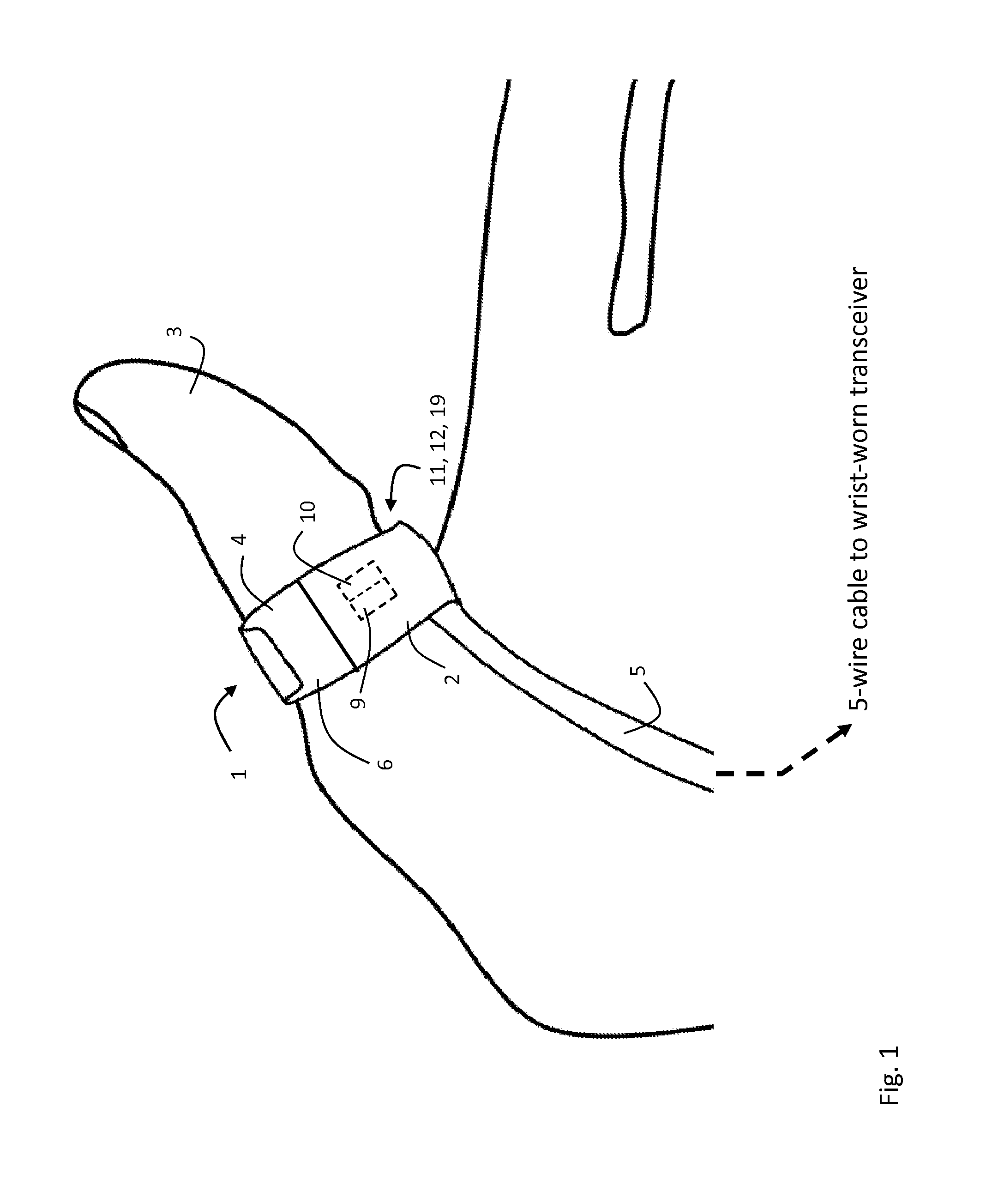
ActiveUS20120179011A1Accurate extractionImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsCable transmissionTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn system that continuously measures pulse oximetry and blood pressure, along with motion, posture, and activity level, from an ambulatory patient. The system features an oximetry probe that comfortably clips to the base of the patient's thumb, thereby freeing up their fingers for conventional activities in a hospital, such as reading and eating. The probe secures to the thumb and measures time-dependent signals corresponding to LEDs operating near 660 and 905 nm. Analog versions of these signals pass through a low-profile cable to a wrist-worn transceiver that encloses a processing unit. Also within the wrist-worn transceiver is an accelerometer, a wireless system that sends information through a network to a remote receiver, e.g. a computer located in a central nursing station.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
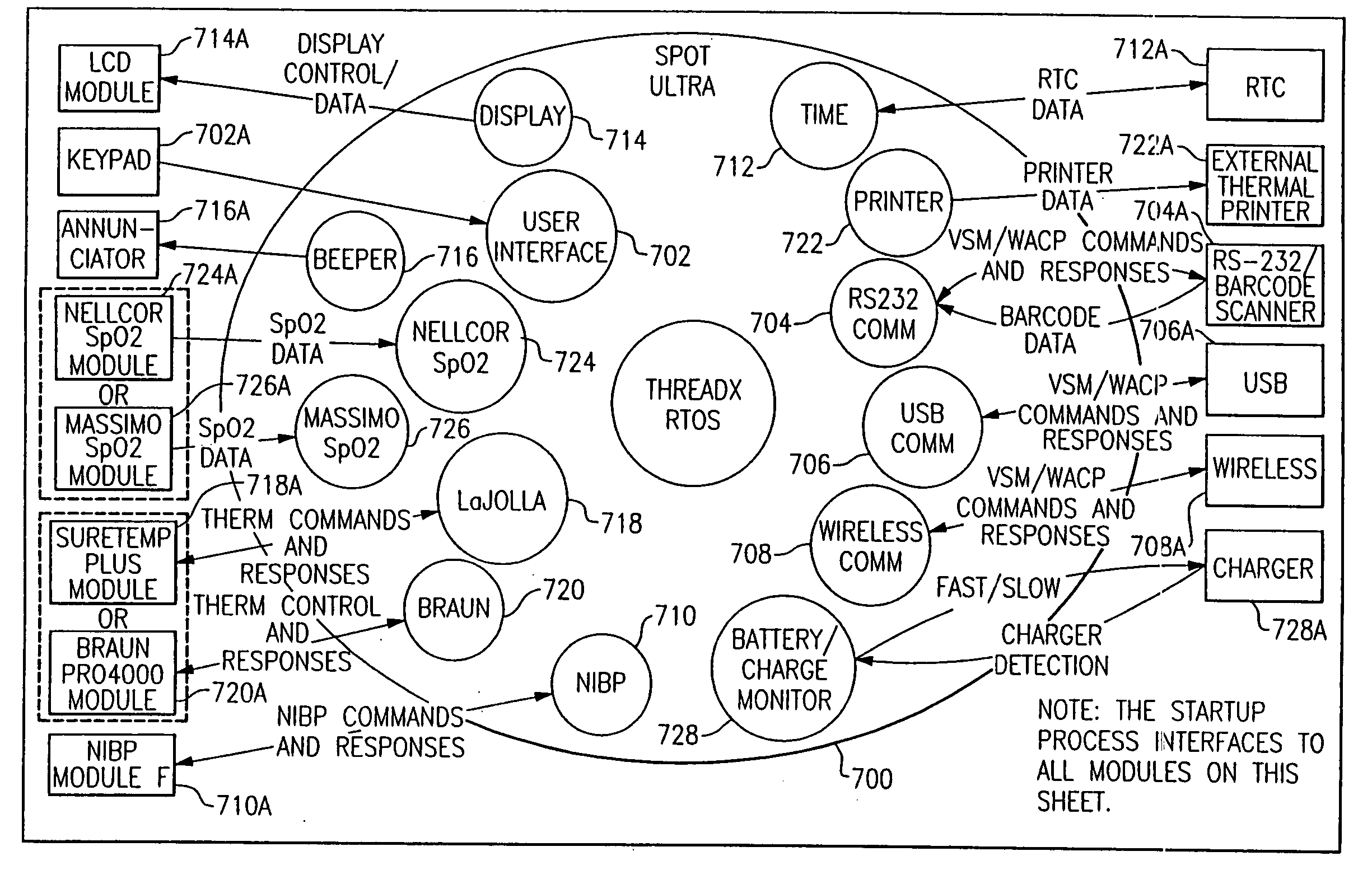
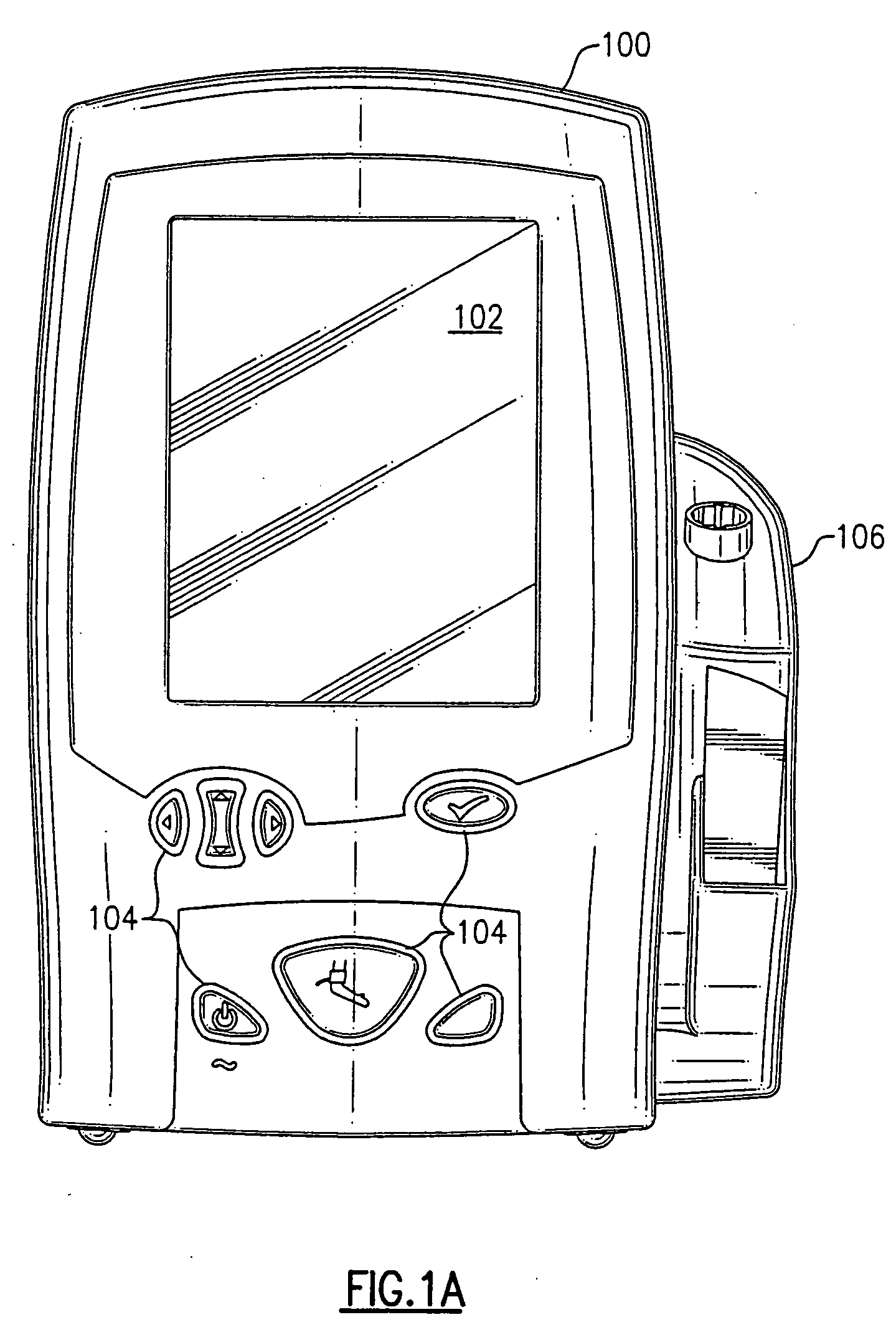
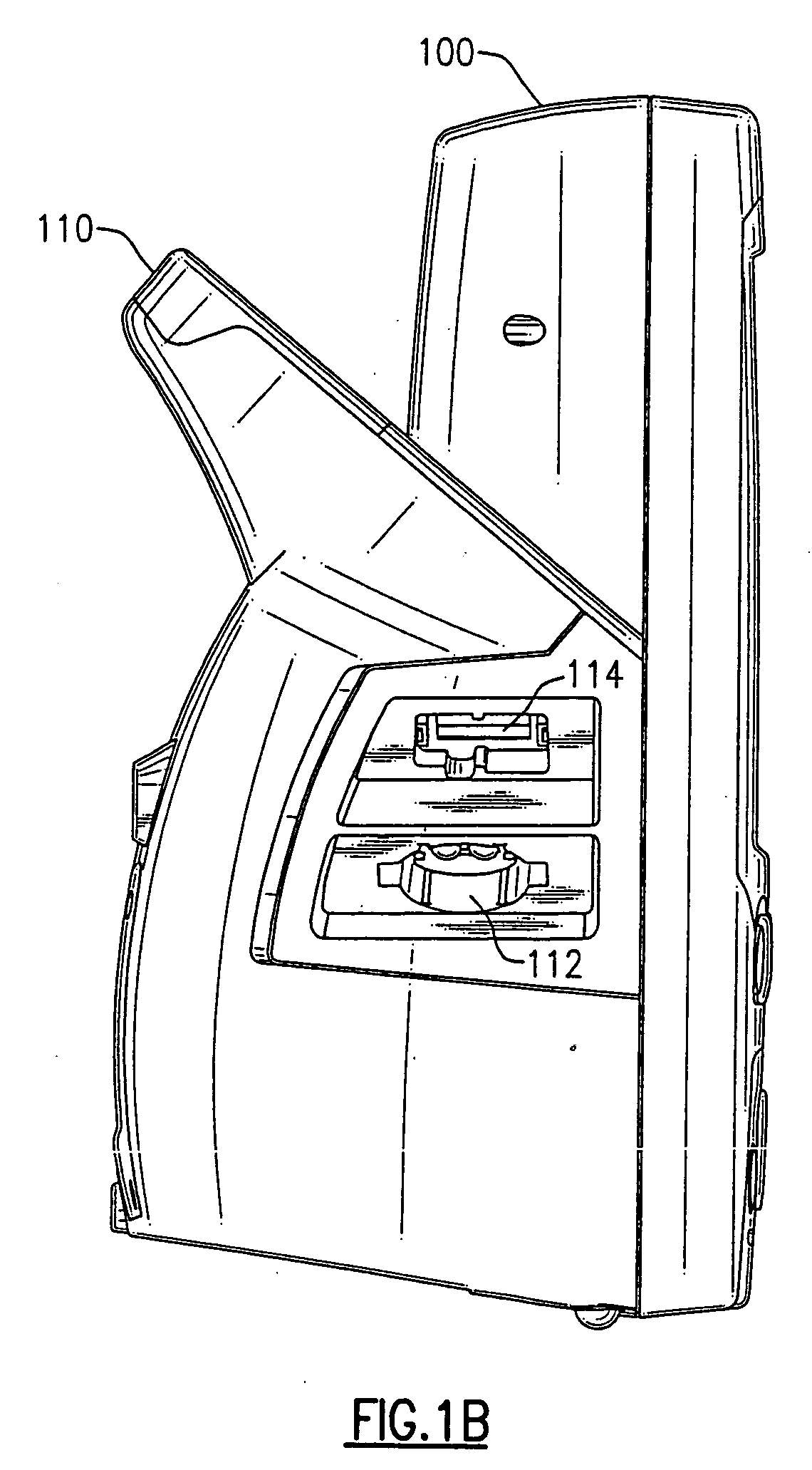
Portable vital signs measurement instrument and method of use thereof
The invention is a portable vital signs measurement instrument, systems and methods that provide a variety of measurement capabilities, including blood pressure, temperature, pulse oximetry, and other indications of patient status. The instrument, systems and methods include the ability to communicate wirelessly, for example using Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11B), with a server, so that information can be entered easily, securely and reliably into a medical database system accessible by way of the server. The systems and methods provide for the instrument to initiate a communication session by attempting to discover a server access point in its vicinity.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
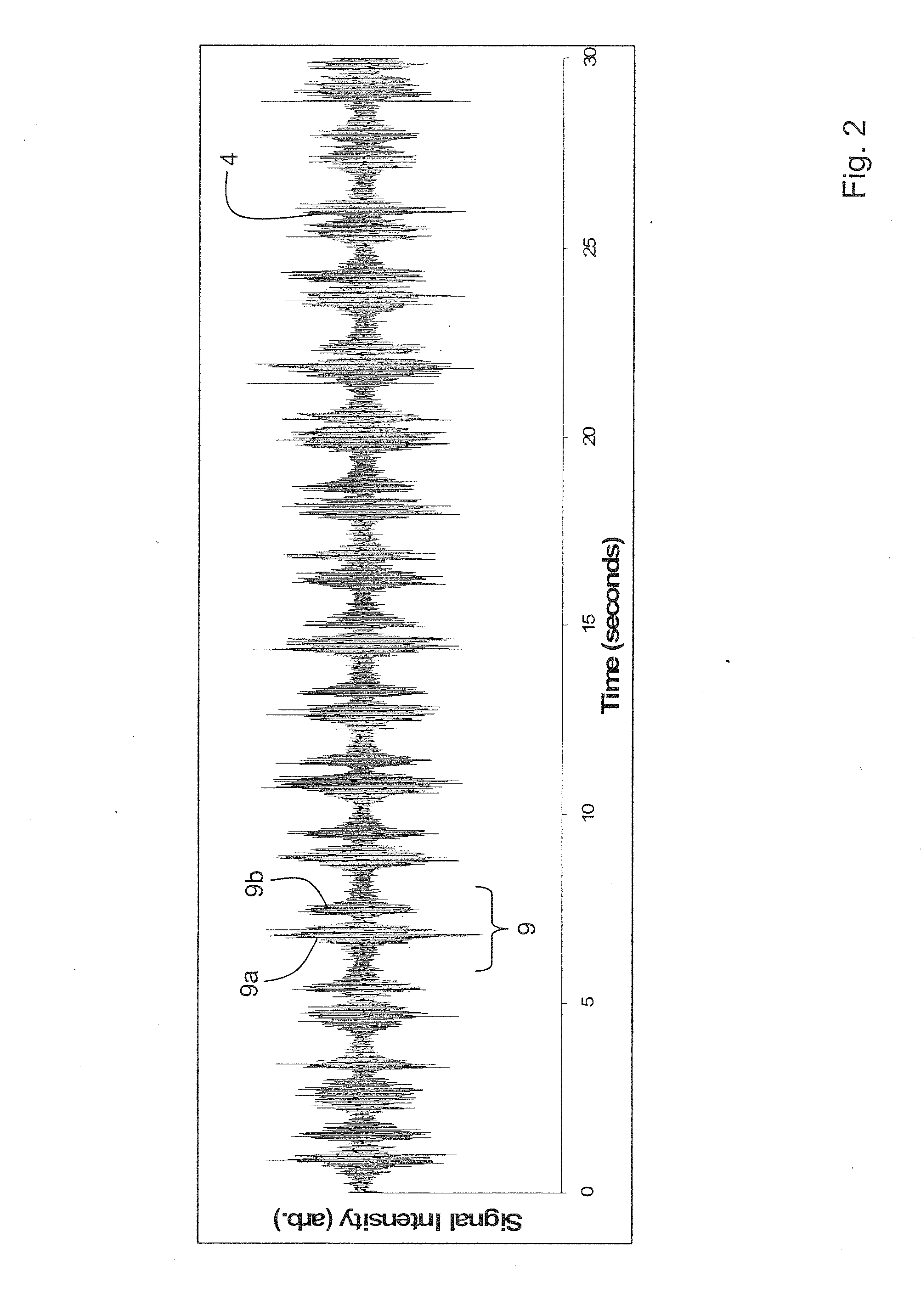
Device for determining respiratory rate and other vital signs
A body-worn sensor that measures respiratory rate and other vital signs using an acoustic sensor (e.g., a small-scale sensor). The body-worn sensor features a chest-worn patch sensor that combines both the acoustic sensor and an ECG electrode into a single adhesive patch. To measure blood pressure, the device additionally performs a ‘composite’ PTT-based measurement that features both pressure-dependent and pressure-free measurements. The acoustic sensor measures respiration rate by recording sounds related to the patient's inspiration and expiration. The acoustic sensor is typically placed near the patient's trachea, but can also be placed on the middle right and left side of the chest, and the middle right and left side of the back.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Method for treating a cardiovascular condition
A pair of vascular interventional devices, at least one of which includes a hollow, flexible tube and a dilator that is adapted for insertion into and through the tube and over a guidewire, may be utilized to treat or study a cardiovascular condition, or to measure the blood pressure across a vascular segment. The first device also includes a hub with an end port through which a second device may be introduced into and through the tube. The hub also includes a side port through which a fluid agent may be injected for delivery through the tube or through which pressures can be measured. A guidewire is inserted into a vessel of the cardiovascular system of a patient in the conventional manner. The dilator of the first device is then inserted into the tube and the dilator and tube are then inserted into the vessel over the guidewire and positioned in the target area. The dilator is then withdrawn through the tube from the cardiovascular system of the patient. A second interventional device is selected to treat or study the cardiovascular condition, and the second device is introduced through the end port of the hub of the first device. The second interventional device is advanced over the guidewire to the distal end of the tube of the first device, and the guidewire is then removed. The second interventional device is employed to treat or study the cardiovascular condition. If a pressure transducer is placed on the side port of the first device, as well as on the second device, the second device may be advanced beyond the end of the first device so that the blood pressure may be measured simultaneously at the end of the tube of the first interventional device (the first location) and at the end of the second interventional device (the second location). The difference in blood pressure, if any, between the first and second locations may then be calculated.
Owner:STRATIENKO ALEXANDER A
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
InactiveUS20060122525A1Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for non-contact registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
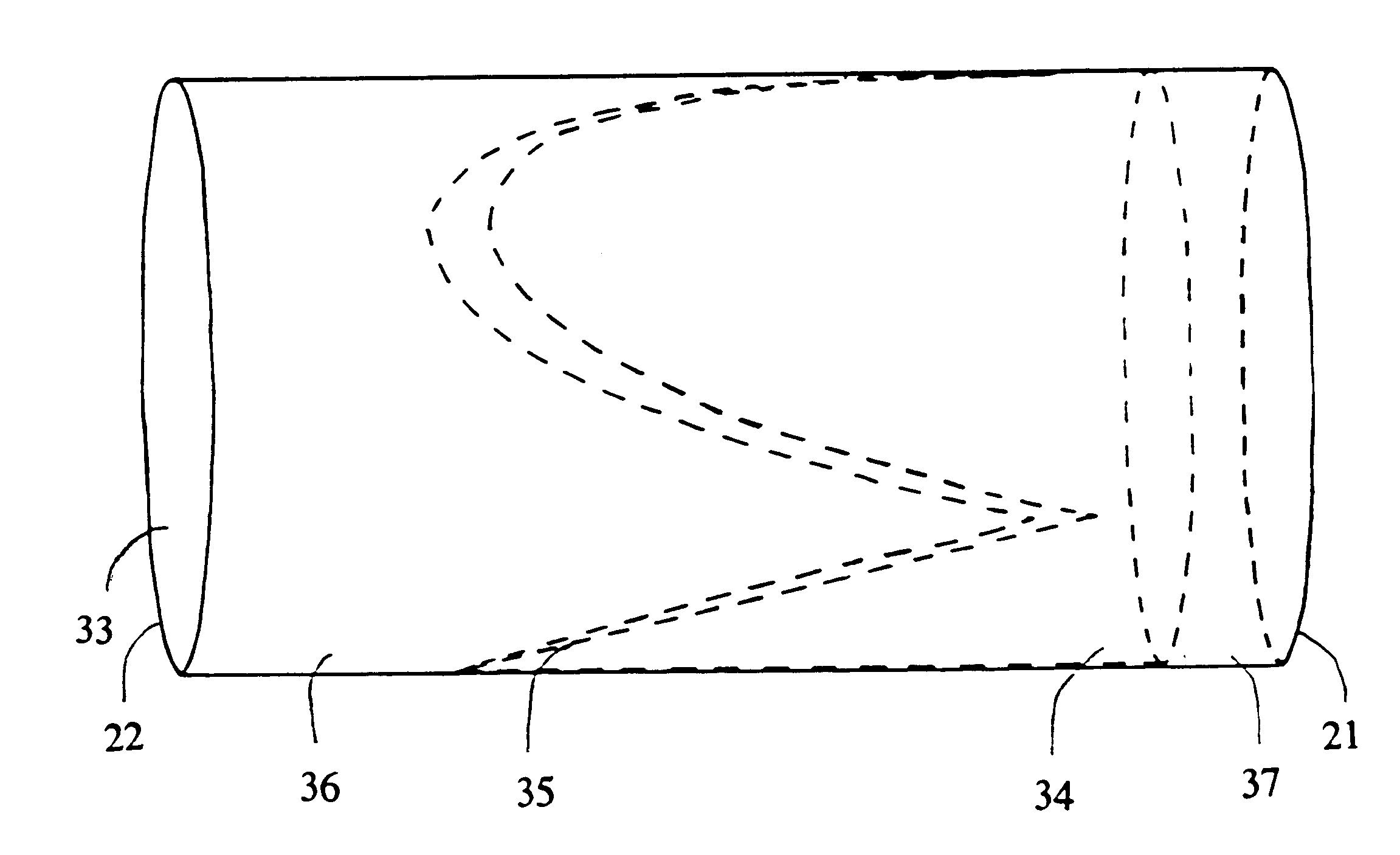
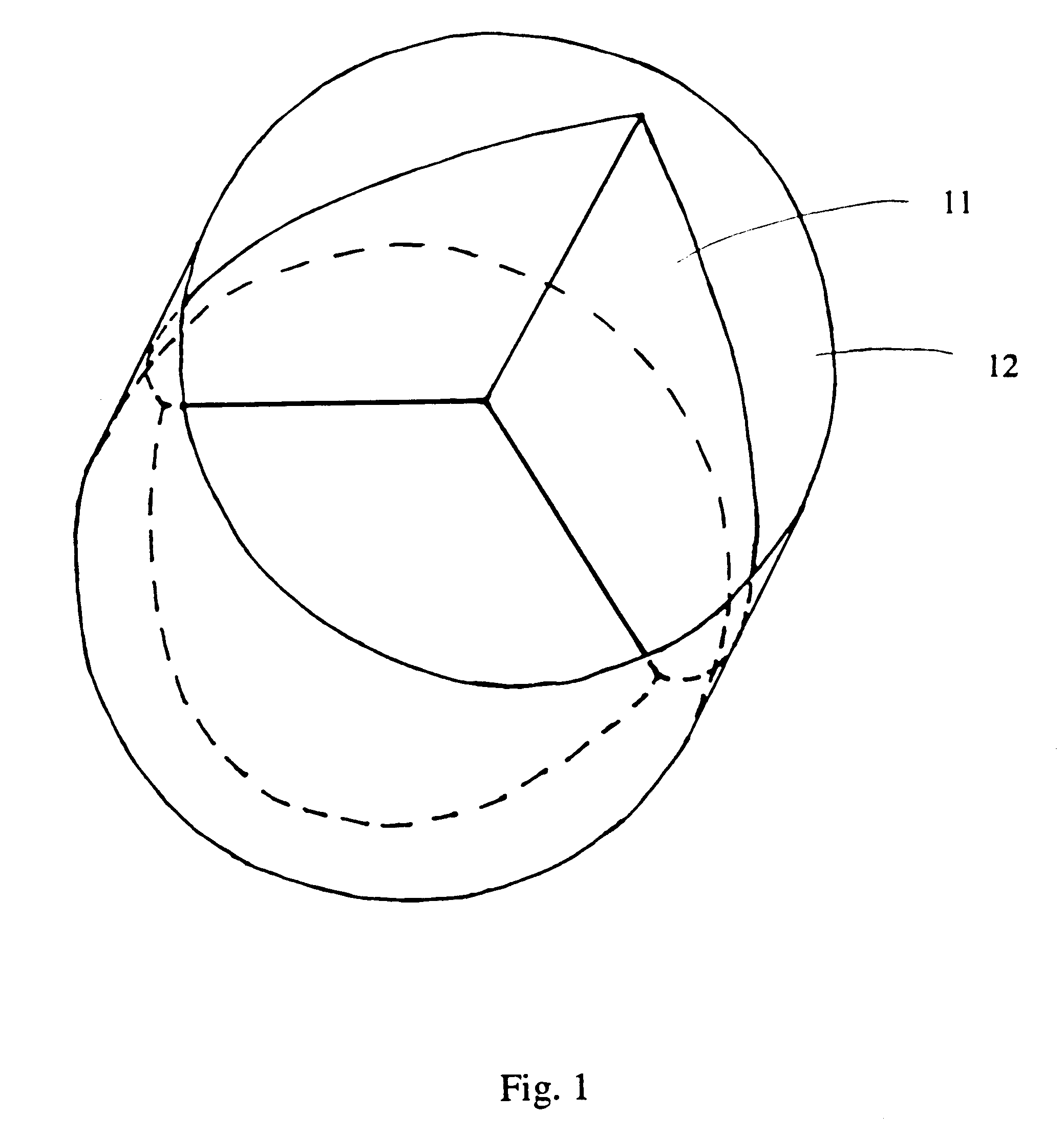
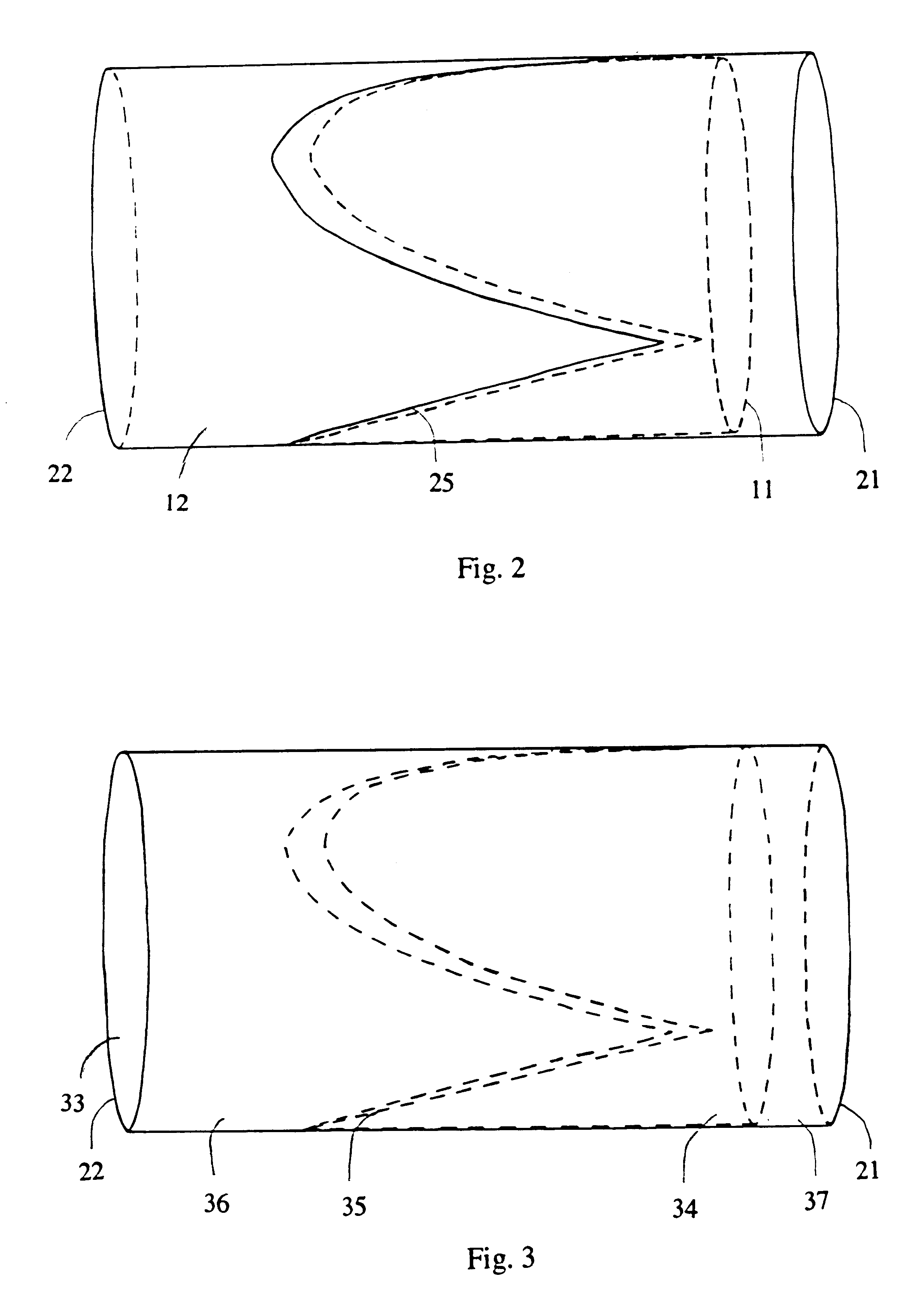
Venous valve and graft combination
A synthetic venous valve and graft combination that exerts no radial force at the valve site is disclosed. The trilobed valve (11) is passively actuated by venous blood pressure changes. When open, the aperture for blood flow is approximately that of the original vein. The prosthesis is useful for replacing nonfunctioning venous valves in the human vasculature.
Owner:WILDER JOHN G +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com