Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1276 results about "Angular orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
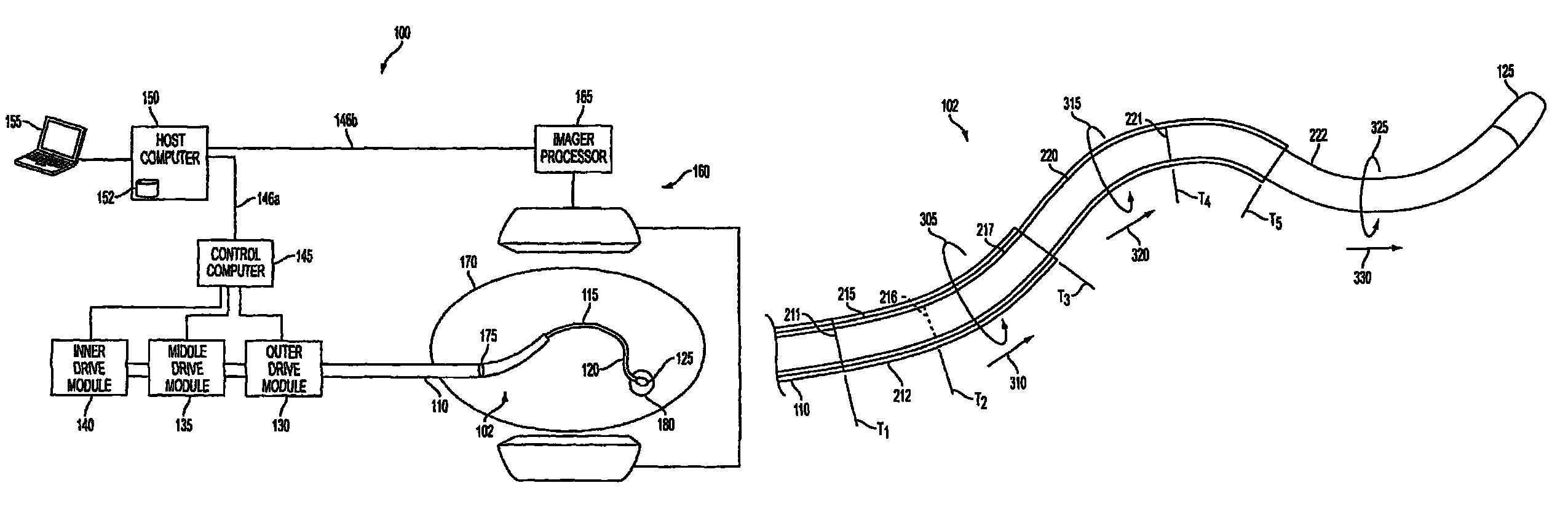
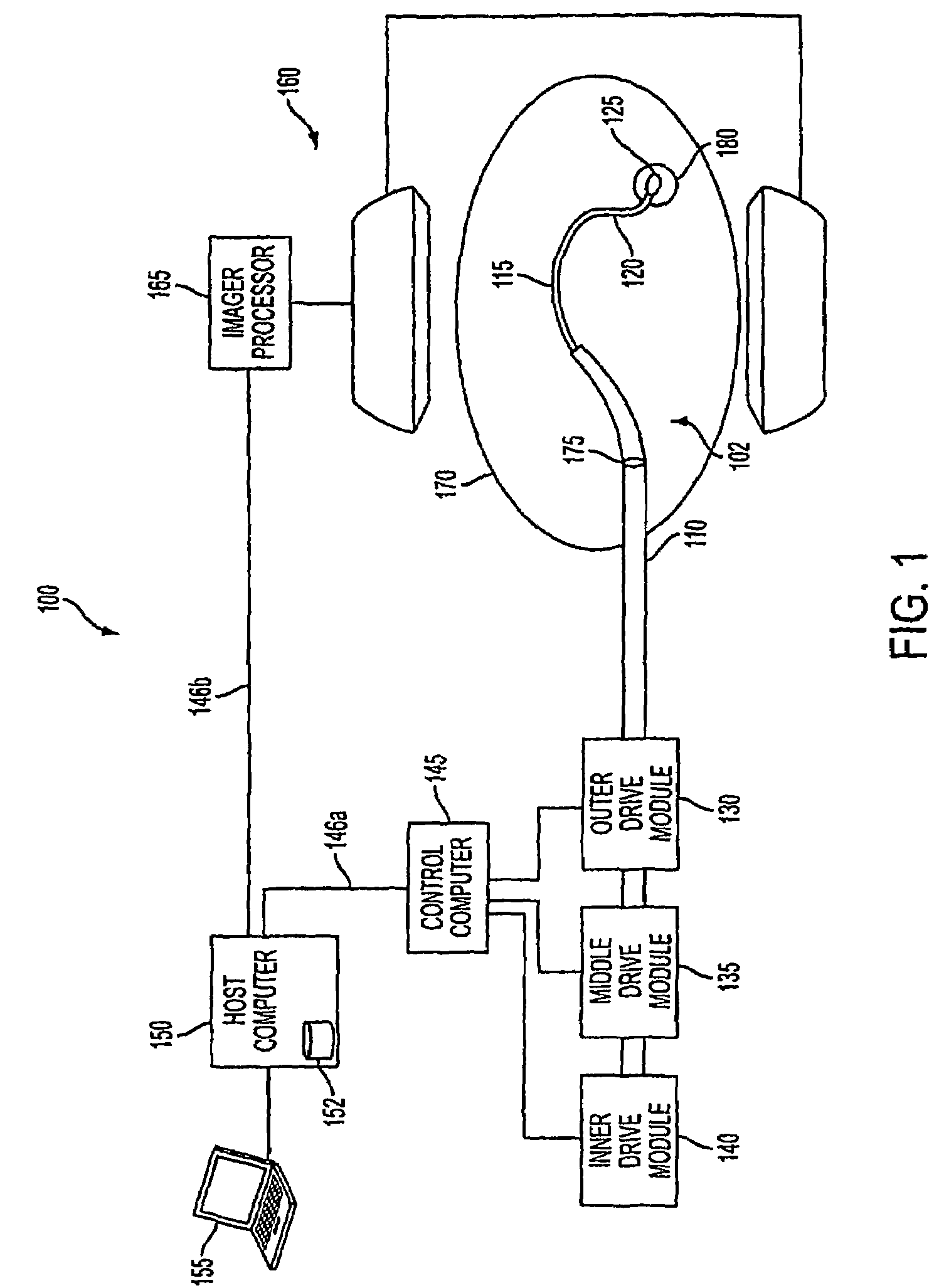
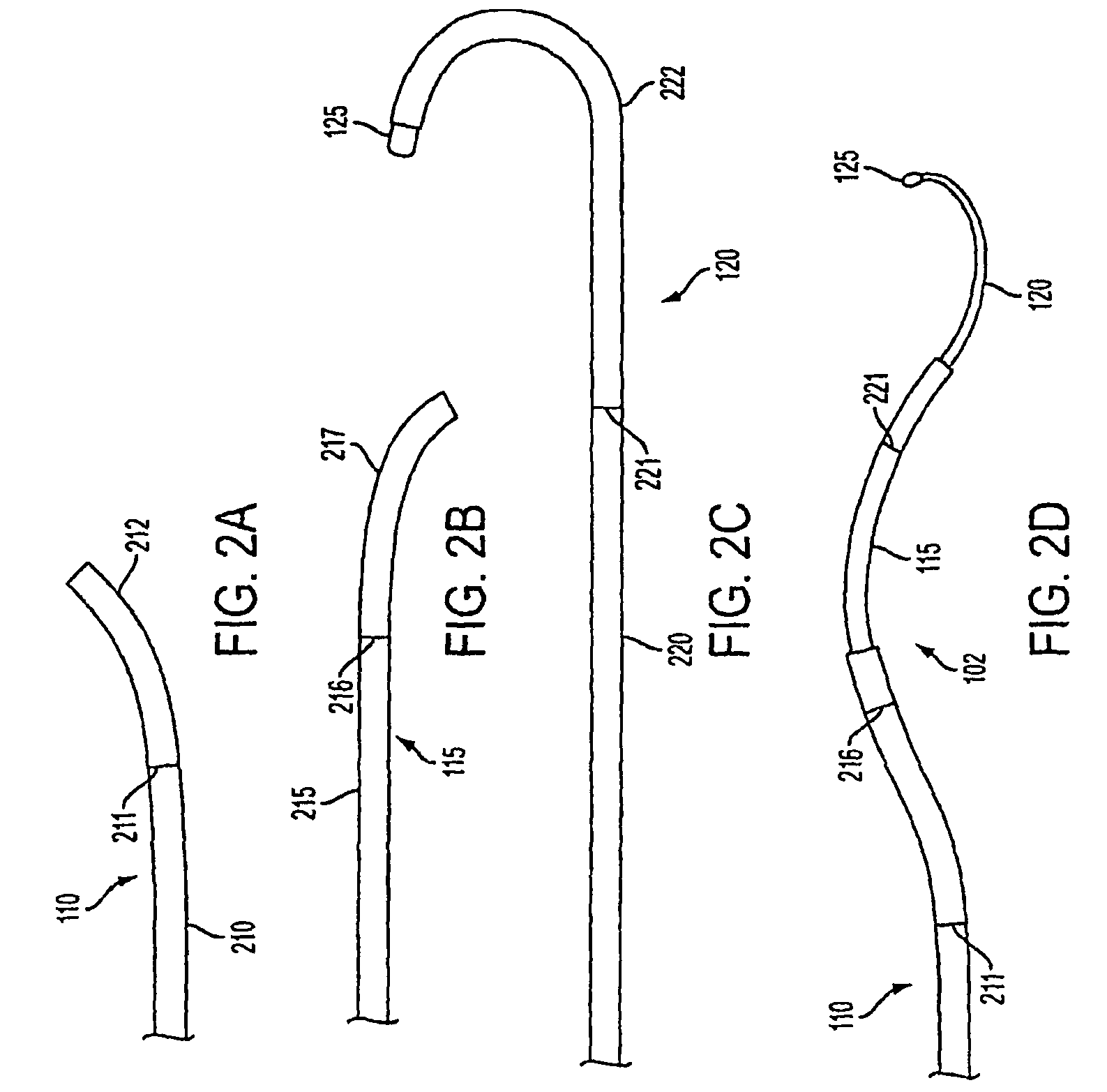
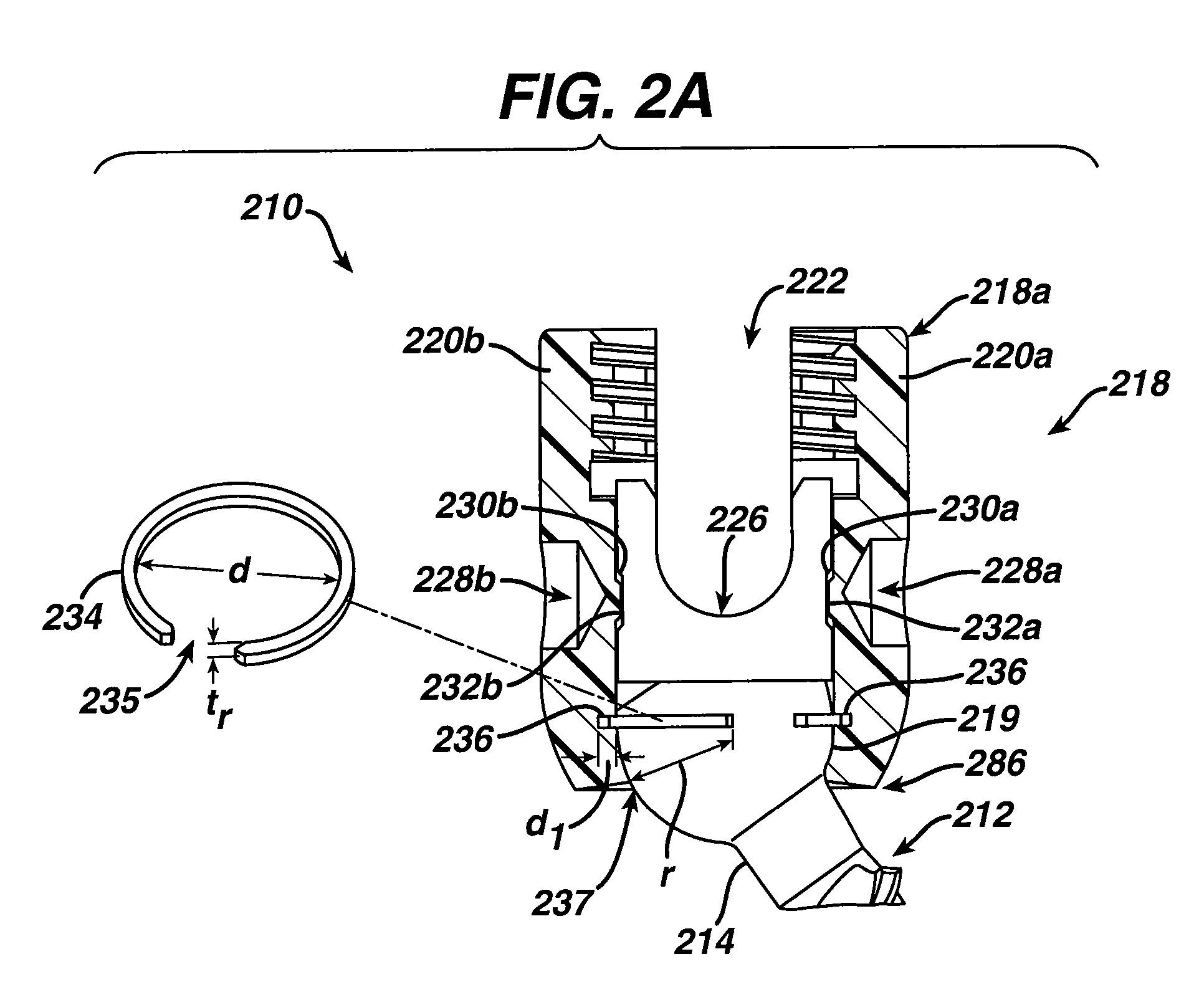
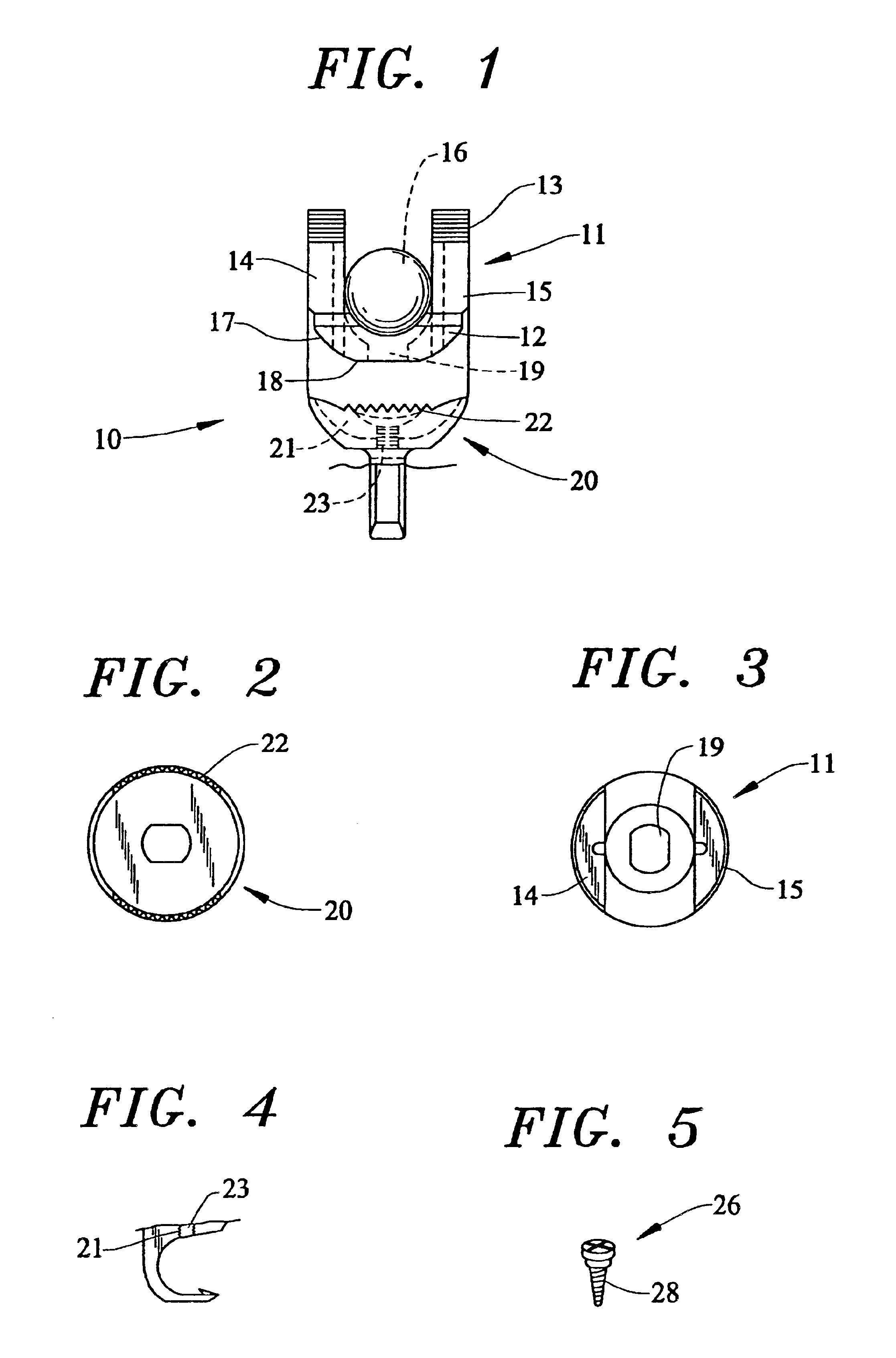
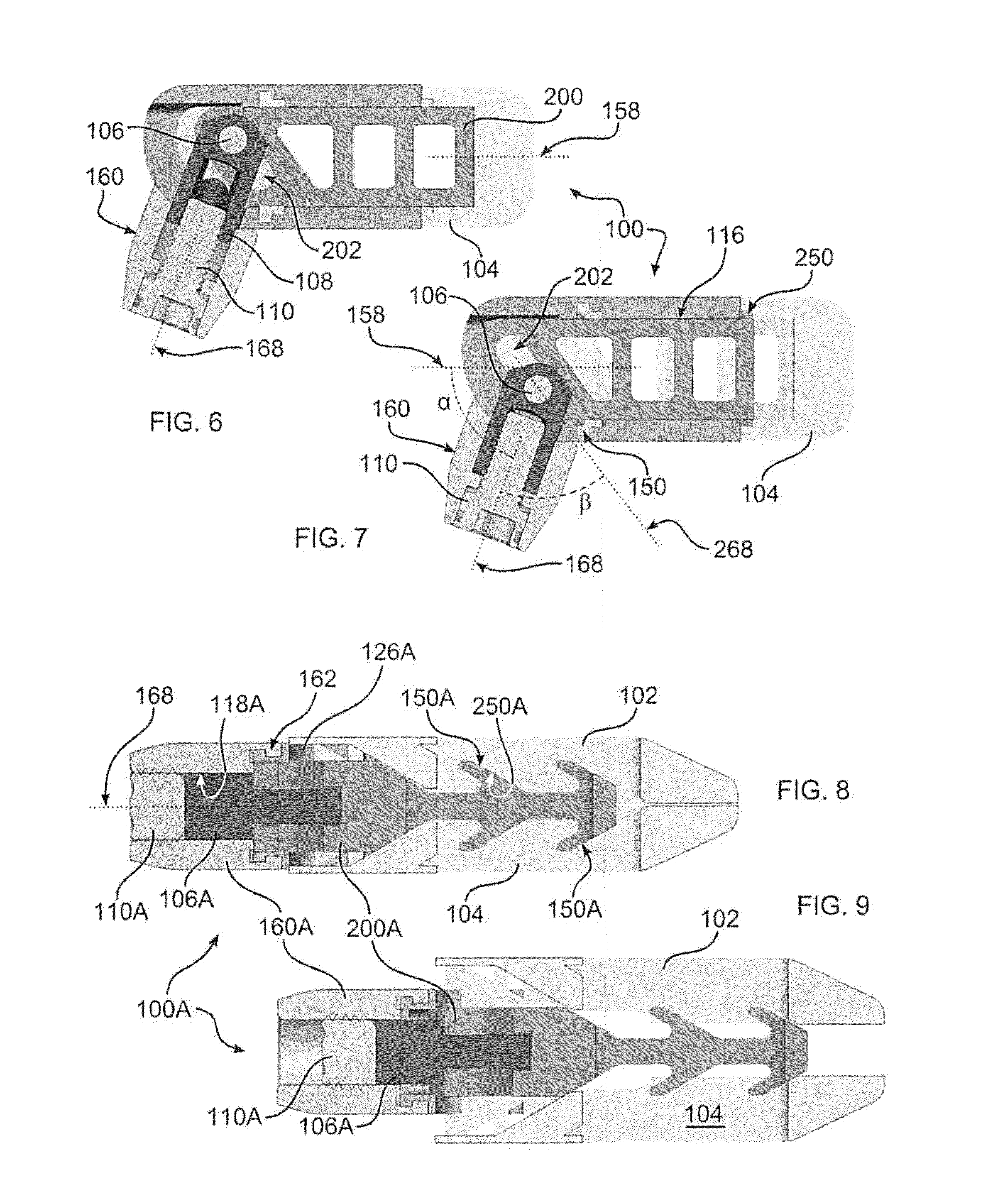
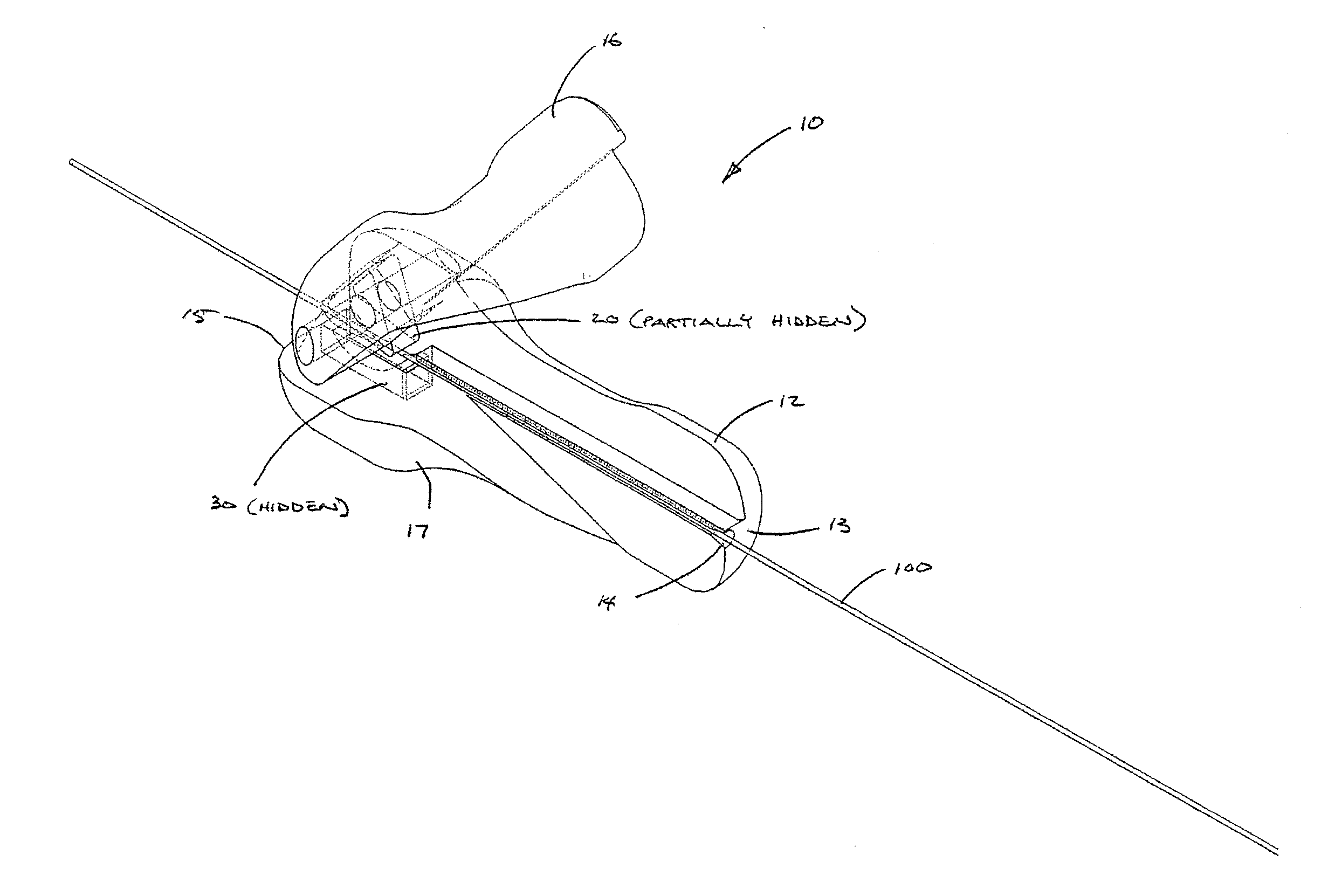
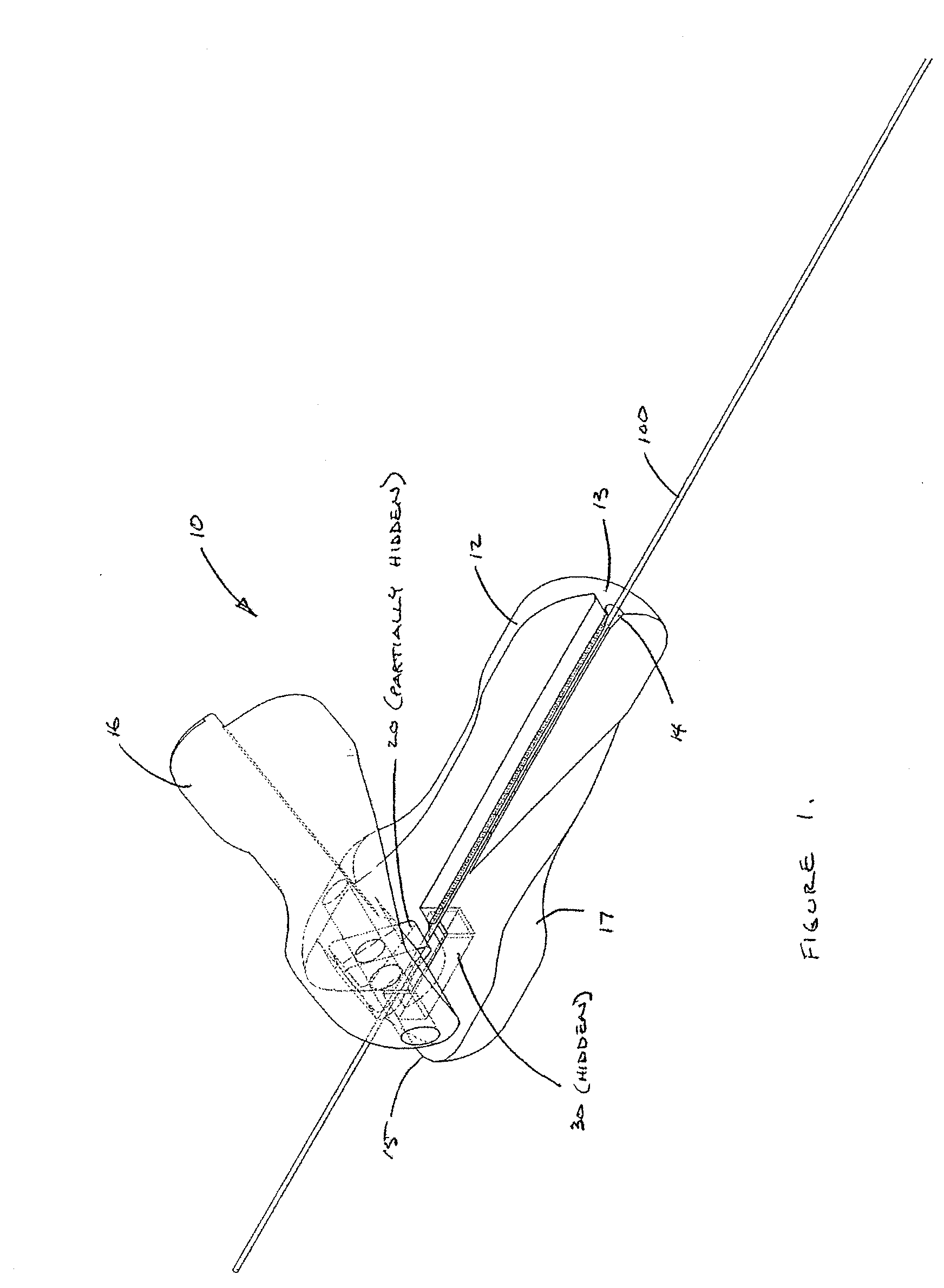
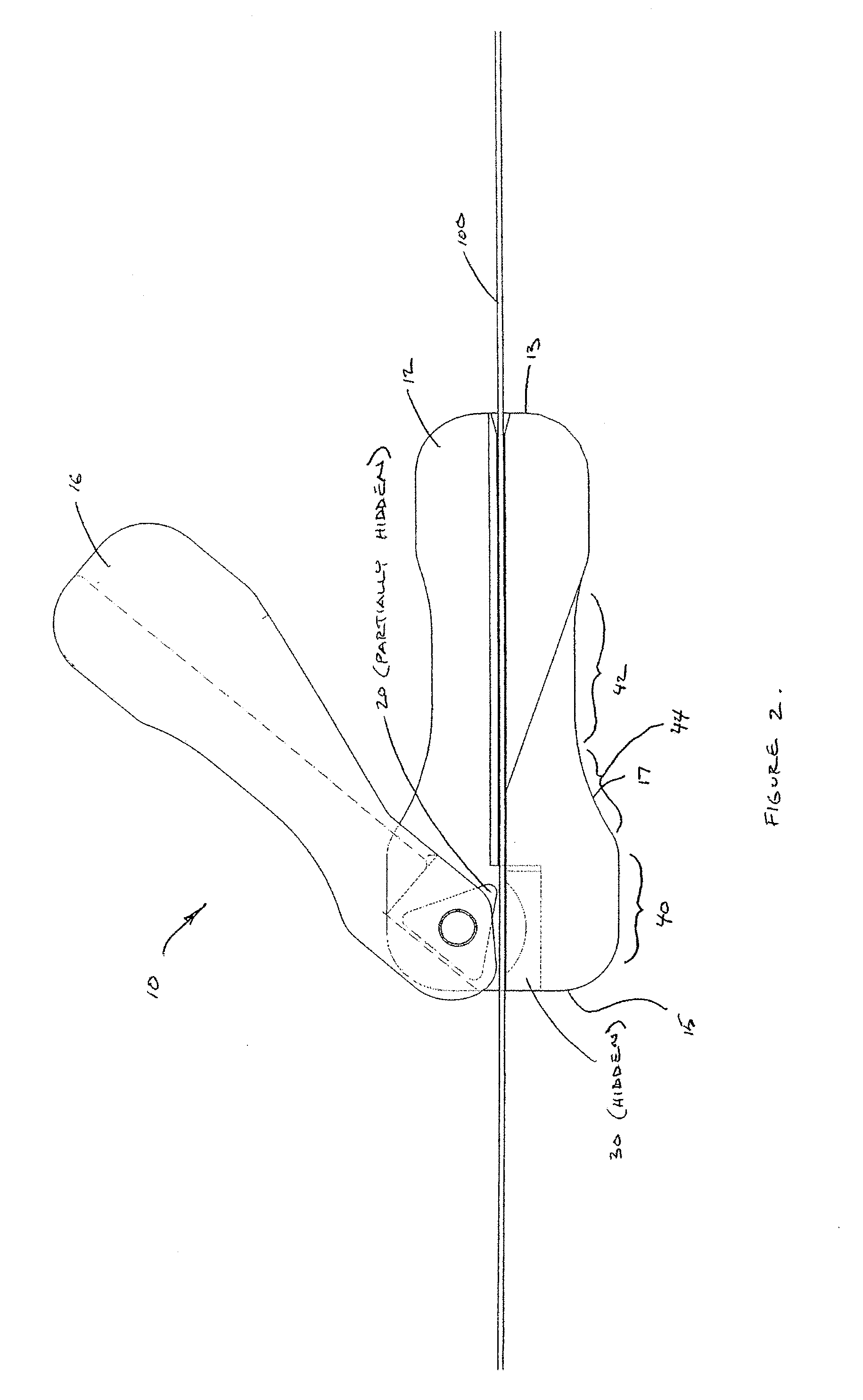
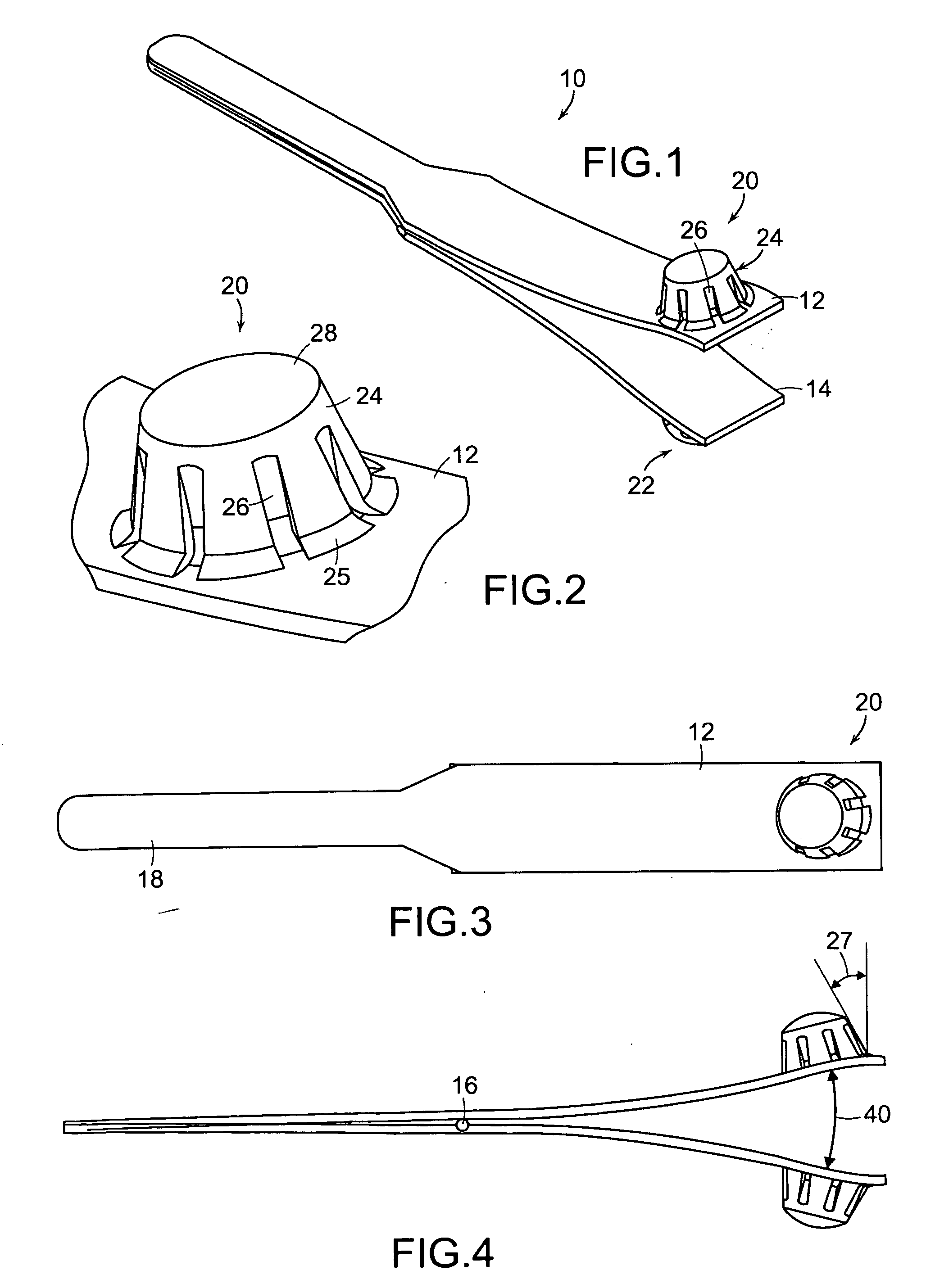
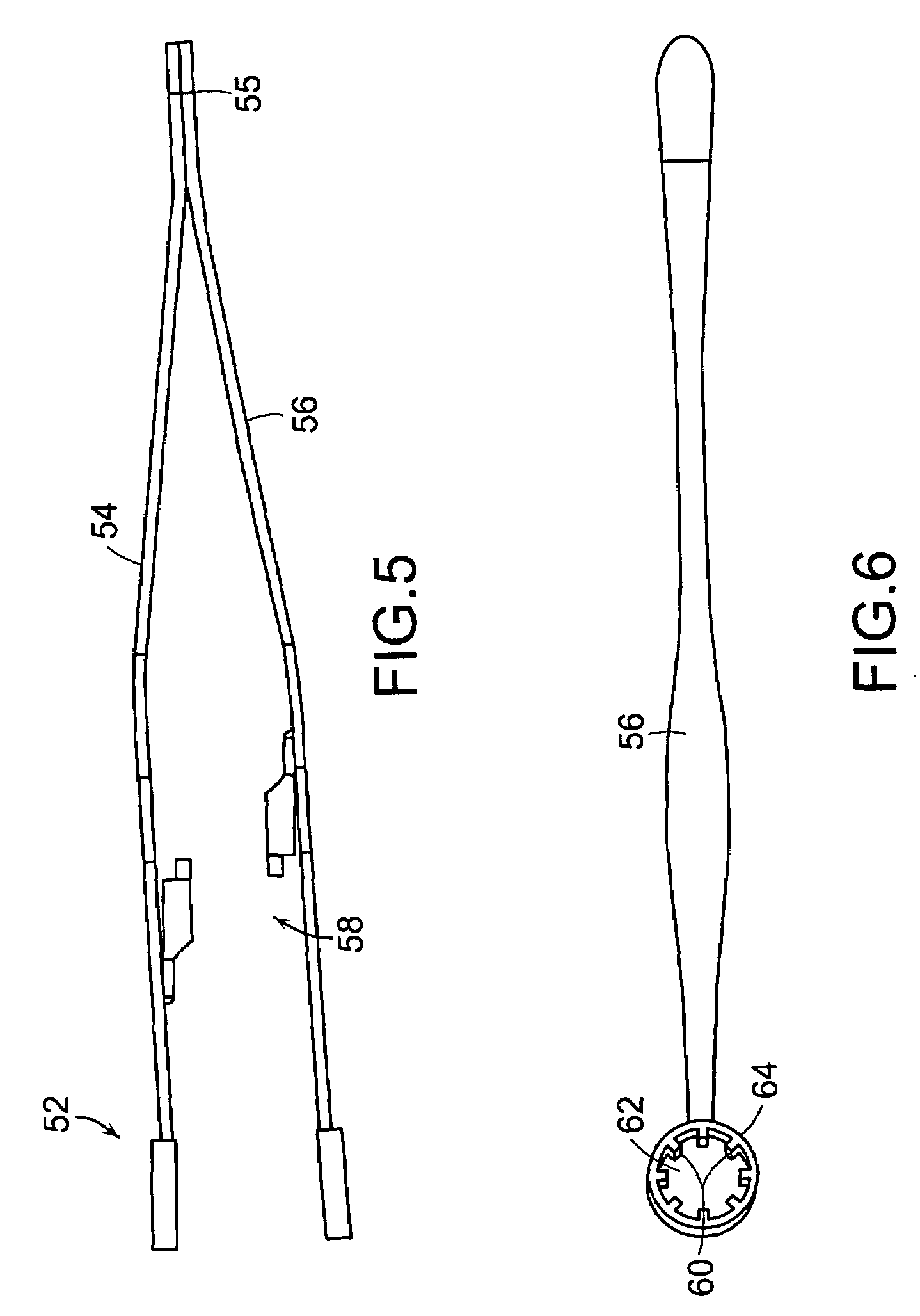
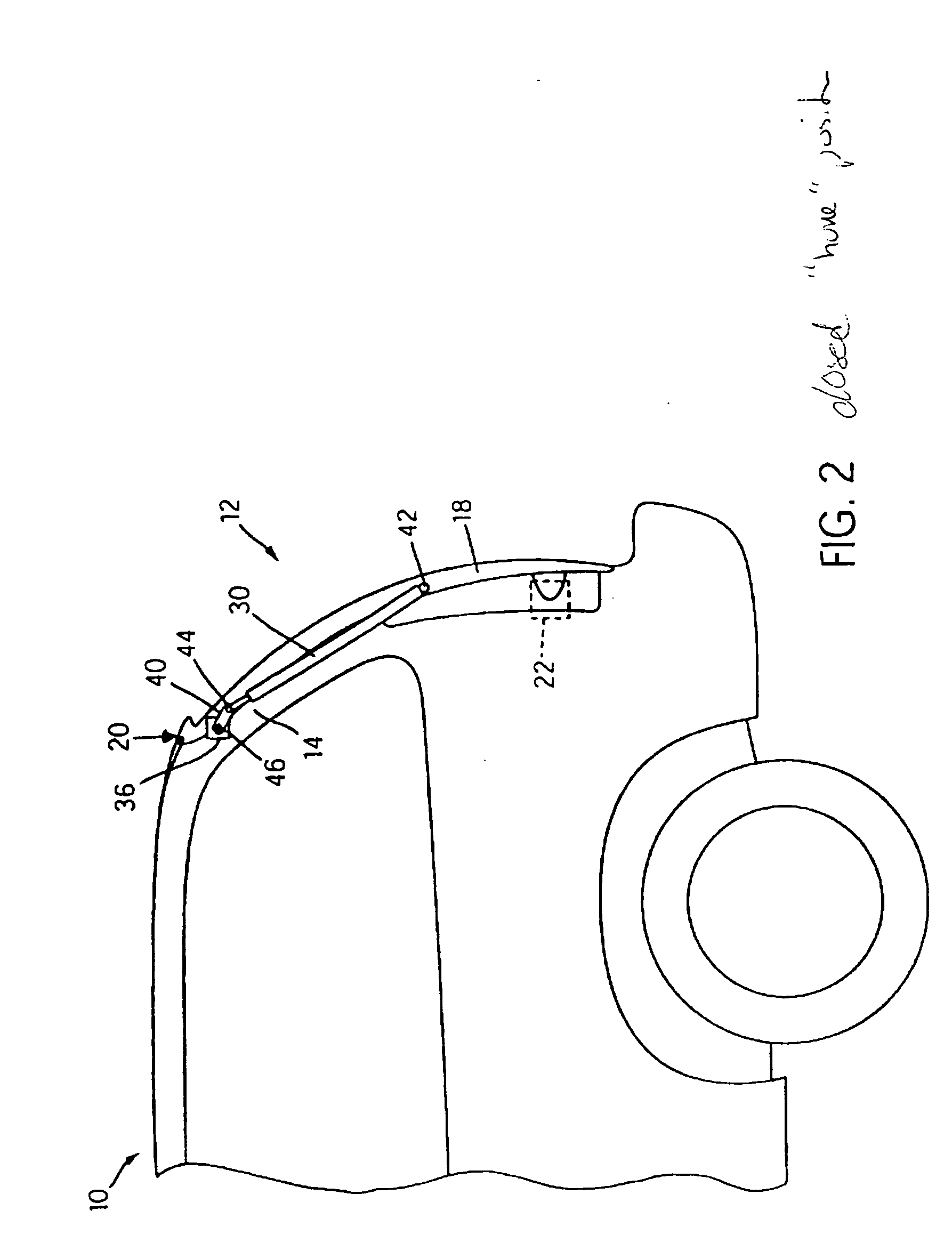
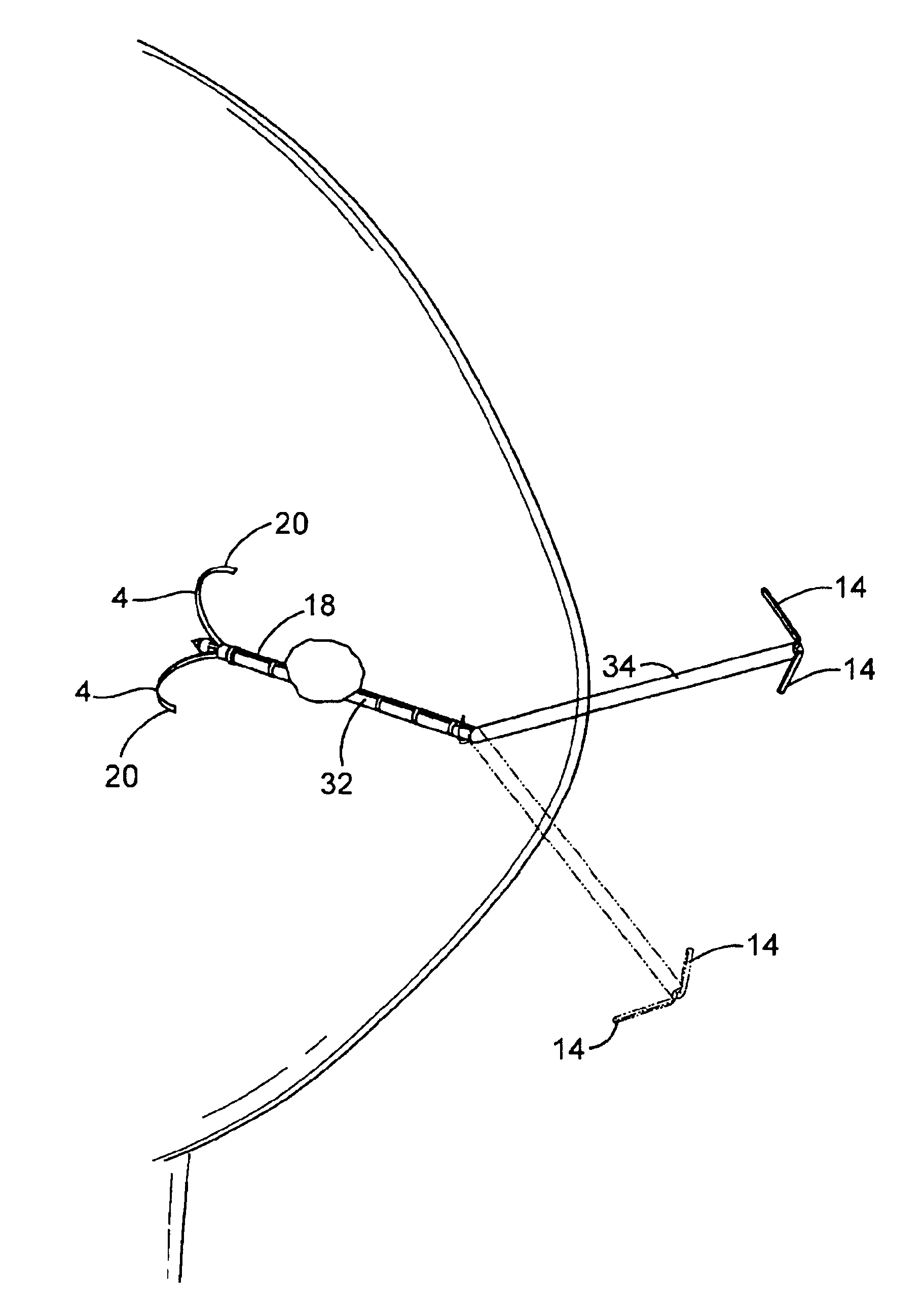
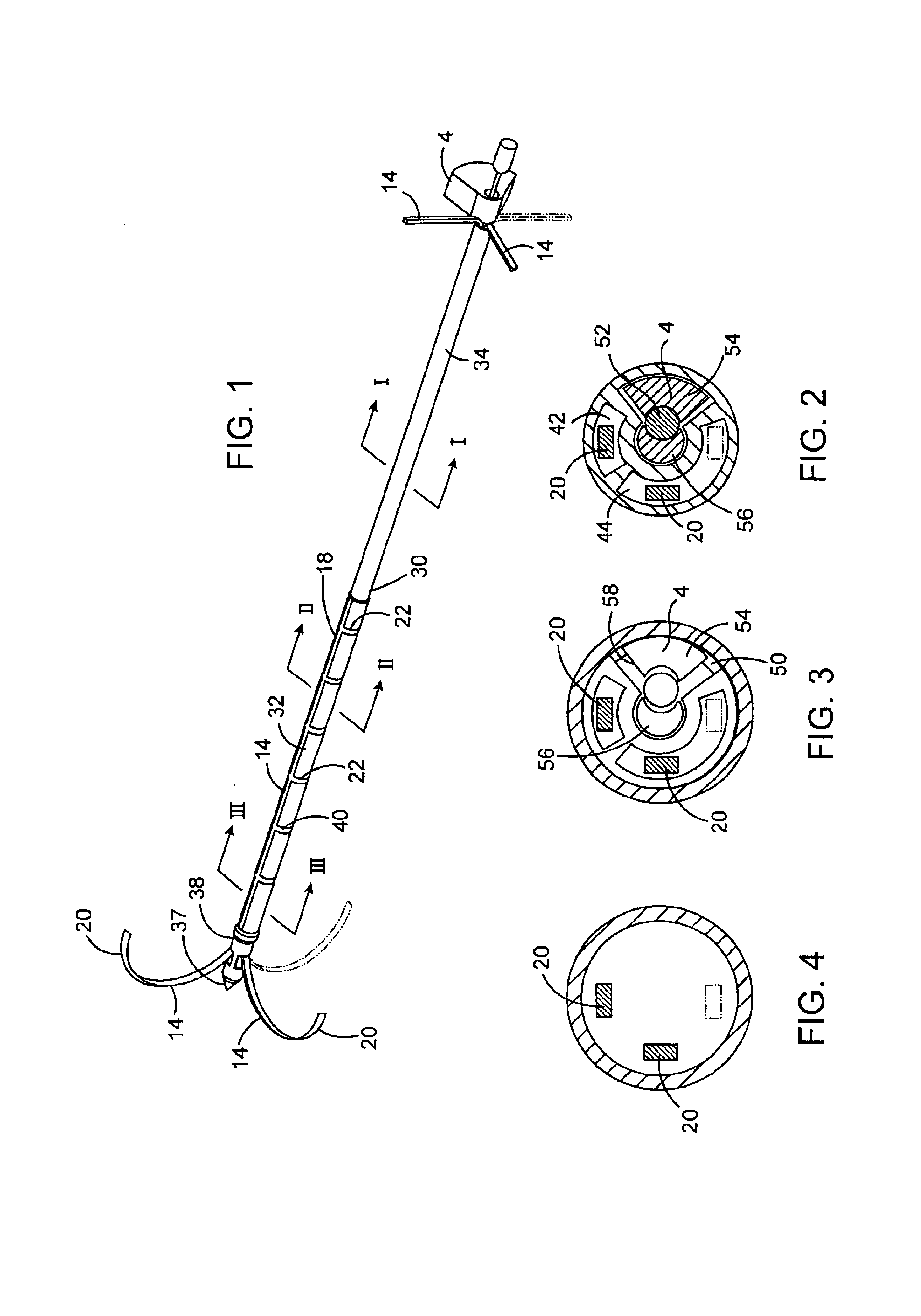
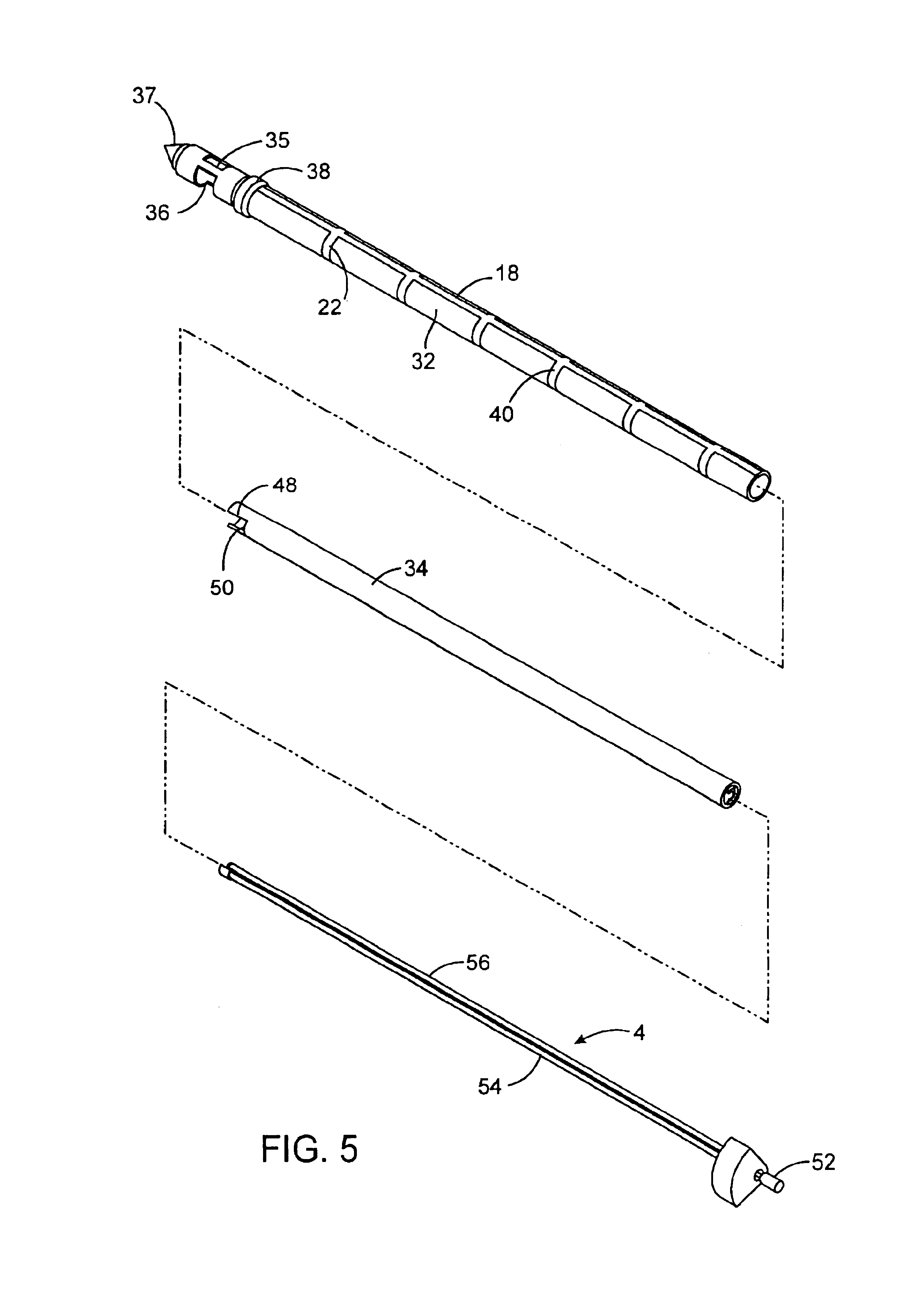
Active cannula for bio-sensing and surgical intervention
ActiveUS8152756B2Easy accessReduces the collateral trauma imposedCannulasSurgical needlesSurgical operationAnatomical structures
Disclosed is a surgical needle, or active cannula, that is capable of following a complex path through cavities and tissue within a patient's anatomy. The needle has a plurality of overlapping flexible tubes, each of which has a pre-formed curvature and a pre-determined flexibility. Each of the plurality of flexible tubes is selected based on their respective preformed curvature and flexibility so that a given overlap configuration causes the combination of overlapping flexible tubes to form a predetermined shape that substantially matches a desired path through the anatomy. By individually controlling the translation and angular orientation of each of the flexible tubes, the surgical needle may be guided through the anatomy according to the desired path.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
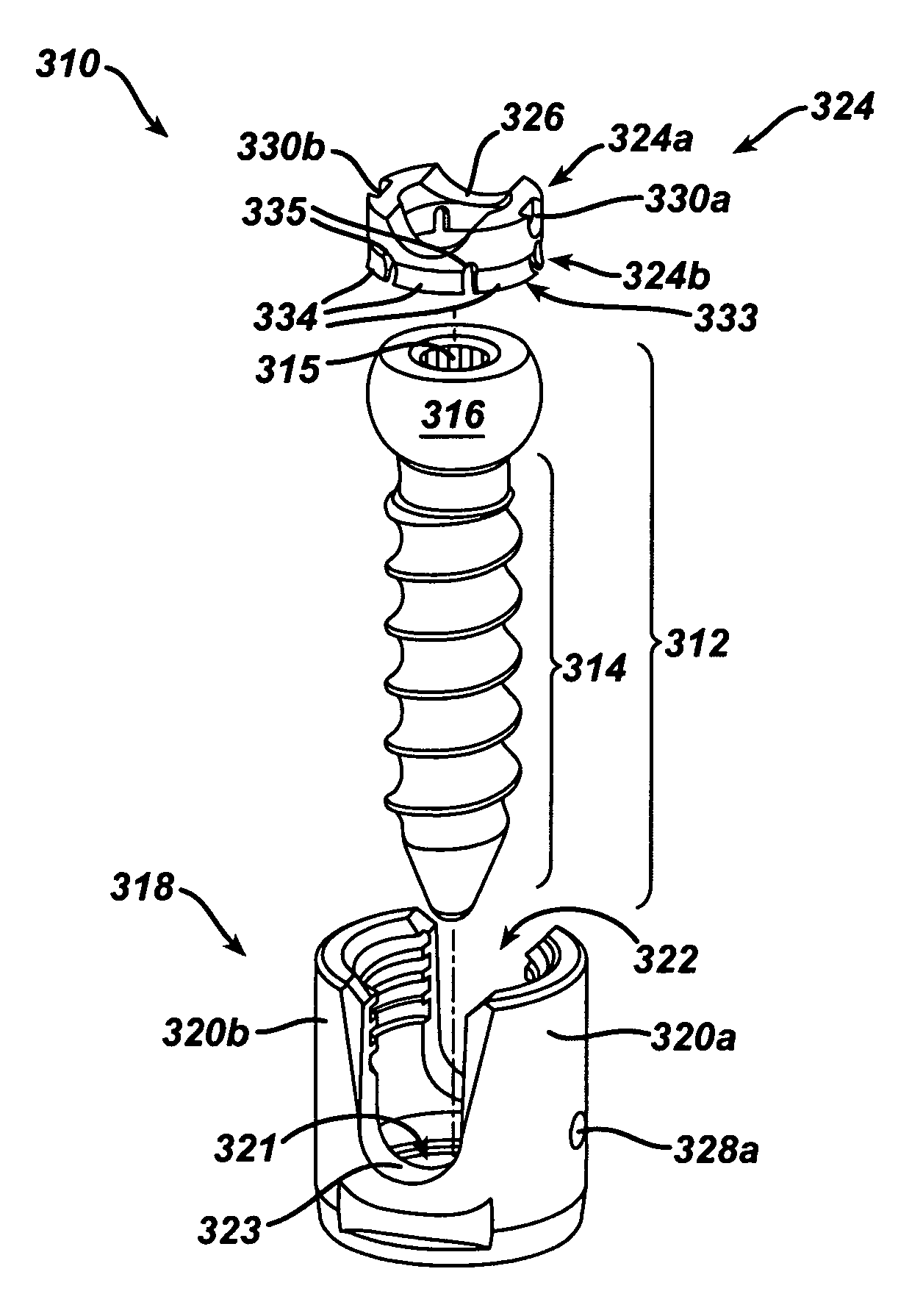
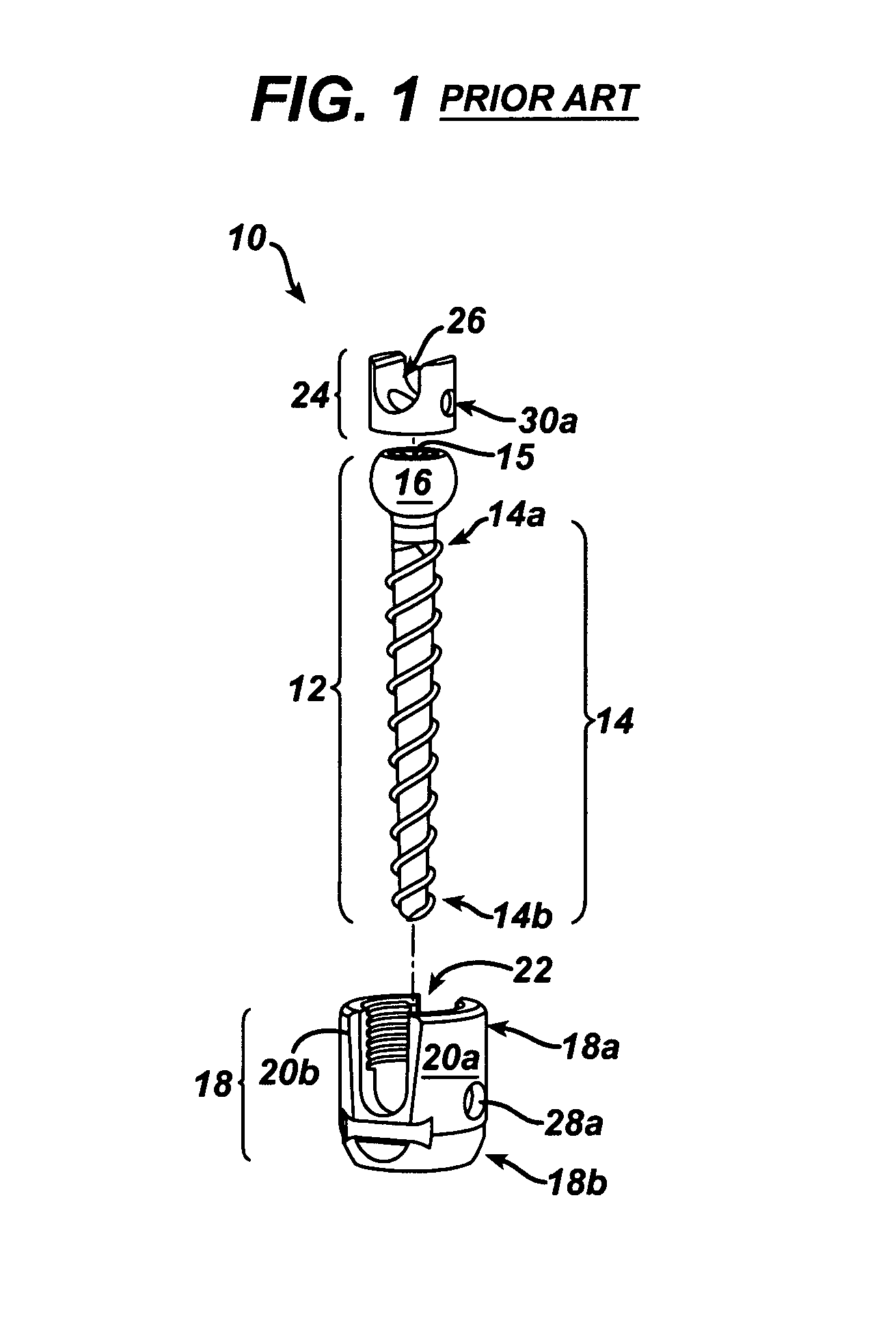
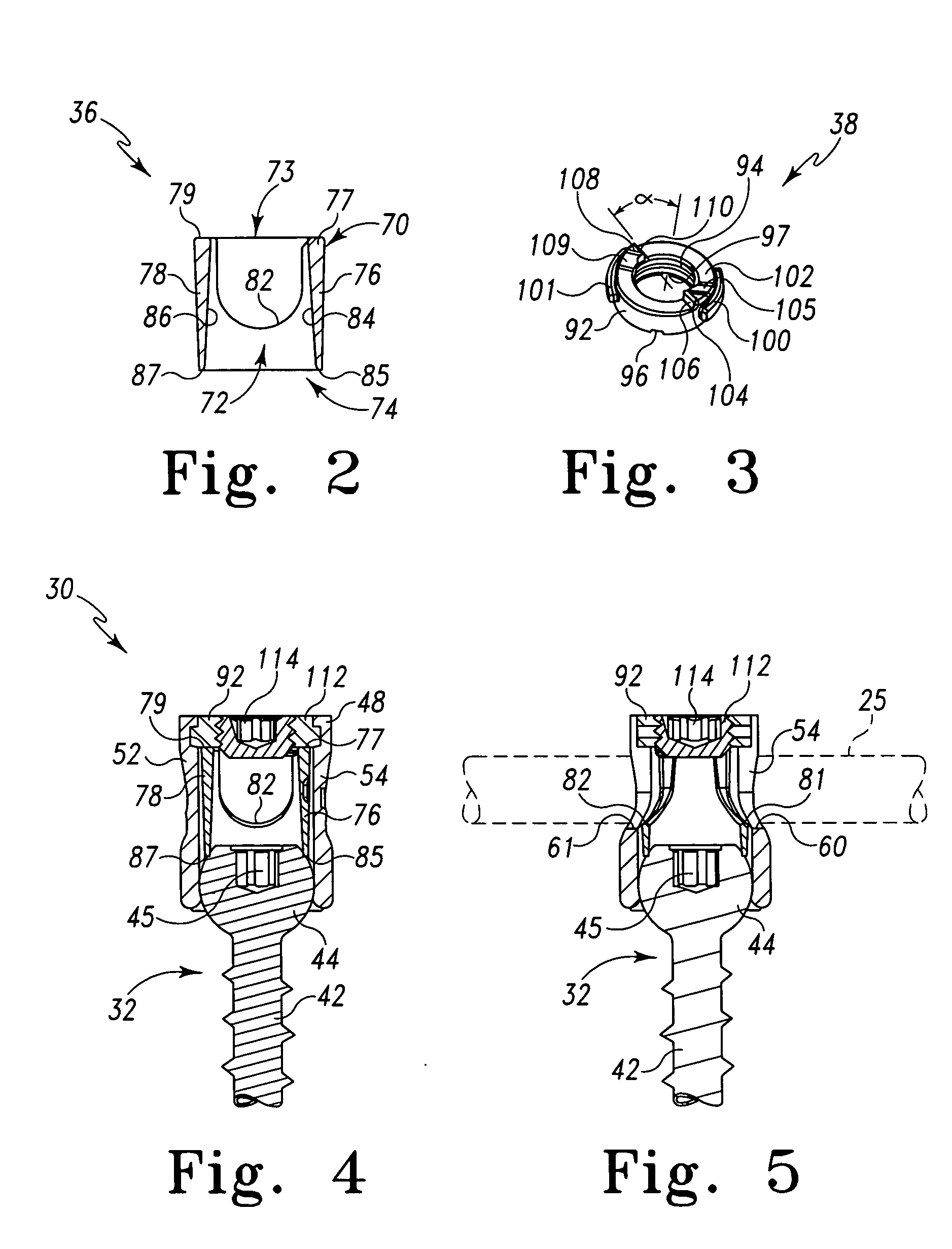
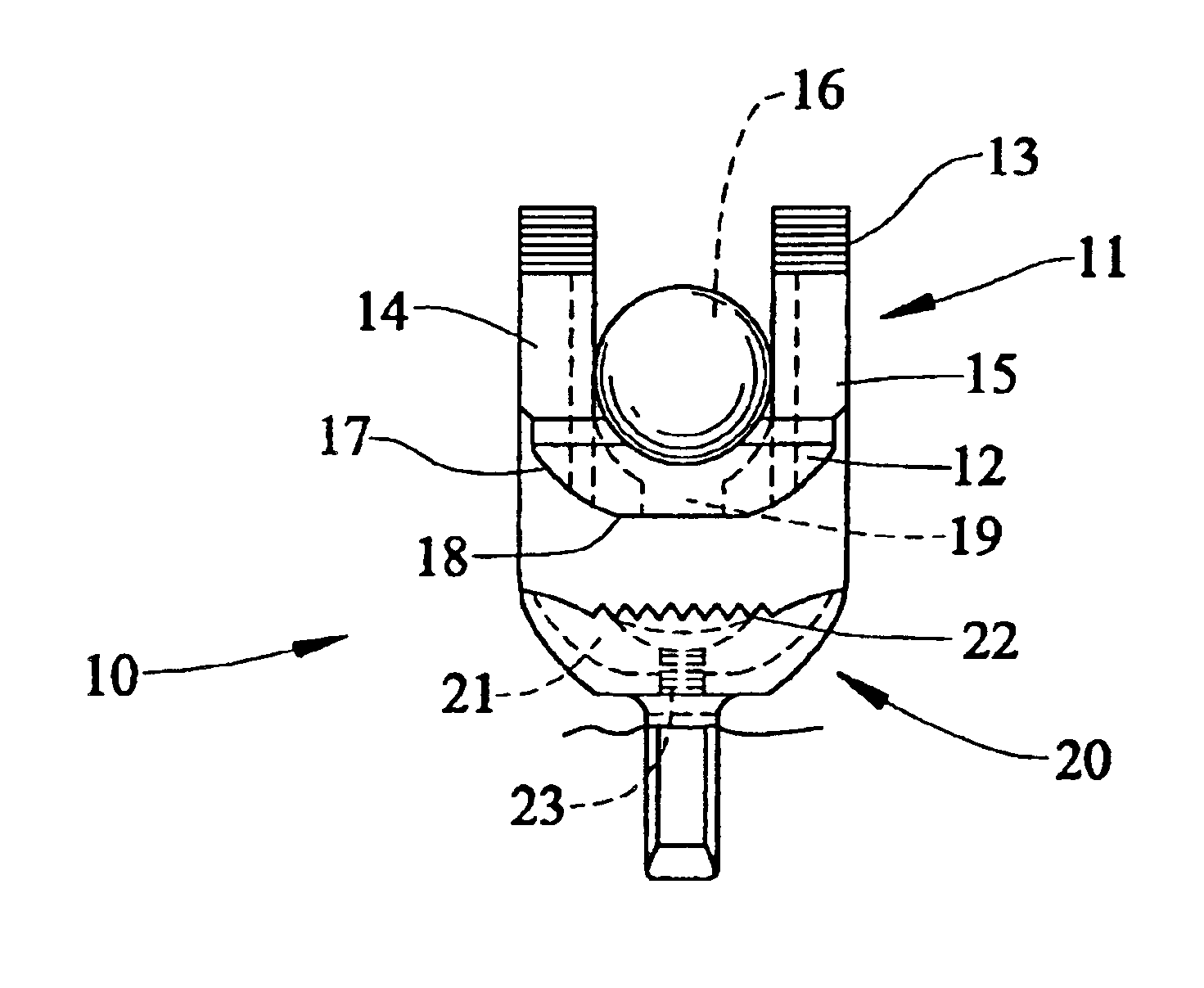
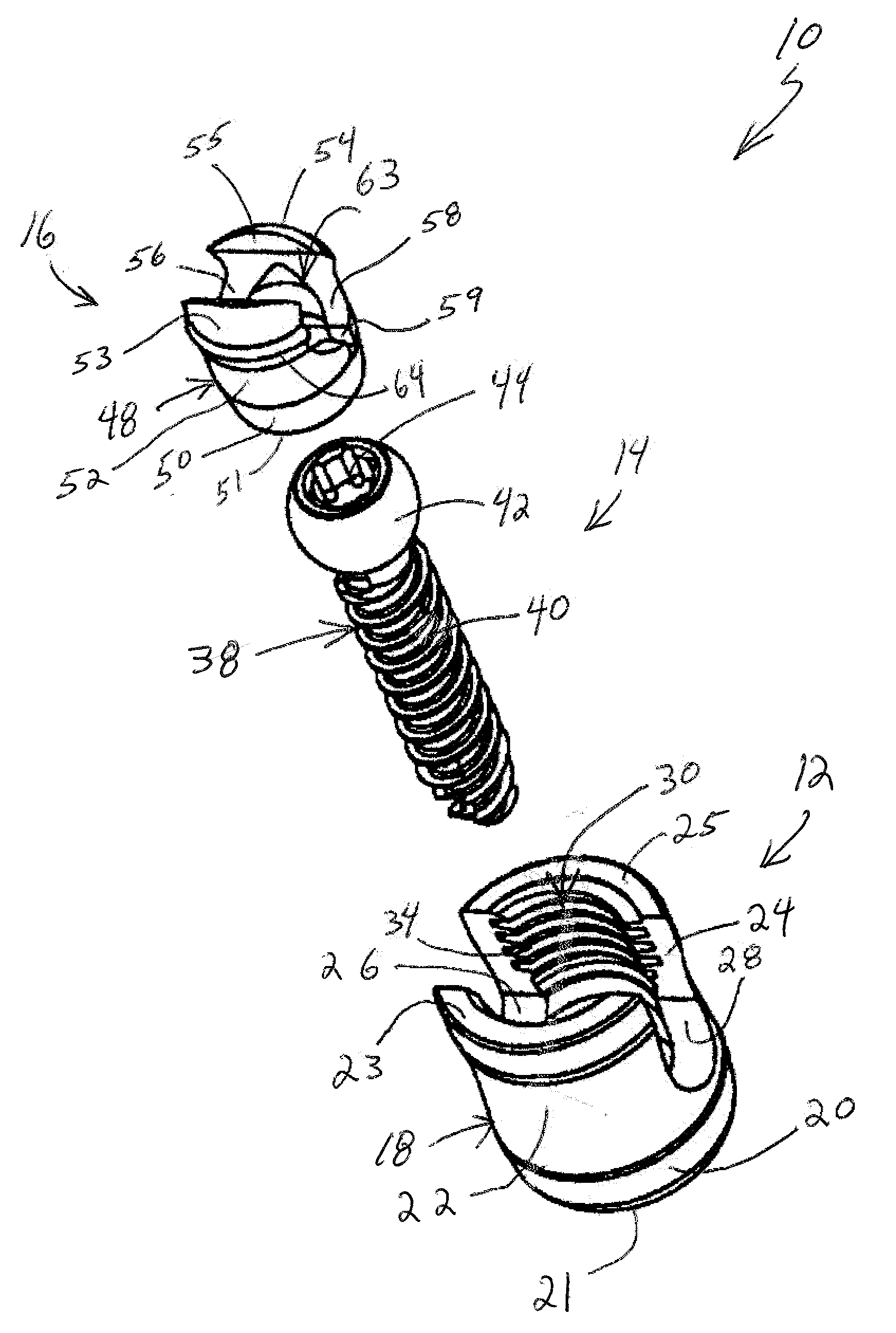
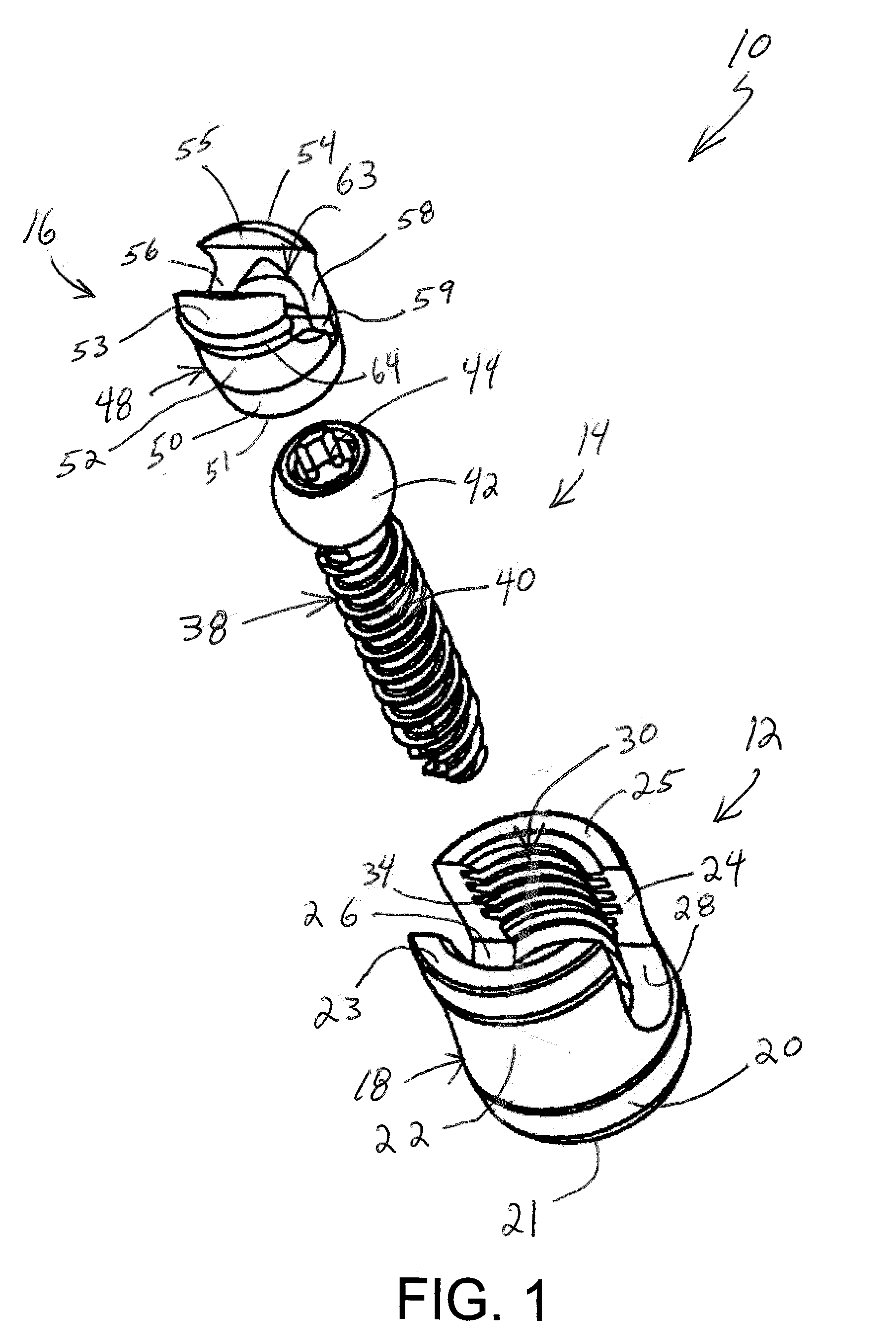
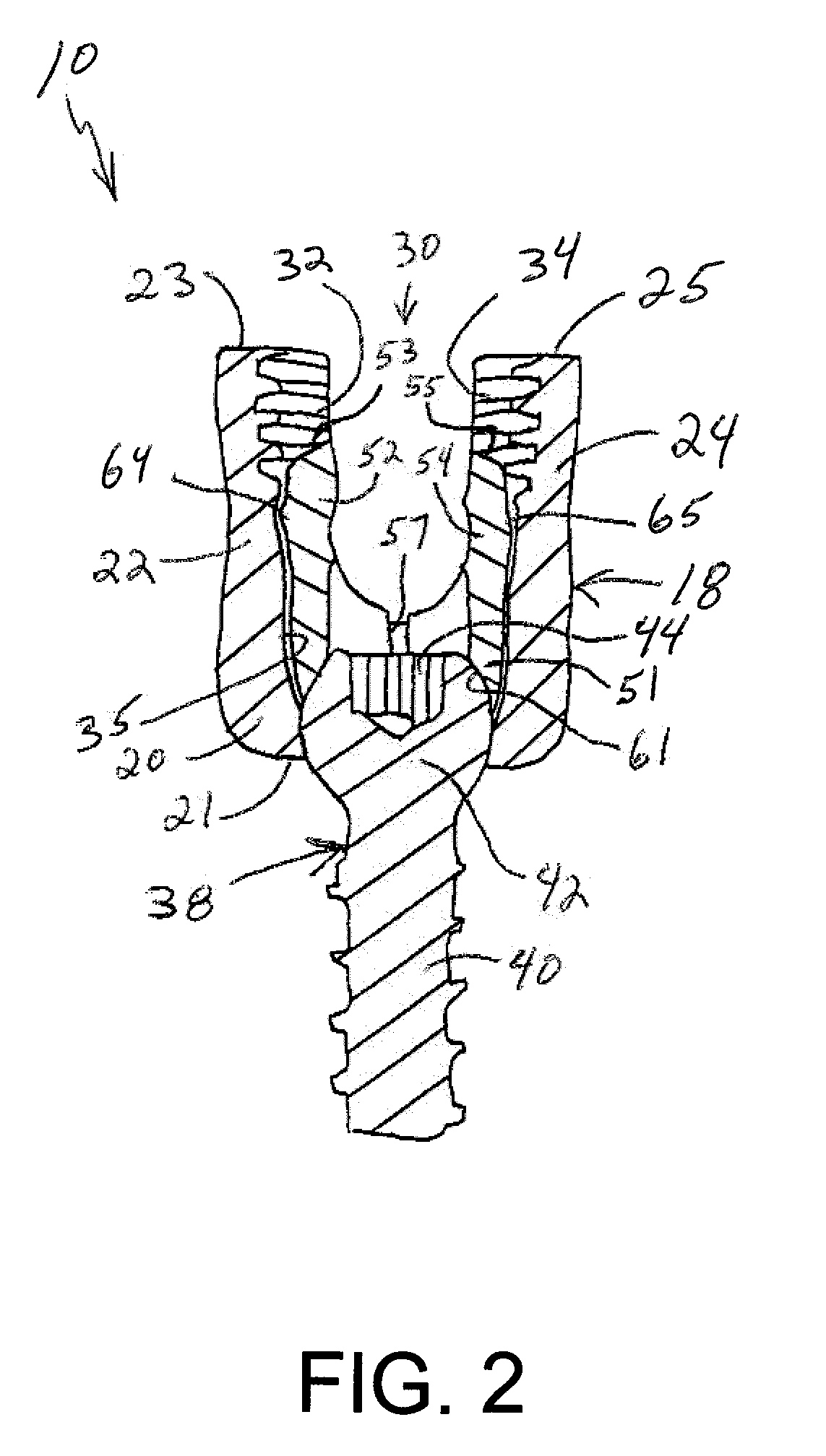
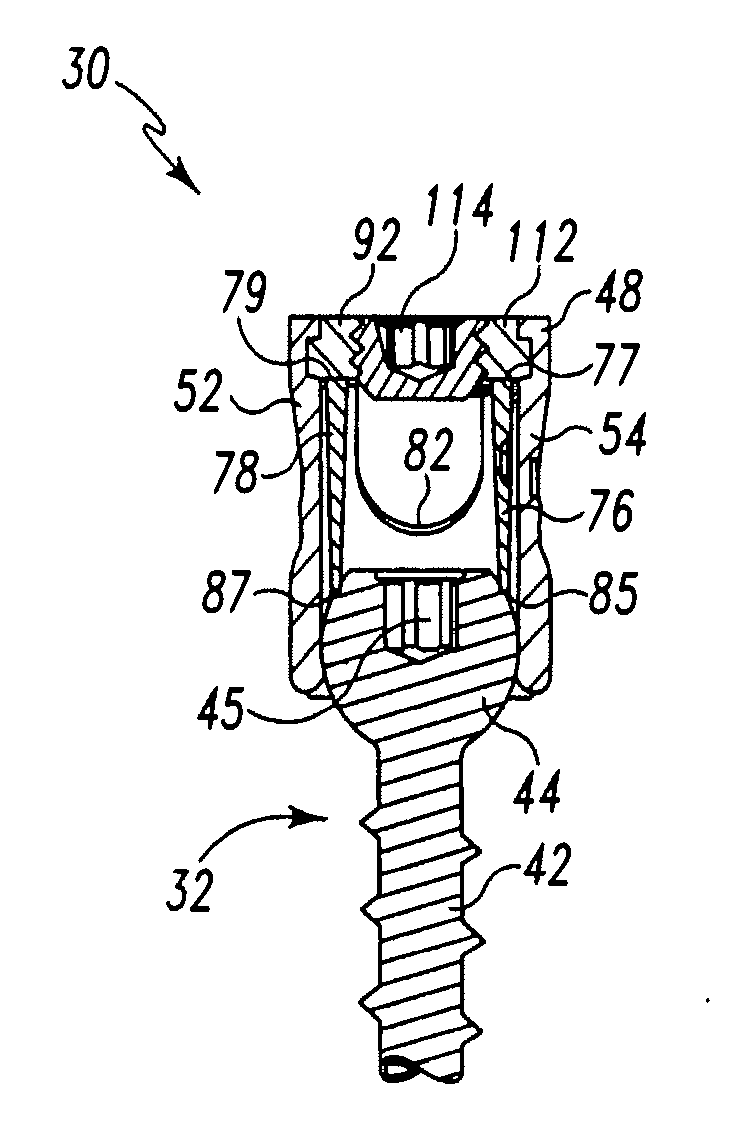
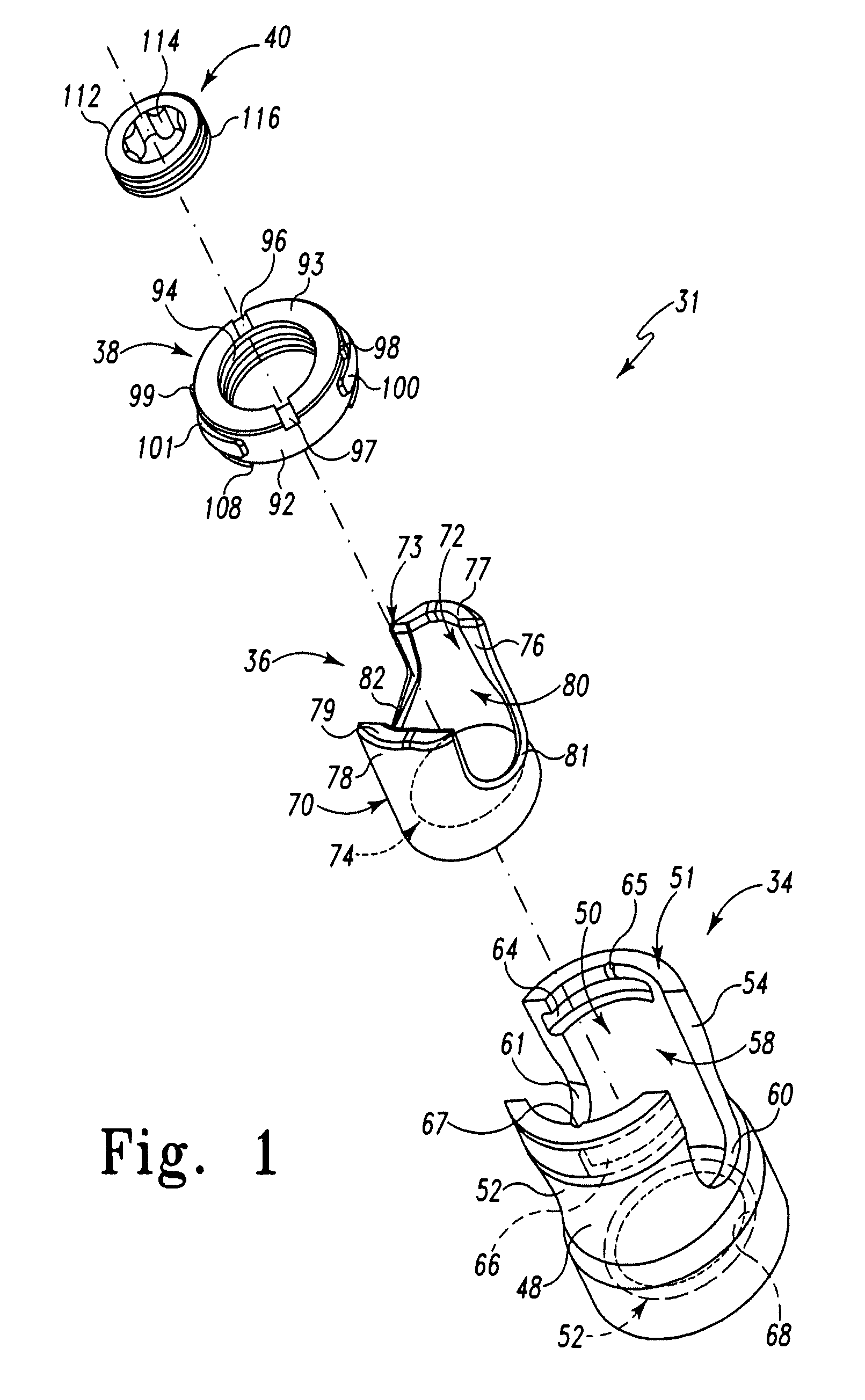
Polyaxial bone screw
ActiveUS7087057B2Efficient retentionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAngular orientationFriction force
The present invention generally provides a polyaxial fixation device having a shank with a spherical head formed on a proximal end thereof, and a receiver member having an axial passage formed therein that is adapted to polyaxially seat the spherical head of the shank. The polyaxial bone screw further includes an engagement member that is adapted to provide sufficient friction between the spherical head and the receiver member to enable the shank to be maintained in a desired angular orientation before locking the spherical head within the receiver member.
Owner:HAND INNOVATIONS +1
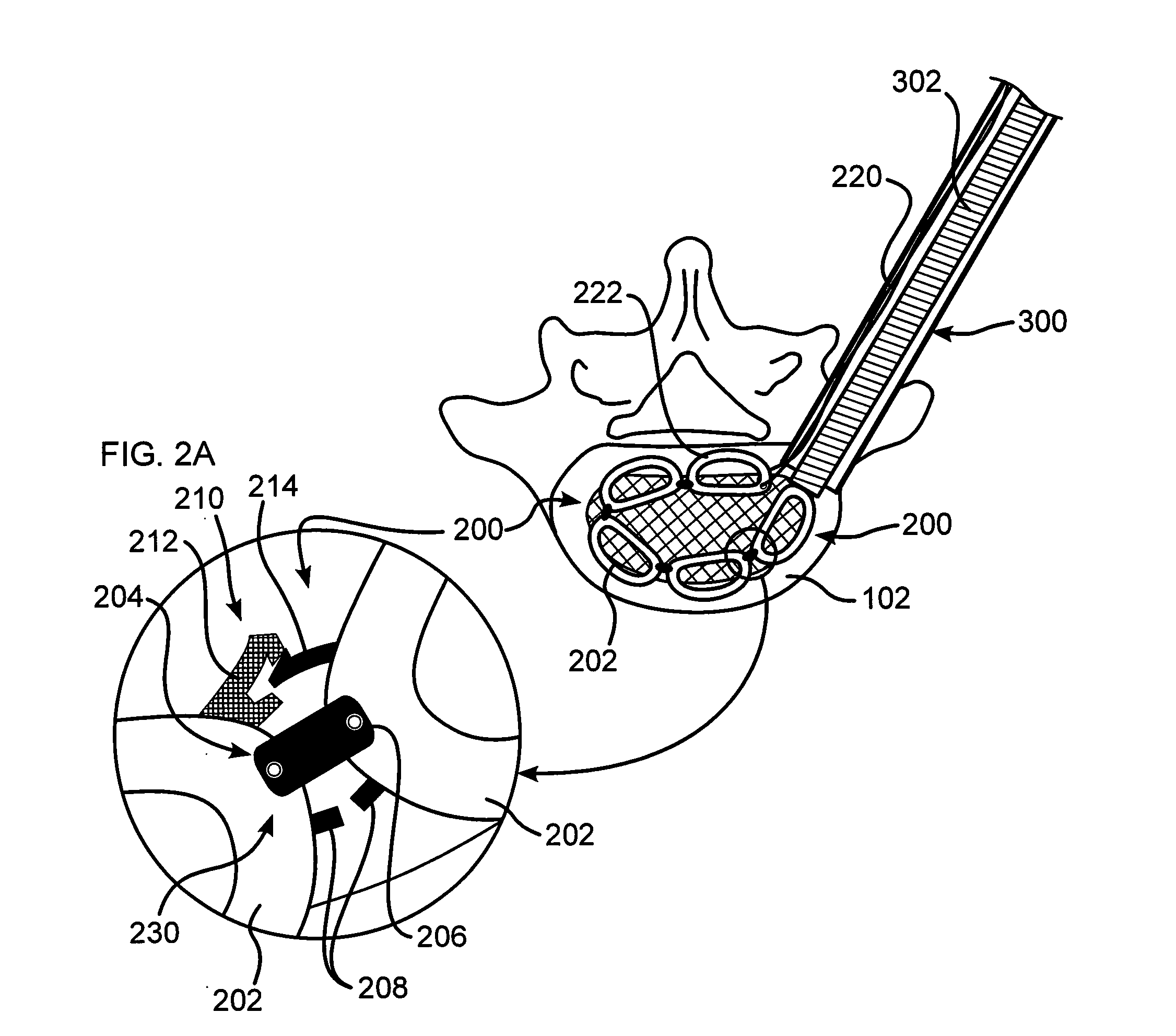
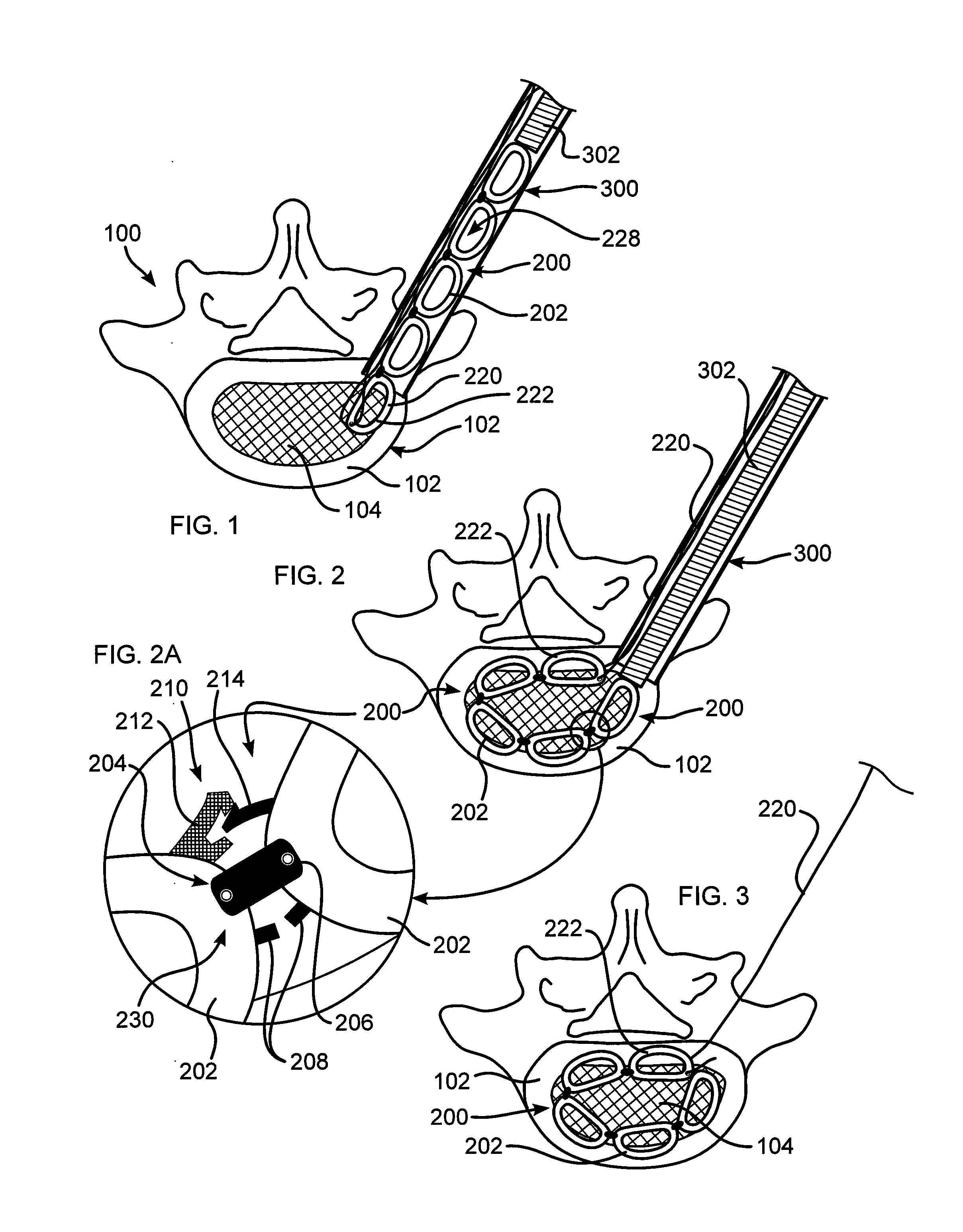
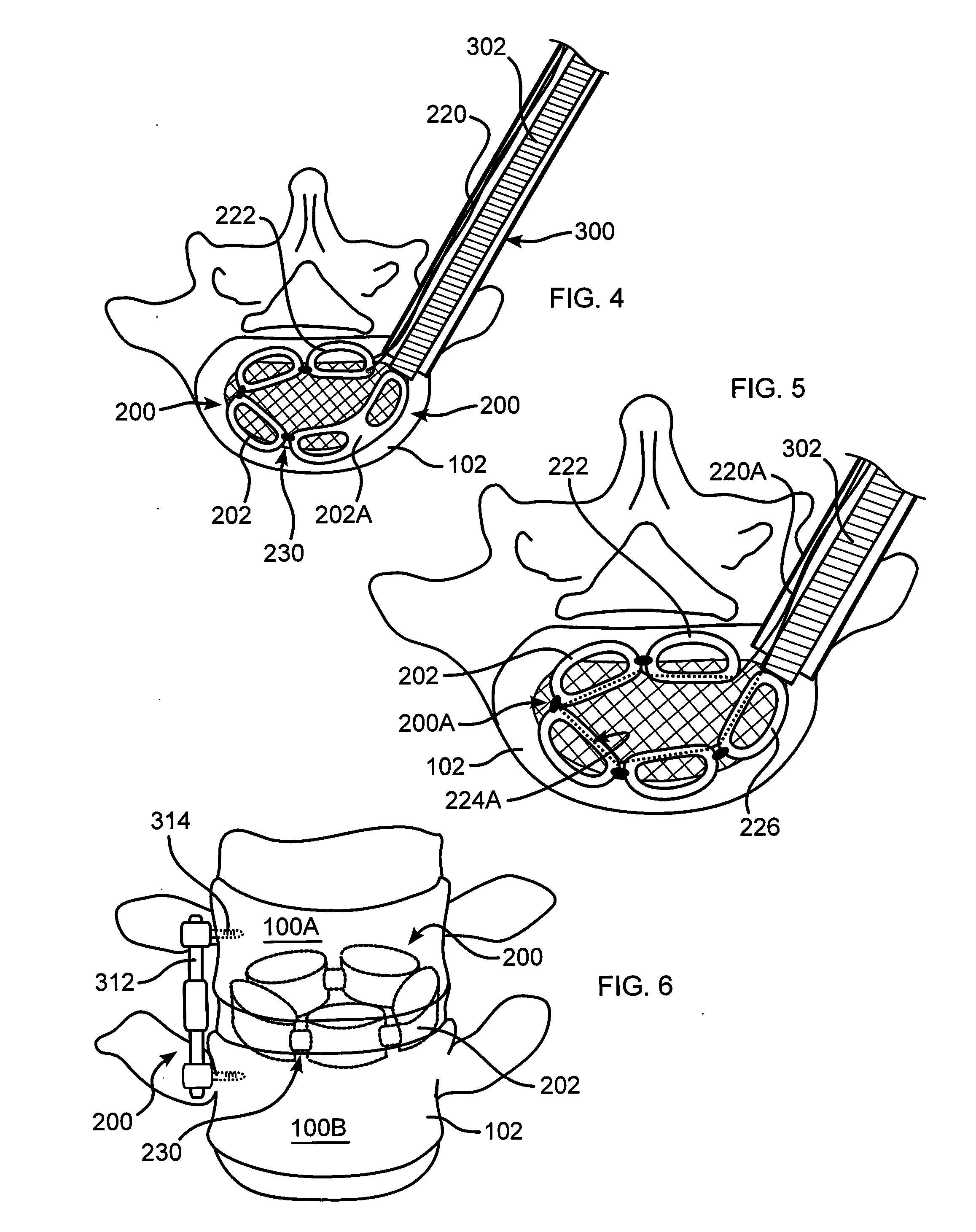
Pedicle screw constructs for spine fixation systems
A pedicle screw coupling construct for a pedicle screw construct provides fixation of angular orientation thereof relative to a pedicle screw independent of fixation of a received spinal rod to the coupling construct. The pedicle screw construct forms one component or element in a spinal fixation system. The independent fixation coupling construct also provides for fixation of the angular orientation of the coupling construct while the coupling construct has received the spinal rod. In another form, a coupling head or construct is configured to allow a pedicle screw shaft to pass therethrough but retain the pedicle screw head for rotation of the coupling head about the pedicle screw head. The coupling head or construct is also configured to allow at least a 45° arc of pivot or articulation about a pedicle screw shaft relative to a longitudinal axis of a spinal rod received in the body. This allows the head with a received spinal rod to fold, bend or pivot relative to the pedicle screw shaft, particularly to a greater degree than the prior art.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
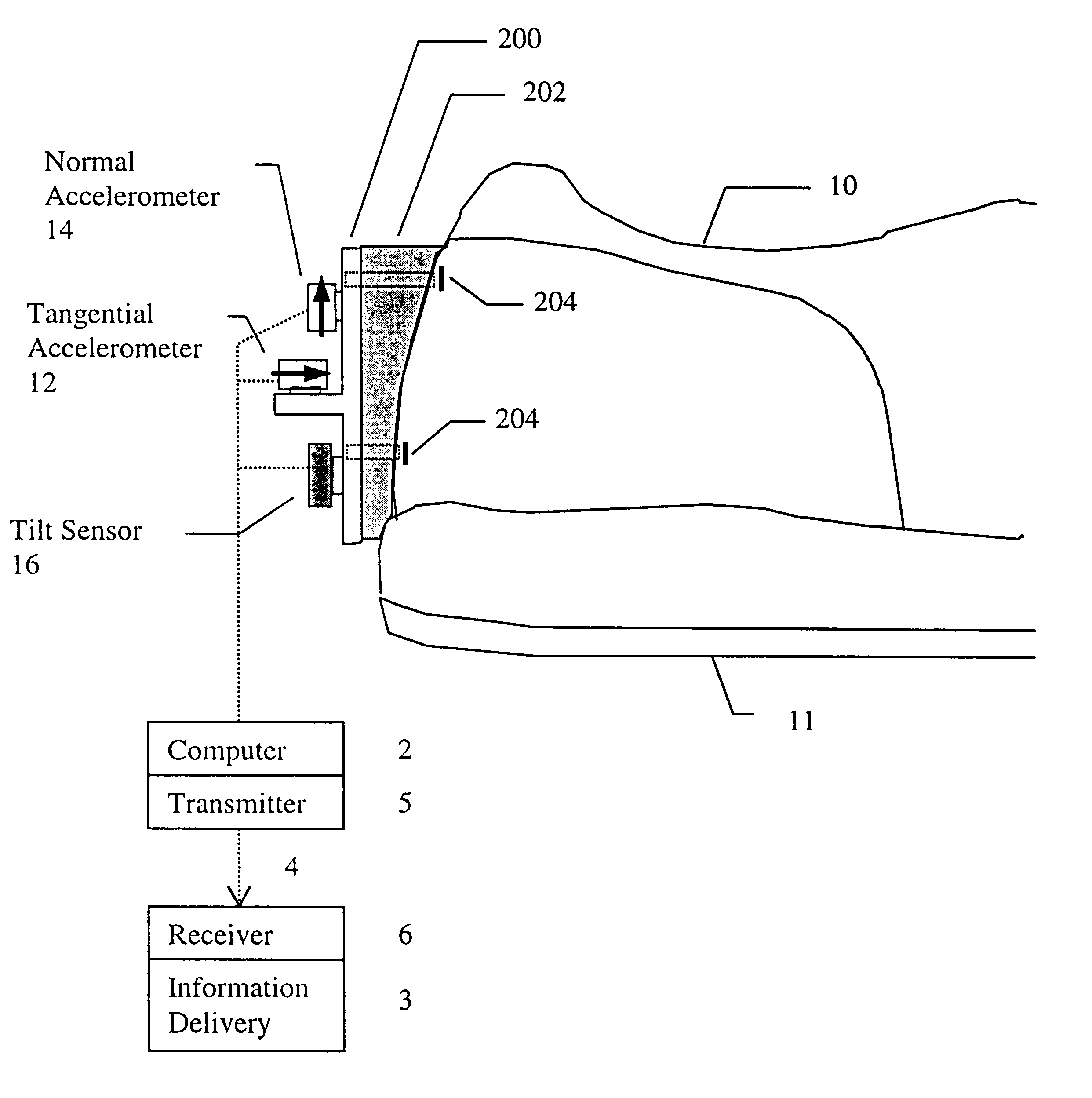
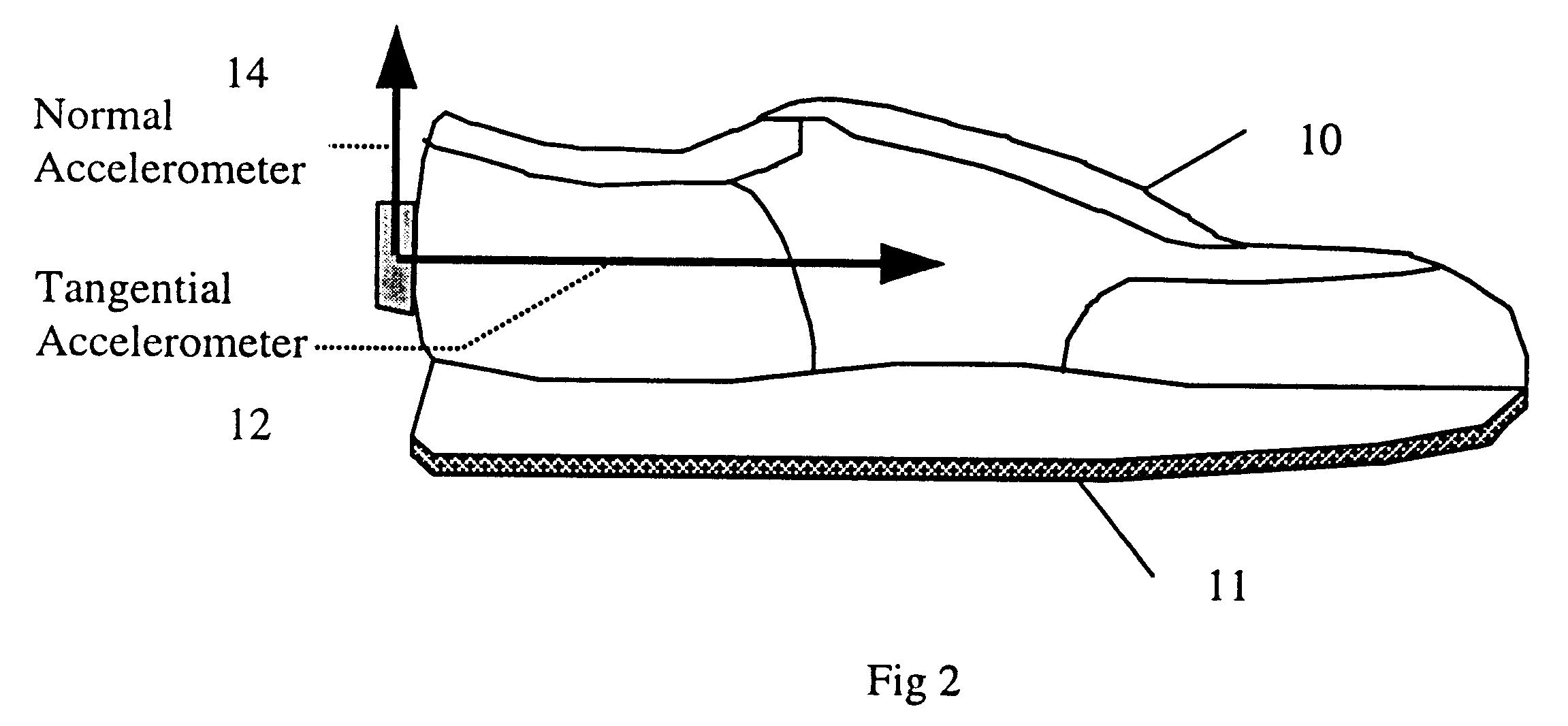
Motion analysis system
InactiveUS6301964B1Accurately determine velocity and distance traveledAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGymnastic exercisingAccelerometerTarget Motion Analysis
A device comprised of at least a pair of accelerometers and a tilt sensor mounted in fixed relation to a datum plane defining surface (sole of a shoe) may be used for extracting kinematic variables including linear and rotational acceleration, velocity and position. These variables may be resolved into a selected direction thereby permitting both relative and absolute kinematic quantities to be determined. The acceleration is determined using a small cluster of two mutually perpendicular accelerometers mounted on a shoe. Angular orientation of the foot may be determined by double integration of the foot's angular acceleration (which requires a third accelerometer substantially parallel to one of the two orthogonal accelerometers). The two orthogonal accelerations are then resolved into a net horizontal acceleration or other selected direction which may be integrated to find the foot velocity in the selected direction. The average of the foot velocity corresponds to the subject's gait speed.
Owner:GARMIN
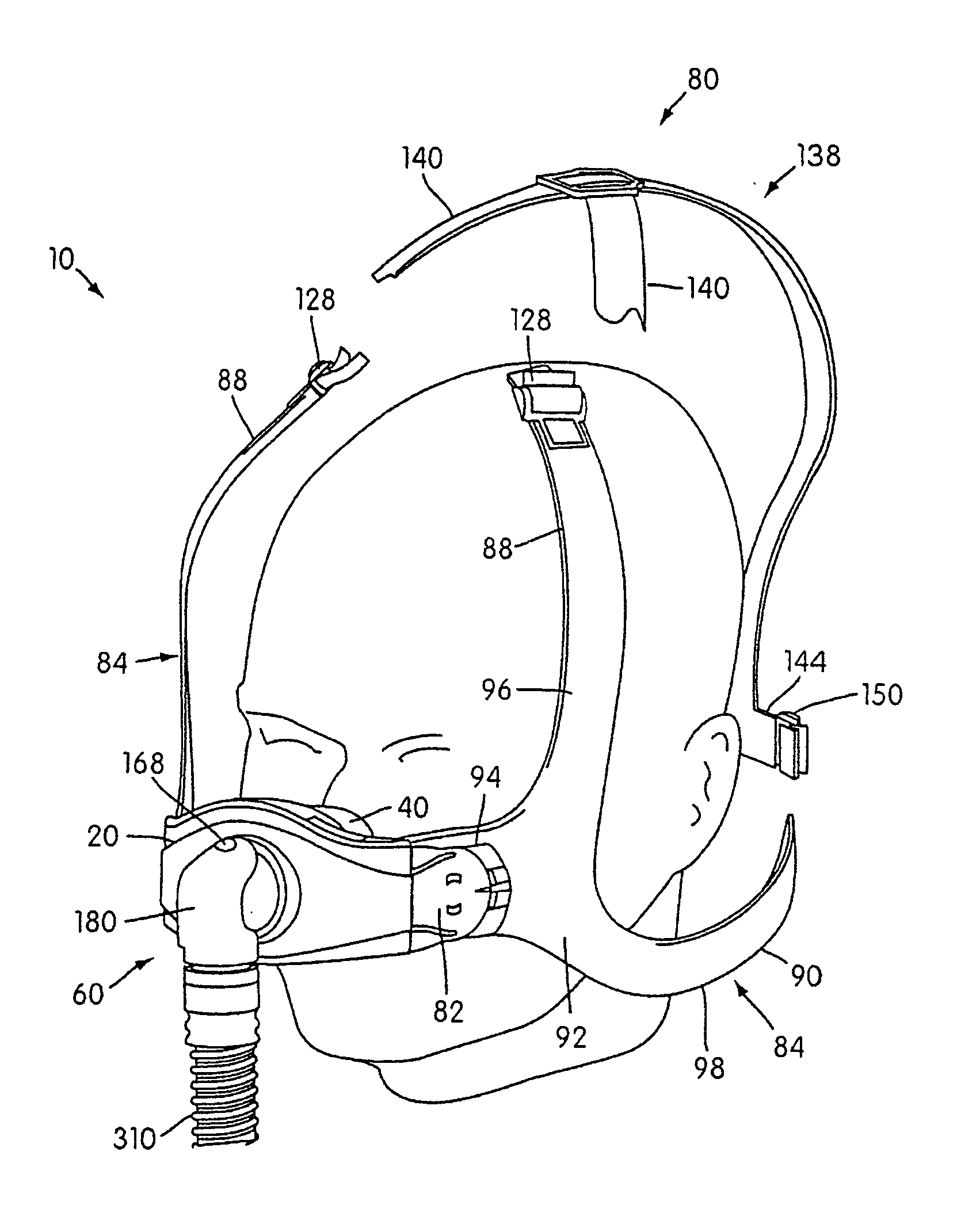
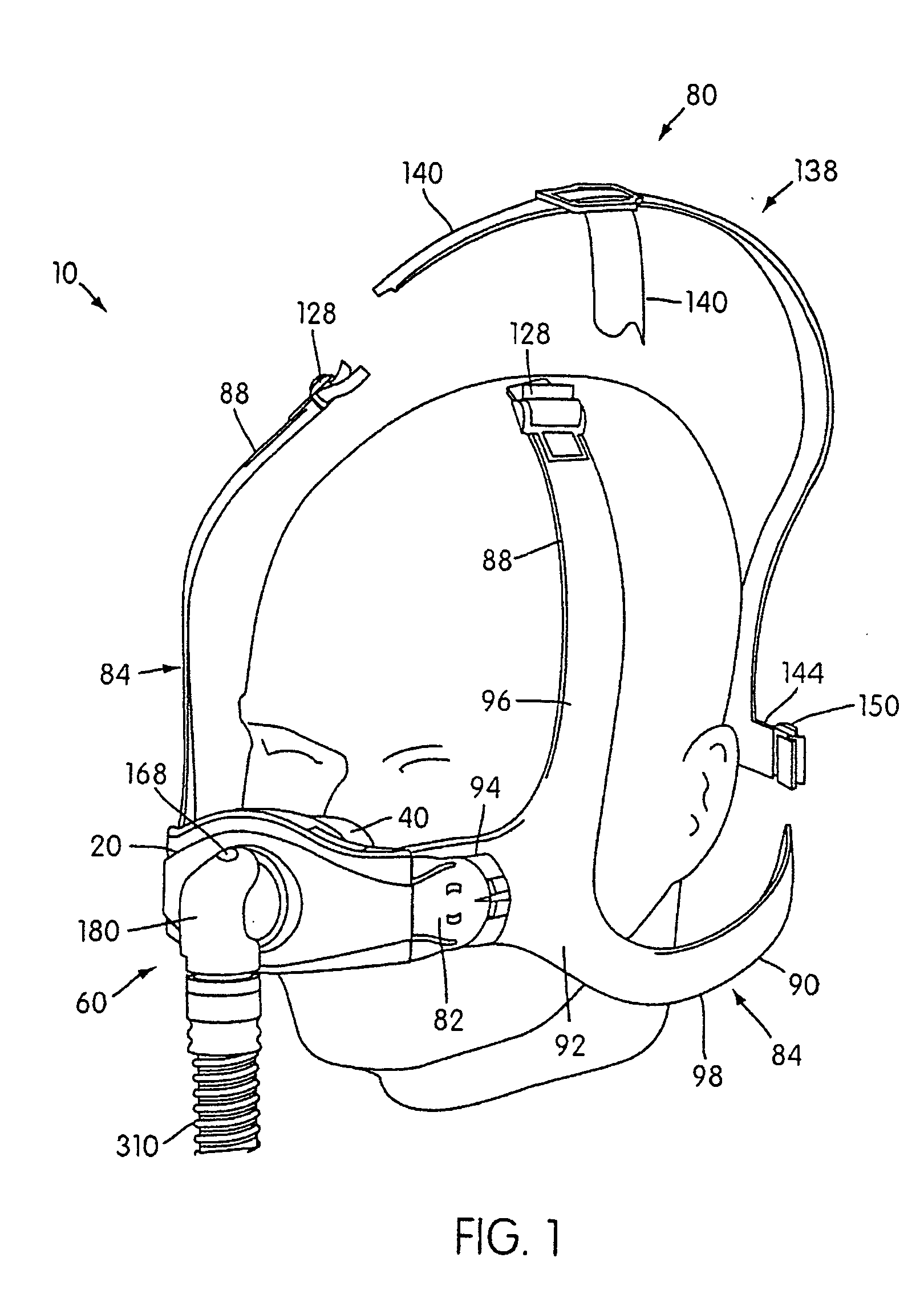
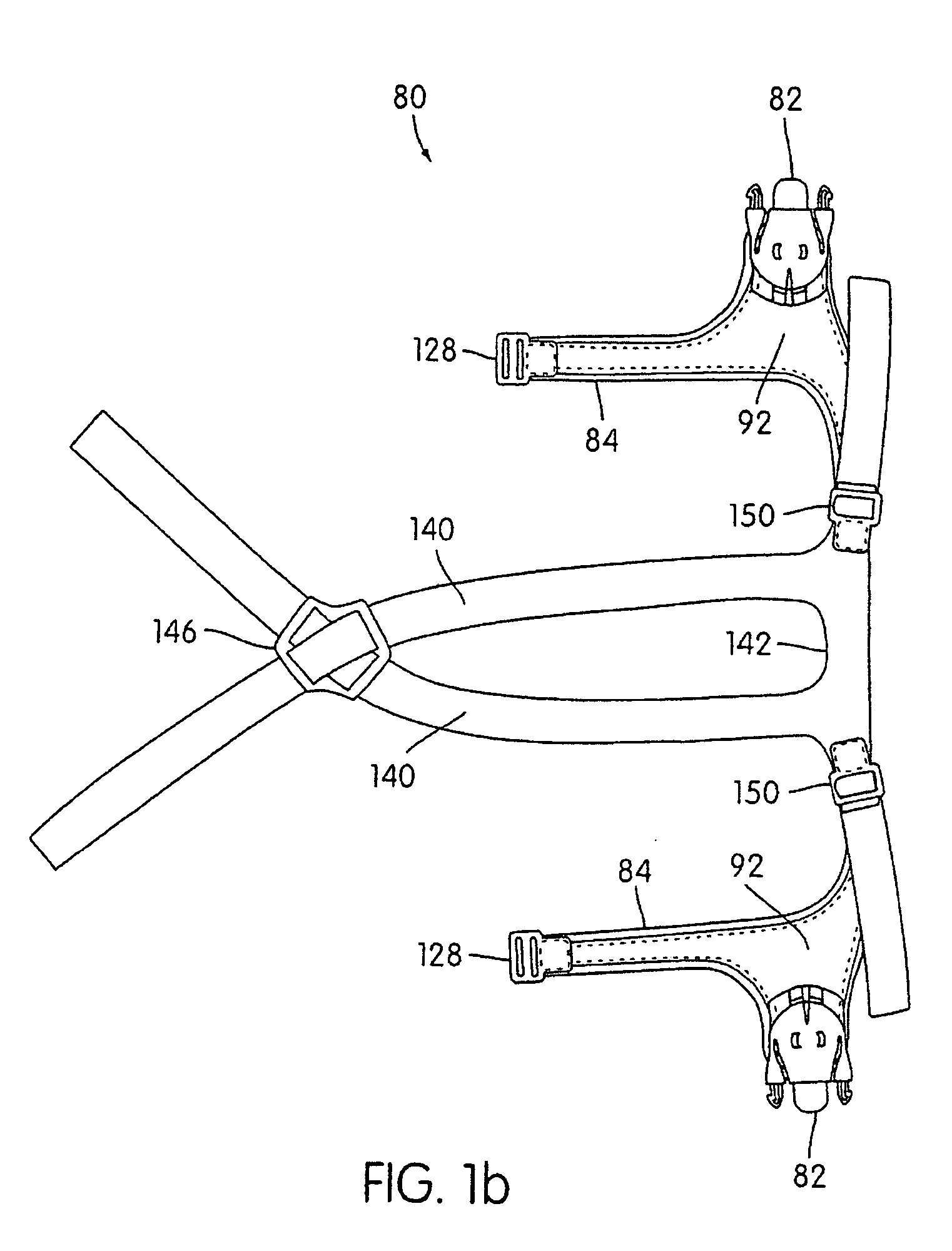
Respiratory mask assembly with magnetic coupling to headgear assembly
ActiveUS20050155604A1Decrease and minimize and numberDecrease and minimize requirementRespiratory masksBreathing masksCouplingBreathing gas
A respiratory mask assembly for delivering breathable gas to a patient includes a frame and a headgear assembly which are adapted to being removeably magnetically coupled to one another at a desired angular orientation therebetween.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Biologically implantable prosthesis and methods of using the same
A heart valve assembly includes a first annular prosthesis for implantation within a tissue annulus, a second valve prosthesis, and a plurality of magnets on the first and second prostheses to secure the second prosthesis to the first prosthesis. In one embodiment, the magnets are arranged to allow the second prosthesis to be secured to the first prosthesis in a predetermined angular orientation. During use, the first annular prosthesis is implanted into the annulus, and the second valve prosthesis is inserted into the annulus. The magnets orient the second prosthesis relative to the first prosthesis to align the second prosthesis with the first prosthesis in a predetermined angular orientation; and secure the second prosthesis to the first prosthesis in the predetermined angular orientation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Polyaxial Bone Screw
InactiveUS20060241599A1Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsAngular orientationBiomedical engineering
The present invention generally provides a polyaxial fixation device having a shank with a spherical head formed on a proximal end thereof, and a receiver member having an axial passage formed therein that is adapted to polyaxially seat the spherical head of the shank. The polyaxial bone screw further includes an engagement member that is adapted to provide sufficient friction between the spherical head and the receiver member to enable the shank to be maintained in a desired angular orientation before locking the spherical head within the receiver member.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Instrument with articulation lock
An articulating tool is provided with an articulation lock. The tool includes proximal, central and distal portions, an articulation mechanism, and first and second articulation locks. The central portion of the tool is pivotably coupled to the proximal portion and the distal portion is pivotably coupled to the central portion. The articulation mechanism is configured to manipulate an angular orientation of the distal portion relative to the central portion. The articulation mechanism includes a pair of links, the pair comprising a proximal link on the proximal portion of the tool and a distal link on the distal portion of the tool. The articulation mechanism is adapted such that movement of the proximal link causes corresponding relative movement of the distal link. The first articulation lock has an engaged position and a disengaged position. When in the engaged position, the first articulation lock impedes movement of the proximal link relative to the central portion about a yaw axis, and corresponding relative movement of the distal link. The second articulation lock also has an engaged position and a disengaged position. When in the engaged position, the second articulation lock impedes movement of the proximal link relative to the central portion about a pitch axis, and corresponding relative movement of the distal link. Methods of operating the articulating tool are also disclosed.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
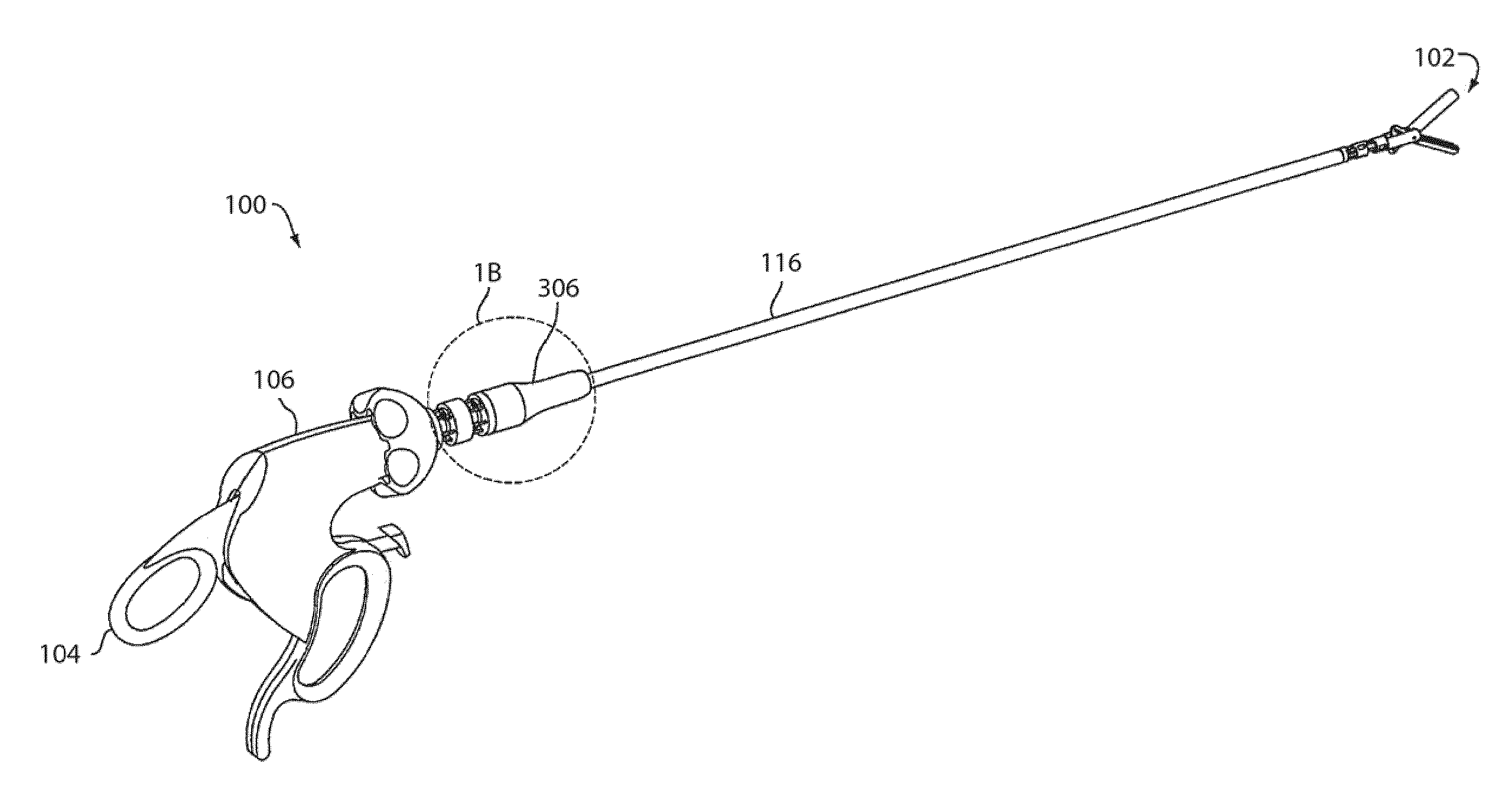
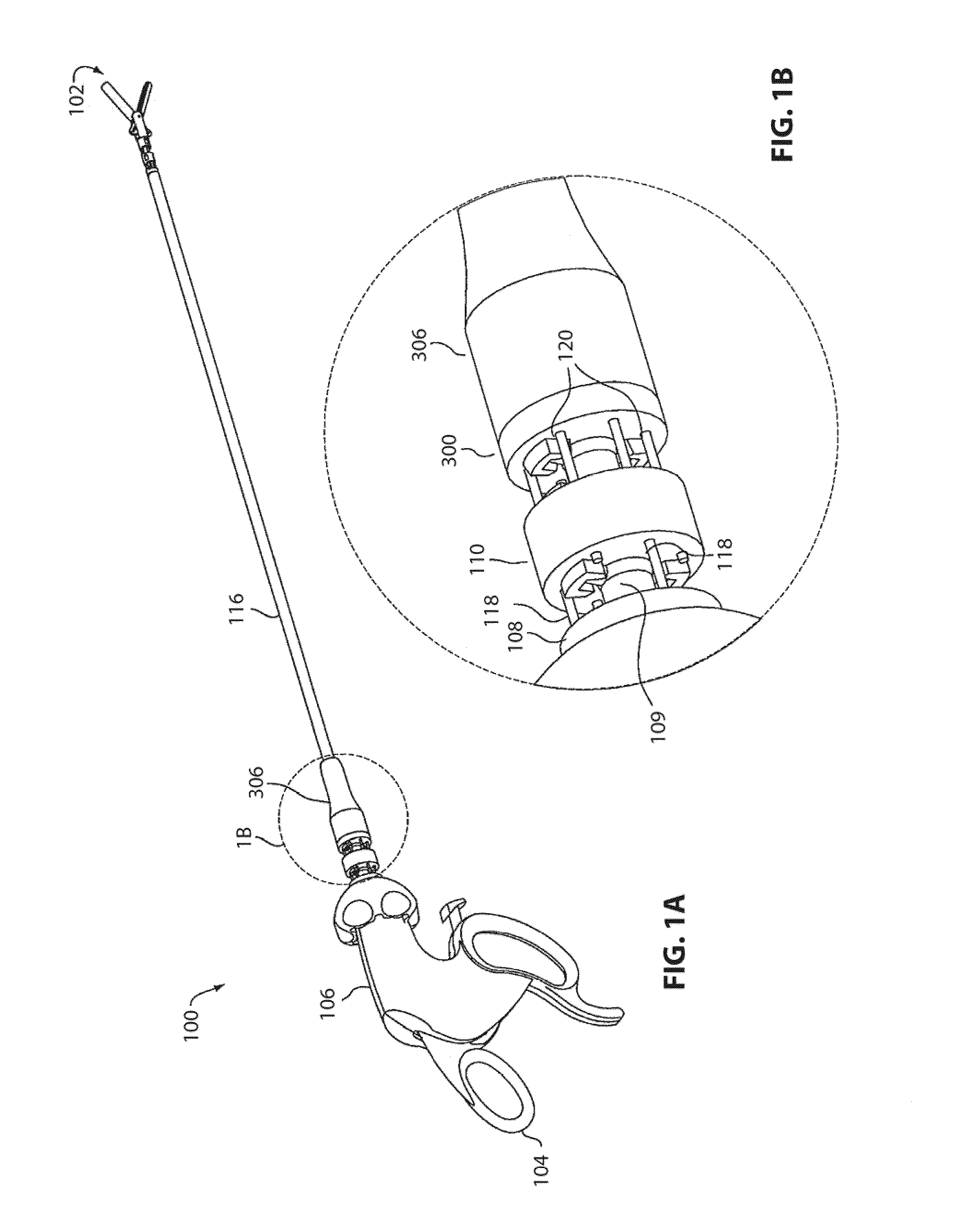
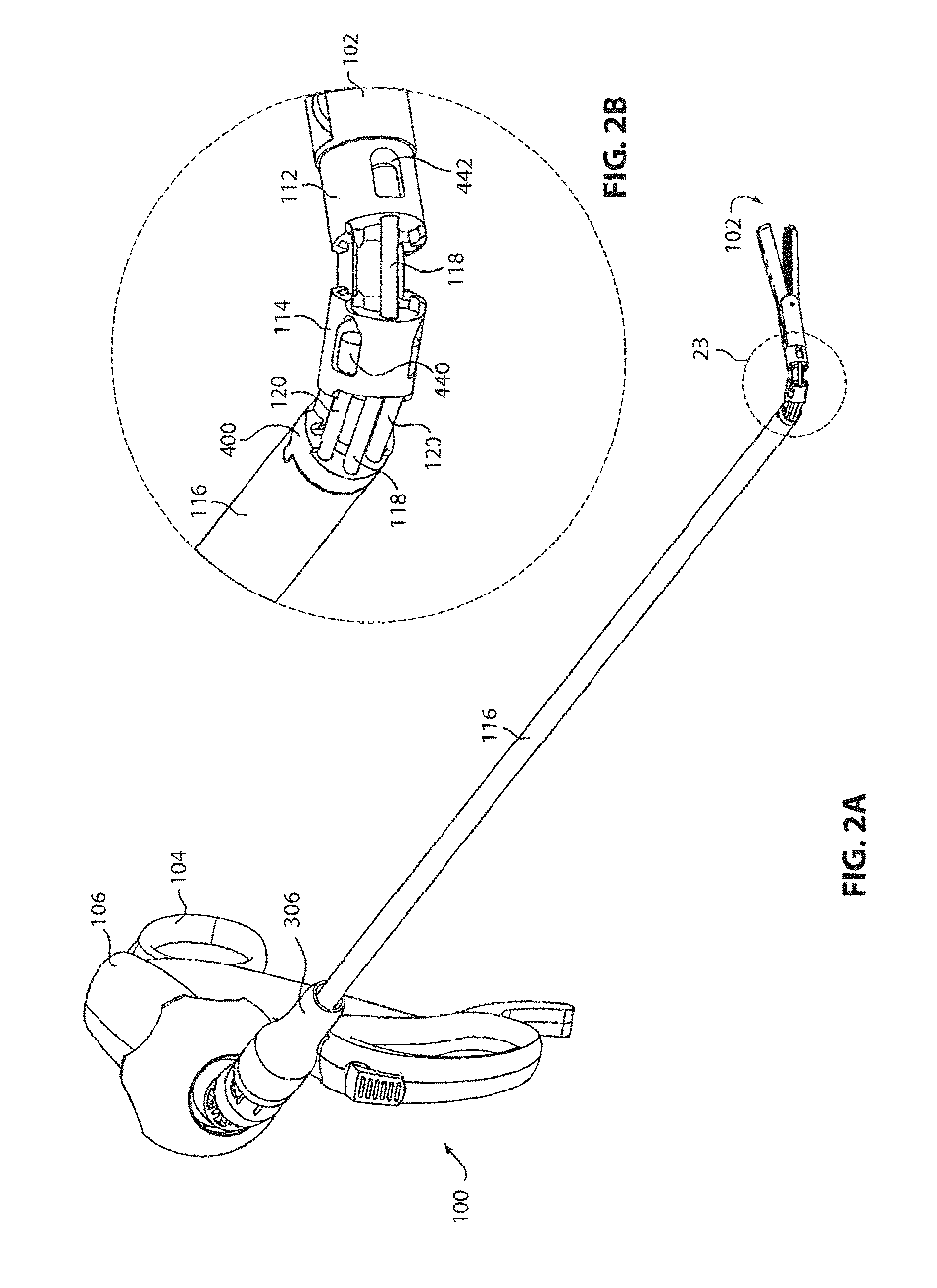
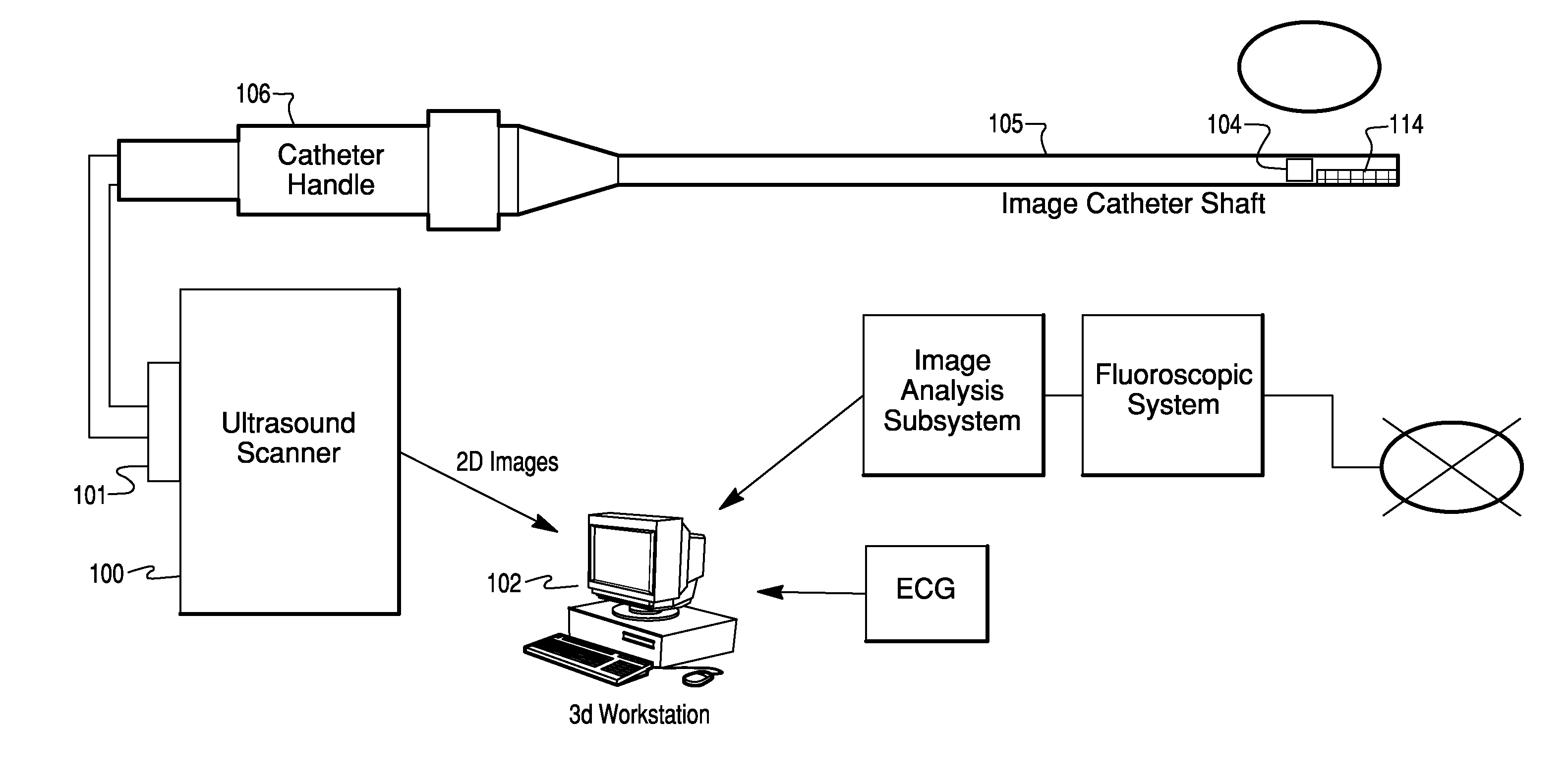
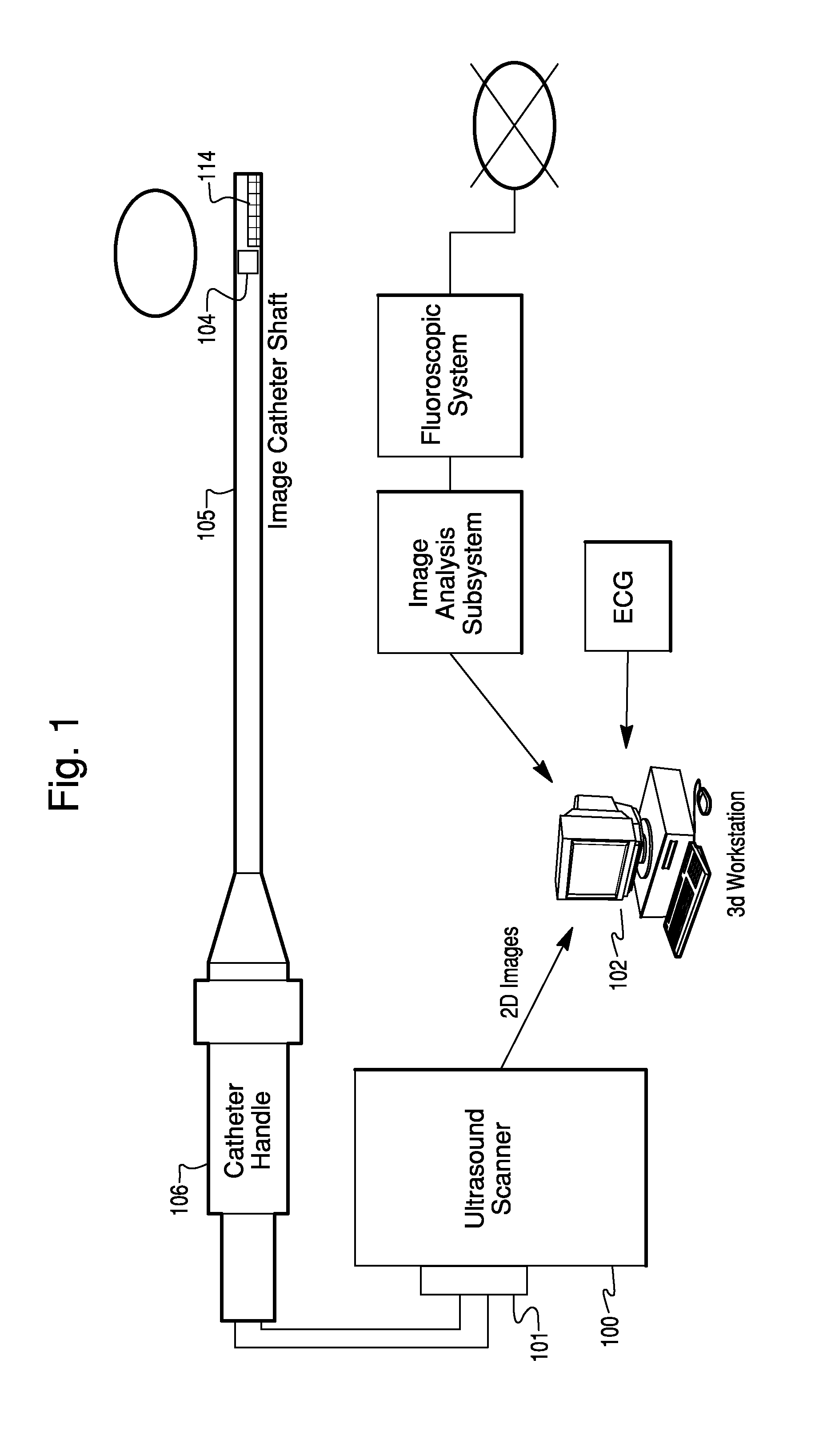
Catheter Position Tracking Methods Using Fluoroscopy and Rotational Sensors
Methods for determine the position and rotational orientation of the transducer array of an ultrasound imaging catheter within a patient include imaging the distal end of the catheter using fluoroscopy and determining the angular orientation based upon the shape and dimensions of the image of the transducer array and wire connecting harness. Additional rotational and translational information may be obtained from sensors located at the proximal end of the catheter. By combining position information obtained using fluoroscopy with information from relative rotation / translation sensors, the imaging transducer position and orientation can be determined more accurately. The resulting accurate imaging transducer position information enables combining multiple images from different positions or orientations to generate multi-dimensional images. Catheters including rotation and translation motion sensors at the proximal end, and radio-opaque materials near the distal end can be provided to enhance the methods.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Expandable interbody fusion cage
An expandable intervertebral device including a body extending generally along a longitudinal axis and including at least two branch portions coupled together adjacent an end portion of the body. The device further includes an expansion member positioned between the at least two branch portions with at least a portion of the expansion member arranged at an angular orientation relative to the longitudinal axis whereby a change in the angular orientation relative to the longitudinal axis urges the at least two branch portions apart to expand the body.
Owner:SOFAMOR
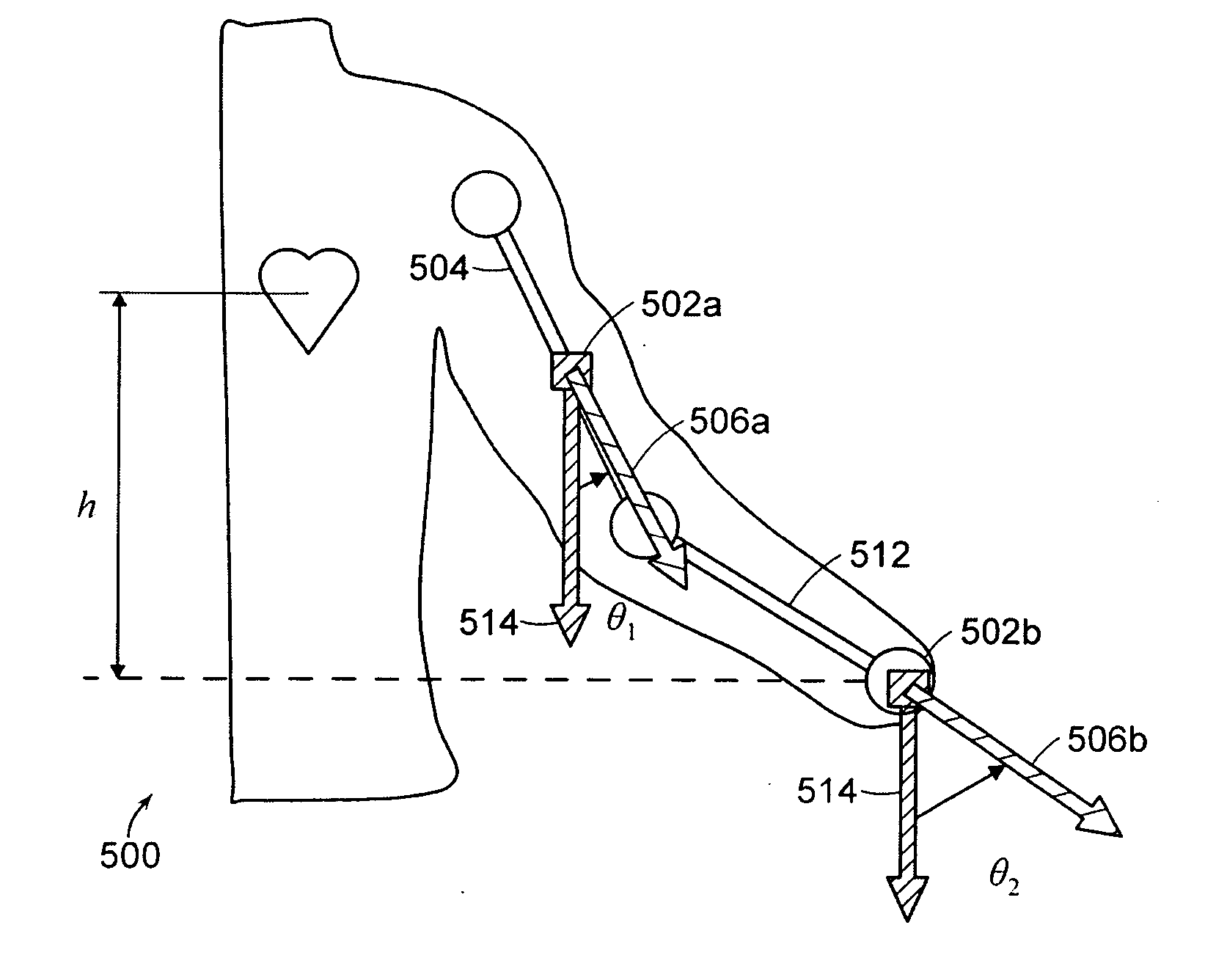
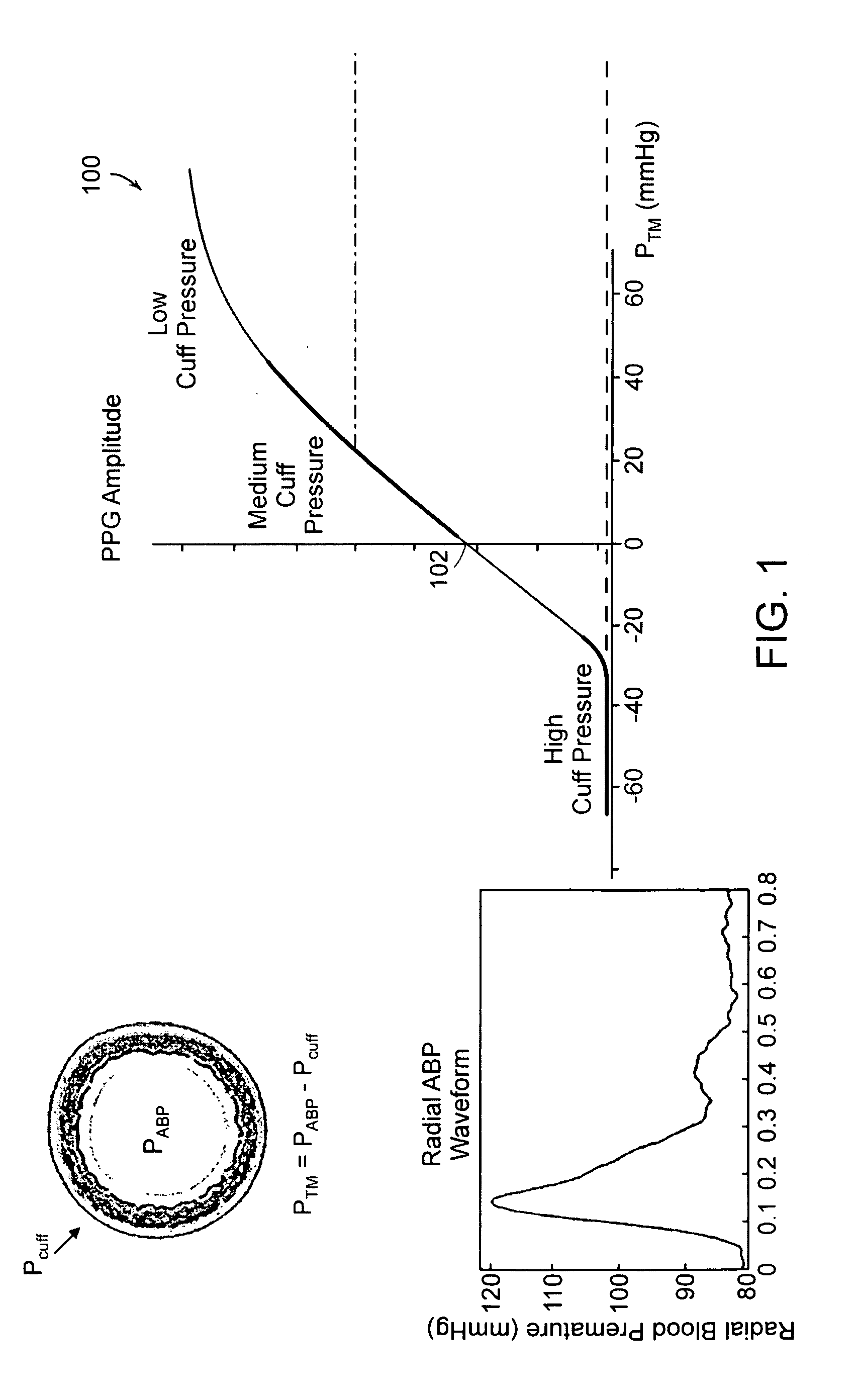
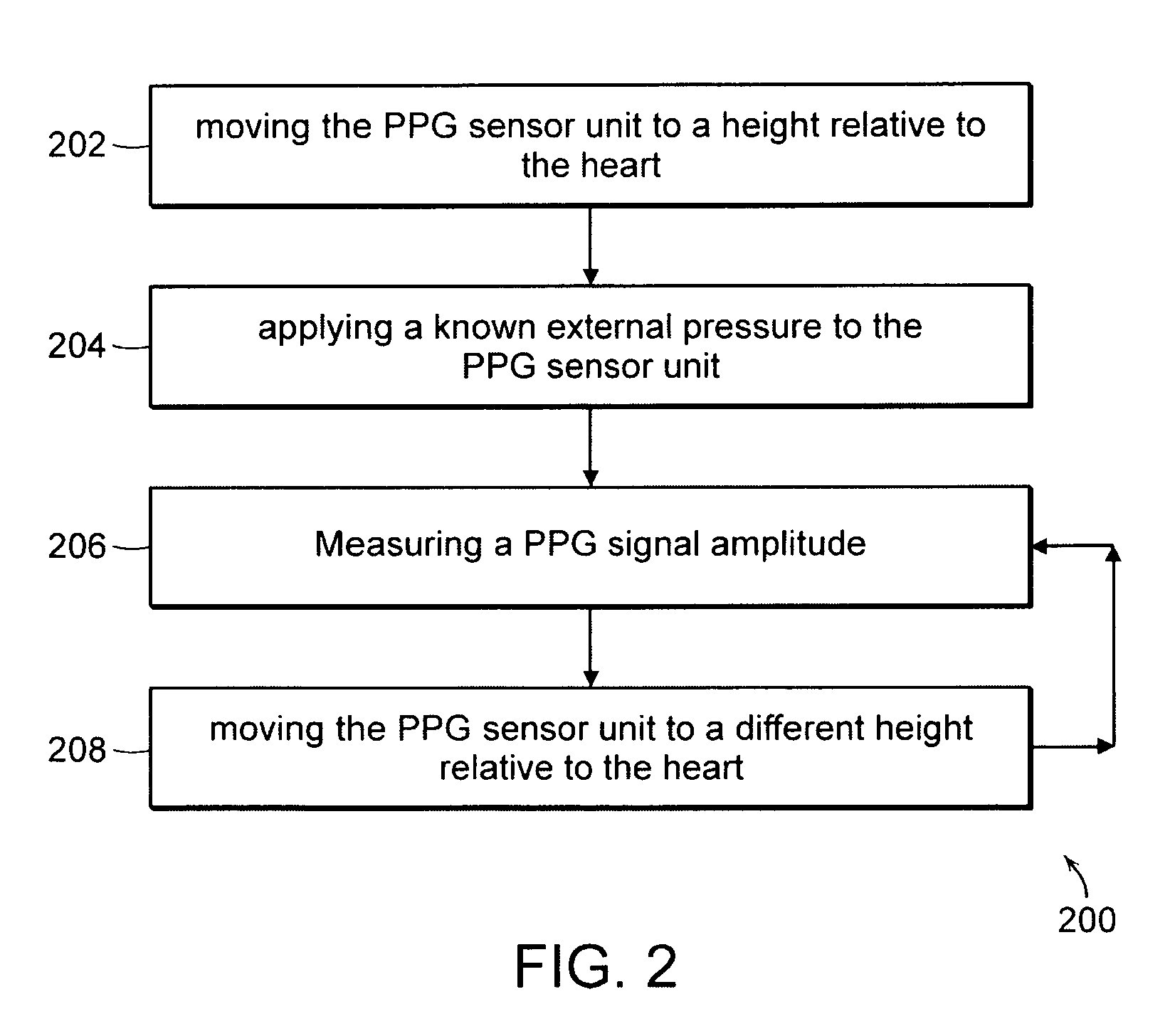
Wearable blood pressure sensor and method of calibration
Methods and apparatus for measuring arterial blood pressure at an extremity of a subject. Arterial blood pressure is derived from a circulatory measurement performed on an extremity of a subject and the circulatory measurement is normalized to account for the instantaneous vertical displacement of the extremity. The vertical displacement of the extremity relative to the heart of the subject is obtained using the angular orientation of the subject's extremity. An improved photoplethysmograph can discriminate light traversing the extremity from ambient light on the basis of differential response. The apparatus may have a conducting polymer actuator for applying pressure to the extremity of the subject. A pulsatile waveform from the photoplethysmographic signal may be obtained at a plurality of externally applied pressures to calibrate the photoplethysmograph.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
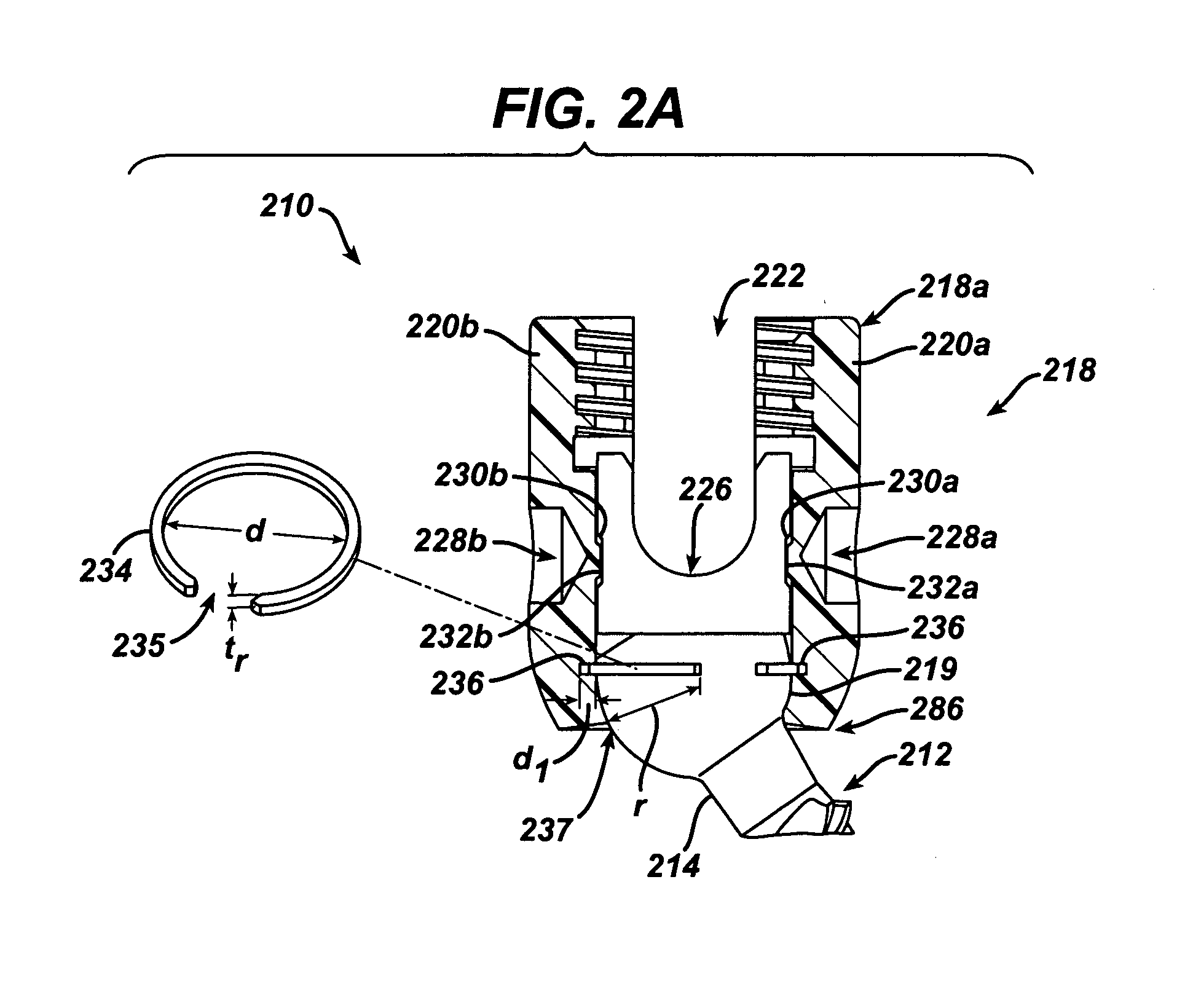
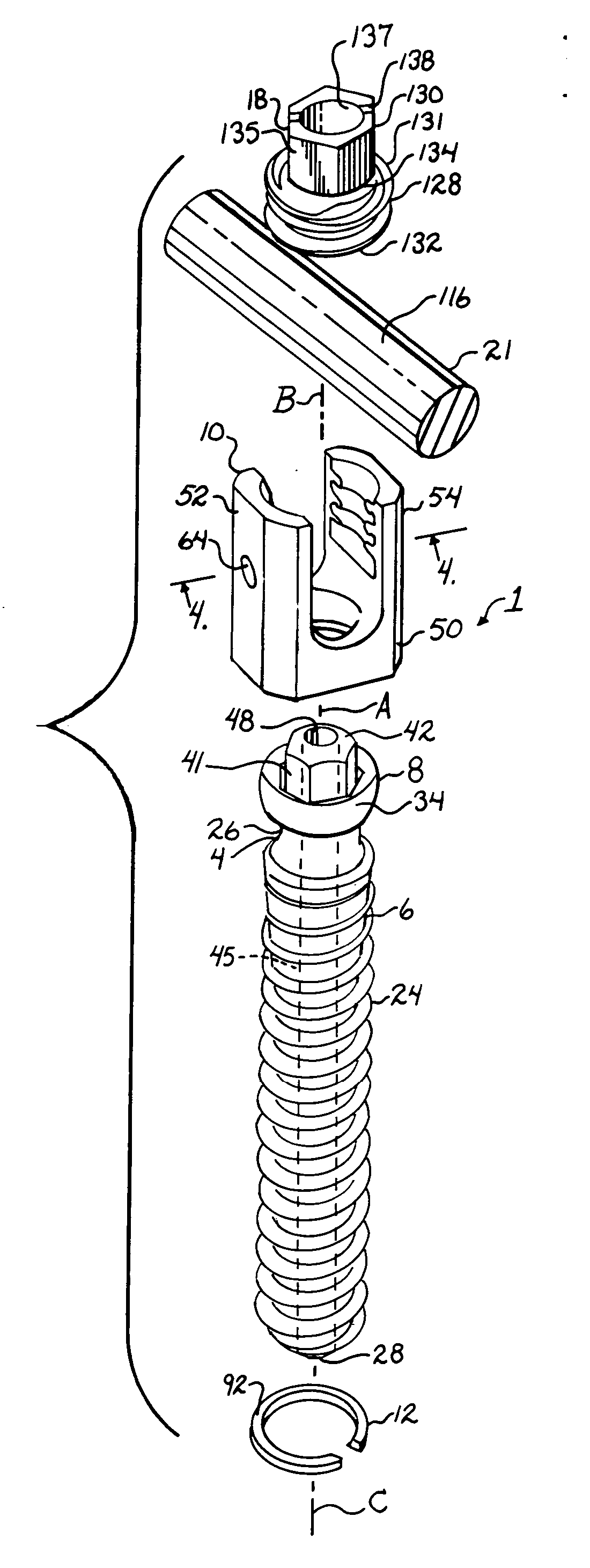
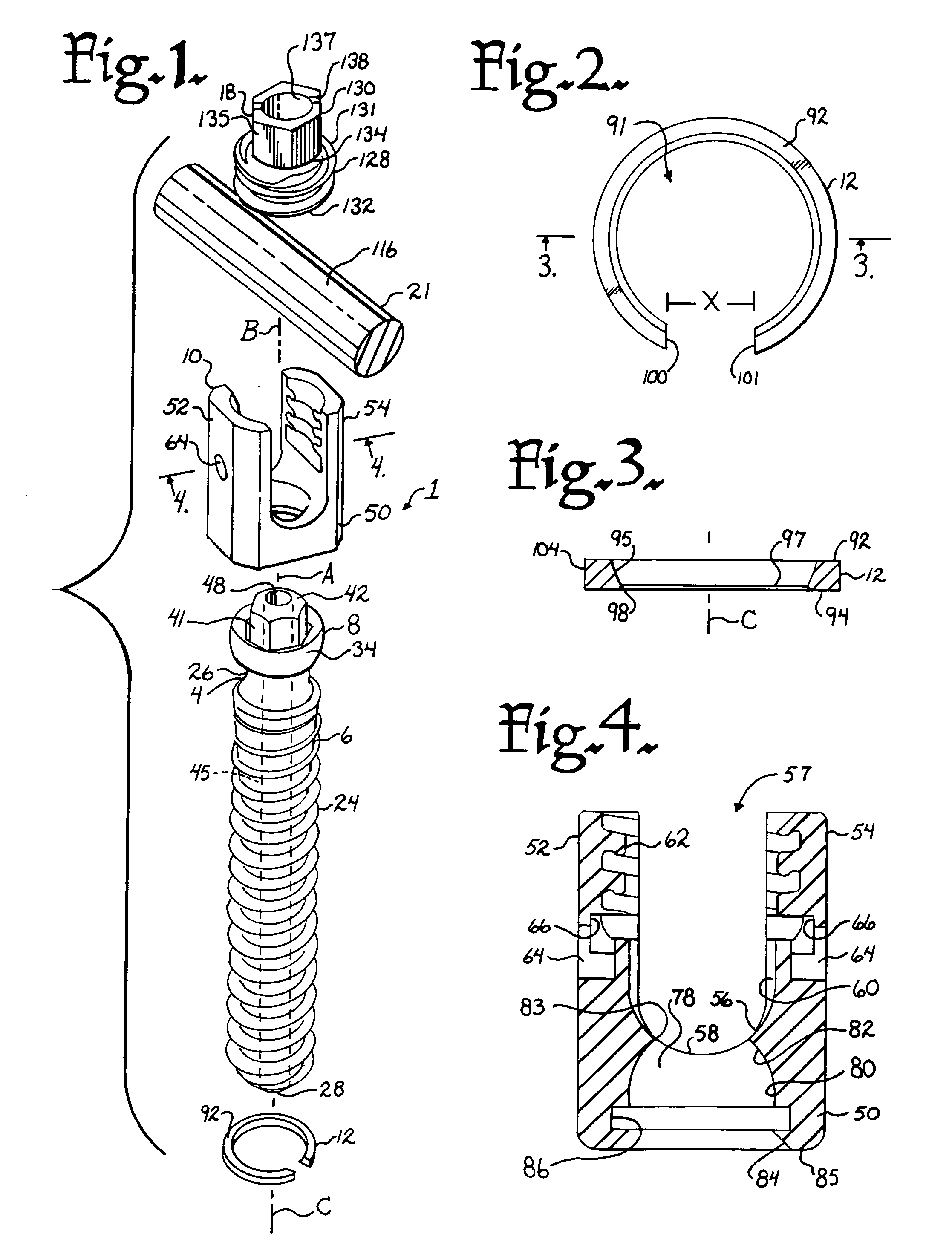
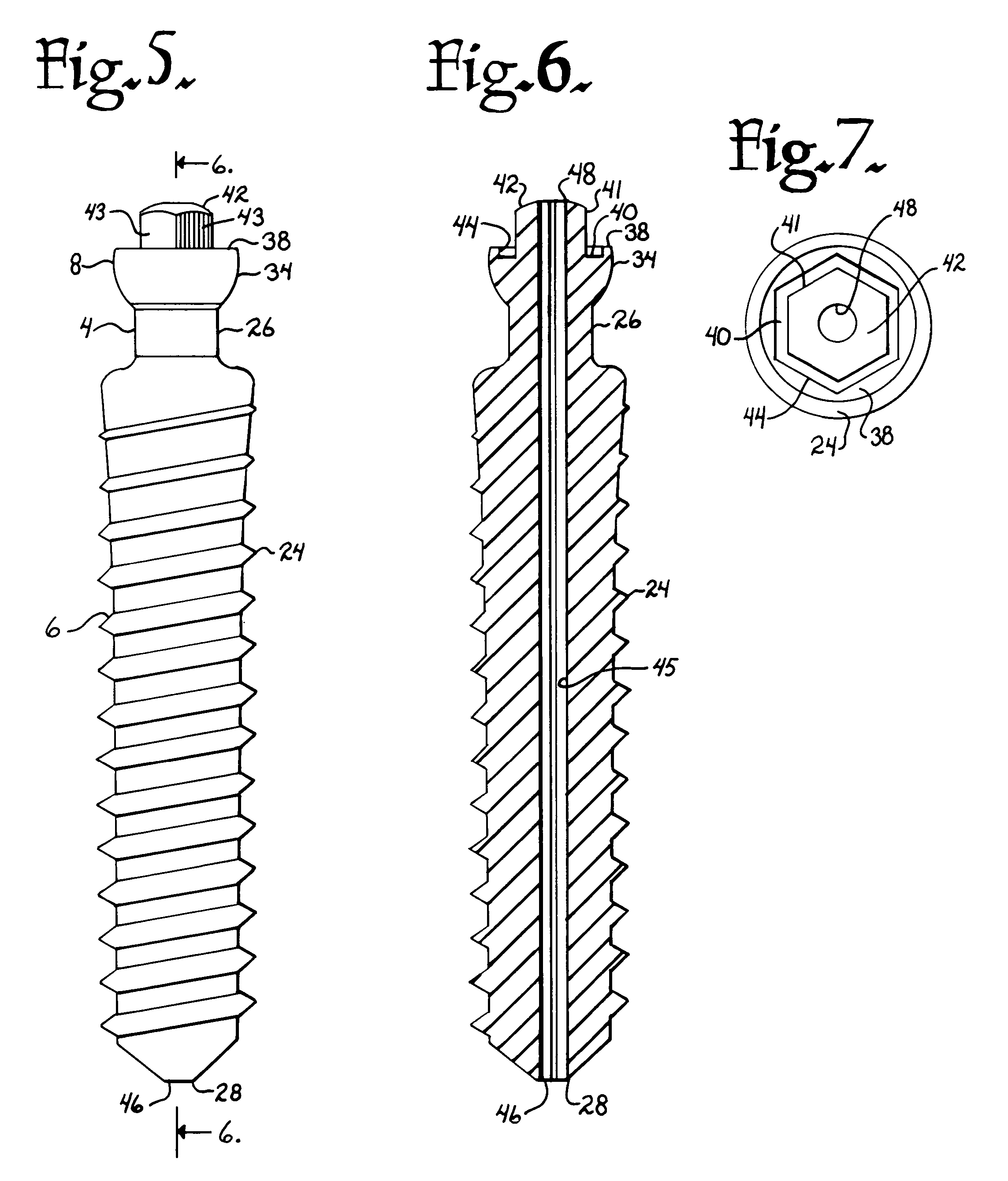
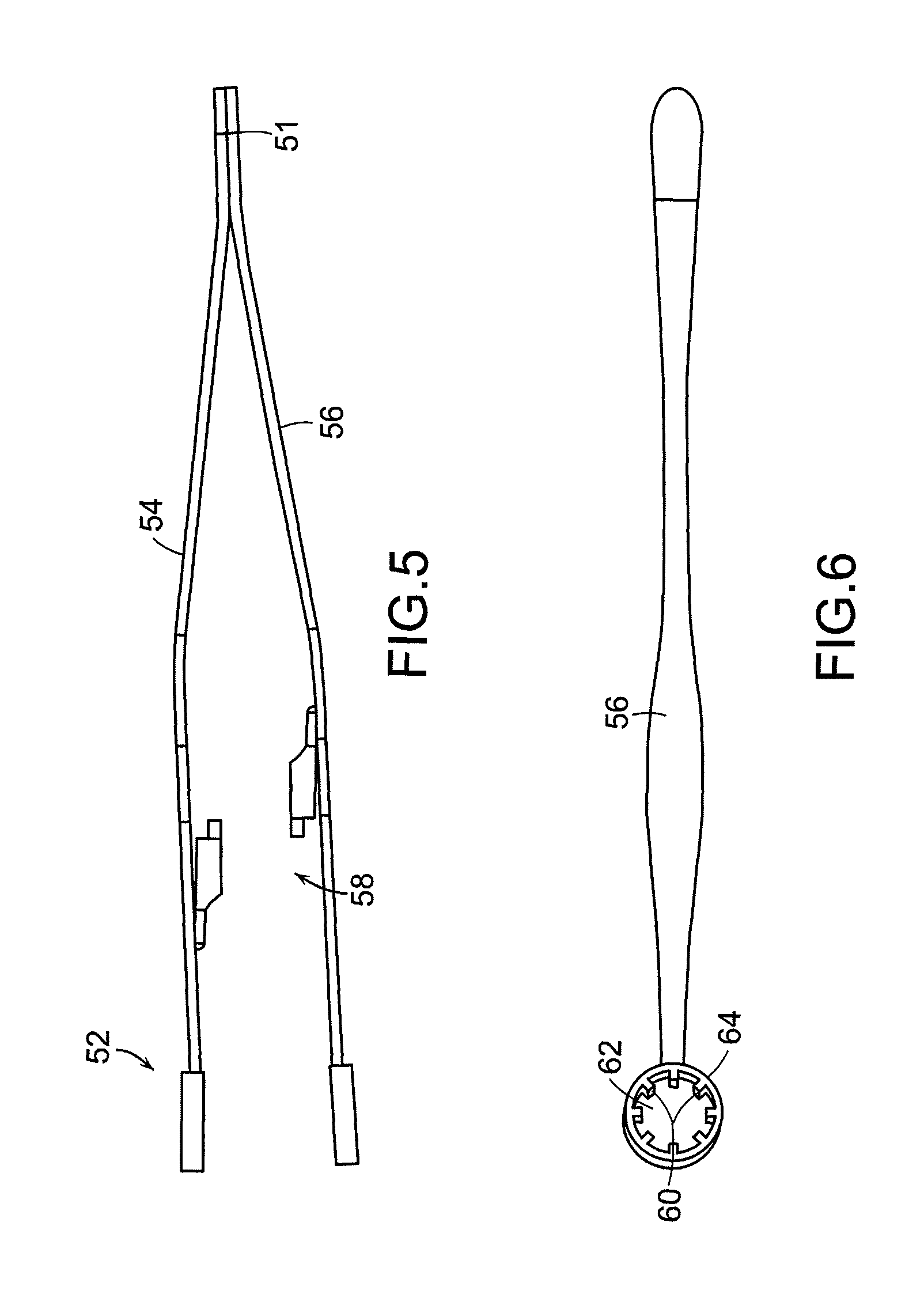
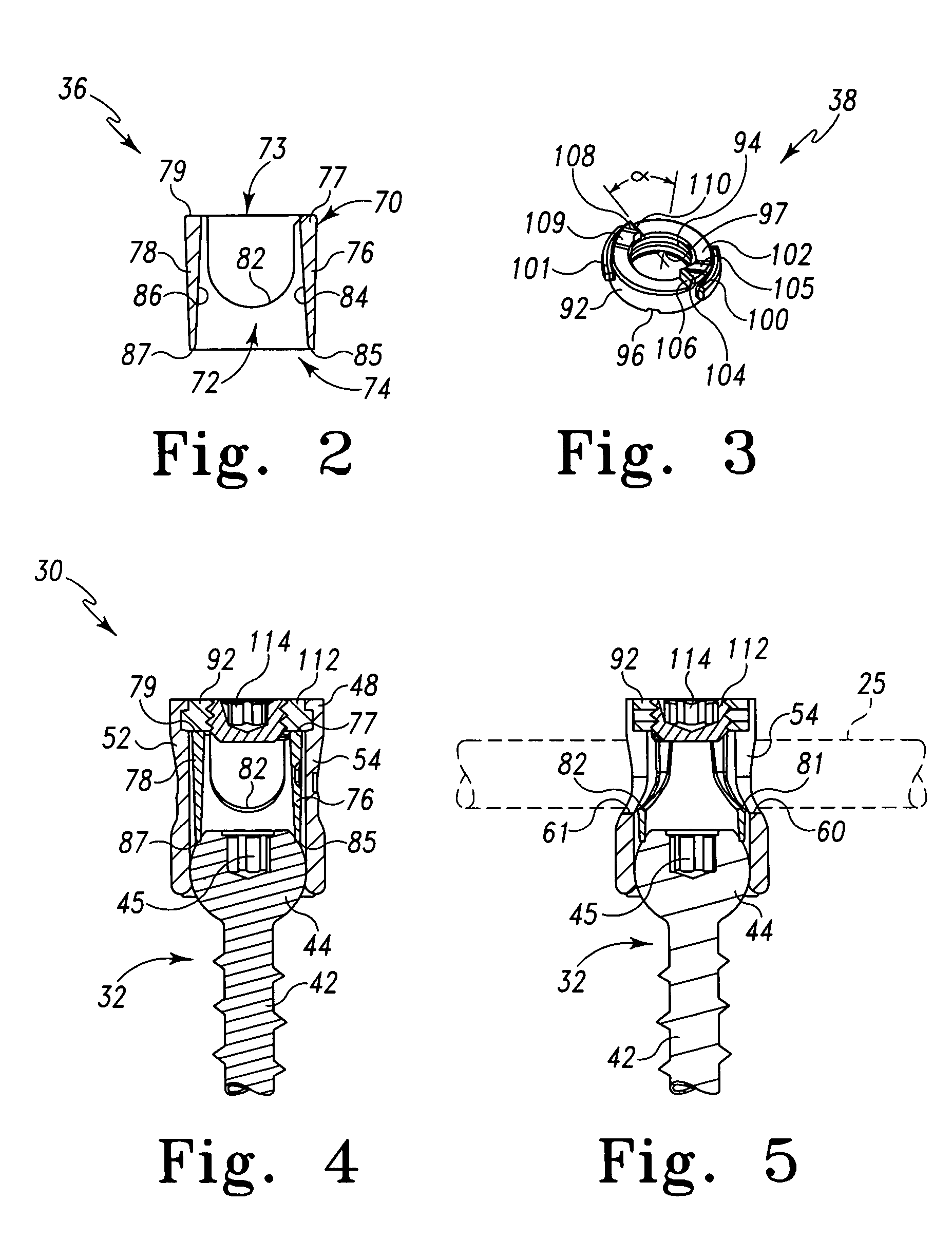
Polyaxial bone screw assembly with fixed retaining structure
A polyaxial bone screw assembly includes a threaded shank body having an integral upper portion receivable in a receiver and retained within the receiver by a retaining structure in the form of an open ring. The retaining structure is compressible, having an opening with two ends that may be pressed toward one another. The receiver has a U-shaped cradle defining a channel for receiving a spinal fixation rod. The receiver channel communicates with a cavity partially defined by an upper spherical surface and a substantially cylindrical surface communicating with a bottom opening of the receiver that allows for bottom loading the shank upper portion and the compressed retaining structure into the receiver, but prevents passage of the retaining structure out of the receiver once the retaining structure expands to an original form thereof and thus retains the shank upper portion within the cavity. The shank upper portion is designed to directly frictionally engage the spinal fixation rod when a closure structure operably urges the rod toward the upper portion, fixing the bone screw shank body in a selected angular orientation with respect to the receiver.
Owner:JACKSON
Polyaxial modular skeletal hook
InactiveUS6932817B2Positively attachingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSet screwComputer module
A modular skeletal hook has an upper module for connecting with larger support apparatus to maintain bones of the skeleton in fixed relationship. The upper module is connected to an attachment module by a modified ball and socket arrangement. The attachment module has a C-shaped hook for engaging the bone. The angular orientation of the upper module and the attachment module may be fixed by a set screw threaded through the upper module and the attachment module.
Owner:ATLAS SPINE
Method and system for interference lithography utilizing phase-locked scanning beams
InactiveUS6882477B1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesActive addressable light modulatorLithographic artistLight beam
A method and system of interference lithography (also known as interferometric lithography or holographic lithography) which utilizes phase-locked, scanning beams (so-called scanning beam interference lithography, or SBIL). The invention utilizes a high-precision stage that moves a substrate under overlapped and interfering pairs of coherent beams. The overlapped beams interfere, generating fringes, which form a pattern “brush” for subsequent writing of periodic and quasi-periodic patterns on the substrate. The phase of the fringes in the overlapped region is phase-locked to the motion of the precision stage. The invention includes methods for forming, overlapping, and phase-locking interfering pairs of beams on a variety of substrates; methods for measuring and controlling the period, phase, and angular orientation of fringes generated by the overlapping beams; and methods for measuring and controlling the effects of stage mechanical and thermal drift and other disturbances during the writing process.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Intervertebral Implant
ActiveUS20140058513A1Different shapesLimited extentBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesAngular orientation
An intervertebral spacer for therapeutic treatment of a patient includes at least one link sized and dimensioned to fit within an intervertebral space in the patient, and is configured to maintain a separation of two adjacent vertebrae for a period of time. A rigid guiding object, which may be a tool or a successive link, is insertable into the patient, to guide other links into the patient using an MIS approach. A pivot is connected between successive links, or between a guide tool and a link, configured to limit a relative range of angular orientation between the link and the guiding tool, or successive links. Multiple links are so joined to form a chain pushable by the last link, and pullable by the first link, to form a chain which may be formed into a curved configuration corresponding to the patient's intervertebral space.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
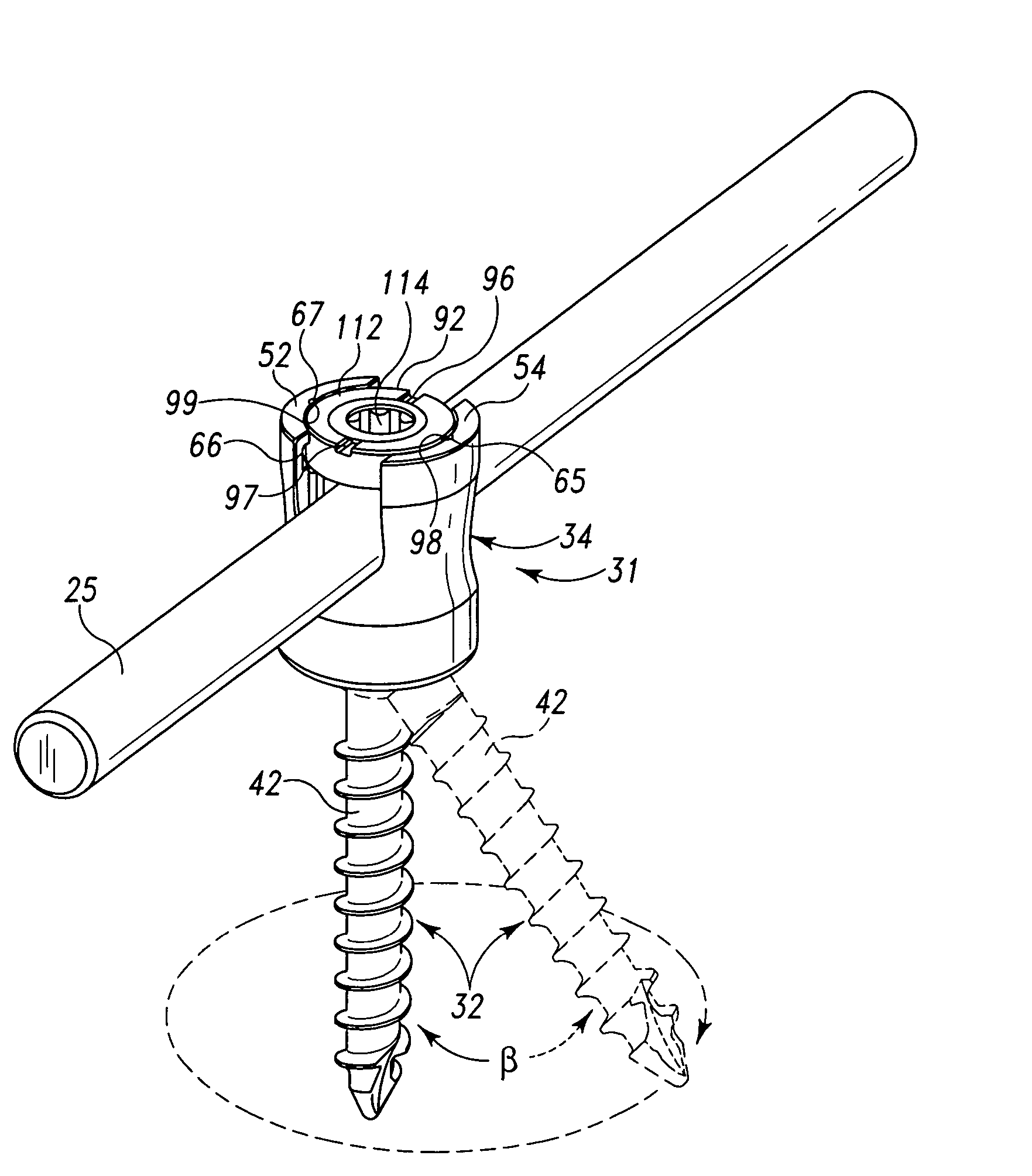
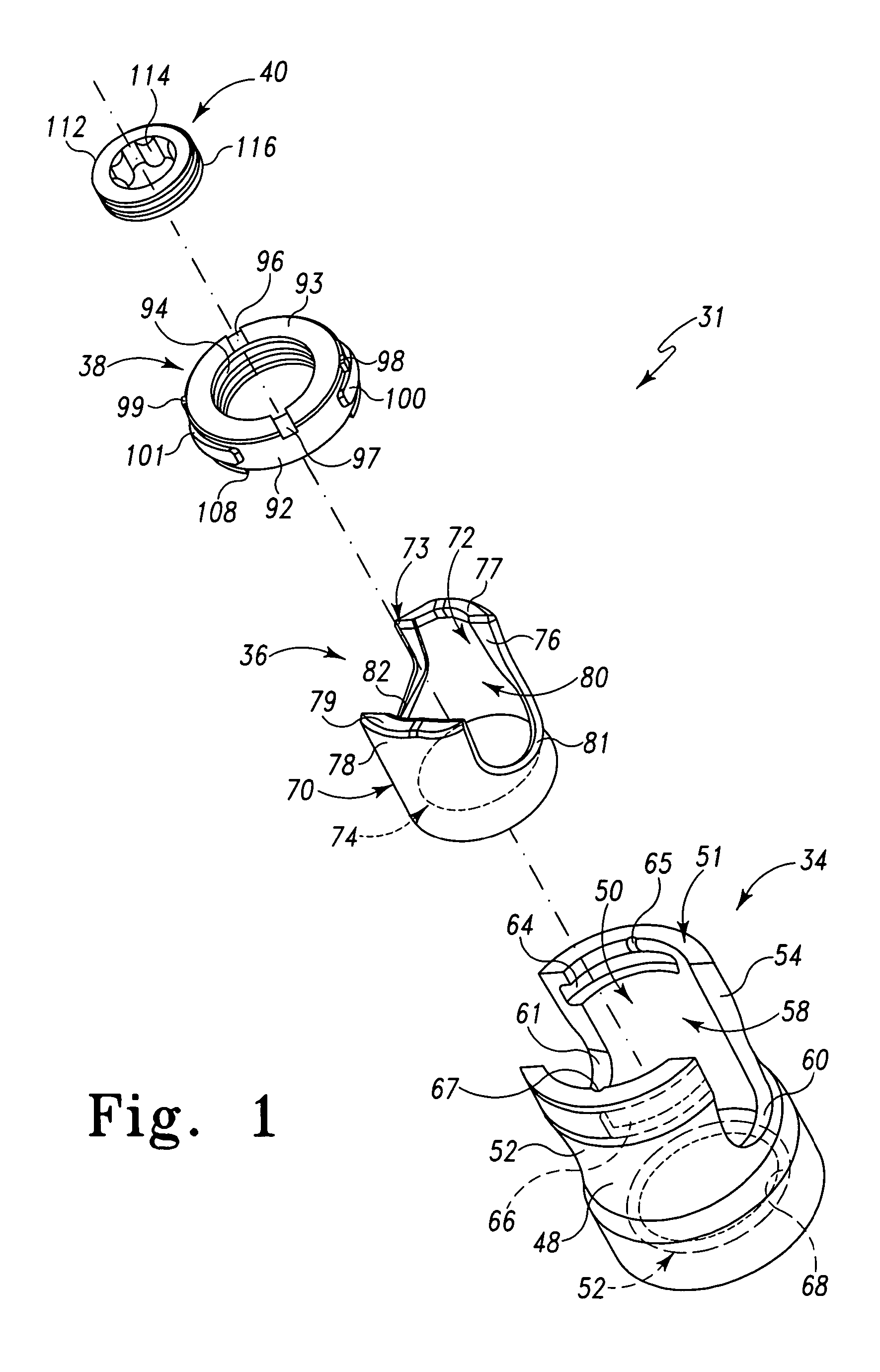
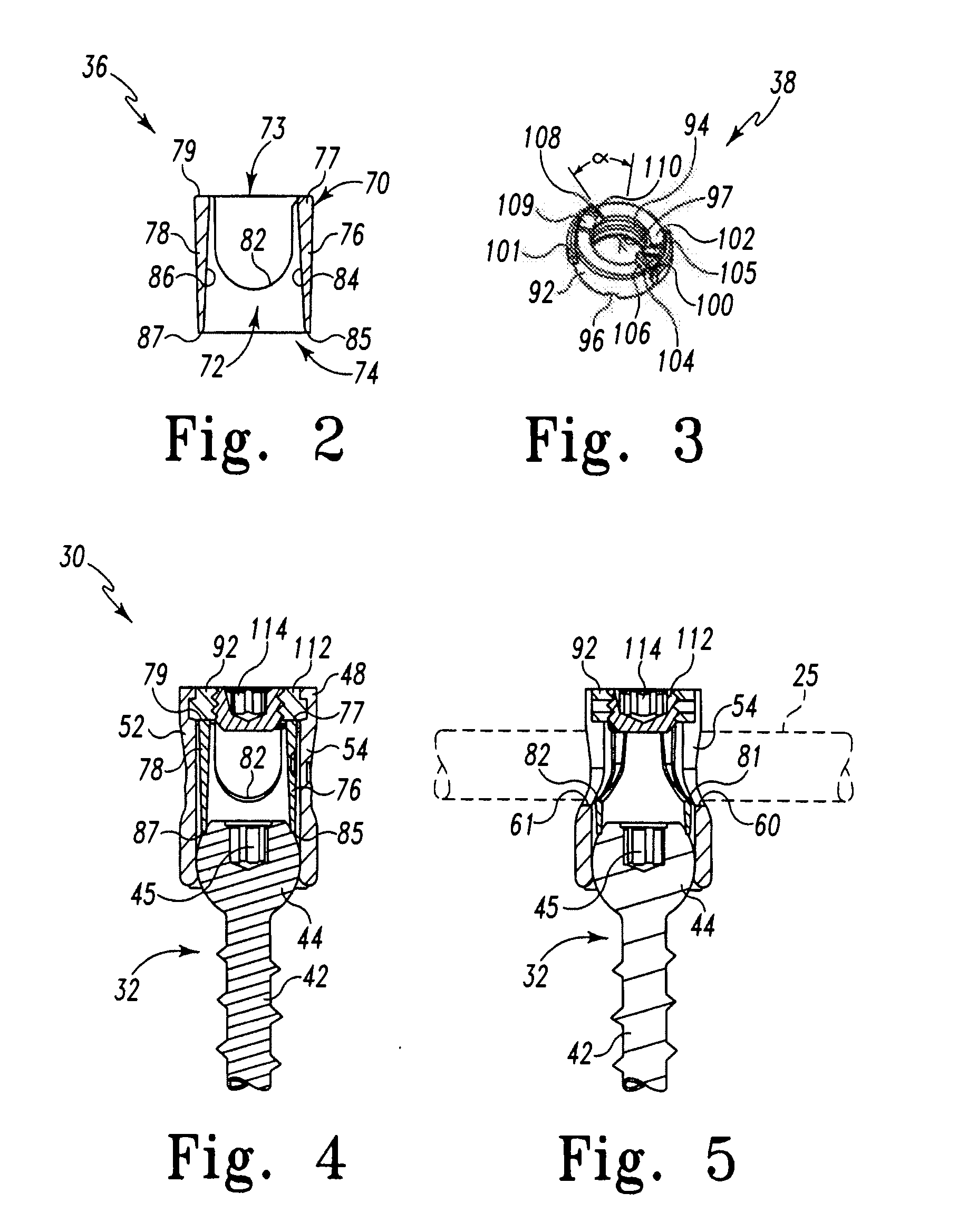
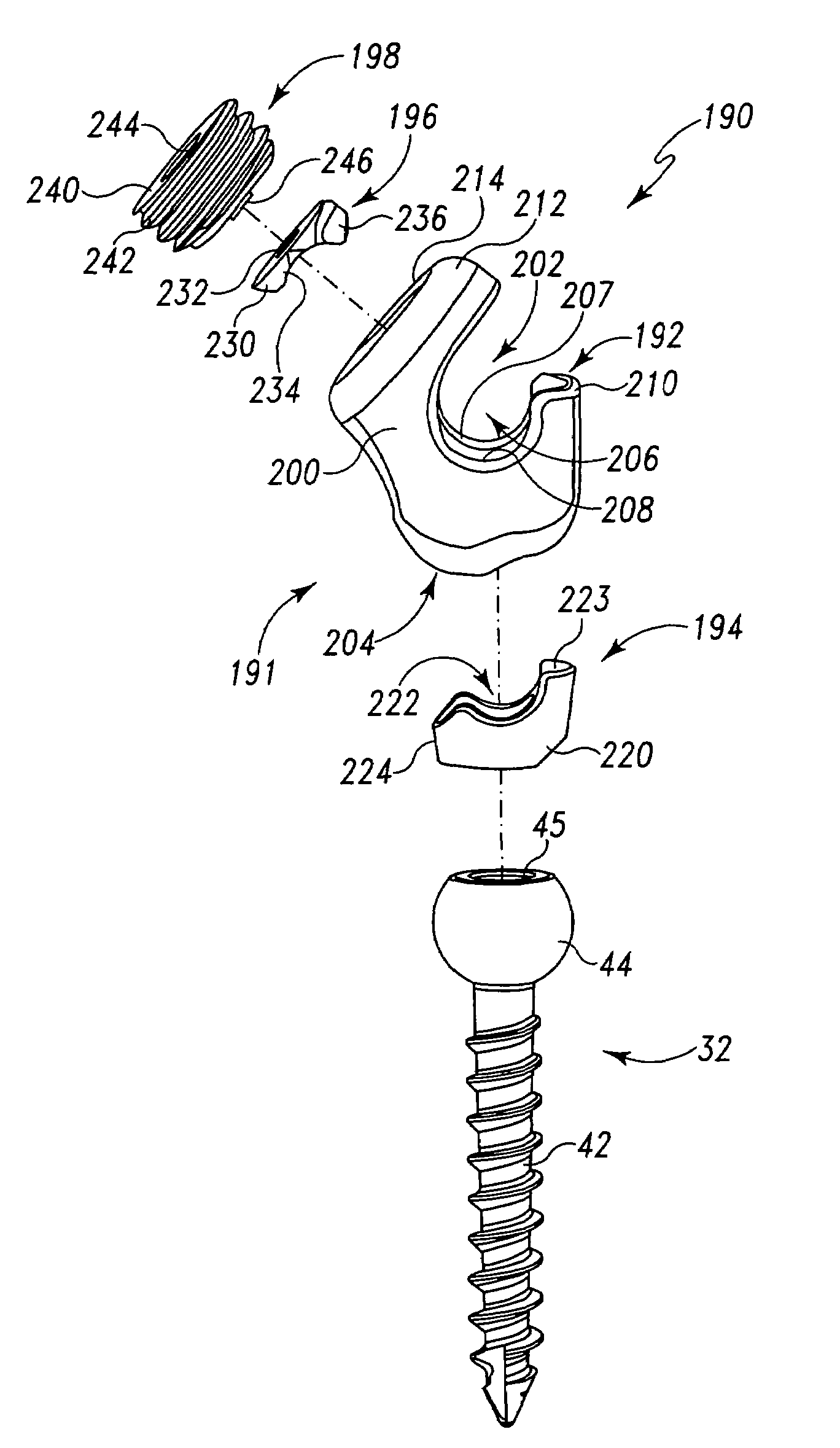
Top Loading Polyaxial Spine Screw Assembly With One Step Lockup
A top loading polyaxial spinal rod screw assembly is configured for simultaneous or one step lockup of angular orientation of a rod holder portion of the screw assembly relative to a bone screw and of a spinal rod within the rod holder portion of the screw assembly. The spinal rod and the angular orientation of the rod holder holding the spinal rod are thus fixed upon receipt of a lockup component of the present assembly. Components of the present spinal rod screw assembly cooperate to allow reception of a spinal rod in a rod holder that is adapted for pivotal retention on a bone screw and to lock or fix the spinal rod within the rod holder while also locking or fixing the angular orientation of the rod holder relative to the bone screw upon receipt of a lockup cap component of the screw assembly in the rod holder. In one form, the present screw assembly is defined by a three-piece polyaxial screw head assembly for a bone screw. The three-piece polyaxial screw head assembly includes a spine rod holder or head configured for pivotal connection with the bone screw, a head insert configured for reception in the spine rod holder, and a lockup (end) cap configured for reception in the spine rod holder. The lockup cap is configured to interact with the head insert to fix an angular position or orientation of the spine rod holder relative to the bone screw at the same time as fixing a spinal rod that has been received in the spine rod holder relative to the spine rod holder.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Articulating Expandable Intervertebral Implant
A spacer for separating bones of a joint includes a frame and a carriage. The carriage has ramped surfaces, and is slideably moveable in relation to the frame. A screw support is moveably connected to the frame to form a changeable angular orientation with respect to the frame. An actuating screw is supported by the screw support, and is connected to the carriage to cause the carriage to slideably move in relation to the frame when the actuating screw is rotated. Opposing endplates are configured to engage opposing bone of the joint, and each has ramped surfaces mateable with the ramped surfaces of the carriage. When the carriage is moved by rotation of the actuating screw, the ramped surfaces of the carriage and the endplates slide against each other, causing the endplates to move relatively apart, to increase the height of the spacer.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
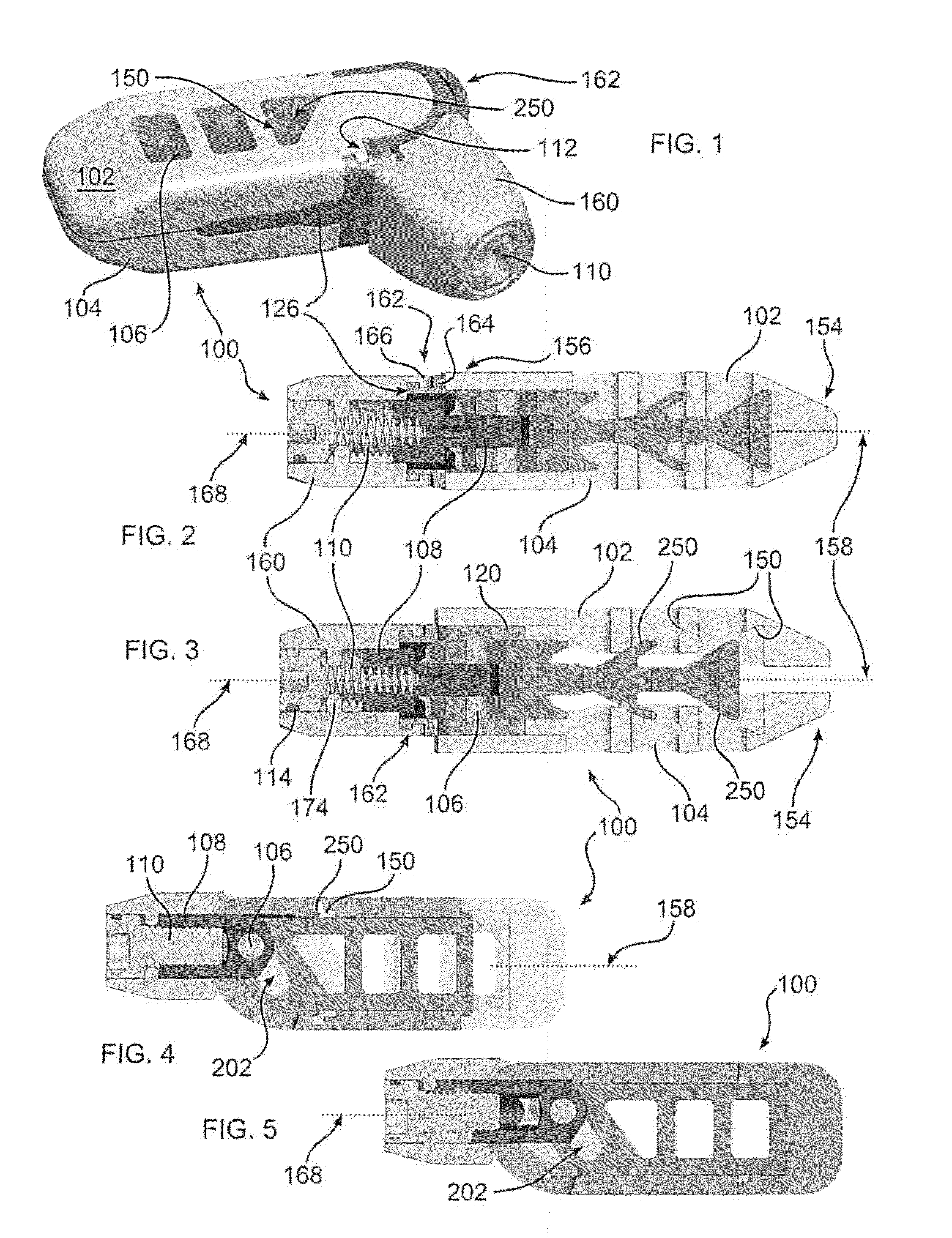
Hyperdexterous surgical system user interface devices
ActiveUS10617484B2Provide flexibilityEasy to operateProgramme controlComputer controlPhysical medicine and rehabilitationControl system
User interface devices are disclosed. The device can include a body that can be held in a user's hand. The body has an outer surface that can be gripped by fingers of the user's hand to facilitate translation and rotation of the body by the user's hand. The device can include one or snore sensors disposed within the body. In some embodiments, the one or more sensor can provide one or both of position and orientation information of the body to a control system. The body can provide feedback to the user via the exterior surface of the body that is gripped by the user's fingers and / or can receive control inputs from the user via one or more of translation of the body, rotation of the body, pressing of the outer surface with the user's fingers, and changing of the angular orientation of the longitudinal axis of the body. Methods of using a user interface device are also provided.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
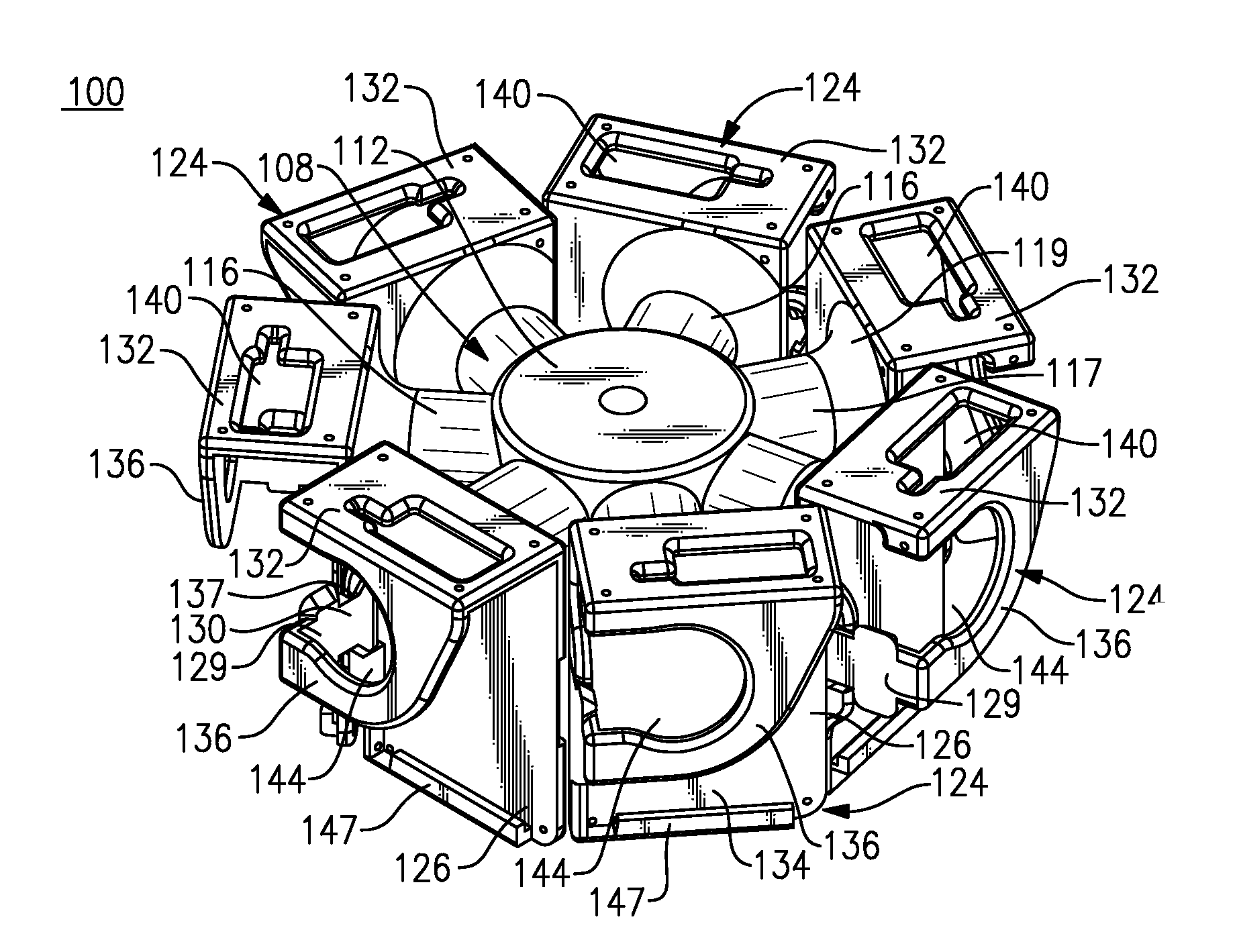
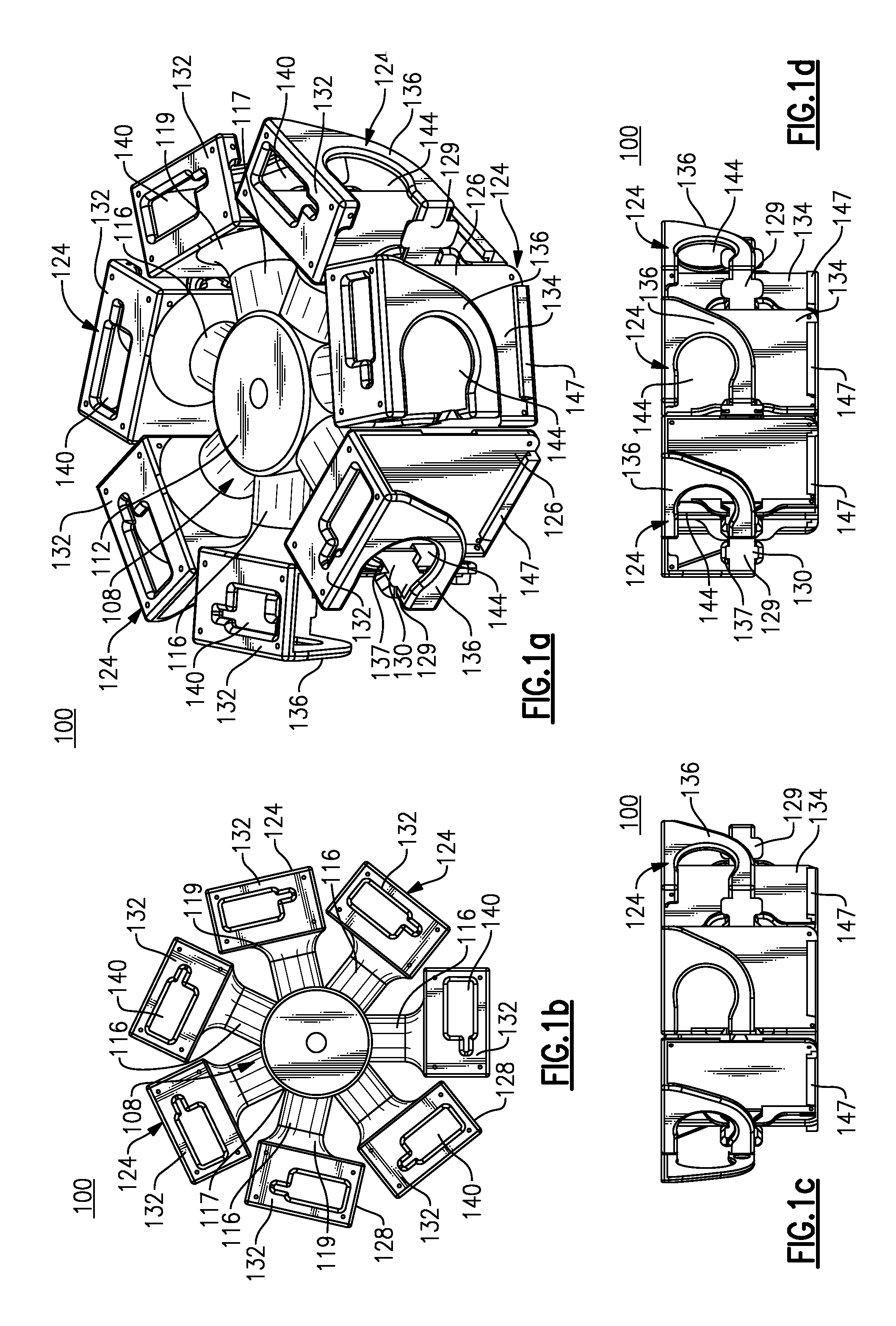
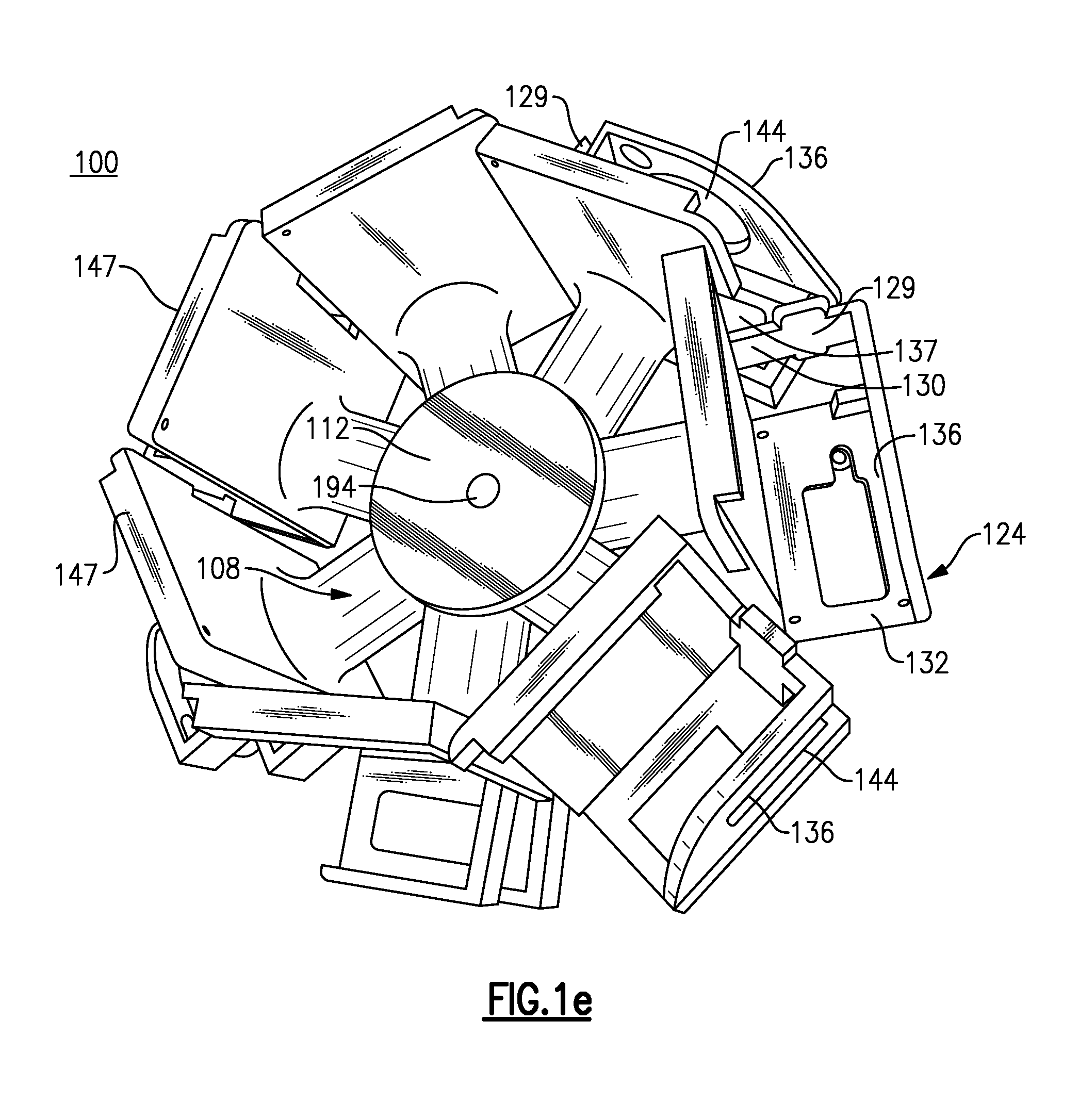
360 Degree Camera Mount and Related Photographic and Video System
ActiveUS20140153916A1Easy to assembleEasy to usePanoramic photographySteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Angular orientation
A camera holding assembly that is configured to hold a plurality of cameras in a predetermined orientation includes a support having a plurality of receptacles. Each of the receptacles include at least one feature enabling a camera to be releasably retained therein as well as at least one and preferably at least three attachment features configured for enabling the camera holding assembly to be secured to another object. The receptacles are oriented about the support so that each camera, when loaded into the defined receptacles, is aimed in a different angular orientation. Images obtained from each retained camera can be stitched to create either a composite 360 degree×180 degree full spherical image or a composite 360 degree composite image of a scene of interest.
Owner:360 HEROS
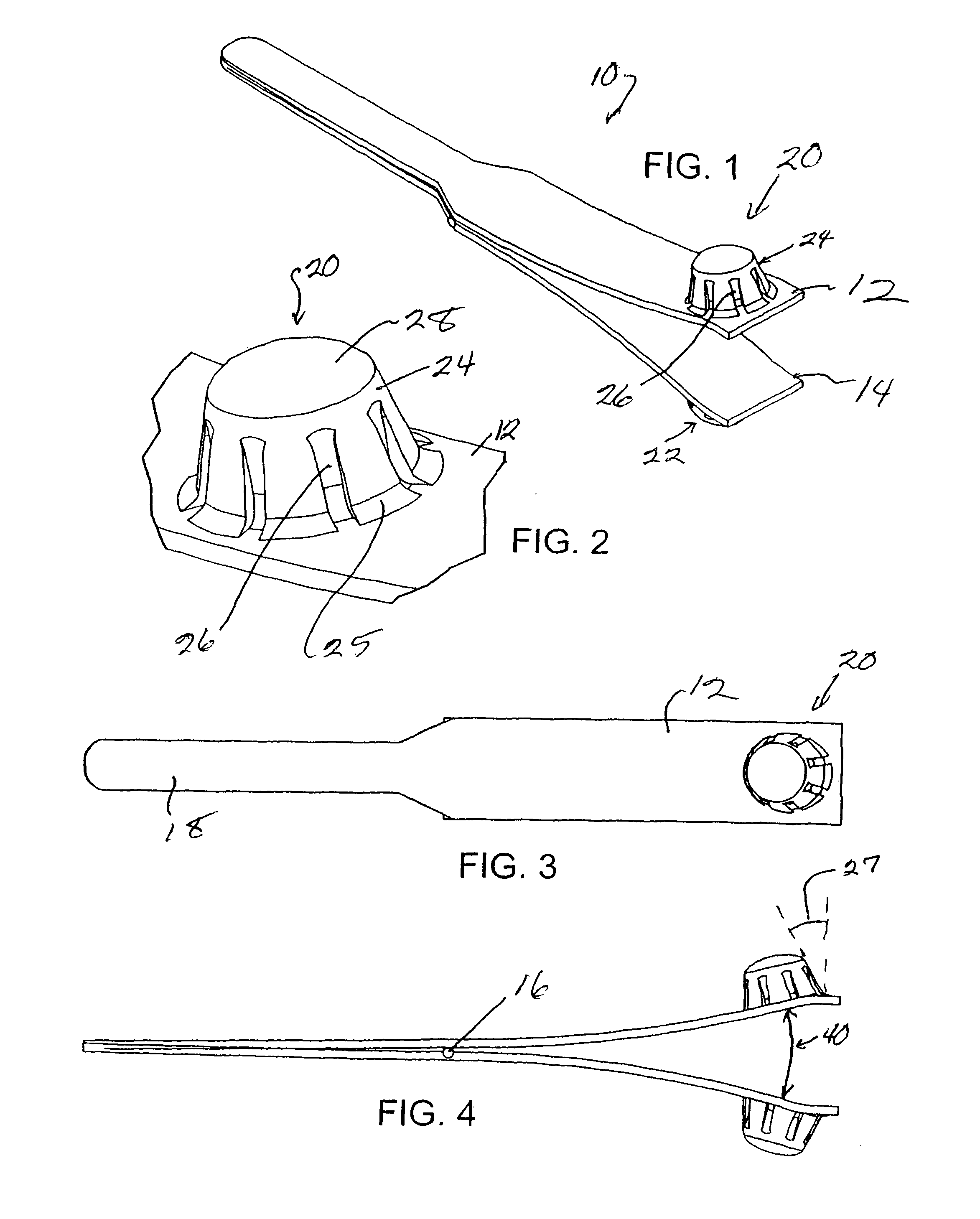
Tissue clamp
InactiveUS7901420B2Avoid premature releasePlace safeSurgical forcepsWound clampsAngular orientationBiomedical engineering
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Pedicle screw constructs for spine fixation systetms
A pedicle screw coupling construct for a pedicle screw construct provides fixation of angular orientation thereof relative to a pedicle screw independent of fixation of a received spinal rod to the coupling construct. The pedicle screw construct forms one component or element in a spinal fixation system. The independent fixation coupling construct also provides for fixation of the angular orientation of the coupling construct while the coupling construct has received the spinal rod. In another form, a coupling head or construct is configured to allow a pedicle screw shaft to pass therethrough but retain the pedicle screw head for rotation of the coupling head about the pedicle screw head. The coupling head or construct is also configured to allow at least a 45° arc of pivot or articulation about a pedicle screw shaft relative to a longitudinal axis of a spinal rod received in the body. This allows the head with a received spinal rod to fold, bend or pivot relative to the pedicle screw shaft, particularly to a greater degree than the prior art.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Dual display system
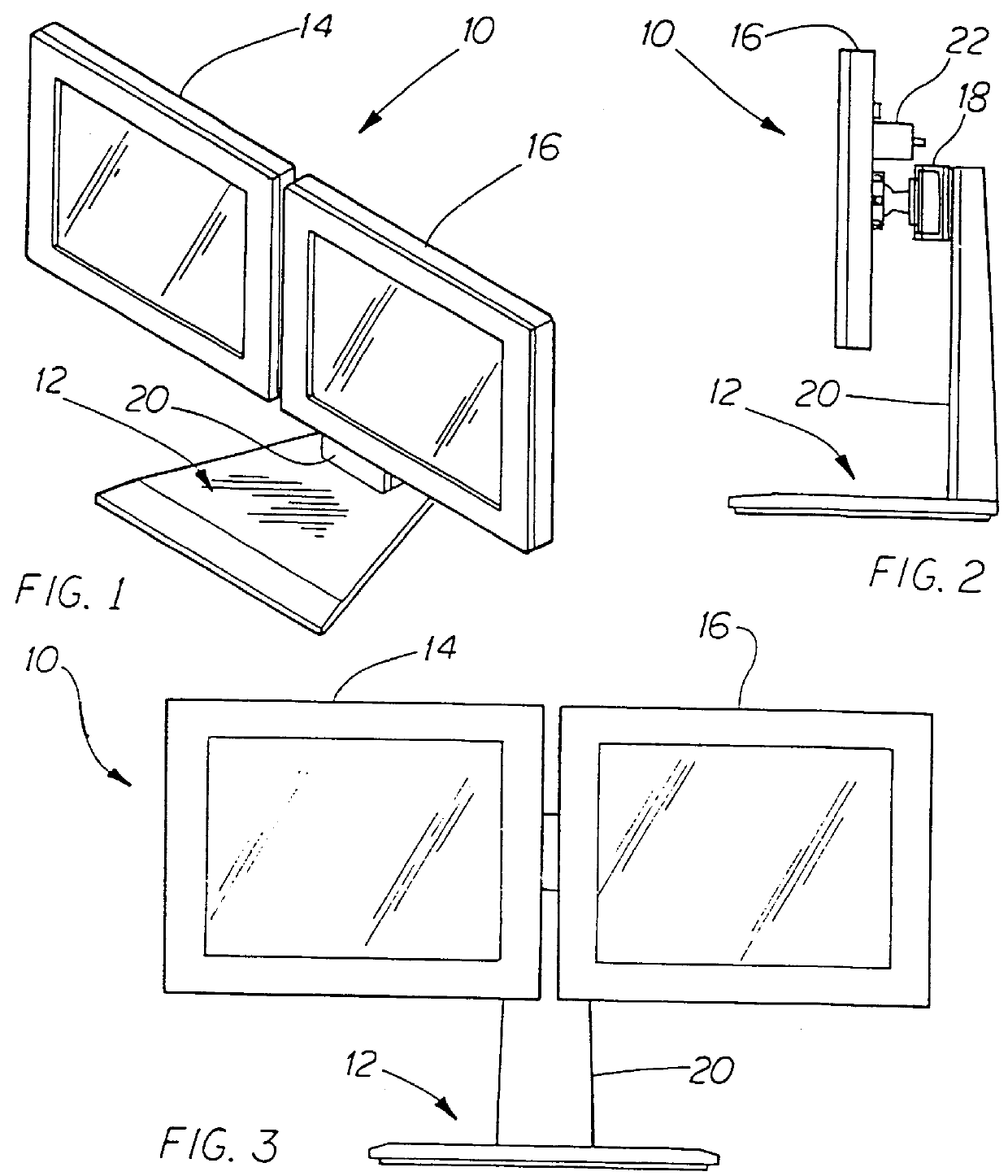
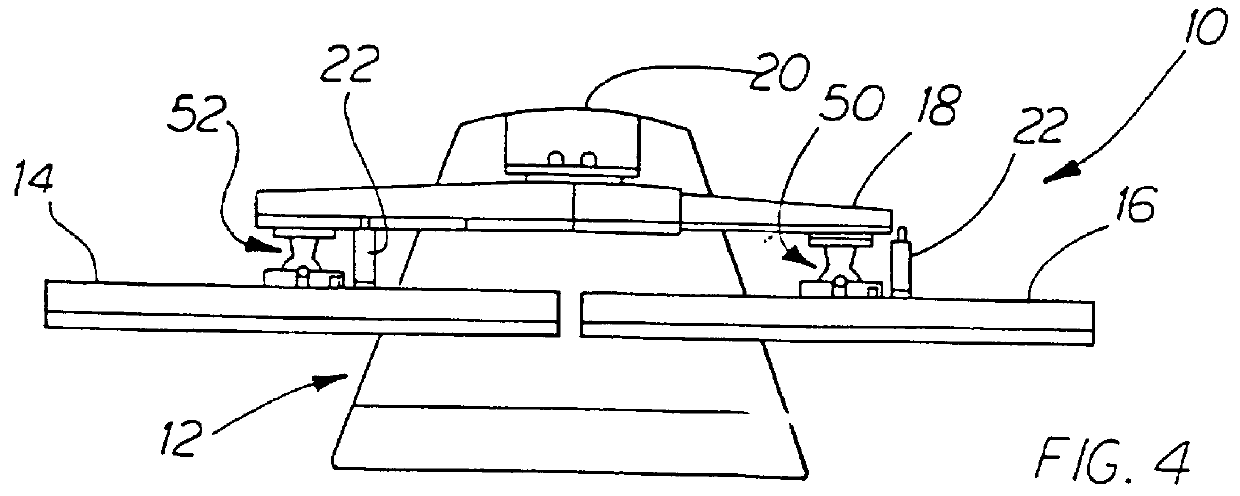
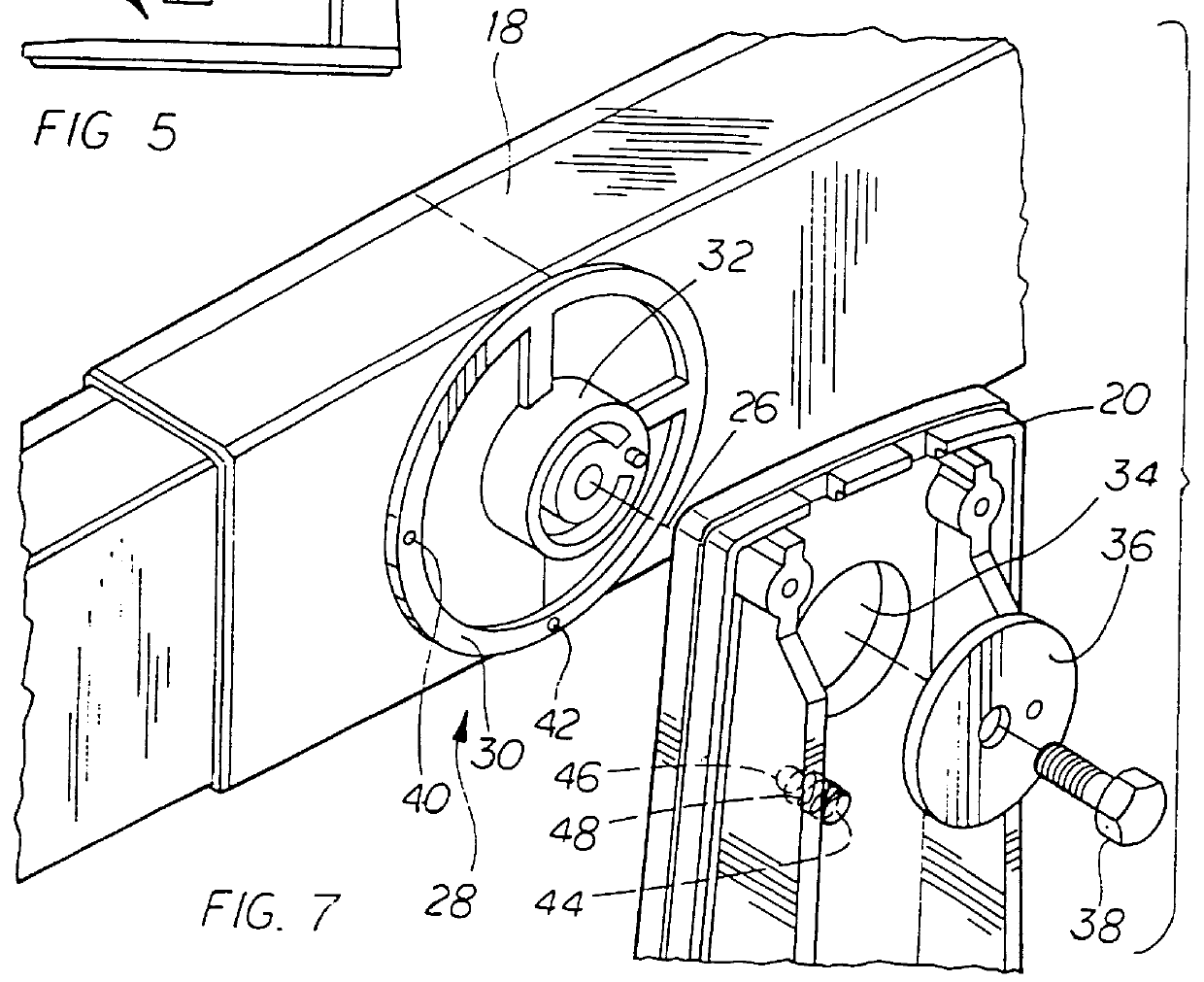
InactiveUSRE36978E1Increase spacingReduce spacingDigital data processing detailsStands/trestlesDisplay deviceAngular orientation
A display system includes a base, a pair of electronic displays, and an arm assembly that supports the displays from the base in vertical or horizontal registration. In one implementation, the arm assembly is a single telescopic member that rotates relative to the base and locks in vertical and horizontal orientations, the displays rotate relative to the member between corresponding extreme angular positions in which the operative angular orientation of the displays relative to horizontal is maintained, and the length of the member is adjusted to minimize separation of the displays. In another implementation, the arm assembly has separate arms rotating about vertically spaced axes and linked to minimize the separation of the displays automatically when vertically or horizontally registered. In a simple implementation, the arm assembly is a rigid arm that releasably attaches to the base only in vertical and horizontal orientations, the displays mounted releasably to the arm in pre-defined angular orientations that preserve their operative angular orientation, and one display can be connected to the arm at spaced apart position to adjust separation of the displays.
Owner:MOSCOVITCH JERRY
Pedicle screw constructs for spine fixation systems
A pedicle screw coupling construct for a pedicle screw construct provides fixation of angular orientation thereof relative to a pedicle screw independent of fixation of a received spinal rod to the coupling construct. The pedicle screw construct forms one component or element in a spinal fixation system. The independent fixation coupling construct also provides for fixation of the angular orientation of the coupling construct while the coupling construct has received the spinal rod. In another form, a coupling head or construct is configured to allow a pedicle screw shaft to pass therethrough but retain the pedicle screw head for rotation of the coupling head about the pedicle screw head. The coupling head or construct is also configured to allow at least a 45° arc of pivot or articulation about a pedicle screw shaft relative to a longitudinal axis of a spinal rod received in the body. This allows the head with a received spinal rod to fold, bend or pivot relative to the pedicle screw shaft, particularly to a greater degree than the prior art.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Telescopic introducer with a compound curvature for inducing alignment and method of using the same
An introducer system for implantation of pacemaker leads into the venous system of the human heart through the coronary sinus is comprised of a flexible, elongate, outer elongate element having a first shape or bias along a portion. The first shape on the outer element may be prebiased or may be initially straight and subsequently biased once deployed in the body chamber. A flexible, elongate, telescopic inner elongate element has a second shape or bias on its distal portion and has the first shape or bias on a more proximal portion. The inner elongate element is telescopically disposed in the outer sheath. The outer and inner elongate elements are rotatable with respect to each other, such that when the inner elongate element is distally extended from the outer sheath, there exists an angular orientation between the inner and outer sheaths which is congruent, when there is at least partial alignment between the distal portion of the outer elongate element and the more proximal portion of the inner sheath, both having the first shape or bias. This results in the rotation of the distal second shape or curve of the inner elongate element into a predetermined three dimensional location.
Owner:PRESSURE PROD MEDICAL SUPPLIES INC
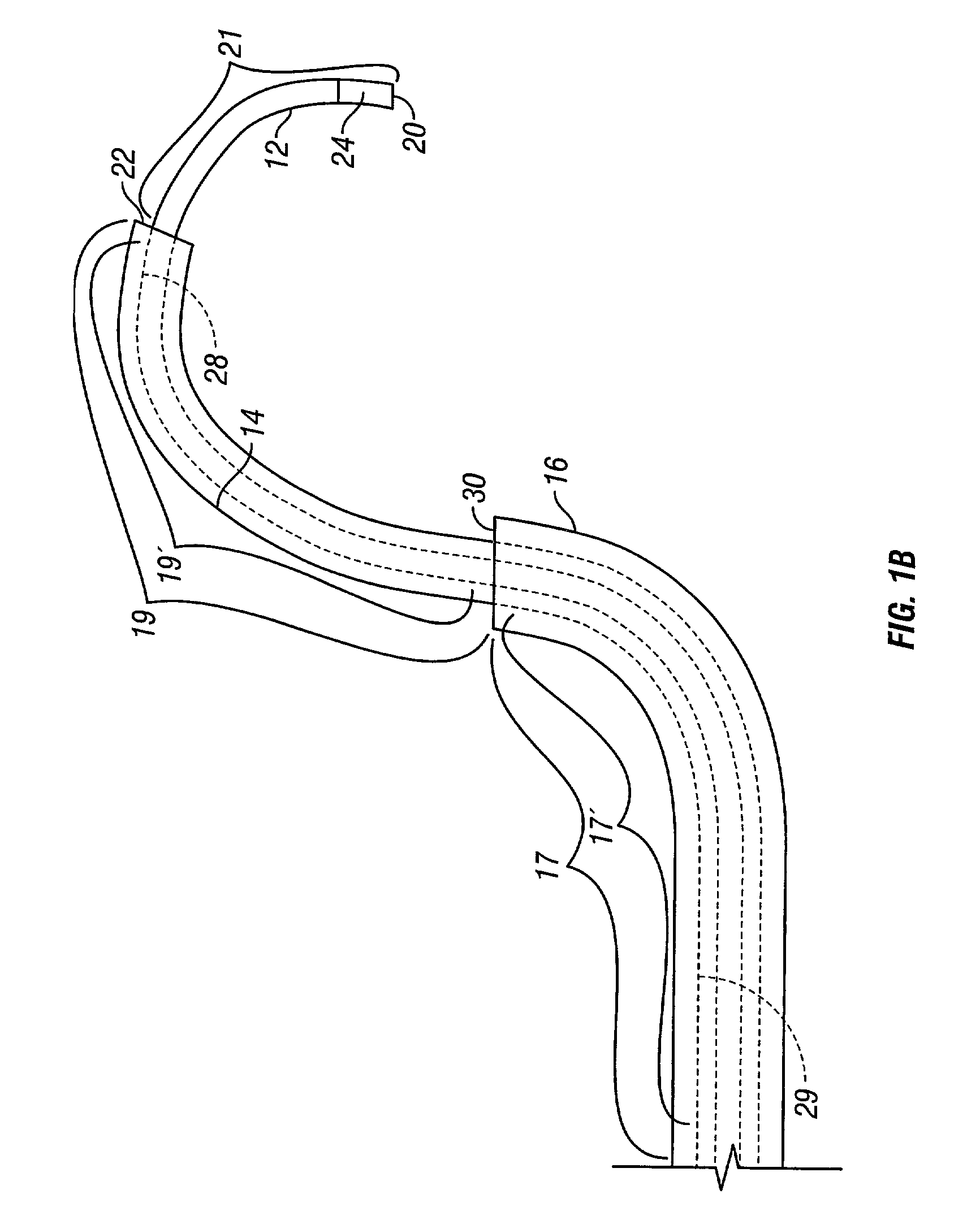
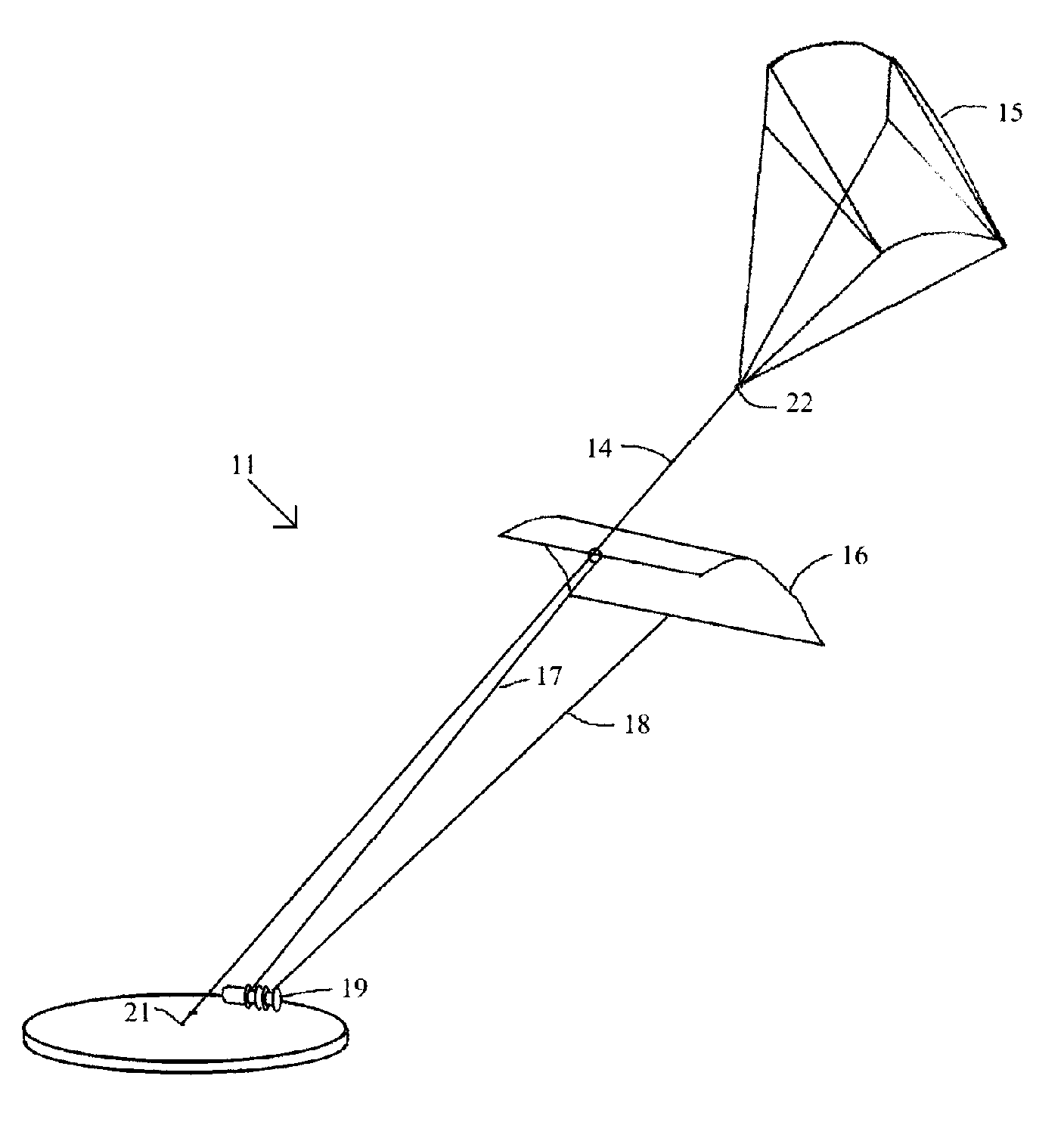
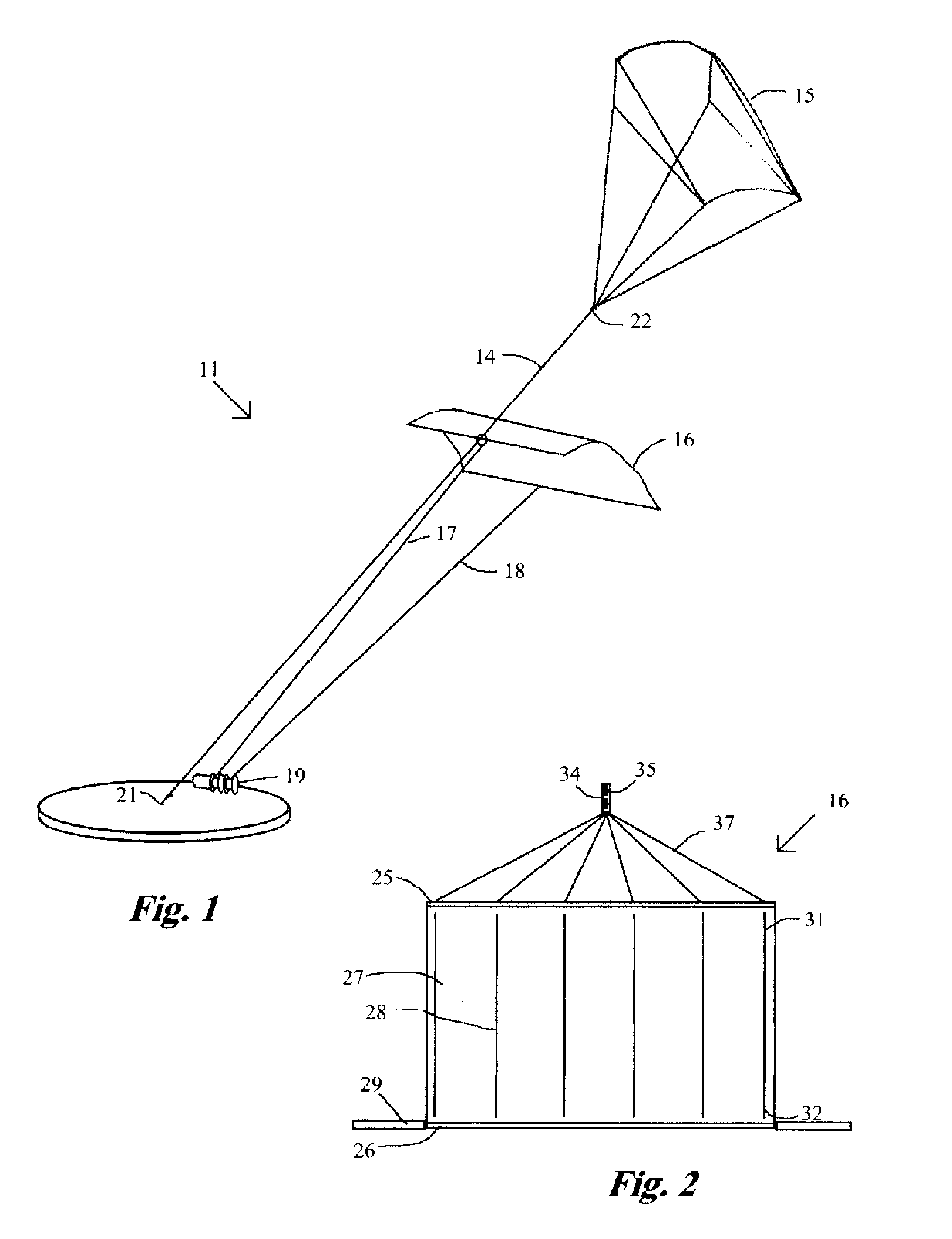
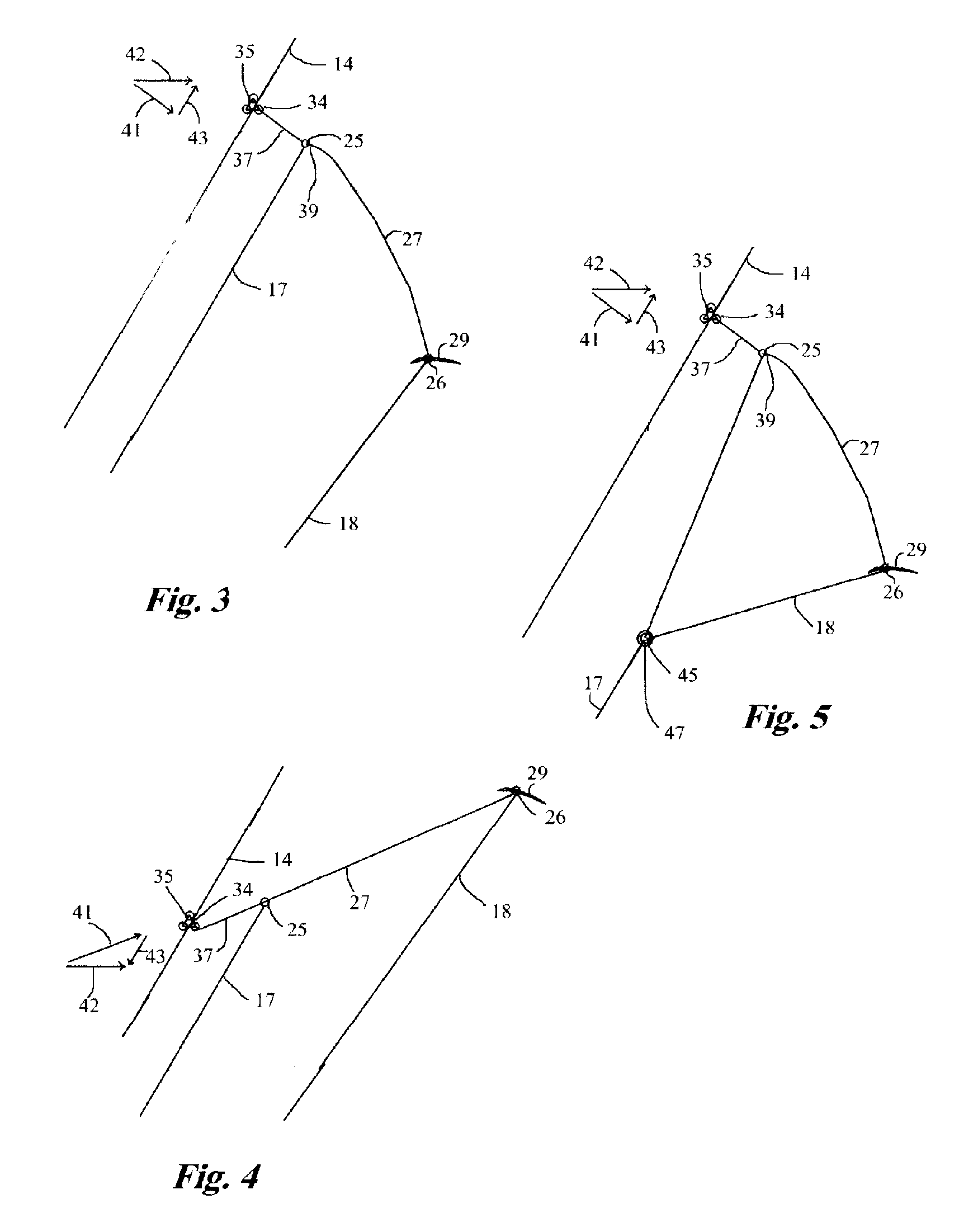
Aerialwind power generation system and method
InactiveUS7188808B1Increase power generationWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesWind drivenAngular orientation
An aerial power generation system includes a guide line supported by a support body. Wind driven elements are configured and shaped to provide maximum force from both lift and drag during the downwind phase of operation and minimum force during the upwind phase. The guide lines add stability to the system and provide better control over angular orientation and direction of motion. Power transfer is through one or more tow lines connected from the driven elements to power generation devices on the ground. Another embodiment of the aerial power generation system includes a revolving apparatus and two or more wind powered driven elements connected by tow lines to the revolving apparatus. The method includes changing the driven elements between high and low force configurations for downwind and upwind operation, and flying the driven elements in a selected pattern perpendicular to the tow line.
Owner:OLSON GAYLORD G
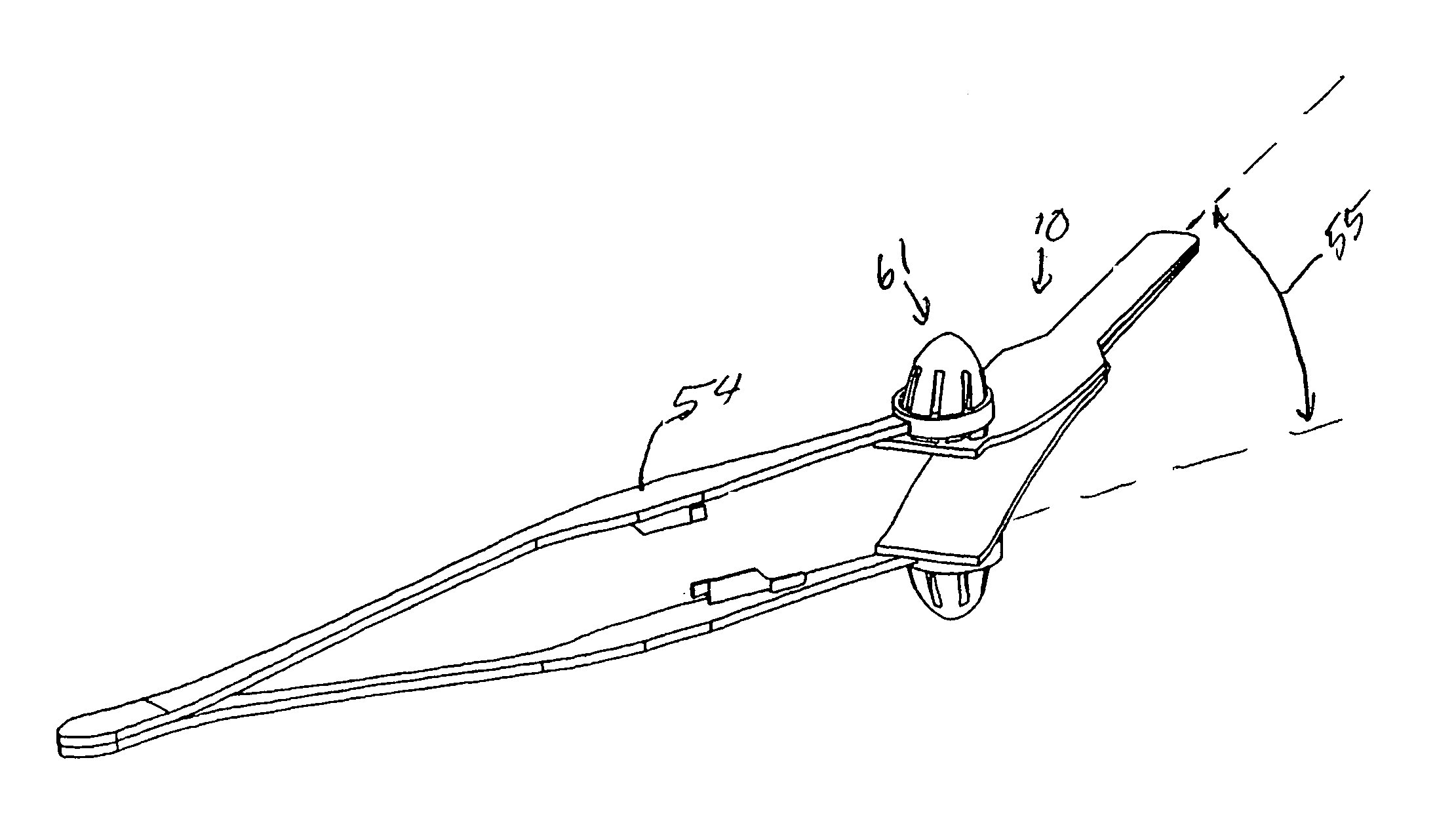
Guidewire handling device
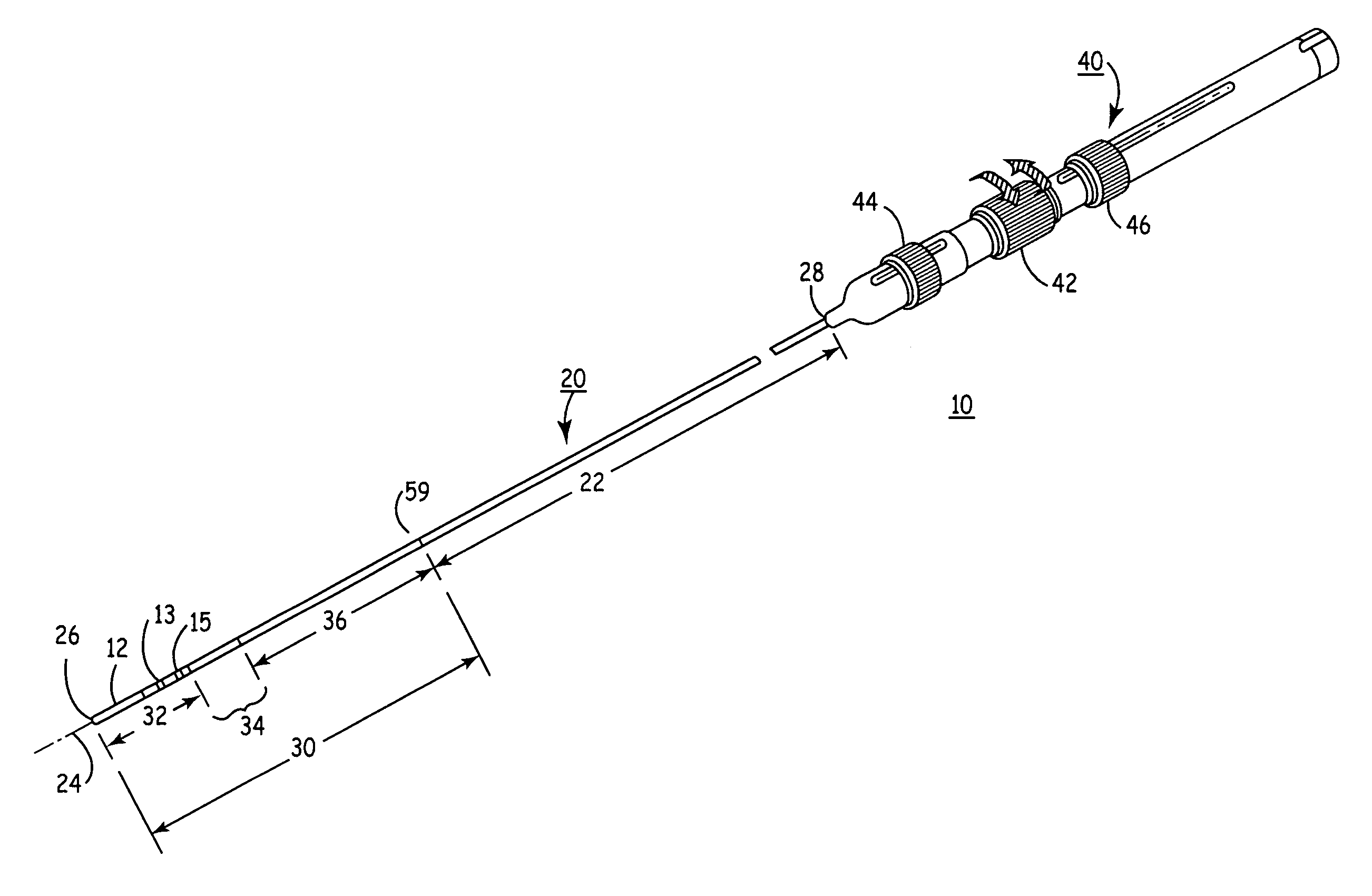
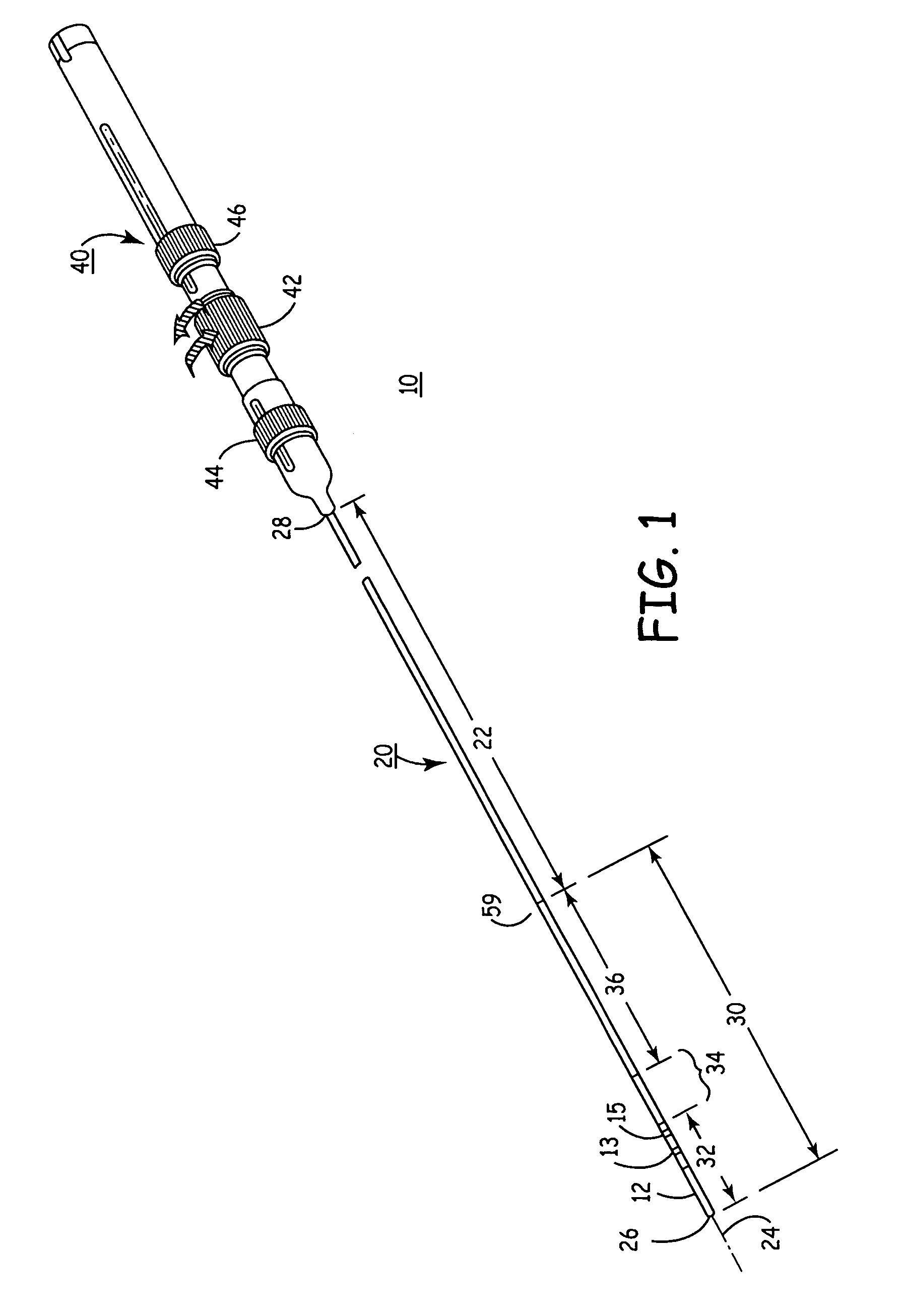
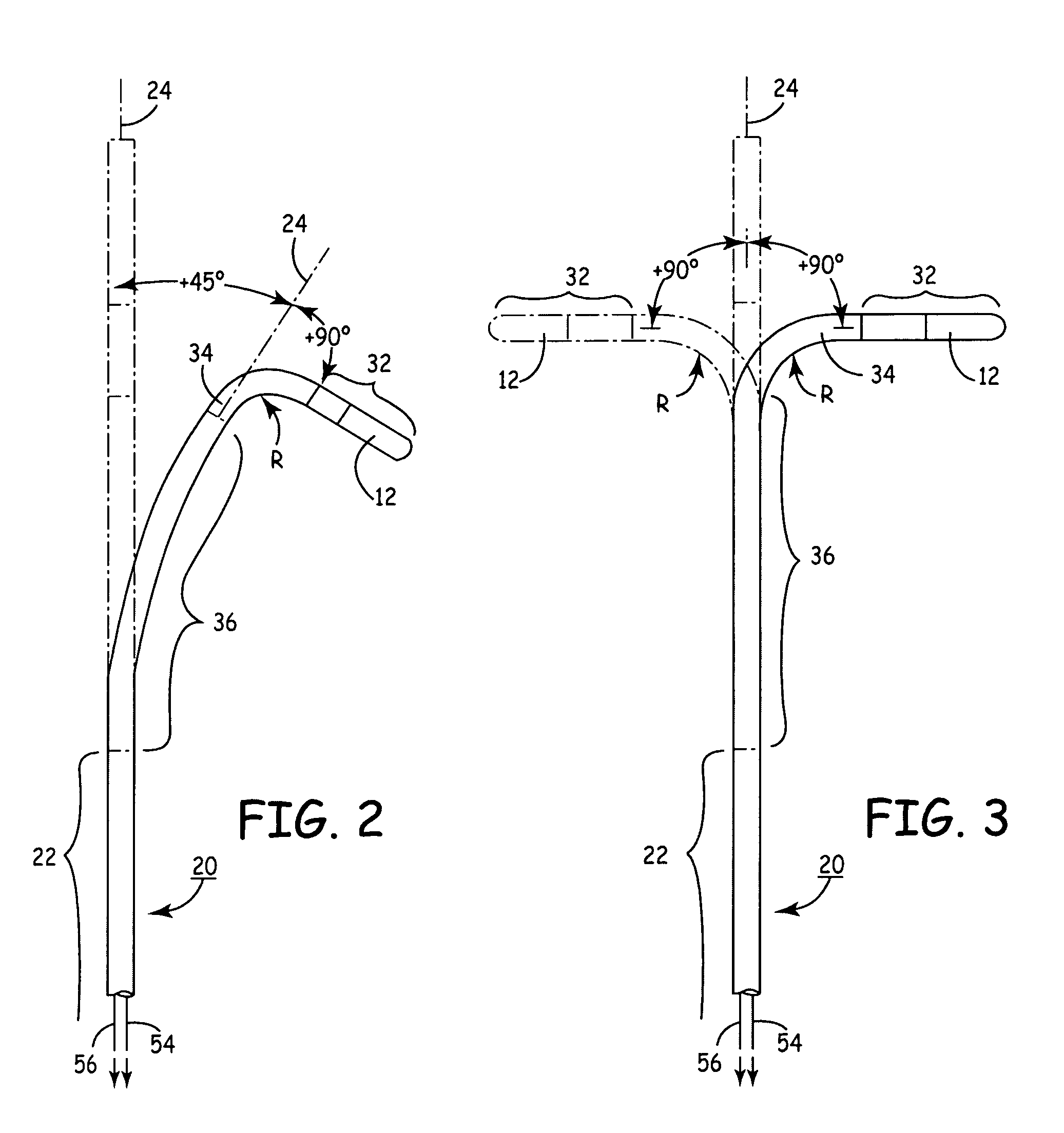
This invention describes a guidewire handling device for creating an indicium and / or urging a guidewire. A guidewire handling device is provided that includes a device body having a guidewire passage sized to receive a guidewire. A clamping member is coupled to the device body and is movable between a first and second position. The guidewire handling device includes a visible marker that provides visible feedback regarding the angular orientation of the guidewire handling device. In addition, the guidewire handling device includes a contoured surface that allows the torque applied to the guidewire handling device to be dependent on the location where the torque is applied.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Tissue clamp
ActiveUS20080249547A1Avoid premature releasePlace safeSurgical pincettesSurgical forcepsEngineeringAngular orientation
The present invention relates to a tissue clamp, a tool for grasping the clamp and a method of using the clamp for surgical procedures. The clamp has a fixture or fixtures positioned on the proximal end of the arms of the clamp so that a tool can be used by the surgeon to securely grasp the clamp during placement thereof on the vasculature or other tissue of the patient. The fixture can have a plurality of channels so that the user can select the angular orientation of the tool relative to the damp.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Low-mounted powered opening system and control mechanism
A power-operated system for actuating the rear doors or liftgates of motor vehicles is disclosed. The system includes an articulating strut mounted between a vehicle frame and the rear door. A motor assembly is operatively coupled between the articulating strut and the vehicle frame for changing the angular orientation and, in turn, mechanical advantage provided by the articulating strut. The articulating strut is moved into angular orientations of greater mechanical advantage in order to effect opening of the rear door and lesser mechanical advantage to effect closing of the rear door.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Devices and methods for performing procedures on a breast
InactiveUS6936014B2Less obtrusiveLess susceptible to inadvertent bumpingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMedicineAngular orientation
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com