Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
342 results about "Distal segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
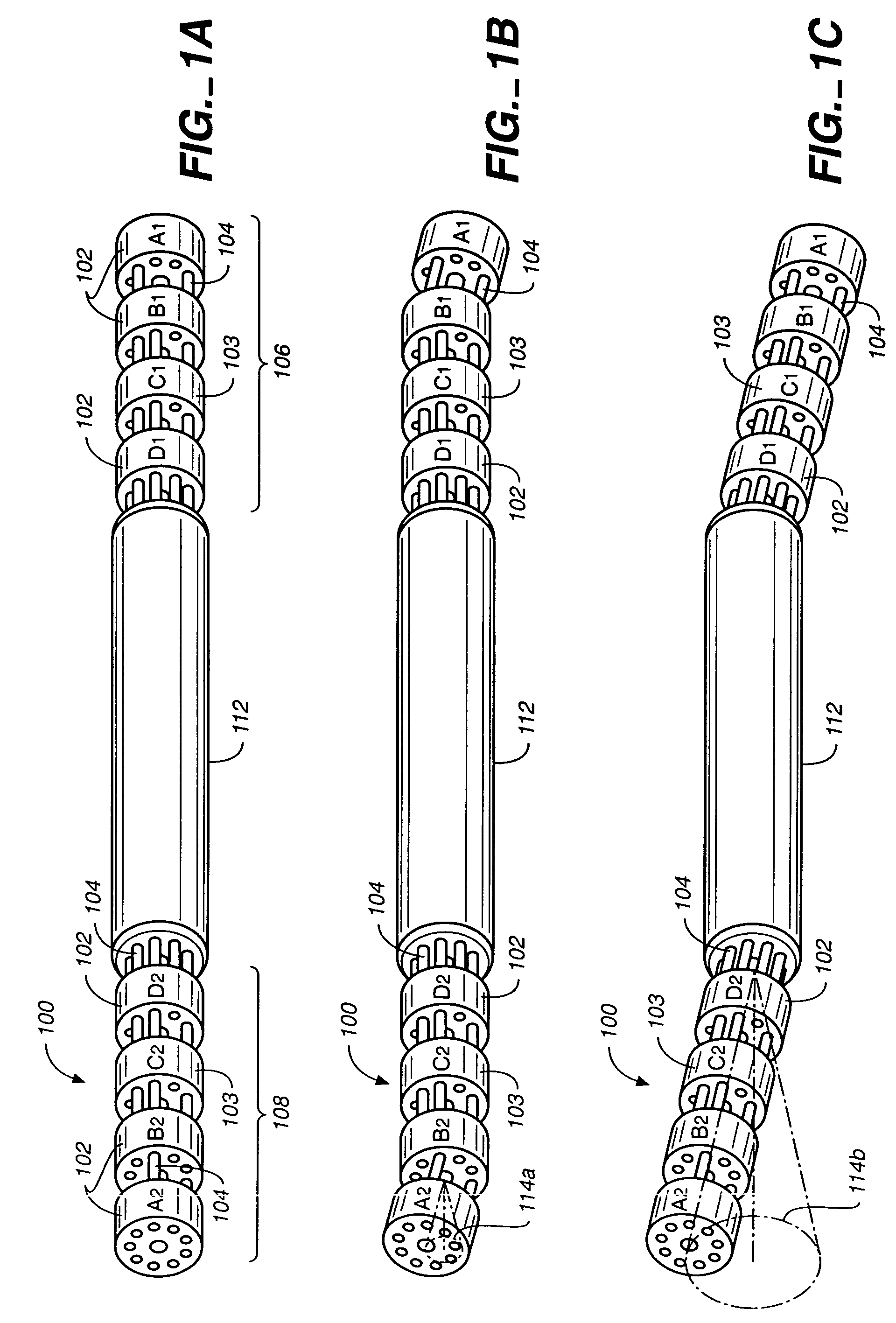
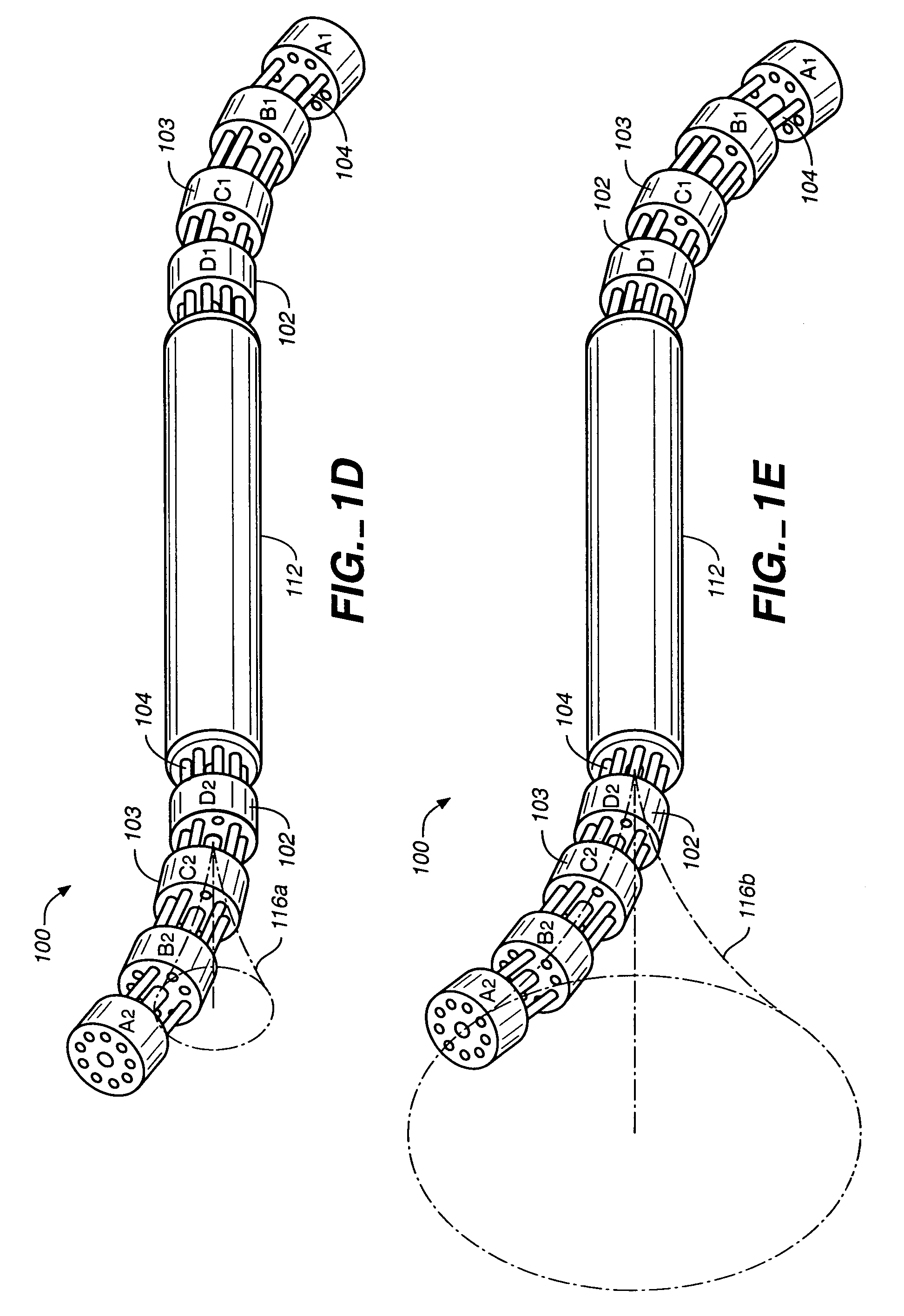
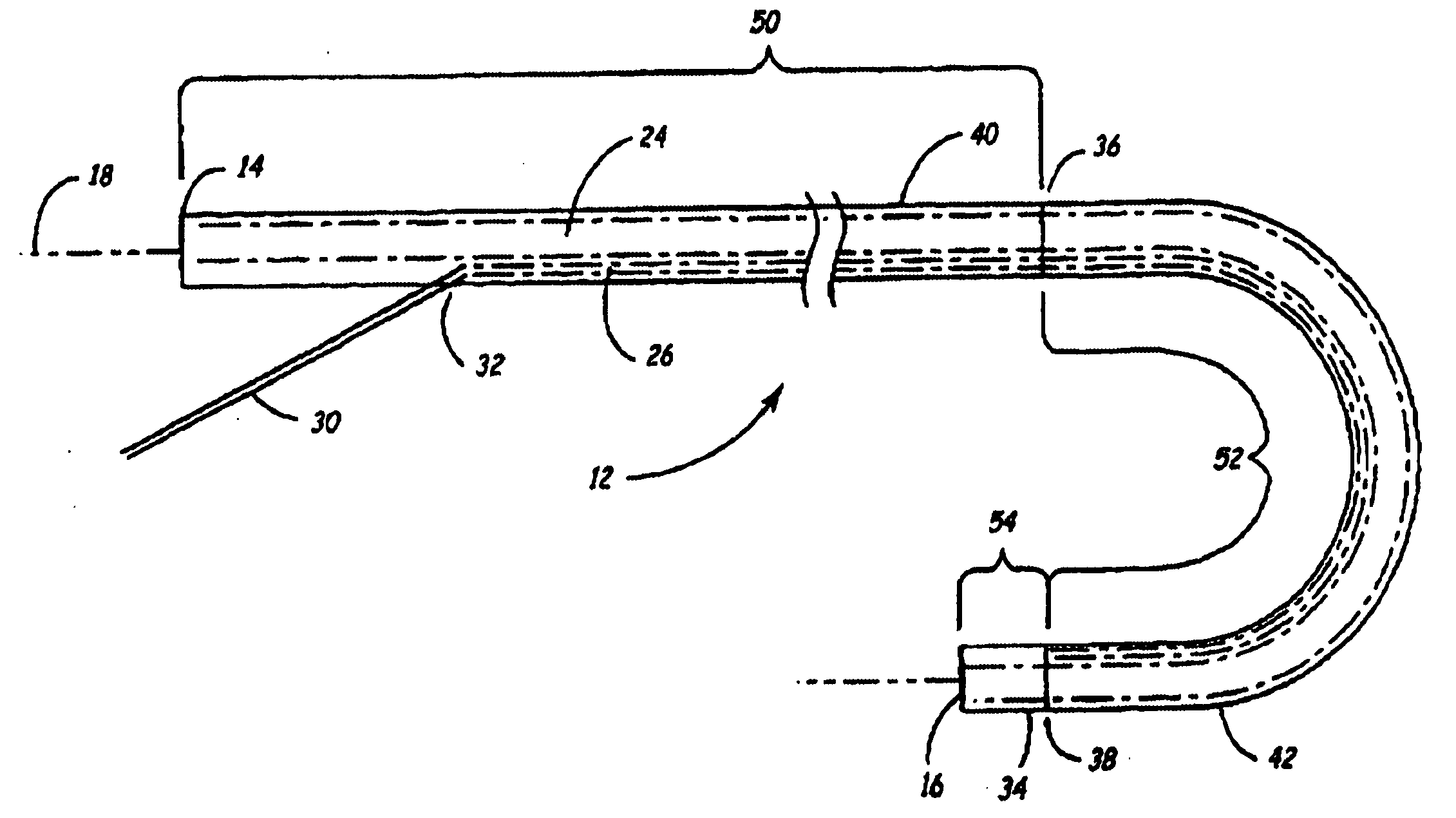
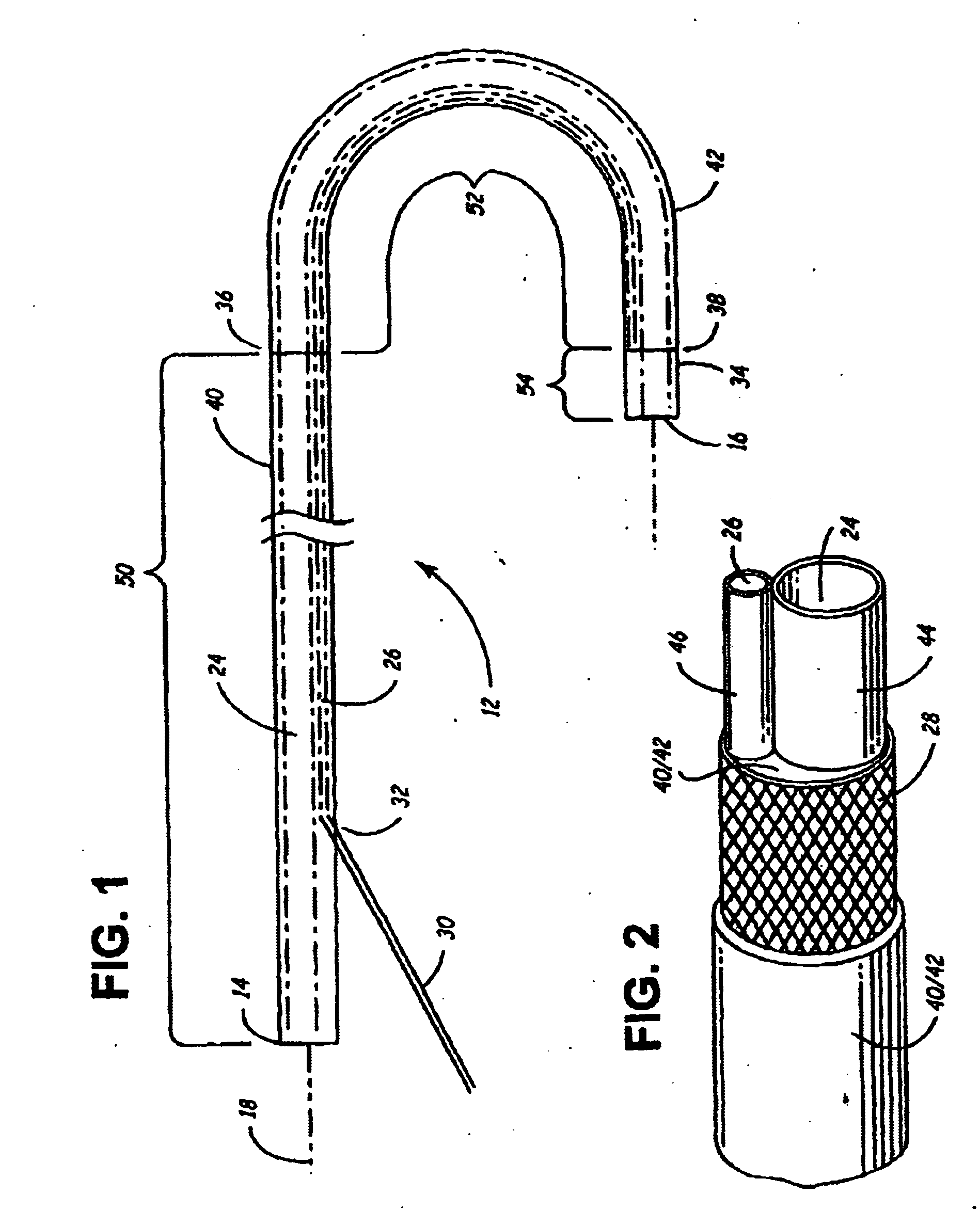
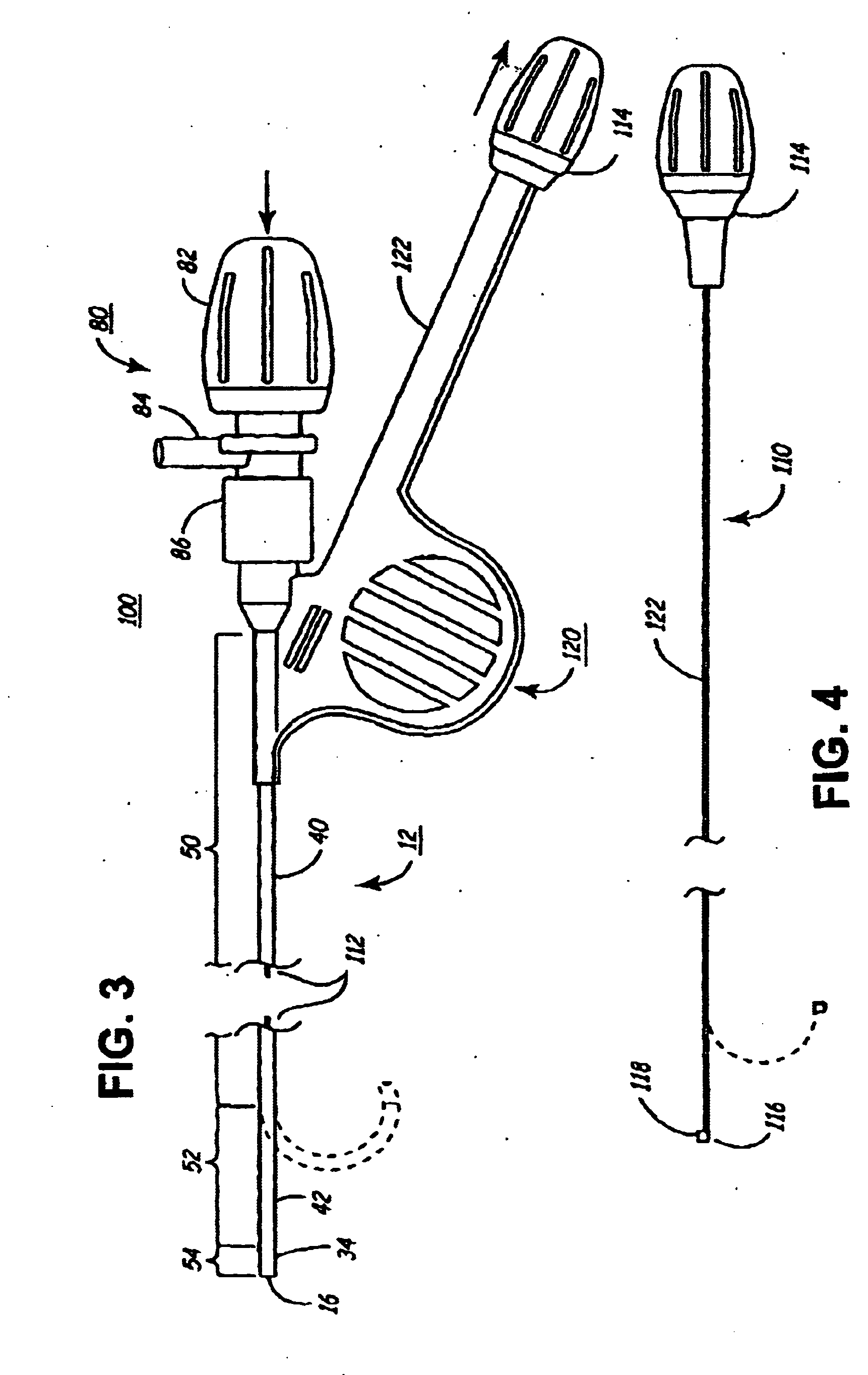
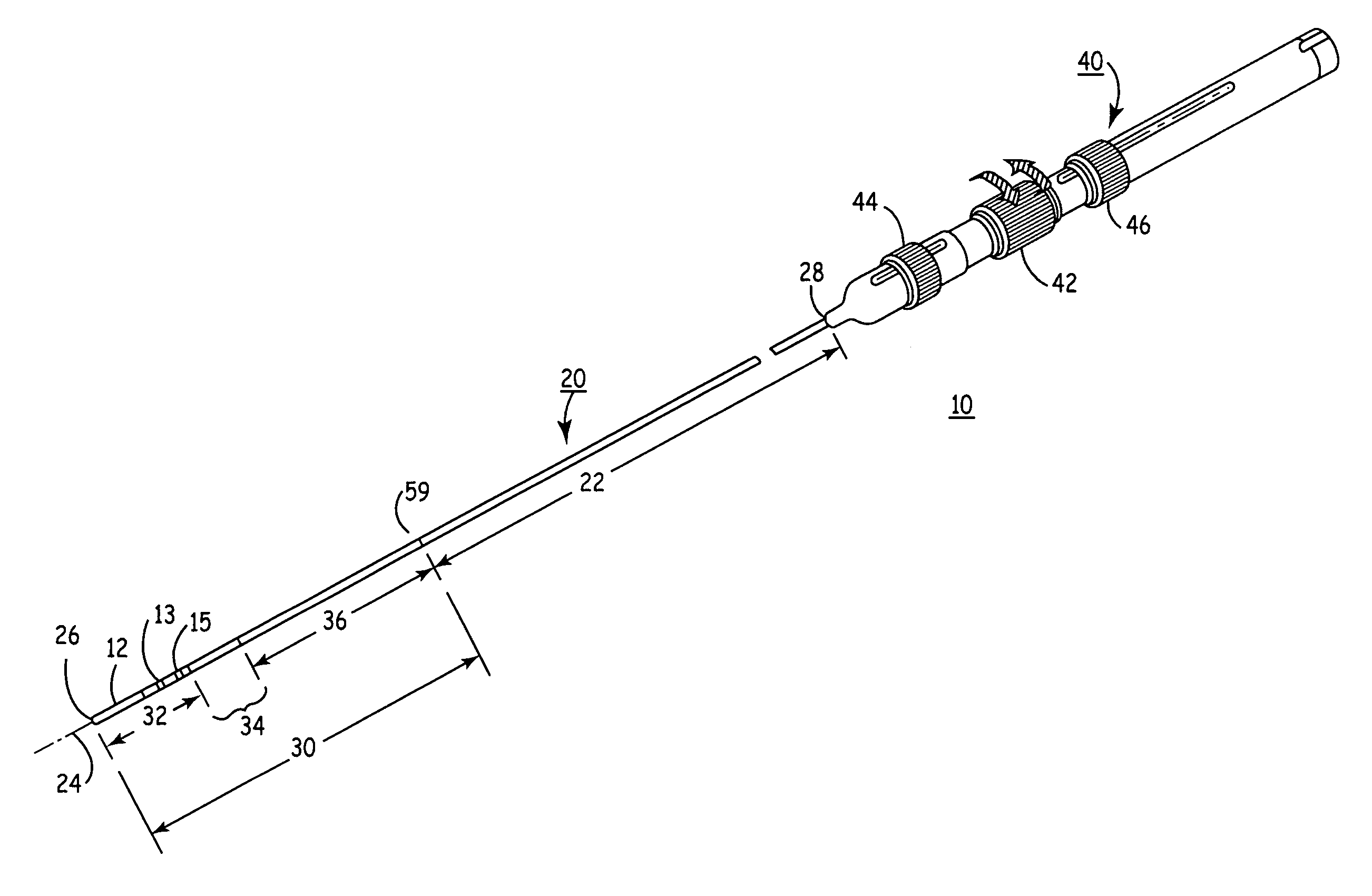
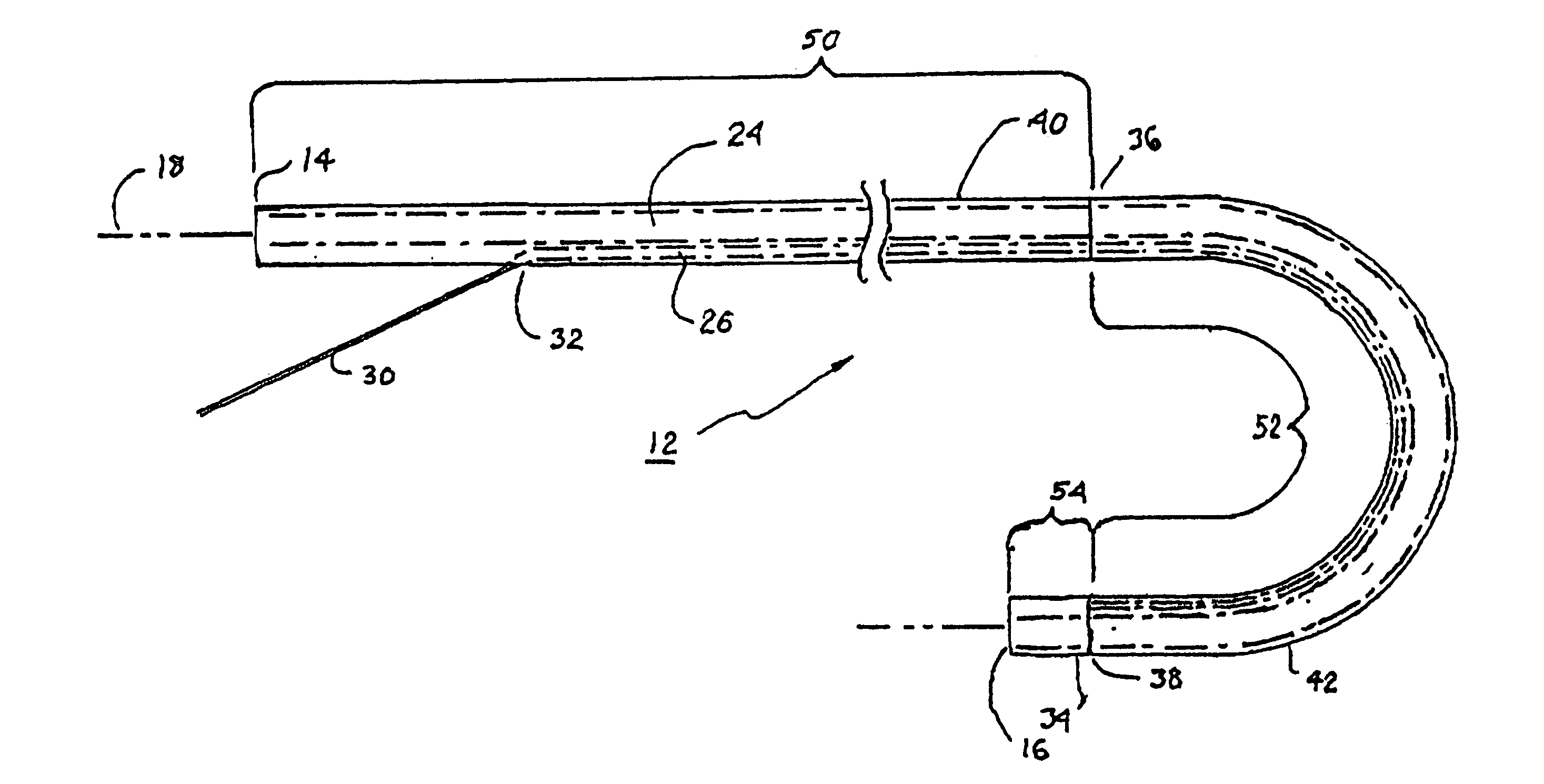
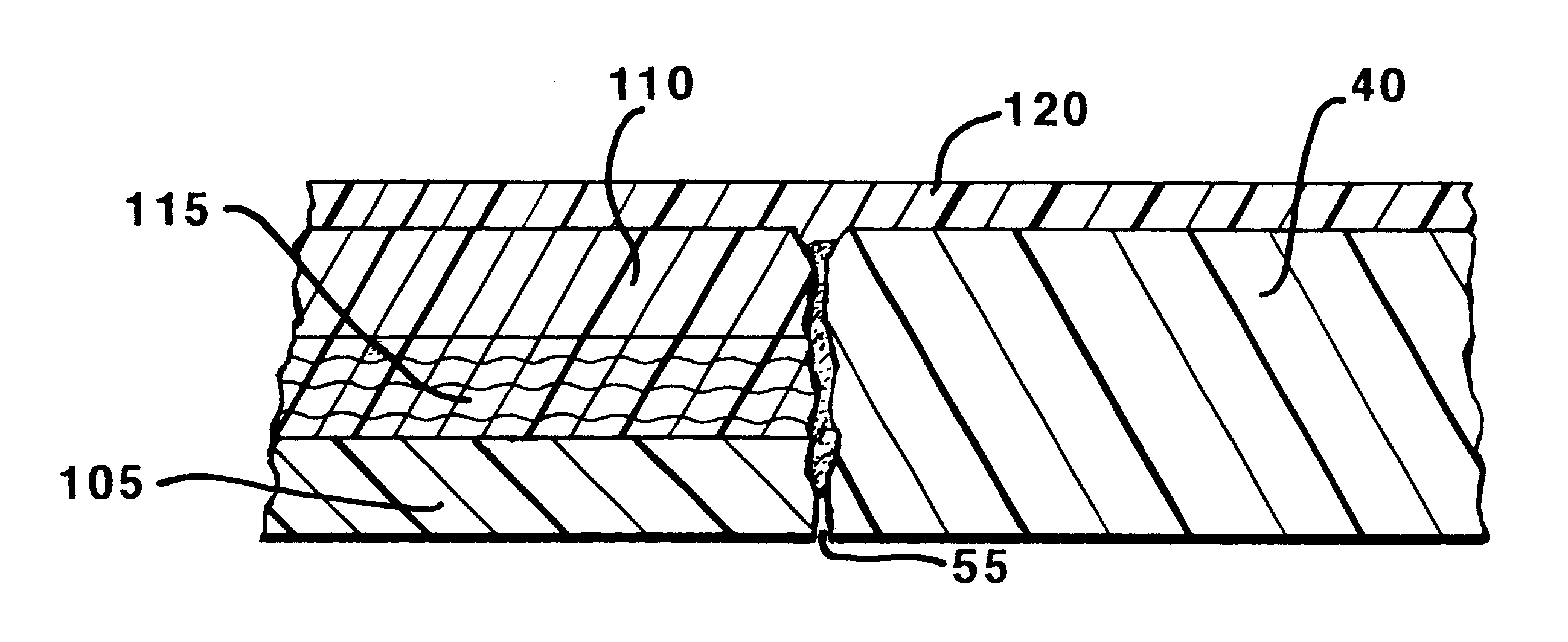
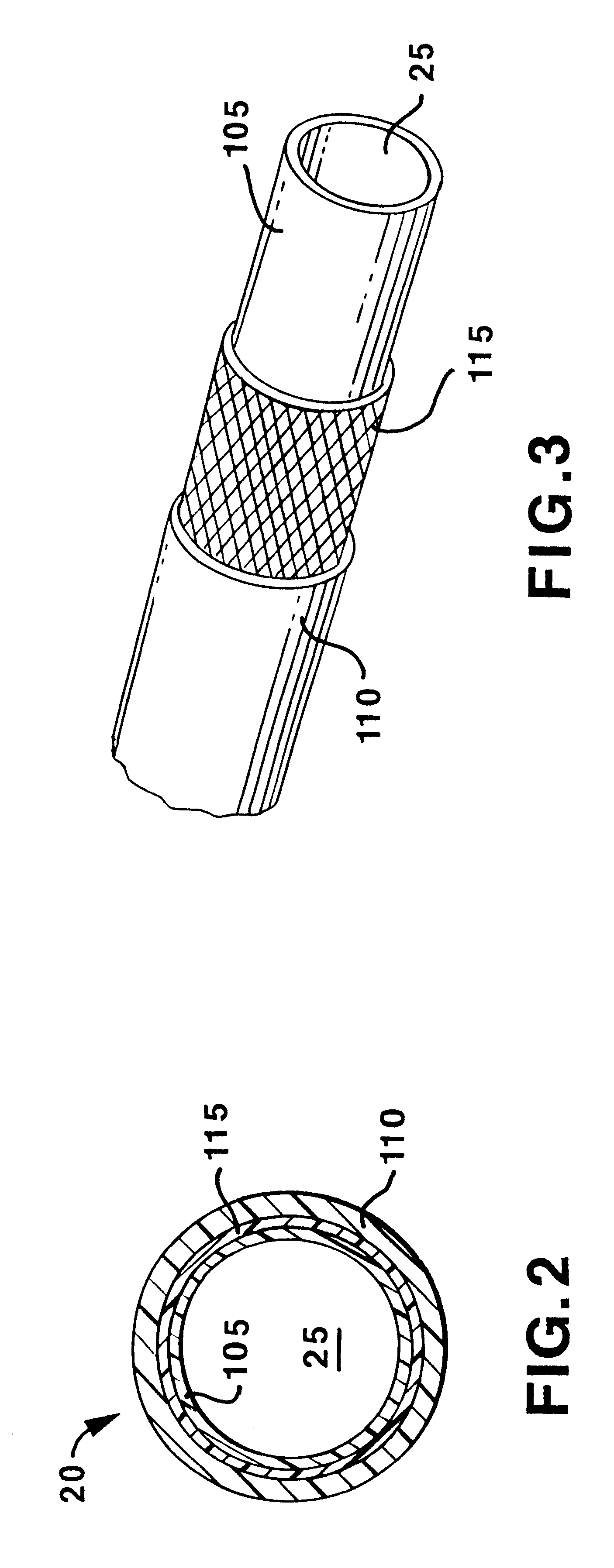
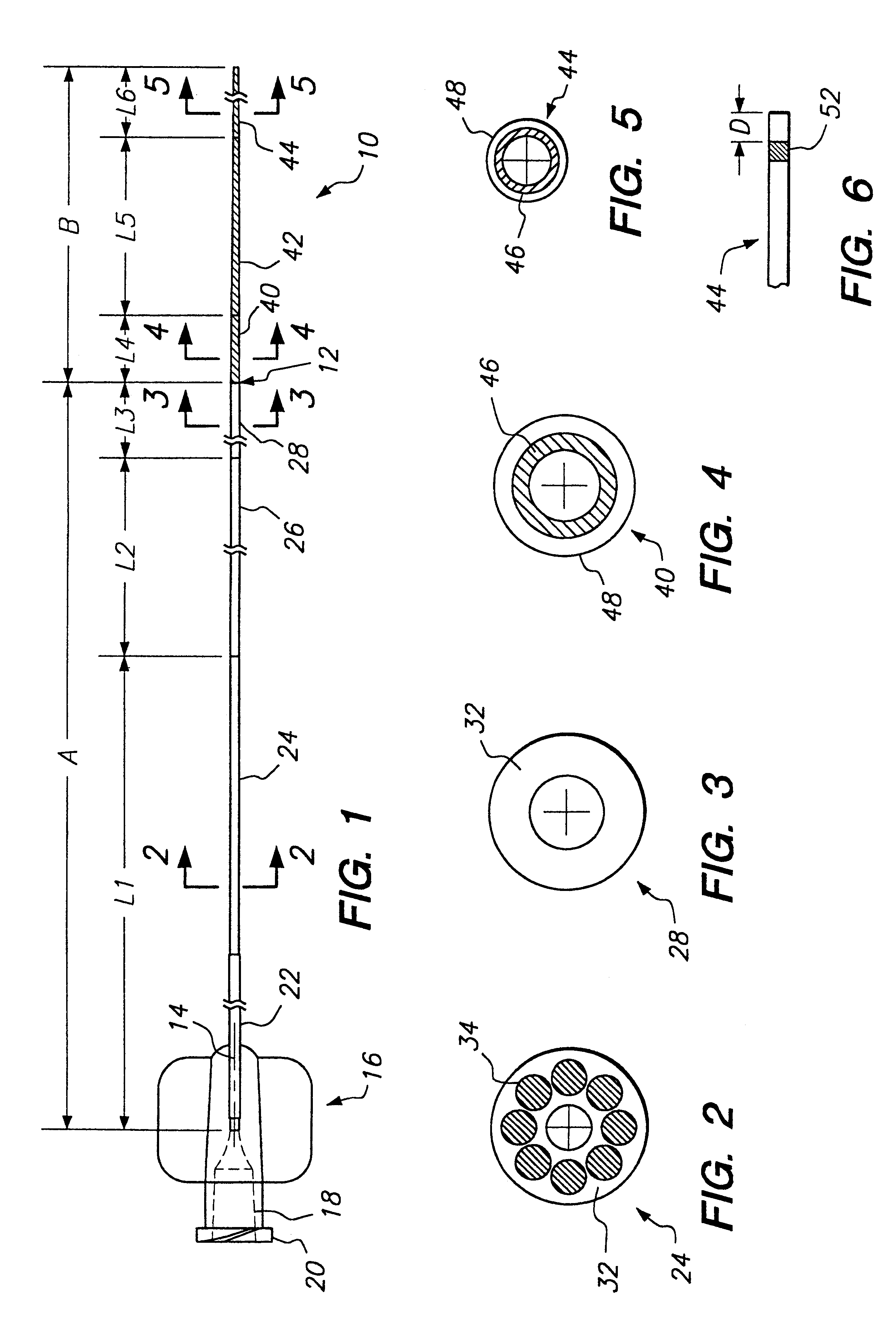
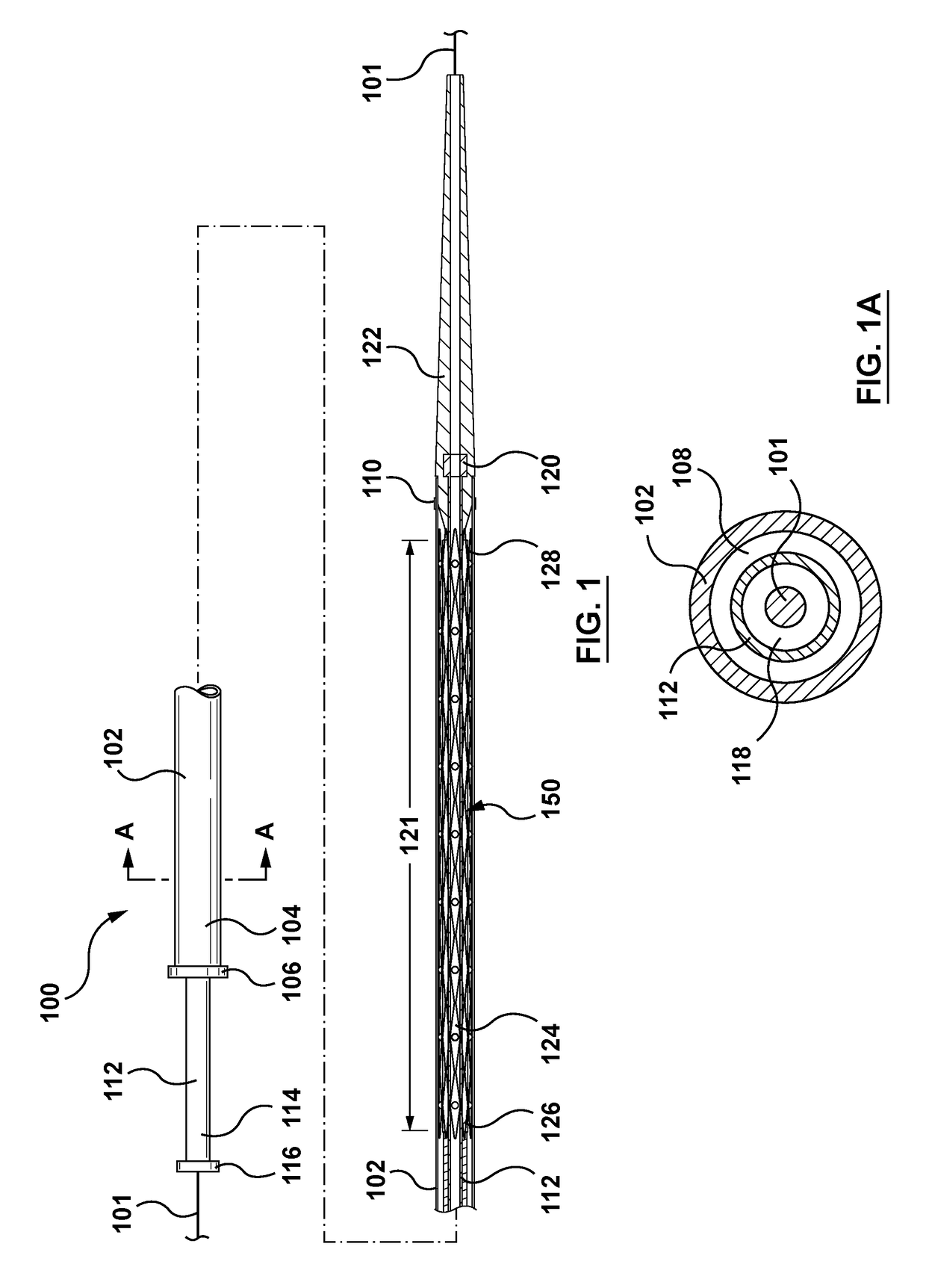
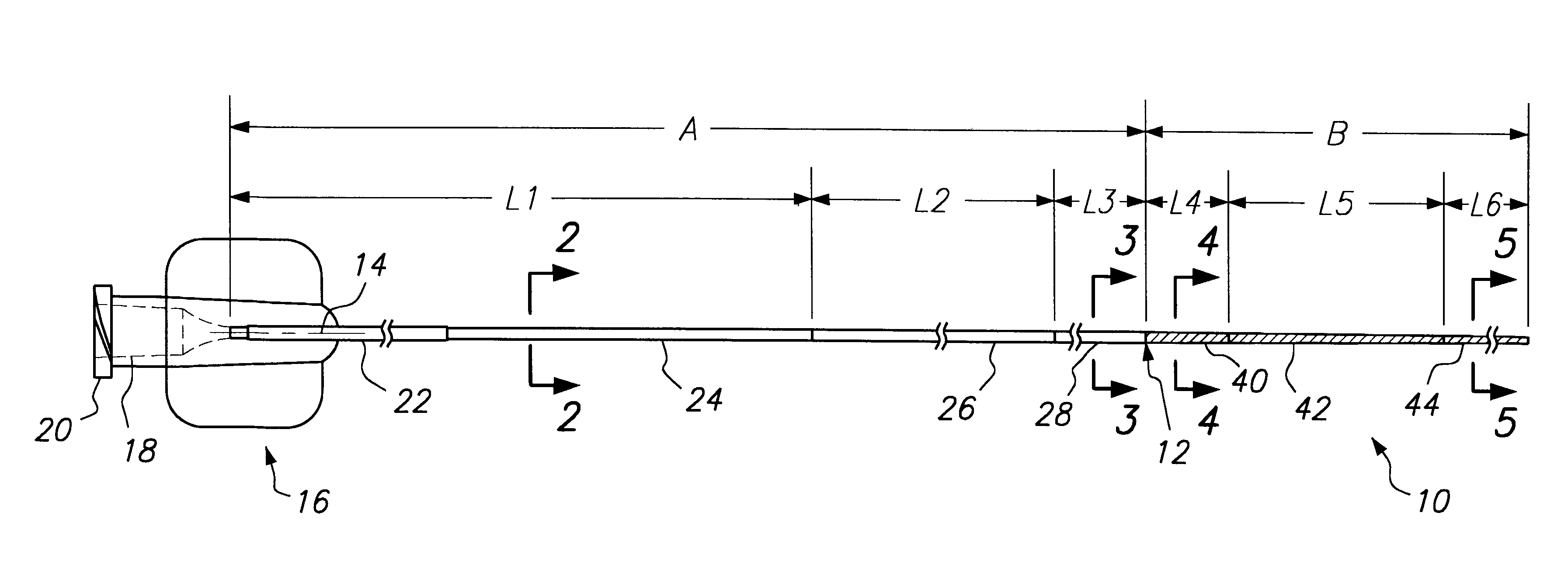
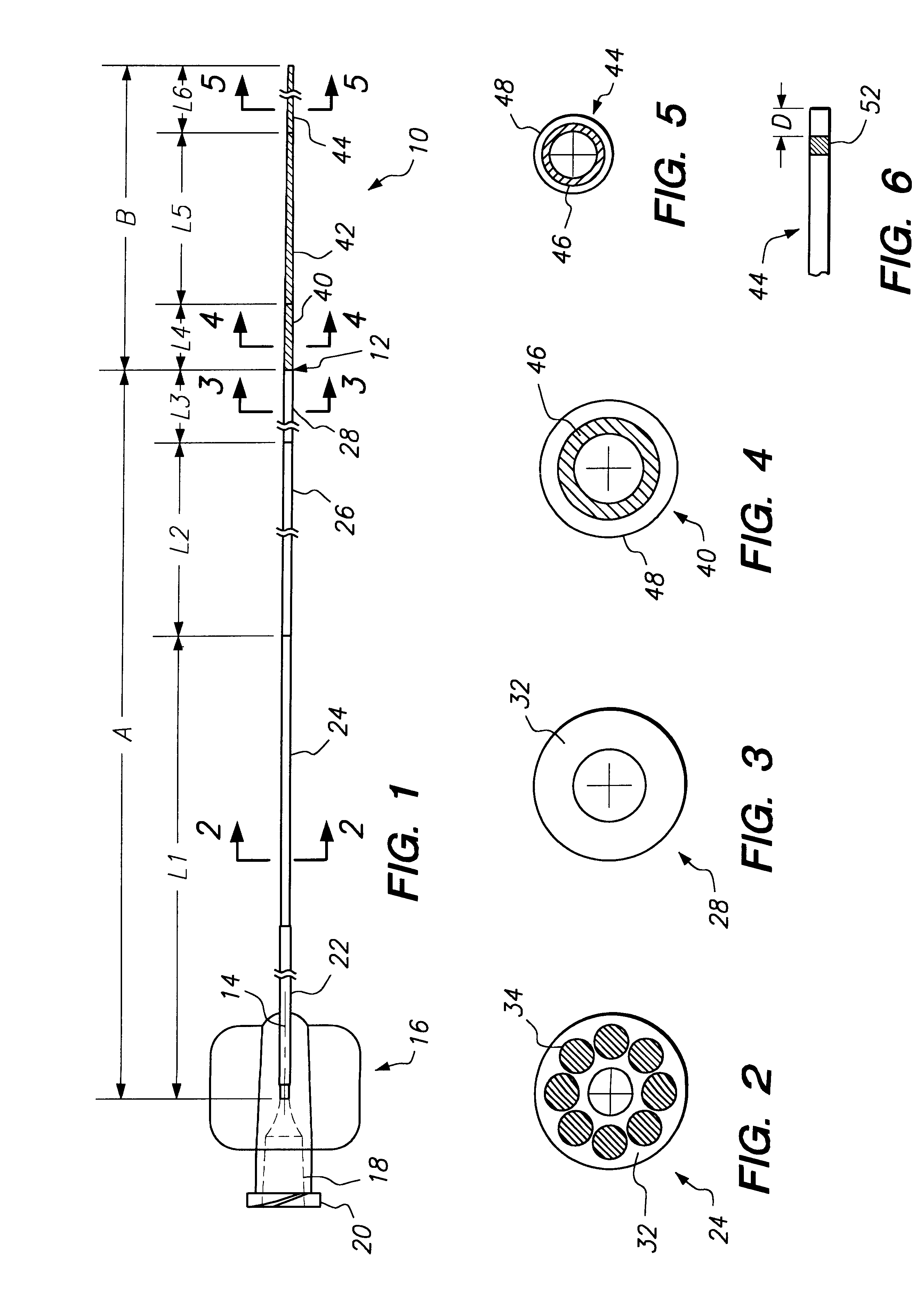
Segment Endpoints. Definition of the proximal or distal end point of a segment is usually done by placing markers near the endpoint of the segment and using one of the following methods.
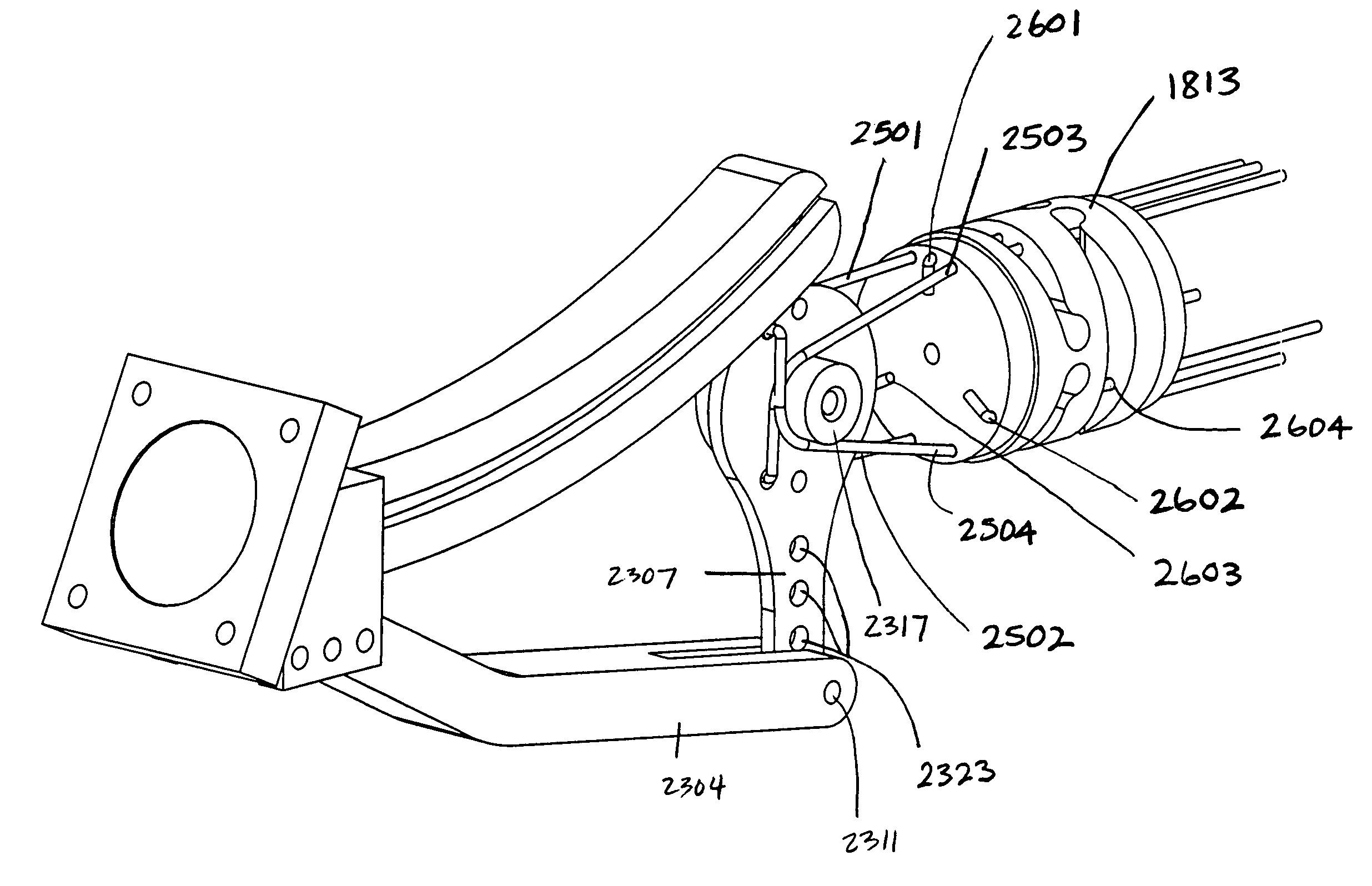
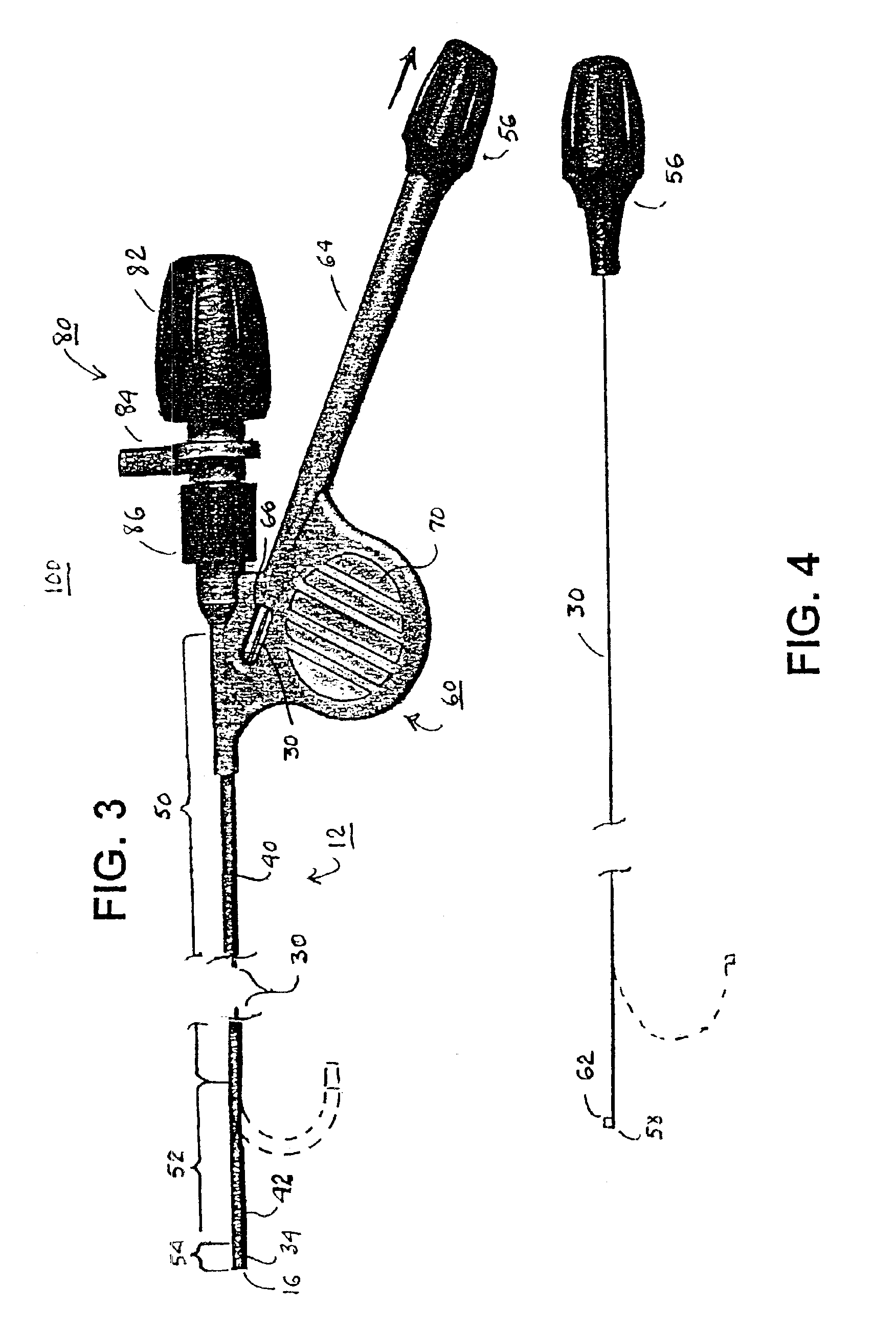
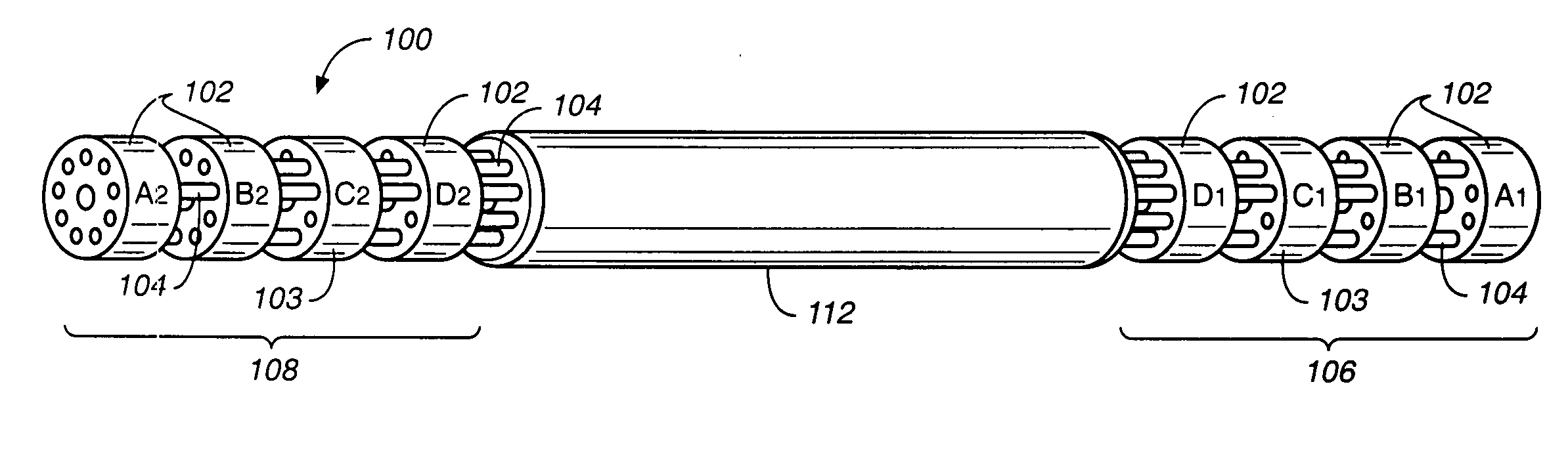
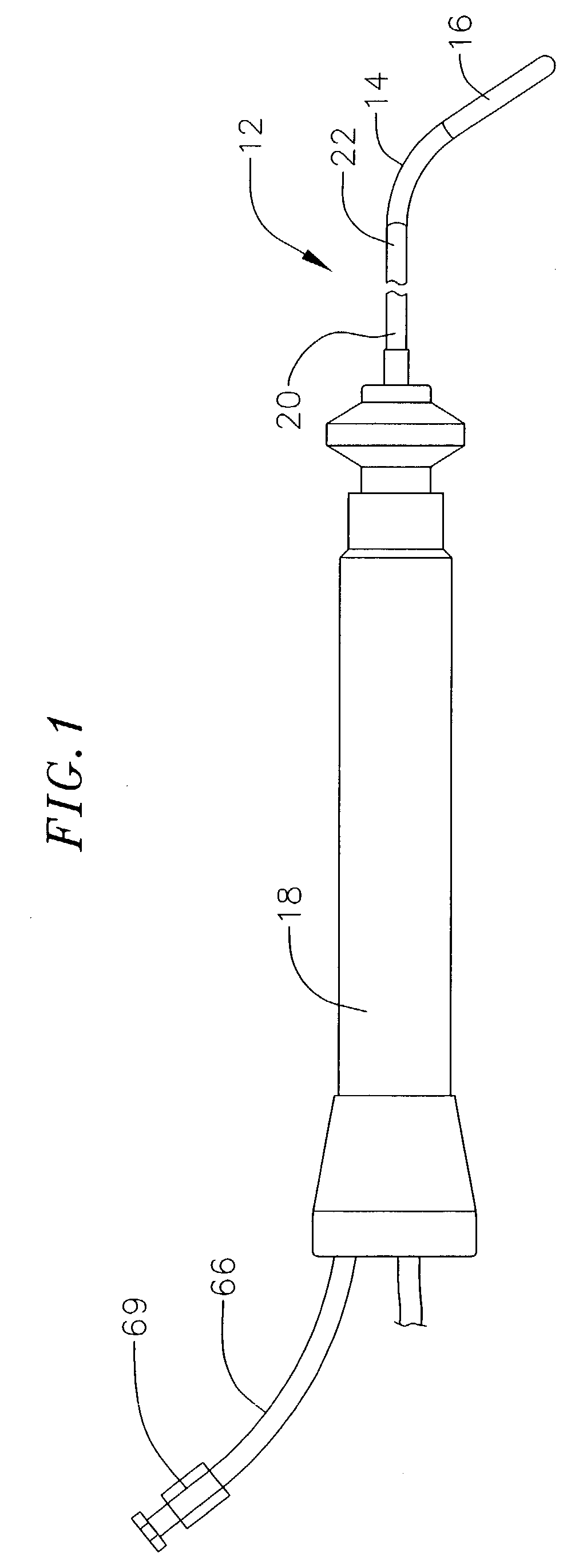
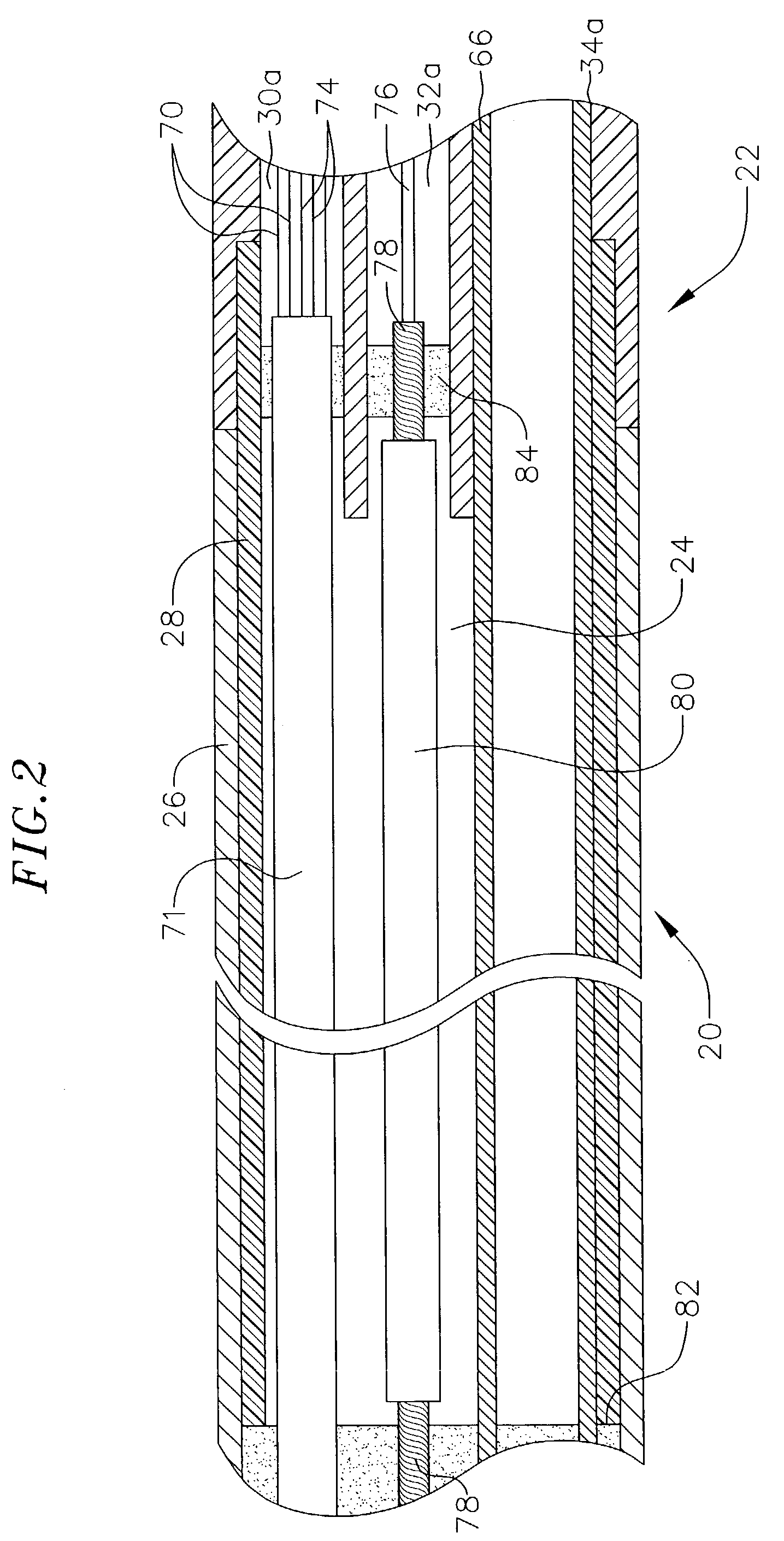
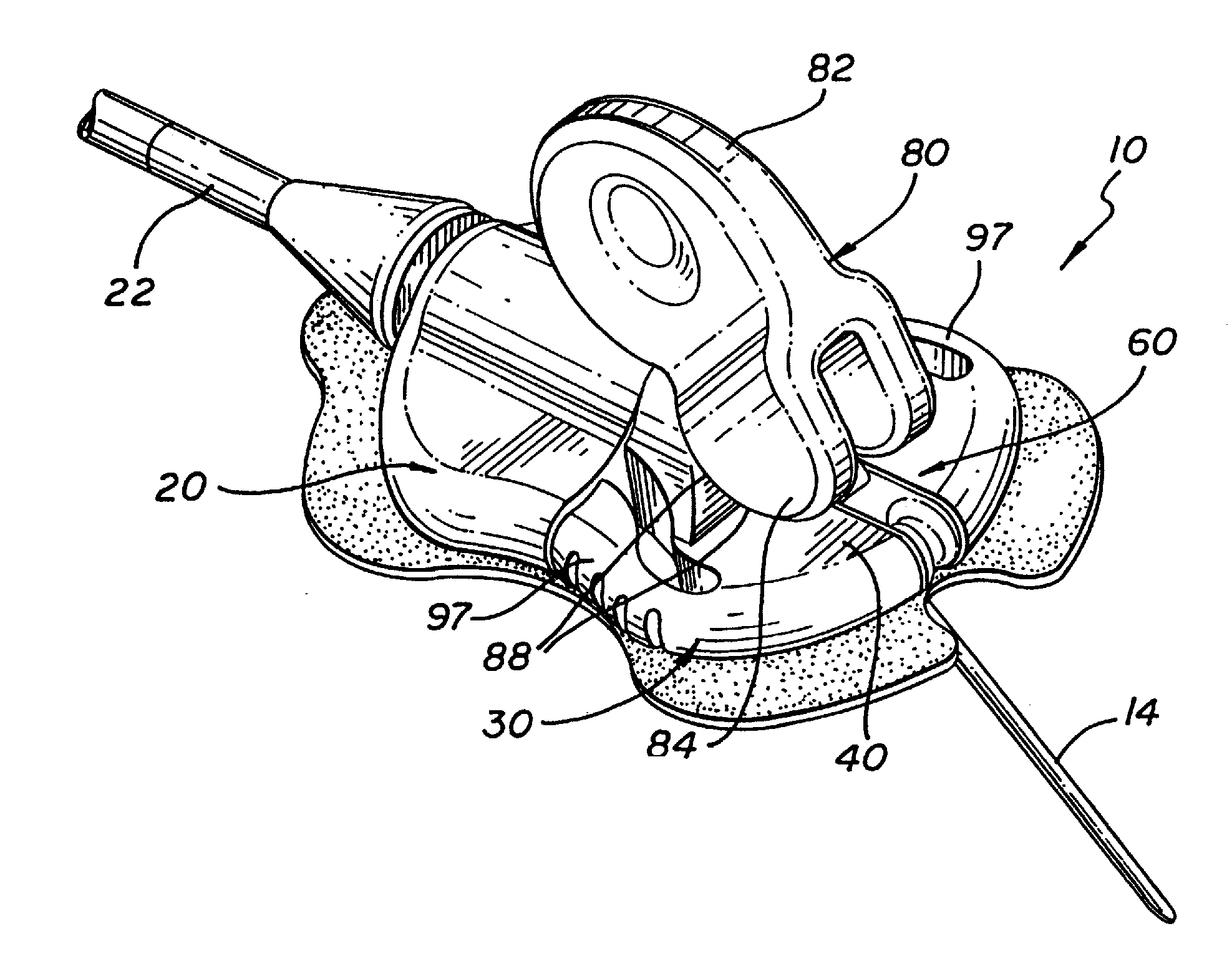
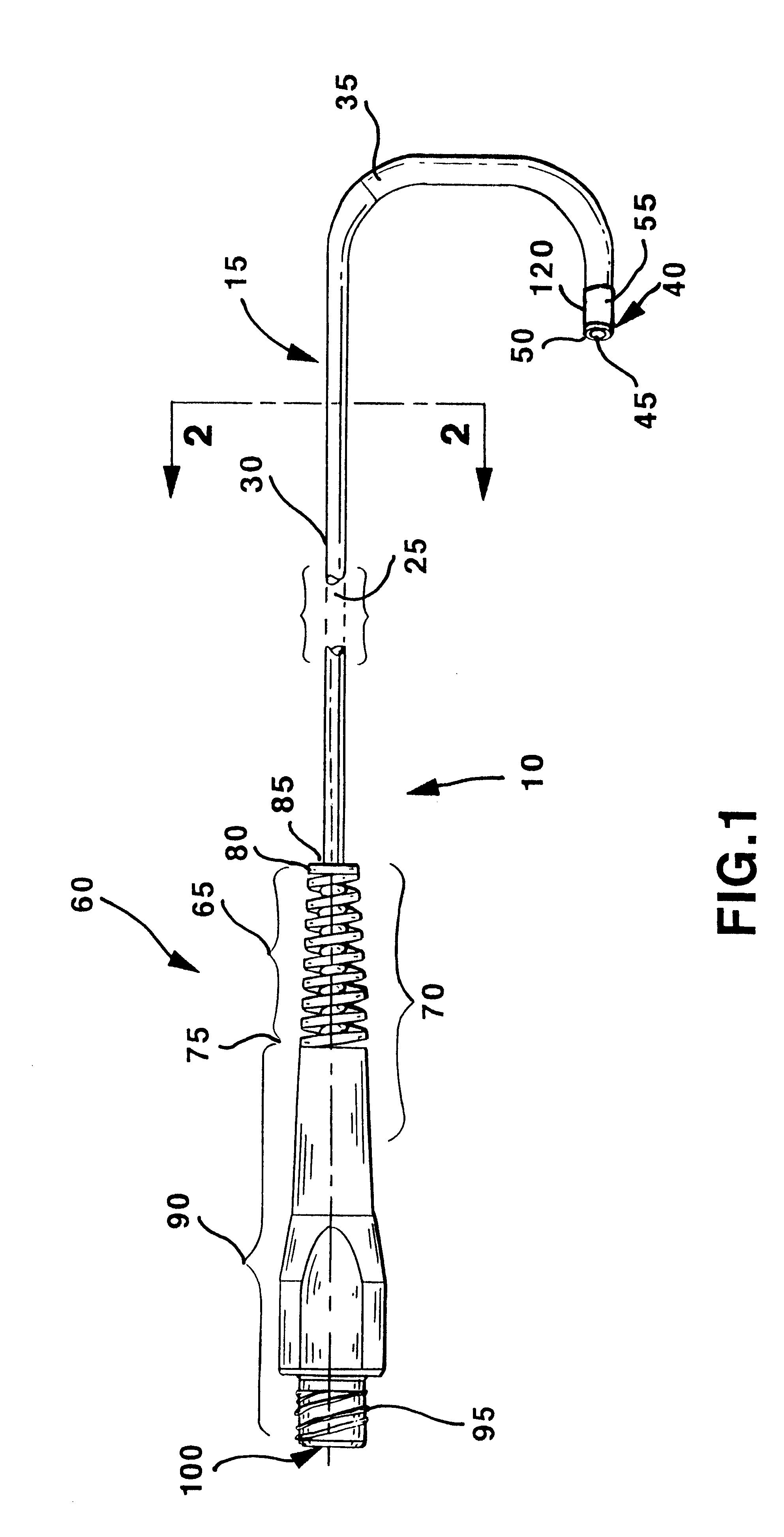
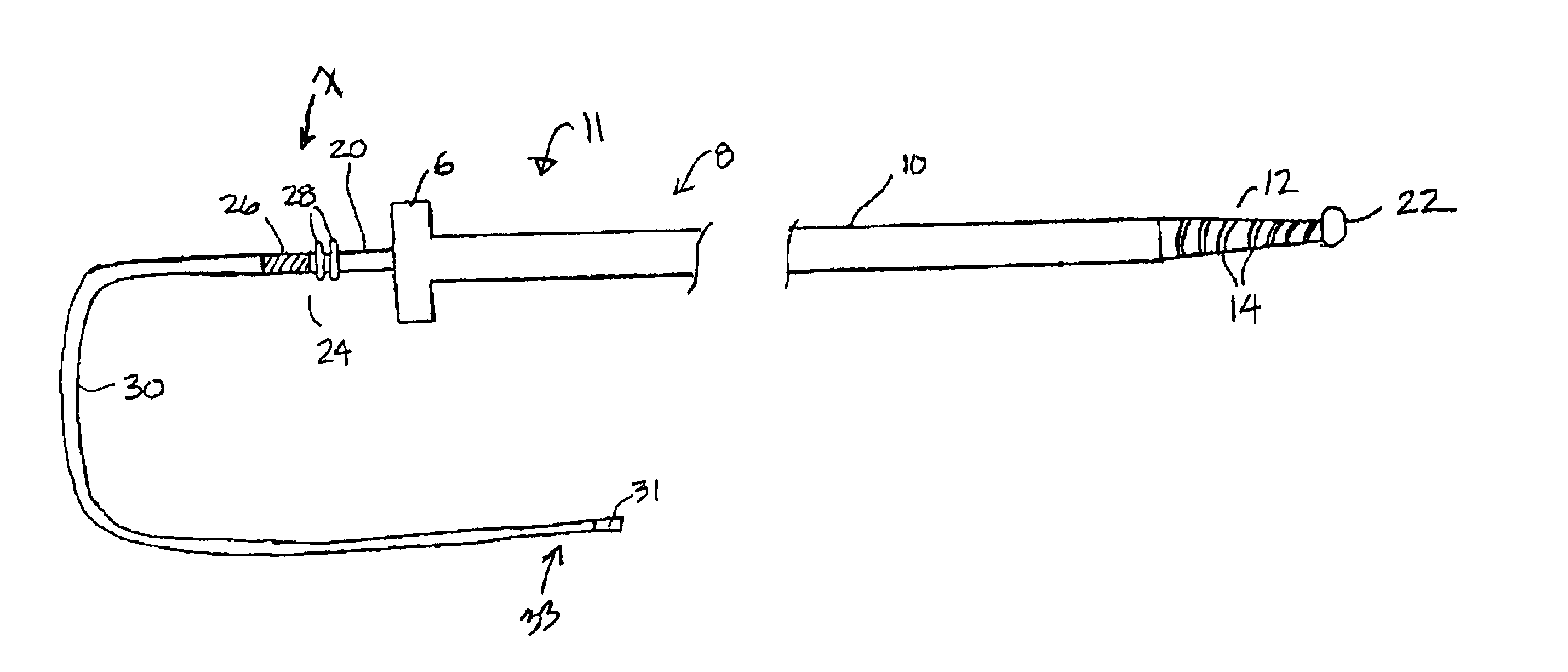
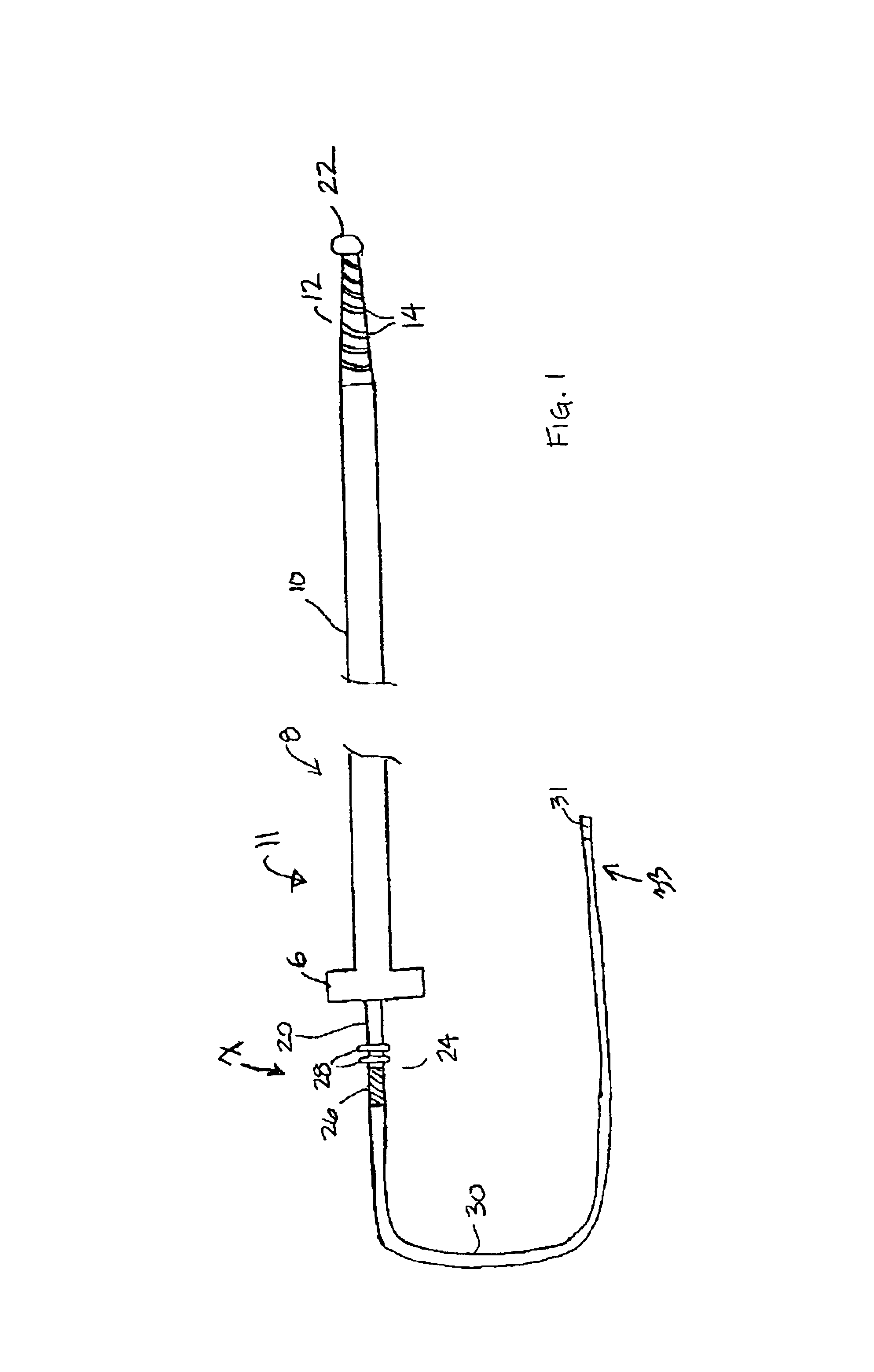
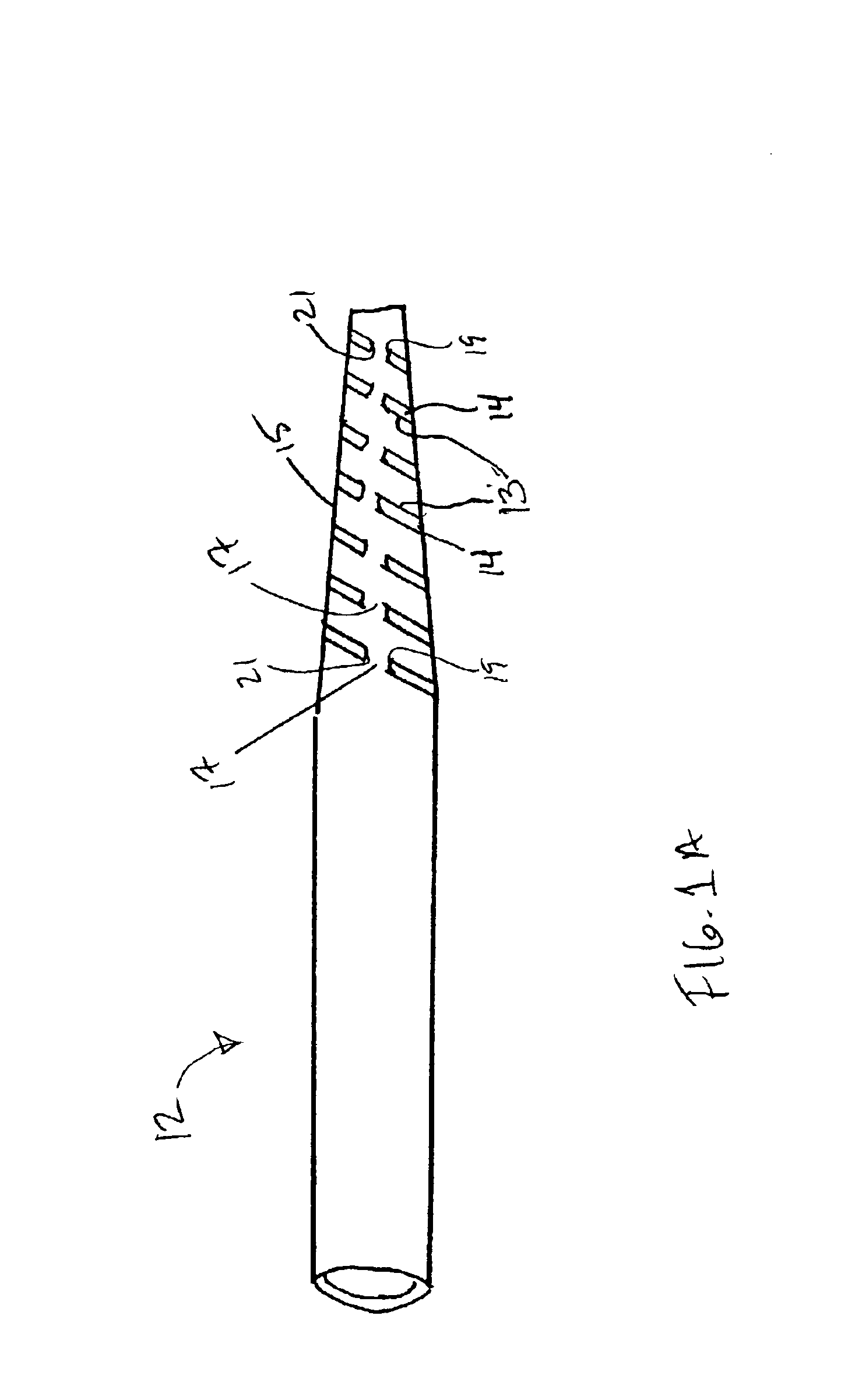
Hand-actuated device for remote manipulation of a grasping tool
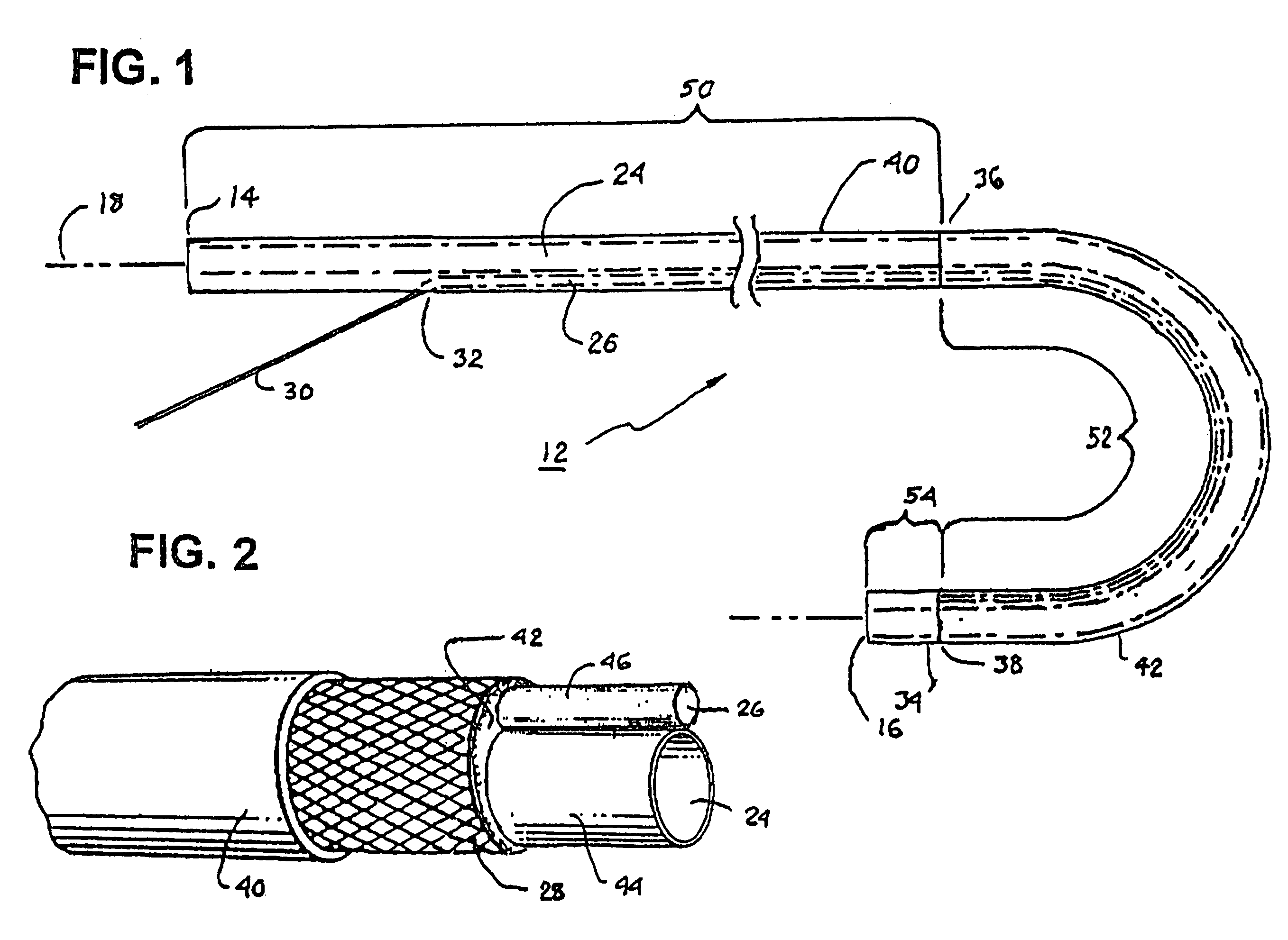
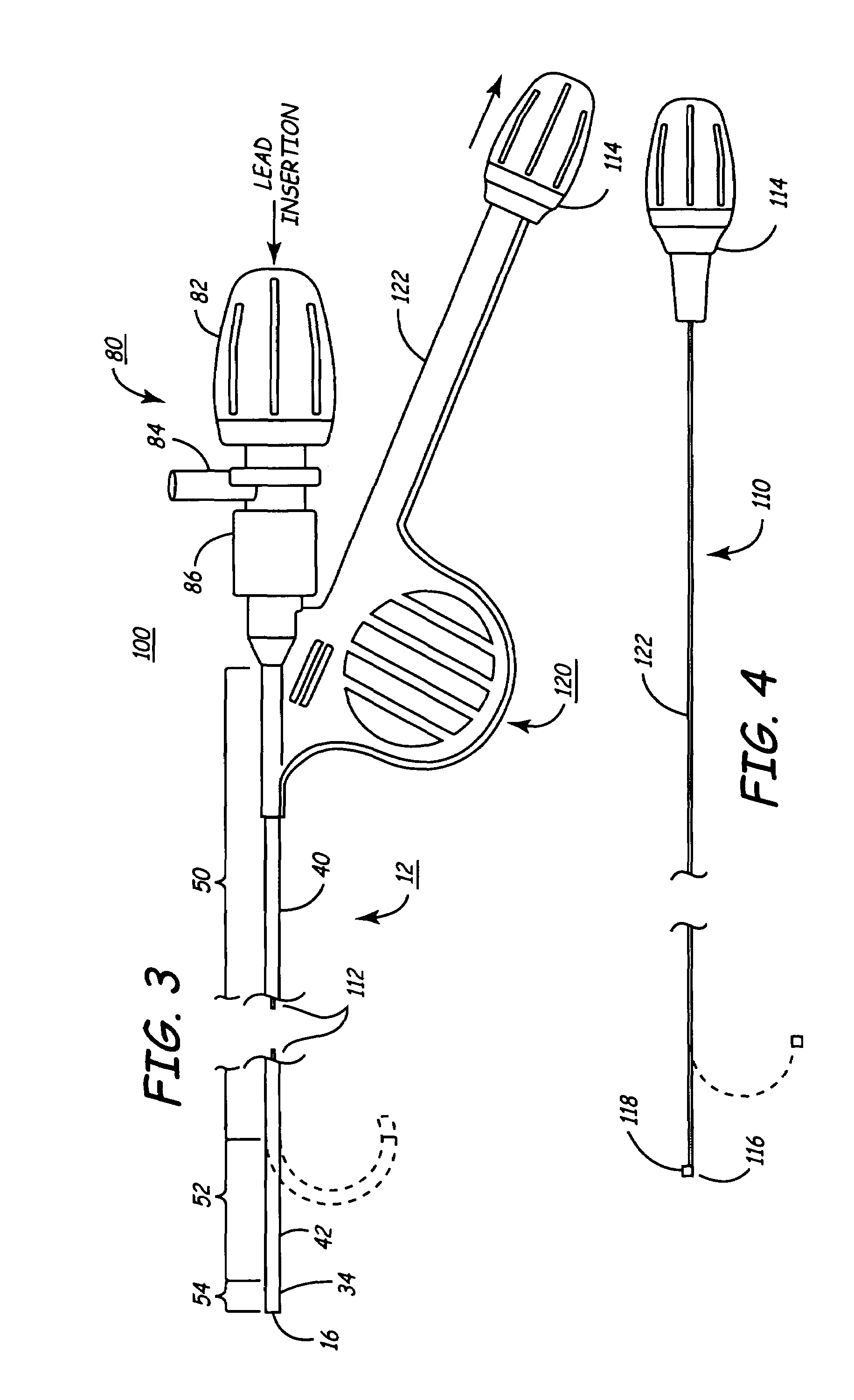
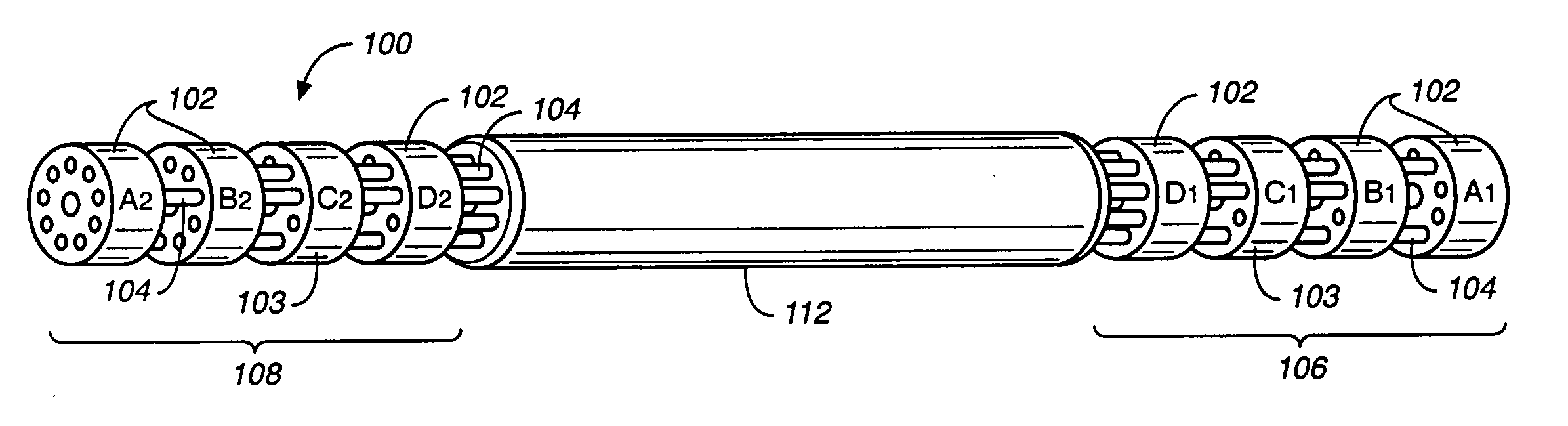
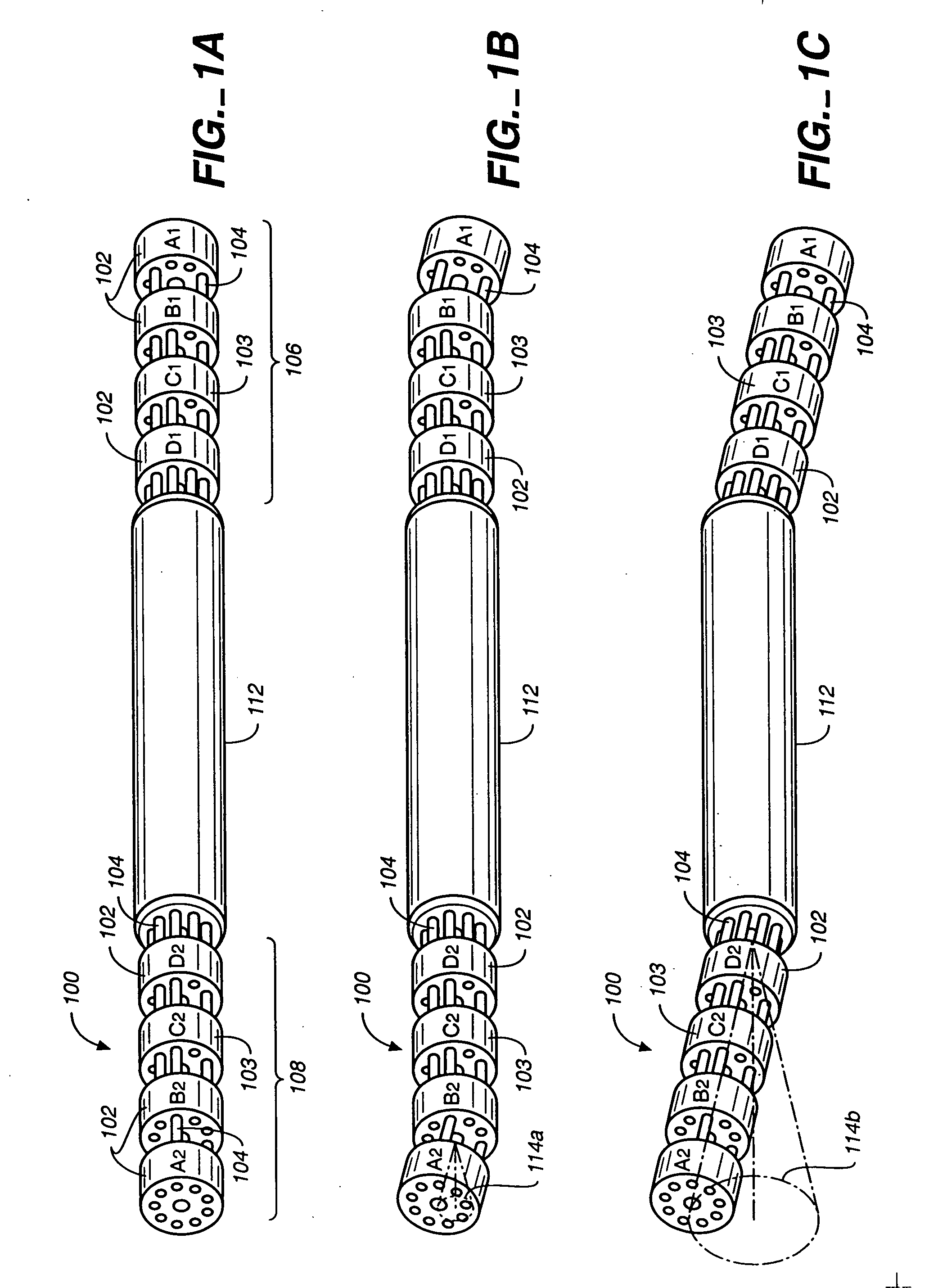
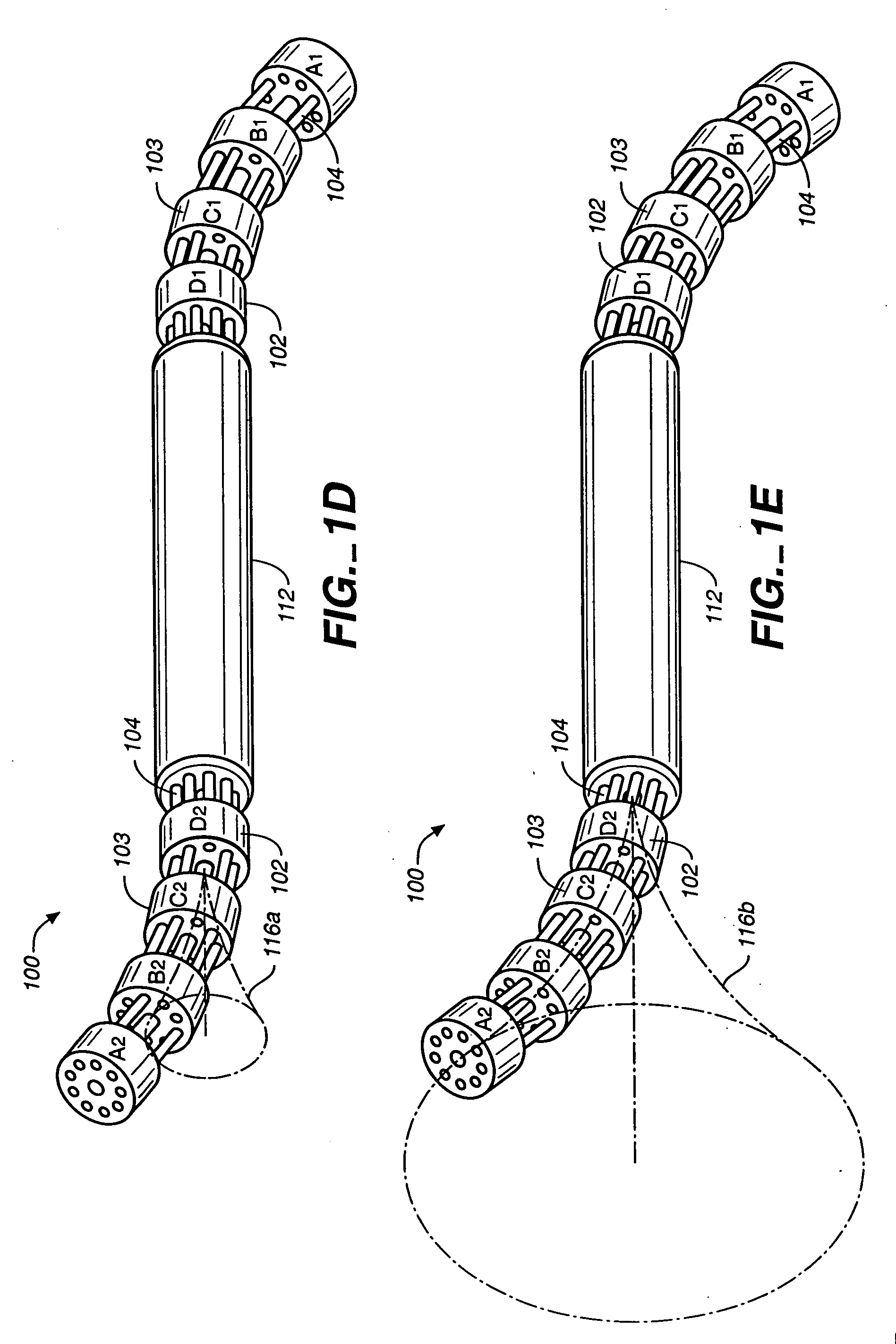
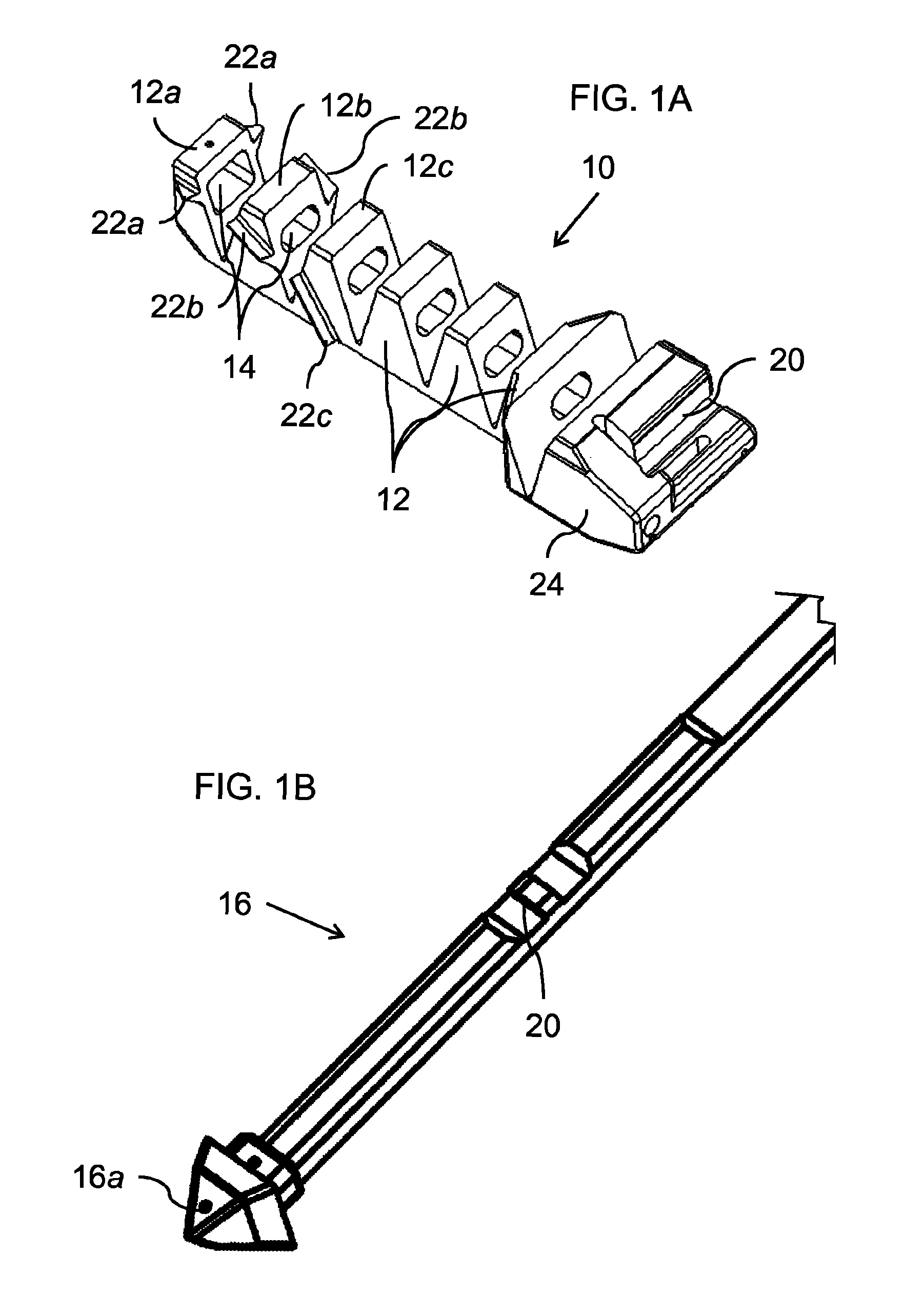
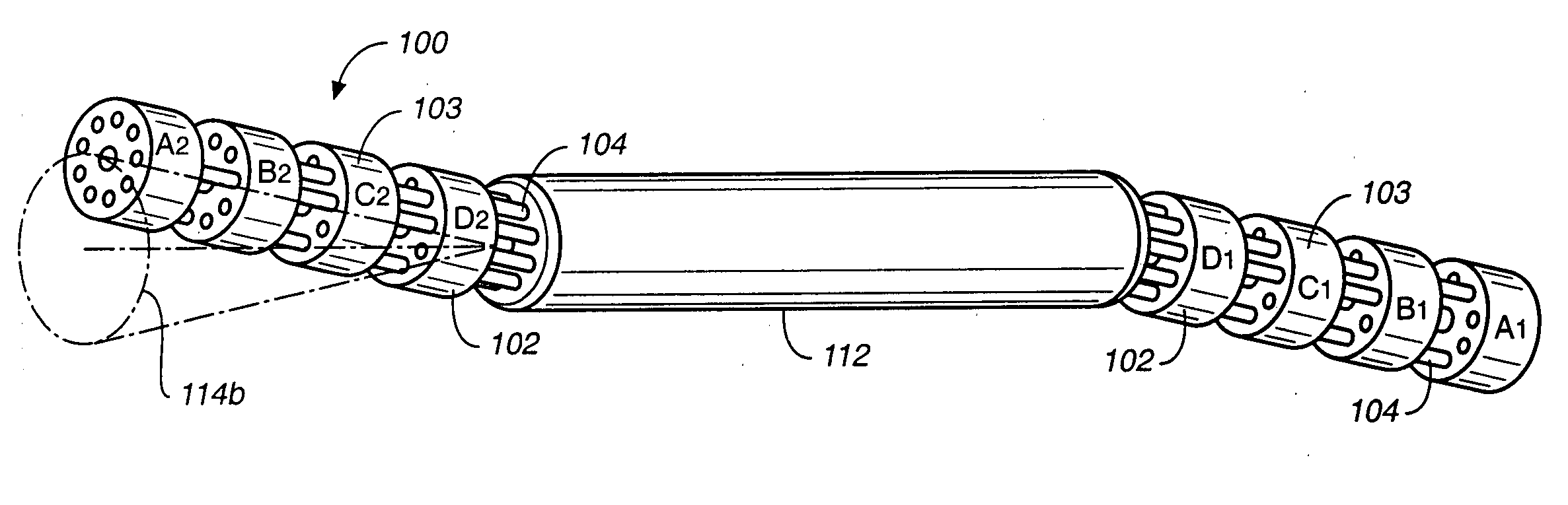
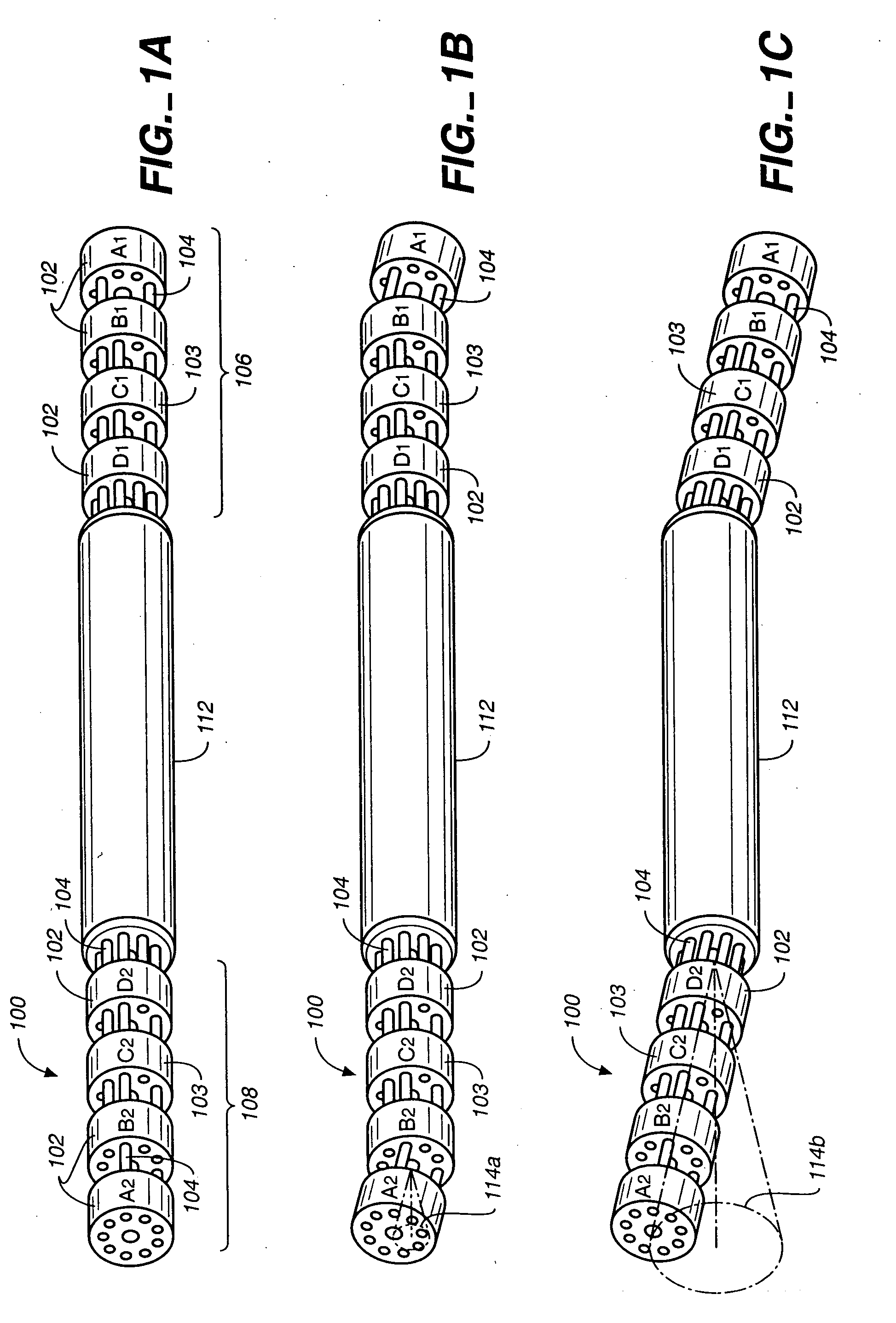
The invention provides an articulating mechanism useful, for example, for remote manipulation of various surgical instruments and diagnostic tools within, or to, regions of the body. Movement of segments at the proximal end of the mechanism results in a corresponding, relative movement of segments at the distal end of the mechanism. The proximal and distal segments are connected by a set of cables in such a fashion that each proximal segment forms a discrete pair with a distal segment. This configuration allows each segment pair to move independently of one another and also permits the articulating mechanism to undergo complex movements and adopt complex configurations. The articulating mechanisms may also be combined in such a way to remotely mimic finger movements for manipulation of an object or body tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Flexible sensor apparatus
ActiveUS20070073129A1Quick and easy transcutaneous placementImprove stabilitySurgical needlesCatheterAnalyteAdhesive
A flexible mounting base to hold a sensor at an infusion site, the sensor being a removable in vivo sensor for monitoring analyte concentration level in a patient, such as blood glucose (BG) level. The mounting base comprises a flexible adhesive that anchors the flexible sensor set at an infusion site to provide stability for the sensor set in a convenient and comfortable manner. Placement of the mounting base onto the patient's skin causes the insertion needle to pierce the skin for transcutaneous placement of the cannula with the sensor therein. The insertion needle can then be withdrawn to leave the cannula and sensor at the selected insertion position, with the distal segment of the sensor being exposed to patient extracellular fluid via apertures formed in the cannula.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
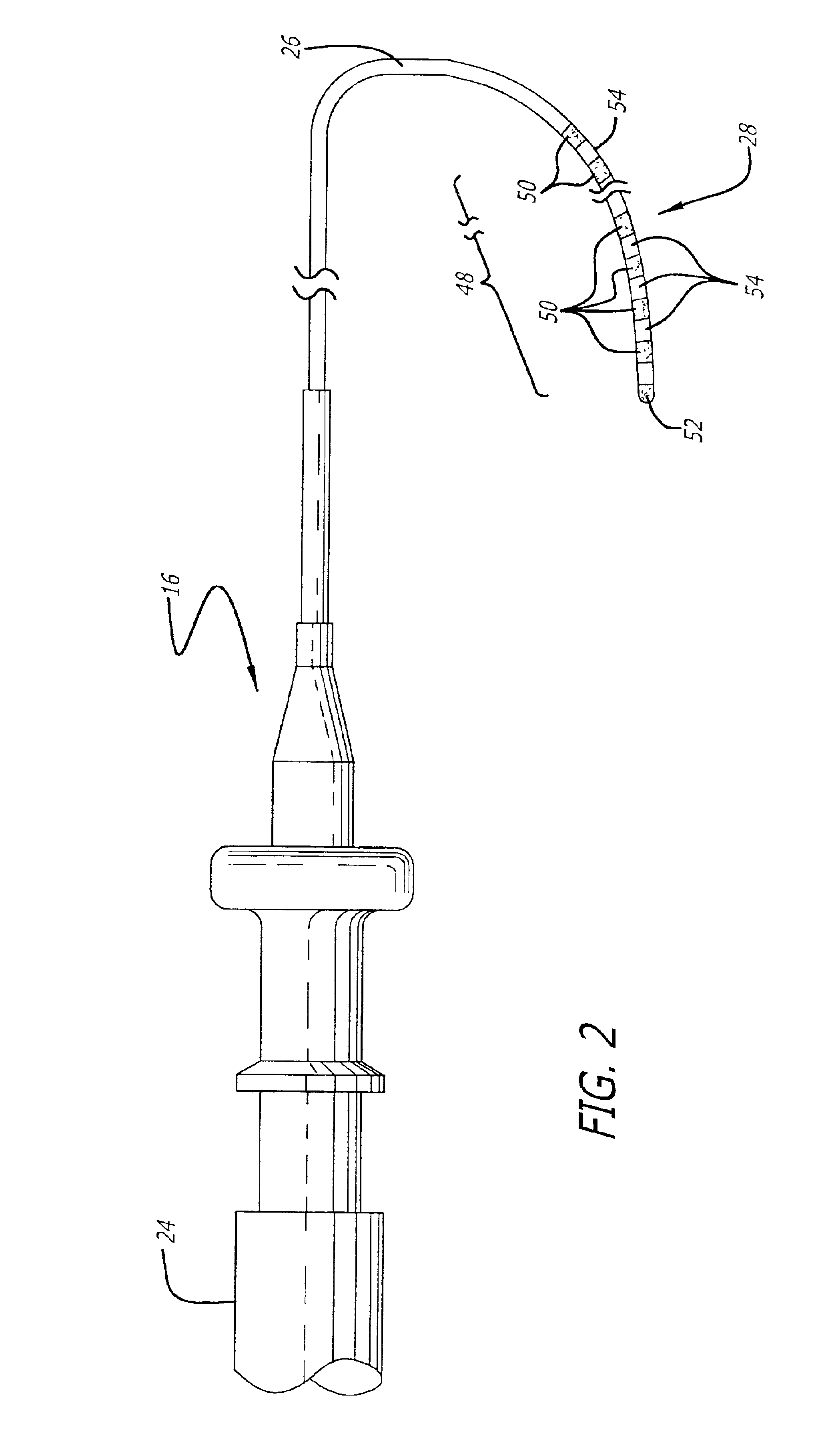
Steerable catheter
InactiveUS6945956B2Easy to insertHigh tensile strengthMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesDistal segmentCatheter device
A steerable catheter and methods of fabrication including a catheter body formed of a continuous wire braid formed of wires braided over a delivery lumen liner and a pull wire lumen liner distal to a pull wire jacket port, braided around the pull wire jacket port to form a braid port, and over at least a portion of the delivery lumen liner proximal to the pull wire jacket port. A pull wire extends from a pull wire proximal end through the pull wire lumen port and through the pull wire lumen to a pull wire distal end. A band is attached to the pull wire distal end and fitted over a distal segment of the wire braid proximal to the catheter body distal end to fix the pull wire distal end to the catheter body and restrain the wire distal end from flaring away from the delivery lumen liner.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Sensor with layered electrodes
ActiveUS20070173711A1Easy and quick to placeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsThin film sensorGlucose sensors
A thin film sensor, such as a glucose sensor, is provided for transcutaneous placement at a selected site within the body of a patient. The sensor includes several sensor layers that include conductive layers and includes a proximal segment defining conductive contacts adapted for electrical connection to a suitable monitor, and a distal segment with sensor electrodes for transcutaneous placement. The sensor electrode layers are disposed generally above each other, for example with the reference electrode above the working electrode and the working electrode above the counter electrode. The electrode layers are separated by dielectric layer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
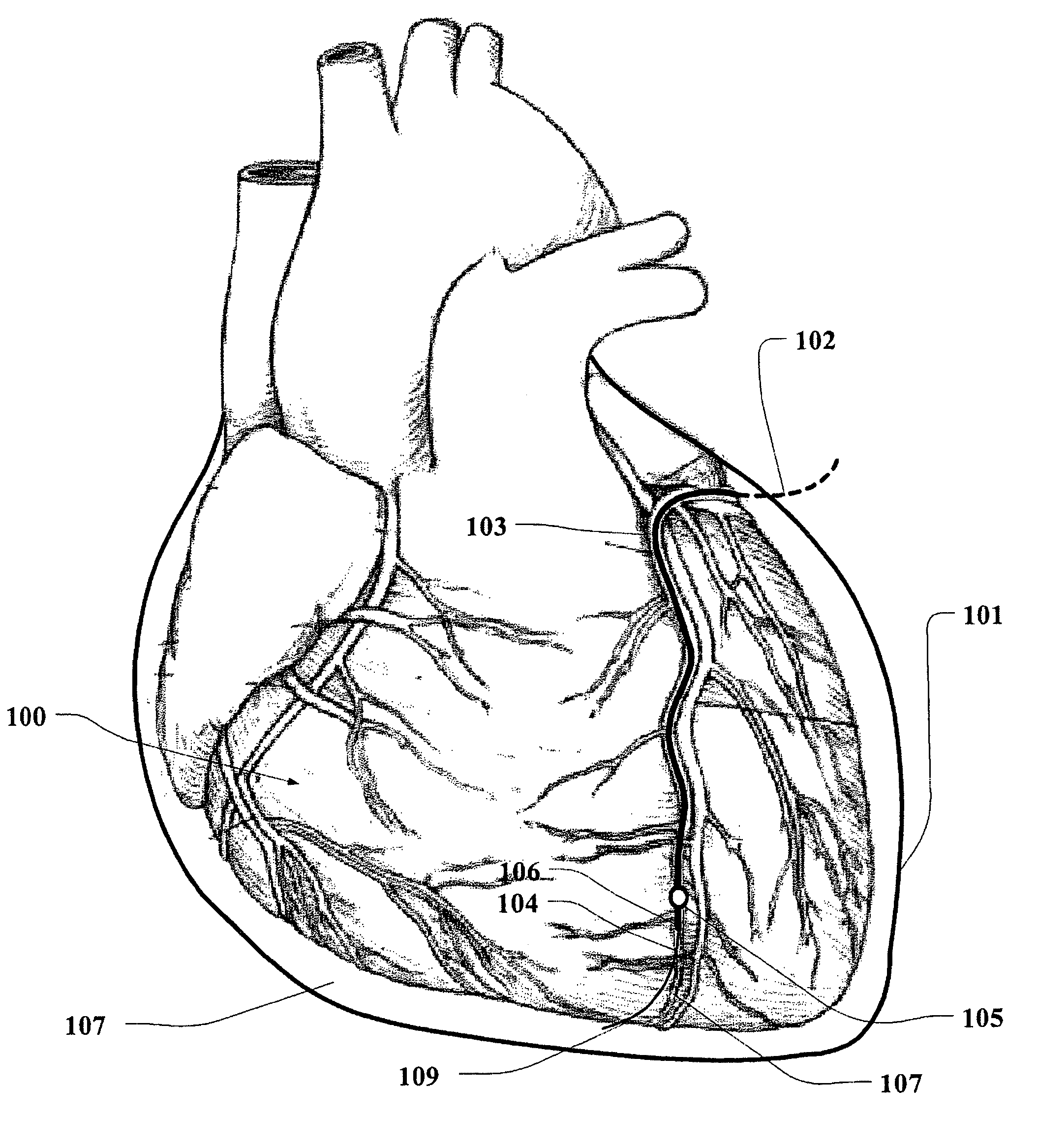
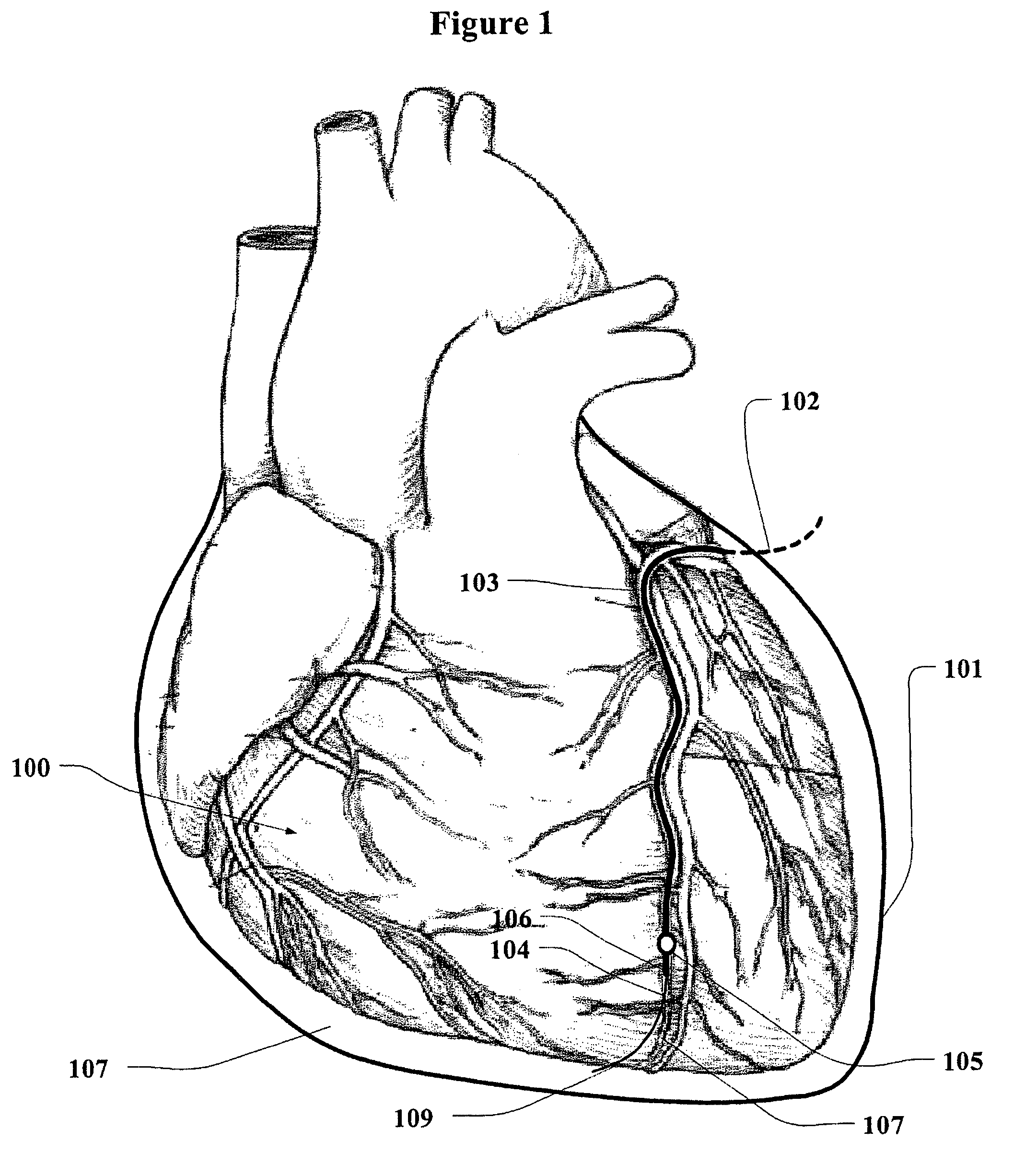
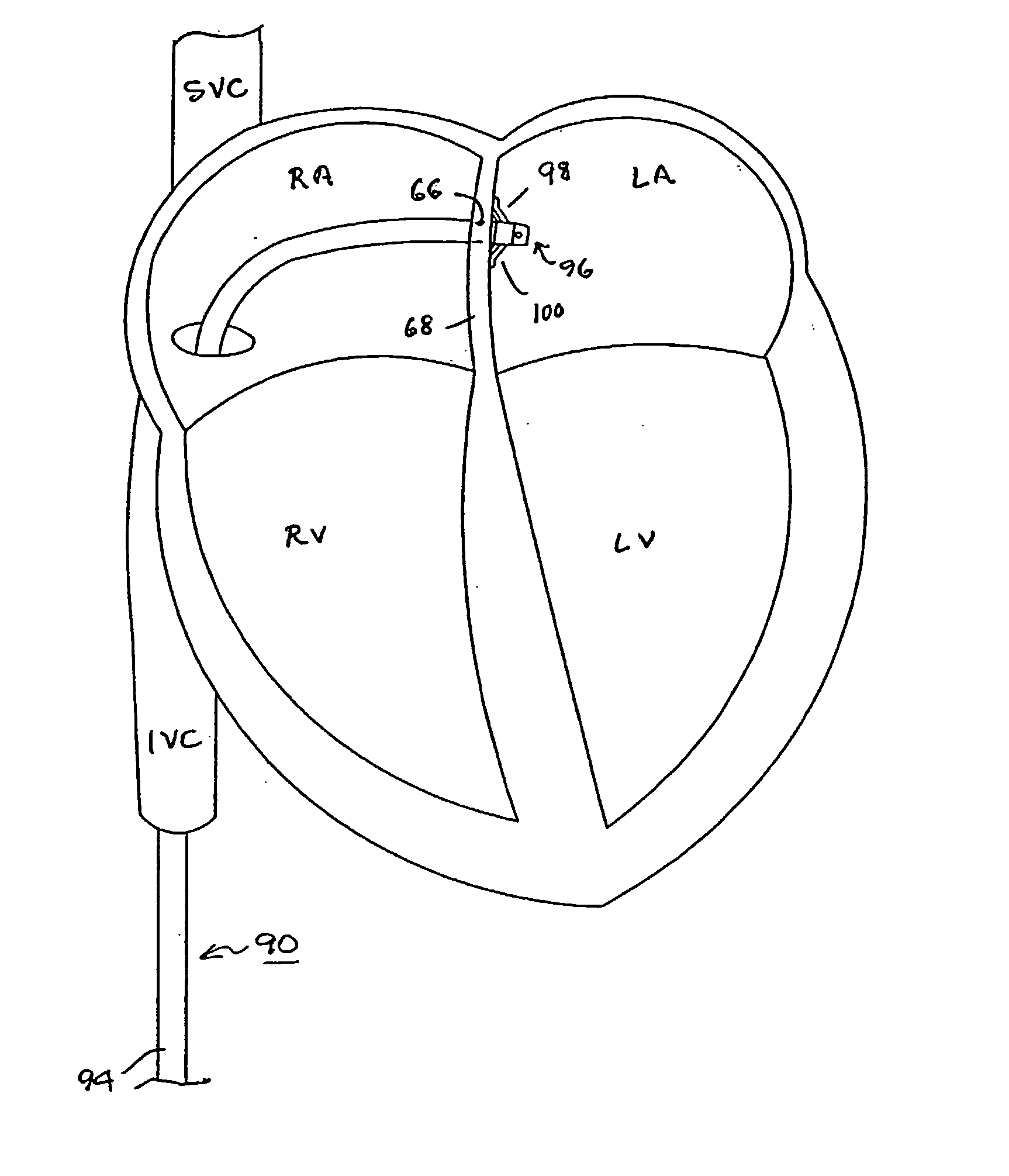
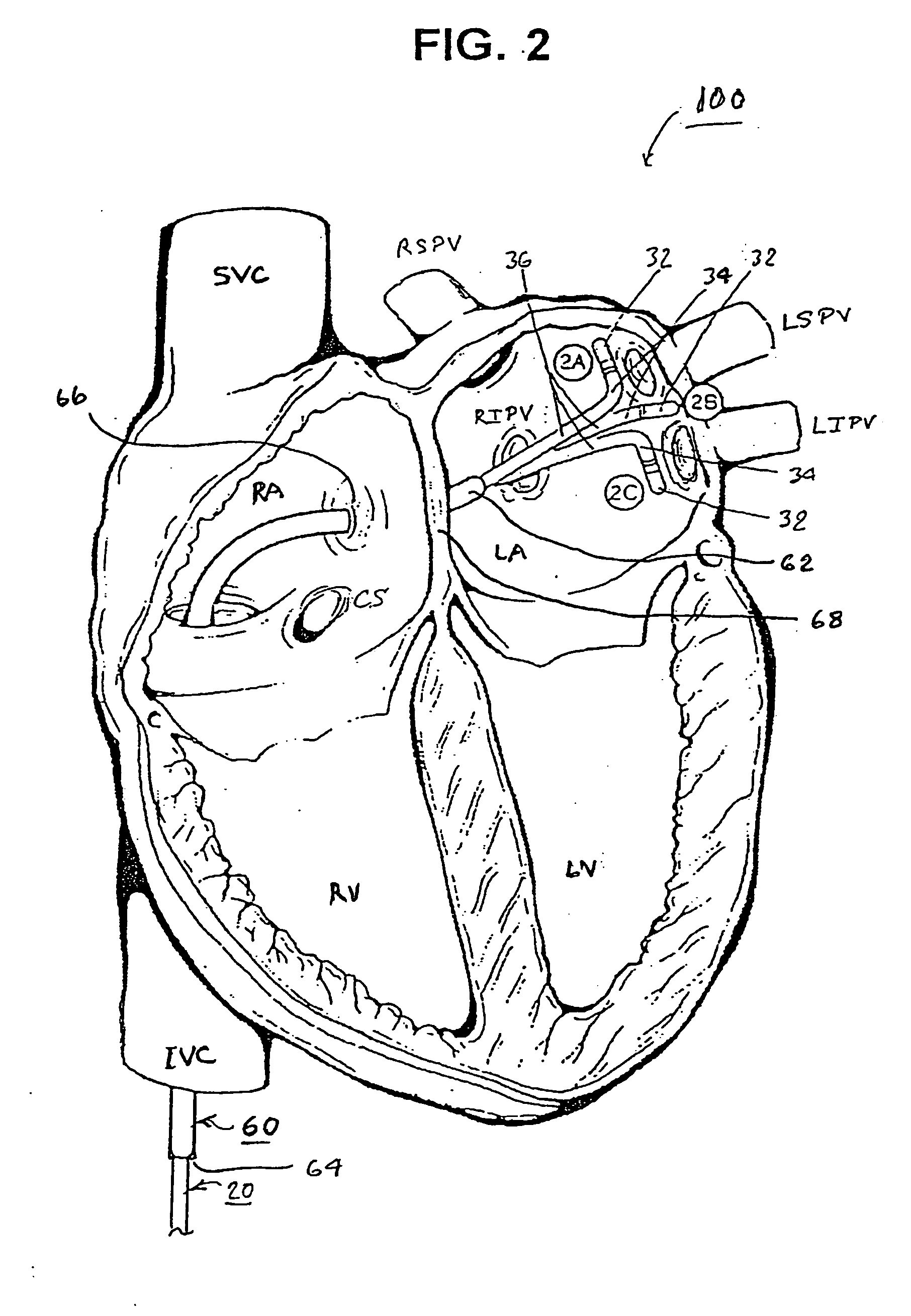
Methods and systems for accessing the pericardial space
Methods and systems for transvenously accessing the pericardial space via the vascular system and atrial wall, particularly through the superior vena cava and right atrial wall, to deliver treatment in the pericardial space are disclosed. A steerable instrument is advanced transvenously into the right atrium of the heart, and a distal segment is deflected into the right atrial appendage. A fixation catheter is advanced employing the steerable instrument to affix a distal fixation mechanism to the atrial wall. A distal segment of an elongated medical device, e.g., a therapeutic catheter or an electrical medical lead, is advanced through the fixation catheter lumen, through the atrial wall, and into the pericardial space. The steerable guide catheter is removed, and the elongated medical device is coupled to an implantable medical device subcutaneously implanted in the thoracic region. The fixation catheter may be left in place.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Transnasal method and catheter for lacrimal system
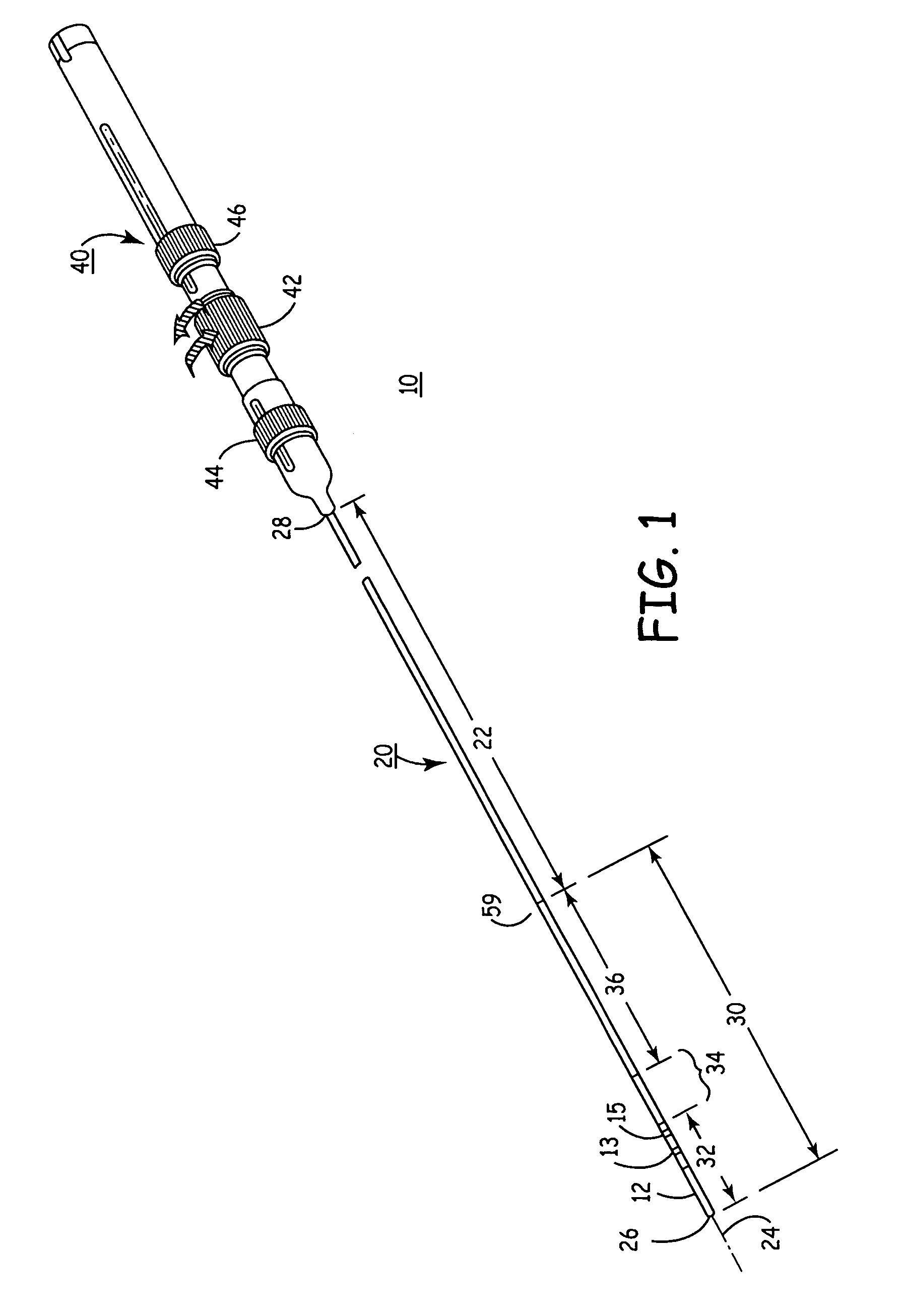
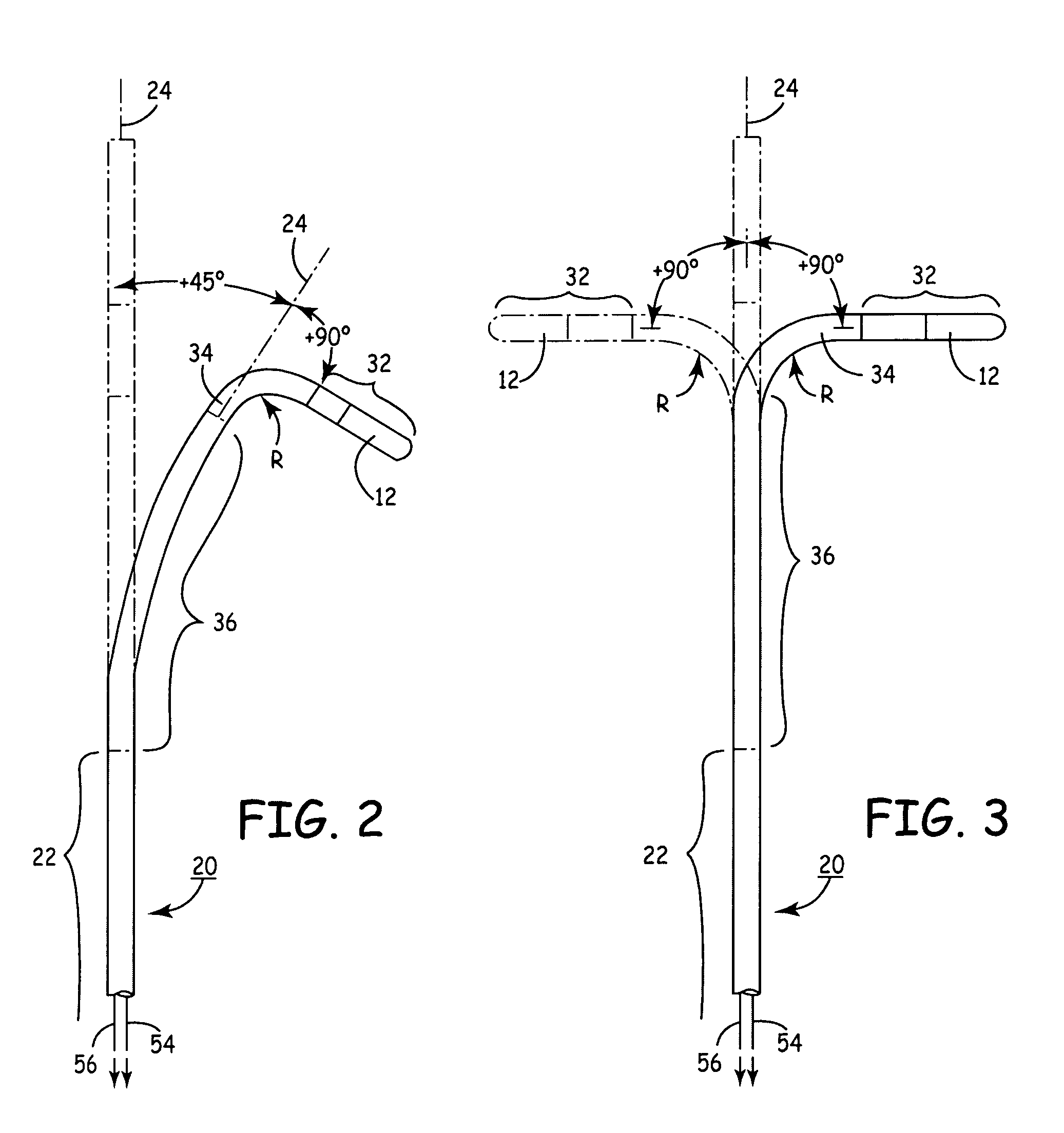
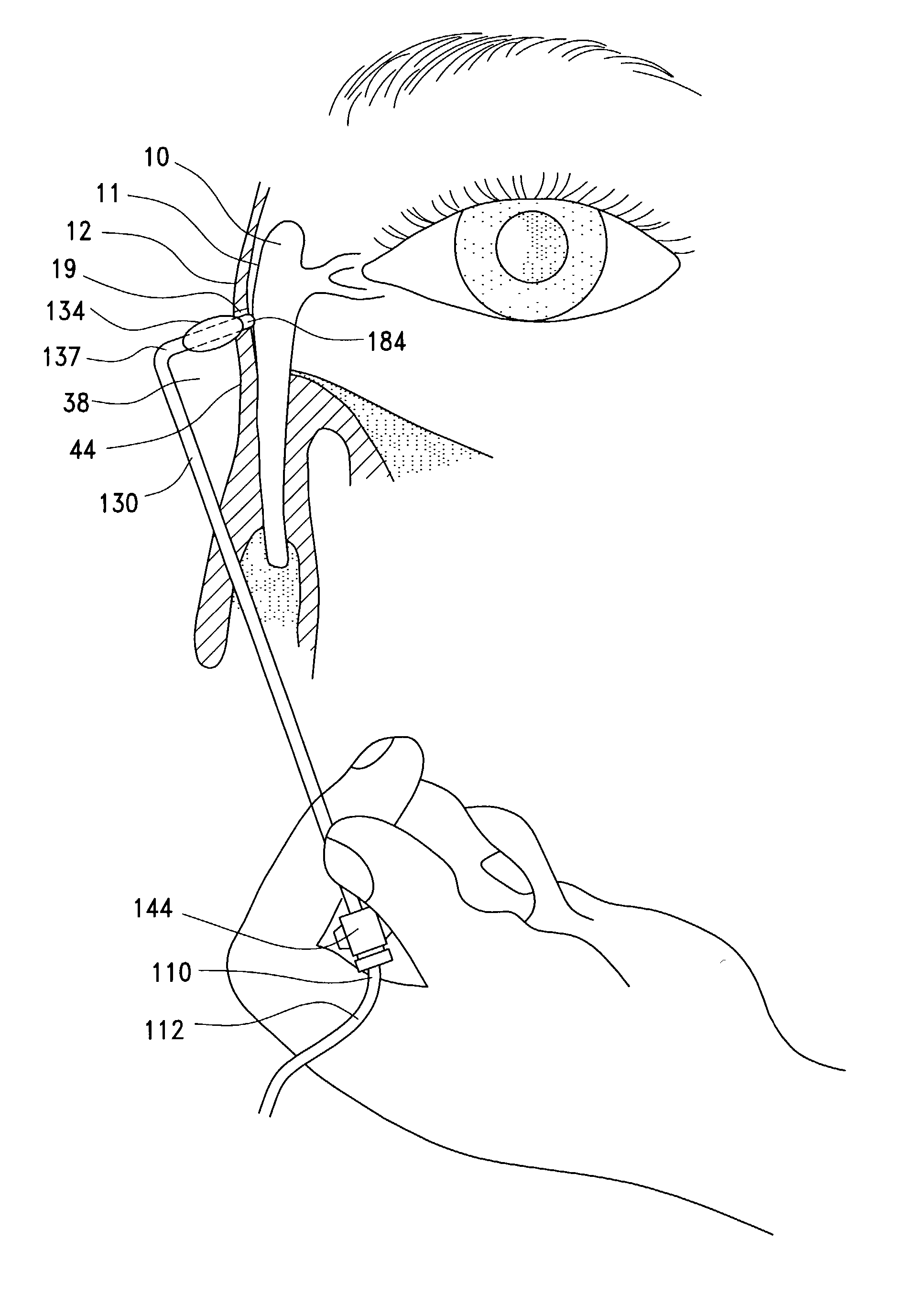
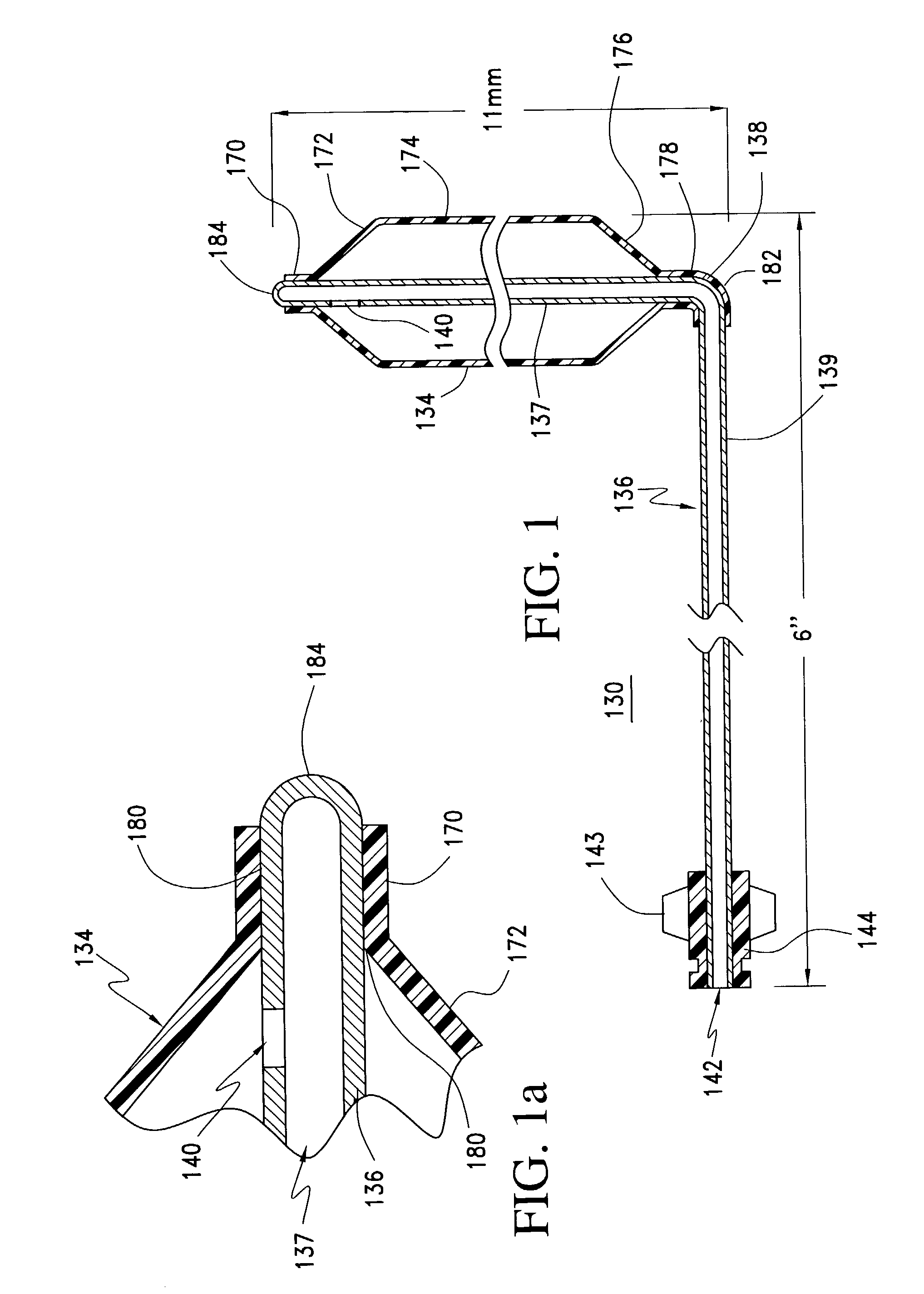
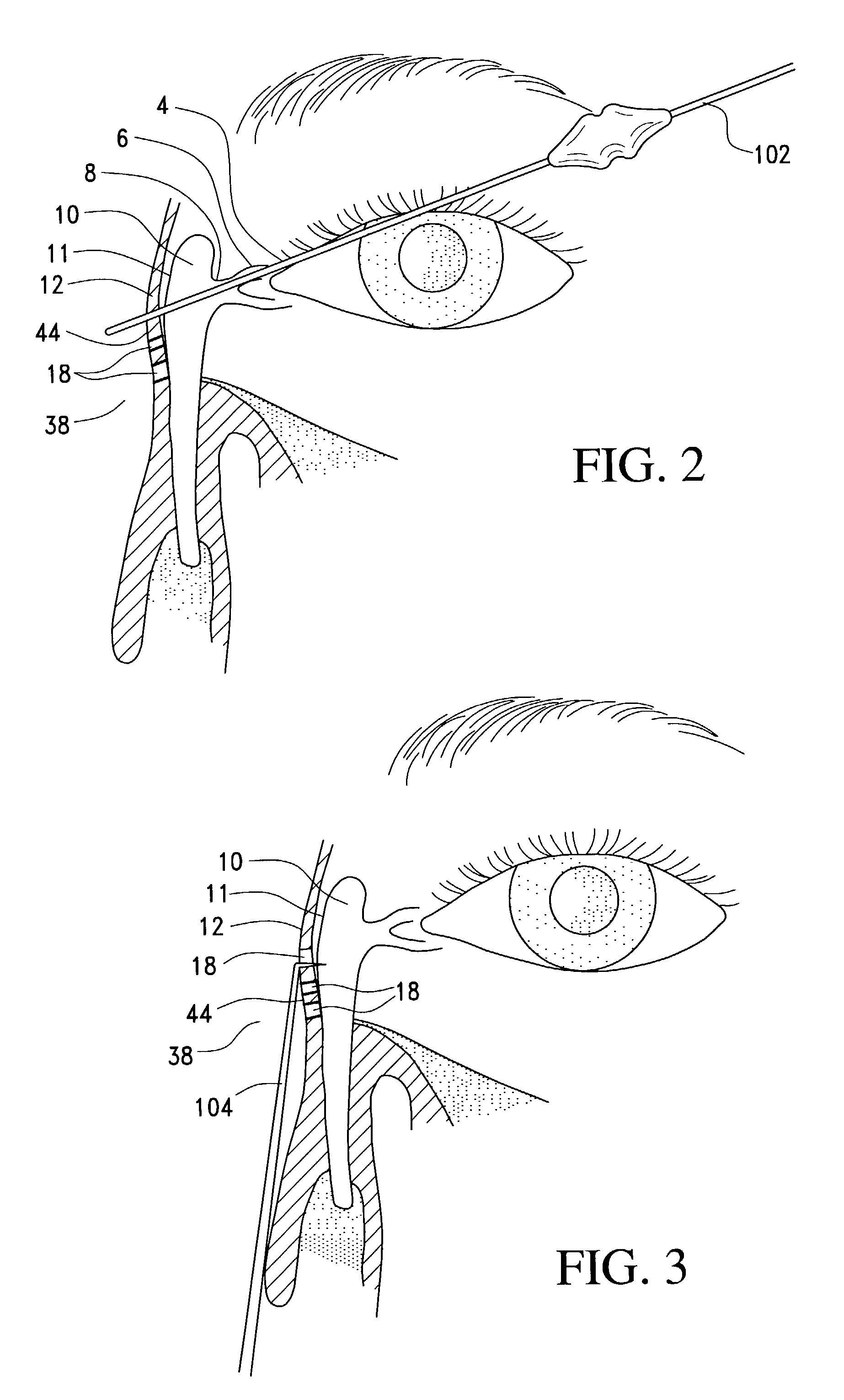
A balloon catheter for treatment of a patient's lacrimal system is applied transnasally without the use of a guide wire or a curve retention member. The catheter uses a stainless steel hypotube of sufficient stiffness and column strength to be pushed from the patent's nasal cavity through an opening-formed through the lateral nasal wall and lacrimal fossa, into the lacrimal sac. The catheter has an inflatable member mounted about a rigid bent distal segment. The opening is first formed by pushing small holes through the medial sac, lacrimal fossa, and lateral nasal wall with an instrument and coalescing the holes. The catheter is then introduced into the nasal cavity and pushed laterally through the opening by manipulating its proximal end. Pressurized fluid is then applied to the catheter to inflate the inflatable member and dilate the opening.
Owner:BECKER BRUCE
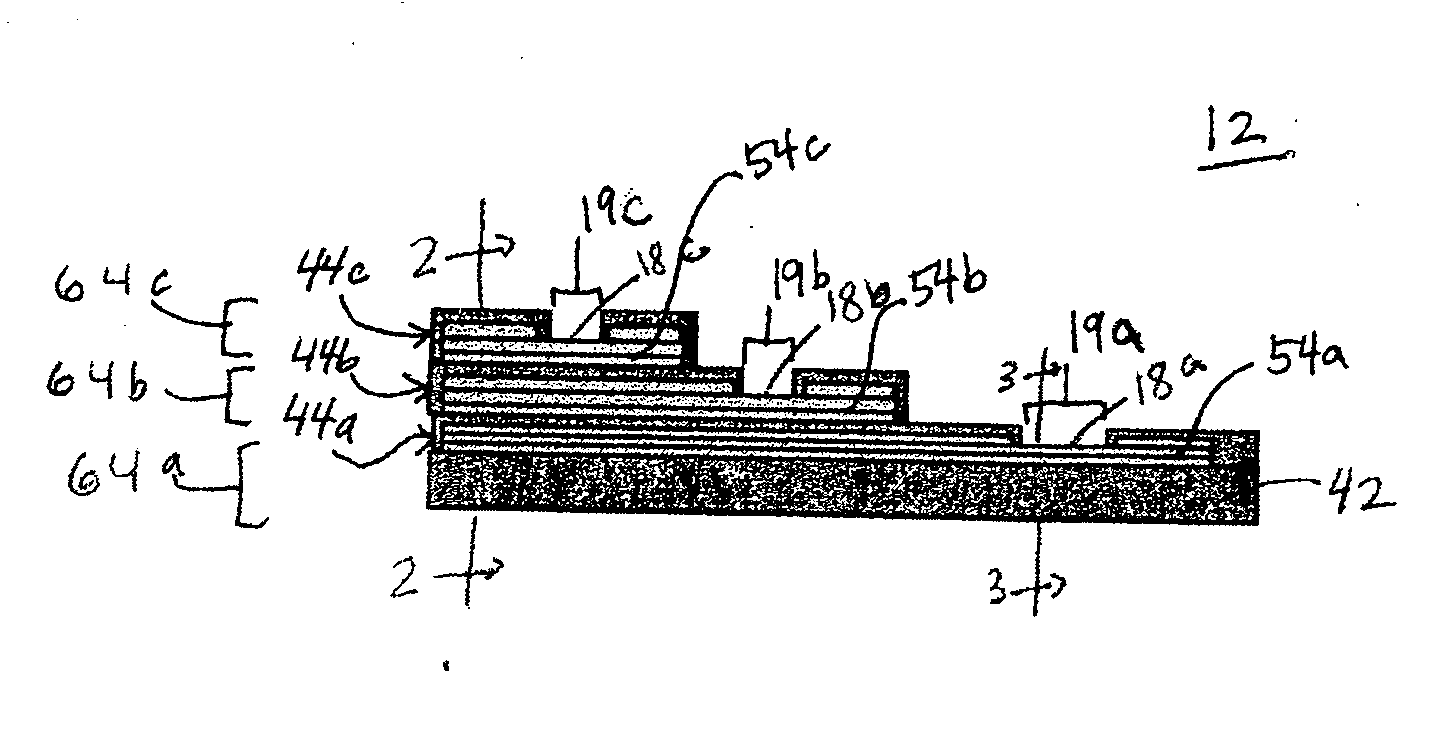
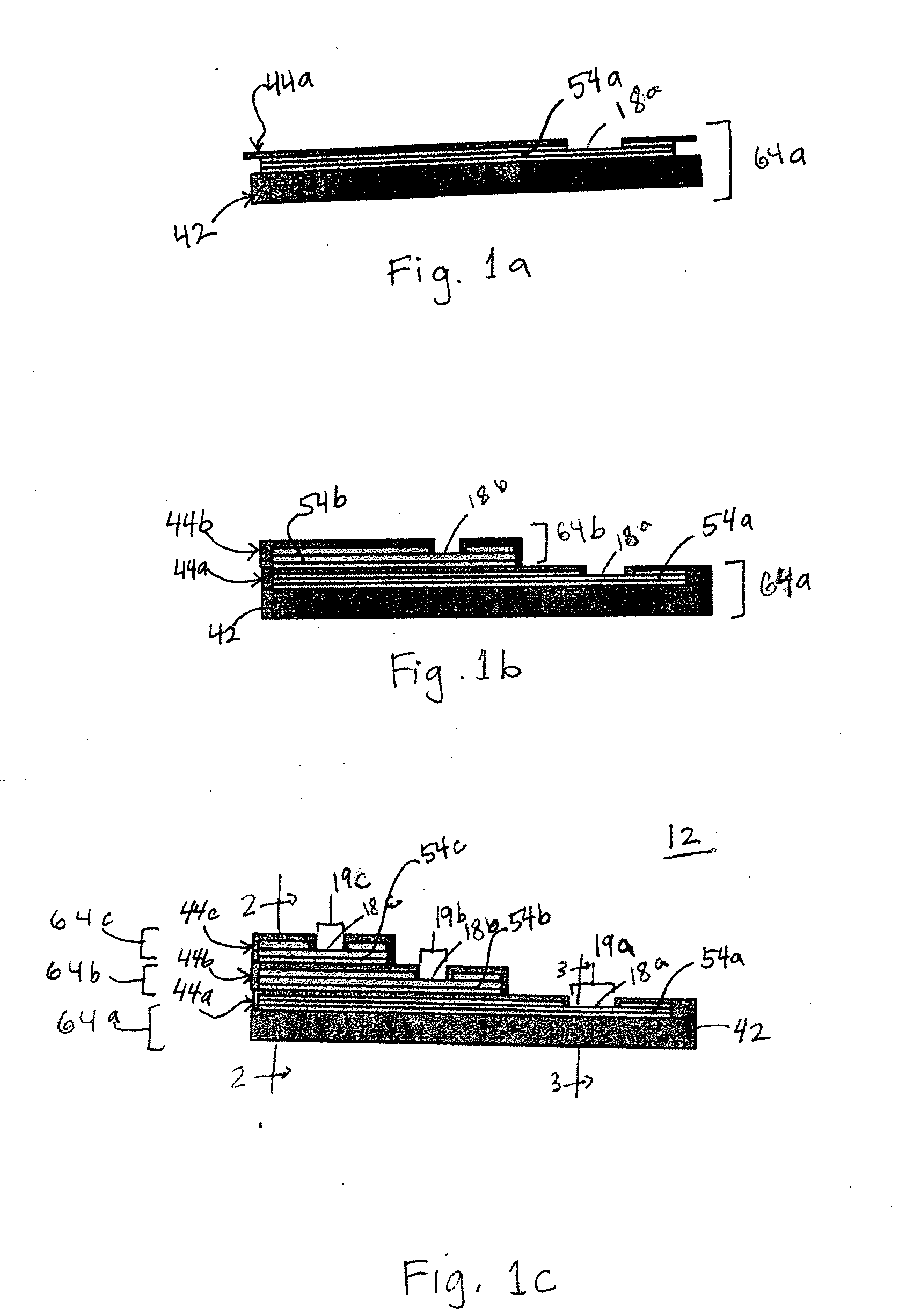
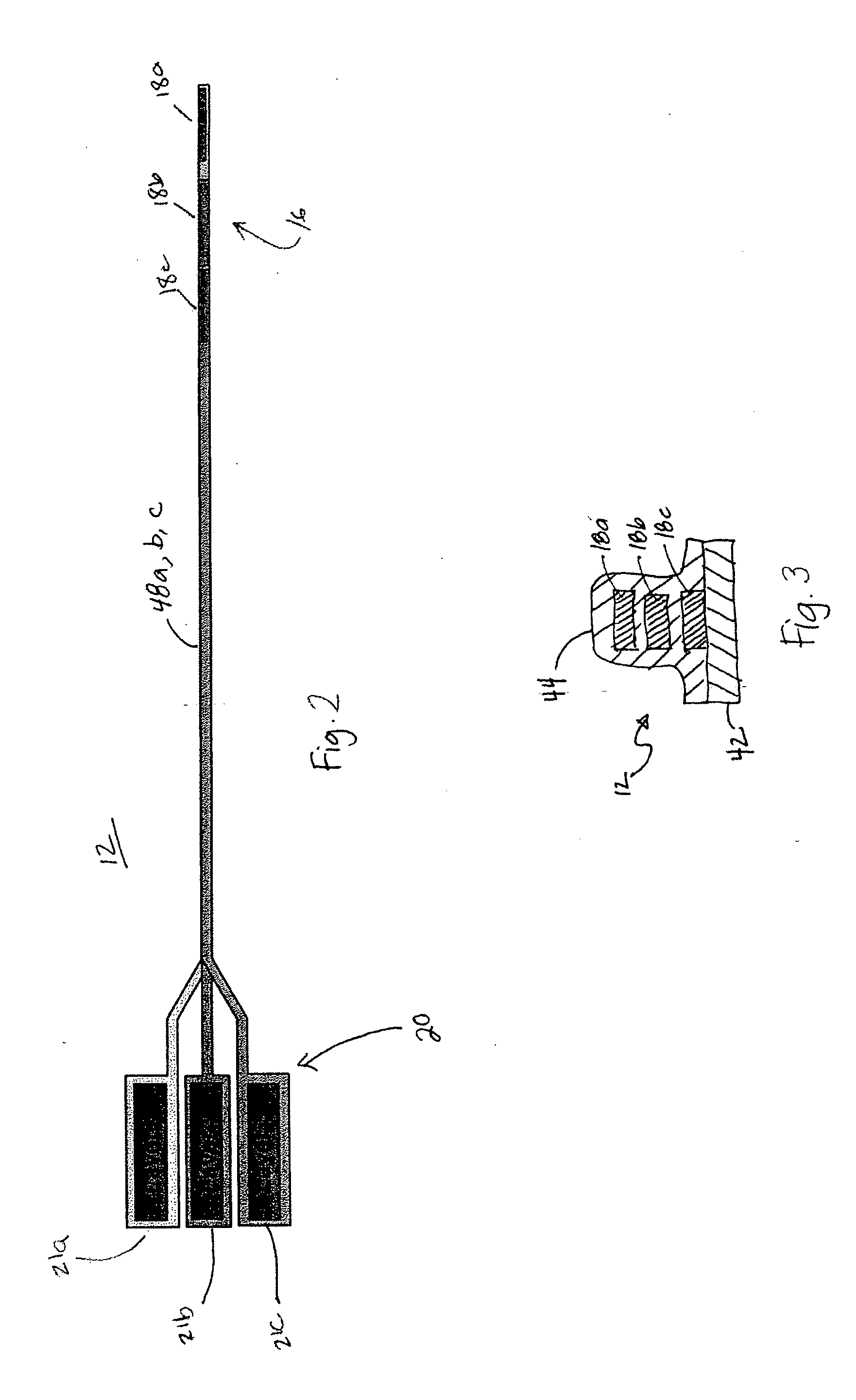
Multi-lumen steerable catheter
Elongated medical devices are disclosed adapted to be inserted through an access pathway into a body vessel, organ or cavity to locate a therapeutic or diagnostic distal segment of the elongated medical device into alignment with an anatomic feature of interest. Multi-lumen steerable catheters having a deflection lumen liner and a delivery lumen liner are adapted to be deflected by a deflection mechanism within or advanced through the deflection lumen liner to enable advancement of the catheter distal end through a tortuous pathway. At least one lumen liner is formed of a no yield elastomer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Hand-actuated device for remote manipulation of a grasping tool
The invention provides an articulating mechanism useful, for example, for remote manipulation of various surgical instruments and diagnostic tools within, or to, regions of the body. Movement of segments at the proximal end of the mechanism results in a corresponding, relative movement of segments at the distal end of the mechanism. The proximal and distal segments are connected by a set of cables in such a fashion that each proximal segment forms a discrete pair with a distal segment. This configuration allows each segment pair to move independently of one another and also permits the articulating mechanism to undergo complex movements and adopt complex configurations. The articulating mechanisms may also be combined in such a way to remotely mimic finger movements for manipulation of an object or body tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Articulation for surgical roboter
A surgical robotic component comprising an articulated terminal portion, the terminal portion comprising: a distal segment having an attachment for a surgical tool; a basal segment for attaching the terminal portion to the remainder of the surgical robotic component; and an intermediate compound joint between the distal segment and the basal segment, the intermediate compound joint permitting relative rotation of the distal segment and the basal segment about first, second and third axes; the terminal portion being arranged such that, in at least one configuration of the intermediate compound joint: (i) the axial direction of the basal segment is parallel to the axial direction of the distal segment, and (ii) the first, second and third axes are transverse to the axial directions of the basal and distal segments.
Owner:CMR SURGICAL LTD
Ablation catheter with transducer for providing one or more of pressure, temperature and fluid flow data for use in controlling ablation therapy
A distal segment of a catheter shaft is adapted to be positioned against tissue in a biological organ. The distal segment has a tissue-contacting area intended to contact the tissue. One or more pressure sensors positioned within the tissue-contacting area provide pressure data indicative of the pressure exerted on the distal segment. The distal segment carries one or more electrodes and the pressure sensors are located either on an electrode or on the catheter shaft near an electrode. The pressure sensors provide pressure data to a processor that analyzes the data to determine if the tissue-contacting area of the distal segment is contacting the tissue. The pressure sensors may also provide temperature data indicative of the temperature at the sensor. A flow sensor, located opposite the pressure sensor on the shaft, provides data related to the flow rate of fluid through the organ.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Torque sensing in a surgical robotic wrist
Owner:CMR SURGICAL LTD
Method and device for accessing a pericardial space
A method for accessing a pericardial space of a heart of a mammalian patient is disclosed comprising: guiding a catheter through a coronary sinus of the heart and to a cardiac vein; advancing said catheter to a distal segment of the cardiac vein; intentionally puncturing the vein with the catheter to access the pericardial space, and performing a therapy or a diagnostic procedure using the catheter an the puncture in the vein and using the pericardial space.
Owner:G&L CONSULTING
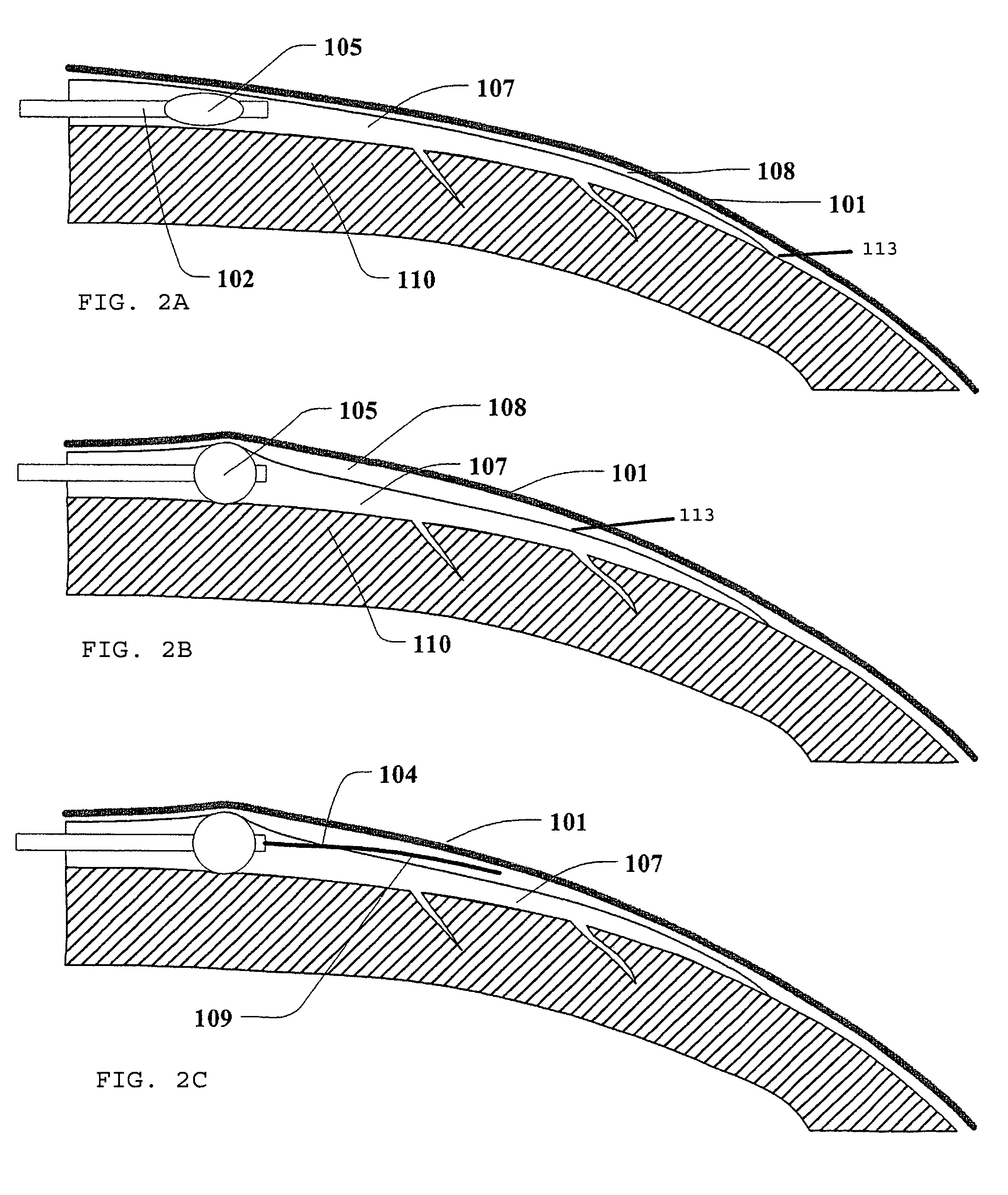
Deflectable catheter with hinge
A deflectable device, such as a catheter, is provided that includes a hinge that enhances the ability of the device to deflect or bend within a predetermined plane. The catheter comprises an elongated tubular catheter body having proximal and distal ends and at least one lumen extending therethrough. A distal segment is provided distal to the distal end of the catheter body. A tubular hinge is provided between the distal end of the catheter body and the proximal end of the distal segment. The hinge has an axis and at least one lumen extending therethrough. The tube includes at least one slot, and preferably a plurality of slots, extending part of the way through the hinge generally transverse to the axis of the hinge.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Methods and apparatus for flow restoration
Methods for restoring blood flow in occluded blood vessels using an apparatus having a self expandable distal segment that is pre-formed to assume a superimposed structure in an unconstrained condition but can be made to take on a volume-reduced form making it possible to introduce it with a microcatheter and a push wire arranged at the proximal end, with the distal segment in its superimposed structure assuming the form of a longitudinally open tube and having a mesh structure of interconnected strings or filaments or struts. In a preferred embodiment, the distal segment has a tapering structure at its proximal end where the strings or filaments or struts converge at a connection point.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Insertion Set for a Transcutaneous Sensor
An improved insertion set is provided for transcutaneous placement of a sensor such as a glucose sensor at a selected site within the body of a patient. The insertion set comprises a mounting base defining an upwardly open channel for receiving and supporting a flexible thin film sensor, in combination with a cap assembled with said mounting base to capture and retain a proximal end of the sensor within said channel. The sensor further includes a distal segment with sensor electrodes thereon which protrudes from the mounting base for transcutaneous placement, wherein the sensor distal segment is slidably carried by a slotted insertion needle fitted through the assembled base and cap. Placement of the insertion set against the patient's skin causes the insertion needle to pierce the skin to carry the sensor electrodes to the desired subcutaneous site, after which the insertion needle can be slidably withdrawn from the insertion set. The mounting base further includes a fitting and related snap latch members for mated slide-fit releasable coupling of conductive contact pads on a proximal end of the sensor to a cable connector for transmitting sensor signals to a suitable monitoring device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
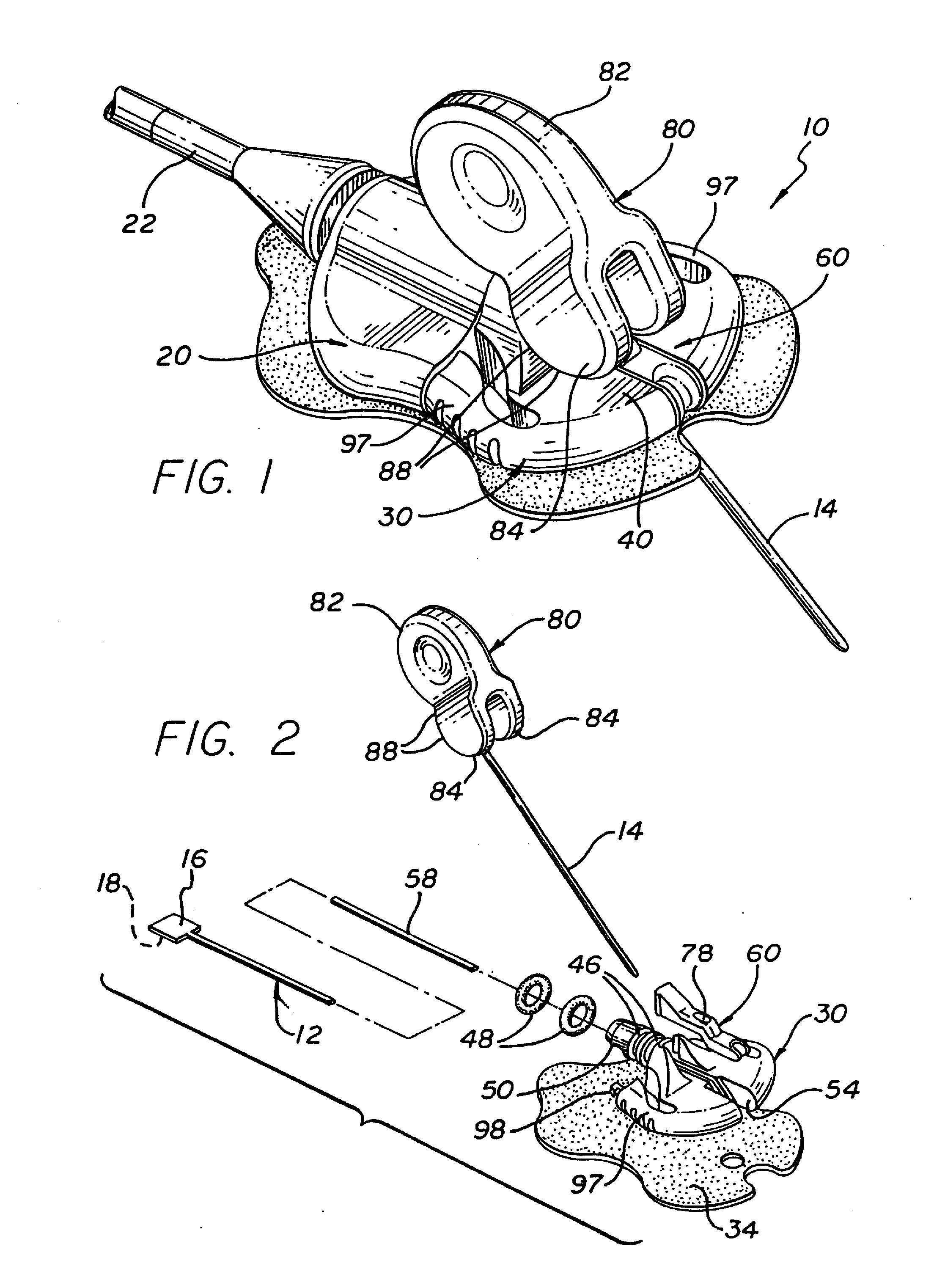
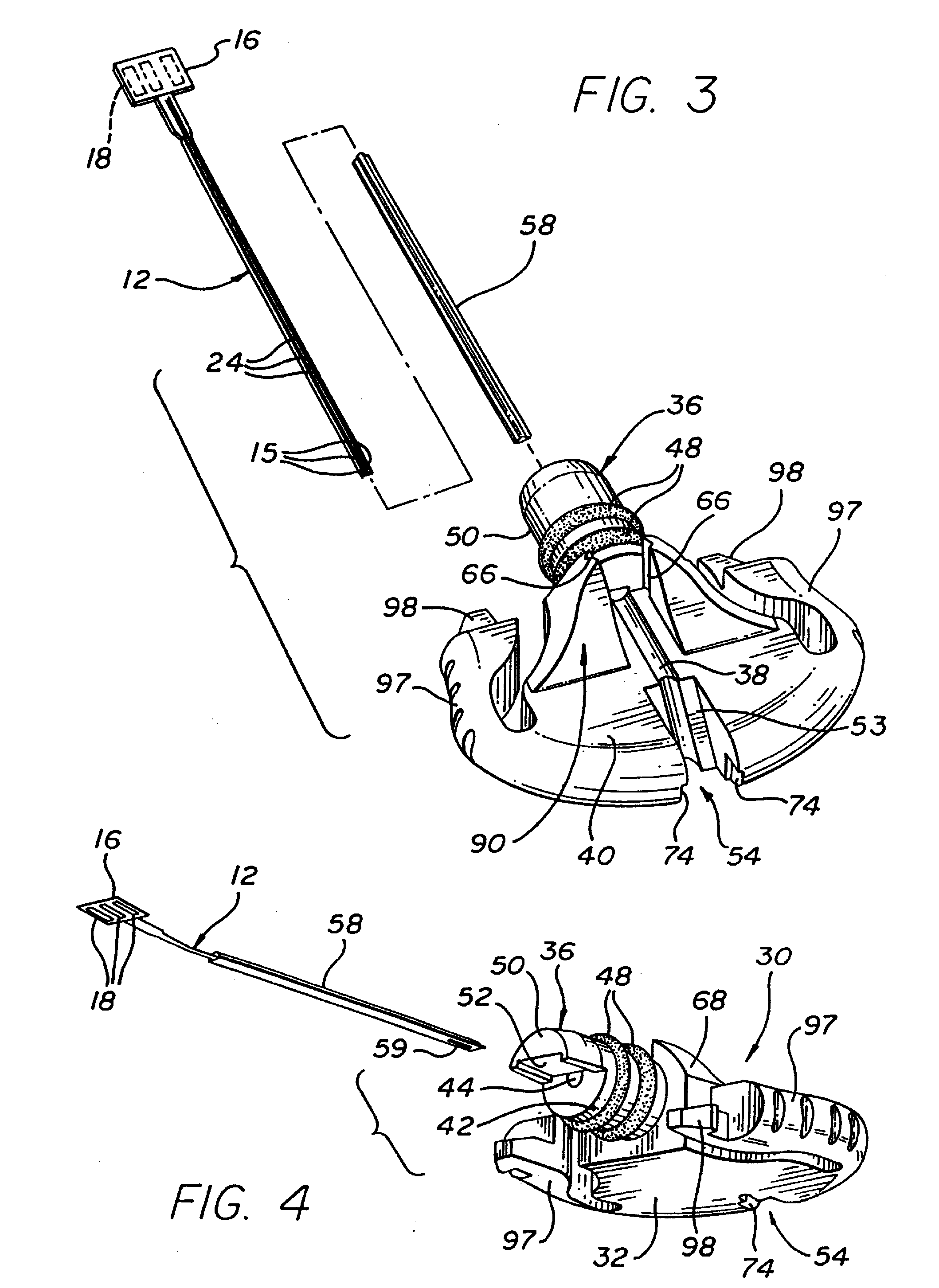
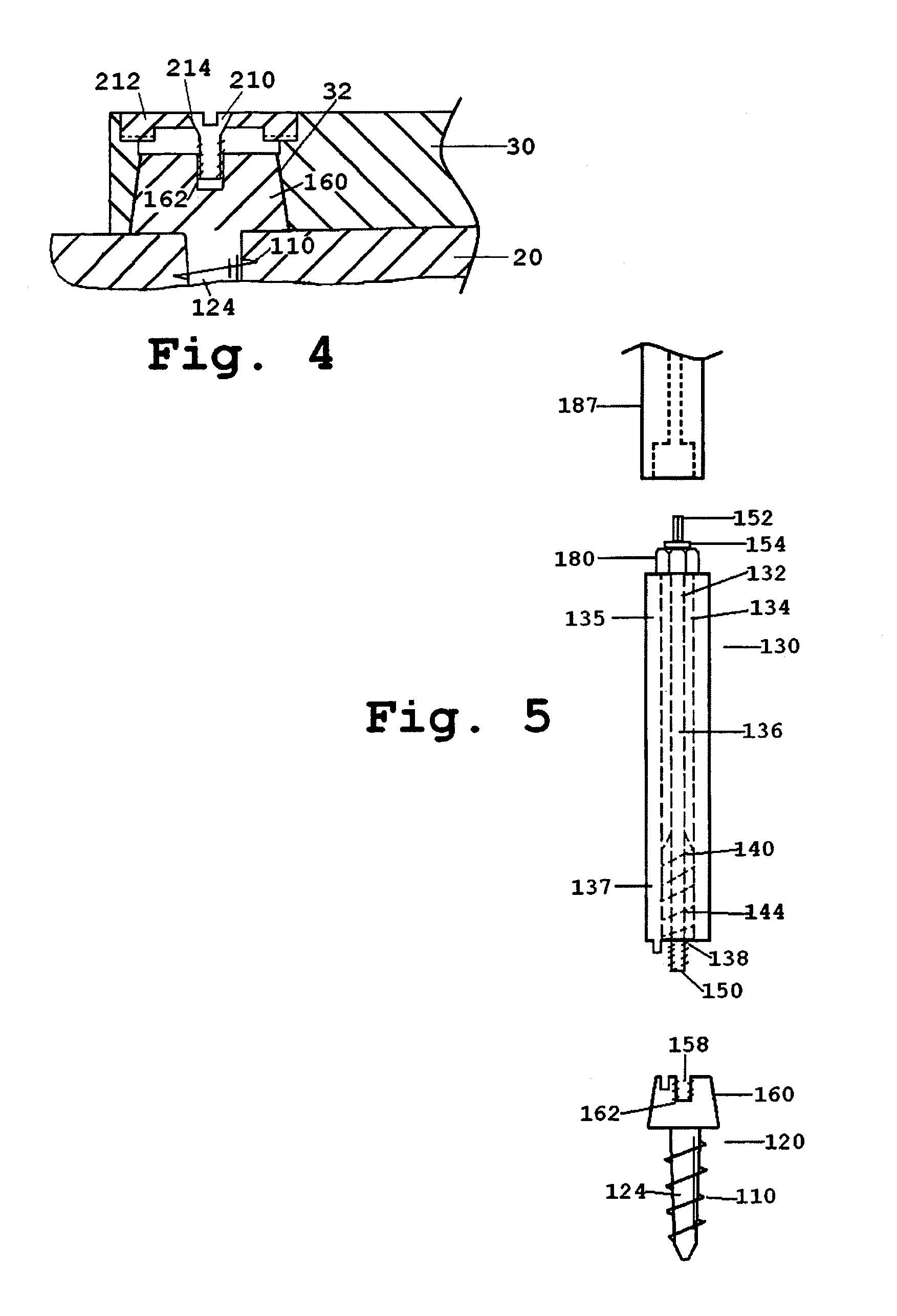
Distraction screw for skeletal surgery and method of use
ActiveUS7476228B2Improve functionalityAccurate placementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDistractionFixation point
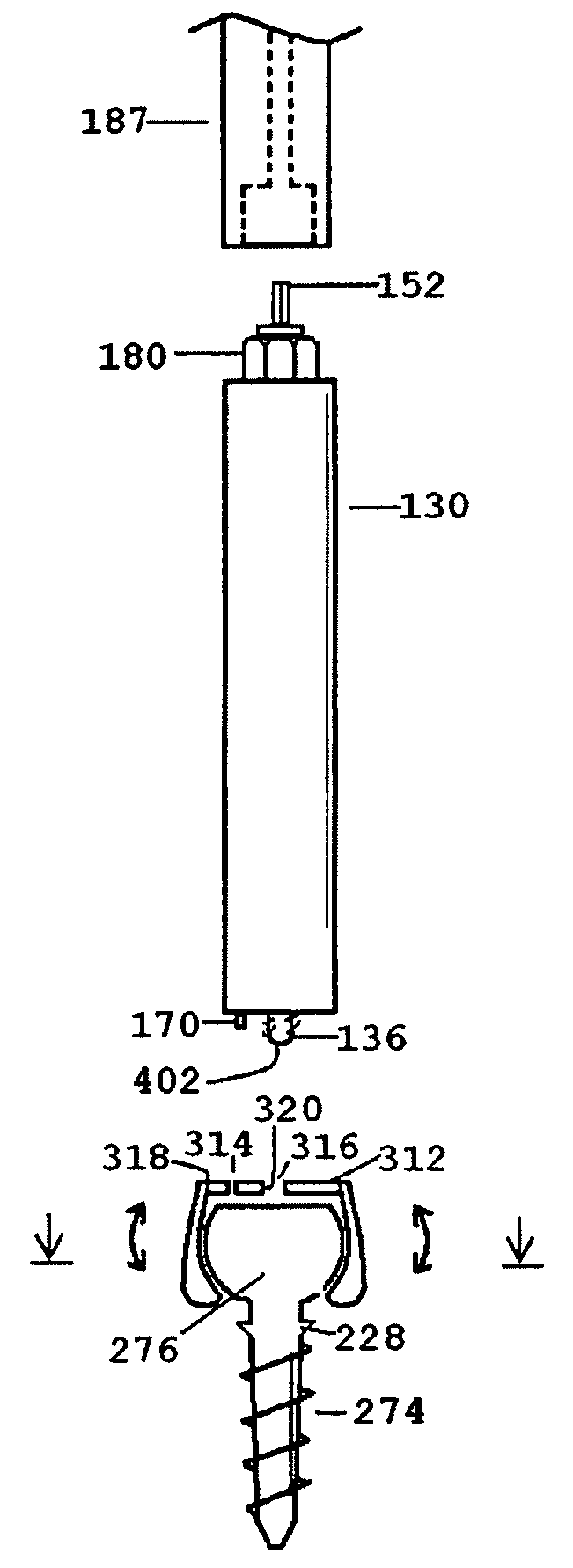
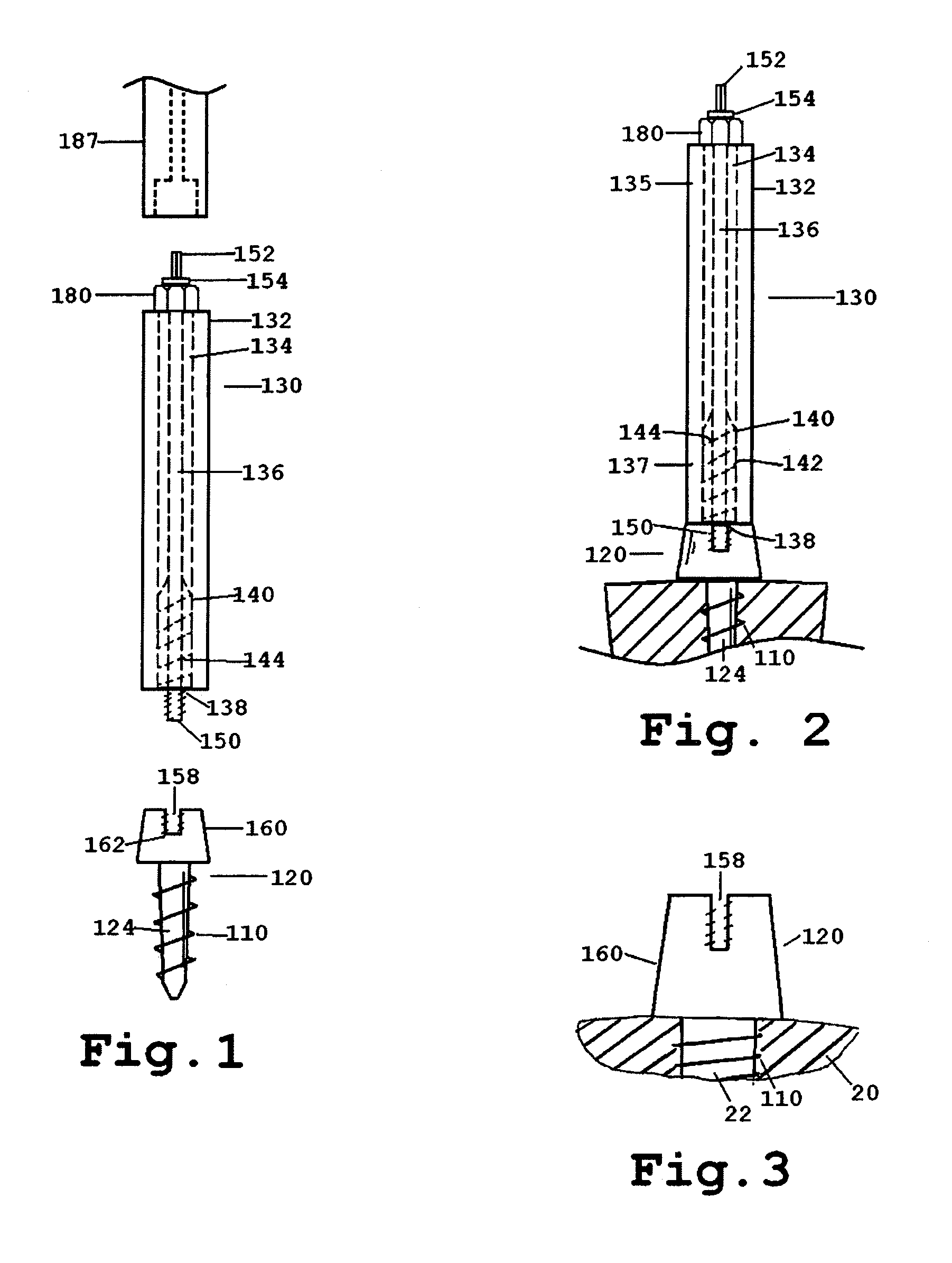
An improved distraction bone screw and a method for its use are described. The distraction screw is comprised of an implantable distal segment and a detachably secured proximal segment. The distal segment includes a head portion and a threaded shank portion. The proximal segment is represented as an elongated body having an internal bore that extends through its length. A deployable member is disposed within the bore, which is extendible outside the internal bore to securely couple to the distal segment. As an assembly, the distraction screw is used to affix and realign bone during surgical reconstruction. Upon completion of the surgical work, the proximal segment is removed and the distal segment is left attached to the reconstructed bone. Securely affixed, the distal segment provides an additional point of fixation for the skeletal plates that are used to preserve the bony alignment while bone healing occurs. The affixed distal segment will also provide a ready mechanism for distraction screw replacement at the time of surgical revision without obligatory plate removal. Different embodiments of the proximal segment, distal segment and the rotational locking mechanisms which inhibit the rotation of one segment relative to the other during deployment were also described. In addition, in cases where the distraction screw must be placed into the bone at an inclined angle, poly-axial heads were provided so that proper skeletal plate placement can still be accomplished.
Owner:ABDOU M SAMY
Methods and systems for accessing the pericardial space
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
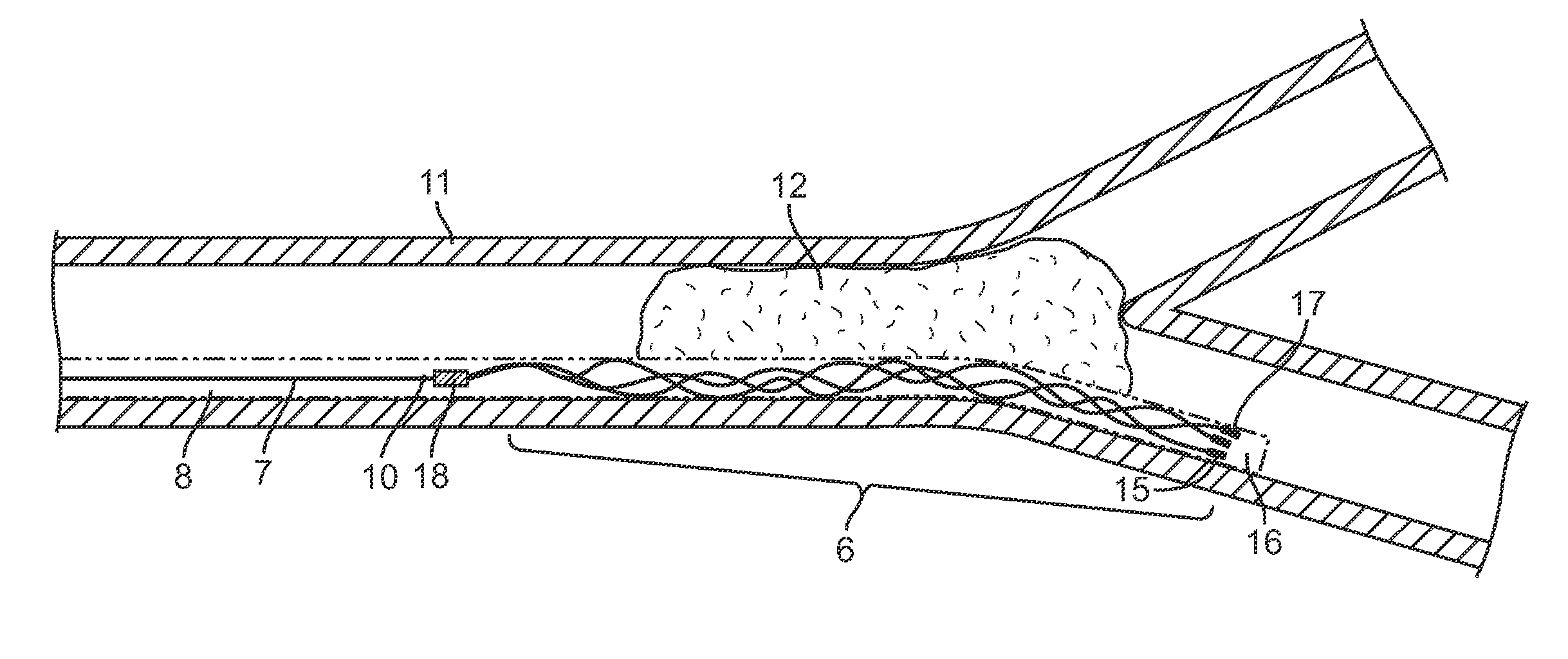
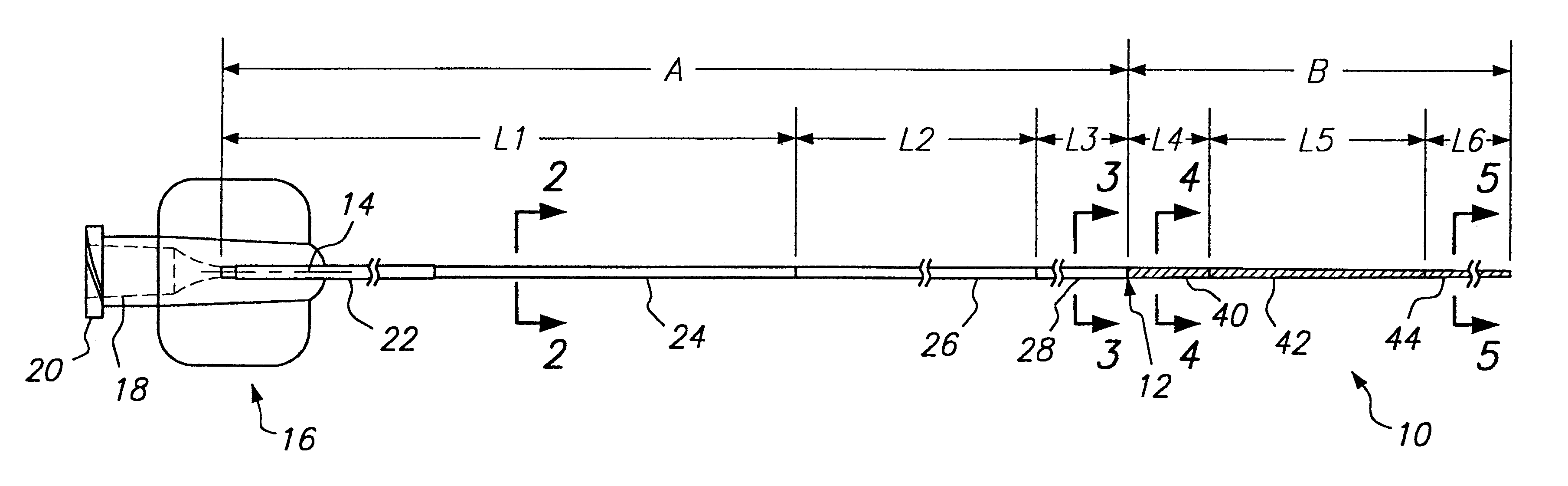
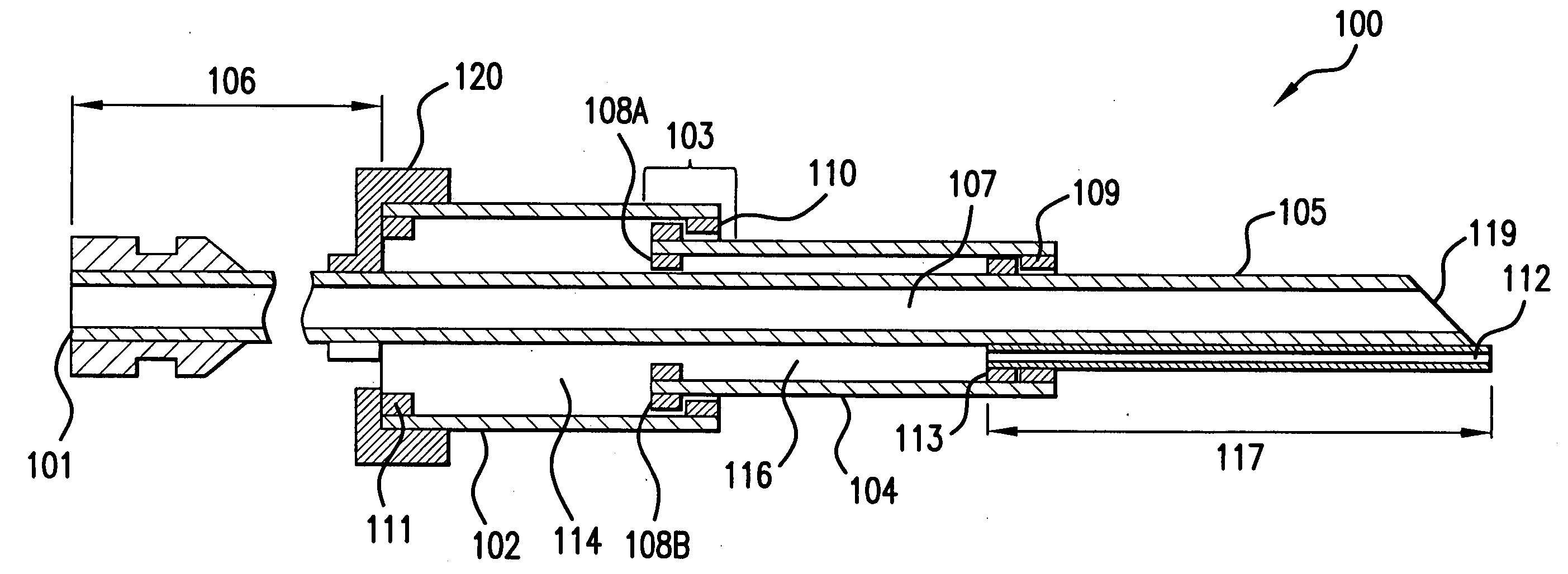
Soft tip guiding catheter and method of fabrication
The present invention relates to medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing ther devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, and particularly to an improved distal soft tip or segment attachment with a relatively stiff proximal catheter shaft. A tubular sleeve is bonded through the application of pressure and heat to a distal portion of the catheter shaft and a proximal portion of the distal segment of soft distal tip bridging the attachment junction. In the preferred method, the catheter shaft distal end is aligned with the distal segment or soft tip proximal end and the sleeve is fitted over the attachment junction. A heat shrink tube is fitted over the sleeve and adjoining portions of the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip and heat is applied. The shrinkage force of the heat shrink tube over the assembly of the tubular sleeve overlying and bridging the attachment junction and the applied heat melts and force the materials of the tubular sleeve and the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip together to fill interstitial spaces of the attachment junction and reduces the outer diameter of the sleeve. The heat shrink tube is removed after the assembly cools and solidifies. Preferably, the catheter shaft distal end and the soft tip or intermediate segment proximal end are each formed with a like plurality of ungular cut sections that are complementary in shape to one another, whereby the ungular cut sections are aligned with and mated together along the attachment junction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Flow directed catheter
InactiveUS6296631B2Similar property of flexibilityPrevent kinkingCatheterCoatingsDistal segmentBiomedical engineering
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Trans-septal catheter with retention mechanism
A trans-septal guide catheter for providing access through the septum separating a first heart chamber from a second heart chamber that includes an elongated guide catheter body extending between guide catheter proximal and distal ends. A distal segment of the guide catheter is adapted to be inserted through the septum to locate the distal segment of the guide catheter within one of the first heart chamber and the second heart chamber. The catheter body encloses a guide catheter lumen adapted to provide access into the one of the first heart chamber and the second heart chamber through a guide catheter lumen proximal end opening and a guide catheter lumen distal end opening. A retention mechanism engages the septum and maintains the distal segment of the guide catheter extending into the one of the first heart chamber and the second heart chamber
Owner:STEWART MARK T +2
Aspiration catheter having a variable over-the-wire length and methods of use
InactiveUS20050027236A1Shortening effective over-the-wire length of catheterBalloon catheterEnemata/irrigatorsDistal segmentAspiration catheter
An aspiration catheter includes an aspiration shaft and a telescoping outer sheath which can be passed over a guidewire. The sheath includes “nesting” proximal and distal tubes. The distal tube slides within a proximal tube lumen, and the aspiration shaft slides within a distal tube lumen. The catheter can be placed in an expanded position by pushing the aspiration shaft, thereby causing the distal tube to be moved distally. The catheter can be retracted by pulling the aspiration shaft proximally so that a distal segment of the aspiration shaft is drawn into the distal tube lumen and the distal tube is drawn into the proximal tube lumen. Alternatively, a middle tube is slidingly disposed over the aspiration shaft between the proximal and distal tubes. In this embodiment, the middle tube nests within the proximal tube lumen and the distal tube nests within a middle tube lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Cardiac vein lead and guide catheter
InactiveUS6871085B2Easy steeringSmall sizeTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsWalking around obstaclesDistal segment
A guide catheter and medical lead are provided wherein the lead may be used as a pull wire to steer the guide catheter. The guide catheter is provided with a flexible distal segment and the lead is provided with a distal engaging member, which may also serve as an electrode. The distal engaging member interacts with the distal catheter end such that traction applied to the proximal lead end causes flexion of the distal segment of the catheter to advance the flexible distal segment between a non-flexed position and a flexed position, allowing the catheter to be steered around obstacles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for imparting curves in implantable elongated medical instruments
InactiveUS6907298B2Stay flexibleSpace maximizationInternal electrodesCatheterDistal segmentMedical device
Elongated medical instruments adapted to be permanently or temporarily implanted in the mammalian body or used to access a site in the body to facilitate introduction of a further medical device, and methods and apparatus for deflecting the distal end and imparting curves in distal segments of such medical instruments within the body by manipulation of a proximal segment of the instrument outside the body are disclosed. Multiple portions of distal segments of a single one or distal segments of coaxially arranged distal segments of deflectable coiled wires are formed each having a line of spacers each functioning as a backbone along a side of the wire coil and formed in a variety of ways. One or more elongated movable wire extends through a coil lumen to one or more attachment point distal to each portion that can be pushed to widen and / or pulled to narrow the spacing of coil turns across the coil diameter from the line to induce a bend in all more proximal portions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Stent-graft delivery system having an inner shaft component with a loading pad or covering on a distal segment thereof for stent retention
A catheter for delivering a self-expanding stent-graft prosthesis includes an inner shaft component having a distal segment over which the stent-graft prosthesis is loaded in a compressed delivery configuration. The distal segment has a covering that is intimately disposed thereover. The covering forms a raised outer surface on the distal segment and includes a plurality of protrusions that extend radially outward from the raised outer surface. An outer shaft component is slidingly disposed over the distal segment of the inner shaft component for holding the stent-graft prosthesis in the compressed delivery configuration. In the compressed delivery configuration, the stent-graft prosthesis is disposed over and makes contact with the covering of the distal segment of the inner shaft component such that at least the plurality of protrusions provide sufficient friction to of the covering secure a longitudinal position of the stent-graft prosthesis relative to the inner shaft component.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Articulating mechanism for remote manipulation of a surgical or diagnostic tool
The invention provides an articulating mechanism useful, for example, for remote manipulation of various surgical instruments and diagnostic tools within, or to, regions of the body. Movement of segments at the proximal end of the mechanism results in a corresponding, relative movement of segments at the distal end of the mechanism. The proximal and distal segments are connected by a set of cables in such a fashion that each proximal segment forms a discrete pair with a distal segment. This configuration allows each segment pair to move independently of one another and also permits the articulating mechanism to undergo complex movements and adopt complex configurations.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Flow directed catheter
A flow directed microcatheter is formed having a gradually changing flexibility and diameter between a proximal end and a distal end of the microcatheter. The changing properties of the microcatheter according to the present invention provide the flexibility of the distal tip needed to allow the microcatheter to be directed by the flow of blood within the vasculature, and the columnar strength and torquability at the proximal end and along the length of the microcatheter needed to advance and direct the distal tip to the target site. A proximal segment of the microcatheter includes a plurality of strands which vary in diameter to change the flexibility of the microcatheter. A distal segment of the microcatheter includes an inner layer which is compatible with solvents, such as DMSO, and an outer layer which provides strength and flexibility. The proximal segment and the distal segment of the microcatheter are joined by a kink resistant fuse joint.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device and method for spinous process distraction
An implant for maintaining a given minimum inter-spinous-process spacing includes an implant body with a number of segments hingedly interconnected so as to assume a straightened state for delivery along a conduit and a curved deployed state. An elongated tightening element is anchored at the distal segment of the implant body and passes along a channel extending along the implant body. Tension applied to the tightening element biases the implant body from the straightened state to the curved deployed state. Preferably, when the tightening element is deflected to reach the curved deployed state, a locking arrangement locks the tightening element relative to the implant body, thereby retaining the implant in the curved deployed state. A distal portion of the implant body is preferably formed with a set of lateral projections to inhibit withdrawal of the distal portion between adjacent spinous processes after deployment.
Owner:SEASPINE
Balloon catheters and methods for treating paranasal sinuses
A set of sinus balloon catheters are provided for treating a patient's paranasal sinus system, including dilating prepared openings, and natural ostia and ducts and excising sinus cavities. These include a balloon catheter with a bend placing a distal segment at 90° to a proximal segment and a balloon catheter which is substantially straight. The catheters have sufficient stiffness and column strength that the balloon carrying distal segment of the catheter can be pushed into the prepared opening, natural ostium or duct, or sinus to be excised. The catheters have appropriate inflated working diameters and appropriate outer diameters with the balloon deflated that will enable the catheter to be pushed into the respective prepared opening, natural ostium or duct, or sinus cavity to be excised. The methods use the balloon catheters to dilate prepared openings to selected parts of the sinus system, to dilate natural ostia and ducts of the sinus system, and / or to dilate sinus cavities to remove them.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Articulating mechanism for remote manipulation of a surgical or diagnostic tool
The invention provides an articulating mechanism useful, for example, for remote manipulation of various surgical instruments and diagnostic tools within, or to, regions of the body. Movement of segments at the proximal end of the mechanism results in a corresponding, relative movement of segments at the distal end of the mechanism. The proximal and distal segments are connected by a set of cables in such a fashion that each proximal segment forms a discrete pair with a distal segment. This configuration allows each segment pair to move independently of one another and also permits the articulating mechanism to undergo complex movements and adopt complex configurations.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com