Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36results about How to "Large profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
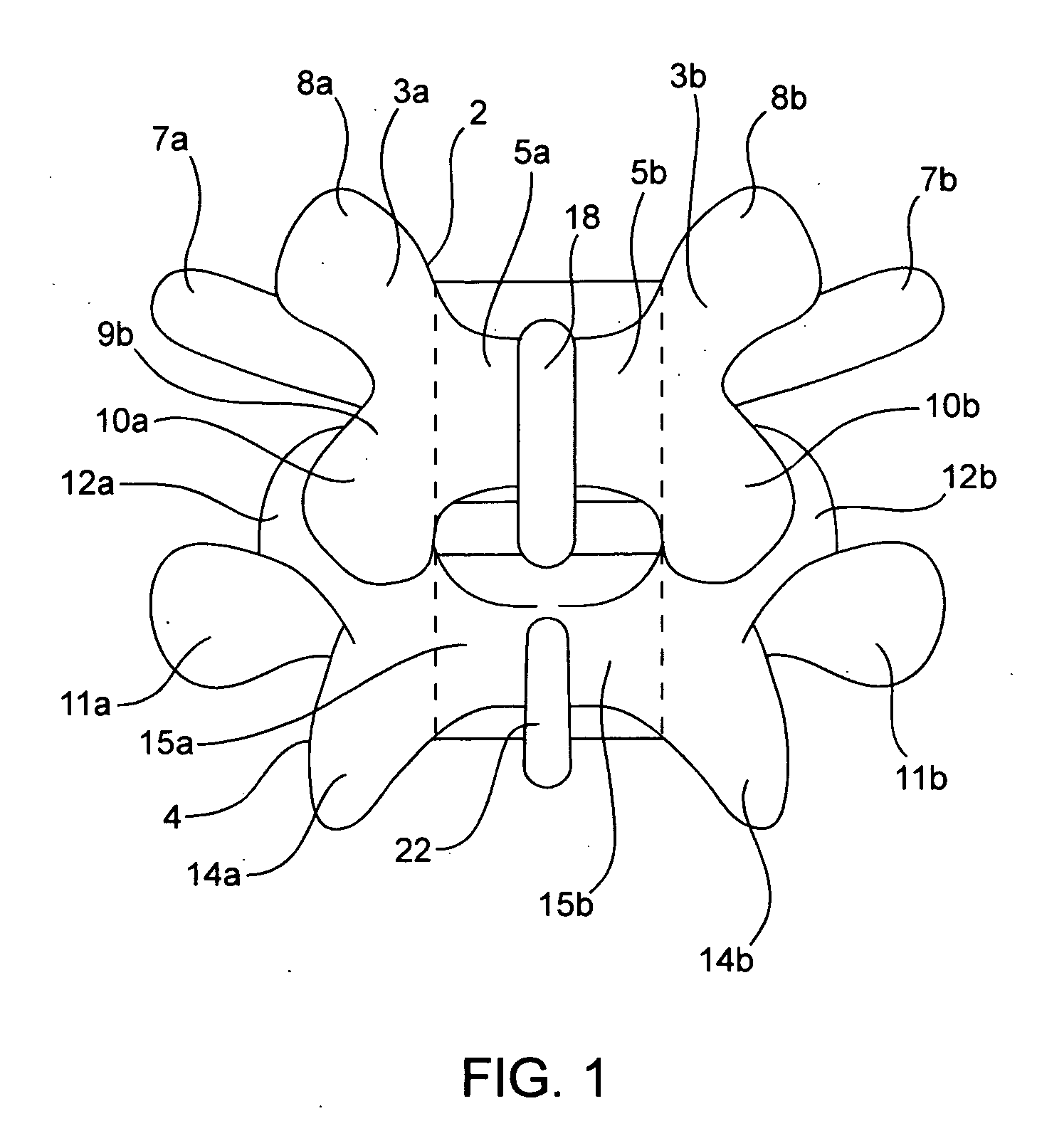
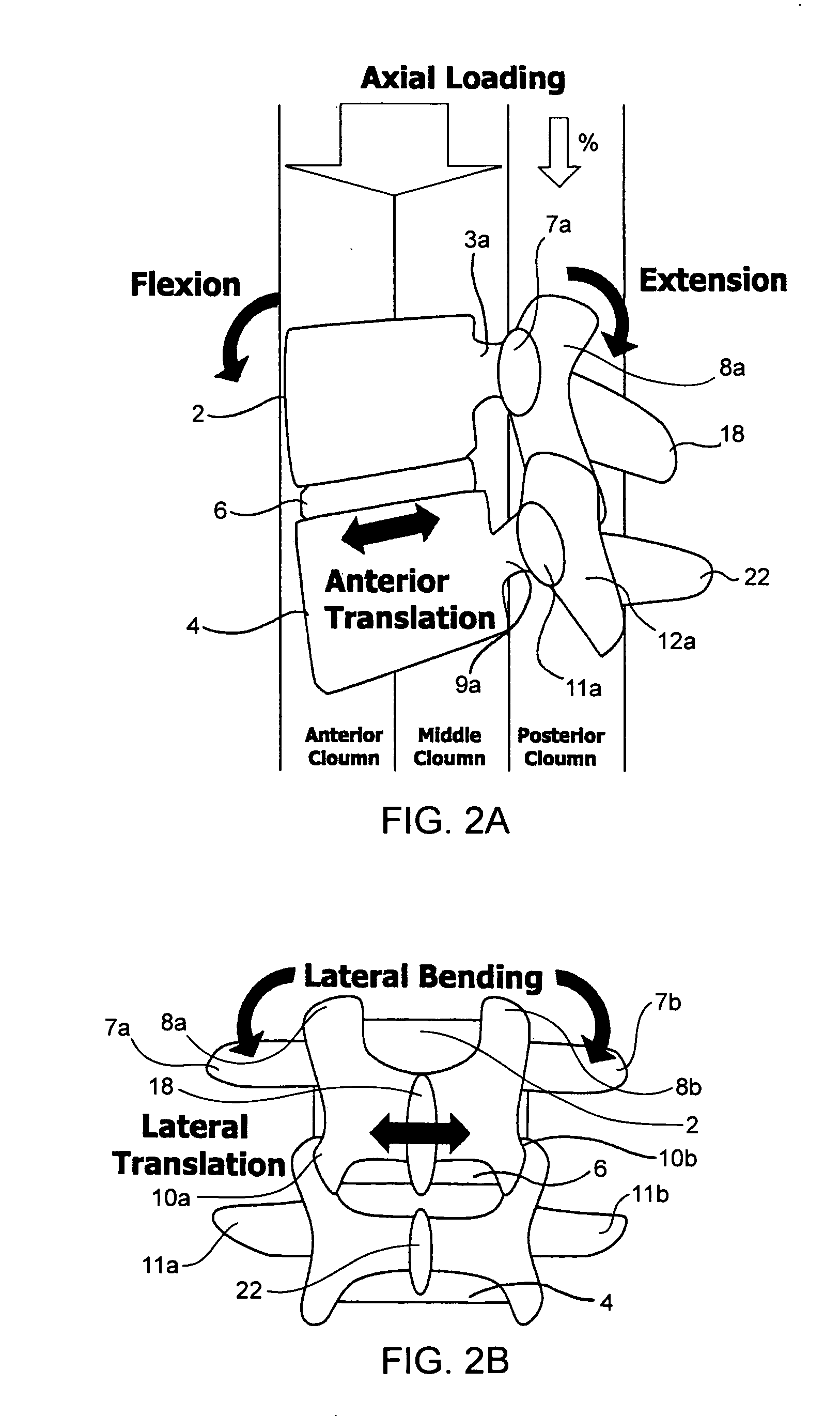
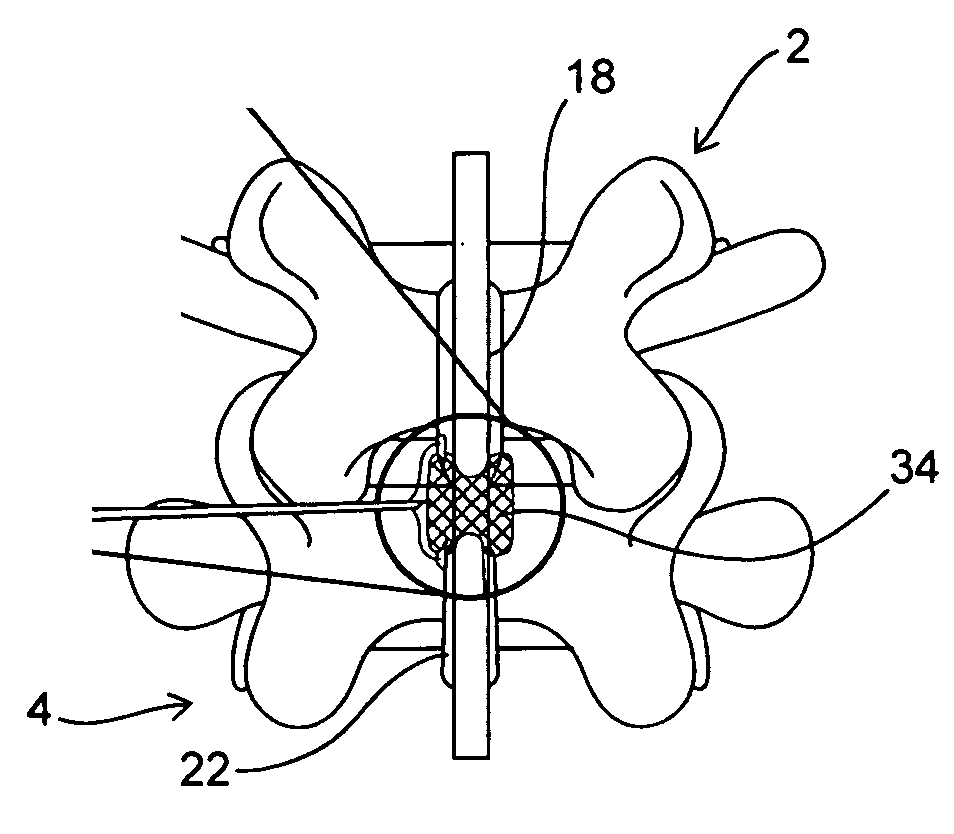
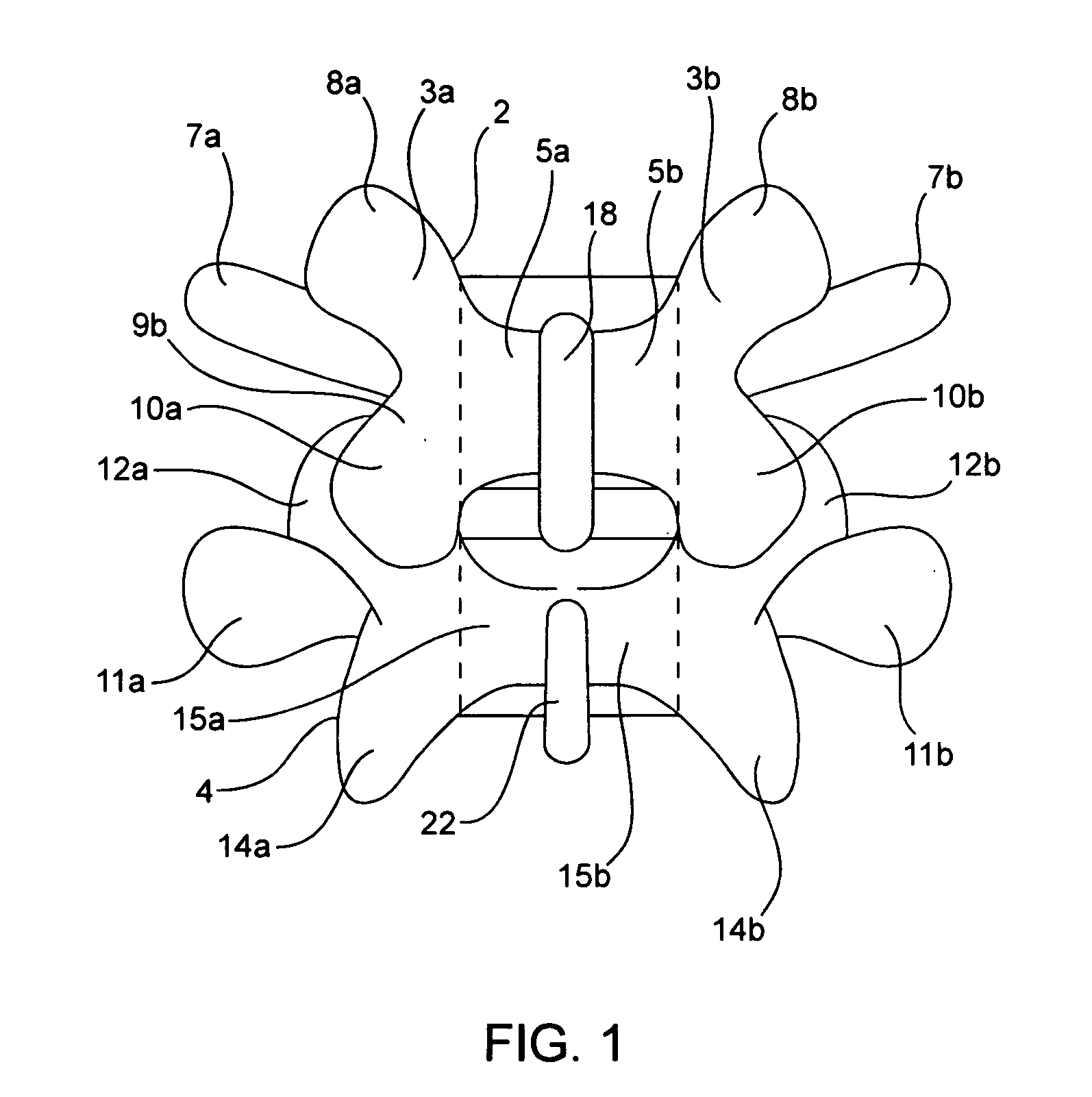
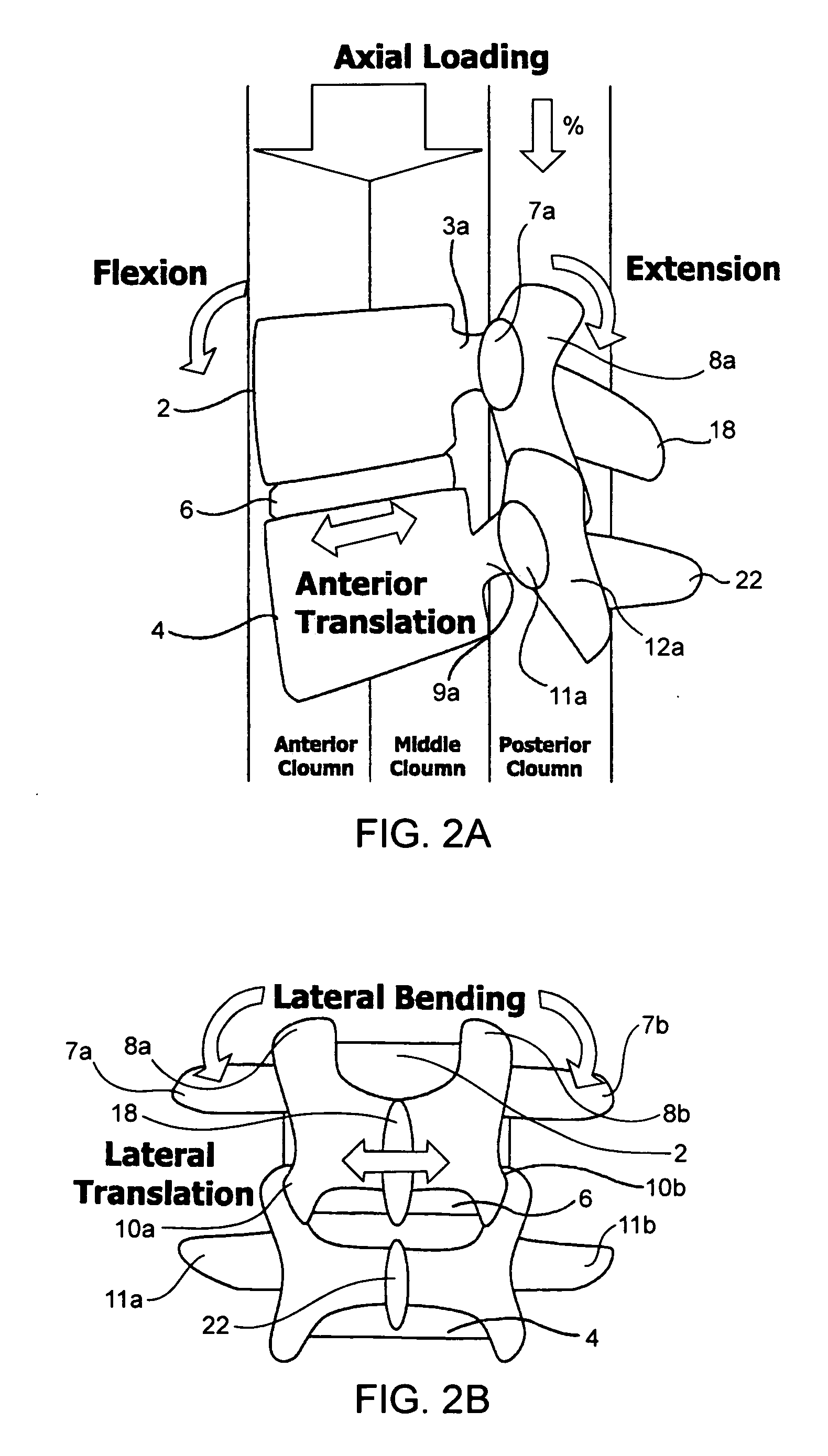
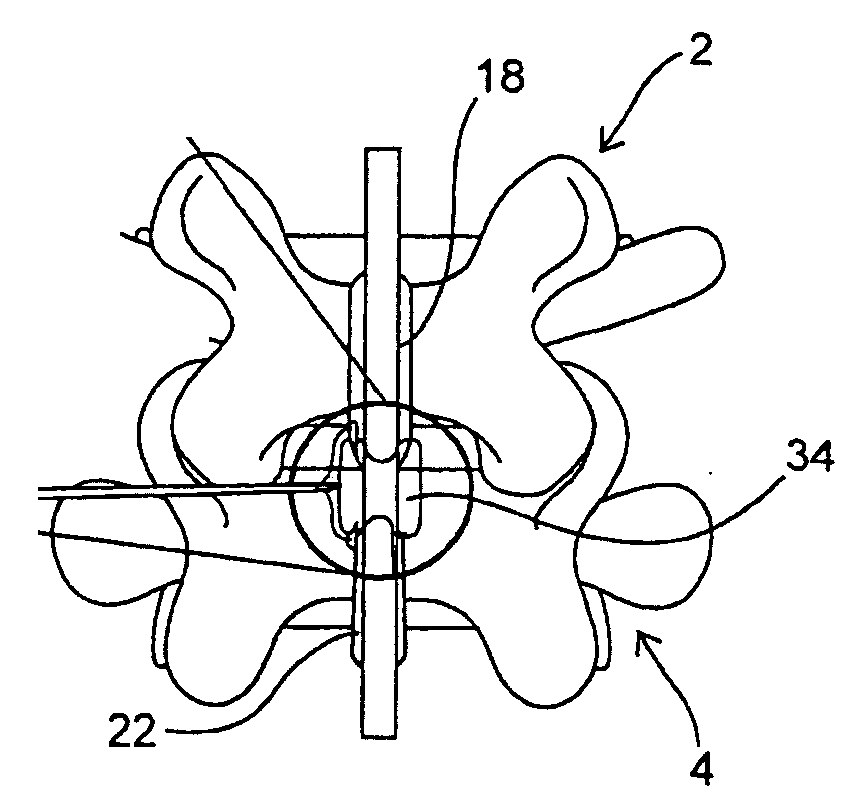
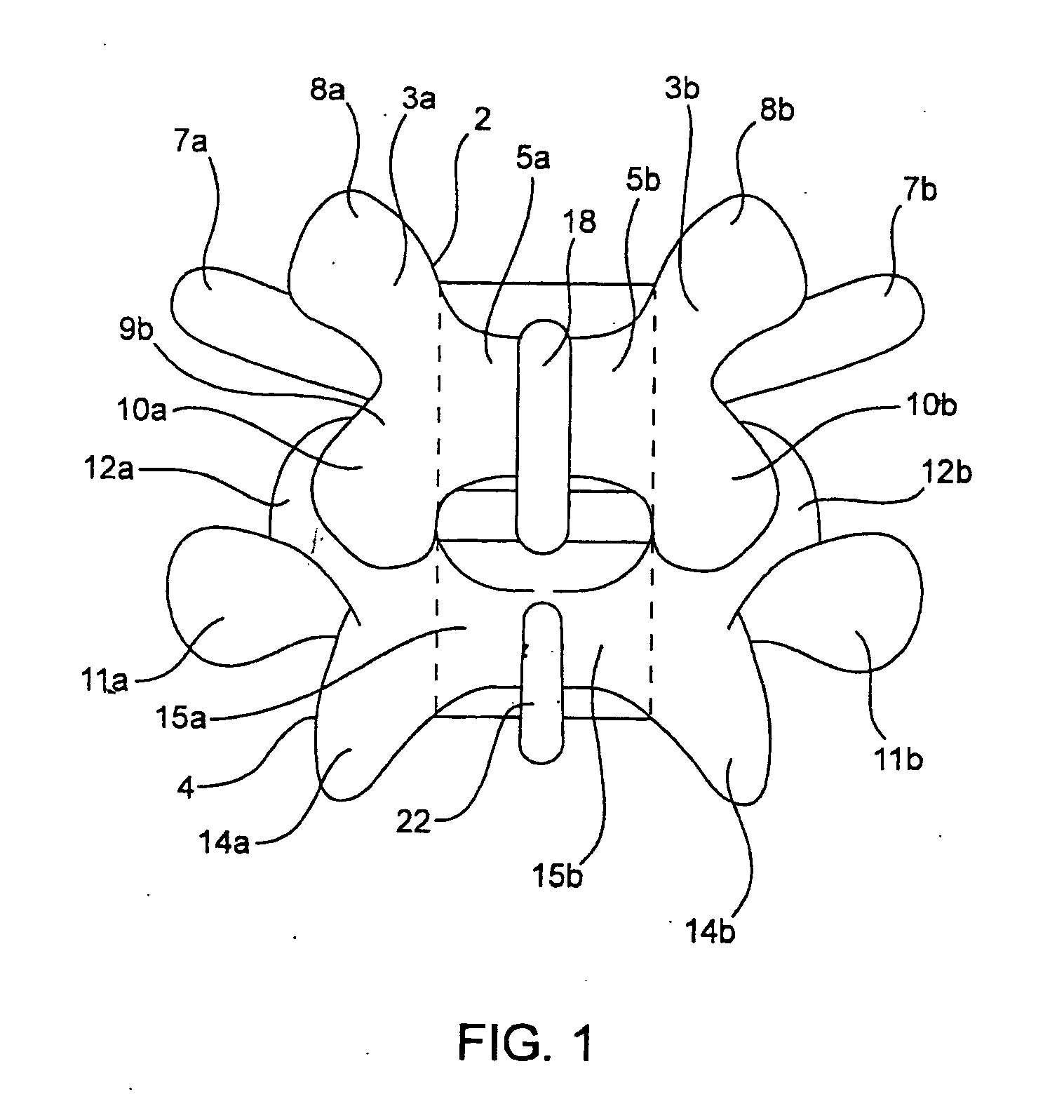
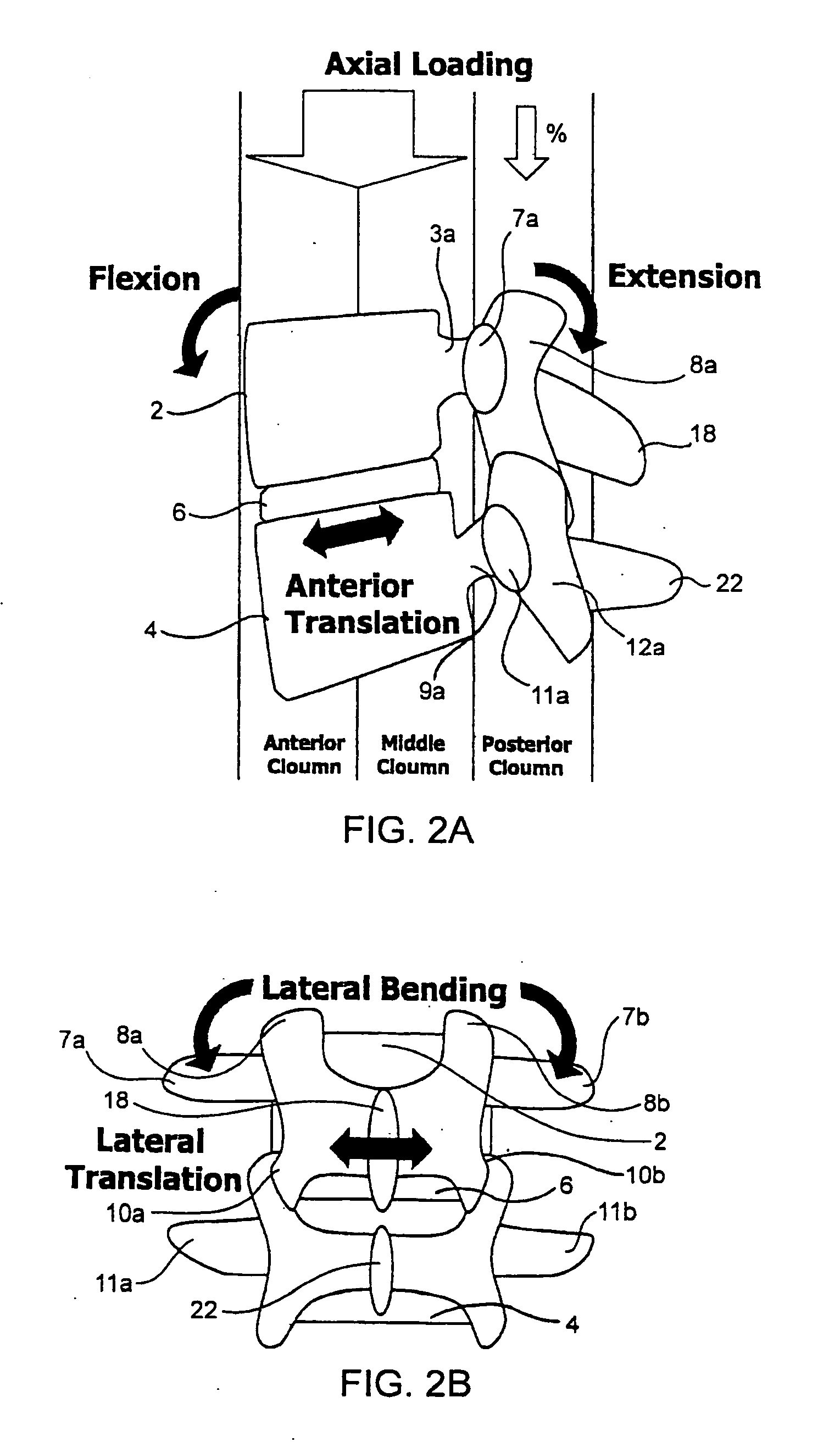
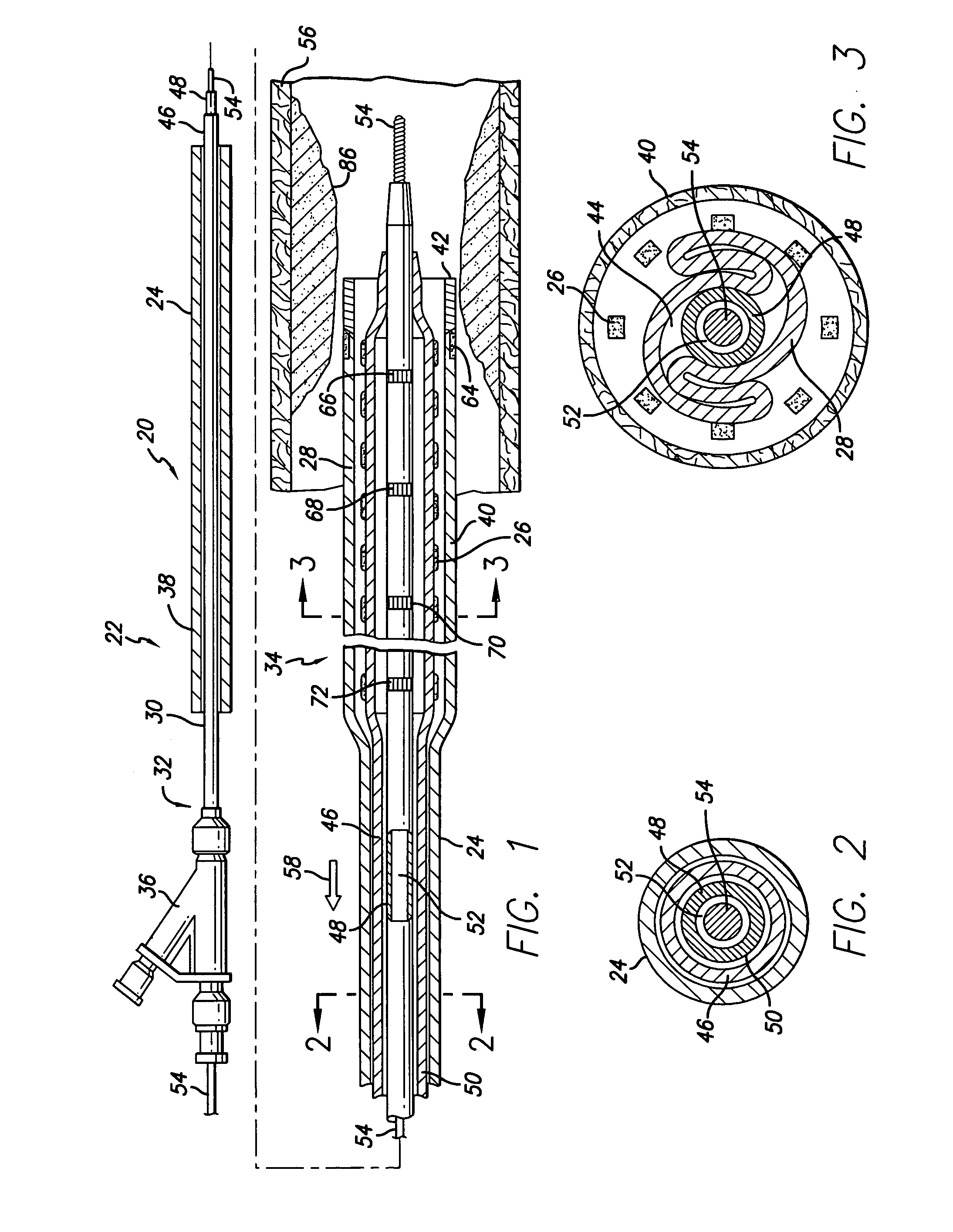
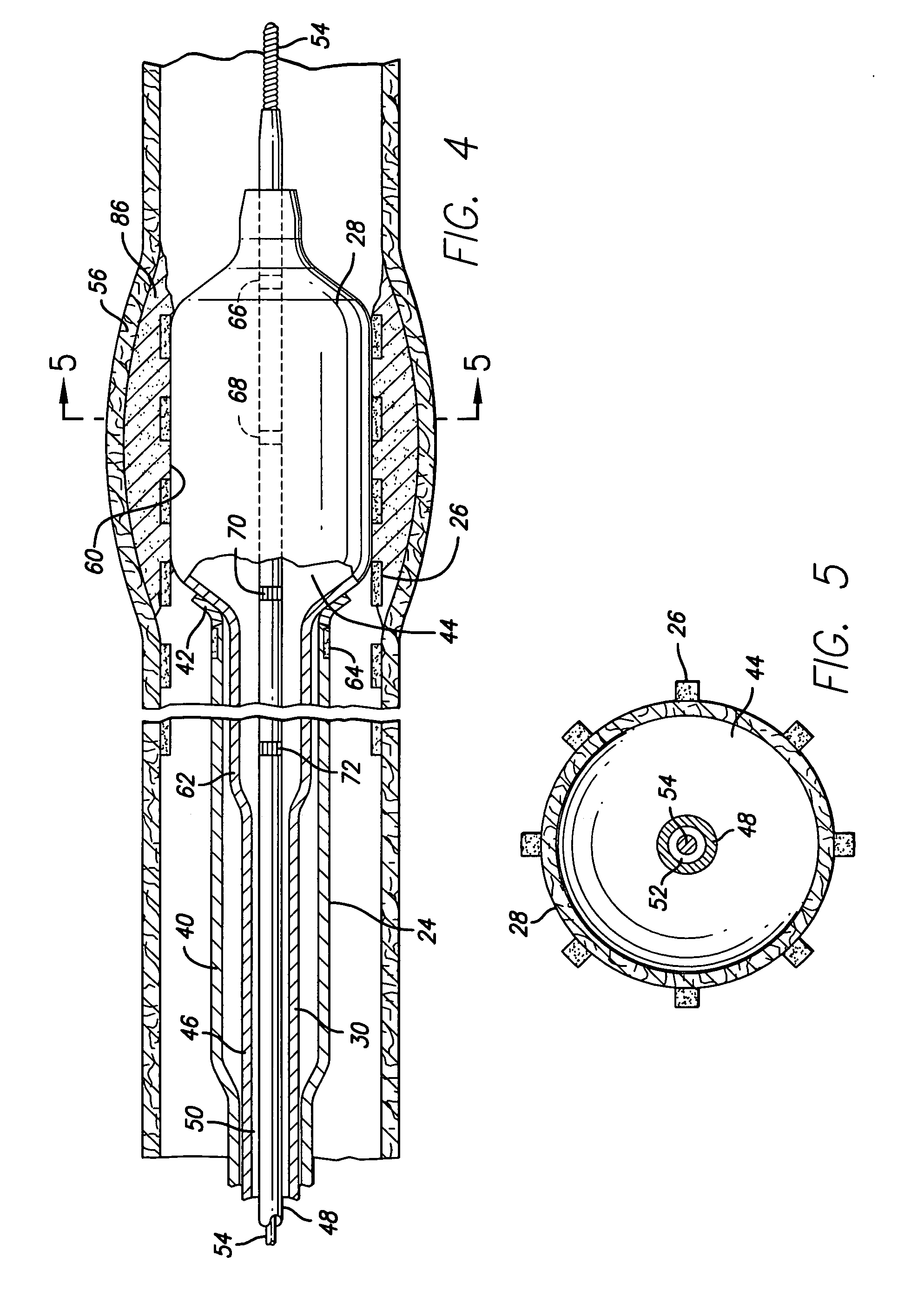
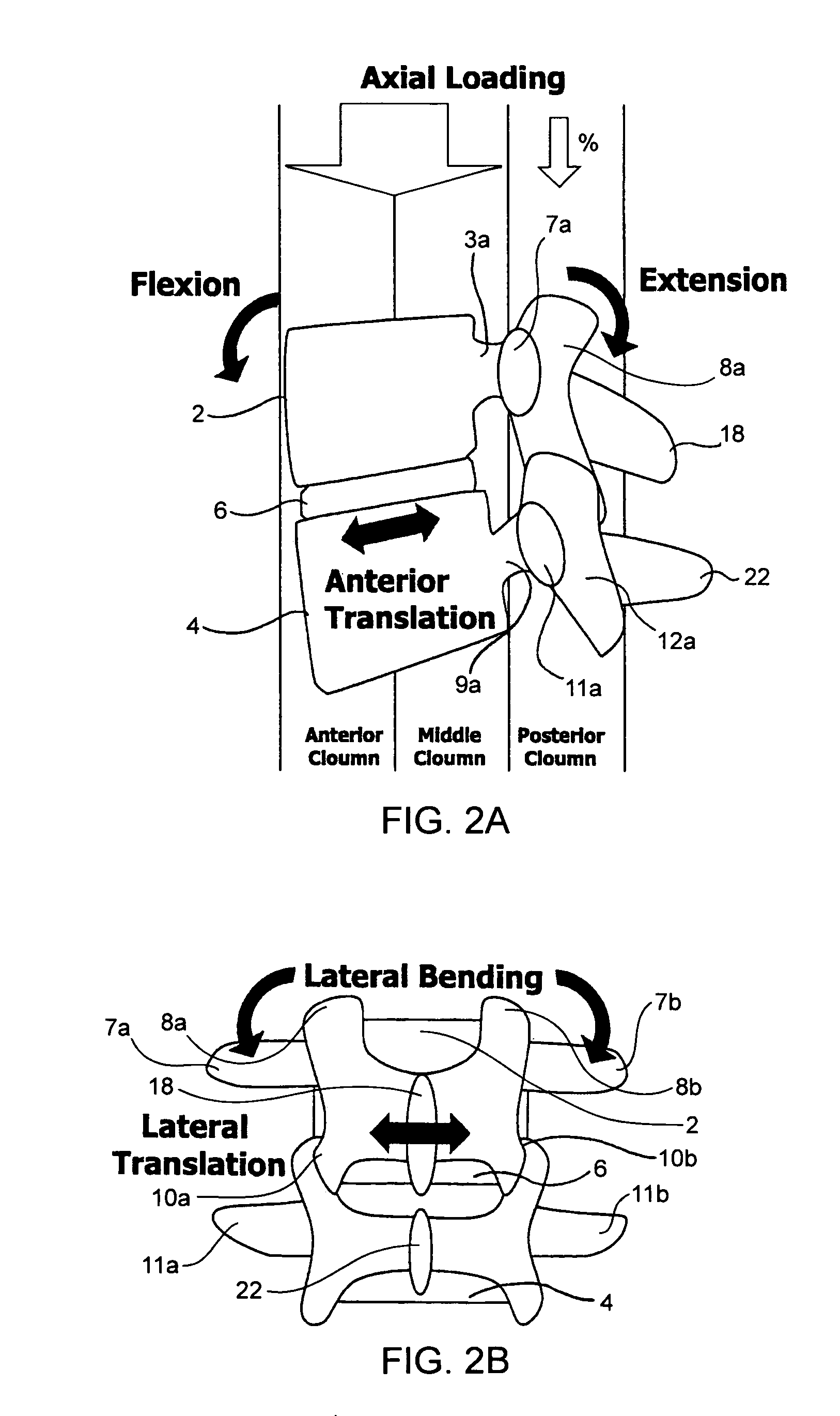
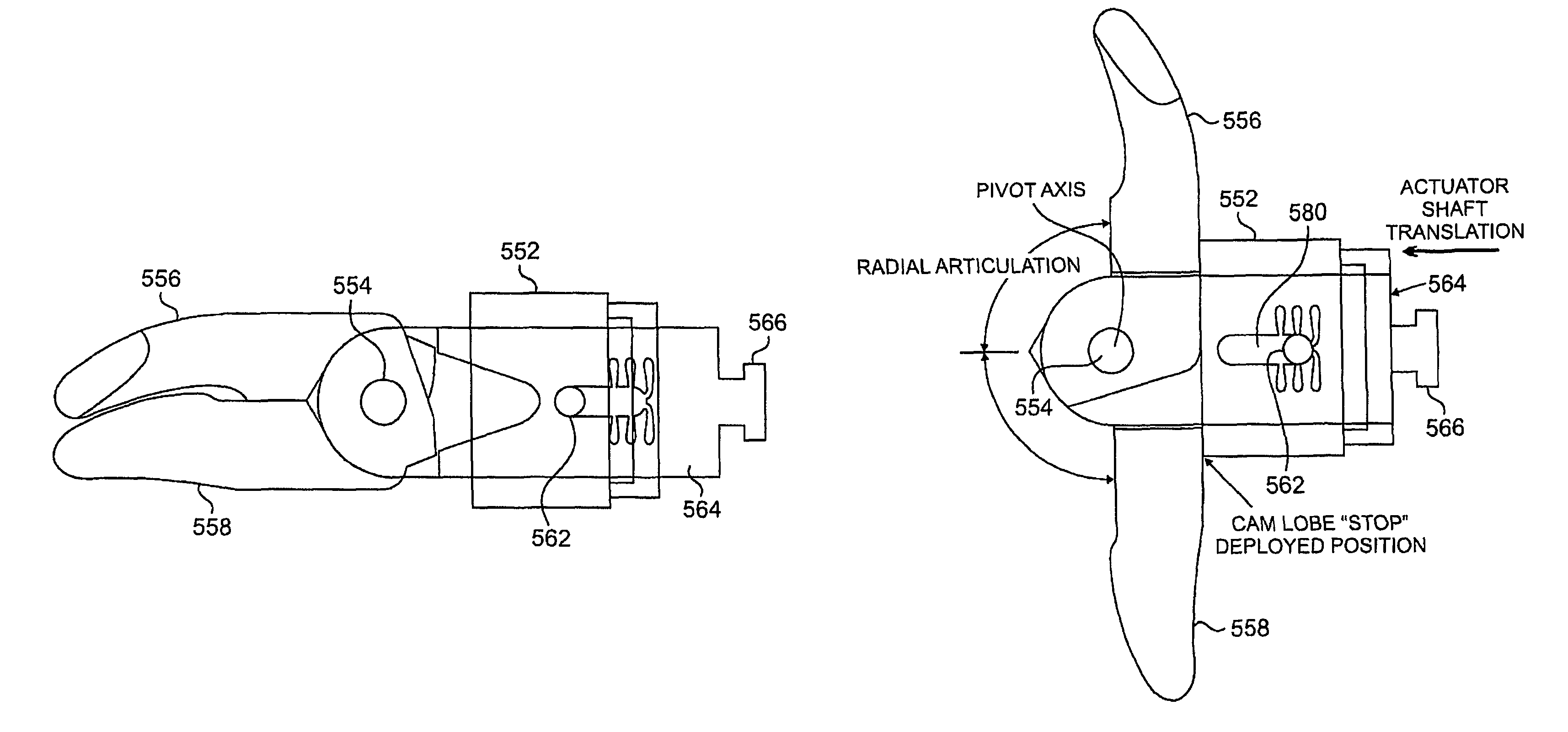
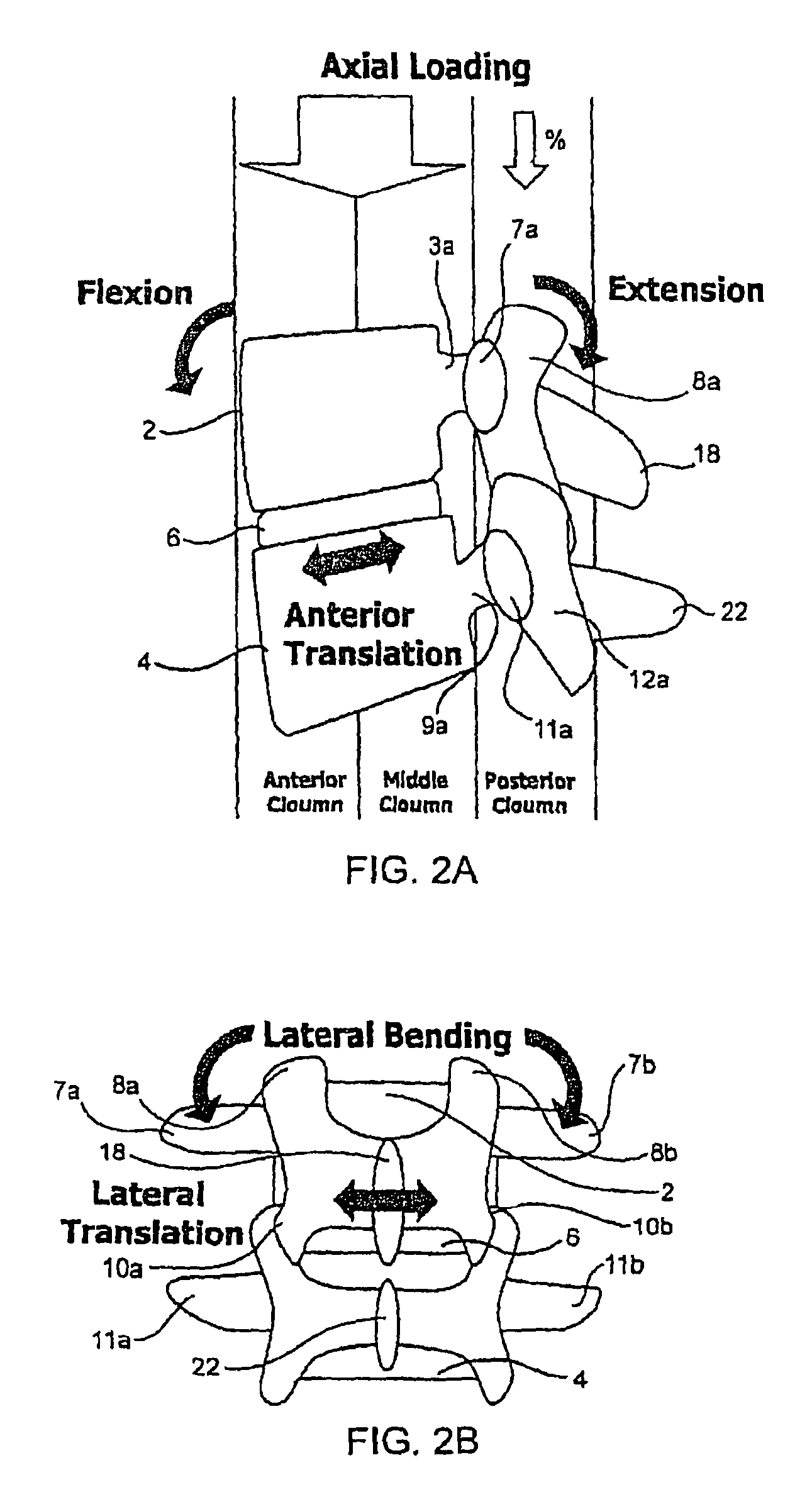
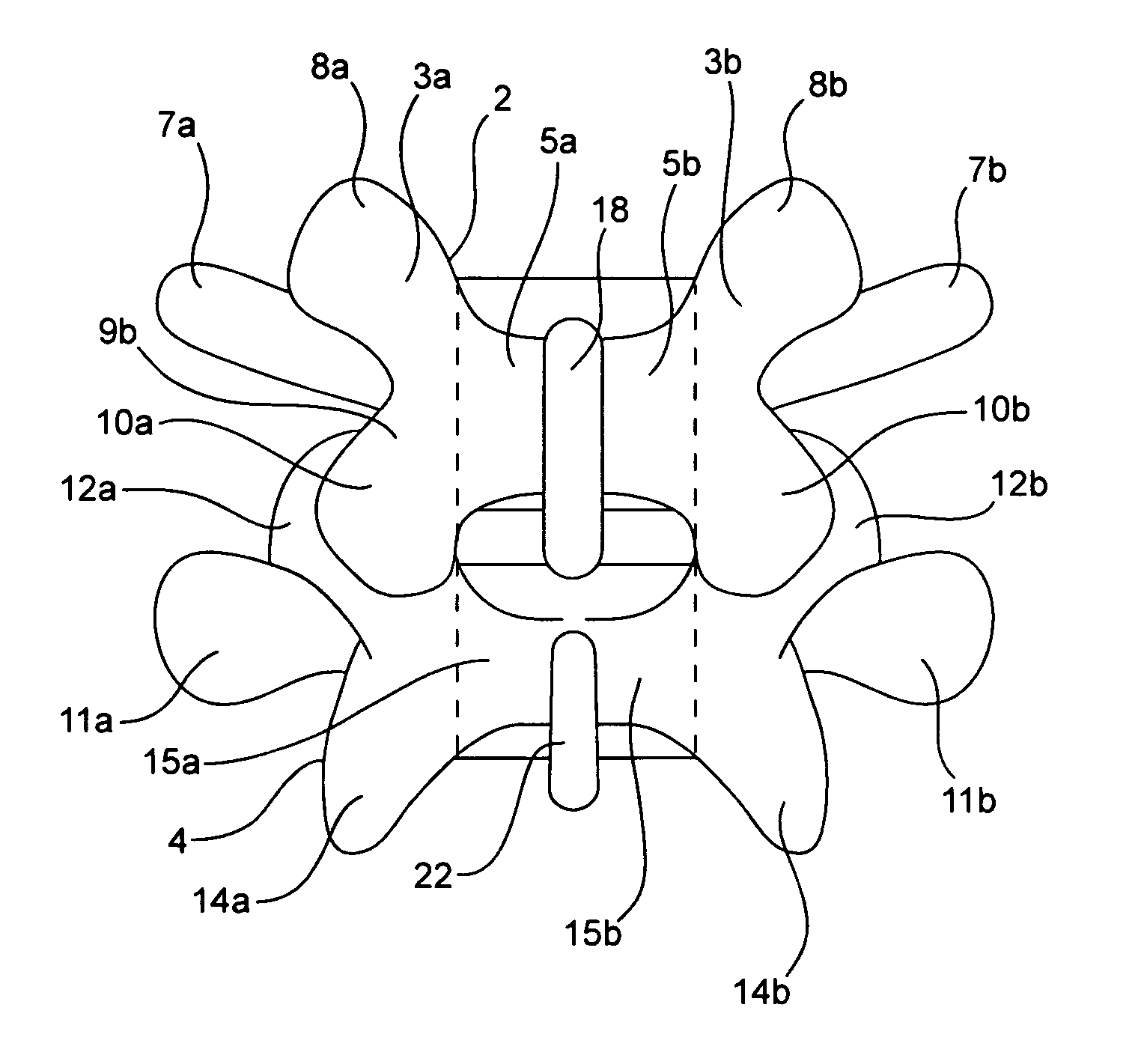
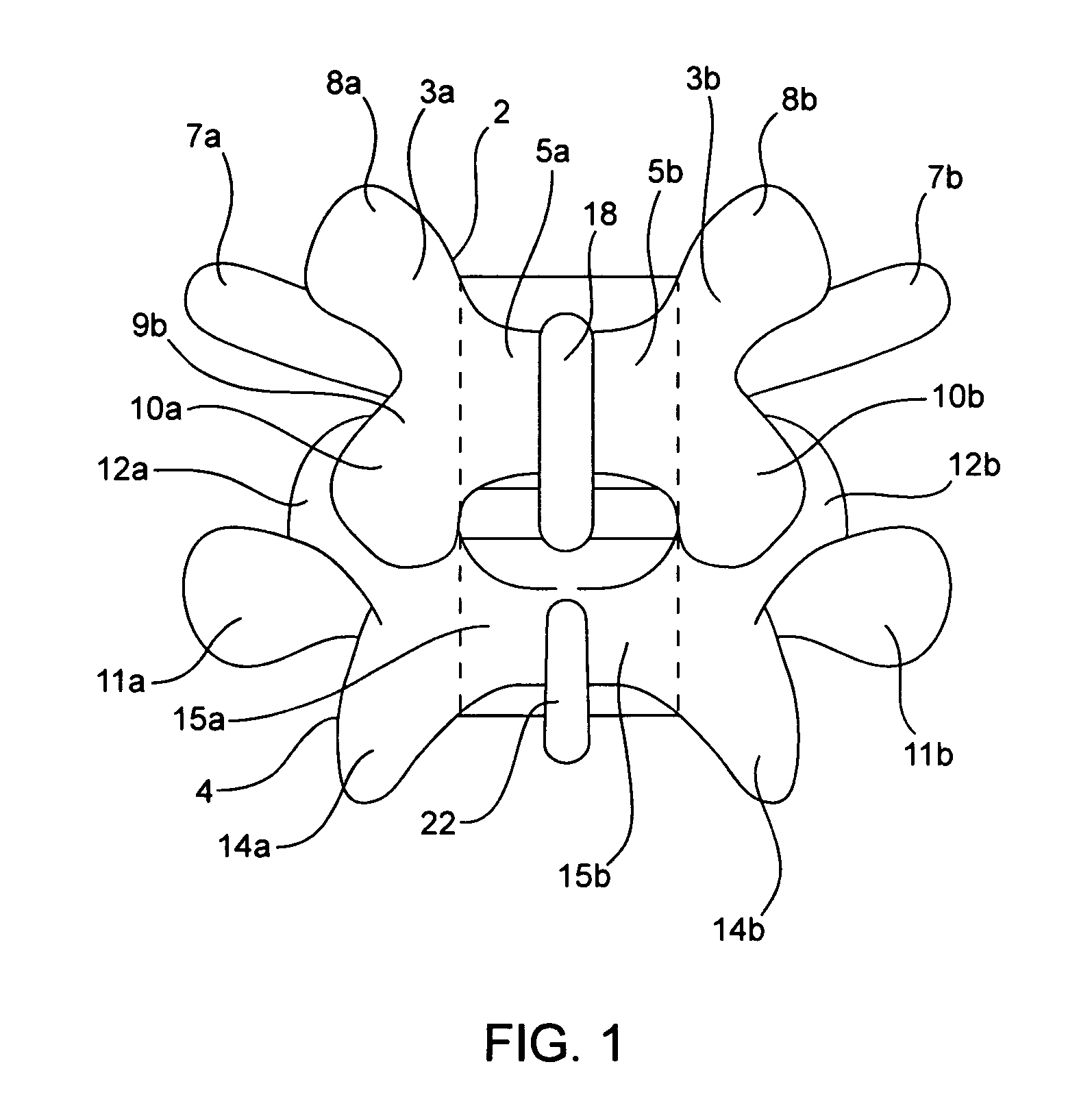
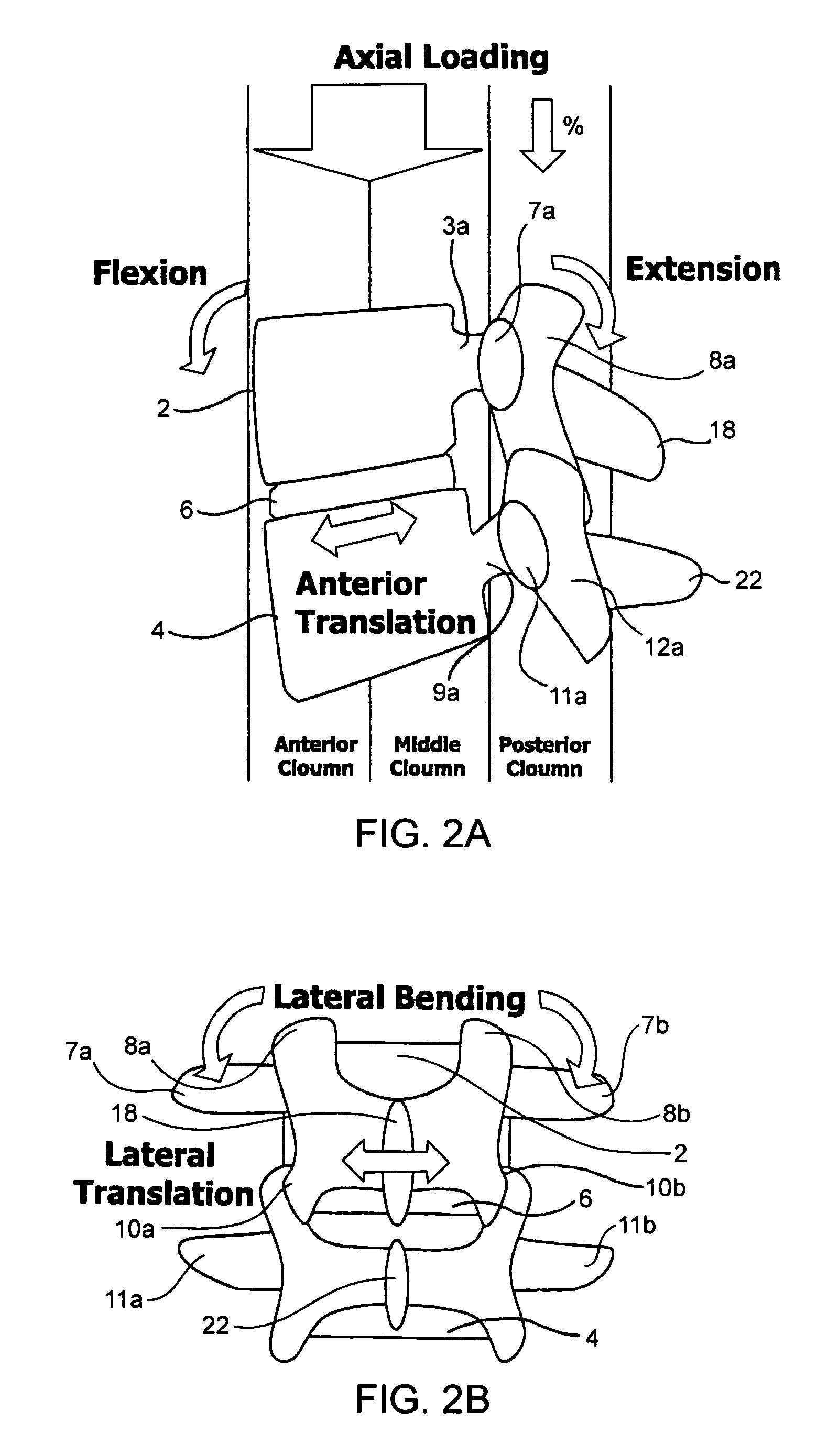
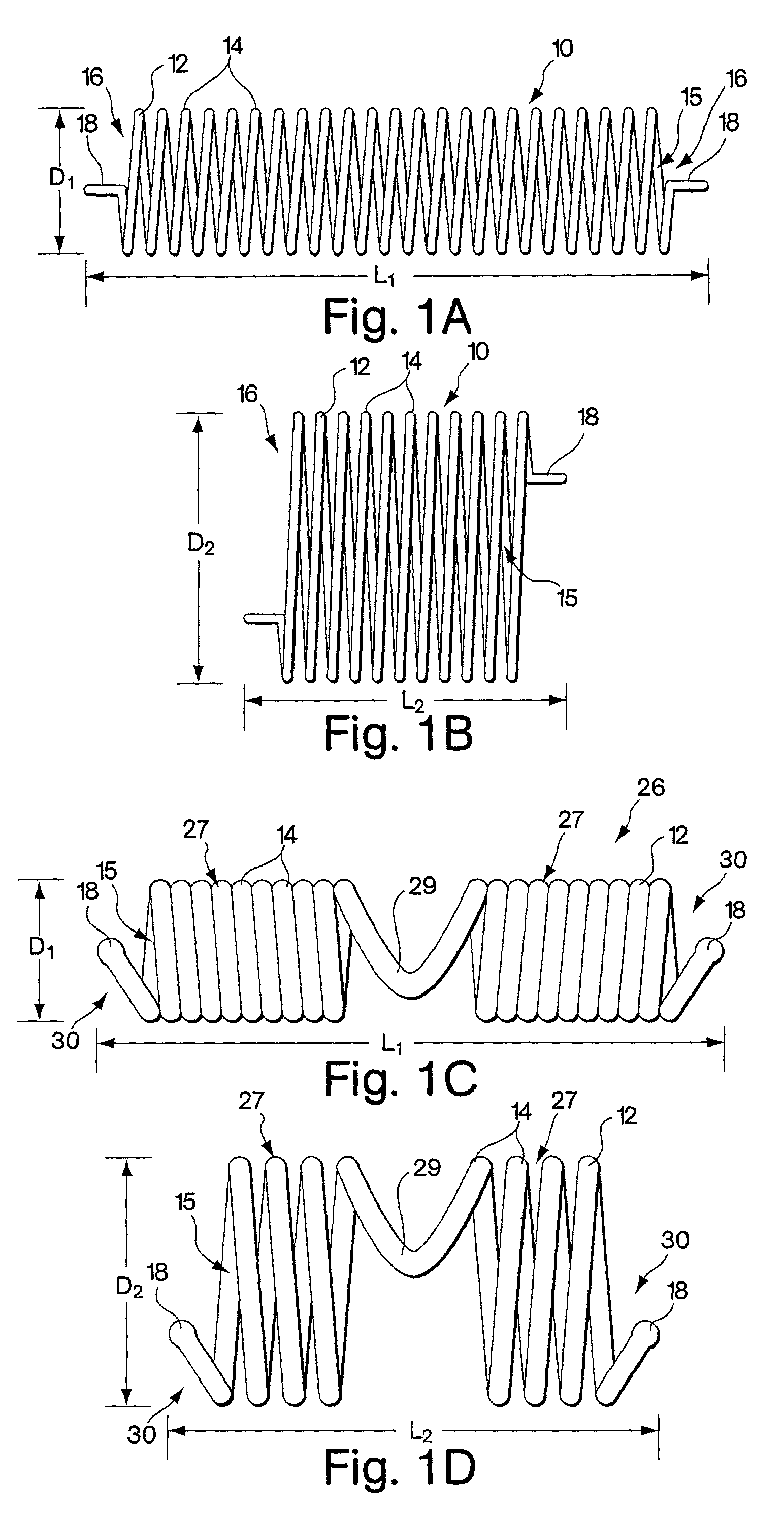
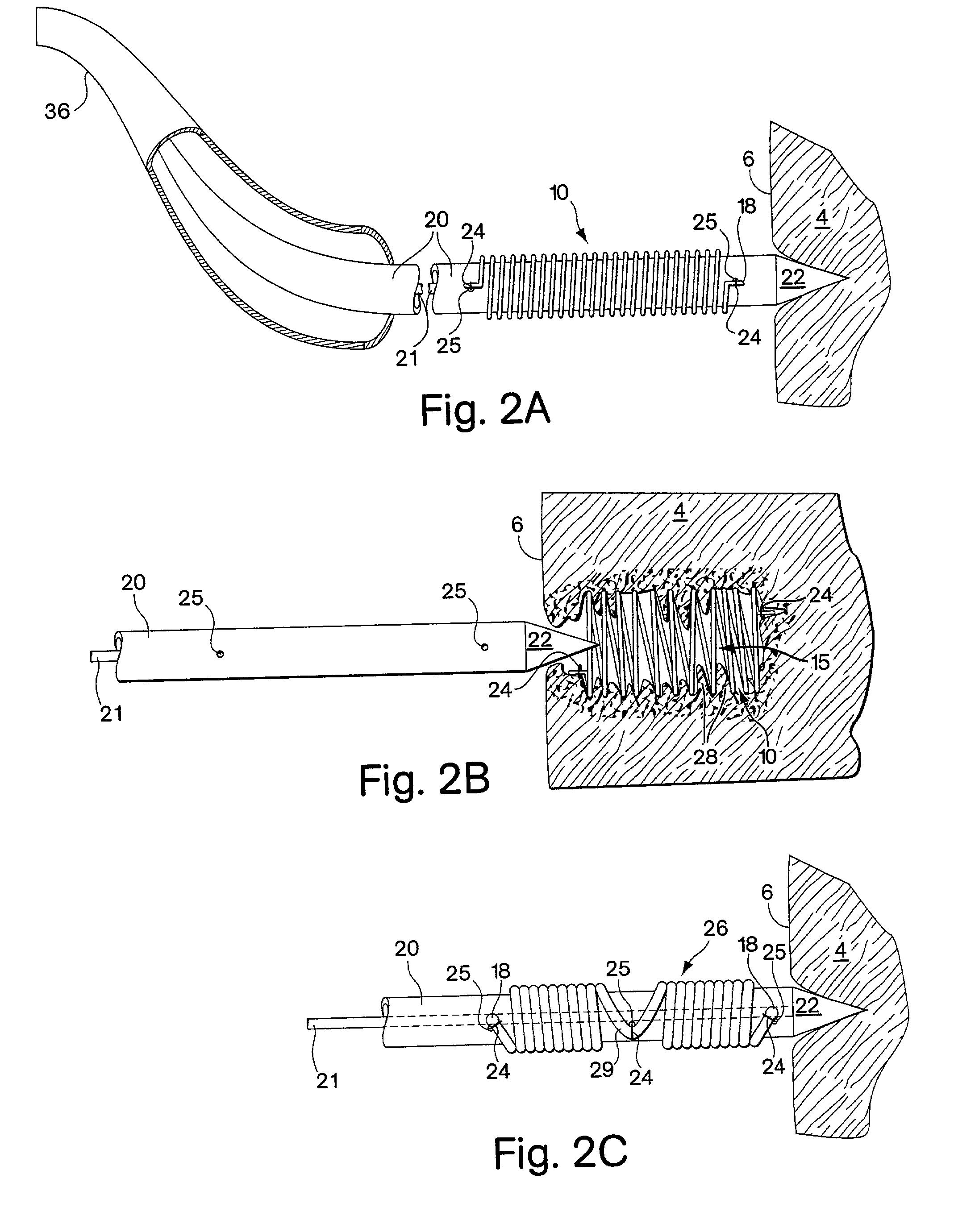
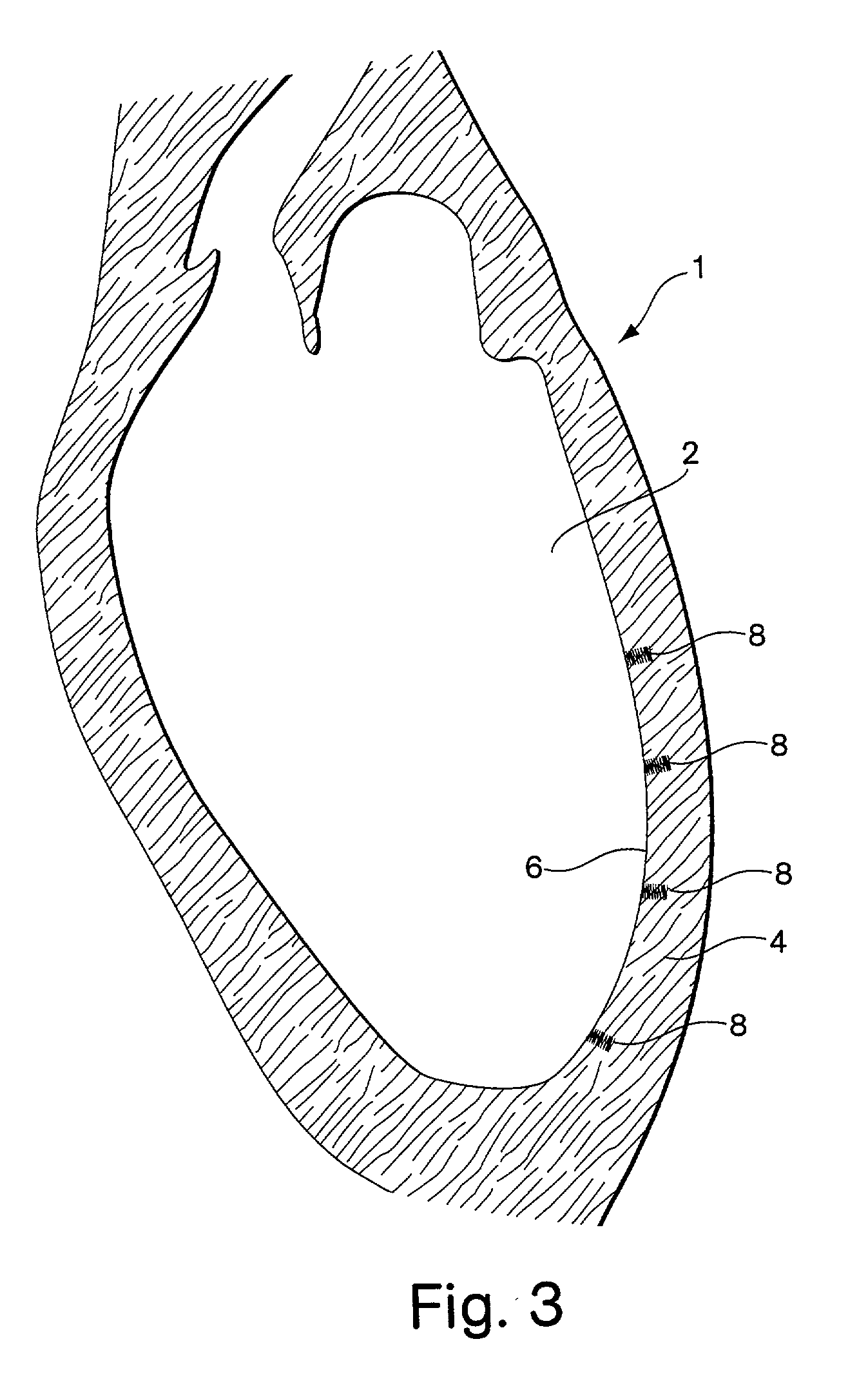
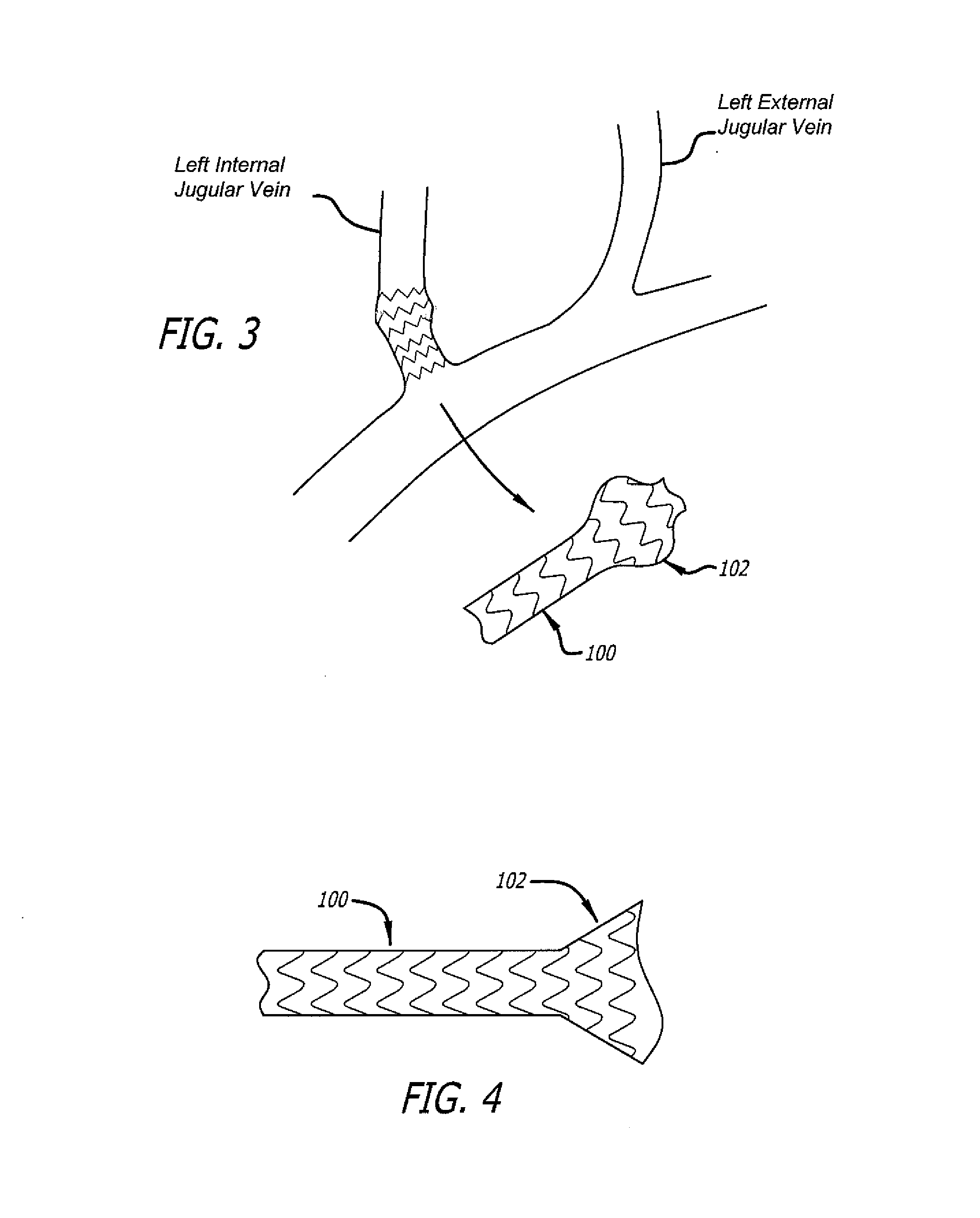
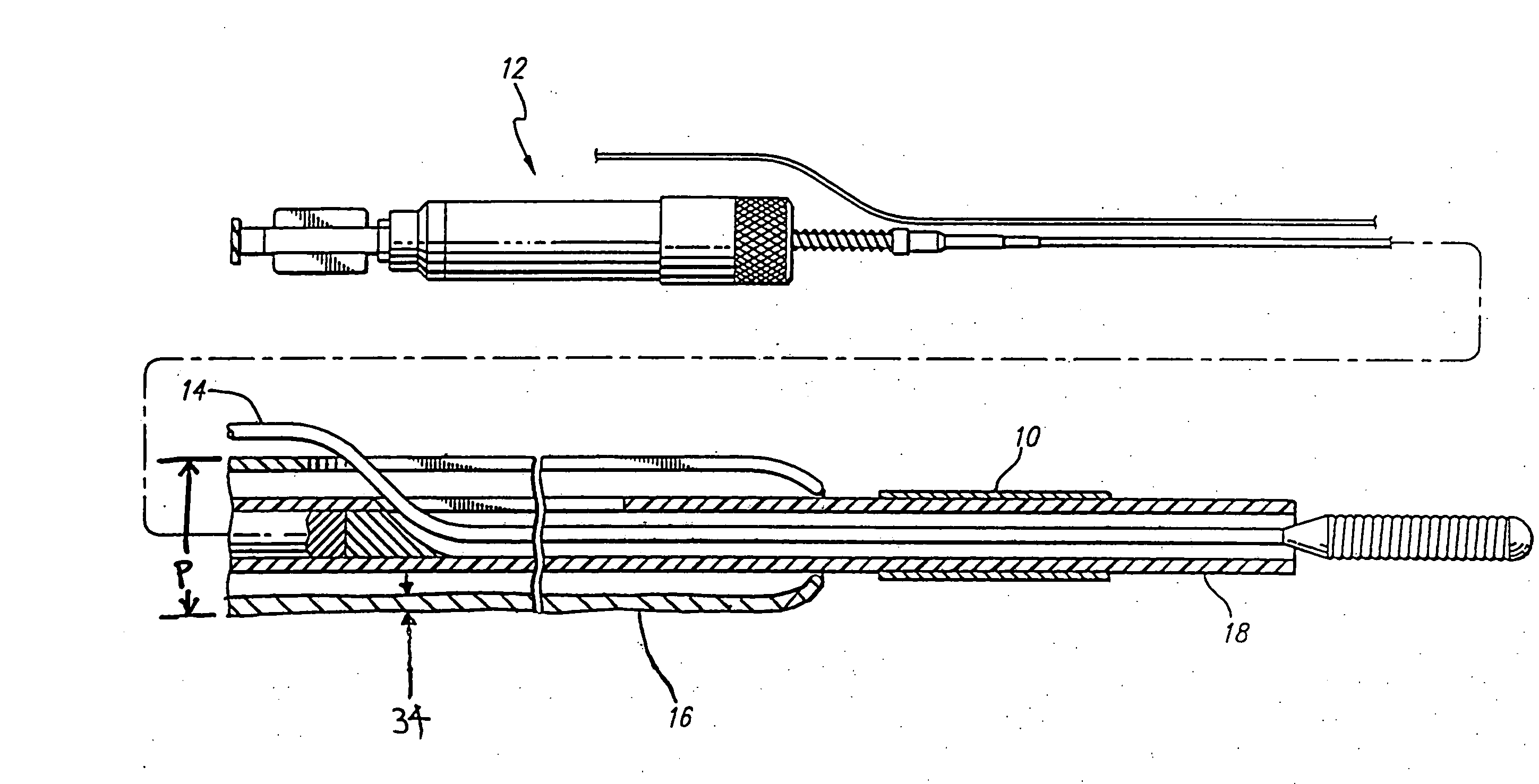
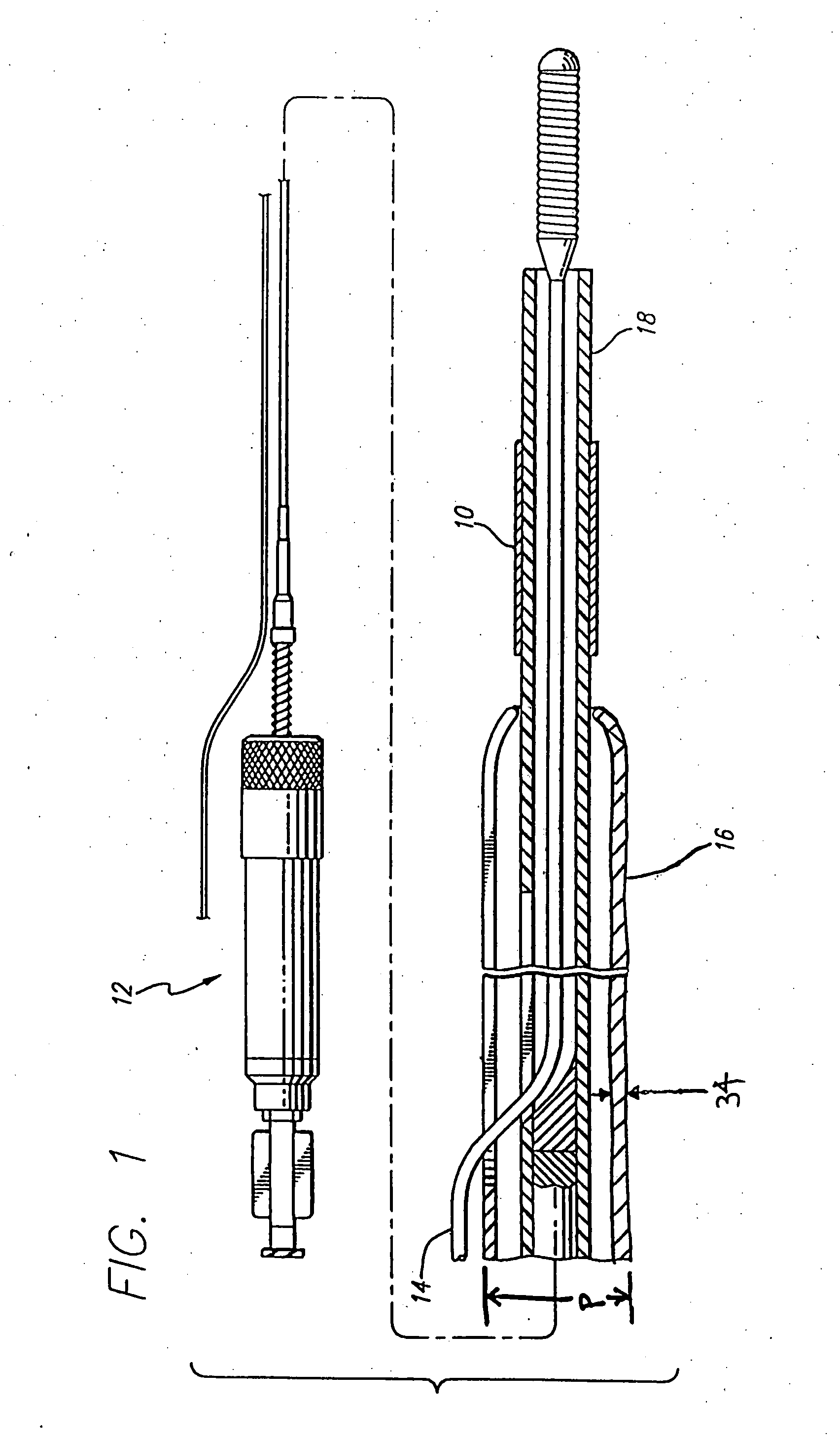
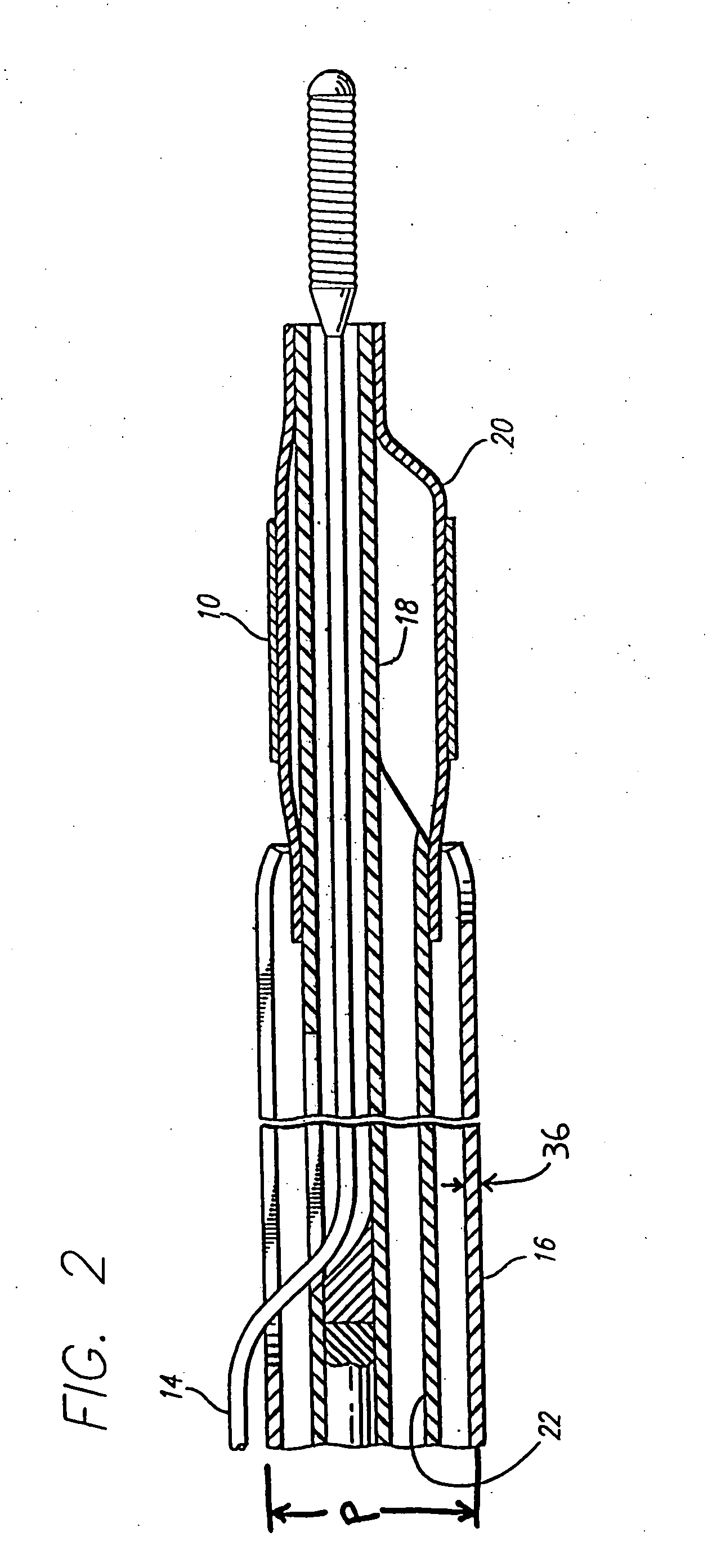
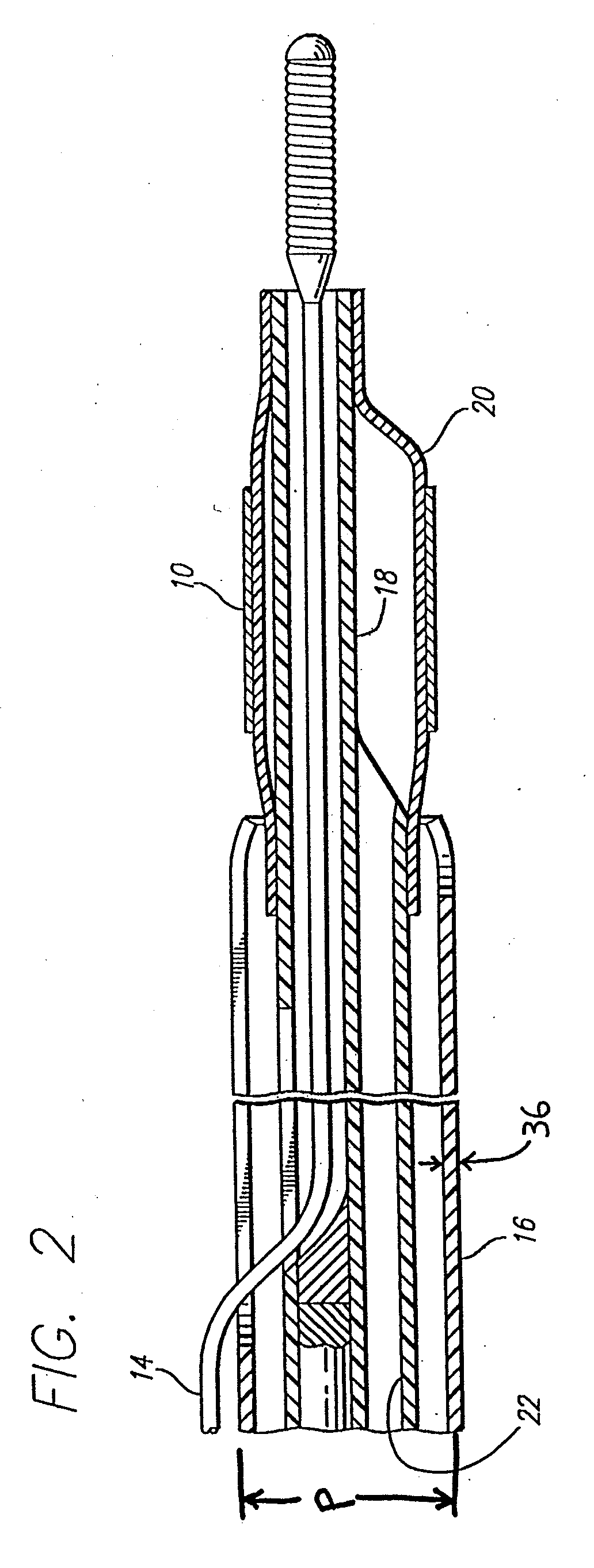
Devices and methods for the treatment of spinal disorders
InactiveUS20050049708A1Permit some movementReducing nerve impingementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDiseaseSpine disorder
Devices and methods for treating a damaged intervertebral disc to reduce or eliminate associated back pain. Dynamic bias devices and reinforcement devices are disclosed, which may be used individually or in combination, to eliminate nerve impingement associated with the damaged disc, and / or to reinforce the damaged disc, while permitting relative movement of the vertebrae adjacent the damaged disc.
Owner:ANULEX TECH
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
InactiveUS20060085070A1Facilitate deliveryLarge profileInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinous processBiomedical engineering
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS20070161991A1Reduce deliveryReduced space requirementsInternal osteosythesisCannulasBiomedical engineeringSpinous process
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS20070173832A1Reduce deliveryReduced space requirementsInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinous processBiomedical engineering
Owner:VERTIFLEX
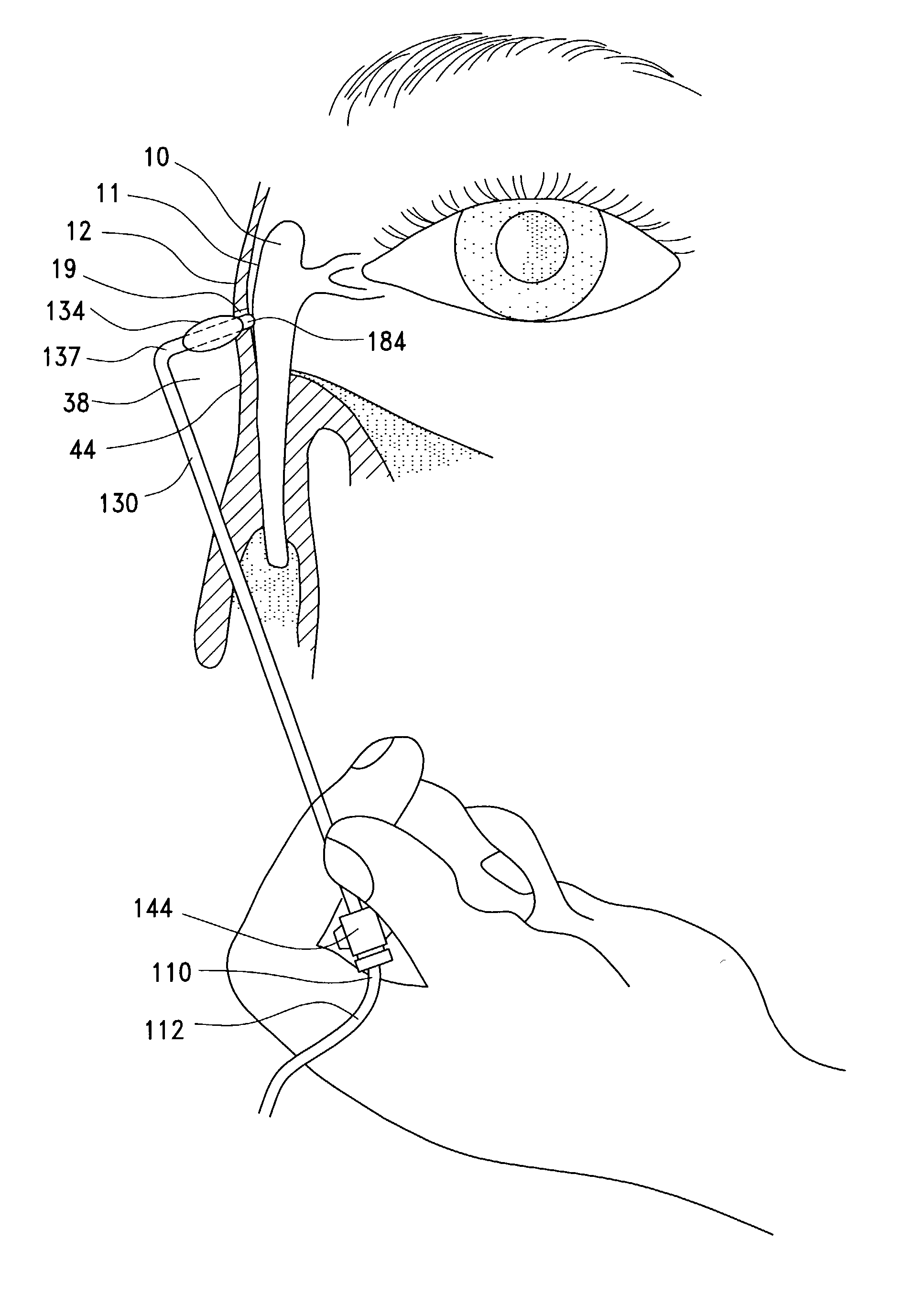
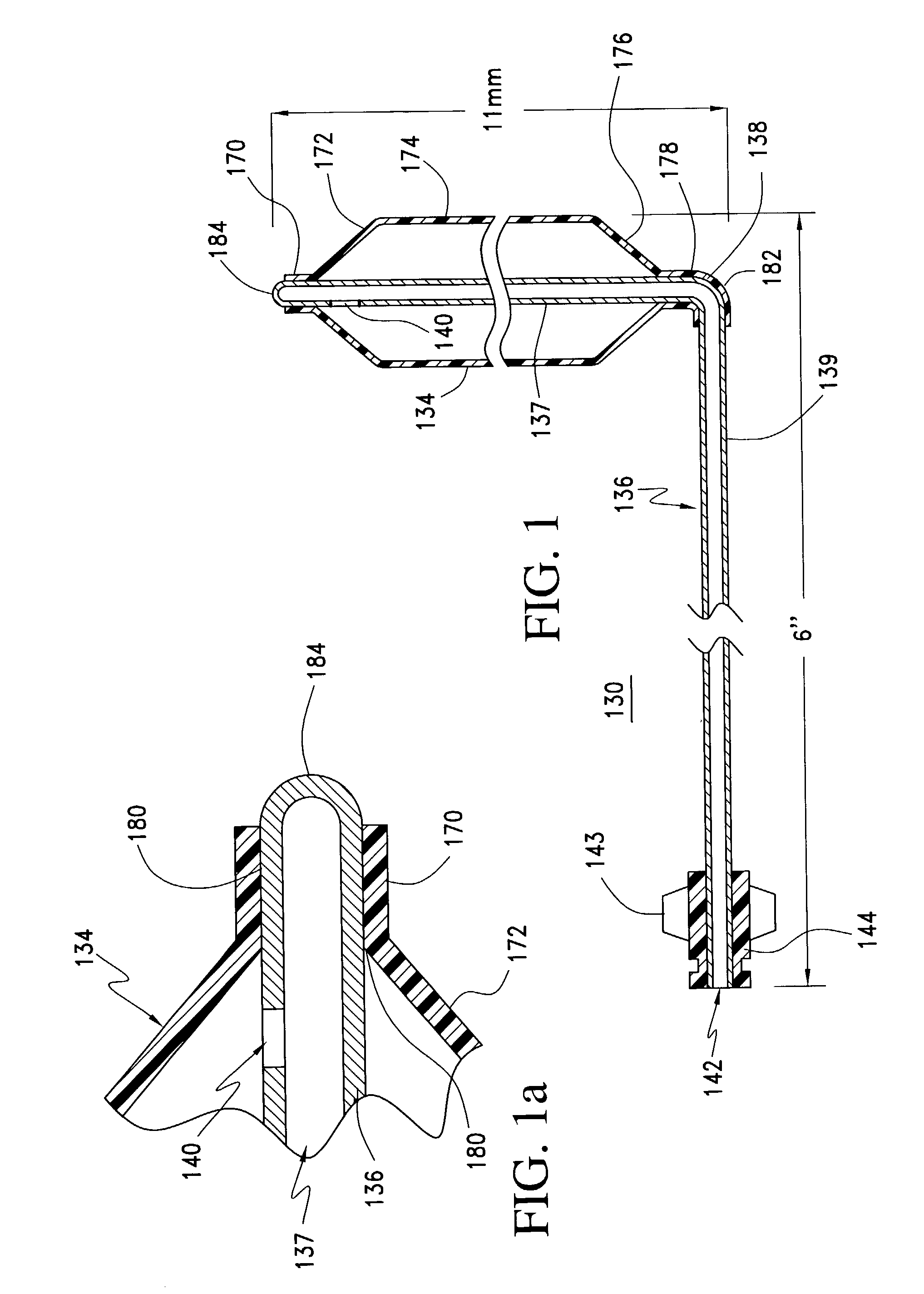
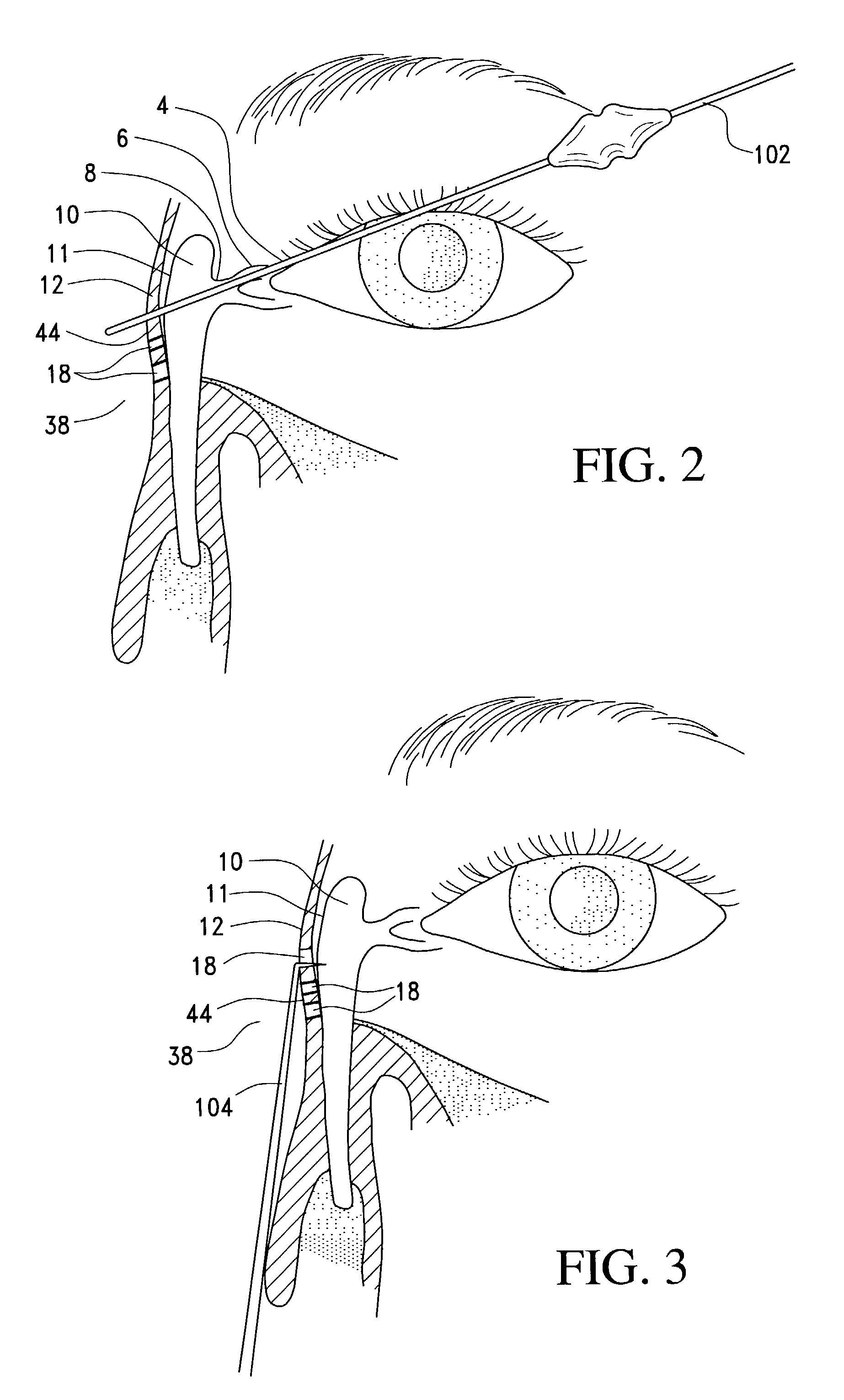
Transnasal method and catheter for lacrimal system
A balloon catheter for treatment of a patient's lacrimal system is applied transnasally without the use of a guide wire or a curve retention member. The catheter uses a stainless steel hypotube of sufficient stiffness and column strength to be pushed from the patent's nasal cavity through an opening-formed through the lateral nasal wall and lacrimal fossa, into the lacrimal sac. The catheter has an inflatable member mounted about a rigid bent distal segment. The opening is first formed by pushing small holes through the medial sac, lacrimal fossa, and lateral nasal wall with an instrument and coalescing the holes. The catheter is then introduced into the nasal cavity and pushed laterally through the opening by manipulating its proximal end. Pressurized fluid is then applied to the catheter to inflate the inflatable member and dilate the opening.
Owner:BECKER BRUCE
Stent delivery system with adjustable length balloon
InactiveUS6884257B1Efficient and cost-effective post-expansion dilationLarge profileStentsSurgeryStentCatheter device
A stent delivery system with an adjustable length balloon. The system includes a stent delivery catheter having an expandable member with an inflated length that can be adjusted according to the length of a stent to be expanded. An exterior sheath having an expandable distal tip is disposed about the expandable member such that the sheath can be longitudinally adjusted so as to expose a desired length of the expandable member. The exposed length of the expandable member provides an effective working length required to expand the stent for deployment. Additionally, where subsequent expansions of the deployed stent may be necessary, post dilitation may be achieved by re-positioning the catheter and re-adjusting the sheath to form an effective working length of the expandable member which corresponds to the length of the stent that needs further expansion.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
InactiveUS8409282B2Reduce deliveryLarge profileInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnVertebral bone
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS8425559B2Reduce deliveryReduced space requirementsInternal osteosythesisCannulasEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS8152837B2Reduce deliveryReduced space requirementsInternal osteosythesisCannulasBiomedical engineeringSpinous process
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
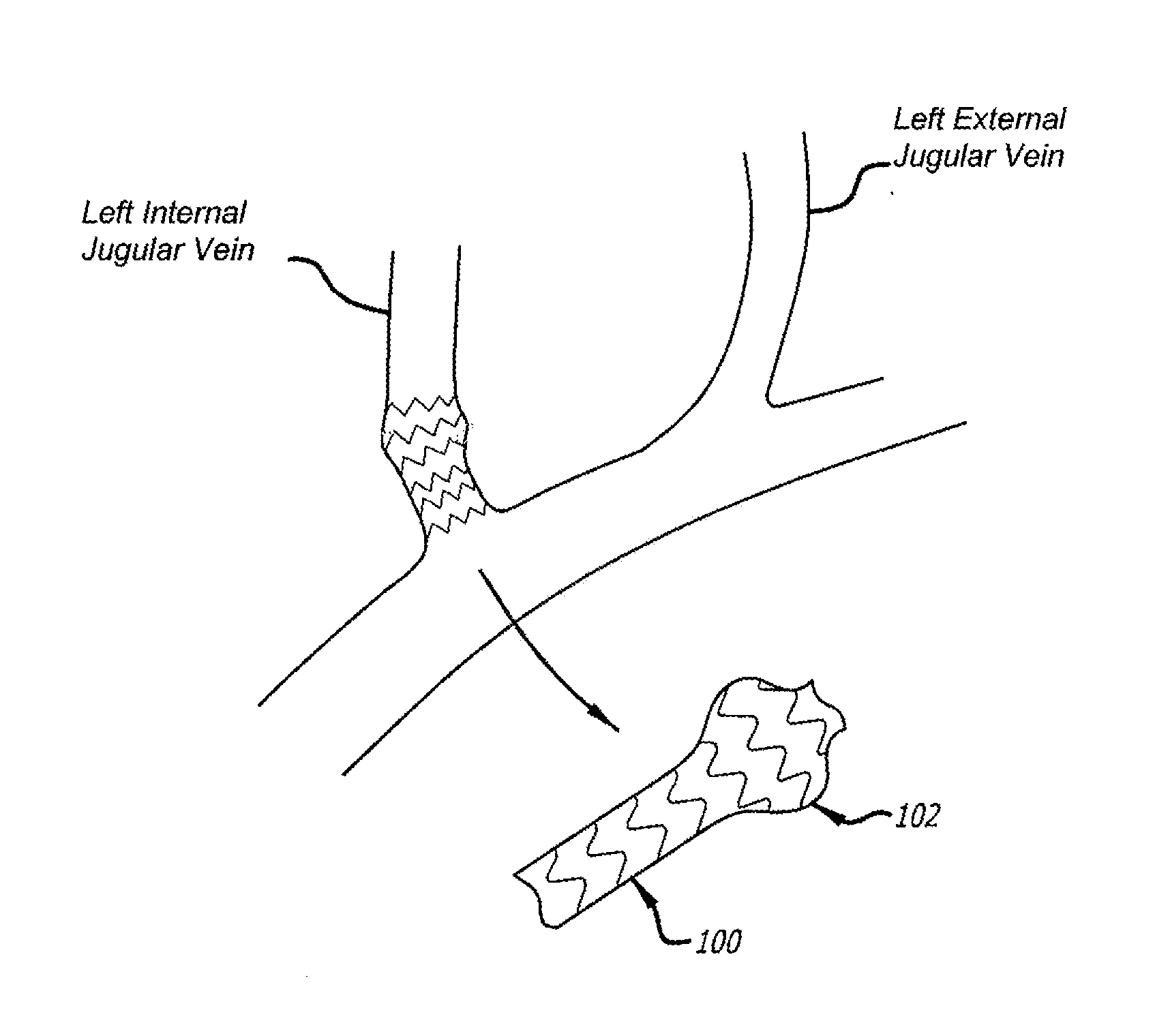
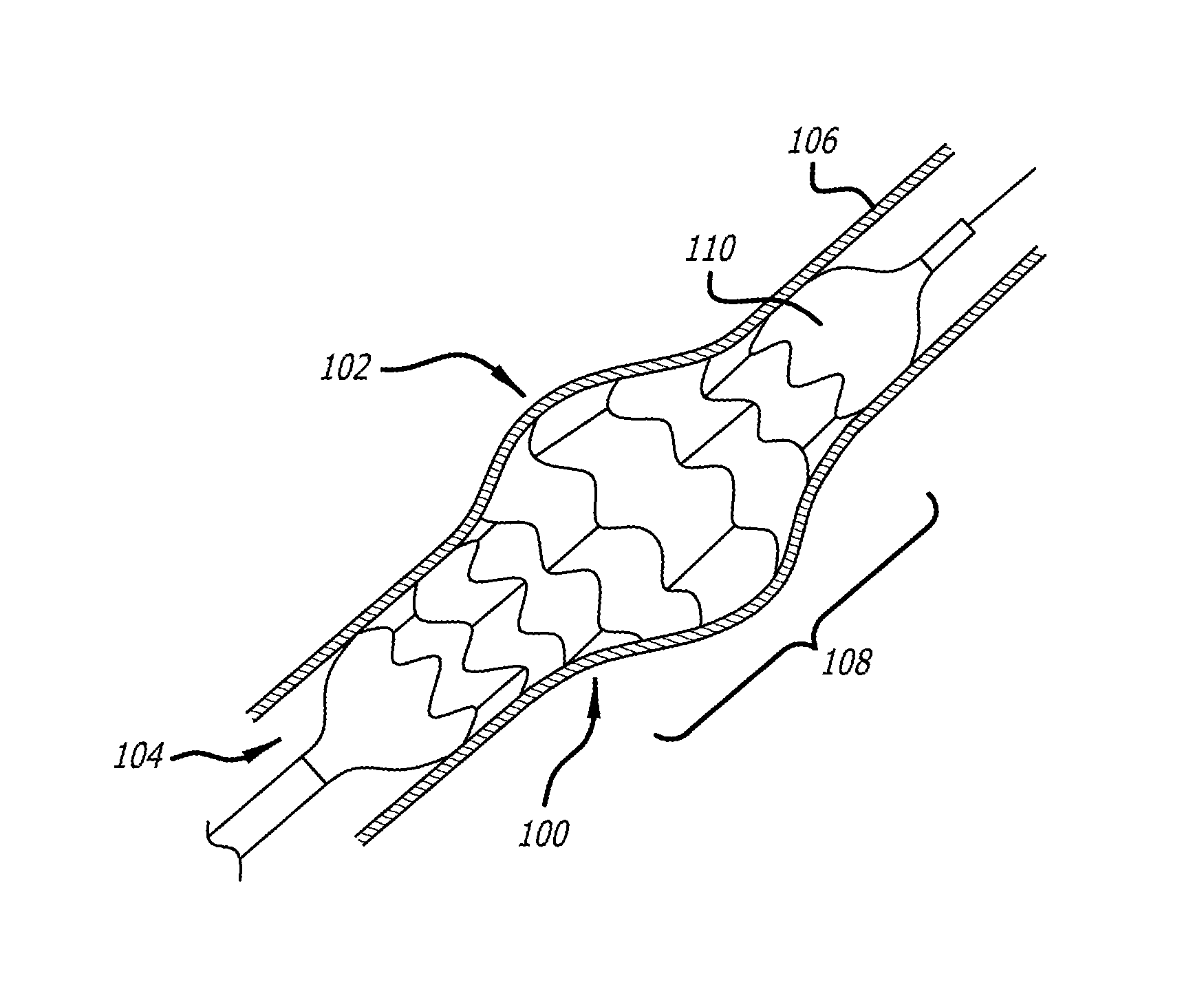
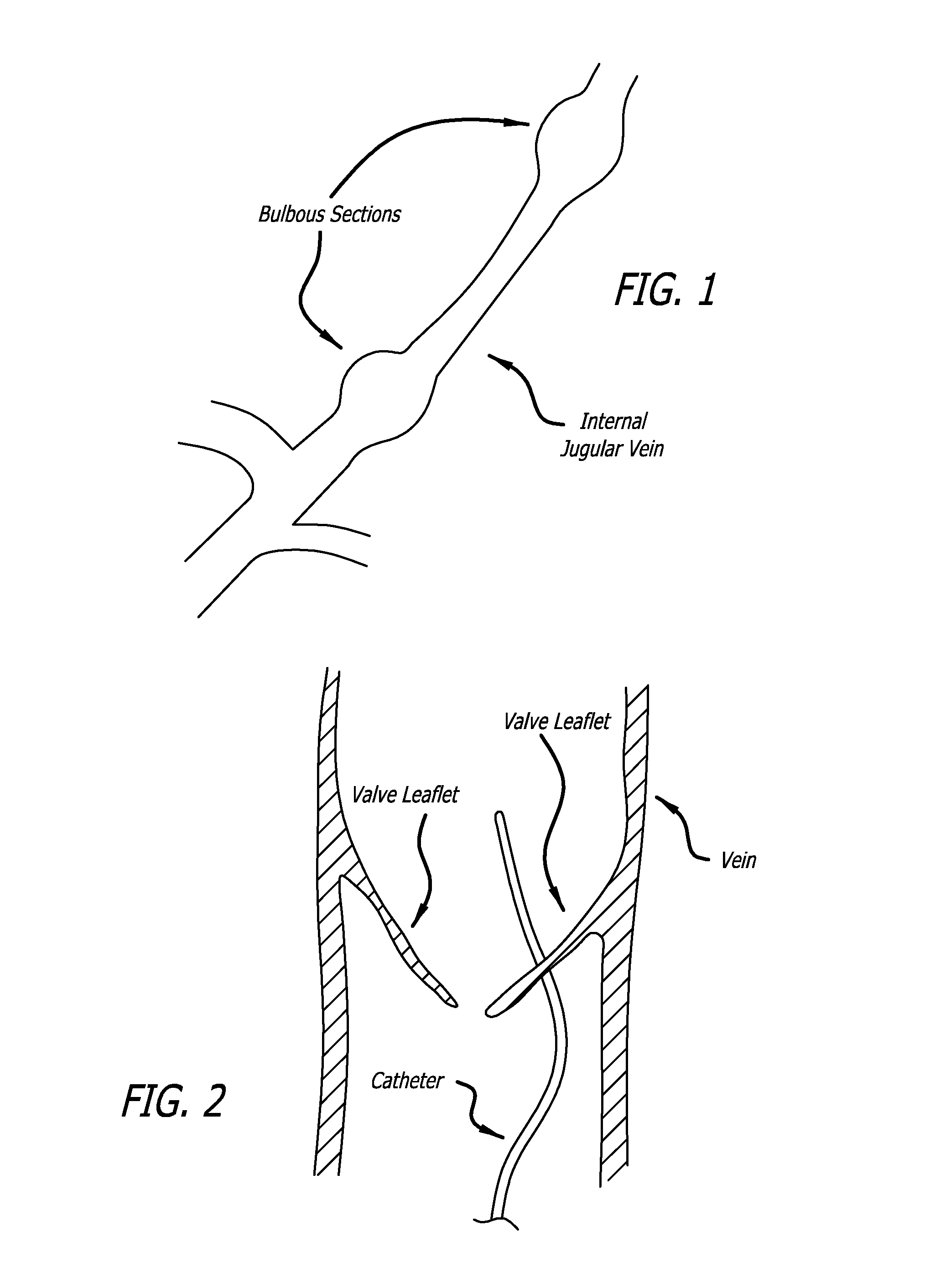
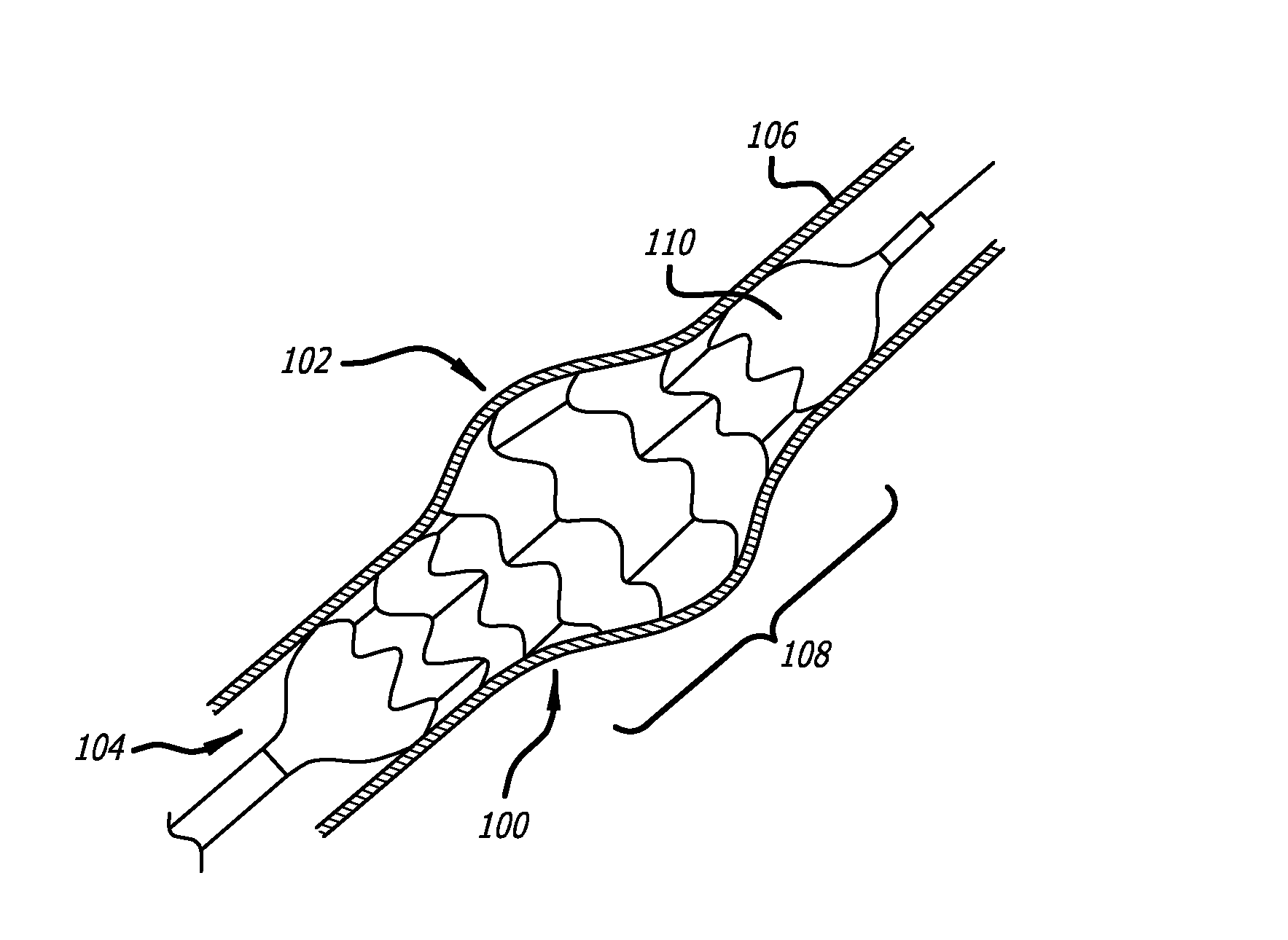
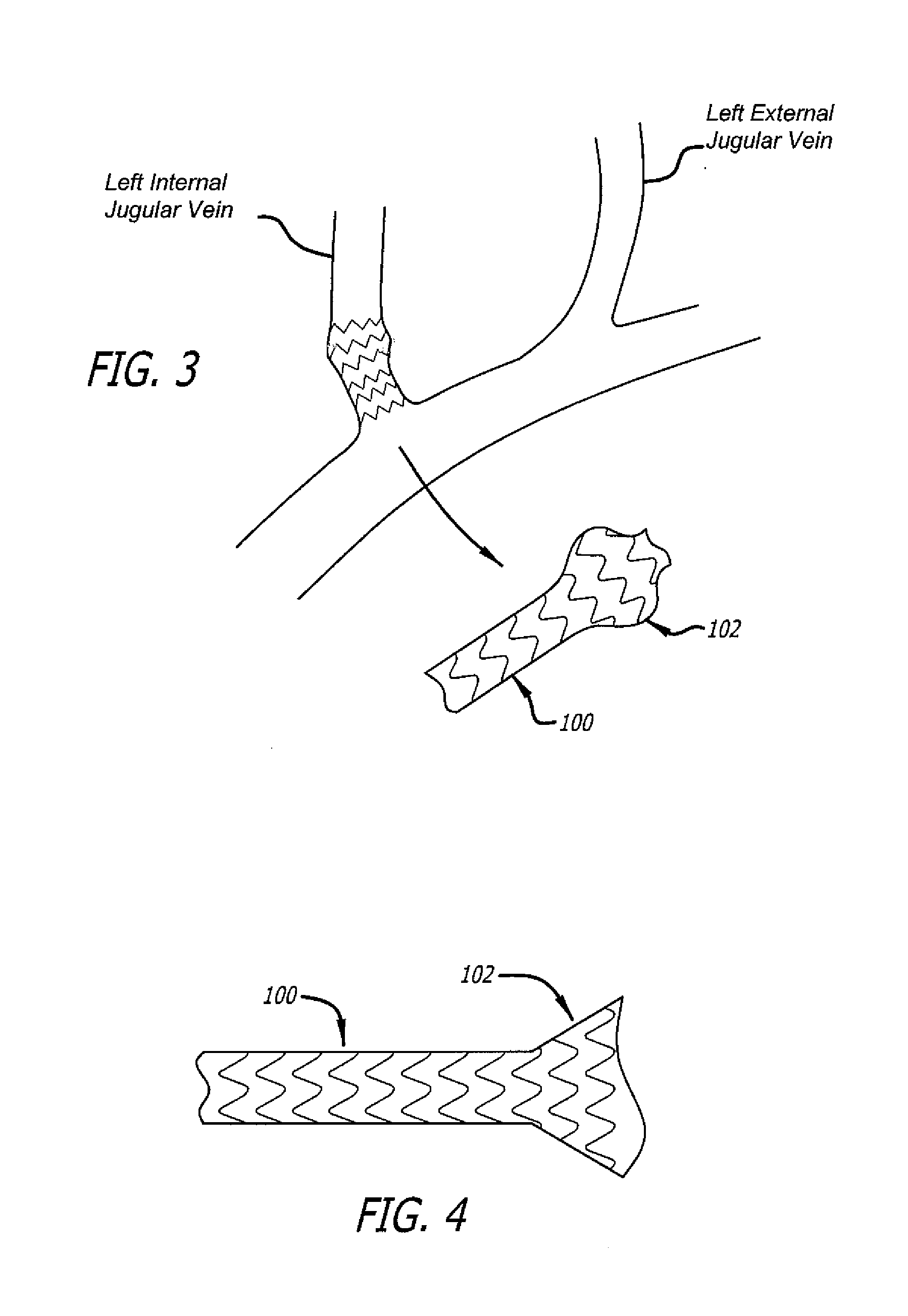
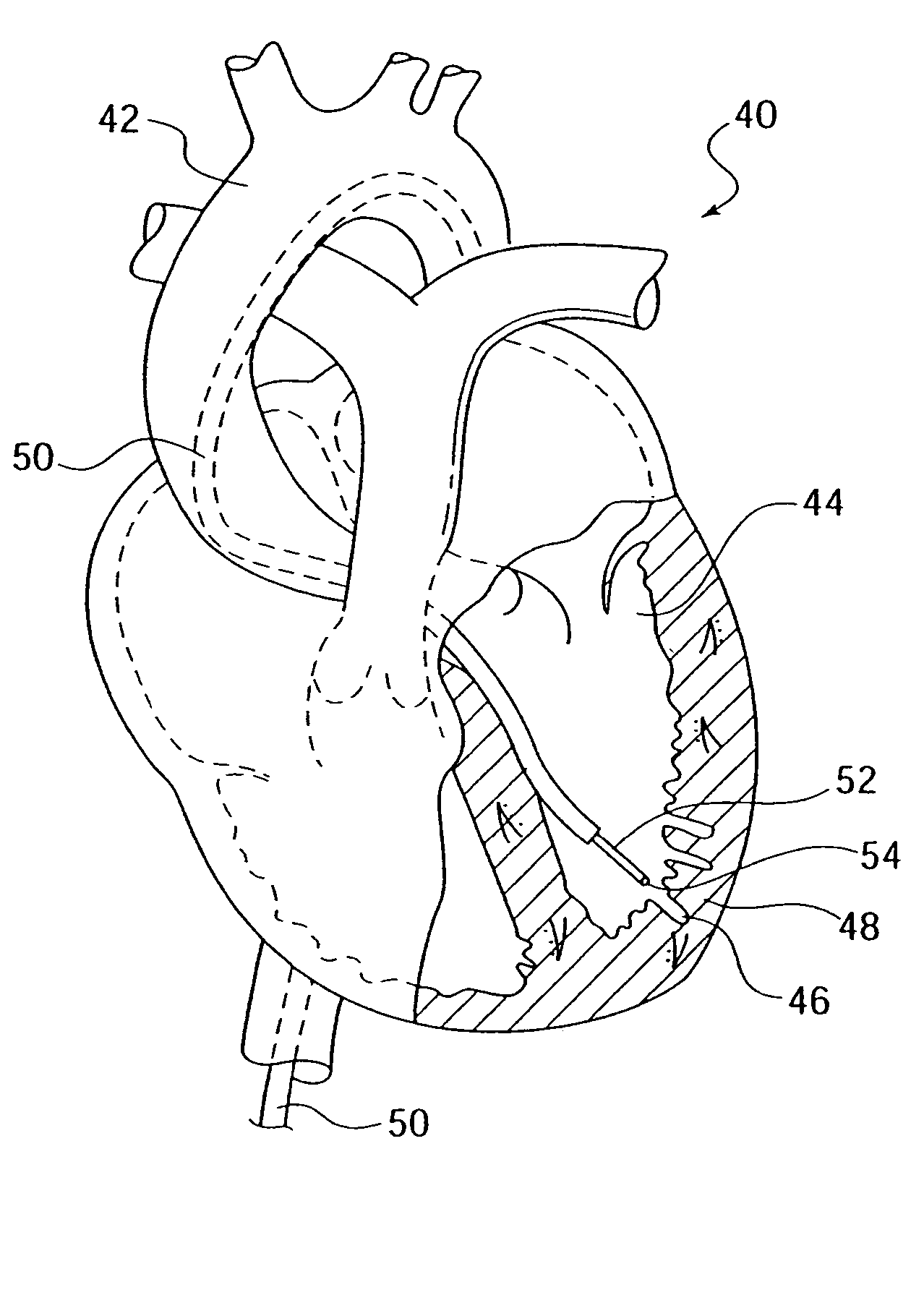
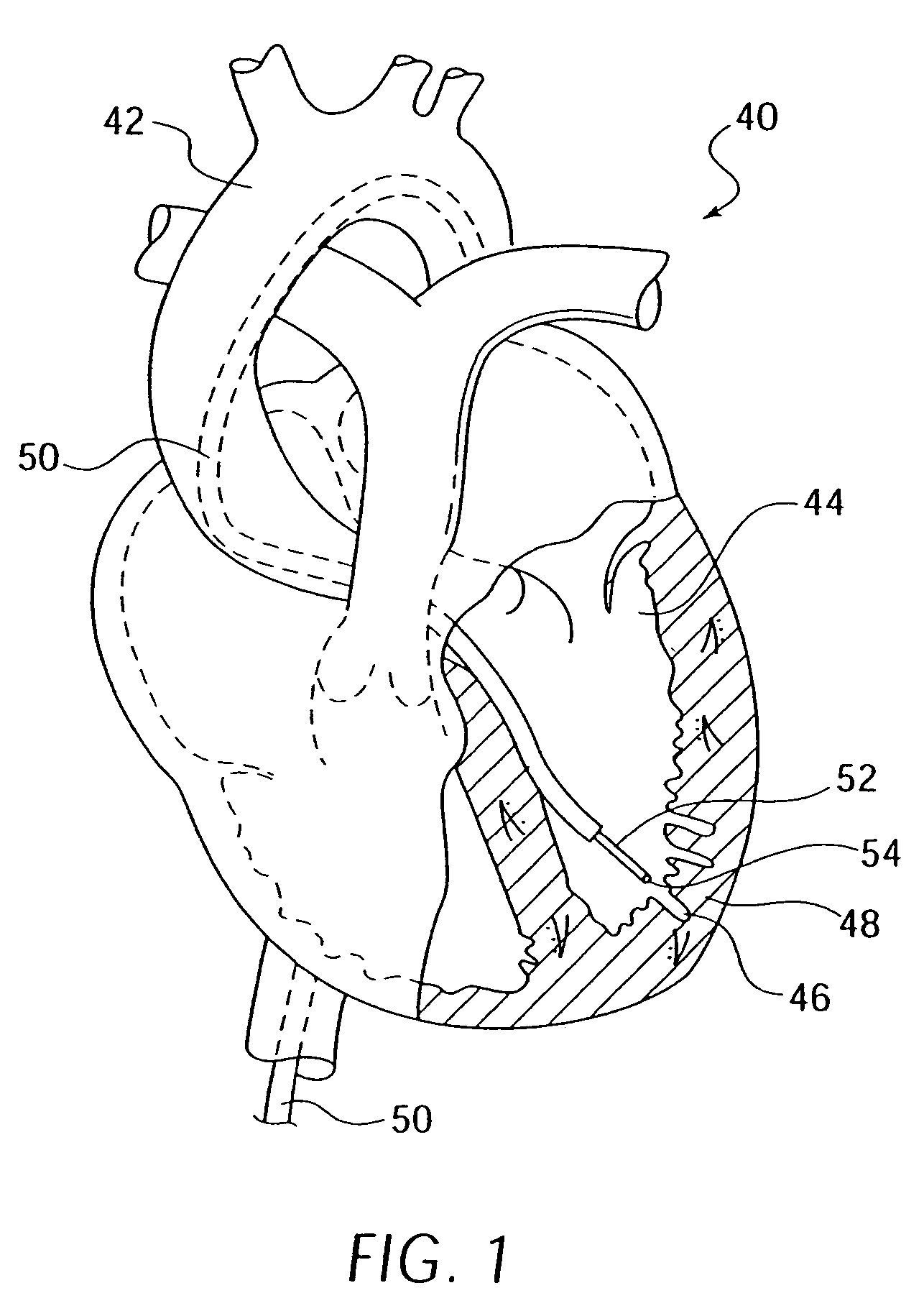
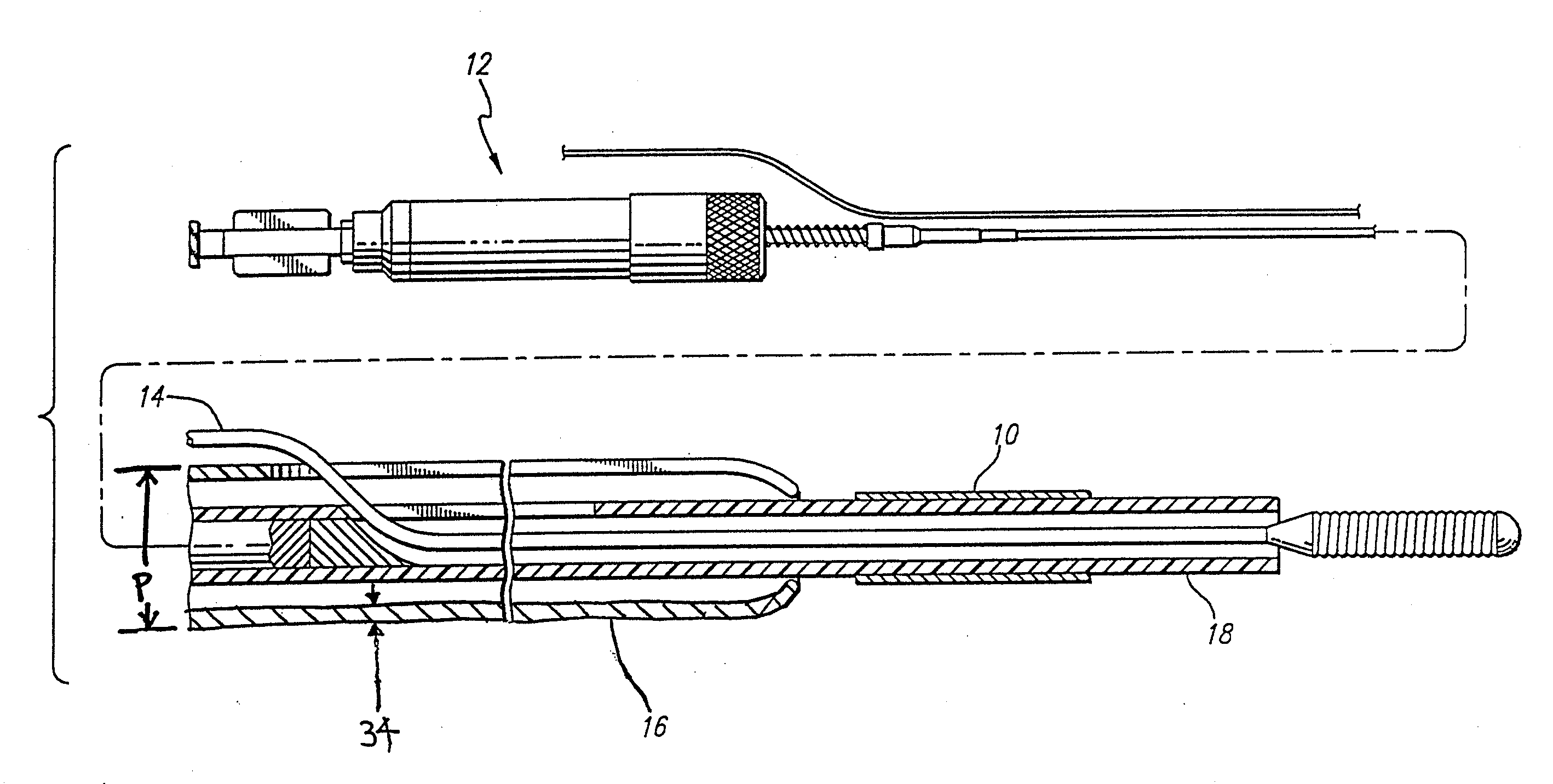
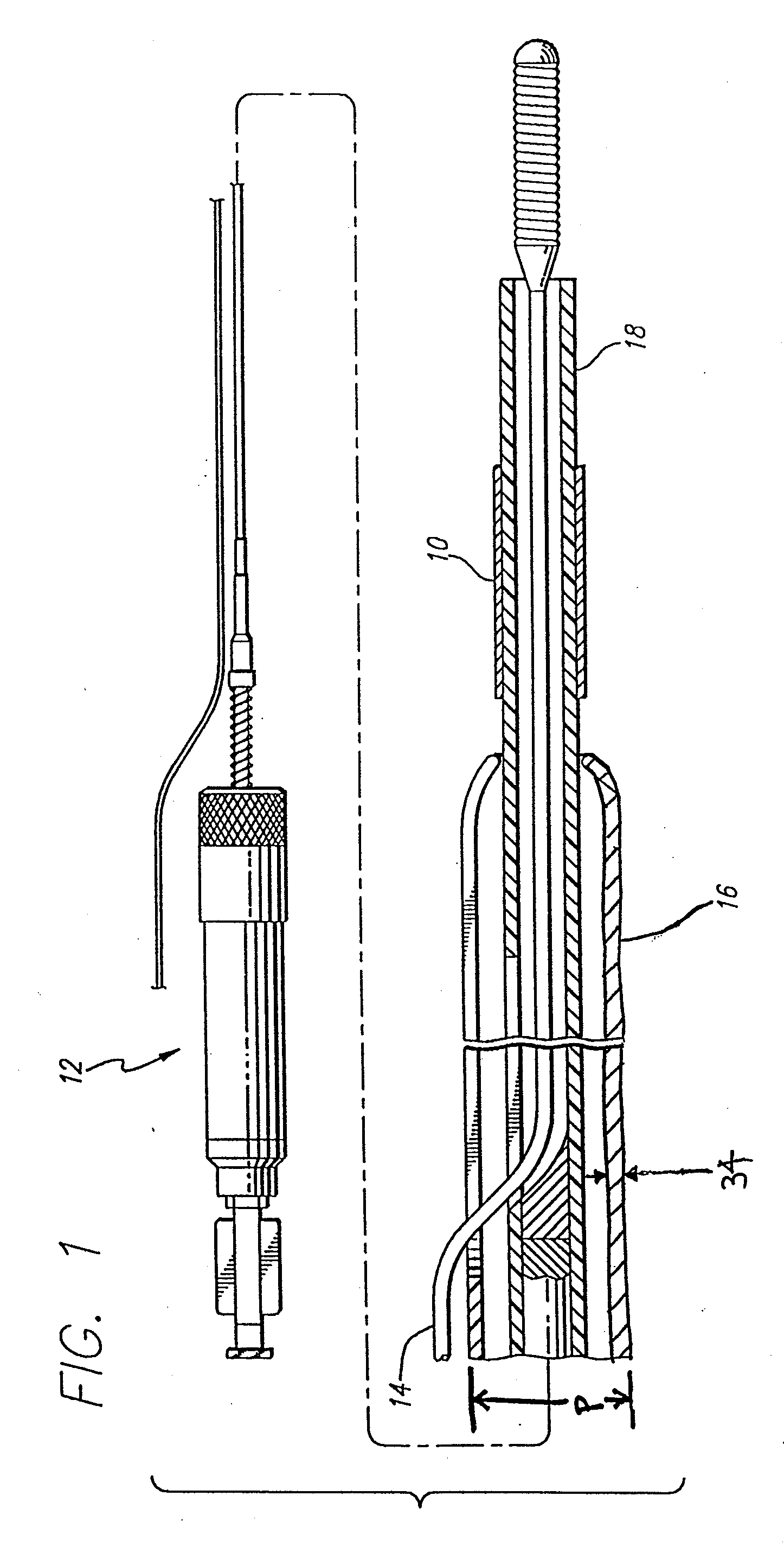
Method of delivering a medical device across a plurality of valves
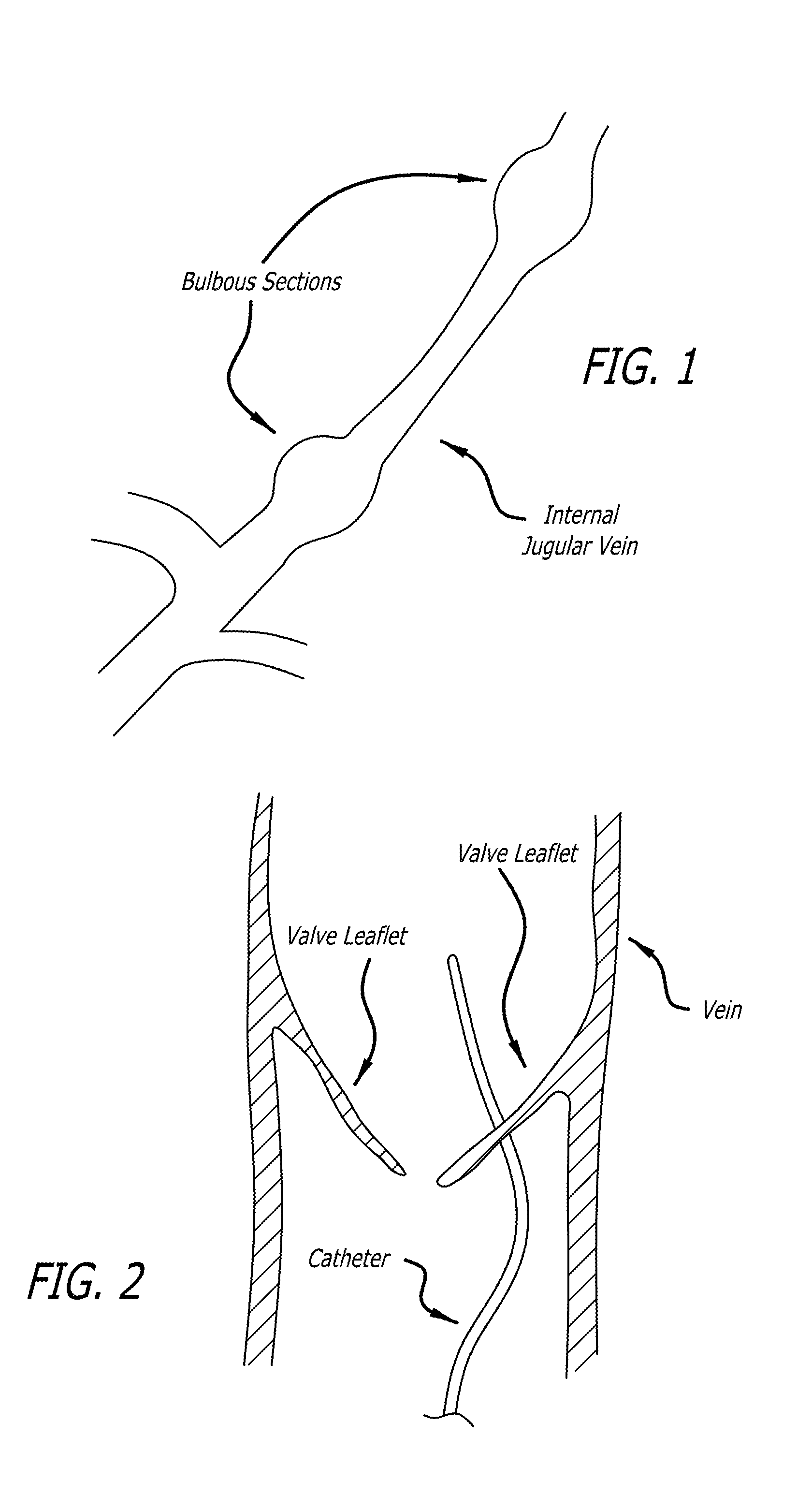
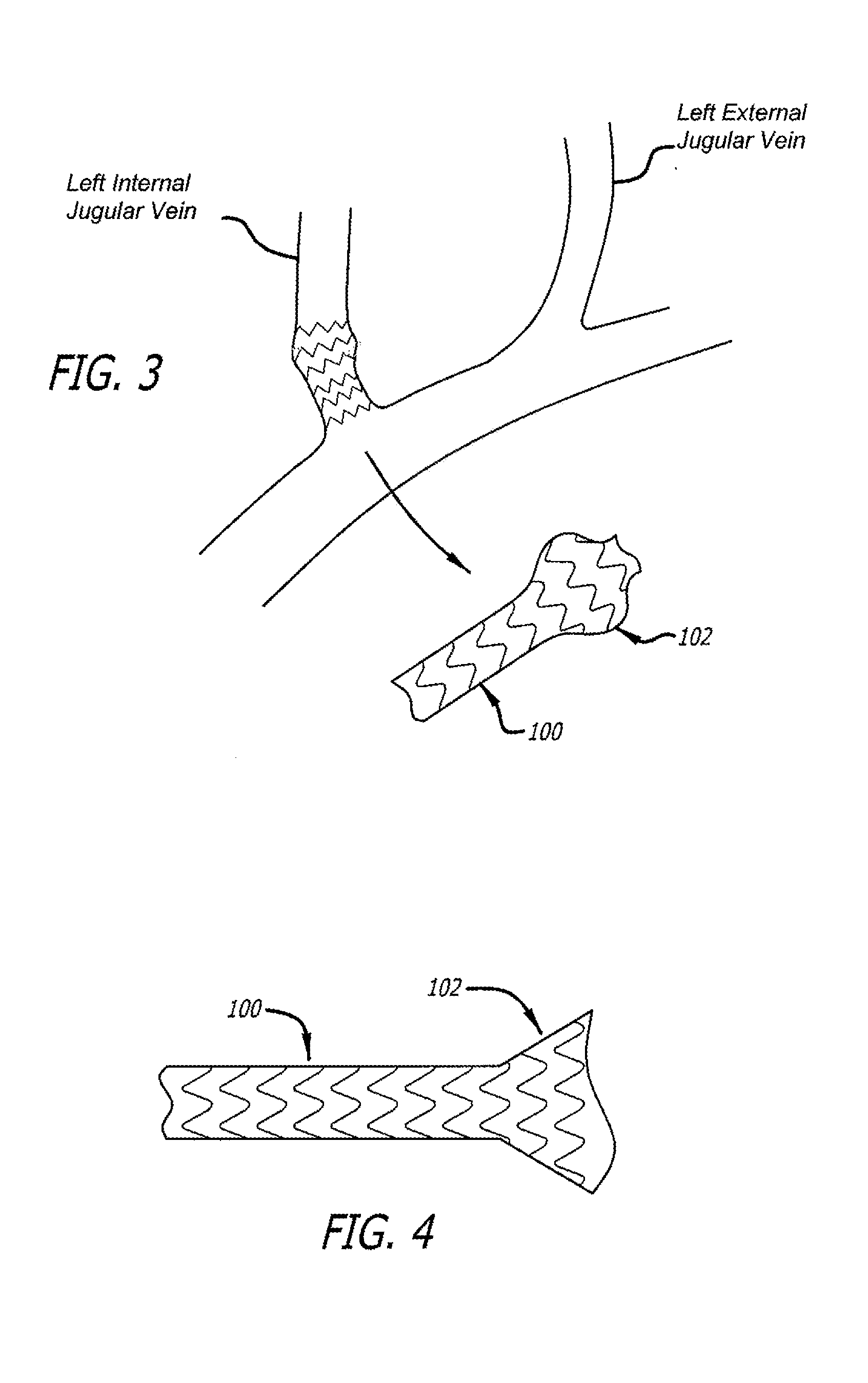
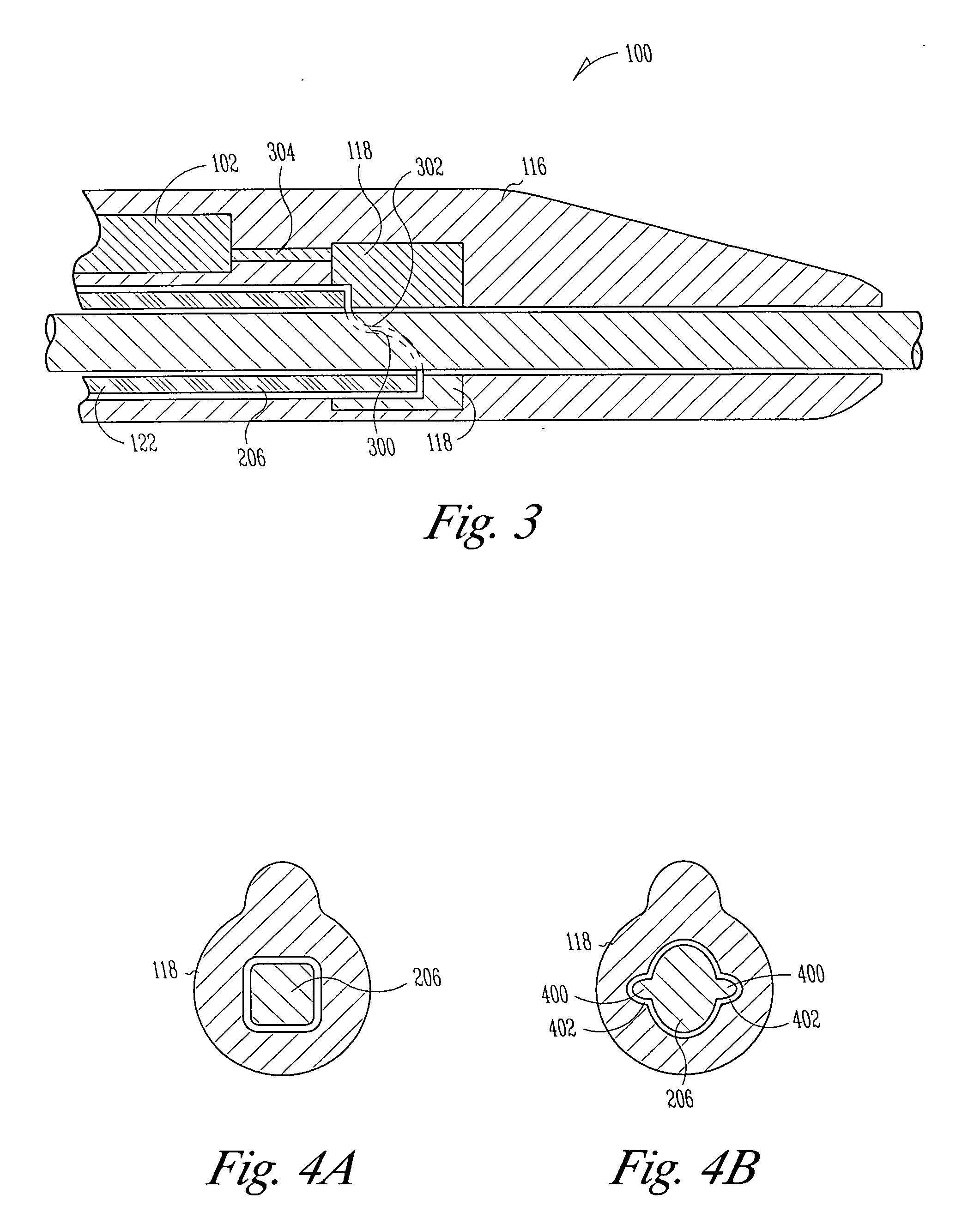
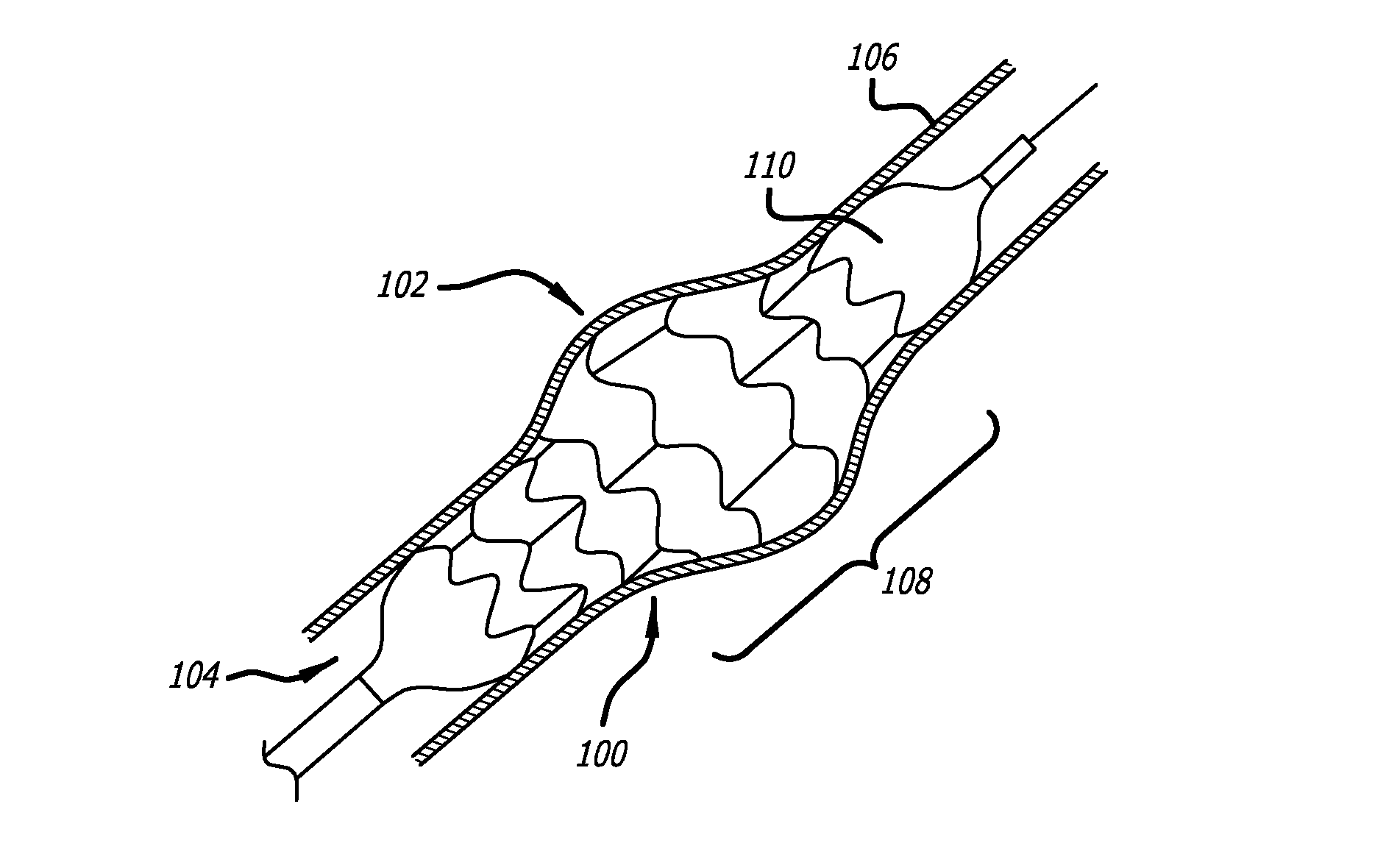
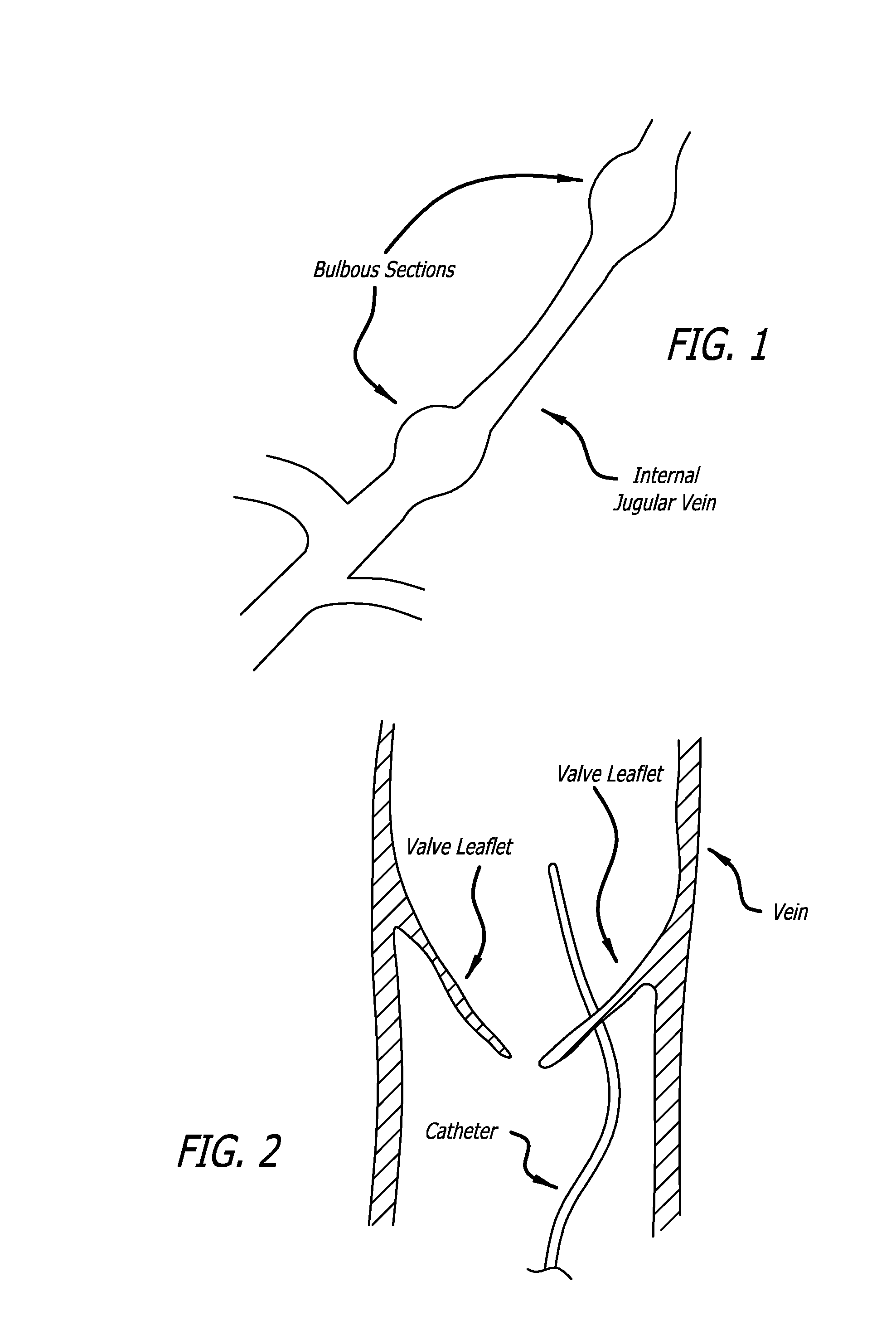
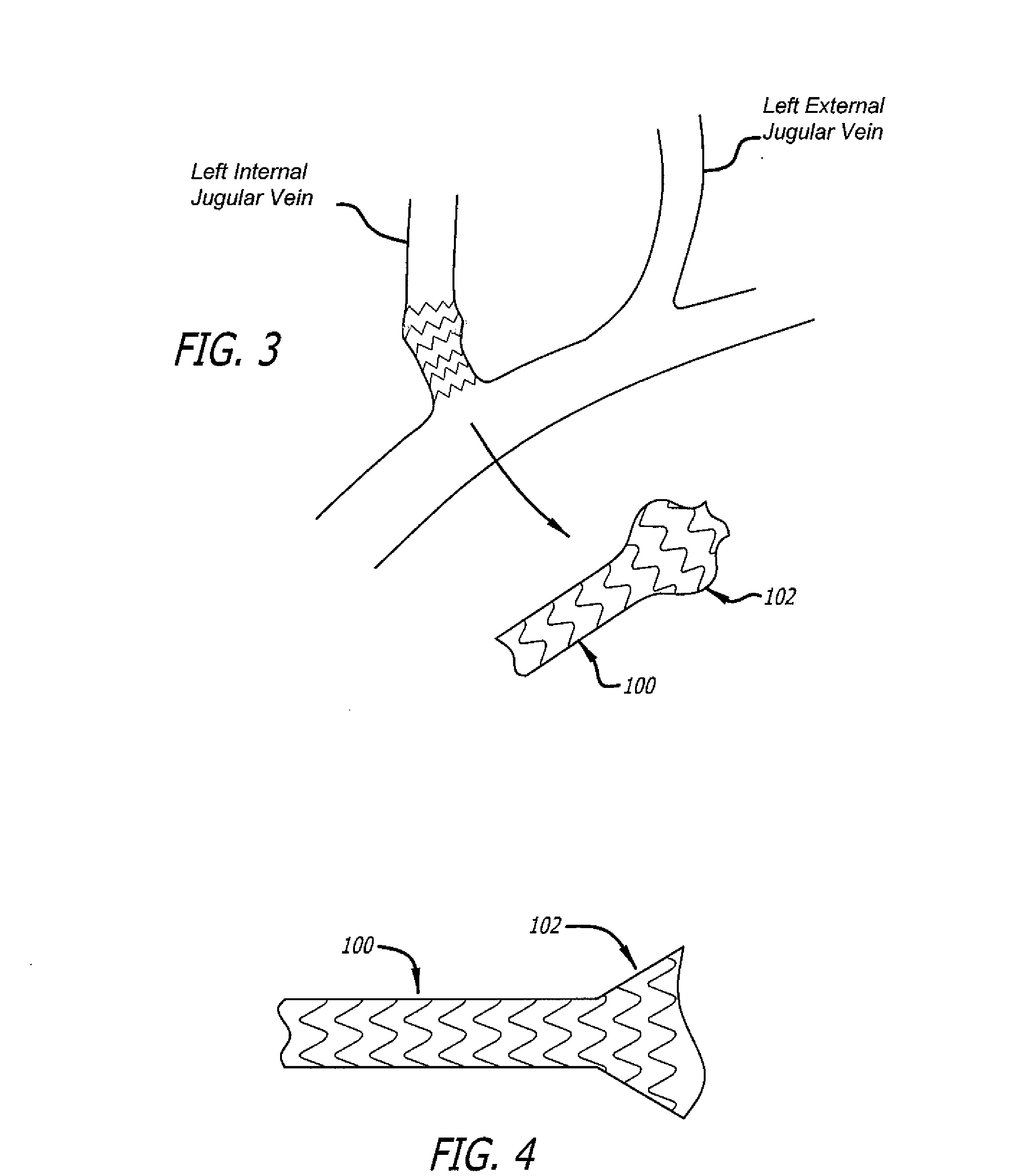
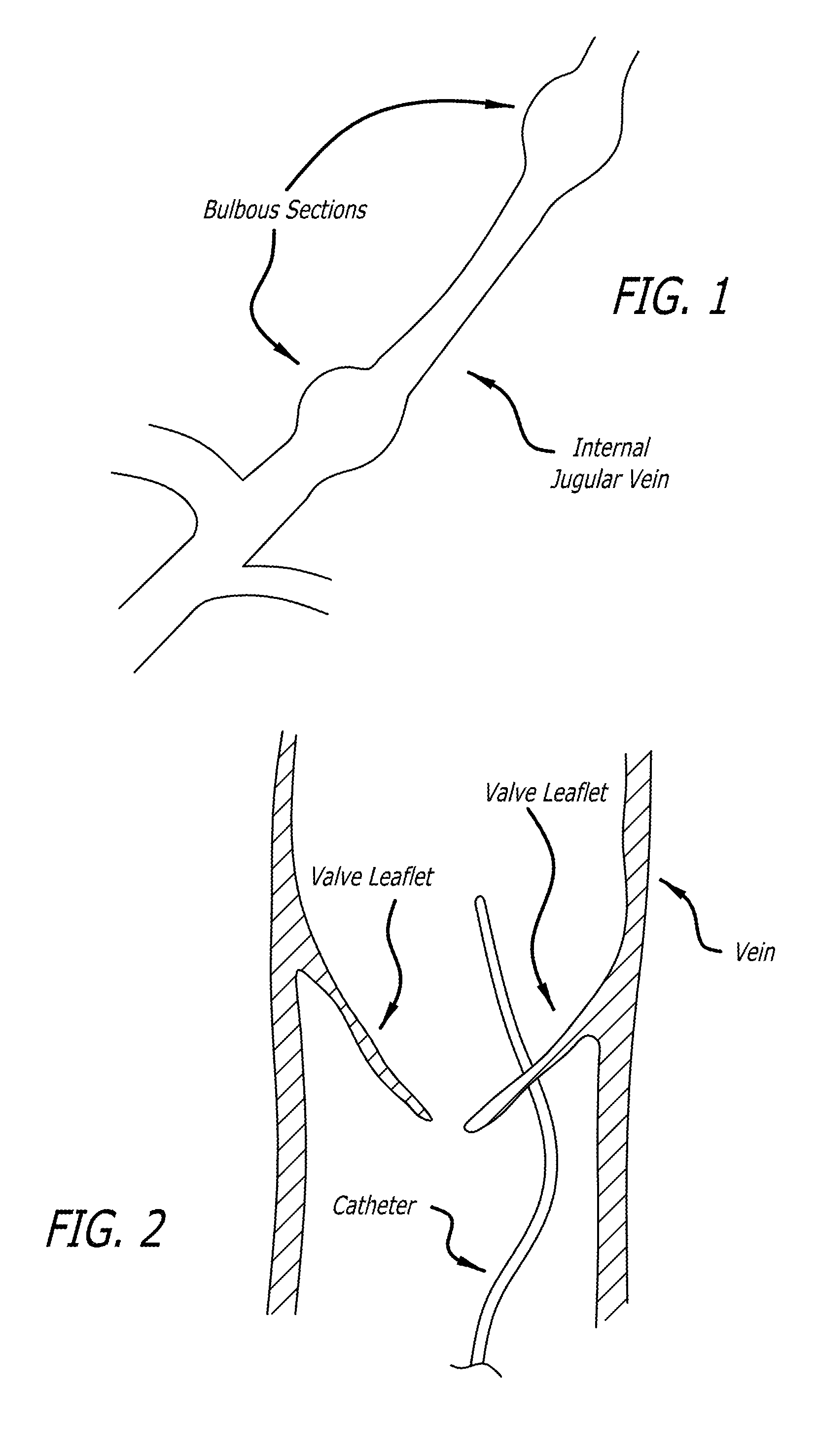
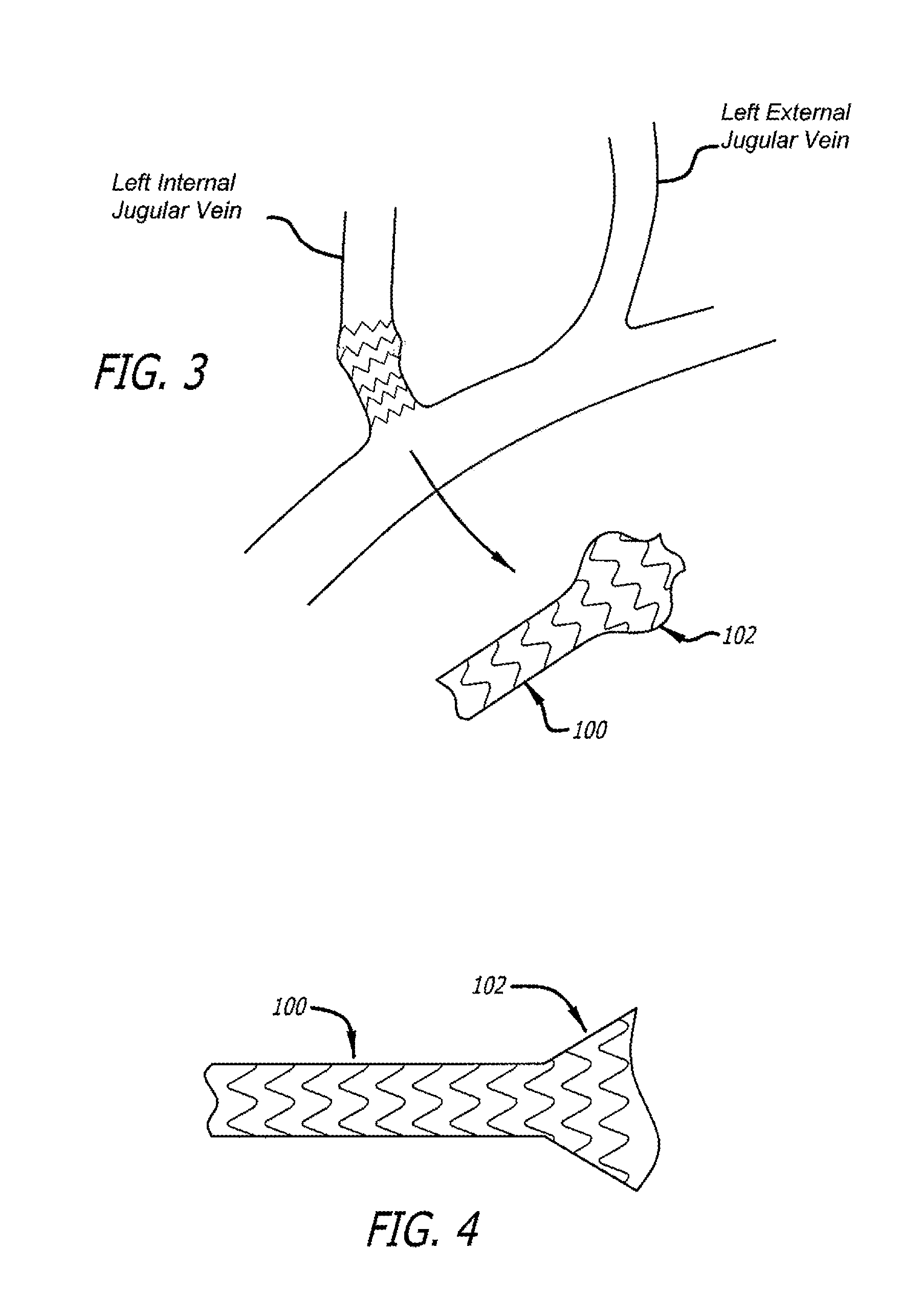
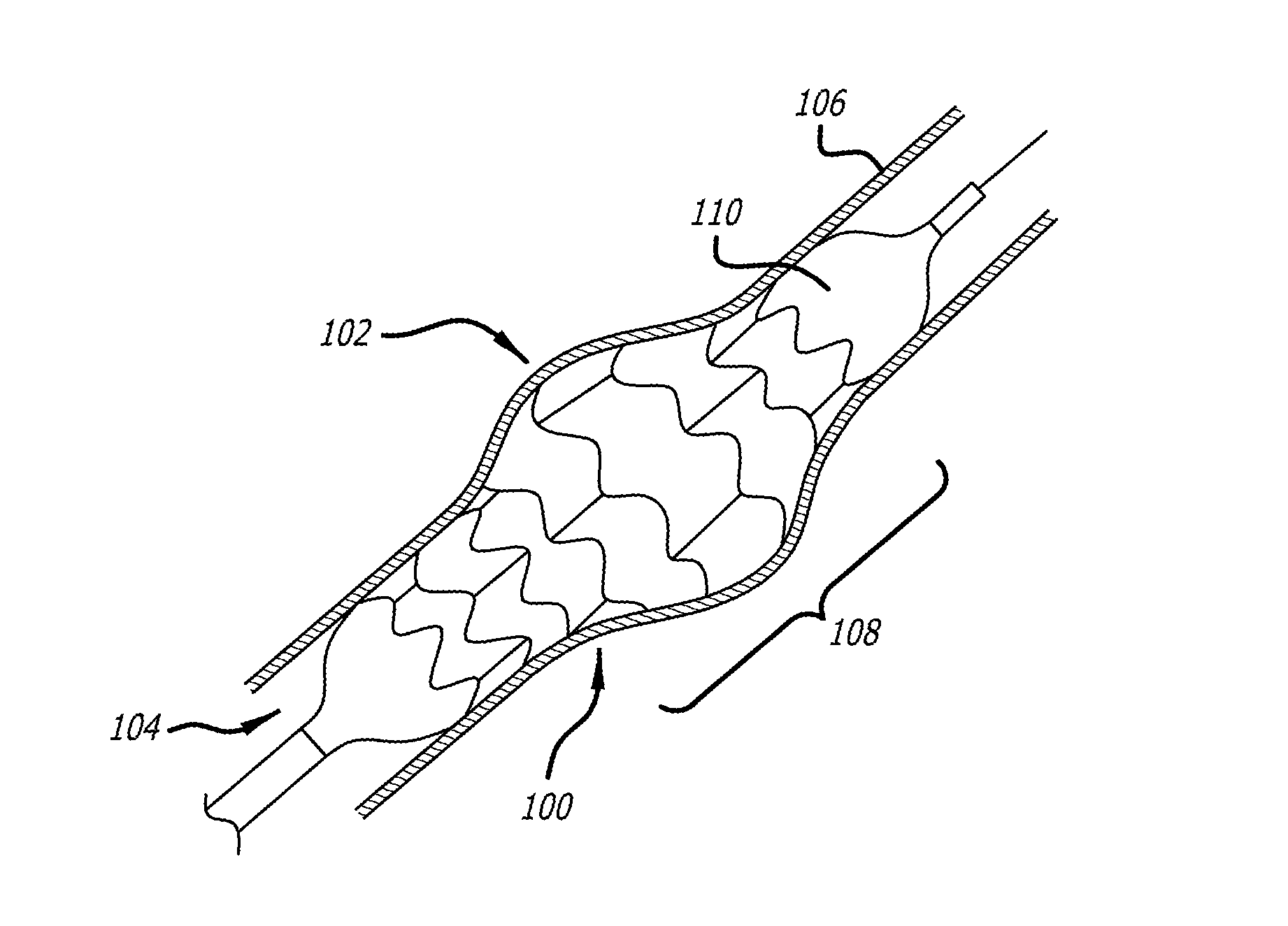
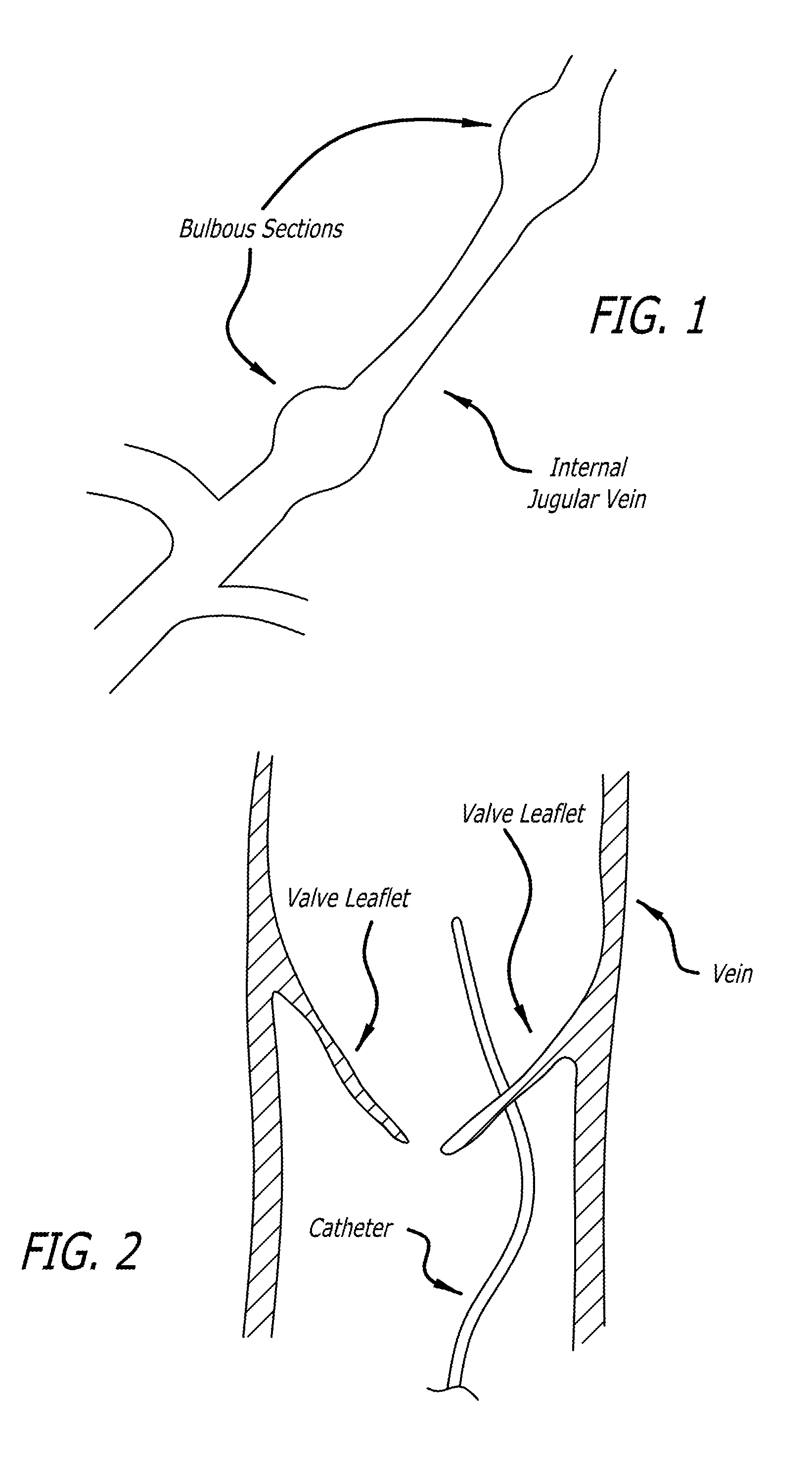
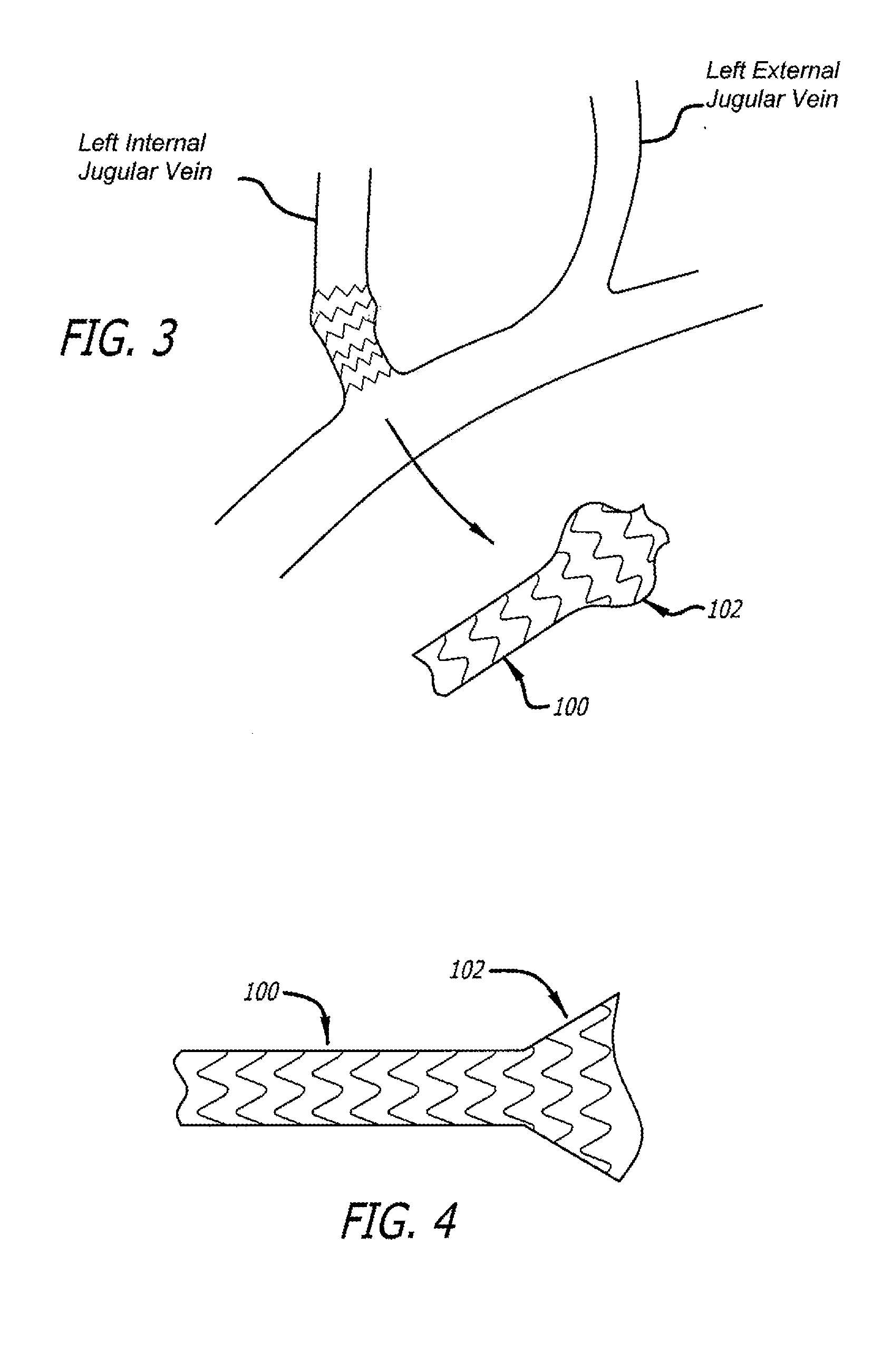
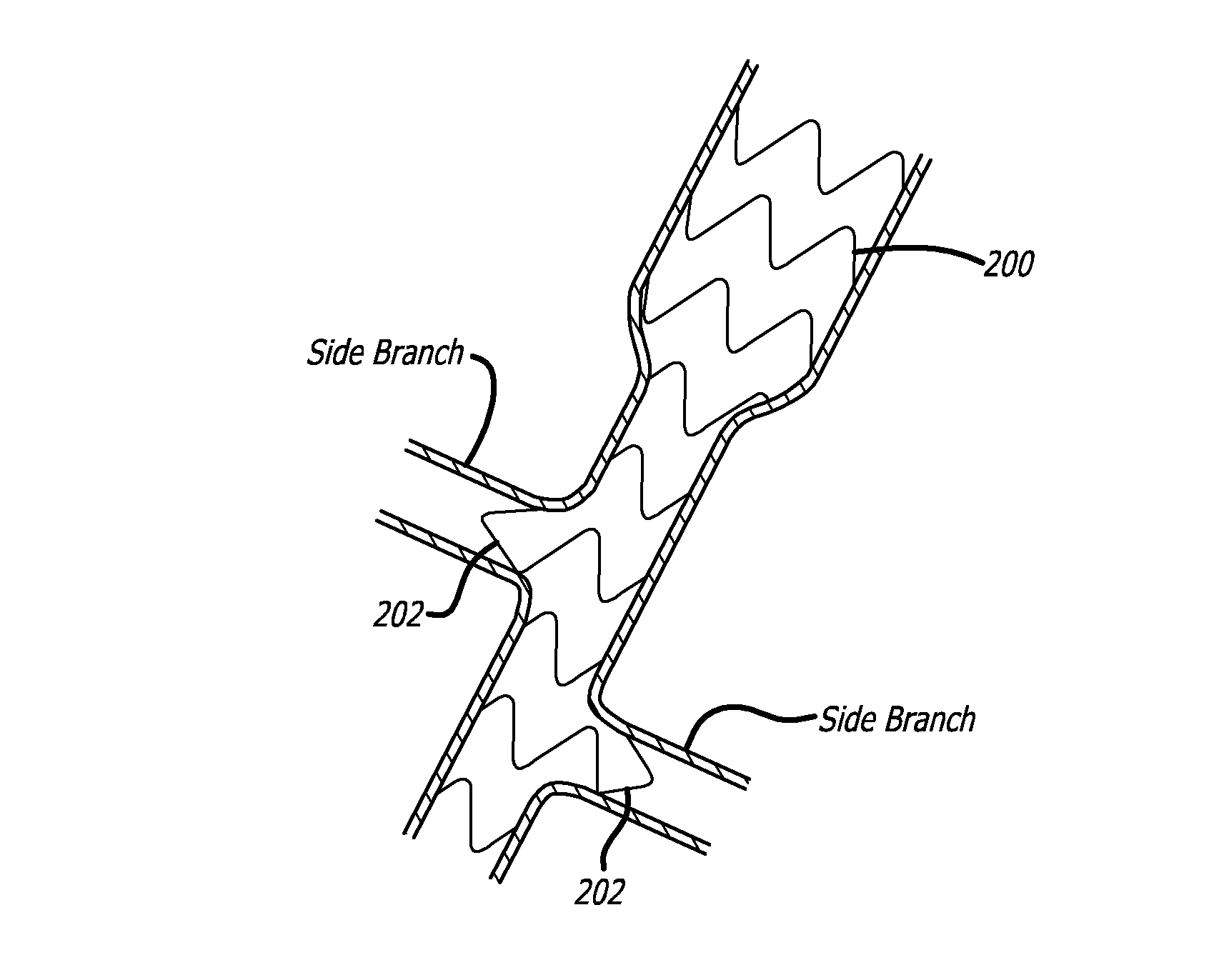
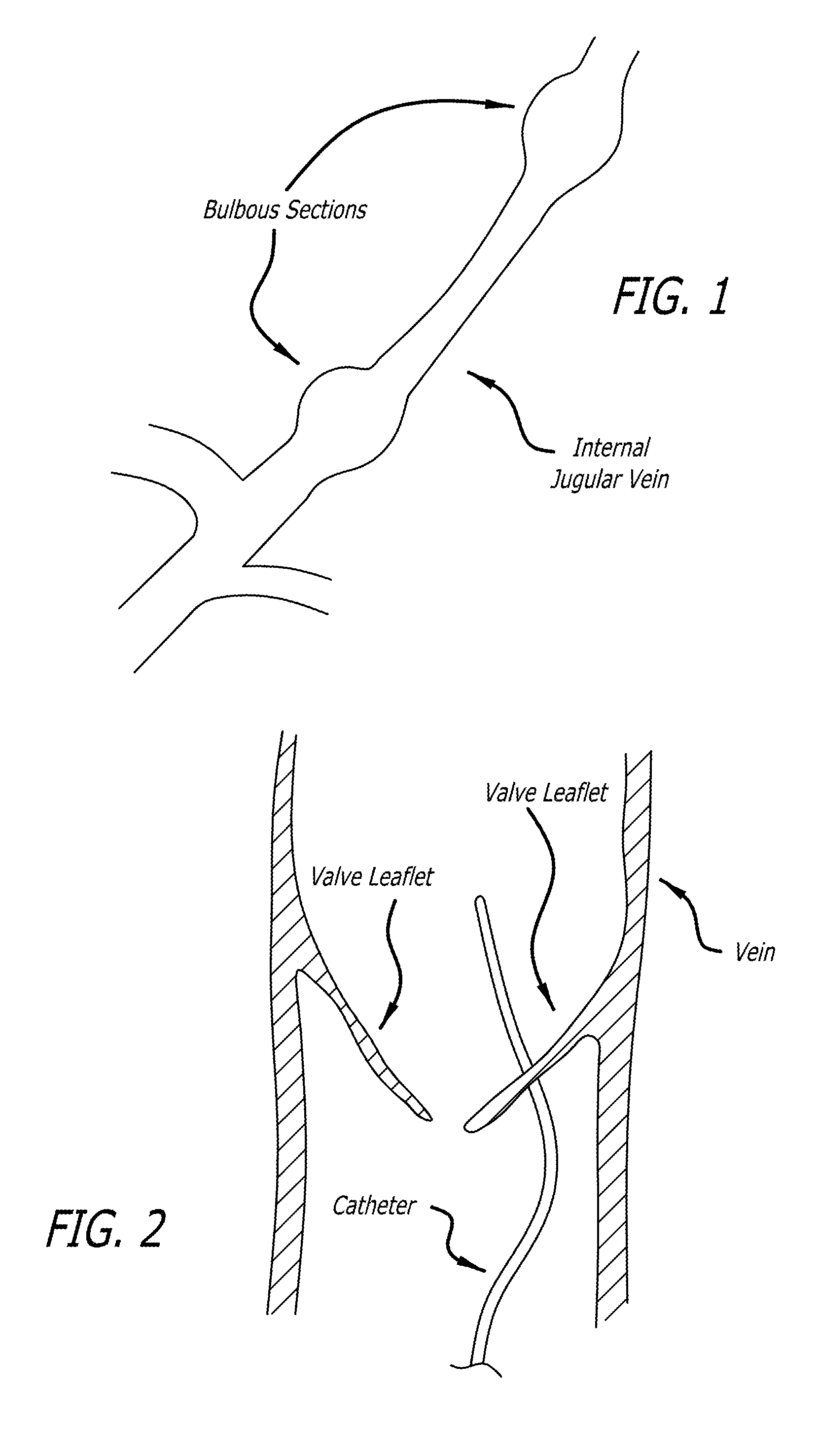
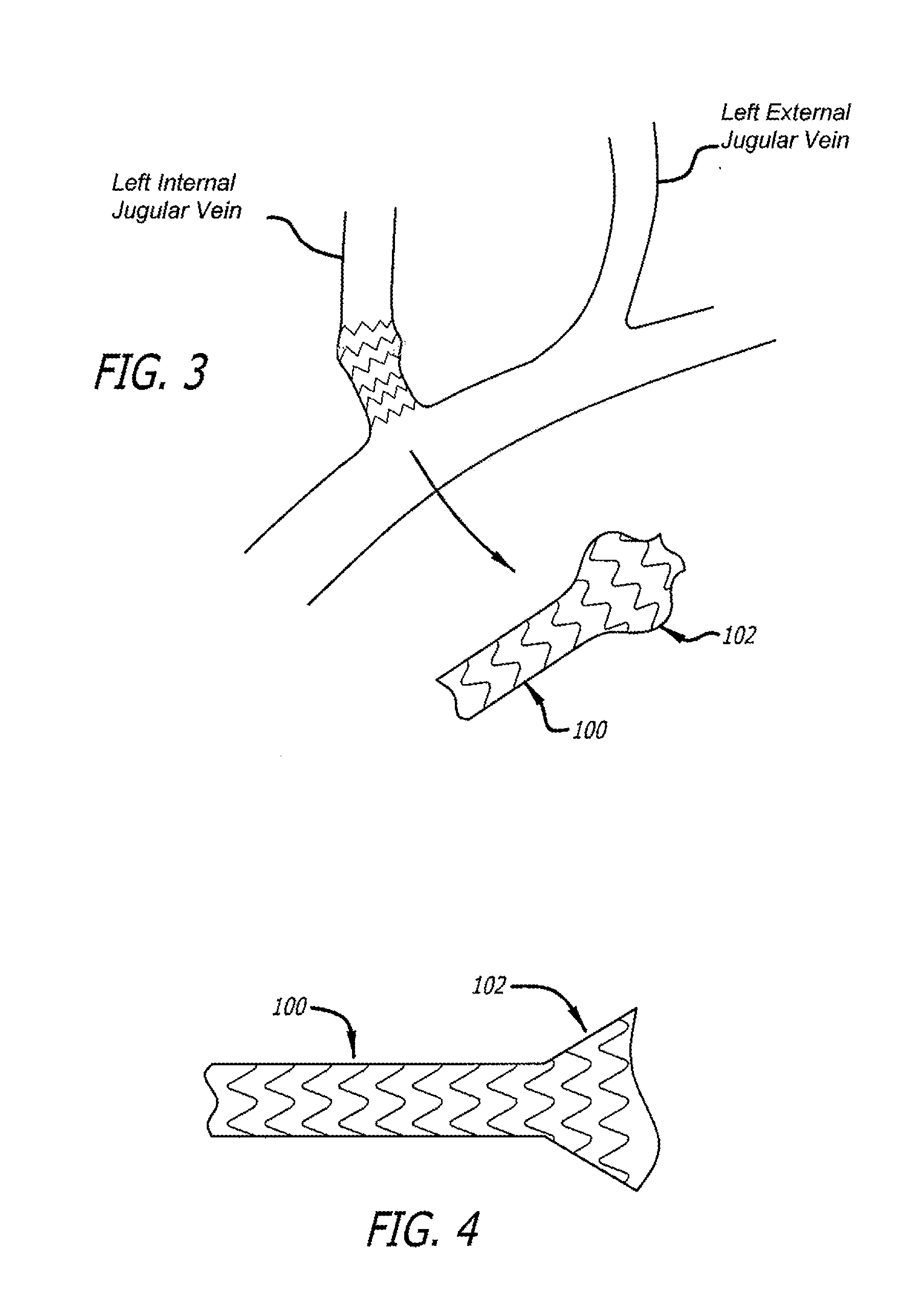
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Lead assembly and methods including a push tube
InactiveUS20060036307A1Easy to browseSmall sectionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
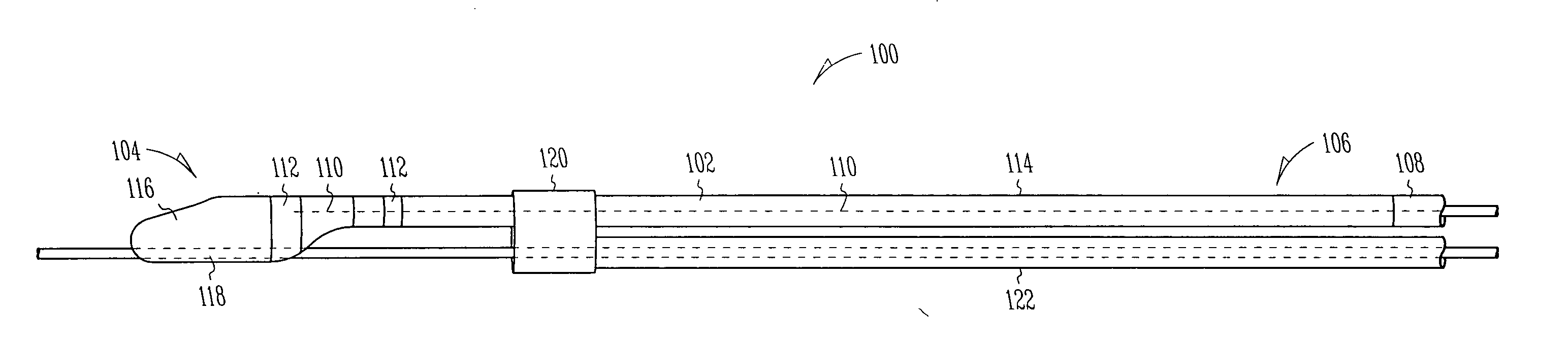
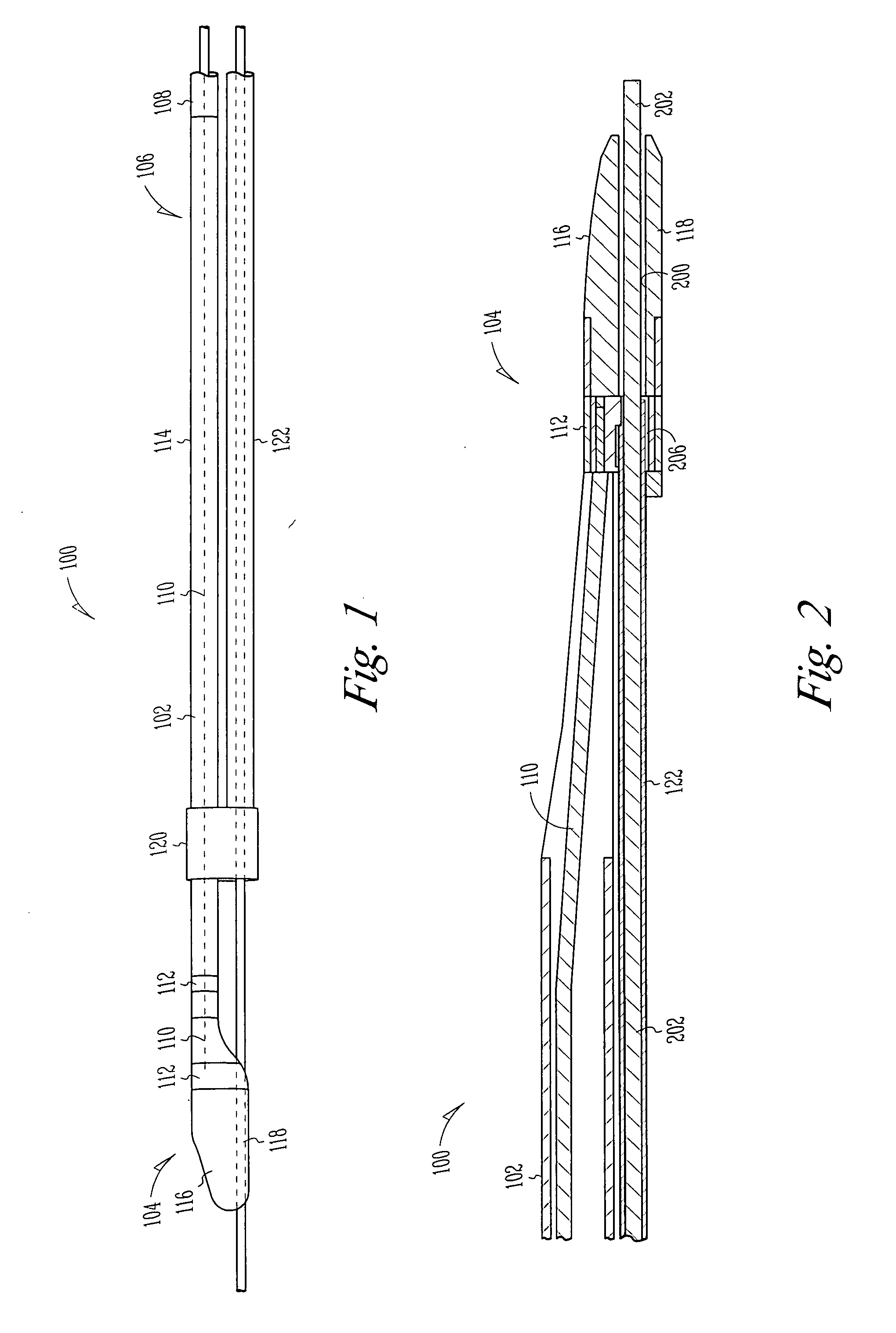
A lead assembly includes an elongate body having a conductor electrically coupled with an electrode coupled to the elongate body. The lead assembly includes a push tube extending along at least a portion of the elongate body. A distal tip is coupled to the elongate body substantially adjacent to the distal end of the elongate body. The distal tip is sized and shaped to couple with a push tube distal end. In one option, the distal tip includes a seat to receive the push tube distal end. In another option, the seat is a side rail seat and a guide wire extends along the elongate body and is slidably coupled with the side rail seat. The lead assembly includes, optionally, an active fixation device slidably coupled with a portion of the elongate body, and the active fixation device is sized and shaped to couple with the push tube.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
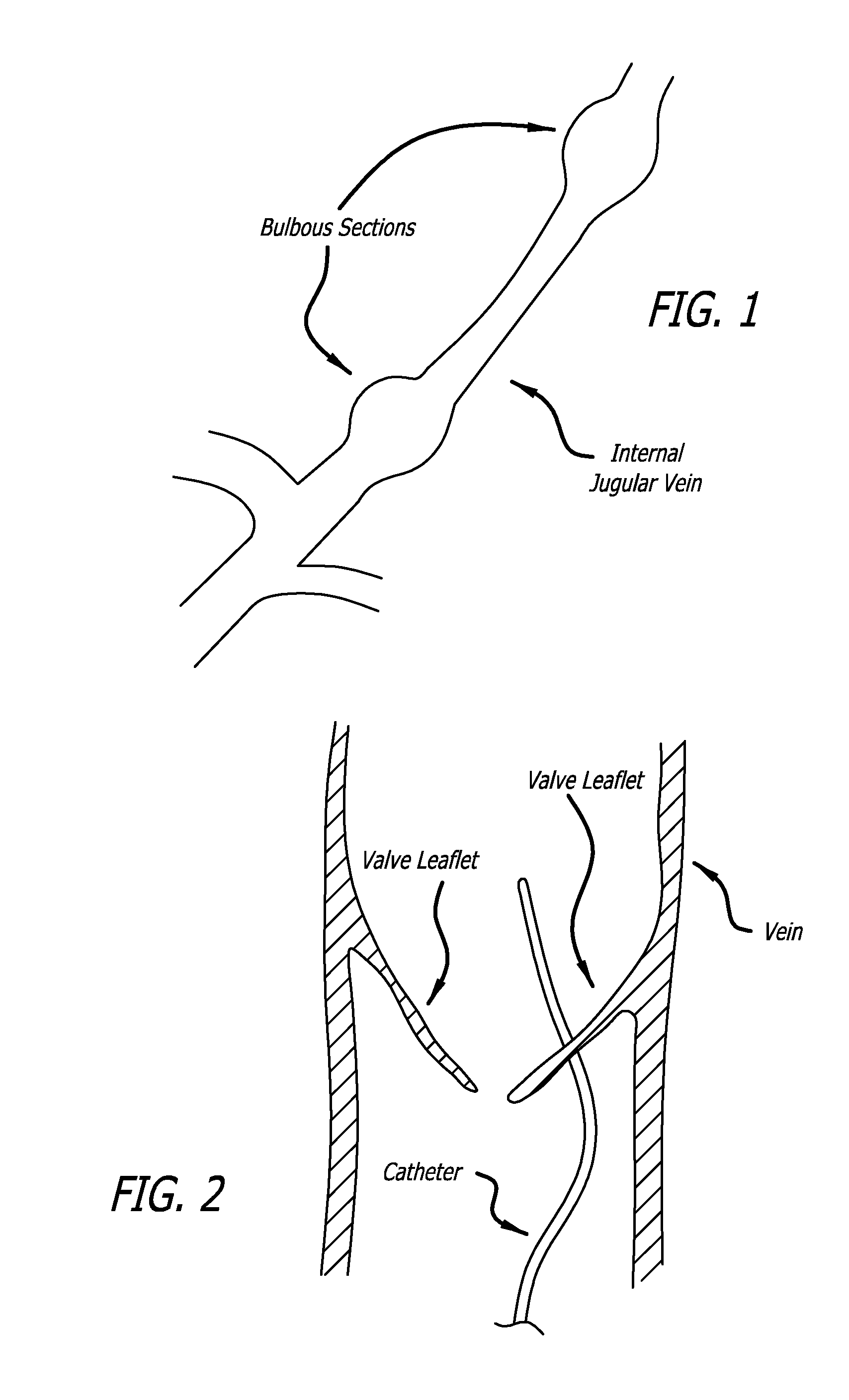
Methods of treating a condition of a vessel in a patient
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Vascular inducing implants
Implants and associated delivery systems for promoting angiogenesis in ischemic tissue are provided. The implants may be delivered percutaneously, thoracically or surgically and are particularly well suited for implantation into the myocardium of the heart. The implants are configured to have a first configuration having a low profile and an expanded, second configuration having a large profile. The implants are delivered to the ischemic tissue location in the first configuration, implanted then expanded to the second configuration. The expanded implants maintain a stress on the surrounding tissue, irritating and slightly injuring the tissue to provoke an injury response that results in angiogenesis. The flow of blood from the surrounding tissue into the implant and pooling of the blood in and around the implant leads to thrombosis and fibrin growth. This healing process leads to angiogenesis in the tissue surrounding the implant. Additionally, the implants may contain an angiogenic substance or a thrombus of blood, preloaded or injected after implantation to aid in initiating angiogenesis.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Method of fabricating an intraluminal scaffold with an enlarged portion
InactiveUS8524132B2Sufficient flexibilityLarge profileButtonsFilament/thread formingVeinSubject matter
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Polymeric marker with high radiopacity
ActiveUS20050064224A1Minimize and prevent flowingReduce wall thicknessMedical devicesDischarge tube main electrodesPolymer resinRadiopaque agent
High radiopacity is achieved in a polymeric marker by combining a polymeric resin, a powdered radiopaque agent having uniformly shaped particles of a specific particle size distribution and a wetting agent. The method to produce the marker calls for the blending and pelletization of these materials followed by extrusion onto support beading. The resulting supported tubing is subsequently cut to length with the beading still in place. After ejection of the beading remnant the marker is slipped into place on the device to be marked and attached by melt bonding. Marking of a guidewire allows lesions to be measured while the marking of balloon catheters allow the balloon to be properly positioned relative to a lesion.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method of delivering a medical device across a valve
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
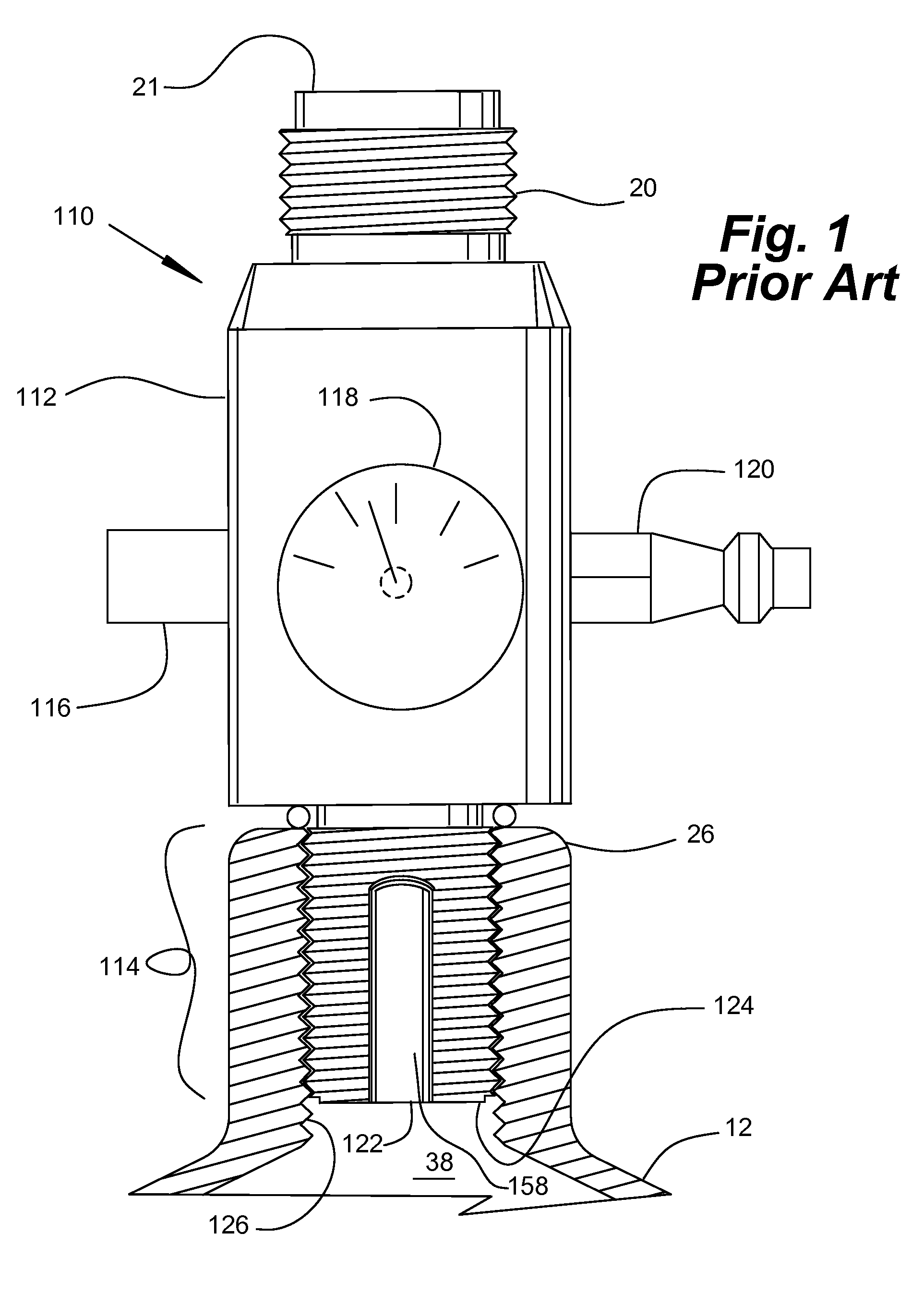
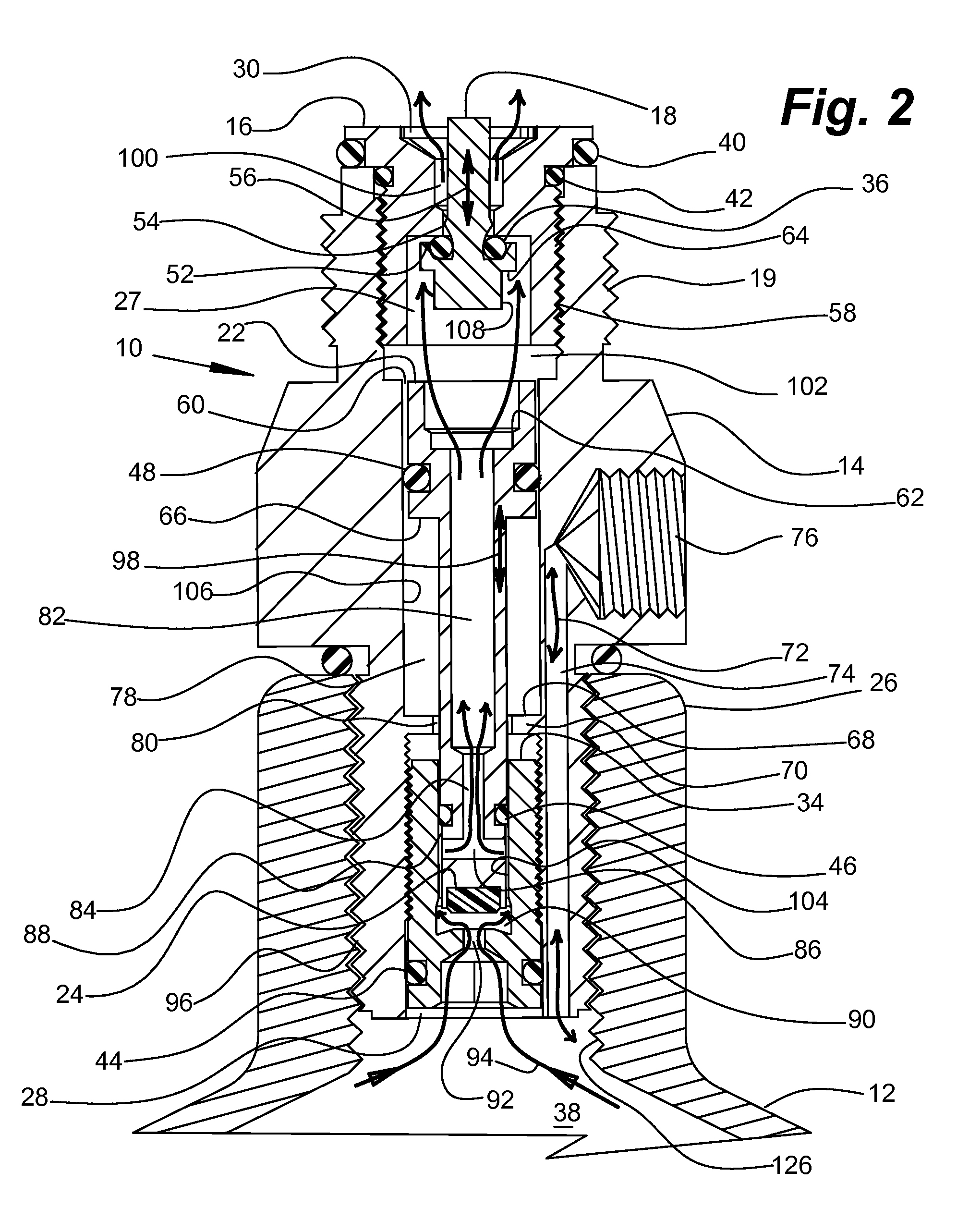
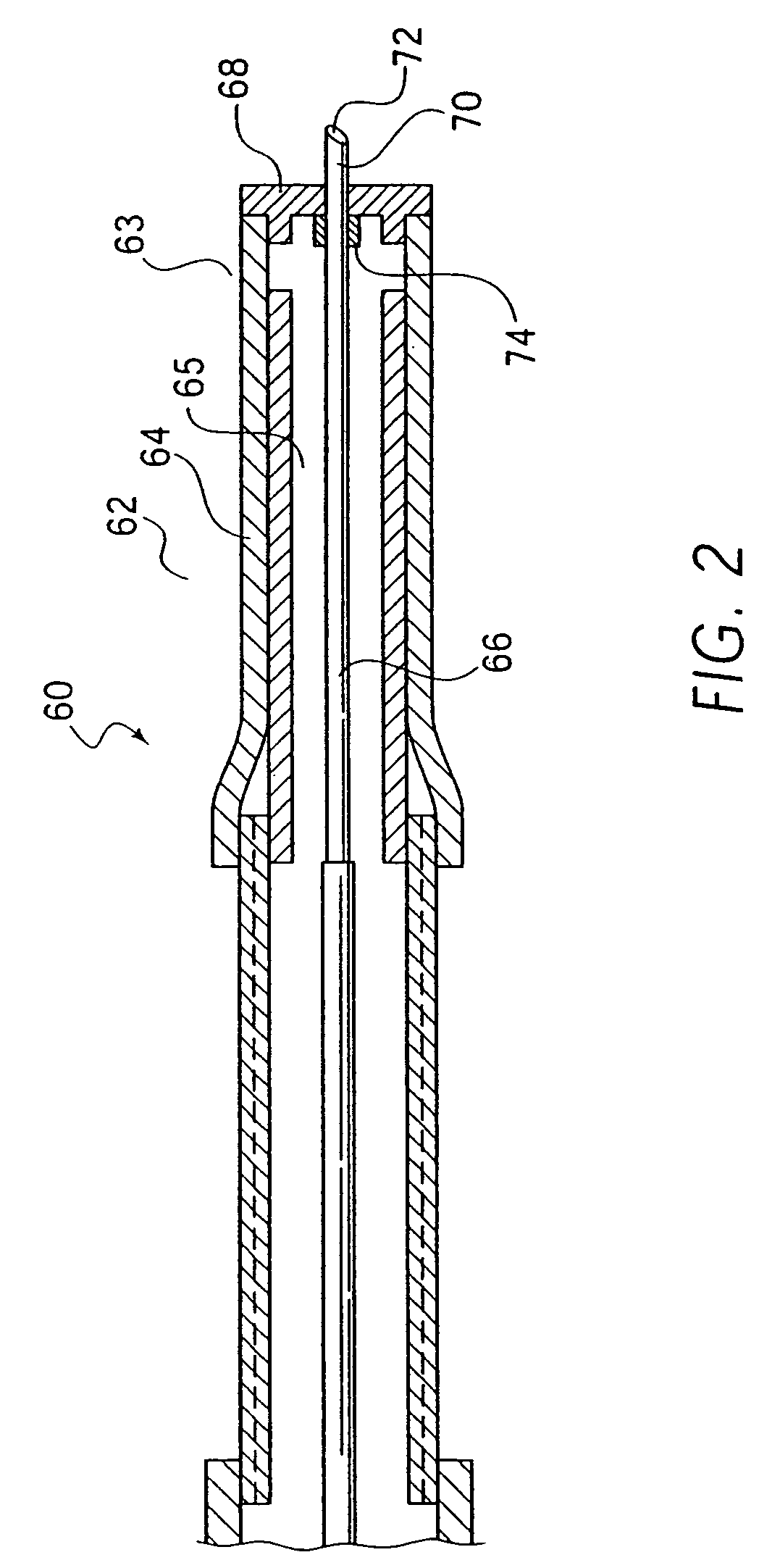
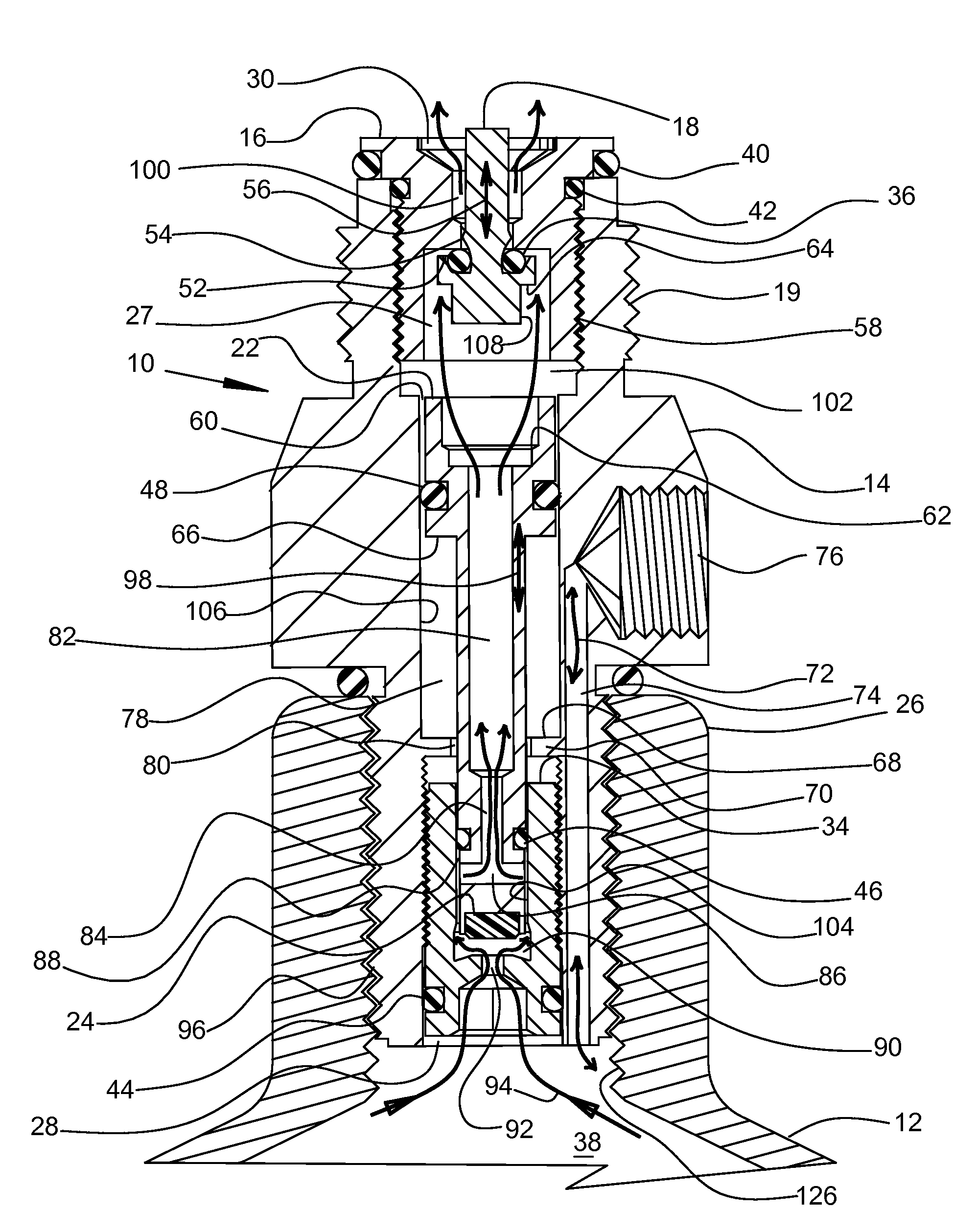
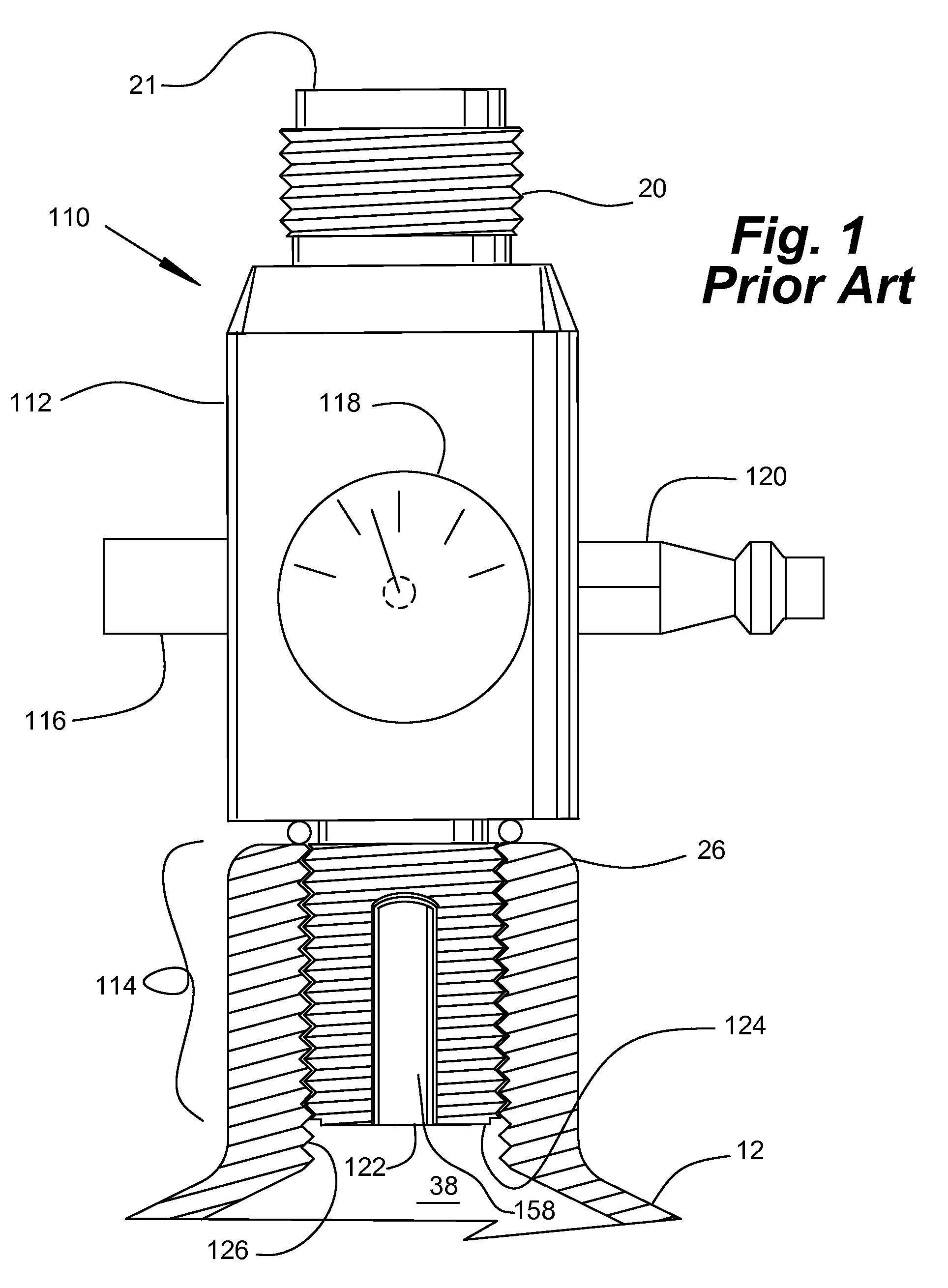
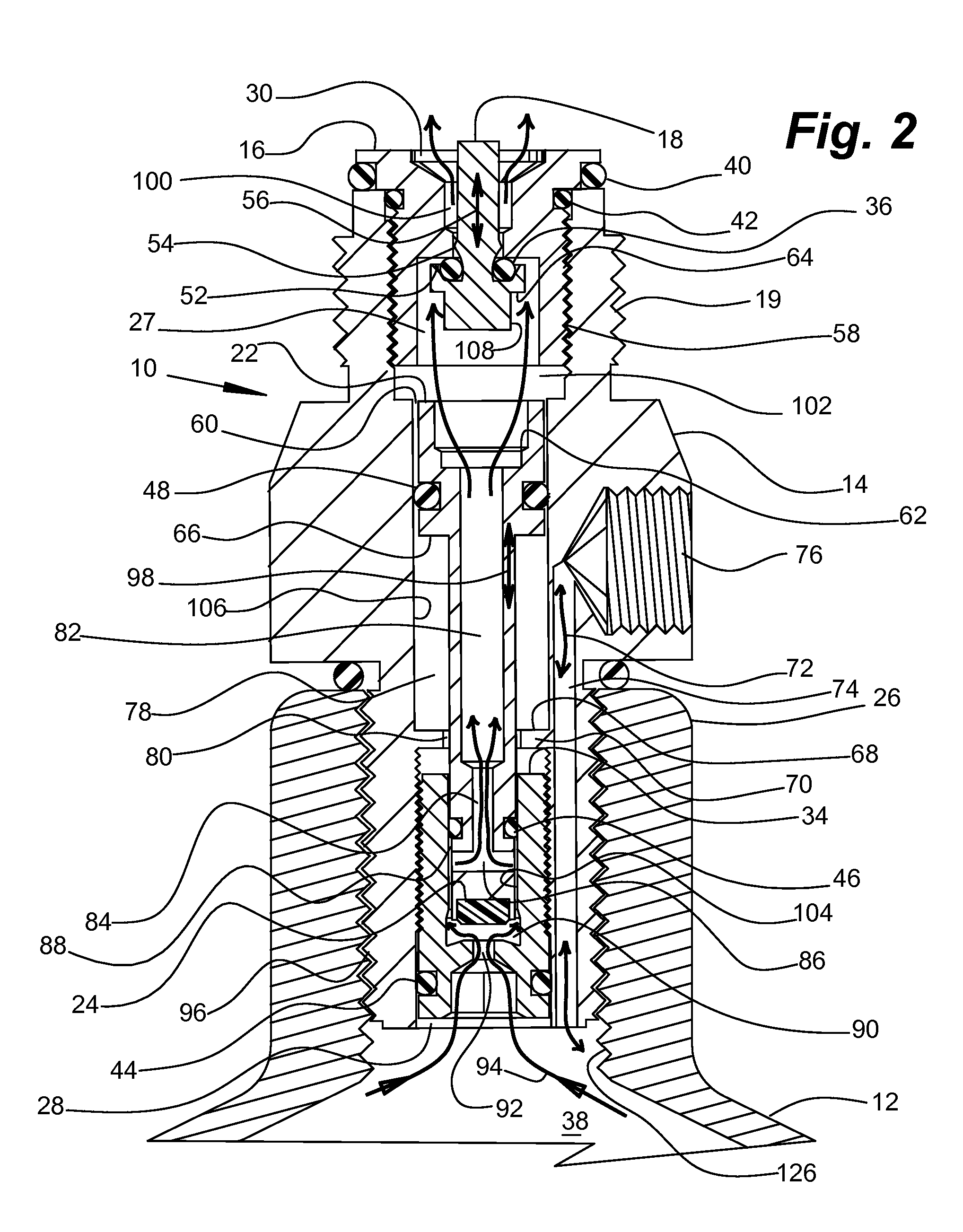
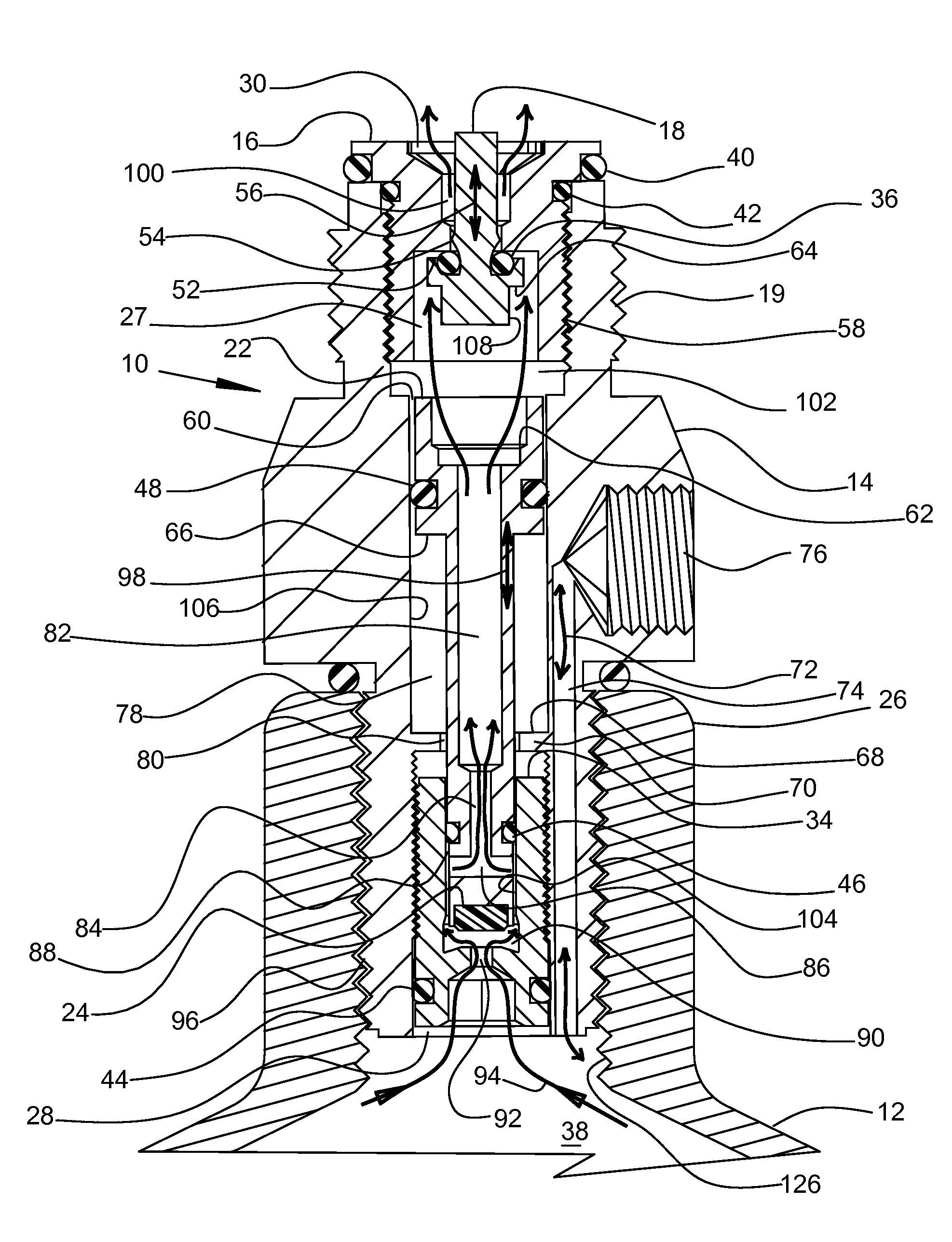
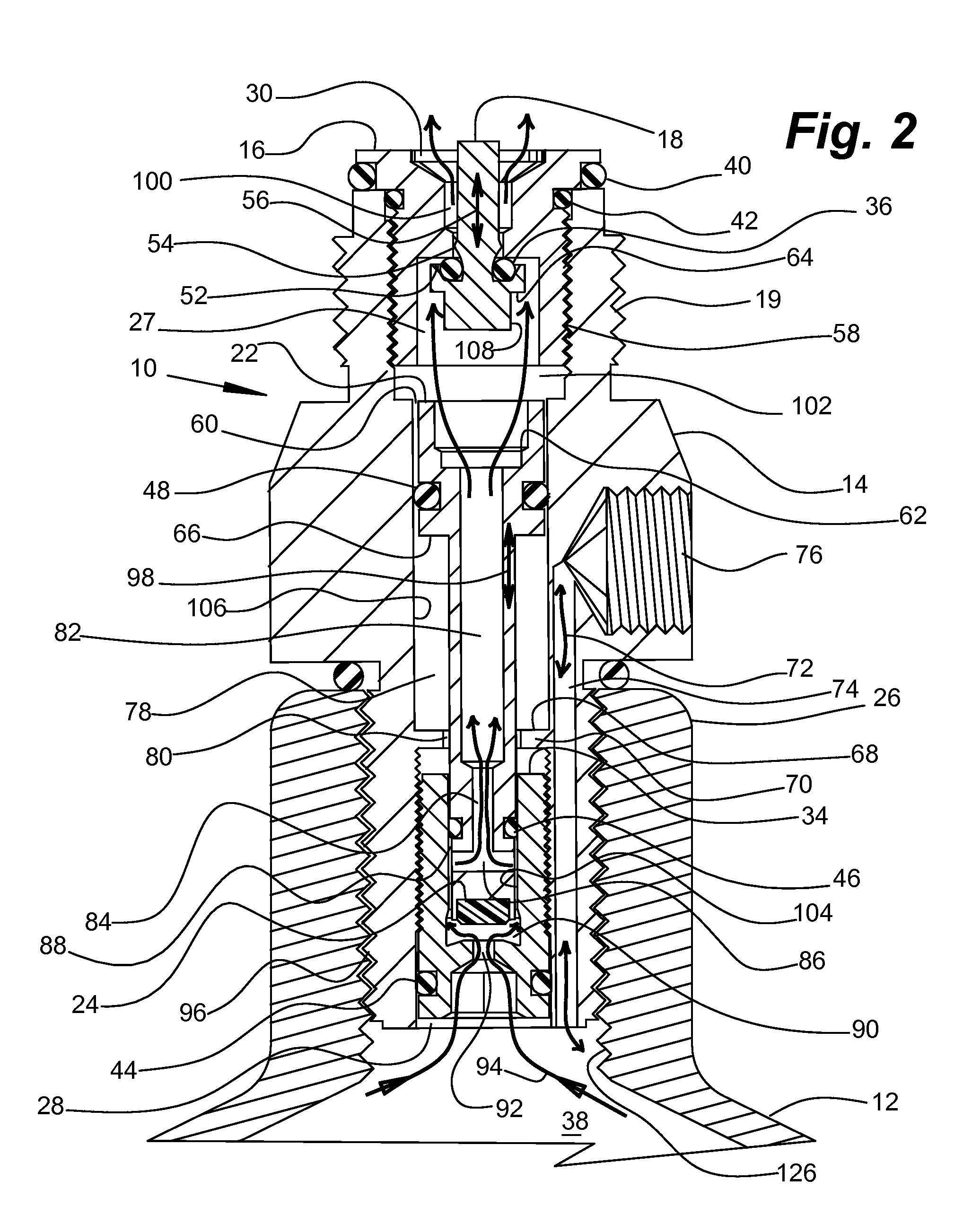
Compressed Air Regulator Apparatus Situated in Canister and Method for Regulating Compressed Air Thereof
ActiveUS20080210210A1Reduced in size and complexity and weightImprove functionalityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLiquid transferring devicesEngineeringPiston
A compressed gas regulator of a piston type is disclosed in which a regulator is configured with an input valve situated entirely inside a compressed air canister, which regulator is then attached to a paintball gun, marker or other device for providing discrete charges of gas at a predetermined pressure to the attached device. The overall size and weight of the regulator are minimized, which allows increased capabilities to the user. A regulator overpressurization port vents behind a conventional safety gauge for safety purposes. Fill, gage, and canister overpressurization rupture ports are interconnected with a fill channel that extends from the canister to the ports without intersecting or interfering with the regulating components within the regulator. The input valve seat face is surrounded by a shallow generally conical surface within an input plenum. The shallow generally conical surface extends at approximately 5 to 15 degrees.
Owner:YSN IMPORTS LLC
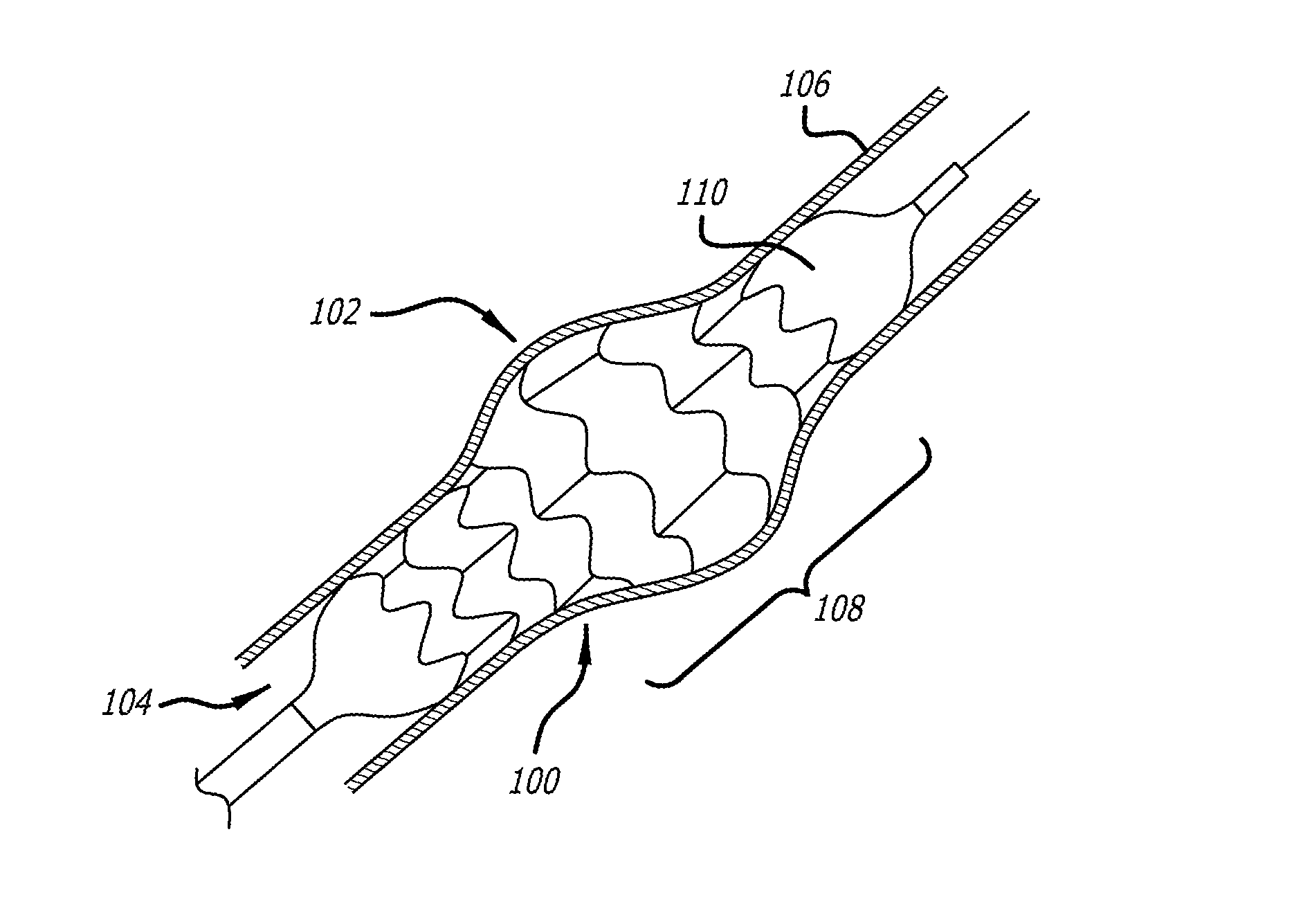
Intraluminal scaffold having an enlarged portion
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Intraluminal scaffold with conforming axial strut
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Nitinol alloy design and composition for medical devices
A stent and a delivery system for implanting the stent in a body lumen is disclosed. The stent is made from a superelastic alloy such as nickel-titanium or nitinol, and includes a ternary element in order to minimize the stress hysteresis of the superelastic material. The stress hysteresis is defined by the difference between the loading plateau stress and the unloading plateau stress of the superelastic material. The resulting delivery system has a small profile and includes a sheath covering the stent that has a thin wall. A guide wire core can also be made from the small stress hysteresis superelastic material.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Remote pick-up devices
ActiveUS20080224488A1Minimized overall profileReduce widthGripping headsLoad-engaging elementsEngineeringFixed position
An improvement to elongate tools for engaging objects from remote distances is disclosed wherein the connection between the rod on which the engagement elements are provided and the handle of the device allows for the orientation of the rod with respect to the handle to occupy at least two pre-selected fixed positions which are at angular positions approximately 90 degrees from one another.
Owner:ONTEL PRODS
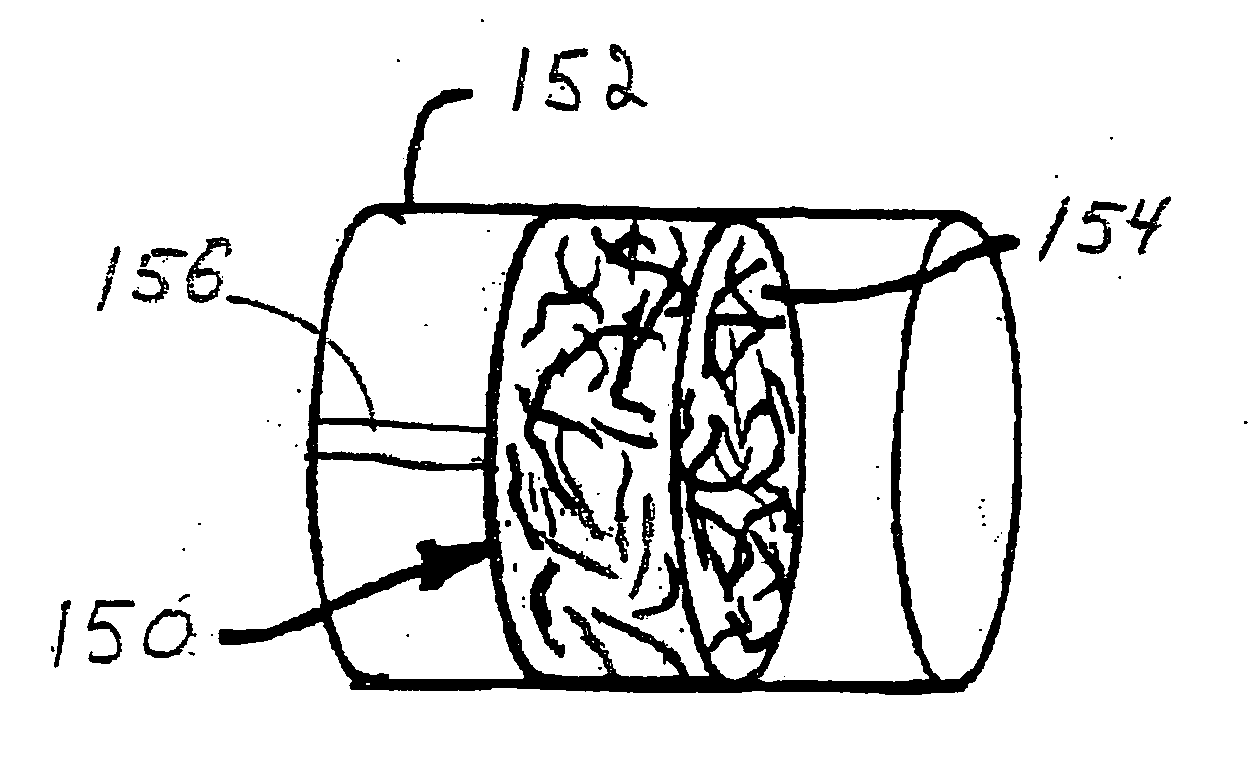
Radiopaque fibers and filtration matrices
Medical devices with radiopaque three dimensional filtration matrices provide for improved visualization of the device within a vessel. In some embodiments, the three dimensional filtration matrix comprises fibers, such as surface capillary fibers. Visualization of the three dimensional filtration matrix provides for an evaluation of the proper deployment of the three dimensional filtration matrix. Radiopaque surface capillary fibers can be advantageously incorporated into other medical devices. Radiopaque surface capillary fibers can be formed by extrusion of a radiopaque polymer or polymer composite.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
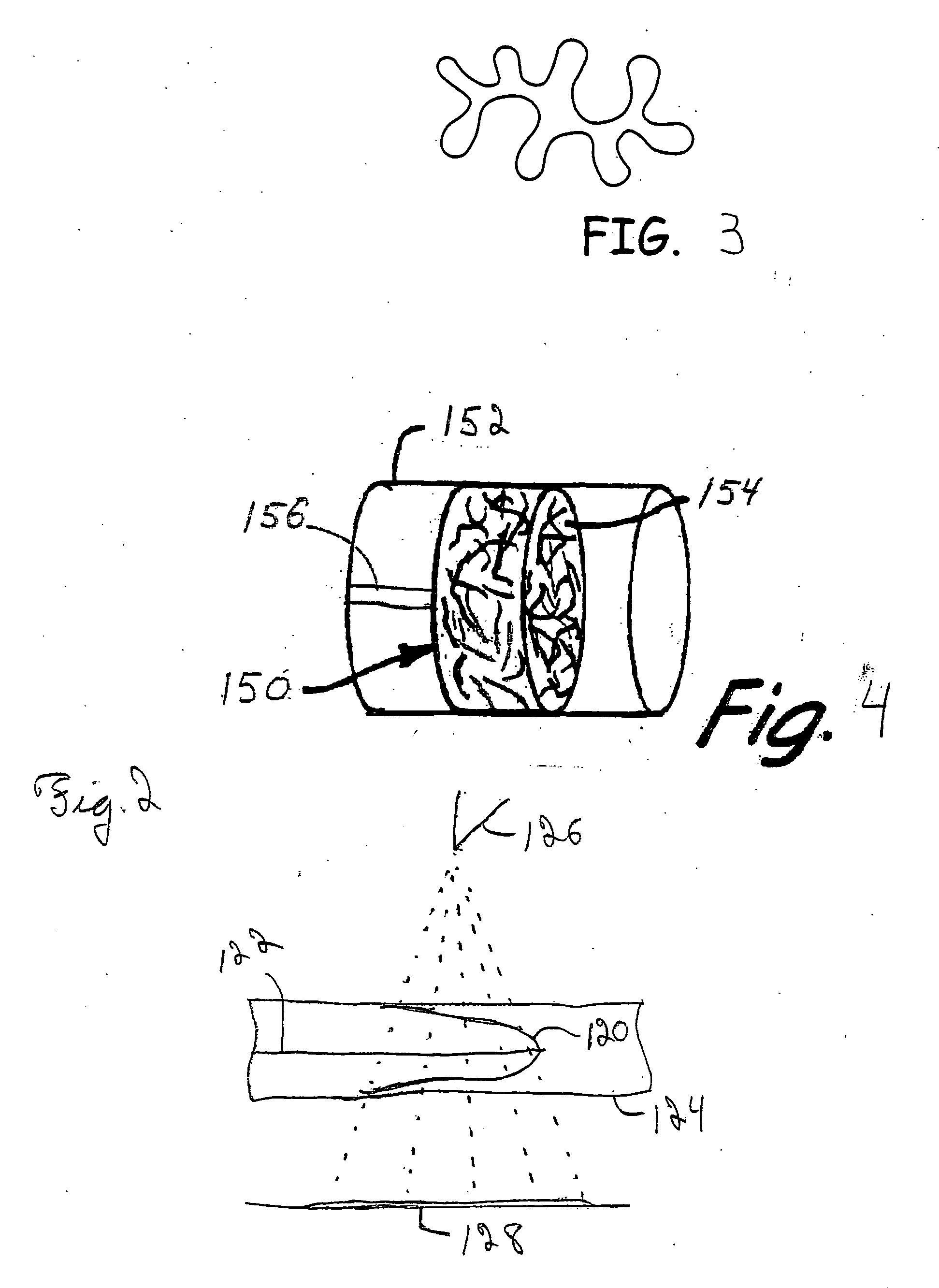
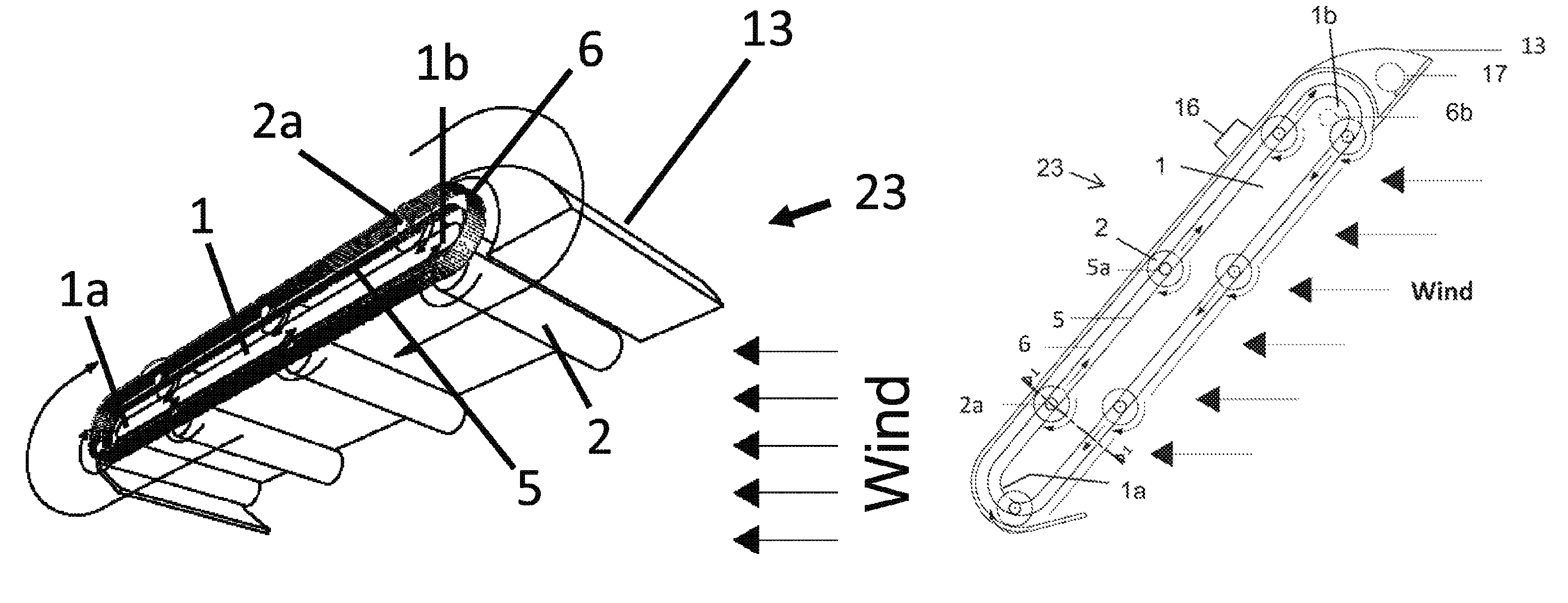
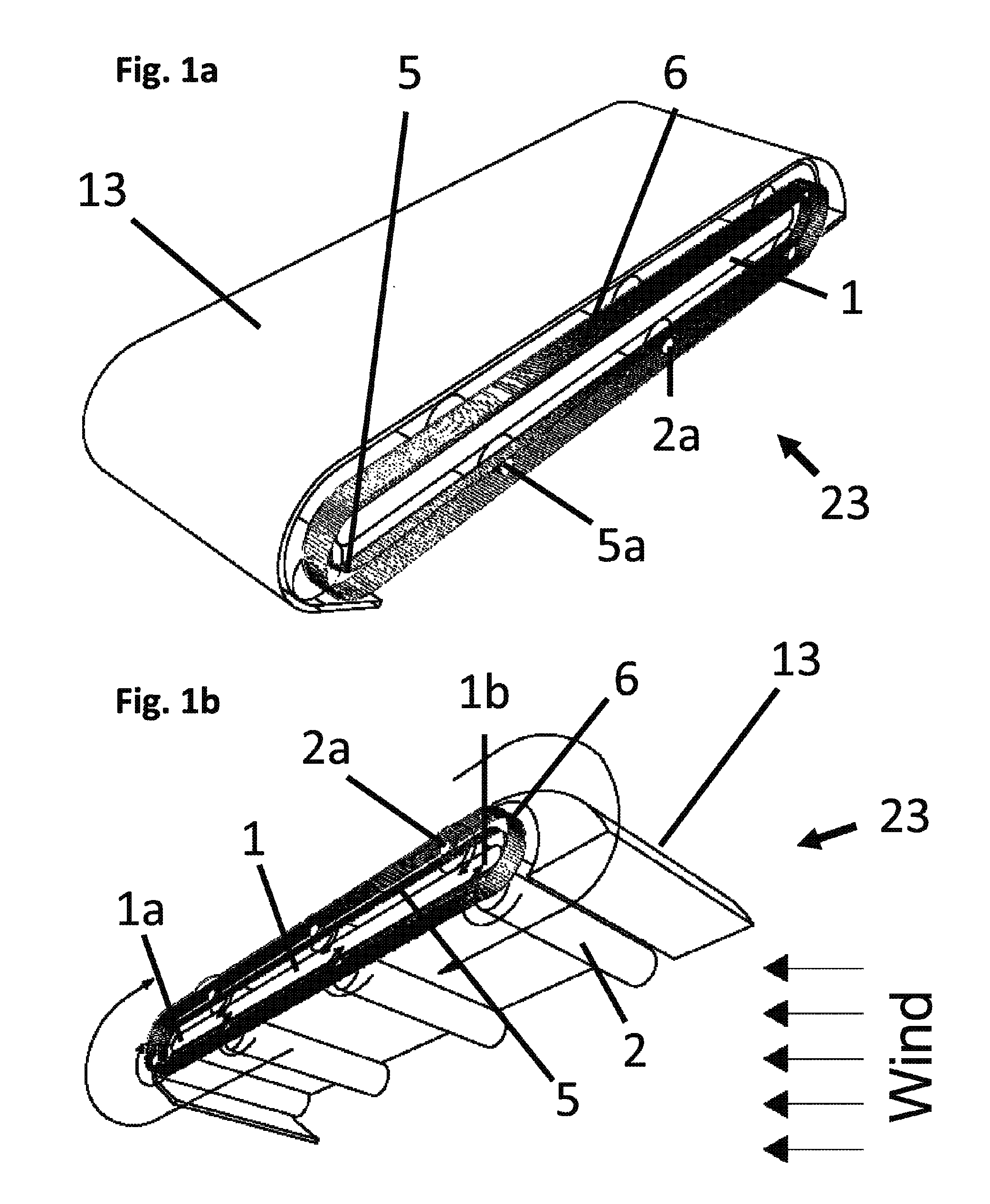
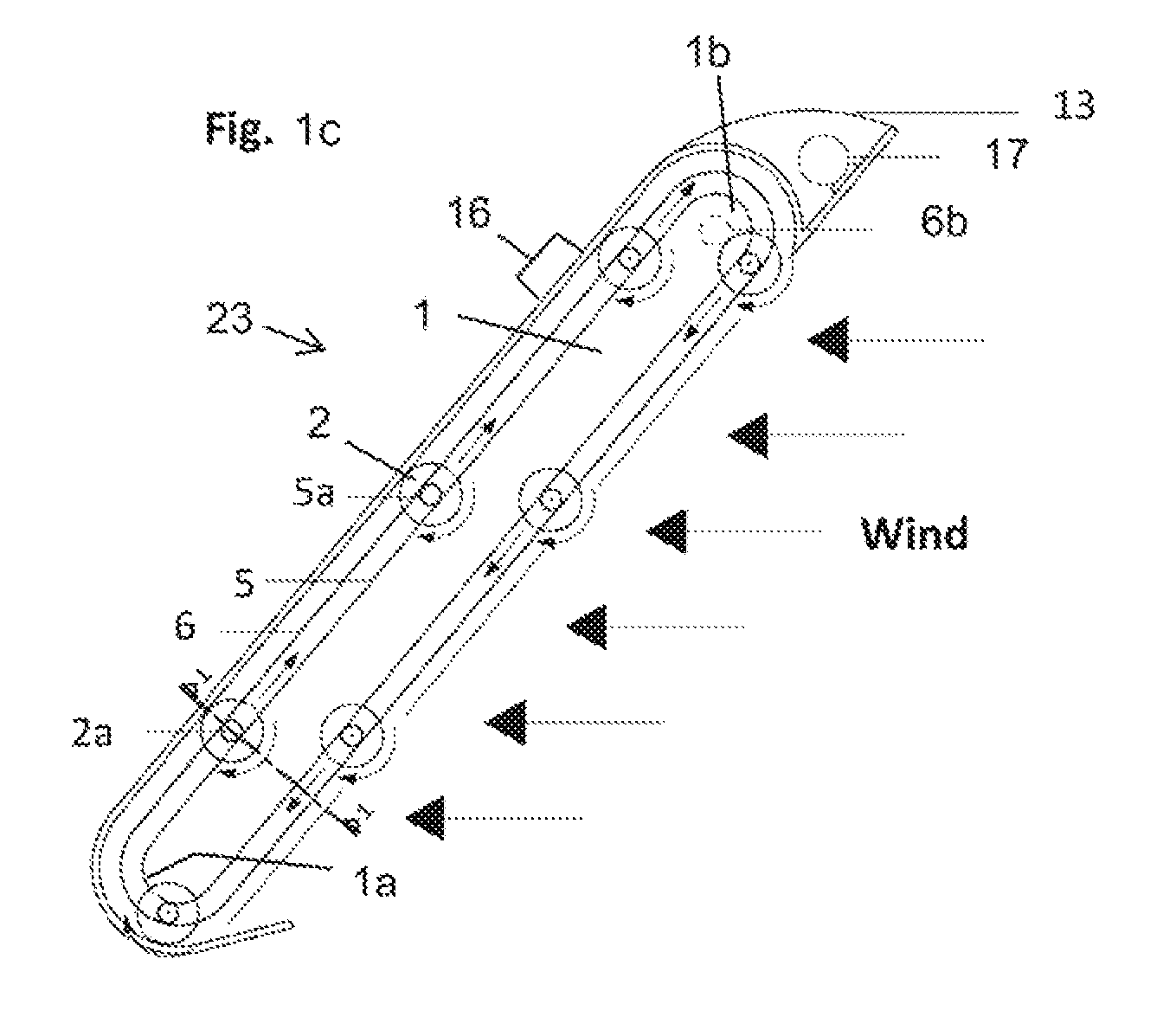
Orbiting drum wind turbine and method for the generation of electrical power from wind energy
InactiveUS20110198857A1Compact designReduced susceptibility to failurePropellersWind motor controlAngle of incidenceGear wheel
A wind turbine captures energy from a flowing fluid medium using drum-shaped drive elements that spin while traveling along a continuous orbiting course around a base. Attached roller bearings engaging stationary raceways can guide the drive elements. Means for spinning the drive elements can include toothed belts engaging drive element cog wheels. Spinning can provide Magnus effect enhancement. Wind energy is captured by the drive element motion, then transferred to the base cog wheels by a toothed belt and finally fed to an output shaft. The invention includes locating drive elements in a moving fluid medium, spinning the drive elements as they are urged by the wind along a continuous orbiting course and capturing energy by linking the motion of the drive elements to an external device. The method includes adjusting the base's azimuth and the angle of incidence of the wind in response to wind direction and speed.
Owner:BECKER ERWIN MARTIN
Remote pick-up devices
ActiveUS7980609B2Minimized overall profileReduce widthGripping headsShop accessoriesAngular degreesEngineering
An improvement to elongate tools for engaging objects from remote distances includes a connection between the rod on which the engagement elements are provided and the handle of the that allows for the orientation of the rod with respect to the handle to occupy at least two pre-selected fixed positions which are angular positions approximately 90 degrees from one another.
Owner:ONTEL PRODS
Method of fabricating an intraluminal scaffold with an enlarged portion
InactiveUS20120043703A1Sufficient flexibilityLarge profileButtonsFilament/thread formingMedical treatmentVein
Devices and methods for treating veins and venous conditions, such as chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, are provided. In one aspect, the disclosed subject matter provides an intraluminal scaffold having a generally tubular body with a lumen defined therethrough, the tubular body having a compressed condition for delivery and an expanded condition for implant within a vessel having a distended portion, at least a length of the tubular body configured to form an enlarged portion in the expanded condition to engage a wall of the distended portion of the vessel. Methods for fabricating and using the scaffold, methods for remodeling a vein, and methods of deploying a medical device in a vessel without negatively impacting the function of a valve of the vessel, are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
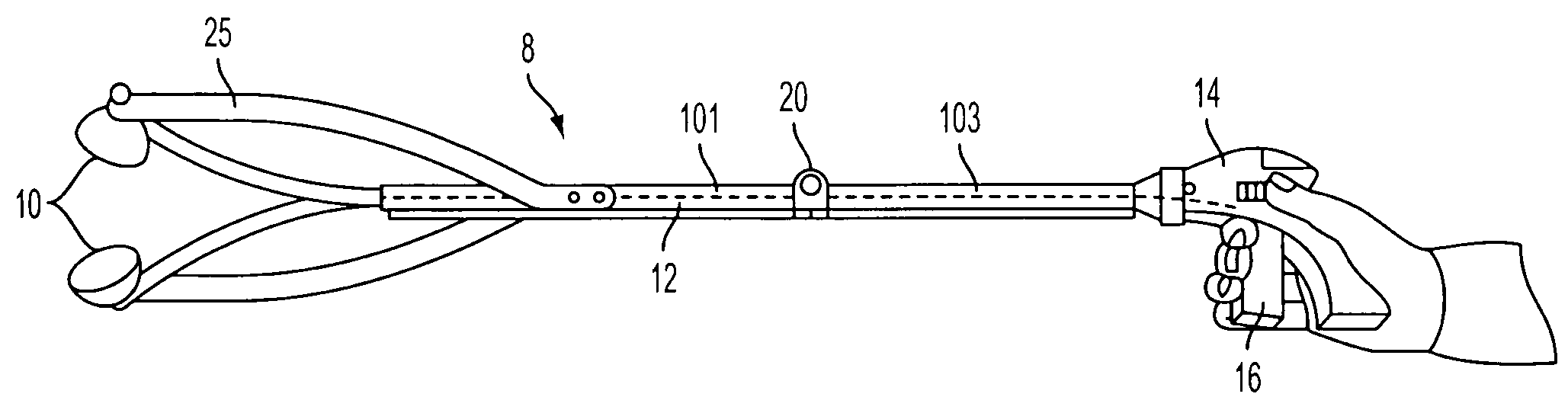
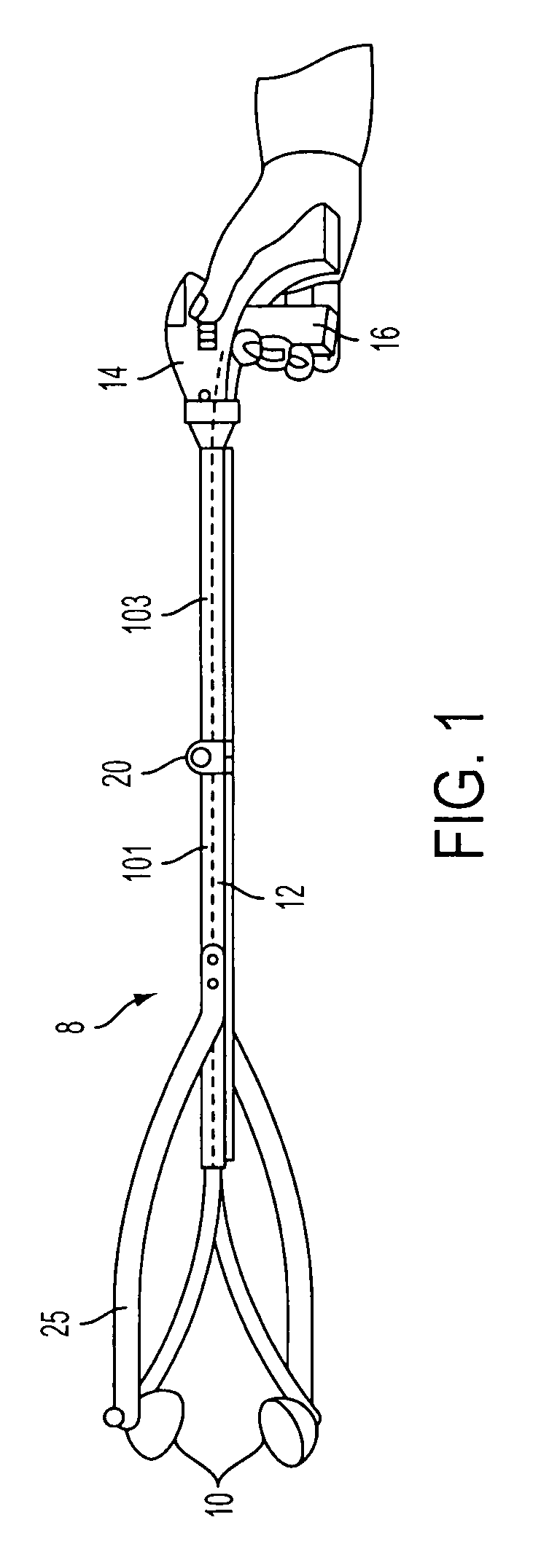
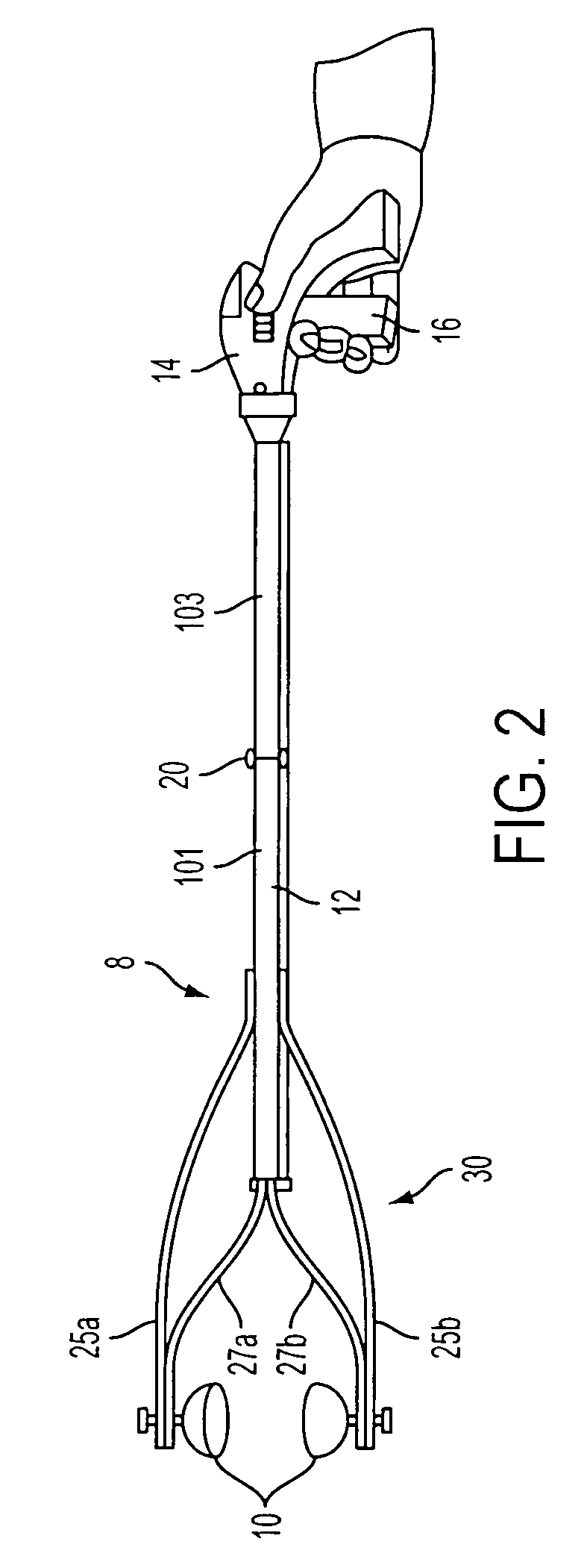
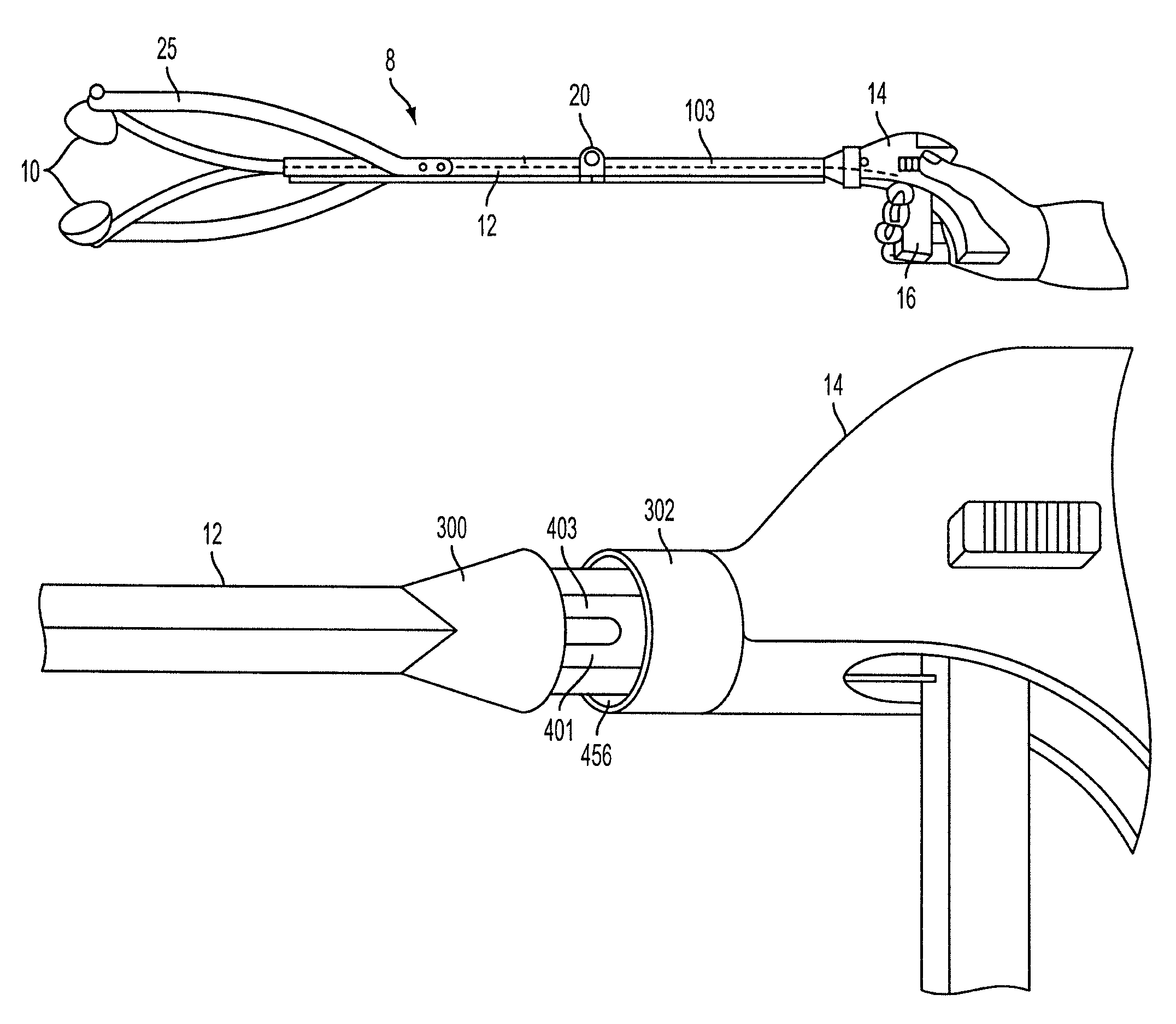
Elongated medical device with functional distal end
InactiveUS7211067B2Reduce the possibilityLarge radial extentBalloon catheterDiagnosticsMedicineMedical device
An elongate medical device that may be used for performing medical procedures on a patient is provided. This elongate medical device may include a first member having an elongated configuration, a second member pivotally coupled to the first member at a pivot area of the first member, and a manipulation member extending through either a first lumen or a second lumen of the first member. The second member of this device may have a first region on one side of the pivot area and a second region on a different side of the pivot area. The medical device may also include a third member slidable within one of the lumens of the first member.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Compressed air regulator apparatus situated in canister and method for regulating compressed air thereof
ActiveUS20090101215A1Increase in sizeWeight increaseVessel mounting detailsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringPiston
A compressed gas regulator of a piston type is disclosed in which a regulator is configured with an input valve situated entirely inside a compressed air canister, which regulator is then attached to a paintball gun, marker or other device for providing discrete charges of gas at a predetermined pressure to the attached device. The overall size and weight of the regulator are minimized, which allows increased capabilities to the user. A regulator overpressurization port vents behind a conventional safety gauge for safety purposes. Fill, gage, and canister overpressurization rupture ports are interconnected with a fill channel that extends from the canister to the ports without intersecting or interfering with the regulating components within the regulator. The input valve seat face is surrounded by a shallow generally conical surface within an input plenum. The shallow generally conical surface extends at approximately 5 to 15 degrees.
Owner:YSN IMPORTS LLC
Compressed air regulator apparatus situated in canister and method for regulating compressed air thereof
ActiveUS8171950B2Reduced in size and complexity and weightImprove functionalityCombustion enginesPipeline systemsEngineeringPiston
A compressed gas regulator of a piston type is disclosed in which a regulator is configured with an input valve situated entirely inside a compressed air canister, which regulator is then attached to a paintball gun, marker or other device for providing discrete charges of gas at a predetermined pressure to the attached device. The overall size and weight of the regulator are minimized, which allows increased capabilities to the user. A regulator overpressurization port vents behind a conventional safety gauge for safety purposes. Fill, gage, and canister overpressurization rupture ports are interconnected with a fill channel that extends from the canister to the ports without intersecting or interfering with the regulating components within the regulator. The input valve seat face is surrounded by a shallow generally conical surface within an input plenum. The shallow generally conical surface extends at approximately 5 to 15 degrees.
Owner:YSN IMPORTS LLC
Orbiting drum wind turbine and method for the generation of electrical power from wind energy
InactiveUS8253264B2Compact designReduce failurePropellersWind motor controlAngle of incidenceTurbine
A wind turbine captures energy from a flowing fluid medium using drum-shaped drive elements that spin while traveling along a continuous orbiting course around a base. Attached roller bearings engaging stationary raceways can guide the drive elements. Means for spinning the drive elements can include toothed belts engaging drive element cog wheels. Spinning can provide Magnus effect enhancement. Wind energy is captured by the drive element motion, then transferred to the base cog wheels by a toothed belt and finally fed to an output shaft. The invention includes locating drive elements in a moving fluid medium, spinning the drive elements as they are urged by the wind along a continuous orbiting course and capturing energy by linking the motion of the drive elements to an external device. The method includes adjusting the base's azimuth and the angle of incidence of the wind in response to wind direction and speed.
Owner:BECKER ERWIN MARTIN
Nitinol alloy design and composition for vascular stents
InactiveUS20090248130A1Large profileWider the hysteresis curveStentsBlood vesselsHysteresisStent implantation
A stent and a delivery system for implanting the stent in a body lumen is disclosed. The stent is made from a superelastic alloy such as nickel-titanium or nitinol, and includes a ternary element in order to minimize the stress hysteresis of the superelastic material. The stress hysteresis is defined by the difference between the loading plateau stress and the unloading plateau stress of the superelastic material. The resulting delivery system has a small profile and includes a sheath covering the stent that has a thin wall.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com