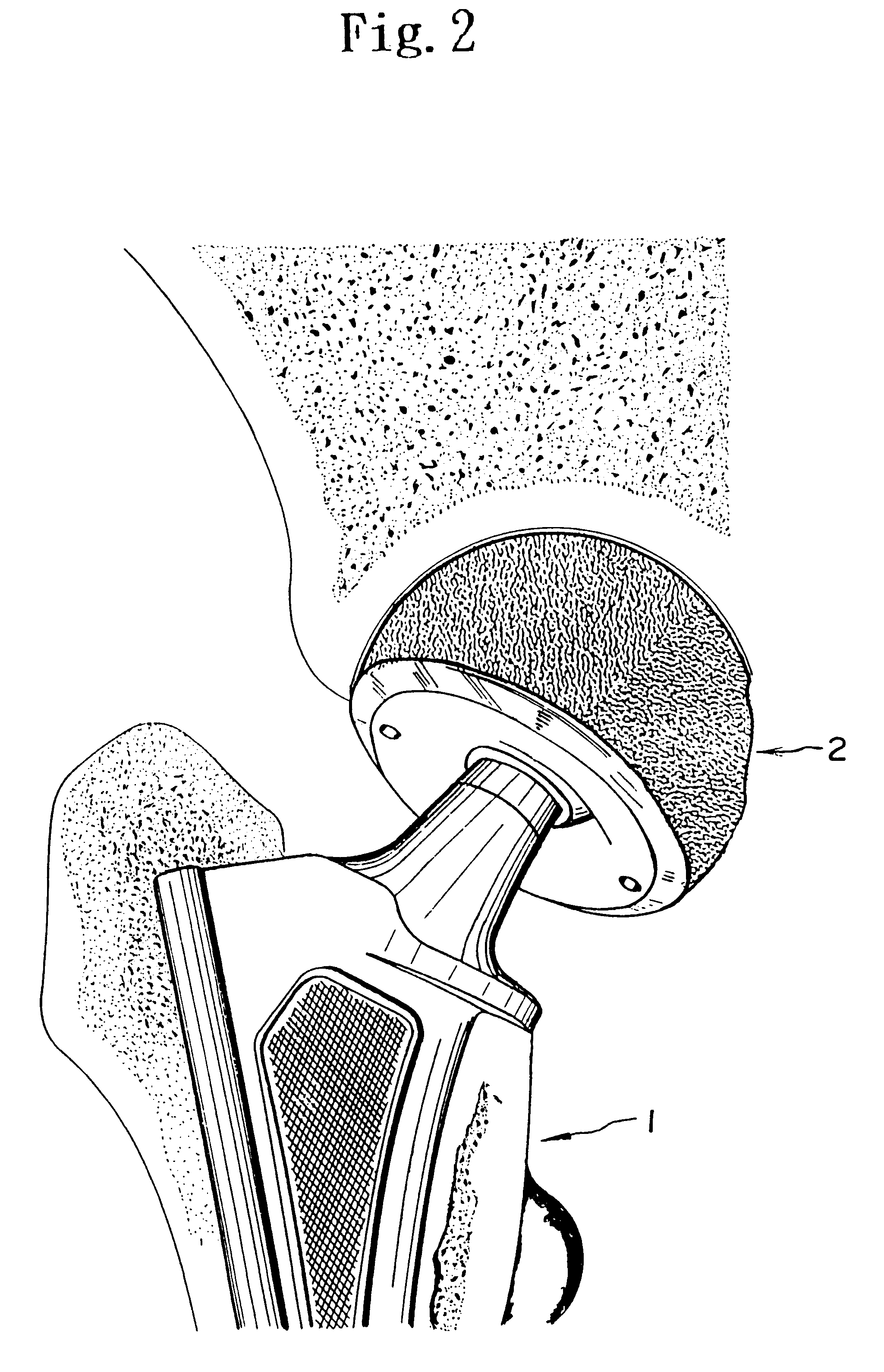Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14833 results about "Titanium alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Titanium alloys are metals that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, the high cost of both raw materials and processing limit their use to military applications, aircraft, spacecraft, bicycles, medical devices, jewelry, highly stressed components such as connecting rods on expensive sports cars and some premium sports equipment and consumer electronics.
Minimally-Invasive Approach to Bone-Obstructed Soft Tissue
InactiveUS20080177268A1Improve shielding effectLow magnetic susceptibilitySurgeryMagnetic susceptibilityImaging quality
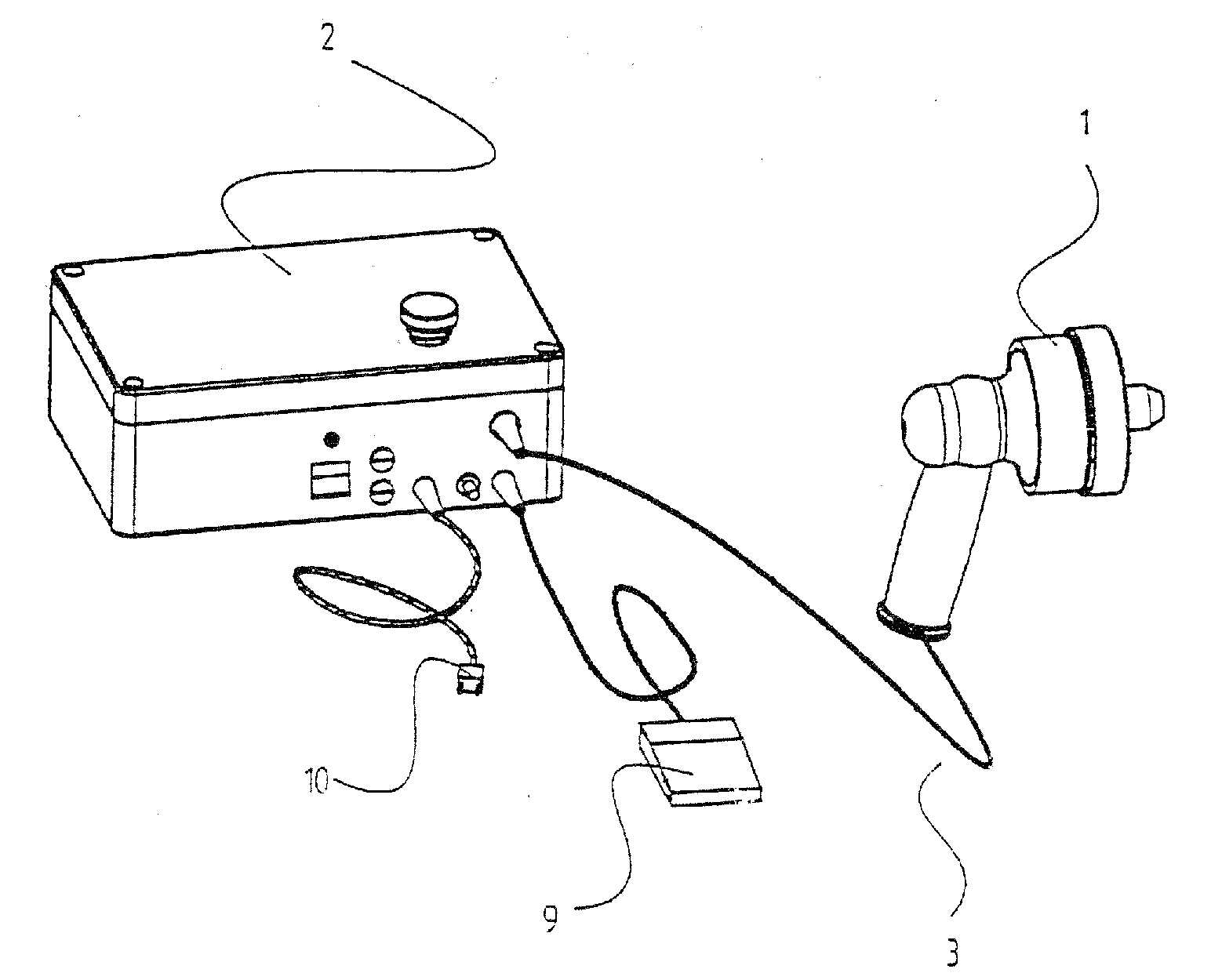
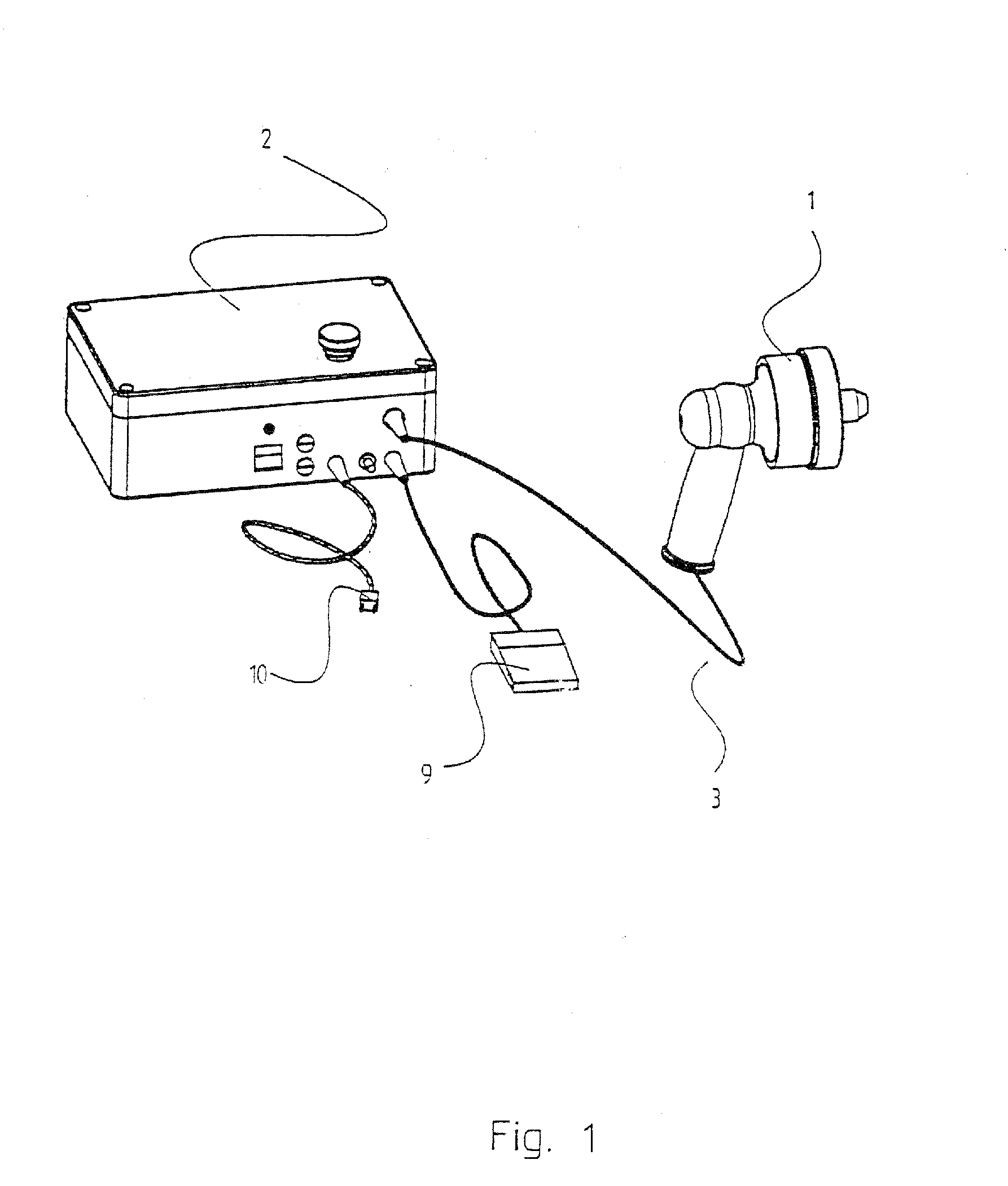
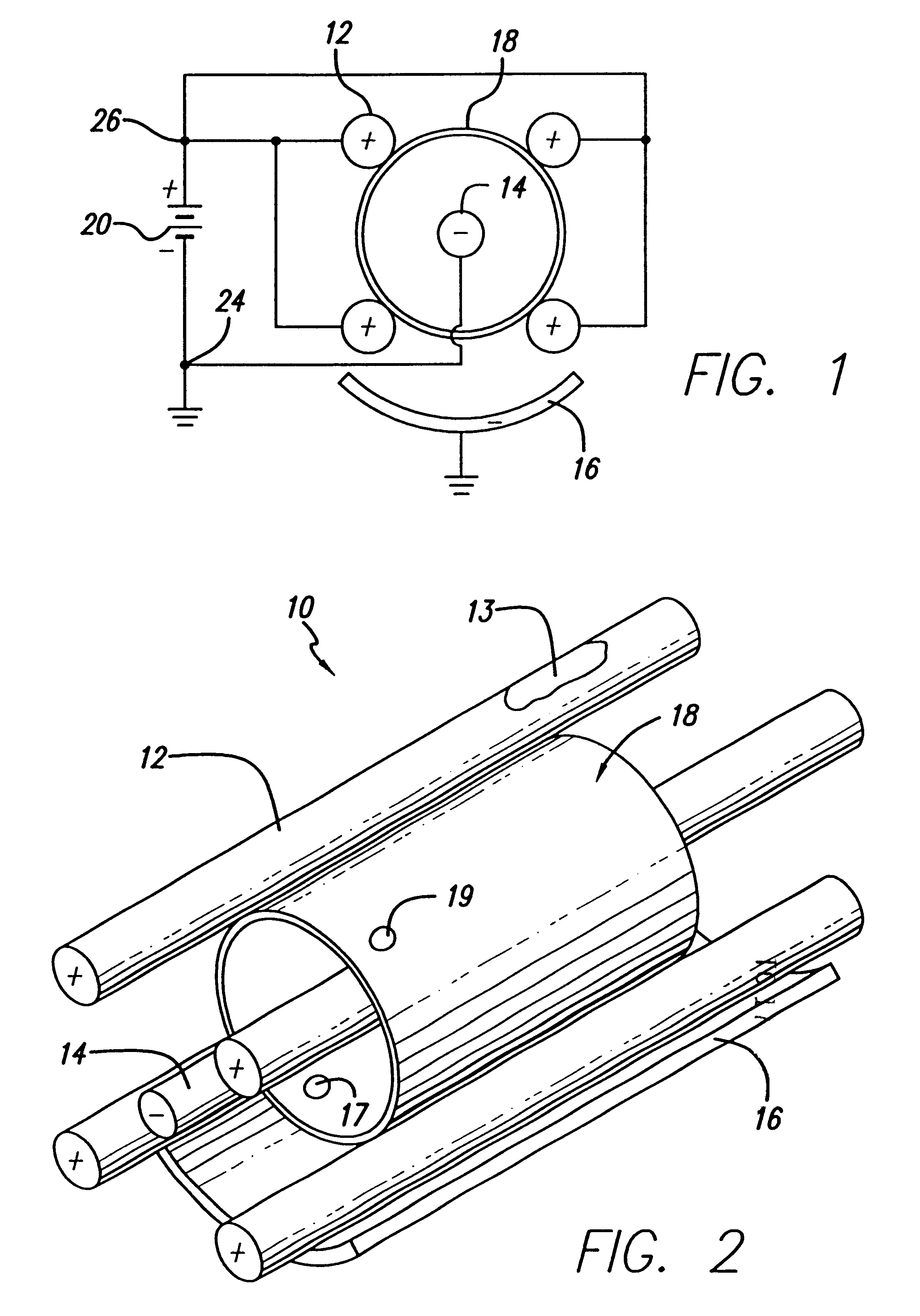
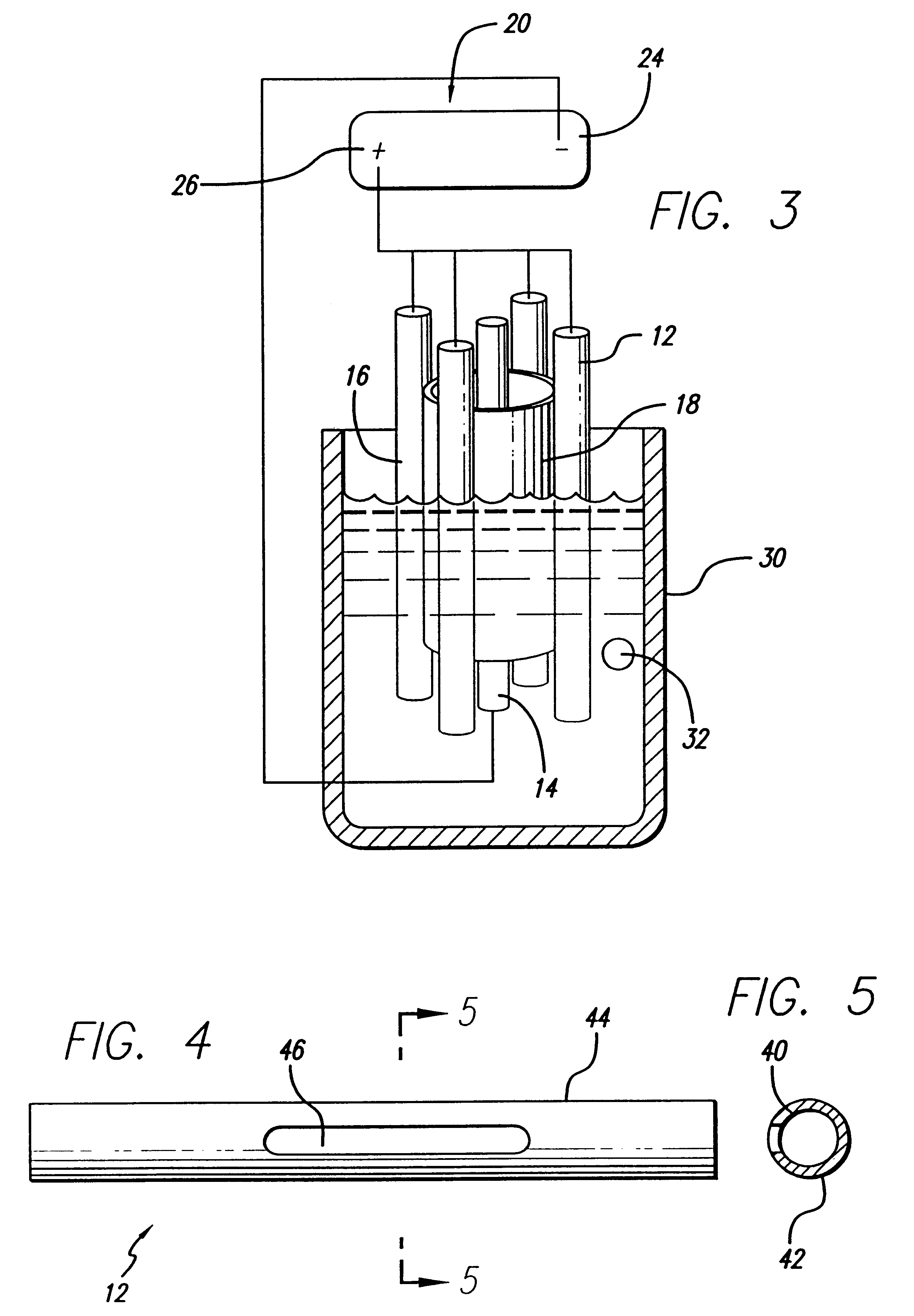
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for placing a minimally-invasive access with respect to a patient's bone or other non-soft tissue. The subject invention can use a drilling machine incorporating an ultrasound motor. The subject drilling machine can be applied to sample, for example, bone biopsies under MRI control. In a specific embodiment, the subject ultrasound motor can be completely manufactured of non-magnetic materials, such as plastics, titanium, and titanium alloy, or ceramics and piezoceramics. The subject drilling apparatus can be placed into an MRI near field without influencing the image quality, and without the drilling apparatus itself being disturbed by the MRI magnet, gradient, or high-frequency field. The subject invention can incorporate good shielding with the subject drilling apparatus use of these materials, and can achieve minimal, if any, image distortions or so-called artifacts. Thus, the subject invention can involve the problem by use of non-magnetic materials of low magnetic susceptibility for the design of an actuation unit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Electro-polishing fixture and electrolyte solution for polishing stents and method
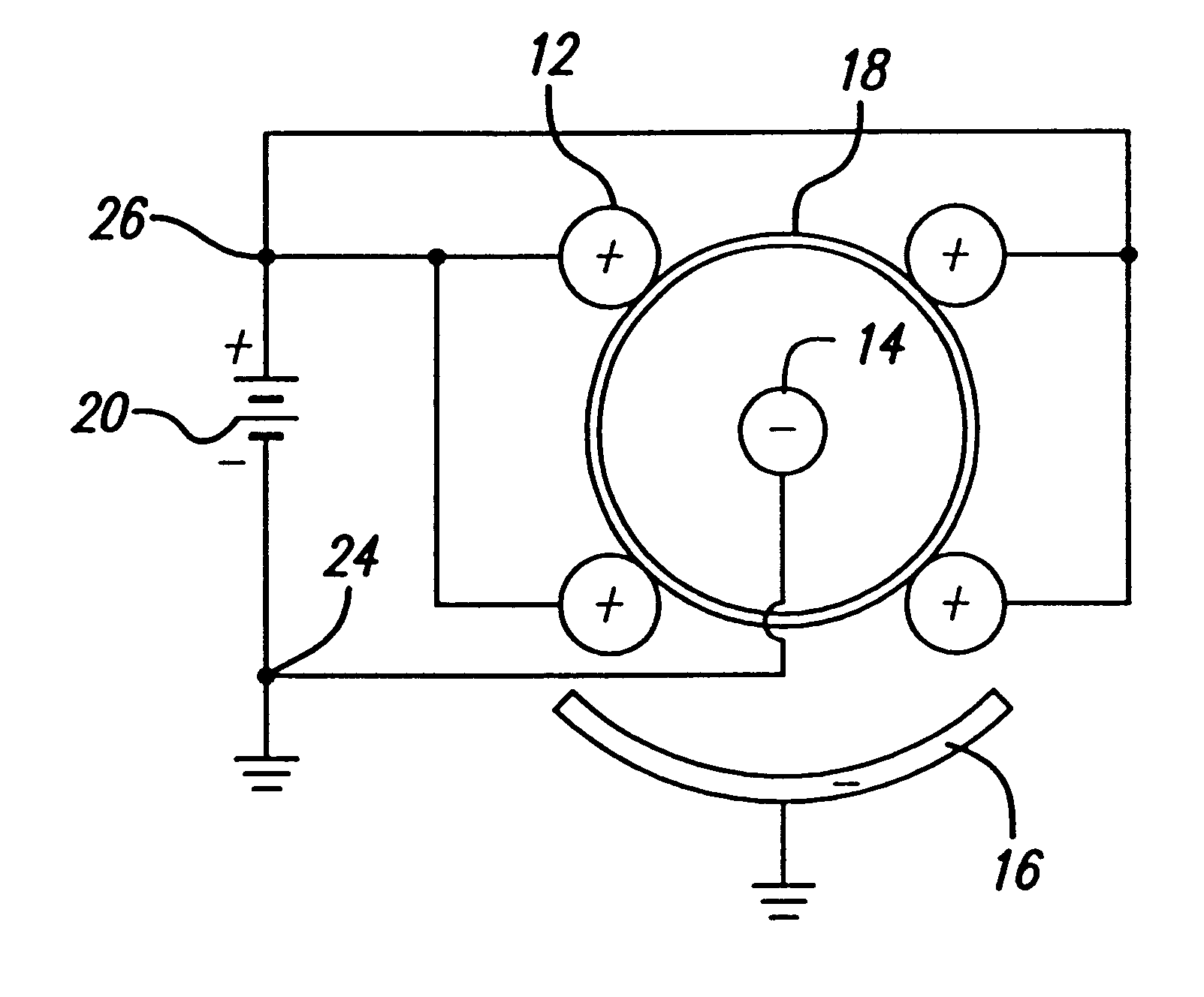
An electro-polishing fixture for polishing stents which incorporates multiple anodes in contact with the stent and a center cathode disposed coaxially within the interior of the stent and a curved exterior cathode disposed about the perimeter of the stent. The invention further includes an electrolyte solution adapted for polishing stents composed of nickel-titanium alloy and a method of using the electrolyte in combination with the electro-polishing fixture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
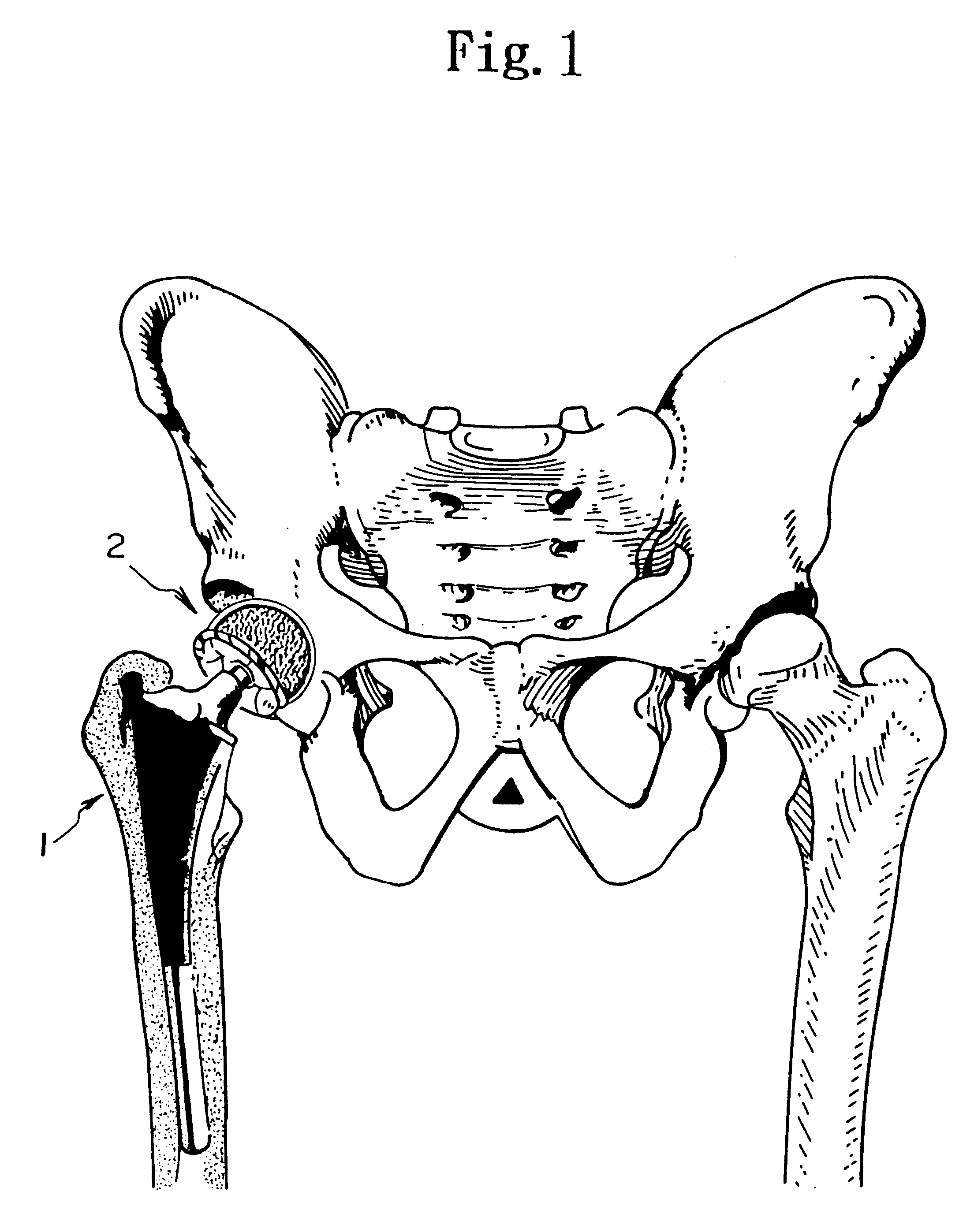
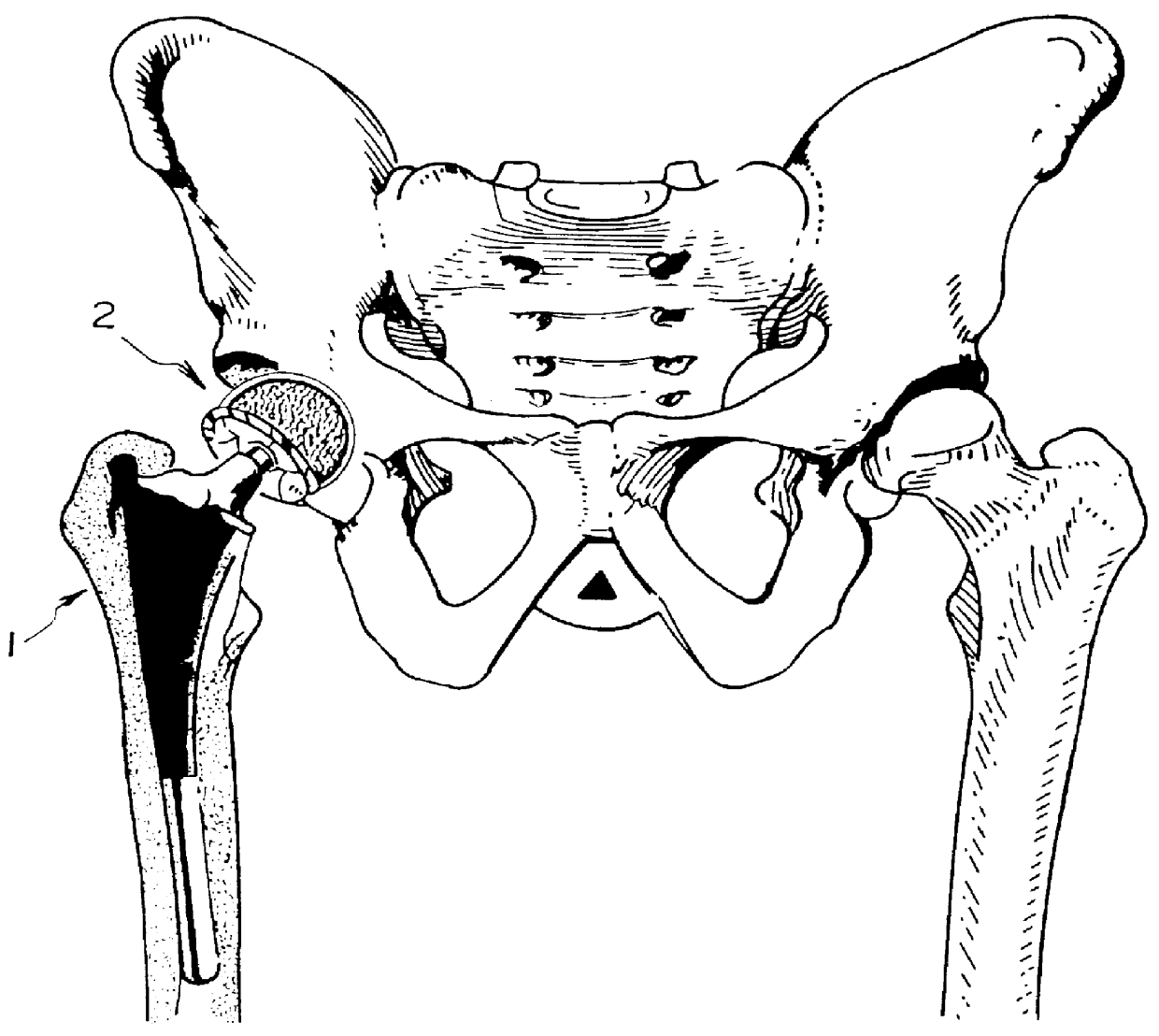
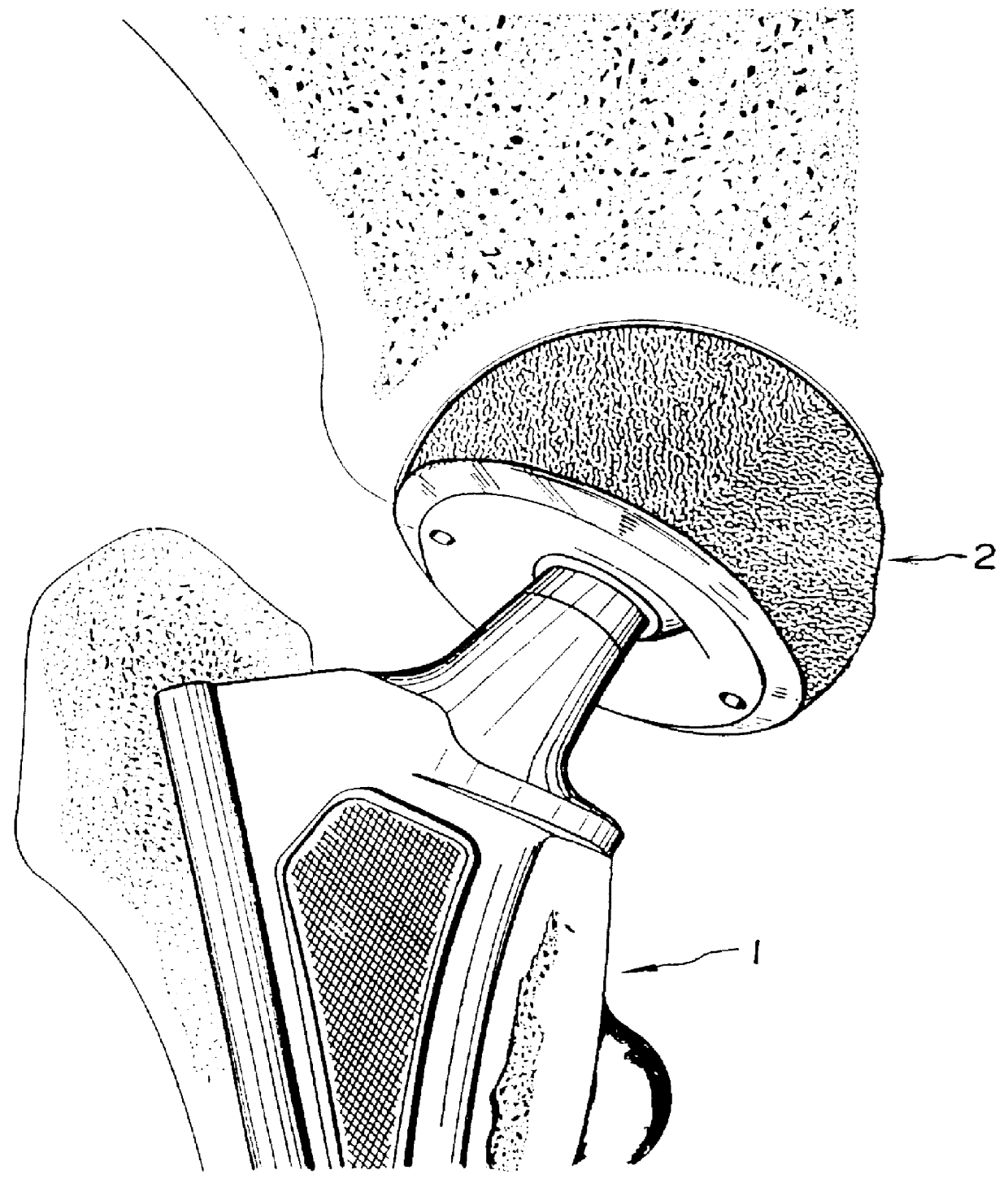
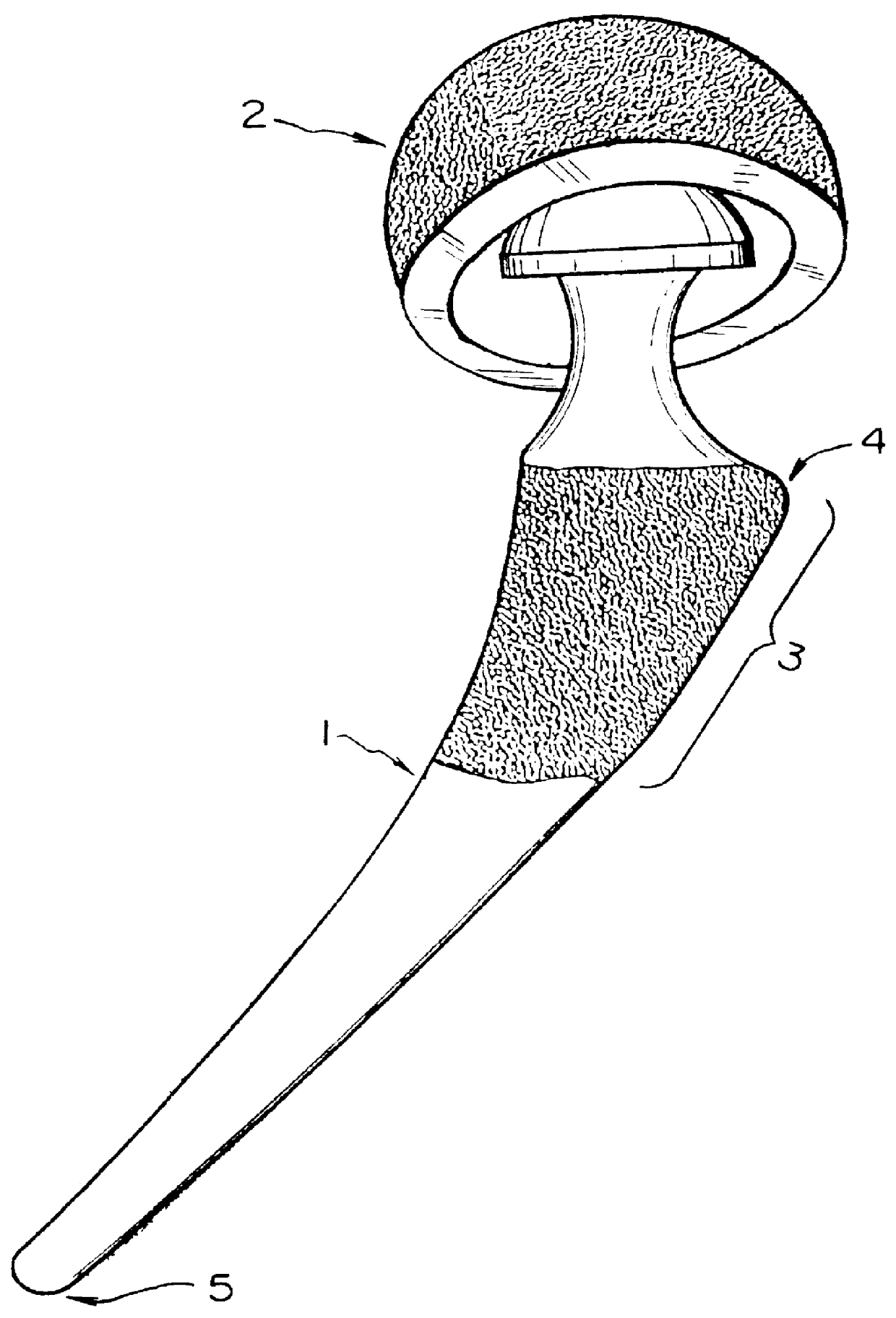
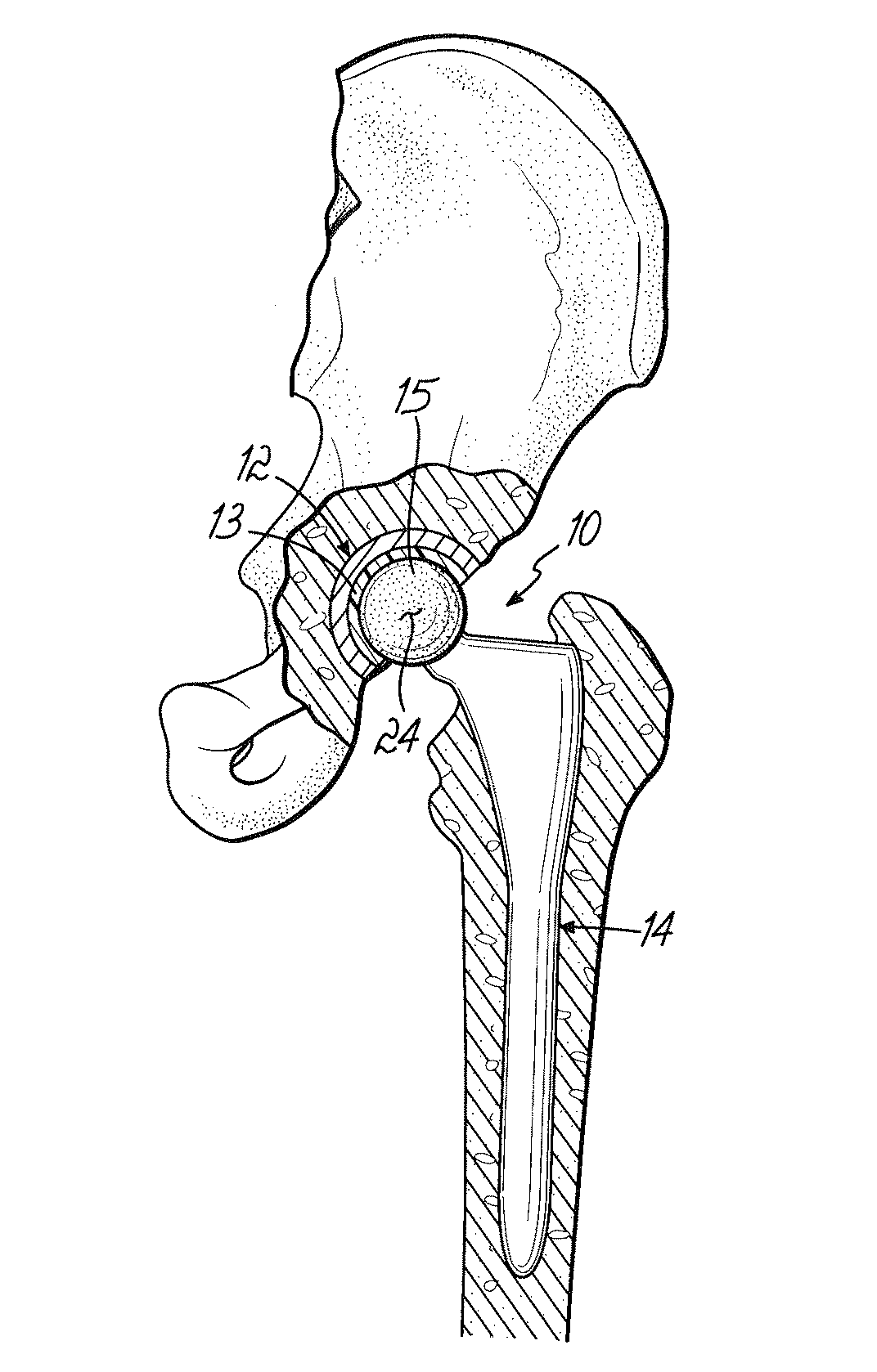
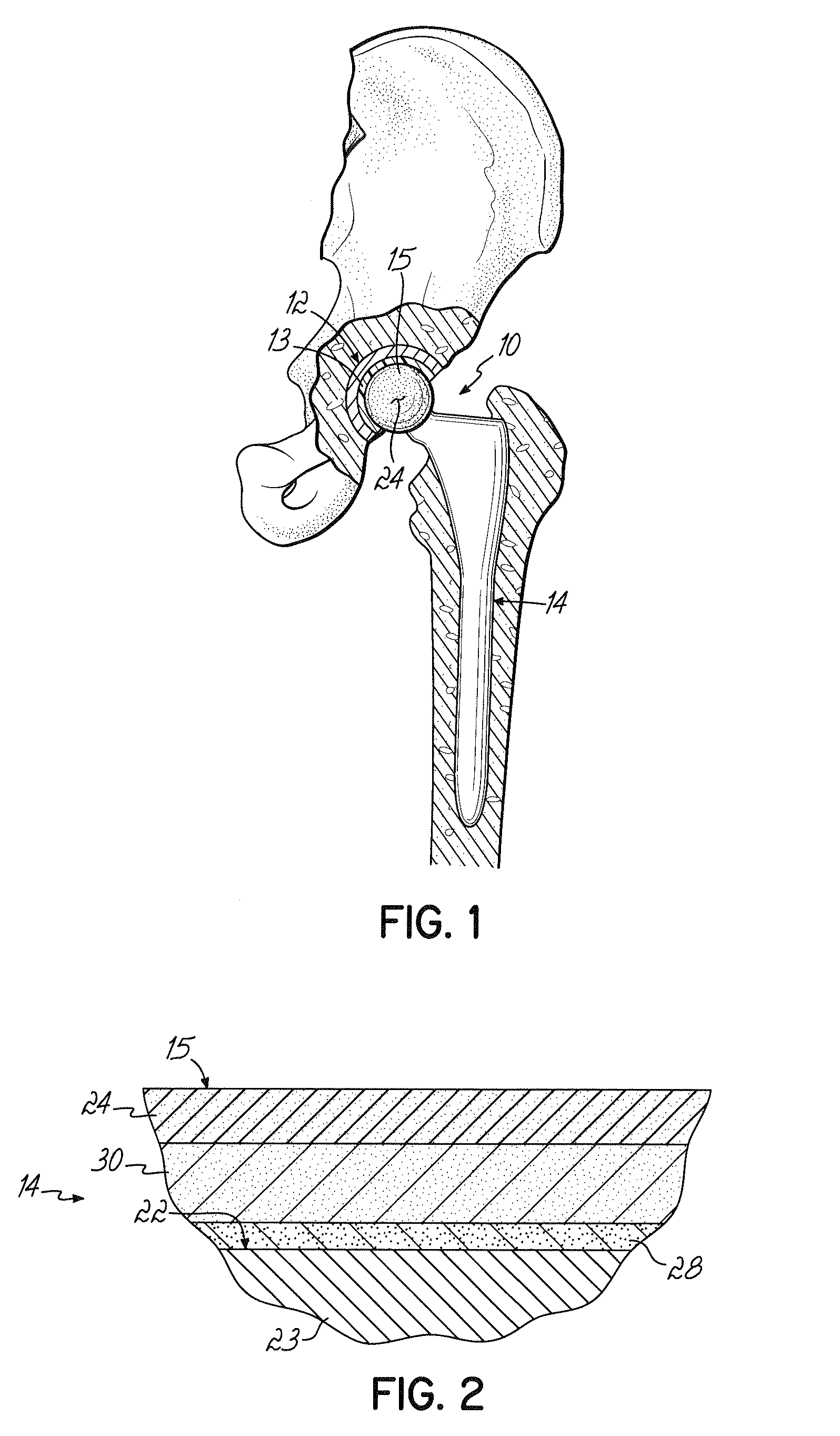
Orthopedic implant system
InactiveUS6312473B1Easy to fixAvoid excessive temperatureSurgical adhesivesBone implantFemoral stemPolymethyl methacrylate
It is an object of the present invention to provide an improved orthopedic implant system with satisfied biological, mechanical and morphological compatibilities.Solid metal femoral stem and solid metal acetabular head are covered with diffusion-bonded foamed-shaped sheet made of commercially pure titanium or titanium alloy(s). The open-cells in said foamed metal sheet are impregnated with biocompatible polymethyl methacrylate resin cement, which is reinforced with selected oxides including alumina, magnesia, zirconia, or a combination of these oxides along with an application of a small amount of a metal primer agent.
Owner:OSHIDA YOSHIKI
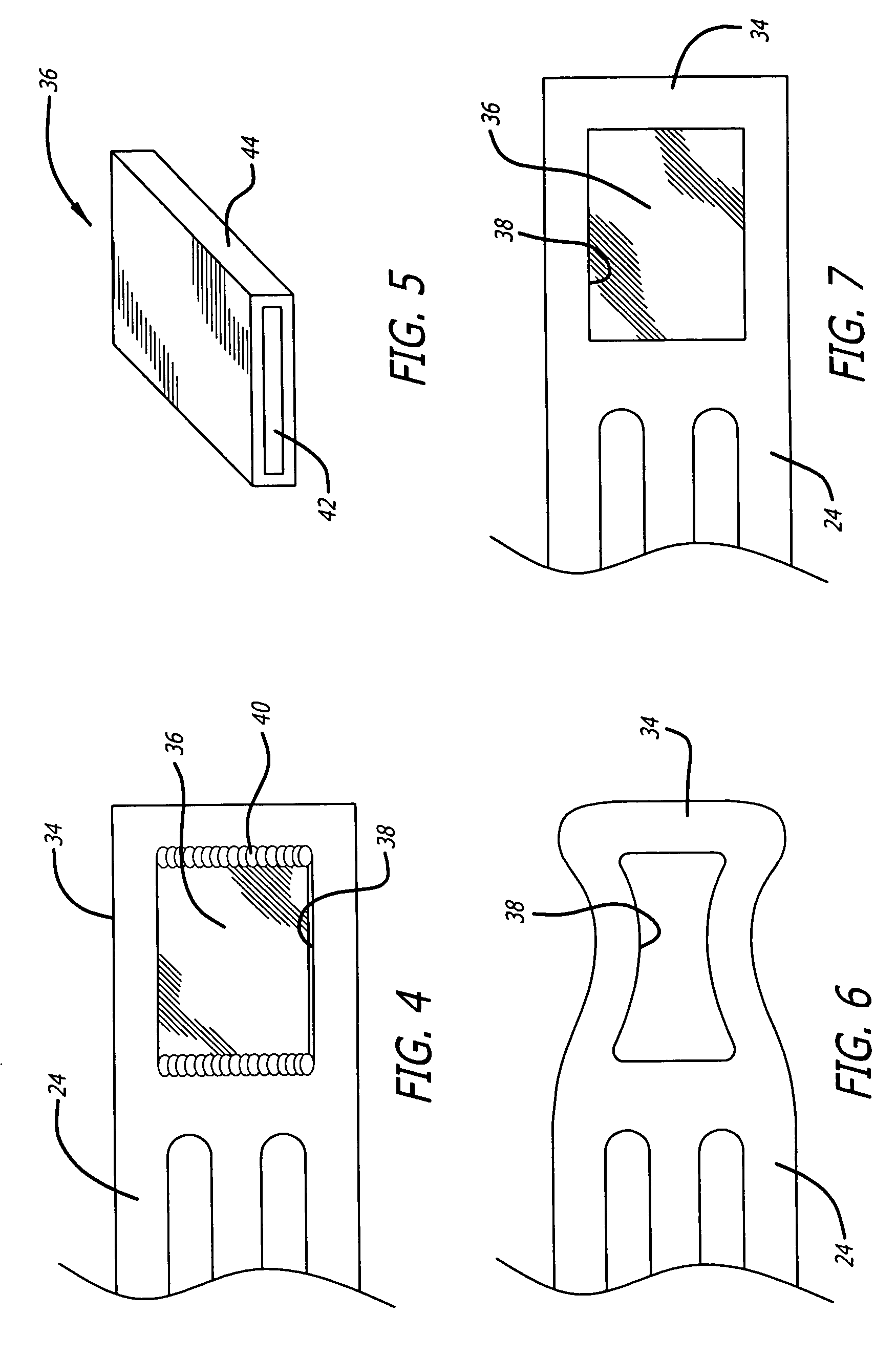
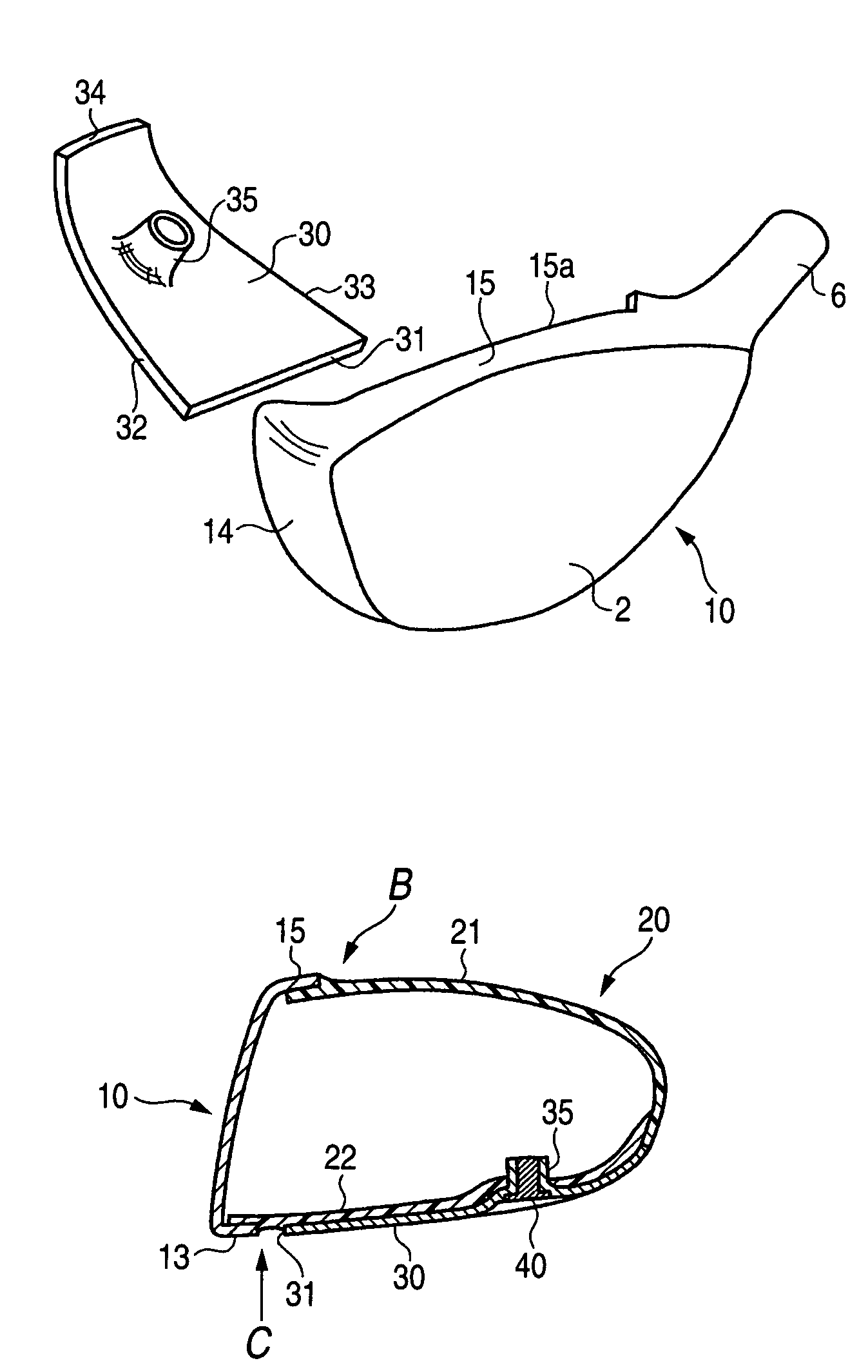
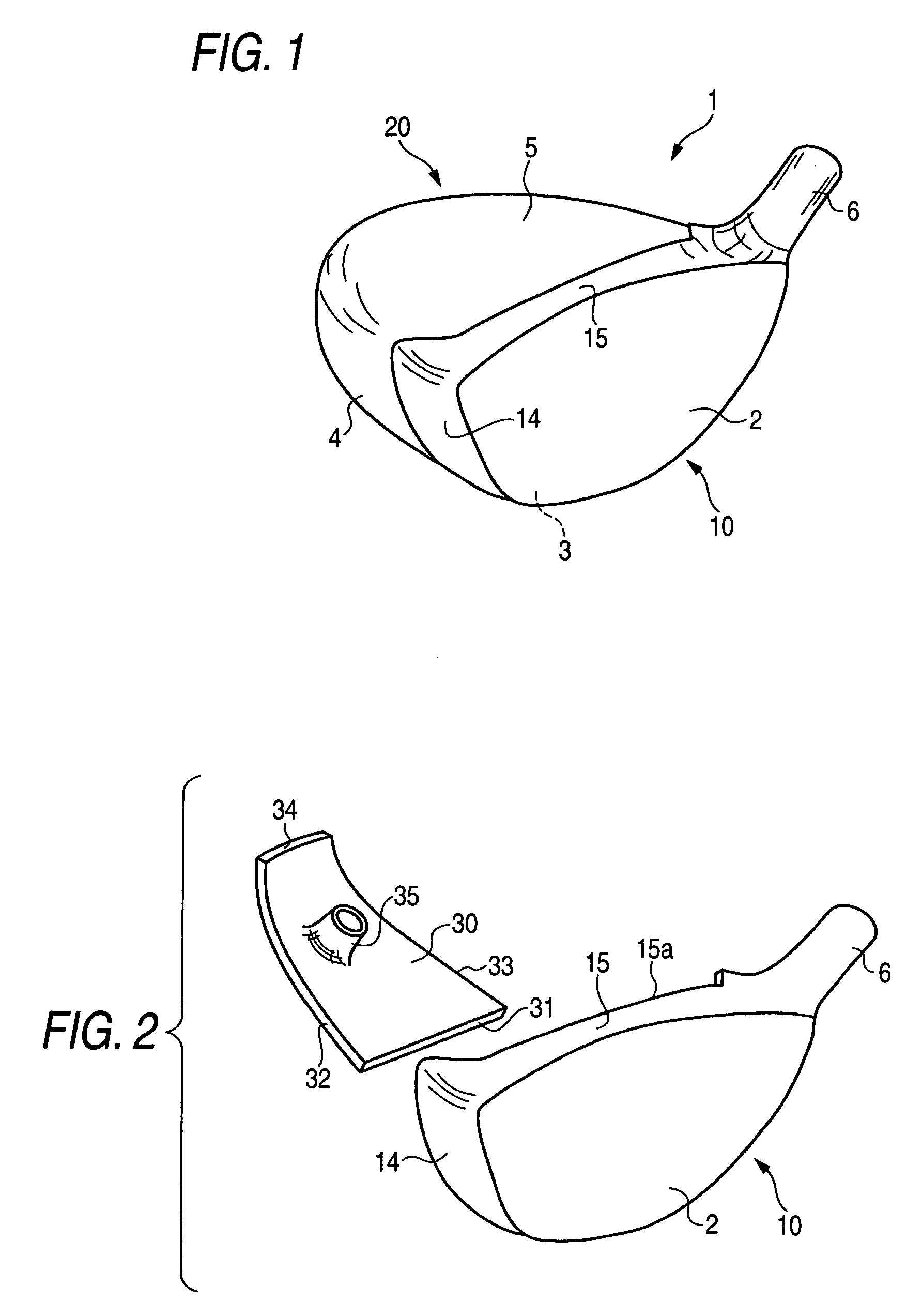
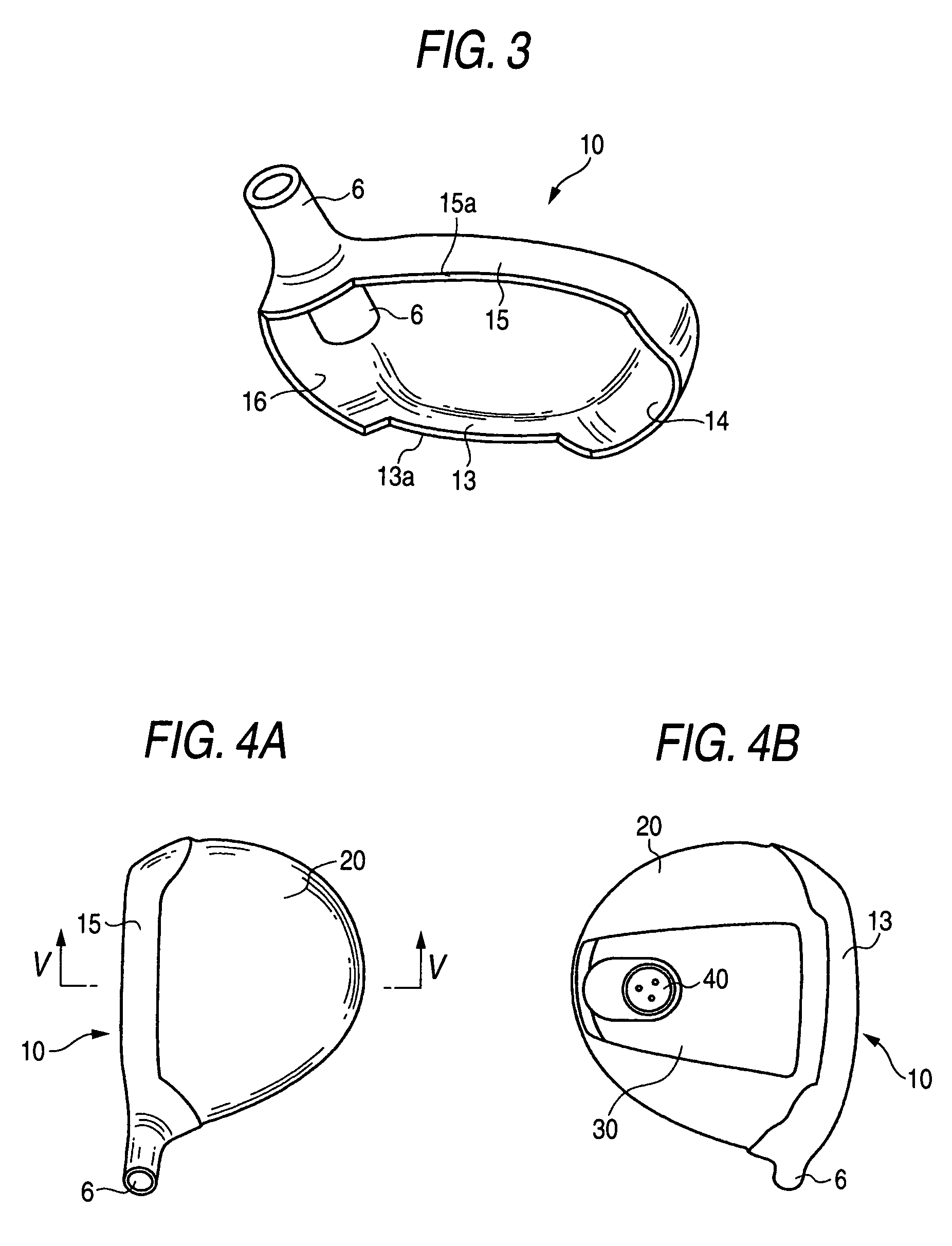
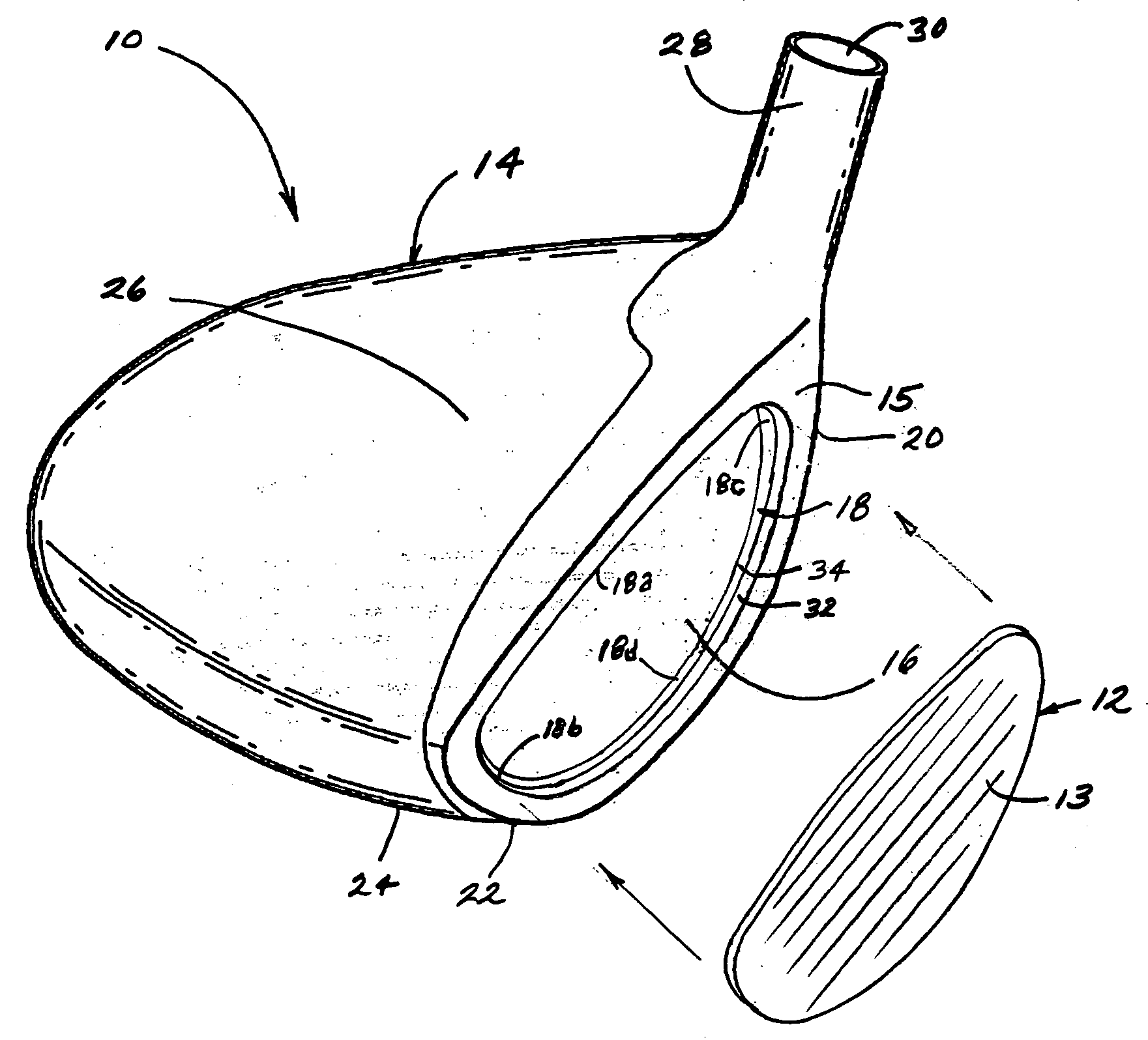
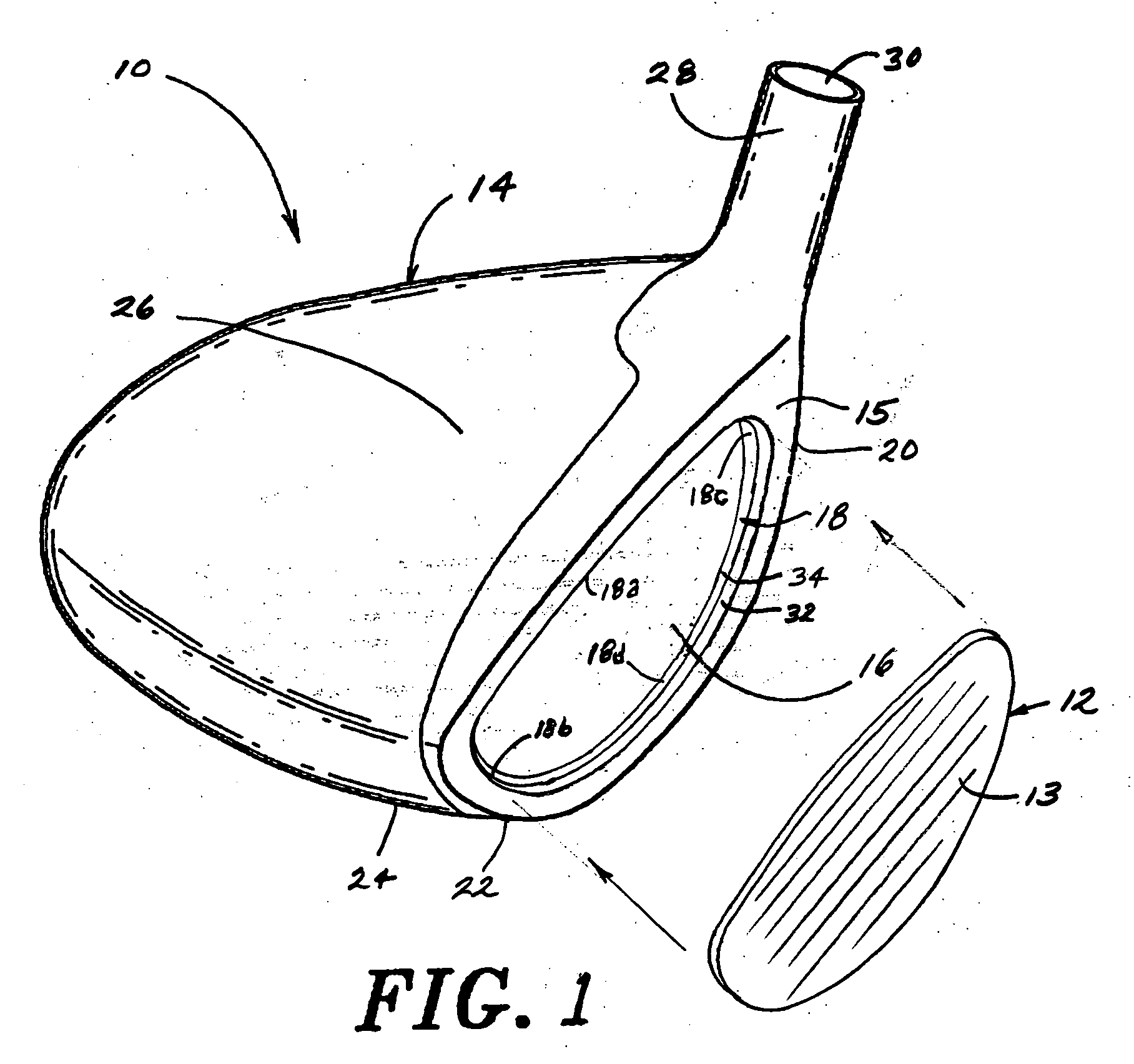
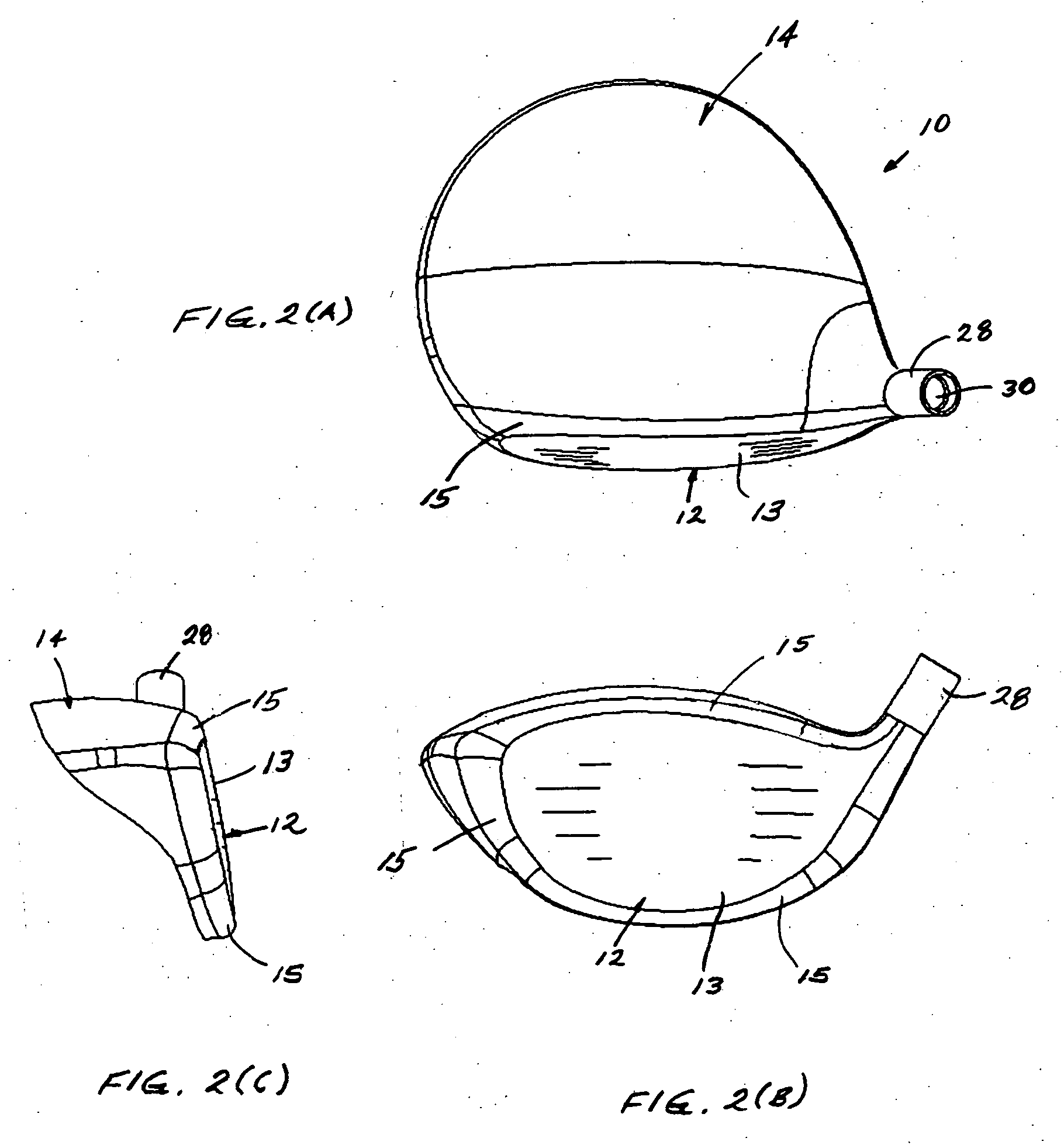
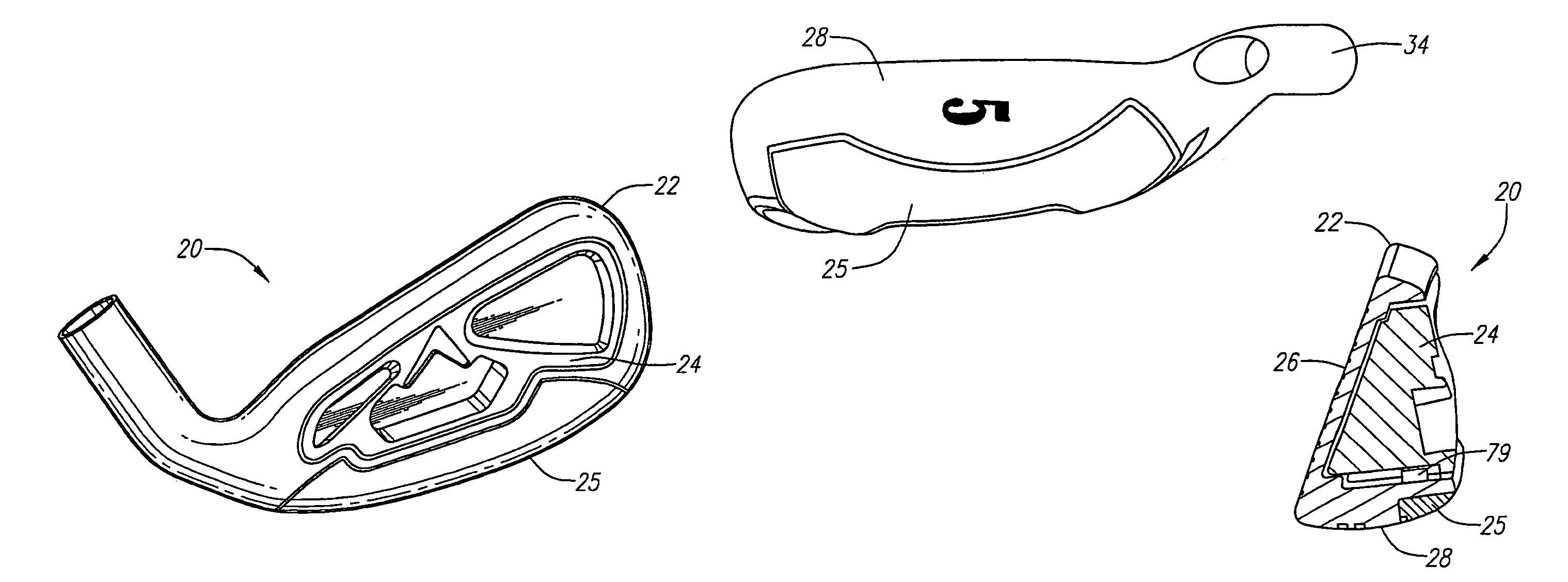
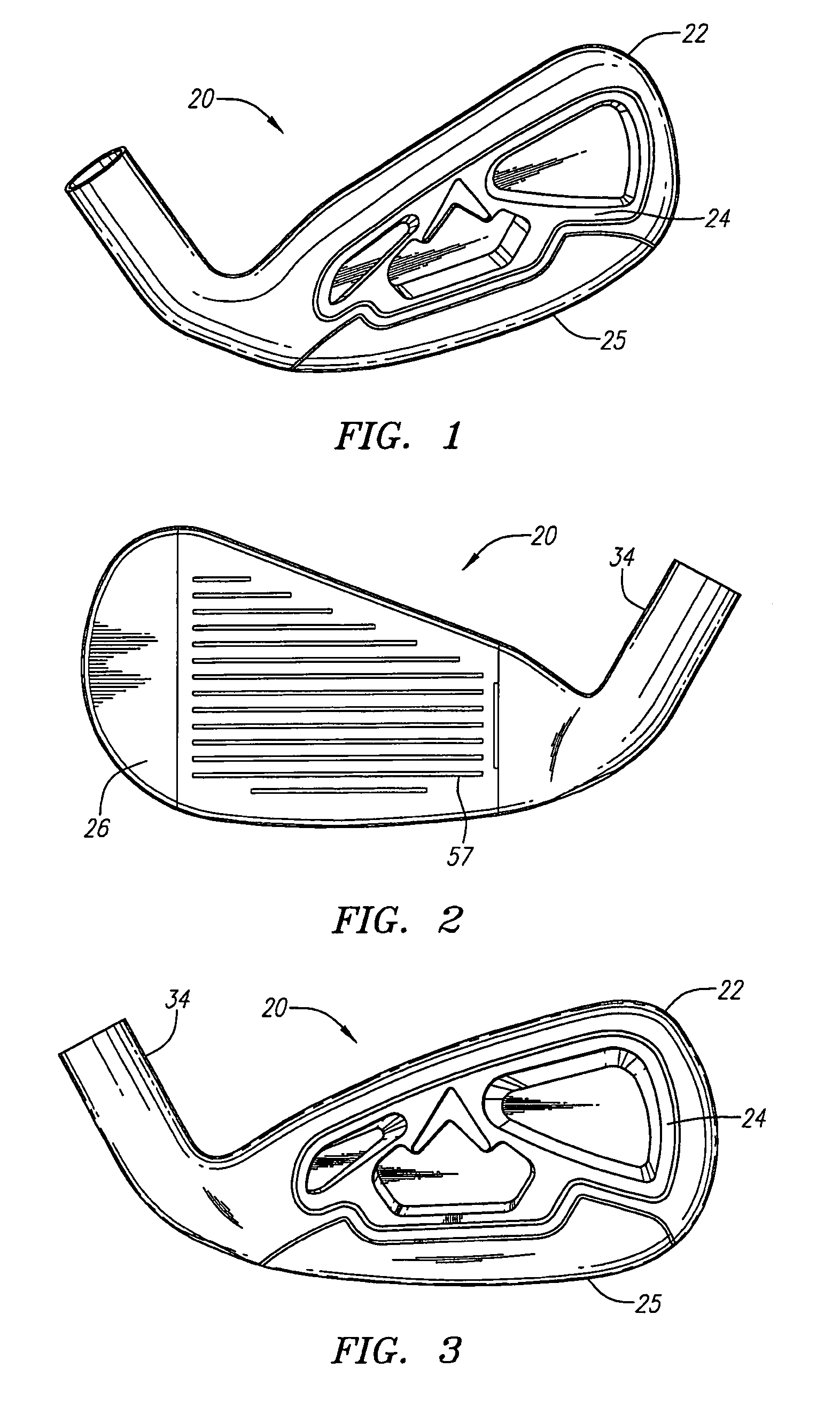
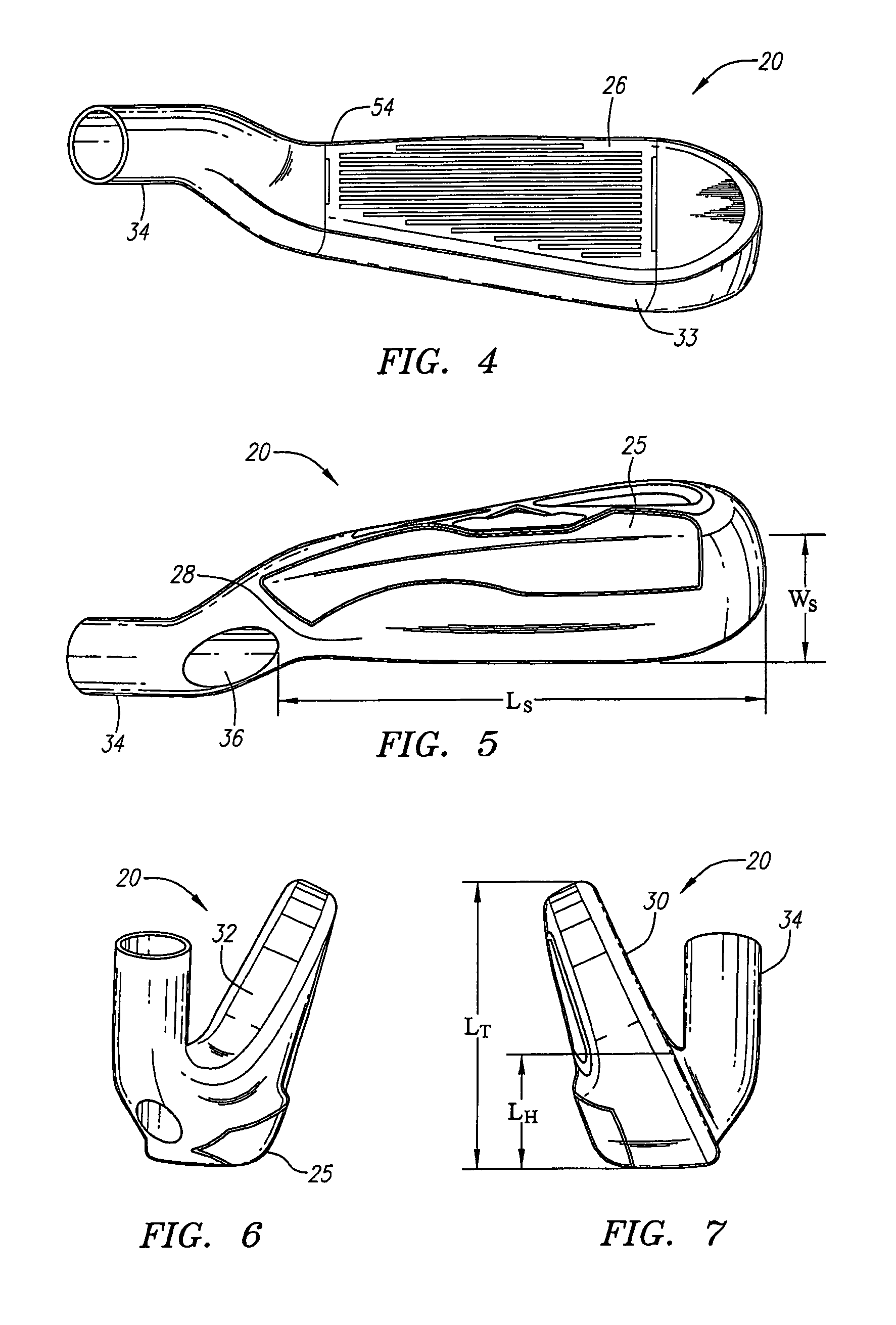
Golf club head
A golf club head includes a front body, a middle body, a back body integrally. The middle body is disposed between the front body and the back body. The middle body includes a middle crown constituting a middle portion of a crown portion in back and forth directions, a middle side constituting middle portions of both side surfaces on a toe side and a heel side in the back and forth directions, a middle sole constituting a middle portion of a sole portion in the back and forth directions. The middle body may include aluminum alloy. The front body and the back body may include titanium alloy.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
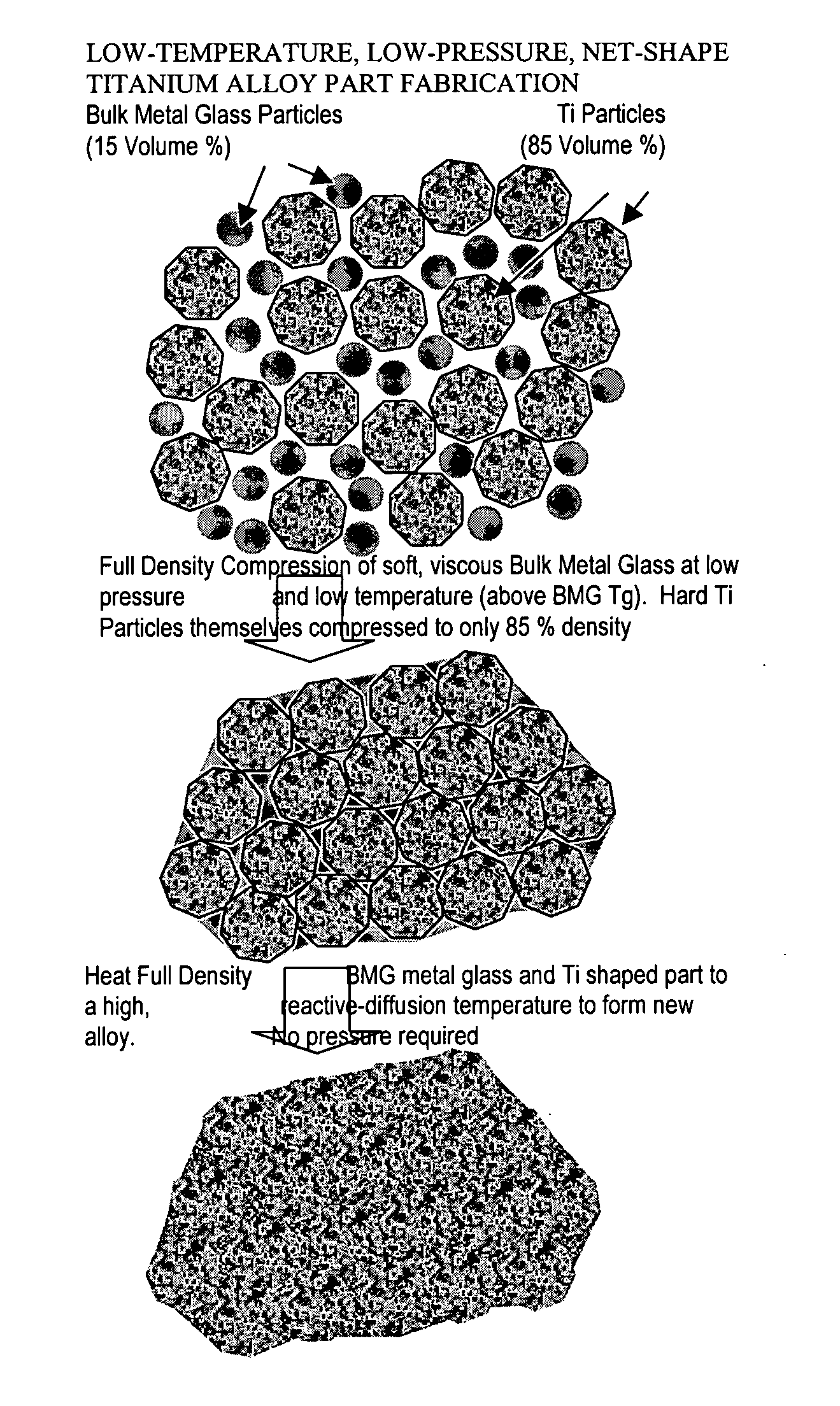
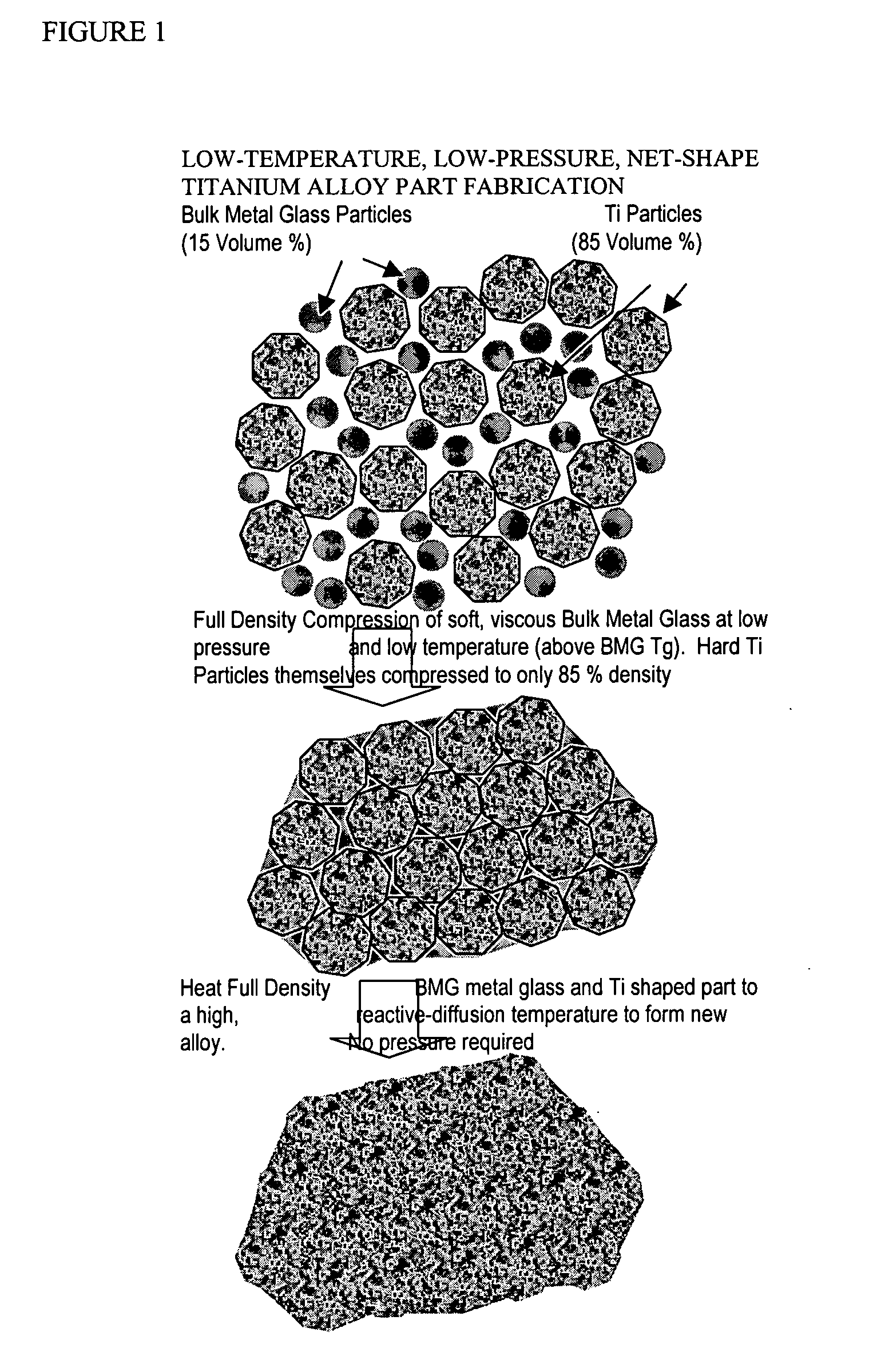
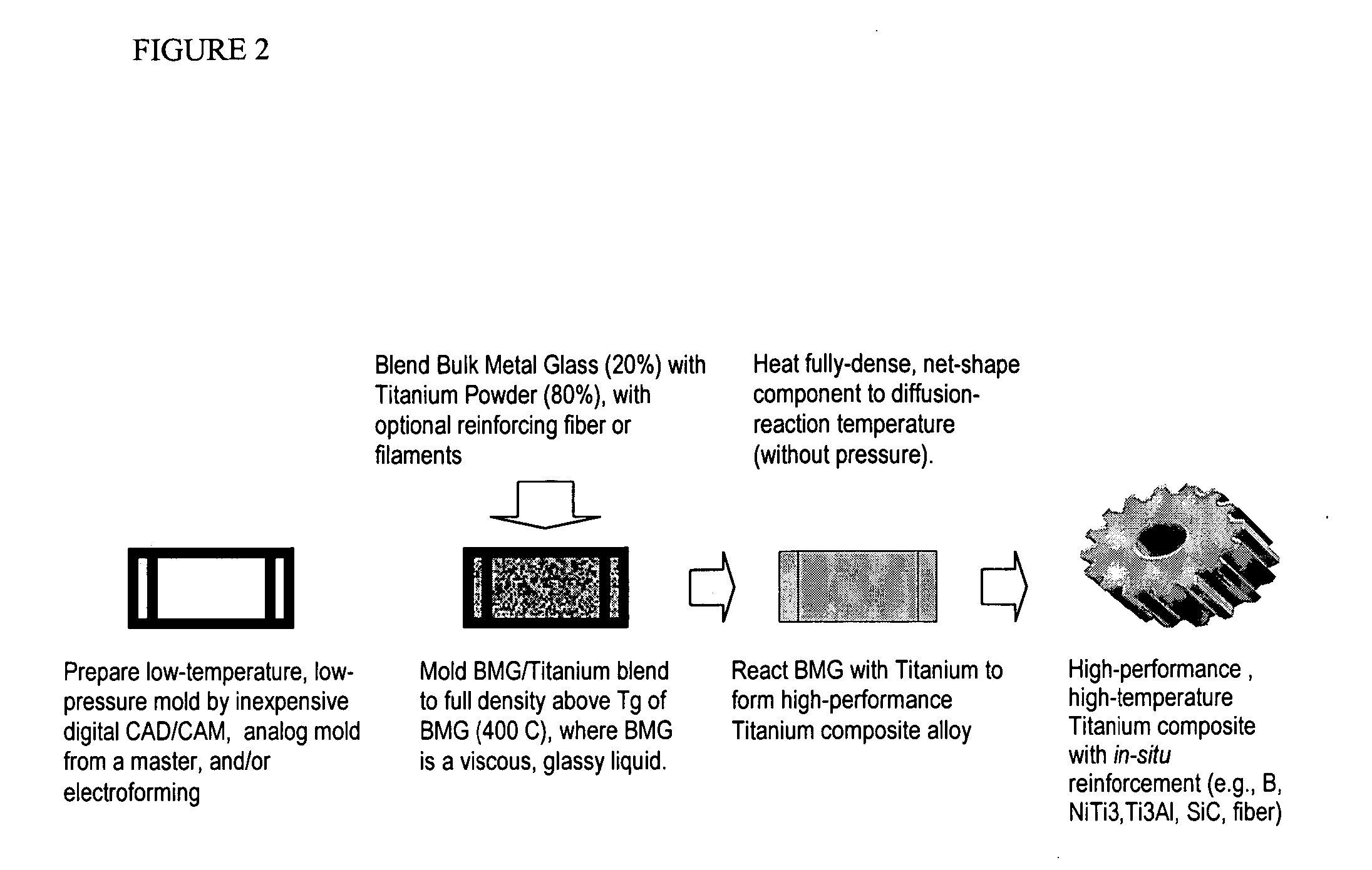
Titanium group powder metallurgy
InactiveUS20050084407A1Excellent cold formabilityImprove hardenabilityVitrificationVolumetric Mass Density
Methods and compositions relating to powder metallurgy in which an amorphous-titanium-based metal glass alloy is compressed above its glass transition temperature Tg with a titanium alloy powder which is a solid at the compression temperature, to produce a compact with a relative density of at least 98%.
Owner:MYRICK JAMES J
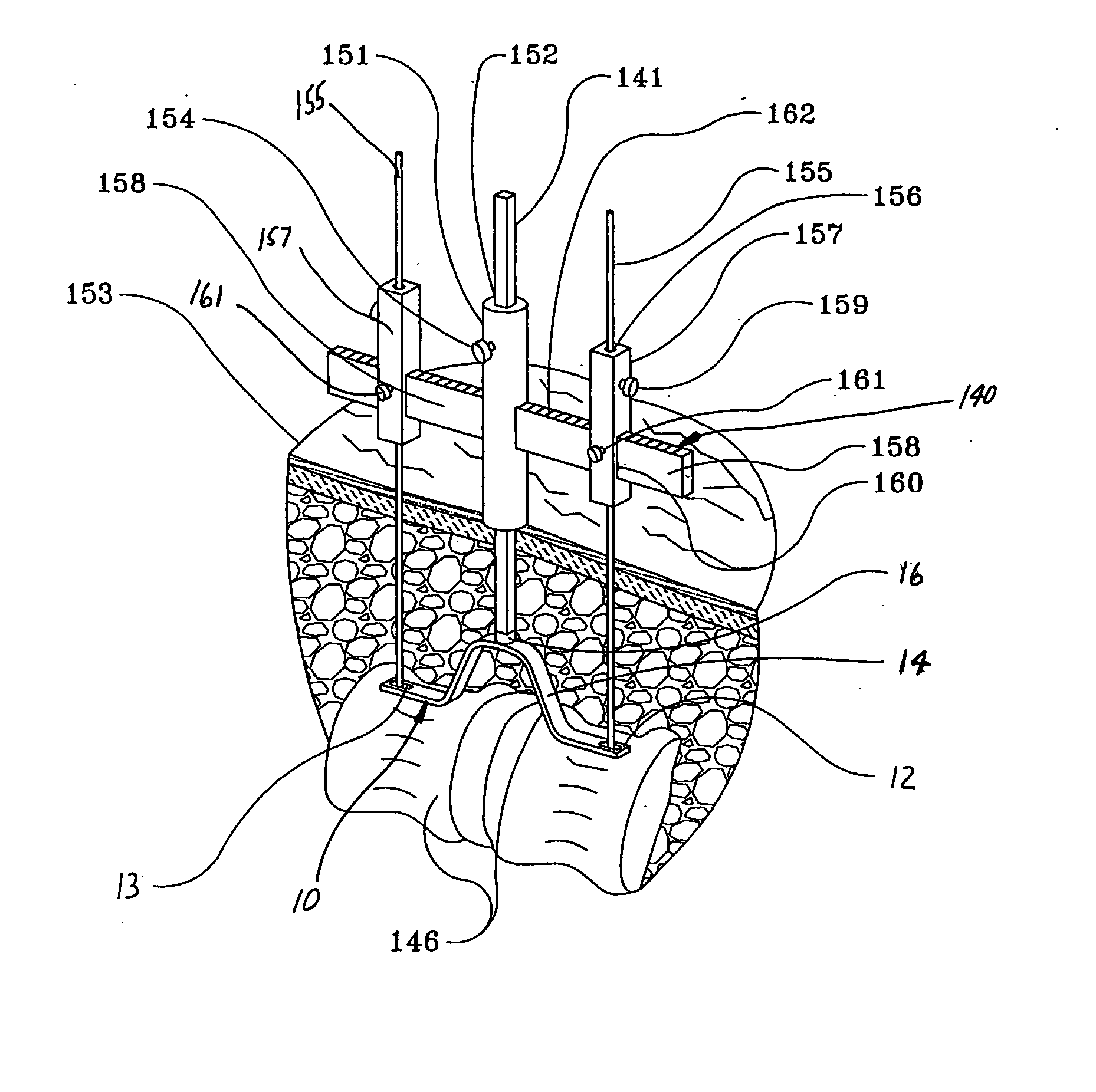
Artificial spinal joints and method of use
InactiveUS20050209694A1Preventing subluxationMaintain strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFiberCarbon fibers
An artificial spinal joint, consisting of a flexible or rigid member or a pair of moveably-joined, flexible or rigid segments, is formed into a spring-like shape, whose distal ends have feet with slots through which screws can be inserted to attach the artificial joint to vertebra whose facets (joints) are non-functional. The artificial spinal joint is able to prevent subluxation of the spine, while retaining the mobility of the spine and permitting angular deflection of the vertebra above and below a non-functional spinal joint. A jig is used to position tools and make passageways for screws to attach the artificial spinal joint to the vertebra or its pedicles or facets in a minimally invasive procedure. The rigid members or segments are bio-compatible and may be made of titanium, a titanium alloy, tantalum, medical grade stainless steel or carbon fibers in a matrix of a rigid, durable plastic. The flexible members or segments may be made of spring steel coated with a durable, bio-compatible material, small diameter carbon fibers in a flexible, durable plastic matrix, or a single shape or dual shape, superelastic memory metal. The feet, made of any of the rigid or flexible materials described above, may also be moveably attached to the proximal ends of the members or segments. Having the feet moveably attached to the segments facilitates insertion of the artificial spinal joint into the body by folding the feet parallel to the axis of the segments during insertion, and then unfolding the feet for attachment to the vertebra or its pedicles or facets. The artificial spinal joint may be inserted and attached to vertebra whose facets are non-functional in minimally invasive, moderately invasive or conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:TRIMEDYNE
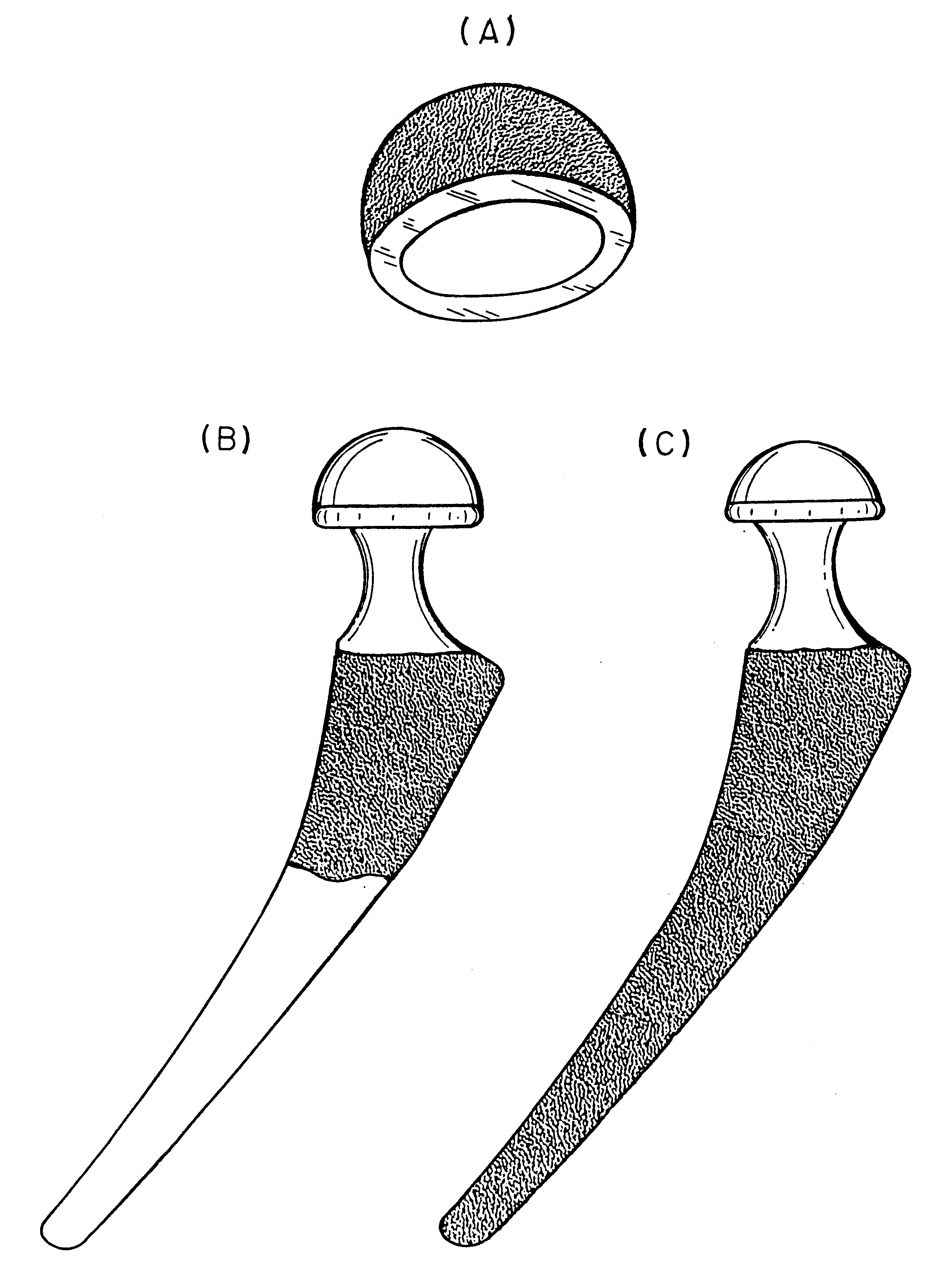
Radiopaque markers for medical devices
InactiveUS20050060025A1High level of radiopacitySufficient radiopacityStentsBlood vesselsIridiumRhenium
An implantable medical device includes a structural body made from a superelastic material and includes one or more marker holders integrally formed on the structural body. Each marker holder is designed to hold a radiopaque marker which has a level of radiopacity greater than the superelastic material. The radiopaque marker can be made from a nickel-titanium alloy which includes a ternary element. The ternary element can be selected from the group of elements consisting of iridium, platinum, gold, rhenium, tungsten, palladium, rhodium, tantalum, silver, ruthenium, and hafnium. In one form, the marker holder includes a pair of projecting fingers connected together at a notched region to cooperatively create a particular-shaped opening. This opening, in turn, is adapted to receive a similarly shaped portion formed on the radiopaque marker. In one form, the radiopaque marker includes an inner core which is partially, or completely, encased by an outer layer. This inner core can be made from a highly radiopaque material while the outer layer is formed from a material that is easier to weld to the marker.
Owner:ABBOTT VASCULAR SOLUTIONS
Golf club head
InactiveUS7344452B2Position of the center of gravity can be designed more easilySimple designGolf clubsRacket sportsMetallic materialsEngineering
A golf club head includes a front body formed of a titanium-based metal material, an FRP body, a metallic sole plate, and a weight member. The front body has a face portion, a metal sole portion, a metal side portion (toe), a metal crown portion, a metal side portion (heel), and a hosel portion. A slight gap is formed between a front side of the sole plate and the metal sole portion. Preferably, the front body is made of a titanium alloy, while the sole plate is made of stainless steel.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Golf club-heads having a particular relationship of face area to face mass
Golf clubs and club-heads for same are disclosed. An exemplary club-head has a hollow body and a face plate. The body defines a front opening and a face support, wherein the face plate is affixed to the face support and covers the front opening. The “face portion” of the club-head has a face area (Af, in mm2) and a face mass (Mf, in grams), wherein Af>5400 mm2, and in a plot of Mf as a function of Af, Mf is below Mf=0.0072(Af)+18. At least a portion of the face plate can be made of composite. E.g., the face plate can include a composite plate made of carbon fiber and cured epoxy resin. The strike face of the face plate can include a composite plate and a cap bonded to the composite plate on the strike face. The cap can be made of a metallic material, such as (but not limited to) titanium alloy or stainless steel.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Immobilizing mediator molecules via anchor molecules on metallic implant materials containing oxide layer
A mediator molecule is immobilized on the surface of a metallic or ceramic implant material. An anchor molecule such as a dialdehyde having a functional group that covalently binds the mediator molecule is covalently bound to the surface, and the mediator molecule is coupled to the functional group of the anchor molecule. The implant material may be composed of titanium, titanium alloy, aluminum, stainless steel or hydroxylapatite. Oxide units on the surface of the implant material can be increased preferably by treating with hot chromic-sulphuric acid for 0.5 to 3 hours at a temperature between 100 to 250° C. prior to binding the anchor molecule. Also, prior to binding the anchor molecule, the surface of the implant material can be activated by reacting with a silane derivative. Mediator molecules include BMP protein, ubiquitin and antibiotics, and the implant material may be an artificial joint or coronary vessel support such as a stent.
Owner:MORPHOPLANT
Method of manufacturing expansile filamentous embolization devices
InactiveUS7014645B2Convenient position controlLow of tissue damageEar treatmentCatheterTitanium alloyBiomedical engineering
An embolization device for occluding a body cavity includes one or more elongated, expansible, hydrophilic embolizing elements non-releasably carried along the length of an elongated filamentous carrier that is preferably made of a very thin, highly flexible filament or microcoil of nickel / titanium alloy. At least one expansile embolizing element is non-releasably attached to the carrier. A first embodiment includes a plurality of embolizing elements fixed to the carrier at spaced-apart intervals along its length. In second, third and fourth embodiments, an elongate, continuous, coaxial embolizing element is non-releasably fixed to the exterior surface of the carrier, extending along a substantial portion of the length of the carrier proximally from a distal tip, and optionally includes a lumenal reservoir for delivery of therapeutic agents. Exemplary methods for making these devices include skewering and molding the embolizing elements. In any of the embodiments, the embolizing elements may be made of a hydrophilic, macro-porous, polymeric, hydrogel foam material. In the second, third and fourth embodiments, the elongate embolizing element is preferably made of a porous, environmentally-sensitive, expansile hydrogel, which can optionally be made biodegradable and / or bioresorbable, having a rate of expansion that changes in response to a change in an environmental parameter, such as the pH or temperature of the environment.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
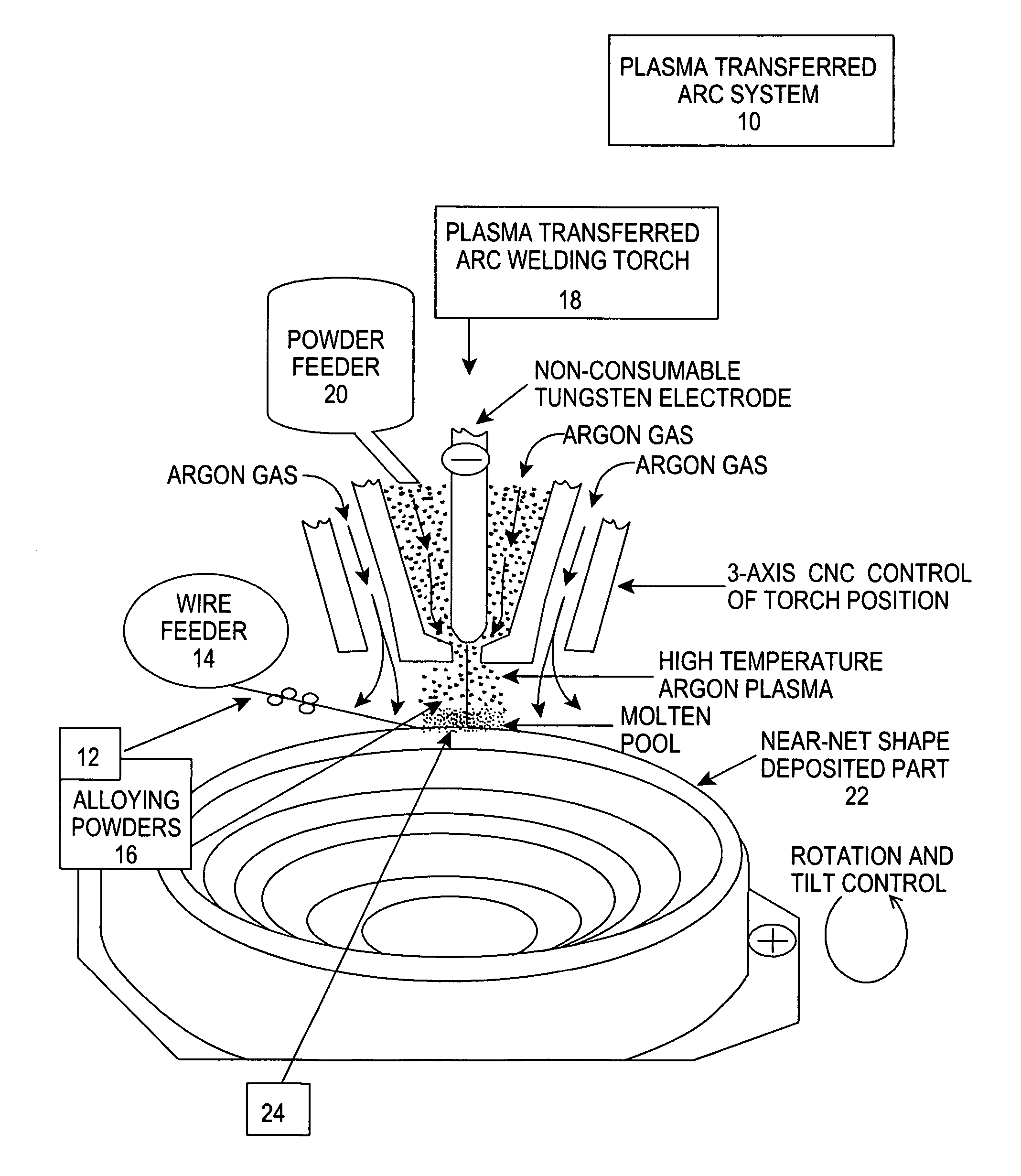
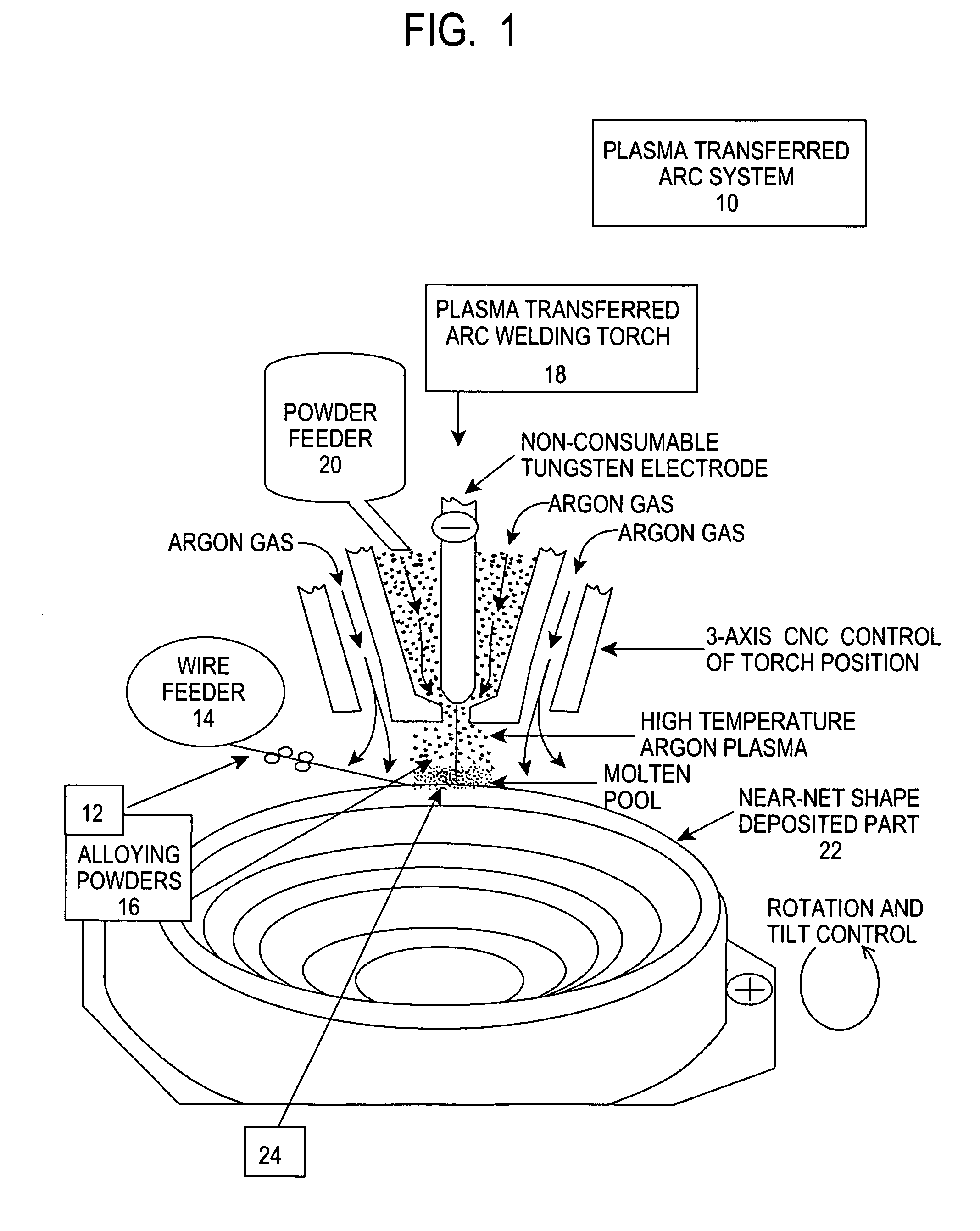
Low cost process for the manufacture of near net shape titanium bodies
InactiveUS20060185473A1Low costAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusHigh energyTitanium
Owner:ATS MER LLC
Combination self-expandable, balloon-expandable endoluminal device
An endoluminal device, such as a stent or a vena cava filter, comprising at least one superelastic section and at least one plastically deformable section. The superelastic section may comprise, for example, a superelastic grade of nitinol, whereas the plastically deformable section may comprise, for example, gold, platinum, tantalum, titanium, stainless steel, tungsten, a nickel alloy, a cobalt ally, a titanium alloy, or a combination thereof. Each plastically deformable section may merely comprise a constrained portion of the superelastic section comprising a plastically deformable material, such as gold. The device enables deployment by a method comprising introducing the device into a body lumen with the device radially constrained in a first configuration having a first diameter; allowing the device to self-expand into a second configuration having a second diameter less than or equal to a fully-self-expanded diameter; and then optionally “fine-tuning” the device by forcibly expanding the device into a third configuration having a third diameter in a range between the second diameter and less than or equal to a fully-forcibly-expanded diameter. The superelastic and plastically deformable sections may be tubular sections placed end-to-end, such that the plastically deformable section can be conformed to fit a tapered section of a lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Titanium tungsten alloys produced by additions of tungsten nanopowder
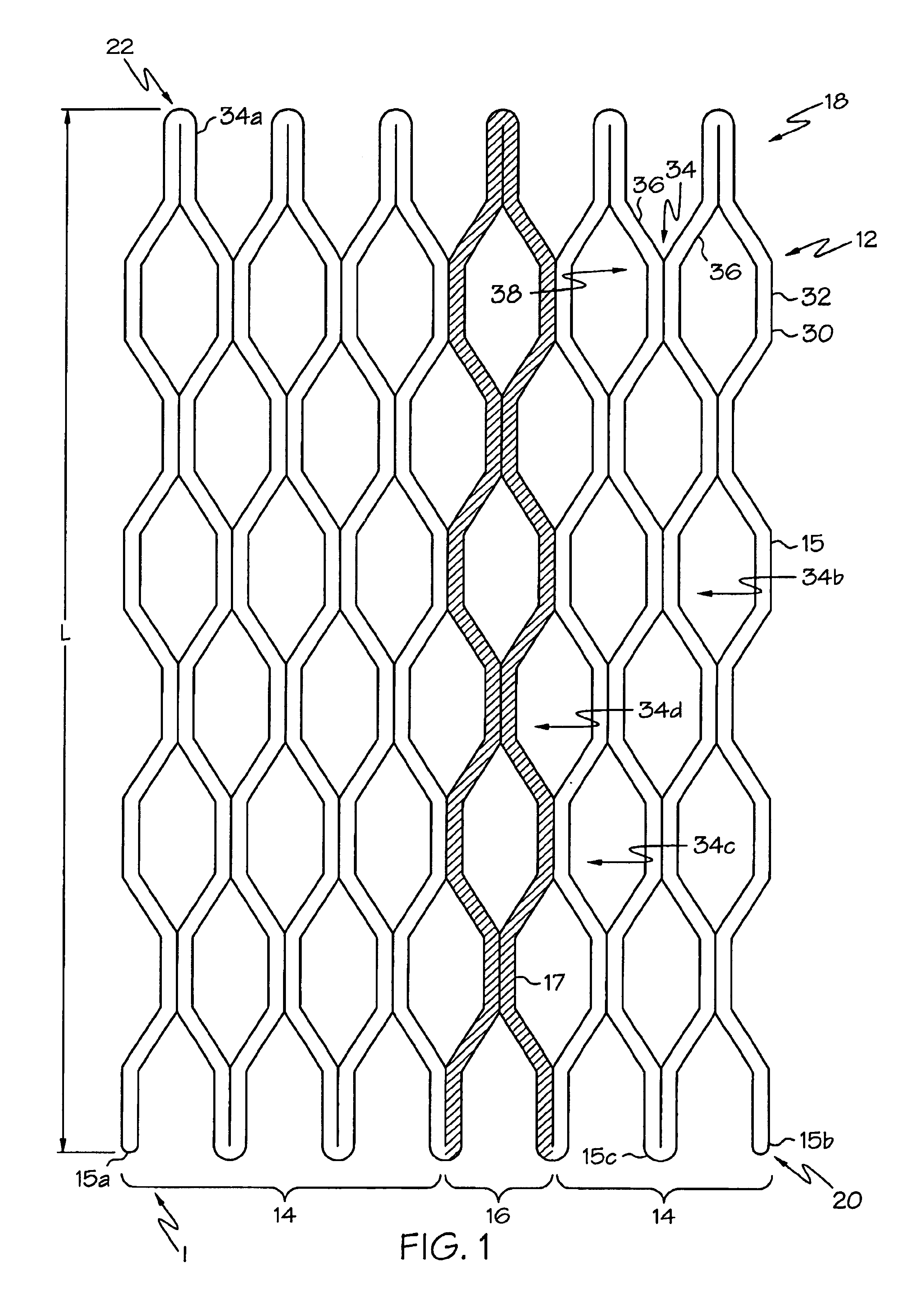
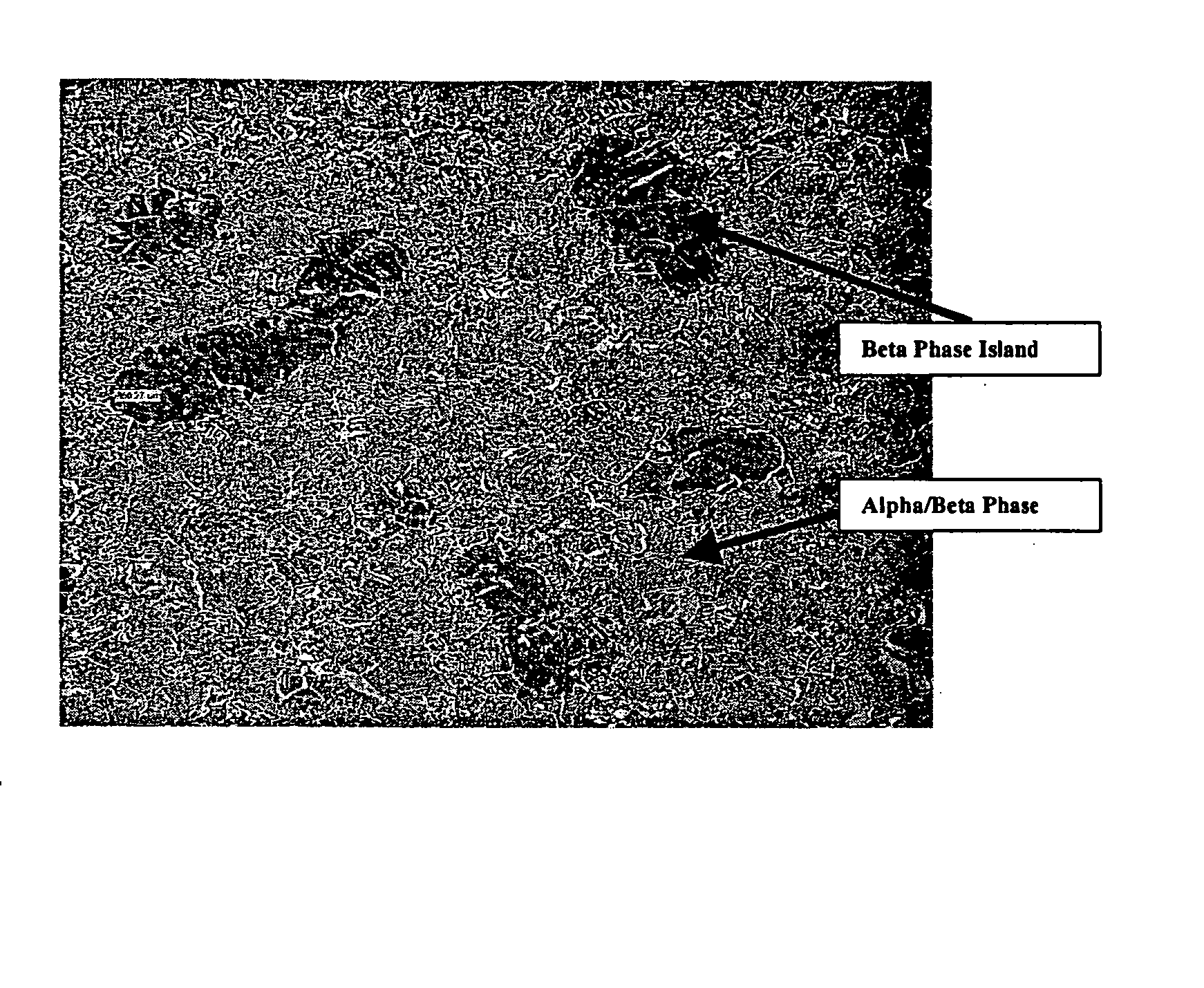
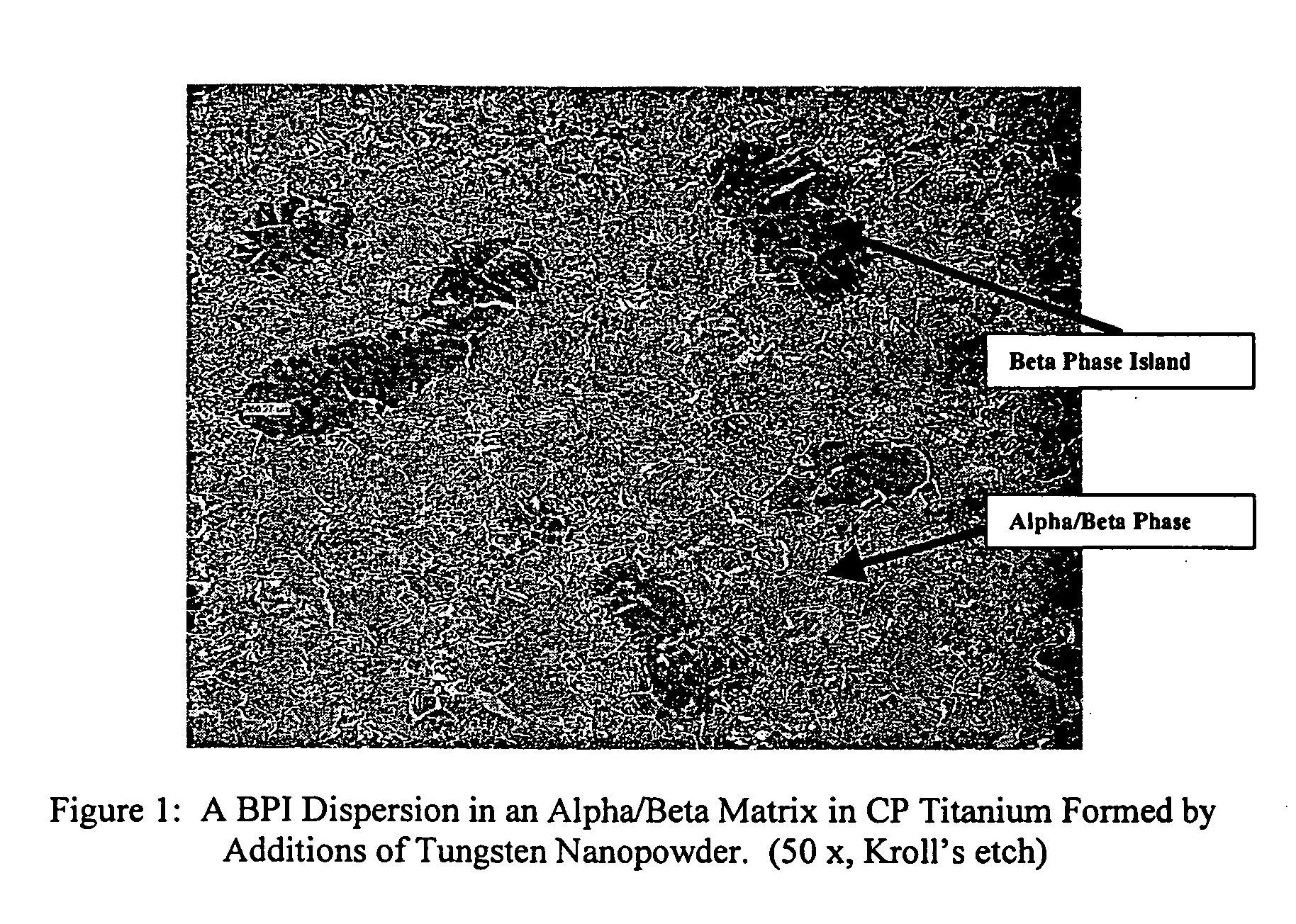
Disclosed herein are titanium-tungsten alloys and composites wherein the tungsten comprises 0.5% to 40% by weight of the alloy. Also disclosed is a method of making such alloys and composites using powders of tungsten less then 3 μm in size, such as 1 μm or less. Also disclosed is a method of making the titanium alloy by powder metallurgy, and products made from such alloys or billets that may be cast, forged, or extruded. These methods of production can be used to make titanium alloys comprising other slow-diffusing beta stabilizers, such as but not limited to V, Nb, Mo, and Ta.
Owner:DYNAMET TECH
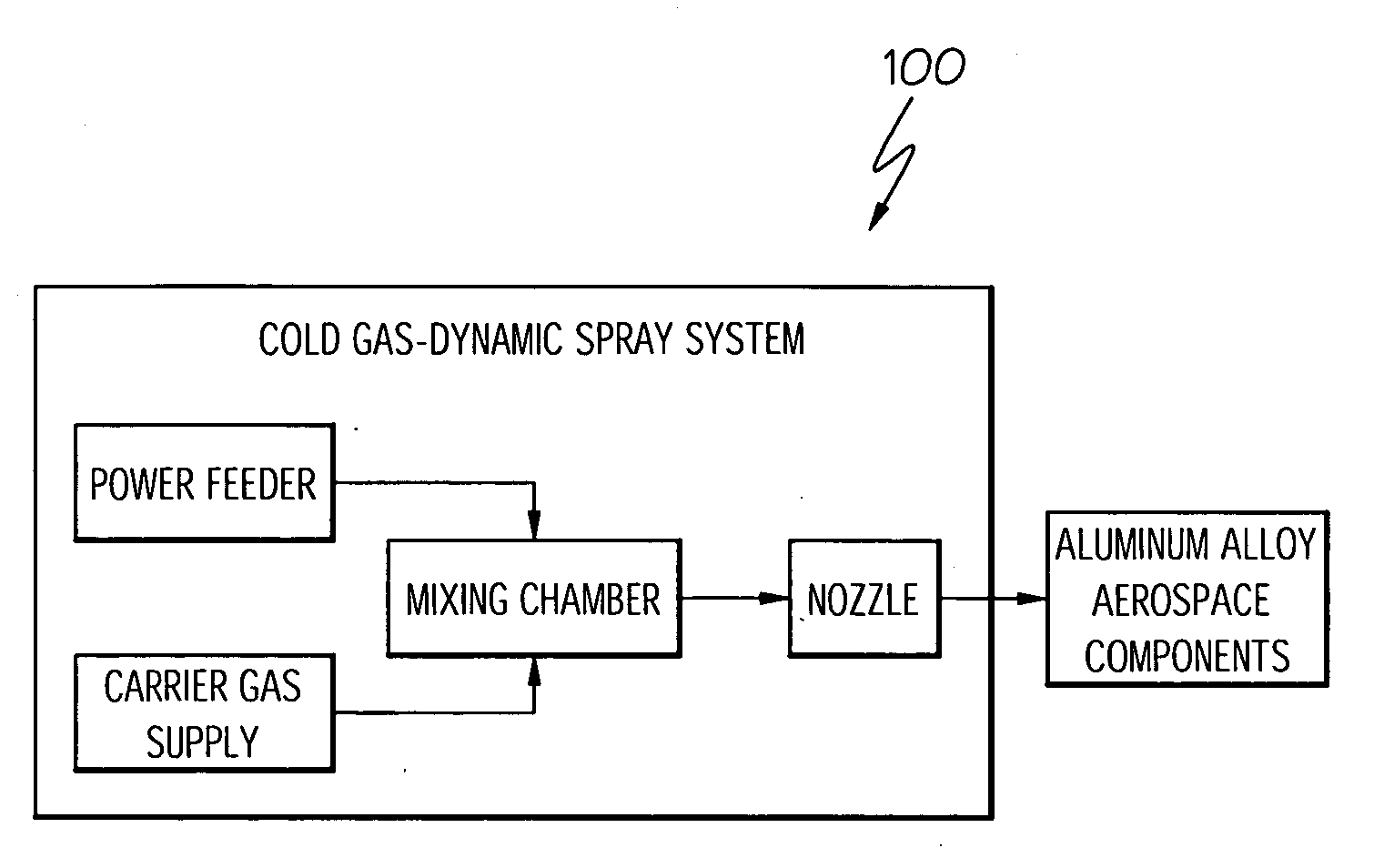
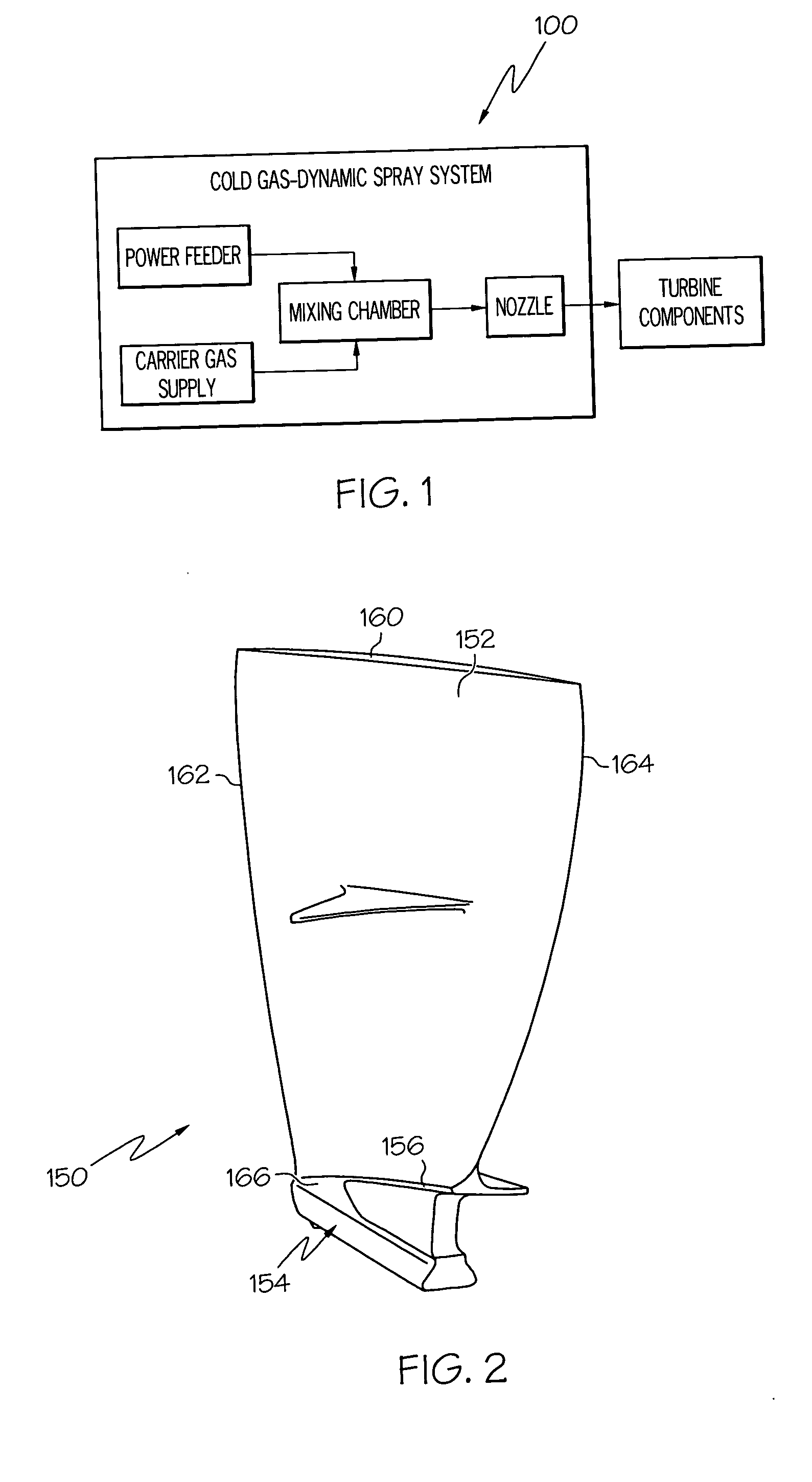
Aluminum articles with wear-resistant coatings and methods for applying the coatings onto the articles
InactiveUS20060093736A1Liquid surface applicatorsSuperimposed coating processWear resistantTitanium alloy
A method for coating a surface of a component formed from aluminum or an alloy thereof includes the step of cold gas-dynamic spraying a powder material on the component surface to form a coating, the powder material comprising at least one alloy from the group consisting of titanium, a titanium alloy, nickel, a nickel alloy, iron, an iron alloy, aluminum, an aluminum alloy, copper, a copper alloy, cobalt, and a cobalt alloy. In one embodiment, the method further includes the step of heat treating the turbine component after the cold gas-dynamic spraying.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
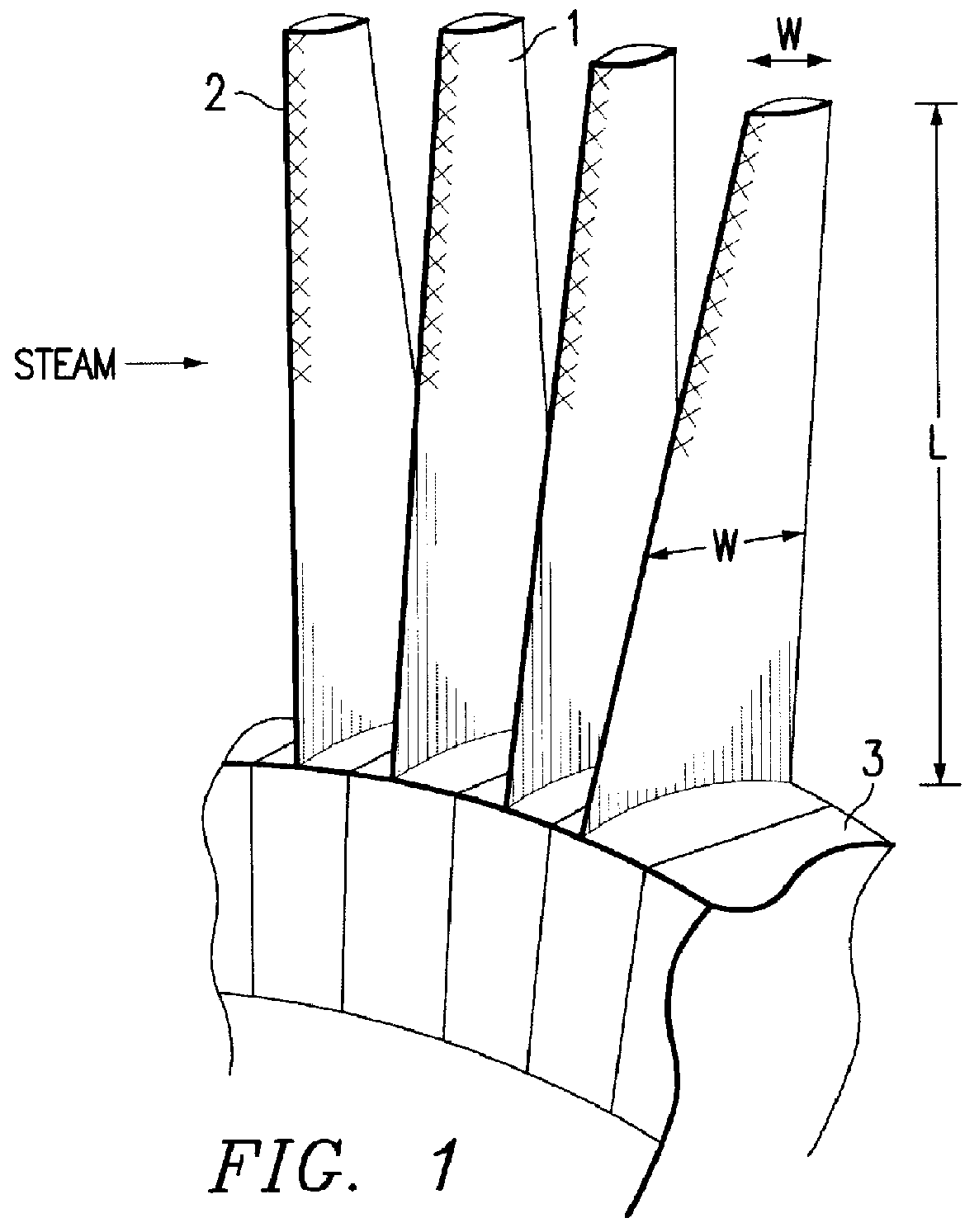
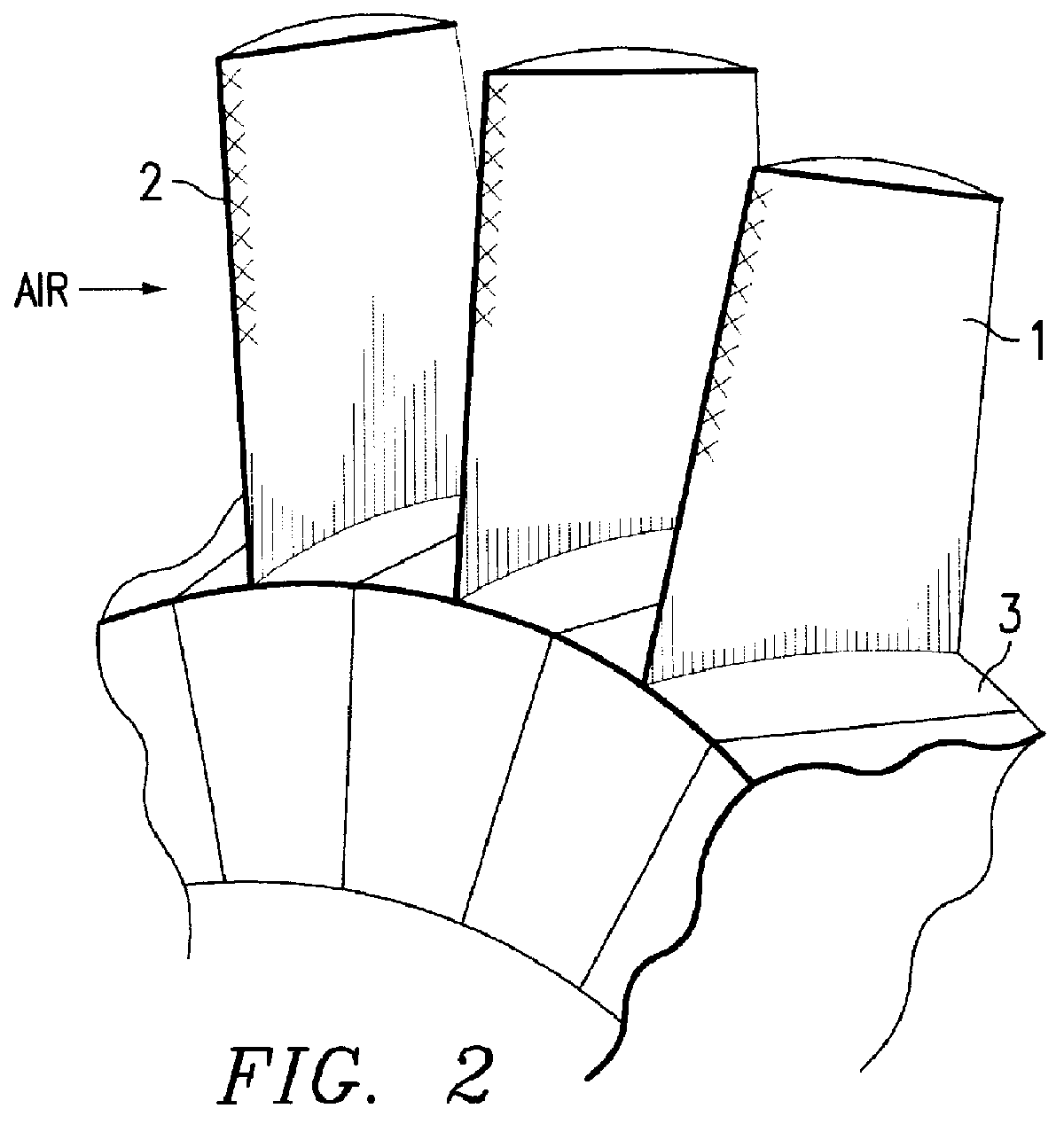
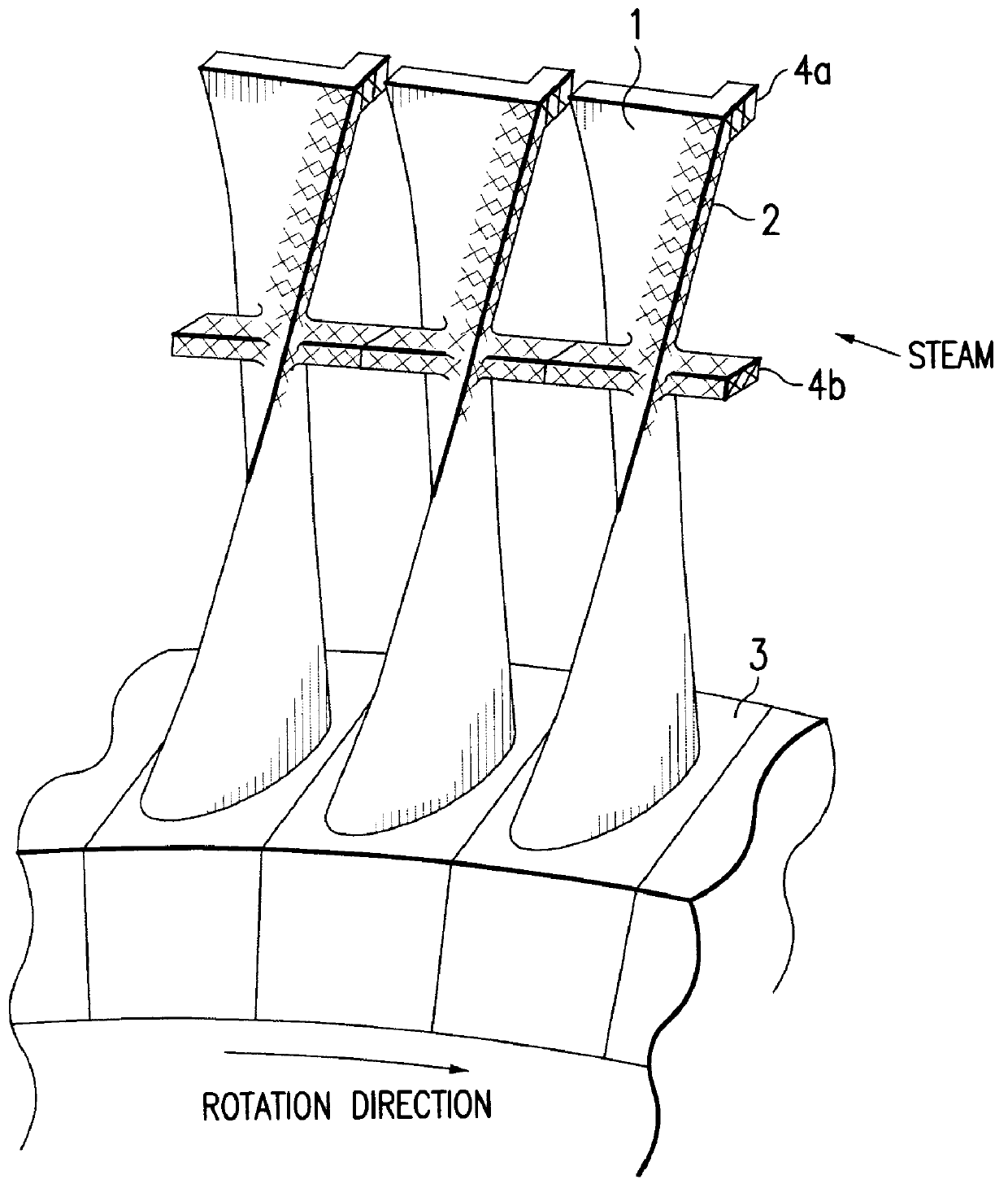
Method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades and titanium alloy turbine blades
InactiveUS6127044ALess abrasionSuperior in water droplet erosion resistancePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTurbine blade
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01817 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 13, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10066 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997A method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades comprising the steps of (a) forming turbine blades of titanium alloy through hot forging or machining, (b) cooling leading edges on tip portions of the turbine blades including covers thereof formed through hot forging or machining faster than blade main body after final hot forging or solid solution treatment, and (c) heat treating the cooled turbine blades. With this method, it is possible to manufacture titanium turbine blades in an economical fashion and obtain titanium alloy turbine blades superior in reliability by preventing erosion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Golf club head with center of gravity adjustability
ActiveUS8956244B1Optimize locationIncrease heightGolf clubsRacket sportsMetallic materialsEngineering
A golf club head comprising an adjustable weighting feature including a tube extending from the crown to the sole of the golf club head is disclosed herein. More specifically, a golf club head formed from three pieces, namely a first piece comprising a face, a crown portion, a sole portion, and a hosel, a second piece comprising a rear end, a crown portion, and a sole portion, and a tube, wherein these pieces are welded to one another, is disclosed herein. Each of these pieces may be separately cast, forged, or formed from a metal material such as stainless steel, titanium alloy, and aluminum alloy.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Orthopedic implant system
InactiveUS6066176AStrong interlocking fixationEasy to fixSurgical adhesivesBone implantPolymethyl methacrylateFemoral stem
It is an object of the present invention to provide an improved orthopedic implant system with satisfied biological, mechanical and morphological compatibilities. Solid metal femoral stem (entirely or partially) and solid metal acetabular head (entirely or partially) are covered with diffusion-bonded foamed-shaped sheet made of commercially pure titanium or titanium alloy(s). The open-cells in said foamed metal sheet are impregnated with biocompatible polymethyl methacrylate resin cement, which is reinforced with selected oxides (e.g., alumina, magnesia, zirconia, or a combination of these oxides) along with an application of a small amount of a metal primer agent.
Owner:OSHIDA YOSHIKI
Titanium alloy with oxidized zirconium for a prosthetic implant
A prosthetic device having a generally fixed member formed from a low friction material such as ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and an articulating titanium member, which includes an articular bearing surface. The articular surface is a zirconium oxide layer formed by applying a coating of zirconium onto the titanium member and heating this in an oxygen-containing environment. This causes the zirconium to oxidize and further causes the zirconium to migrate into the titanium member forming a titanium zirconium diffusion layer, which prevents delamination.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
High-temperature titanium alloy with high heat resistance and high thermal stabilization
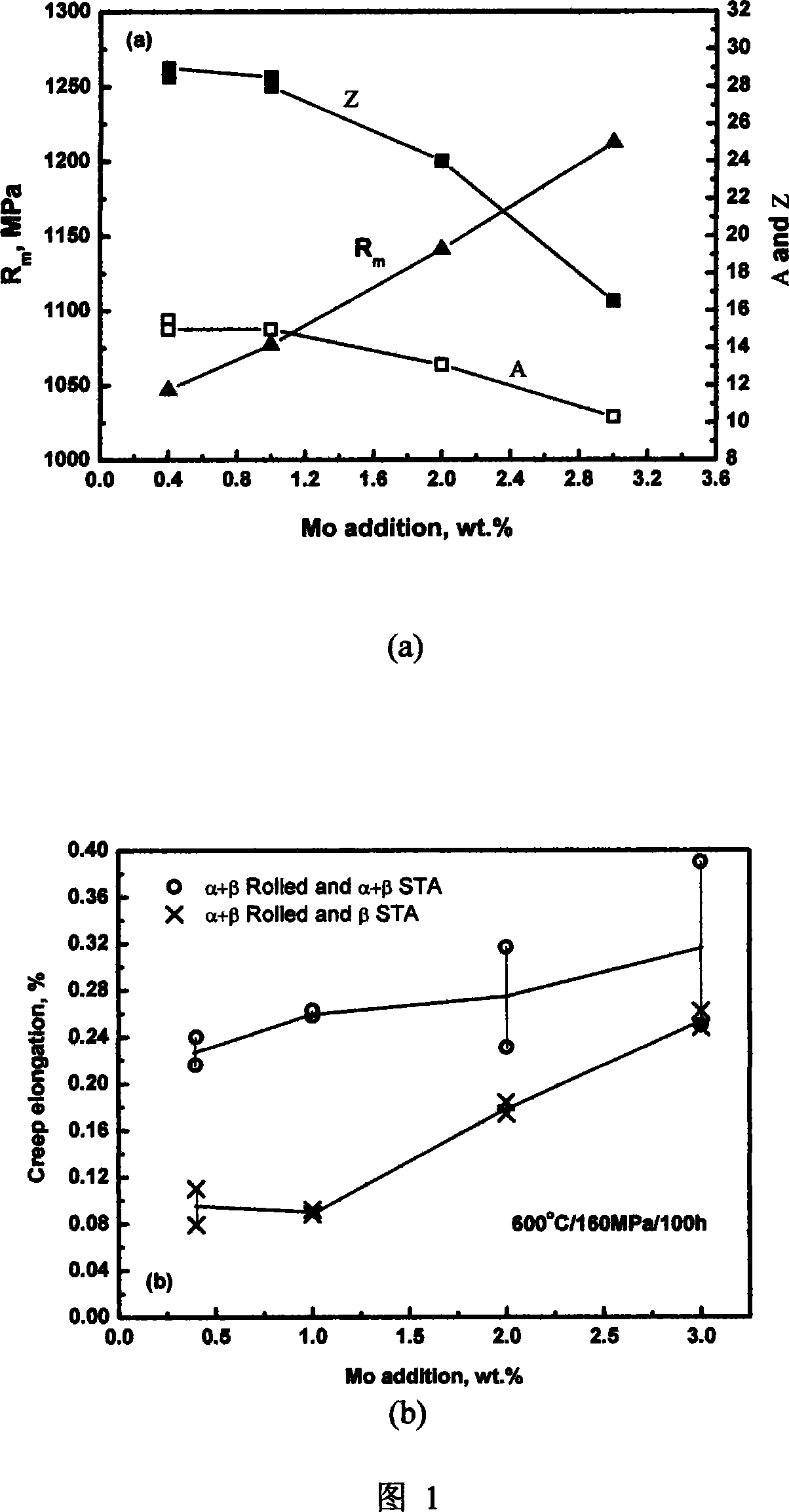
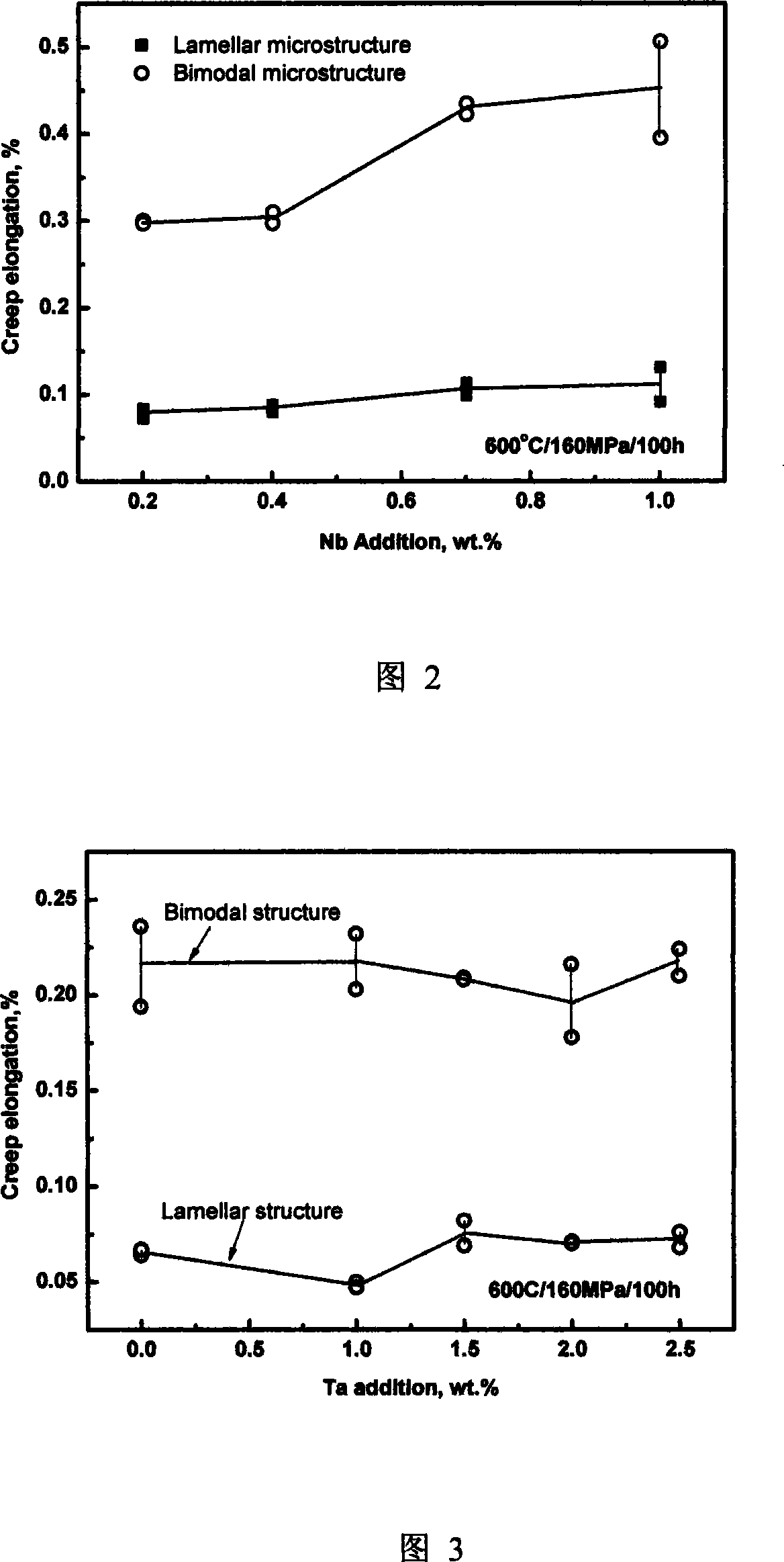
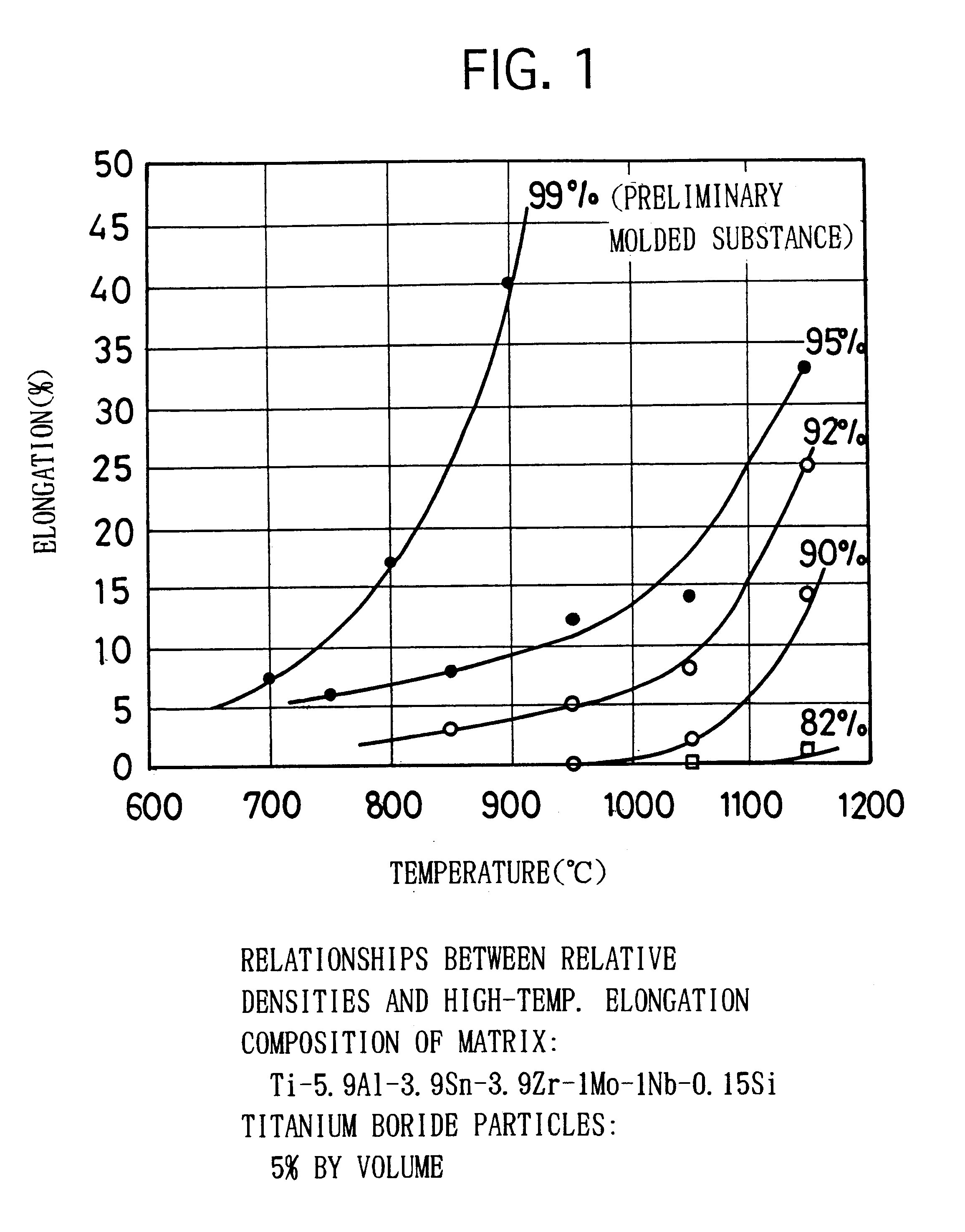
The invention provides a novel high-temperature Ti alloy with high heat resistance and high heat stability. The alloy contains eutectic Nb, Ta and Mo elements. Based on the appropriate proportion of these three elements, the alloy is superior in high resistance and stability to heat and good antioxidant effect. The alloy contains (by weight) Al 5.0-6.3 percent, Sn 3.0-5.0 percent, Zr 2.5-7.0 percent, Mo 0.2-1.5 percent, Si 0.20-0.55 percent, Nb 0.2-1.0 percent, Ta 0.2-3.0 percent, C 0.01-0.09 percent, and Ti and other inevitable impurities in balance. The alloy is an ideal alternative material for high-temperature parts of aircraft engine, such as wheel disk, drum barrel, barrel shaft and blade.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
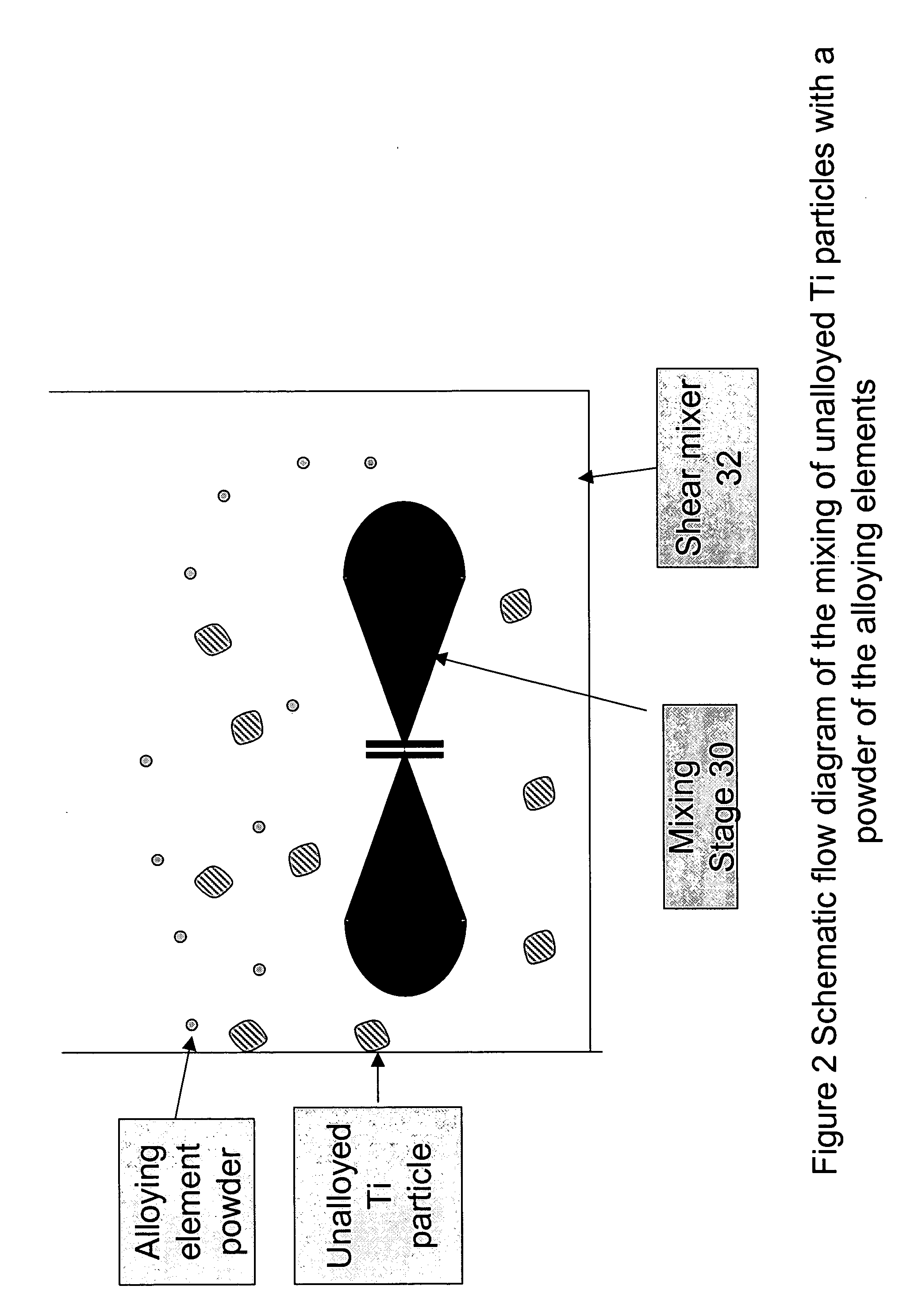
Method for manufacturing titanium alloy wire with enhanced properties
A method for producing reinforced titanium alloy wire, comprising forming a billet of titanium alloy with grains of a precipitated discontinuous reinforcement material such as TiB and / or TiC. The billet may be formed by the hot consolidation of a titanium alloy powder formed by gas atomization. The billet is then hot formed to reduce it to rod or coil form. The rod or coil is then subjected to successive cold drawing operations to form a reinforced titanium alloy wire of reduced diameter. The cold drawing includes periodic annealing operations under low oxygen conditions to relieve work hardening and to recrystallize the reinforcement material grains to reduce the size thereof.
Owner:FMW COMPOSITE SYST
Biocompatible low modulus titanium alloy for medical implant
A biocompatible titanium alloy with low modulus comprising alpha'' phase as a major phase and containing from about 6 to about 9 wt % of molybdenum, from 0 to about 1 wt % of an alloying element and the balance titanium. The alloying element is niobium and / or zirconium. The biocompatible titanium alloy is suitable for use as a material for a medical prosthetic implant.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV +1
Iron golf club
InactiveUS7338387B2Lower center of gravityHigh moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsHigh densityMetallic materials
The iron golf club head (20) of the present invention is preferably composed of three main components: a main body (22), a central member (24) and a mass member (25). The Mass member (25) is preferably composed of a high density material such as a nickel-tungsten alloy. The central member (24) is preferably composed of a lightweight, non-metal material. The main body (22) is preferably composed of a titanium alloy material. The iron golf club head (20) preferably has high moments of inertia Izz and Ixx, and a low center of gravity.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
All-inside double-bundle acl reconstruction
An “all-inside double-bundle” ACL reconstruction technique, according to which two femoral sockets and two closed tibial sockets are provided to accommodate retrograde fixation of two grafts (for example, two semitendonosus allografts) within the four sockets. At least one of the tibial sockets is formed by using a retrograde drill device provided with a retrograde drill cutter detachable from a retrograde drill guide pin. The femoral tunnels or sockets may be formed by the retrograde drill method or by a conventional method, and may be carried out before or after the formation of the tibial sockets. The grafts (for example, two semitendonosus allografts) are secured in the knee by employing a continuous loop / button construct provided with a button, preferably of titanium alloy, and a continuous loop of suture attached to the button.
Owner:ARTHREX
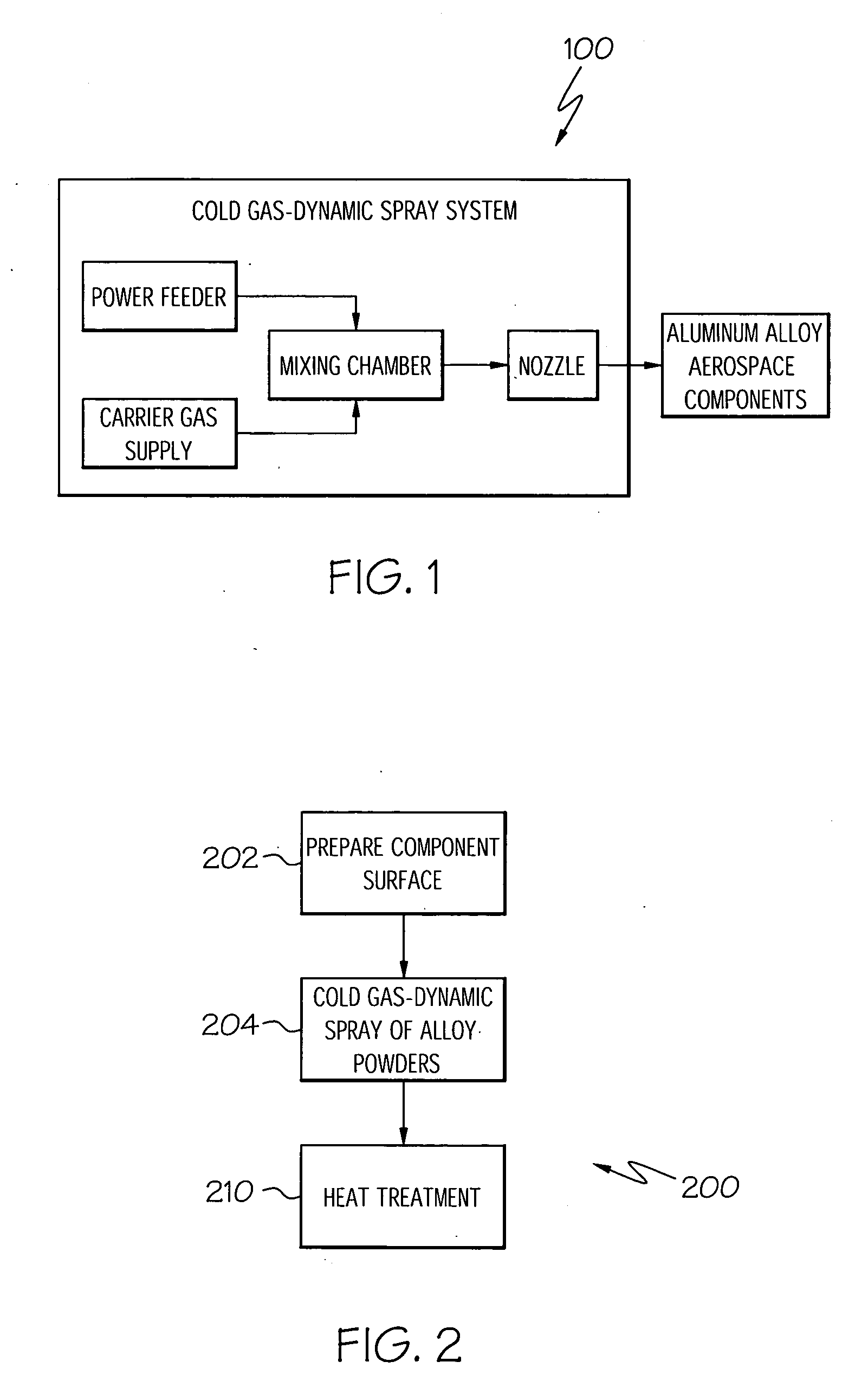
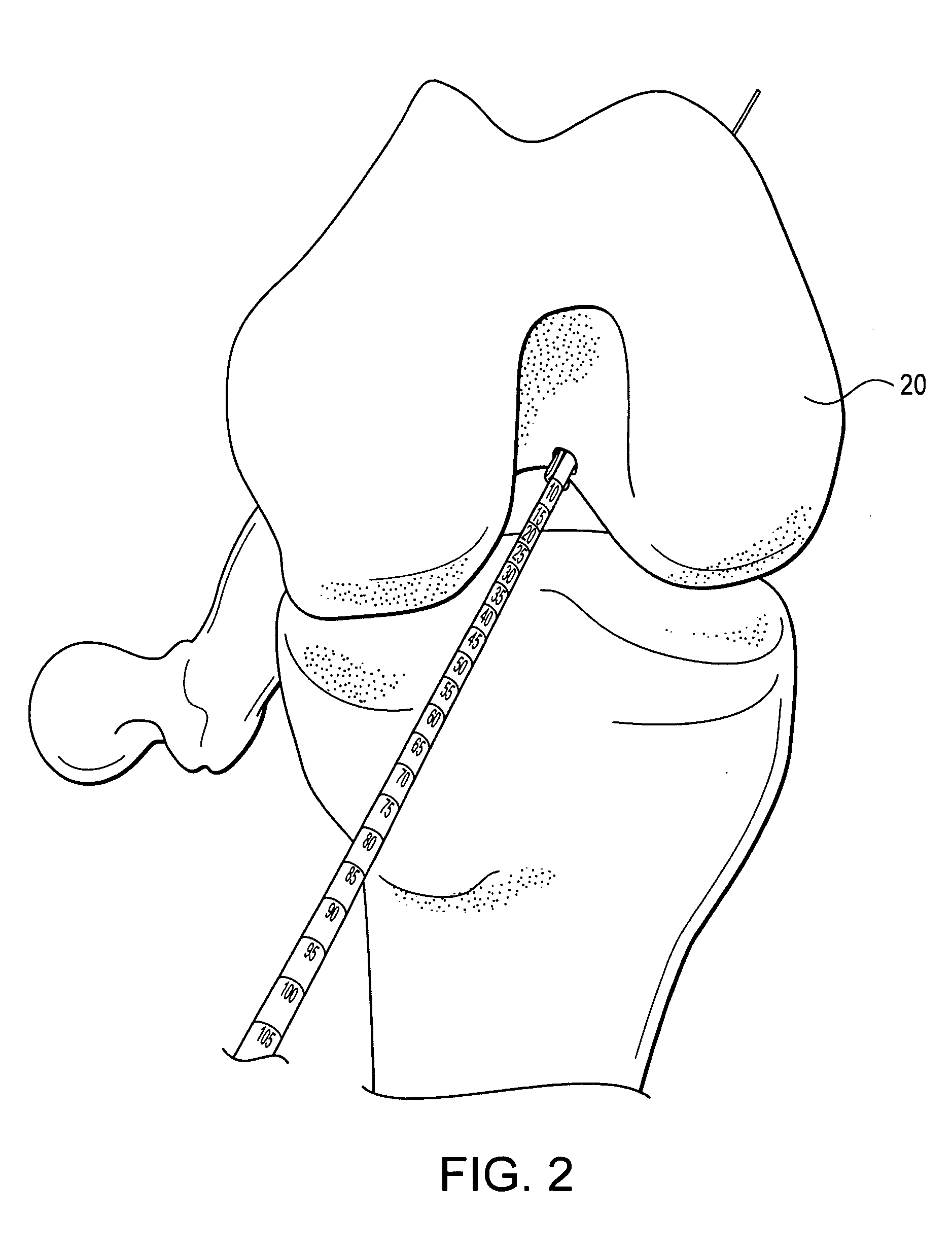
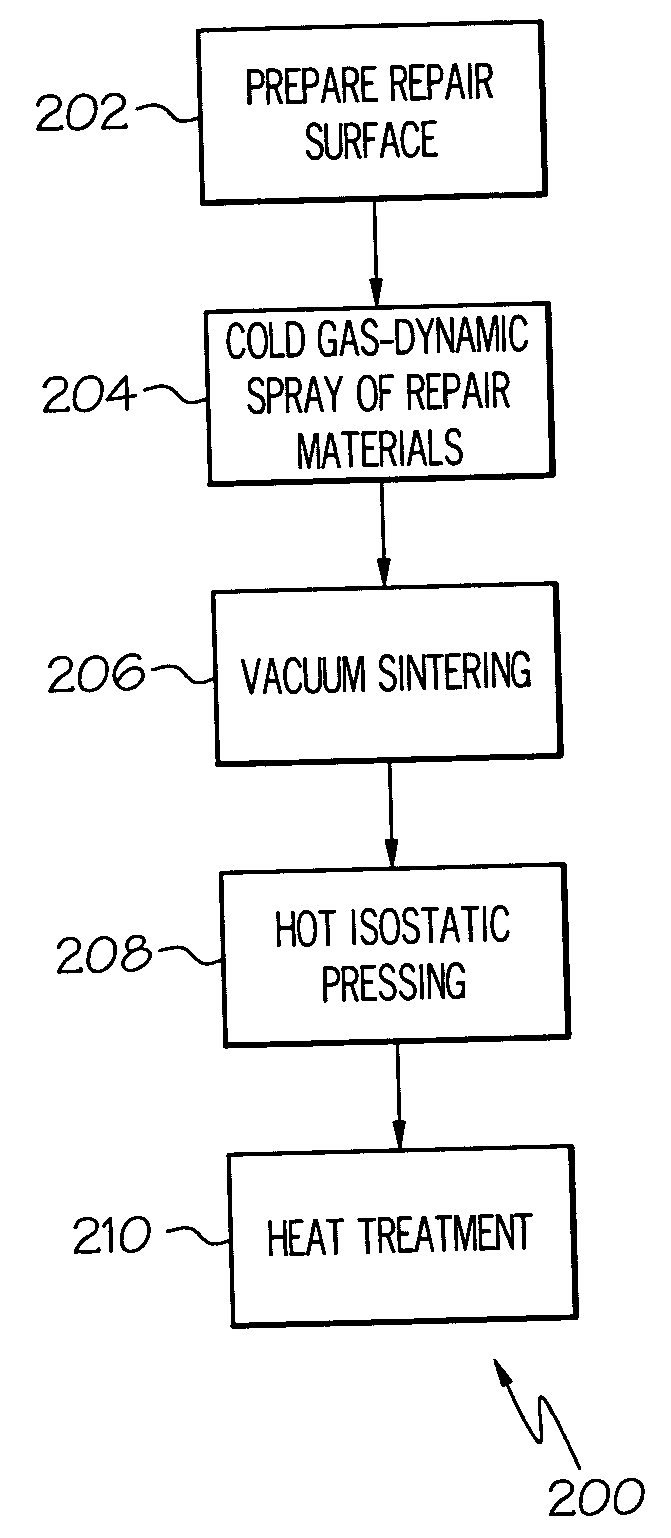
Method for repairing titanium alloy components
A method for repairing a titanium alloy surface of a turbine component includes the step of cold gas-dynamic spraying a powder material comprising at least one titanium alloy directly on the titanium alloy surface. The method may further include the steps of hot isostatic pressing the cold gas-dynamic sprayed turbine component, and performing a separate heat treating step after the hot isostatic pressing. Thus, the cold gas-dynamic spray process and post-spray processing can be employed to effectively repair degraded areas on compressor turbine components.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
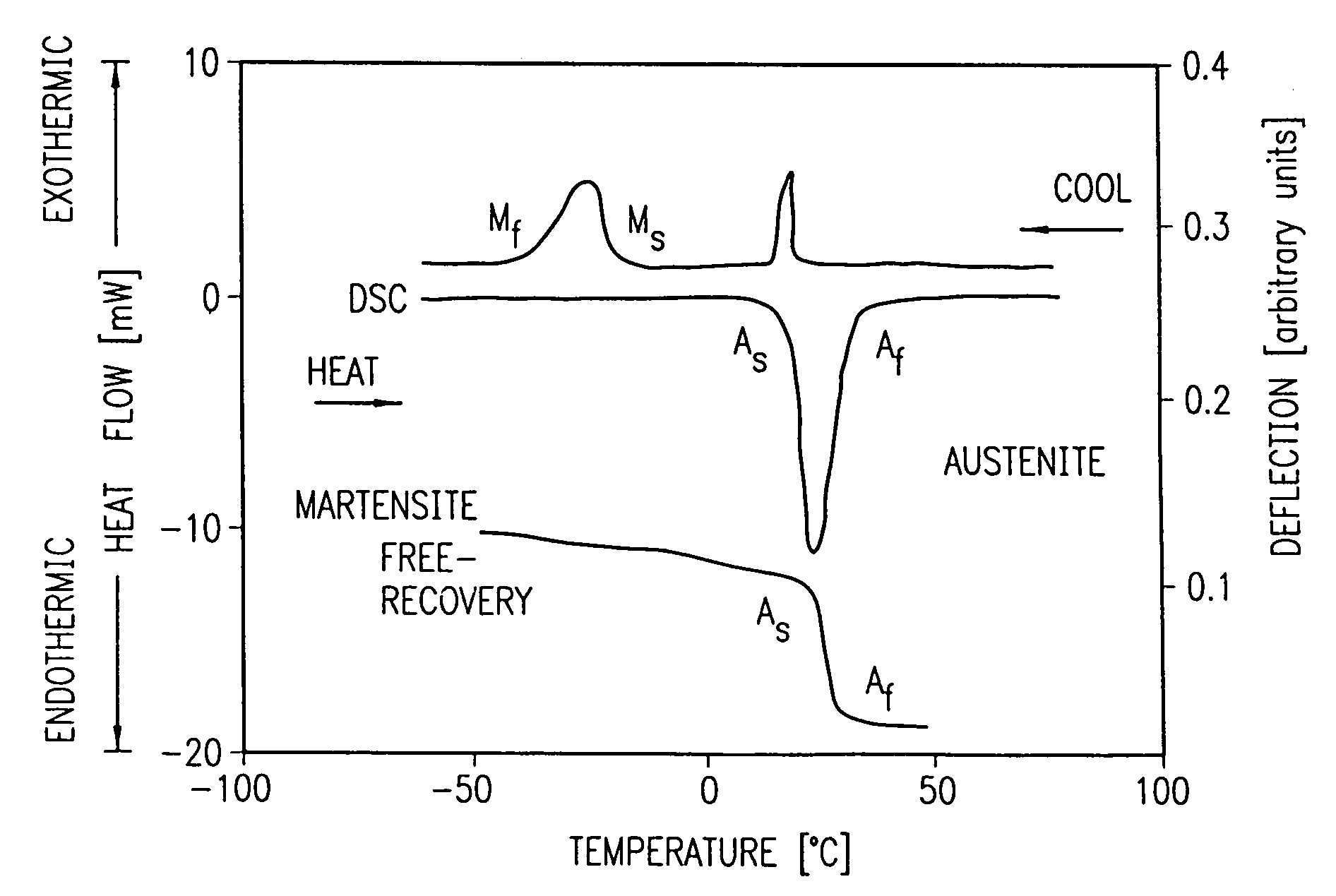
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Prosthetic valves for medical application
A prosthetic valve in the form of a flap valve which includes one or more flaps arranged to allow movement of liquid through the valve only in one direction, in which the or each flap is made of a flexible open work structure of a medically acceptable metal such as titanium or a titanium alloy.
Owner:SHAW DAVID PETER
Process for forging titanium-based material, process for producing engine valve, and engine valve
InactiveUS6599467B1Degradation can be suppressedReduced strengthMetal-working apparatusMachines/enginesTitaniumEngine valve
The invention provides a process for forging a titanium-based material comprises the steps of: preparing a titanium-based sintered workpiece including at least one of ceramics particles and pores in a total amount of 1% or more by volume, the ceramics particles being thermodynamically stable in a titanium alloy; and heating the workpiece to a forging temperature and forging the same. In the production process, the pores or the ceramics particles inhibit the grain growth during forging. Accordingly, it is possible to carry out the forging at a relatively high temperature at which the titanium-based material exhibits a small resistance to deformation. Moreover, the titanium-based material can maintain an appropriate microstructure even after the forging. Consequently, the impact value and the fatigue strength are inhibited from decreasing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Porous Interbody Spacer
Orthopedic implants, particularly interbody spacers, have a combination of correct pore size and stiffness / flexibility. When the implants have the proper pore size and stiffness, osteocytes are able to properly bridge the pores of the implant and then experience a proper compressive load to stimulate the bone cells to form bone within the pores. An implant includes a body formed of an osteoconductive material and having a stiffness of between 400 megapascals (MPa) and 1,200 MPa. Additionally, the body includes a plurality of pores having an average size of between 150 microns and 600 microns. The pores permit the growth of bone therein. The body is formed of packs of coils which may be formed using an additive manufacturing process and using traditional orthopedic implant materials such as titanium and titanium alloys while still achieving desired stiffness and pore sizes of the implants.
Owner:NEXUS SPINE L L C
Processing method of titanium and titanium alloy strip coils
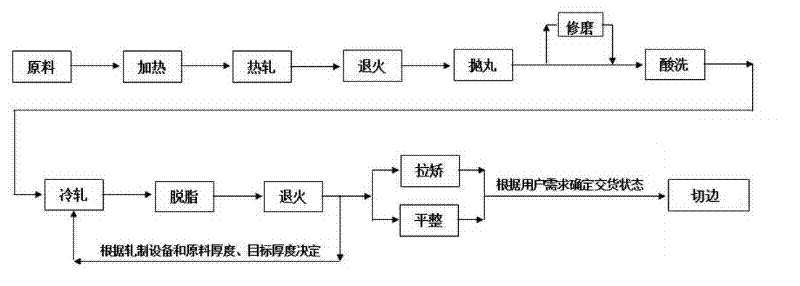
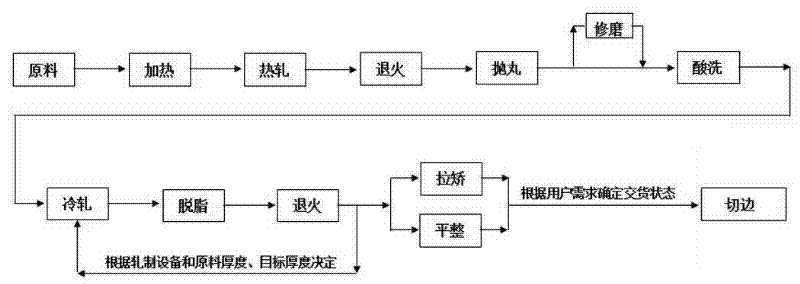
ActiveCN102310314ASolve the shortage of titanium-free surface processing technologyImprove processing efficiencyWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsSingle plateTitanium
The invention provides a processing method of titanium and titanium alloy strip coils, which comprises the steps of raw material preparation, heating, rolling, annealing, shot blasting treatment, coping, pickling, cold rolling, derosination, annealing, straightening or flattening, edge scraping, and product obtaining. According to the method, existing large steel rolling equipment of various types in the steel processing industry is fully utilized, the defect that no titanium material surface processing and treatment technology exists in the steel processing industry is overcome, the advantages of the steel processing industry are combined with the uniqueness of the titanium material processing industry, and the essential leap of titanium material processing from single plate rolling to long strip rolling plus collection and coiling is completed. By using the method, goods can be delivered in a coiled state as well as a flat plate state, the titanium material processing efficiency is improved, the titanium material processing yield is increased, and conditions are created and high quality raw materials are provided for the processing of titanium welded pipes with various diametersand longer lengths, so high efficiency, energy conservation and economization of titanium material processing are realized.
Owner:YUNNAN TITANIUM IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com