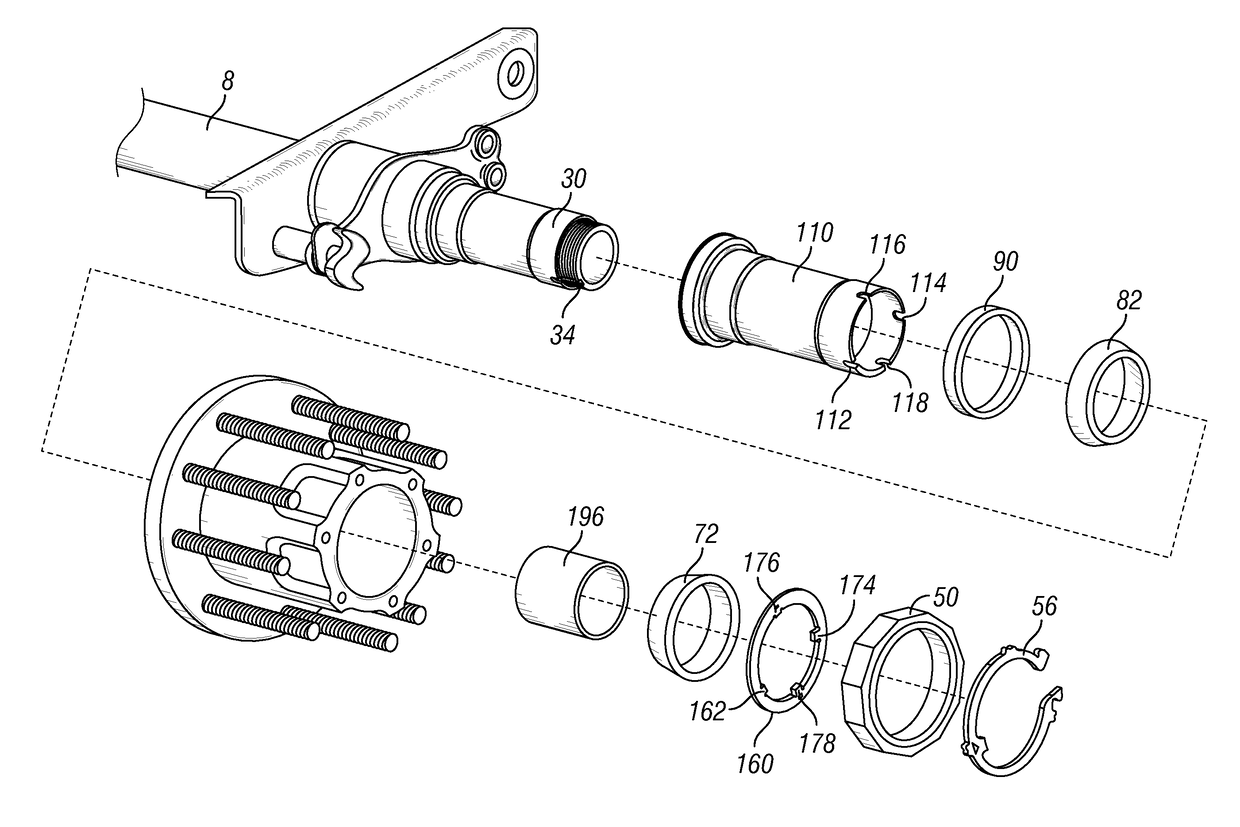
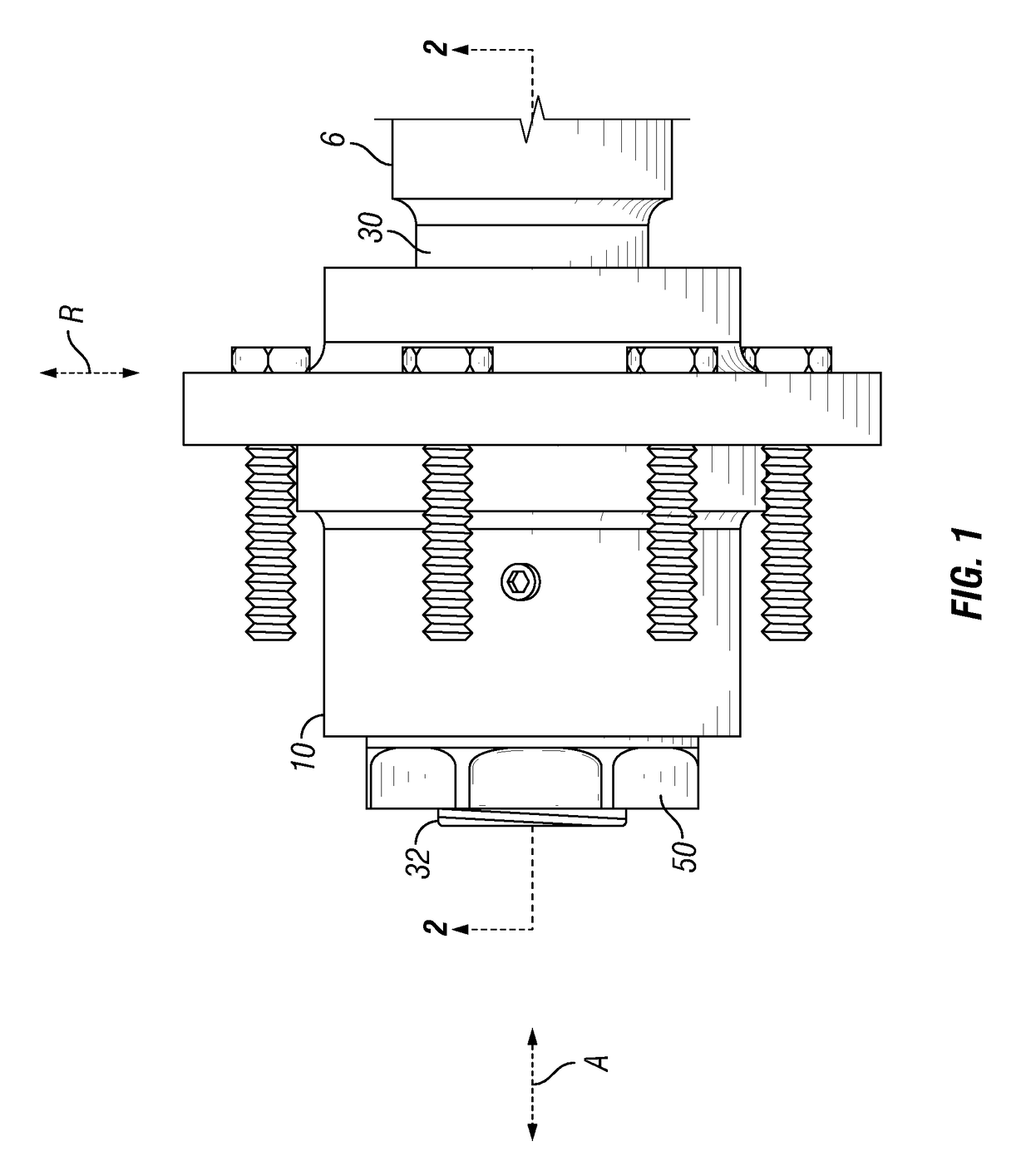
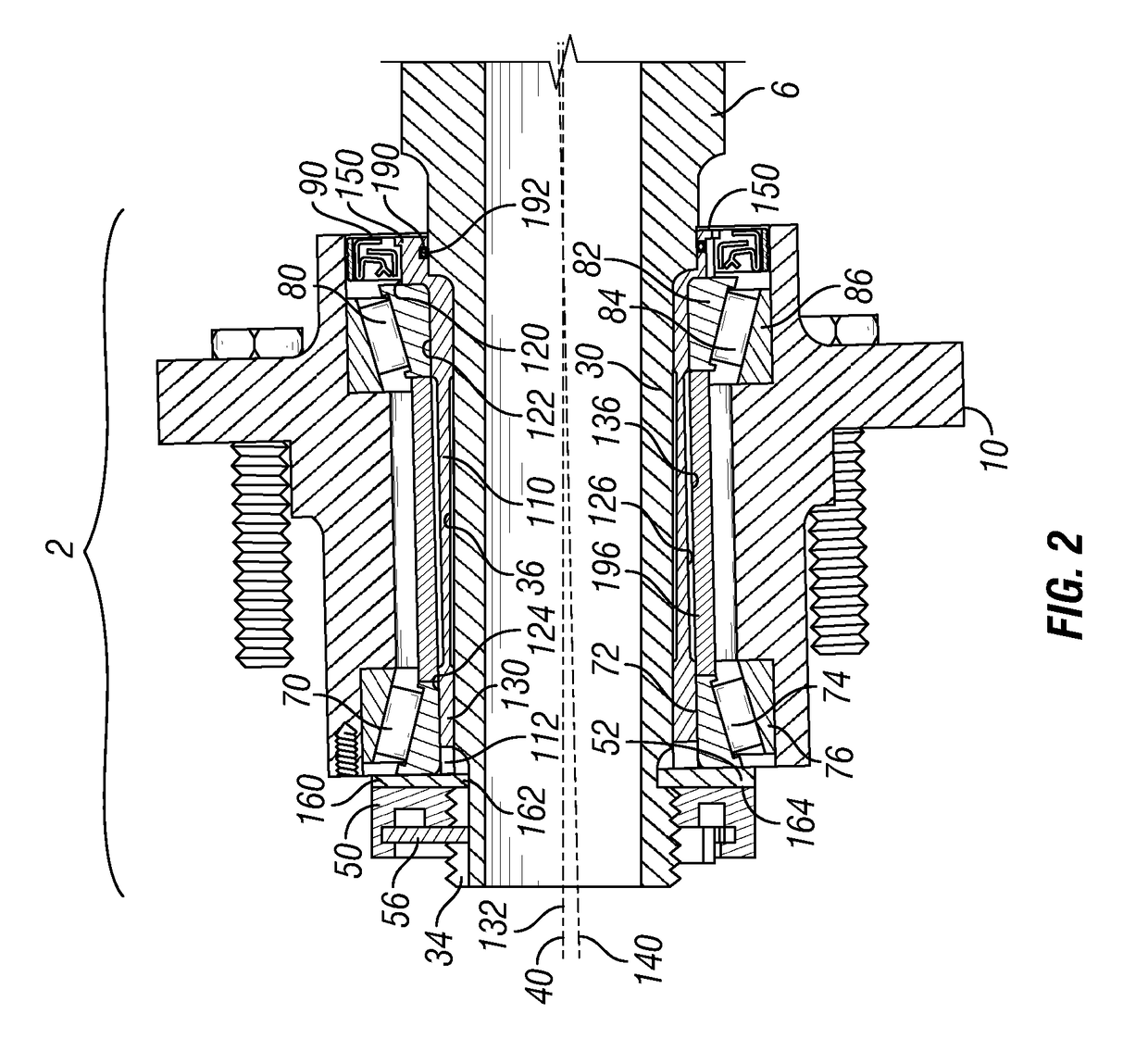
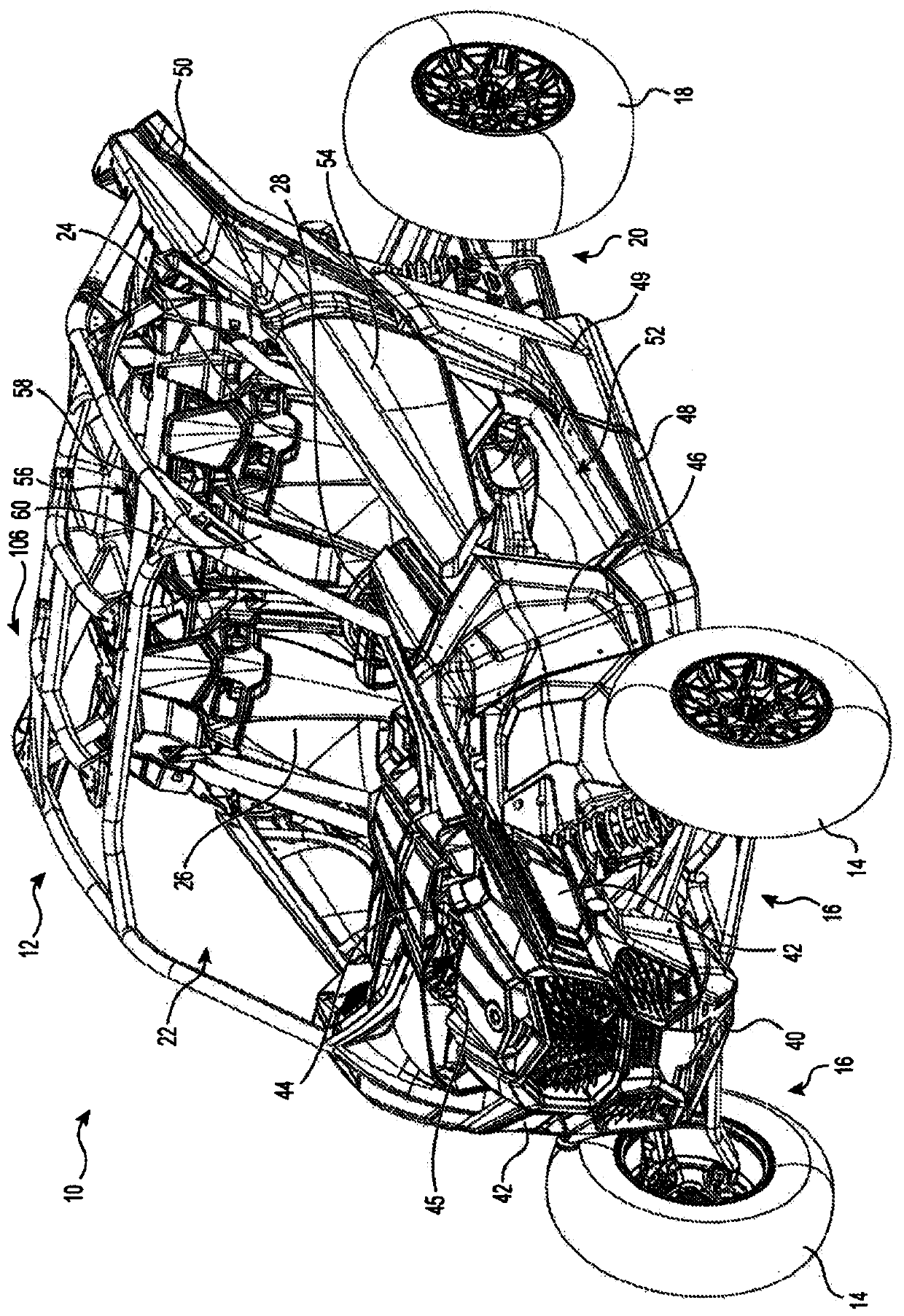
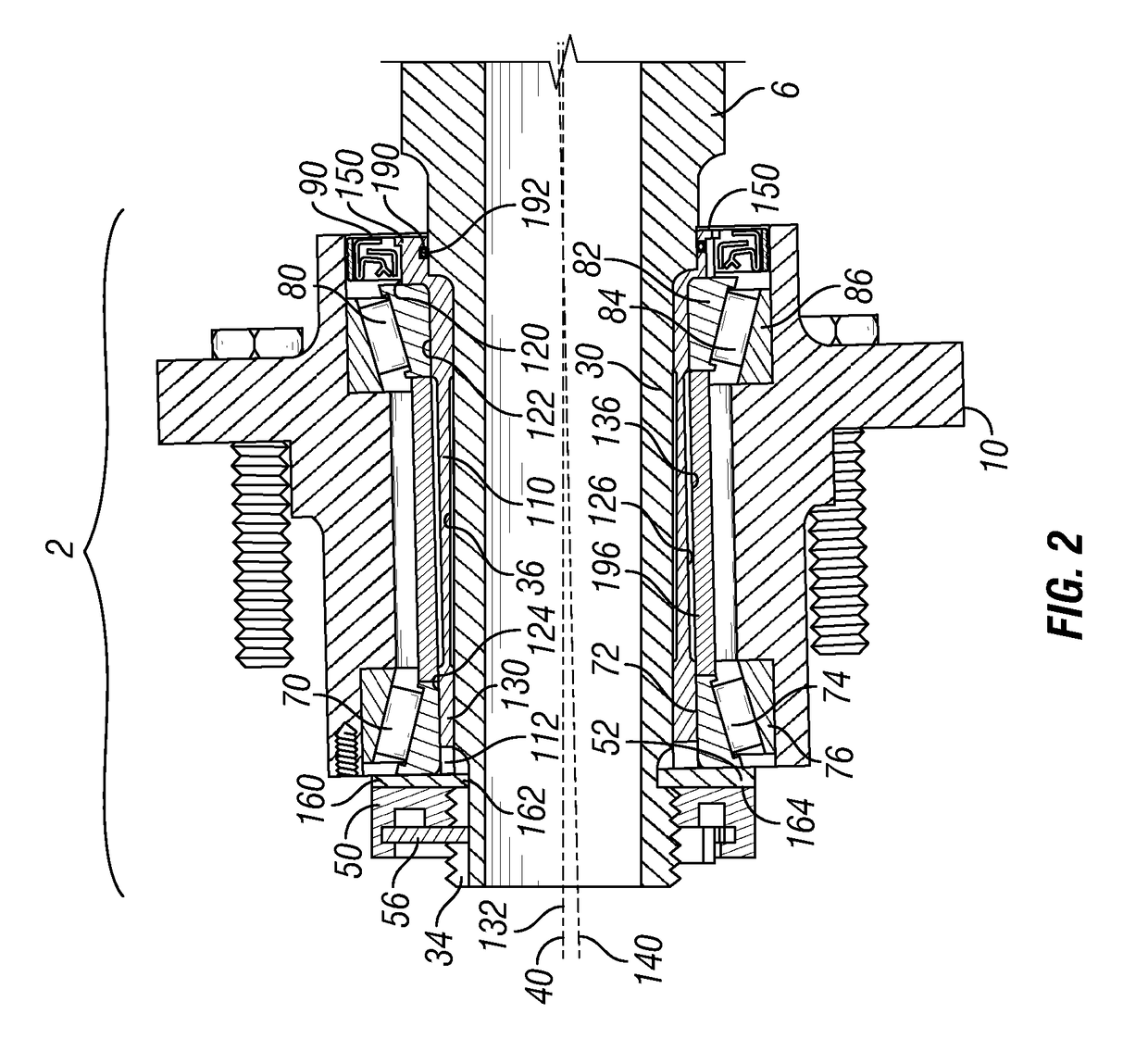
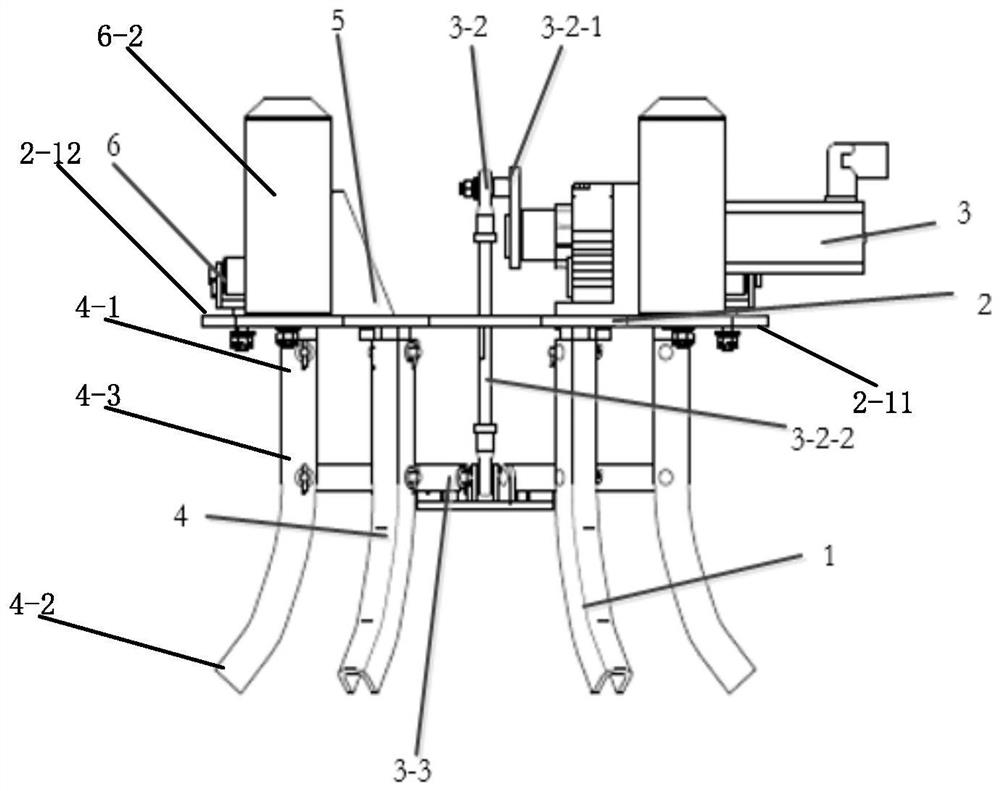
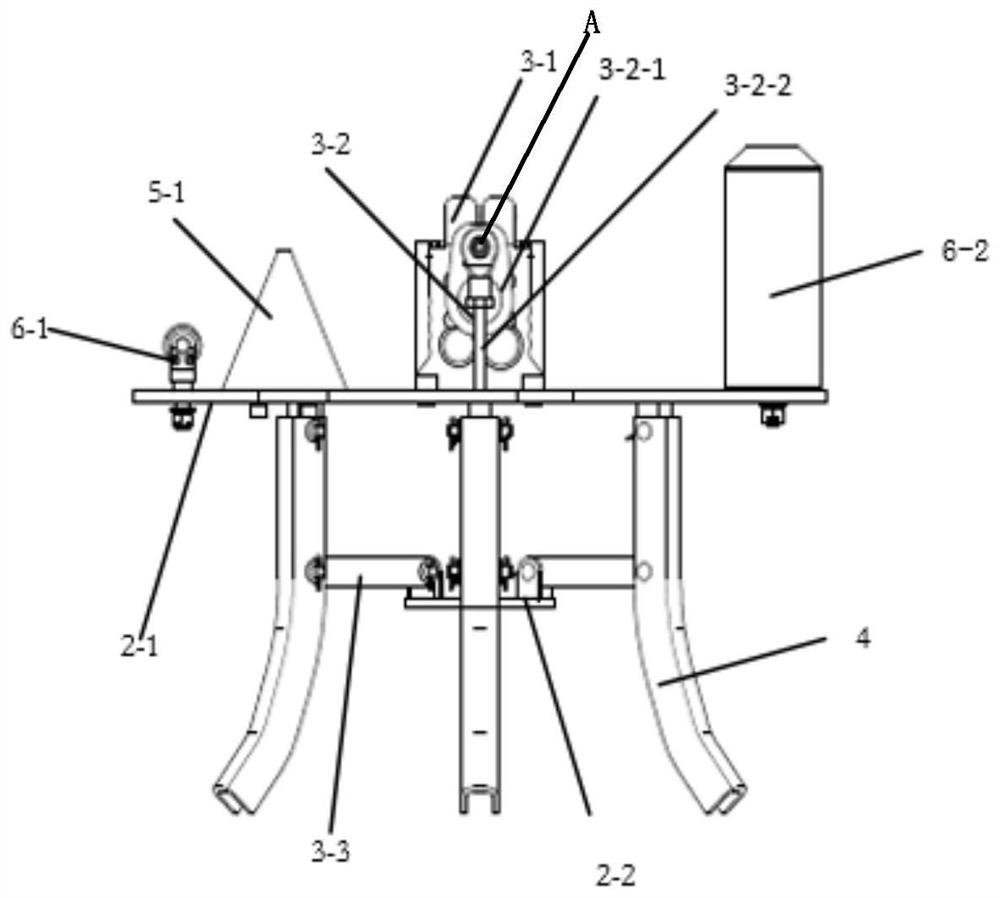
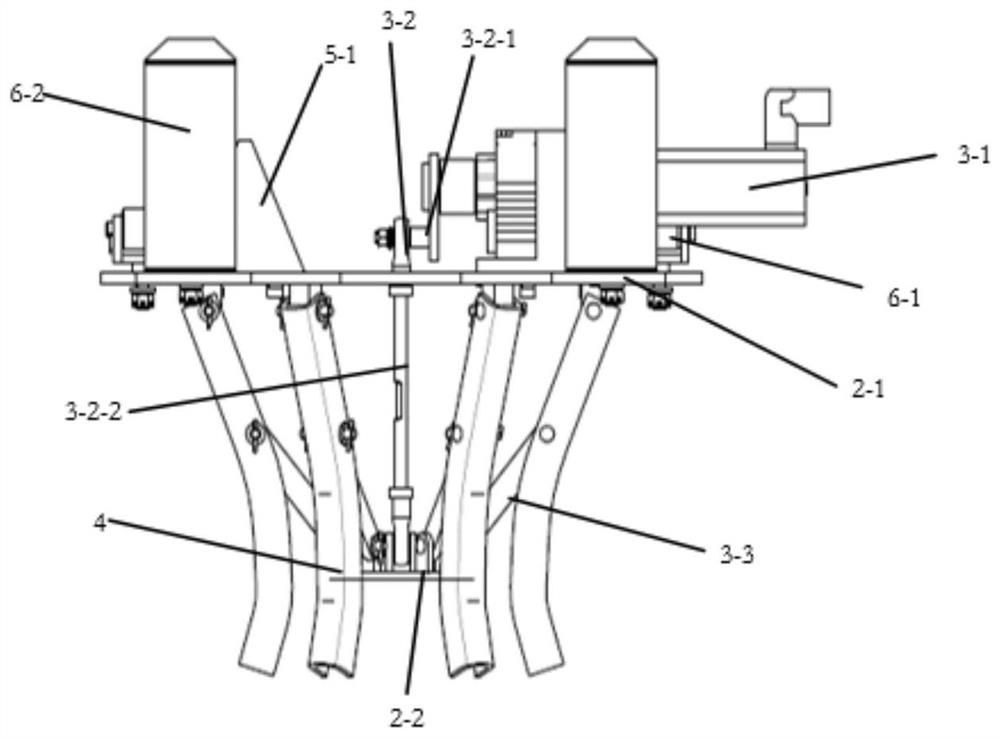
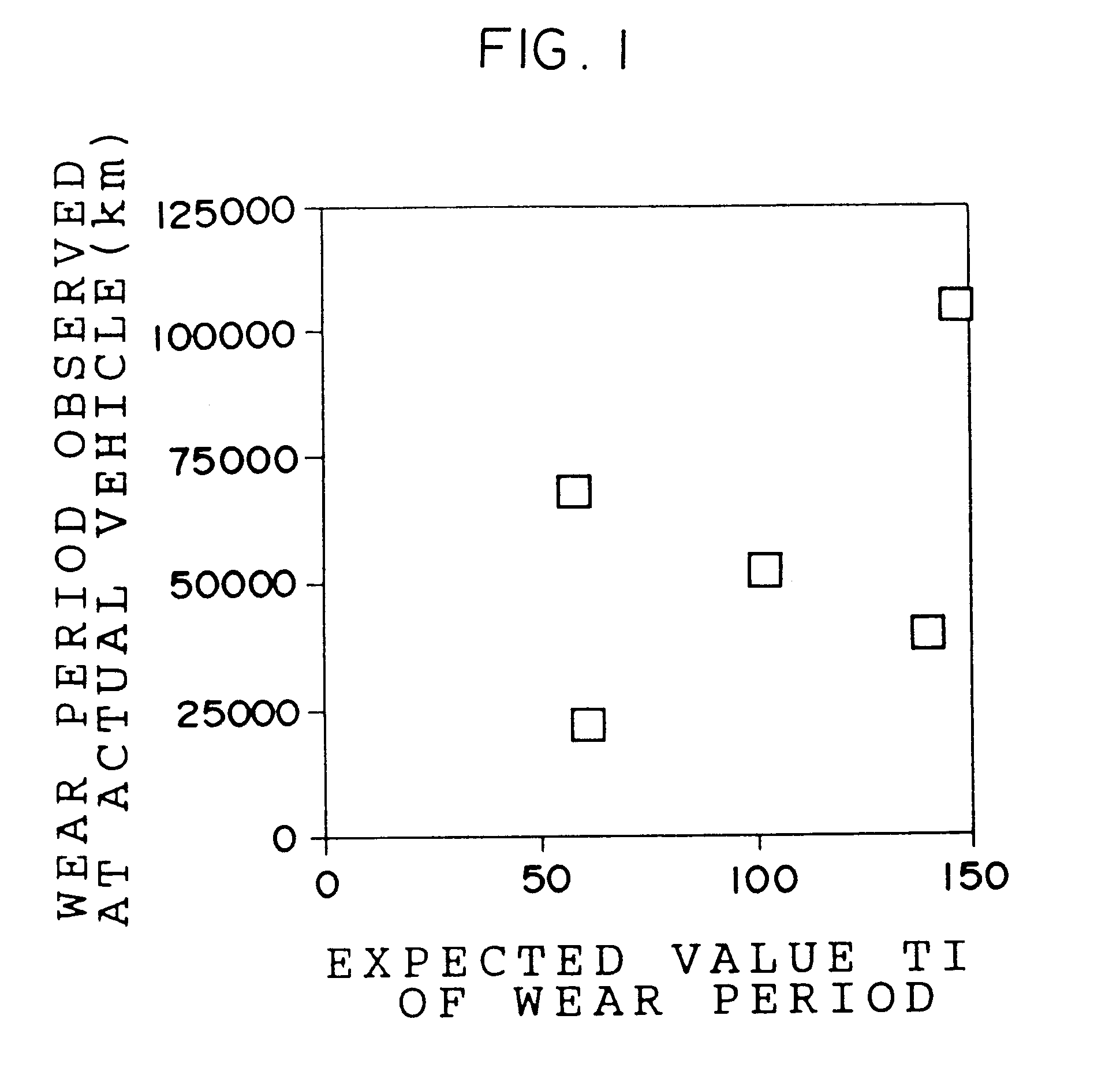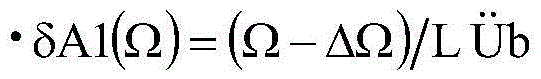Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109 results about "Toe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
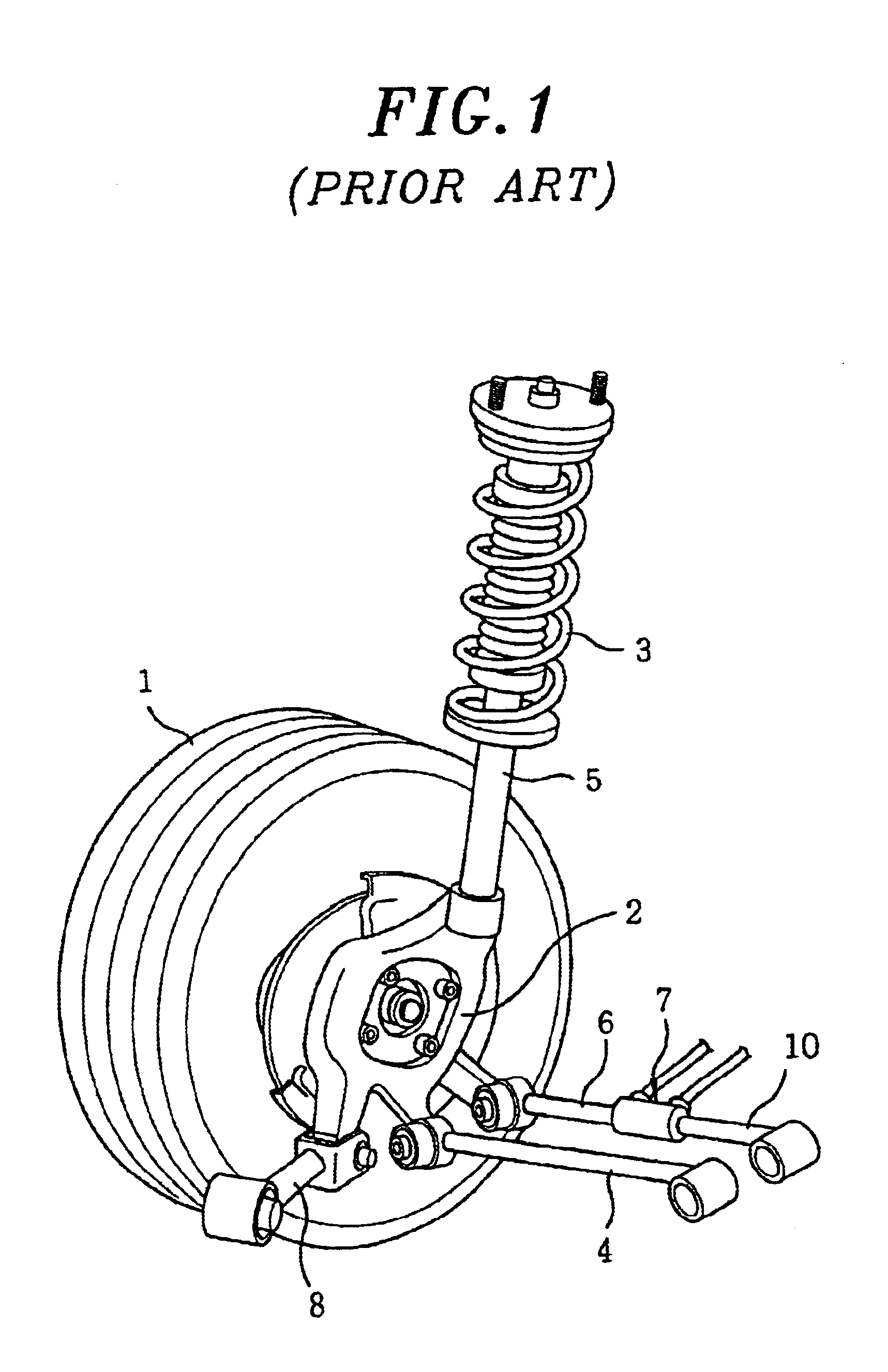
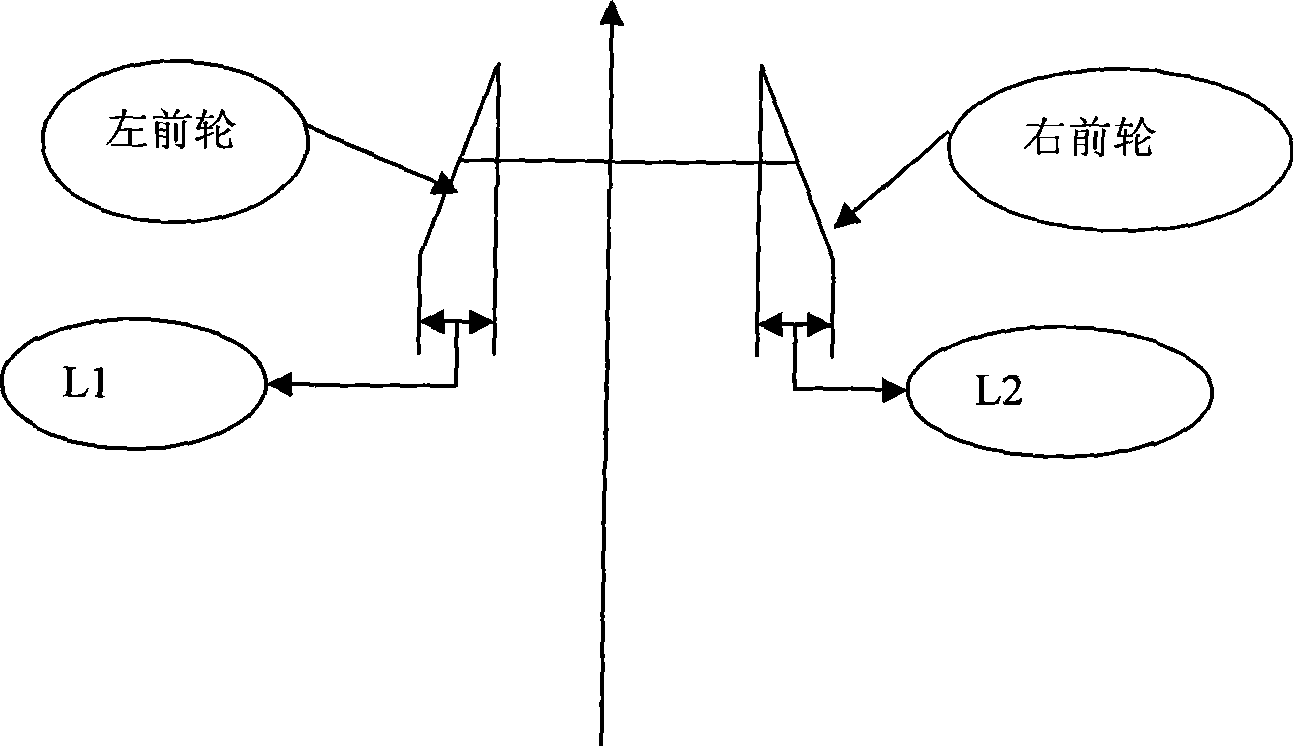
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as tracking, is the symmetric angle that each wheel makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a function of static geometry, and kinematic and compliant effects. This can be contrasted with steer, which is the antisymmetric angle, i.e. both wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly). Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel pointing away from the centerline of the vehicle. Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel pointing towards the centerline of the vehicle. Toe can be measured in linear units, at the front or rear of the tire, or as an angular deflection.
Wheel alignment gauge
InactiveUS20060185180A1Accurately indicatedAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringSpoke
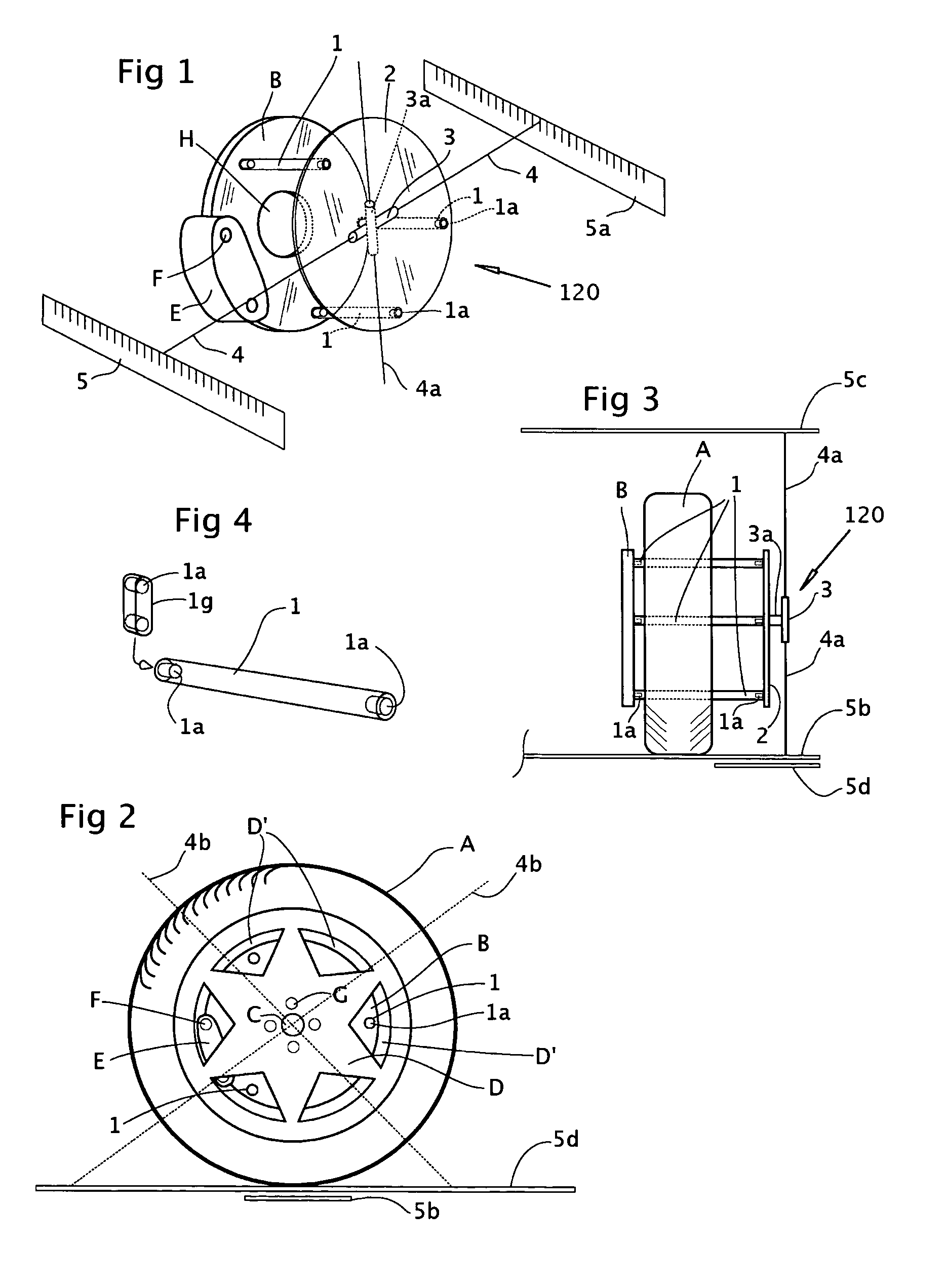
The present invention is a wheel alignment gauge for checking the ‘toe’ and ‘camber’ of the wheels. The gauge can be used with the vehicle on the ground. The gauge uses three identical magnet-ended extension rods which are inserted through the vent holes or spokes of the wheels. The rod's inboard ends magnetically attach to the disc brake rotor surface leaving the outboard ends clear of the vehicle's wheel and bodywork. Flat plates rest on the ground and magnetically attach to the outboard ends to create a plane parallel to the rotor and wheel. Laser-ended alignment arms magnetically attach to the plates, are level, and have forward ends that extend beyond the front of the vehicle allowing the lasers to project ate target sheets centered on the lasers. Each arm also has a perpendicular location arm that contacts the front of the wheel (or rotor when the wheels are removed). The laser's dots provide a off-center measurement, which, along with the arm's spacing, one can calculate the trigonometric SINE of the wheel's angle. The gauge can be quickly changed from vertical to horizontal for camber or toe measurements respectively. If adjustment is required, the vehicle is raised on its suspension, the wheels are removed and the gauge re-attached to locate on the rotors to direct alignment adjustments.
Owner:MACKELVIE WINSTON
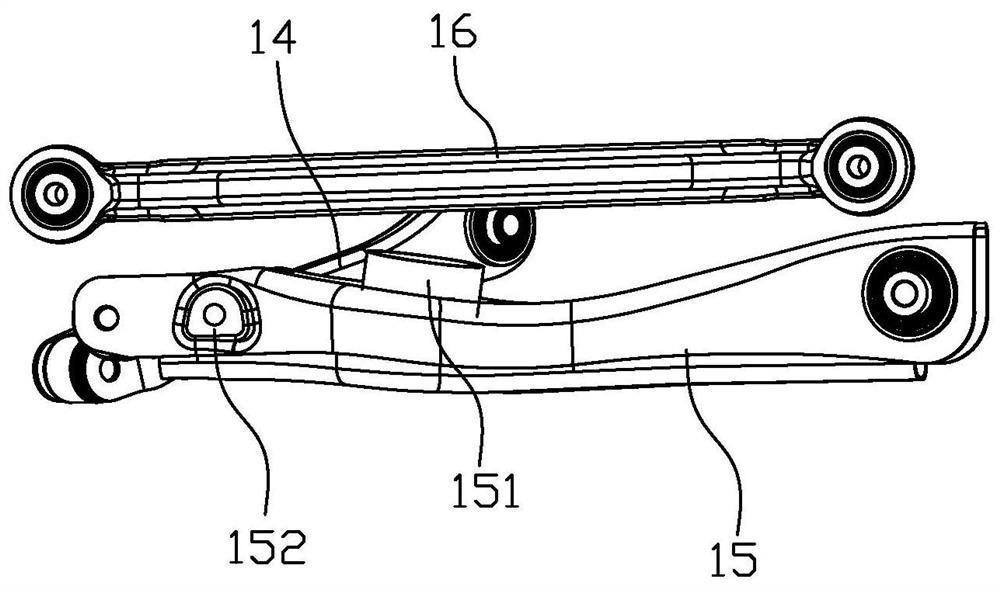
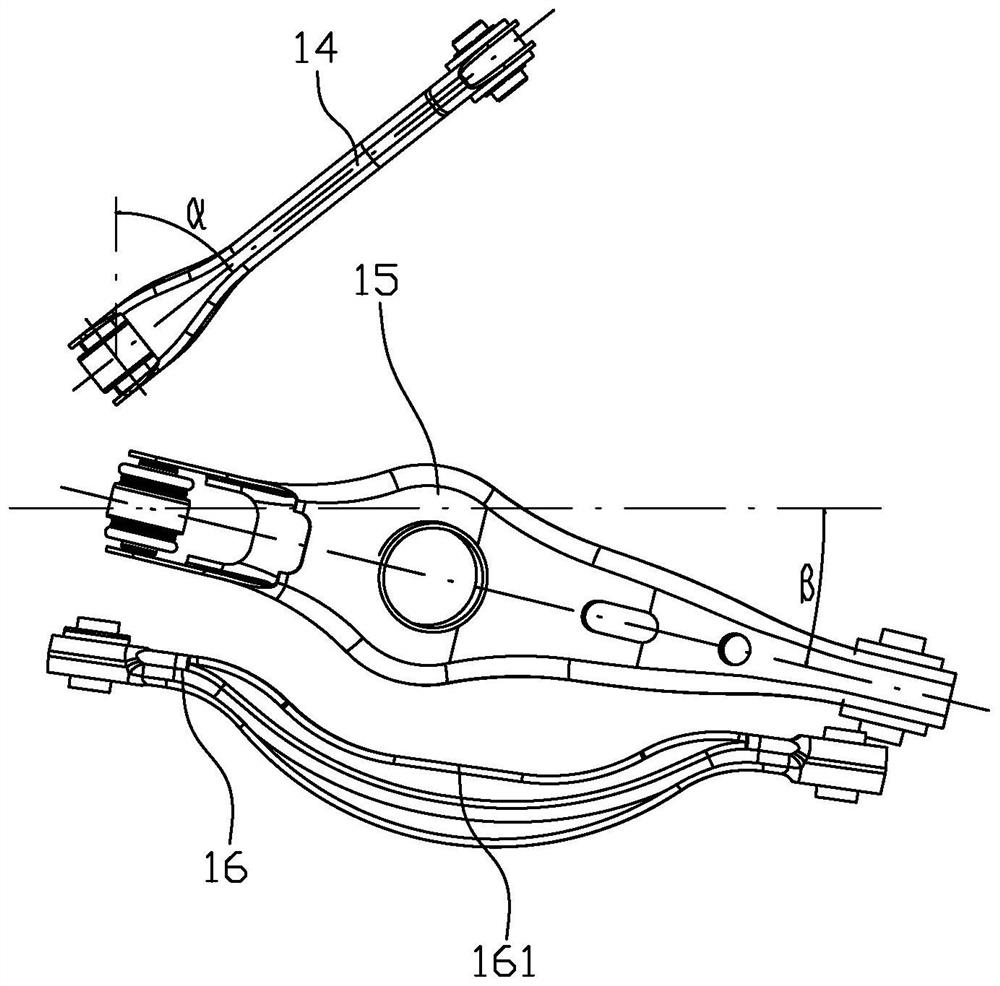
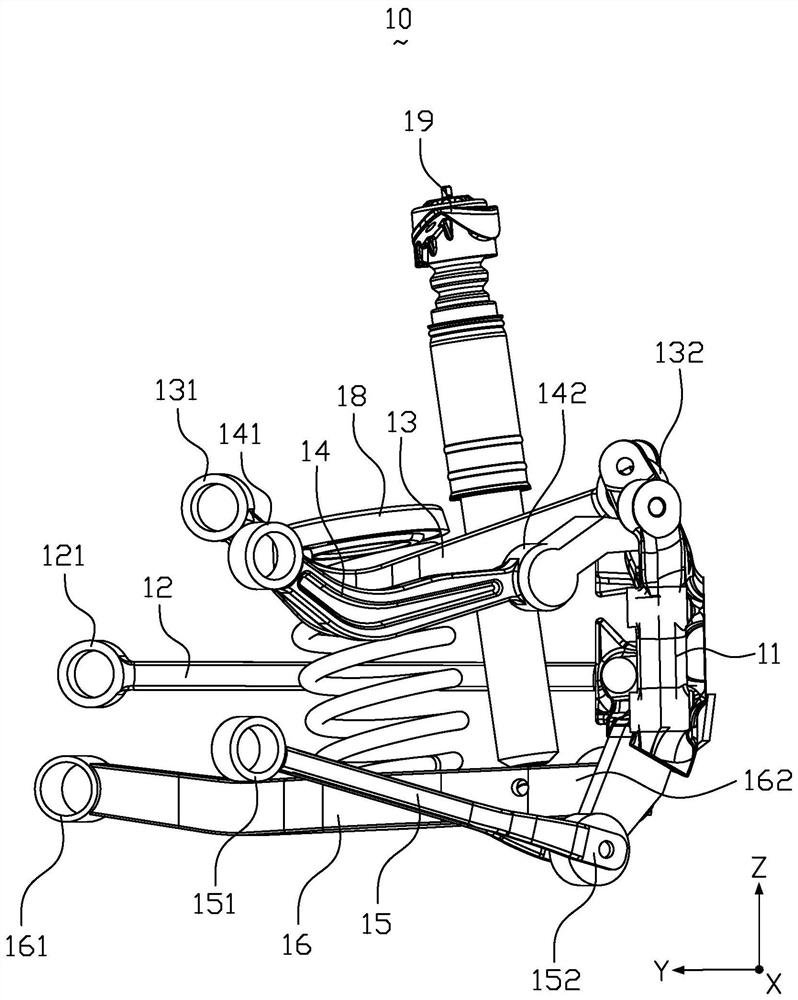
Self compensation floating swing arm independent suspension system
ActiveCN102363408AIdeal handlingIdealized securityInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsAnti-roll barCamber angle
The invention provides a self compensation floating swing arm independent suspension system, comprising a self compensation floating swing arm independent suspension device and a centrifugal force control scissors-type anti-roll bar device. The two mechanisms can be used in combination or independently and are applicable to both front wheels and rear wheels. The self compensation floating swing arm independent suspension system guarantees that wheels perform line bounce along a vertical direction of a car body on various kinds of road surfaces when a car runs at a low speed or at a high speed or makes turns and guarantees maximum contact area between the wheels and the road surfaces, with the parameters of king pin angle, toe-in angle, camber angle, wheel track, and axle base being maintained the same as original parameters; and, when the car makes turns, the centrifugal force control scissors-type anti-roll bar device works automatically, offsets a roll force with a force equal to the roll force in magnitude and opposite to the roll force in direction, and enables the car body to lower automatically, thereby improving anti-roll capacity and realizing idealization of controllability, safety, stability and comfort of the car. The self compensation floating swing arm independent suspension system has a simple structure, excellent performance, and low cost, and is easy to realize.
Owner:侯贺
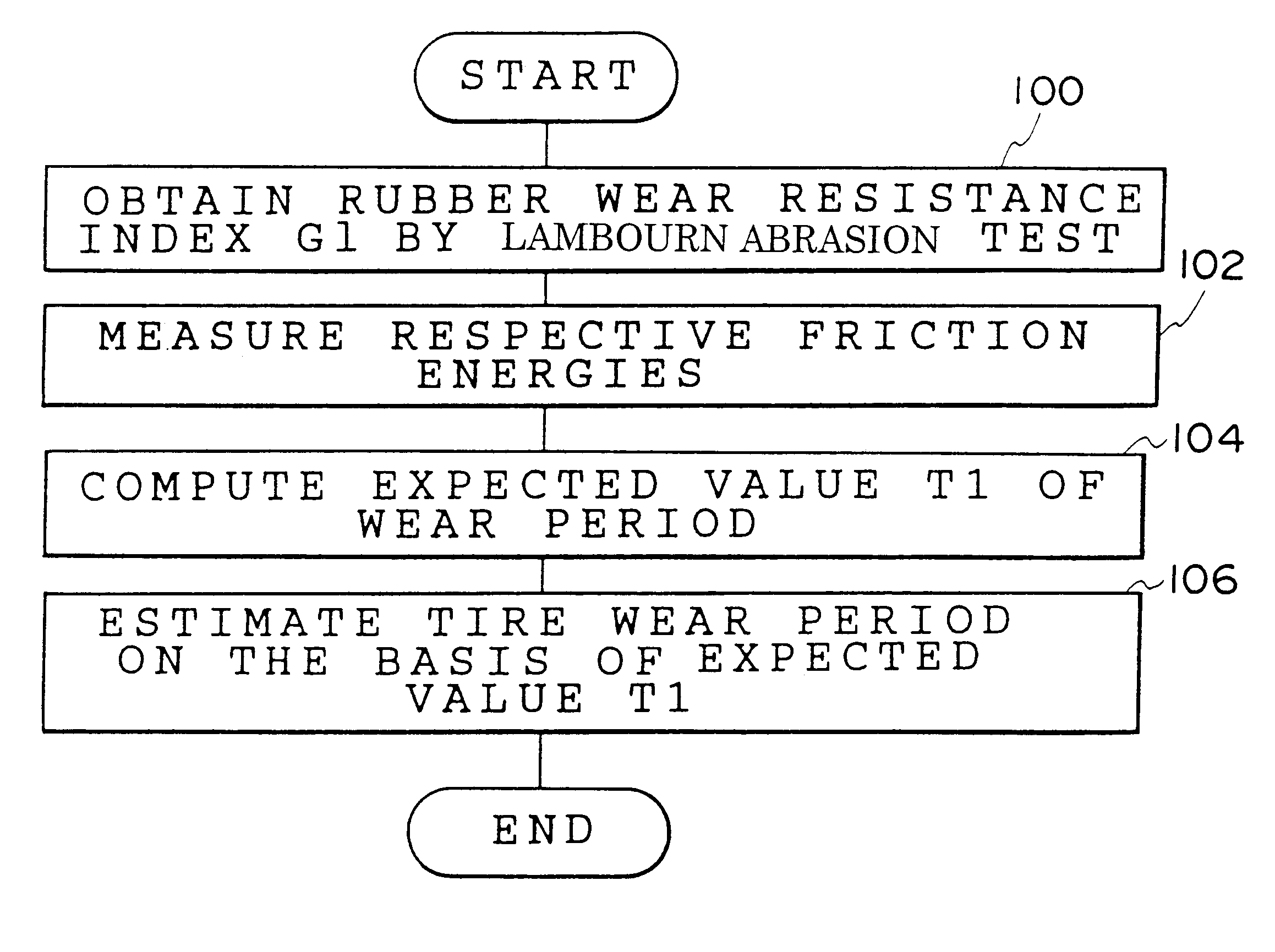
Method for estimating a tire wear life
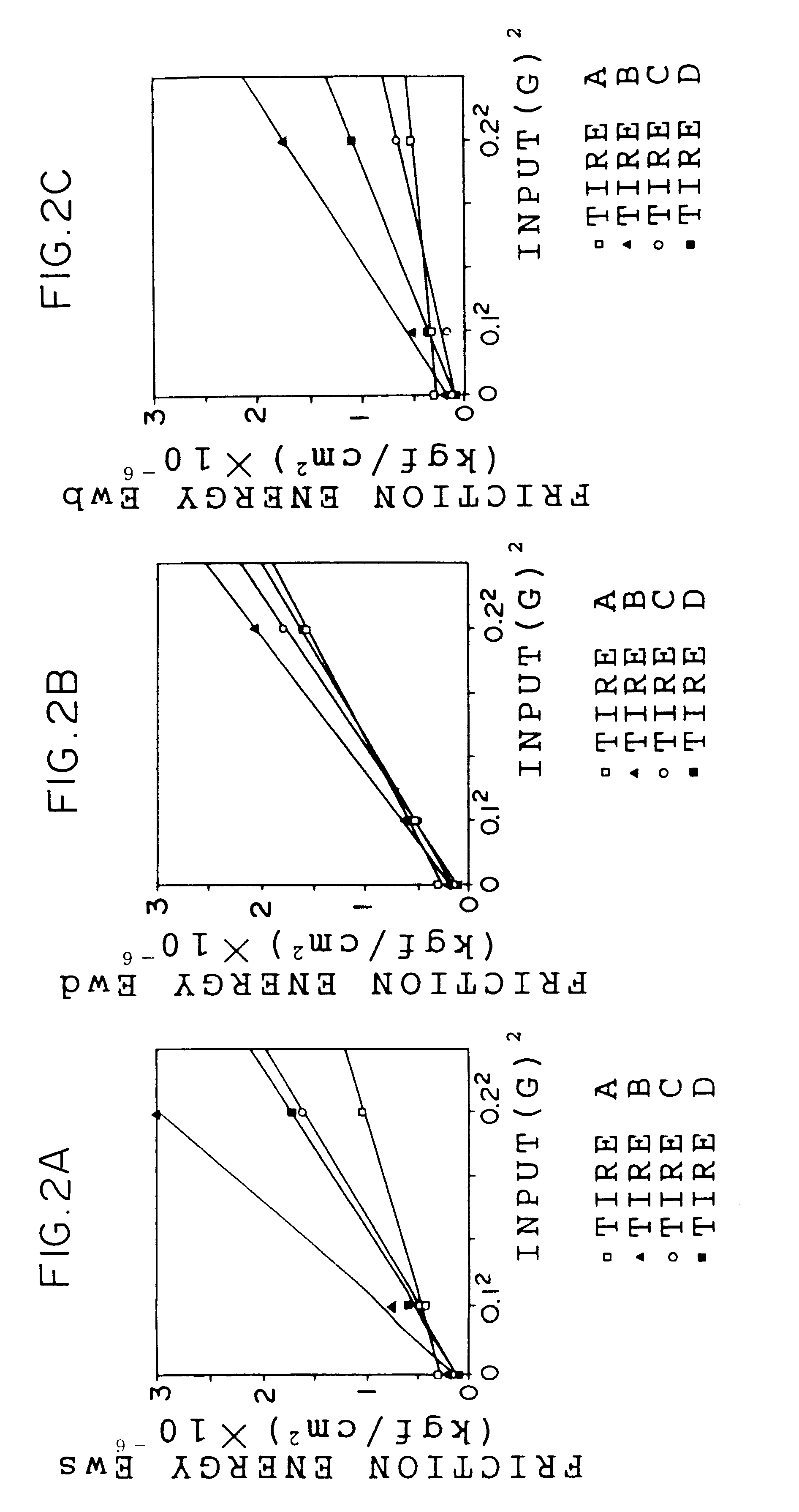
A wear resistance index G1 of a tire whose wear life is to be estimated is measured by the Lambourn abrasion tester. Then, friction energies in free rolling, when the tire is fitted with a toe angle, under application of a side force, under application of a braking force and under application of a driving force of the tire are measured. An expected value of the wear life T1 is calculated using the wear resistance index G1 and the friction energies thus obtained and the wear life of the tire is estimated on the basis of the expected value of the wear life T1. The wear life of a tire can be estimated accurately in a short time in accordance with the method for estimating a tire wear life of the present invention.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20070102085A1Improve drivabilityEfficient dischargeTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesGroove widthTransverse groove
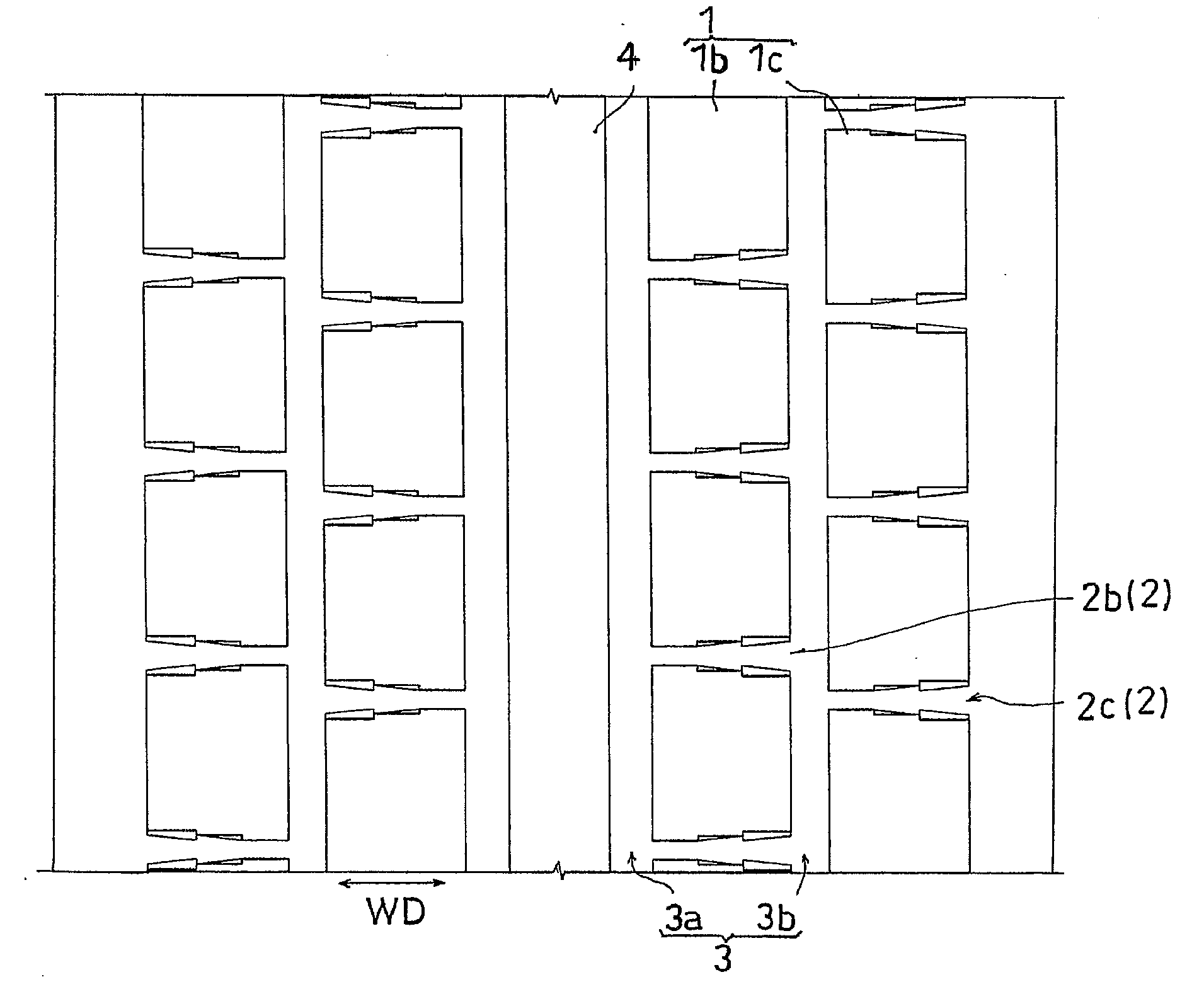
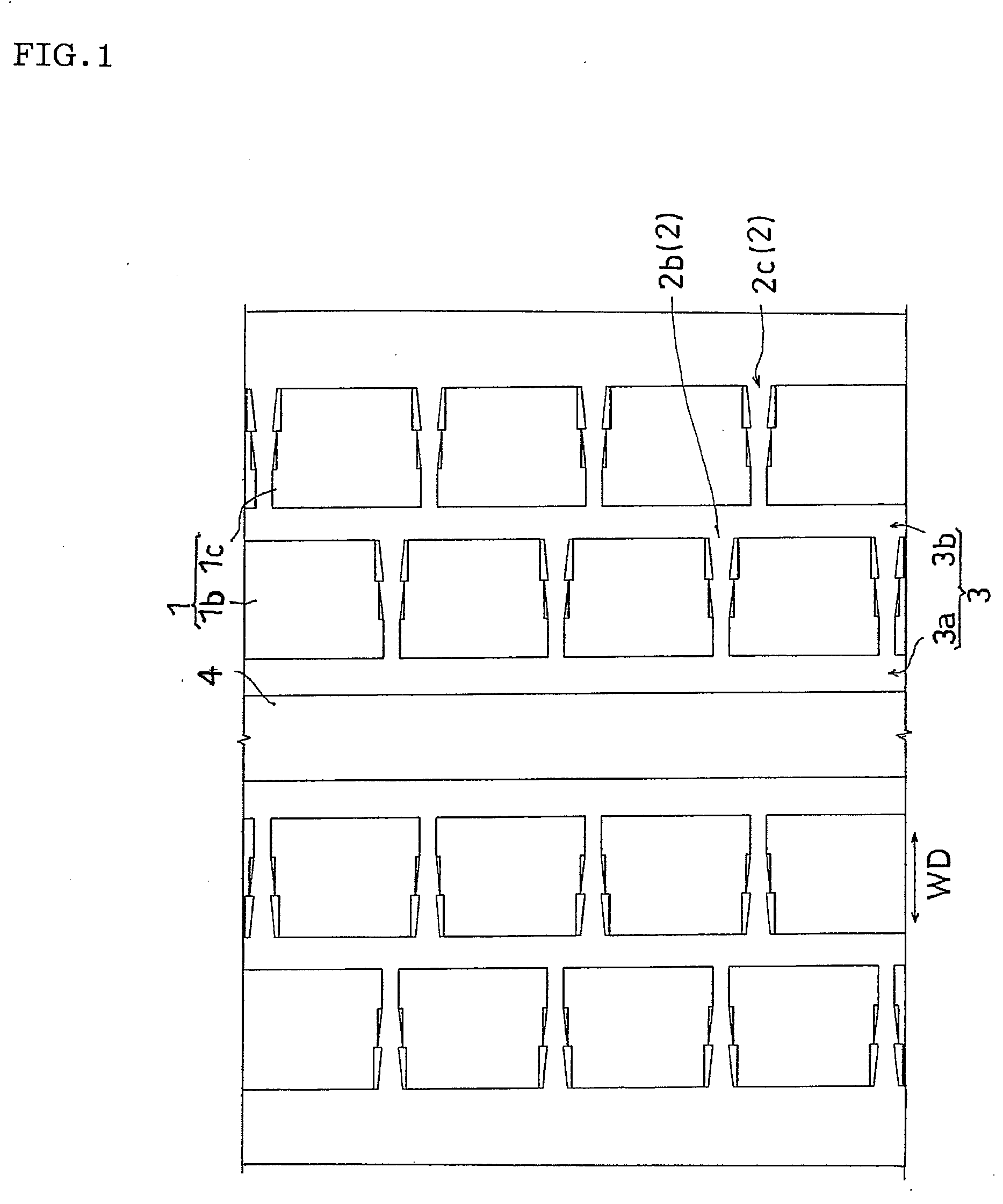
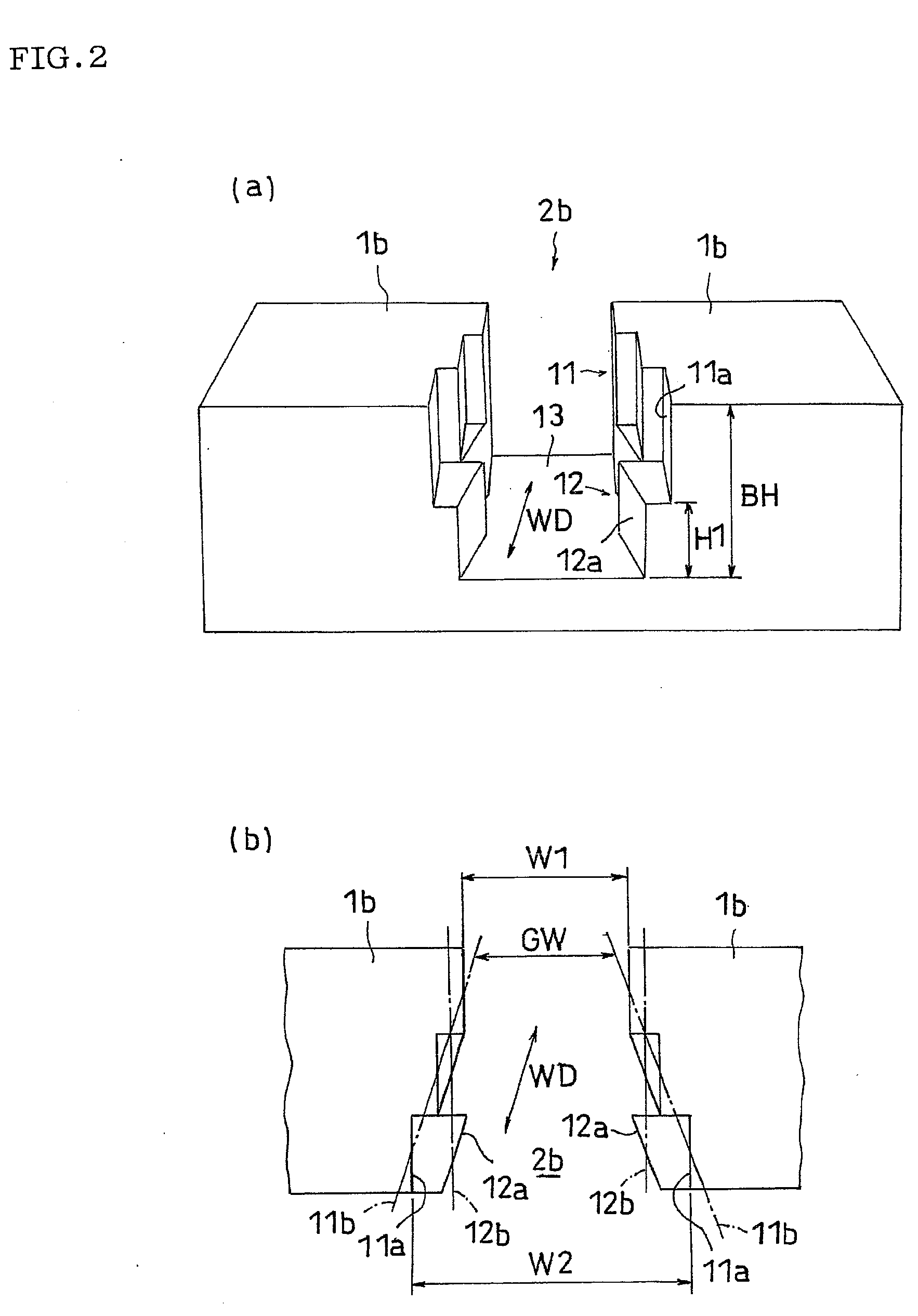
The invention provides a pneumatic tire which can increase a driving performance on a road surface of a so-called sherbet snow, and in which a biased wear such as a toe-and-heel wear or the like is hard to be generated. In a pneumatic tire provided with a tread pattern having a transverse groove 2b formed between a plurality of blocks 1b, the transverse groove 2b is provided with a top side groove portion 11 extending while a groove width GW expands to a tread end side, and a bottom side groove portion 12 extending with a roughly fixed groove width GW.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Vehicle wheel alignment technology
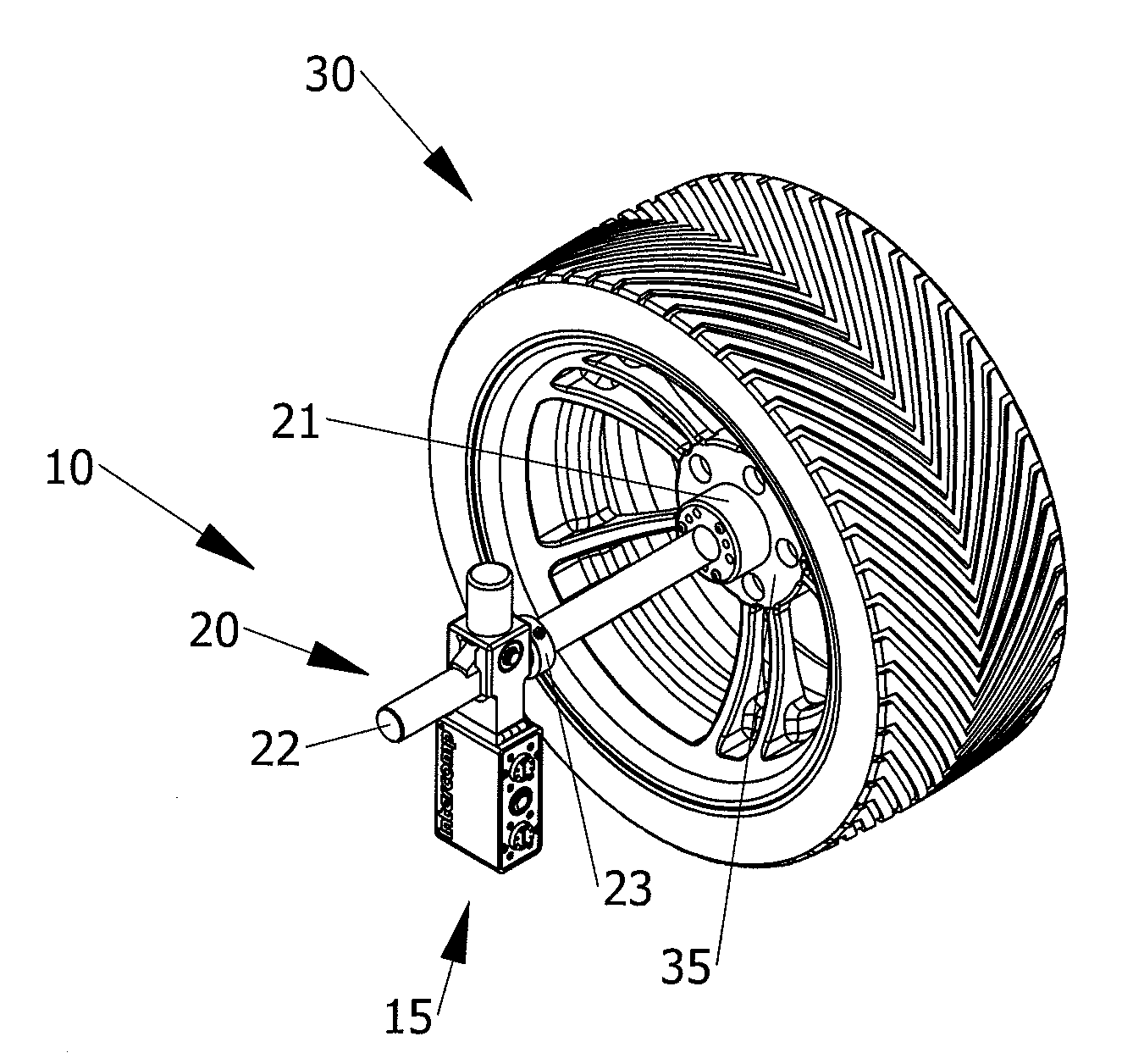
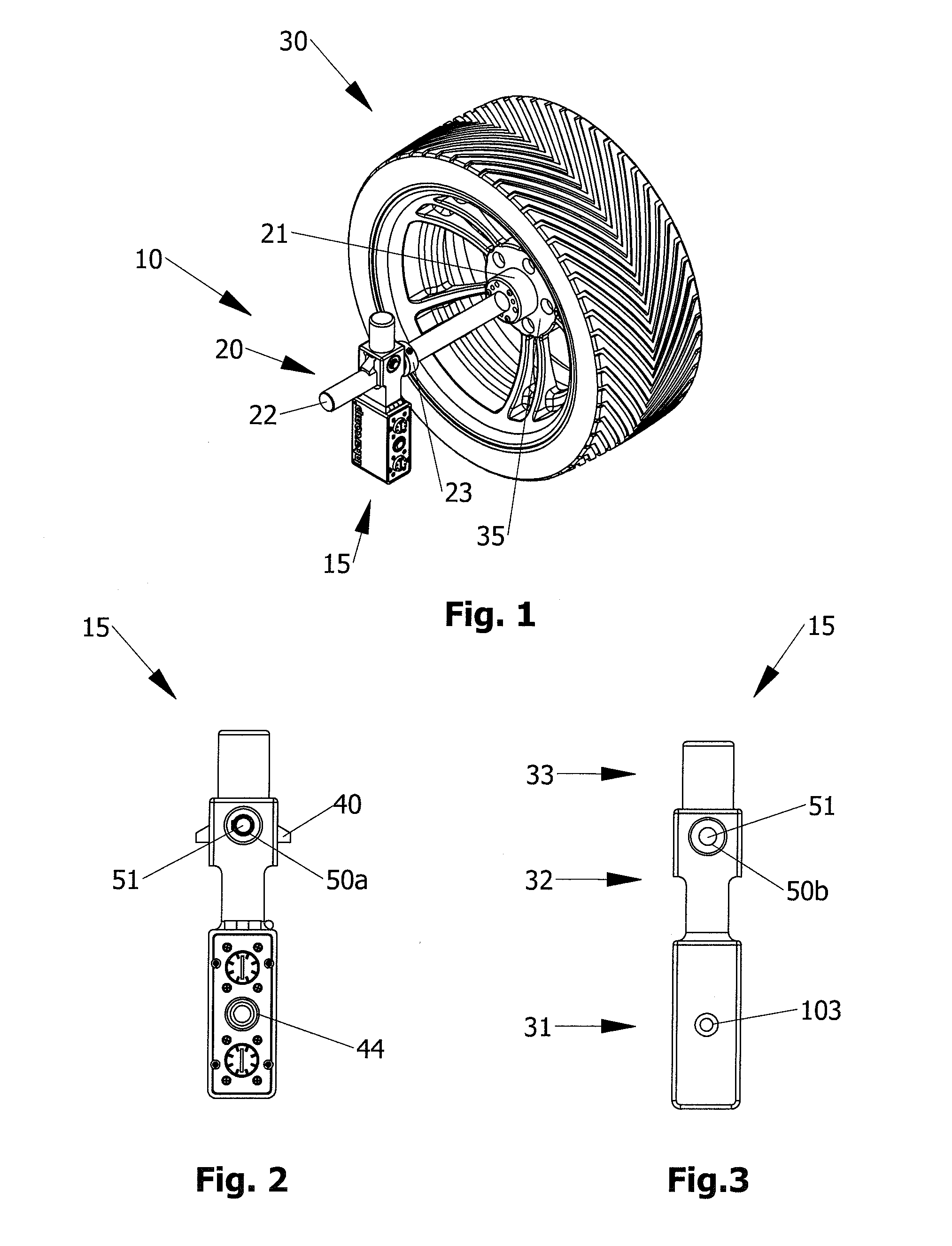
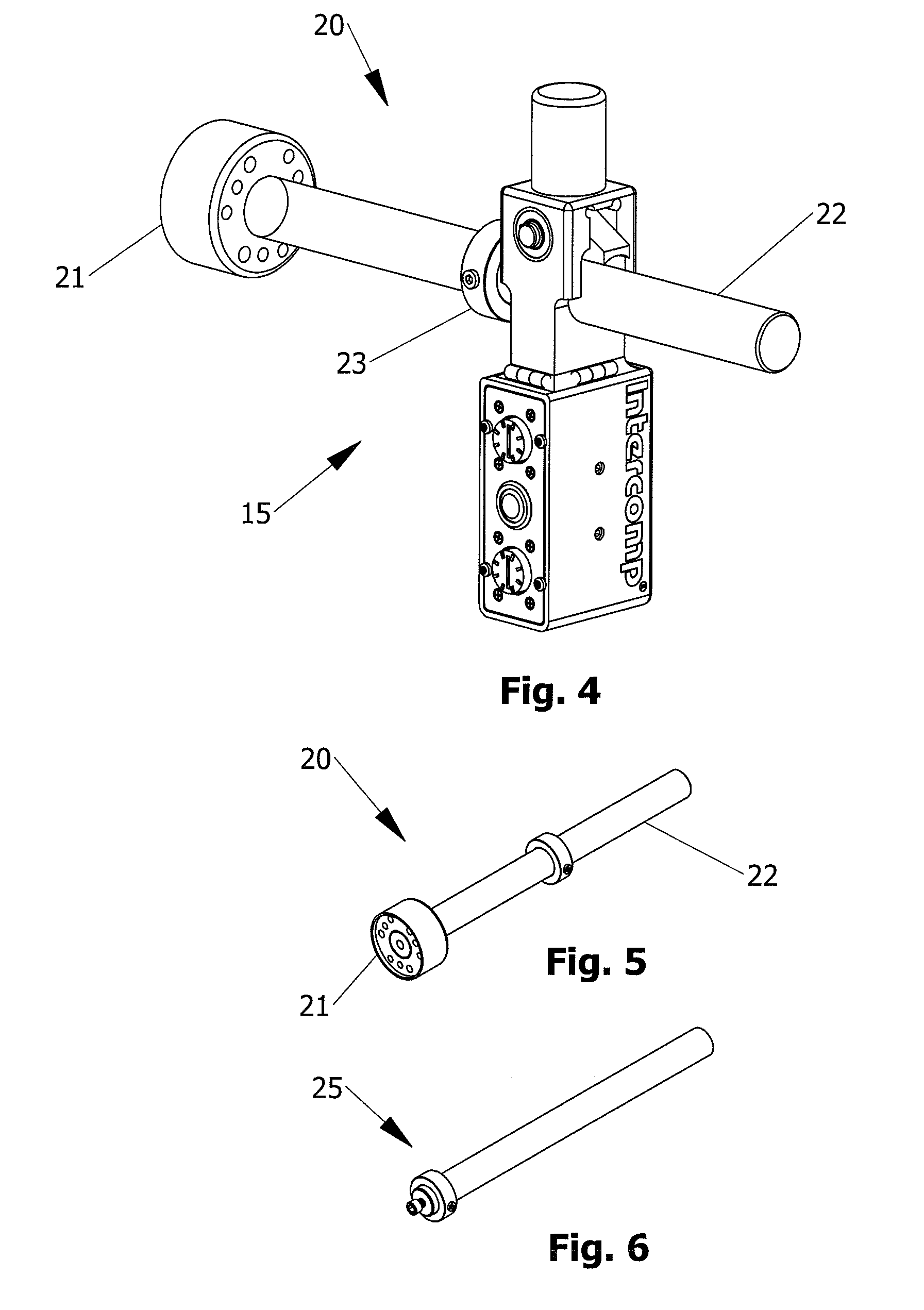
ActiveUS20130239420A1Accurate and repeatable referencePractical and reliable and accurate and efficientUsing optical meansMechanical measuring arrangementsVehicle frameEngineering
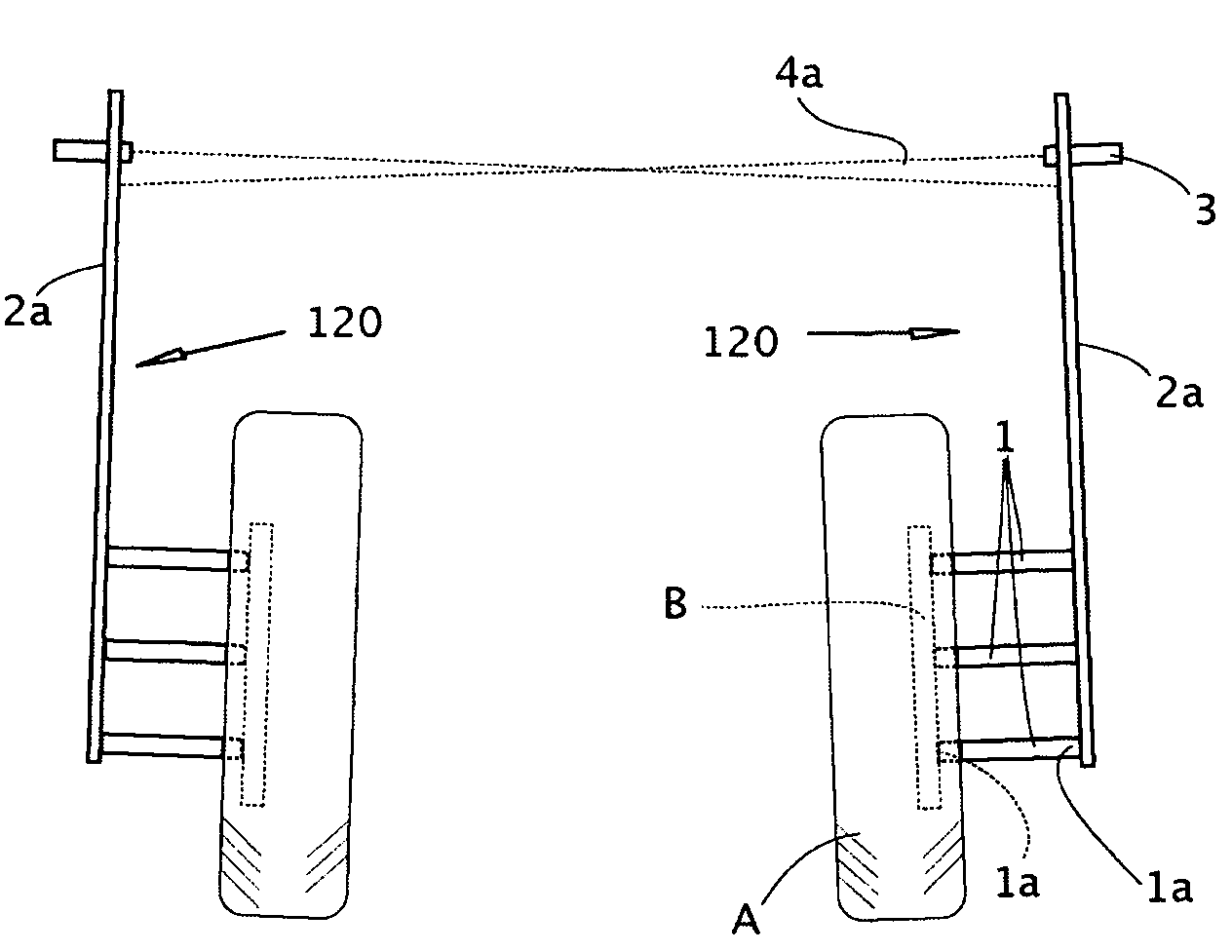
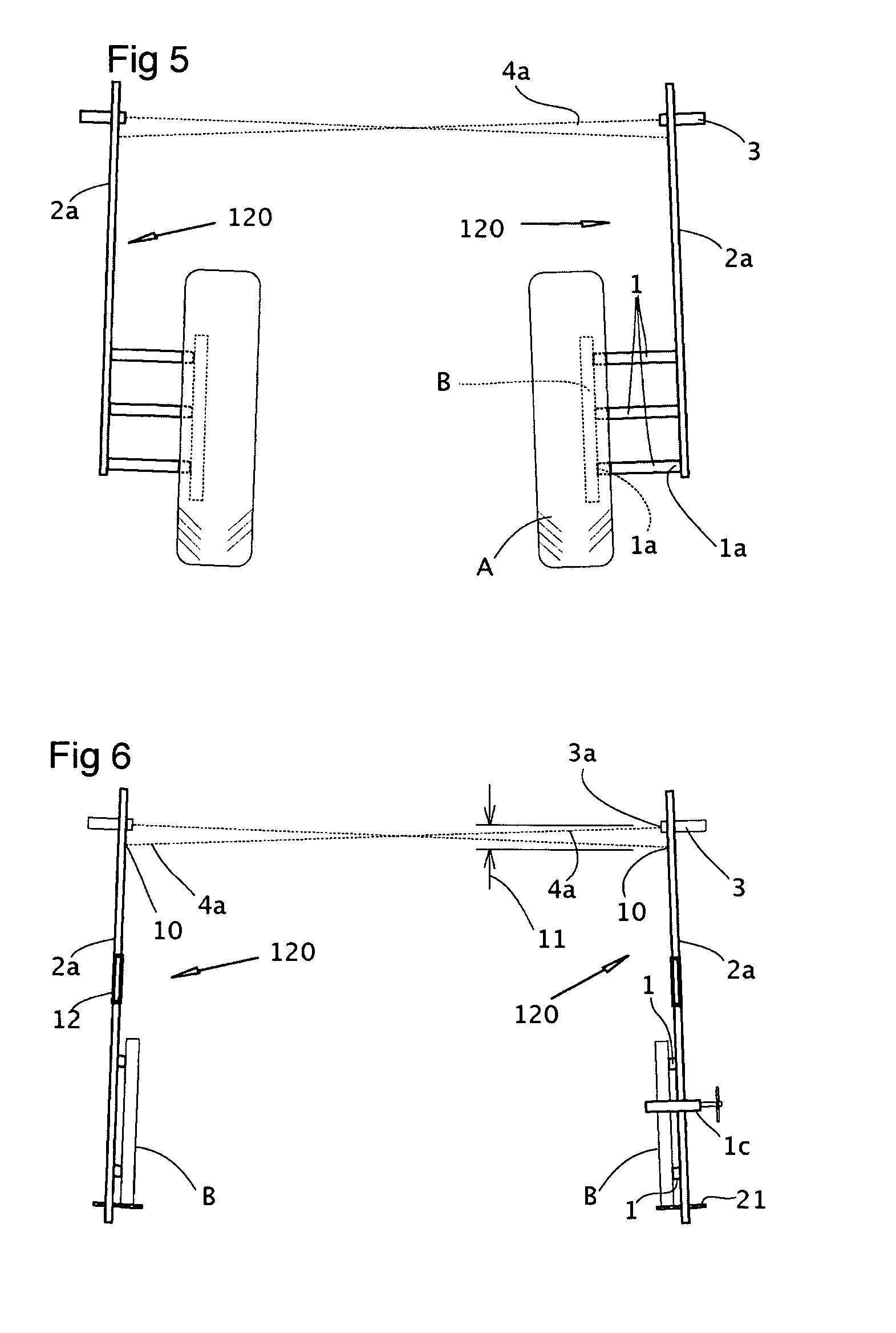
A laser square gauge for use with an automobile for measuring camber, toe and wheel offset. The laser square gauge generates a vertical laser datum line off of the wheel. The visible line replaces the cumbersome use of jigs and string lines. The gauge is operable by a single user and generates an accurate, repeatable reference. The reference can be used to easily measure camber, offset, toe-in and toe-out of the other wheels, as well as car body and frame dimensions. The gauge permits easy maintenance of records to check set-up dimensions of each car for each environment, such as a race track. The gauge is particularly useful for setting up the alignment and suspension of high performance racing automobiles.
Owner:INTERCOMP
Active toe angle adjustment mechanism
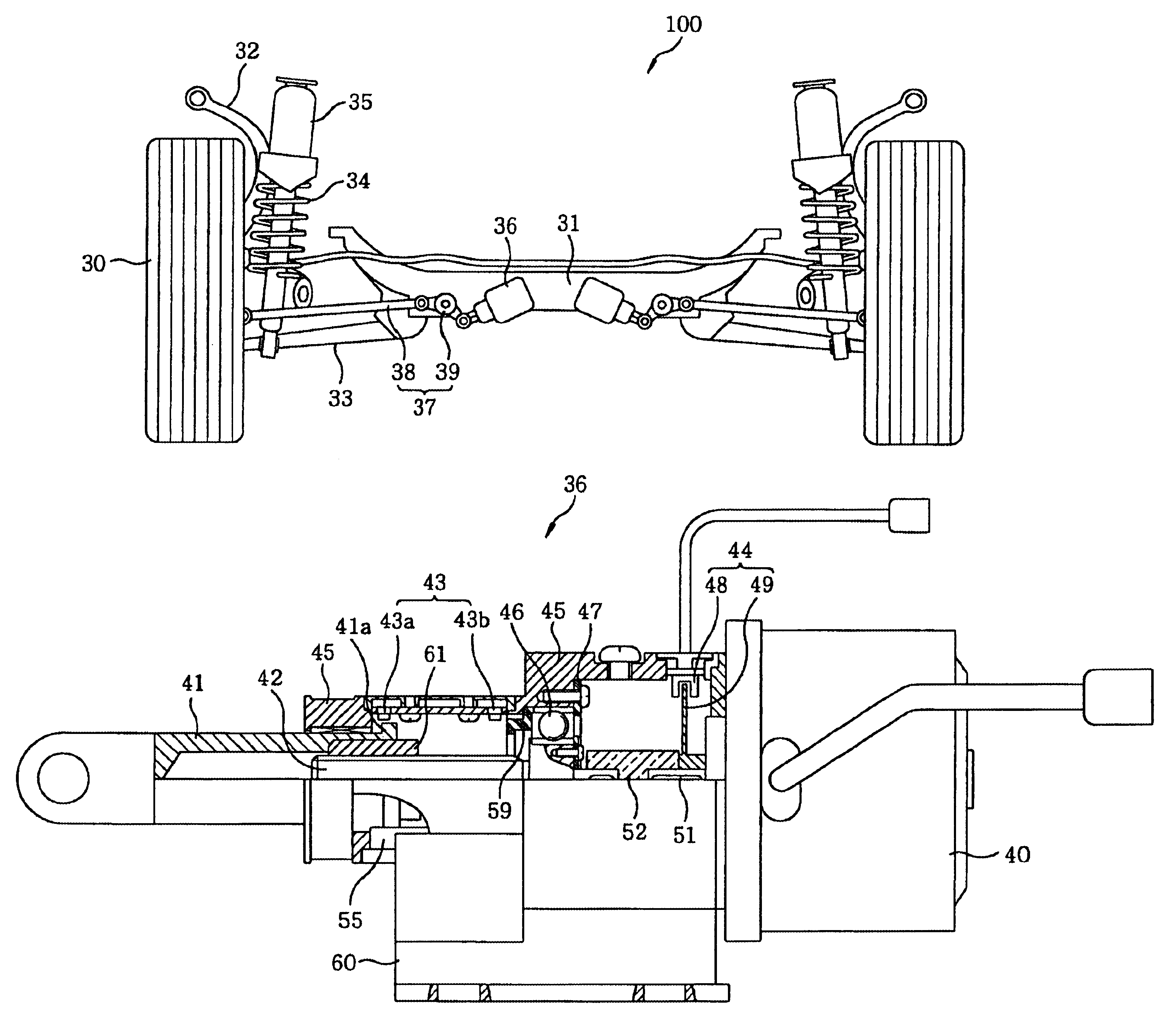
InactiveUS6962355B2Short response timeReduce occupationVehicle testingSteering linkagesJoystickBall screw
A toe angle adjustment mechanism includes an electrical linear actuator, a control lever, and an interconnection arm, wherein the electrical linear actuator is mounted on a rear cross member of a vehicle having a pair of rear wheels. The control lever, pivotally attached to the rear cross member, pivotally interconnects the electrical linear actuator with the interconnection arm, which is pivotally connected with a steering knuckle rotationally coupled with a corresponding rear wheel. The electrical linear actuator includes a housing, a motor, a ball screw rotated by the motor, a ball nut operatively mounted on the ball screw for linear movement therealong in response to rotation of the ball screw by the motor, and an actuator rod attached to the ball nut.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Apparatus and method for determining the orientation of an object such as vehicle wheel alignment
ActiveUS7710555B2Easy to adjustEasy alignmentVehicle testingSurveying instrumentsFresnel lensCamber angle
An apparatus for determining wheel assembly alignment comprises a contact assembly, a light source, and a light beam receiving assembly. The contact assembly engages the wheel assembly to define a plane of orientation of the wheel assembly and the light source projects a beam of light with respect to the contact assembly. The light beam receiving assembly receives the light beam and forms an image of the light beam indicating the orientation of the wheel assembly with respect to a predetermined position. The receiving assembly may include a Fresnel lens for directing the received light beam to a target and a camera device for imaging the light beam on the target, with the camera device adapted to provide toe and camber information of the wheel assembly based on the location at which the light beam impinges upon the target. The contact assembly may be pressed against the wheel assembly without being secured thereto.
Owner:BURKE E PORTER MACHINERY
Apparatus and method for determining the orientation of an object such as vehicle wheel alignment
ActiveUS20080007016A1Easy to adjustEasy alignmentVehicle testingSurveying instrumentsFresnel lensLight beam
An apparatus for determining wheel assembly alignment comprises a contact assembly, a light source, and a light beam receiving assembly. The contact assembly engages the wheel assembly to define a plane of orientation of the wheel assembly and the light source projects a beam of light with respect to the contact assembly. The light beam receiving assembly receives the light beam and forms an image of the light beam indicating the orientation of the wheel assembly with respect to a predetermined position. The receiving assembly may include a Fresnel lens for directing the received light beam to a target and a camera device for imaging the light beam on the target, with the camera device adapted to provide toe and camber information of the wheel assembly based on the location at which the light beam impinges upon the target. The contact assembly may be pressed against the wheel assembly without being secured thereto.
Owner:BURKE E PORTER MACHINERY
Spindle system for wheel alignment correction with brake adjustment
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
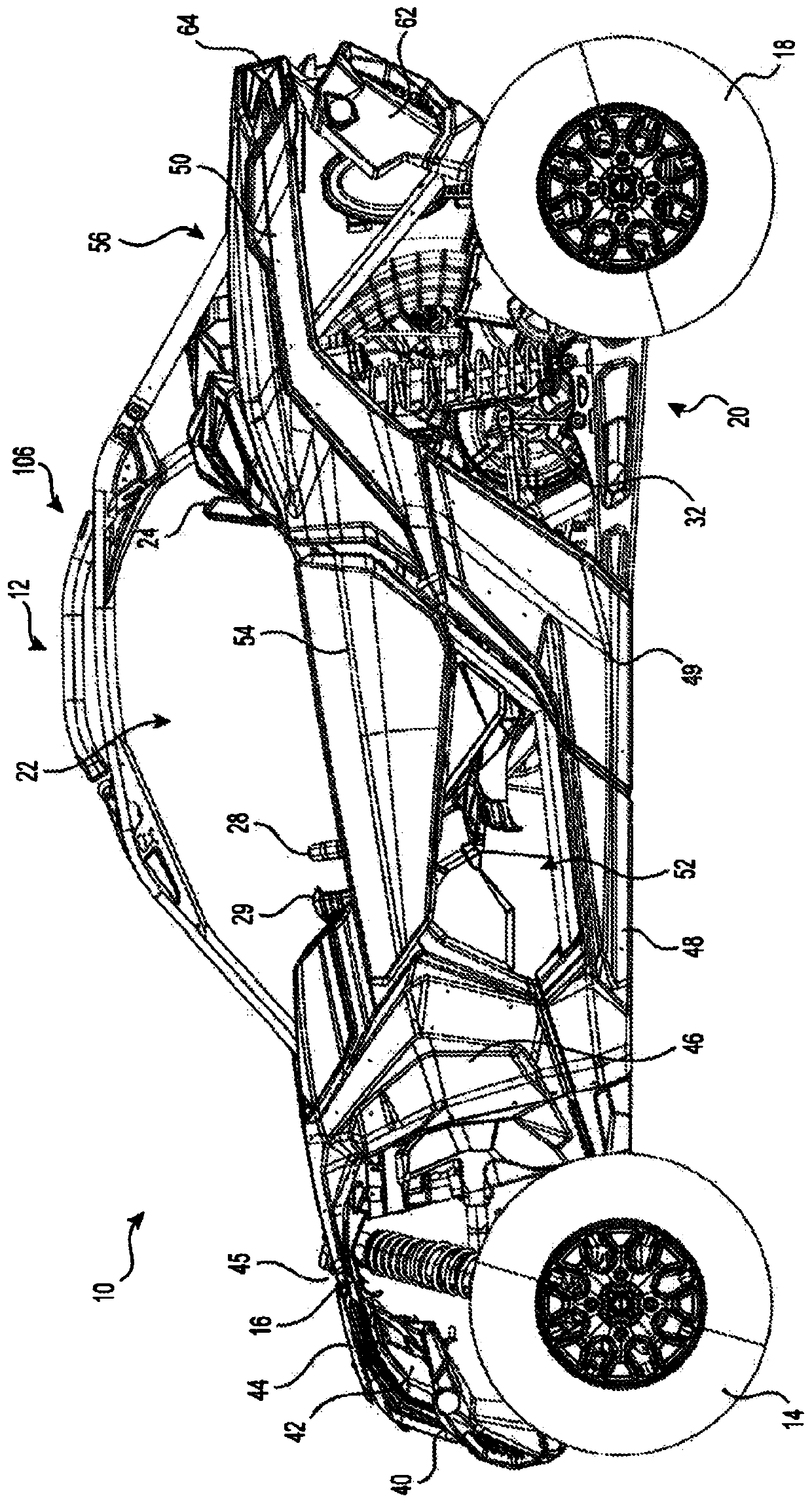
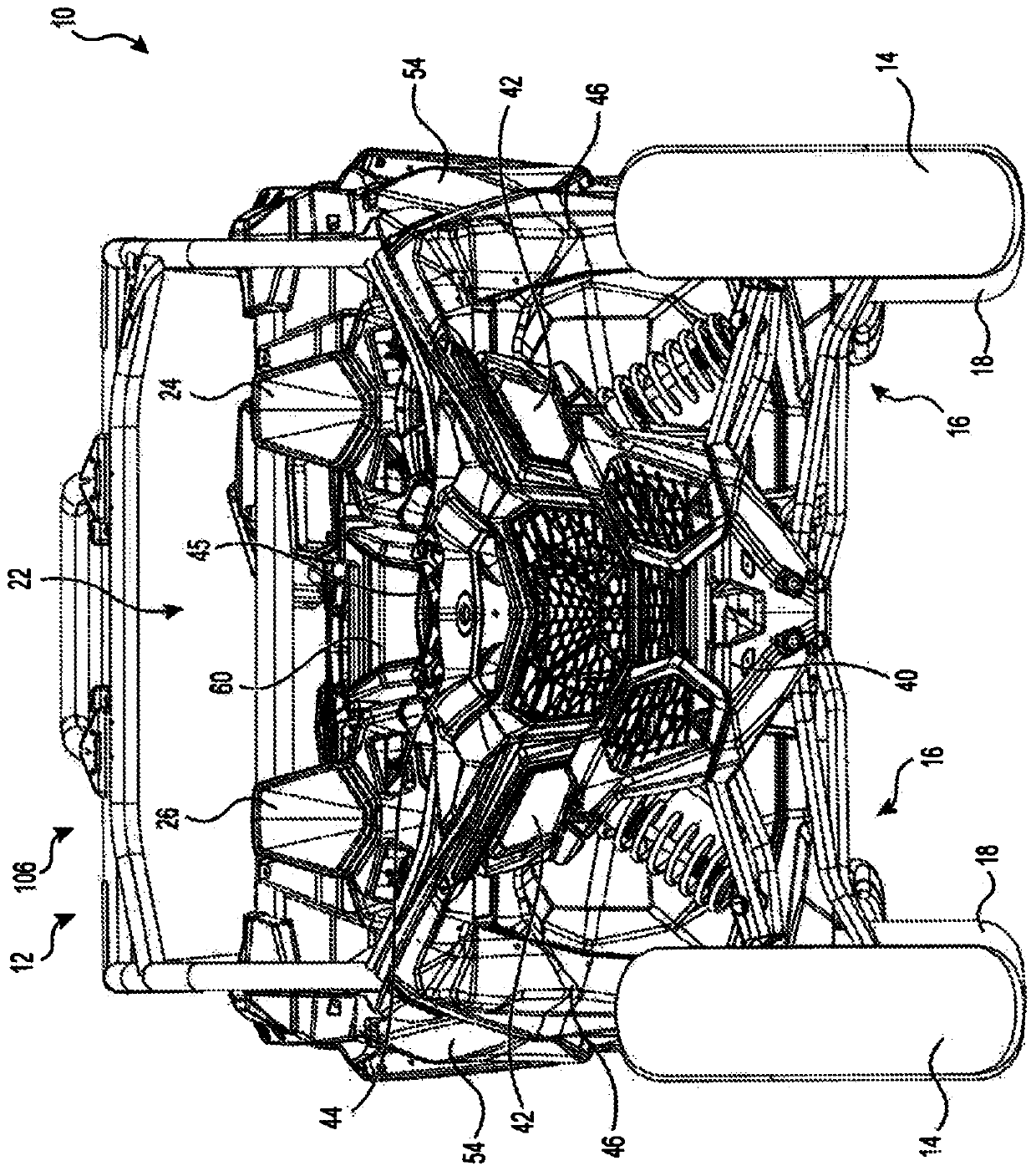
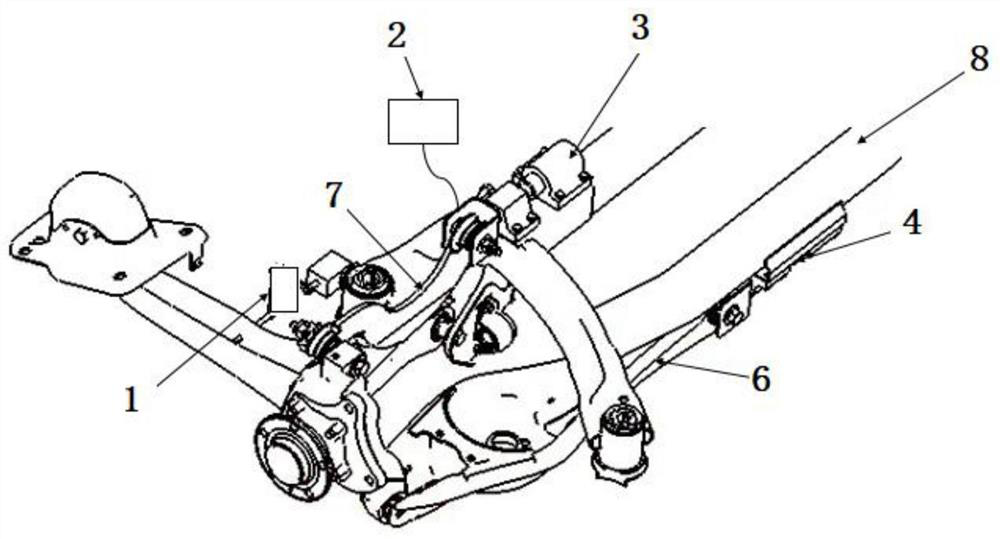
Rear suspension assembly for an off-road vehicle
A vehicle has a frame, a driver and passenger seats, two front and two rear suspension assemblies, two front and two rear wheels, and a motor operatively connected to the at least two wheels. Each rear suspension assembly has a trailing arm having a front end pivotally connected to the frame; a knuckle pivotally connected to a rear portion of the trailing arm; a lower link having a laterally outward end pivotally connected to the trailing arm and a laterally inward end pivotally connected to the frame; an upper link having a laterally outward end pivotally connected to the trailing arm and a laterally inward end pivotally connected to the frame; and a toe link having a laterally outward end pivotally connected to the knuckle and a laterally inward end pivotally connected to the frame.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
Spindle system for wheel alignment correction with brake adjustment
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
A clamping device in the process of tire transportation
The invention discloses a clamping device used in a tire conveying process. The clamping device comprises a clamping arm, an installing seat and a driving mechanism, wherein one end of the clamping arm is installed on the installing seat, and the other end of the clamping arm extends in the direction opposite to a tire; the clamping arm extends into the annular space inside the tire under the action of a conveying cart lifting mechanism and is opened in the direction near a toe mouth of the tire under the driving of the driving mechanism, and the clamping arm abuts against the toe mouth of thetire; the clamped tire can be moved to an appointed position along with a conveying cart; after the tire is in place, the clamping arm is closed in the direction away from the toe mouth under the driving of the driving mechanism; and under the action of the lifting mechanism, the clamping arm is contracted from the annular space of the tire and is separated from the tire. The clamping device is simple in structure, the manufacturing and conveying cost can be lowered, the clamping device is convenient to repair by workers, and the workpiece conveying efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:湖北迪迈威智能装备有限公司
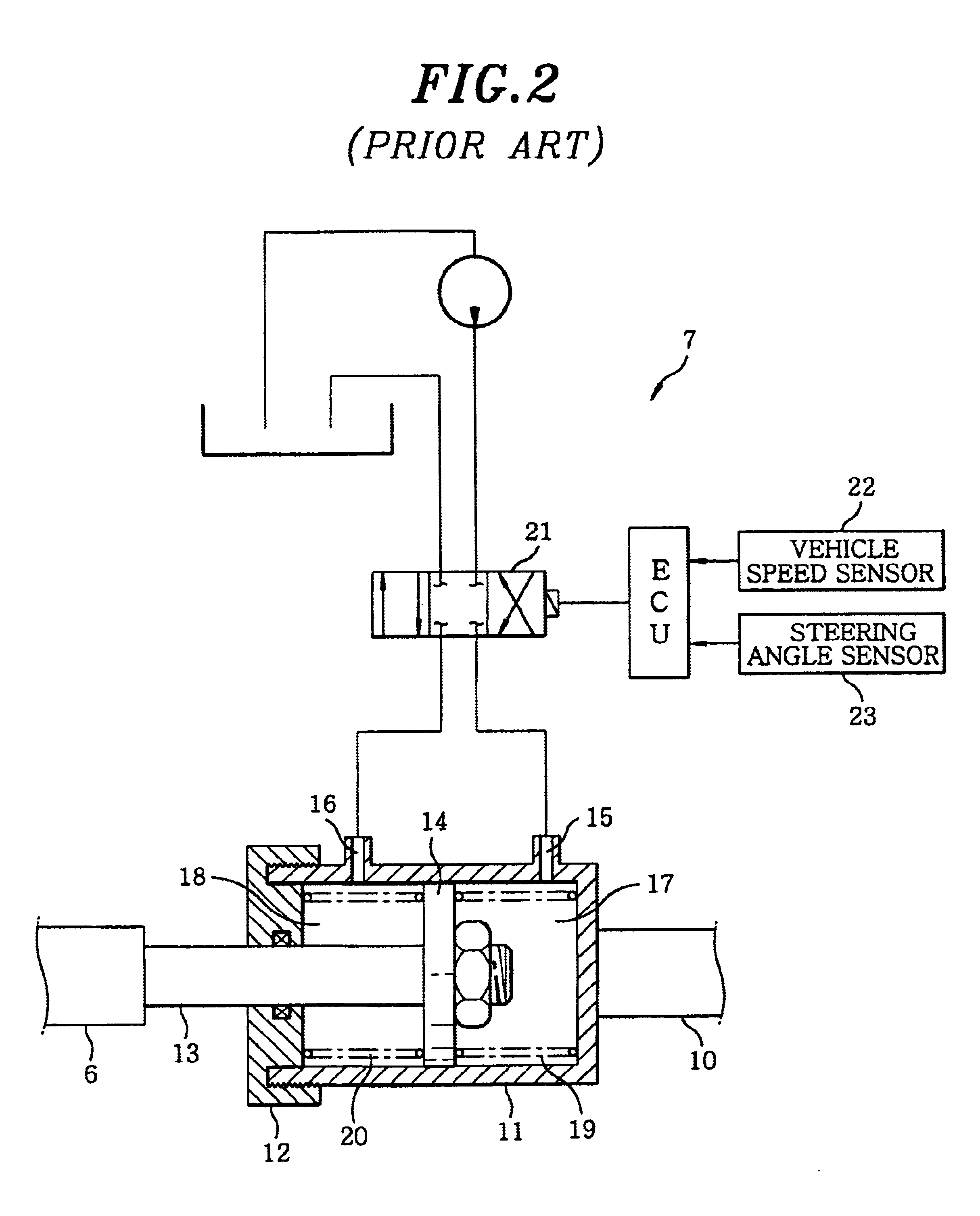
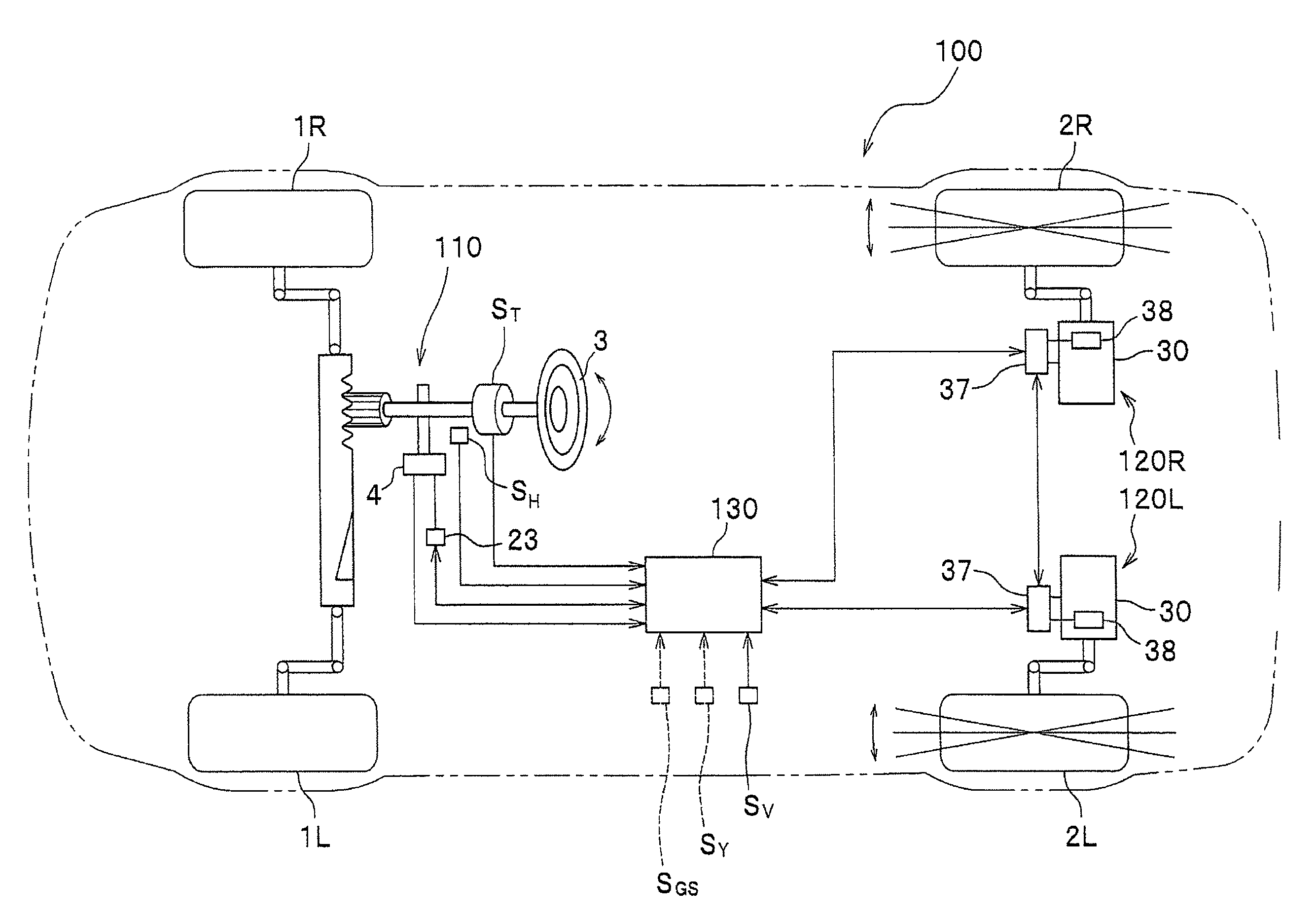
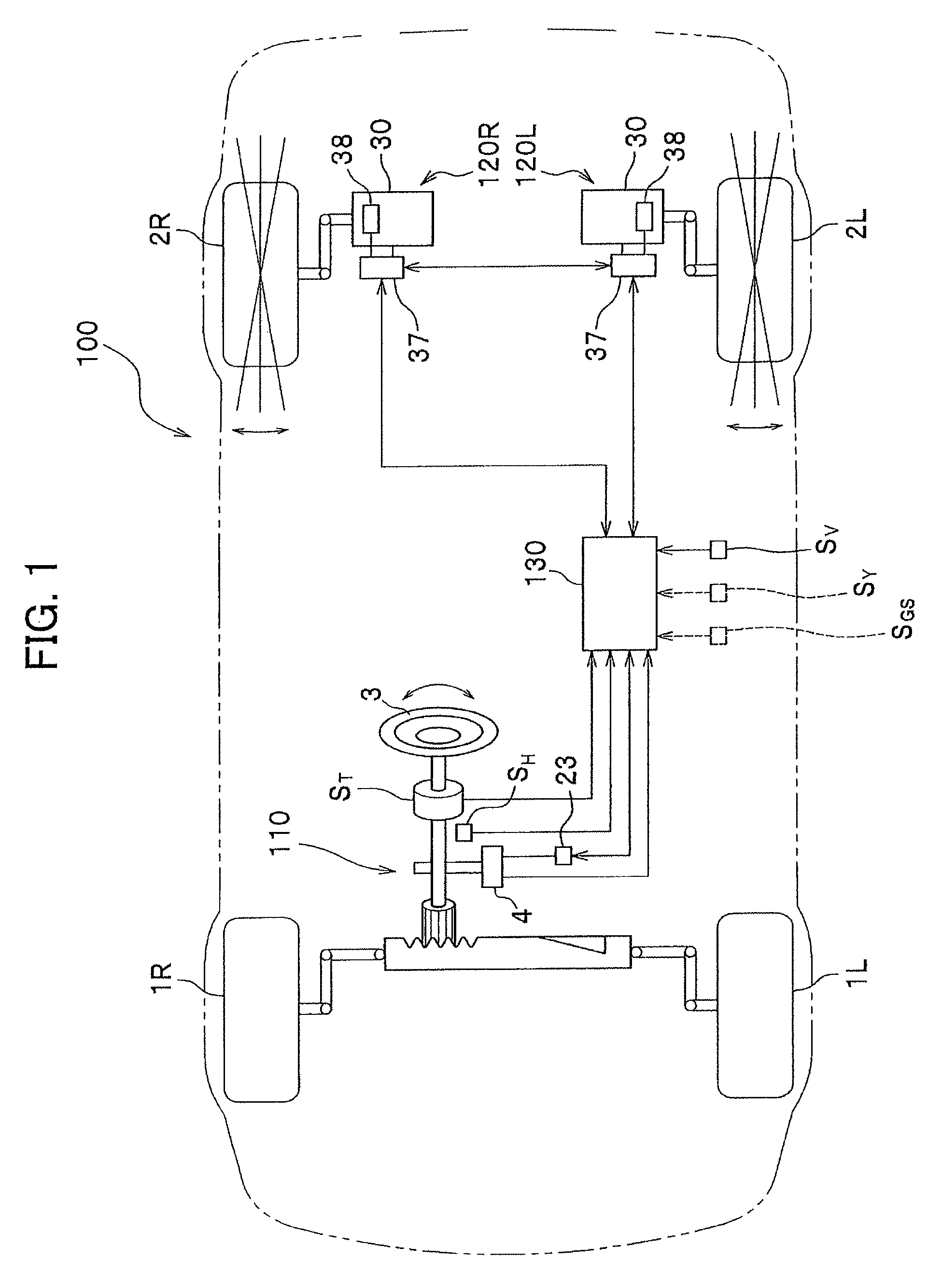
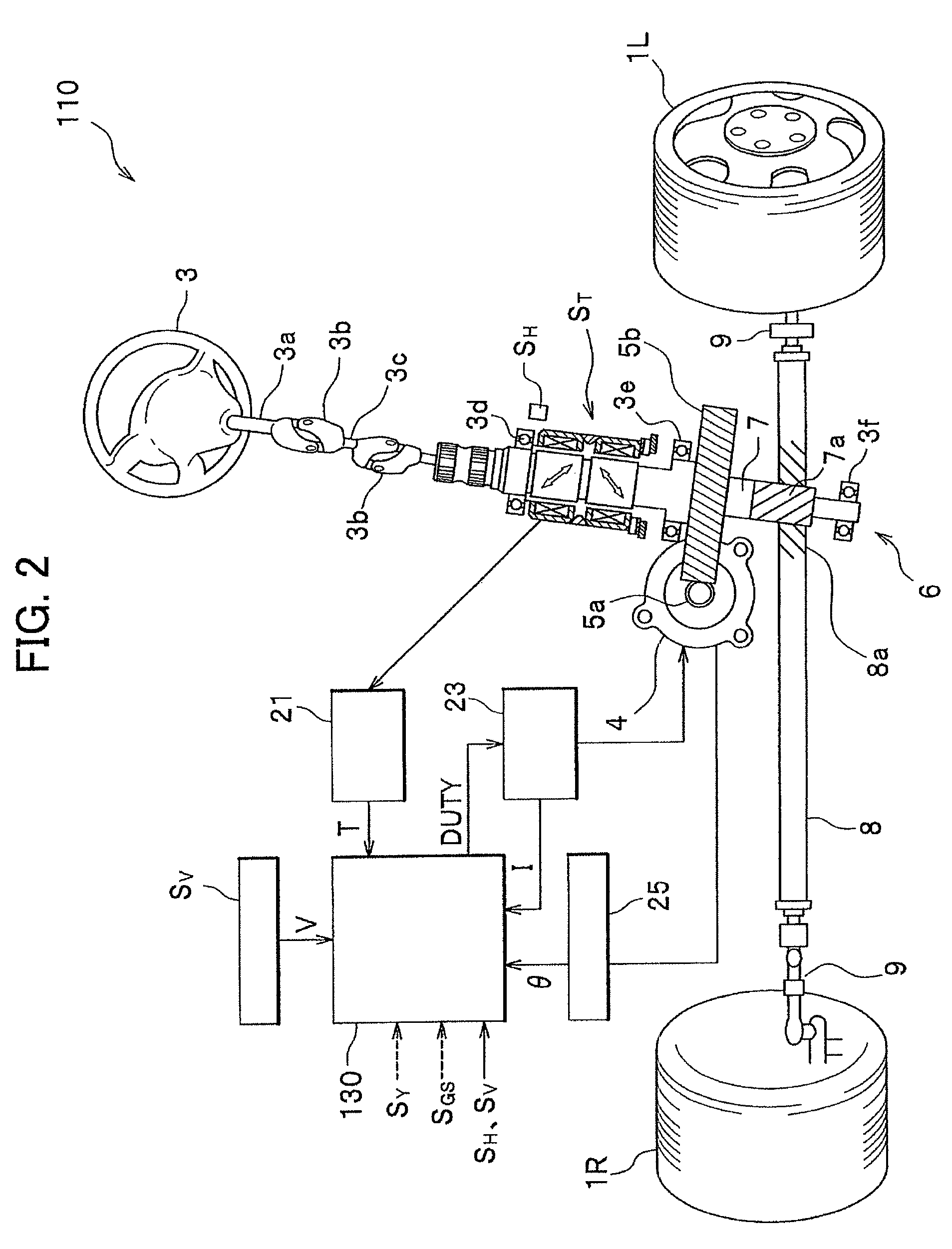
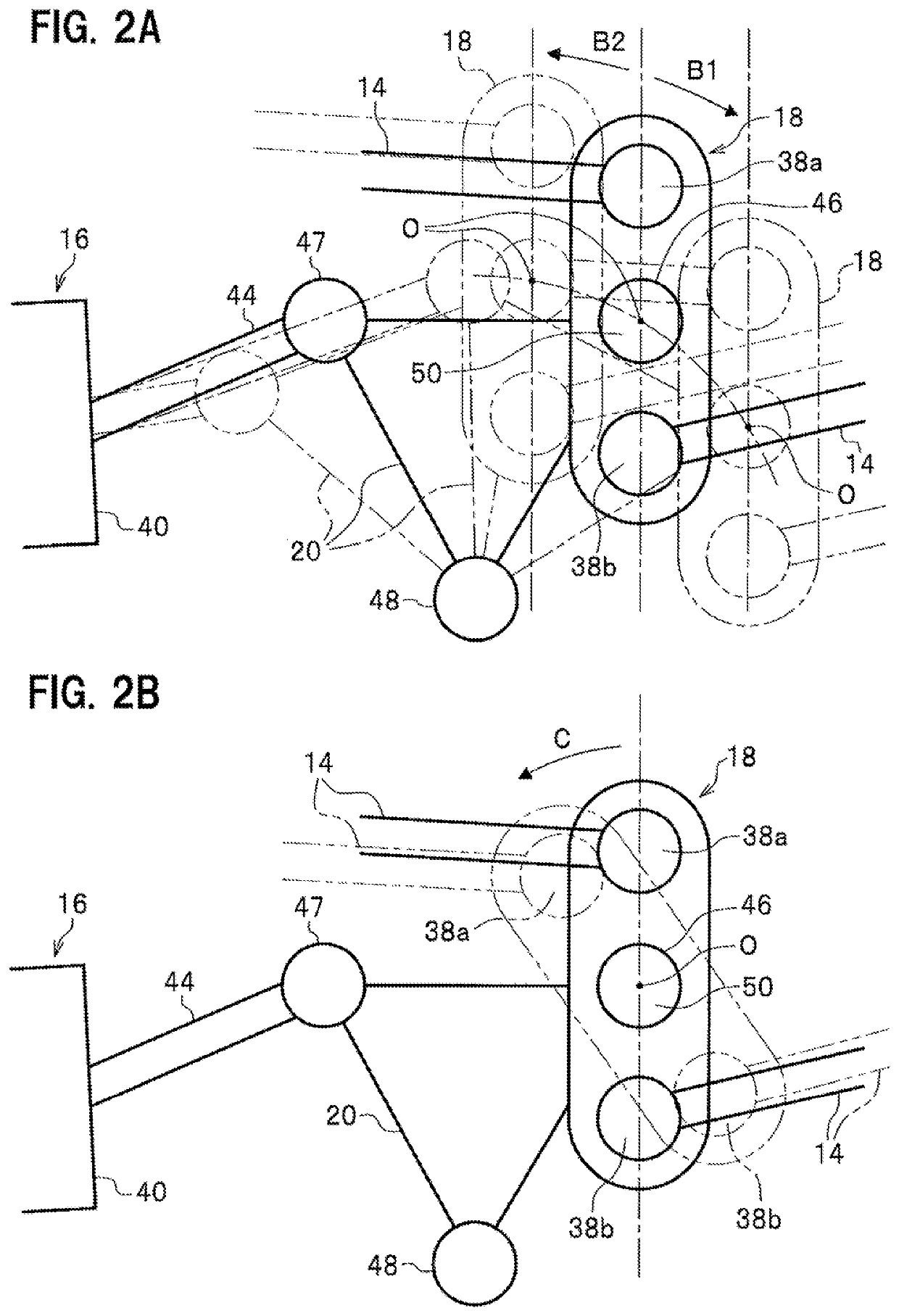
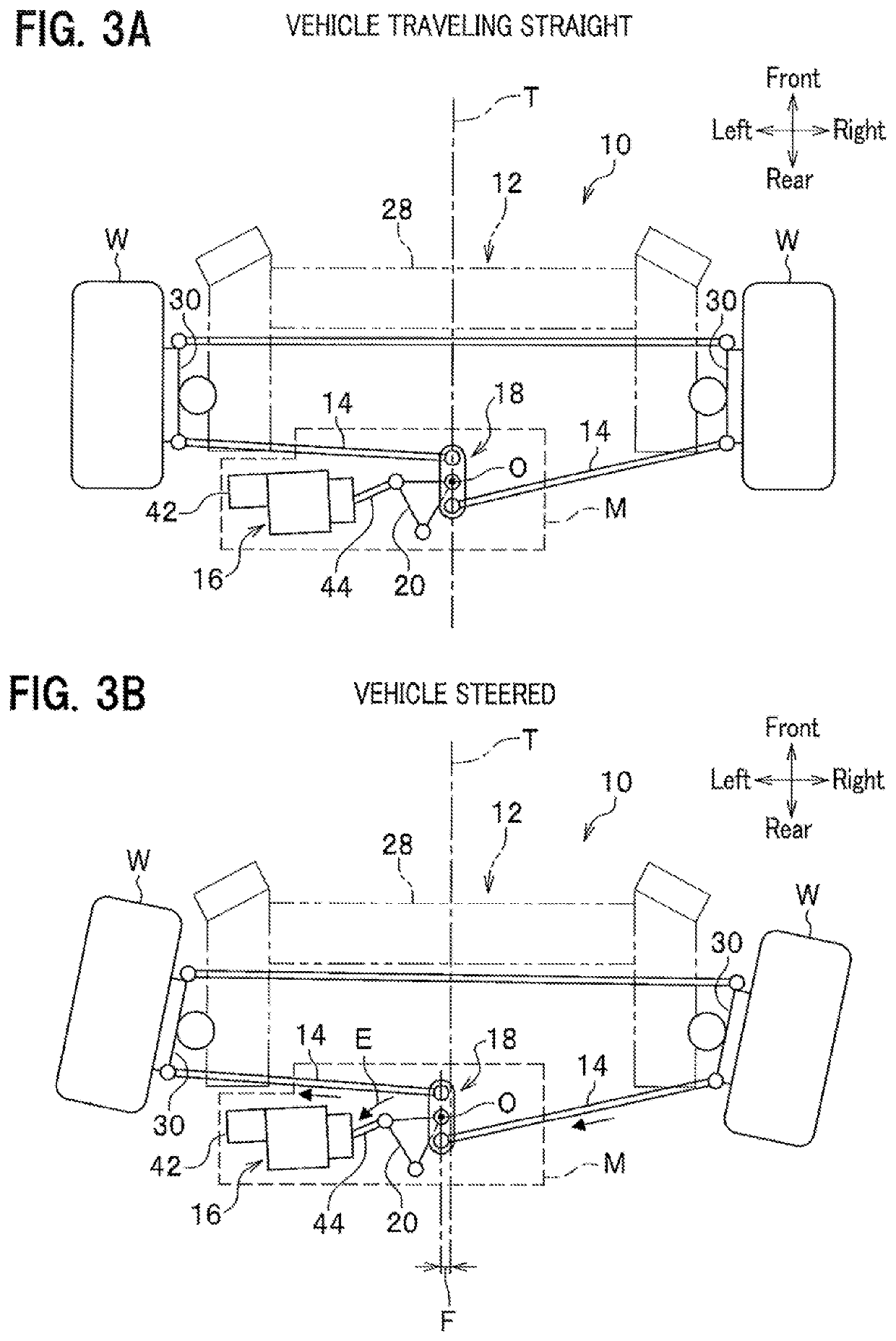
Steering system
ActiveUS8051942B2Improve responsivenessDigital data processing detailsSteering linkagesSteering angleMechanical engineering
The present invention improves response characteristics in turning traveling of a vehicle while traveling stability at the time of turning is kept. The present invention provides a system in which toe angles of left and right rear wheels are controlled based on a steering angular velocity, not a steering angle of a steering. In a steering system in which toe angles of left and right rear wheels are controlled independently, a steering angular velocity is calculated from a steering angle, and toe angle changers are controlled to tilt the toe angle of the right rear wheel to the left when the steering angular velocity is on the left side, and is controlled to tilt the toe angle of the left rear wheel to the left when the steering angular velocity is on the right side.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
All-region bionic wheel of off-road vehicle
PendingCN113043795AGood envelopmentImprove local stiffnessTyre tread bands/patternsControl theoryTread
An all-terrain bionic wheel for off-road vehicles belongs to the technical field of tire tread pattern structure design, and is characterized in that 30-36 pattern blocks in each of two pattern block groups are uniformly distributed on the circumference of a wheel surface and are symmetrically arranged on the left and right sides of a groove; regular hexagonal column structures which are uniformly distributed are arranged in the peripheral contour line of the single pattern block, and the bottom structure L2 of the pattern block is 10-15mm; the side length L4 of the regular hexagon ranges from 15 mm to 20 mm; and the height L5 of the regular hexagonal column is 10-13 mm. And along with the change of the tire pressure, the distance between the adjacent regular hexagons is 0-5mm. According to the invention, a camel toe structure and a tree frog foot biological structure are used for reference, and a pattern structure suitable for various ground environments is formed by changing the distance between the pattern blocks, so that the adhesion capability of the tire on low-adhesion roads such as soft, muddy, frozen and slippery roads can be improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Four-wheel aligner calibrating device based on belt drive
The invention discloses a four-wheel aligner calibrating device based on belt drive. The four-wheel aligner calibrating device aims to solve the problem that quality arbitration cannot be carried out on a 3D four-wheel aligner. The four-wheel aligner calibrating device comprises a toe-in zero-point test frame, a front rack test portion, a rear rack test portion, a right belt drive device and a left belt drive device. The left belt drive device comprises a driving pulley, a front driven pulley, a front sensor clamping sleeve, a rear sensor clamping sleeve, a rear driven pulley and a belt. The outer end of the long ground foot wheel shaft of a front left combined supporting leg in the toe-in zero-point test frame is sleeved with and in key connection with the driving pulley, the left end of a front cross shaft in a left rack test portion is sleeved and locked with the right end of the front sensor clamping sleeve, the middle portion of the front sensor clamping sleeve is sleeved with the front driven pulley which is in key connection, the left end of a rear cross shaft in a left rack test portion is sleeved with the right end of the rear sensor clamping sleeve which is locked, the middle portion of the rear sensor clamping sleeve is sleeved with the rear driven pulley which is in key connection, and the belt is arranged in the pulley groove of the driving pulley, the pulley groove of the front driven pulley and the pulley groove of the rear driven pulley.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
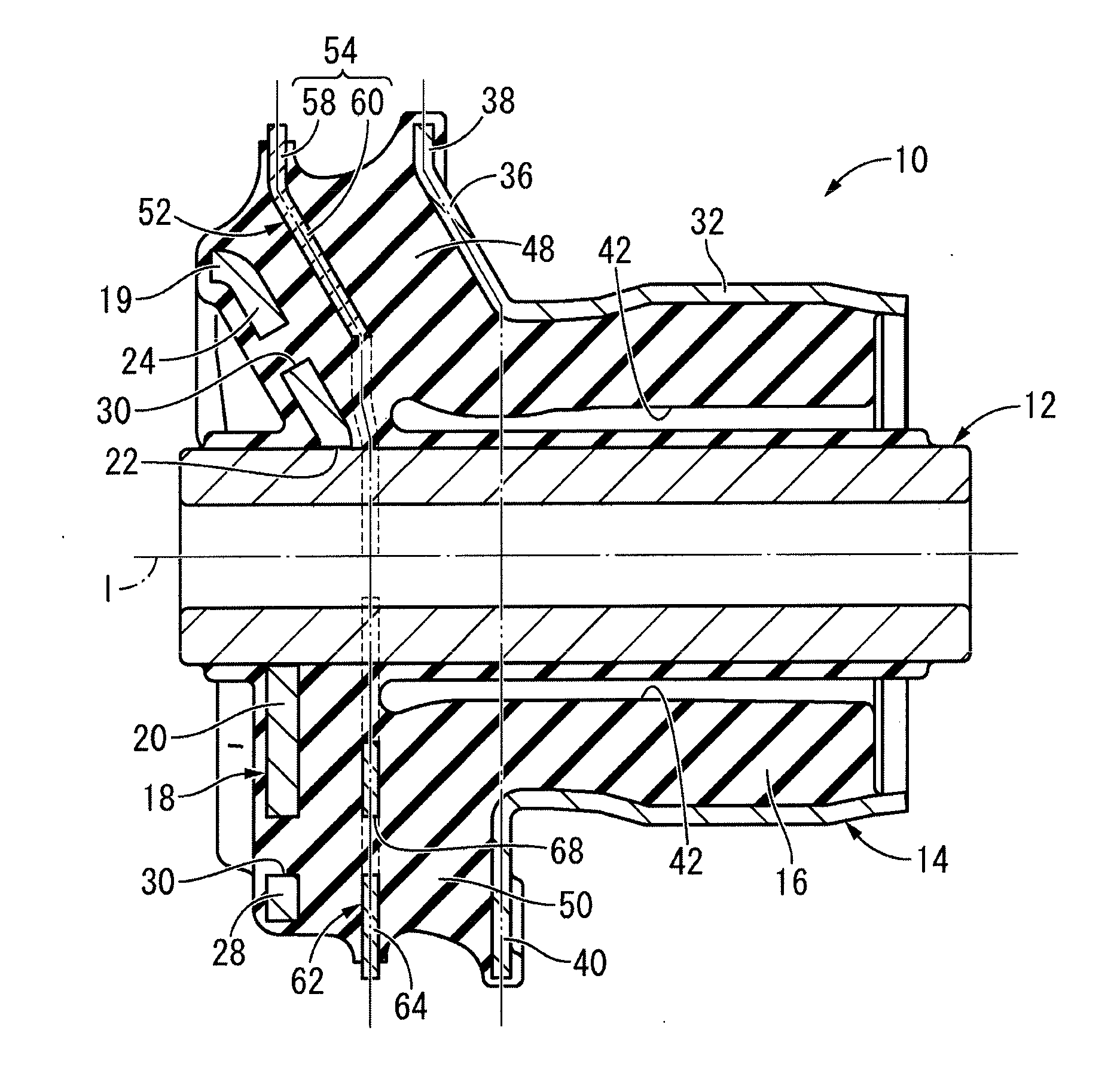
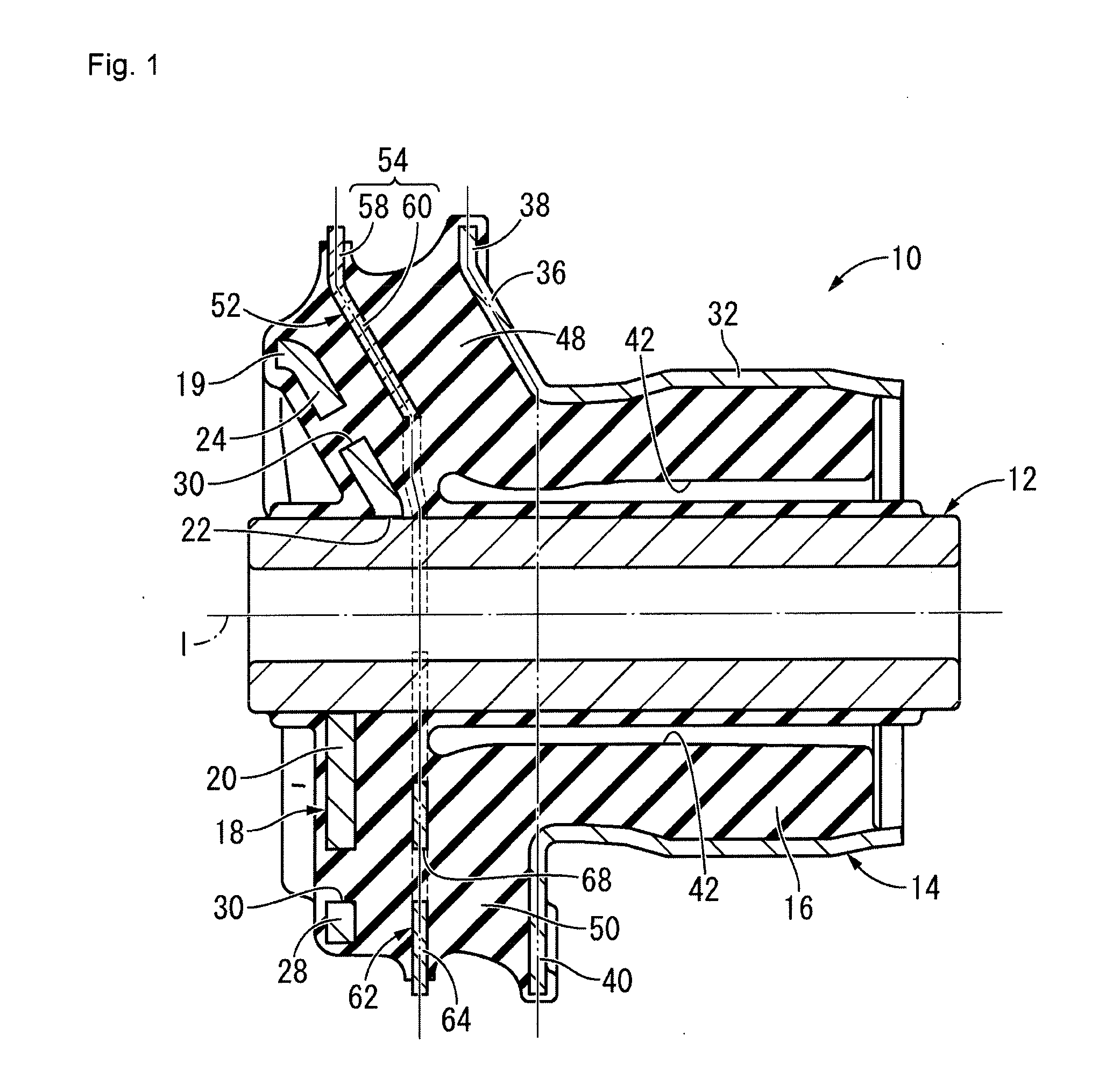
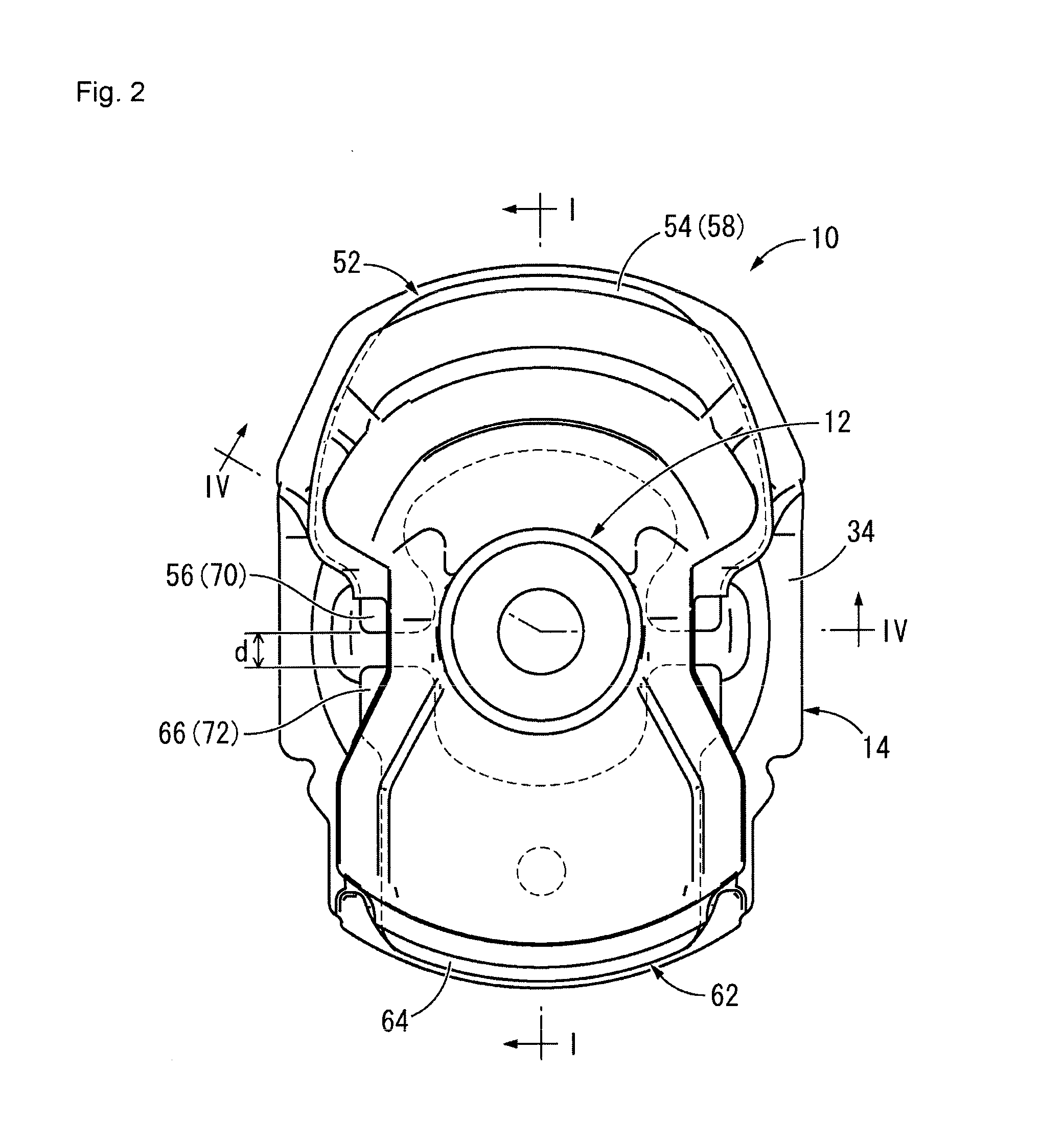
Toe correct bush
ActiveUS20130001915A1Increased durabilityImprove running stabilityInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsEngineeringFlange
To provide a toe correct bush having excellent durability and a novel structure, the toe correct bush effectively achieving improvement in running stability during steering with a toe correction function and improvement in straight line performance with an intermediate restraining plate. A first intermediate restraining member is provided between opposing surfaces of an inner inclined portion and an outer inclined portion and is fixed to a compression rubber, the first intermediate restraining member spreading and being isolated from the opposing surfaces of the inner inclined portion and the outer inclined portion. A second intermediate restraining member is provided independent from the first intermediate restraining member between opposing surfaces of an inner flange and an outer flange and is fixed to a connecting rubber, the second intermediate restraining member spreading and being isolated from the opposing surfaces of the inner flange and the outer flange.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
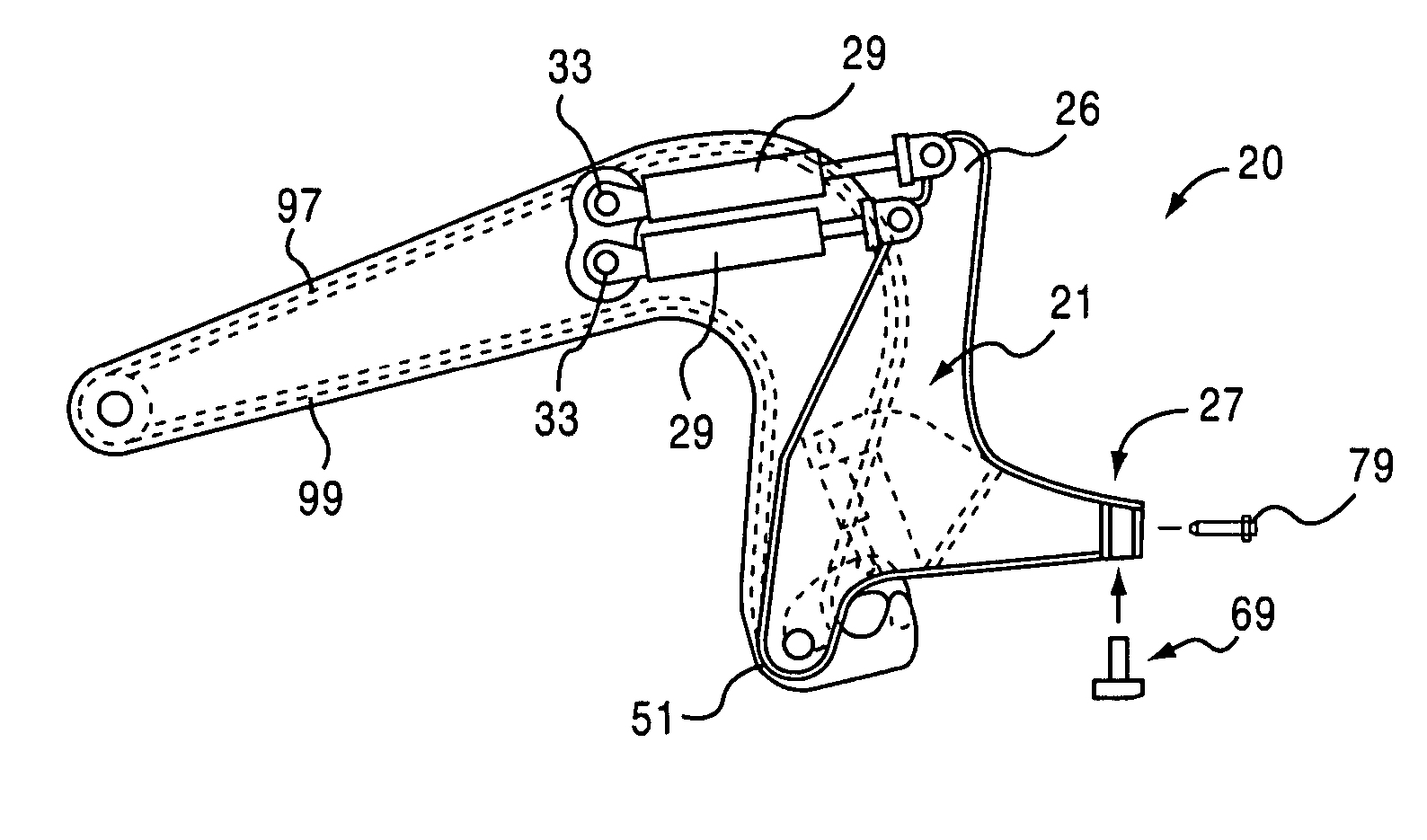
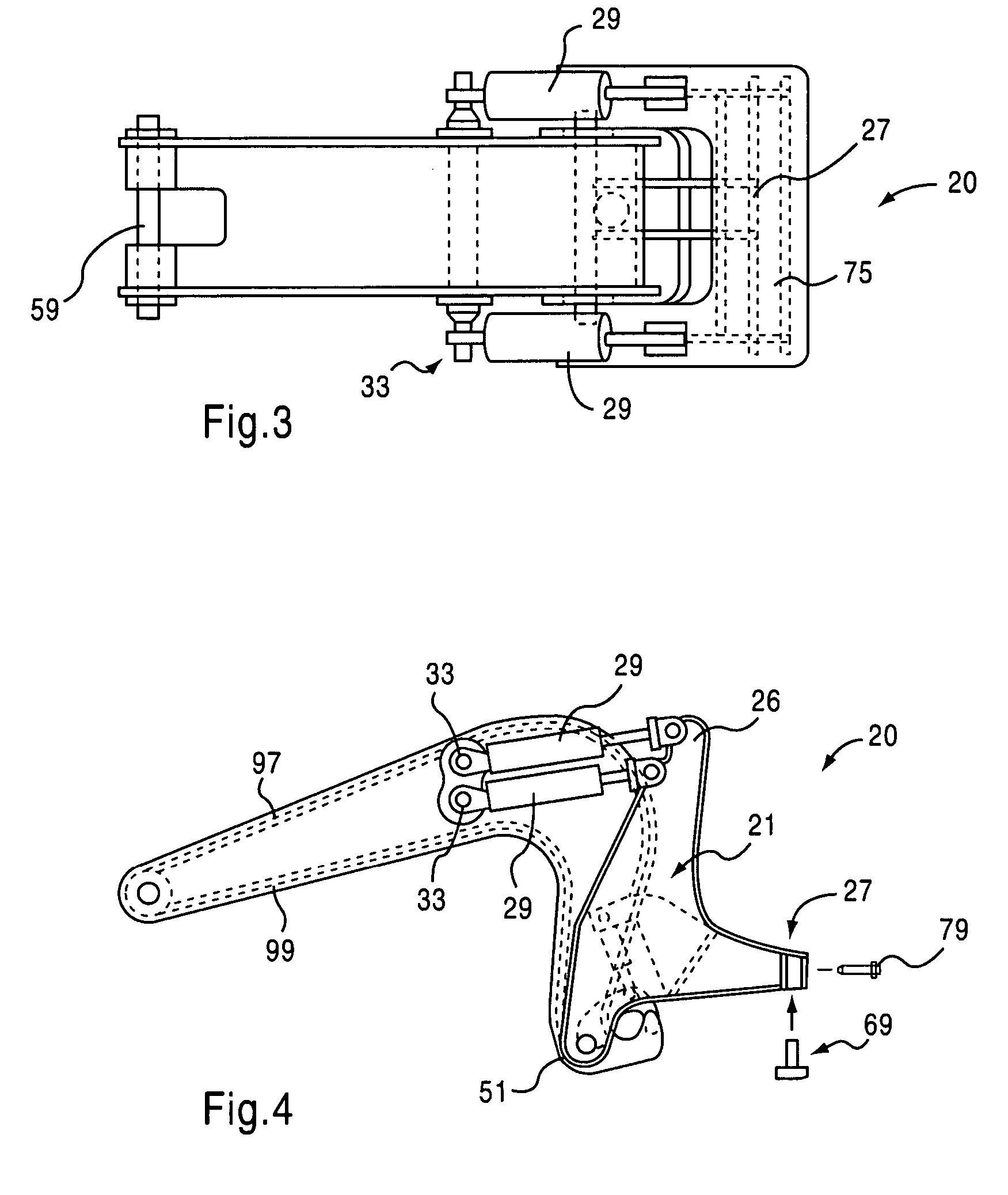
Gooseneck hitch assembly with u-shaped toe and method of use
ActiveUS20060125207A1Increase typeSimple designTractor-trailer combinationsHand carts with one axisEngineeringMechanical engineering
A gooseneck hitch assembly adapted for use with a towing vehicle comprises a gooseneck hitch and a u-shaped toe. The u-shaped toe has legs straddling sides of the gooseneck hitch assembly, the legs connected to one or more powered cylinders mounted to the gooseneck assembly. The u-shaped toe also has an enlarged toe end to reduce the bearing pressuring encountered during a hitching operation. The u-shaped toe can include a wear pad mounted to an underside of the toe end to reduce wear during towing use. A wear pad of the bearing plate assembly can further include a beveled surface to accommodate the change in orientation of a free end of the toe during the hitching operation.
Owner:GROUND FORCE MFG
Wheel toe-in camber full-dynamic control device and method for multi-link suspension
ActiveCN113335381AExtended service lifeImprove handlingSteering partsCamber angleControl engineering
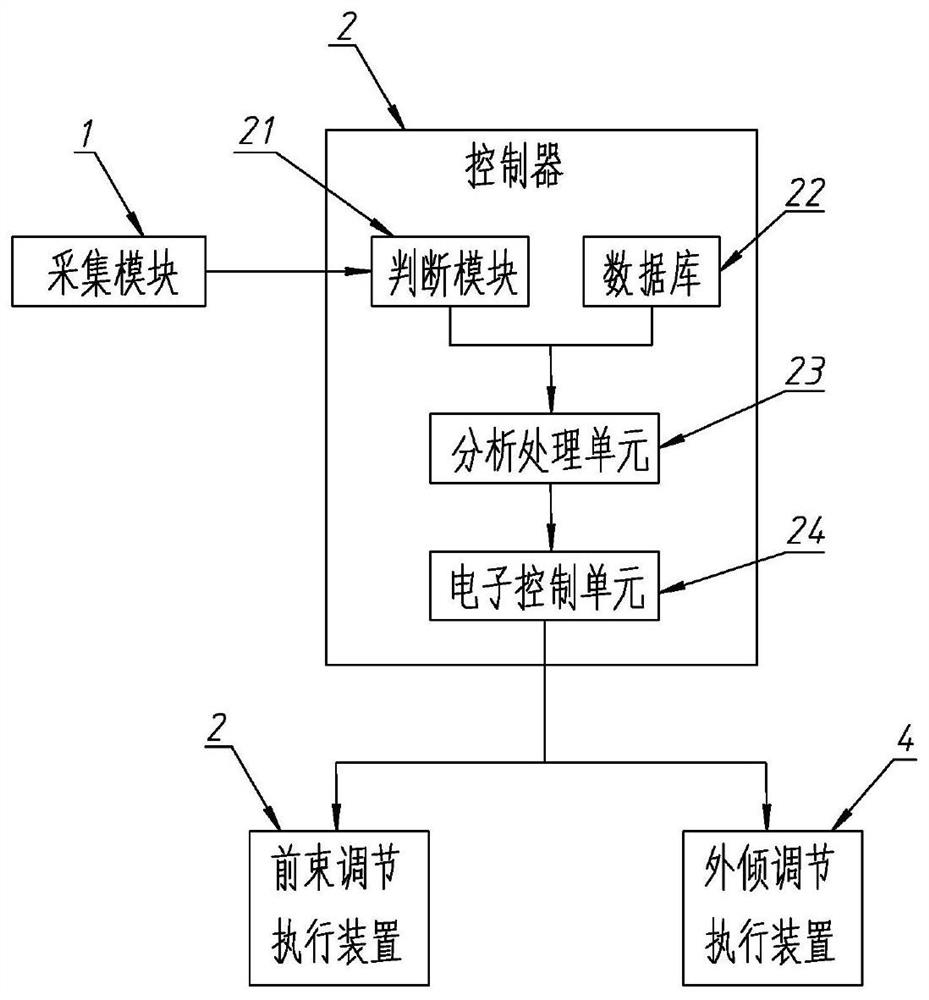
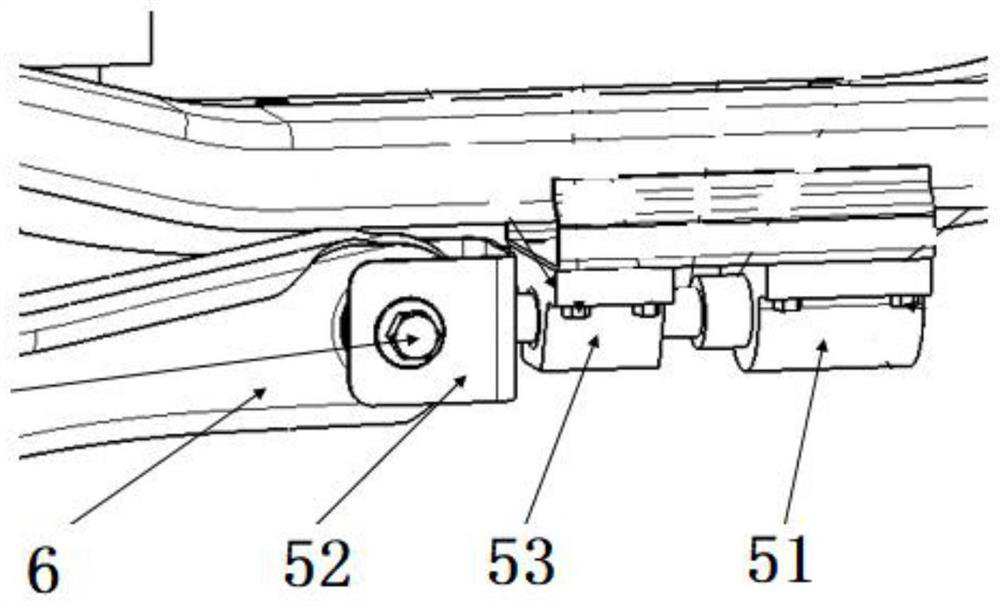
The invention discloses a wheel toe-in camber full-dynamic control device and method for a multi-link suspension. The dynamic control device comprises an acquisition module, a controller, a toe-in adjustment execution device and a camber adjustment execution device, various real-time motion parameters of a vehicle are collected through the acquisition module, the current motion working condition of the vehicle is judged, and then the real-time toe-in control arm adjustment amount and the camber control arm adjustment amount of the vehicle are calculated, and the toe-in control arm and the camber control arm are adjusted to achieve the optimal ideal toe-in camber angle so that the wheel has proper toe-in angle and camber angle under various motion working conditions facing different road conditions, the safety of the wheel is improved, the tire wear is effectively reduced, and the service life of the tire is prolonged. According to the dynamic control method, the wheels have proper camber angles under various motion working conditions, and the toe-in angles corresponding to the camber angles are matched in real time.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR GRP
Device and method for measuring and determining relevant parameters for the adjustment of the directions of travel of two steerable axles of a vehicle in relation to each other
ActiveCN105555644AMeasurement devicesRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringControl theory
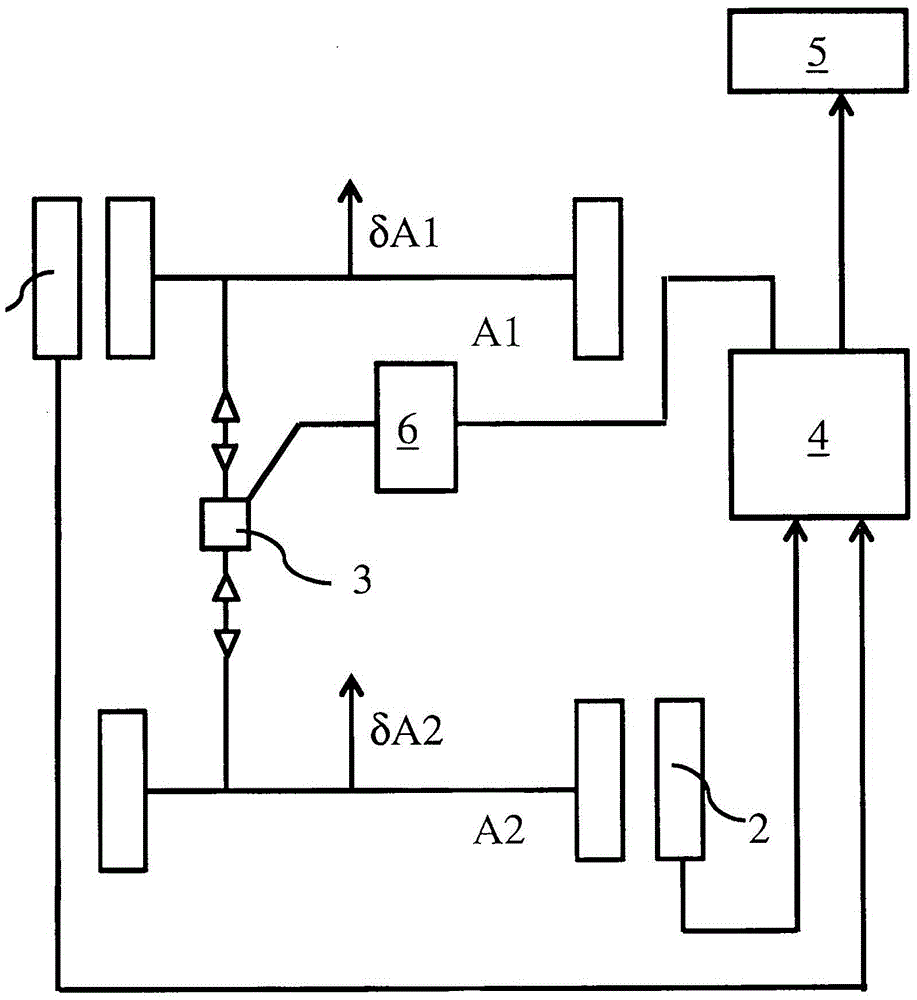
The invention relates to a device and to a method for measuring and determining relevant parameters for the adjustment of the directions of travel of two steerable axles of a vehicle in relation to each other, wherein only one measuring unit for measuring the individual toe angle of a wheel associated with said measuring unit is present on each vehicle side in such a way that a first measuring unit is associated with the wheel of the first of the steerable axles on the left vehicle side and the second measuring unit is associated with the wheel of the second of the steerable axles on the right vehicle side, wherein the output signals of the measuring units are fed to an evaluating unit, wherein the difference of the directions of travel of the two steerable axles or a parameter representing said difference is determined in the evaluating unit from the fed signals of the measuring units and is provided as an output signal of the evaluating unit. The invention further relates to a method for adjusting the directions of travel of two steerable axles of a vehicle in relation to each other, wherein the adjustment of the directions of the two steerable axles in relation to each other is performed by means of only one measuring unit per vehicle side, in that the difference of the directions of travel of the two steerable axles or a parameter representing said difference is determined from a measurement of the toe angle of the right wheel of a first of the two axles and the measurement of the toe angle of the left wheel of the second axle, wherein the adjustment of the directions of travel of the two steerable axles in relation to each other is performed in such a way that the difference or the parameter representing said difference is smaller in magnitude than a threshold value.
Owner:DURR ASSEMBLY PROD GMBH
Cantilever brake device
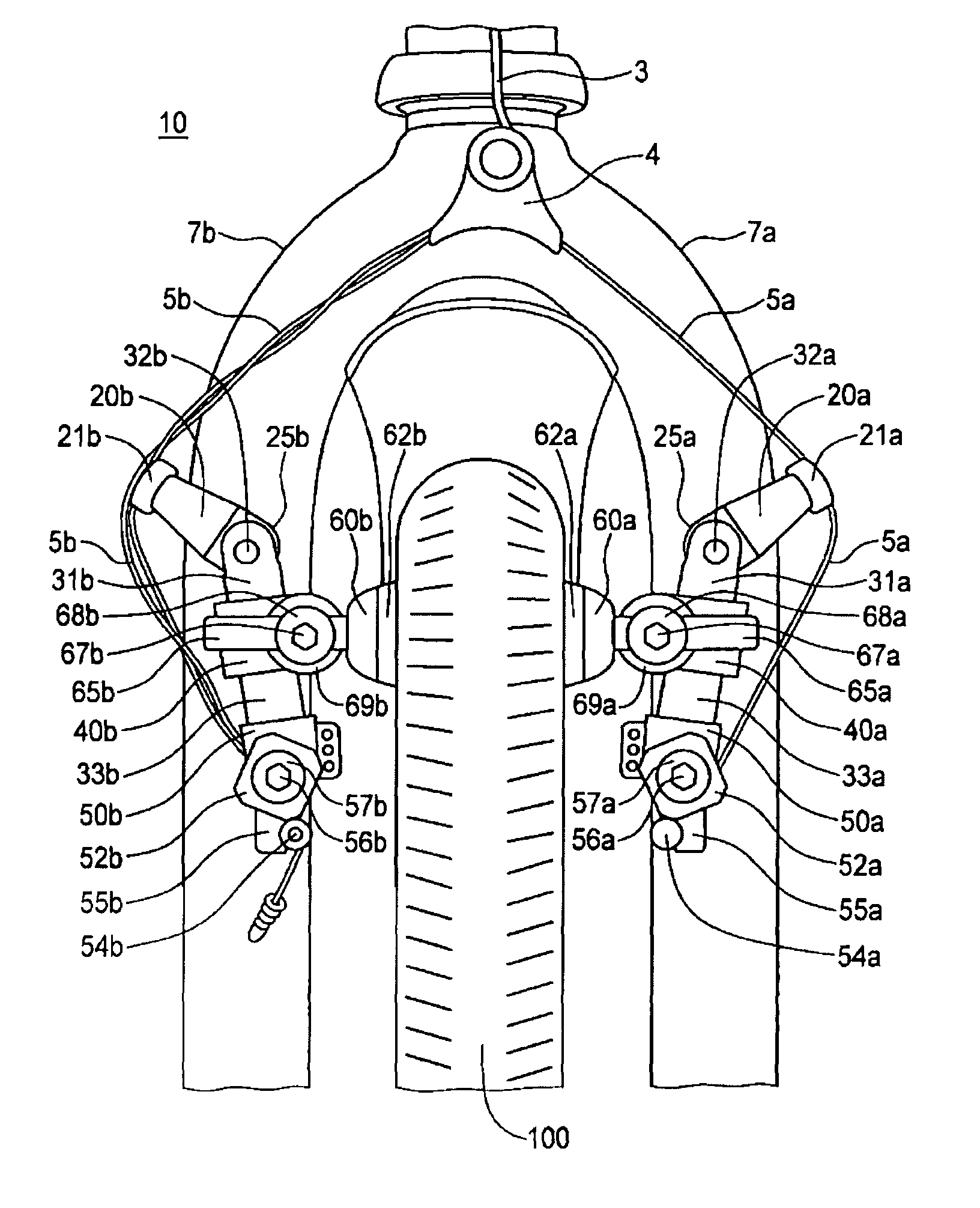
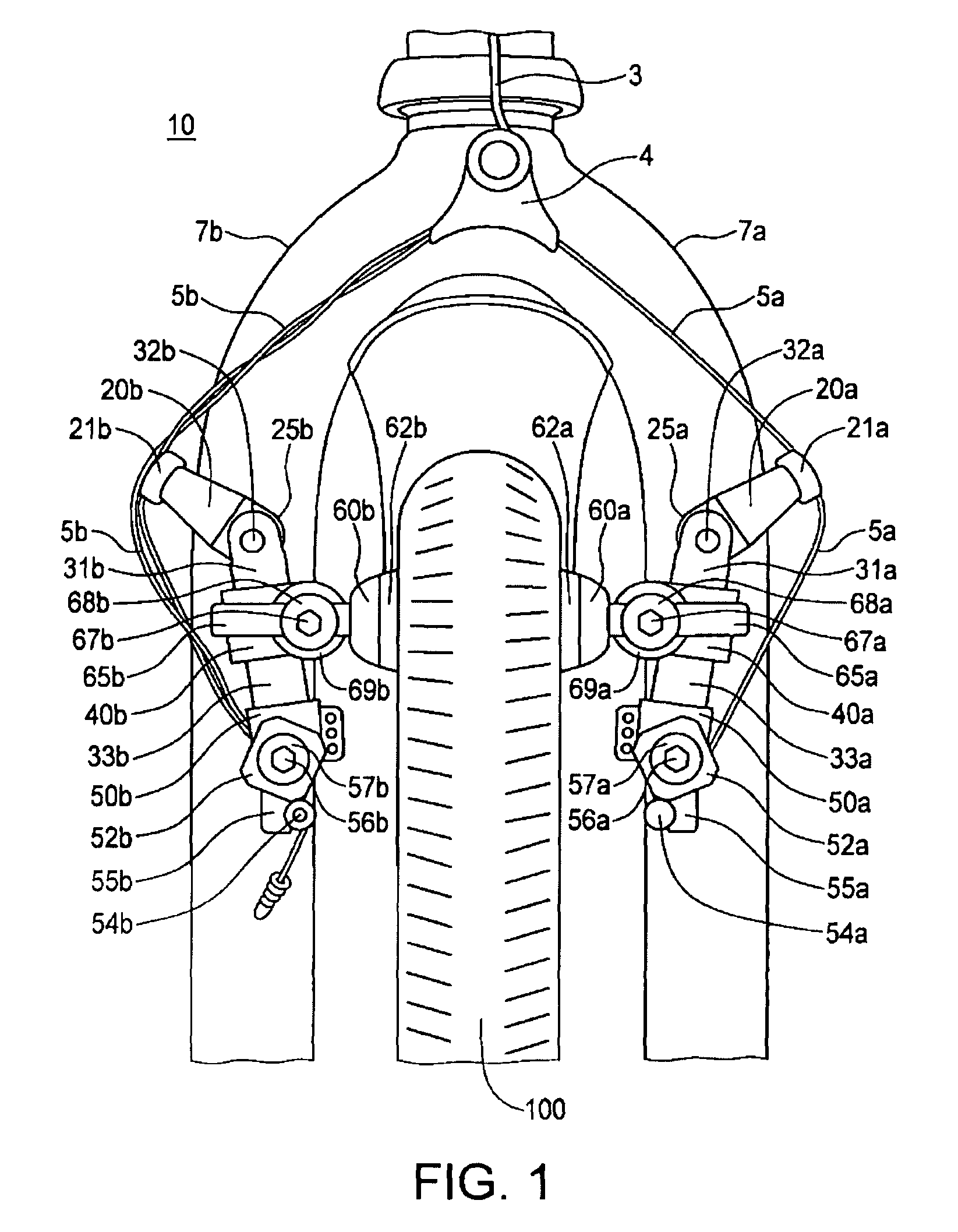
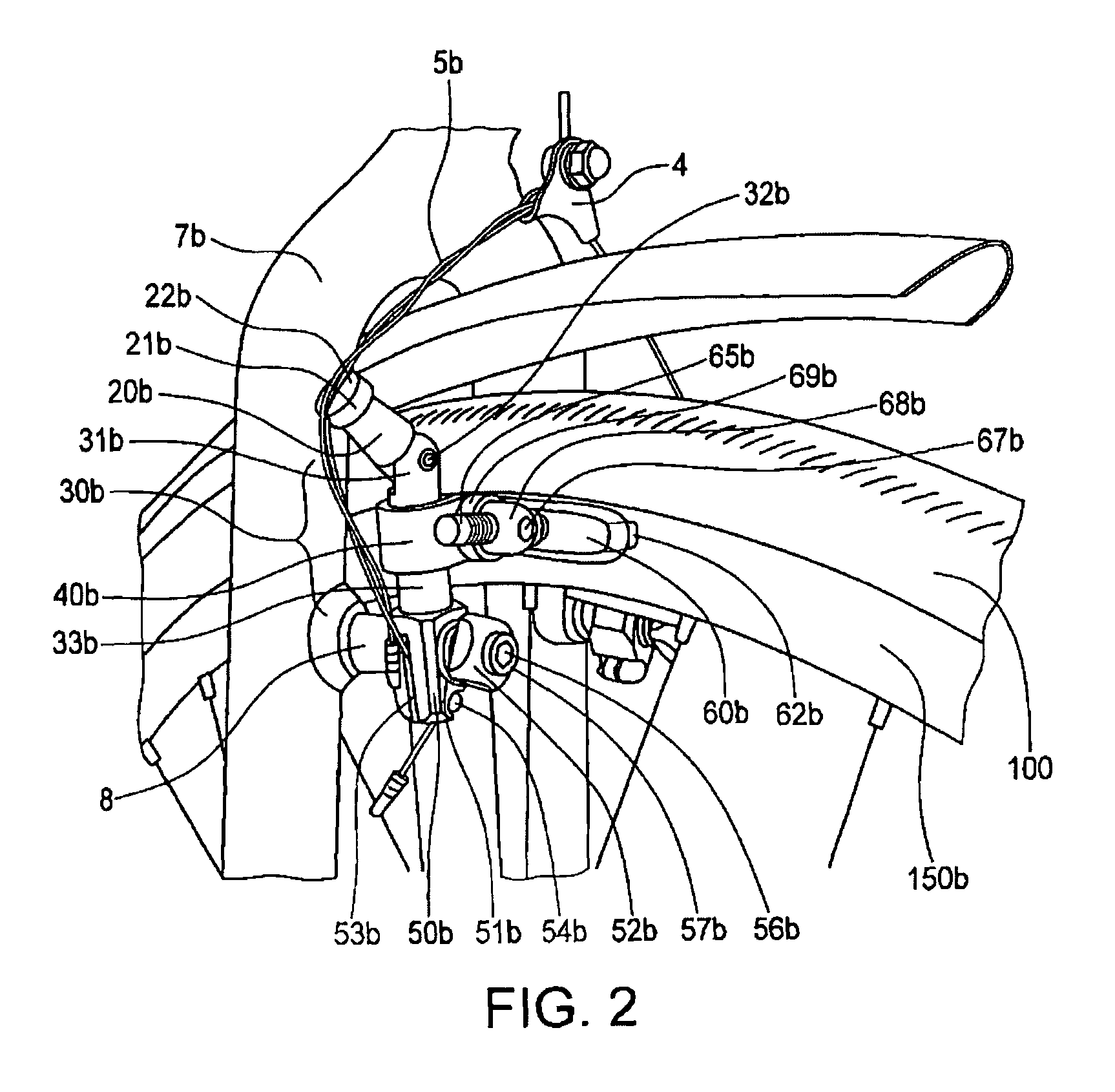
InactiveUS8127896B2Easy to adjustReduce noiseBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesHorizontal axisCantilever
A cantilever brake device is disclosed having a pair of opposing brake arm assemblies with cable tension or the traction point at the distal end of the body members at the bottom trunk portions rather than at the upper level by the adjustable arm members. By moving the cable tension and traction point to the bottom level of the body members, the brakes are applied more evenly and uniformly against and onto the rim surface for greater braking power and mechanical advantage. The cantilever brake device is also disclosed having a shoe housing member that is easily adjustable on a y-axis for height adjustment of the brake shoes since the brake shoes are each mounted on the shoe housing member and allows uniform adjustment of both shoe housing members holding the brake shoes. The shoe housing member is easily rotatable to modify the pitch angle of the brake shoes on a pivotal, horizontal axis to align the brake pads squarely against the rim surface so that the top and bottom portions of the brake pads touch the rim surface equally and uniformly when brakes are applied. Consequently, all of the vertical, horizontal, roll angle, pitch angle, and toe-in adjustments are easily achievable for fine tuning the brakes by using the present cantilever brake device.
Owner:BIKEBIZ III
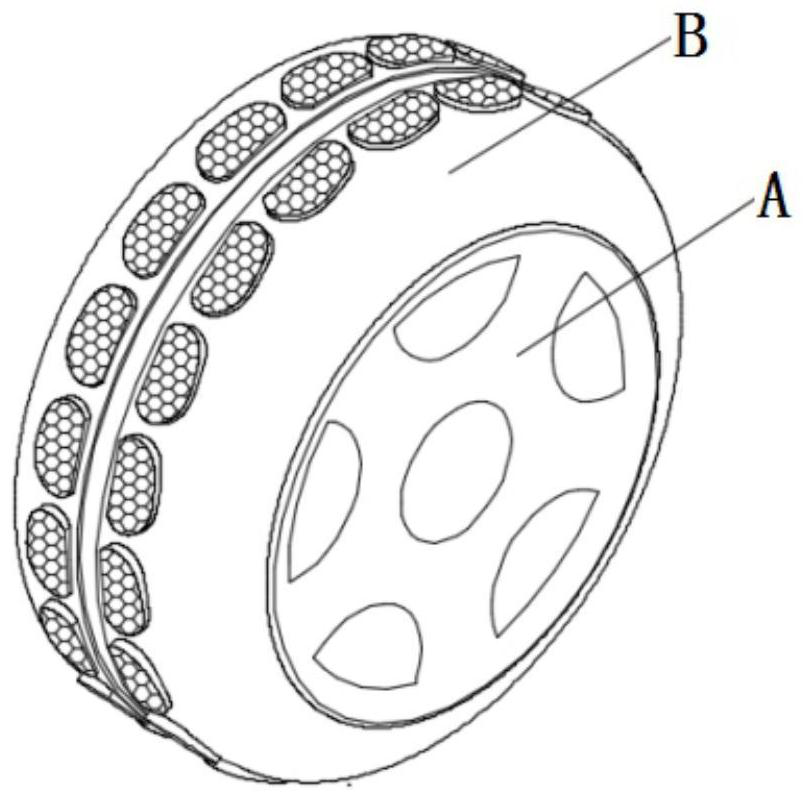
Low-flying-dust high-traction bionic walking wheel on lunar surface
ActiveCN112848791AImprove traction performanceImprove hitch tractionRolling resistance optimizationHigh resiliency wheelsLunar soilBionics
A low-flying-dust high-traction bionic walking wheel on a lunar surface belongs to the technical field of engineering bionics, is formed by simulating the curved surface morphology of the sole of an ostrich, the contour of a toenail and the motion characteristics of the third toe, is composed of a hub, a tire assembly and a wheel thorn group, and is mainly applied to a manned rapid lunar rover. In the rolling process of a bionic walking wheel, the extending length of the wheel thorns can be adjusted in a self-adaptive mode according to the load on the wheel and the lunar surface condition, and the traction force and passing ability of the bionic walking wheel are improved. In the contact process of a tire tread and the lunar surface, the surface structure of the tire tread fixes lunar soil under the wheel, and the disturbance of the wheel to the lunar soil is reduced. Simulation analysis shows that compared with a screen wheel, the low-flying-dust and high-traction bionic walking wheel for the moon surface has the advantages that the hook traction force is increased by about 90%, the flying dust amount is reduced by about 51%, and the low-flying-dust and high-traction bionic walking wheel is simple in structure, light in weight, free of inflation and good in traction performance and flying dust suppression effect; and the adhesiveness, the traction property and the dust suppression property of the manned lunar rover can be improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
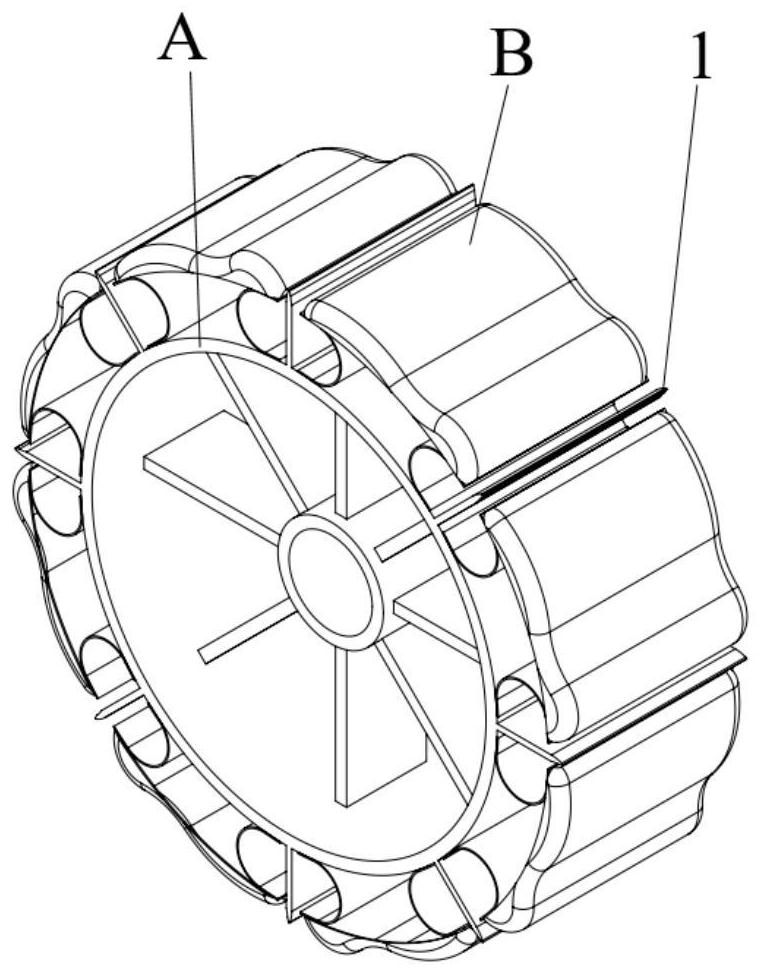
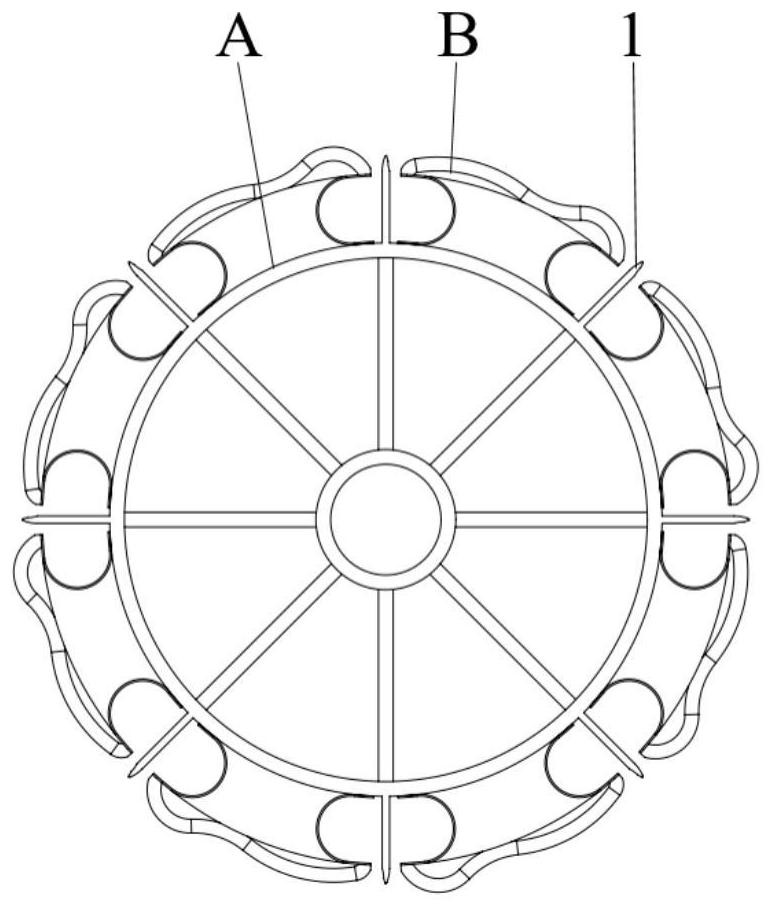
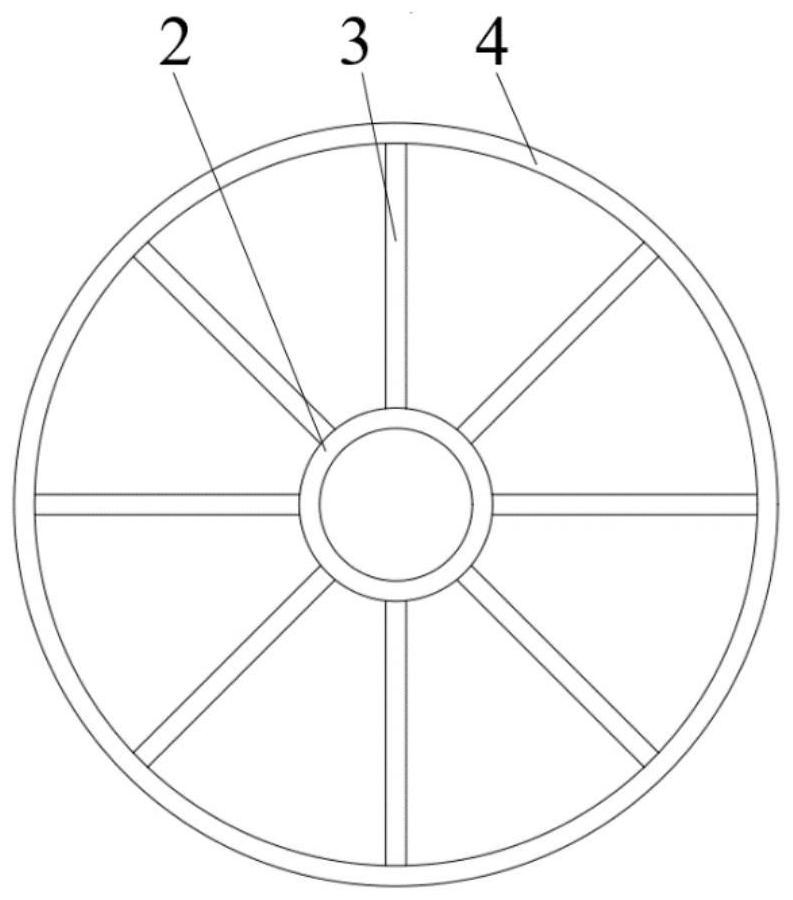
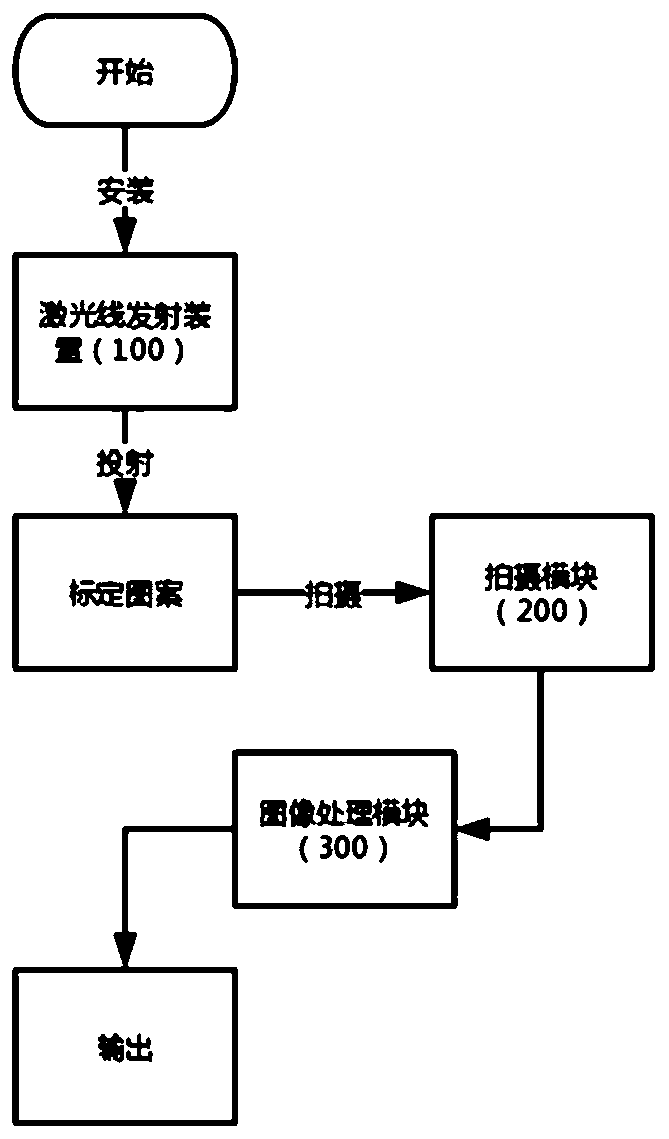
Method and system for measuring toe-in angle of wheel based on image
ActiveCN111220399AReduce computational complexityImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingEngineering
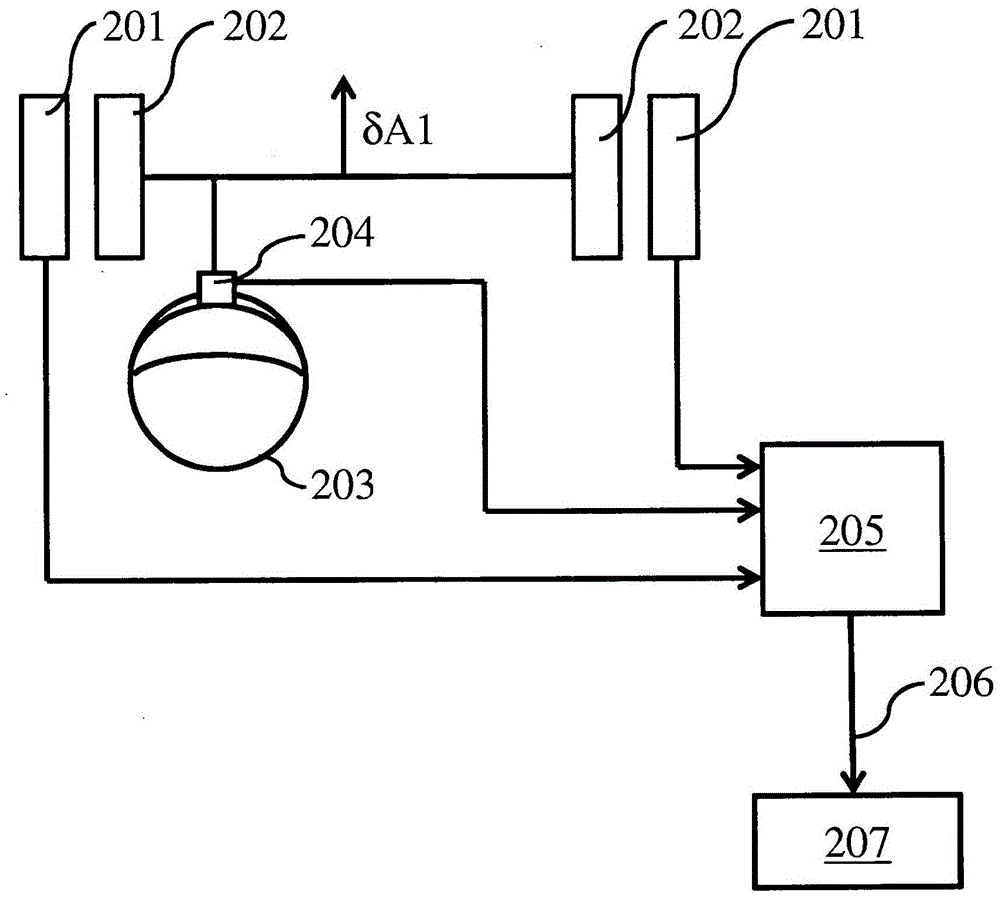
The invention discloses a method and system for measuring a toe-in angle of a wheel based on an image, and the method comprises the following steps of clamping a laser ray transmitting device on the side surface of the wheel of a to-be-detected vehicle; projecting the laser rays of the laser ray emitting device towards the ground, and placing a calibration pattern at the side of a projection area;projecting the laser rays to the side of a calibration pattern placed on the ground; using a shooting module to shoot the laser rays and the calibration pattern; and using an image processing moduleto calculate the three-dimensional position relationship among the laser rays to obtain the toe-in angle of each tire of the vehicle to be detected. The beneficial effects of the invention are that byadopting a laser line calibration scheme, the calculation complexity is reduced, the detection precision is improved, the calculation is simple, the implementation is convenient, and the precision ishigh.
Owner:的卢技术有限公司
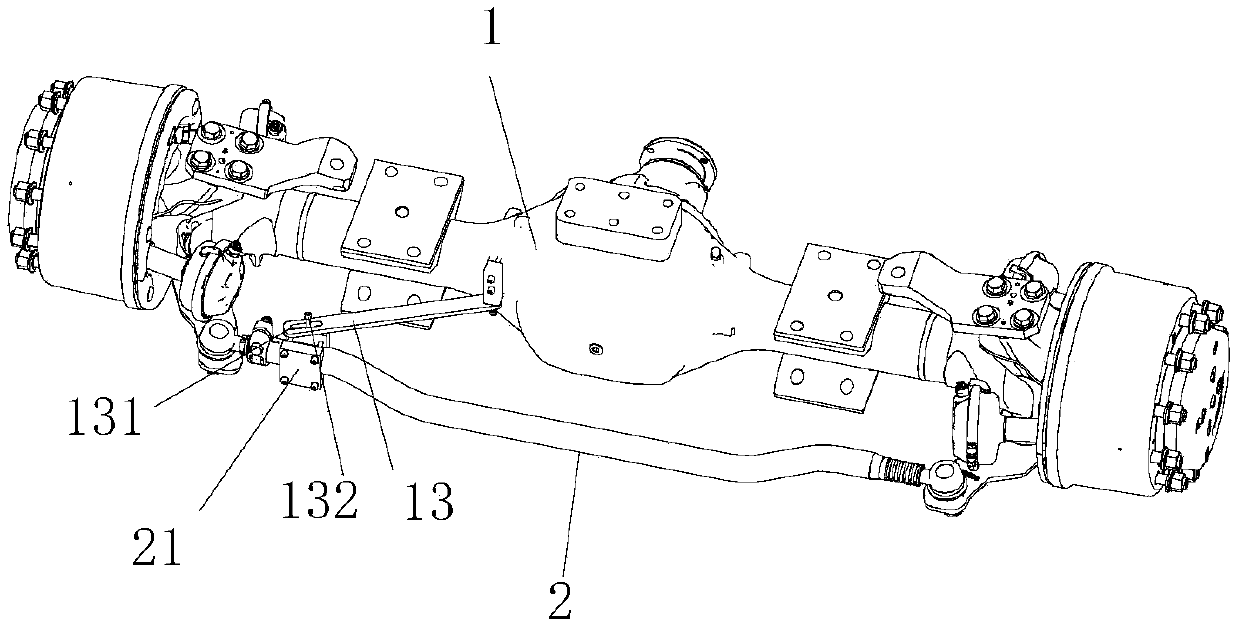
Adjusting method of synchronization and toe-in of double-front-axle steering vehicle
ActiveCN101519063AAccurate measurementAccurate adjustment effectVehicle servicing/repairingVehicle wheel testingTruckControl theory
The invention relates to an adjusting method of synchronization and toe-in of a double-front-axle steering vehicle, which is characterized by comprising the steps of preparing for the adjustment of tyre toe-in and asynchronization, adjusting the asynchronization between steering axles after a vehicle being parked in a correct place, and adjusting the toe-in of the vehicle. The positional parameters of front wheels can be measured and adjusted simply, effectively and accurately by adopting the method. The method solves the problem of abnormal abrasion of tyres caused by asynchronization among the toe-in and the steering axles. The method is effectively verified and used in the road tests of trucks.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
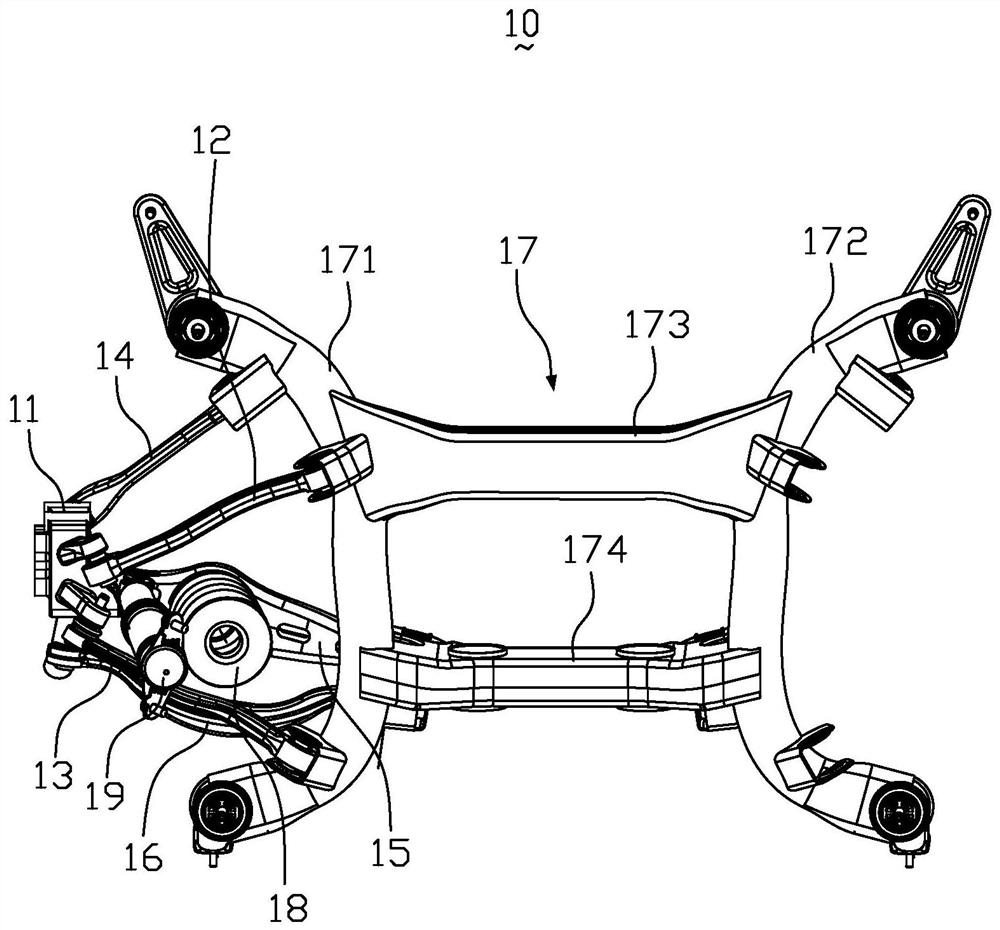
Five-link suspension system and vehicle
PendingCN112078314AGood for weight lossOptimize spaceResilient suspensionsPivoted suspension armsVehicle frameClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a five-link suspension system which comprises a steering knuckle, an upper front arm, an upper rear arm, a lower oblique arm, a lower transverse arm, a toe-in arm, an auxiliary frame, a spring and a shock absorber. The length direction of a vehicle body is defined as the longitudinal direction, and the width direction of the vehicle body is defined as the transverse direction, wherein the longitudinal direction is perpendicular to the transverse direction. One ends of the upper front arm, the upper rear arm, the lower oblique arm, the lower transverse arm and the toe-in arm are hinged to the steering knuckle, the other ends of the upper rear arm, the lower oblique arm, the lower transverse arm and the toe-in arm are hinged to the auxiliary frame, the lower transverse arm is obliquely arranged in the transverse direction, the spring is opposite to the shock absorber, one ends of the spring and the shock absorber are connected to the lower transverse arm, and theother end of the shock absorber is connected to a side beam of the vehicle body. According to the five-link suspension system, the spring and the shock absorber are separated and linearly arranged above the lower transverse arm, weight reduction of the lower transverse arm and space release are facilitated, a larger luggage space can be obtained, and road noise is reduced. The invention also relates to a vehicle.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Rubber wheel bogie train wheel positioning method
ActiveCN111076959APrecise positioningAvoid duplicate detectionRailway vehicle testingBogieVehicle frame
The invention discloses a rubber wheel bogie train wheel positioning method which comprises the following steps: S1, before each rubber wheel bogie is subpackaged, adjusting wheel ends to enable leftand right toe-in values to be equal, adjusting a steering tie rod to enable a total toe-in value to be zero, and then locking to finish pre-positioning; S2, installing all the rubber wheel bogies withthe completion of pre-positioning on a whole vehicle, symmetrically installing multiple sets of detection targets on a left side and a right side of a vehicle body, and installing a camera sensor inthe center of each rubber wheel; S3, detecting the detection target by the camera sensor to obtain positioning parameters of each rubber wheel, wherein the toe-in value of the wheel is adjusted to a target value by adjusting a steering tie rod; if a propelling angle deviates leftwards, a cushion block is additionally arranged on a lower thrust rod on the left side; otherwise, a cushion block is added to a lower thrust rod on the right side, wherein the adding thickness is h, h = L*cos alpha, L is the distance between the lower thrust rod and the center of a frame, and alpha is the propelling angle. The method has the advantages of simple steps, no need of repeated detection, capability of quickly eliminating the thrust angle and the like.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST +1
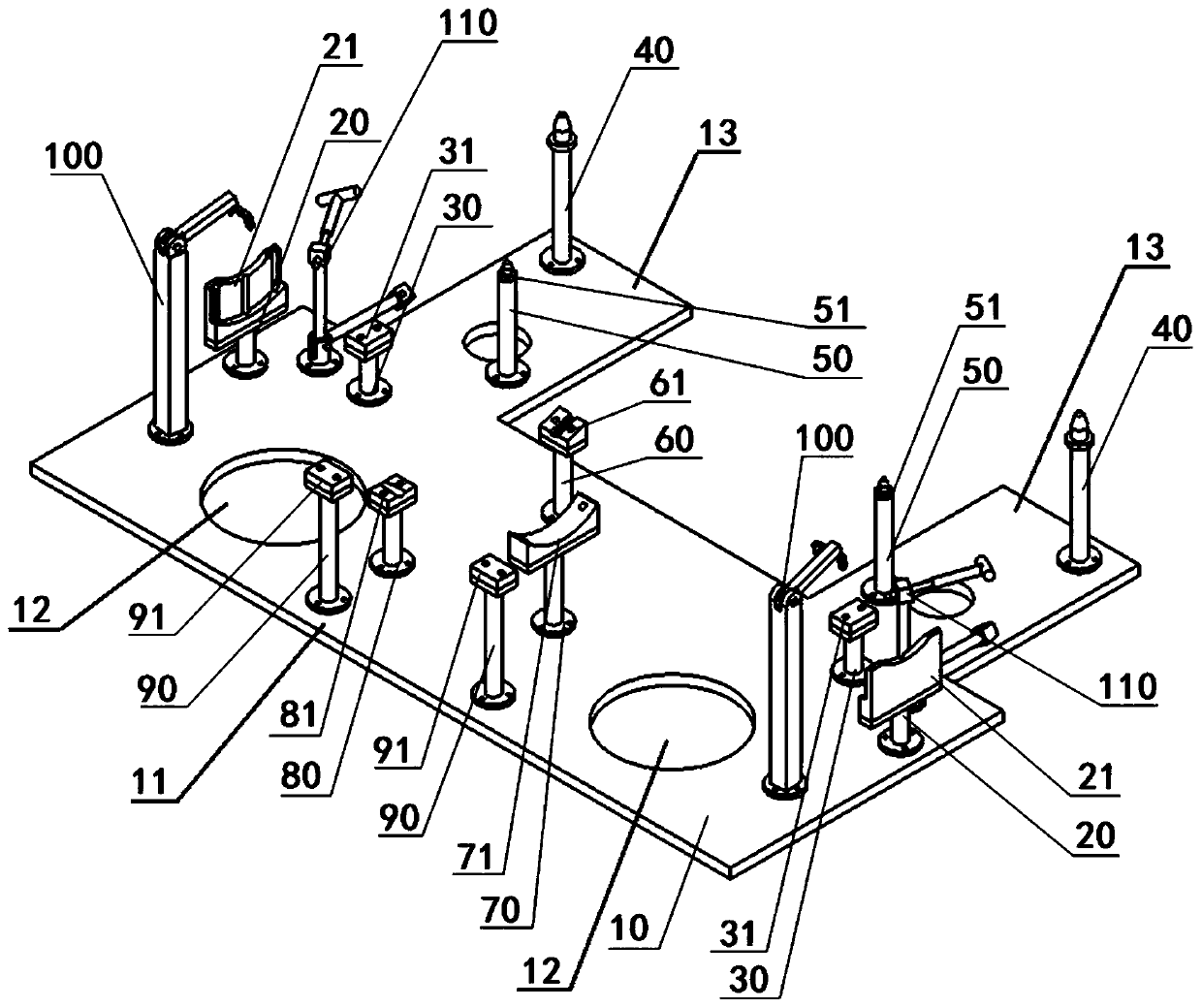
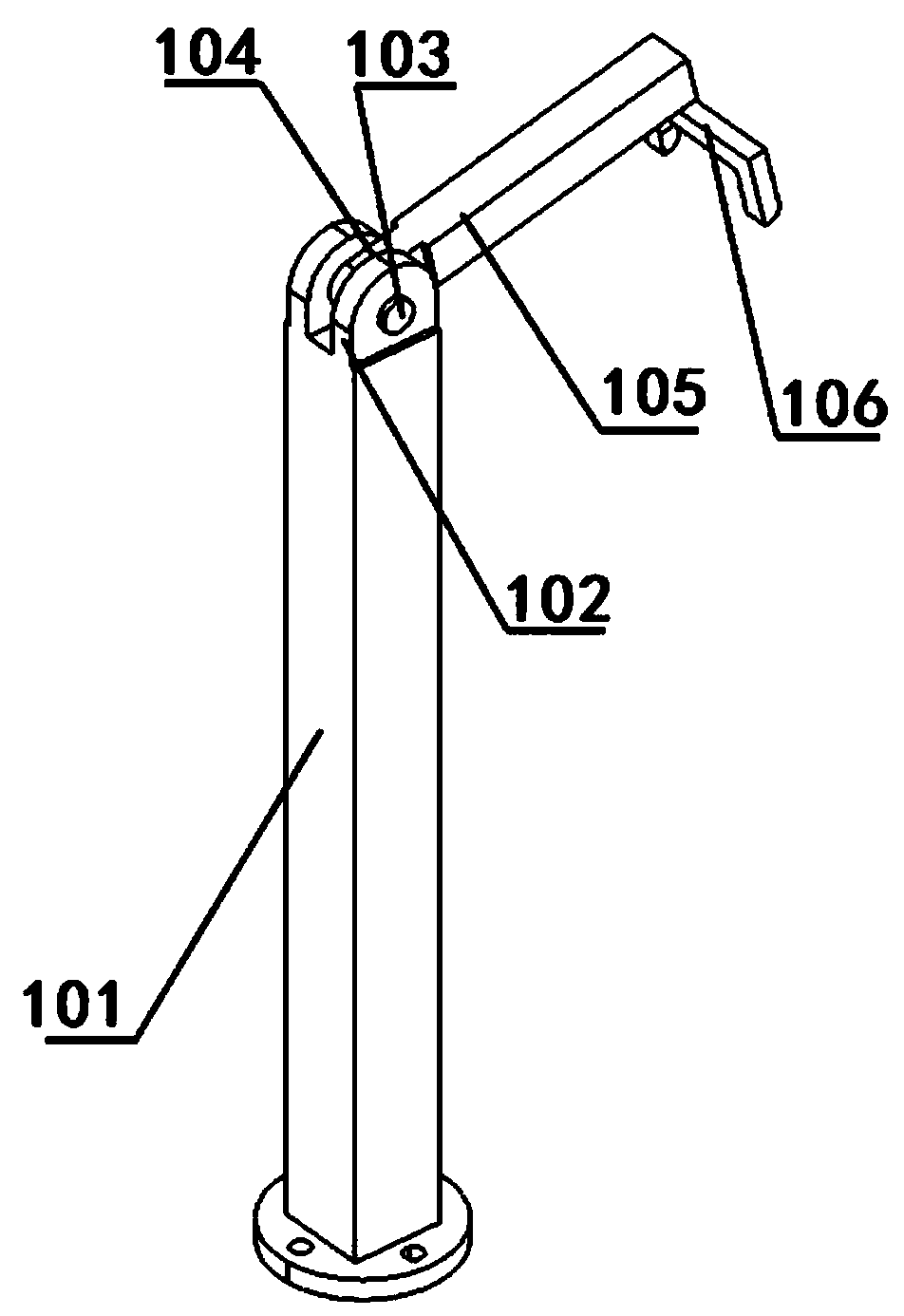
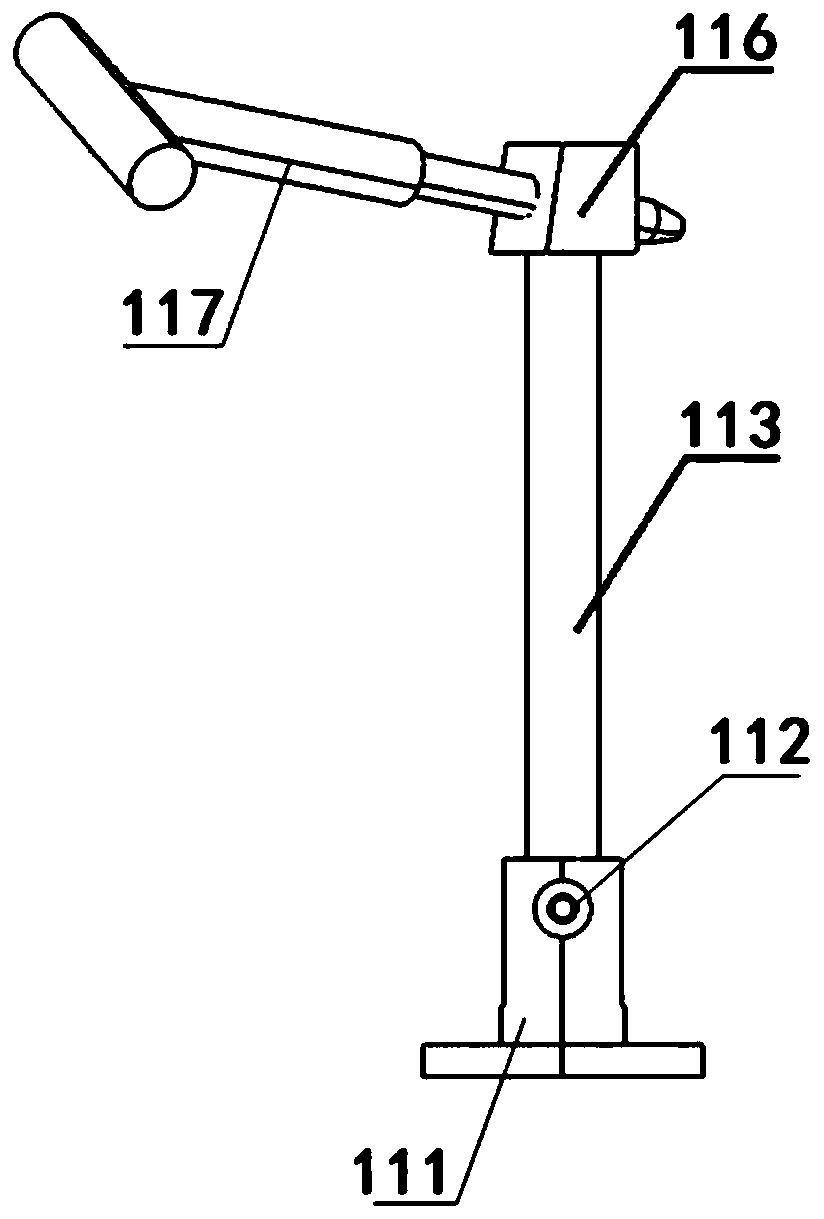
Rear suspension line lower adjusting tool structure
PendingCN111422282ARealize offline adjustmentImprove packaging accuracyVehiclesCamber angleVehicle frame
The invention relates to a rear suspension line lower adjusting tool structure, which belongs to the technical field of automobile production and manufacturing. The rear suspension line lower adjusting tool structure comprises a rear auxiliary frame positioning pin structure, a rear auxiliary frame auxiliary supporting structure, a rear brake disc supporting structure, a swing arm supporting structure, a swing arm supporting structure, a motor supporting structure, a rear wheel toe-in positioning structure, a rear wheel camber angle positioning structure and a vehicle body assembling positioning structure which are arranged on a base plate. The rear suspension line lower adjusting tool structure is a tool structure integrating rear suspension sub-assembly, rear suspension combined assemblyand rear suspension adjustment, what is guaranteed is that the camber angle and toe-in of the rear wheel are consistent with the design state and are assembled in place at a time by designing a positioning structure on the tool, and the procedure of adjusting the camber angle and toe-in of the rear wheel on a detection line is omitted.
Owner:IAT AUTOMOBILE TECH
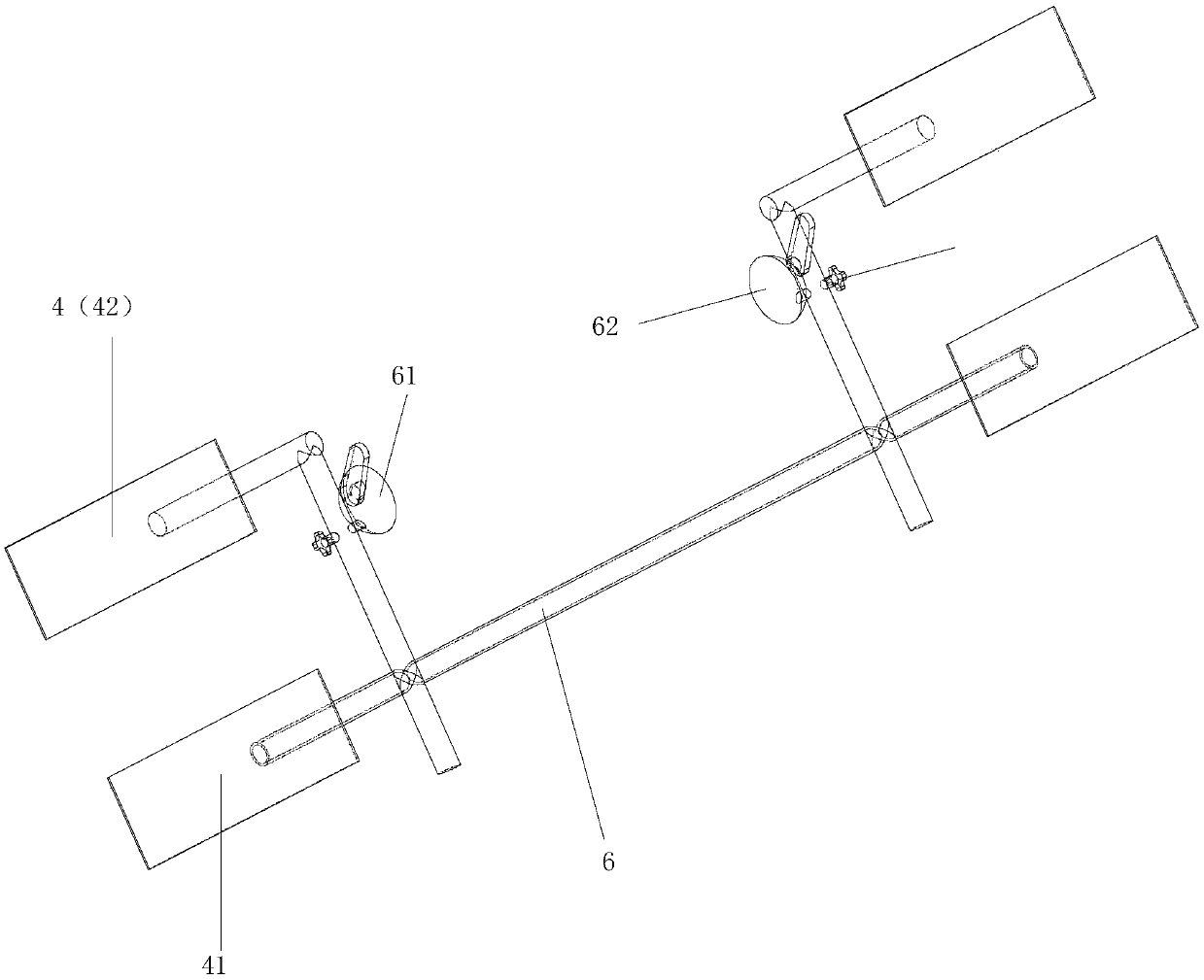
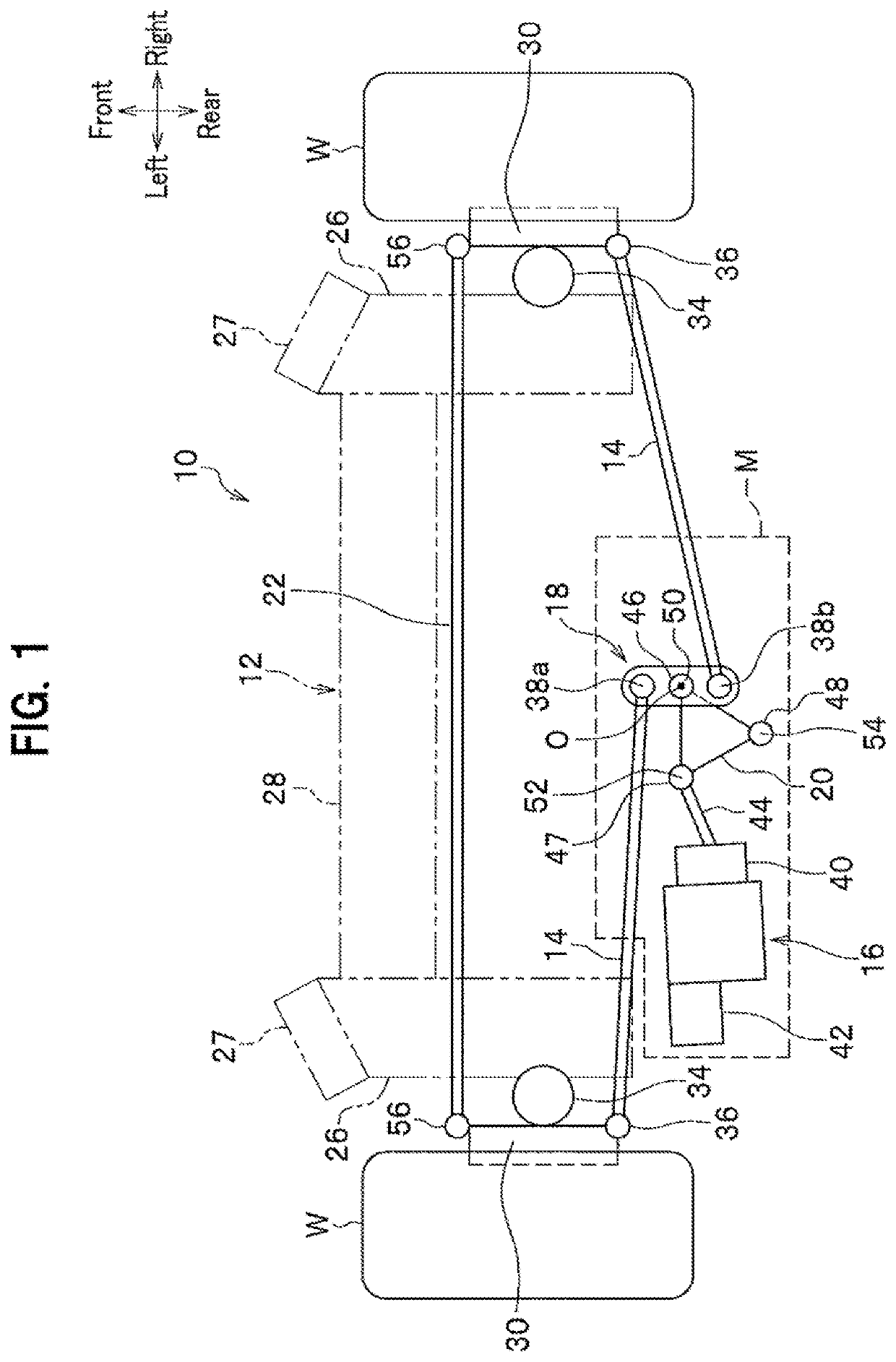
Wheel steering system
ActiveUS10836425B2Improve the environmentSlow changeSteering linkagesMechanical steering gearsSuspension (vehicle)Actuator
A wheel steering system is provided that improves an environment of an actuator being mounted and reduces changes in toe angles of wheels at the time of a suspension stroke. The system includes: right and left hub carriers supported by a rear suspension mechanism; right and left tie rods having outer ends in a vehicle width direction thereof pivotally connected to the right and left hub carriers; and a Watts link having inner ends in the vehicle width direction of the right and left tie rod pivotally attached thereto so as to be pivotable about a pivot axis, wherein the actuator and the Watts link are arranged above springs, and the Watts link is connected with the actuator so as to be displaceable substantially along the vehicle width direction when a driving force of the actuator is inputted to the Watts link.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Five-link suspension system and vehicle
A five-link suspension system comprises a steering knuckle, a toe-in arm, a transverse swing arm, a guide arm, a longitudinal swing arm and a control arm. The coordinates of a first connecting shaft of the toe-in arm are 3155-3165 mm, -279--289 mm and 15-25 mm, and the coordinates of a second connecting shaft of the toe-in arm are 3050-3060 mm, -732--742 mm and 14-24 mm; the coordinates of a thirdconnecting shaft of the transverse swing arm are 2981-2991 mm, -382--392 mm and 154-164 mm, and the coordinates of a fourth connecting shaft of the transverse swing arm are 2916-2926 mm, -729--739 mmand 169-179 mm; the coordinates of a fifth connecting shaft of the guide arm are 2810-2820 mm, -650--660 mm and 96-106 mm, and the coordinates of a sixth connecting shaft of the guide arm are 2672-2682 mm, -422--432 mm and 114-124 mm; the coordinates of a seventh connecting shaft of the longitudinal swing arm are 2677-2687 mm, -408--418 mm and -37--47 mm, and the coordinates of an eighth connecting shaft of the longitudinal swing arm are 2849-2859 mm, -693--703 mm and -120--130 mm; and the coordinates of a ninth connecting shaft of the control arm are 2958-2968 mm, -713--723 mm and -69--79 mm, and the coordinates of a tenth connecting shaft of the control arm are 3099-3109 mm, -265--275 mm and -70--80 mm. The toe-in curve of the five-link suspension system has very high linearity. The invention also relates to a vehicle.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Power-driven shoe device wheel configuration with combined translational and rotational hinge mechanism and integrated gear-bushing assembly
Disclosed is a power-driven shoe. The shoe includes a shoe sole having a plurality of rotatable wheels arranged below the shoe sole in an overlapping fashion. The distance between the rotational axis of the wheels is less than or equal to the diameter of the wheel, such that vertical obstacles can be overcome in both the positive and negative displacement directions for increased ground stability. The shoe sole includes a toe part and a sole part that are connected to each other, via a hinge, in both a rotational and translational configuration, such that at least one front wheel or at least one middle wheel are independently in contact with the ground while maintaining at least one rear wheel in contact with the ground throughout a bi-pedal gait cycle, allowing for comfort during a user's natural range of motion.
Owner:NIMBUS ROBOTICS INC
All-steel radial tire toe opening structure
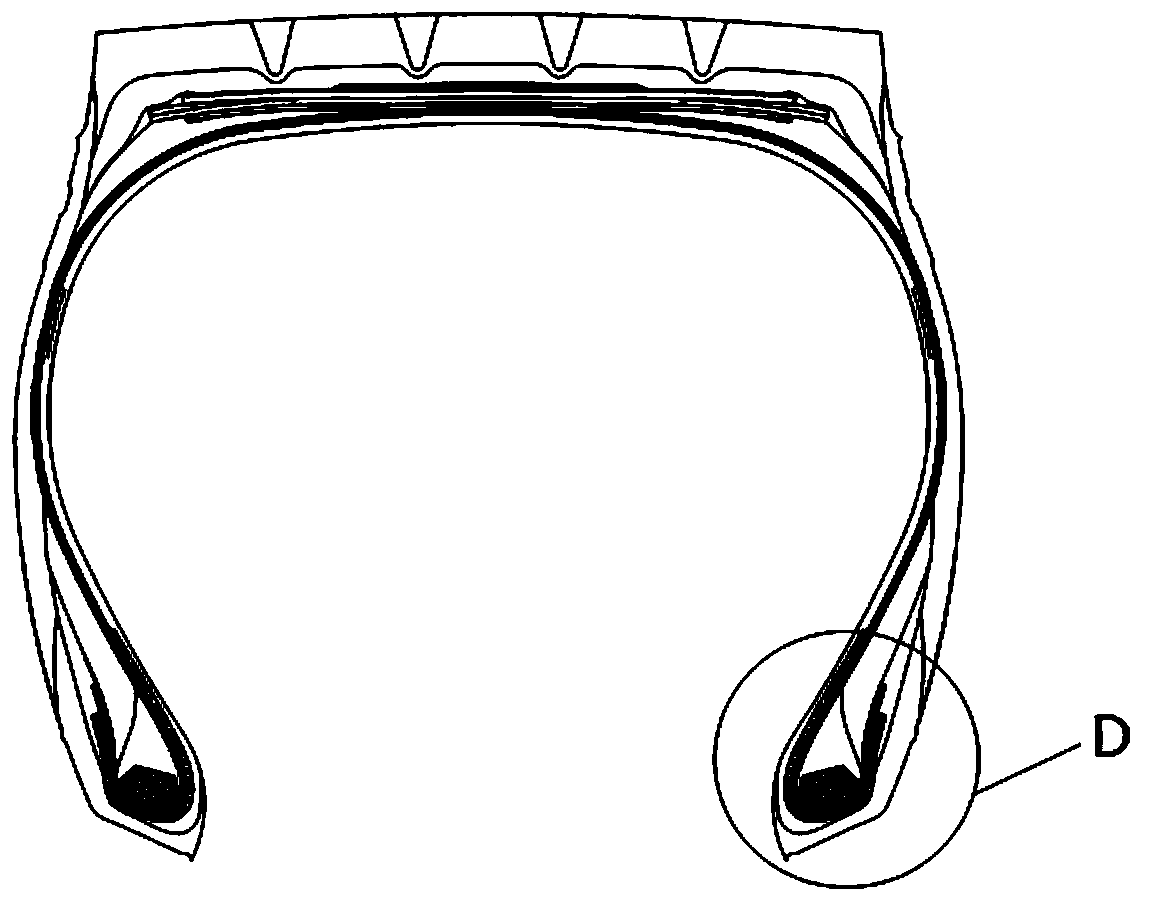
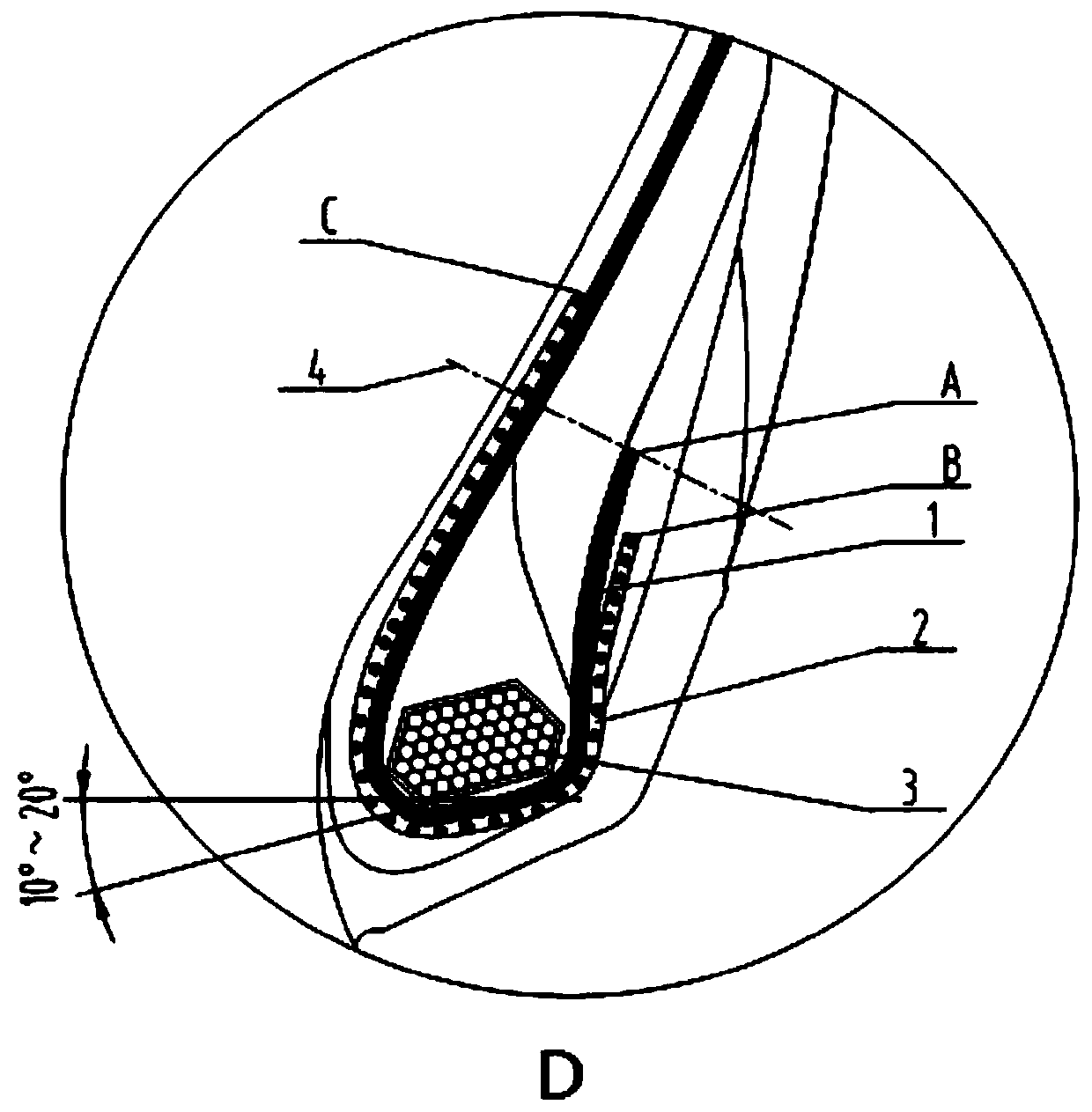
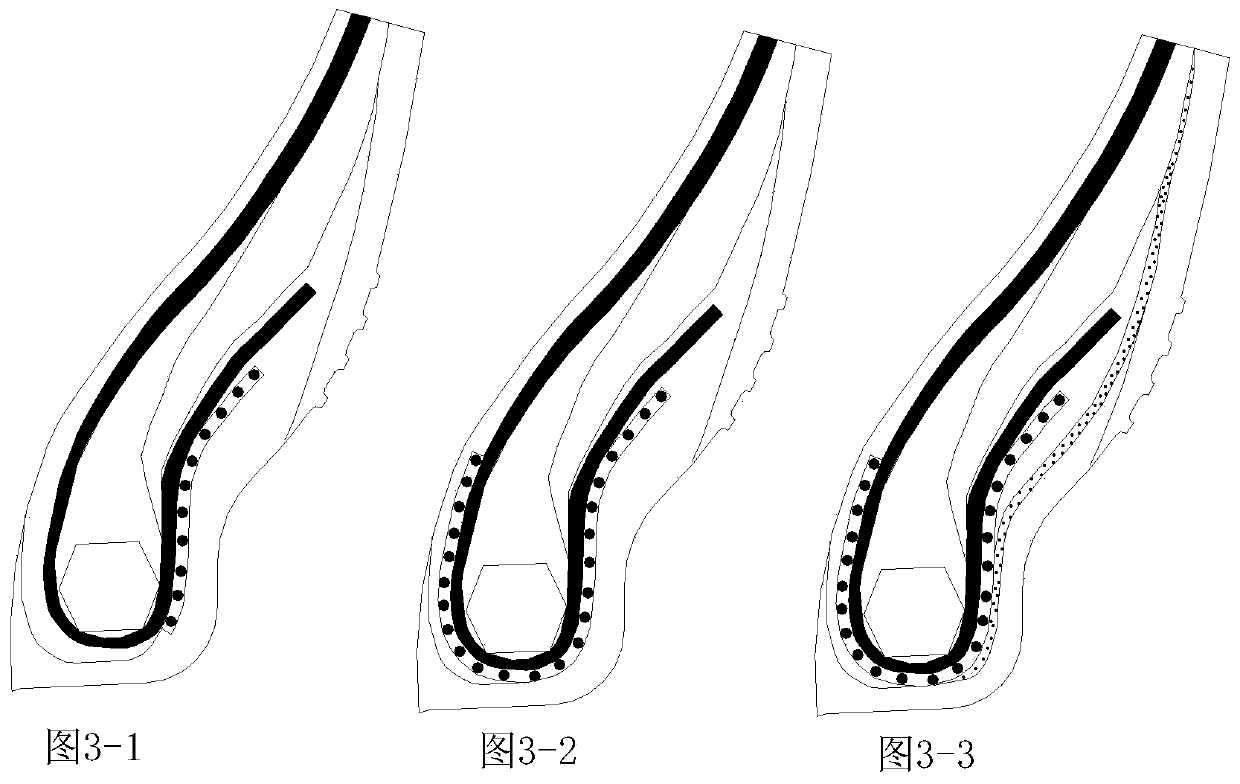
The invention provides an all-steel radial tire toe opening structure. The all-steel radial tire toe structure comprises a carcass ply surrounding toe opening steel wire rings and a toe opening reinforcing layer, the steel wire rings are obliquely arranged at an angle of 10-30 degrees, namely, the inclination angle between the bottom surfaces of the steel wire rings and the tire tread is 10-30 degrees; the toe opening reinforcing layer is reversely wrapped around the toe opening steel wire rings; the vertical line is a vertical line which passes through the carcass ply turn-up endpoint A and is vertical to the carcass ply; the vertical position of the toe opening reinforcing layer positive wrapping end point C is higher than the vertical position of the intersection point of the vertical line and the toe opening reinforcing layer; the vertical position of the toe reinforcing layer turn-up endpoint B is lower than the vertical position of the carcass ply turn-up endpoint A, so that theproblem that cracks are easily generated at the carcass ply turn-up endpoint is solved, and the bearing capacity of the all-steel radial tire, particularly the toe opening part, is greatly improved. The invention belongs to the technical field of tire structure optimization.
Owner:GUIZHOU TIRE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com