Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4118results about "Axially engaging brakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
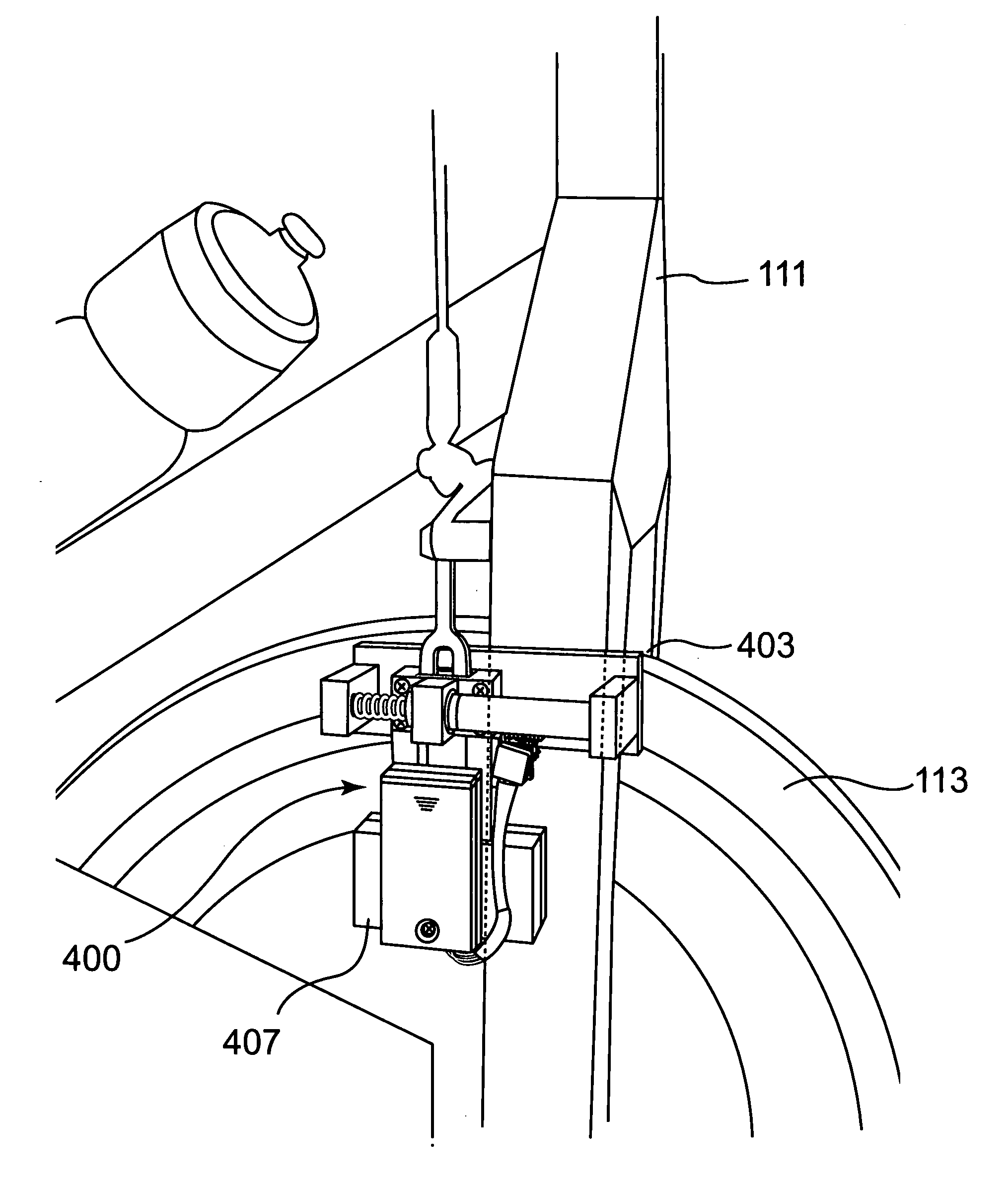
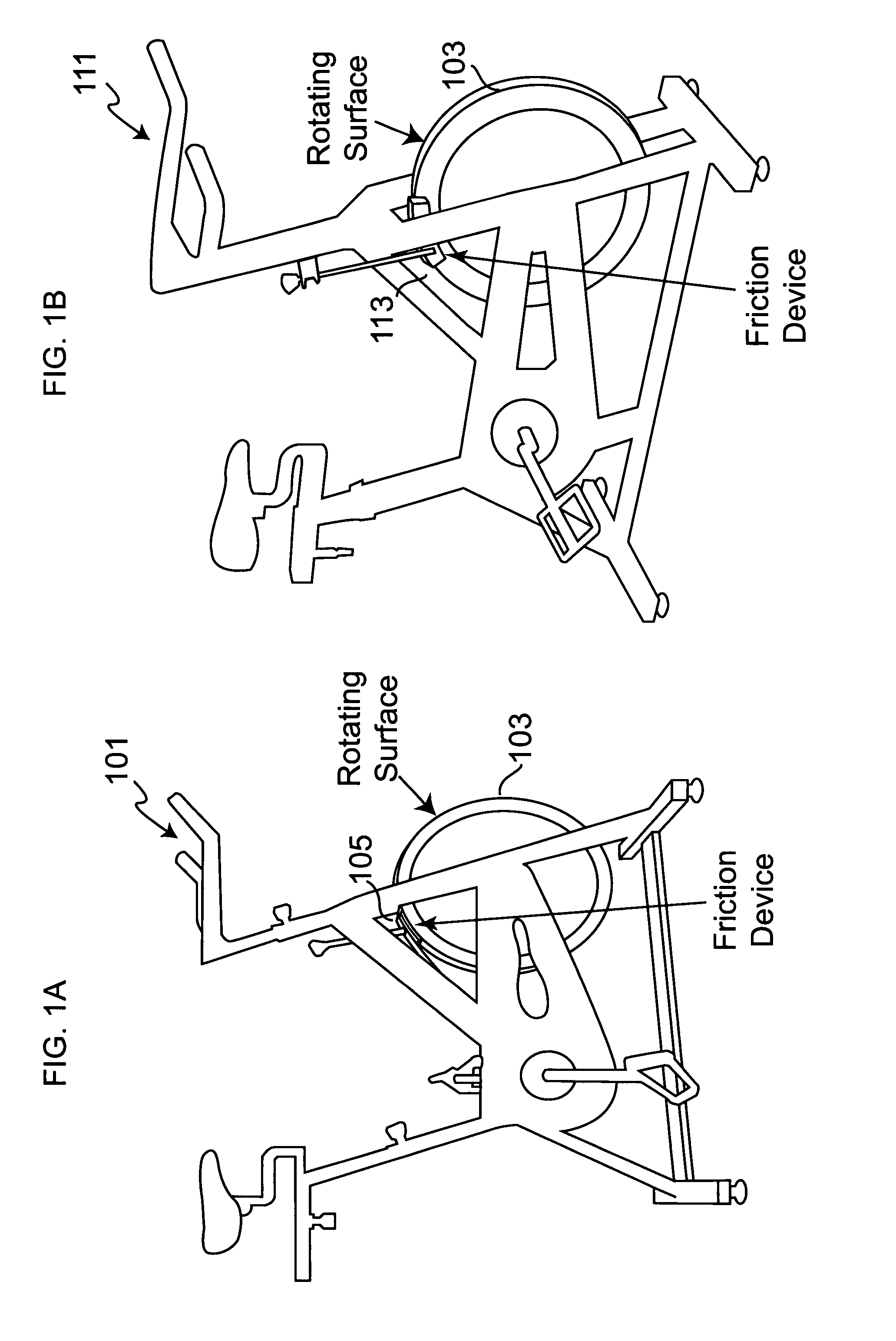
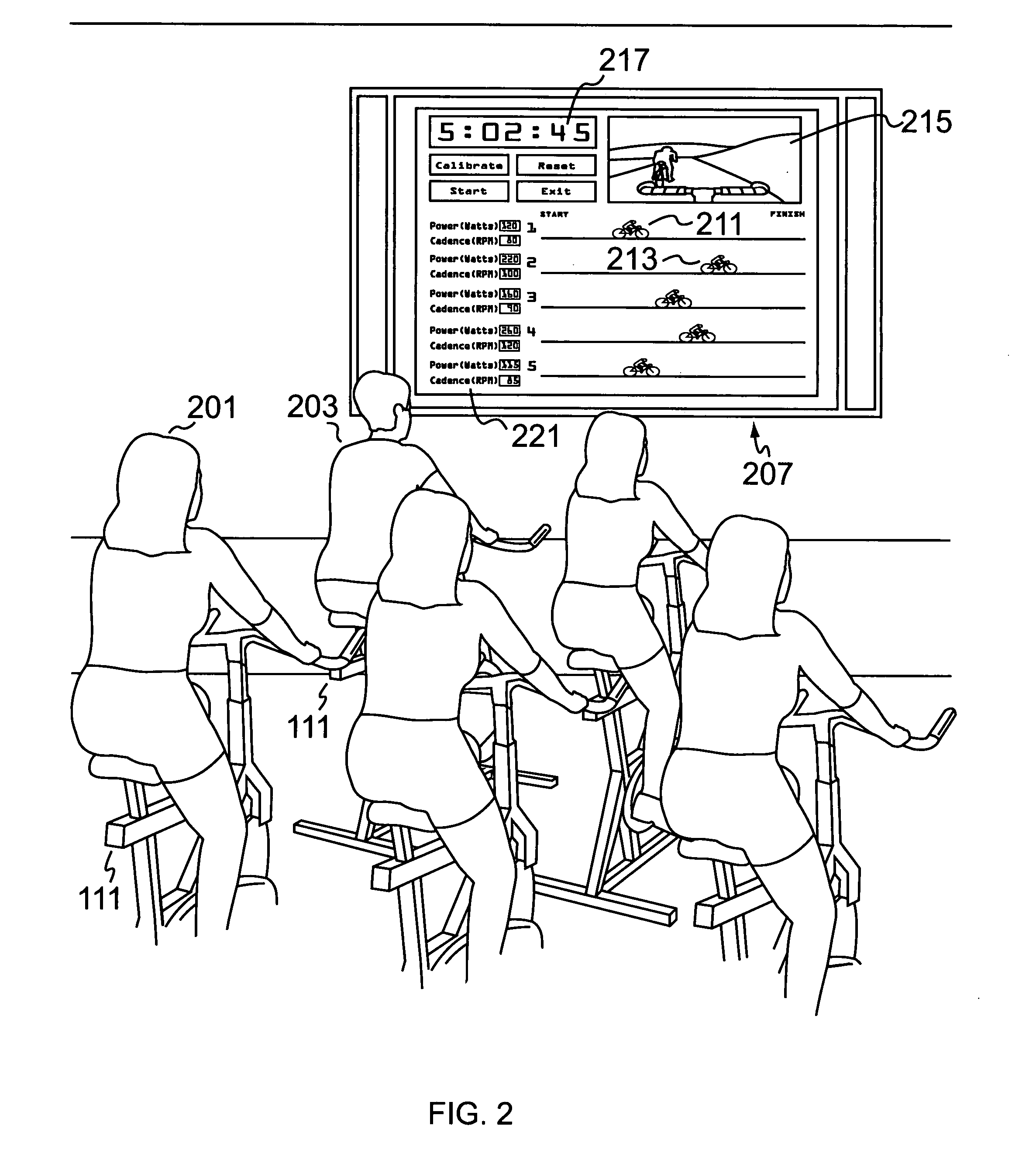
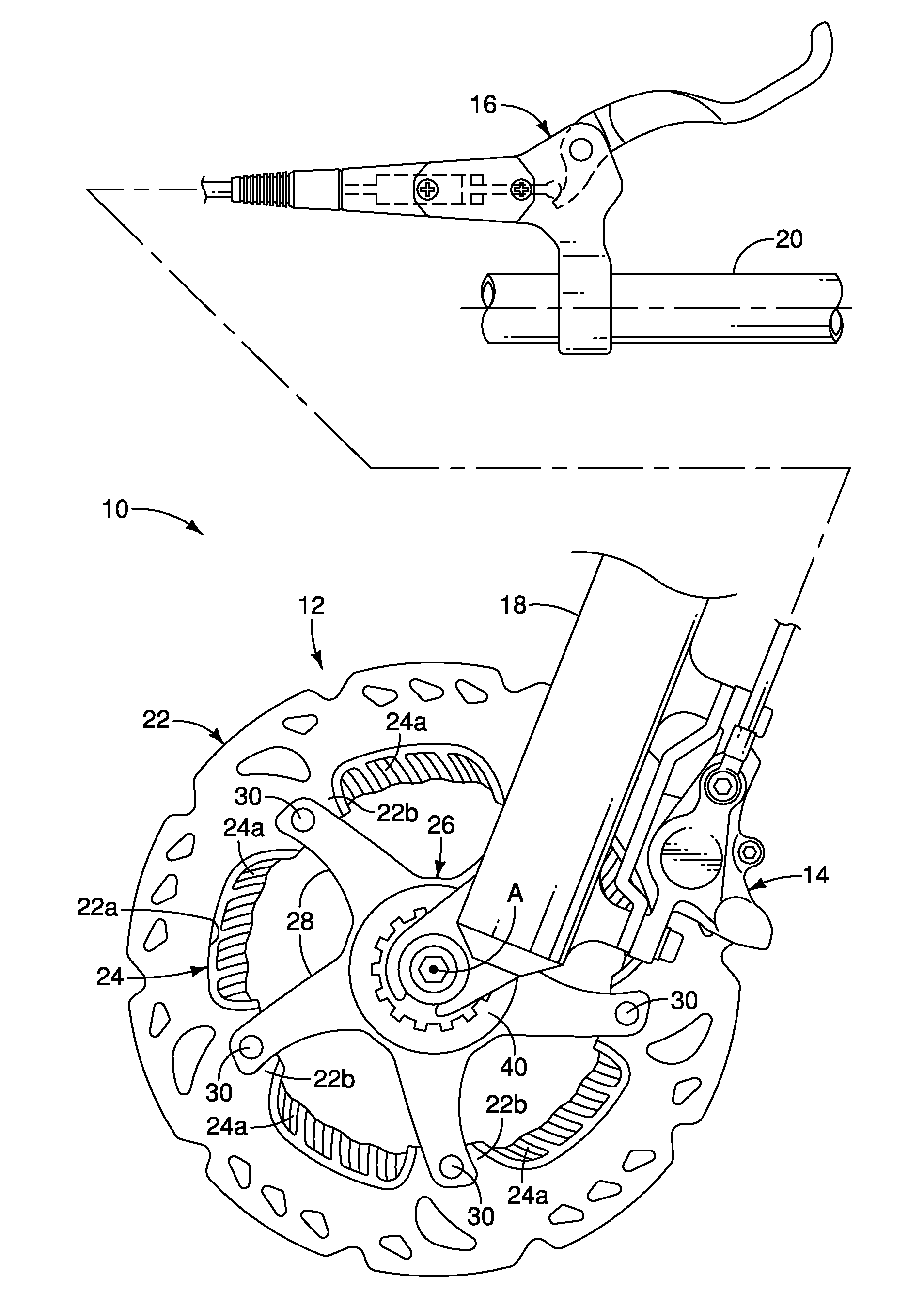
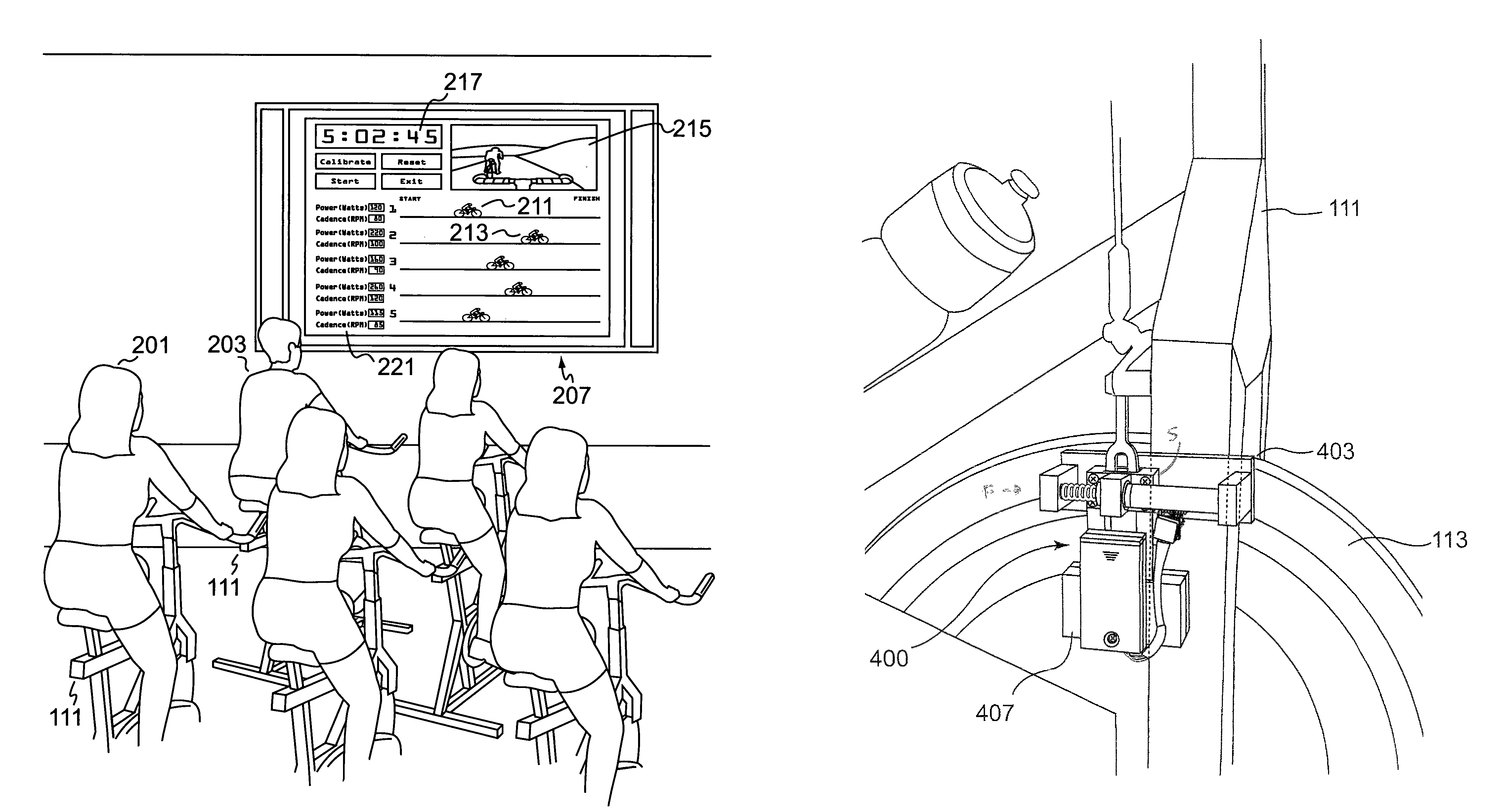
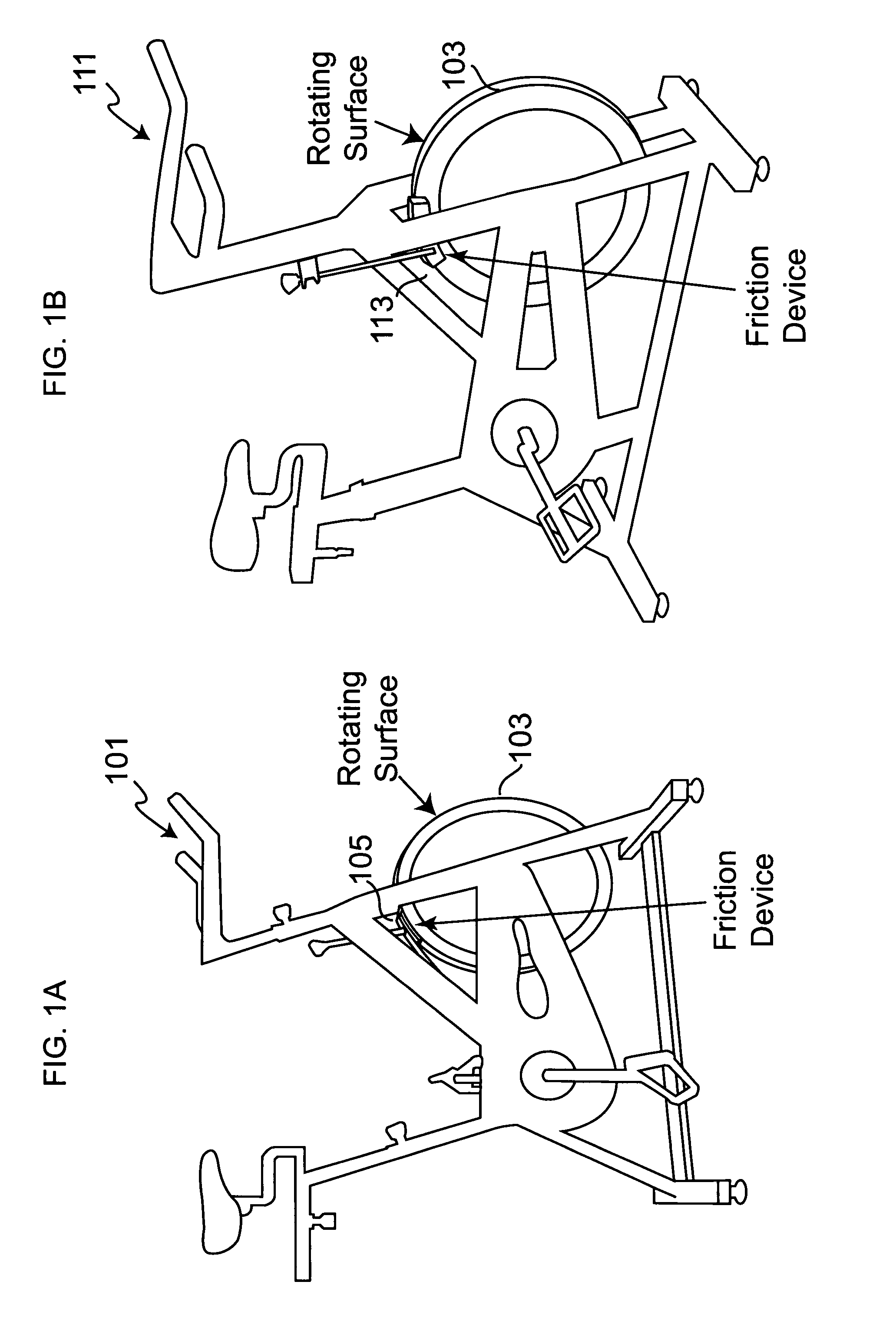
Method and apparatus for measuring exercise performance
ActiveUS20080015089A1High levelPhysical therapies and activitiesAxially engaging brakesExercise performanceDisplay device
An integrated sensor apparatus capable of detecting exercise equipment parameters such as power output and cadence is designed so as to be easily retrofittable to existing equipment. To the extent that a particular sensor uses friction measurement, it can supplant an existing friction causing device on the equipment. Additionally, the sensor can communicate, wirelessly if desired, with a processing device. The processing device is capable of receiving and processing a plurality of sensor signals. The processing device can then output processed signals to a display, so that a plurality of people joining in a group exercise or competition can easily track their relative performance in real-time.
Owner:ARTIS LLC
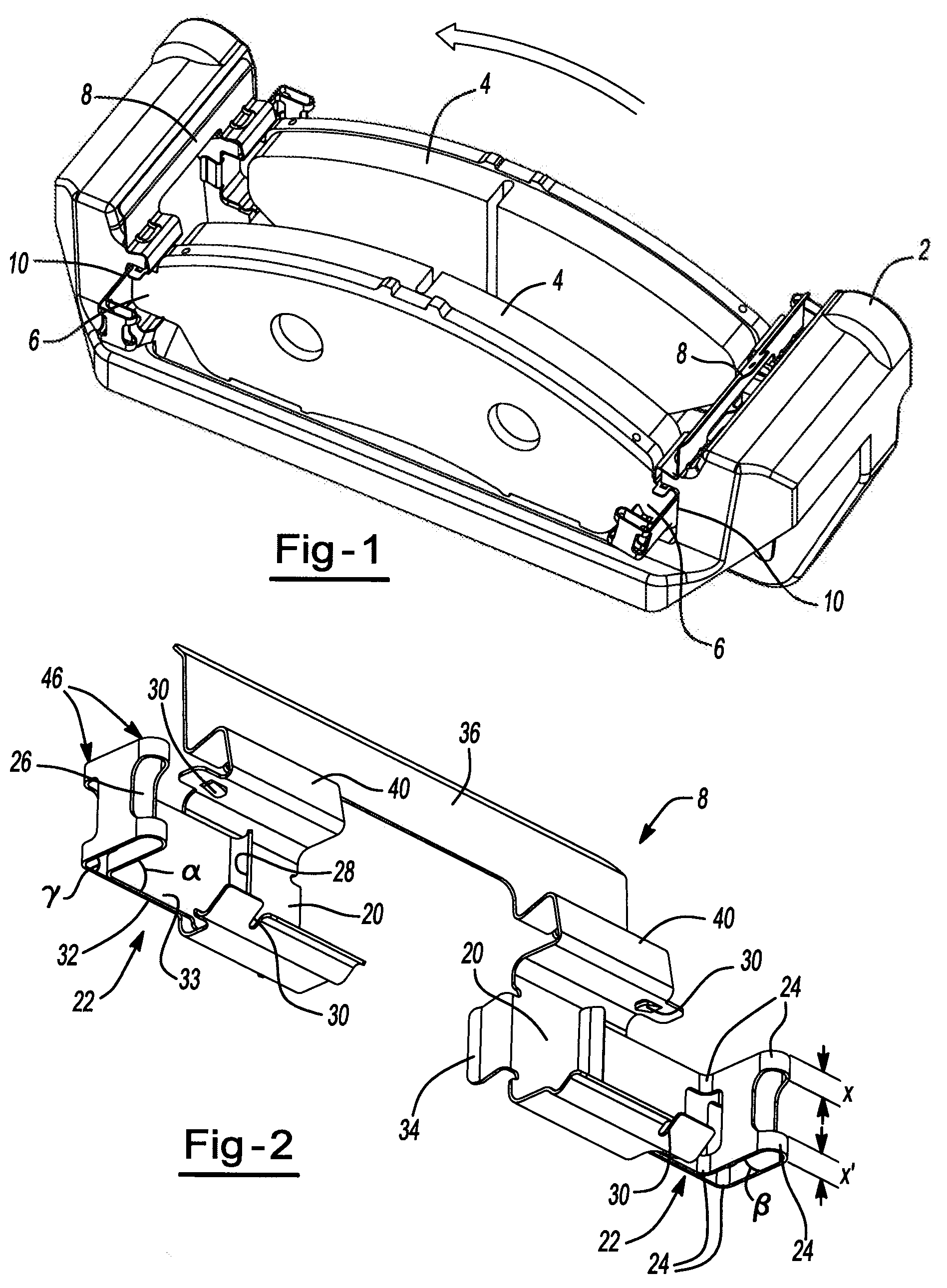
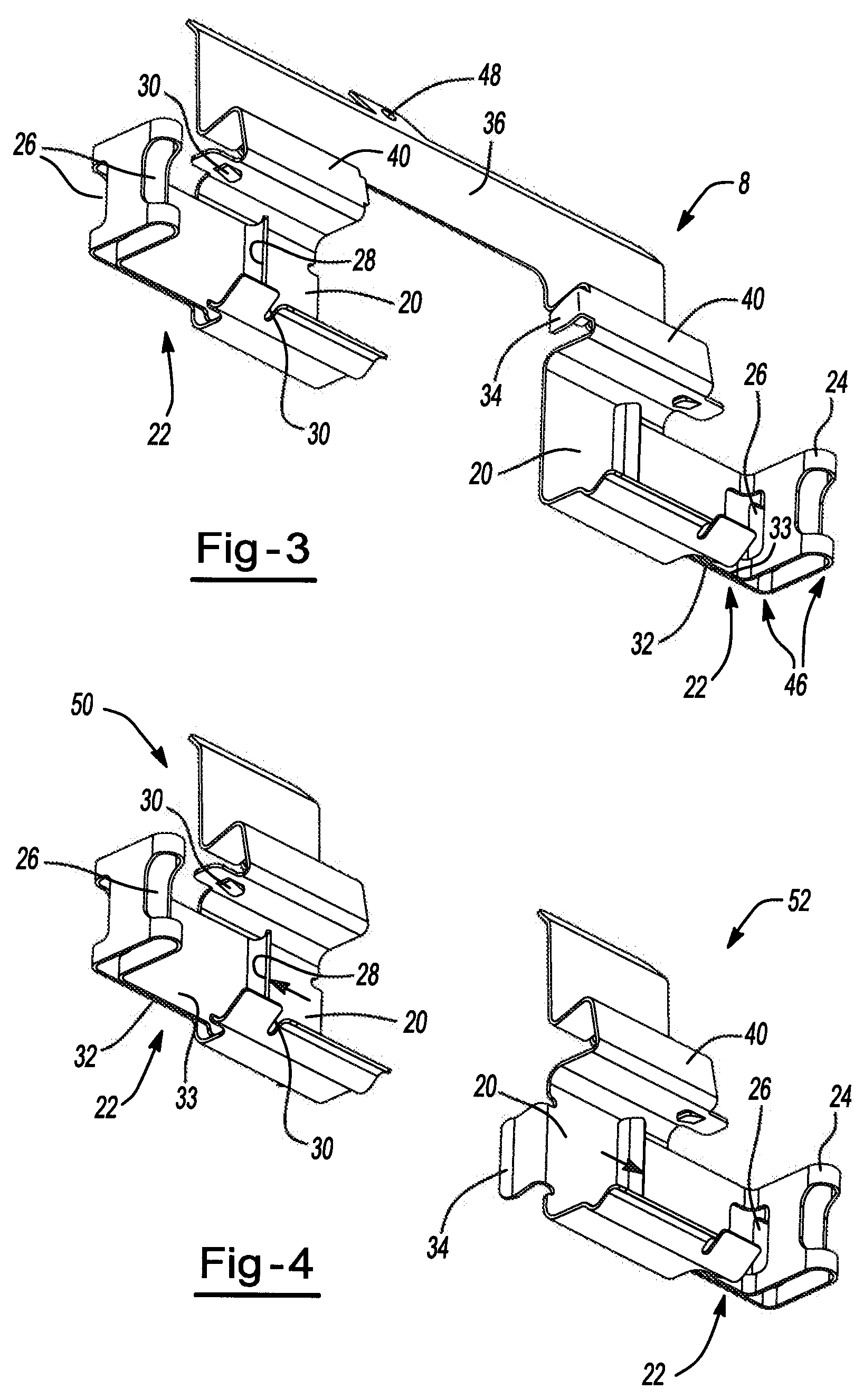
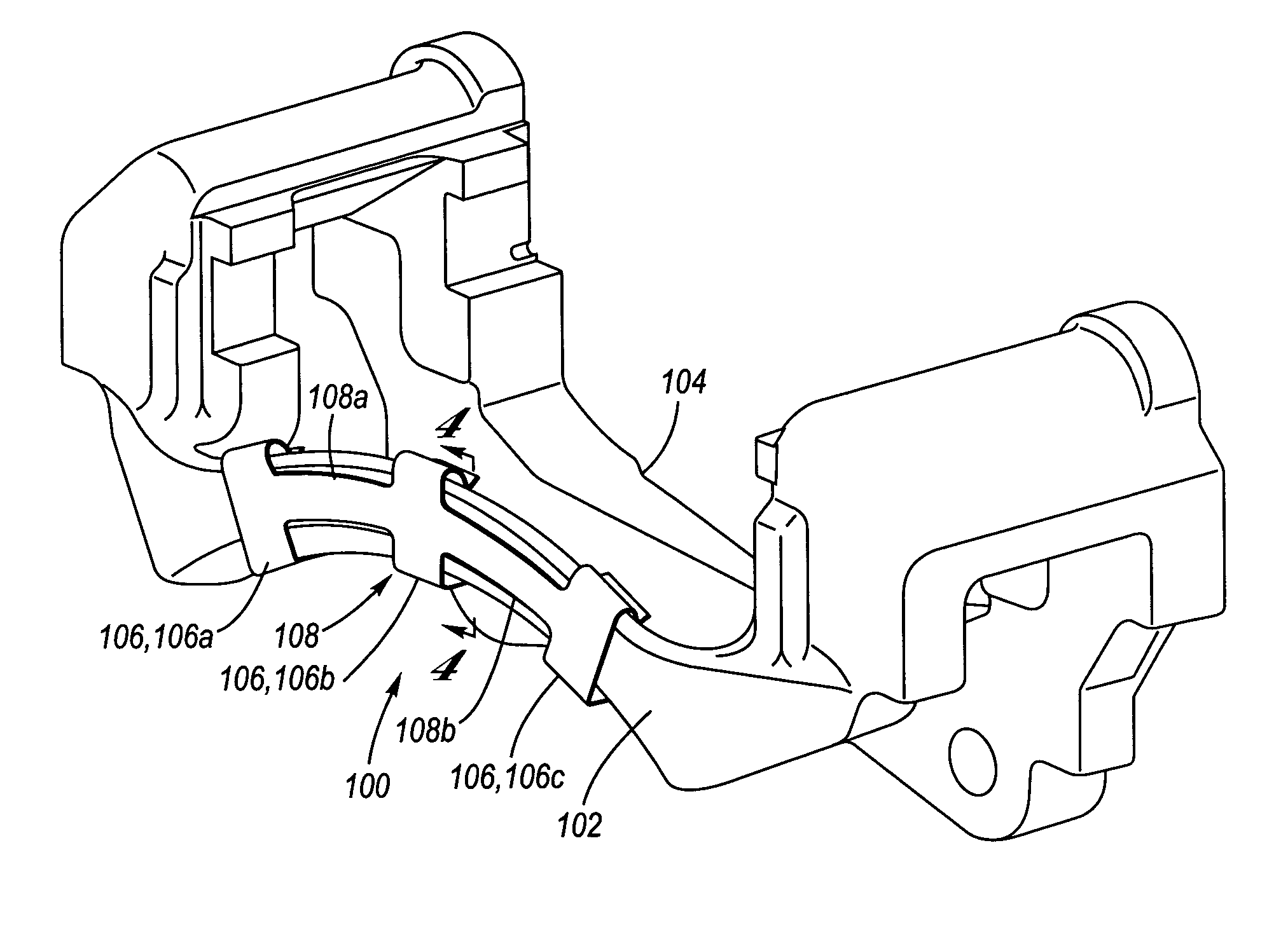
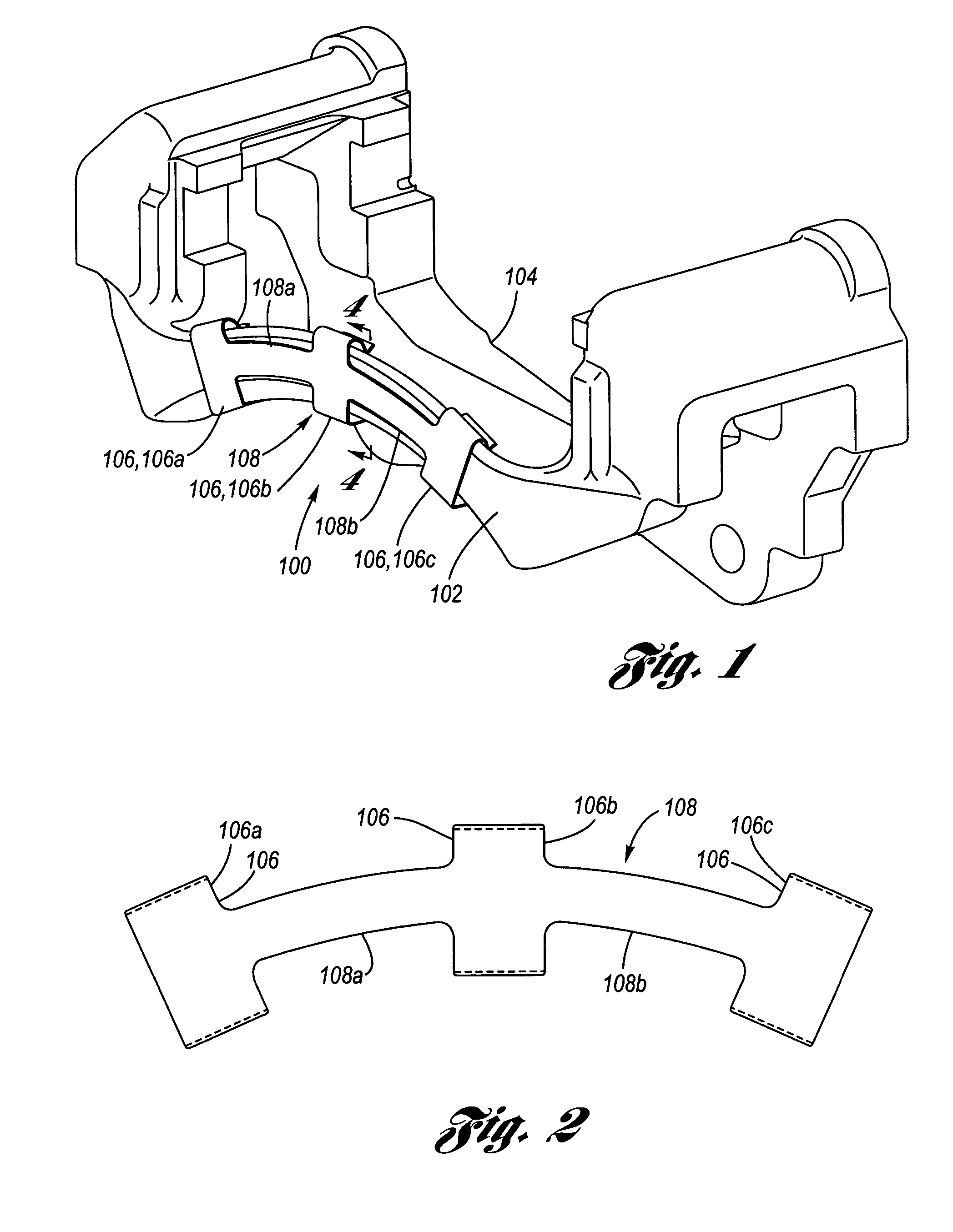
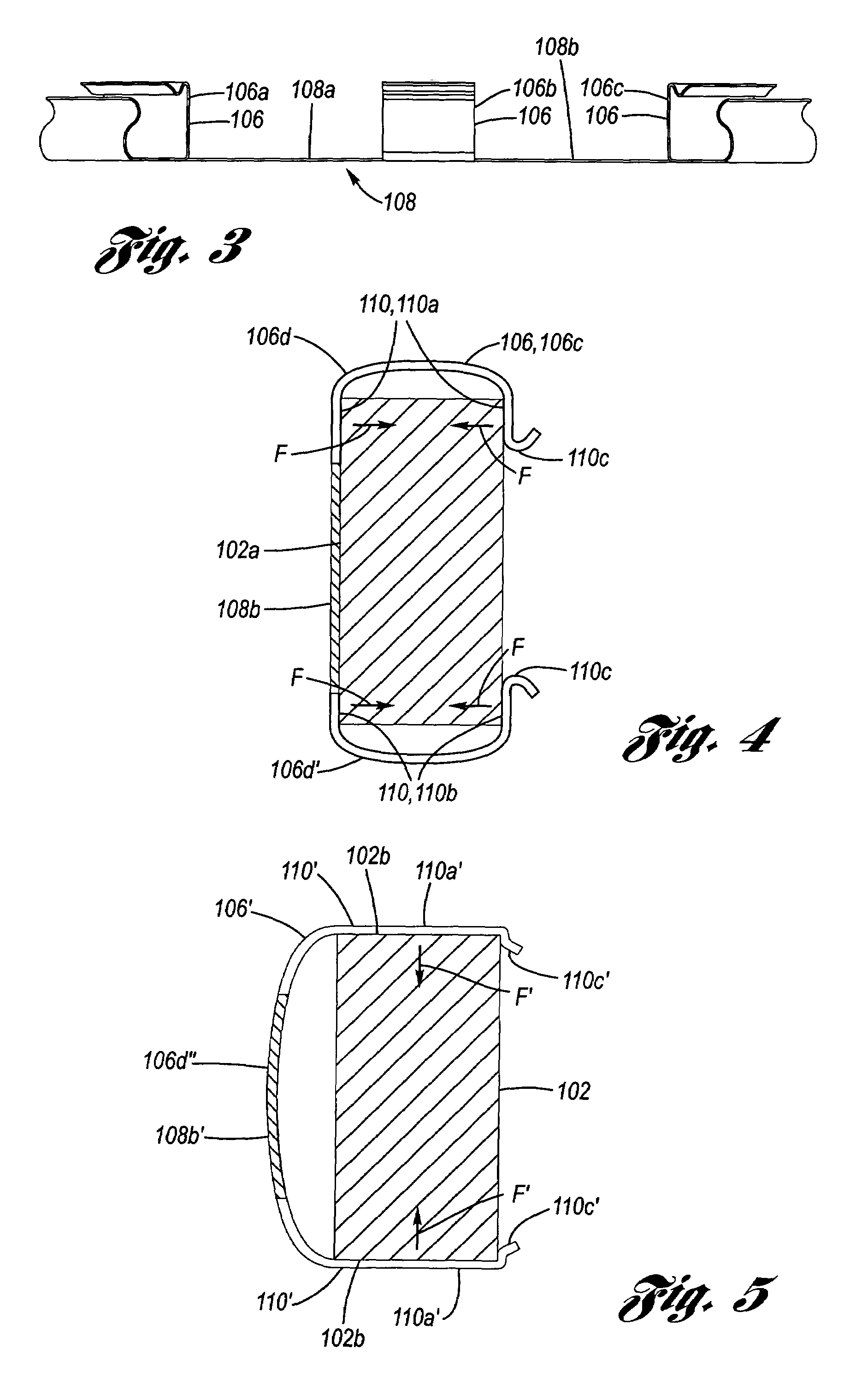
Pad retraction device
InactiveUS20110168503A1Constant forceRemove debrisSnap fastenersAxially engaging brakesBiomedical engineeringBody segment
A clip comprising: a body portion; one or more arms connected to the body portion and projecting away from the body portion; a deformable portion of the one or more arms that is distal from the body portion; and a lip on the one or more arms that is proximate to the body portion.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
LSI package provided with interface module, and transmission line header employed in the package
InactiveUS20050230795A1High frequencyAxially engaging brakesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterposerComputer module
An LSI package encompasses a transmission line header embracing a header-base, a transmission line held by the header-base, and an interface IC chip mounted on the header-base, an interposer substrate having a plurality of board-connecting joints, which facilitate connection with the printed wiring board; an LSI chip mounted on the interposer substrate; and a receptacle having a lead terminal and being mounted on the interposer substrate, configured to accommodate the transmission line header so that the interface IC chip electrically connects to the LSI chip through the lead terminal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Device for fixing a ventilated brake disk axially on the hub of a motor vehicle wheel
InactiveUS6446765B1Easy to controlHigh speed usBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An axial fixing device for axially fixing an annular brake disk on a wheel hub of a motor vehicle, the annular brake disk having the same axis of rotation as the hub and including radial ventilation ducts regularly distributed about its periphery. According to the invention, the hub has axial guide pieces in relief, or "lugs", for co-operating with fluting in an inner peripheral edge of the disk to center the disk, to lock it angularly, and to guide it axially relative to the hub, each lug of the hub having a radial through channel for co-operating with a corresponding ventilation duct of the disk, and the disk is held axially in the hub with play by axial holding means disposed between the disk and the hub.
Owner:MESSIER BUGATTI INC
Method of making brake discs and rotors with open slots and brake discs and rotors made therewith
InactiveUS20050252739A1Improve cooling effectGood cooling propertiesBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesEngineering
The present invention broadly comprises a brake disc having superior cooling characteristics and a method for manufacturing brake discs with superior cooling characteristics. The brake disc has at least one slot arranged at an angle greater than zero degrees and less than ninety degrees with respect to a radius of said disc passing through said slot. The angle can be selected to enhance cooling under specified conditions. Slots in the disc can open to an inner or outer perimeter of the disc or may be fully enclosed within the disc. The shape and width of the slots and the spacing between the slots can be selected to enhance cooling properties of the disc.
Owner:CALLAHAN FRED J +1
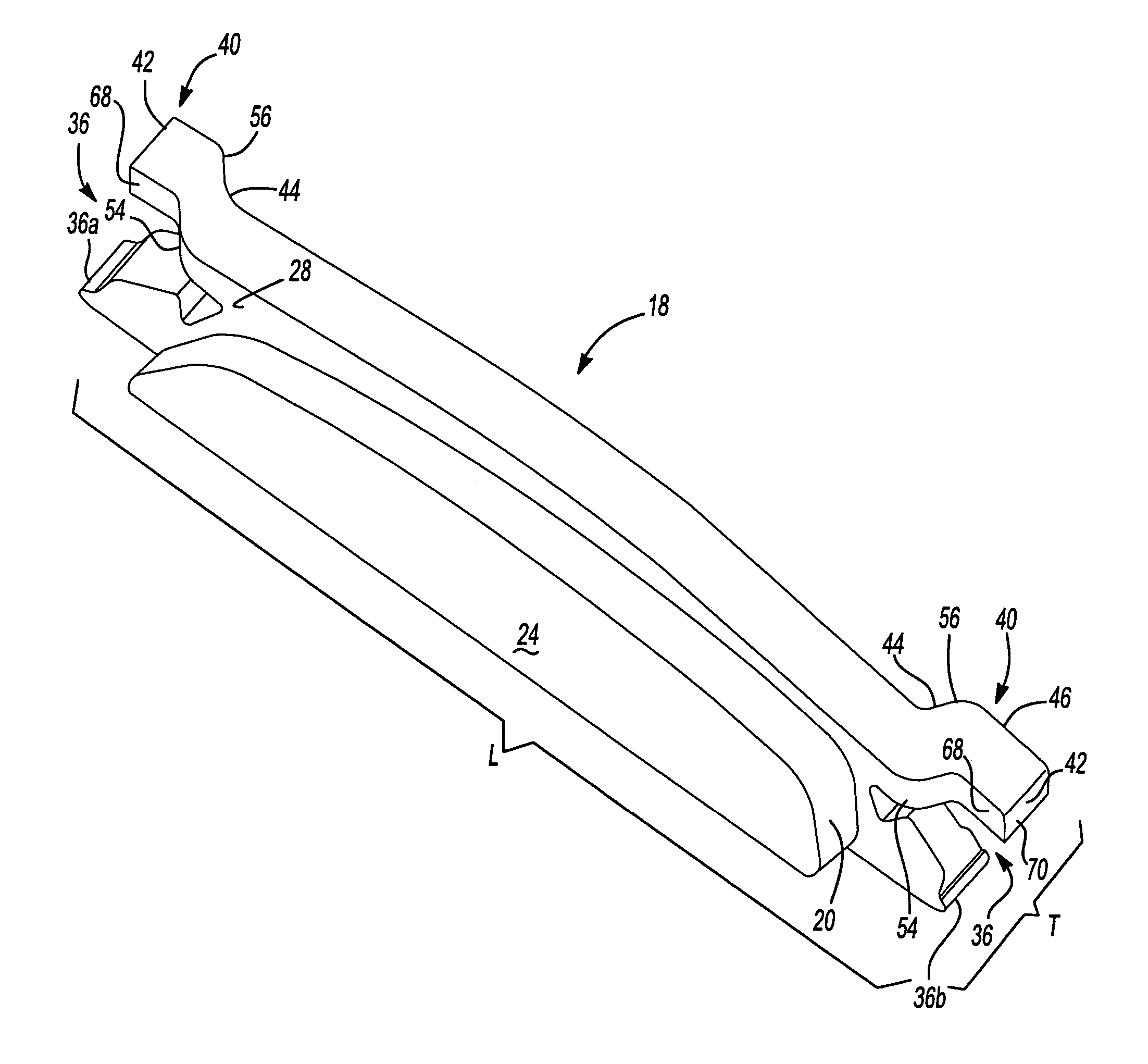
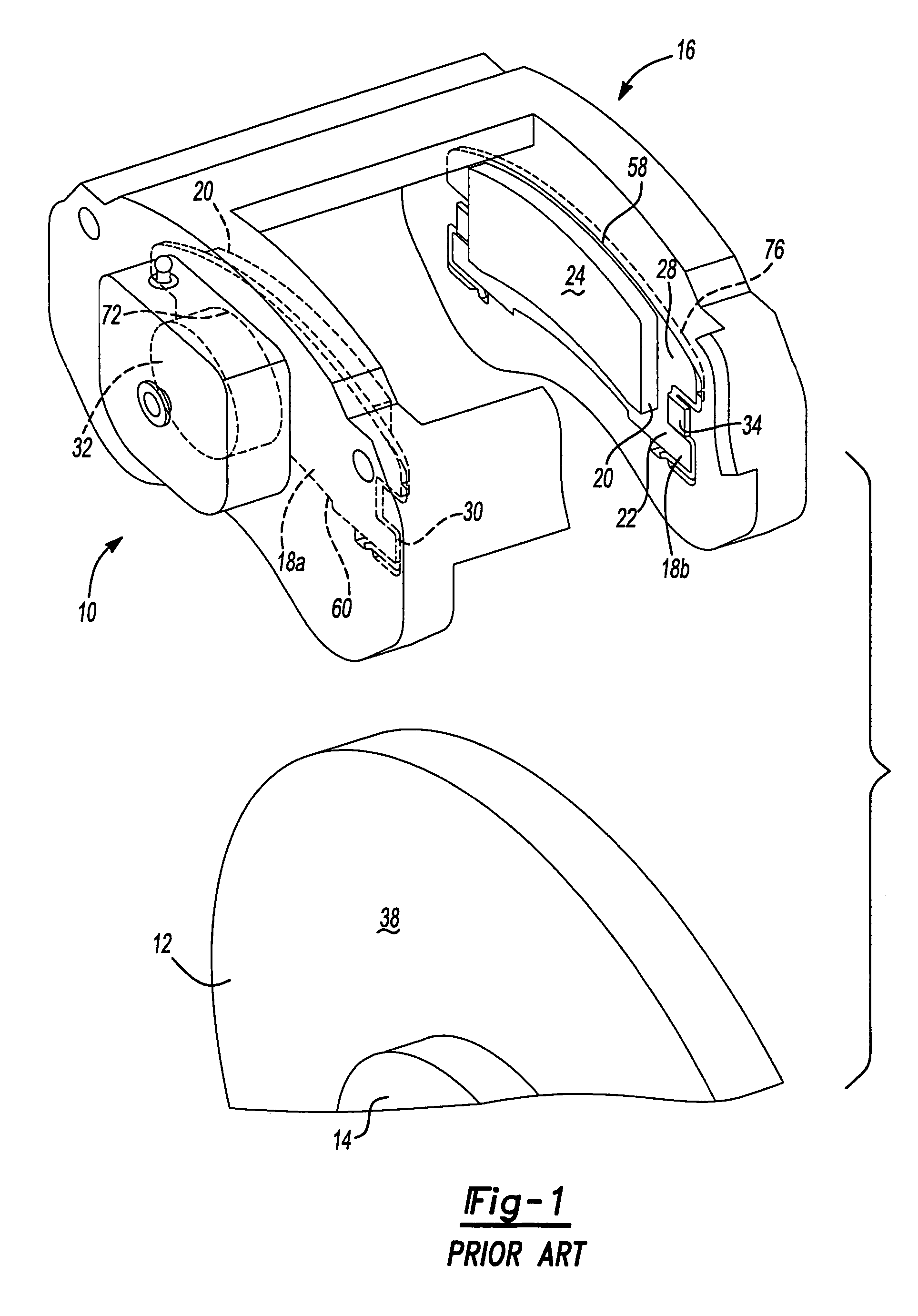
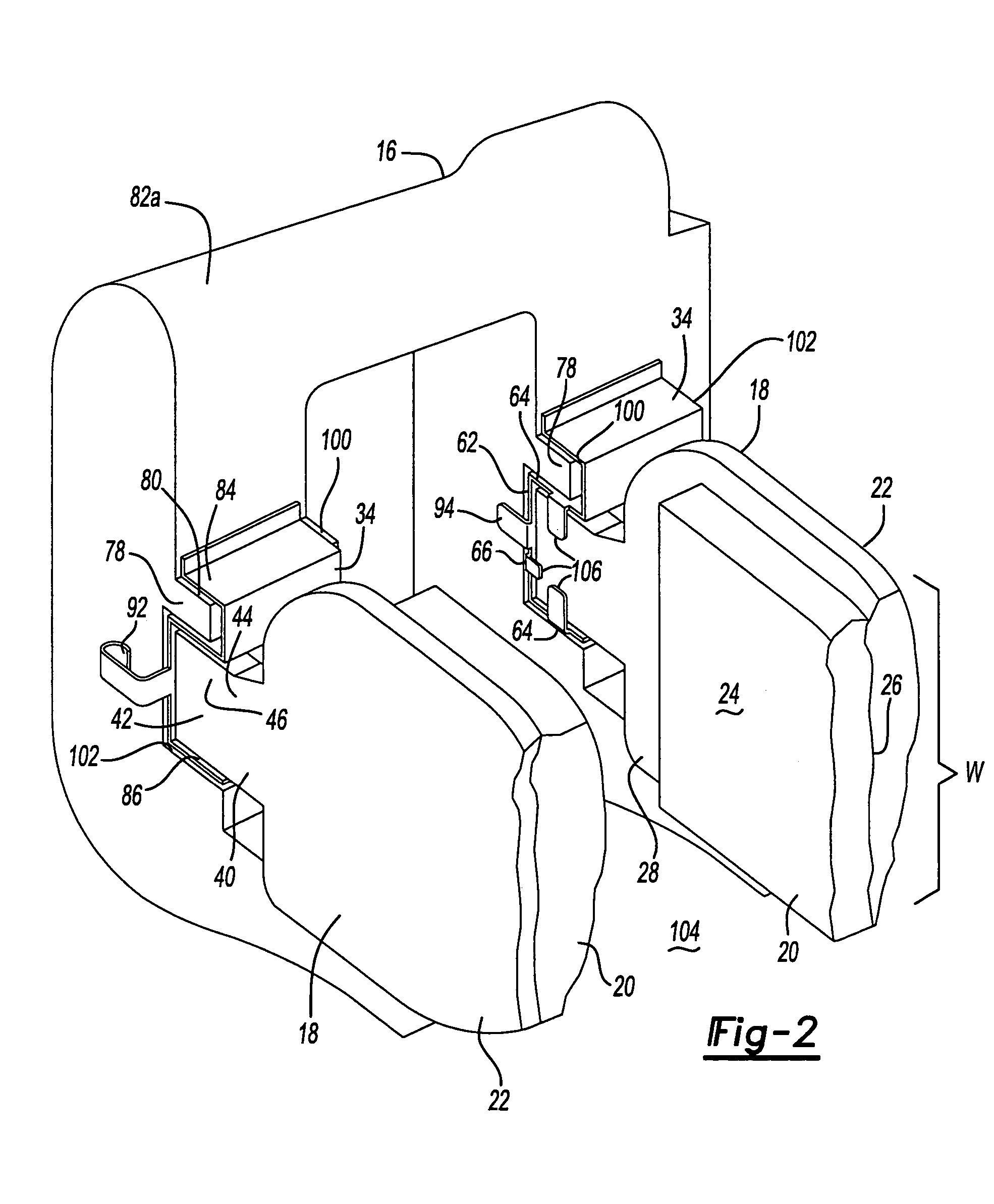
Pad retaining clips
A brake caliper mounting clip is disposed between a brake caliper having a brake pad channel and a brake pad having an edge member. The edge member moves in the brake pad channel between a rotor gap and a caliper housing. The clip further comprises a pad holding portion slidingly engaged with the edge member and having a plurality of pad retaining members. The pad retaining members are connected to the pad holding portion and disposed between the edge member and the rotor gap. The plurality of the pad retaining members is further configured to prevent the brake pad from falling into the rotor gap. Additionally the edge member of the brake pad and the plurality of pad retaining members are configured to prevent improper installation of the brake pads in the caliper.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Coiled spreader spring
InactiveUS20140339026A1Movement is minimized and eliminatedMinimizes and eliminates DVT growthAxially engaging brakesBraking elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A spreader spring comprising: (a) a locking arm that connects the spreader spring to a brake component; (b) a retraction arm; and (c) a bias device located between the locking arm and the retraction arm; wherein the bias device includes six helical loops or more that store energy during a brake apply and once the brake apply is complete assist in retracting a brake pad.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
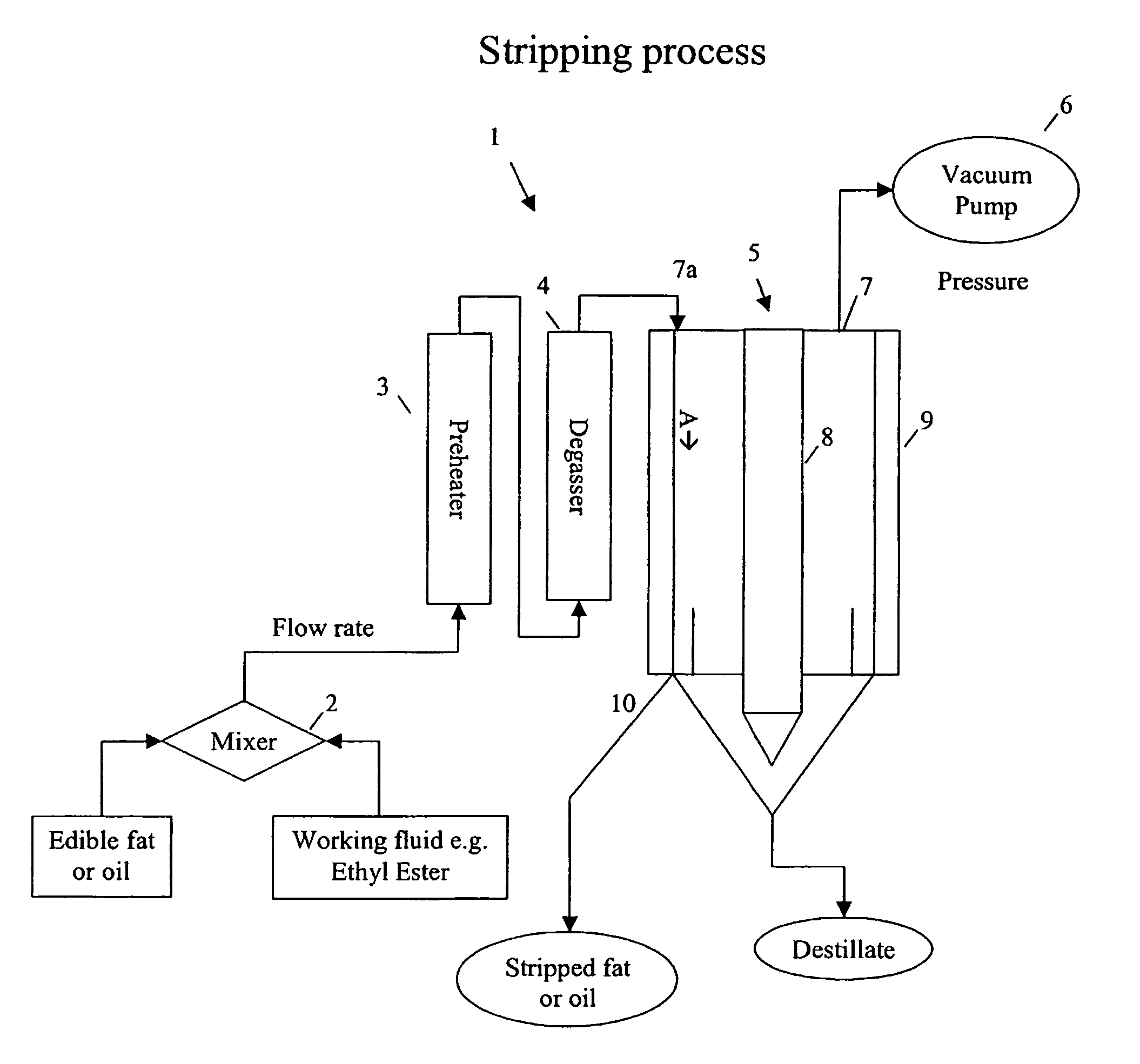
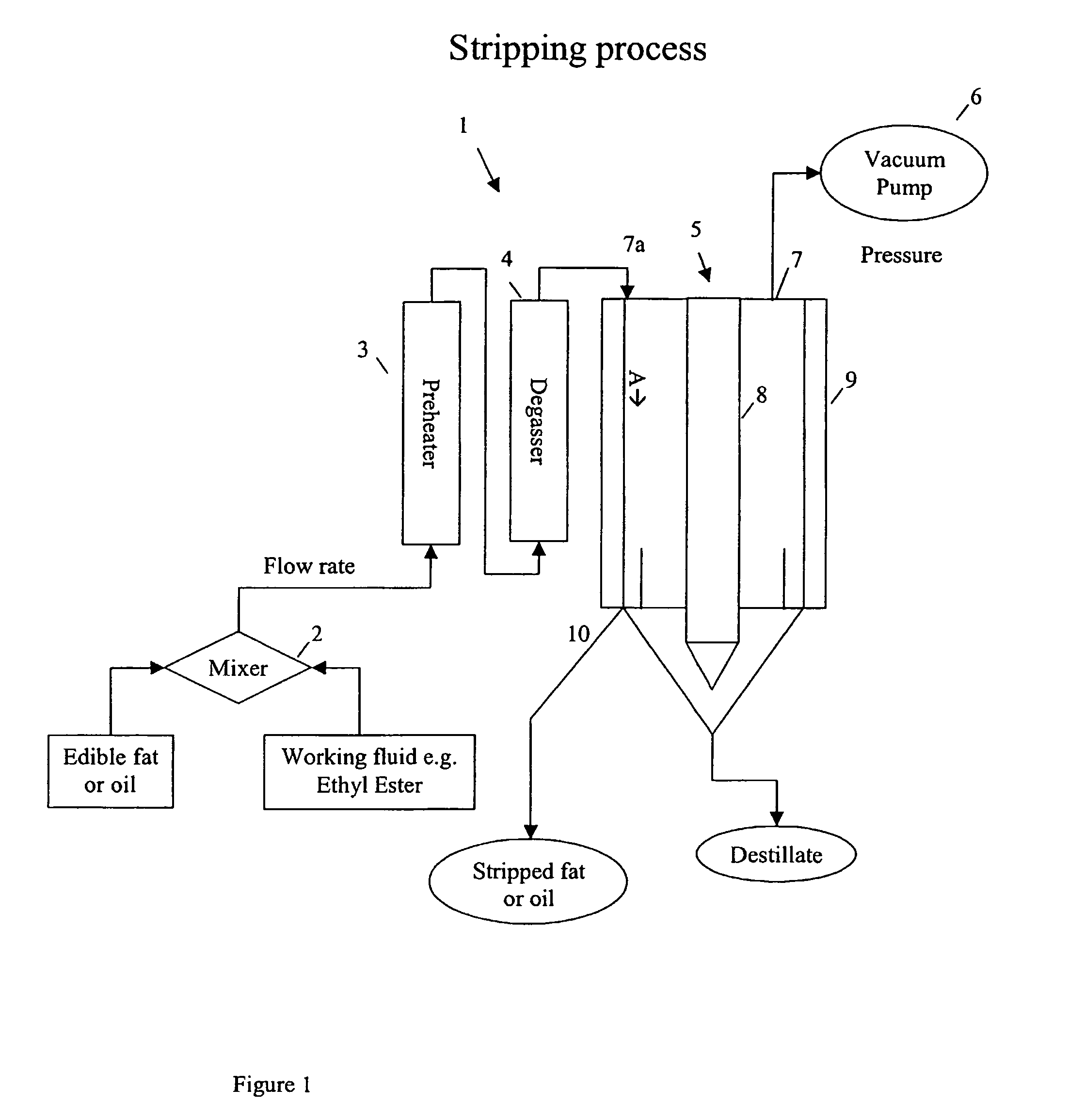
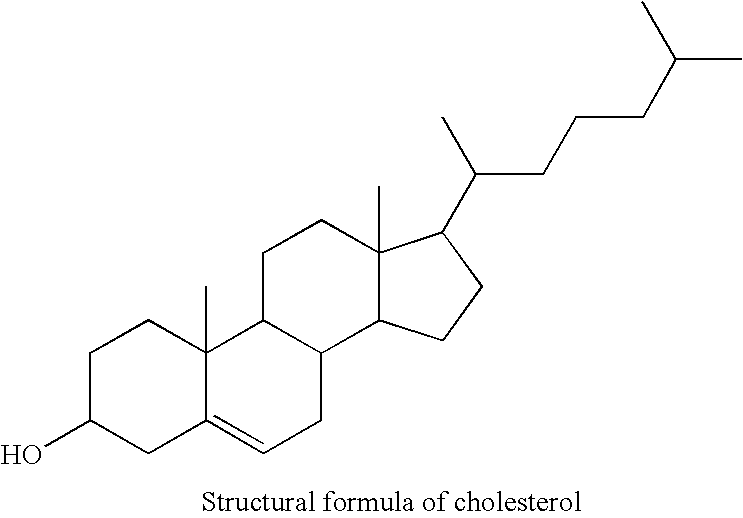
Process for decreasing the amount of cholesterol in a marine oil using a volatile working fluid
ActiveUS7678930B2Lower cholesterol levelsPoint becomes highCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderWorking fluidFree form
The invention relates to a process for decreasing the amount of cholesterol in a mixture comprising a marine oil, the marine oil containing the cholesterol, which process comprises the steps of adding a volatile working fluid to the mixture, where the volatile working fluid comprises at least one of a fatty acid ester, a fatty acid amide and a hydrocarbon, and subjecting the mixture with the added volatile working fluid to at least one stripping processing step, in which an amount of cholesterol present in the marine oil in free form is separated from the mixture together with the volatile working fluid. The present invention also relates to a volatile cholesterol decreasing working fluid and a health supplement and a pharmaceutical, based on a marine oil, prepared according to the process mentioned above.
Owner:PRONOVA BIOPHARMA NORGE
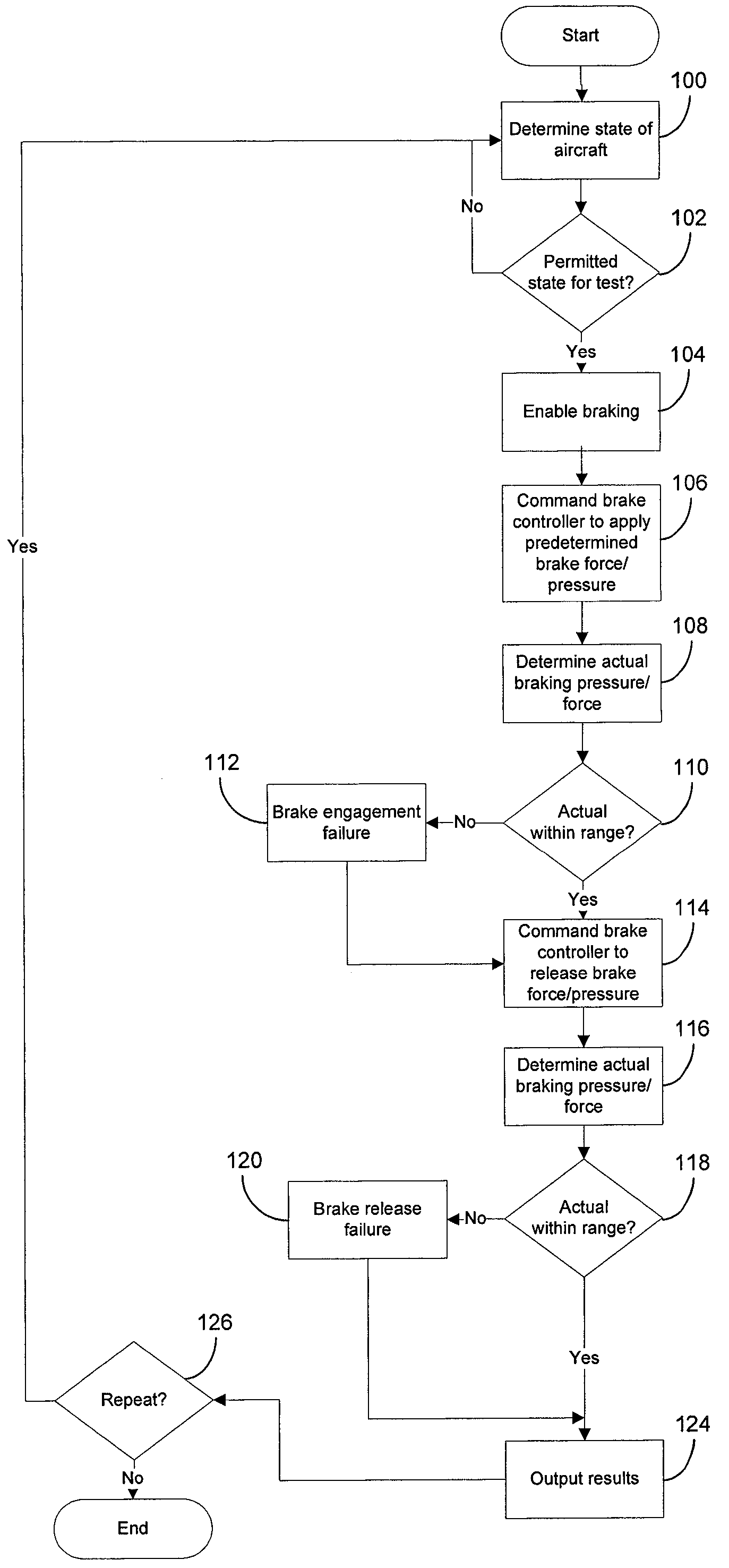
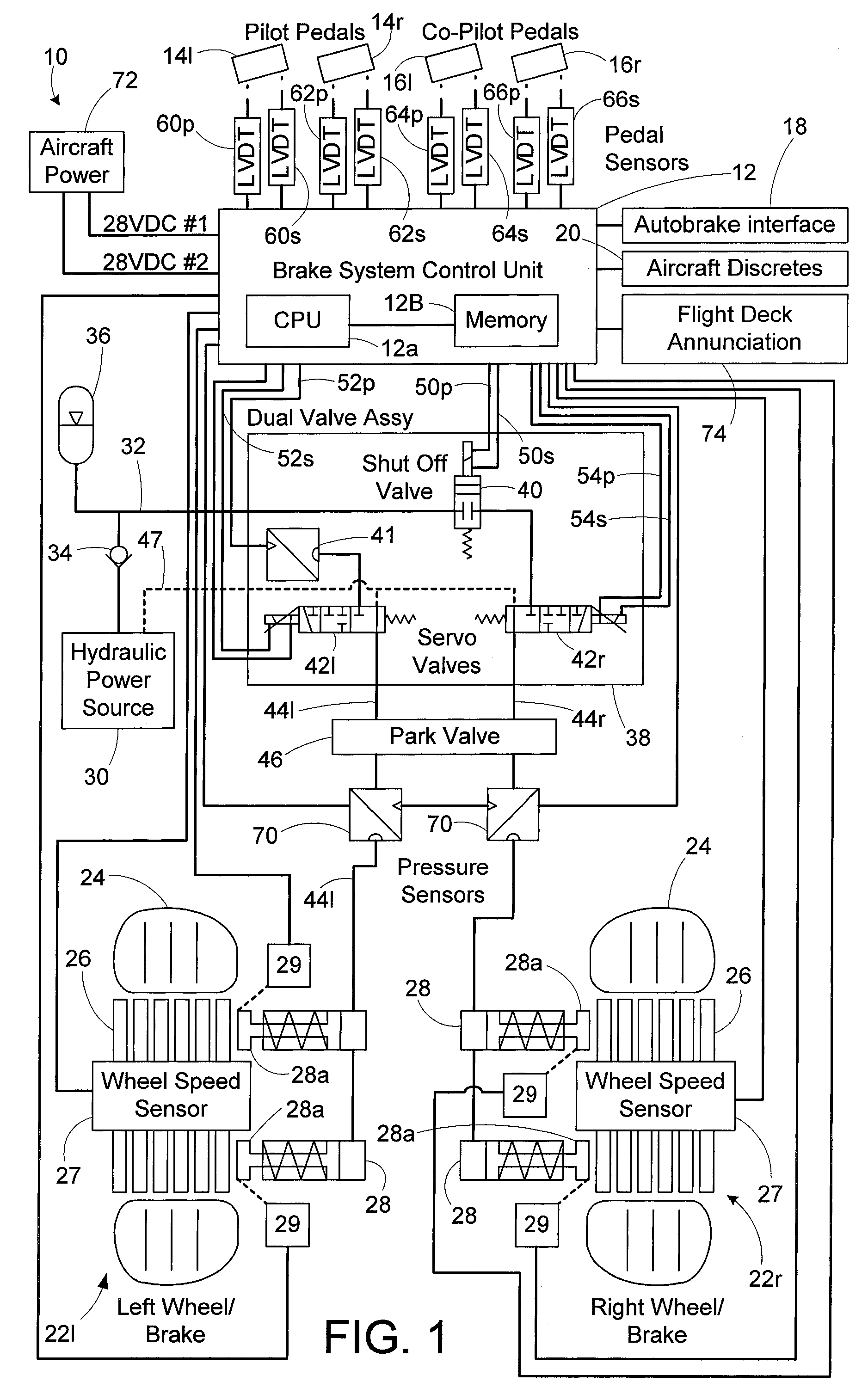
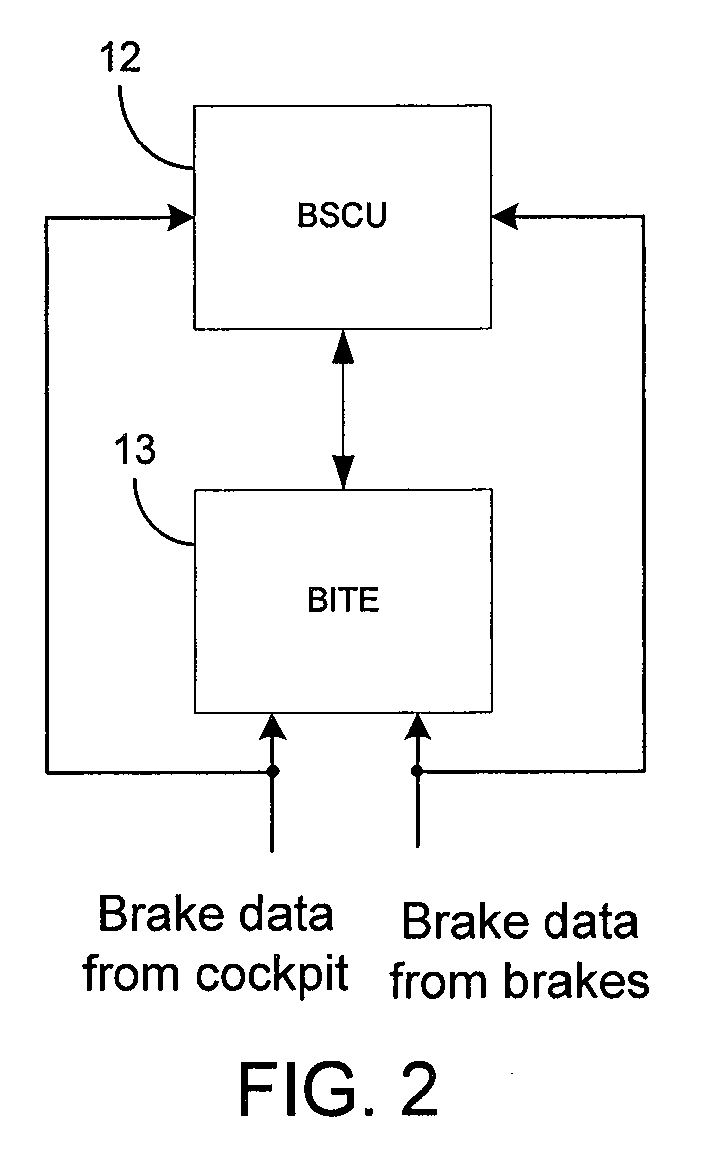
Brake operation built-in test equipment
A system, apparatus and method provide a means for testing operation of vehicle brake system. More particularly, a brake actuator is automatically commanded to engage a brake disk stack while the vehicle is in a benign state. An engagement force applied to the brake-disk stack by the actuator then is determined, and the engagement force is compared to a first threshold value. If the engagement force is within a predetermined range of the first threshold value, it is concluded that the brake system is operating normally, otherwise it is concluded that the brake system is operating abnormally.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
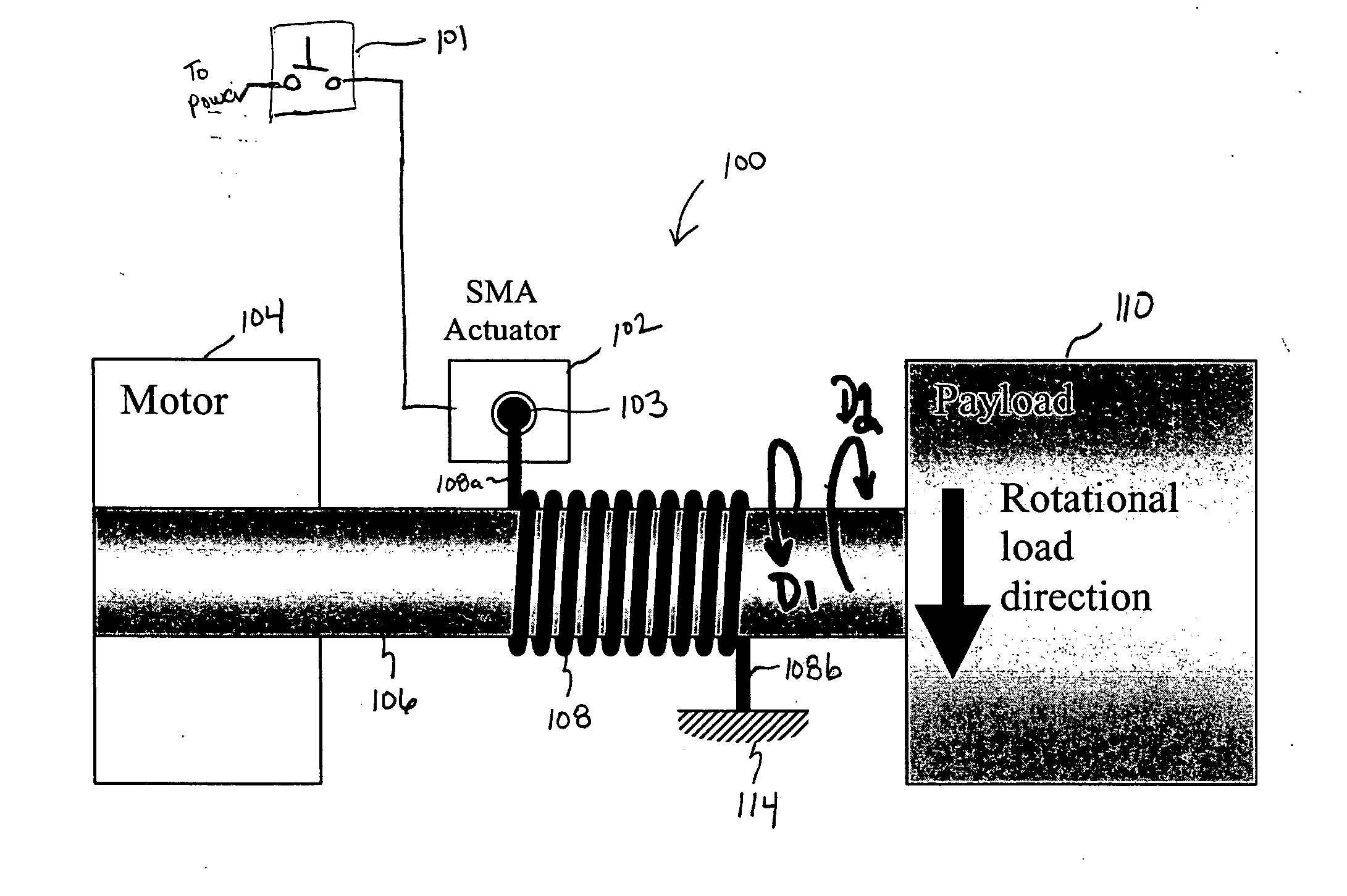
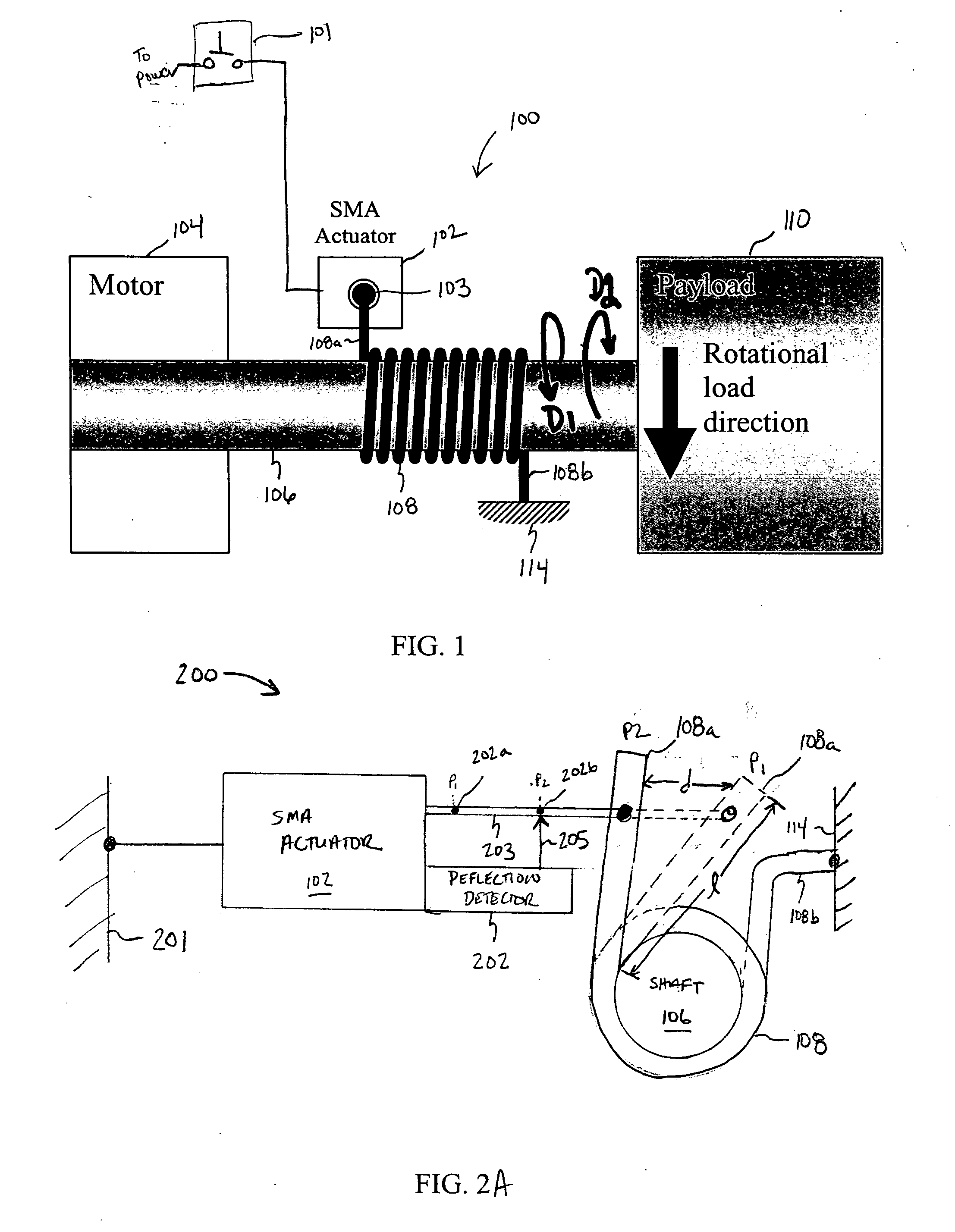
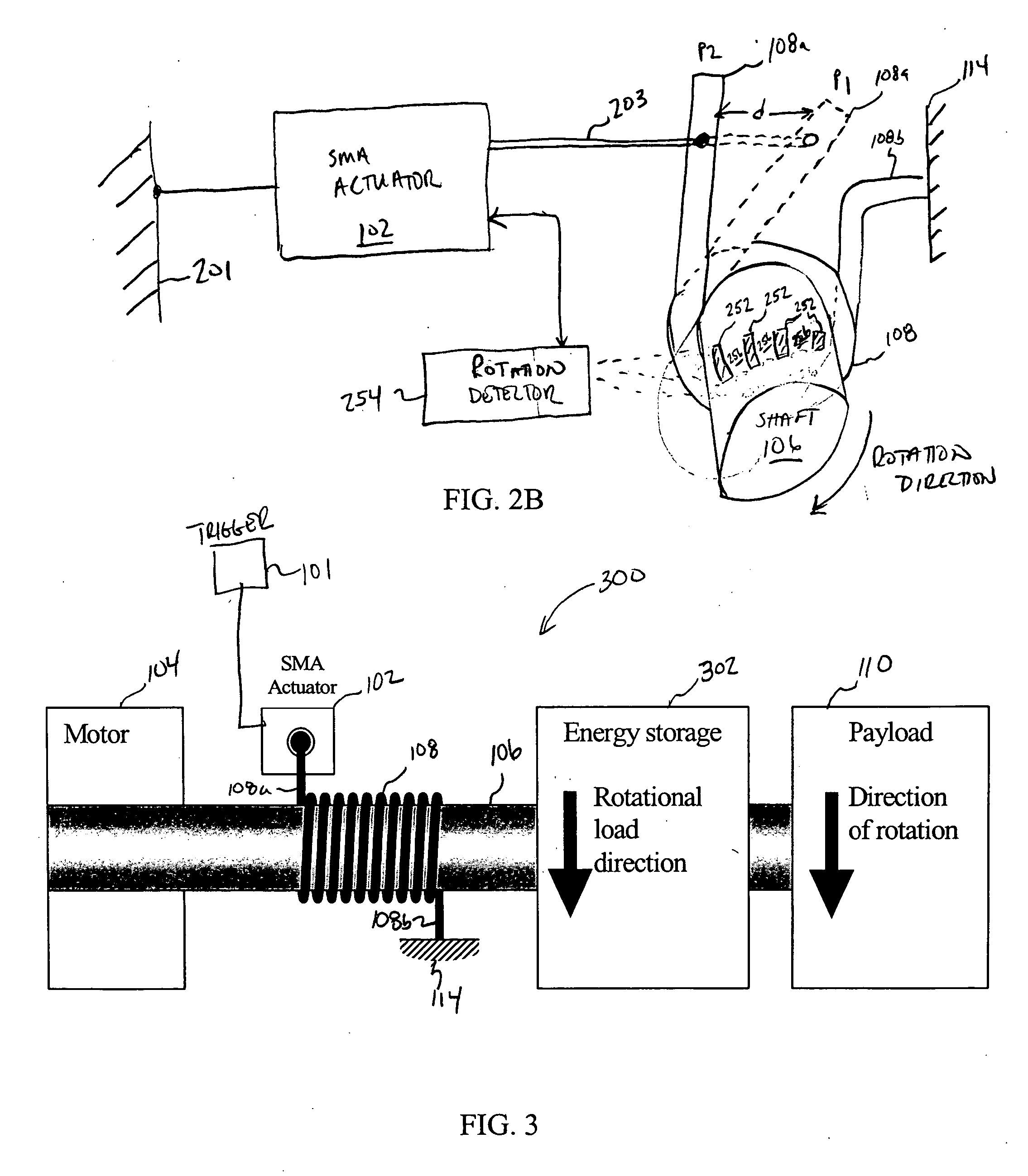
Shape memory alloy-actuated and bender-actuated helical spring brakes
In one embodiment of the present invention, a shape memory alloy (“SMA”)-actuated helical spring brake comprises a rotatable member and a helical wrap spring arranged concentrically about the rotatable member. The spring has a first spring end and a second spring end and includes a number of turns that are based radially inward and are configured to frictionally engage the rotatable member. The turns permit rotation of the rotatable member in a first direction and inhabit rotation in a second direction. The SMA-actuate helical spring brake also include an anchor point coupled to the second spring end, and an SMA actuator having an output drive member coupled to the first spring end. The SMA actuator is configured to, for example, deflect the first spring end to permit the rotatable member to rotate.
Owner:ALFMEIER PRAZISION BAUGRUPPEN & SYSTLOSUNGEN
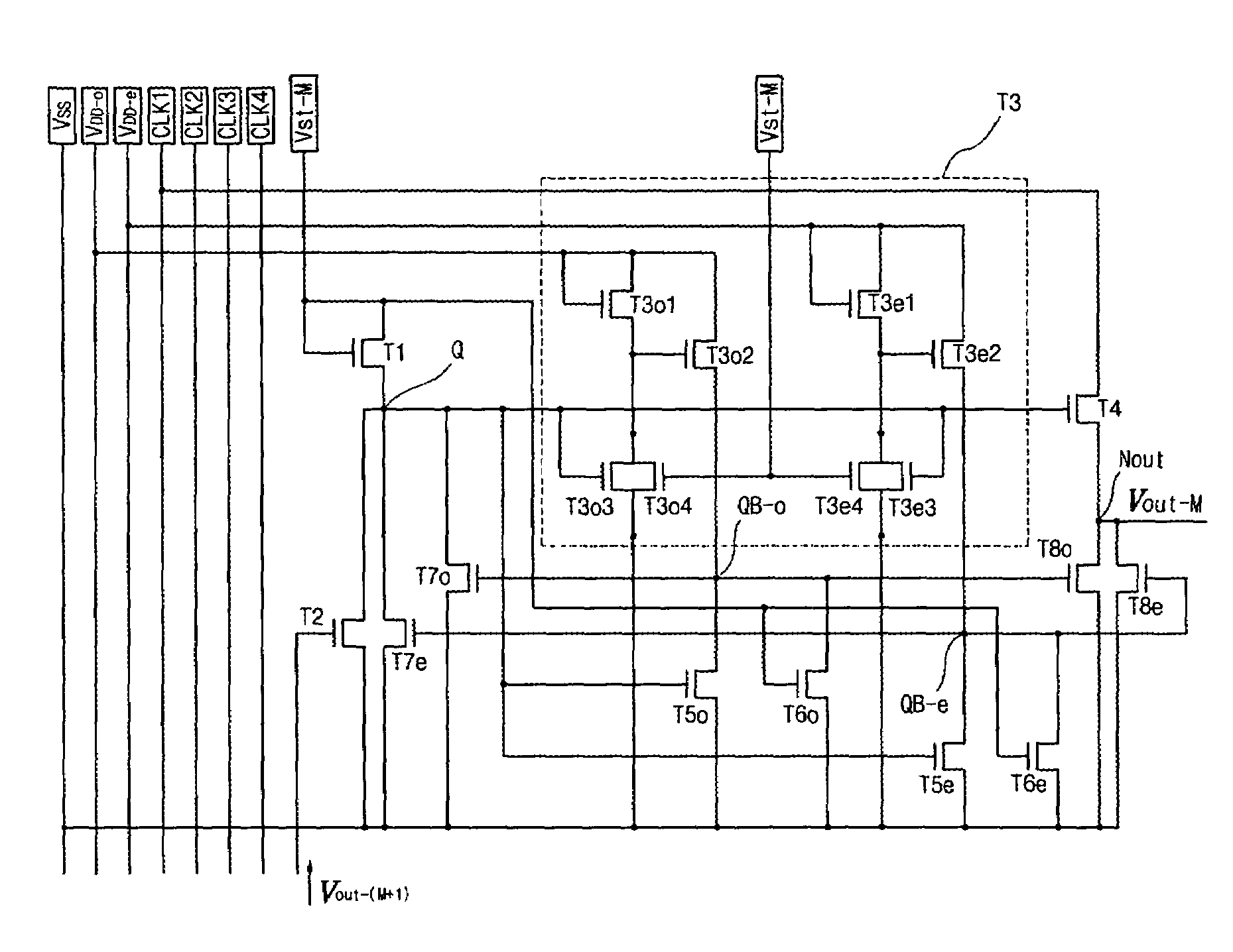
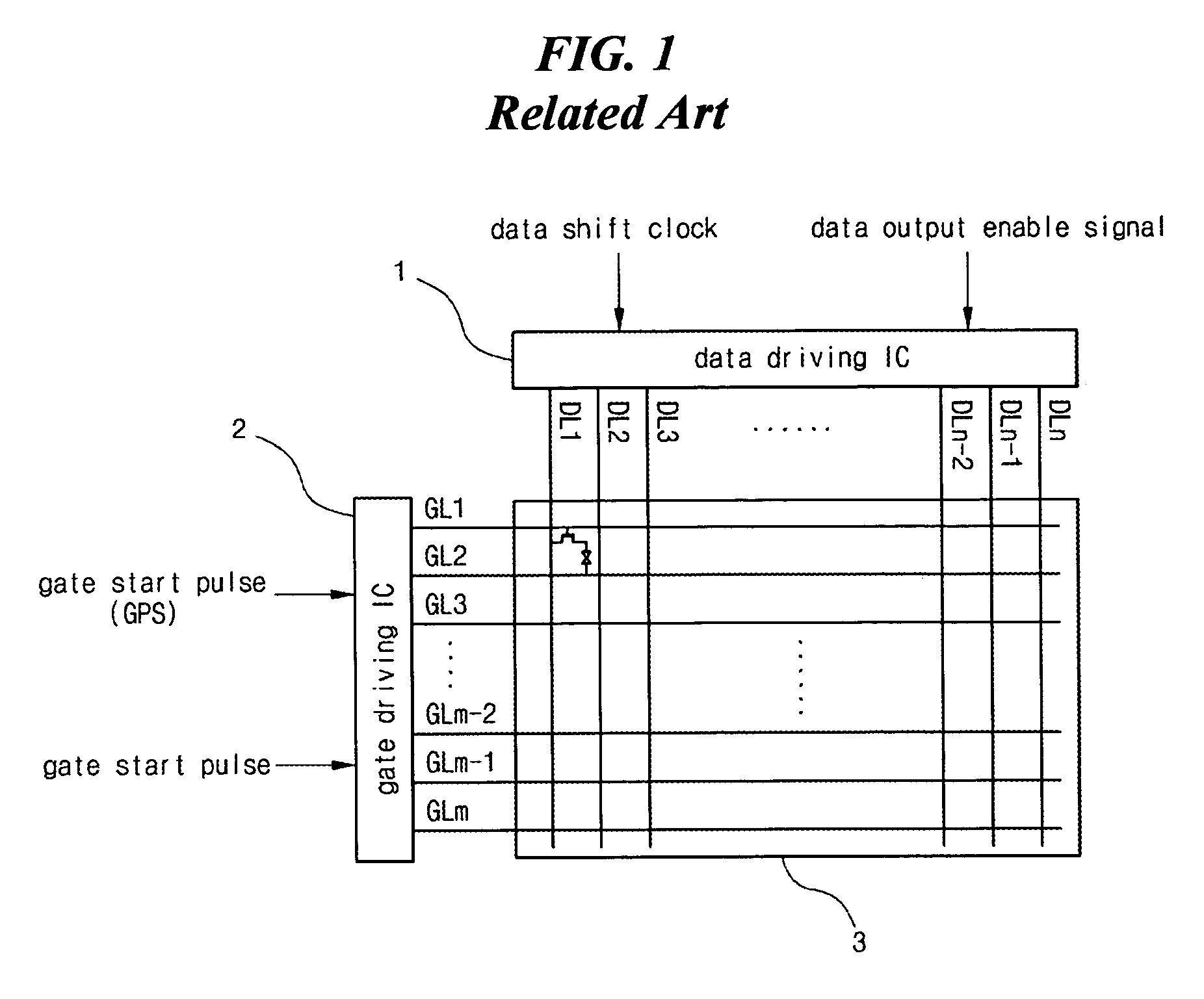
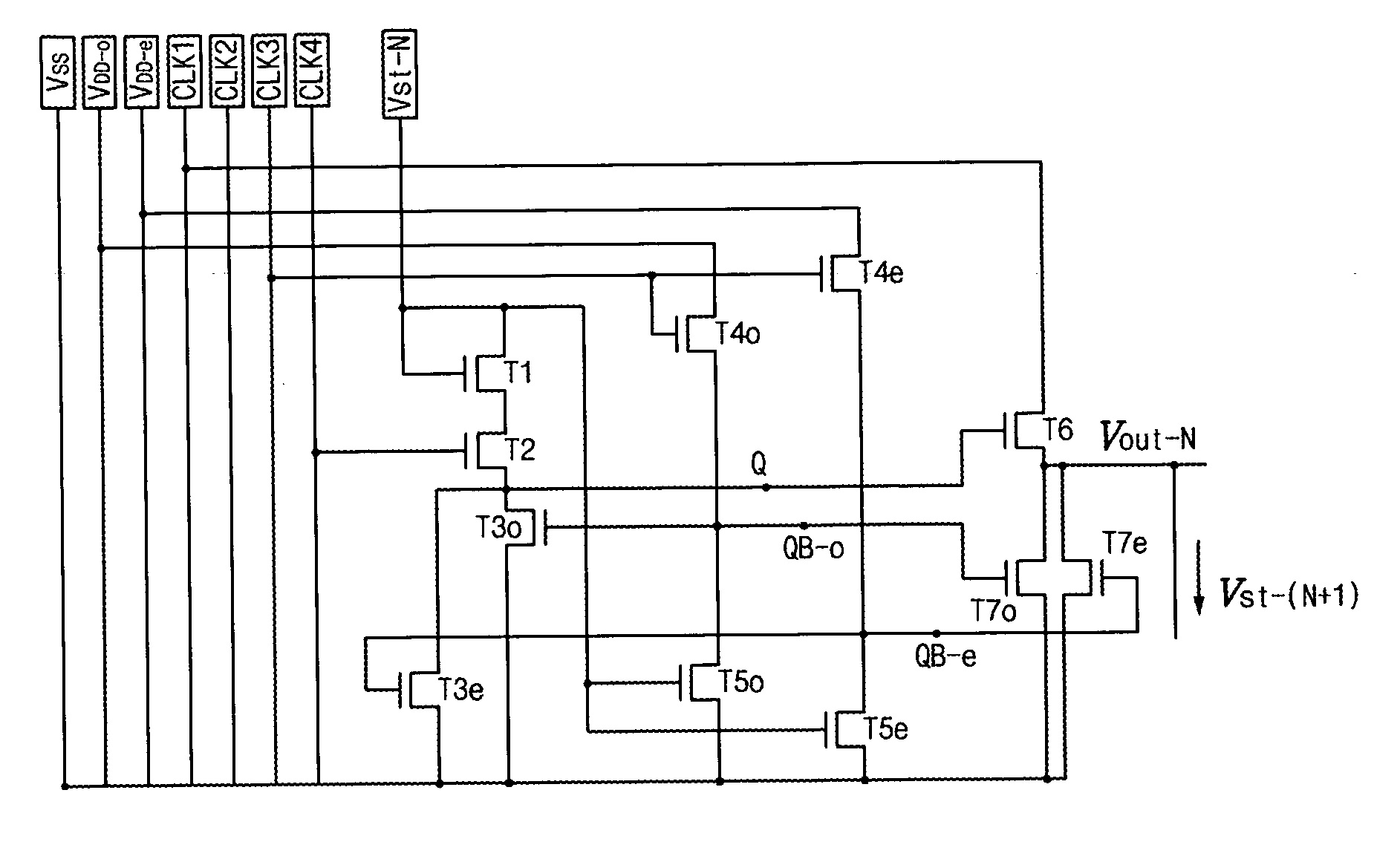
Driving circuit including shift register and flat panel display device using the same
ActiveUS7528820B2Increase contrastImprove display qualityAxially engaging brakesStatic indicating devicesShift registerEngineering
A driving circuit for a flat panel display device includes shift register stages, each containing: a first TFT charging a Q node according to a start signal; a second TFT discharging the Q node according to an output voltage of a next shift register stage; a pull-up unit increasing an output voltage according to the Q node voltage; an odd pull-down unit decreasing the output voltage in an odd frame according to a QB-o node voltage; and an even pull-down unit decreasing the output voltage in an even frame according to a QB-e node voltage. A gate and drain of a third odd TFT connected to the QB-o node are connected to each other and receive an odd source voltage. A gate and drain of the third even TFT connected to the QB-e node are connected to each other and receive an even source voltage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Disk Brake And Production Method For A Disk Brake
ActiveUS20130008749A1Less componentsImprove stabilityBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesSpring forceEngineering
A disk brake having a brake caliper and a brake actuation mechanism being supported in it, in which the brake actuation mechanism includes an amplification mechanism for introducing a clamping force, an adjustment device for compensation of lining wear with a torque clutch, a thrust element for transmitting the clamping force onto a brake disc and a reset device, which components are arranged around a rod, in which the torque clutch, for example, is formed as a roller-ramp-mechanism. A spring force can act onto the torque clutch by means of the reset device thereby forming a torque limit. Furthermore the invention relates to an assembly method for such a disc brake.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD AB
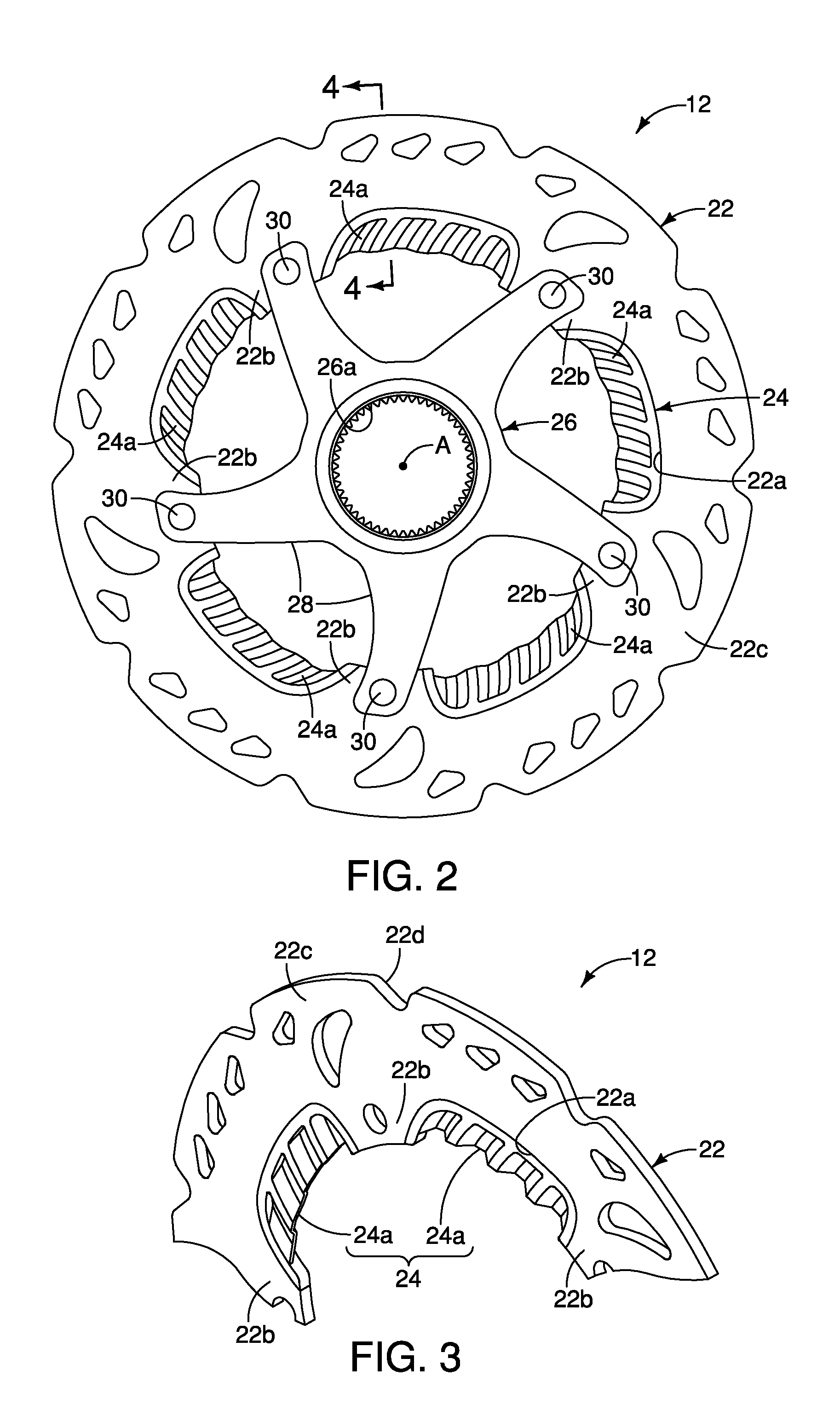
Bicycle disc brake rotor
ActiveUS20130168193A1Improve performanceEffective coolingAxially engaging brakesBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A bicycle disc brake rotor basically has an outer portion and a cooling fin. The outer portion has first and second base surfaces facing in opposite axial directions. The cooling fin is disposed radially offset from at least one of the first and second braking surfaces.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
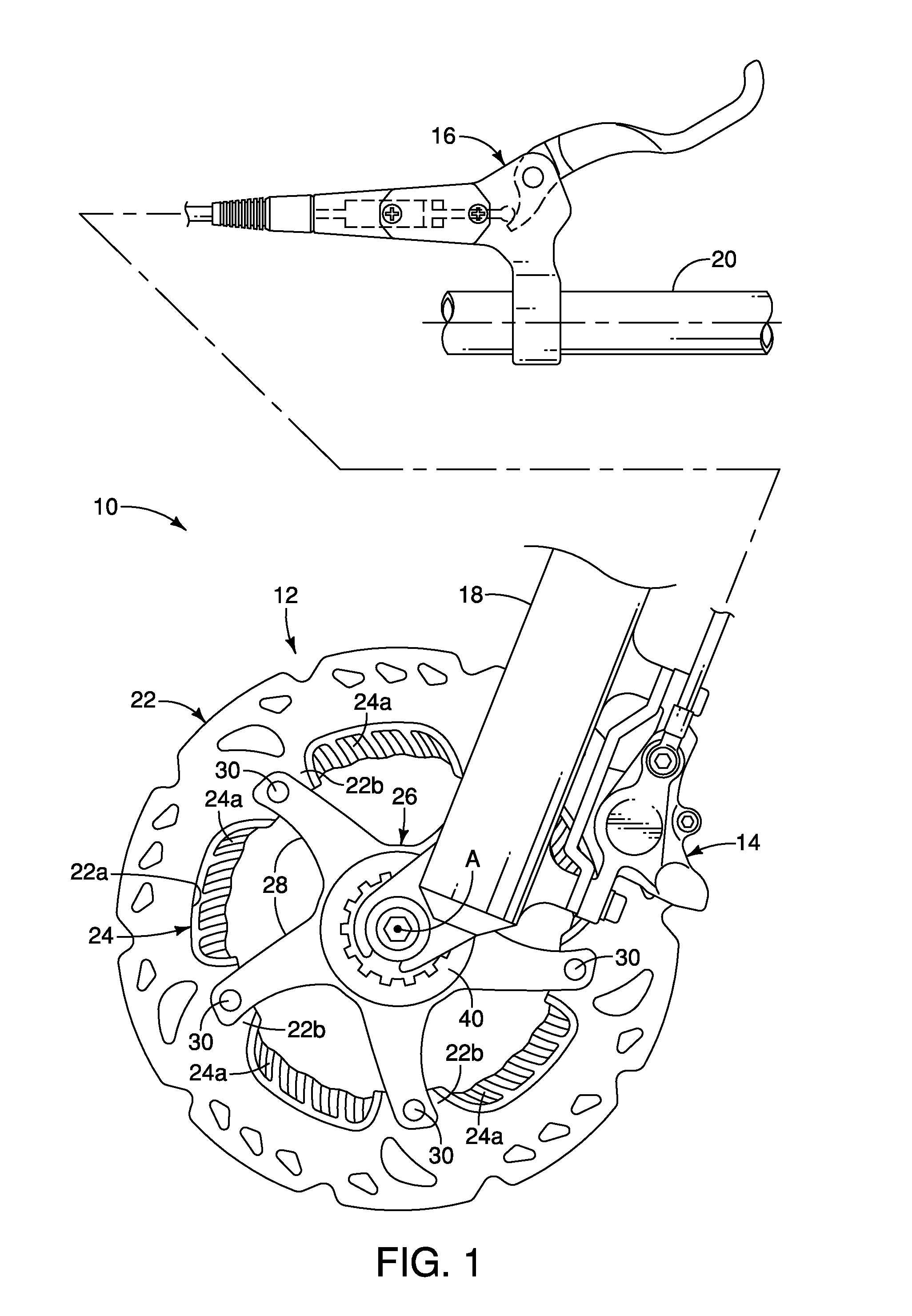
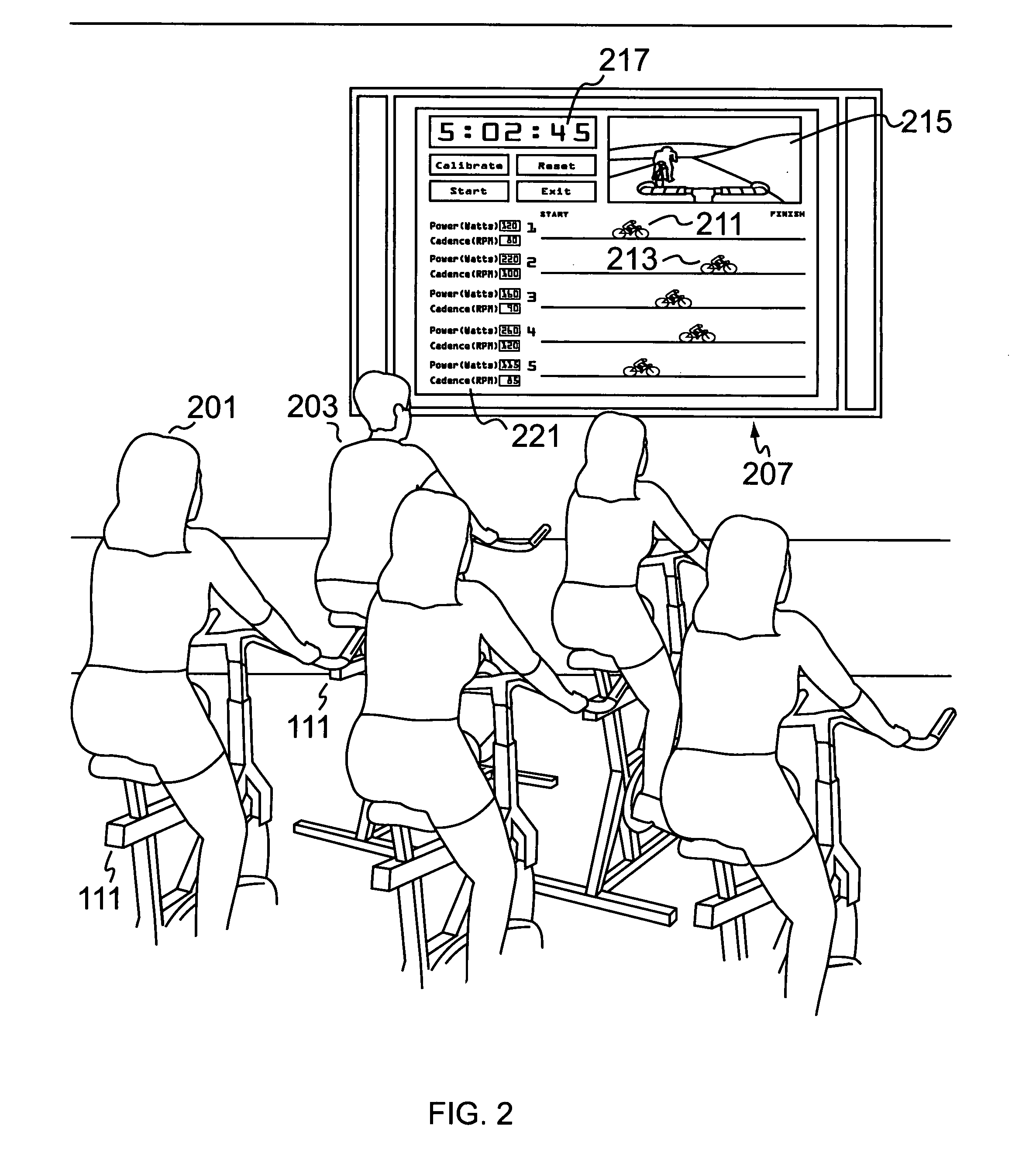
Apparatus for measuring exercise performance
ActiveUS7874957B2High levelPhysical therapies and activitiesAxially engaging brakesExercise performanceDisplay device
An integrated sensor apparatus capable of detecting exercise equipment parameters such as power output and cadence is designed so as to be easily retrofittable to existing equipment. To the extent that a particular sensor uses friction measurement, it can supplant an existing friction causing device on the equipment. Additionally, the sensor can communicate, wirelessly if desired, with a processing device. The processing device is capable of receiving and processing a plurality of sensor signals. The processing device can then output processed signals to a display, so that a plurality of people joining in a group exercise or competition can easily track their relative performance in real-time.
Owner:ARTIS LLC
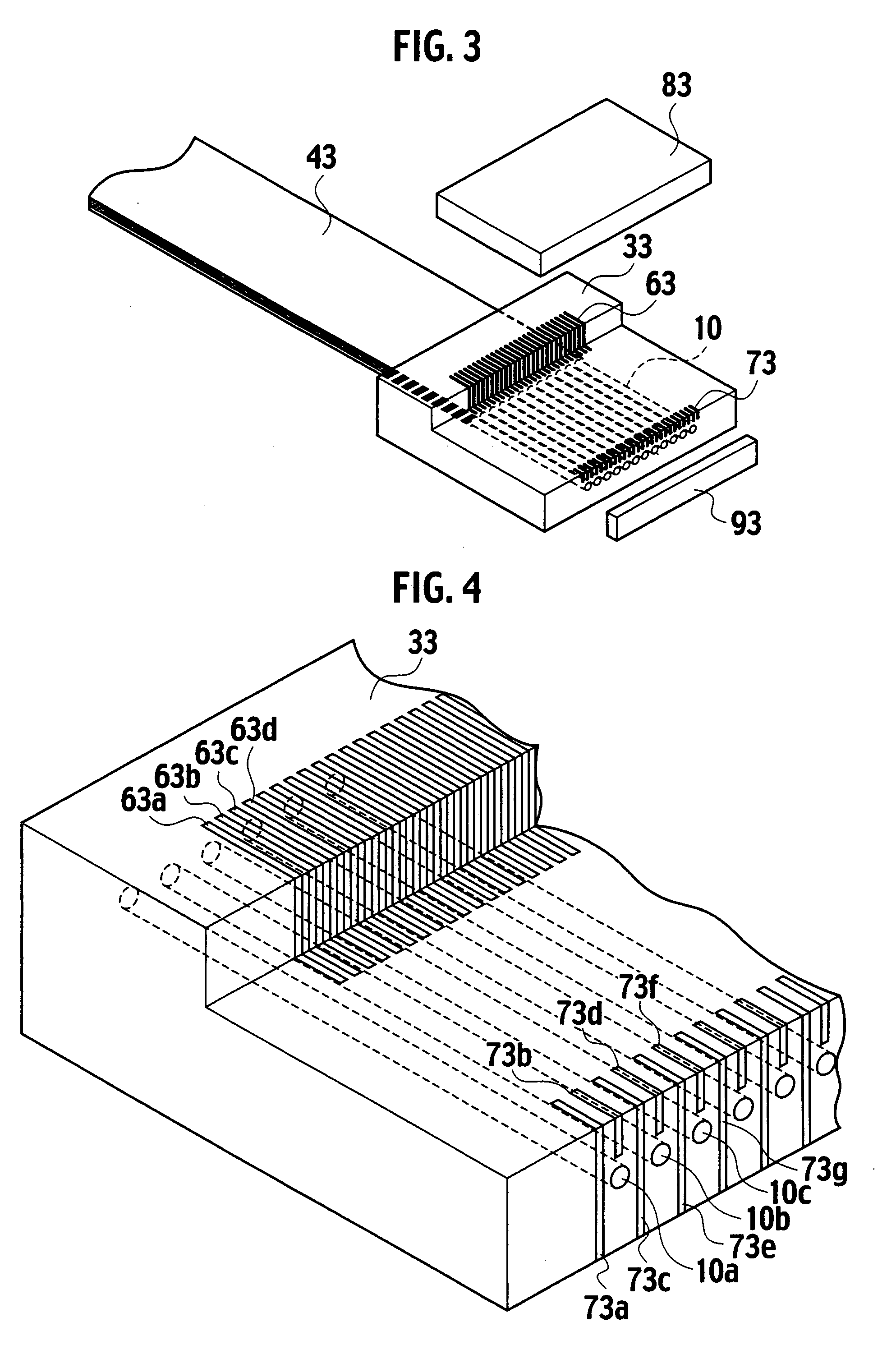
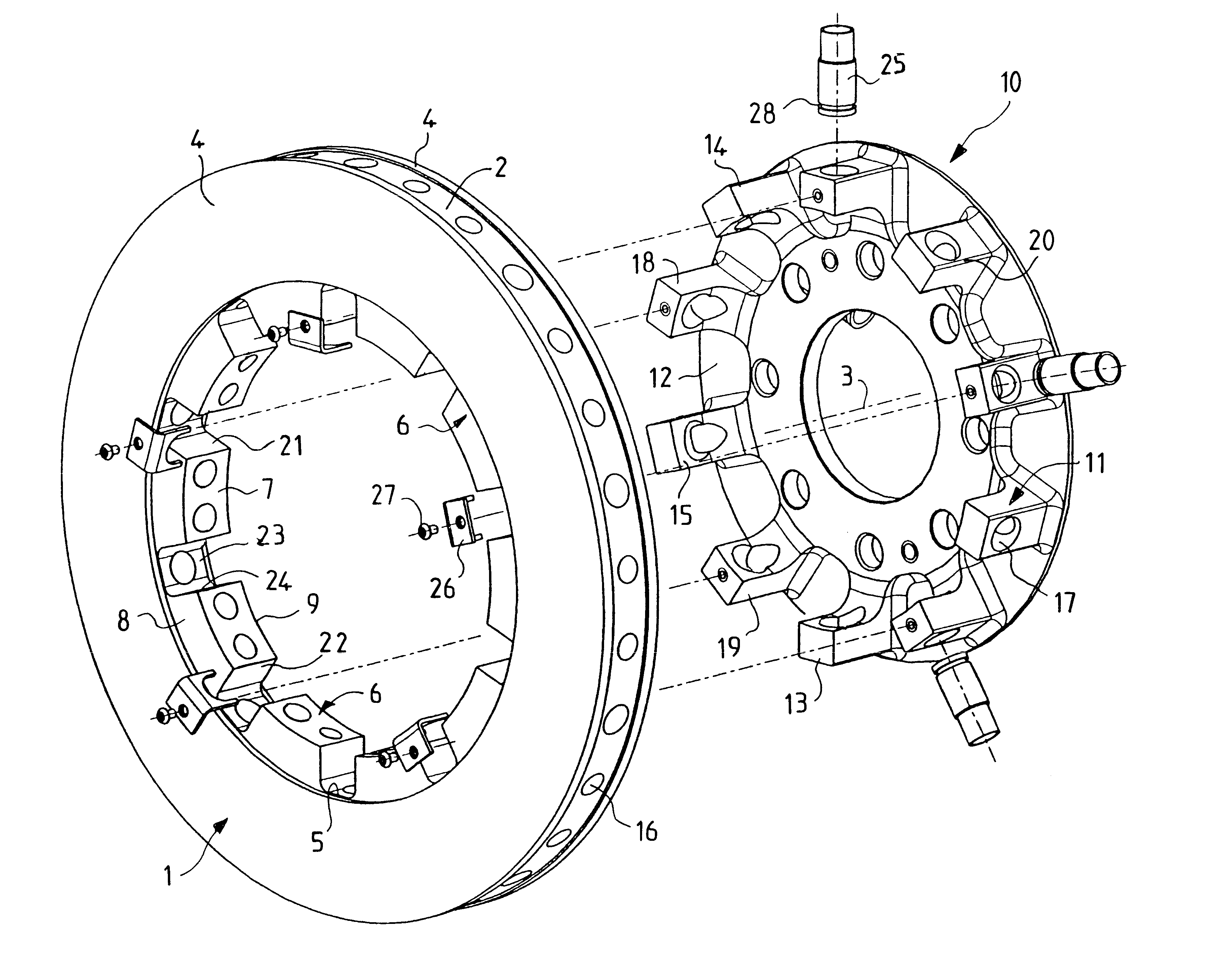
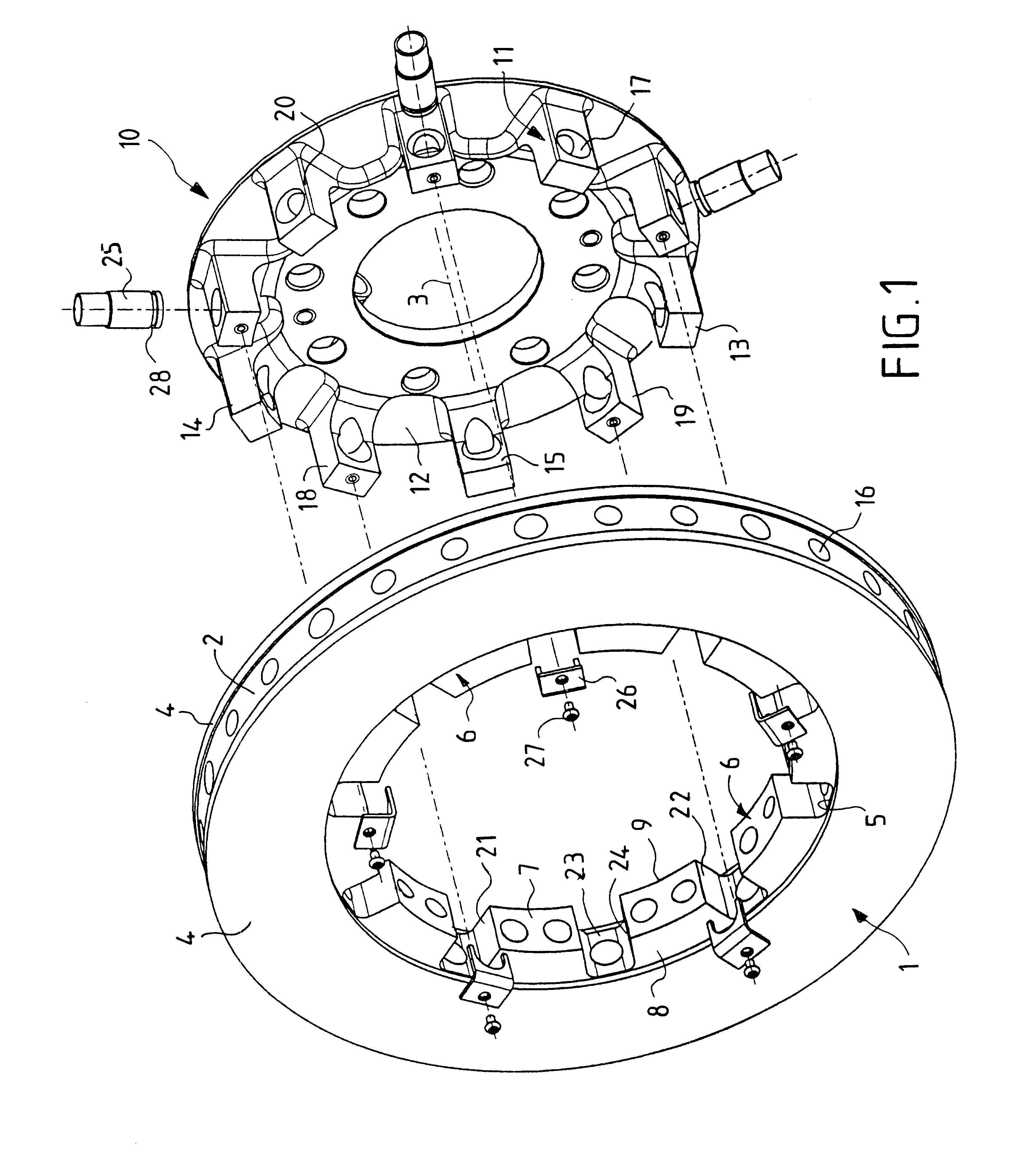
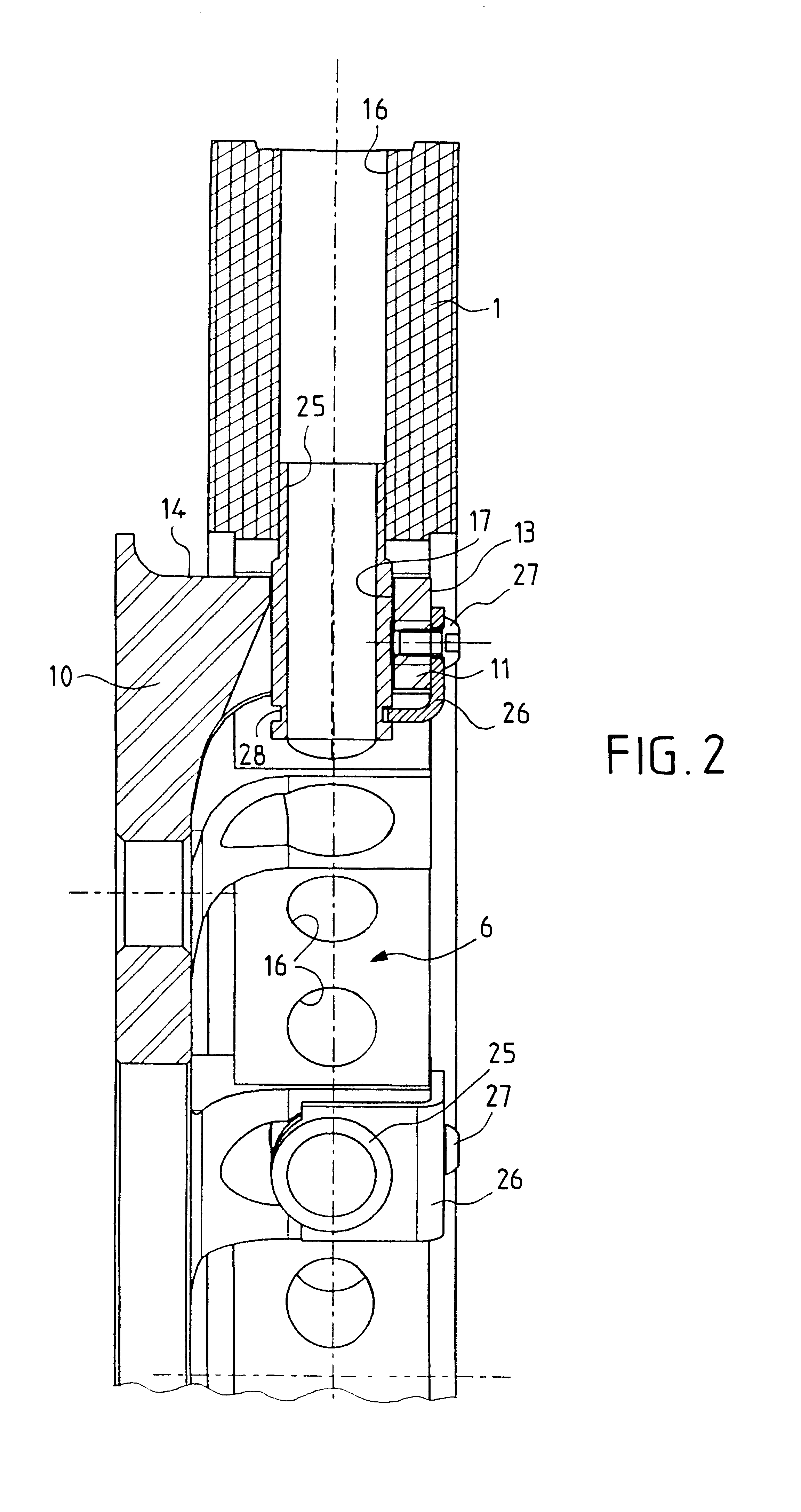
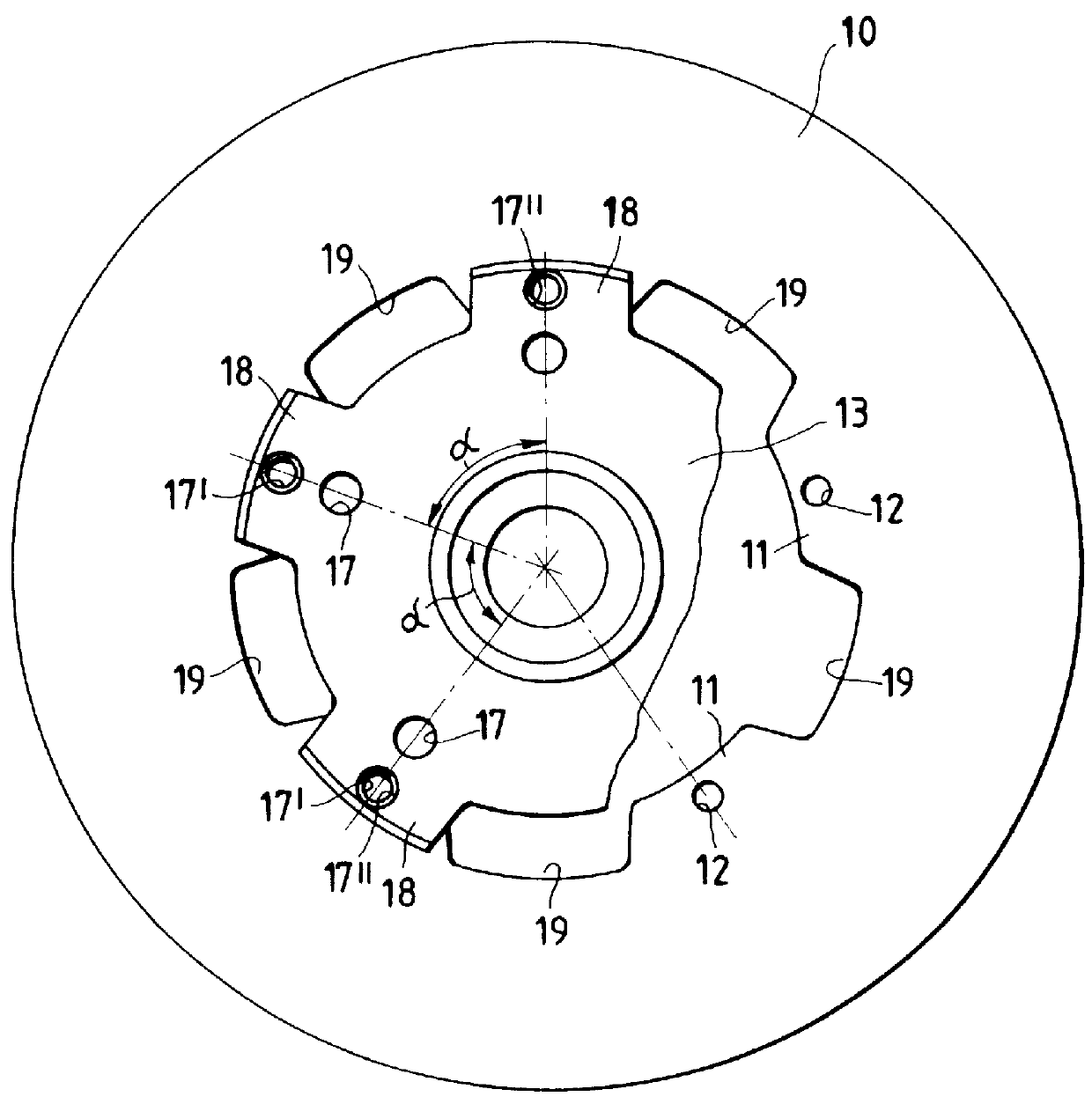
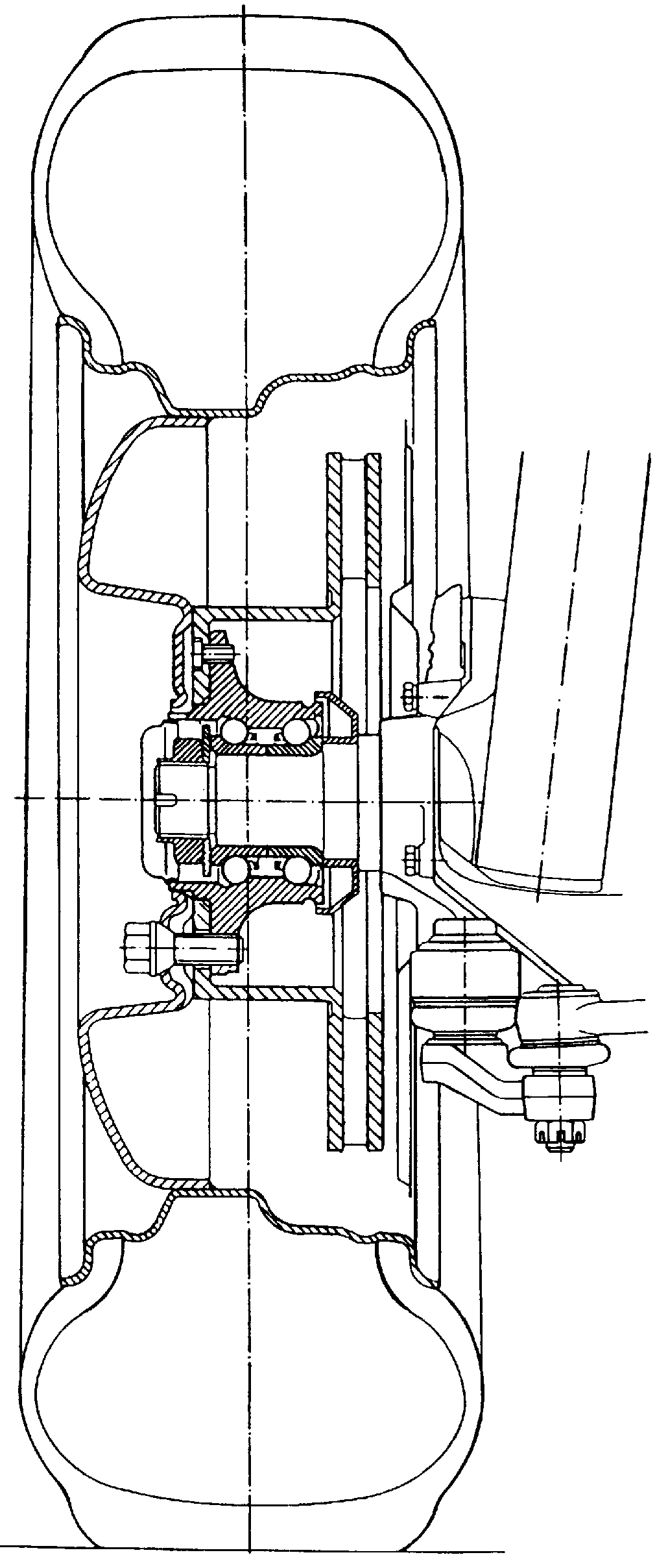
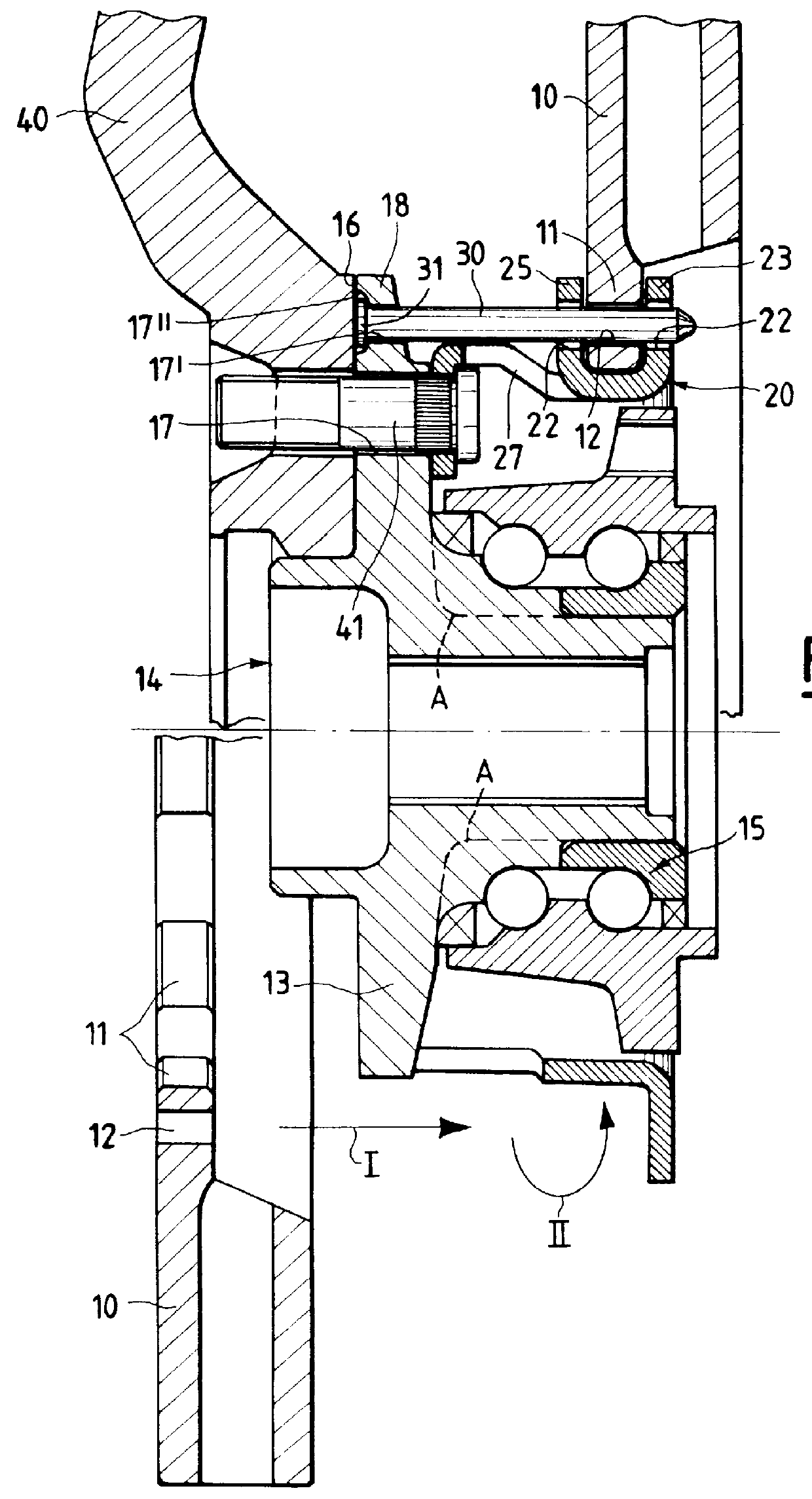
Wheel hub or hub unit allowing improved mounting and removal of a brake member
There is disclosed a wheel hub or hub unit of the type having a radial hub flange (13) providing connection to the wheel (40) and to a brake member (10) having an annular disc portion having a plurality of ears (11) radially protruding from its inner edge. The hub flange (13) defines a plurality of axial passages, in the form of peripheral radial recesses (19) or bores (17, 17') for slipping a plurality of axial pins (30) to be fitted in holes (12) obtained in the brake member ears (11) and in openings (22) obtained in at least one radial wall (23) of a brake carrier (20) rotatably fast with the hub (14) to rotationally secure the brake member (10) to the hub. When the wheel (40) is mounted on the outside of the hub flange, axial movement of the pins towards the outside is stopped by the wheel.
Owner:SKF IND SPA
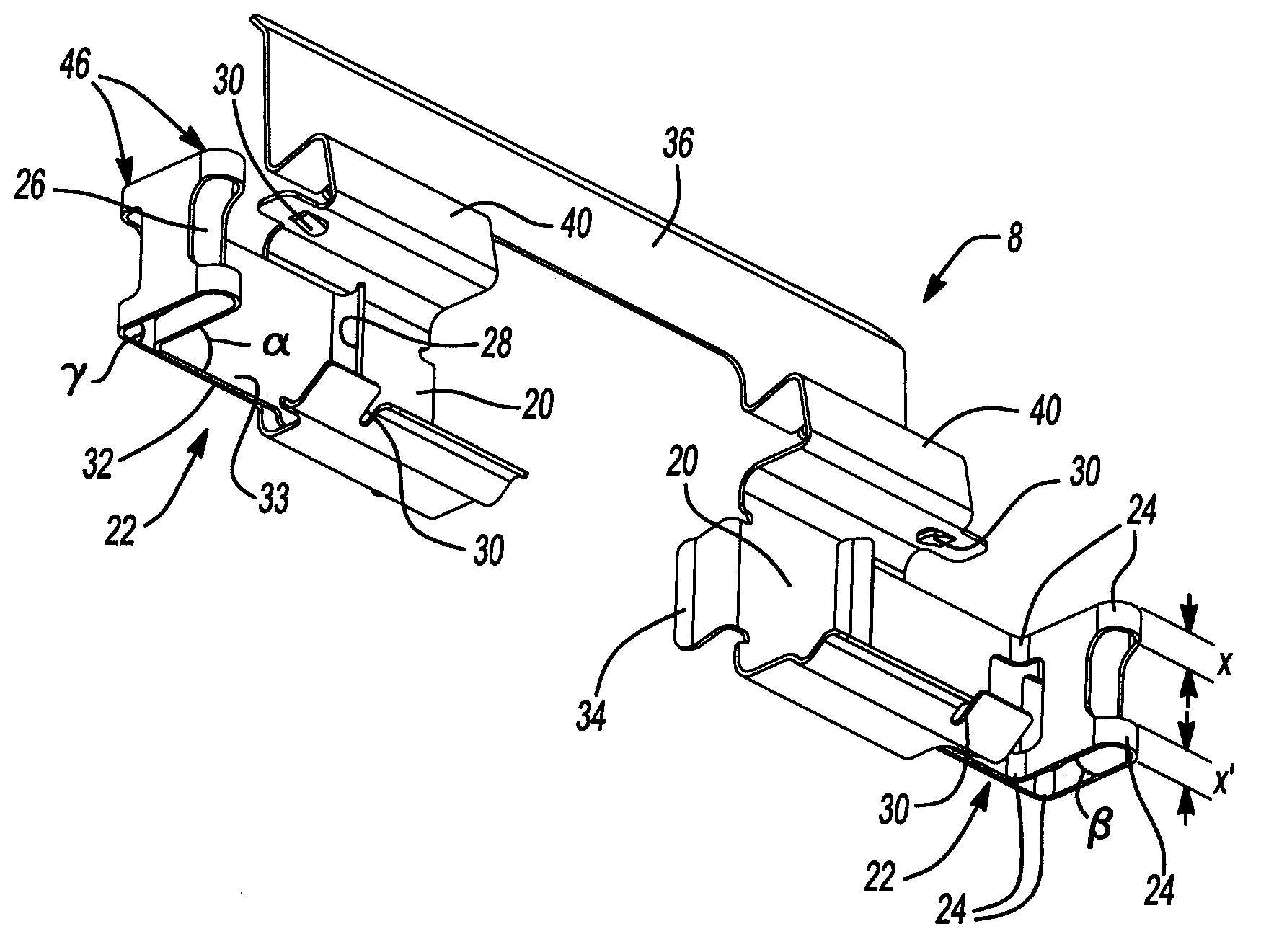
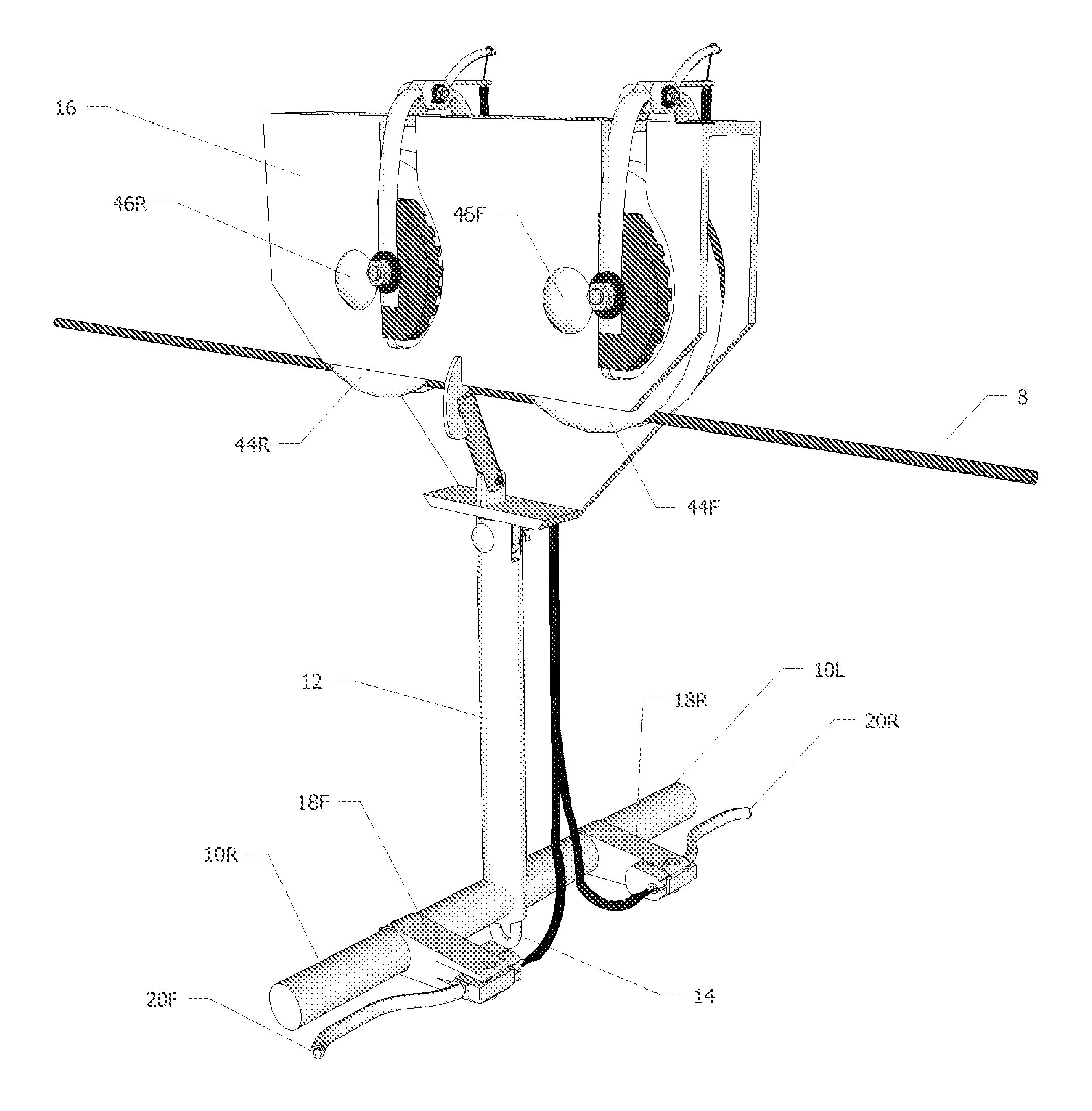
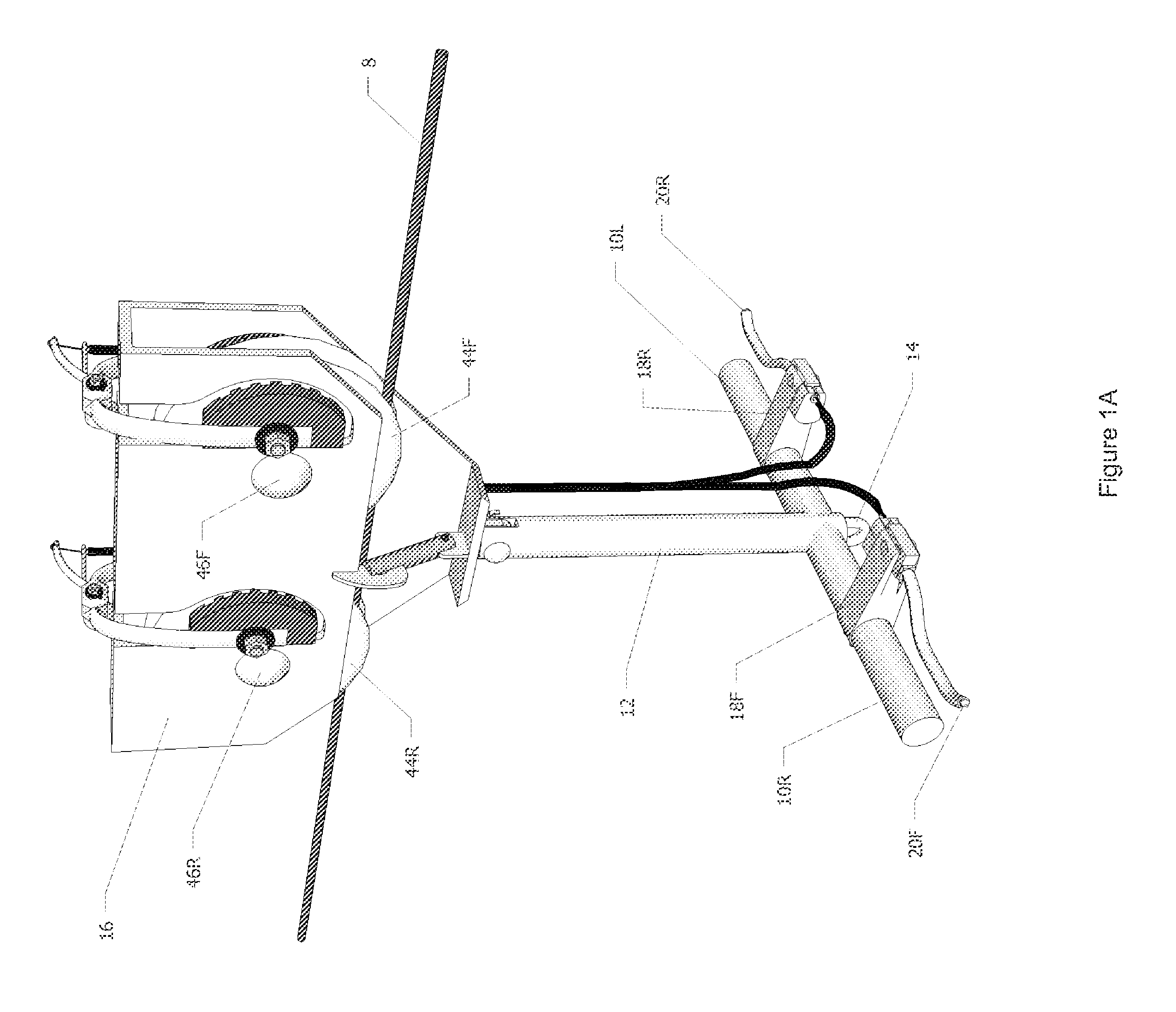
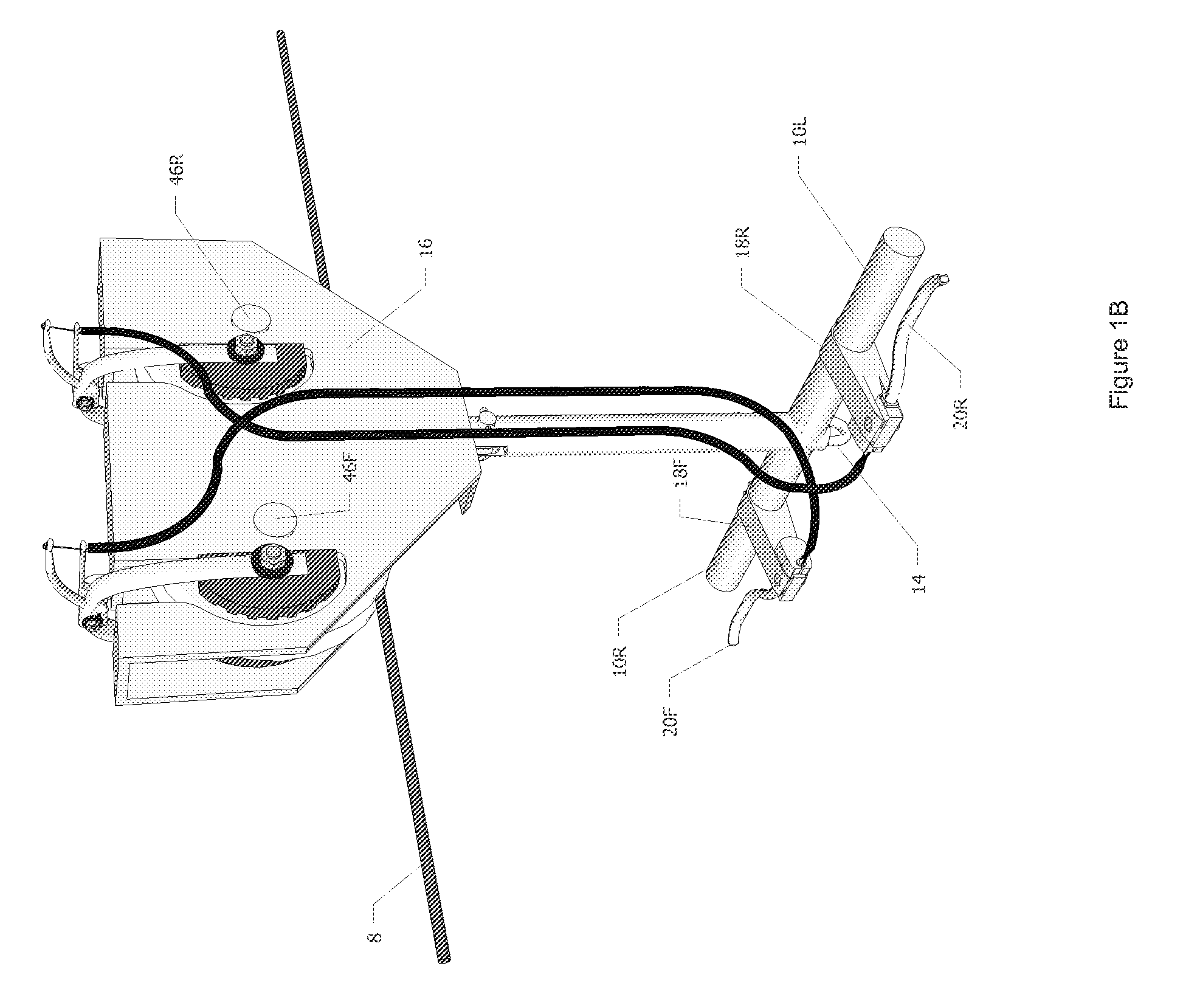
Rider controlled zip line trolley brake
An improved zip line trolley allowing a rider control of his or her speed while traversing along a suspended cable (8) as seen in FIGS. 1A and 1B. The trolley comprises front and rear pulleys (44F) and (44R) conjoined via pulley housing (16) with left and right horizontal handles (10L) and (10R) attached to vertical shaft (12). Front and rear hand brake levers (20F) and (20R) are mounted onto left and right horizontal handles (10L) and (10R). When front and rear hand brake levers (20F) and (20R) are squeezed by the rider, they create a constricting force on front left and right calipers (32FL) and (32FR) along with rear left and right calipers (32RL) and (32RR) of FIGS. 2A and 3A. Thus, friction is applied to front and rear pulleys (44F) and (44R) via front left and right brake pads (34FL) and (34FR) along with rear left and right brake pads (34RL) and (34RR). This frictional force slows the rider's speed to his or her desired rate and brings the rider to a safe stop at a precise location along suspended cable (8).
Owner:BRANNAN KENTON MICHAEL
Pad retaining clips
A brake caliper mounting clip is disposed between a brake caliper having a brake pad channel and a brake pad having an edge member. The edge member moves in the brake pad channel between a rotor gap and a caliper housing. The clip further comprises a pad holding portion slidingly engaged with the edge member and having a plurality of pad retaining members. The pad retaining members are connected to the pad holding portion and disposed between the edge member and the rotor gap. The plurality of the pad retaining members is further configured to prevent the brake pad from falling into the rotor gap. Additionally the edge member of the brake pad and the plurality of pad retaining members are configured to prevent improper installation of the brake pads in the caliper.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disc brake with parking function
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
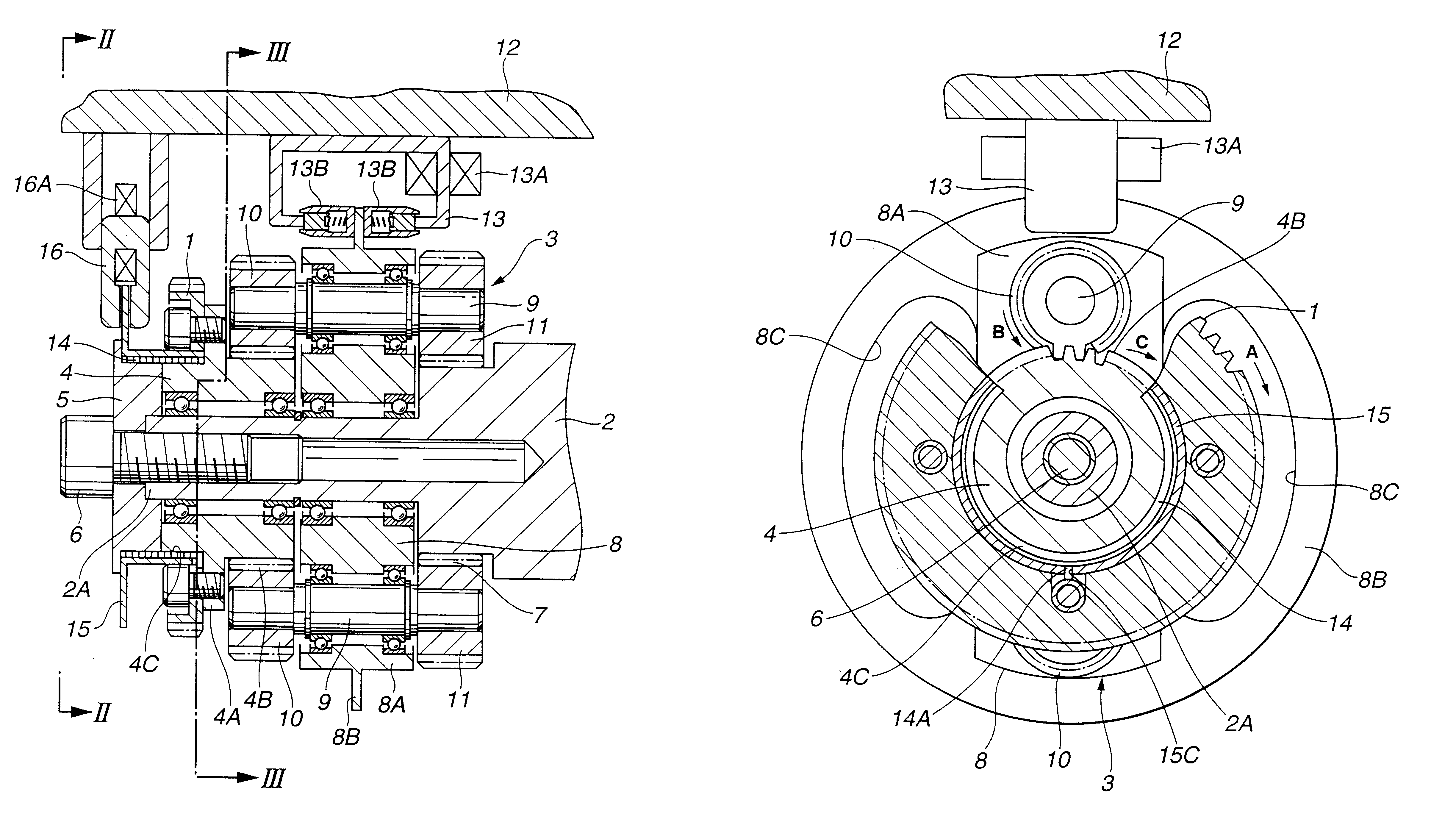
Disk brake
ActiveUS20070251772A1High strengthAvoid deformationAxially engaging brakesSlack adjustersMechanical engineeringDisc brake
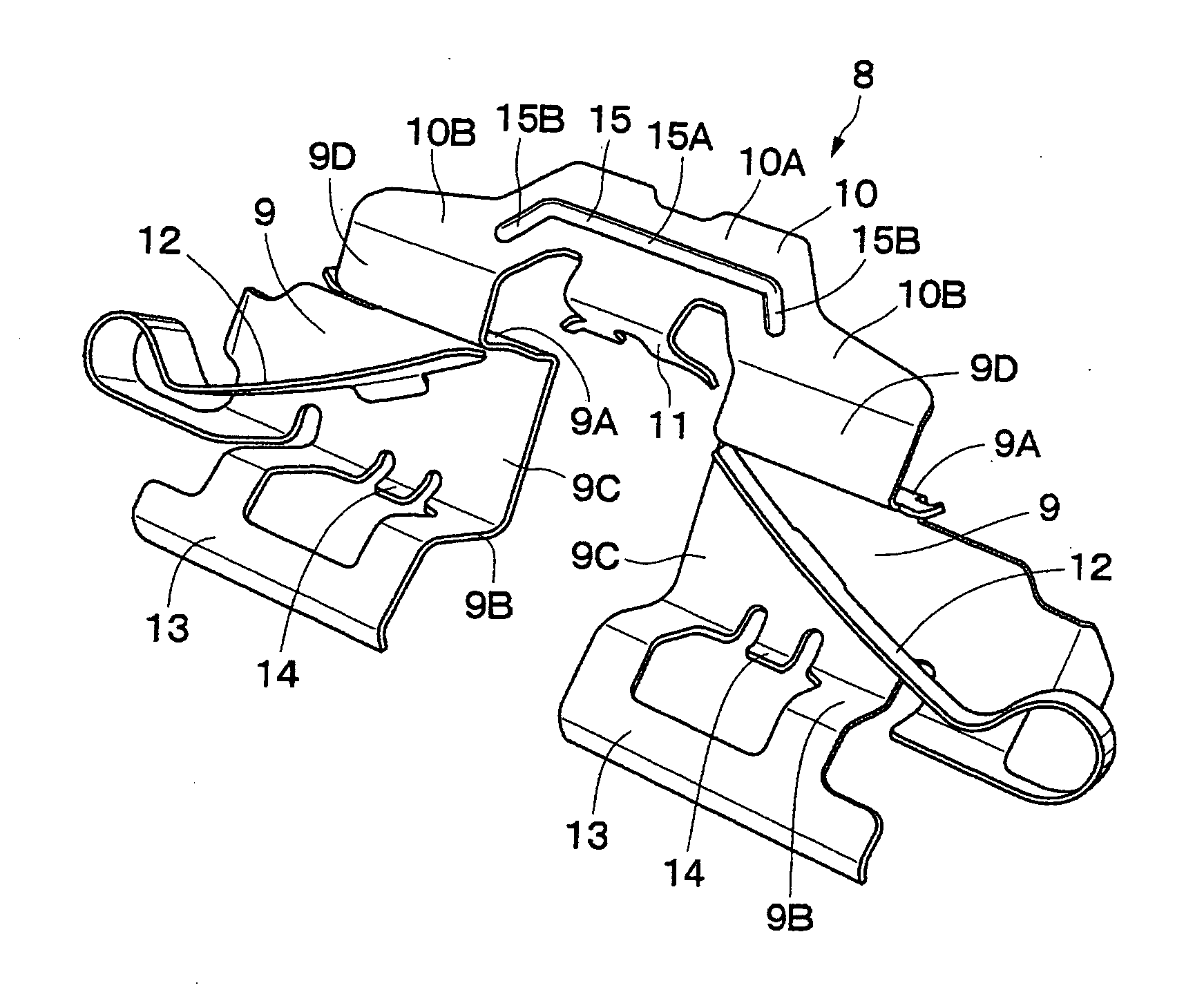
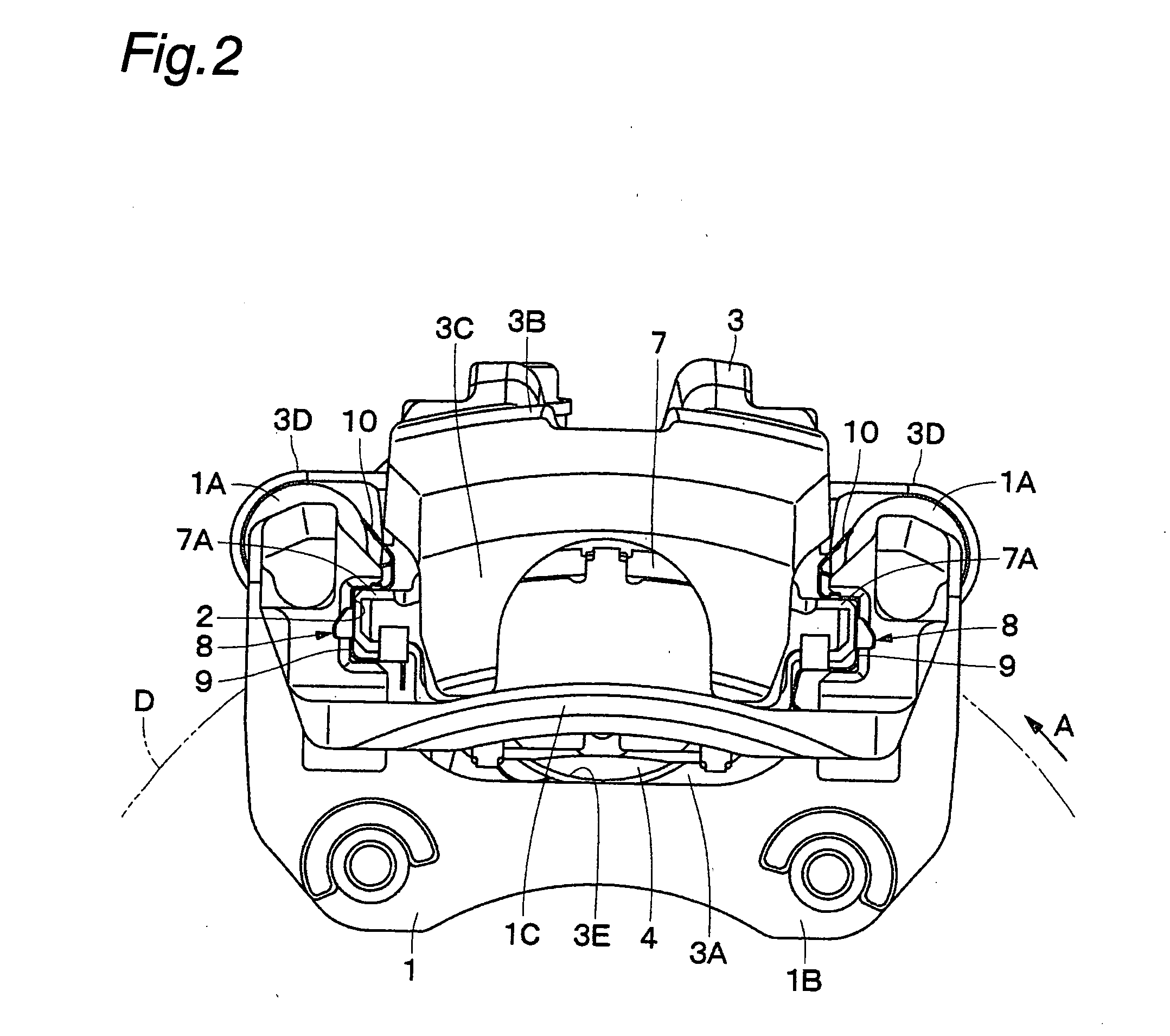
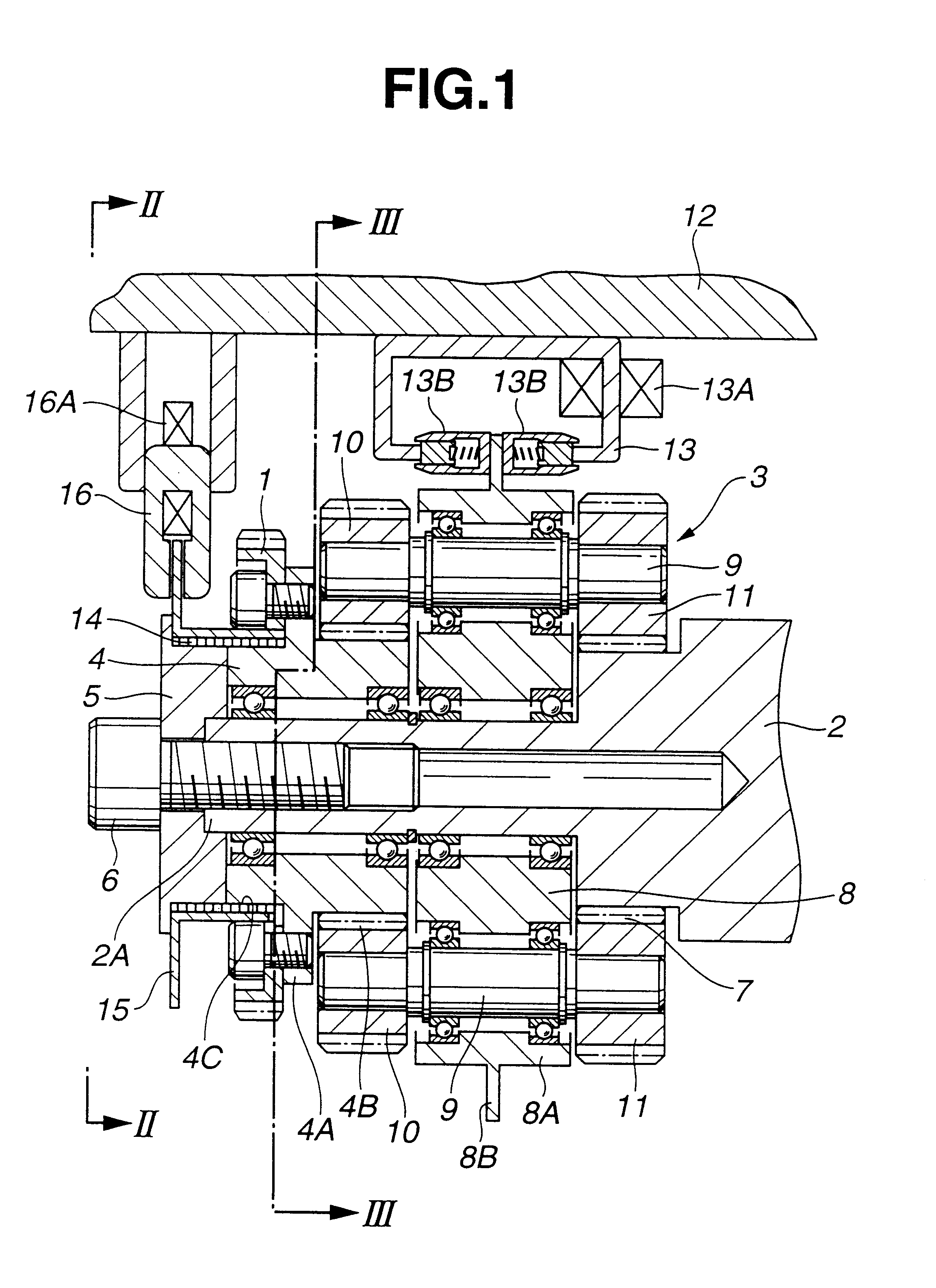
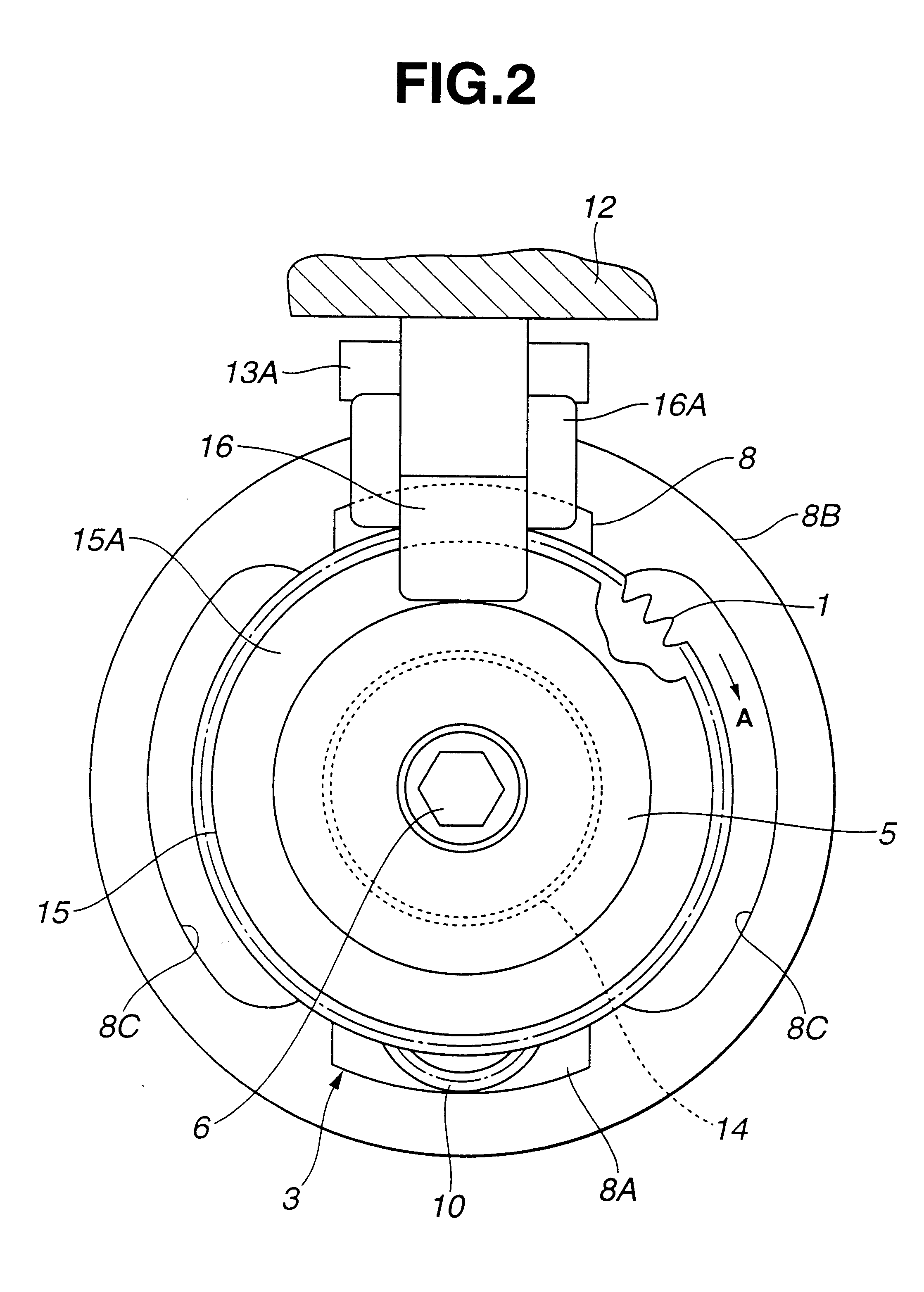
The strength and rigidity of pad springs are increased with a simple structure to prevent deformation and so forth of the pad springs caused by external force. A mounting member 1 is provided with pad springs 8 for resiliently supporting friction pads 7. Each pad spring 8 has guide plates 9, a connecting plate 10, an engagement plate 11, radially urging portions 12, circumferentially urging portions 13, reinforcement 15, etc. The reinforcement 15 includes a rectilinear reinforcement 15A formed on a flat plate portion 10A of the connecting plate 10 by embossing, for example, and oblique reinforcements 15B formed on joint portions 10B of the connecting plate 10. Thus, the joint portions 10B and so forth of the pad springs 8 can be prevented from being deformed by external force when the brake is activated or during assembling operation, for example, and hence it is possible to prevent positional displacement of the guide plates 9, etc. that would otherwise be caused by the deformation of the joint portions 10B.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Electric parking brake system and control method for the electric parking brake
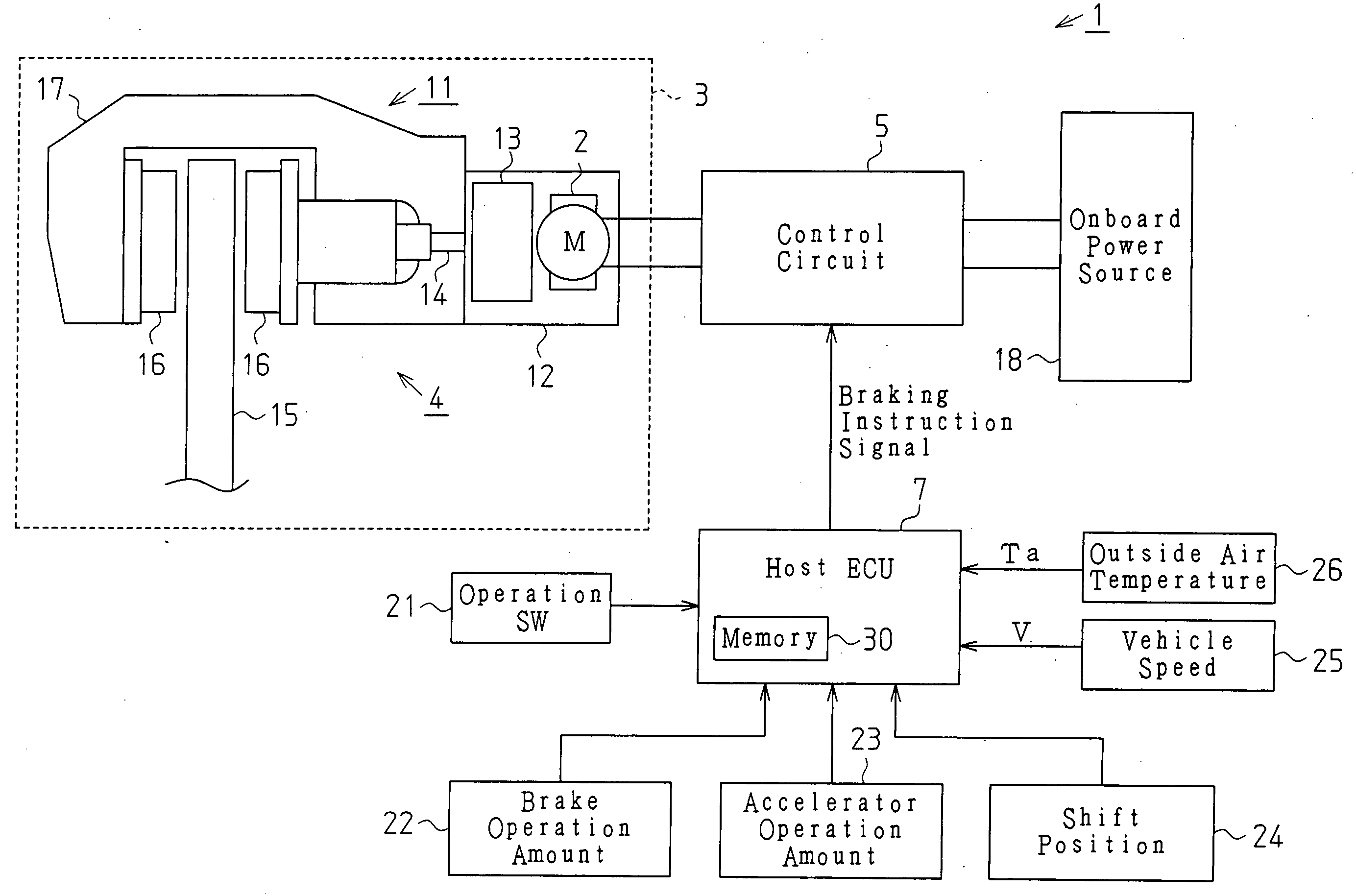
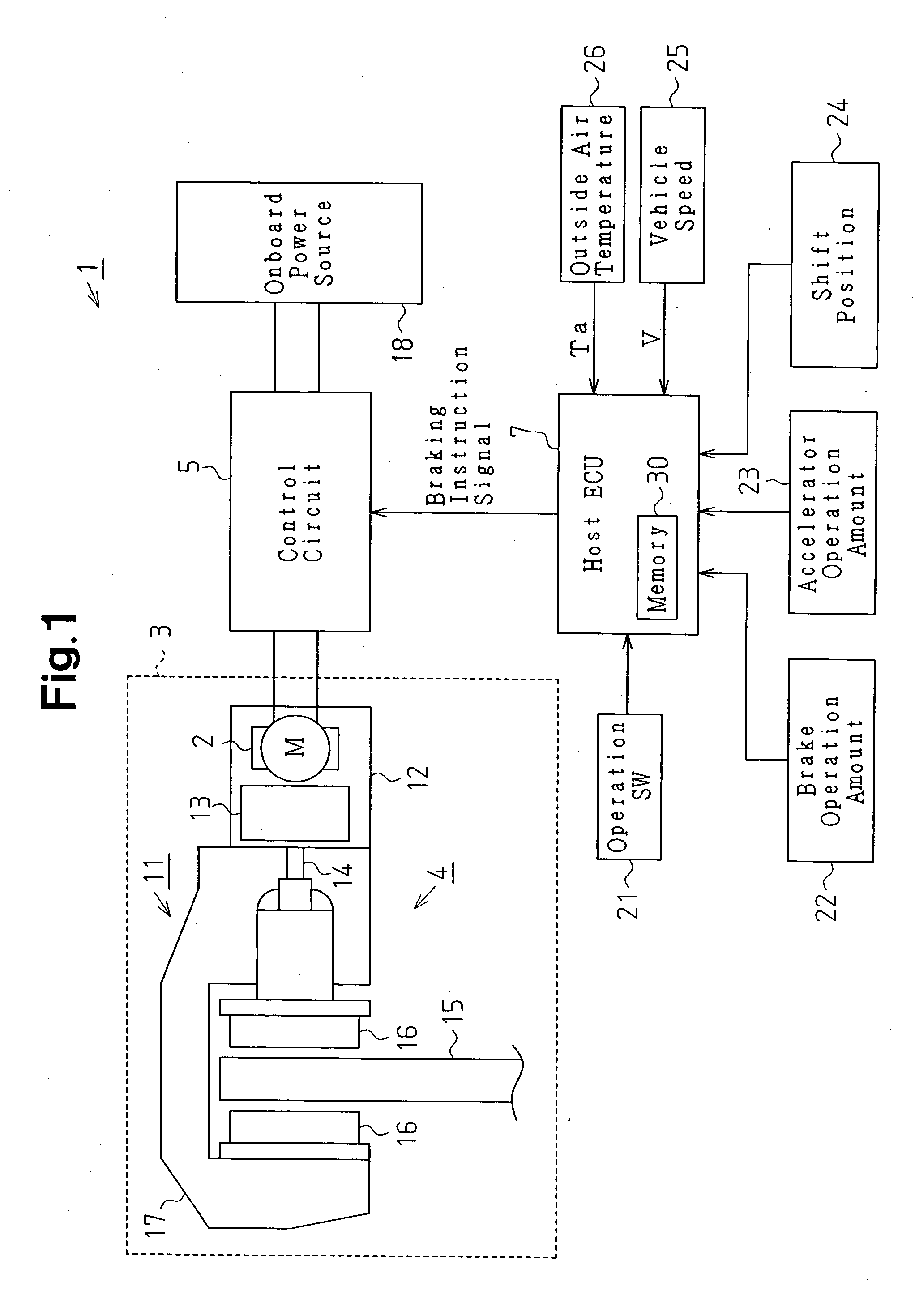
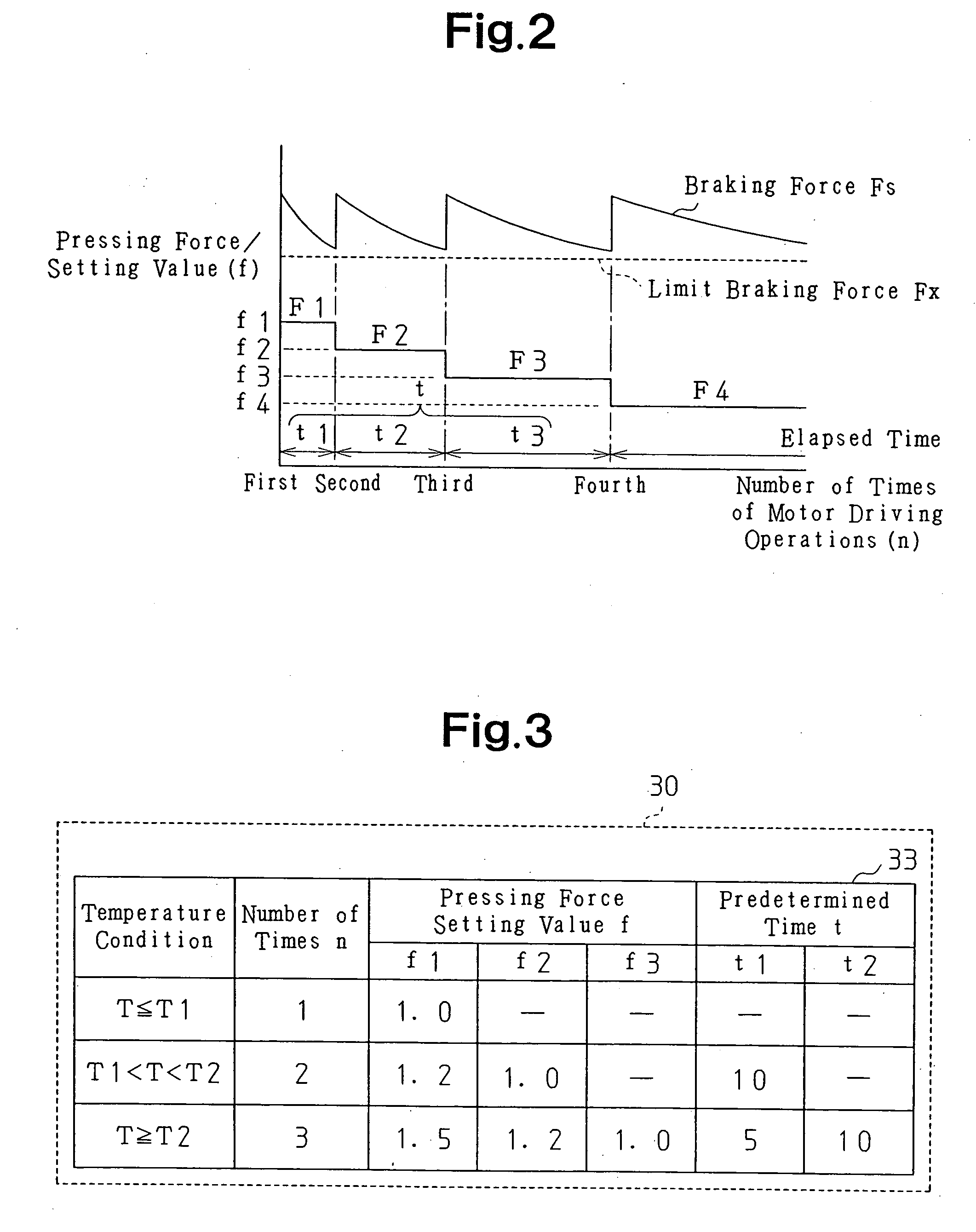
InactiveUS20050077783A1Steady braking forceImprove efficiencyAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionElectric parking brakeControl circuit
A friction member driven by a motor is pressed against a rotating element that rotates integrally with a wheel to give a pressing force to the rotating element, thereby applying braking force to the wheel. Control means controls the control circuit that controls the motor. In order to apply braking force to the wheel, the control means commands the control circuit to drive the motor once or a plurality of times at a predetermined time interval. Determining means determines a temperature of the friction member at the time when the parking brake starts braking the wheel. Setting means sets at least one of the number of driving of the motor, the time interval, and the target value of the pressing force. Therefore, a steady braking force with high efficiency is generated.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brake assembly with brake pad position and wear sensor
A brake assembly includes a sensor mounted to a brake component, and which is in communication with a transceiver. The sensor provides position information of the brake component, which is combined with known mechanical relationships between various brake components, to determine a wear state of a brake pad and a clearance between the brake pad and a rotor. The clearance is then adjusted based on signals from the sensor and the known mechanical relationship between the various brake components to maintain the clearance within desired limits.
Owner:MERITOR HEAVY VEHICLE BRAKING SYST (UK) LTD
Electric-motor brake apparatus
InactiveUS6173820B1Generation of braking forceConstant actuation travel of the brake apparatus are assuredAxially engaging brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsParking brakeAutomotive engineering
The invention relates to a brake apparatus with an electric service motor, which serves to actuate the brake via an actuating device. To enable setting an air clearance, the apparatus includes a readjuster for setting the air clearance, the brake is actuated with the readjuster and then reversed by a defined length. To realize a parking braking function, the apparatus includes a parking brake that can be repositioned from a released position to a braking position and that acts on the actuating device.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
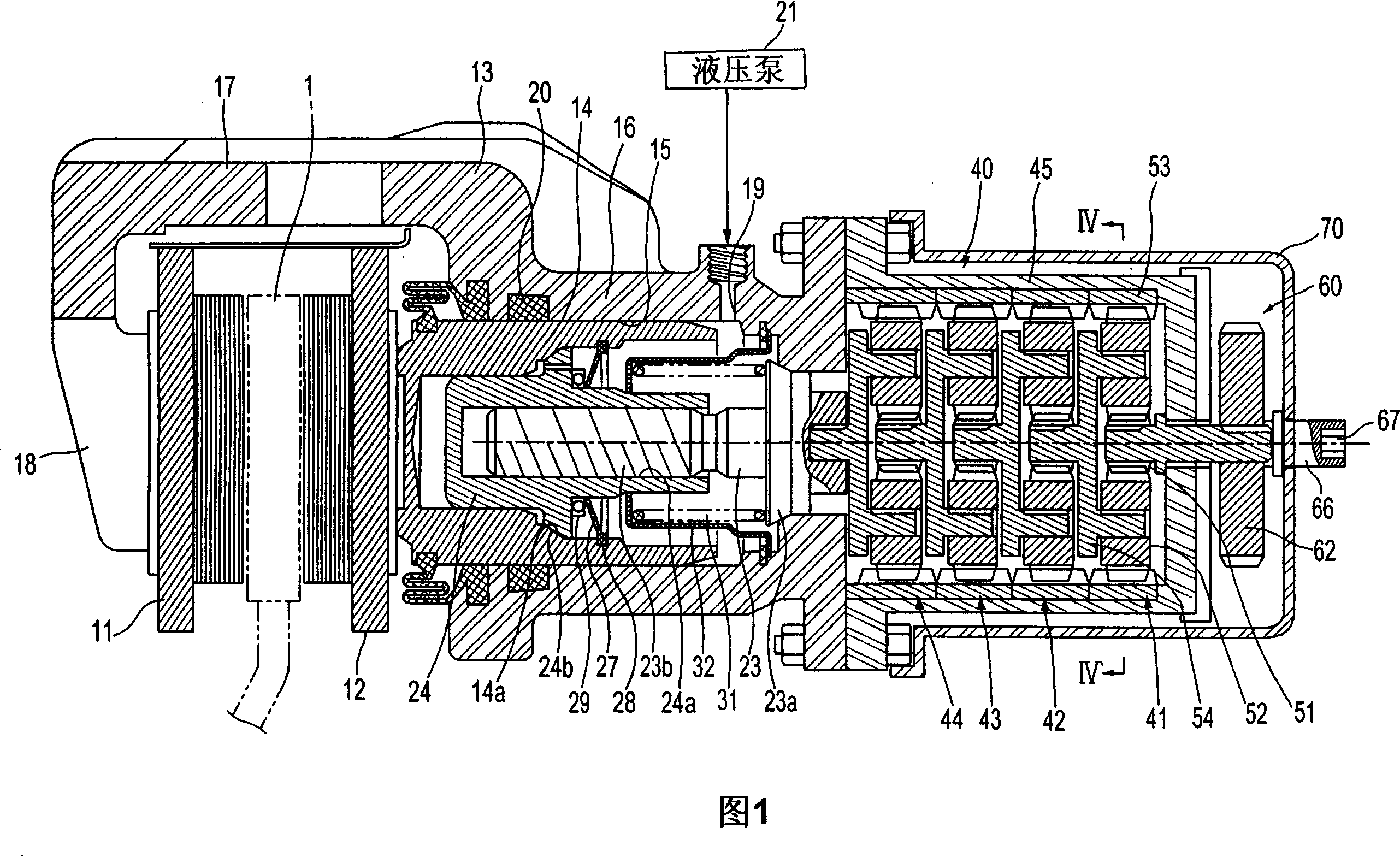
Automobile brake controlled by wire
ActiveCN102853000ASave installation spaceIt has the function of deceleration and torque increaseAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsAuto regulationLinear motion
The invention discloses an automobile brake controlled by a wire, which comprises a brake disc, wherein a friction plate is arranged on each of the two sides of the brake disc; the friction plates are fixedly connected with a piston which can axially move along a brake caliper body and is connected with a trapezoid nut; the trapezoid nut can axially move along an inner hole of the piston and is in fit connection with a trapezoid threaded end of a screw rod; a driving nut is movably arranged on a ball screw section of the screw rod and is fixedly connected with a worm gear; the worm gear is engaged with a worm which is fixedly connected with an output end of a driving motor of the brake to covert the rotation motion of the driving motor of the brake into linear motion; and the driving motor of the brake is perpendicular to a brake caliper of the brake. The automobile brake controlled by the wire has automatic regulation and parking braking functions, can improve reinforcement effect, is high in braking performance, simple in structure, convenient to mount, easy to maintain and less in energy consumption, and can ensure the constancy of brake response speed of a vehicle so as to further ensure the braking performance.
Owner:RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV TAIZHOU
Driving circuit including shift register and flat panel display device using the same
ActiveUS20060139292A1Increase contrastHigh color reproductionAxially engaging brakesStatic indicating devicesShift registerEngineering
A driving circuit for a flat panel display device includes shift register stages, each containing: a first TFT charging a Q node according to a start signal; a second TFT discharging the Q node according to an output voltage of a next shift register stage; a pull-up unit increasing an output voltage according to the Q node voltage; an odd pull-down unit decreasing the output voltage in an odd frame according to a QB-o node voltage; and an even pull-down unit decreasing the output voltage in an even frame according to a QB-e node voltage. A gate and drain of a third odd TFT connected to the QB-o node are connected to each other and receive an odd source voltage. A gate and drain of the third even TFT connected to the QB-e node are connected to each other and receive an even source voltage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Adsorption of nucleic acids to a solid phase
ActiveUS20050214926A1Eliminate needImprove propertiesSugar derivativesAxially engaging brakesLysis bufferLiquid phase
The present invention is directed to a method for adsorbing, i.e. non-covalently binding, nucleic acids to a solid phase using a two-step procedure. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to a method for isolating nucleic acids from a biological sample. In the first step of the procedure, lysis is effected by mixing the biological sample with an aequous lysis buffer containing a chaotropic agent and incubating the mixture; in the second step, the concentration of the chaotropic agent in the mixture is increased and the mixture is contacted with the solid phase, whereby the nucleic acids in the liquid phase is adsorbed to the solid phase.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
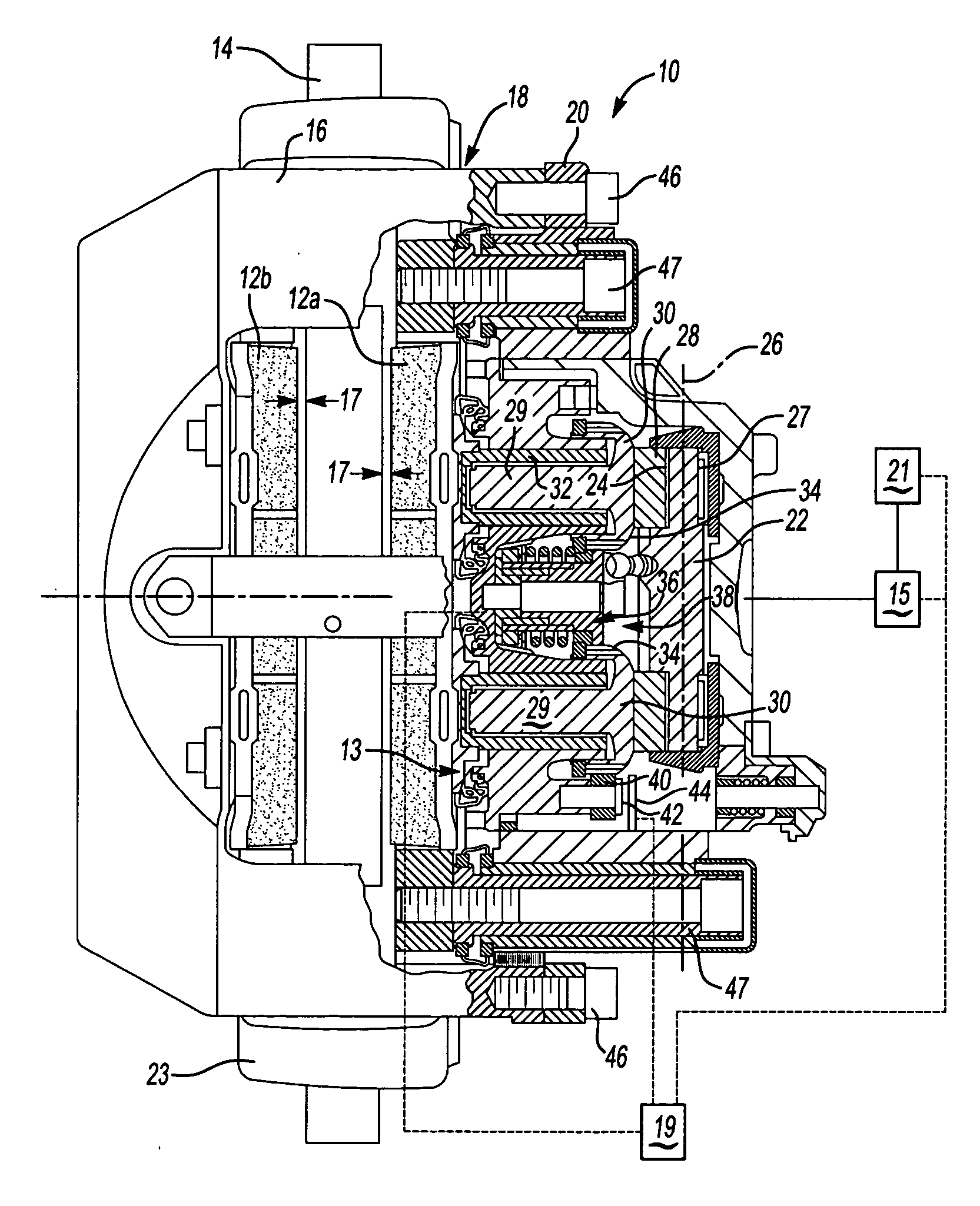
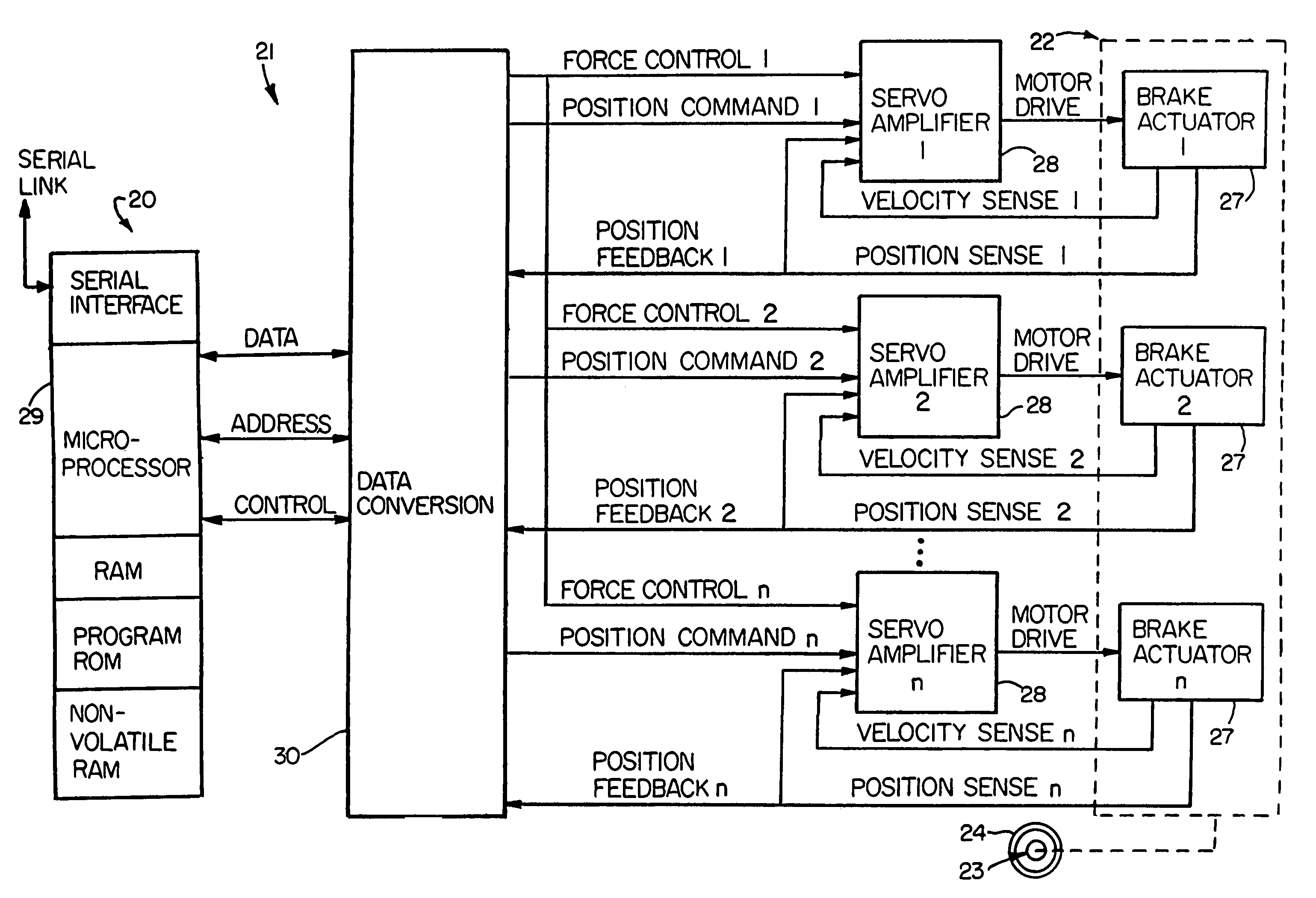
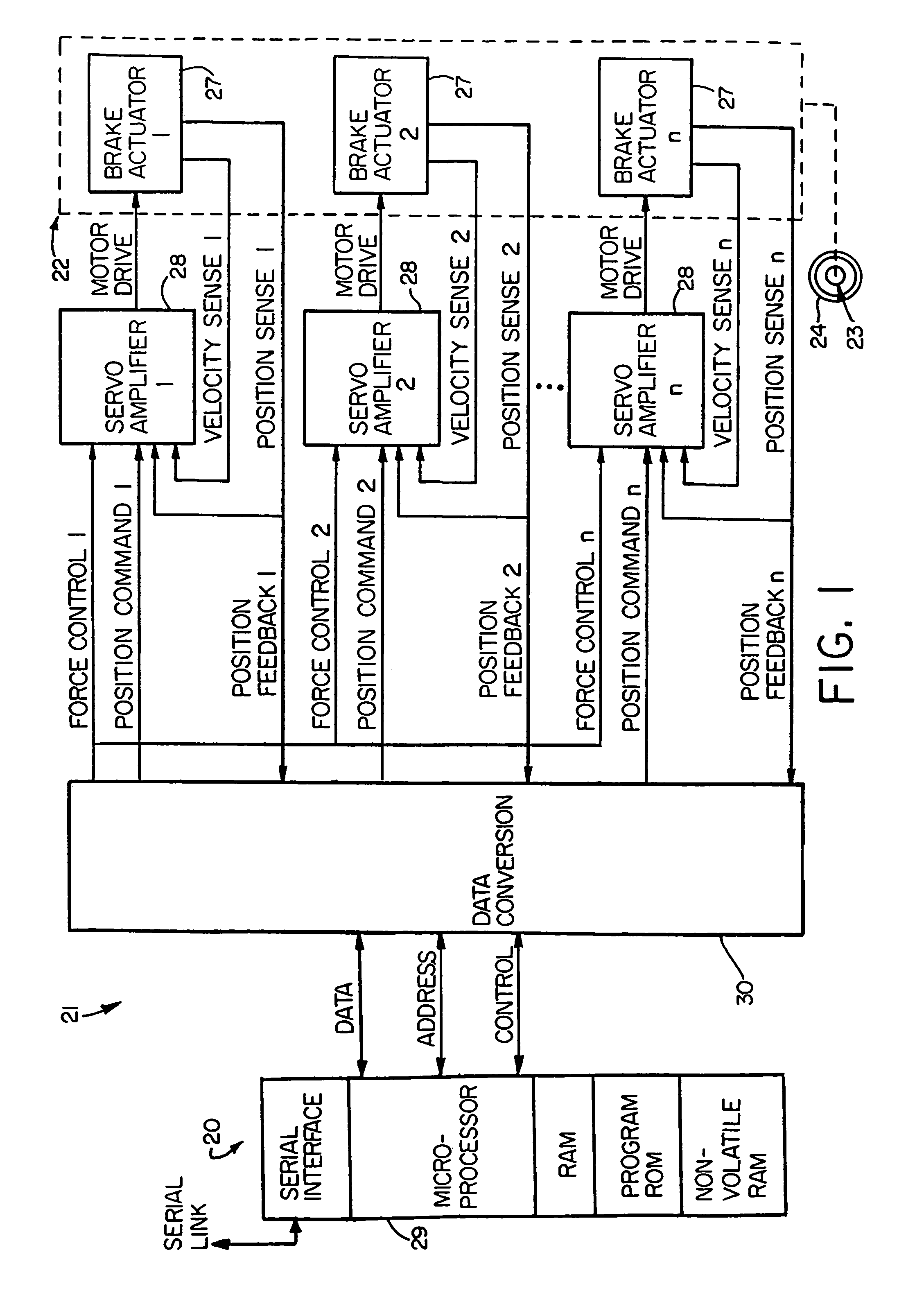
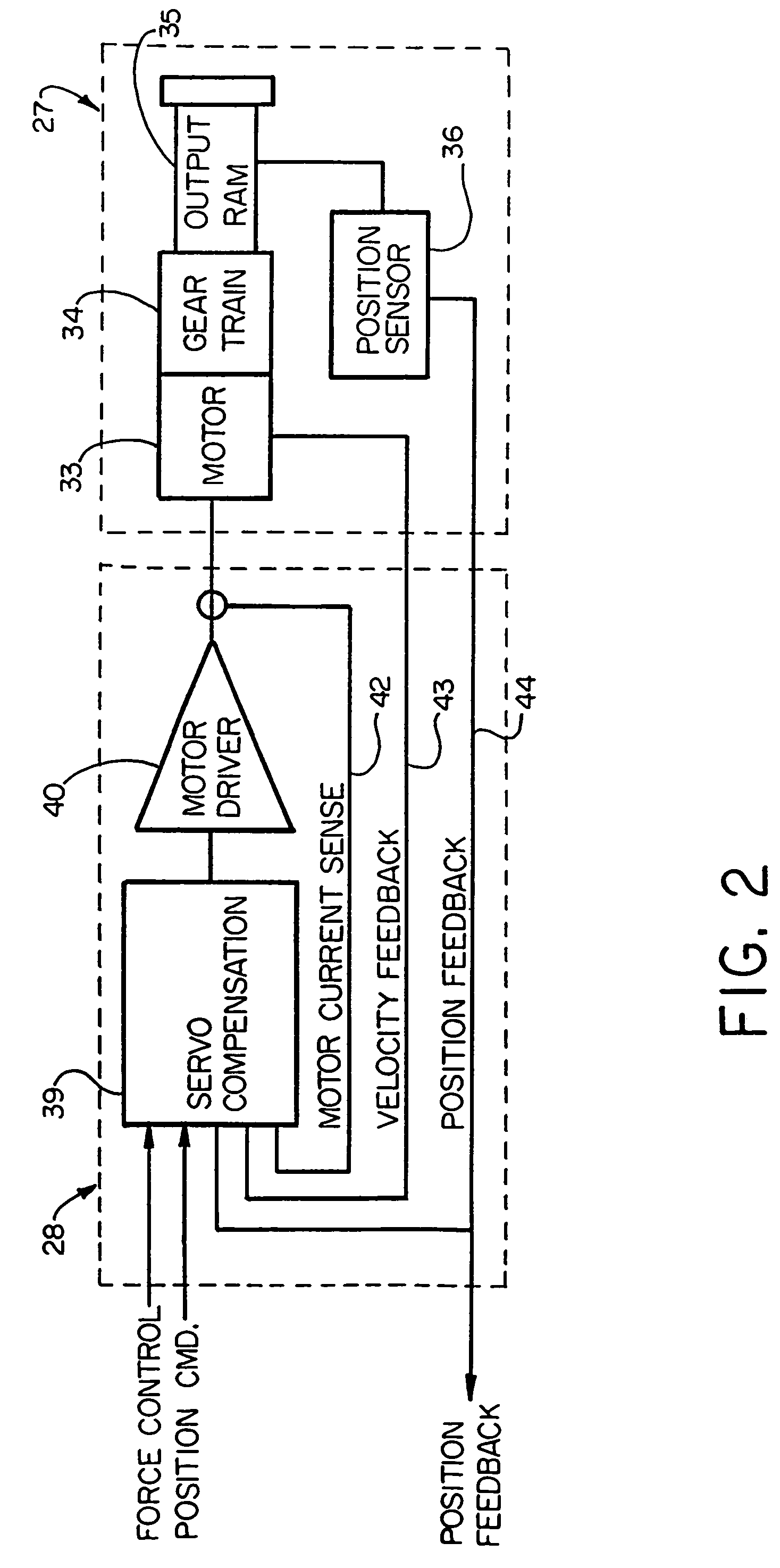
Electronic aircraft braking system with brake wear measurement, running clearance adjustment and plural electric motor-actuator ram assemblies
InactiveUS7108107B2Easy maintenanceIncrease weightAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionElectric aircraftActuator
An electrically actuated aircraft brake system and method which provides for brake wear measurement, brake running clearance adjustment, ram position-based control and improved construction and operation. Brake wear and running clearance measurement are obtained by analyzing the output of position sensing circuitry. The position sensing circuitry, preferably including a LVDT position sensor, is also used to determine braking load, a brake controller including circuitry for effecting displacement of one or more reciprocating rams to load a brake disk stack by a predetermined amount based on a present displacement value of the position signal obtained from the position sensor. The position sensor preferably includes a LVDT transducer connected between the reciprocating ram and a brake housing, and the motive device preferably includes a servo motor. Also provided is an actuator housing including a guideway for each ram, the guideway and ram having the same polygonal cross-section, whereby the ram nut is guided and restrained from rotation by the guideway as it is translated by a ball screw in threaded engagement with the ram nut for selective movement into and out of forceful engagement with the brake disk stack for applying and releasing braking force on a rotatable wheel. An electric motor is drivingly connected to each ball screw by a first gear integral with the ball screw, a second gear in mesh with the first gear, and a pinion on a rotating drive shaft of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Valve timing control system for internal combustion engine
A valve timing control system includes; a rotor rotated by a crankshaft of the internal combustion engine; a camshaft rotated according to the rotation of the rotor to open and close an intake valve and an exhaust valve of the internal combustion engine; and a rotational phase controller for variably controlling a rotational phase of the camshaft relative to the rotor. The rotational phase controller is disposed between the rotor and the camshaft. The rotational phase controller includes; a clutch selectably put in one of a holding state for forbidding a relative rotation between the rotor and the camshaft in at least one of rotational directions and a releasing state for allowing the relative rotation; and a generator for generating a holding toque directing to the rotational direction forbidden by the clutch and applying the holding torque to the clutch when the clutch is put in the holding state.
Owner:UNISIA JECS CORP
Brake apparatus
ActiveUS20160032995A1Less discomfortSmooth brake release operationBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesPower flowCalipers
A brake apparatus comprising: a caliper having a piston configured to move a brake pad to be pressed on a disc rotor rotating with a wheel; a thrust retaining mechanism located in the caliper to thrust the piston and maintain braking force exerted by the thrust piston; an electric motor mounted on the caliper to operate the thrust retaining mechanism; and a controller configured to apply electric current to the electric motor in response to an application command or a release command, thereby perform control according to the commands, wherein the controller, upon receiving a release command, configured to operate the electric motor to reduce braking force exerted by the piston by performing current maintenance control which continuously applies electric current to the electric motor and switching control which successively switches between a larger and a smaller amount of electric current applied to the electric motor.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Brake carrier
A brake carrier for a heavy vehicle disc brake includes an actuating side carrier portion including a support for an actuating side brake pad having a first material having a first property. The brake carrier also includes a separate reaction side carrier portion having a support for a reaction side brake pad for securement to the actuating side carrier portion. The actuating side carrier portion includes a first material having a first property, and the reaction side carrier portion includes a second material having a second property, wherein the second property differs from the first property.
Owner:MERITOR HEAVY VEHICLE BRAKING SYST (UK) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com