Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44385 results about "Road surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A road surface or pavement is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkway. In the past, gravel road surfaces, cobblestone and granite setts were extensively used, but these surfaces have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base course. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the twentieth century. Road surfaces are frequently marked to guide traffic. Today, permeable paving methods are beginning to be used for low-impact roadways and walkways. Pavements are crucial to countries such as US and Canada, which heavily depend on road transportation. Therefore, research projects such as Long-Term Pavement Performance are launched to optimize the life-cycle of different road surfaces.
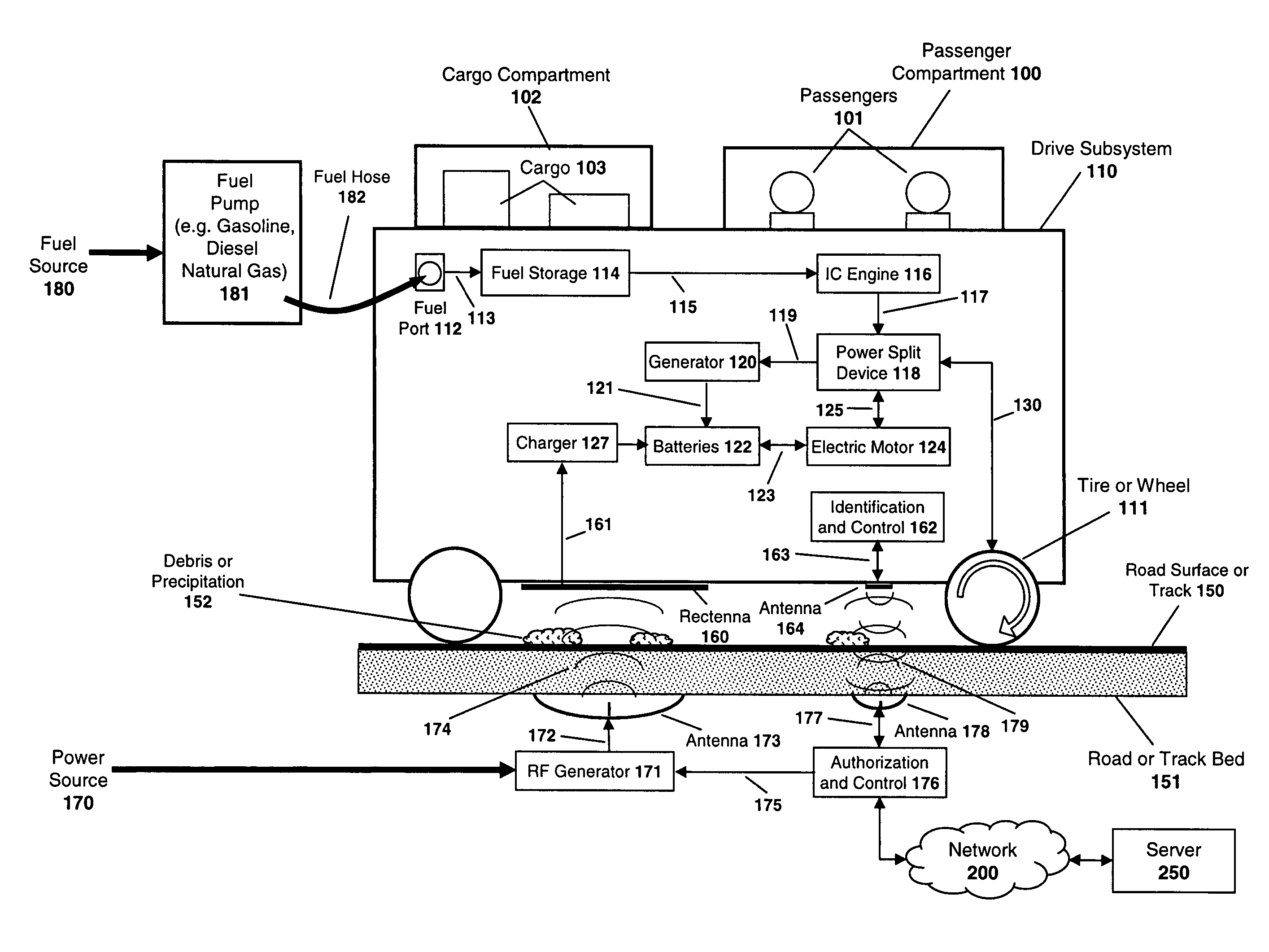
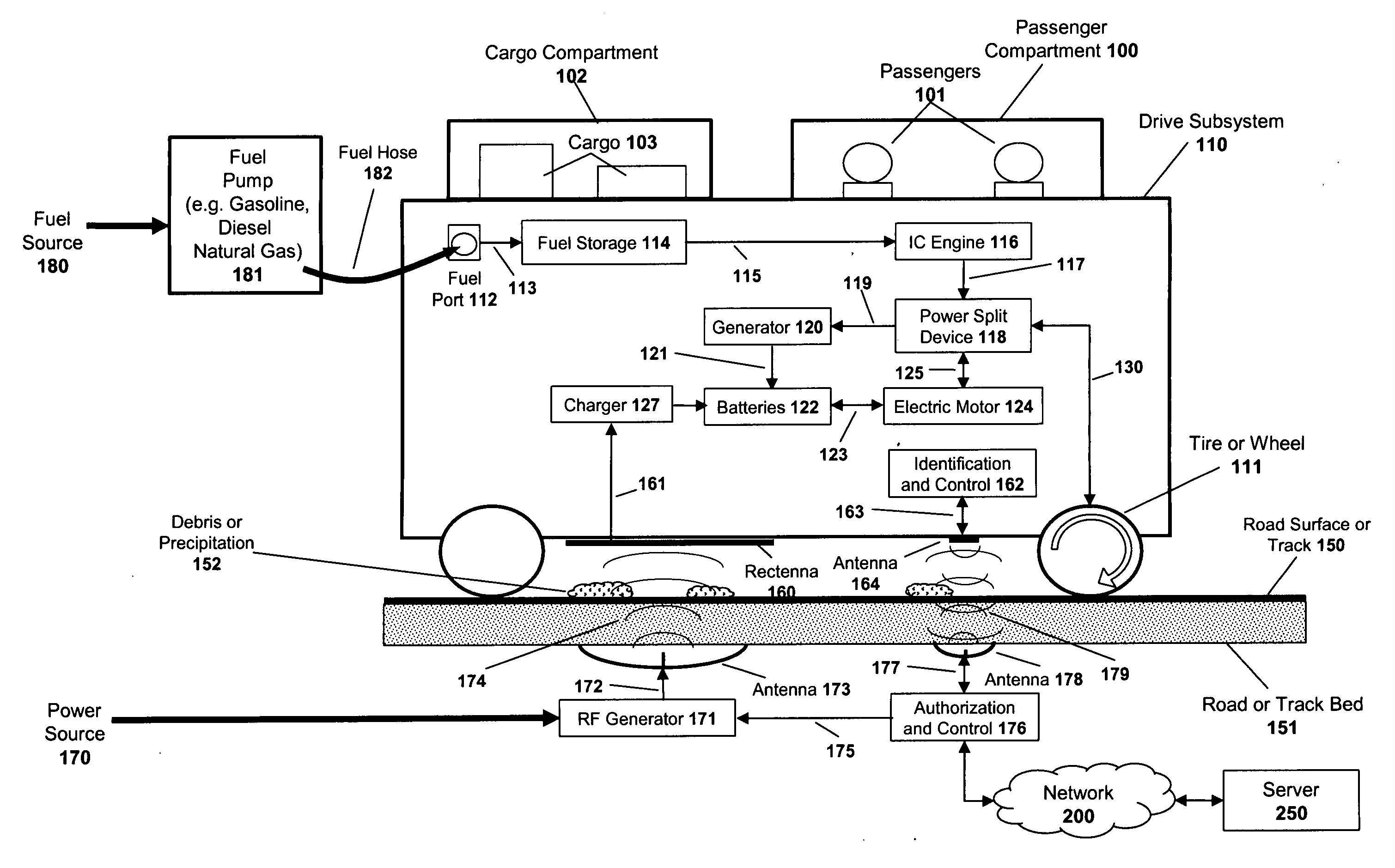
System and method for powering a vehicle using radio frequency generators
A system and method are described for powering a vehicle using radio frequency (“RF”) signals. For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: positioning a plurality of RF generators beneath the road surface of a roadway, the RF generators configured to transmit RF signals in the direction of vehicles traveling over the roadway; coupling a rectenna on a vehicle, the rectenna configured to receive the RF signals transmitted from the RF generators and to generate power from the RF signals; and using the power generated by the rectenna to power the vehicle.
Owner:REARDEN
System and method for powering vehicle using radio frequency signals and feedback
ActiveUS20100044123A1Improve power efficiencyCharging stationsElectromagnetic wave systemChannel state informationRadio frequency signal
A system and method are described for powering a vehicle using radio frequency (“RF”) signals. For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: positioning an antenna array beneath or on the road surface of a roadway, the antenna array configured to transmit RF signals responsive to RF processing logic and / or circuitry; coupling a rectenna array to a vehicle, the rectenna array configured to receive the RF signals transmitted from the antenna array and to generate power from the RF signals; providing feedback signals from the vehicle to the RF processing logic and / or circuitry, the feedback signals including channel state information (CSI) defining a current state of the channels between the antenna array and the rectenna array, the RF processing logic and / or circuitry using the channel state information to adjust the RF signal transmissions from the antenna array to improve the efficiency of the power generated by the rectenna array; and using the power generated by the rectenna array to power the vehicle.
Owner:REARDEN
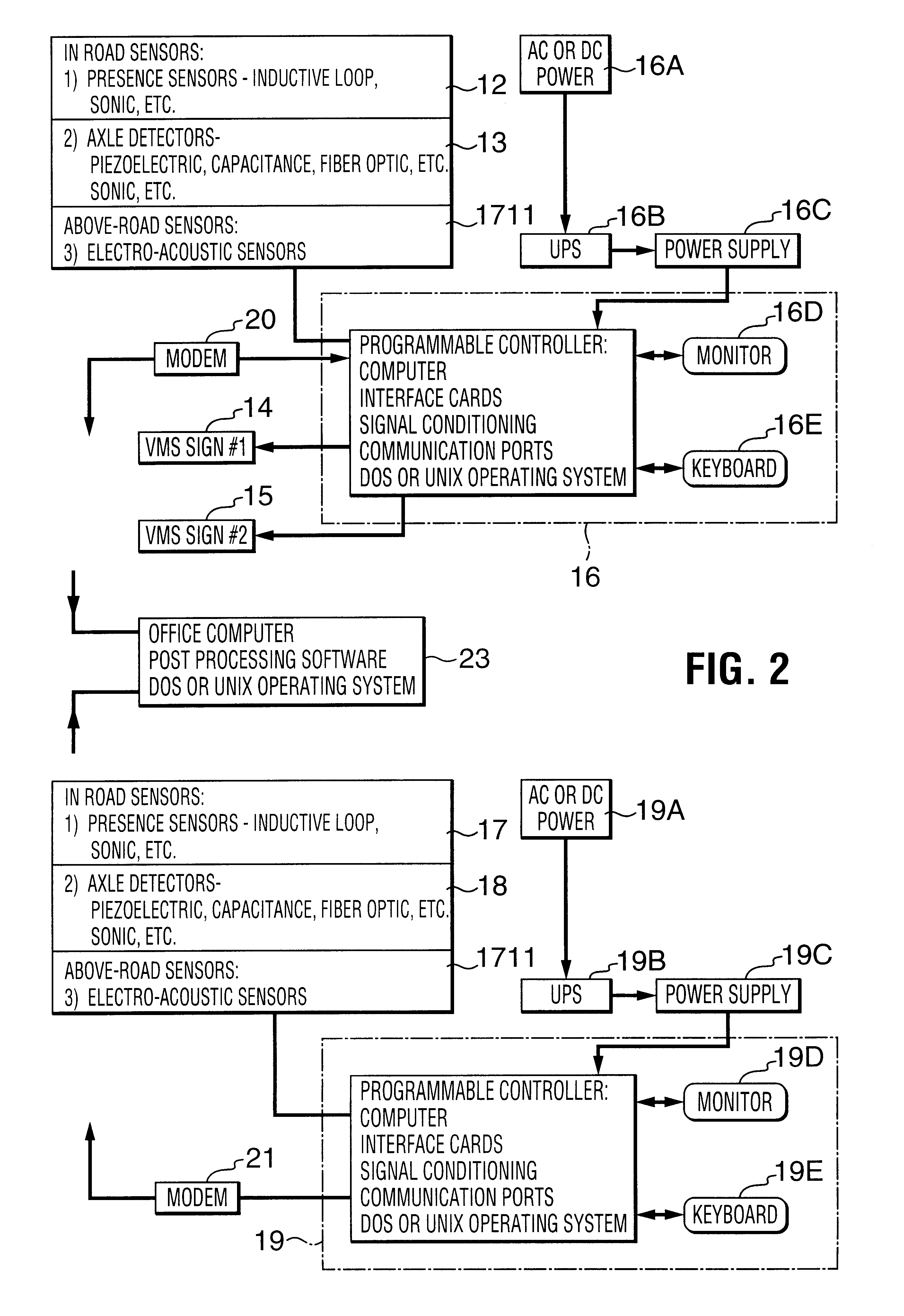
Truck traffic monitoring and warning systems and vehicle ramp advisory system
InactiveUS6204778B1Prevent rolloverControlling traffic signalsAnalogue computers for vehiclesTruckSensor array
Traffic monitoring and warning systems and vehicle ramp advisory systems are provided herein. Such system includes a set of sensor arrays comprising a set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays which is disposed above a traffic lane approaching a hazard for producing signals which are indicative of whether the vehicle is an automobile or a truck and, if it is a truck, to record the presence of such truck, and to provide signals which are indicative of the speed of such truck. A processor is provided which has a memory for storing site-specific data related both to the geometry of the hazard and to signals which have been received from the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays. A traffic signalling device is associated with the traffic lane and is disposed downstream of the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays, the traffic signalling device being controlled by the processor. The processor is responsive to the signals from the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays for computing an actual speed of the truck and for computing a computed maximum safe speed for such truck at the hazard. The computed maximum safe speed of the truck is derived from the site-specific dimensional data of the hazard and from at least the initial speed of the truck, the computed maximum safe speed of the truck being a maximum safe speed for that truck safely to negotiate the hazard. The processor compares the computed actual speed of the truck with the computed maximum safe speed for the truck. Then, the processor automatically operates the traffic signalling device if the computed actual speed of the truck exceeds the computed maximum safe speed for the truck. The processor also discontinues operating the traffic signalling device if the computed actual speed of the truck no longer exceeds the computed maximum safe speed for the truck.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL ROAD DYNAMICS
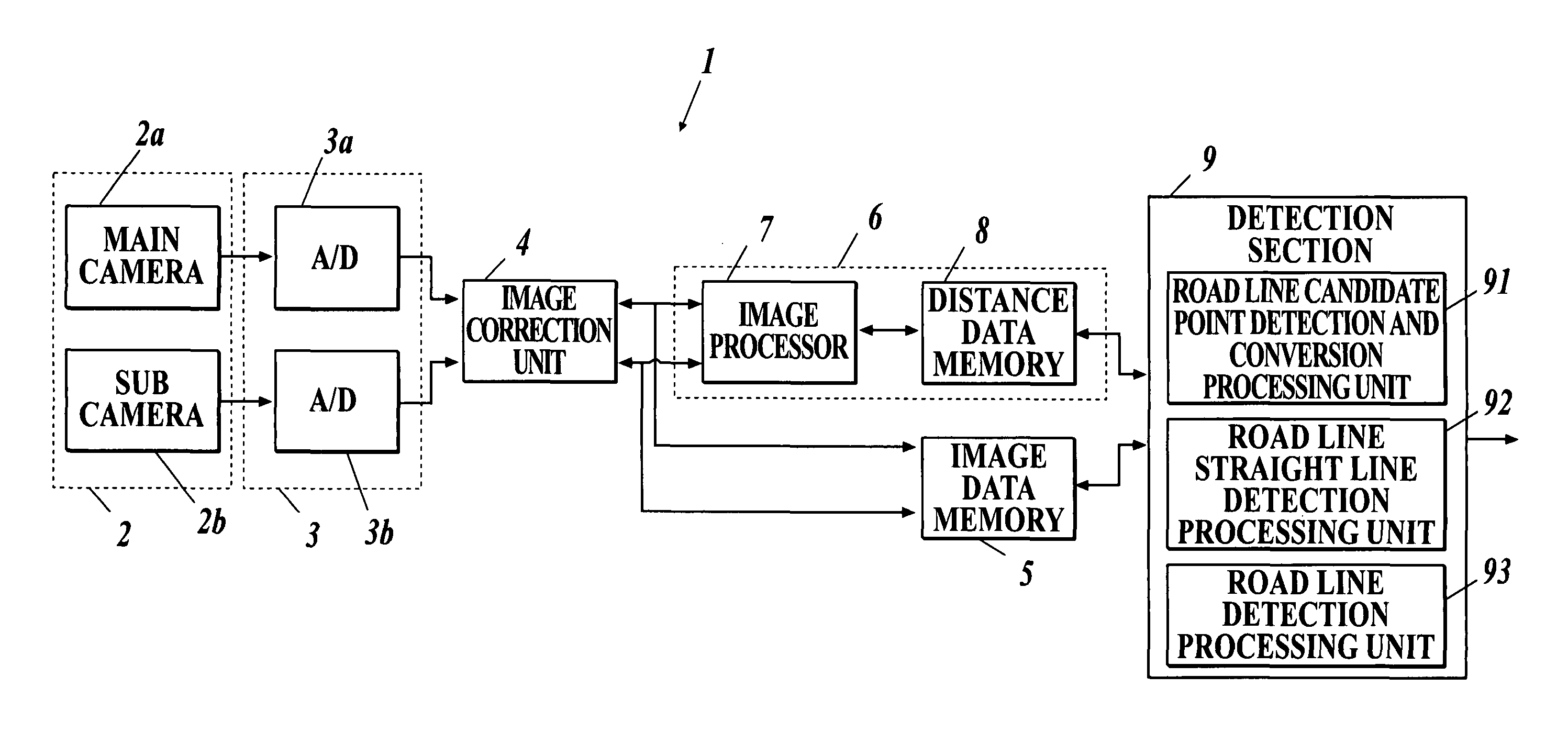
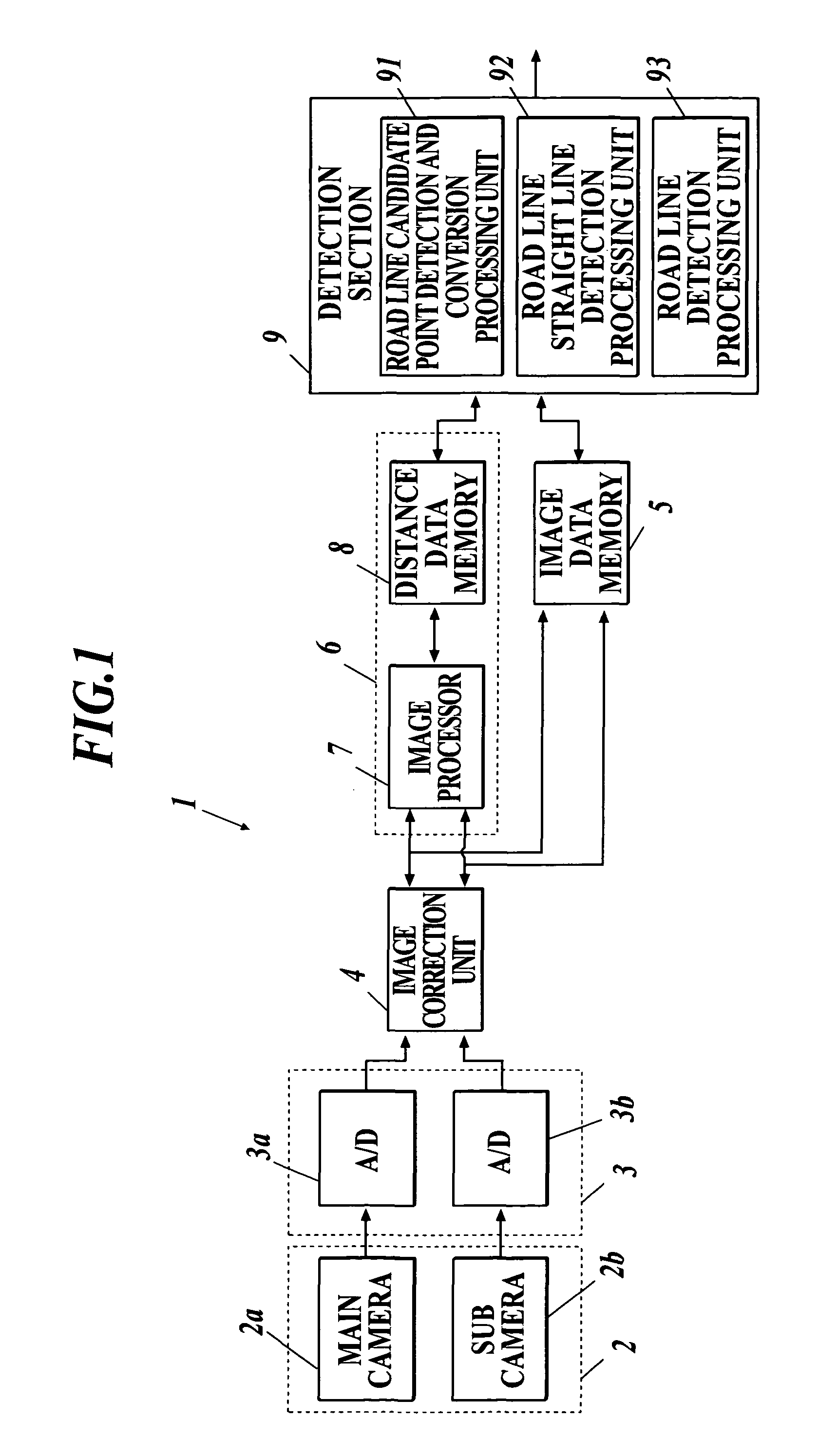
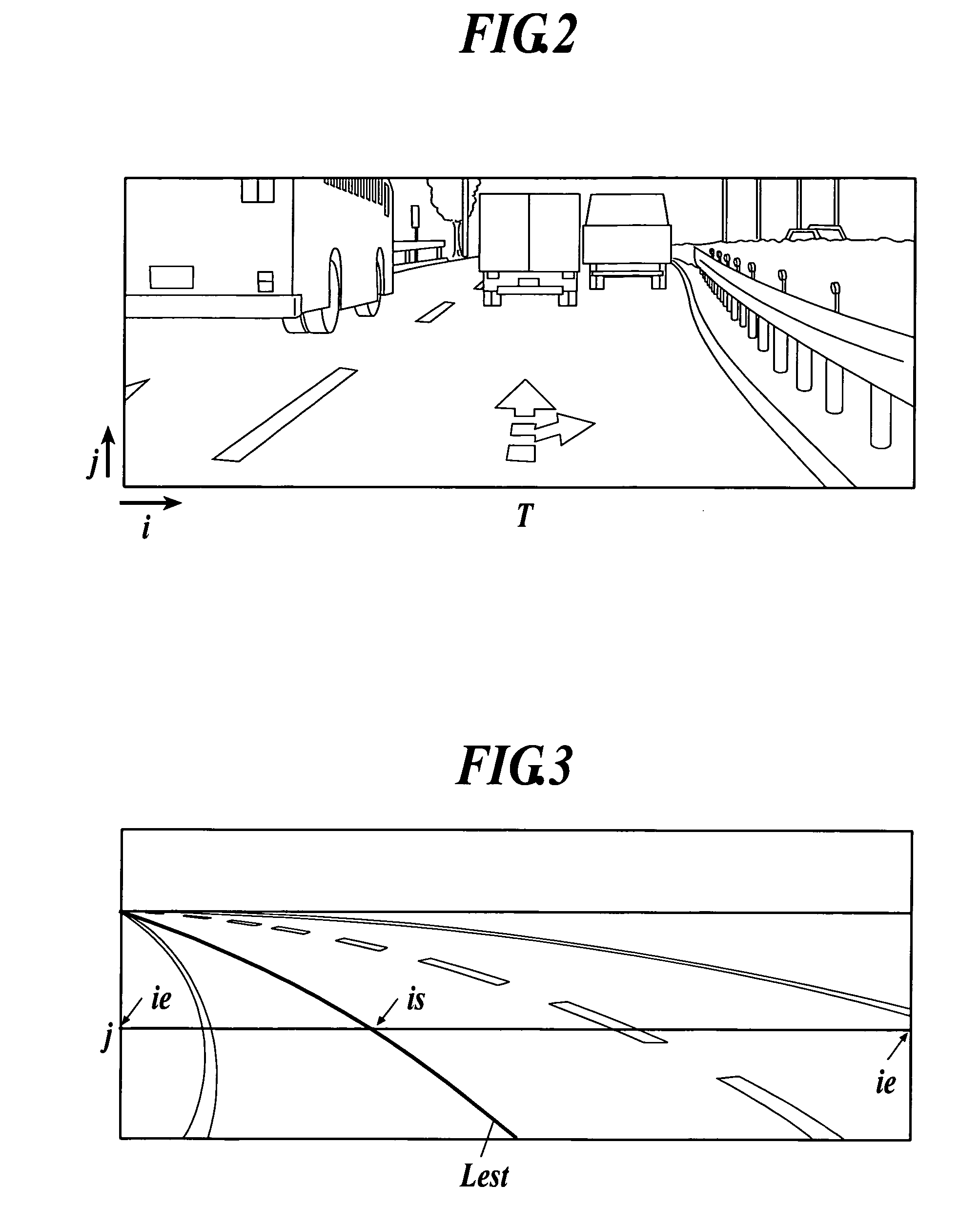
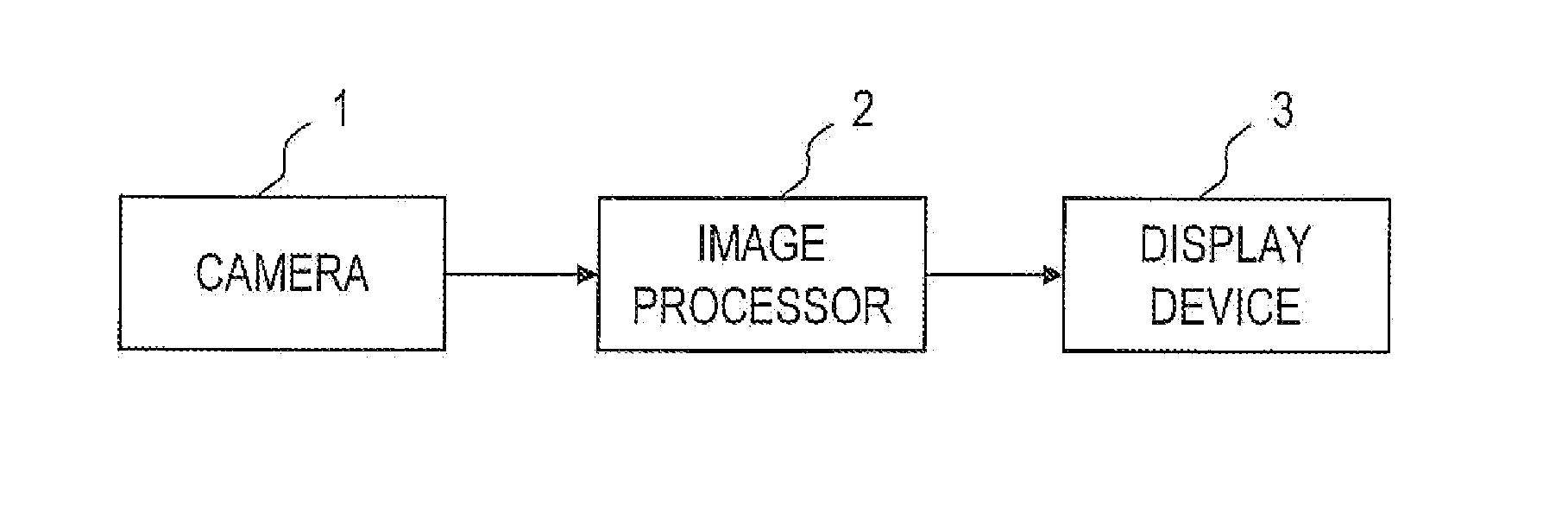
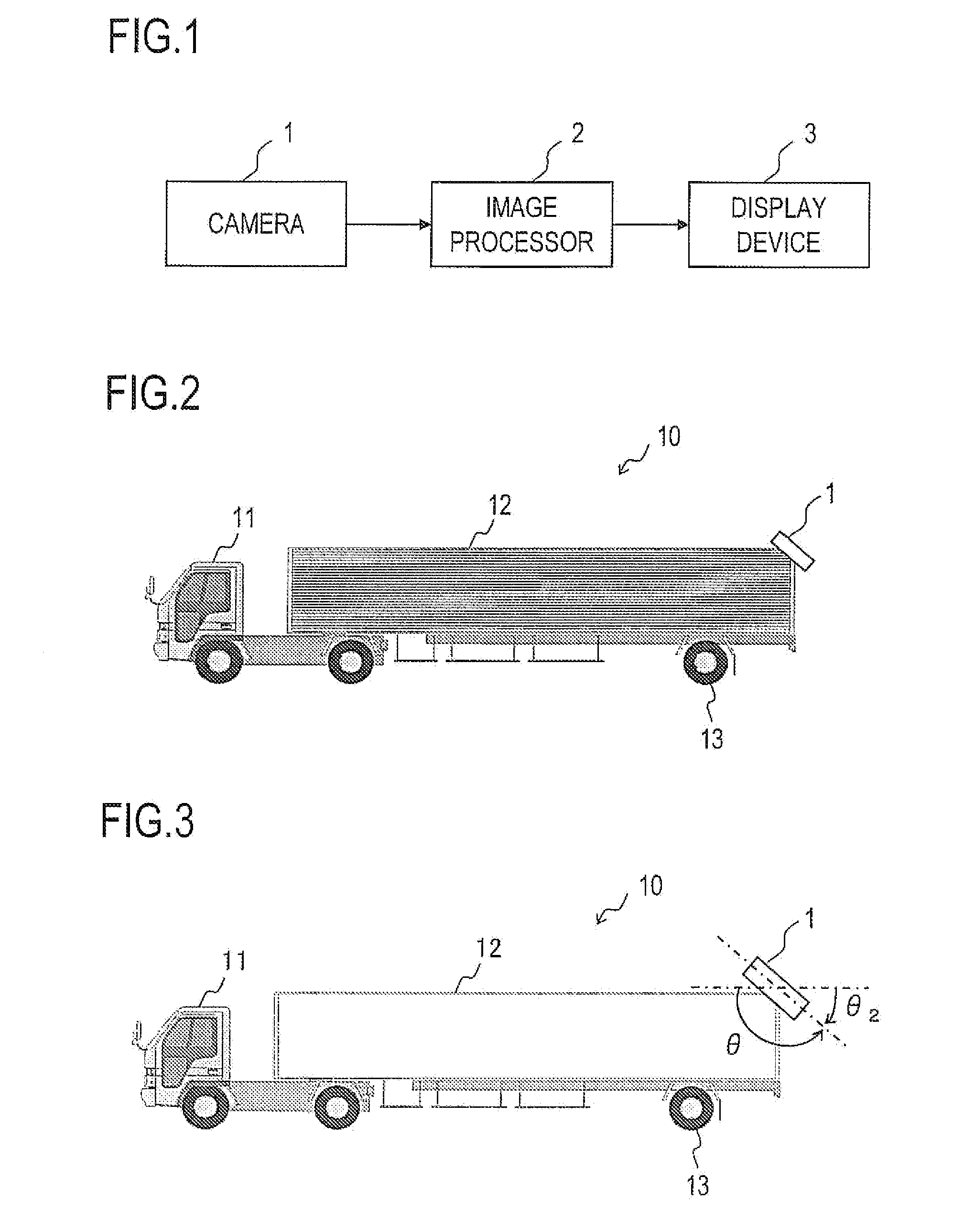
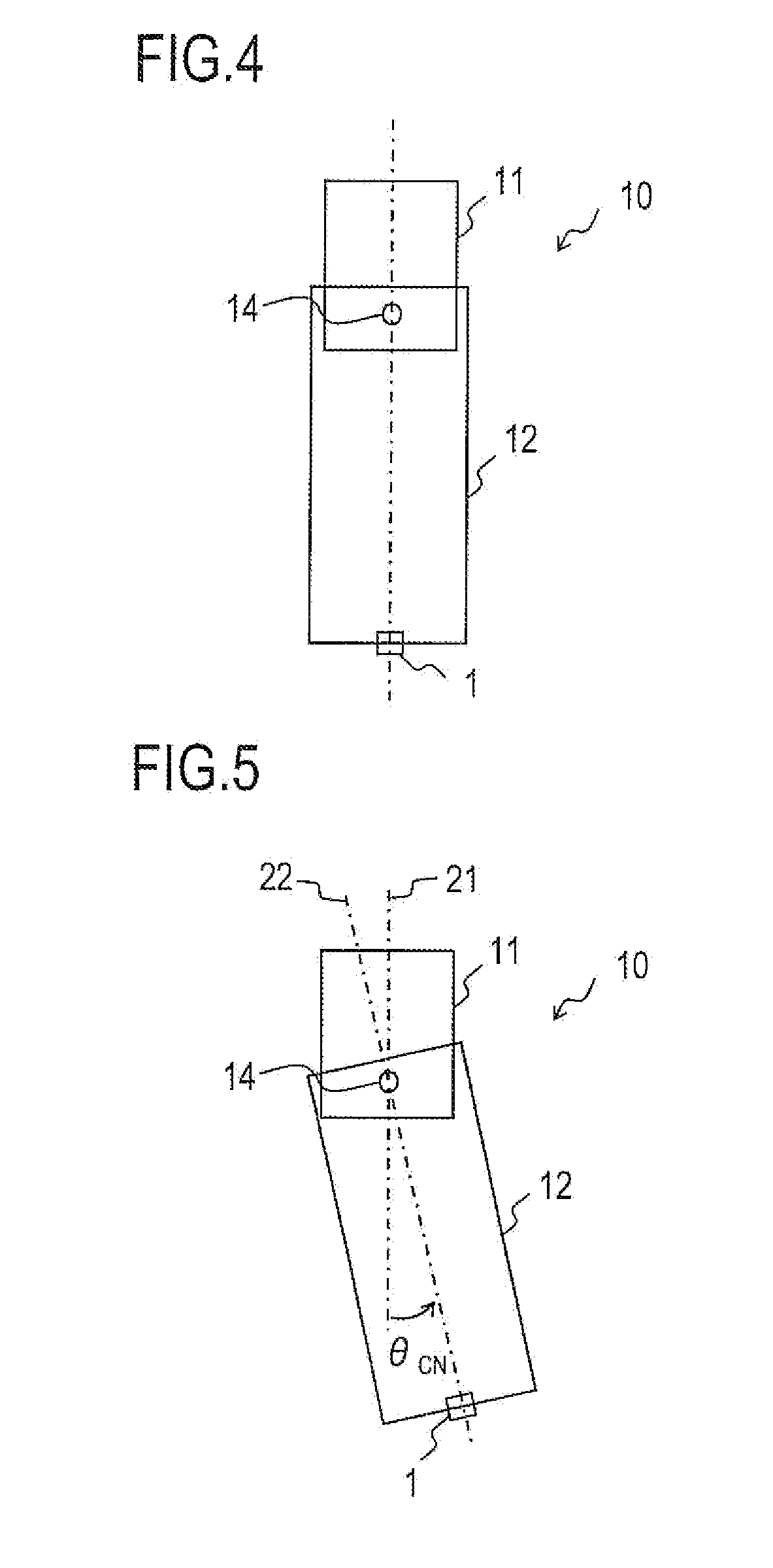
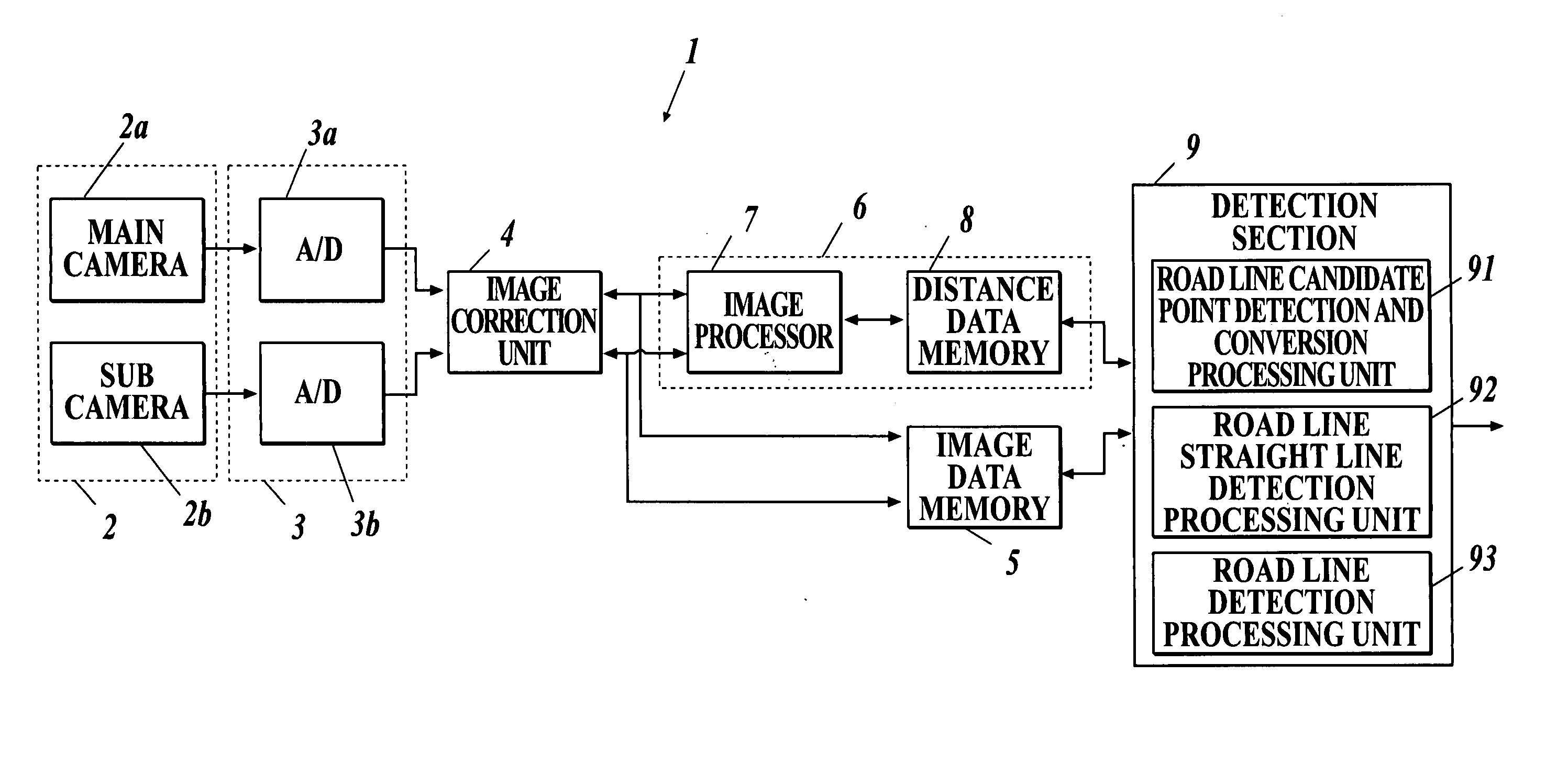
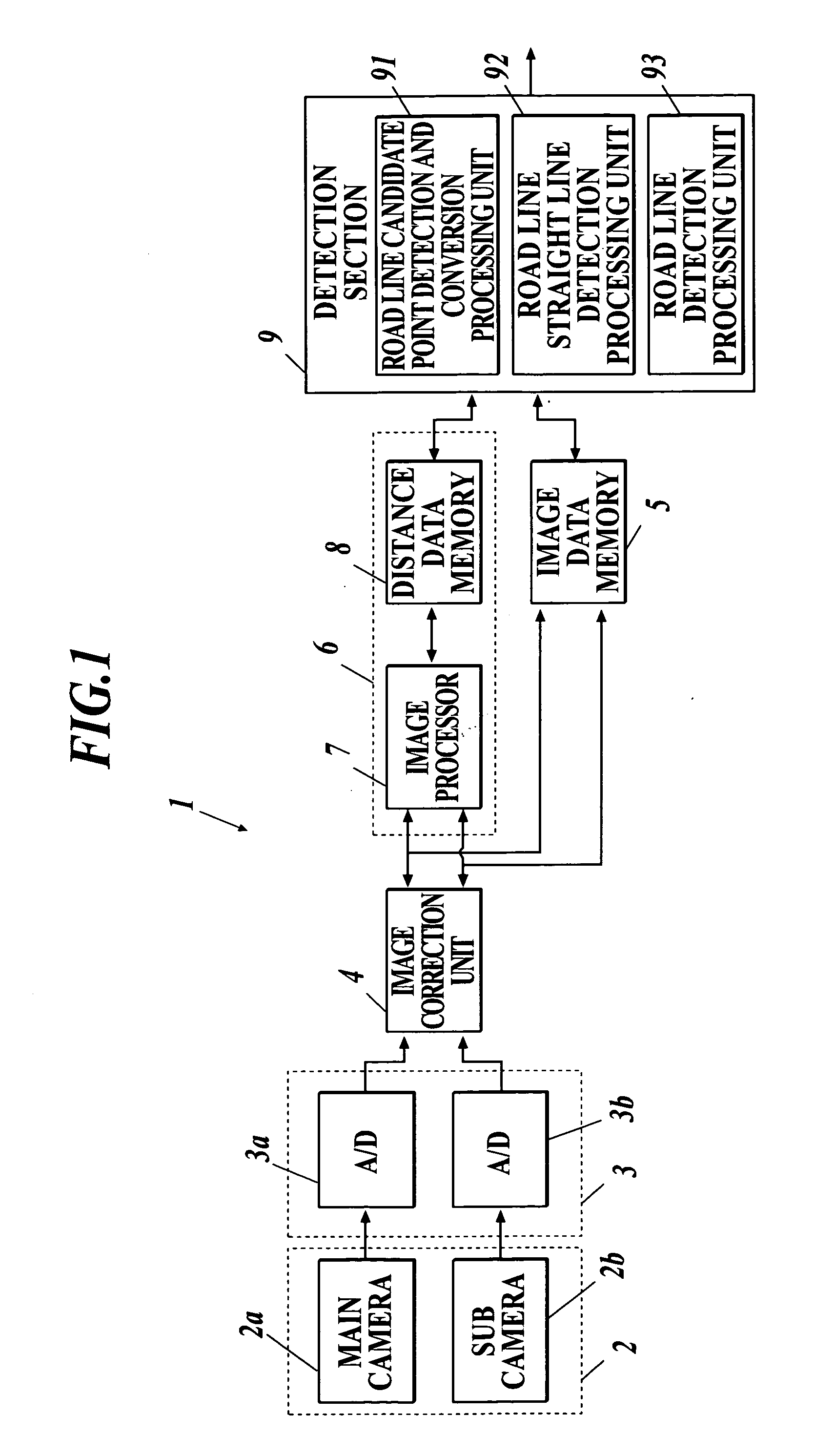
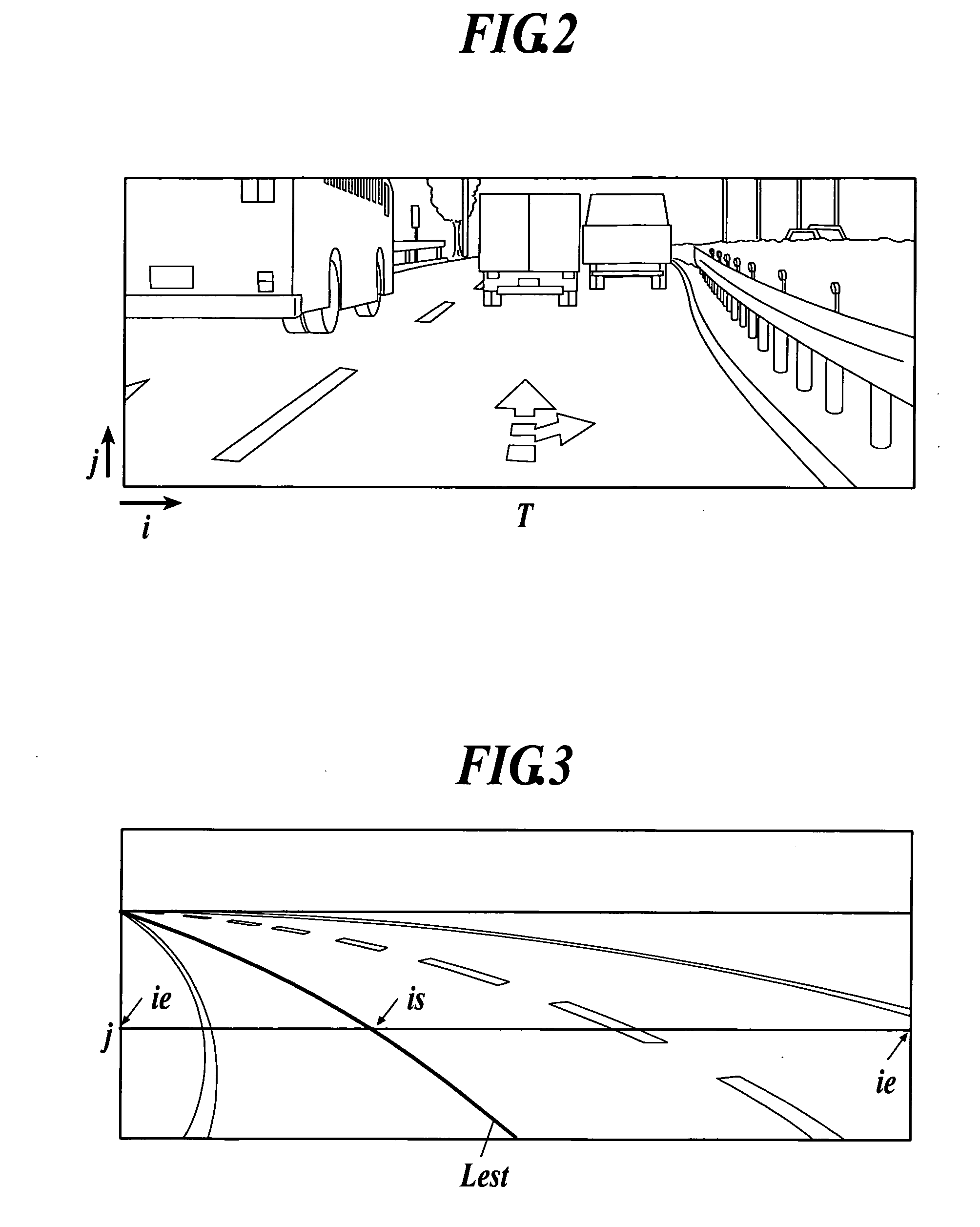
Road line recognition apparatus
ActiveUS8224031B2Stable detectionAccurate detectionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficImaging processingRoad surface
A road line recognition apparatus, including: an imaging section imaging a progress path of a own vehicle including a road to output a couple of images; an image processing section calculating a distance in a real space in a set region of at least an image on one side based on the imaged couple of images; and a detection section detecting a road line; wherein the detection section includes: a road line candidate point detection and conversion processing unit detecting a pixel on a road surface as a road line candidate point based on luminance and the distance with regard to the image on one side, and performing Hough conversion of the road line candidate point; a road line straight line detection processing unit detecting one straight line proper to the road line on each of a right side and a left side of the own vehicle based on at least a position or a behavior of the own vehicle between straight lines obtained by the Hough conversion; and a road line detection processing unit detecting the road line of a shape of a straight line or a curved line by recording a road line position which is a road line candidate point indicating a road line among the road line candidate points based on the detected straight line.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
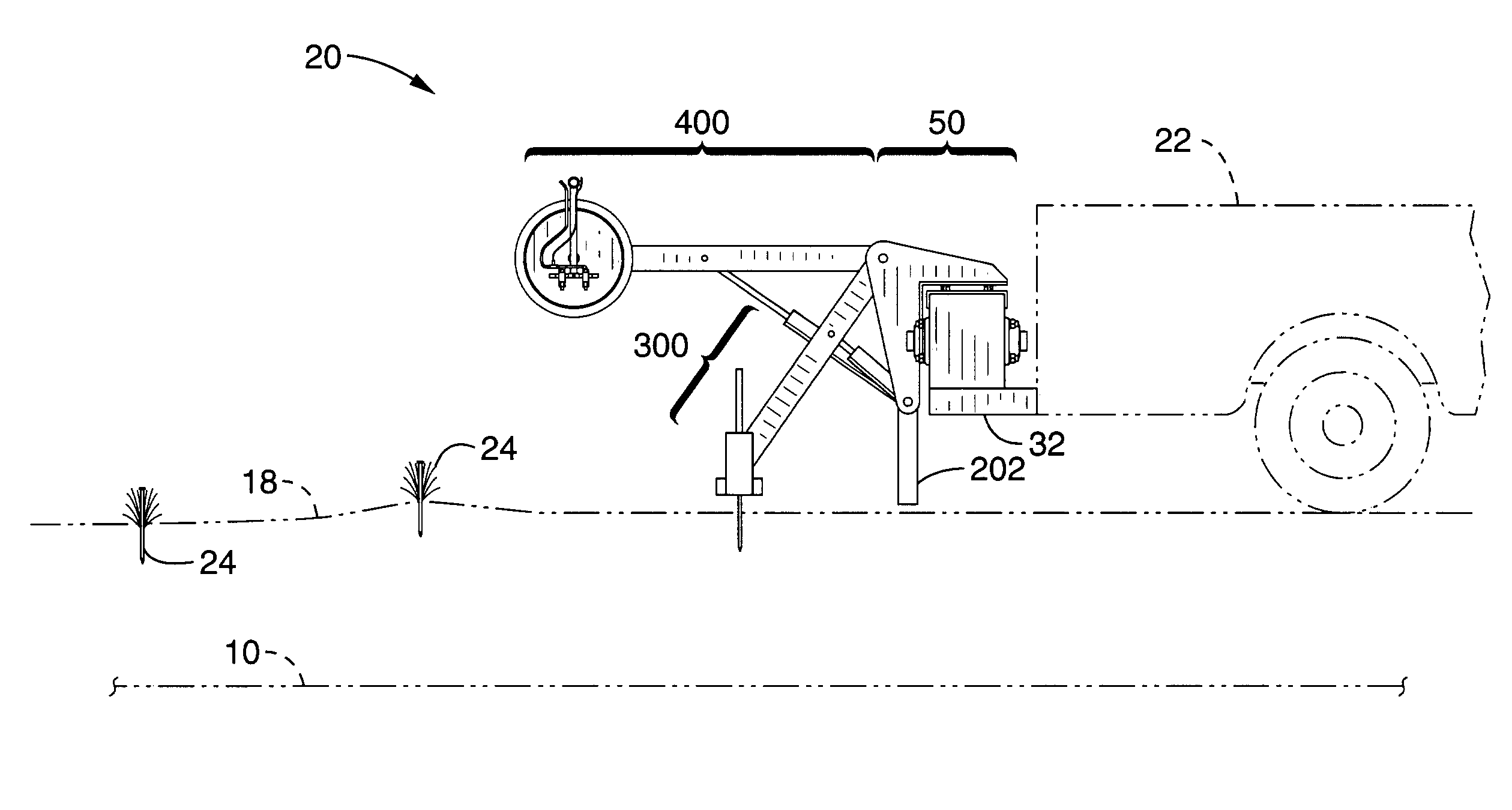
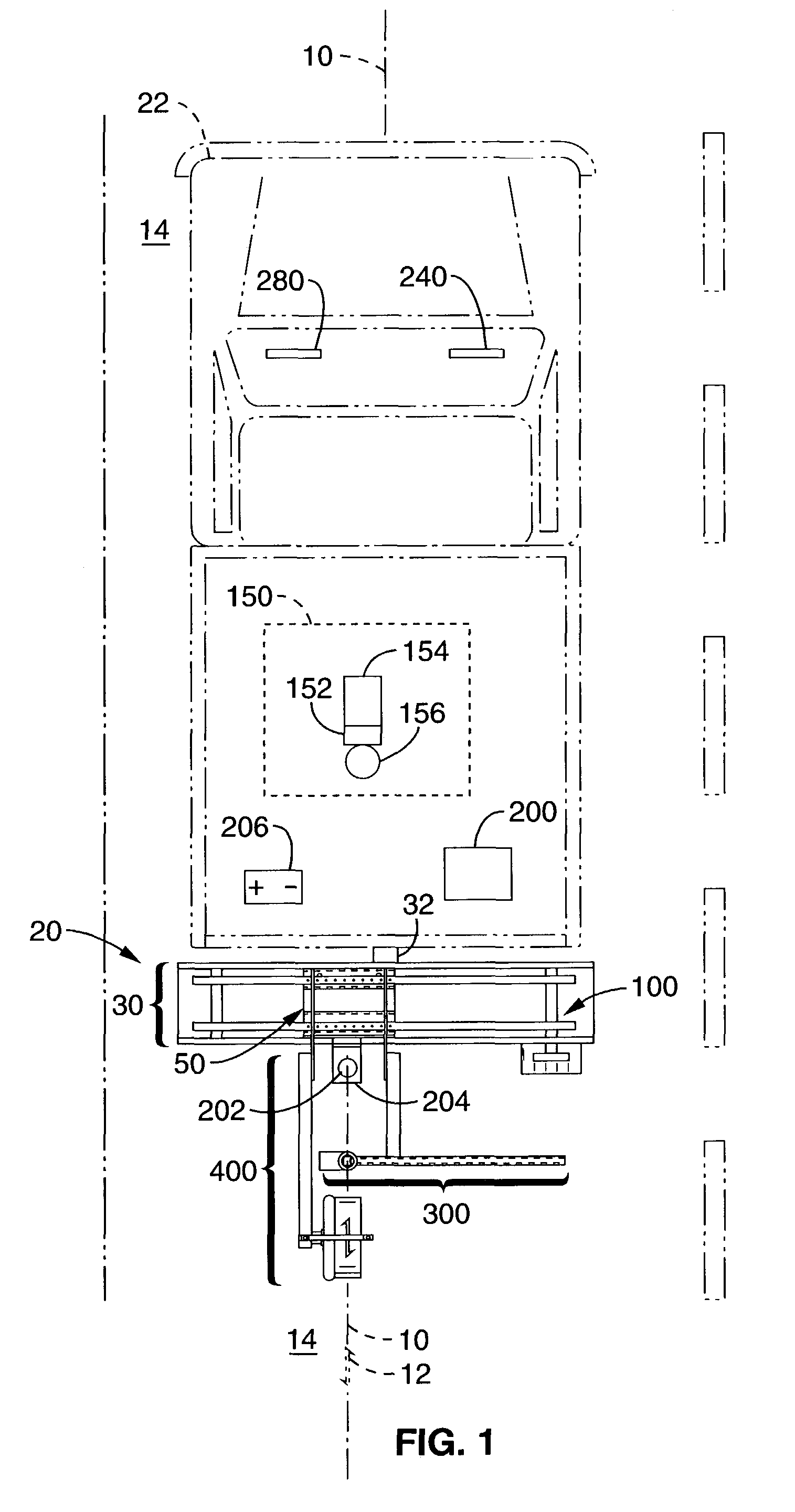
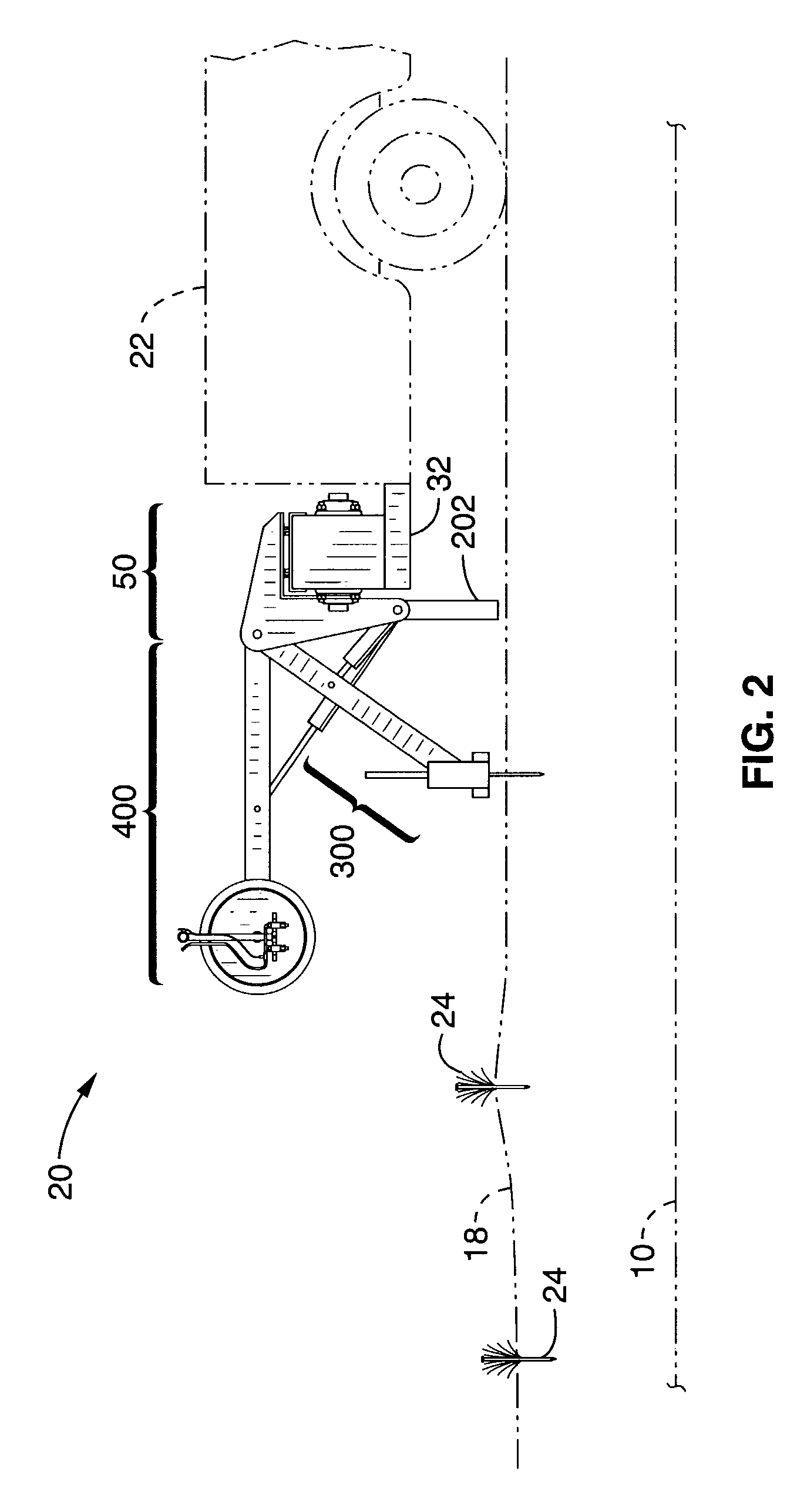
Apparatus and method for locating and marking an underground utility
InactiveUS7372247B1Safely mark surface positionIncrease speedMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementProximateRoad surface
An apparatus and method to locate and mark the surface position of an underground utility while maneuvering along the path of the utility. The apparatus uses an underground utility detector that responds to the location of an underground utility to continually position a carriage proximate vertical of the utility. Marker systems are aligned with the carriage and apply either a unique paint symbol on pavement or a spike in the ground. The apparatus is configured to use an underground utility detector or positioning equipment that generate positional signals. The apparatus may be configured to mark utility positions at predetermined intervals and mark utility offset positions. The apparatus may be attached to a vehicle, towed by a vehicle, motorized or propelled by a person.
Owner:TRI SITE
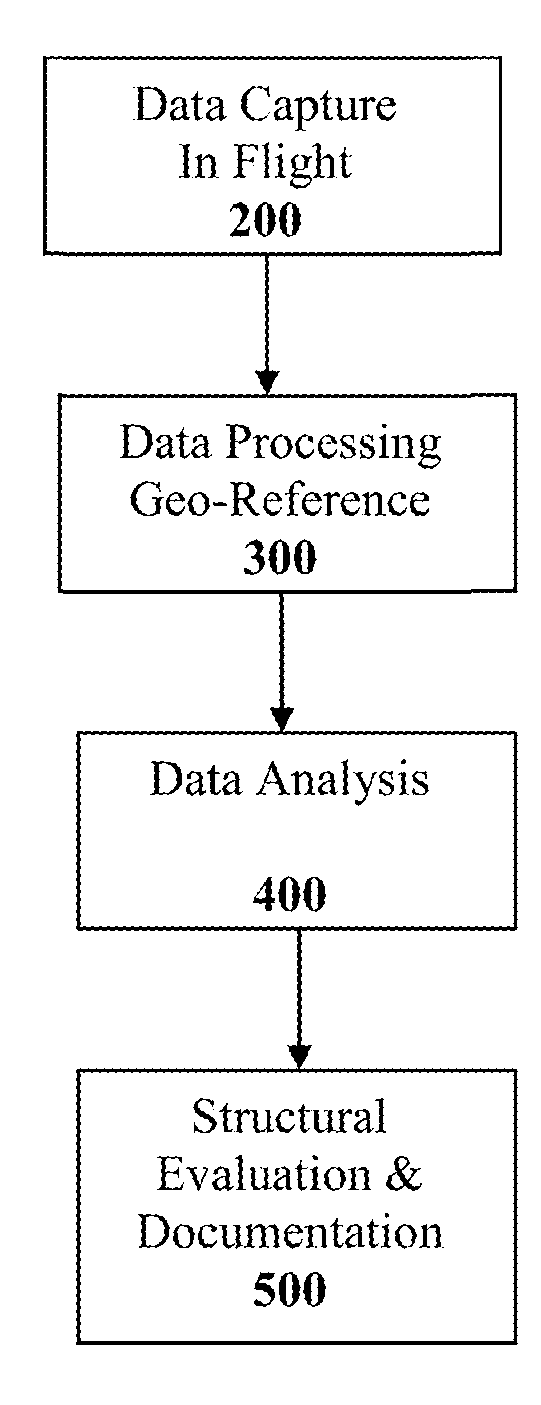
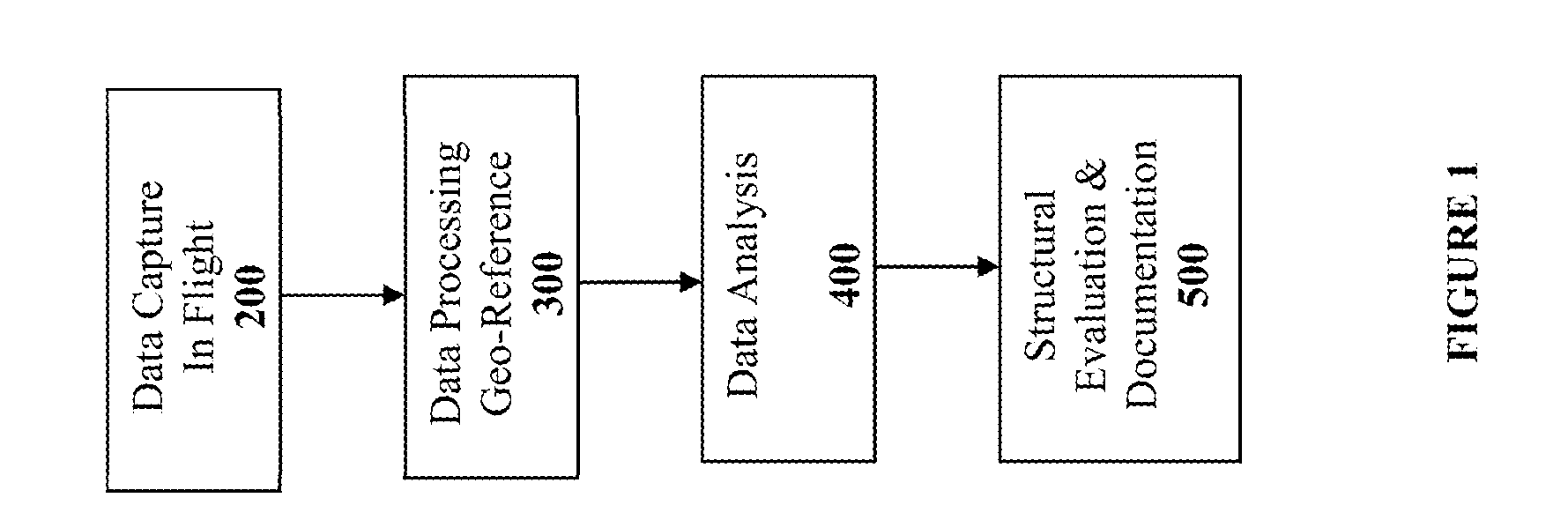
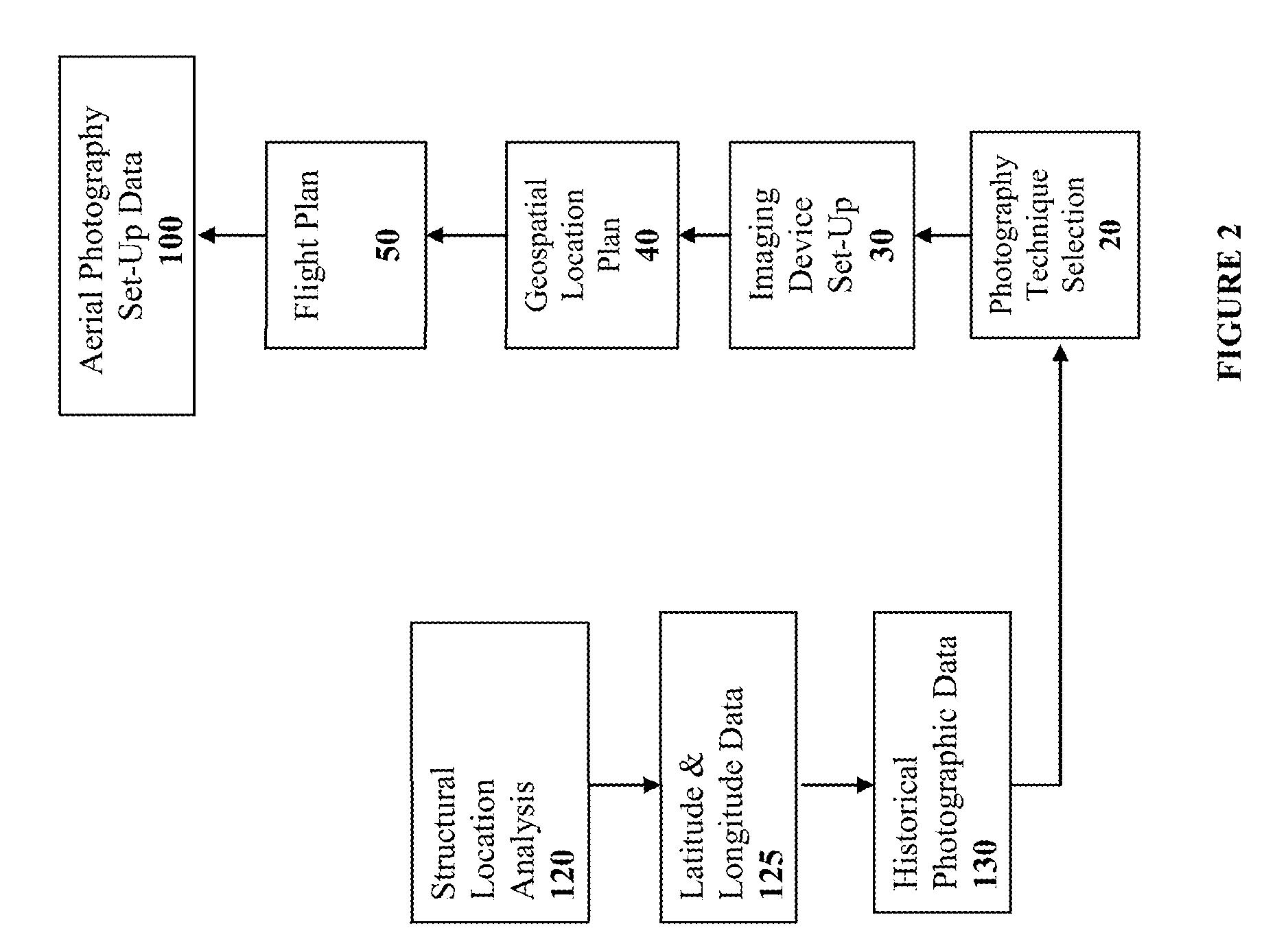
Method and System for Remotely Inspecting Bridges and Other Structures
ActiveUS20130216089A1Facilitating spatial integrationFacilitating automated damage detectionImage enhancementImage analysisJet aeroplaneOn board
Spatially Integrated Small-Format Aerial Photography (SFAP) is one aspect of the present invention. It is a low-cost solution for bridge surface imaging and is proposed as a remote bridge inspection technique to supplement current bridge visual inspection. Providing top-down views, the airplanes flying at about 1000 feet can allow visualization of sub-inch (large) cracks and joint openings on bridge decks or highway pavements. On board Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to help geo-reference images collected and facilitate damage detection. Image analysis is performed to identify structural defects such as cracking. A deck condition rating technique based on large crack detection is used to quantify the condition of the existing bridge decks.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
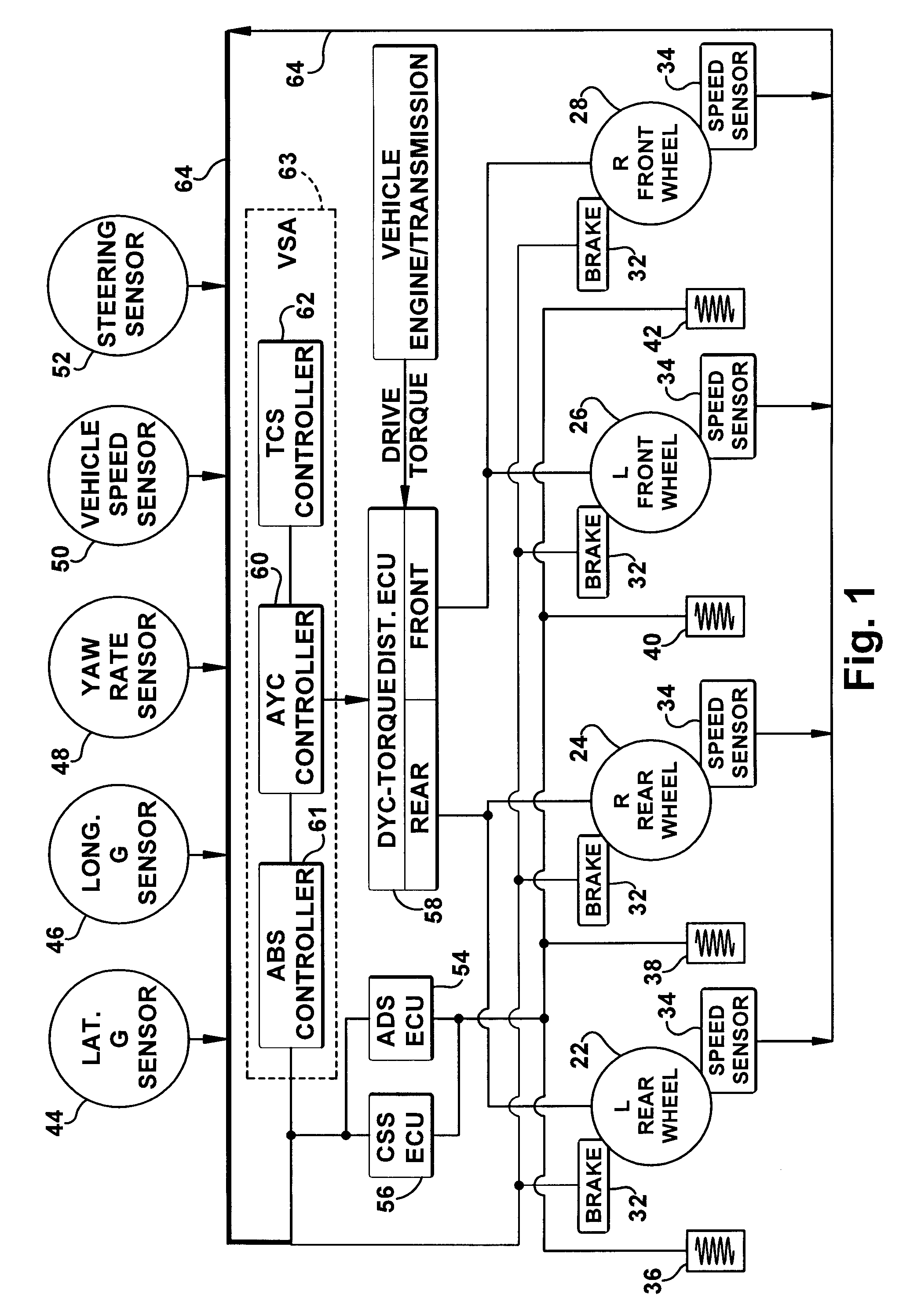
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
InactiveUS20080183353A1Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemTraction control system
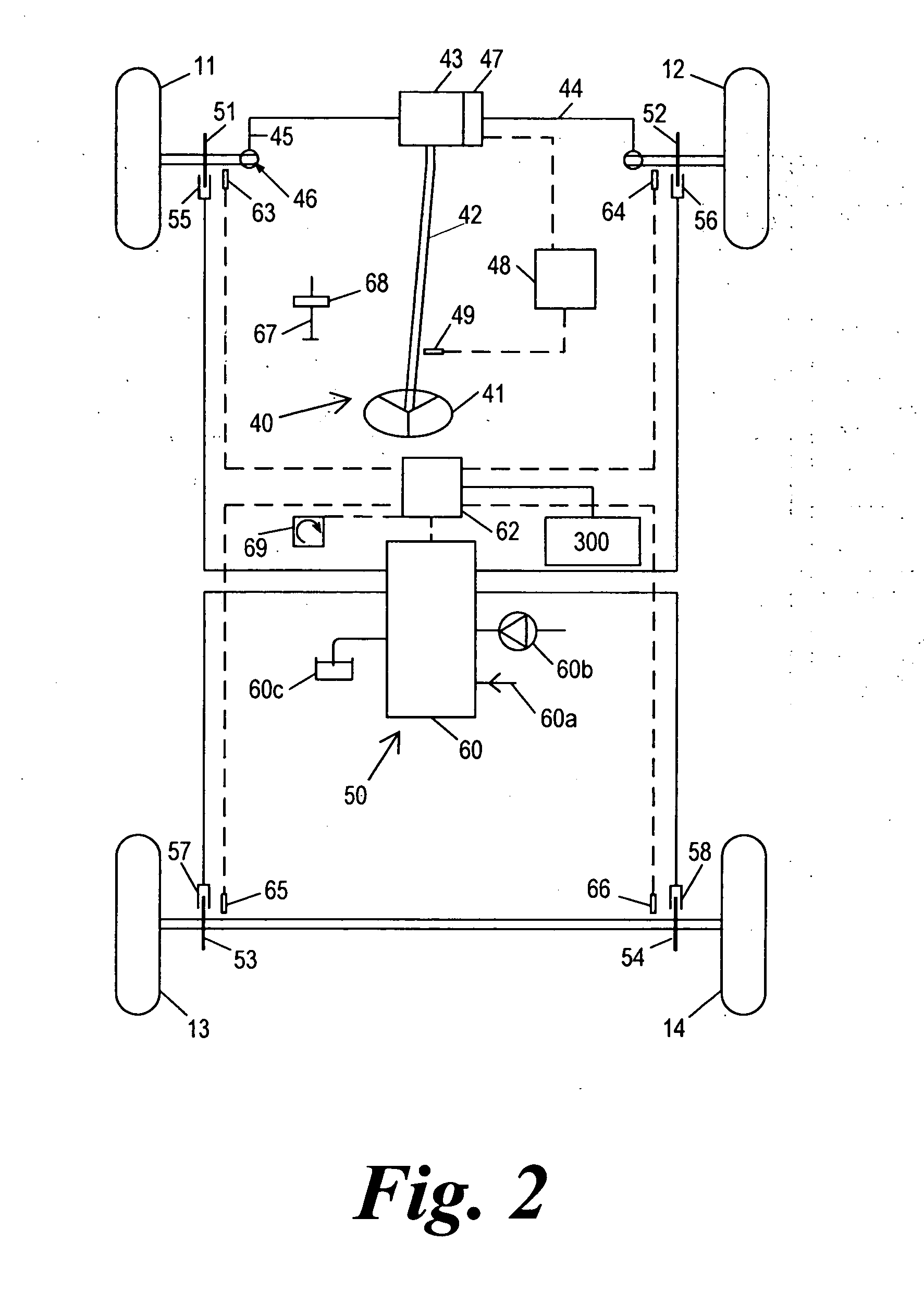
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle classification and axle counting sensor system and method
InactiveUS20020140924A1Accurately determinedAccurate detectionOptical rangefindersDetection of traffic movementRoad surfaceVehicle detection
A vehicle detection and classification sensor provides accurate 3D profiling and classification of highway vehicles for speeds up to 100 mph. A scanning time-of-flight laser rangefinder is used to measure the distance to the highway from a fixed point above the road surface and then measure the distance to the surfaces of any vehicle that is viewed by the sensor. The beam is pulsed at a high repetition rate for determining vehicle speeds with a high accuracy and uses the calculated speed and consecutive range measurements as the vehicle moves past the sensor to develop a three-dimensional profile of the vehicle. An algorithm is applied to the three-dimensional profile for providing a vehicle-classification. A laser is also used to count the number of axles associated with the vehicle.
Owner:WANGLER RICHARD J +3
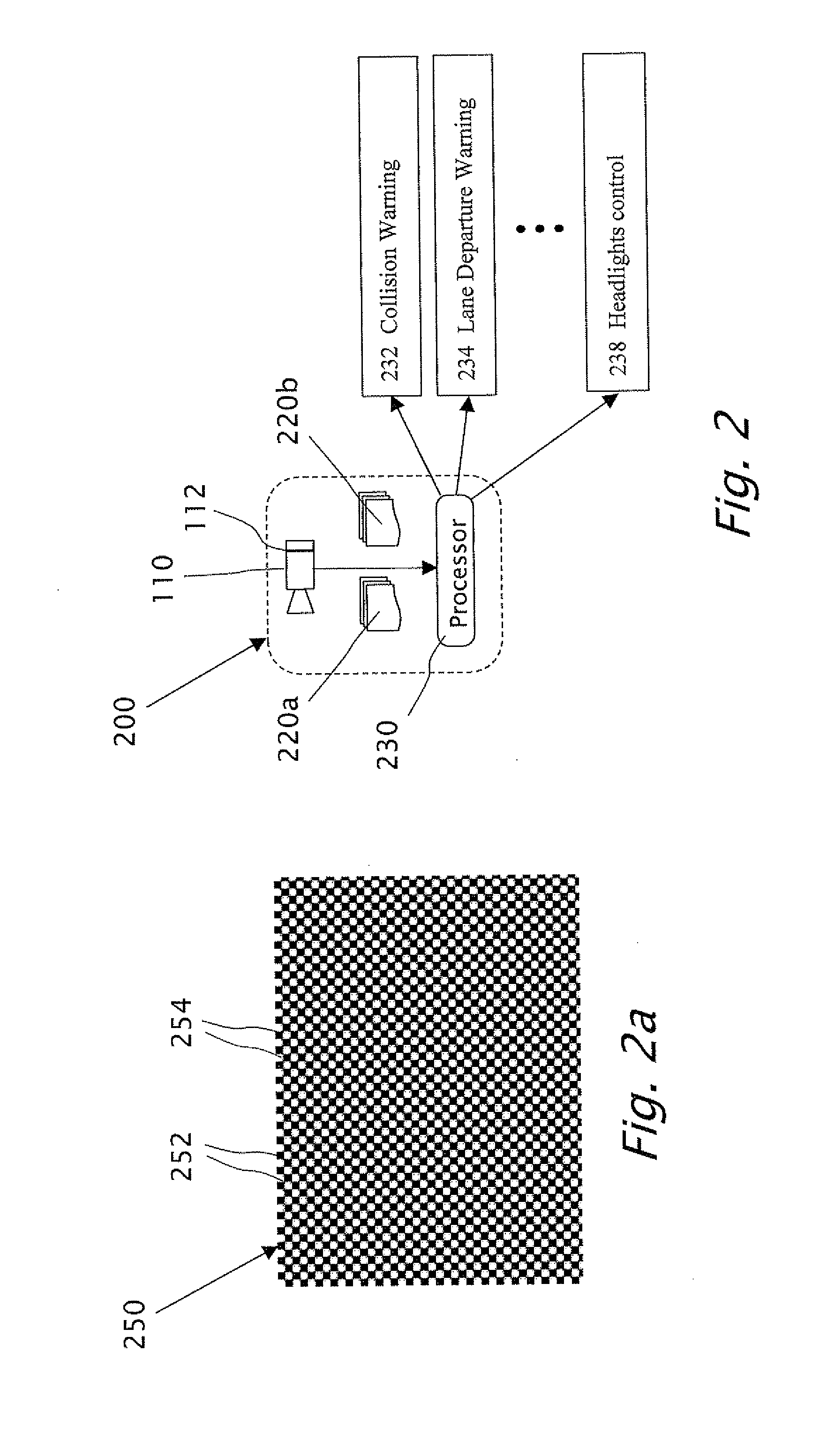
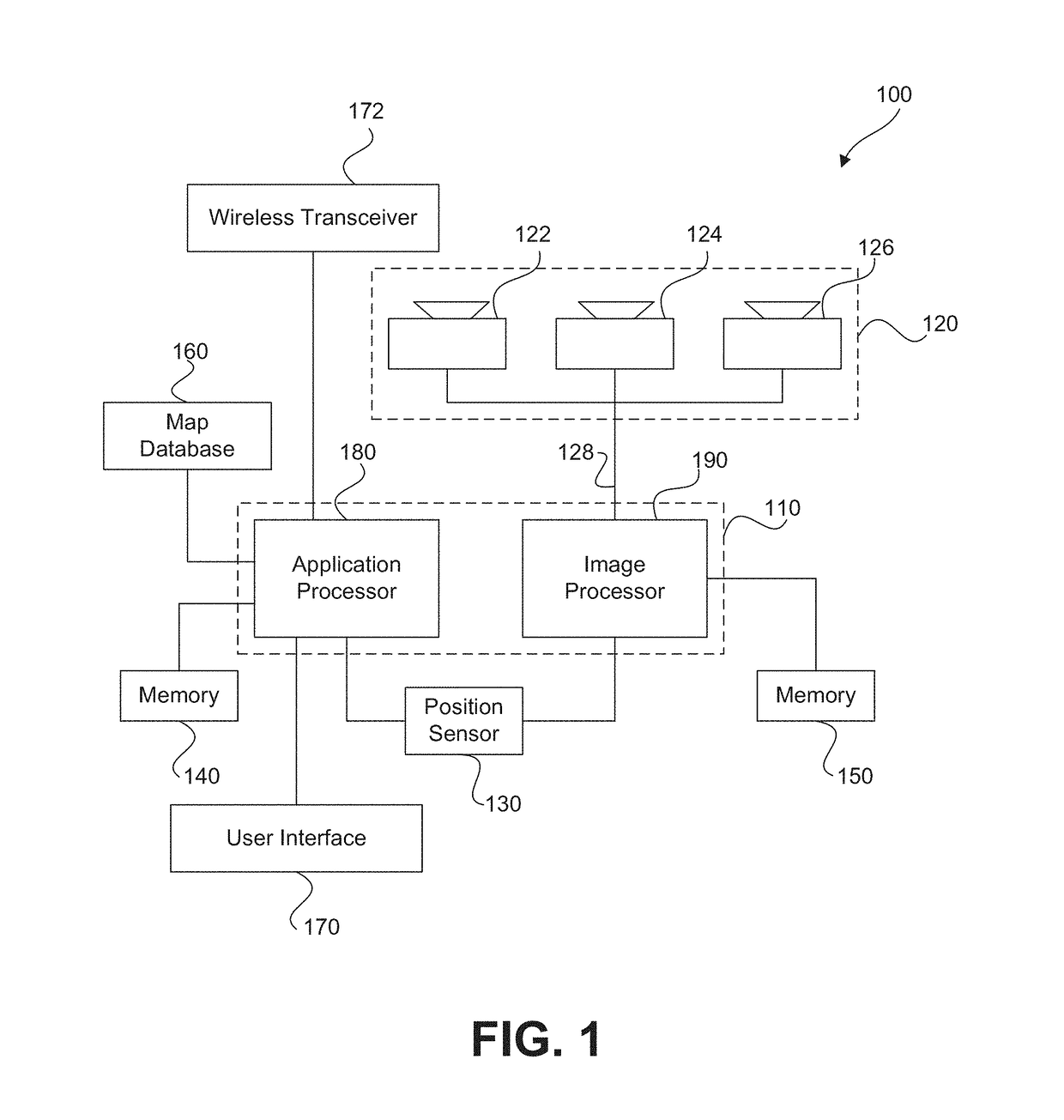
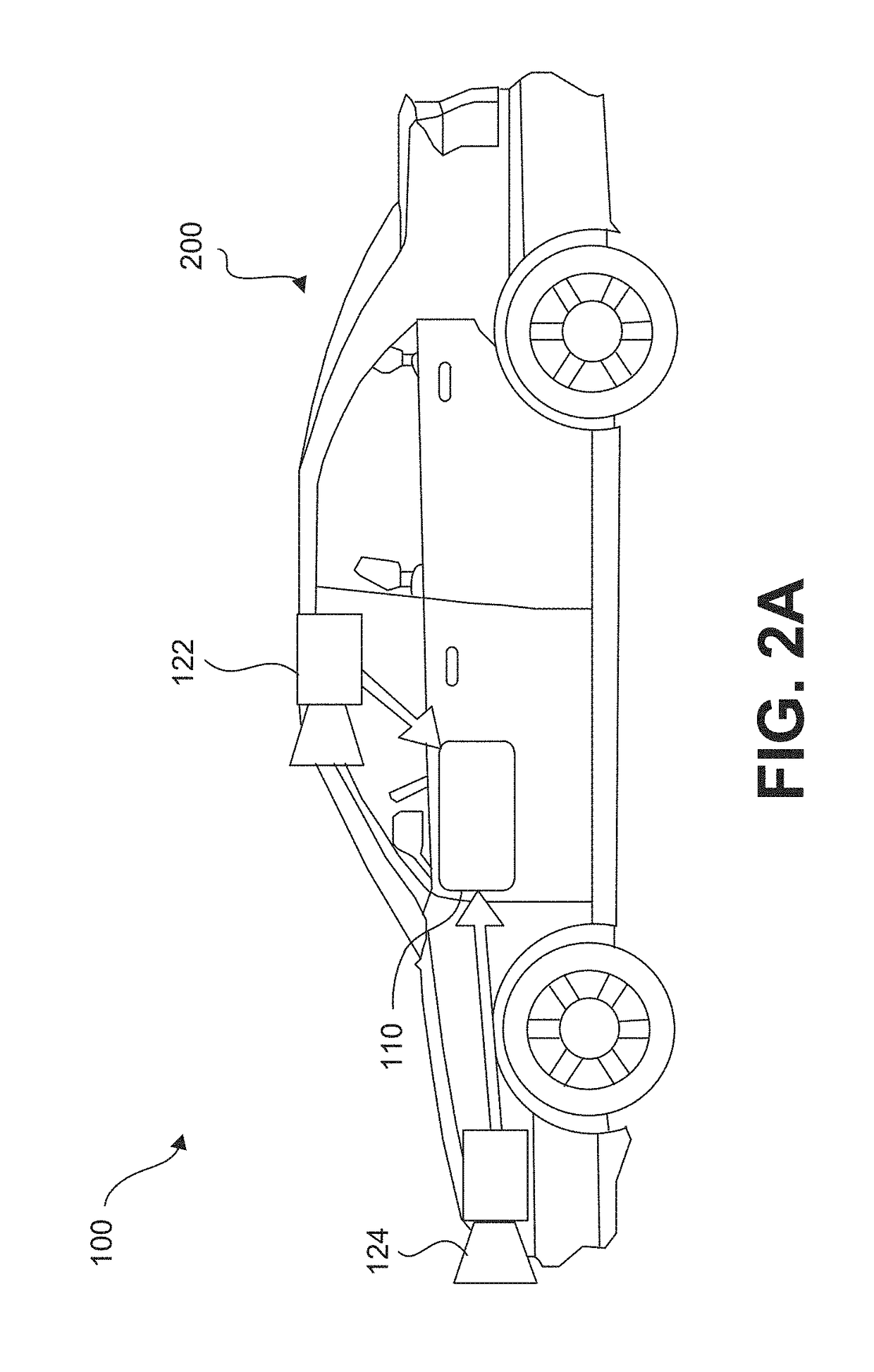
Symmetric filter patterns for enhanced performance of single and concurrent driver assistance applications
InactiveUS20080043099A1Avoid saturationReduce intensityVehicle headlampsRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorReal time analysis
A system mounted on a vehicle for performing vehicle control applications and driver warning applications, the system including a camera configured to acquire a plurality of images of the environment in front of the camera. The camera includes a filter wherein the filter is installed at the focal plane of the camera and wherein designated portions of the filter transmit selective light wavelength. The preferred filter has a checkerboard pattern. The system further including an image processor capable of analyzing in real time a plurality of respective image sequences acquired from at least one of the portions of the filter and is capable of detecting yellow lane markings on a concrete road surface.
Owner:MOBILEYE TECH
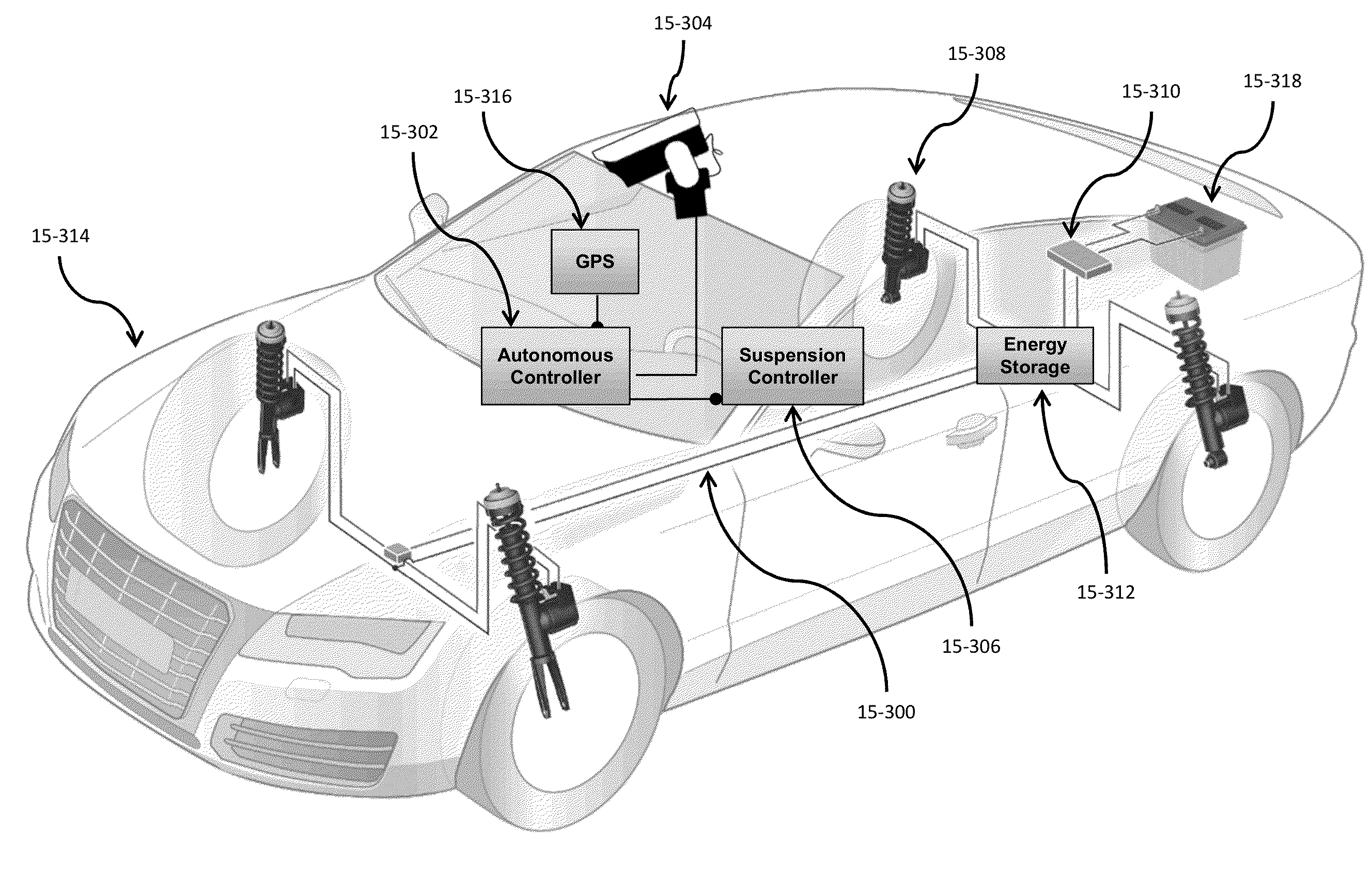
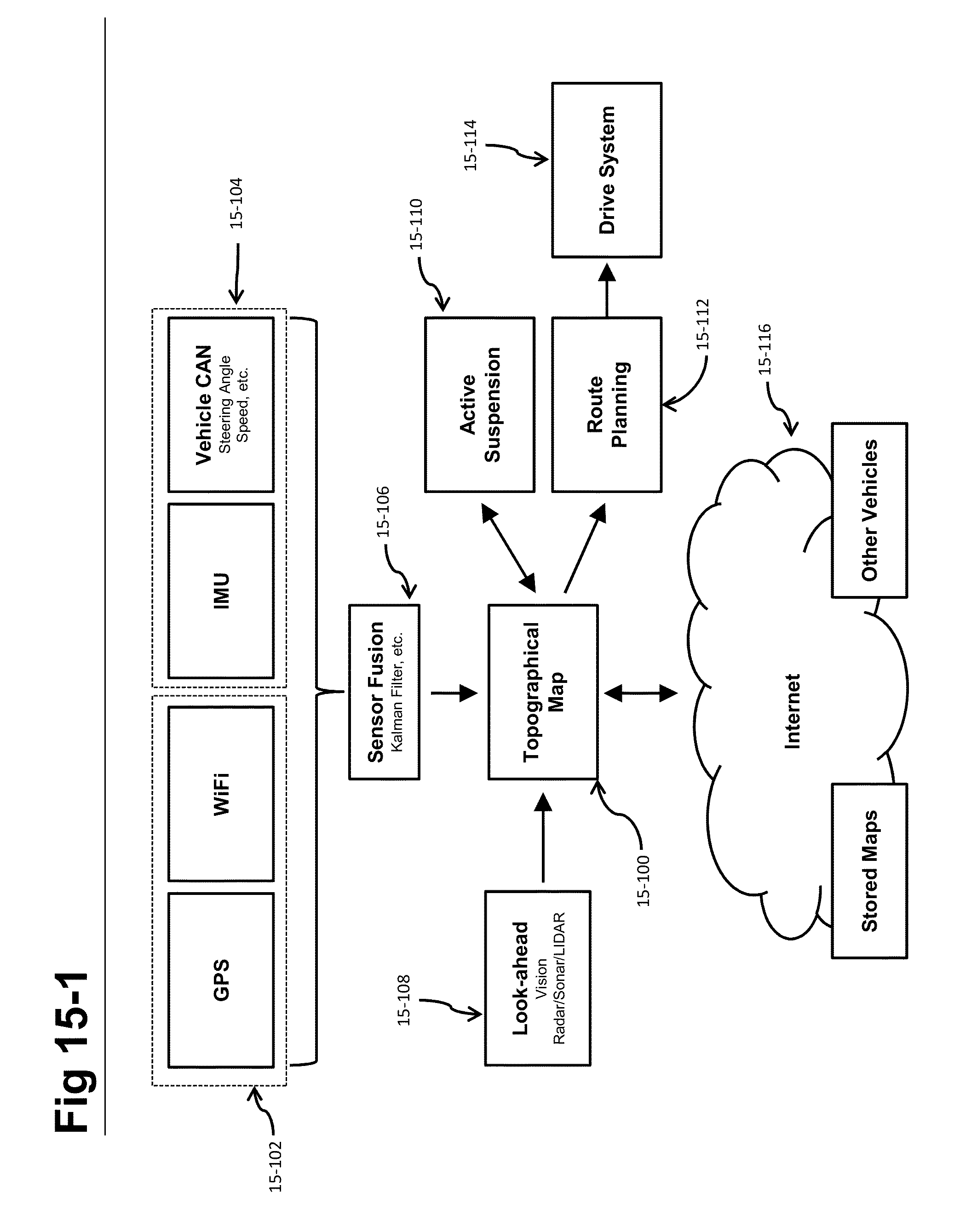
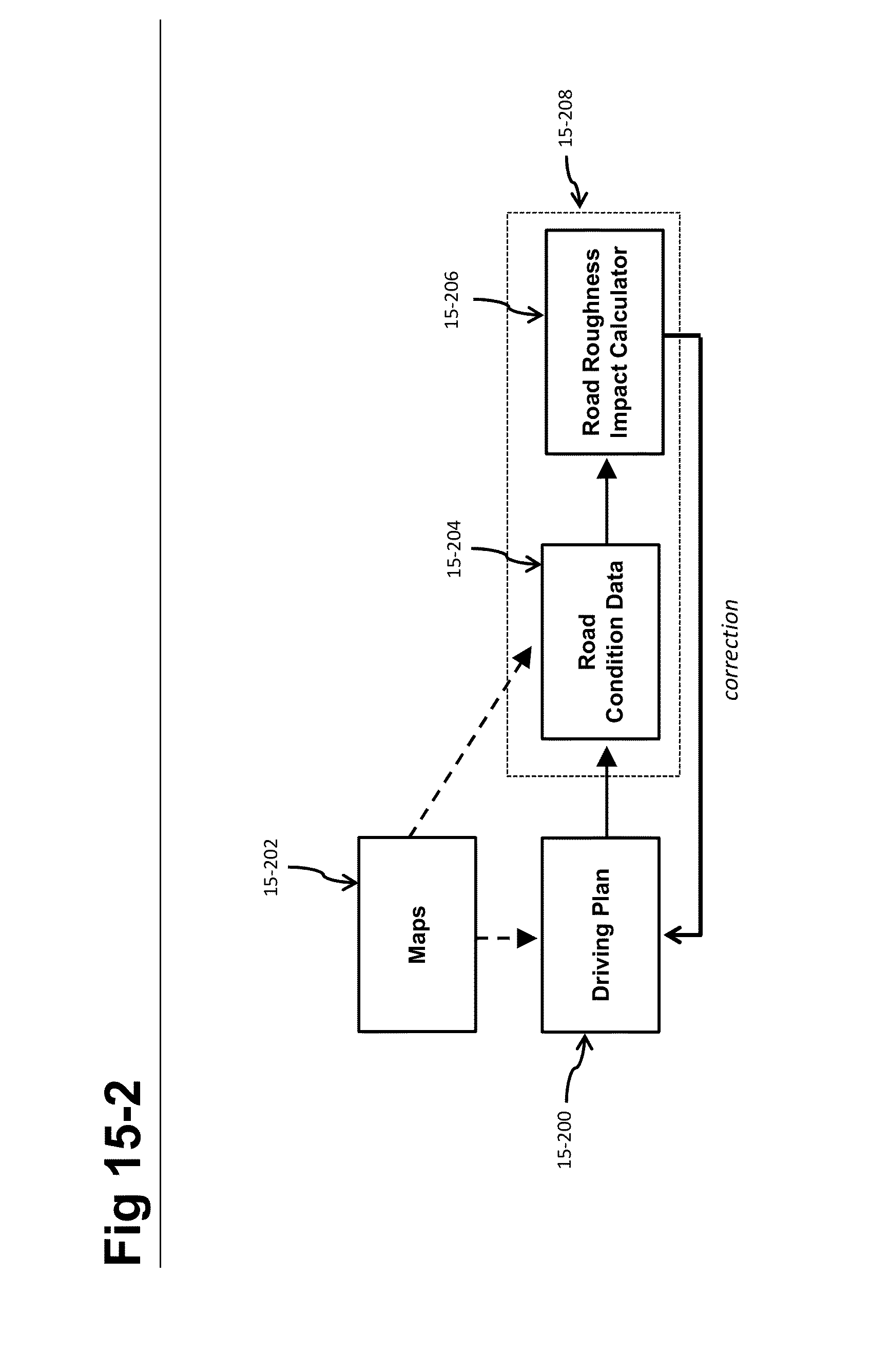
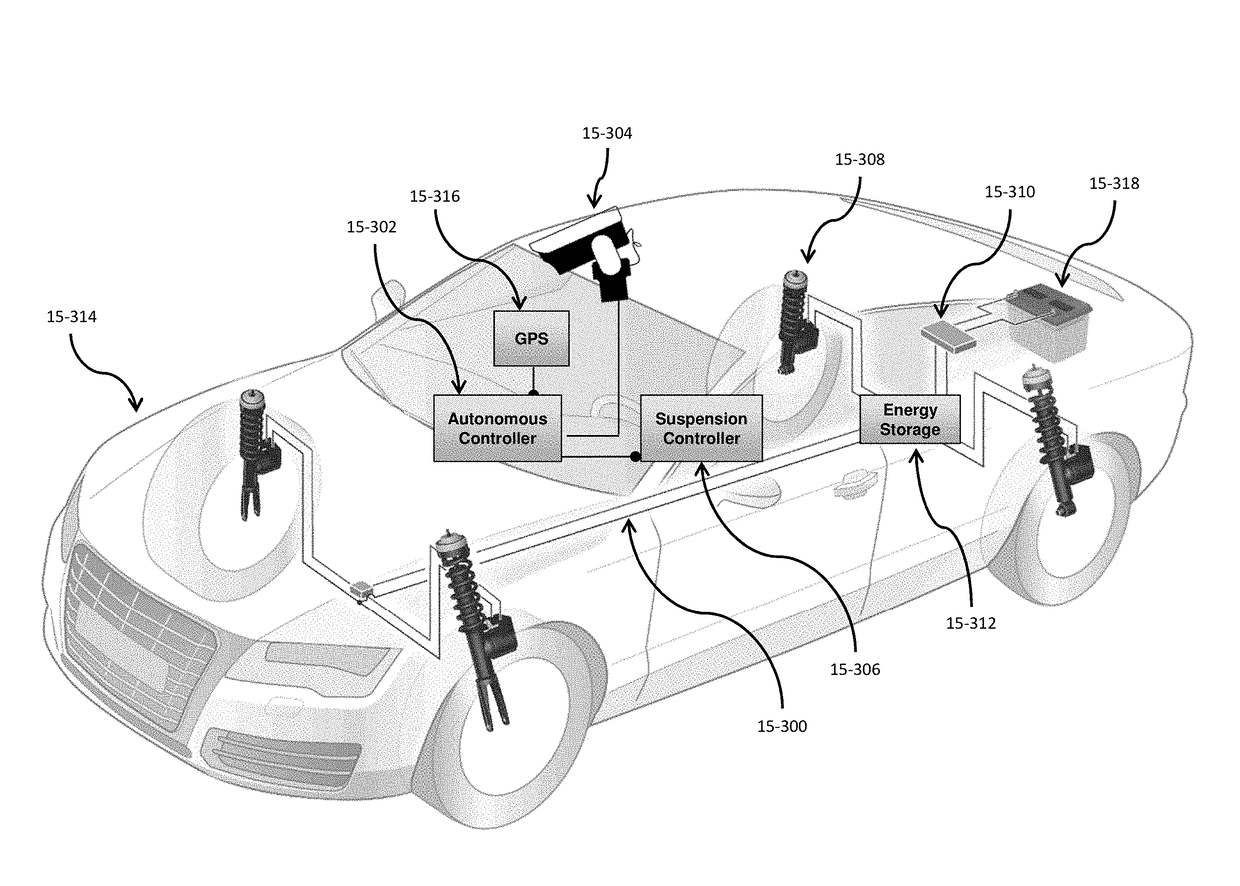
Self-driving vehicle with integrated active suspension
InactiveUS20140297116A1Improve ride comfort performanceActive suspension technologiesDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesRoad surfaceEngineering
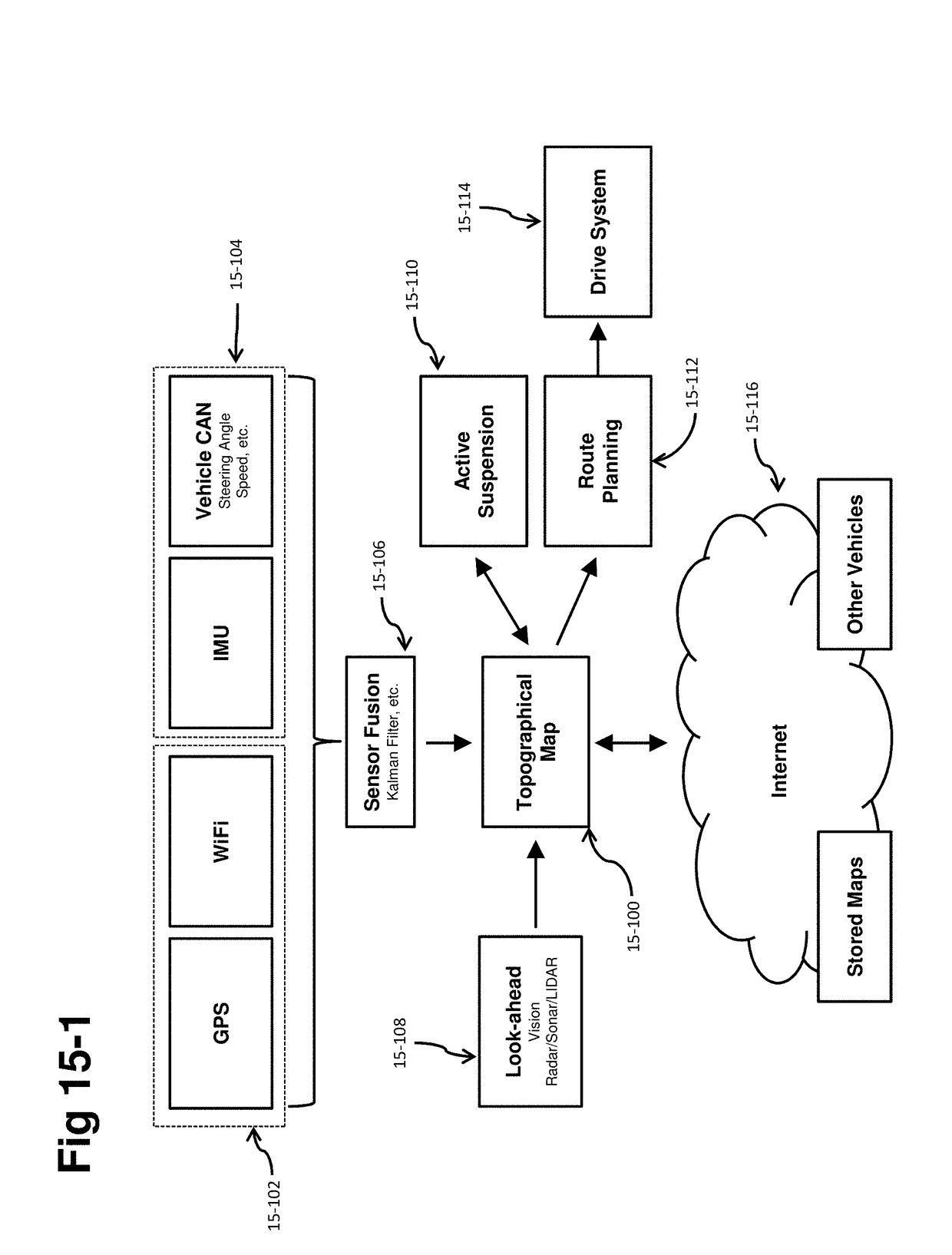
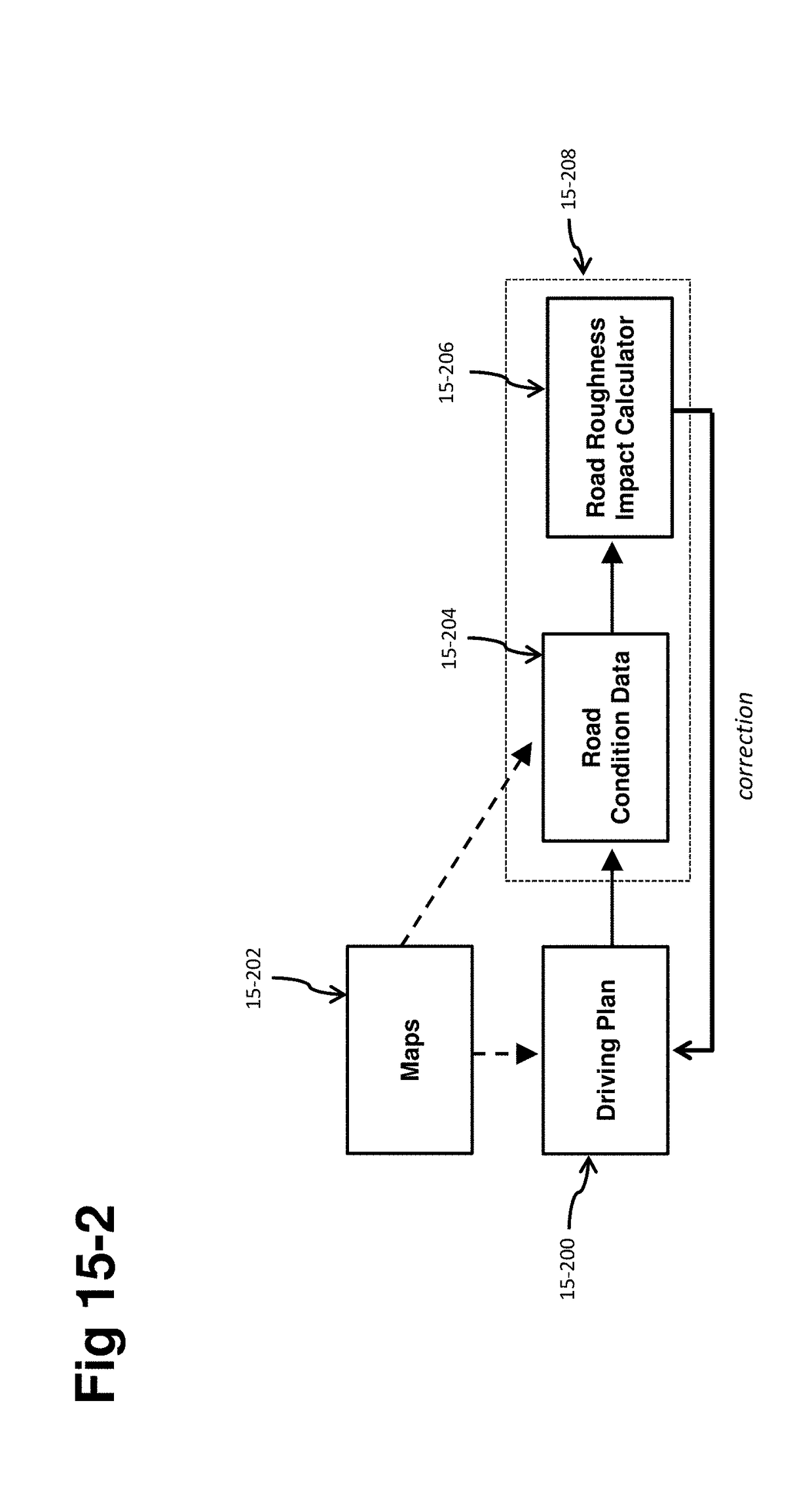
A self-driving vehicle with an integrated fully-active suspension system. The fully-active suspension utilizes data from one or more sensors used for autonomous driving (e.g. vision, LIDAR, GPS) in order to anticipate road conditions in advance. The system builds a topographical map of the road surface. Suspension and road data is delivered back to the vehicle in order to change autonomous driving behavior including route planning. Energy storage is regulated based on a planned route. Forward and lateral acceleration feel is mitigated through active pitch and tilt compensation. The fully-active suspension pushes and pulls the suspension in three or more operational quadrants in order to deliver superior ride comfort, handling, and / safety of the vehicle.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
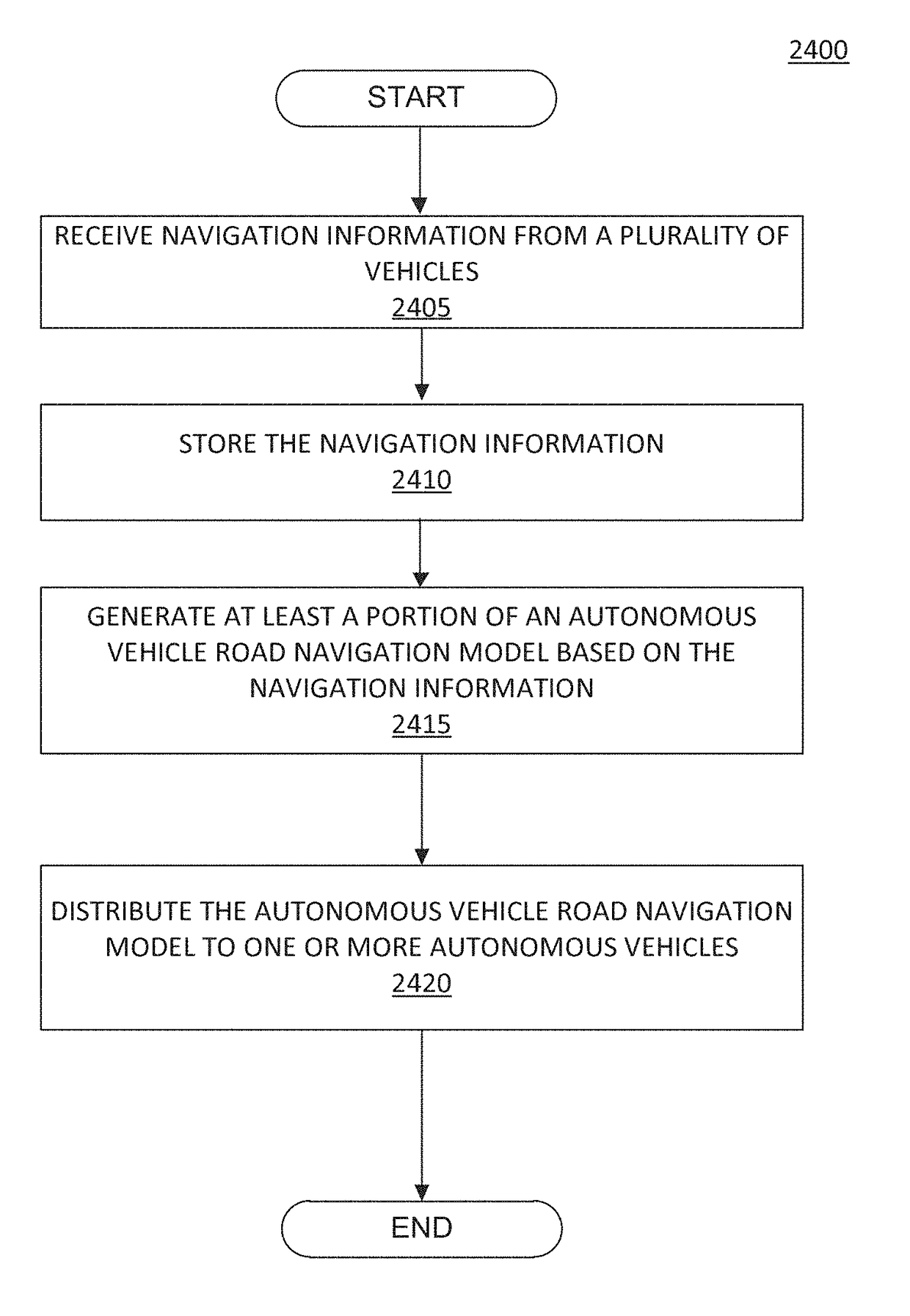
Unmanned vehicle navigation driving method based on cloud database
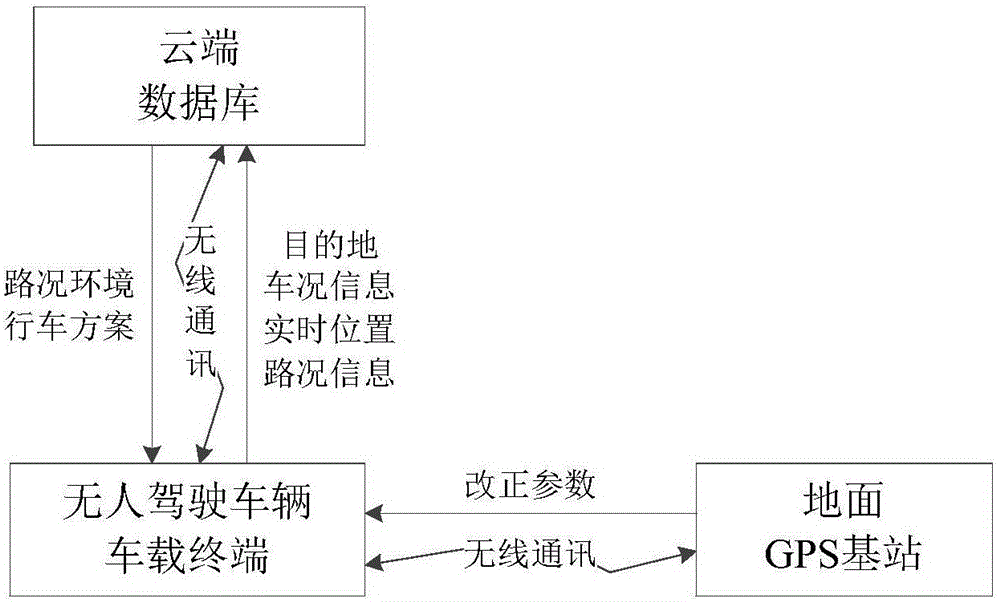
ActiveCN105741595AImprove driving efficiencyImprove driving safetyDetection of traffic movementPosition/course control in two dimensionsRoad surfaceBase station
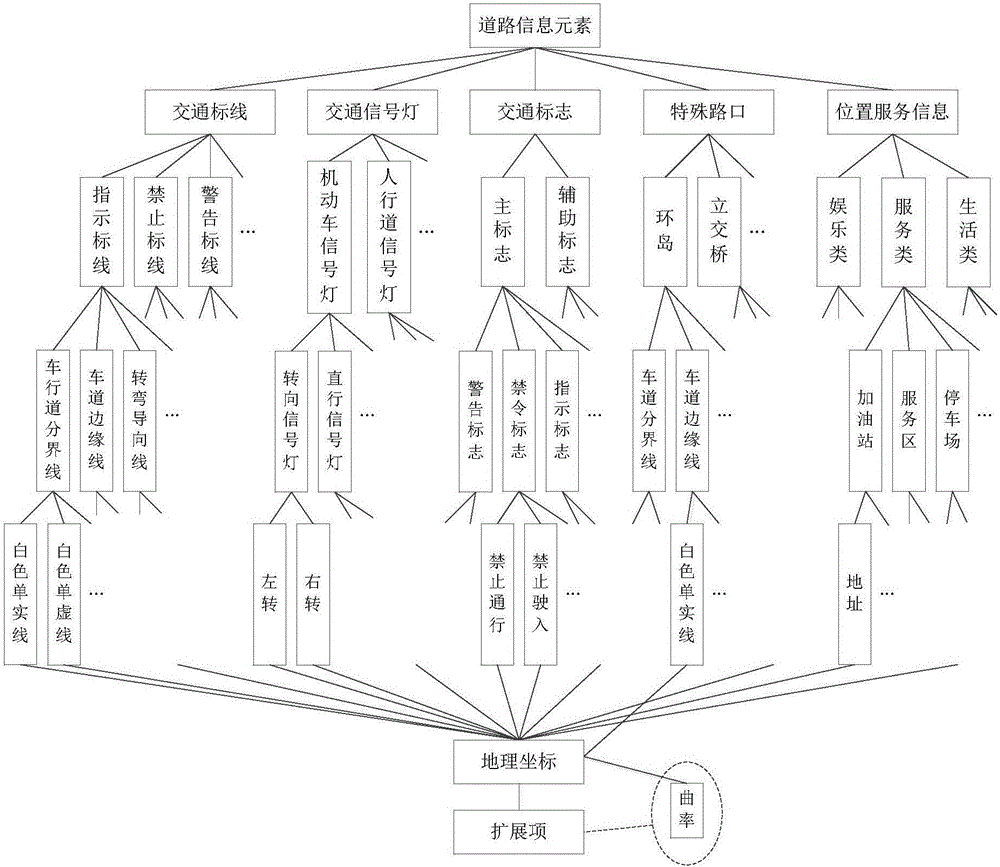
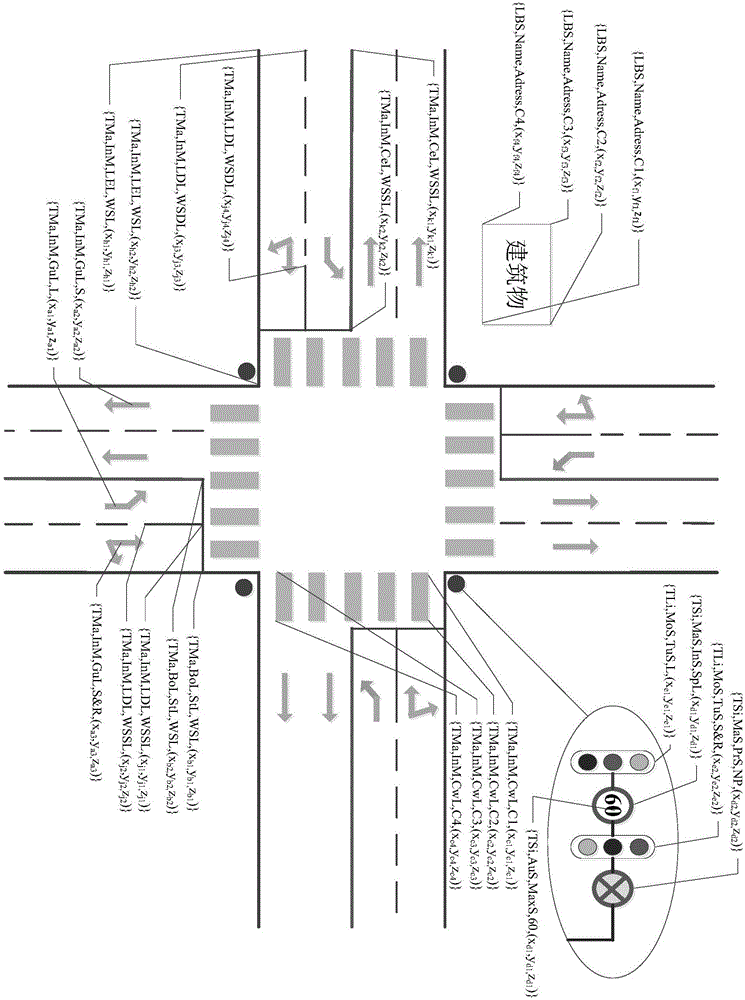
The invention provides an unmanned vehicle navigation driving method based on a cloud server. A device according to the method comprises three modules, namely the cloud database, an on-vehicle terminal and a ground GPS base station. In the unmanned vehicle, a destination is input through the on-vehicle terminal of the vehicle. Furthermore the destination information, position information and vehicle condition information of the vehicle are transmitted to the cloud database. The cloud database integrates all related information for performing calculation planning, and transmits an optimal driving plan to a vehicle system for execution by a vehicle control system. Furthermore, surrounding environment information is acquired in real time in vehicle driving and is uploaded to the cloud database, thereby realizing real-time synchronous updating of the cloud database and ensuring high reliability and high real-time performance of cloud data. The unmanned vehicle navigation driving method can supply detailed map information for the vehicle on special conditions of rainy or snowy weather, insufficient light at night, covered road surface or covered sign plate, etc.
Owner:ORDOS CITY PUDU TECH CO LTD
Linear lighting system
InactiveUS20090207602A1Prevent escapeNon-electric lightingMechanical apparatusLight equipmentLinear matrix
A linear light system, and a linear luminaire used in the system, for lighting a traffic surface. The linear luminaire has a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) disposed in a linear matrix along the length of the traffic surface, and a plurality of refractive lenses for directing the emitted light from the LEDs at the traffic surface. The traffic surface is typically the roadway of a tunnel. A refractor lens is used to direct the emitted light from the LEDs predominantly toward at least the traffic surface.
Owner:LSI INDS
Vehicle control method and apparatus
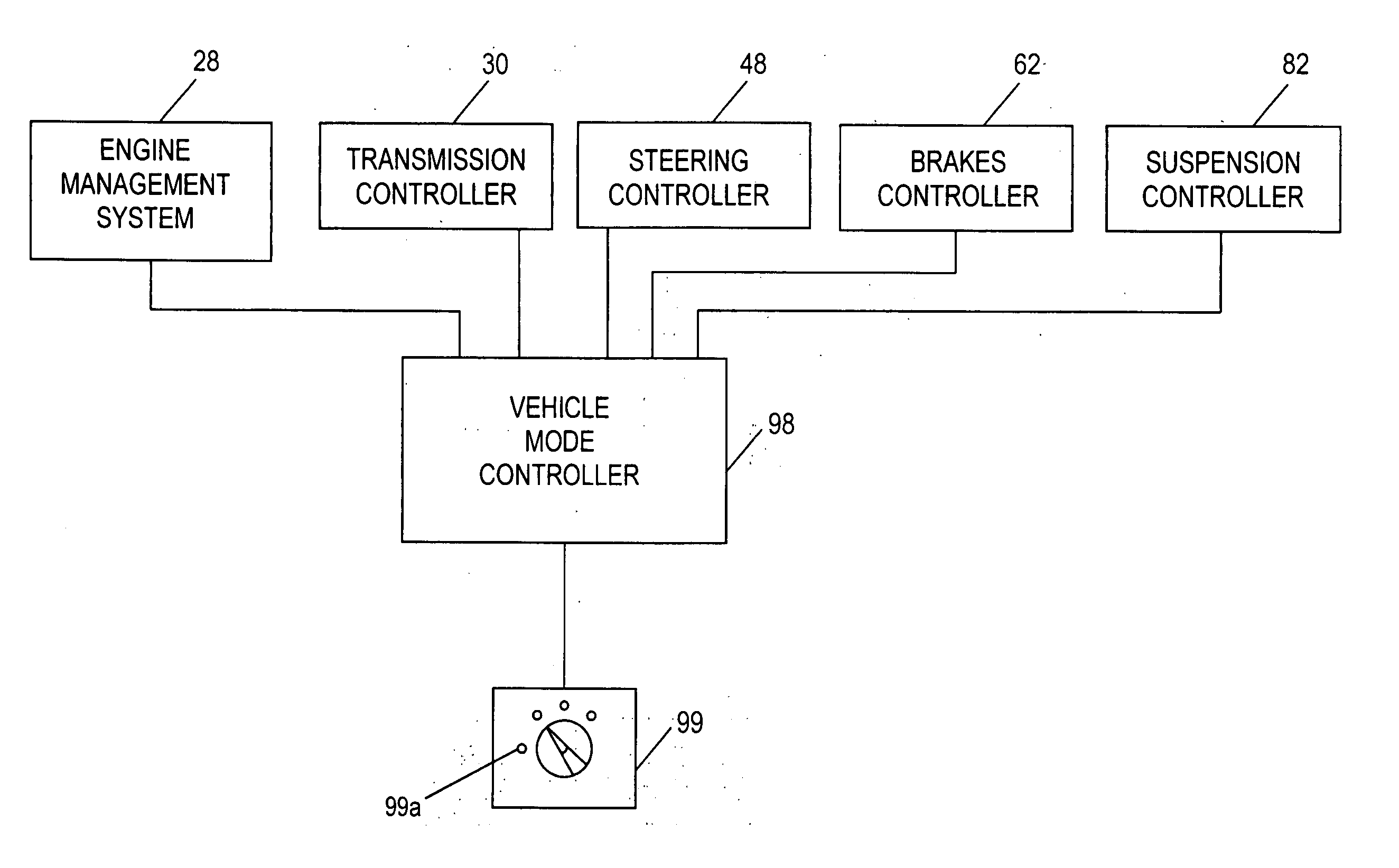
ActiveUS20050004732A1Minimizes combinationMaximize controlVehicle body stabilisationDigital data processing detailsTerrainMode control
A vehicle mode controller, a driving mode collecting means, and a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system, a transmission controller, a steering controller, a brakes controller and a suspension controller, provide an improved system and method of operating a vehicle control system in a host vehicle in a manner suitable for a respective driving surface in a plurality of different off-road surfaces and terrains such as might be encountered when driving off-road. An improved method is provided for controlling a vehicle control system by avoiding unplanned combinations of subsystem configuration modes and minimizing the transition time when changing between subsystem configuration modes.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Vehicle surroundings monitoring device, and image production method/program
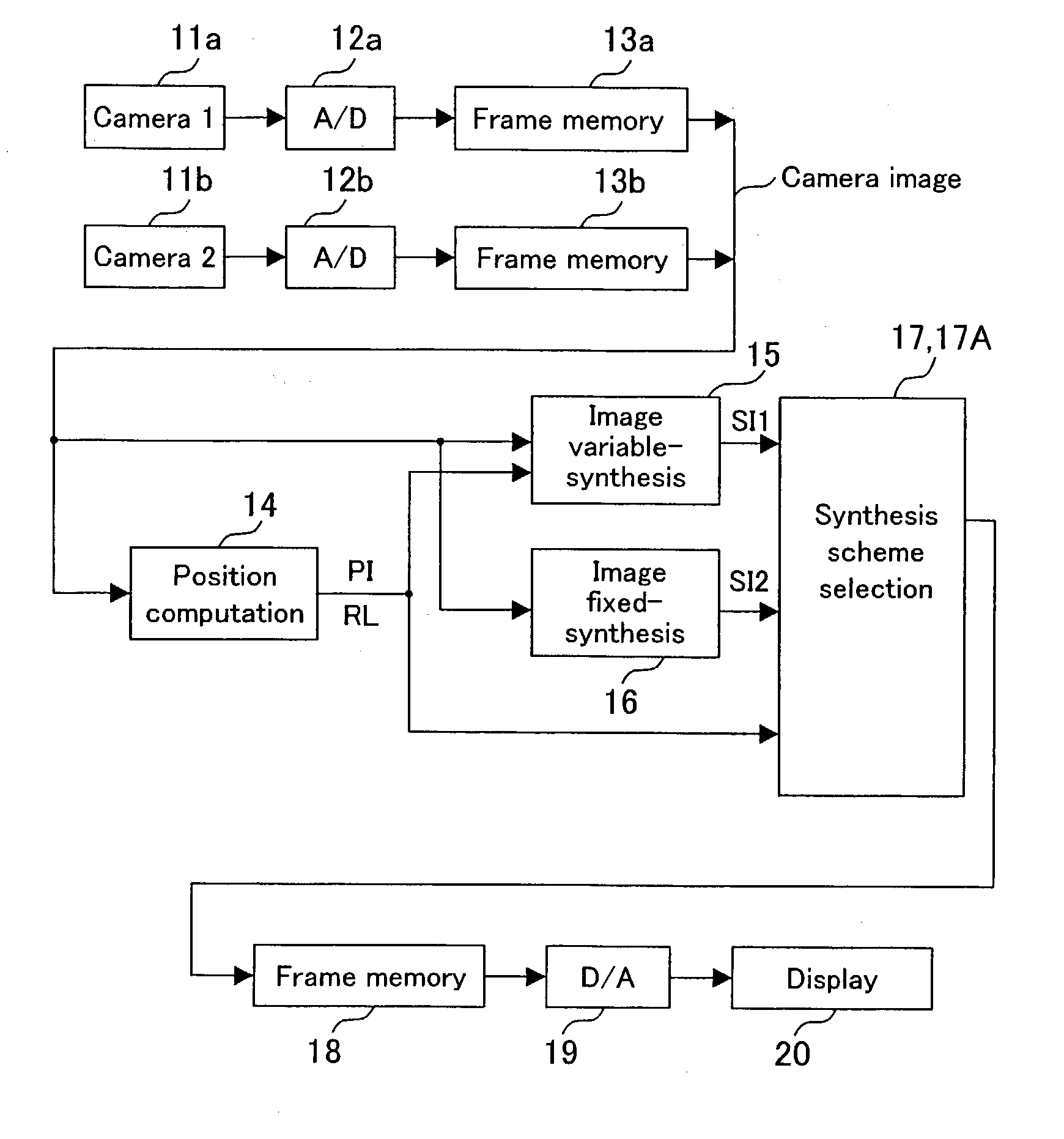
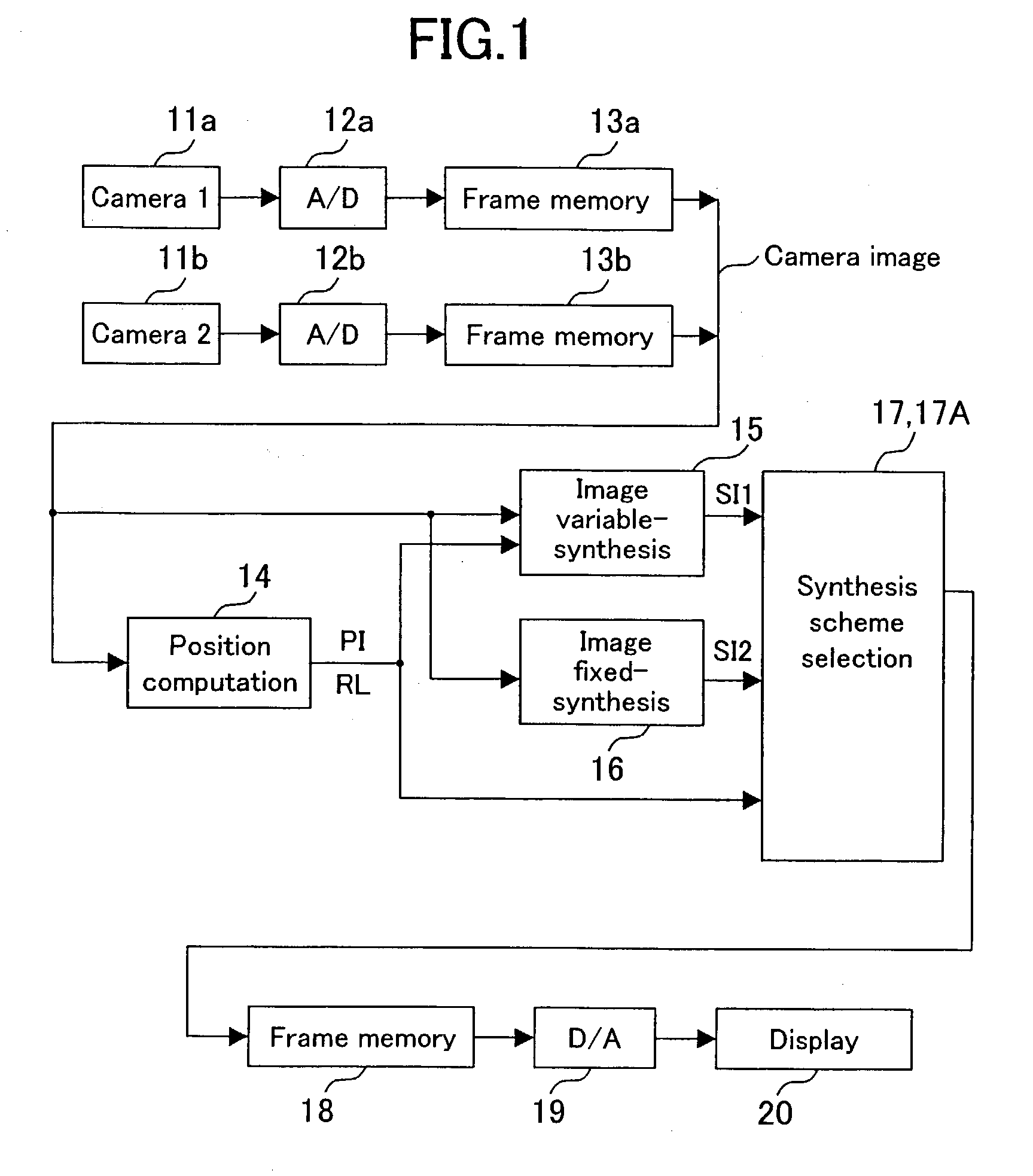
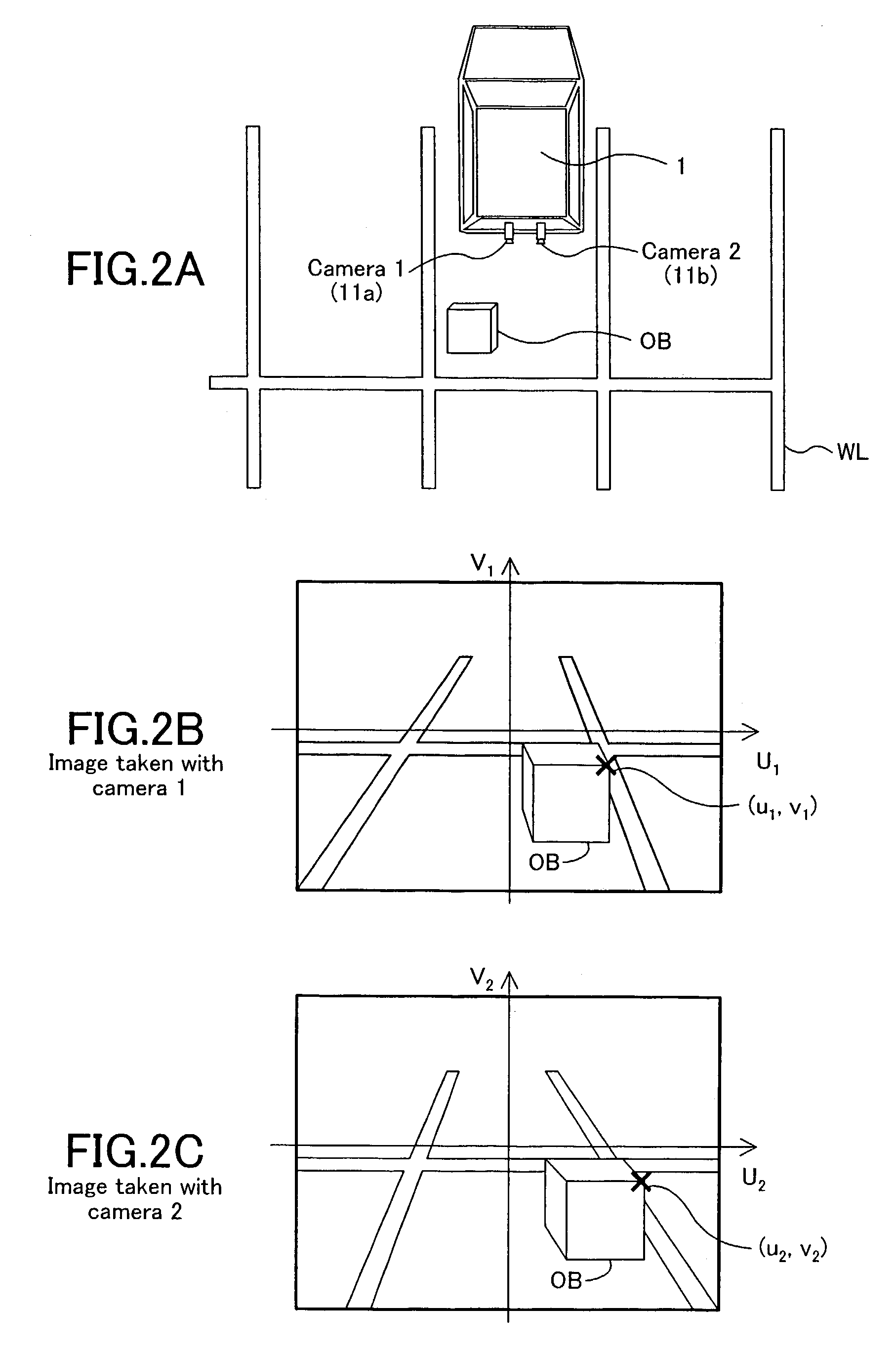
InactiveUS7110021B2Small distortionImage analysisPosition fixationCamera imageComputer graphics (images)
A synthesized image showing the situation around a vehicle is produced from images taken with cameras capturing the surroundings of the vehicle and presented to a display. A position computation section computes position information and the reliability of the position information, for a plurality of points in the camera images. An image variable-synthesis section produces a first synthesized image from the camera images using the position information. An image fixed-synthesis section produces a second synthesized image by road surface projection, for example, without use of the position information. A synthesis scheme selection section selects either one of the first and second synthesized images according to the reliability as the synthesized image to be presented.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of plasmon-enhanced properties of materials and applications thereof
InactiveUS20050164169A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyInfraredThermochromism
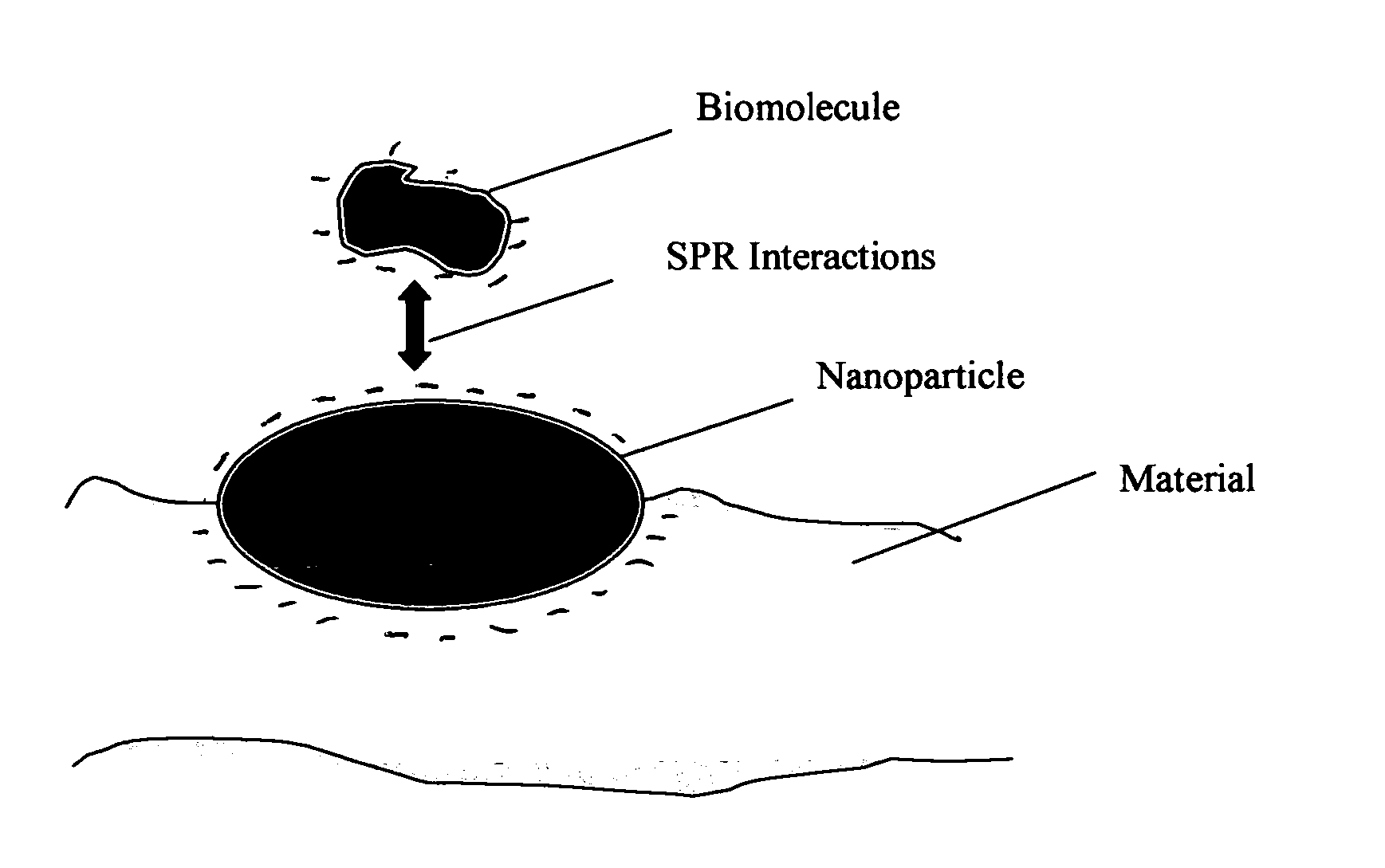
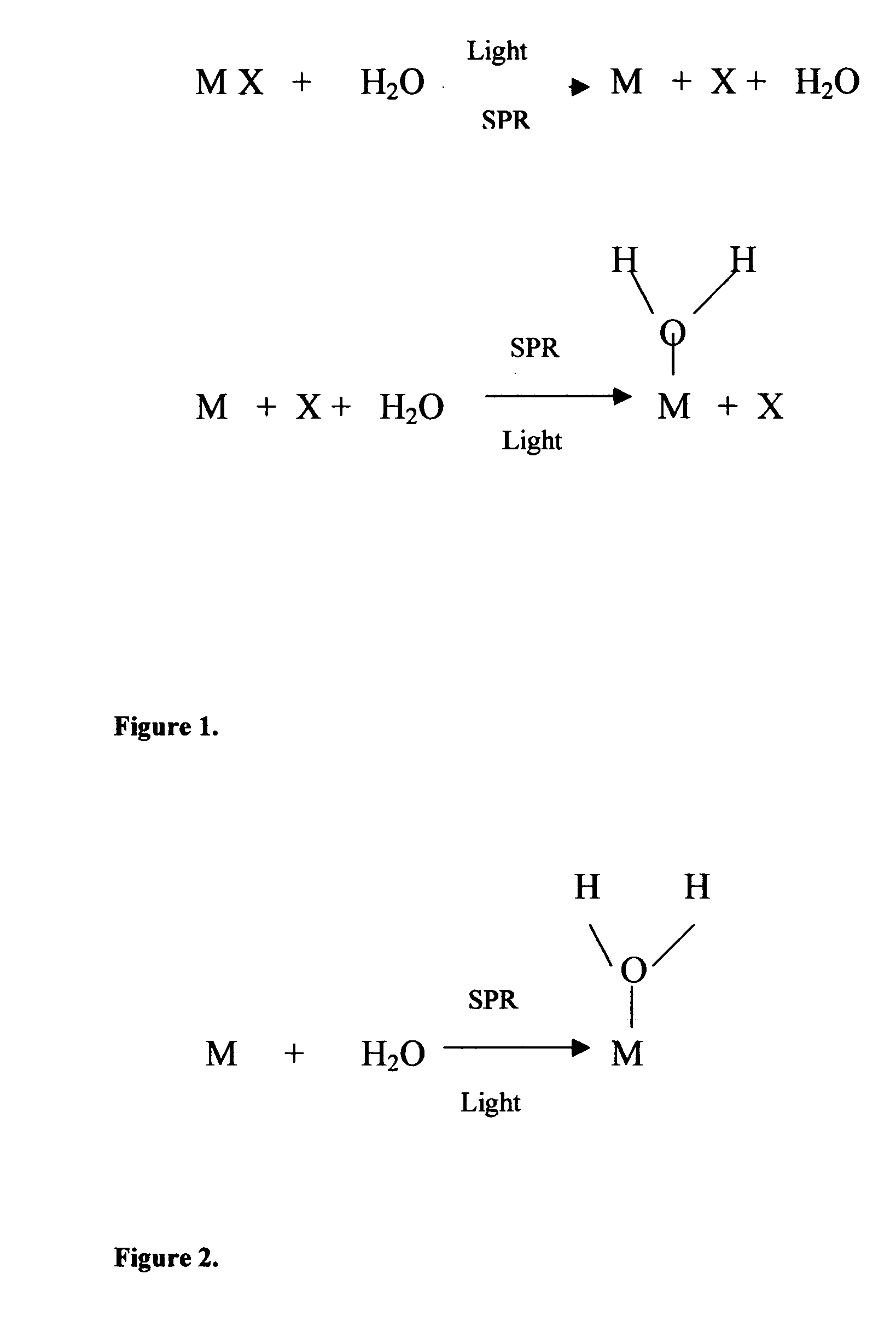
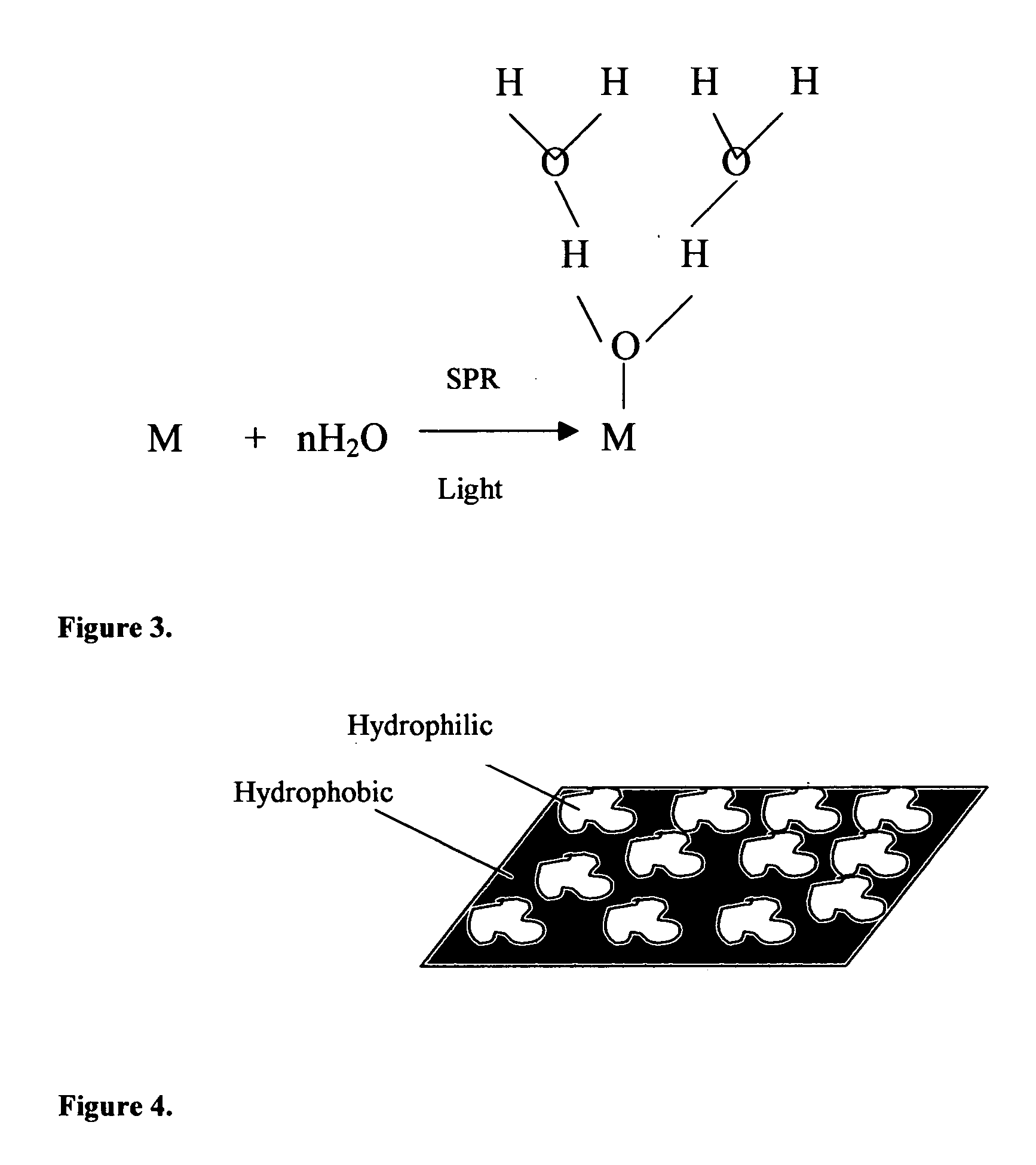
Methods and applications of surface plasmon resonance-enhanced antibacterial, anti-adhere, adhere, catalytic, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, spectral change, biological and chemical decomposition properties of materials with embedded nanoparticles are disclosed. A method of the nonlinear generation of surface plasmon resonance enables the use of light with wavelengths from X-Ray to IR to enhance properties of materials by several orders of magnitude. The nanoparticle size is crucial for the enhancement and their size is considered to be in the proposed methods and applications within a range of 0.1 nm to 200,000 nm. The nanoparticles preferably are made of noble metals and / or semiconductor oxides. The invention describes a very broad spectrum of applications of surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of materials with embedded nanoparticles, from environmental cleanup by road pavement and construction materials, self-cleaning processes of surface materials, thermochromic effects on heat blocking materials, corrosion preventing paint, to sanitization by antibacterial textile fabrics, filters, personal clothing, contact lenses and medical devices.
Owner:SPR ADVANCED TECH INC
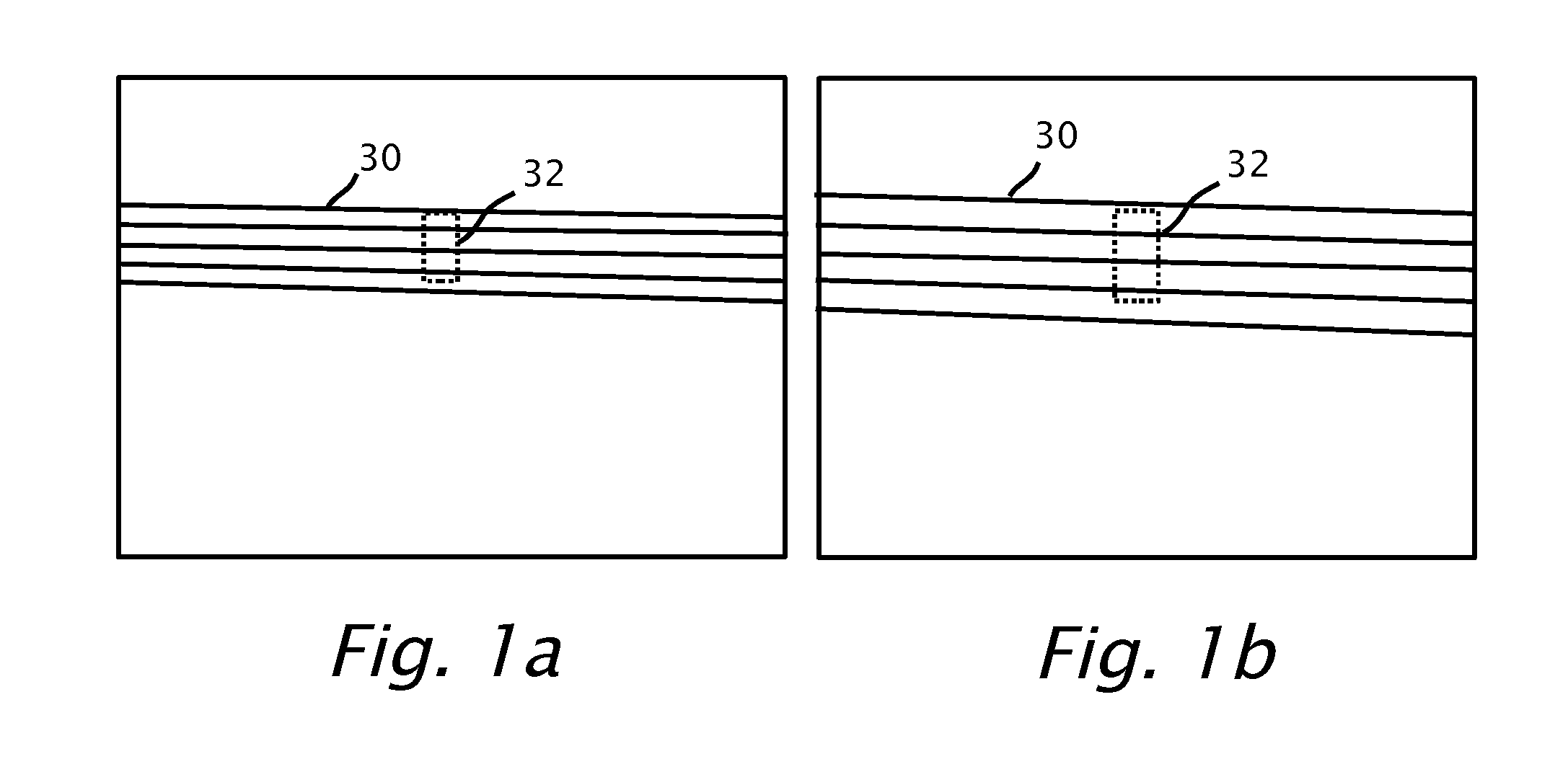
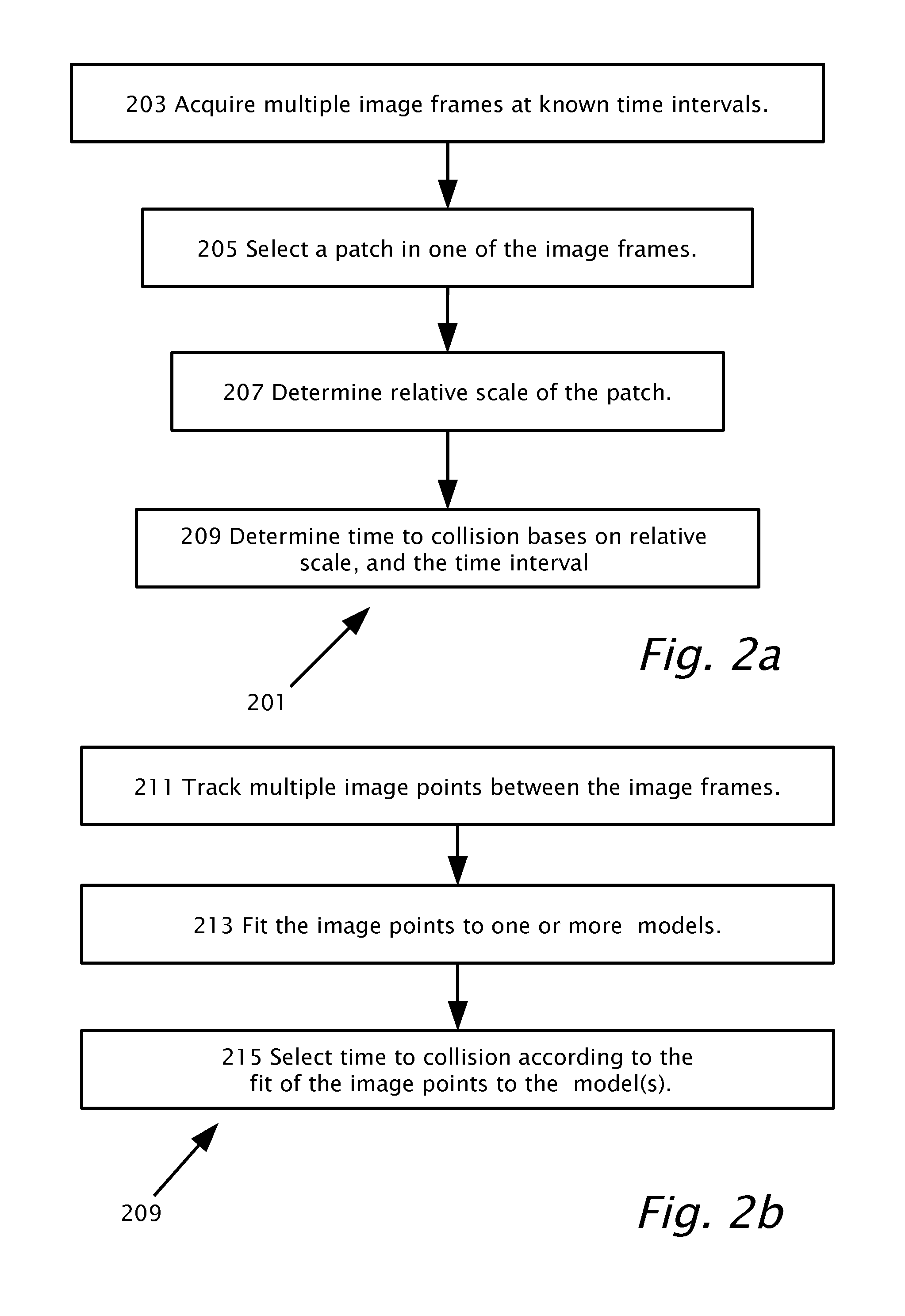
Forward collision warning trap and pedestrian advanced warning system
A method for providing a forward collision warning using a camera mountable in a motor vehicle. The method acquires multiple image frames at known time intervals. A patch may be selected in at least one of the image frames. Optical flow may be tracked between the image frames of multiple image points of the patch. Based on the fit of the image points to a model, a time-to collision (TTC) may be determined if a collision is expected. The image points may be fit to a road surface model and a portion of the image points is modeled to be imaged from a road surface. A collision is not expected based on the fir of the image points to the road surface model.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
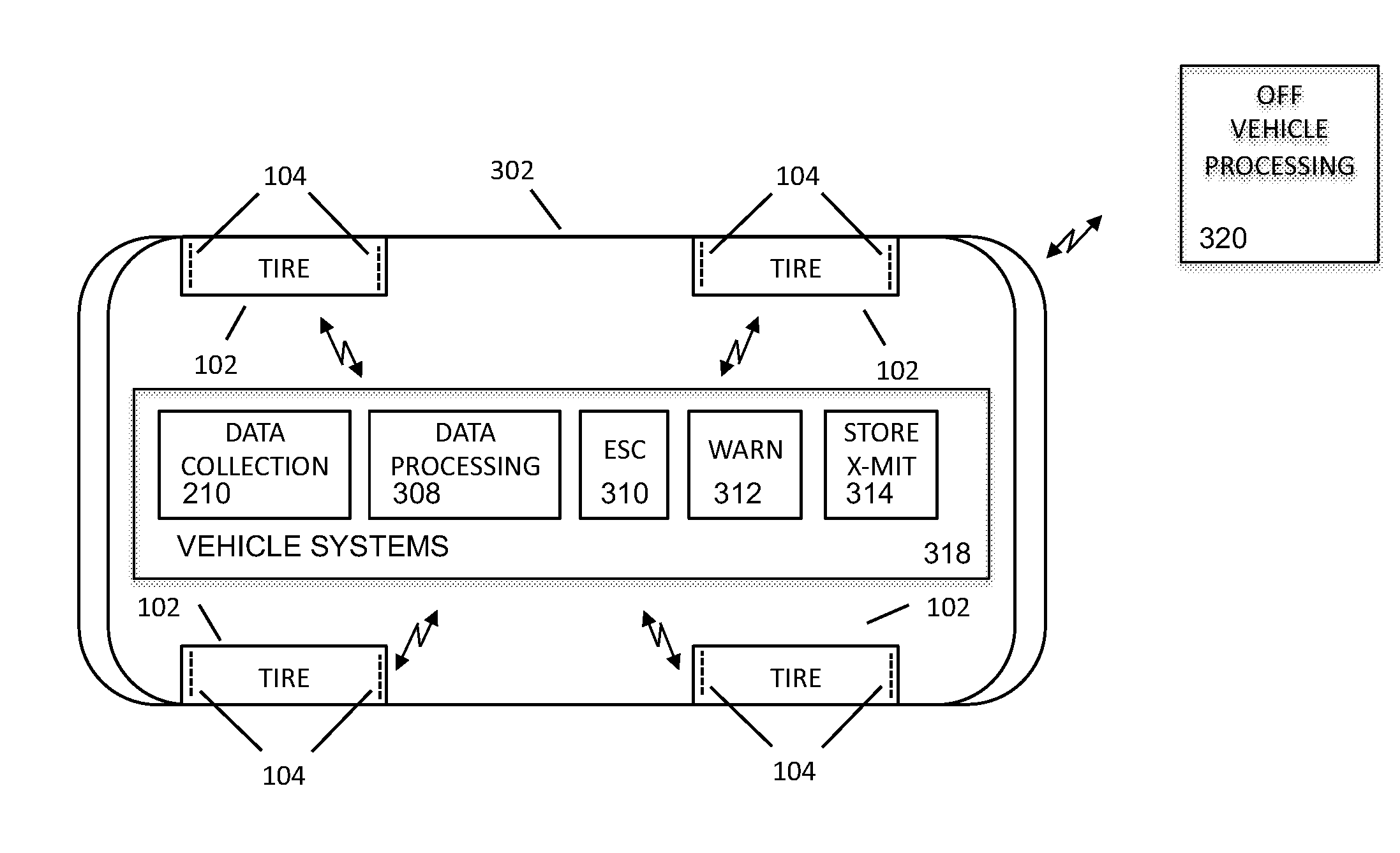
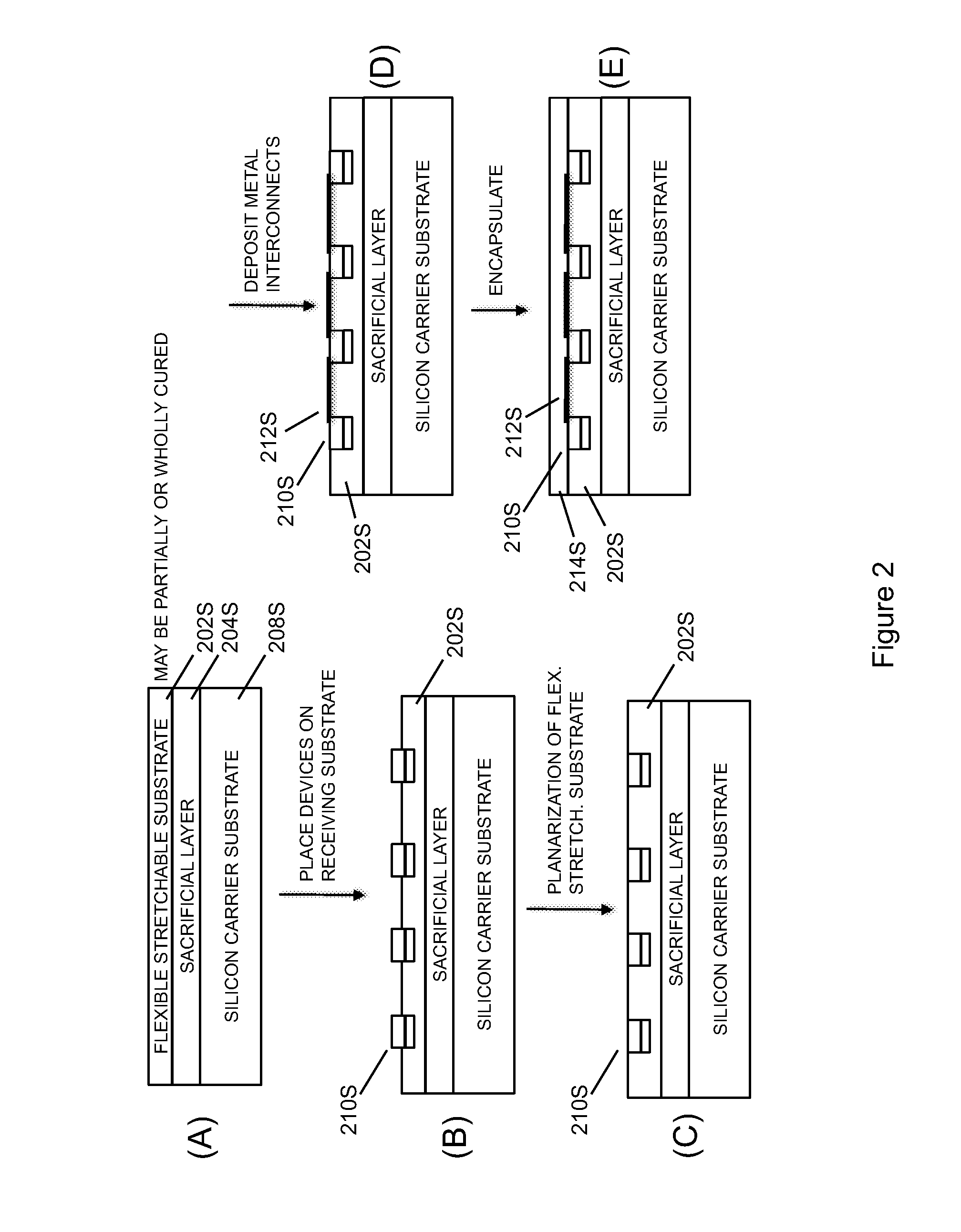
Systems, devices, and methods utilizing stretchable electronics to measure tire or road surface conditions
InactiveUS20100271191A1Improve performanceIncrease motivationTyre measurementsRoads maintainenceStretchable electronicsRoad surface
In embodiments, the present invention may comprise a sensor-based tire data collection facility integrated with the body of a vehicle tire, wherein the sensor-based tire data collection facility includes a stretchable electronics circuit and a wireless communications facility for communicating data collected by the sensor-based tire data collection facility to a vehicle data collection facility external to the body of the vehicle tire.
Owner:MC 10 INC
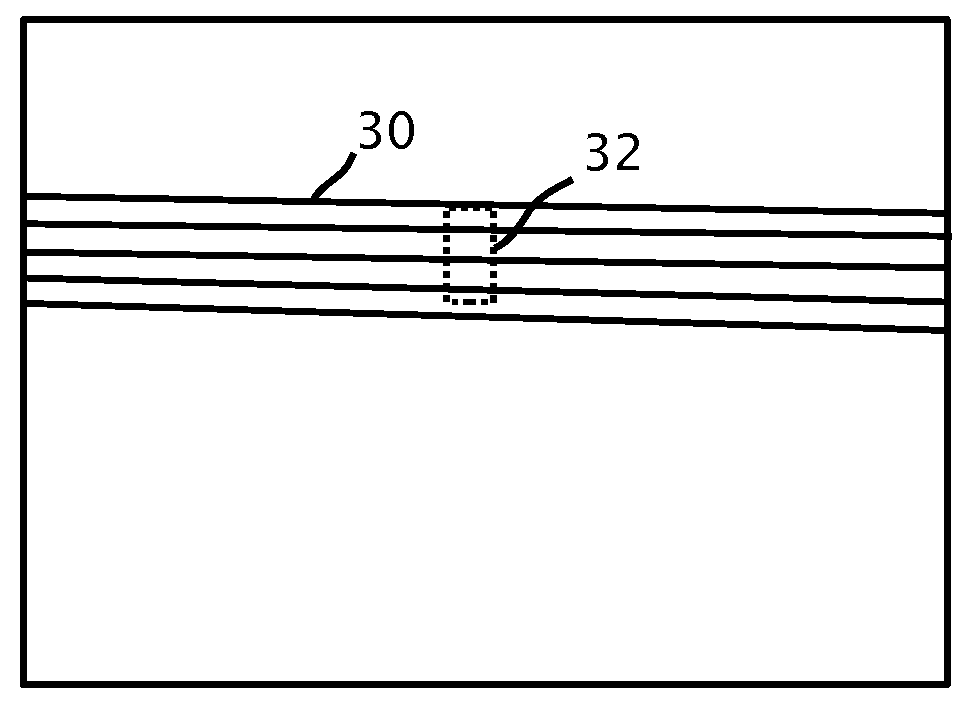
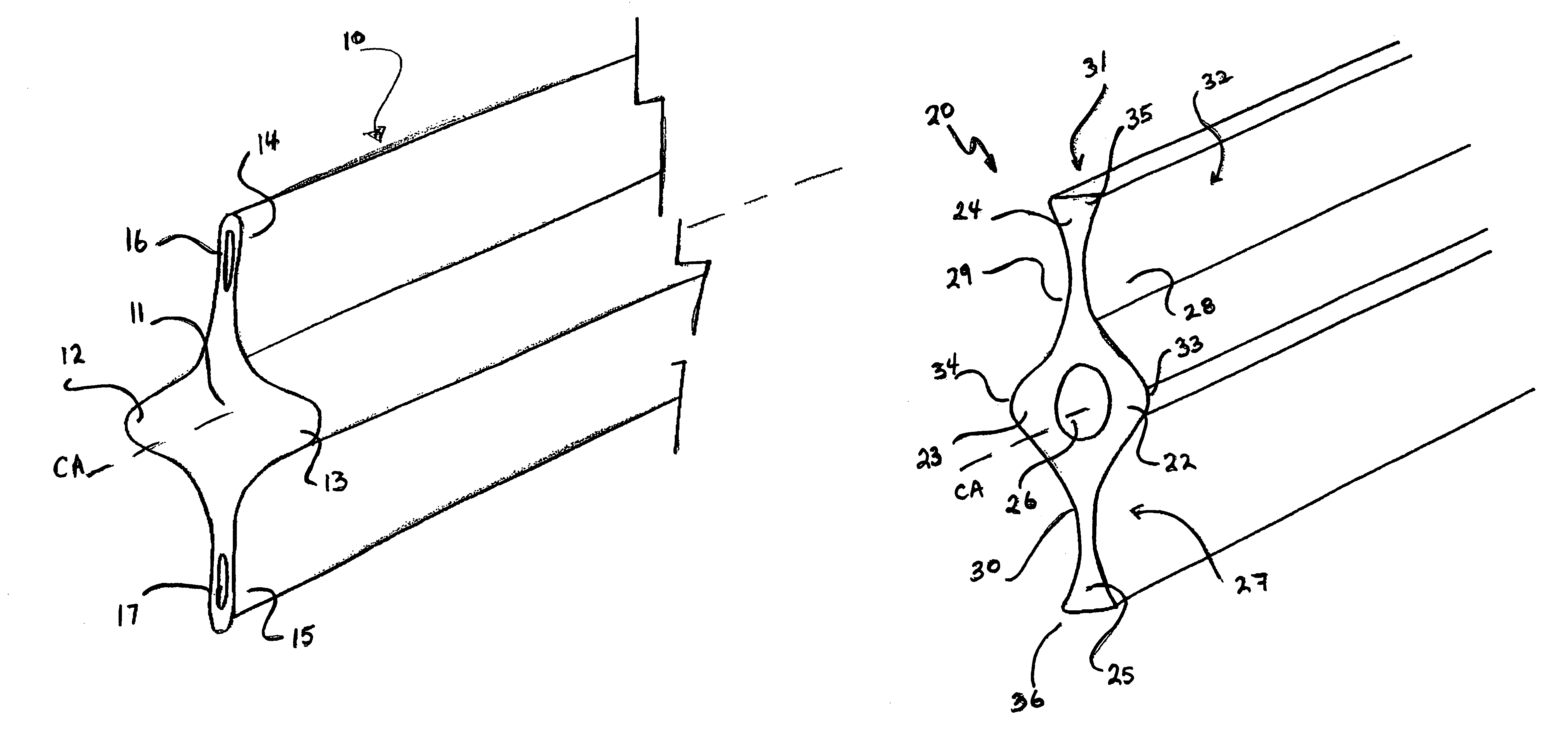
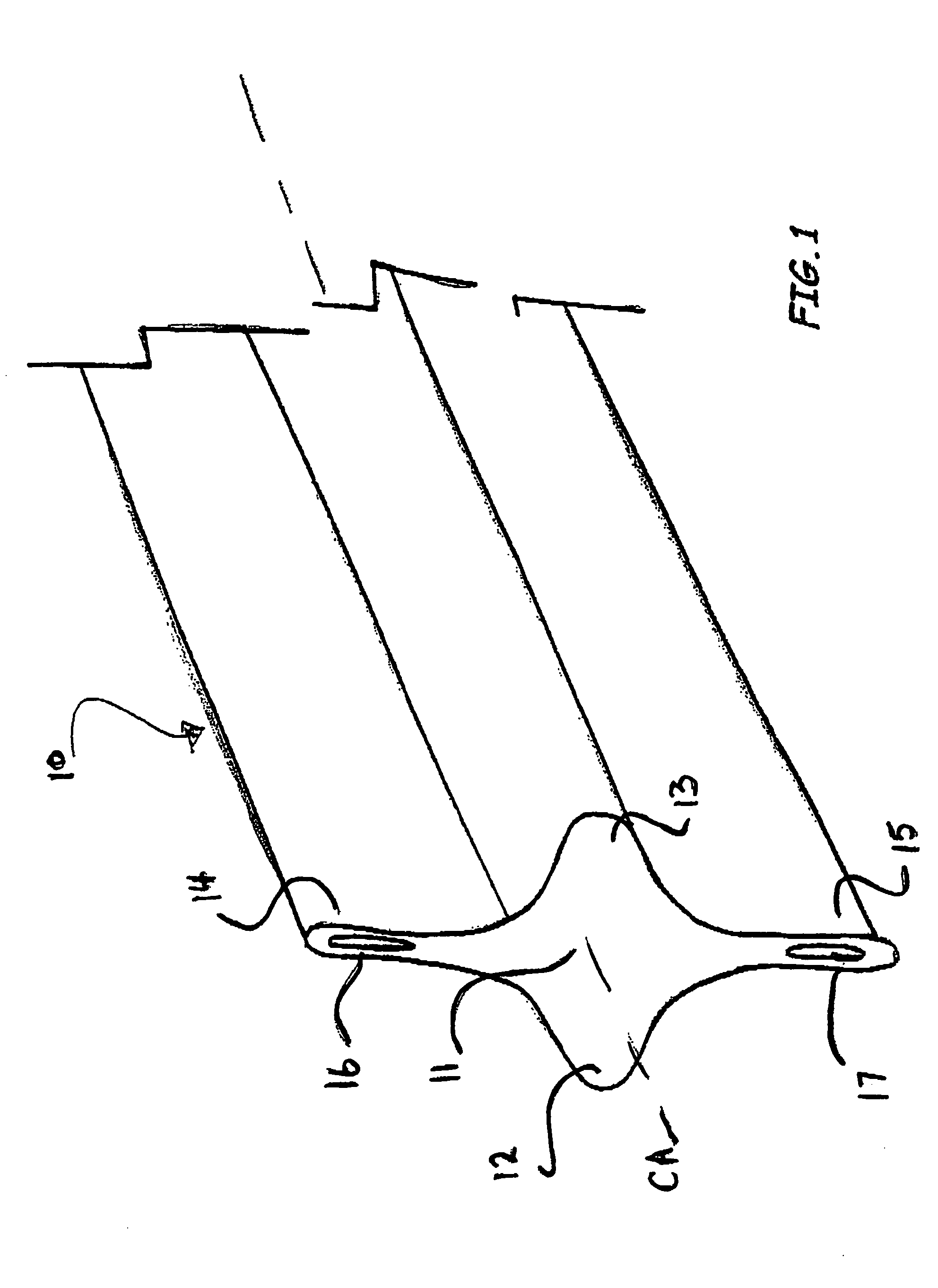
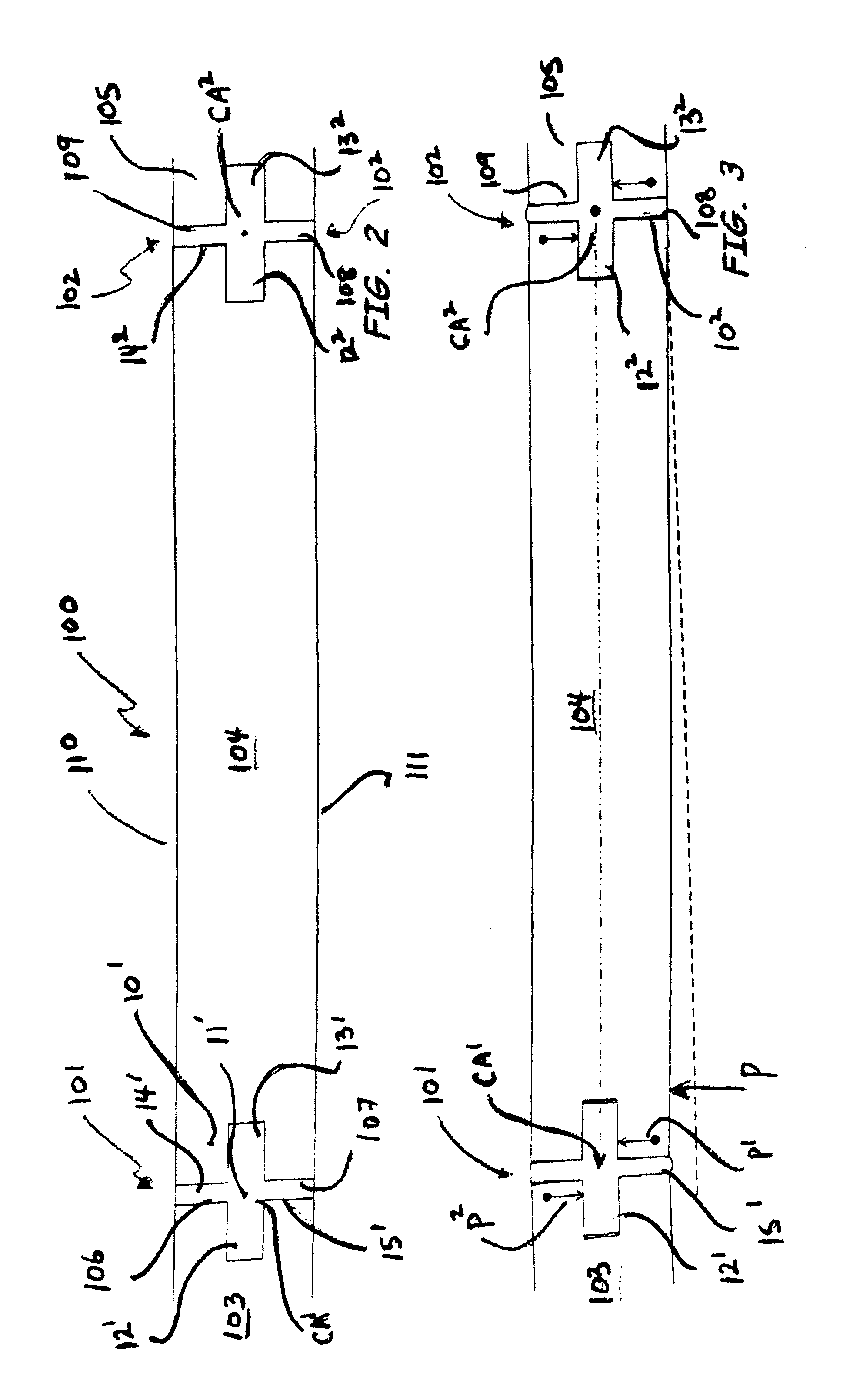
Pavement joint
InactiveUS7806624B2Reduce wastePotential tripping hazards to pedestrians are reducedPaving detailsBuilding insulationsRoad surfaceEngineering
A pavement joint 101, 102 disposed between two contiguous pavement slabs 103, 104 and 105 incorporating a shear key (12, 13, 22 and 23) and at least one hinge (37, 38, 39 and 40). The shear key and the at least one hinge are operative when at least one of the slabs is subjected to out-of-plane action P with the shear key transferring shear between the slabs, and the at least one hinge accommodating angular displacement of the slabs relative to the joint axis in at least one direction. In one form, a joint member 10, 20, 40, 50 and 60 is disposed between the slabs to provide the shear key and hinge. A joint member and pavement slab for use in the joint is also described.
Owner:TRIPSTOP TECH
Driving Assistance System And Connected Vehicles
InactiveUS20100171828A1Assist driving of inexpensively and satisfactorilySignificance and benefits of the inventionImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceOptical flow
A tractor and a trailer are connected together and a camera is installed on the trailer side of the connected vehicles. The camera captures images behind the trailer. A driving assistance system projects the captured images on bird's-eye view coordinates parallel with a road surface to convert the images into bird's-eye view images and obtains on the bird's-eye view coordinates an optical flow of a moving image composed of the captured images. The connection angle between the tractor and the trailer is estimated based on the optical flow and on movement information on the tractor, and further, a predicted movement trajectory of the trailer is obtained from both the connection angle and the movement information on the tractor. The predicted movement trajectory is overlaid on the bird's-eye view images and the resulting image is outputted to a display device.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Road line recognition apparatus
ActiveUS20060239509A1Accurate detectionStable detectionDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionLocation detectionImaging processing
A road line recognition apparatus, including: an imaging section imaging a progress path of a own vehicle including a road to output a couple of images; an image processing section calculating a distance in a real space in a set region of at least an image on one side based on the imaged couple of images; and a detection section detecting a road line; wherein the detection section includes: a road line candidate point detection and conversion processing unit detecting a pixel on a road surface as a road line candidate point based on luminance and the distance with regard to the image on one side, and performing Hough conversion of the road line candidate point; a road line straight line detection processing unit detecting one straight line proper to the road line on each of a right side and a left side of the own vehicle based on at least a position or a behavior of the own vehicle between straight lines obtained by the Hough conversion; and a road line detection processing unit detecting the road line of a shape of a straight line or a curved line by recording a road line position which is a road line candidate point indicating a road line among the road line candidate points based on the detected straight line.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
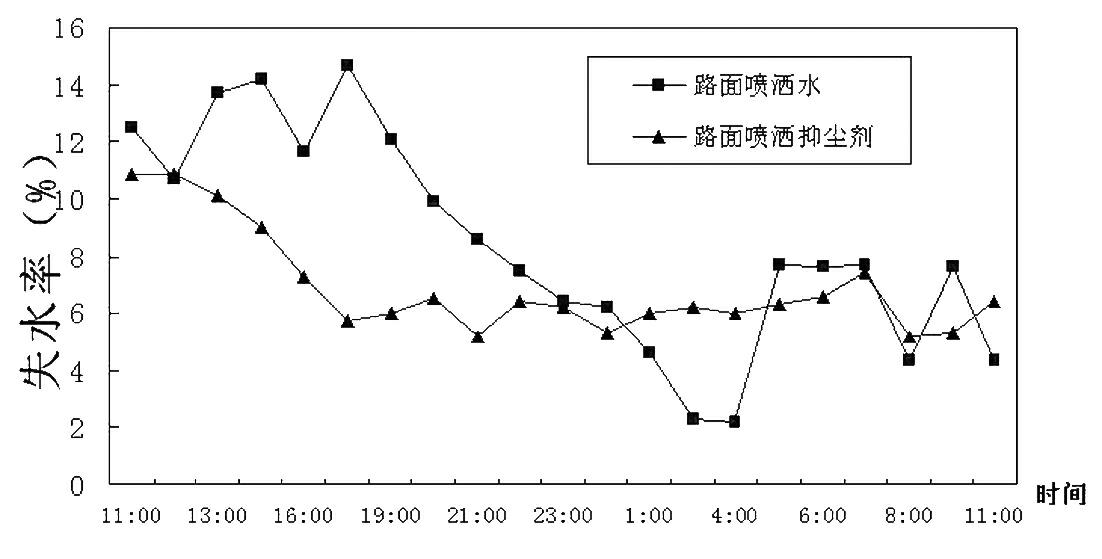
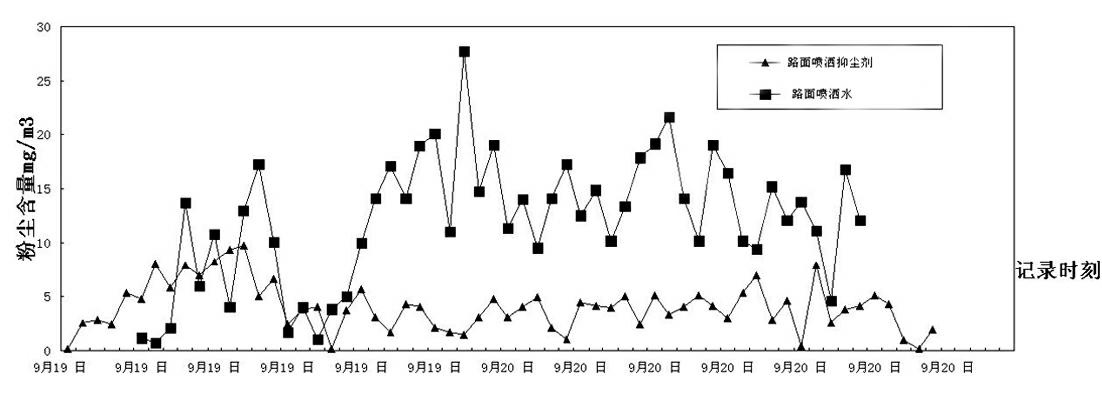
Road dust suppressant
ActiveCN102660227AStrong anti-pressure functionLarge particle sizeOther chemical processesLiquid productEvaporation
The invention discloses a road dust suppressant, which is prepared by mixing and blending 0.1-2.0% of water-soluble high molecular polymer, 20-50% of moisture absorption humectant, 1.0-5.0% of preservative, 0.5-5.0% of penetrating agent and the balance water. The road dust suppressant is a dynamic dust-proof and dust-suppressing liquid product which combines functions of wetting, bonding, permeating, adsorbing moisture and the like into a whole and has extremely strong pressurization-resistant function. The road dust suppressant has the advantages of obvious anti-evaporation performance and good water retention hygroscopicity, and dust on the road surface can be coagulated and is unlikely to fly. The road dust suppressant disclosed by the invention not only can be applied to road dust suppressing but also can be simultaneously used for the aspects, such as the mine exploration and transportation environment, storage yards of coal ash, coal and other ores, and the treatments of municipal construction earthwork dust raise.
Owner:山西兴源盛科技有限公司
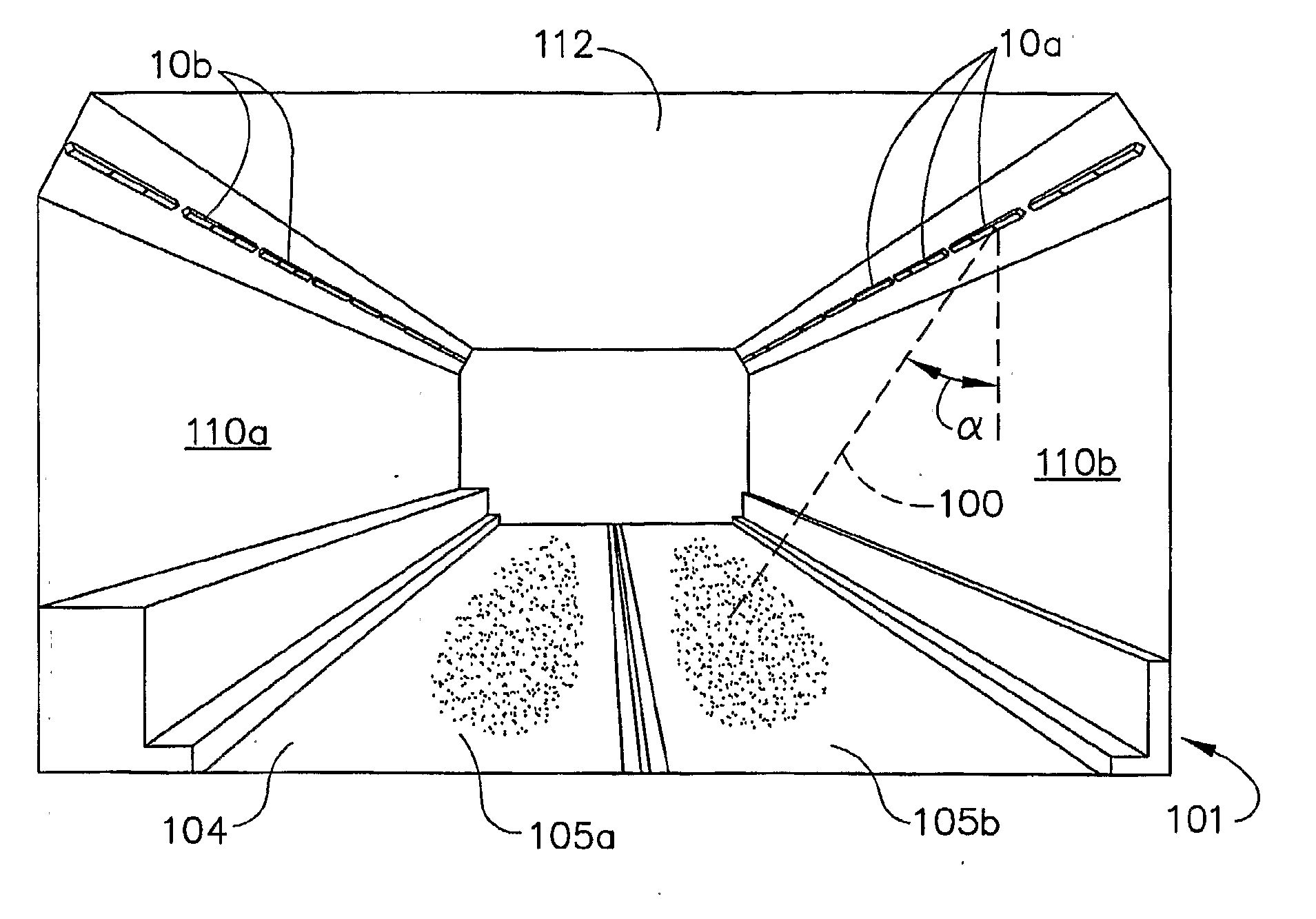
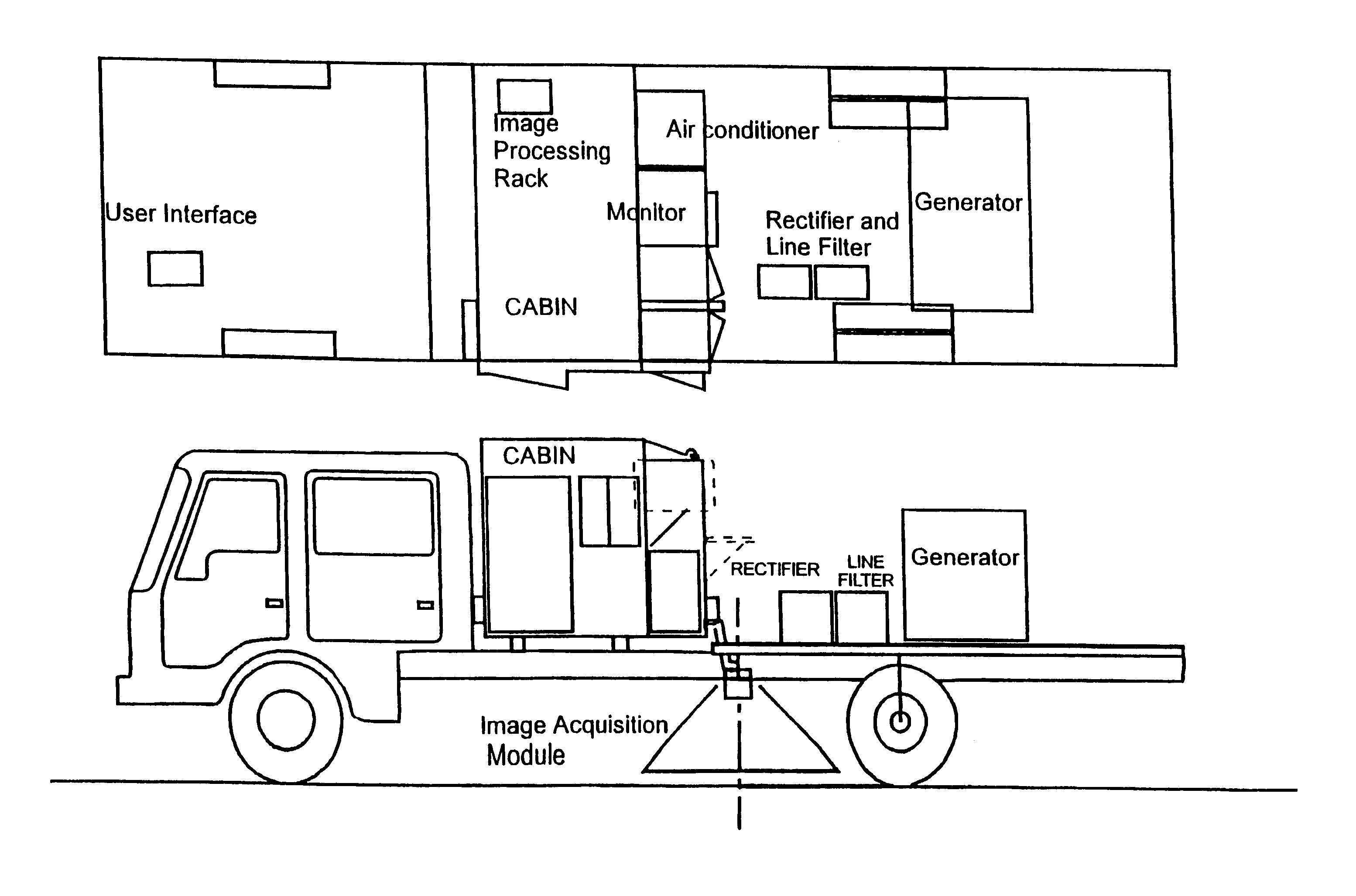
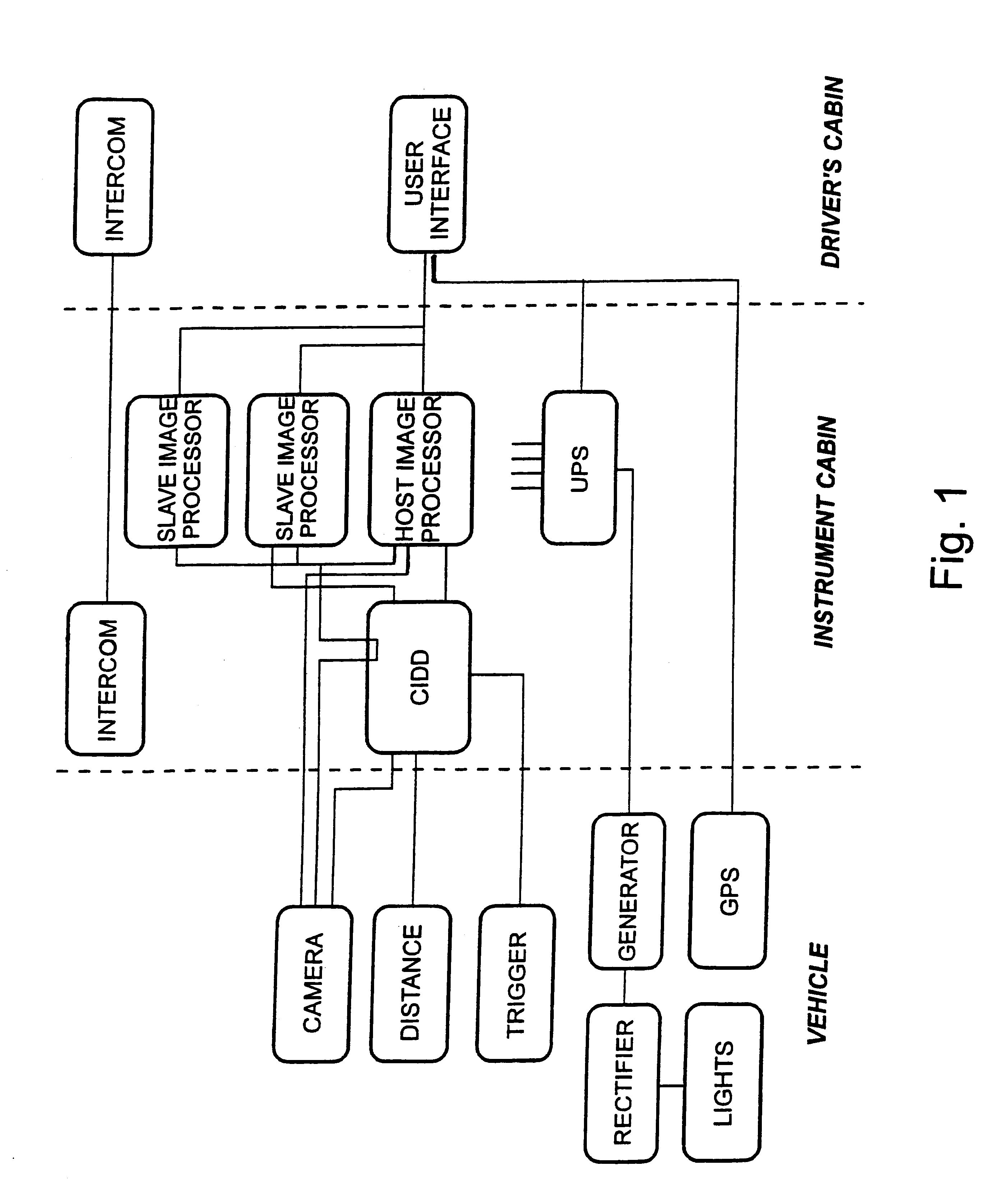
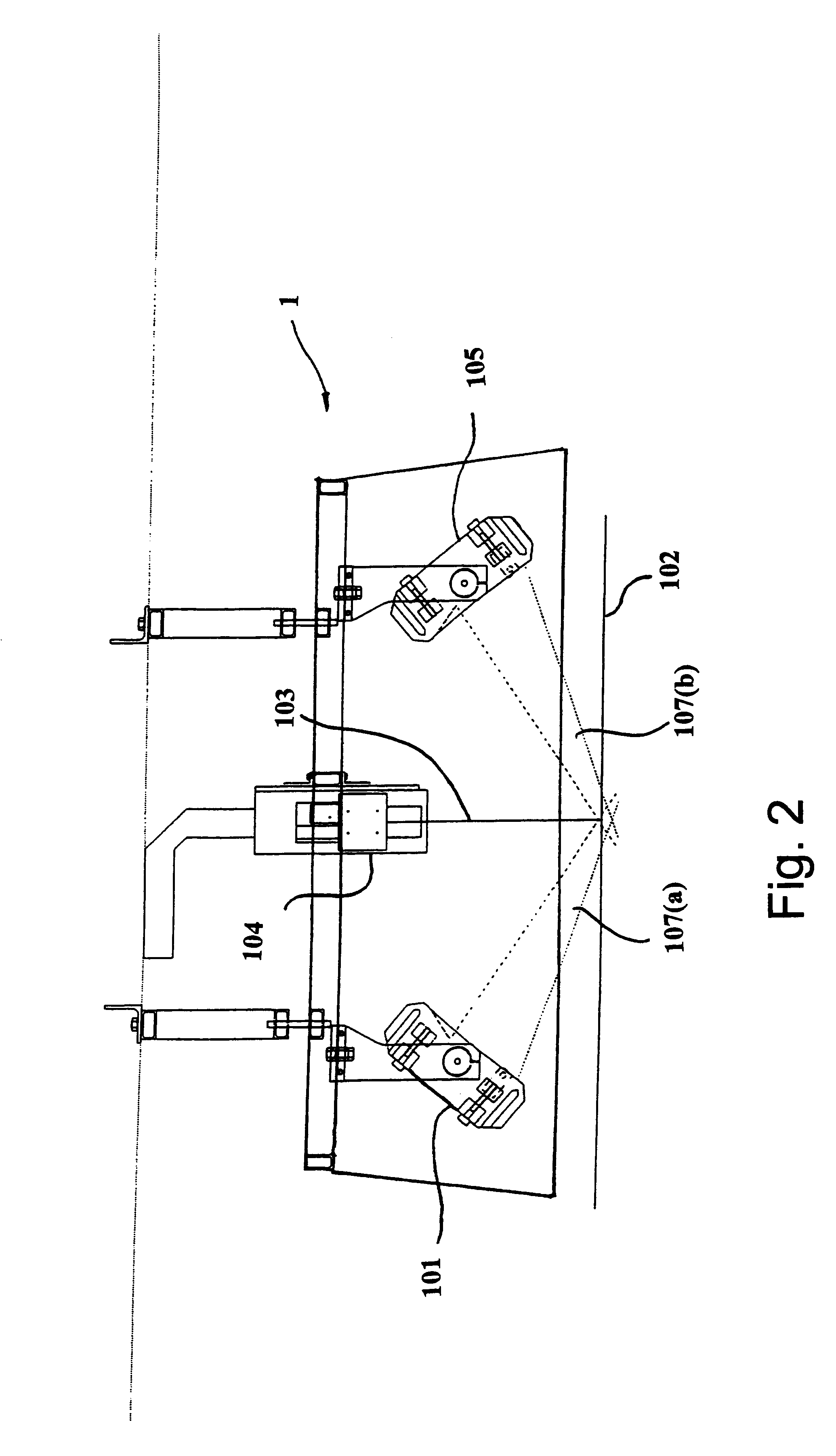
Road pavement deterioration inspection system
InactiveUS6615648B1Reduce the risk of injuryReduce transferDigital computer detailsMeasurement arrangements for variableRoad surfaceDigital camera
A system for acquiring, processing, storing, analyzing and reporting data relating to the condition of a road or other pavement surface (102) in real time. The system includes a digital camera (104) mounted on a vehicle and positioned relative to a pavement surface (102) so as to capture images of the pavement surface (102) while the camera (104) is moving relative to the surface (102). The system also includes an illumination assembly (100) to illuminate the region from which an image is taken and an interface between the digital camera (104) and at least one computer. The system also includes a processor in the computer for processing the images to detect and classify cracks and other pavement surface (102) features.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Alerting illumination device
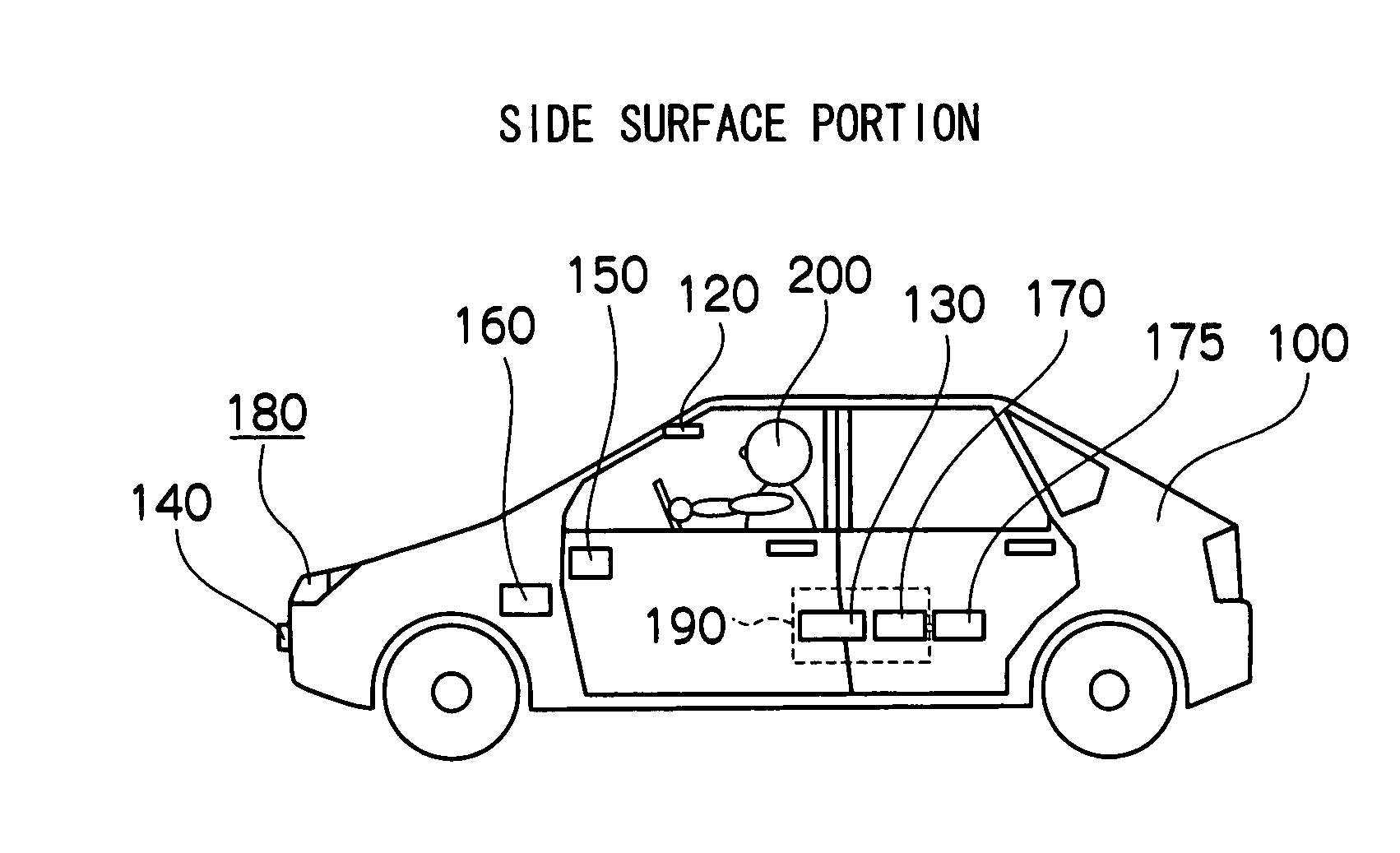
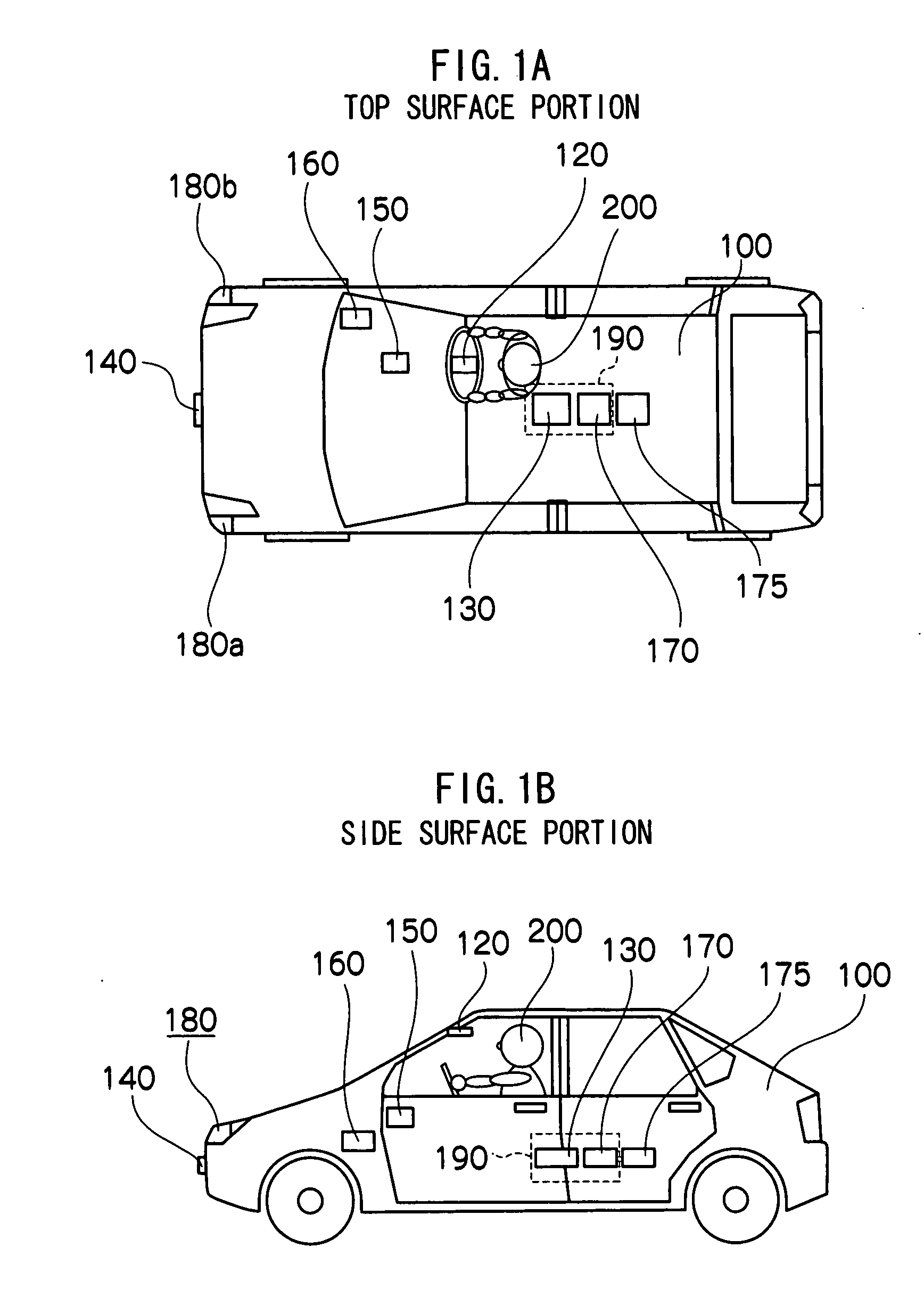
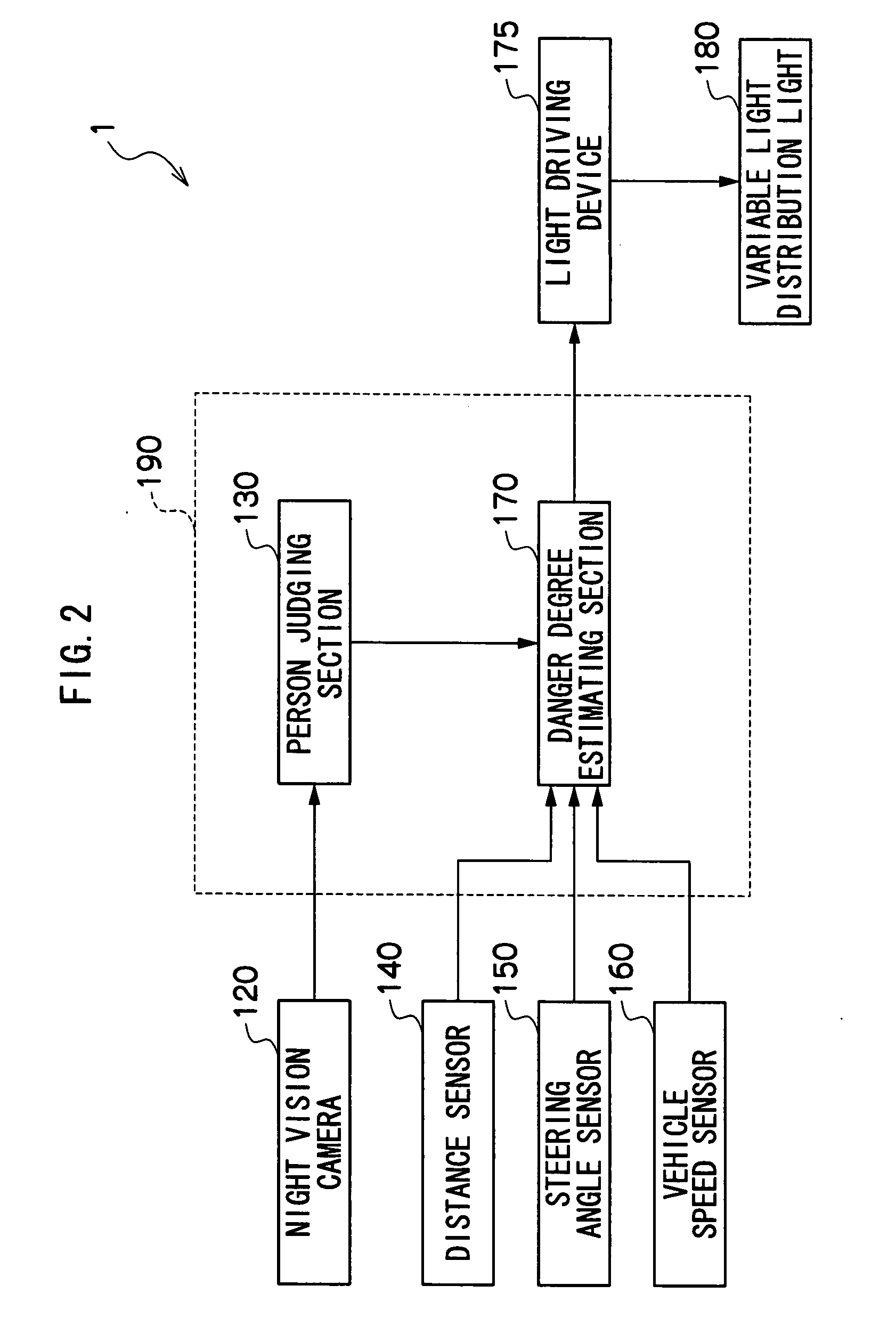
An alerting illumination device, which includes a detecting component, a danger degree estimating component, a danger assuming component, an illuminating component and a controlling component, is provided. The danger degree estimating component estimates a degree of danger, with respect to a subject vehicle, of the person detected by the detecting component. The danger assuming component, on the basis of the estimated degree of danger, assumes whether or not the person detected by the detecting component is a danger with respect to the subject vehicle. The illuminating component illuminates light. The controlling component, in a case in which the danger assuming component assumes that the person is a danger, controls the illuminating component such that light, which shows a direction of the person who is assumed to be a danger and a distance to the person, is illuminated onto a road surface.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Self-driving vehicle with integrated active suspension
ActiveUS20180154723A1Improve ride comfort performanceActive suspension technologiesAssociation with control/drive circuitsSpringsEngineeringRoad surface
A self-driving vehicle with an integrated fully-active suspension system. The fully-active suspension utilizes data from one or more sensors used for autonomous driving (e.g. vision, LIDAR, GPS) in order to anticipate road conditions in advance. The system builds a topographical map of the road surface. Suspension and road data is delivered back to the vehicle in order to change autonomous driving behavior including route planning. Energy storage is regulated based on a planned route. Forward and lateral acceleration feel is mitigated through active pitch and tilt compensation. The fully-active suspension pushes and pulls the suspension in three or more operational quadrants in order to deliver superior ride comfort, handling, and / safety of the vehicle.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
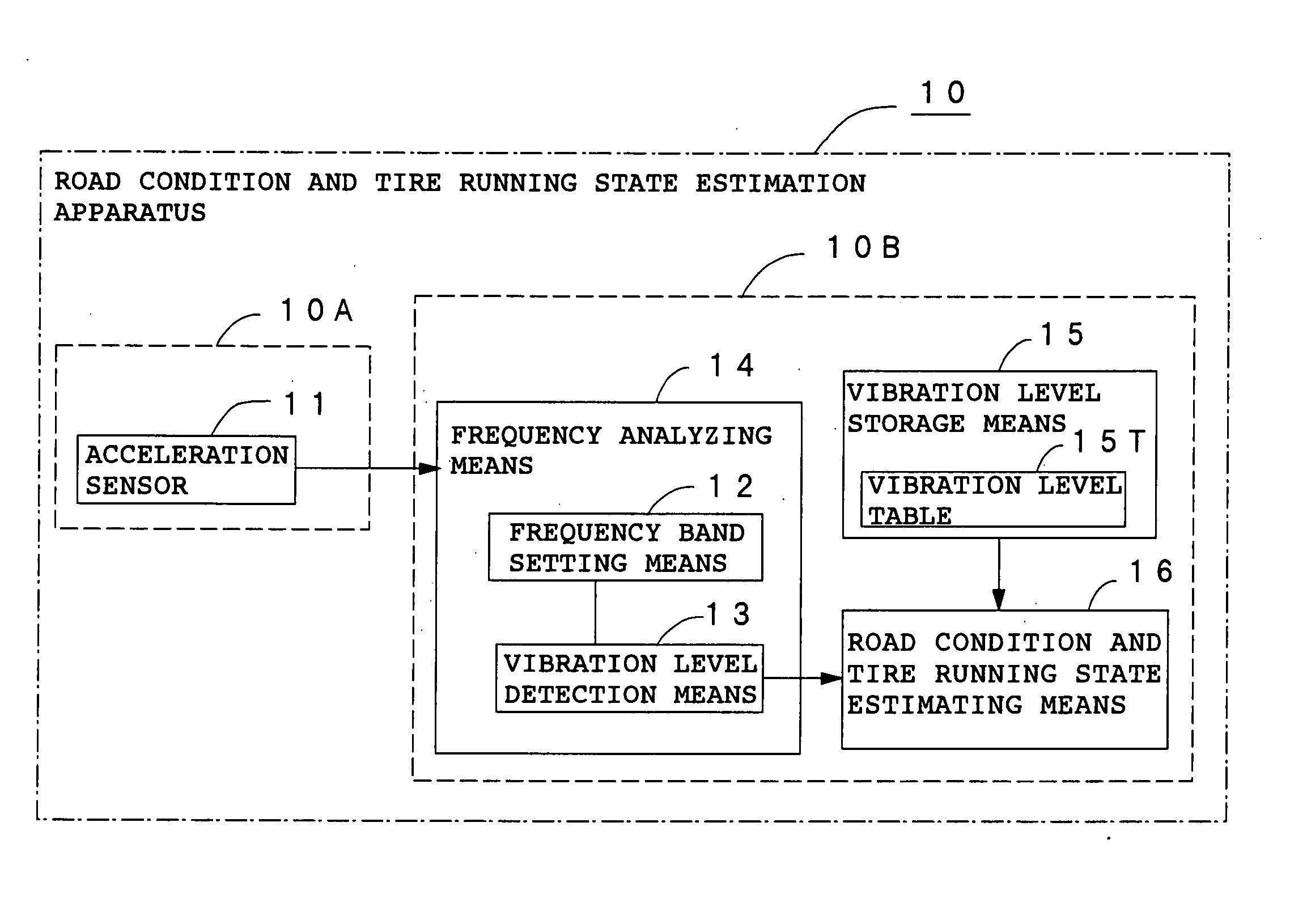
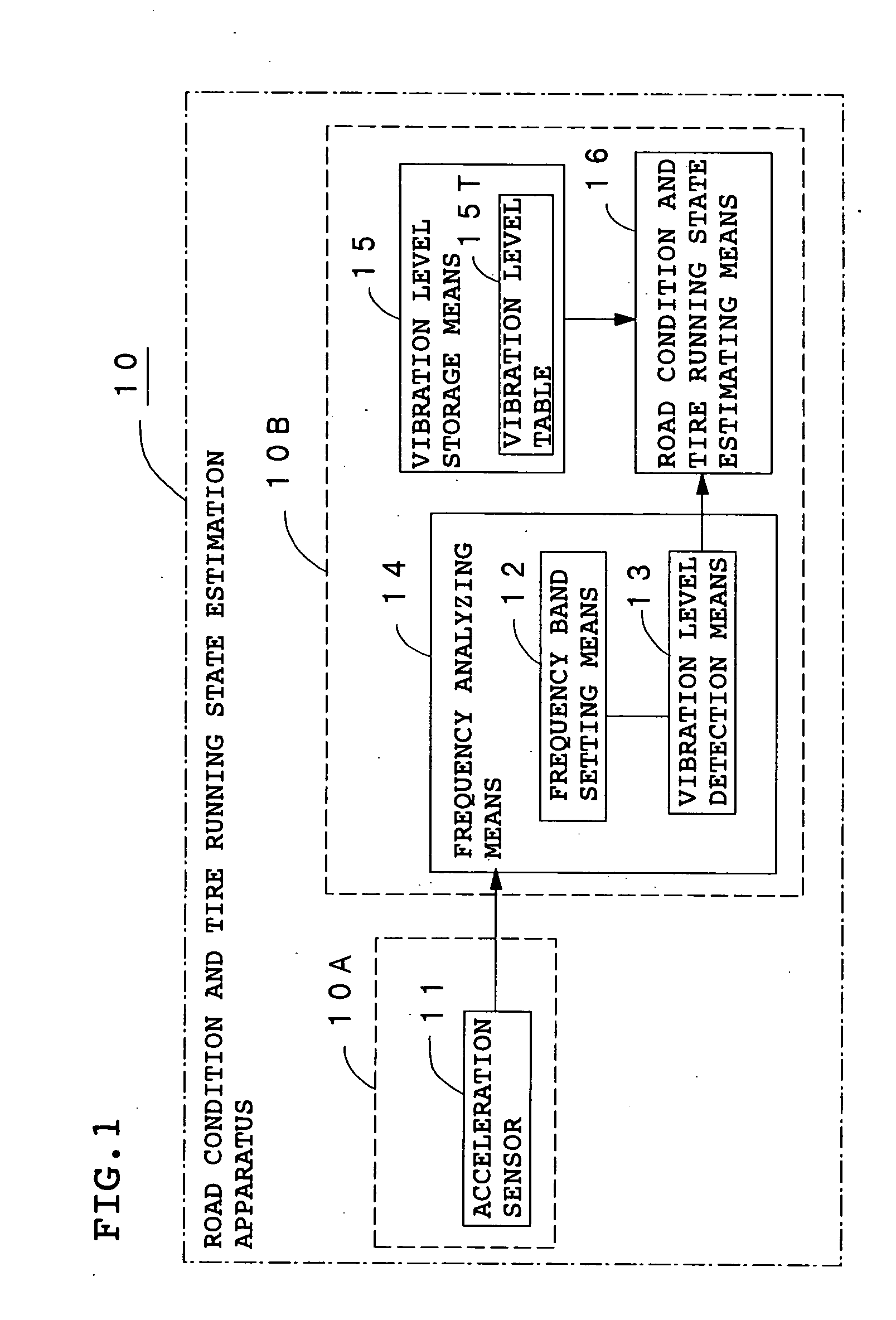
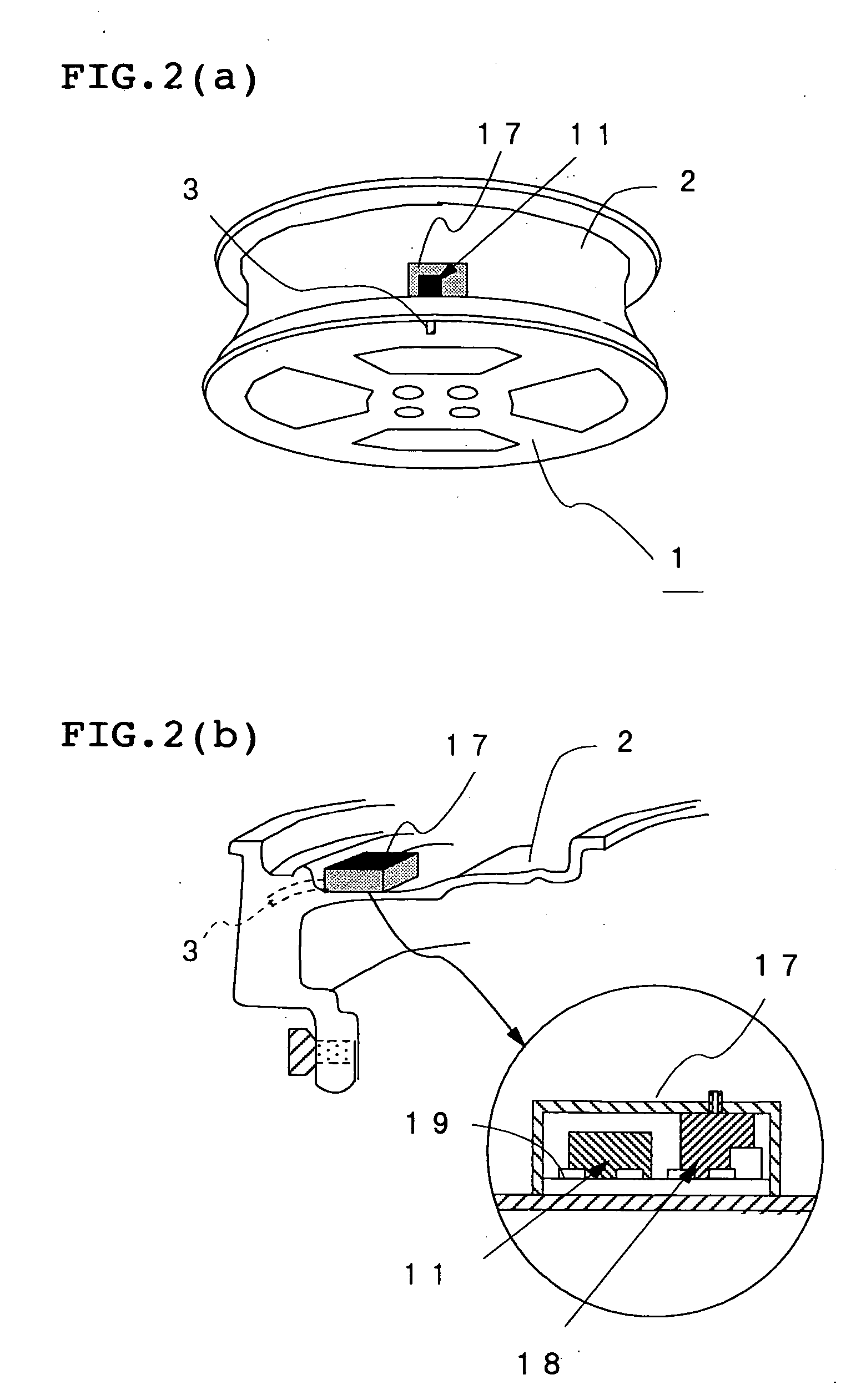
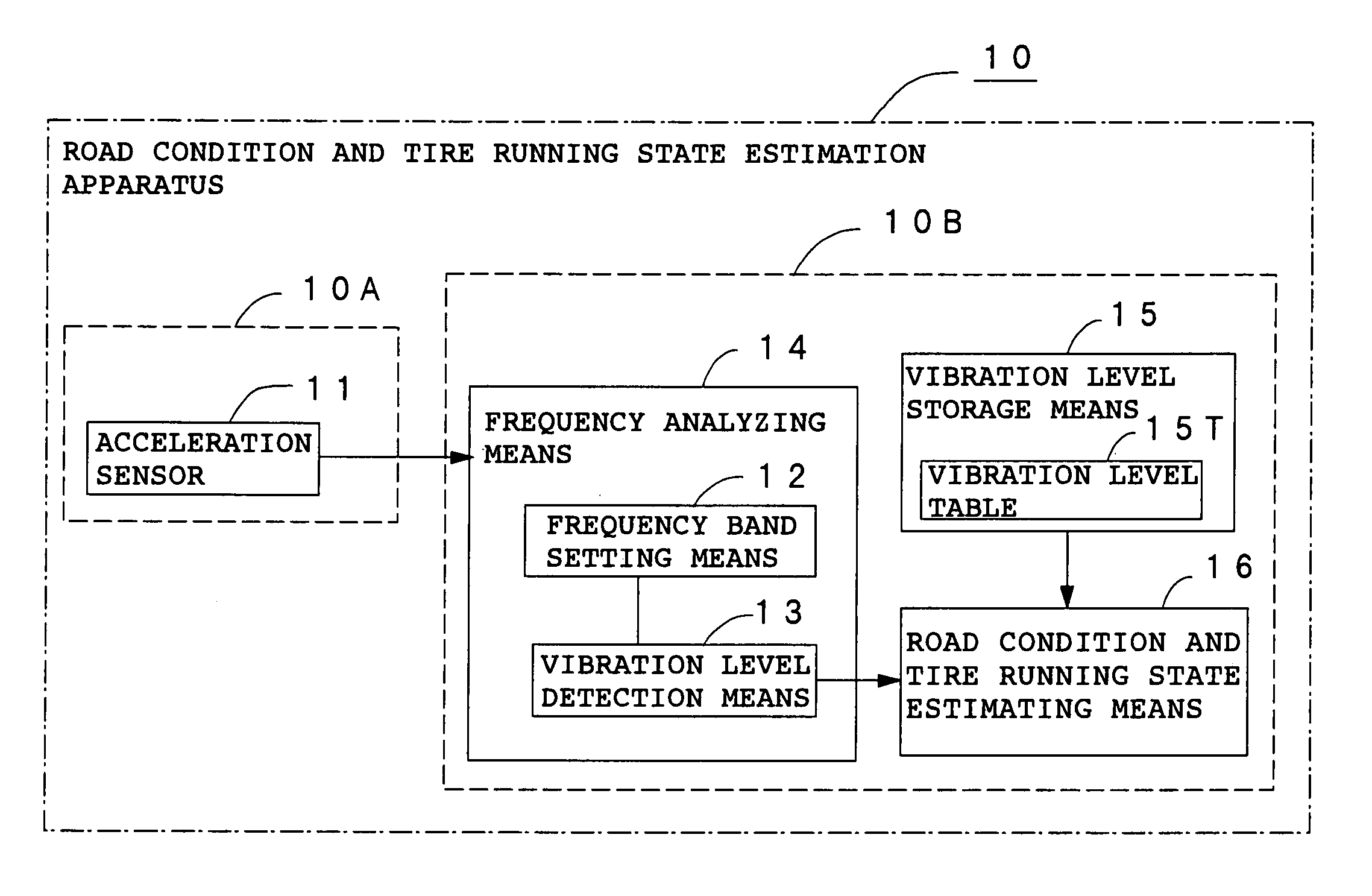
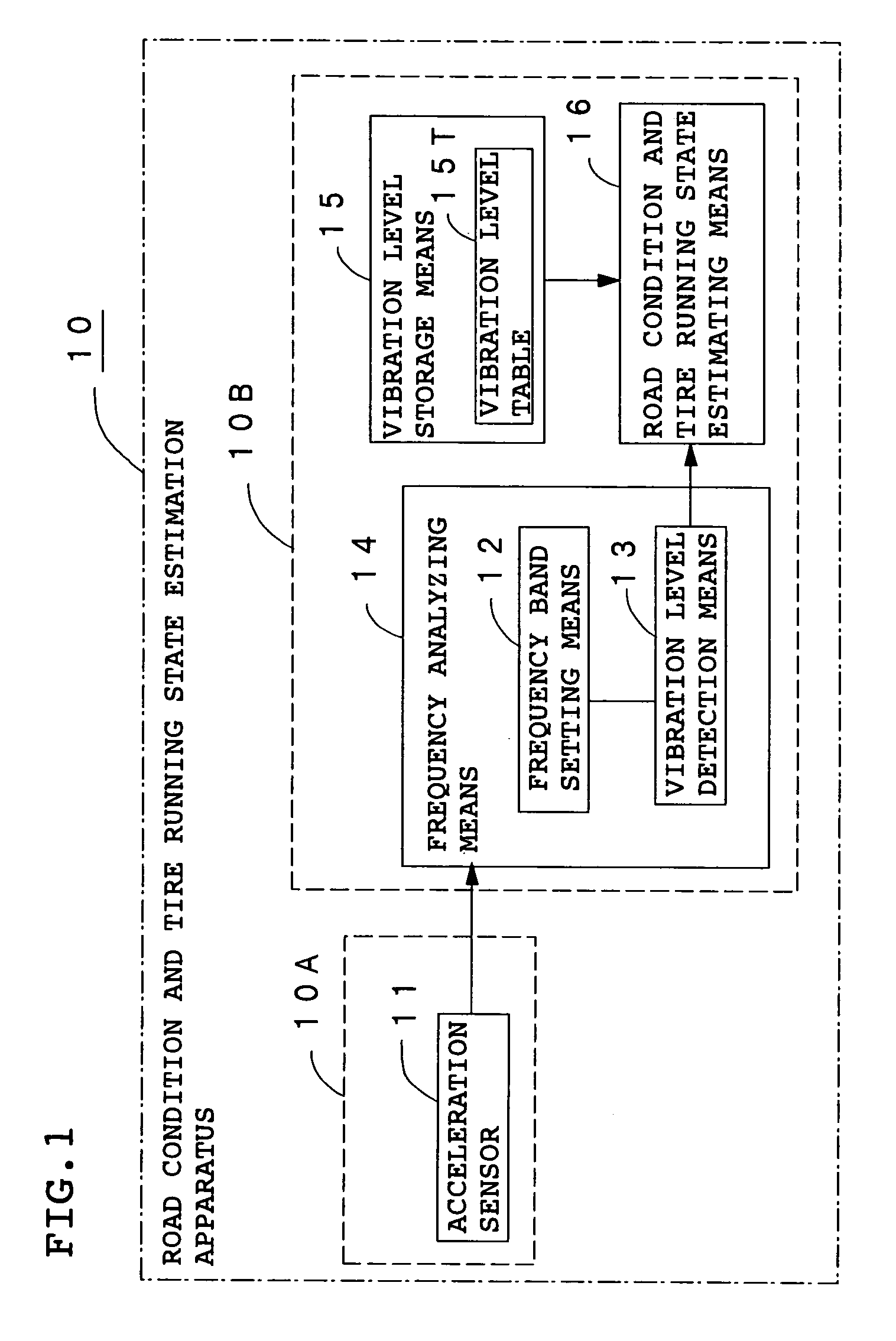
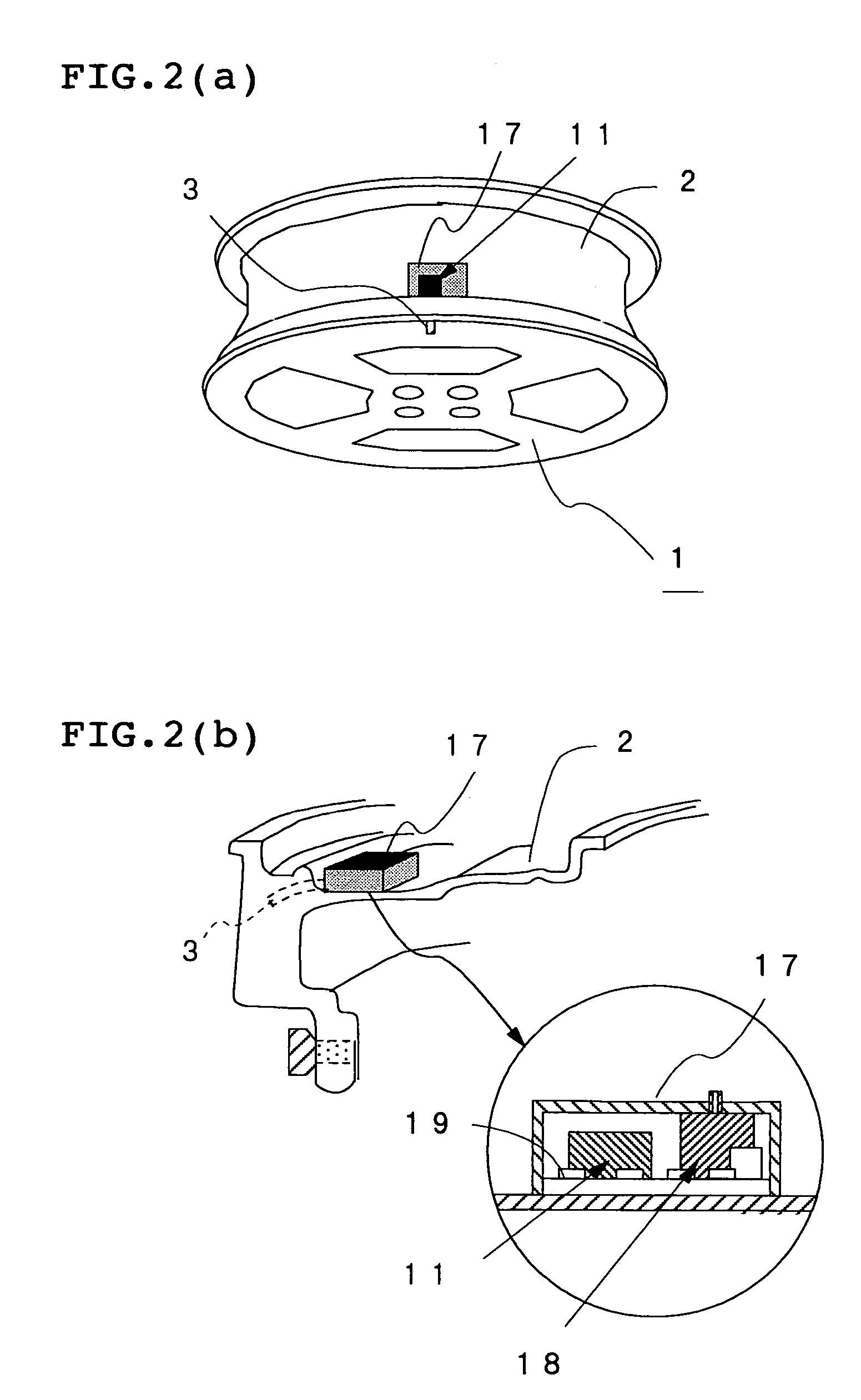
Method and apparatus for estimating road surface state and tire running state, abs and vehicle control using the same
InactiveUS20050085987A1Accurate estimateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsRoad surfaceVehicle control
The frequency of an information signal indicative of the vibration of a wheel detected by an acceleration sensor 11 mounted to a wheel 1 or the frequency of an information signal indicative of a change in the pressure of a gas in a tire detected by a pressure sensor 31 installed in the tire is analyzed by frequency analyzing means 14 (34), the band value of the obtained vibration spectrum or pressure change spectrum is detected, and a vibration level or pressure change level at the detected frequency band is compared with a vibration level table 15T showing the relationship between road friction coefficient μ and vibration level stored in vibration level storage means 15, or a pressure change level table 35T showing the relationship between road friction coefficient μ and pressure change level stored in pressure change level storage means 35 to estimate a road friction coefficient μ. Therefore, it is possible to estimate the value of road friction coefficient μ accurately and improve the safety of a car.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Crowdsourcing the collection of road surface information
ActiveUS20180025235A1Sufficient informationImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationRoad surfaceInformation system
Systems and methods are provided for crowdsourcing road surface information collection. In one implementation, a method of collecting road surface information for a road segment may include receiving at least one image representative of a portion of the road segment, identifying in the at least one image at least one road surface feature along the portion of the road segment, determining a plurality of locations associated with the road surface feature according to a local coordinate system of the vehicle, and transmitting the determined plurality of locations from the vehicle to a server. The determined locations may be configured to enable determination by the server of a line representation of the road surface feature extending along the road segment.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
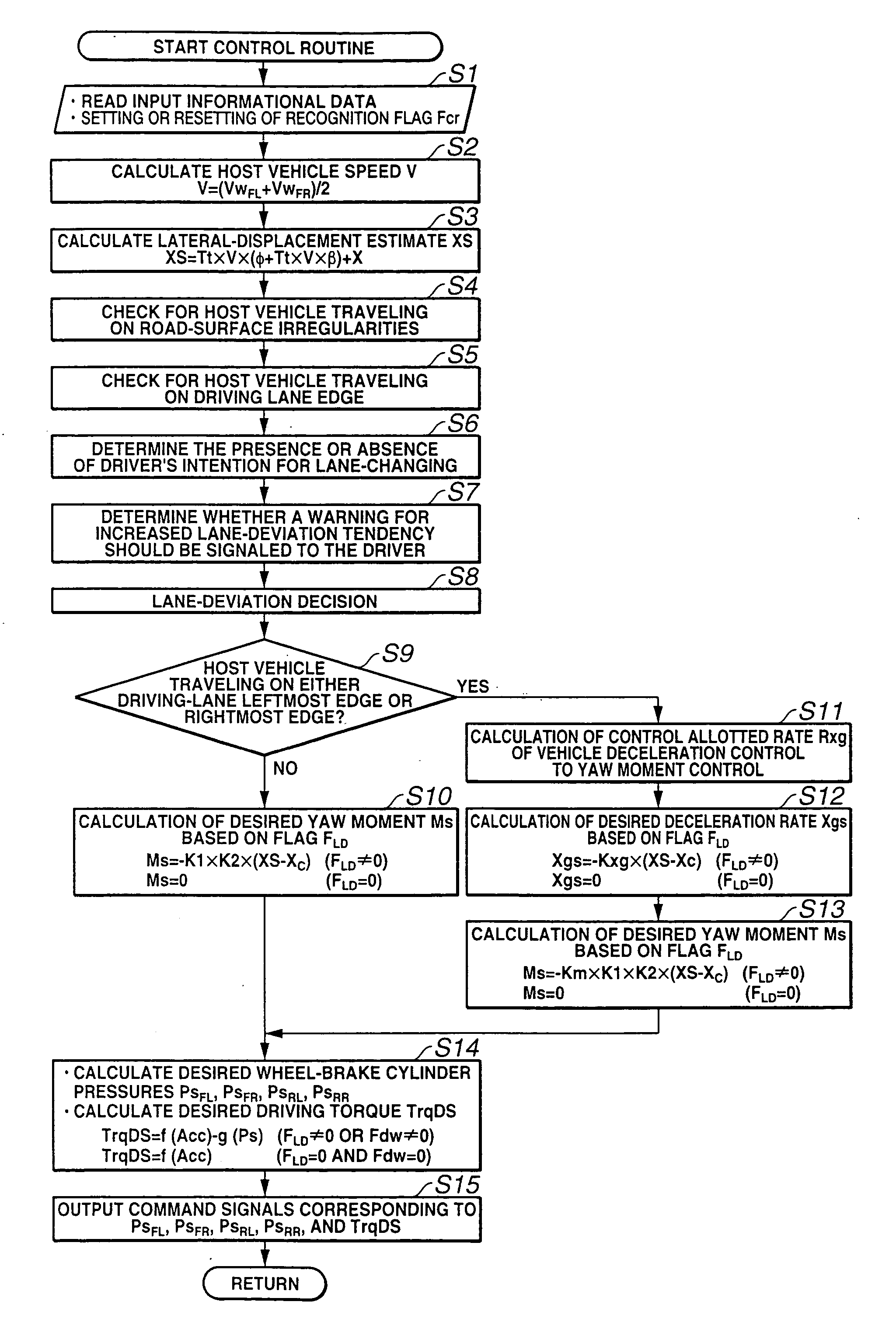
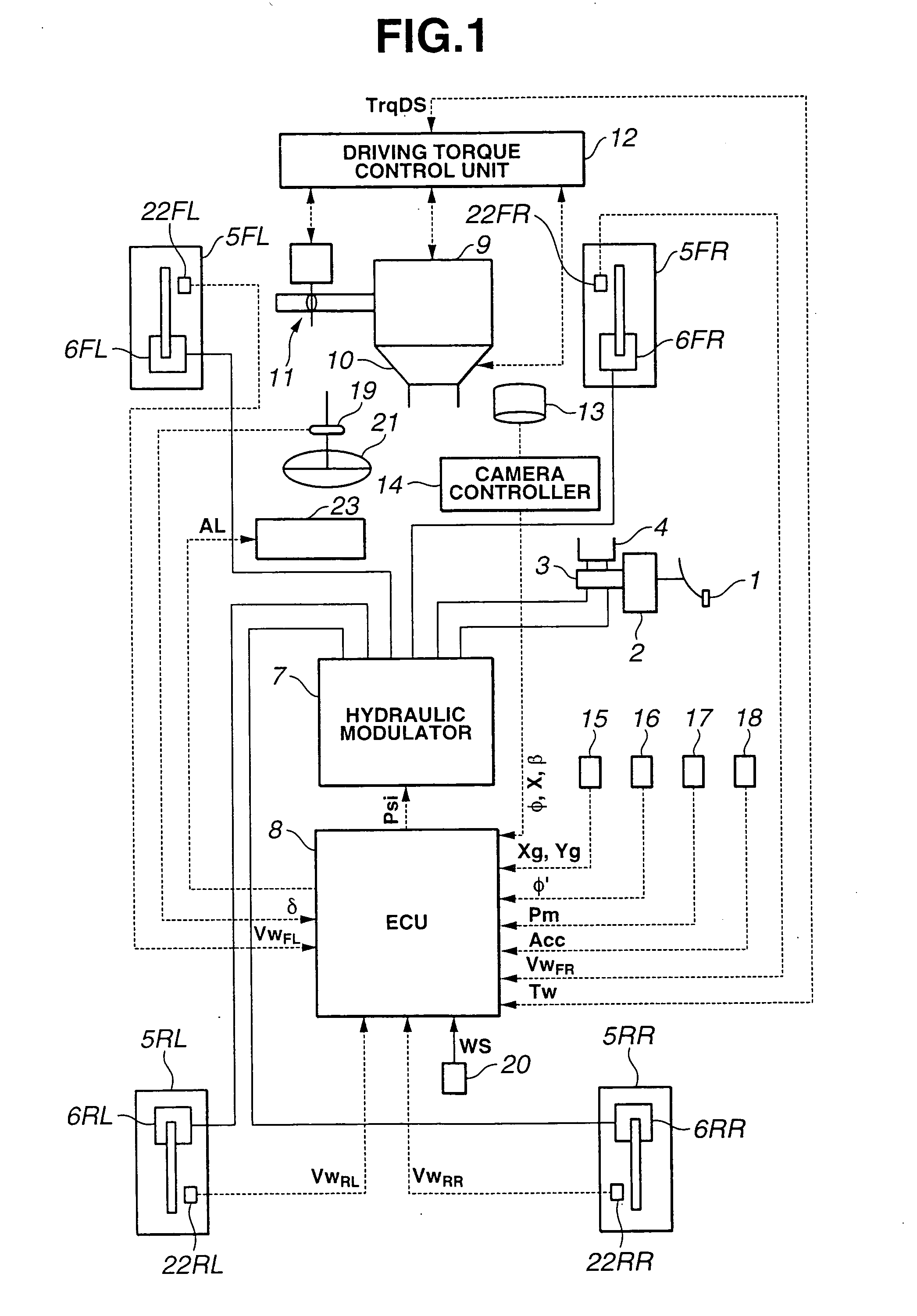
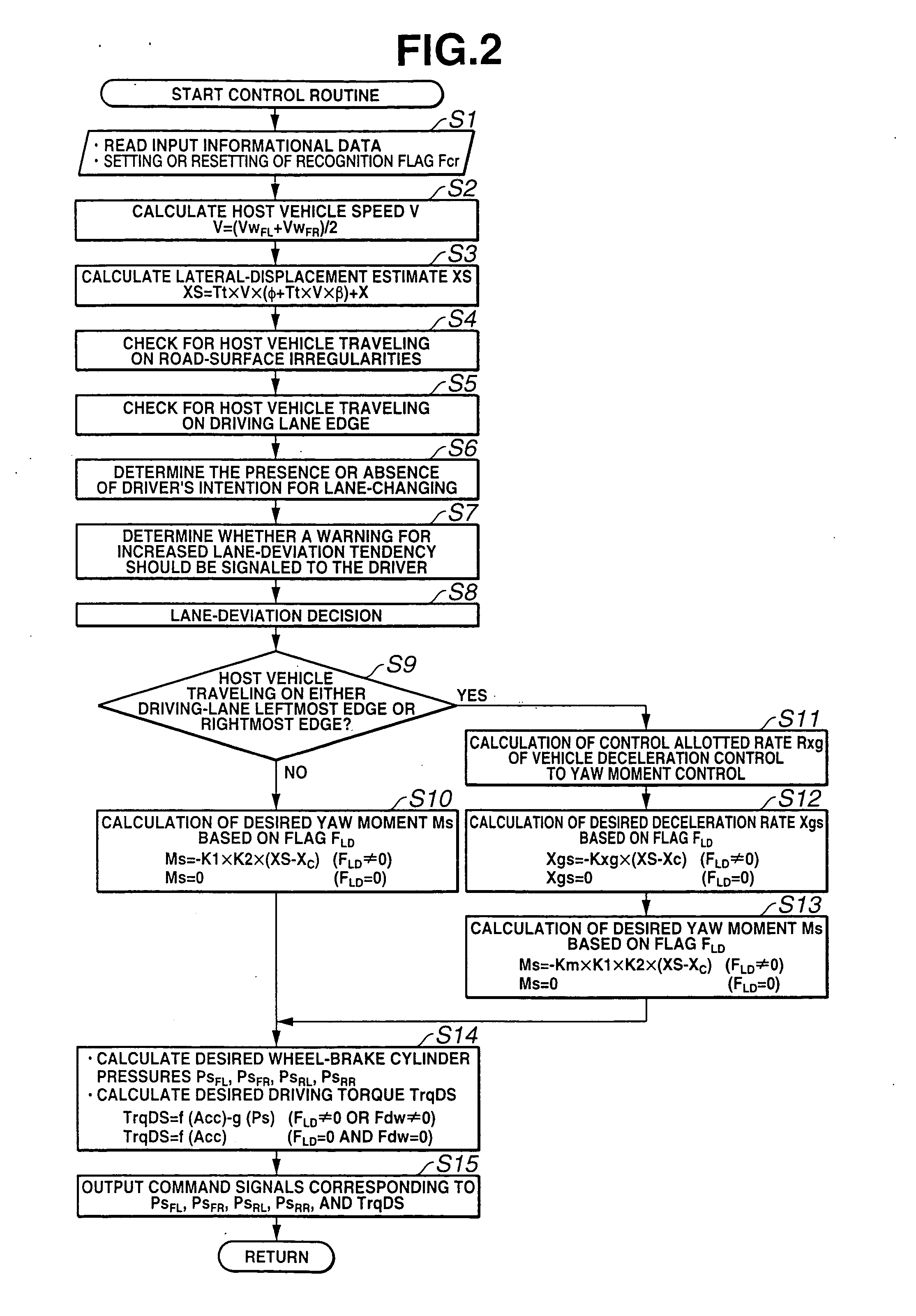
Automotive lane deviation prevention apparatus
ActiveUS20050125153A1Improve securityVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsRoad surfaceControl unit
An automotive lane deviation prevention (LDP) apparatus includes a control unit detecting whether a host vehicle is in a specific state where the host vehicle is traveling on road-surface irregularities formed on or close to a lane marking line. The control unit actively decelerates the host vehicle when the host vehicle is in the specific state where the host vehicle is traveling on the road-surface irregularities.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for estimating road surface state and tire running state, ABS and vehicle control using the same
InactiveUS7203579B2Accurate estimateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsRoad surfaceVehicle control
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Lane keeping assist system and lane keeping assist method
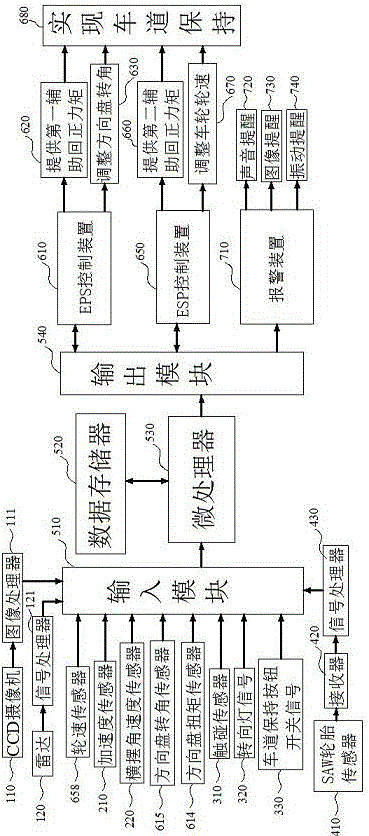
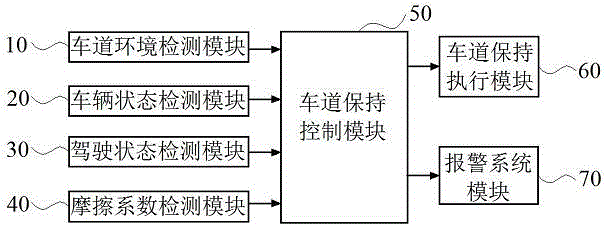
ActiveCN105711588AImprove driving safetyEnsure driving safetyExternal condition input parametersDriver input parametersElectric power steeringDriver/operator
The invention proposes a lane keeping assist system and a lane keeping assist method. The method comprises the steps of comprehensively detecting a people-vehicle-road driving environment through a lane environment detection module, a vehicle state detection module, a driver driving state detection module and a vehicle and road surface rolling friction coefficient detection module; calculating a corresponding detection signal through a lane keeping control module; judging whether a vehicle deviates from a lane or not; performing transverse lane return-to-center control through cooperative control of an electric power steering system (EPS) and an electronic stability program (ESP), and keeping a longitudinal safety distance through ESP control; and giving an alarm for reminding. Through the technical scheme provided by the invention, the driving safety of vehicle driving is remarkably improved; and the lane keeping is realized through the cooperative control of the EPS and the ESP, so that on the premise of ensuring the driving safety of the vehicle, the working comfort of the lane keeping assist system can be improved to the maximum extent.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
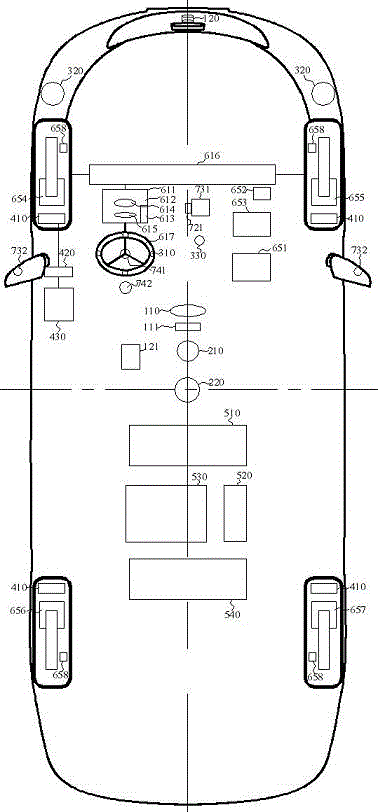
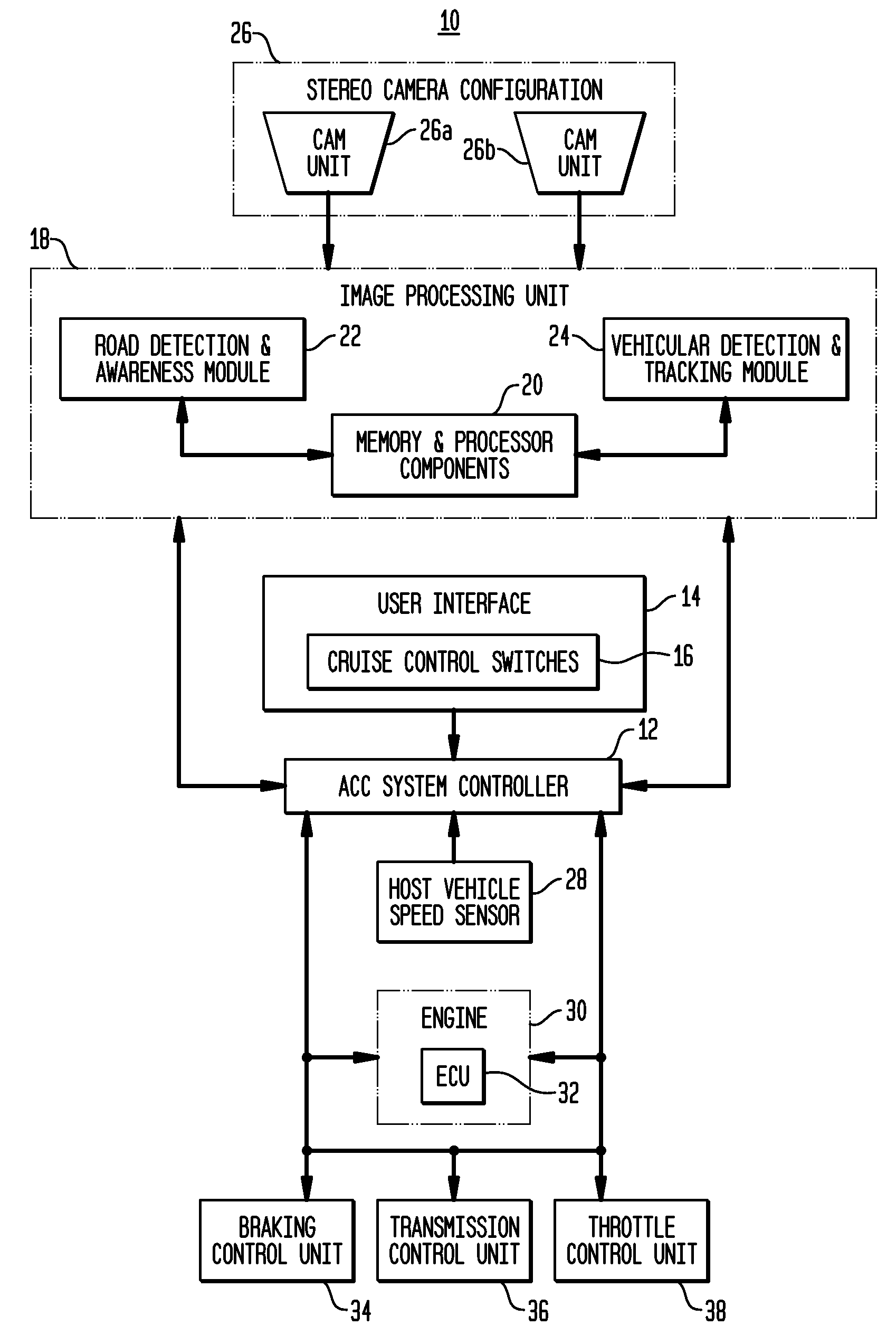
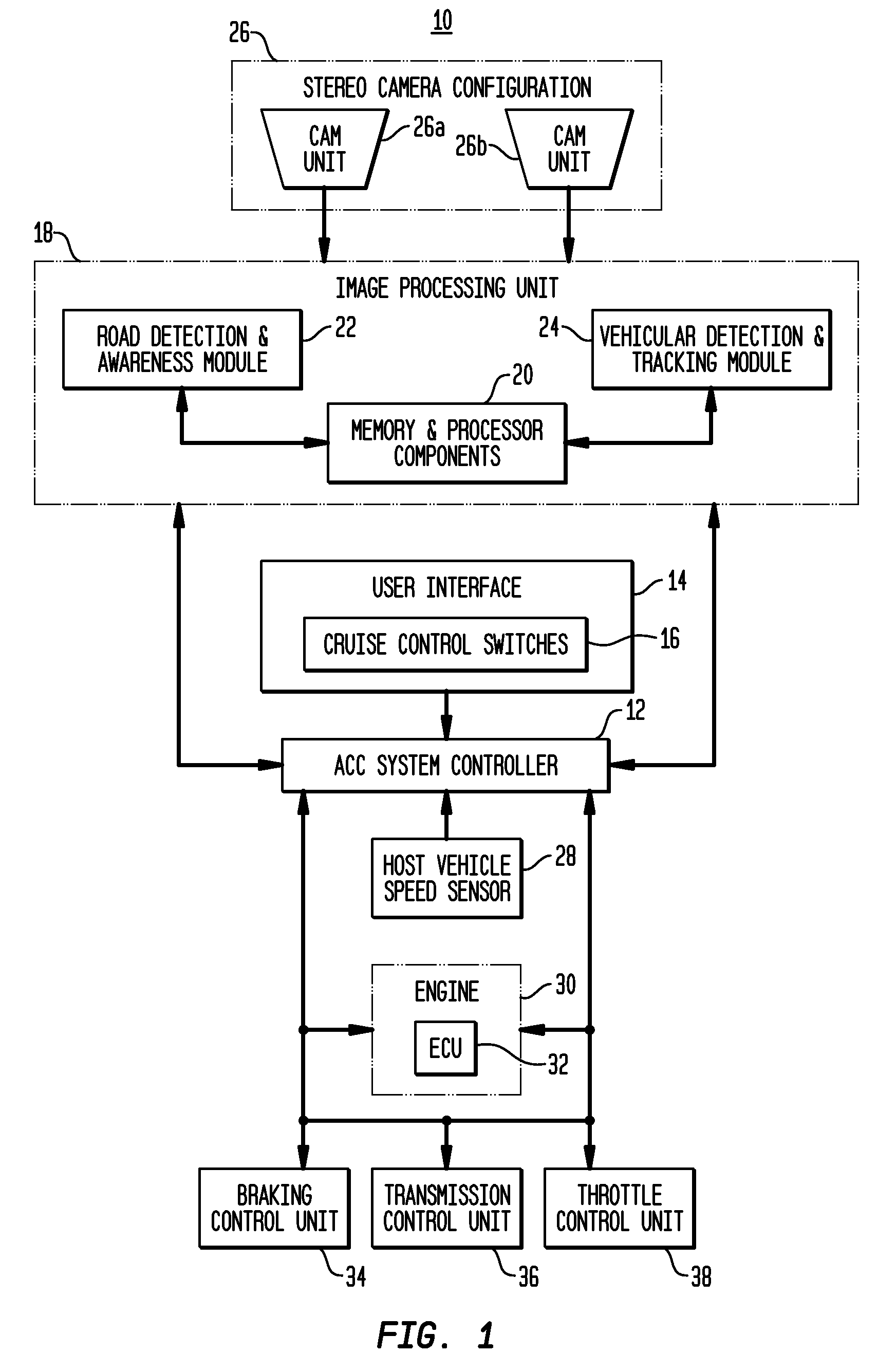
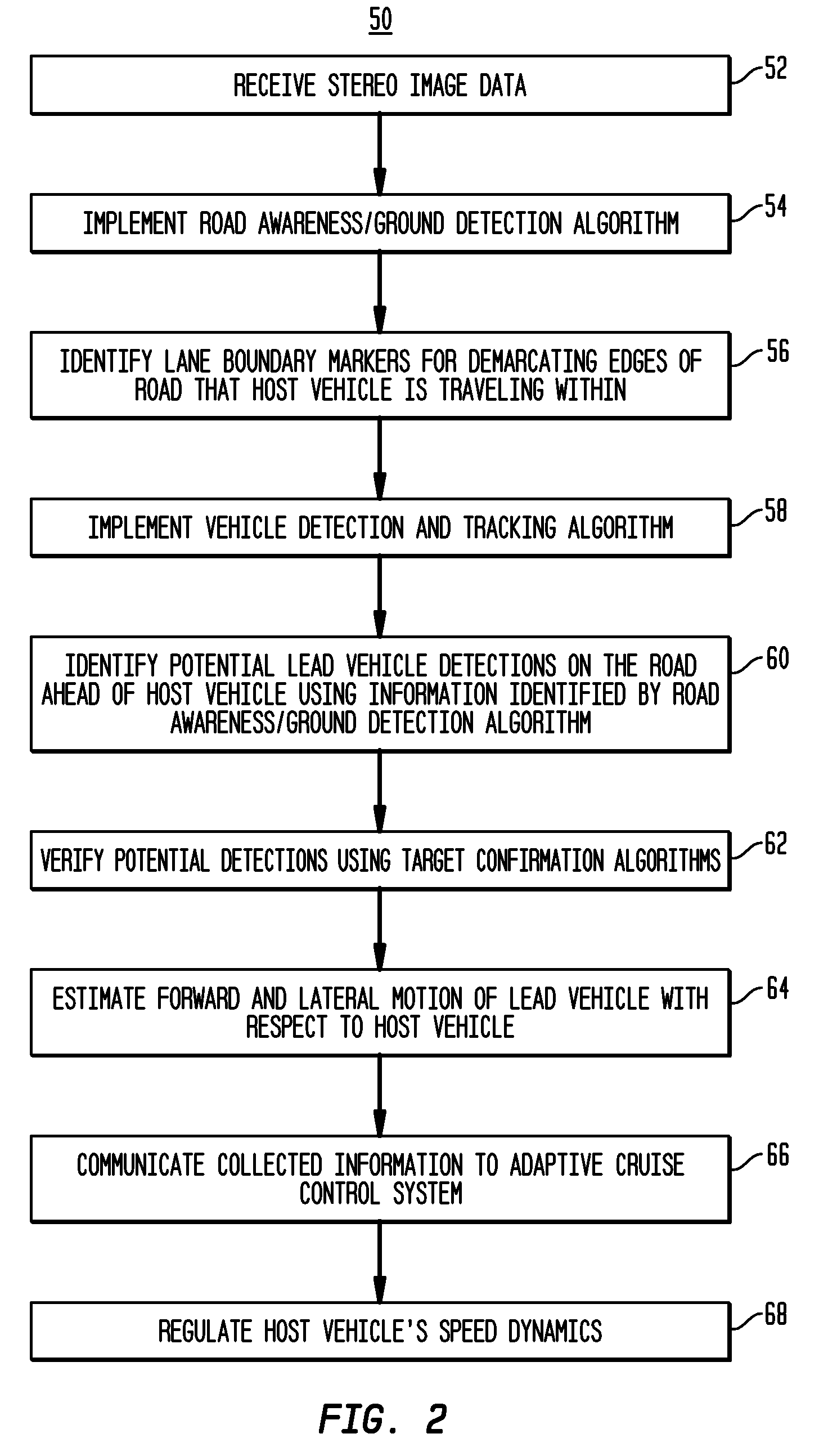
Apparatus and method for object detection and tracking and roadway awareness using stereo cameras
ActiveUS20070255480A1Performance-enhanced approachComponent is expensiveImage analysisDigital data processing detailsControl systemStereo cameras
The present invention provides a collision avoidance apparatus and method employing stereo vision applications for adaptive vehicular control. The stereo vision applications are comprised of a road detection function and a vehicle detection and tracking function. The road detection function makes use of three-dimensional point data, computed from stereo image data, to locate the road surface ahead of a host vehicle. Information gathered by the road detection function is used to guide the vehicle detection and tracking function, which provides lead motion data to a vehicular control system of the collision avoidance apparatus. Similar to the road detection function, stereo image data is used by the vehicle detection and tracking function to determine the depth of image scene features, thereby providing a robust means for identifying potential lead vehicles in a headway direction of the host vehicle.
Owner:ZAMA INNOVATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com