Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2019 results about "Signal correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
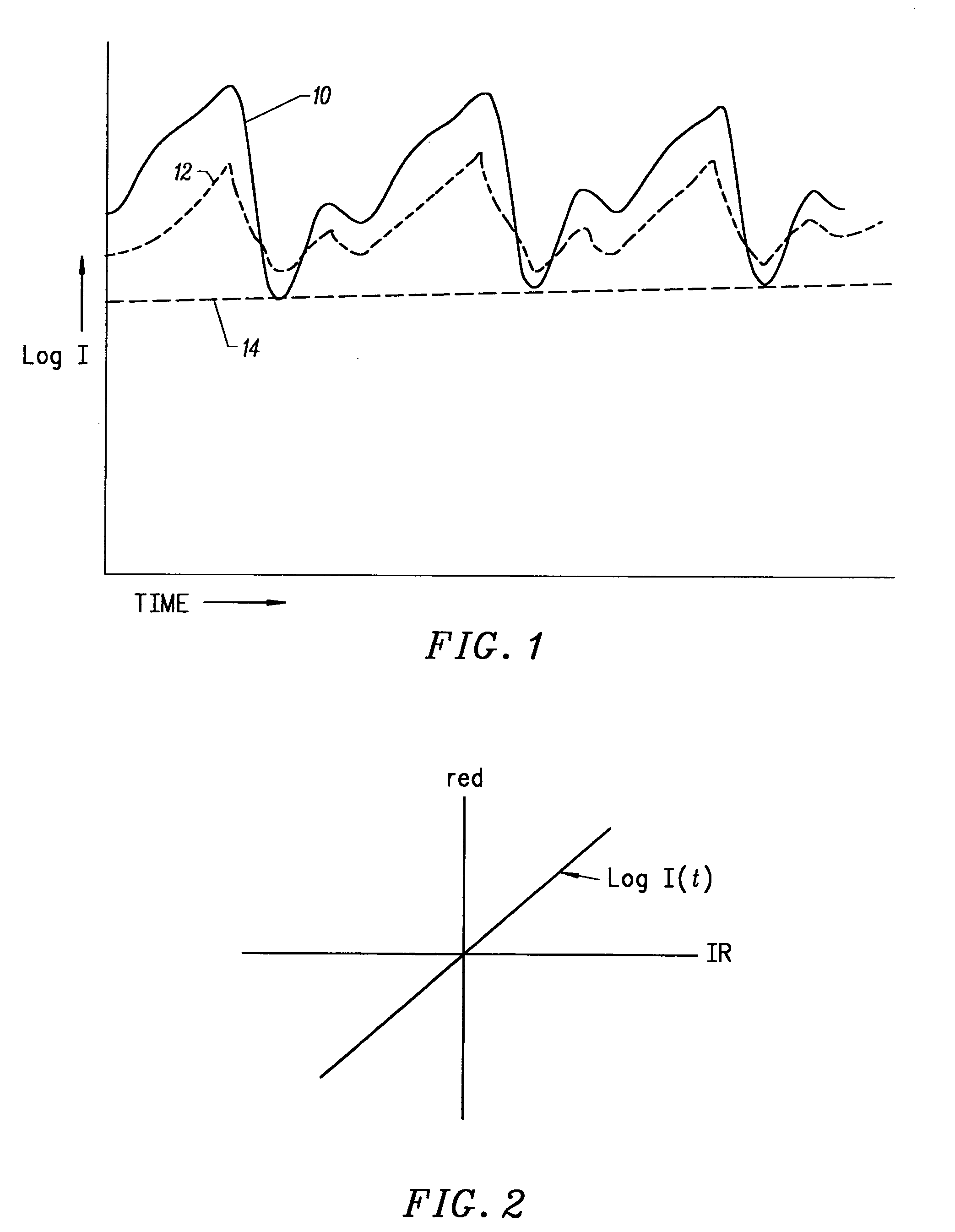
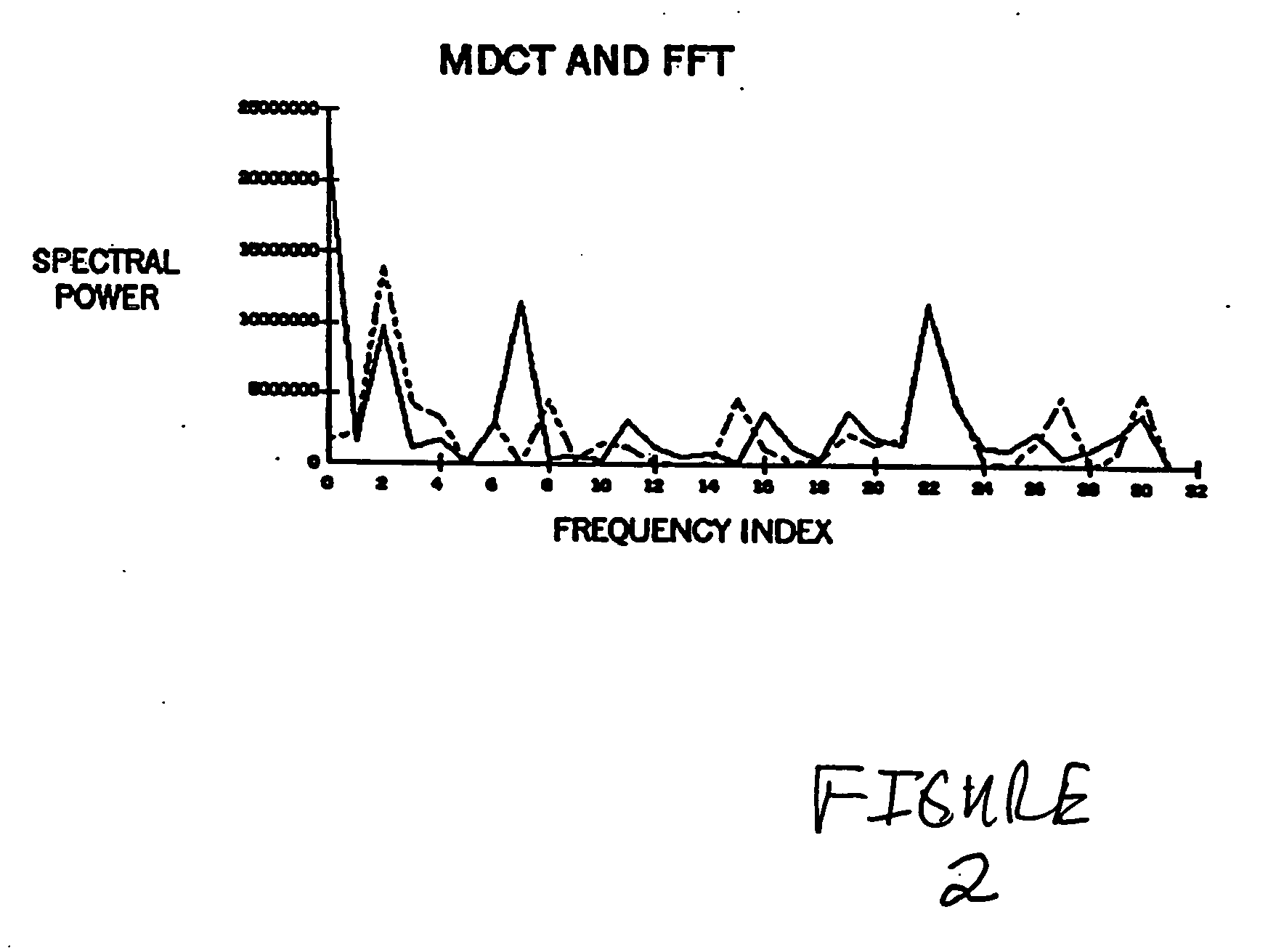
CORRELATION SIGNAL CORRELATION. When two signals tend to point in the same direction, we say that they are correlated. Signals show a positive correlation if they tend to increase and decrease together. Signals show a negative correlation if one tends to increase when the other decreases, and vice-versa.
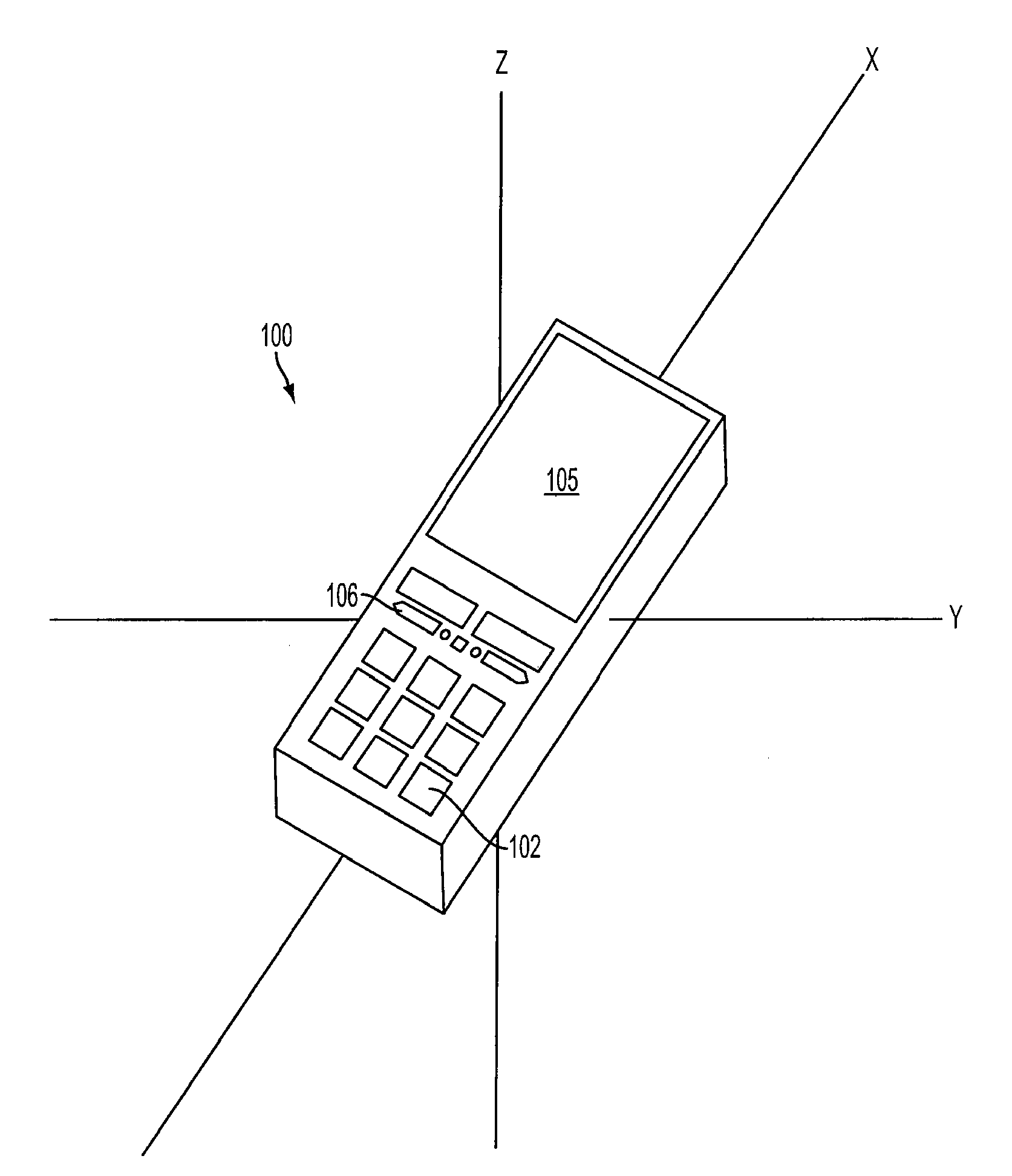
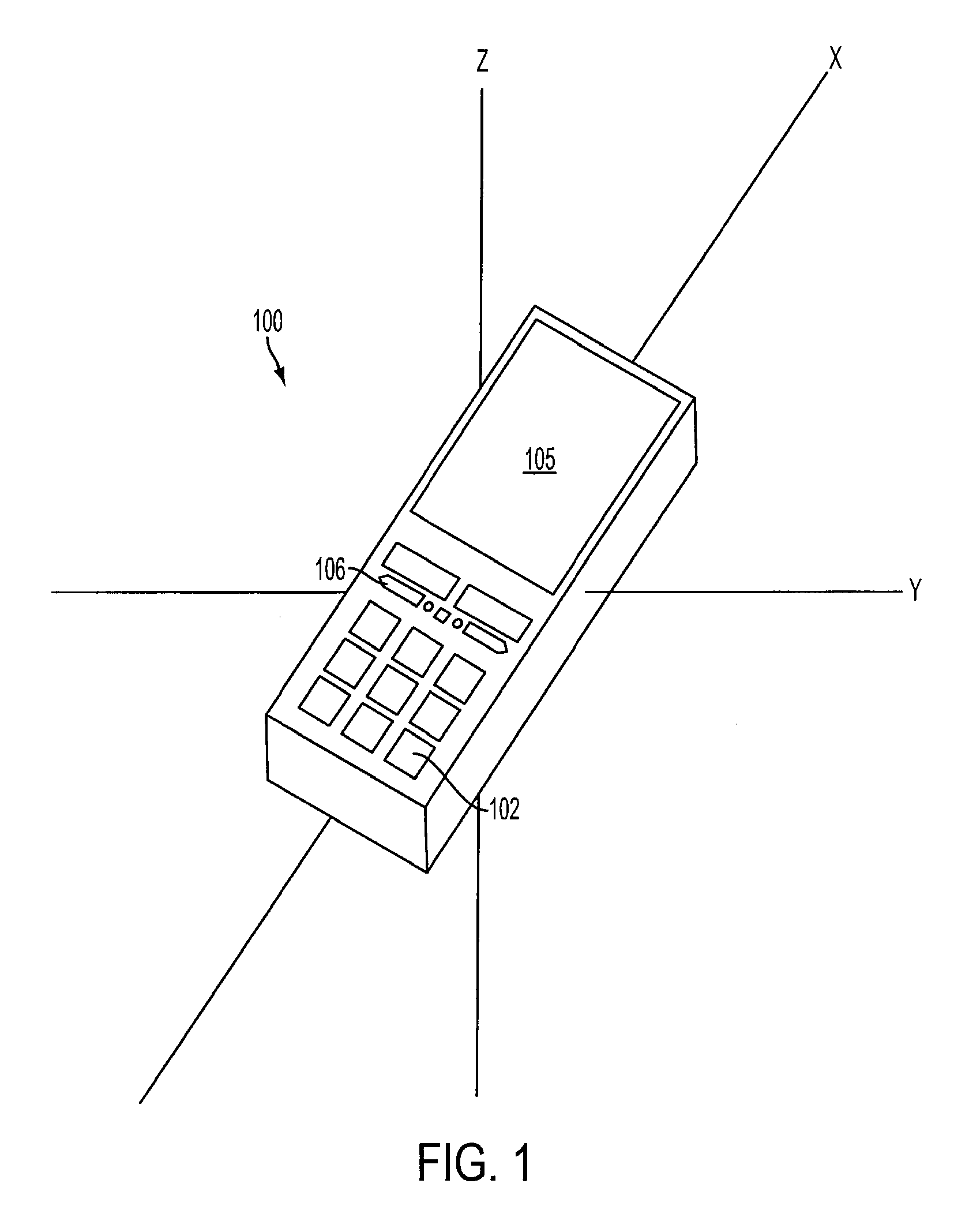
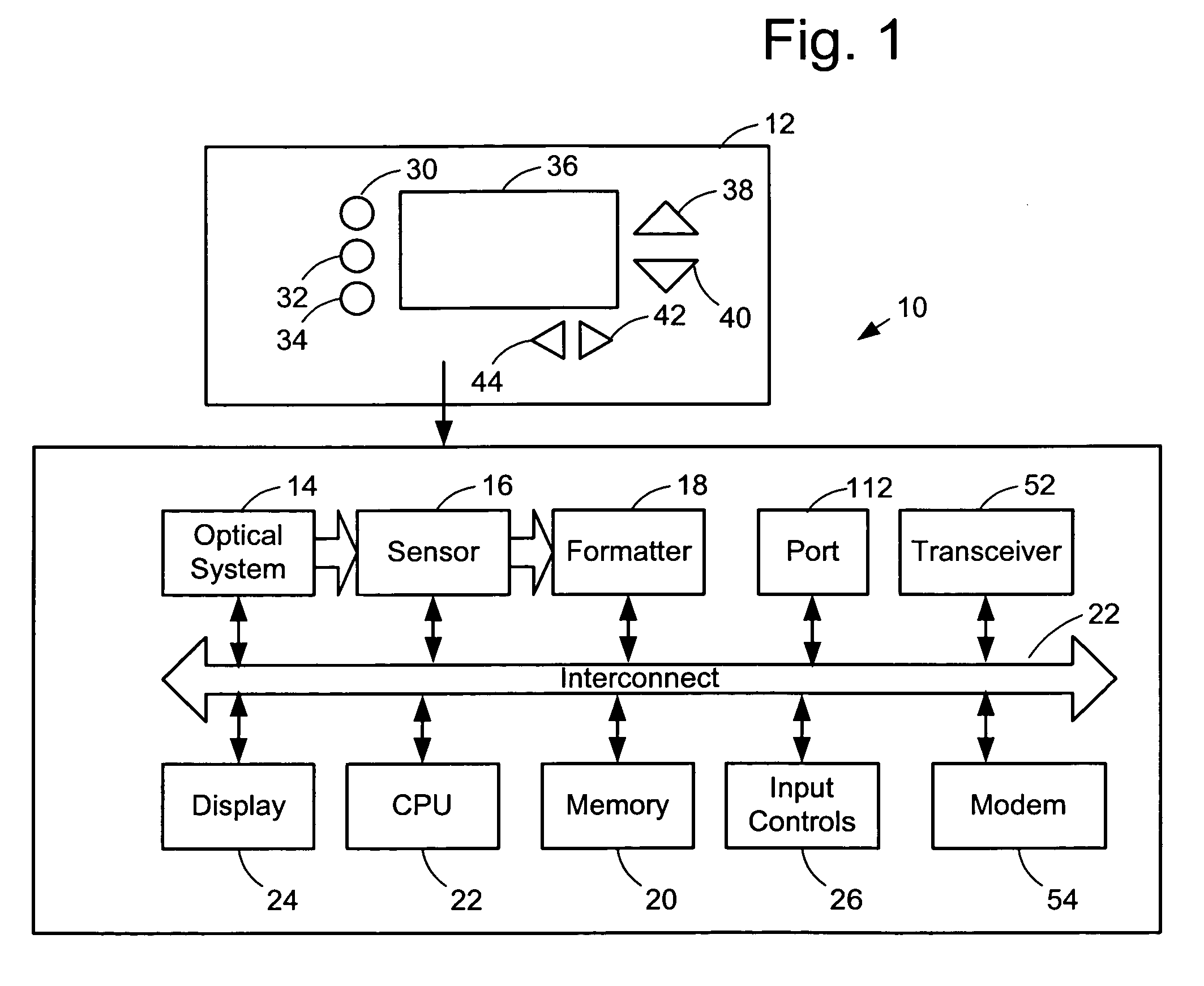
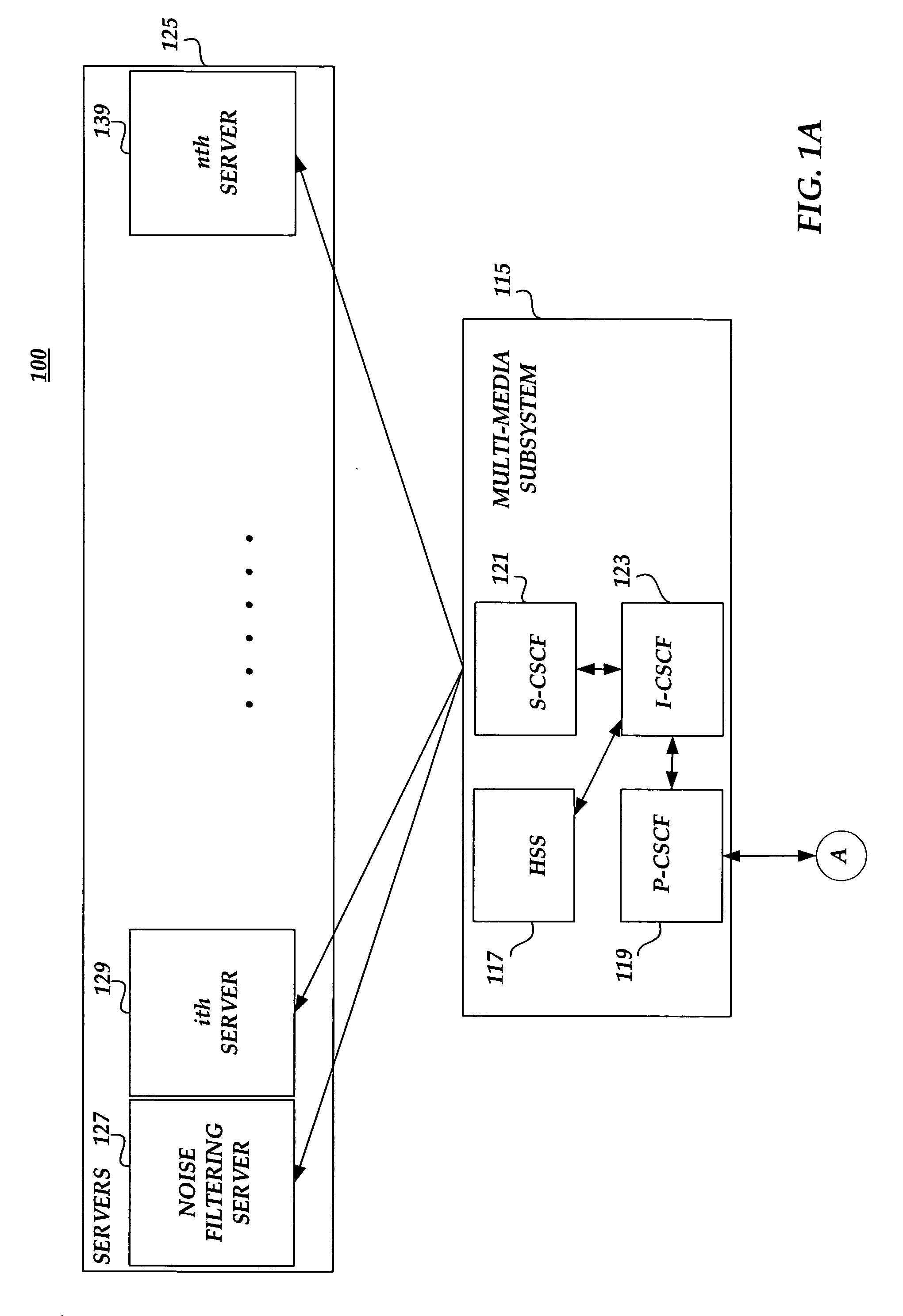
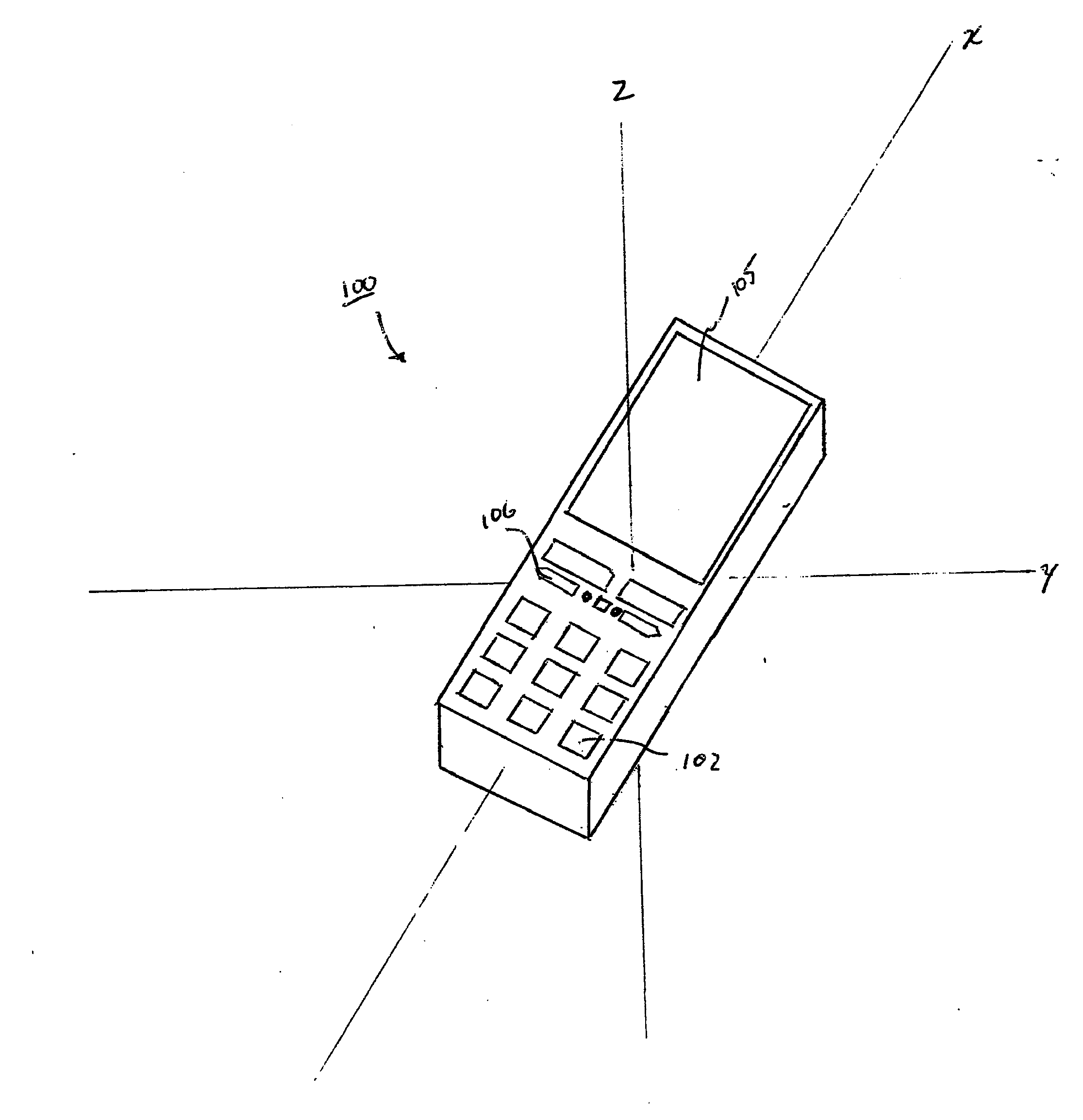
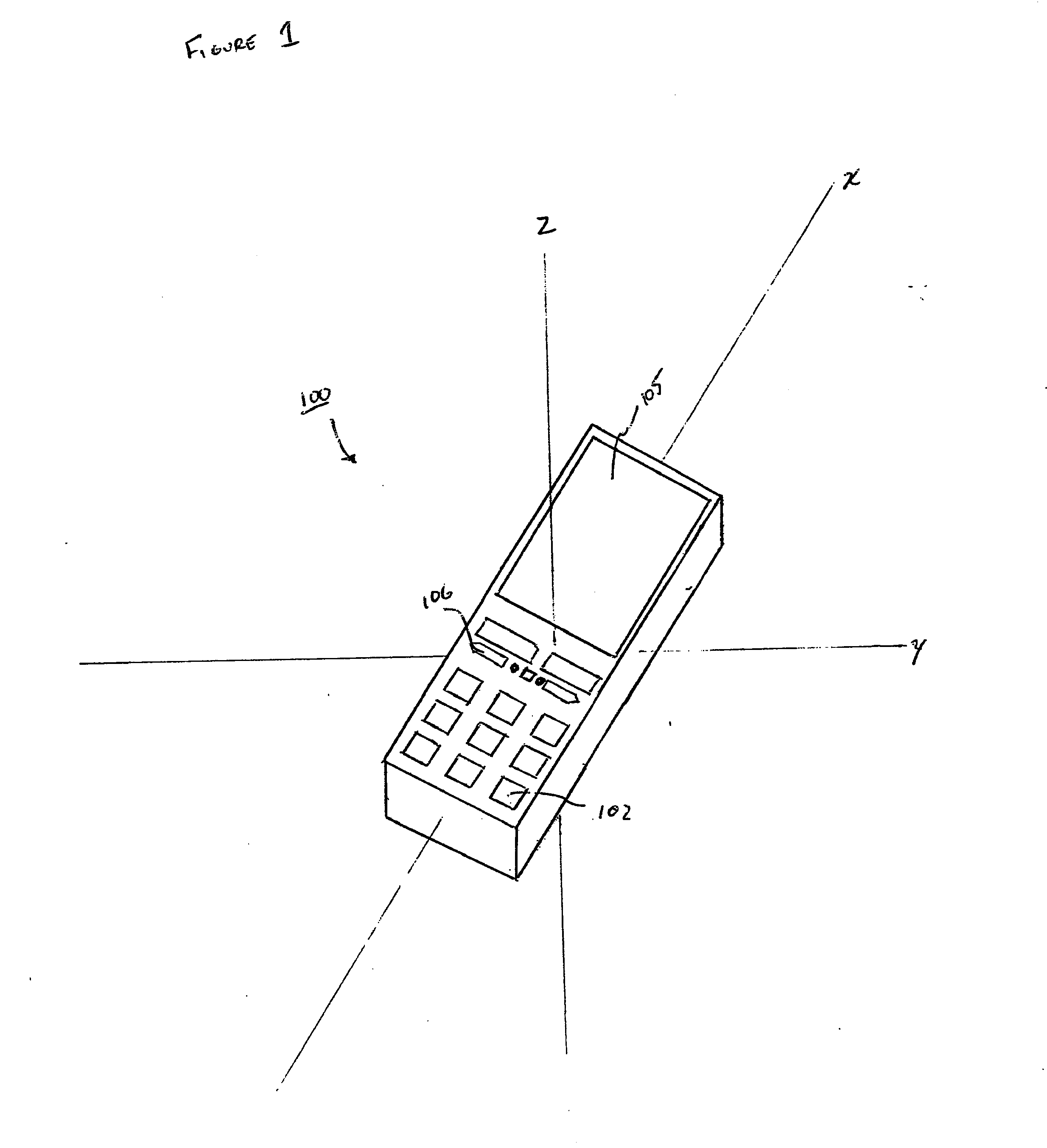
Orientation-sensitive signal output
The selection and output of a signal, such as an alphanumeric character, is provided depending upon the orientation of a device, such as a mobile telephone. In particular, a neutral position of a device is determined in relation to at least a first axis, the device including at least a first control associated with a first plurality of output signals, and an angular displacement of the device is measured about at least the first axis. A selection of the first control is also received, and one of the first plurality of output signals is output based at least upon the selection and the angular displacement.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
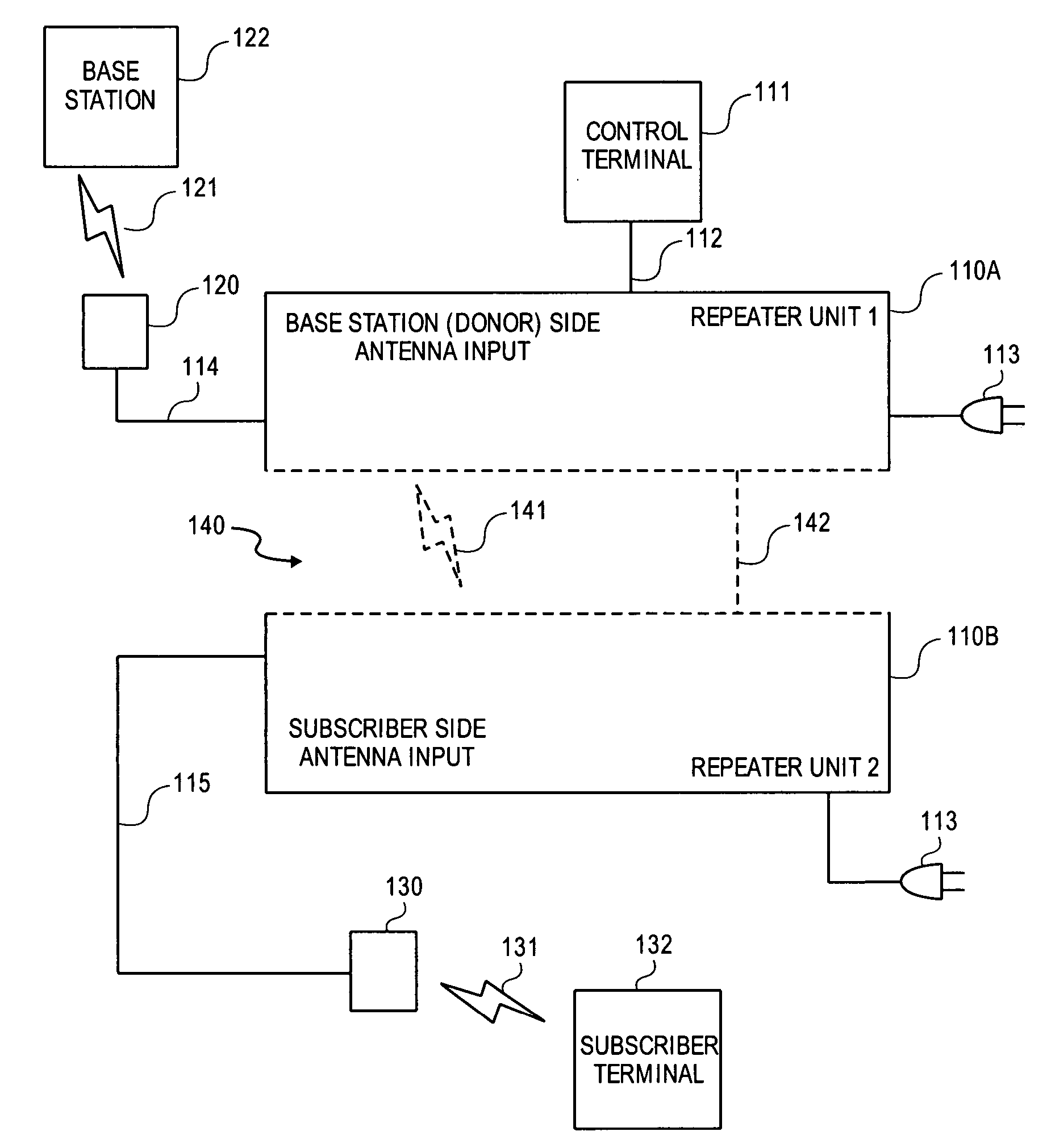
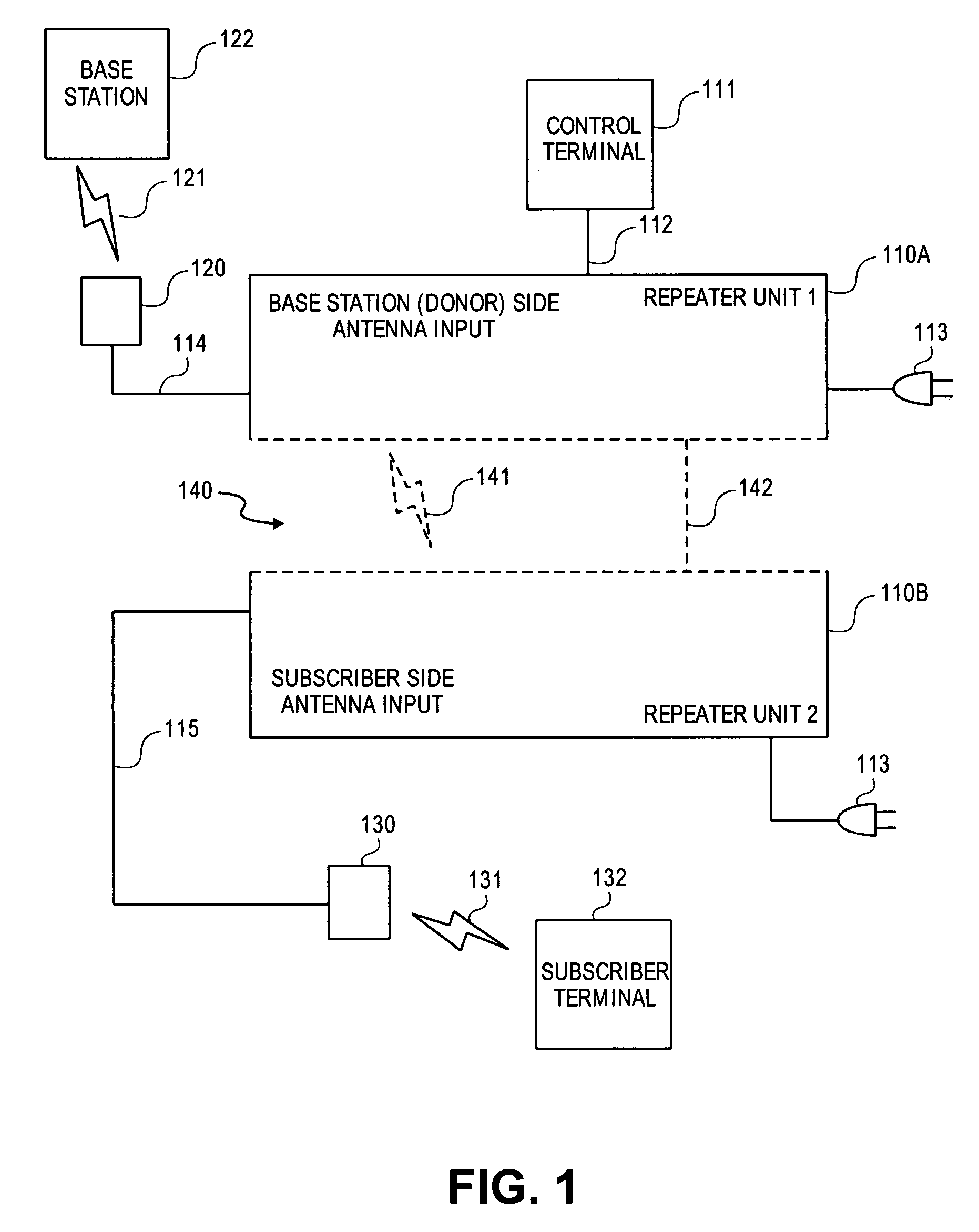
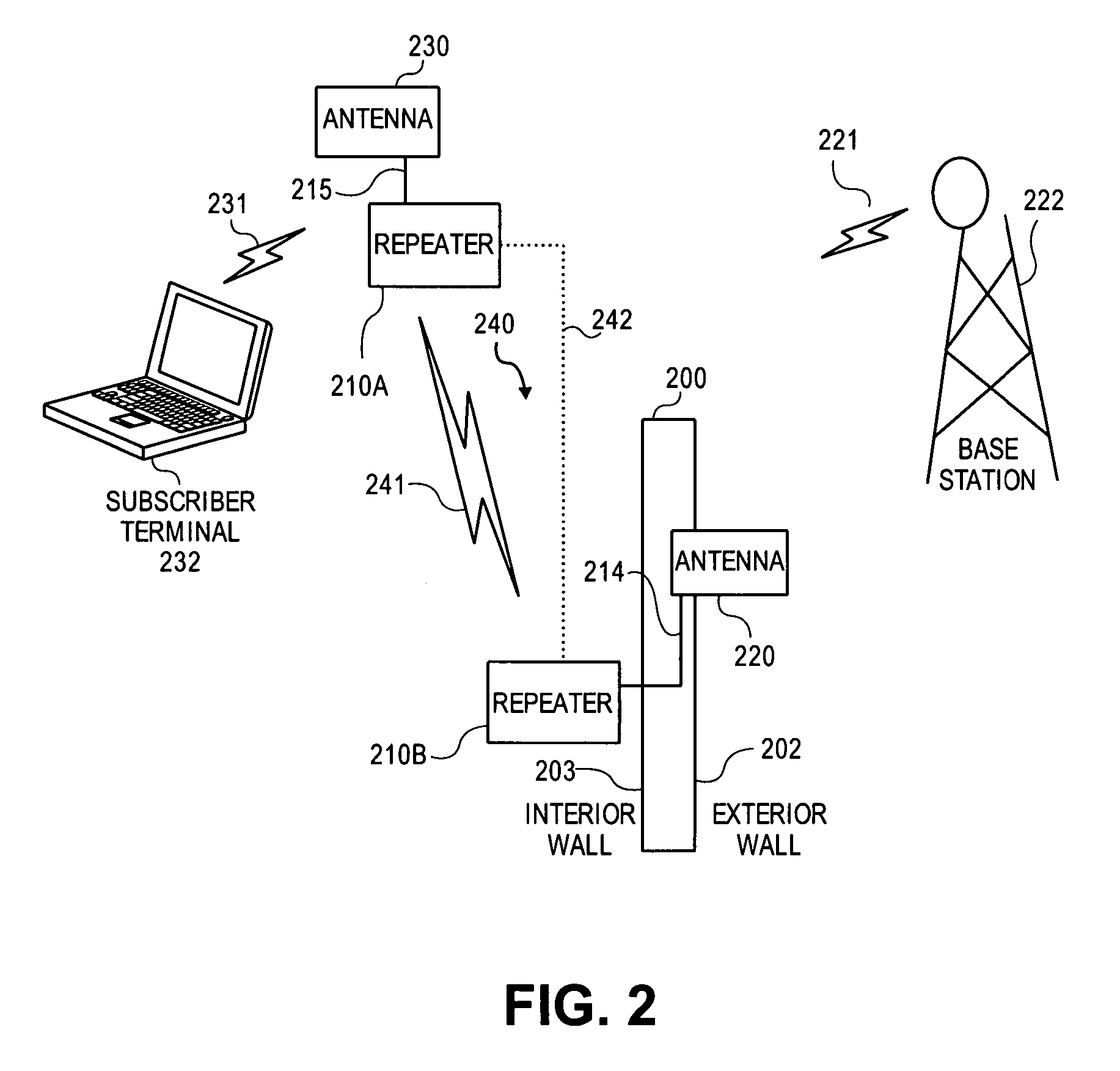
Enhanced physical layer repeater for operation in WiMAX systems
A method and repeater are described for repeating using a time division duplex (TDD) radio protocol. A signal is transmitted from a first station to a second station using a downlink and an uplink. The signal can be detected on the uplink or the downlink. The repeater can synchronize to time intervals associated with the detected signal that are measured during an observation period. The signal can be retransmitted from the second station to the first station if the signal is detected on the uplink and re-transmitted from the first station to the second station if the signal is detected on the downlink. A gain value associated with the downlink can be used to establish a gain value associated with the uplink.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
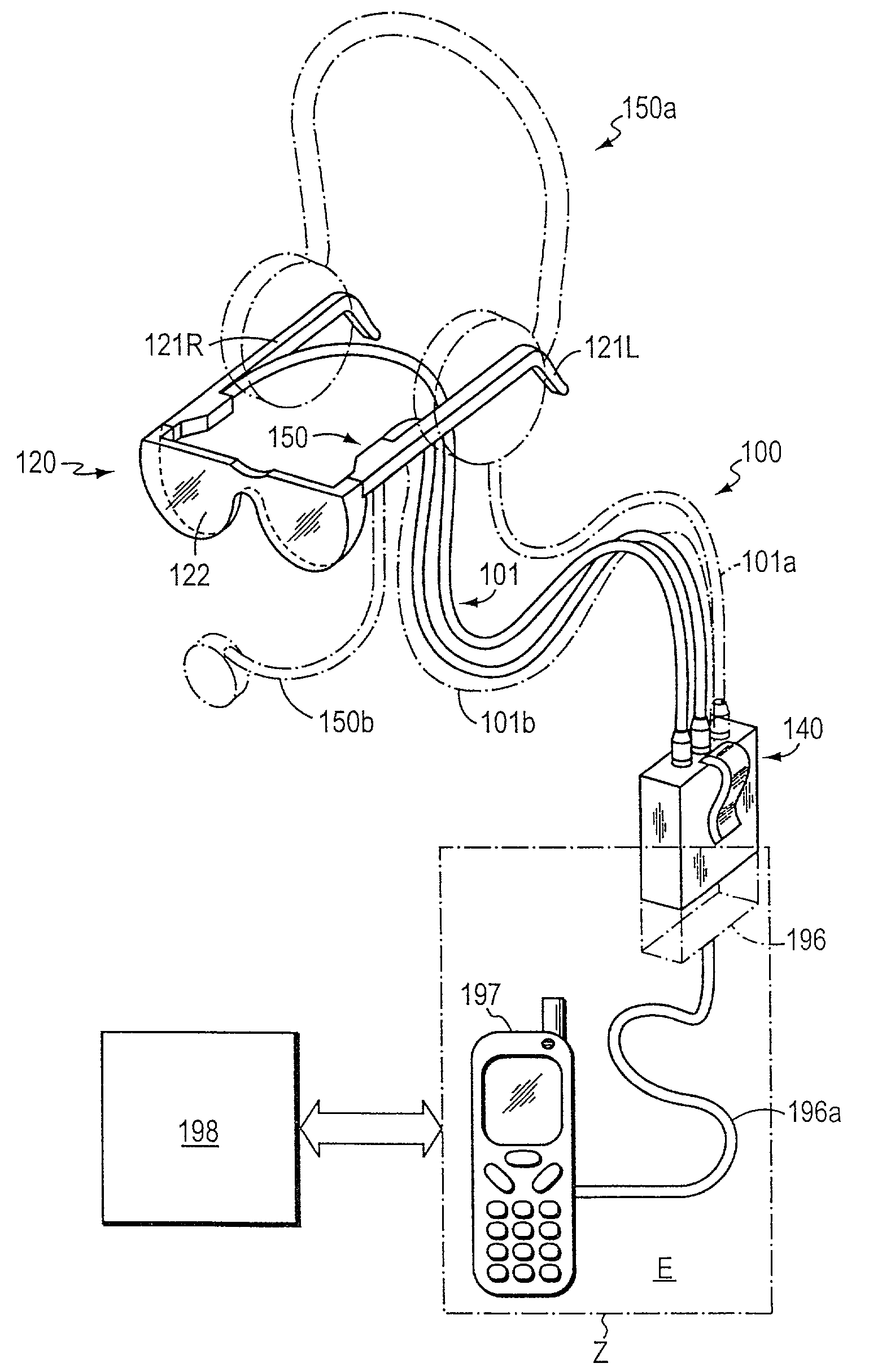
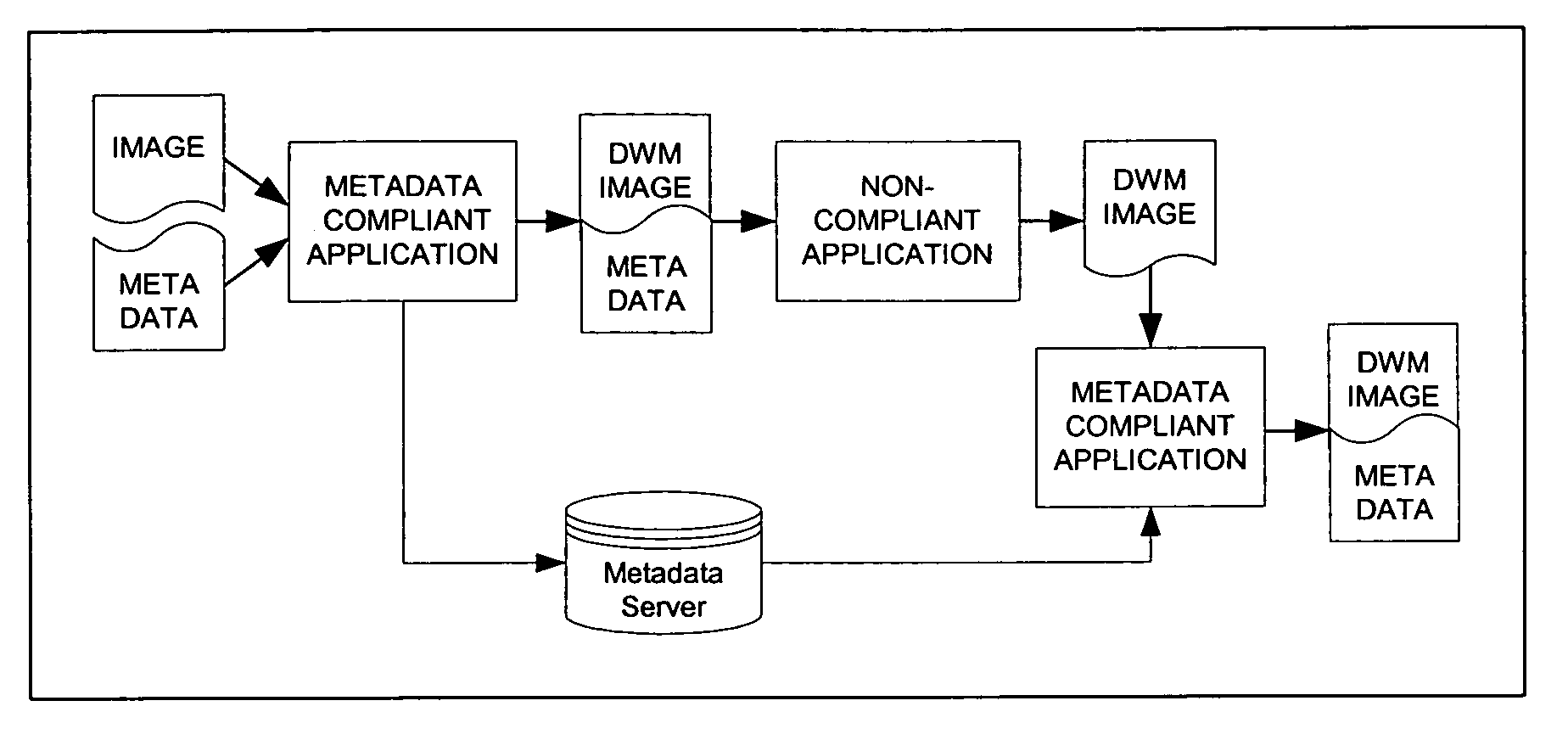
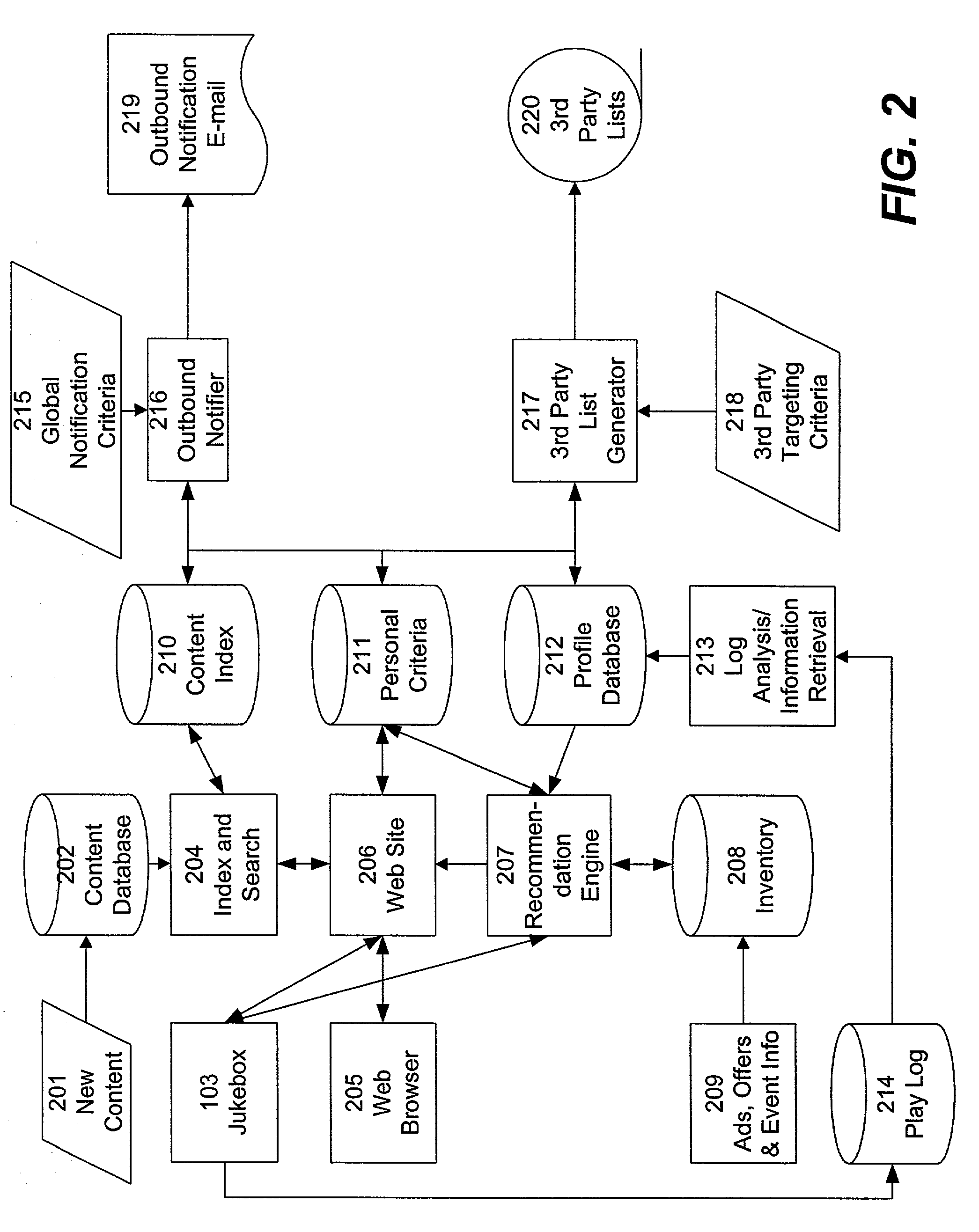
Interactive data view and command system
InactiveUS7245273B2Improved system characteristicGood basisInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCommunication unitData view
A method and information system for capturing signals, for processing signals, and for providing signals at least partially based on, or bearing correlation to, the captured signals is disclosed. The information system includes a signal input unit, a wireless communication unit, and an output unit. The signal input unit (preferably an optical signal unit) is constructed and is positionable to capture signals associated with an eye. The output unit is constructed to provide information based on the captured signals or to provide information as a function of the captured signals or in correlation with the captured signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
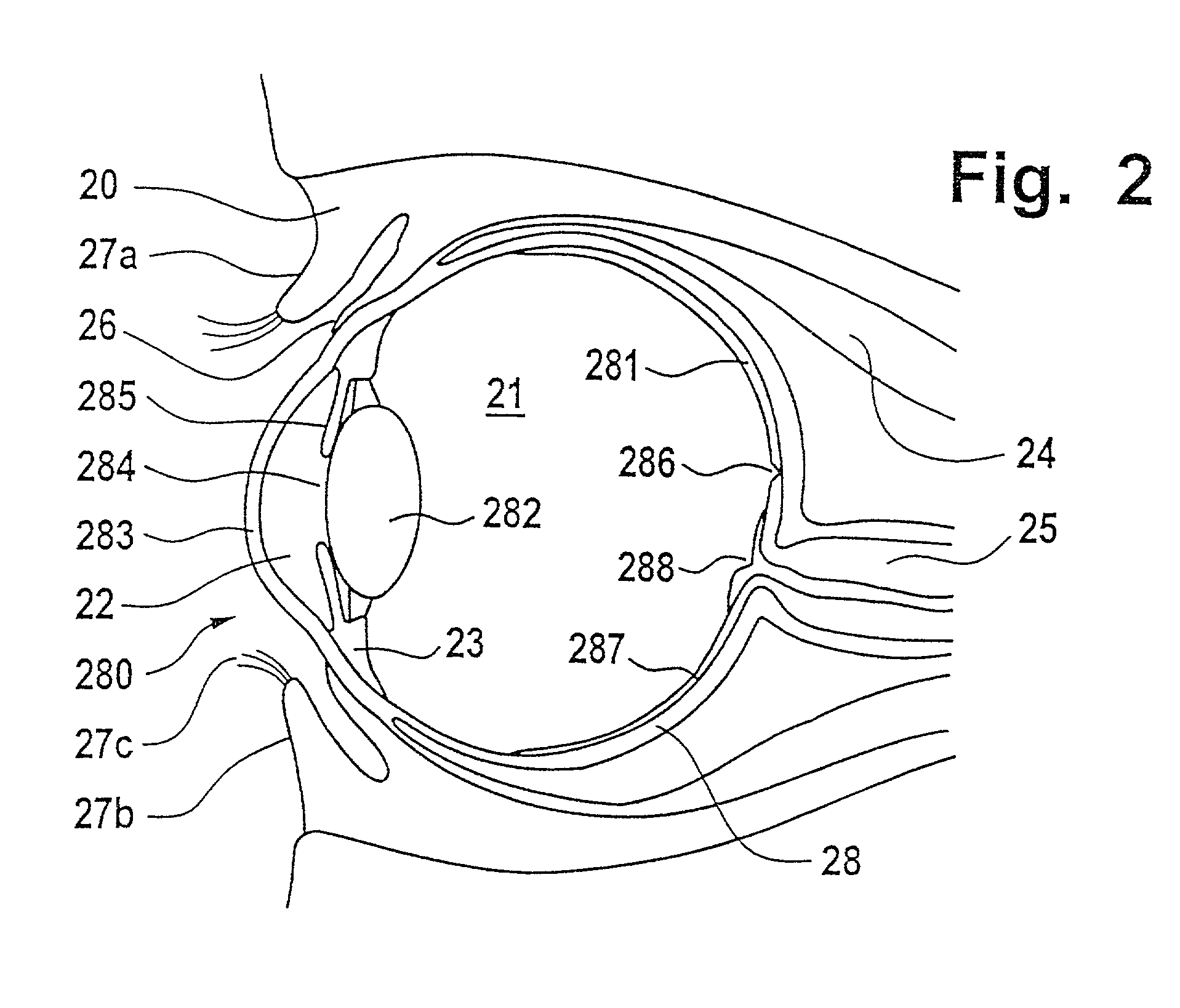
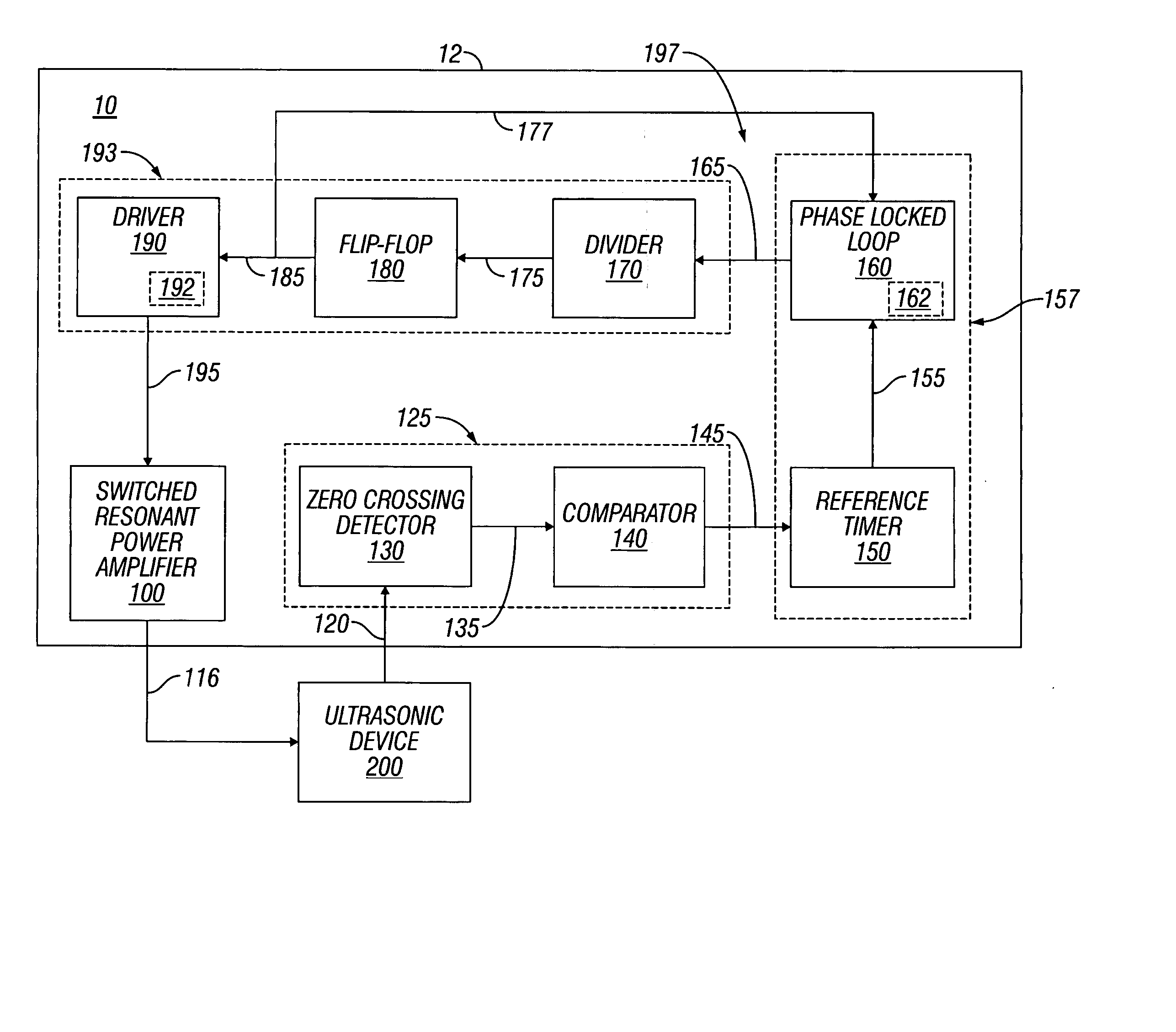
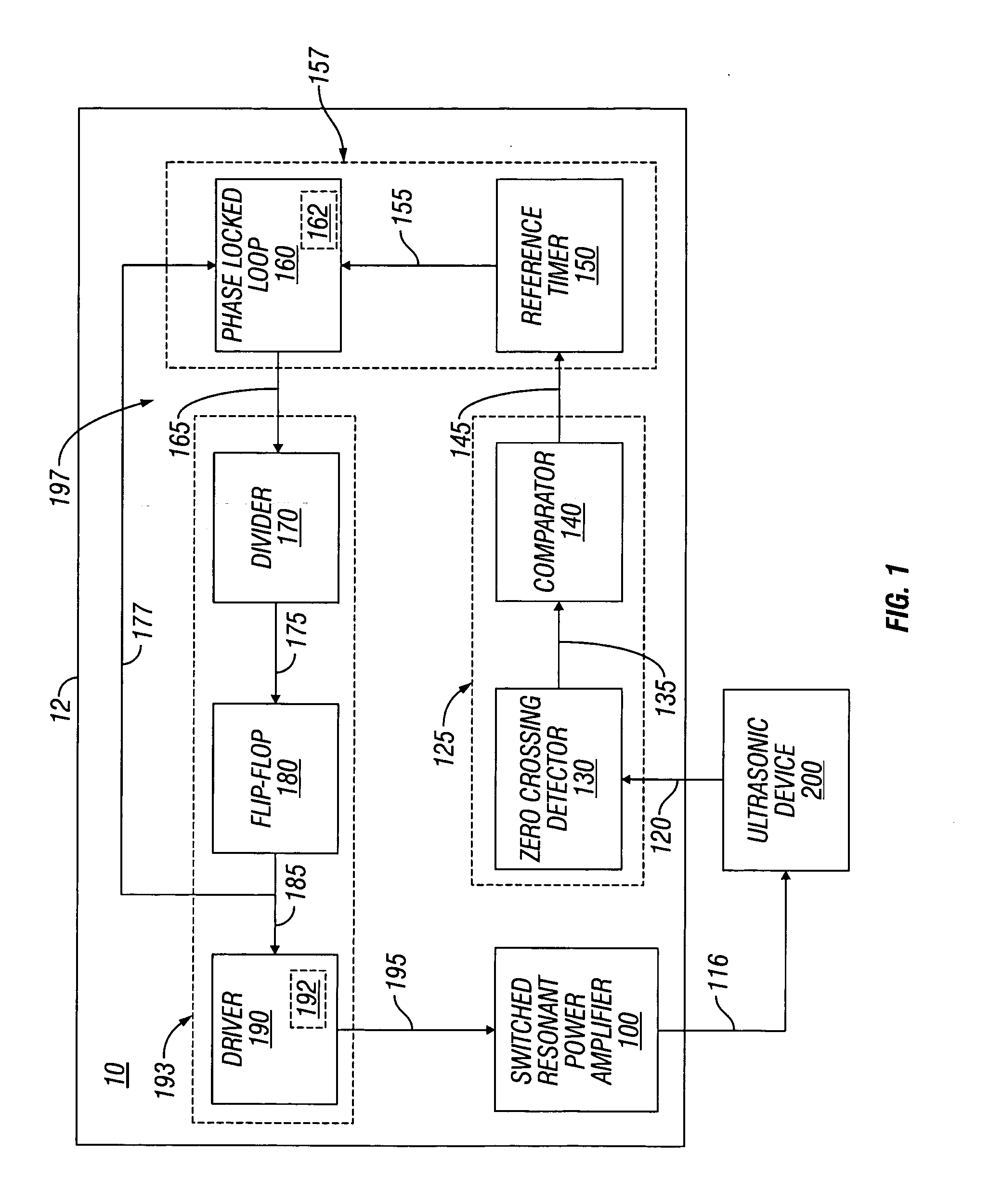
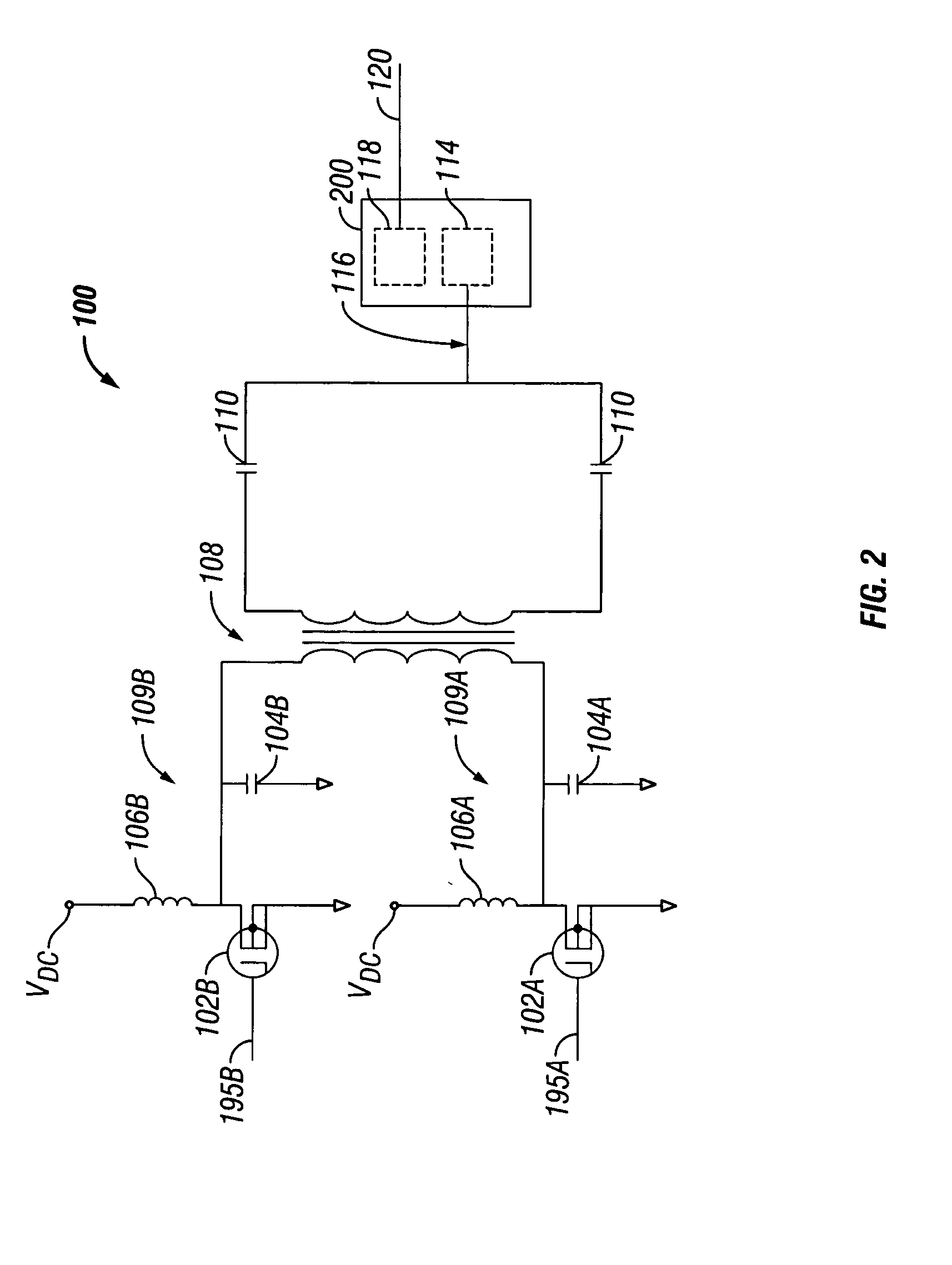
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS7396336B2Operation efficiency can be improvedSmall footprintUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyHemt circuitsControl ultrasound
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
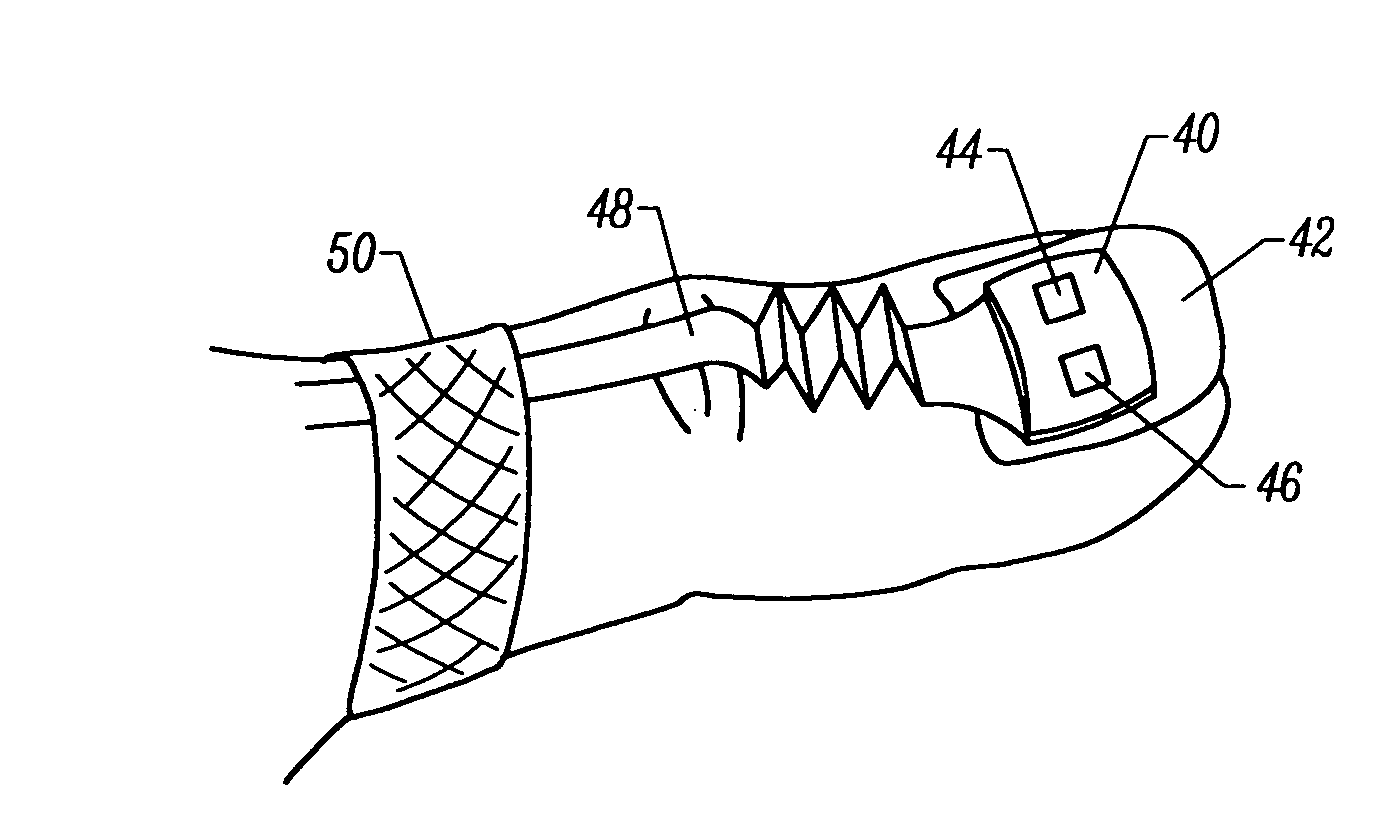
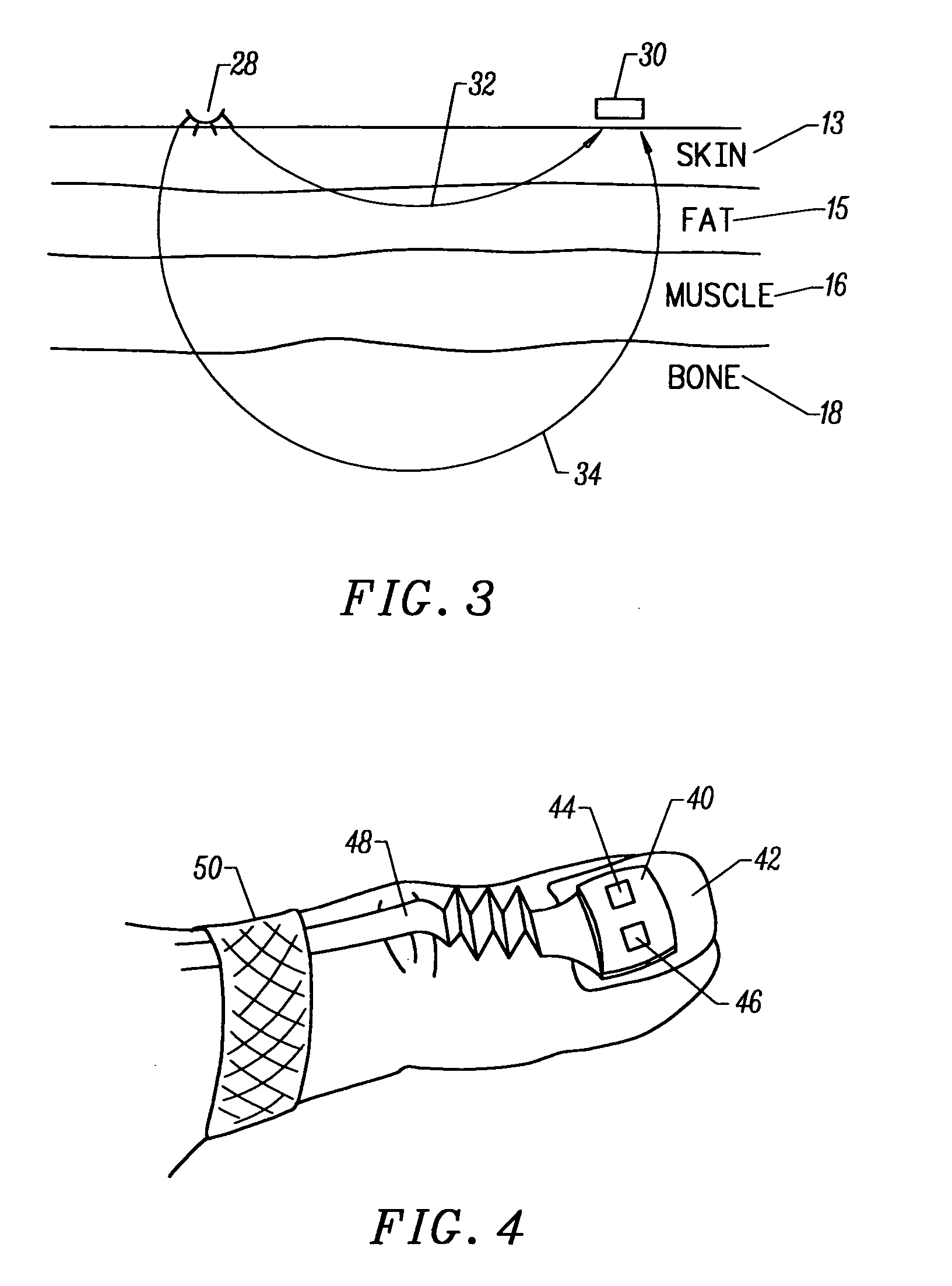
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS20050070773A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
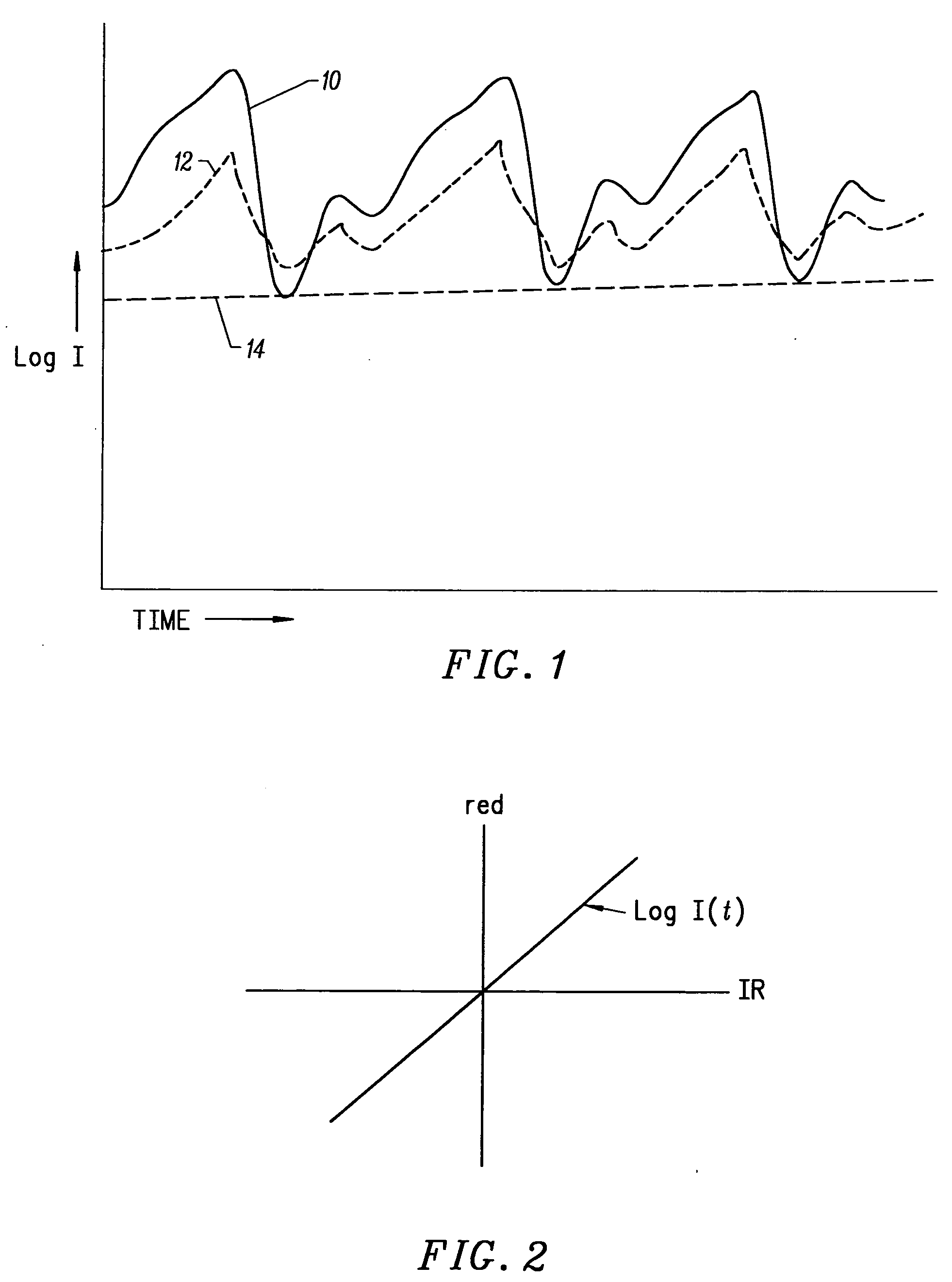
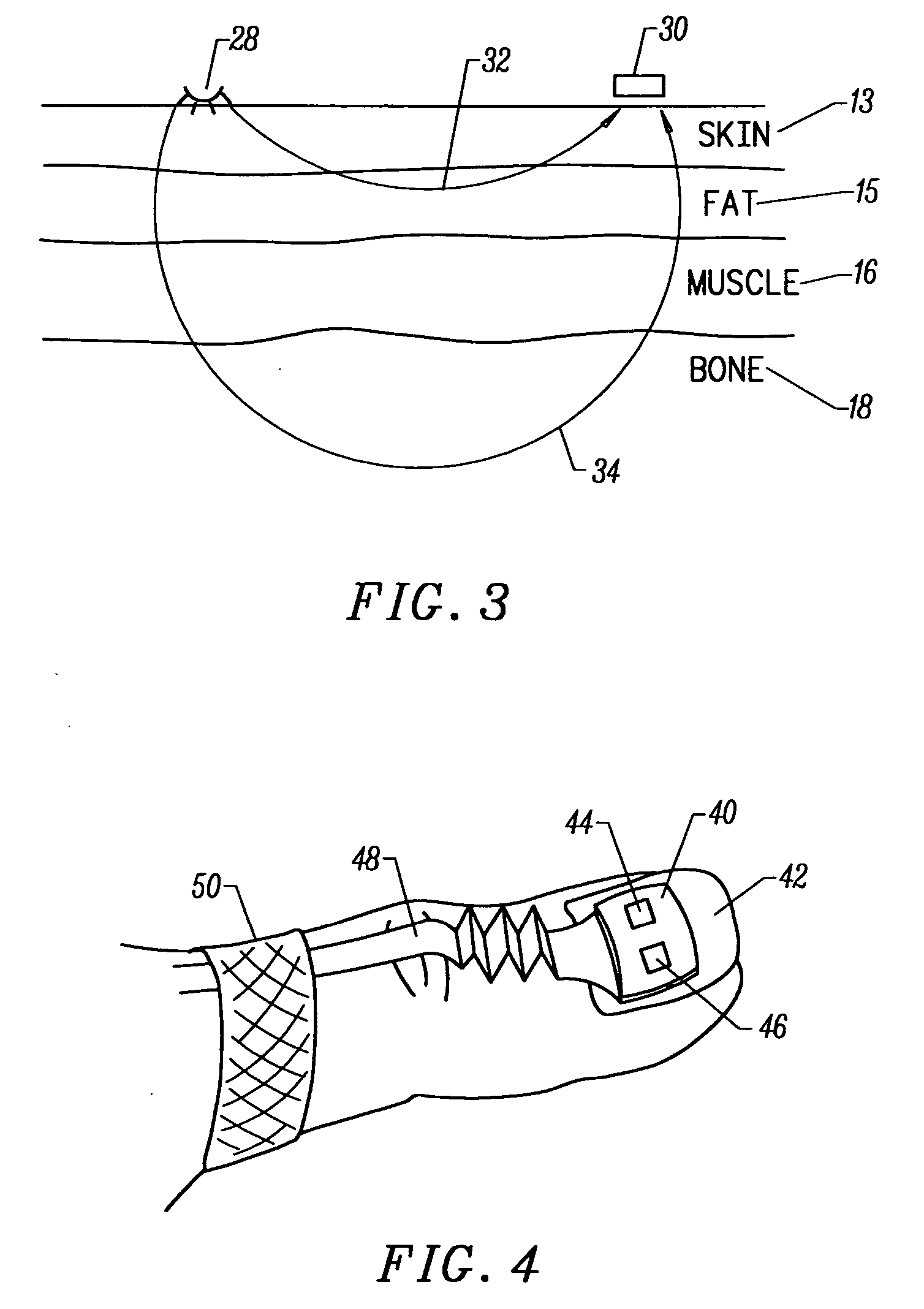
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
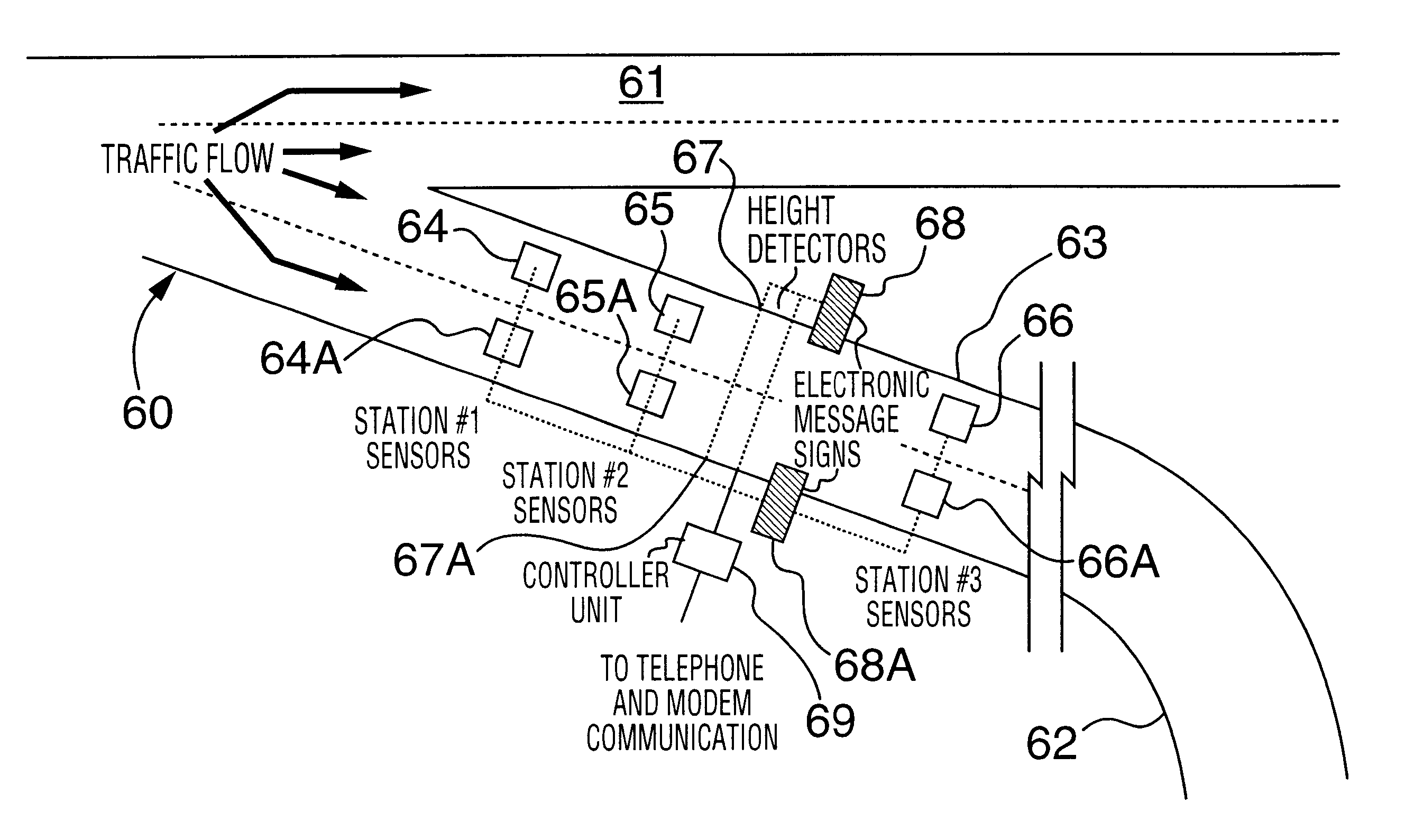
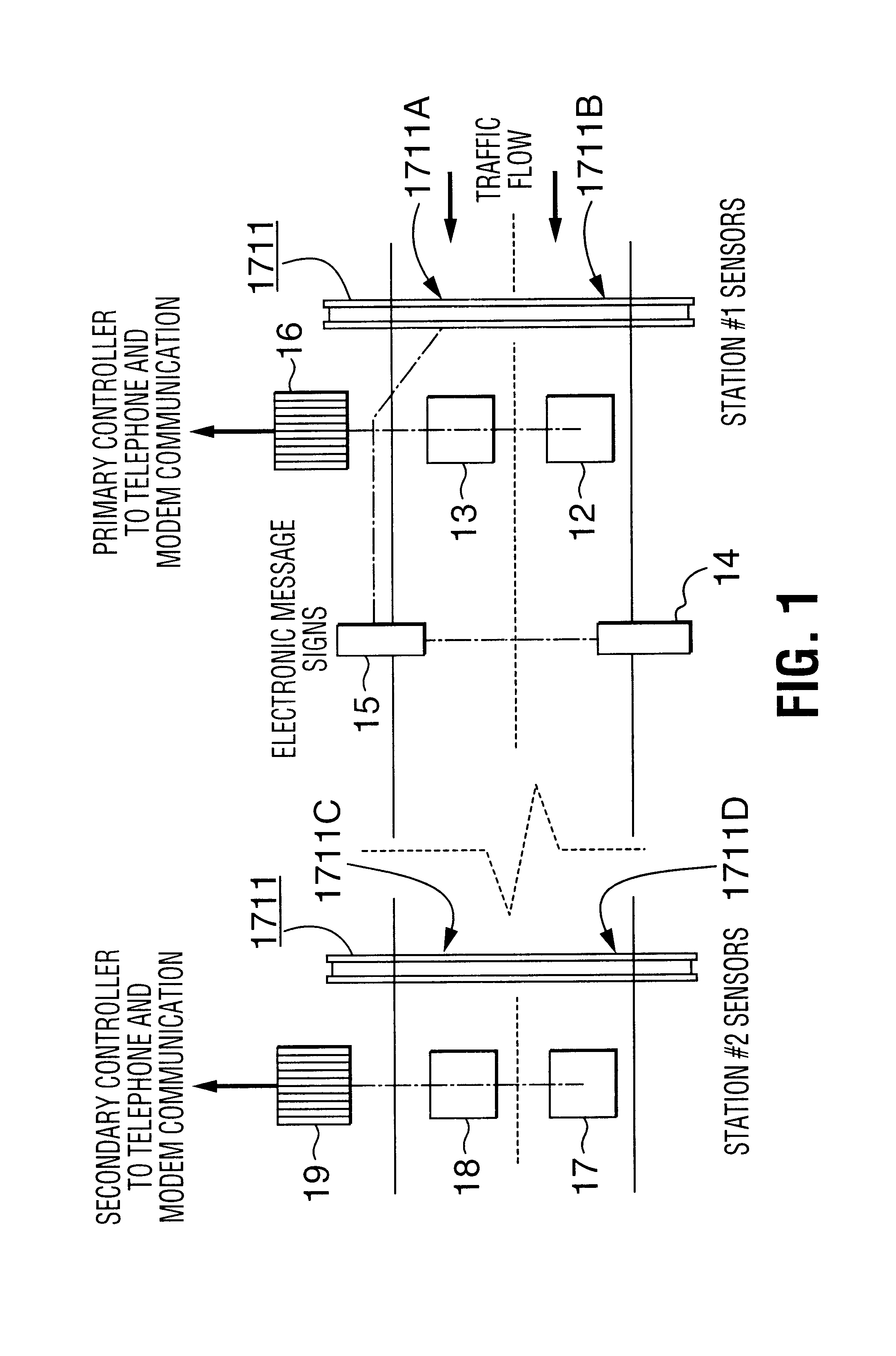
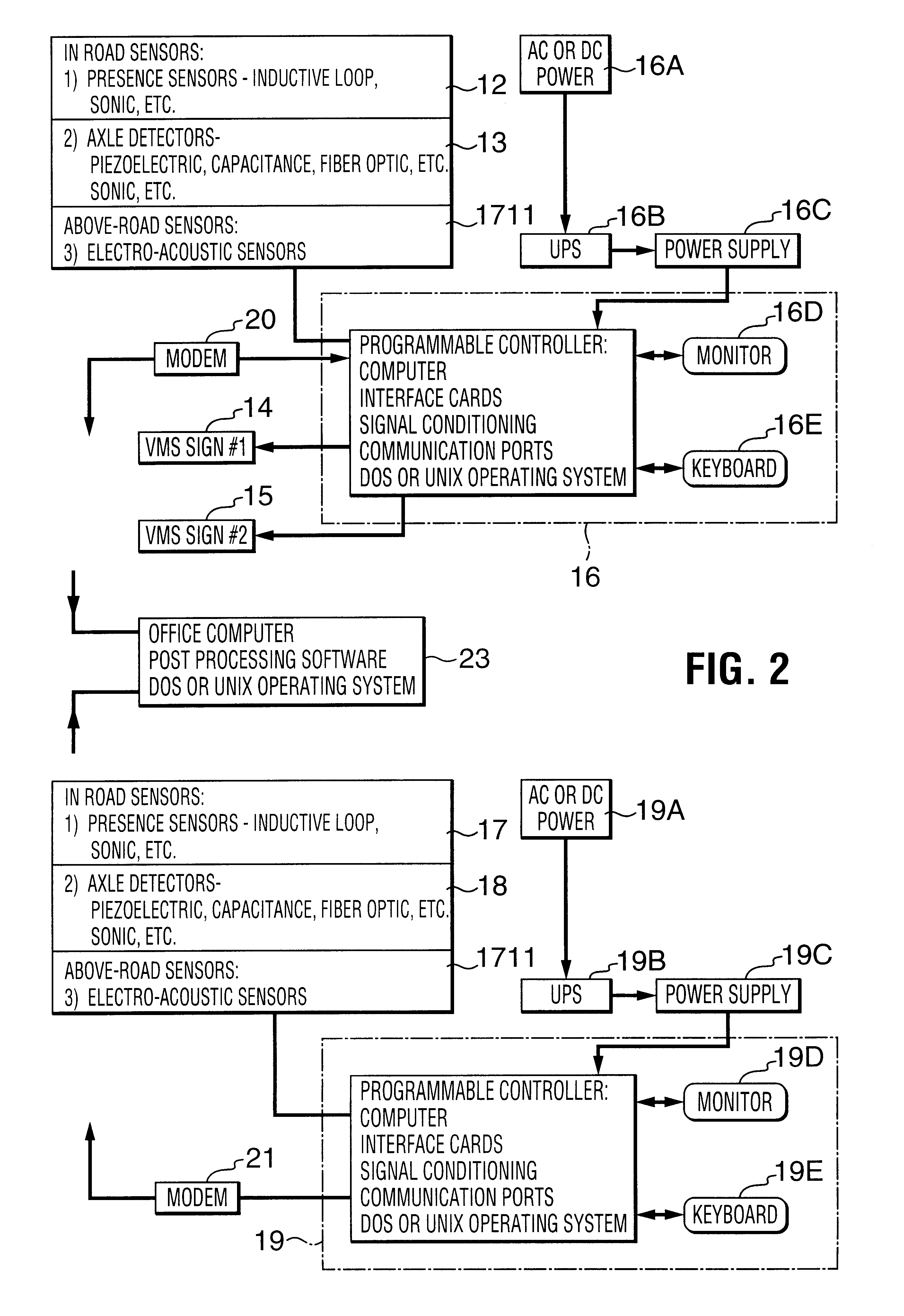
Truck traffic monitoring and warning systems and vehicle ramp advisory system
InactiveUS6204778B1Prevent rolloverControlling traffic signalsAnalogue computers for vehiclesTruckSensor array
Traffic monitoring and warning systems and vehicle ramp advisory systems are provided herein. Such system includes a set of sensor arrays comprising a set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays which is disposed above a traffic lane approaching a hazard for producing signals which are indicative of whether the vehicle is an automobile or a truck and, if it is a truck, to record the presence of such truck, and to provide signals which are indicative of the speed of such truck. A processor is provided which has a memory for storing site-specific data related both to the geometry of the hazard and to signals which have been received from the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays. A traffic signalling device is associated with the traffic lane and is disposed downstream of the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays, the traffic signalling device being controlled by the processor. The processor is responsive to the signals from the set of above-road electro-acoustic sensor arrays for computing an actual speed of the truck and for computing a computed maximum safe speed for such truck at the hazard. The computed maximum safe speed of the truck is derived from the site-specific dimensional data of the hazard and from at least the initial speed of the truck, the computed maximum safe speed of the truck being a maximum safe speed for that truck safely to negotiate the hazard. The processor compares the computed actual speed of the truck with the computed maximum safe speed for the truck. Then, the processor automatically operates the traffic signalling device if the computed actual speed of the truck exceeds the computed maximum safe speed for the truck. The processor also discontinues operating the traffic signalling device if the computed actual speed of the truck no longer exceeds the computed maximum safe speed for the truck.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL ROAD DYNAMICS
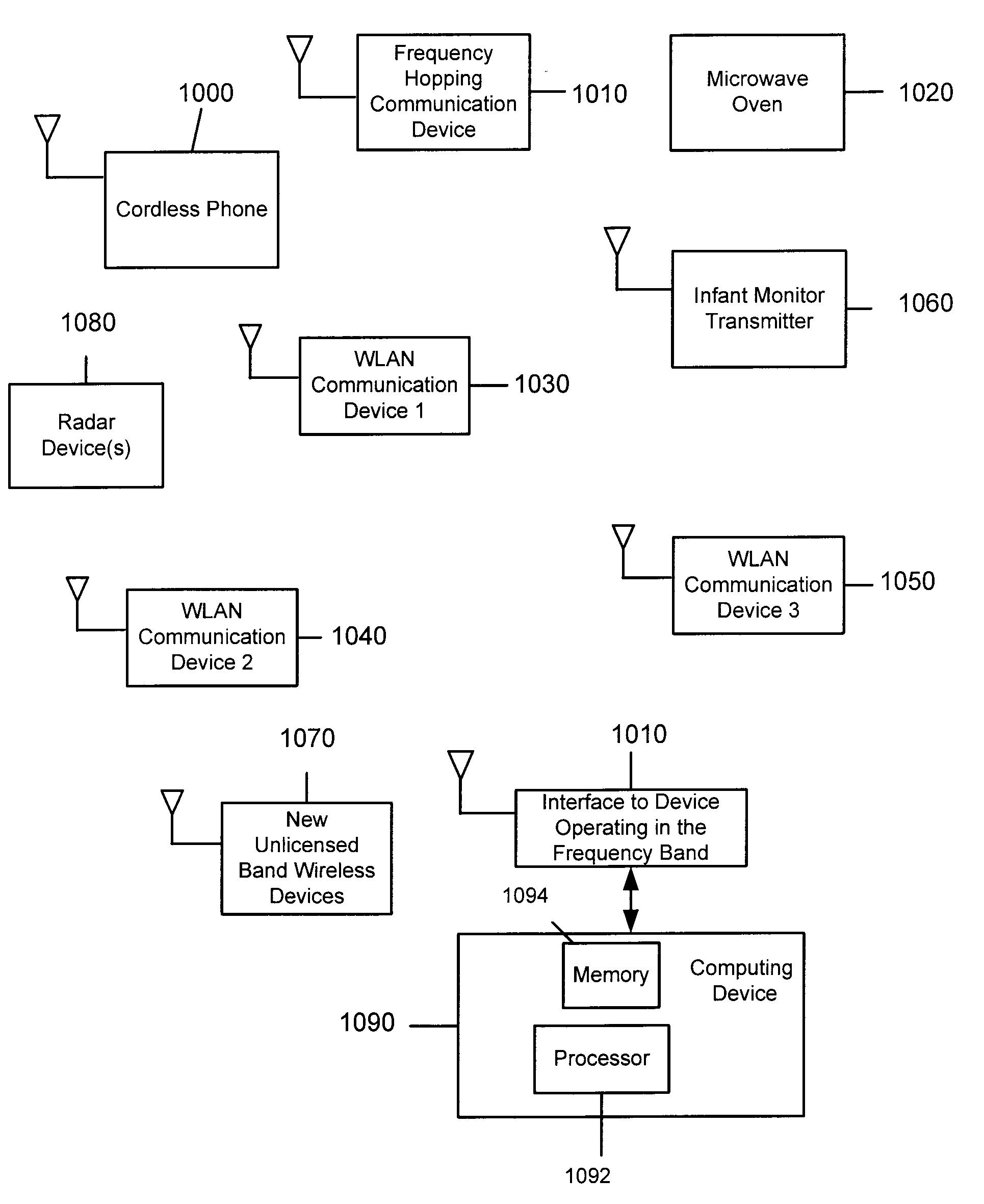
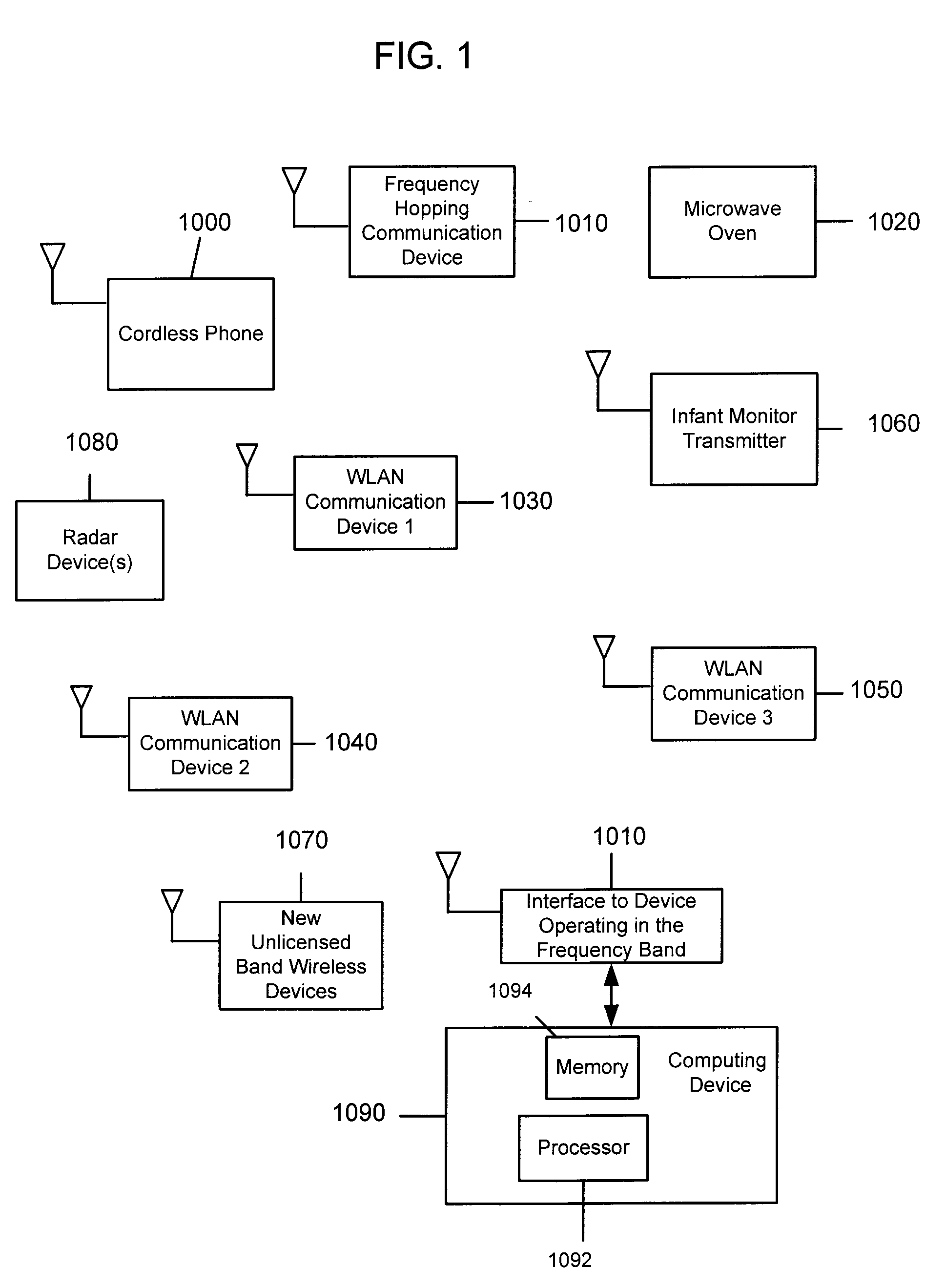
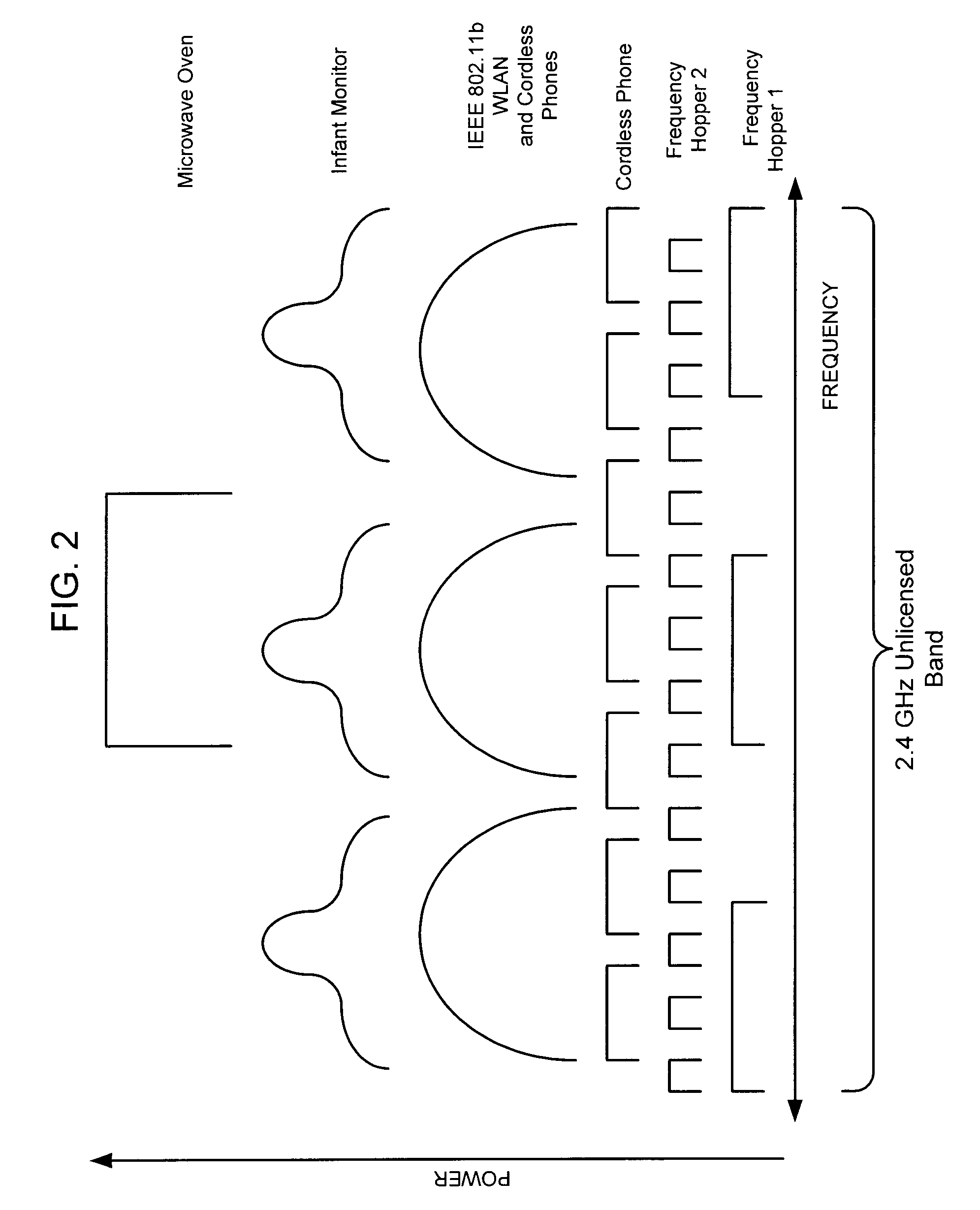
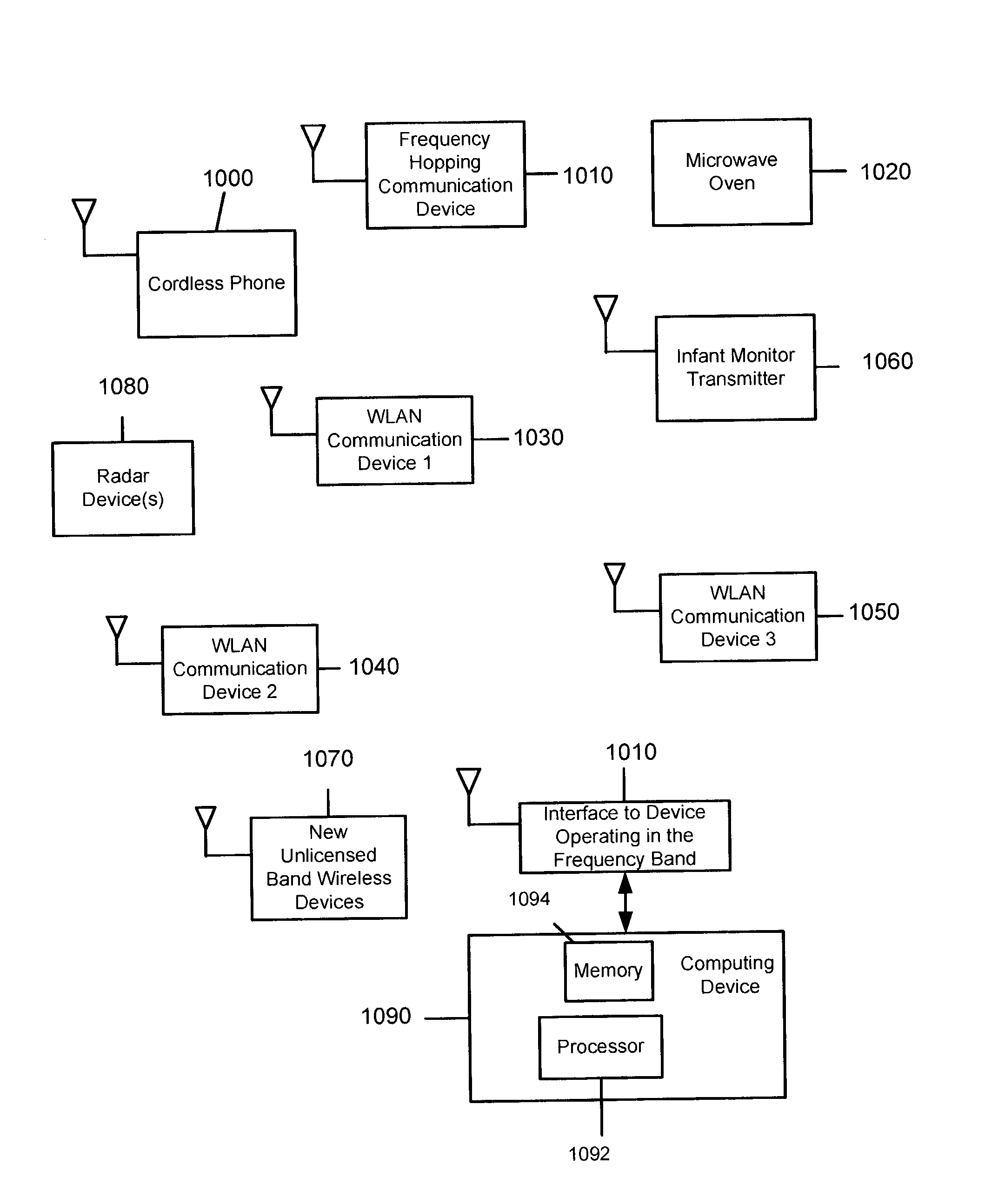
System and Method for Spectrum Management of a Shared Frequency Band
ActiveUS20030198200A1Avoid interferenceEasy to useError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumSignal classification
Abstract of Disclosure A system and method for managing the spectrum utilization of a frequency band that is shared, both in frequency and time, by multiple devices. At one or more devices operating in the frequency band, pulses associated with signals occurring in the frequency band are detected by sampling part or all the frequency band for a time interval. From the detected signal pulses, the signals can be classified. In addition, overall spectrum activity can be measured. Using classification information for signals detected in the frequency band, policies can be executed so that a device may take certain actions in order to avoid interfering with other signals, or to optimize simultaneous use of the frequency band with the other signals. Signal detection occurs at one or more devices operating in a frequency band. Signal classification and measurement, as well as policy execution may occur within a processor of the same device where signal detection occurs, or in another device (located remotely or within the operating region of the frequency band).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
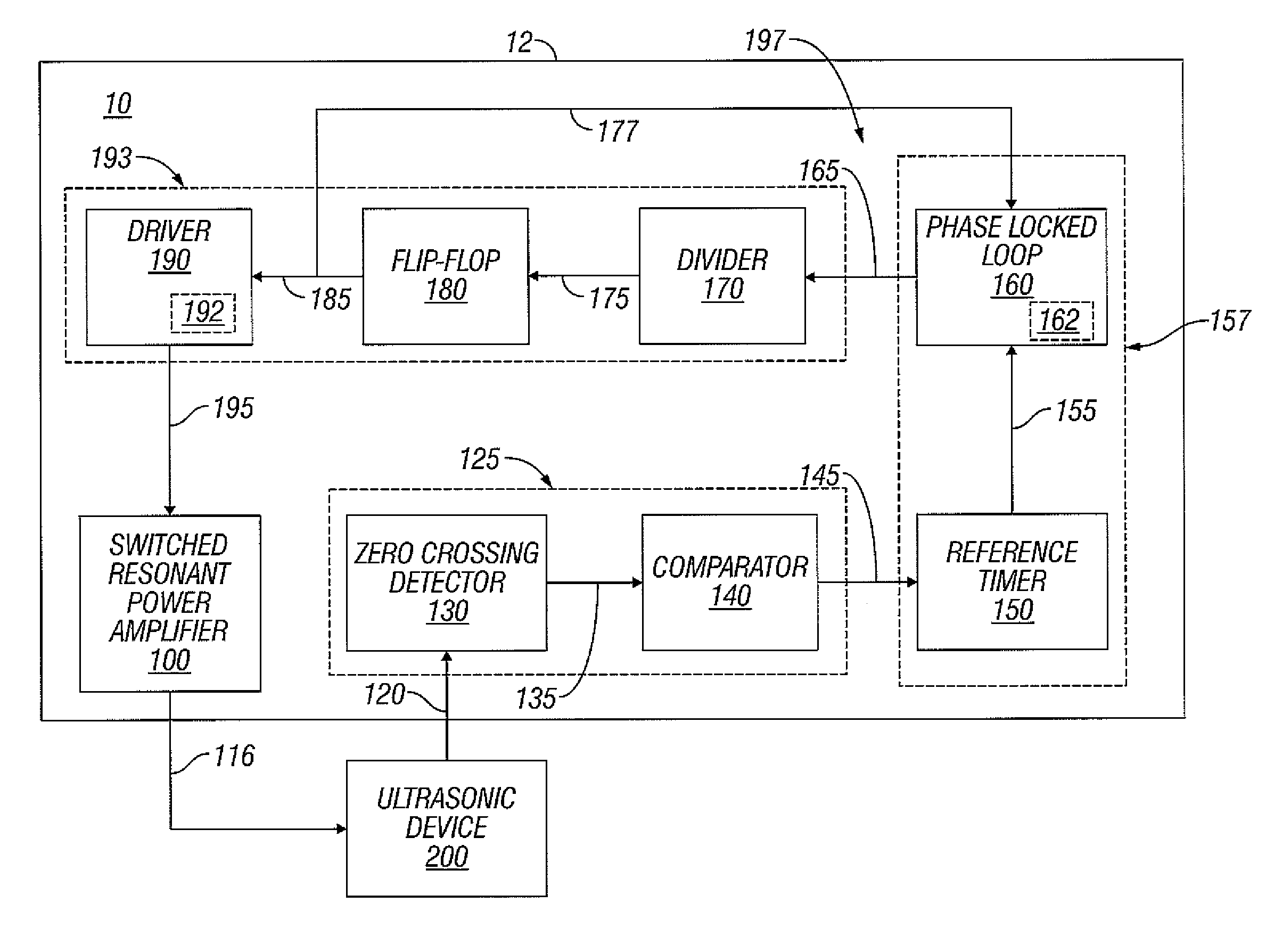
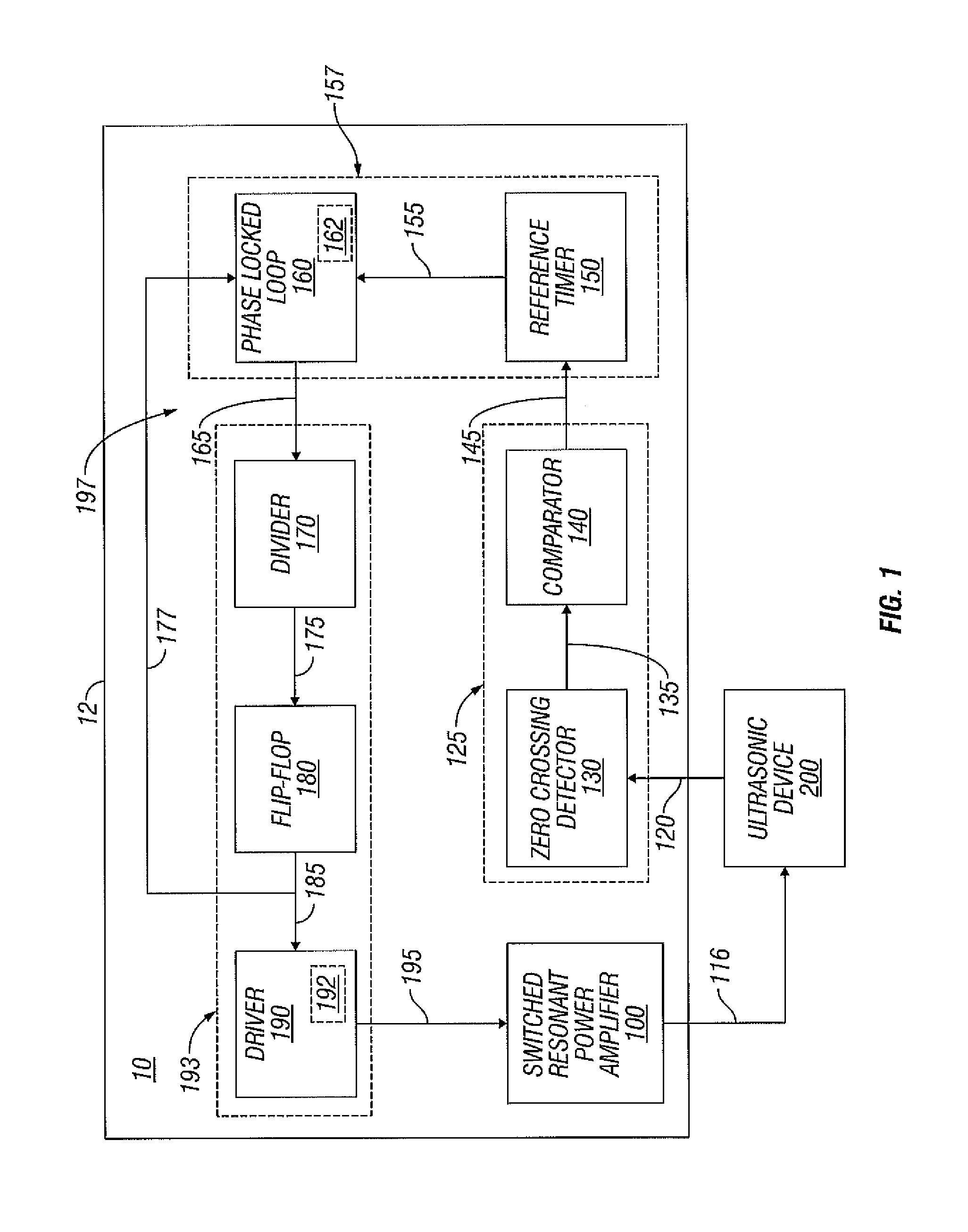
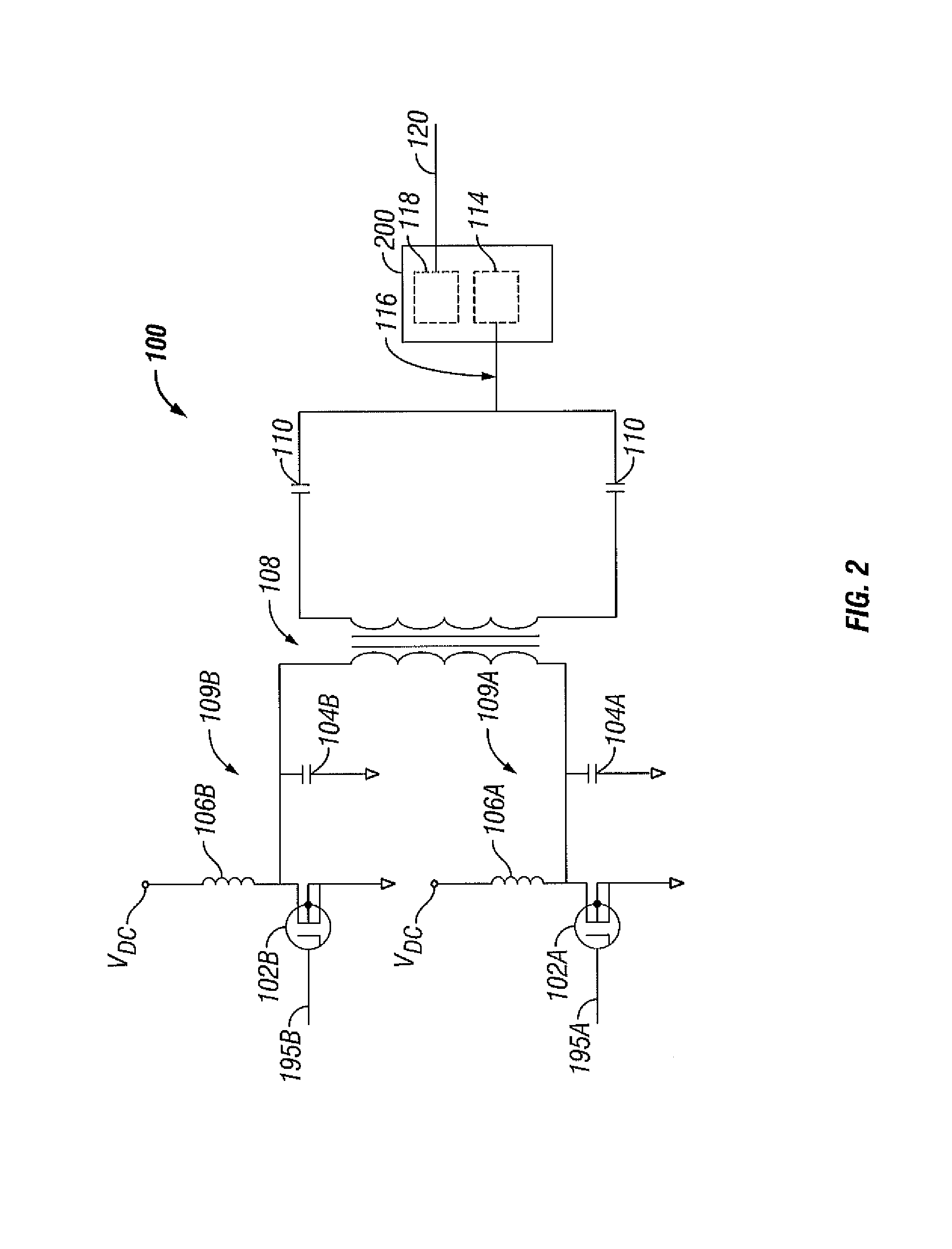
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS20050149151A1Reduce frequencyControl outputUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencySonificationAudio power amplifier
A switched resonant power amplifier system for ultrasonic transducers is disclosed. The system includes an amplifier that receives and processes a driver output signal for generating a drive signal that is provided to an ultrasonic device for controlling output of the ultrasonic device. An output control circuit receives and processes a signal related to a feedback signal generated by the ultrasonic device and a divider reference signal, and generates a compensated clock signal that is adjusted for at least one of phase and frequency differences between the received feedback signal and the divider reference signal. A compensated drive circuit receives and processes the compensated clock signal for generating the divider reference signal, and for generating the driver output signal.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
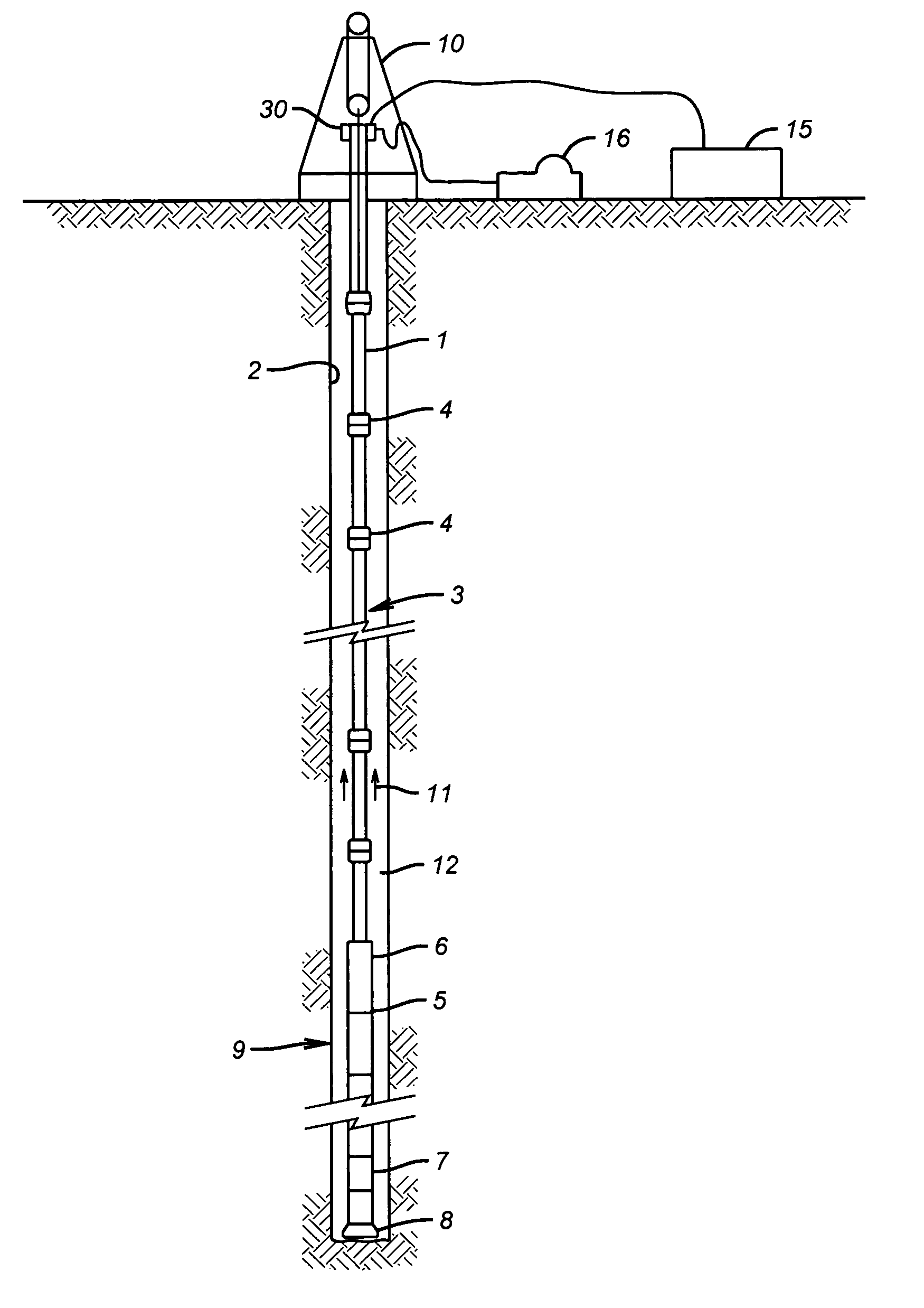
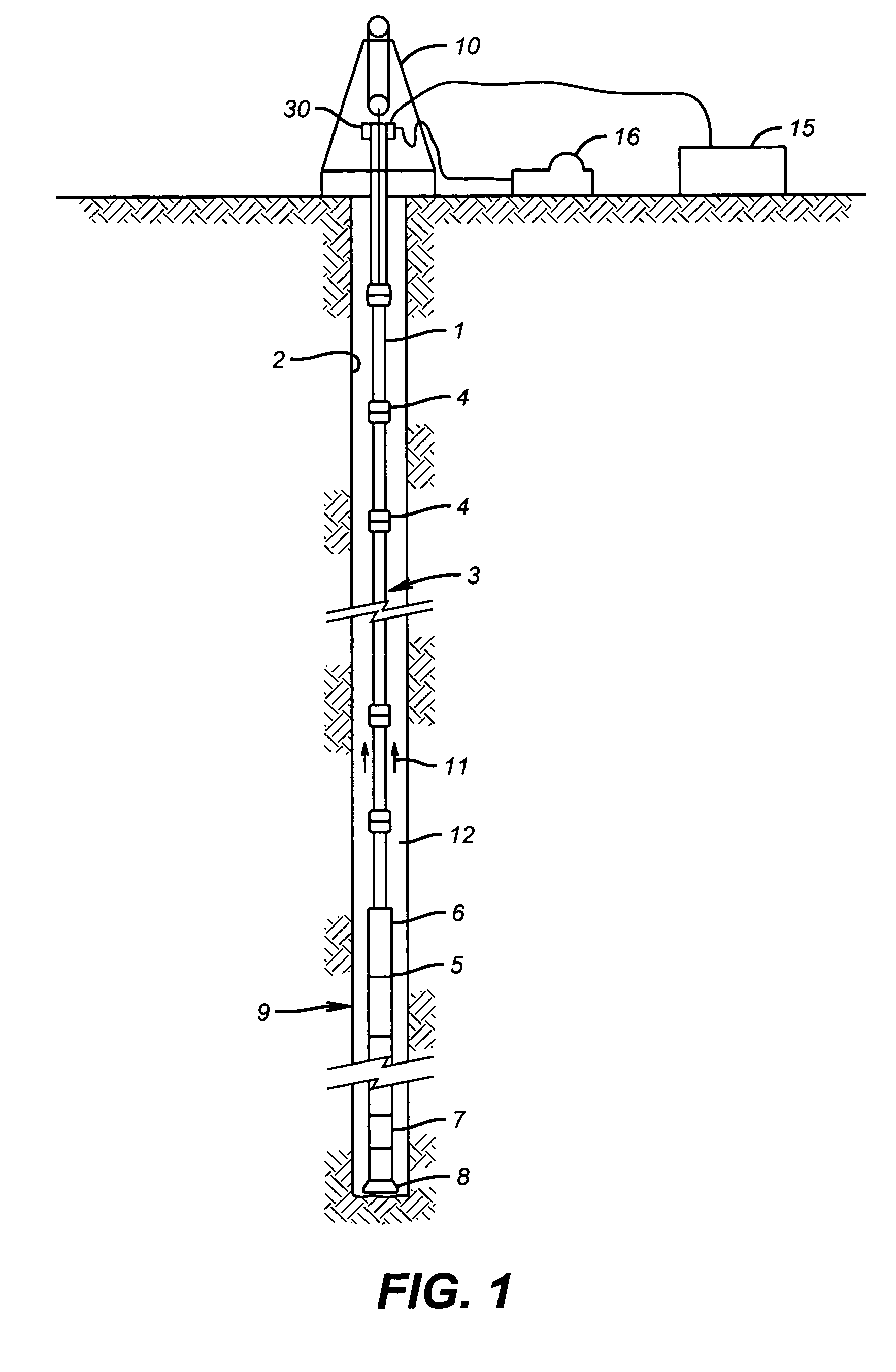
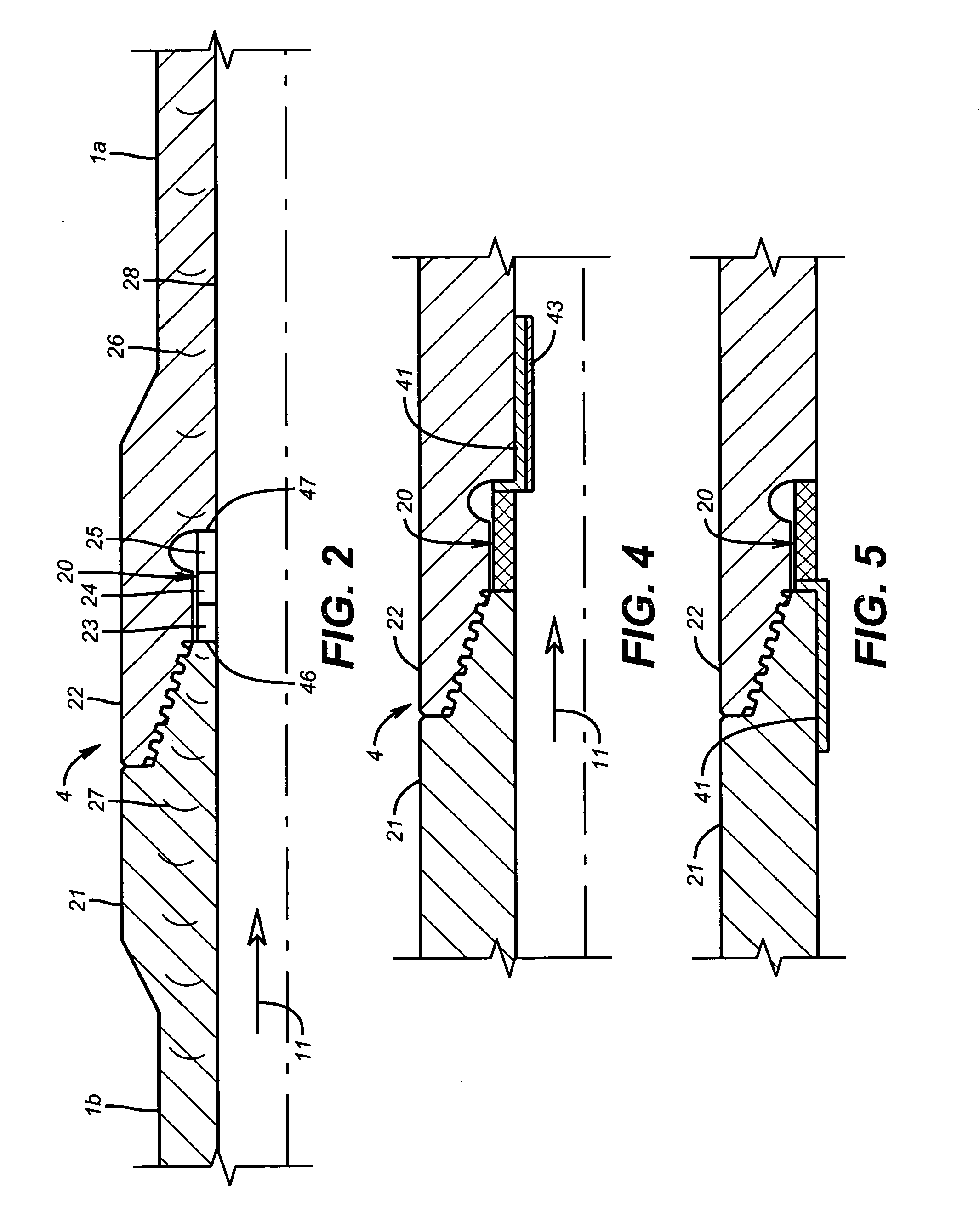
Apparatus and methods for self-powered communication and sensor network
A measurement and communication system for use with a tubular string, comprises a tubular string having a plurality of self-powered, autonomous telemetry stations disposed at predetermined locations along the tubular string. Each autonomous telemetry station is adapted to receive at least one first signal and transmit at least one second signal related to the at least one first signal. Power is extracted from potential energy sources proximate each autonomous telemetry station. A method of communicating information along a tubular string comprises, disposing an autonomous telemetry station at predetermined locations along the tubular string. A preferred transmission path is autonomously determined at each of the autonomous telemetry stations. Information is transmitted along the tubular string according to the autonomously determined preferred path.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and System for Determining the Position of a Mobile Station
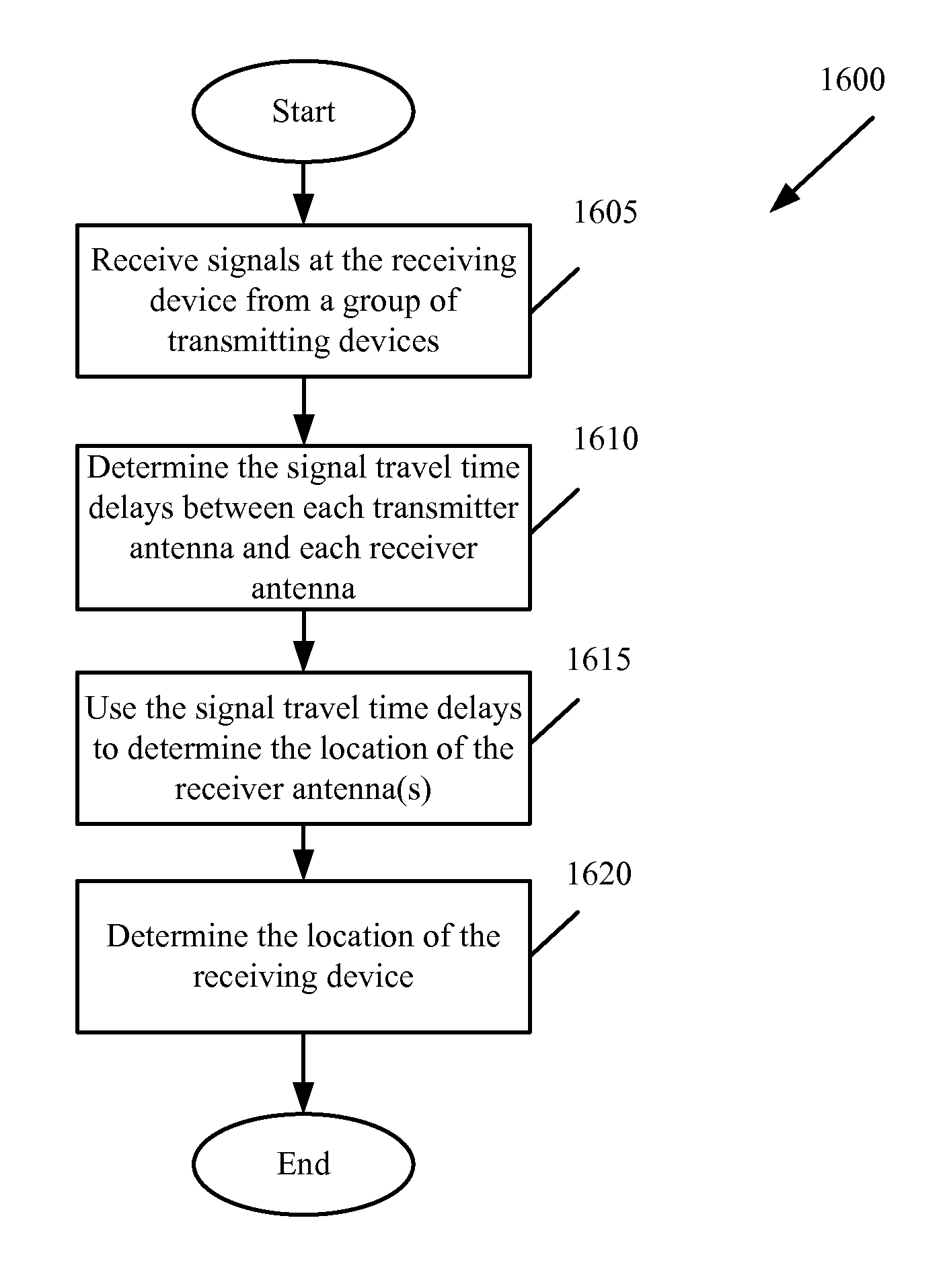
InactiveUS20100271263A1Low costRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationEngineeringMobile station
A method of determining the location of a mobile device is provided. The method receives a signal with a known radio transmission pattern at the mobile device from each of several transmitting devices. The method correlates each received signal with a corresponding signal that has a same known radio transmission pattern to determine the time the signal traveled between the corresponding transmitting device and the mobile device. The method determines the location of the mobile device based on the time the signal travelled between the corresponding transmitting device and the mobile device. In some embodiments, determining the location of the mobile device does not require calculating a distance between the mobile device and any of the transmitting devices. In some embodiments determining the location of the mobile device includes solving a function that is dependent on the time the signals traveled between each corresponding transmitting device and the mobile device.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
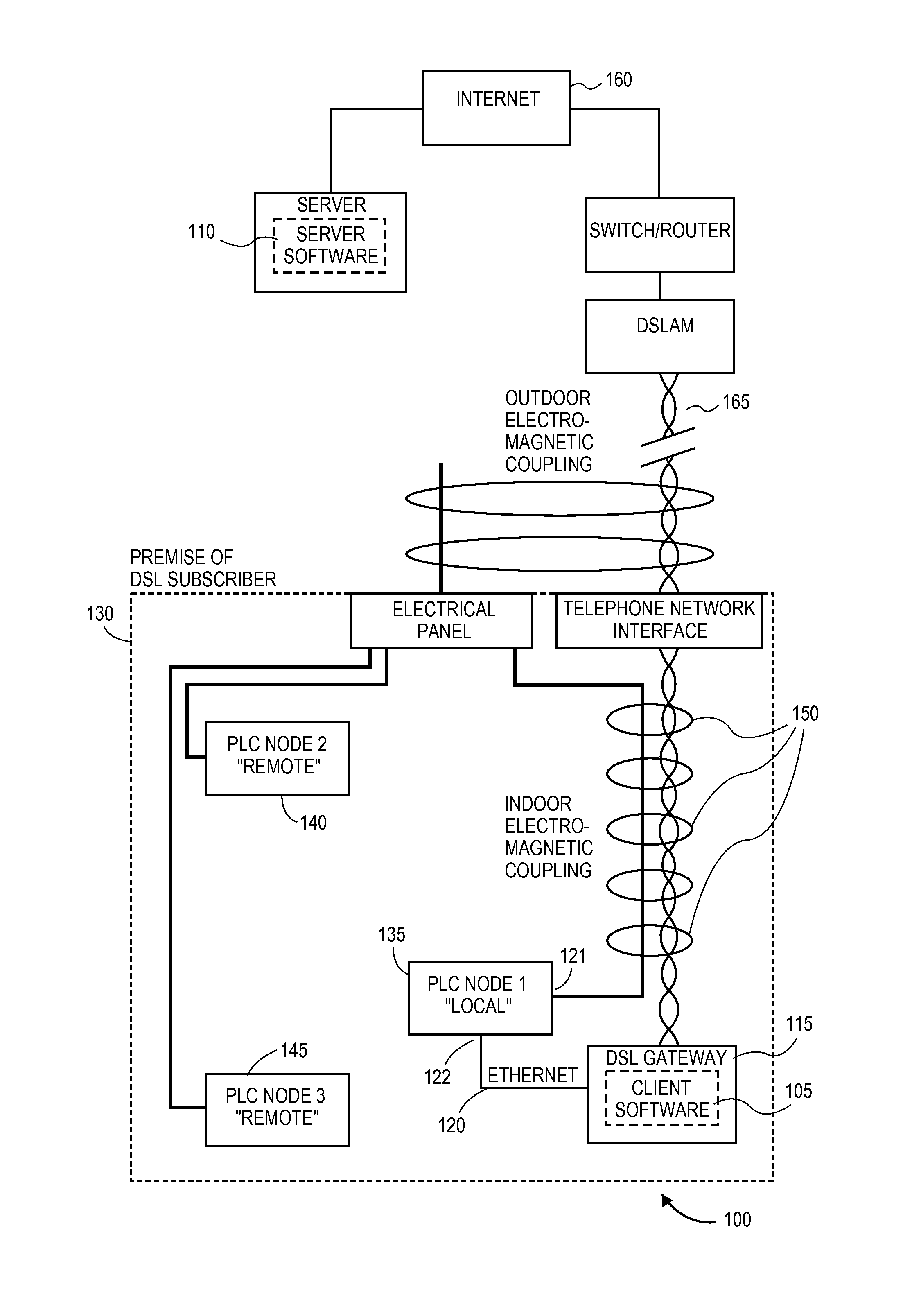
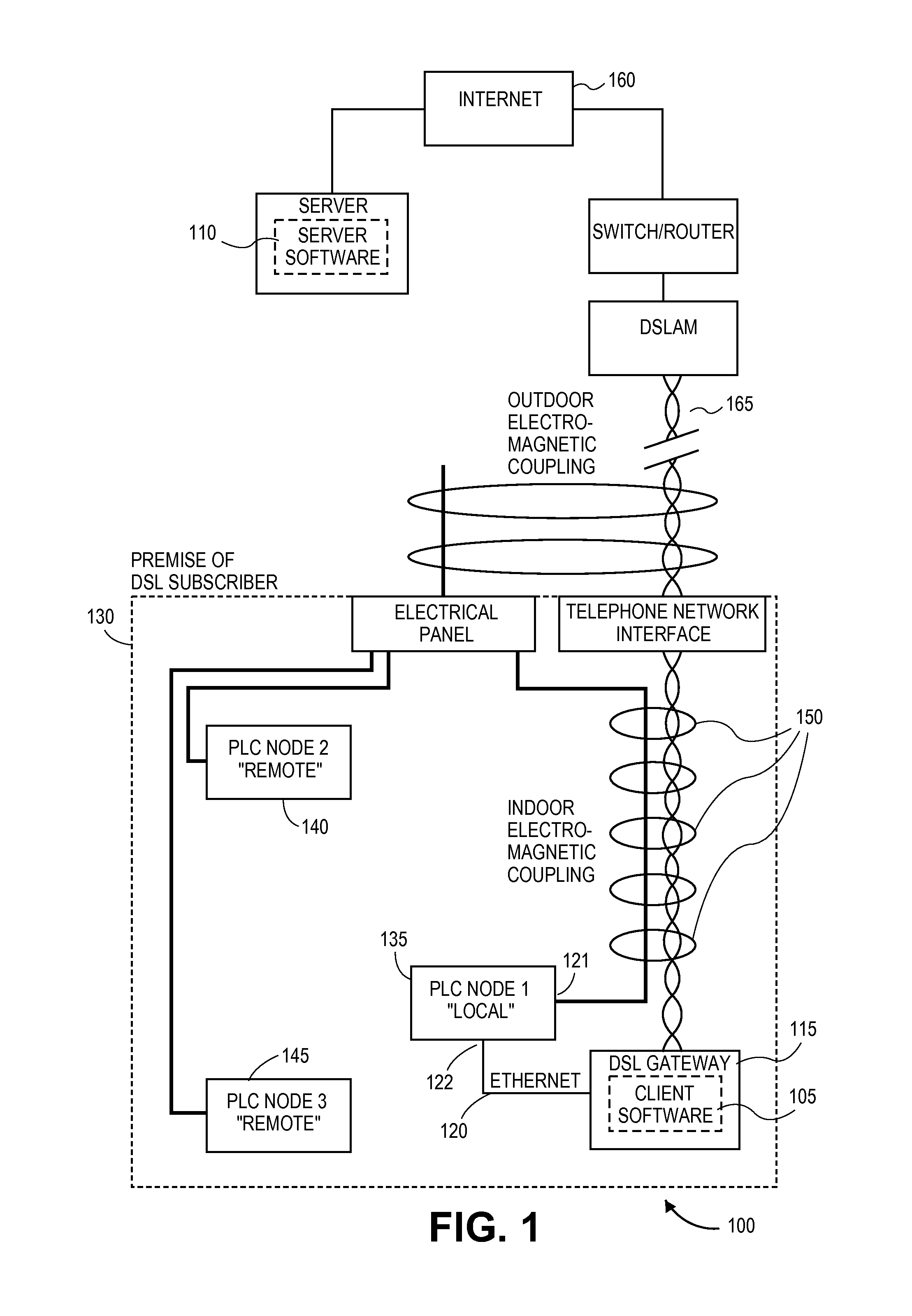
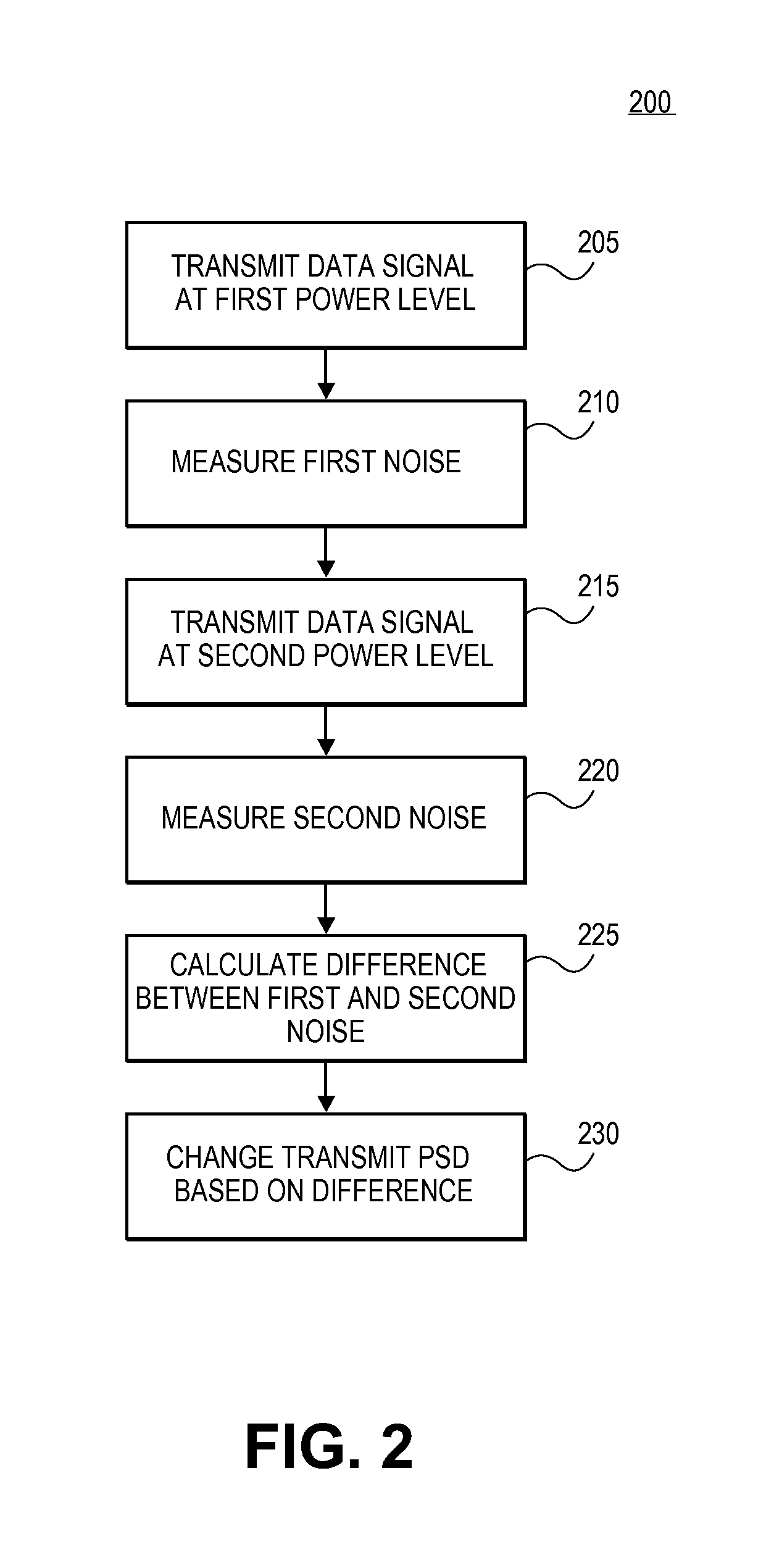
Method and apparatus for reducing the power of a signal electromagnetically coupled from a PLC medium to a DSL medium
ActiveUS20140369430A1Reduce impactDecrease phenomenonPower managementSystems with measurements/testing channelsDigital subscriber lineTransmitted power
Reducing a power of a signal electromagnetically coupled from a PLC medium to a digital subscriber line (DSL) medium. The method involves transmitting a data signal over the PLC medium at a first average power level from one of a plurality of PLC transmitters coupled to the PLC medium, then measuring first noise associated with a first signal received at a DSL receiver coupled to the DSL communication medium caused at least in part by the data signal transmitted over the PLC medium at a second average power level from the one PLC transmitter, the second average power level different than the first average power level, followed by measuring second noise associated with a second signal received at the DSL receiver coupled to the DSL communication medium caused at least in part by the data signal transmission over the PLC medium at the second average power level. A transmit power spectral density (PSD) for the data signal transmitted by the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium is then changed, based on a difference between the first noise and the second noise, such that the changed transmit PSD for the data signal transmitted by the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium reduces the power of the signal electromagnetically coupled from the PLC medium to the DSL medium caused by the data signal transmission from the one PLC transmitter over the PLC medium.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
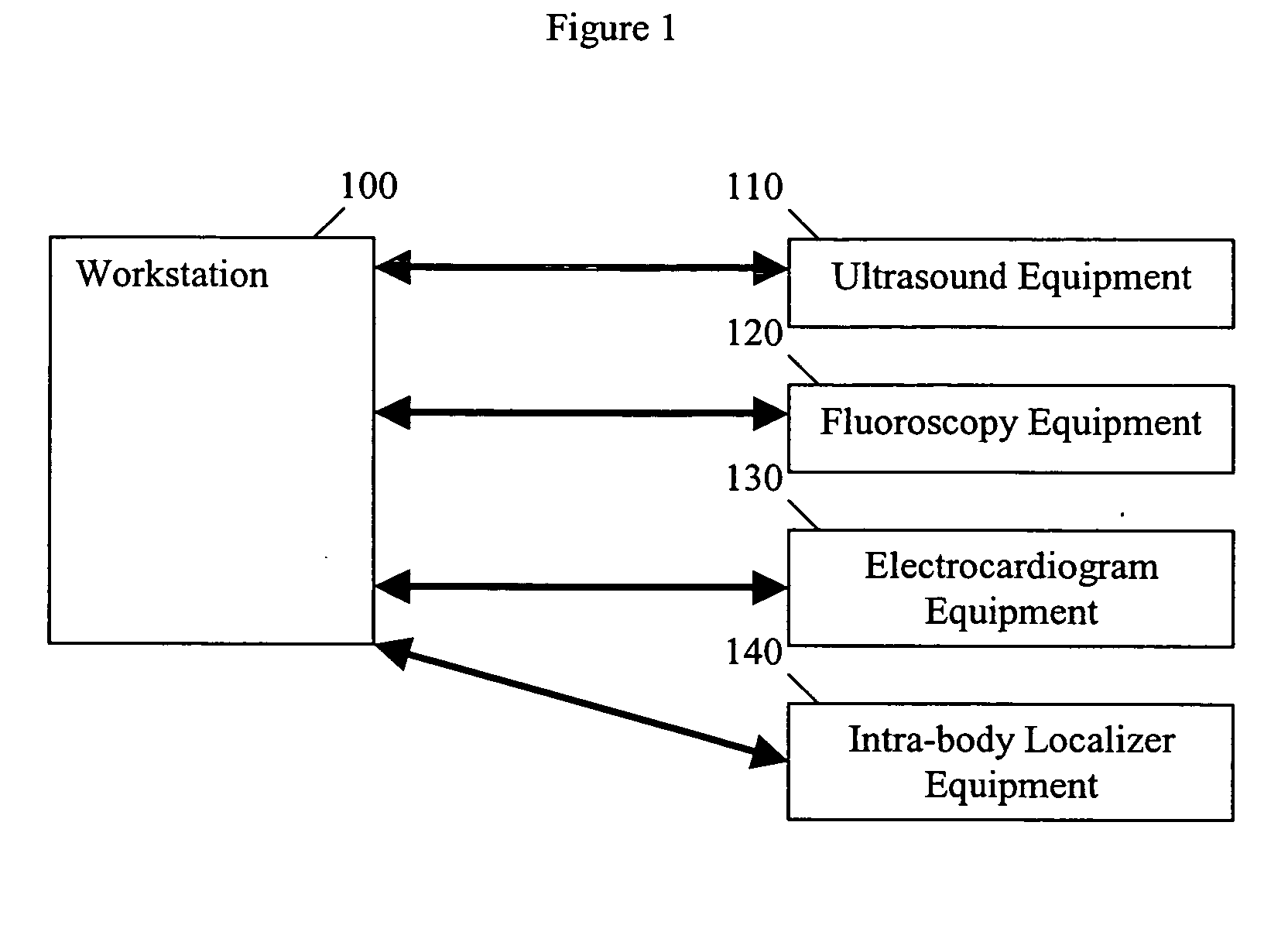
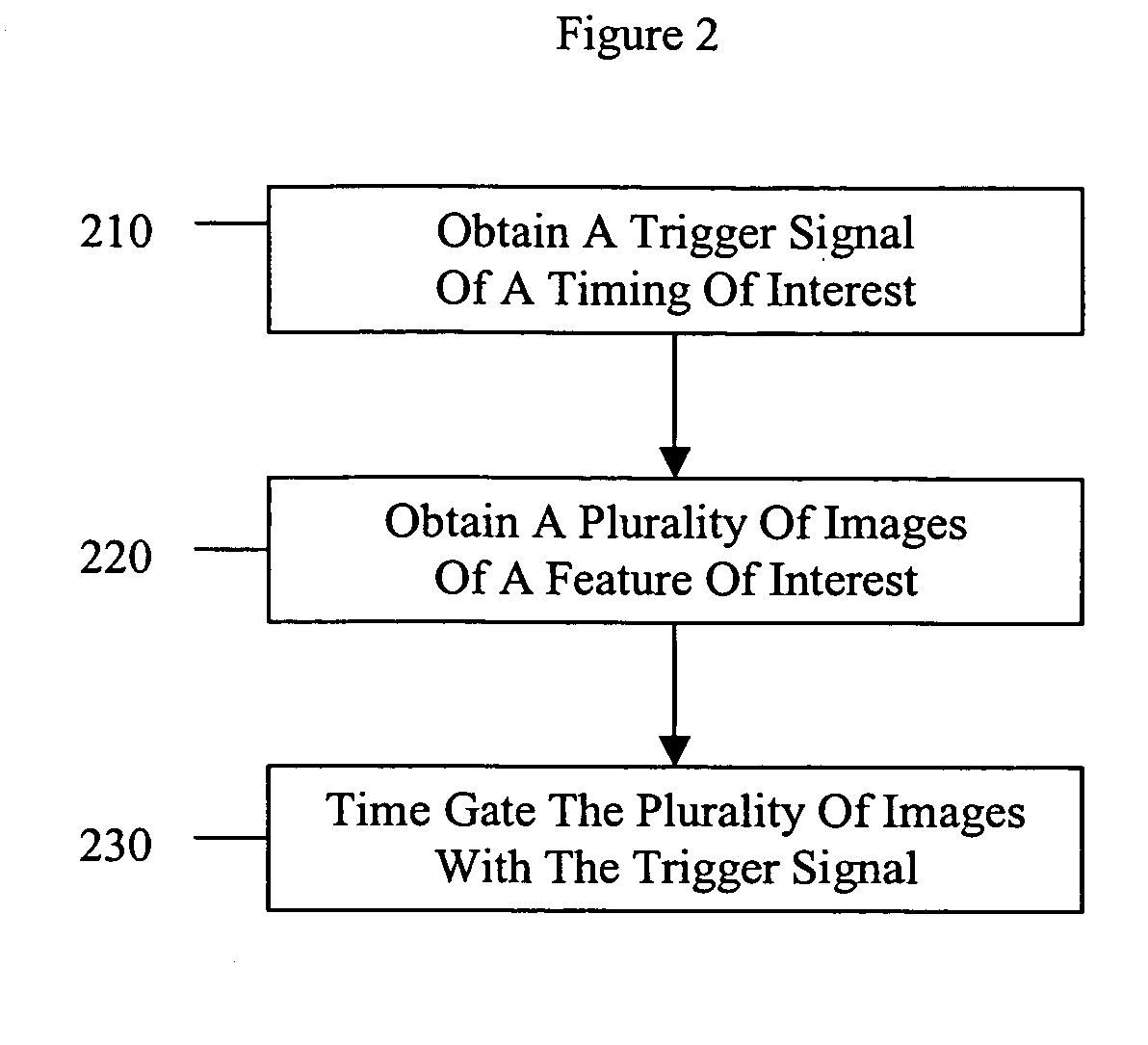
Method and apparatus for time gating of medical images
ActiveUS20050080336A1Blood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesTime gatingMedical imaging
A medical imaging system is provided which includes a signal generator configured to obtain a trigger signal corresponding to a timing of interest, imaging equipment configured to obtain a plurality of images of a feature of interest, and a processor programmed to correlate the plurality of images with the trigger signal. Also provided is a method of correlating a plurality of medical images by obtaining a trigger signal of a timing of interest, obtaining a plurality of images of a feature of interest, and correlating the plurality of images with the trigger signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for spectrum management of a shared frequency band
ActiveUS7269151B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumSignal classification
A system and method for managing the spectrum utilization of a frequency band that is shared, both in frequency and time, by multiple devices. At one or more devices operating in the frequency band, pulses associated with signals occurring in the frequency band are detected by sampling part or all the frequency band for a time interval. From the detected signal pulses, the signals can be classified. In addition, overall spectrum activity can be measured. Using classification information for signals detected in the frequency band, policies can be executed so that a device may take certain actions in order to avoid interfering with other signals, or to optimize simultaneous use of the frequency band with the other signals. Signal detection occurs at one or more devices operating in a frequency band. Signal classification and measurement, as well as policy execution may occur within a processor of the same device where signal detection occurs, or in another device (located remotely or within the operating region of the frequency band).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and systems for providing noise filtering using speech recognition
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing noise filtering using speech recognition. The disclosed systems and methods may include performing a speech recognition process on a signal. Furthermore, the disclosed systems and methods may include determining a first frequency range based on the performed speech recognition process, the first frequency range corresponding to an expected voice associated with the signal. In addition, the disclosed systems and methods may include attenuating a second frequency range in the signal, the second frequency range being outside the first frequency range and the extemporaneous noise in the first frequency.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
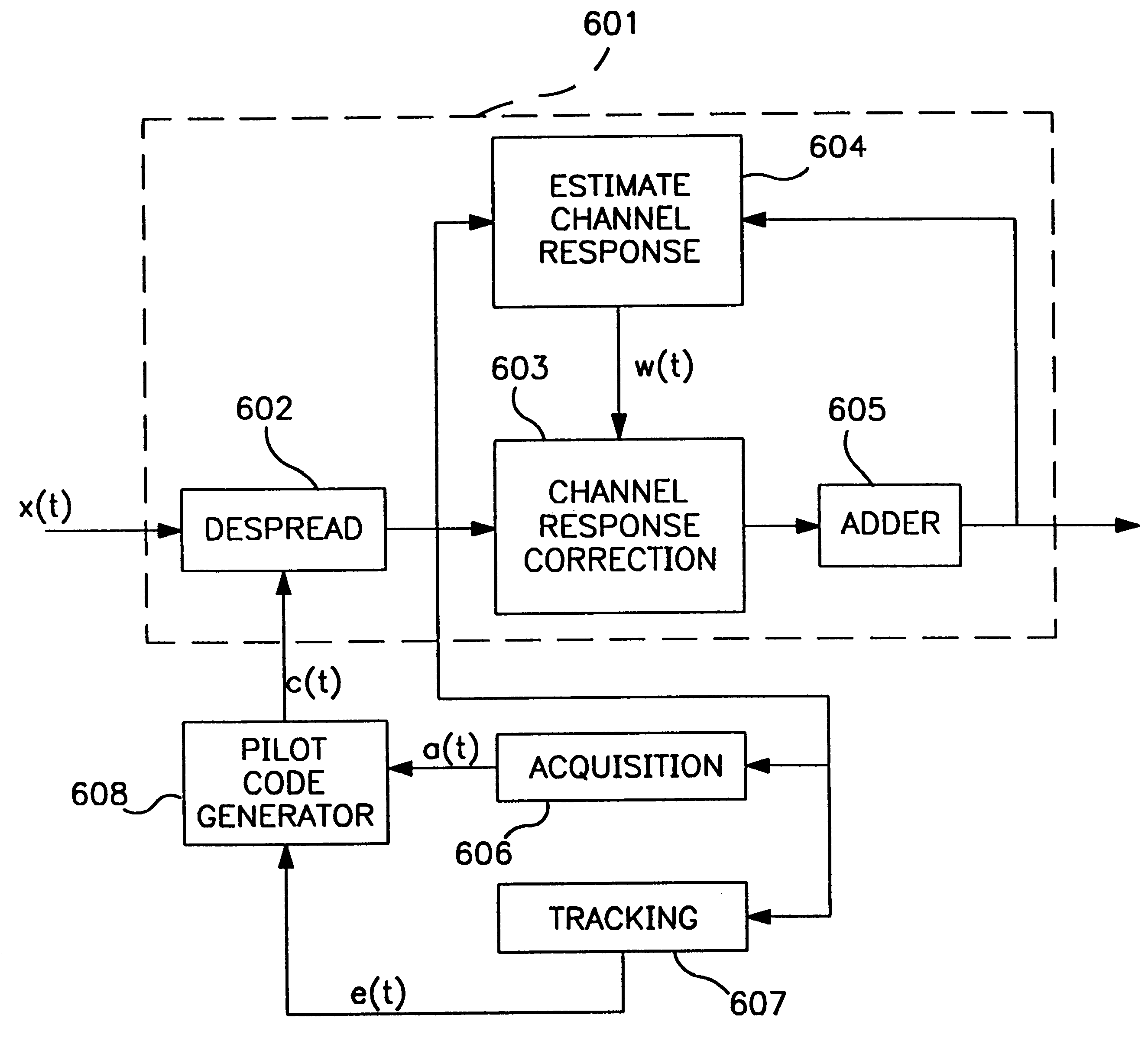
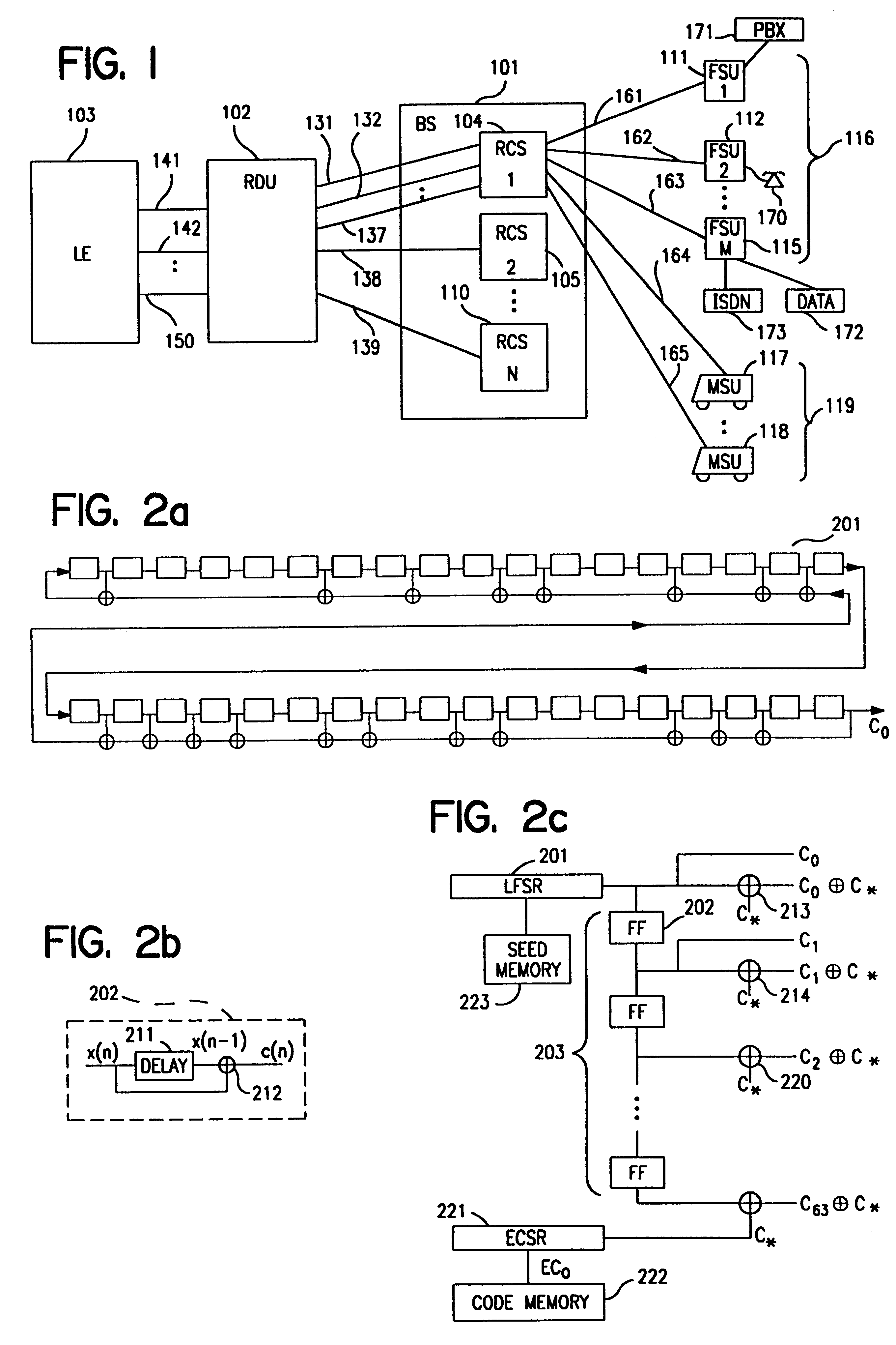
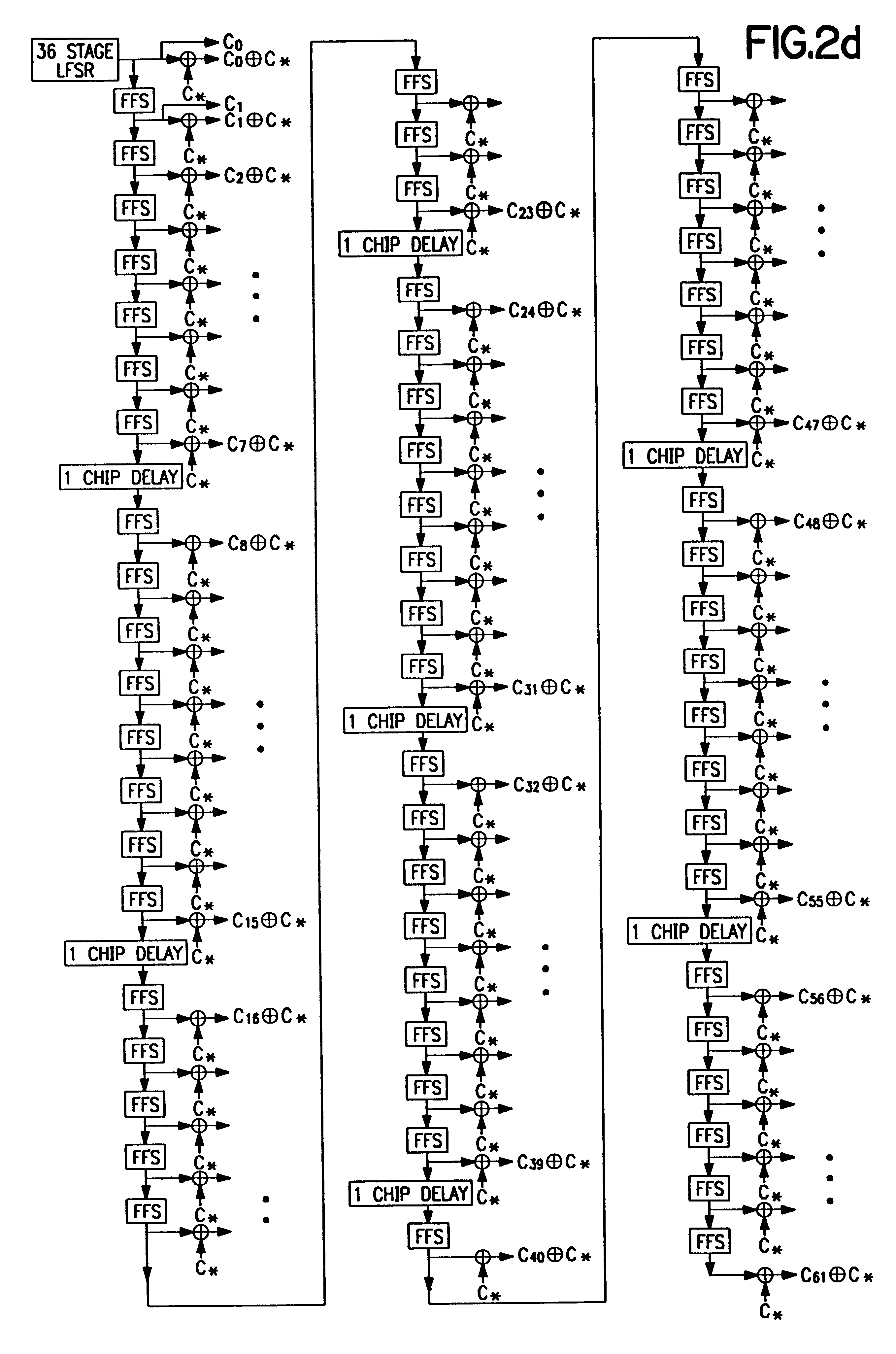
Code sequence generator in a CDMA modem
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals: a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Information retrieval engine
InactiveUS7162482B1Tag information accurately and efficientlyAccurate and efficient retrievalElectrophonic musical instrumentsData processing applicationsSignal correlationLog likelihood
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS20050070775A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
Audio signature extraction and correlation
InactiveUS20050232411A1Interconnection arrangementsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsFrequency spectrumSignal correlation
A signature is extracted from the audio of a program received by a tunable receiver such that the signature characterizes the program. In order to extract the signature, blocks of the audio are converted to corresponding spectral moments. At least one of the spectral moments is then converted to the signature. Also, a test audio signal from a receiver is correlated to a reference audio signal by converting the test audio signal and the reference audio signal to corresponding test and reference spectra, determining test slopes corresponding to coefficients of the test spectrum and reference slopes corresponding to coefficients of the reference spectrum, and comparing the test slopes to the reference slopes in order to determine a match between the test audio signal and the reference audio signal.
Owner:NIELSEN COMPANY US LLC THE A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
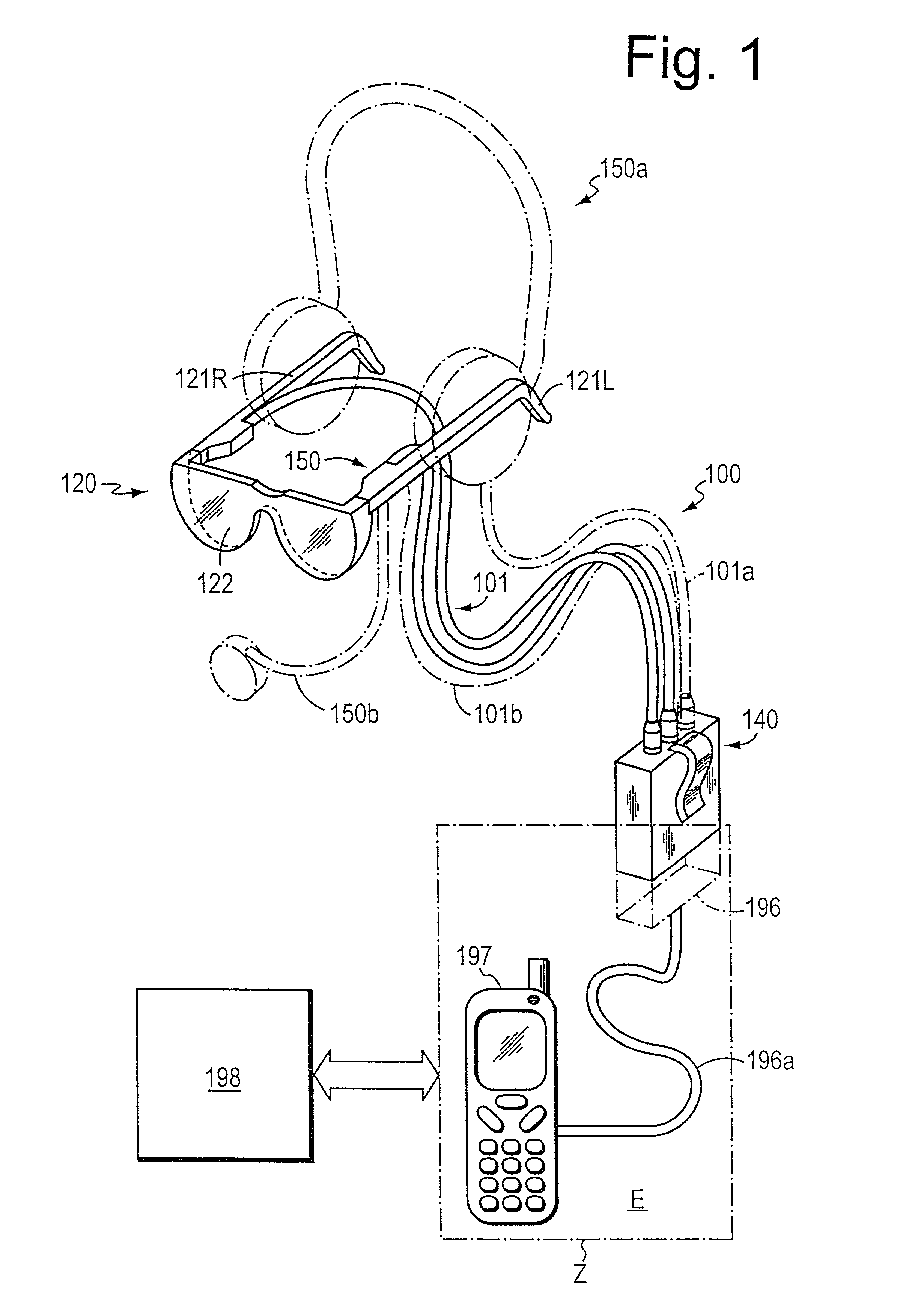
Interactive data view and command system
ActiveUS20080157946A1Good basisTime-consume to performInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionCommunication unitData view
A method and information system for capturing signals, for processing signals, and for providing signals at least partially based on, or bearing correlation to, the captured signals is disclosed. The information system includes a signal input unit, a wireless communication unit, and an output unit. The signal input unit (preferably an optical signal unit) is constructed and is positionable to capture signals associated with an eye. The output unit is constructed to provide information based on the captured signals or to provide information as a function of the captured signals or in correlation with the captured signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
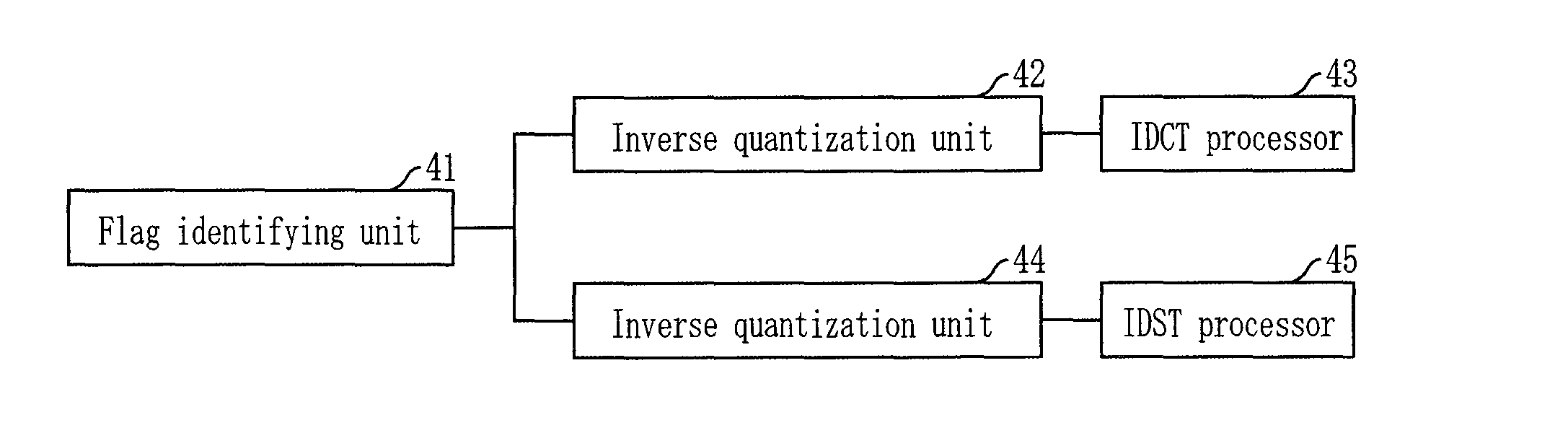
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
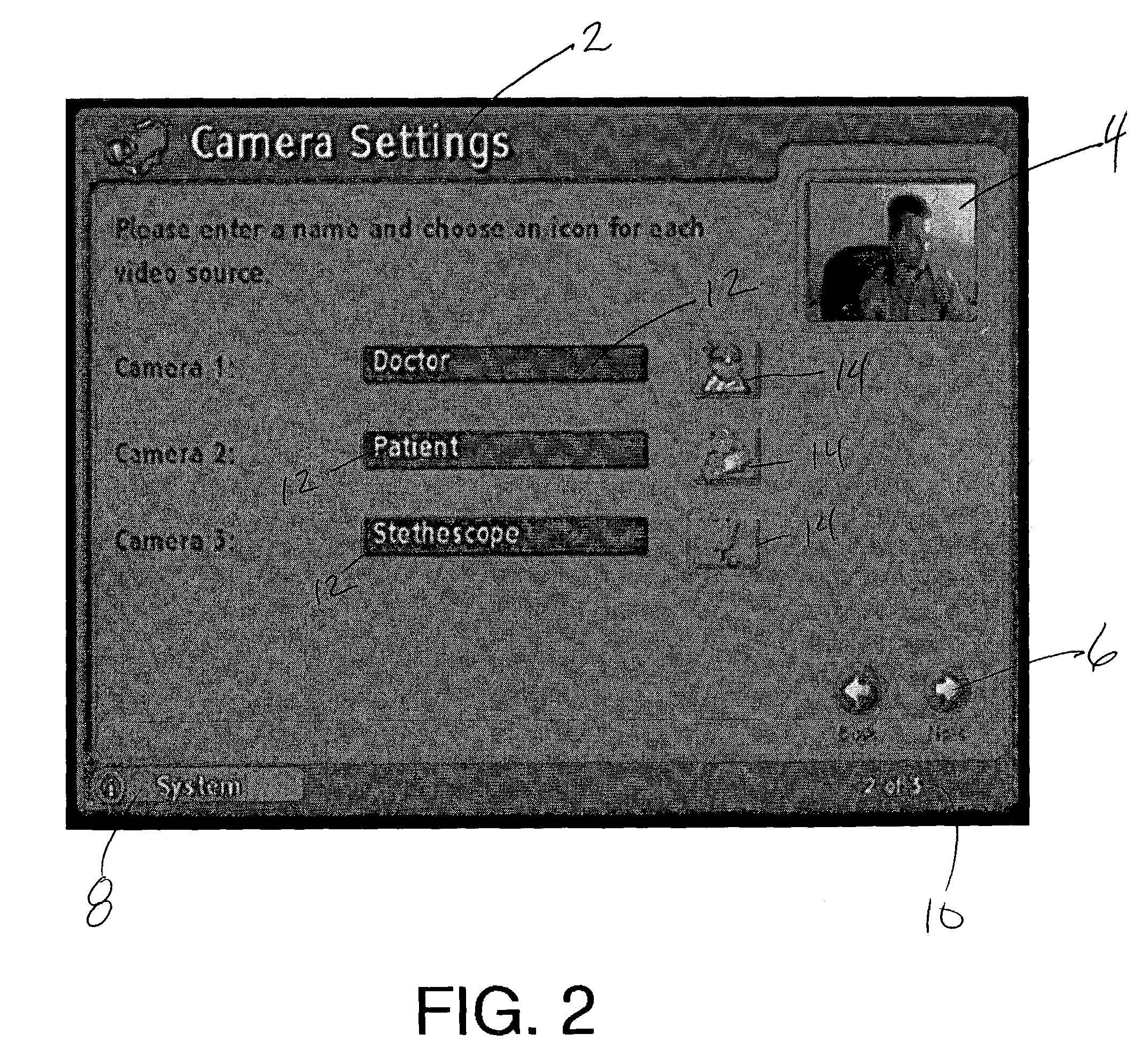
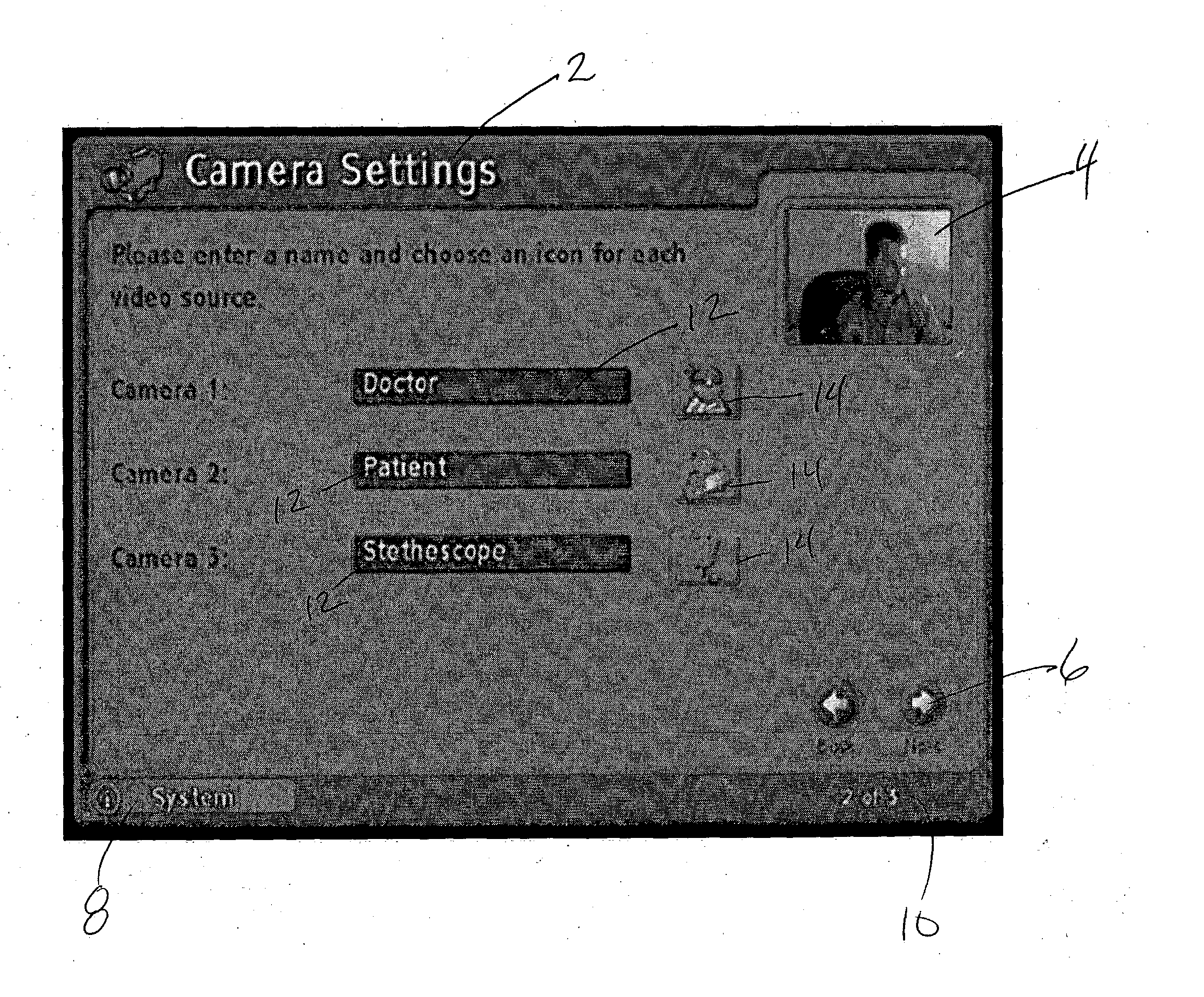
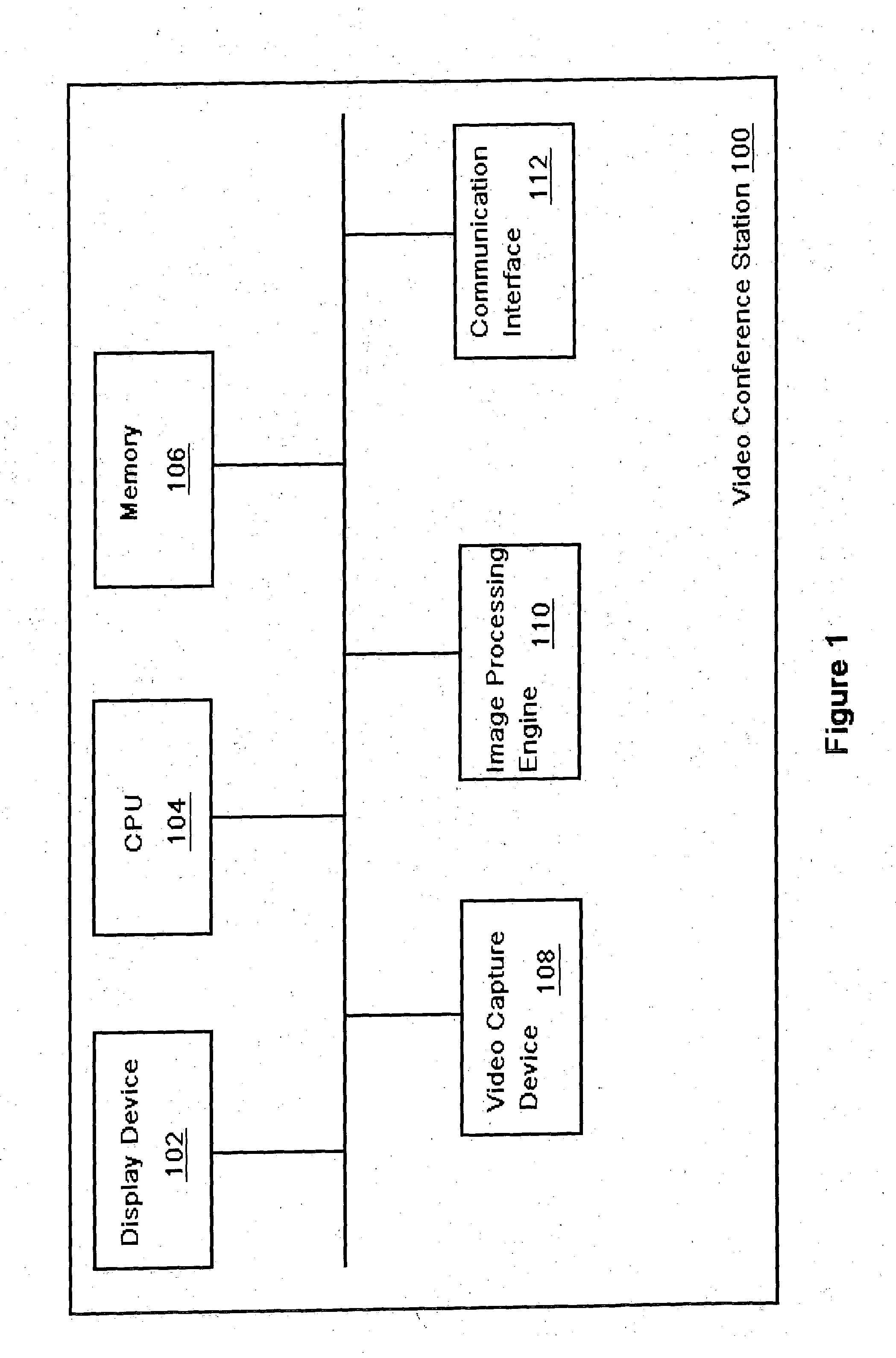
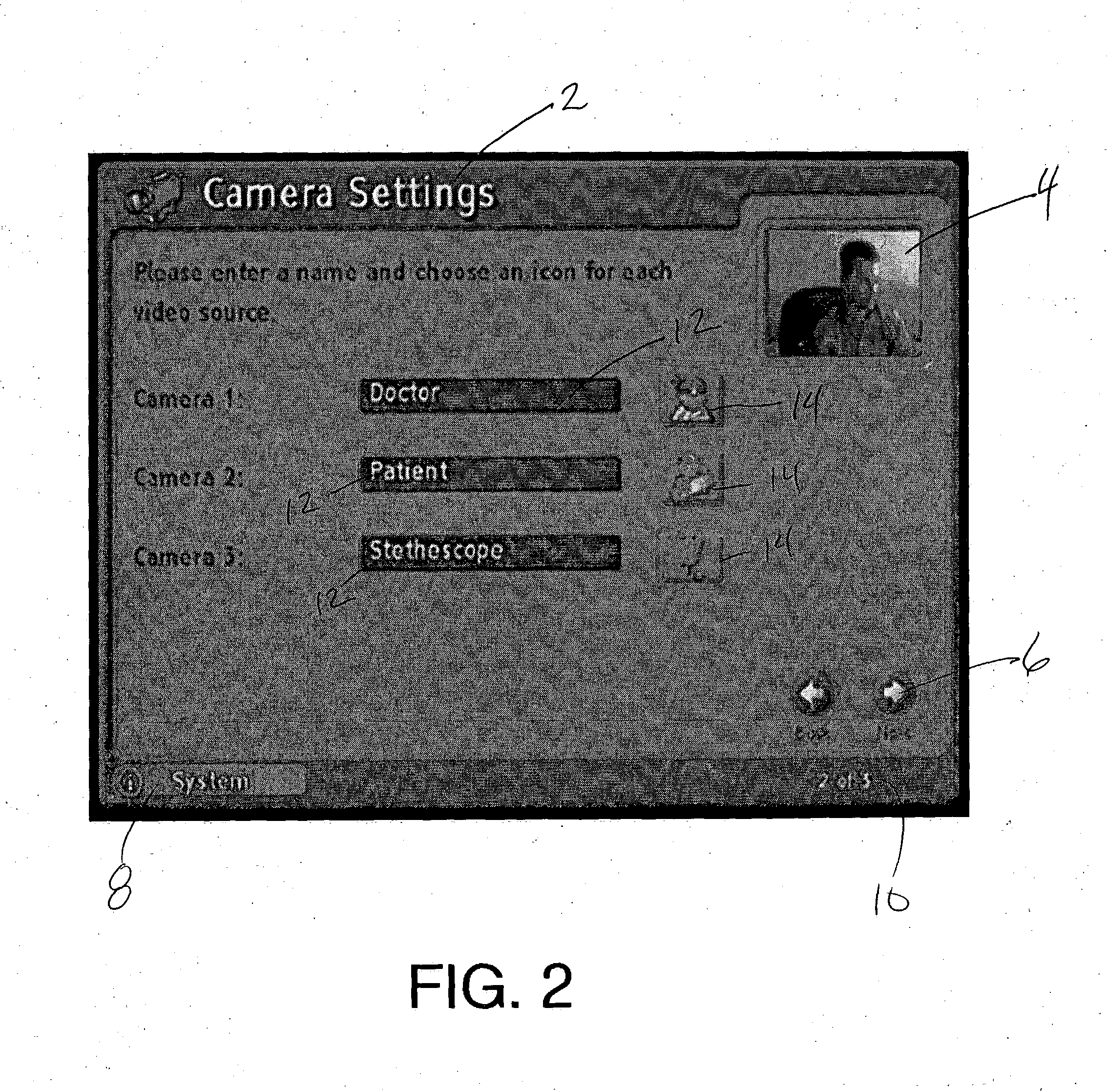
Graphical user interface for video feed on videoconference terminal
InactiveUS7133062B2Television system detailsTelevision conference systemsGraphicsGraphical user interface
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) of a videoconference terminal is provided with user-selectable icons which are associated by the user with various video signals. Textual labels for the various video signals may also be provided. This information may be exchanged with the “far end” participant in the video conference. During the videoconference participants may then simply select an icon to dynamically switch video feeds without having to remember by number the particular camera or other video signal associated with a desired video feed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
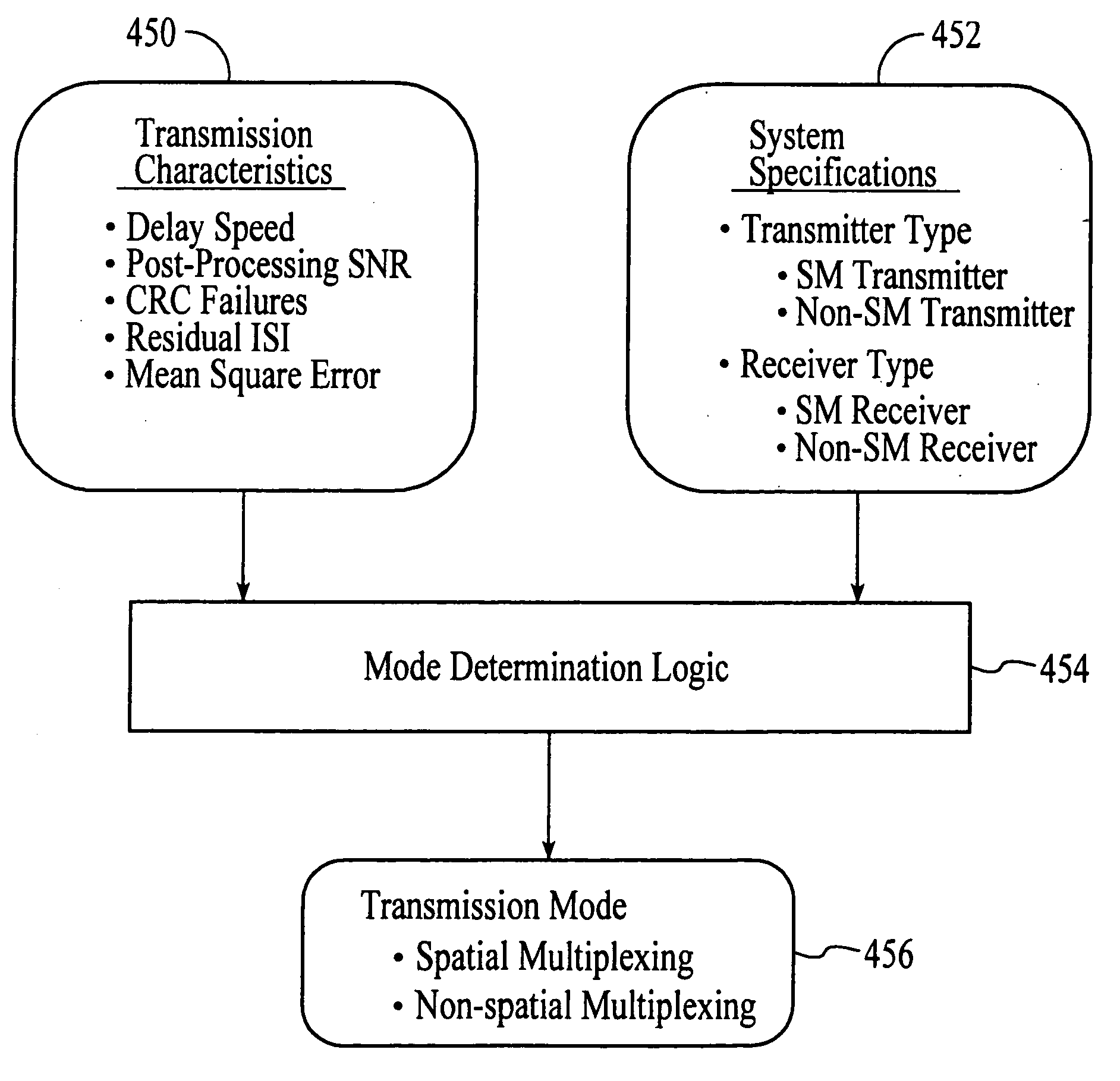
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for providing control for switch-mode power supply
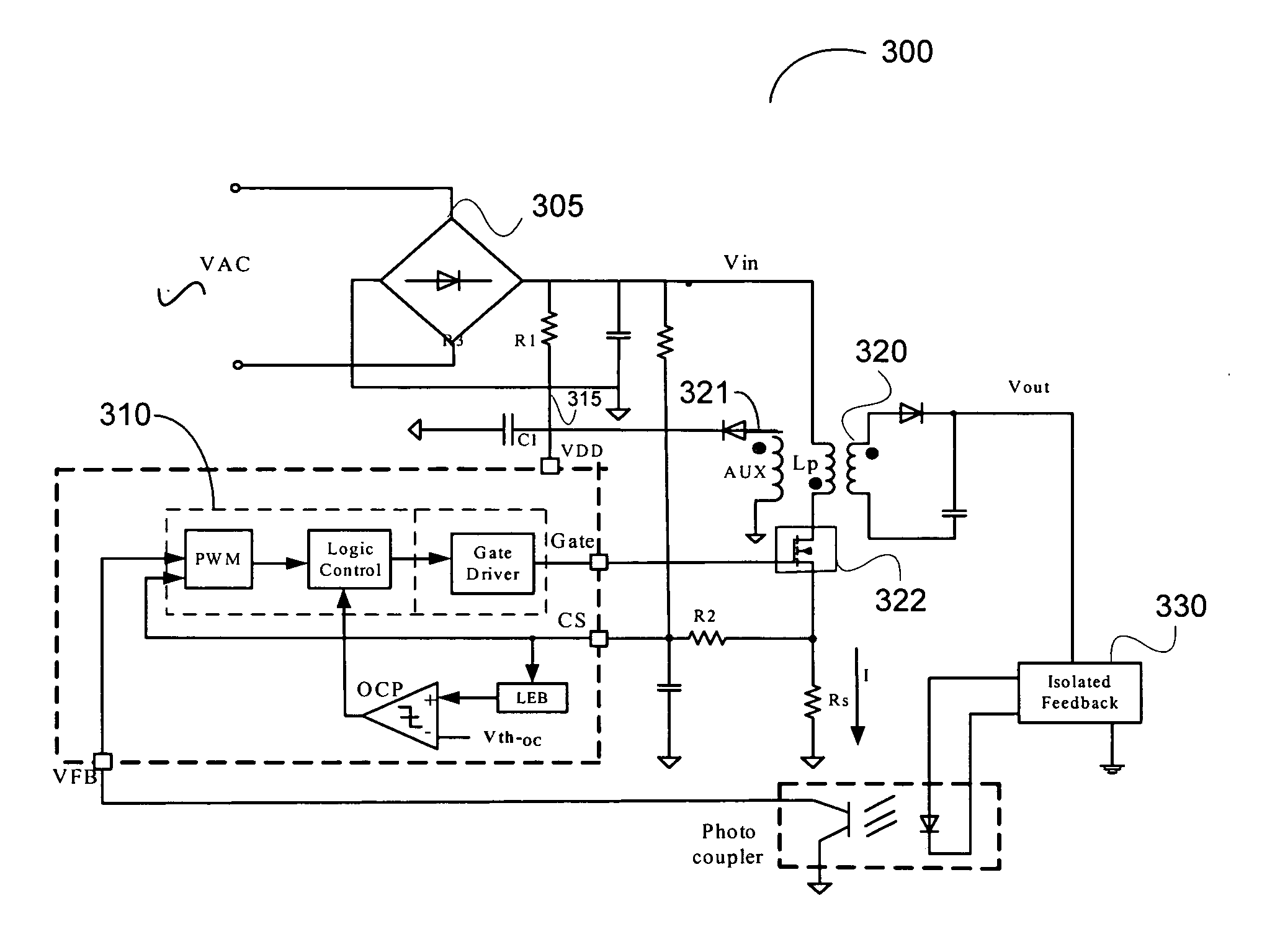
ActiveUS20080043504A1Reduce standby power consumptionImprove system efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringProcess information
System and method for providing control for switch-mode power supply. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a system for regulating a power converter. The system comprises a signal processing component that is configured to receive a first voltage and a second voltage, to process information associated with the first voltage and the second voltage, to determine a signal based on at least information associated with the first voltage and the second voltage, and to send the signal to a switch for a power converter. The switch is regulated based on at least information associated with the signal. The signal processing component is further configured to determine the signal to be associated a first mode, if the first voltage is higher than a first threshold.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
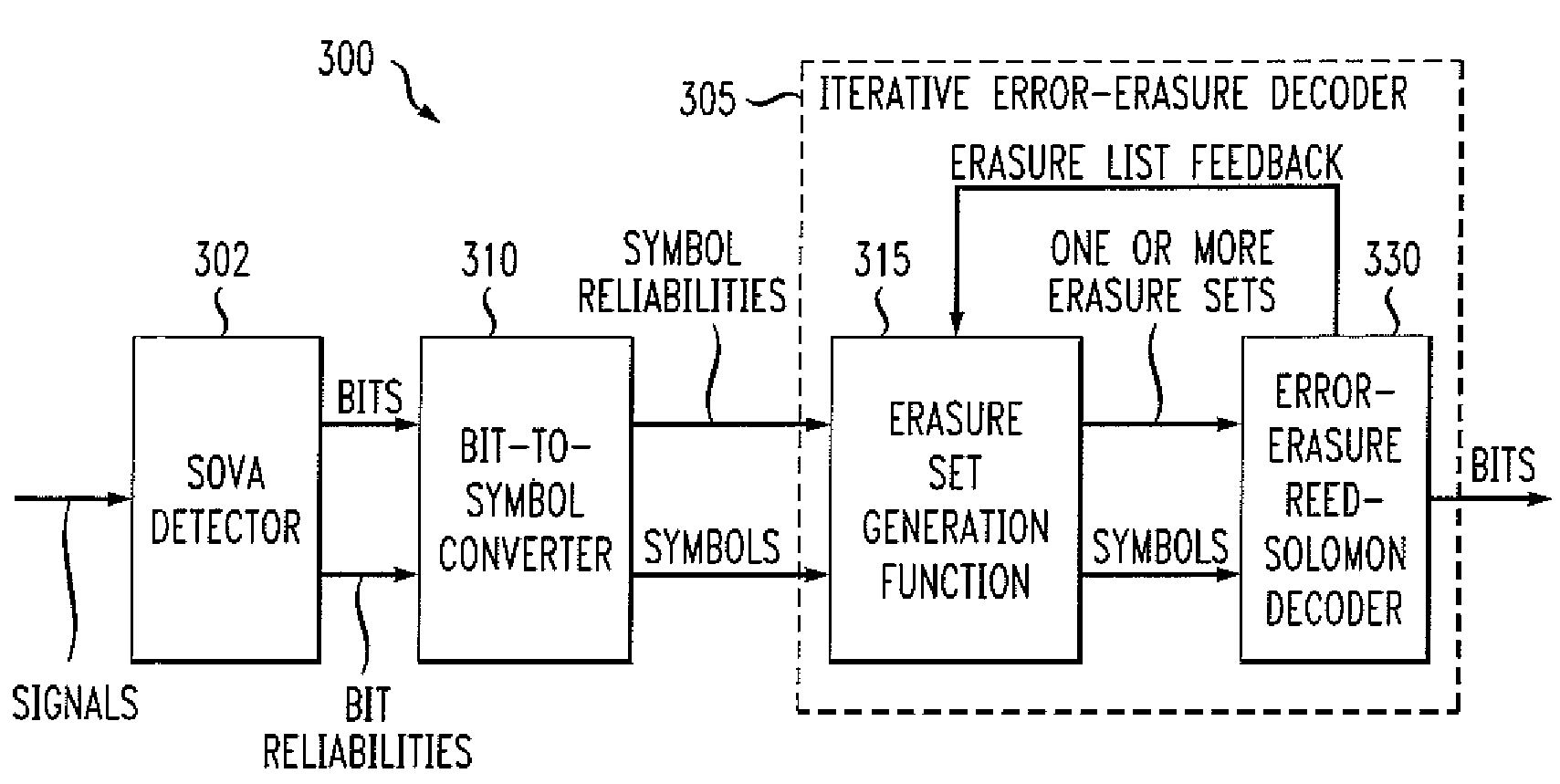
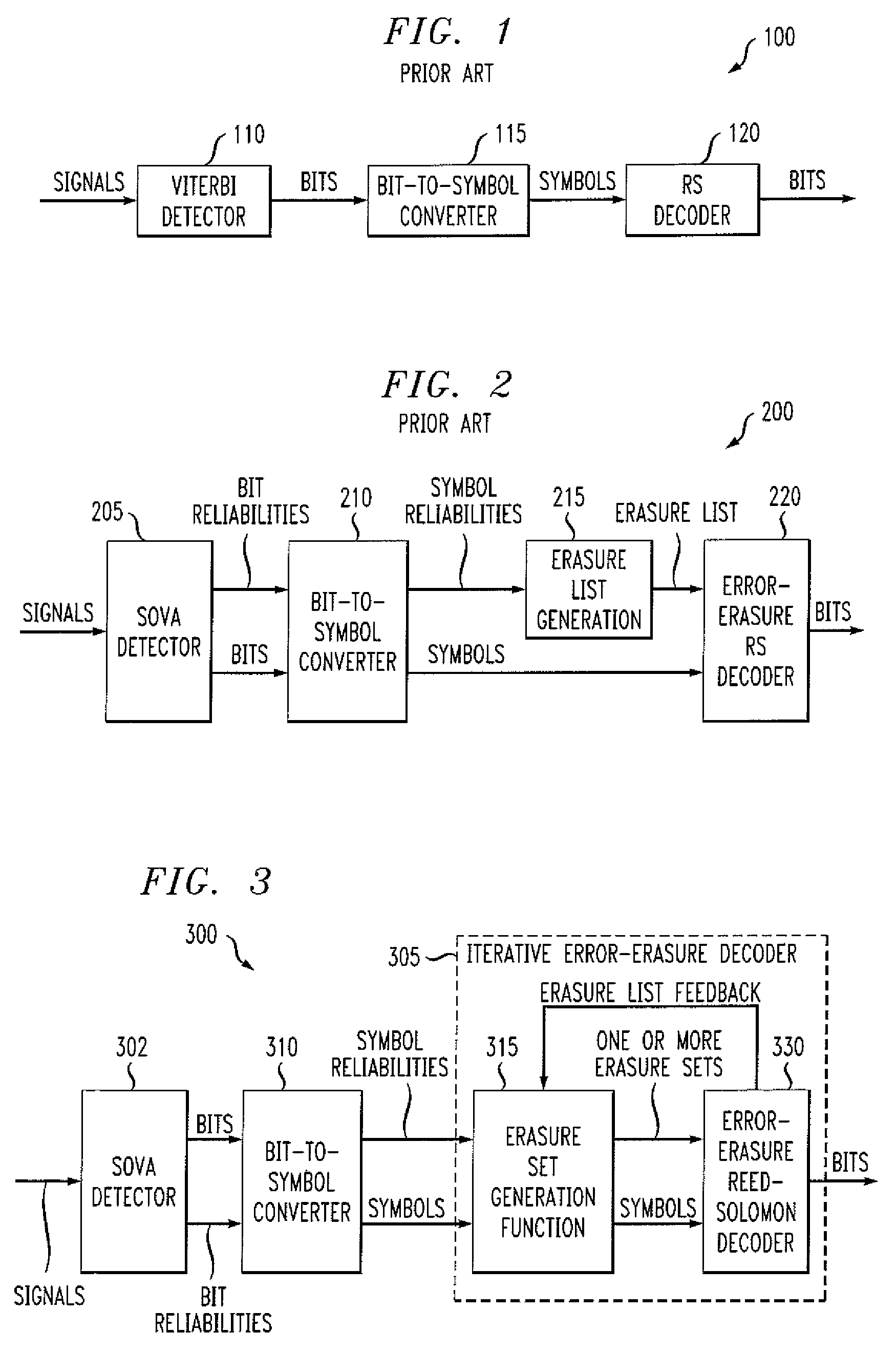
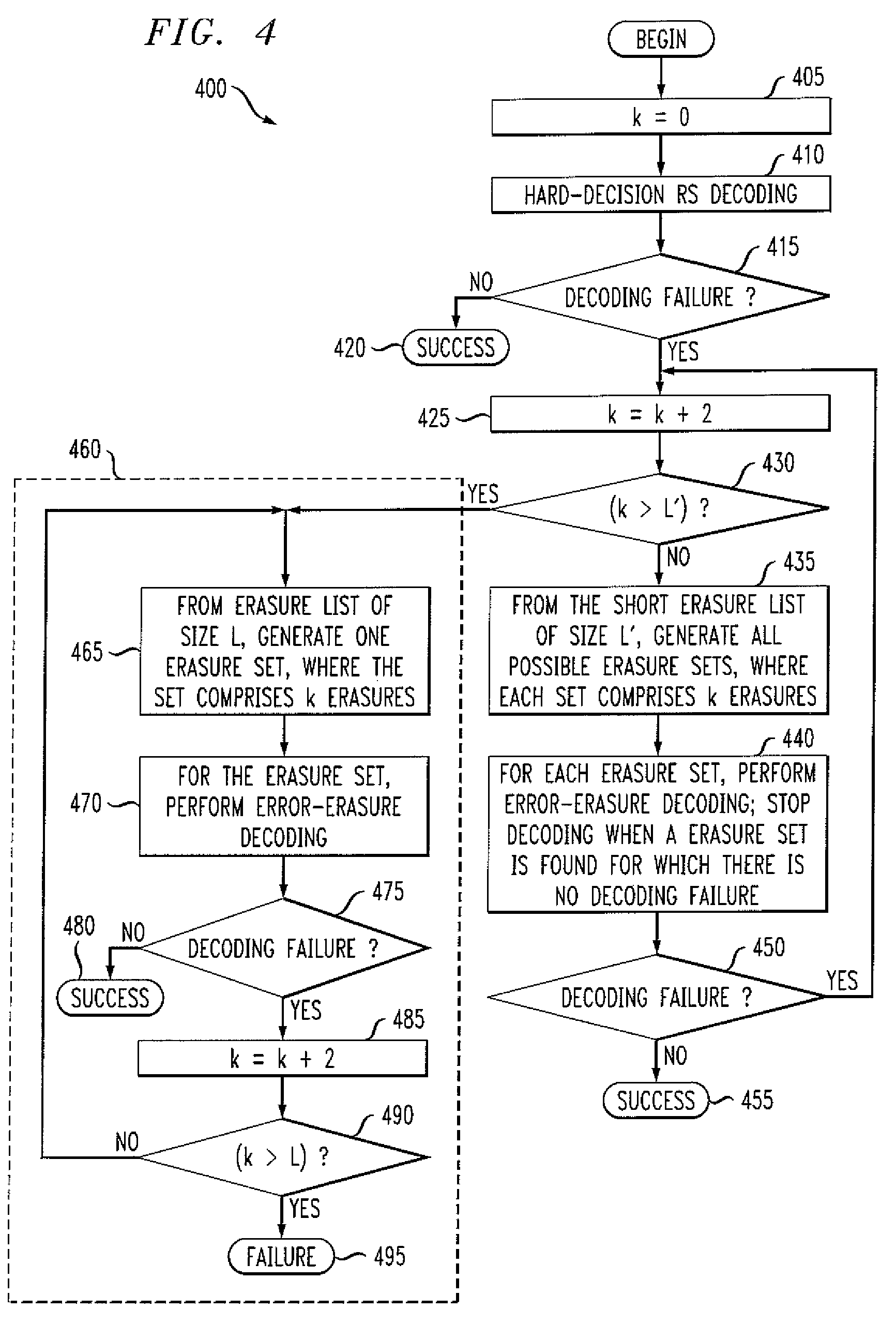
Method and apparatus for iterative error-erasure decoding
Methods and apparatus are provided for improved iterative error-erasure decoding. A signal is decoded by obtaining a plurality of symbols associated with the signal and one or more corresponding reliability values; generating at least one erasure list comprised of L symbols and at least one shortened erasure list comprised of L′ symbols, where L′ is less than L; and constructing an erasure set by taking erasures from at least one of the erasure list and the shortened erasure list. A signal is also processed by generating one or more reliability values using a soft-output detector; generating an erasure list of symbols by comparing the reliability values to at least one reliability threshold value (or by sorting); and performing error erasure decoding using the erasure list. The size of the erasure list can optionally be adjusted using feedback information.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Graphical user interface for system status alert on videoconference terminal
InactiveUS20050024485A1Television system detailsTelevision conference systemsGraphicsGraphical user interface
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) of a videoconference terminal is provided with user-selectable icons which are associated by the user with various video signals. Textual labels for the various video signals may also be provided. This information may be exchanged with the “far end” participant in the video conference. During the videoconference participants may then simply select an icon to dynamically switch video feeds without having to remember by number the particular camera or other video signal associated with a desired video feed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
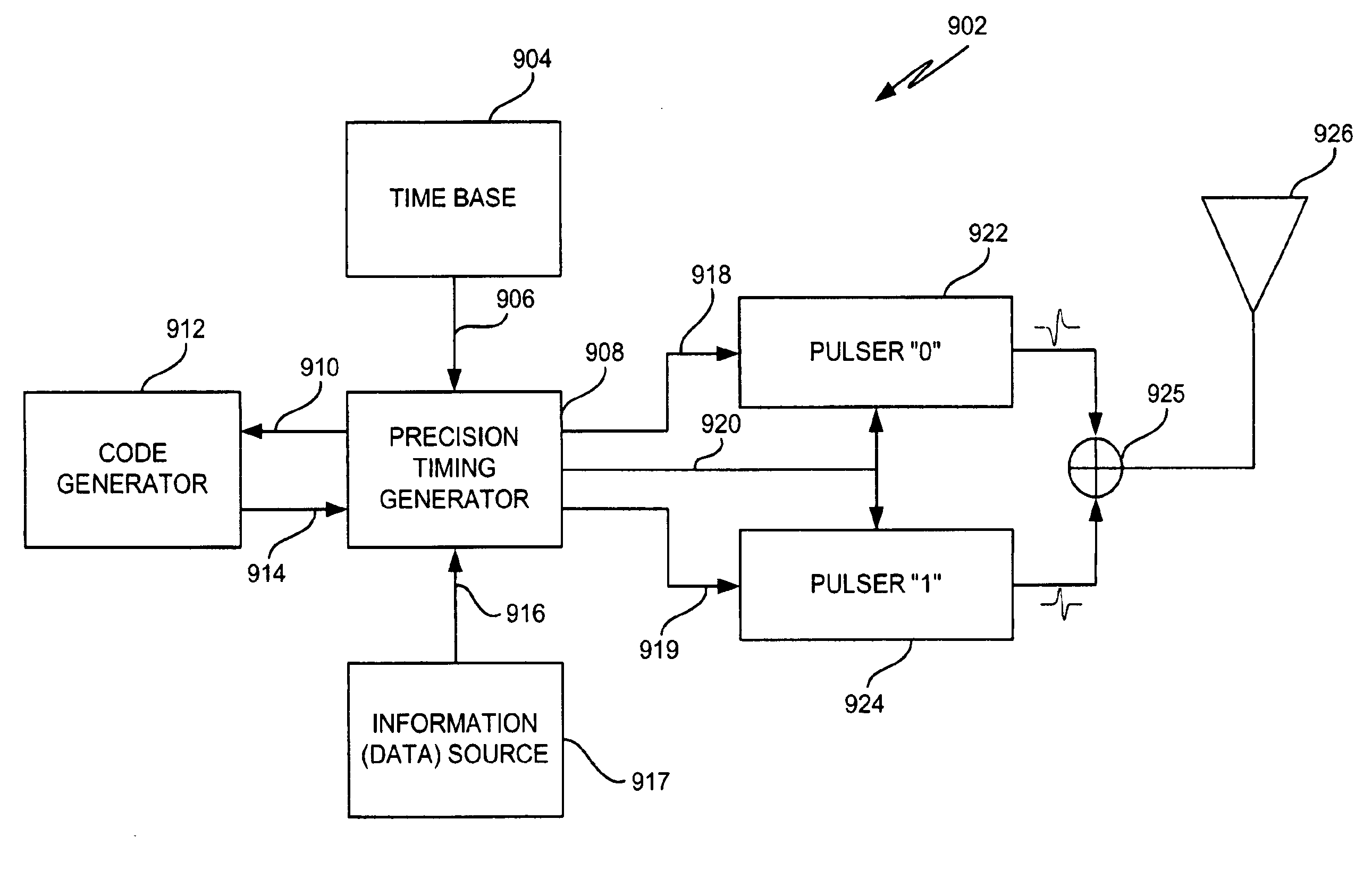
Apparatus, system and method for flip modulation in an impulse radio communications system
Apparatuses, systems and methods for transmitting and receiving modulated impulse radio signals. An impulse radio receiver includes a time base, a precision timing generator, a template generator, a delay, first and second correlators, a data detector and a time base adjustor. The time base produces a periodic timing signal that is used by the precision timing generator to produce a timing trigger signal. The template generator uses the timing trigger signal to produce a template signal. A delay receives the template signal and outputs a delayed template signal. When an impulse radio signal is received, the first correlator correlates the received impulse radio signal with the template signal to produce a first correlator output signal, and the second correlator correlates the received impulse radio signal with the delayed template signal to produce a second correlator output signal. The data detector produces a data signal based on at least the first correlator output signal. The time base adjustor produces a time base adjustment signal based on at least the second correlator output signal. The time base adjustment signal is used to synchronize the time base with the received impulse radio signal.
Owner:ALEREON
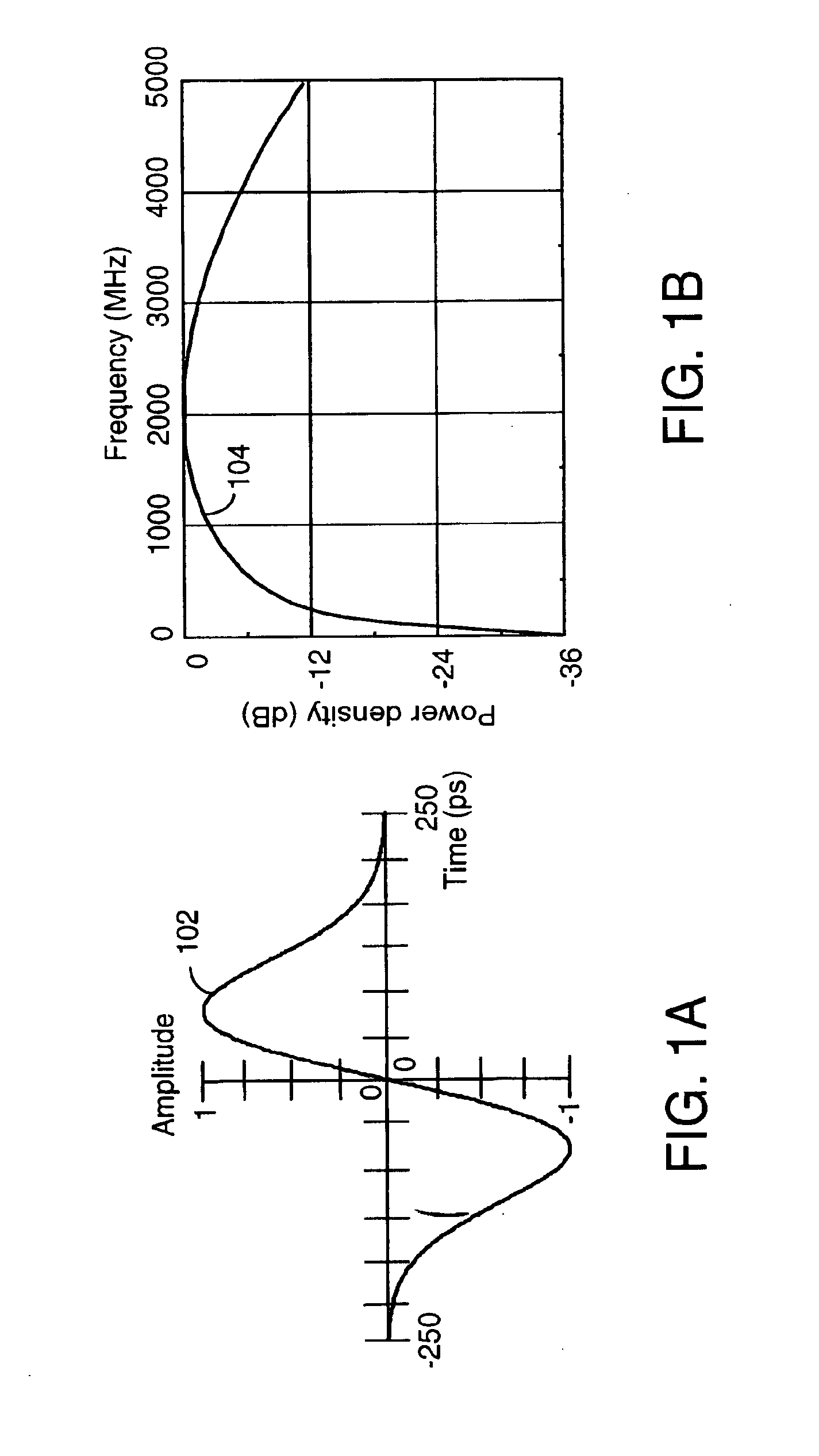
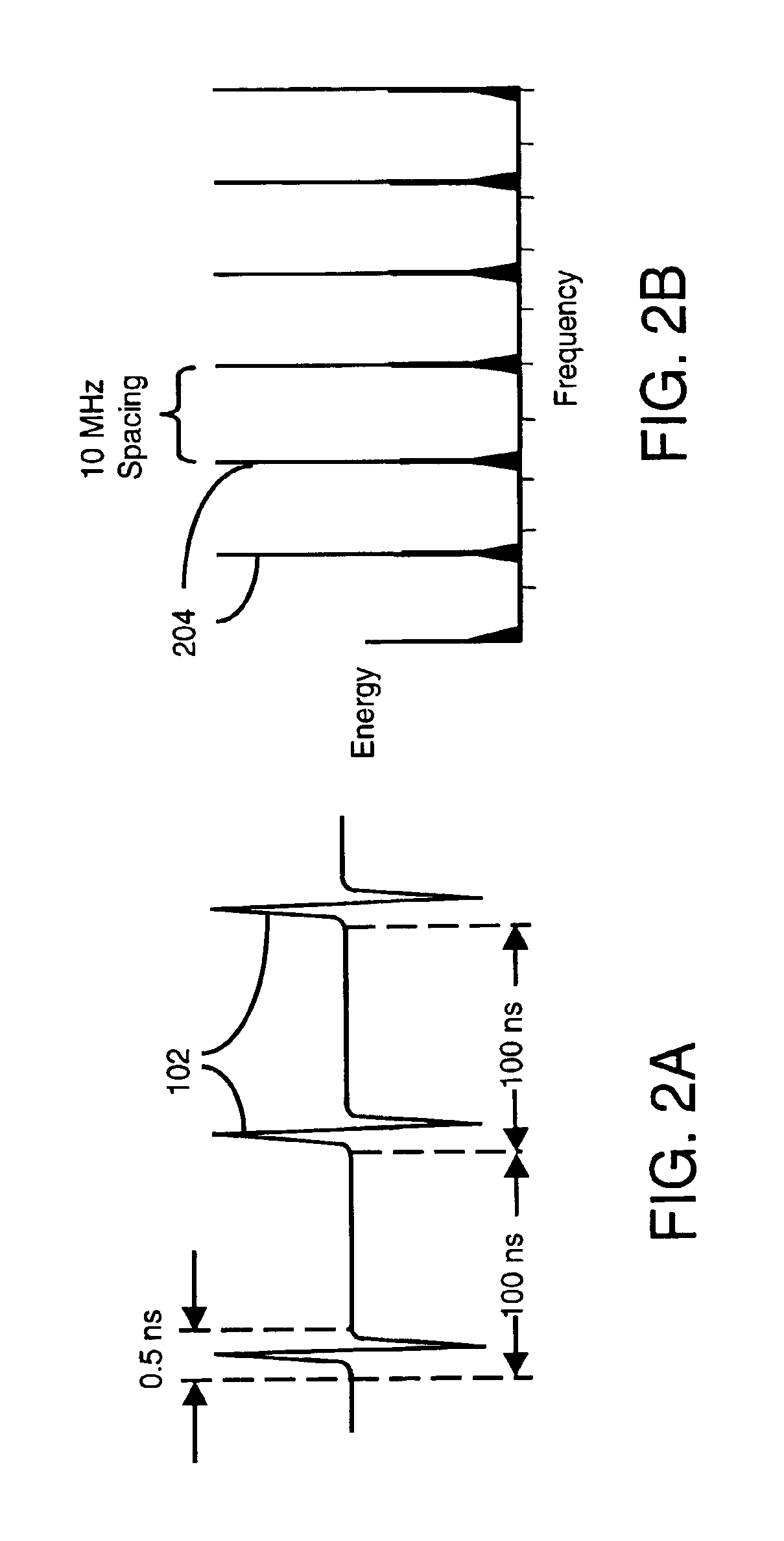
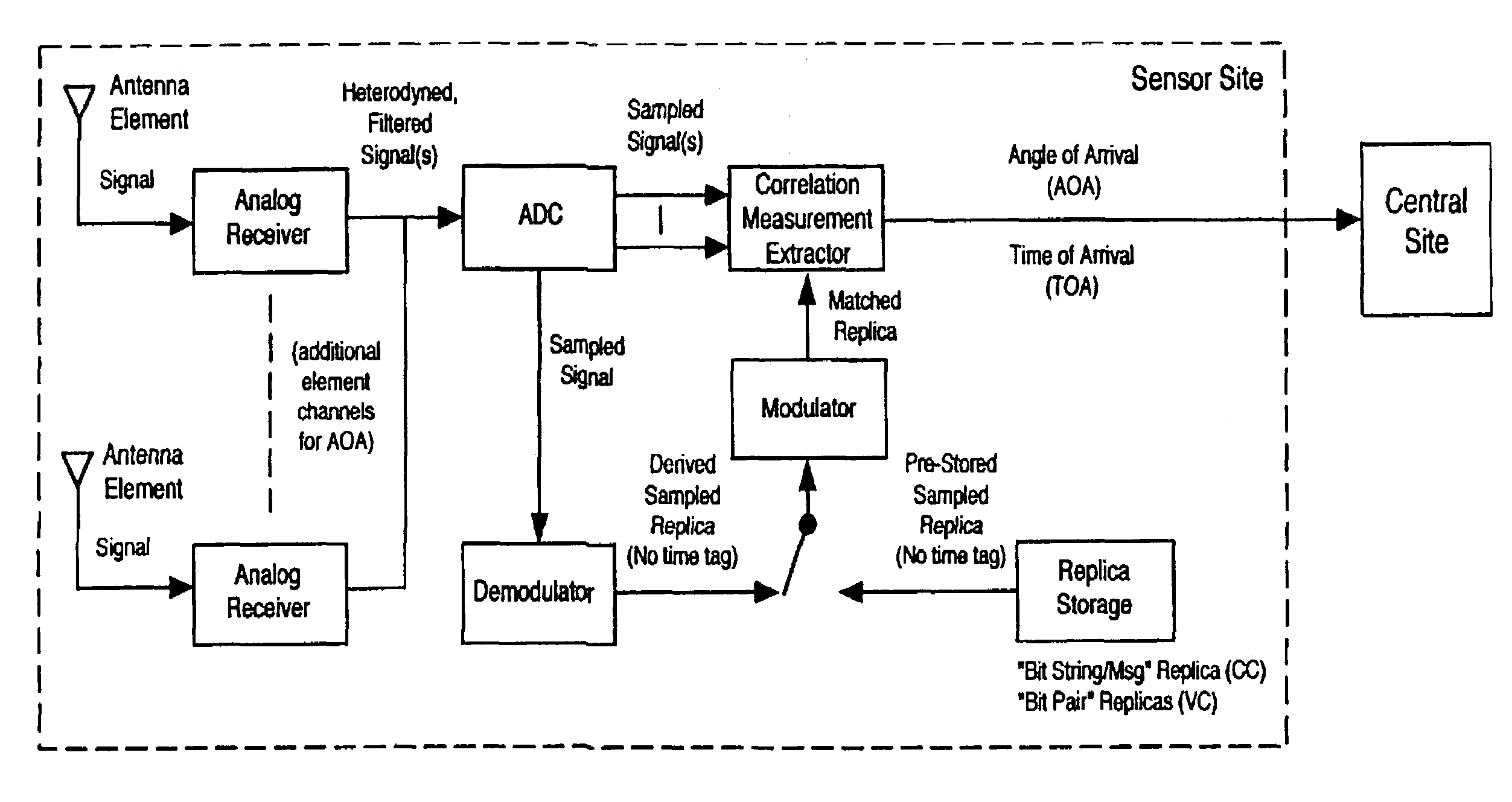
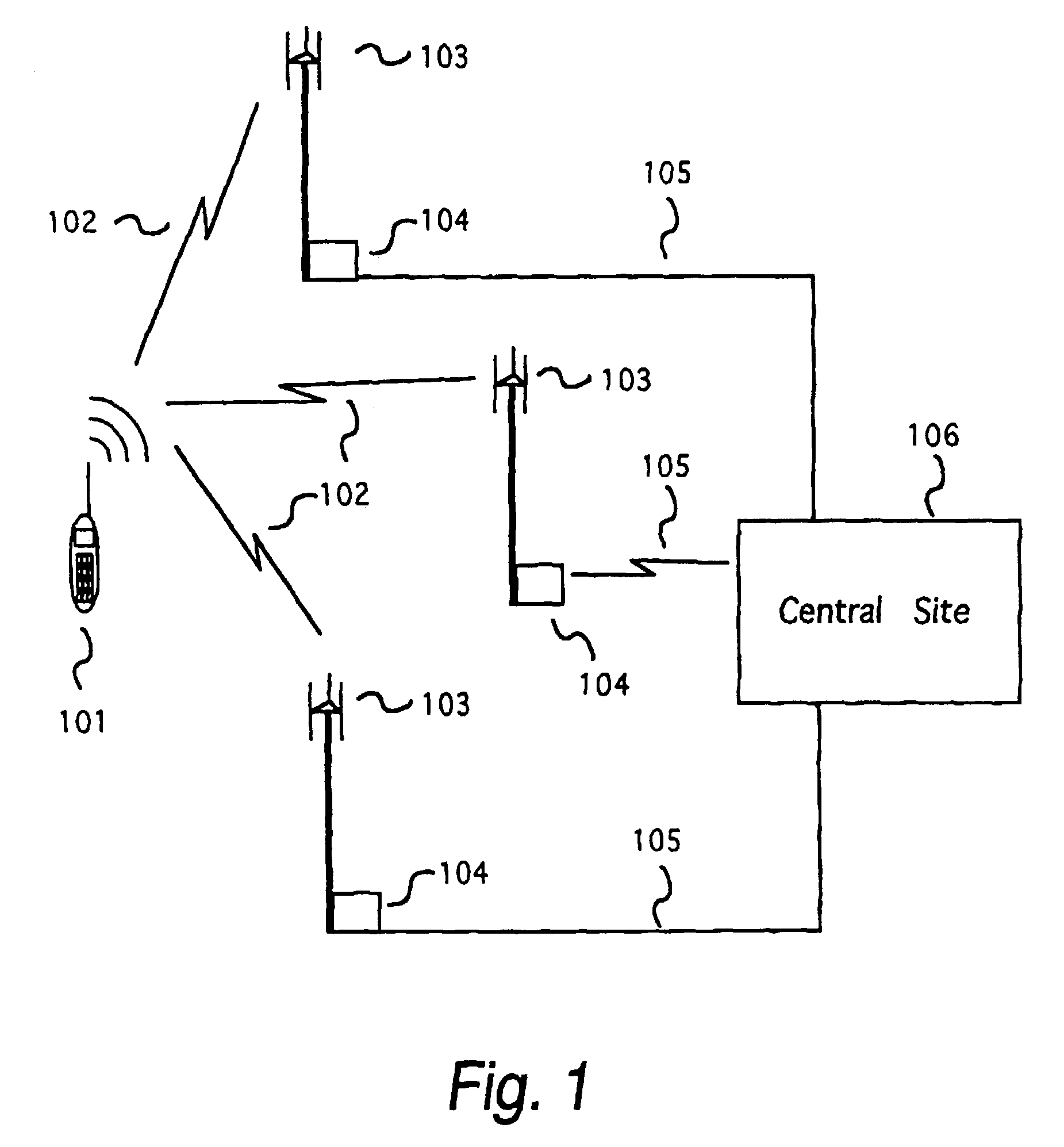
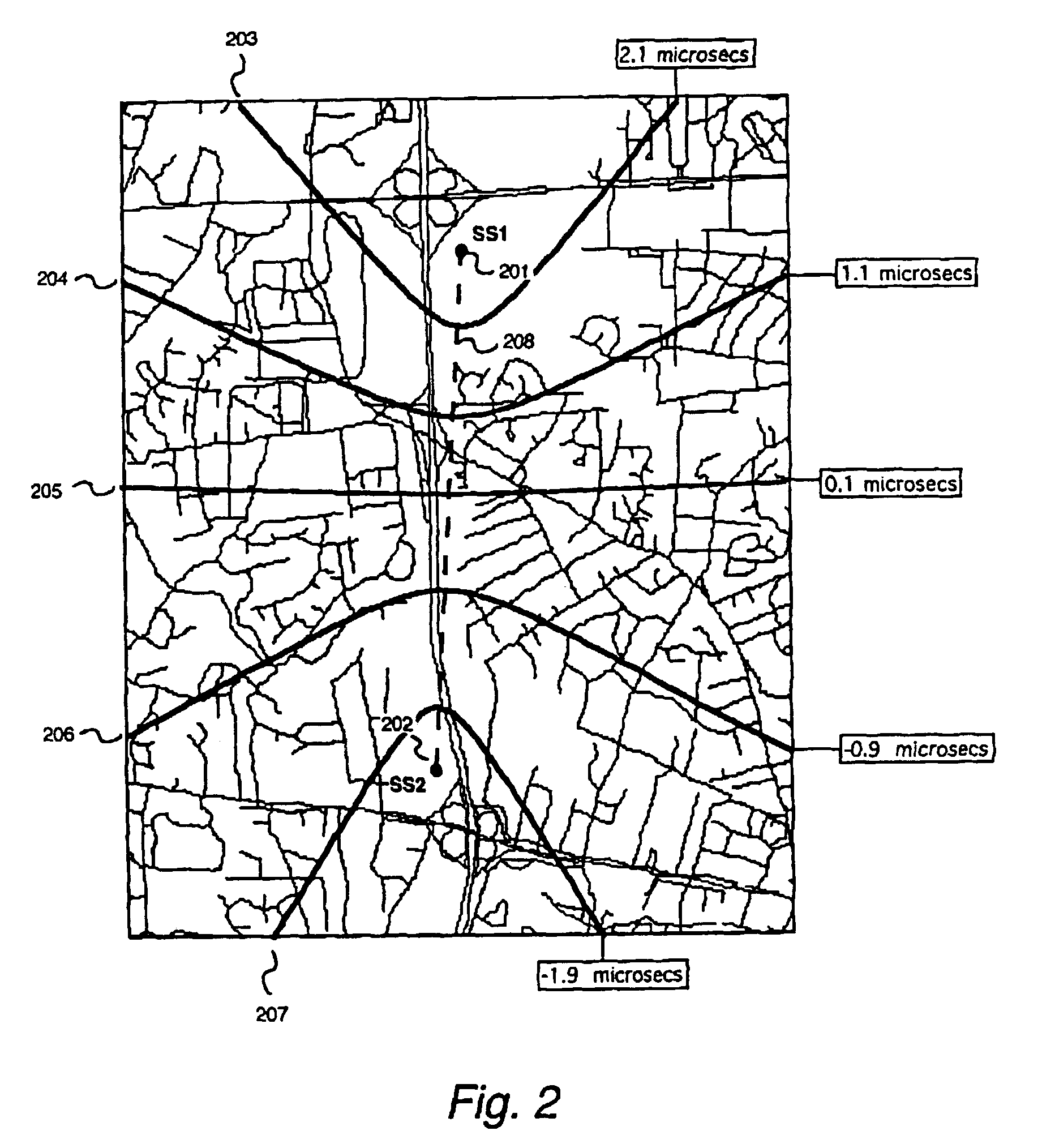
Robust, efficient, localization system
InactiveUS7340259B2Quick responseEasy to measure in real timeDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Orientation-sensitive signal output
ActiveUS20060281453A1Digital data processing detailsDevices with sensorEngineeringSignal correlation
The selection and output of a signal, such as an alphanumeric character, is provided depending upon the orientation of a device, such as a mobile telephone. In particular, a neutral position of a device is determined in relation to at least a first axis, the device including at least a first control associated with a first plurality of output signals, and an angular displacement of the device is measured about at least the first axis. A selection of the first control is also received, and one of the first plurality of output signals is output based at least upon the selection and the angular displacement.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
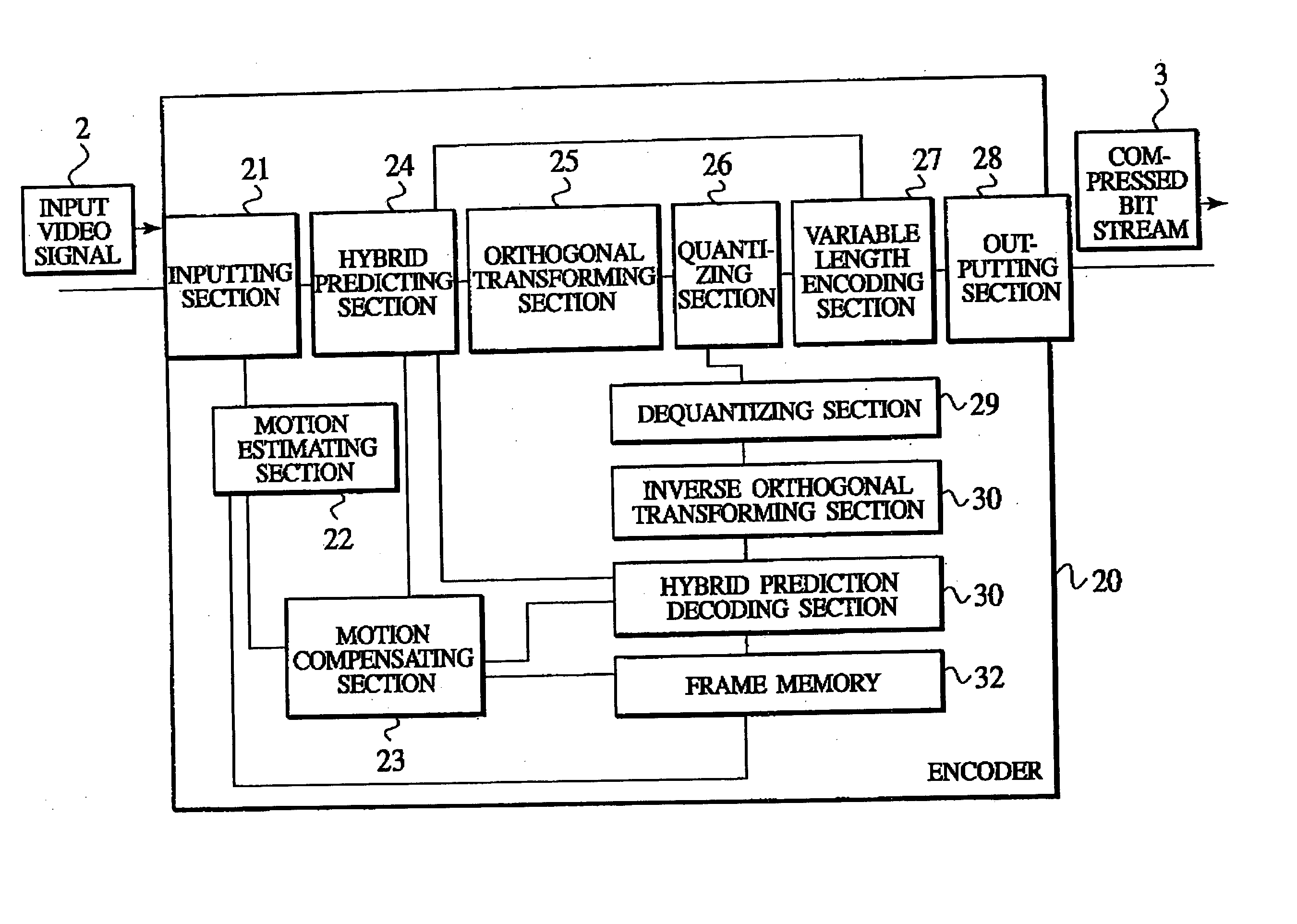
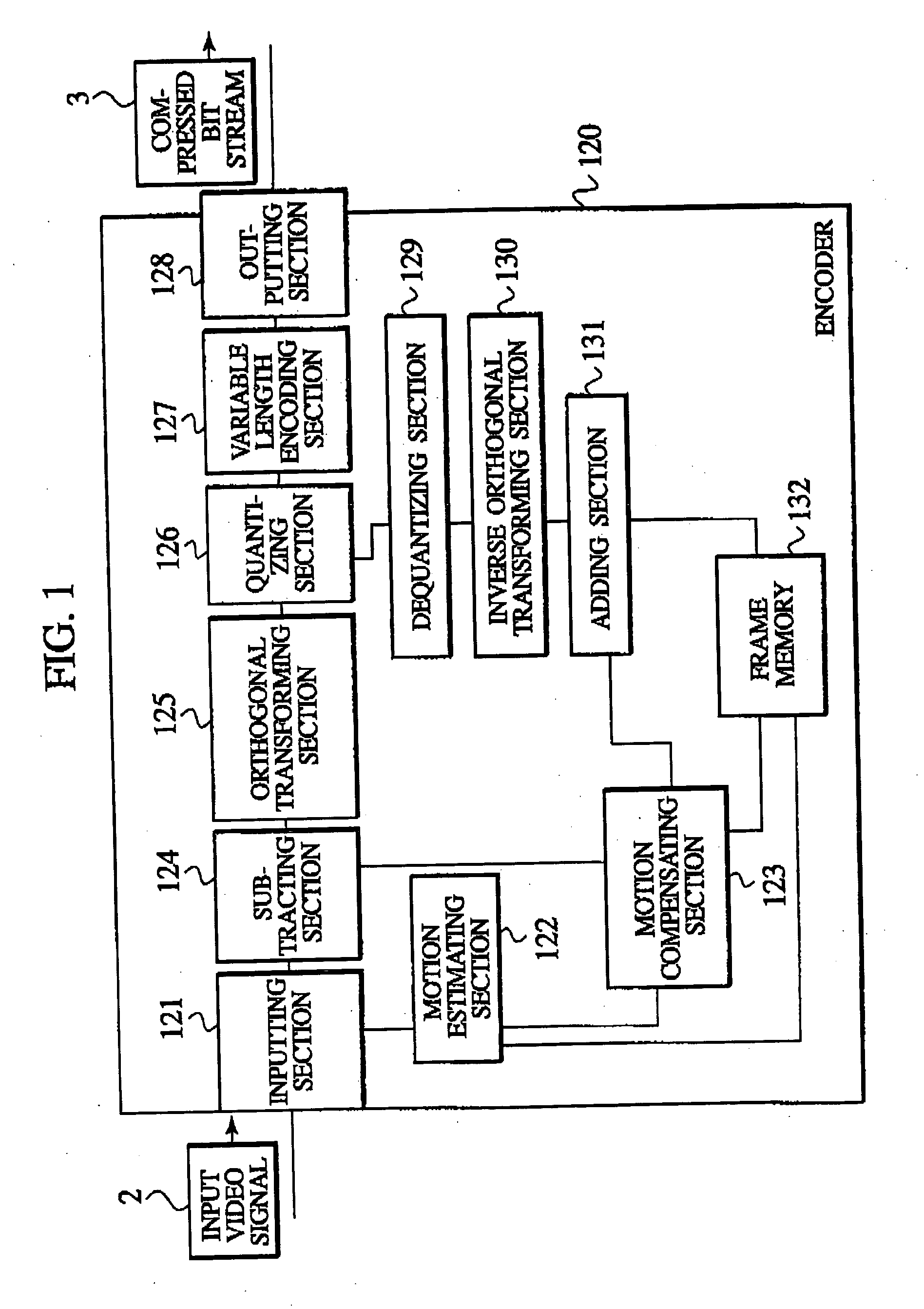
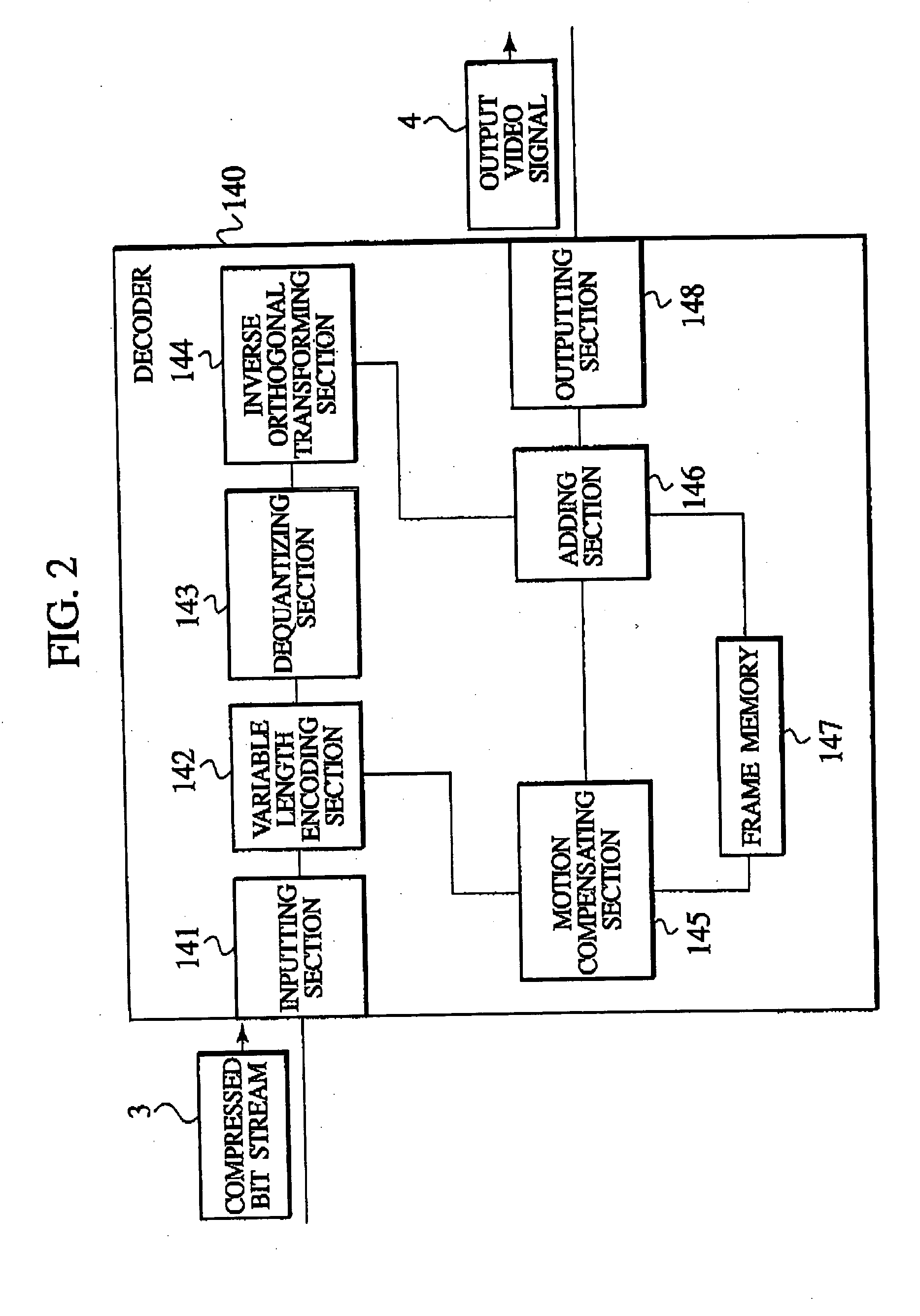
Moving picture encoding/transmission system, moving picture encoding/transmission method, and encoding apparatus, decoding apparatus, encoding method decoding method and program usable for the same
ActiveUS20040233989A1Inhibit deteriorationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSignal correlationIntra-frame
An object of the present invention is to allow portions which are subjected to a coding in inter-frame prediction mode and portions which are subjected to coding in intra-frame prediction mode to be mixed in one macro block without changing the framework of macro blocks. The present invention provides an encoder which encodes each of first image blocks of a video. The encoder includes prediction mode selection information generating means for generating prediction mode selection information which indicates that a first prediction mode for reducing temporal redundancy is applied to each of second image blocks or that a second prediction mode for reducing spatial redundancy is applied to each of the second image blocks. The second image blocks are obtained by dividing the first image blocks. The encoder includes predictive residual signal generating means for generating a predictive residual signal by applying the selected first or second prediction mode to each of the second image blocks. The encoder includes transmitting means for transmitting the prediction mode selection information in association with the predictive residual signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com