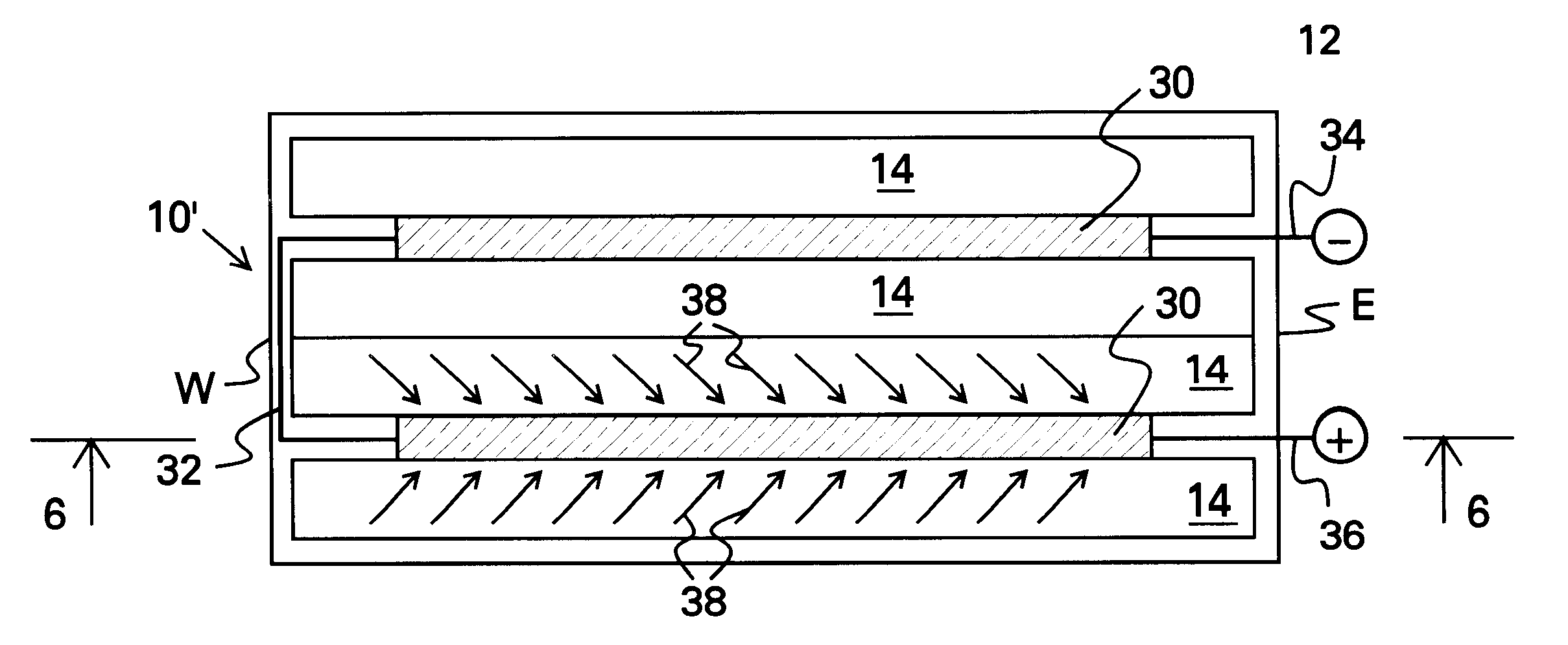
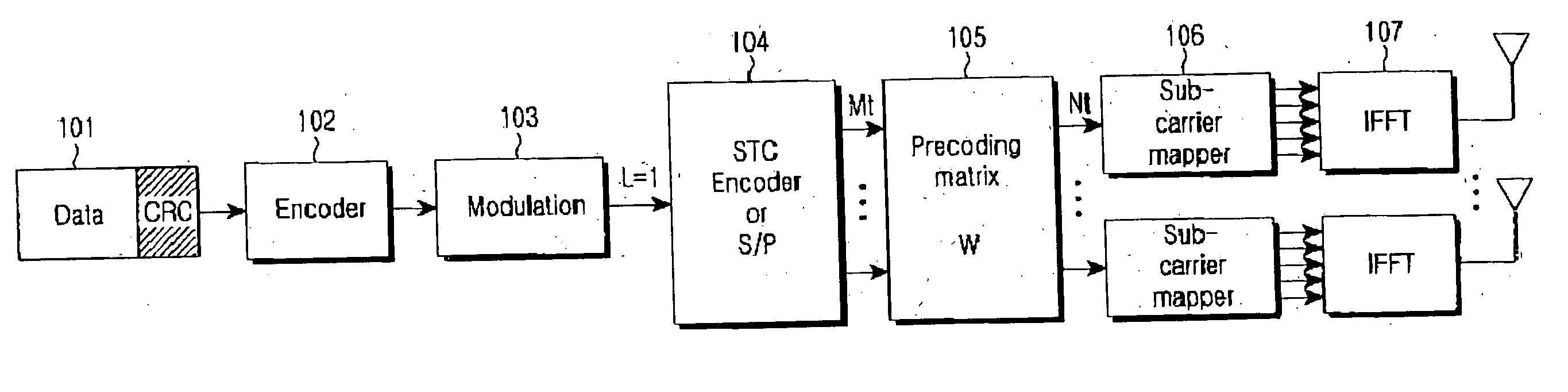
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
993 results about "Spatial multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
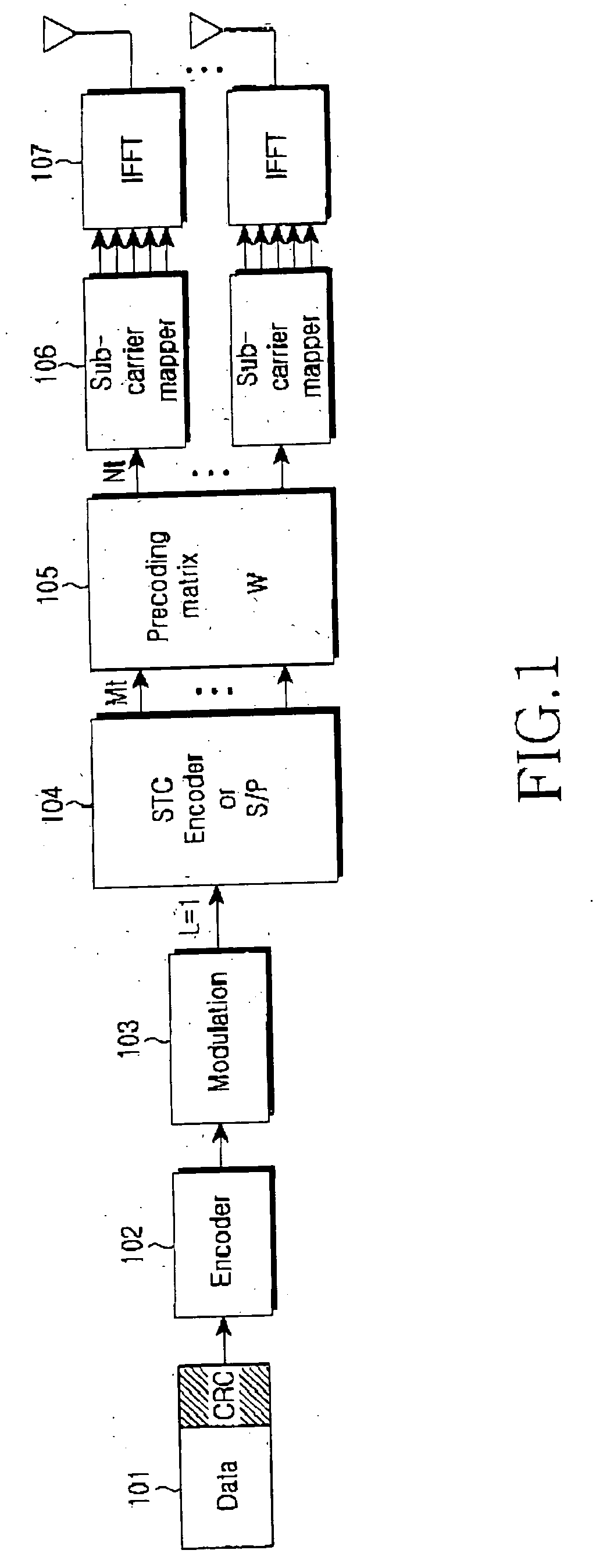
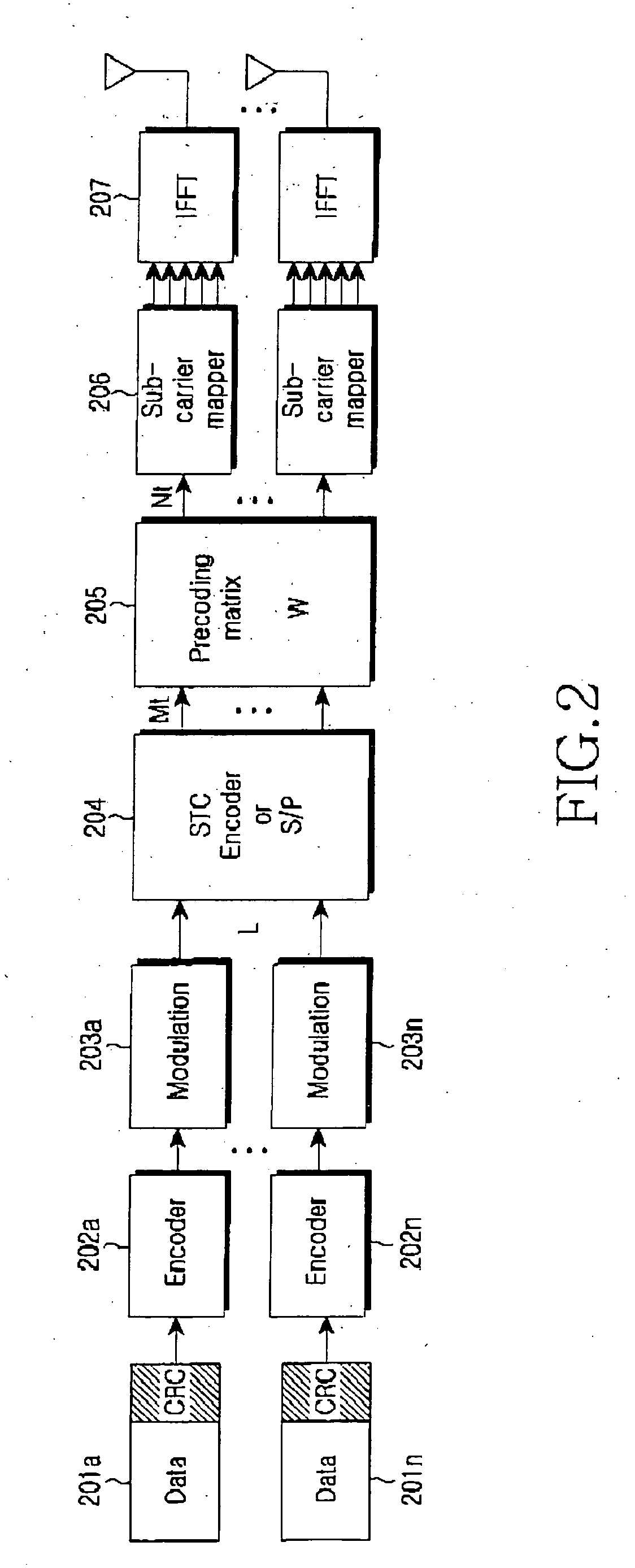
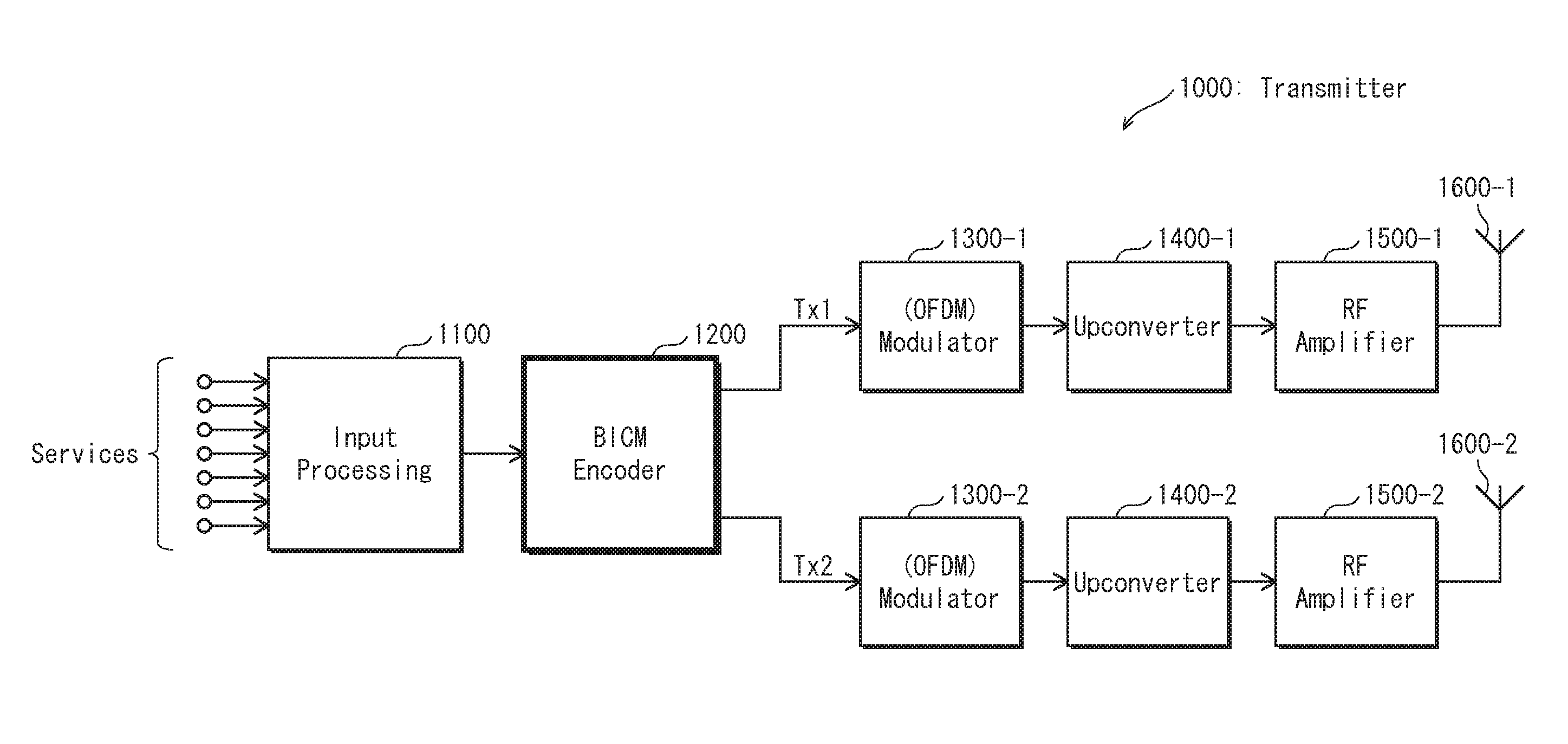
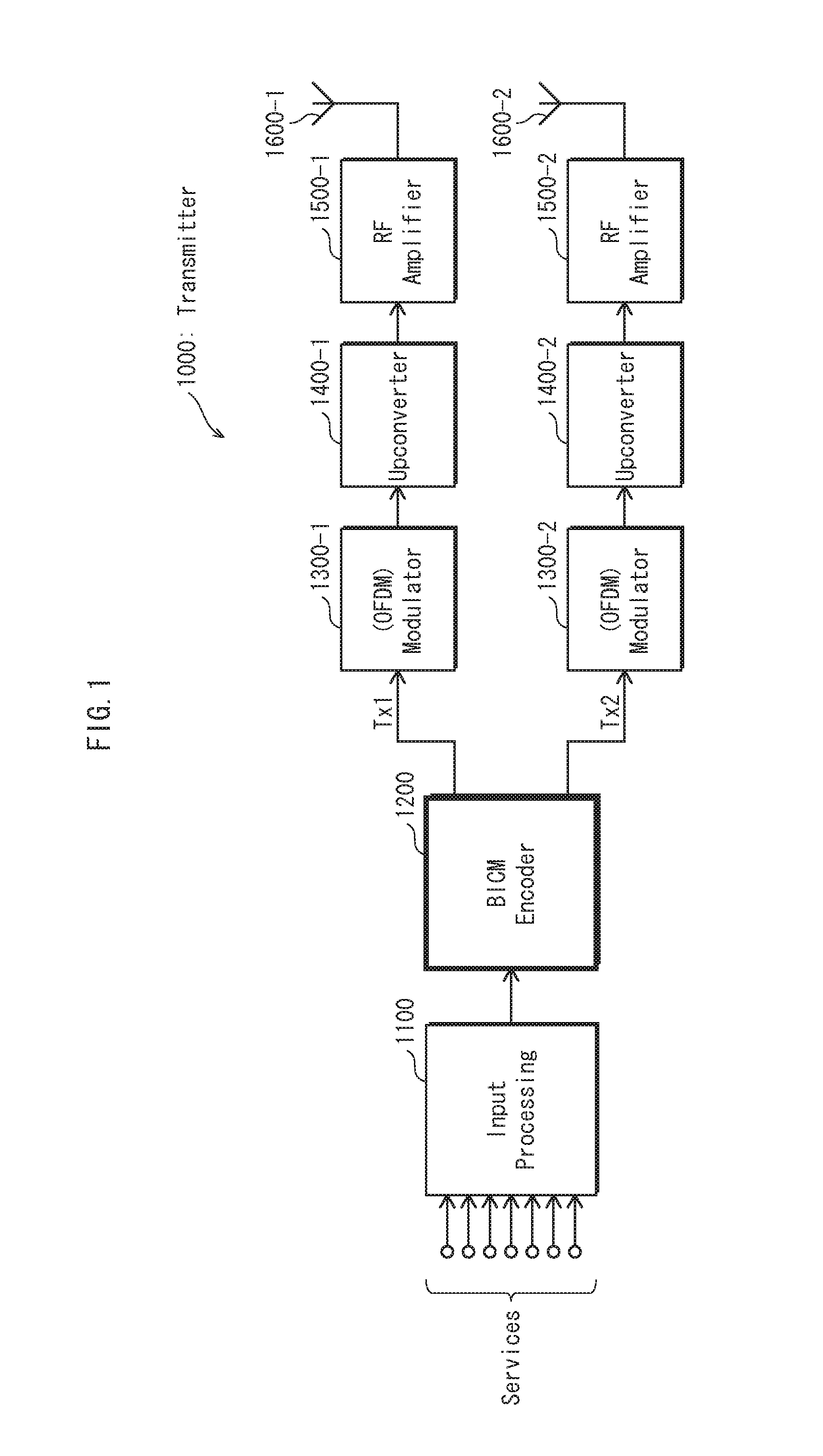
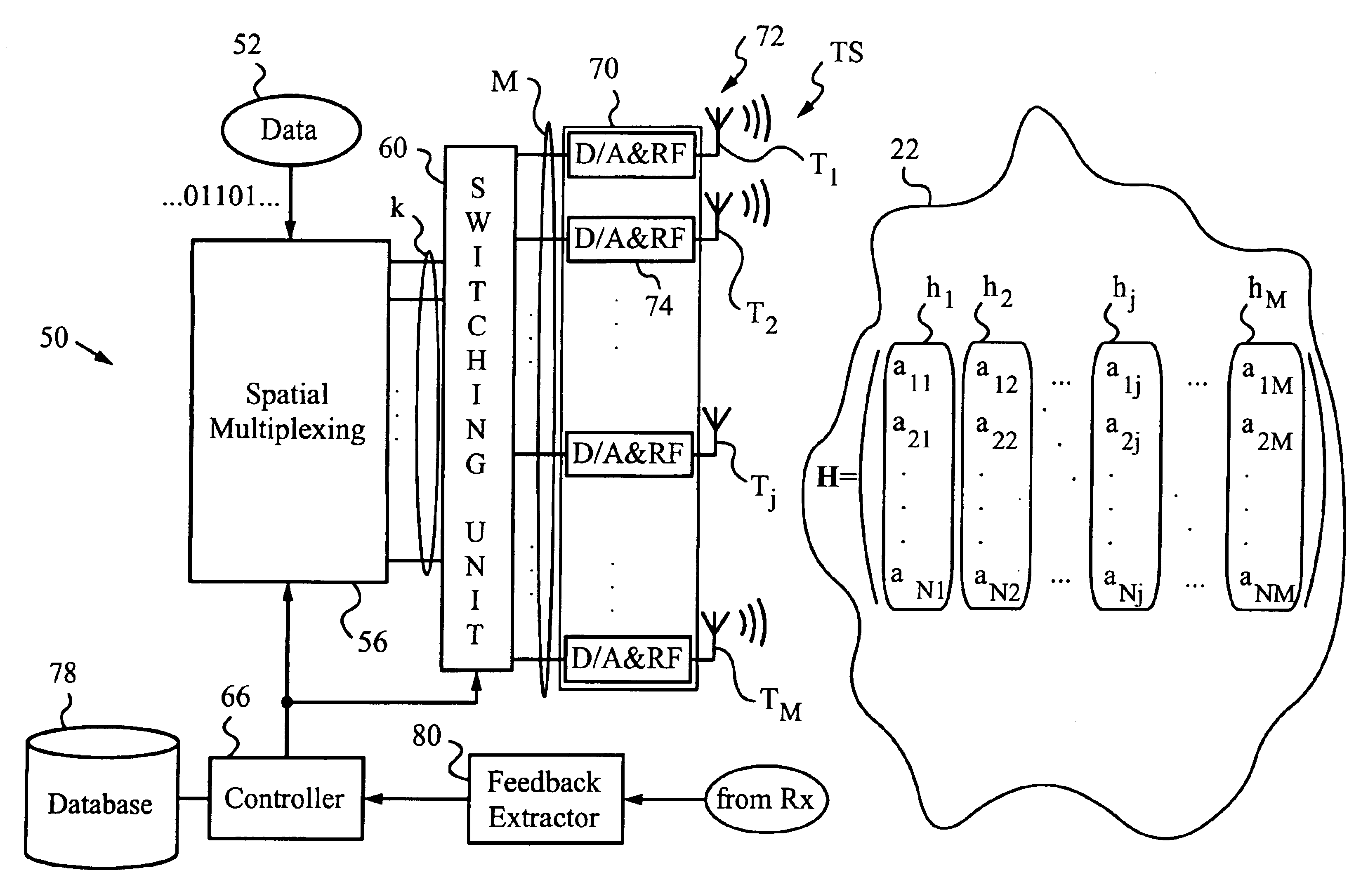
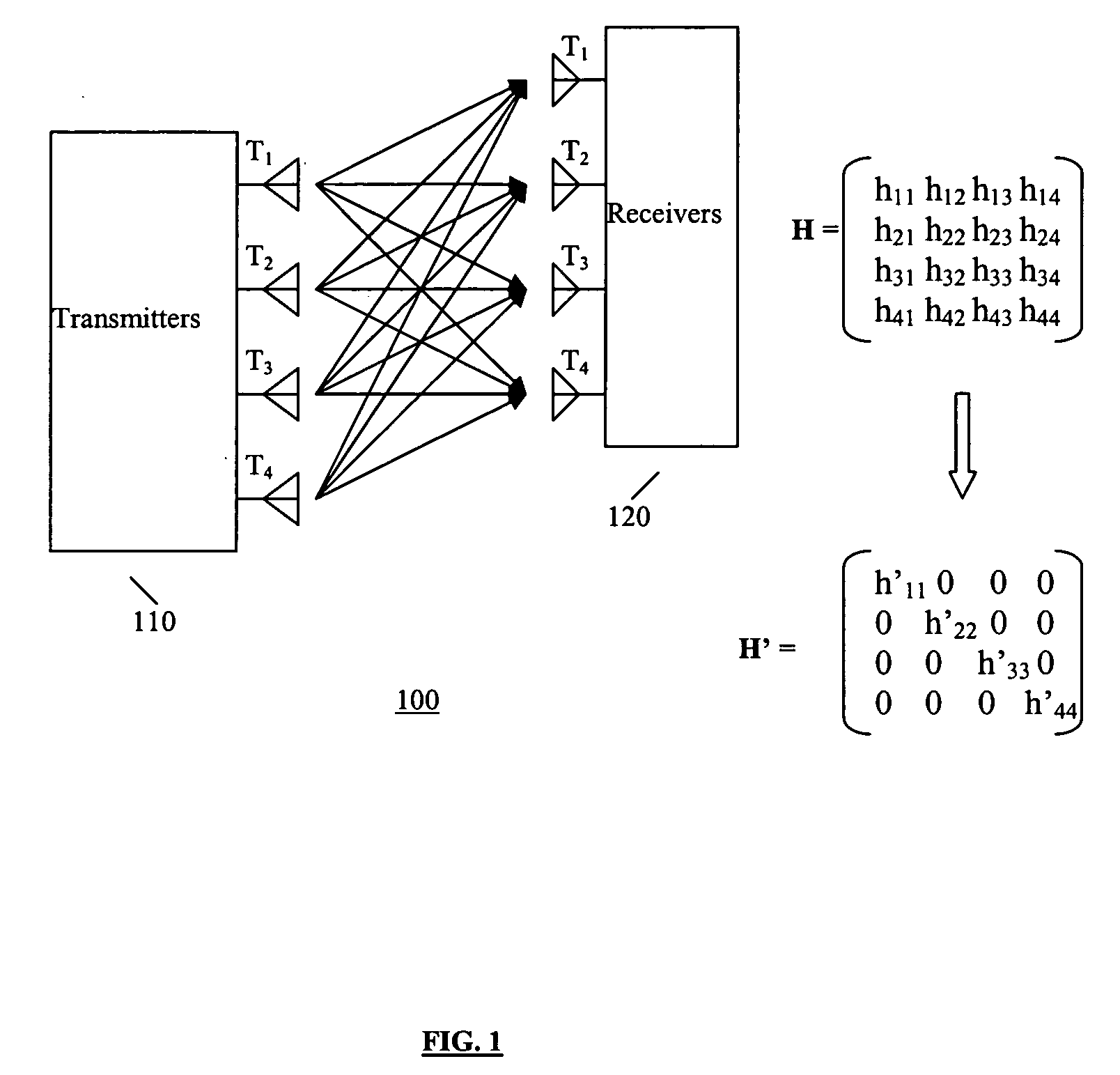
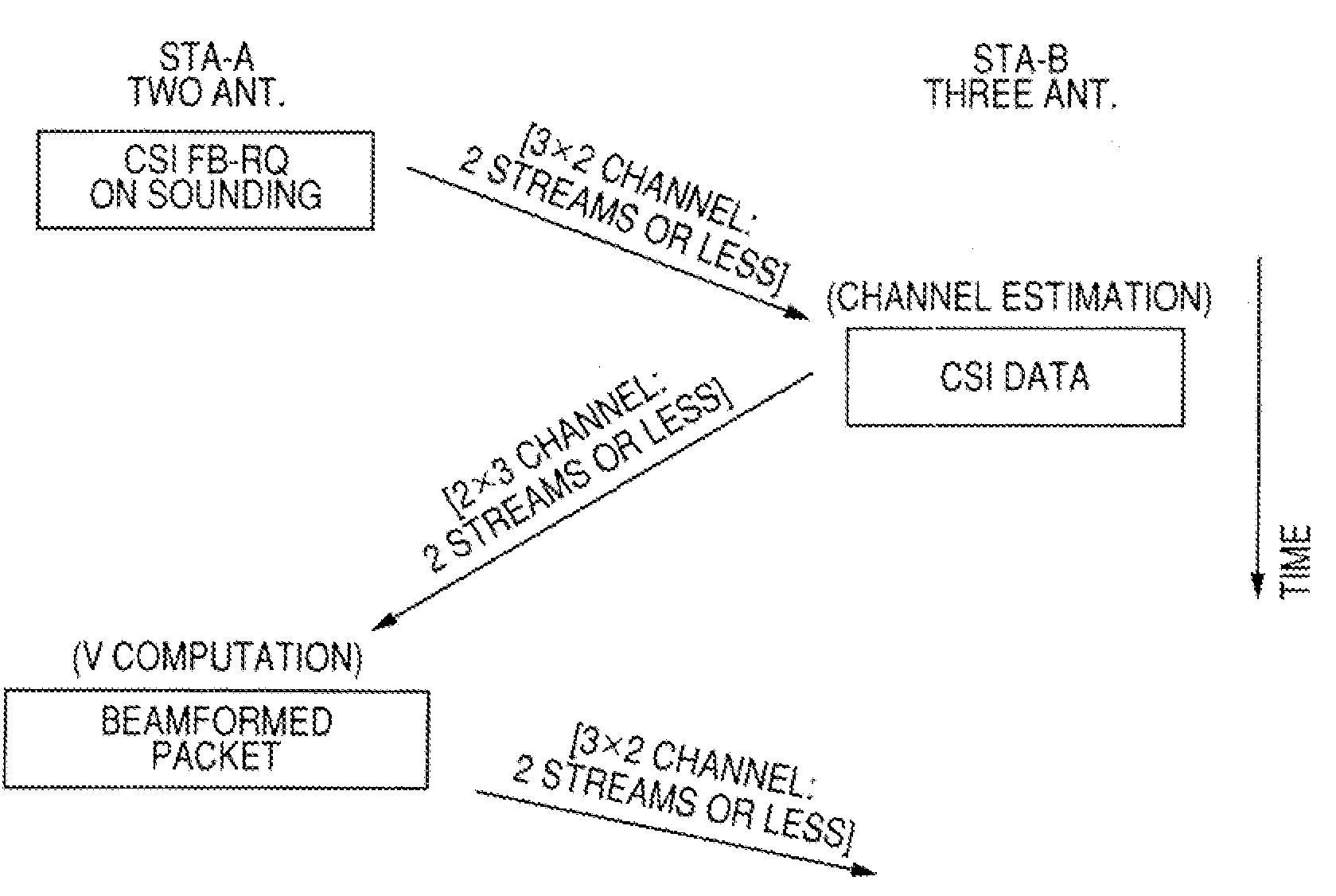
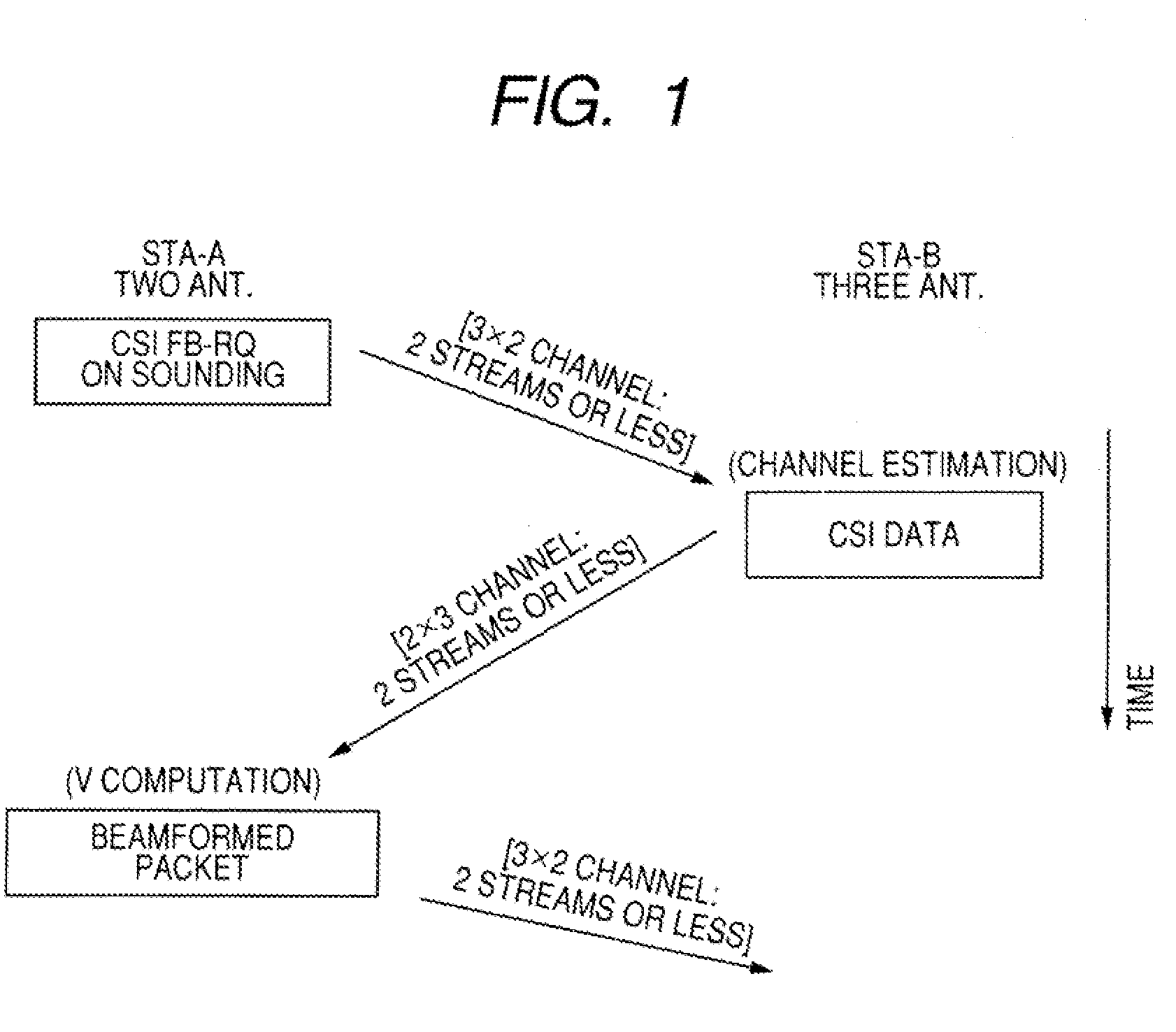
Spatial multiplexing (often abbreviated SM or SMX) is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication, Fibre-optic communication and other communications technologies to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, known as "streams". Therefore, the space dimension is reused, or multiplexed, more than one time. If the transmitter is equipped with Nₜ antennas and the receiver has Nᵣ antennas, the maximum spatial multiplexing order (the number of streams) is, Nₛ=min(Nₜ,Nᵣ) if a linear receiver is used.
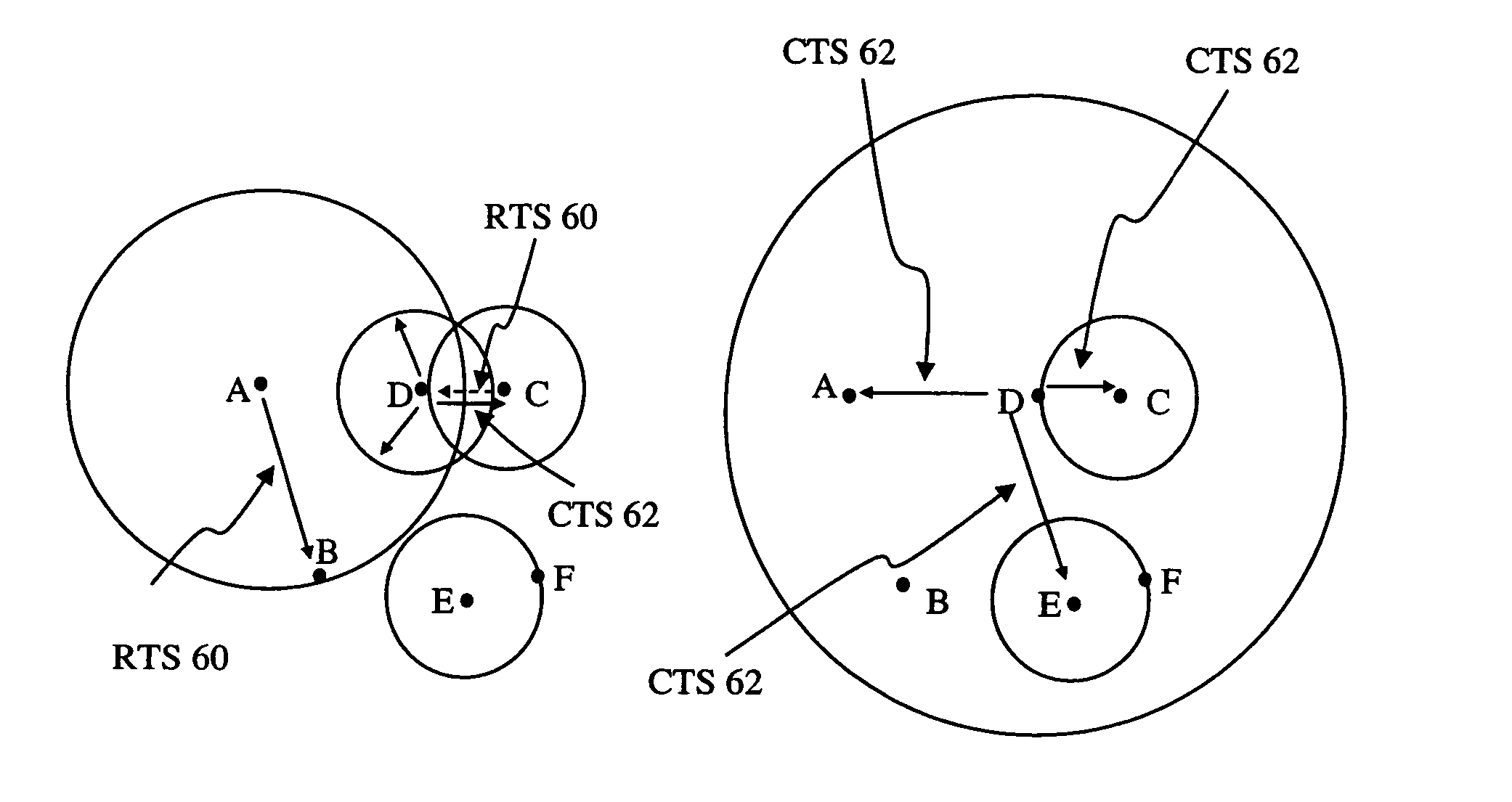
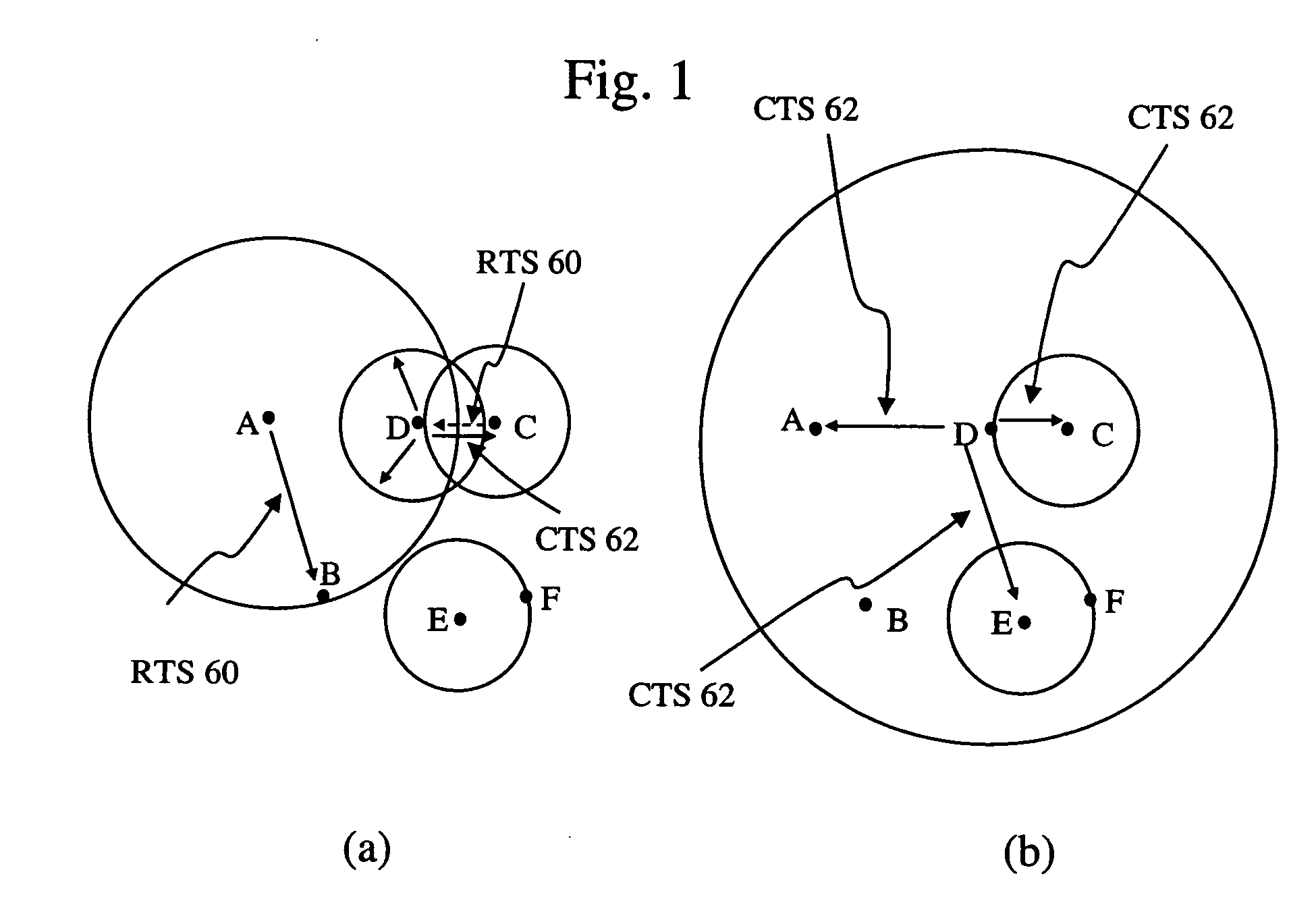
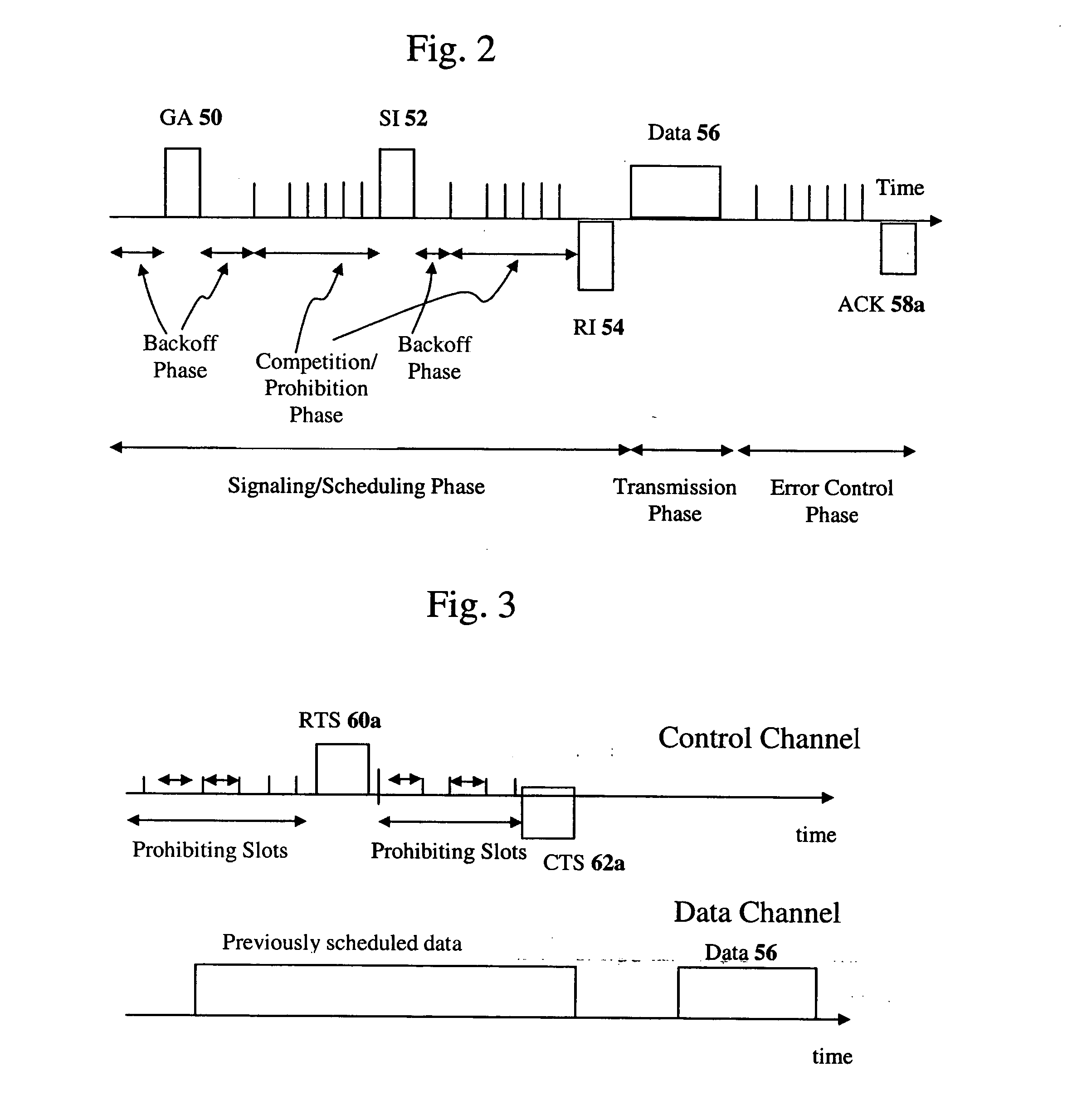
Method of interference management for interference/collision avoidance and spatial reuse enhancement
InactiveUS20050058151A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove channel utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A method called the evolvable interference management (EIM) method is disclosed in this patent for avoiding interference and collision and increasing network throughput and energy efficiency in wireless networks. EIM employs sensitive CSMA / CA, patching approaches, interference engineering, differentiated multichannel, detached dialogues, and / or spread spectrum techniques to solve the interference and QoS problems. EIM-based protocols can considerably increase network throughput and QoS differentiation capability as compared to IEEE 802.11e in multihop networking environments. Due to the improvements achievable by EIM, the techniques and mechanisms presented in this application may be applied to obtain an extension to IEEE 802.11 to better support differentiated service and power control in ad hoc networks and multihop wireless LANs. New protocols may also be designed based on EIM.
Owner:YEH CHIHSIANG
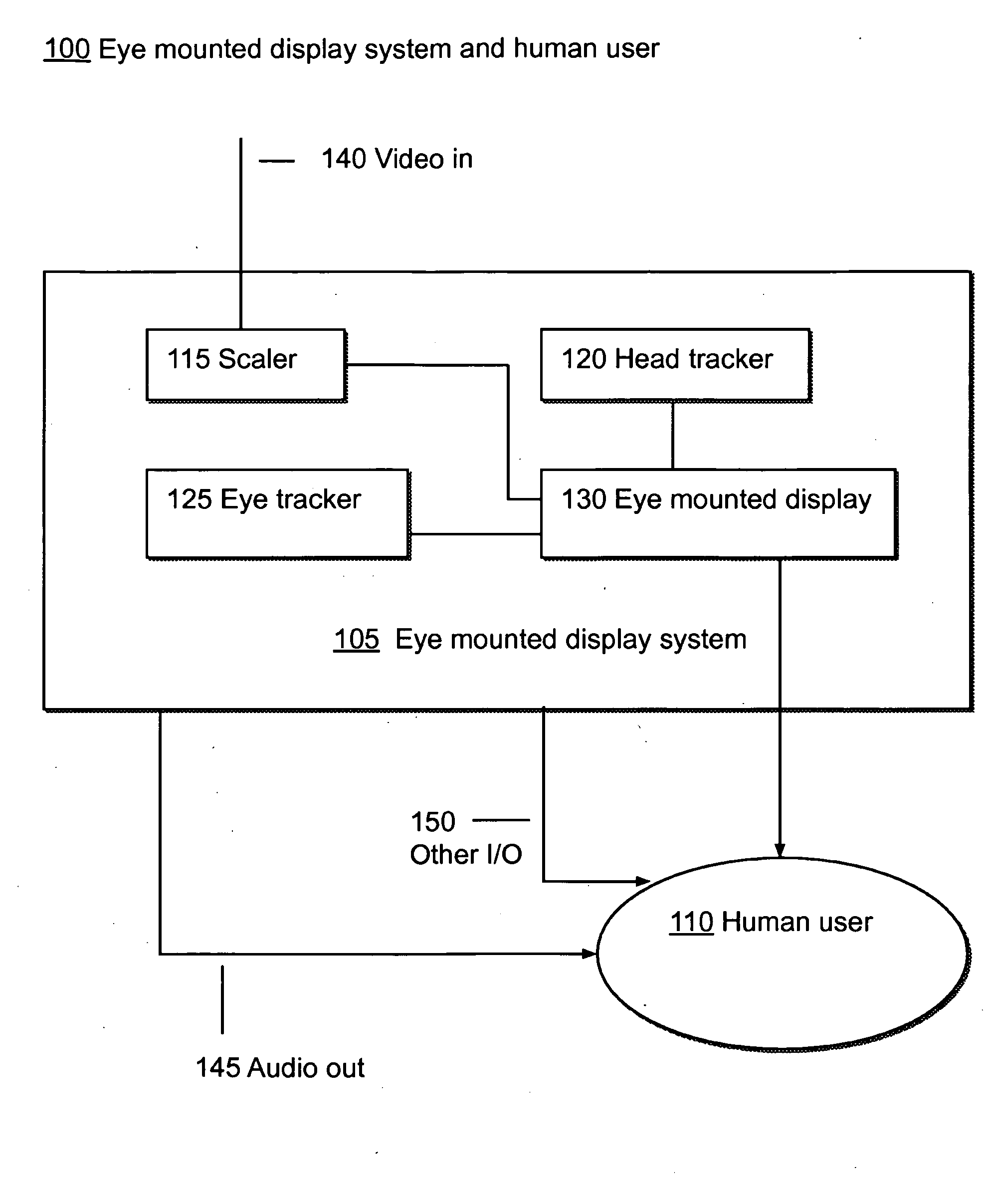
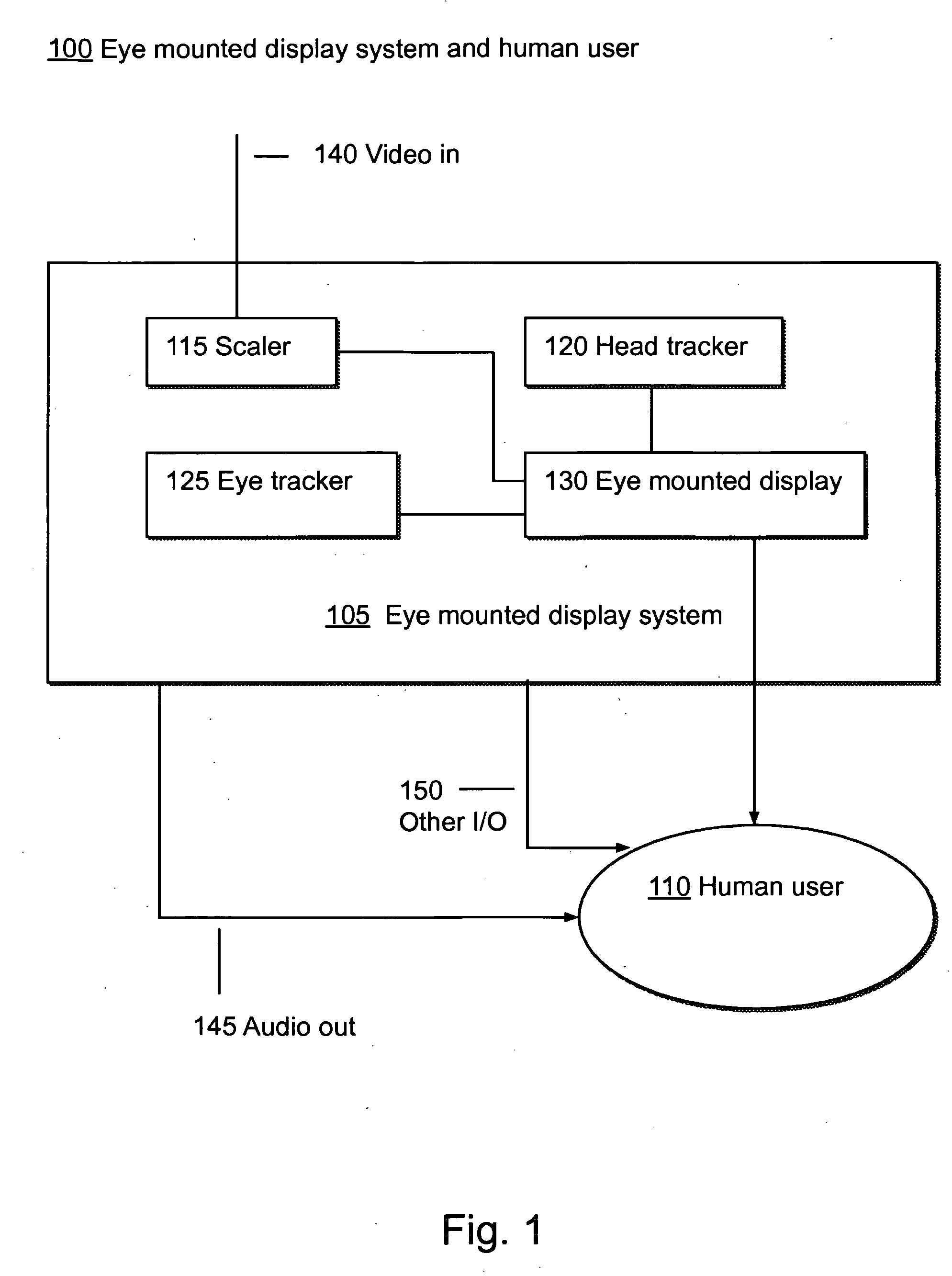
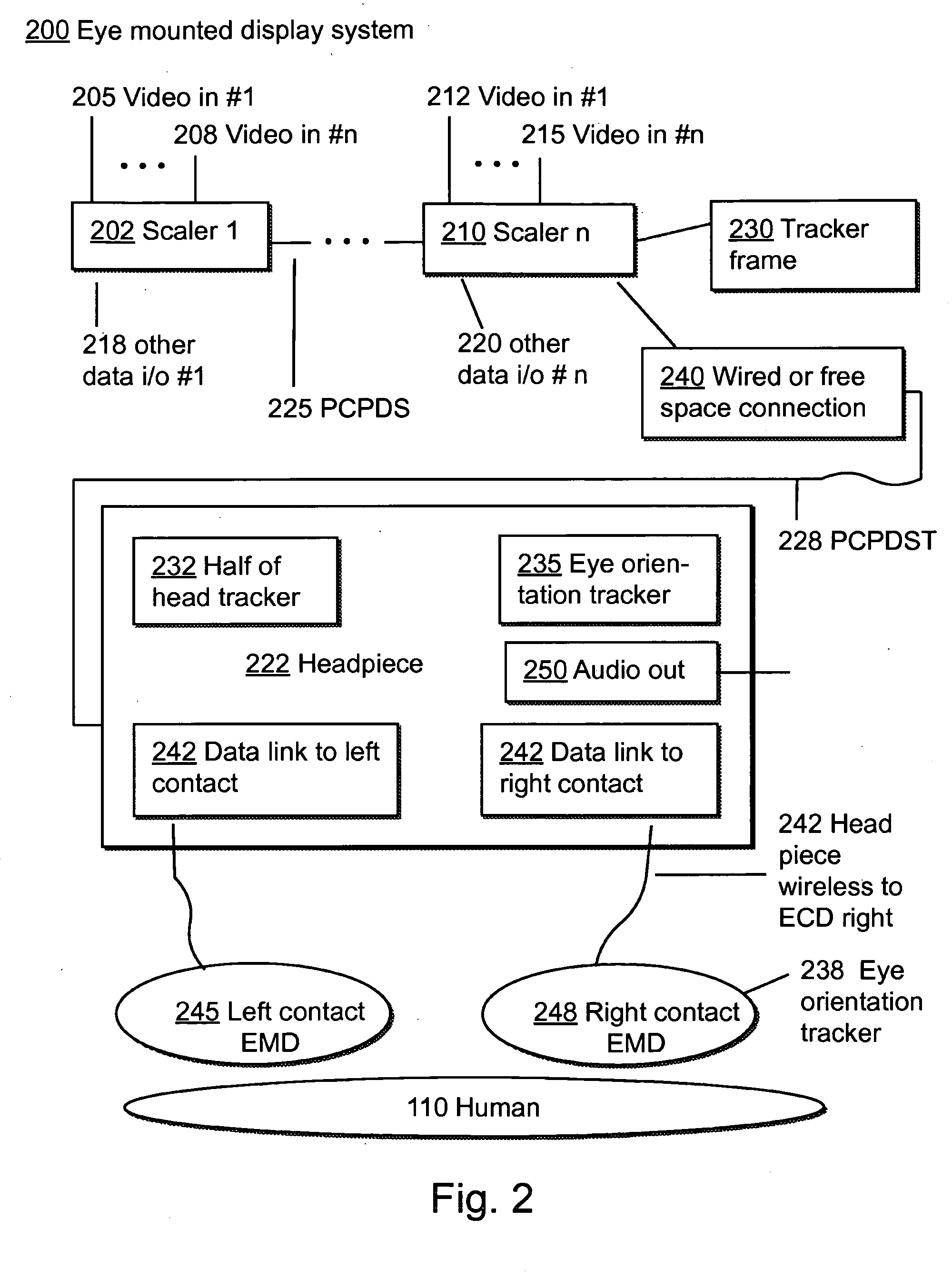
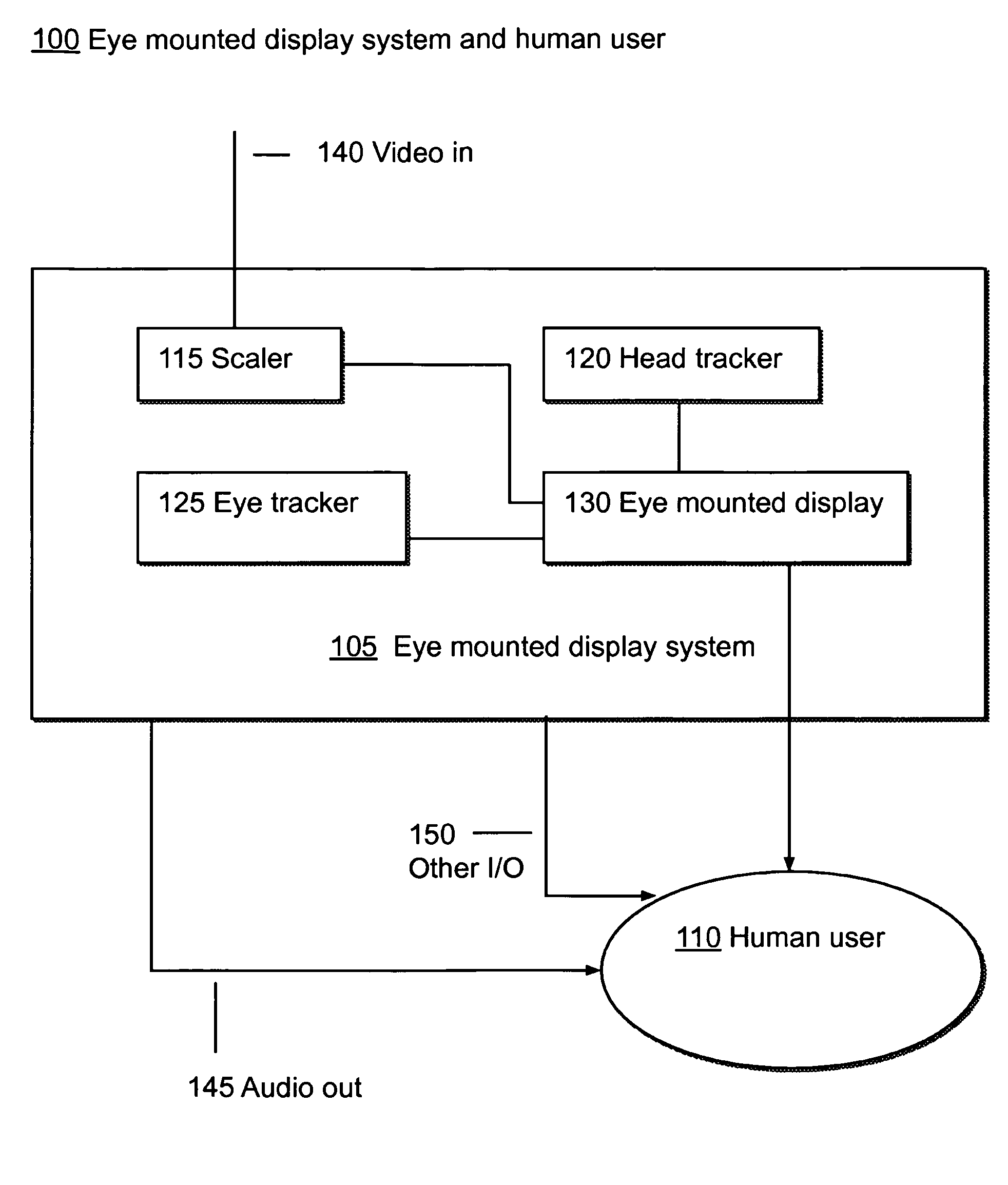
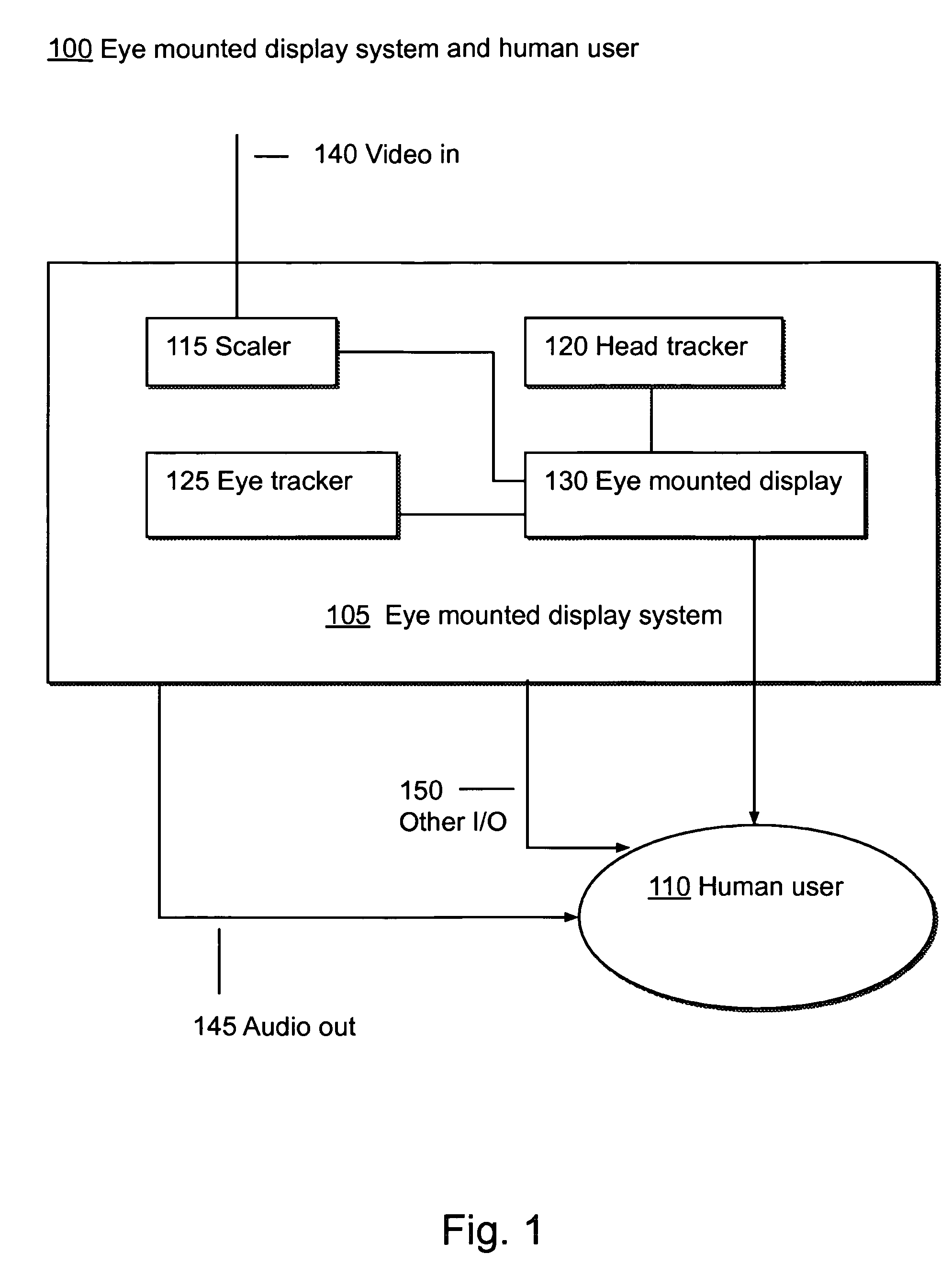
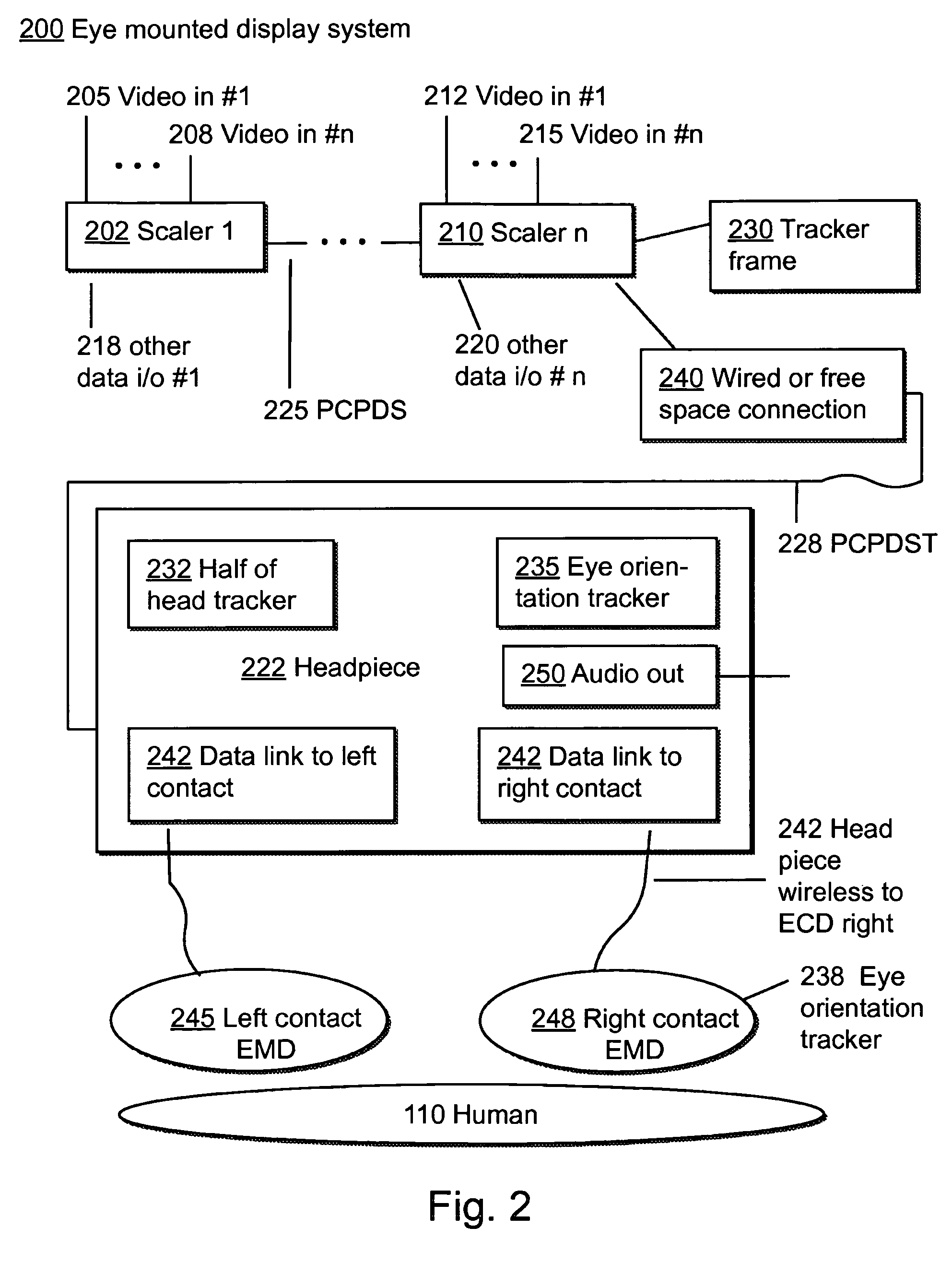
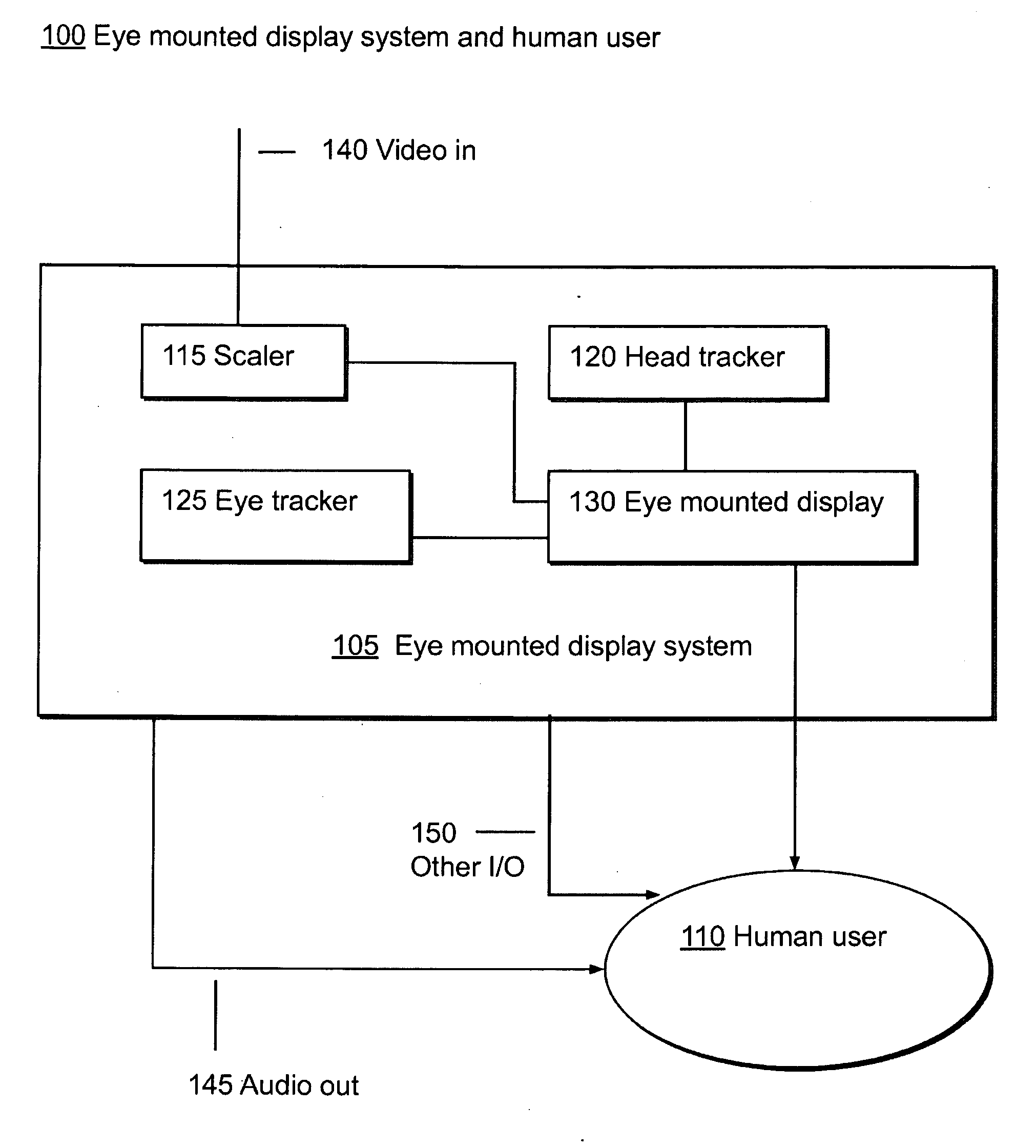
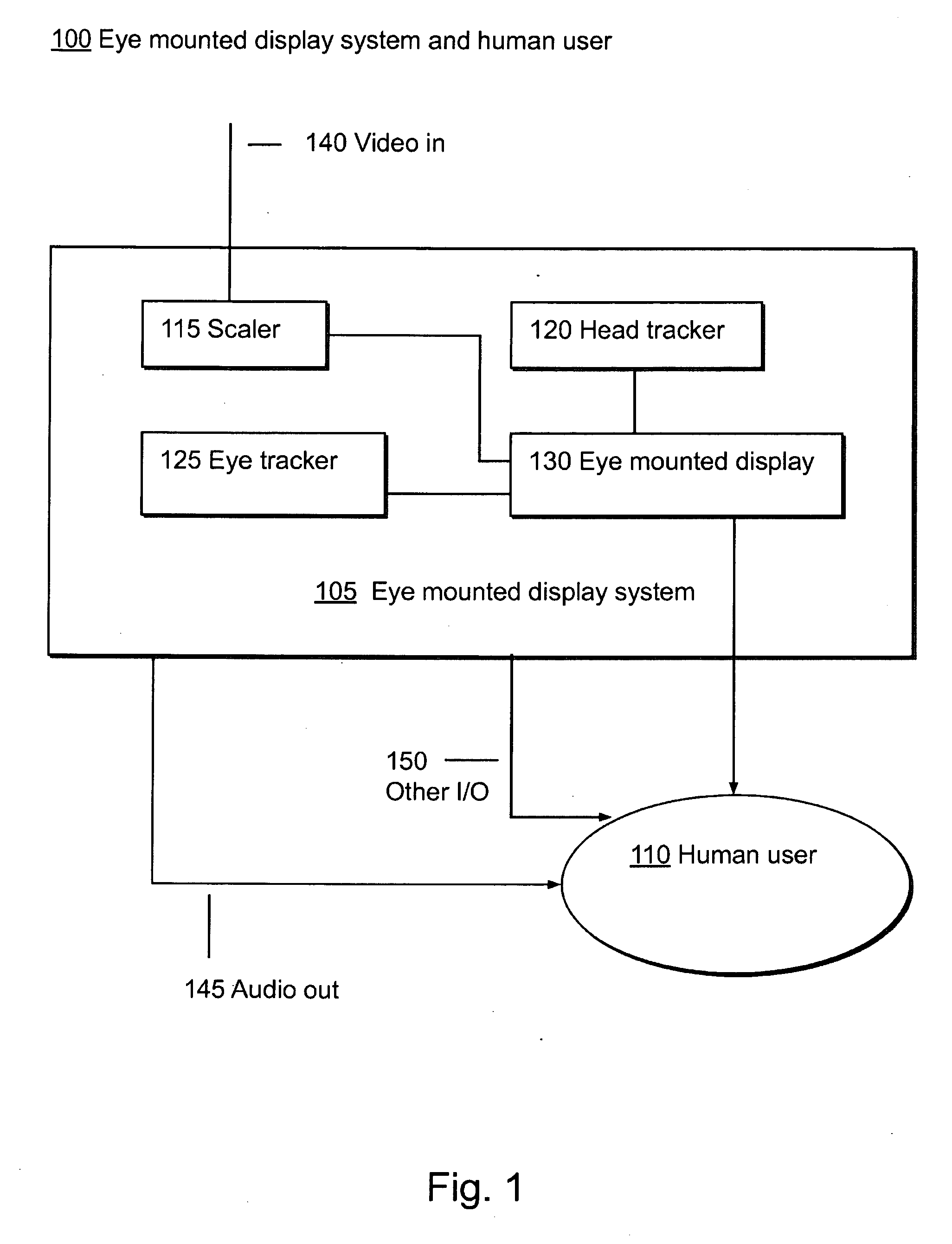
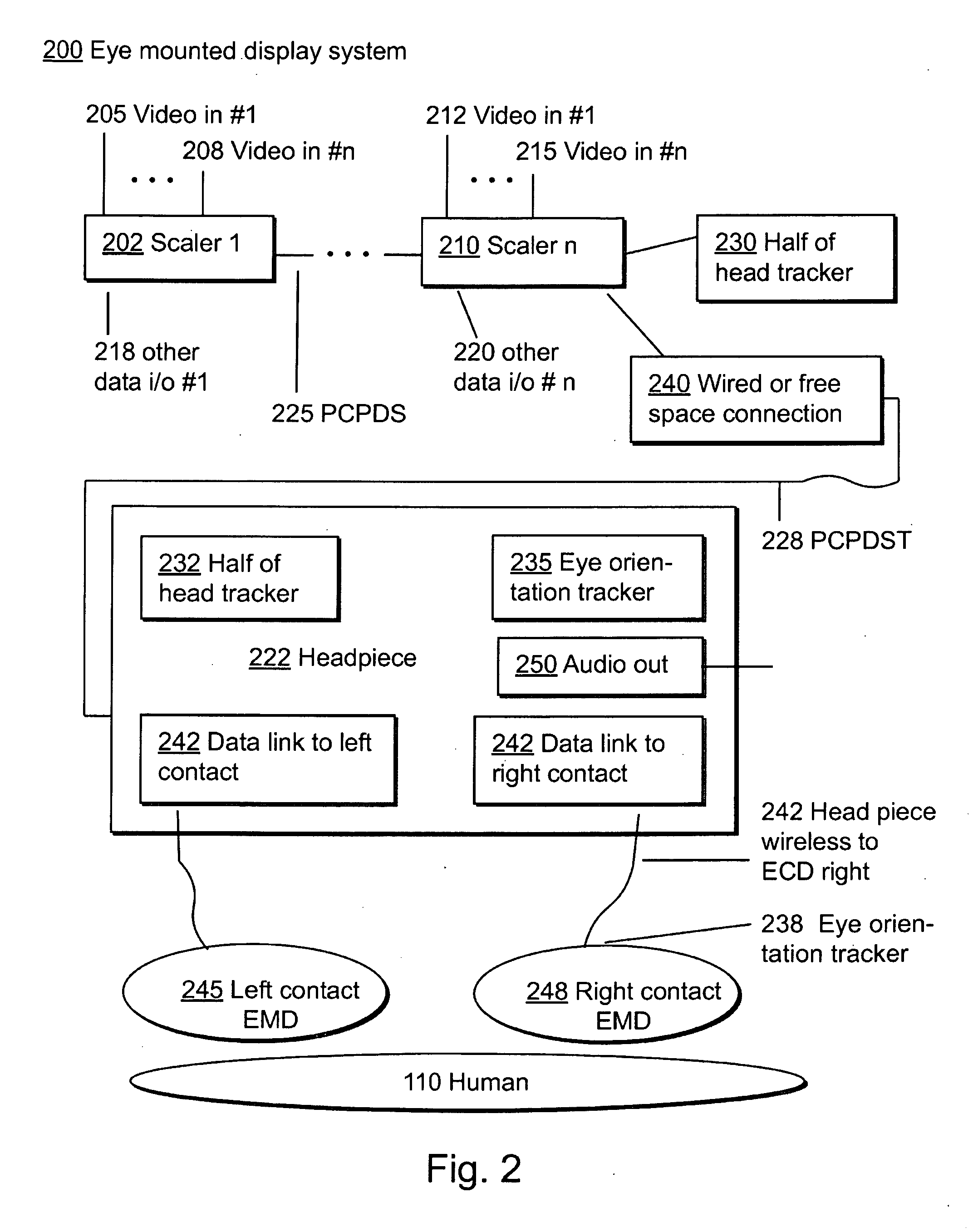
Systems Using Eye Mounted Displays
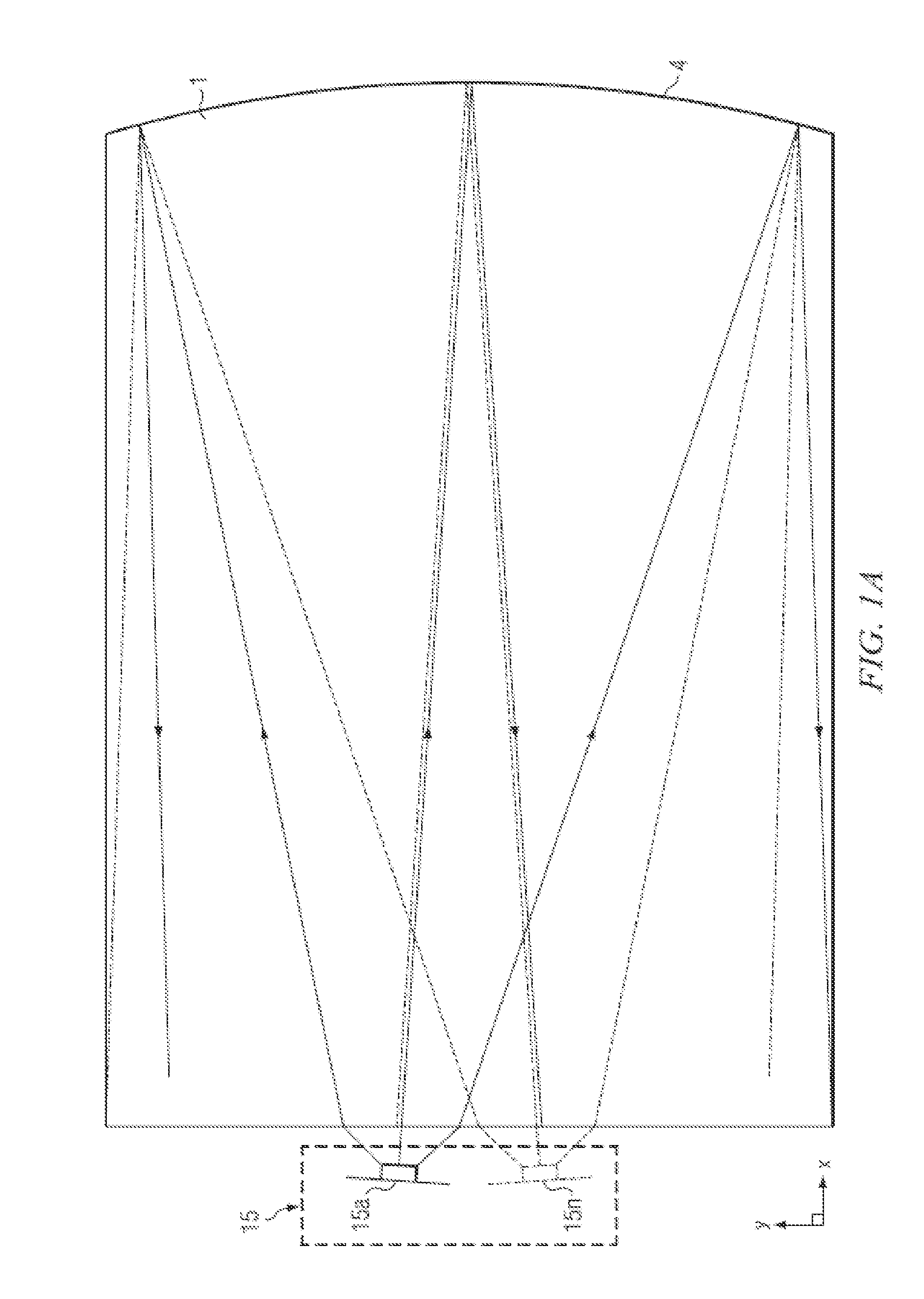
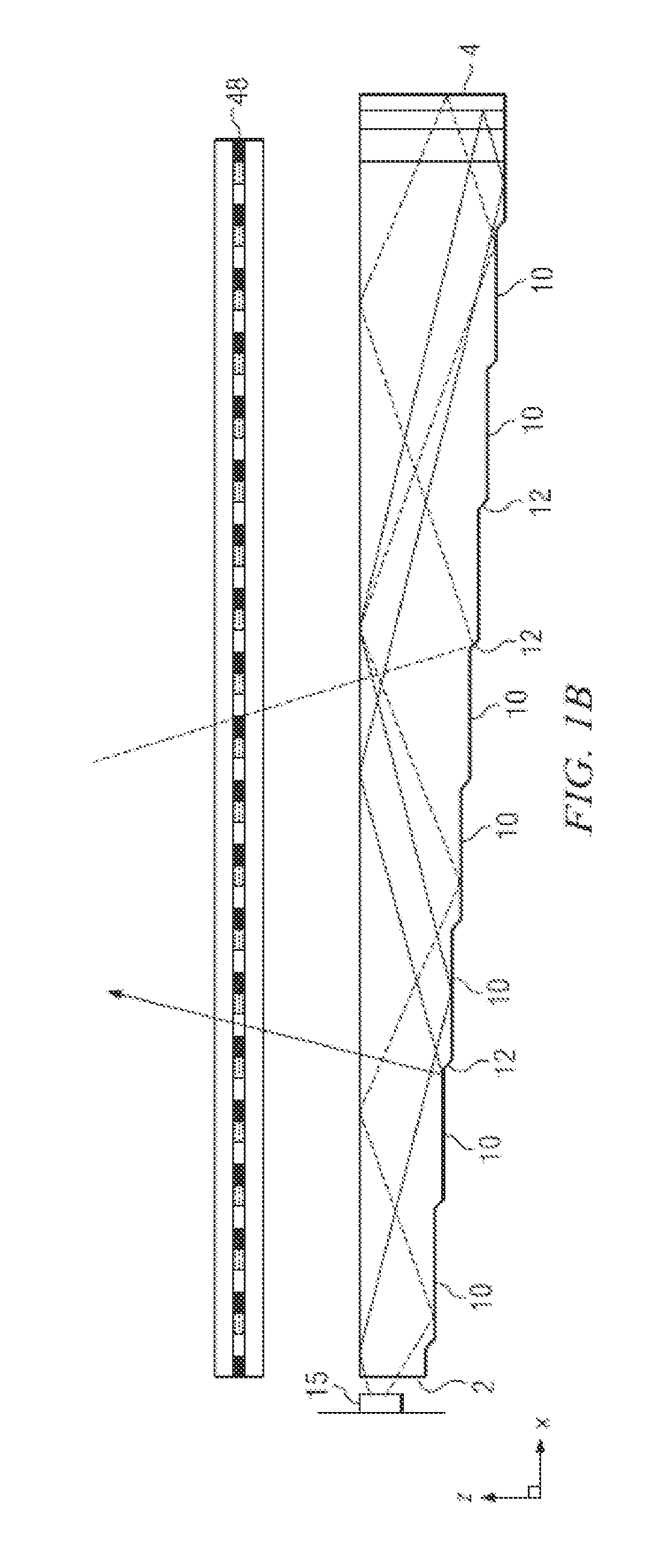
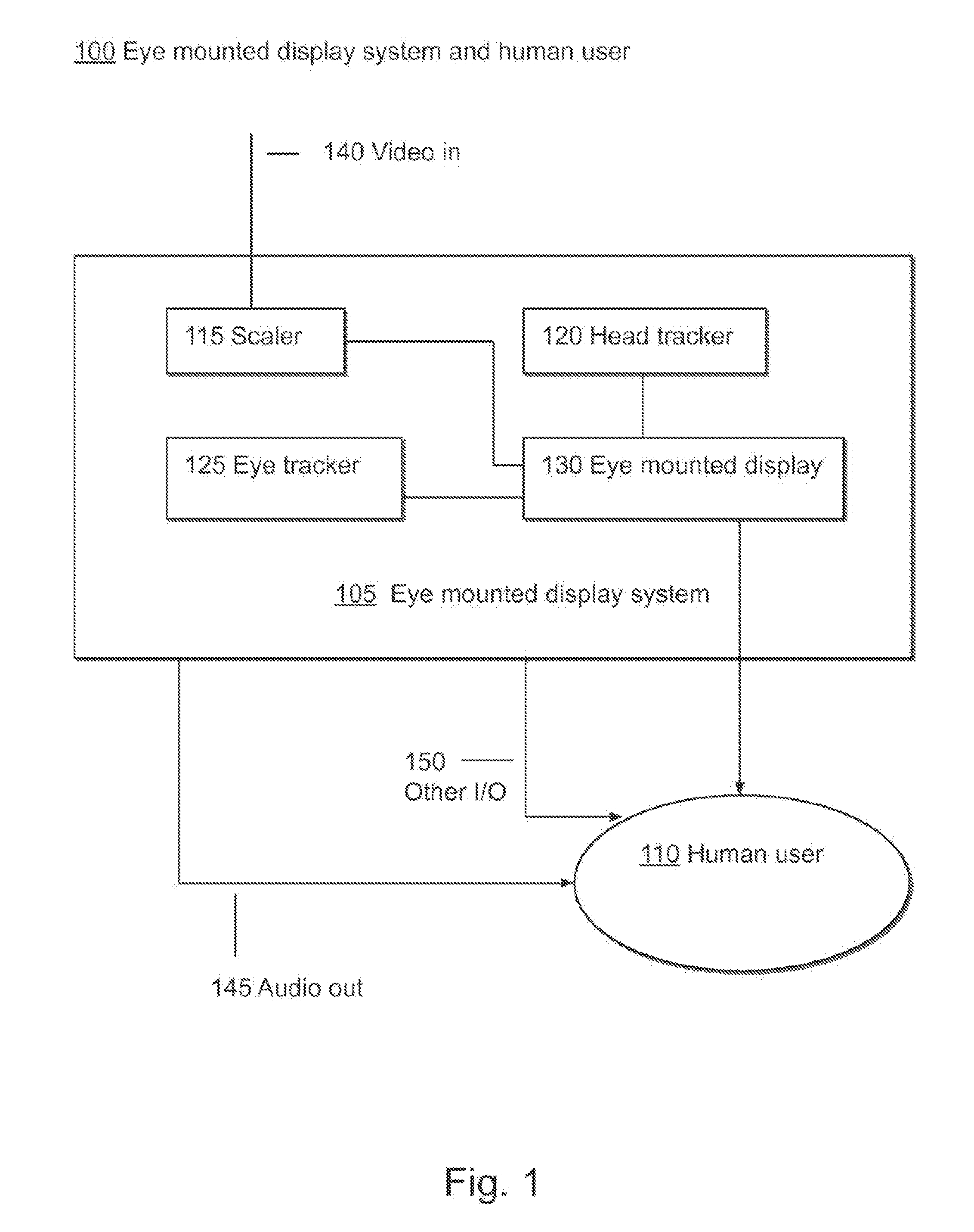
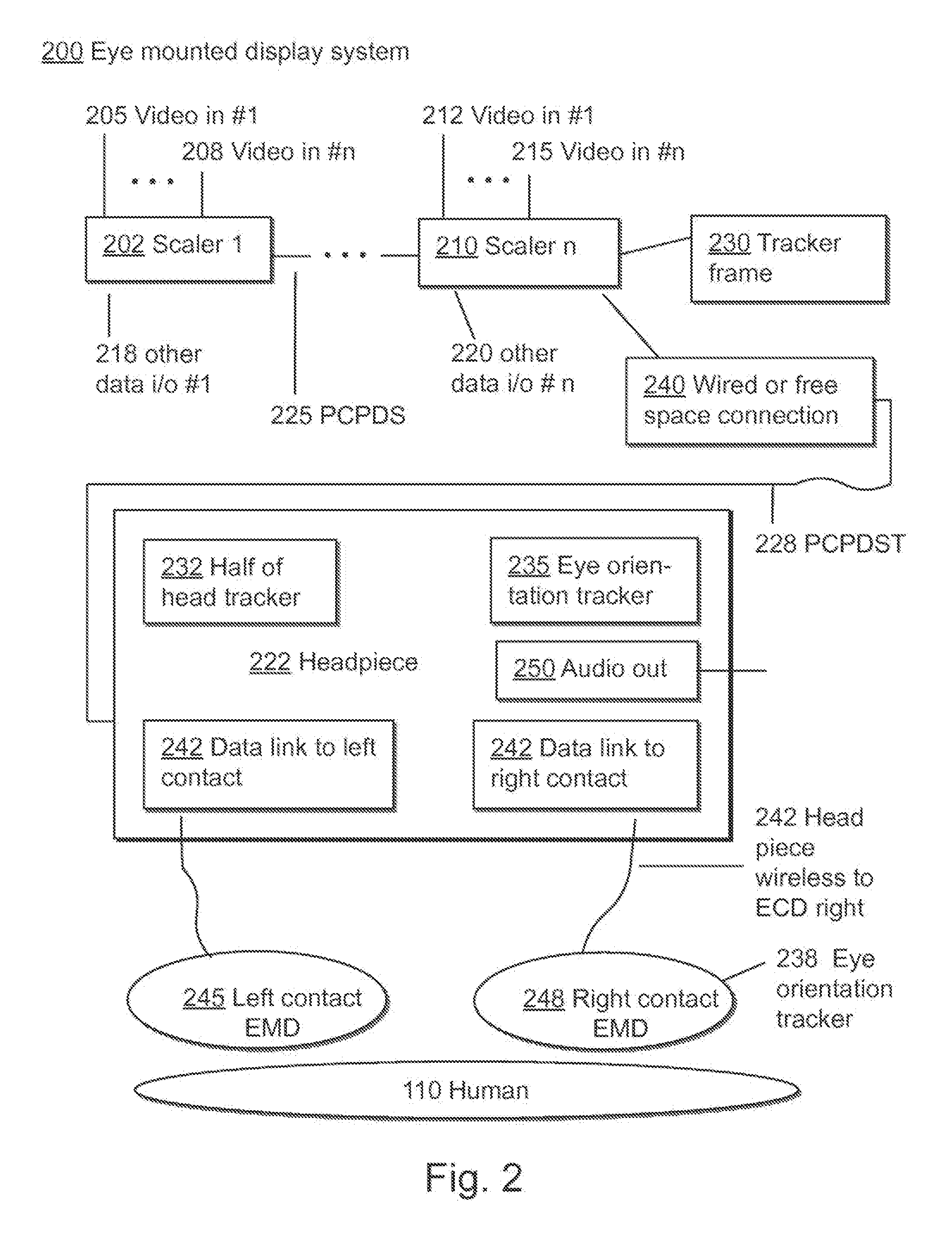
ActiveUS20090189974A1Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
Spatial multiplexing in a cellular network
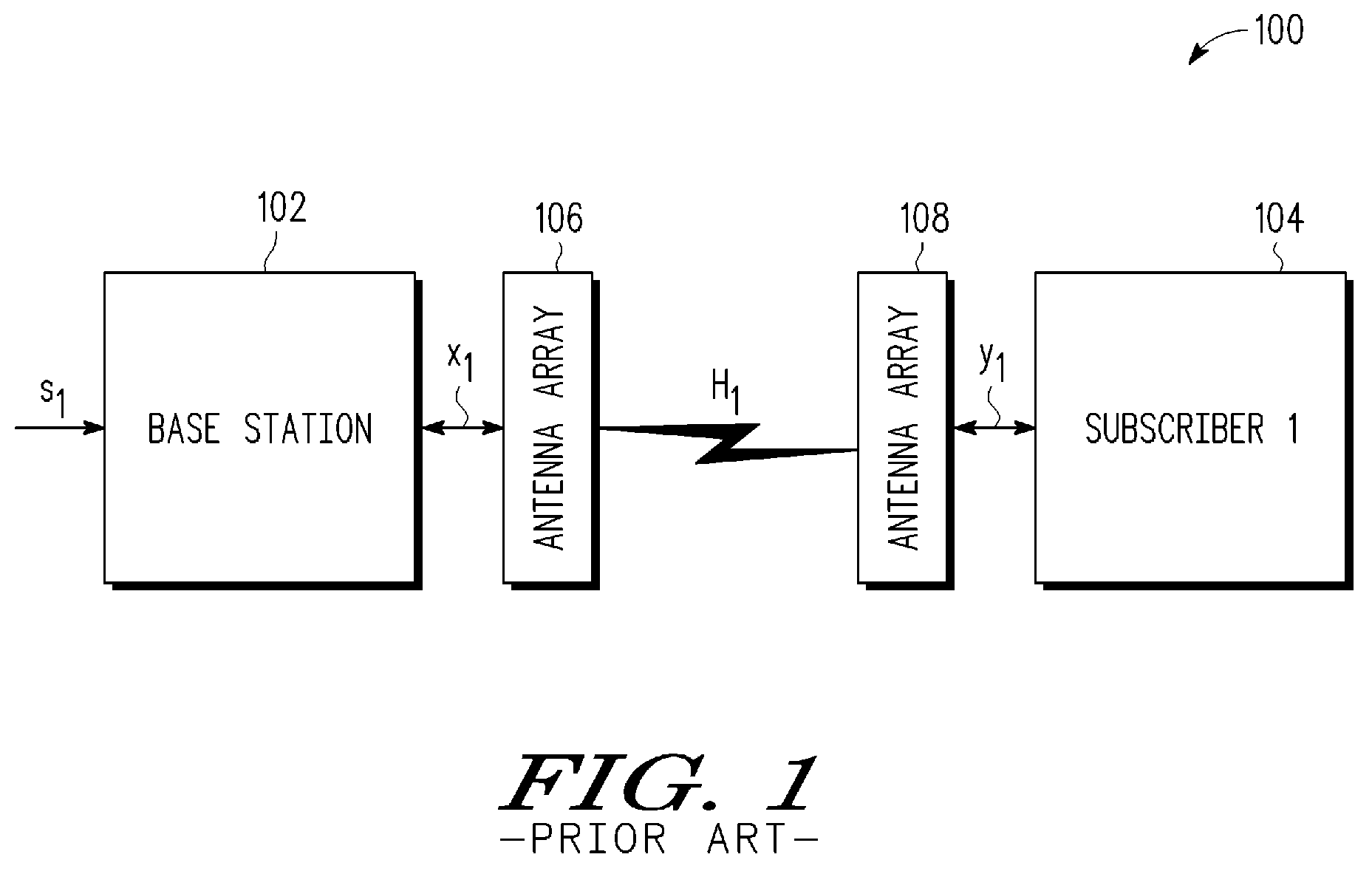
InactiveUS6067290ASpatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementData streamControl signal
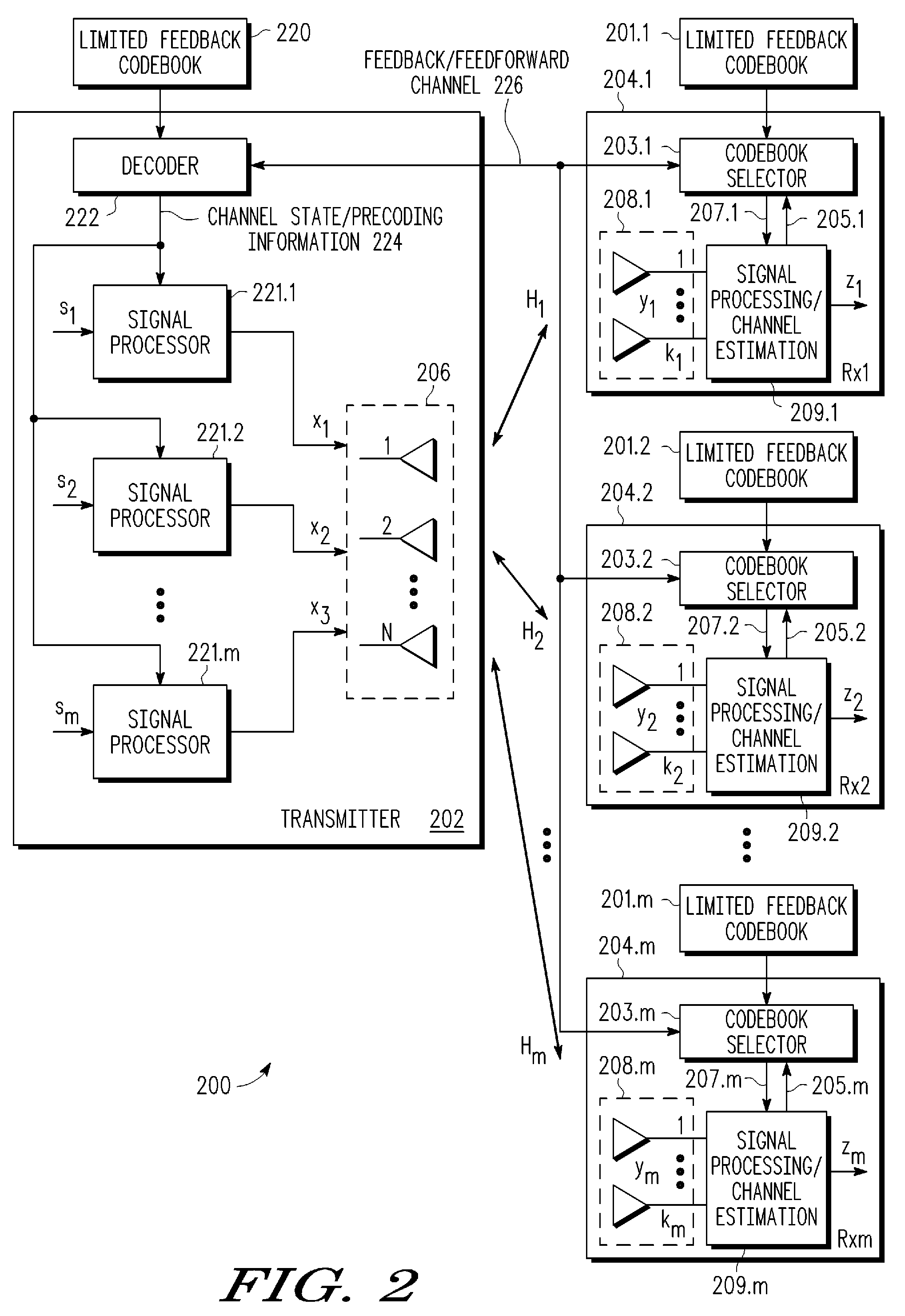
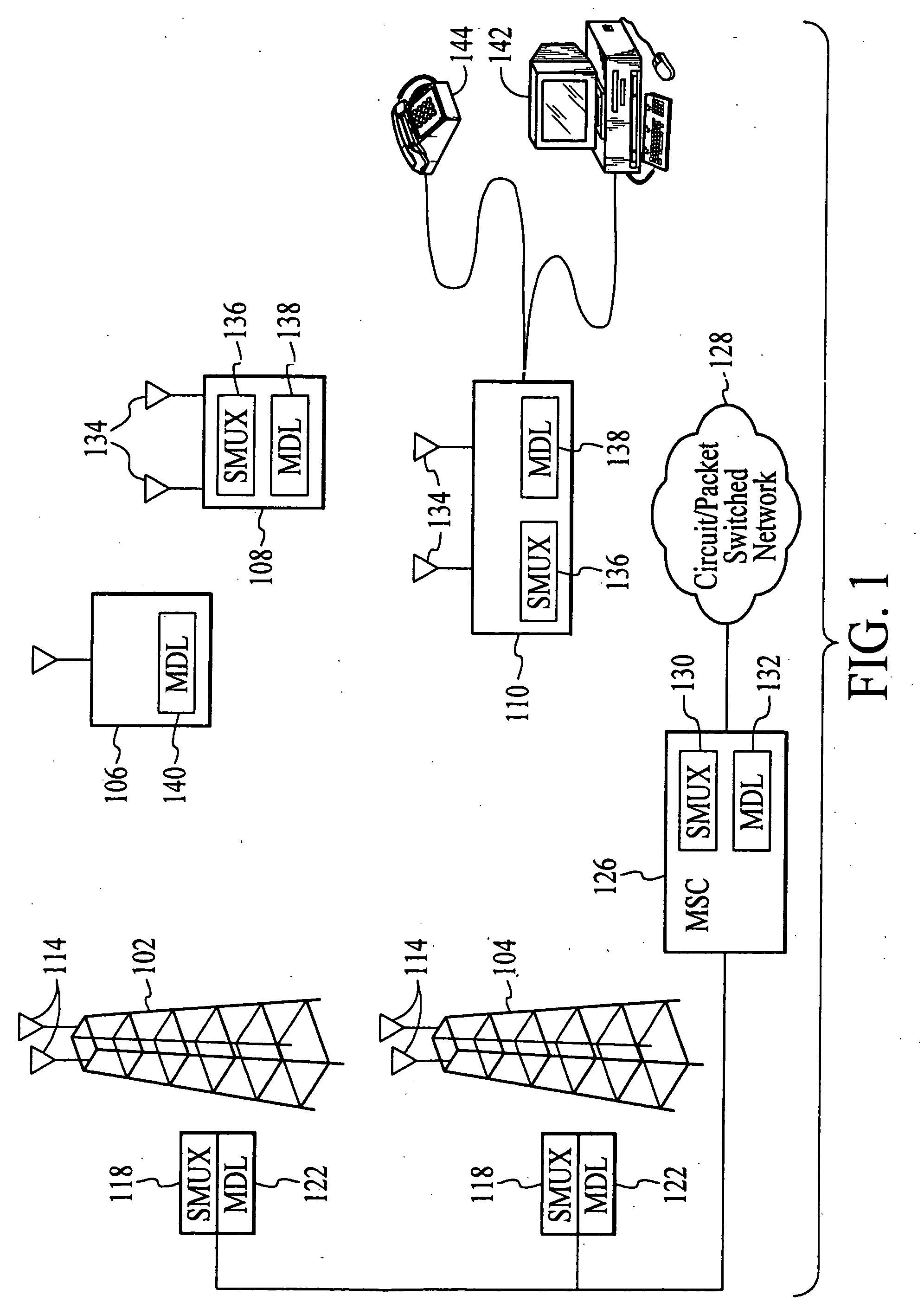
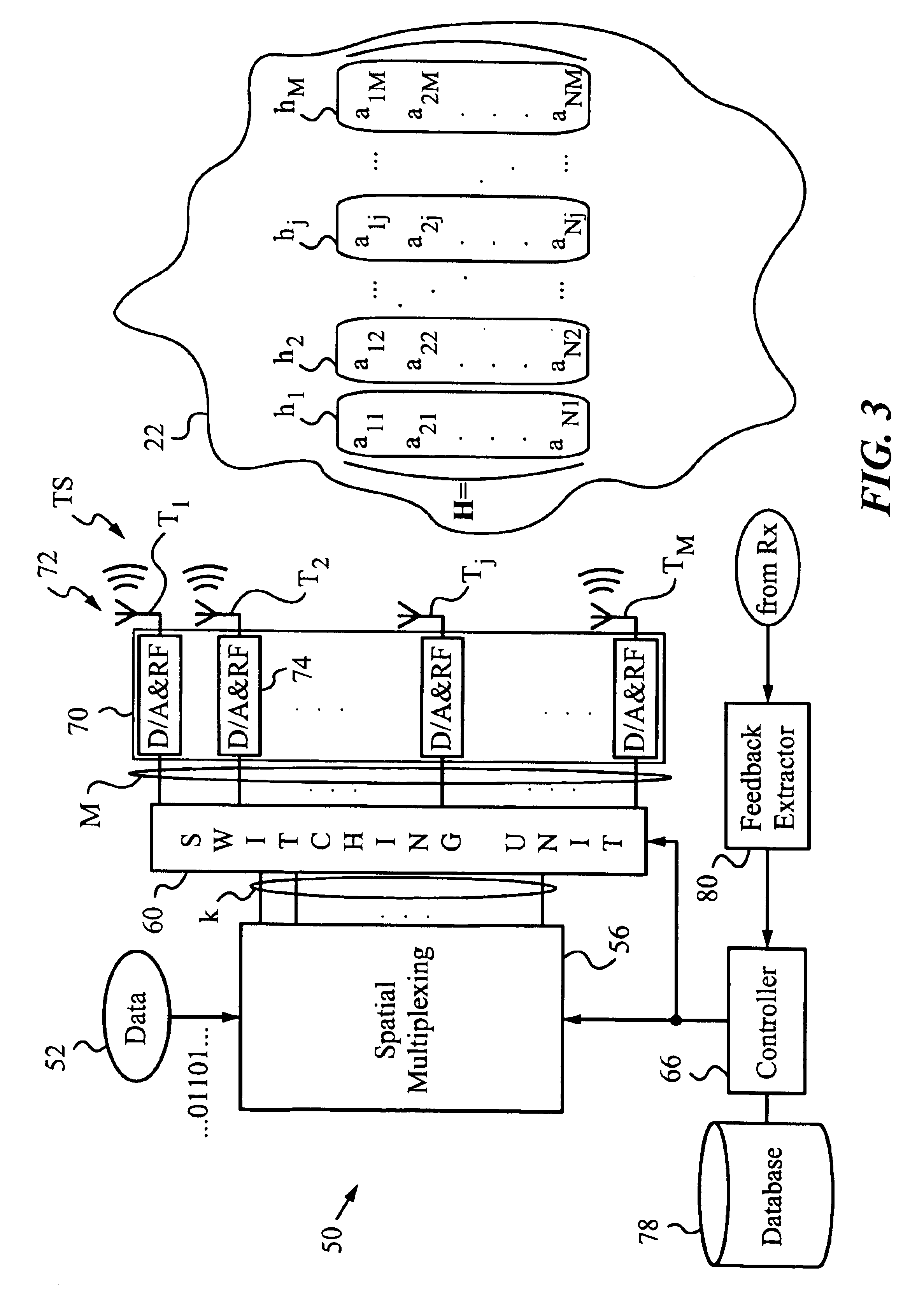
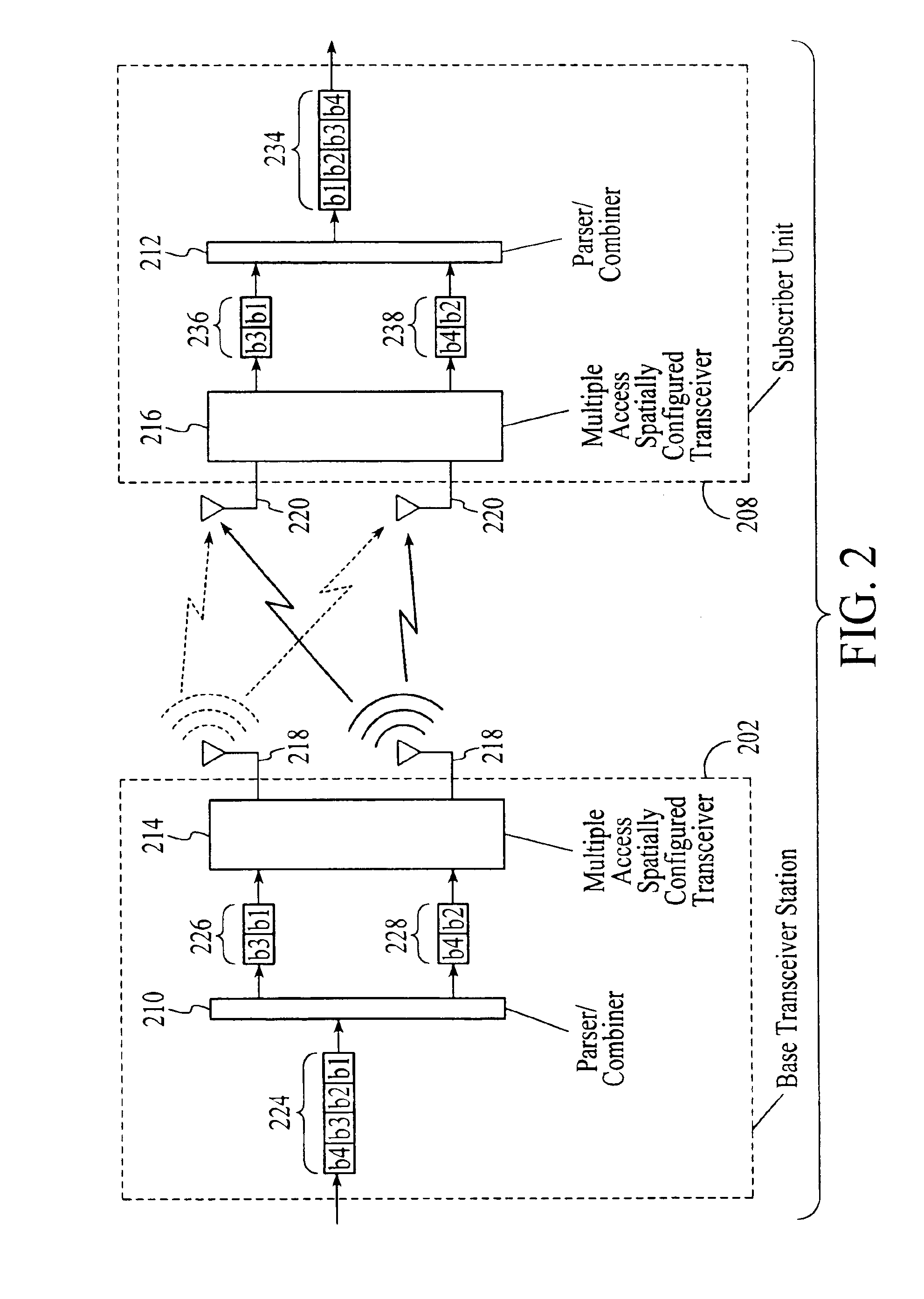
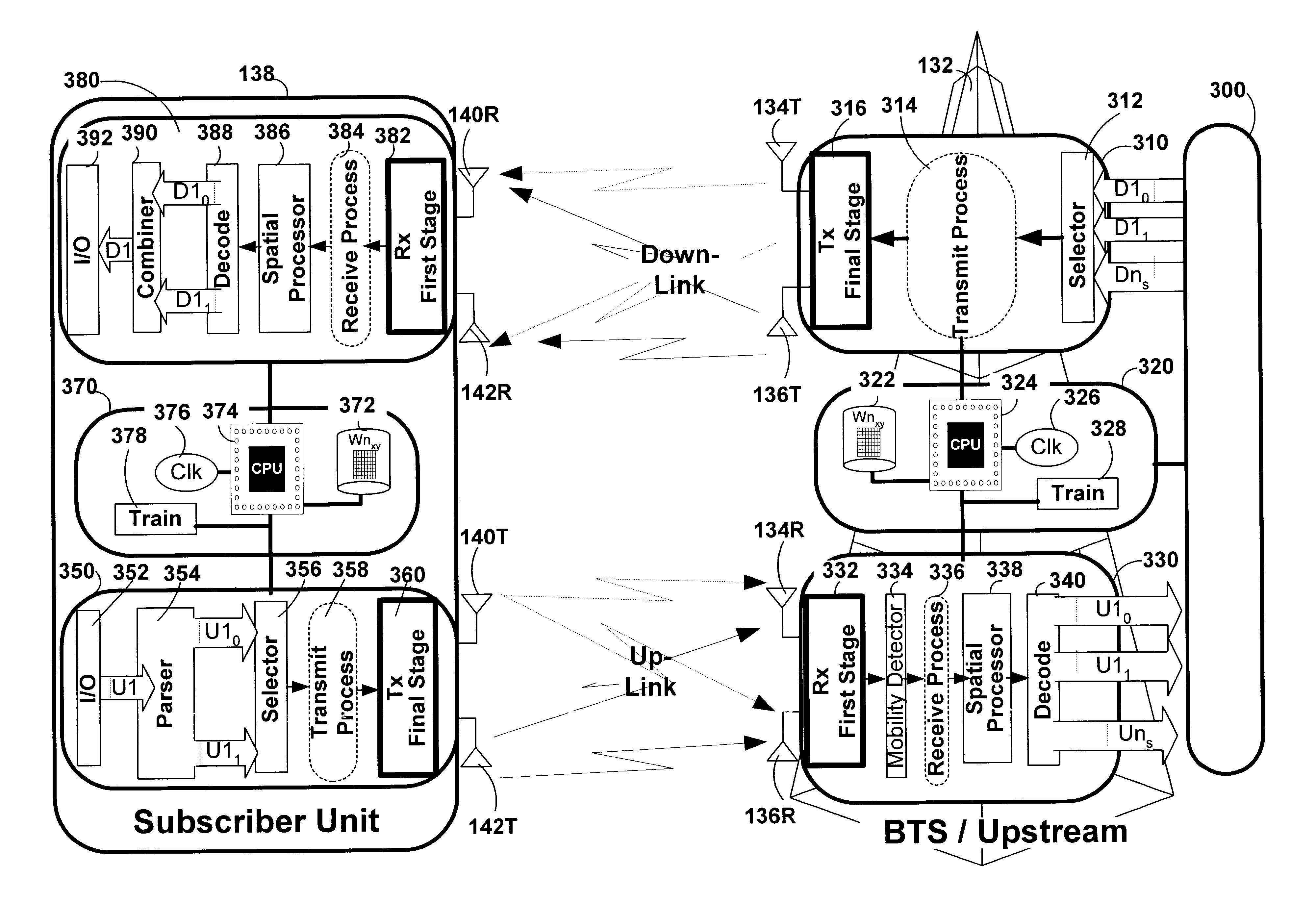
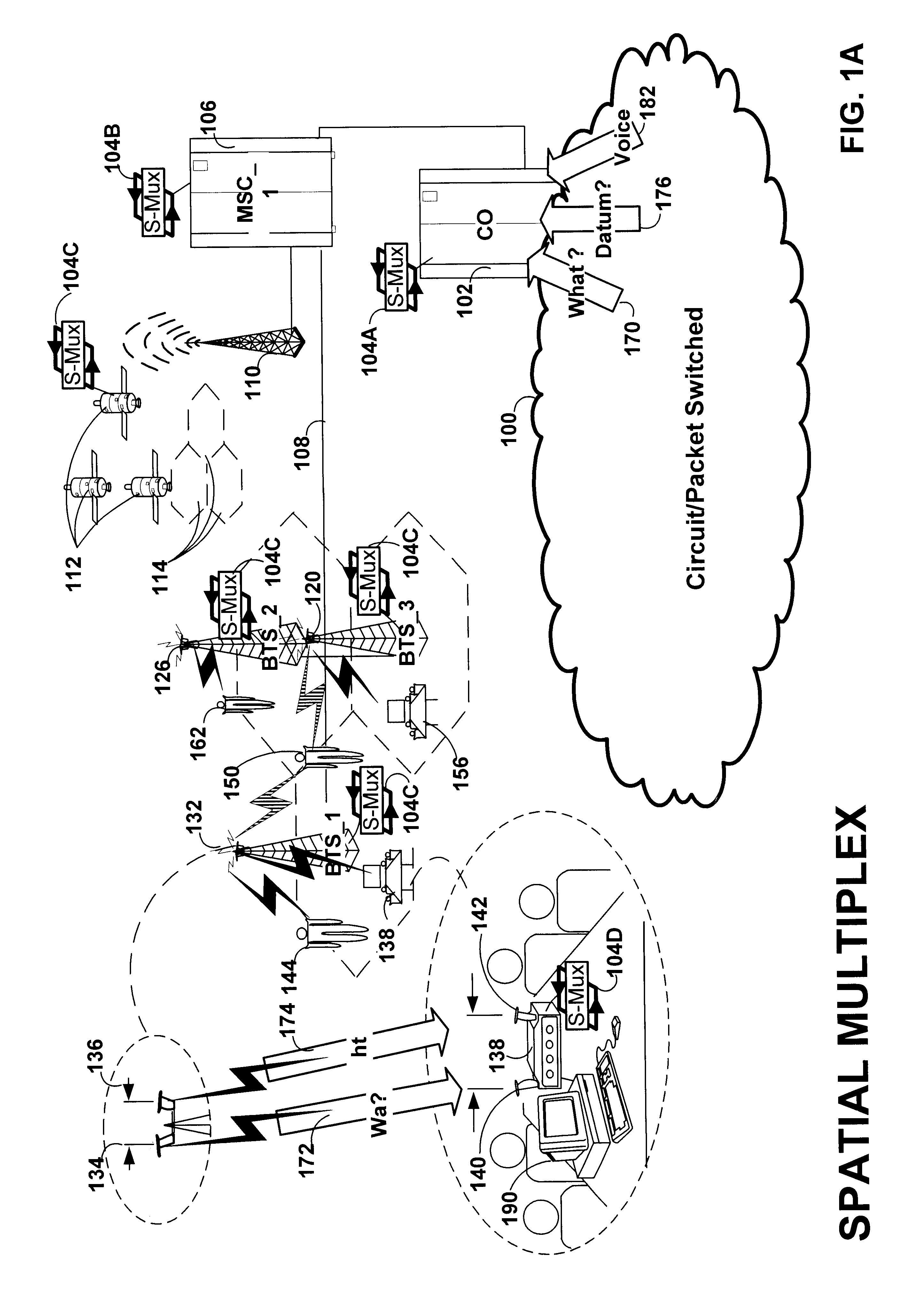
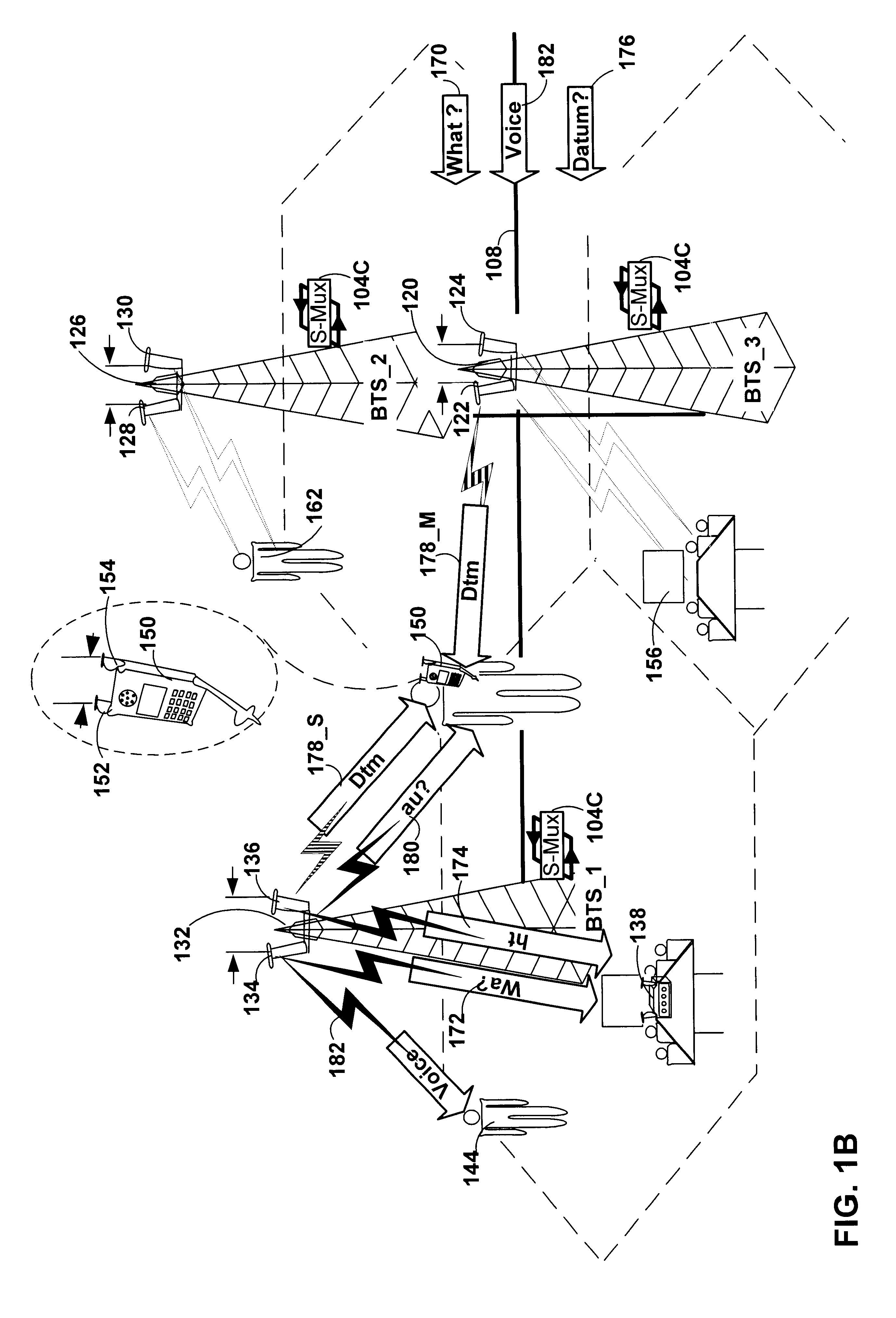
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for implementing spatial multiplexing in conjunction with the one or more multiple access protocols during the broadcast of information in a wireless network. A wireless cellular network for transmitting subscriber datastream(s) to corresponding ones among a plurality of subscriber units located within the cellular network is disclosed. The wireless cellular network includes base stations and a logic. The base stations each include spatially separate transmitters for transmitting, in response to control signals, selected substreams of each subscriber datastream on an assigned channel of a multiple access protocol. The logic communicates with each of the base stations. The logic assigns an available channel on which to transmit each subscriber datastream. The logic routes at least a substream of each datastream to at least a selected one of the base stations. The logic also generates control signals to configure the at least a selected one of the base stations to transmit the selected substreams to a corresponding one among the plurality of subscriber units on the assigned channel. A subscriber unit for use in a cellular system is also disclosed. The subscriber unit includes: spatially separate receivers, a spatial processor, and a combiner. The spatially separate receivers receive the assigned channel composite signals resulting from the spatially separate transmission of the subscriber downlink datastream(s). The spatial processor is configurable in response to a control signal transmitted by the base station to separate the composite signals into estimated substreams based on information obtained during the transmission of known data patterns from at least one of the base stations. The spatial processor signals the base stations when a change of a spatial transmission configuration is required. The combiner combines the estimated substreams into a corresponding subscriber datastream.
Owner:INTEL CORP
WLAN capacity enhancement using SDM
ActiveUS20050047384A1Increase capacityMaximize signal powerNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesSignal responseTelecommunications
A method for communication over a wireless local area network (WLAN) includes receiving uplink signals from a plurality of stations in the WLAN. Responsively to the uplink signals, a set of the stations is selected for inclusion in a spatial multiplexing group. Downlink signals are transmitted simultaneously to the stations in the set using spatial division multiplexing (SDM).
Owner:WAVION
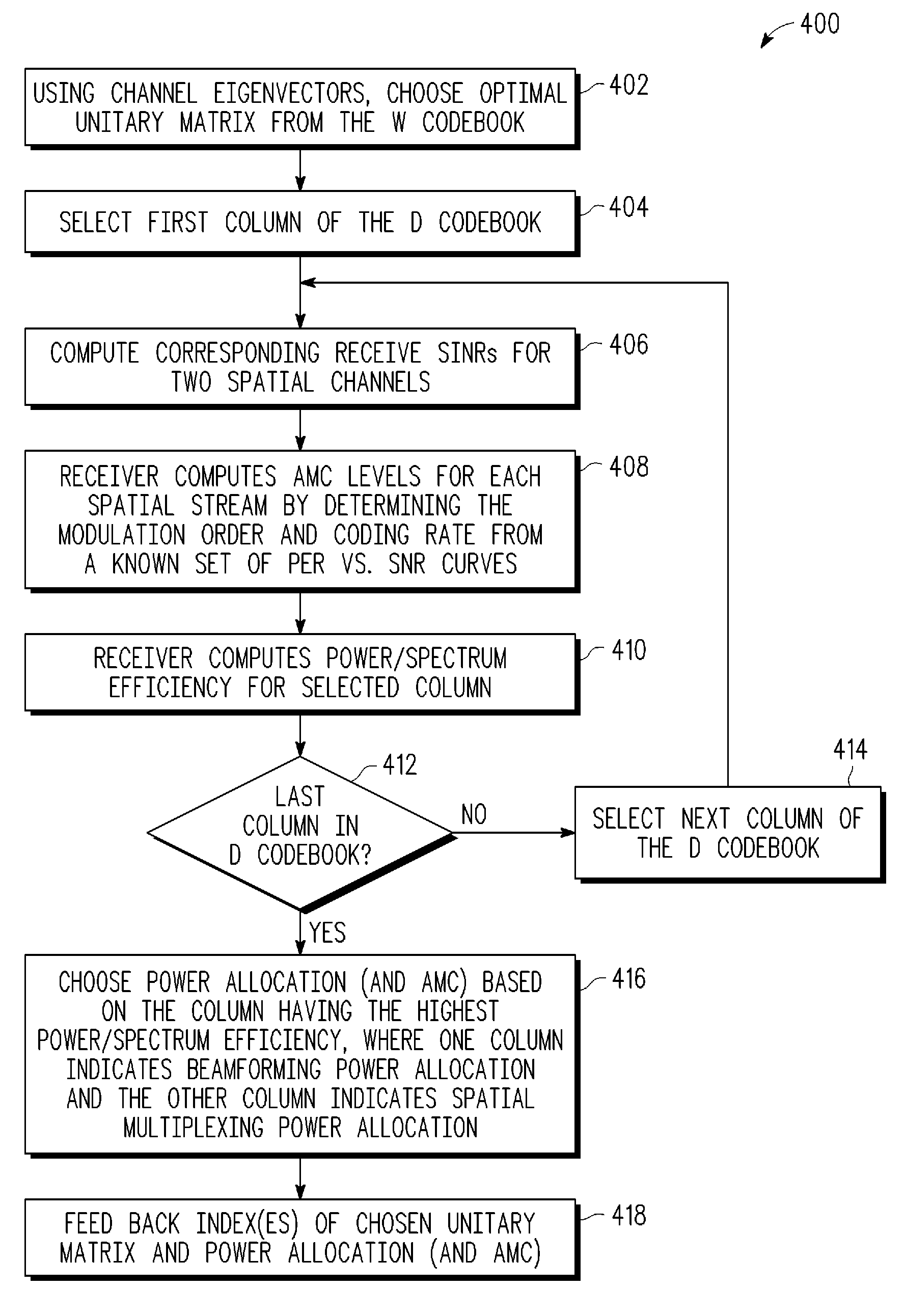
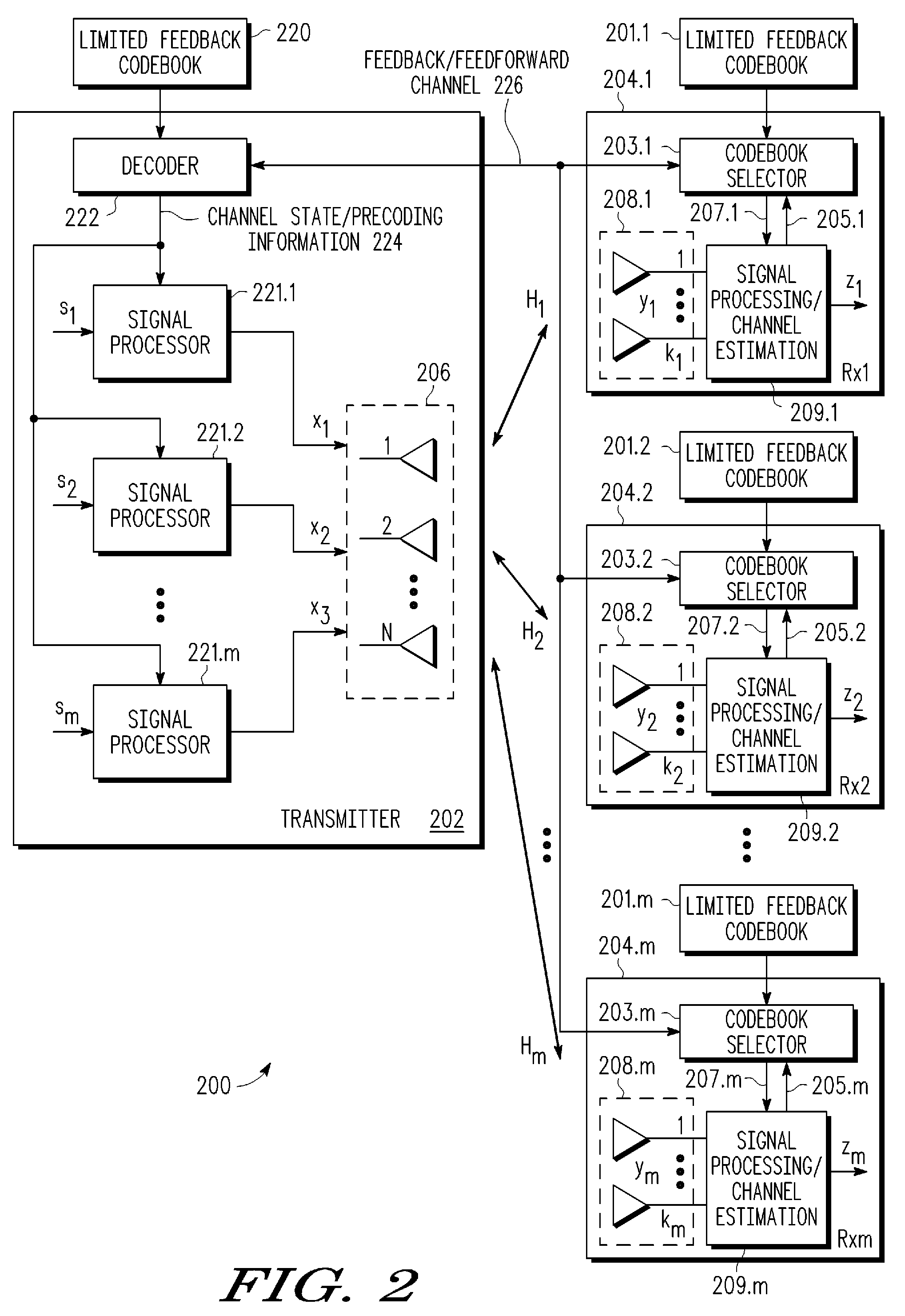
MIMO precoding enabling spatial multiplexing, power allocation and adaptive modulation and coding
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based feedback mechanism is provided to enable non-unitary precoding for multi-stream transmission, where in each stream is optimized with suitable transmission power allocation and AMC. The codebook-based feedback mechanism uses a precoding codebook having a power allocation matrix which is constrained to specify that beamforming always applies full power to a predetermined beam. With this constraint, a one-bit power allocation feedback index may be used to switch between beamforming and spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems using eye mounted displays
ActiveUS8786675B2Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationNon-optical adjunctsCathode-ray tube indicatorsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
Eye Mounted Displays
InactiveUS20090189830A1Avoid and reduce interferenceVarious limitationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
Device for concentrating optical radiation
InactiveUS6274860B1Minimizes waste heatLow costSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueOptical radiationFiber
A holographic planar concentrator (HPC) for collecting and concentrating optical radiation is provided. The holographic planar concentrator comprises a planar highly transparent plate and at least one multiplexed holographic optical film mounted on a surface thereof. The multiplexed holographic optical film has recorded therein a plurality of diffractive structures having one or more regions which are angularly and spectrally multiplexed. Two or more of the regions may be configured to provide spatial multiplexing. The HPC is fabricated by: (a) recording the plurality of diffractive structures in the multiplexed holographic optical film employing angular, spectral, and, optionally, spatial multiplexing techniques; and (b) mounting the multiplexed holographic optical film on one surface of the highly transparent plate. The recording of the plurality of diffractive structures is tailored to the intended orientation of the holographic planar concentrator to solar energy. The HPC is mounted in the intended orientation for collecting solar energy and at least one solar energy-collecting device is mounted along at least one edge of the holographic planar concentrator. Examples of suitable solar energy-collecting devices include photovoltaic cells and fiber optic light guides for transmitting collected light into an interior of a building for illumination purposes and for transmitting collected solar radiation into a hot water tank for heating. The HPC permits efficient collection of solar energy without expensive requirements, while minimizing energy losses.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for supporting various multi-antenna schemes in BWA system using multiple antennas
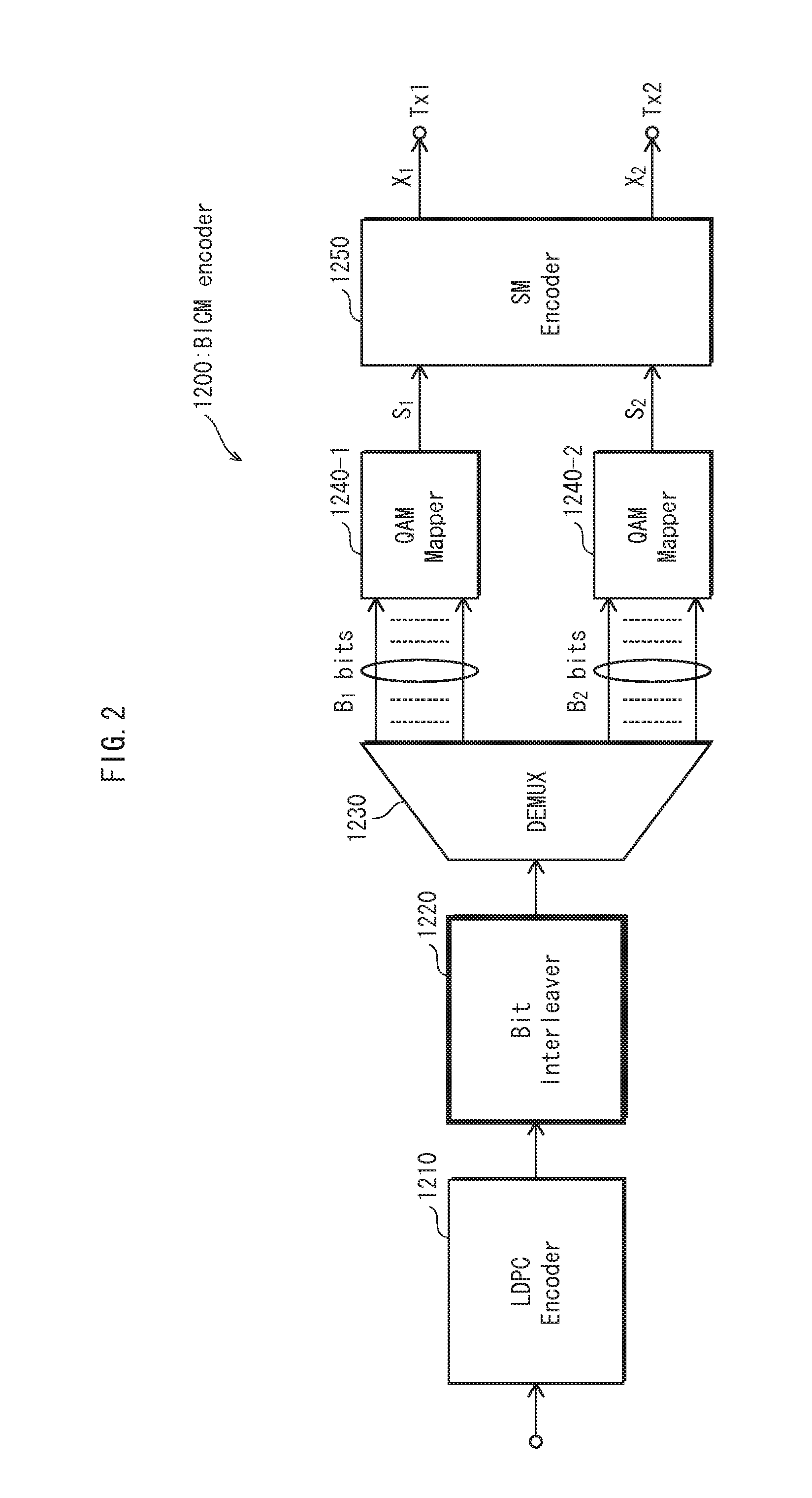
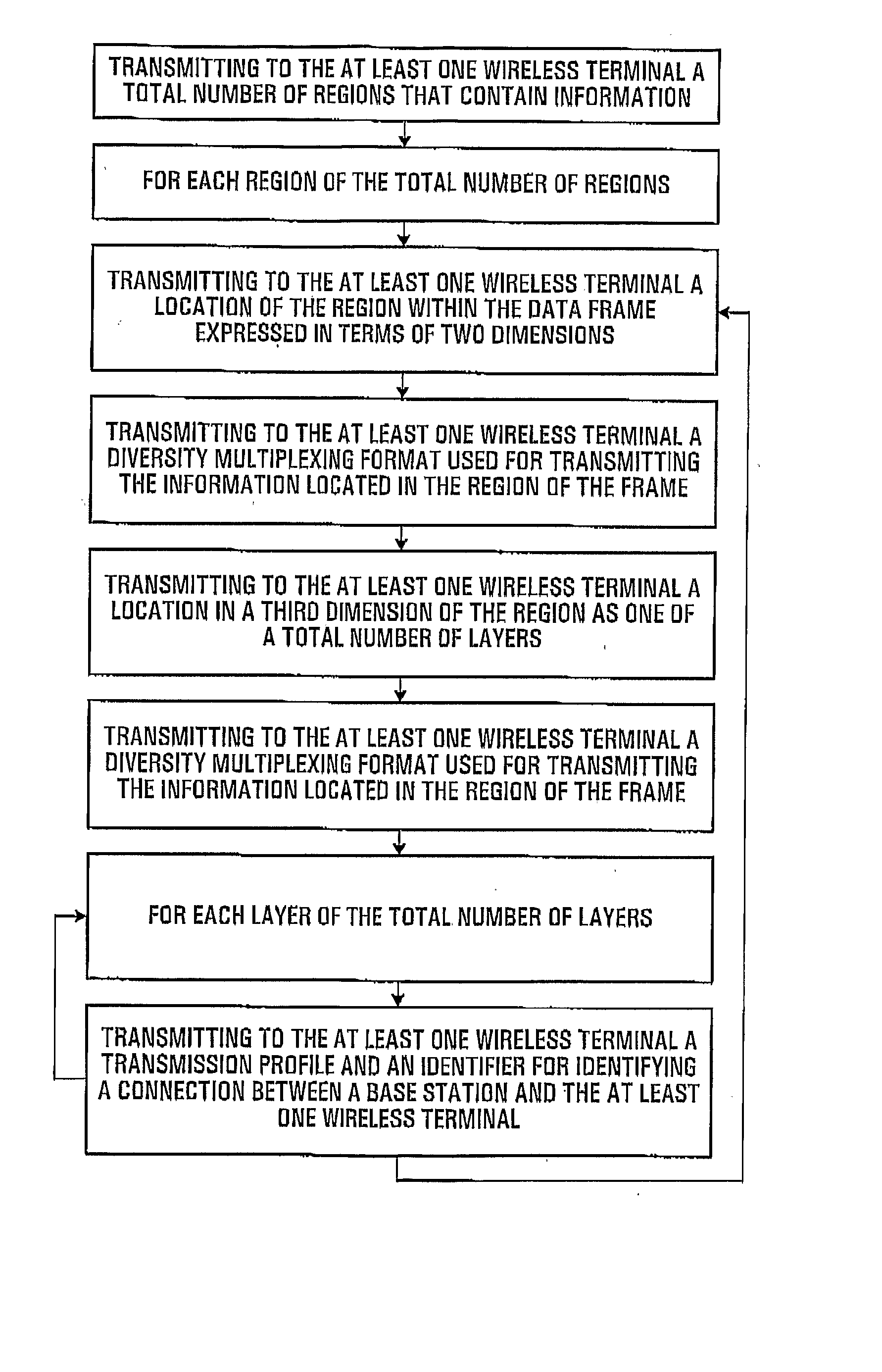
Disclosed is a method for using various multiple antenna schemes in a baseband wireless access system is provided. According to the method, a downlink MAP message is constructed in order to support various multiple antenna schemes based on a multiple-input multiple output (MIMO), which is one of the multiple antenna schemes, so that compatibility with exiting MIMO technology having no MIMO feedback can be achieved and overhead occurring in transmission of an MAP information element can be reduced. Further, it is possible to efficiently support spatial multiplexing technology capable of transmitting multiple layers having different modulation and coding in a MIMO system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interleaving method and deinterleaving method
ActiveUS20130216001A1Improve reception performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesChecking code calculationsCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An interleaving method performed by a transmitter for a communication system with quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes, spatial multiplexing, and T transmit antennas is used for applying permutation to N cyclic blocks of a codeword in order to map bits of the permutated cyclic blocks onto T constellation words constituting multiple spatial-multiplexing blocks from the codeword. Each cyclic block consists of Q bits.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
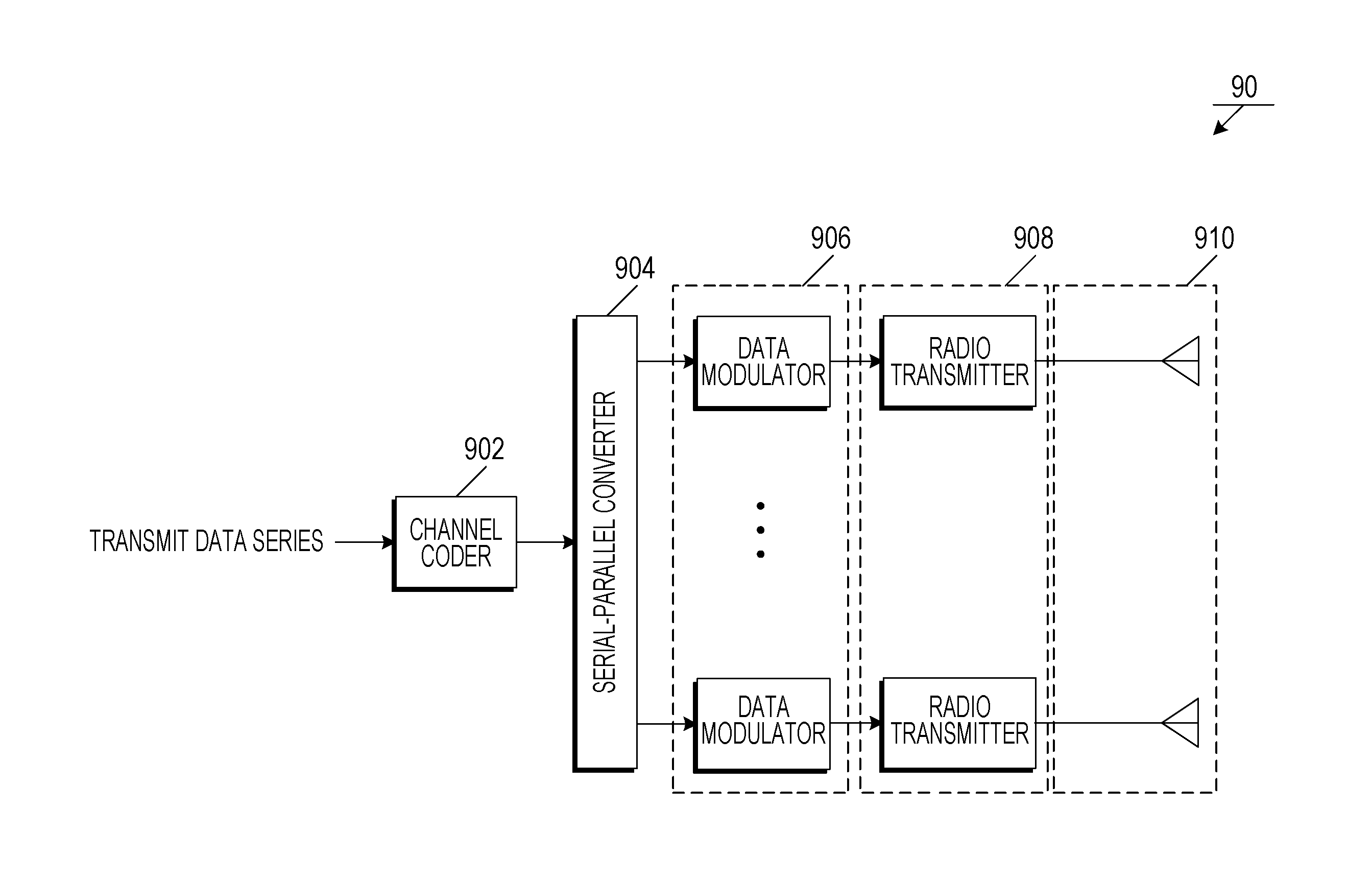
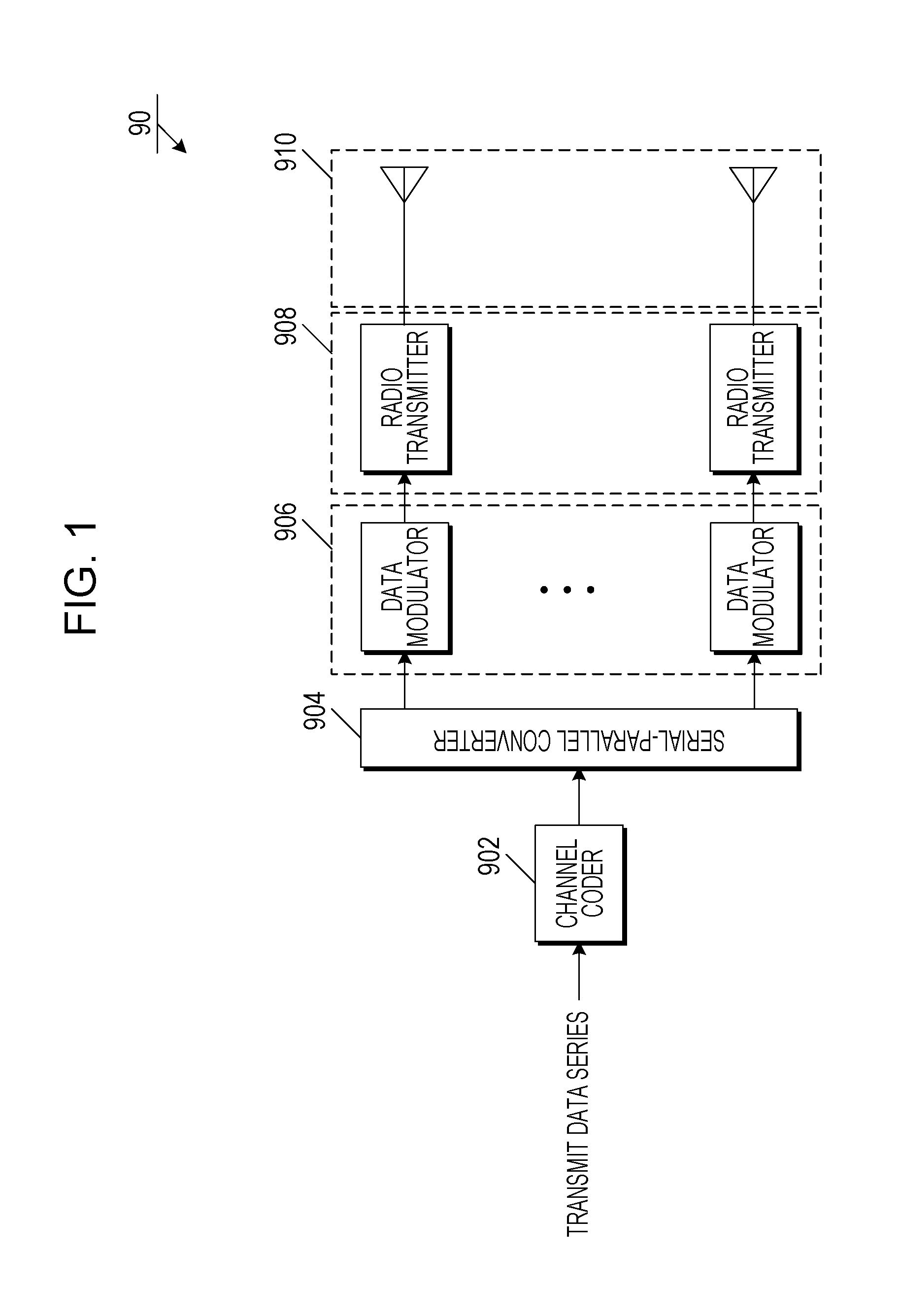
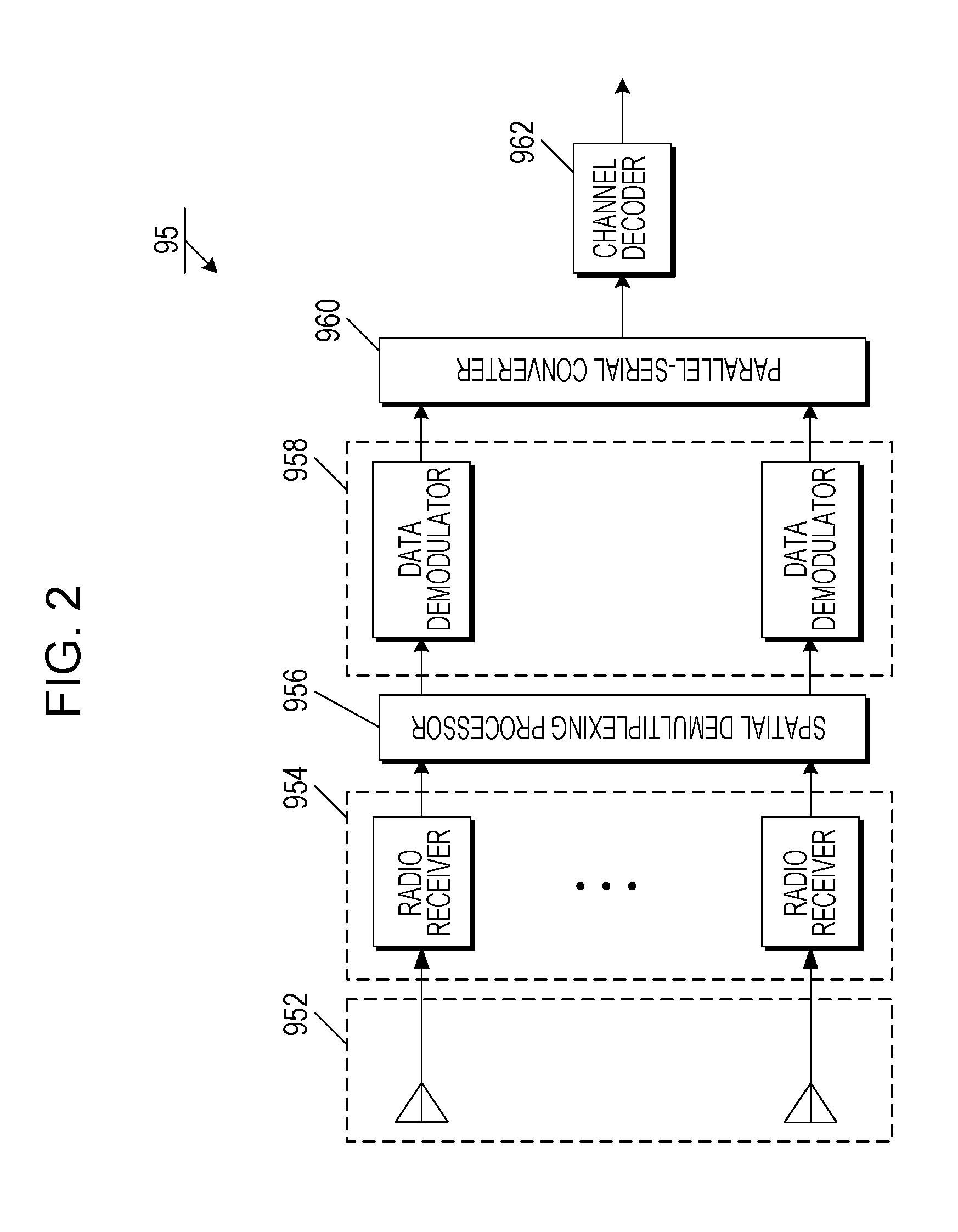
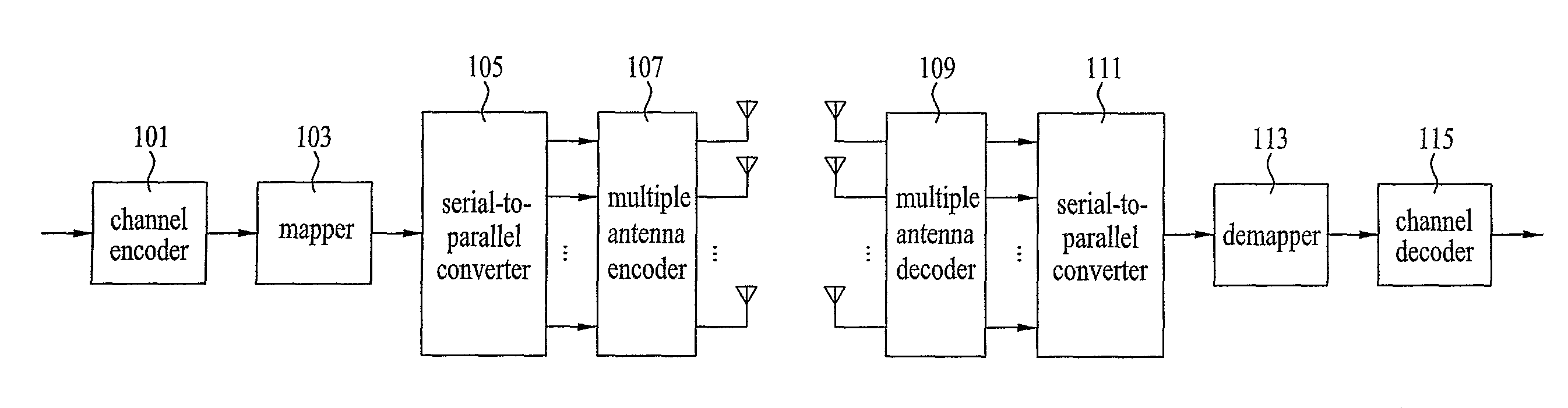
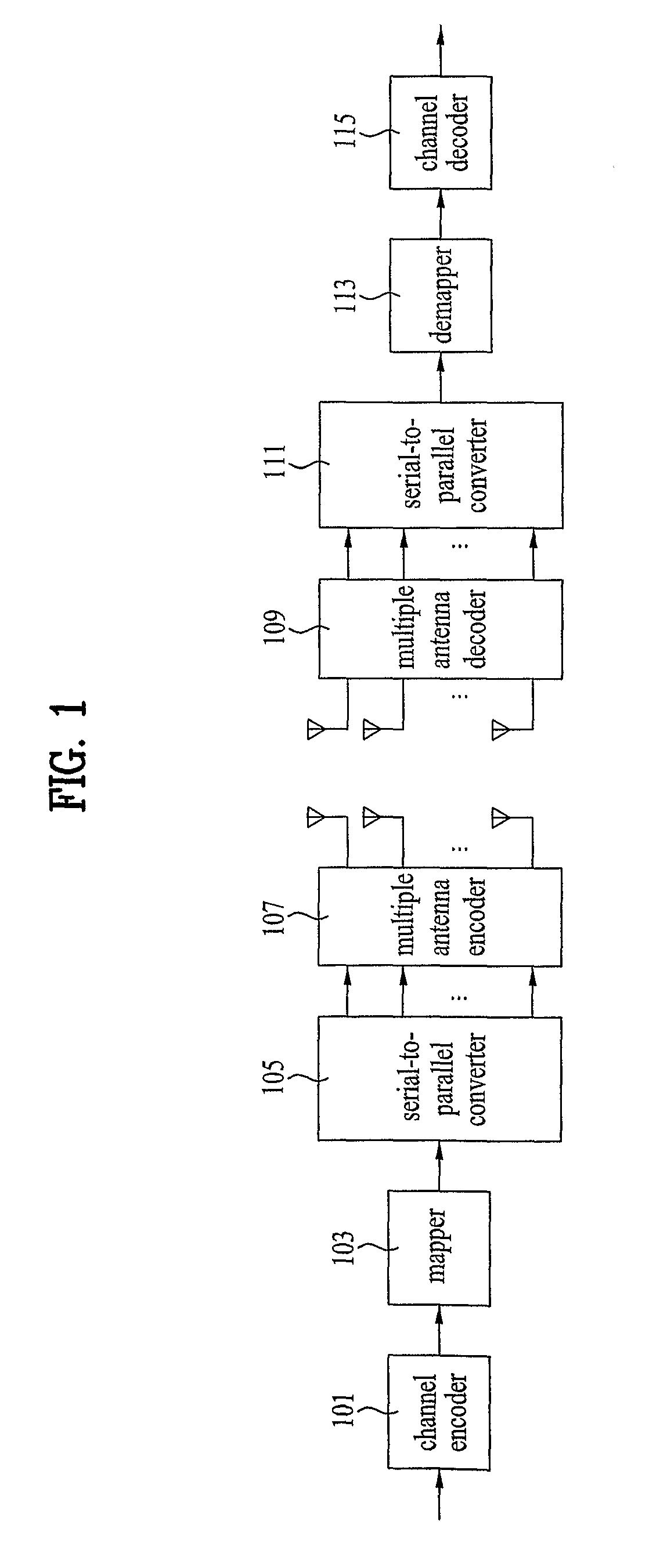
Methods For Supporting Mimo Transmission In Ofdm Applications
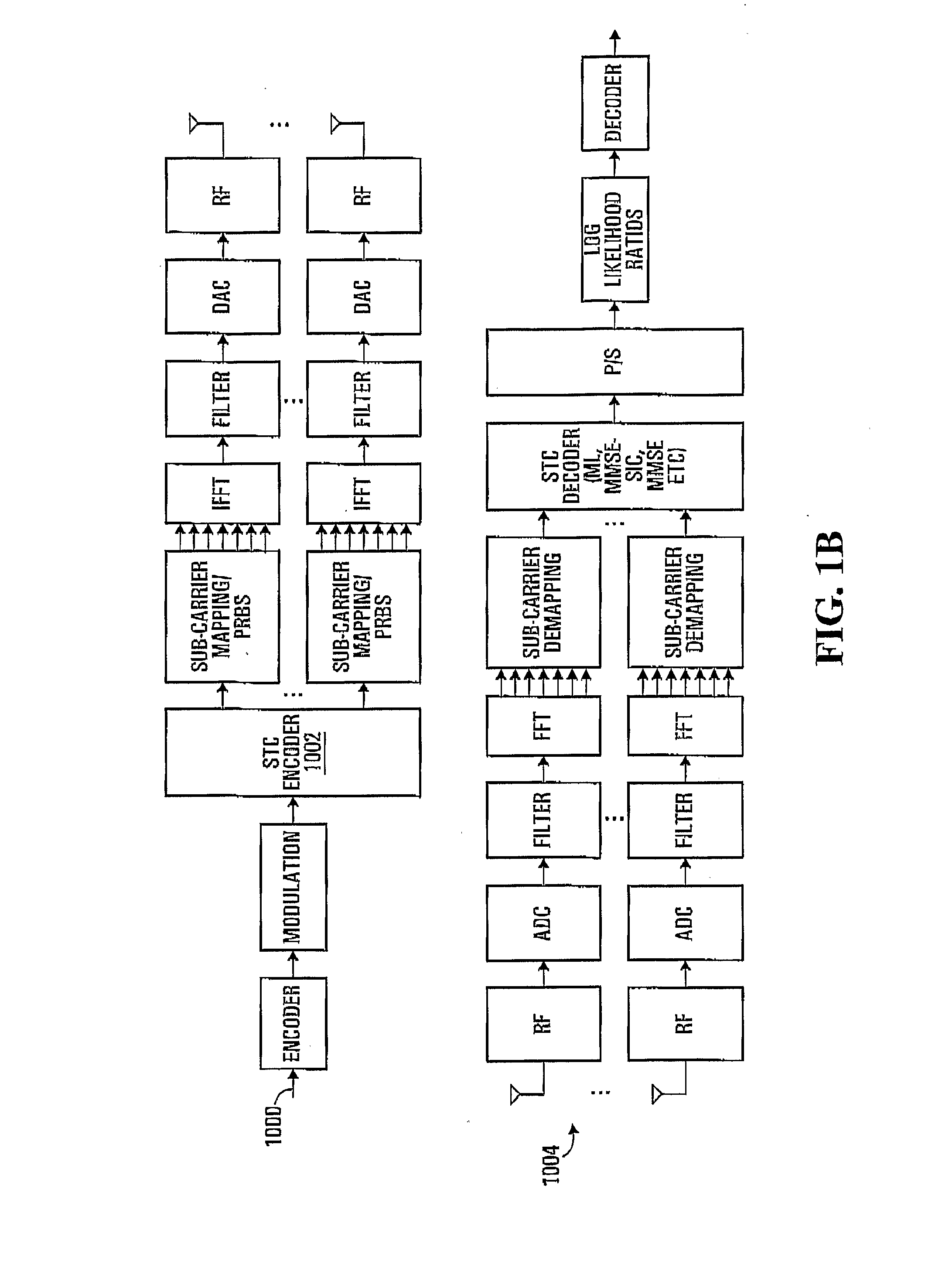
ActiveUS20070274253A1Spatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionSpace time transmit diversityMimo transmission
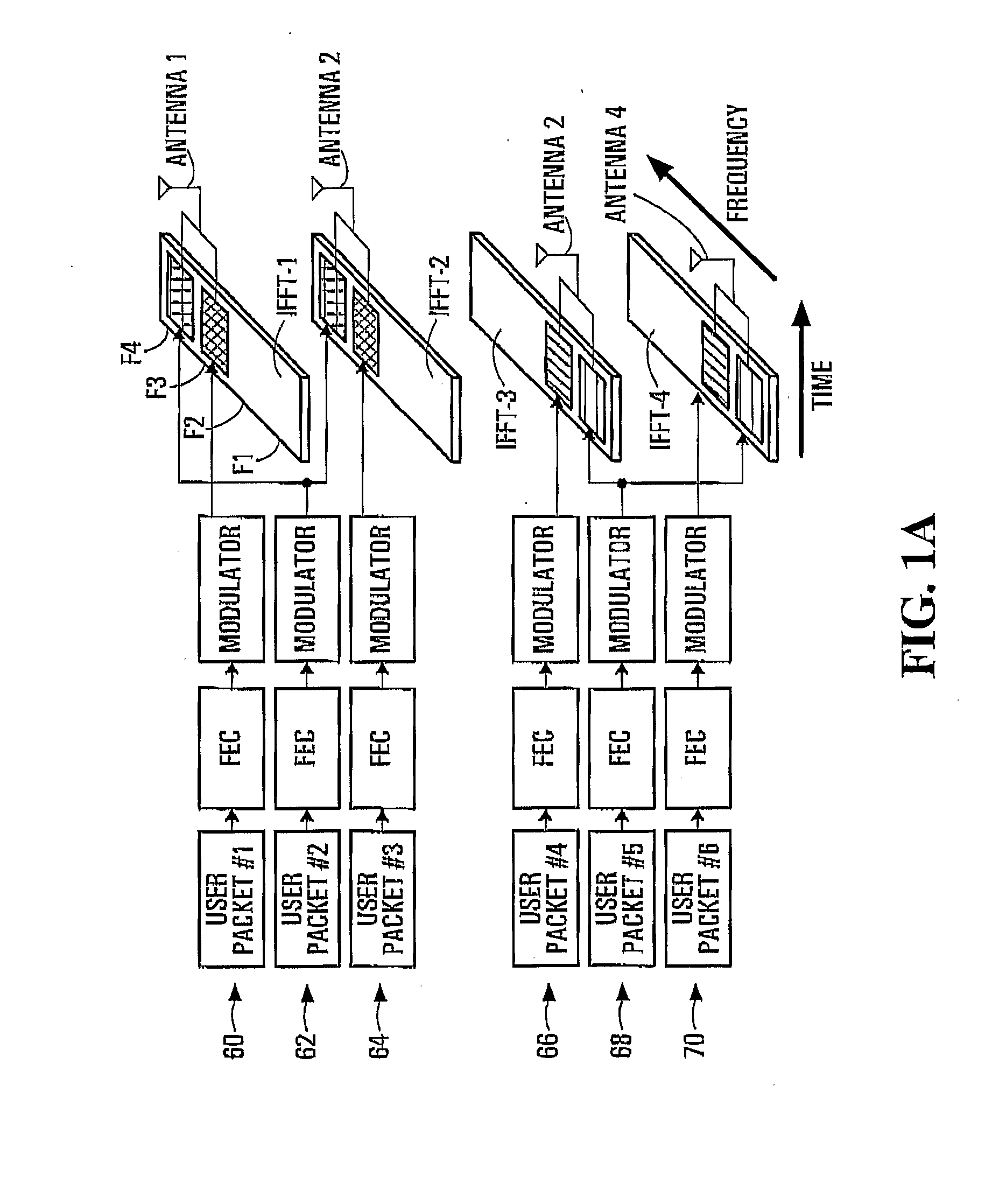
Aspects of the present invention provide MAC enhancements to support the PHY features of a MIMO-OFDMA framework. The MAC enhancements involve DL burst assignment to support adaptive MIMO transmission, UL burst assignment to support adaptive MIMO transmission, fast feedback channel operation to support wireless terminal dynamic feedback of MIMO mode selection, for example space time transmit diversity (STTD) or spatial multiplexing (SM), and / or permutation mode selection, for example diversity or adjacent subcarrier mode, dynamic CQICH allocation and de-allocation and the use of CQICH_ID for DL burst allocation. One or more of these enhancements is included in a given implementation. Methods are also provided for implementing the MAC enhancements.
Owner:APPLE INC
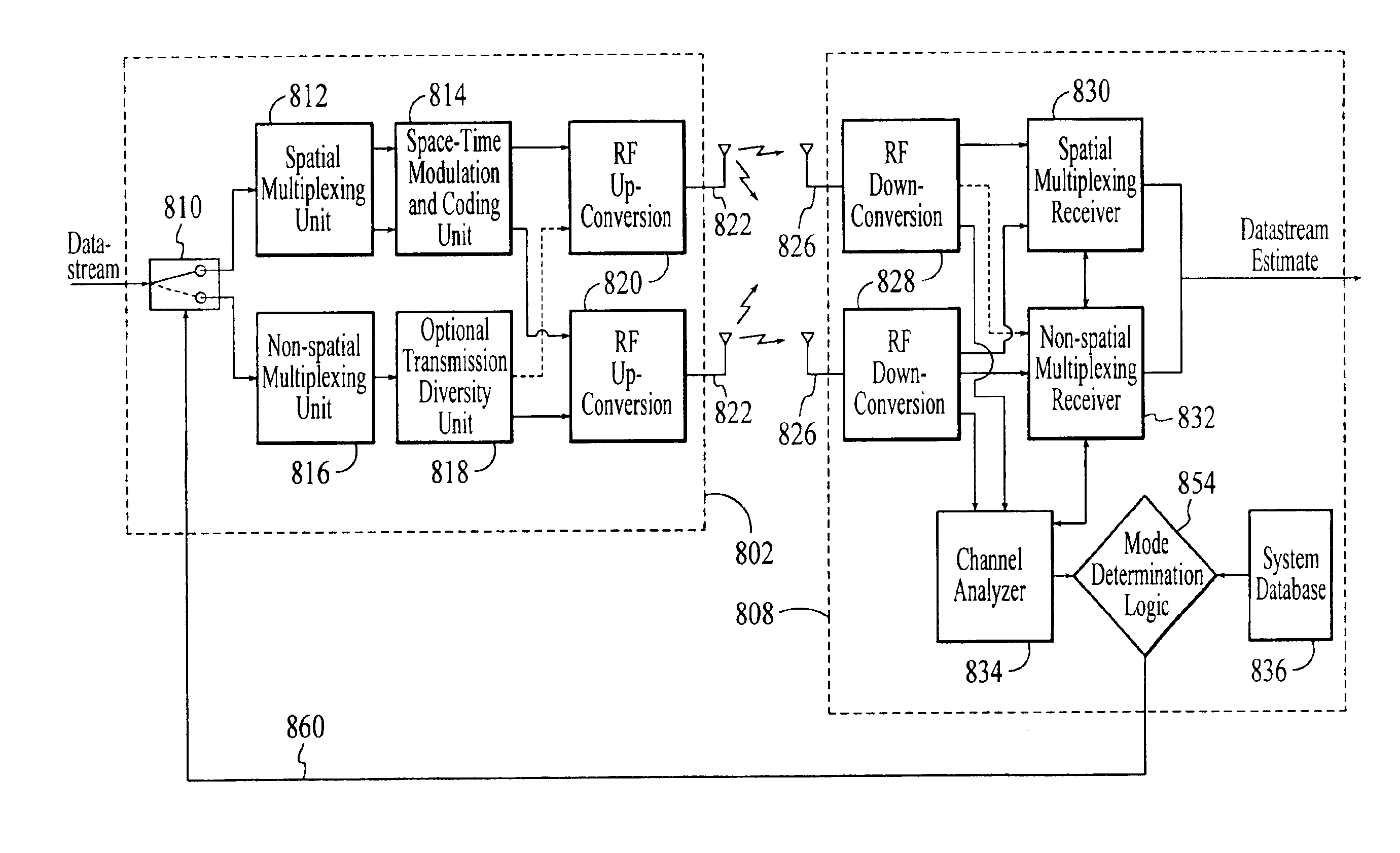
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
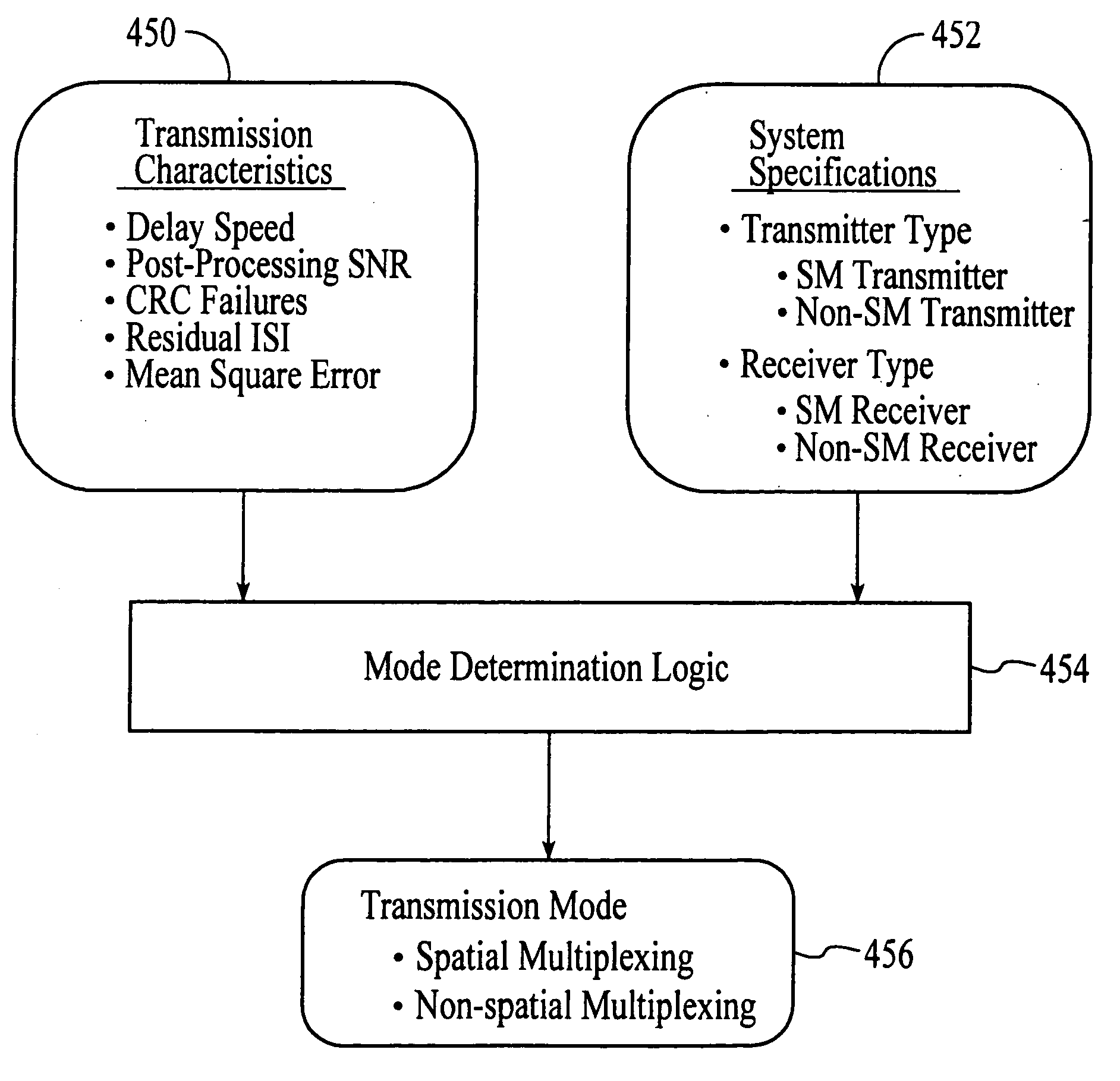
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for mode adaptation in wireless communication
InactiveUS6922445B1Improve quality parametersSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and system for selective mode adaptation for transmitting data by spatial multiplexing applicable in communications systems with a transmit unit having multiple transmit antennas or multiple transmit units and a receive unit having multiple receive antennas. A channel descriptor, such as channel matrix H or a channel matrix filter , with has sub-descriptors corresponding to the transmit antennas is determined and a quality parameter, such as signal-to-interference and noise ratio, signal-to-noise ratio or power level are chosen. The quality parameter is assigned a threshold and the sub-descriptor or sub-descriptors whose quality parameters do not meet the threshold are identified and deactivated.
Owner:INTEL CORP
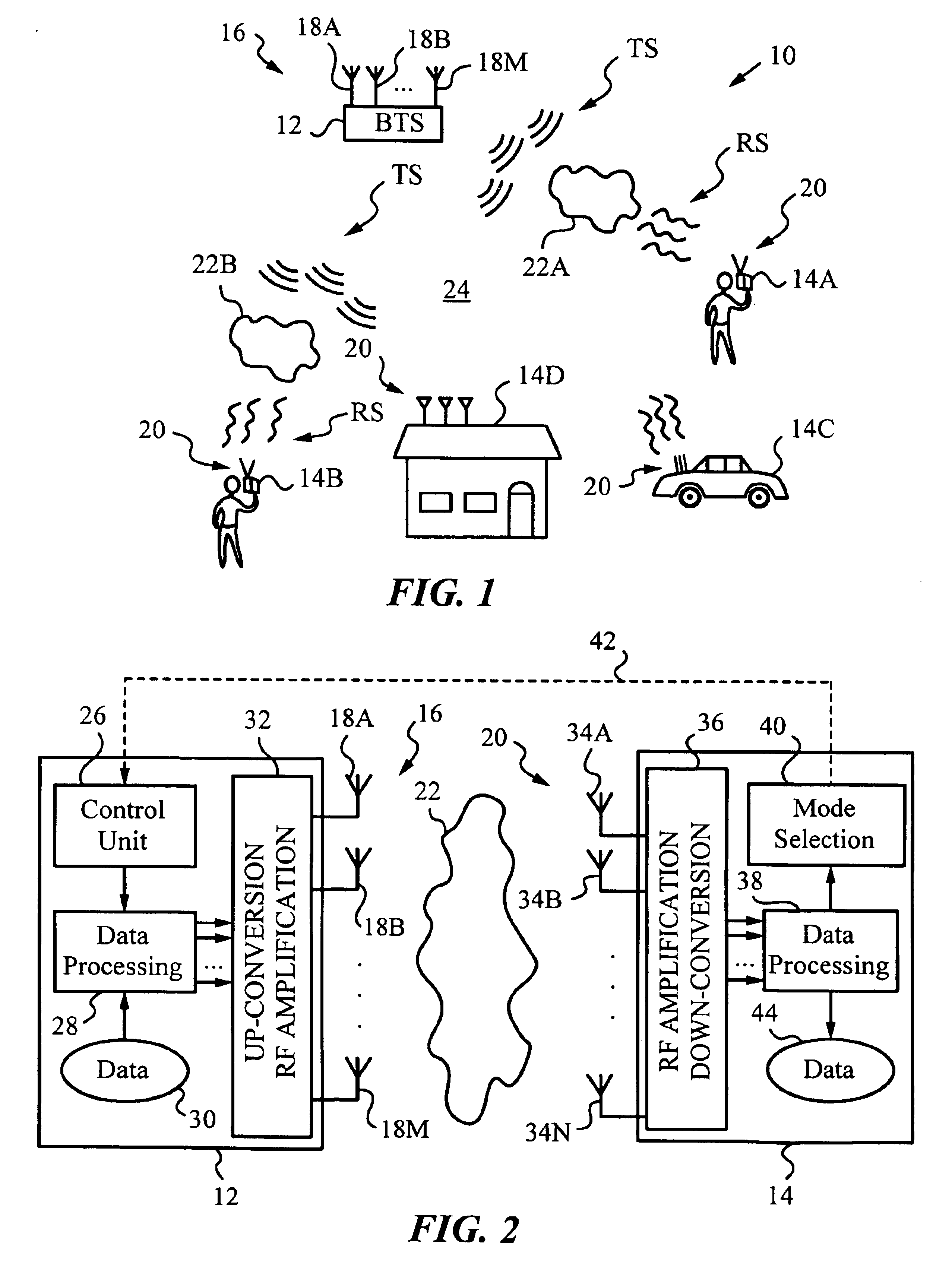
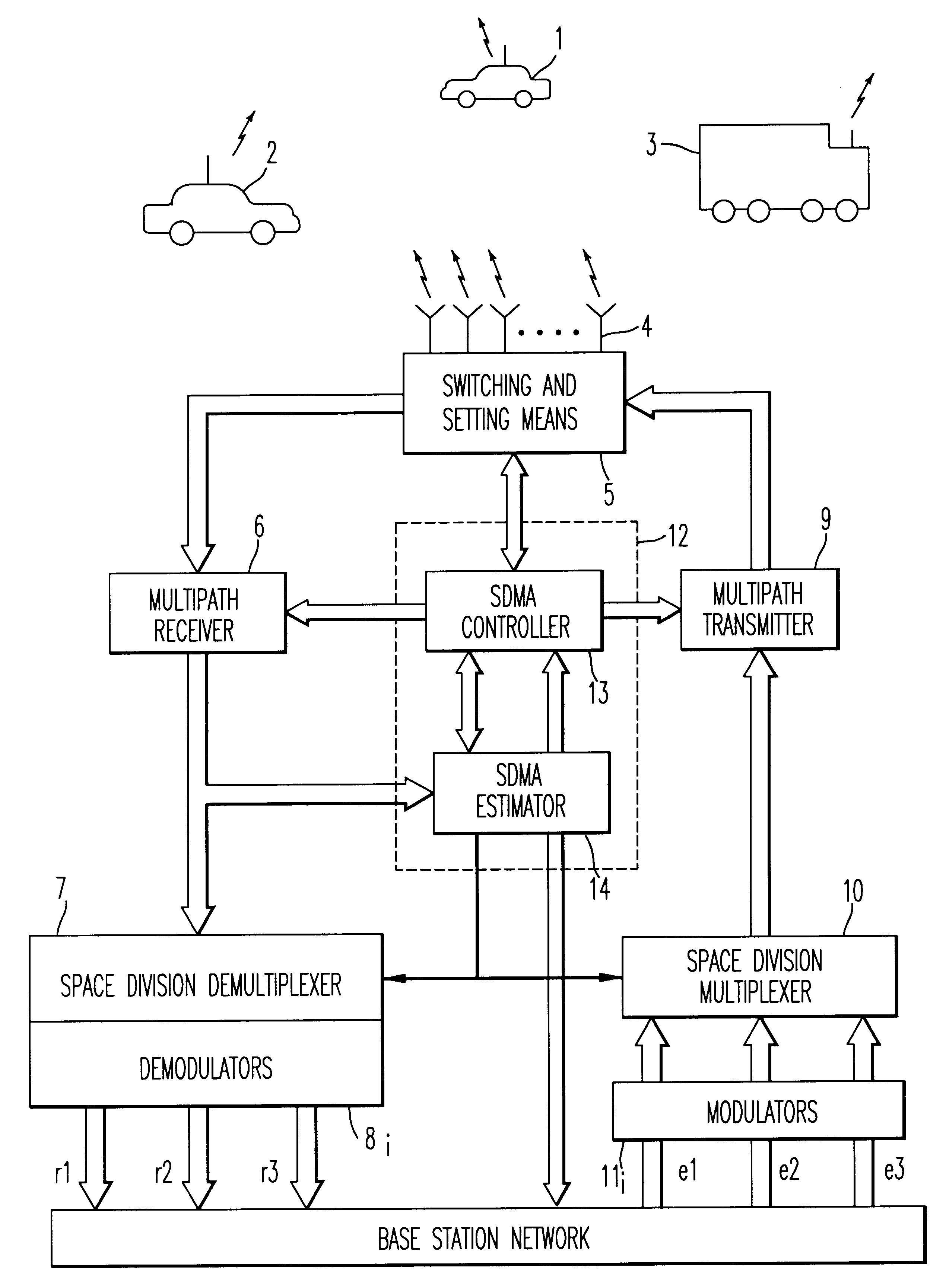
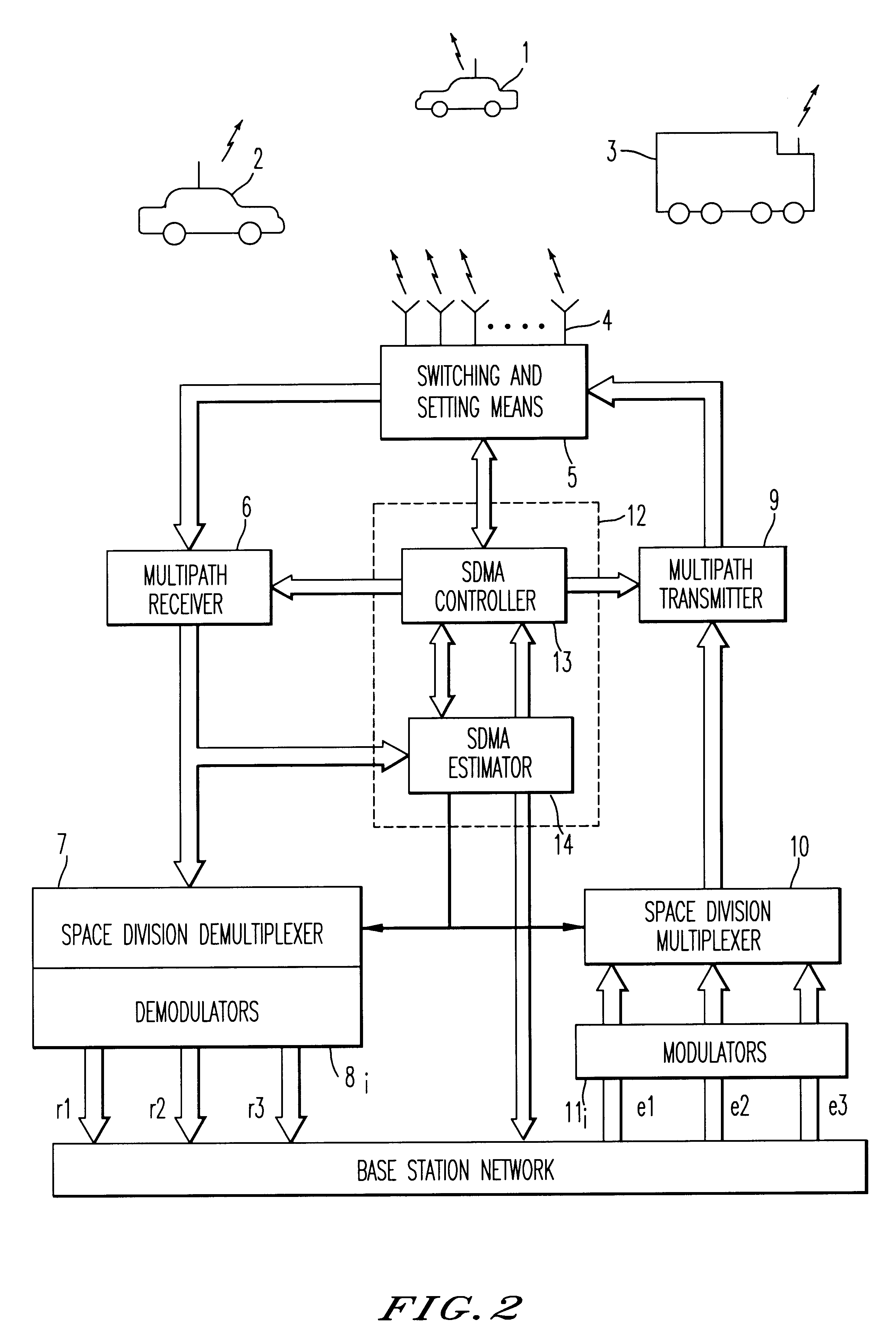
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Wireless communication system, base station device, and terminal device
ActiveUS20130336418A1Frequency utilization efficiency can be improvedIncrease frequencySpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionChannel state informationCommunications system
A terminal device notifies a base station device about control information associated with a receive quality of the terminal device. The base station device performs data modulation on a plurality of pieces of transmit data for the terminal device, by using a plurality of different data modulation schemes one by one, based on the control information, and spatially multiplexes the plurality of pieces of transmit data after the data modulation over a single wireless resource and transmits a spatially multiplexed signal. The terminal device receives the signal with the plurality of pieces of transmit data spatially multiplexed, and detects desirable transmit data from the receive signal, based on a first channel matrix which represents channel state information between the base station device and the terminal device and a second channel matrix in which the first channel matrix is multiplied by a transform matrix. Accordingly, an adaptive modulation technology is applied even to MIMO spatial multiplexing transmission using a LR technology, and hence a wireless communication system and so forth that can contribute to improvement in frequency utilization efficiency can be provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
Signal generation using phase-shift based pre-coding
InactiveUS20070274411A1Less complexImprove scalabilitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPrecodingPhase shifted
A phase-shift based pre-coding scheme used in a transmitting side and a receiving side that has less complexity than those of a space-time coding scheme, that can support various spatial multiplexing rates while maintaining the advantages of the phase-shift diversity scheme, that has less channel sensitivity than that of the pre-coding scheme, and that only requires a low capacity codebook is provided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
MIMO precoding enabling spatial multiplexing, power allocation and adaptive modulation and coding
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based feedback mechanism is provided to enable non-unitary precoding for multi-stream transmission, where in each stream is optimized with suitable transmission power allocation and AMC. The codebook-based feedback mechanism uses a precoding codebook having a power allocation matrix which is constrained to specify that beamforming always applies full power to a predetermined beam. With this constraint, a one-bit power allocation feedback index may be used to switch between beamforming and spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for achieving transmit diversity and spatial multiplexing using antenna selection based on feedback information
InactiveUS20090316807A1Eliminate the problemSecret communicationRadio transmissionFast Fourier transformData stream
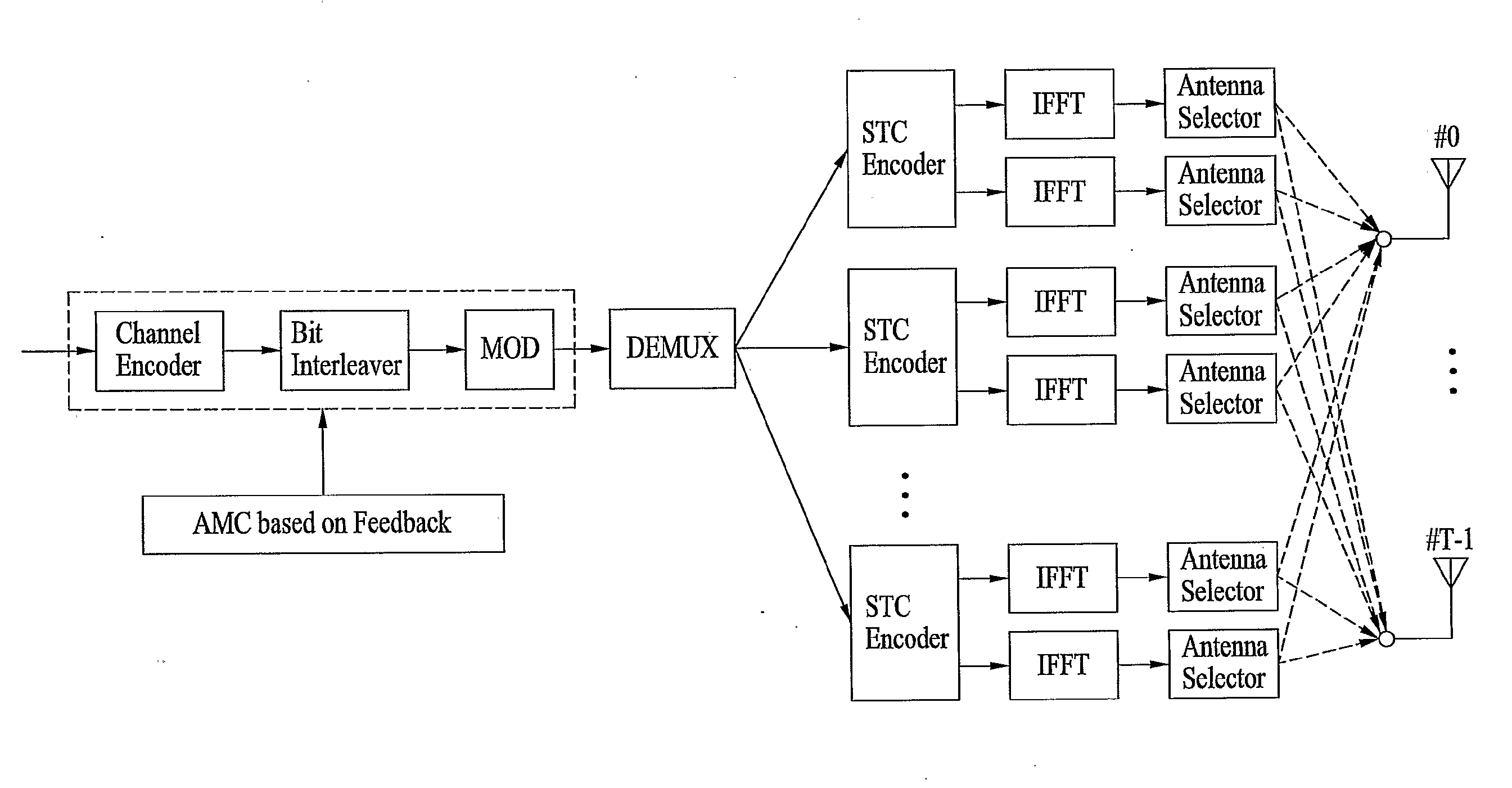
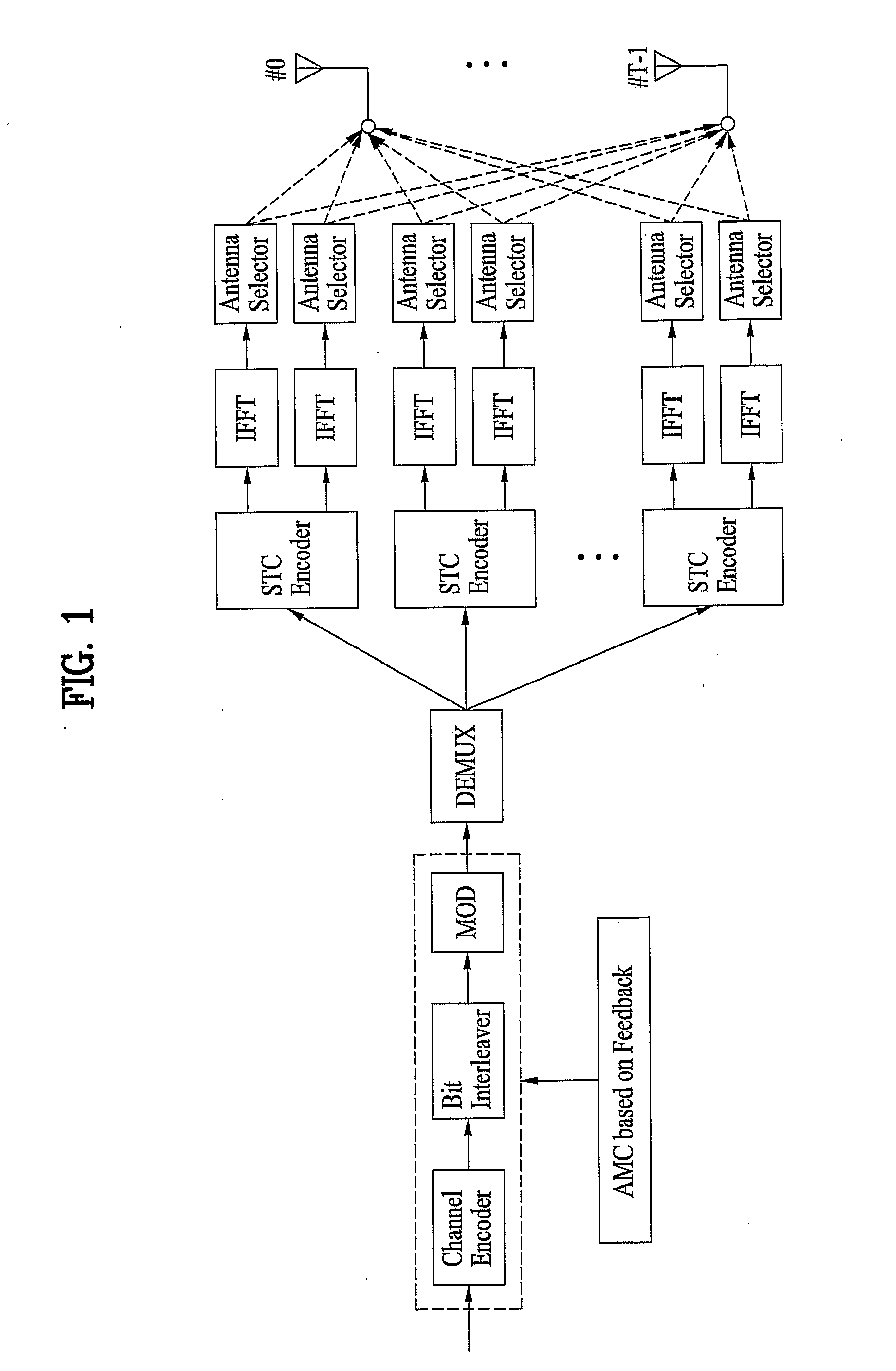
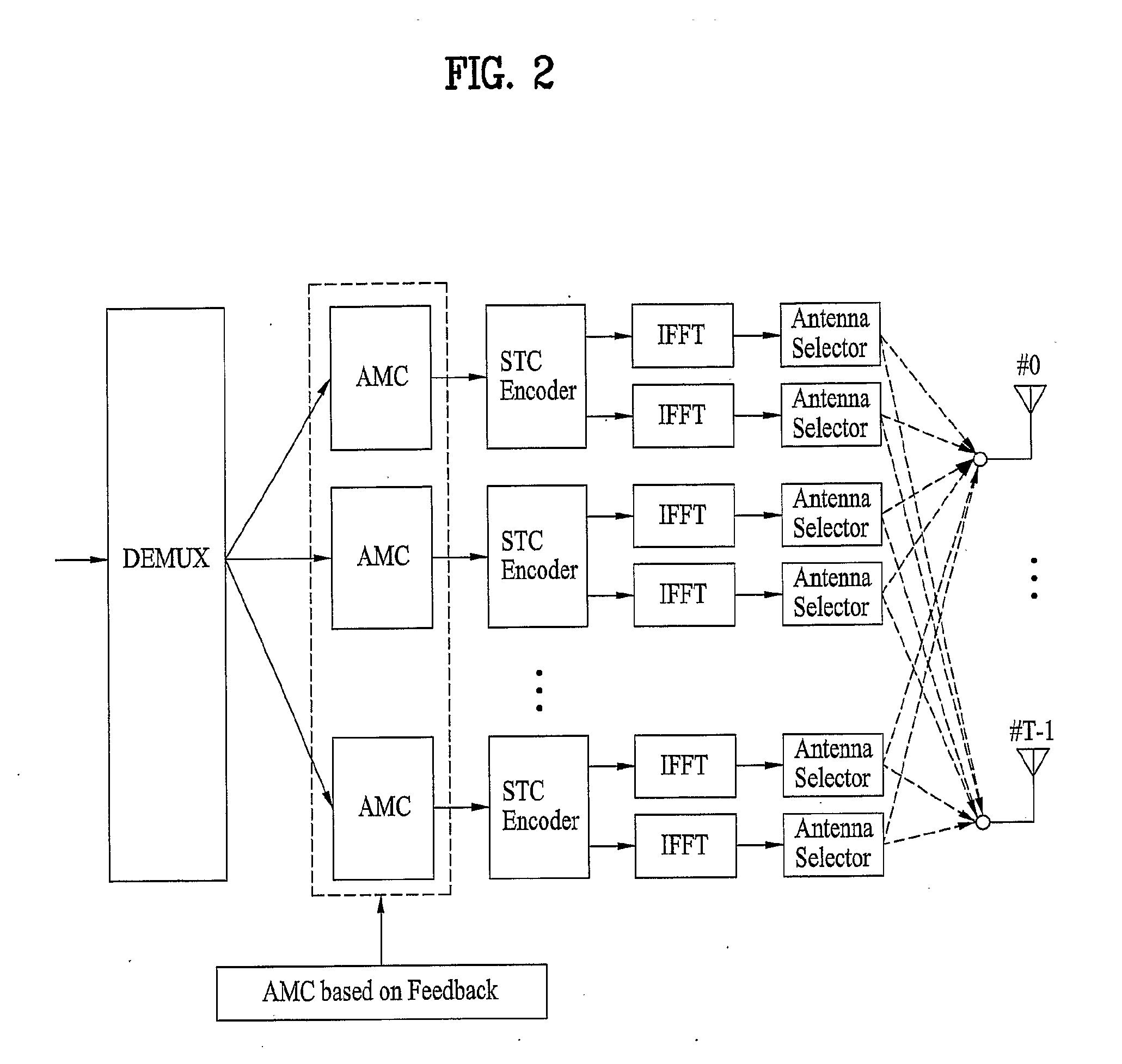
A method of achieving transmit diversity in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The method comprises encoding and modulating data stream based on feedback information, demultiplexing symbols to at least one encoder block, encoding the demultiplexed symbols by the at least one encoder block, transforming the encoded symbols by at least one inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) block, and selecting antennas for transmitting the symbols based on the feedback information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method of maximizing MIMO system performance by joint optimization of diversity and spatial multiplexing
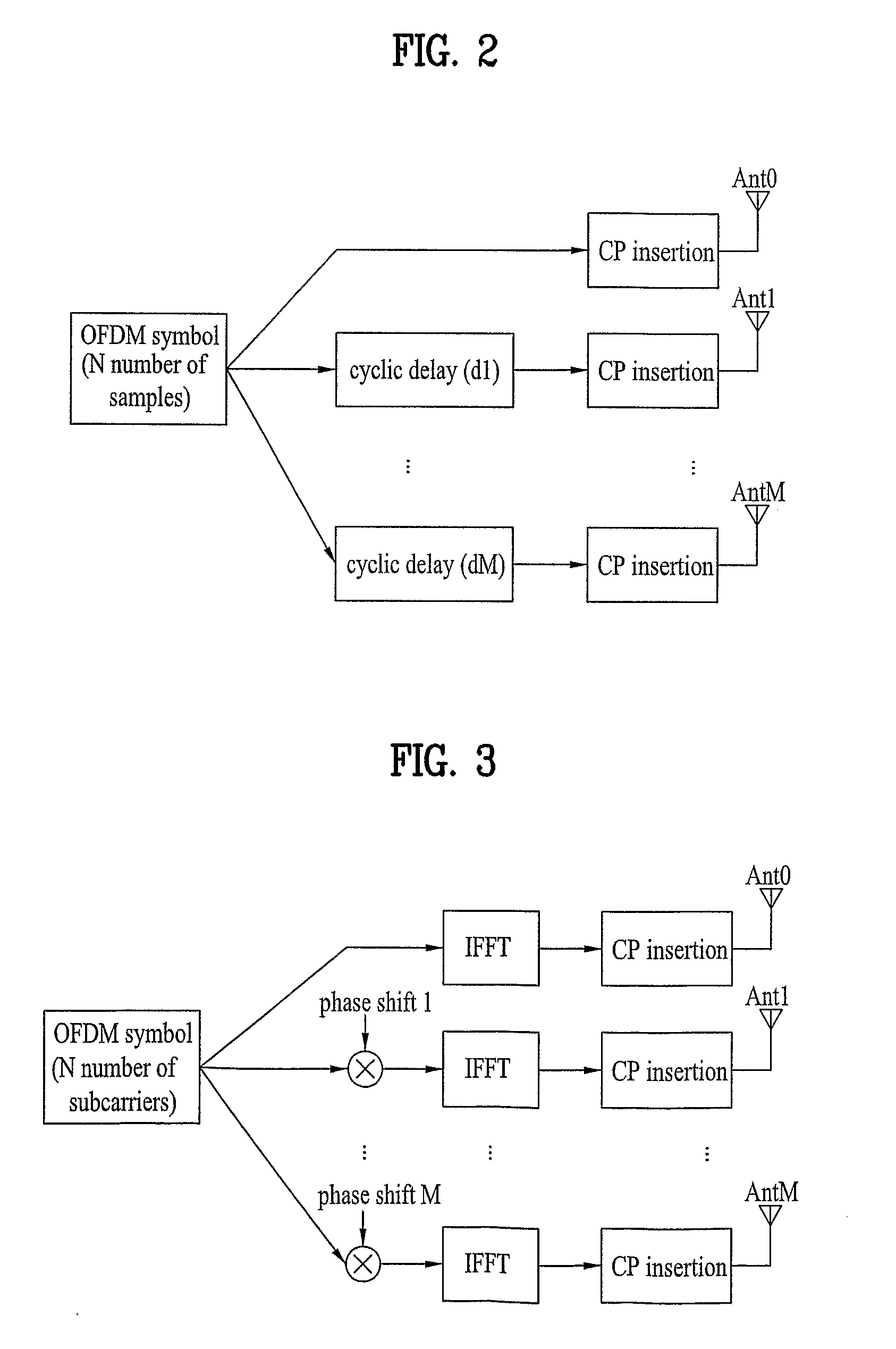
InactiveUS20060098760A1Increase communication robustnessImprove spectral efficiencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTime domainCommunications system
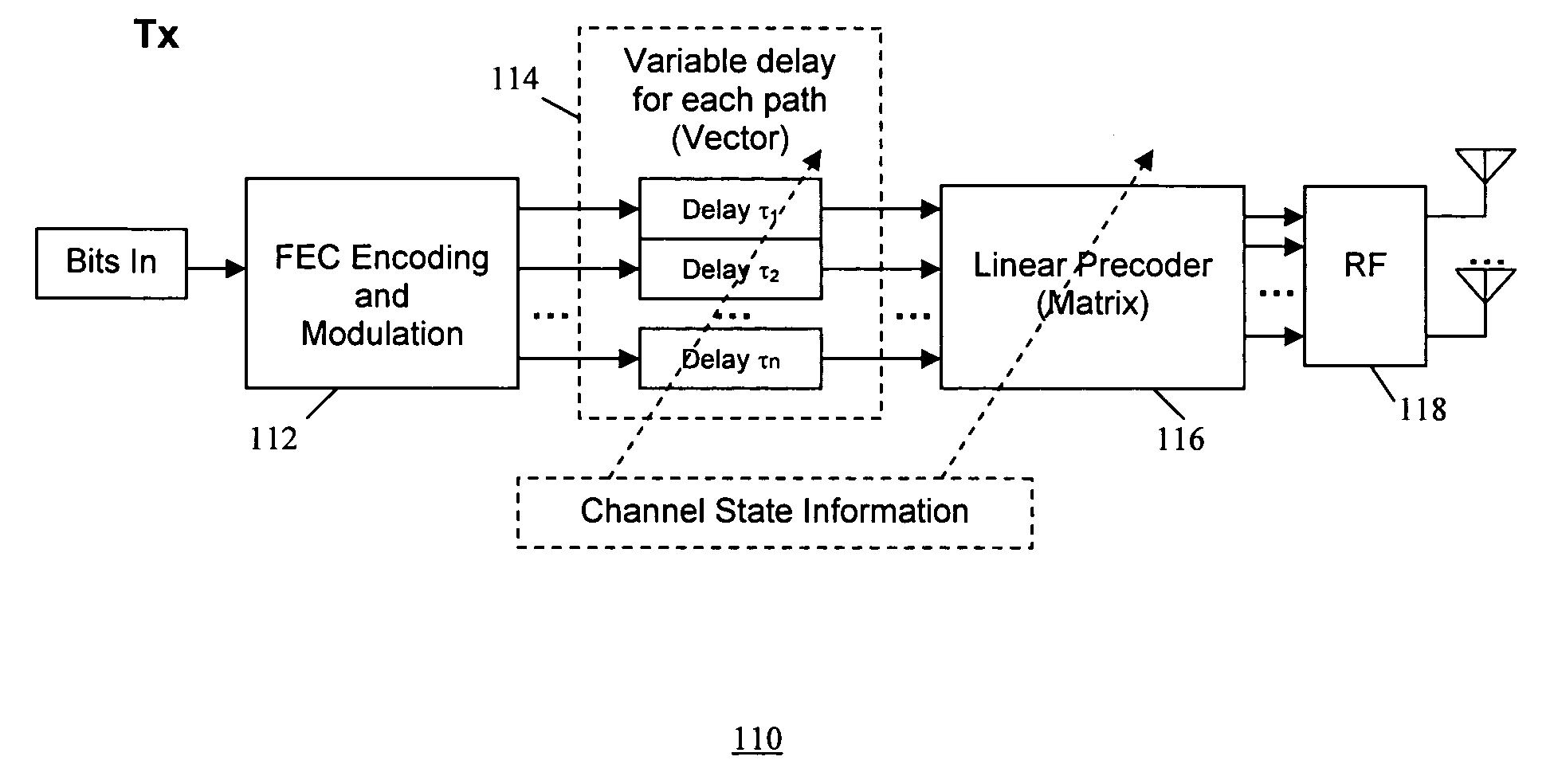
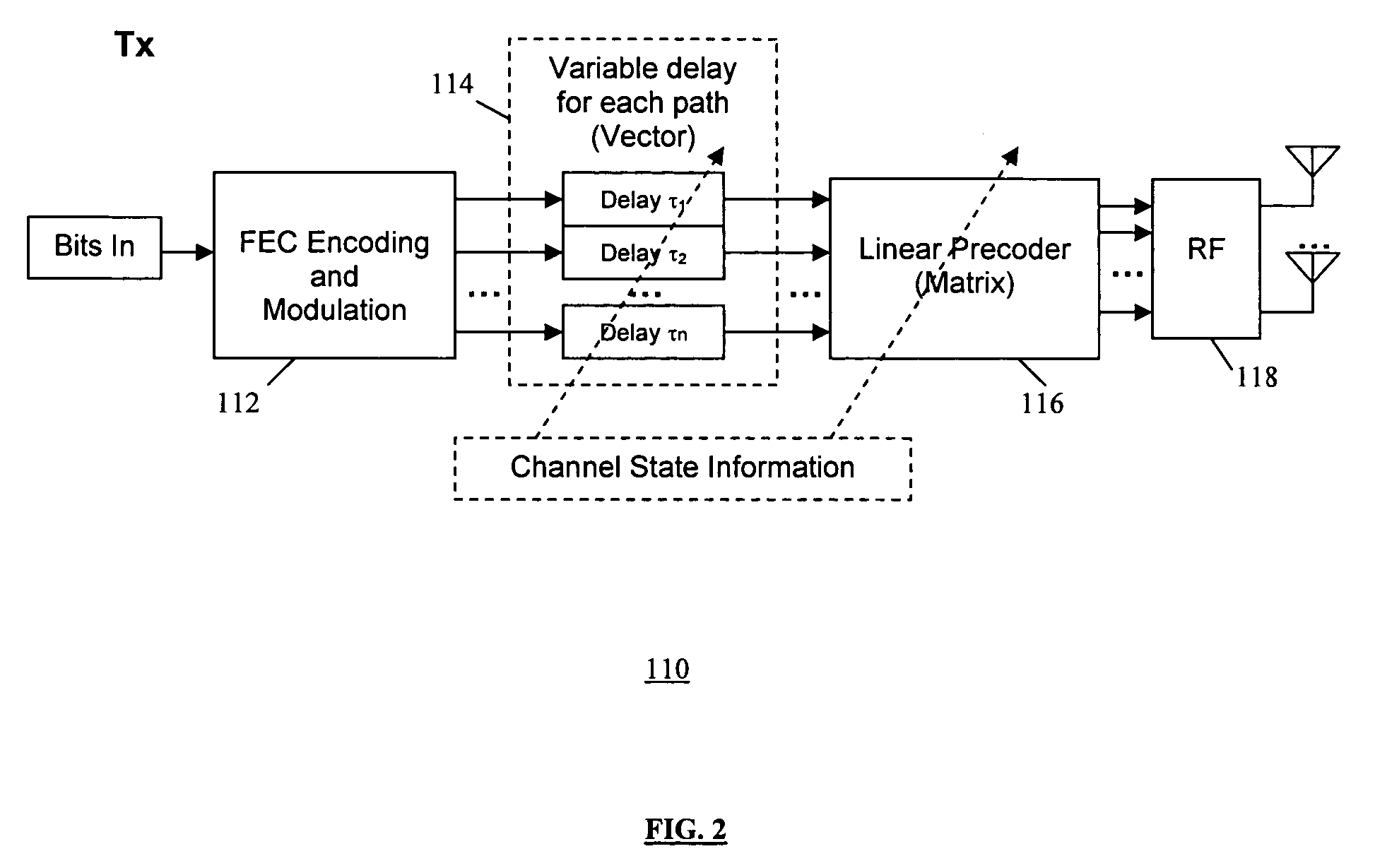
A method of transmission in a wireless communication system having a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter: signals are encoded using a space-domain precoder for spatial multiplexing, time-domain variable delay is introduced at each signal communication path for time diversity, and the signal are transmitted to the receiver. In the receiver the signal transmissions from the transmitter are decoded using a space-domain decoder, wherein time diversity and spatial multiplexing are combined, to increase communication robustness and spectral efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
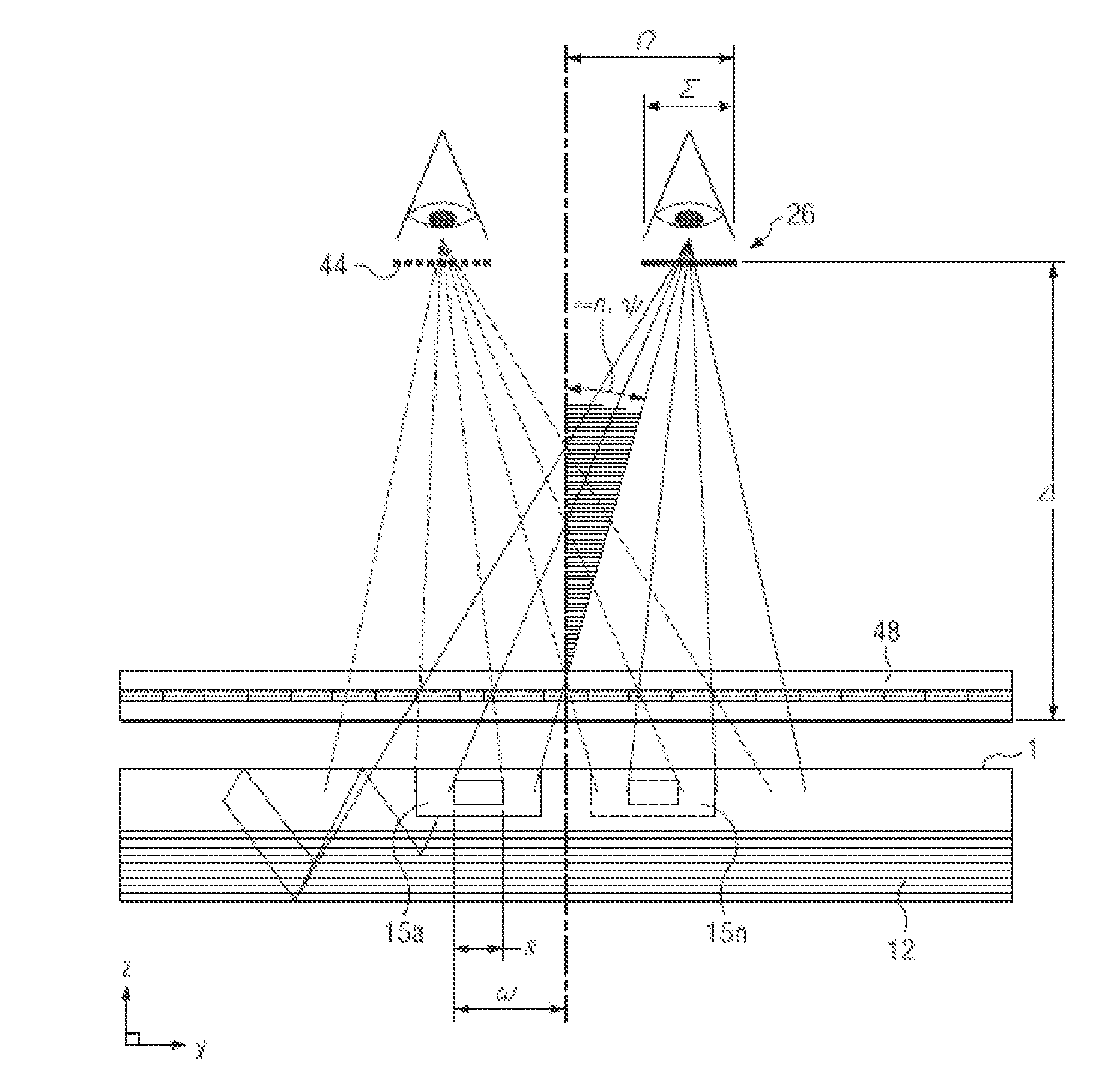
Directional backlight
InactiveUS20150268479A1High resolutionReduce thicknessSteroscopic systemsOptical light guidesParallaxSpatial light modulator
A directional display may include a waveguide. The waveguide may include light extraction features arranged to direct light from an array of light sources by total internal reflection to an array of viewing windows and a reflector arranged to direct light from the waveguide by transmission through extraction features of the waveguide to the same array of viewing windows. A further spatially multiplexed display device comprising a spatial light modulator and parallax element is arranged to cooperate with the illumination from the waveguide. An efficient and bright autostereoscopic display system with low cross talk and high resolution can be achieved.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Eye Mounted Displays and Systems Using Eye Mounted Displays
ActiveUS20150049004A1Avoid and reduce interferenceOvercome limitationsImage analysisGeometric image transformationCorneal surfaceEntire pupil
A display device is mounted on and / or inside the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. The projected light propagates through the pupil but does not fill the entire pupil. In this way, multiple sub-displays can project their light onto the relevant portion of the retina. Moving from the pupil to the cornea, the projection of the pupil onto the cornea will be referred to as the corneal aperture. The projected light propagates through less than the full corneal aperture. The sub-displays use spatial multiplexing at the corneal surface. Various electronic devices interface to the eye mounted display.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
Spatially multiplexed imaging directional backlight displays
InactiveUS20130328866A1Slow responseReduce complexityMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
Disclosed is an imaging directional backlight that cooperates with a spatial light modulator to direct light into a first viewing window for one set of image pixels and into a second viewing window for a second set of image pixels. The waveguide may comprise a stepped structure, where the steps further comprise extraction features hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Such an apparatus may be used to achieve an autostereoscopic display with a flat structure, not requiring fast response speed spatial light modulators.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
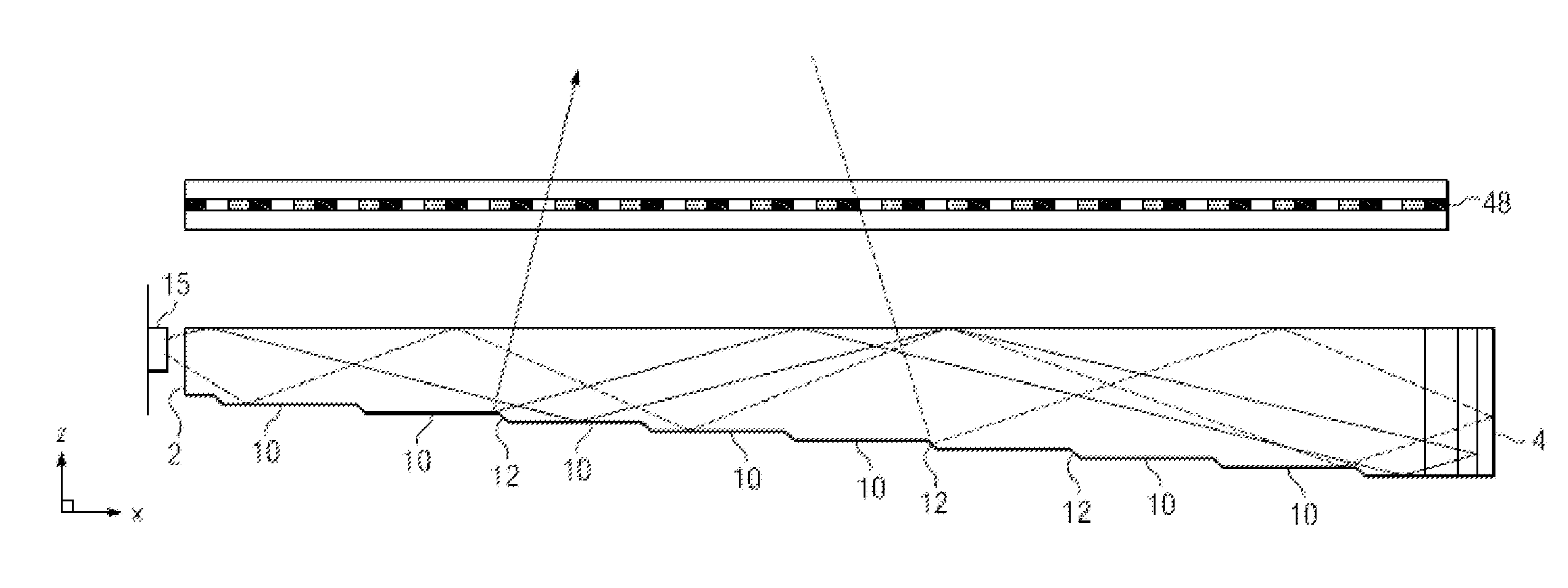
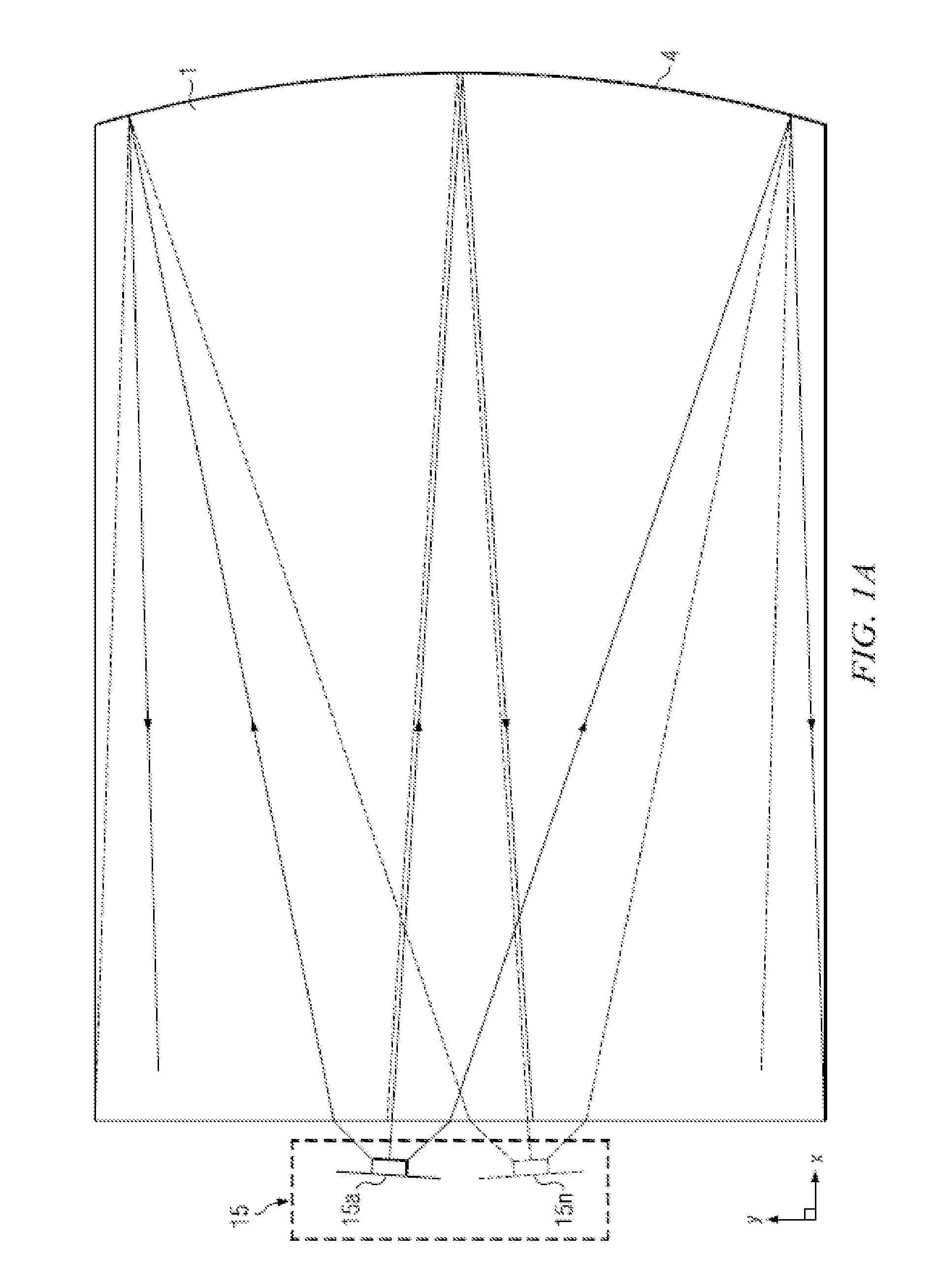
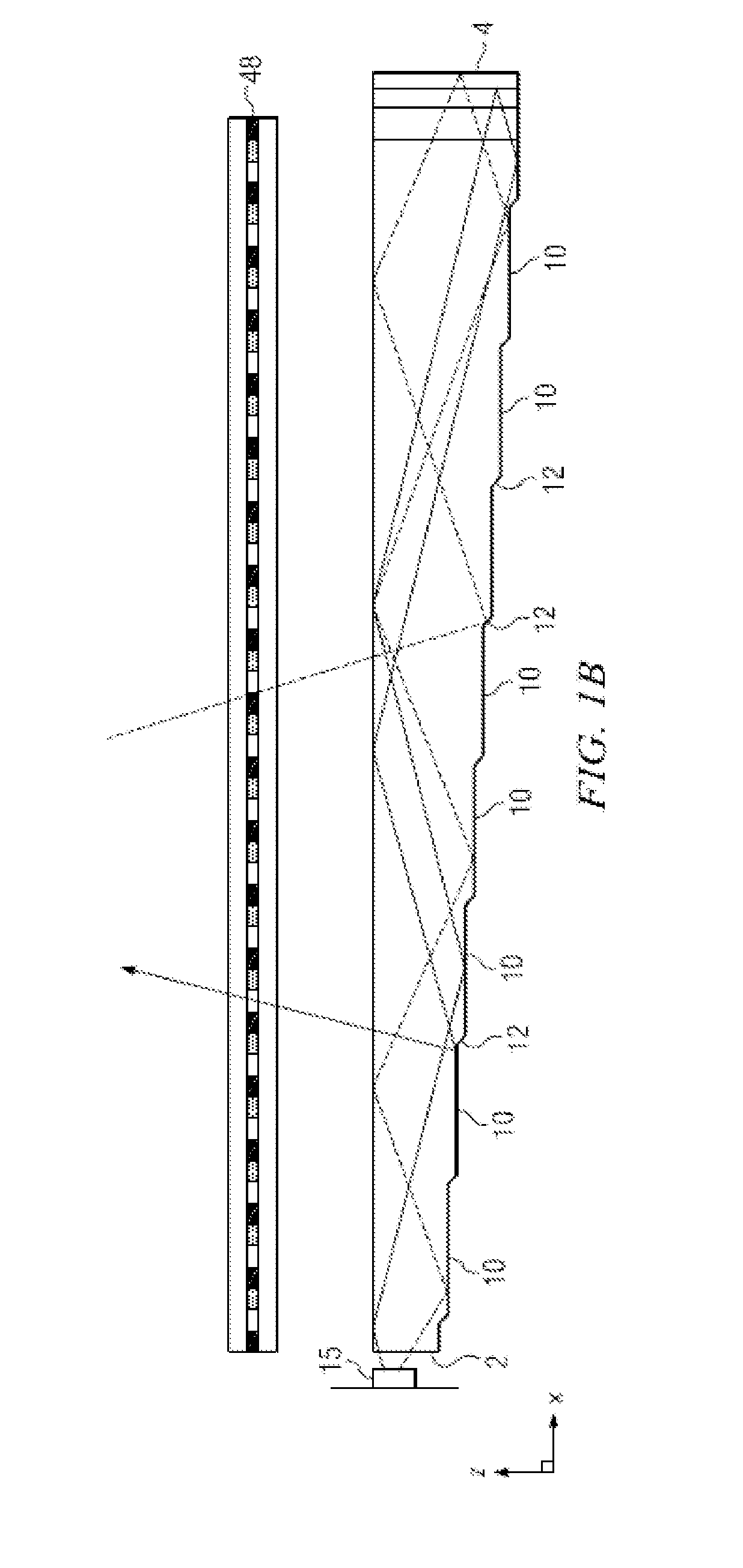
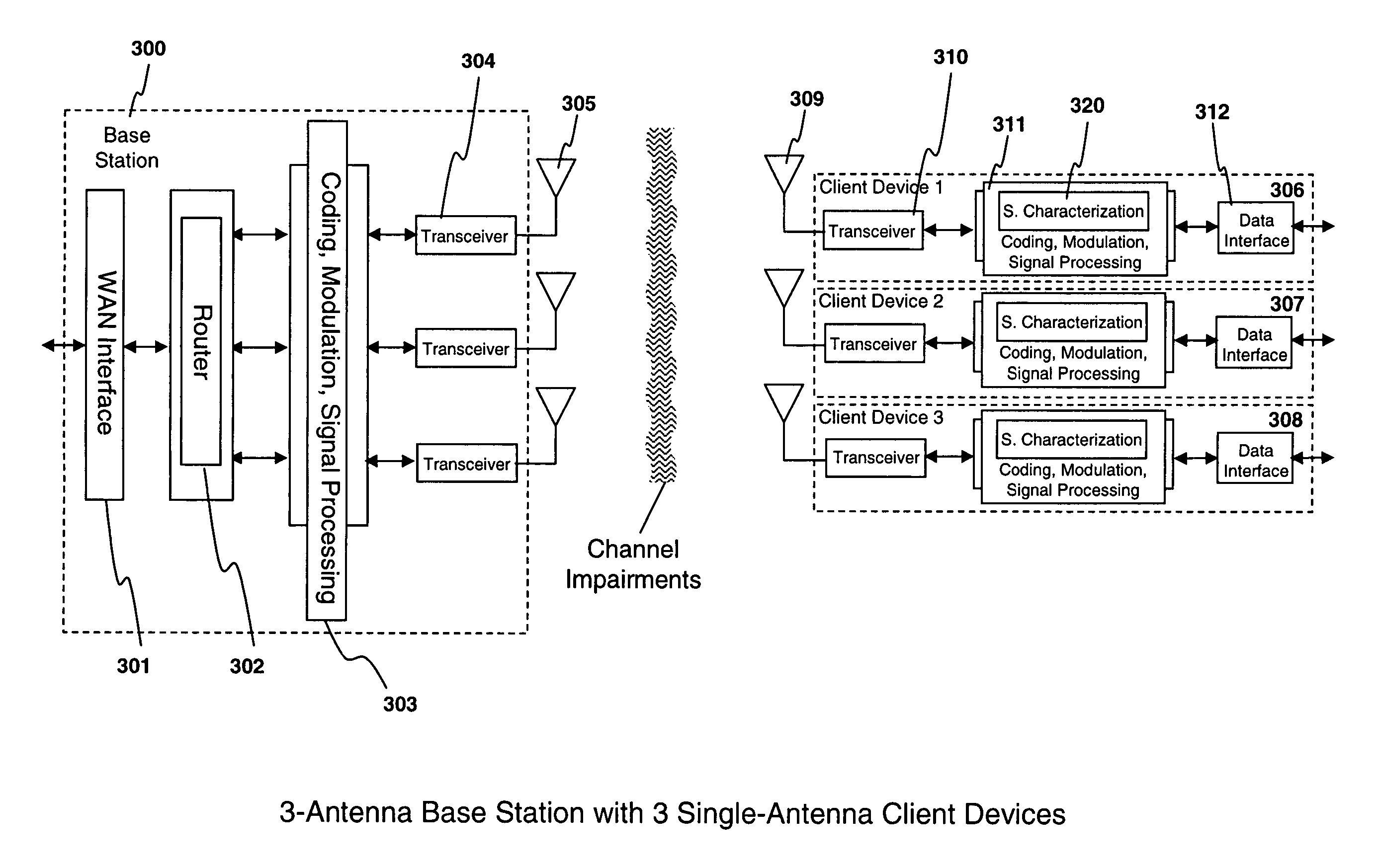
System and method for spatial-multiplexed tropospheric scatter communications
A method is described comprising: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of client devices utilizing tropospheric scatter, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and transmitting the channel characterization data back to the base station utilizing tropospheric scatter; storing the channel characterization data for each of the plurality of client devices; receiving data to be transmitted to each of the client devices; and precoding the data using the channel characterization data associated with each respective client device to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN
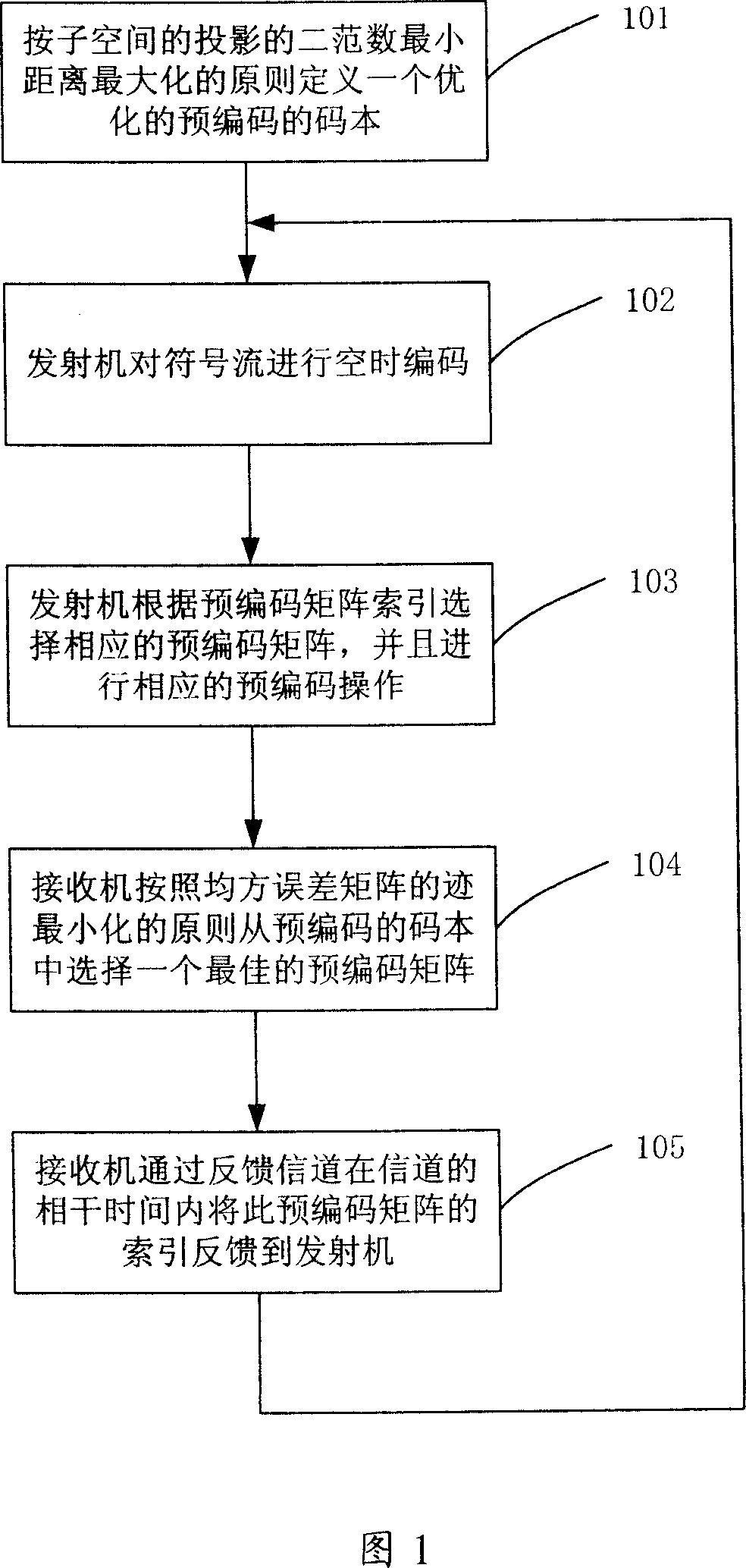
Multi-input multi-output space multiplexing precoding method of wireless communication system
InactiveCN101136718AImprove communication performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMulti inputCoherence time
Using precoded space multiplexing of limited fed back, the method defines a group of set of precoded matrix (i.e. precoded codebook) known by transmitter and receiver. Using algorithm of channel estimation to obtain current state information of channel, the receiver selects an optimal precoded matrix from precoded codebooks according to minimized principles of trace of mean square error matrix as well as through a feedback channel, feeds index of the precoded matrix back to the transmitter within coherence time of channel. Based on the said index of the precoded matrix, the transmitter obtains the precoded matrix, and then carries out precoded operations on vectors of transmit signal based on the precoded matrix. Precoded codebook can be designed based on maximized principle of minimum distance between two norms of projections of subspaces. Using limited bit number fed back, the invention raises communication performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
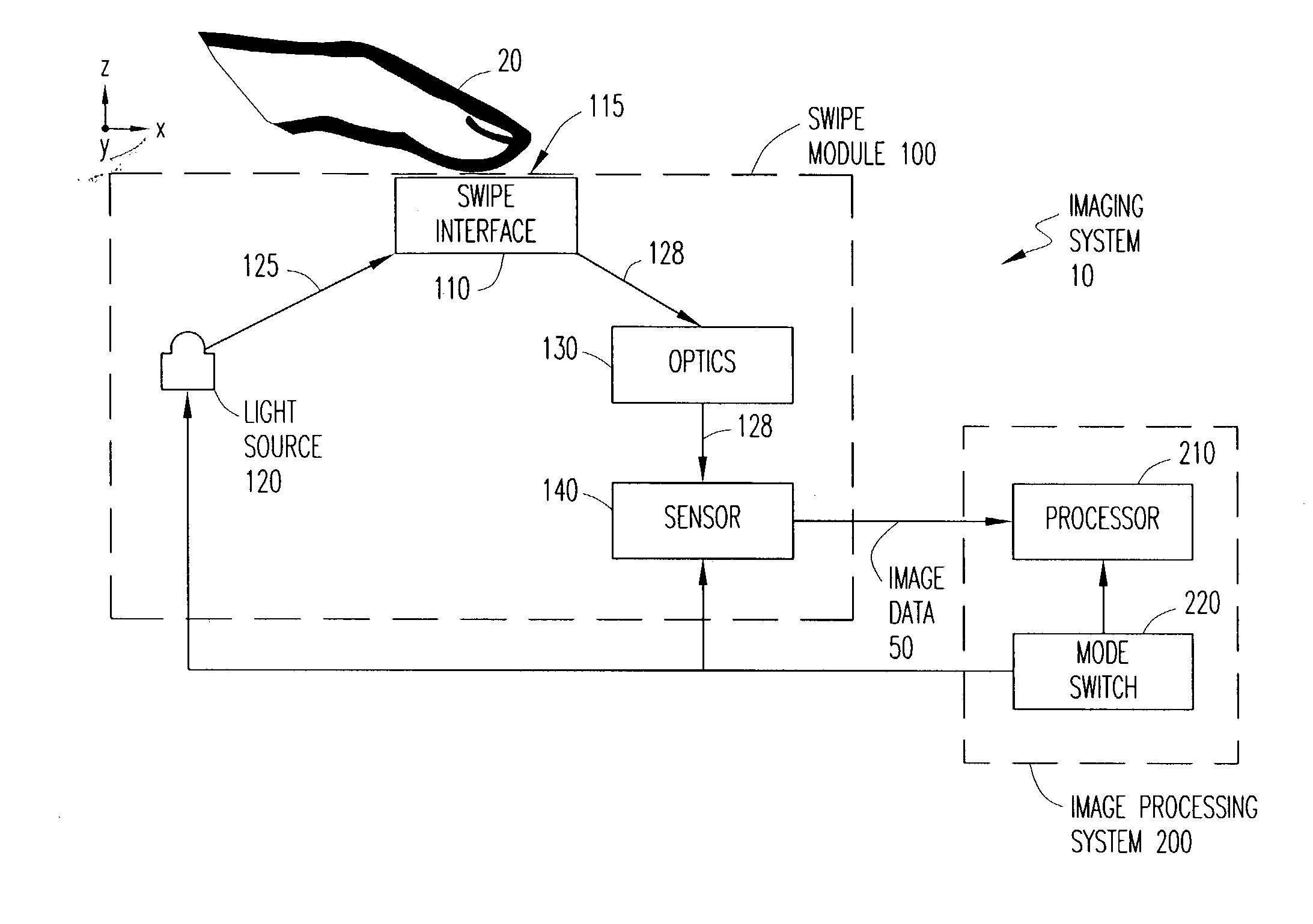
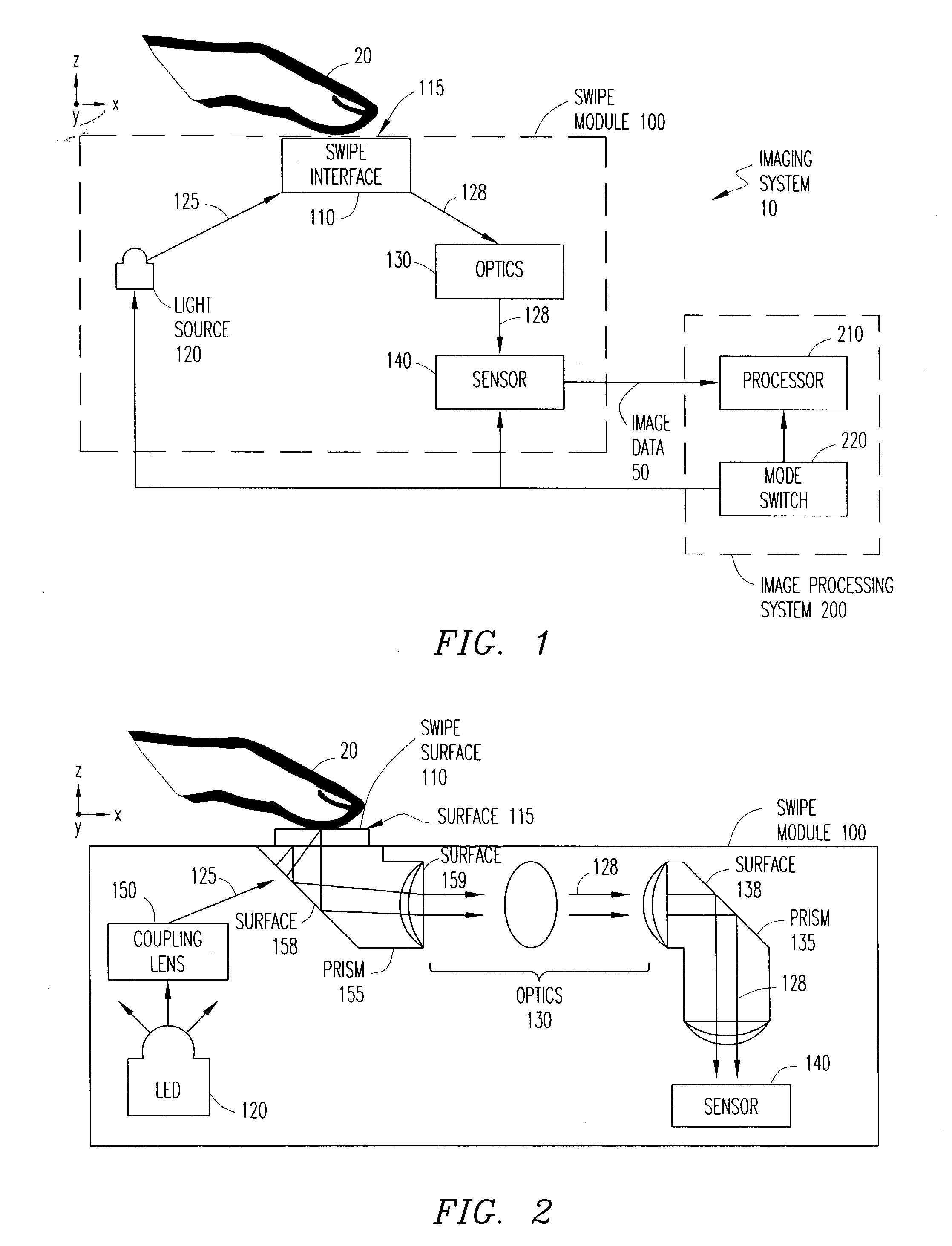
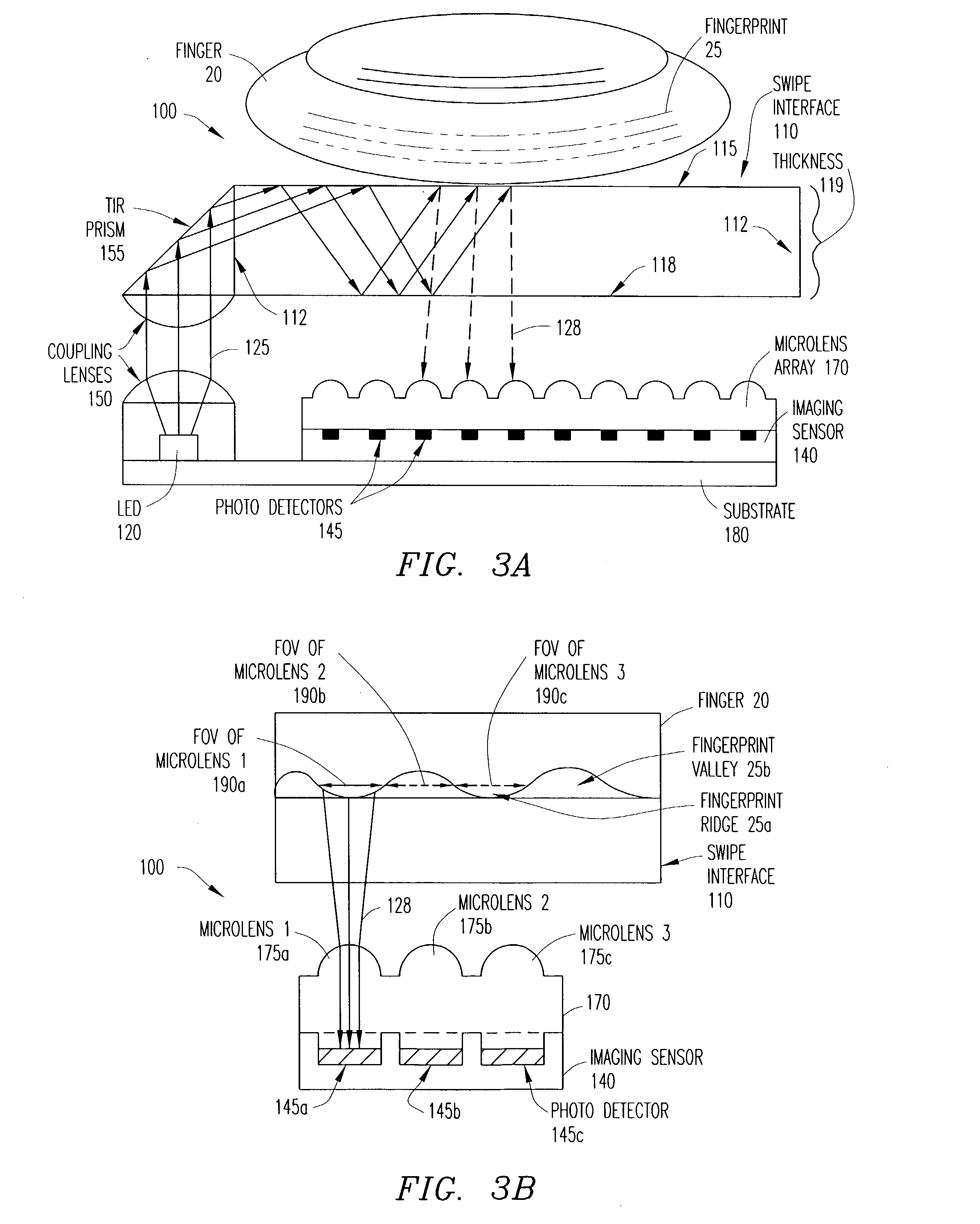
System and method for time-space multiplexing in finger-imaging applications
ActiveUS20040208347A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital reflexOperation mode
An apparatus for imaging a fingerprint operates in a selected mode to provide a finger recognition and / or a finger navigation application. Multiple light sources are capable of being sequentially selected for illumination of corresponding partitions of a finger interface upon which a user places a finger (or thumb). The selection of light sources is based on the selected mode of operation. A single sensor captures light reflected from the digit in all illuminated partitions as sequential partition images. The sensor further outputs image data corresponding to the captured partition images for processing in the selected mode.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Method and apparatus for correcting errors in a multiple subcarriers communication system using multiple antennas
ActiveUS20090307558A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemPhase shifted
A method for correcting errors in a multiple antenna system based on a plurality of sub-carriers and a transmitting / receiving apparatus supporting the same are disclosed. The method includes determining a phase shift based precoding matrix phase shifted at a predetermined phase angle, initially transmitting each sub-carrier symbol to a receiver in a packet unit by using the phase shift based precoding matrix, reconstructing the phase shift based precoding matrix to reduce a spatial multiplexing rate if a negative reception acknowledgement (NACK) is received from the receiver, and retransmitting the initially transmitted sub-carrier symbol by using the reconstructed phase shift based precoding matrix or by changing the phase shift based precoding matrix using offset information fed back from the receiver or random offset information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
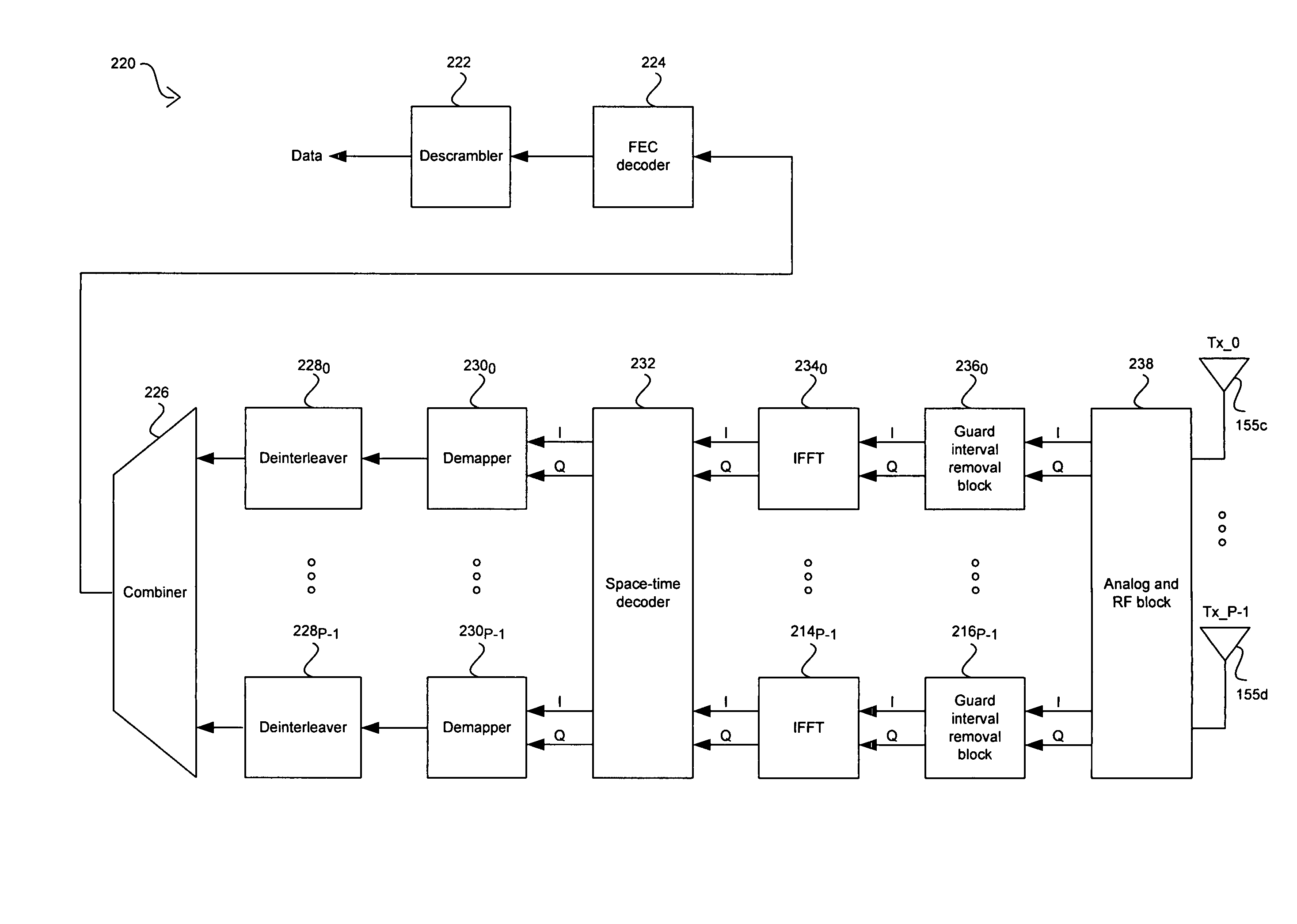
Method and system for increasing data rate in a mobile terminal using spatial multiplexing for DVB-H communication
A method and system for increasing data rate in a mobile terminal using spatial multiplexing for digital video broadcasting for handhelds (DVB-H) communication are provided. A reconfigurable orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) chip may be utilized in a mobile terminal to process received spatially multiplexed signals. The mobile terminal may be utilized in a spatially multiplexed multiple-input-multiple-output (SM-MIMO) wireless system. The spatially multiplexed signals may be quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) modulated and may utilize OFDM subcarries. A processor may be utilized to configure the OFDM chip to process signals such as IEEE 802.11 and 802.16, and DVB. The OFDM chip may generate channel weights to be applied to the spatially multiplexed signals received in multiple receive antennas. The weighted signals may be combined to generate multiple RF received signals from which channel estimates may be generated. Subsequent channel weights may be dynamically generated from generated channel estimates.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Subscriber unit in a hybrid link incorporating spatial multiplexing
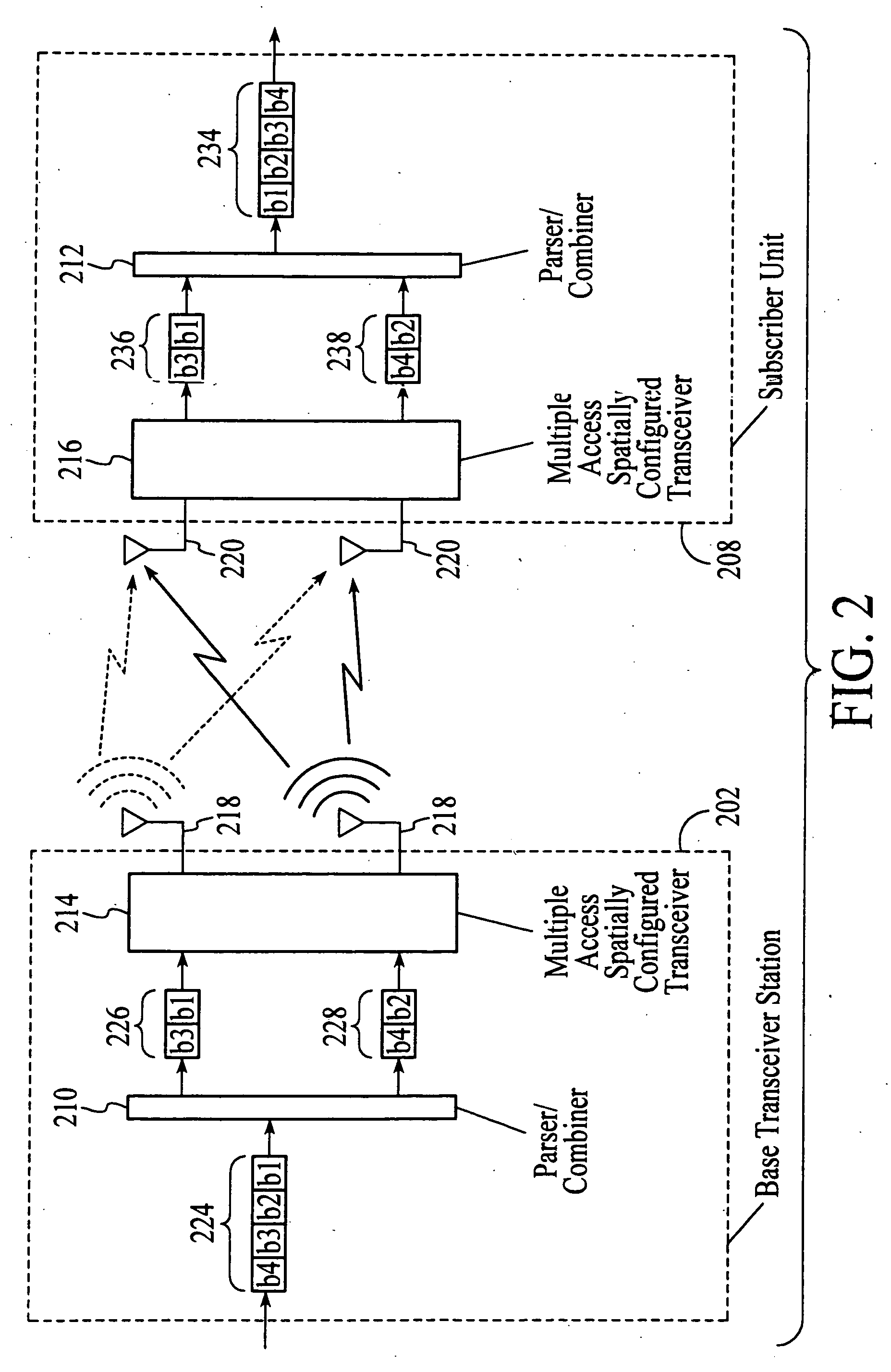
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for implementing spatial multiplexing in conjunction with the one or more multiple access protocols during the broadcast of information in a wireless network. A subscriber unit for use in a cellular system is disclosed. The subscriber unit includes a plurality of spatially separate antennas and a transmitter for transmitting a plurality of substreams of a datastream on an assigned channel or slot of a multiple access protocol. The transmitter is arranged to apply each substream to an associated one of the spatially separate antennas.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Wireless Communication System, Wireless Communication Apparatus, and Wireless Communication Method
ActiveUS20090207765A1Improve process capabilityReduce circuit sizeMultiplex communicationNetwork topologiesCommunications systemData transmission
A wireless communication system is disclosed. The wireless communication system performs data transmission using spatially multiplexed streams from a first terminal including N antennas to a second terminal including M antennas (N and M are integers larger than or equal to 2 and N>H).
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com