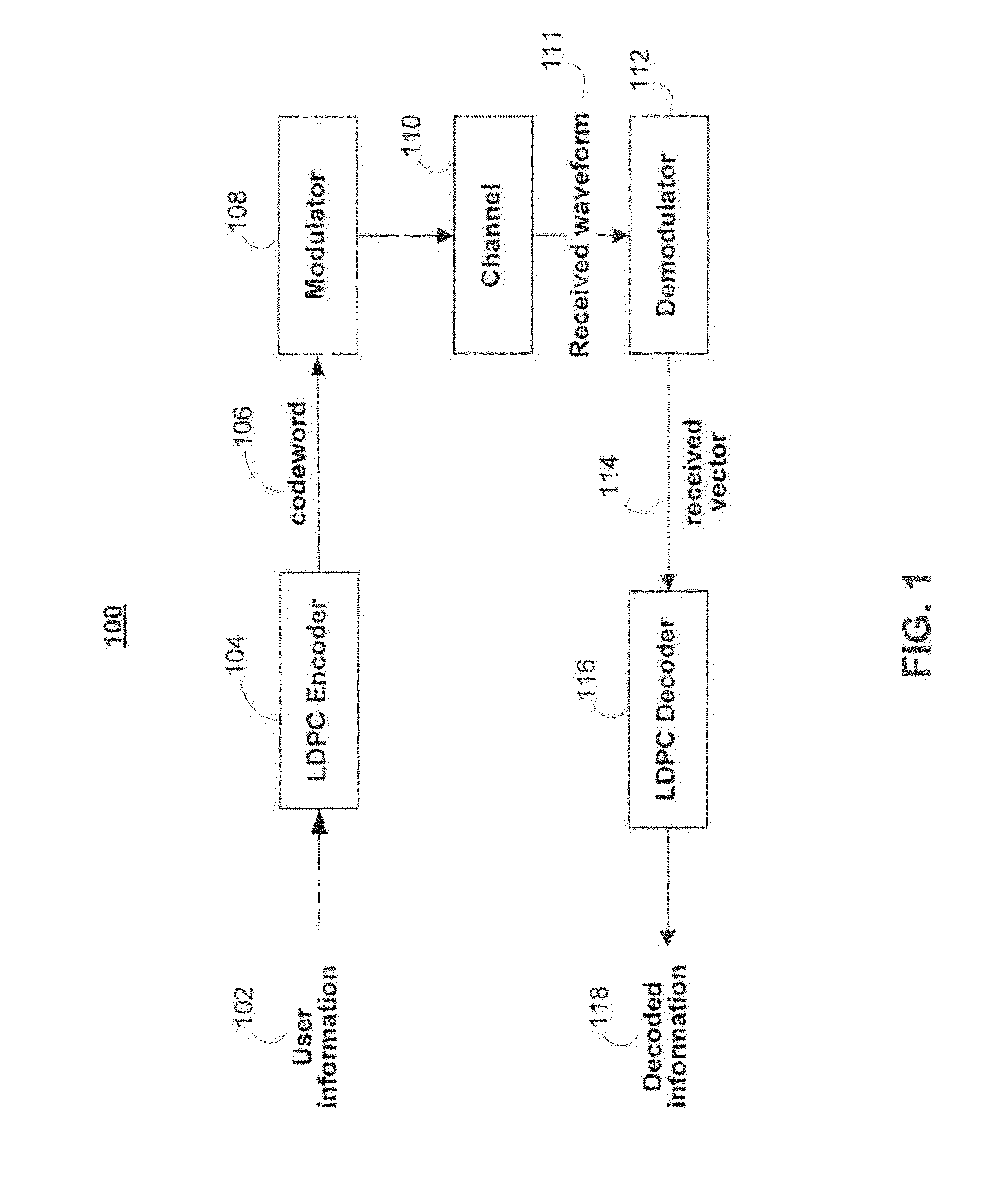
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
438results about "Checking code calculations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
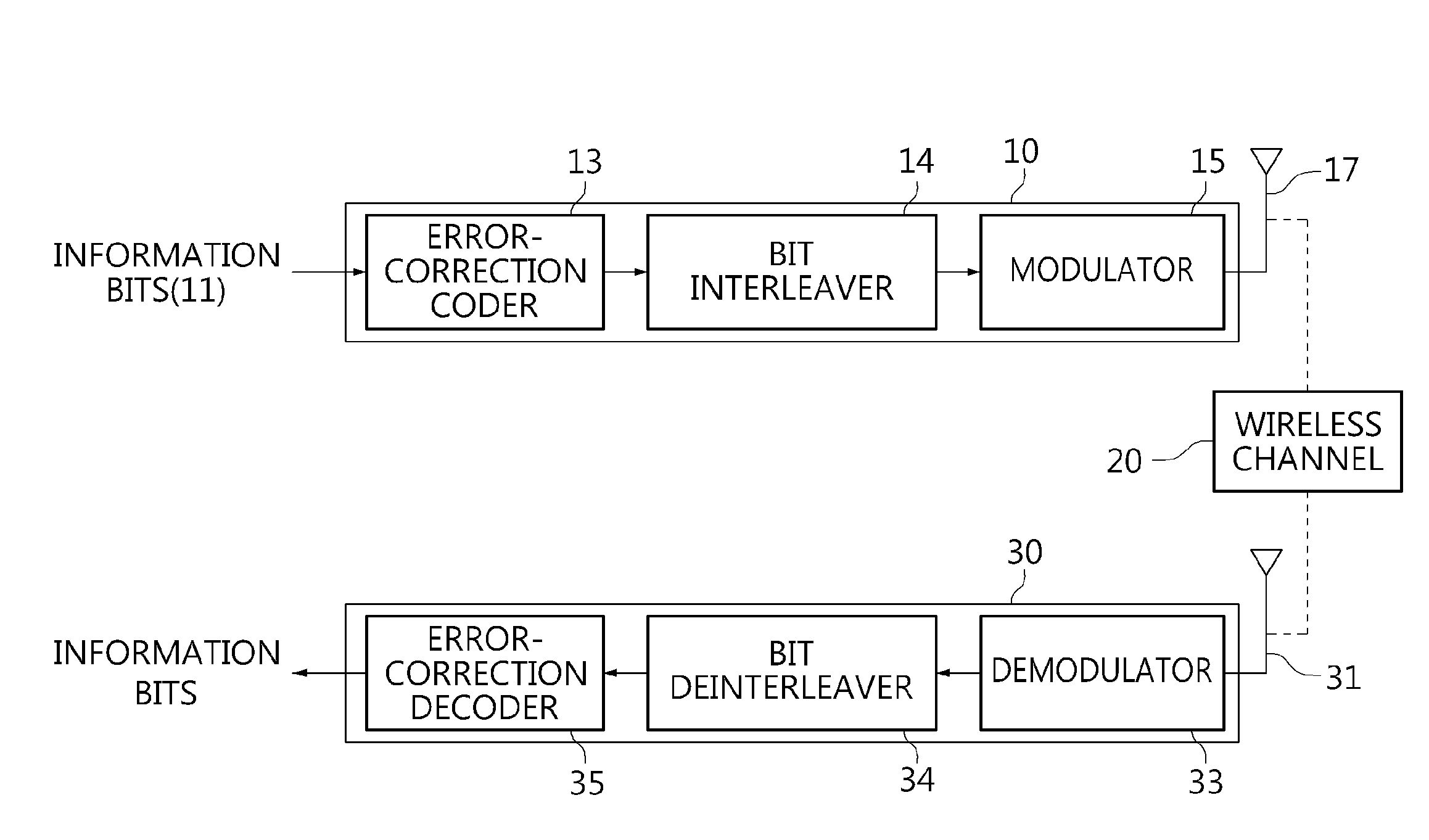
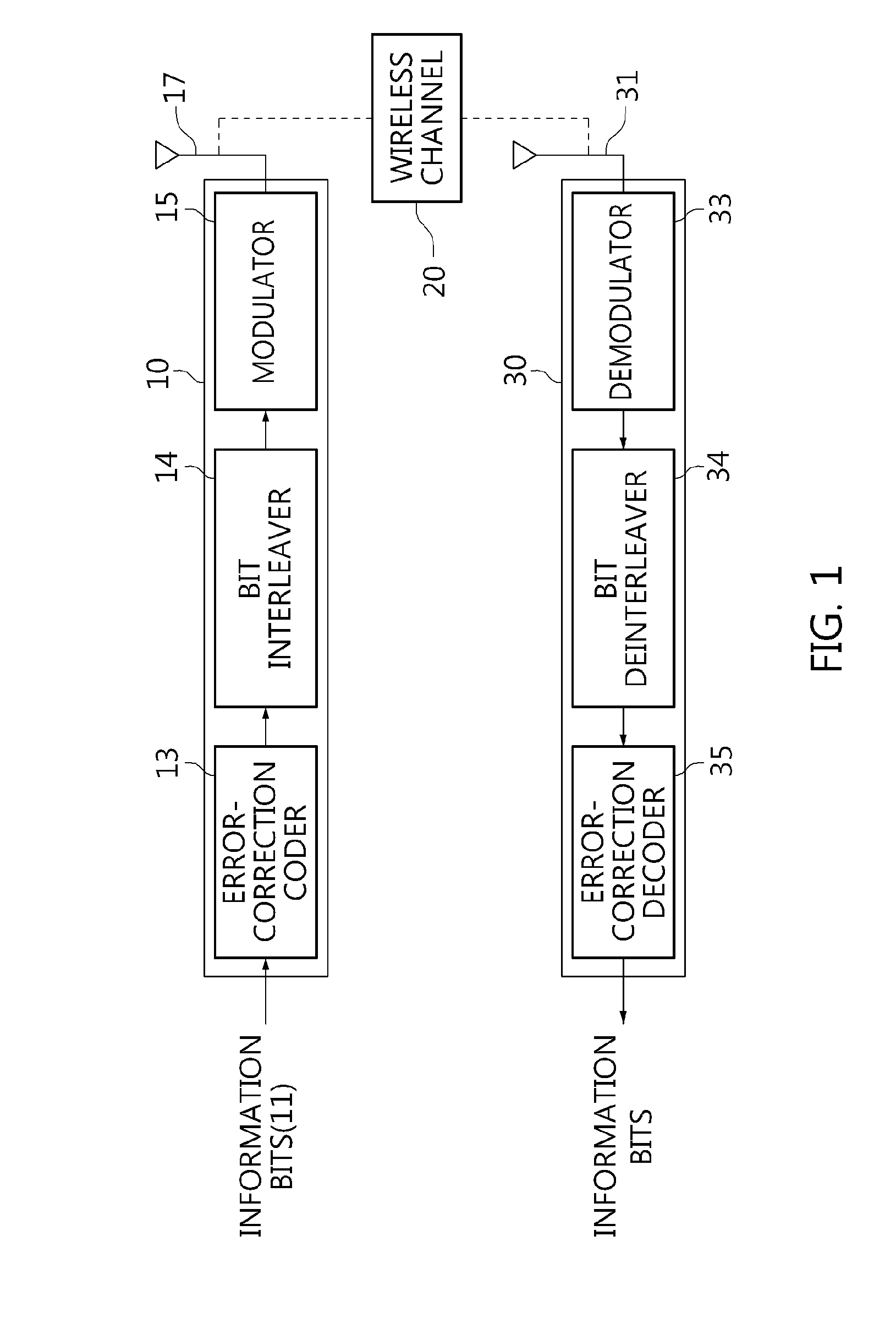
Interleaving method and deinterleaving method
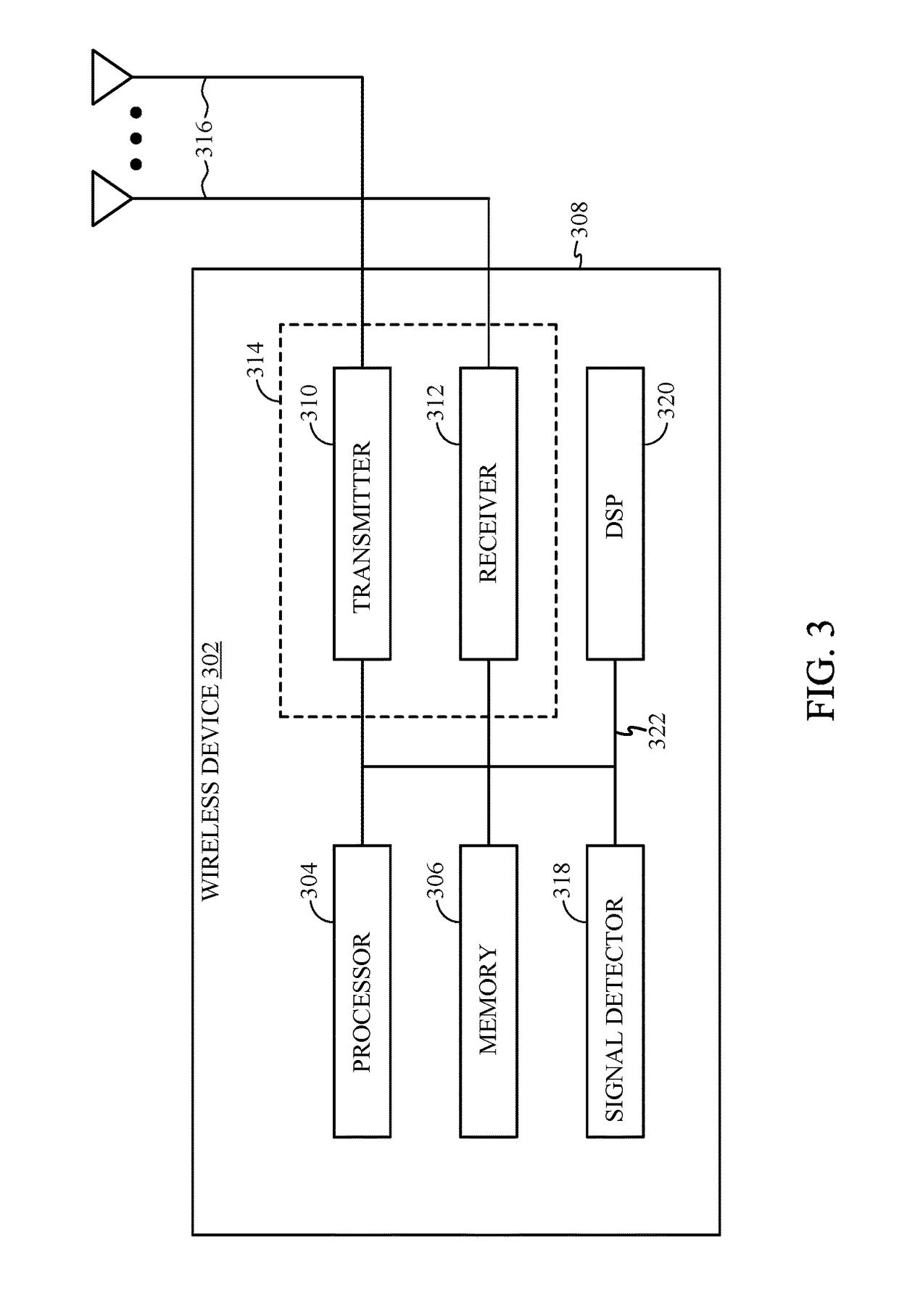
ActiveUS20130216001A1Improve reception performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesChecking code calculationsCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An interleaving method performed by a transmitter for a communication system with quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes, spatial multiplexing, and T transmit antennas is used for applying permutation to N cyclic blocks of a codeword in order to map bits of the permutated cyclic blocks onto T constellation words constituting multiple spatial-multiplexing blocks from the codeword. Each cyclic block consists of Q bits.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
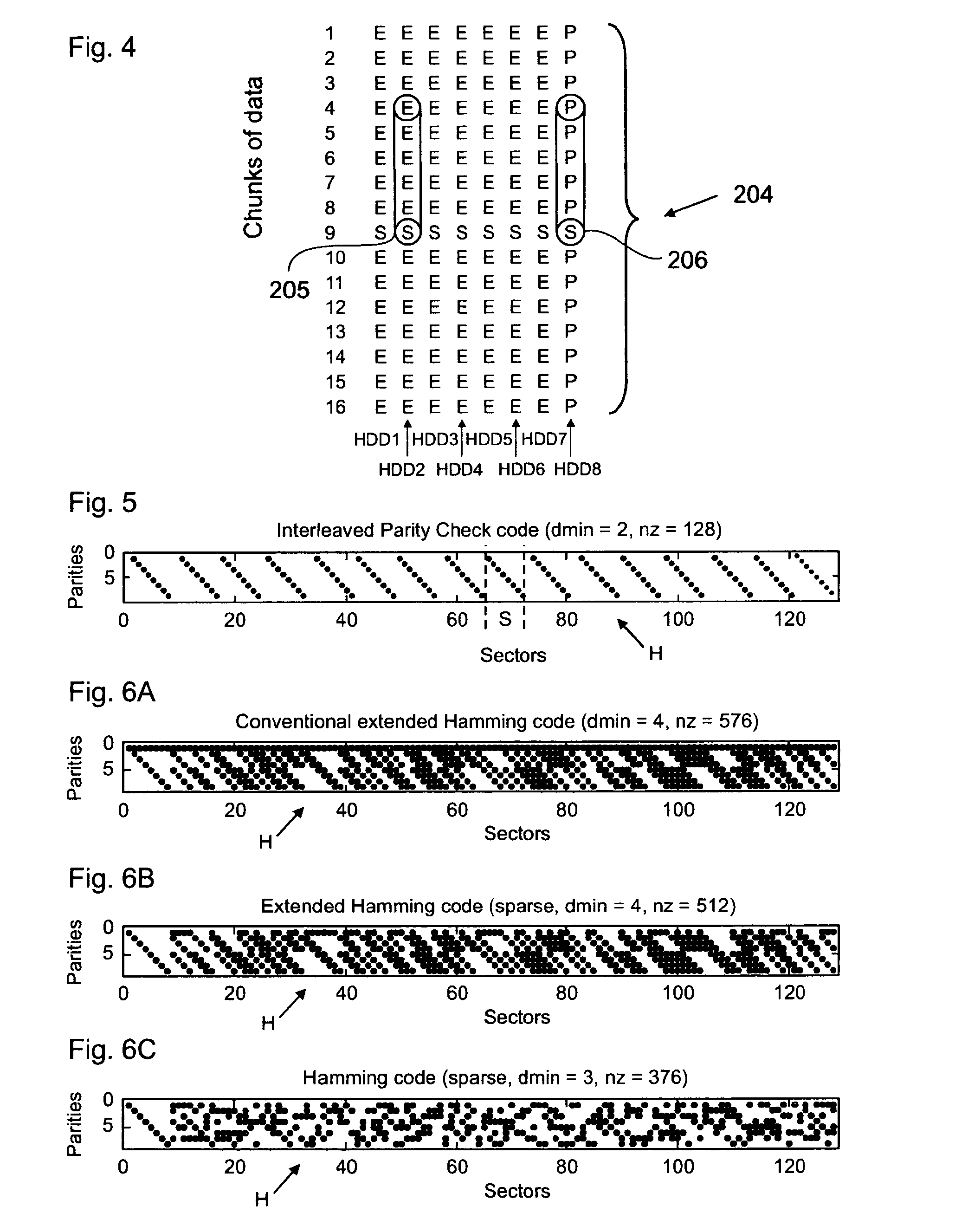
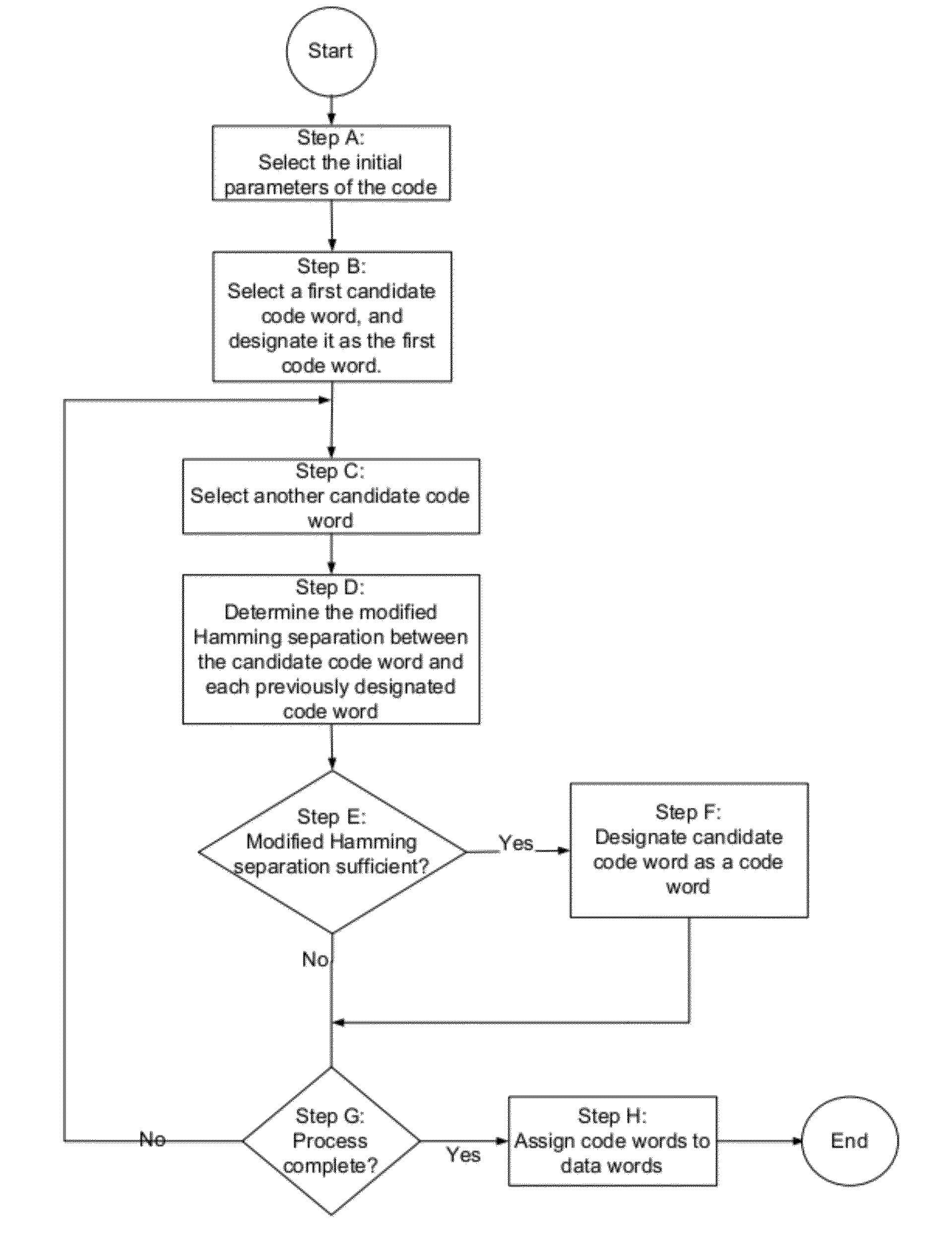
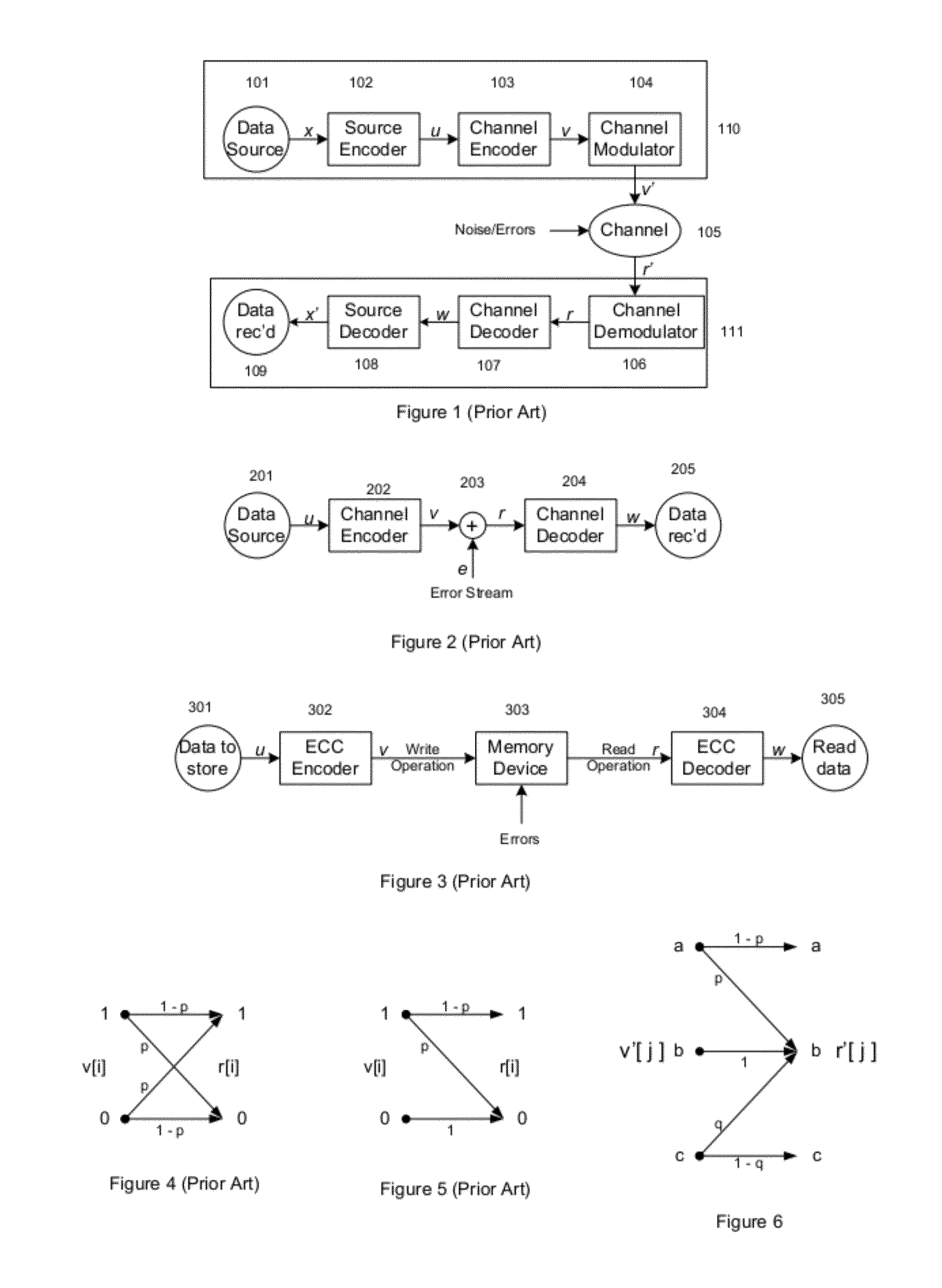
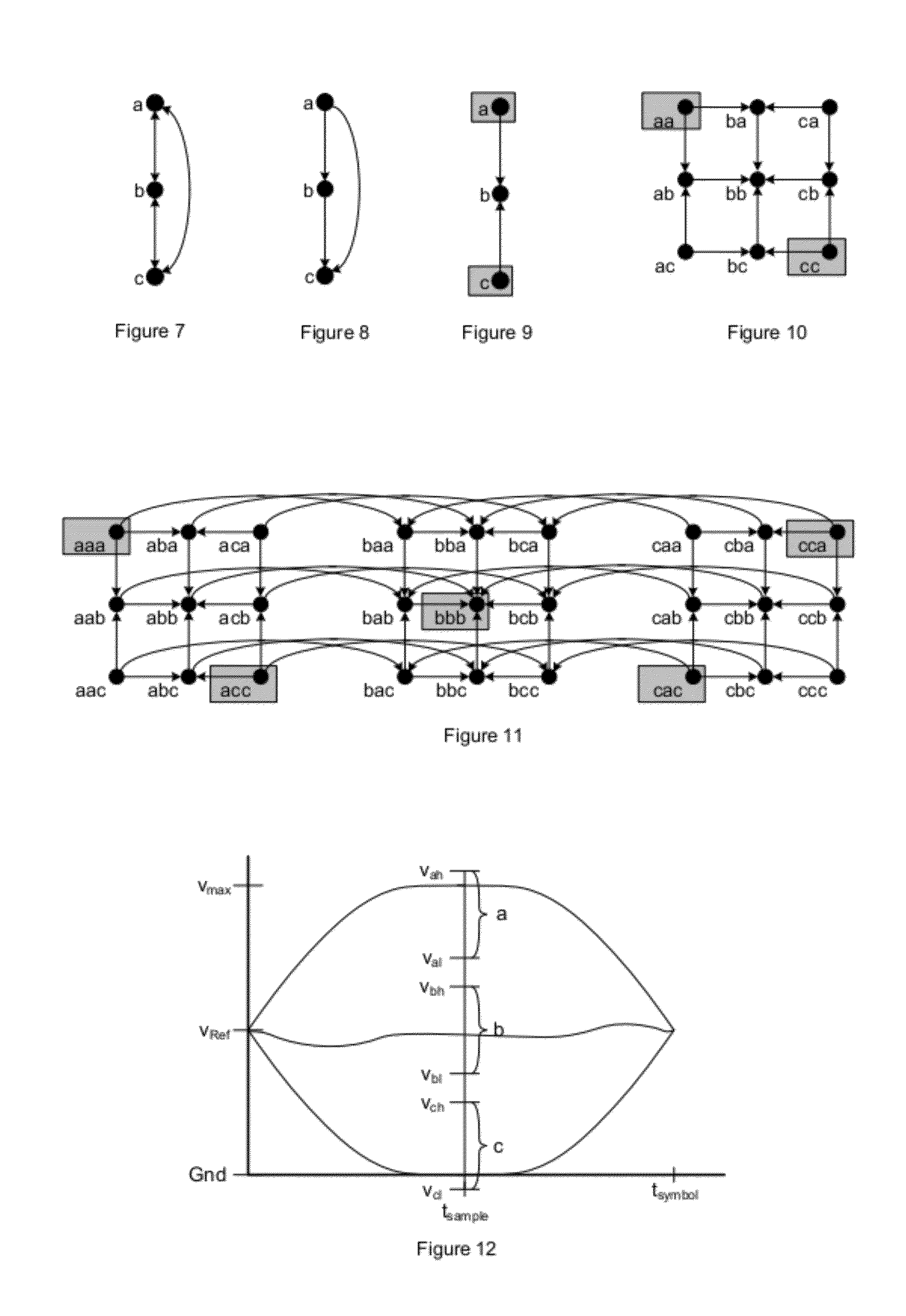
Error detection and correction codes for channels and memories with incomplete error characteristics
InactiveUS8429495B2Efficient error-correcting codeOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionParallel computingErrors and residuals
A channel has a first and a second end. The first end of the channel is coupled to a transmitter. The channel is capable of transmitting symbols selected from a symbol set from the first end to the second end. The channel exhibits incomplete error introduction properties. A code comprises a set of code words. The elements of the set of code words are one or more code symbols long. The code symbols are members of the symbol set. The minimum modified Hamming separation between the elements of the set of code words in light of the error introduction properties of the channel is greater than the minimum Hamming distance between the elements of the set of code words. A memory device, a method of using the channel, and a method of generating the code are also described.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
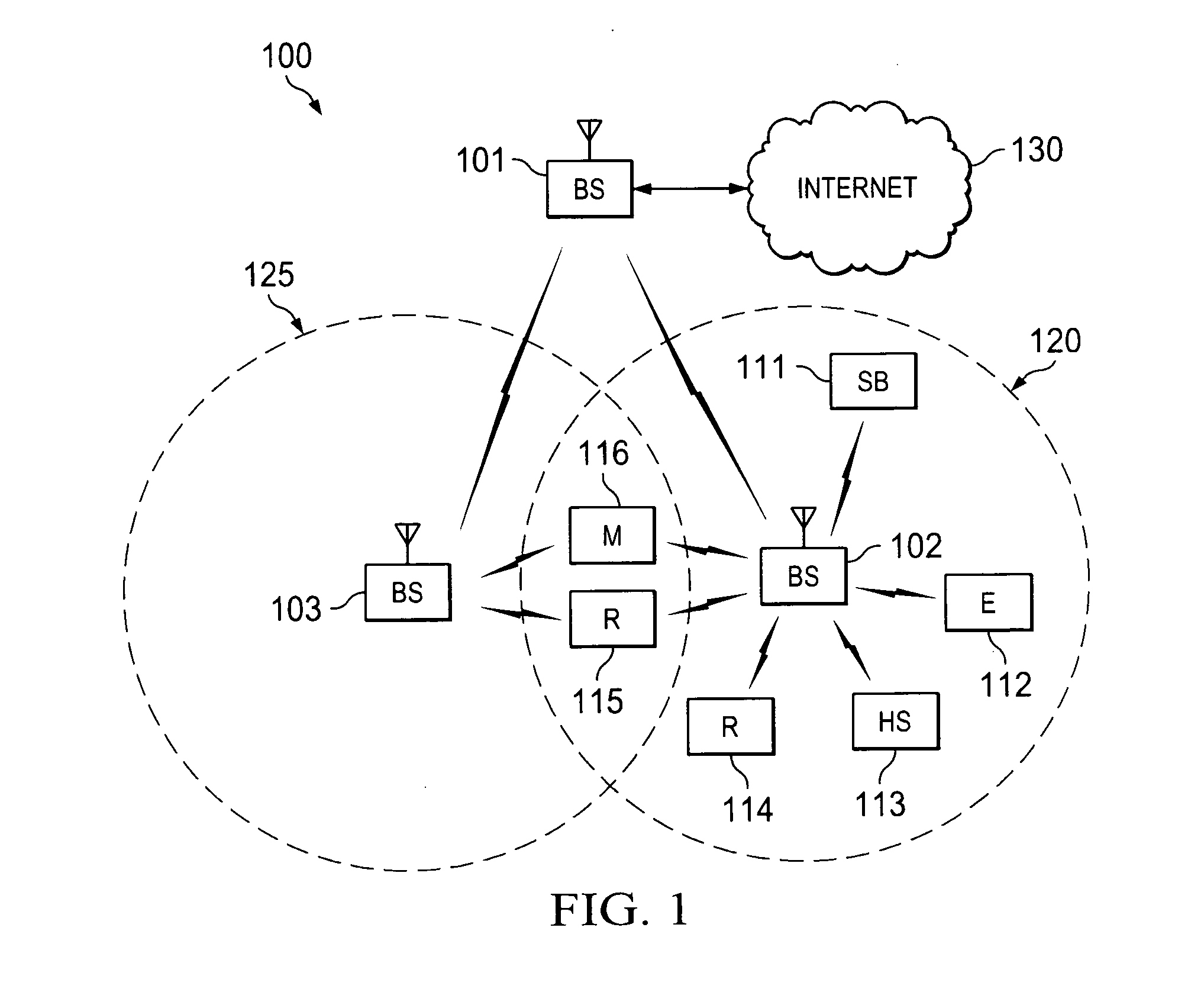
Apparatus, and associated method, for allocating communications in a multi-channel communication system
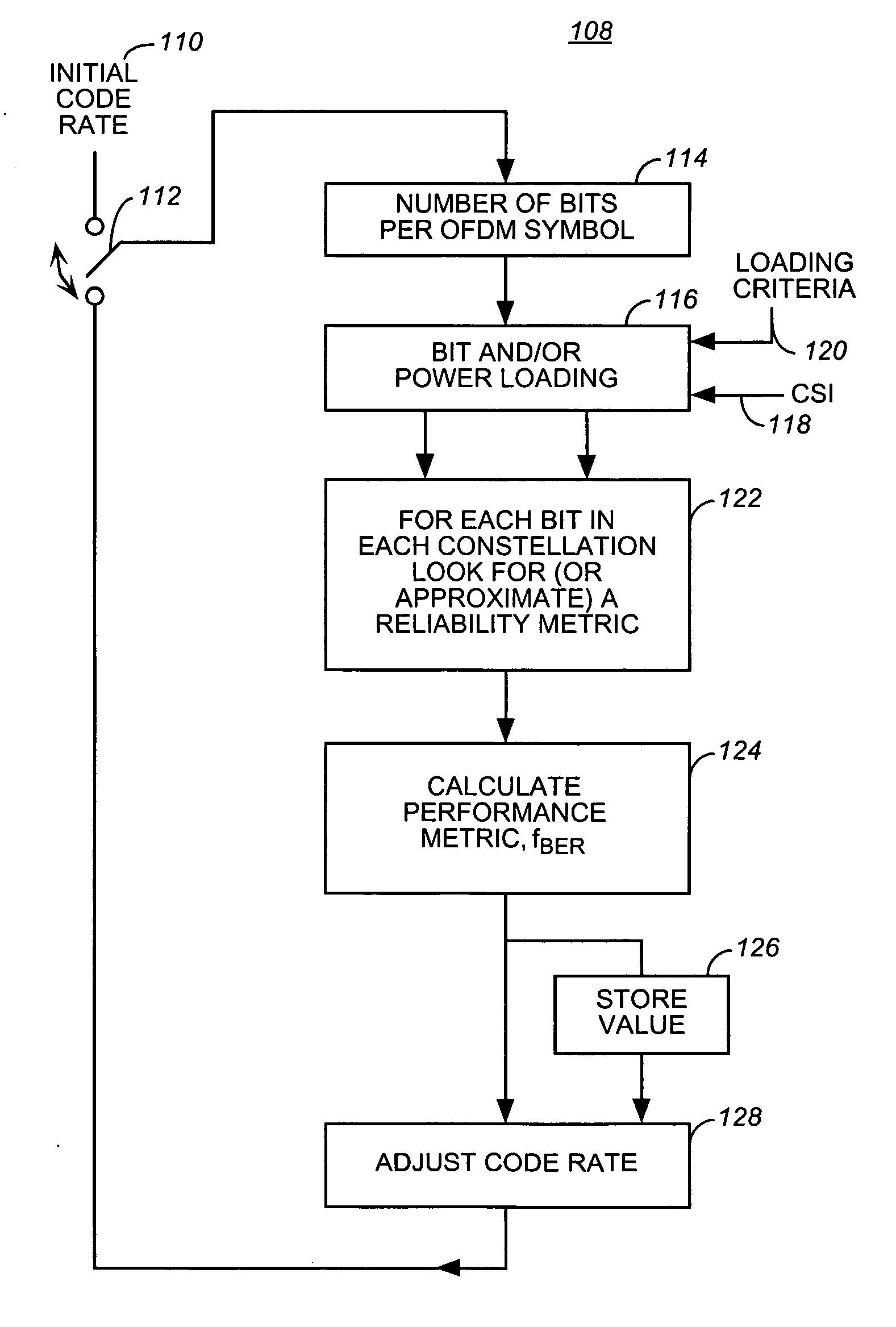
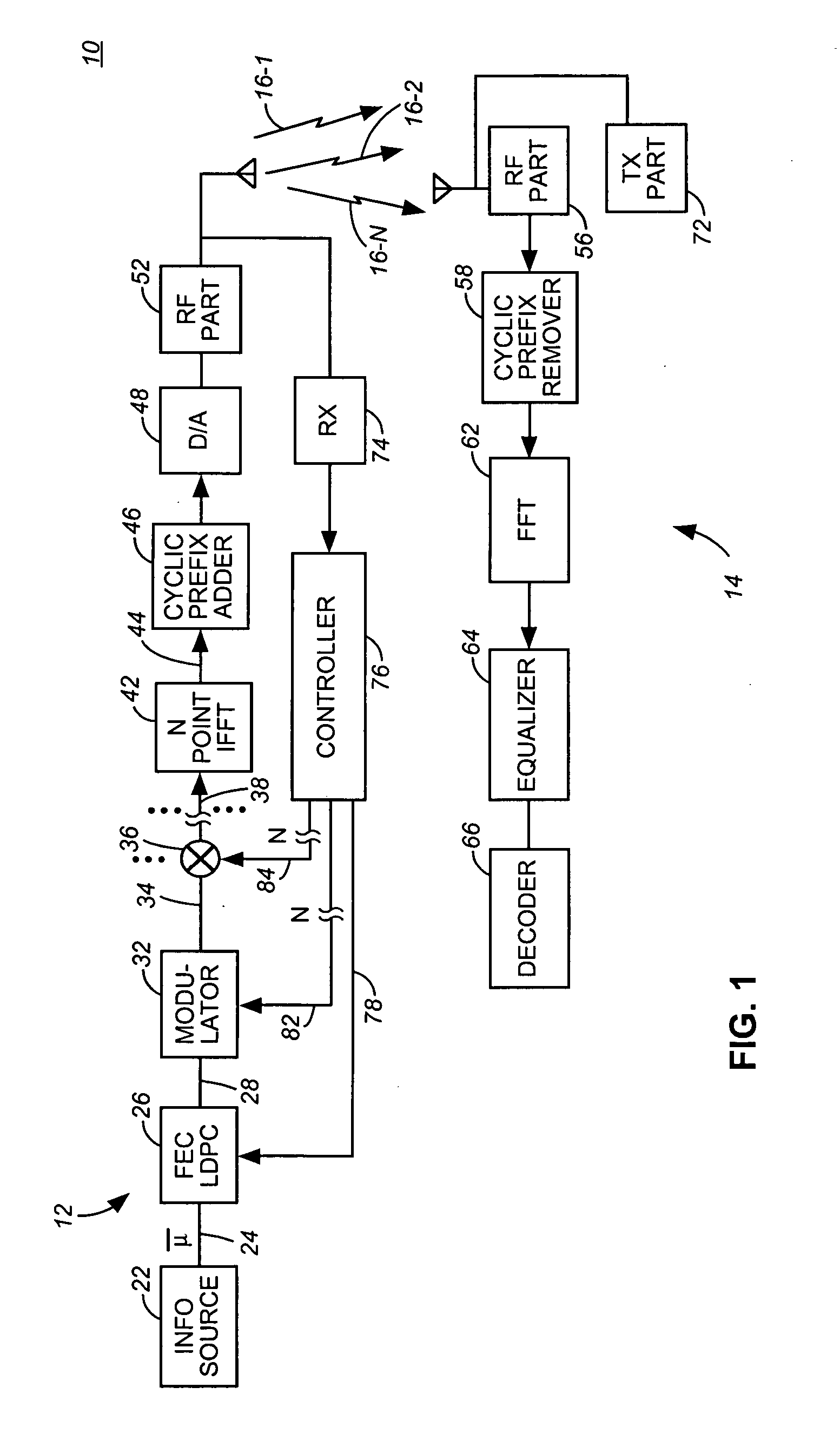
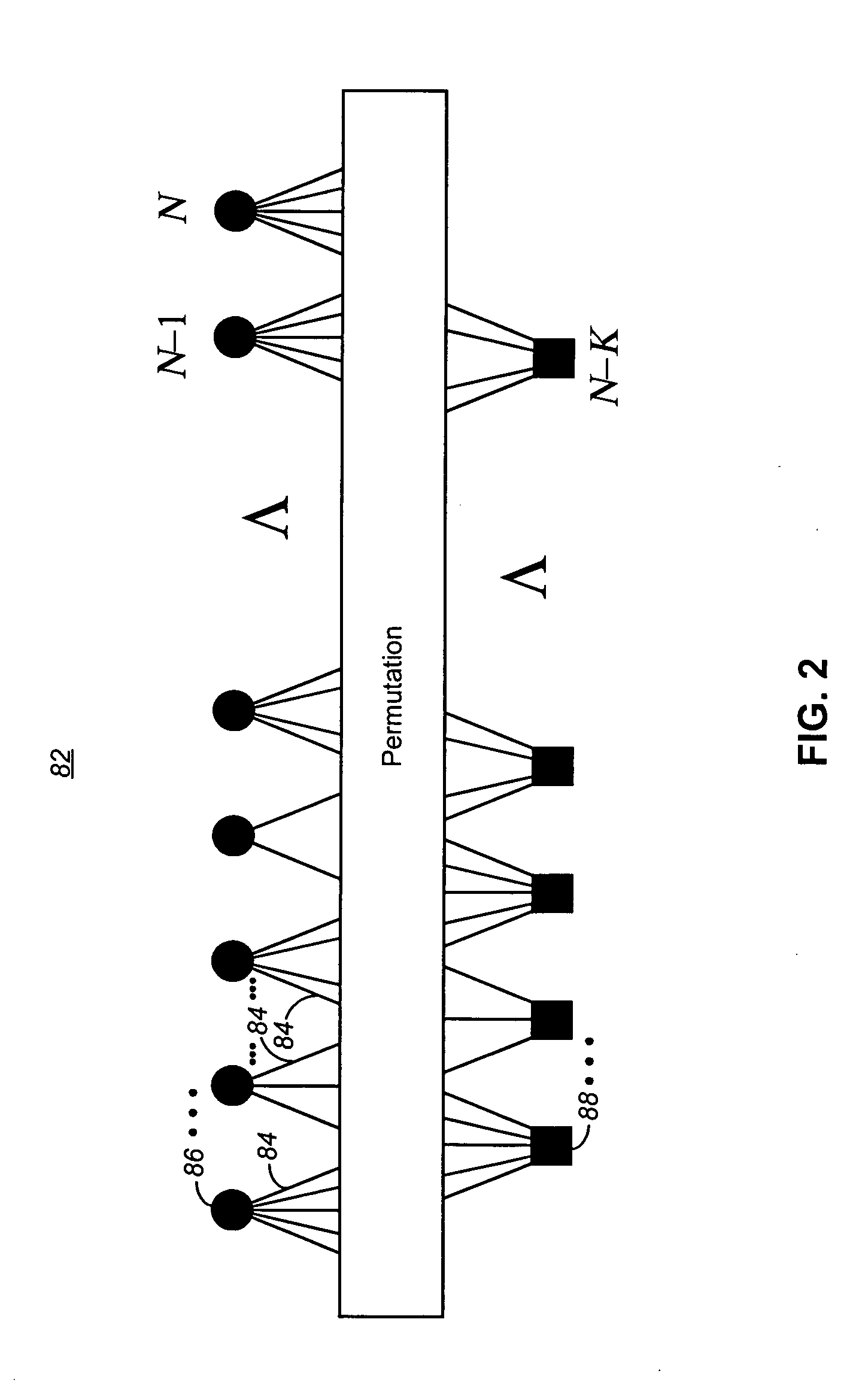
InactiveUS20060013181A1Transmission path divisionError correction/detection using LDPC codesCommunications systemSelf adaptive
Apparatus, and an associated method, for allocating communication data for communication in a multi-channel communication system, such as an OFDM system. An adaptive bit, power, and code rate scheme for a sending station that utilizes LDPC codes selects together bit, power, and code rates of data that are to be communicated upon different ones of the channels in manners that optimize a selected performance criteria.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
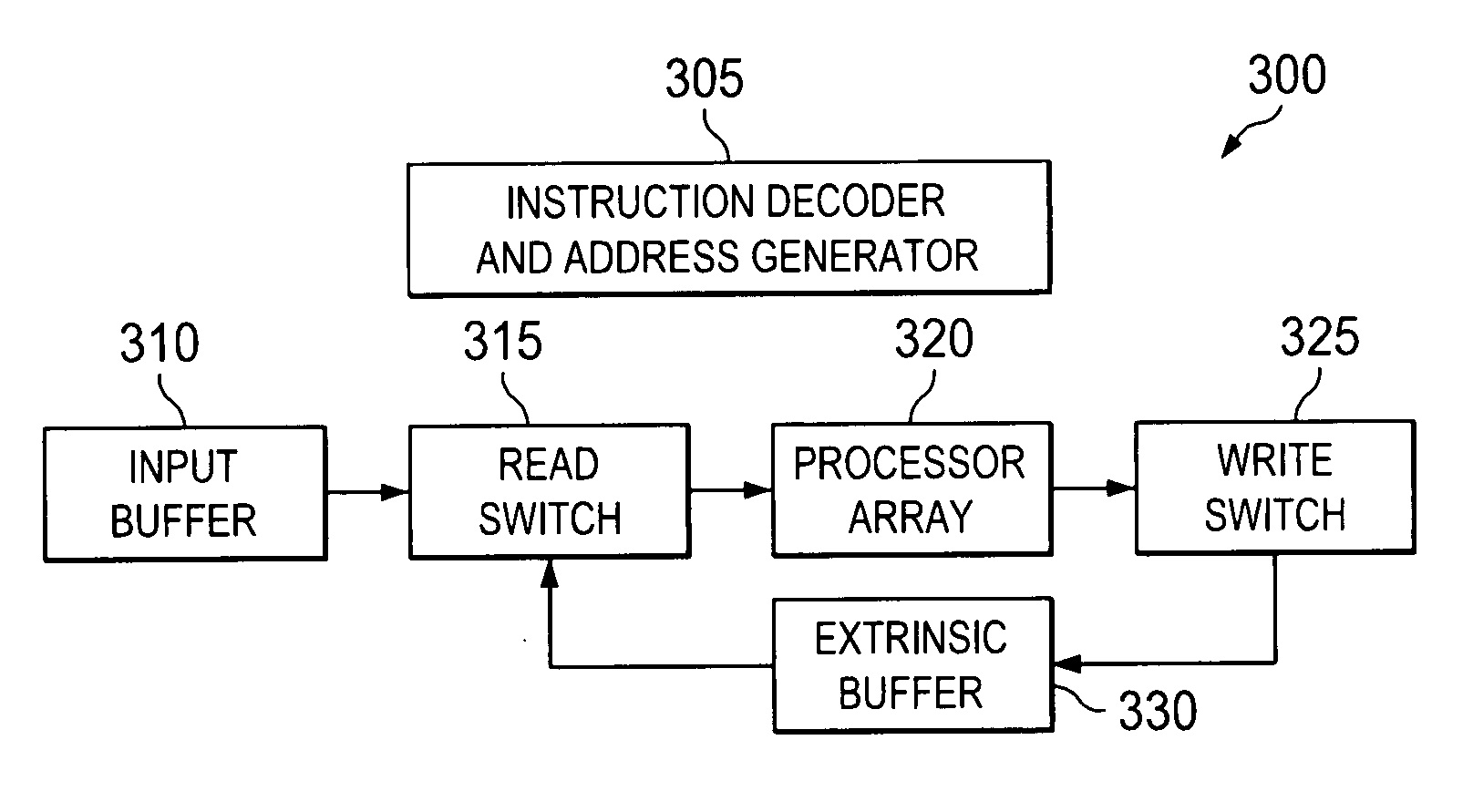
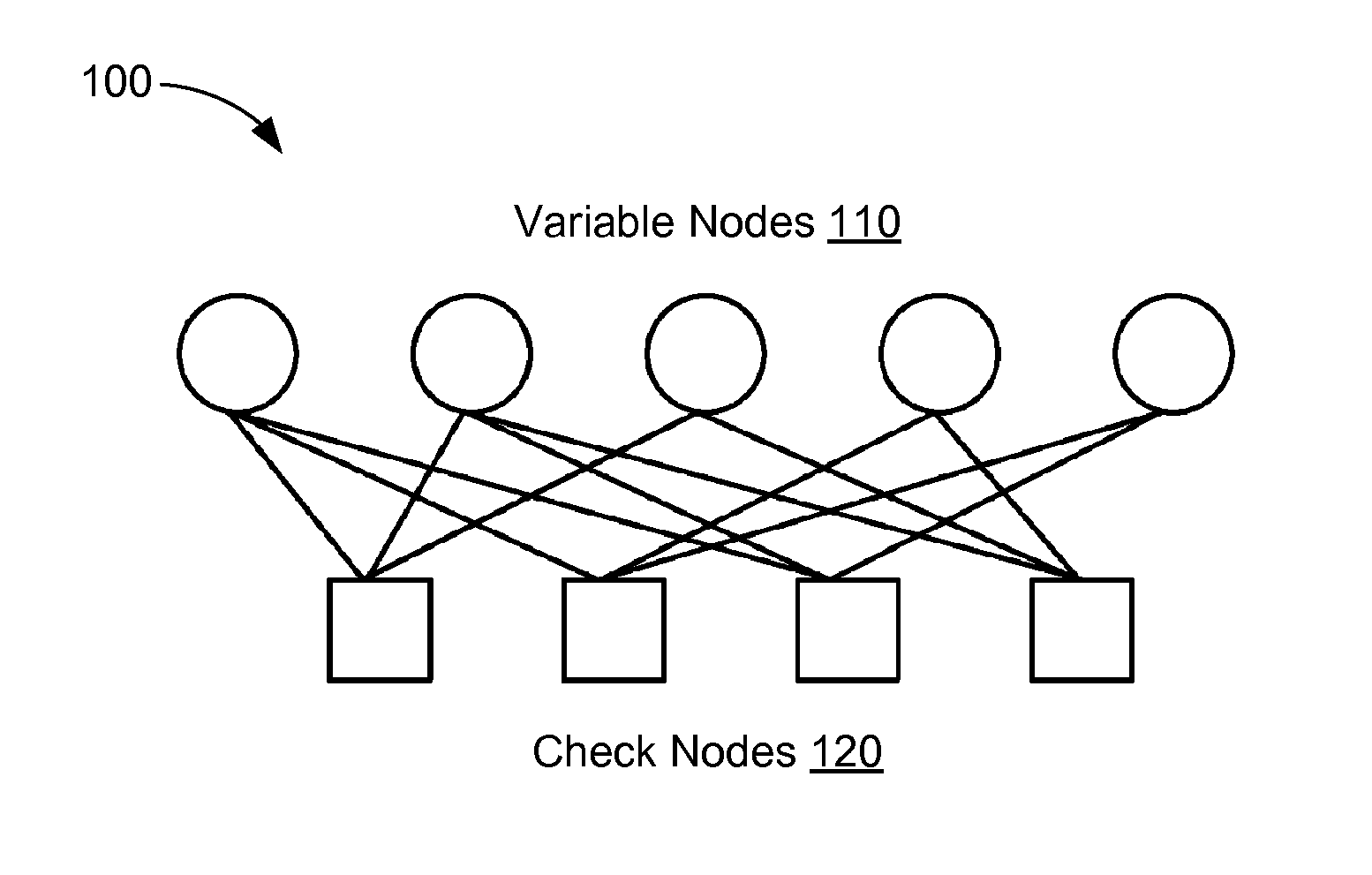
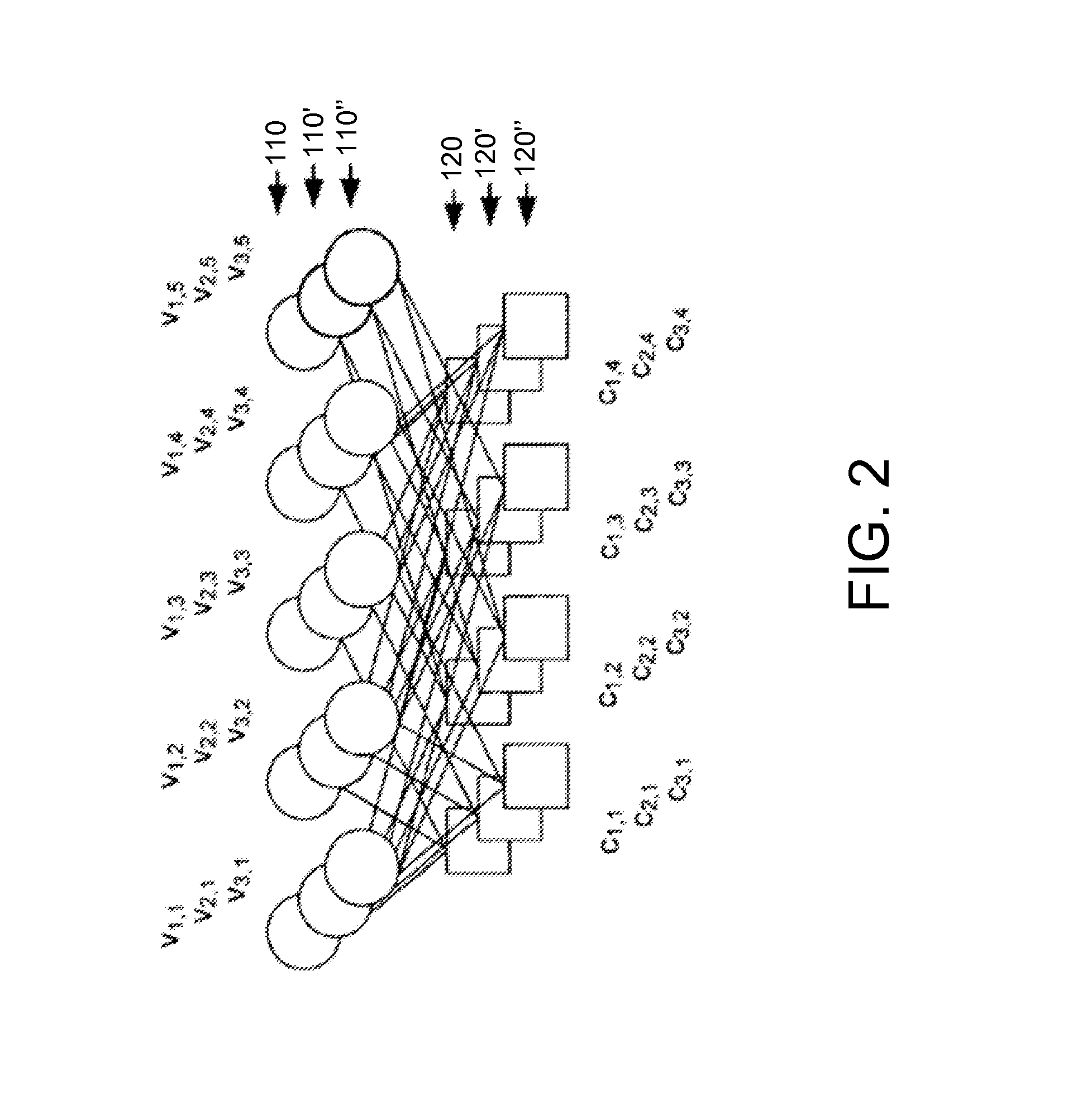
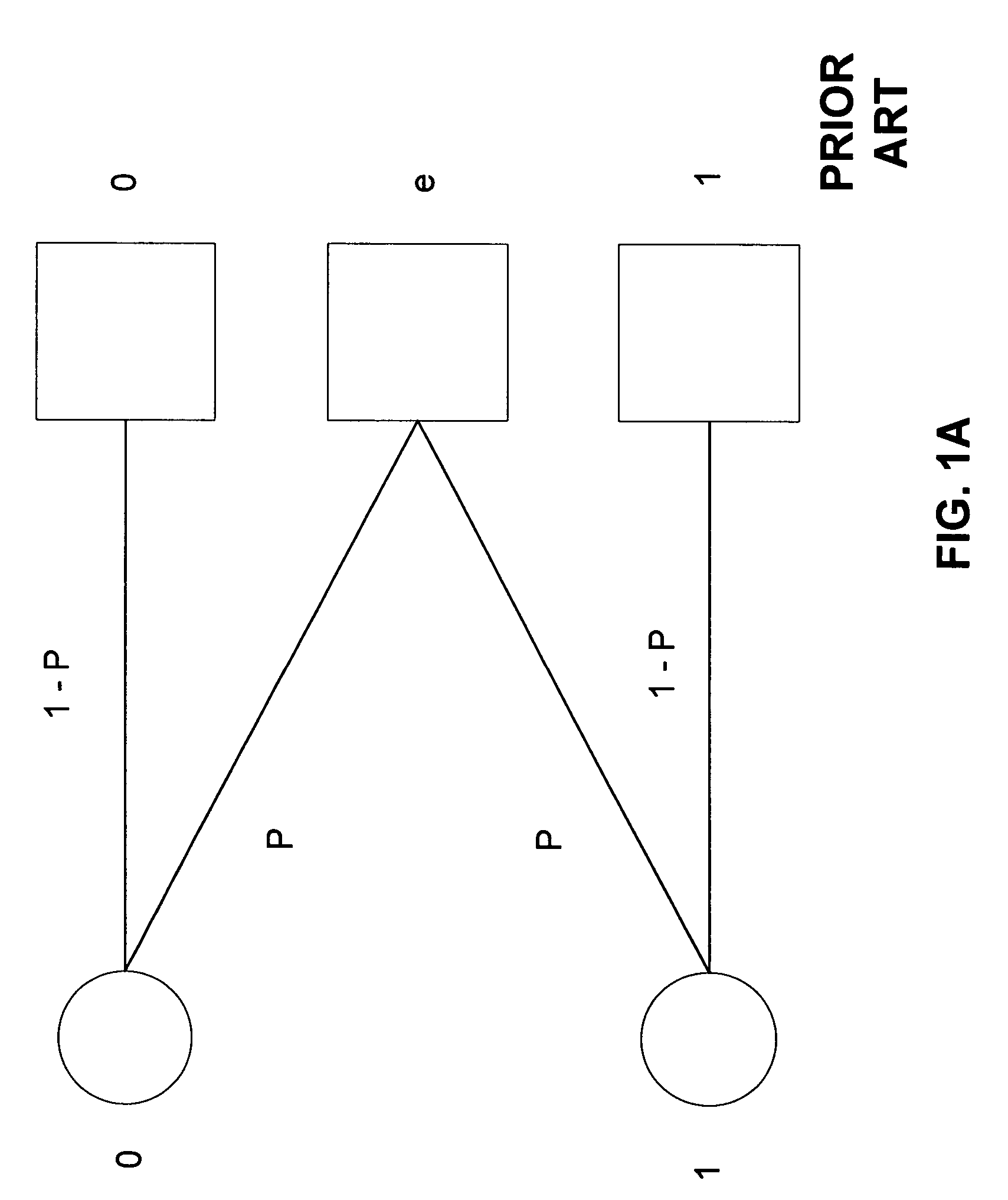
[01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement
ActiveUS20150303949A1Minimal costMinimize the numberError detection/correctionCode conversionNode countDistributed database
An apparatus or method for minimizing the total accessing cost, such as minimizing repair bandwidth, delay or the number of hops including the steps of minimizing the number of nodes to be engaged for the recovery process using a polynomial-time solution that determines the optimal number of participating nodes and the optimal set of nodes to be engaged for recovering lost data, where in a distributed database storage system, for example a dynamic system, where the accessing cost or even the number of available nodes are subject to change results in different values for the optimal number of participating nodes. An MDS code is included which can be reused when the number of participating nodes varies without having to change the entire code structure and the content of the nodes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
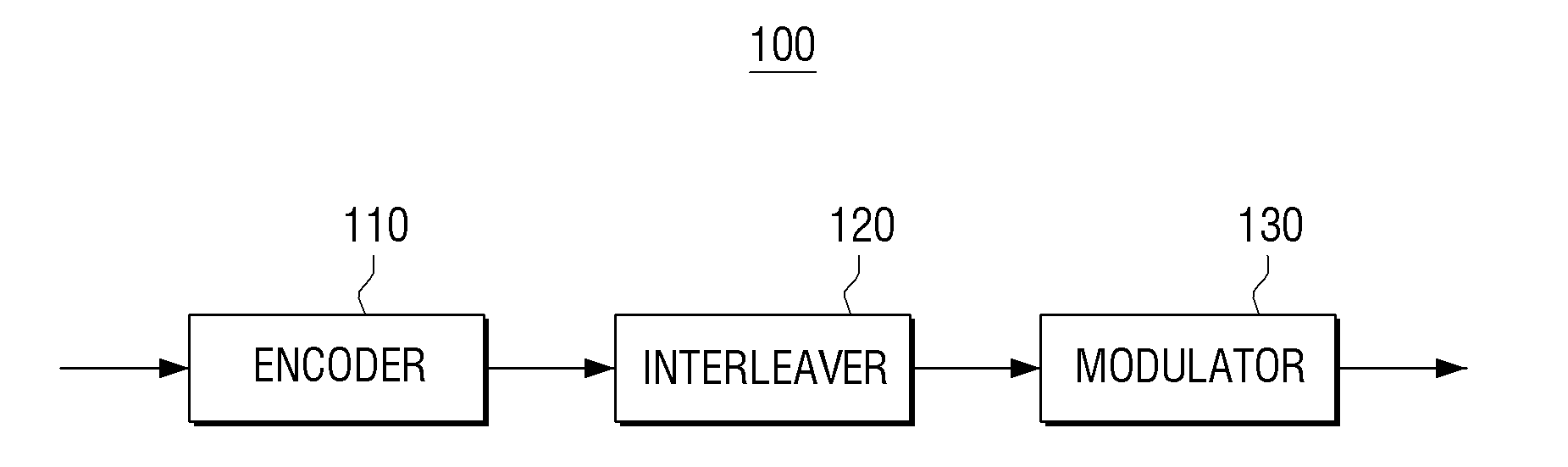
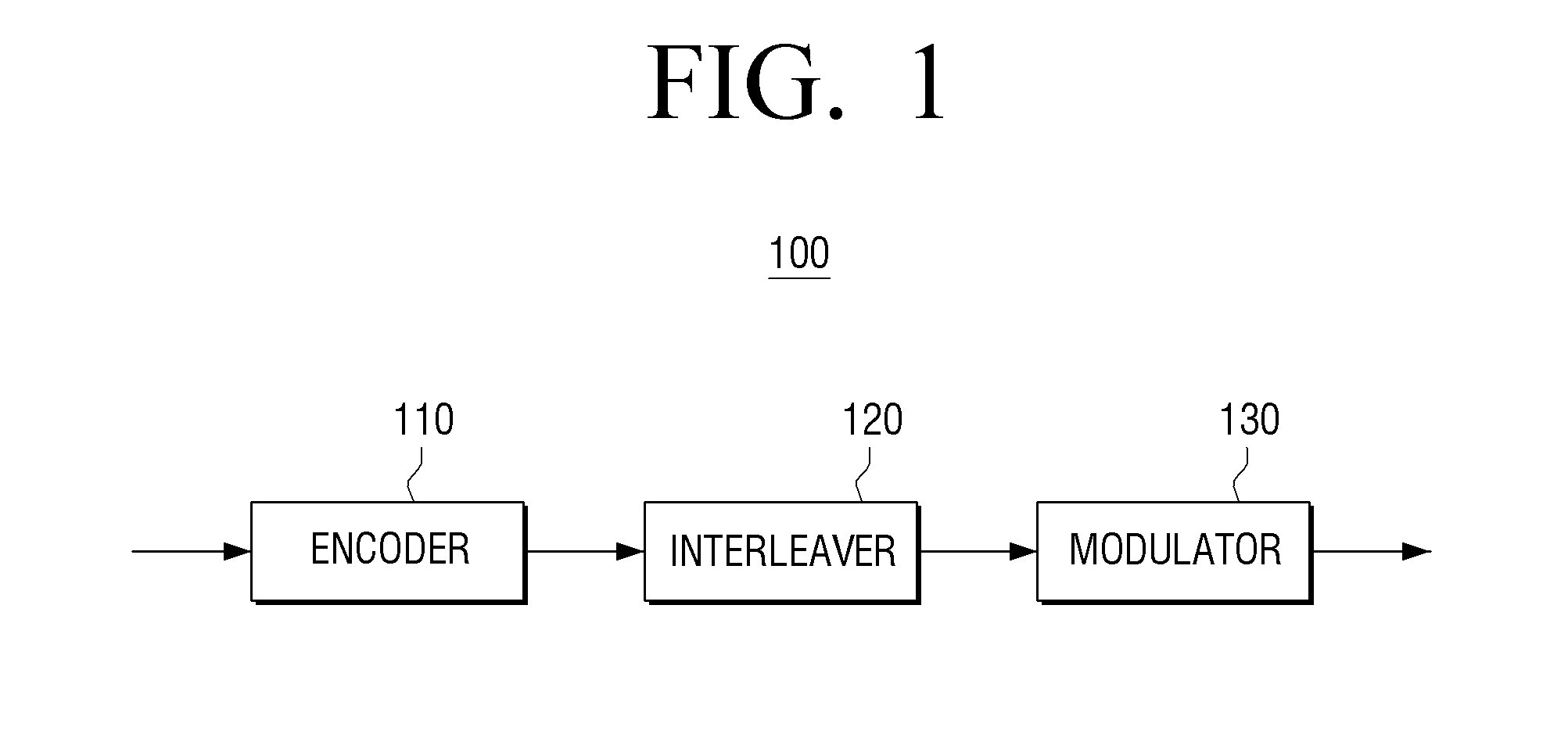
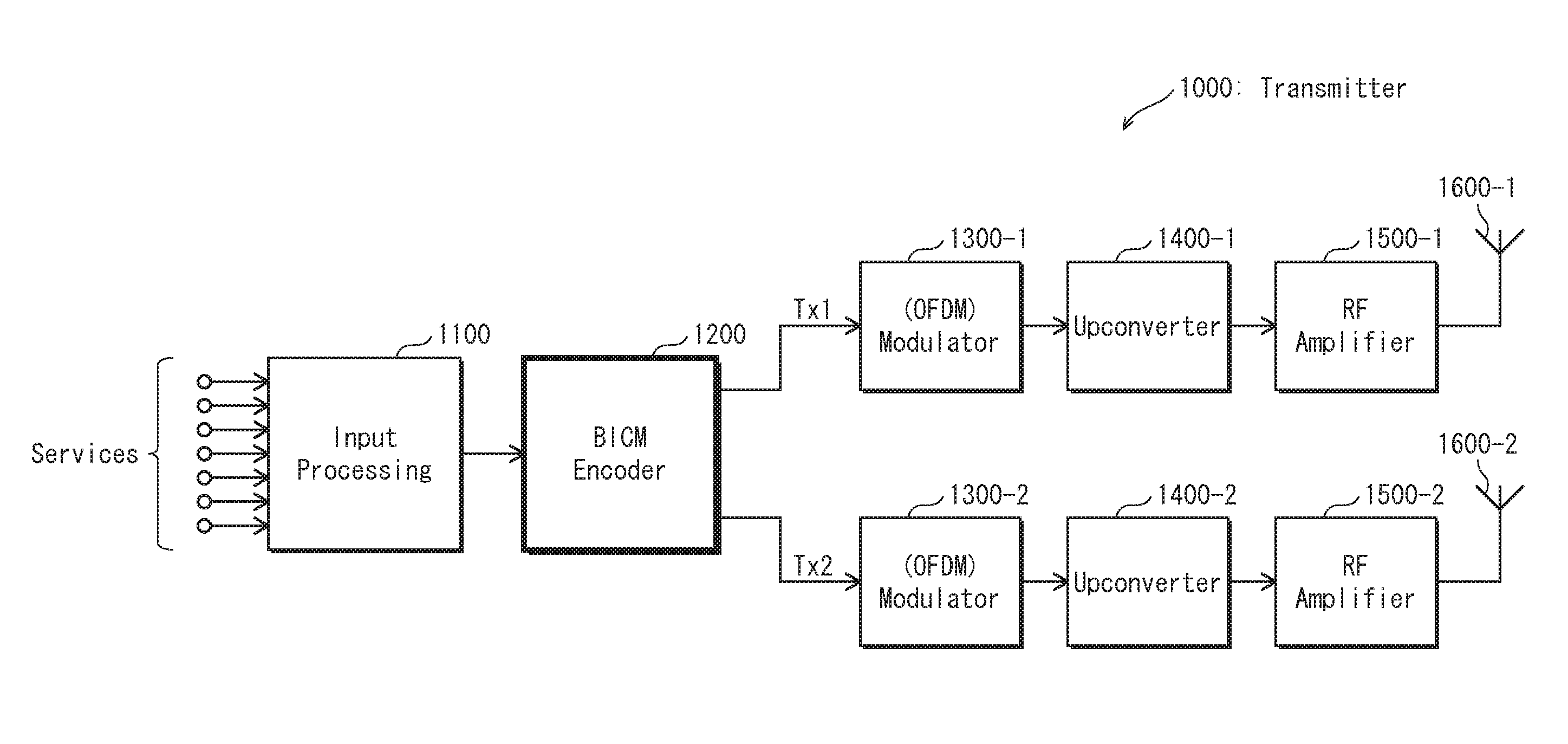
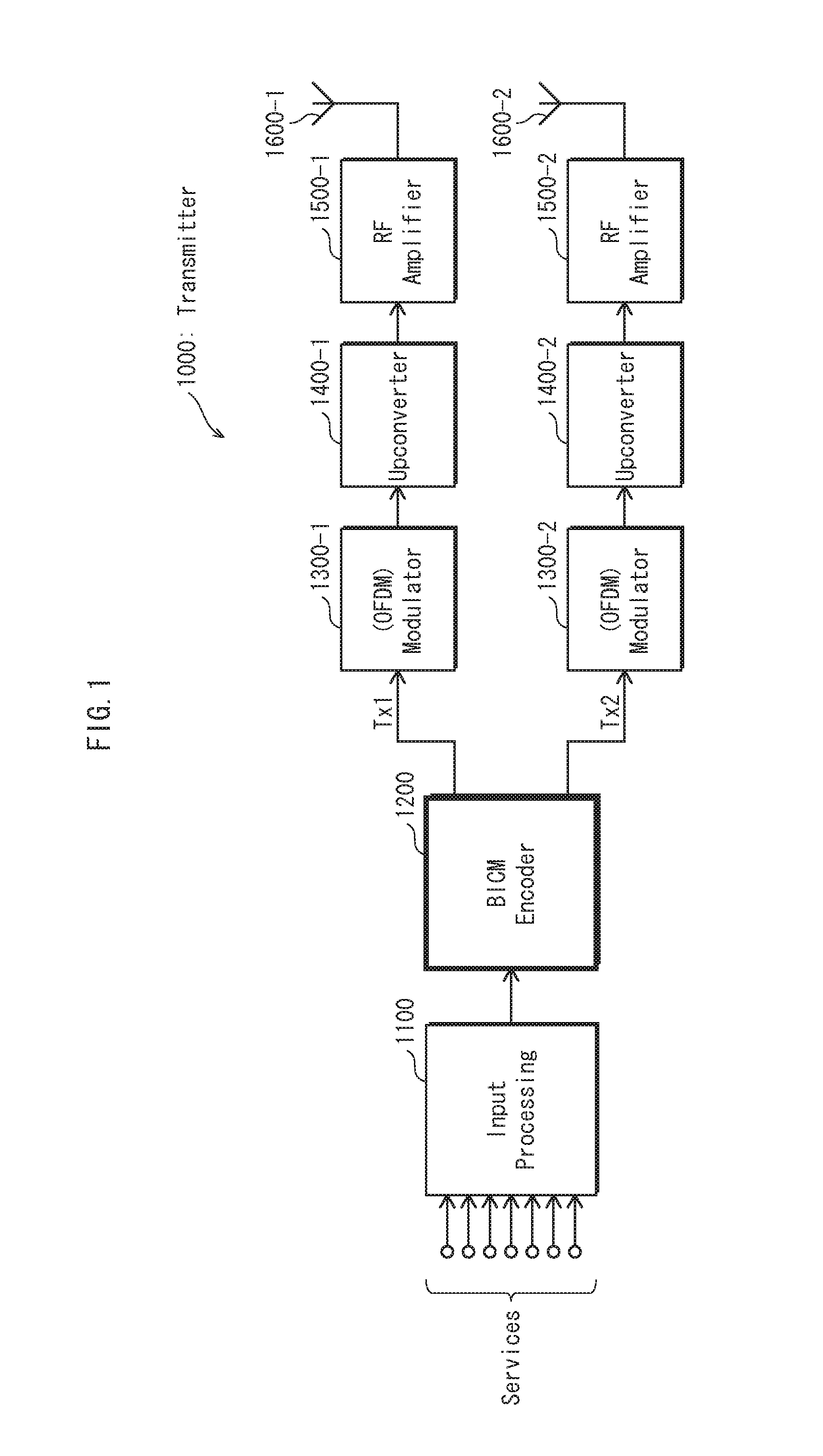
Transmitting apparatus and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20150128005A1Overcome disadvantagesError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeLow density
A transmitting apparatus and a receiving apparatus are provided. The transmitting apparatus includes an encoder configured to generate a low density parity check (LDPC) codeword by performing LDPC encoding, an interleaver configured to interleave the LDPC codeword, and a modulator configured to modulate the interleaved LDPC codeword according to a modulation method to generate a modulation symbol. The interleaver performs interleaving by dividing the LDPC codeword into a plurality of groups, rearranging an order of the plurality of groups in group units, and dividing the plurality of rearranged groups based on a modulation order according to the modulation method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
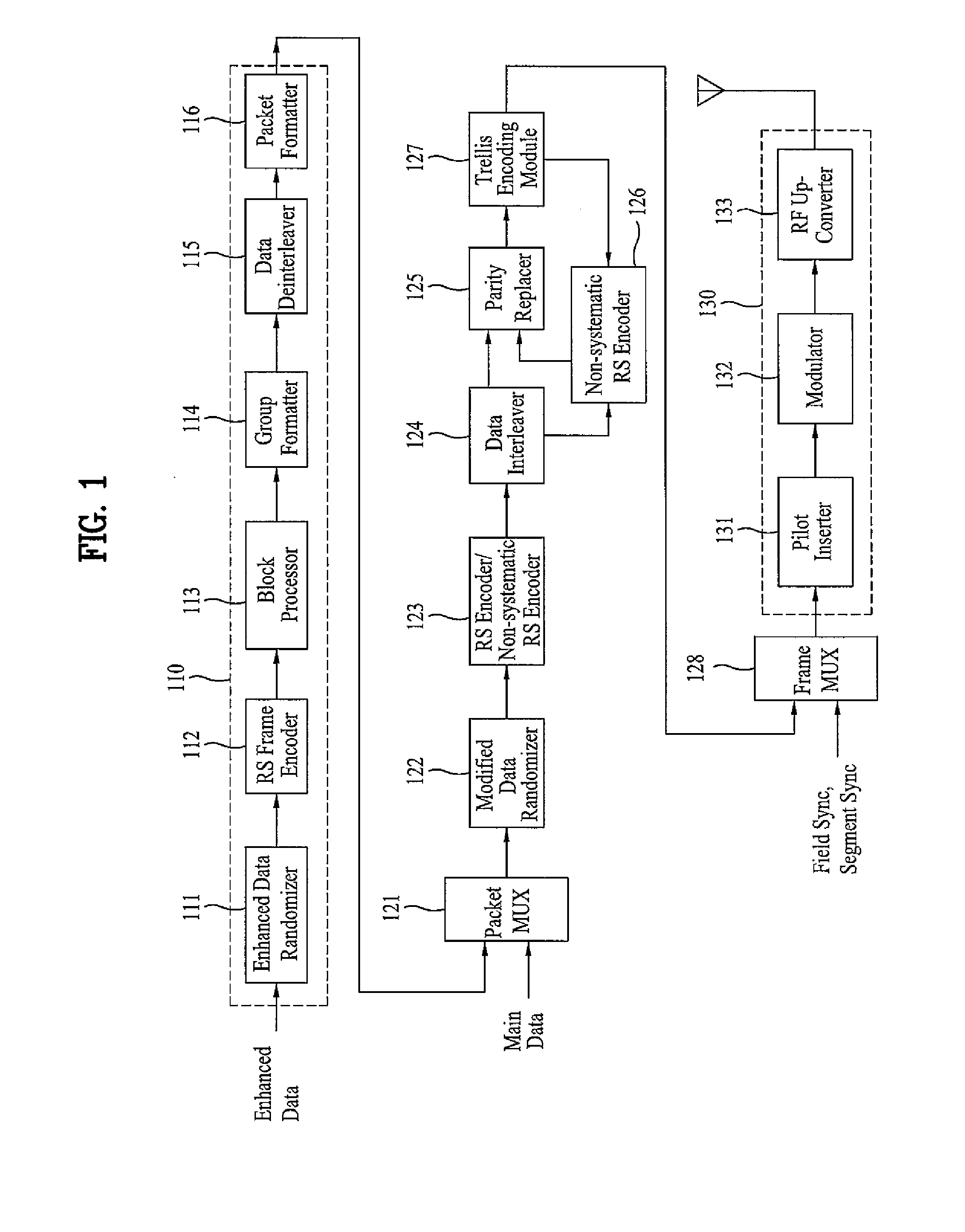
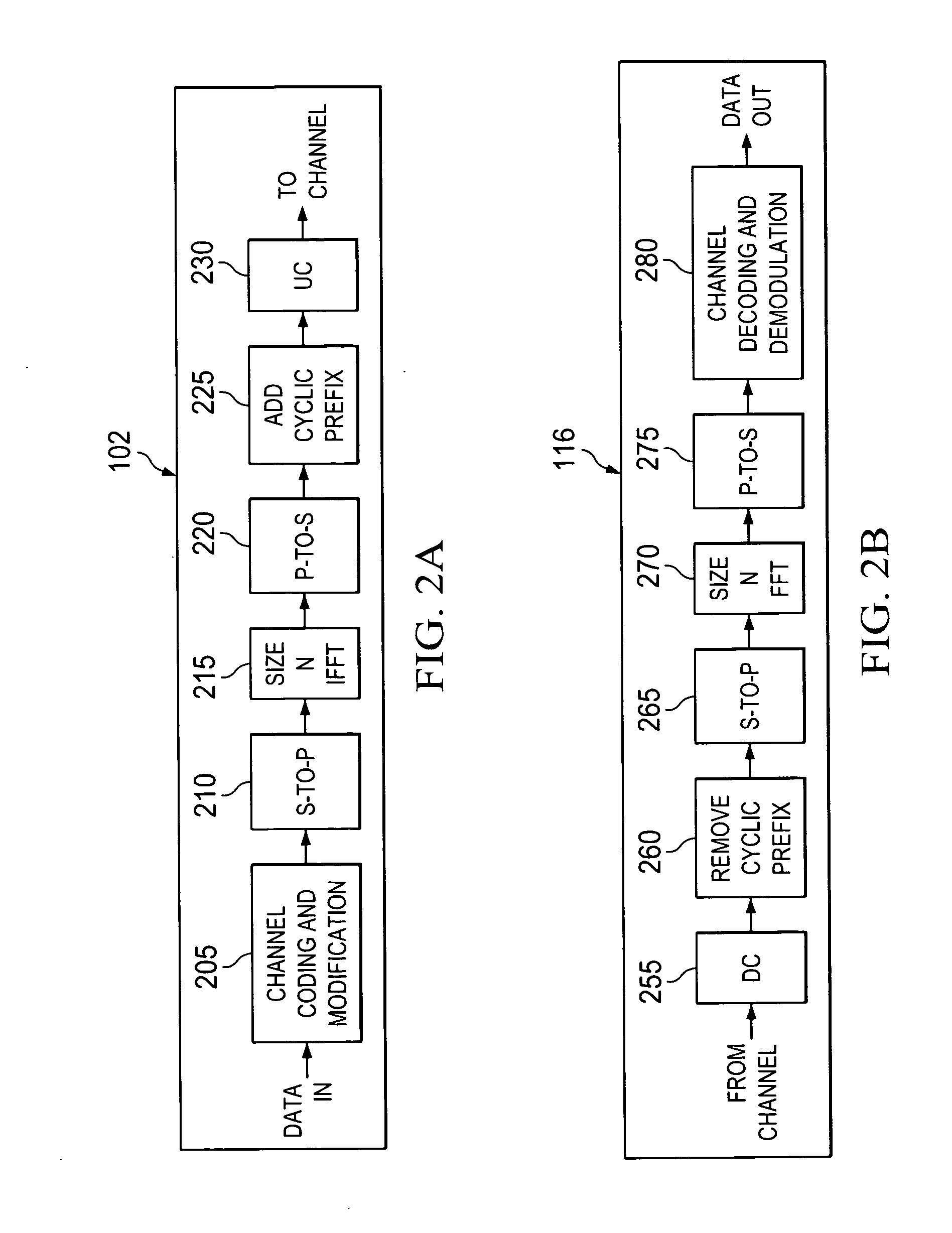
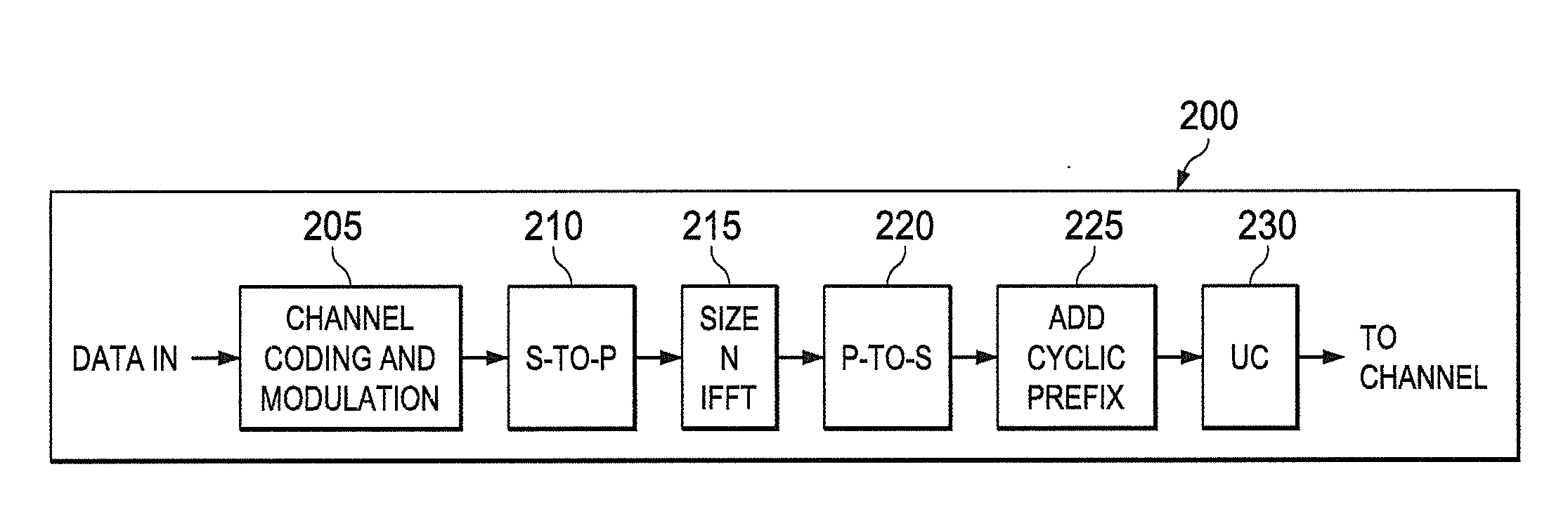
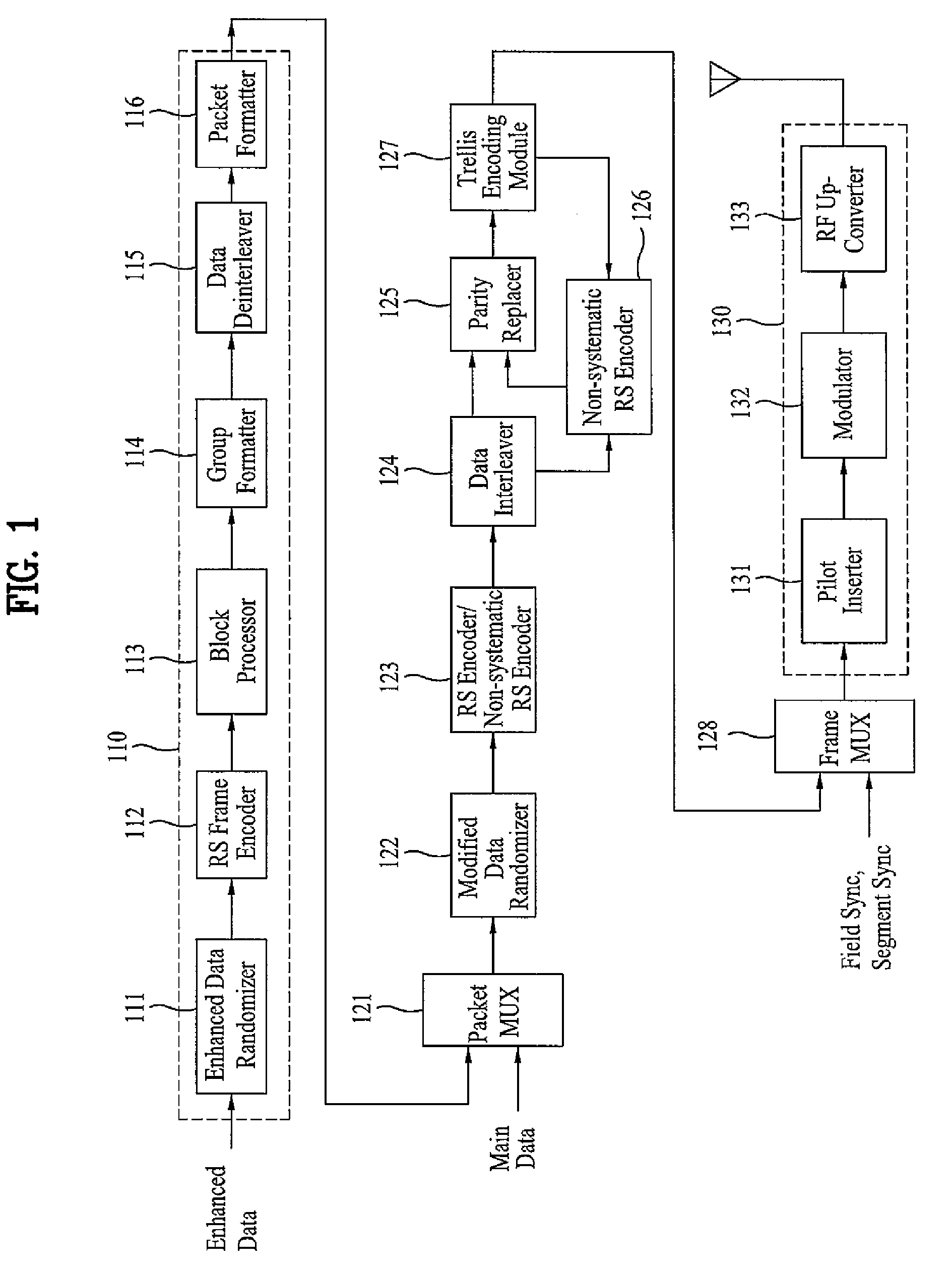
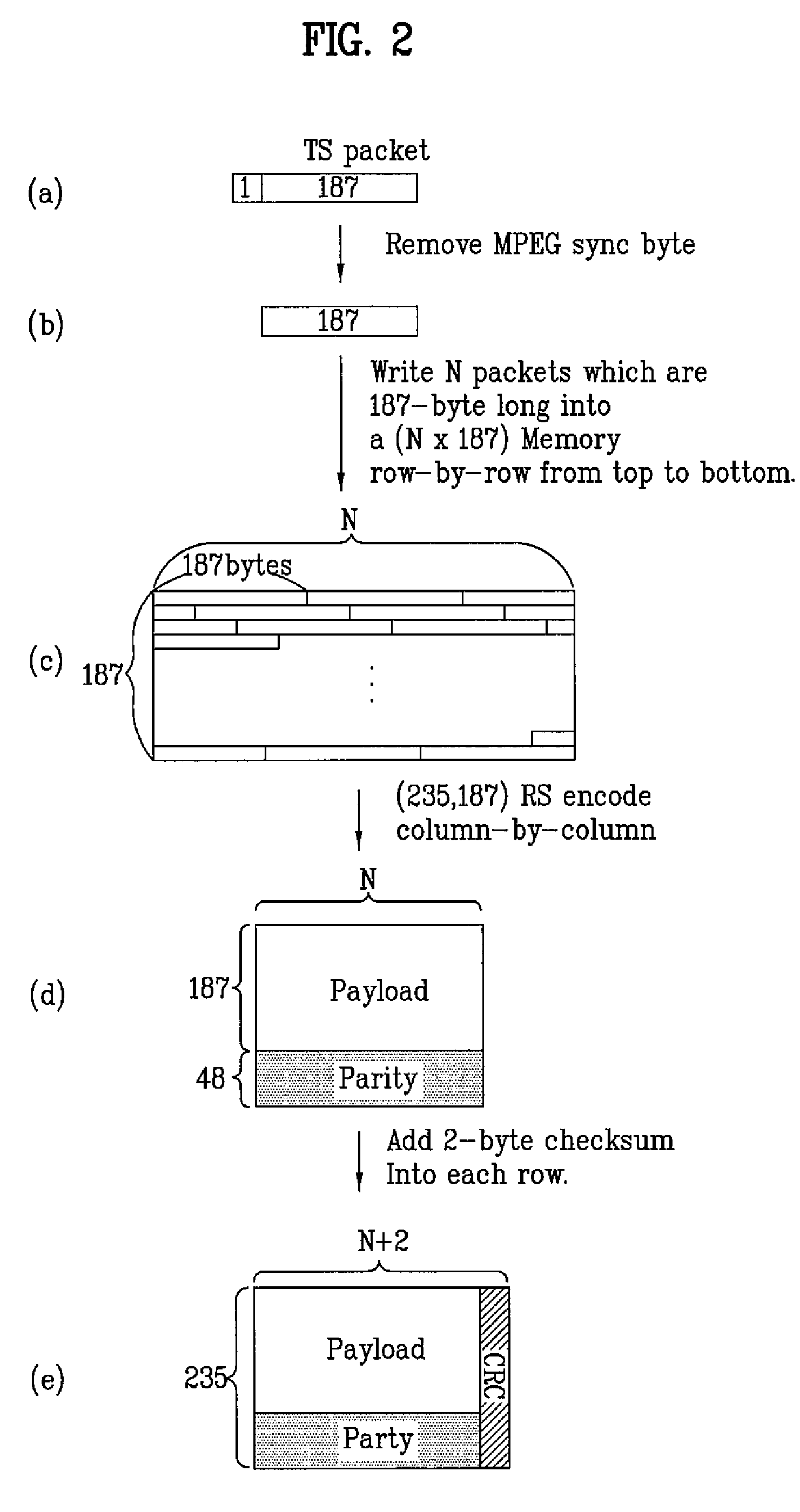
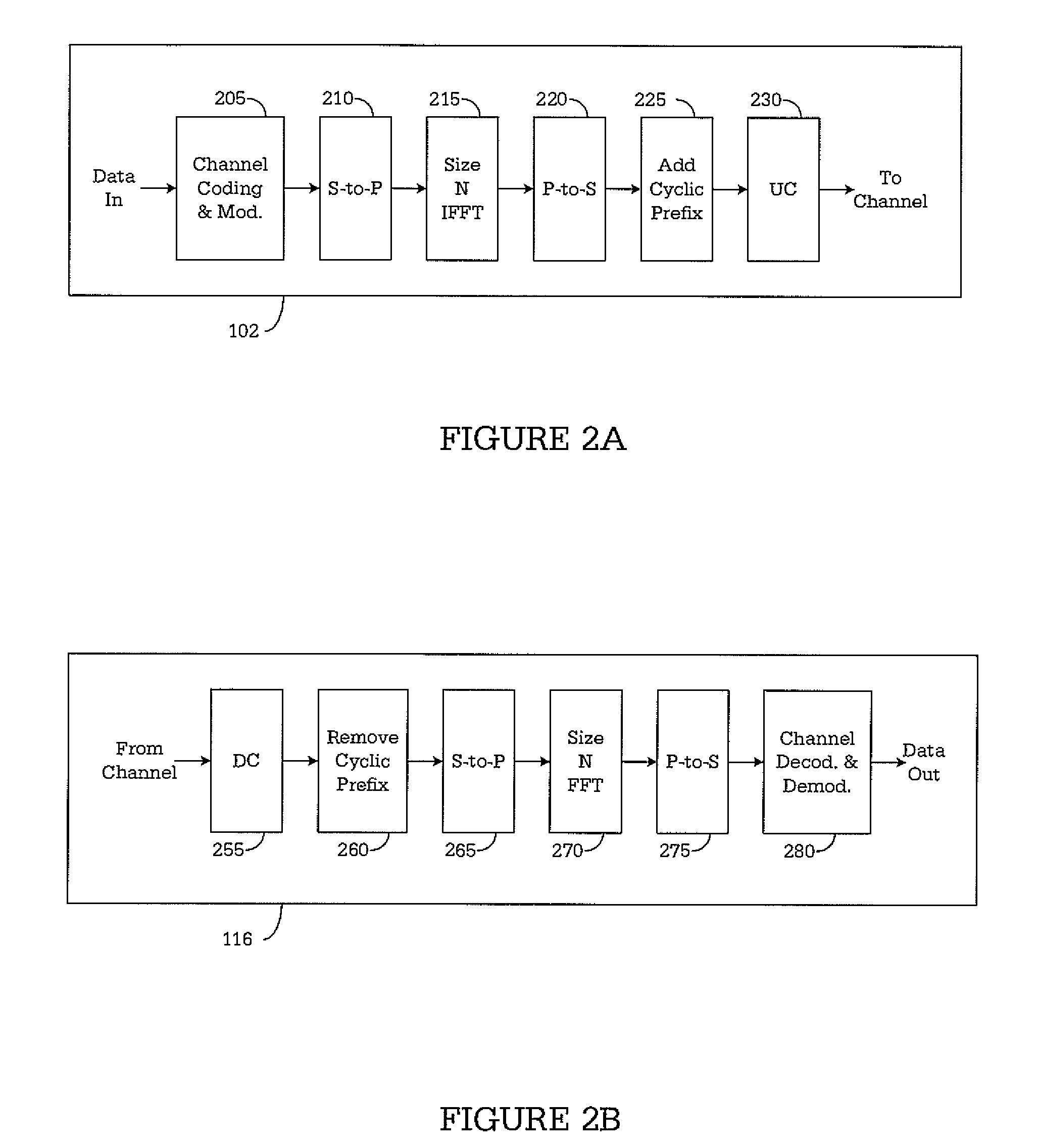
DTV transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcast data
ActiveUS20080069147A1Improve performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexerBroadcast data
A digital television transmitting system includes a frame encoder, a block processor, a group formatter, and a multiplexer. The frame encoder forms an enhanced data frame and encodes the data frame for error correction and for error detection. The block processor further encodes the encoded data frame at a rate of ½ or ¼, and the group formatter divides the encoded data frame into a plurality of enhanced data blocks and maps the divided data blocks into a plurality of enhanced data groups, respectively. The multiplexer multiplexes the enhanced data groups with main data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
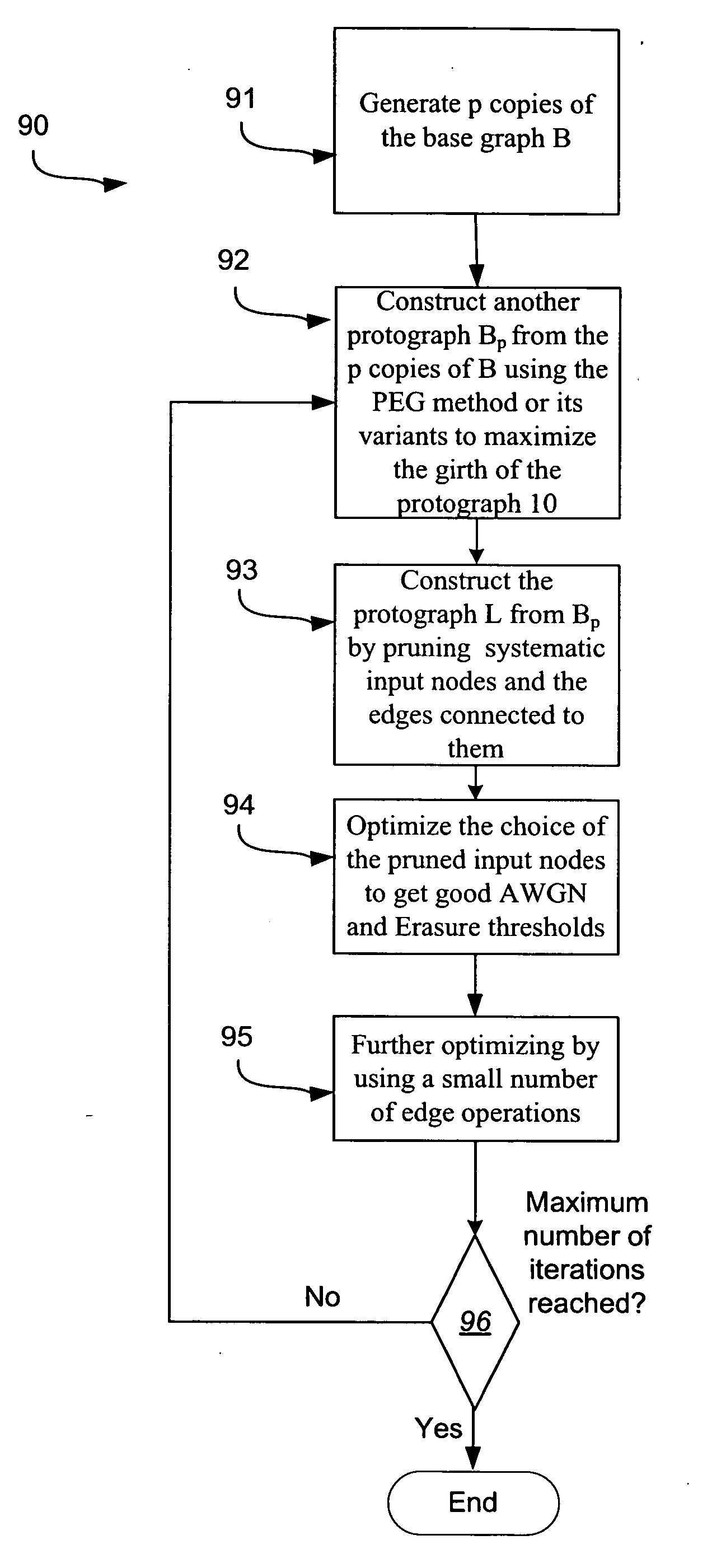
System and method for providing H-ARQ rate compatible codes for high throughput applications
ActiveUS20070162815A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsHigh rateTheoretical computer science
In one embodiment, the present patent application comprises a method and apparatus to generate low rate protographs from high rate protographs, comprising copying a base graph; permuting end points of edges of a same type in copies of the base graph to produce a permuted graph; and pruning systematic input nodes in the permuted graph and the edges connected to them. In another embodiment, the present patent application comprises a method and apparatus to generate high-rate codes from low-rate codes, comprising puncturing a subset of codeword bits, wherein the step of puncturing a subset of codeword bits comprises regular-irregular puncturing the subset of codeword bits, random puncturing variable nodes, or progressive node puncturing variable nodes to obtain a desired code from a preceding code.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
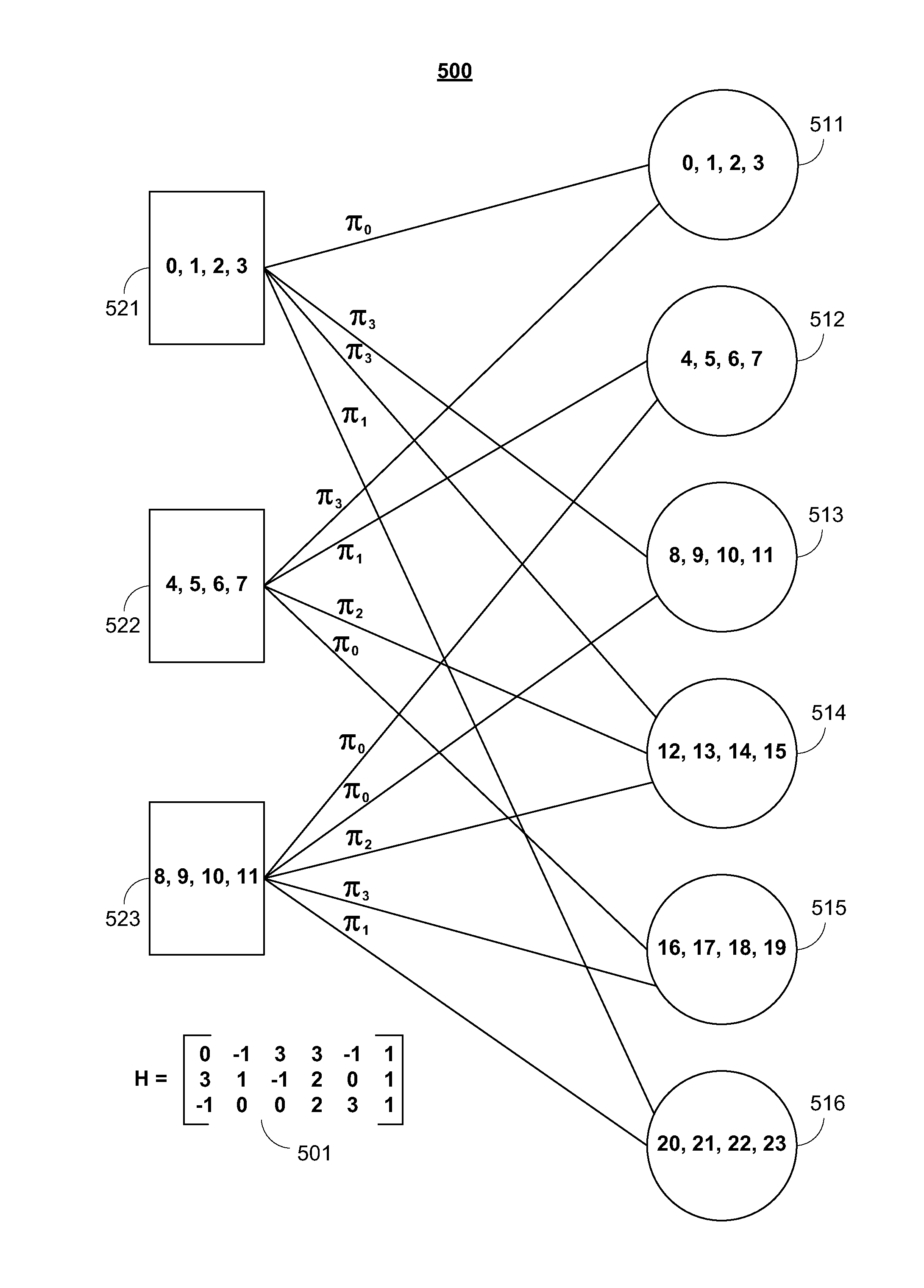
Encoding method, decoding method, encoding device and decoding device of structured LDPC codes
ActiveCN104868925ASolving inefficienciesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionProduction lineExpansion factor
An encoding method, decoding method, encoding device and decoding device for a structured LDPC. The method comprises: determining a basic matrix used for encoding and containing K0 pairs which are adjacent up and down; and according to the basic matrix and an expansion factor corresponding thereto, completing an LDPC encoding operation of obtaining Nb × z bits of code words from (Nb - Mb) × z bits of source data, where z is the expansion factor, and z is a positive integer which is greater than or equal to 1. The provided technical solution is suitable for the encoding and decoding of structured LDPC, thereby realizing the encoding and decoding of LDPC at high production line speed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
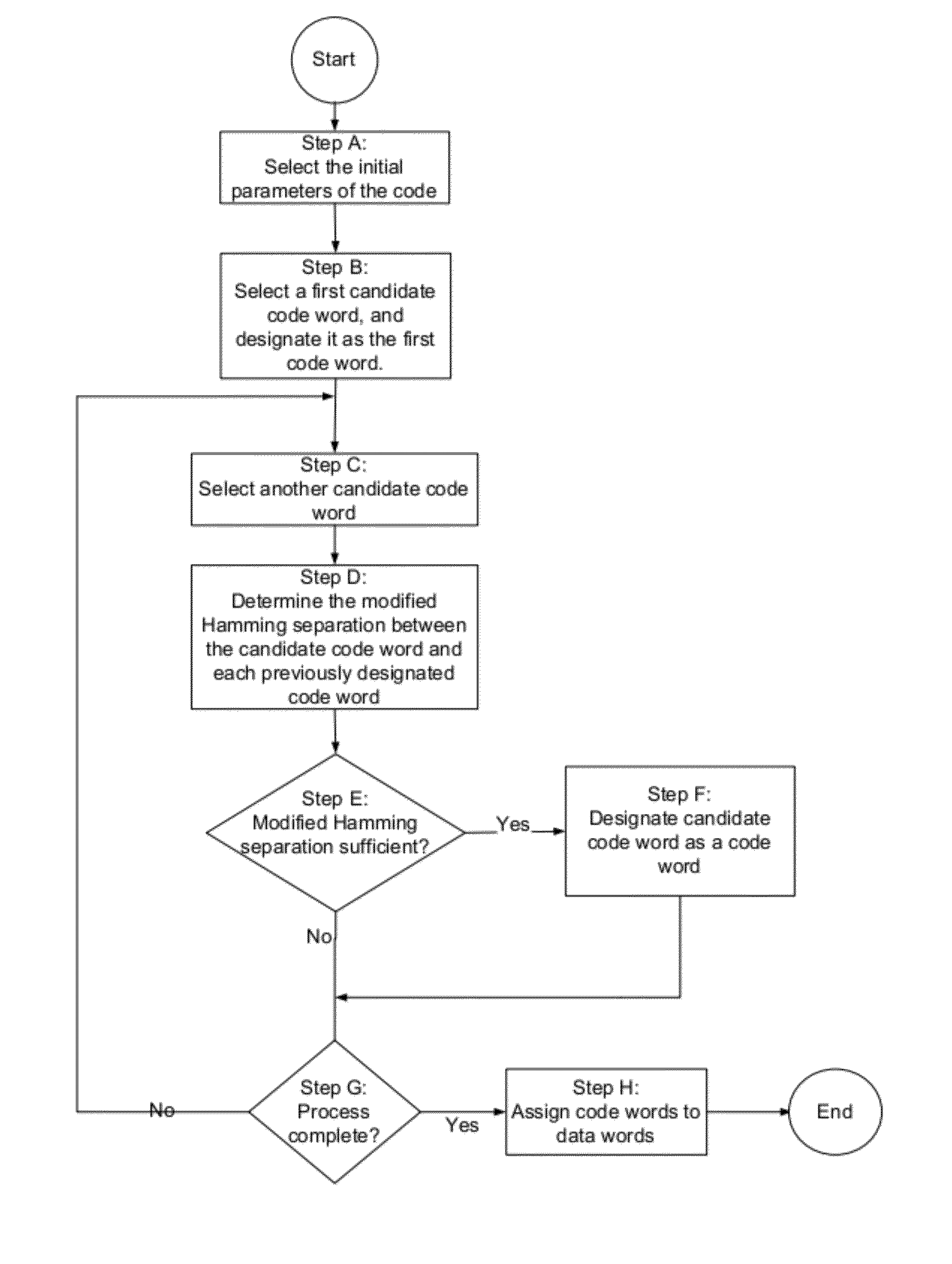
Method for creating an error correction coding scheme
InactiveUS20080244353A1Reduce data lossEasy constructionBurst error correctionCode conversionMain diagonalData set
The present invention relates to a method for reducing data loss comprising a first computing step for computing an intermediate result for each redundancy information entity of a redundancy set by processing respectively associated data information entities of a given data set on at least two main diagonals of a parity check matrix representing an error correction coding scheme. The method further comprises a second computing step for computing the information content of the respective redundancy information entity dependent on the respective intermediate result.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Error detection and correction codes for channels and memories with incomplete error characteristics
InactiveUS20120096330A1Efficient error-correcting codeOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionParallel computingHamming distance
A channel has a first and a second end. The first end of the channel is coupled to a transmitter. The channel is capable of transmitting symbols selected from a symbol set from the first end to the second end. The channel exhibits incomplete error introduction properties. A code comprises a set of code words. The elements of the set of code words are one or more code symbols long. The code symbols are members of the symbol set. The minimum modified Hamming separation between the elements of the set of code words in light of the error introduction properties of the channel is greater than the minimum Hamming distance between the elements of the set of code words. A memory device, a method of using the channel, and a method of generating the code are also described.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
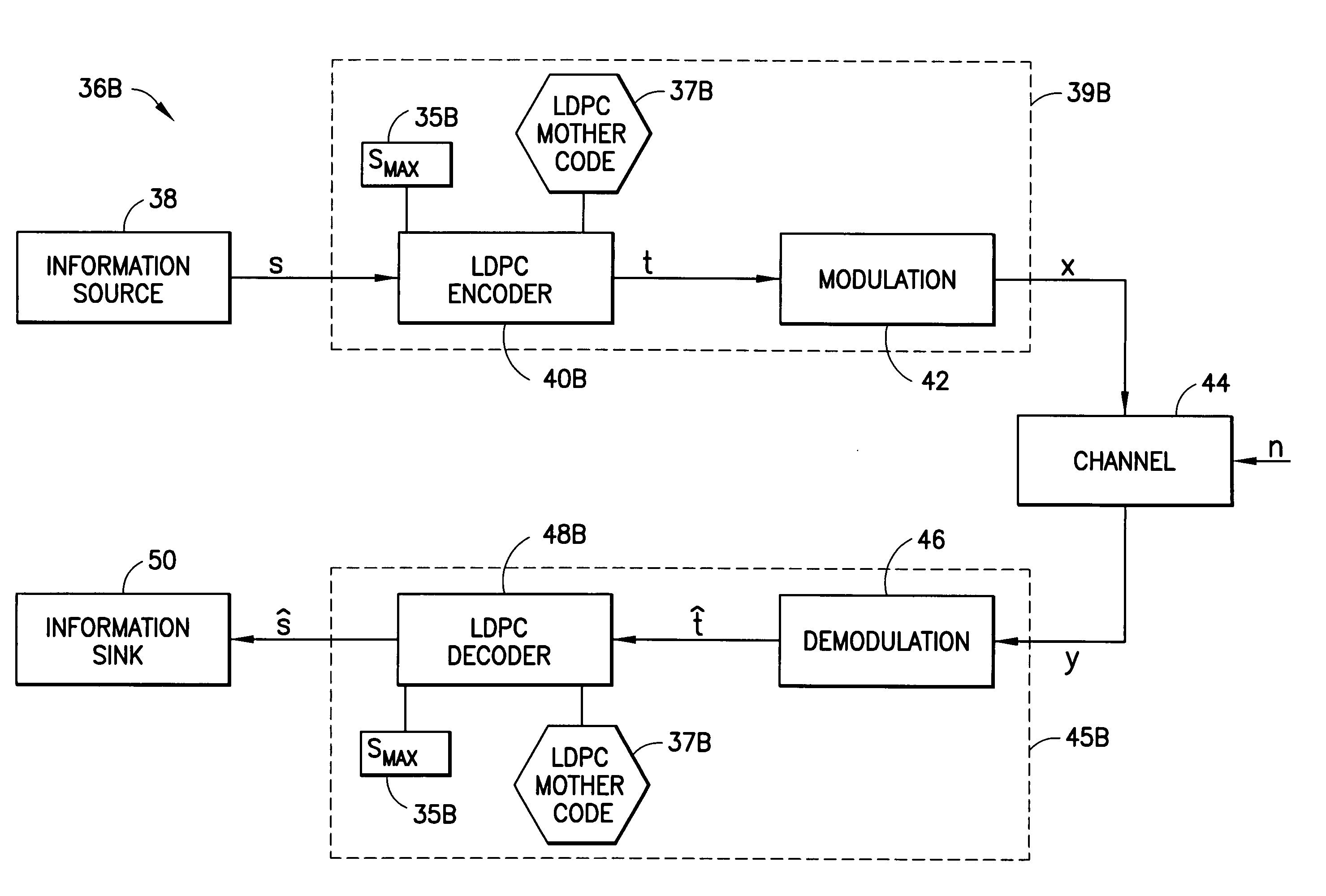
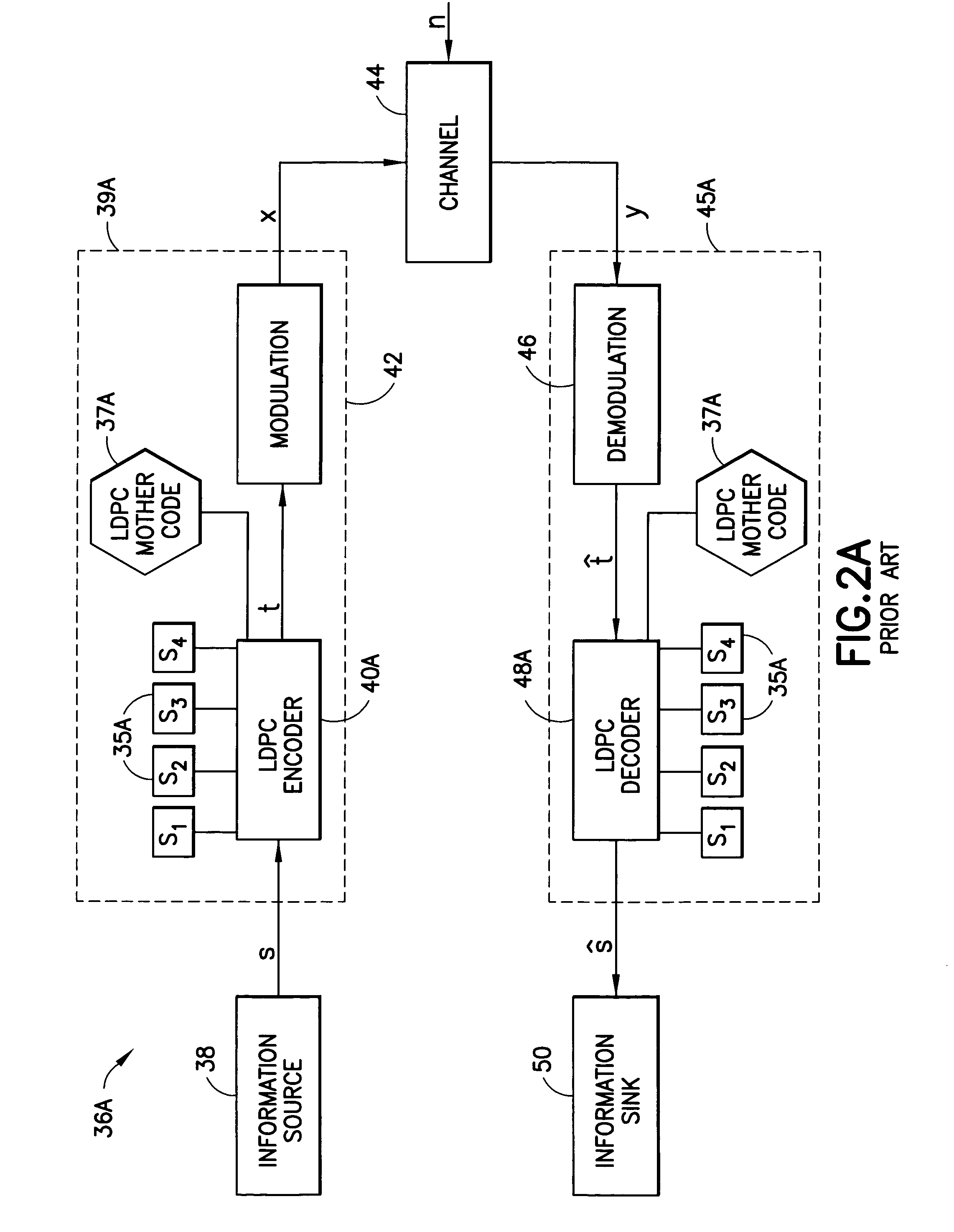
Low-density parity-check codes for multiple code rates
InactiveUS7222284B2Lower requirementReduce memory requirementsDigital variable displayError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeParallel computing
Puncture sequences S1, S2, etc. for code rates R1, R2, etc. less than a maximum code rate Rmax are defined subsets of a maximum rate puncture sequence Smax that corresponds to the maximum code rate Rmax. Each puncture sequence Si for a code rate Ri is related to the puncture sequence Si−1, of the previous code rate Ri−1, and preferably S1⊂S2⊂ . . . ⊂Smax−1⊂Smax. The puncture sequences are groups of one or more memory elements, each of which is a variable degree, a variable node location, a check degree, or a check node location. A method for deriving such a puncture sequence for variable code rates is also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
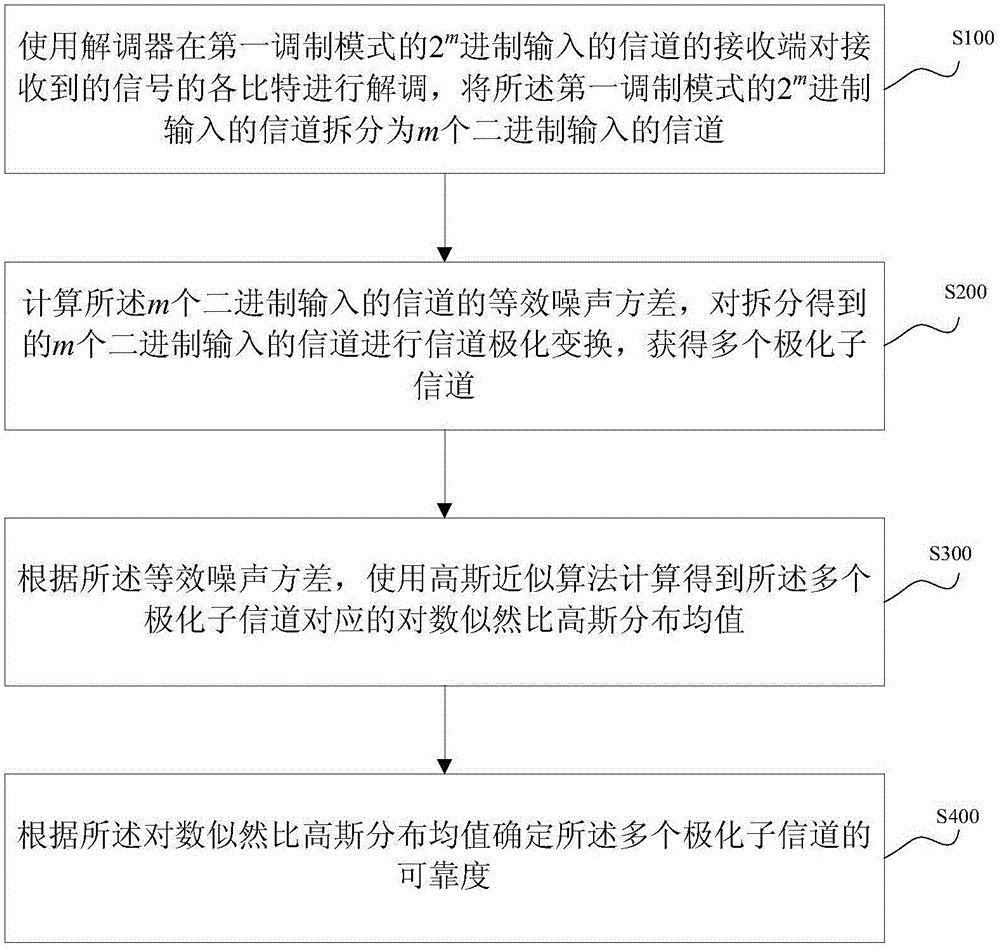
Method and device for determining channel reliability in polarization coding modulation
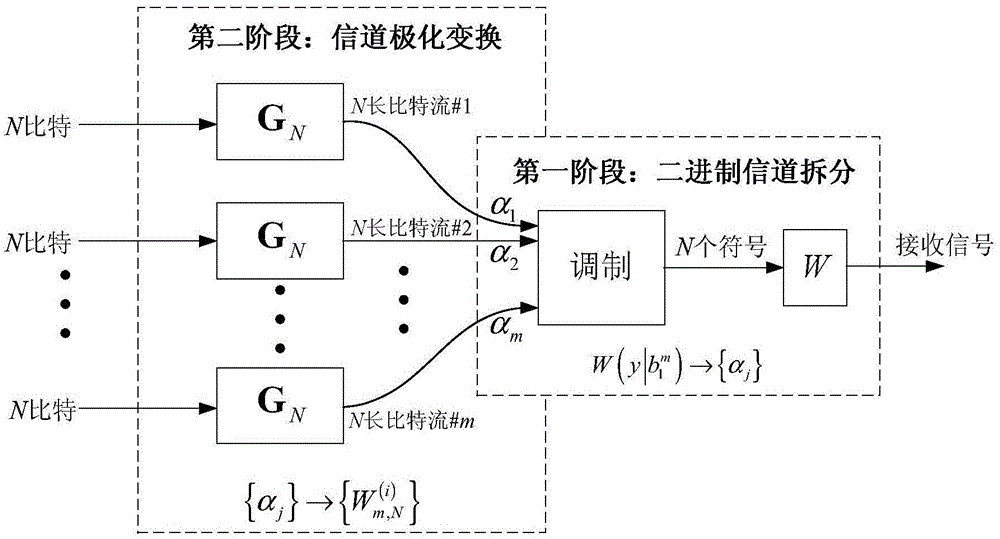
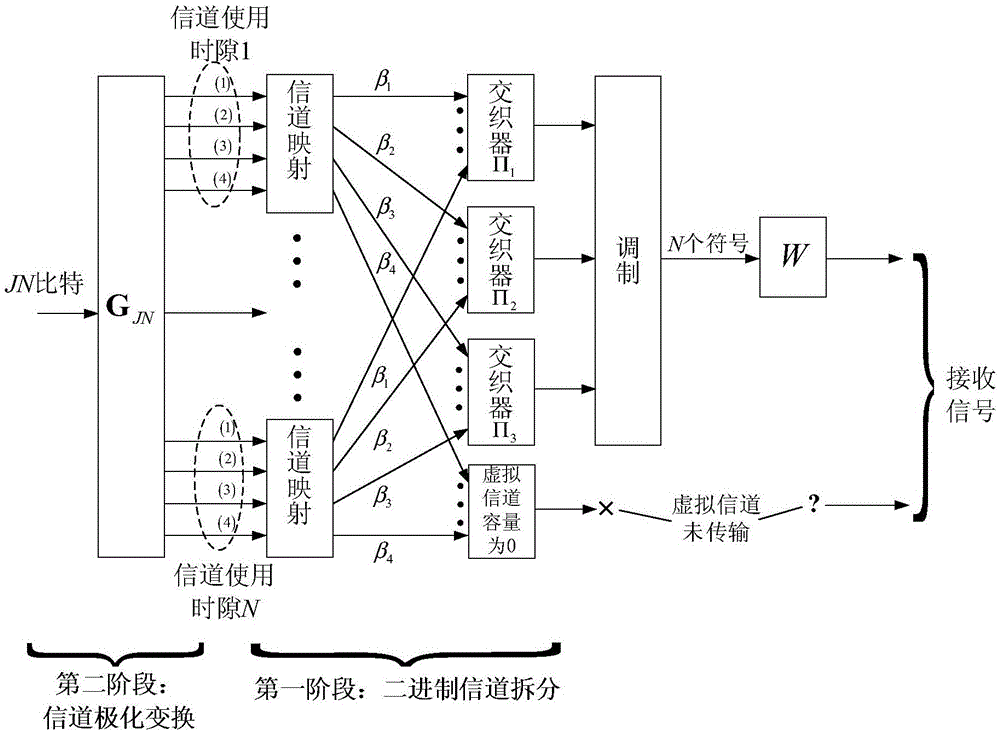
ActiveCN105099622AAvoid the problem of computational complexityReduce complexityChecking code calculationsChannel coding adaptationComputation complexityChannel polarization
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and device for determining channel reliability in polarization coding modulation. The method comprises: dividing a channel into m binary input channels, carrying out channel polarization transformation, and using a Gaussian approximation algorithm to calculate a log likelihood ratio Gaussian distribution mean corresponding to the polarization sub-channels according to the equivalent noise variance of the binary input channels obtained by splitting, so as to determine the reliability of the polarization sub-channels. Since the method provided by the invention adopts the Gaussian approximation algorithm, the problem of calculation complexity caused by calculating the channel reliability by using a density evolution tool is avoided. Compared with the scheme of calculating the channel reliability by using the density evolution tool, the calculation complexity of the method provided by the invention is obviously reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and system for providing low density parity check (LDPC) encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20110202820A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
An approach is provided for processing structure Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. Memory storing edge information and a posteriori probability information associated with a structured parity check matrix used to generate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) coded signal are accessed. The edge information represent relationship between bit nodes and check nodes, and are stored according to a predetermined scheme that permits concurrent retrieval of a set of the edge information.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
System and method for structured LDPC code family with fixed code length and no puncturing
InactiveUS20110047433A1Low parityHigh bit rateError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceLow density
A family of low density parity check (LDPC) codes is generated based on a mother code having a highest code rate. The low density parity check (LDPC) codes include a codeword size of at least 1344. The LDPC codes also include a plurality of parity bits in a lower triangular form. The mother code is constructed by: selecting m number of rows and n number of columns; setting maximum column weights and row weights; designing a protograph matrix based on the set column weights and row weights and selected m and n; and selecting circulant blocks based on the protograph matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Puncturing for structured low density parity check (LDPC) codes
ActiveUS20170141798A1Facilitate communicationError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesTheoretical computer scienceLow density
Certain aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to techniques for puncturing of structured low density parity check (LDPC) codes. A method for wireless communications by wireless node is provided. The method generally includes encoding a set of information bits based on a LDPC code to produce a code word, the LDPC code defined by a matrix having a first number of variable nodes and a second number of check nodes, puncturing the code word to produce a punctured code word, wherein the puncturing is performed according to a first puncturing pattern designed to puncture bits corresponding to one or more of the variable nodes having a certain degree of connectivity to the check nodes, and transmitting the punctured code word
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Layered quasi-cyclic LDPC decoder with reduced-complexity circular shifter
ActiveUS8291283B1Improve computing efficiencyDecreased routing congestionError detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityParallel computing
This disclosure relates generally to data decoding, and more particularly to iterative decoders for data encoded with a low-density parity check (LDPC) encoder. LDPC decoders are disclosed that use reduced-complexity circular shifters that may be used to decode predefined or designed QC-LDPC codes. In addition, methods to design codes which may have particular LDPC code performance capabilities and which may operate with such decoders using reduced-complexity circular shifters are provided. The generation of quasi-cyclic low density parity check codes and the use of circular shifters by LDPC decoders, may be done in such a way as to provide increased computational efficiency, decreased routing congestion, easier timing closure, and improved application performance.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
LDPC code family for millimeter-wave band communications in a wireless network
InactiveUS20120240001A1Increase in sizeCode conversionChecking code calculationsWireless mesh networkTheoretical computer science
A method constructs a family of low-density-parity-check (LDPC) codes. The method includes identifying a code rate for an LDPC code in the family, identifying a protograph for the LDPC code, and constructing a base matrix for the LDPC code. The base matrix is constructed by replacing each zero in the protograph with a ‘−1’, selecting a corresponding value for an absolute shift for each one in the protograph based on constraining a number of relative shifts per column of the LDPC code to one and increasing a size of a smallest cycle in a graph of the LDPC code, and replacing each one in the protograph with the corresponding value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
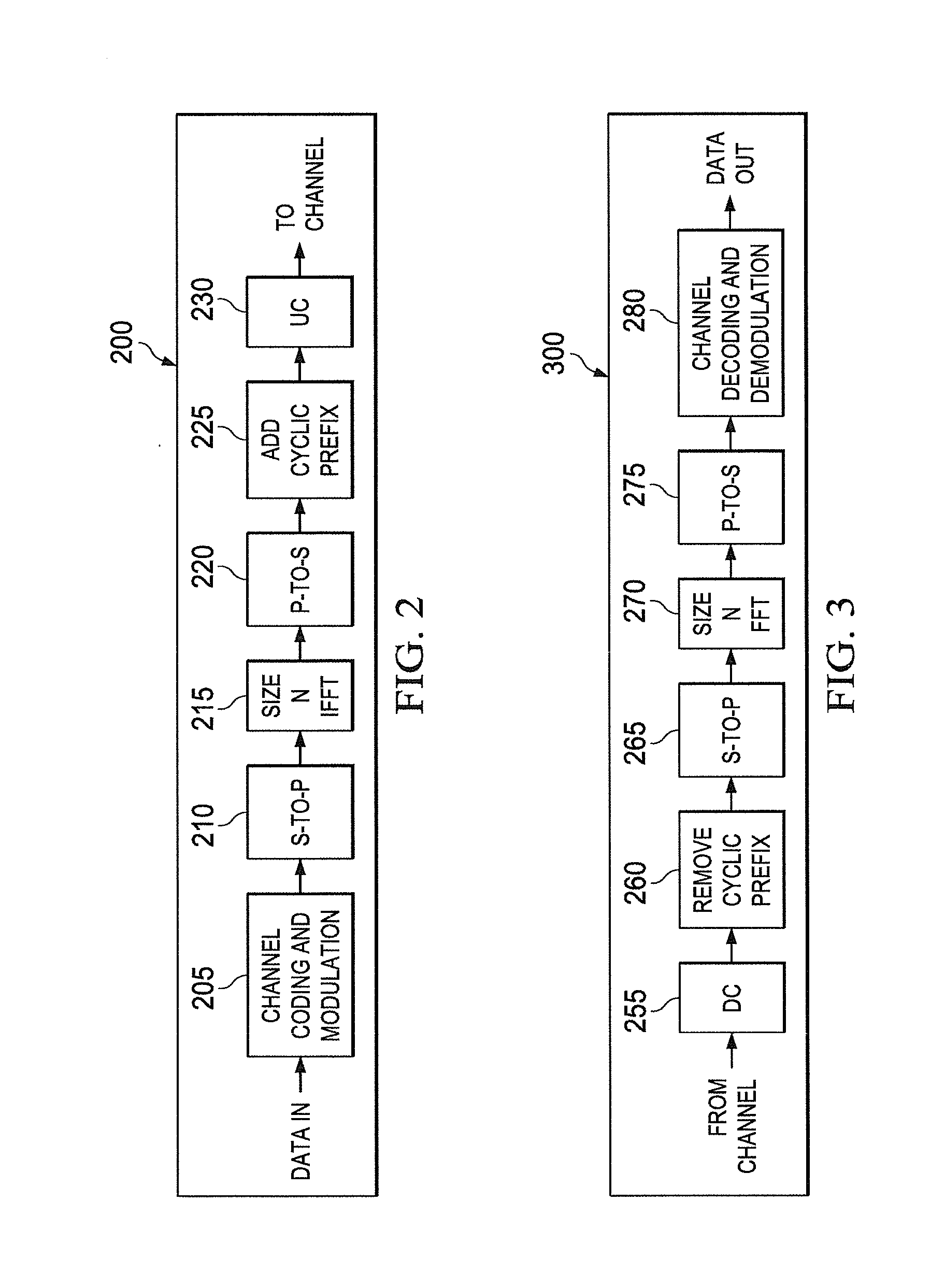
DTV receiving system and method of processing broadcast data therein
ActiveUS7782958B2Improve performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A digital television transmitting system includes a frame encoder, a block processor, a group formatter, and a multiplexer. The frame encoder forms an enhanced data frame and encodes the data frame for error correction and for error detection. The block processor further encodes the encoded data frame at a rate of ½ or ¼, and the group formatter divides the encoded data frame into a plurality of enhanced data blocks and maps the divided data blocks into a plurality of enhanced data groups, respectively. The multiplexer multiplexes the enhanced data groups with main data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System and method for structured LDPC code family
InactiveUS20110066916A1Low densityError preventionChecking code calculationsTheoretical computer scienceLow density
A low density parity check (LDPC) family of codes is constructed by: determining a protograph for a mother code for the LDPC family of codes. The protograph is lifted by a lifting factor to design code specific protograph for a code. The method also includes constructing a base matrix for the code. The base matrix is constructed by replacing each zero in the code specific protograph with a ‘−1’; and replacing each one in the code specific protograph with a corresponding value from the mother matrix. The LDPC code includes a codeword size of at least 1344, a plurality of information bits, and a plurality of parity bits. The LDPC code is based on a mother code of code length 672.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
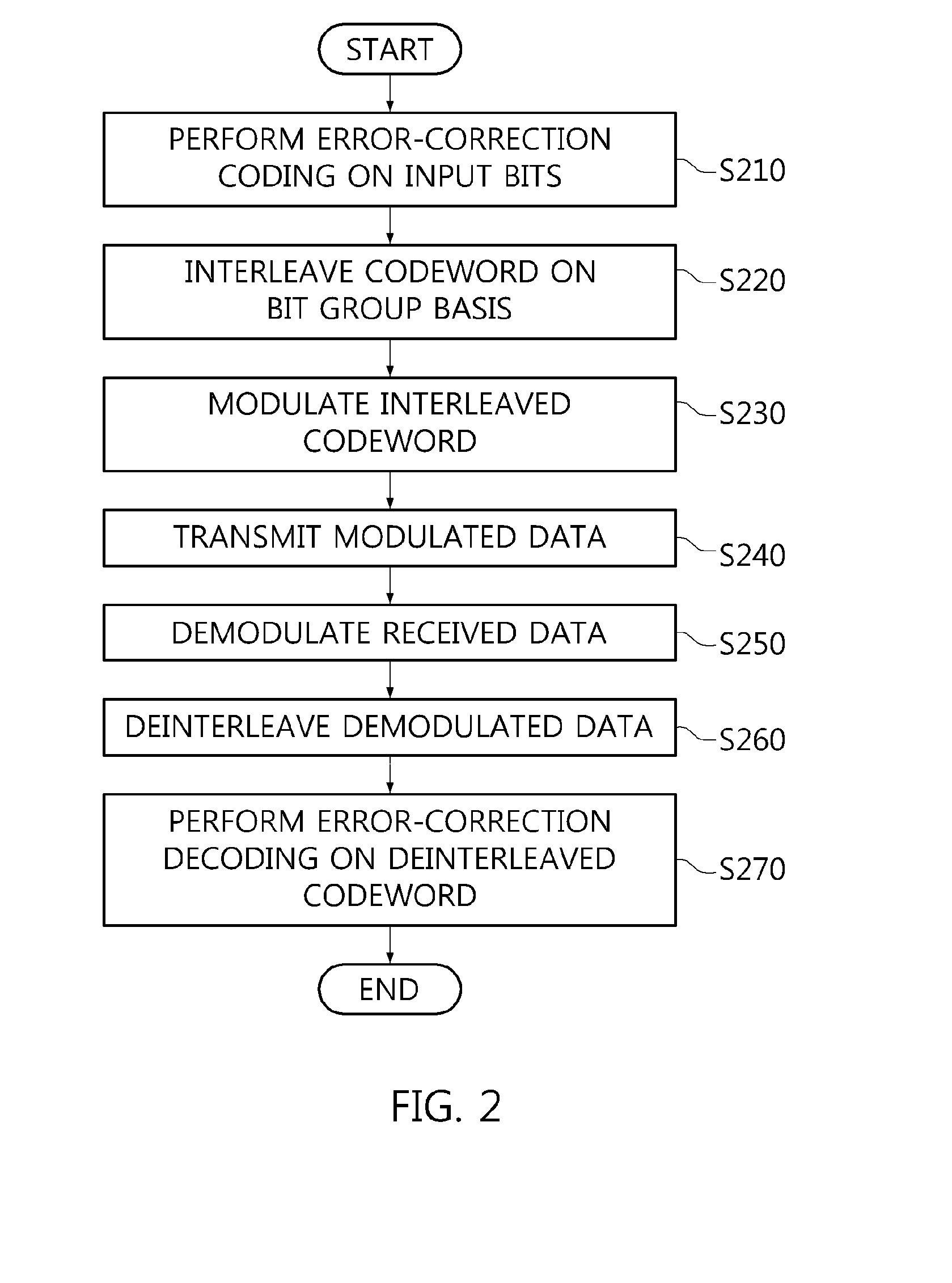
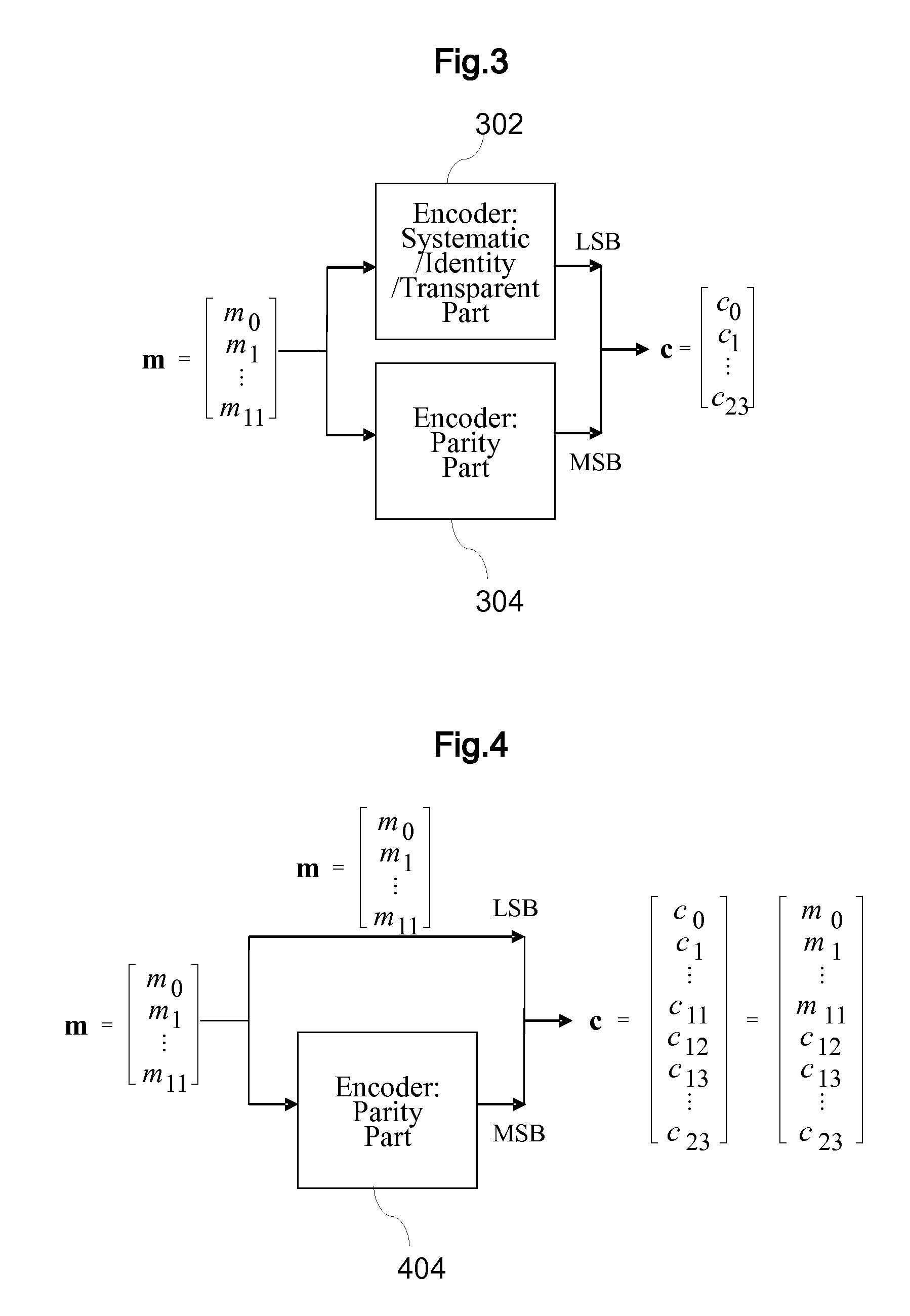
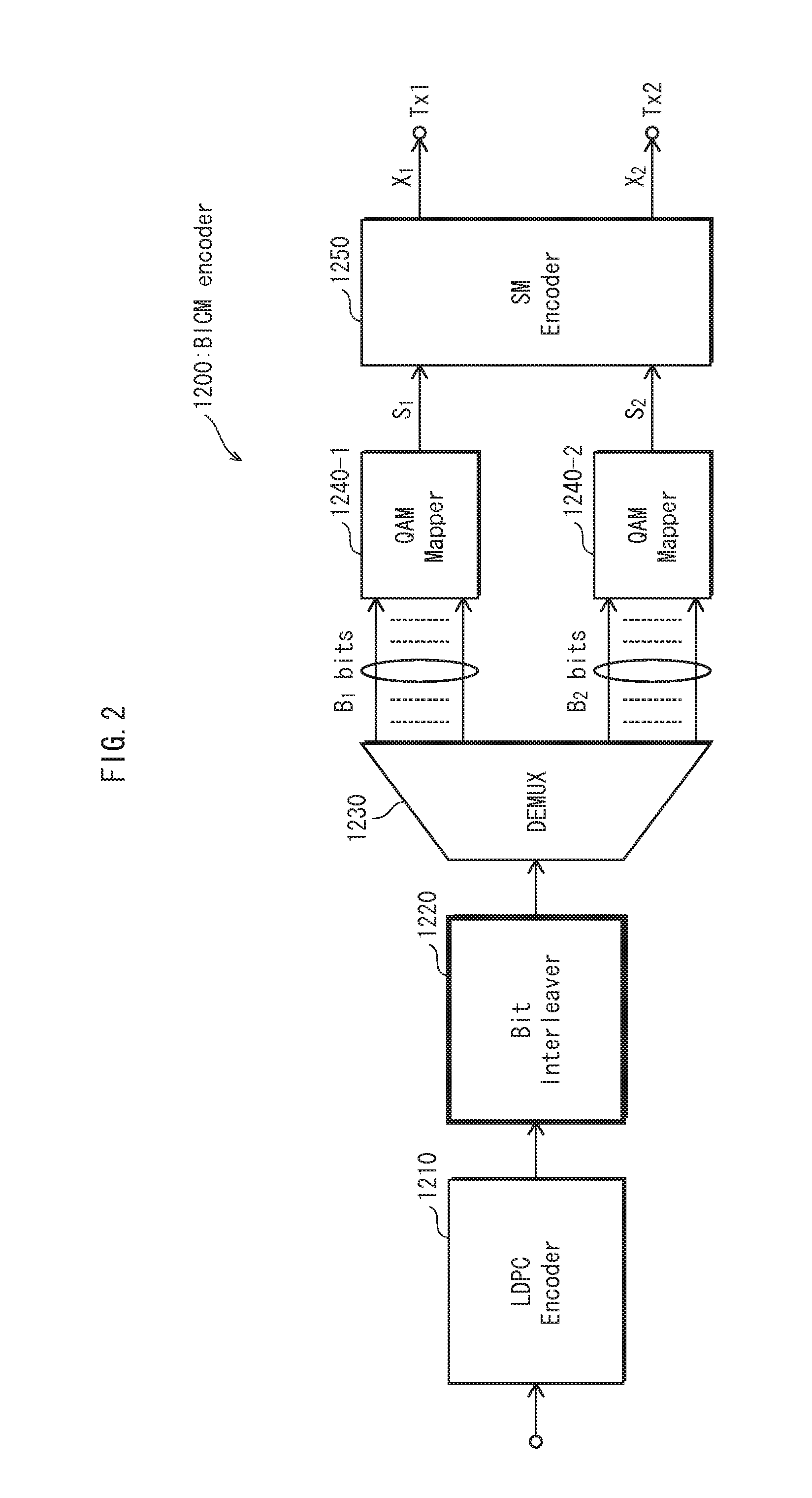
Bit interleaver for low-density parity check codeword having length of 64800 and code rate of 3/15 and 16-symbol mapping, and bit interleaving method using same
ActiveUS20150236722A1Effective distributionEfficiently distributedError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSymbol mappingParallel computing
A bit interleaver, a bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) device and a bit interleaving method are disclosed herein. The bit interleaver includes a first memory, a processor, and a second memory. The first memory stores a low-density parity check (LDPC) codeword having a length of 64800 and a code rate of 3 / 15. The processor generates an interleaved codeword by interleaving the LDPC codeword on a bit group basis. The size of the bit group corresponds to a parallel factor of the LDPC codeword. The second memory provides the interleaved codeword to a modulator for 16-symbol mapping.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
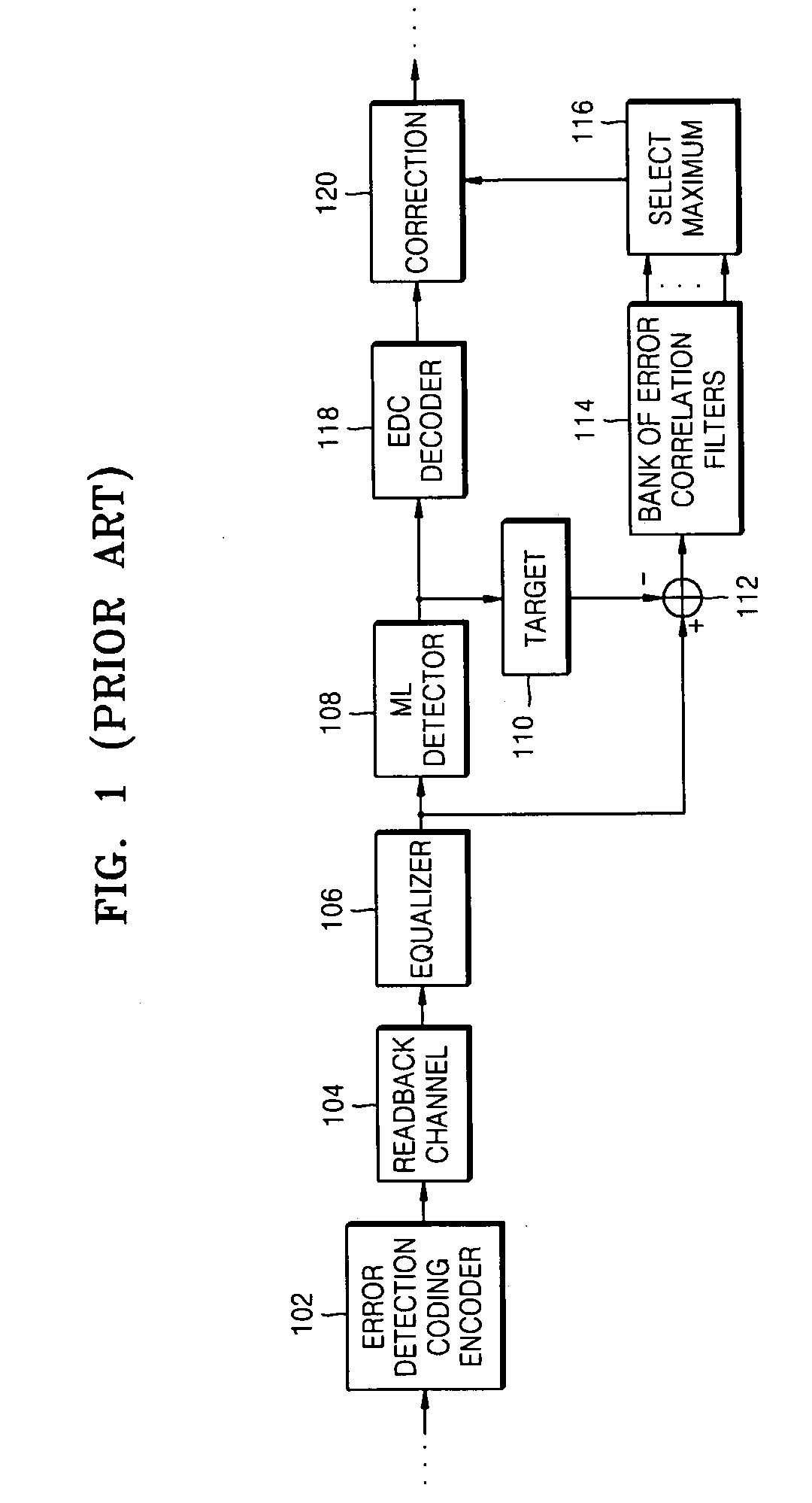
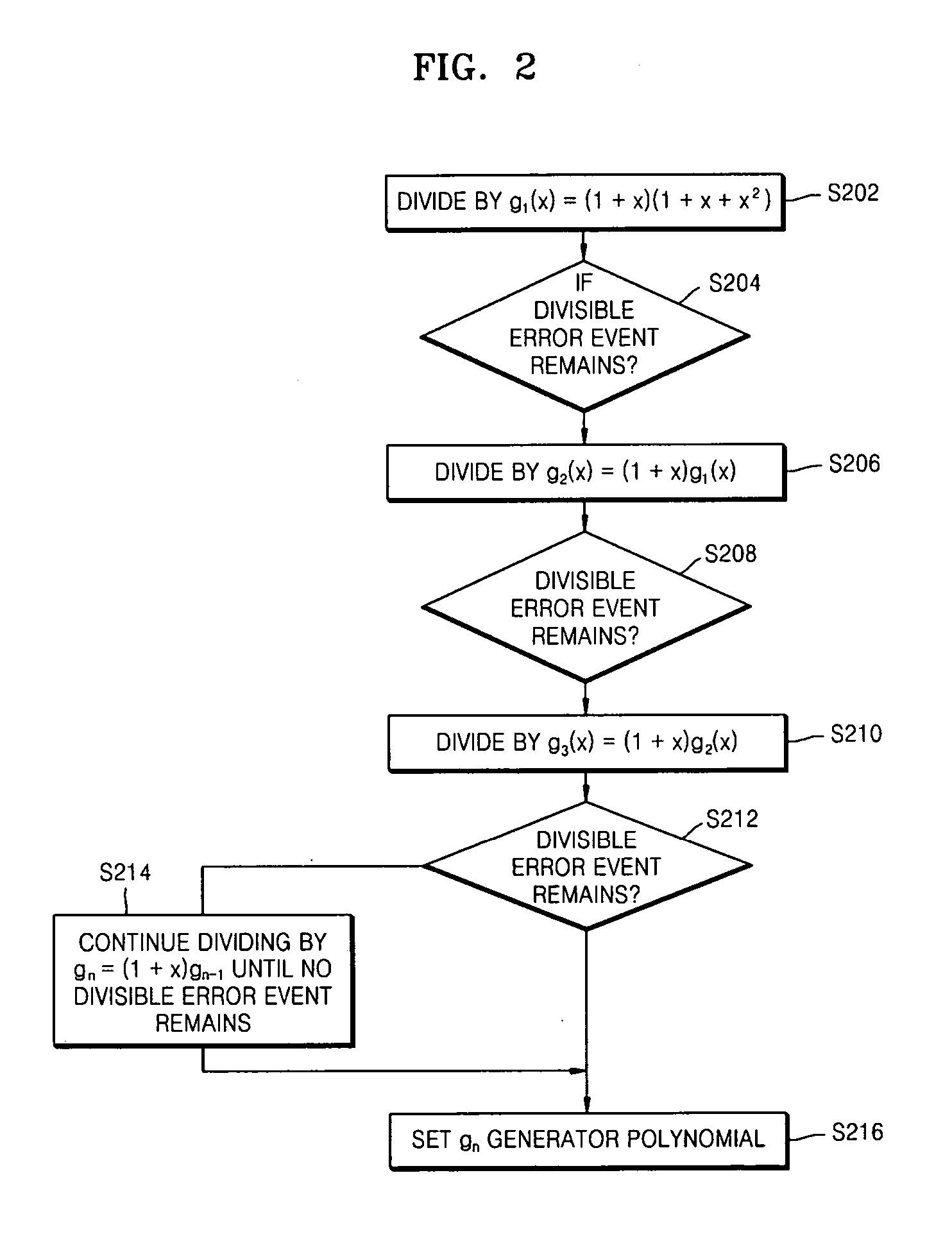
Method of detecting and correcting a prescribed set of error events based on error detecting code
InactiveUS20070061689A1Code conversionChecking code calculationsComputer hardwareIntersymbol interference
A method of constructing an effective generator polynomial for error correction by which a unique set of syndromes for each error event is produced is provided. The method includes preparing a set of dominant error events from the intersymbol interference characteristics of media; and generating a codeword from the data using a non-primitive generator polynomial that produces a unique syndrome set which can completely specify each dominant error event.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
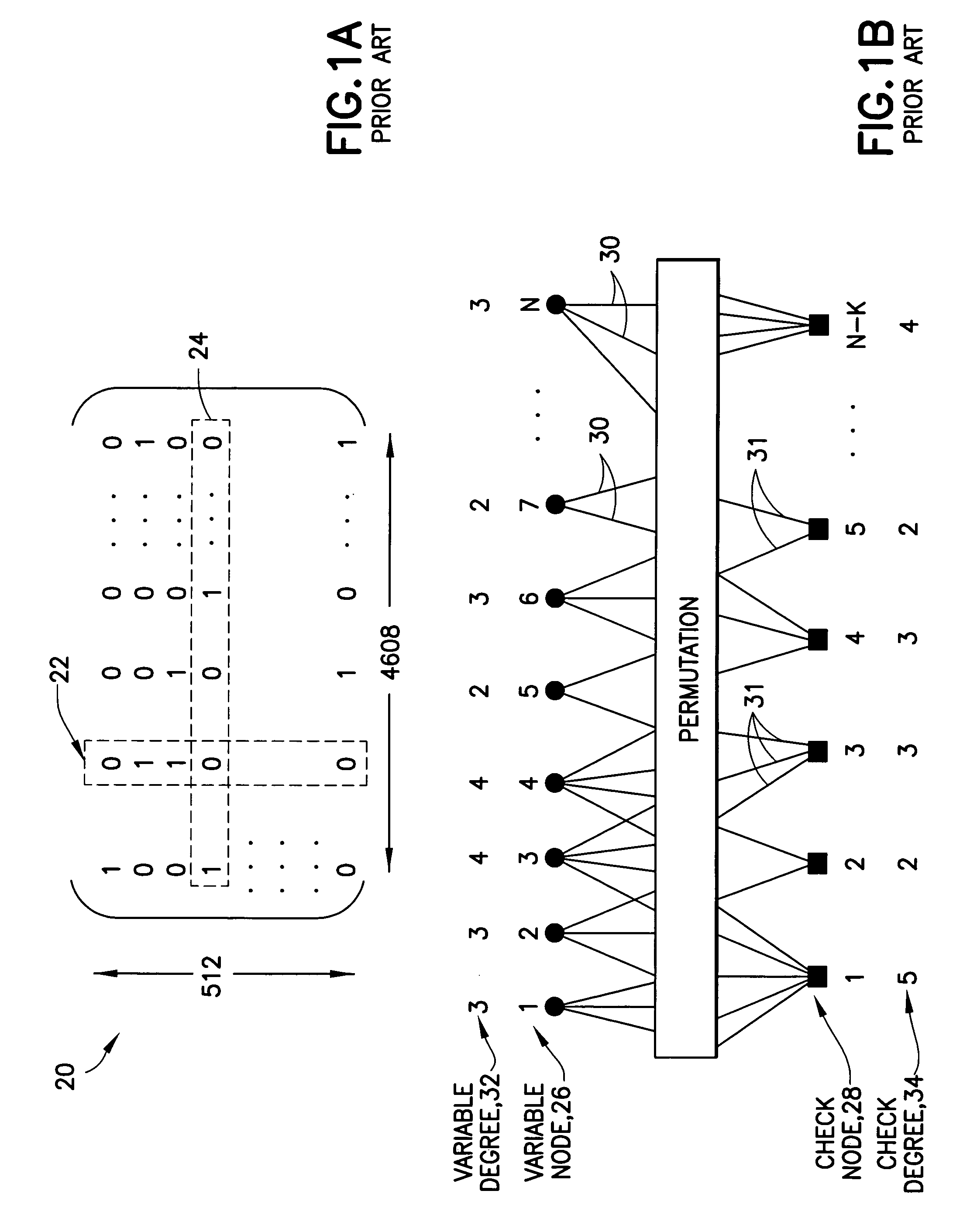
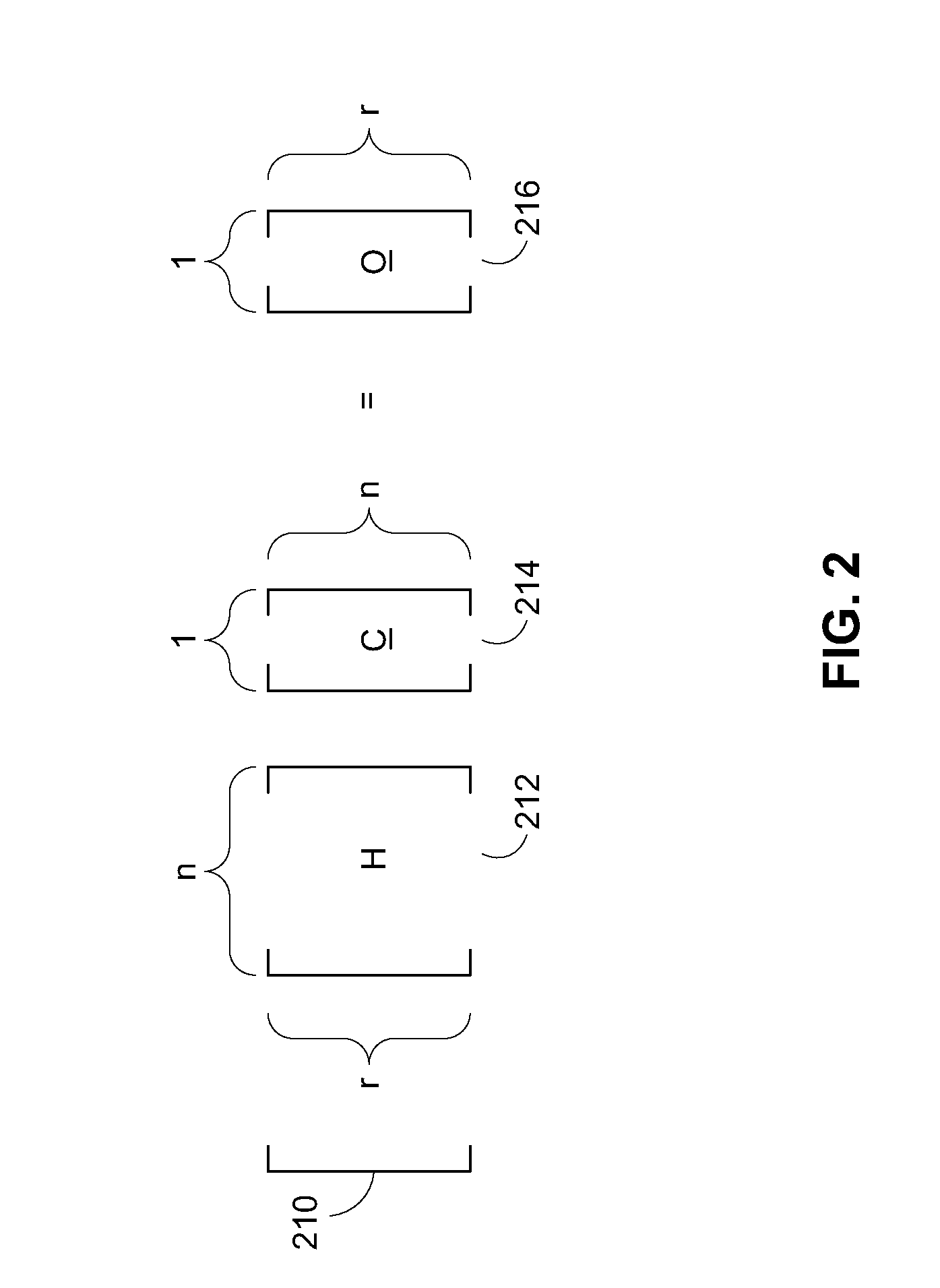
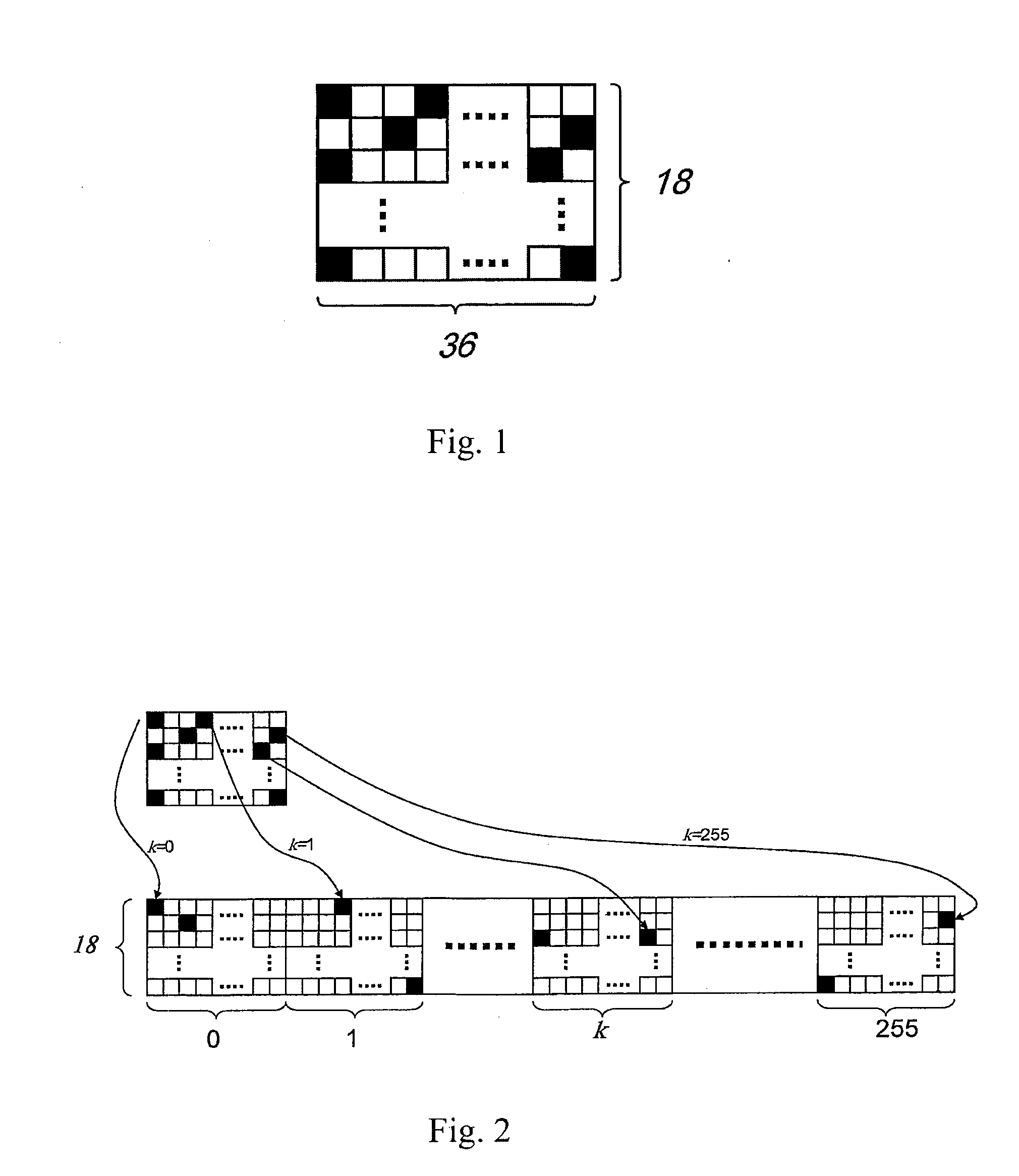
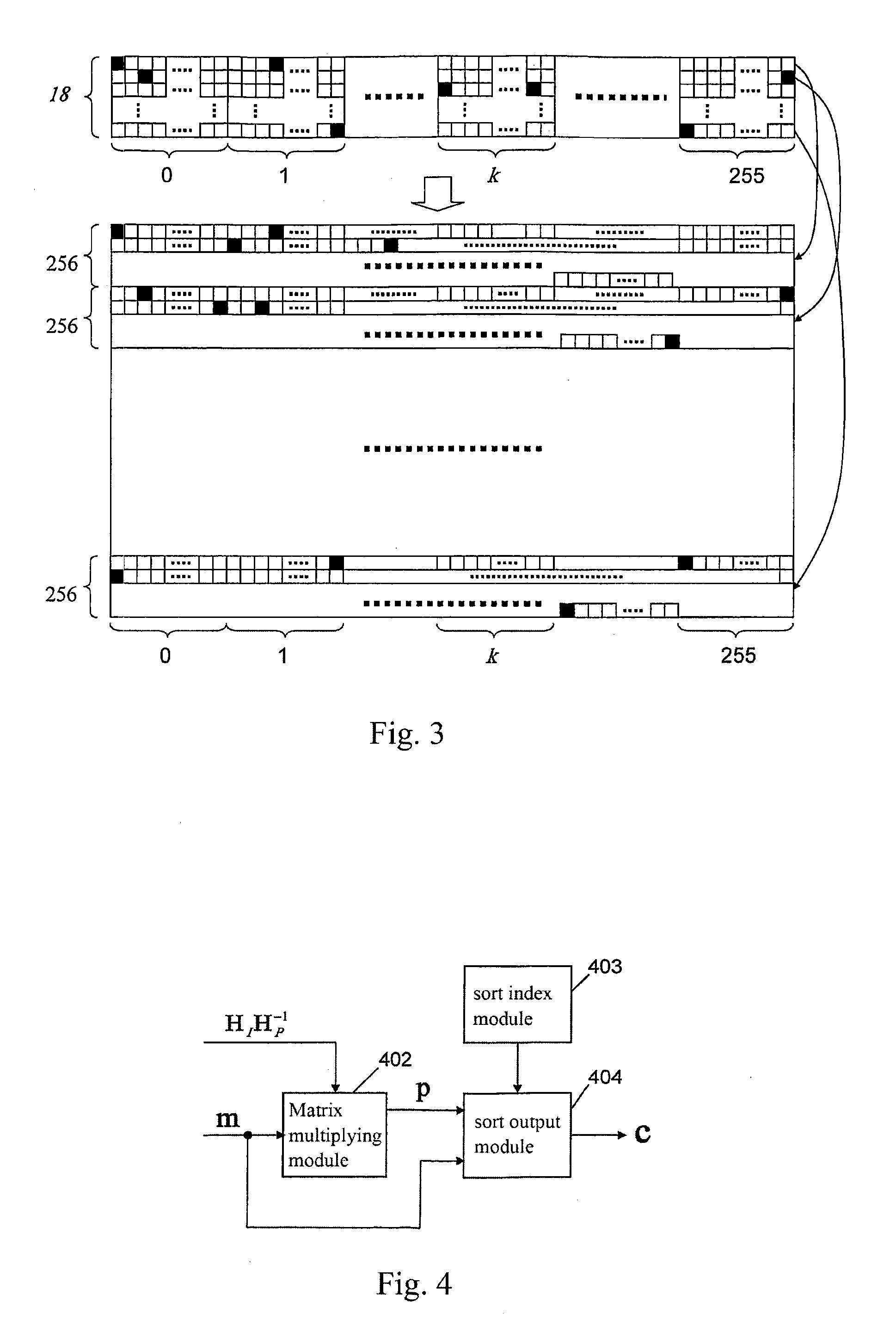
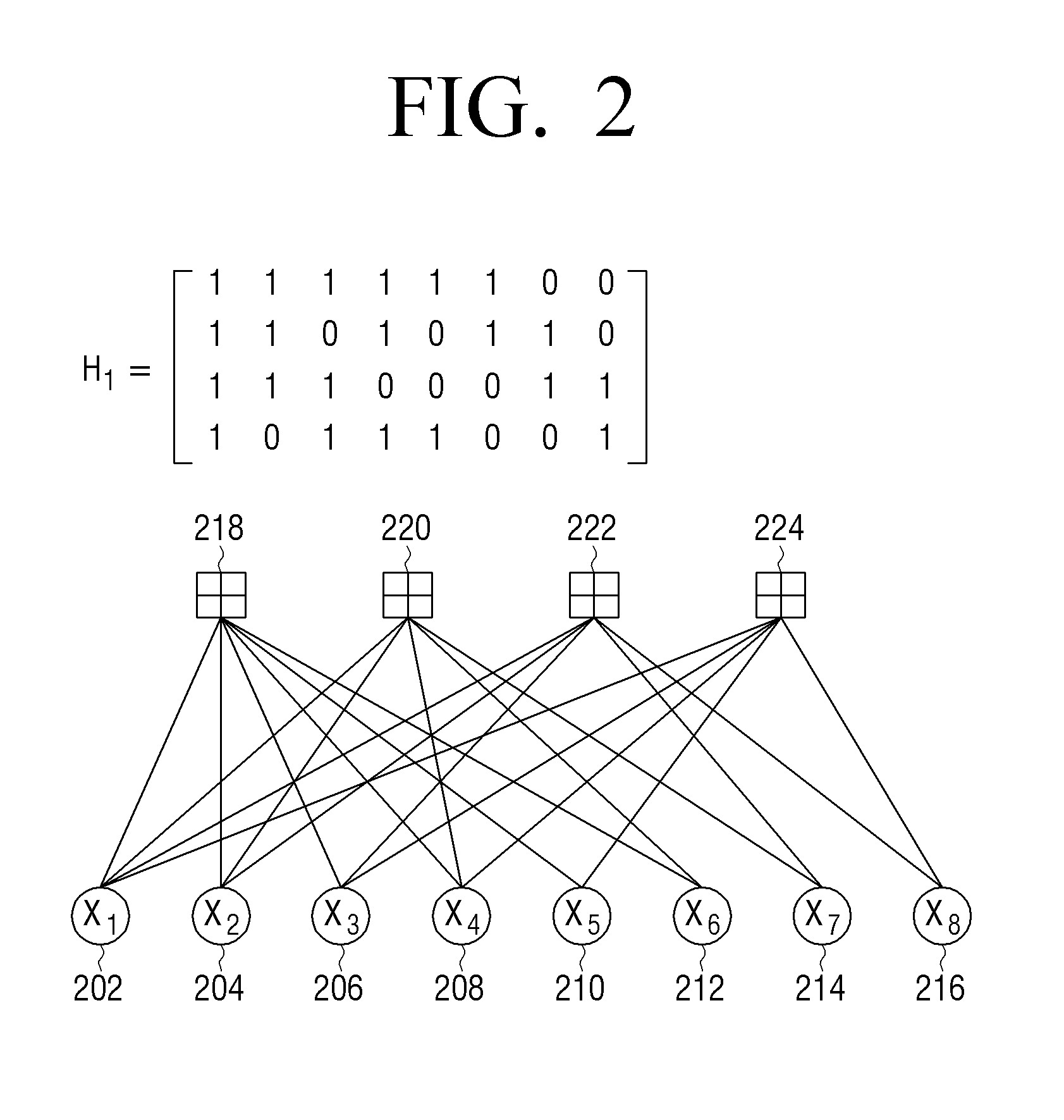
Method for constructing checking matrix of LDPC code and coding and decoding apparatus utilizing the method
InactiveUS20110239077A1Improve performanceLess occupiedError preventionCode conversionAlgorithmEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for constructing LPDC code check matrix and encoding and decoding devices using the same. The encoding device encodes the inputted binary information and outputs the encoded system code sequence of position transformation. The encoding device comprises: a matrix multiplication module outputting a check sequence p which is obtained through the binary information sequence m multiplied with a matrix; a sorting index module having N memory units storing index values of a sorting table IDX in turn; and a sorting output module for sorting the m and p and outputting a code word c based on the index value stored in the sorting index table. The present invention constructs the LDPC code check matrix using an algebraic structure, obtaining the LDPC code with stable performance. In addition, the encoding and decoding devices of the present invention occupy less memory, which is preferable for optimization of the devices.
Owner:TIMI TECH
LDPC design for high parallelism, low error floor, and simple encoding
ActiveUS20140229789A1Yield with good performanceHigh error floorError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsChecking code calculationsTheoretical computer scienceData encoding
A method of data encoding is disclosed. An encoder receives a set of information bits and performs an LDPC encoding operation on the set of information bits to produce a codeword based on a matched lifted LDPC code. The matched lifted LDPC code is based on a commutative lifting group and includes a number of parity bits and a submatrix to determine values of the parity bits. An order of the lifting group (Z) corresponds with a size of the lifting. A determinant of the submatrix is a polynomial of the form: ga+(g0+gL)P, where g0 is the identity element of the group, g0=gL2<sup2>k< / sup2>, and P is an arbitrary non-zero element of a binary group ring associated to the lifting group.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
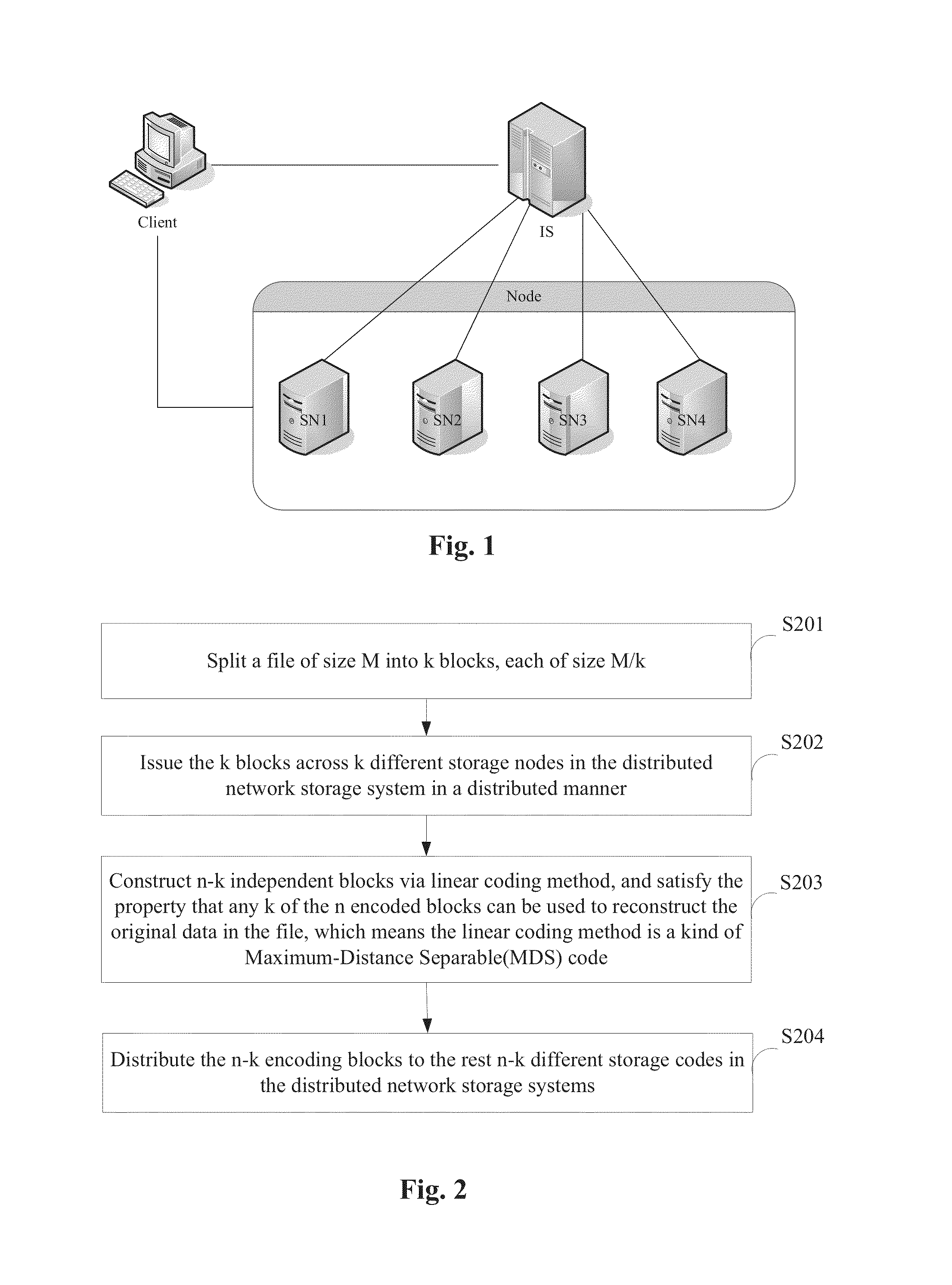
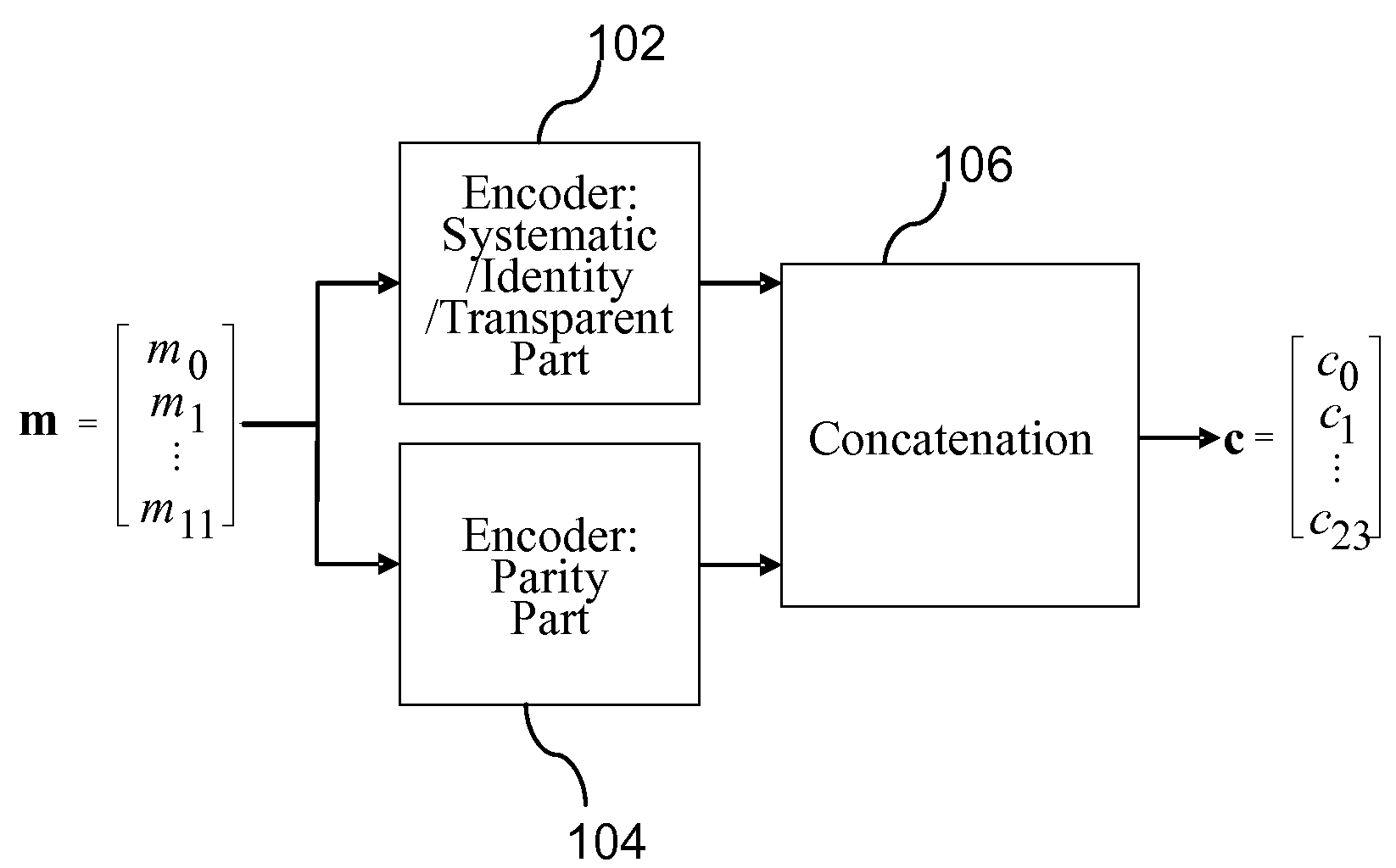
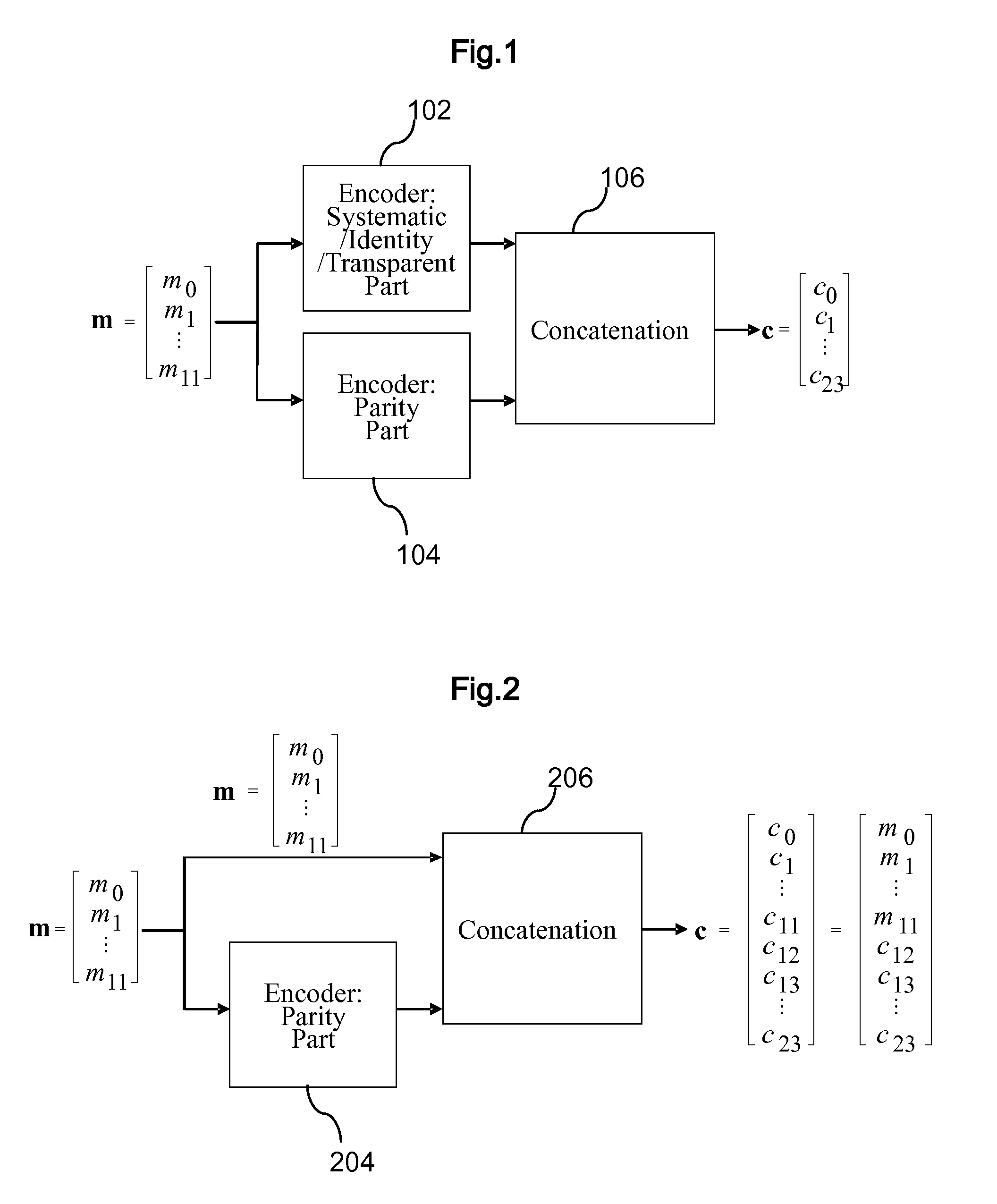
Data Storage Method, Device and Distributed Network Storage System
ActiveUS20140317222A1Ensure reliabilitySatisfactory propertyError detection/correctionChecking code calculationsComputer hardwareLinear coding
A method, device and system disclosed used in storage technique, comprising: splitting a file of size M into k blocks, that is to say, each block is of size M / k; issuing the above k blocks across k different storage nodes in the distributed network storage system in a distributed manner; using the k blocks, constructing n−k independent blocks via linear coding method, and satisfying the property that any k of the n encoded blocks can be used to reconstruct the original data in the file, which means the linear coding method is a kind of Maximum-Distance Separable (MDS) code; distribute the n−k encoded blocks to the rest n−k different storage codes in the distributed network storage systems.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
System and method for providing H-ARQ rate compatible codes for high throughput applications
ActiveUS8132072B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsGraphicsHigh rate
In one embodiment, the present patent application comprises a method and apparatus to generate low rate protographs from high rate protographs, comprising copying a base graph; permuting end points of edges of a same type in copies of the base graph to produce a permuted graph; and pruning systematic input nodes in the permuted graph and the edges connected to them. In another embodiment, the present patent application comprises a method and apparatus to generate high-rate codes from low-rate codes, comprising puncturing a subset of codeword bits, wherein the step of puncturing a subset of codeword bits comprises regular-irregular puncturing the subset of codeword bits, random puncturing variable nodes, or progressive node puncturing variable nodes to obtain a desired code from a preceding code.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
LDPC design for high rate, high parallelism, and low error floor
InactiveUS20140229788A1Increase the number ofImprove encoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMultiple edgesHigh rate
A method of data encoding is disclosed. An encoder receives a set of information bits and performs a lifted LDPC encoding operation on the information bits to produce a codeword. The encoder then punctures all lifted bits of the codeword that correspond to one or more punctured base bits of a base LDPC code used for the LDPC encoding operation. The base LDPC code has no multiple edges, and the one or more punctured base bits are those that correspond with one or more punctured base nodes, respectively, of the base LDPC code. For some embodiments, the one or more punctured base nodes correspond to one or more degree 2 variable nodes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
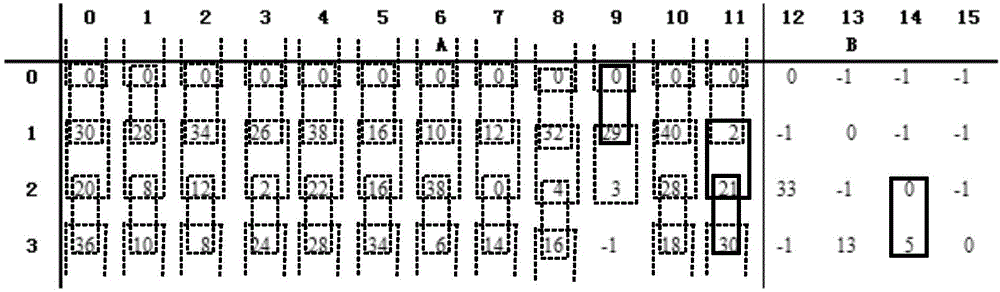
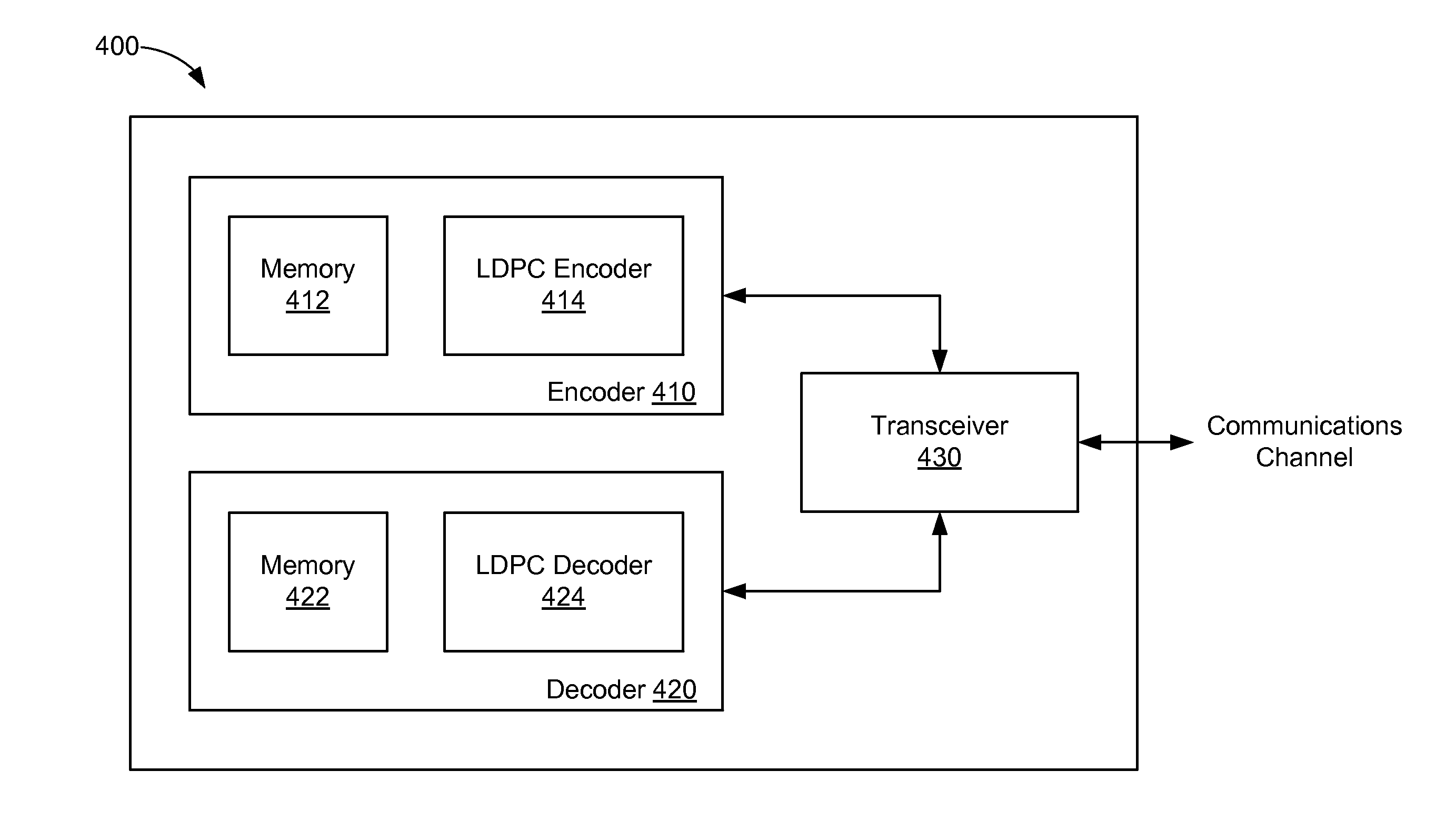
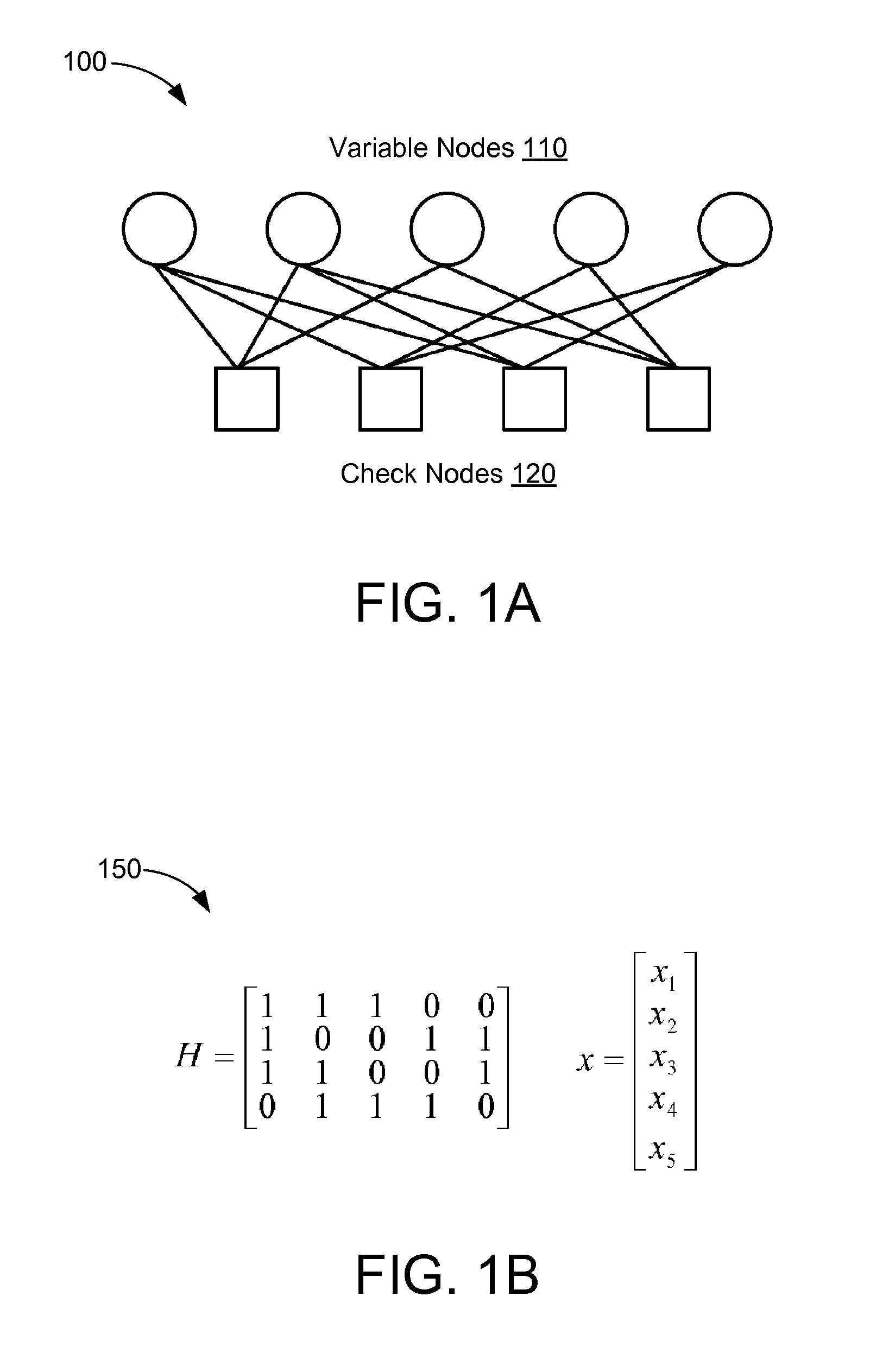
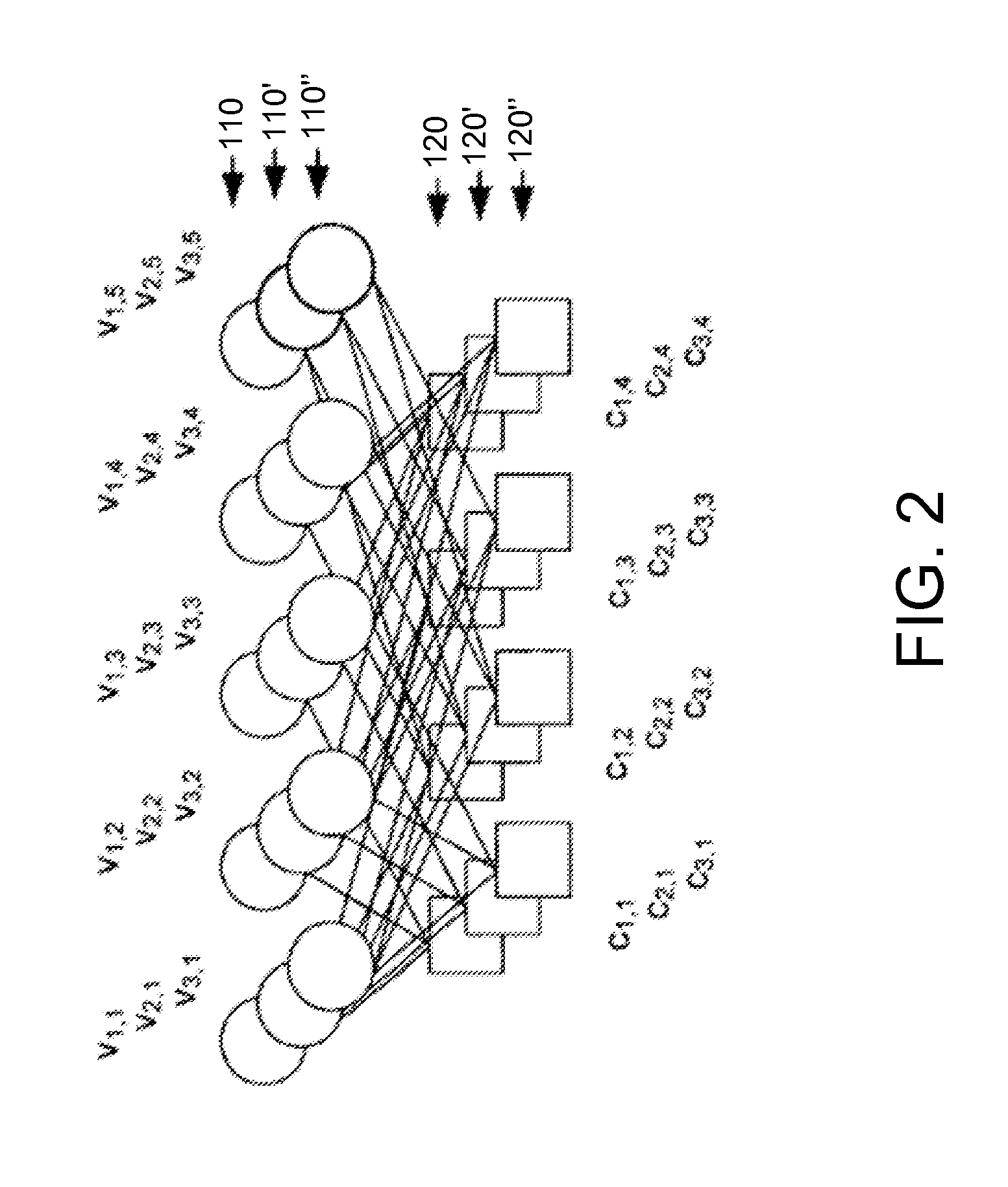
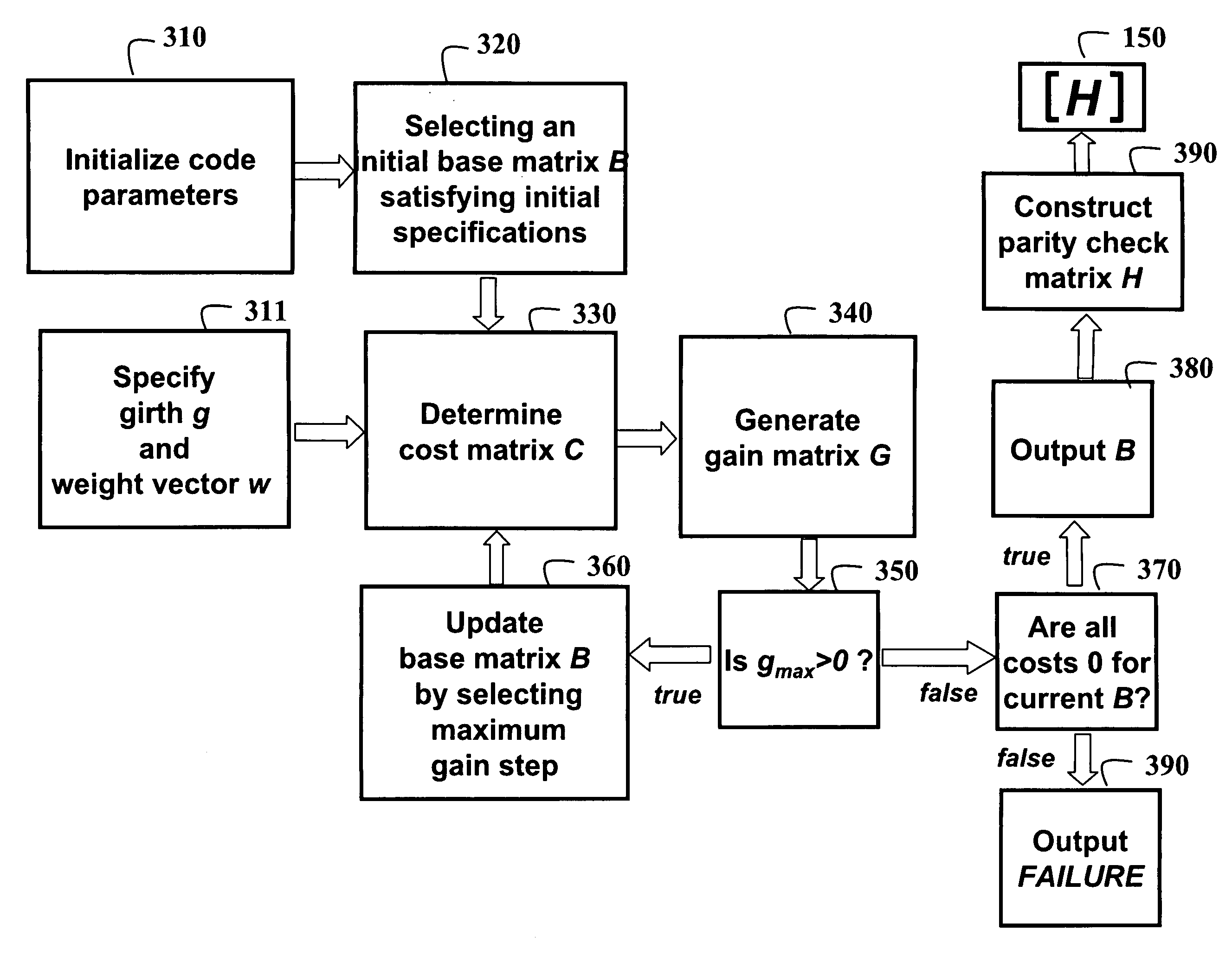
Method for constructing large-girth quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS8103931B2Short block-lengthLess timeCode conversionChecking code calculationsSingle elementTheoretical computer science
A method constructs a code, wherein the code is a large-girth quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check code. A base matrix is selected for the code. A cost matrix corresponding to the base matrix is determined. A single element in the base is changed repeatedly maximize a reduction in cost. A parity check matrix is constructing for the code from the base matrix when the cost is zero, and an information block is encoded as a code word using the parity check matrix in an encoder.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
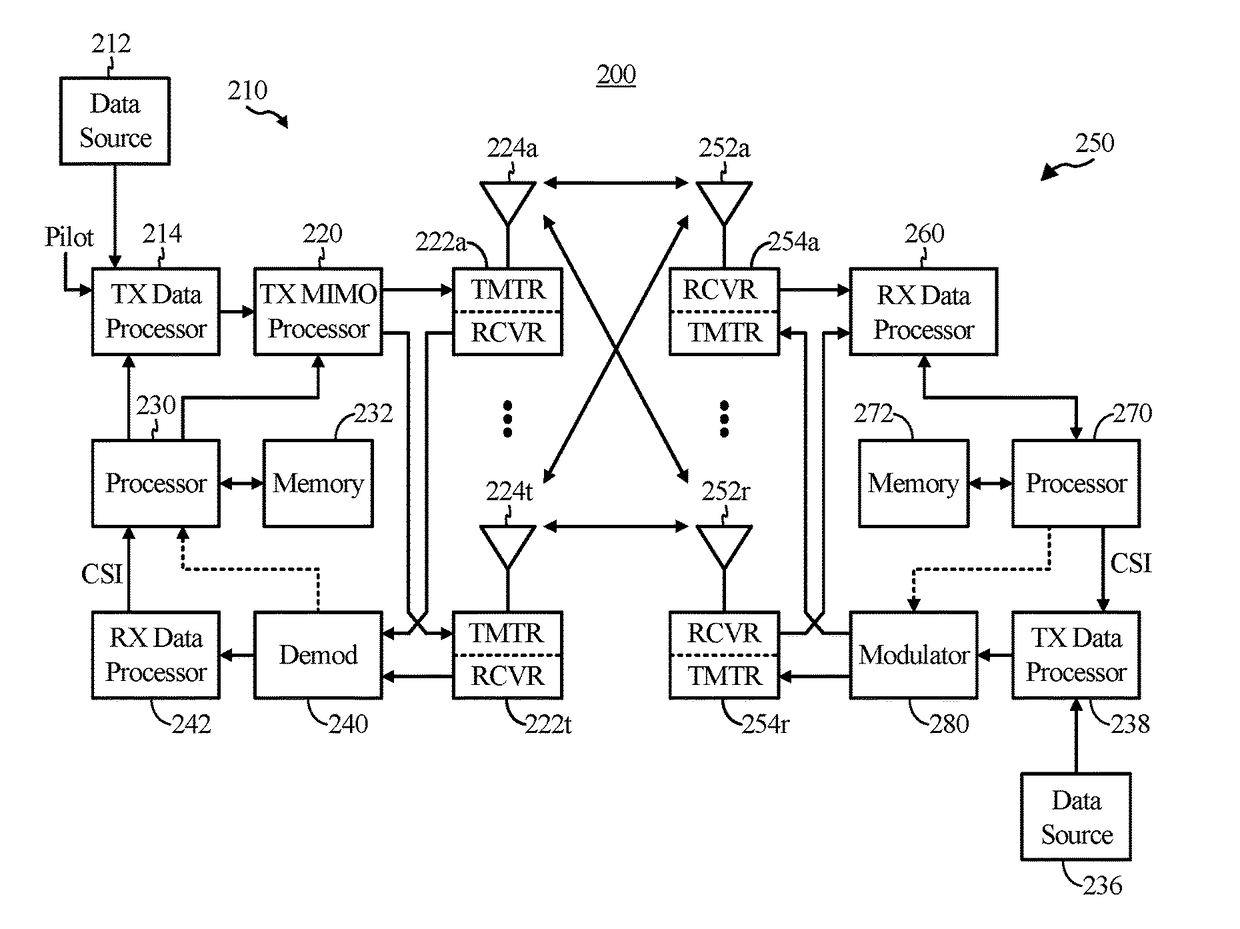
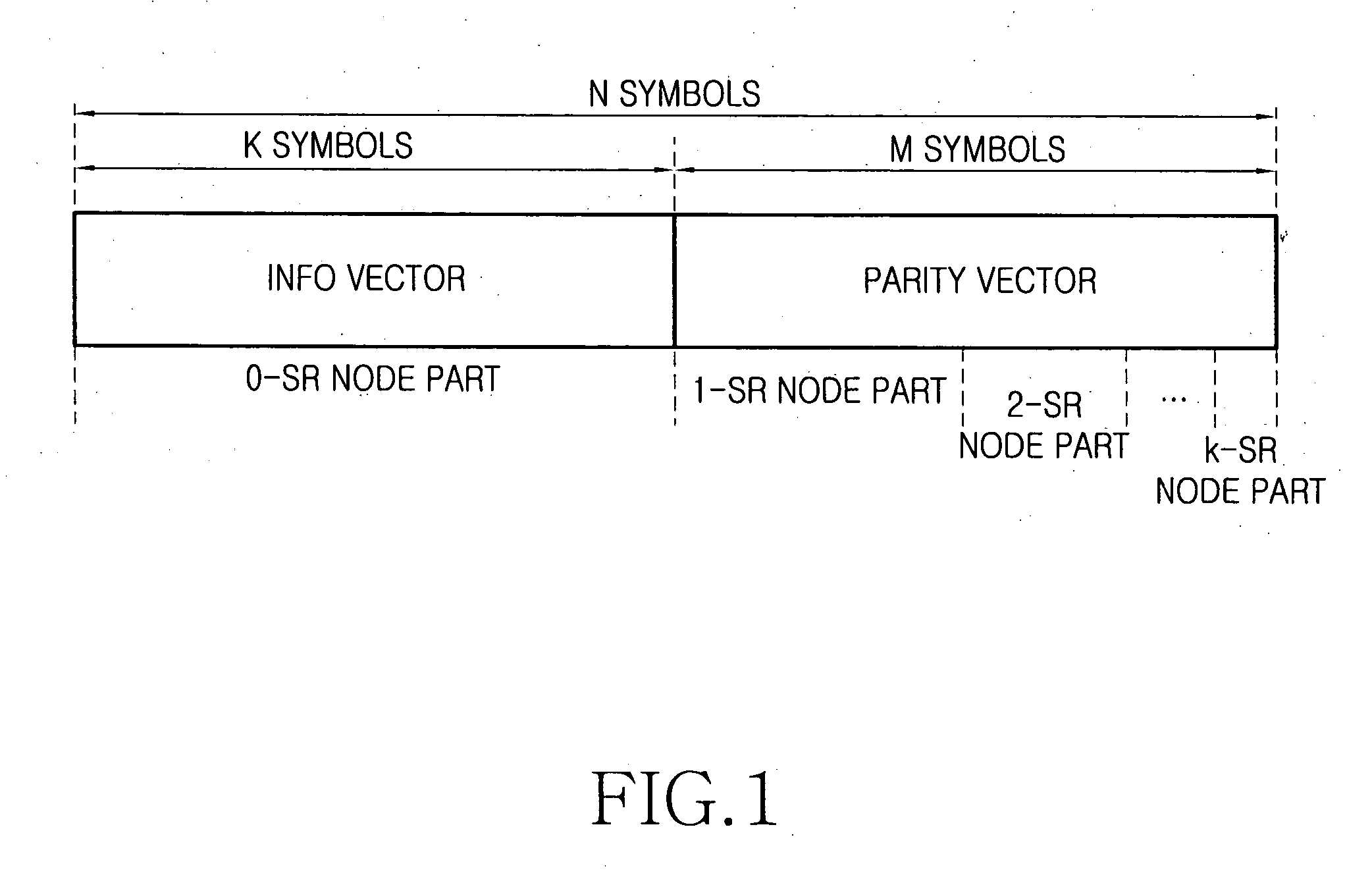
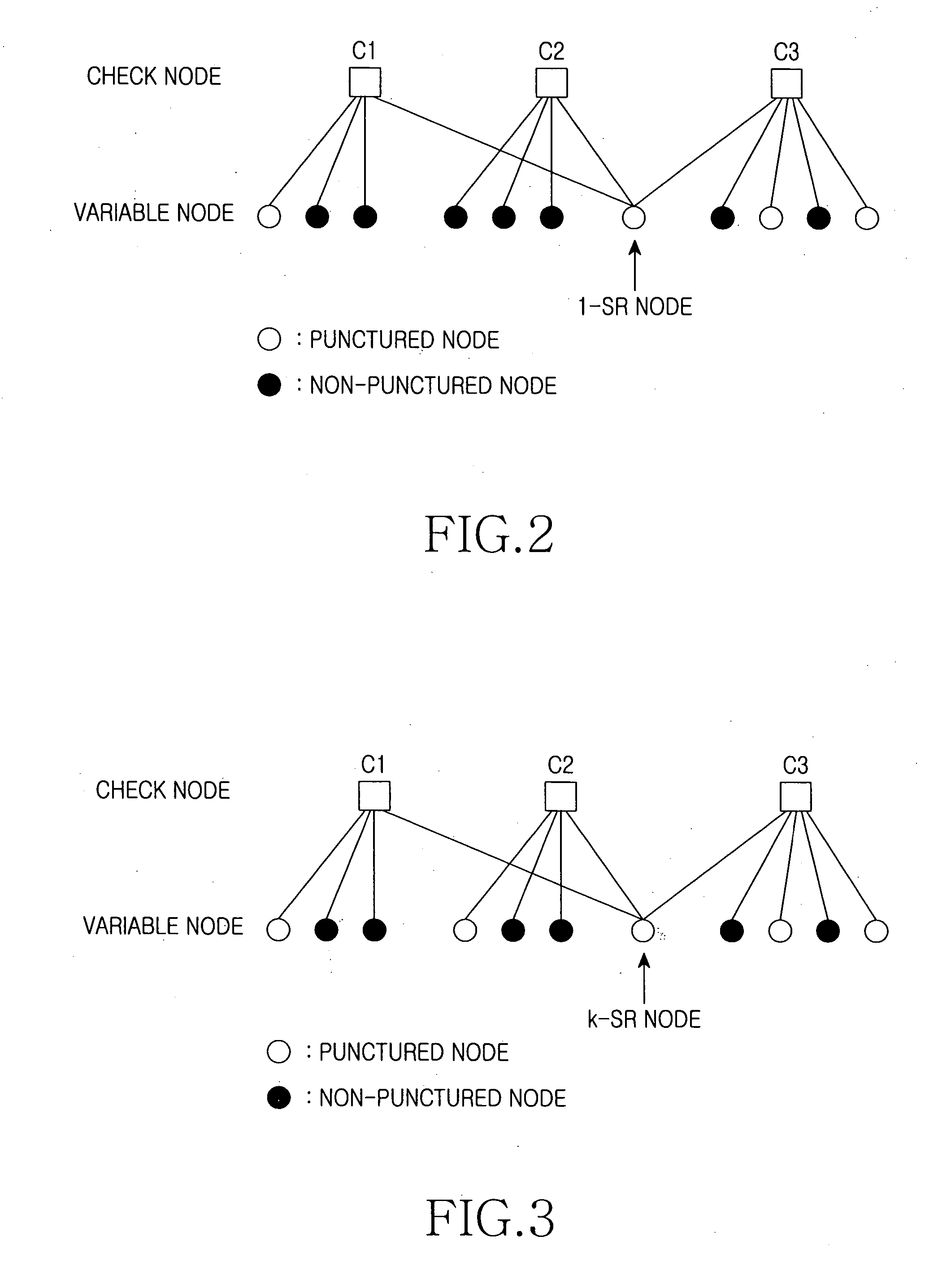
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving signal in a communication system
ActiveUS20070226583A1Error preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCommunications systemLow density
In a communication system, a signal transmission apparatus includes an encoder for encoding an information vector into a low density parity check (LDPC) codeword with an LDPC coding scheme, and a puncturer for puncturing the LDPC codeword according to a coding rate using a puncturing scheme. A signal reception apparatus includes a ‘0’ inserter for inserting ‘0’ symbols in a received signal according to a coding rate used in a signal transmission apparatus, and a decoder for decoding the ‘0’ symbol-inserted signal with a decoding scheme corresponding to a low density parity check (LDPC) coding scheme used in the signal transmission apparatus, thereby detecting an information vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Generation of golay-based systematic block code supporting various sizes
ActiveUS20090217139A1Strong resistanceEffectively generating codesError preventionModulated-carrier systemsComputer hardwareBlock code
A method for generating block codes from Golay code and a method and apparatus for encoding data are provided. The method can effectively generate codes having various lengths, various dimensions, and superior hamming weight distribution, and encodes data such as control information having various lengths into codes having strong resistance to channel errors, resulting in an increase of error correction performance.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
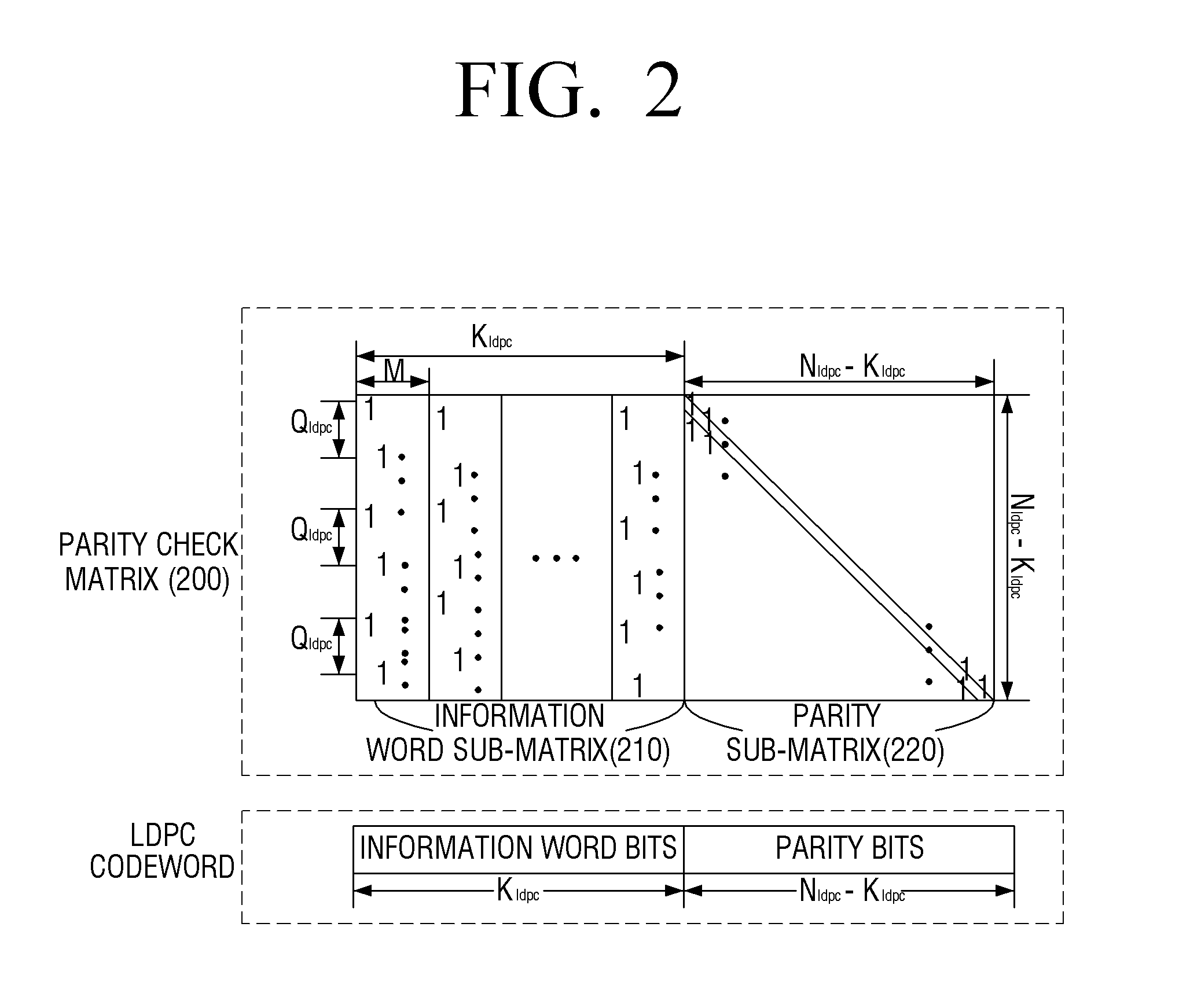
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding of low density parity check codes
ActiveUS20140372825A1Improve decoding performanceImprove codec performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAlgorithmParity-check matrix
An encoding apparatus is provided. The encoding includes a low density parity check (LDPC) encoder which performs LDPC encoding on input bits based on a parity-check matrix to generate an LDPC codeword formed of 64,800 bits, in which the parity-check matrix includes an information word sub-matrix and a parity sub-matrix, the information word sub-matrix is formed of a group of a plurality of column blocks each including 360 columns, and the parity-check matrix and the information word sub-matrix are defined by various tables which represent positions of value one (1) present in every 360-th column.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement [01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9653ab0-f18e-444f-8212-6db105d9530a/US20150303949A1-20151022-D00000.PNG)
![[01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement [01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9653ab0-f18e-444f-8212-6db105d9530a/US20150303949A1-20151022-D00001.PNG)
![[01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement [01] cost-efficient repair for storage systems using progressive engagement](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9653ab0-f18e-444f-8212-6db105d9530a/US20150303949A1-20151022-D00002.PNG)