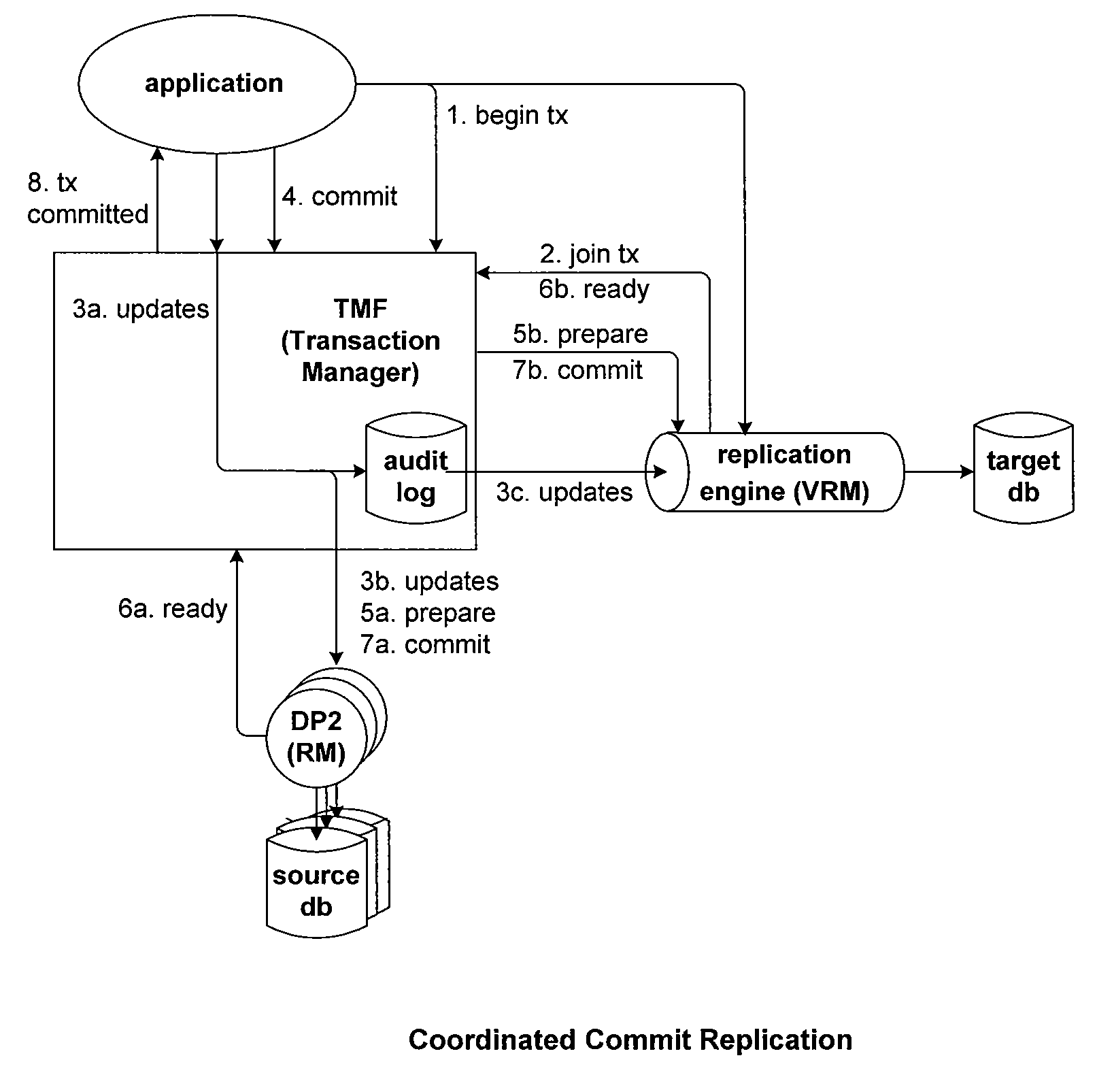
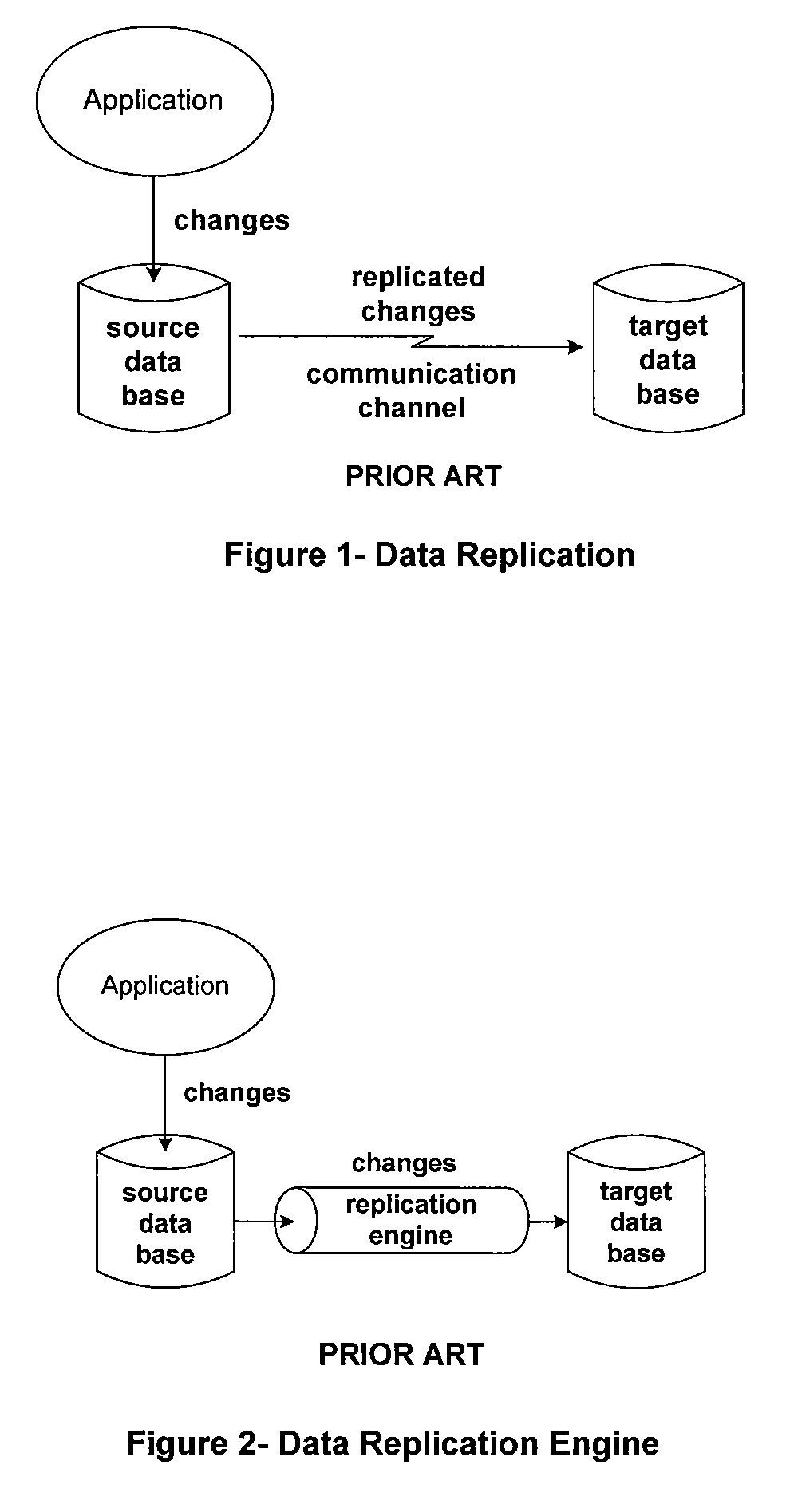
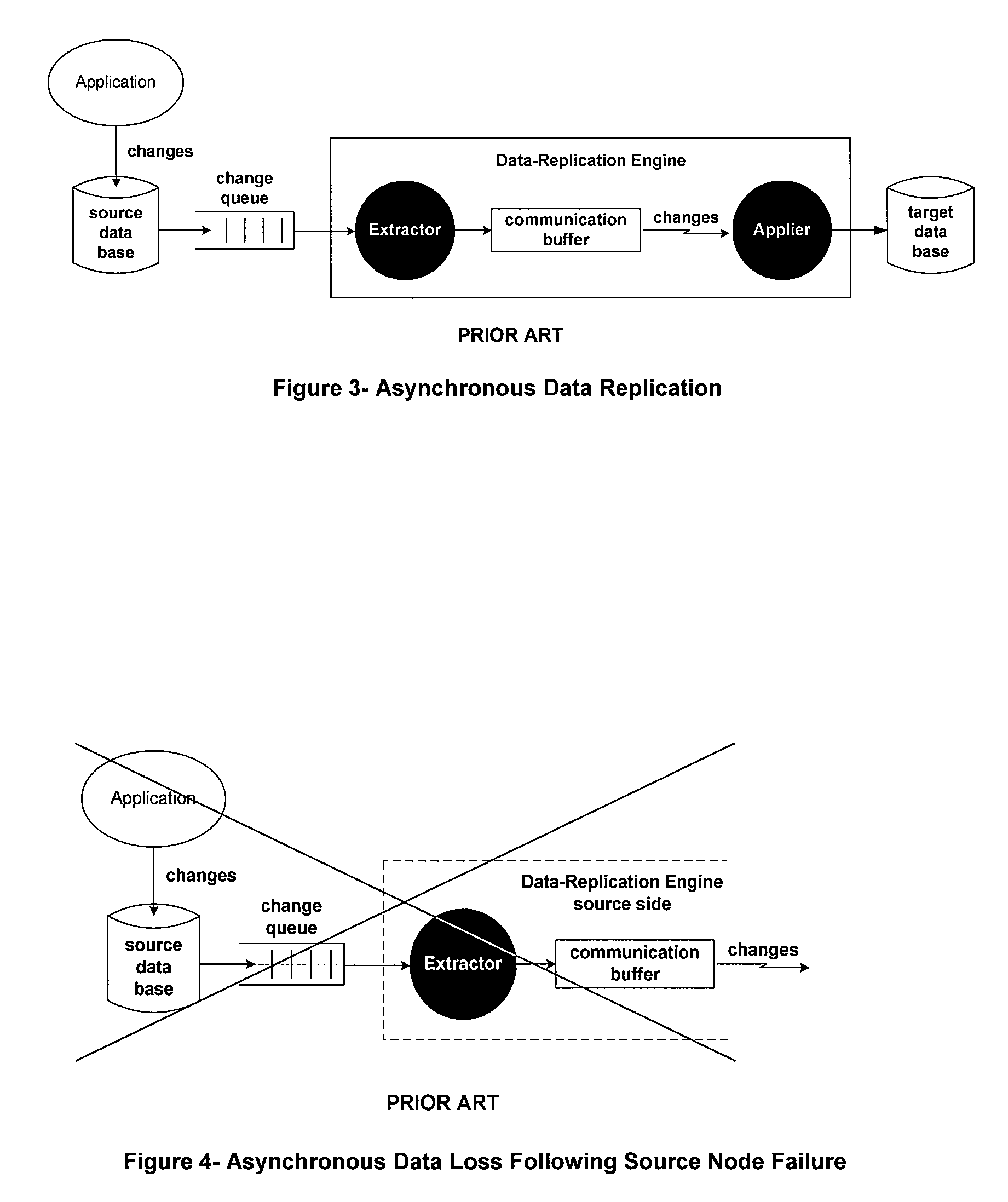
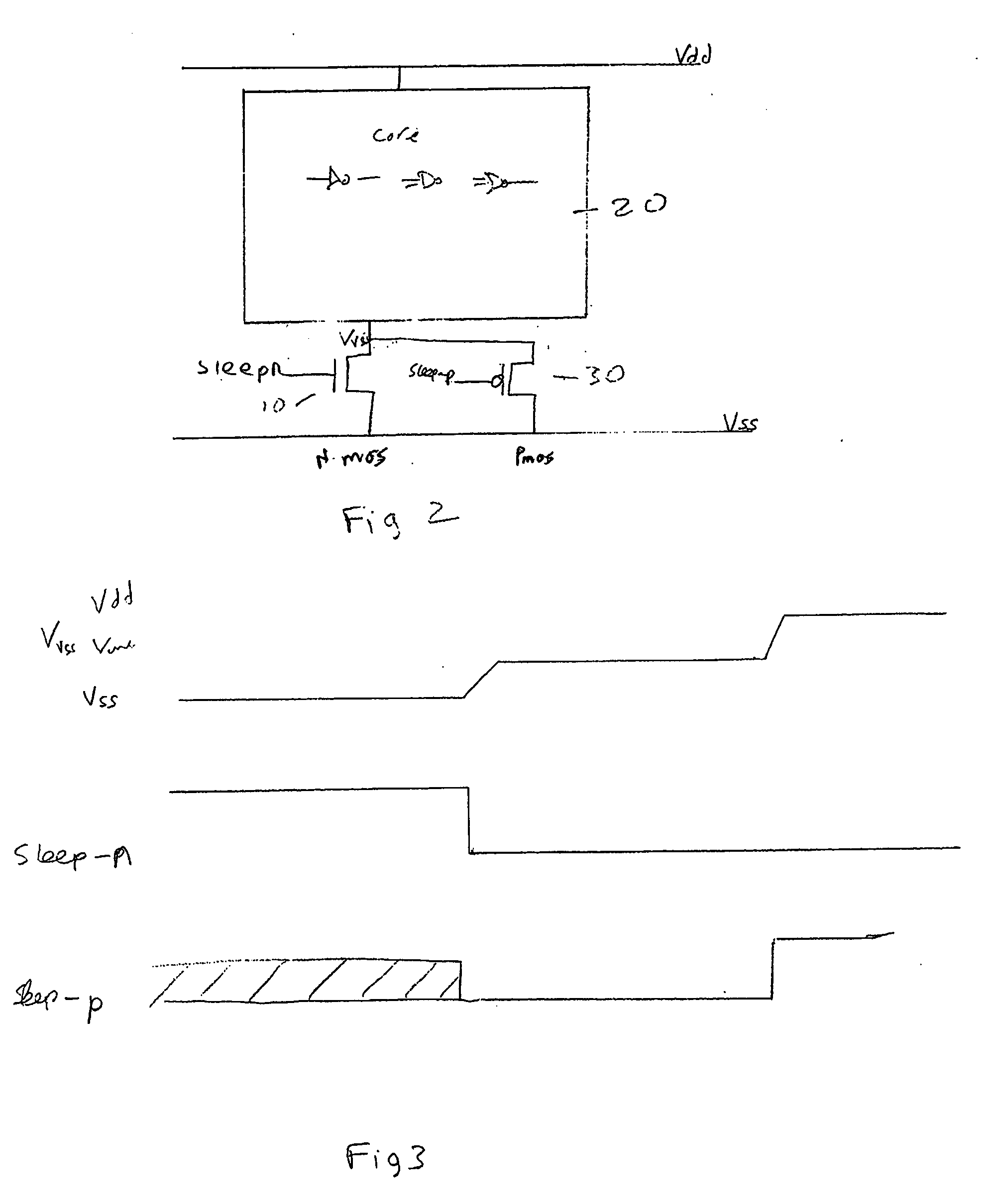Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198results about How to "Reduce data loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mixed mode synchronous and asynchronous replication system
ActiveUS8301593B2Reduce stepsAvoid data lossDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionAsynchronous communicationApplication software
A replication system that includes an asynchronous replication mode and a synchronous replication mode replicates data associated with a plurality of transactions. The replication system includes one or more target nodes connected via communication media in a topology. Each target node includes a database and a plurality of appliers allocated thereto. Each transaction has one or more transaction steps or operations. A first set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on an object-by-object basis when the replication system operates in asynchronous replication mode. A second set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on a transaction-by-transaction basis when the replication system operates in synchronous replication mode. The replication system further includes one or more originating nodes, and the requests for the first and second sets of transaction steps or operations to execute on an originating node can be initiated during the same time period.
Owner:RPX CORP
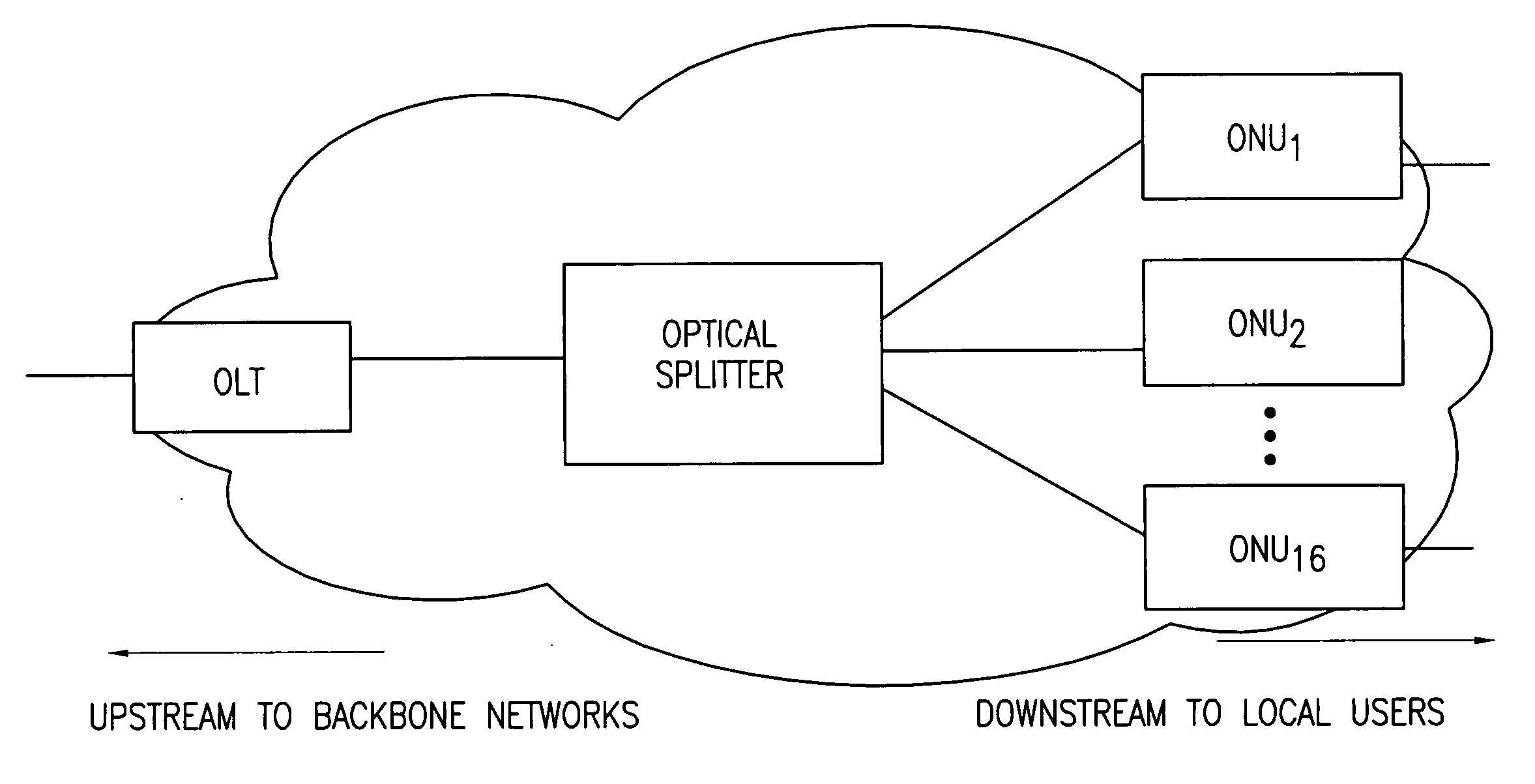
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
System and method for synchronizing data trasnmission across a variable delay interface
InactiveUS20020089927A1Significant overheadLimitation in wireless bandwidthError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsSufficient timeComputerized system
A method of synchronizing data transmission between a host computer system and a transmitter across an interface with variable delay or latency. The host computer system marks transition frames between successive transmission intervals and transfers the outgoing frames across the variable interface to the transmitter. The transmitter enqueues outgoing frames into one or more FIFO transmission queue(s) and processes the enqueued frames as appropriate for the communication protocol in use. Marked frames are detected as they reach the head of the appropriate transmit queue. In particular, while bypassing is not active, the transmitter transmits unmarked frames until the end of the current interval, or until there is insufficient time in the interval to transmit another frame or until a marked frame is detected. While bypassing is not active, the transmitter terminates transmission from the transmit queue when a marked frame is detected during each interval. While bypassing is active, the transmitter discards unmarked frames without transmission until a marked frame is detected. During each interval, the transmitter activates bypassing if a marked frame has not been detected and deactivates bypassing if a marked frame is detected while bypassing is active. The transmitter enables queue mark operation if a marked frame is detected while queue mark operation is not enabled. The transmitter increments a bypass counter each time an interval ends without detecting a marked frame, and disables queue mark operation if the bypass counter reaches a predefined limit.
Owner:CONEXANT
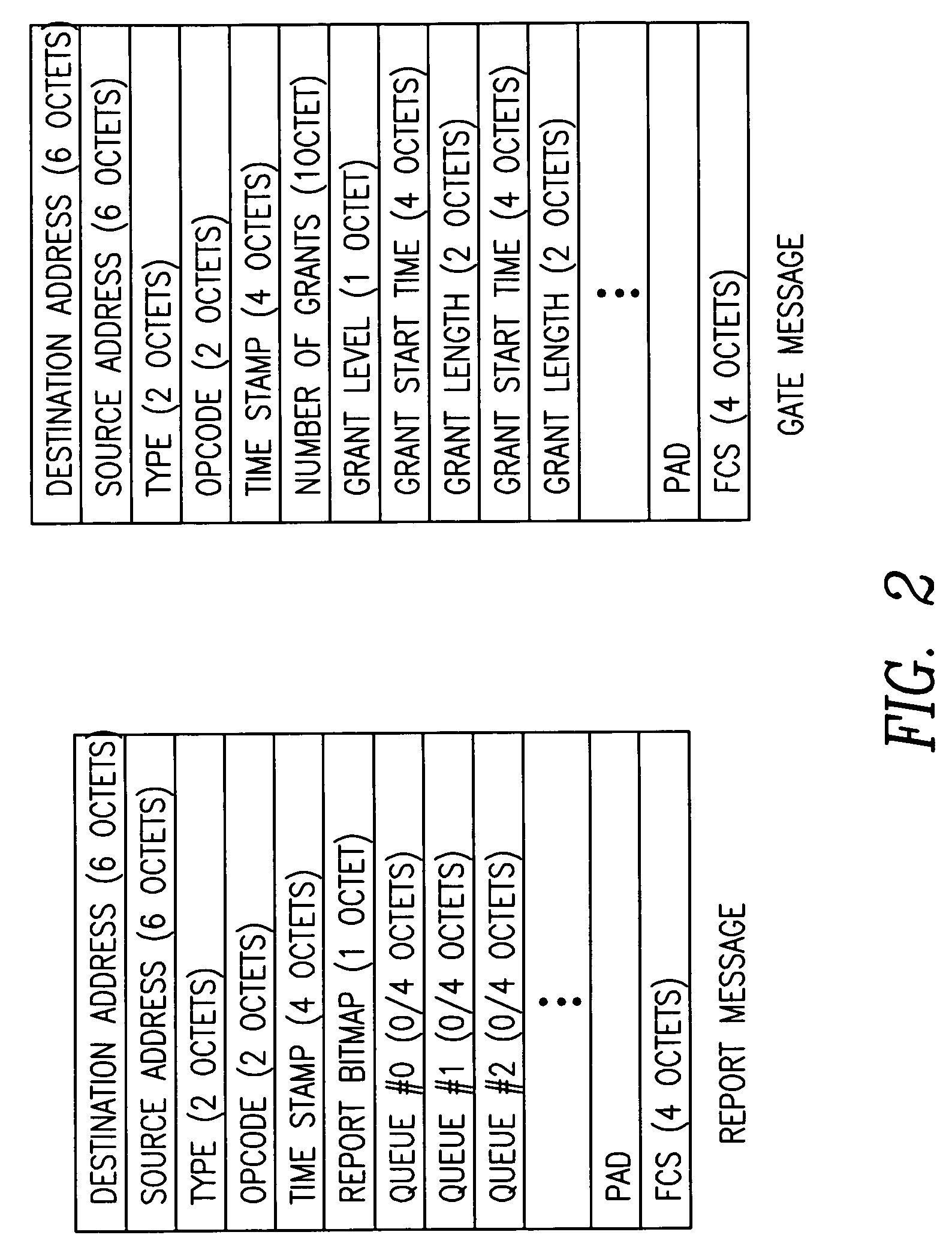
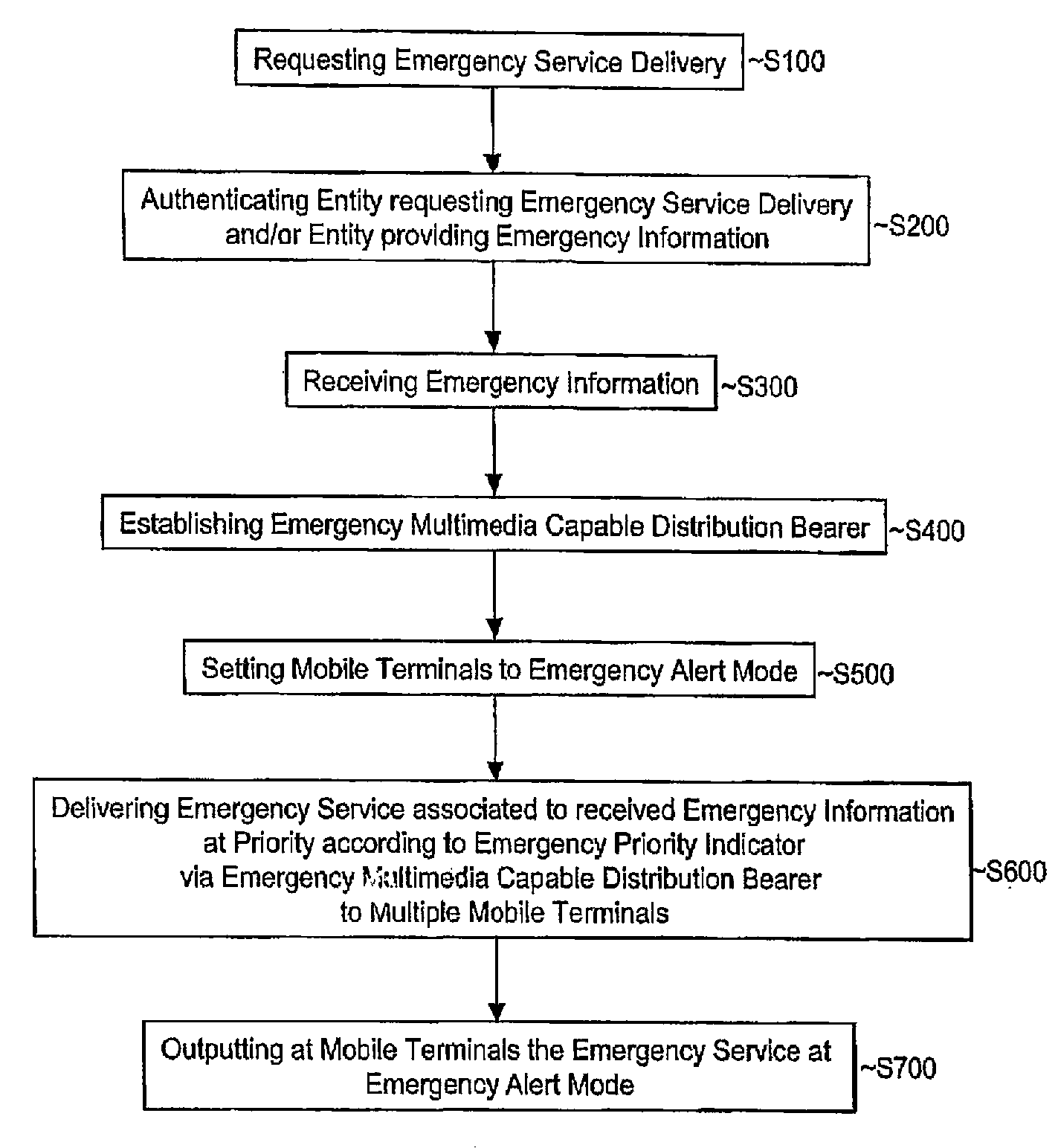
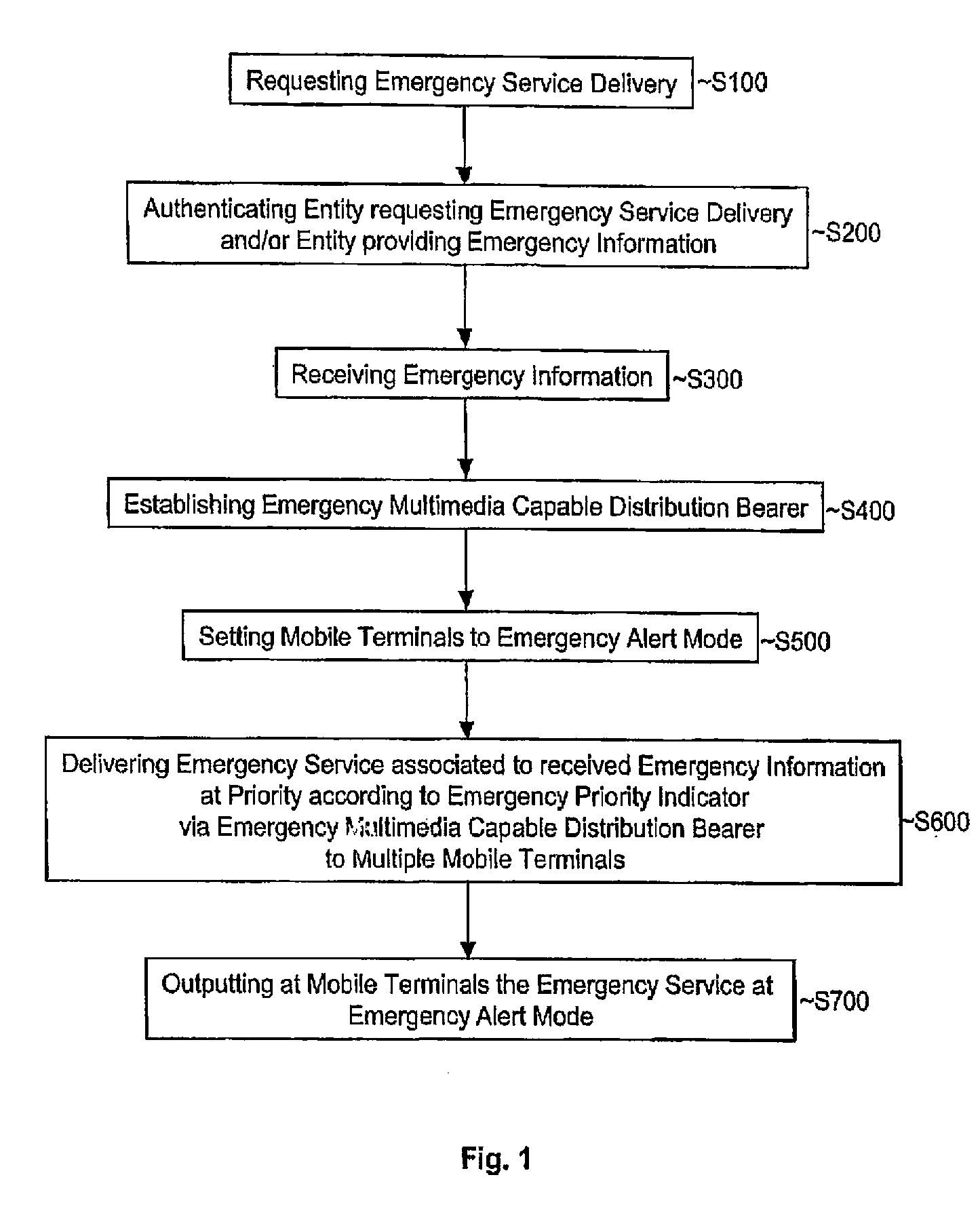
Method for Informing Multiple Mobile Terminals of an Emergency Event
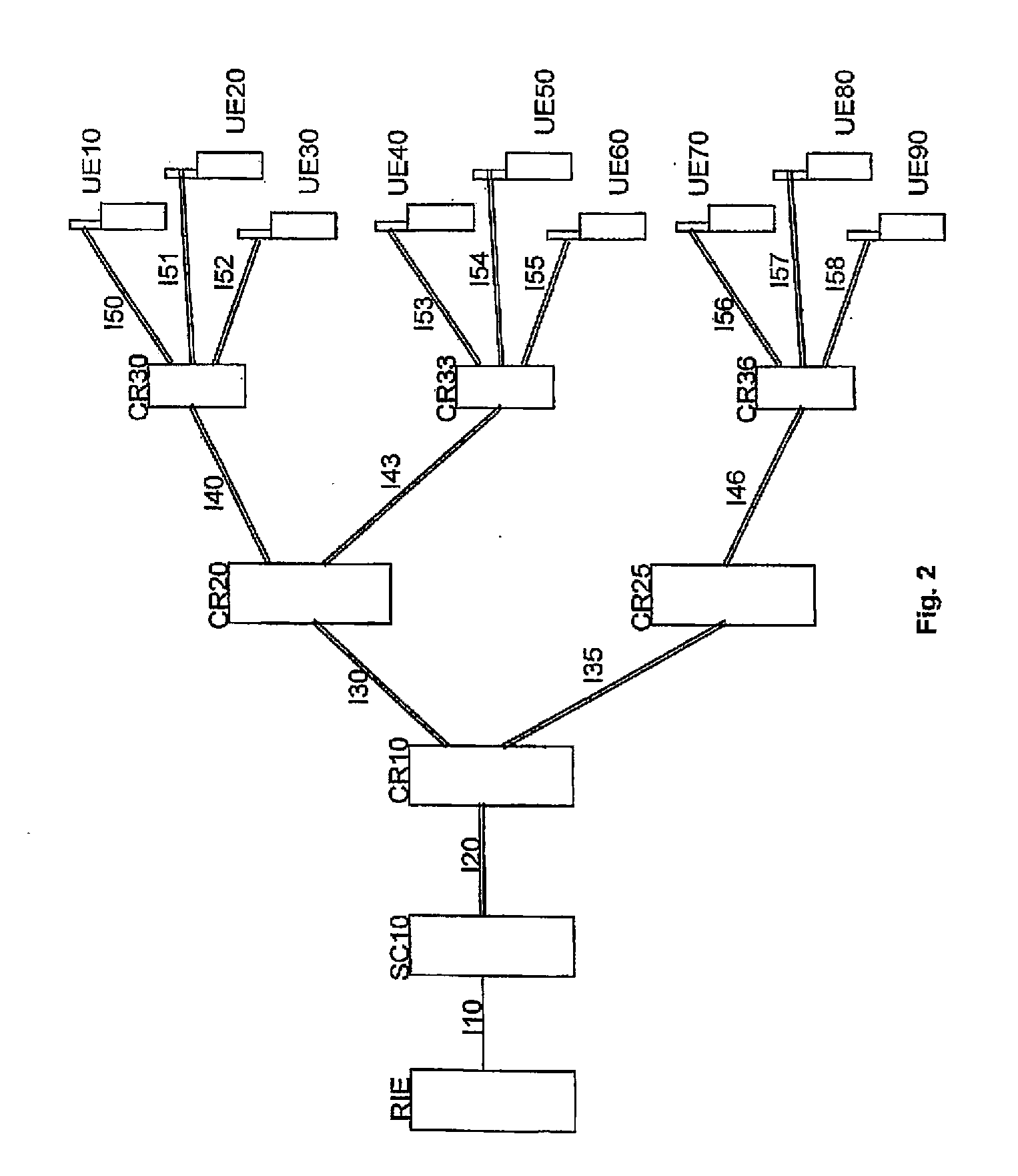
ActiveUS20080261554A1Reduce data lossImprove service qualityTelephonic communicationBroadcast service distributionComputer scienceComputer program
A method, devices, a system, and computer programs for informing multiple mobile terminals (UE10-90) of an emergency event are disclosed. The method comprises the steps of receiving (S300) emergency information associated with the emergency event, establishing (S400) an emergency multimedia capable distribution bearer for a delivery of an emergency service associated with the received emergency information, the emergency multimedia capable distribution bearer being associated with an emergency priority indicator indicating a higher priority for the emergency multimedia capable distribution bearer compared to further communication being not associated with the emergency priority indicator, and delivering (S600) the emergency service via the emergency multimedia capable distribution bearer to the multiple mobile terminals (UE10-90).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
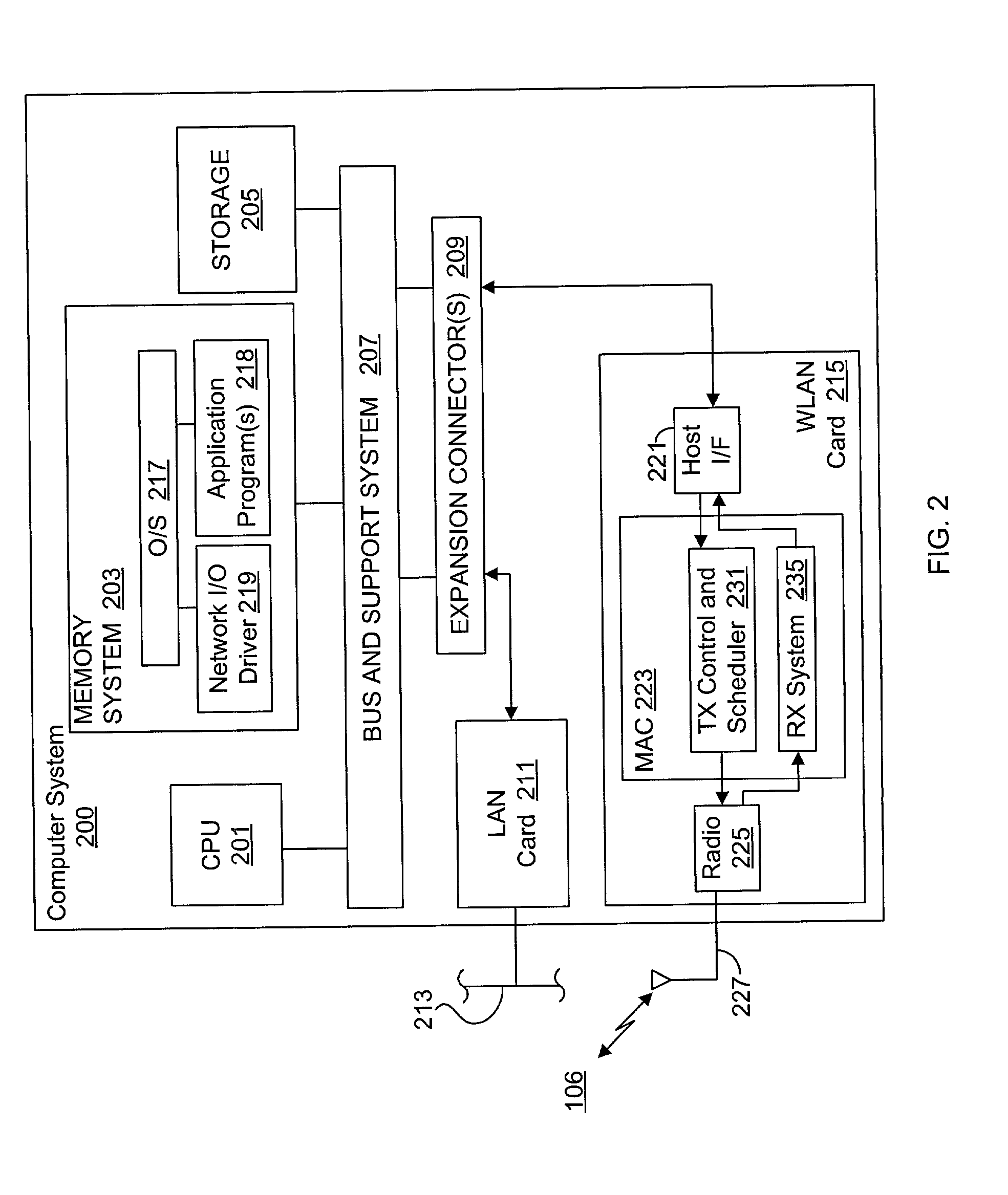
System and method for providing a selectable retry strategy for frame-based communications
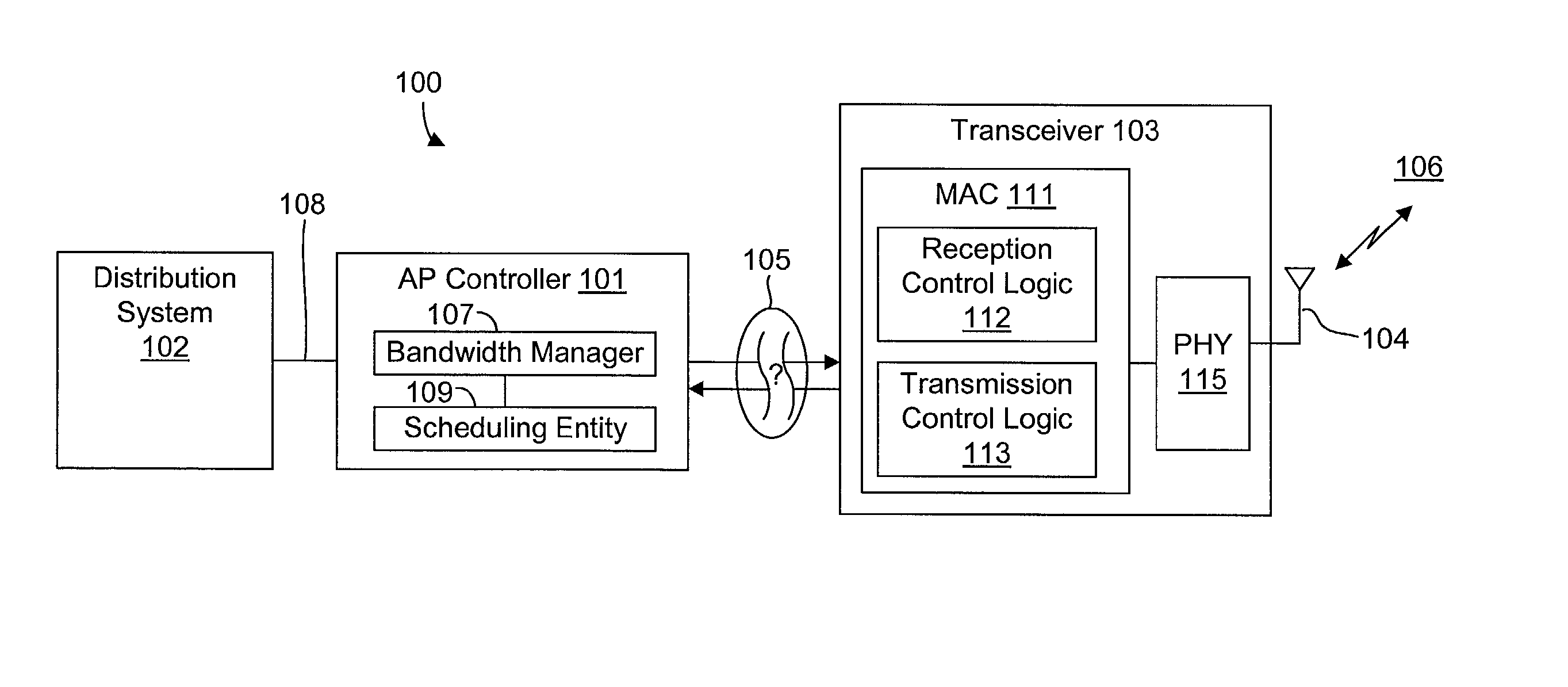
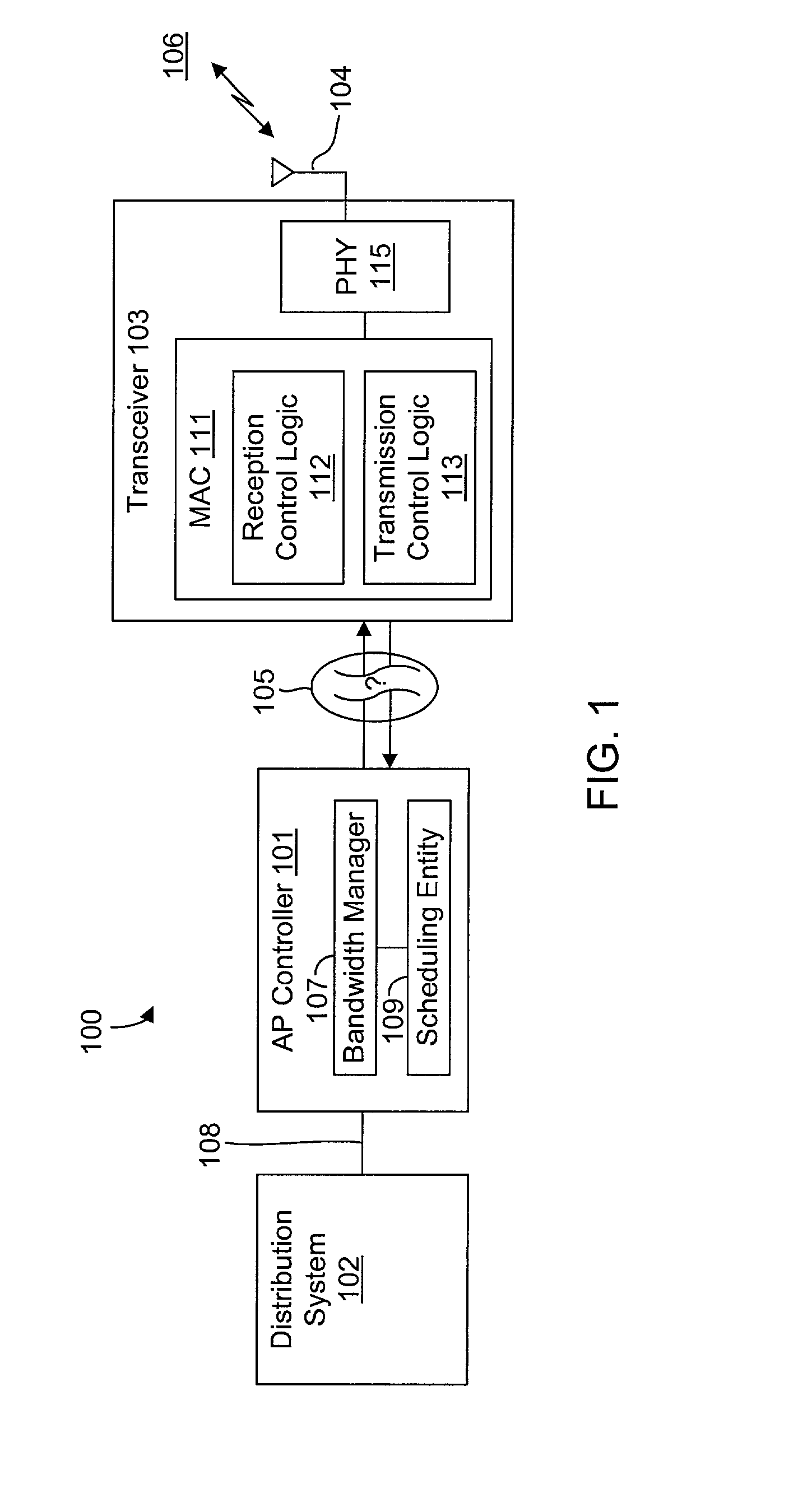
InactiveUS20020089959A1Eliminate timeBroaden applicationError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTransceiverCommunications system
A frame-based communications system with selectable retry strategy including a controller that programs a retry strategy field of a frame descriptor of a frame, where the retry value indicates a selected one of a normal retry count, an alternative retry count, and at least one "no retry" option. The system includes a transceiver that attempts retransmission of the frame up to as many times indicated by a selected retry count or until expiration of a frame transmit duration, or that does not attempt retransmission if the retry value indicates no retry. The no retry options may include treating the first attempt as successful or returning an unsuccessful attempt as a failure. The frame itself may be programmed with a request to not acknowledge a successfully received frame to recapture the time normally allocated to acknowledgement frames. The transceiver may include acknowledgement logic that is configured to suppress an acknowledgement frame.
Owner:CONEXANT
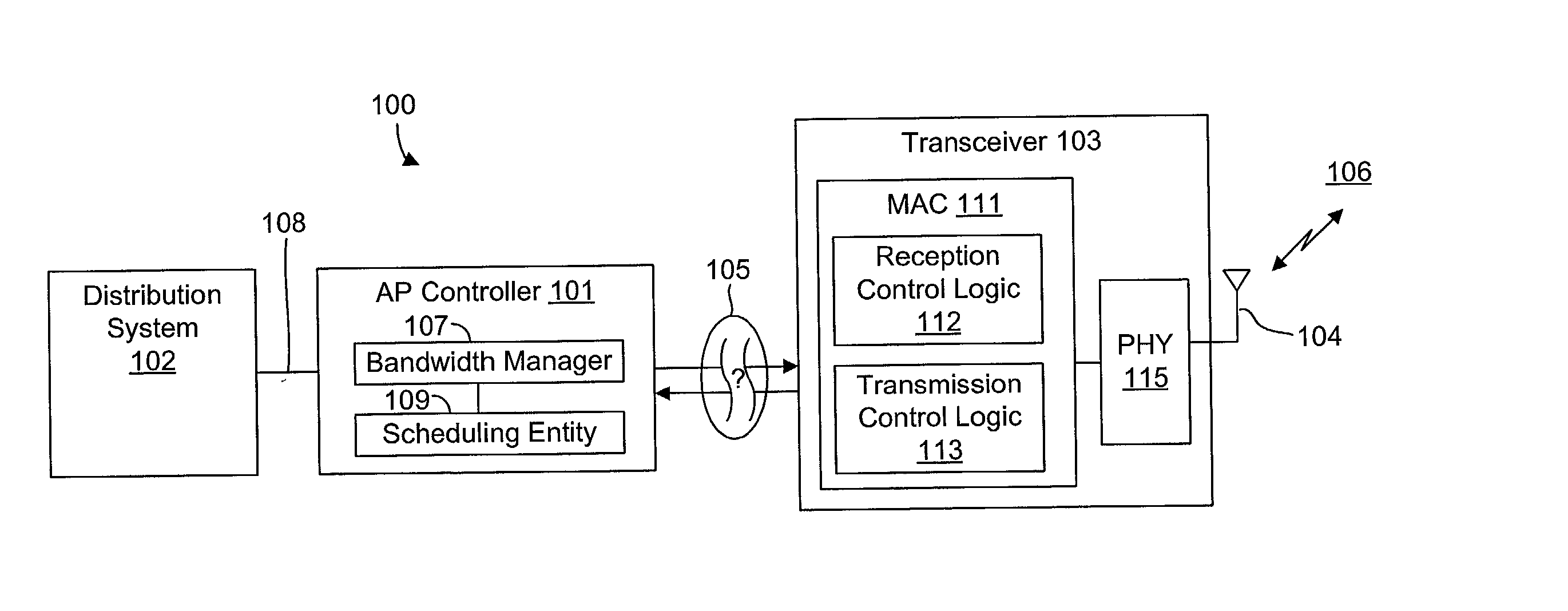
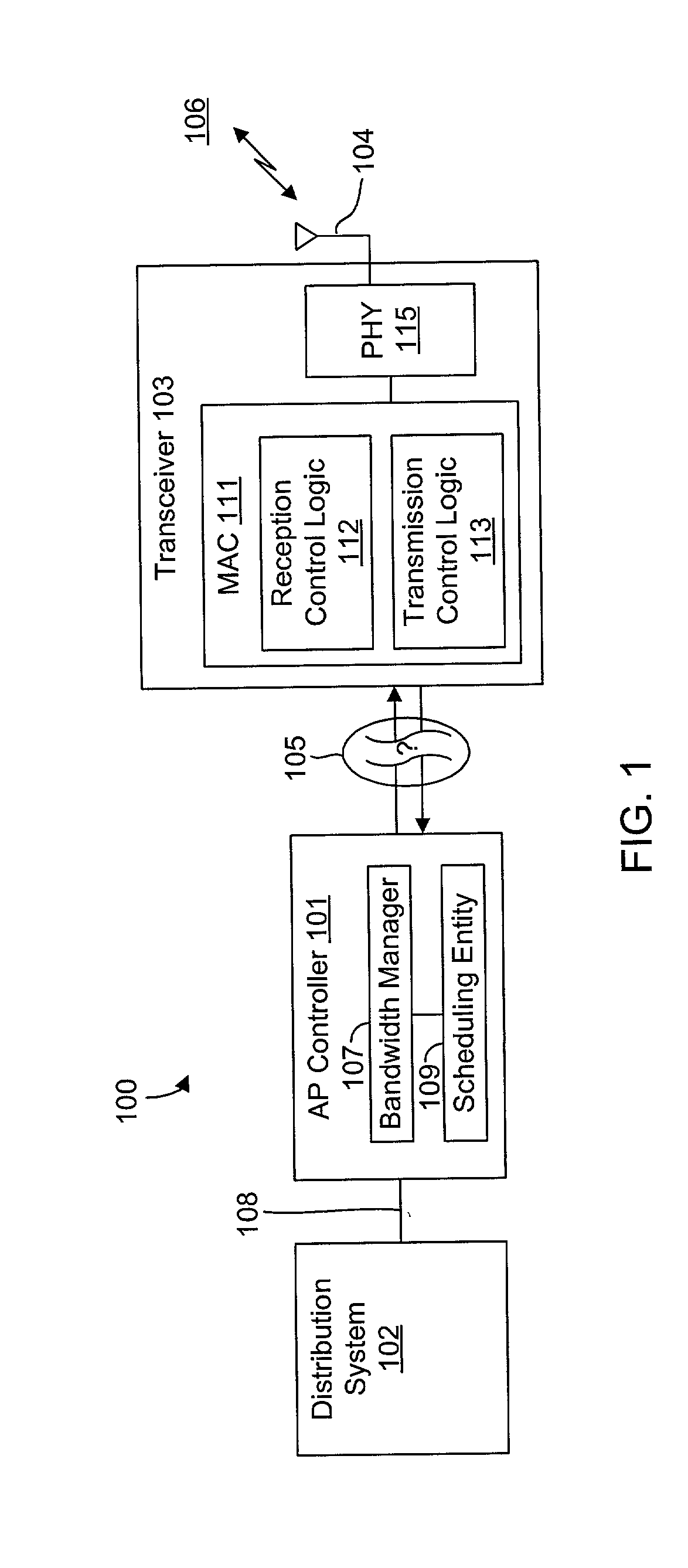
System and method of repetitive transmission of frames for frame-based communications
InactiveUS20020089994A1Function increaseLower latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemFrame based
A communications system including a scheduling entity and a transceiver coupled across a variable timing interface. The scheduling entity forwards frames for transmission and identifies selected frames as persistent. The transceiver includes a queue, a frame manager and a transmission scheduler. The frame manager receives and enqueues forwarded frames and the transmission scheduler dequeues and transmits frames from the queue and forwards persistent frames back to the frame manager. The transmission scheduler includes persistence logic that detects a persistent mark and asserts a persistent signal that is detected by the transmission scheduler. The scheduling entity identifies a persistent frame by setting a bit in a transmit control field of the frame descriptor. The scheduling entity sends a clear persistence command to the transceiver to clear a persistent mark of an identified frame. The transceiver may be configured for wireless communications.
Owner:CONEXANT
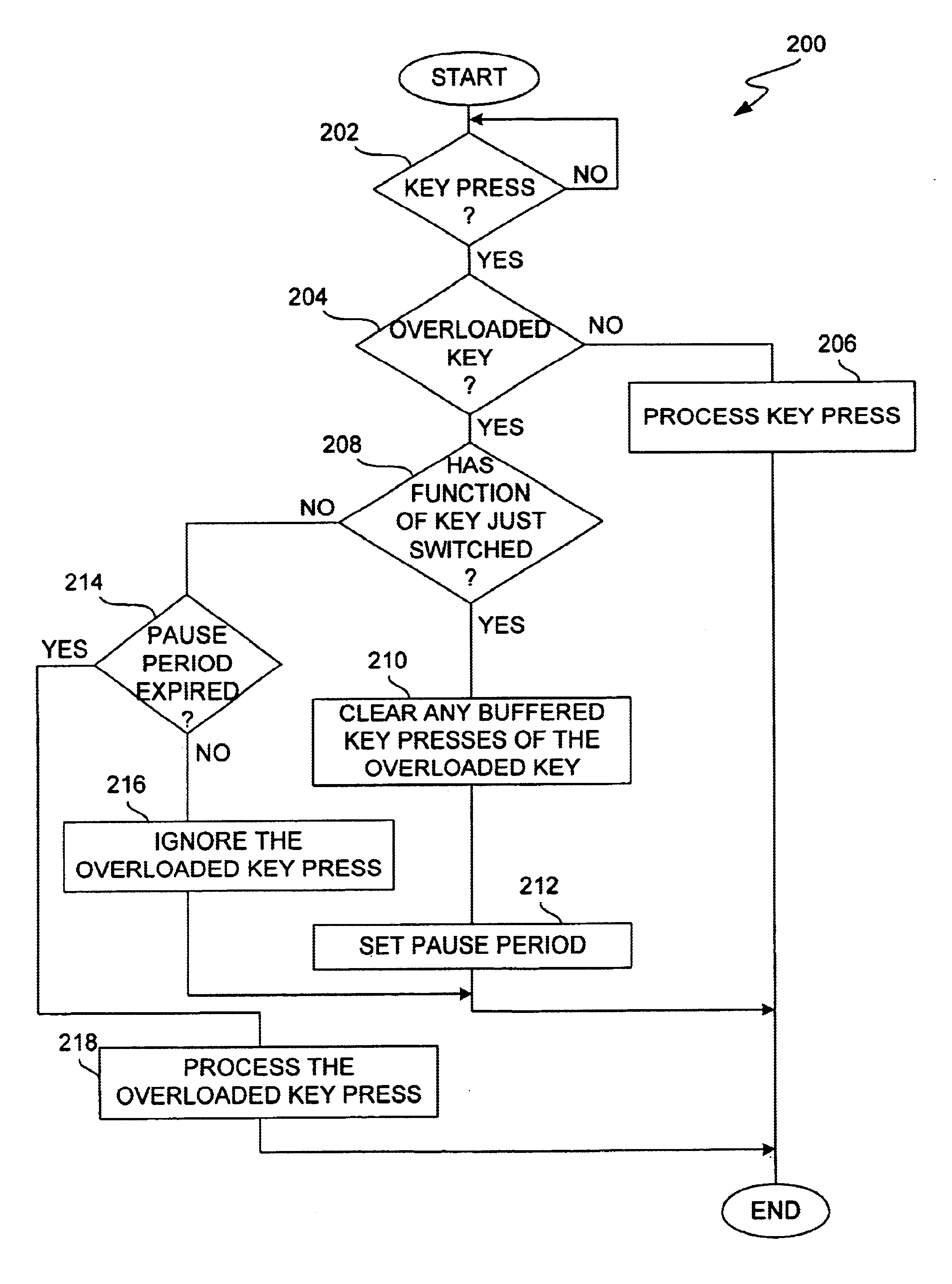
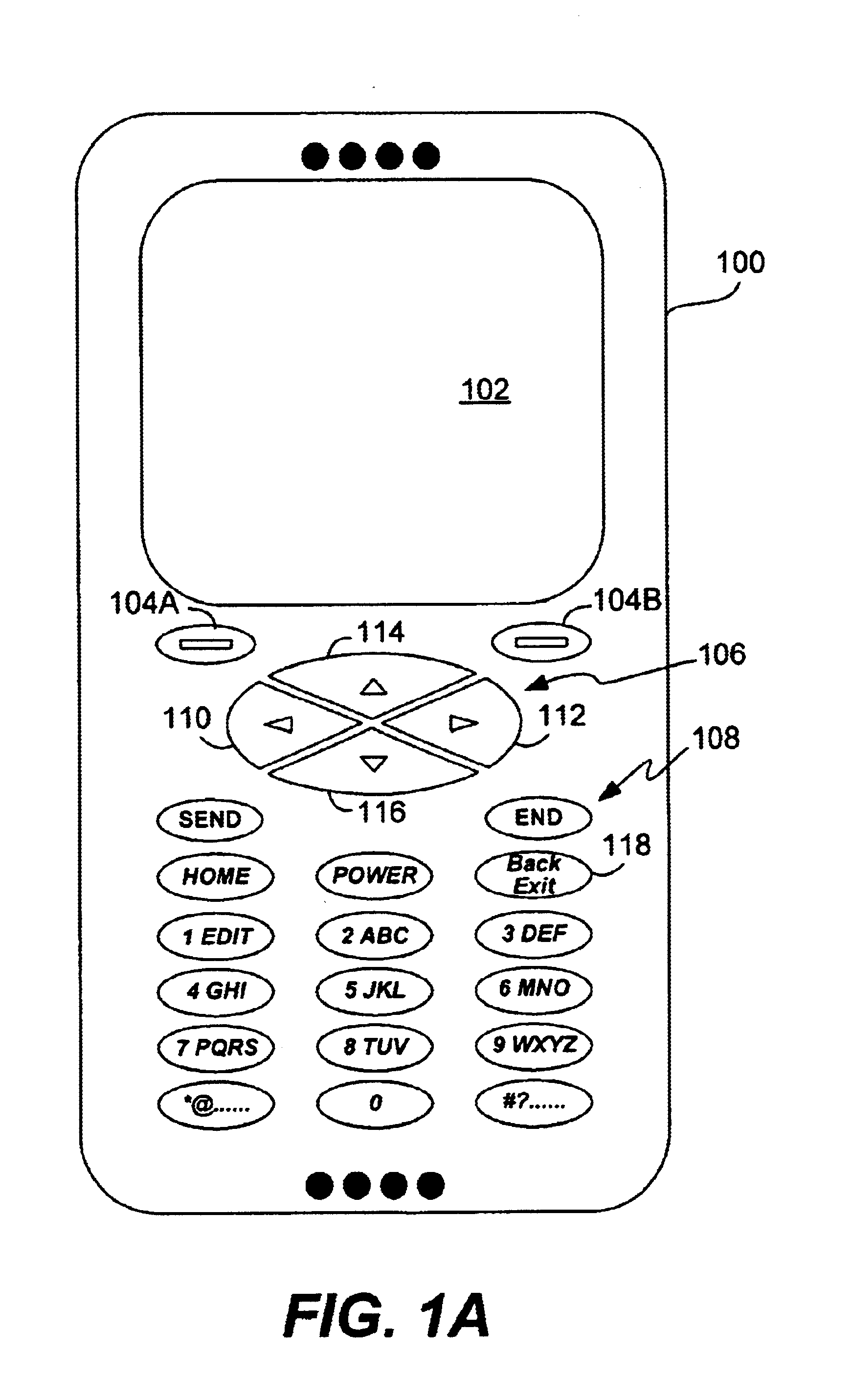
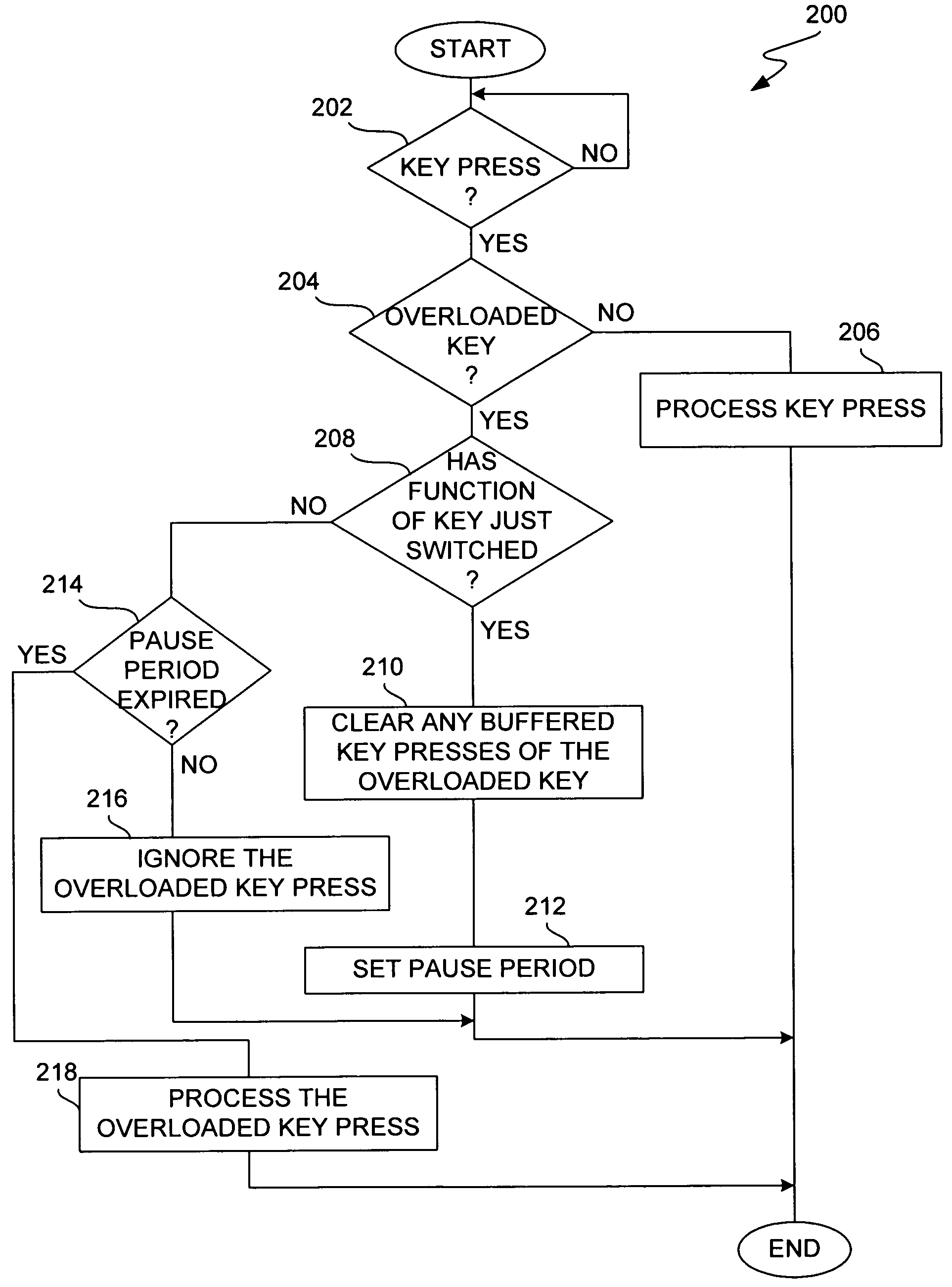
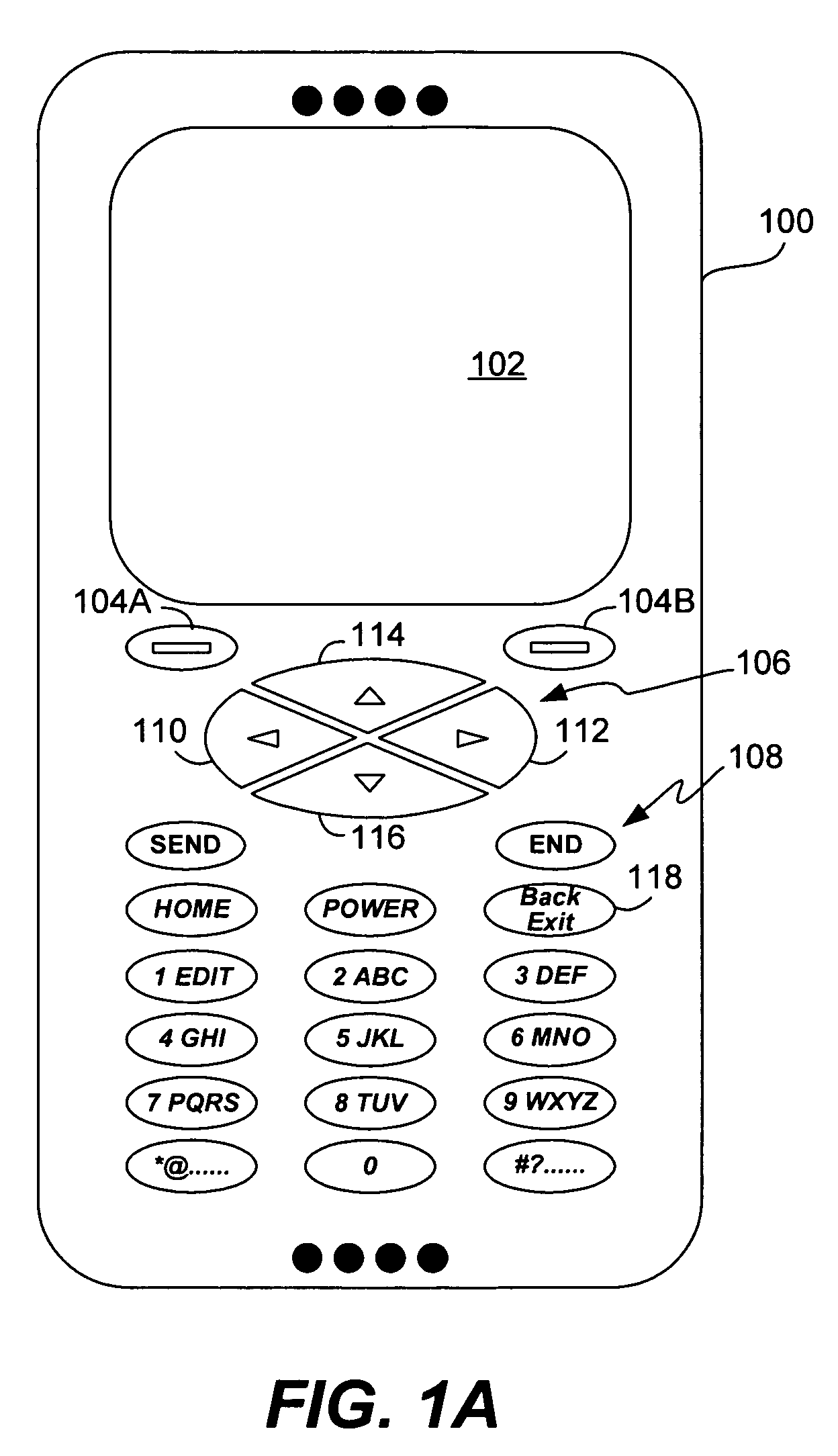
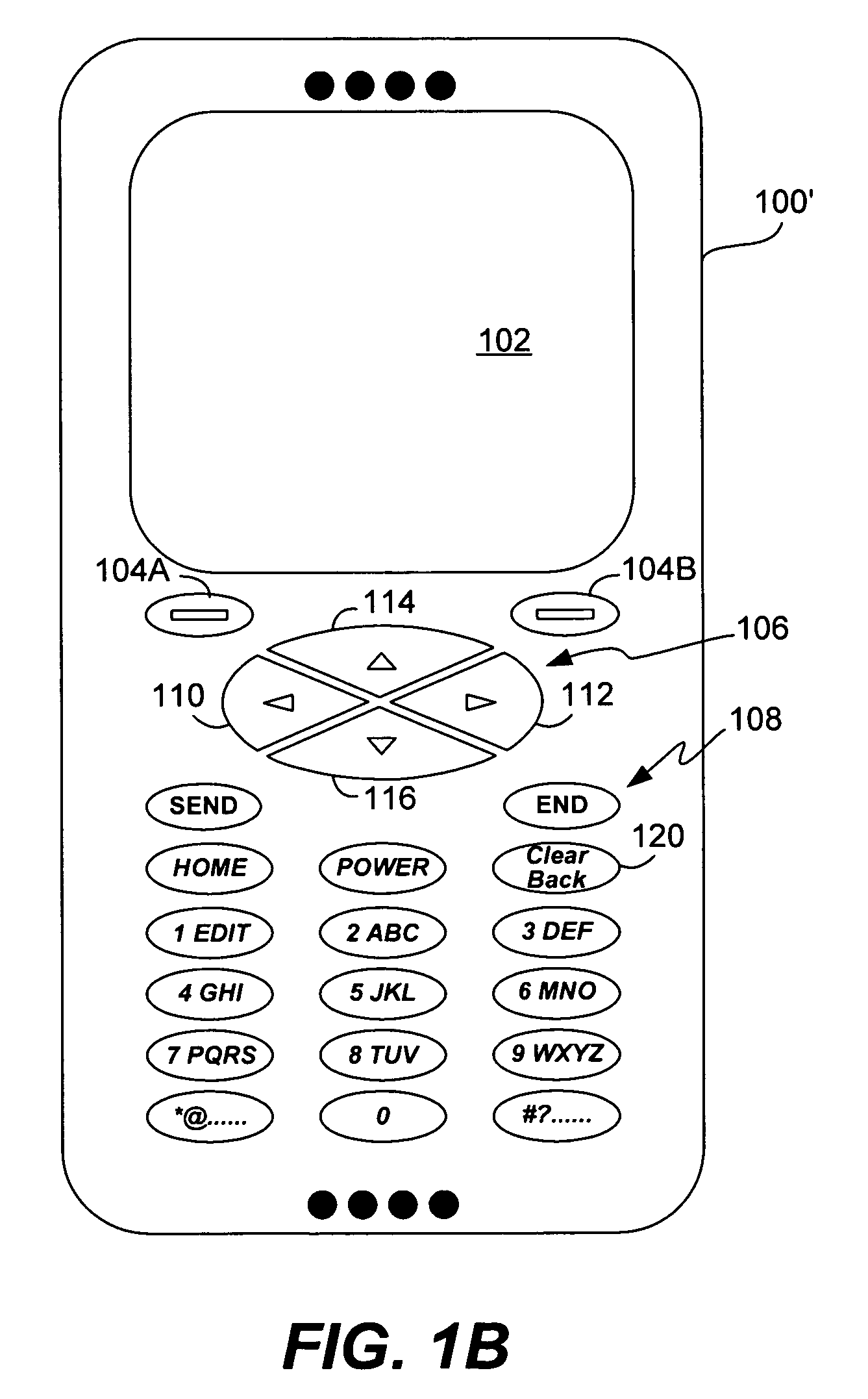
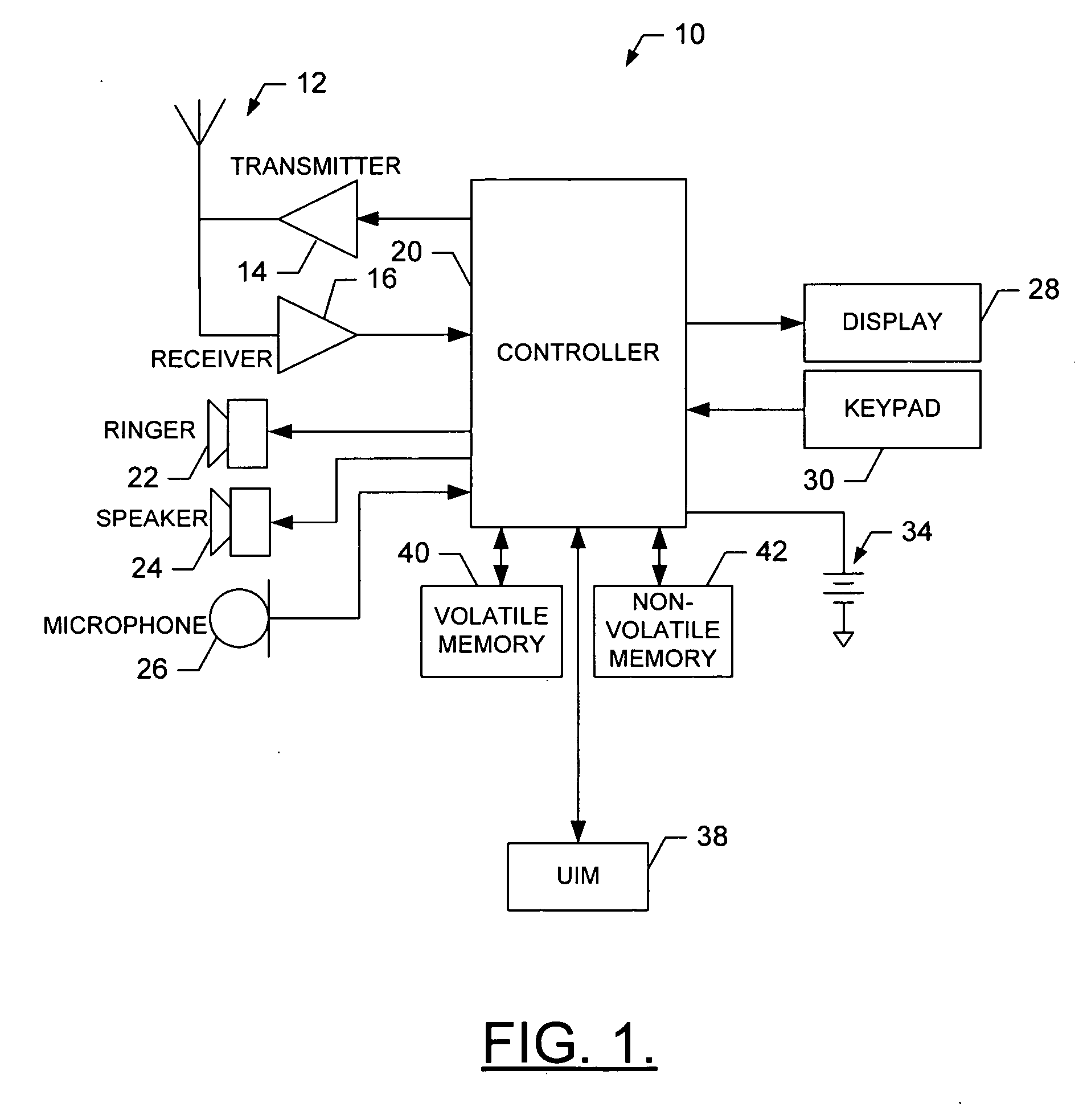
Method and system for processing overloaded keys of a mobile device
InactiveUS6907273B1Few mistakeReduce data lossTransmissionTelephone set constructionsComputer hardwareKey pressing
Improved approaches are disclosed for processing overloaded keys substantially more in accordance with user's expected behavior. With the improved approaches, users are less likely to undergo unexpected processing in response to overloaded key presses. In one embodiment, the processing ignores certain overloaded key presses and / or imposes delays to ensure that users have an opportunity to appreciate when an overloaded key has switched to another function. These approaches are particularly well suited for small scale mobile devices having reduced size displays and overloaded keys such as mobile phones (e.g., cellular phones), two-way pagers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), or other two-way mobile communication devices.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
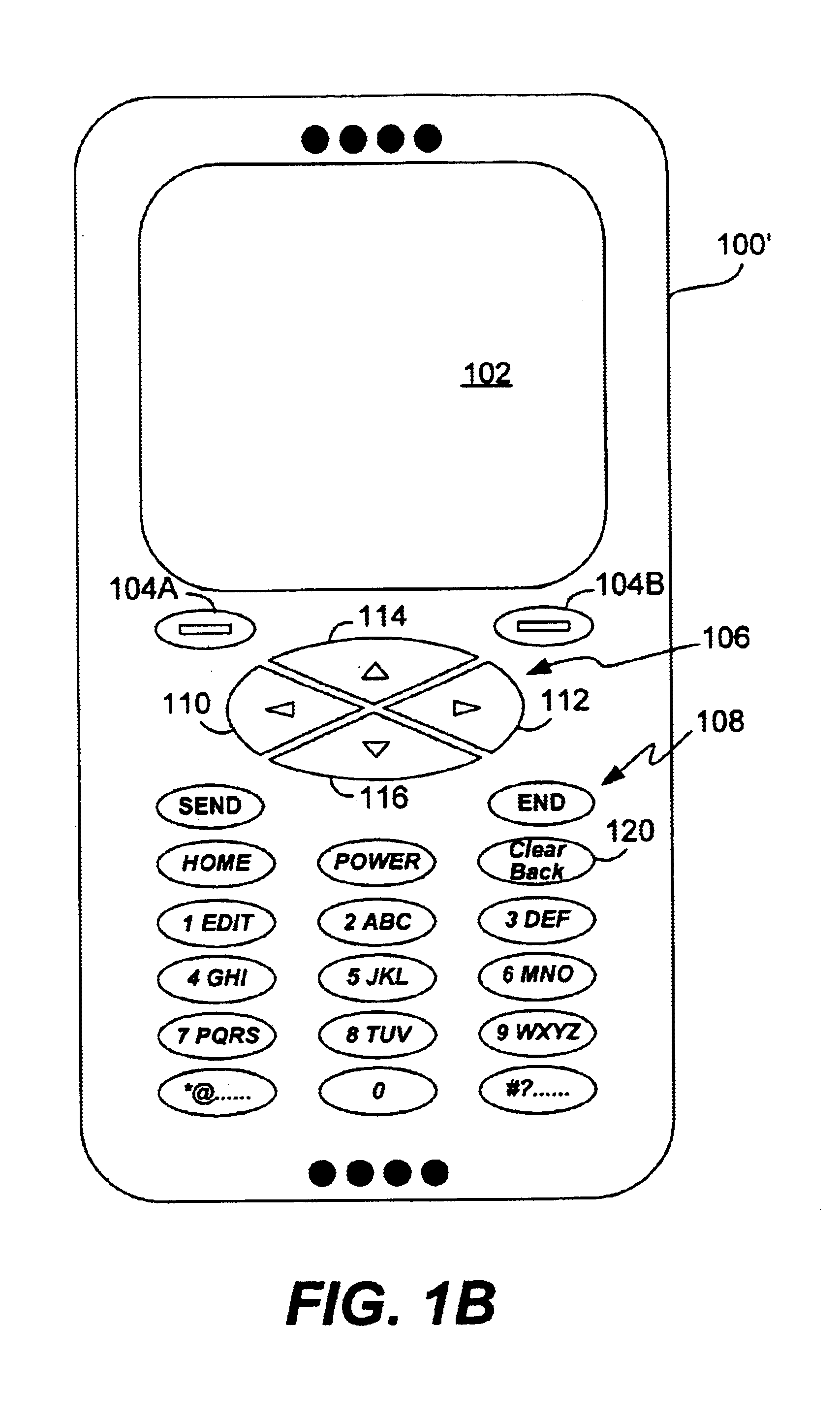
Method and system for processing overloaded keys of a mobile device
InactiveUS7065386B1Few mistakeReduce data lossInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer hardwareKey pressing
Improved approaches are disclosed for processing overloaded keys substantially more in accordance with user's expected behavior. With the improved approaches, users are less likely to undergo unexpected processing in response to overloaded key presses. In one embodiment, the processing ignores certain overloaded key presses and / or imposes delays to ensure that users have an opportunity to appreciate when an overloaded key has switched to another function. These approaches are particularly well suited for small-scale mobile devices having reduced size displays and overloaded keys such as mobile phones (e.g., cellular phones), two-way pagers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), or other two-way mobile communication devices.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
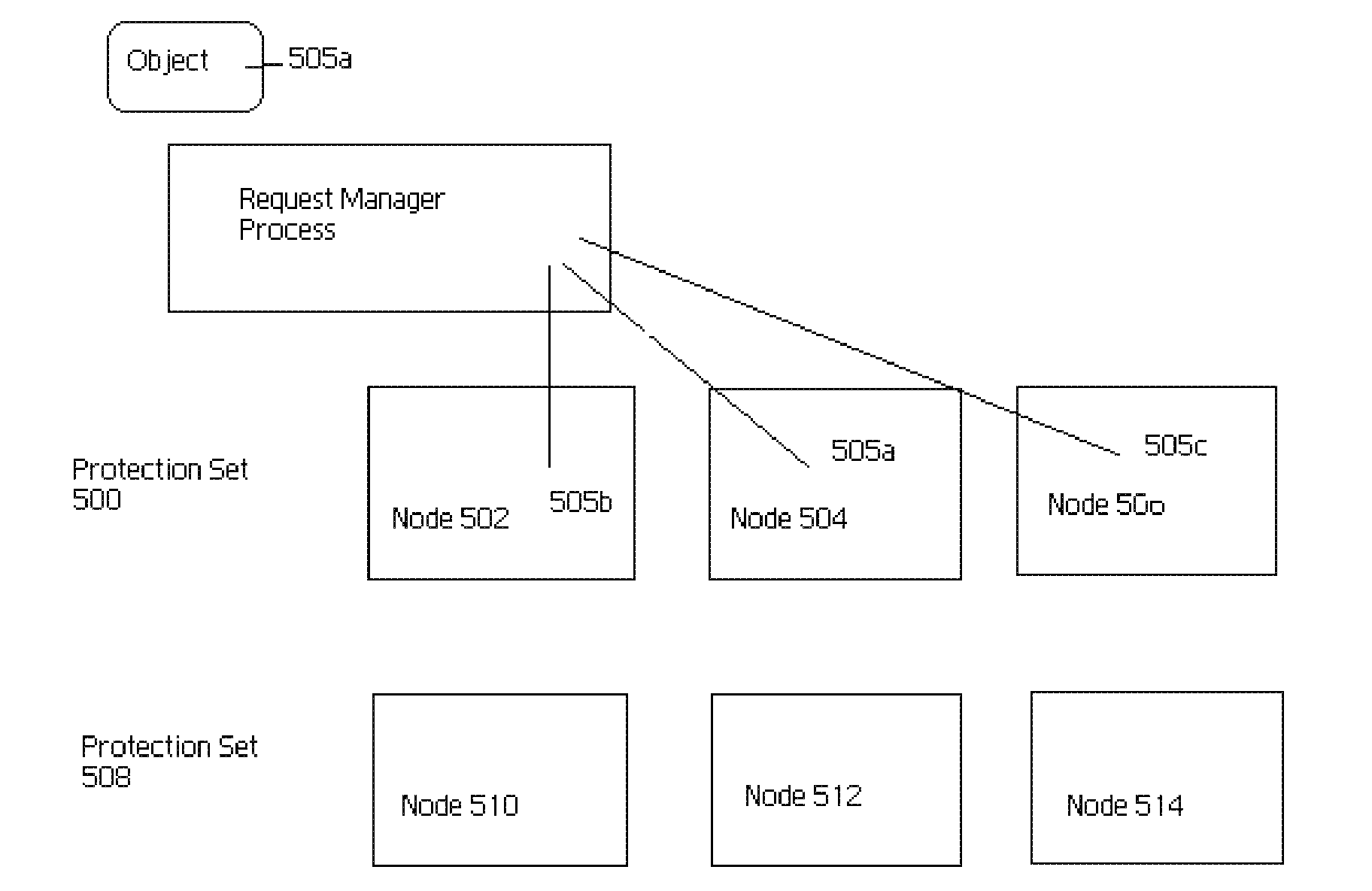
Method for improving mean time to data loss (MTDL) in a fixed content distributed data storage
ActiveUS20070189153A1Improve mean time between failuresReduce data lossDigital data information retrievalError preventionMultiple failureMean time to data loss
An archival storage cluster of preferably symmetric nodes includes a data protection management system that periodically organizes the then-available nodes into one or more protection sets, with each set comprising a set of n nodes, where “n” refers to a configurable “data protection level” (DPL). At the time of its creation, a given protection set is closed in the sense that each then available node is a member of one, and only one, protection set. When an object is to be stored within the archive, the data protection management system stores the object in a given node of a given protection set and then constrains the distribution of copies of that object to other nodes within the given protection set. As a consequence, all DPL copies of an object are all stored within the same protection set, and only that protection set. This scheme significantly improves MTDL for the cluster as a whole, as the data can only be lost if multiple failures occur within nodes of a given protection set. This is far more unlikely than failures occurring across any random distribution of nodes within the cluster.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Method for creating an error correction coding scheme
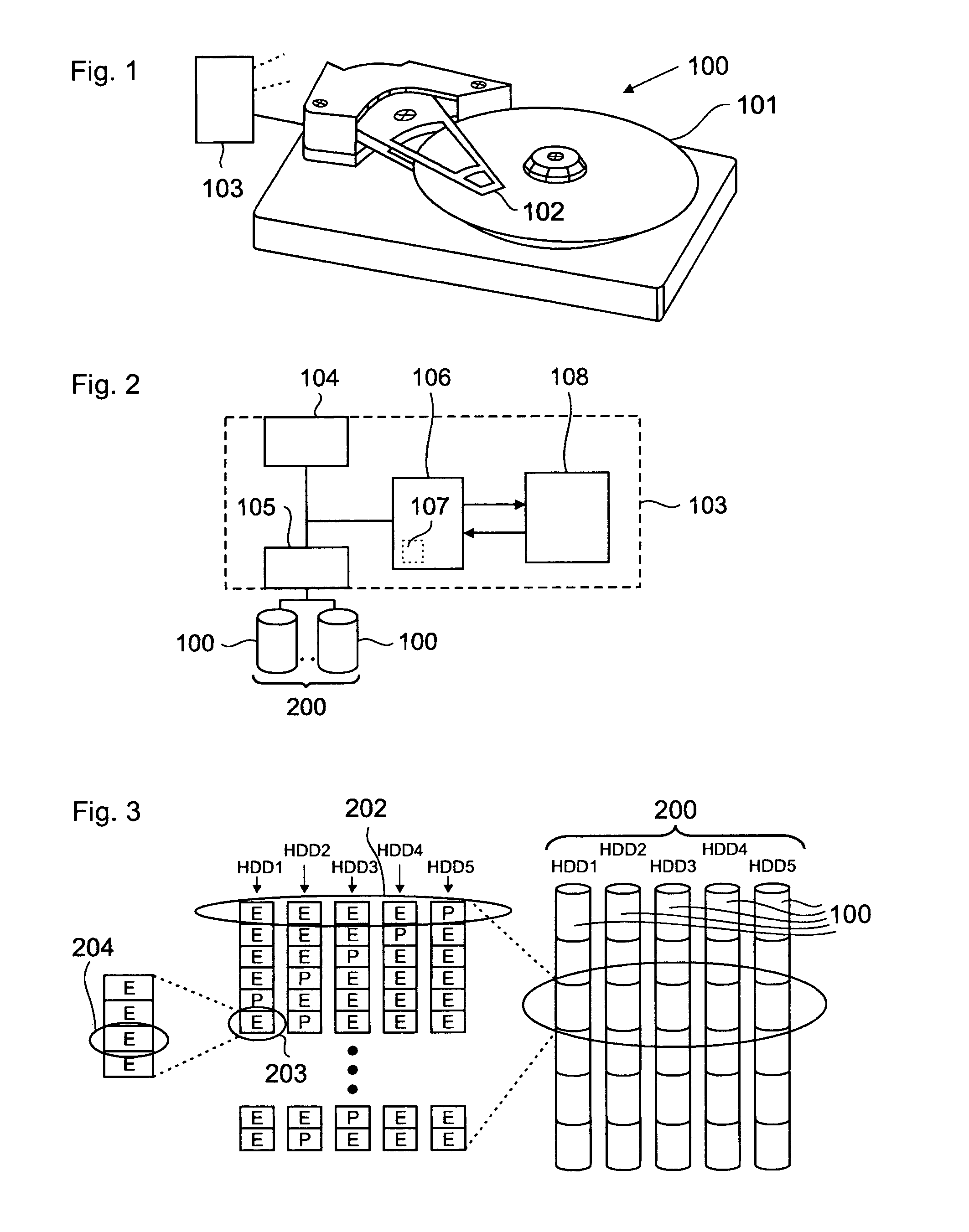
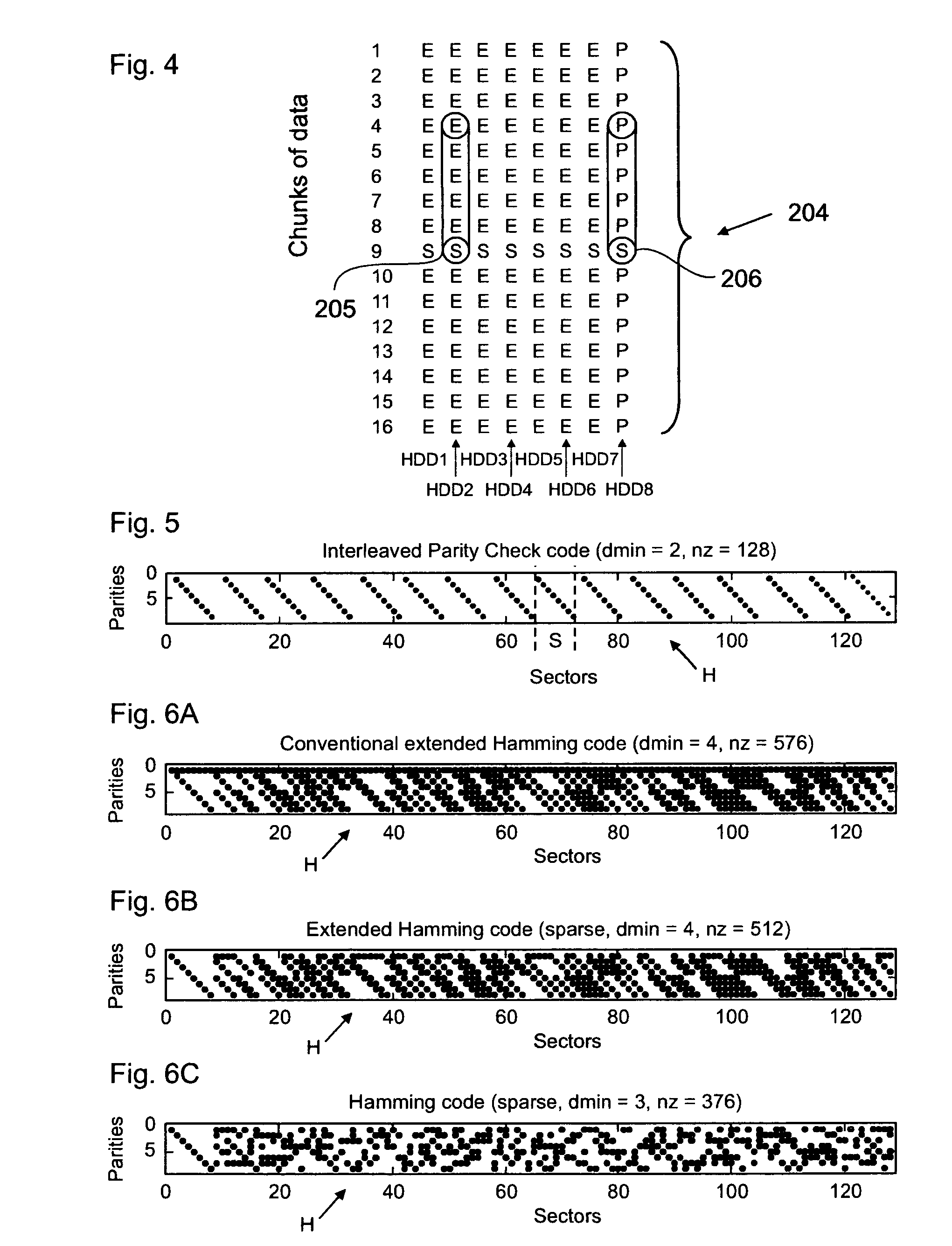
InactiveUS20080244353A1Reduce data lossEasy constructionBurst error correctionCode conversionMain diagonalData set
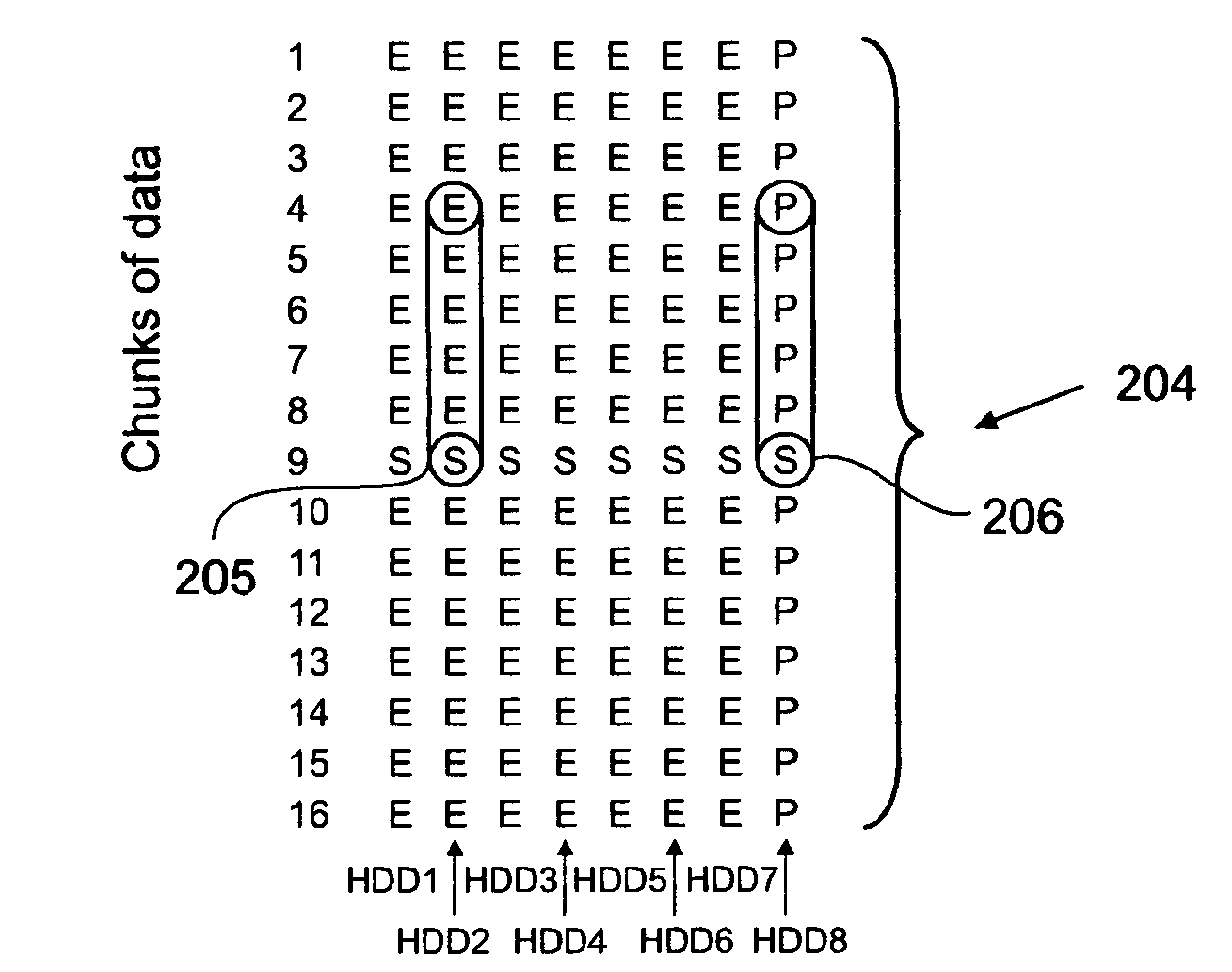
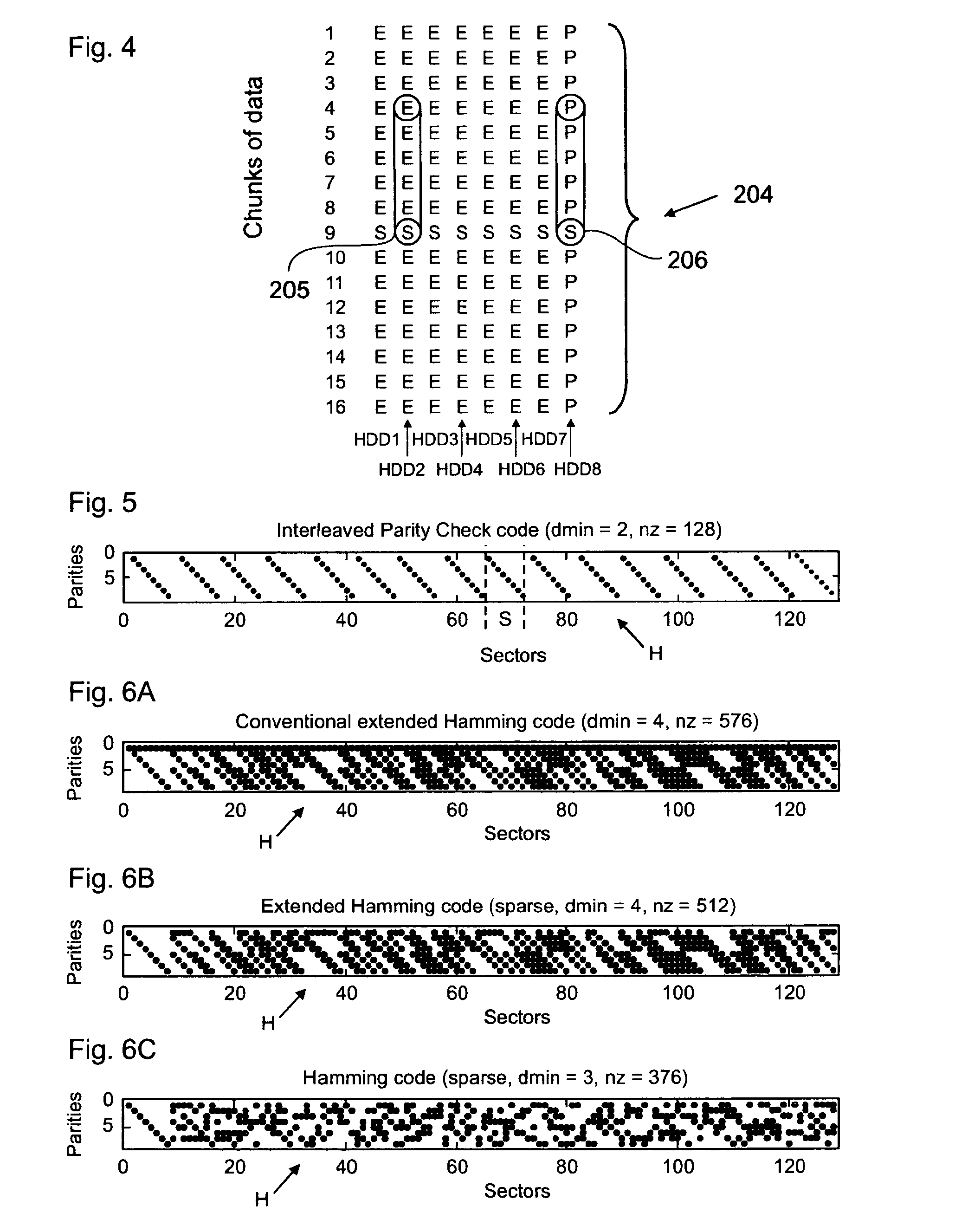
The present invention relates to a method for reducing data loss comprising a first computing step for computing an intermediate result for each redundancy information entity of a redundancy set by processing respectively associated data information entities of a given data set on at least two main diagonals of a parity check matrix representing an error correction coding scheme. The method further comprises a second computing step for computing the information content of the respective redundancy information entity dependent on the respective intermediate result.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS7808913B2Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
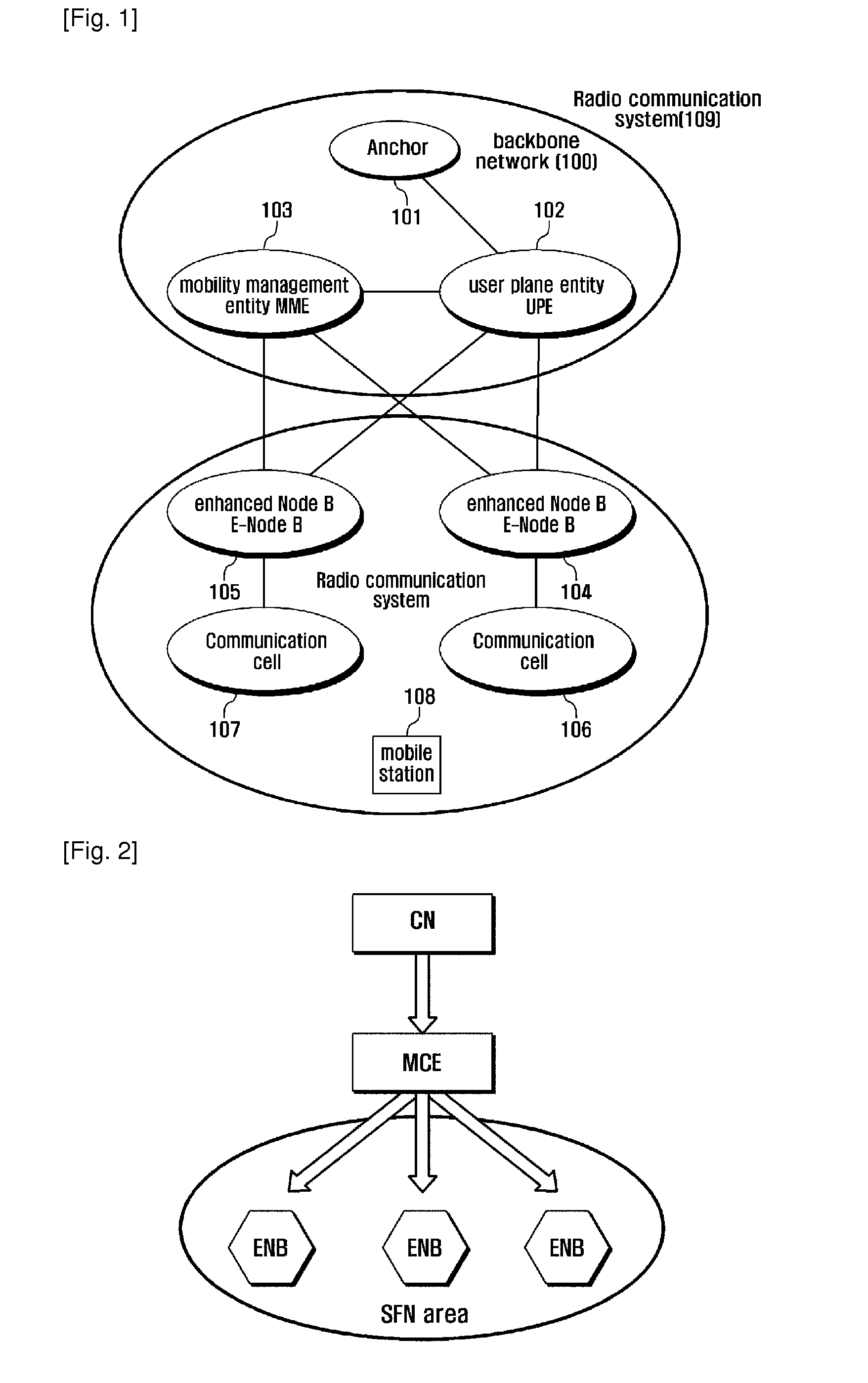
Method for supporting continuous reception of evolved broadcast and multicast service data
ActiveUS20100254352A1Reduce MBMS data lossReduce data lossConnection managementOrthogonal multiplexCurrent cellTransfer mode
The method for supporting continuous reception of enhanced broadcast service data comprising steps of: an MCE receiving an “MBMS Session Start Request” message from a core network; after the MCE receives the message, transmitting a response message to the core network; MCE transmitting an “MBMS Session Start Request” message to an ENB, the message including information of adjacent cells; and the ENB broadcasting the information of adjacent cells on a current cells. With the scheme of present invention, if a user wants to move to a common cell when he / she receives MBMS service in an SFN edge cell, he / she can enter the active mode and switch into the common cell so as to reduce MBMS data loss. When a UE moves from a cell with SC-PTM transmission mode into a cell with SC-PTM transmission mode, data loss can also be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
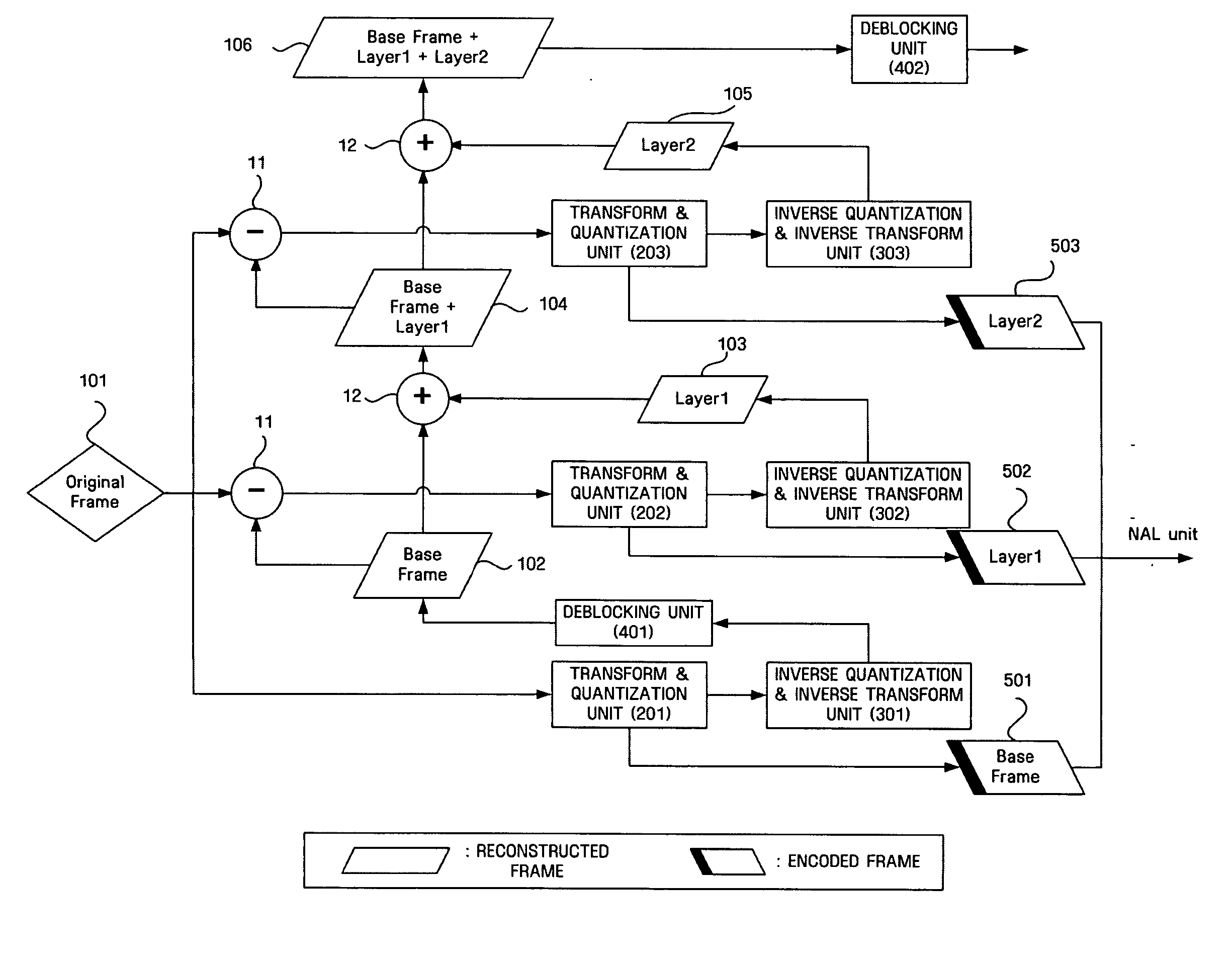
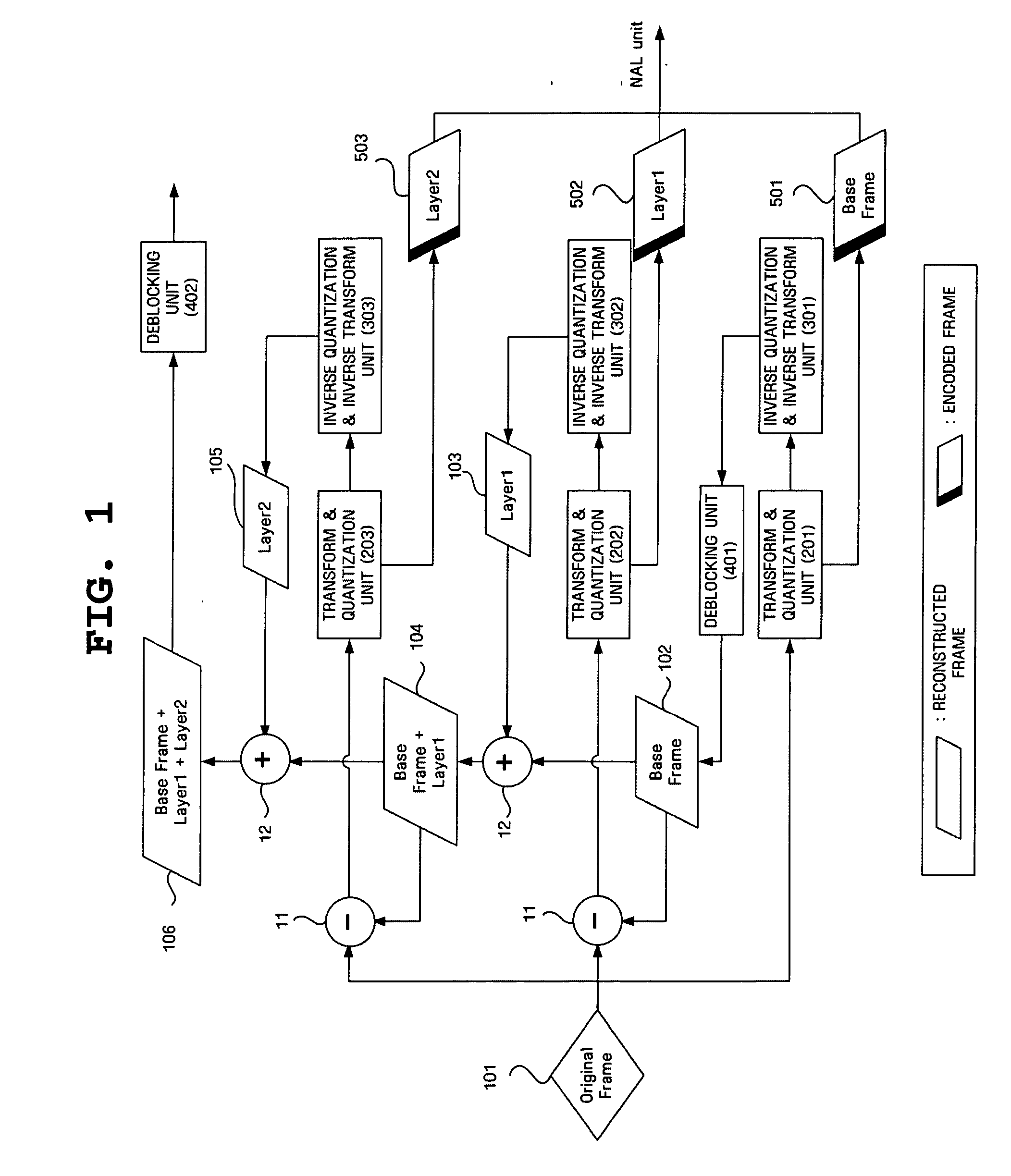
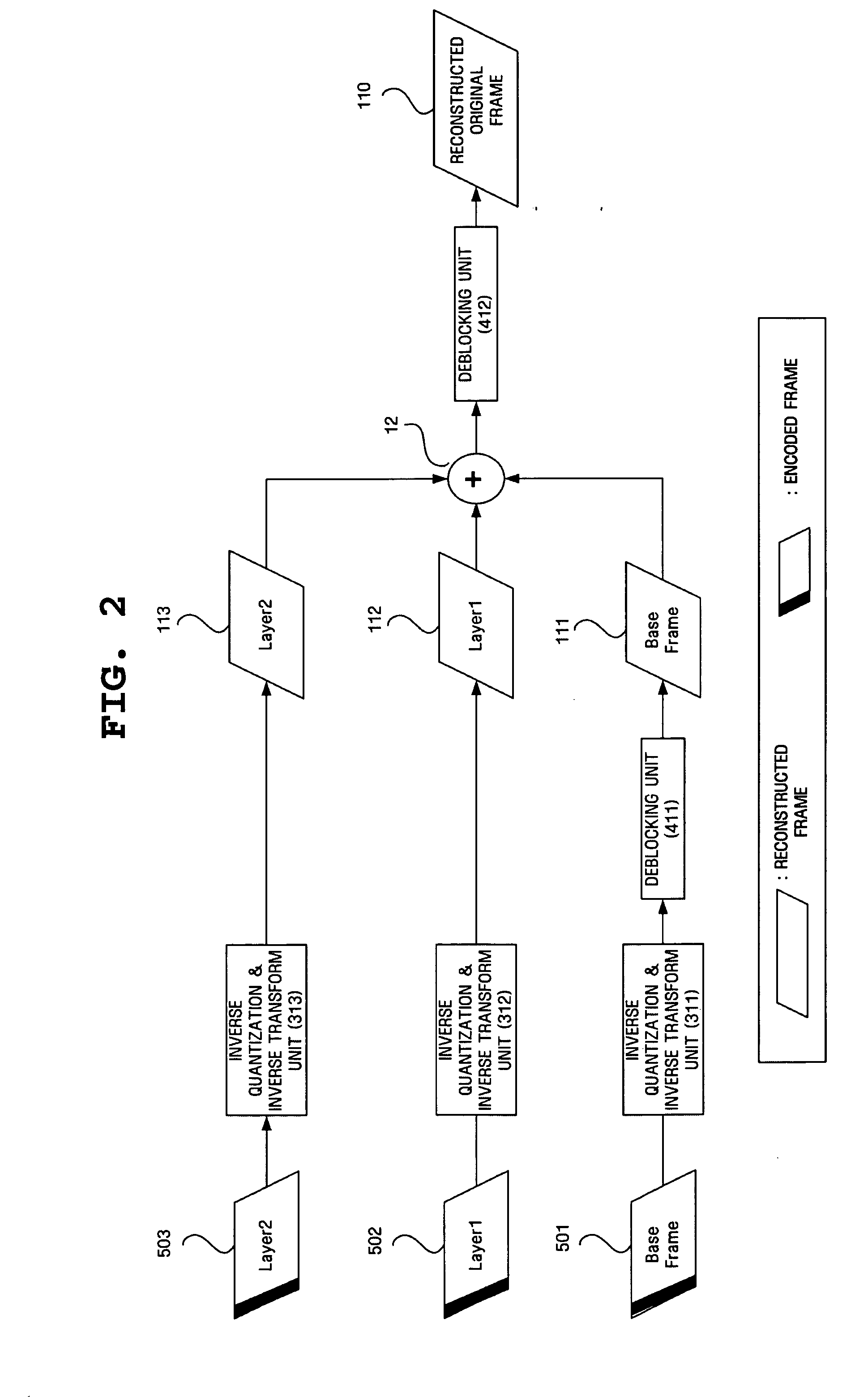
Fine granularity scalable video encoding and decoding method and apparatus capable of controlling deblocking
InactiveUS20060159359A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEnhanced signalCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationGranularityVideo encoding
Disclosed herein is a Fine Granularity Scalability (FGS)-based video encoding and decoding method and apparatus capable of controlling deblocking. In the video decoding method according to the present invention, original video data is received and a base layer is generated based on the original data. Next, the difference between the original data and data that is obtained by reconstructing the base layer and deblocking the reconstructed base layer is obtained, thus generating an enhancement layer. Then, a reconstructed frame is generated based on the data that is obtained by reconstructing the enhancement layer, and data that is obtained by reconstructing and deblocking the reconstructed base layer. Finally, the reconstructed frame is deblocked at a lower intensity than that of deblocking performed in the first two steps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
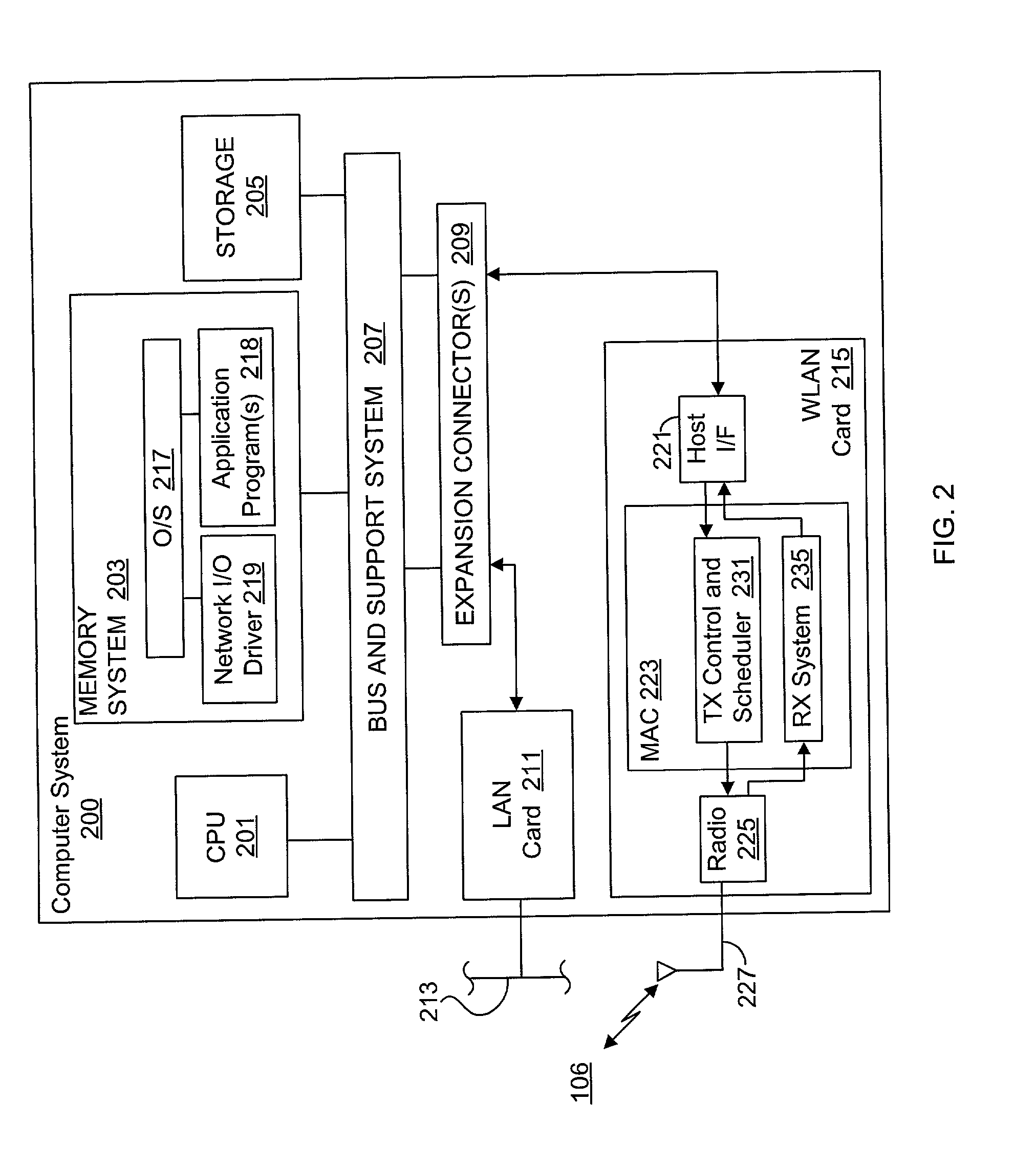
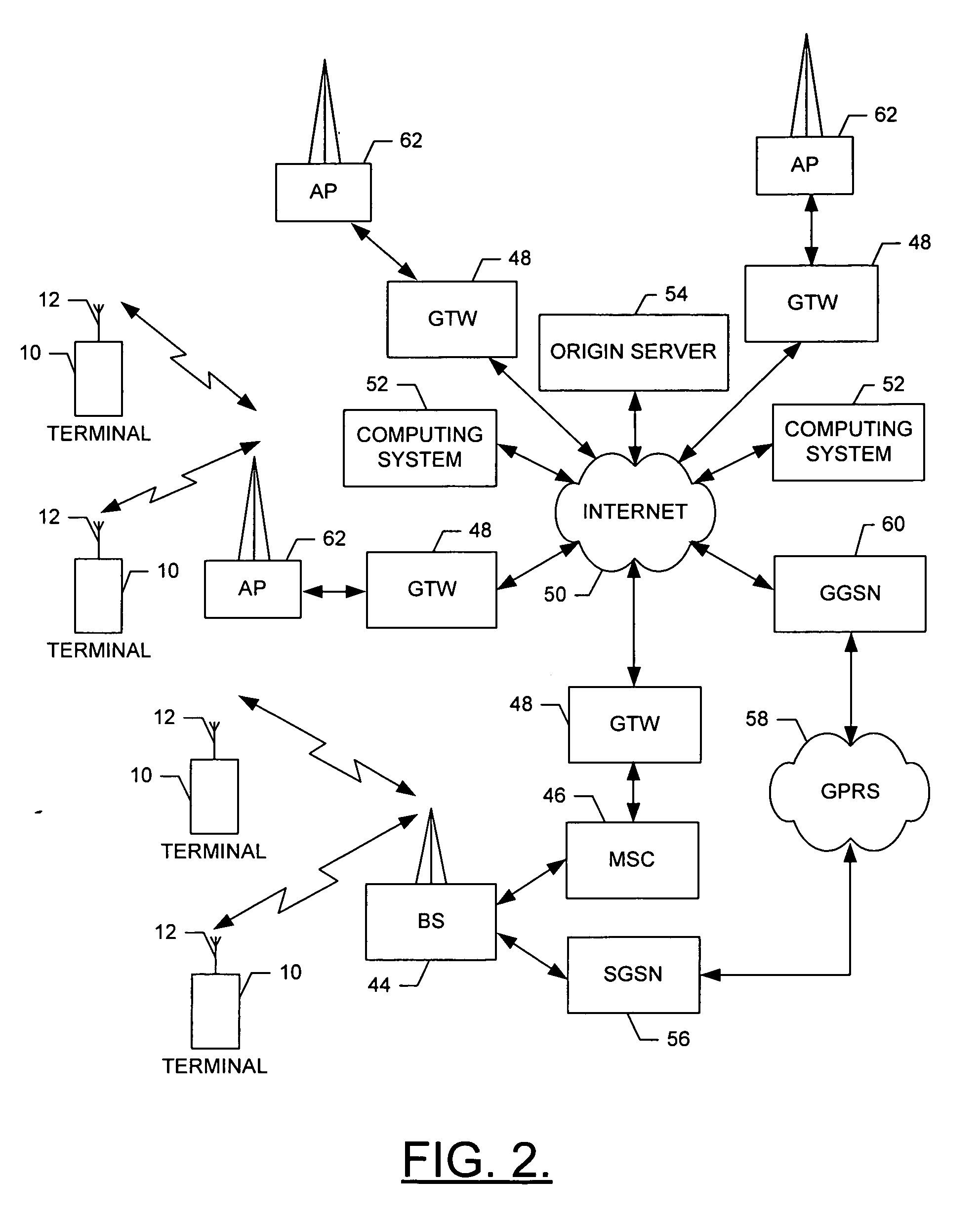
Method and apparatus for handing off a mobile terminal between a mobile network and a wireless lan
InactiveUS20050021586A1Reduce data lossEliminate needAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesMobile WebHand-off
A method for performing a handover of a mobile terminal between a 3G cell and a WLAN cell when the mobile terminal moves within a 3G cell into the coverage area of the WLAN cell. The present invention proposes that the handover be performed when there are no active calls. If there are ongoing calls, method proposes to wait until the calls are terminated before the handover is performed. After the ongoing calls are terminated, the handover is performed by disassociating from the radio access network of the 3G cell and associating with the access point of the WLAN, using the relatively straightforward disassociation and association procedures. The handover method according to the present invention obviates the need for complex and expensive protocols to ensure a seamless and error free handover of calls when moving from the coverage of the 3G cell to the coverage of the WLAN cell. This method can be used with either the loose coupling arrangement or the tight coupling arrangement.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
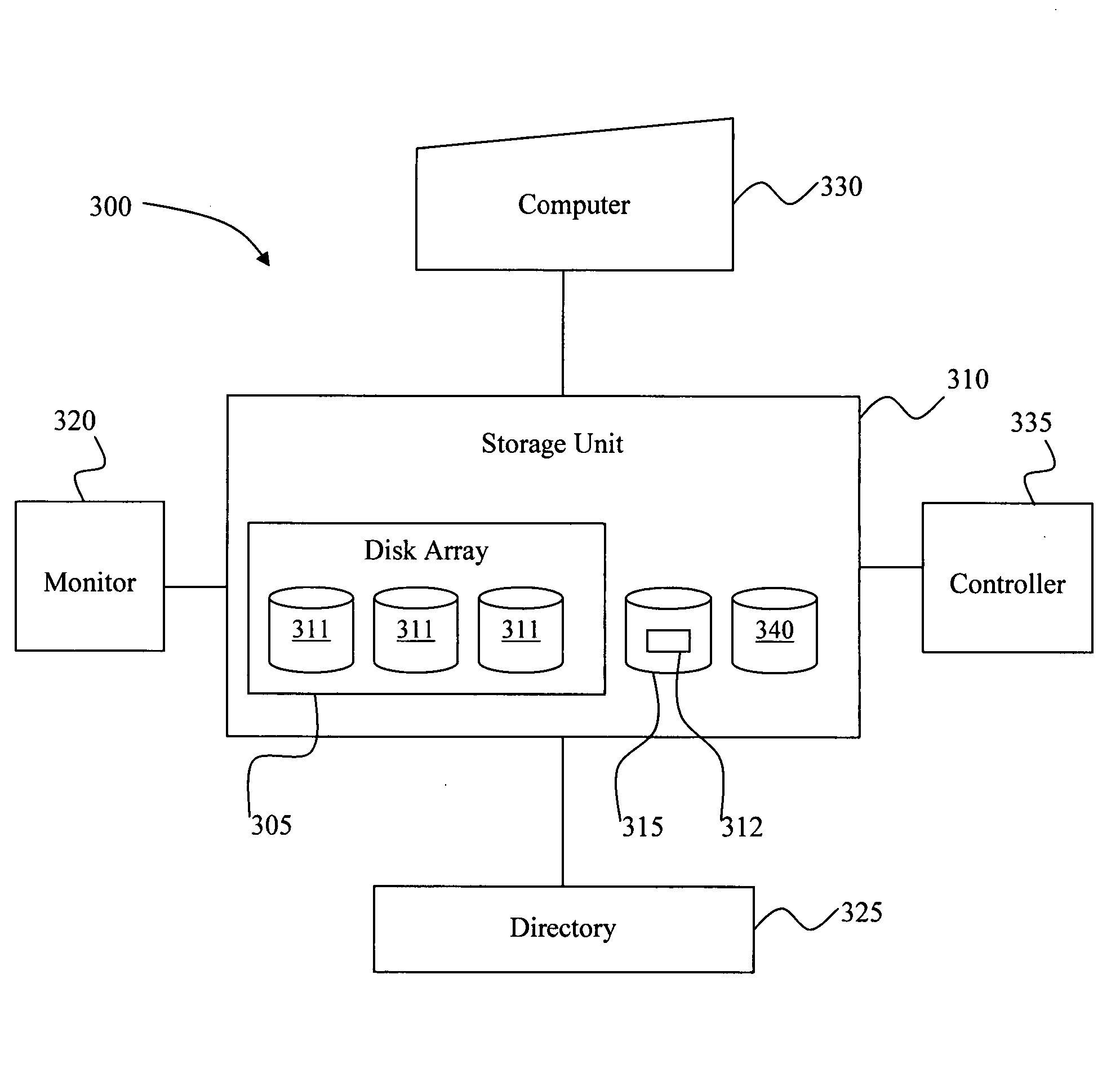
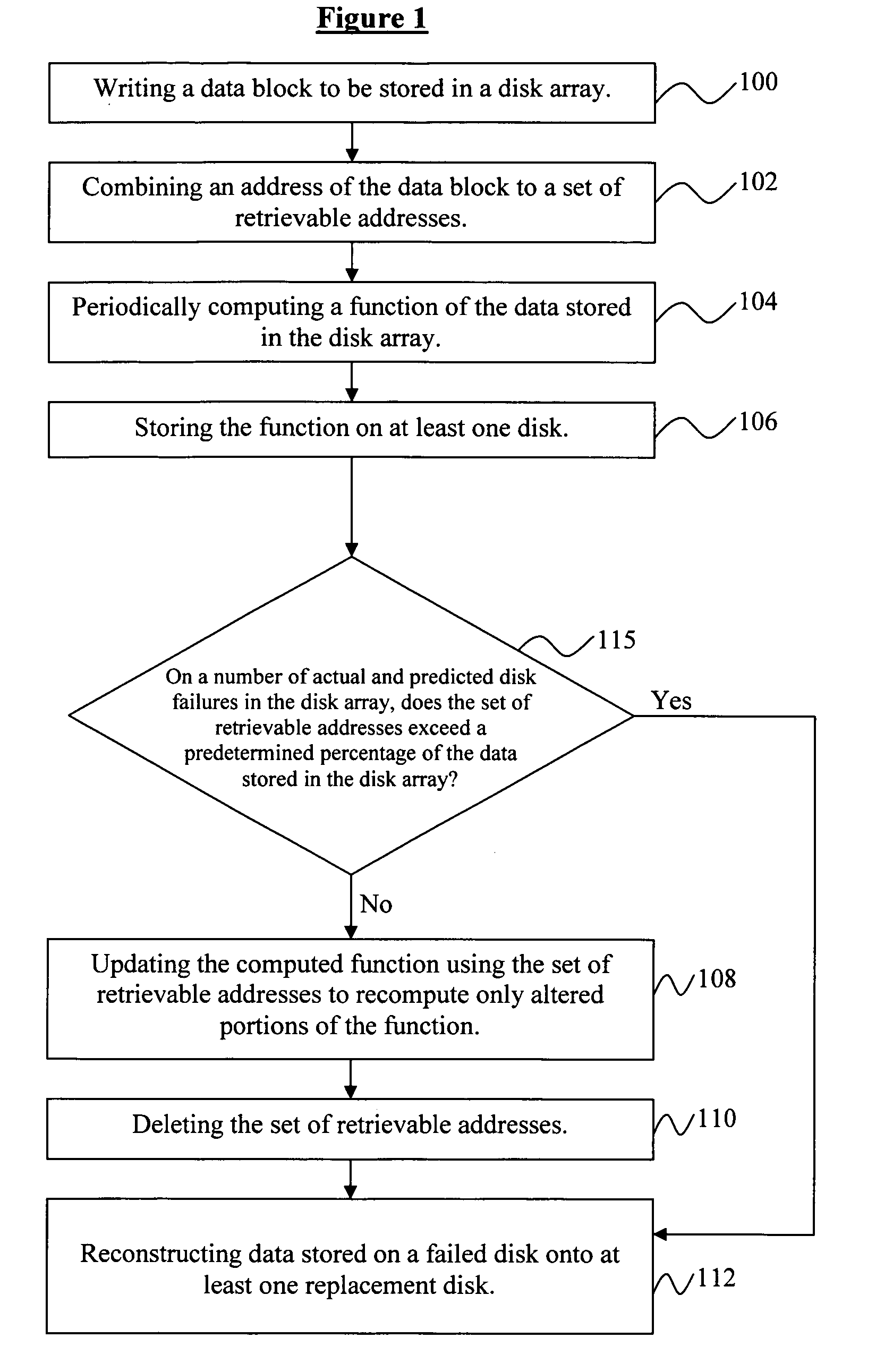
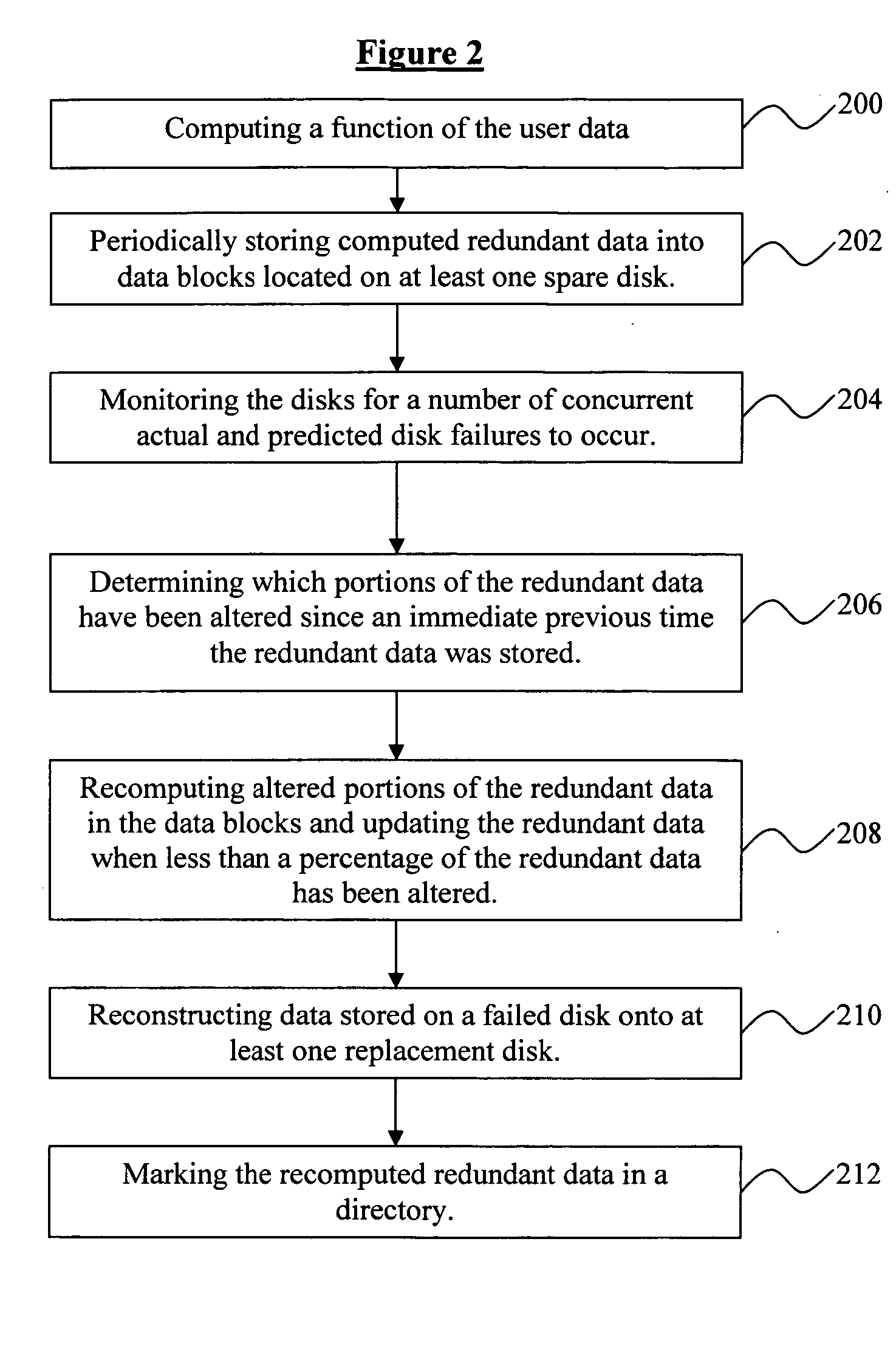
System and method for reducing data loss in disk arrays by establishing data redundancy on demand
InactiveUS20050091452A1Increase the number ofImprove the level ofRedundant data error correctionMemory systemsDisk arrayData reconstruction
Disclosed is a system and method for reducing data loss in a disk array comprising computing redundant data of the user data in the disk array, periodically storing the computed redundant data into data blocks located on at least one disk; monitoring the disks for a number of concurrent actual and predicted disk failures to occur; determining which portions of the redundant data have been altered since an immediate previous time the redundant data was stored; re-computing altered portions of the redundant data and updating the corresponding data blocks when said number of concurrent disk failures occur and less than a fraction of the redundant data has been altered, reconstructing data stored on a failed disk onto at least one replacement disk; and marking the recomputed redundant data in a directory, wherein the disk array comprises one of the standard RAID arrays.
Owner:IBM CORP
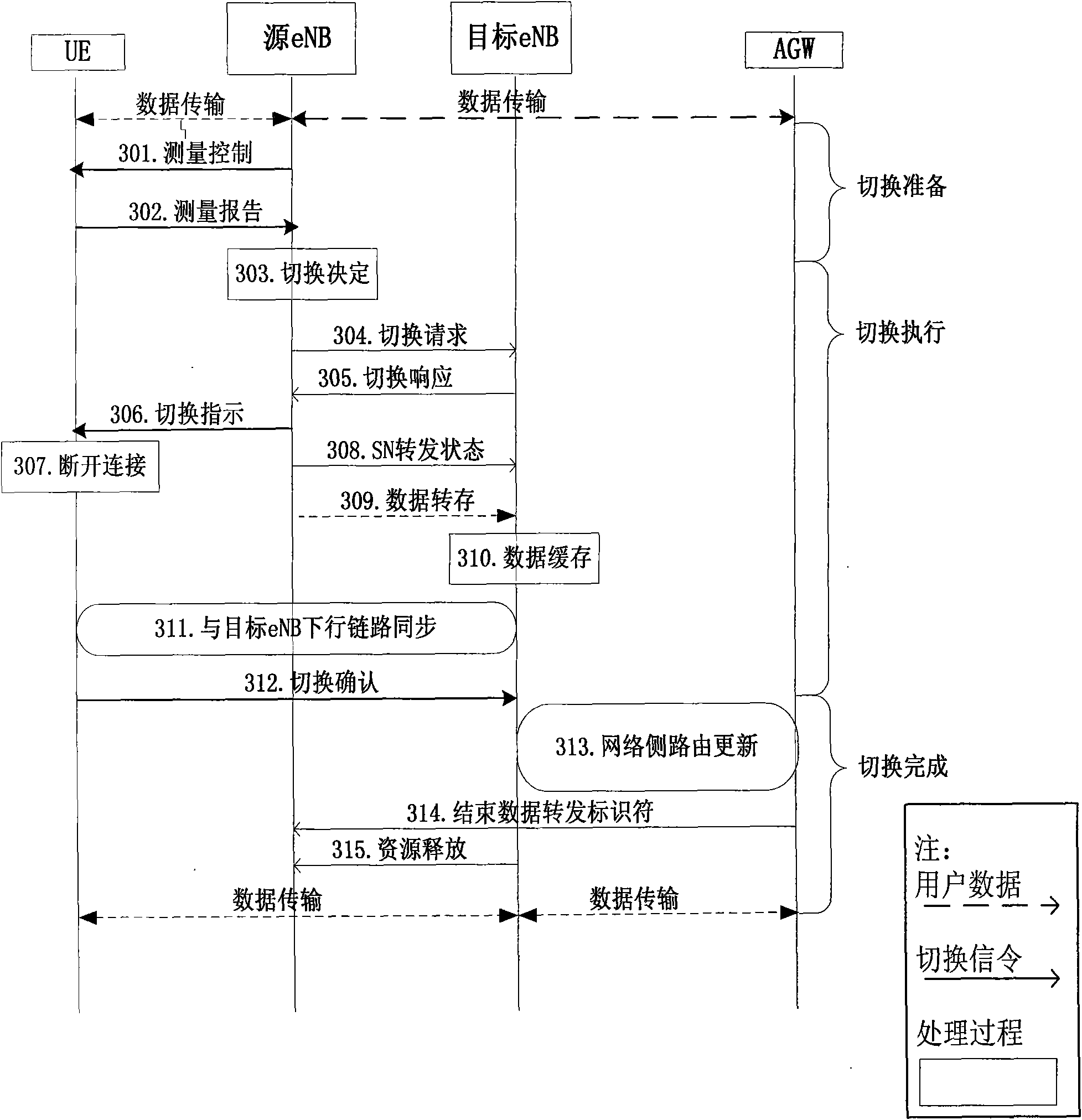
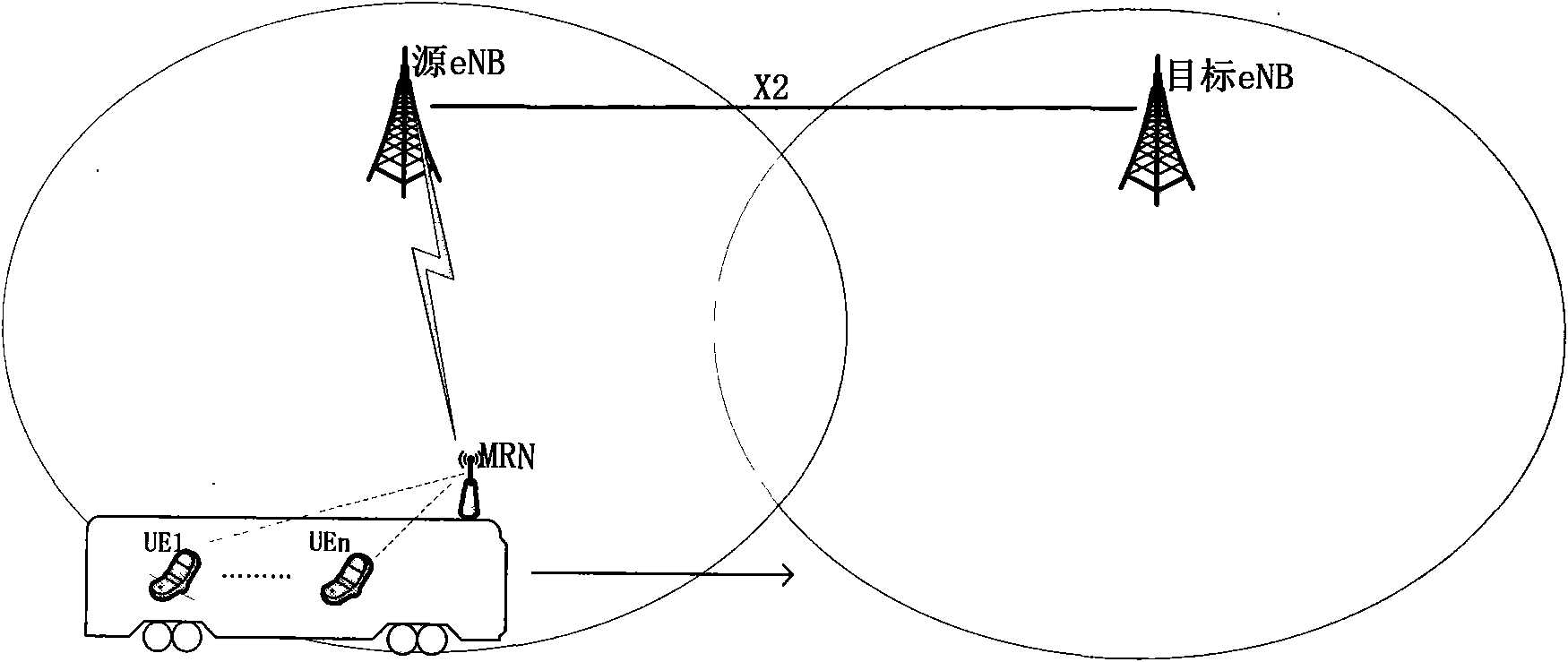
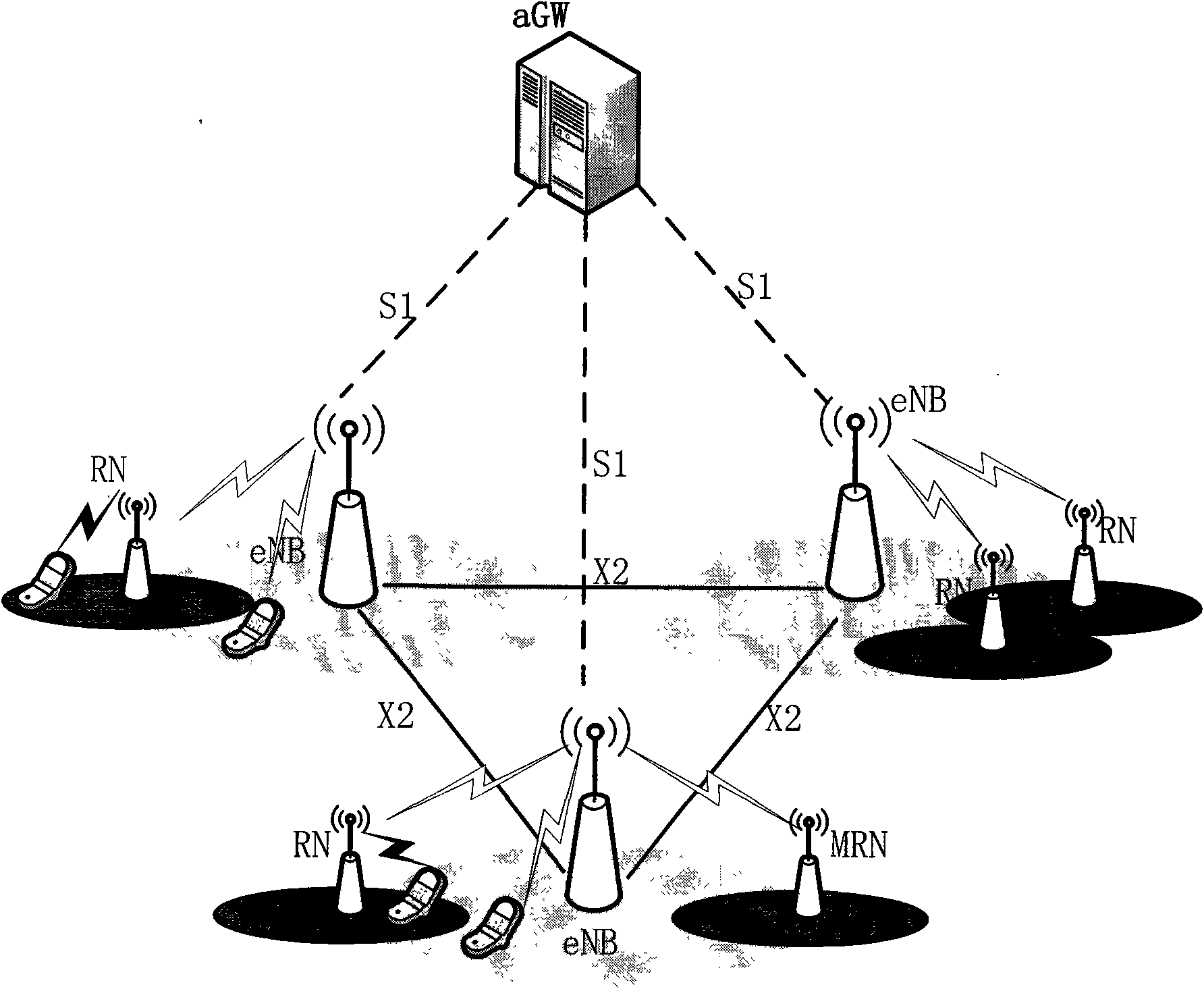
Method for switching group users in mobile-relay system
InactiveCN101626565AReduce data lossReduce the chance of users dropping callsNetwork data managementData transmissionActive mode
The invention discloses a method for switching cells of group users in a wireless communication system, relating to the technology of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: accessing the group users via a mobile-relay node and establishing a user information list stored in an ACTIVE mode on the mobile-relay node andbase stations, initializing the list when the users establish RRC connection with the mobile-relay node, automatically updating during switching; during switching execution, completing the context synchronization between the source base station and subordinate users of the mobile-relay node via information in the ACTIVE list by a source base station so as to enable users data transmission not to be broken, and reestablishing the context synchronization of the subordinate users by using the information in the ACTIVE list by the mobile-relay node after completing the switching among the base stations. The invention can be used in the mobile-relay system, can realize cross-regional soft switching of the group users and solves the problem of continuity met by the group users during switching.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO MOBILE TECH CO LTD
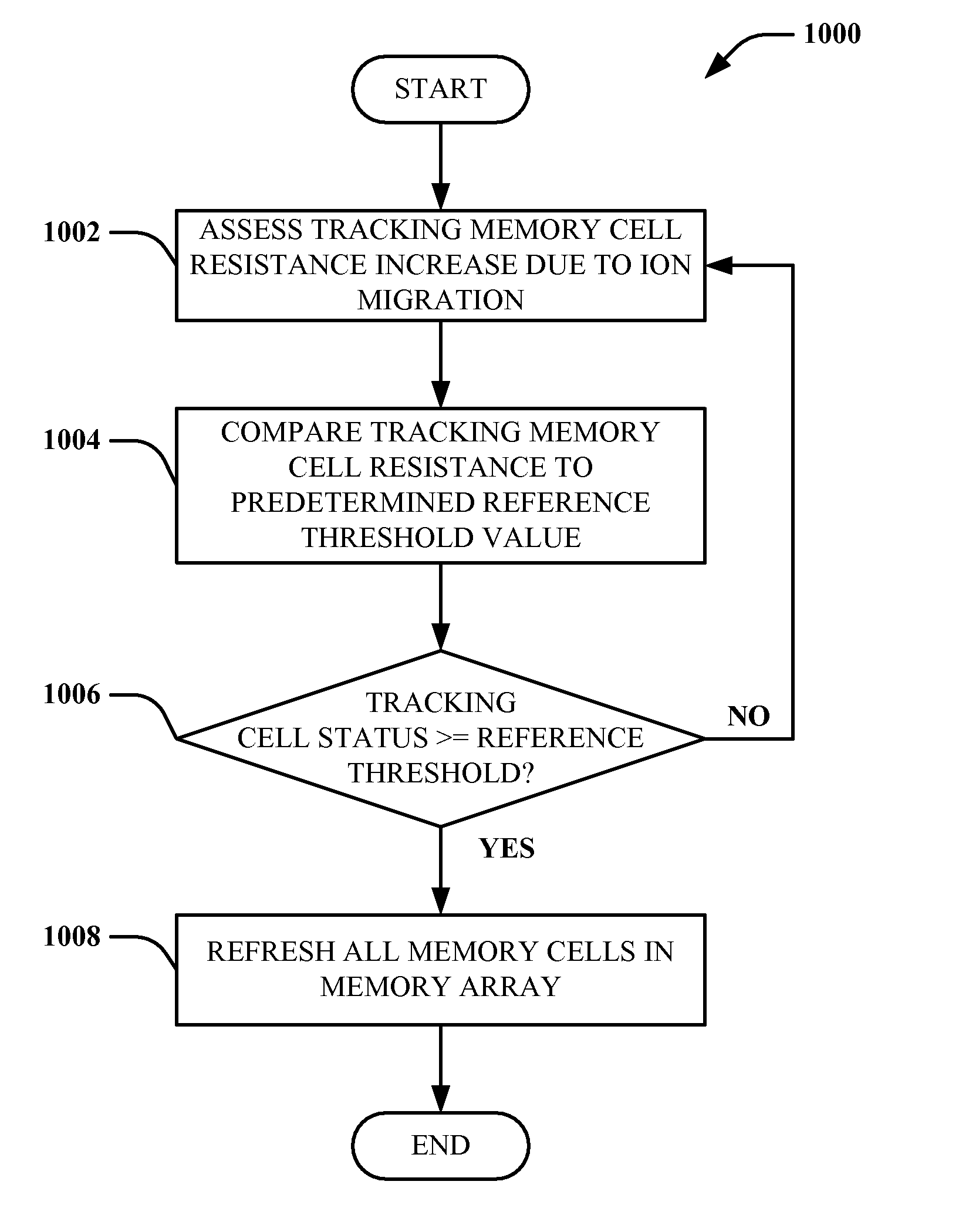
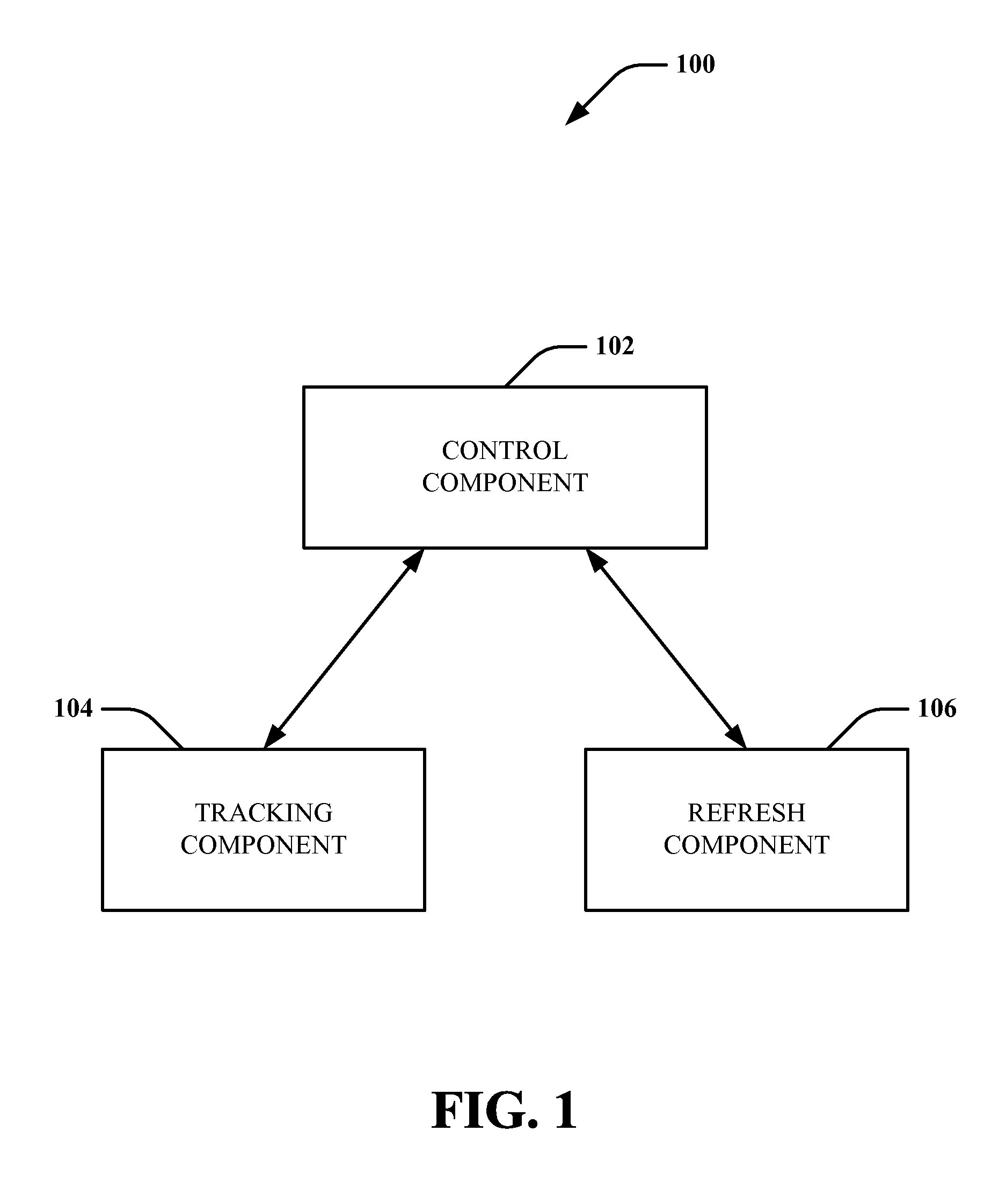
Use of periodic refresh in medium retention memory arrays
ActiveUS20080151669A1Accurate measurementReduce generationRead-only memoriesDigital storageRetention memoryEngineering
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate extending data retention time in a data retention device, such as a nanoscale resistive memory cell array, via assessing a resistance level in a tracking element associated with the memory array and refreshing the memory array upon a determination that the resistance of the tracking element has reached or exceeded a predetermined reference threshold resistance value. The tracking element can be a memory cell within the array itself and can have an initial resistance value that is substantially higher than an initial resistance value for a programmed memory cell in the array, such that resistance increase in the tracking cell will cause the tracking cell to reach the threshold value and trigger refresh of the array before data corruption / loss occurs in the core memory cells.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
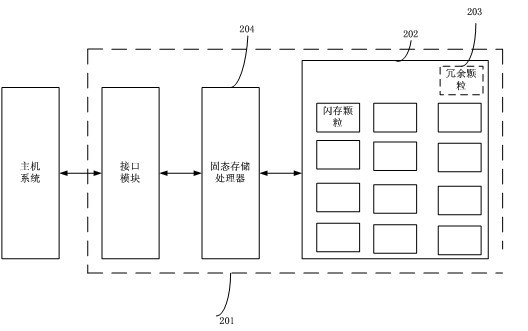
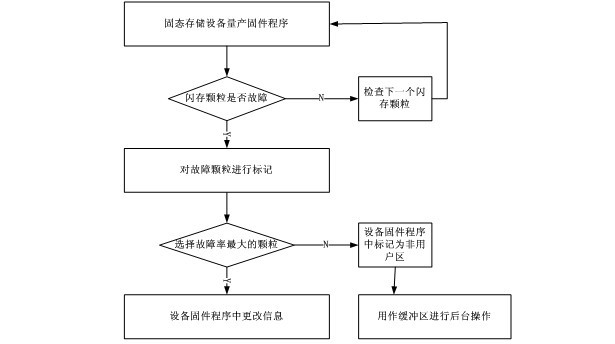
Fault tolerance design method for solid-state memory device
ActiveCN102043689AWill not affect the excellent rateExtended service lifeRedundant hardware error correctionSolid-state storageError-tolerant design
The invention discloses a fault tolerance design method for a solid-state memory device, in which standby redundant memory particles are additionally added in design of a circuit board of a memory device, when the device has flash memory fault in production back-end test or usage, the failed particles are substituted by the redundant memory particles, thereby ensuring that excellent rate of production of the memory device cannot be influenced even encapsulation test is not performed on the particles; simultaneously, service life of the device is effectively prolonged by adding the redundant memory particles in the method, when the flash memory particles in the device reach certain service life, the flash memory particles are substituted by the redundant particles or idle particles, so that the service life of the device is effectively prolonged through the continuous substitution. The method can be implemented in process of device production test and / or usage.
Owner:WUHAN SOLIC CZECHOSIOVAKIA DATA SCI & TECH +1
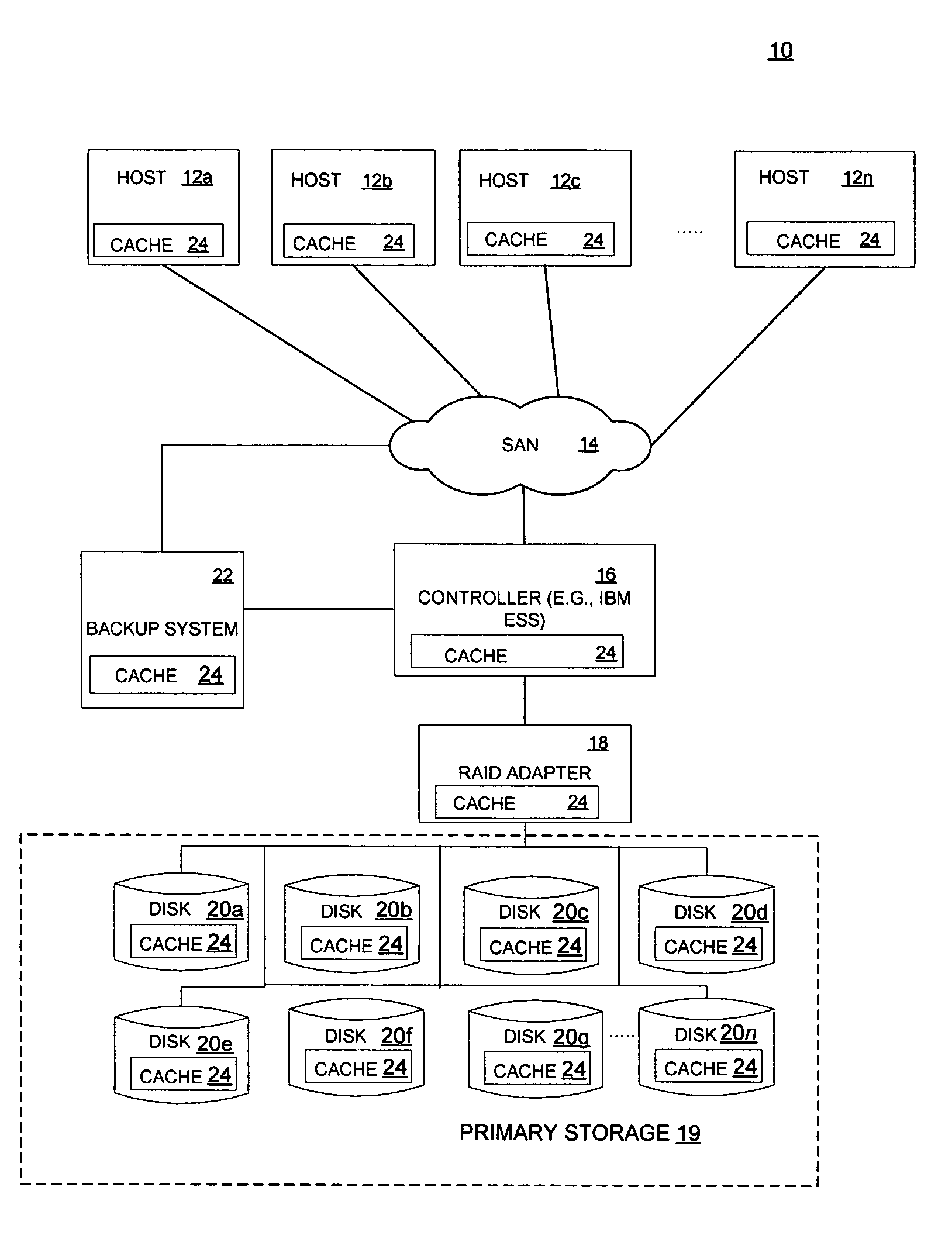
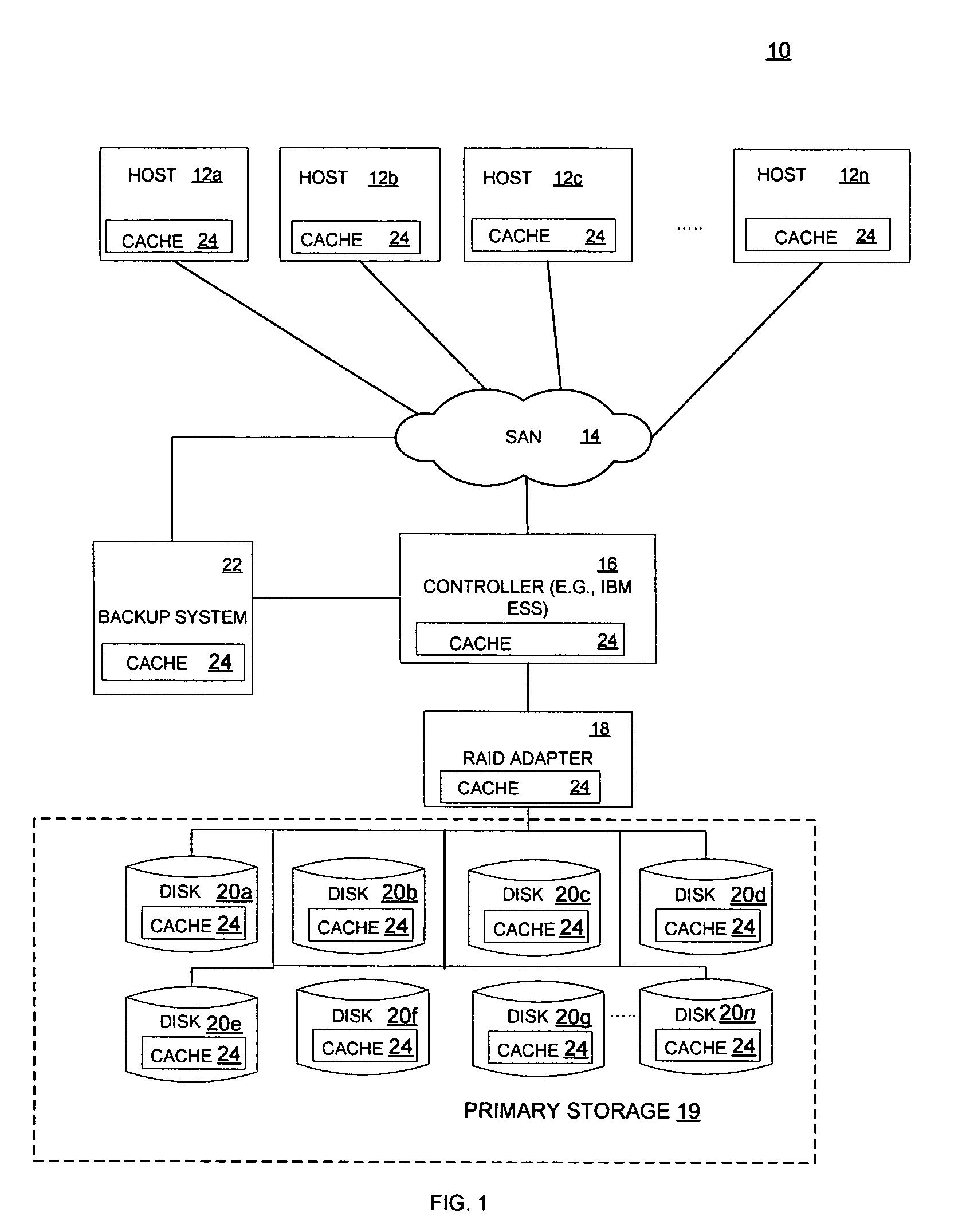
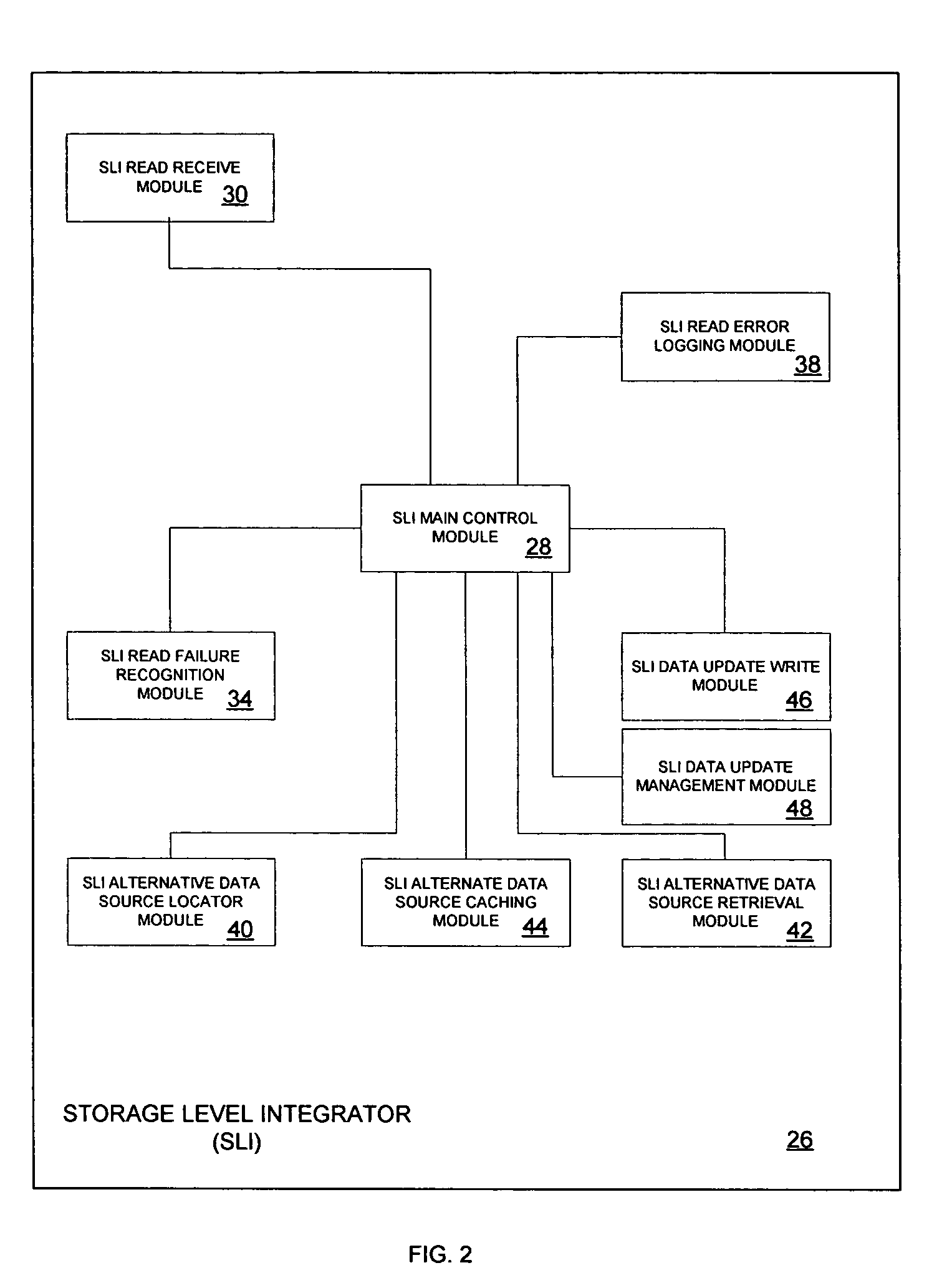
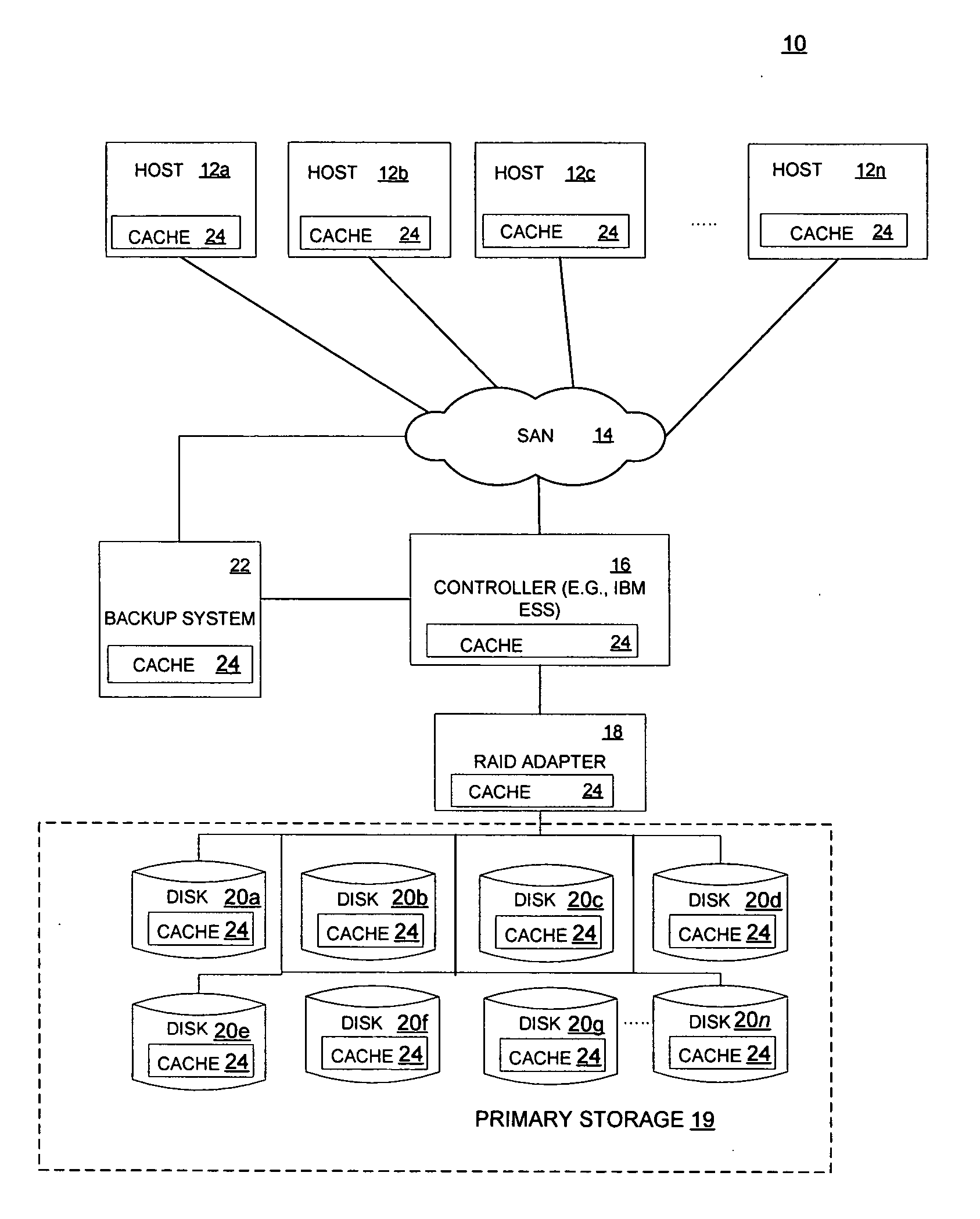
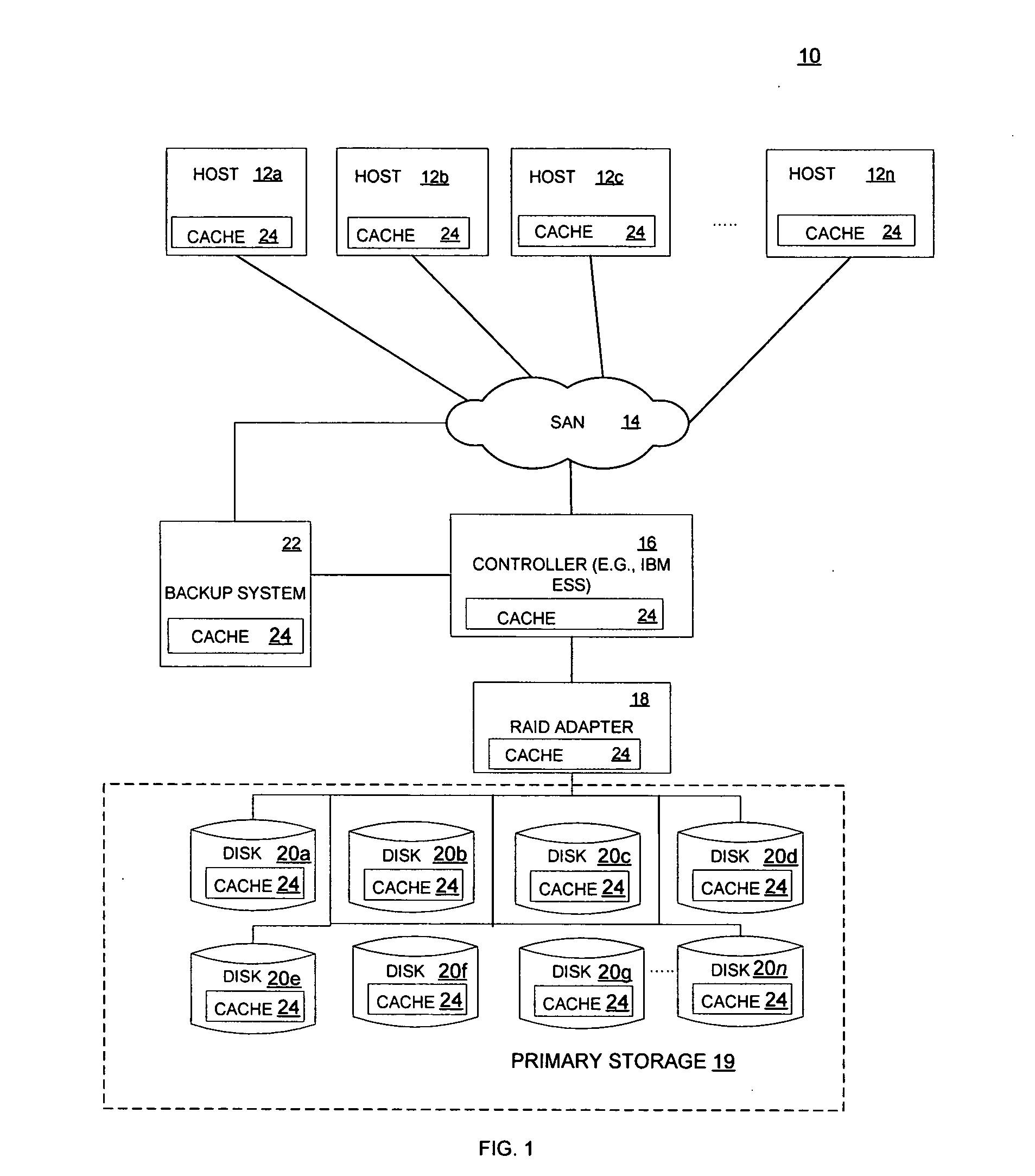
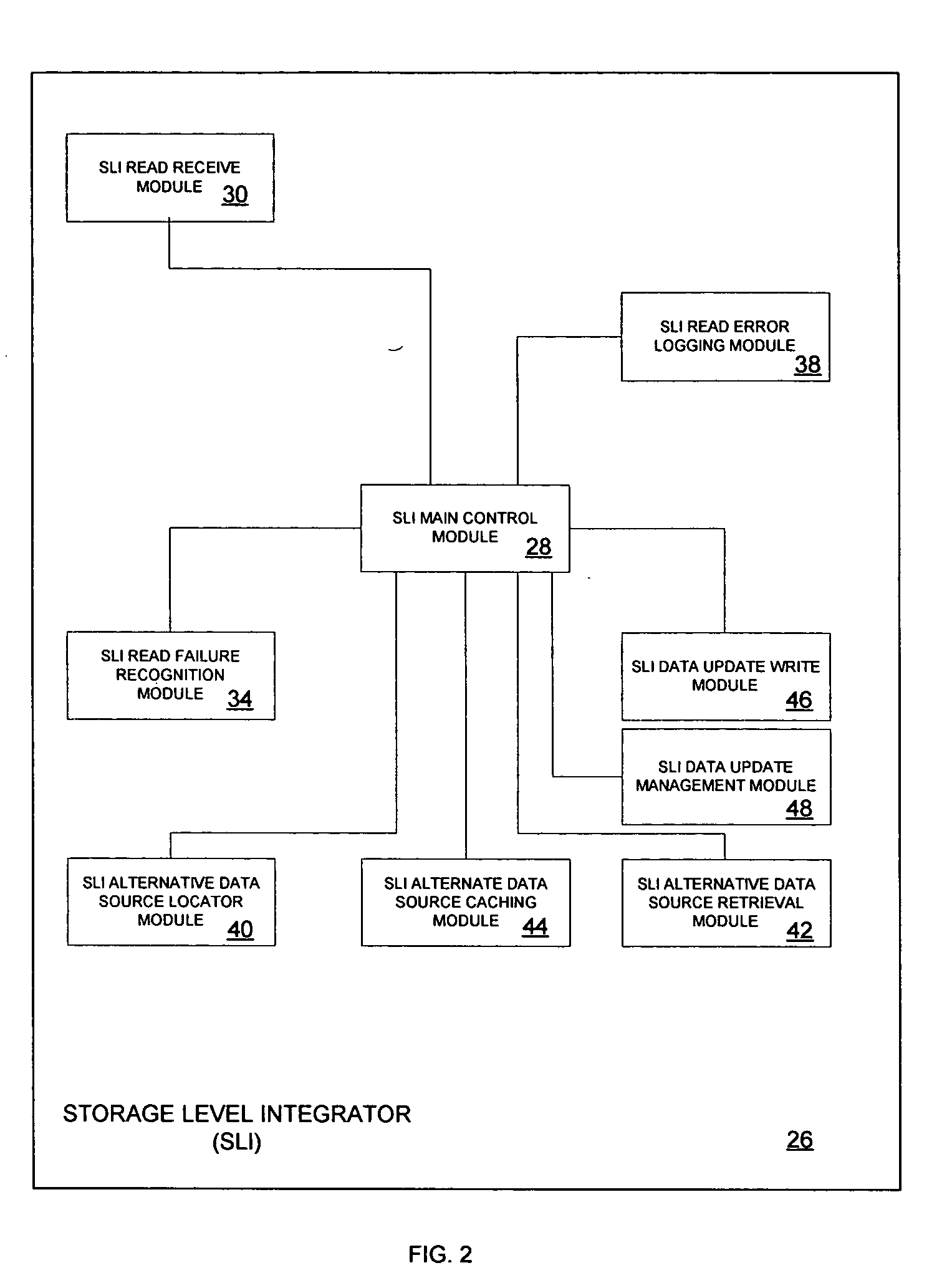
Method for reducing data loss and unavailability by integrating multiple levels of a storage hierarchy
InactiveUS7461101B2Reduce data lossReduce dataData processing applicationsError detection/correctionMemory hierarchyData loss
A method for reducing data loss and unavailability by integrating multiple levels of a storage hierarchy is provided. The method includes receiving a read request. In addition, the method includes recognizing a data failure in response to the read request. The method further includes locating an alternate source of the data to be read in response to recognizing the data failure. The alternate source includes data cached at devices in the storage hierarchy, data in a backup system, and cumulative changes to the data since the last backup. Moreover, the method includes responding to the read request with data from the alternate source.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reducing data loss and unavailability by integrating multiple levels of a storage hierarchy
InactiveUS20060015767A1Reduce data lossReduce unavailabilityData processing applicationsError detection/correctionMemory hierarchyData loss
A method for reducing data loss and unavailability by integrating multiple levels of a storage hierarchy is provided. The method includes receiving a read request. In addition, the method includes recognizing a data failure in response to the read request. The method further includes locating an alternate source of the data to be read in response to recognizing the data failure. The alternate source includes data cached at devices in the storage hierarchy, data in a backup system, and cumulative changes to the data since the last backup. Moreover, the method includes responding to the read request with data from the alternate source.
Owner:IBM CORP
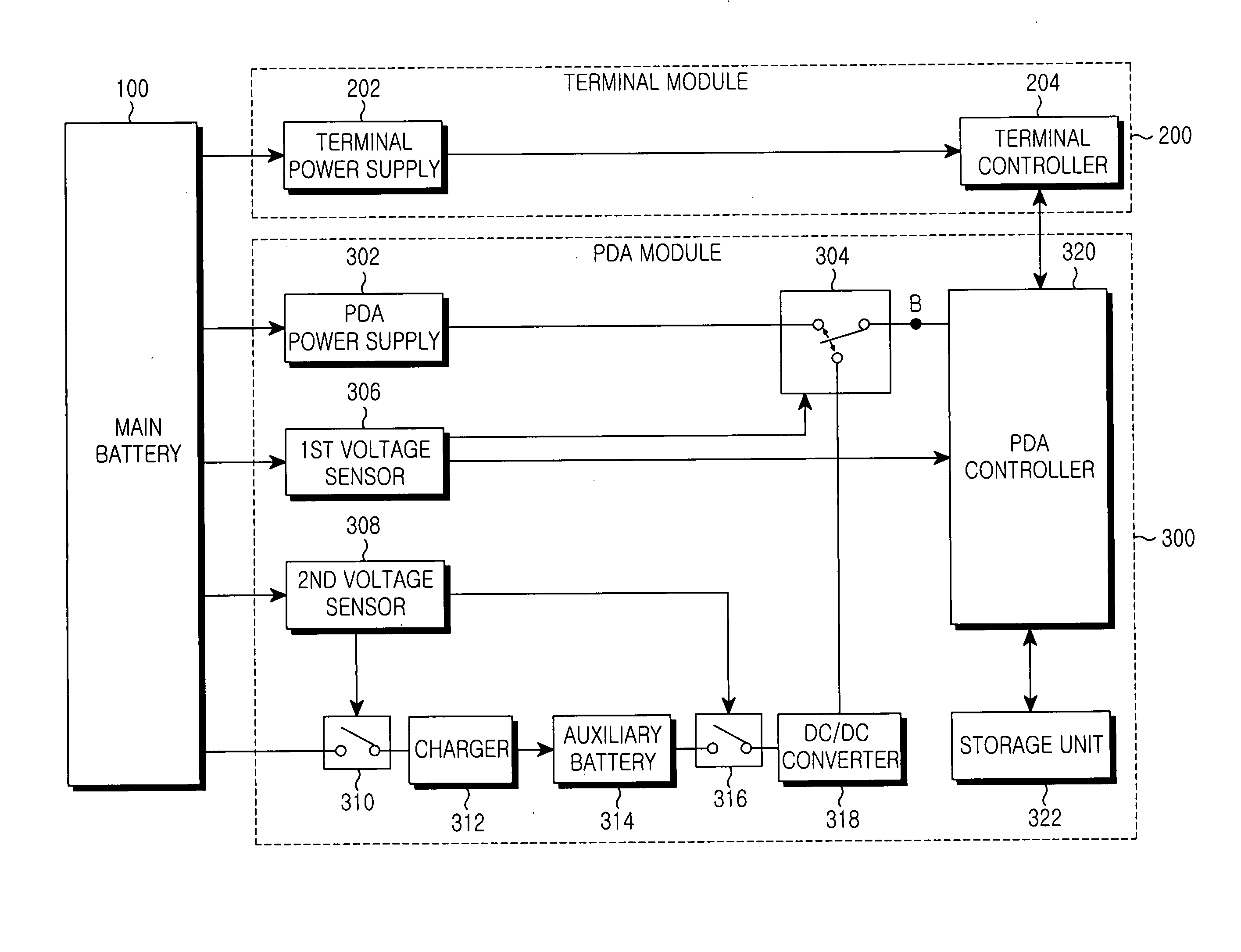
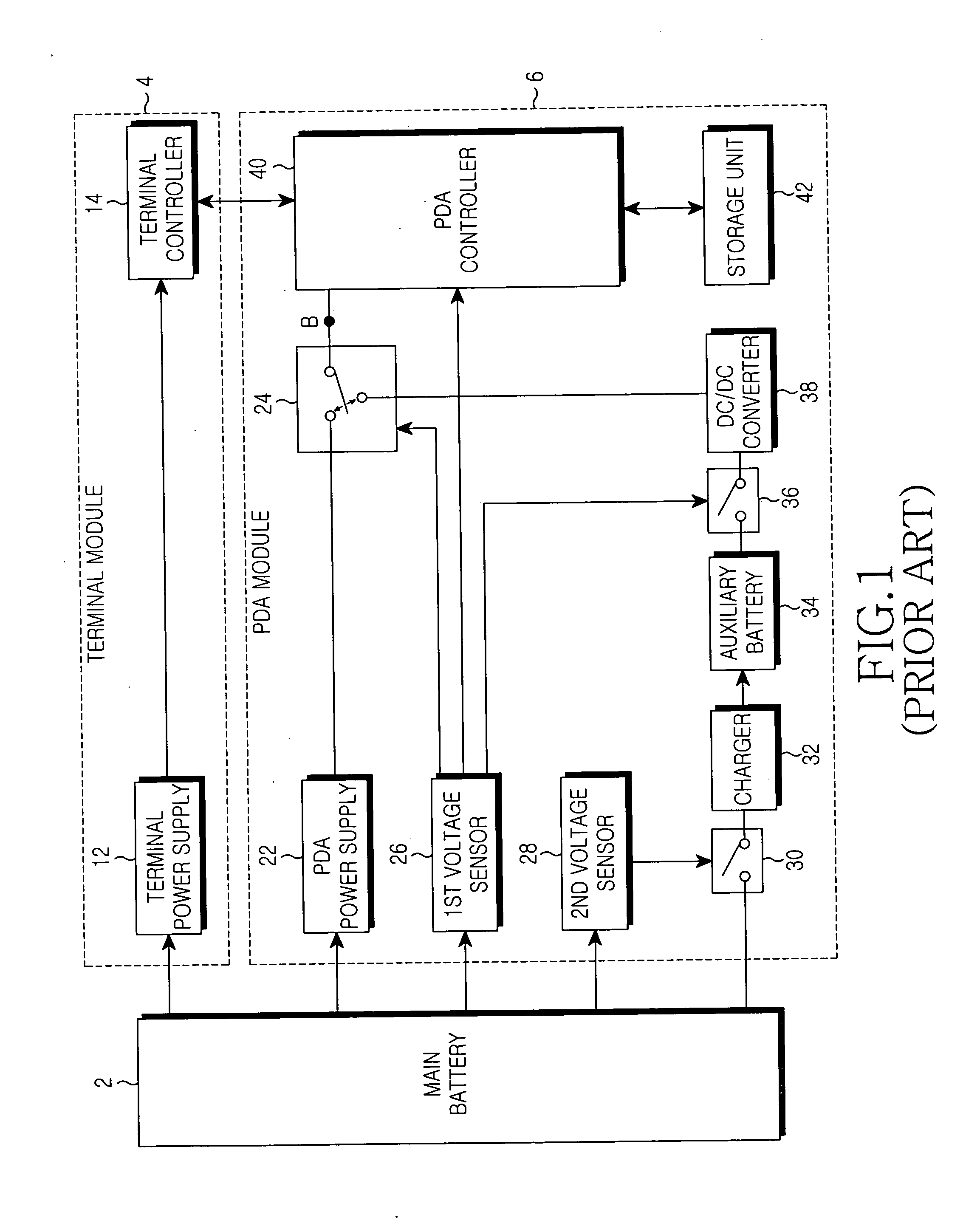
Power control apparatus of a complex terminal
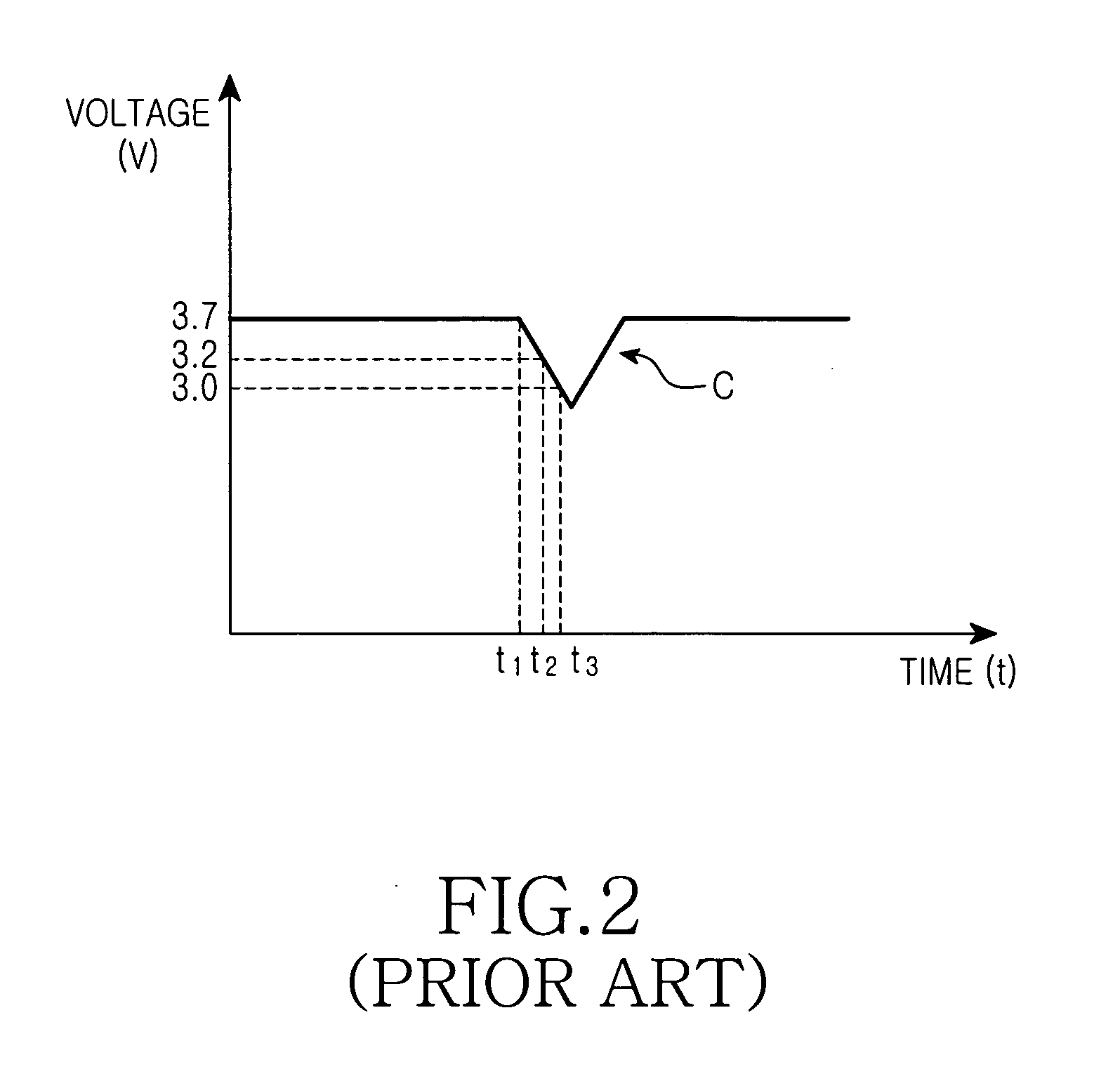
InactiveUS20050041352A1Reduce data lossEasy to operateBatteries circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical batteryVoltage sensor
Disclosed is a power control apparatus of a complex terminal which includes a main battery and an auxiliary battery. The power control apparatus includes: a DC / DC converter for outputting an auxiliary power supplied from the auxiliary battery after adjusting a level of voltage of the auxiliary power to a required input voltage level of the complex terminal; a second voltage sensor for measuring voltage of a main power outputted from the main battery, and controlling the auxiliary power of the auxiliary battery to be inputted to the DC / DC converter before the measured voltage of the main power becomes lower than a predetermined voltage; and a first voltage sensor for interrupting supply of the main power from the main battery to the complex terminal and controlling the auxiliary power outputted from the DC / DC converter to be supplied to the complex terminal, when the measured voltage of the main power becomes lower than the predetermined voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
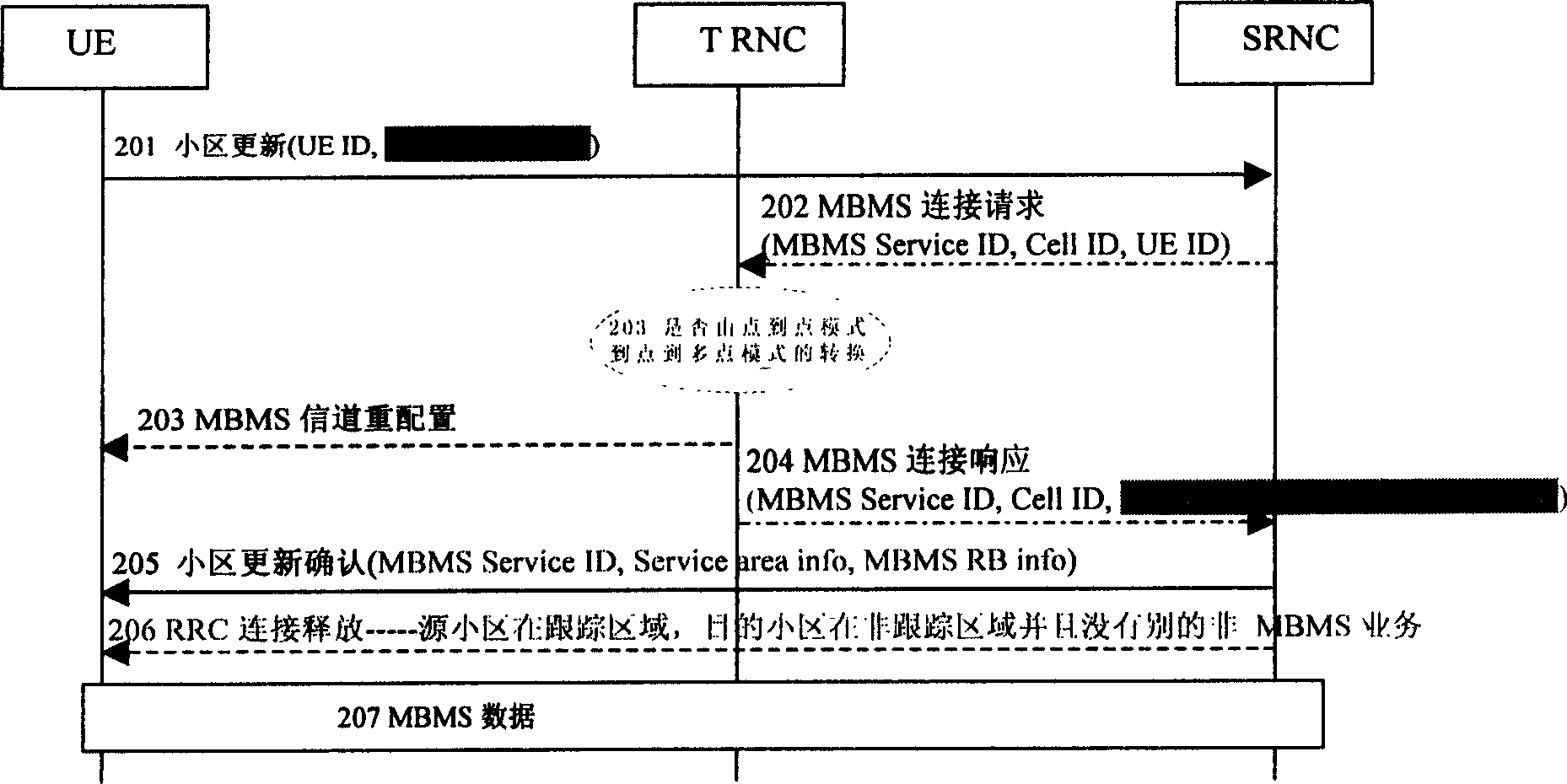
Method for moving UE in RRC connection mole
InactiveCN1518255AImprove efficiencyReduce signal transmissionSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionTelecommunicationsCell ID
A method for moving UE in RRC connection mode, that is, moving the UE in the CELL-FACH or CELL-PCH state and receiving MBMS service to anothe cell, includes such steps as transmitting a 'cell update' message with MBMS service ID from UE to new cell, receiving the messag by RNC, transmitting 'MBMS connection request' message containing MBMS service ID, UE identity and cell ID, or not transmitting if the new cell is in same RNC, RNC transmitting 'MBMS channel relocating' to all UEs in the cell if the UE leads to the channel type change from PTP to PTM, RNC transmitting 'MBMS connection response' to SRNC, and RNC transmitting 'cell updating acknowledge' to the UE.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
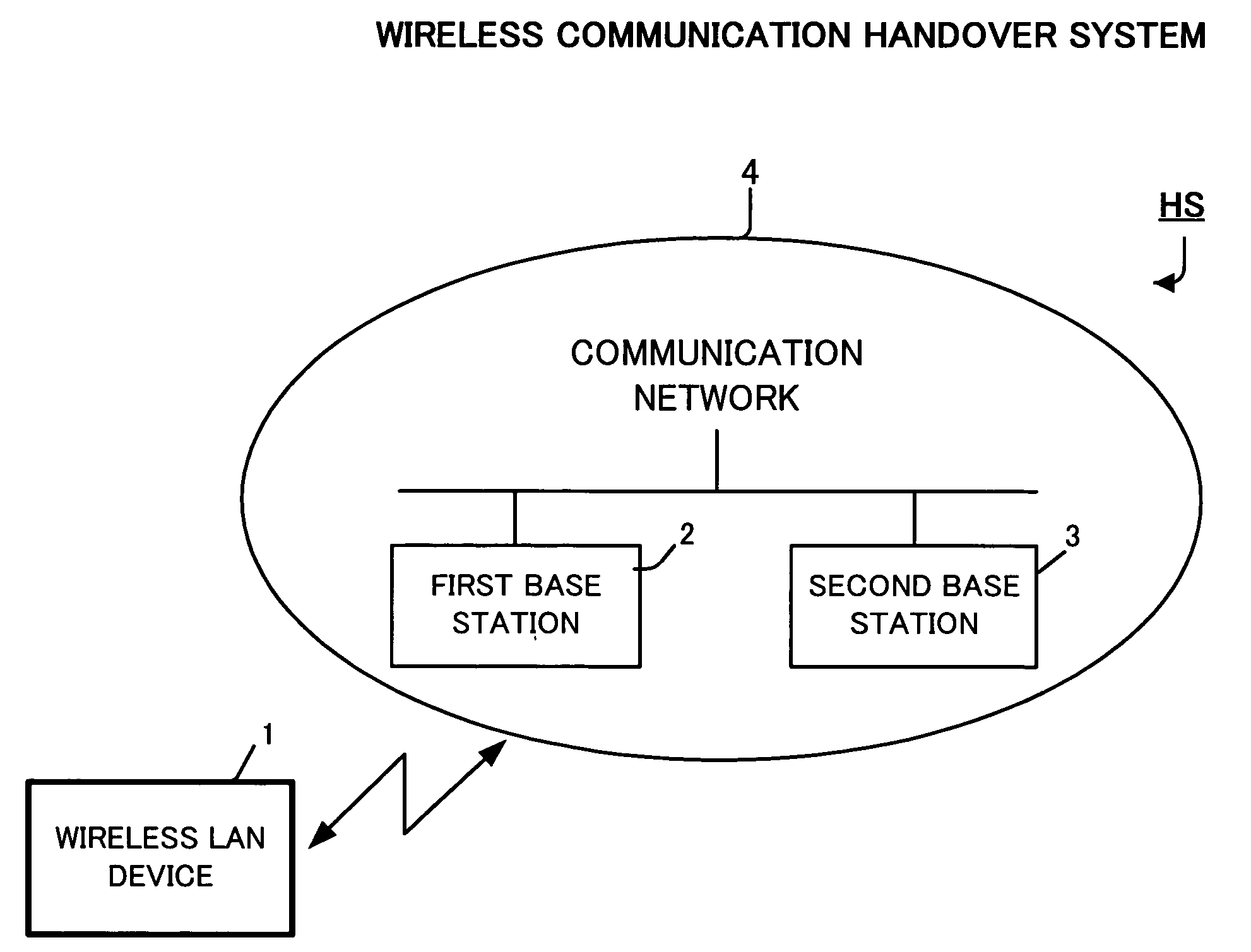
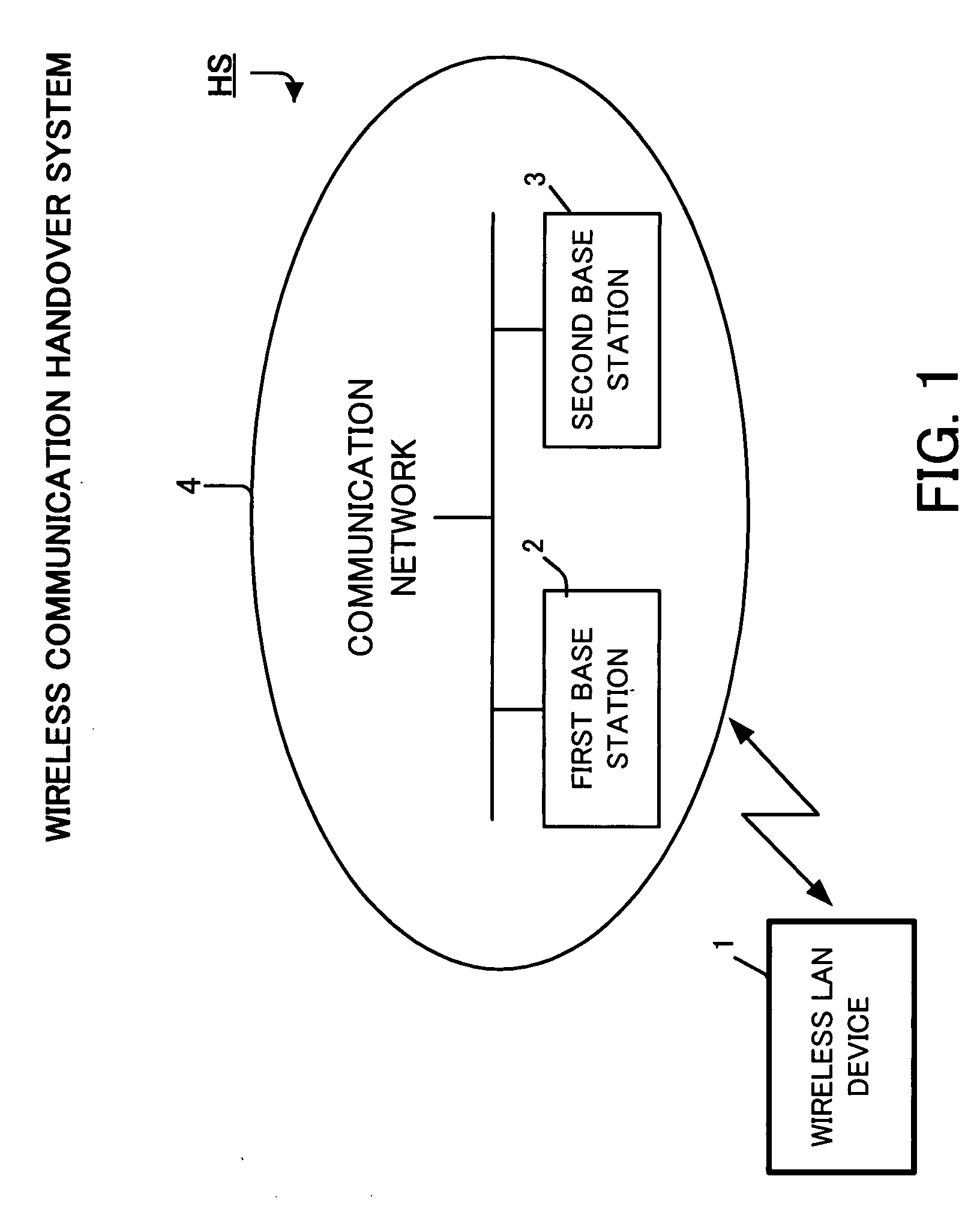
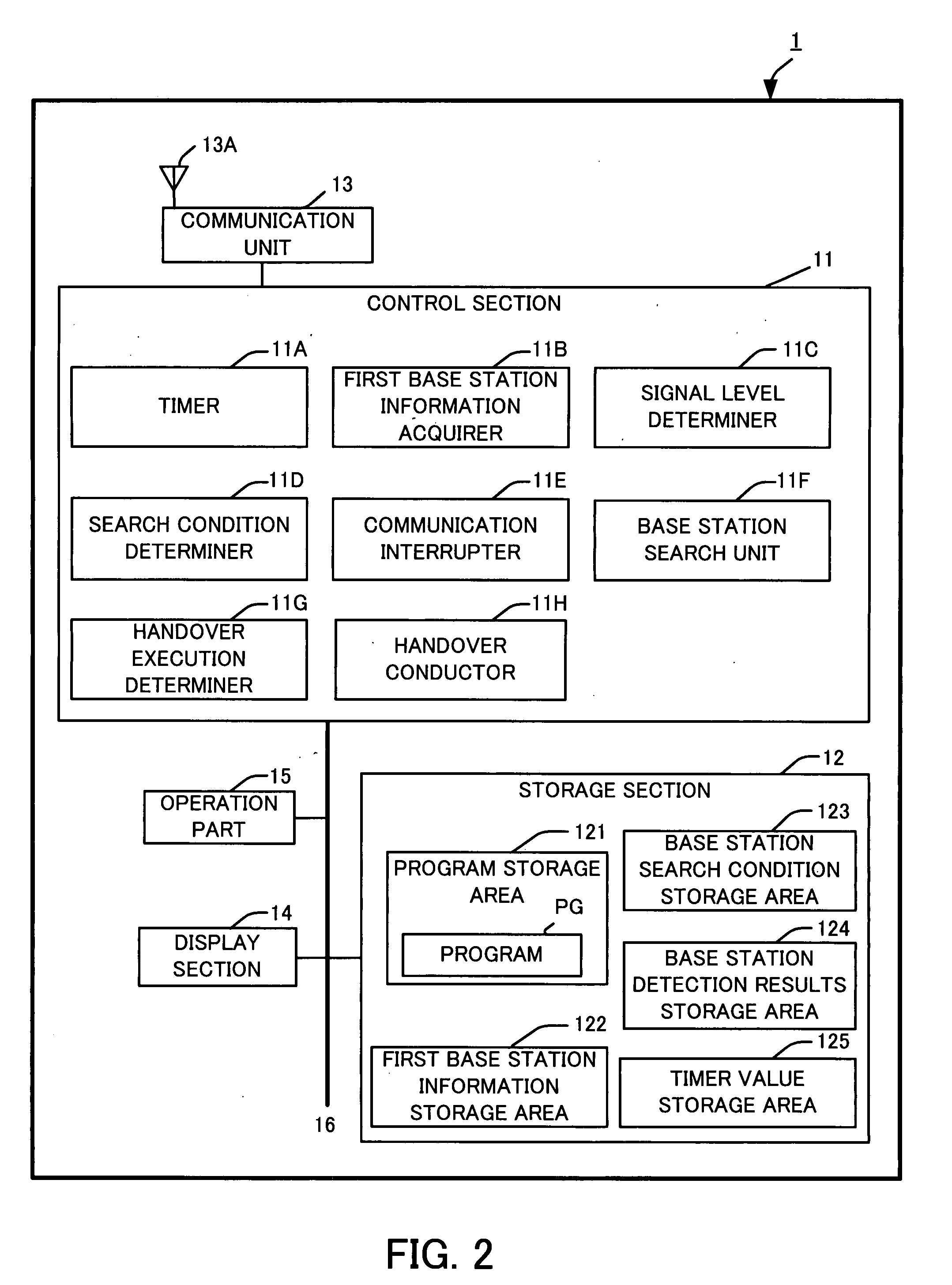
Method for handover in wireless communication, mobile electronic device, and wireless communication handover system
InactiveUS20080119192A1Duration time is shortenedReduce data lossAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesWireless lanHandover
A wireless LAN device determines whether there is a necessity to search for a base station based on base station information as to a currently associated first base station, and selects all or a part of base station search conditions stored in advance to search for the base station when there is the necessity for searching the base station. When detecting at least one base station, the wireless LAN device determines whether there is a necessity to execute a handover based on base station information of each of the detected base station and the first base station. If the handover is necessary, the wireless LAN device determines the second base station from the base stations and associates the wireless LAN device with the second base station.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Method for creating an error correction coding scheme
InactiveUS20070198890A1Reduce lossReduce data lossBurst error correctionCode conversionMain diagonalParity-check matrix
The present invention relates to a method for reducing data loss comprising a first computing step for computing an intermediate result for each redundancy information entity of a redundancy set by processing respectively associated data information entities of a given data set on at least two main diagonals of a parity check matrix representing an error correction coding scheme. The method further comprises a second computing step for computing the information content of the respective redundancy information entity dependent on the respective intermediate result.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
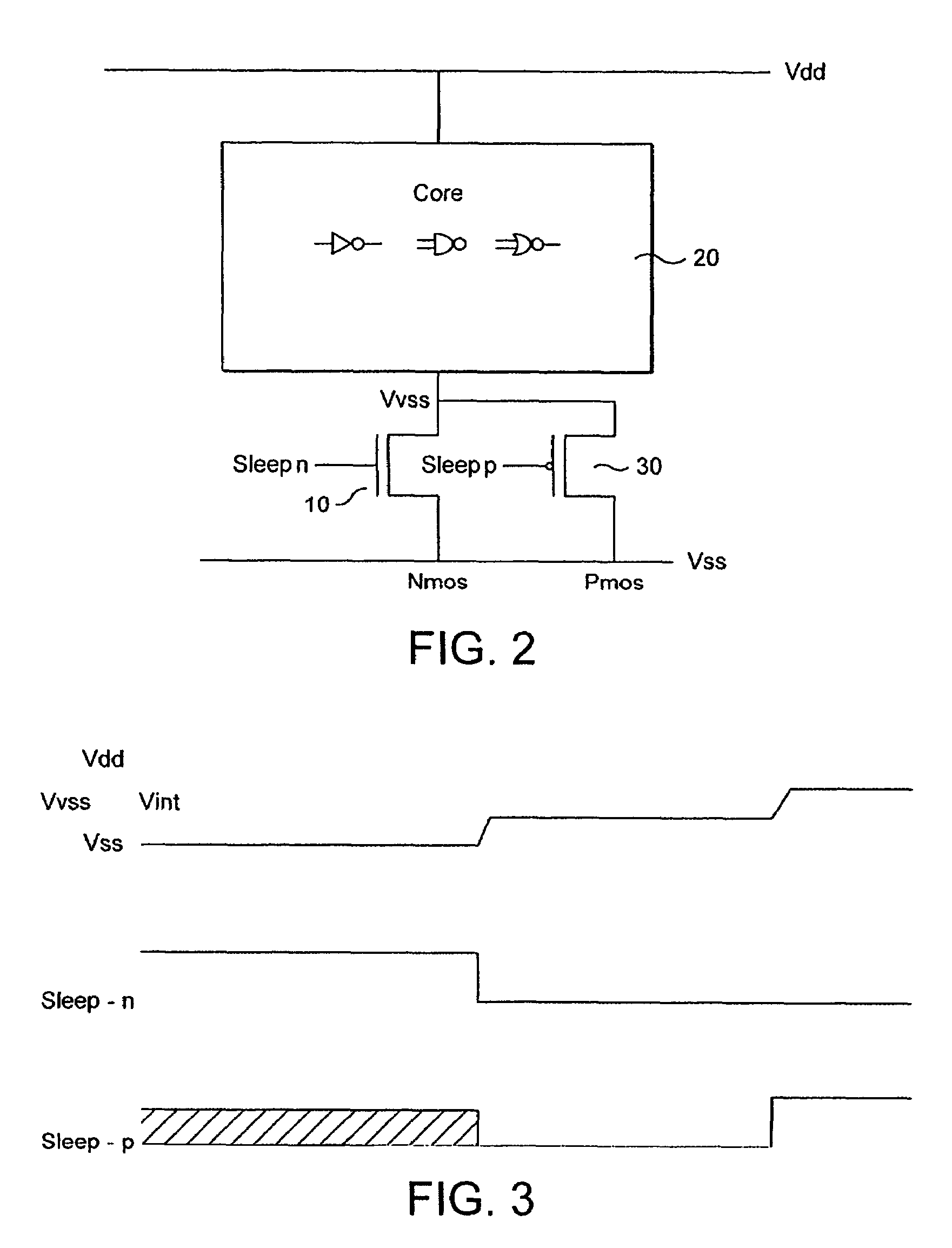
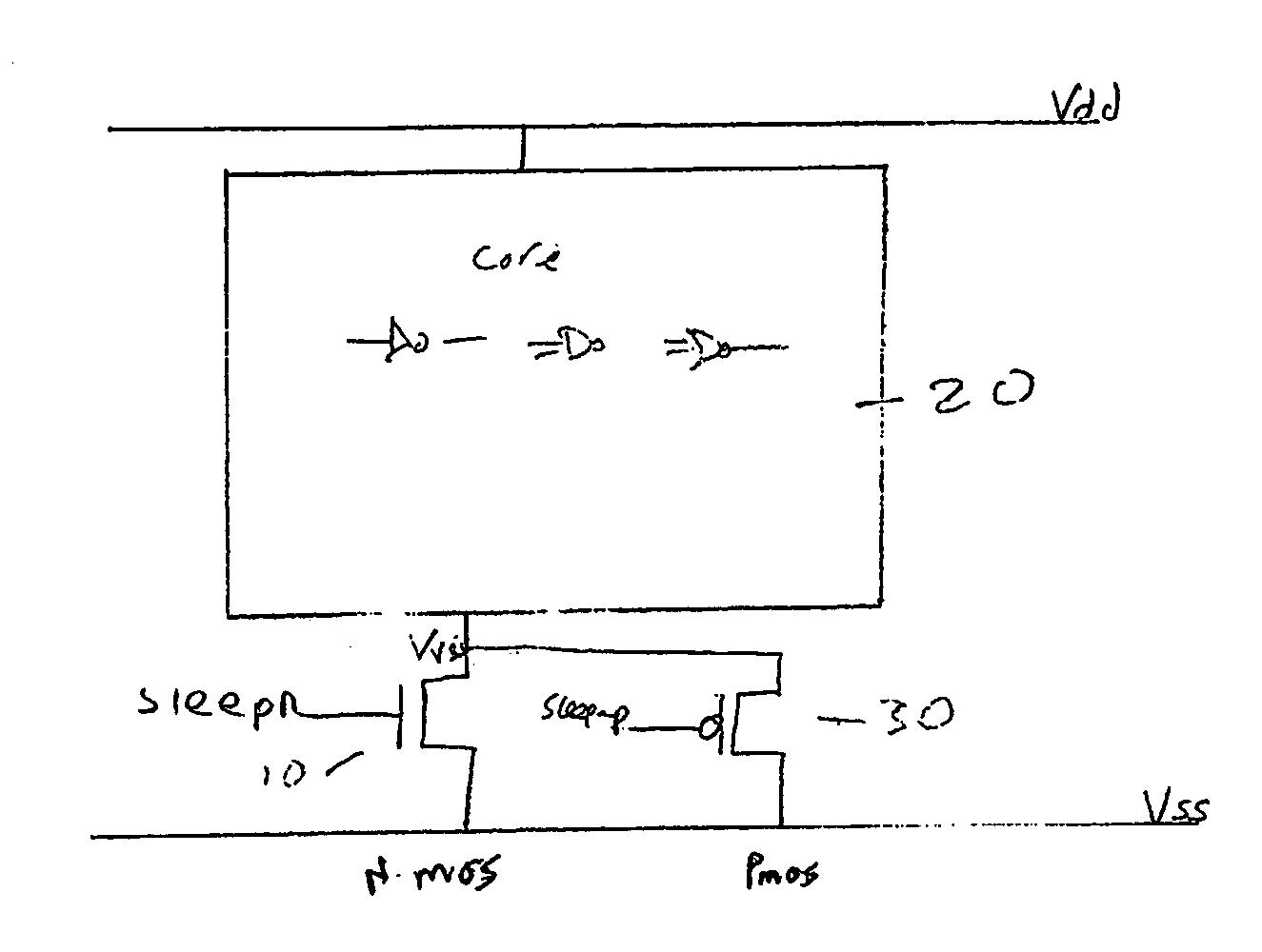
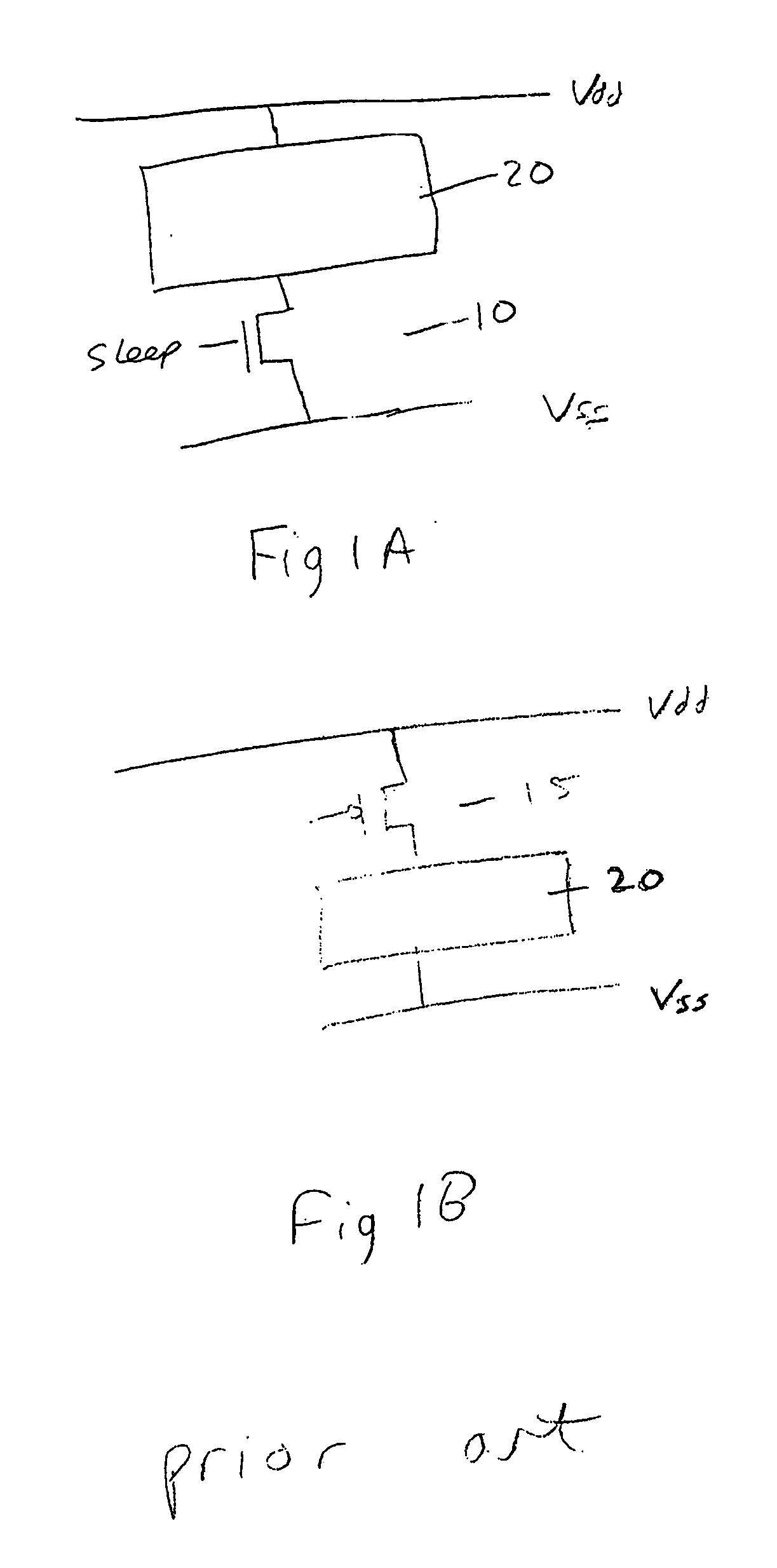
Method and apparatus for controlling a voltage level
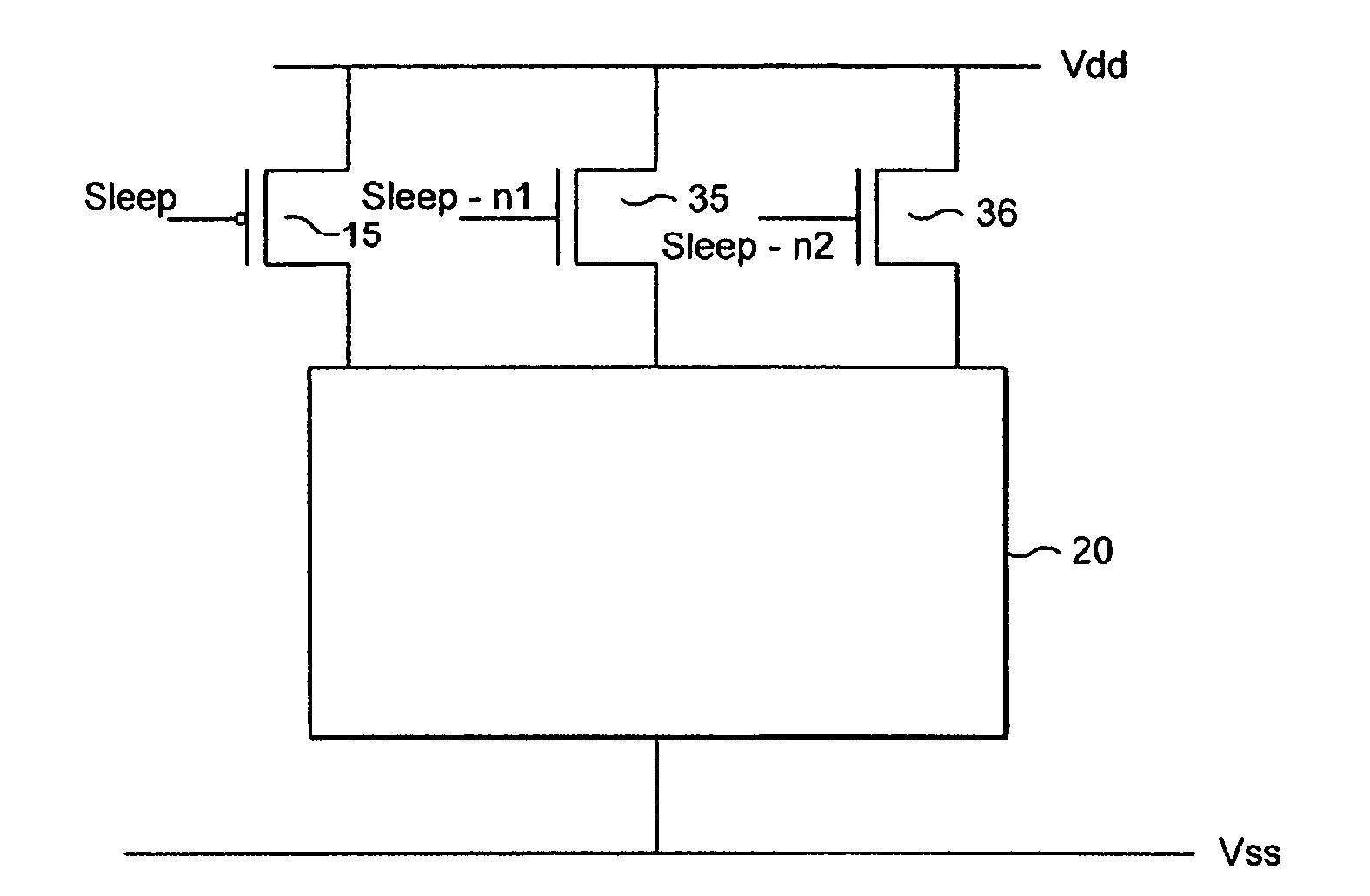
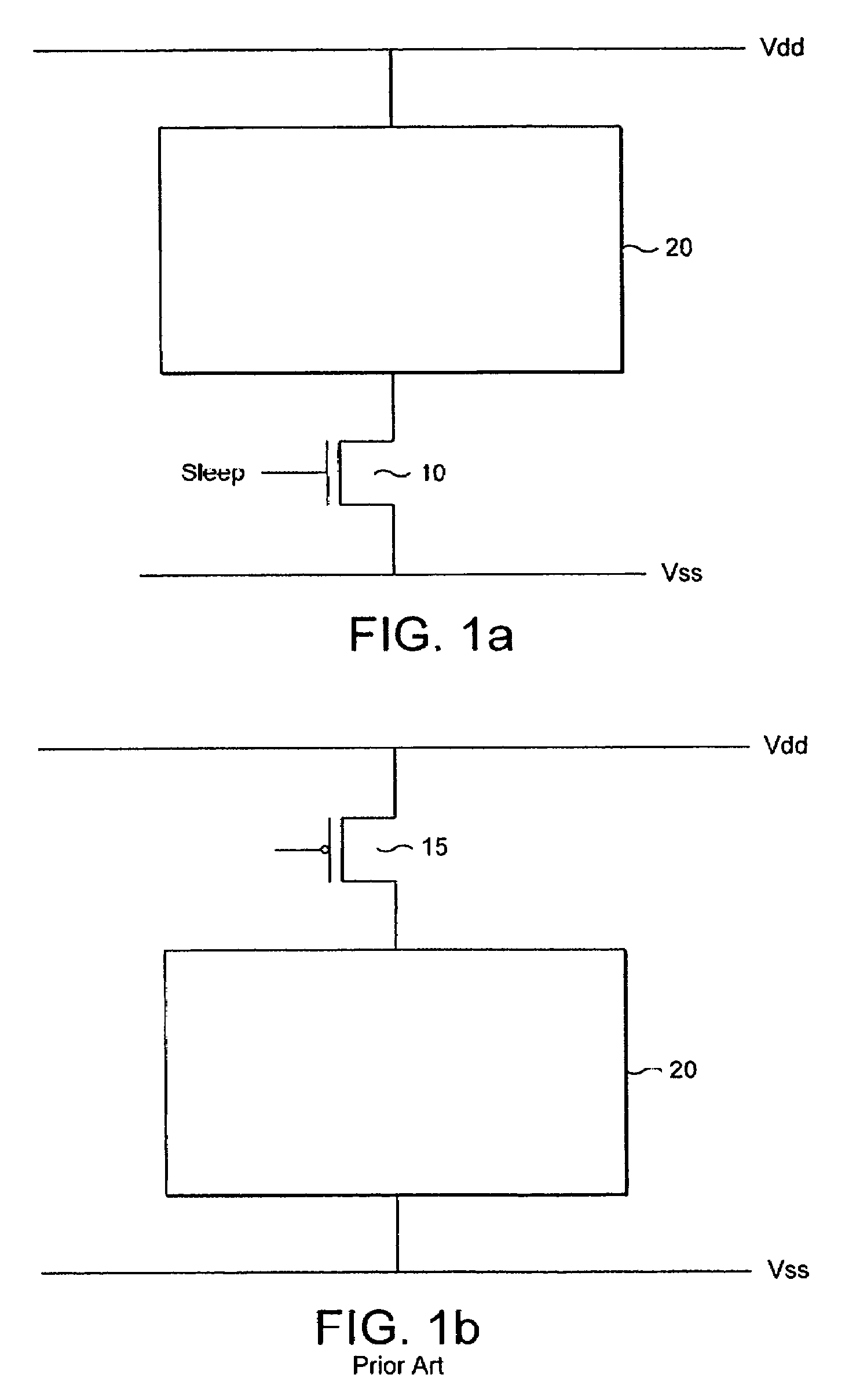
ActiveUS7262631B2Reduce voltageReduce power lossReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalVoltage sourceTransistor
A voltage level control device operable to control a voltage level supplied from a first voltage level source to circuitry, said circuitry being arranged between said first voltage level source and a second voltage level source, said first and second voltage level sources being operable to output different voltage levels; said voltage level control device comprising: a power transistor operable to be connected between said first voltage level source and said circuitry, said power transistor comprising a sleep signal input operable to receive a sleep signal; a switching device arranged in parallel with said power transistor and comprising a sleep signal input operable to receive a pseudo sleep signal; wherein said voltage level control device is operable in dependence upon said sleep signal and said pseudo sleep signal to output to said circuitry an output voltage said output voltage comprising one of three voltage levels, said three voltage levels lying between voltage levels output by said first and second voltage sources.
Owner:ARM LTD
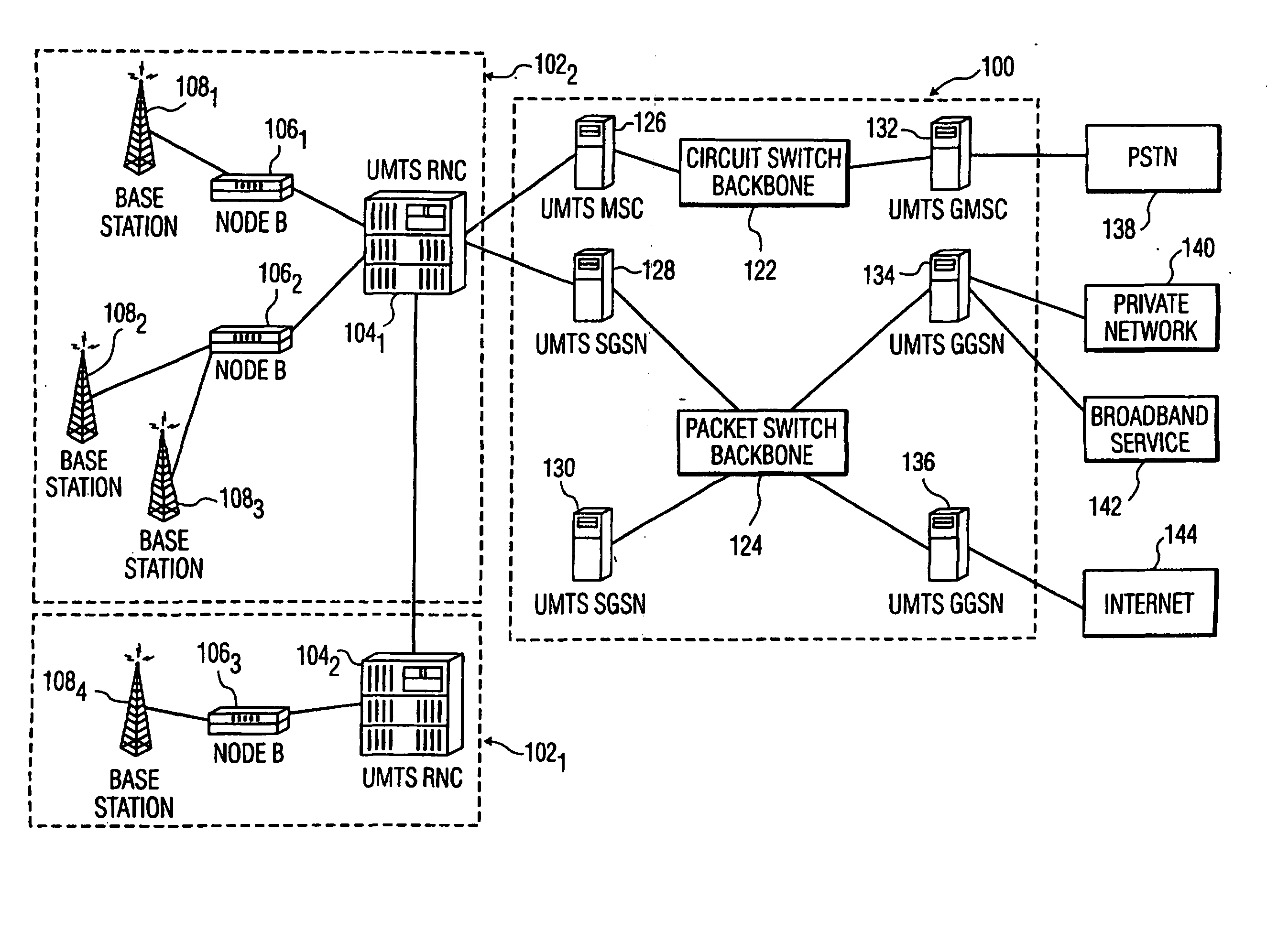
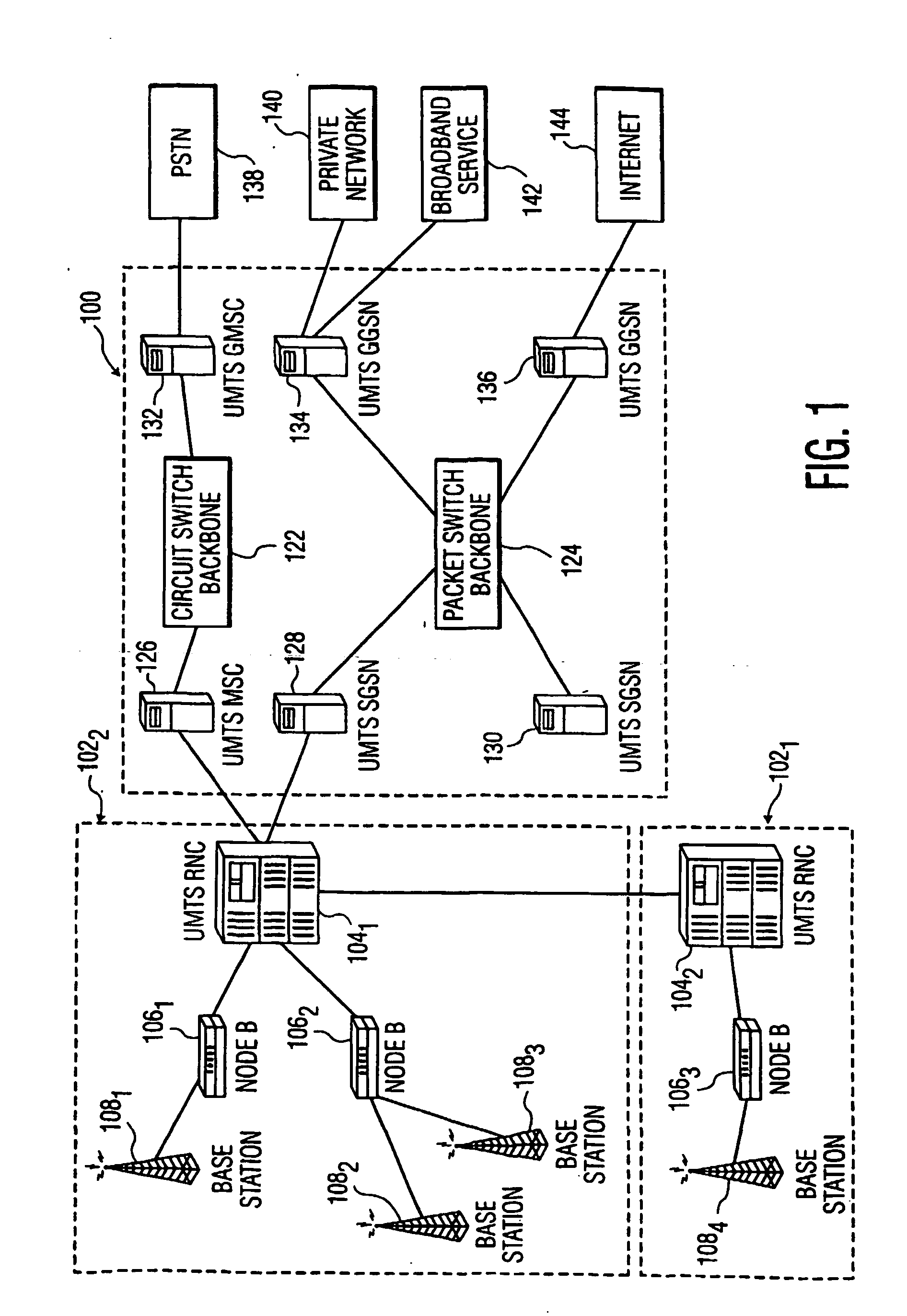
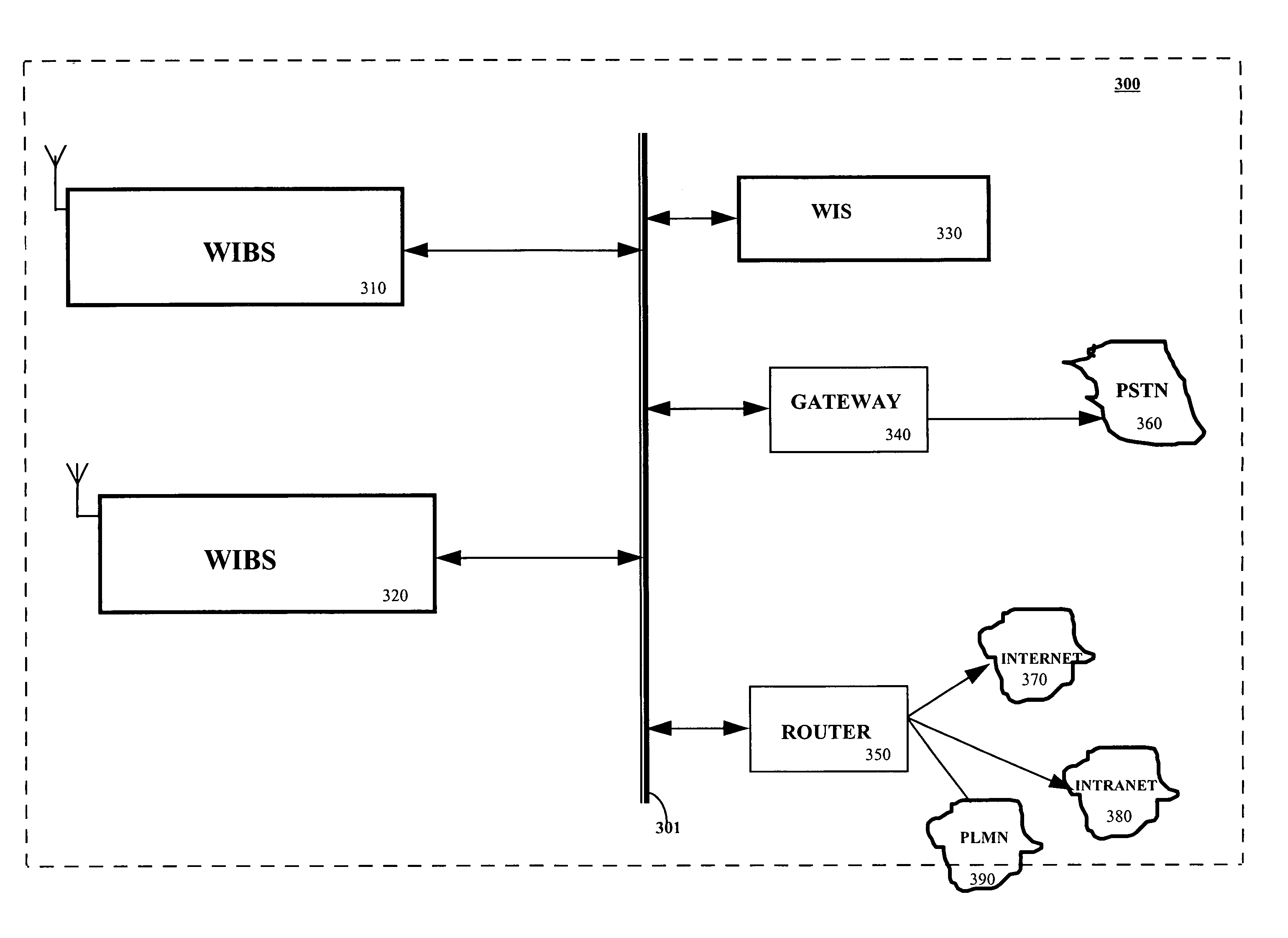
In-building code division multiple access wireless system and method
InactiveUS6967938B1Shorten the timeReduce data lossFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunication unitCommunications system
A wireless office communication system including a wireless internet base station (WIBS) encompassing a base station controller, a mobile switch controller, and an ethernet interface module for coupling the WIBS to an existing internet protocol (IP) based network. The interface module provides for coupling the WIBS to an ethernet back-bone, a mobile communication unit and a public switch telephone network (PSTN). In one embodiment, the wireless communication system includes a wireless internet server which also encompasses base station controller and mobile switch controller functions to enable the wireless communication system to manage call mobility with the system. In one embodiment, communication between the WIBS and the PSTN is in an IP data protocol format. The WIBs provides control and sequencing of all call control operations by handling both voice and data calls which are transmitted over the ethernet back-bone to the PSN or the internet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a voltage level
ActiveUS20060226869A1Reduce voltageReduce power lossReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalVoltage sourceTransistor
A voltage level control device operable to control a voltage level supplied from a first voltage level source to circuitry; said circuitry being arranged between said first voltage level source and a second voltage level source, said first and second voltage level sources being operable to output different voltage levels; said voltage level control device comprising: a power transistor operable to be connected between said first voltage level source and said circuitry, said power transistor comprising a sleep signal input operable to receive a sleep signal; a switching device arranged in parallel with said power transistor and comprising a sleep signal input operable to receive a pseudo sleep signal; wherein said voltage level control device is operable in dependence upon said sleep signal and said pseudo sleep signal to output to said circuitry an output voltage said output voltage comprising one of three voltage levels, said three voltage levels lying between voltage levels output by said first and second voltage sources.
Owner:ARM LTD
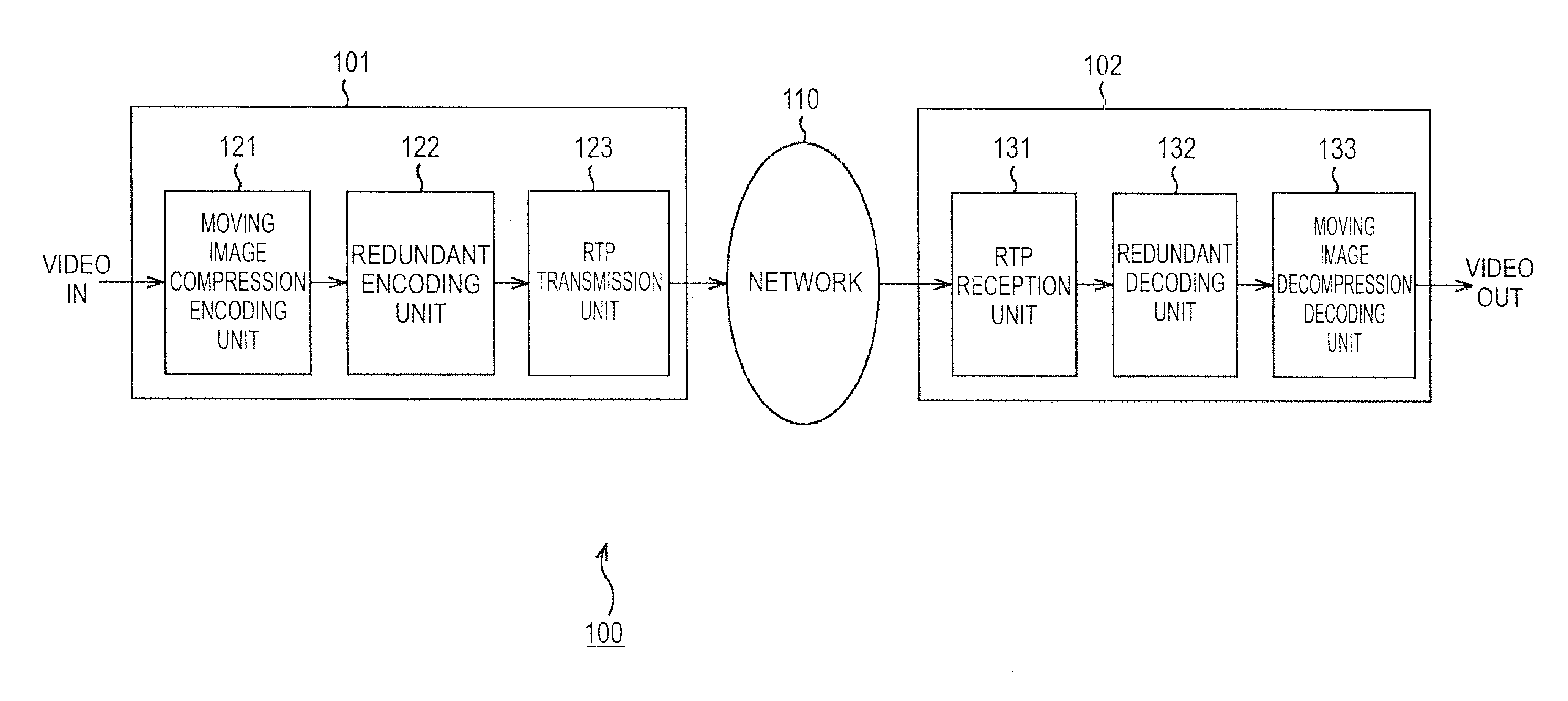
Information processing device, method and program
ActiveUS20110252287A1Increase in unnecessary delayQuality is lostError preventionCode conversionInformation processingDummy data
An information processing device includes: an obtaining means for obtaining encoded data obtained by encoding image data formed by blocks with predetermined data unit, for each block, and redundant data for the encoded data obtained by encoding the encoded data using a forward error correction method; a decoding means for decoding each block using the encoded data and intermediate data generated during a decoding process if the encoded data is all collected or using dummy data, the encoded data, and intermediate data generated during a decoding process if the encoded data is not all collected; a forward error correction method decoding means for decoding the encoded data and the redundant data and recovers lost encoded data; and a setting means for decoding the encoded data and setting intermediate data obtained during the decoding to be used to decode a subsequent block as intermediate data during a decoding process for a block which has been decoded.
Owner:SONY CORP
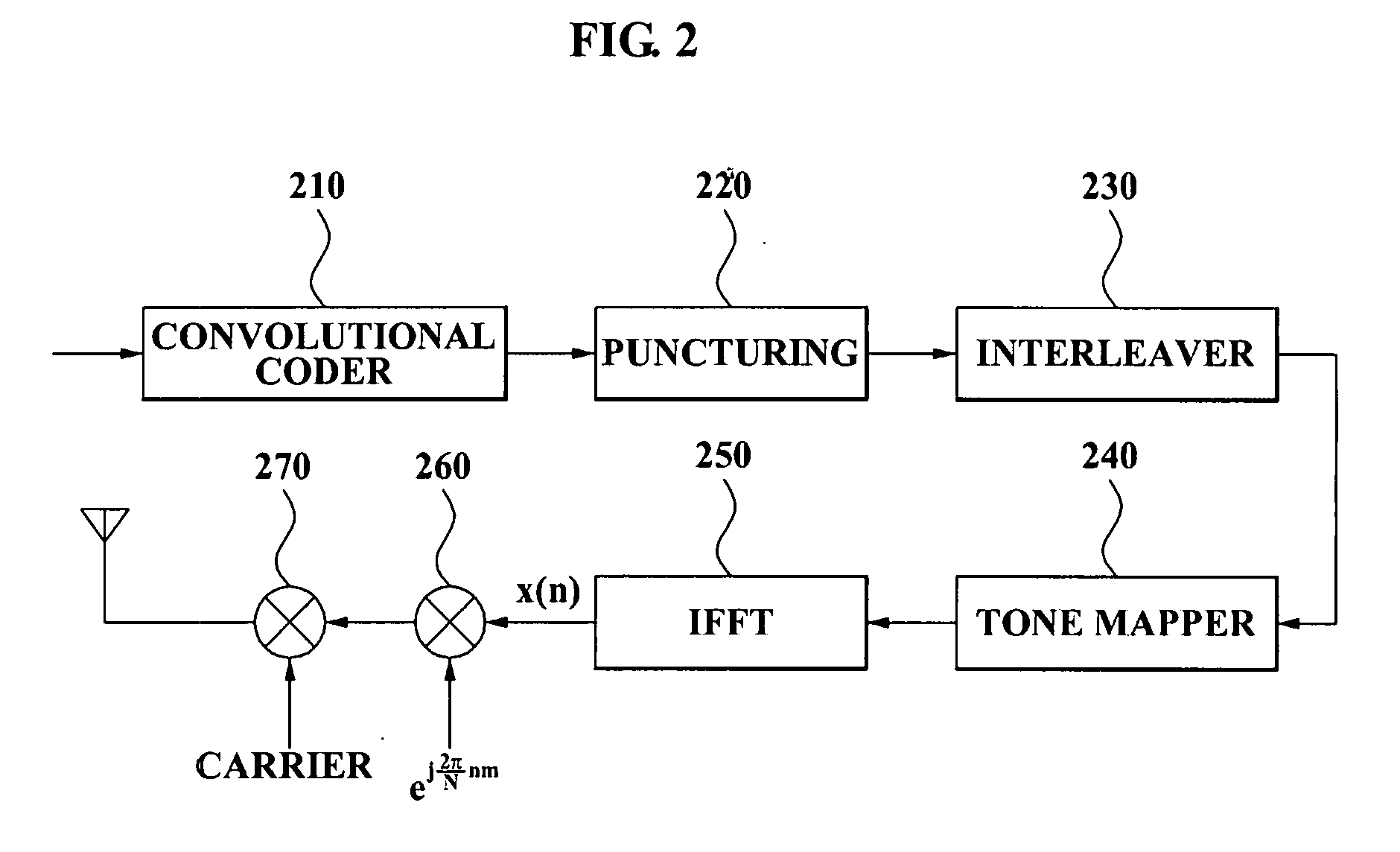
Method for detection and avoidance of ultra wideband signal and ultra wideband device for operating the method
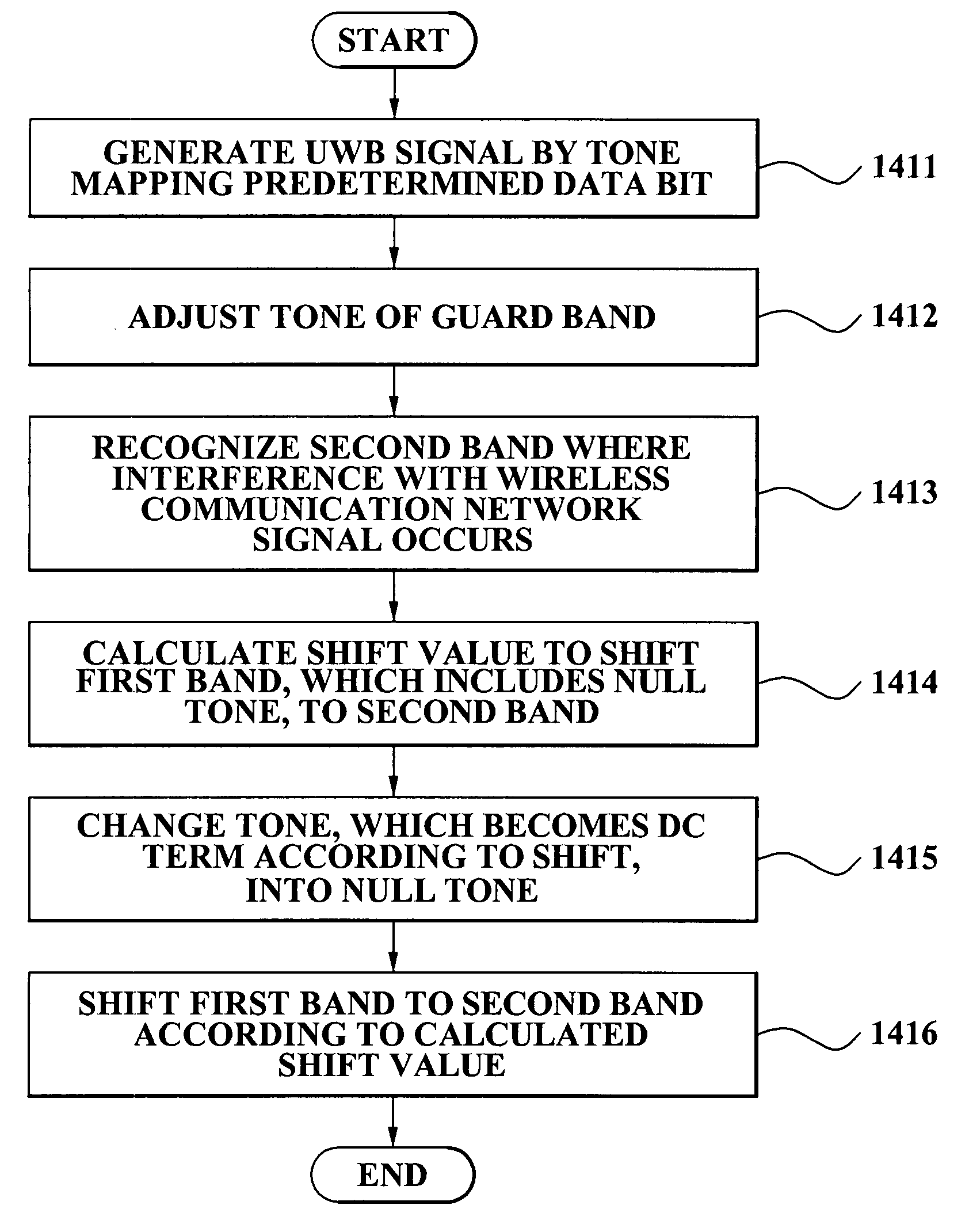
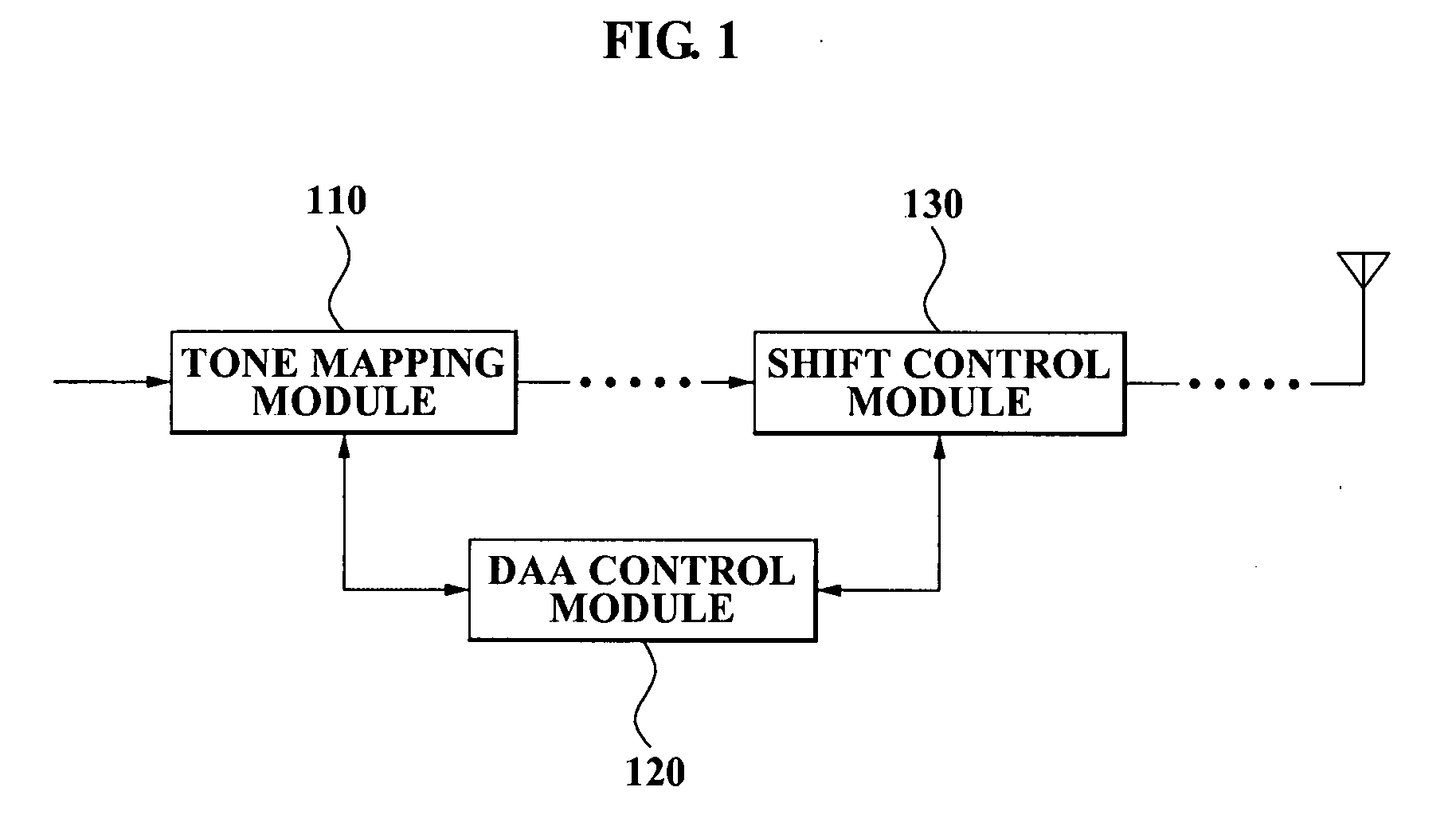
InactiveUS20080069181A1Efficient solutionSimple planNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionUltra-widebandTone mapping
A DAA method of a UWB signal with respect to a WiMax signal, the method including: generating the UWB signal by tone mapping a predetermined data bit; and controlling a first band to shift to a second band where an interference with the WiMax signal occurs, the first band including a null tone among mapped tones of the UWB signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
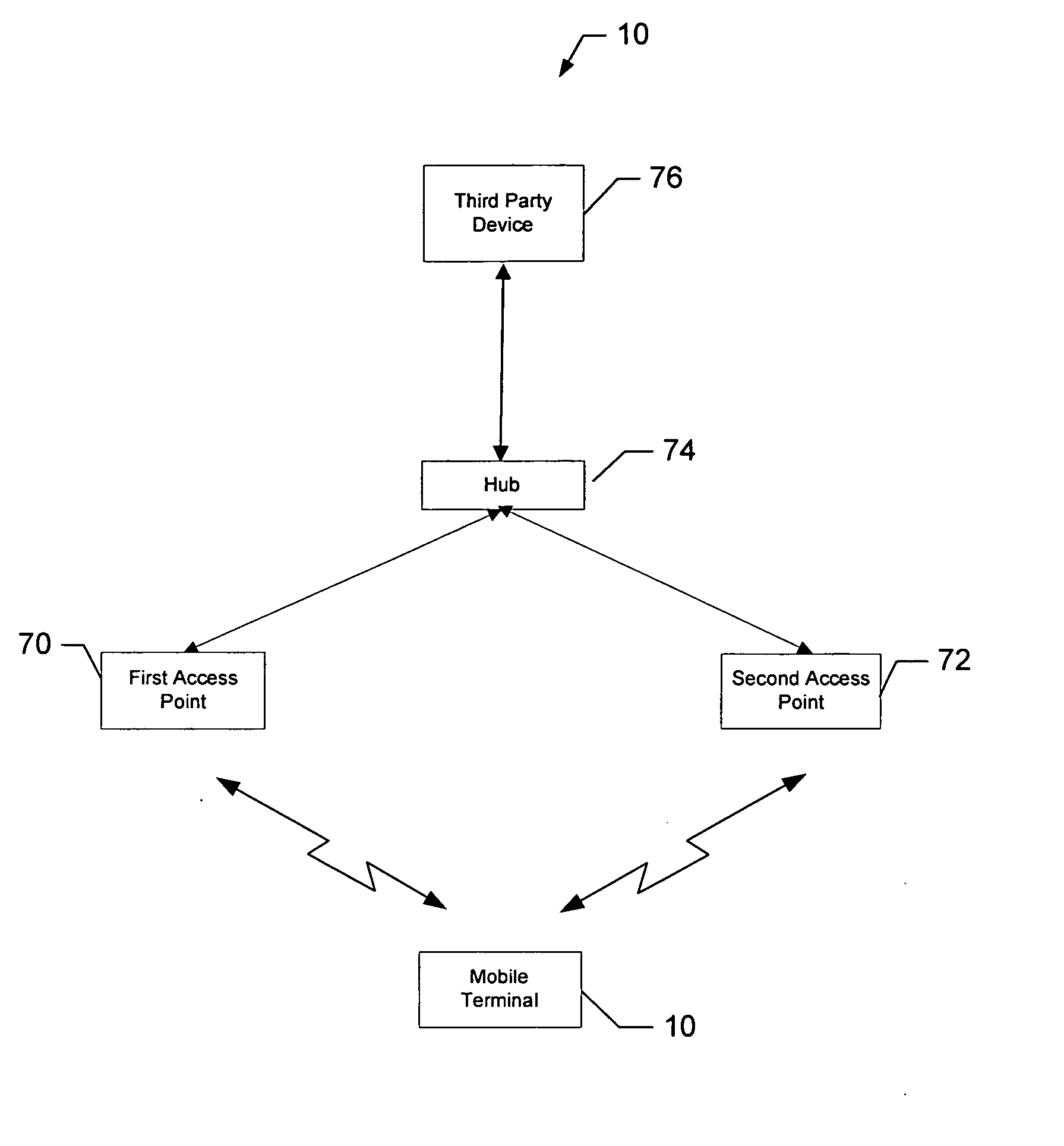
System and method for proactive, early network switching
ActiveUS20060135165A1Inhibition transitionReduce data lossRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationData storingData loss
A mobile terminal for reduction of data loss during transitioning of the mobile terminal between network devices includes a controller. The controller is capable of transmitting a request to transition and receiving queued data from an original network device prior to transition from the original network device to a target network device. The queued data is content data intended for and undelivered to the mobile terminal that is temporarily stored at the original network device from a time when the request to transition is transmitted to when the transition occurs. The controller is also capable of transitioning from the original network device to the target network device and receiving data stored at the target network device responsive to the request to transition following transition from the original network device to the target network device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com