Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
680 results about "Matrix multiplication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, matrix multiplication or matrix product is a binary operation that produces a matrix from two matrices with entries in a field, or, more generally, in a ring or even a semiring. The matrix product is designed for representing the composition of linear maps that are represented by matrices. Matrix multiplication is thus a basic tool of linear algebra, and as such has numerous applications in many areas of mathematics, as well as in applied mathematics, statistics, physics, economics, and engineering.
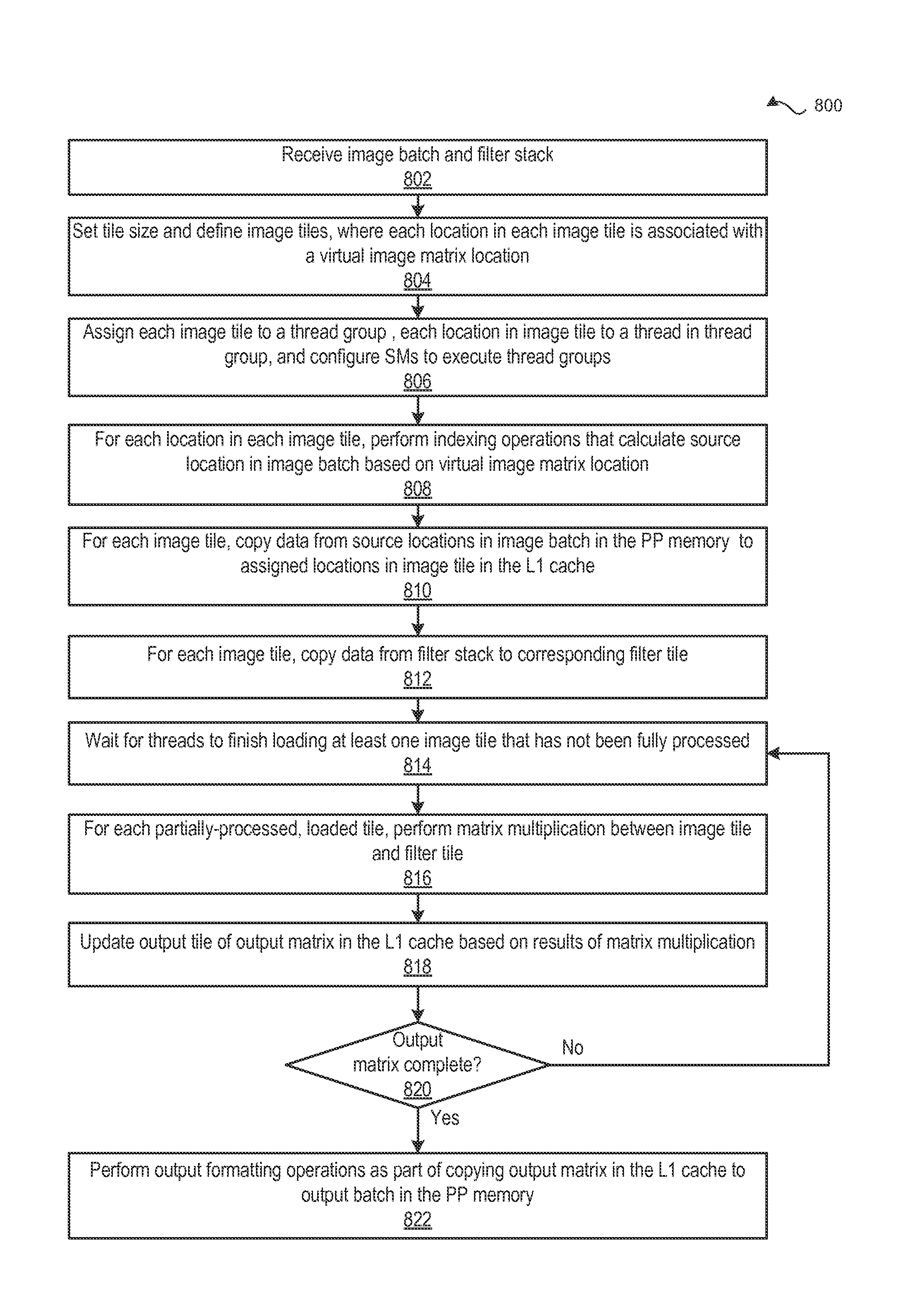
Performing multi-convolution operations in a parallel processing system
ActiveUS20160062947A1Easy to operateOptimizing on-chip memory usageBiological modelsComplex mathematical operationsLine tubingParallel processing
In one embodiment of the present invention a convolution engine configures a parallel processing pipeline to perform multi-convolution operations. More specifically, the convolution engine configures the parallel processing pipeline to independently generate and process individual image tiles. In operation, for each image tile, the pipeline calculates source locations included in an input image batch. Notably, the source locations reflect the contribution of the image tile to an output tile of an output matrix—the result of the multi-convolution operation. Subsequently, the pipeline copies data from the source locations to the image tile. Similarly, the pipeline copies data from a filter stack to a filter tile. The pipeline then performs matrix multiplication operations between the image tile and the filter tile to generate data included in the corresponding output tile. To optimize both on-chip memory usage and execution time, the pipeline creates each image tile in on-chip memory as-needed.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Speed up big-number multiplication using single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architectures
InactiveUS20130332707A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsMatrix multiplicationSIMD
A processing apparatus may be configured to include logic to generate a first set of vectors based on a first integer and a second set of vectors based on a second integer, logic to calculate sub products by multiplying the first set of vectors to the second set of vectors, logic to split each sub product into a first half and a second half and logic to generate a final result by adding together all first and second halves at respective digit positions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
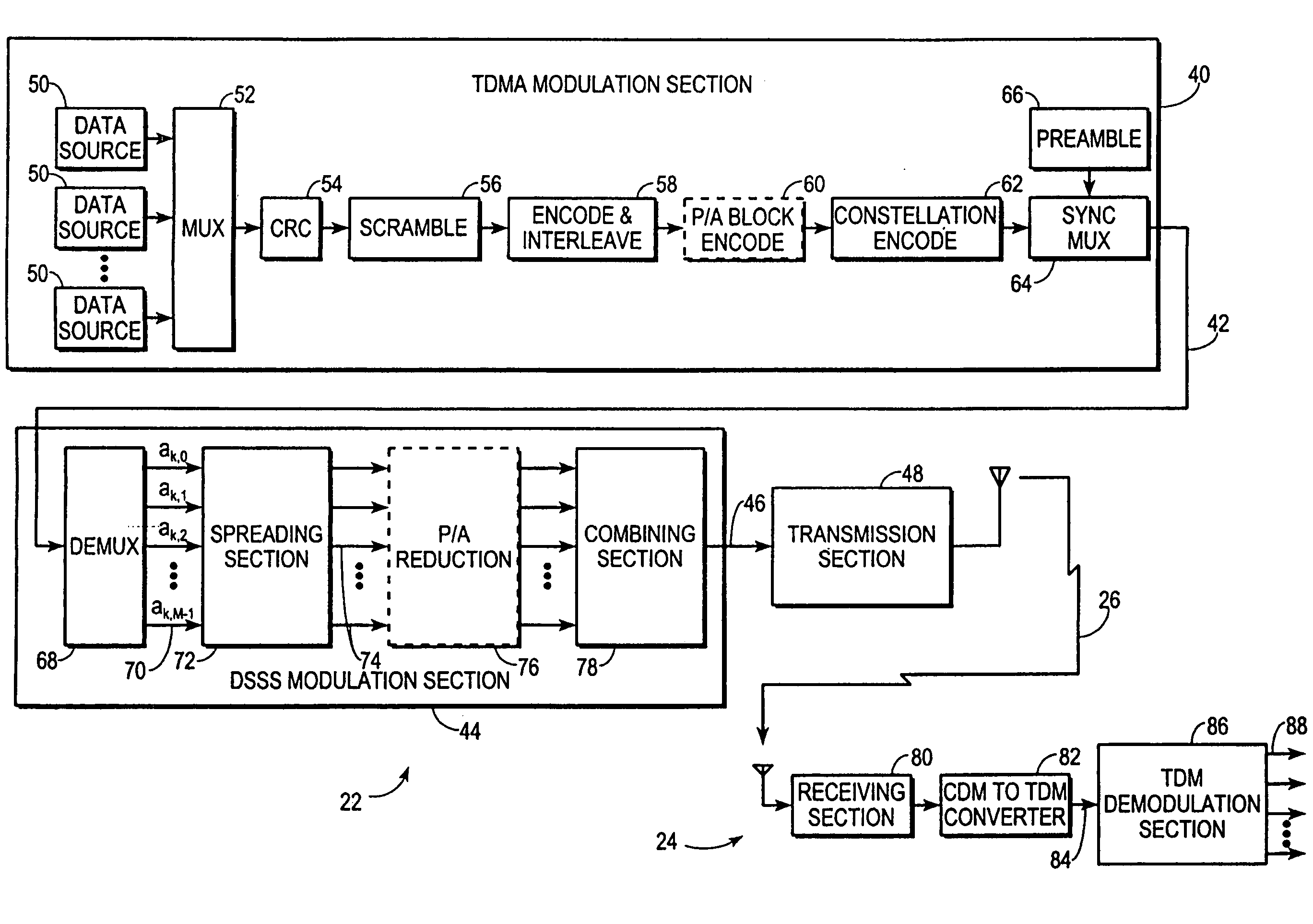
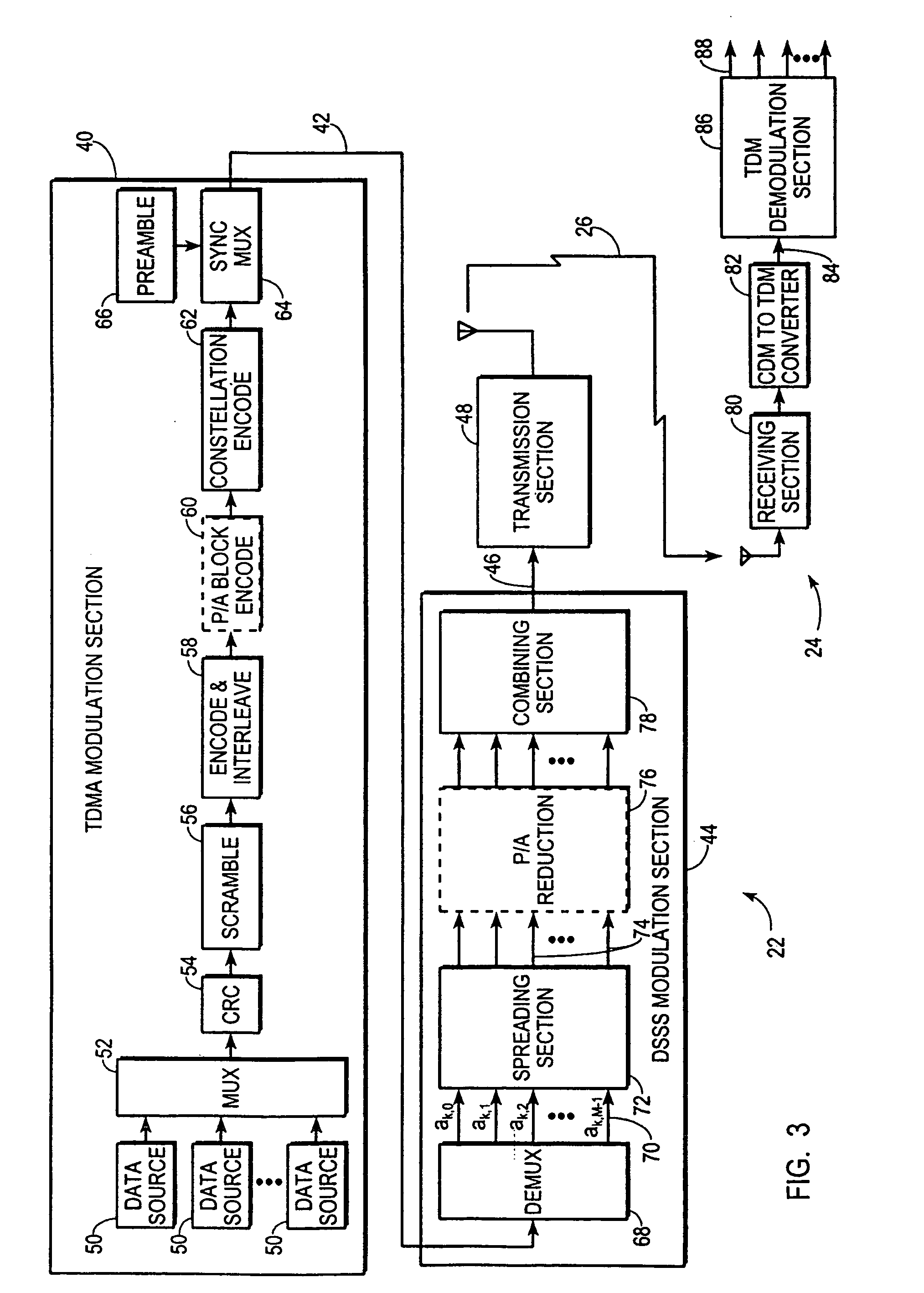
CDMA/TDMA communication method and apparatus for wireless communication using cyclic spreading codes
A communication system (20) uses TDMA techniques to distinguish intended recipients of a communication signal (26) from one another, and direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) techniques to encode and distinguish diverse parallel substreams (70, 74) of each user's data stream. Parallel unspread substreams (70) are spread using cyclic variations of a common spreading code (38). In one embodiment, the common spreading code (38) is chosen for low aperiodic autocorrelation sidelobes and a substantially flat spectral analysis. In another embodiment the common spreading code (38) is chosen for low periodic autocorrelation sidelobes and a substantially flat spectral analysis. In one embodiment, the use of cyclic variations of the spreading code (38) along with a cyclic prefix (114) enables the mathematical communicative matrix multiplication property, thereby permitting equalization for multipath to occur following or in conjunction with despreading.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
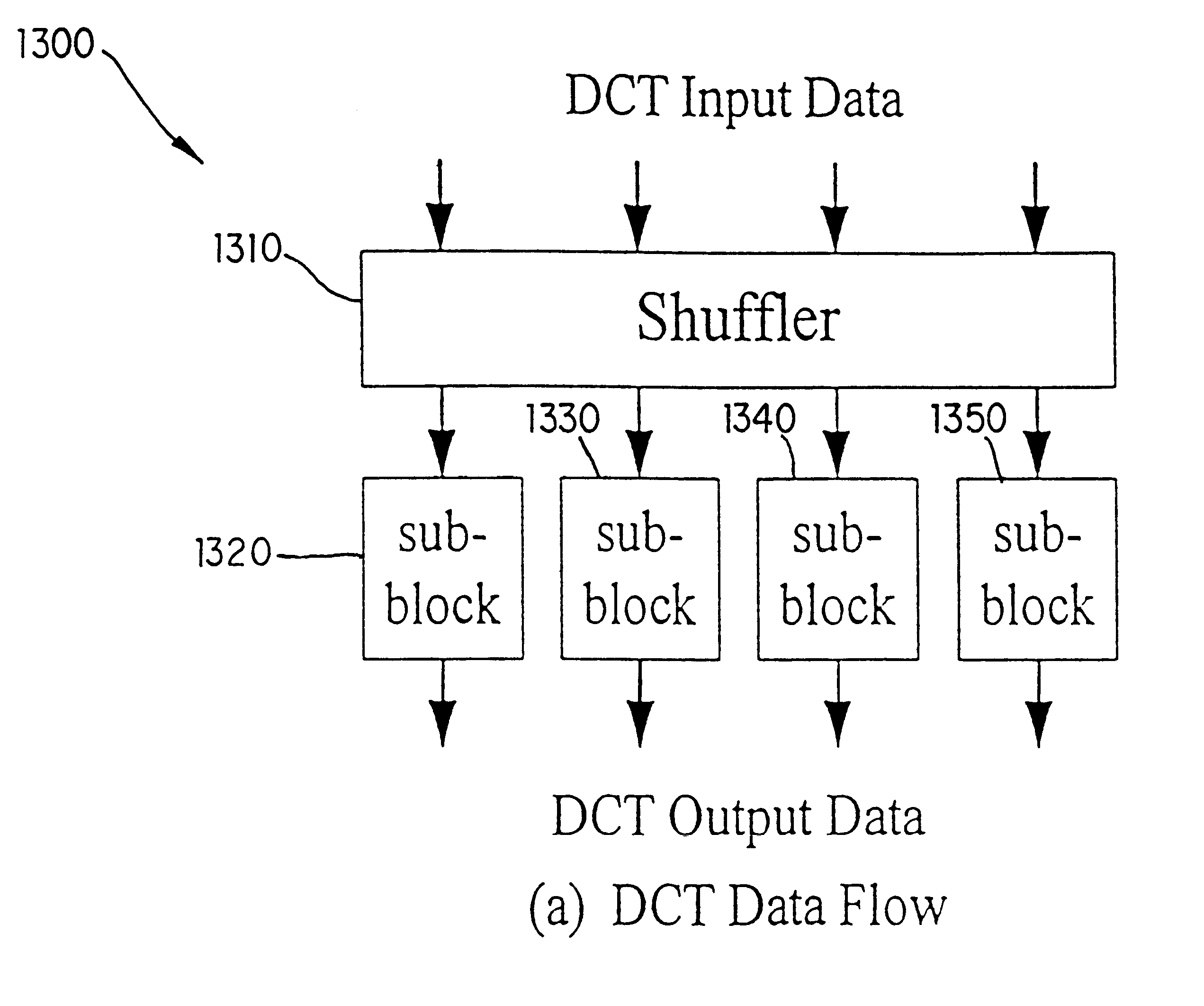
Method and system for computing 8x8 DCT/IDCT and a VLSI implementation
InactiveUS6587590B1Character and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsVlsi implementationsVideo processing
A method and system for computing 2-D DCT / IDCT which is easy to implement with VLSI technology to achieve high throughput to meet the requirements of high definition video processing in real time is described. A direct 2-D matrix factorization approach is utilized to compute the 2-D DCT / IDCT. The 8x8 DCT / IDCT is computed through four 4x4 matrix multiplication sub-blocks. Each sub-block is half the size of the original 8x8 size and therefore requires a much lower number of multiplications. Additionally, each sub-block can be implemented independently with localized interconnection so that parallelism can be exploited and a much higher DCT / IDCT throughput can be achieved.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
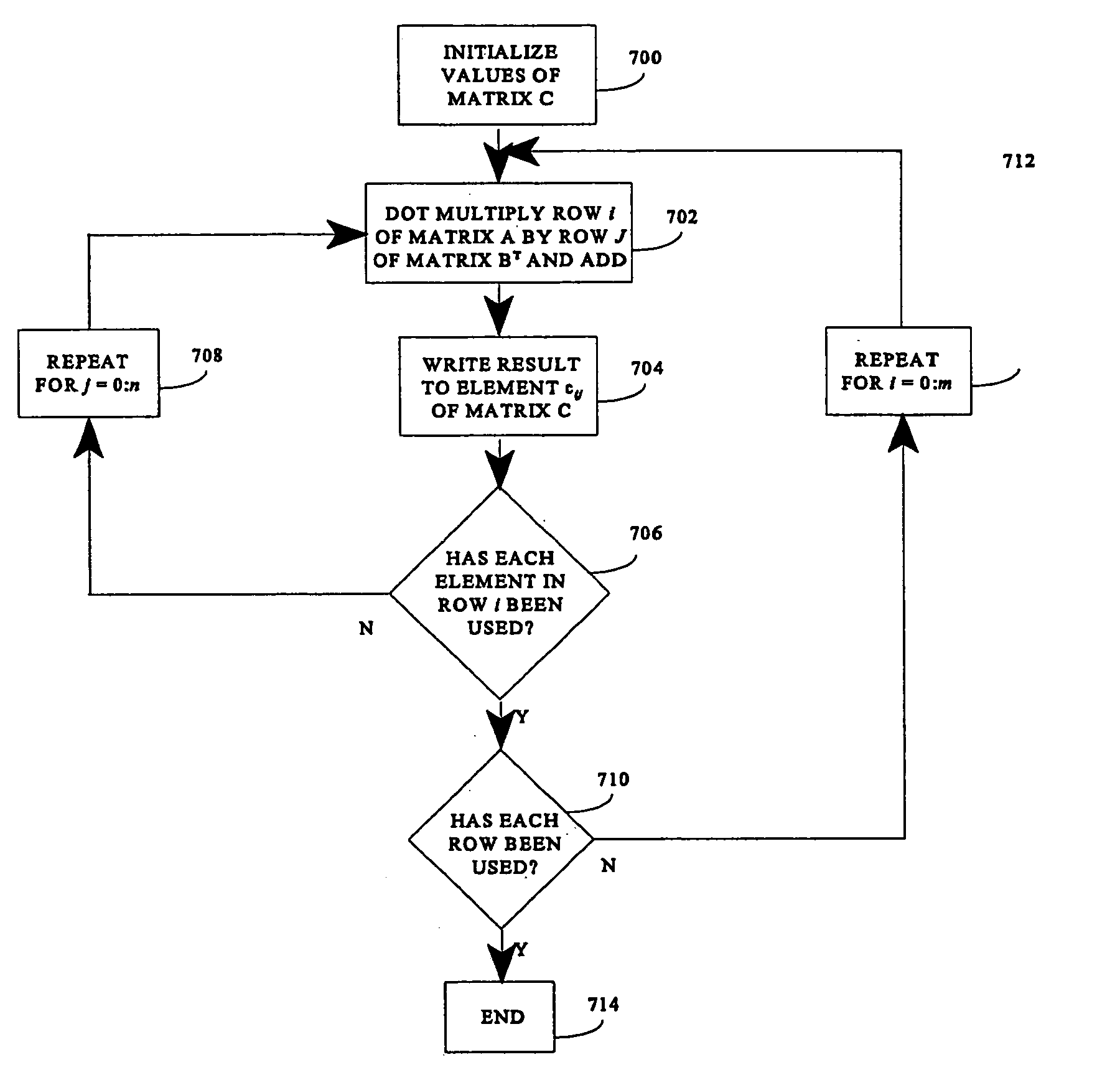
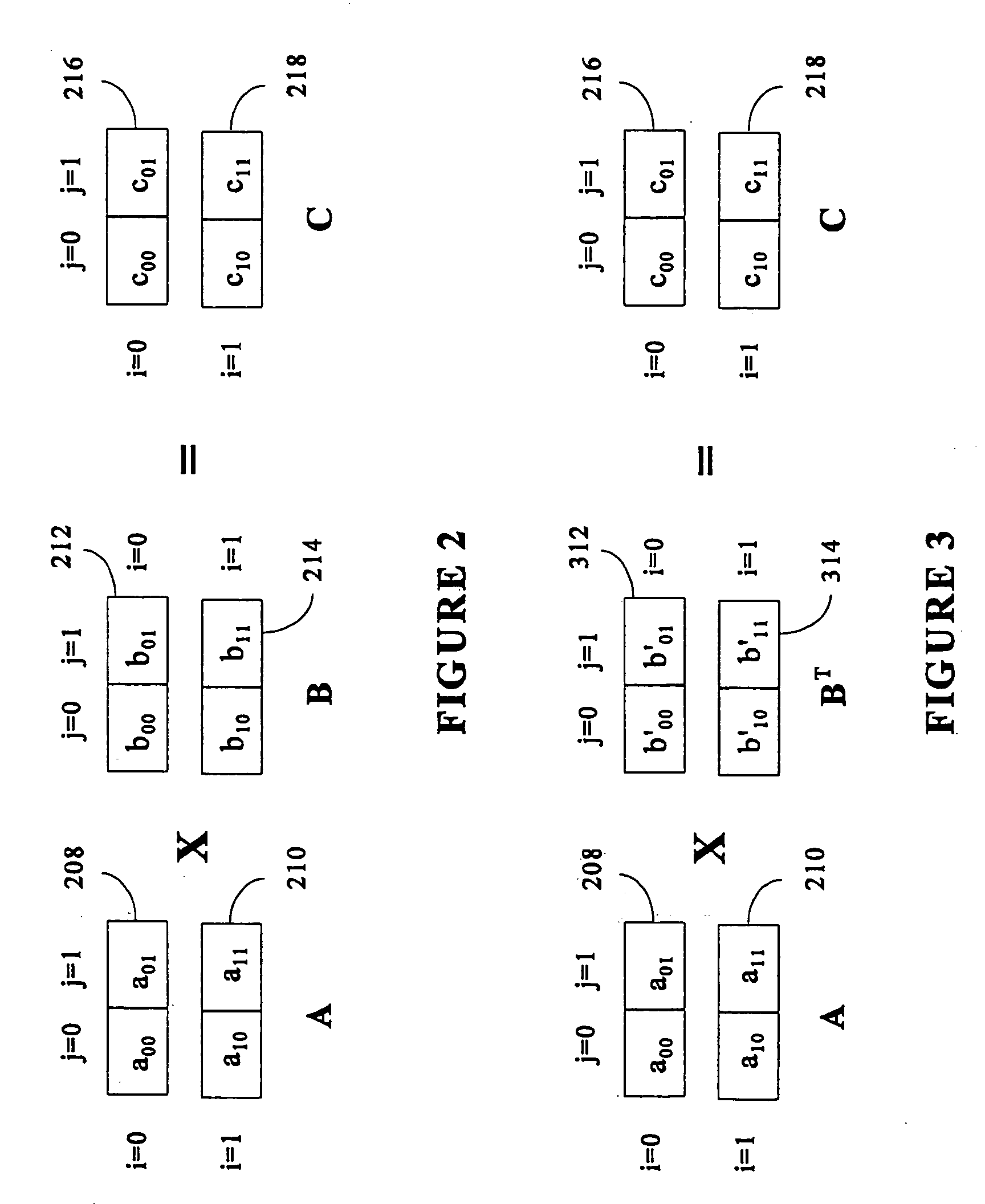
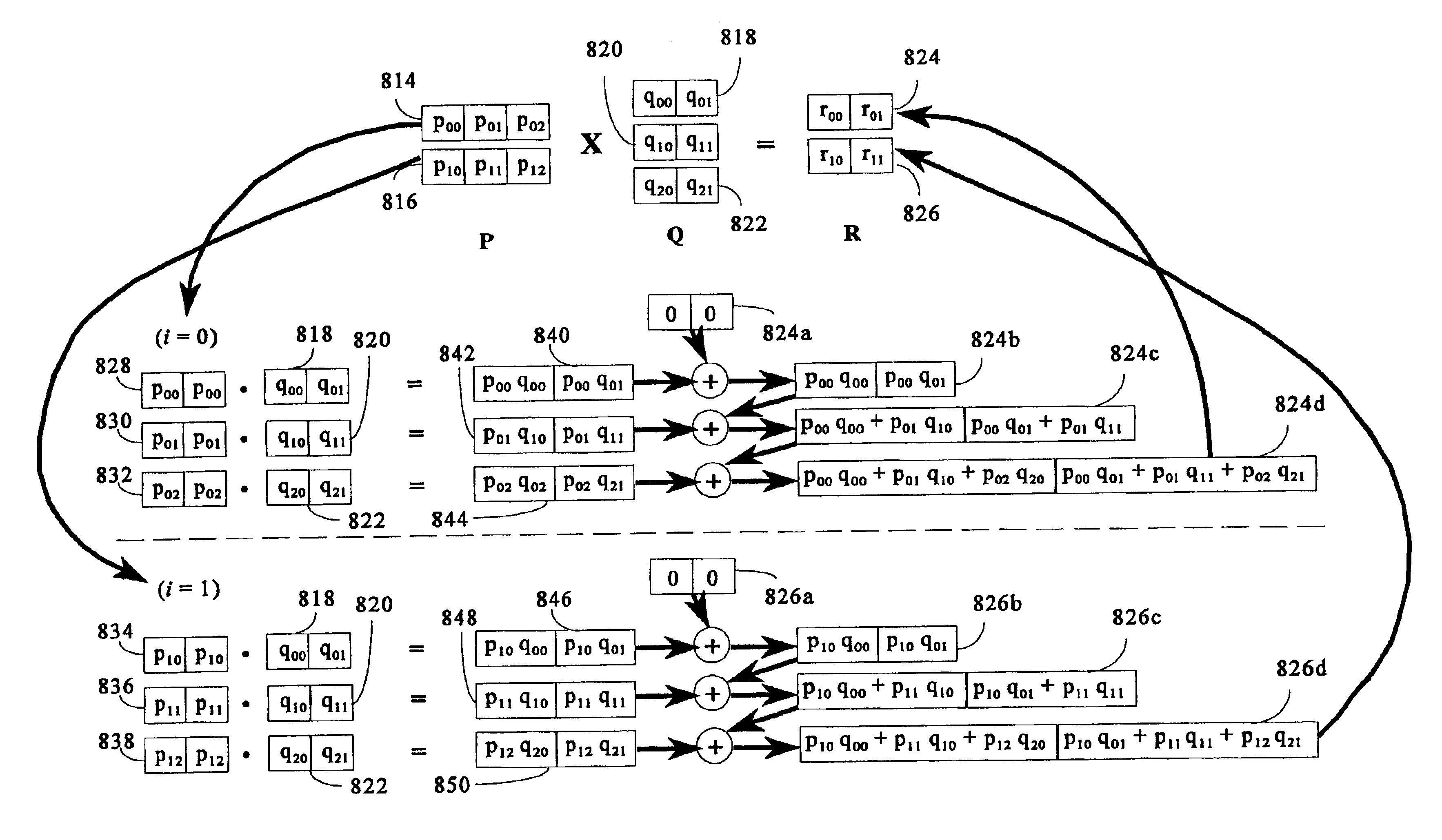
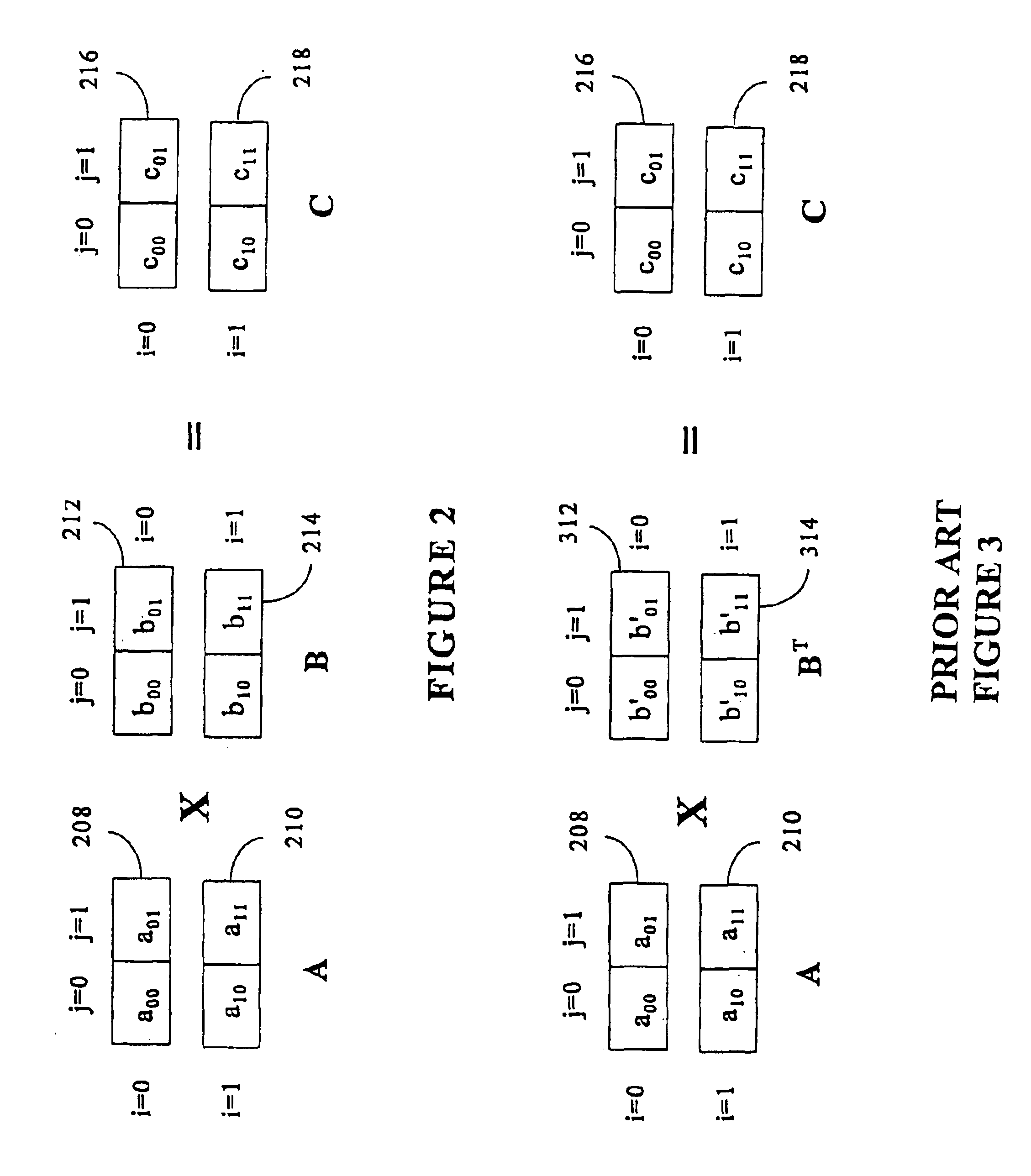
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS20050193050A1Efficient and rapid matrix multiplicationEfficient executionComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlAlgorithmProcessor register
To perform multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system, partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which form a product matrix. Each matrix can be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for network service path analysis
InactiveUS20090097418A1Minimized in sizeData switching by path configurationDirected graphDecomposition
Systems and methods for network service path analysis analyze and manage the delivery of applications over a network. A program running on a computer utilizes a Layer 3 topology of a computer network to create a directed graph representing deliverability of packets across the network. By analyzing access control lists and firewall rule sets from the network, along with modeling routing protocol behavior and policy as packet filters, the program performs a series of matrix multiplications, using an optimized decomposition of the IP packet space. The resulting matrix contains all of the path information for all deliverable packets. The matrix populates a network path database that captures the set of packets deliverable between any pair of Internet Protocol addresses in the network.
Owner:ALTERPOINT
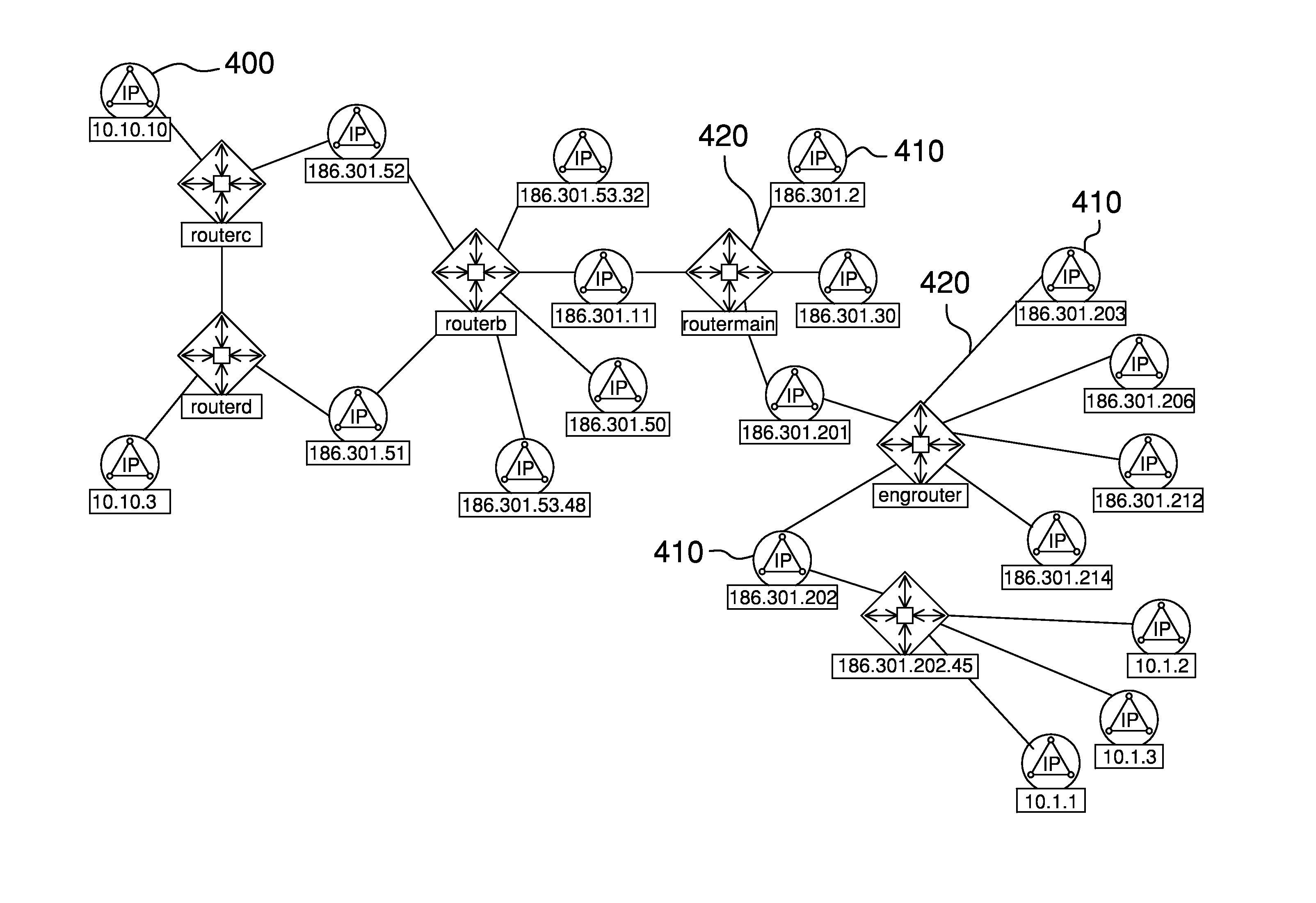
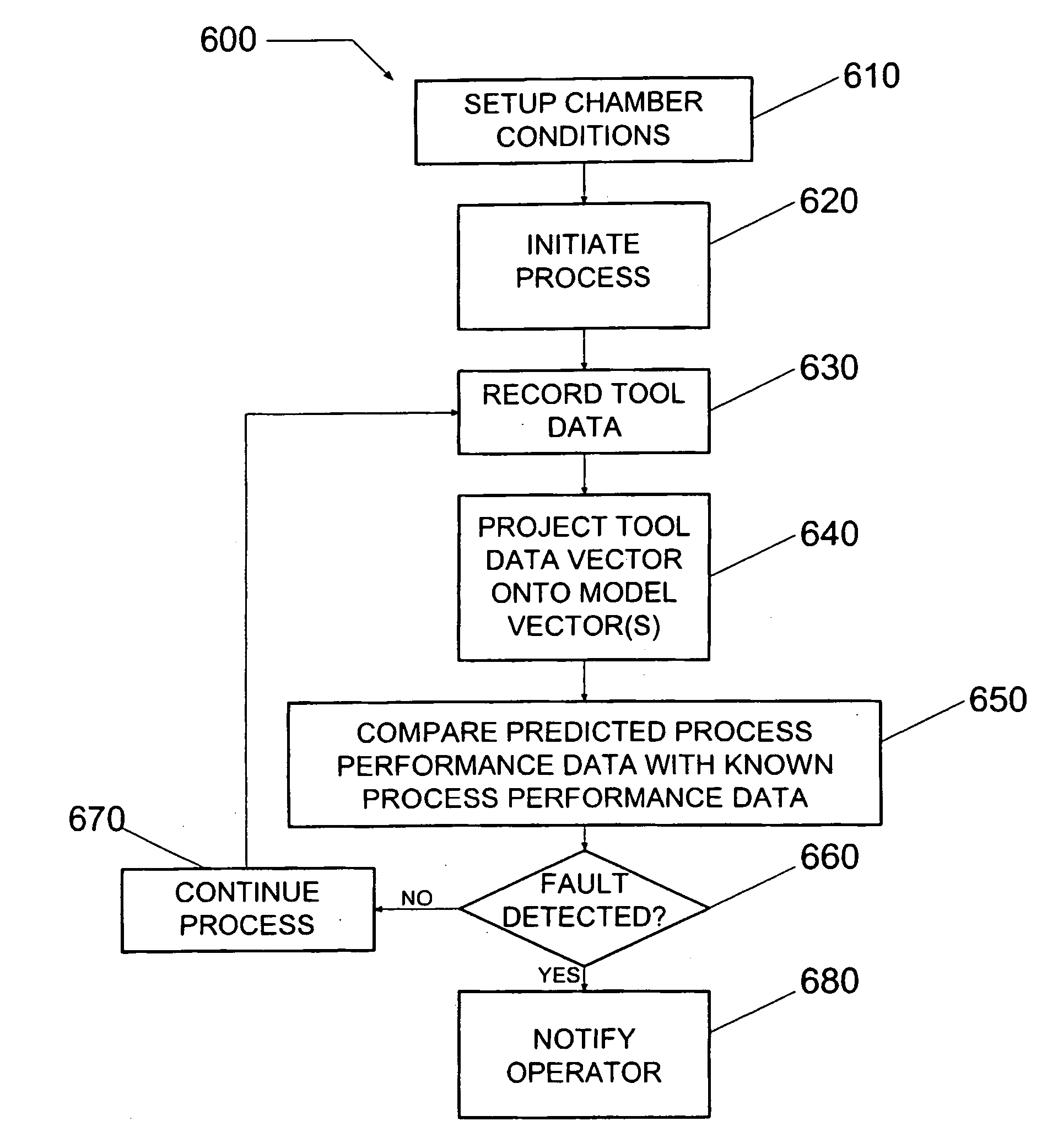
Method and system for predicting process performance using material processing tool and sensor data
InactiveUS20050252884A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesEngineeringMaterials processing
A material processing system including a process tool and a process performance prediction system. The performance prediction system includes sensors coupled to the tool to measure tool data and a controller coupled to the sensors to receive tool data, where the controller is configured to predict the process performance for the tool using the tool data. A method for detecting a fault in a material processing system using a process performance prediction model is also provided. The method includes preparing the tool, initiating a process in the tool, and recording tool data to form to a tool data matrix. The method also includes performing a matrix multiplication of the tool data matrix and a correlation matrix to form predicted process performance data, where the correlation matrix includes the performance prediction model, comparing the predicted data with target data, and determining a fault condition of the processing system from the comparing step.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Efficient implementation of block-based transform on graphics processing unit
ActiveUS20060204119A1Improve processing speedPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputational scienceGraphics
Implementations of transforms, such as a discrete cosine transform (DCT) and inverse DCT on a graphics processing unit (GPU), use direct matrix multiplication. GPU features such as parallel graphics pipelines, multi-channel capability, and multiple render targets are used to obtain significantly faster processing speeds than on a conventional central processing unit (CPU). Various rendering modes may be used, such as point rendering mode, line rendering mode, and triangle or quadrilateral rendering mode.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
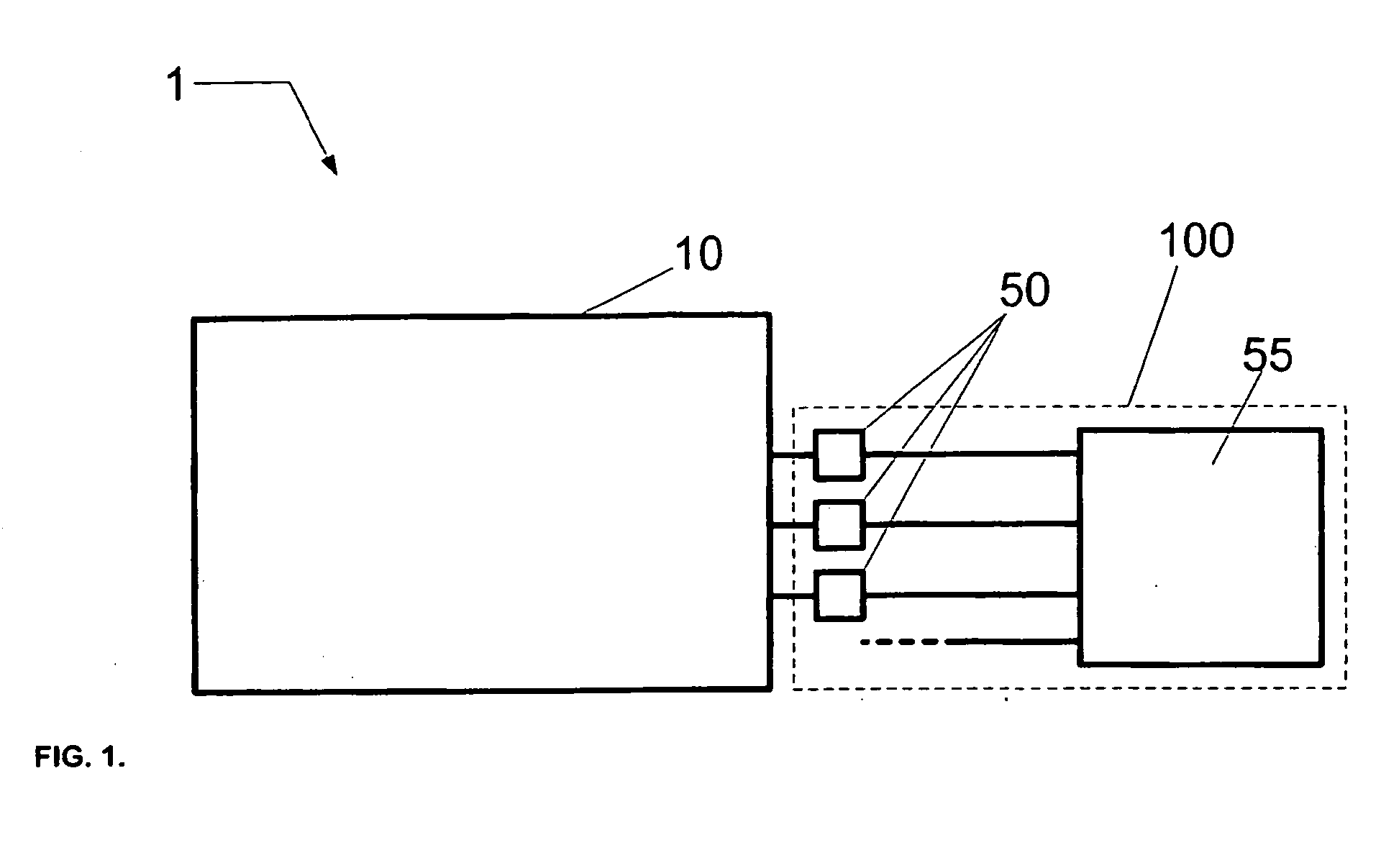
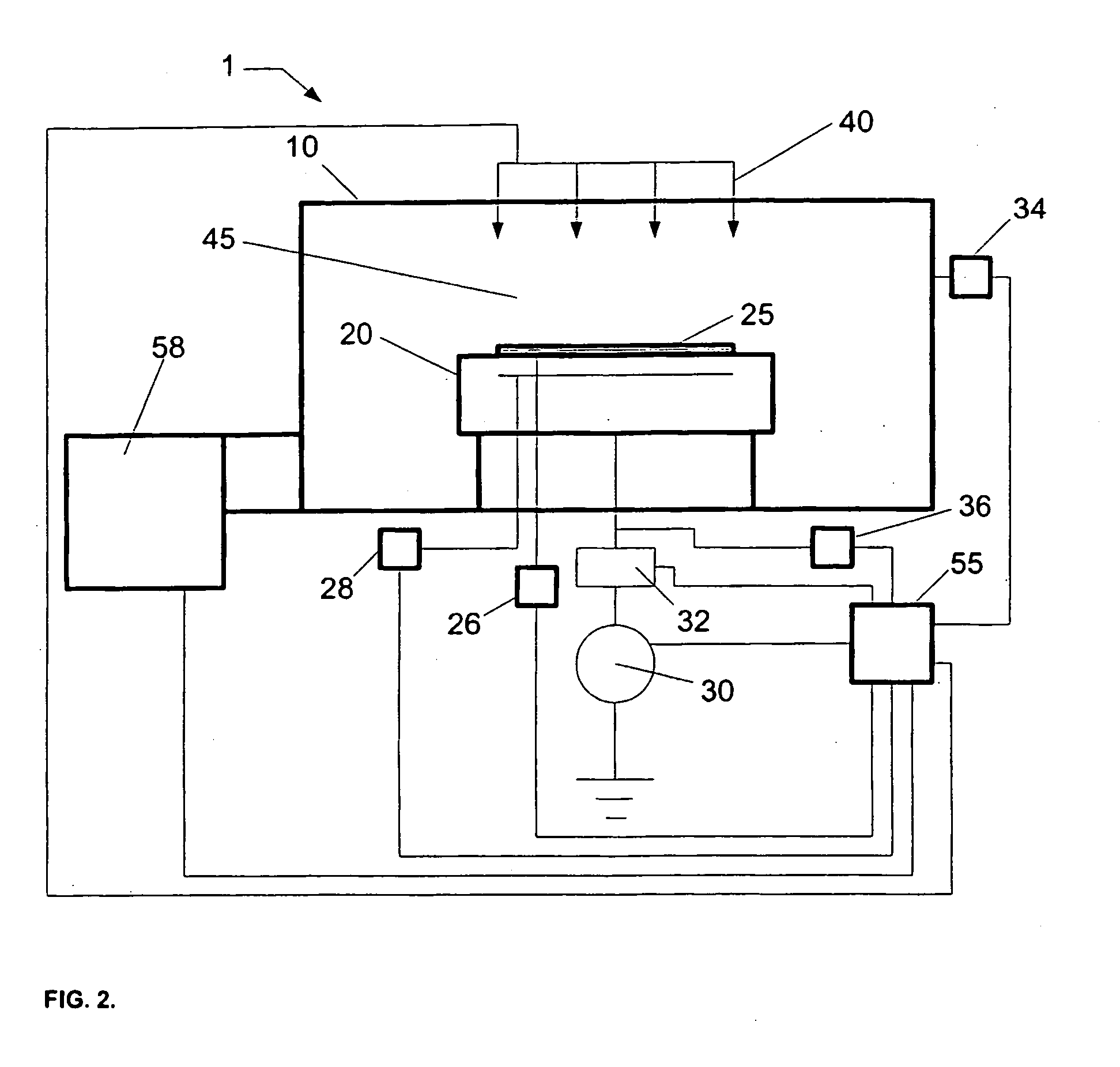
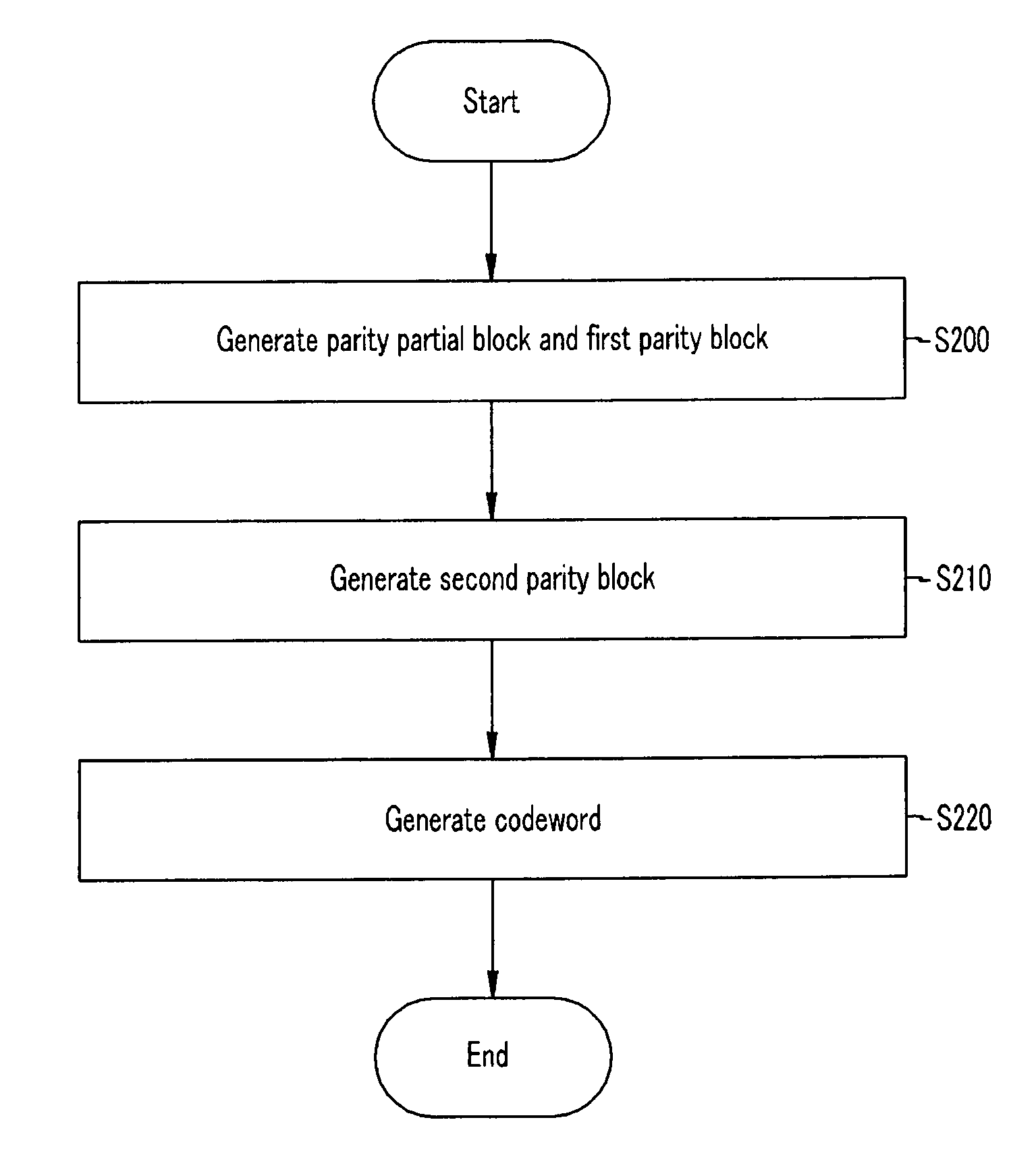
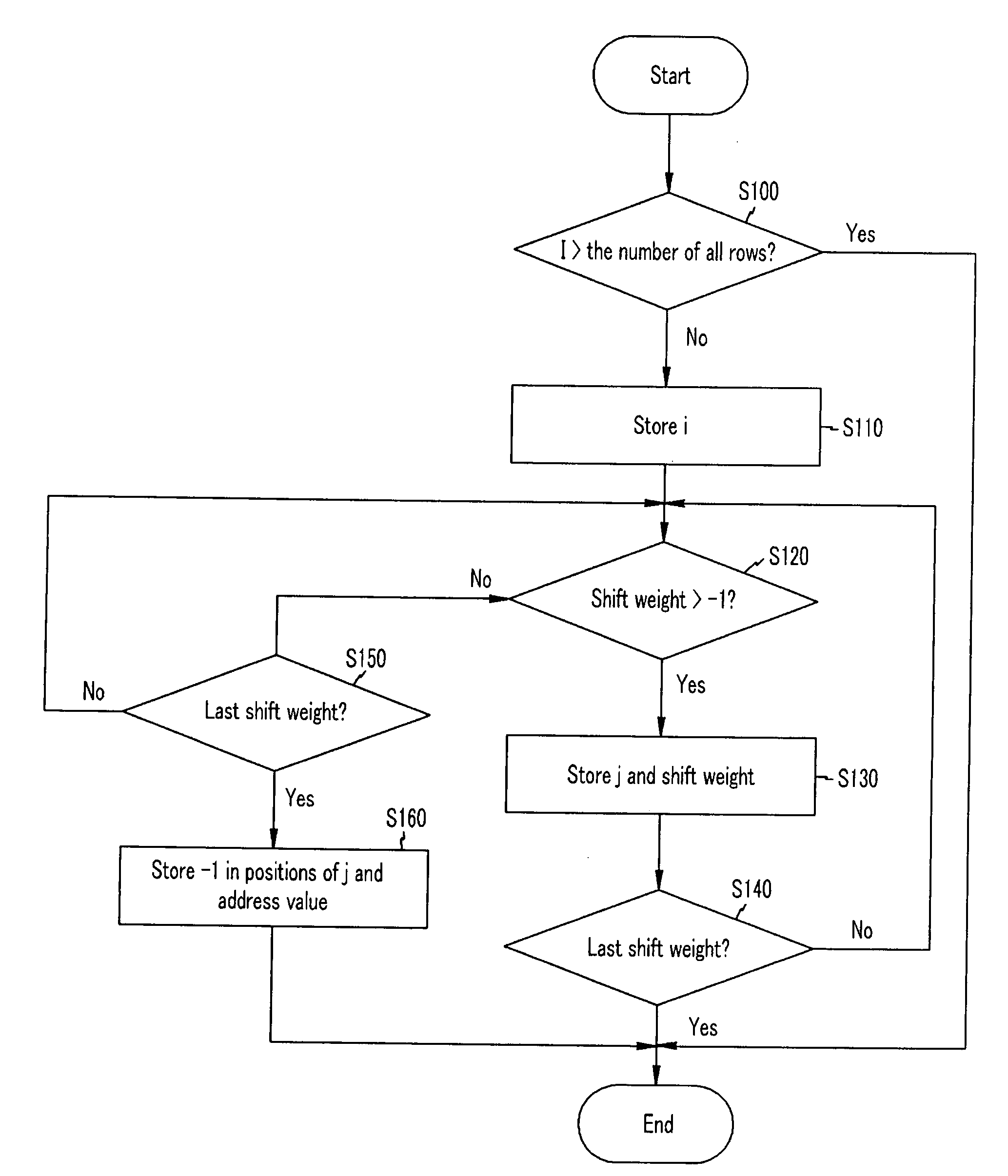
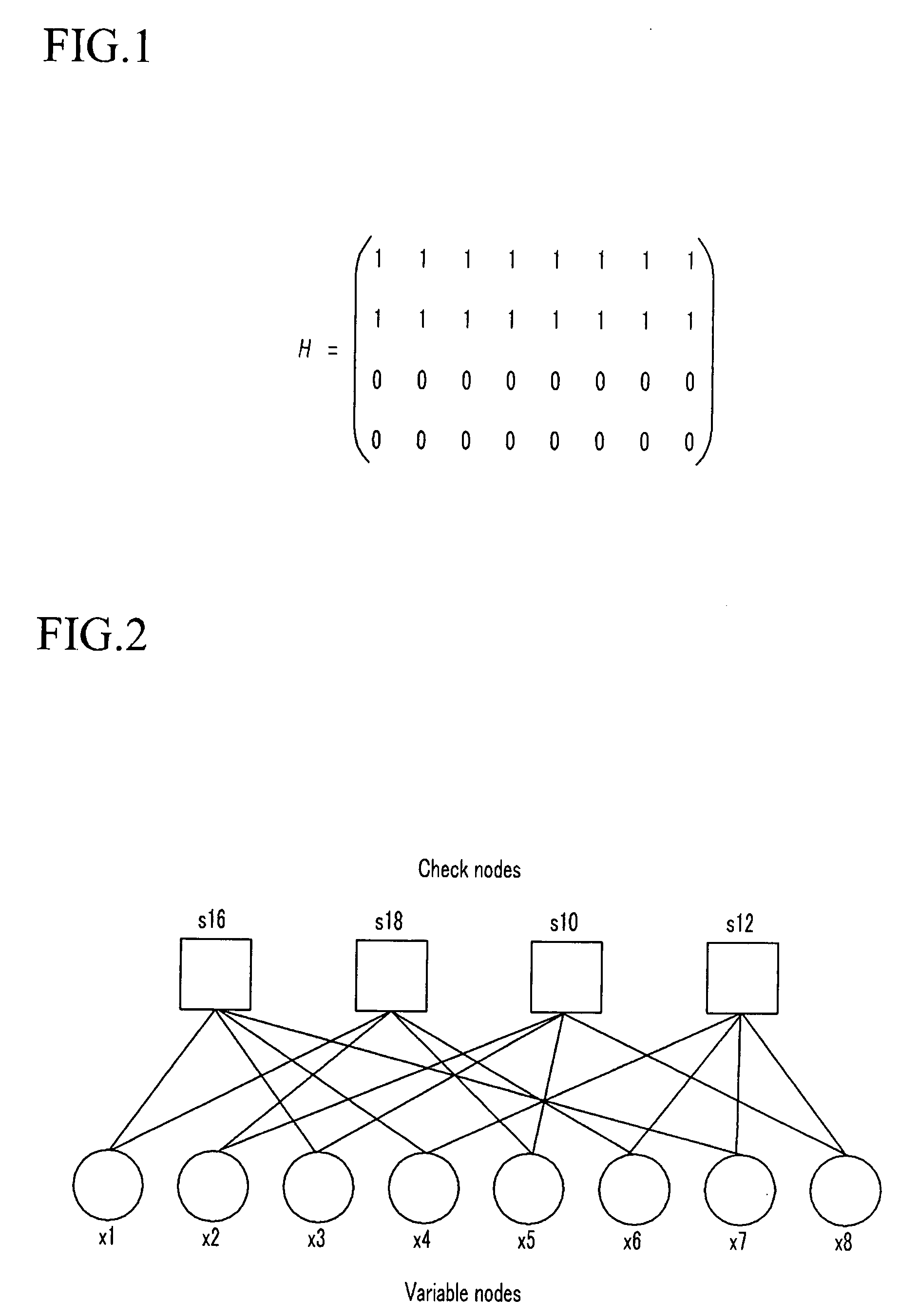
Parity check matrix storing method, block LDPC coding method, and apparatus using parity check matrix storing method
ActiveUS8190967B2Low density parity check (LDPC)Minimize complexityError detection/correctionError coding/decoding sychronisationParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a low density parity check (LDPC) encoding method and an apparatus thereof. In the LDPC encoding method, a matrix multiplication corresponding to ET−1 and T−1 is eliminated according to a structural characteristic in an encoding process. Accordingly, shift weights that are not −1 among shift weights corresponding to partial blocks A, B, and C of a parity check matrix are used to perform an encoding operation, and a cyclic shift operation of an information unit block is performed in parallel so that a first parity block and a second parity block may be simultaneously generated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Parity check matrix storing method, block LDPC coding method, and apparatus using parity check matrix storing method
ActiveUS20080140686A1Minimize complexityReducing requiredDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
The present invention relates to a low density parity check (LDPC) encoding method and an apparatus thereof. In the LDPC encoding method, a matrix multiplication corresponding to ET−1 and T−1 is eliminated according to a structural characteristic in an encoding process. Accordingly, shift weights that are not −1 among shift weights corresponding to partial blocks A, B, and C of a parity check matrix are used to perform an encoding operation, and a cyclic shift operation of an information unit block is performed in parallel so that a first parity block and a second parity block may be simultaneously generated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
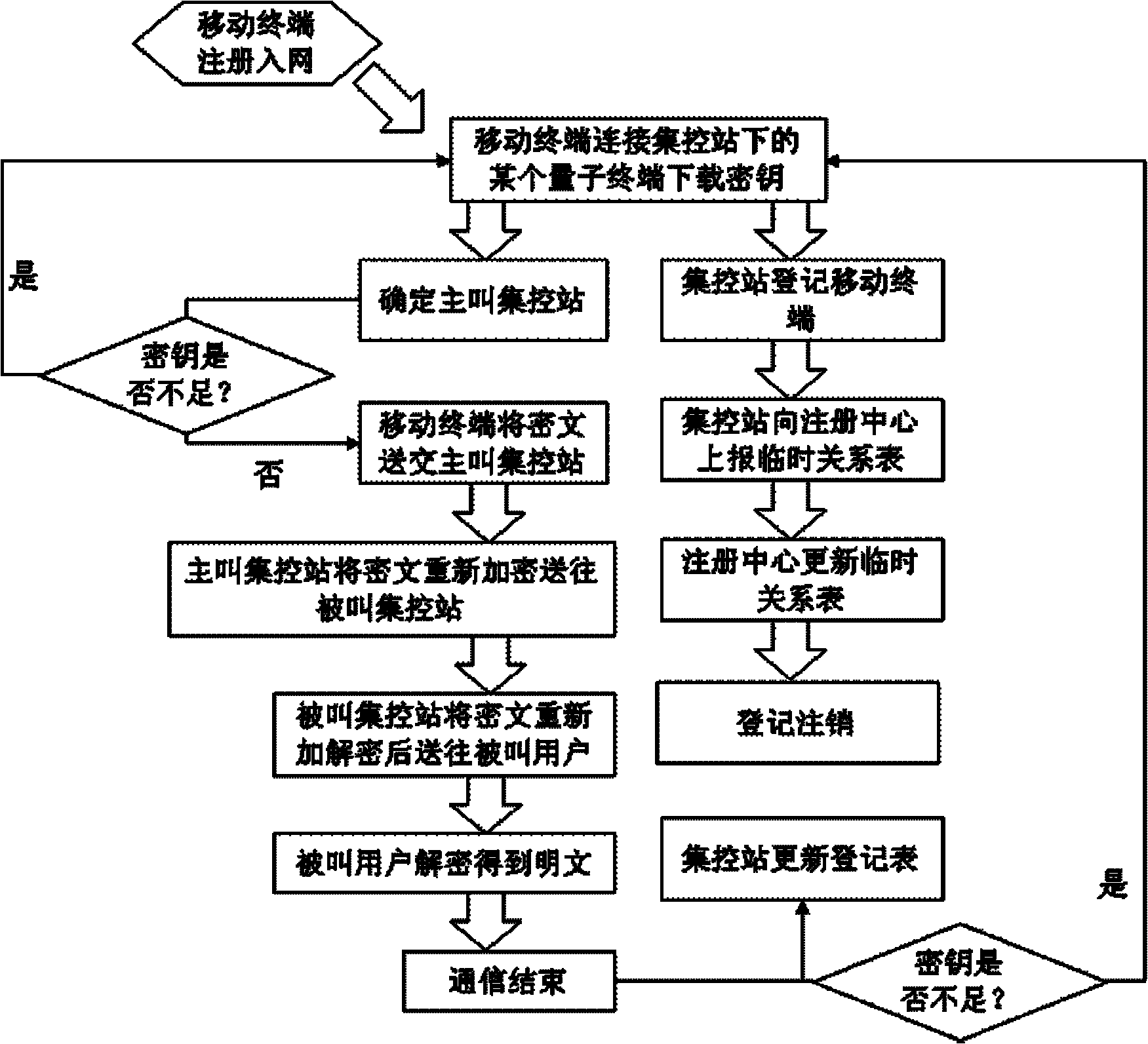
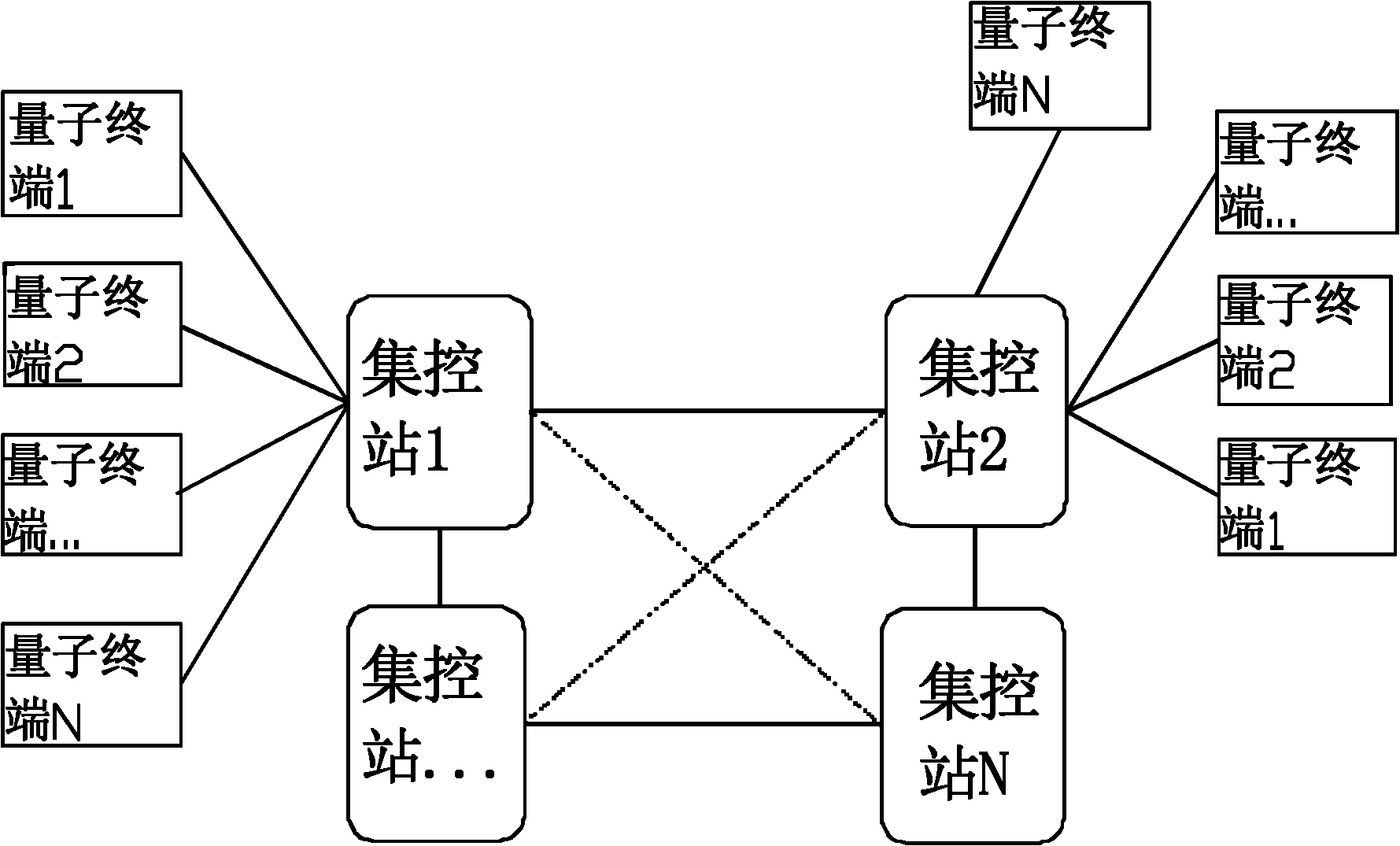
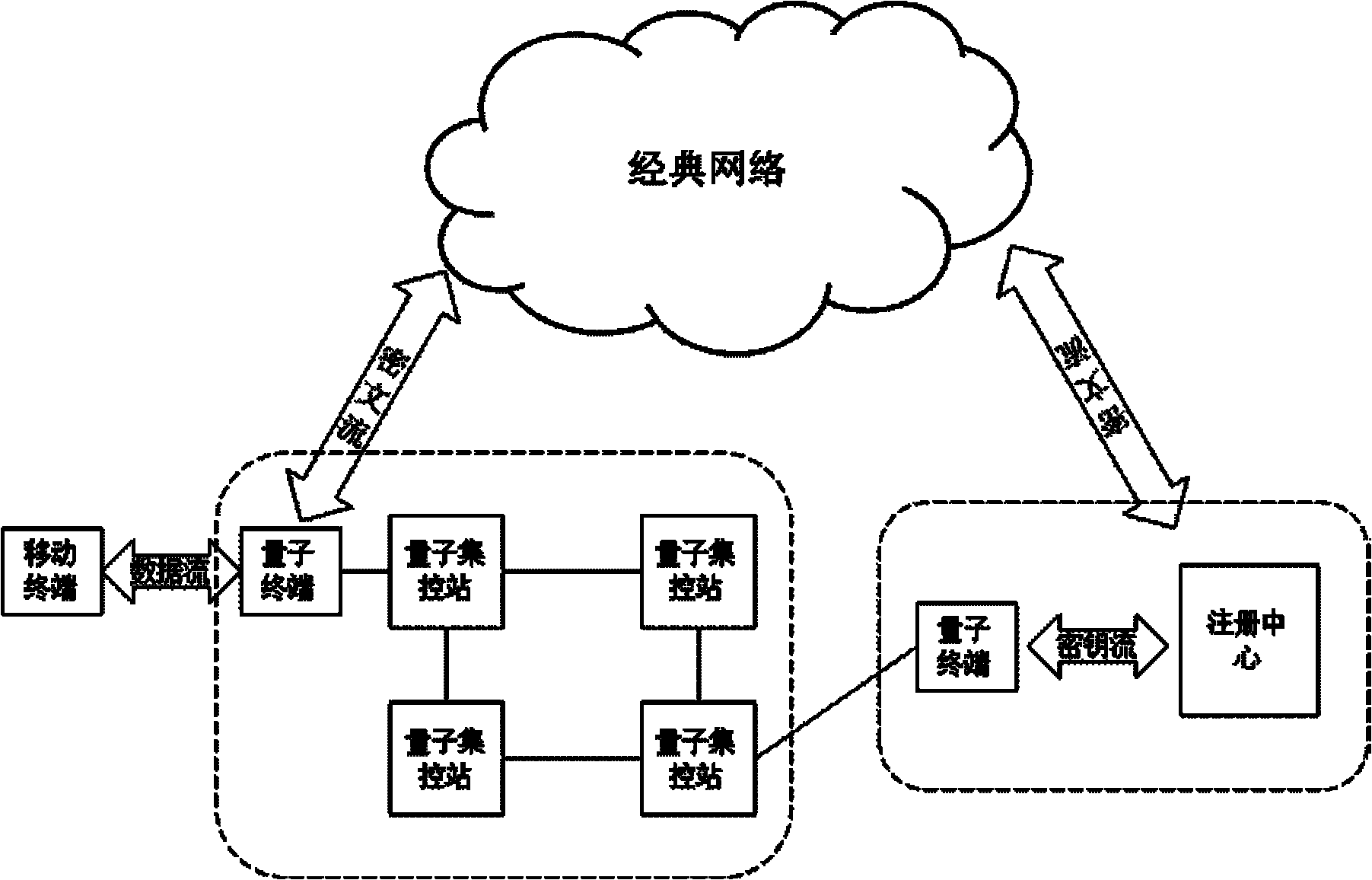
Quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and communication method thereof
ActiveCN102196425AReduce computationGuaranteed distribution securitySecurity arrangementPlaintextTelecommunications
The invention discloses a quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and a communication method thereof. The method comprises that: a mobile terminal is registered in a network; the registered mobile terminal is connected with any quantum terminal by a key updating interface, and applies for the downloading of shared keys in a certain data volume to the quantum terminal; after the mobile terminal downloads the keys, the quantum terminal transmits a quantum centralized control station address to the mobile terminal for updating, and the mobile terminal takes a centralized control station on the quantum centralized control station address as a calling centralized control station; after the calling centralized control station is determined, the mobile terminal submits a cipher text to the calling centralized control station; the calling centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called centralized control station; the called centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called user; and after the called user decrypts the re-encrypted cipher text to obtain a plaintext, the communication is finished. In the method, the encryption does not require multiple matrix multiplication operations, so the computational load of the encryption is greatlyreduced; and simultaneously, the key distribution security of the highest level can be ensured in the key distribution of a quantum key distribution network.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK +1
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Accounting allocation method
InactiveUS6014640AQuantity minimizationEasy and efficient implementationComplete banking machinesFinanceDistribution methodParallel computing
An expense allocation method utilizes matrix multiplication to transform a set of reciprocal or cascading allocation rules into a new set of one-step allocation rules. The new set of rules reallocates amounts directly to the ultimate destination without going through numerous intermediate levels of reallocation. By taking advantage of the specific structure of the matrix, and partitioning the matrix into four (4) subparts, the matrix multiplication process is greatly simplified. The expense allocation method can be easily and efficiently implemented on a computer system, including computers based upon parallel or vector architectures. This invention permits most allocation work to be done before the end of an accounting period, allowing end-of-period accounting work to be completed sooner. Alternatively, expenses can be allocated as they occur, rather than waiting until the end of a period.
Owner:BENT KIRKE M
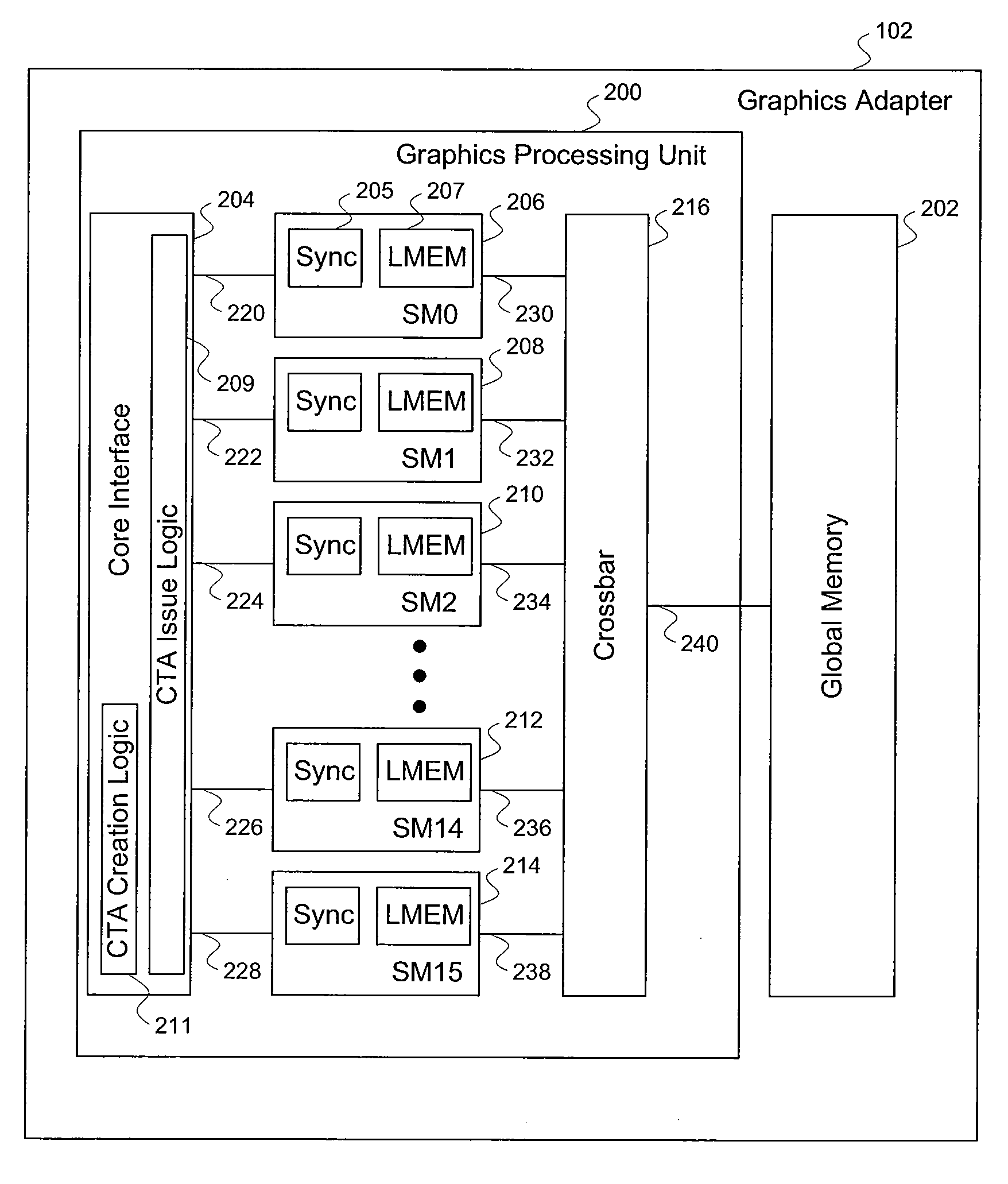
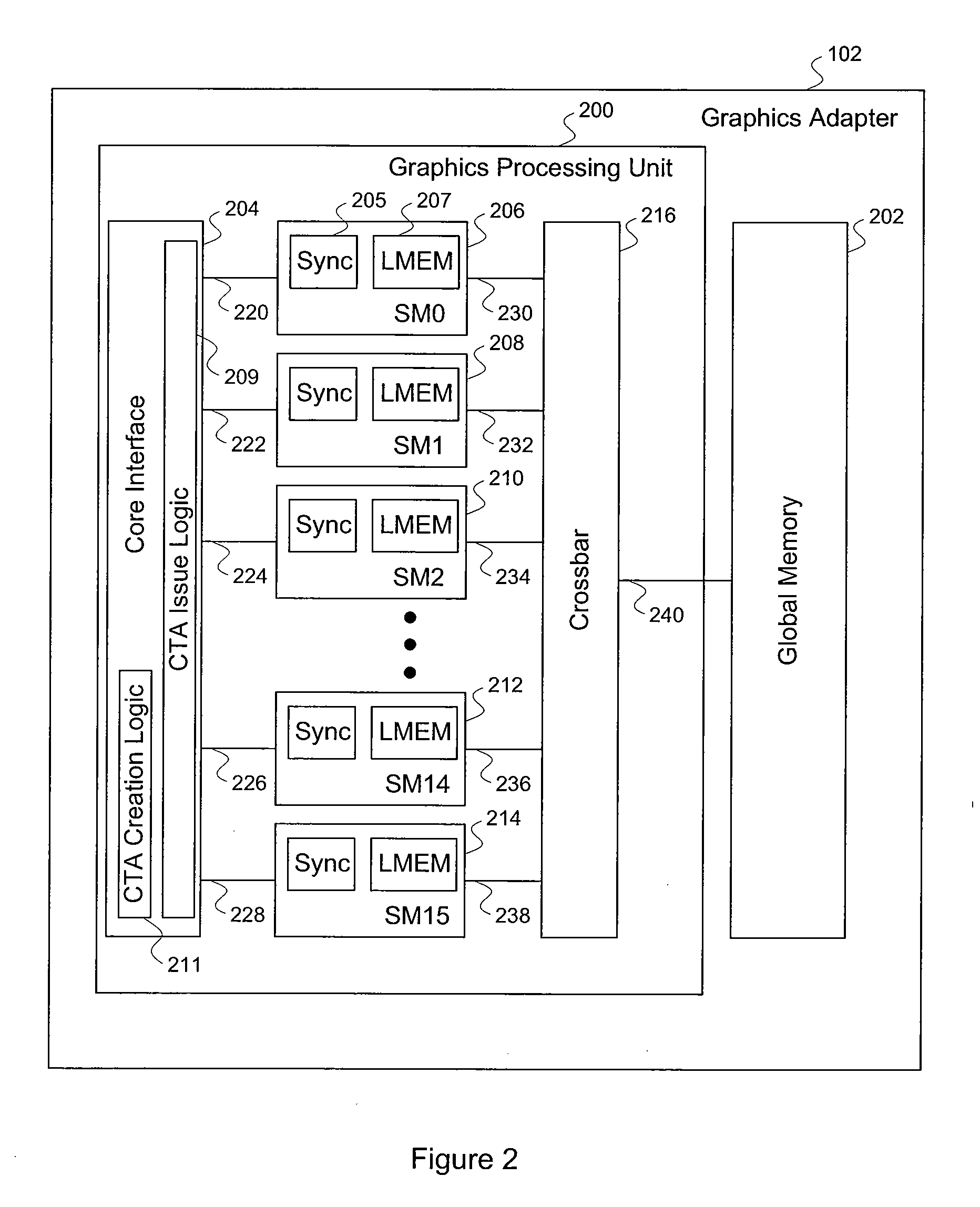
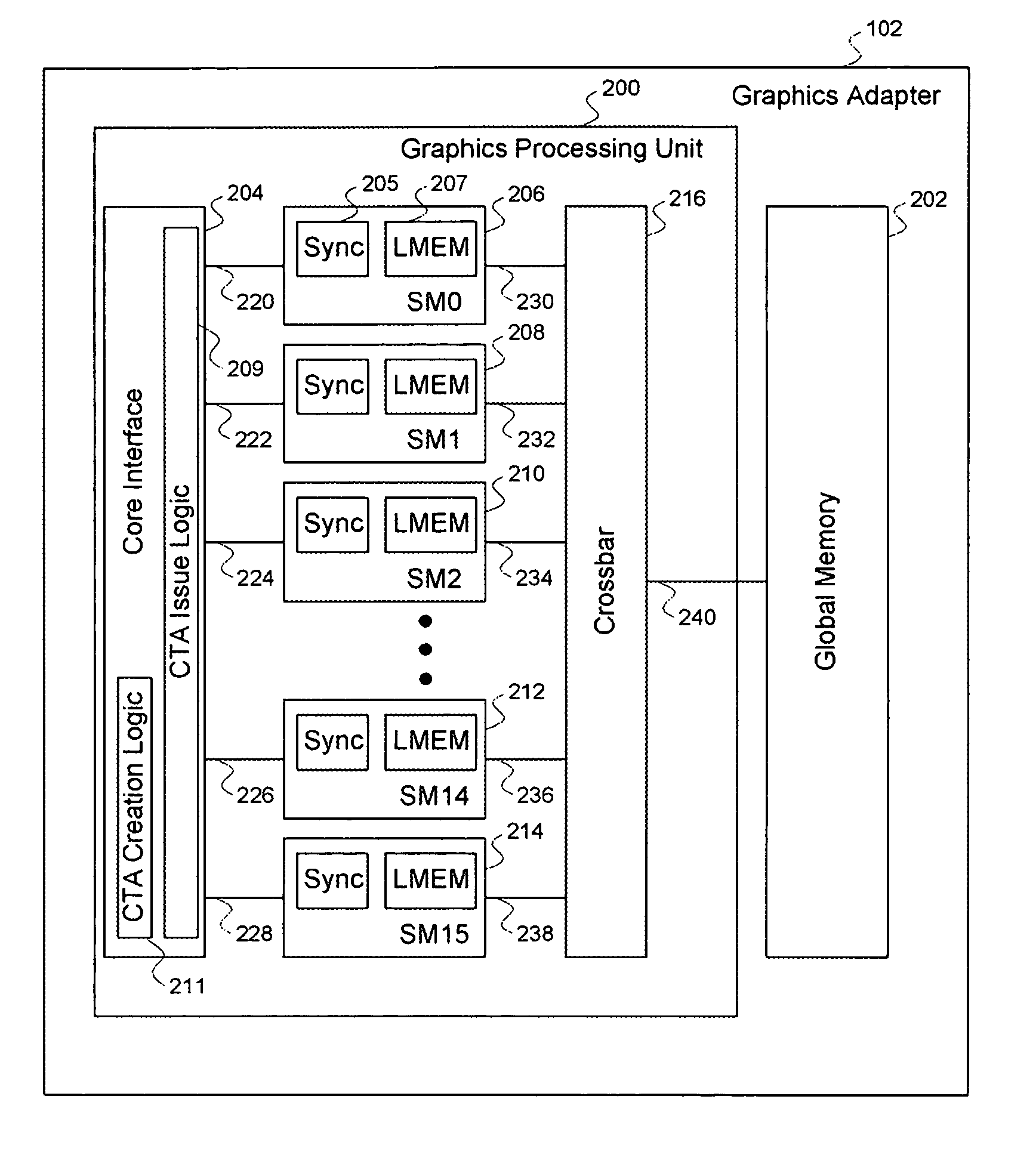
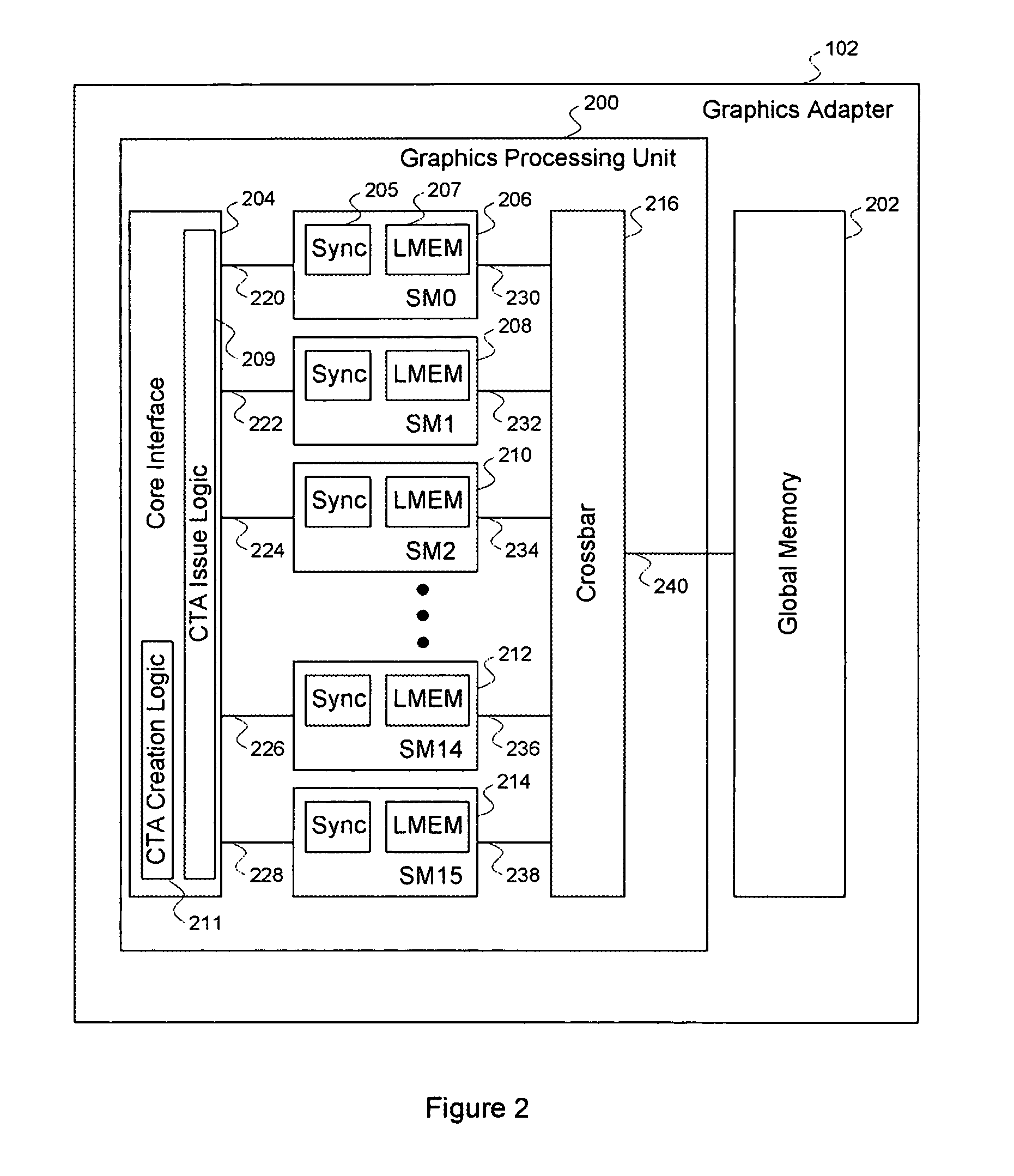
Efficient matrix multiplication on a parallel processing device
ActiveUS20100325187A1Significant processing efficiencyReduce the number of timesComputation using non-contact making devicesData mergingMulti processorParallel processing
The present invention enables efficient matrix multiplication operations on parallel processing devices. One embodiment is a method for mapping CTAs to result matrix tiles for matrix multiplication operations. Another embodiment is a second method for mapping CTAs to result tiles. Yet other embodiments are methods for mapping the individual threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for result tile computations, source tile copy operations, and source tile copy and transpose operations. The present invention advantageously enables result matrix elements to be computed on a tile-by-tile basis using multiple CTAs executing concurrently on different streaming multiprocessors, enables source tiles to be copied to local memory to reduce the number accesses from the global memory when computing a result tile, and enables coalesced read operations from the global memory as well as write operations to the local memory without bank conflicts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
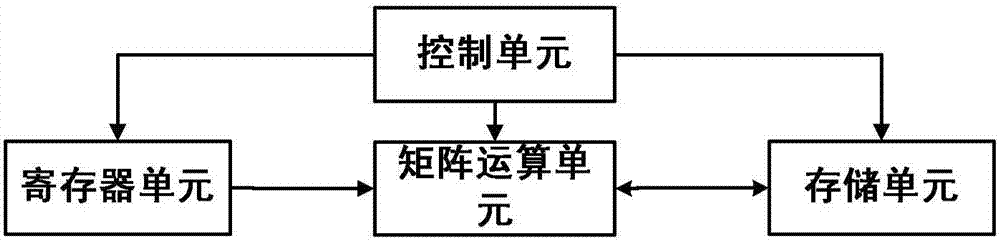
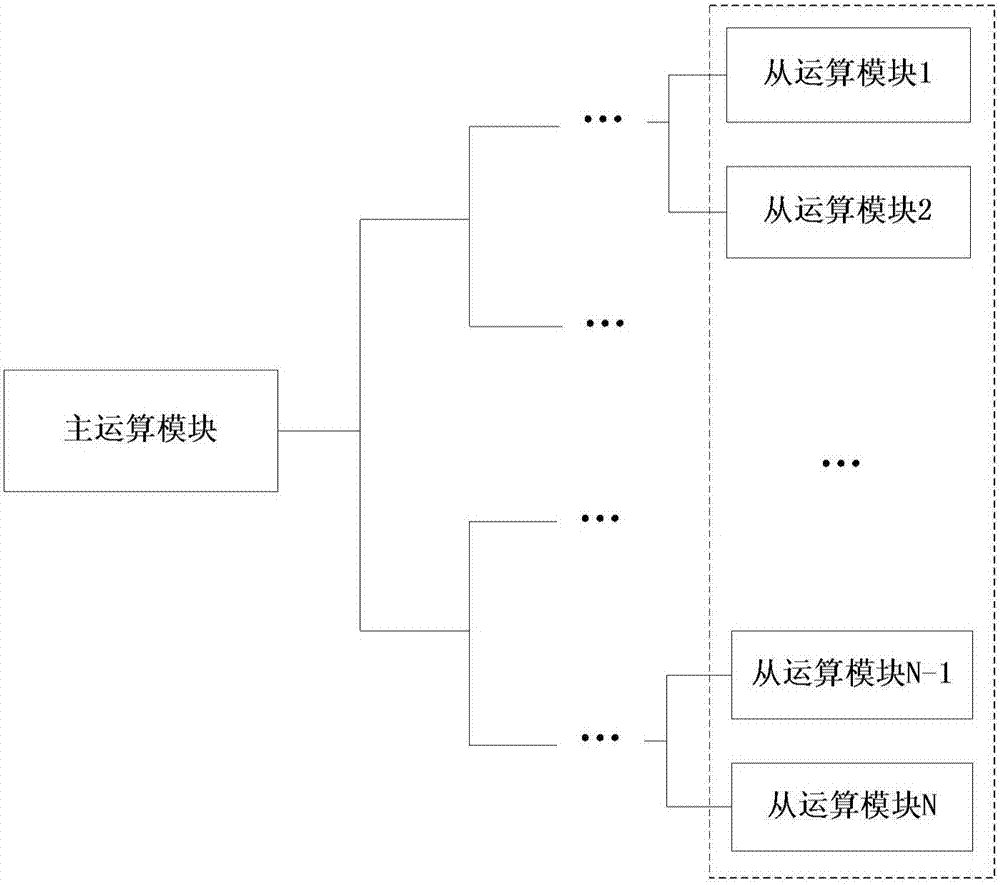
Apparatus and method used for executing matrix multiplication operation
ActiveCN107315574ADigital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesMatrix multiplicationControl unit
The invention discloses an apparatus and a method used for executing matrix multiplication operation. The apparatus is characterized by comprising a storage unit used for storing matrix data related with a matrix operation instruction, a register unit used for storing scalar data related with the matrix operation instruction, a control unit used for decoding the matrix operation instruction and controlling an operation process of the matrix operation instruction, and a matrix operation unit used for performing the matrix multiplication operation on an input matrix according to the decoded matrix operation instruction, wherein the matrix operation unit is a customized hardware circuit.
Owner:ANHUI CAMBRICON INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Efficient matrix multiplication on a parallel processing device
ActiveUS7792895B1Significant processing efficiencyReduce the number of timesComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsLocal memoriesMatrix multiplication
The present invention enables efficient matrix multiplication operations on parallel processing devices. One embodiment is a method for mapping CTAs to result matrix tiles for matrix multiplication operations. Another embodiment is a second method for mapping CTAs to result tiles. Yet other embodiments are methods for mapping the individual threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for result tile computations, source tile copy operations, and source tile copy and transpose operations. The present invention advantageously enables result matrix elements to be computed on a tile-by-tile basis using multiple CTAs executing concurrently on different streaming multiprocessors, enables source tiles to be copied to local memory to reduce the number accesses from the global memory when computing a result tile, and enables coalesced read operations from the global memory as well as write operations to the local memory without bank conflicts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Modular multiplier
ActiveUS20030212729A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsModular multiplierKaratsuba algorithm
Modular multiplication of two elements X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), where m is a field degree, may utilize field degree to determine, at least in part, the number of iterations. An extra shift operation may be employed when the number of iterations is reduced. Modular multiplication of two elements X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), may include a shared reduction circuit utilized during multiplication and reduction. In addition, a modular multiplication of binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), may utilize the Karatsuba algorithm, e.g., by recursively splitting up a multiplication into smaller operands determined according to the Karatsuba algorithm.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for fast tensor-vector multiplication
InactiveUS20140181171A1Computation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmMatrix multiplication
A method and a system for fast tensor-vector multiplication provide factoring an original tensor into a kernel and a commutator, multiplying the kernel obtained by the factoring of the original tensor, by the vector and thereby obtaining a matrix, and summating elements and sums of elements of the matrix as defined by the commutator obtained by the factoring of the original tensor, and thereby obtaining a resulting tensor which corresponds to a product of the original tensor and the vector.
Owner:DOURBAL PAVEL
Method and apparatus for computing matrix transformations
A method and apparatus for performing matrix transformations including multiply-add operations and byte shuffle operations on packed data in a processor. In one embodiment, two rows of content byte elements are shuffled to generate a first and second packed data respectively including elements of a first two columns and of a second two columns. A third packed data including sums of products is generated from the first packed data and elements from two rows of a matrix by a multiply-add instruction. A fourth packed data including sums of products is generated from the second packed data and elements from two more rows of the matrix by another multiply-add instruction. Corresponding sums of products of the third and fourth packed data are then summed to generate two rows of a product matrix. Elements of the product matrix may be generated in an order that further facilitates a second matrix multiplication.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Programmable matrix processor
A matrix processor and processing method, the processor including a data encoder for receiving an input data stream; a data controller coupled to the data encoder for arranging the input data in an operand matrix, at least one processing unit for processing the data in matrix form by Boolean matrix-matrix multiplication with a selected operator matrix, and an output control module coupled to the processing unit for outputting desired results therefrom.
Owner:RUSNANO
Sparse Matrix-Vector Multiplication on Graphics Processor Units
InactiveUS20110078226A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsGraphicsMatrix multiplication
Techniques for optimizing sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) on a graphics processing unit (GPU) are provided. The techniques include receiving a sparse matrix-vector multiplication, analyzing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication to identify one or more optimizations, wherein analyzing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication to identify one or more optimizations comprises analyzing a non-zero pattern for one or more optimizations and determining whether the sparse matrix-vector multiplication is to be reused across computation, optimizing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication, wherein optimizing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication comprises optimizing global memory access, optimizing shared memory access and exploiting reuse and parallelism, and outputting an optimized sparse matrix-vector multiplication.
Owner:IBM CORP
Mapping the threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for efficient matrix multiplication
ActiveUS7912889B1Significant processing efficiencyReduce the number of timesComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsLocal memoriesMatrix multiplication
The present invention enables efficient matrix multiplication operations on parallel processing devices. One embodiment is a method for mapping CTAs to result matrix tiles for matrix multiplication operations. Another embodiment is a second method for mapping CTAs to result tiles. Yet other embodiments are methods for mapping the individual threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for result tile computations, source tile copy operations, and source tile copy and transpose operations. The present invention advantageously enables result matrix elements to be computed on a tile-by-tile basis using multiple CTAs executing concurrently on different streaming multiprocessors, enables source tiles to be copied to local memory to reduce the number accesses from the global memory when computing a result tile, and enables coalesced read operations from the global memory as well as write operations to the local memory without bank conflicts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System, transmitter, method, and computer program product for utilizing an adaptive preamble scheme for multi-carrier communication systems
InactiveUS20060045193A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemEngineering
A system, transmitter, method, and computer program product apply a performance improvement characteristic, such as phase rotation or power allocation, to both a known preamble and a data payload of a transmitted data packet, such that existing multi-carrier receivers are capable of decoding the data payload with the performance improvement characteristic applied. The performance improvement characteristic is applied by vector-matrix multiplication of the preamble and the data payload by the performance improvement characteristic.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
High speed and efficient matrix multiplication hardware module
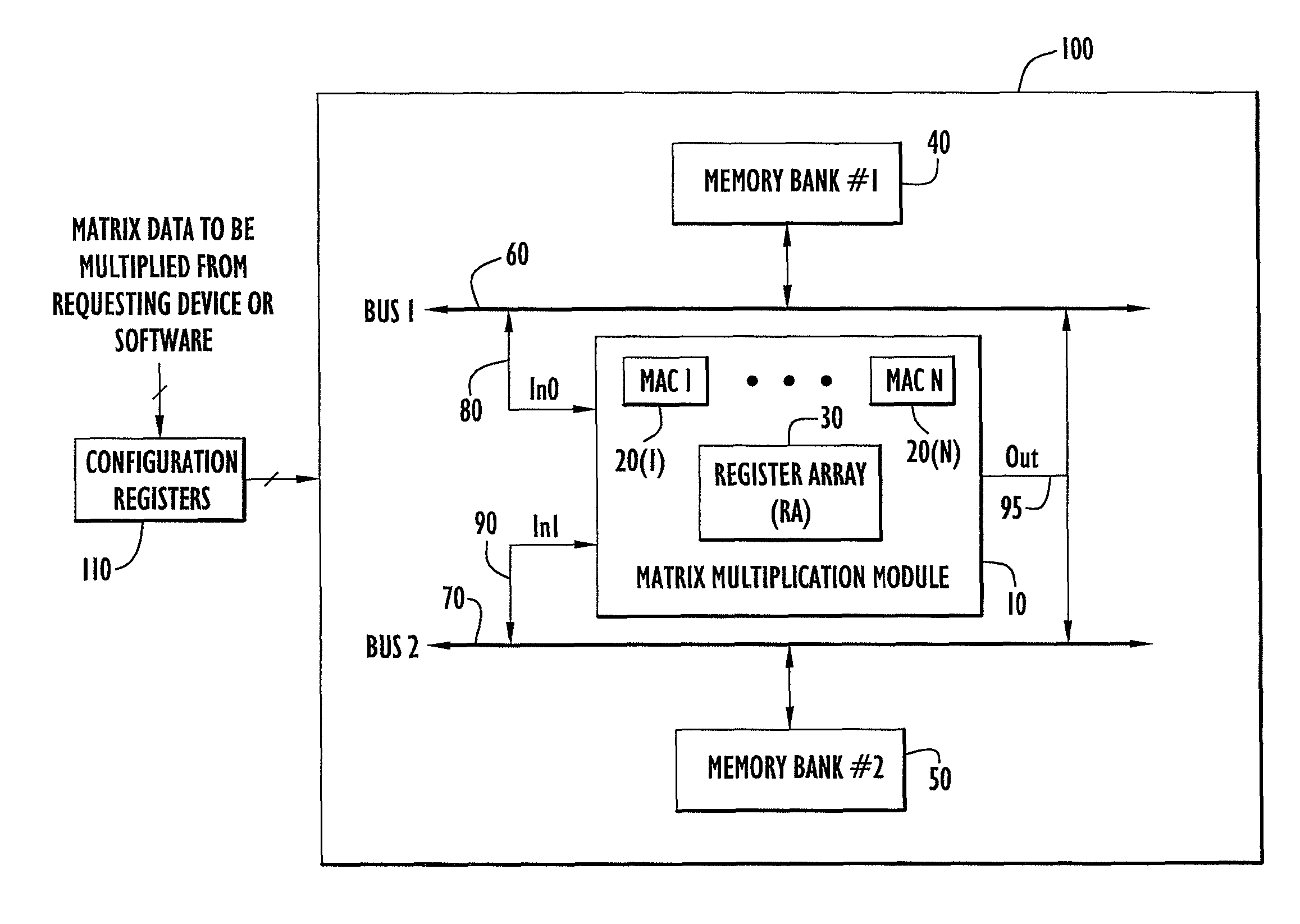
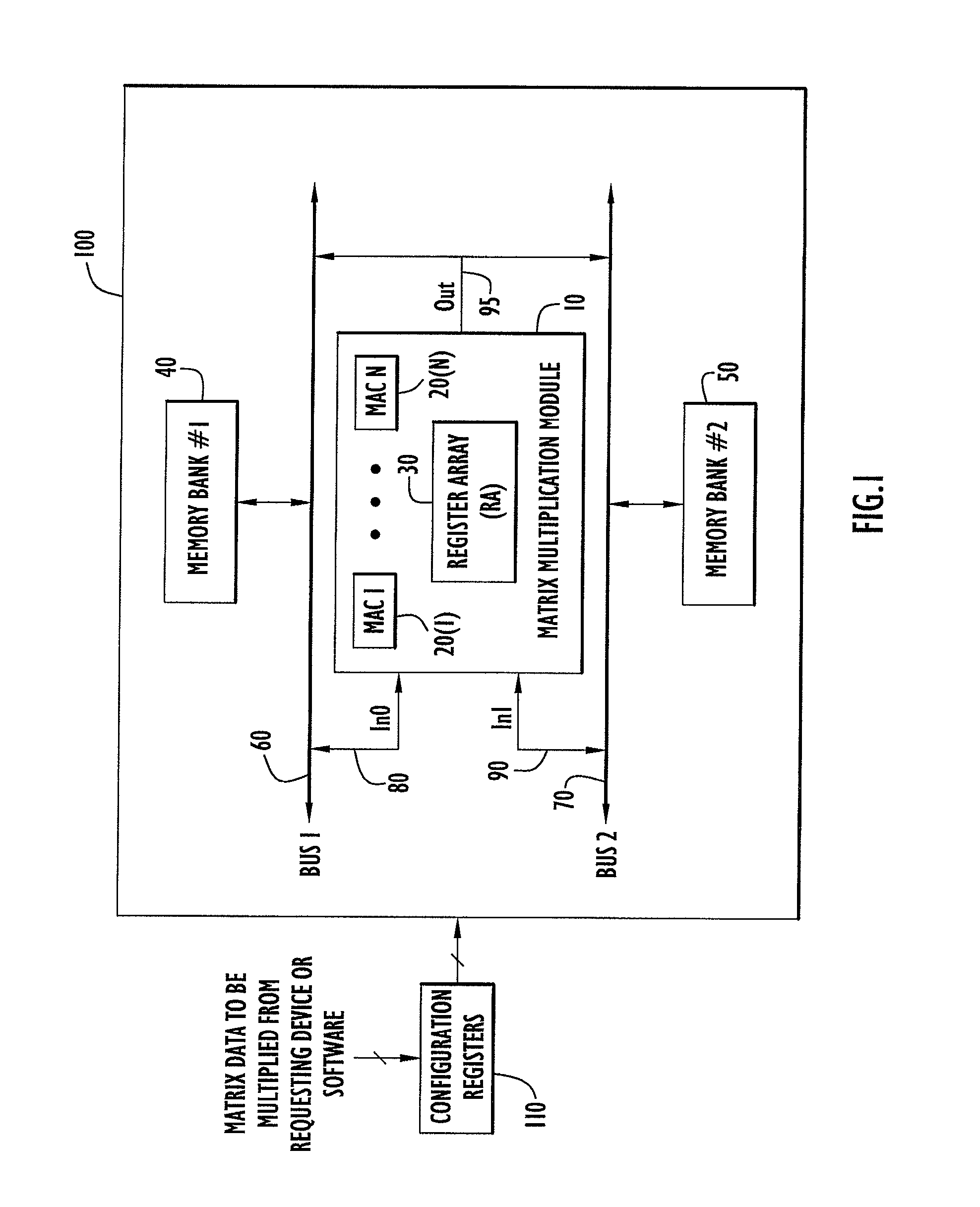
ActiveUS8051124B2Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlClock rateComputer module
A matrix multiplication module and matrix multiplication method are provided that use a variable number of multiplier-accumulator units based on the amount of data elements of the matrices are available or needed for processing at a particular point or stage in the computation process. As more data elements become available or are needed, more multiplier-accumulator units are used to perform the necessary multiplication and addition operations. To multiply an N×M matrix by an M×N matrix, the total (maximum) number of used MAC units is “2*N−1”. The number of MAC units used starts with one (1) and increases by two at each computation stage, that is, at the beginning of reading of data elements for each new row of the first matrix. The sequence of the number of MAC units is {1, 3, 5, . . . , 2*N−1} for computation stages each of which corresponds to reading of data elements for each new row of the left hand matrix, also called the first matrix. For the multiplication of two 8×8 matrices, the performance is 16 floating point operations per clock cycle. For an FPGA running at 100 MHz, the performance is 1.6 Giga floating point operations per second. The performance increases with the increase of the clock frequency and the use of larger matrices when FPGA resources permit. Very large matrices are partitioned into smaller blocks to fit in the FPGA resources. Results from the multiplication of sub-matrices are combined to form the final result of the large matrices.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Matrix multiplication acceleration method for supporting variable blocks
ActiveCN104899182AImprove computing efficiencyImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix multiplicationLinked list
The invention discloses a matrix multiplication acceleration method for supporting variable blocks. The steps include: a matrix A and a matrix B are inputted, the size Si of a subblock is determined according to the scales of the matrix A and the matrix B, the matrix A is partitioned in lines regarding the subblock with the scale of Si*N as the unit, the matrix B is partitioned in rows regarding the subblock with the scale of N*Si as the unit, a DMA descriptor is generated for required data of multiplication operation of each subblock, all the DMA descriptors are constructed to a DMA descriptor list, for the multiplication operation of each subblock, the required data of the multiplication operation of the subblocks is read according to the DMA descriptor list in a main memory, the multiplication operation of the subblocks is conducted via a processing unit chain of a matrix multiplication accelerator, and the result is written back to the main memory via the DMA. The method is advantageous in that variable blocks can be supported, the number of employed processing units can be adjusted according to the size of the blocks, and the acceleration efficiency for accelerating the multiplication operation of non-uniform matrixes is high.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Precision improvement method for the Strassen/Winograd matrix multiplication method
ActiveUS7209939B2Reduce rounding errorsReduce errorsComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmComputerized system
A computer system for multiplying a first matrix and a second matrix that reduces rounding error, including a processor, a memory, a storage device, and software instructions stored in the memory for enabling the computer system, under the control of the processor, to perform obtaining a first set of dimension values for the first matrix and a second set of dimension values for the second matrix, selecting one of a plurality of multiplication permutations if the first set of dimension values and the second set of dimension values are greater than a crossover value, multiplying the first matrix by the second matrix using the multiplication permutation and a Strassen-Winograd method, recursively sub-dividing the first matrix and the second matrix producing a set of sub-matrix products and a recursion tree, and propagating the set of sub-matrix products up the recursion tree to produce a product matrix.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
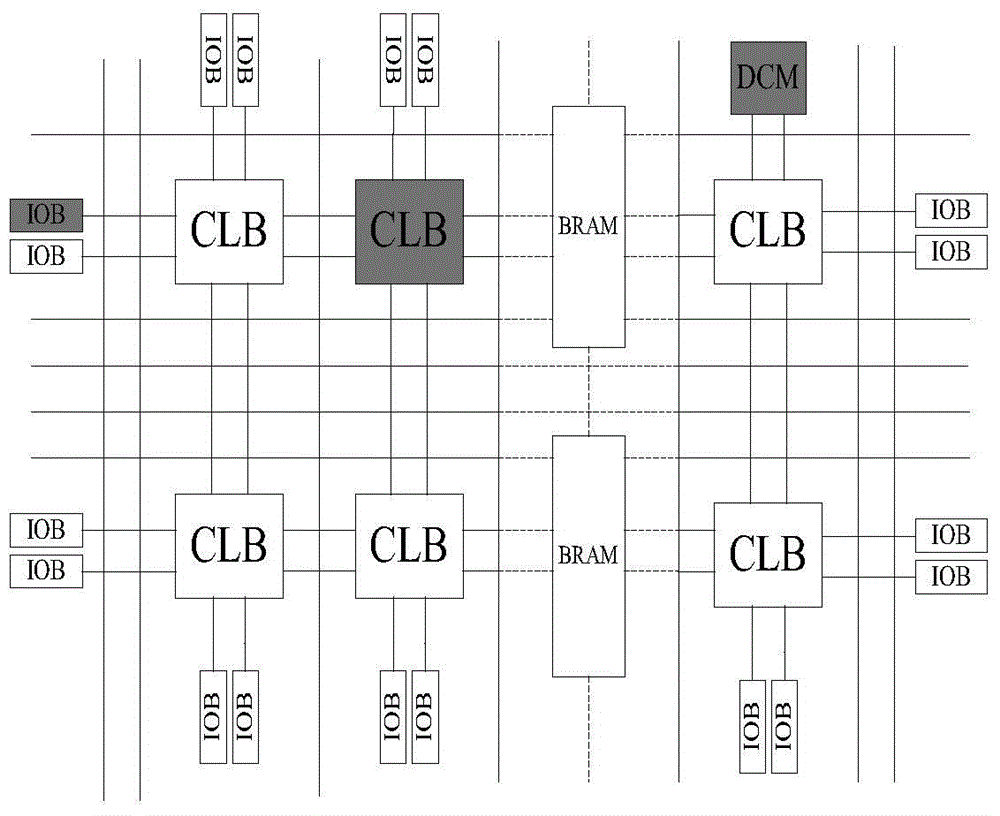
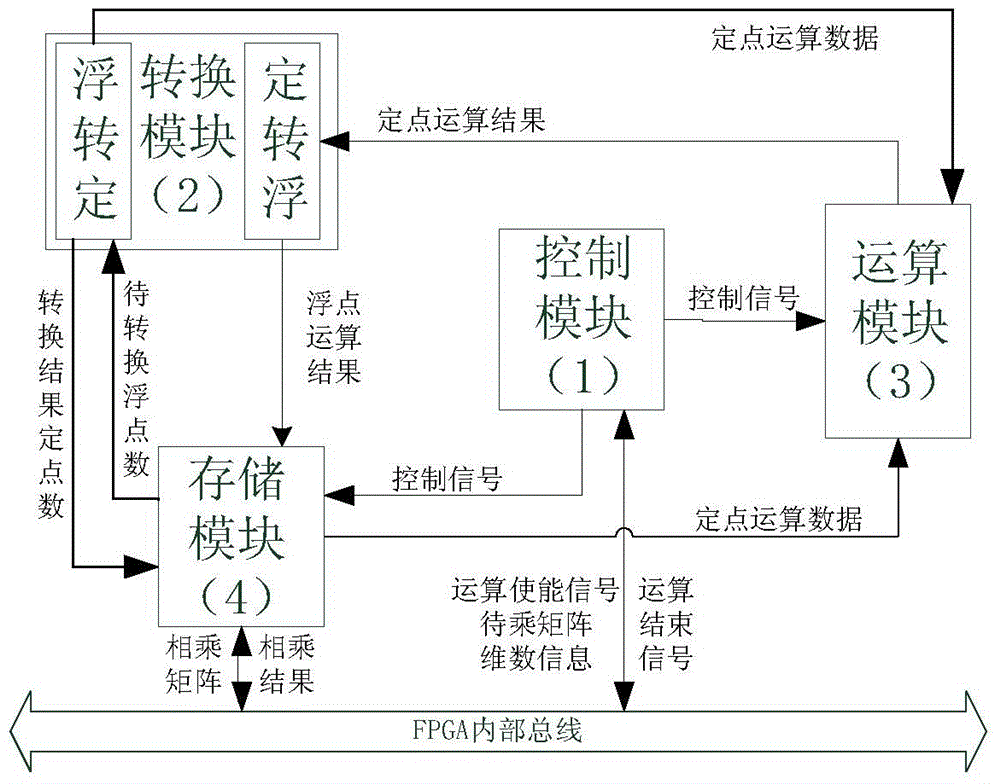
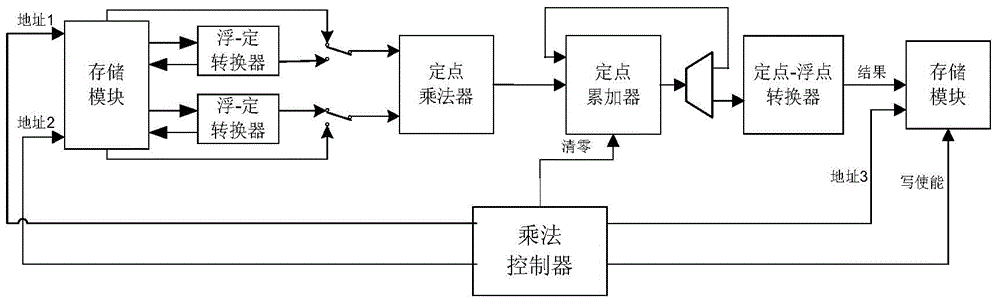
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based general matrix fixed-point multiplier and calculation method thereof
ActiveCN104572011AImprove computing efficiencyImprove performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral matrixControl signal
The invention discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based general matrix fixed-point multiplier. An internal structure of the multiplier consists of a control module, a conversion module, an operation module and a storage module. The control module is used for generating a control signal according to dimension of a to-be-operated matrix. The conversion module is responsible for performing conversion between a fixed-point number and a floating-point number during operation. The operation module is used for reading operation data from the storage module and the conversion module, performing fixed-point multiplication and fixed-point accumulating operation and storing a result in the storage module. The storage module is used for caching to-be-operated matrix data and result matrix data, providing an interface compatible with a bus signal and allowing access of other components on a bus. The characteristic of high fixed-point calculation efficiency in hardware is fully utilized; by using a unique operation structure, simultaneous conversion and operation of the data are realized to improve the overall operation speed, and a plurality of matrix fixed-point multipliers can be simultaneously used to perform parallel calculation; thus the fixed-point multiplication of an arbitrary dimension matrix can be supported, and meanwhile extremely high calculation efficiency is guaranteed. Compared with matrix multiplication performed by using the floating-point number, the multiplier has the advantage that the calculation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:上海碧帝数据科技有限公司
RF signal processing in multi-antenna systems
A method for antenna subset selection by joint processing in RF and baseband in a multi-antenna systems. Lt input data streams are generated in a transmitter for either diversity transmission or multiplexing transmission. These streams are modulated to RF signals. These signals are switched to the t branches associated with the t transmit antennas, and a phase-shift transformation is applied to the RF signals by a t×t matrix multiplication operator Φ1, whose output are t≧Lt RF signals. These signals are transmitted over a channel by t antennas. The transmitted signals are received by r antennas in a receiver. A phase-shift transformation is applied to the r RF signals by a r×r matrix multiplication operator Φ2. Lr branches of these phase shifted streams are demodulated and further processed in baseband to recover the input data streams.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION
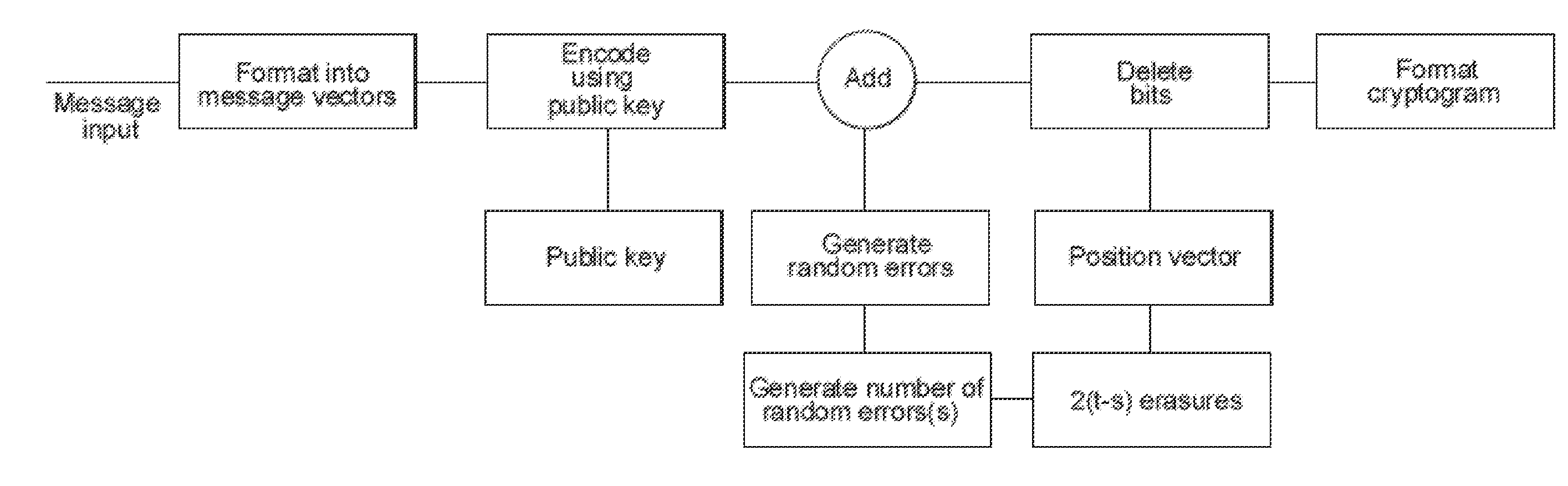
Methods, systems and apparatus for public key encryption using error correcting codes
InactiveUS20150163060A1Improve securityEasy to broadcastKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareTrade offs
This invention provides improved security of the McEliece Public Key encryption system adding features which make full use of random number generation for given message and cryptogram parameters. Different embodiments of the invention are described which enable the level of security to be traded-off against cryptogram size and complexity. Message vectors are encoded with a scrambled generator matrix, using matrix multiplication to form codeword vectors. Shortened corrupted codewords are generated by corrupting each codeword vector and omitting a predefined number of bits, whereby a cryptogram is formed from the shortened corrupted codewords. Measures are included to defeat attacks based on information set decoding. A number of different applications are given.
Owner:PQ SOLUTIONS LTD
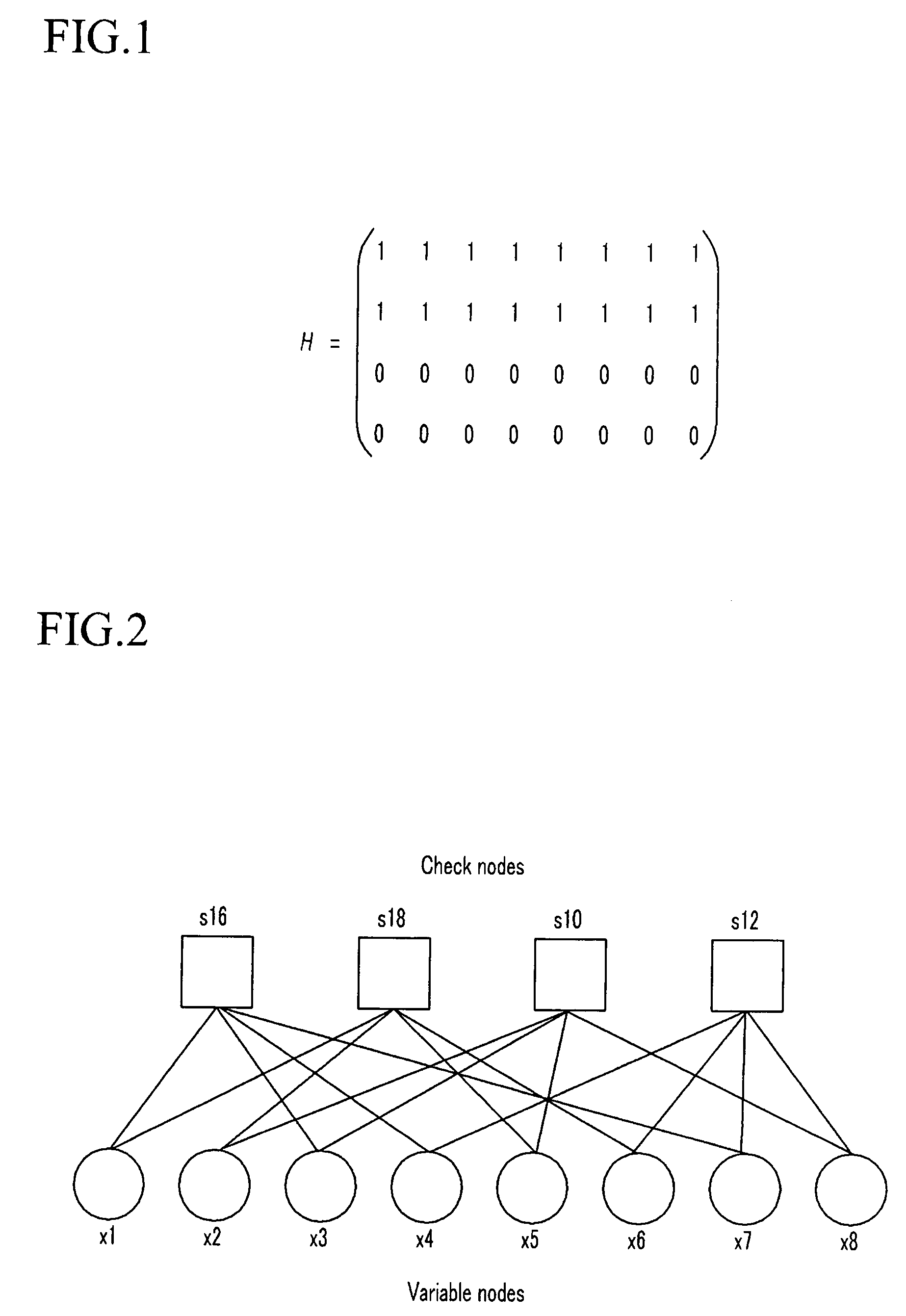
Method for constructing checking matrix of LDPC code and coding and decoding apparatus utilizing the method
InactiveUS20110239077A1Improve performanceLess occupiedError preventionCode conversionAlgorithmEngineering
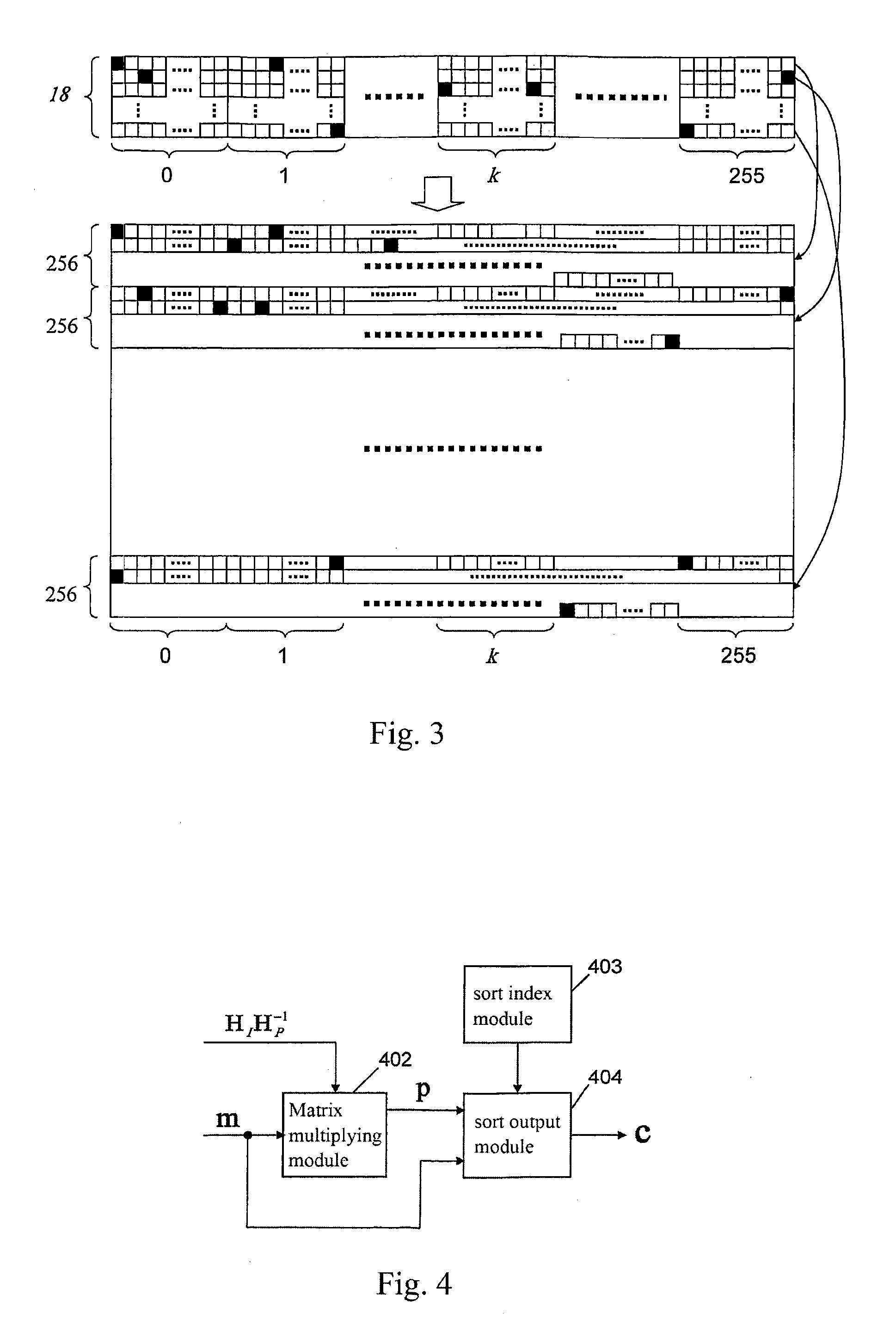
The present invention relates to a method for constructing LPDC code check matrix and encoding and decoding devices using the same. The encoding device encodes the inputted binary information and outputs the encoded system code sequence of position transformation. The encoding device comprises: a matrix multiplication module outputting a check sequence p which is obtained through the binary information sequence m multiplied with a matrix; a sorting index module having N memory units storing index values of a sorting table IDX in turn; and a sorting output module for sorting the m and p and outputting a code word c based on the index value stored in the sorting index table. The present invention constructs the LDPC code check matrix using an algebraic structure, obtaining the LDPC code with stable performance. In addition, the encoding and decoding devices of the present invention occupy less memory, which is preferable for optimization of the devices.
Owner:TIMI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com